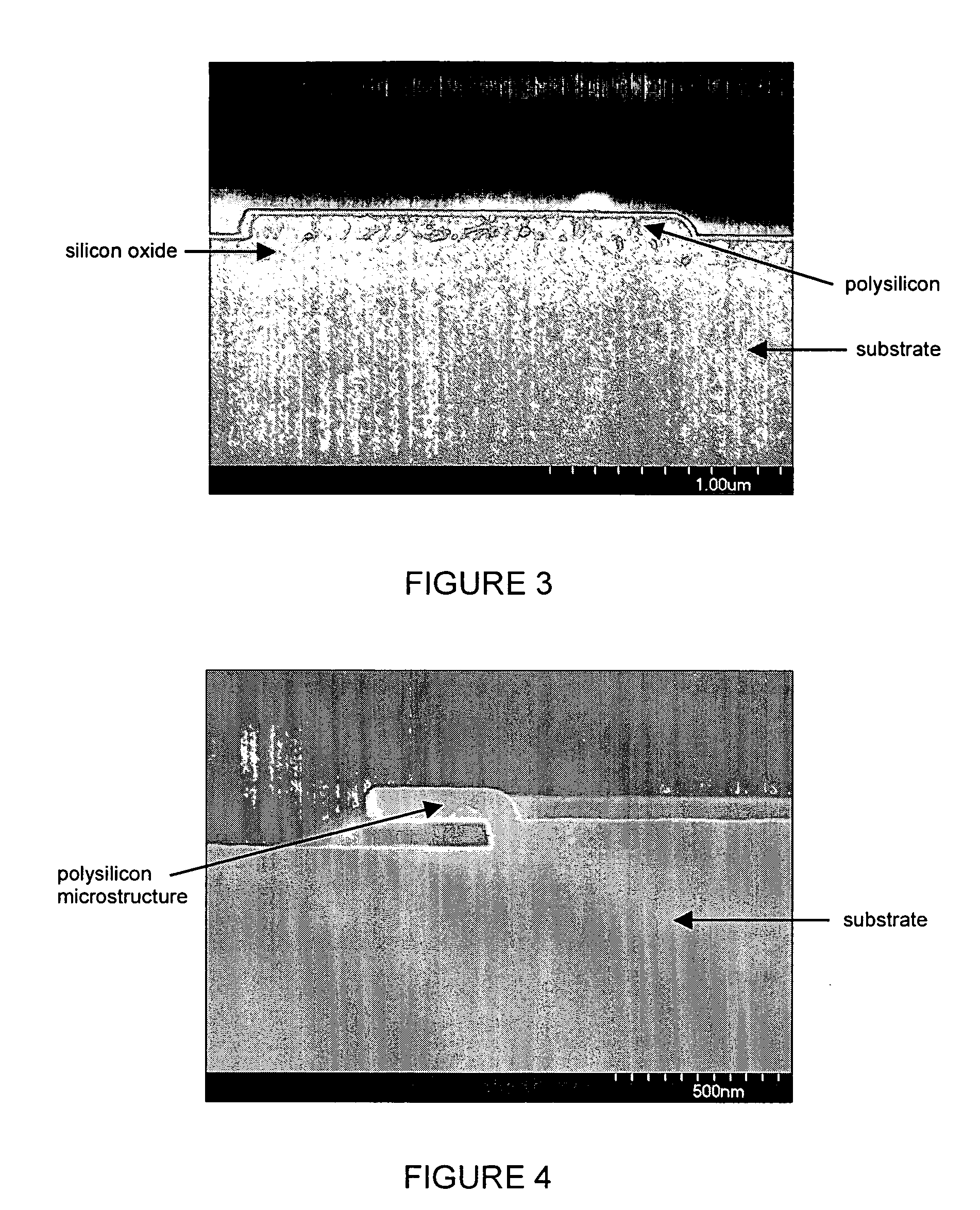
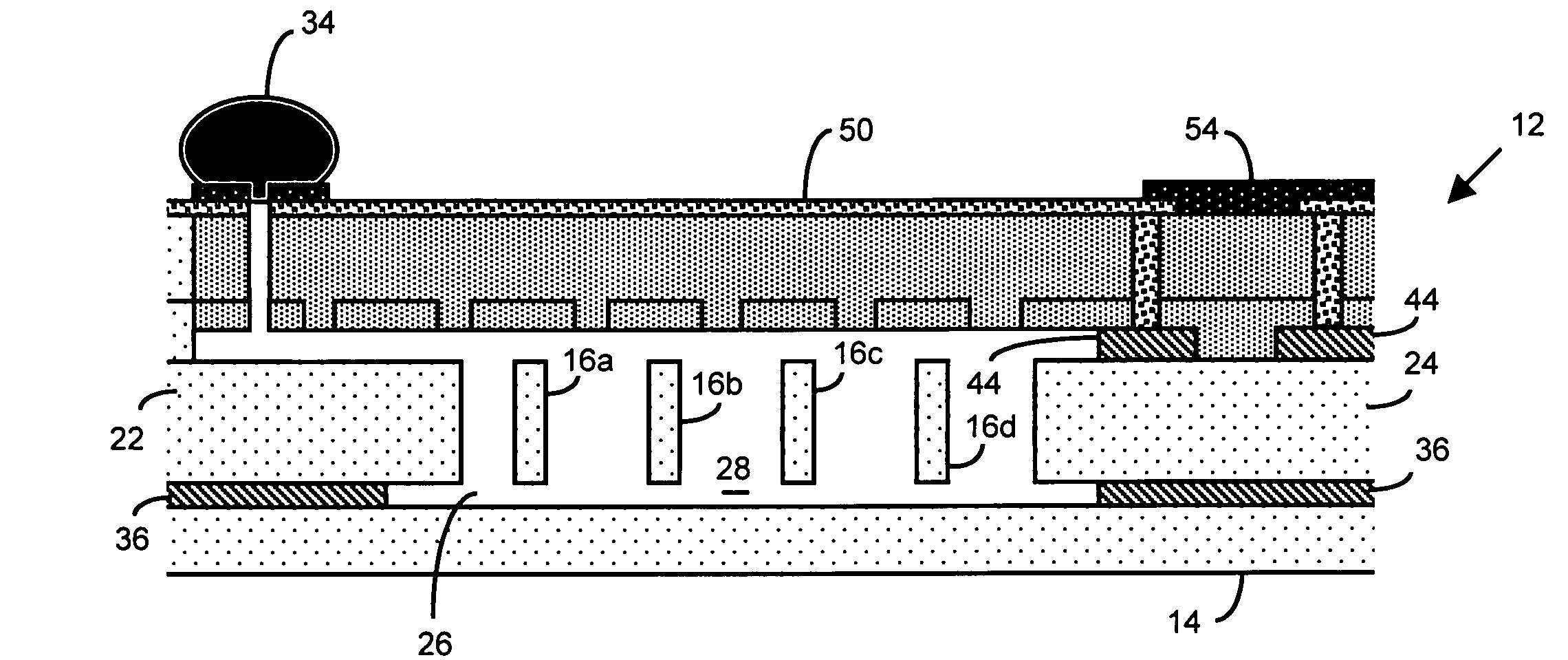
Patents
Literature
249 results about "Stiction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stiction is the static friction that needs to be overcome to enable relative motion of stationary objects in contact. The term is a portmanteau of the words static and friction, perhaps also influenced by the verb stick.
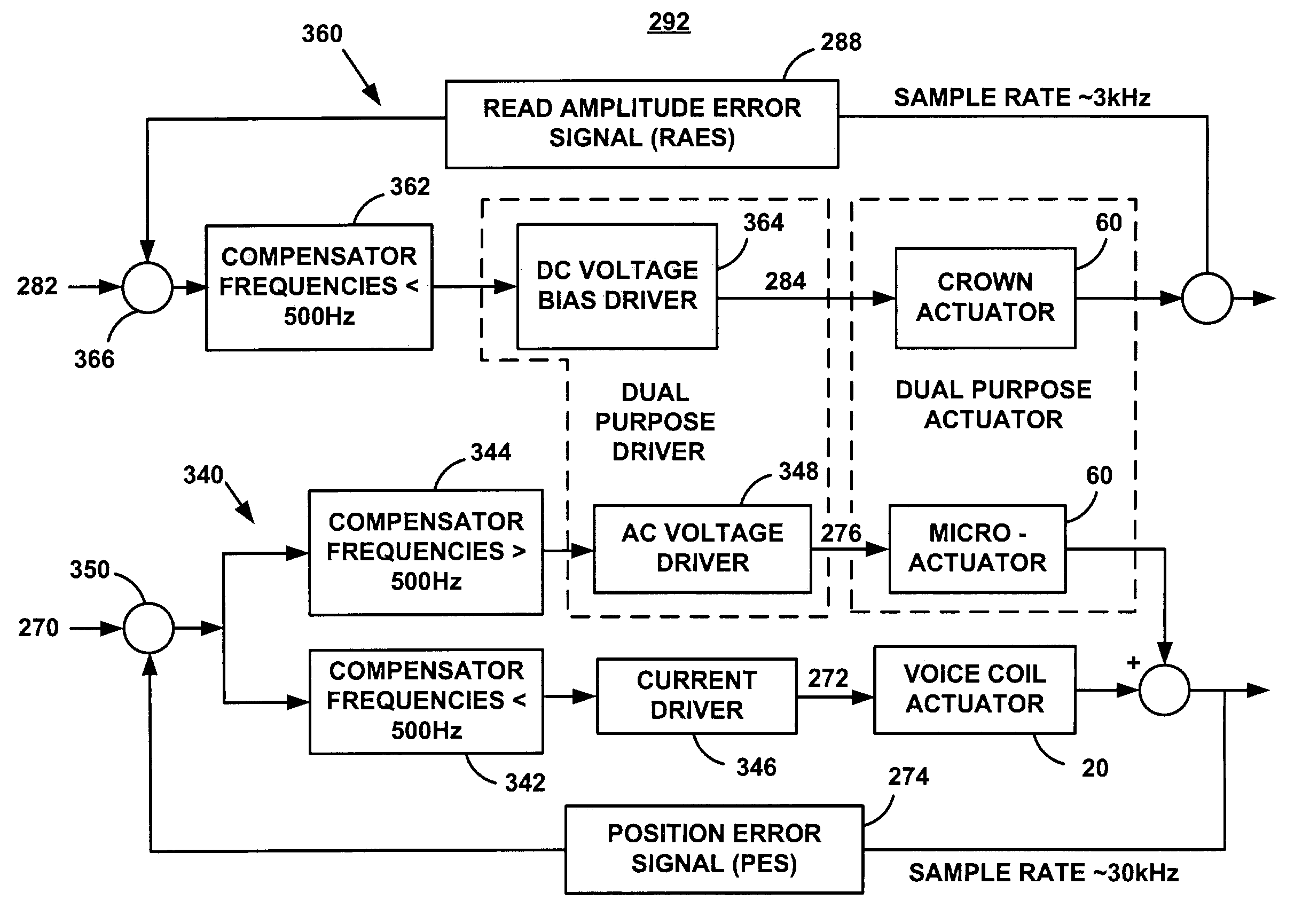
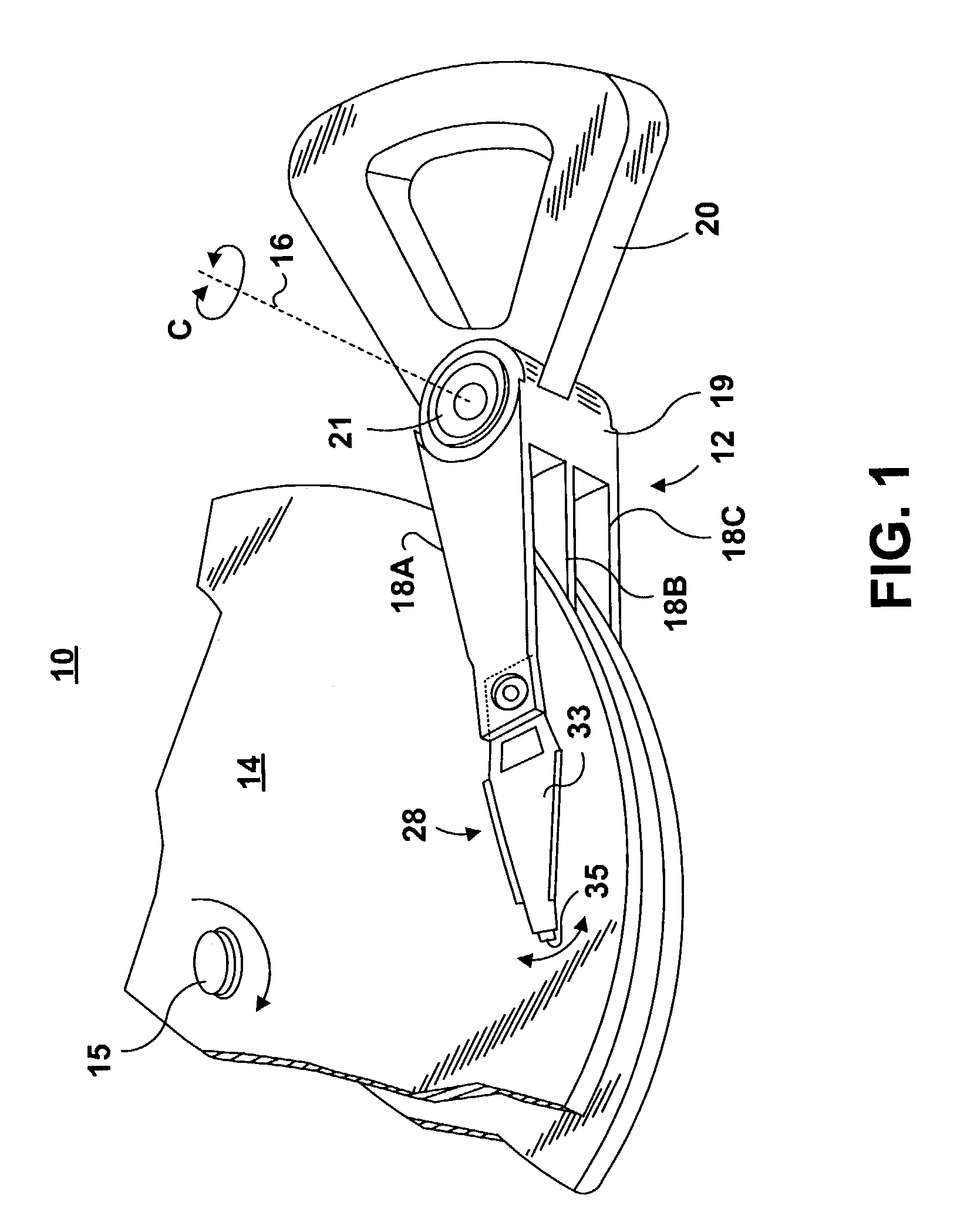
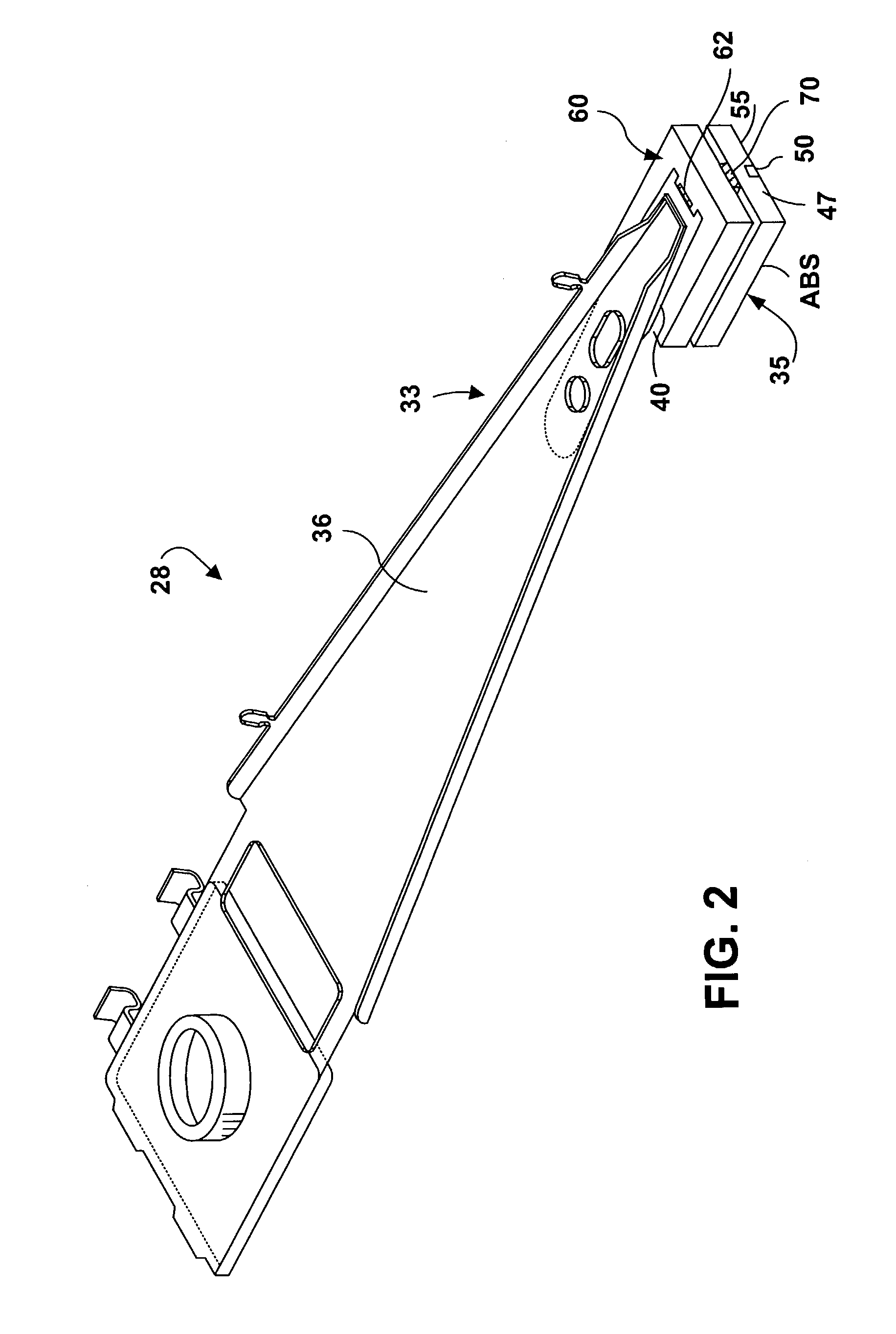
Active fly height control crown actuator
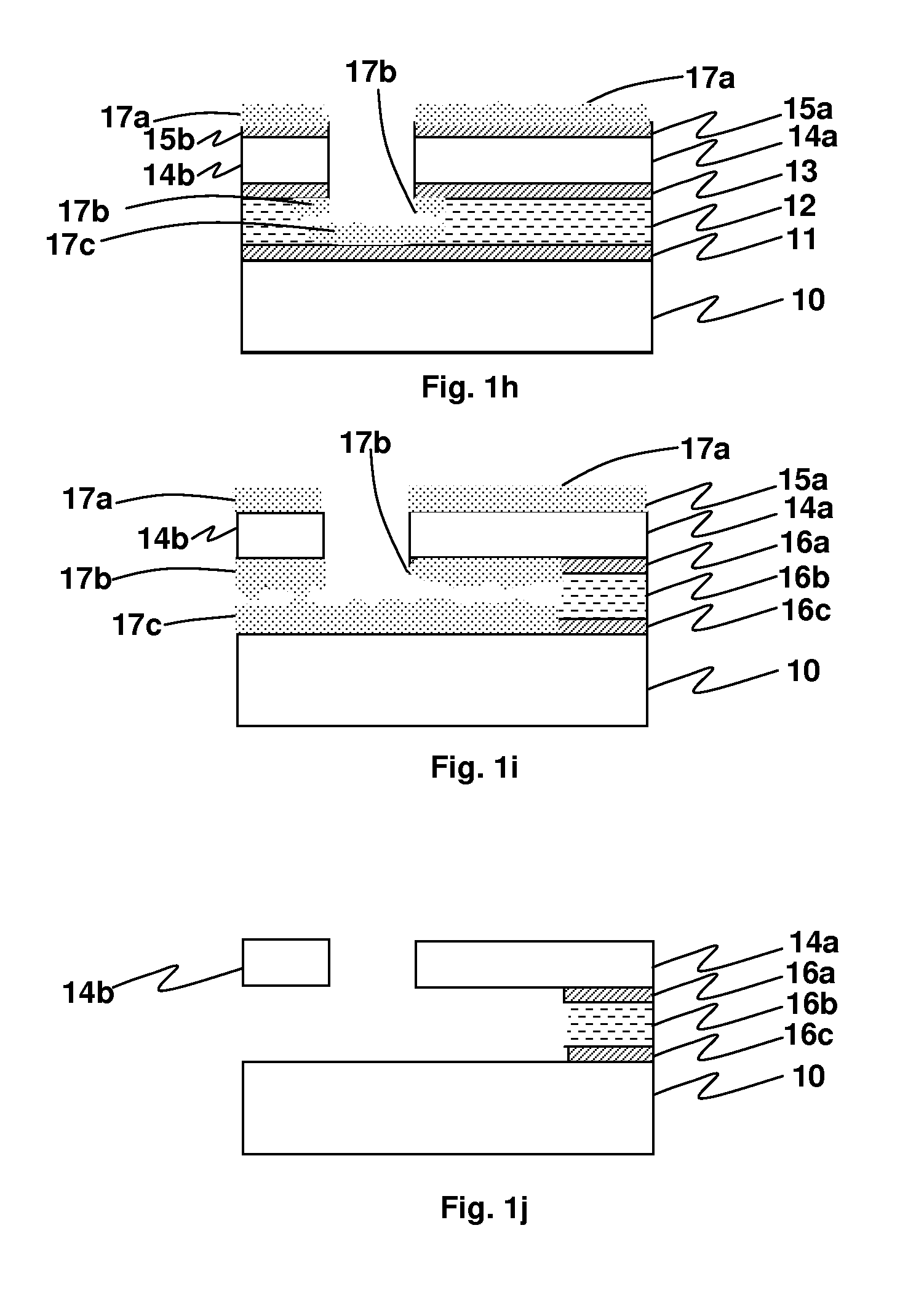
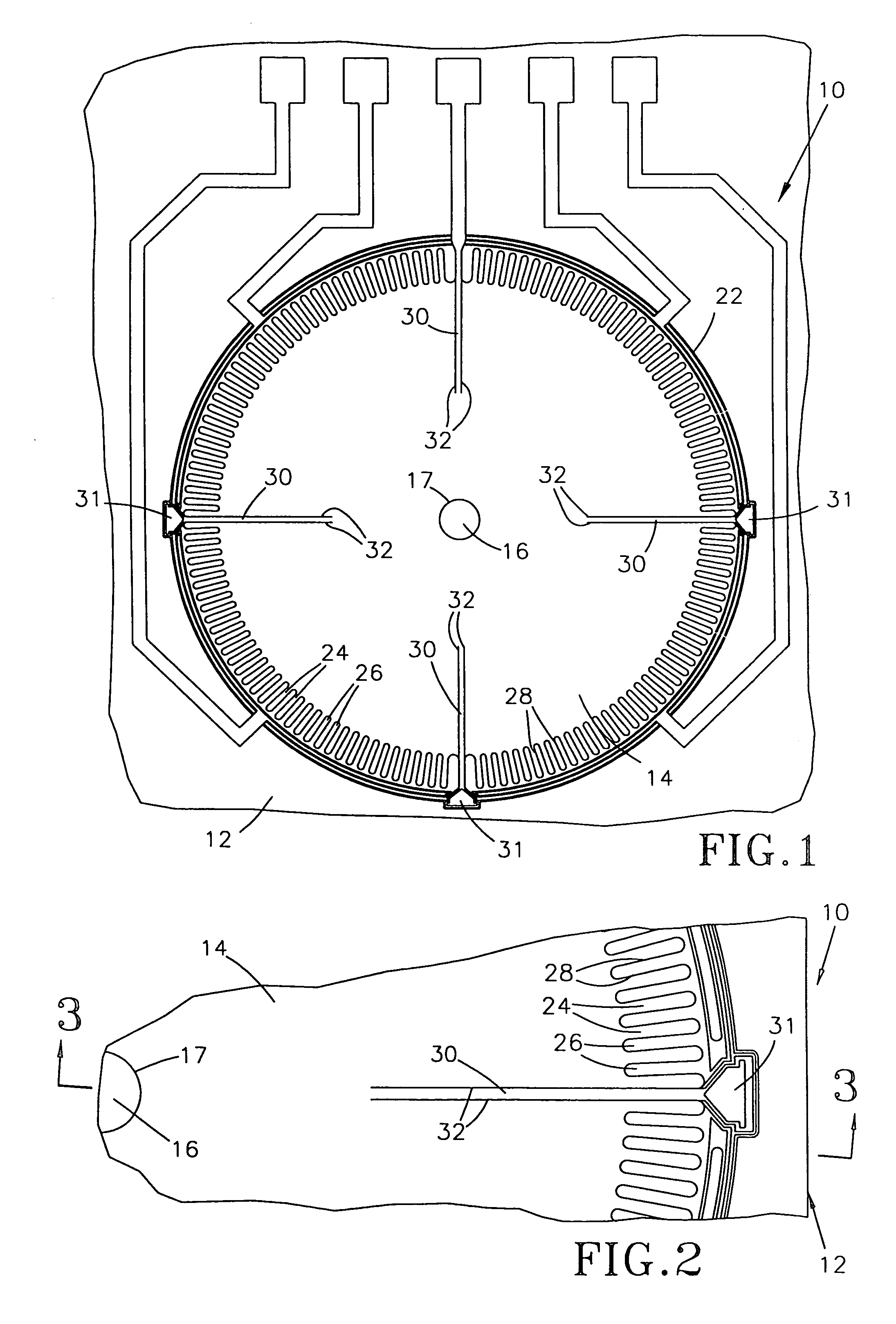
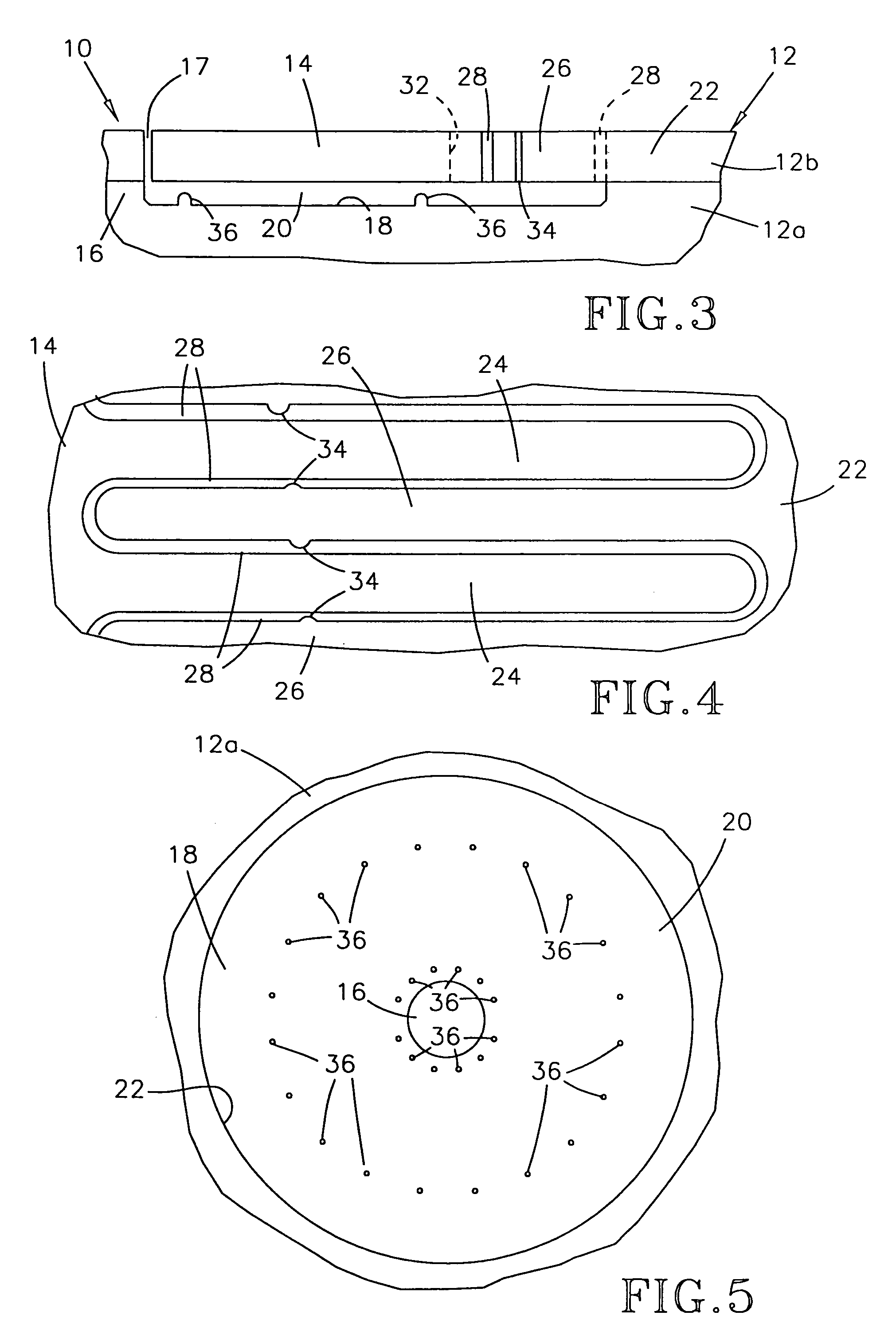
InactiveUS6950266B1Improve production efficiencyReduced altitude sensitivityAnalogue recording/reproducingDriving/moving recording headsData integrityMicro actuator
A micro-actuator is comprised of a piezoelectric motor mounted on a flexure tongue with offsetting hinges, to perform a fine positioning of the magnetic read / write head. The substantial gain in the frequency response greatly improves the performance and accuracy of the track-follow control for fine positioning. The simplicity of the enhanced micro-actuator design results in a manufacturing efficiency that enables a high-volume, low-cost production. The micro-actuator is interposed between a flexure tongue and a slider to perform an active control of the fly height of the magnetic read / write head. The induced slider crown and camber are used to compensate for thermal expansion of the magnetic read / write head, which causes the slider to be displaced at an unintended fly height position relative to the surface of the magnetic recording disk. The enhanced micro-actuator design results in reduced altitude sensitivity, ABS tolerances, and reduced stiction. The controlled fly height of the magnetic read / write head prevents a possibility of a head crash, while improving the performance and data integrity.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method of cleaning and treating a semiconductor device including a micromechanical device
InactiveUS6024801ADecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical compoundEngineering
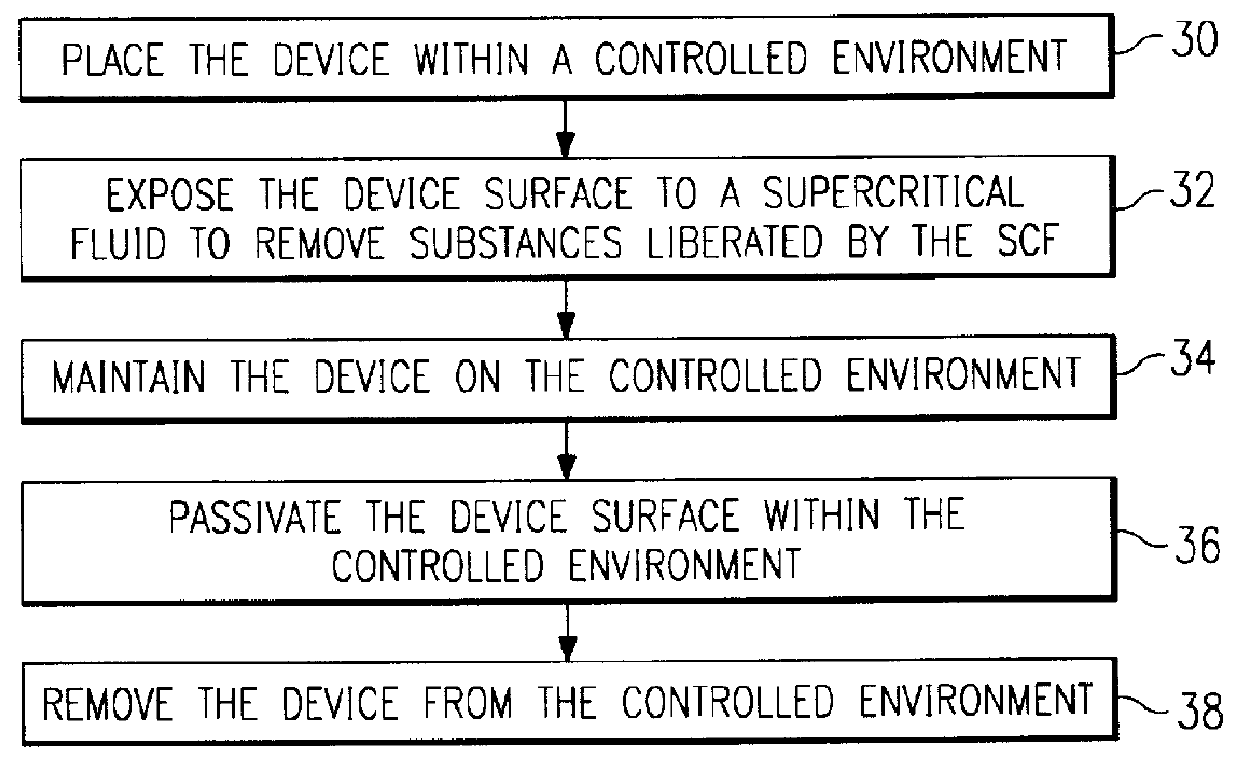
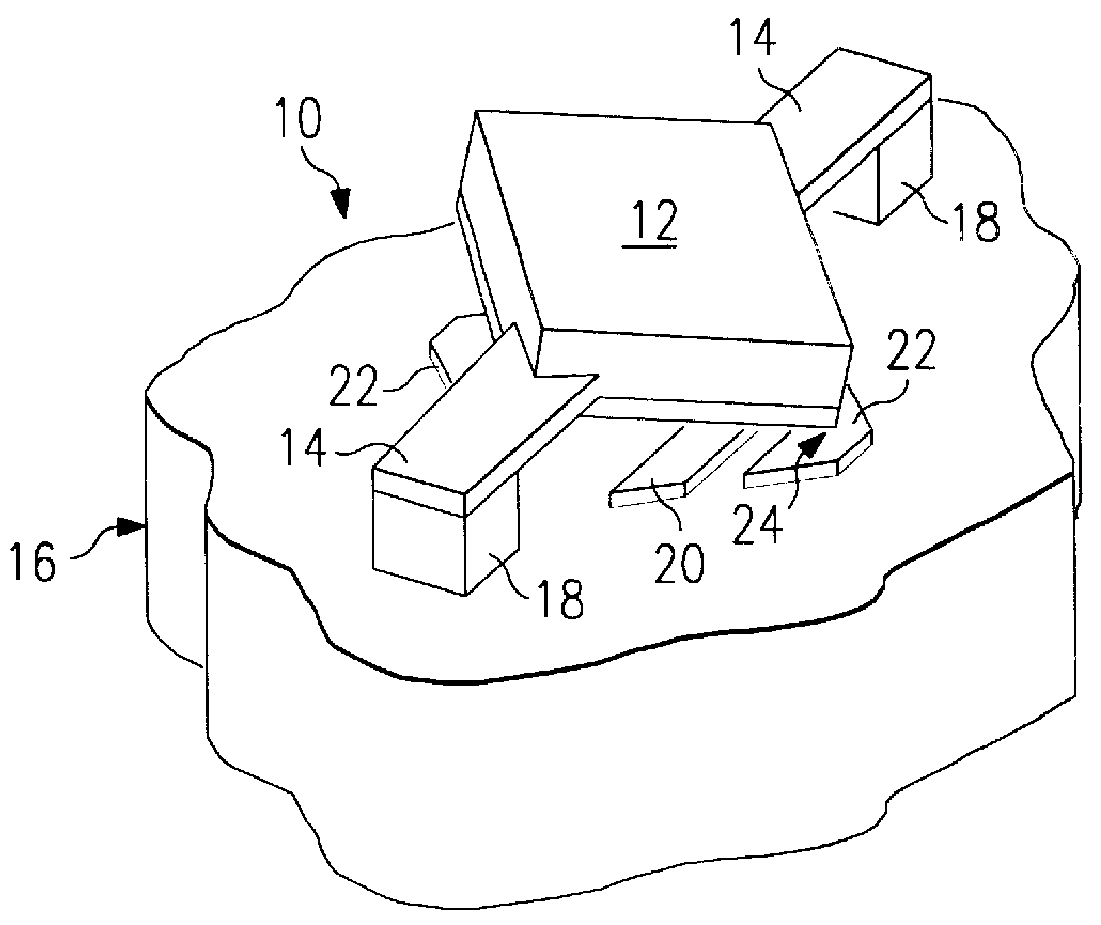
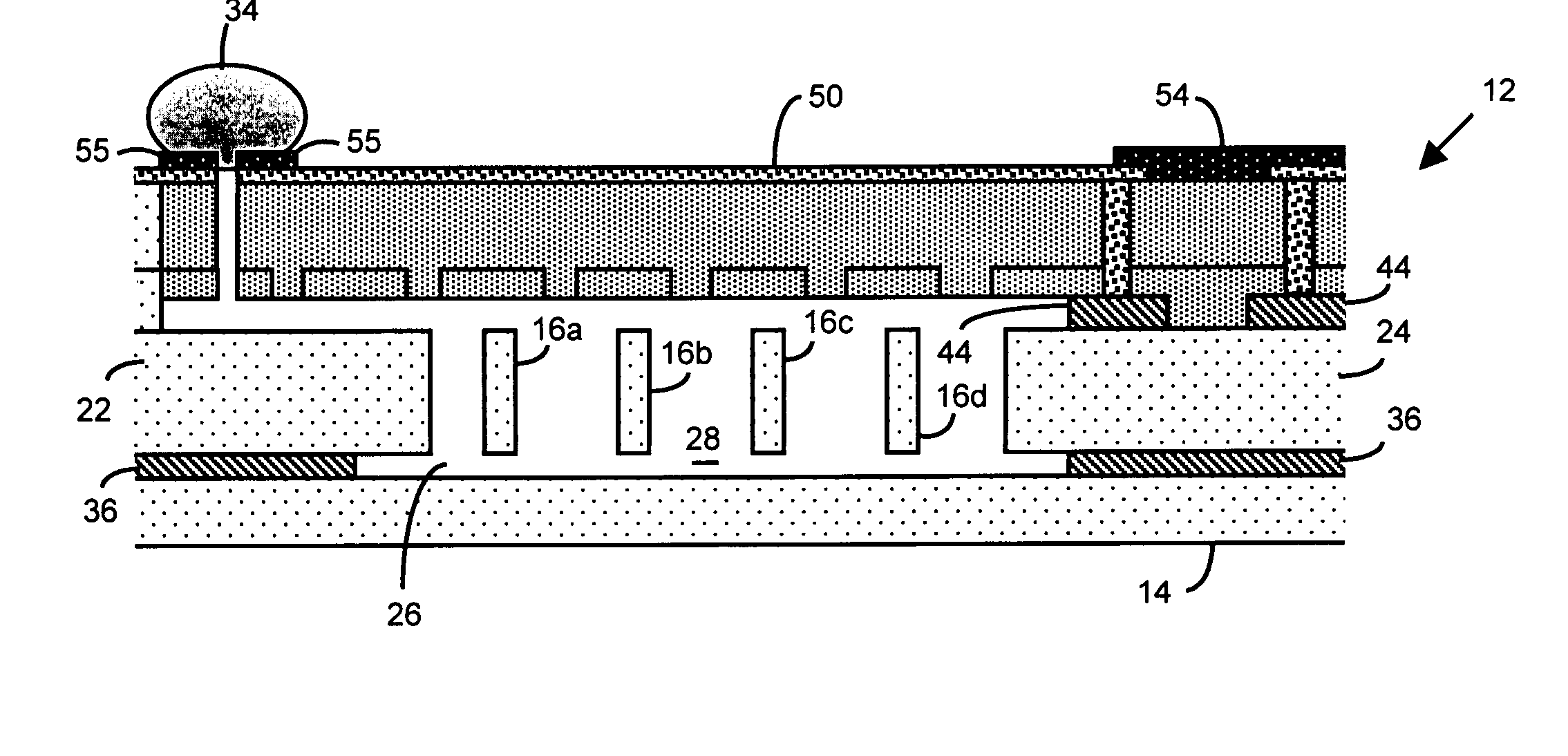
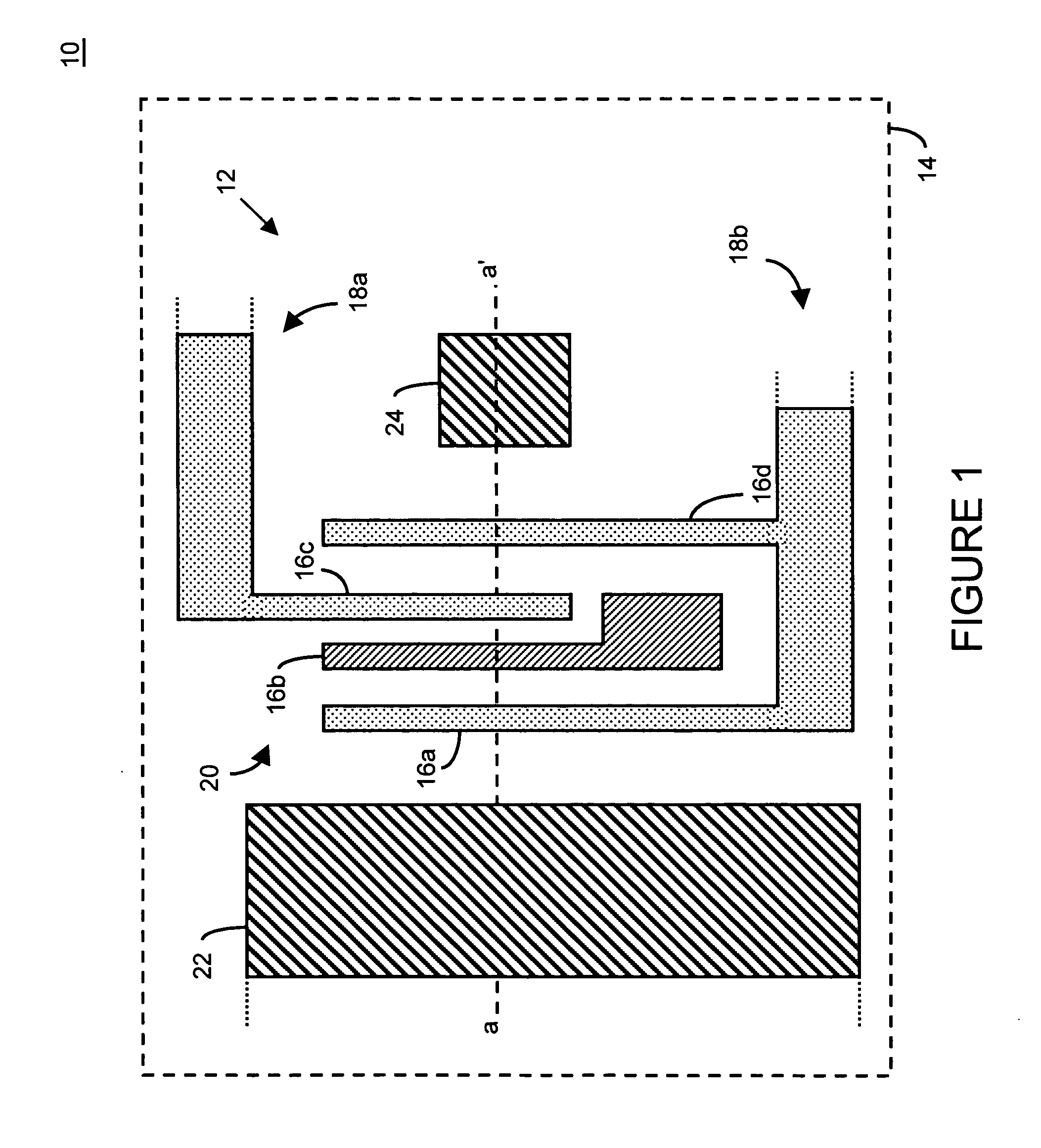
A method of cleaning and treating a device, including those of the micromechanical (10) and semiconductor type. The surface of a device, such as the landing electrode (22) of a digital micromirror device (10), is first cleaned with a supercritical fluid (SCF) in a chamber (50) to remove soluble chemical compounds, and then maintained in the SCF chamber until and during the subsequent passivation step. Passivants including PFDA and PFPE are suitable for the present invention. By maintaining the device in the SCF chamber, and without exposing the device to, for instance, the ambient of a clean room, organic and inorganic contaminants cannot be deposited upon the cleaned surface prior to the passivation step. The present invention derives technical advantages by providing an improved passivated surface that is suited to extend the useful operation life of devices, including those of the micromechanical type, reducing stiction forces between contacting elements such as a mirror and its landing electrode. The present invention is also suitable for cleaning and passivating other surfaces including a surface of semiconductor wafers, and the surface of a hard disk memory drive.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
