Patents
Literature
288results about How to "Blocking phenomenon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
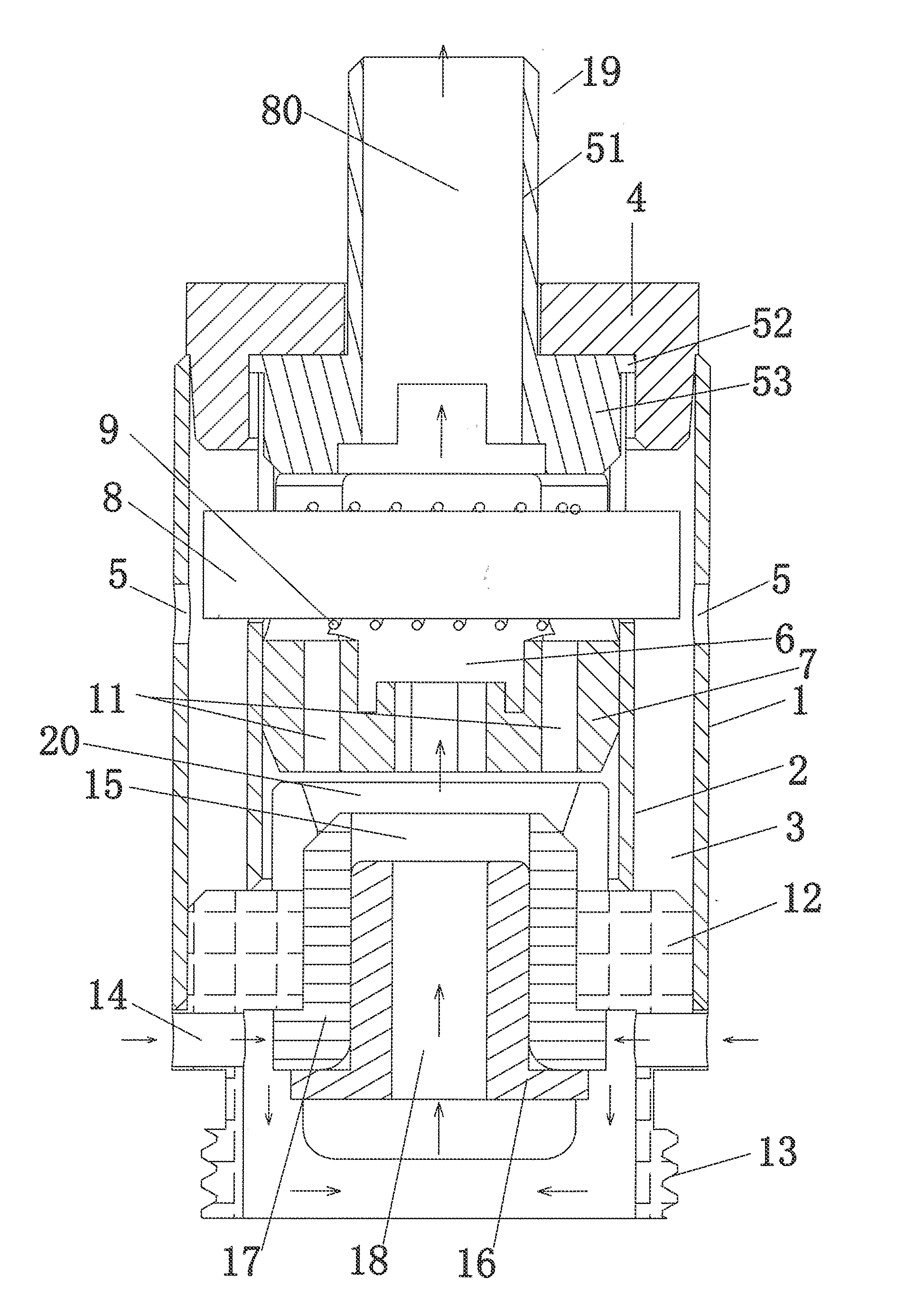
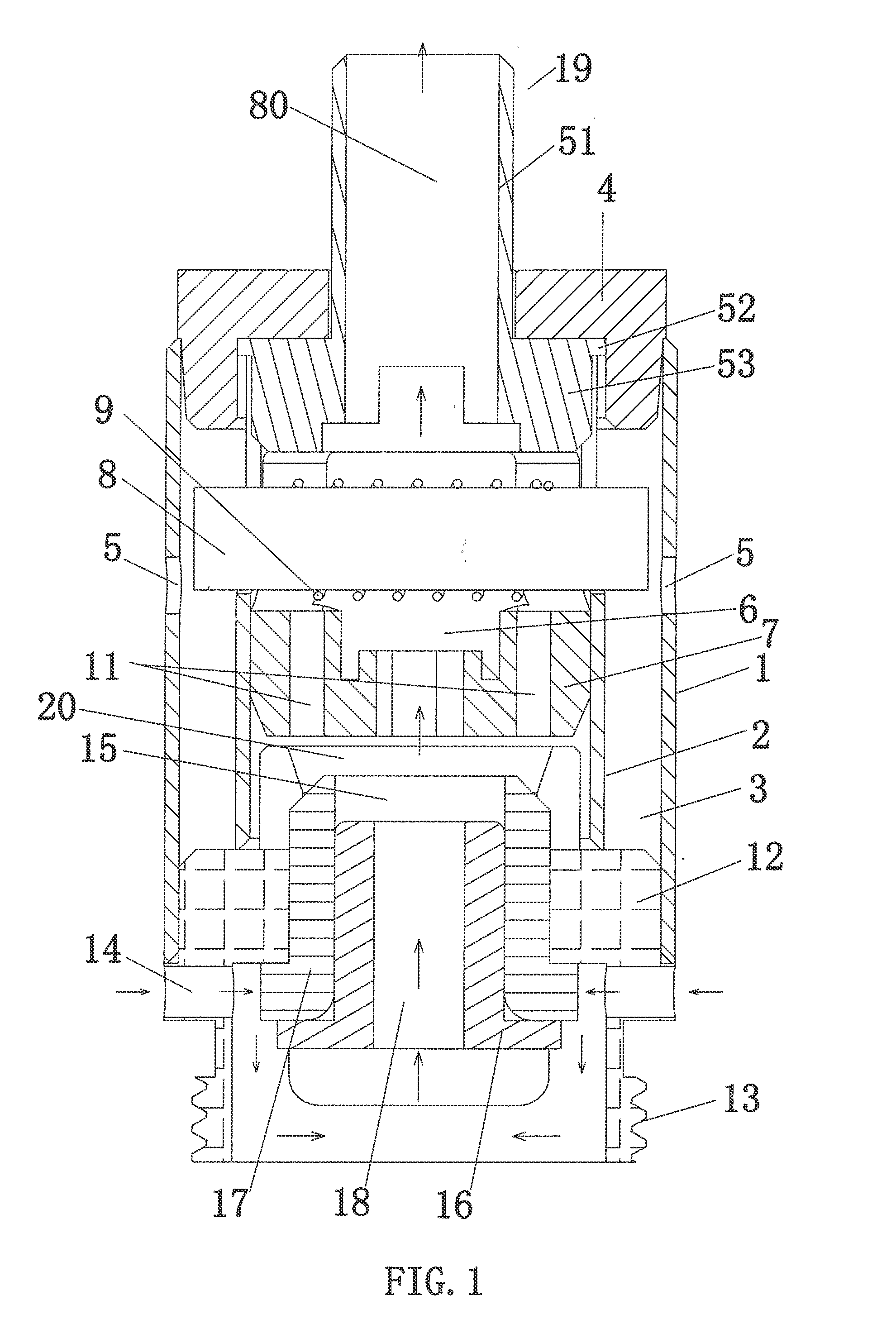
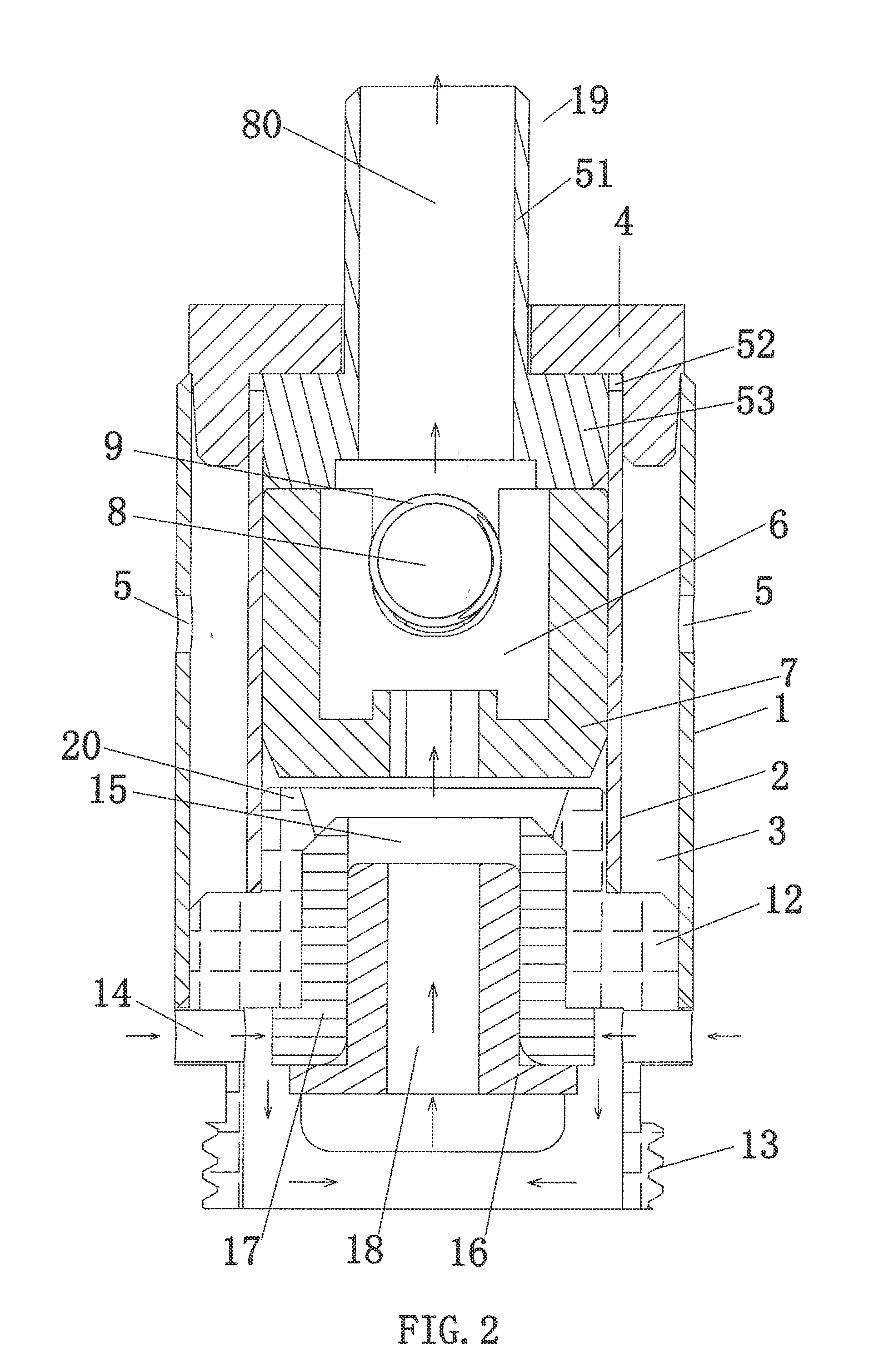
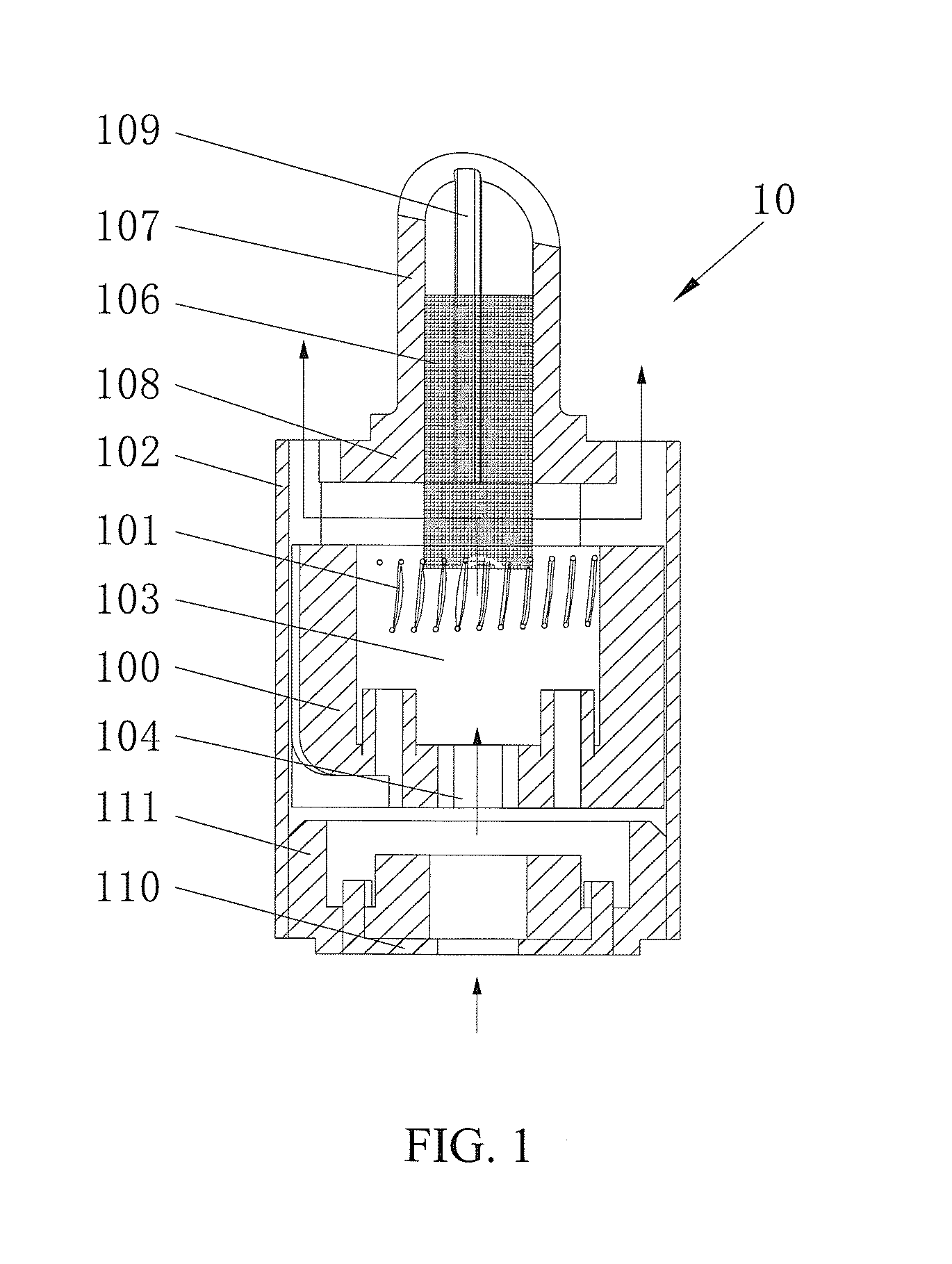
Atomizing Head
ActiveUS20150059787A1Simple structureAccelerate liquid flowLighting and heating apparatusTobacco pipesEngineeringVoltage
The present invention discloses an atomizer head assembly, comprising: an outer tube; an inner tube disposed in the outer tube, having a outer supporter openings formed on a lateral side of wall of the inner tube; a liquid storage chamber formed between the inner tube and the outer tube; a liquid inlet opening formed on a lateral side of wall of the outer tube; and an atomizing member having an end arranged in the one or more outer supporter openings. Moreover, the atomizing head assembly of the present invention comprises a plurality of atomizing members for atomizing liquid electrically connected in parallel and spatially arrange in various configurations, such that the atomizer head assembly can operated with an elevated voltage such that the heat generated per unit time by the atomizer head assembly is increased and the volume of atomized cigarette liquid in the atomizing chamber is increased accordingly.
Owner:JOYETECH CHANGZHOU ELECTRONICS
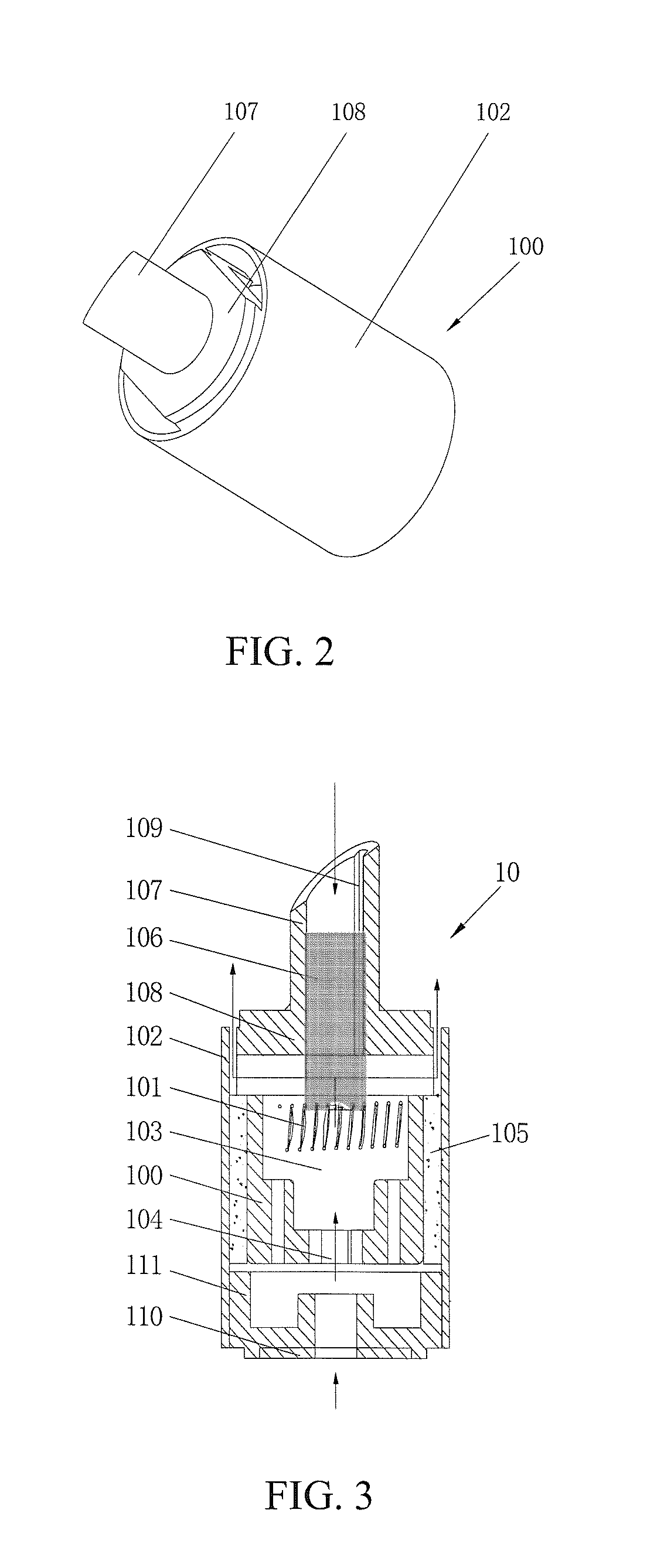
Replaceable universal atomizing head
InactiveUS20140190477A1Prevention of dry burningSimple structureMedical devicesTobacco devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
The present invention discloses a replaceable universal atomizing head, wherein the heating device is fixed in the atomizing chamber of the support base, and said liquid guiding member comprises a liquid guiding rope, a liquid guiding nozzle and a liquid guiding nozzle seat connected integrally with the liquid guiding nozzle, wherein one end of the liquid guide rope pierced from the liquid guiding nozzle seat and reaches heating device, further comprising a conductive ring, wherein said support base is fixed in the middle of the conductive ring cavity, pressing a wire connected to one end of the heating device between the conductive ring and the support base; the wall surface of the inner hole of the liquid nozzle and the liquid guiding nozzle seat provides a liquid guiding slot; one end of the liquid guiding nozzle seat is inserted into one end of the conductive ring cavity; the other end of conductive ring cavity provides a conductive member, which comprises a conductor and an insulator, wherein the conductor is fixed on the insulator and welds with wire connected to the other end of the heating device, wherein the insulator with vent holes is fastened in the conductive ring cavity. Atomizing head of the present invention has a simple structure, is easy to assemble, and is able to prevent dry combustion.
Owner:JOYETECH CHANGZHOU ELECTRONICS
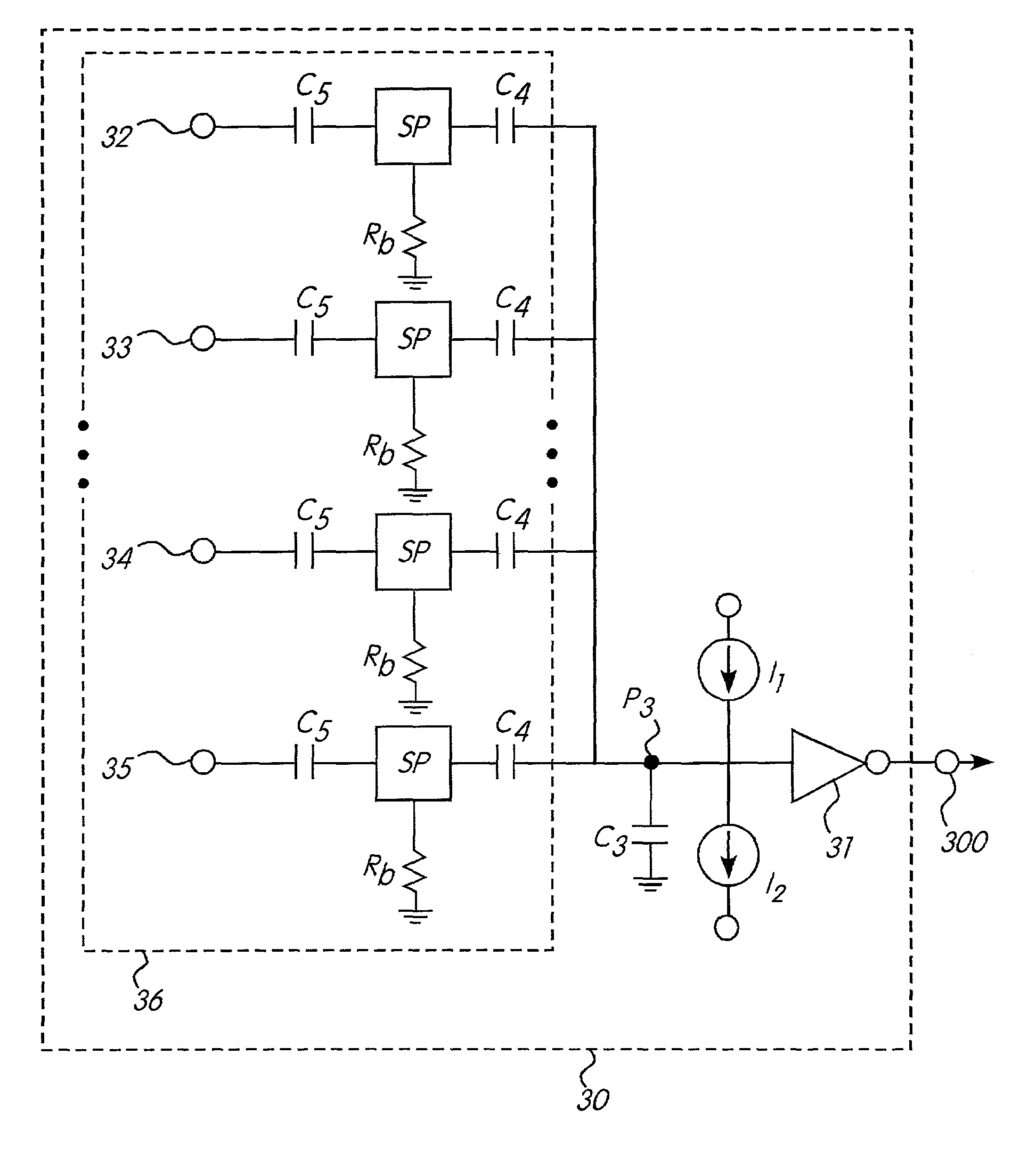
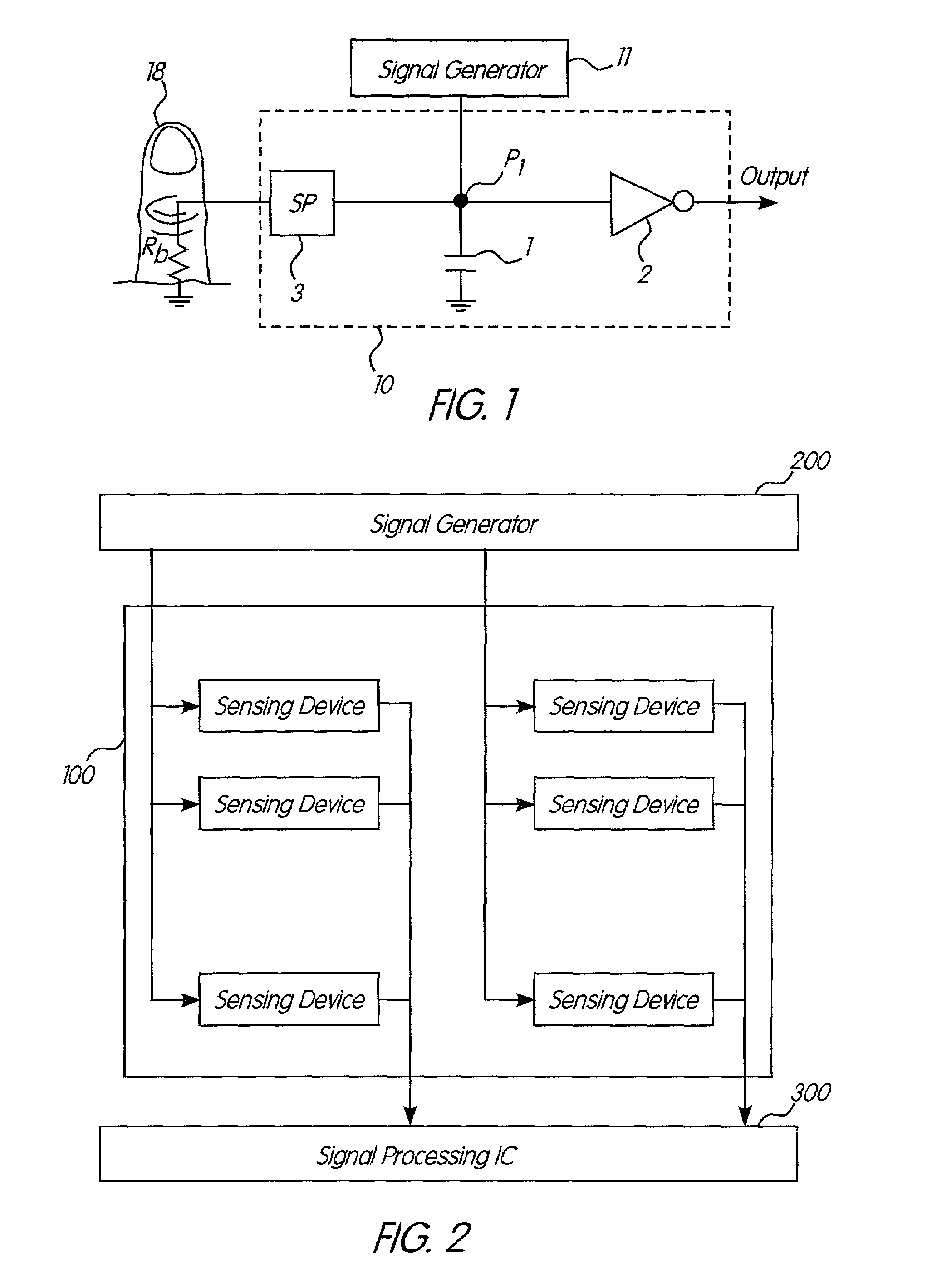
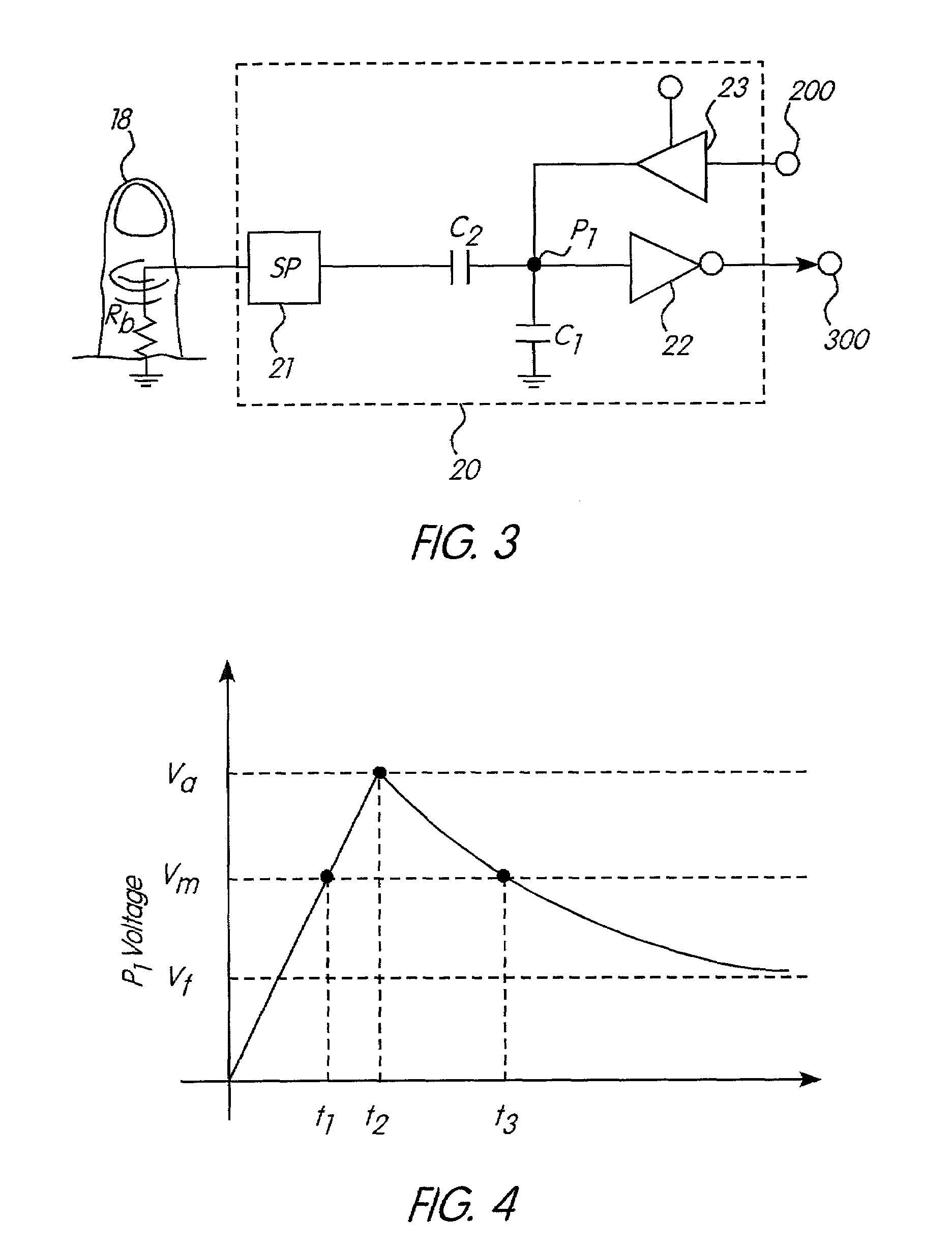
Apparatus and method for sensing the degree and touch strength of a human body on a sensor
InactiveUS7006078B2Decrease power consumptionMinimize amountTransmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsResistive elementImage resolution
An improvement in sensor for detecting contact with a human resistive element is disclosed. This design uses additional components to avoid discharging capacitors through the human resistive element, thereby sparing the user the uncomfortable sensation associated therewith and increasing the power requirements of the device. In addition, designs are utilized which multiple sensing points are multiplexed to achieve greater resolution while with a lower pin count at the signal processing chip.
