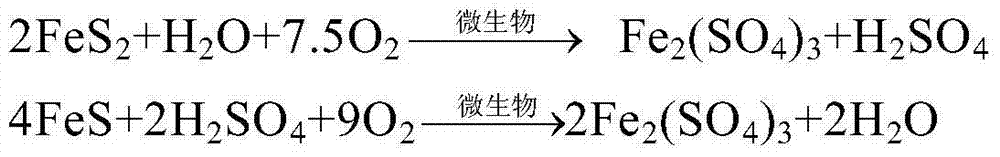
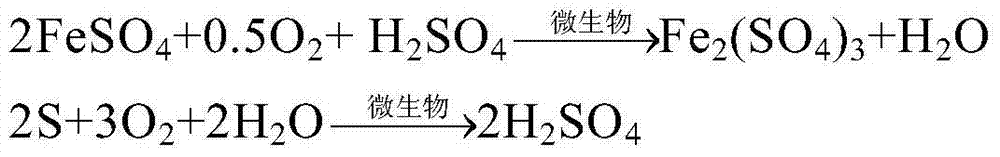
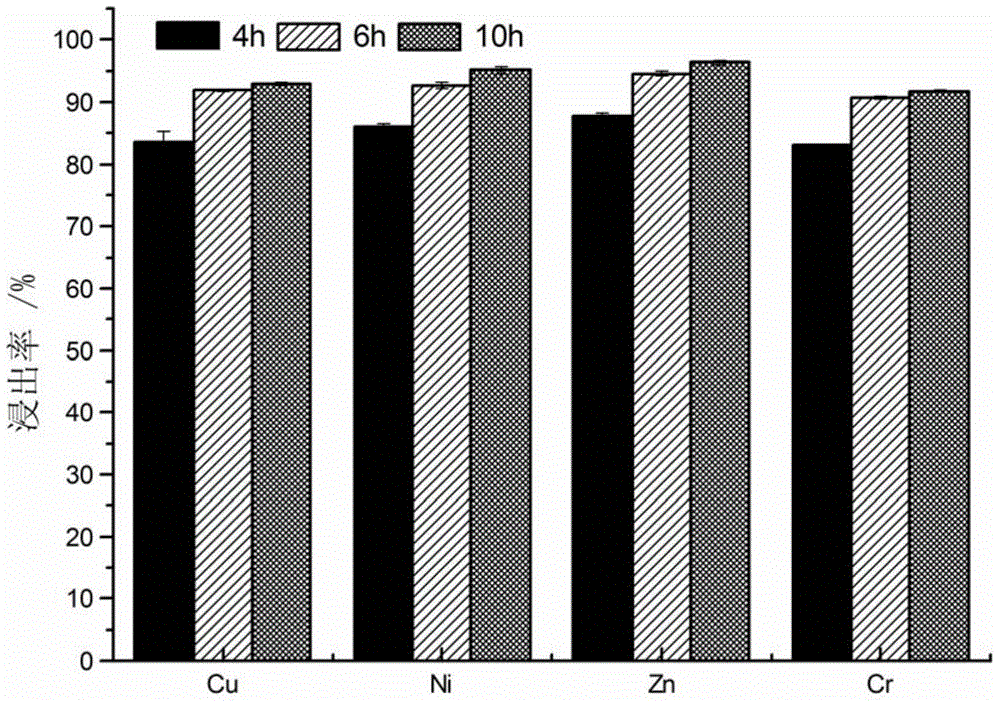
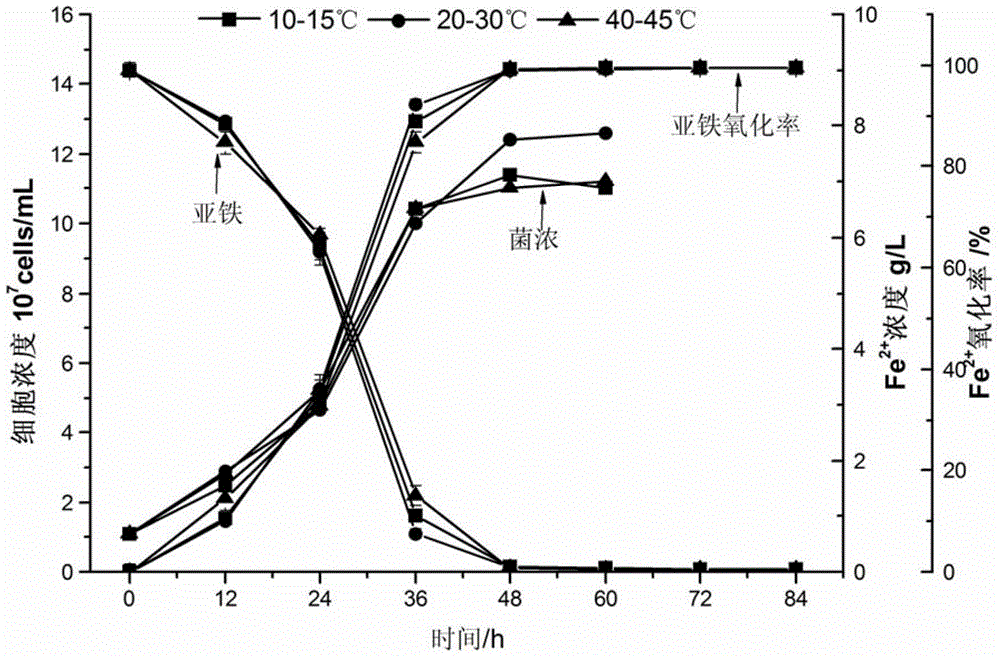
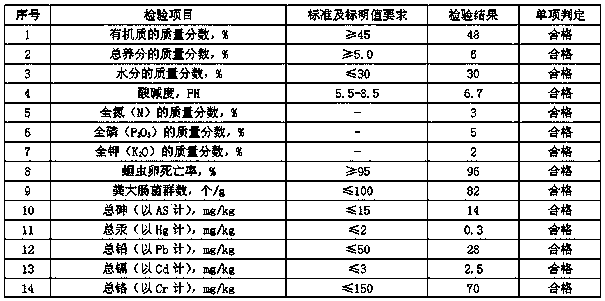
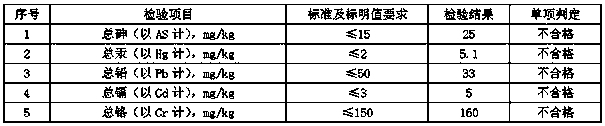
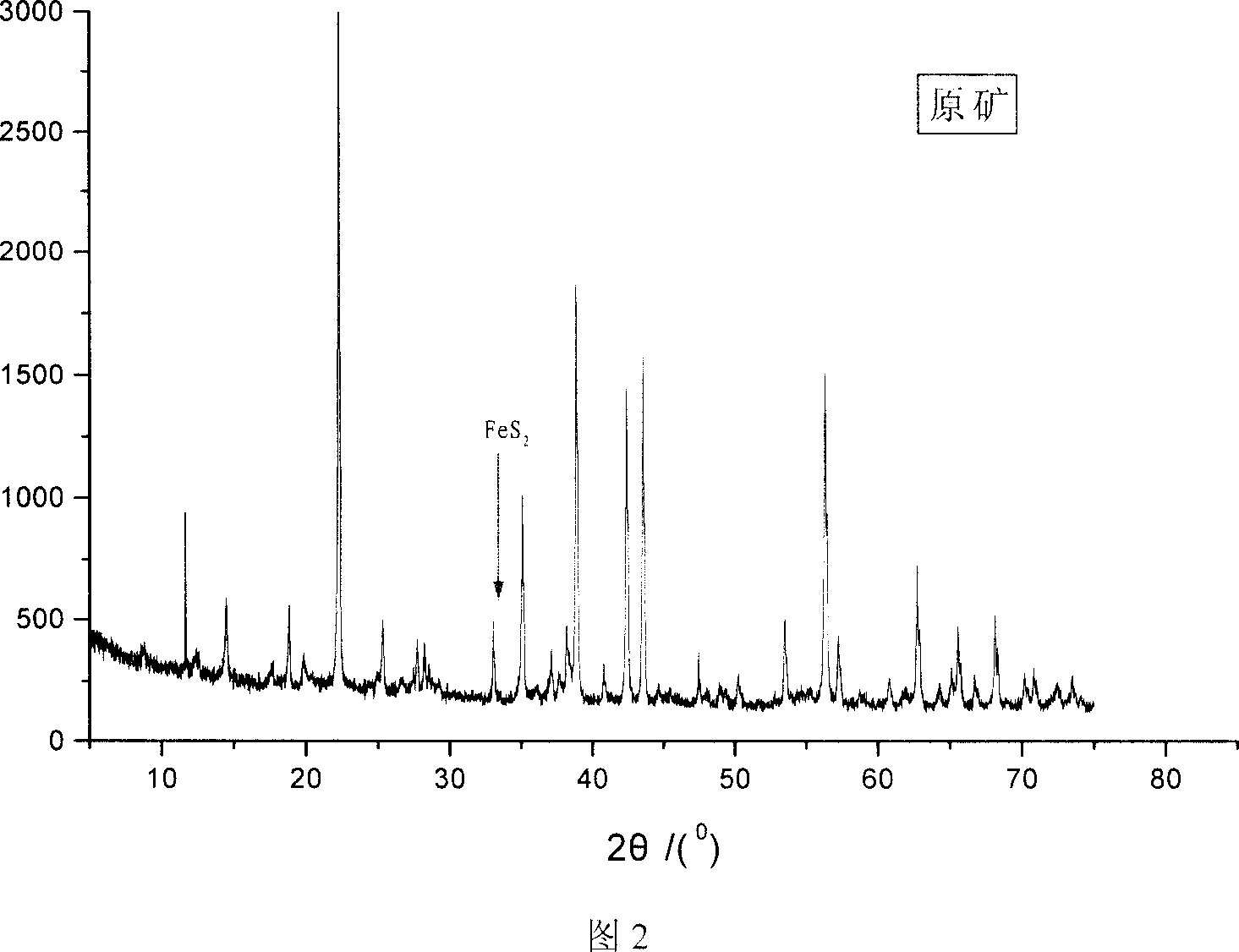
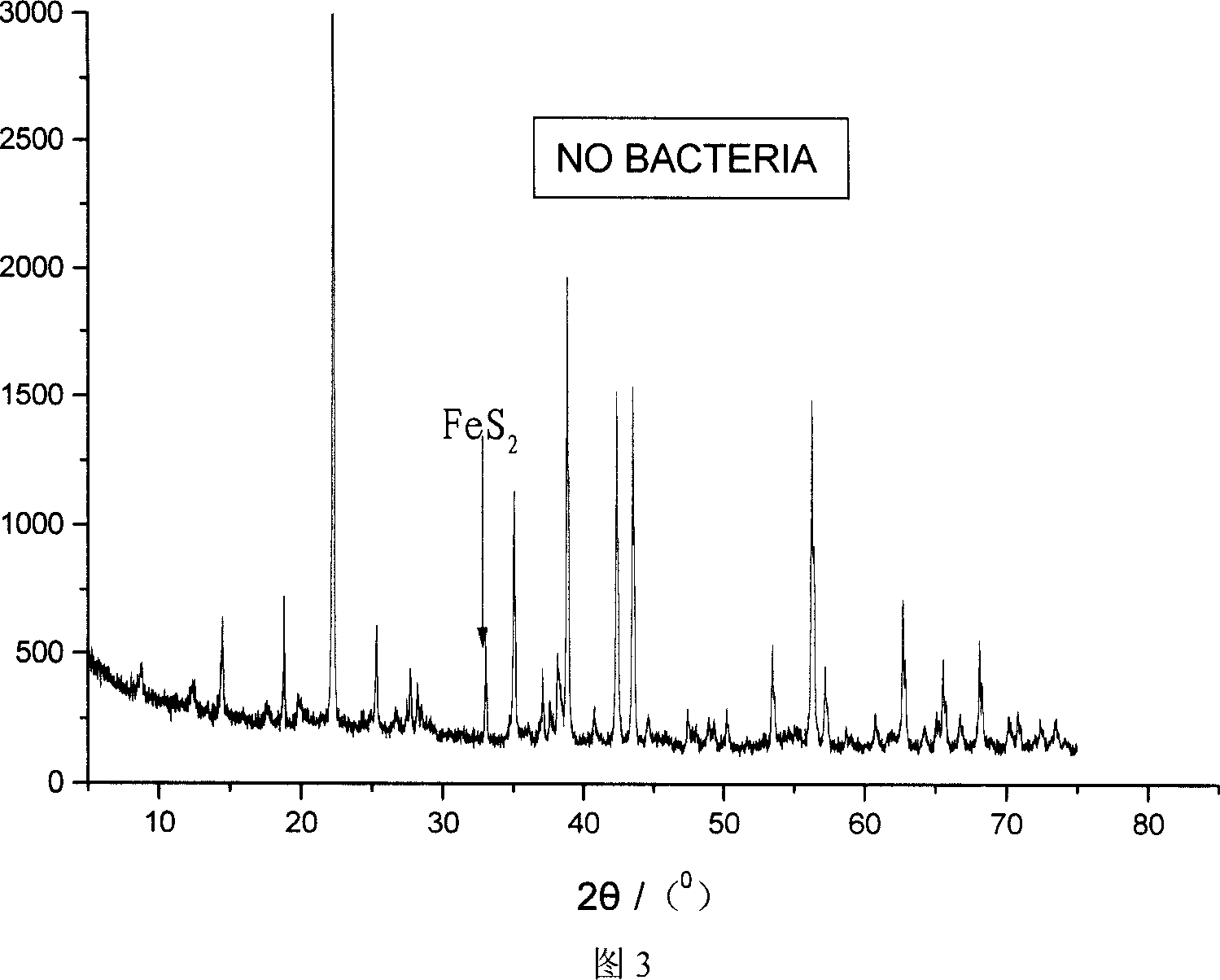
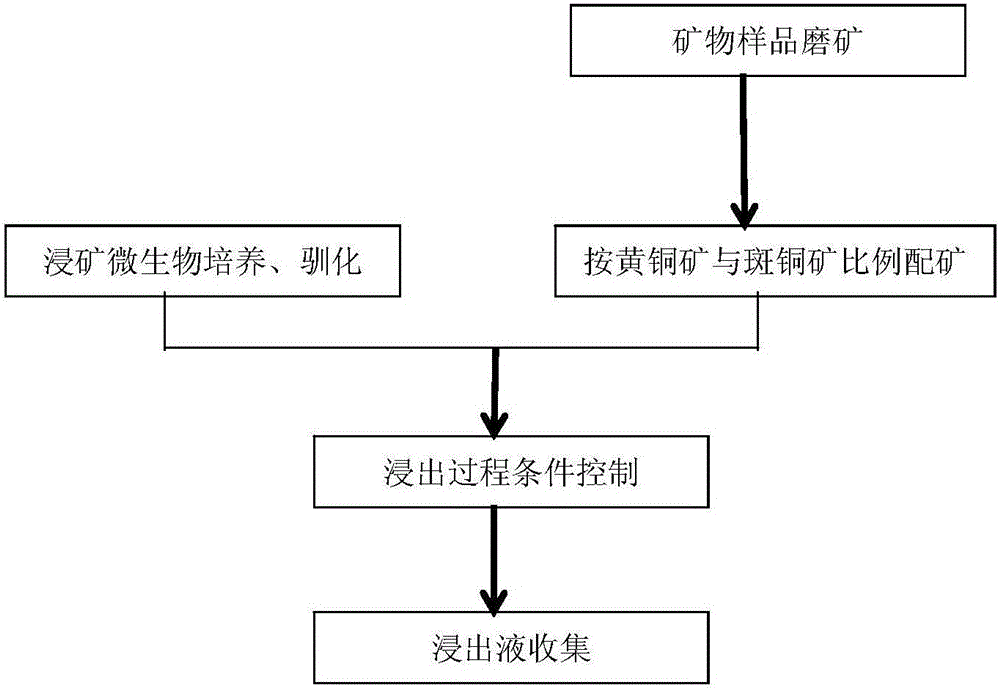
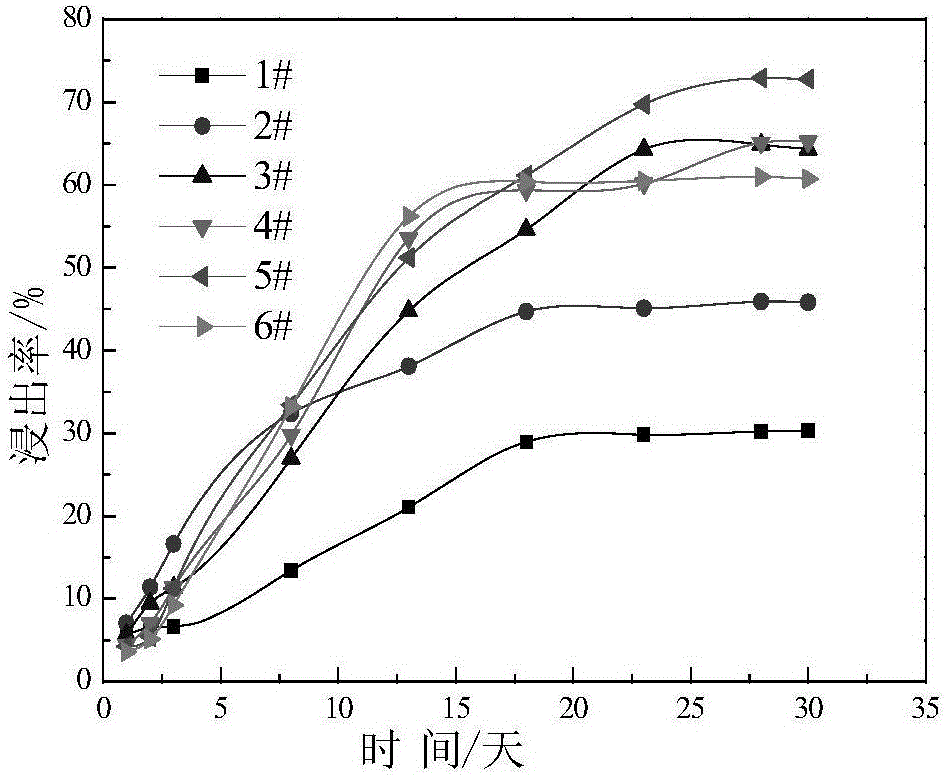
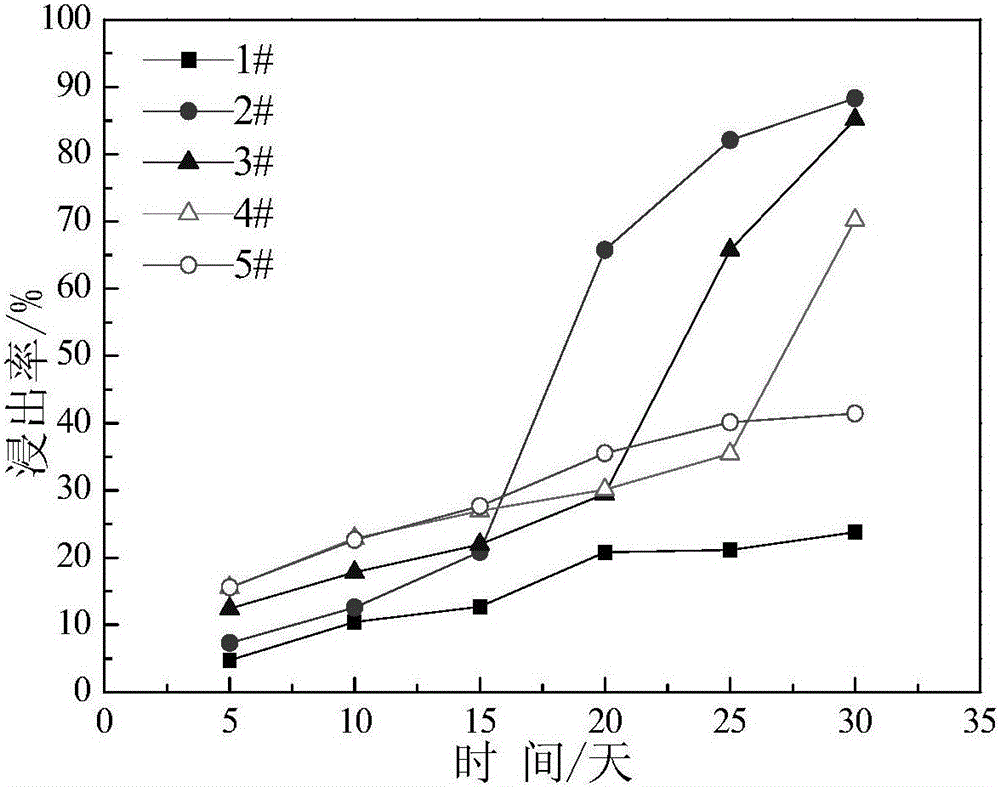
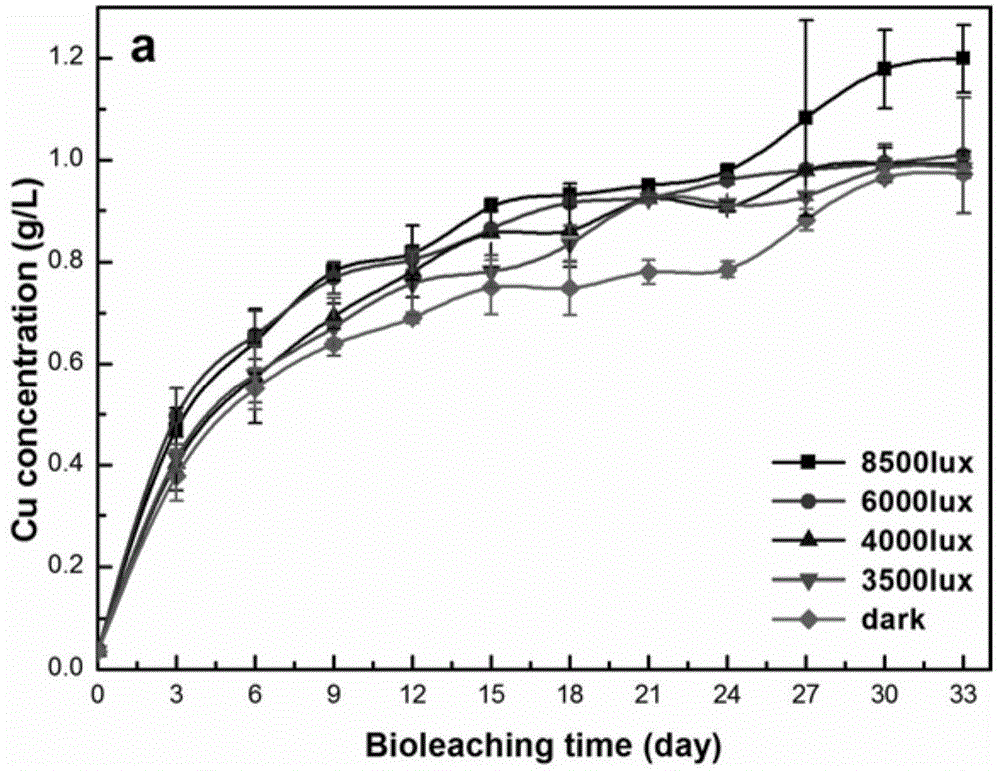
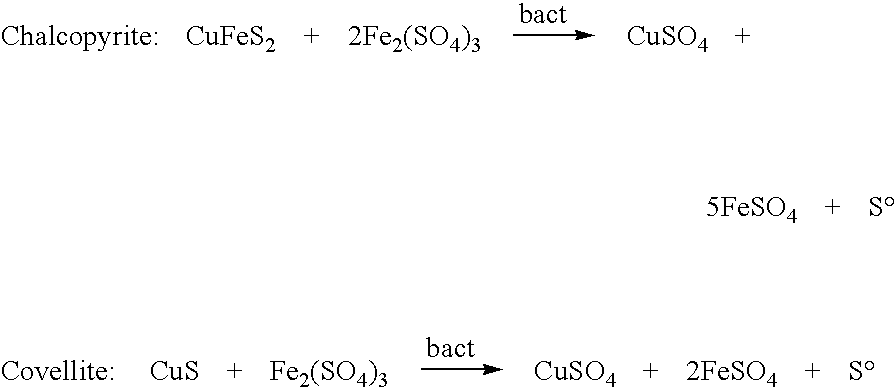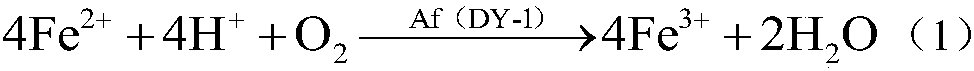Patents
Literature
113 results about "Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for microbiological leaching of uranium-molybdenum ore and enrichment and separation of uranium and molybdenum
The invention discloses a method for microbiological leaching of uranium-molybdenum ore and enrichment and separation of uranium and molybdenum. The method comprises a microbiological leaching method of uranium-molybdenum ore and an enrichment and separation method of uranium and molybdenum in a leachate; in the leaching method, an oxidizing agent for leaching the uranium-molybdenum ore is biological high iron, namely an acidophilous acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans solution containing the biological high iron. The method comprises the following specific steps: firstly crushing the uranium-molybdenum ore so that the crushed materials with the granularity of above 200 meshes account for more than 50% of the total amount and the crushed materials with the granularity of 30 meshes account for not more than 10% of the total amount; then infiltrating the crushed uranium-molybdenum ore in a biological oxidizing agent solution, carrying out solid-liquid separation after infiltrating, and then carrying out ion exchange on the microbiological leachate of the uranium-molybdenum ore by using 201*7 resins, and carrying out iron elution, uranium elution and molybdenum elution. In the method, the uranium leaching rate is above 80%, the molybdenum leaching rate is within the range from 60% to 70% or above, and the molybdenum leaching rate is increased by 20-30%; the uranium, molybdenum and iron in the leachate are eluted by using a PH1.0 solution by virtue of an ion exchange column, and the removal rate of the iron is above 95%, the adsorption rate of the uranium and the molybdenum is not affected, the uranium and the molybdenum adsorbed on the resin are desorbed by using different desorption reagents step by step, and the recovery rate of the uranium and the molybdenum is above 80%.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Efficient desulfurizing bacreria and use method thereof in removal of sulfur in iron ore
InactiveCN104745495ANo pollution in the processLess investmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMixed cultureSulfur
