Patents
Literature
73 results about "Autostereogram" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
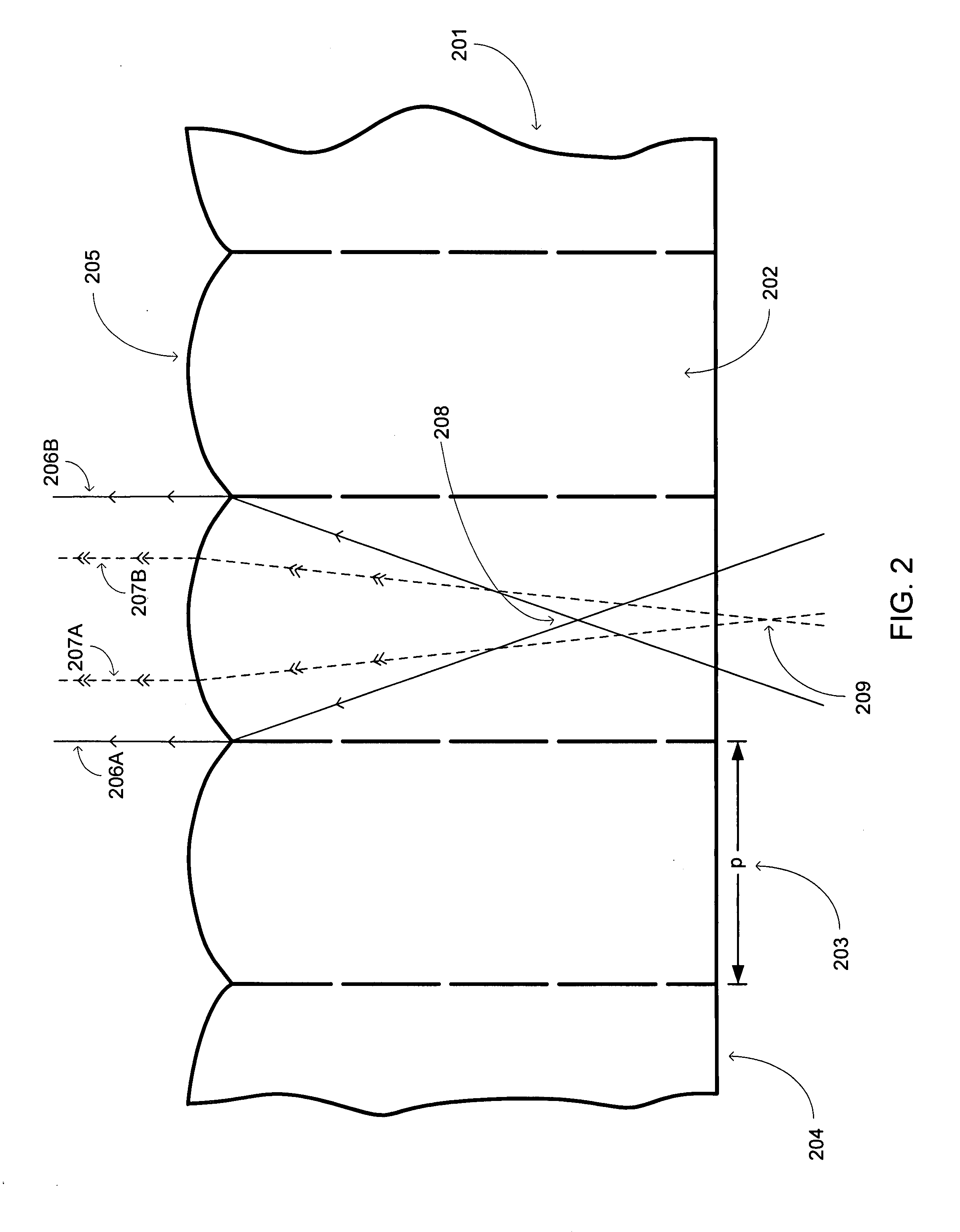
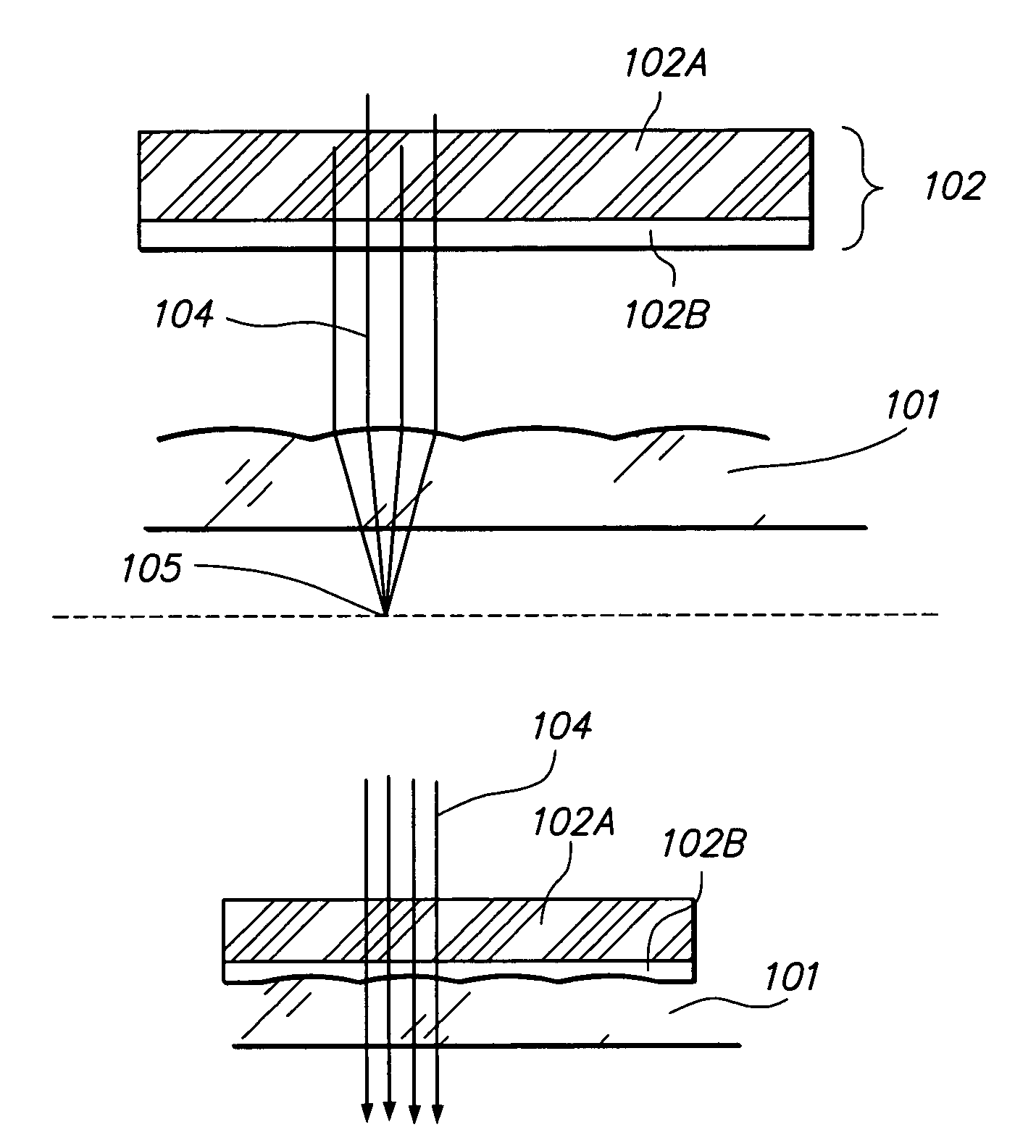
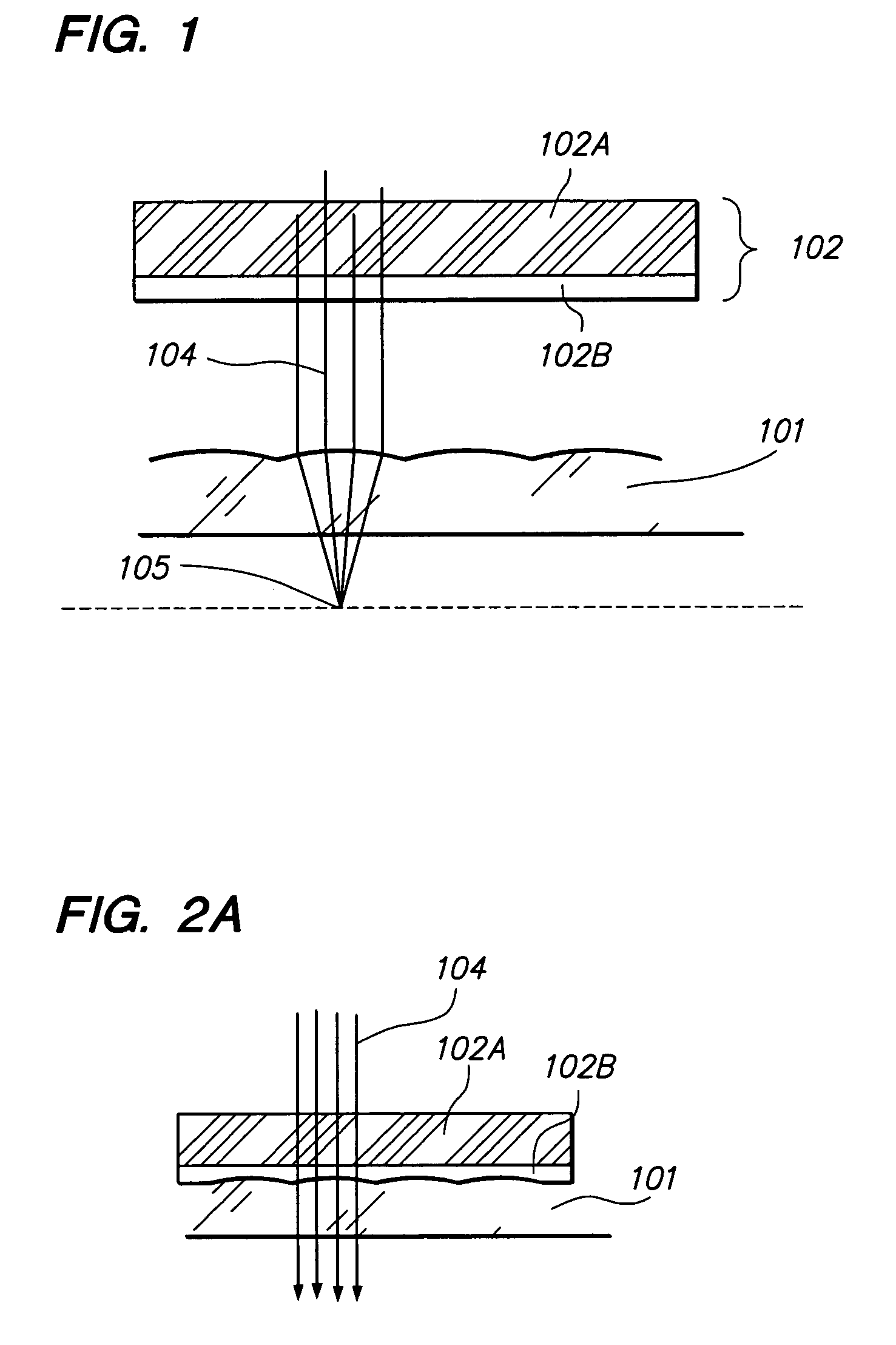
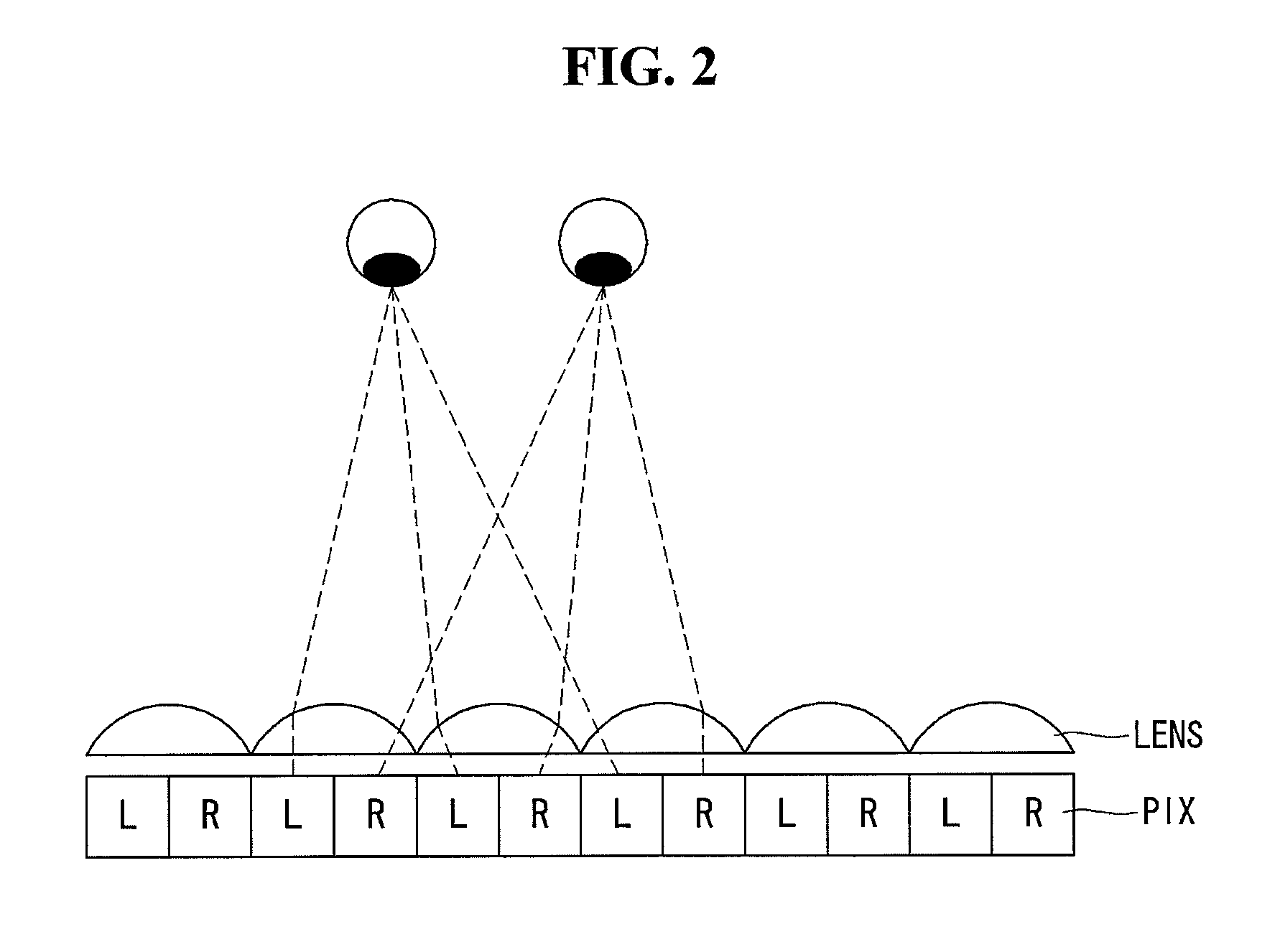
An autostereogram is a single-image stereogram (SIS), designed to create the visual illusion of a three-dimensional (3D) scene from a two-dimensional image. In order to perceive 3D shapes in these autostereograms, one must overcome the normally automatic coordination between accommodation (focus) and horizontal vergence (angle of one's eyes). The illusion is one of depth perception and involves stereopsis: depth perception arising from the different perspective each eye has of a three-dimensional scene, called binocular parallax.