Owner:MCQUINT
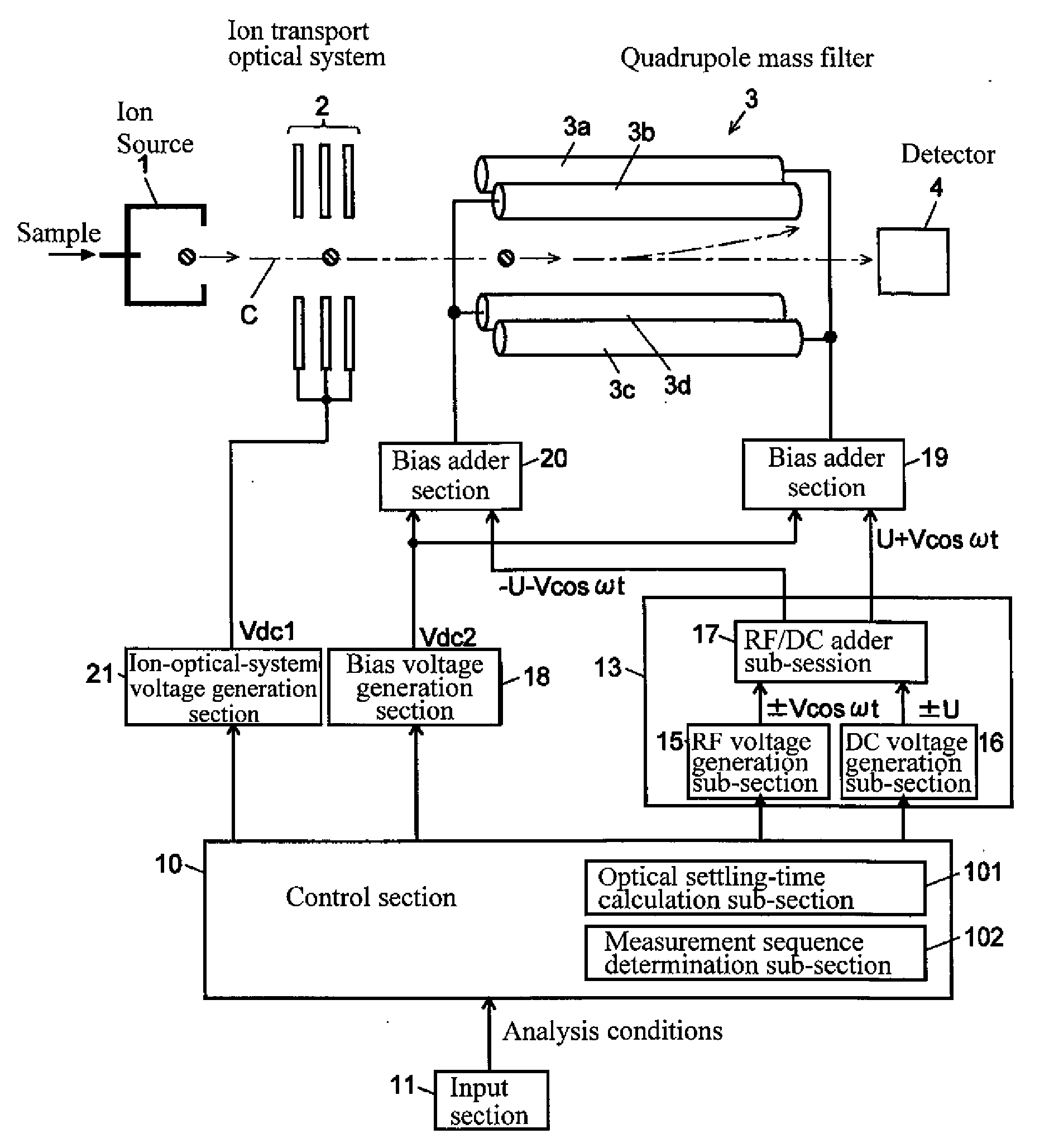
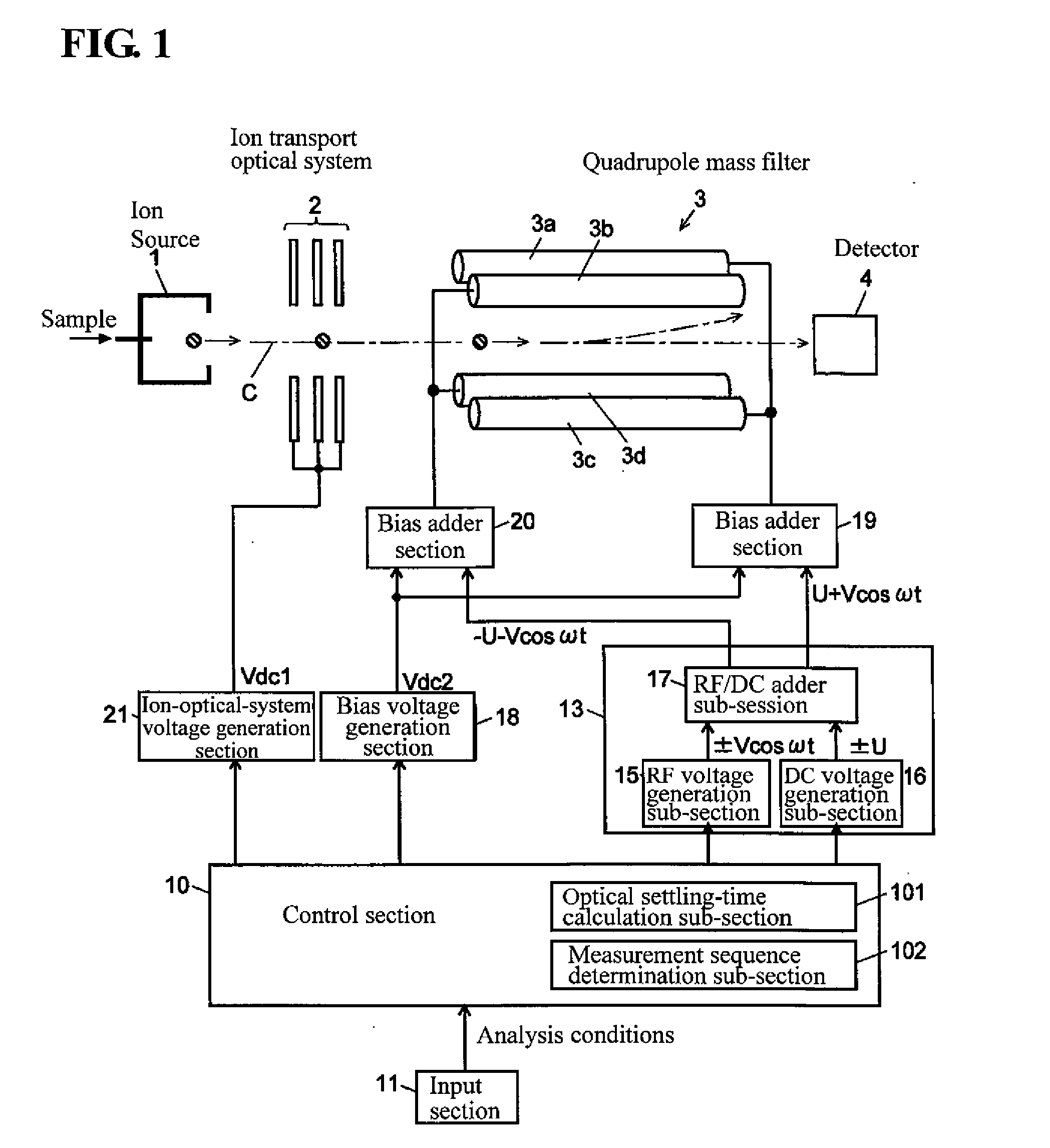
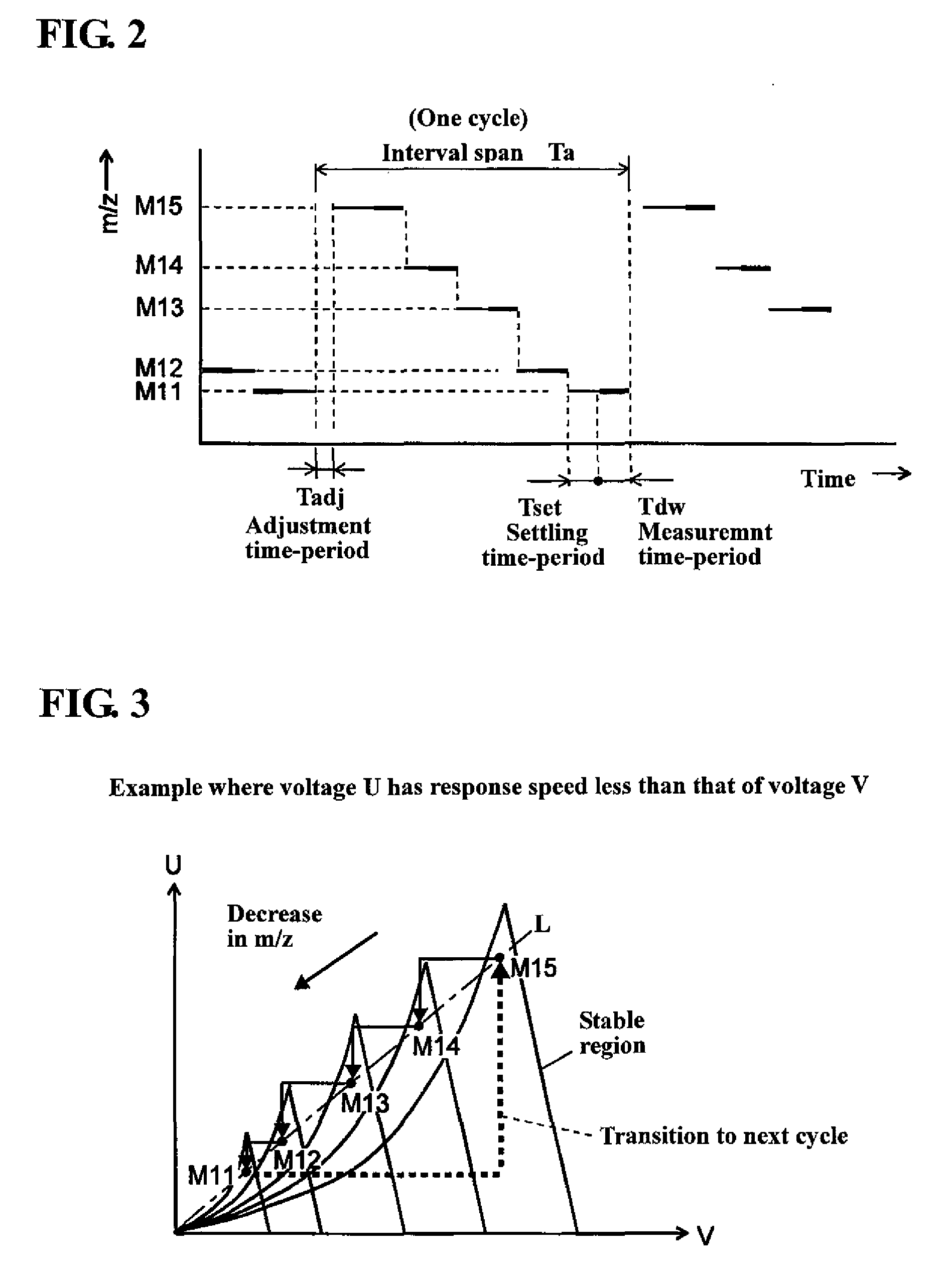
Quadrupole mass spectrometer
ActiveUS20100084552A1Improve time resolutionRaise the ratioStability-of-path spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionClassical mechanicsQuadrupole
Disclosed is a quadrupole mass spectrometer, which is capable of, during an SIM measurement, maximally reducing a settling time-period necessary for an operation of changing an input voltage to a quadrupole mass filter in a staircase pattern, and preventing unwanted ions from excessively entering a detector during a course of changing between a plurality of mass values. Under a condition that a response speed of a DC voltage U to be applied to quadrupole electrodes is less than that of an amplitude of a high-frequency voltage V, a control section 10 is operable to rearrange the mass values in descending order of mass value, and an optimal settling-time calculation sub-section 101 is operable to determine a settling time-period for each of the mass values, based on a mass-value difference and a post-change mass value.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
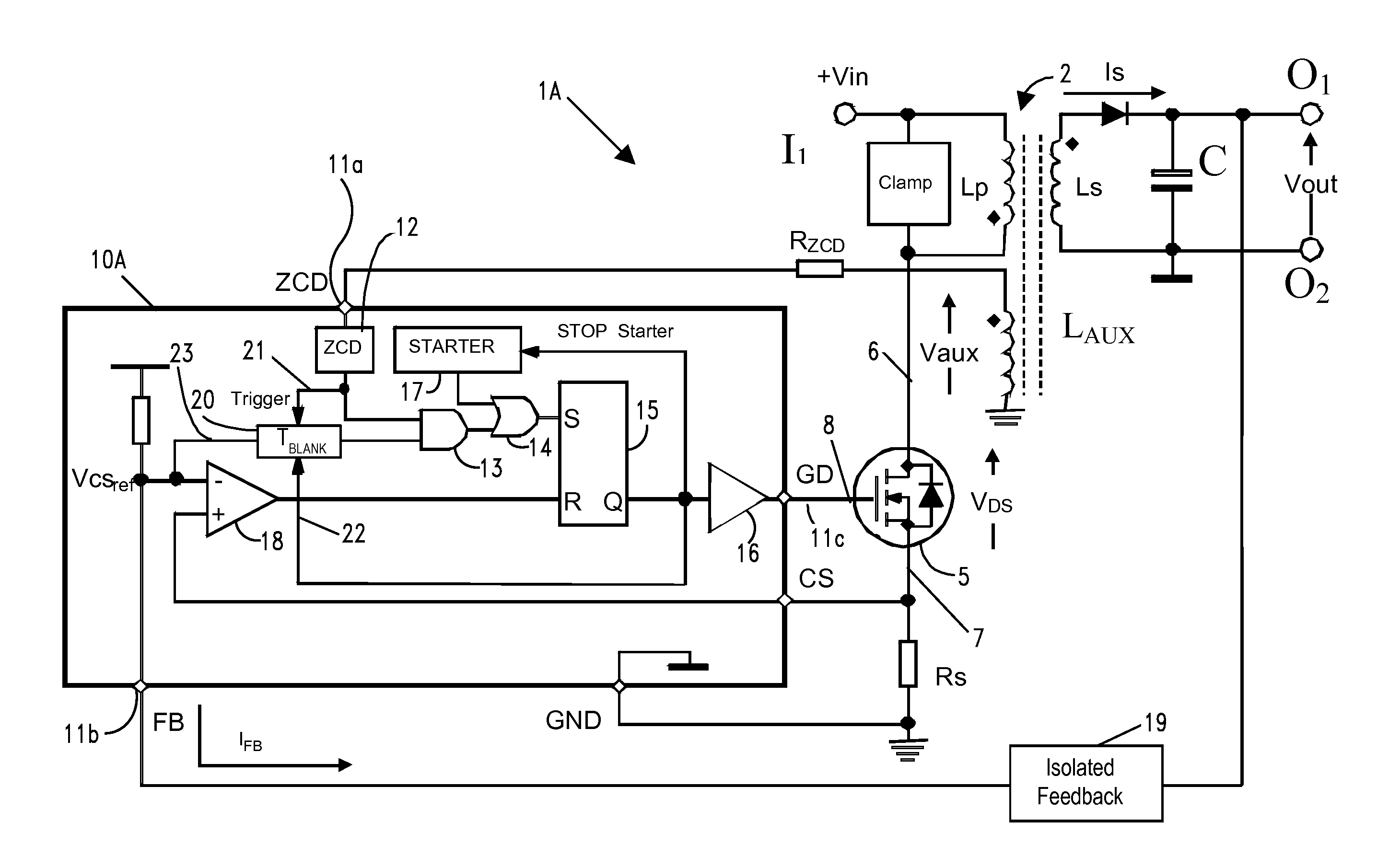
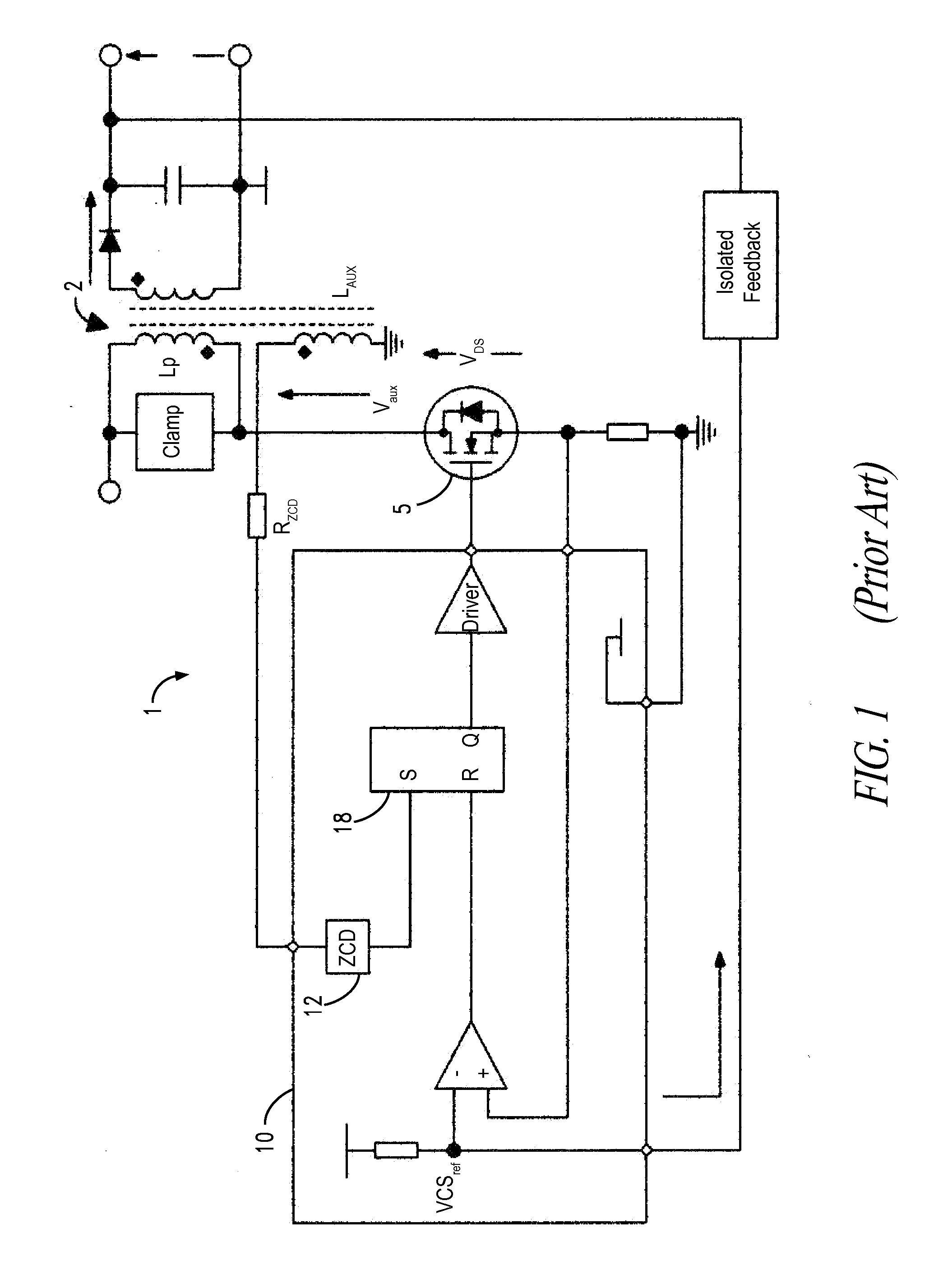
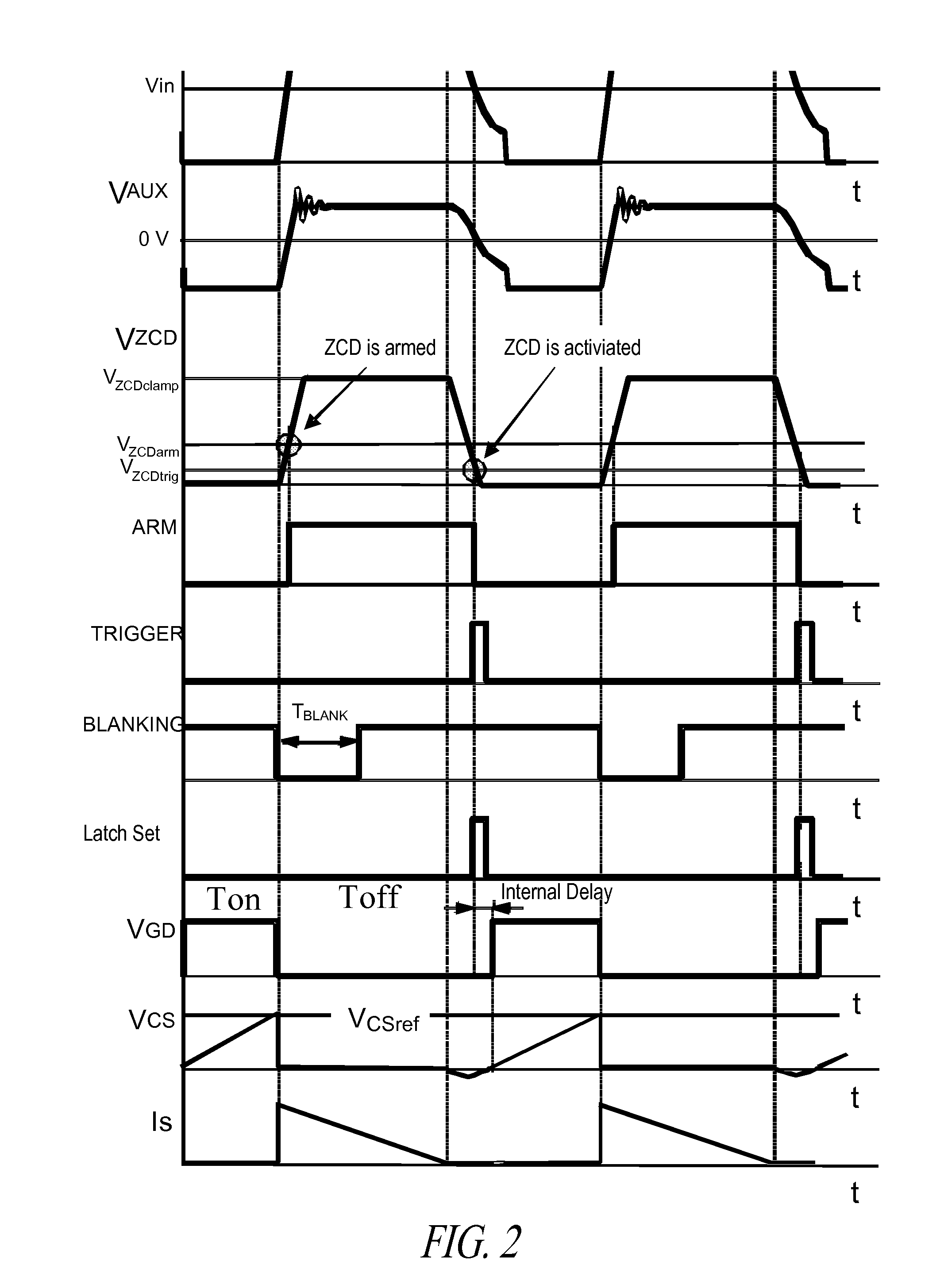
Method and circuit for controlling a switching regulator
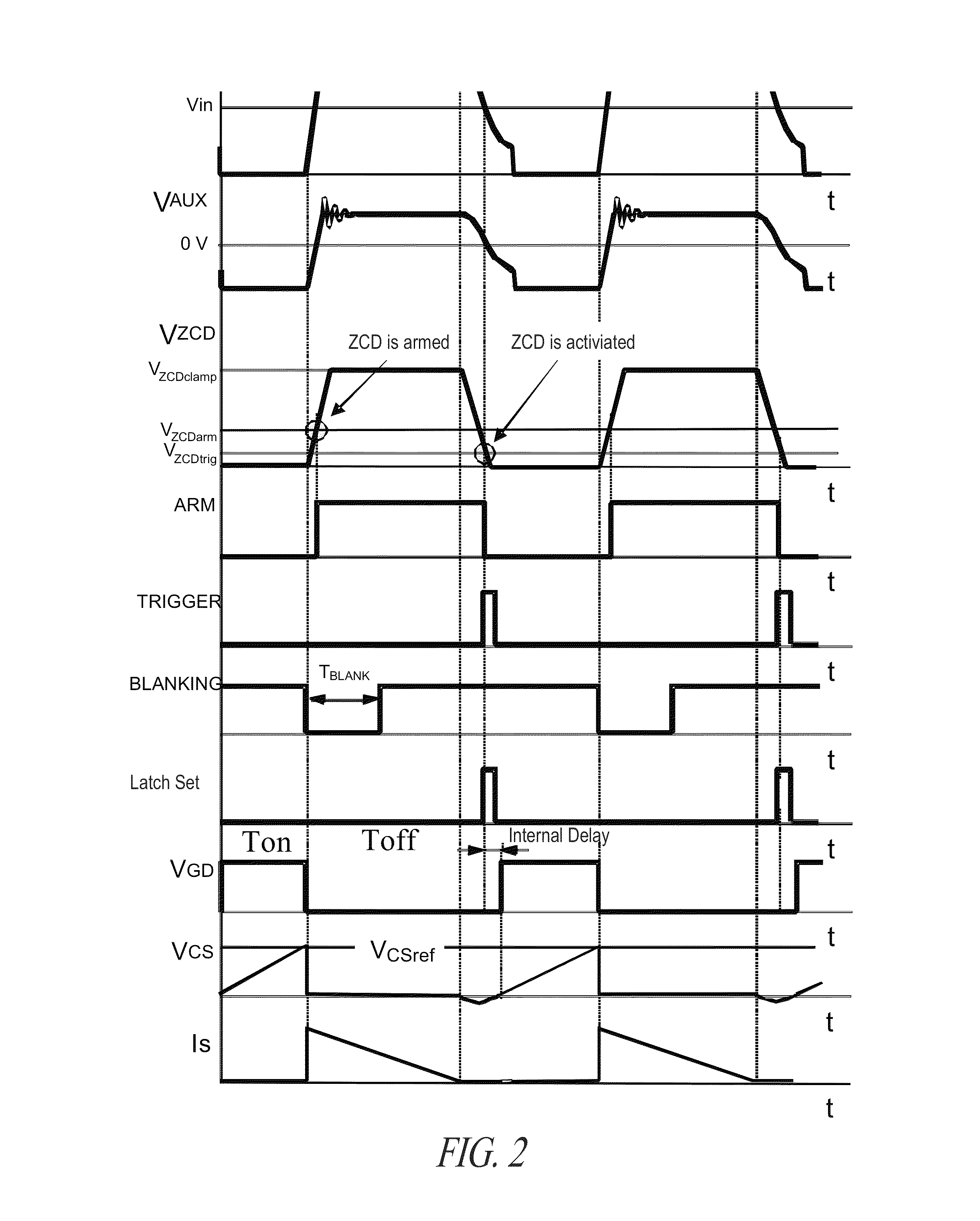
ActiveUS20140029316A1Reduce noiseEfficient workEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionSwitching cycleControl switch
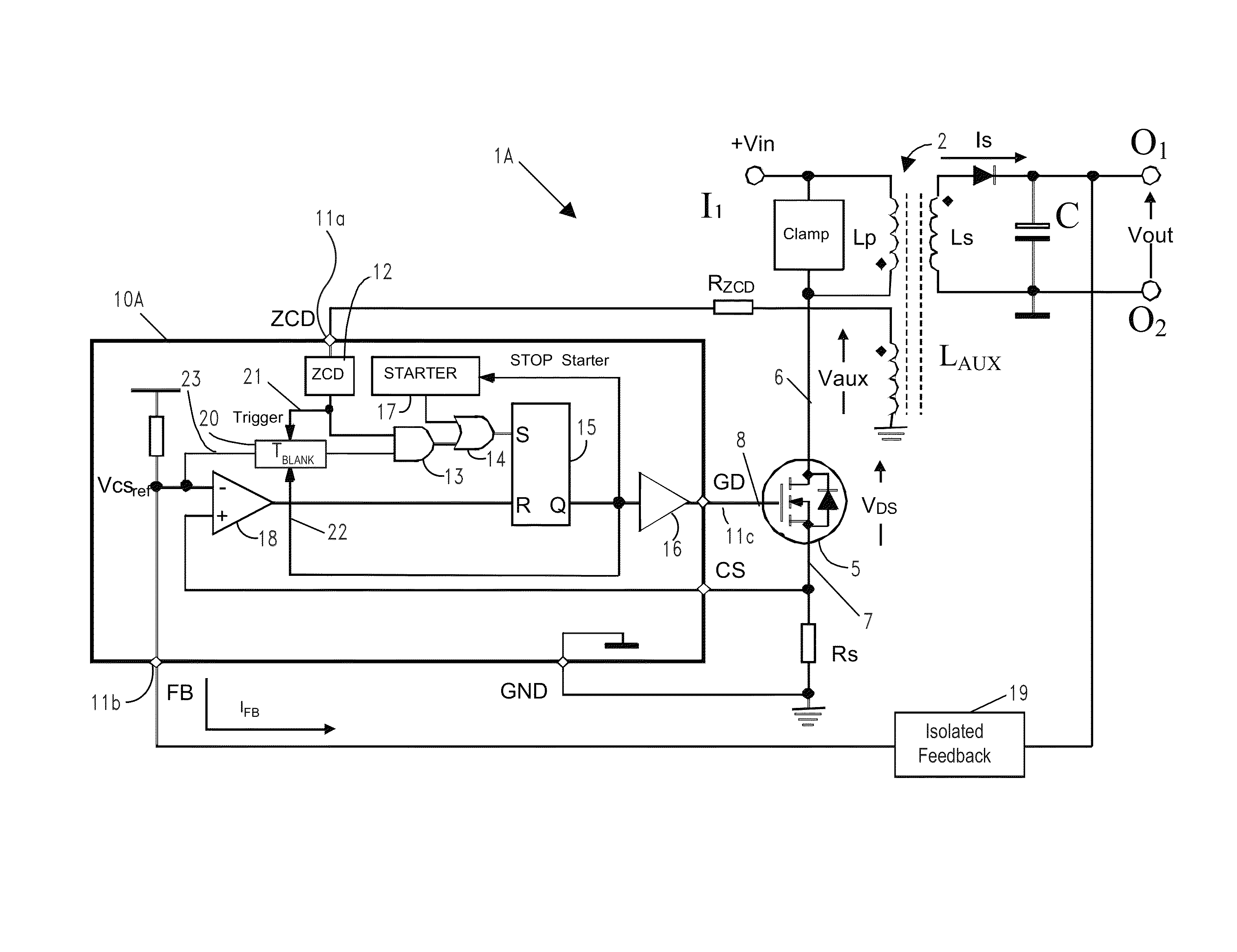
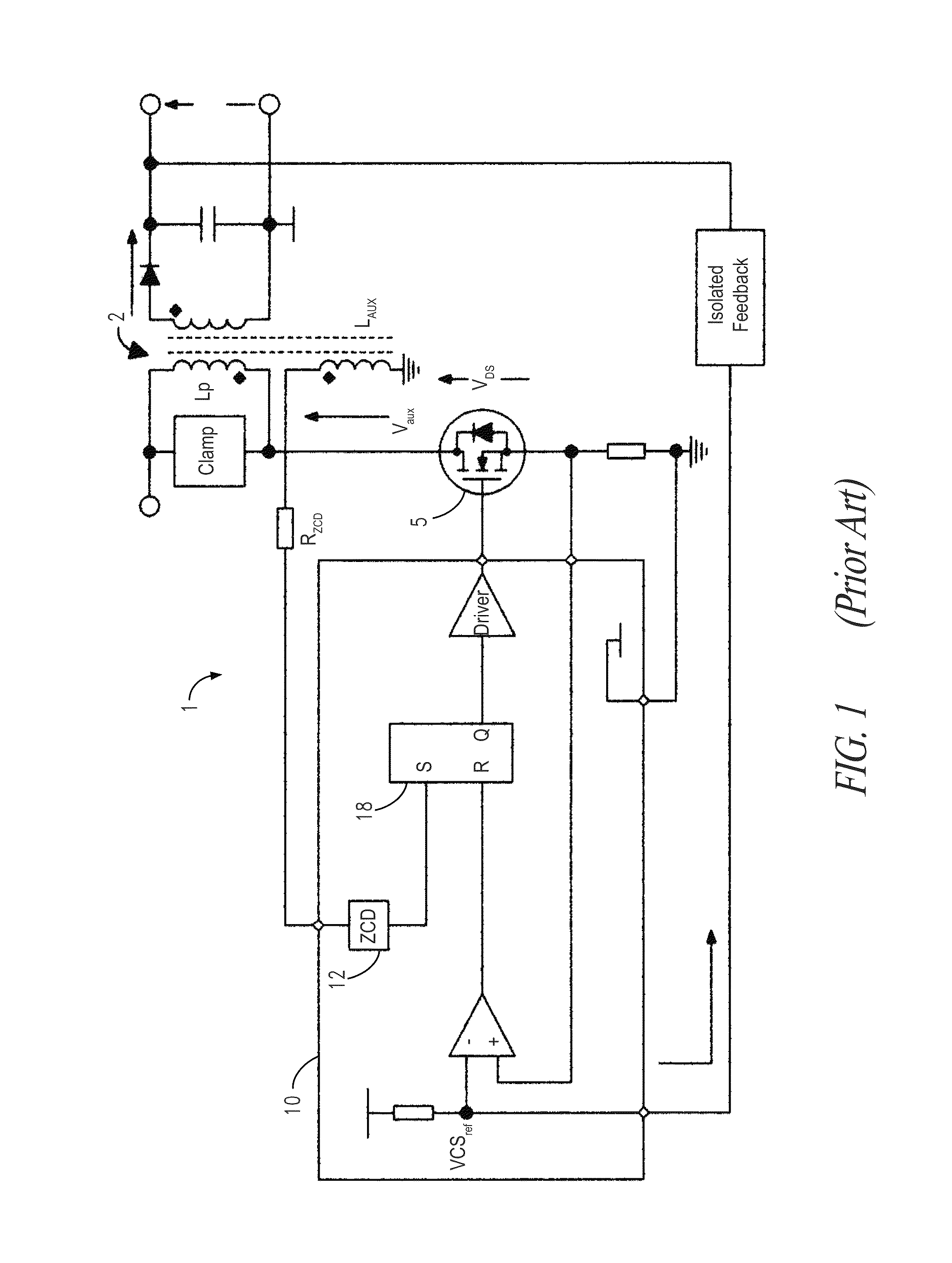
A method for controlling a switching regulator includes defining a waiting time during which a trigger signal corresponding to a recirculation signal of the switching regulator is ignored holding a control switch in an open condition, and detecting a number of local valleys of the recirculation signal during the waiting time. In particular, defining the waiting time is performed for each switching cycle by adding a first value, which is determined on the basis of a load on the regulator, to a second variable value, which is proportional to the number valleys detected during the waiting time of the preceding switching cycle.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
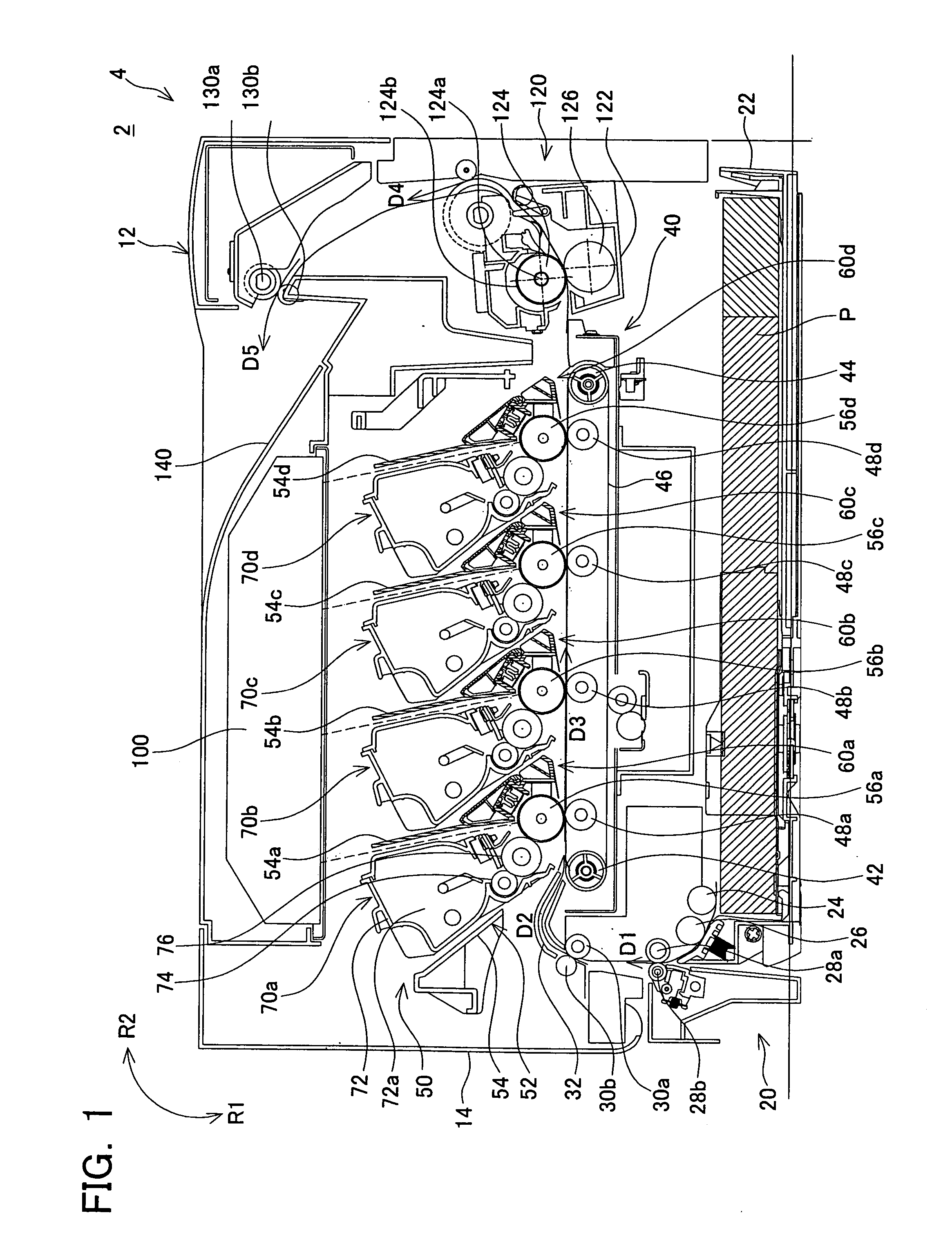
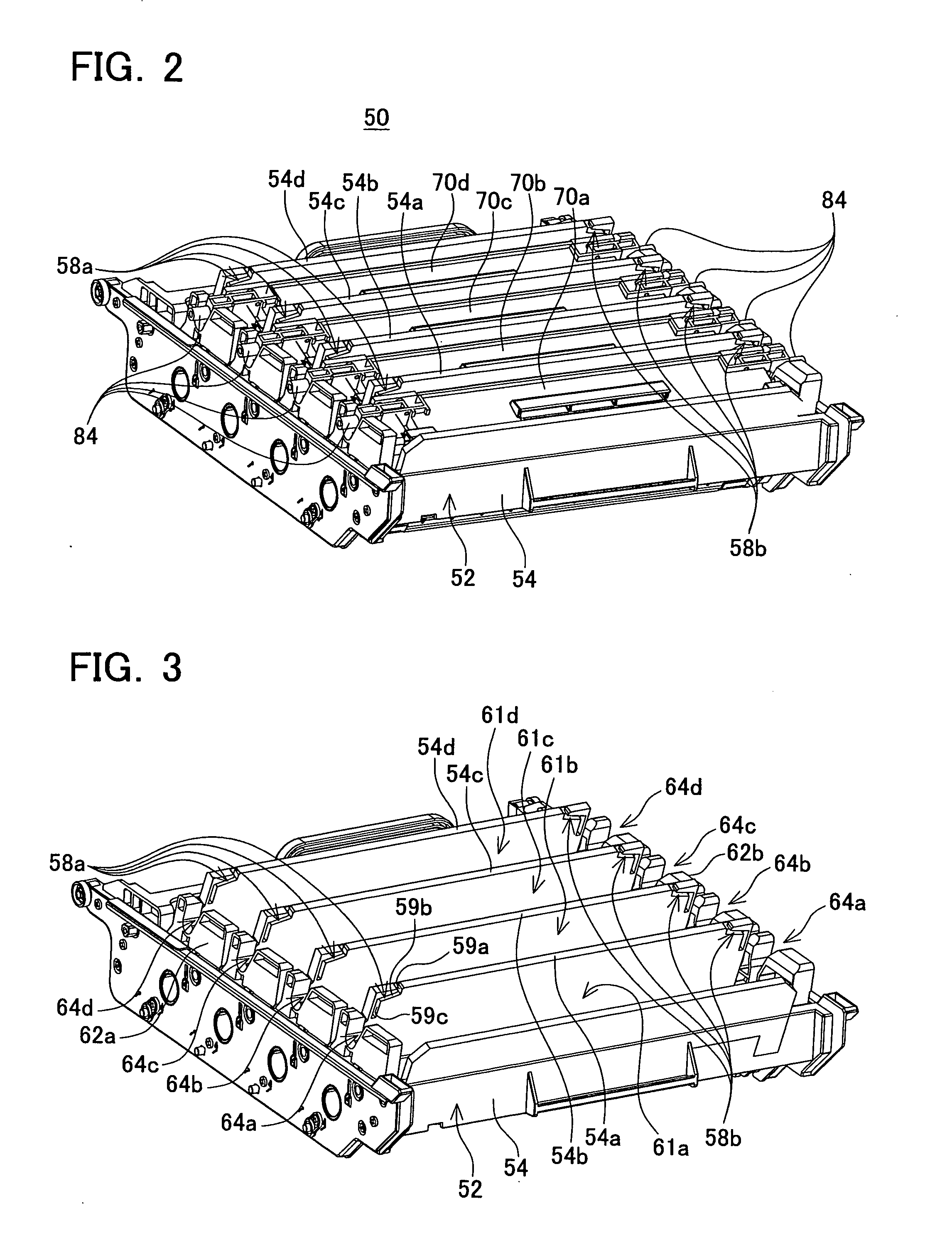
Developing unit and image forming device
ActiveUS20070147890A1Avoid damageMaintain positionElectrographic process apparatusImage formationMechanical engineering
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
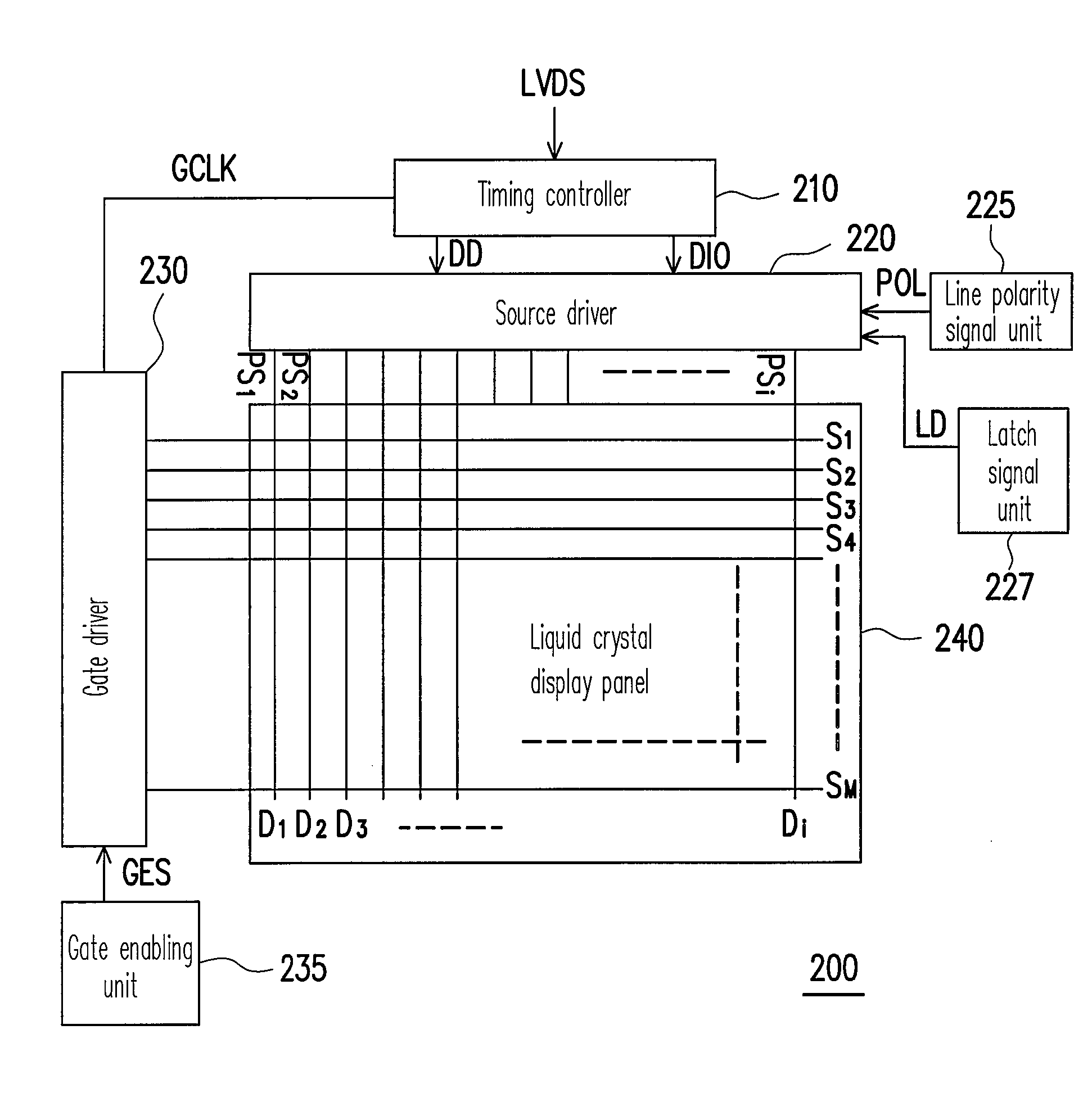
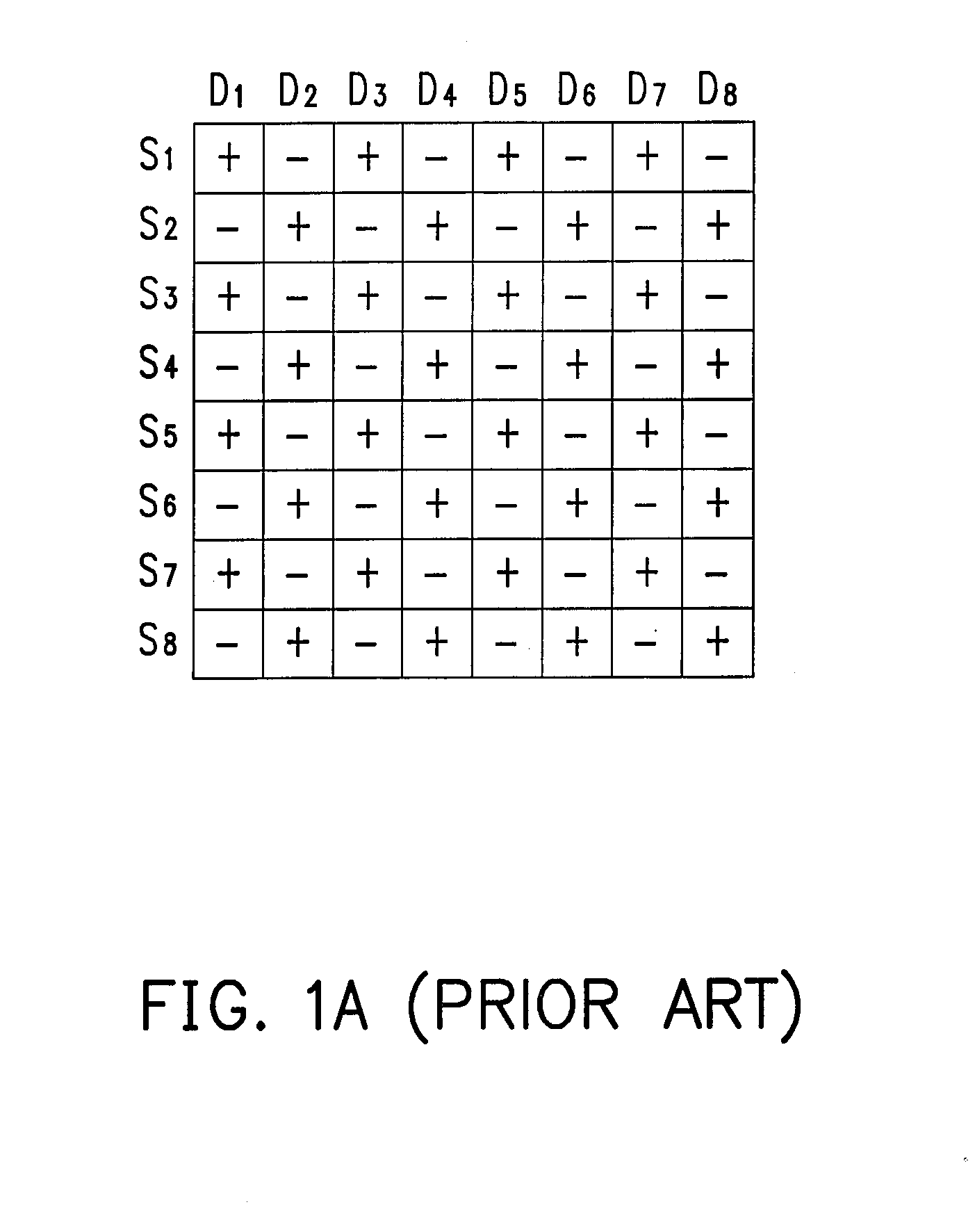
Display driving apparatus and multi-line inversion driving method thereof
InactiveUS20070262941A1Polarity switching frequencyReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesScan lineElectrical polarity