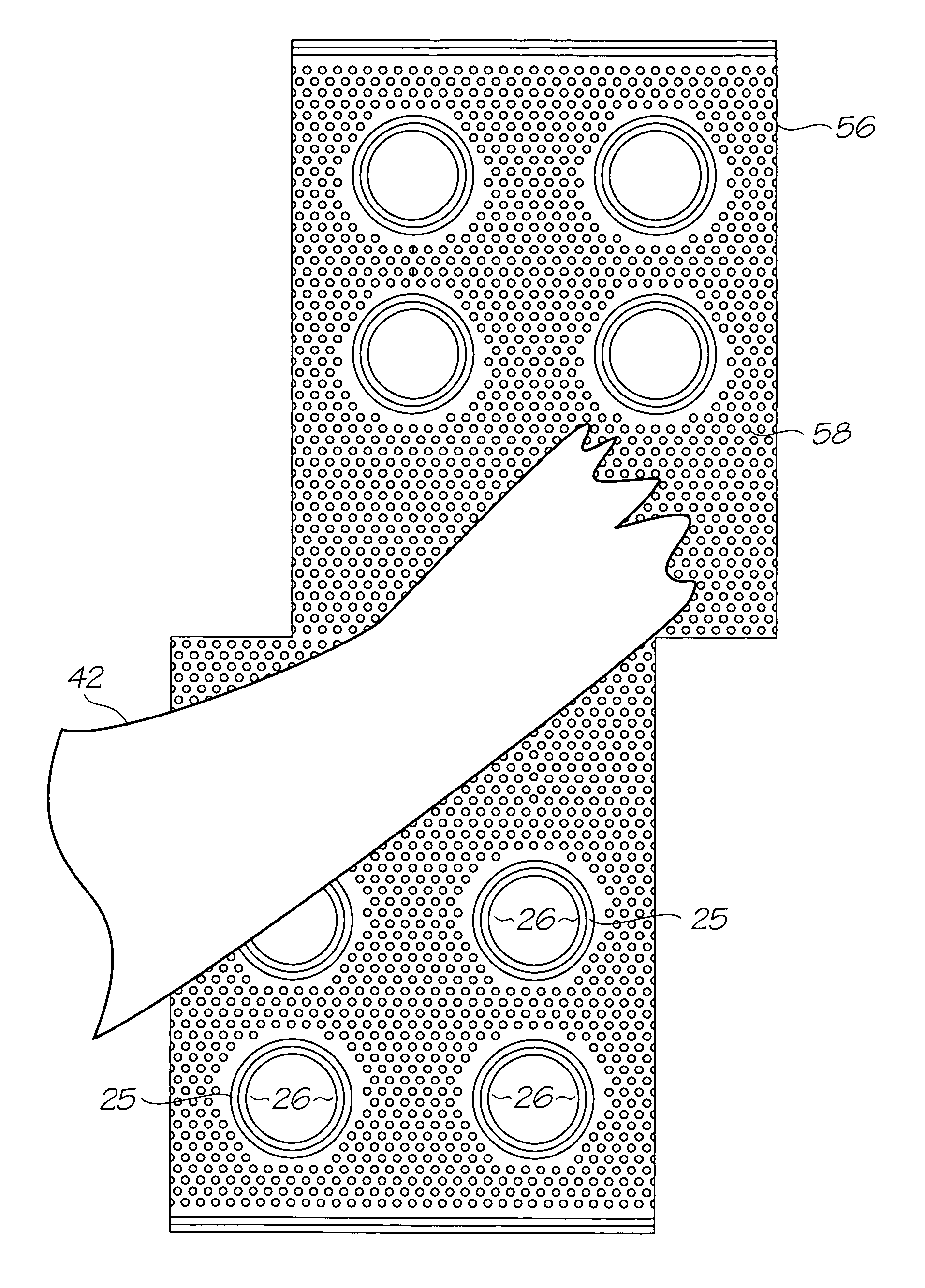
Anti-stiction technique for electromechanical systems and electromechanical device employing same
ActiveUS20060246631A1Operating environment limitedMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesMetal foilEngineering
A mechanical structure is disposed in a chamber, at least a portion of which is defined by the encapsulation structure. A first method provides a channel cap having at least one preform portion disposed over or in at least a portion of an anti-stiction channel to seal the anti-stiction channel, at least in part. A second method provides a channel cap having at least one portion disposed over or in at least a portion of an anti-stiction channel to seal the anti-stiction channel, at least in part. The at least one portion is fabricated apart from the electromechanical device and thereafter affixed to the electromechanical device. A third method provides a channel cap having at least one portion disposed over or in at least a portion of the anti-stiction channel to seal an anti-stiction channel, at least in part. The at least one portion may comprise a wire ball, a stud, metal foil or a solder preform. A device includes a substrate, an encapsulation structure and a mechanical structure. An anti-stiction layer is disposed on at least a portion of the mechanical structure. An anti-stiction channel is formed in at least one of the substrate and the encapsulation structure. A cap has at least one preform portion disposed over or in at least a portion of the anti-stiction channel to seal the anti-stiction channel, at least in part.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Alignment methods in fluid-filled MEMS displays
InactiveUS20080037104A1Improve electromechanical performanceGood optical performanceTube/lamp screens manufactureStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
This invention relates to MEMS display apparatus and methods for assembly thereof that include a plurality of light modulators having components substantially surrounded in a liquid that reduces the effects of stiction and improves the optical and electromechanical performance of the display apparatus. The invention also relates to methods for aligning components of a MEMS display to establish a correspondence between the plurality of light modulators and a plurality of apertures to regulate the transmission of light through the apparatus.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Methods for manufacturing fluid-filled mems displays
InactiveUS20080283175A1Improve performanceReduce static frictionHollow inflatable ballsHollow non-inflatable ballsDisplay deviceEngineering
This invention relates to methods of manufacturing fluid-filled MEMS displays, where the fluid is sealed in the display assembly and substantially surrounds the moving components of the display to reduce the effects of stiction and to improve the optical and electromechanical performance of the display.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Anti-stiction technique for thin film and wafer-bonded encapsulated microelectromechanical systems