Display Device
InactiveUS20080316303A1Quick displayCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsAutostereogramLiquid-crystal display
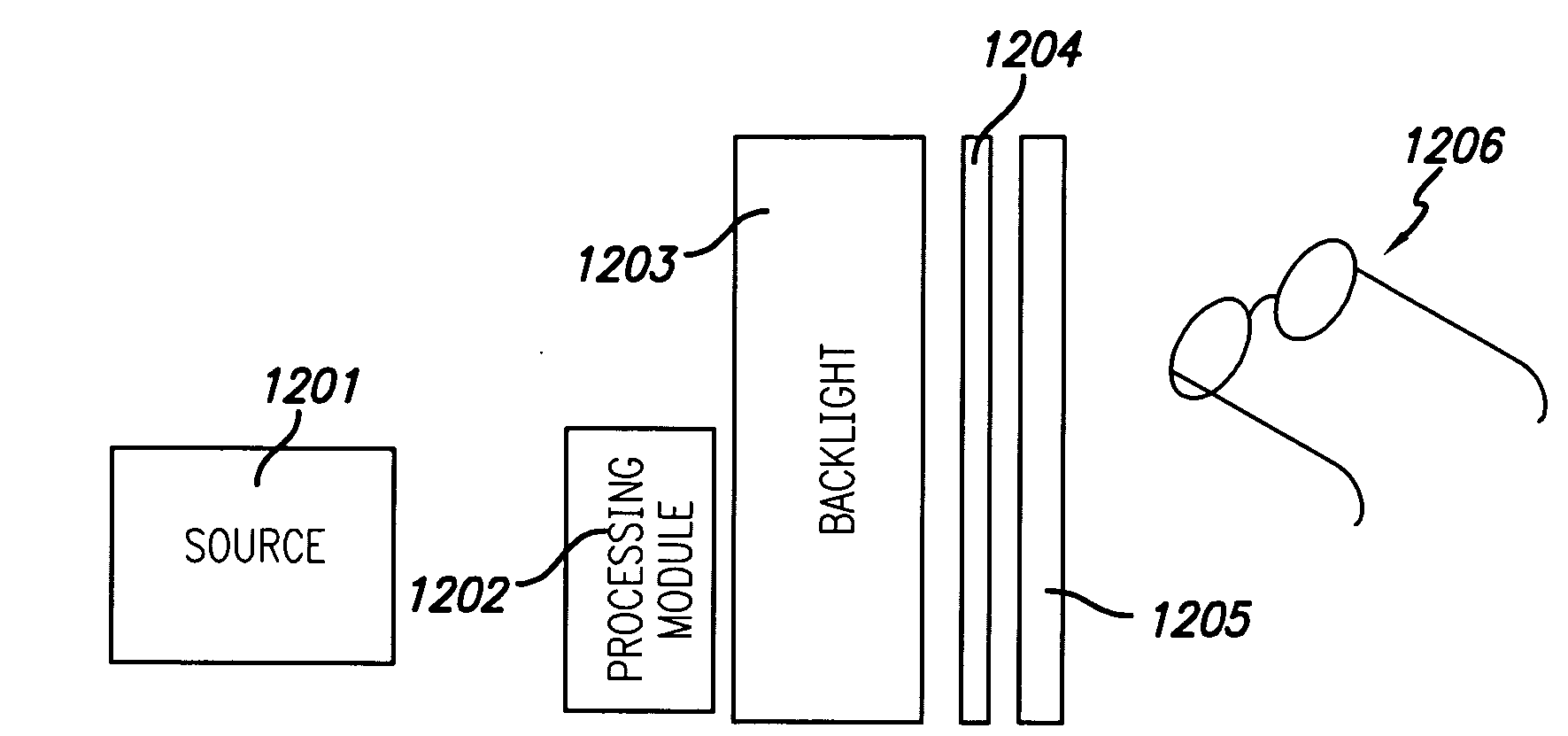
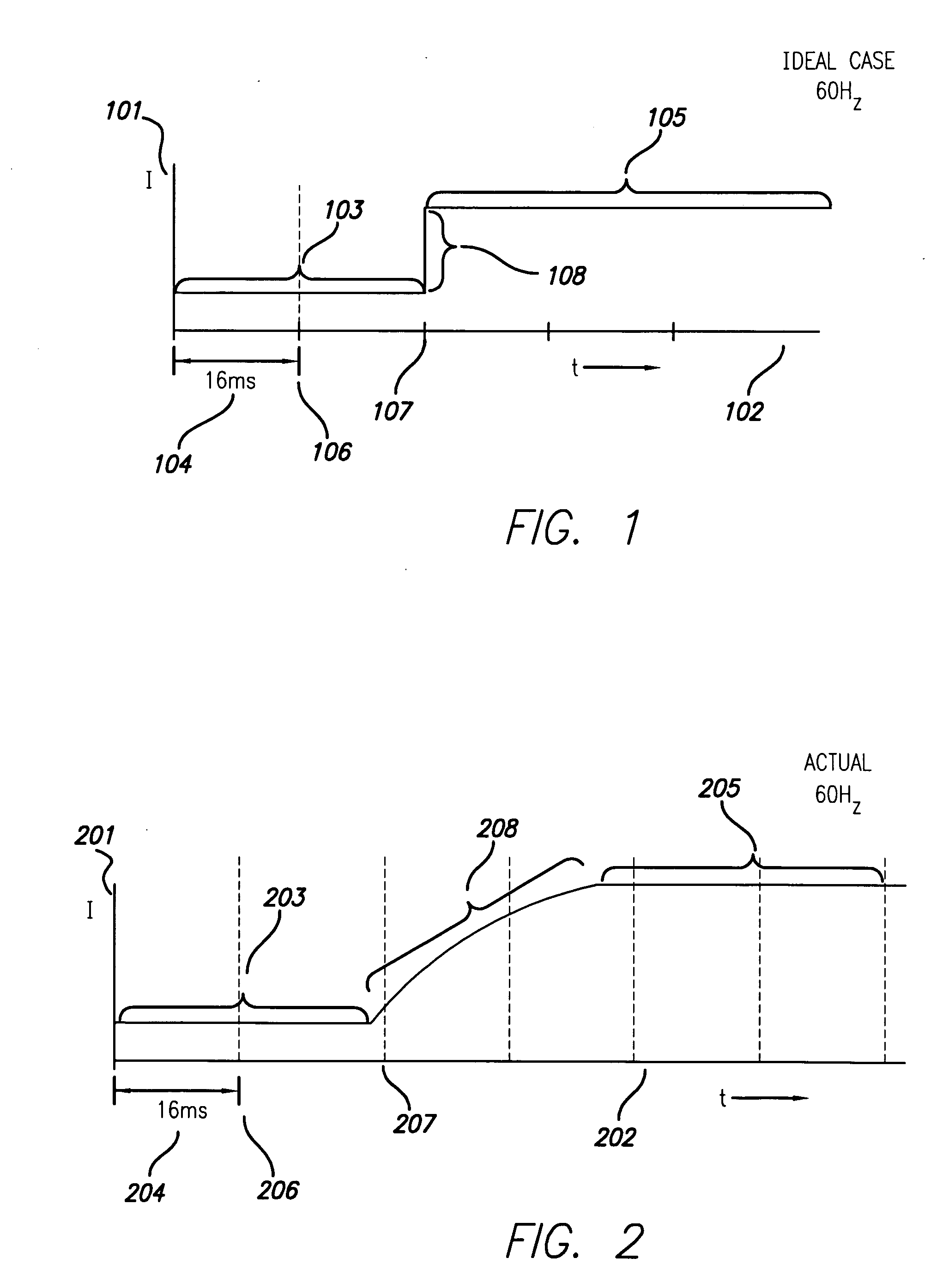
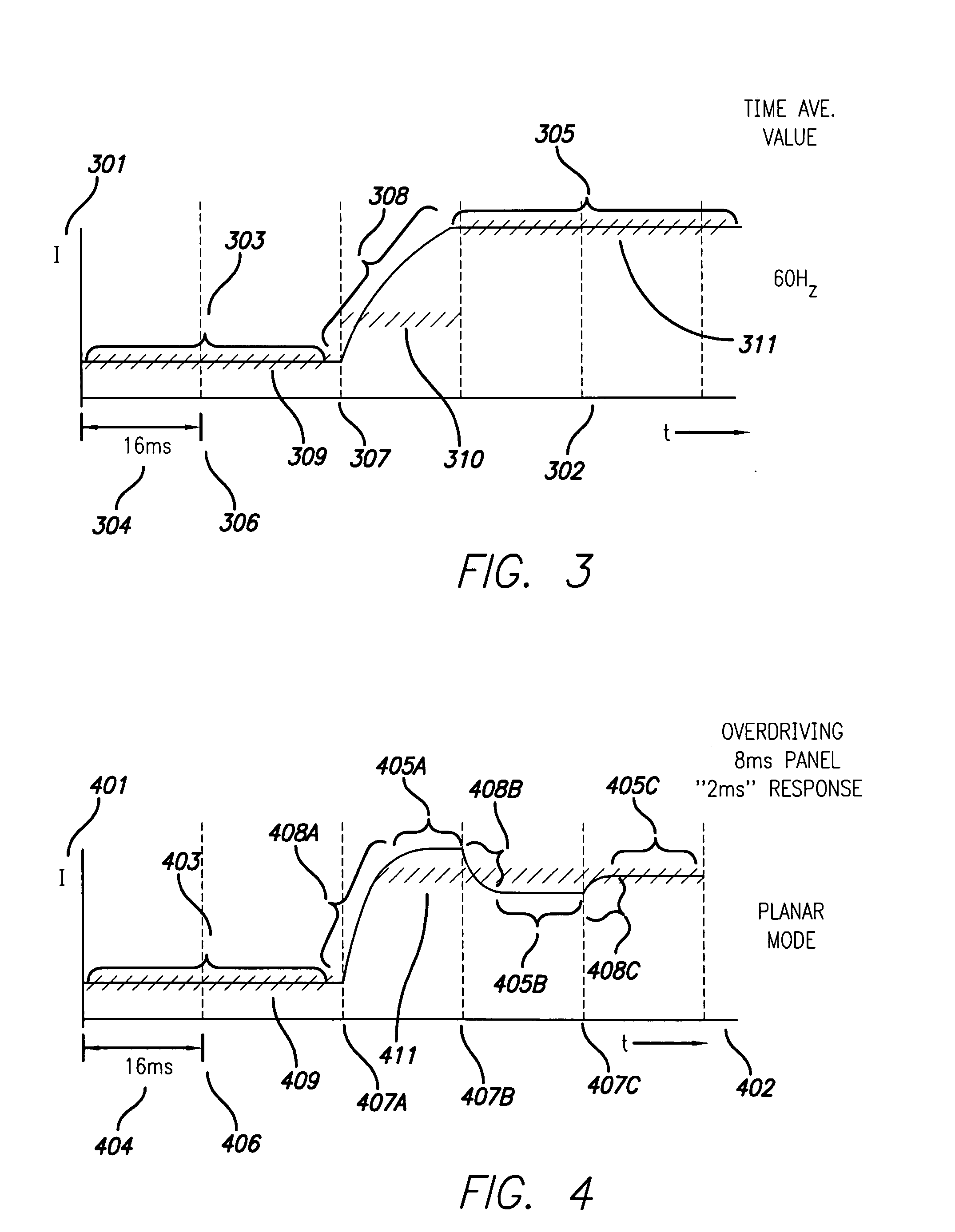
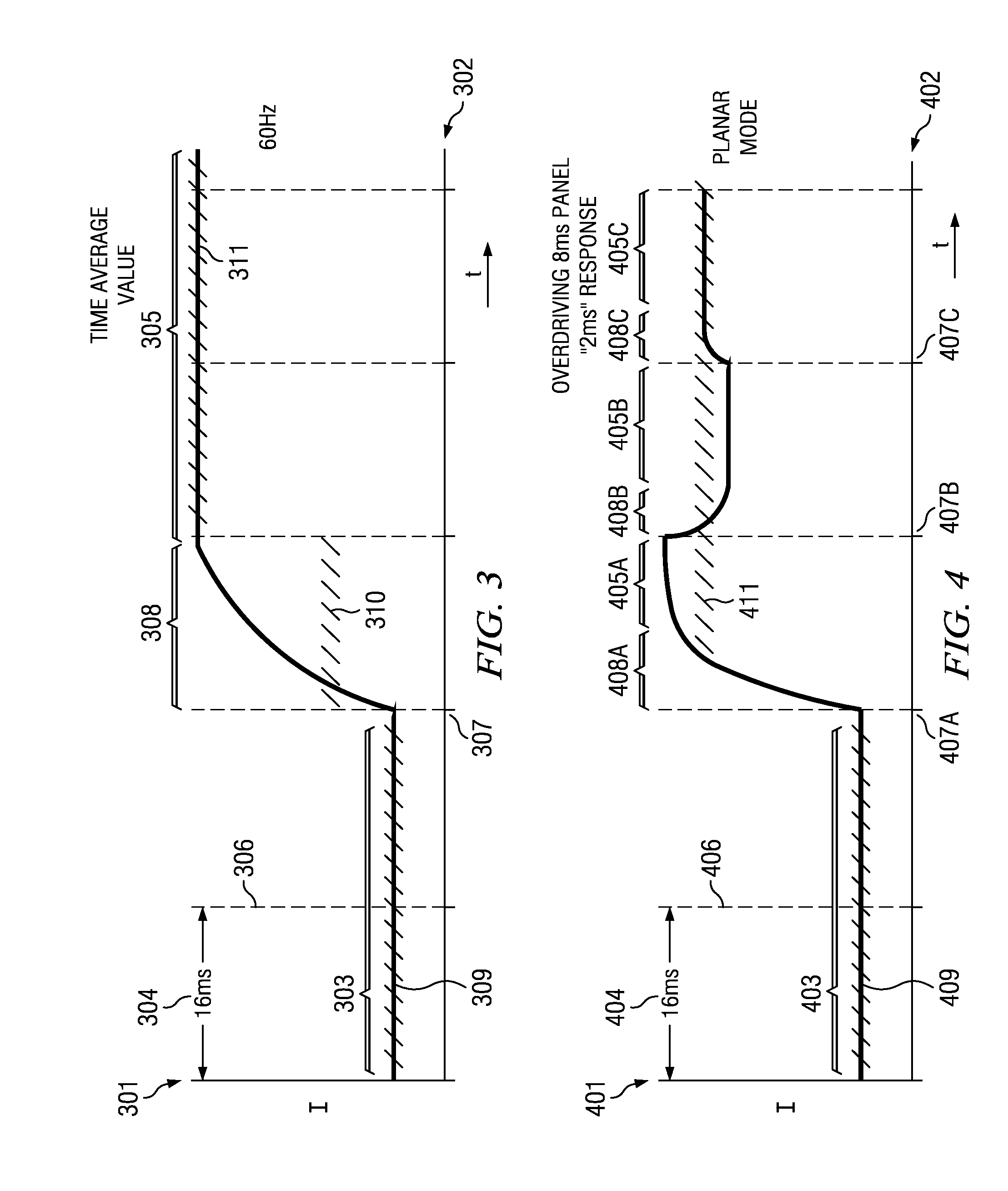
An enhanced liquid crystal display design is provided having relatively fast response time particularly useful in high speed or highly intense applications, such as stereoscopic or autostereoscopic image display. The liquid crystal display device is configured to display stereoscopic images, and comprises an LCD panel and control electronics configured to drive the LCD panel to a desired stereoscopic display state. The control electronics are configured to employ transient phase switching and overdrive the LCD panel to a desired state to enable relatively rapid display of stereoscopic images.