A display driving apparatus and a multi-line inversion driving method thereof are provided. The apparatus includes a gate driver, a source driver, a gate enabling unit and a line polarity signal unit. Every time after a plurality of scan lines is turned on, the source driver inverts the polarity of the sub pixel driving signal according to a line polarity signal output by the line polarity signal unit. Thereby, the polarity inversion operating frequency of the sub pixel driving signal is lowered to reduce the power consumption of the source driver.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Laminated-type piezoelectric element
InactiveUS20060232172A1Easily connectDecrease thermal stressPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesOptoelectronicsElectrically conductive adhesive
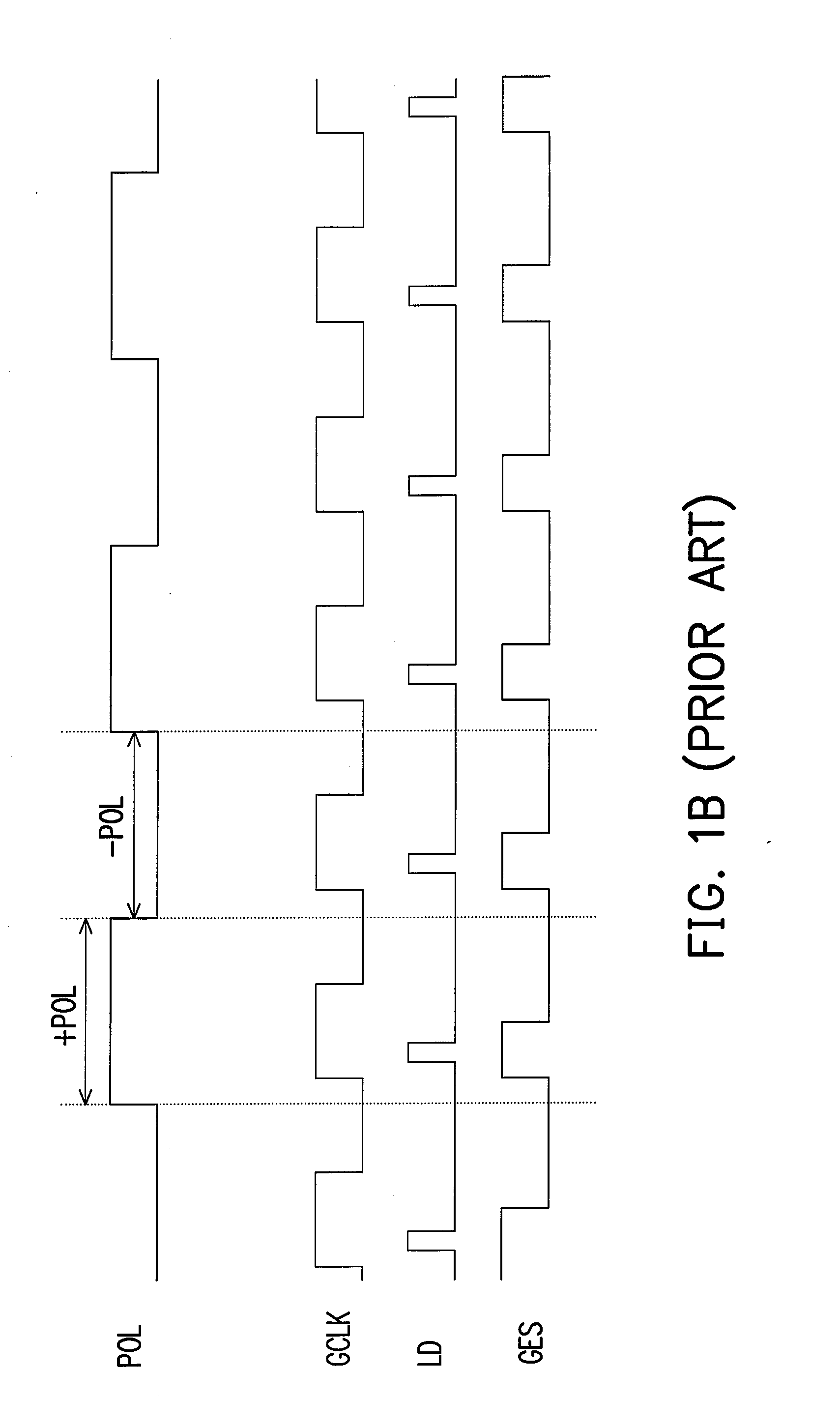
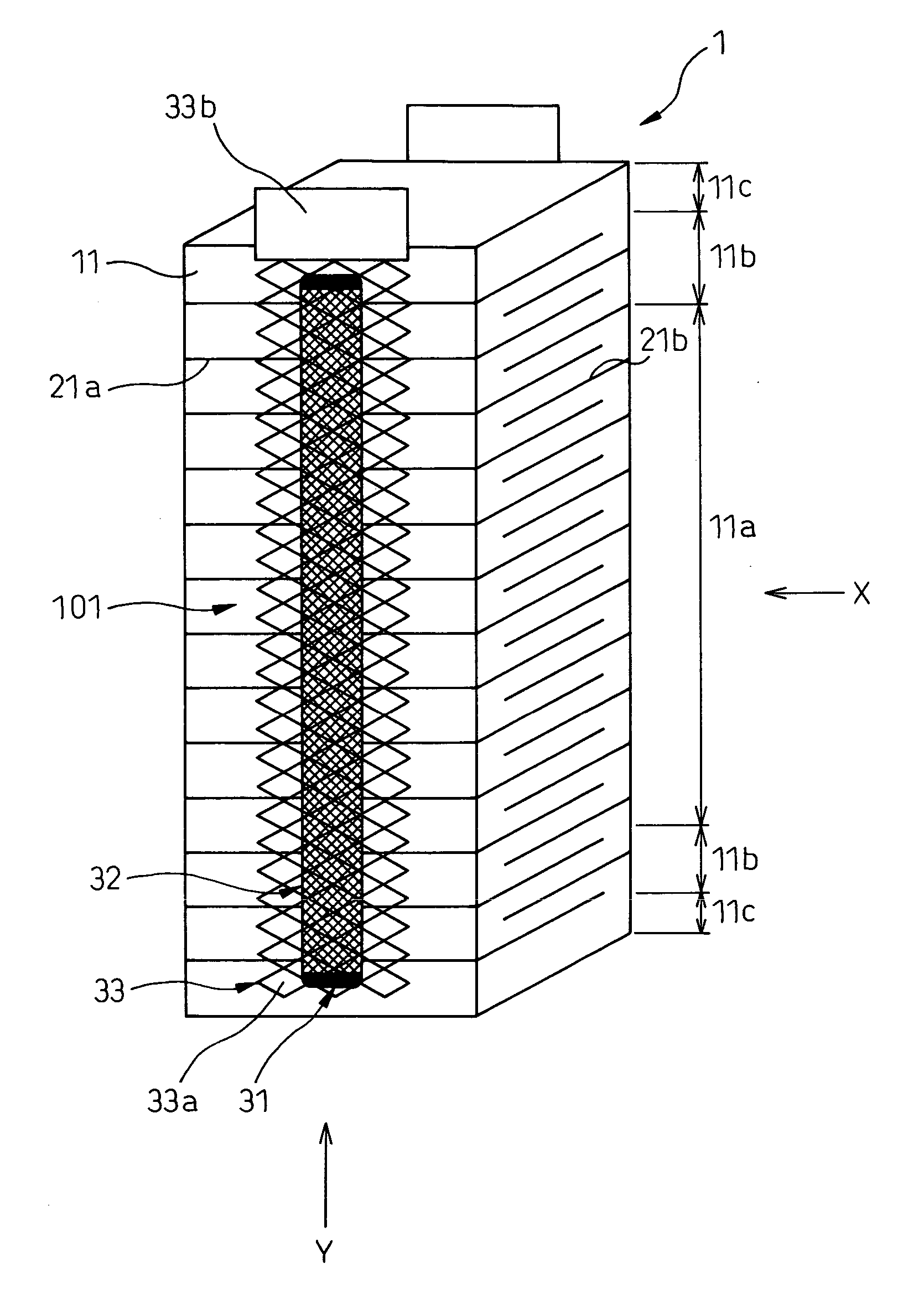
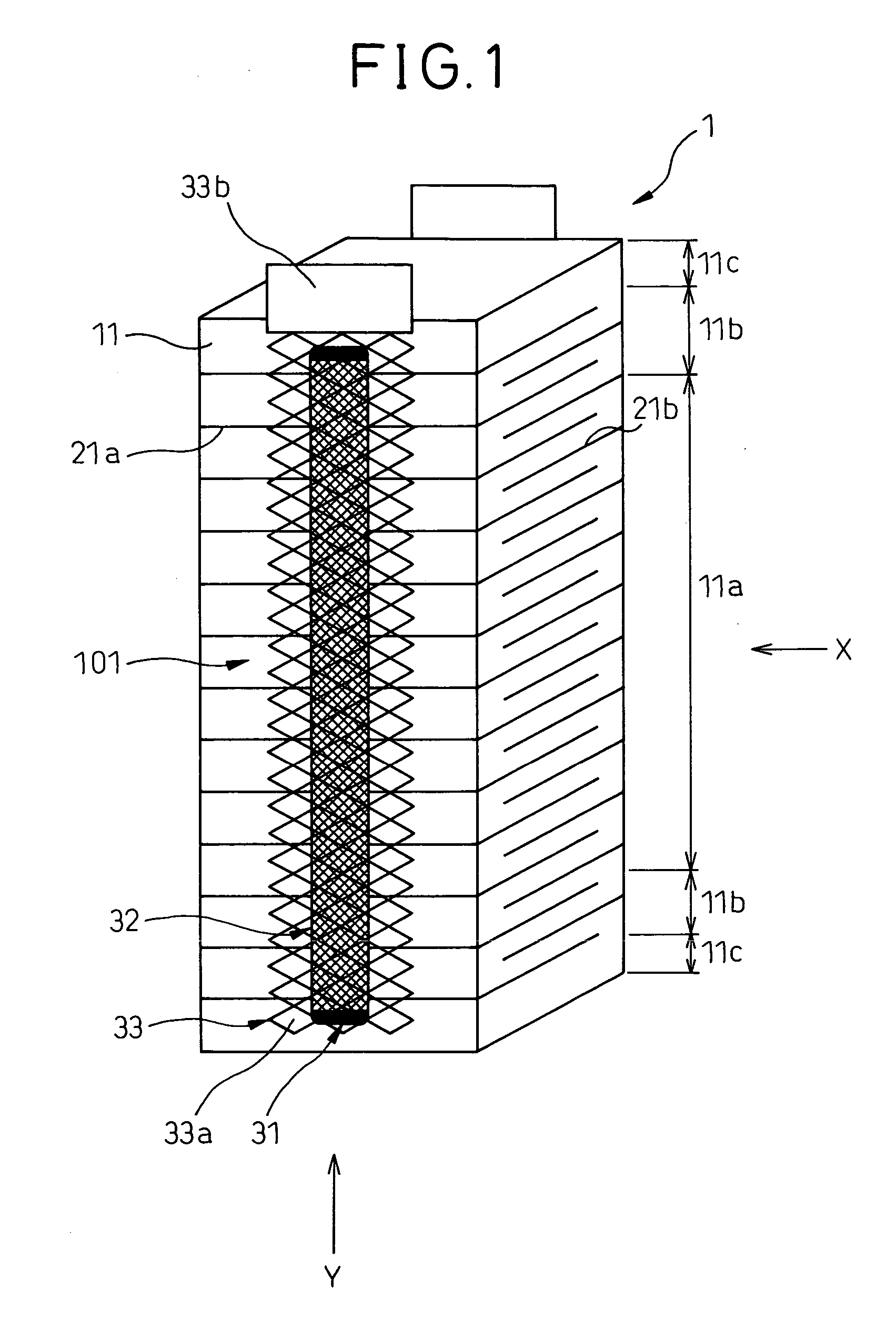
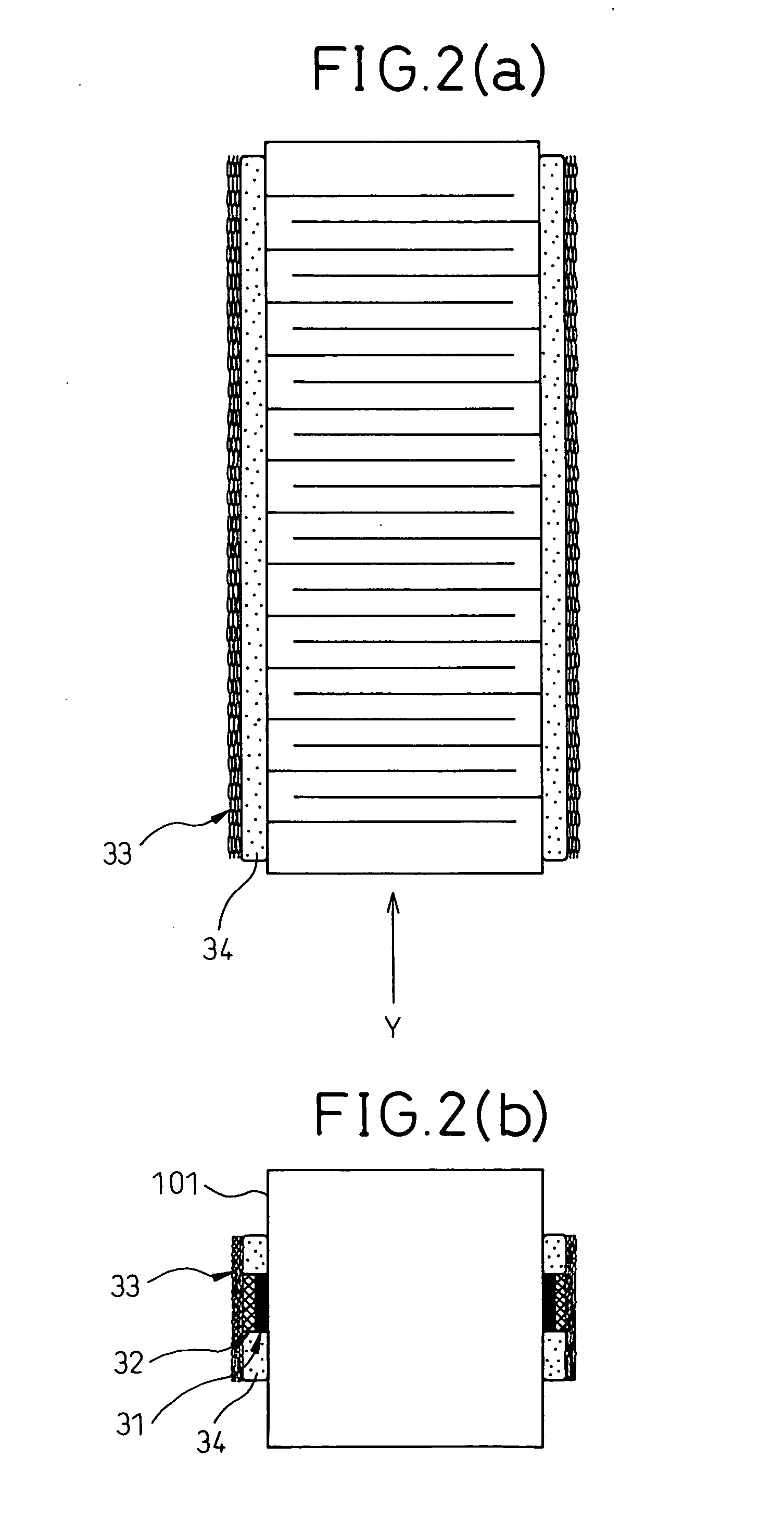
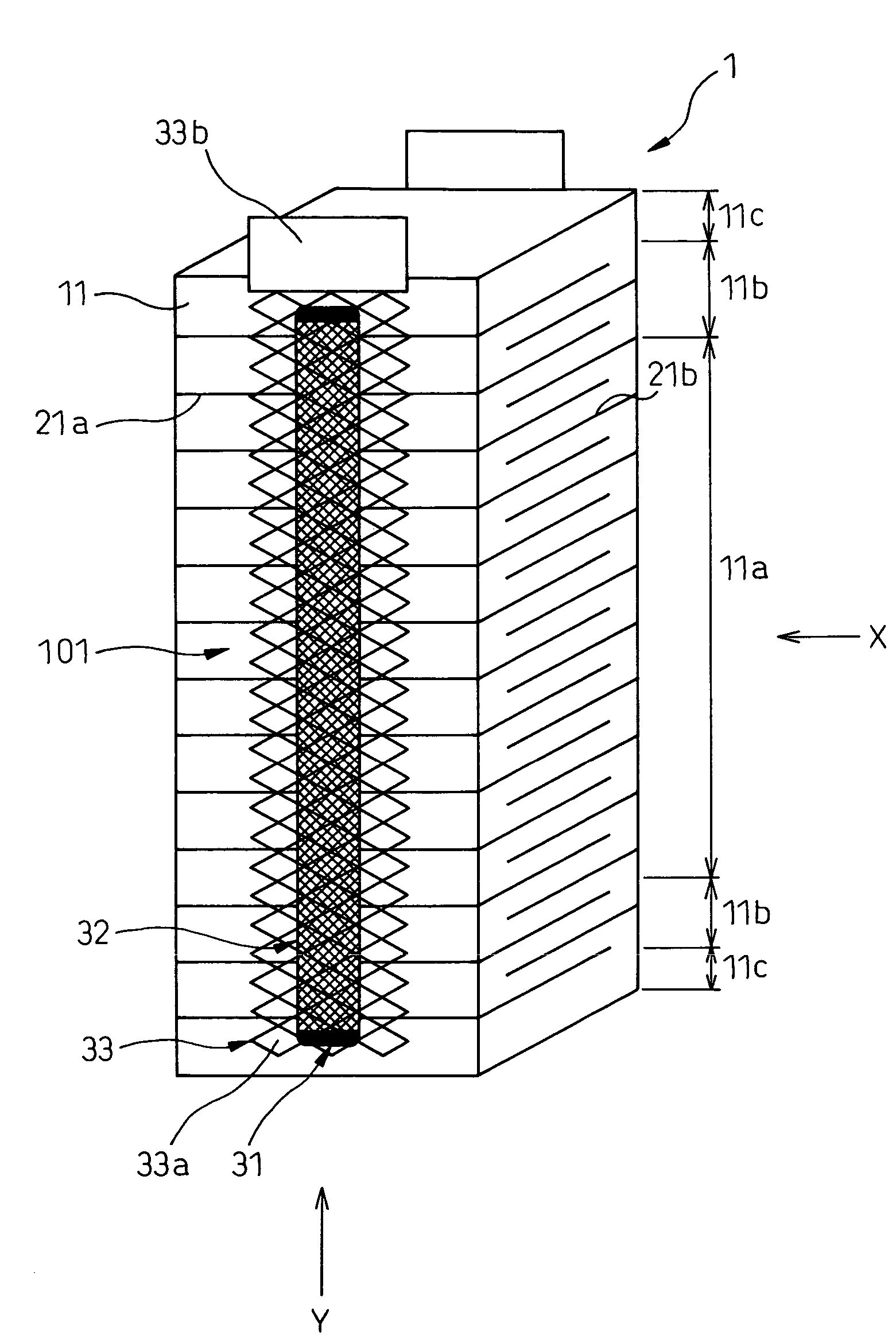
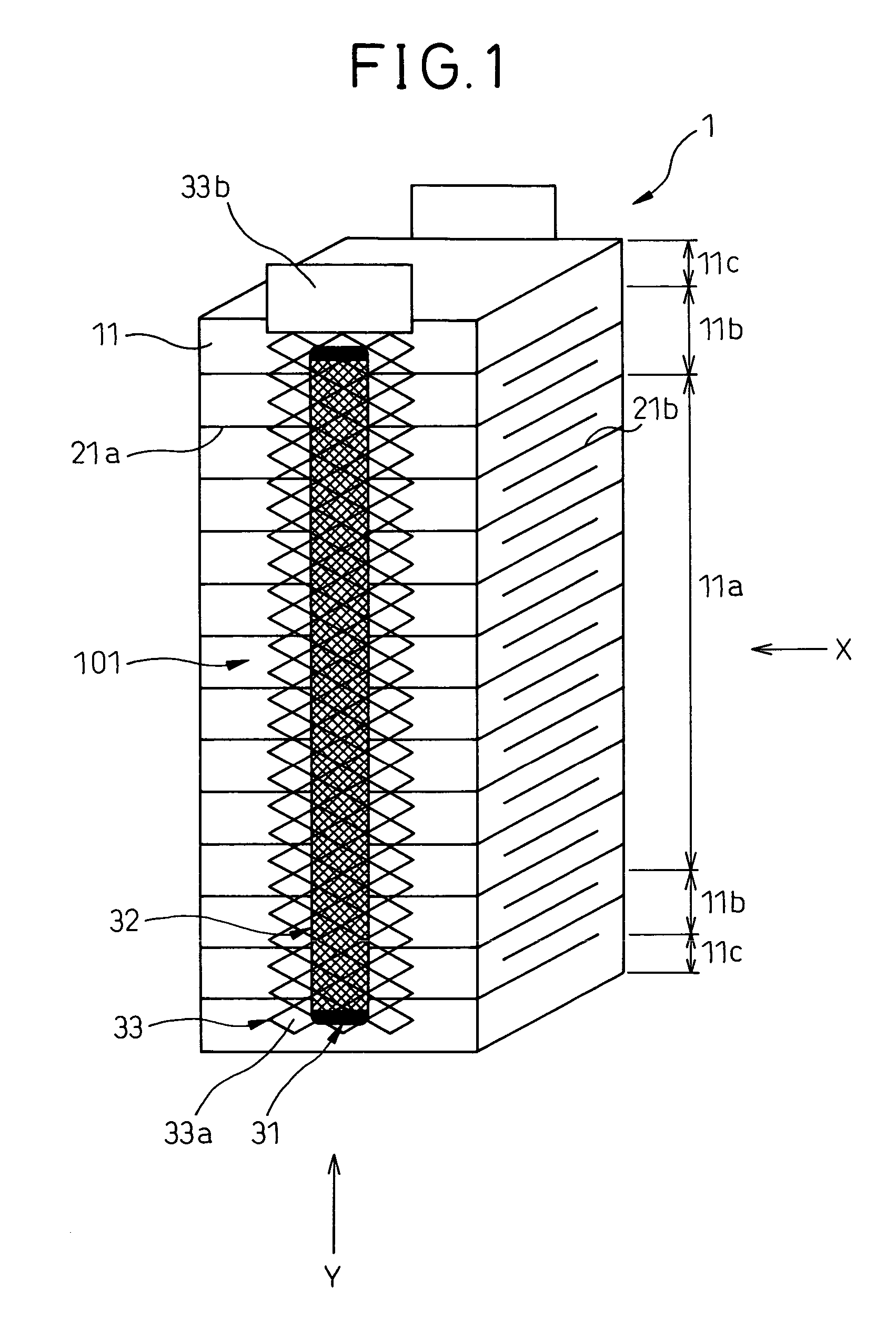
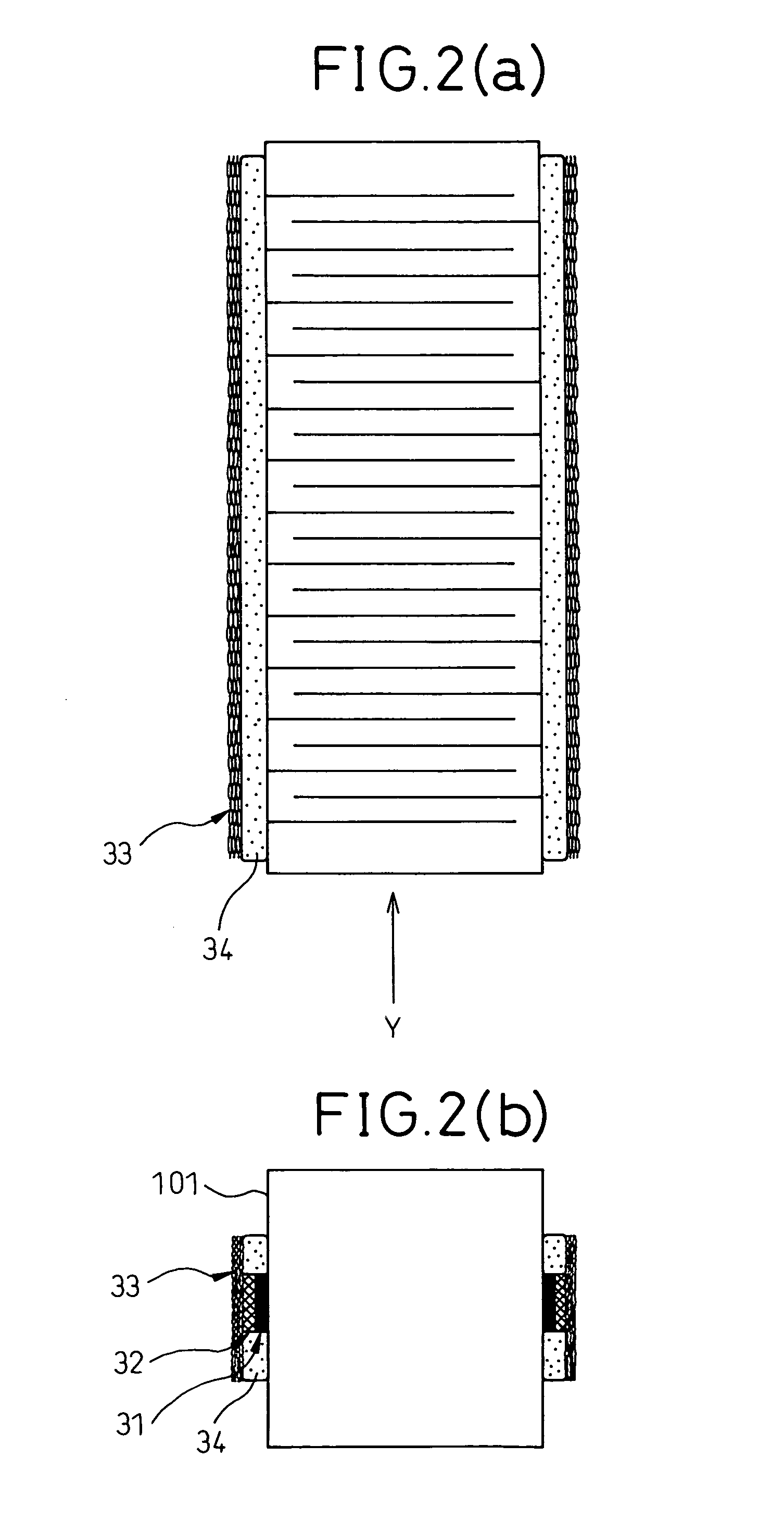
A laminated-type piezoelectric element 1 is provided, which comprises a first external electrode layer 33, which is located at a side area of the laminated-type piezoelectric element 1, is electrically continuous to internal electrode layers 21, and comprises plural expansible and contractible opening portions 33a in a stacking direction of the laminated-type piezoelectric element 1. As the first external electrode layer 33 is connected to the laminated-type piezoelectric element 1 with an electrically conductive adhesive member 32 and the electrically conductive adhesive member 32 is narrower than the first external electrode layer 33, the electrically conductive adhesive member 32 penetrates into the opening portions 33a of the first external electrode layer 33 to form connections in a shape of an anchor. Therefore, the first external electrode layer 33 is firmly connected to the laminated-type piezoelectric element 1.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Laminated-type piezoelectric element
InactiveUS7439655B2Displacement properties do not easily changeReduced strengthPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesOptoelectronicsElectrically conductive adhesive
A laminated-type piezoelectric element 1 is provided, which comprises a first external electrode layer 33, which is located at a side area of the laminated-type piezoelectric element 1, is electrically continuous to internal electrode layers 21, and comprises plural expansible and contractible opening portions 33a in a stacking direction of the laminated-type piezoelectric element 1. As the first external electrode layer 33 is connected to the laminated-type piezoelectric element 1 with an electrically conductive adhesive member 32 and the electrically conductive adhesive member 32 is narrower than the first external electrode layer 33, the electrically conductive adhesive member 32 penetrates into the opening portions 33a of the first external electrode layer 33 to form connections in a shape of an anchor. Therefore, the first external electrode layer 33 is firmly connected to the laminated-type piezoelectric element 1.