The invention relates to efficient desulfurizing bacreria and use method thereof in removal of sulfur in iron ore, the desulfurizing bacreria is a mixed culture of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, leptospirillum ferriphilum and ferroplasma acidiphilum, the desulfurizing bacreria is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), and the preservation number is CGMCC NO.8337. The method includes the following steps: (1) the sulfurous iron ore is broken and ground into ore powder; (2) the ore powder is prepared into ore pulp by use of water; (3) the ore pulp pH is adjusted to 1.0-3.5, the mixed bacteria liquid of the desulfurizing bacreria is inoculated; and (4) oxidation process temperature is controlled at 10 DEG C to 55 DEG C, and the period is 5-60 days. The efficient desulfurizing bacreria is suitable for the microbial oxidation desulfurization of various kinds of sulfurous iron ores, the investment is little, the production cost is low, and no waste gas and environment pollution are produced.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
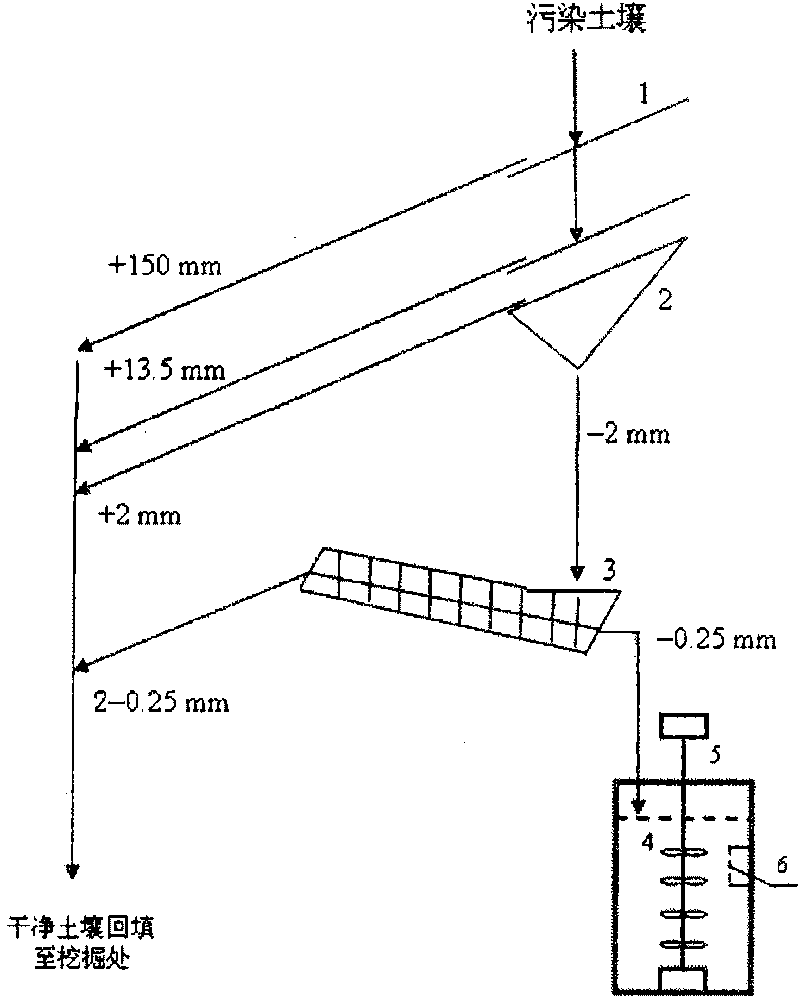
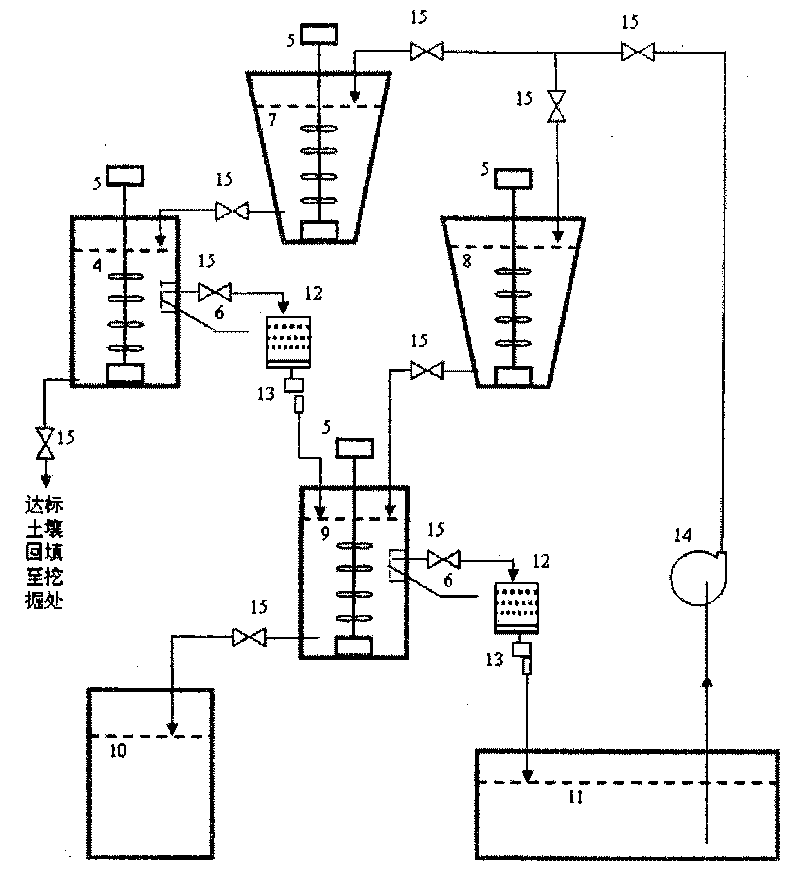
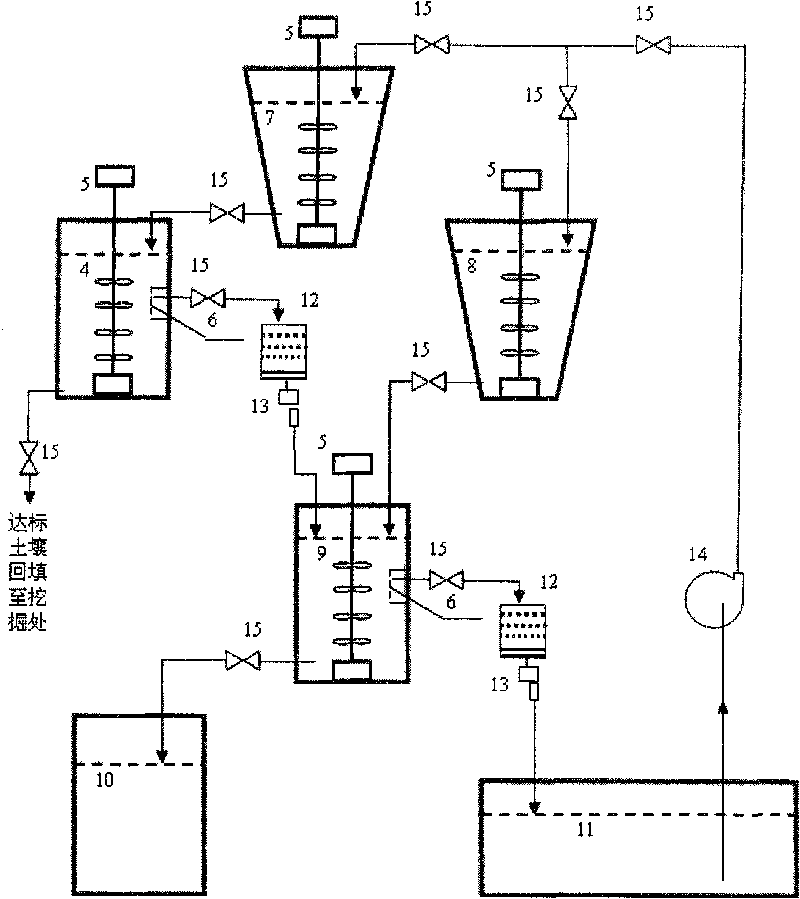
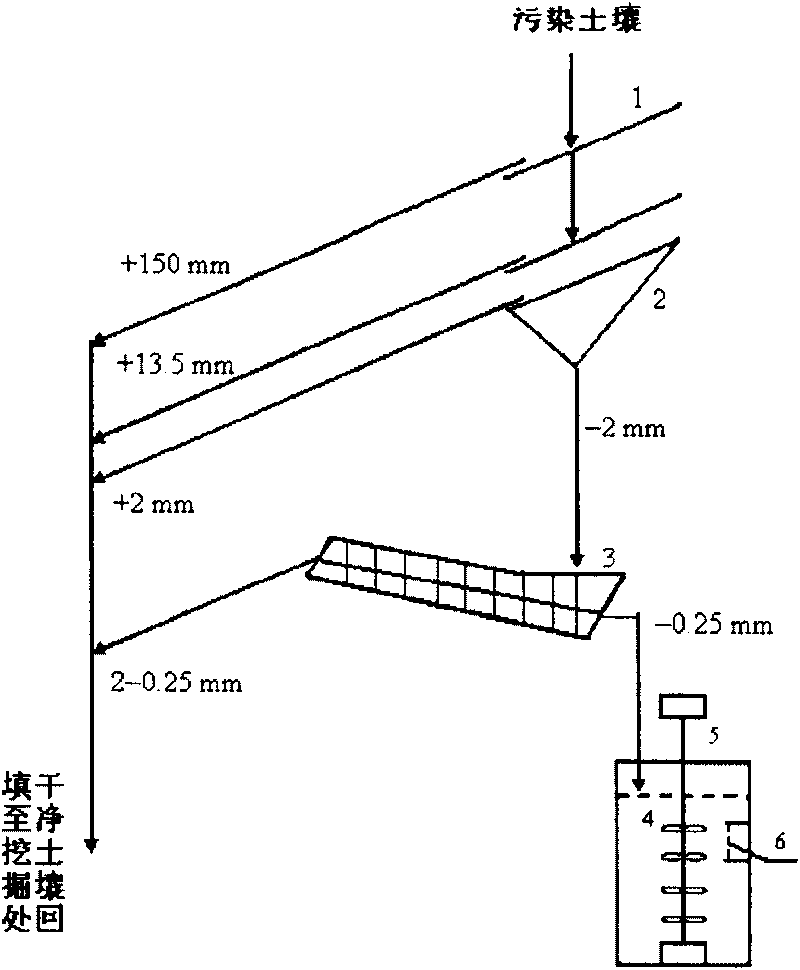
Treatment method of soil contaminated by uranium or cesium
InactiveCN101745528AQuick removalEfficient removalBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationSulfate-reducing bacteriaFiltration
The invention belongs to the technical field of the microorganism, and in particular to a treatment method of soil contaminated by radioactive nuclide uranium or cesium. The invention adopts a bar screen, a double-plate screen and a spiral screen to screen the soil contaminated by uranium or cesium. The soil particles with the particle size more than 0.25mm are clean soil particles, the soil particles with the particle size less than 0.25mm are soil contaminated by uranium or cesium; and the soil particles with the particle size less than 0.25mm are mixed with active acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans for treatment, and the settlement is clean soil after filtration, the filtrate is transferred and mixed with active sulfate reducing bacteria for treatment, then the uranium or cesium is precipitated and can be recovered through filtering separation, and the water can also be recovered. The invention has the advantages of simple operation and low cost, and realizes the rapid and efficient removal of the uranium or cesium in the slightly contaminated soil.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Method for recovering metal copper in waste circuit board
InactiveCN102363890AImprove leaching rateLow copper contentPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementPhosphoric acidRaffinate