Owner:REAID INC
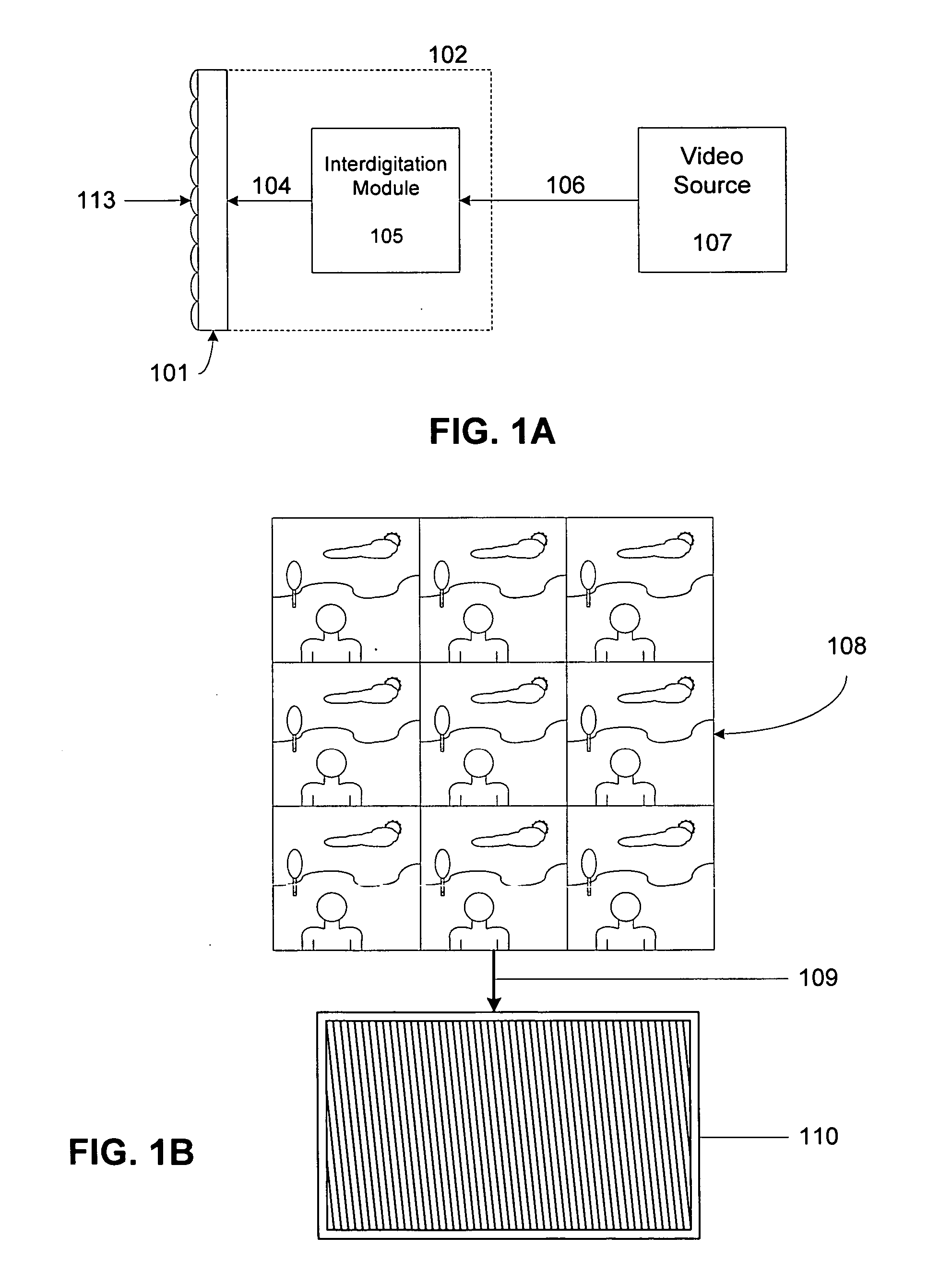
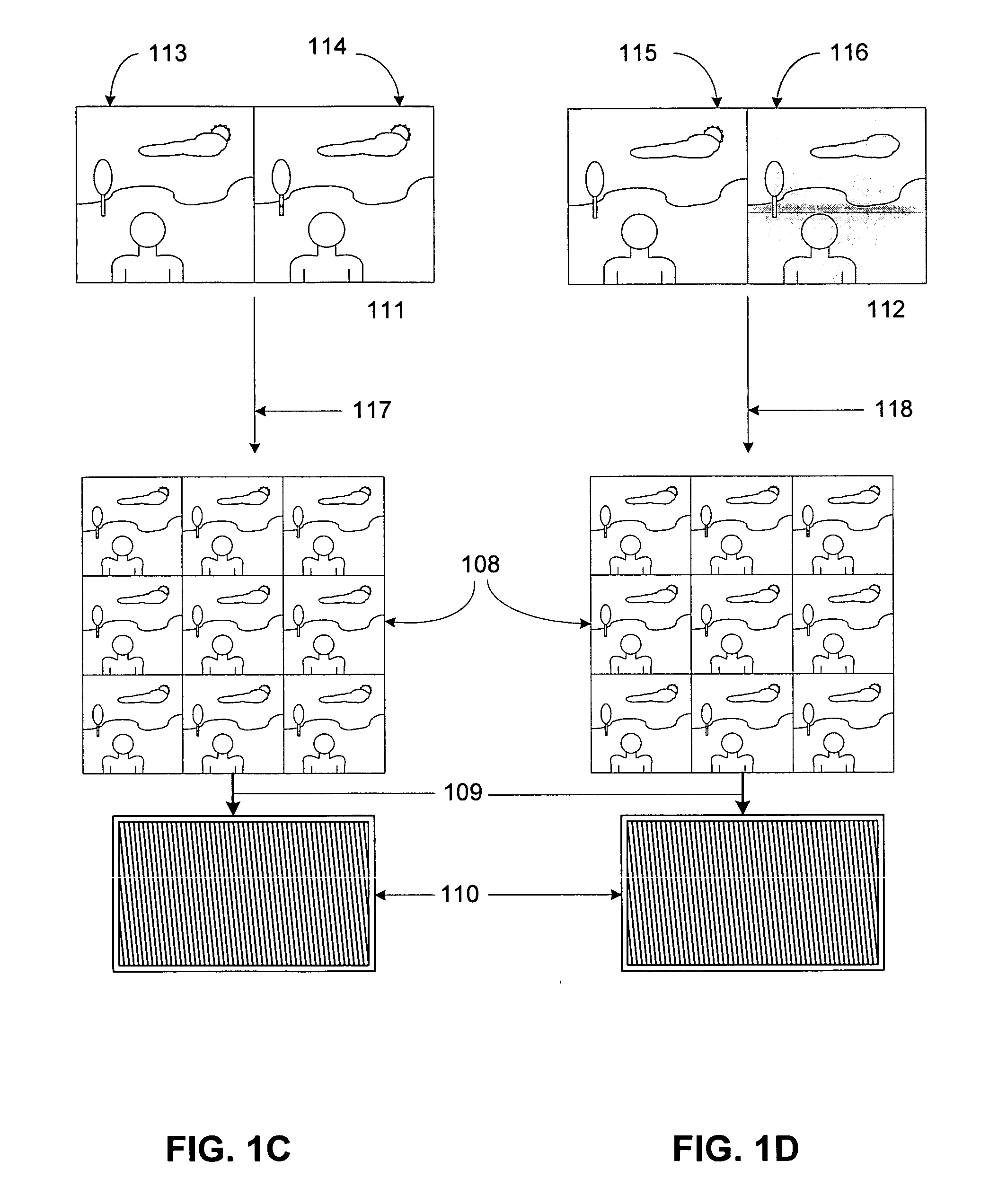
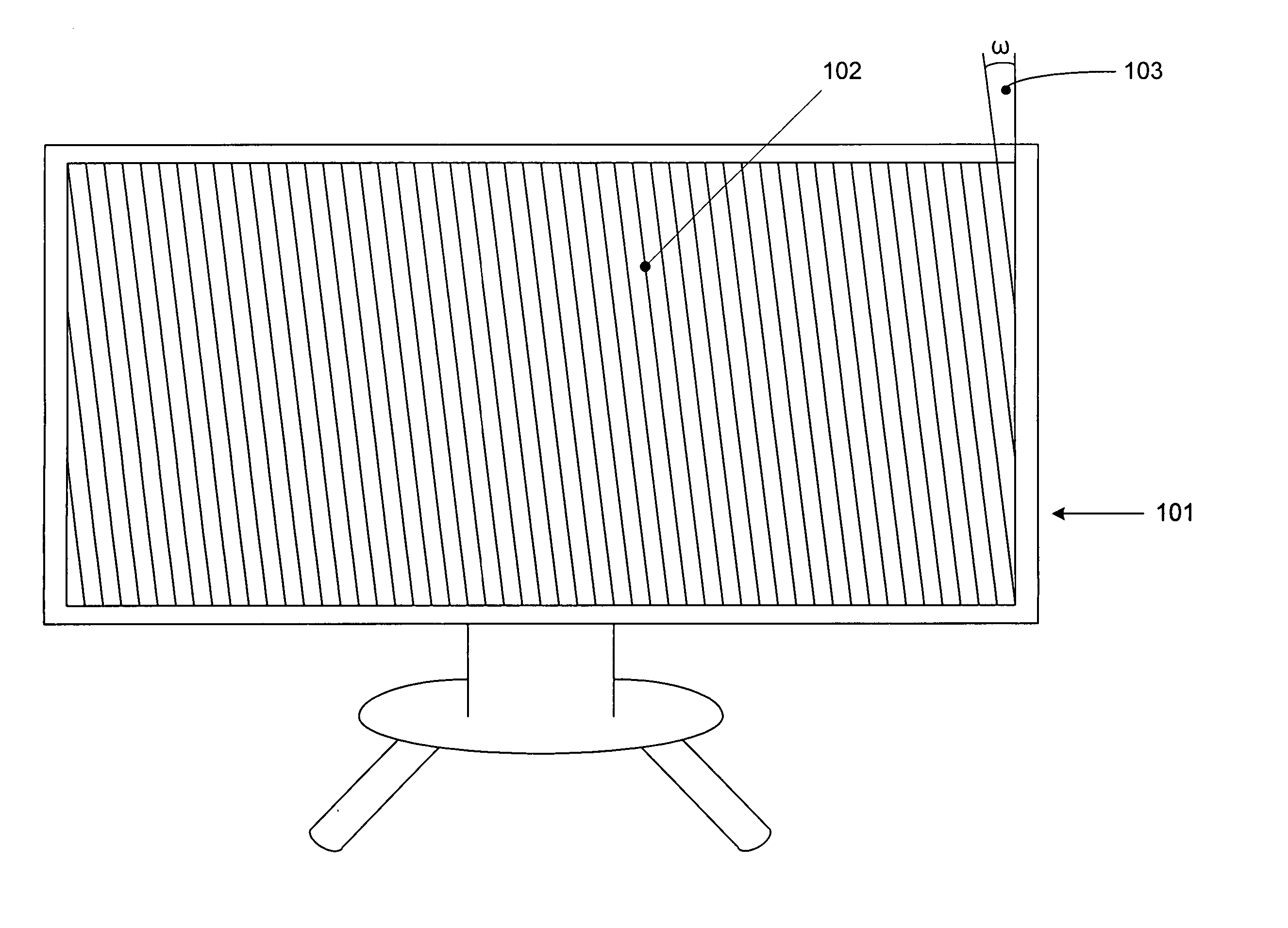
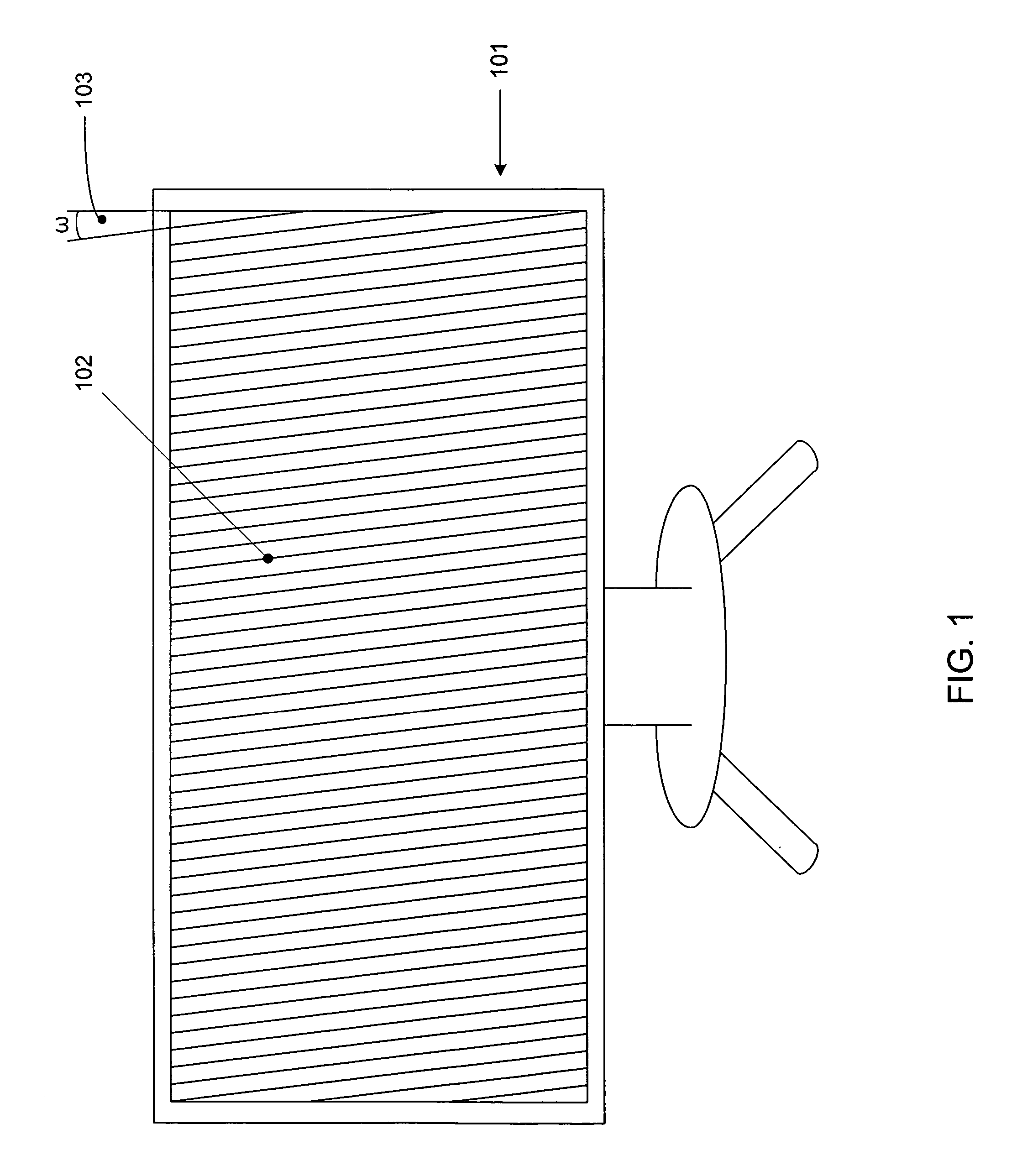
Monitor with integral interdigitation
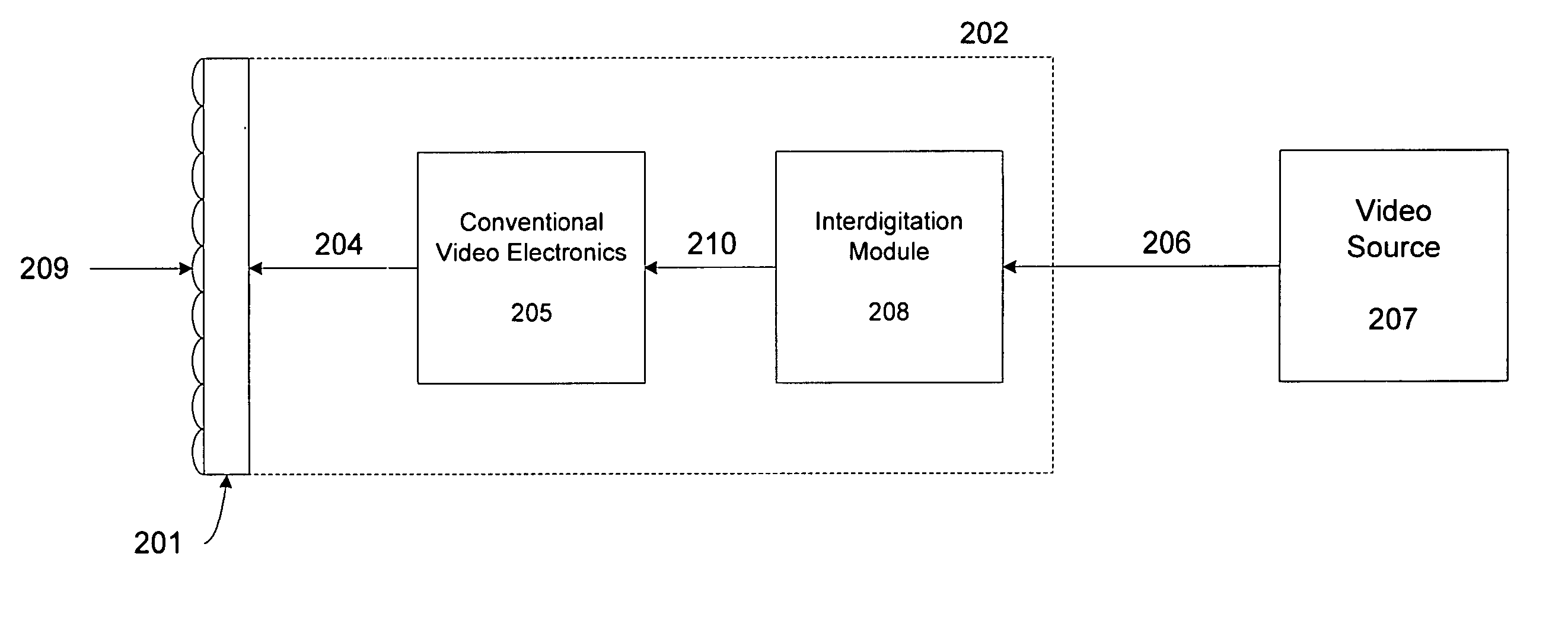
InactiveUS20070109401A1Color television detailsSteroscopic systemsAutostereogramComputer graphics (images)
An autostereoscopic system is provided. The autostereoscopic system comprises a video source configured to provide video content in a video source format and a monitor system coupled to the video source and configured to receive the video content in the video source format. The monitor system comprises an interdigitation module configured to receive the video content in the video source format and interdigitate the video content in the video source format into an autostereoscopic image, a video rendering module coupled to the interdigitation module configured to receive the autostereoscopic image from the interdigitated module and provide a rendered autostereoscopic image, a display coupled to the video rendering module and configured to receive the rendered autostereoscopic image, and a lenticular screen held in juxtaposition with the display. Temperature compensation may be employed within the system.