Owner:DENSO CORP
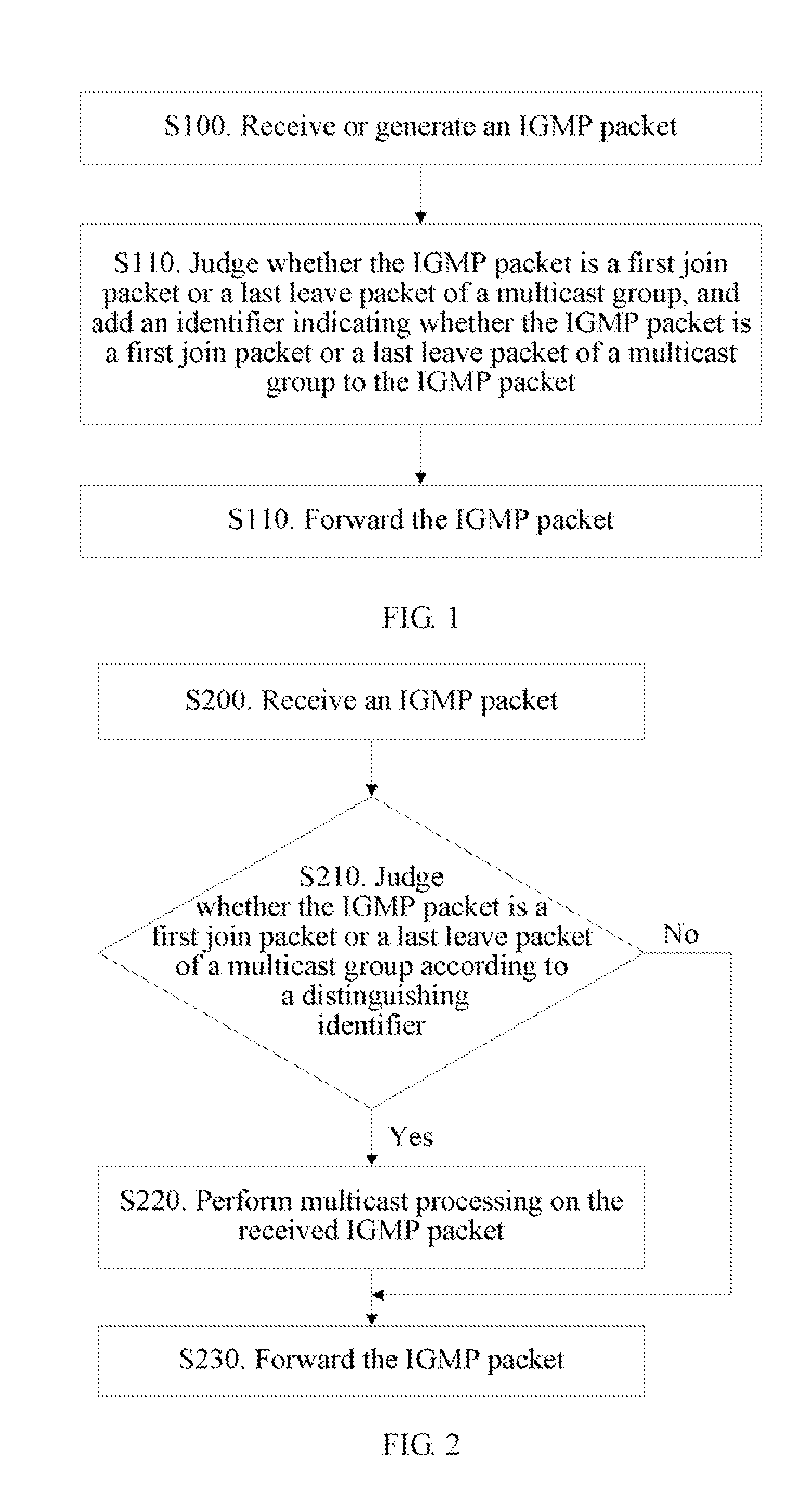
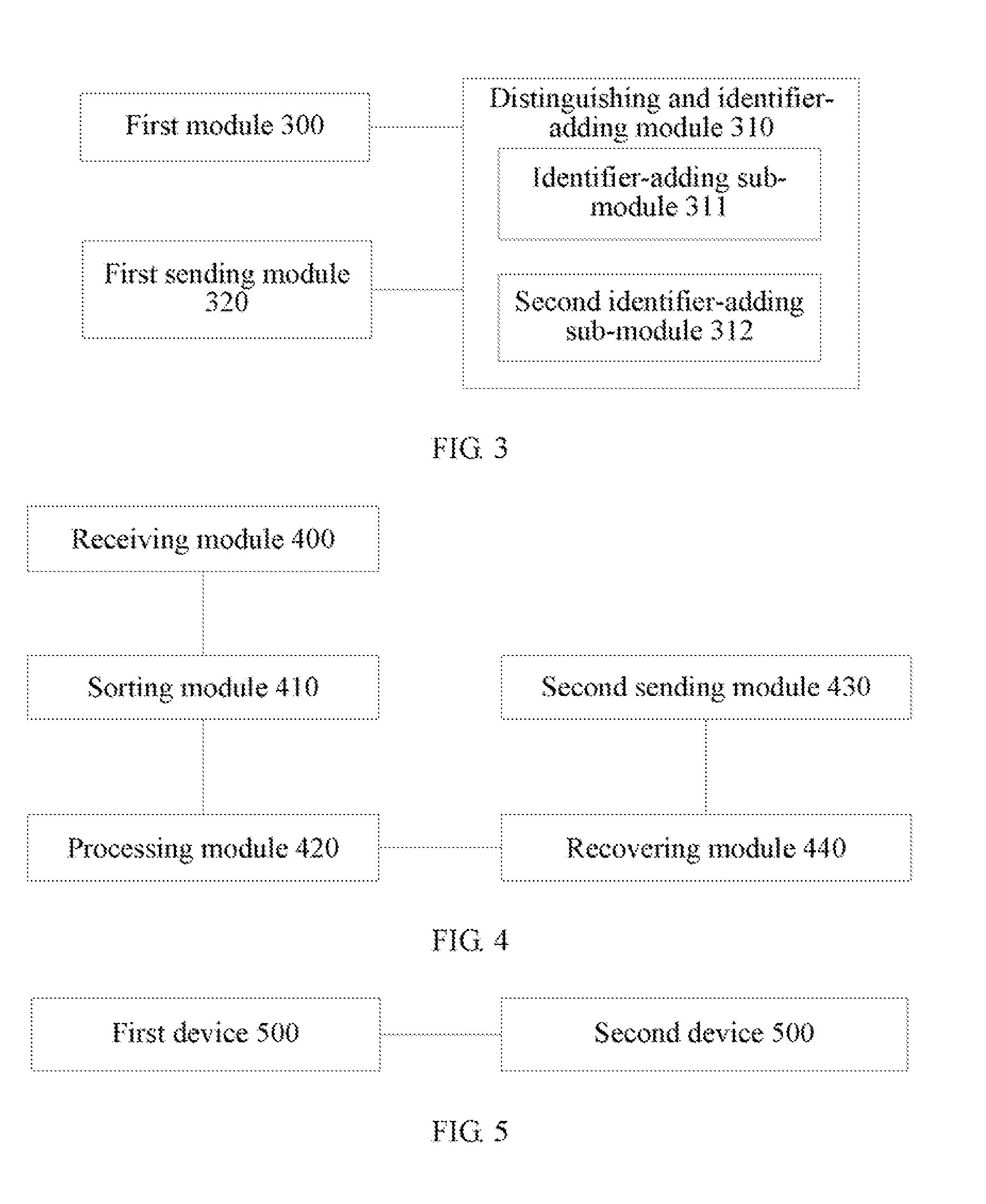
Method, device and system for implementing multicast
ActiveUS20120281697A1Relieve packet processing pressureMeet the requirementsData switching by path configurationTTEthernetThe Internet
A method for implementing multicast includes: receiving or generating an internet group management protocol IGMP packet; judging whether the packet is a first join packet or a last leave packet of a multicast group, and adding an identifier indicating whether the IGMP packet is a first join packet or a last leave packet of a multicast group to the IGMP packet, where the identifier is used for a subsequent entity not to perform multicast processing on the IGMP packet when judging that the IGMP packet is not the first join packet or the last leave packet of the multicast group according to the identifier; and forwarding the IGMP packet to the subsequent entity. Therefore, the packet processing pressure on the network apparatus is relieved, and meanwhile, the IGMP packet requirements in the practical network are met.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
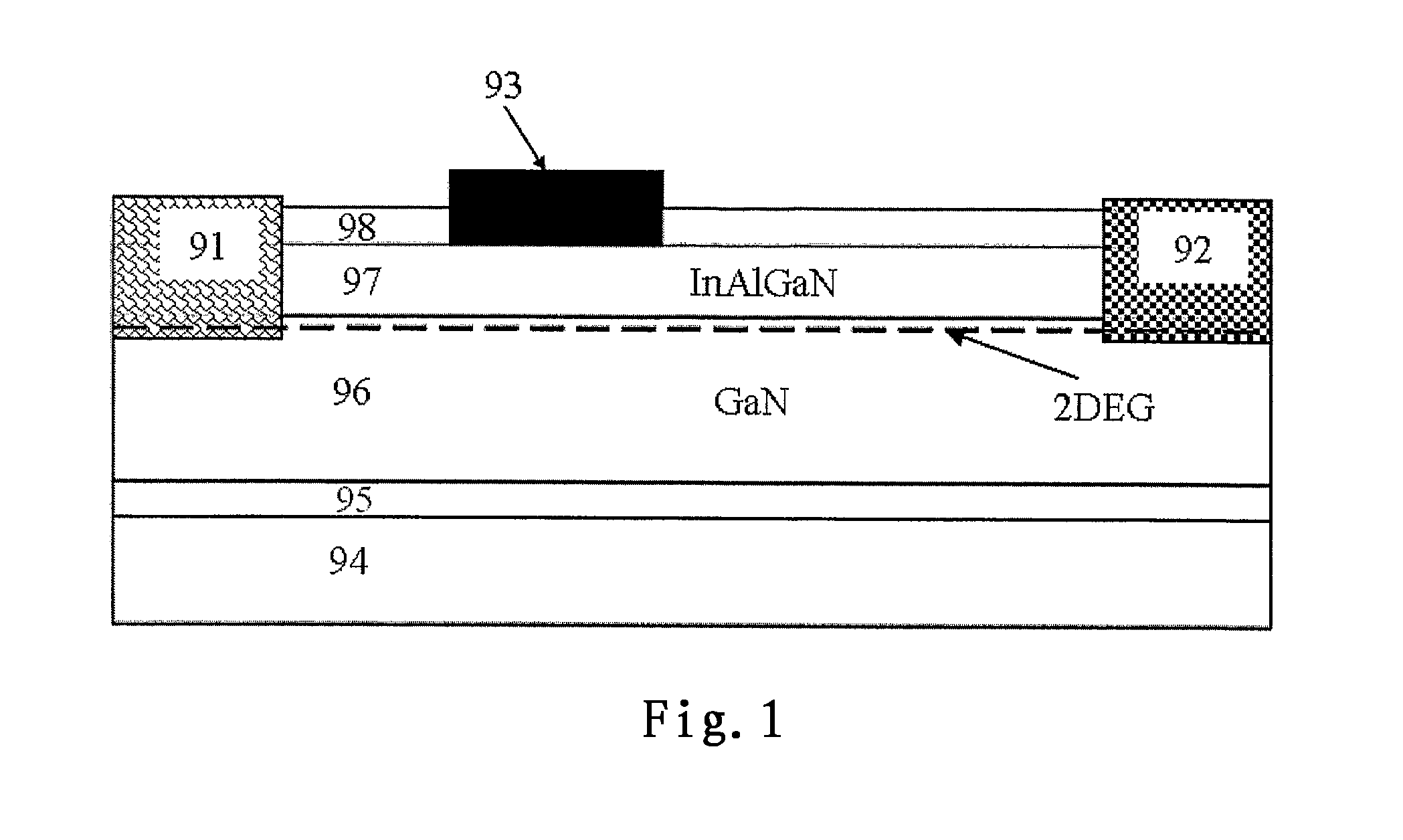
Semiconductor device and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20120280280A1Improve breakdown voltageIncrease unit areaSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor packageIsolation layer
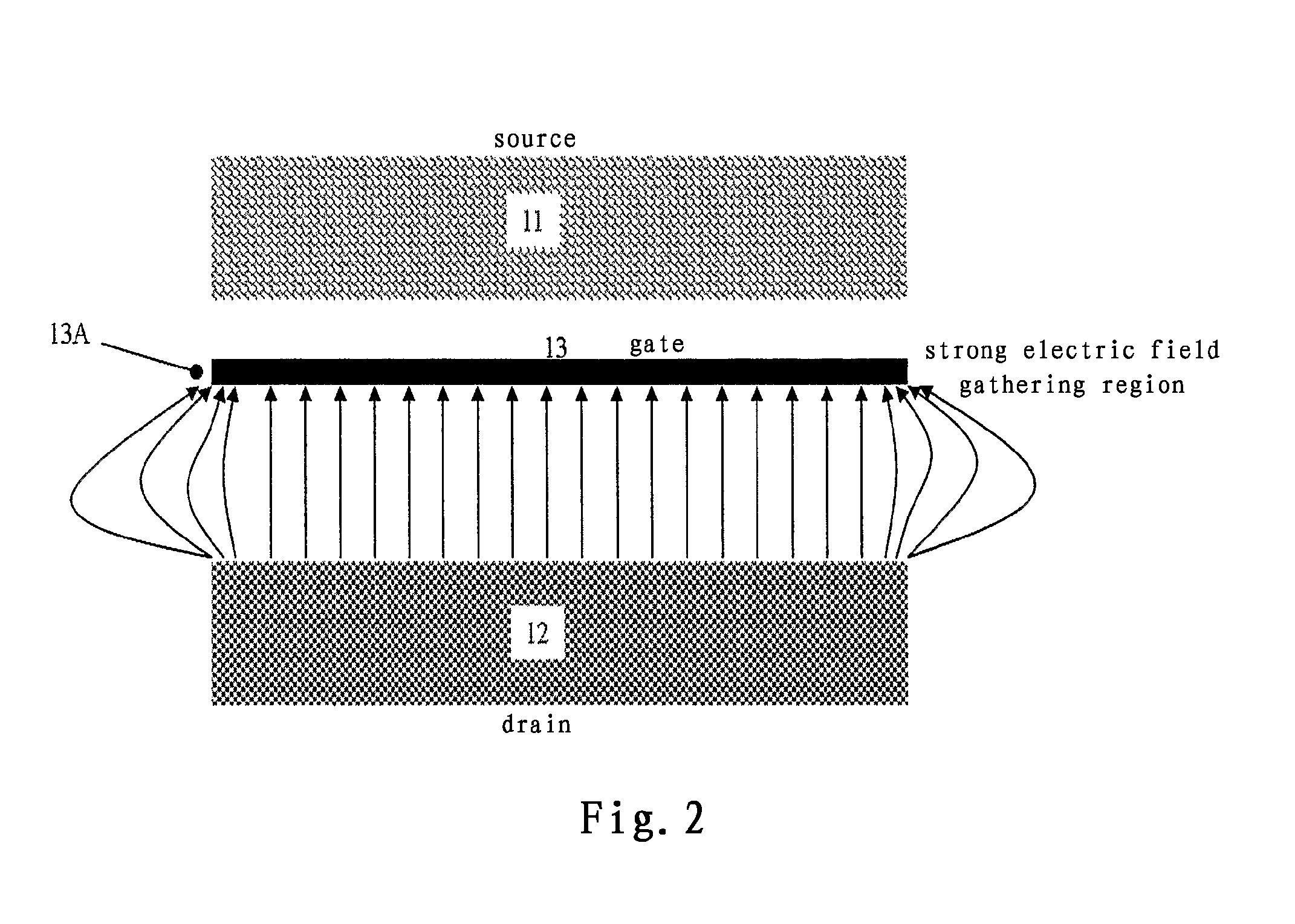
The invention relates to a semiconductor device and a fabrication method thereof. A semiconductor device according to an aspect of the invention comprising: a semiconductor layer on a substrate; an isolation layer on the semiconductor layer; a source and a drain which are in contact with the semiconductor layer, each of the source and the drain comprises multiple fingers, and the multiple fingers of the source intersect the multiple fingers of the drain; and a gate on the isolation layer, the gate is located between the source and the drain and comprises a closed ring structure which encircles the multiple fingers of the source and the drain.
Owner:GPOWER SEMICON
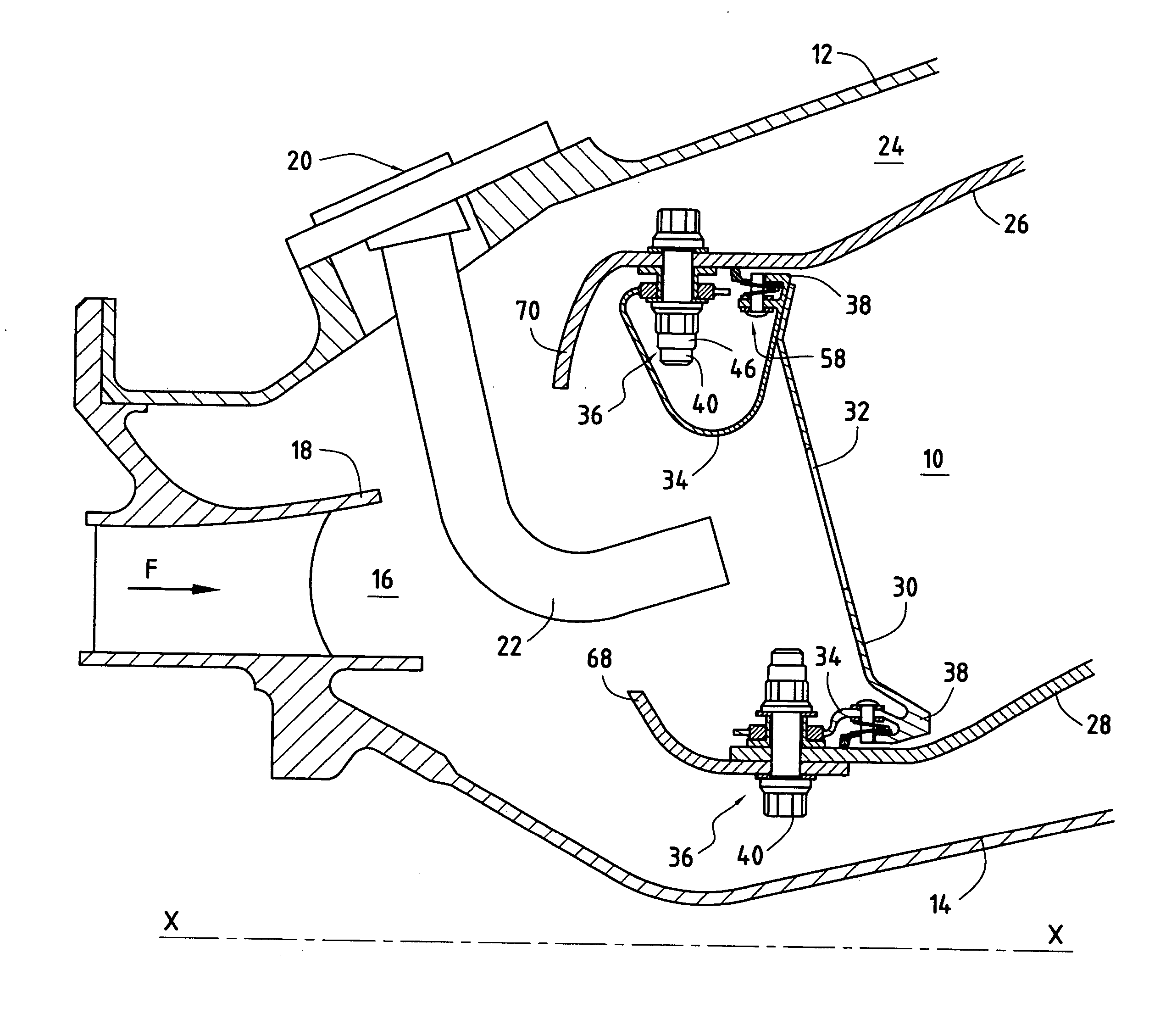
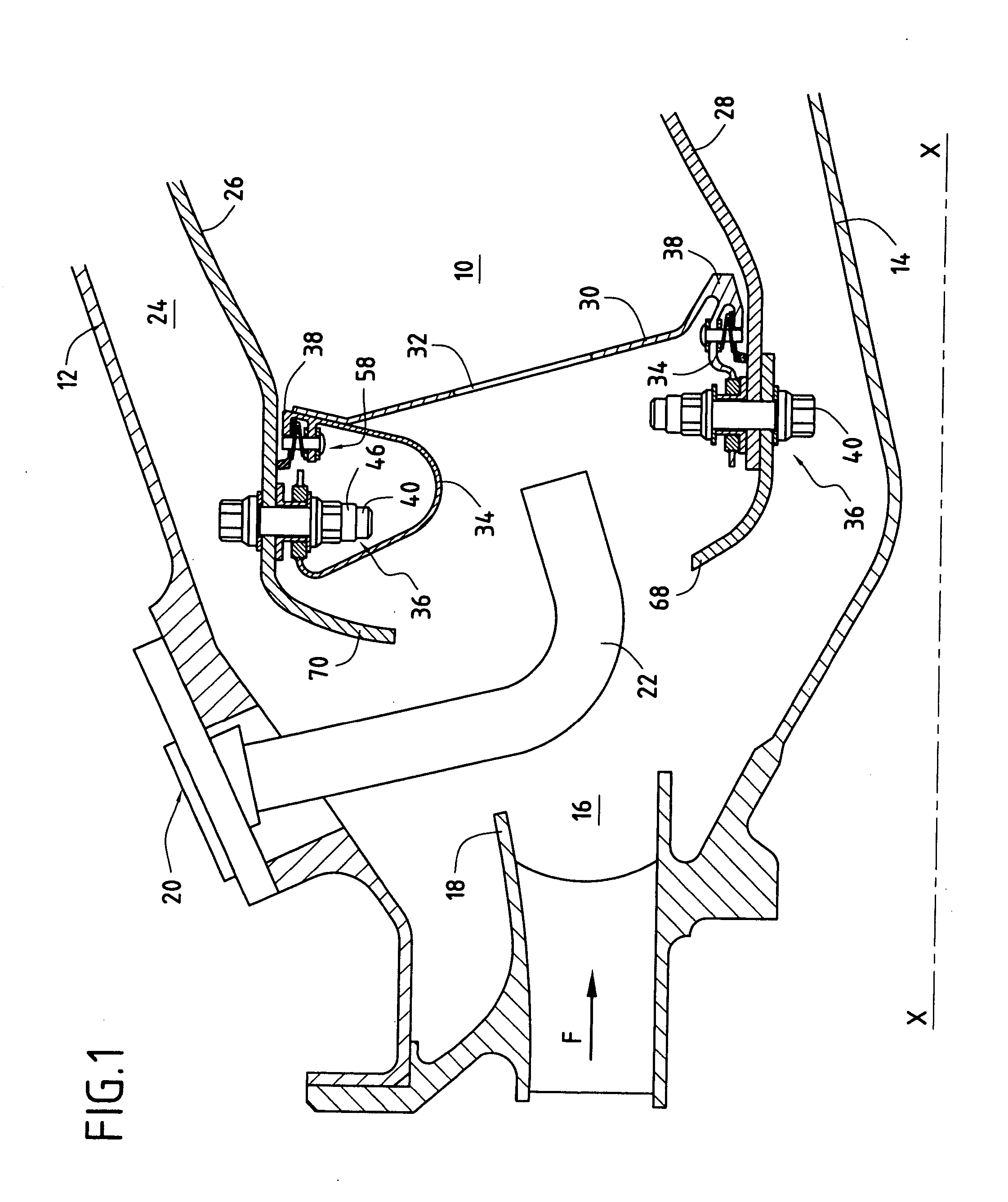
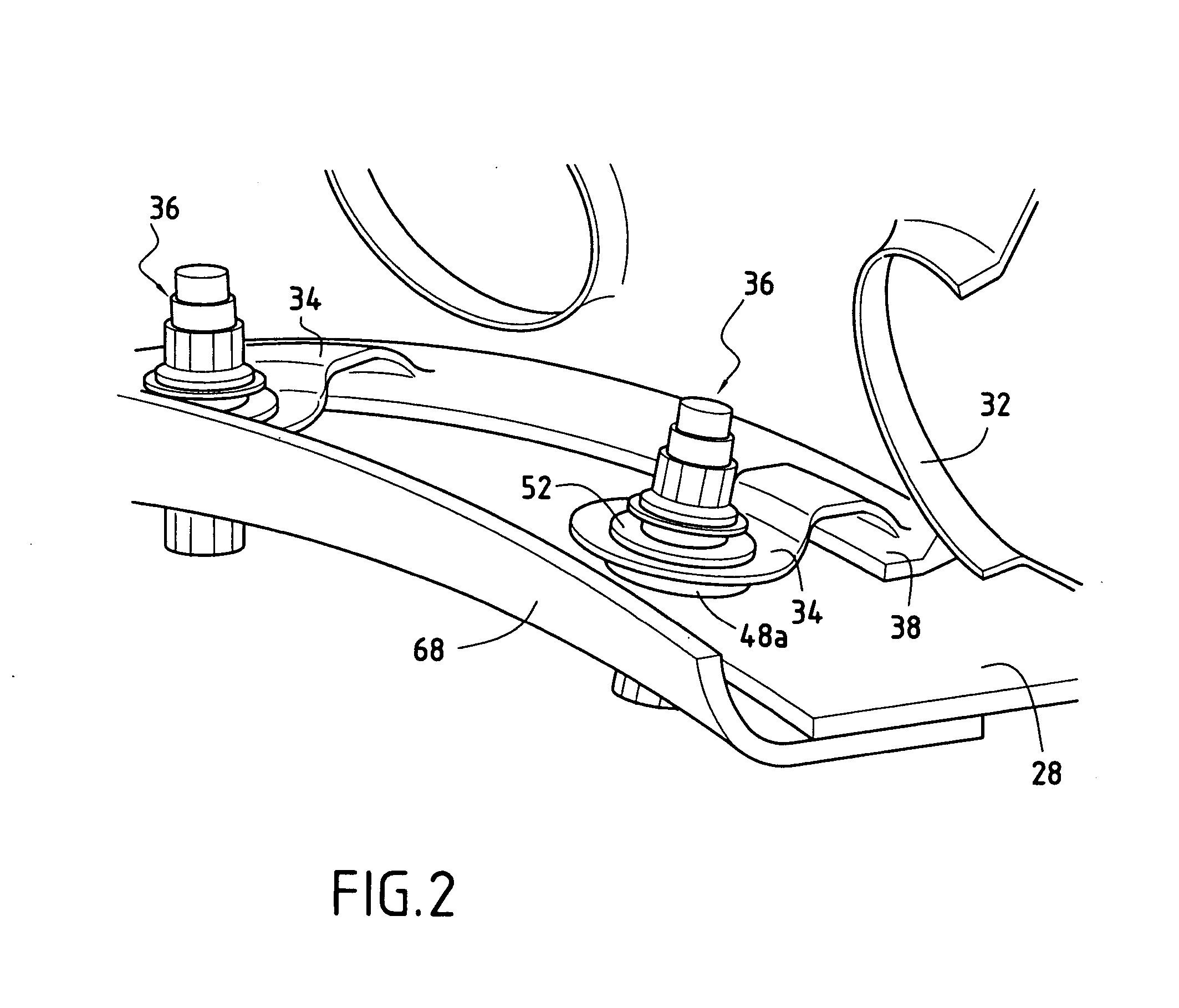
Assembling an annular combustion chamber of a turbomachine
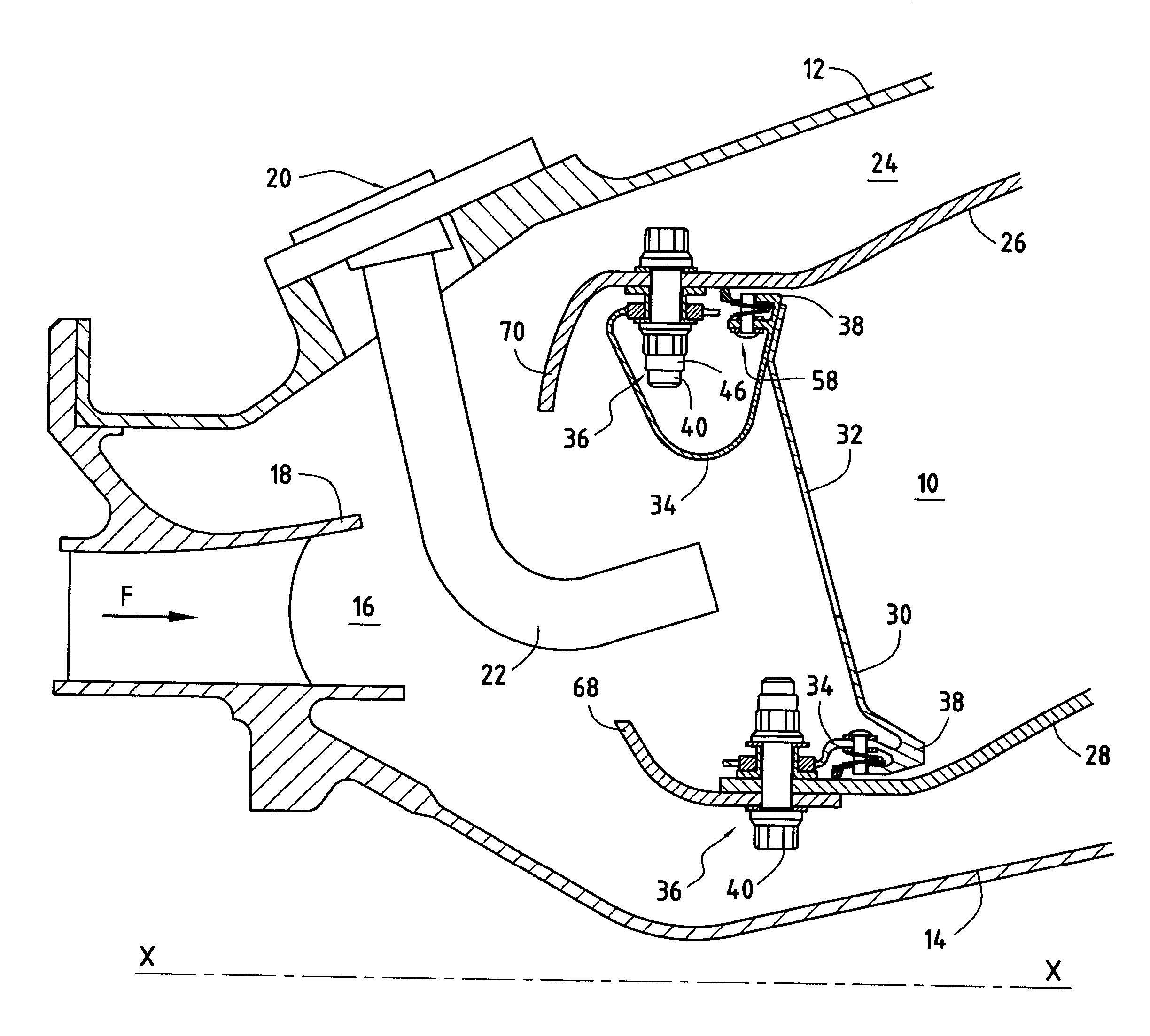
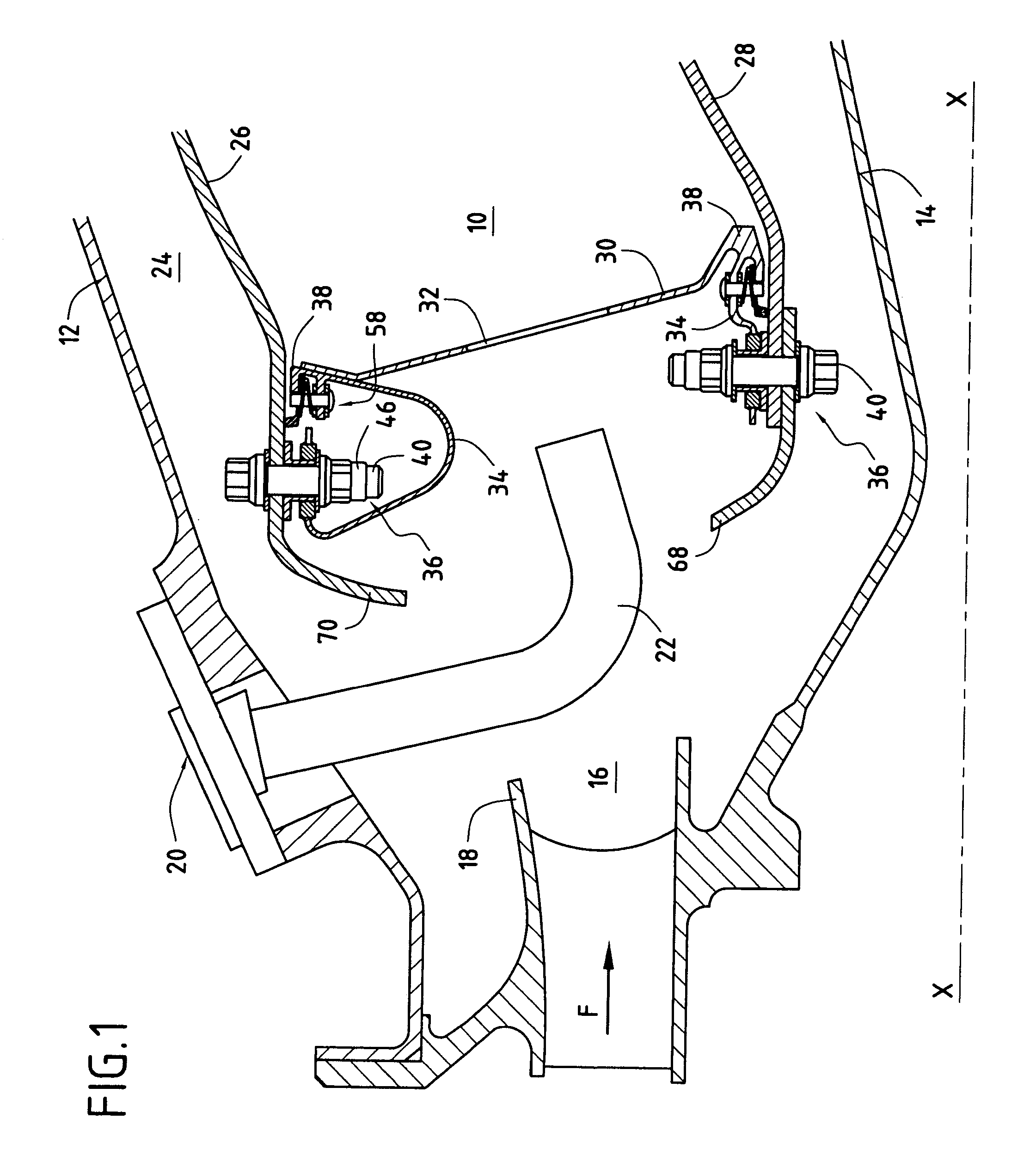
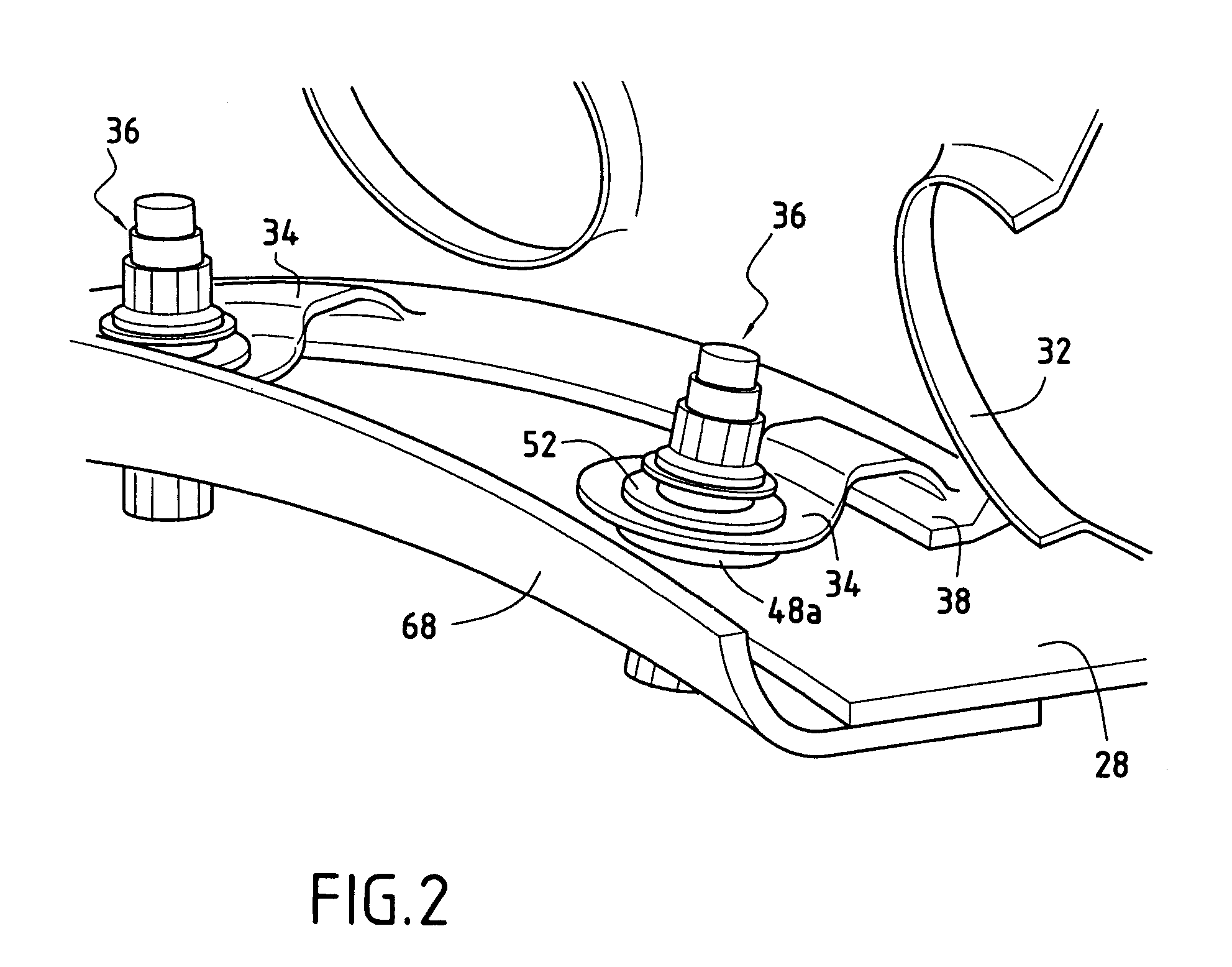
ActiveUS7849696B2Effective dampingMitigate such drawbackContinuous combustion chamberCombustion enginesCombustion chamberThermal expansion
An annular combustion chamber comprising axial walls interconnected by a chamber end wall having a coefficient of thermal expansion that is different from that of the axial walls, the chamber end wall being provided with a plurality of inner and outer fastener tabs secured by fastener systems to the end portions of the axial walls. Each fastener system comprises a bolt, a nut tightened onto one of the ends of the bolt, and a slideway bushing disposed around the bolt between the nut and the end portion of the corresponding axial wall, a determined amount of radial clearance being provided between the nut and the end portion of the axial wall so as to enable the chamber end wall to expand radially freely in operation relative to the axial walls.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
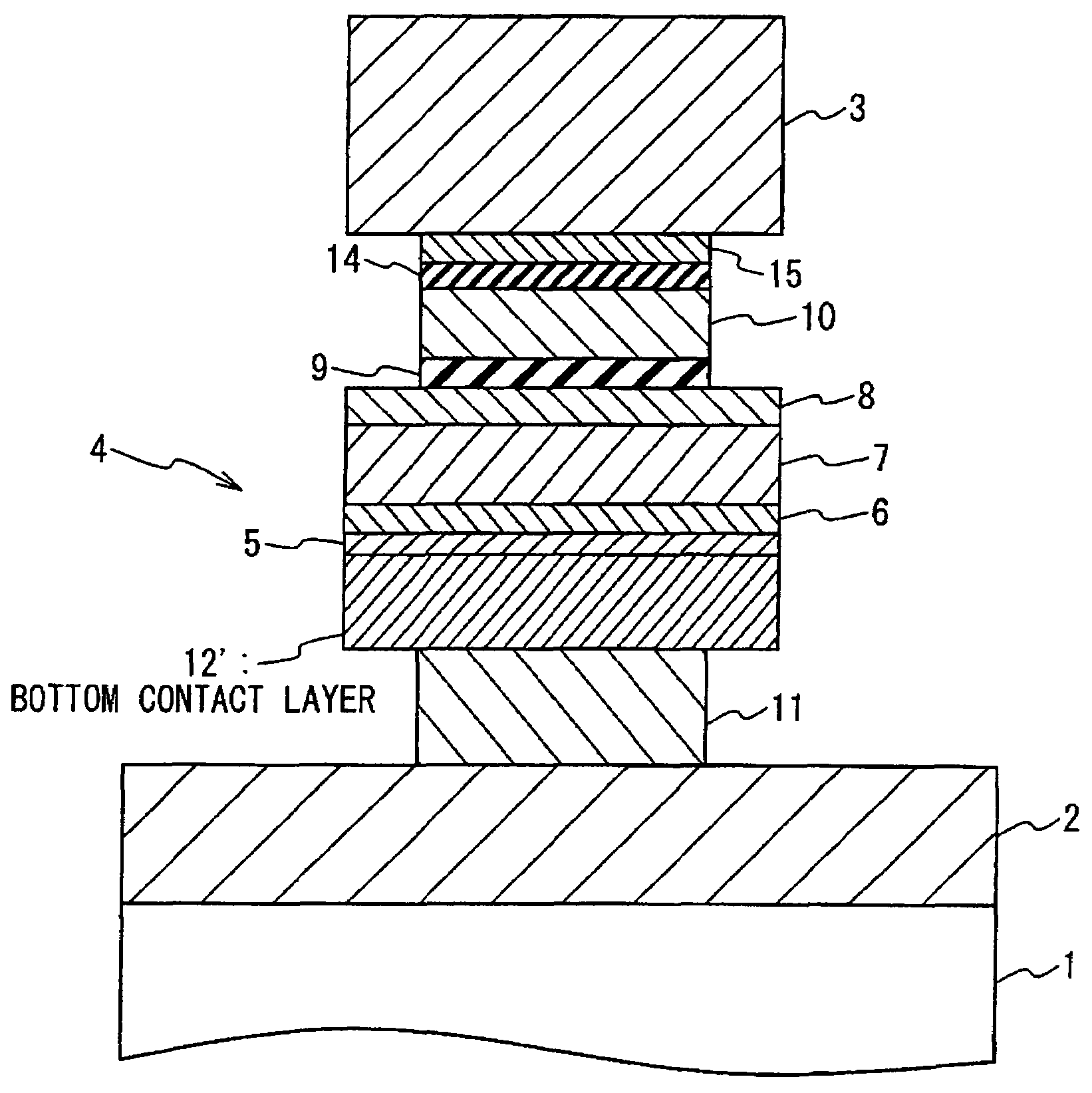
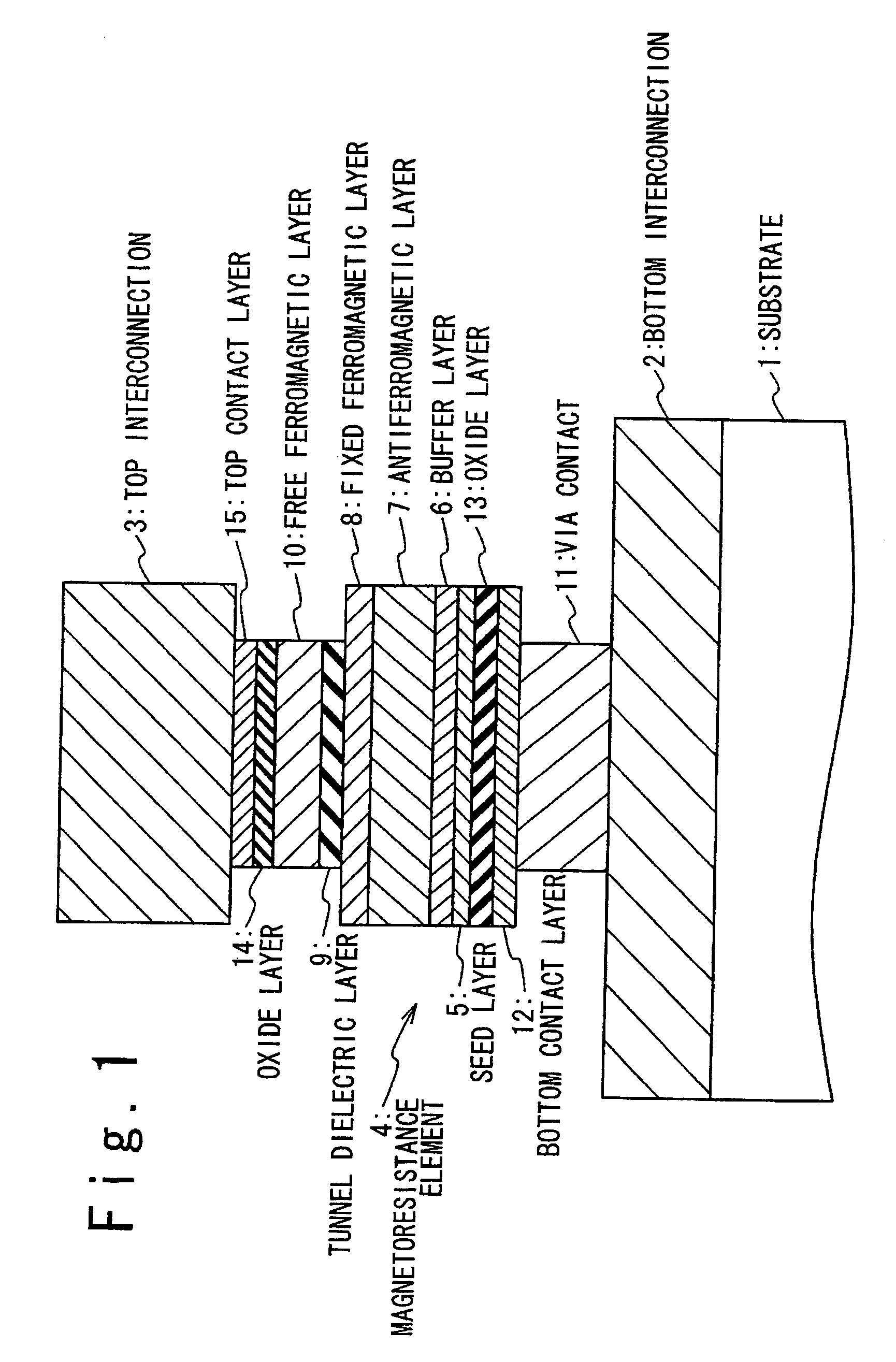
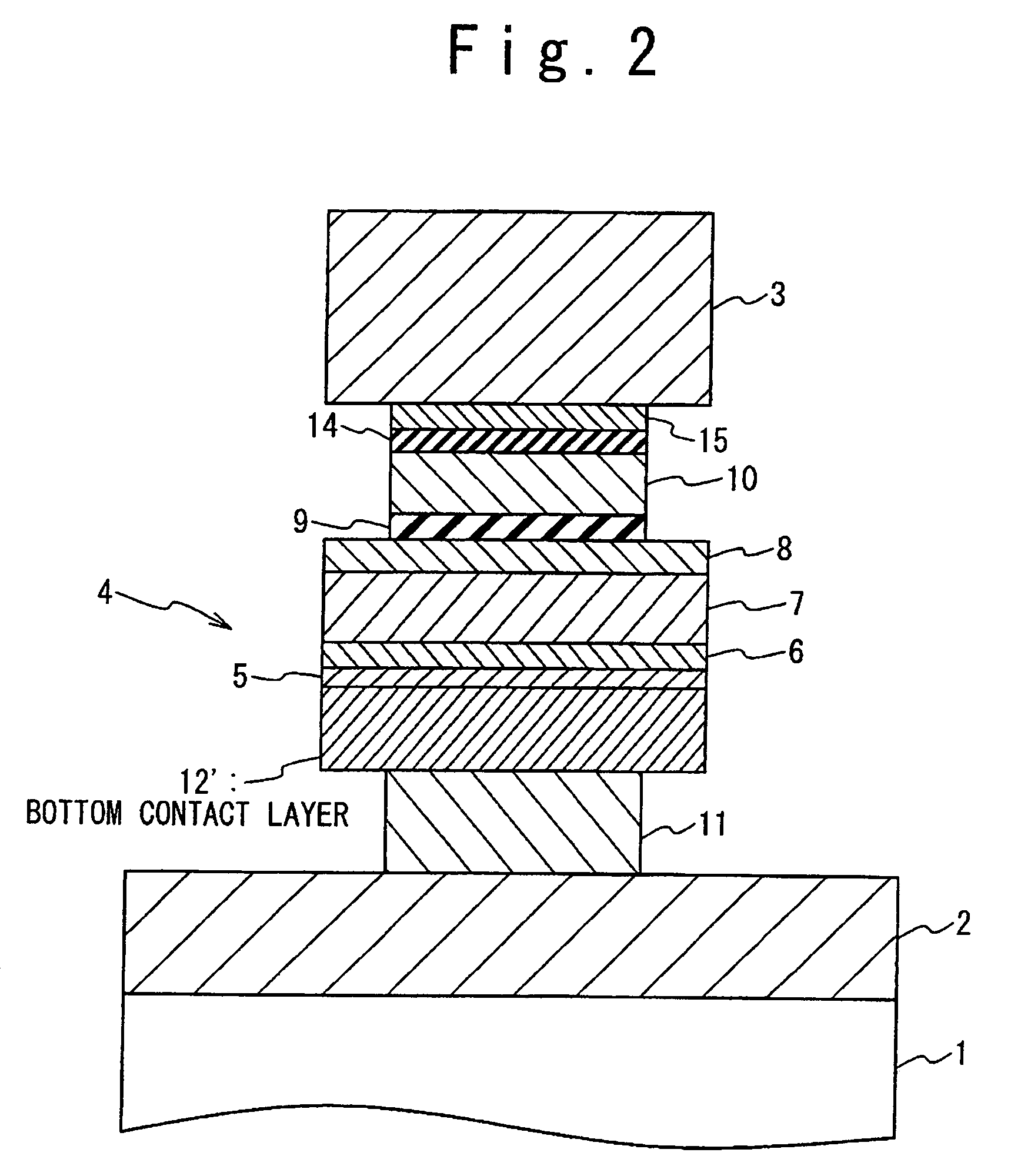
Magnetoresistance device with a diffusion barrier between a conductor and a magnetoresistance element and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS7394626B2Improve thermal stabilityPrevent interdiffusionNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismElectrical conductorMagnetic reluctance
Owner:NEC CORP
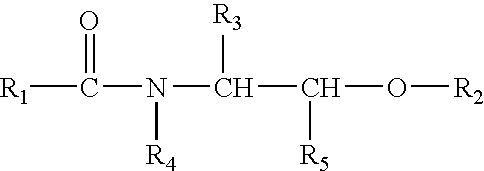
Composition containing at least one hydroxy acid, at least one mono- or disaccharide and at least one ceramide, and methods
ActiveUS20070226916A1Reduce in quantityBlocking phenomenonCosmetic preparationsHair removalAlpha hydroxy acidDisaccharide
Composition which, in a preferred embodiment, contains, in a cosmetically acceptable medium, at least one monosaccharide and / or disaccharide, at least one α-hydroxy acid, and at least one ceramide compound. Uses include topical application for the treatment of keratinous substances, in particular keratinous fibres, especially the hair.