The invention discloses a method for recovering metal copper in a waste circuit board. The method is characterized by consisting of the following steps of: preparing bacterial culture solution by taking acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans as a leaching strain and taking ammonium sulfate, potassium chloride, potassium acid phosphate, calcium nitrate and ferrous sulfate as a culture medium; circularly spraying the bacterial culture solution to obtain copper sulfate solution; extracting copper sulfate solution by taking Lix984 as an extracting agent and 260# kerosene as a diluting agent to obtain copper-carrying organic phase and raffinate; reversely extracting the copper-carrying organic phase by taking sulfuric acid aqueous solution as the extracting agent, until Cu<2+> concentration in the sulfuric acid aqueous solution reaches 43-48g / L; electrodepositing the sulfuric acid aqueous solution with Cu<2+> concentration of 43-48g / L and separating copper out at a cathode. The method has the advantages of environmental friendliness, mild reaction, shortened flow and metal copper recovery rate of 99.5 percent, and is suitable for recovering the metal copper in the waste circuit board.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RES INST OF NON FERROUS METALS
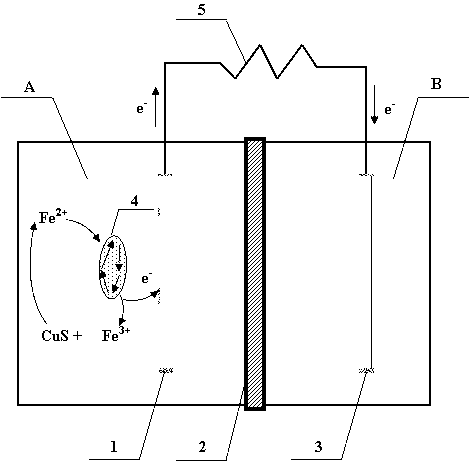
Bio-electrochemical system used for copper sulfide ore leaching
The invention belongs to the bioleaching field and relates to a bio-electrochemical system used for copper sulfide ore leaching. The system utilizes the electron transfer capability of microbes to improve the copper sulfide leaching efficiency, recover elemental sulfur and generate electricity. The system is composed of an anode chamber, a cathode chamber, a cation exchange membrane and an external circuit. Fe<2+> in the anode chamber is oxidized to Fe<3+> under the action of ore leaching bacteria Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, copper sulfide reacts with the oxidation product Fe<3+> to obtain Cu<2+> and elemental sulfur, and Fe<3+> is reduced to Fe<2+> which is reused by the ore leaching bacteria. The transfer of electrons to a cathode from an anode promotes the oxidation of Fe<2+> to Fe<3+> and indirectly promotes the leaching of Cu<2+>. The bio-electrochemical system used in the invention has the advantages of simple technology, easy operation, and low operation cost, and has practical application values.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
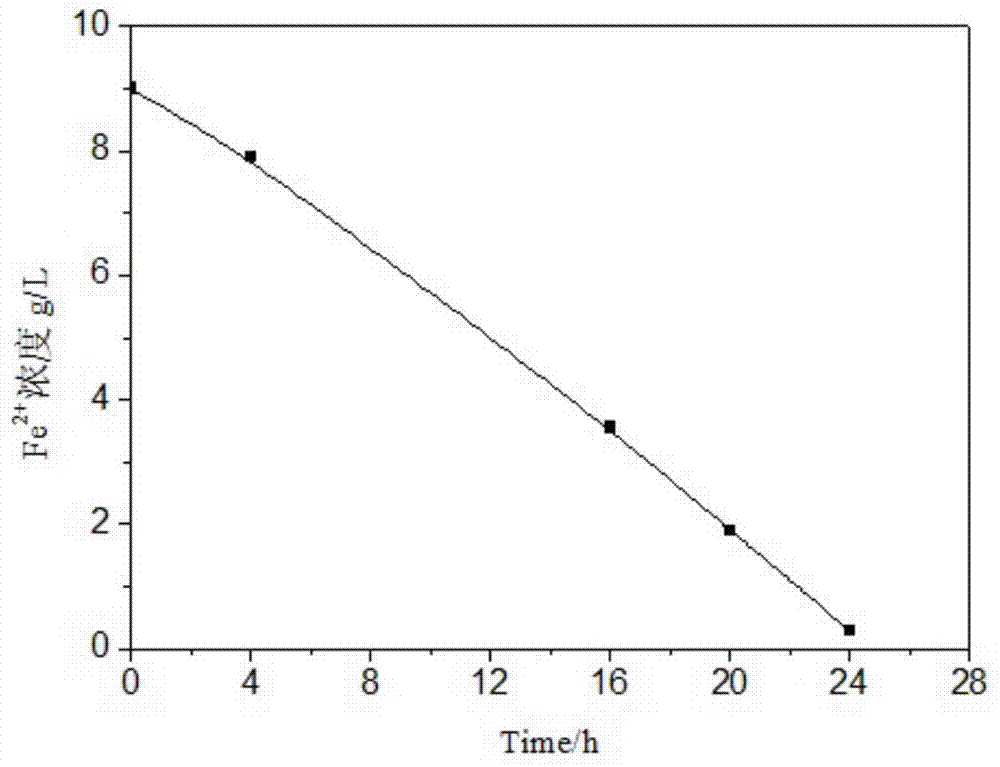
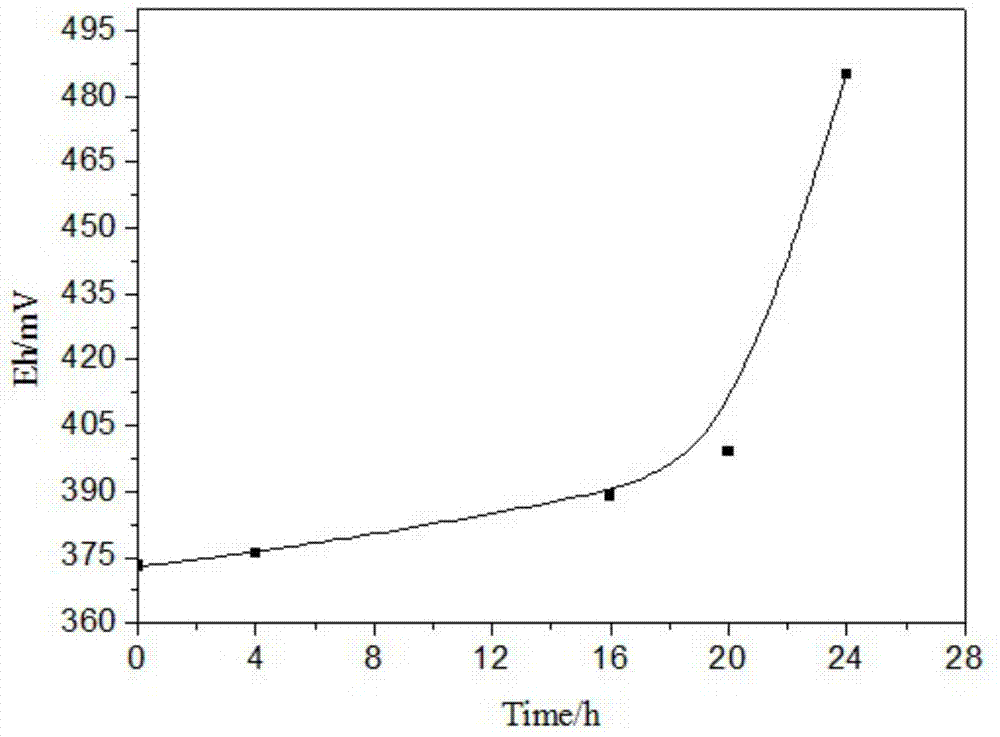
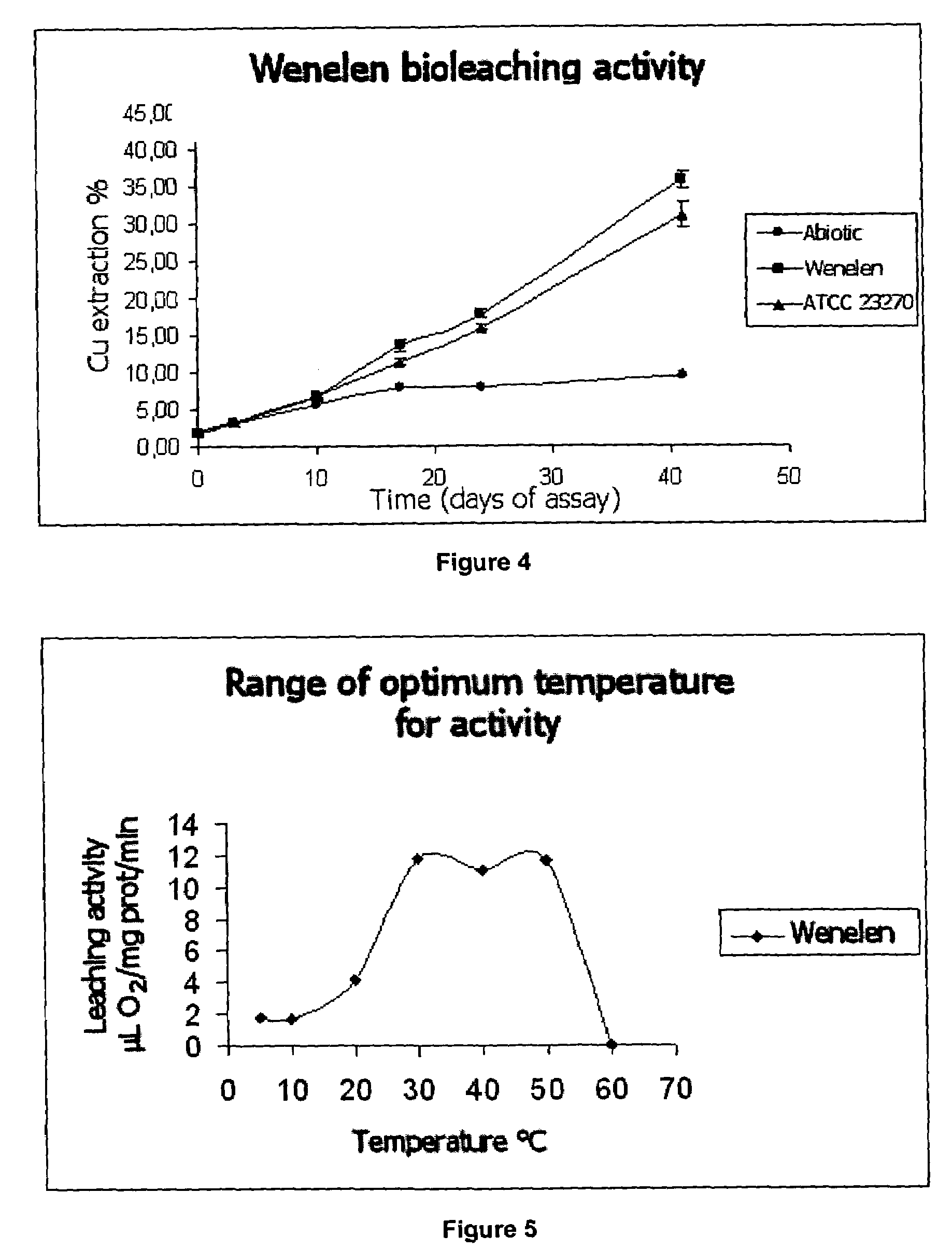
Bacteria strain wenelen DSM 16786, use of said bacteria for leaching of ores or concentrates containing metallic sulfide mineral species and leaching processes based on the use of said bacteria or mixtures that contain said bacteria