Owner:REAID INC
Autostereoscopic display with planar pass-through
InactiveUS20060284974A1Increase heightTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAutostereogramStereoscopic imaging
A method and system for presenting both autostereoscopic images and planar images in a single display is disclosed. The design comprises processing the planar images received in the form of planar image data. The processing comprises at least one from a group comprising selectively employing bleed-through processing to enhance the planar image data when viewed through a lens sheet comprising slanted lenticules, selectively introducing blurring into the planar image data, and selectively employing anti-alias processing to the planar image data. Certain super pixels may be computed that differ from standard pixels, and lenticules in the data sheet may be slanted at desired angles. The physical lenticules may cause bleed-through that may be processed. Resolution may be computed after processing, and the resolution implemented for display. Mode switching between planar and autostereoscopic imaging may be provided in the form of Metadata or visible flags.
Owner:REAID INC
3D portable game system
InactiveUS7371163B1More visibilityQuicker and accurate recognitionVideo gamesSpecial data processing applicationsViewpointsControl character
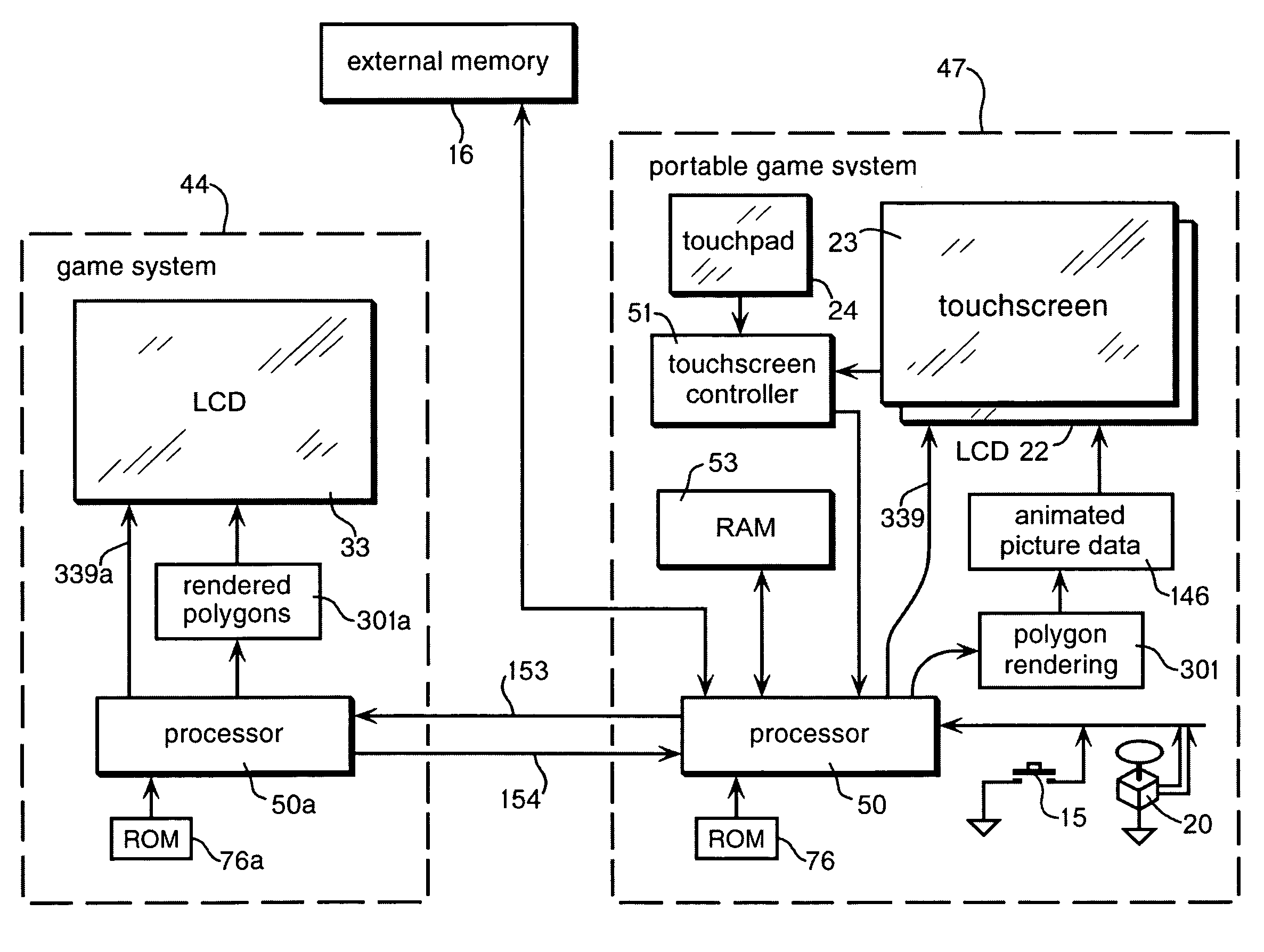
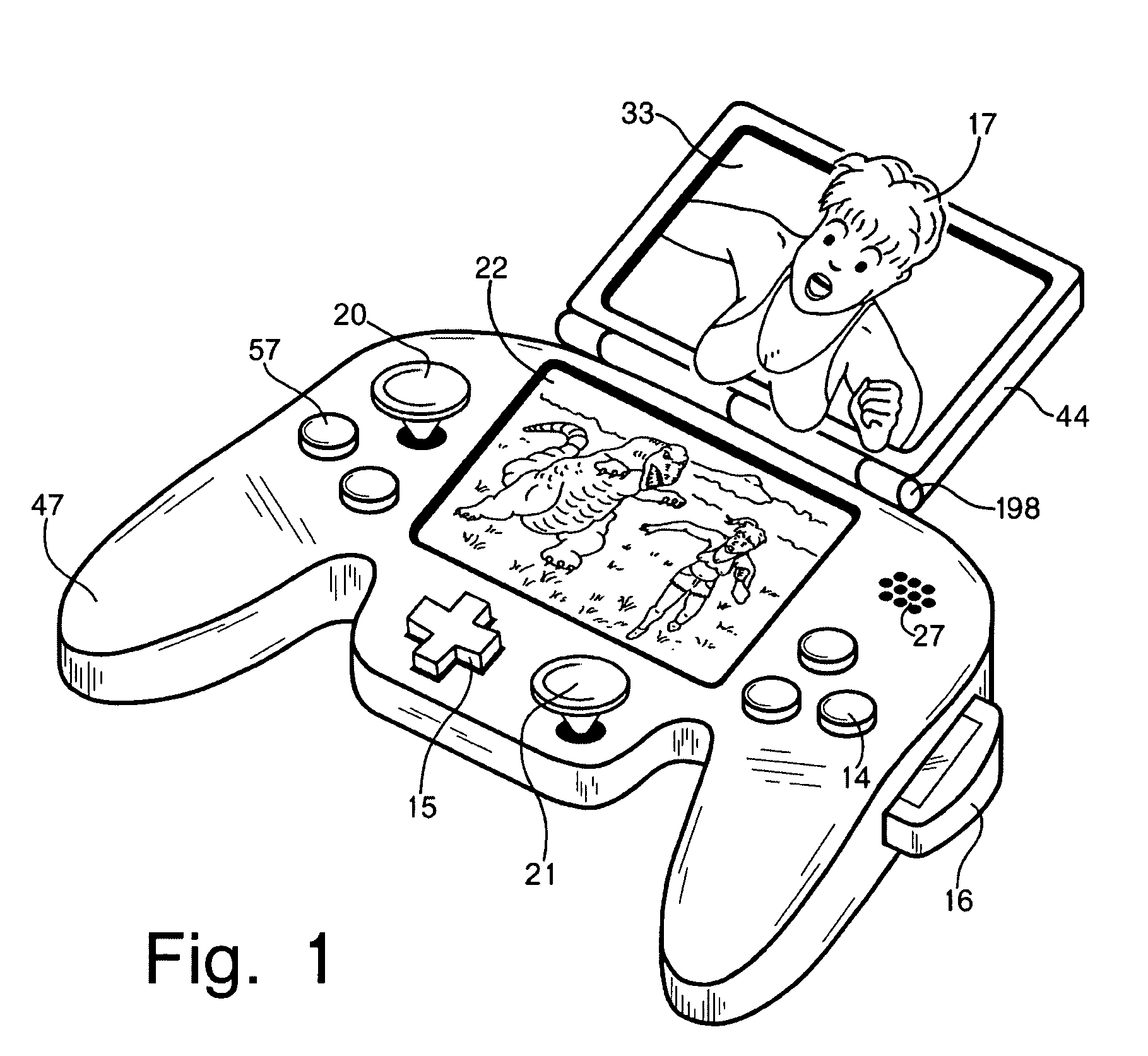
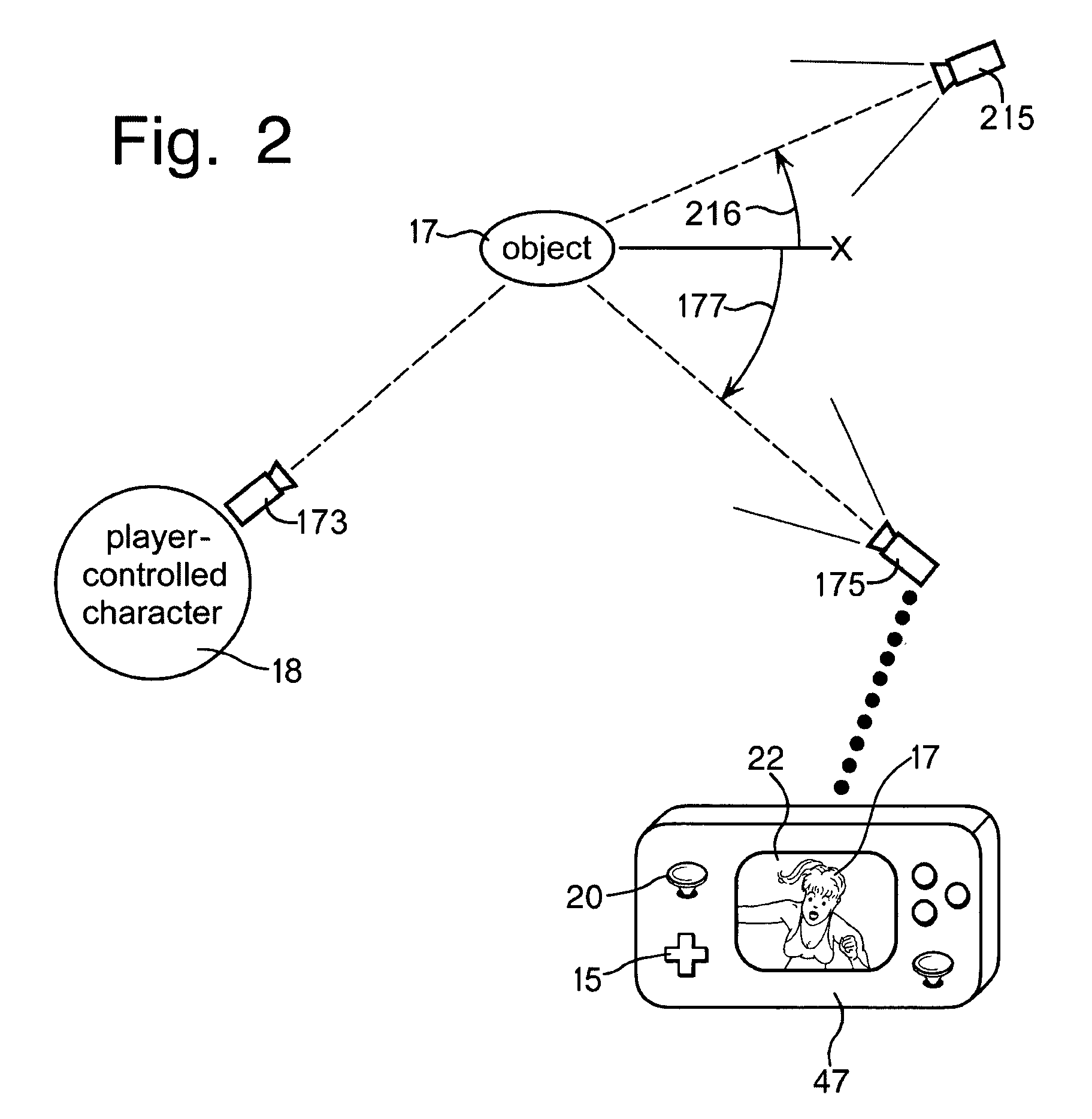
A portable game system that contains an LCD touchscreen that displays 3D player-controlled characters moving in a simulated 3D game world and viewed from variable 3D viewpoints. The LCD touchscreen displays autostereoscopic images (without using glasses) so that a game player can reach into the game world and move virtual objects in 3D by pointing to them using the autostereoscopic touchscreen.