Owner:LOREAL SA
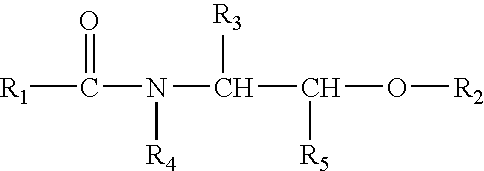
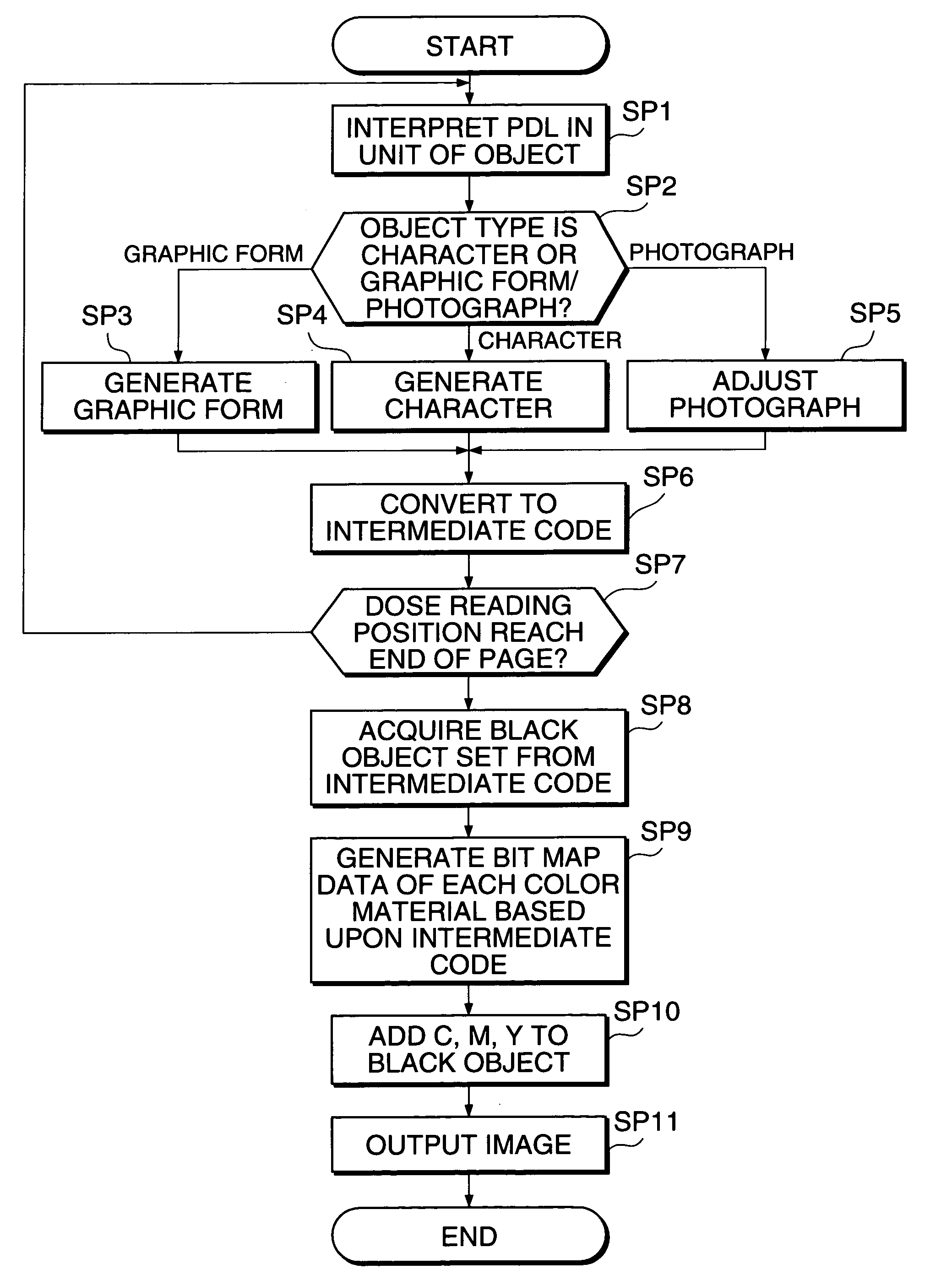
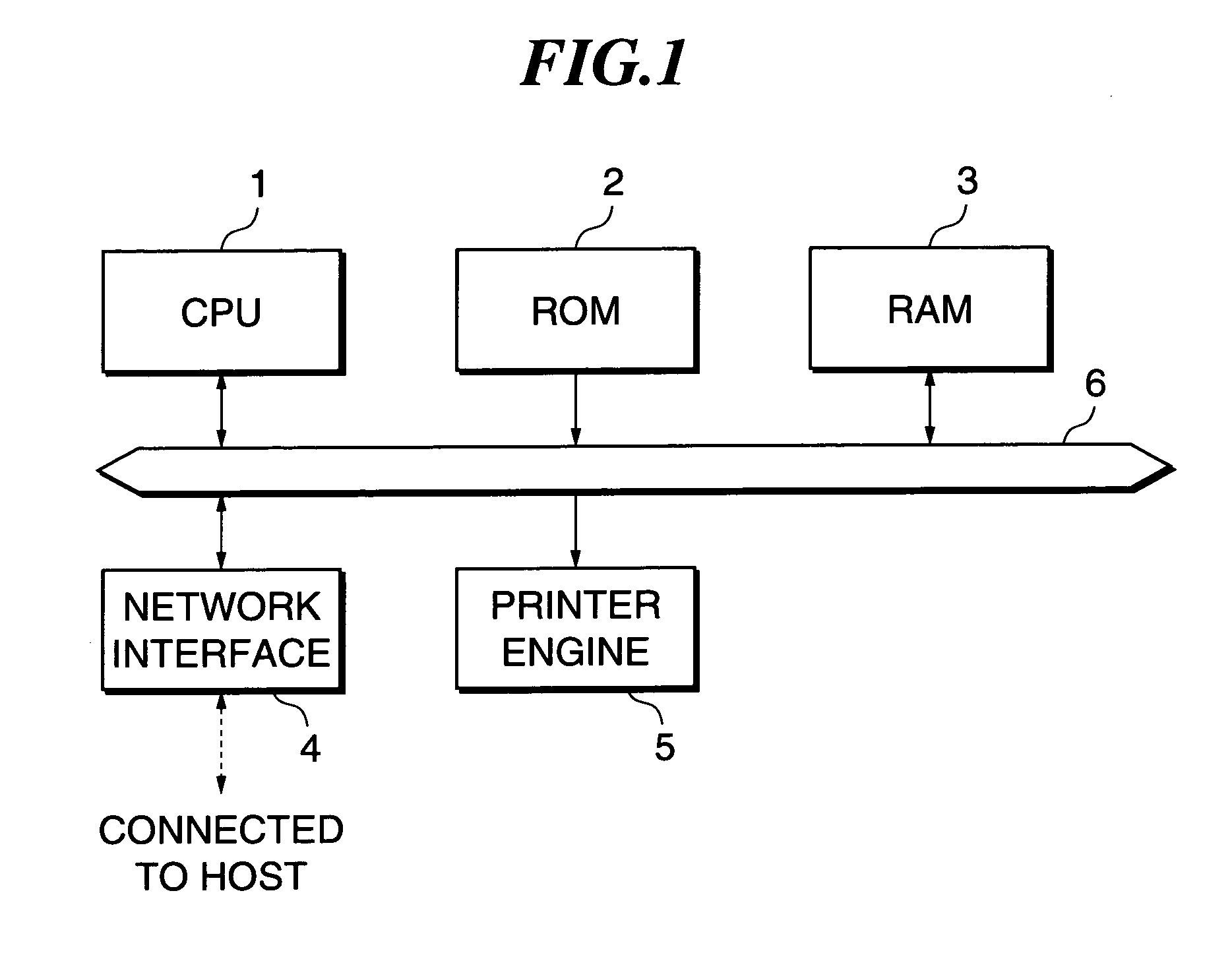
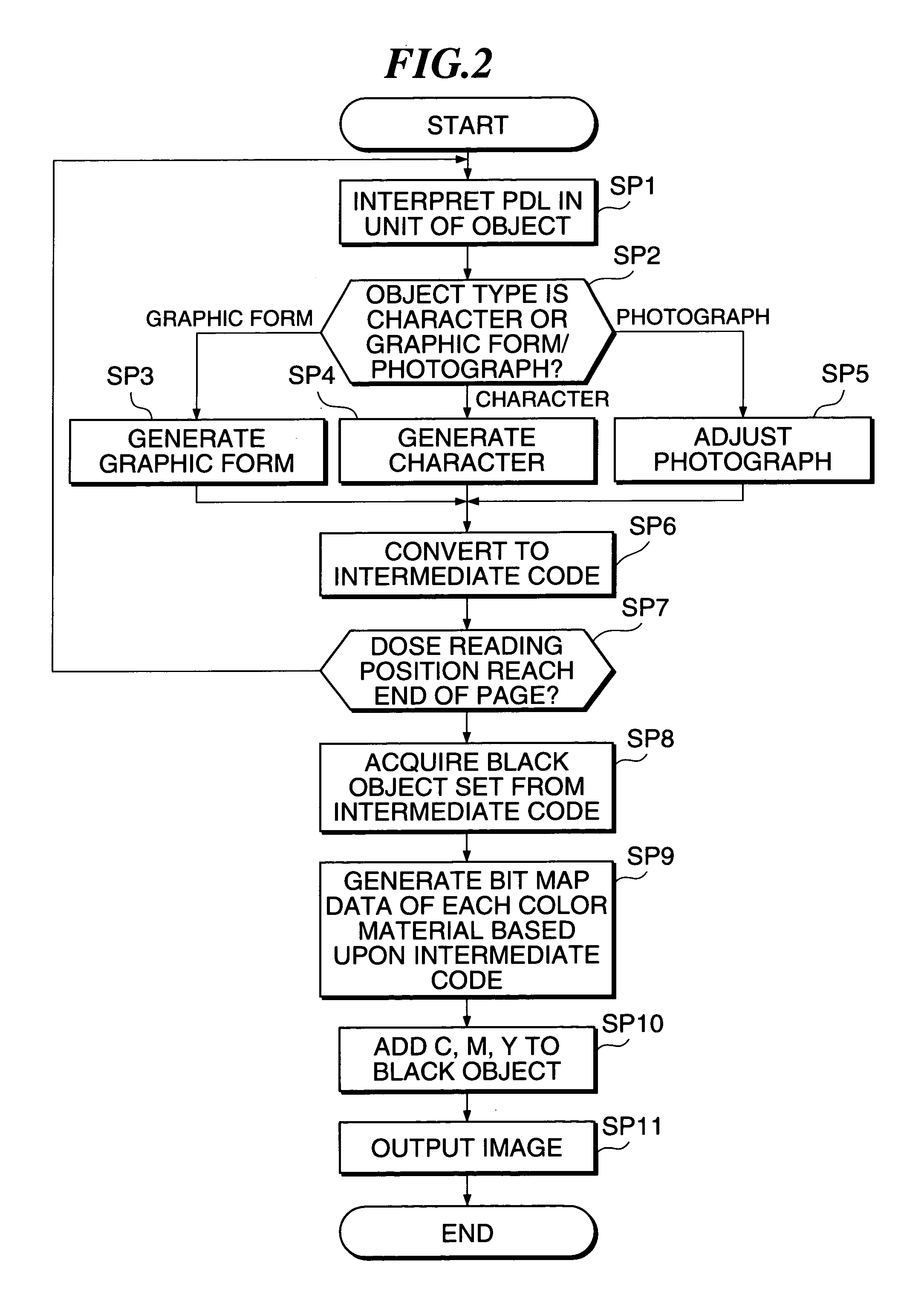
Image processing device and image processing method thereof
InactiveUS7362467B1Blocking phenomenonEffectively preventing a phenomenonImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersImaging processingCopying
The image processing device and method of the present invention prevent a problem such as misregistration and a phenomenon that an edge pales, and enable high speed output in a color printer and a color copying machine. The color materials of Y, M, C of a predetermined amount are output onto a black object regardless of peripheral pixel values and thereby a phenomenon that an edge pales is prevented. In the edge of the black object, trapping processing according to peripheral pixel values is executed and a problem due to misregistration is made inconspicuous.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
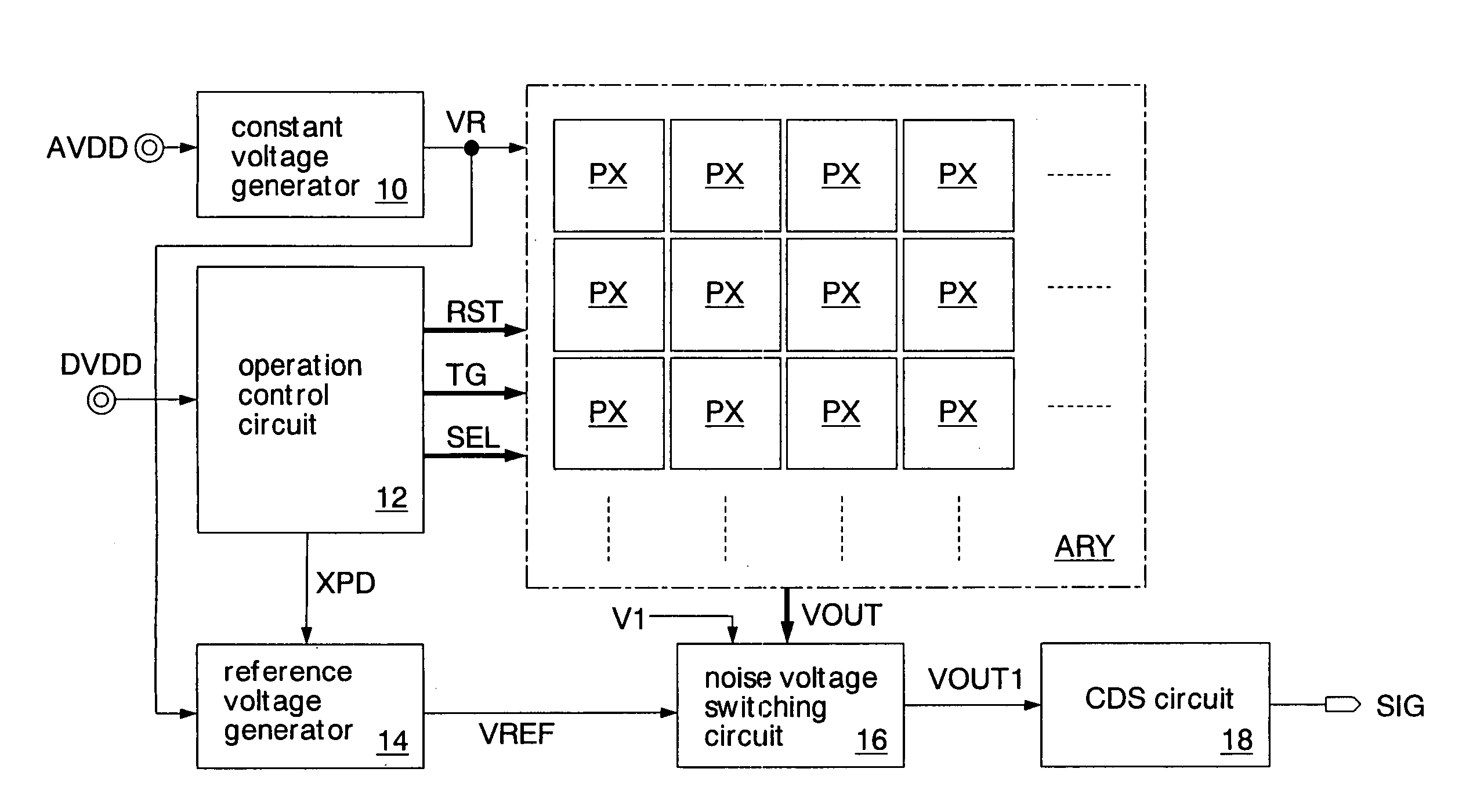
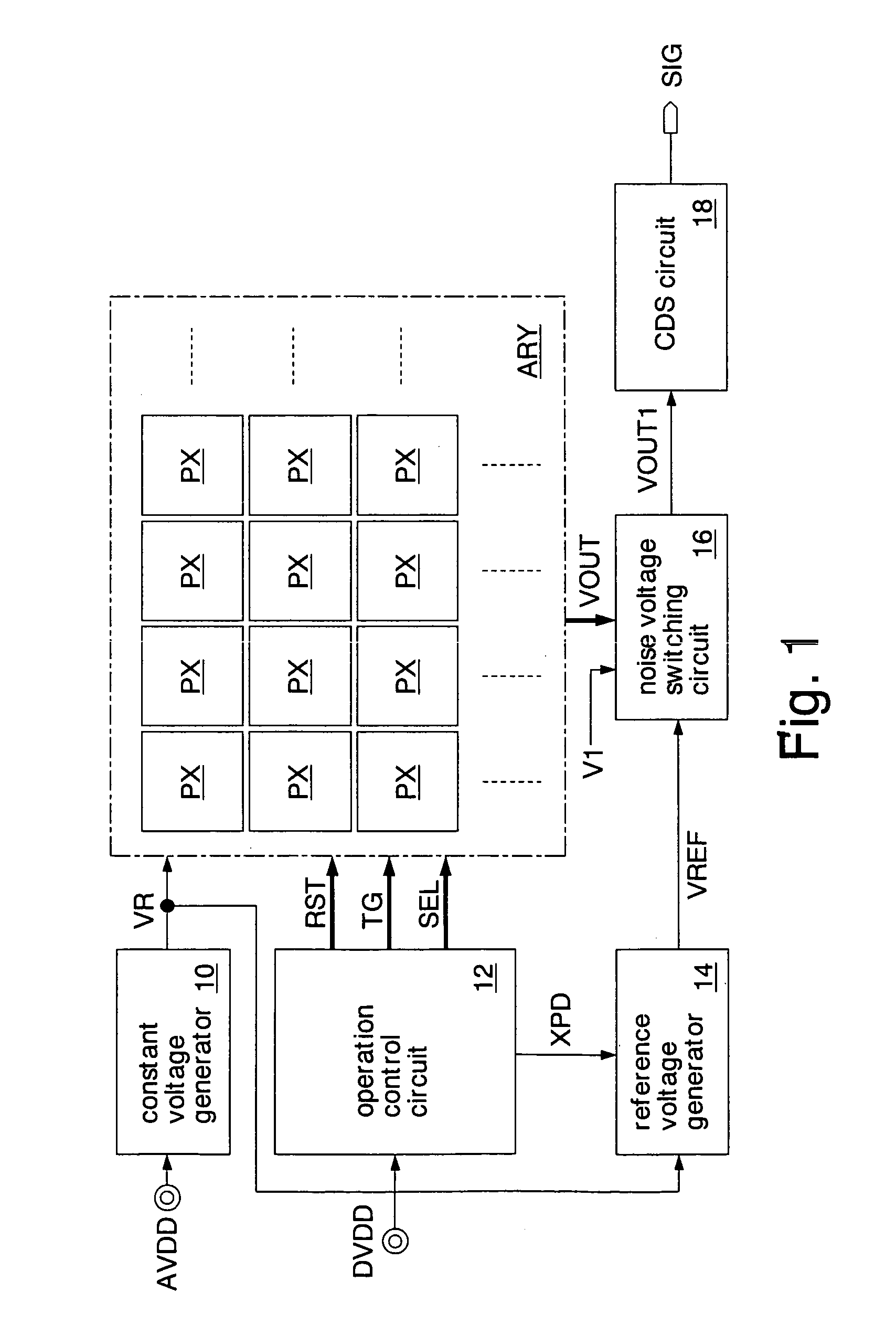
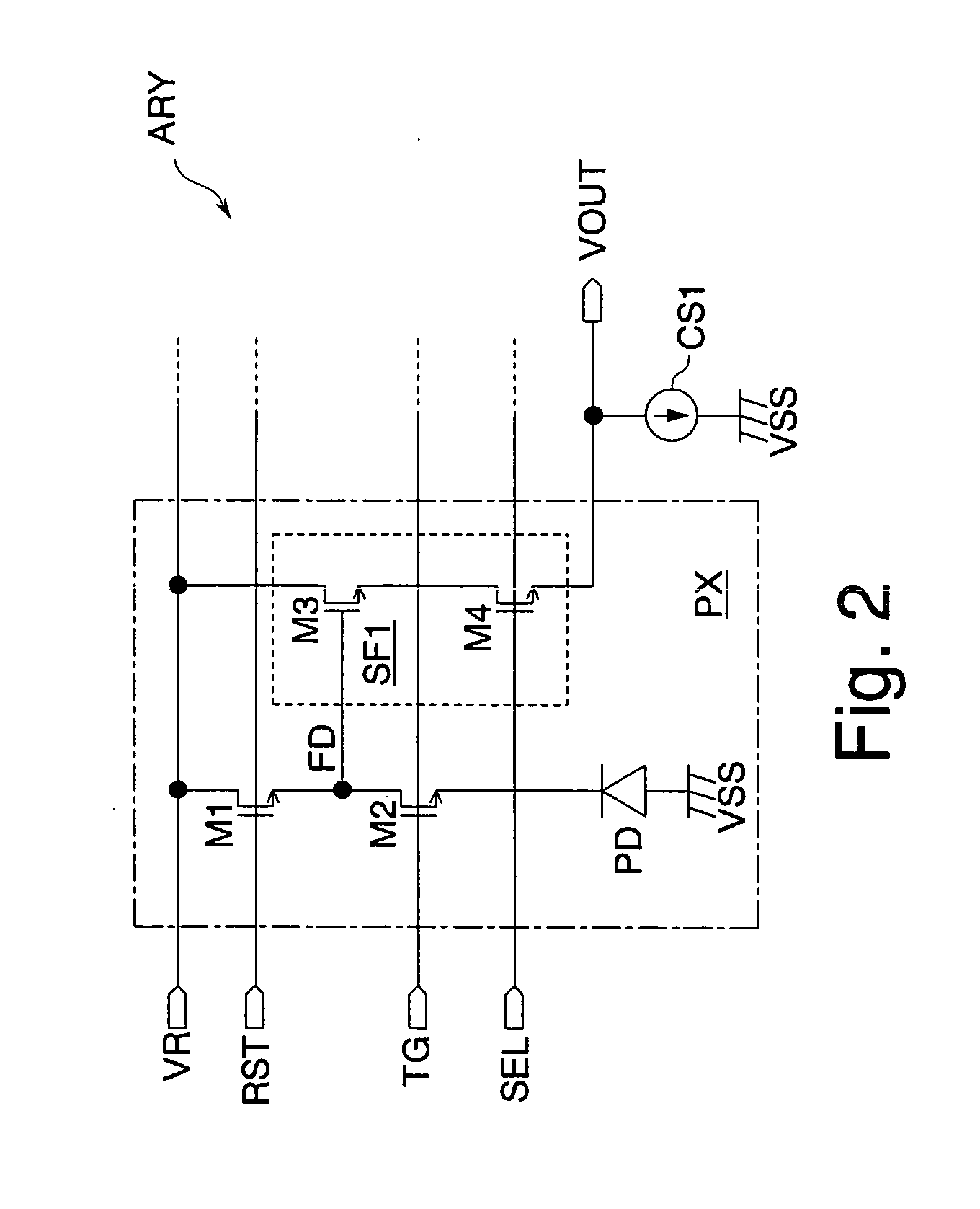
Imaging device
InactiveUS20060170794A1Improve accuracyIncrease volumeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsVoltage generatorImaging quality
A second source follower circuit of a reference voltage generator includes a transistor having the same characteristics as a first source follower circuit of a pixel. Accordingly, the second source follower circuit can generate a second reference voltage according to the change in characteristics of the first source follower circuit. A noise voltage switching circuit outputs a first voltage as a noise voltage to a pixel signal generator when the noise voltage is equal to or lower than the second reference voltage. In a reset state, the noise voltage and the second reference voltage always have a predetermined voltage difference. Therefore, deterioration in image quality can be prevented even when capturing a subject having high brightness. Since a trimming circuit or the like selecting any one of a plurality of reference voltages according to characteristics of a formed transistor becomes unnecessary, the cost of an imaging device can be reduced.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Assembling an annular combustion chamber of a turbomachine
ActiveUS20070107710A1Effective dampingMitigate such drawbackContinuous combustion chamberCombustion enginesCombustion chamberEngineering
An annular combustion chamber comprising axial walls interconnected by a chamber end wall having a coefficient of thermal expansion that is different from that of the axial walls, the chamber end wall being provided with a plurality of inner and outer fastener tabs secured by fastener systems to the end portions of the axial walls. Each fastener system comprises a bolt, a nut tightened onto one of the ends of the bolt, and a slideway bushing disposed around the bolt between the nut and the end portion of the corresponding axial wall, a determined amount of radial clearance being provided between the nut and the end portion of the axial wall so as to enable the chamber end wall to expand radially freely in operation relative to the axial walls.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
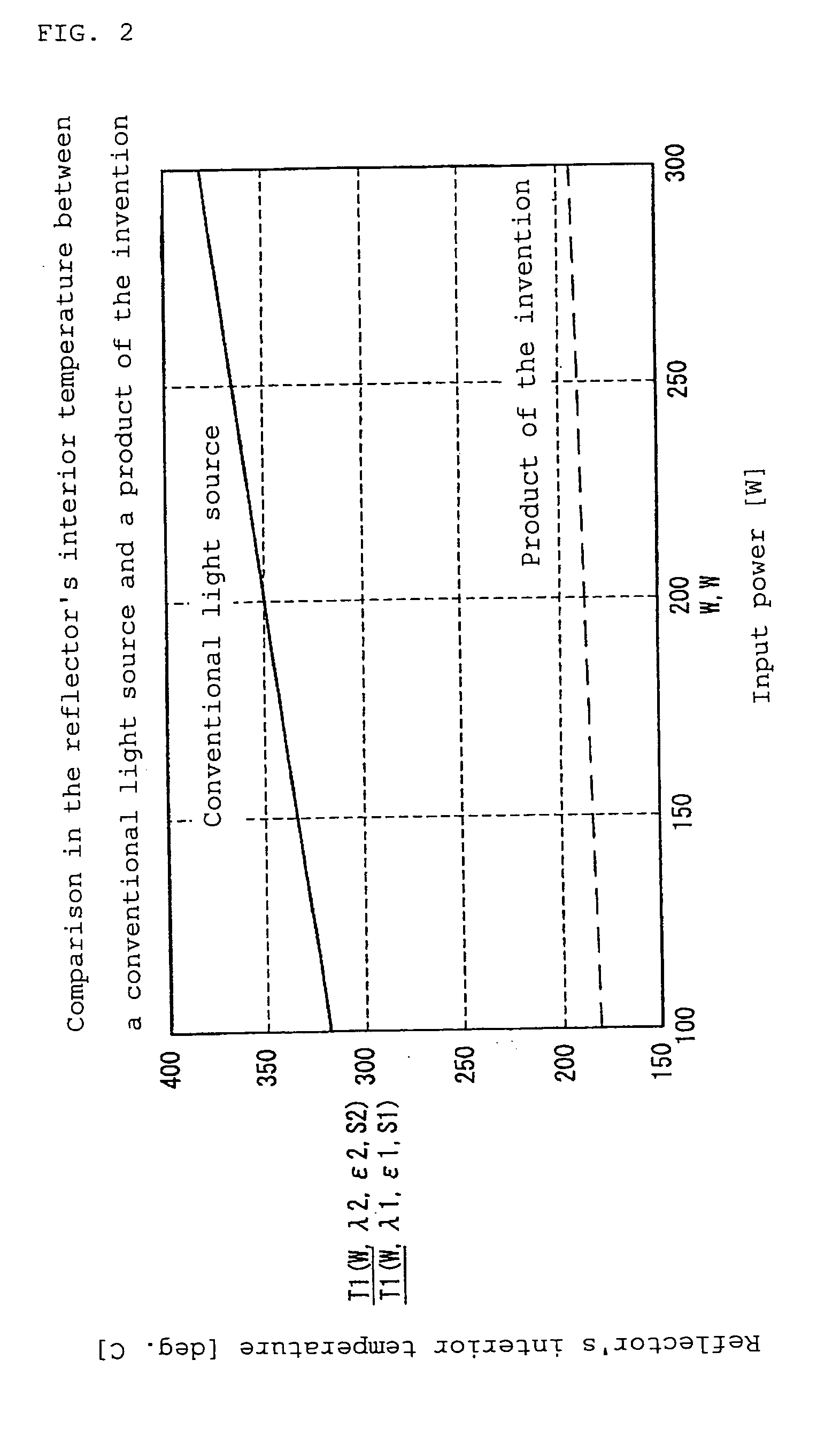
Reflector, light source device and projection display apparatus
InactiveUS20070041197A1Efficiently convertSuppress deformationMirrorsPoint-like light sourceAnodic oxidationThermal conductivity
A concave mirror substance 1 constituting a reflector is composed of a base material having a high thermal conductivity such as aluminum etc. An infrared-to-heat converting layer 2 is film-formed by anodizing the substrate formed of aluminum etc., so as to absorb light in a wavelength range which passes through a visible light reflecting layer 4 and convert it into heat. A gloss-forming buffer layer 3 is film-formed by calcining Si resin or polyimide resin over the inner side (the light source-side surface) of infrared-to-heat converting layer 2 at high temperatures, so as to buffer the two layers in a manner that does not allow infrared-to-heat converting layer 2 and visible light reflecting layer 4 to be in direct contact with each other, and so as to reduce the influence of projections and indentations present on infrared-to-heat converting layer 2 and smoothen the light source-side surface of visible light reflecting layer 4. In this way, it is possible to suppress performance degradation by efficient discharge of heat by converting light into heat and by alleviating thermal stress and strain due to the difference in expansion coefficient between components, and it is also possible to achieve reduction in cost, miniaturization and weight reduction.
Owner:SHARP KK
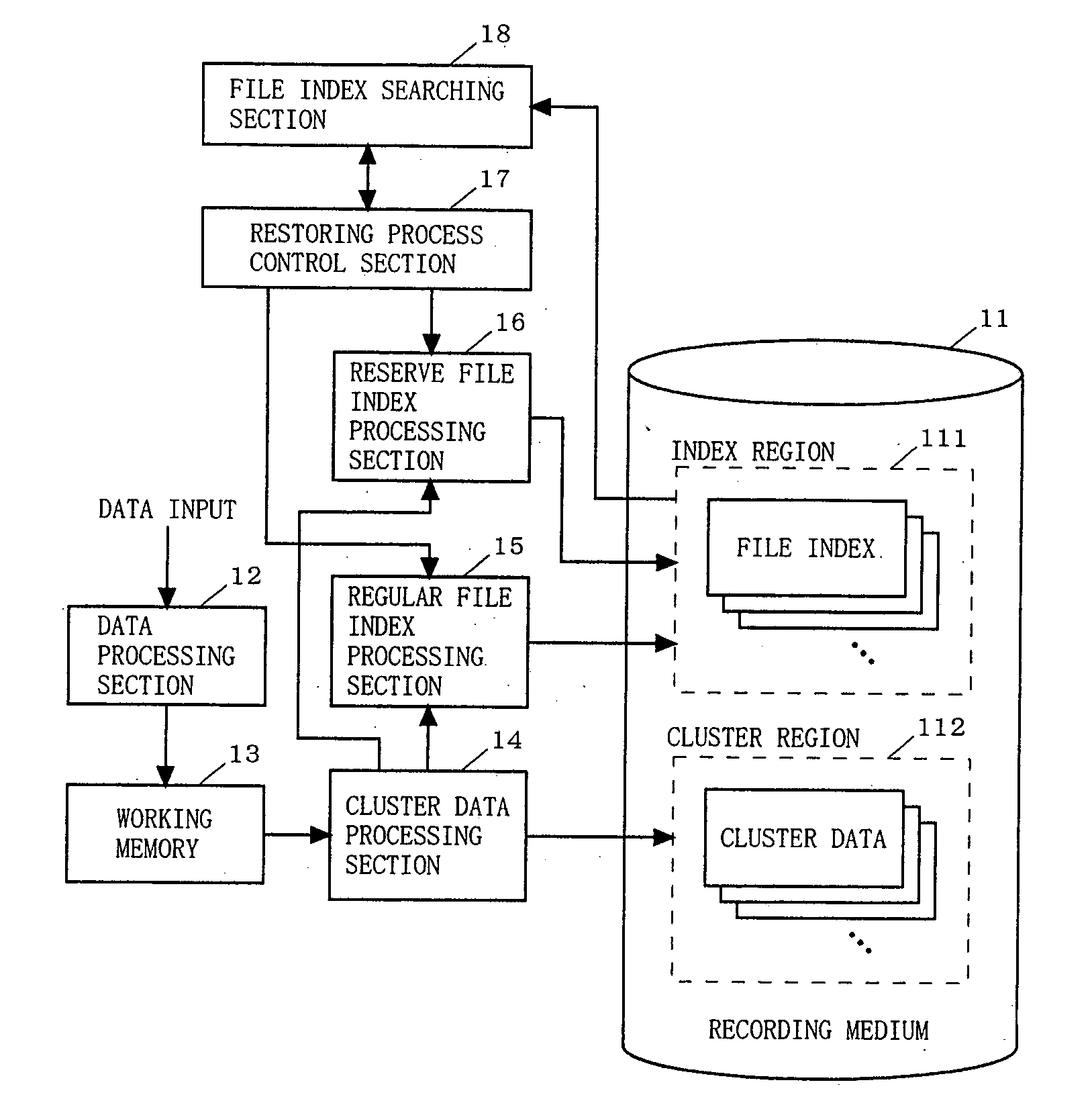
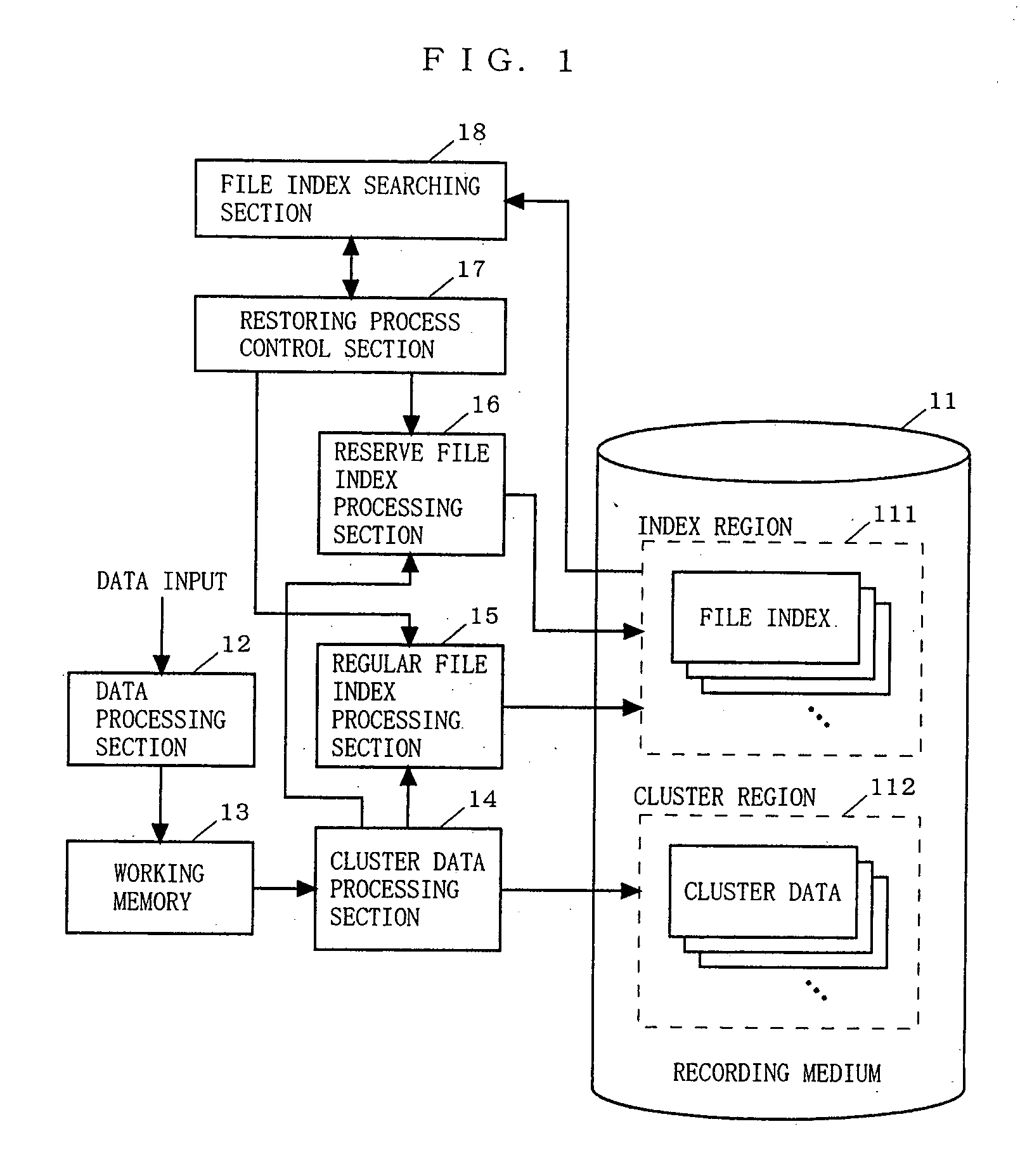
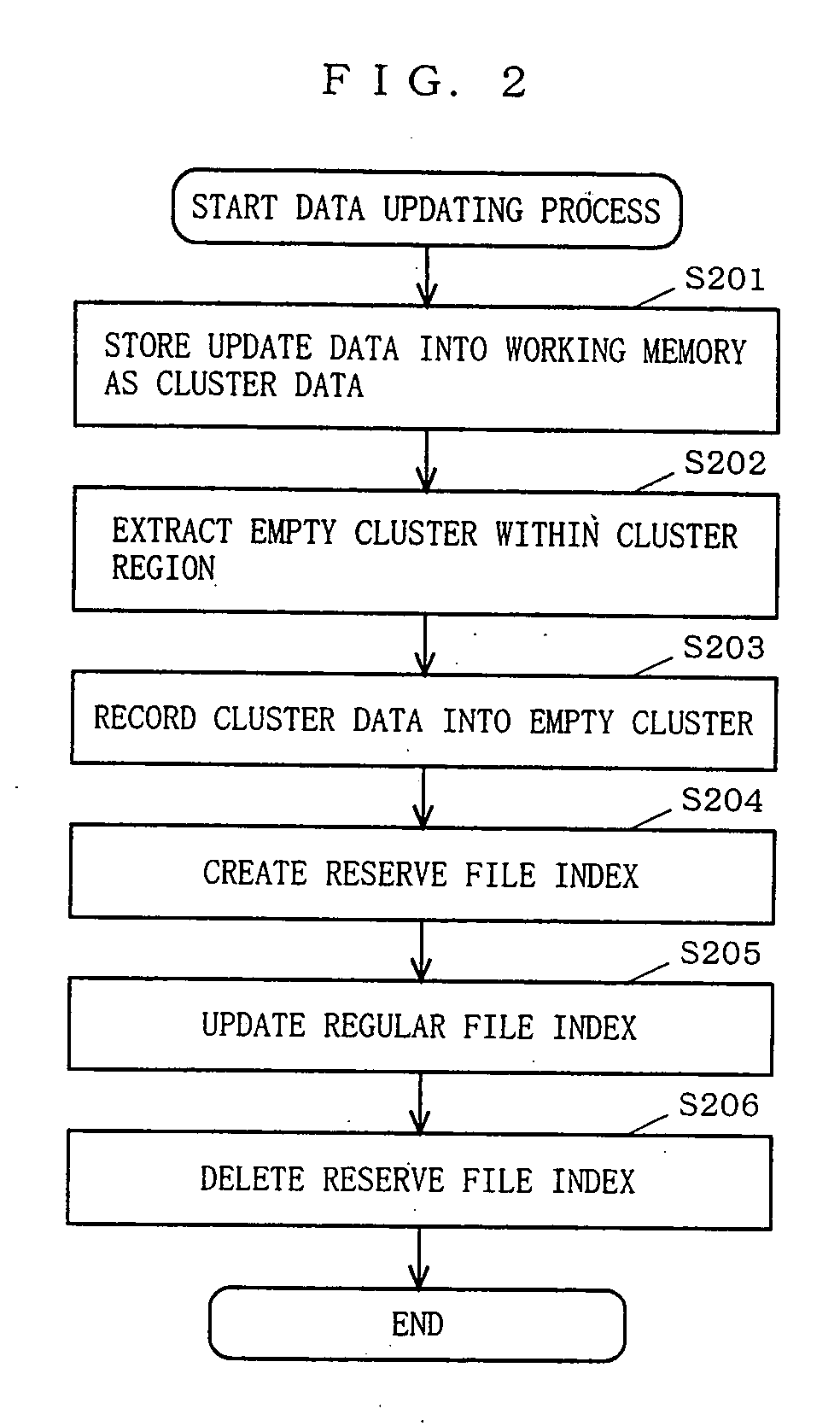