InactiveUS6930367B2Operating environment limitedMaterial nanotechnologyAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSelf-assembled monolayerEngineering
There are many inventions described and illustrated herein. In one aspect, there is described a thin film or wafer encapsulated MEMS, and technique of fabricating or manufacturing a thin film or wafer encapsulated MEMS employing anti-stiction techniques. In one embodiment, after encapsulation of the MEMS, an anti-stiction channel is formed thereby providing “access” to the chamber containing some or all of the active members or electrodes of the mechanical structures. Thereafter, an anti-stiction fluid (for example, gas or gas-vapor) is introduced into the chamber via the anti-stiction channel. The anti-stiction fluid may deposit on one, some or all of the active members of the mechanical structures thereby providing an anti-stiction layer (for example, a monolayer coating or self-assembled monolayer) and / or out-gassing molecules on such members or electrodes. After introduction and / or application of the anti-stiction fluid, the anti-stiction channel may be sealed, capped, plugged and / or closed.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method and apparatus for an improved micro-electrical mechanical switch
InactiveUS6127744ABatteries circuit arrangementsBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsElectricityFriction effect
A method, device and circuit which applies an electrostatic repulsion pushing force to a MEM switch armature during an opening process. The repulsive force adds to the spring restoration force on the armature, increasing the opening speed of the switch and aids in overcoming stiction effects. The inventive switch includes a contact electrically connected to a first terminal of the switch. A throw is electrically connected to a second terminal of the switch. Finally, a mechanism is provided for opening the switch by electrostatically causing the throw to disengage the contact. In the illustrative implementation, the mechanism for opening the switch includes a first charge storage structure mounted on the throw and a second charge storage structure mounted in proximity to the first charge storage structure. When charges are applied between the first and the second charge storage structures, a force of repulsion is created or a force of attraction is created depending on the polarity of the potential.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
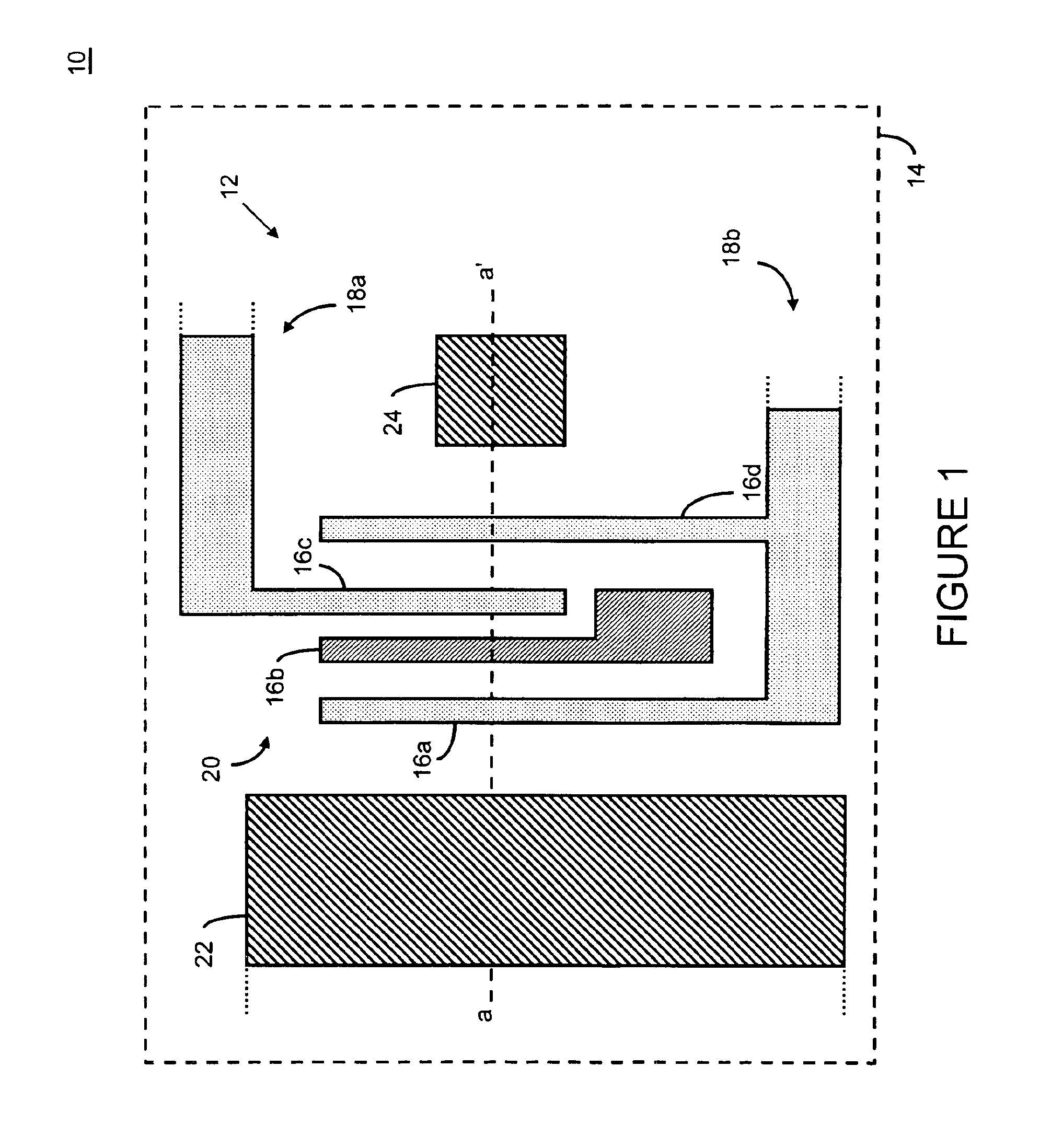
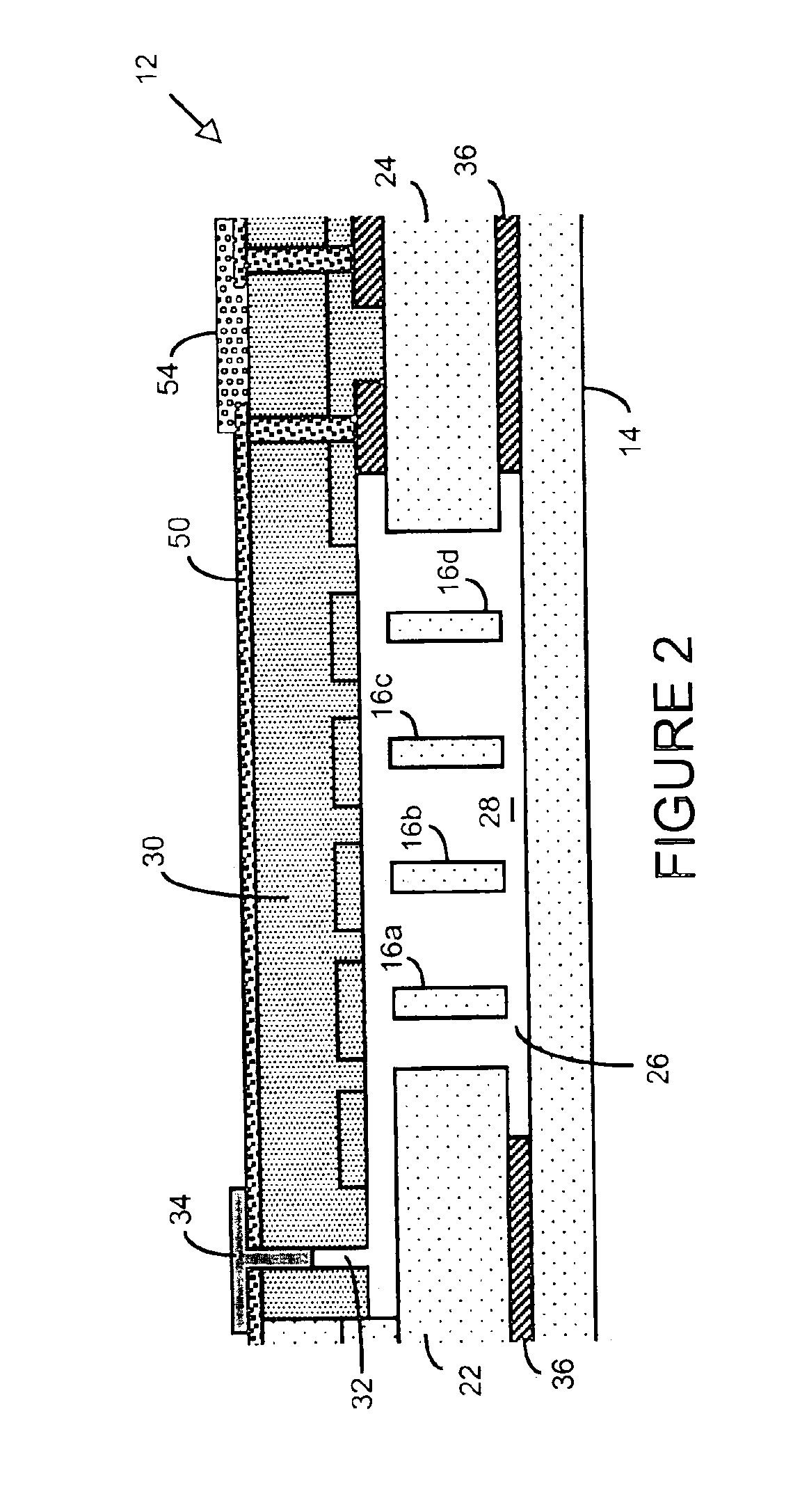
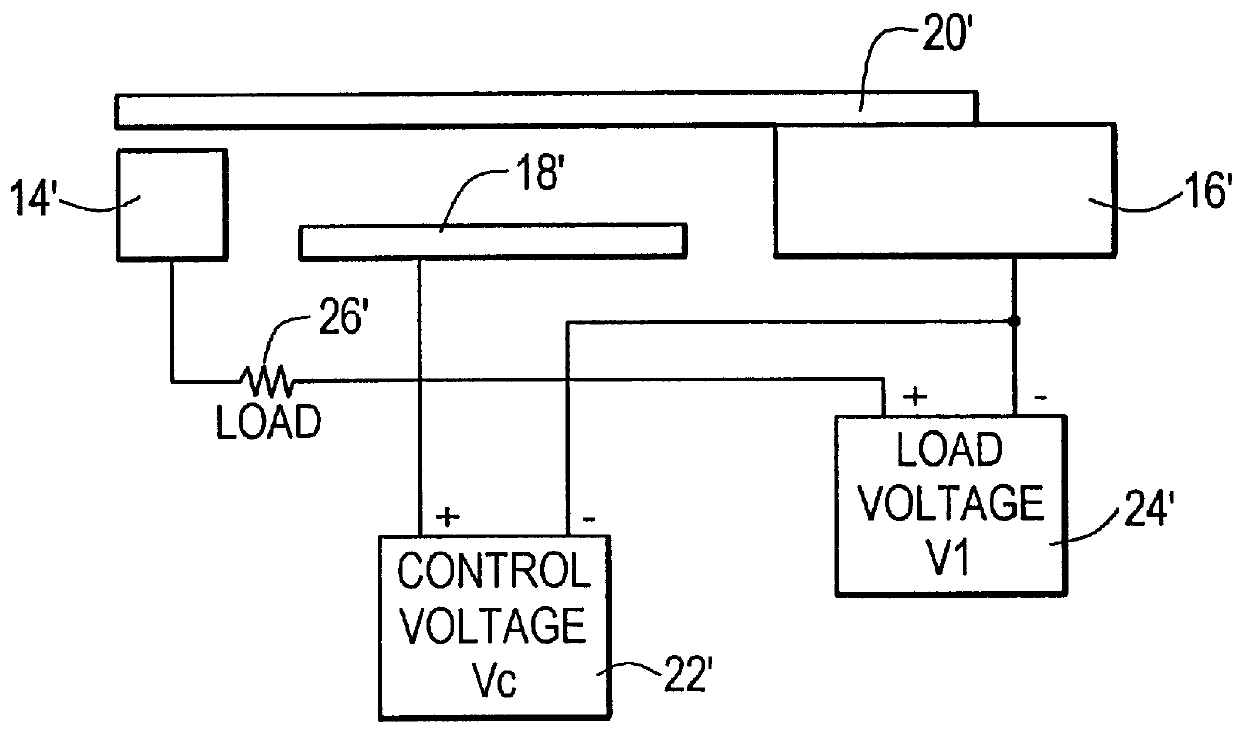
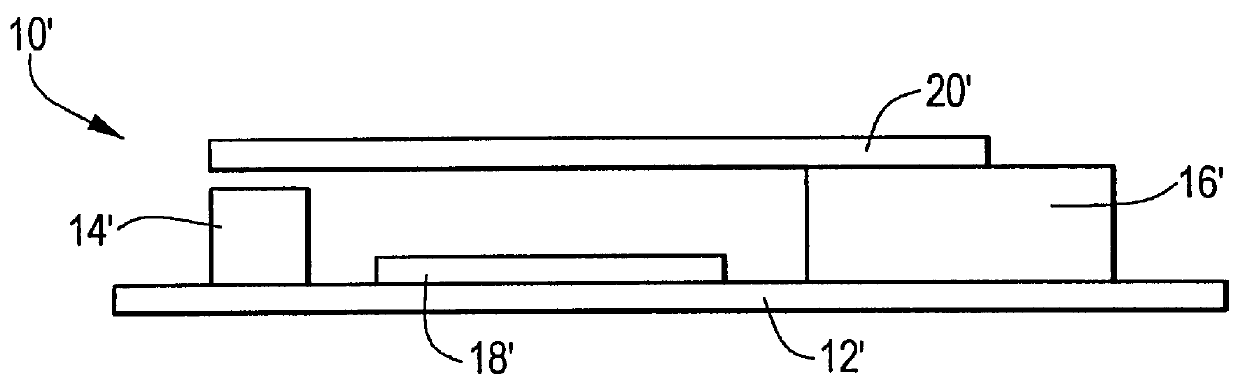
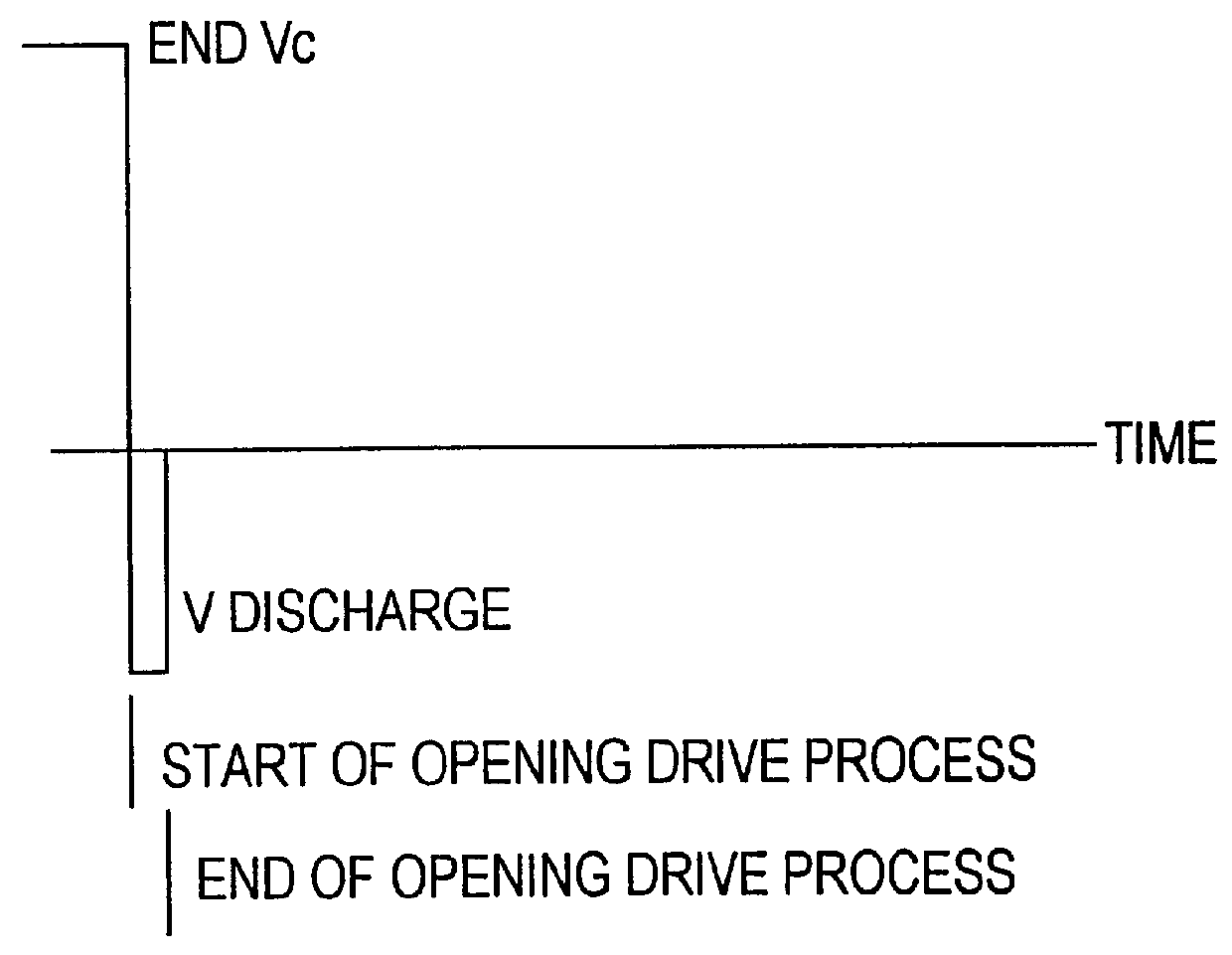
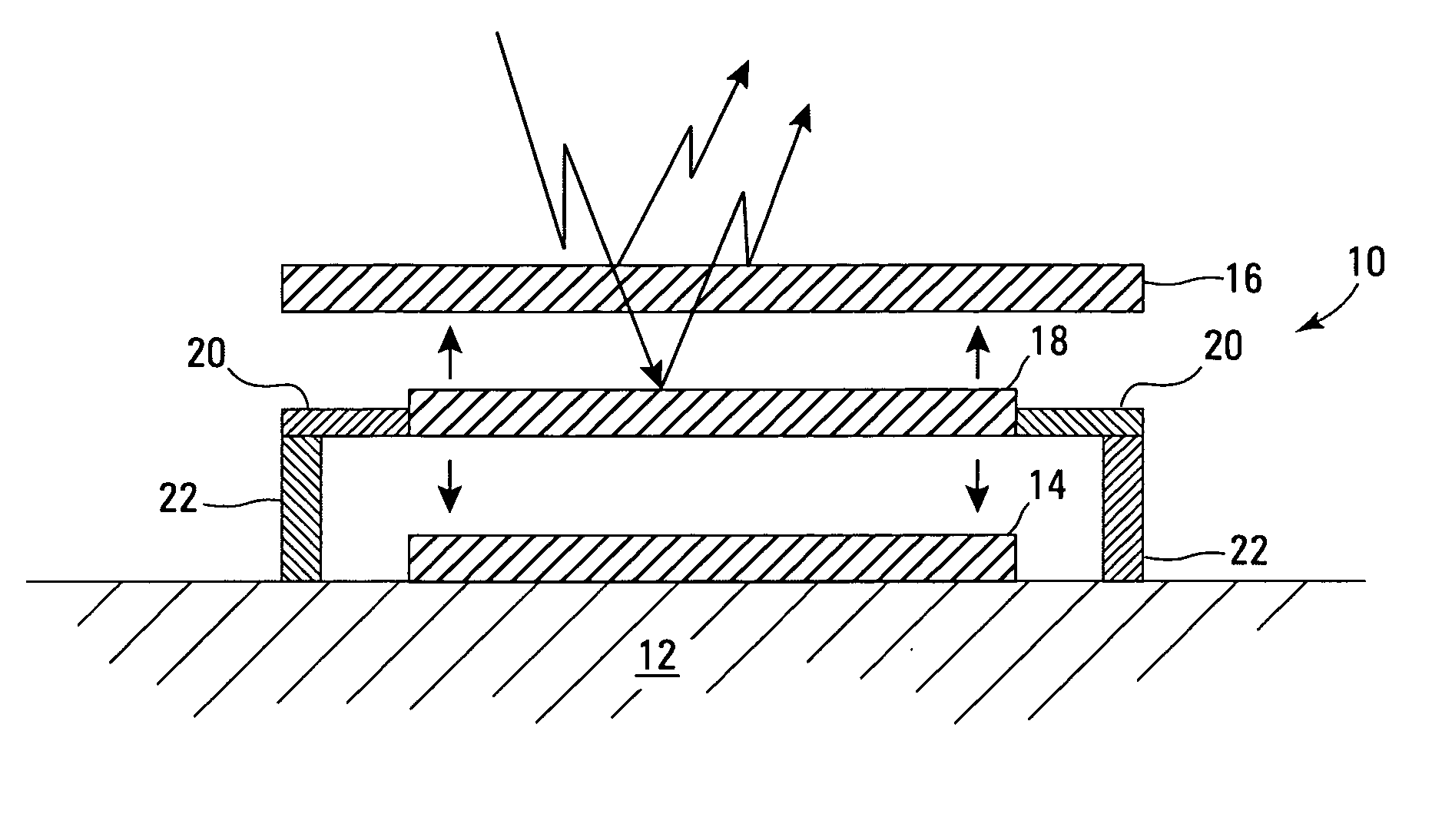
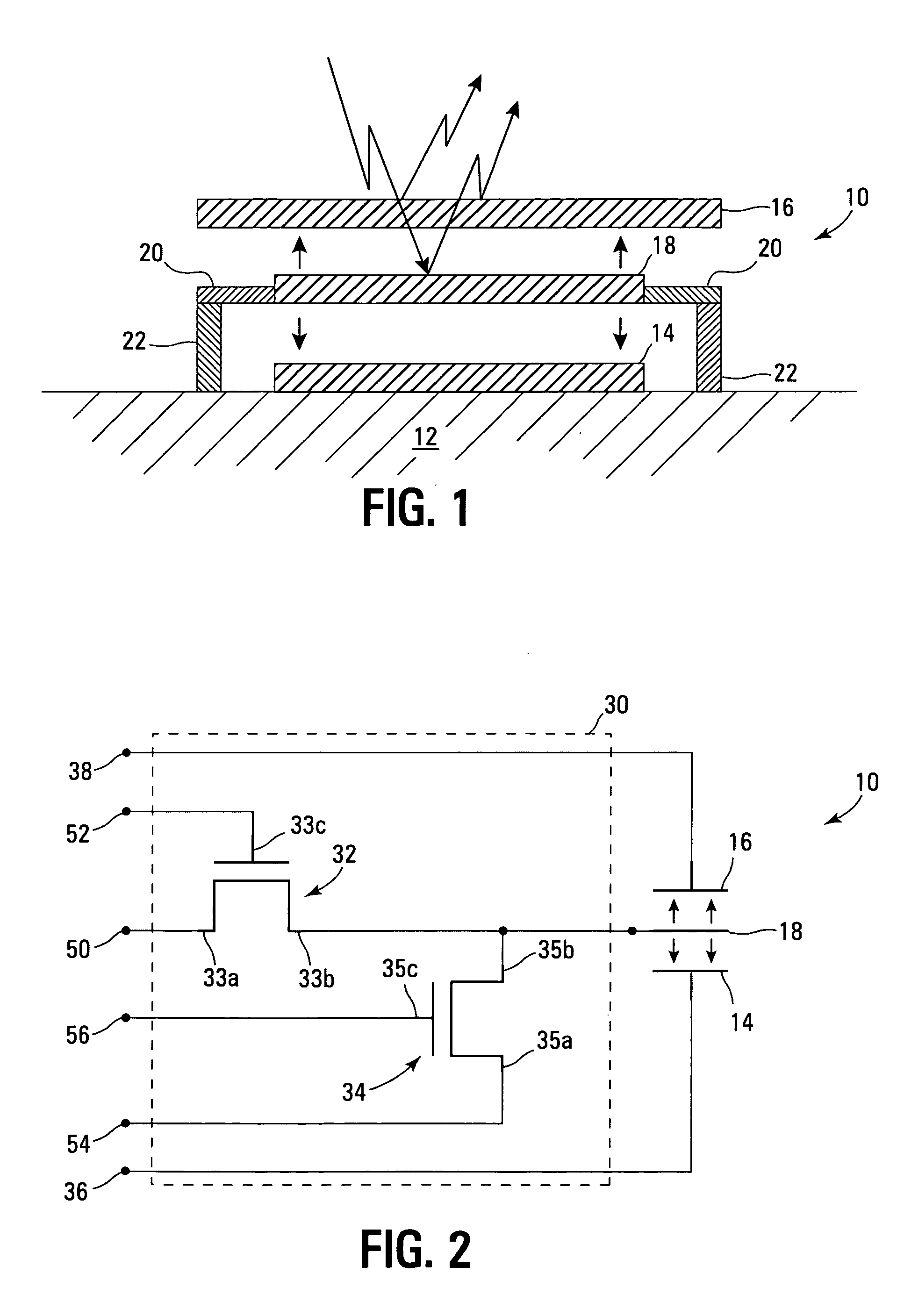
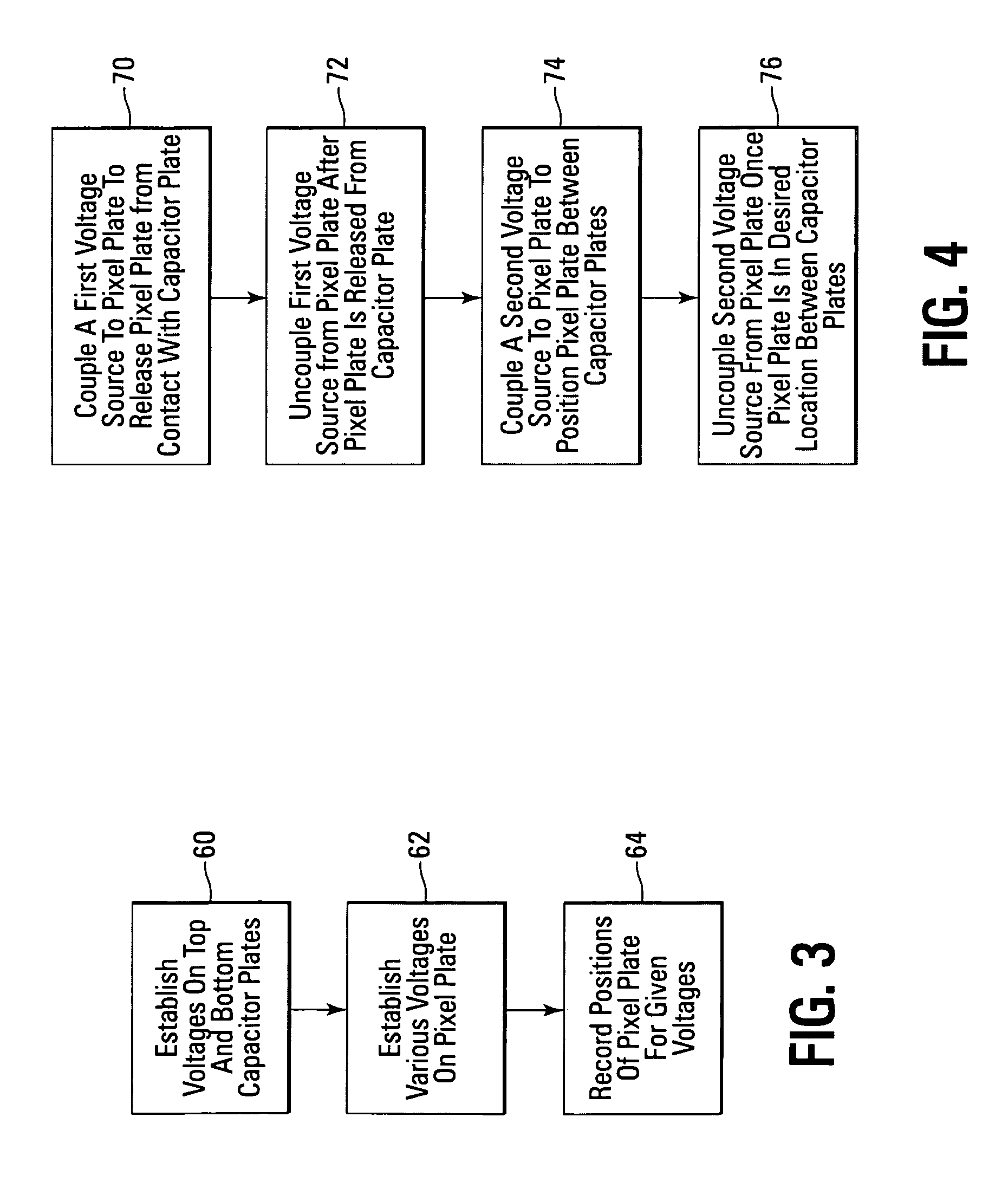
Control circuit for overcoming stiction
InactiveUS20070075942A1Static indicating devicesMicrostructural device manufactureEngineeringControl circuit