Owner:BEST ROBERT M
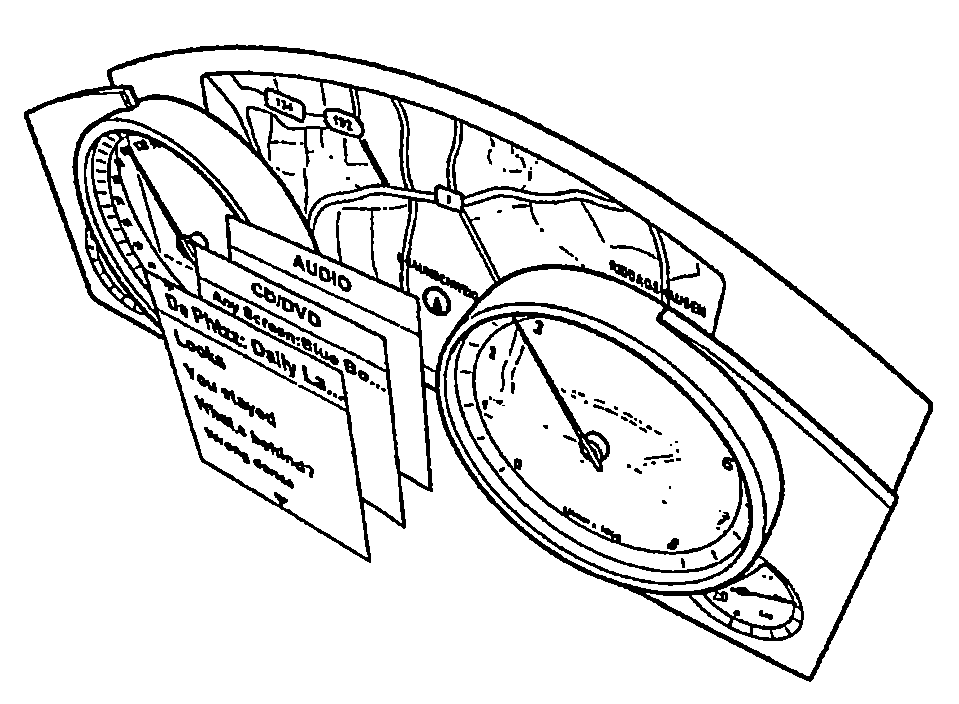
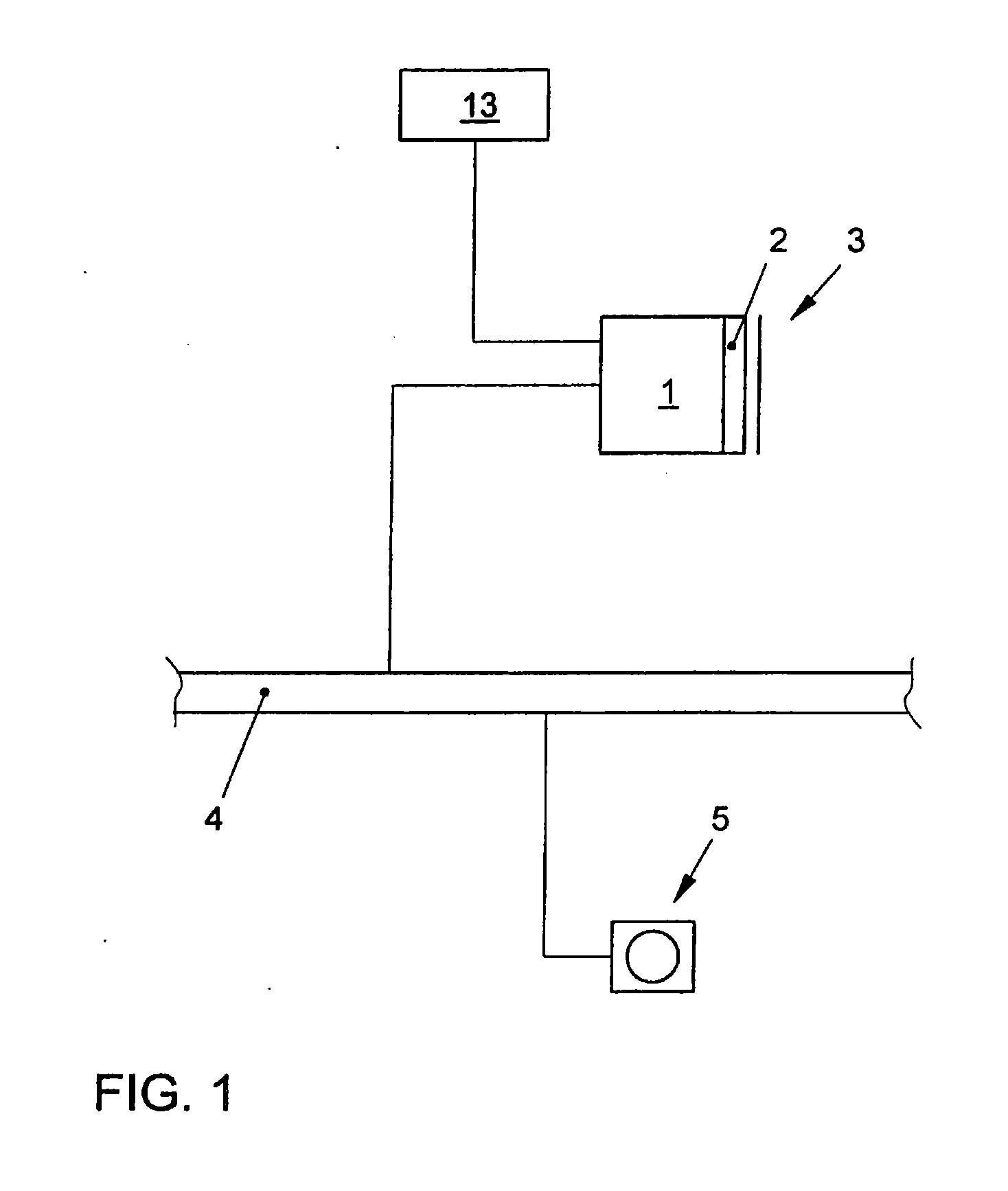
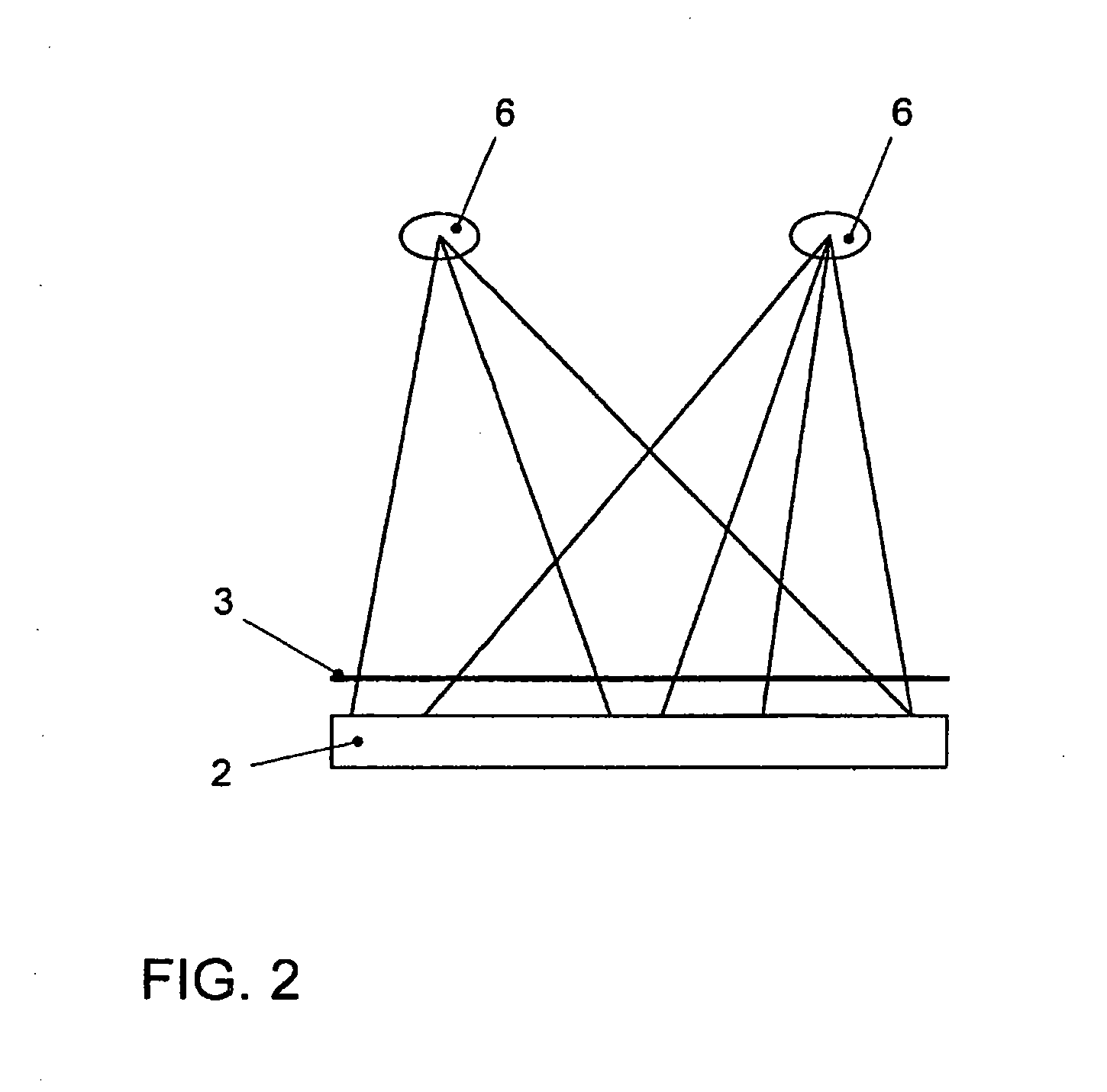
Method for Representing Items of Information in a Means of Transportation and Instrument Cluster for a Motor Vehicle
ActiveUS20080161997A1Easy to displaySpace minimizationDigital data processing detailsInstrument arrangements/adaptationsAutostereogramMobile vehicle
In a method for displaying items of information in a transportation device, the items of information are displayed in the form of hierarchical menu structures. A device for displaying items of information includes a control unit and a display unit for the stereoscopic and / or autostereoscopic display of items of information. In the method, the display is implemented stereoscopically, at least two different menus or menu items being displayed to the viewer at different distances. The instrument cluster includes the placement of a mask in front of the display of a display unit, the mask modifying the light emission of the light emitted by the display so as to result in a display of autostereoscopic images.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG
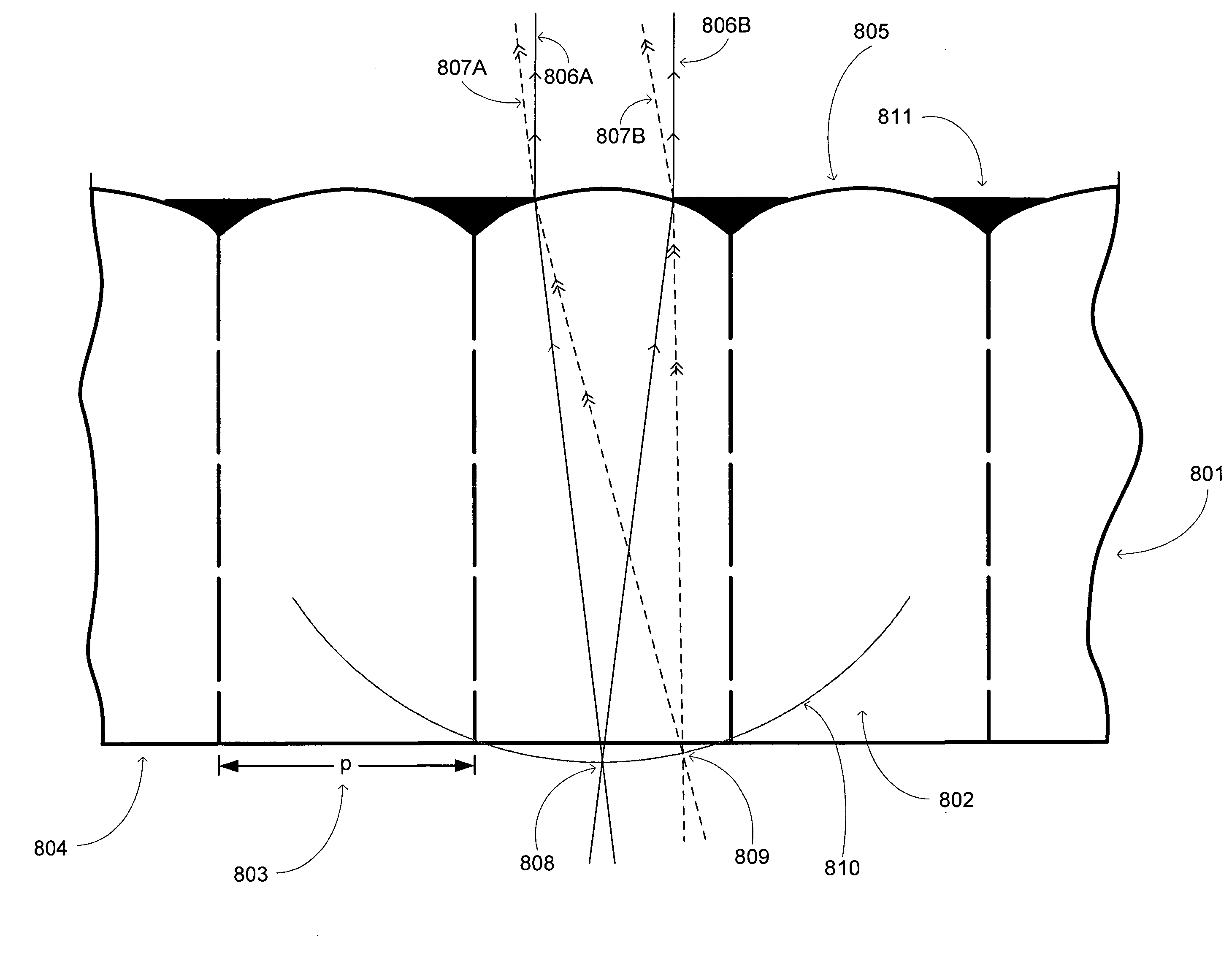
Aperture correction for lenticular screens
ActiveUS20080186573A1Increase heightReduce in quantitySpecial surfacesCoatingsAutostereogramComputer graphics (images)
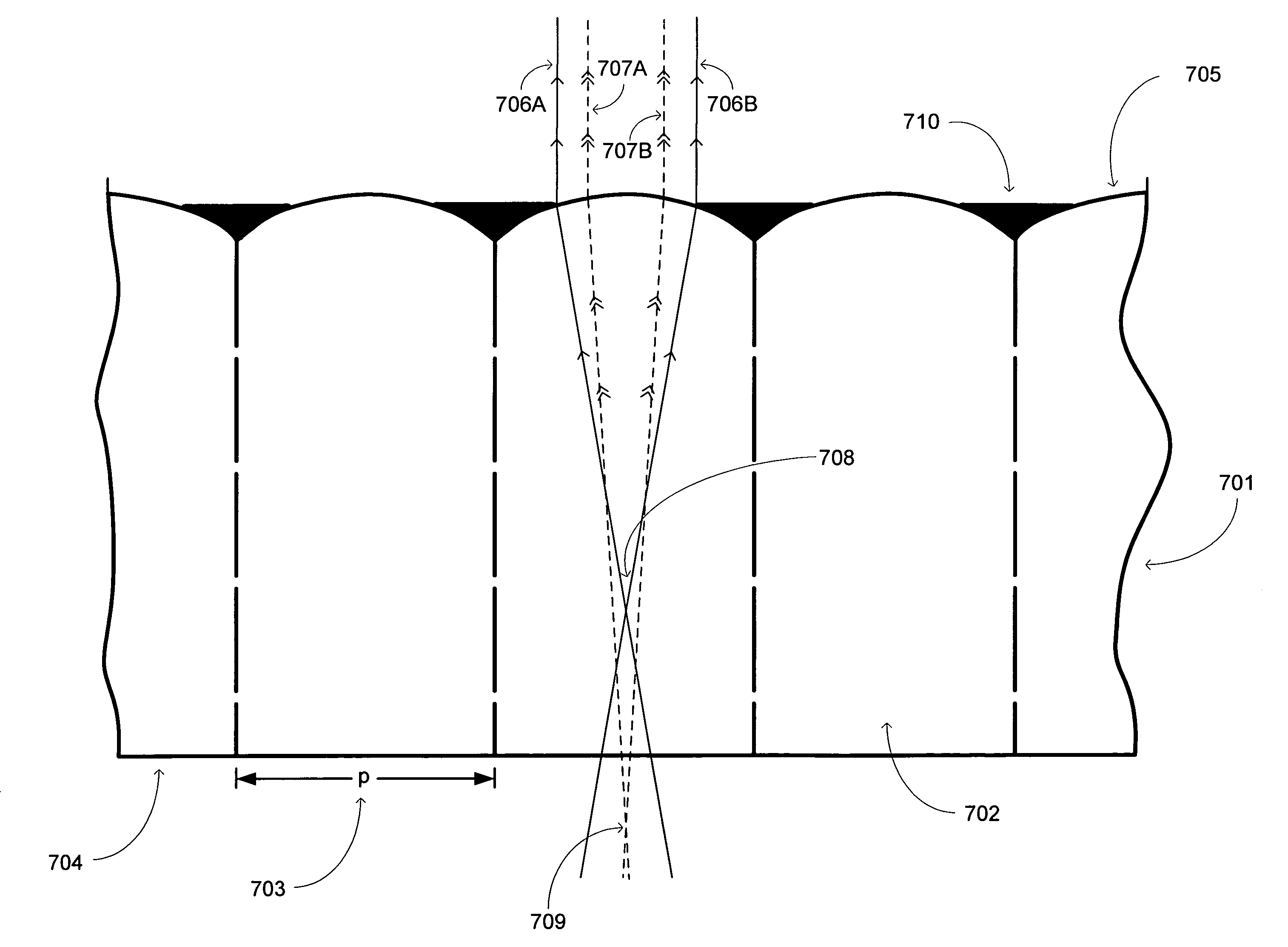
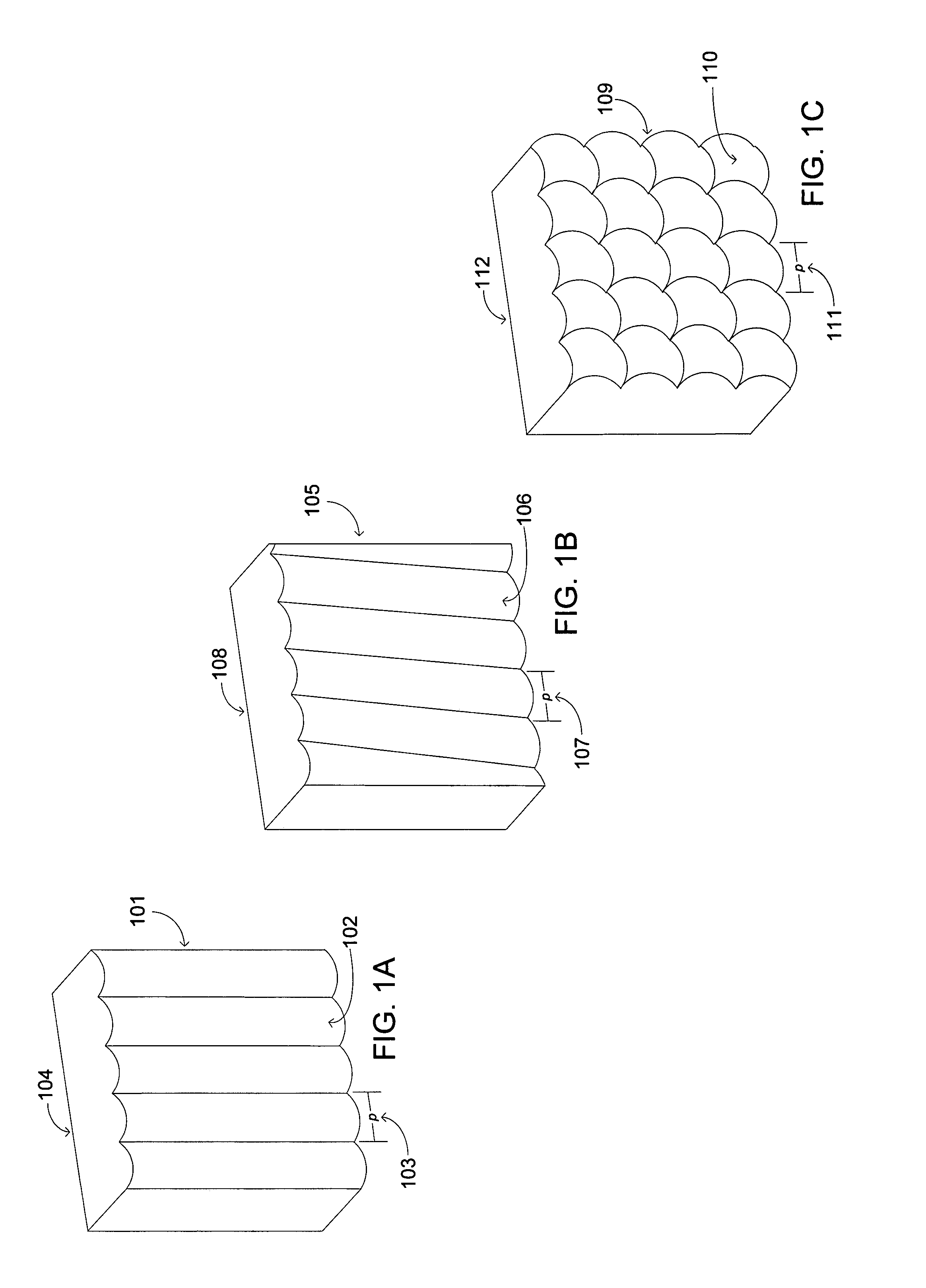
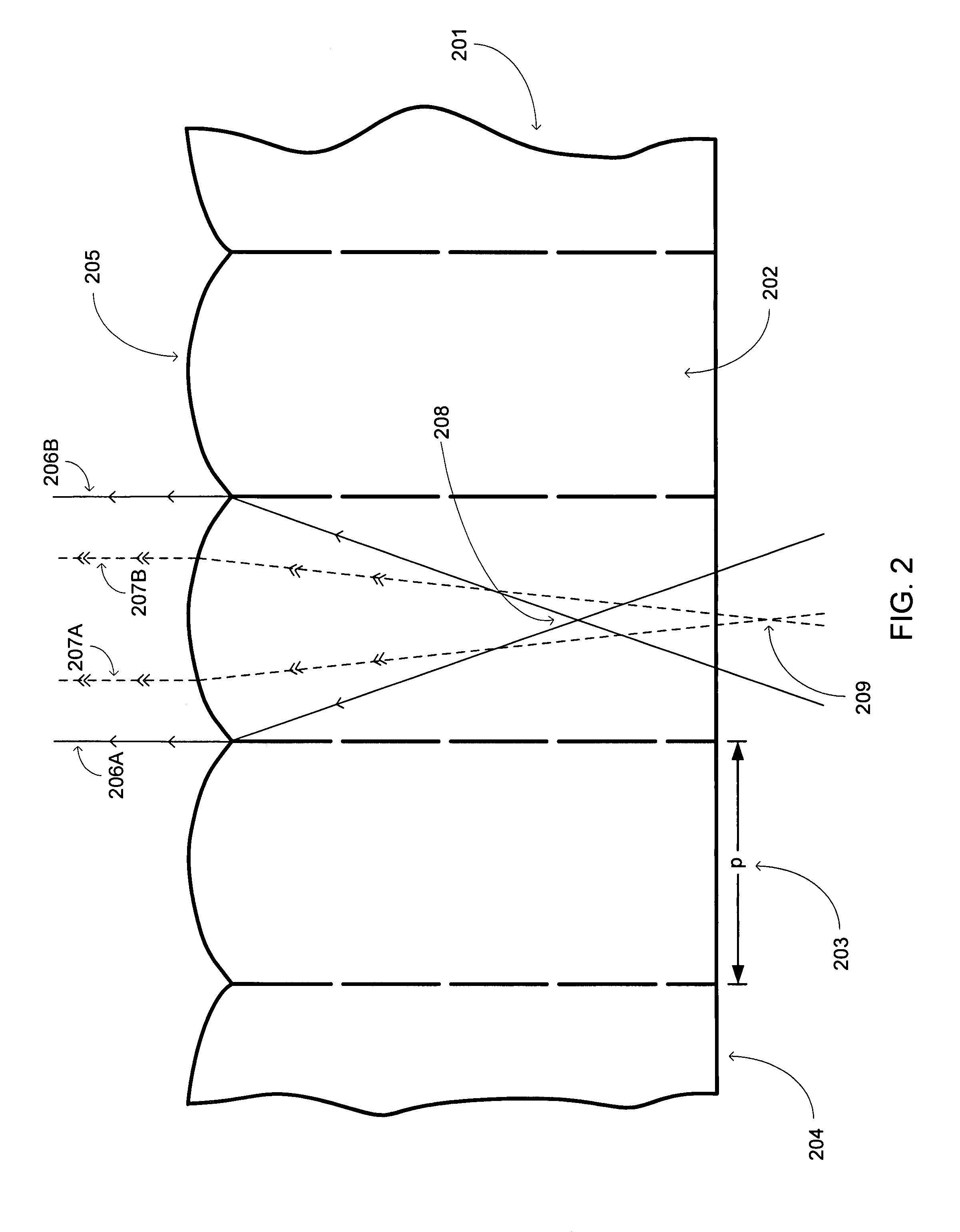
An apparatus including an autostereoscopic image selection device and an overcoat opaque material applied to the autostereoscopic image selection device. The autostereoscopic image selection device and overcoat opaque material operate together to provide a self-locating aperture in association with the autostereoscopic selection device. The associated method entails applying an opaque overcoat material to an image selection device comprising a plurality of lenticules and removing selected portions of the opaque overcoat material from the image selection device. The applying and removing operate together with the image selection device to reduce a numerical aperture for at least one lenticule.
Owner:REAID INC
Soft aperture correction for lenticular screens
An apparatus including an autostereoscopic image selection device having a plurality of lenticules is provided. The autostereoscopic image selection device has an opaque material applied thereto in gaps between the plurality of lenticules. The opaque material is applied to the autostereoscopic image selection device in a soft aperturing manner, the soft aperturing manner comprising applying the opaque material such that the opaque material is tapered from the gaps over the plurality of lenticules. The opaque material can be applied in accordance with a windowing function.
Owner:REAID INC
Neutralizing device for autostereoscopic lens sheet
A neutralizing sheet for an autostereoscopic image viewing system. The image viewing system includes a lenticular sheet covering a display screen. The neutralizing sheet including a pliable portion and is movable between a first position and a second position. The pliable portion has a refractive index similar to the lenticular sheet. When pressed into the lenticular sheet to define the first position, the pliable portion deforms to assume the shape of the lenticular sheet. Thus, refraction through the lenticular sheet is neutralized and viewing of planar images is enabled. In the second position, the neutralizing sheet is separated from the lenticular sheet and viewing of stereoscopic images is enabled.