Data recording apparatus, data recording method, program for implementing the method, and program recording medium
InactiveUS20050262033A1Blocking phenomenonSolve large capacityInput/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsClustered dataData recording
The present invention provides a data recording apparatus which allows data to be read on the next access after recording of cluster data or a file index is interrupted by power disconnection or the like caused during a data updating process. A cluster data processing section 14 searches a cluster region 112 of a recording medium 11 for an empty cluster and records cluster data into the empty cluster. A reserve file index processing section 16 creates anew reserve file index for the recorded cluster data within the index region 111 of the recording medium 11. Then, a regular file index processing section 15 updates the contents of an existing regular file index corresponding to update data to the contents of the reserve file index. Thereafter, the reserve file index processing section 16 deletes the reserve file index from the index region 111.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and equipment for implementing synchronous switching of CLOS cross connection matrix
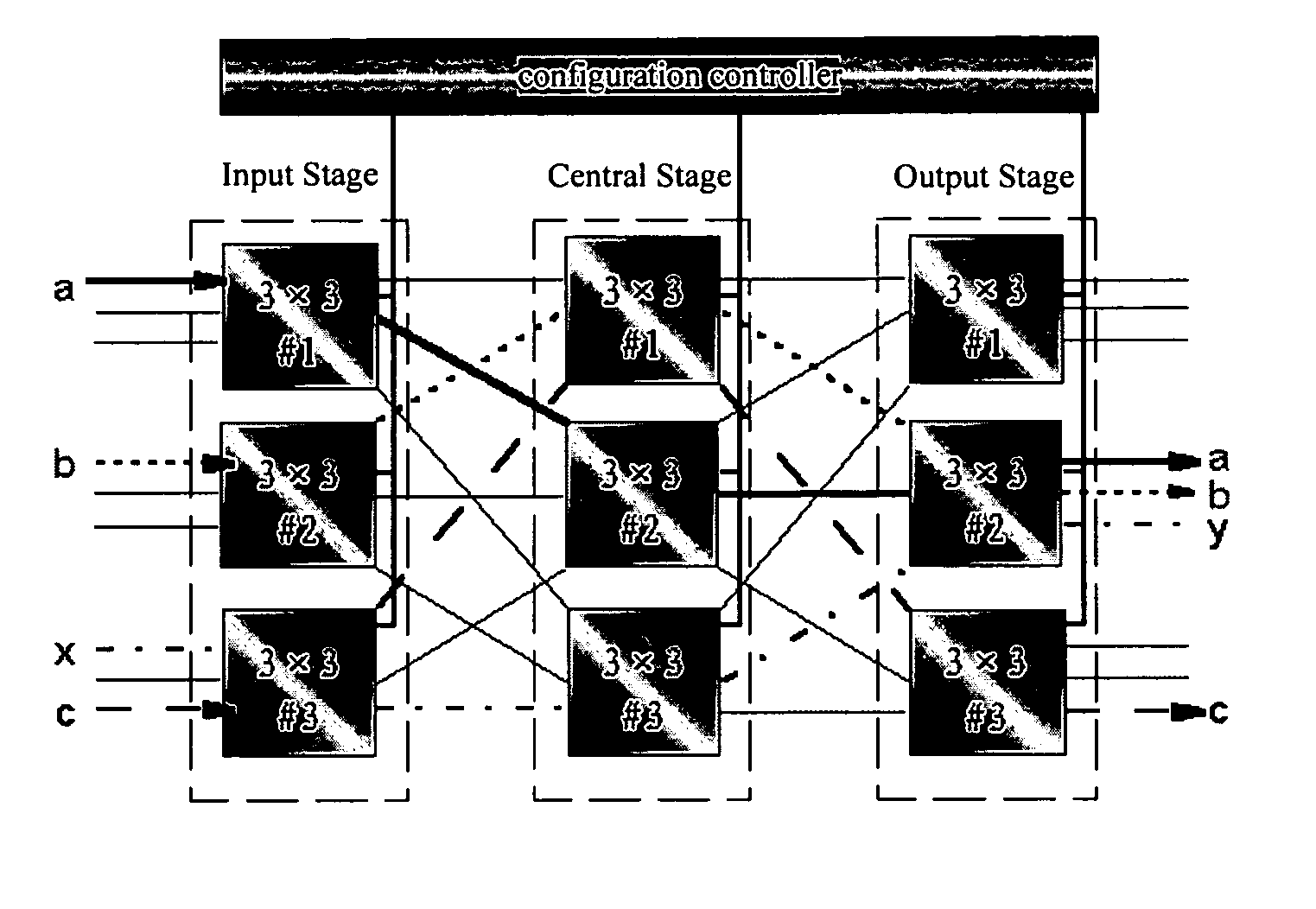
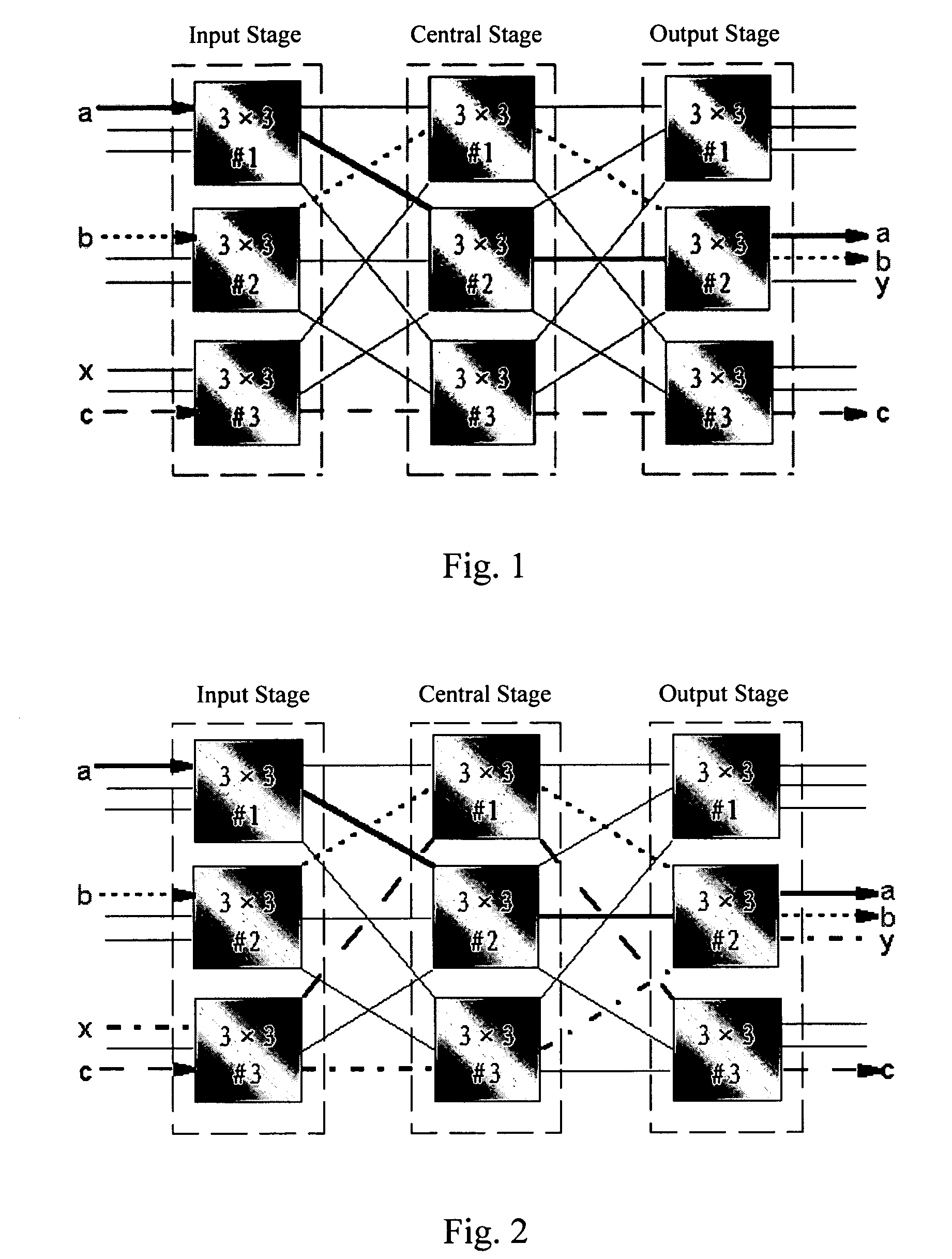
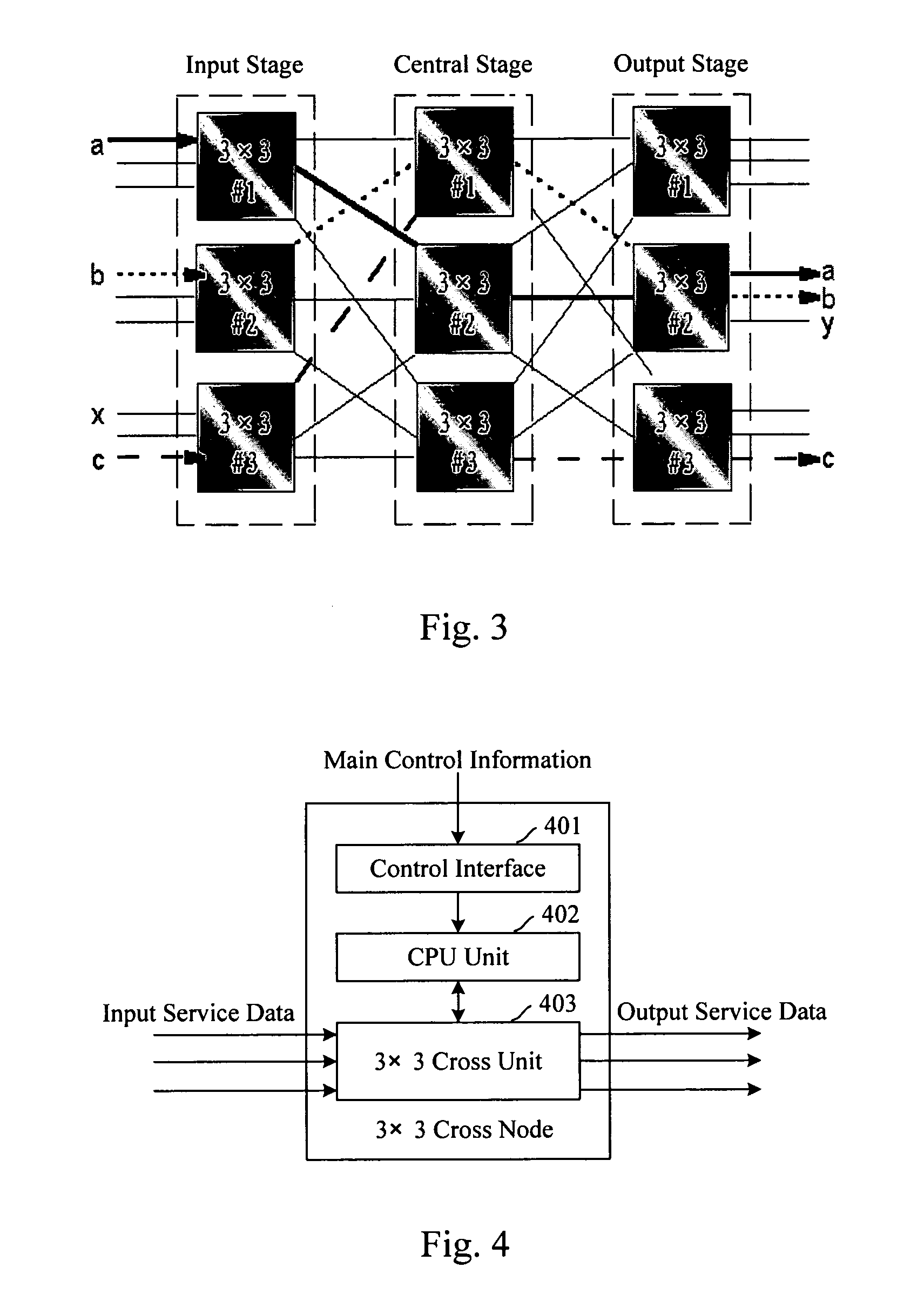
InactiveUS20060209816A1Blocking phenomenonGuaranteed normal switchingData switching by path configurationCircuit switching systemsCross connectionAgricultural engineering
The present invention discloses a method for implementing synchronous switching of cross connections of a CLOS cross connection matrix, comprising: the configuration controller calculating a new CLOS cross connection matrix according to the cross request, sending this new CLOS cross connection matrix to the cross nodes requiring synchronous switching, and sending synchronous switching signal to all the cross nodes requiring synchronous switching after receiving the ready signals returned by all the cross nodes requiring synchronous switching, and the cross nodes performing the synchronous switching immediately after receiving the synchronous switching signal. The present invention also discloses a digital cross connection equipment containing a configuration controller for implementing synchronous switching of a CLOS cross connection matrix. With the present invention, synchronous switching of the input stage, the central stage and the output stage can be guaranteed without instantaneous disconnections.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
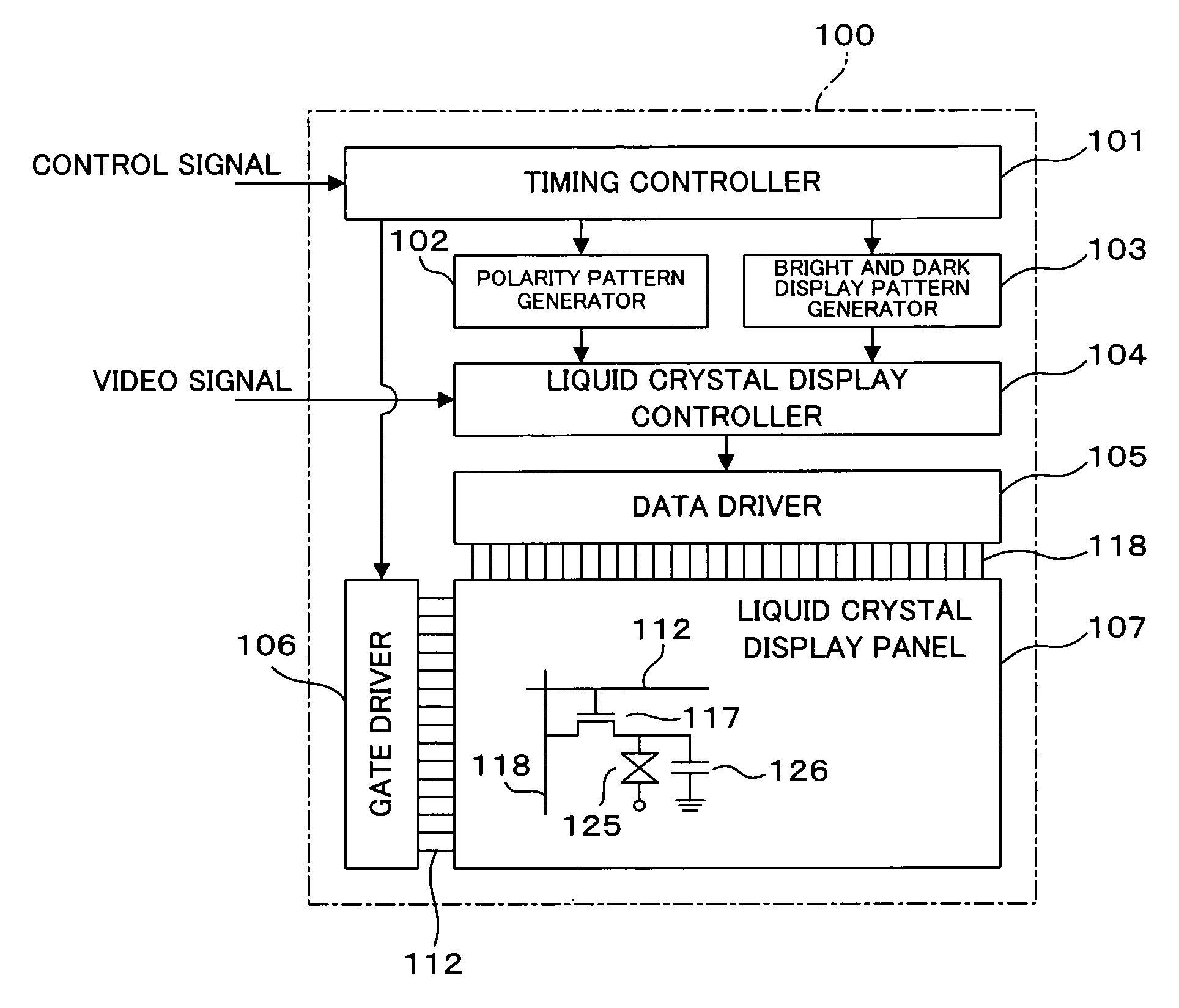
Method of driving liquid crystal display device and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20060055648A1Avoid rising manufacturing costsReduce oblique leakage of lightStatic indicating devicesOperating tablesLiquid-crystal displayElectrical polarity
A combination of a bright and dark display pattern and a polarity pattern is used to drive a liquid crystal display device. In the bright and dark display pattern, bright display picture elements and dark display picture elements alternate with each other every one picture element in horizontal and vertical directions. In the polarity pattern, positive-polarity picture elements and negative-polarity picture elements alternate with each other every two picture elements in the horizontal and vertical directions. This driving method allows preventing a phenomenon in which a screen becomes whitish when viewed from any oblique angle (i.e., washing out), that is, what the effect of HT technique based on time division is aiming at, while preventing the occurrence of flicker and burn-in on the screen. Moreover, the driving method enables coarseness-free excellent display, because the bright display picture elements and the dark display picture elements alternate with each other every one picture element.
Owner:SHARP KK
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20080210978A1Improve ESD toleranceImprove the immunityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsContact formationEngineering
A semiconductor device includes: a gate electrode formed above a semiconductor region; a drain region and a source region formed in portions of the semiconductor region located below sides of the gate electrode in a gate length direction, respectively; a plurality of drain contacts formed on the drain region to be spaced apart in a gate width direction of the gate electrode; and a plurality of source contacts formed on the source region to be spaced apart in the gate width direction of the gate electrode. The intervals between the drain contacts are greater than the intervals between the source contacts.
Owner:PANNOVA SEMIC
Packing box, corrugated cardboard blank sheet and ruling wheel assembly
InactiveUS20110226847A1Inhibit potential serpentine folding lineIncreased bending stiffnessMechanical working/deformationBoxes/cartons making machineryCardboardEngineering