The present invention is related to an isolated chemolithotrophic bacterial strain belonging to the specie Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, named “Wenelen” and deposited at the Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH—DSMZ under classification number DSM 16786, the use of said bacteria for leaching ores or concentrates containing of metallic sulfide species and leaching processes based on the use of said bacteria or mixtures that contain said bacteria. This Wenelen DSM 16786 strain has an increased oxidizing activity, especially regarding chalcopyrite, when compared to known bacteria. Due to the former feature, this bacteria strain show great interest for biomining applications and it is presently being subjected to annotation processes after sequencing.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
Bacterial strains capable of being used for preparing acidophilic iron oxidizing microbial compound agent and application thereof
The invention discloses five bacterial strains capable of being used for preparing an acidophilic iron oxidizing microbial compound agent. The bacterial strains comprise ferroplasma acidiphilum CS1, acidithiobacillus ferrivorans CS12, acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans CS9, leptospirillum ferriphilum CS13 and sulfobacillus acidophilus CS5. The five bacterial strains are blended to prepare the acidophilic iron oxidizing microbial compound agent which can be used for extracting heavy metals in comprehensive or quality-divided electroplating sludge. The bacterial strain disclosed by the invention is simple in formula, good in economical efficiency, good in adaptability and efficient in universality, and can be efficiently used for extracting heavy metals in electroplating sludge.
Owner:长沙鑫蓝生物科技有限公司
Treatment process applicable to industrial wastewater and application of industrial wastewater in preparation of bacterial manure
InactiveCN104086001ASimple processEasy to handleBiological water/sewage treatmentFertilizer mixturesBacillus megateriumBacillus cereus
The invention belongs to the field of wastewater treatment and discloses a treatment process applicable to industrial wastewater. The treatment process applicable to the industrial wastewater comprises the following steps: 1) preparing complex microbial inoculant; 2) precipitating wastewater; 3) purifying the wastewater; 4) preparing bacterial manure. The prepared complex microbial inoculant comprises 5-6 parts of micrococcus luteus, 4-5 parts of bacillus mucilaginosus, 3-4 parts of paracoccus denitrificans, 2-3 parts of rhodococcus, 2-3 parts of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, 1-2 parts of bacillus megaterium and 1-2 parts of bacillus cereus. The invention also discloses bacterial manure prepared by utilizing the treatment process applicable to the industrial wastewater. The treatment process applicable to the industrial wastewater is simple and feasible, the industrial wastewater can be effectively treated, and the bacterial manure is prepared by utilizing the treatment process applicable to the industrial wastewater.
Owner:东莞市统泉环保科技有限公司
Method for treating radioactive cesium-137 polluted soil
InactiveCN101745530AReduce dependenceResidue reductionBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationEcological environmentSludge