A circuit and method for controlling a micro-electromechanical system is herein disclosed. In one embodiment of a micro-electromechanical system having top and bottom capacitor plates with a pixel plate movably positioned therebetween, a release voltage sufficient to overcome stiction forces adhering the pixel plate to one of the capacitor plates is applied to the pixel plate to cause the pixel plate to be attracted to the pixel plate opposite the capacitor plate to with which the pixel plate is in contact. After the pixel plate has moved a predetermined distance away from the capacitor plate to which it had been adhered by stiction forces, the release voltage is removed. Thereafter, an positional voltage is applied to the pixel plate to move the pixel plate to a desired location between the capacitor plates. Release and positional voltages are coupled to and decoupled from the pixel plate by one or more switching mechanisms.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Integrated method for release and passivation of MEMS structures
InactiveUS6902947B2Preventing undesirable etchingHigh speedMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsHydrogenSelf-assembled monolayer
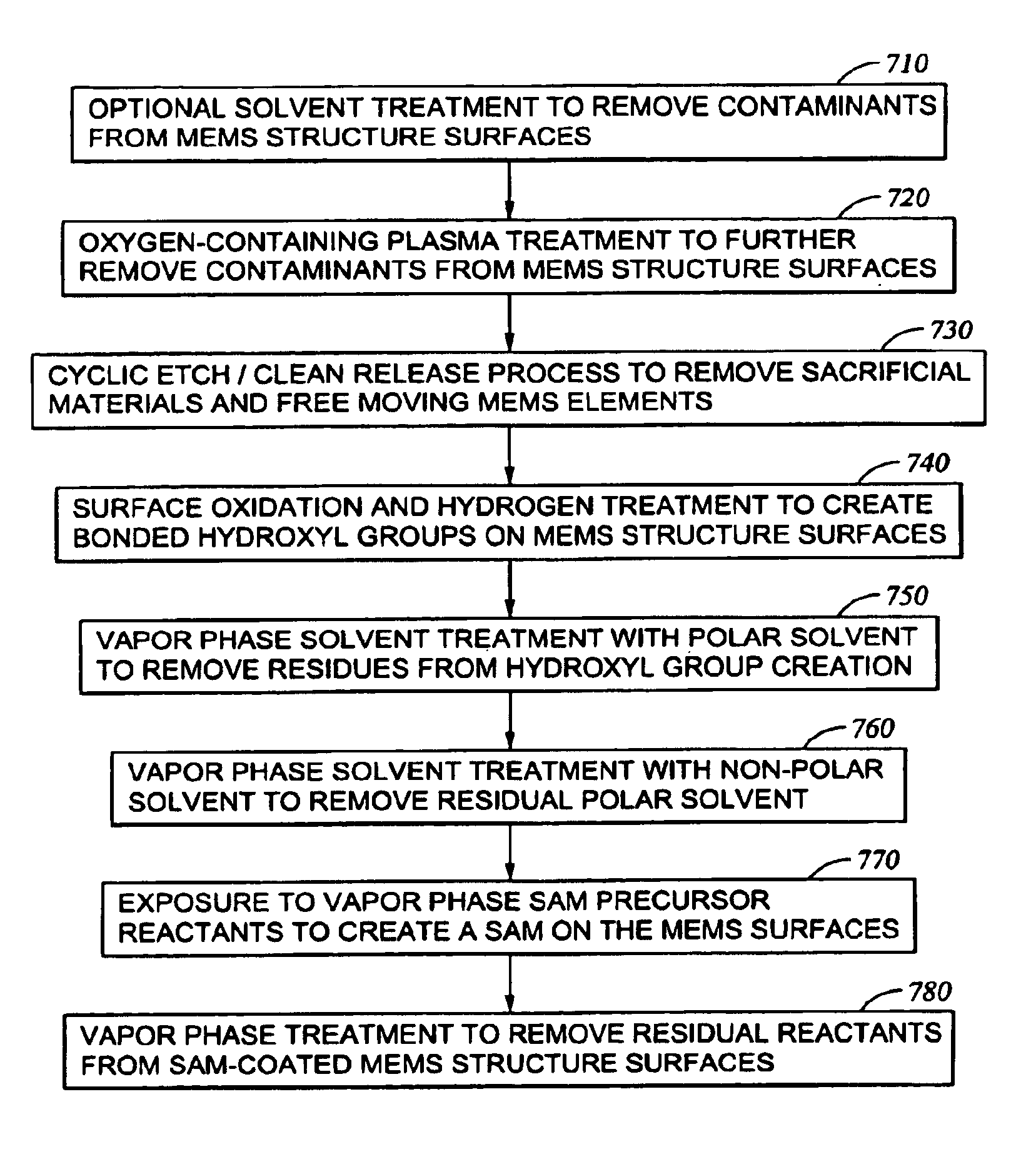
Disclosed herein is a method of improving the adhesion of a hydrophobic self-assembled monolayer (SAM) coating to a surface of a MEMS structure, for the purpose of preventing stiction. The method comprises treating surfaces of the MEMS structure with a plasma generated from a source gas comprising oxygen and, optionally, hydrogen. The treatment oxidizes the surfaces, which are then reacted with hydrogen to form bonded OH groups on the surfaces. The hydrogen source may be present as part of the plasma source gas, so that the bonded OH groups are created during treatment of the surfaces with the plasma. Also disclosed herein is an integrated method for release and passivation of MEMS structures which may be adjusted to be carried out in a either a single chamber processing system or a multi-chamber processing system.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Ground strap for suppressing stiction during MEMS fabrication
ActiveUS7544531B1Impedence networksSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGround StrapConductive materials
To suppress stiction of a MEMS resonator during fabrication, conductive structures of the MEMS resonator are electrically coupled via a ground strap during the step of forming isolation trenches around their contact structures. After the isolation trenches have been formed, the ground strap is transformed into a non-conductive material to complete the electrical isolation of the conductive structures. An etch mask formed on top of the ground strap prevents etching of the ground strap during the formation of the trenches. Depending on the etching process, the ground strap may be formed as a bridge that suspends above the isolation trench or as a column that extends down to the bottom of the isolation trench.
Owner:SITIME
Process for manufacturing electro-mechanical systems
ActiveUS9139425B2Minimizing and eliminating effectReduce fluxTransducer detailsDecorative surface effectsEngineeringStiction
