Patents
Literature
2359 results about "Nano sized" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
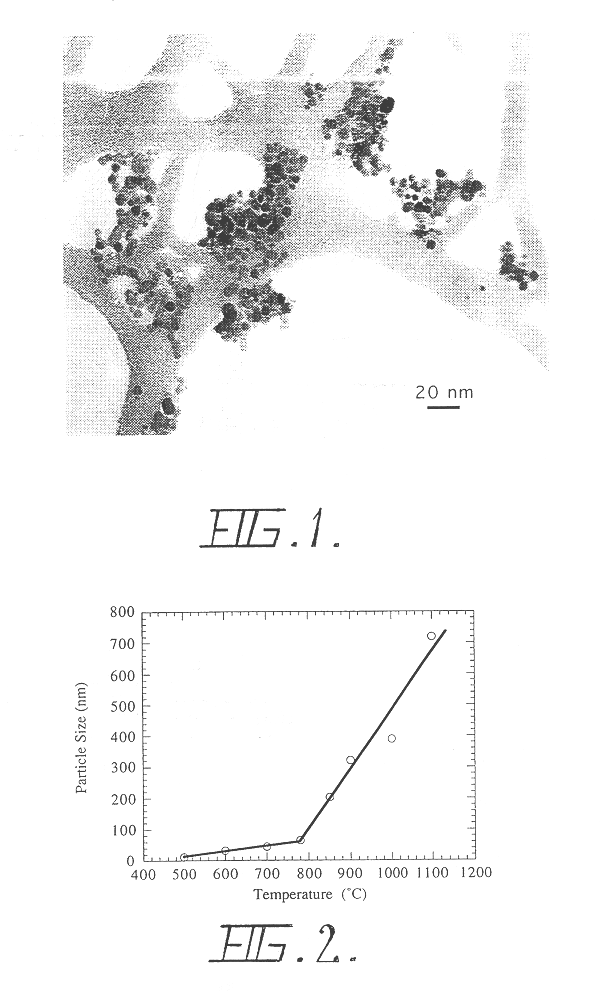
Just how small is “nano?” In the International System of Units, the prefix "nano" means one-billionth, or 10 -9; therefore one nanometer is one-billionth of a meter. It’s difficult to imagine just how small that is, so here are some examples:
Fiber adhesive material
InactiveUS20040071870A1Improve adhesion performanceMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricFiber
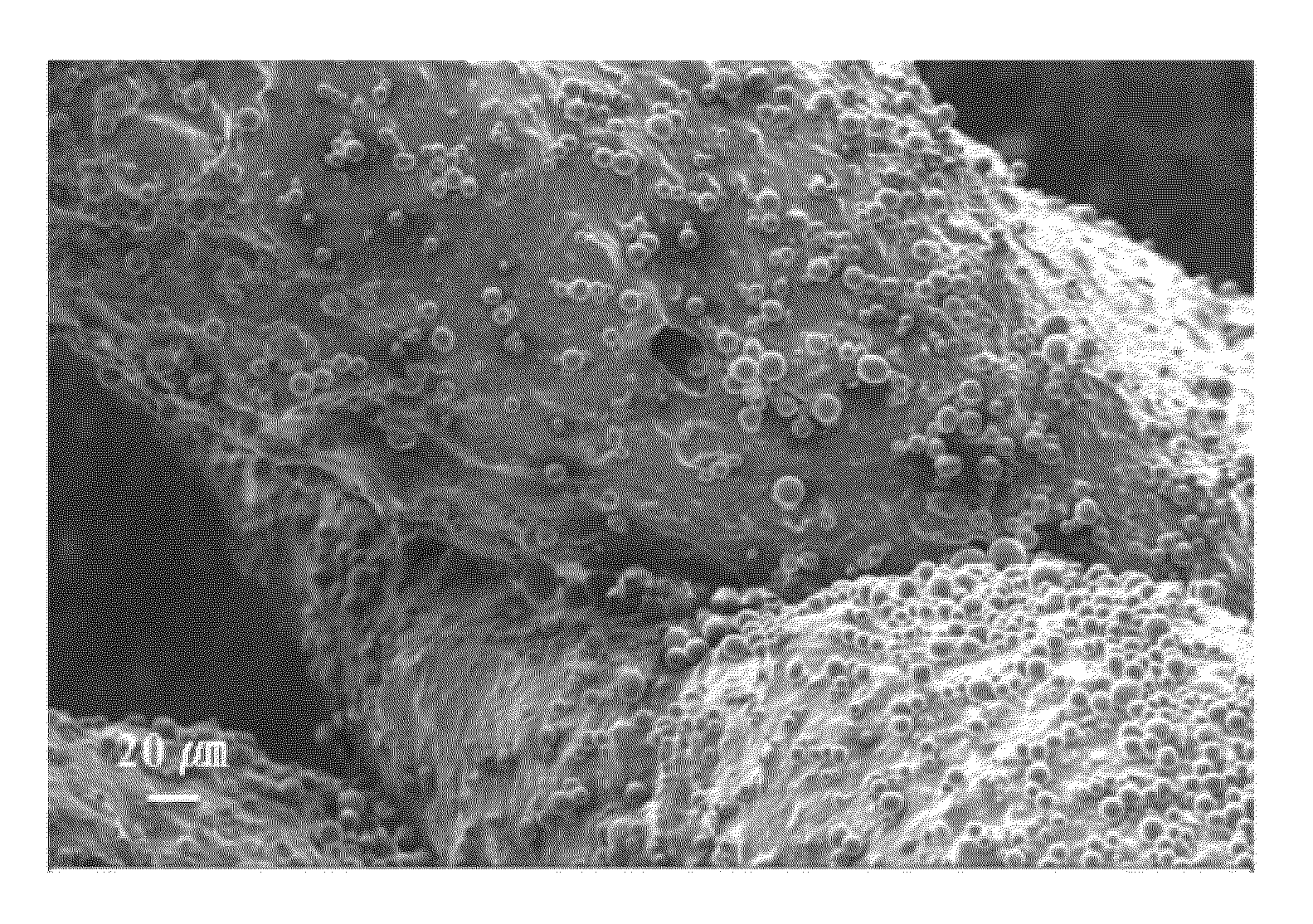
A fiber velvet comprising nano-size fibers or nanofibrils attached to micro-size fibers is disclosed. Methods of manufacturing the velvet as well as various uses of the velvet are also described. For example, the fiber velvet can be used as a thermal interface or as an adhesive material. The nanofibrils may be attached to a flat base or membrane, or may be attached to the tip portions of the micro-size or larger diameter fibers. Various attributes of the micro-size fibers and of the nano-size fibers, for example, geometry (e.g. size, length, packing density) material type (e.g. carbon, metal, polymer, or ceramic) and properties (e.g. conductivity, modulus, surface energy, dielectric constant, surface roughness) can be selected depending on the desired attributes of the fiber velvet. The nanofibrils have a diameter of less than about 1 micron, and may advantageously be formed from single walled and / or multi-walled carbon nanotubes.
Owner:KULR TECH
Method for making a nano-stamp and for forming, with the stamp, nano-size elements on a substrate
The stamping process and a method of fabrication of nano-stamps with characteristic dimensions below 1 nm and up to 100 nm intended for usage in making patterns of characteristic dimensions the same as those of the nano-stamp on surface of a substrate is provided. In the process a very hard stamp is fabricated by first depositing alternating layers of two materials, one of which has very high hardness, on some sacrificial substrate via PVD, CVD or any other deposition procedure that produces alternating layers of selected thickness, from sub 1 nm to above 100 nm. The layered film is then polished to an atomically smooth finish perpendicular to the plane of the layers and etched to produce dips in the softer layers. These steps produce a grid of parallel elevations and valleys on the etched surface, which now can be used as a stamp to stamp out patterns on a substrate of lower hardness than the hardness of the elevated layers. If the substrate is stamped twice with a turning of the stamp 90 degrees between first and second stampings, a square pattern of elevations or hills and valleys is formed, which can be used for magnetic memory storage by subsequently sputtering magnetic material on the tops of the elevations or hills.
