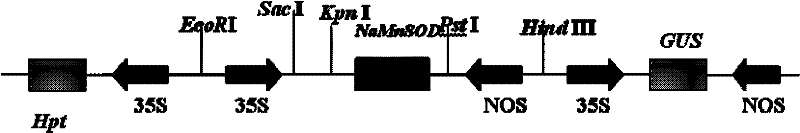Application of extremely halophilic archaea NaSOD gene in improving rice salt tolerance
A technology of extreme halophilic archaea and salt tolerance, which is applied in the application field of extreme halophilic archaea NaSOD gene in improving the salt tolerance of rice, and can solve problems such as yield reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1 Construction of expression vector p1301-NaSOD
[0024] Cultivate Escherichia coli containing the plasmid pGEX-SOD (patent application 200810163748.8), use the specific primers of the NaSOD gene of the halophilic archaea (respectively adding Pst I and Kpn I restriction sites) to carry out bacterial liquid PCR, and recover the purified PCR product Connected to the intermediate vector pMD19-T, transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α. Positive clones were picked and identified by PCR and sequencing. Shake the correct bacterial solution to extract the plasmid pMD19-NaSOD. The plasmid pMD19-NaSOD was double-digested with Pst I and Kpn I, then inserted into the multiple cloning site of pCAMBIA1301, and the CaMV35S promoter and NOS terminator were respectively inserted before and after the target gene to obtain the plant expression vector p1301-NaSOD (such as figure 1 shown). After the recombinant was identified by enzyme digestion, it was introduced into Agrobacter...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2 Genetic transformation of rice mediated by Agrobacterium
[0029] The mature embryos of rice were used as explants to induce and culture the callus, and the embryogenic callus was selected as the transformation recipient. According to Hiei et al. (Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T, Kumashiro T. Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA [J]. Plant. 1994, 6: 271-82.), through transforming Agrobacterium tumefaciens EHA105 carrying the plant expression vector p1301-NaMnSOD into rice callus tissue, and through a series of screening, transgenic rice was differentiated. details as follows:
[0030] (1) Induction and subculture of rice mature embryo callus: After the mature seeds of Oryza sativa L.cv.Nipponbare were dehulled, they were disinfected with 70% alcohol for 2 minutes, and 20% (V / V) sodium hypochlorite solution (plus 2 ~3 drops of Tween-200) soaked for 30min, washed the seeds wi...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3 Identification of transgenic plants
[0037] Hygromycin screening: After the regenerated seedlings are transplanted into the greenhouse, select new leaves in the same position, take 2-3 cm, and soak them in sterile water containing 50 mg / L hygromycin and 1.0 mg / L 6-BA. After 5 days, the leaves of non-transgenic rice plants turned yellow and brown, the leaves of false positive plants also turned yellow, and the leaves of transformed plants remained green.
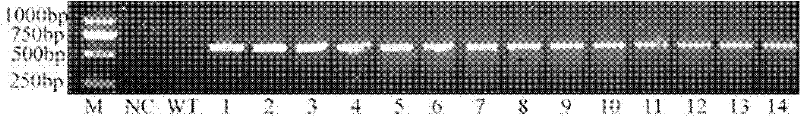
[0038] PCR detection of transgenic rice: the total DNA of rice leaves was extracted by SDS method, amplified with NaSOD specific primers, and all 14 transgenic samples had a band at 621bp (such as figure 2 shown).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com