A method of avoiding stiction during vapor hydrofluoride (VHF) release of a microelectromechanical system (MEMS) or nanoelectromechanical system (NEMS) composed of a mechanical device and a substrate is described. A silicon nitride layer is provided between the substrate and a sacrificial oxide layer and / or between a device layer and the sacrificial oxide layer, and / or on a side of the device layer facing away from the sacrificial oxide layer, and converted to thicker ammonium hexafluorosilicate with VHF while simultaneously removing a portion of the sacrificial oxide. The ammonium hexafluorosilicate acts as a temporary support, shim, wedge, or tether which limits device movement during fabrication and is later removed by sublimation under heat and / or reduced pressure.
Owner:SPTS TECH LTD
Systems and methods for overcoming stiction
InactiveUS6856068B2Stiction force can be overcomePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCoupling light guidesEngineeringStiction
A number of methods and systems for overcoming stiction are provided. The systems include electro-mechanical systems capable of exerting a variety of forces upon areas prone to stiction. The systems can be MEMS arrays or other types of devices where stiction related forces occur. The methods include a variety of ways of causing movement in areas prone to stiction forces. Such movement can be vibrational in nature and is sufficient to overcome stiction, allowing a trapped element to be moved to a desired location.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Stiction-free drying process with contaminant removal for high-aspect ratio semiconductor device structures
ActiveUS20140144462A1Reduces and eliminates negative effectReduces and eliminates stictionElectrostatic cleaningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringStiction
Embodiments of the invention generally relate to a method of cleaning a substrate and a substrate processing apparatus that is configured to perform the method of cleaning the substrate. More specifically, embodiments of the present invention relate to a method of cleaning a substrate in a manner that reduces or eliminates the negative effects of line stiction between semiconductor device features. Other embodiments of the present invention relate to a substrate processing apparatus that allows for cleaning of the substrate in a manner that reduces or eliminates line stiction between semiconductor device features formed on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Recessed electrode for electrostatically actuated structures
InactiveUS7064637B2Reduce the starting voltageReduce gap distanceElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysElectrostrictive/piezoelectric relaysStictionVoltage
An electro-statically actuated switch having a reduced gap distance between electrodes for reducing actuation voltage is provided. The invention provides more reliable electro-statically actuated switches. The invention provides a micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) that includes a recessed, movable electrode. The invention provides electro-statically actuated switches that reduce the likelihood of stiction and beam deformation and that allows lower actuation voltage for electrostatically actuated structures such as switches and mirrors. A method for fabricating such a design is provided that allows lower actuation voltage.