Owner:VIGIL THOMAS R +1
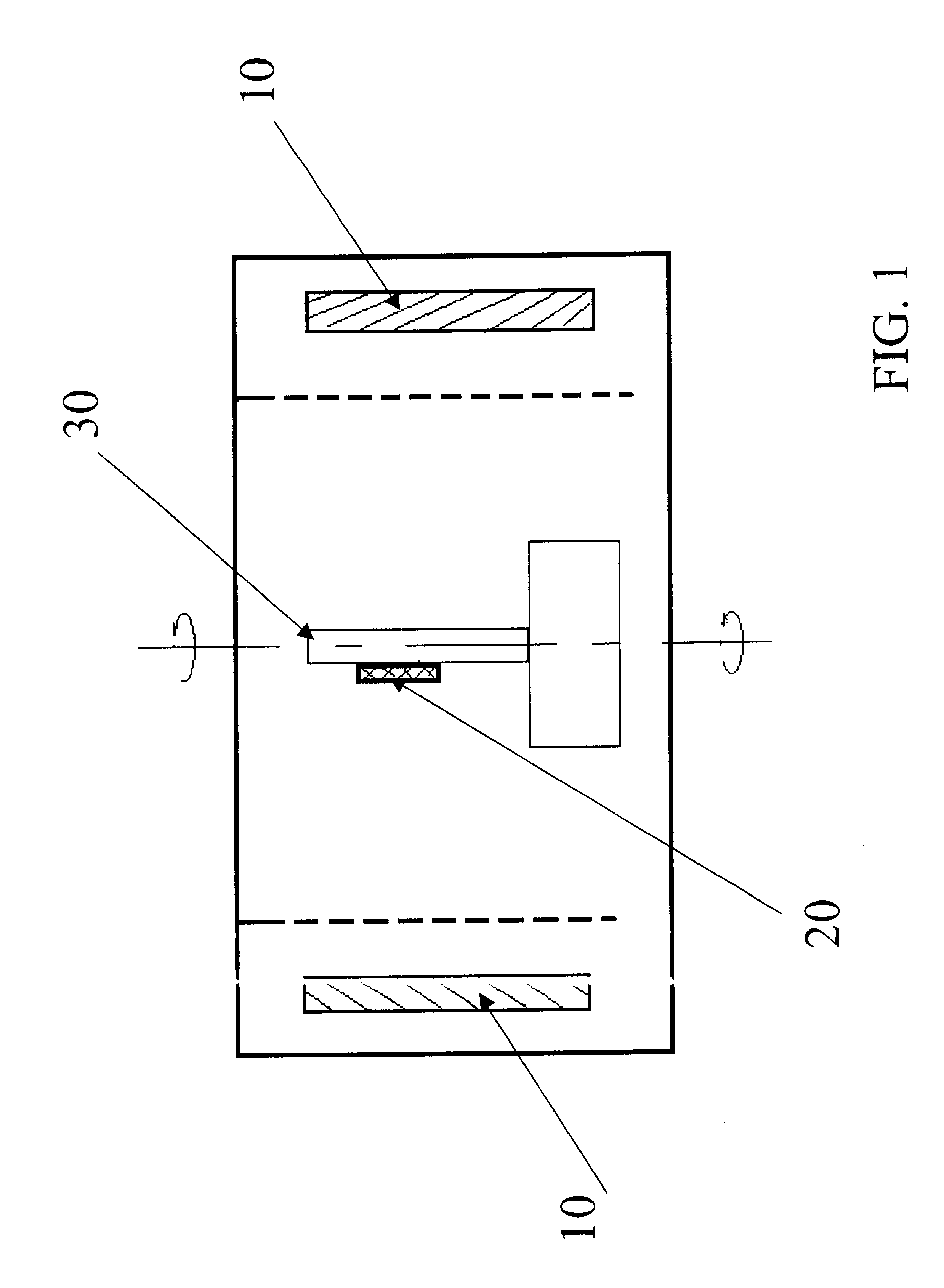
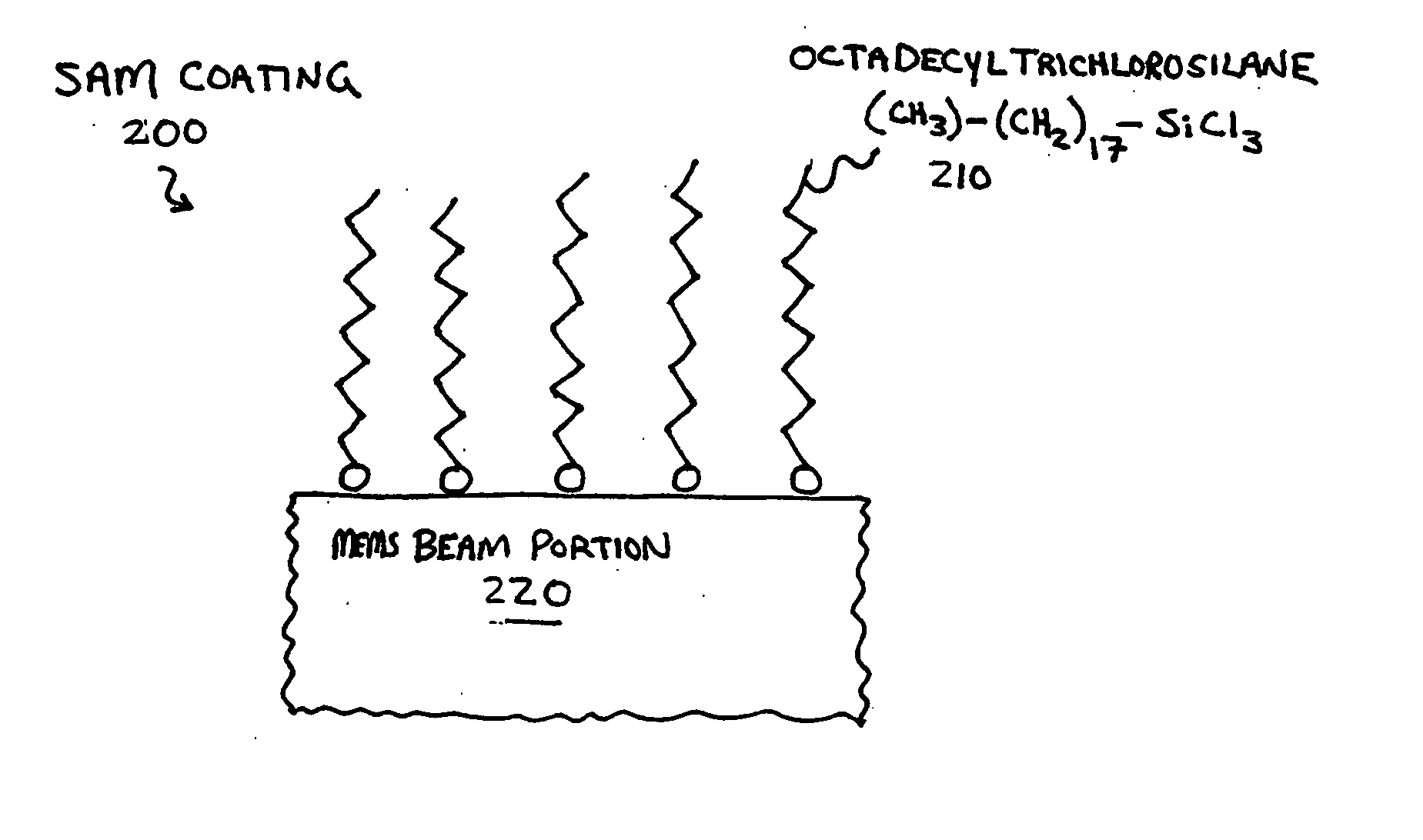
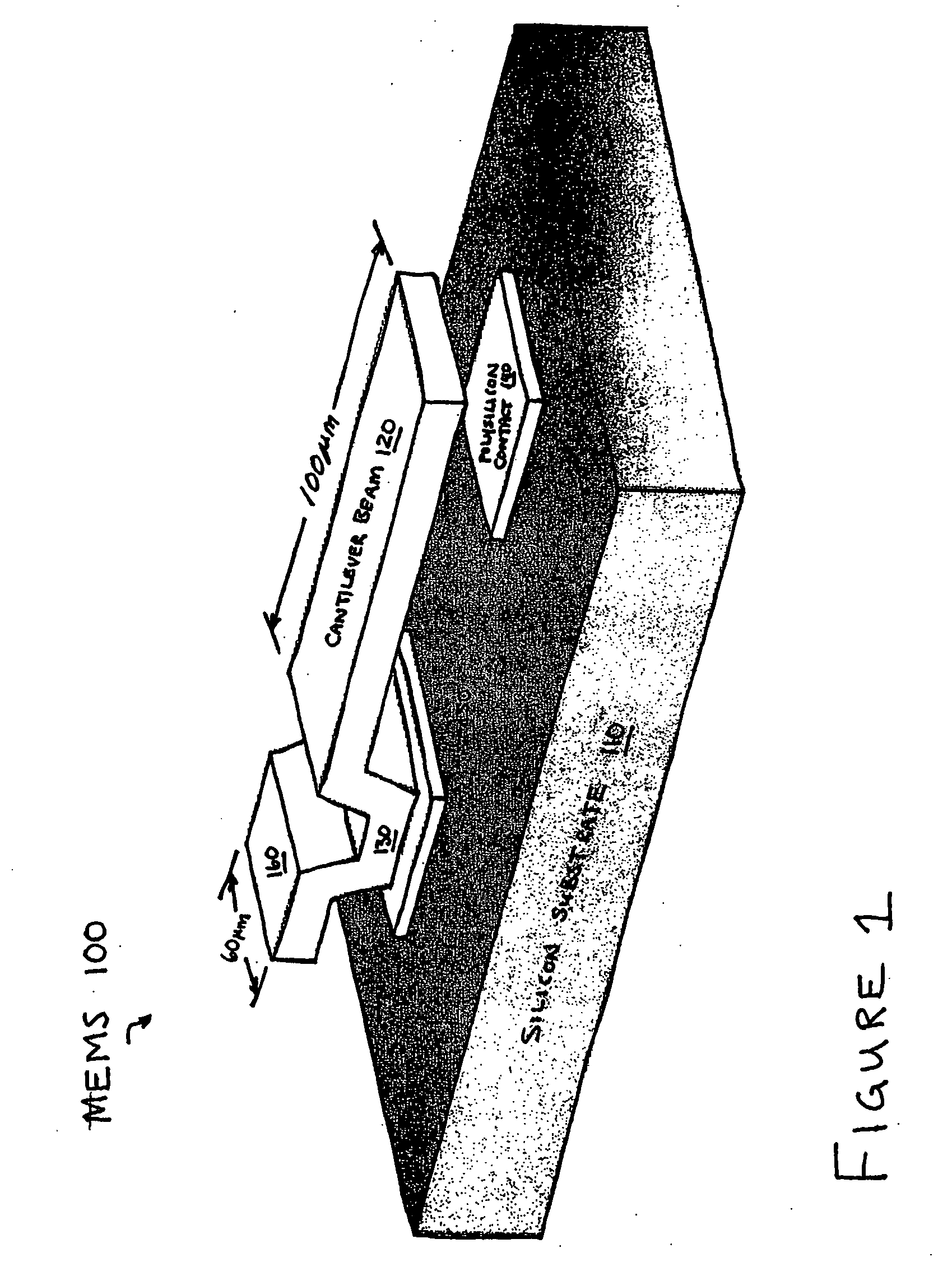
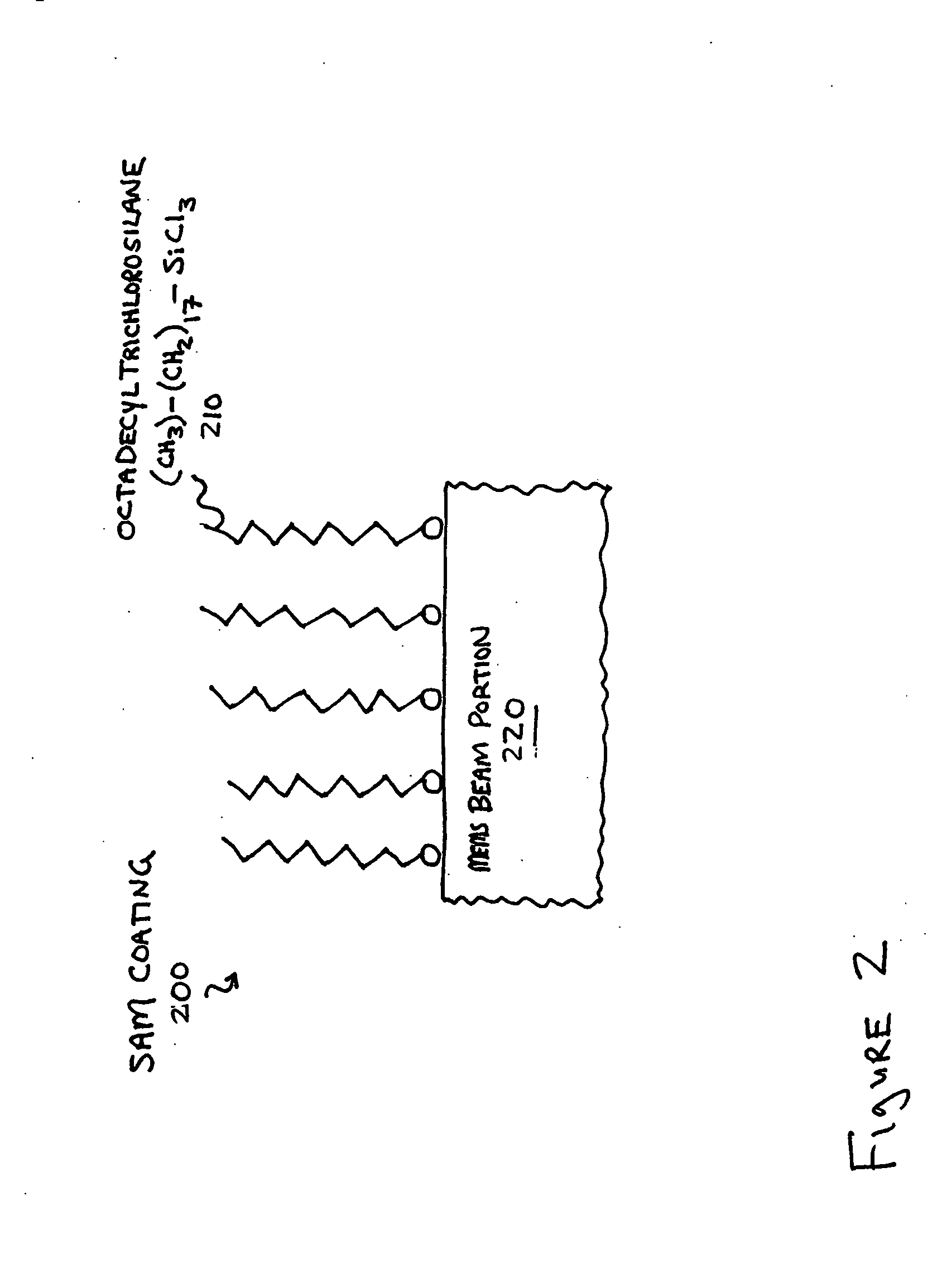
Al2O3 atomic layer deposition to enhance the deposition of hydrophobic or hydrophilic coatings on micro-electromechcanical devices
Micro-mechanical devices, such as MEMS, having layers thereon, and methods of forming the layers, are disclosed. In one aspect, a method may include forming a layer including an oxide of aluminum over at least a portion of a micro-mechanical device, and coating the layer by bonding material to surface hydroxyl groups of the layer. In another aspect, a method may include introducing a micro-mechanical device into an atomic layer deposition chamber, and substantially filling nanometer sized voids of the micro-mechanical device by using atomic layer deposition to introduce material into the voids. In a still further aspect, a method may include introducing an alkylaminosilane to a micro-mechanical device having a surface hydroxyl group, and bonding a silane to the micro-mechanical device by reacting the alkylaminosilane with the surface hydroxyl group.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Microparticles
InactiveUS6669961B2Minimal deformationHardening of the spheresPowder deliveryNanostructure manufactureMicroparticleNanometre
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Non-toxic, heavy-metal free sensitized explosive percussion primers and methods of preparing the same
ActiveUS8206522B2Metal azide explosive compositionsMetal fulminate explosive compositionsEngineeringOxidizing agent
A non-toxic, non-hydroscopic percussion primer composition and methods of preparing the same, including at least one explosive component that has been traditionally considered a moderately insensitive explosive or secondary explosive, and at least fuel particle component having a particle size of about 1.5 microns to about 12 microns, which allows the use of moderately active metal oxidizers. The sensitivity of the primer composition is created by the interaction between the moderately insensitive explosive and the fuel agent such that traditional primary explosives such as lead styphnate or DDNP are not needed. The primer composition also eliminates the risks and dangers associated with traditional nano-sized fuel particles.
Owner:FEDERAL CARTRIDGE
Apparatus for imaging using an array of lenses
An imaging system / camera consisting of multiple nano-sized optical elements arranged in an array format with more than one pixel per optical element will have a higher resolution than each element would be capable of individually, since each element being at a different point gathers slightly different overlapping information. Hence by processing such information one can obtain a clear image. Furthermore multiple information from sectors of an array of sensors can be processed to obtain 3-D, stereotypic and panoramic imaging and may be connected to each other allowing seeing around obstacles as well as enabling full 3-D tracking and / or metric determination of an unknown object. Color / spectroscopic imaging can be achieved by utilizing equally sized lenses and multi-wavelength sensing layers below the lenses. However, color / spectroscopic imaging and / or spectroscopy can be achieved by taking advantage of unique optical properties of nano-scaled lenses accepting various wavelengths below their diffraction limits.