Owner:REDEBT LLC +1
Autostereoscopic display
InactiveUS7375885B2Improve efficiencyPoor efficiencyProjectorsSteroscopic systemsAutostereogramDisplay device
In an autostereoscopic display, a cylindrical lens focuses collimated light emitted from pixels of a display array, and a scanning device sequentially provides the light to openings in a display screen. The image information is provided in the display area at a rate corresponding to the frequency of the scanning of the openings in the display screen to provide the autostereoscopic image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Neutralizing device for autostereoscopic lens sheet
A neutralizing sheet for an autostereoscopic image viewing system. The image viewing system includes a lenticular sheet covering a display screen. The neutralizing sheet including a pliable portion and is movable between a first position and a second position. The pliable portion has a refractive index similar to the lenticular sheet. When pressed into the lenticular sheet to define the first position, the pliable portion deforms to assume the shape of the lenticular sheet. Thus, refraction through the lenticular sheet is neutralized and viewing of planar images is enabled. In the second position, the neutralizing sheet is separated from the lenticular sheet and viewing of stereoscopic images is enabled.
Owner:REDEBT LLC +1
Controlling the angular extent of autostereoscopic viewing zones
A method and system for providing an increased angular extent of autostereoscopic viewing zones received from a display is presented. The design comprises providing a first column of data having a baseline number of views associated therewith, said first column of data provided to at least one lenticule in a lens sheet associated with the display. The design further comprises altering the first quantity of columns of data to a second quantity of columns of data provided to the at least one lenticule. The second quantity of columns comprises more views than the baseline number of views. Employing the second quantity of columns when constructing an autostereoscopic image provides a display having relatively clear viewing of autostereoscopic images for specific viewing distances.
Owner:REAID INC
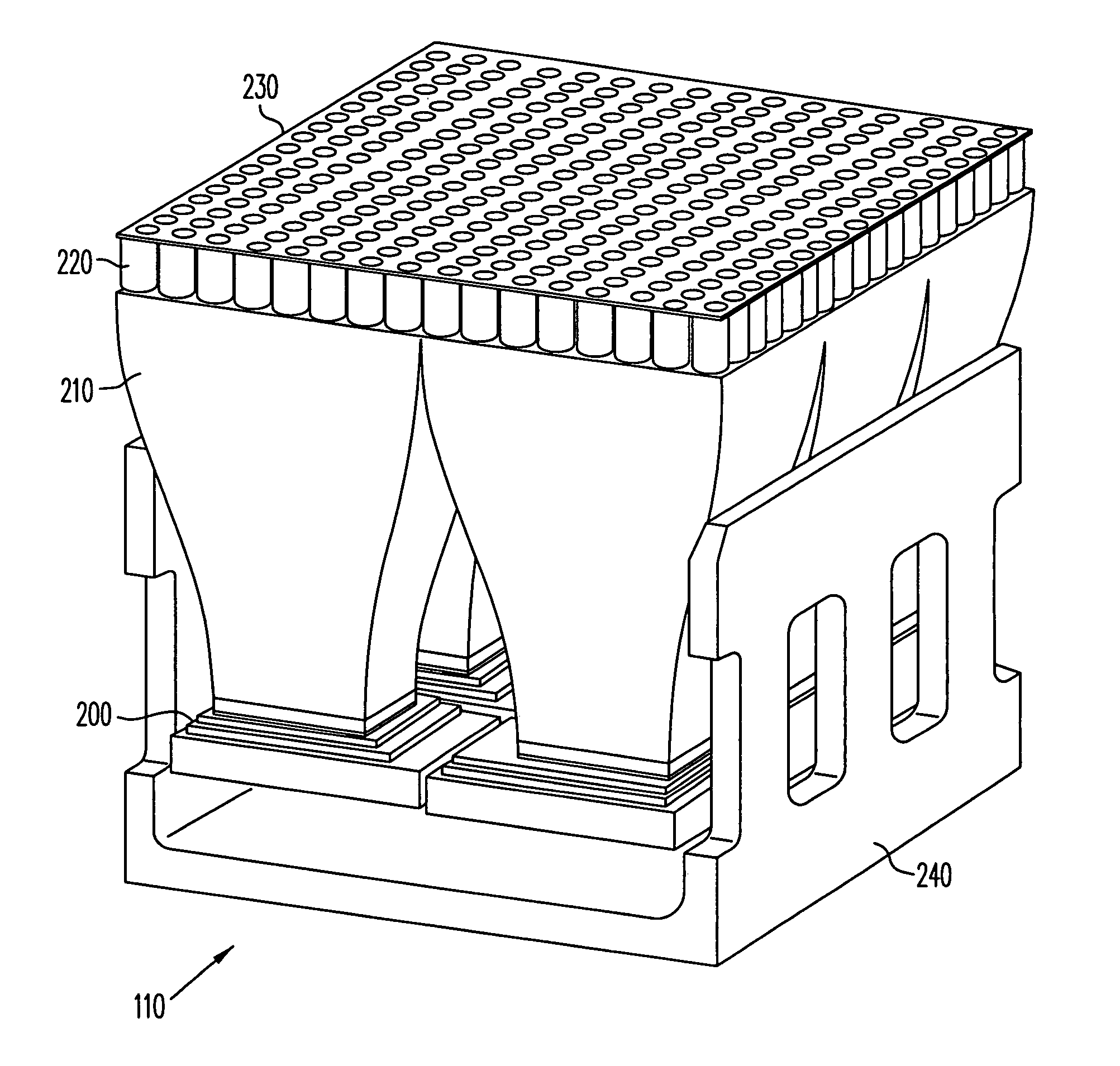
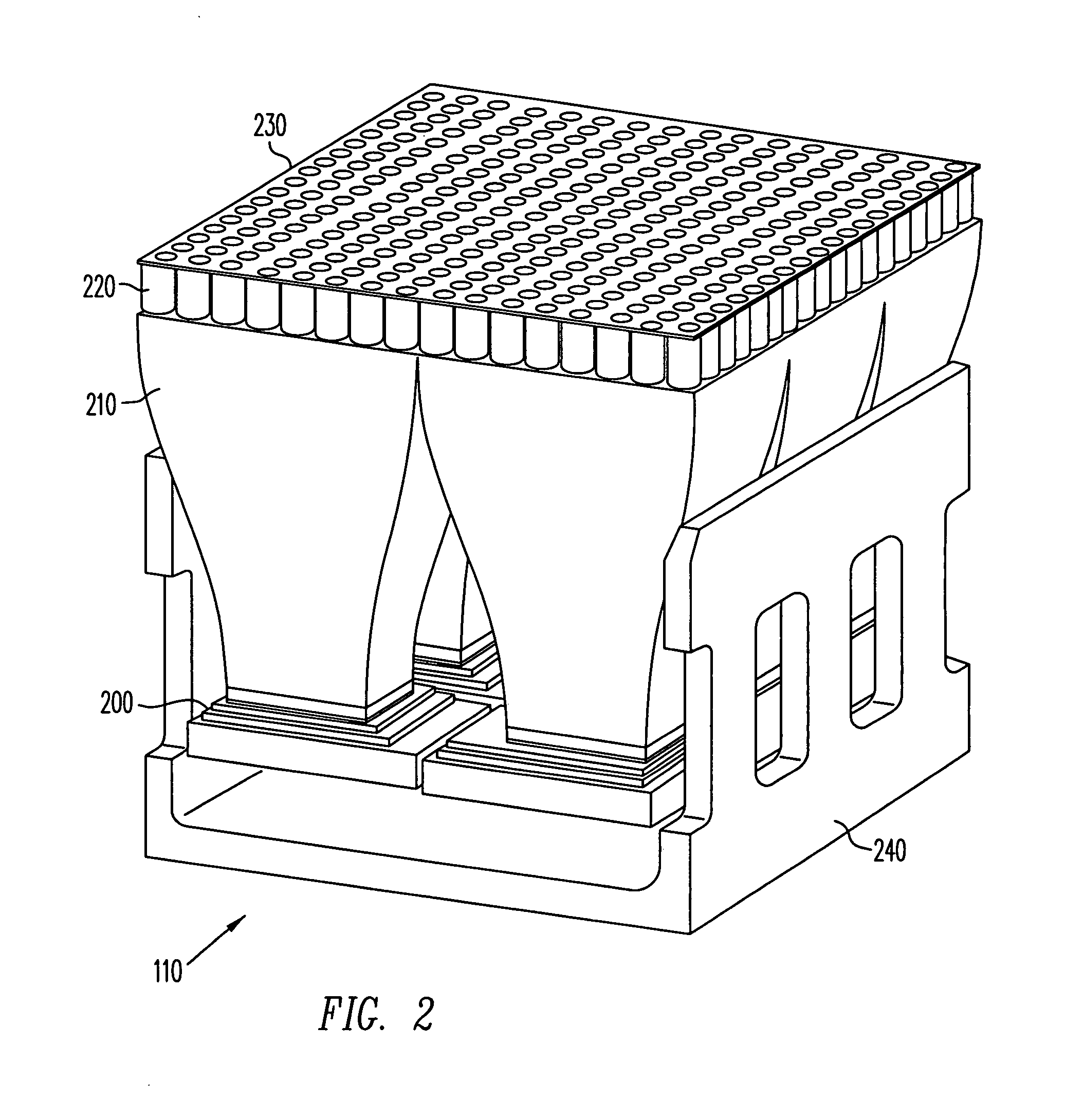
Dynamic autostereoscopic displays
It has been discovered that emissive display devices can be used to provide display functionality in dynamic autostereoscopic displays. One or more emissive display devices are coupled to one or more appropriate computing devices. These computing devices control delivery of autostereoscopic image data to the emissive display devices. A lens array coupled to the emissive display devices, e.g., directly or through some light delivery device, provides appropriate conditioning of the autostereoscopic image data so that users can view dynamic autostereoscopic images.