Owner:AAC TECH PTE LTD
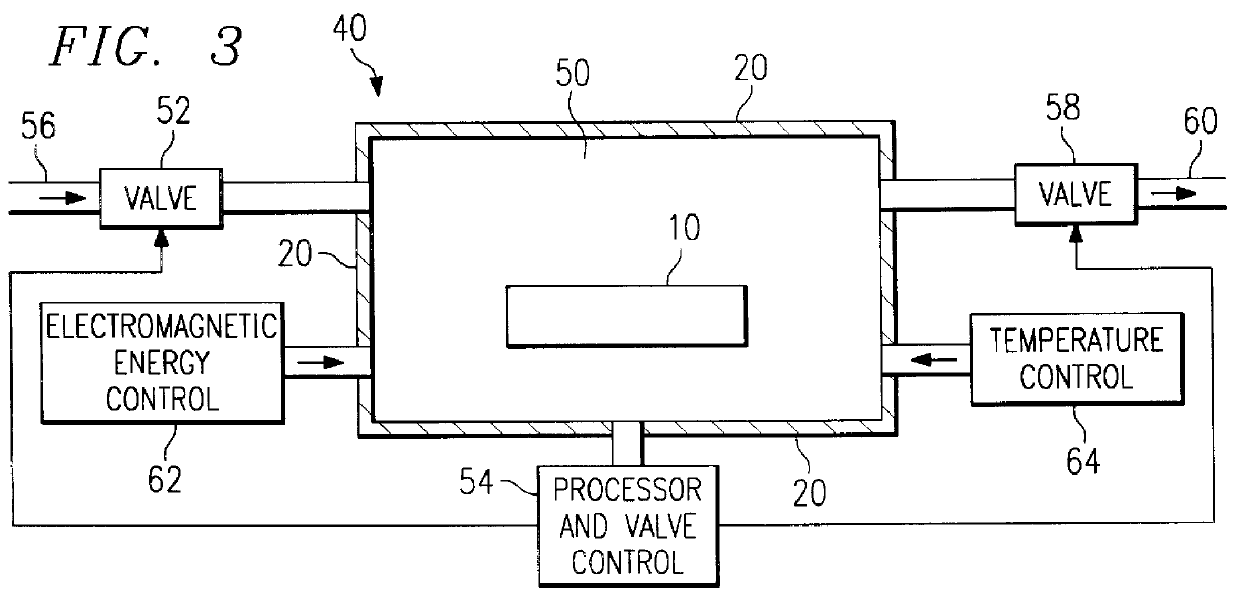
Removal of MEMS sacrificial layers using supercritical fluid/chemical formulations
InactiveUS20050118832A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesCompound (substance)Stiction
A method and composition for removing silicon-containing sacrificial layers from Micro Electro Mechanical System (MEMS) substrates having such sacrificial layers is described. The etching compositions include a supercritical fluid, an etchant species, a co-solvent, and optionally a surfactant. Such etching compositions overcome the intrinsic deficiency of SCFs as cleaning reagents, viz., the non-polar character of SCFs and their associated inability to solubilize polar species that must be removed from the semiconductor substrate. The resultant etched MEMS substrates experience lower incidents of stiction relative to MEMS substrates etched using conventional wet etching techniques.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
Anti-stiction technique for electromechanical systems and electromechanical device employing same
InactiveUS7449355B2Operating environment limitedMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesMetal foilEngineering
A mechanical structure is disposed in a chamber, at least a portion of which is defined by the encapsulation structure. A first method provides a channel cap having at least one preform portion disposed over or in at least a portion of an anti-stiction channel to seal the anti-stiction channel, at least in part. A second method provides a channel cap having at least one portion disposed over or in at least a portion of an anti-stiction channel to seal the anti-stiction channel, at least in part. The at least one portion is fabricated apart from the electromechanical device and thereafter affixed to the electromechanical device. A third method provides a channel cap having at least one portion disposed over or in at least a portion of the anti-stiction channel to seal an anti-stiction channel, at least in part. The at least one portion may comprise a wire ball, a stud, metal foil or a solder preform. A device includes a substrate, an encapsulation structure and a mechanical structure. An anti-stiction layer is disposed on at least a portion of the mechanical structure. An anti-stiction channel is formed in at least one of the substrate and the encapsulation structure. A cap has at least one preform portion disposed over or in at least a portion of the anti-stiction channel to seal the anti-stiction channel, at least in part.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Capacitive microphone and method for making the same
ActiveUS20070154040A1Avoid static frictionAvoid driftingElectrostatic transducer microphonesDeaf-aid setsEngineeringStiction
A capacitive microphone and method for making the same are provided. A backplate with a plurality of holes is formed on a substrate with at least one cavity, and a diaphragm is formed above the backplate. There is an air gap between the backplate and the diaphragm. The air gap and the cavity communicate with each other by each hole. The diaphragm and the backplate are separated by a first distance and a second distance which is smaller than the first distance, such that the difference is formed on the diaphragm. The second distance area is fastened through surface stiction produced by mist or other fluids.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Dry etch release of MEMS structures
InactiveUS6666979B2Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingParticulatesEtching
The present invention pertains to a method of fabricating a surface within a MEM which is free moving in response to stimulation. The free moving surface is fabricated in a series of steps which includes a release method, where release is accomplished by a plasmaless etching of a sacrificial layer material. An etch step is followed by a cleaning step in which by-products from the etch step are removed along with other contaminants which may lead to stiction. There are a series of etch and then clean steps so that a number of "cycles" of these steps are performed. Between each etch step and each clean step, the process chamber pressure is typically abruptly lowered, to create turbulence and aid in the removal of particulates which are evacuated from the structure surface and the process chamber by the pumping action during lowering of the chamber pressure. The final etch / clean cycle may be followed by a surface passivation step in which cleaned surfaces are passivated and / or coated.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Detection and Quantification of Stiction
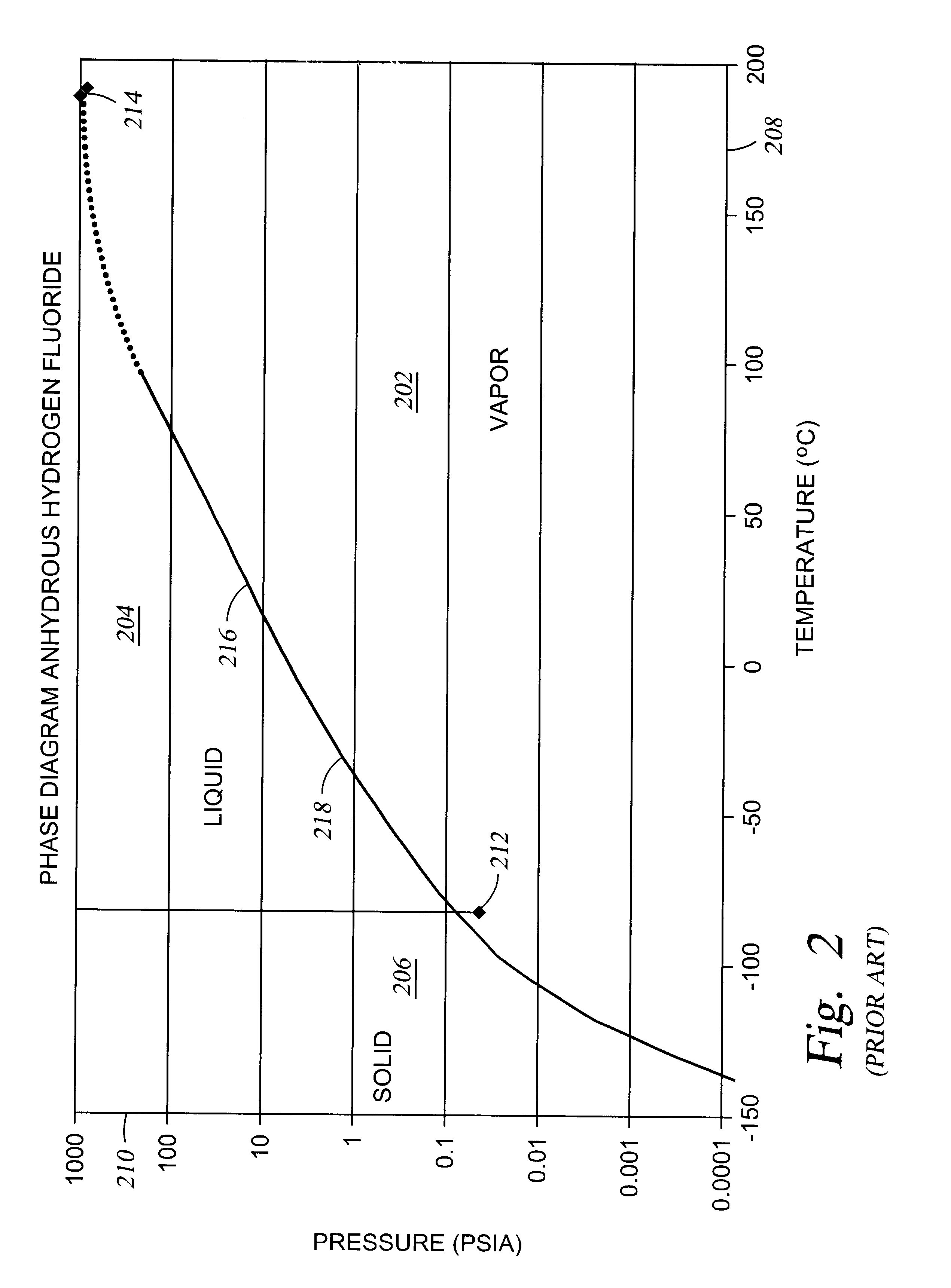
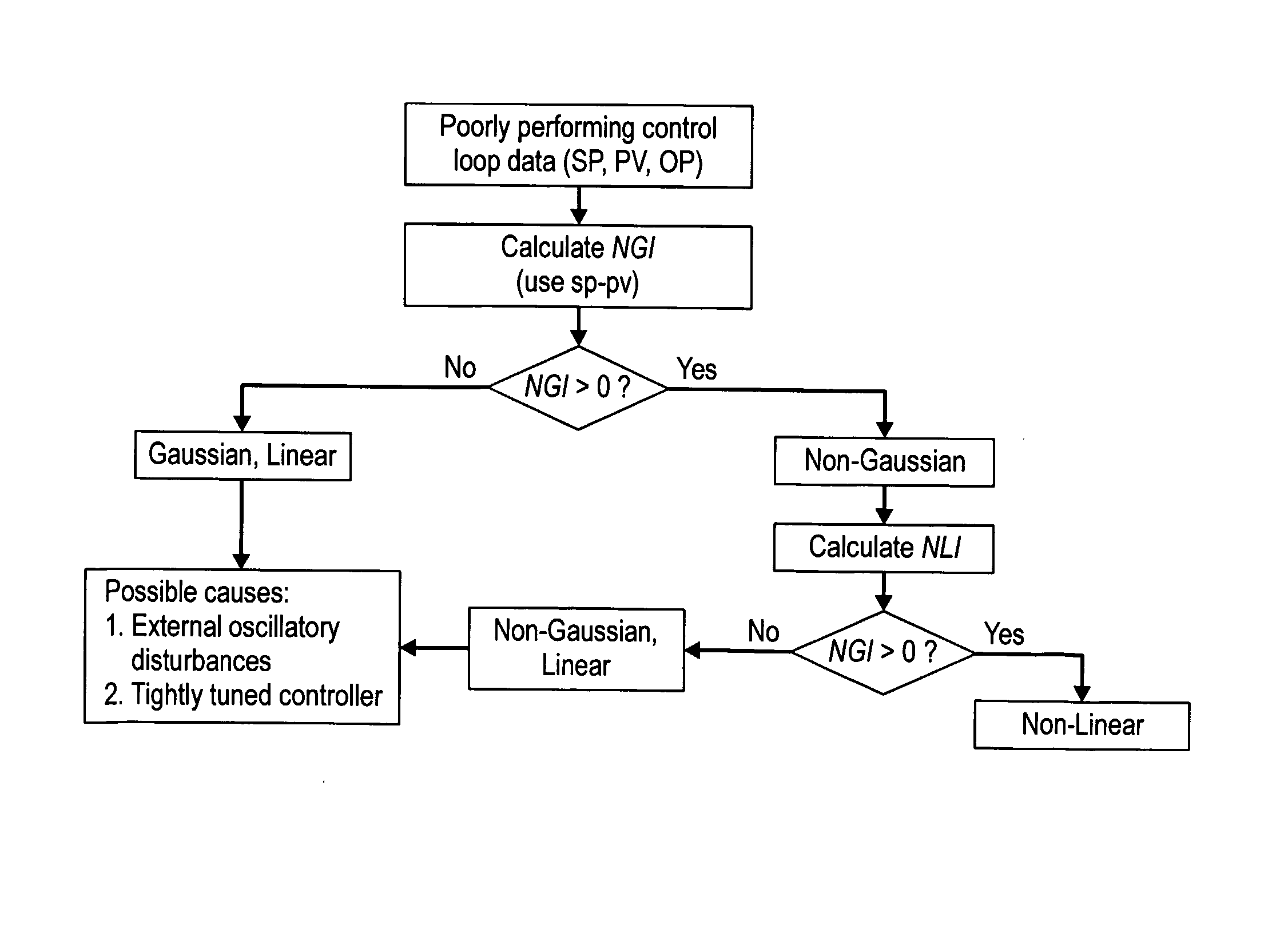
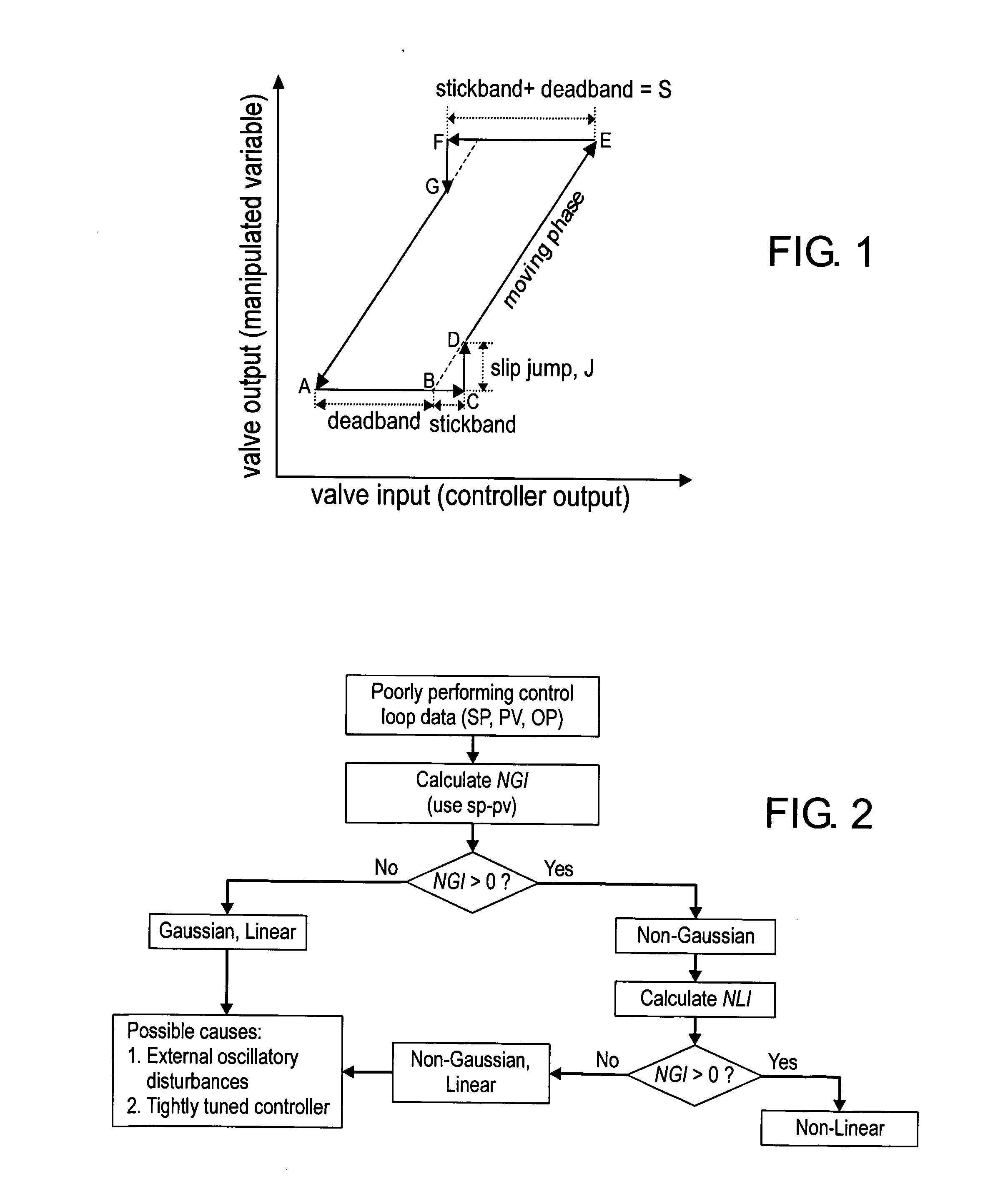
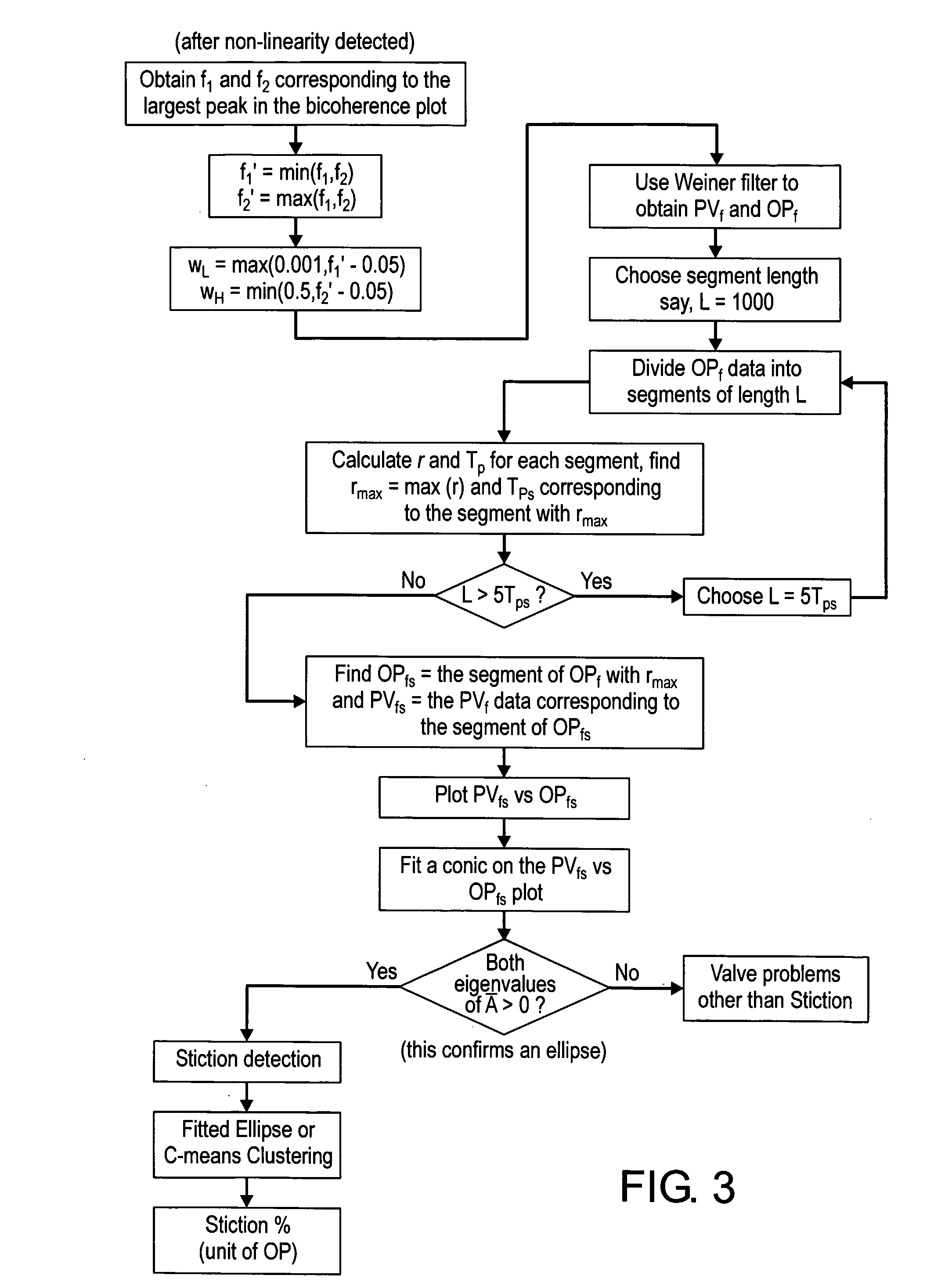
An effective non-intrusive data-based monitoring method may reduce the cost of control loop performance maintenance by screening and short-listing those control loops or valves that need maintenance. The invention comprises a data-based, model-free, non-invasive method that can automatically detect and quantify stiction present in control valves. The method does not require the implementation of any additional valve travel test or, as commonly known, bump test of the control loop. The method may detect and quantify stiction using controlled variable (pv), controller output (op) and set point (sp) data. It does not require valve positioner (mv) data.