Owner:NANOLIGHT TECH
Nanocomposites with high thermoelectric figures of merit
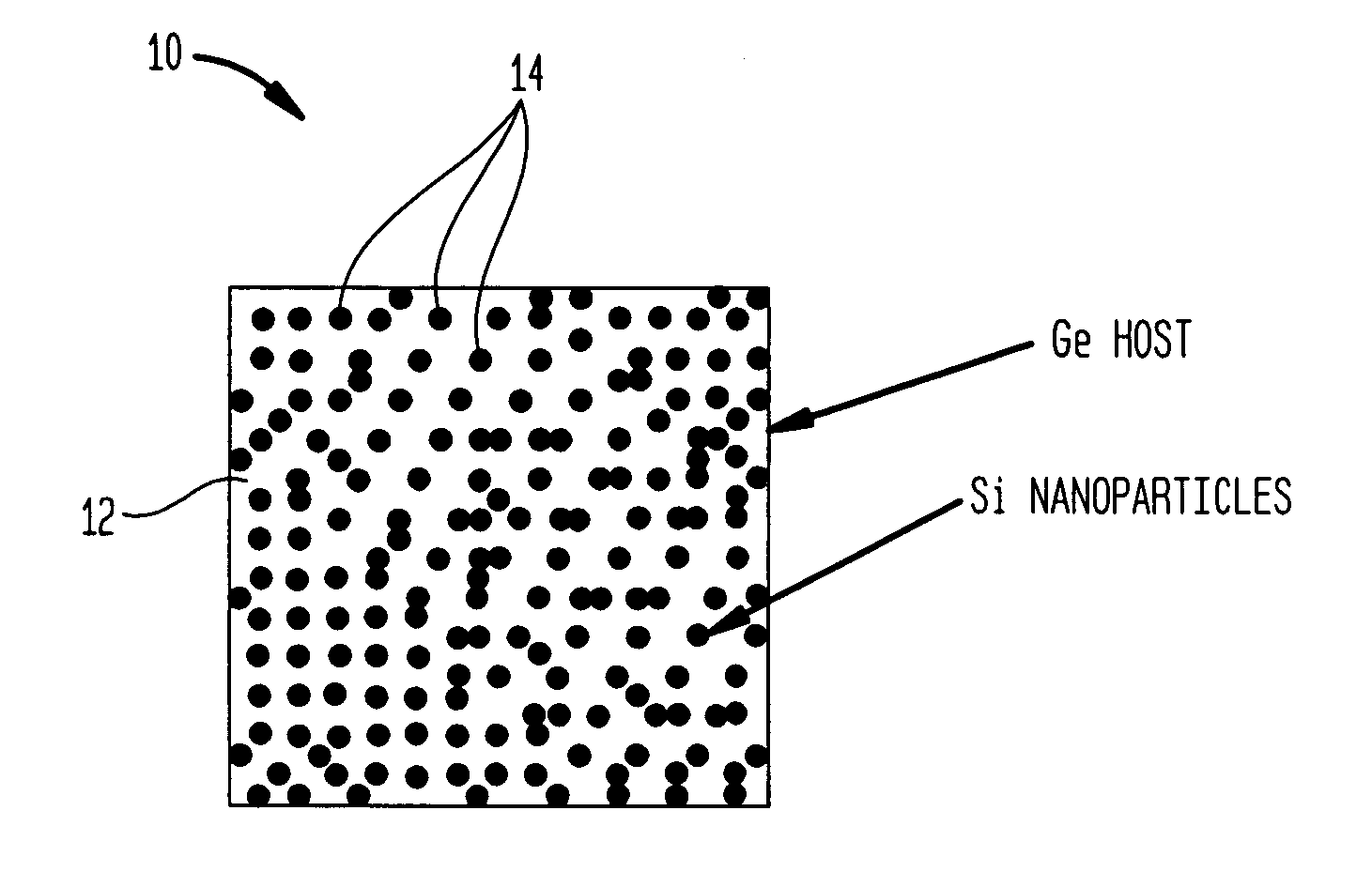
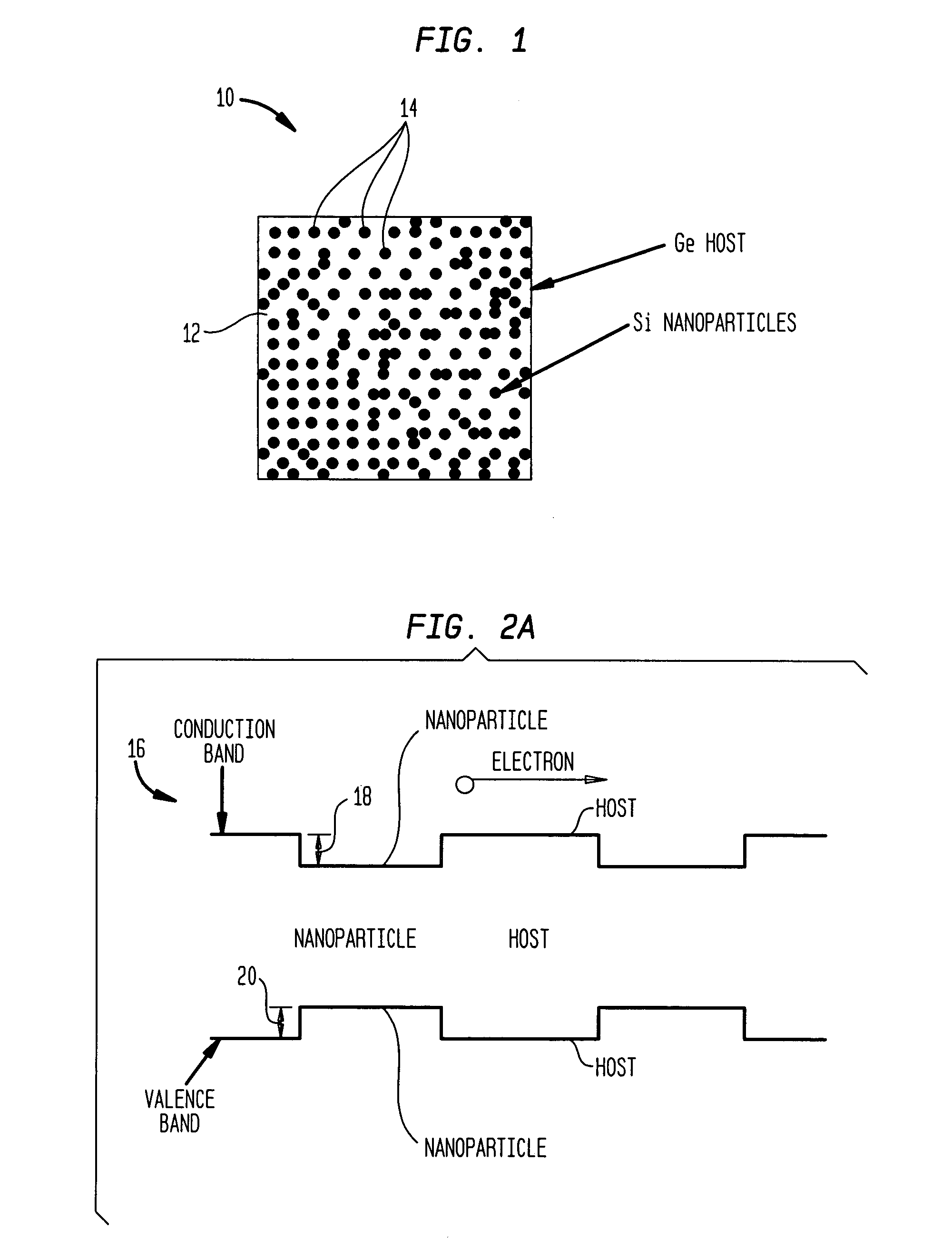
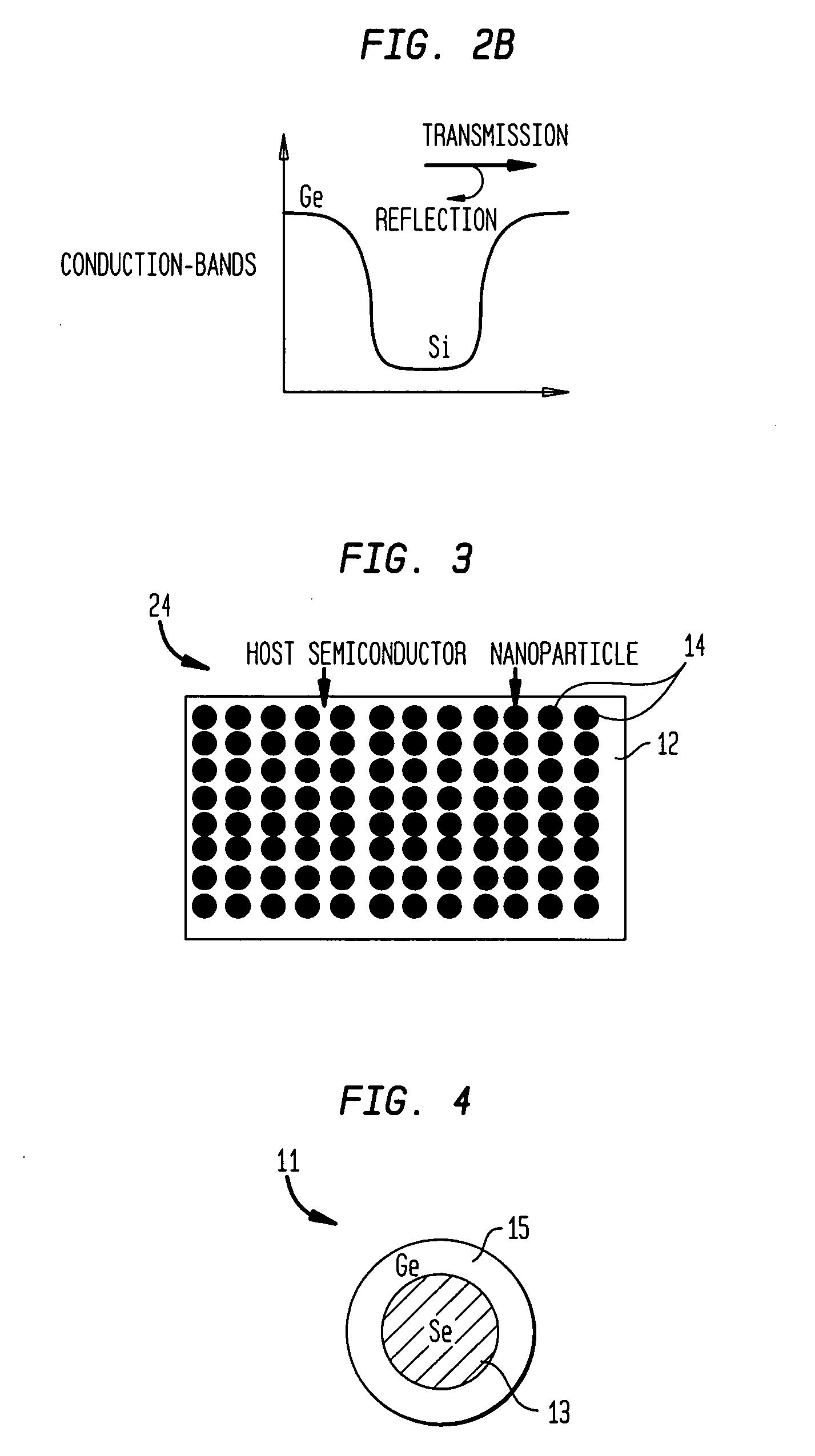
InactiveUS20060102224A1Improve thermoelectric performanceLow thermal conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectValence bandConduction band
The present invention is generally directed to nanocomposite thermoelectric materials that exhibit enhanced thermoelectric properties. The nanocomposite materials include two or more components, with at least one of the components forming nano-sized structures within the composite material. The components are chosen such that thermal conductivity of the composite is decreased without substantially diminishing the composite's electrical conductivity. Suitable component materials exhibit similar electronic band structures. For example, a band-edge gap between at least one of a conduction band or a valence band of one component material and a corresponding band of the other component material at interfaces between the components can be less than about 5 kBT, wherein kB is the Boltzman constant and T is an average temperature of said nanocomposite composition.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE +1
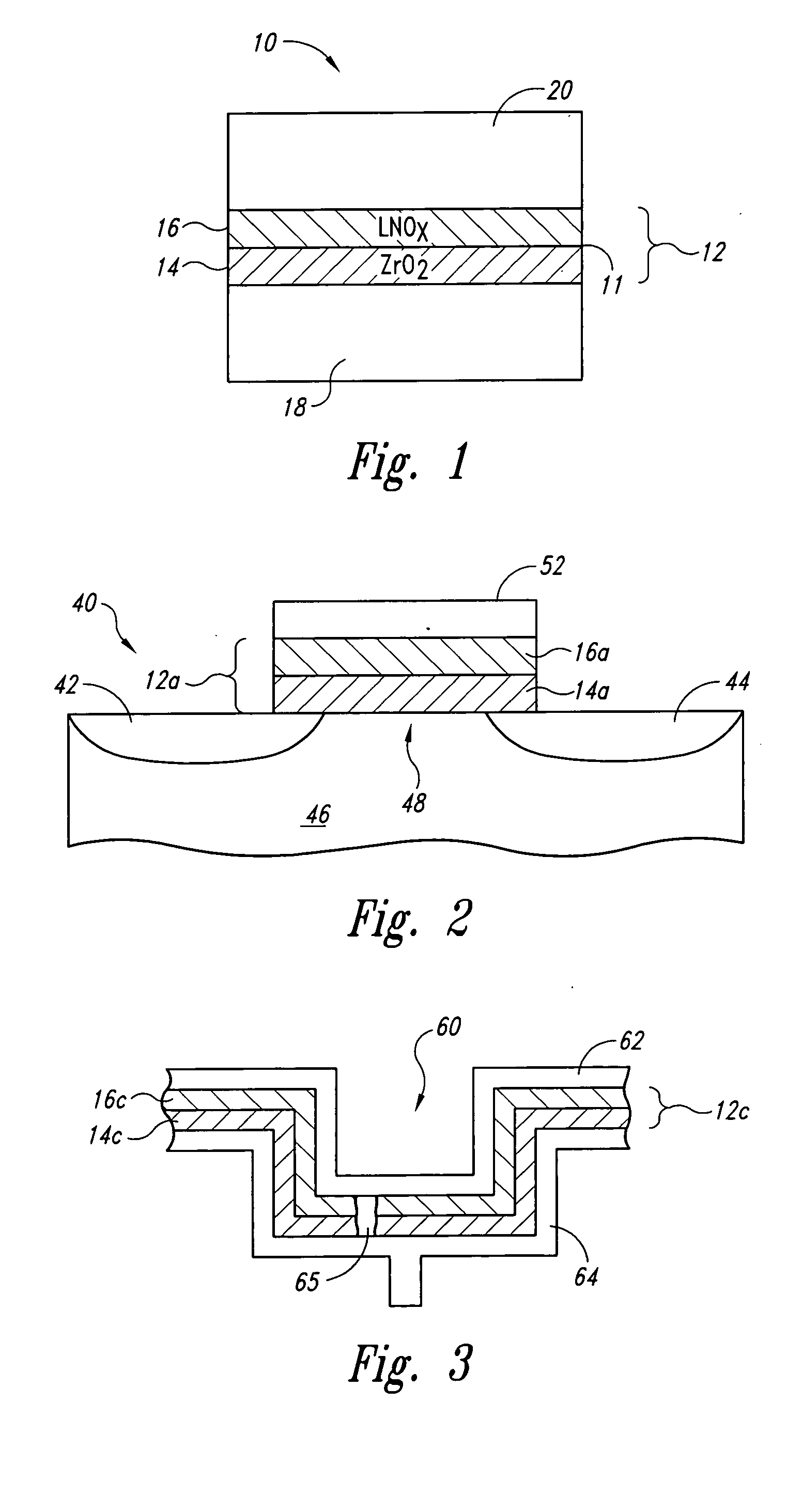
Lanthanide oxide/zirconium oxide atomic layer deposited nanolaminate gate dielectrics
The invention provides a laminated dielectric layer for semiconductor devices formed by a combination of ZrO2 and a lanthanide oxide on a semiconductor substrate and methods of making the same. In certain methods, the ZrO2 is deposited by multiple cycles of reaction sequence atomic layer deposition (RS-ALD) that includes depositing a ZrI4 precursor onto the surface of the substrate in a first pulse followed by exposure to H2O / H2O2 in a second pulse, thereby forming a thin ZrO2 layer on the surface. After depositing the ZrO2 layer, the lanthanide oxide layer is deposited by electron beam evaporation. The composite laminate zirconium oxide / lanthanide oxide dielectric layer has a relatively high dielectric constant and can be formed in layers of nanometer dimensions. It is useful for a variety of semiconductor applications, particularly for DRAM gate dielectric layers and DRAM capacitors.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Composite scintillators for detection of ionizing radiation
InactiveUS20060054863A1High transparencyHigh luminous intensityMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesOptical transparencyLength wave
Applicant's present invention is a composite scintillator having enhanced transparency for detecting ionizing radiation comprising a material having optical transparency wherein said material comprises nano-sized objects having a size in at least one dimension that is less than the wavelength of light emitted by the composite scintillator wherein the composite scintillator is designed to have selected properties suitable for a particular application.