Owner:FOVI 3D INC
Soft aperture correction for lenticular screens
An apparatus including an autostereoscopic image selection device having a plurality of lenticules is provided. The autostereoscopic image selection device has an opaque material applied thereto in gaps between the plurality of lenticules. The opaque material is applied to the autostereoscopic image selection device in a soft aperturing manner, the soft aperturing manner comprising applying the opaque material such that the opaque material is tapered from the gaps over the plurality of lenticules. The opaque material can be applied in accordance with a windowing function.
Owner:REAID INC
Autostereoscopic image acquisition method and system
InactiveUS6262743B1Color television detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsAutostereogramStereoscopic video
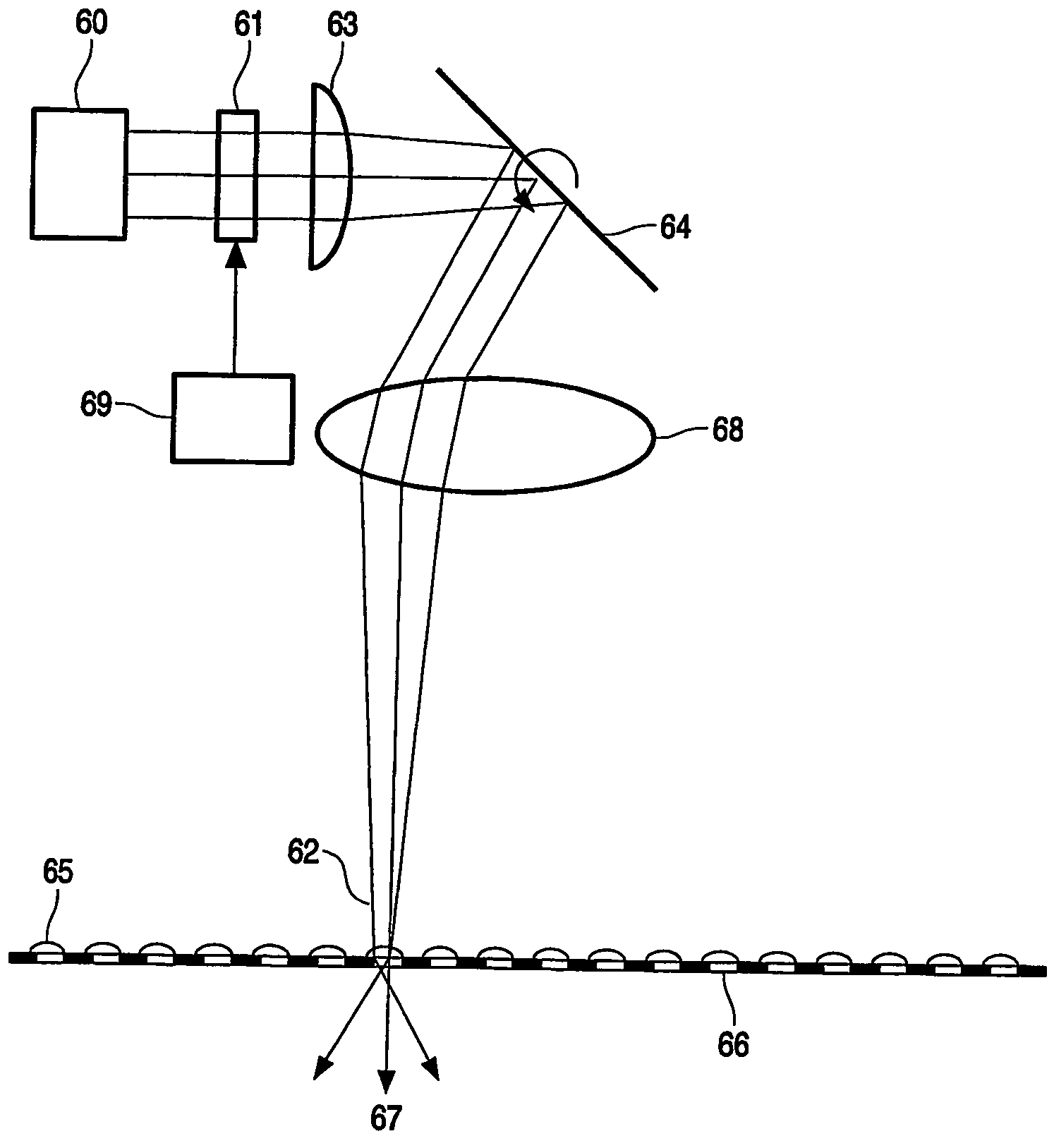
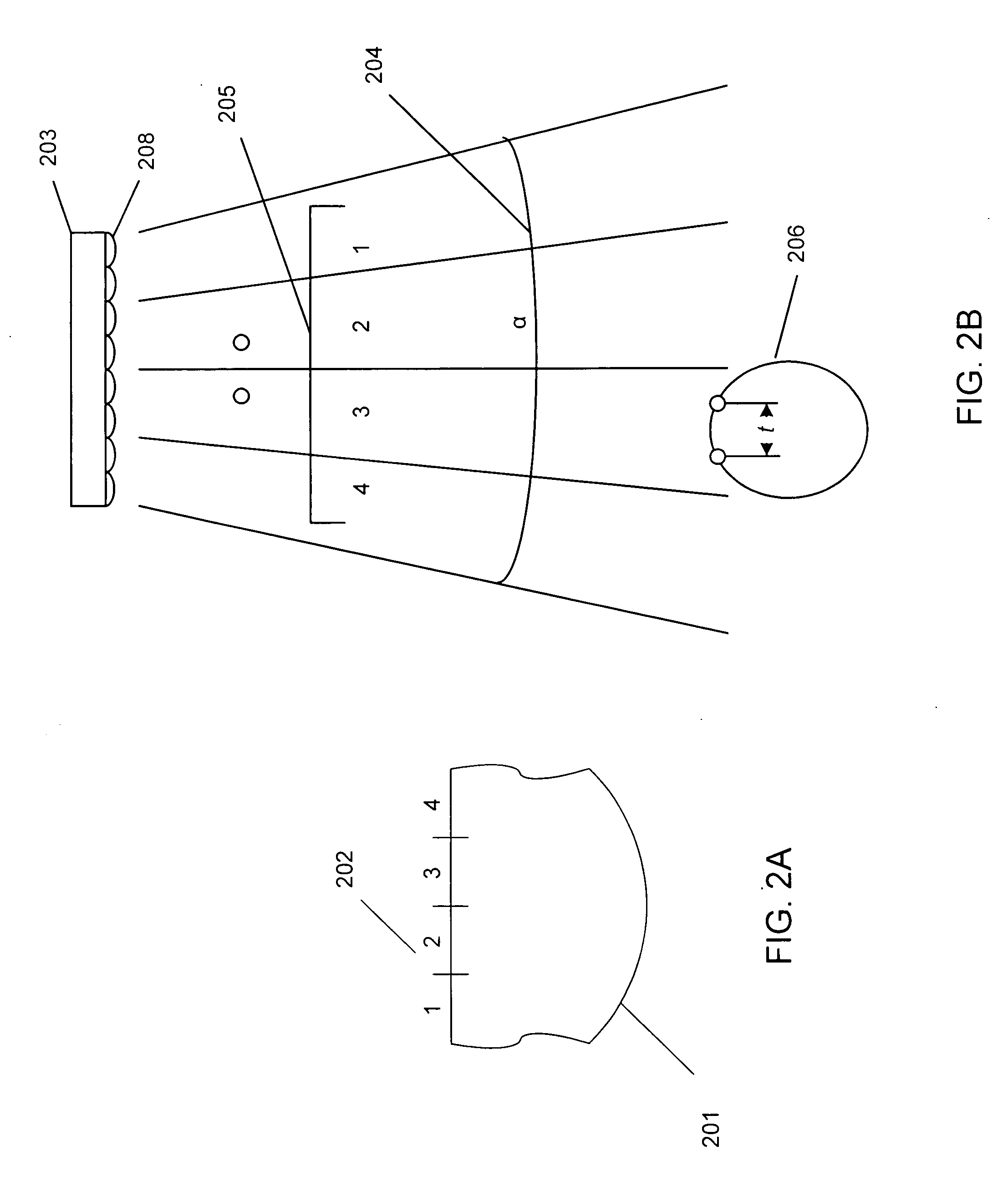
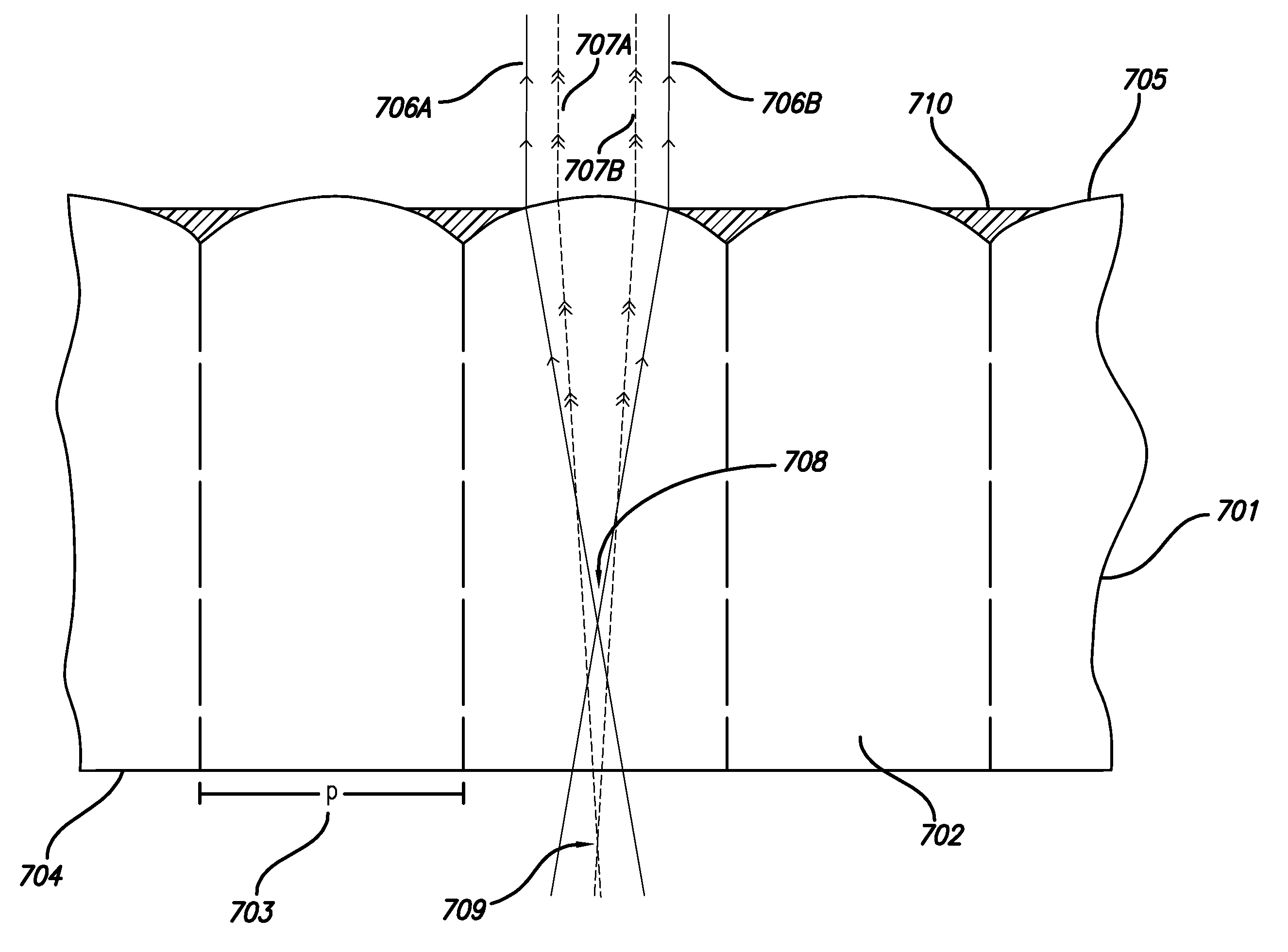
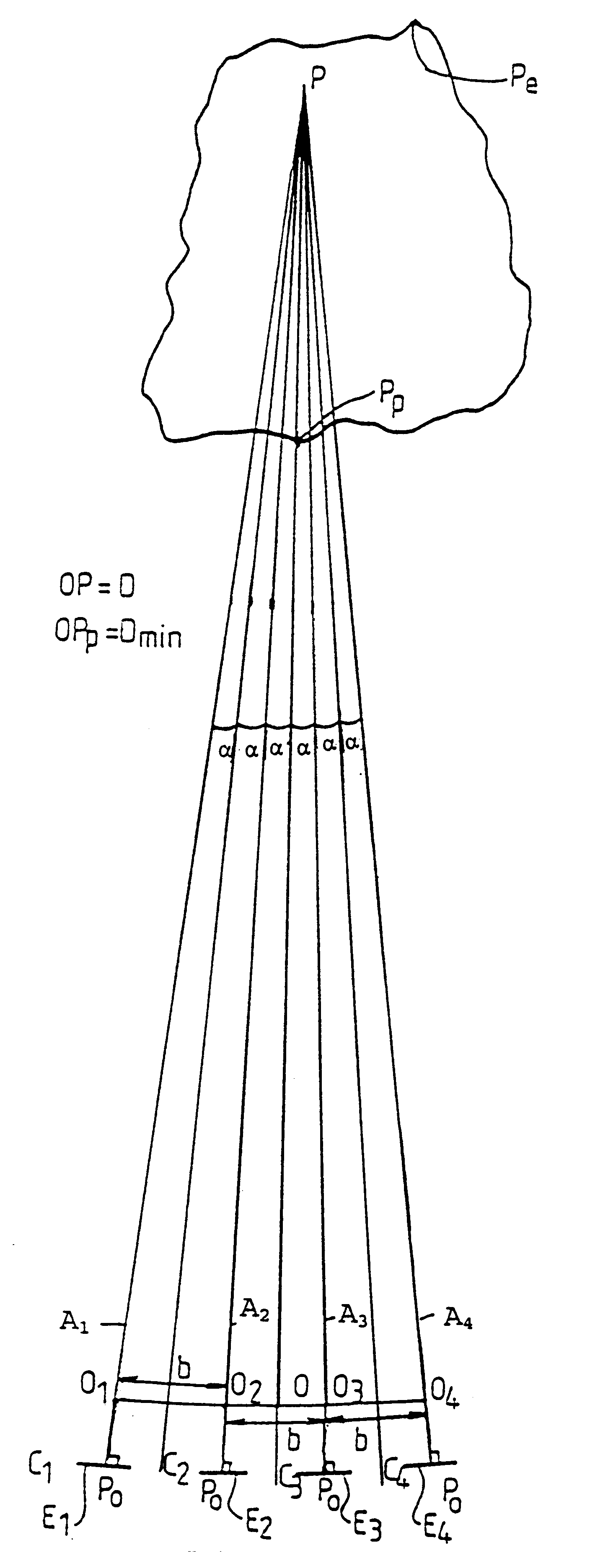
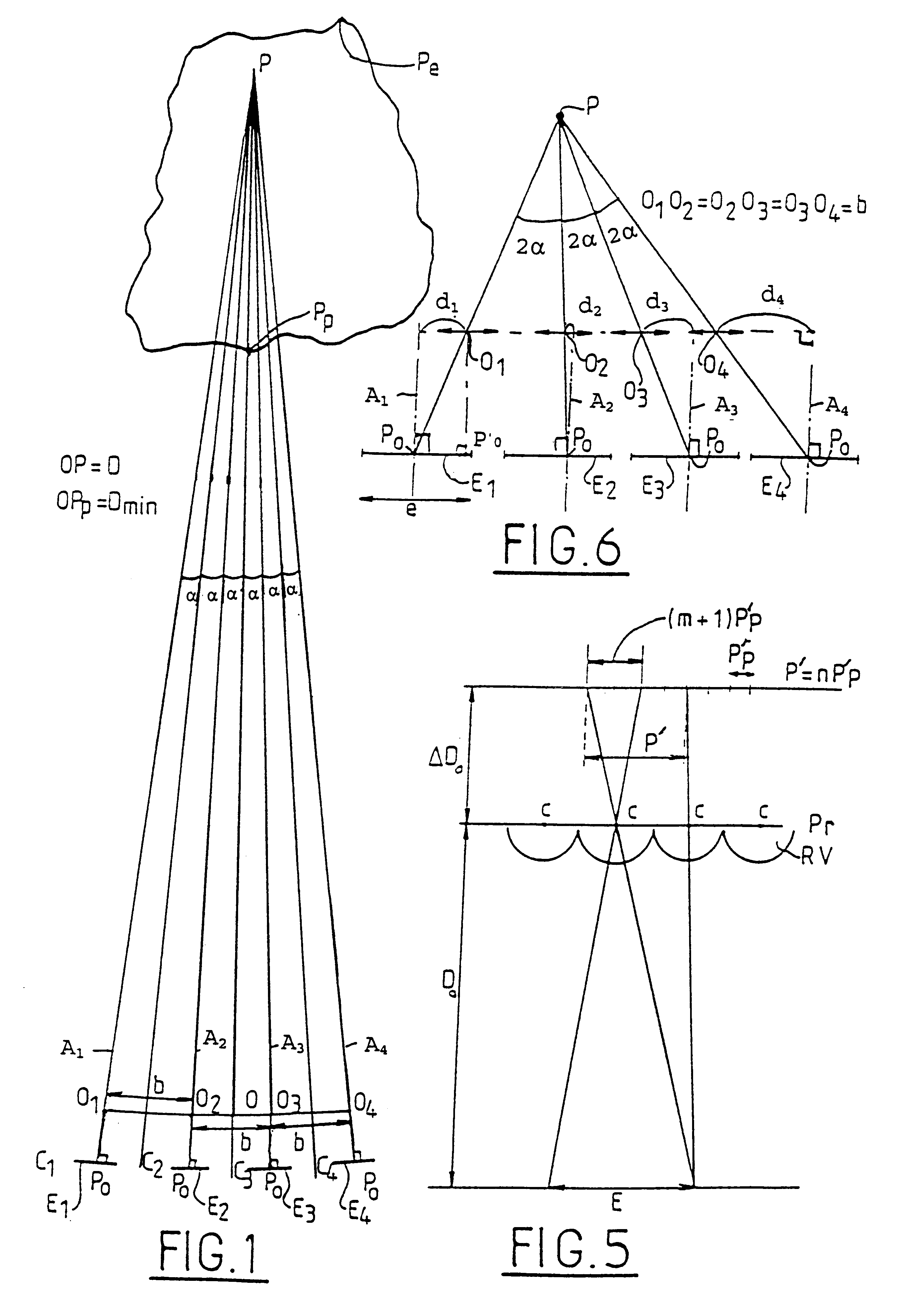
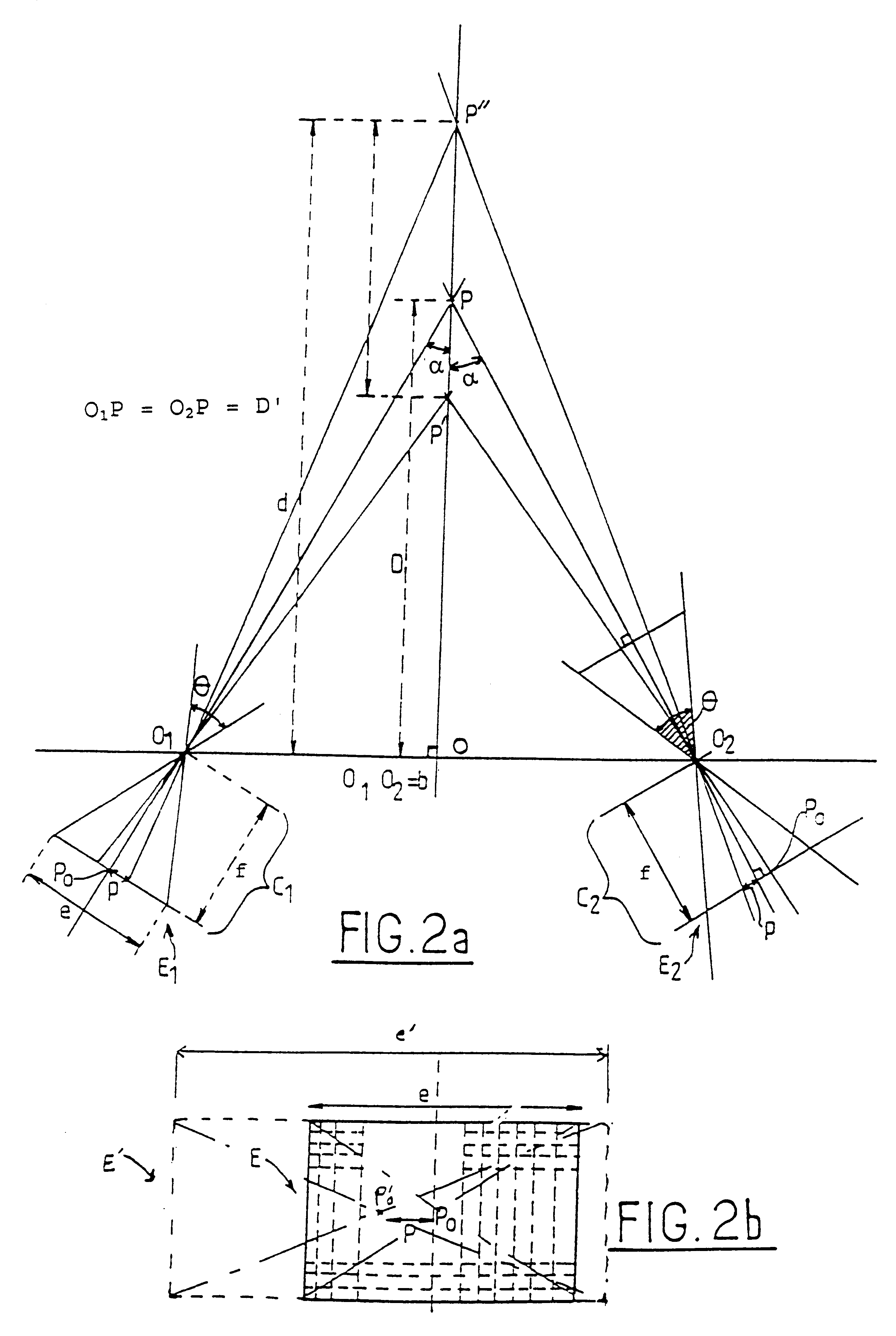