An object of the present invention is to provide a packing box having its ridge(s) collapsed so that there would be no body bulging occurring in the box and potential serpentine folding line would be avoided.Provided is a packing box having a top panel 3, a bottom panel 7, two long side panels and two short side panels, in which at least either one of a ridge defined between said top panel and said long side panel or a ridge defined between said bottom panel and said long side panel is formed by at least two parallel rules configured to be different in depth from adjacent one.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
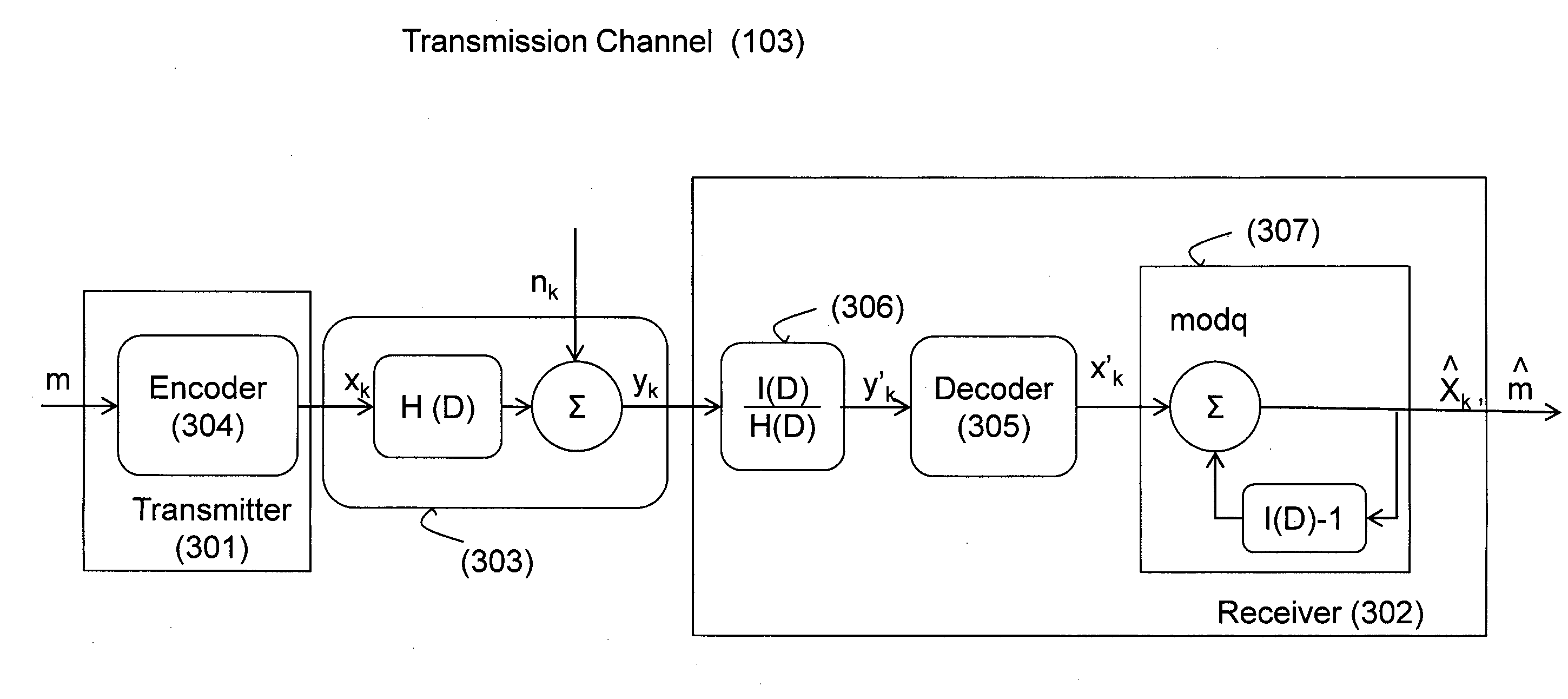
Transmission system with isi channel and method of operating thereof
InactiveUS20120300828A1Reduce outputBlocking phenomenonMultiple-port networksError preventionComputer hardwareTransfer system
There is provided a transmission system and method of operating thereof. The method comprises: dividing a data sequence to be transmitted into a plurality of data blocks; encoding one or more data blocks with one or more linear systematic cyclic codes thus giving rise to encoded data blocks; transmitting said encoded data blocks over an ISI transmission channel; upon receiving, applying a linear integer-forcing (IF) equalization to the received data blocks; processing the output of the IF equalization thereby detecting for each encoded data block a valid codeword with maximal likelihood of decoding; and reconstructing the data blocks using the respective detected valid codewords.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
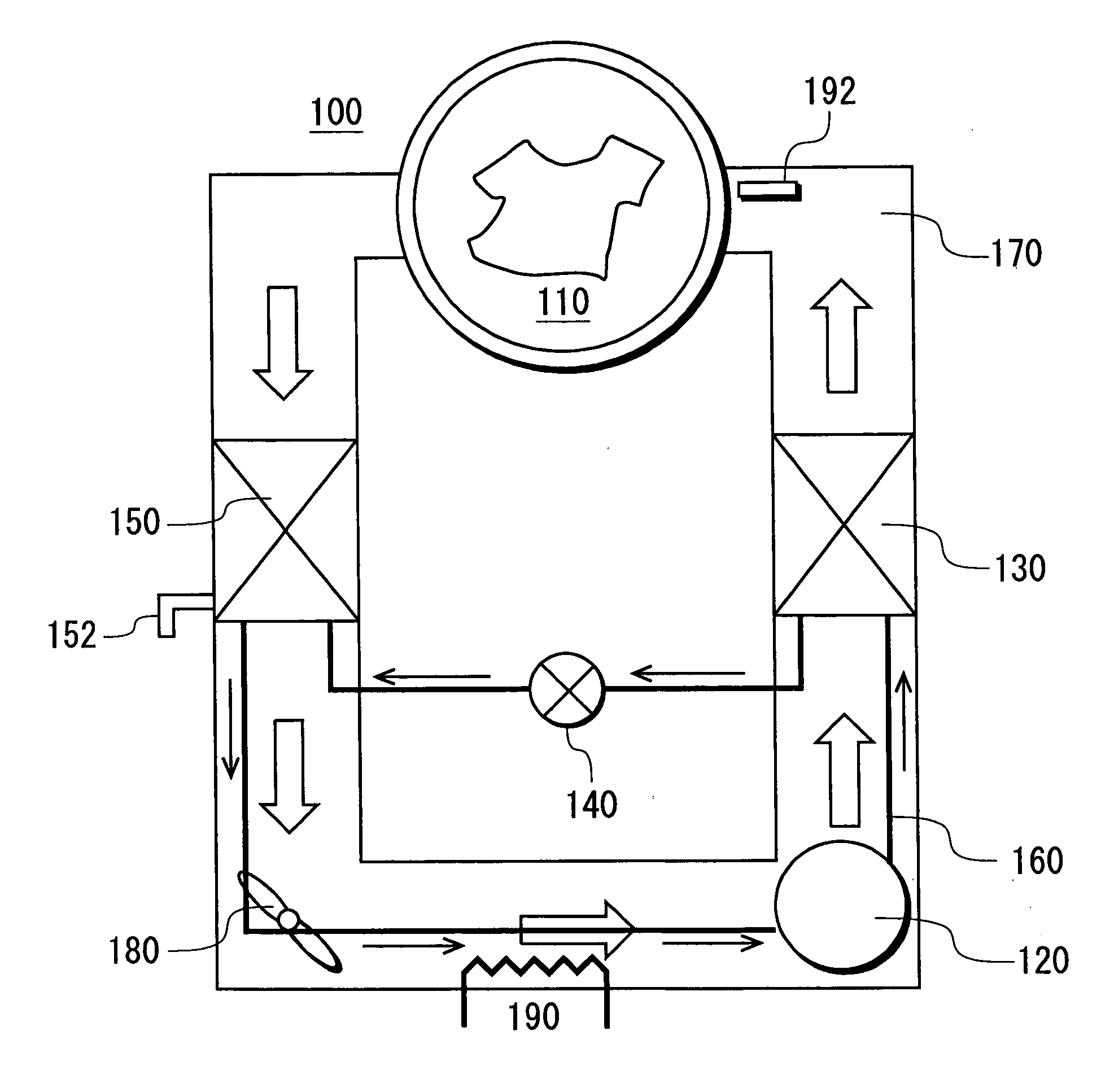
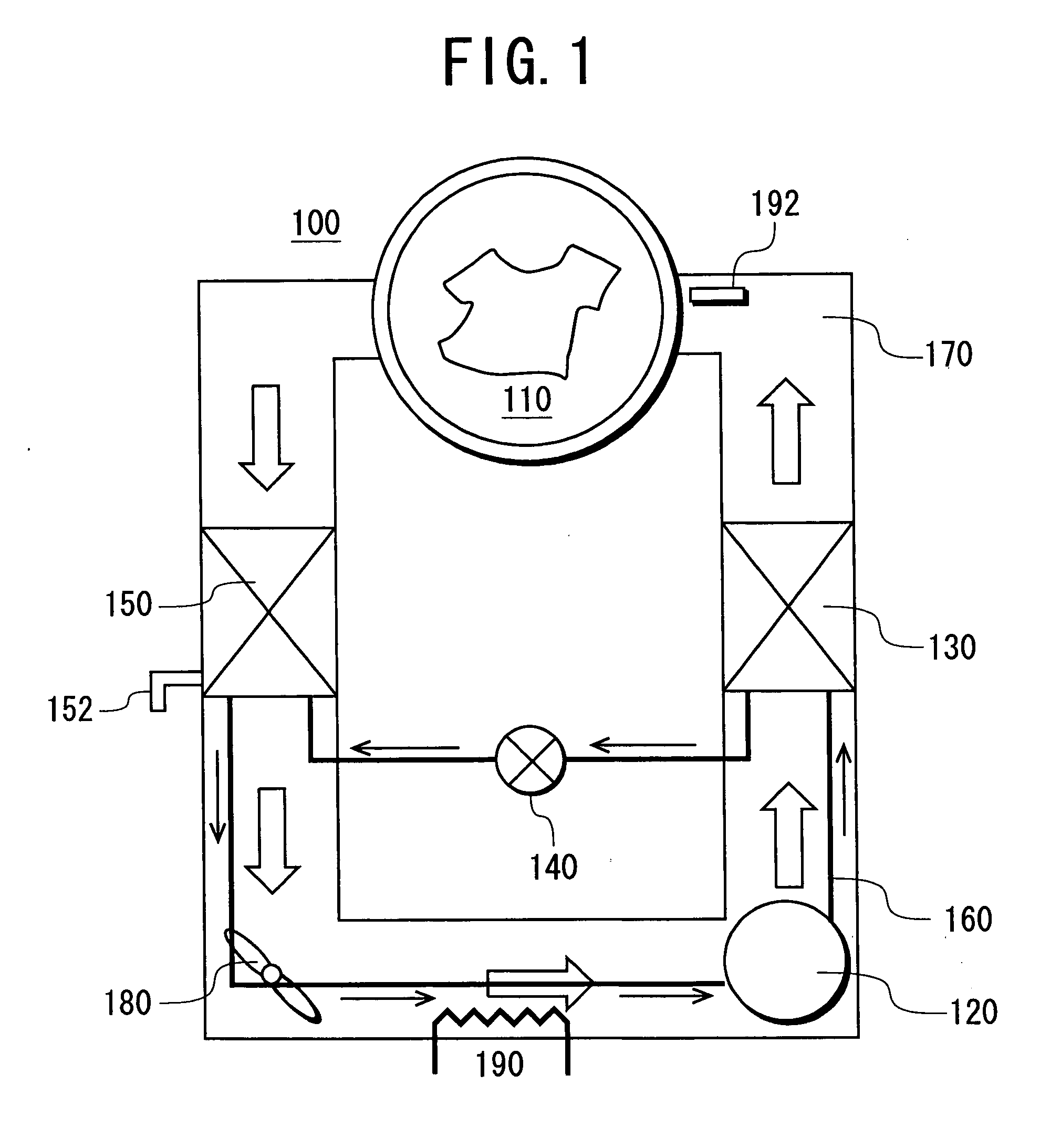
Drying apparatus, washing/drying apparatus, and operation methods of the apparatuses
InactiveUS20060080974A1Shorten the timeIncreased durabilityDrying solid materials with heatCompression machinesAir cycleStable state
An object is to provide an energy-saving drying apparatus which prevents liquid backflow, reduces time for a refrigeration cycle to be in a steady state, and can significantly reduce a time required for drying. The drying apparatus comprises: a drying chamber for accommodating a thing to be dried; a refrigerant circuit in which a compressor, a radiator, a decompression device and a heat sink are successively connected to one another in an annular form via a piping; an air circulation path in which air in the drying chamber exchanges heat with the radiator and the heat sink and circulates; and air circulation means provided in the air circulation path for circulating the air, wherein at least part of the piping from the decompression device to the compressor of the refrigerant circuit is provided within the air circulation path, and the air circulation path is equipped with heating means.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
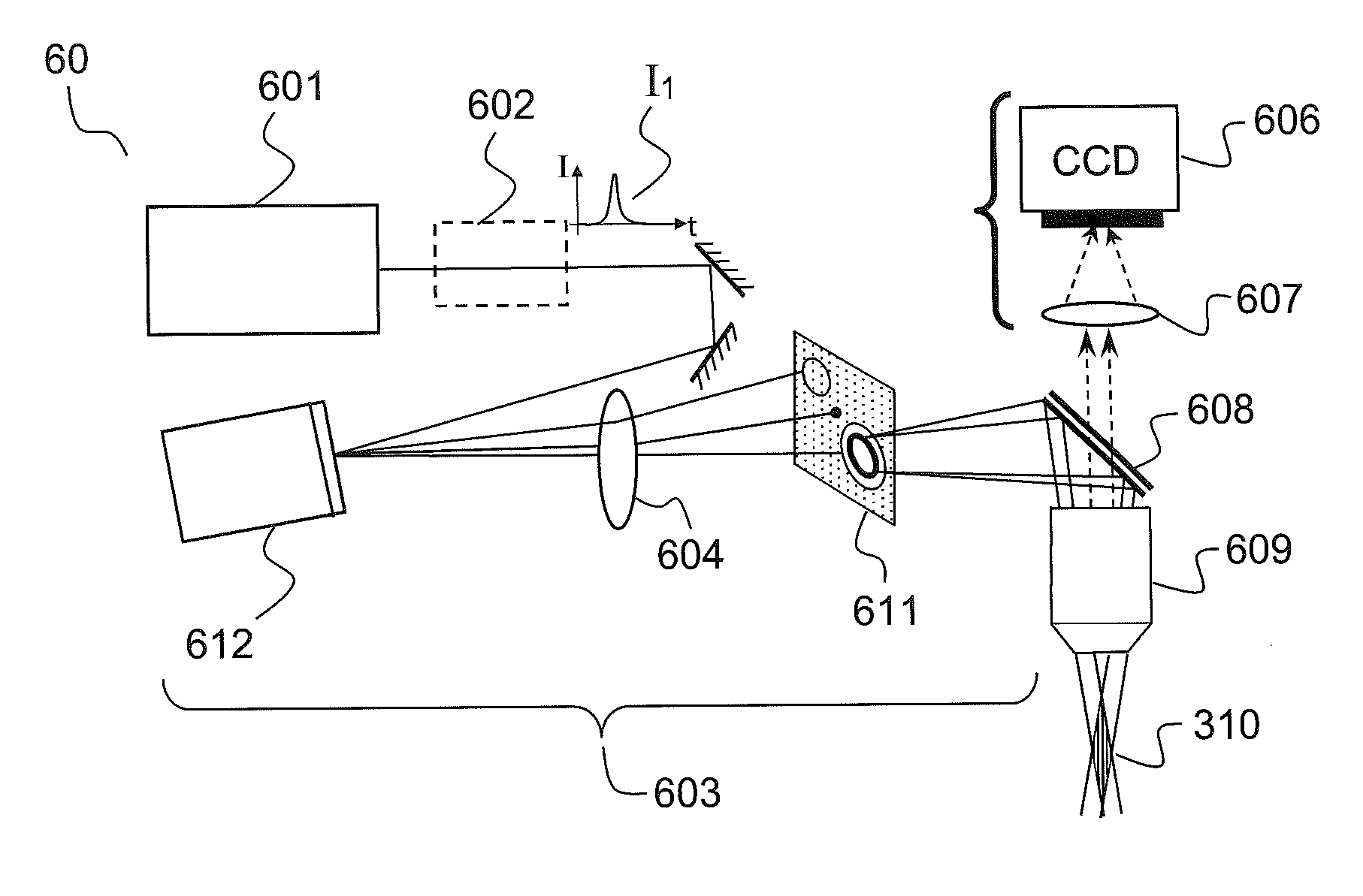
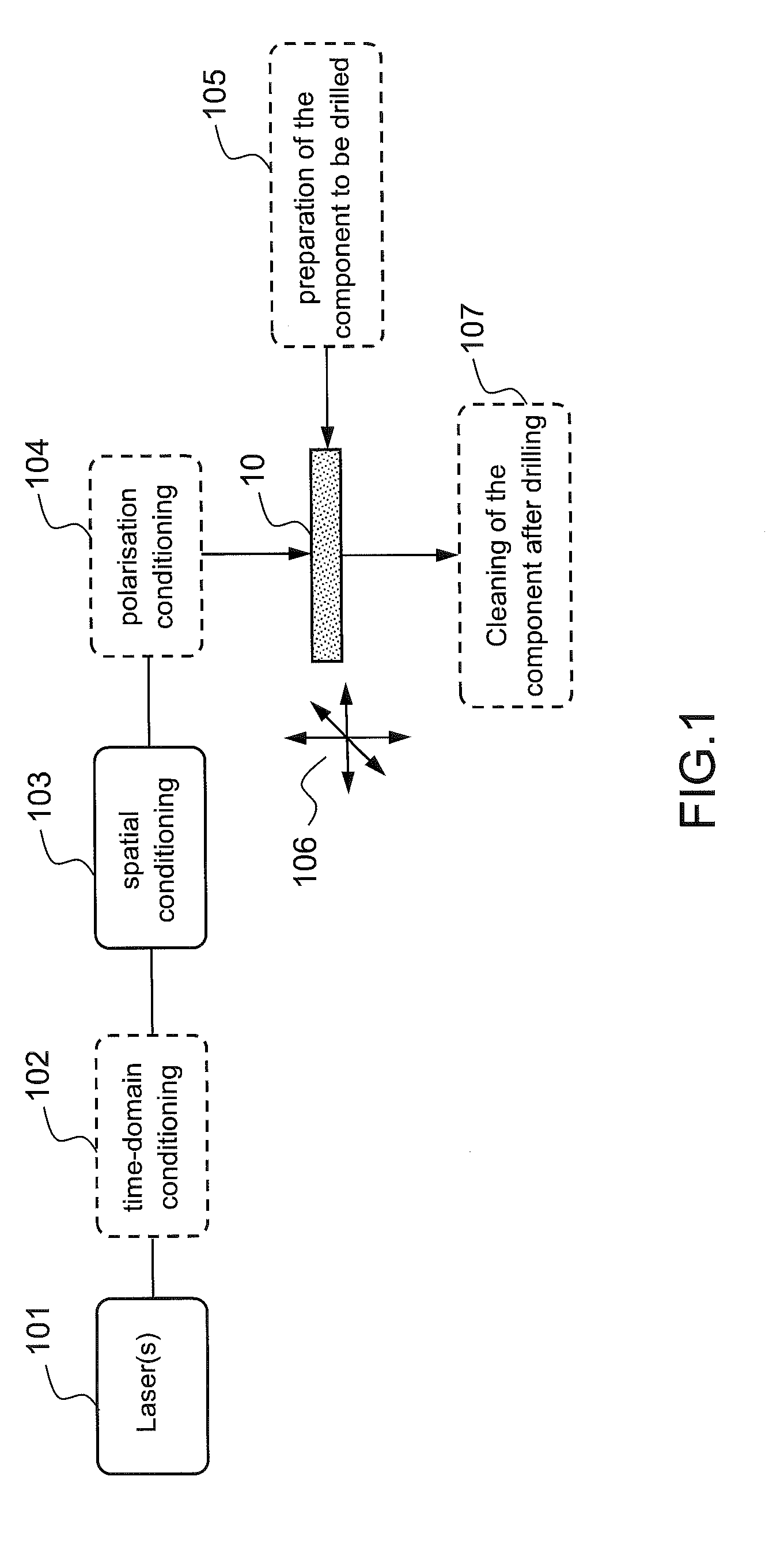
Method and device for laser micromachining
ActiveUS20160271727A1Blocking phenomenonWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusOptical axisLight beam
The invention, according to an aspect thereof, relates to a device (60) for laser micromachining a sample made of a given material, which includes a focusing module enabling a nondiffracting beam to be generated from a given incident beam, said nondiffracting beam being focused along a focusing cylinder that is oriented generally along the optical axis of the focusing module, means (601) for transmitting at least one first light pulse (11) suitable for generating, after said focusing module focuses in the sample, a plasma of free charges by multiphotonic absorption in a volume of the sample located on the side surface of said focusing cylinder
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
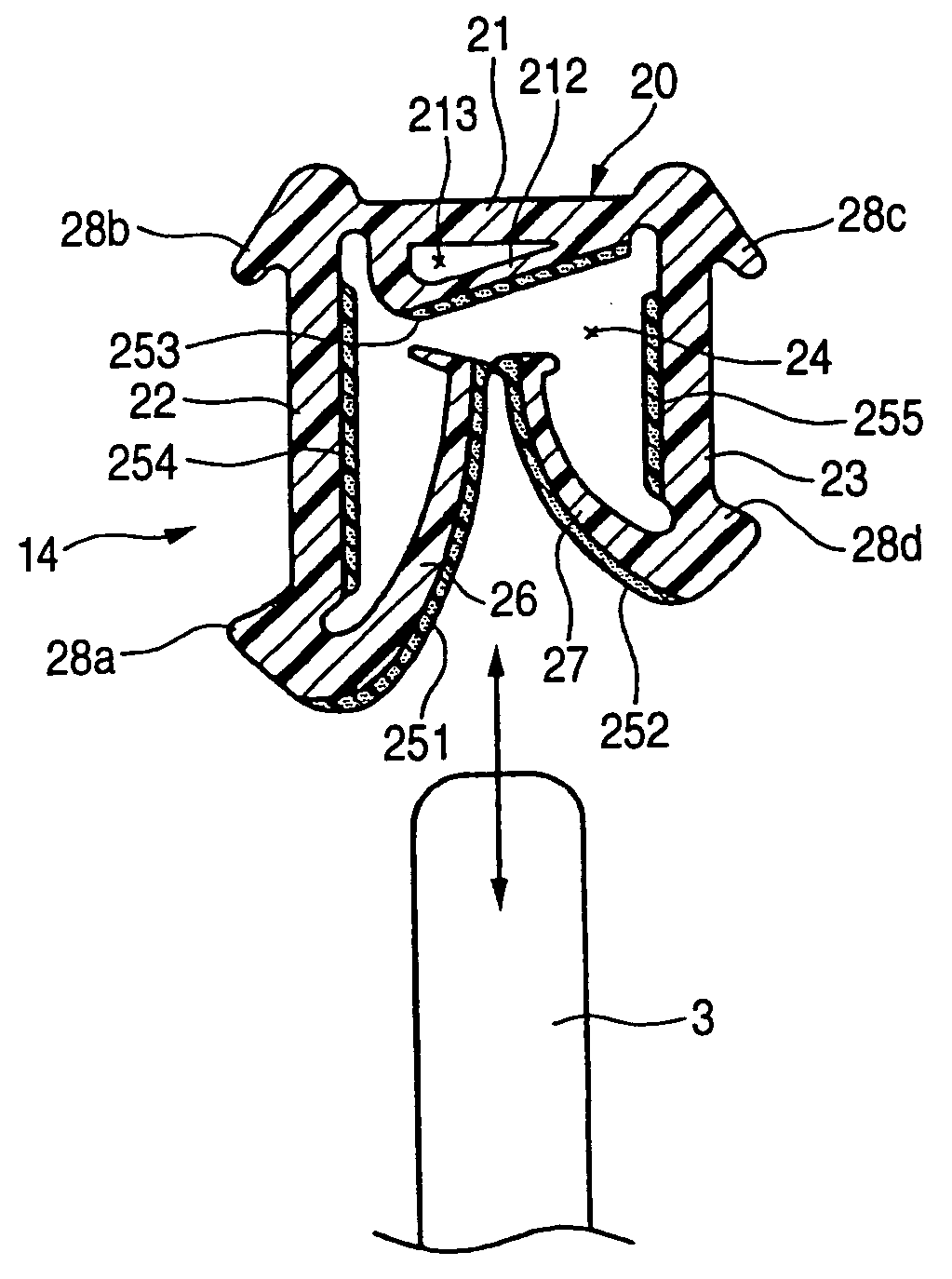
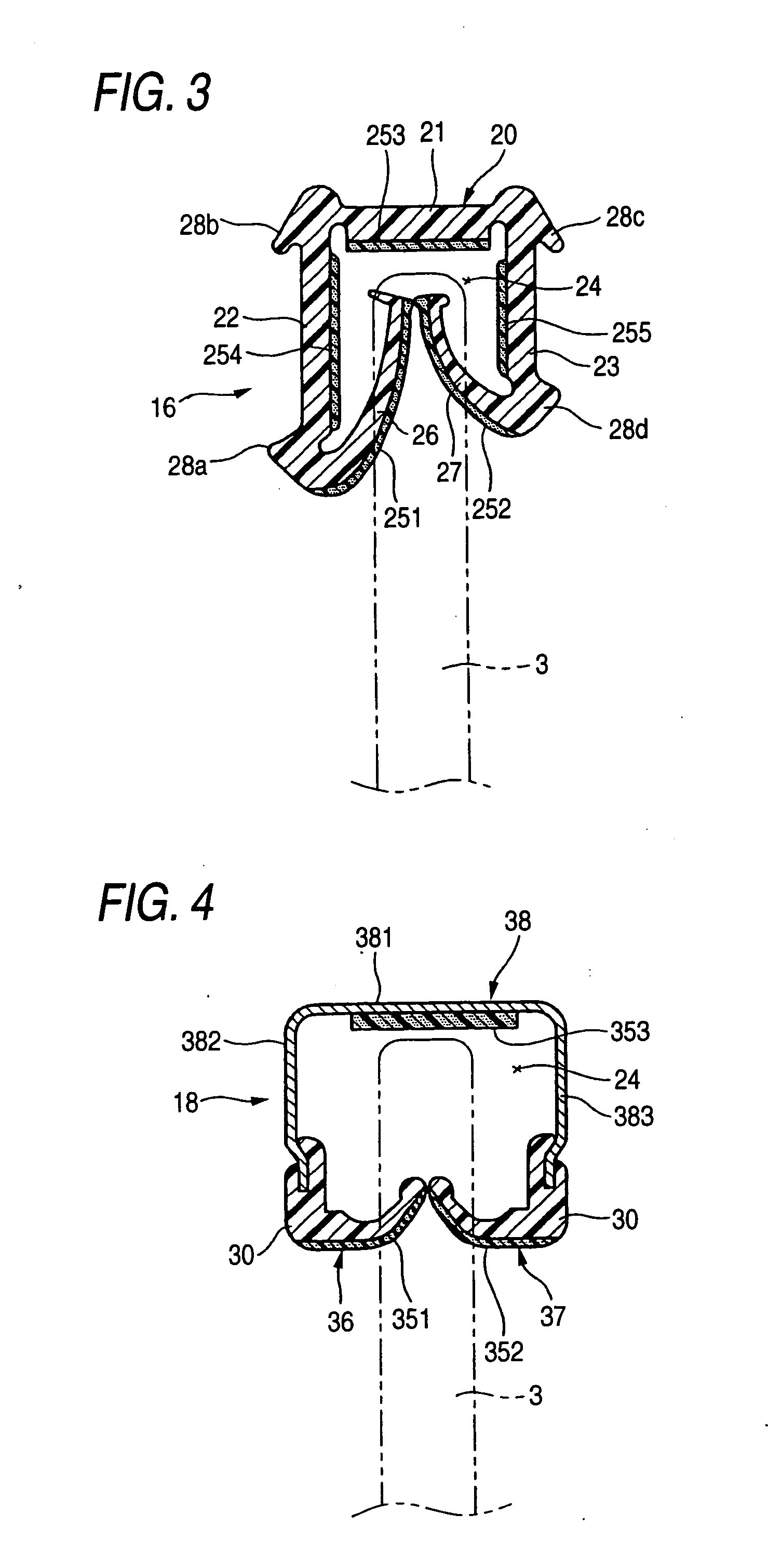
Weather strip and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050003158A1Blocking phenomenonWell formedEngine sealsLayered productsRough surfacePolyolefin
A long weather strip includes an attach portion attachable along a window frame for vehicle, and a lip portion for sealing a glass window pane for vehicle. The lip portion protrudes from the attach portion toward the glass window pane to be in contact therewith. The glass window pane is movable within the window frame. The lip portion includes a rough surface portion pressed onto a face of the glass window pane and made of a molding material containing the following (a) to (c) : (a) olefin thermoplastic elastomer in which a content ratio of polyolefin resin as a hard segment is 50 mass % or more as a whole, (b) solid particles having an average particle diameter in a range from 1 to 100 μm, and (c) liquid lubricant. The rough surface portion has a surface formed in a corrugation state with a number of small projections with the solid particles.