Owner:BWXT Y 12 +1
Optical Fiber Illumination Systems and Methods
ActiveUS20110122646A1Efficient deliveryReduce dependenceGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreFiberUltrasound attenuation
An illumination system generating light having at least one wavelength within 200 nm a plurality of nano-sized structures (e.g., voids). The optical fiber coupled to the light source. The light diffusing optical fiber has a core and a cladding. The plurality of nano-sized structures is situated either within said core or at a core-cladding boundary. The optical fiber also includes an outer surface. The optical fiber is configured to scatter guided light via the nano-sized structures away from the core and through the outer surface, to form a light-source fiber portion having a length that emits substantially uniform radiation over its length, said fiber having a scattering-induced attenuation greater than 50 dB / km for the wavelength(s) within 200 nm to 2000 nm range.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for fabricating magnetoresistive read head having a bias structure with at least one dusting layer
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Microparticles
InactiveUS20020054912A1Poor controlControlling drug release ratePowder deliveryNanostructure manufactureEngineeringPhysics
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Nanosize electropositive fibrous adsorbent
InactiveUS6838005B2Improve the immunityEfficient precipitationIon-exchanger regenerationLoose filtering material filtersFiberParticulates
Aluminum hydroxide fibers approximately 2 nanometers in diameter and with surface areas ranging from 200 to 650 m2 / g have been fount to be highly electropositive. When dispersed in water they are able to attach to and retain electronegative particles. When combined into a composite filter with other fibers or particles they can filter bacteria and nano size particulates such as viruses and colloidal particles at high flux through the filter. Such filters can be used for purification and sterilization of water, biological, medical and pharmaceutical fluids, and as a collector / concentrator for detection and assay of mirobes and viruses. The alumina fibers are also capable of filtering sub-micron inorganic and metallic particles to produce ultra pure water. The fibers are suitable as a substrate for growth of cells. Macromolicules such as proteins may be separated from each other based on their electronegative charges.
Owner:ARGONIDE CORP
Process for the production of ultrafine powders of metal oxides
InactiveUS6503475B1Low costHigh yield rateAlkaline earth titanatesMaterial nanotechnologyDiluentBiological activation
A process for the production of ultrafine powders that includes subjecting a mixture of precursor metal compound and a non-reactant diluent phase to mechanical milling whereby the process of mechanical activation reduces the microstructure of the mixture to the form of nano-sized grains of the metal compound uniformly dispersed in the diluent phase. The process also includes heat treating the mixture of nano-sized grains of the metal compound uniformly dispersed in the diluent phase to convert the nano-sized grains of the metal compound into a metal oxide phase. The process further includes removing the diluent phase such that the nano-sized grains of the metal oxide phase are left behind in the form of an ultrafine powder.