The invention relates to a method for treating radioactive cesium micro-polluted soil. The method comprises the following steps: screening out coarse soil particles from the radioactive cesium micro-polluted soil by adopting a bar screen, a double-plate screen and a spiral screen, and then mixing the volume-reduced radioactive cesium micro-polluted soil and active bacteria liquid of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans in a microbial dissolution promoting reactor to promote the dissolution of the radioactive cesium in the micro-polluted soil to a liquid phase; transferring the radioactive cesium containing solution to a microbial adsorption precipitation reactor, and further precipitating the radioactive cesium transferred to the liquid phase by adjusting the pH value and using active bacteria liquid of sulfate reducing bacteria; filtering the treated soil suspension and recycling the water; and reducing the volume of the sludge adsorbing the radioactive cesium. The method has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, economy, feasibility, high safety, no secondary pollution to the ecological environment, and capacity of efficiently and quickly removing the radioactive cesium from the micro-polluted soil.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Acidithiobacillus and application thereof
ActiveCN102174425AStrong molybdenum resistancePromote growthBacteriaProcess efficiency improvementSulfideAcidithiobacillus
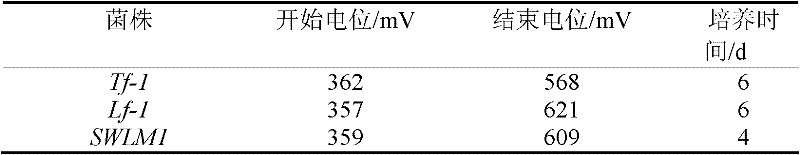
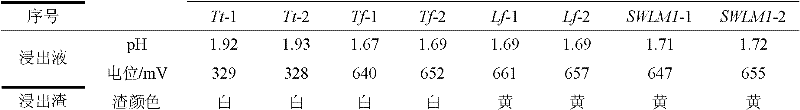
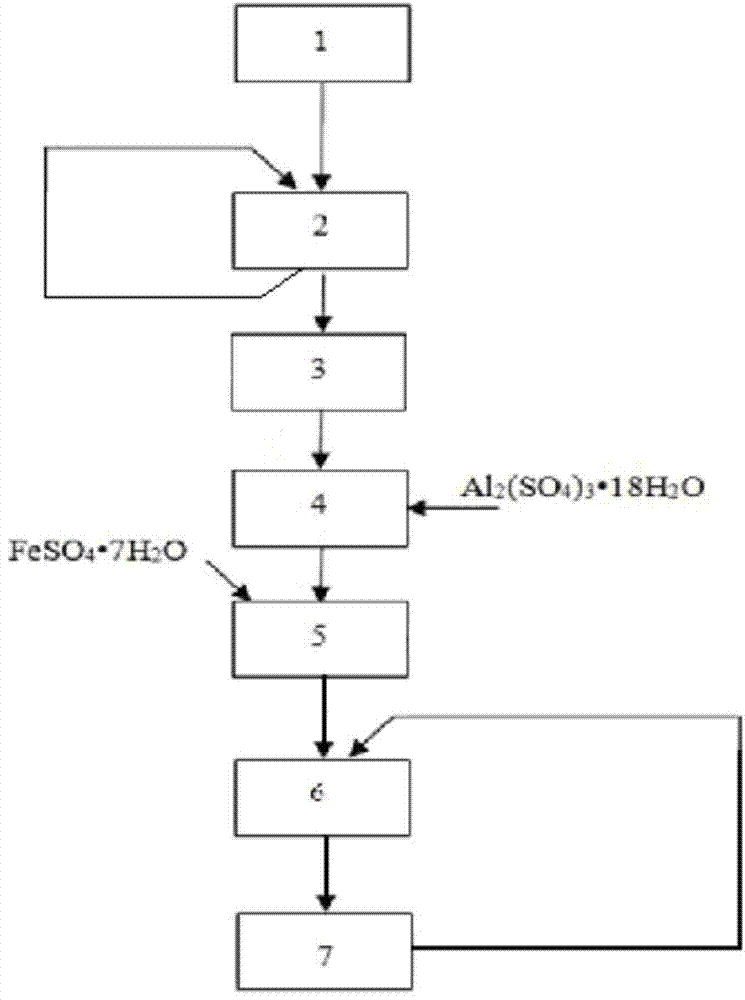
The invention relates to an acidithiobacillus and application thereof. The preserving number of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans SWLM1 of the acidithiobacillus is CGMCC No.3265. The invention also provides the application of the acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans in metallurgy, particularly the acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is applied to the leaching of molybdenum ore containing Fe2<+> or sulfides. In the invention, the acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is added into the molybdenum ore pulp containing the Fe2<+>, the leaching temperature is between 28 DEG C and 32 DEG C, the leaching pH is between 1 and 3, and the Fe2<+> is oxidized into Fe3<+>; the acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is also added into the molybdenum ore pulp containing Fe2<+> and sulfides, the leaching temperature is between 28 DEG C and 32 DEG C, the leaching pH is between 1 and 3, and the Fe2<+> and the sulfides are oxidized into Fe3<+> and sulfuric acid or sulfate respectively. The acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans provided by the invention has a stronger molybdenum resisting characteristic, can also grow well when the content of the molybdenum is 1.6 g / L, and can be widely applied to the leaching of molybdenum-bearing minerals.