Owner:THE UNIV OF ALBERTA +1
Dry etch release of MEMS structures
InactiveUS20030080082A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingParticulatesEtching
The present invention pertains to a method of fabricating a surface within a MEM which is free moving in response to stimulation. The free moving surface is fabricated in a series of steps which includes a release method, where release is accomplished by a plasmaless etching of a sacrificial layer material. An etch step is followed by a cleaning step in which by-products from the etch step are removed along with other contaminants which may lead to stiction. There are a series of etch and then clean steps so that a number of "cycles" of these steps are performed. Between each etch step and each clean step, the process chamber pressure is typically abruptly lowered, to create turbulence and aid in the removal of particulates which are evacuated from the structure surface and the process chamber by the pumping action during lowering of the chamber pressure. The final etch / clean cycle may be followed by a surface passivation step in which cleaned surfaces are passivated and / or coated.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Moving a free-standing structure between high and low adhesion states
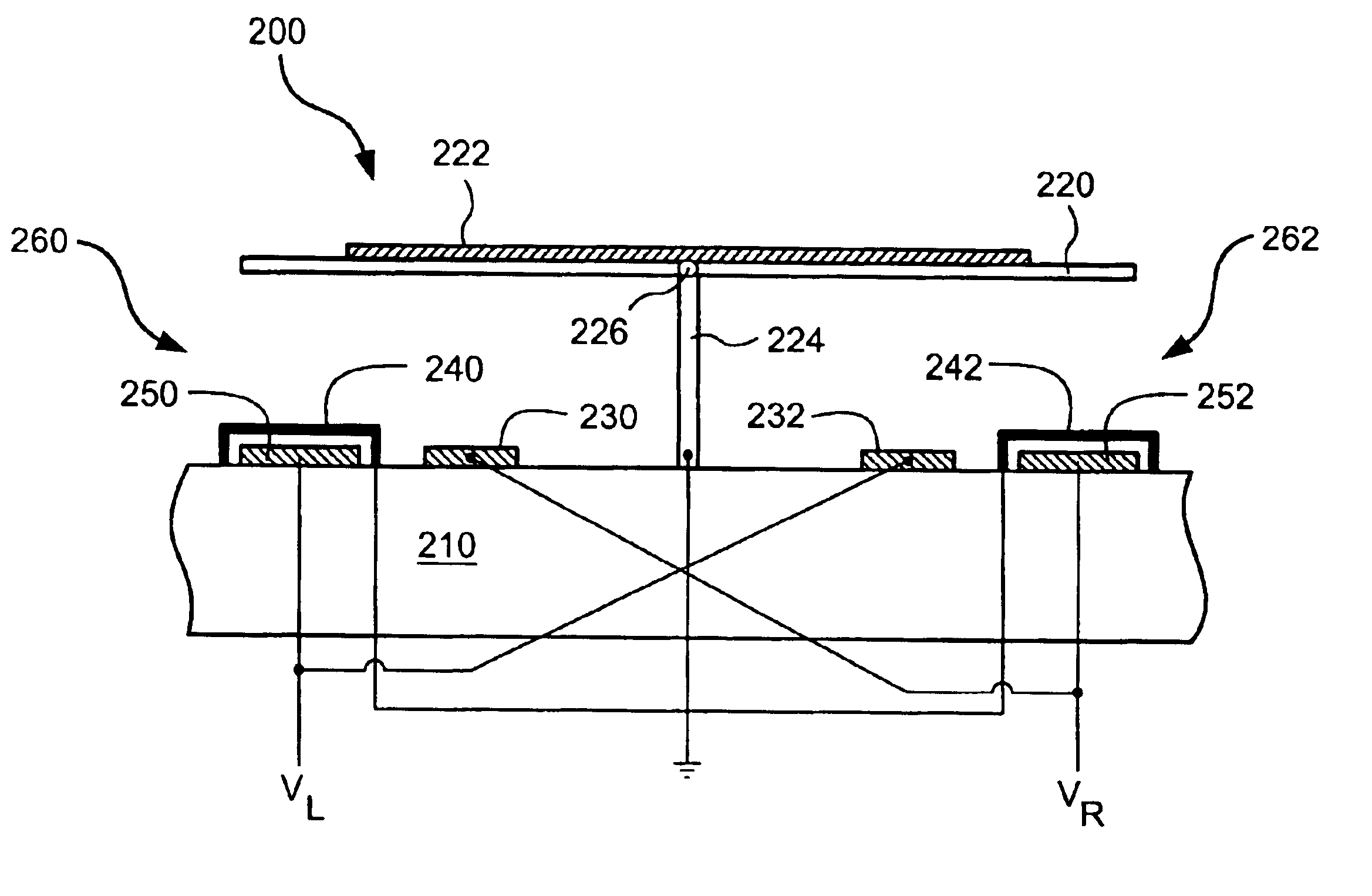
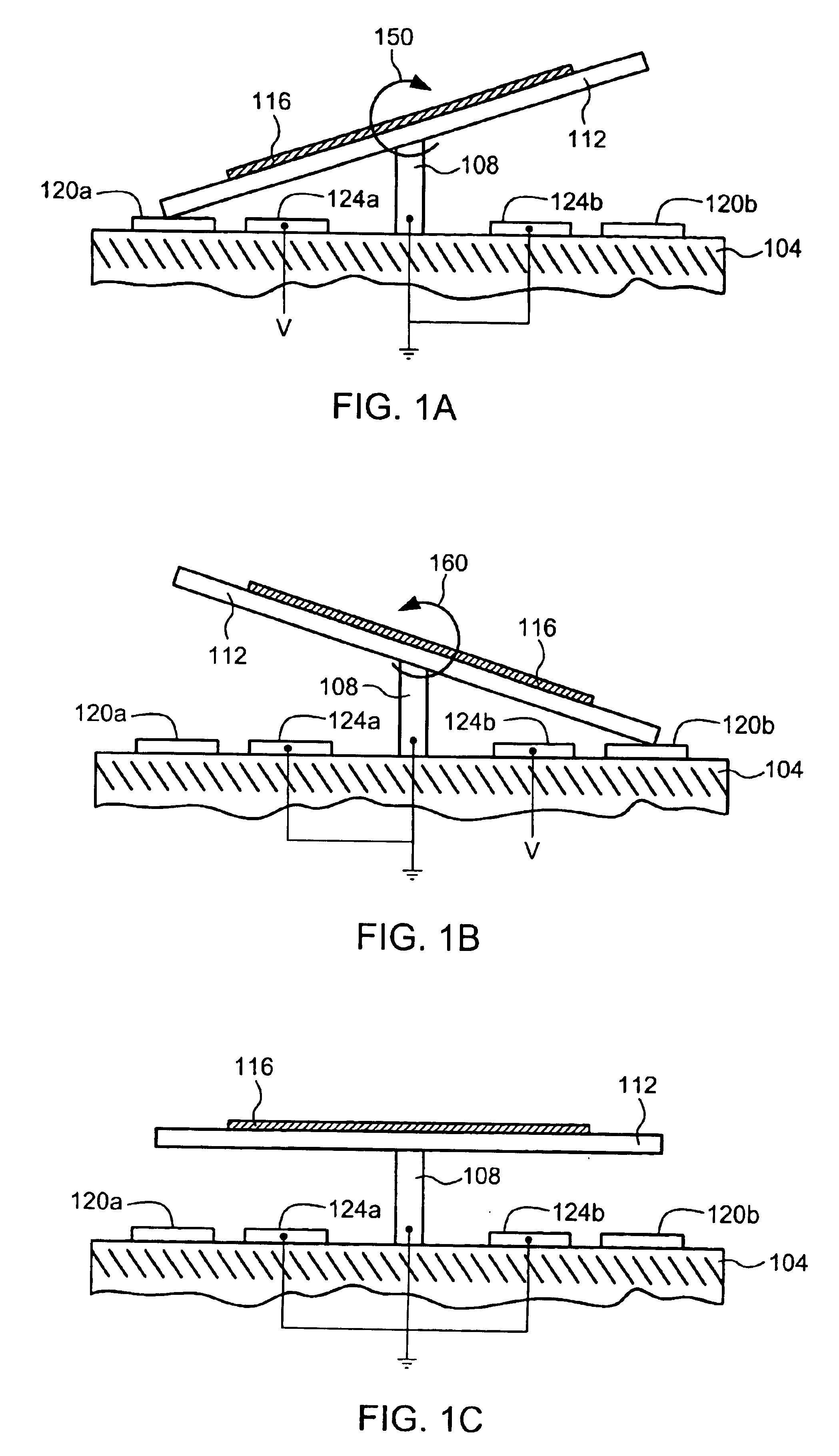
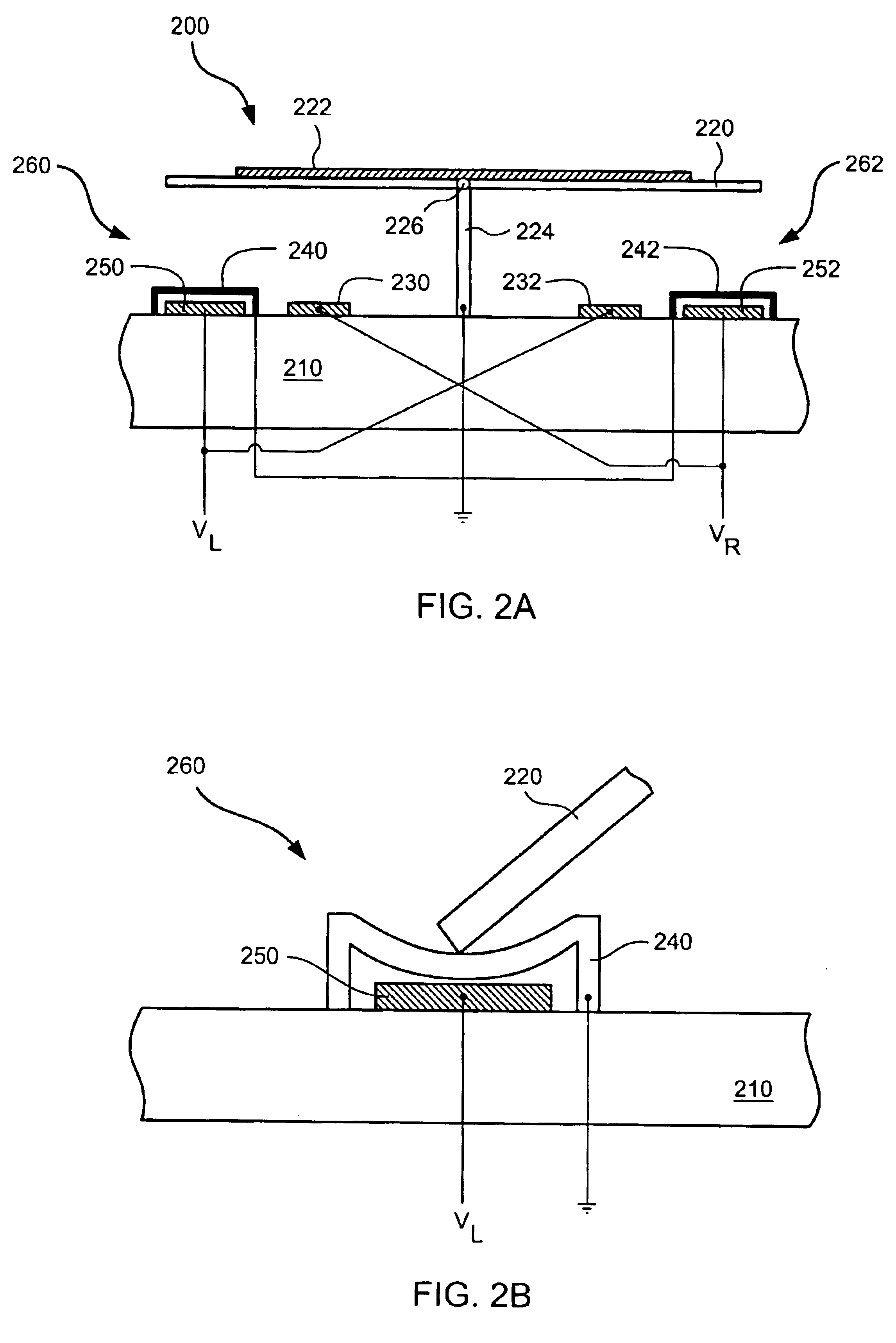
Embodiments disclosed herein generally solve a stiction problem in switching devices by using a series of pulses of force which take the switch from being strongly adhered to a landing electrode to the point where it is only weakly adhered. Once in the low adhesion state, the switch can then be pulled away from contact with a lower force provided by either the spring constant of the switch and / or the electrostatic forces resulting from low voltages applied to nearby electrodes.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Slider having a textured air bearing surface, head stack assembly and disk drive using same
InactiveUS6937439B1Reduce static frictionRecord information storageFluid-dynamic spacing of headsAir bearingTransducer
A disk drive includes a disk having a recording surface and a head stack assembly. The head stack assembly includes a body portion that includes a bore defining a pivot axis, an actuator arm cantilevered from the body portion and a head gimbal assembly supported at the actuator arm. The head gimbal assembly includes a load beam, a gimbal coupled to the load beam and a slider coupled to the gimbal, the slider including a transducer for reading and writing on the recording surface. The slider includes an air bearing surface that is configured to form a shallow recessed surface and a deep recessed surface. The air-bearing surface includes a leading air bearing region and one or more insular regions configured to reduce stiction with the disk. The shallow recessed surface is disposed between the air bearing surface and the deep recessed surface.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Vapor deposition of dihalodialklysilanes
InactiveUS20030161949A1Liquid surface applicatorsChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseDeposition process
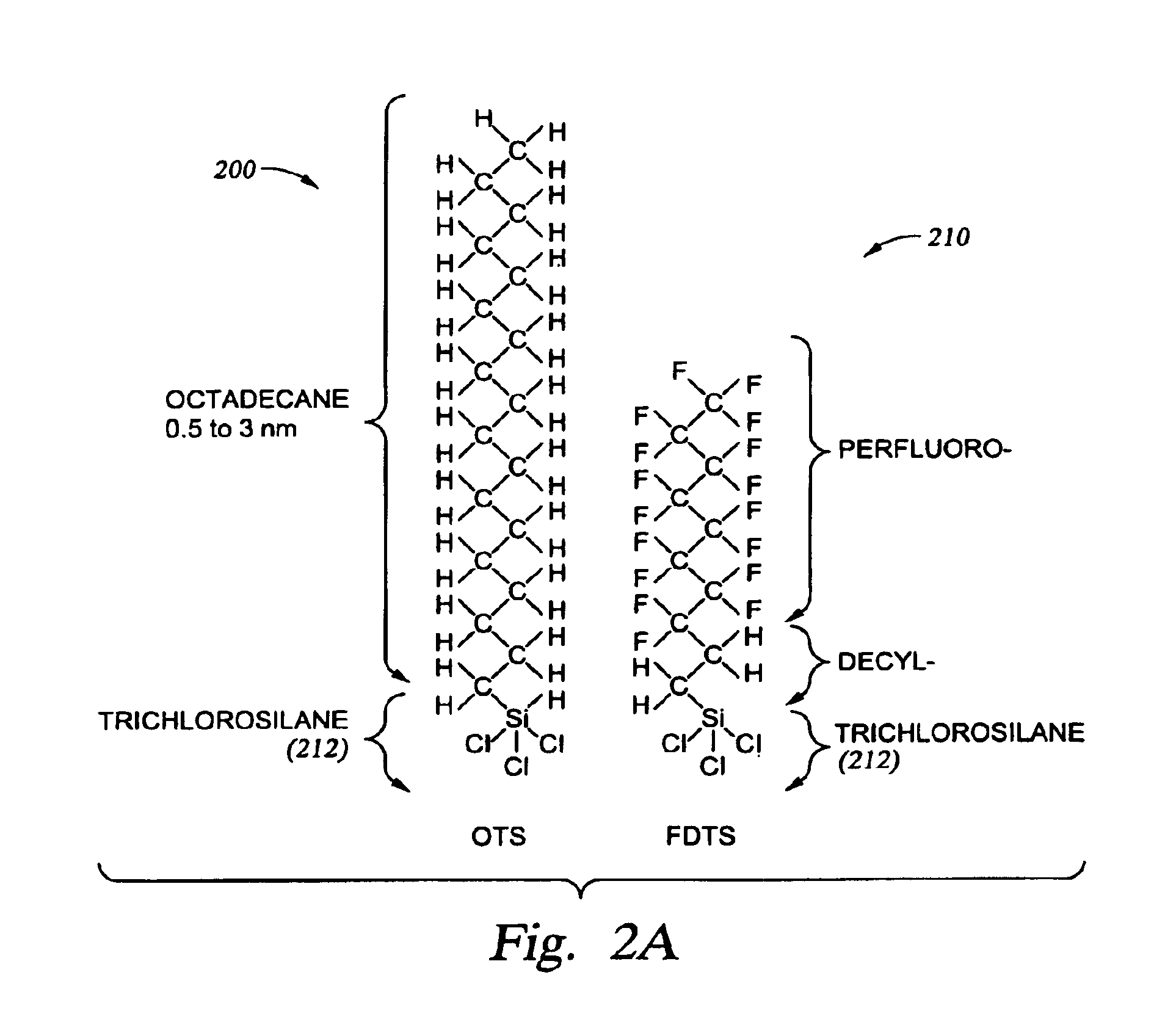
Coatings of dialkylsilyloxy groups are applied to water-wettable surfaces by chemical vapor deposition using dihalodialkylsilanes with short-chain alkyl groups. Some of the surfaces which will benefit from the application of these coatings are hydroxyl-terminated silicon surfaces of microelectromechanical systems, nanoelectromechanical systems, and biomicroelectromechanical systems, while surfaces of other chemistries will benefit as well. When applied to a microstructure on an MEMS surface, the coating reduces stiction in the microstructure. The use of the vapor phase as a deposition medium facilitates the deposition process and permits close control over the reaction conditions and the characteristics of the resulting coating.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Polishing composition and method for defect improvement by reduced particle stiction on copper surface
InactiveUS20060278614A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical chemistryEther
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Removal of MEMS sacrificial layers using supercritical fluid/chemical formulations
InactiveUS20070111533A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface treatment compositionsCompound (substance)Stiction
A method and composition for removing silicon-containing sacrificial layers from Micro Electro Mechanical System (MEMS) and other semiconductor substrates having such sacrificial layers is described. The etching compositions include a supercritical fluid (SCF), an etchant species, a co-solvent, and optionally a surfactant. Such etching compositions overcome the intrinsic deficiency of SCFs as cleaning reagents, viz., the non-polar character of SCFs and their associated inability to solubilize polar species that must be removed from the semiconductor substrate. The resultant etched substrates experience lower incidents of stiction relative to substrates etched using conventional wet etching techniques.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
Metal-insulator-metal (MIM) switching devices
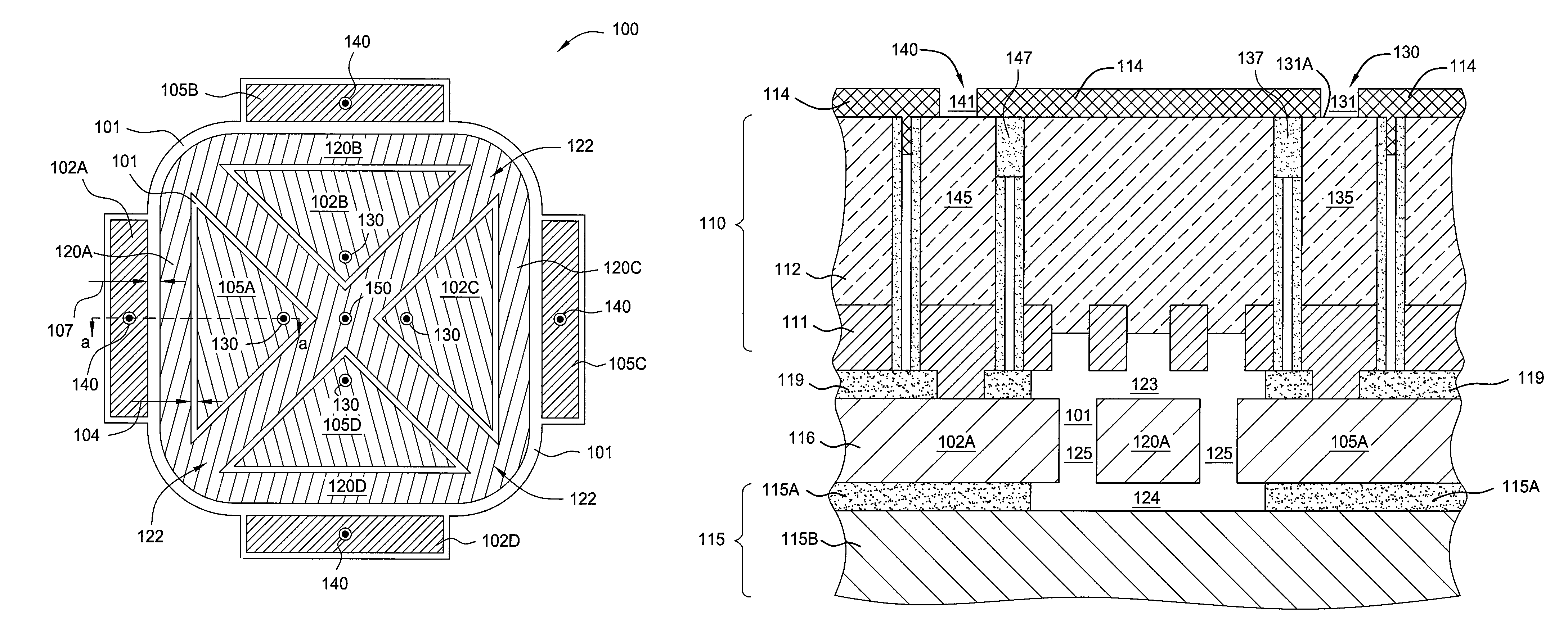
ActiveUS20090128221A1Excellent on-state conductanceWide operating temperature rangeTransistorCircuit-breaking switches for excess currentsMetal-insulator-metalHigh temperature electronics