Owner:SAMSUNG CORNING PRECISION MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Method to Produce Nanometer-Sized Features with Directed Assembly of Block Copolymers
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Electrically conductive adhesives
InactiveUS20070131912A1Material nanotechnologyNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesElastomerMetal particle
The present invention provides an electrically conductive adhesive composition having cured low modulus elastomer and metallurgically-bonded micron-sized metal particles and nano-sized metal particles. The low modulus elastomer provides the mechanical robustness and reliability by relieving the stresses generated; and the metallurgically-bonded micron-sized metal particles and nano-sized metal particles provide a continuous conducting path with minimized interface resistance. Addition of nano-sized metal particles lowers the fusion temperature and allows the metallurgical-bonding to occur at manageable temperatures.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Non-woven media incorporating ultrafine or nanosize powders
InactiveUS20080026041A1Improve efficiencyLarge capacityMaterial nanotechnologyTreatment involving filtrationFiberActivated carbon
The invention is a fibrous structure for fluid streams that is a mixture of nano alumina fibers and second fibers arranged in a matrix to create asymmetrical pores and to which fine, ultrafine, or nanosize particles such as powdered activated carbon are attached without the use of binders. The fibrous structure containing powdered activated carbon intercepts contaminants from fluid streams. The invention is also a method of manufacturing and using the fibrous structure.
Owner:ARGONIDE CORP
Nanocarbon-activated carbon composite
InactiveUS20090220767A1Percolation limitAvoid combiningPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compositesPorosity
The present invention relates to carbon-carbon composite material comprising a carbonaceous carrier and nanosize carbon structures (e.g. CNT or CNF), wherein the nanosize carbon structures are grown on the carbonaceous carrier. The carrier may be porous, as in activated carbon or consists of carbon black particles. In accordance with the invention, nanocarbon growth in the pores of porous carriers can be realized. The process for the manufacture of a this carbon-carbon-composite material comprises the steps of treating a carbonaceous carrier material with a metal-containing catalyst material, said metal being capable of forming nanosize carbon structures, and growing nanosize carbon structures by means of a CVD (chemical vapour deposition) method on the treated carrier in a gas atmosphere comprising a carbon-containing gas, followed by an optional surface modification step. This process allows optimising porosity, hydrodynamical properties and surface chemistry independently from each other, which is particularly beneficial in respect of the use of the composite for water purification. Carbon black-based composites are particularly useful for filler applications.