Owner:BEIJING RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING AND METALLURGY
Fluoride-resistant ore leaching bacterium and application thereof in efficient leaching process of high-fluoride uranium ore
ActiveCN104745498AStrong fluorine resistanceAchieve protectionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh fluorideUranium ore
The invention relates to a fluoride-resistant ore leaching bacterium and application thereof in an efficient leaching process of high-fluoride uranium ore. The fluoride-resistant acidophilus Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is collected at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC for short) on July 1, 2013 and has a collection number of CGMCC NO.7836. The strain can grow in a fluorine-containing solution under an acidic condition, has fluorine resistance of 3.0g / L or above and also has a relatively good capability of oxidizing Fe<2+> into Fe<3+>. When the fluoride-resistant strain (CGMCC NO.7836) is applied to simulated biological dump leaching process of fluorine-containing uranium ore, 55-day uranium leaching rate is improved by 3.70% as compared with that in an acid leaching method; the uranium leaching rate is improved obviously and production cost is reduced; moreover, since adsorption tail liquid during uranium leaching can be recycled, environment pollution can be reduced. Therefore, the strain can be widely applied to biological leaching.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Bacteria strain wenelen DSM 16786, use of said bacteria for leaching of ores or concentrates containing metallic sulfide mineral species and leaching processes based on the use of said bacteria or mixtures that contain said bacteria
The present invention is related to an isolated chemolithotrophic bacterial strain belonging to the specie Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, named “Wenelen” and deposited at the Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH—DSMZ under classification number DSM 16786, the use of said bacteria for leaching ores or concentrates containing of metallic sulfide species and leaching processes based on the use of said bacteria or mixtures that contain said bacteria. This Wenelen DSM 16786 strain has an increased oxidizing activity, especially regarding chalcopyrite, when compared to known bacteria. Due to the former feature, this bacteria strain show great interest for biomining applications and it is presently being subjected to annotation processes after sequencing.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
Method for producing composite microorganism phosphate using low grade ground phosphate rock
InactiveCN101328089AIncrease profitIncrease available phosphorus contentFungiOrganic fertilisersMicroorganismPyrite
The invention relates to a method for producing a compound microorganism phosphate fertilizer using a low grade rock phosphate powder which comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a first bacteria solution of candidakrissii and a first bacteria solution of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans; 2) preparing a secondary bacteria solution of candidakrissii and a secondary bacteria solution of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans; 3) preparing the compound microorganism phosphate fertilizer accoring to the following weight percentage: (1) rice, wheat or corn stalk 20-30%, (2) ammonium sulphate 5-10%, (3) pyrite powder(200-300 mesh) 10-20%, (4) lowgrade phosphate rock(200-300 mesh) 10-20%, (5) the secondary bacteria solution of candidakrissii 15-20%, (6) the secondary bacteria solution of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans 15-20%. The method has advantage of low cost and can improve the phosphate fertilizer utilization efficiency.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
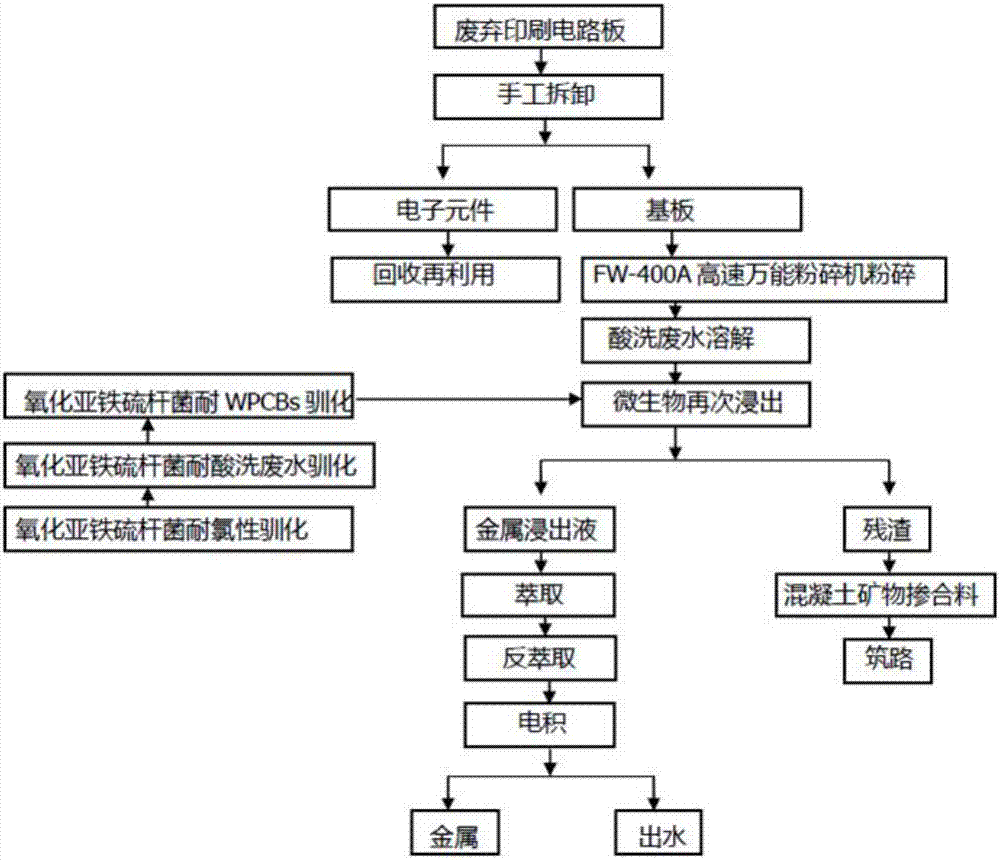
Recycling method of waste printed circuit board
InactiveCN106947866AAvoid recontaminationSolve the problem of high iron content that is difficult to removePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementWastewaterCopper
The invention discloses a recycling method of a waste printed circuit board. Chemical-biological joint leaching is used for lixiviating metal in the waste printed circuit board by using strong acidity and high ferroic of pickling waste water. The recycling method includes the steps of conducting chemical leaching by using the pickling waste water to lixiviate Pb, Zn, Al, Fe, Sn and the like metal completely till the leaching rate of Cu reaches to 30% and over, and adding domesticated acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans to conduct microbial leaching till the leaching rate of Cu reaches to 90% and over. By adoption of the recycling method, the waste printed circuit board and the pickling waste water can be utilized comprehensively, the principle of using waste to eliminate waste is fully carried out, maximal resource recycling and treatment of the two wastes are achieved, not only the heavy metal in the waste printed circuit board is leached completely, but also the effective treatment of the pickling waste water is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Acidophilic iron-oxidizing composite microbial agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104862250AAchieve leachingAchieve recyclingBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSludgeMicrobial agent
The invention discloses an acidophilic iron-oxidizing composite microbial agent which comprises the following communities: a ferroplasma acidiphilum-containing strain, an acidithiobacillus ferrivorans-containing strain, an acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans-containing strain, a leptospirillum ferriphilum-containing strain and a sulfobacillus acidophilus-containing strain, wherein a preparation method of the composite microbial agent comprises the following steps: the aforementioned five strains are placed in a specific basic iron salt / nutrient-containing culture medium, and are subjected to the temperature gradient compounding culture, tolerance mixed-heavy-metal gradient pressure type domestication, temperature cycling gradient type domestication, ferrous oxidation activity improvement and tolerance high-iron domestication, so as to obtain the acidophilic iron-oxidizing composite microbial agent. According to the invention, the acidophilic iron-oxidizing composite microbial agent is simple in formulation, economical, adaptable, versatile and efficient, and can be used for the efficient extraction of heavy metals in electroplating sludge.
Owner:HUNAN AIGE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Preparation and method for treating high-arsenic and high-sulfur gold ore
ActiveCN103014336APromote symbiosisEfficient decompositionProcess efficiency improvementPollutionGold leaching
Owner:SHANDONG GOLD GUILAIZHUANG MINING CO LTD
Microorganism chelating agent for producing bio-organic fertilizer by removing organic solid waste heavy metal
InactiveCN103864483AHigh removal rateSolve the problem of excessive heavy metal ion contentBio-organic fraction processingWater/sewage treatmentRapeseedAspergillus niger
The invention discloses a microorganism chelating agent for producing bio-organic fertilizer by removing organic solid waste heavy metal, wherein the microorganism chelating agent comprises a culture medium and a fermenting chelating bacteria in weight ratio of 1:9, the culture medium comprises the following materials in parts by weight: 60 parts of turf, 10 parts of activated carbon, 10 parts of sugar mud, 5 parts of rapeseed meal and 5 parts of wheat bran; the fermenting chelating bacteria comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 0.5 part of aspergillus niger, 0.5 part of white-rot fungi, 1 part of cyanobacteria, 1.5 part of candida pseudotropical, 1.5 part of lactic acid bacteria, 0.5 part of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, 0.5 part of streptomycete, 1.5 part of cellulose, 1.5 part of glucoamylase and 1 part of non-ionic surfactant. The microorganism chelating agent is capable of removing the heavy metal ion in the organic solid waste so as to sufficiently utilize the organic waste resource, the waste is avoided, the pollution is prevented, and the environment friendliness is achieved.
Owner:广东利大德环保科技有限公司
Method of bacterial eliminating sulfur in high sulfur bauxite
ActiveCN1924042APhysical and chemical properties have no effectBacteriaProcess efficiency improvementSulfurMaceral
The invention discloses a desulfurizing method in the high-sulfur alumina ore through alumina bacteria, which comprises the following steps: adopting Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans to immerse high-sulfur alumina ore; breaking alumina ore; grinding; adopting water culture medium to immerse ore with density at 5-30%; setting the immersing temperature at 25-35 deg.c and rotary speed of shaker at 150-250r / min; making the bulk density of vaccination quantity of enriched bacterial liquid at 5%-10%; leaching for 10-20d; extracting leached ore; washing; desulfurizing.