Owner:TOKAI KOGYO CO LTD
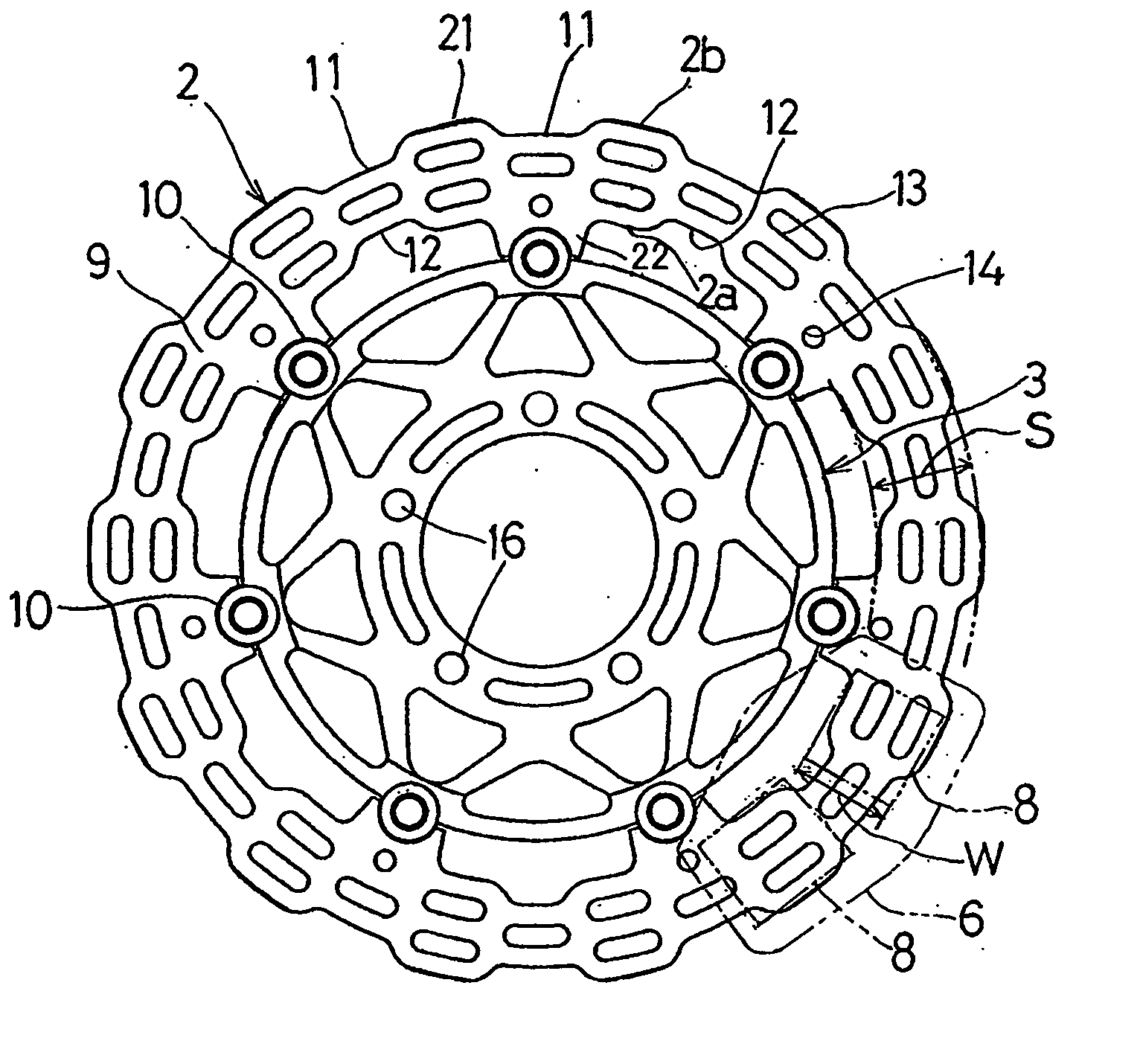
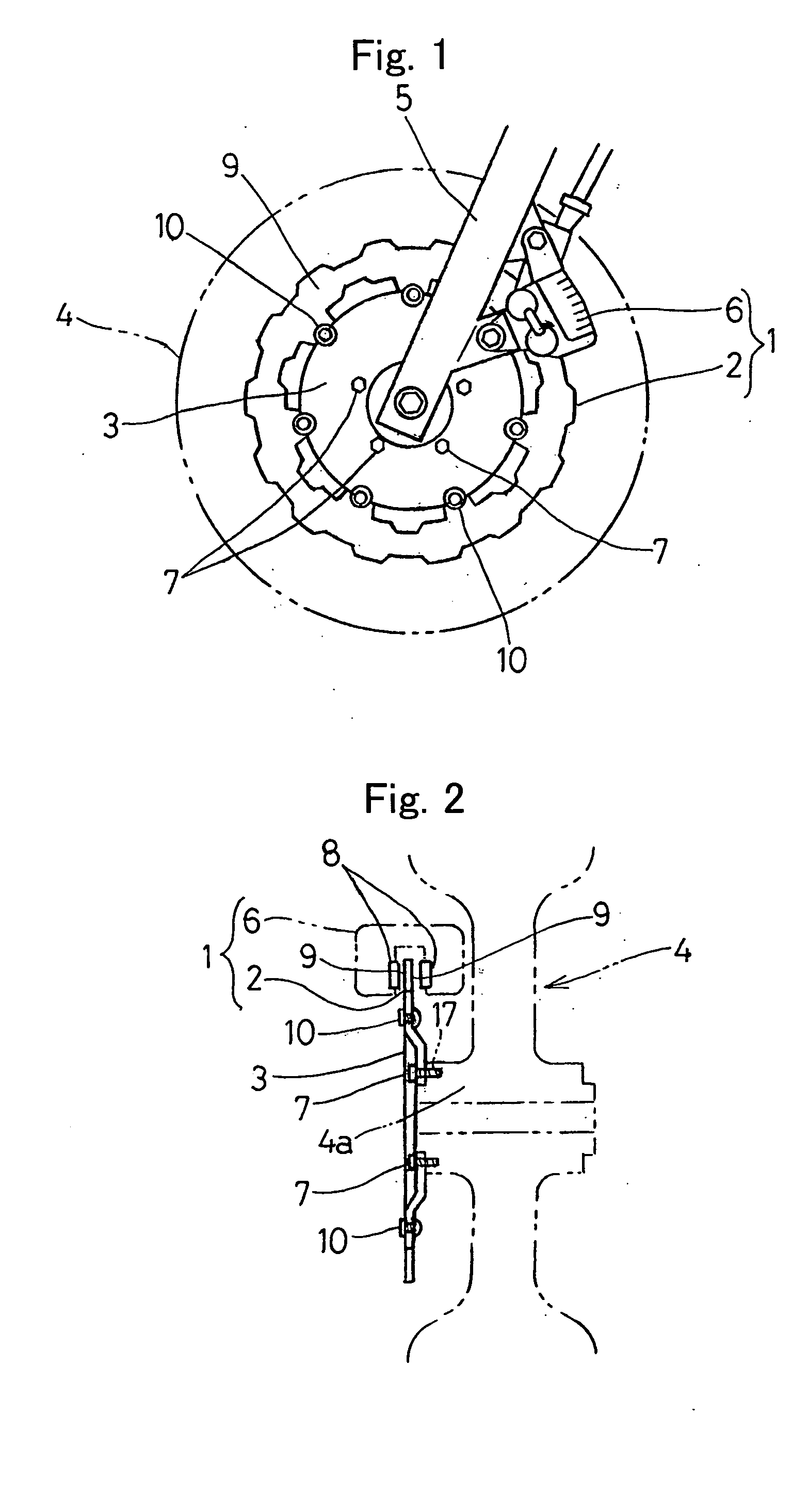
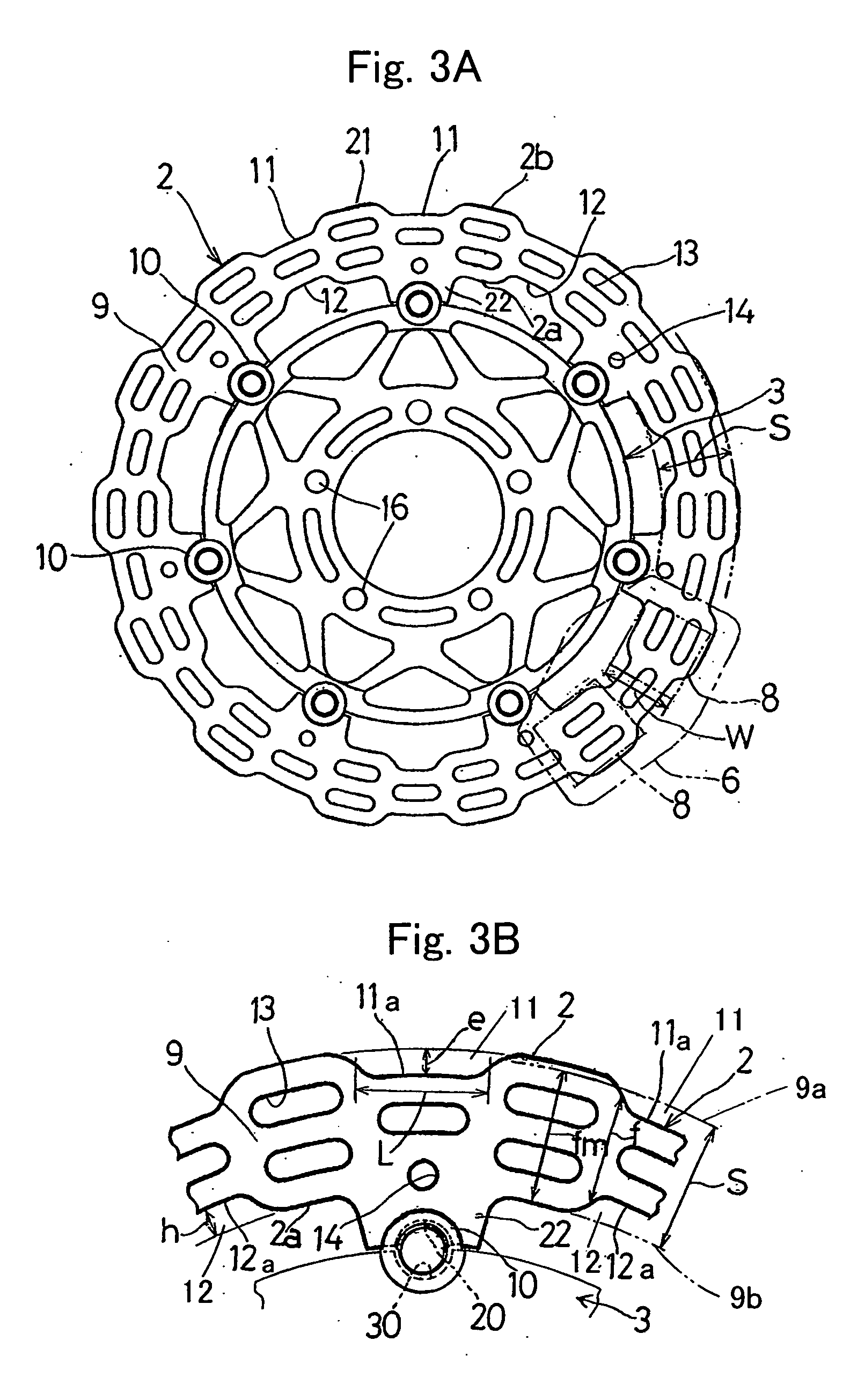
Brake disc for automotive disc brake assembly
ActiveUS20050092561A1Prevent thermal deformationPrevent brake noiseBraking discsCycle brakesThermal deformationEngineering
There is provided a brake disc in a disc brake for a vehicle, which can be manufactured lightweight, suppress the thermal deformation and is effective to prevent the brake noises. This brake disc (2) is supported by a wheel 4 through a plurality of support members (10) and is operable to exert a braking force when sandwiched by frictional pads (8, 8). The brake disc (2) has an outer peripheral face (2b) formed with a plurality of outer recesses (11) deploying in a circumferential direction. Accordingly, the radial width (f) of the braking surfaces (9), with which the frictional pads (8) is engageable, varies in a direction circumferentially thereof.
Owner:KAWASAKI MOTORS LTD
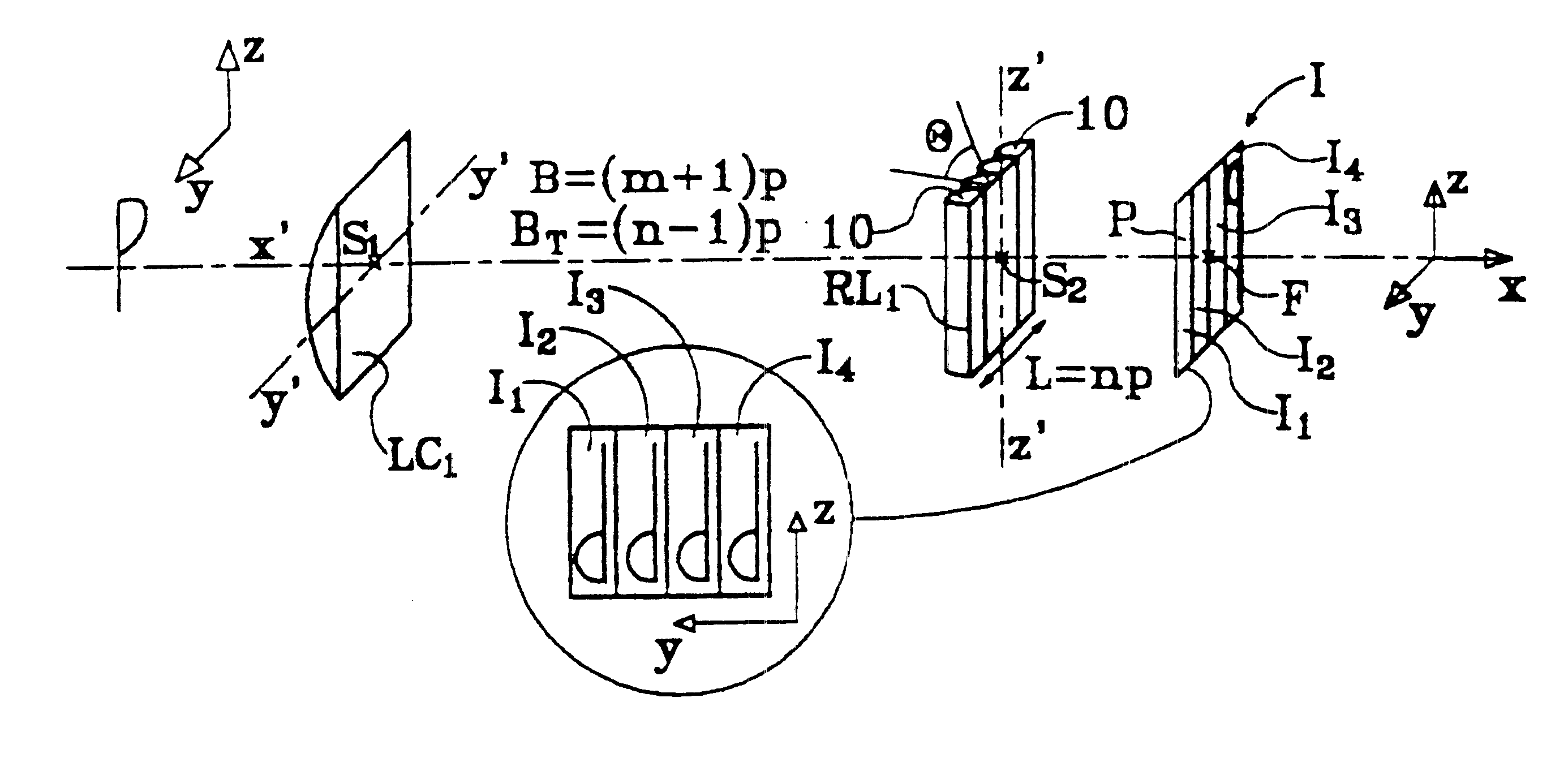
Autostereoscopic imaging device and system comprising it
InactiveUS6574042B2Blocking phenomenonColor television detailsStereoscopic photographyAutostereogramViewpoints
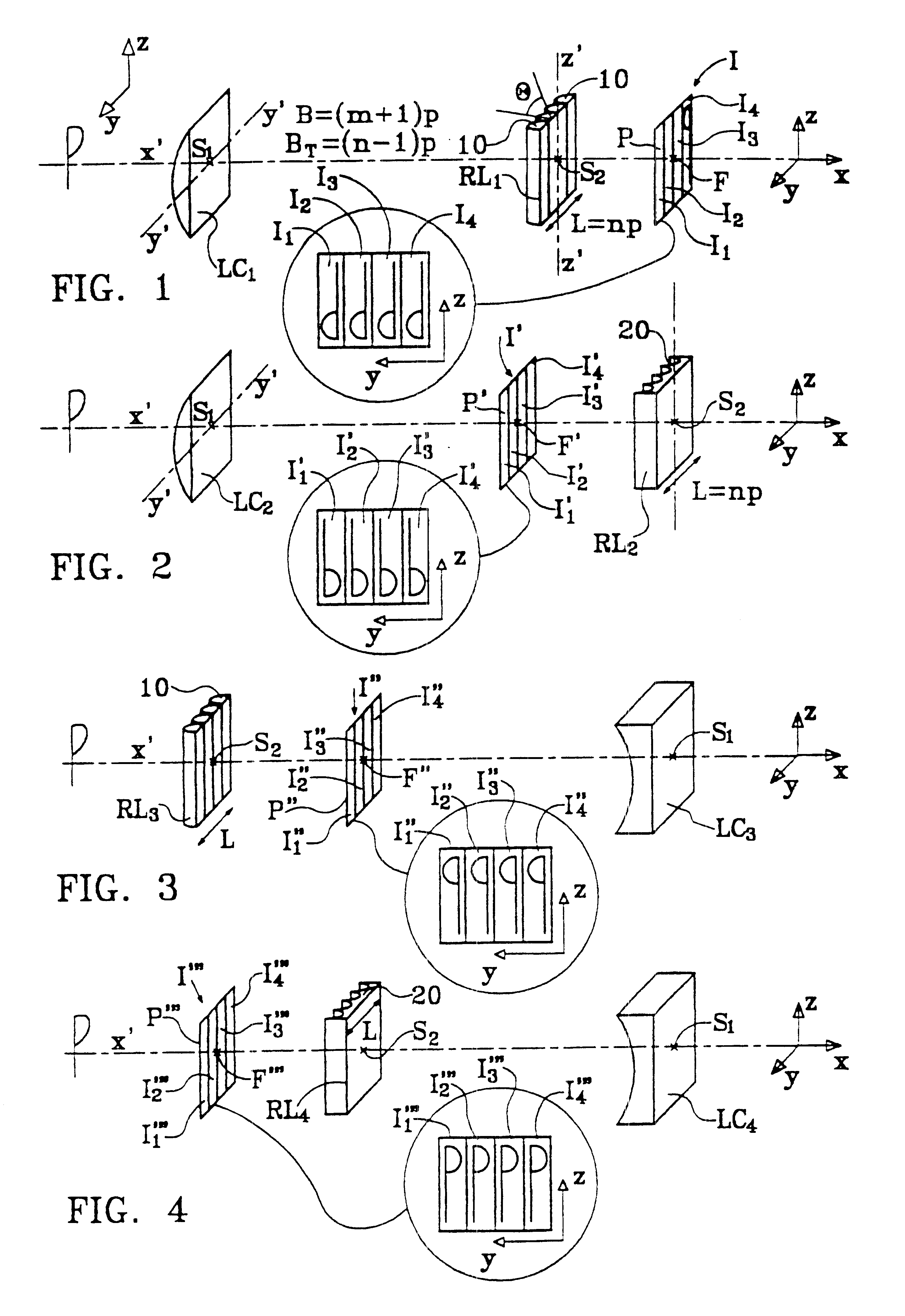
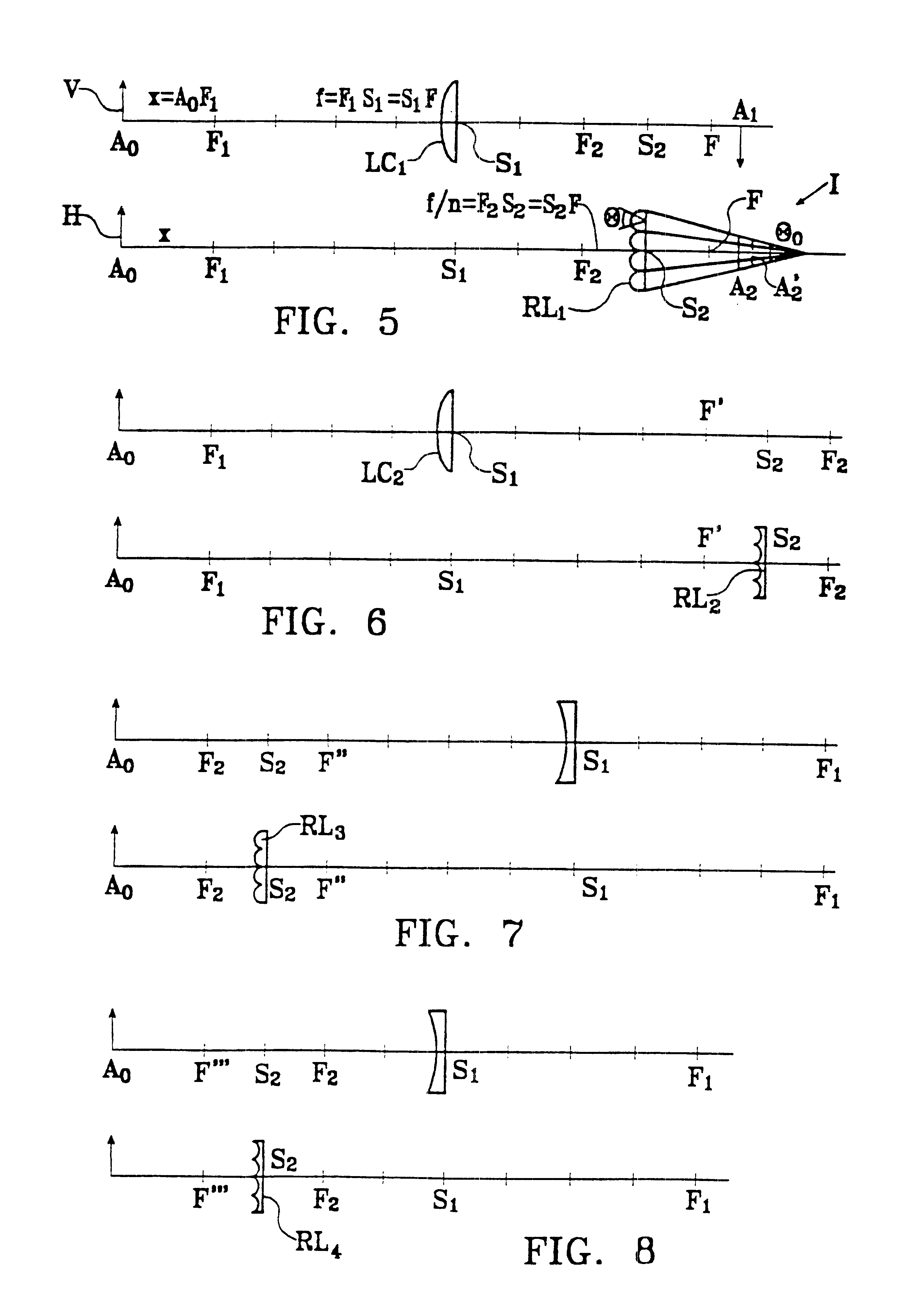
A device for forming an autostereoscopic image having n viewpoints, the device including a lens array (RL1) comprising cylindrical lens (10) having longitudinal axes parallel to a direction (zz') perpendicular to an optical axis (x'x) of the device. The device includes a cylindrical optical assembly whose longitudinal axis is perpendicular to zz' and to xx'. The lens array (RL1) comprises n cylindrical lens (10). The lens array (RL1) and the cylindrical optical assembly (LC1) share a common focusing plane (P) corresponding to a focusing distance DELTA. The absolute value of the ratio between the focal length of the cylindrical optical assembly and that of the lens array is substantially equal to n. Also provided is projection device implementing said image-forming device, and a projector projecting n flat elementary images, and a screen fitted with at least a projection array.
Owner:ALIOSCOPY
Method and circuit for controlling a switching regulator
ActiveUS9083250B2Reduce noiseEfficient workEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionSwitching cycleControl switch
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com