Owner:SUD CHEM IP GMBH & CO KG
Process for the production of ultrafine particles
A new, cost effective process for the production of ultrafine particles which is based on mechanically activated chemical reaction of a metal compound with a suitable reagent. The process involves subjecting a mixture of a metal compound and a suitable reagent to mechanical activation to increase the chemical reactivity of the reactants and / or reaction kinetics such that a chemical reaction can occur which produces a solid nano-phase substance. Concomitantly, a by-product phase is also formed. This by-product phase is removed so that the solid nano-phase substance is left behind in the form of ultrafine particles. During mechanical activation a composite structure is formed which consists of an intimate mixture of nano-sized grains of the nano-phase substance and the reaction by-product phase. The step of removing the by-product phase, following mechanical activation, may involve subjecting the composite structure to a suitable solvent which dissolves the by-product phase, while not reacting with the solid nano-phase substance. The process according to the invention may be used to form ultrafine metal powders as well as ultrafine ceramic powders. Advantages of the process include a significant degree of control over the size and size distribution of the ultrafine particles, and over the nature of interfaces created between the solid nano-phase substance and the reaction by-product phase.
Owner:WESTERN AUSTRALIA UNIV OF THE
Carbon annotate-based device and method for making carbon nanotube based device
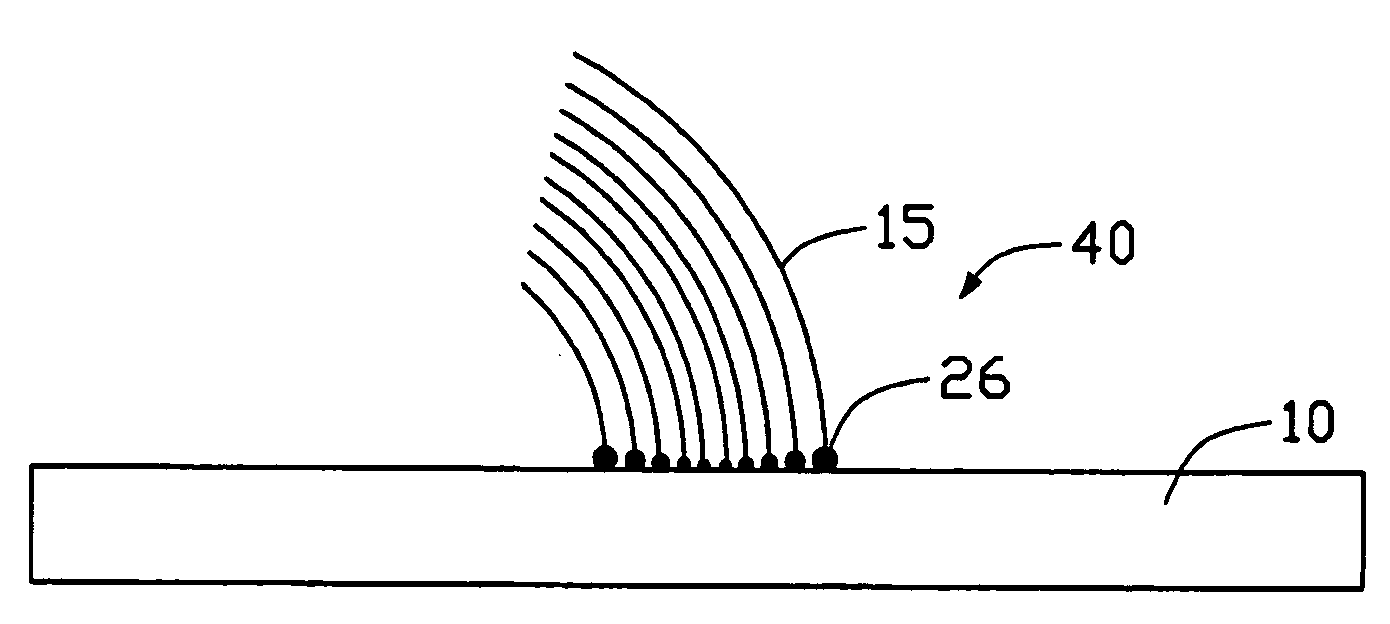
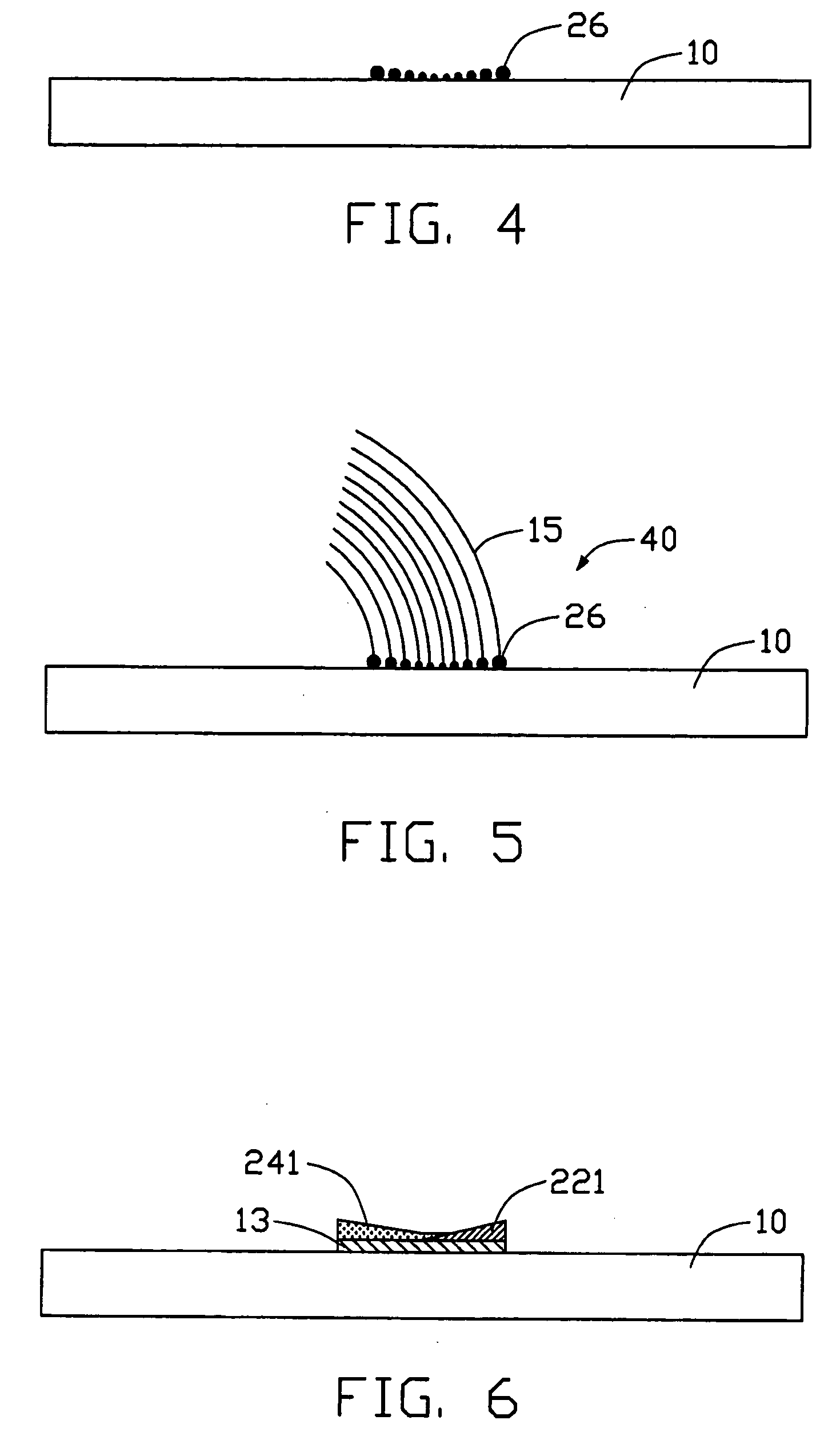
ActiveUS20040136896A1Easy to controlWide applicationMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsGas phaseAlloy
A carbon nanotube-based device (40) includes a substrate (10), a number of alloyed, nano-sized catalytic particles (26) formed on the substrate, and an array of aligned carbon nanotubes (15) extending from the alloyed, nano-sized catalytic particles. The nanotube array bends in an arcuate configuation. A method for making the carbon nanotube-based device includes the steps of: providing a substrate; depositing a catalyst layer on the substrate; depositing two different layers of catalyst-doped materials on different areas of the catalyst layer for accelerating or decelerating the rate of synthesis of the aligned carbon nanotube array; annealing the catalyst and the catalyst-doped materials in an oxygen-containing gas at a low temperature; introducing a carbon source gas; and forming an array of aligned carbon nanotubes extending from the alloyed, nano-sized catalytic particles using a chemical vapor deposition method.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Nano-sized polymer-metal composites
A polymer nanoparticle is provided. The nanoparticle includes an inner layer having alkenylbenzene monomer units. The nanoparticle further includes an outer layer having monomer units selected from conjugated dienes, alkylenes, alkenylbenzenes, and mixtures thereof. The nanoparticle has at least one functional group associated with the outer layer. The nanoparticle further has at least one metal complexed with said functional group. The nanoparticles can be used as a templates for preparation of nano-sized metal crystals and polymer-metal nanocomposite.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Graphite intercalation and exfoliation process
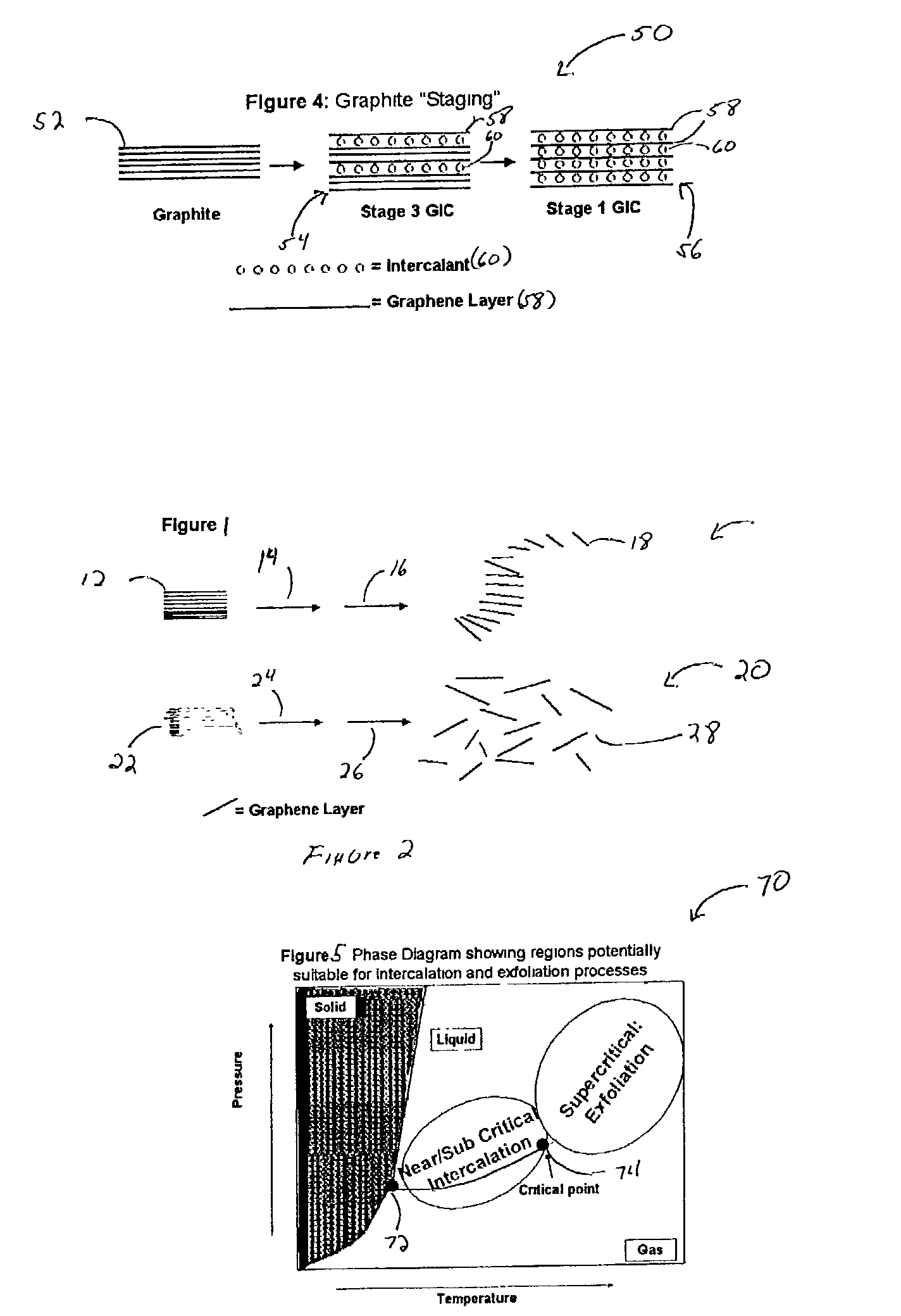
InactiveUS7105108B2Improve volume expansionReduce needMaterial nanotechnologyGraphiteConductive polymerGraphite particle