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND
Method for leaching vanadium out of vanadium-bearing shale through acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans
The invention relates to a method for leaching vanadium out of vanadium-bearing shale through acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the sequential steps of pretreatment of the vanadium-bearing shale; preparation of a domestication culture medium; preparation of a mineral leaching culture medium; strain domestication; and microbiological leaching ofthe vanadium. By means of the method, the ferrous adding amount in a 9K culture medium is reduced, and powdered sulfur is supplemented as an energy substance for bacteria; the acid production capacity of the acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is increased, and meanwhile, iron hydrolytic precipitation occurring in the leaching process is reduced; the adverse effect of iron precipitation on the vanadium leaching process is reduced, and thus the leaching rate of the vanadium is increased; the concentration of iron ions in leachate is reduced; and subsequent vanadium purification and enrichment can be conducted conveniently.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for strengthening biological leaching of chalcopyrite and bornite
The invention provides a method for strengthening biological leaching of chalcopyrite and bornite. One or more of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, acidithiobacillus caldus and leptospirillum ferriphilum are used as mineral leaching microorganisms. The ratio of the chalcopyrite to the bornite is controlled to be 5:1-1:5. In the leaching process, the stirring speed is controlled to be 100-600 rpm. The pH value of a solution is controlled to be 1.5-2.5, the electric potential of the solution is 350-480 mV (Ag / AgCl is a reference electrode), the chalcopyrite and the bornite can be leached in a cooperative mode, and the Cu leaching rate is obviously increased. According to the method, through reasonable ore blending of the chalcopyrite and the bornite, proper leaching technological conditions are controlled, and the biological leaching efficiency of the chalcopyrite and the bornite is improved. The method is efficient, simple and easy to operate.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Decarbonizing and desulphurizing bacterium agent for difficultly-selected gold ore and application thereof
ActiveCN103205381APromote symbiosisEfficient decompositionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAlicyclobacillusMicrobiology
The invention belongs to the field of metallurgical technology, and relates to a decarbonizing and desulphurizing bacterium agent for a difficultly-selected gold ore. The bacterium agent is formed by mixing alicyclobacillus, acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, pseudomonas aeruginosa, bacillus subtilis, bacillus megatherium and burkholderia bacteria. The invention further discloses the method for treating the difficultly-selected gold ore by utilizing the decarbonizing and desulphurizing bacterium agent. The bacterium agent provided by the invention can be used for treating the high-carbon high-sulfur gold ore containing the sulfur content above 15% and the carbon content above 8%, and greatly lowering the quantity of sodium cyanide required for extracting the gold in a cyaniding manner. As a result, the industrial cost is lowered.
Owner:SHANDONG GOLD GUILAIZHUANG MINING CO LTD
Method for removing arsenic in soil by combining microorganisms with electric repairing
ActiveCN104741367AGreen and efficient removalImprove mobilityContaminated soil reclamationElectrokinetic remediationArsenic pollution
The invention provides a method for removing arsenic in soil by combining microorganisms with electric repairing. The method comprises the following steps: in a process for pollution governance on arsenic in soil by adopting an electric repairing method, introducing the microorganisms (acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans) into soil which is being repaired; and adding a mixed liquid of HNO3 and microorganisms at an anode, and adding HNO3 at a cathode, so that, due to the action of microorganisms and arsenic and synergistic action of electrostatic force in the electric repairing process, the arsenic which is difficult to remove independently by an electric repairing method in soil is effectively removed. The method has the advantages that by virtue of the action of the microorganisms and the arsenic in soil, the arsenic is changed into an ionic state, and is removed from the soil by the electric repairing method, coordination of two effects is realized; the target of effectively removing arsenic pollution in the soil is reached; the method is simple to operate and low in price; and new pollution is not generated in the implementation process.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Strain of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and its application in environmental treatment
ActiveCN108018250AStrong metal resistanceChange in surface activityBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismMetal adsorption
The invention discloses a strain of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and its application in environmental treatment. The Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans DY-1 and has a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2017806. Through good biological oxidation, bio-acidic effect, strong metal tolerance and metal adsorption capacity, the Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans DY-1 can produce significant effects in decoloration and deodorization of black and odor water and ecological restoration of sediments and does not damage the existing water system. The Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans DY-1 can be used as a vanguard for the treatment on severely polluted water and lay a good water quality and ecological micro-environment foundation for water quality improvement and water ecological balance of the later treatment methods using other microorganisms and aquatic plants.
Owner:武汉新禹智水环保科技有限公司
Refractory gold ore desulfurizing and dearsenifying method
ActiveCN103031434APromote symbiosisEfficient decompositionProcess efficiency improvementBacillus subtilisGold ore
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgy and relates to a refractory gold ore desulfurizing and dearsenifying method. A preparation used by the refractory gold ore desulfurizing and dearsenifying method is prepared from 30% of burkholderia, 20% of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, 20% of sulfolobus solfataricus, 20% of bacillus subtilis and 10% of pseudomonas aeruginosa. The microbial preparation used by the refractory gold ore desulfurizing and dearsenifying method is reasonable in compatibility and synergistic, so that a relatively good desulfurizing and dearsenifying effect can be achieved; the gold leaching rate is also greatly improved; and the microbial preparation can be recycled and is environment-friendly and pollution-free.