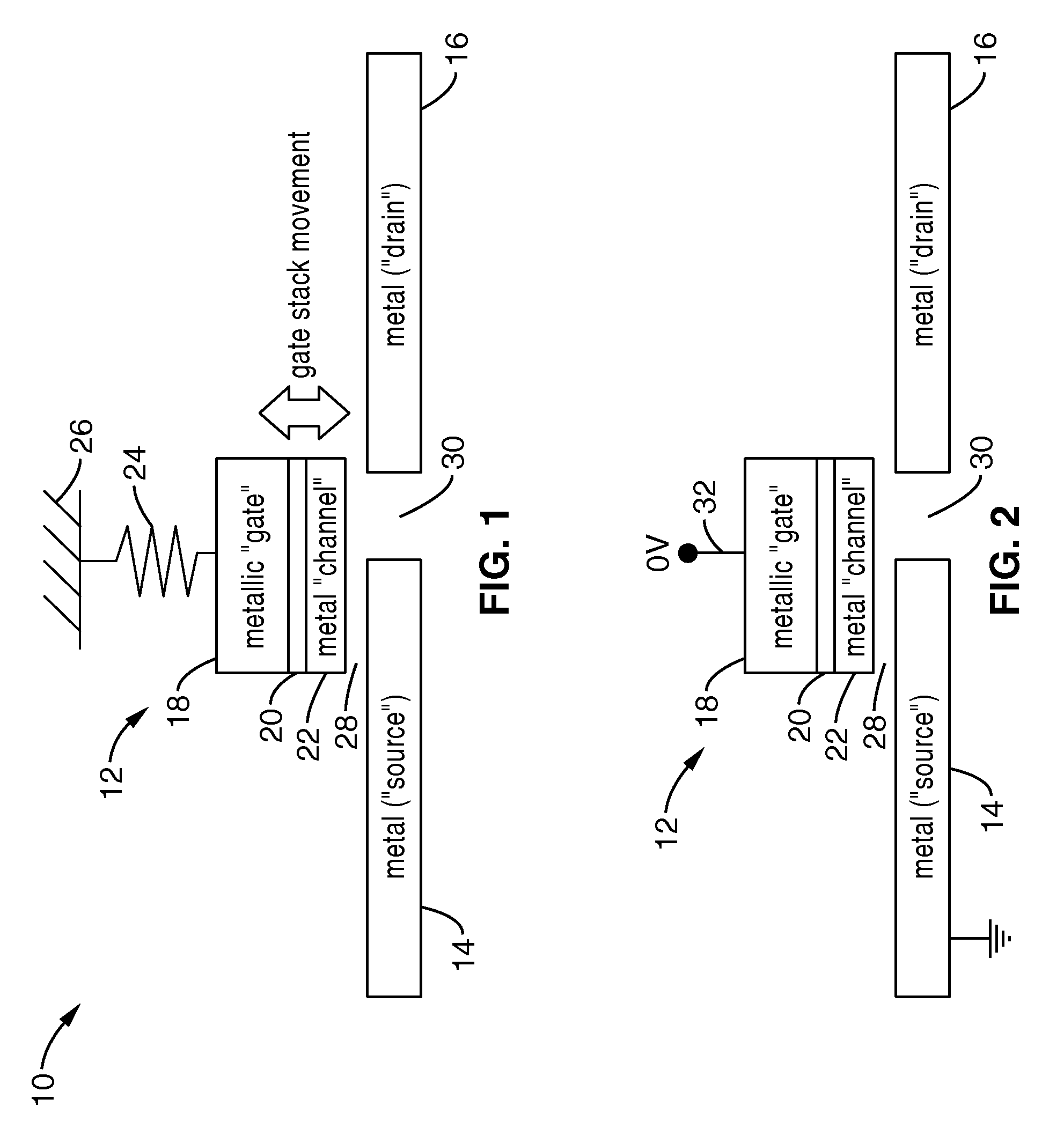
A gated nano-electro-mechanical (NEM) switch employing metal-insulator-metal (MIM) technology and related devices and methods which can facilitate implementation of low-power, radiation-hardened, high-temperature electronic devices and circuits. In one example embodiment a gate electrode is configured as a cantilever beam whose free end is coupled to a MIM stack. The stack moves into bridging contact across a source and drain region when the applied gate voltage generates a sufficient electrostatic force to overcome the mechanical biasing of the cantilever beam. A second set of contacts can be added on the cantilever beam to form a complementary switching structure, or to a separate cantilever beam. The switching can be configured as non-volatile in response to stiction forces. NEM circuits provide a number of advantages within a variety of circuit types, including but not limited to: logic, memory, sleep circuits, pass circuits, and so forth.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
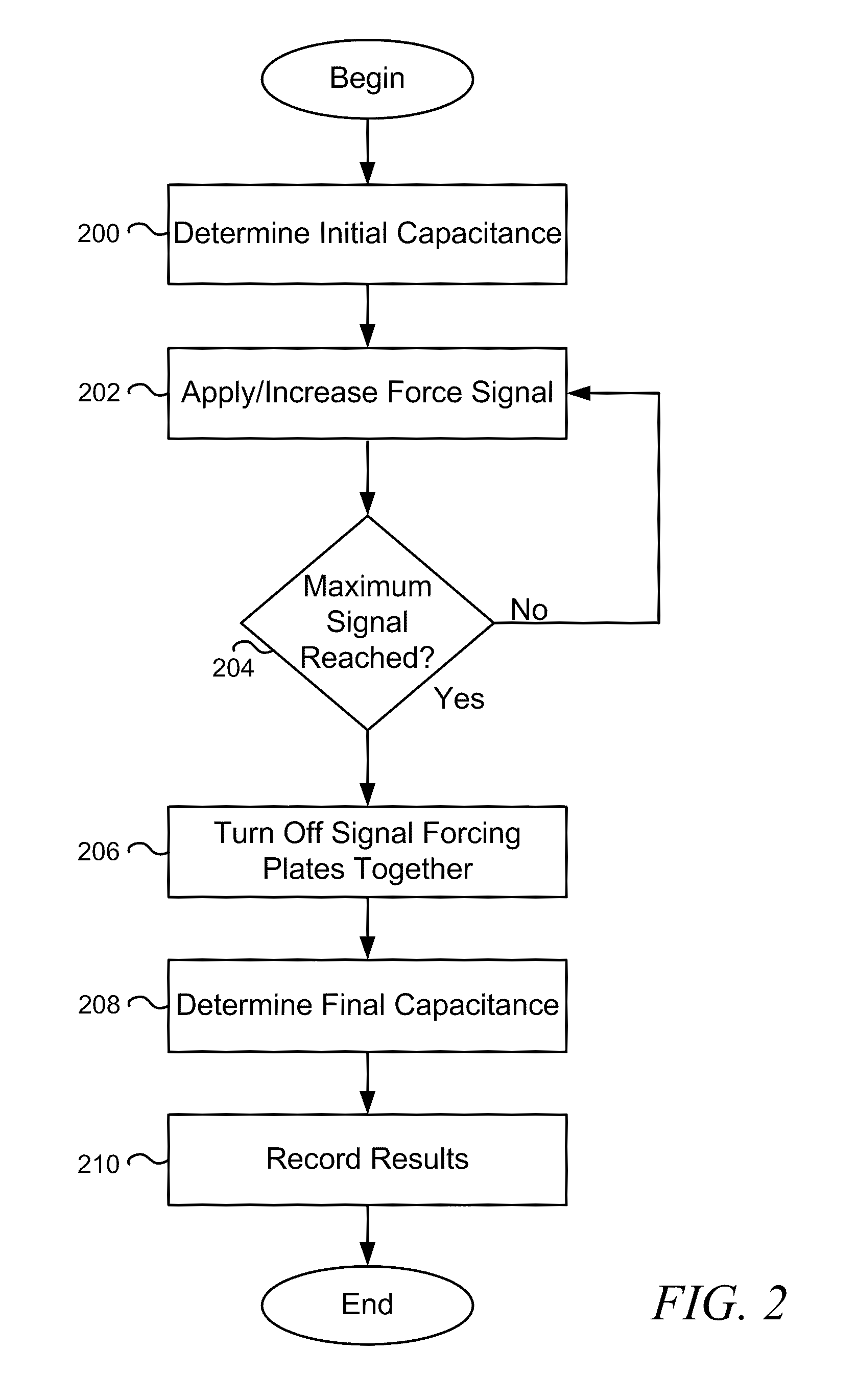
MEMS Stiction Testing Apparatus and Method
ActiveUS20090320557A1Attenuation of electrical signalSolution value is not highTesting dielectric strengthUsing mechanical meansElectricityStiction
A MEMS stiction testing method applies a first electrical signal to a MEMS device having two opposing surfaces to cause the two opposing surfaces to make physical contact. The two opposing surfaces produce a second electrical signal when in physical contact. The method then substantially mitigates the first electrical signal after detecting that the second electrical signal has reached a prescribed maximum value.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Removal of MEMS sacrificial layers using supercritical fluid/chemical formulations
InactiveUS7160815B2Non-surface-active detergent compositionsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCompound (substance)Stiction
A method and composition for removing silicon-containing sacrificial layers from Micro Electro Mechanical System (MEMS) and other semiconductor substrates having such sacrificial layers is described. The etching compositions include a supercritical fluid (SCF), an etchant species, a co-solvent, and optionally a surfactant. Such etching compositions overcome the intrinsic deficiency of SCFs as cleaning reagents, viz., the non-polar character of SCFs and their associated inability to solubilize polar species that must be removed from the semiconductor substrate. The resultant etched substrates experience lower incidents of stiction relative to substrates etched using conventional wet etching techniques.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
Reduced stiction printhead surface
ActiveUS7510267B2Reduction factorPrintingFlexible microstructural devicesStatic friction coefficientPaper dust
An inkjet printhead with a nozzle plate that has an exterior surface with formations for reducing its co-efficient of static friction. By reducing the co-efficient of static friction, there is less likelihood that paper dust or other contaminants will clog the nozzles in the nozzle plate. Static friction, or “stiction” as it has become known, allows dust particles to “stick” to nozzle plates and thereby clog nozzles. By patterning the exterior of the nozzle plate with raised formations, dust particles can only contact the outer extremities of each formation. This reduces friction between the particles and the nozzle plate so that any particles that contact the plate are less likely to attach, and if they do attach, they are more likely to be removed by printhead maintenance cleaning cycles.
Owner:SILVERBROOK RES PTY LTD +1
Deep reactive ion etching process and microelectromechanical devices formed thereby
InactiveUS7077007B2Uniform widthConstant gap widthAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDecorative surface effectsDevice formEngineering
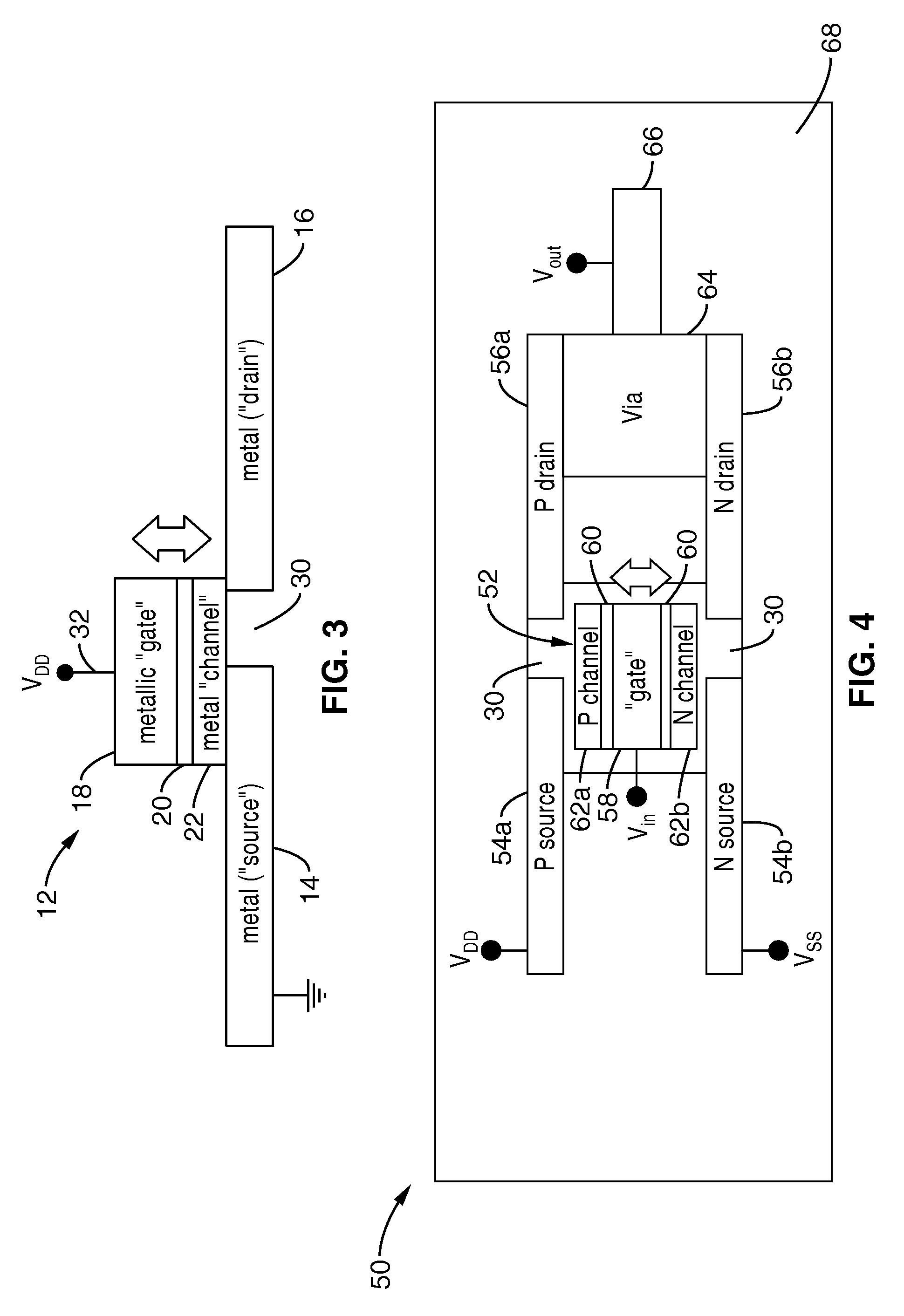
A process for forming a microelectromechanical system (MEMS) device by a deep reactive ion etching (DRIE) process during which a substrate overlying a cavity is etched to form trenches that breach the cavity to delineate suspended structures. A first general feature of the process is to define suspended structures with a DRIE process, such that the dimensions desired for the suspended structures are obtained. A second general feature is the proper location of specialized features, such as stiction bumps, vulnerable to erosion caused by the DRIE process. Yet another general feature is to control the environment surrounding suspended structures delineated by DRIE in order to obtain their desired dimensions. A significant problem identified and solved by the invention is the propensity for the DRIE process to etch certain suspended features at different rates. In addition to etching wider trenches more rapidly than narrower trenches, the DRIE process erodes suspended structures more rapidly at greater distances from anchor sites of the substrate being etched. At the masking level, the greater propensity for backside and lateral erosion of certain structures away from substrate anchor sites is exploited so that, at the completion of the etch process, suspended structures have acquired their respective desired widths.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com