The invention relates to expanded graphite and methods of making the graphite and products that can be made from the graphite made from the inventive process. The invention includes the step of introducing a fluid into at least one of a plurality of interstices of graphite flake, wherein the fluid comprises at least one of a sub-critical point fluid, a near critical point fluid, or a supercritical fluid. The graphite flake is also intercalated with an intercalant and optionally an oxidizing agent. The invention may further include novel techniques of exfoliating the graphite. The invention may be practiced to make nano-sized graphite particles and also graphite composites. Preferred composites which may be made in accordance with the invention include conductive polymeric composites (thermally or electrically), paint composites, battery composites, capacitor composites, and pollution abatement catalyst support composites.
Owner:GRAFTECH INT HLDG INC
Nanostructured compositions
InactiveUS7166663B2Reduce light transmittanceMaterial nanotechnologySpecial tyresParticulatesNanostructured materials
A material composition made of a matrix material, a nano-sized particulate fraction and a micron-sized particulate fraction. A process of making a nano-structured composition. A nano-structured material is provided to initiate a mixture. A micron-sized particulate material is added to the mixture. A matrix material is added to the mixture. Finally, the mixture is utilized to fabricate a nano-structured structure.
Owner:NANOPHASE TECH CORP
Method for preparing polymeric biomaterials having immobilized drug delivery system comprising bioactive molecules loaded particle carrier
InactiveUS20130045266A1Improve low histocompatibilityGood wound healing effectAntibacterial agentsImpression capsMedicineWound site
A new polymeric material for biological tissue regeneration or treatment with a drug delivery system which contains therapeutic agents and / or bioactive molecules to reduce infection and inflammatory reaction at a wound site and maximize tissue regeneration and wound healing is provided. The new bioactive molecule-loaded polymeric material is prepared by (1) preparing micrometer or nanometer sized bioactive molecule-loaded particles; (2) modifying the surface of the prepared particles and immobilizing the particles on the surface of the polymeric material; and (3) physically treating the surface of the polymeric material to improve binding strength of the particles immobilized thereon.
Owner:CHUNGBUK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND +2
Optical Fiber Illumination Systems and Methods
ActiveUS20130088888A1Efficient deliveryReduce dependenceCladded optical fibreElectric discharge tubesFiberLighting system
An illumination system that includes at least one light-diffusing optical fiber is disclosed. The illumination system includes at least one low-scatter light-conducting optical fiber that optically couples the at least one light-diffusing optical fiber to at least one light source. The light-diffusing optical fiber includes a light-source fiber portion having a length over which scattered light is continuously emitted. The light-source fiber portion can be bent, including wound into a coil shape. The light-diffusing optical fiber includes a plurality of nano-sized structures configured to scatter guided light traveling within the light-diffusing optical fiber out of an outer surface of the fiber.
Owner:CORNING INC
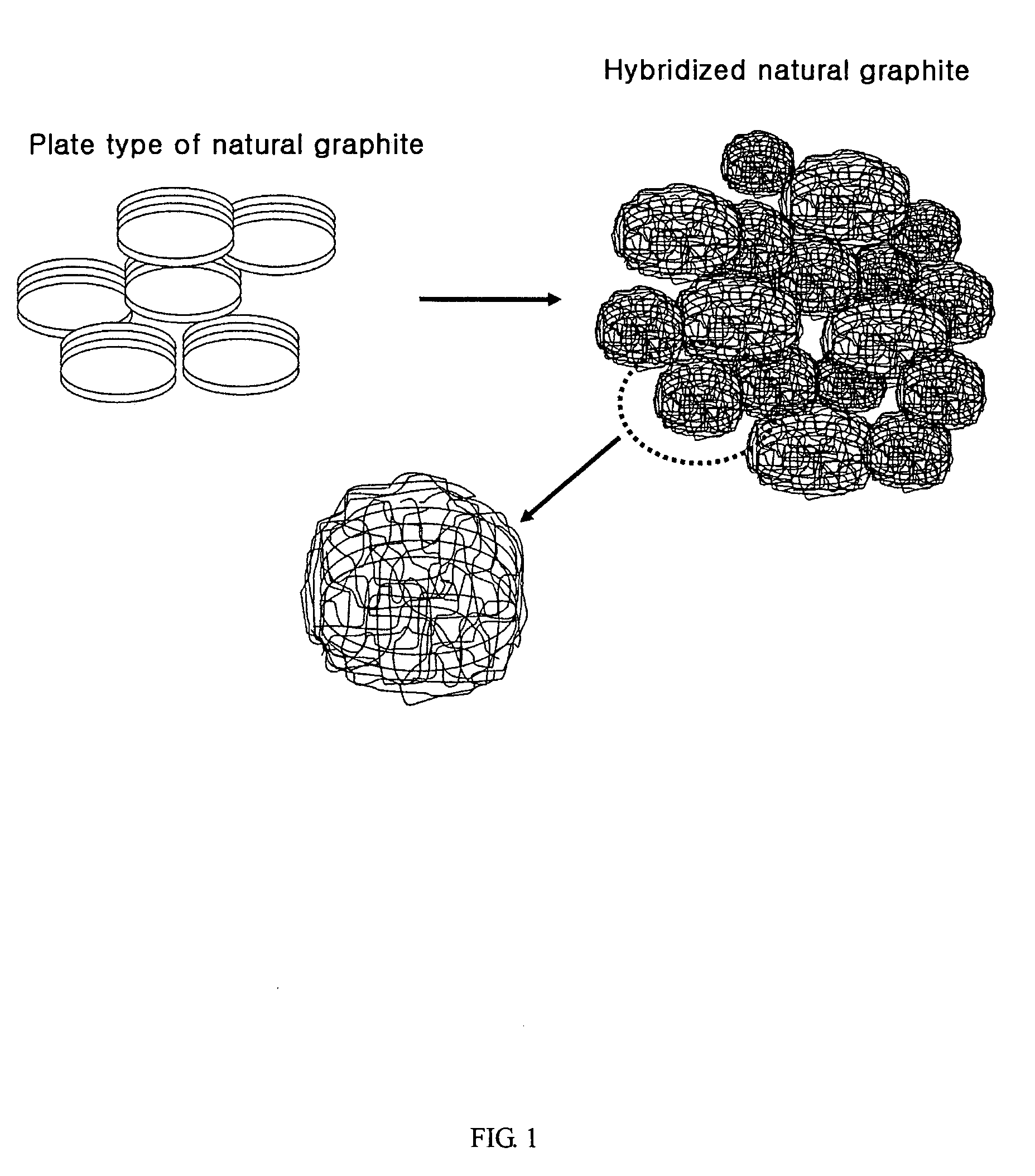
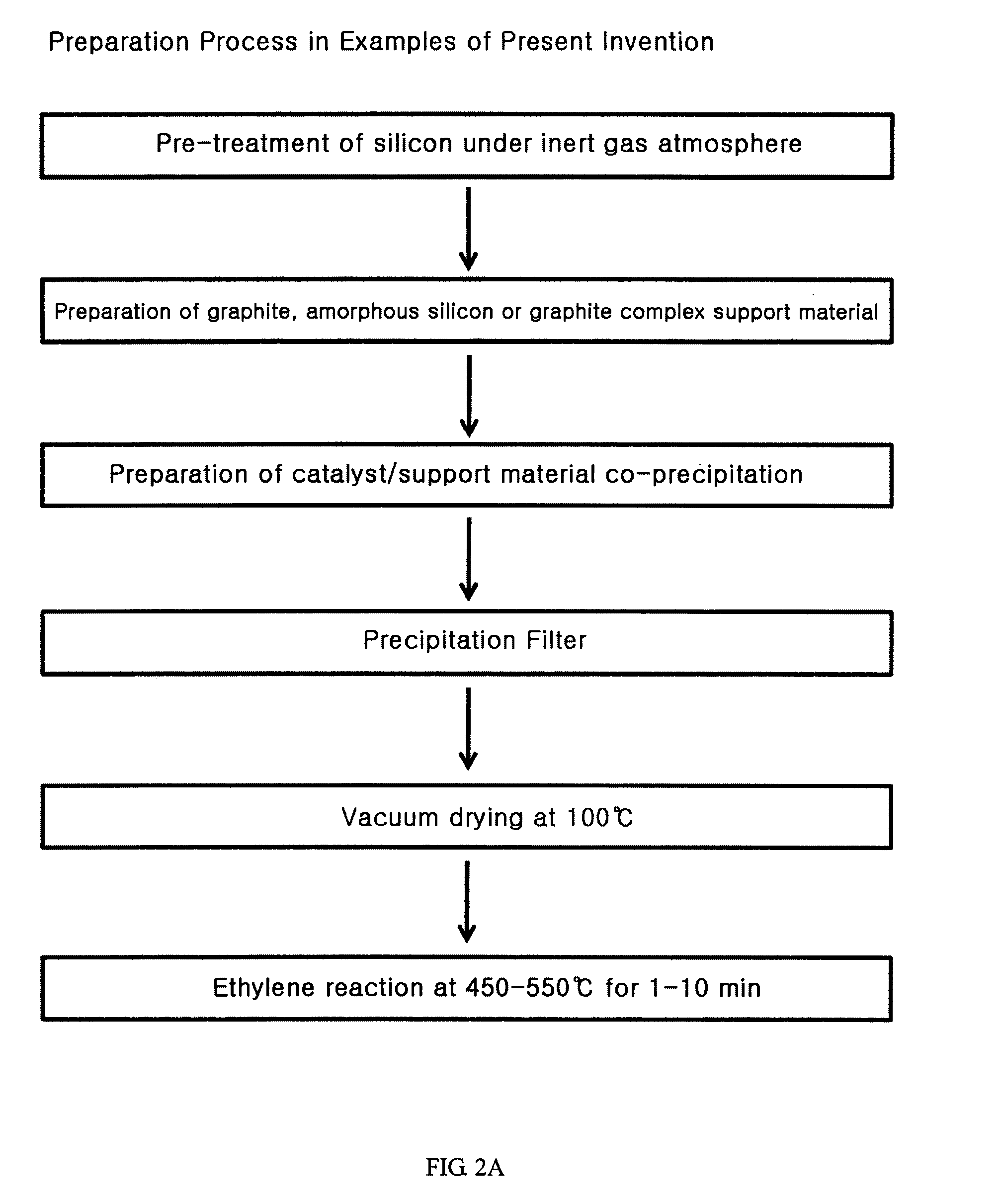
Anode active material hybridizing carbon nano fibers for lithium secondary battery
The present invention is to provide anode active material hybridized with carbon nano fibers for lithium secondary battery prepared by following steps comprising, i) dispersing the nano size metal catalyst to the surface of anode material selected from graphite, amorphous silicon or the complex of graphite and amorphous silicon; and ii) growing the carbon nano fiber by chemical vapor deposition method, wherein carbon nano fibers are grown in a vine form and surround the surface of anode active material.