Owner:SHANDONG GOLD GUILAIZHUANG MINING CO LTD
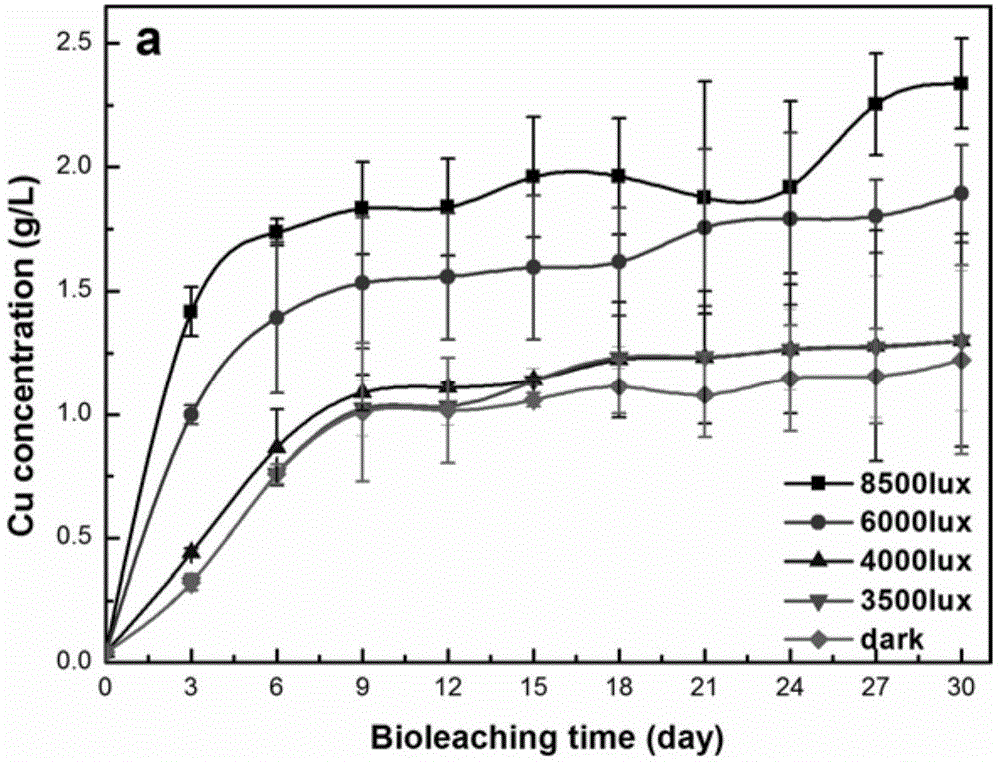
Light-intensified bioleaching method for semiconductor minerals
ActiveCN104561544AImprove bioleaching rateConditions are easy to controlProcess efficiency improvementPyriteBottle
The invention discloses a light-intensified bioleaching method for semiconductor minerals. Under the conditions of illumination and darkness of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, respectively shaking a bottle; aerating; piling; and making a column and leaching out copper pyrites. Under the illumination condition, the leaching efficiencies of copper pyrites of these modes are higher than that under a dark condition, and particularly the shake-flask culture effect under the illumination condition is remarkable. The method has important significance in improving level of comprehensive utilization of minerals (copper pyrites) of semiconductor property and applying the semiconductor minerals as an optical catalyst in mineral leaching industry.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Microbial agent capable of efficiently biologically converting form of cadmium in polluted soil
The invention discloses a microbial agent capable of efficiently biologically converting a form of cadmium in polluted soil. The microbial agent can be utilized for efficiently converting cadmium difficult to utilize in the polluted soil into soluble cadmium and mainly contains the following components in percentage by weight: 25%-35% of Candida utilis 15%-20% of Sporotrichum sp., 15%-20% of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, 15%-20% of Sulfobacillus acidophilus and 5%-15% of Shewanella oneidensis. By processing the soil by virtue of the microbial agent, the removal rate of cadmium is 82%-95%. Compared with an existing cadmium polluted soil converting and restoring technique, the microbial agent is capable of efficiently converting the form of cadmium, short in cycle, low in cost and easy to generalize.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Preparation method of acidithiobacillus ferrooxidian genetic engineering strain with quick growth speed and strong uranium and heat resistance capacities as well as application thereof
InactiveCN101659962AMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionAcidithiobacillusGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a preparation method of an acidithiobacillus ferrooxidian genetic engineering strain with quick growth speed and strong uranium and heat resistance capacities as well as the application thereof, wherein the strain is Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans QEY-6(pJRD215-PT-rcs), CCTCCM 209156; and the preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, augmenting a T5 promoter and a T0 terminator of pQE30, and establishing a shuttle expression vector pJRD215-PT together with pJRD 215; secondly, augmenting and cloning a micrococcus luteus rpf gene, a caulobacter crescentuscc3302 gene and a sulfolobus shibatae ss10b gene to a T vector; thirdly, establishing a recombined shuttle expression vector pJRD215-PT-rcs; and fourthly, establishing the acidithiobacillus ferrooxidian genetic engineering strain which fusedly expresses rpf, cc3302 and ssh10b genes. The invention has simple operation and good repeatability, and can shorten the uranium leaching period, improve theleaching rate and reduce the acid-consuming rate.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans genetic engineering bacteria and use thereof
InactiveCN101935621AImproved ability to oxidize ferrous ionsBacteriaDispersed particle separationThiobacillus ferrooxidansSludge
The invention discloses Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans genetic engineering bacteria, which are A. ferrooxidans pTCYC1 with high ferrous oxidization activity, and are characterized in that: the bacteria are named Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, and the strain was collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with a collection number of CGMCC No.3549 on December 28th, 2009. The genetic engineering bacteria of the invention have higher ferrous oxidization activity and more stable performance than wild thiobacillus ferrooxidans and have a promising application prospect in fields of biological leaching, smoke desulfuration, acid mine water processing, sludge heavy metal removal and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Recovery method for waste circuit board
InactiveCN102218437AComponent greenComponent economySolid waste disposalPlastic recyclingRecovery methodKerosene
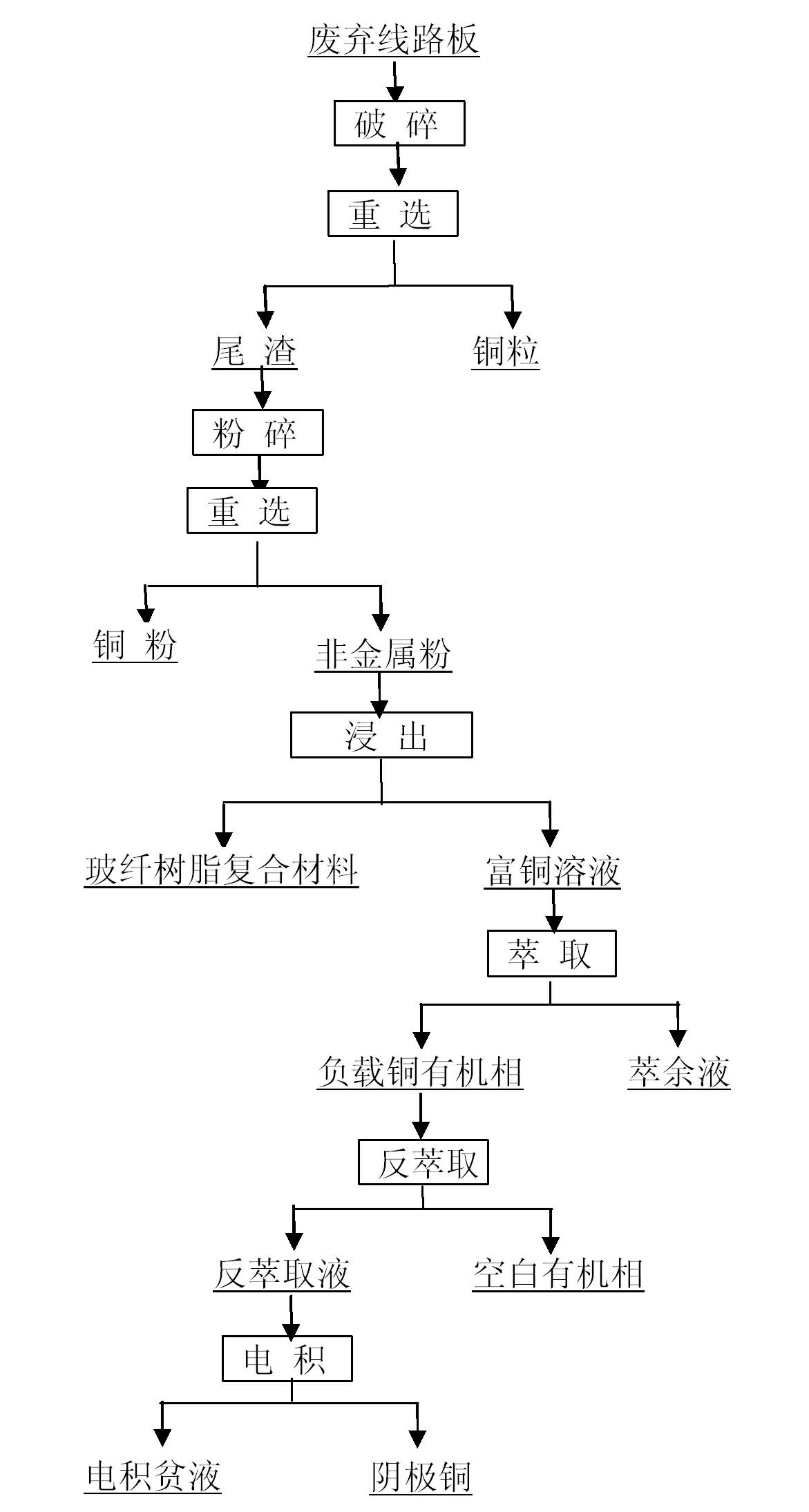
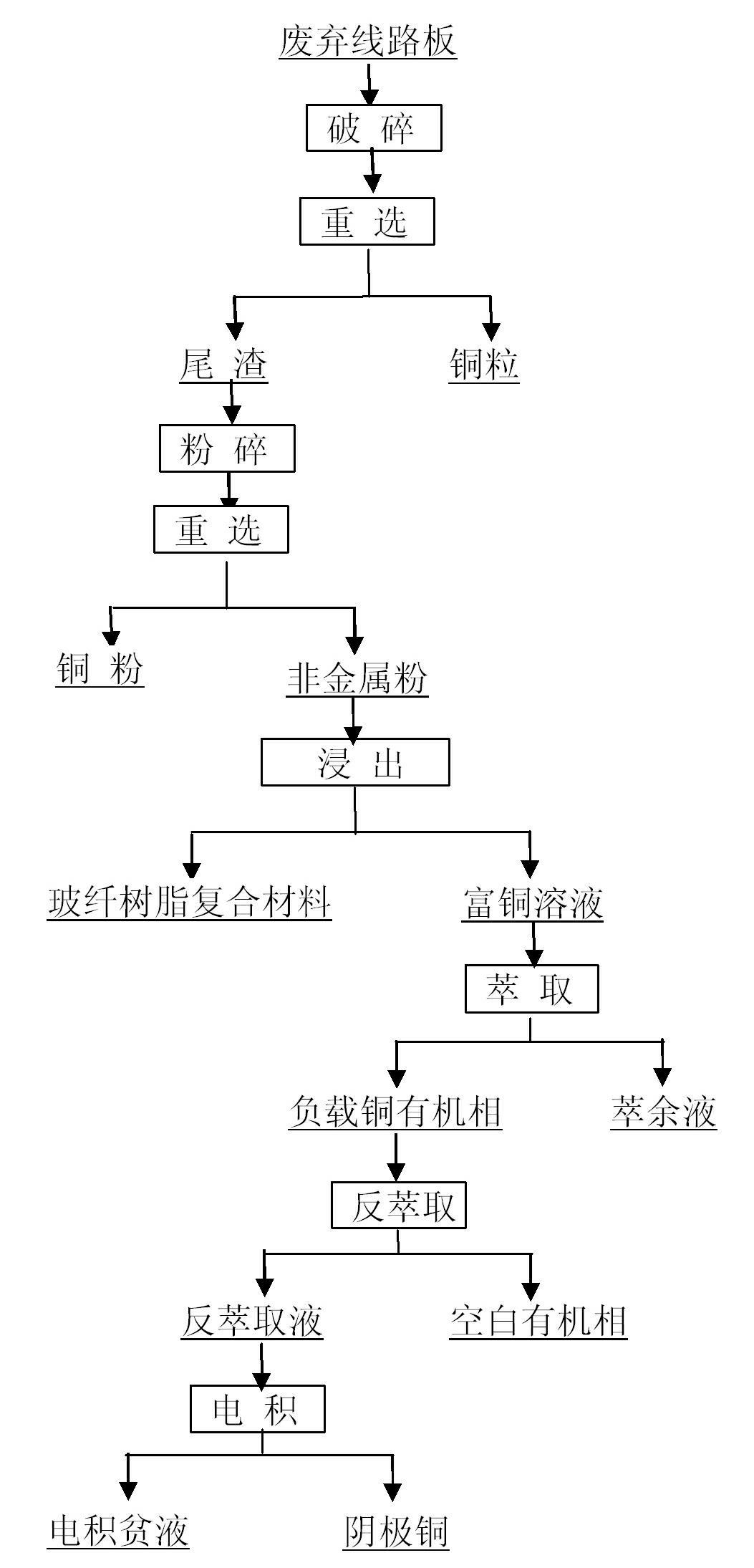
The invention discloses a recovery method for a waste circuit board, which is characterized in that: the waste circuit board is cracked and reselected to obtain shot copper and tailings; the tailings are cracked and reselected to obtain copper powder and nonmetallic powder; an H2SO4 liquid is added into the nonmetallic powder so that a pH value is 1.5-3.5; acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is used as a leaching strain under a temperature of 20-35 DEG C for leaching to obtain a copper-rich liquid and fiberglass resin composite material; an extracting agent with a volume ratio of hydroxyl aldoxime extracting agent to hydroxyl ketoxime extracting agent to kerosene being 5-20:5-20:60-90 to extract the copper-rich liquid is adopted to obtain loaded copper organic phase and raffinate; a 10-30 percent sulphuric acid liquid is used for re-extracting the loaded copper organic phase to obtain a re-extracting liquid and blank organic phase; and then electrodeposition is implemented on the re-extracting liquid to obtain cathode copper and electrodeposition barren liquor. The recovery method for the waste circuit board realizes green, economic and full-value recovery of the waste circuit board, has the advantages of short flow, less investment, high efficiency and low processing cost, and is suitable for recycling various waste circuit boards.
Owner:广东省资源综合利用研究所
Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and applications thereof
ActiveCN103232953AHigh activityEfficient leaching rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLeaching rateAcidithiobacillus ferrooxidans
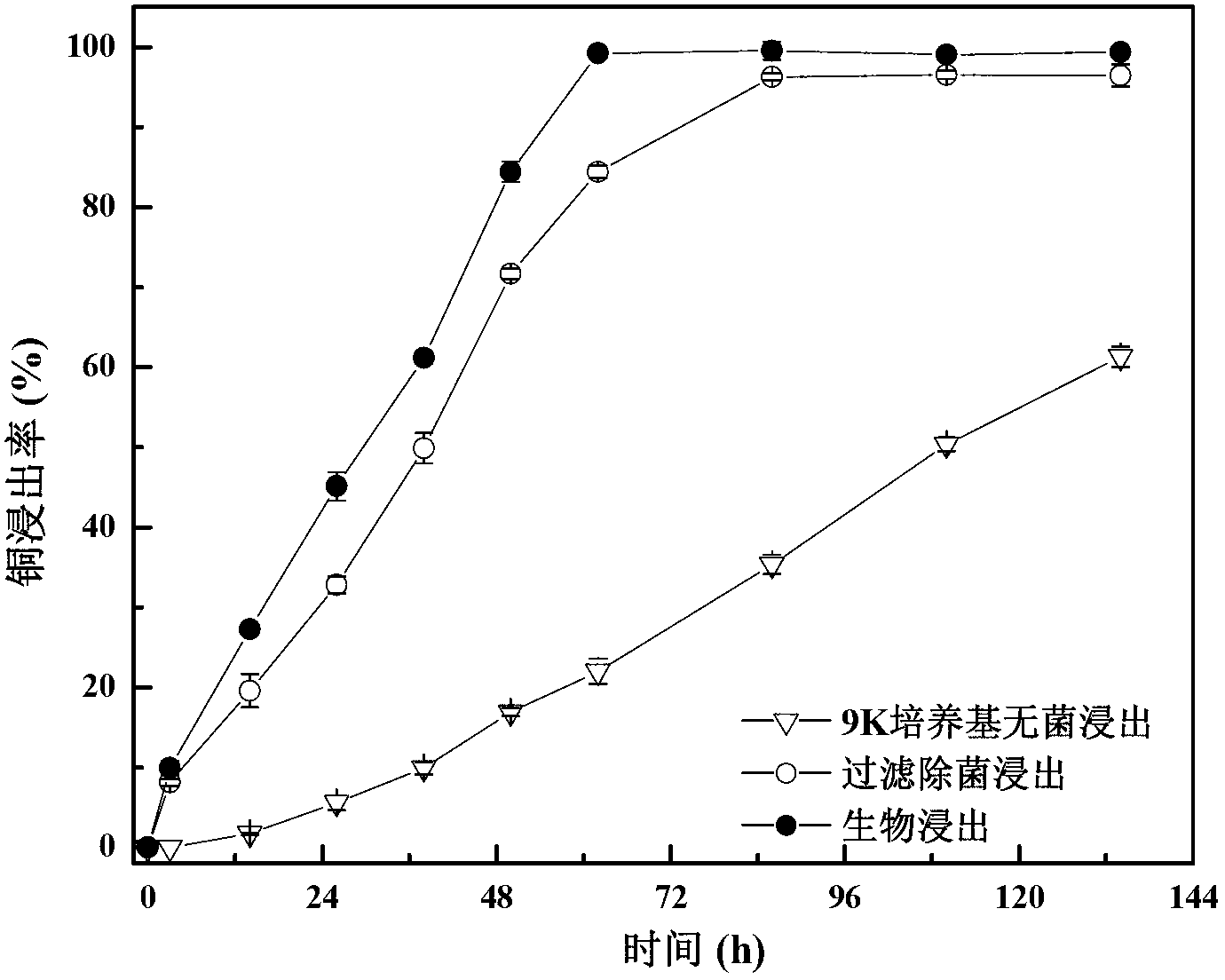
The present invention discloses a strain of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, and applications thereof. The Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans Z1, and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (short for CCTCC) on March 25, 2013, wherein a preservation number is CCTCC NO:M2013102. With the Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, valuable metals in waste PCB can be leached under an aerobic condition. The Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans has characteristics of efficient bio-leaching, efficient leaching rate, and good environment adaptability.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com