Owner:KOREA KUMHO PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Discontinuous conductive filler polymer-matrix composites for electromagnetic shielding
A medical electrical lead having a conductor assembly covered by an insulating layer, and a shield covering positioned adjacent or proximate to at least a portion of the insulating layer in order to shield the conductor assembly from one or more electromagnetic fields. The shield covering is formed of a polymer-matrix composite. The polymer-matrix composite includes a polymeric resin having discontinuous conductive fillers provided therein. The discontinuous conductive fillers include one or more of nano-sized metal structures and nano-sized non-metallic conductive structures. The nano-sized non-metallic conductive structures can have a coating formed of one or more metals. The nano-sized non-metallic conductive structures can be formed of carbon. In turn, the nano-sized non-metallic conductive structures can include one or more of carbon nanofibers, carbon filaments, carbon nanotubes, and carbon nanoflakes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
High-entropy alloy with dispersion nano-sized precipitate strengthening effect and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN104694808AWide range of ingredientsControl mechanical propertiesElectric arc furnaceHigh entropy alloys
The invention discloses high-entropy alloy with the dispersion nano-sized precipitate strengthening effect and a preparing method thereof. The method comprises the steps of removing oxidized skin of a metal material, and then conducting weighing and burdening accurately according to a ratio; conducing smelting in an electric-arc furnace in an argon shield atmosphere of titanium absorbed oxygen to obtain an initial high-entropy alloy ingot, and conducting cold rolling, wherein rolling reduction is 20-50%; placing the ingot in a heat treatment furnace with a temperature ranging from 900 DEG C to 1000 DEG C for heat preservation for 0.5-2 hours, and conducting quenching; placing the ingot in a heat treatment furnace with a temperature ranging from 700 DEG C to 800 DEG C for heat preservation for 2-18 hours, and conducting quenching. By means of precipitation strength, on the premise that high plasticity is kept, yield strength and tensile strength are improved greatly. The room-temperature tensile strength of (FeCoNiCr)94Ti2Al4 in the final state reaches 1094 MPa, plastic elongation is 35%, work hardening effect is remarkable, comprehensive room-temperature mechanical property is prominent, high-temperature tensile strength can reach 400 MPa at the temperature of 800 DEG C and strain rate of 10<-3>, steady creep rate is smaller than or equal to 10<-8> under the stress of 100 MPa and at the temperature of 750 DEG C, and high-temperature tensile strength and creep mechanical property are excellent.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Coating system exhibiting cool dark color
A layered coating composition for use in producing a cool dark coating composition. The coating system includes an IR reflecting layer, having IR-reflective pigments in a resinous binder. A radiation absorbing layer is coated onto the IR reflecting layer. The radiation absorbing layer includes nano-sized pigments dispersed in a resinous binder.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
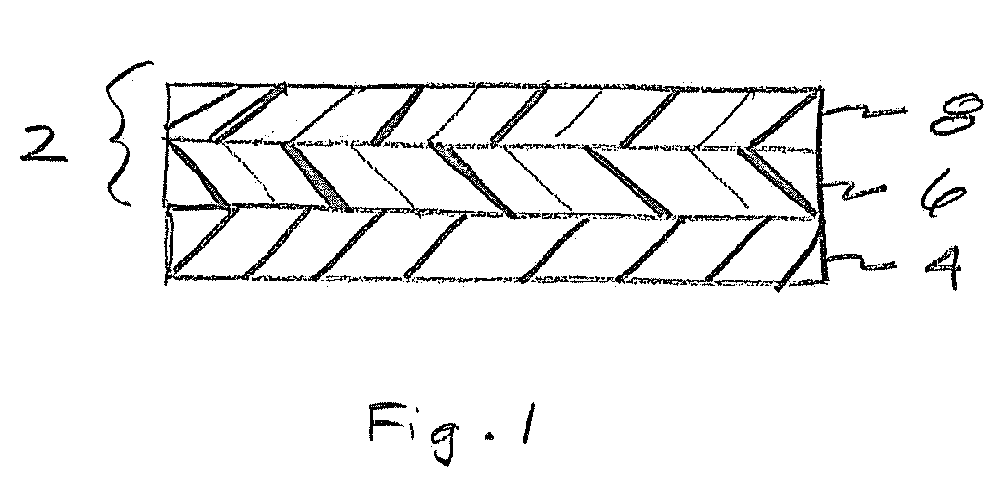
Nano-sized self-assembled liquid dilutable vehicles
Owner:NUTRALEASE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com