The invention relates to a method of acquiring simulated autostereoscopic video images of a scene to be viewed. On the basis of stored data containing three-dimensional information, it implements n simulated cameras, with n>=3, each generating an image of a scene on a given optical axis. The optical axes of the simulated cameras converge at a point situated at the same distance D from the simulated cameras. The scene to be viewed has a nearest point Pp and a farthest point Pe, and the inter-camera distance and the distance Dmin between the simulated cameras and the nearest point Pp are selected in such a manner that for focus varying between the nearest point Pp and the farthest point Pe the angle 2alpha between two adjacent simulated cameras varies between a value not greater than 4.5° for the point Pp and a value not less than 0.2° for the point Pe.
Owner:ALIOSCOPY
Method for displaying multiple-view stereoscopic images
InactiveUS20050012814A1Efficient processQuality improvementSteroscopic systemsAutostereogramComputer graphics (images)
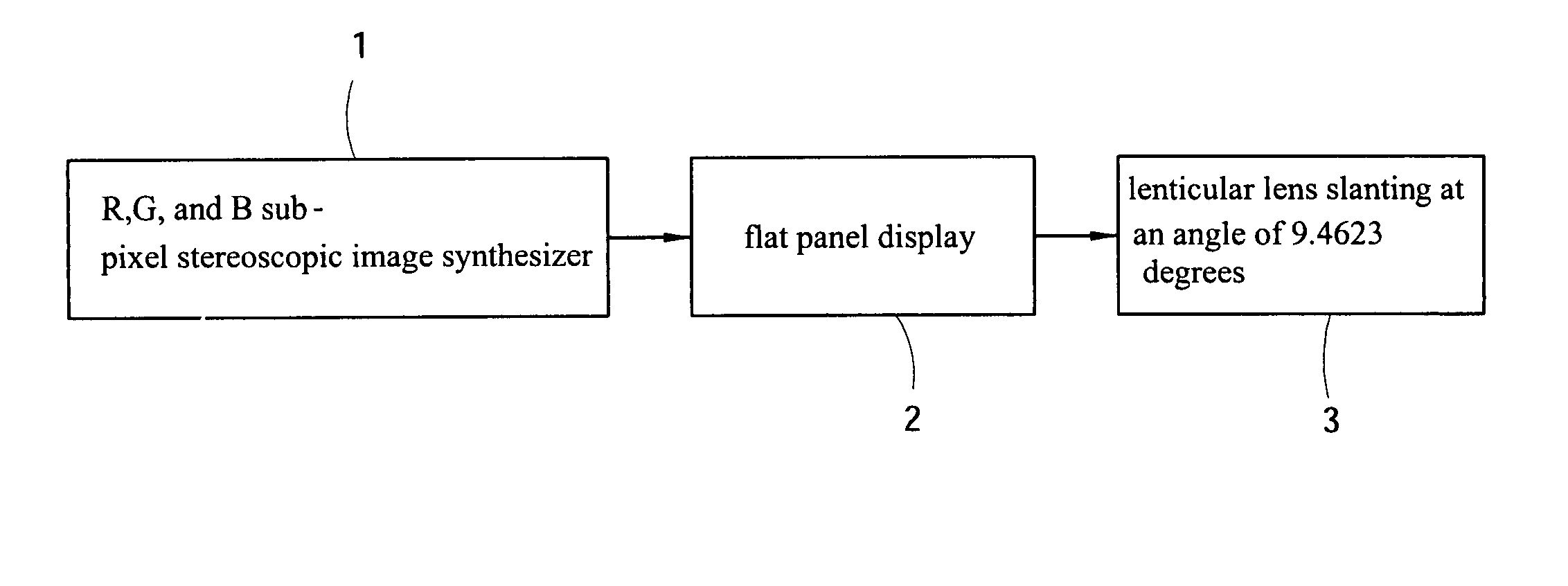
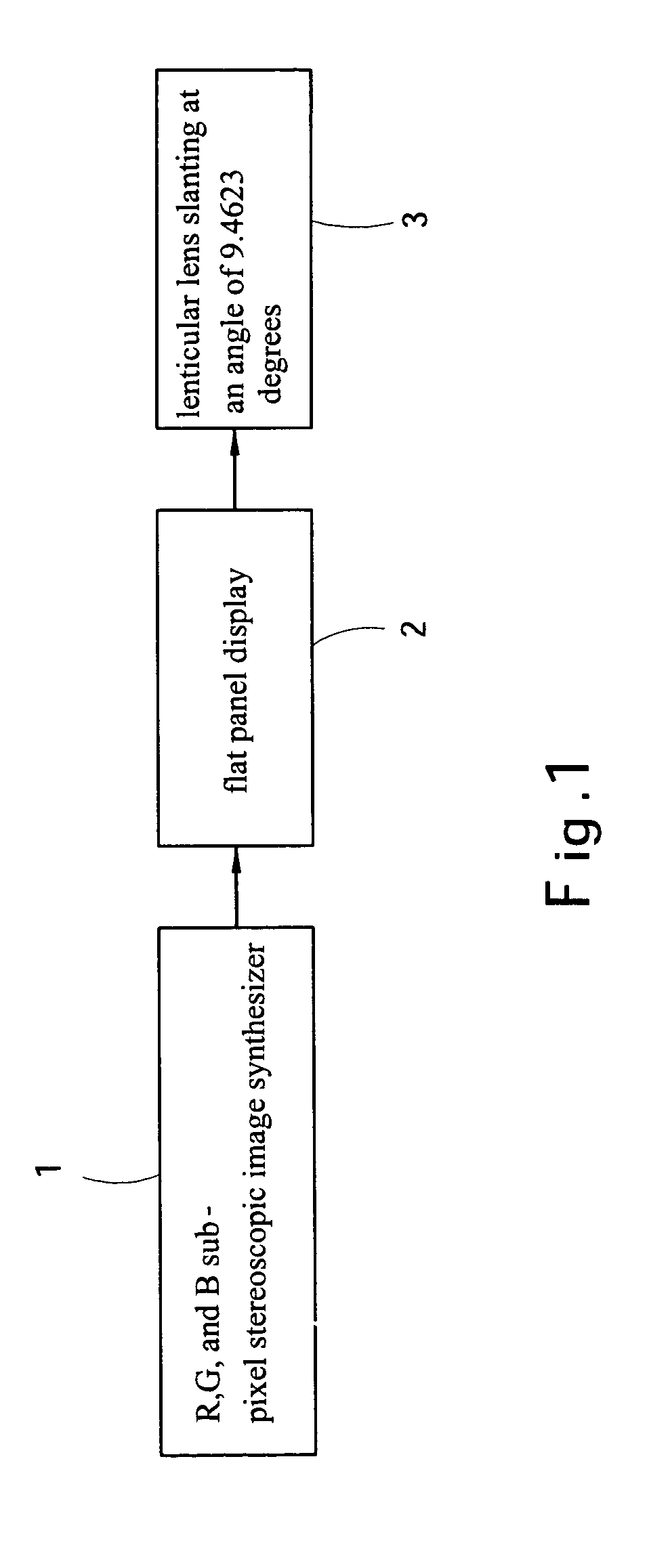
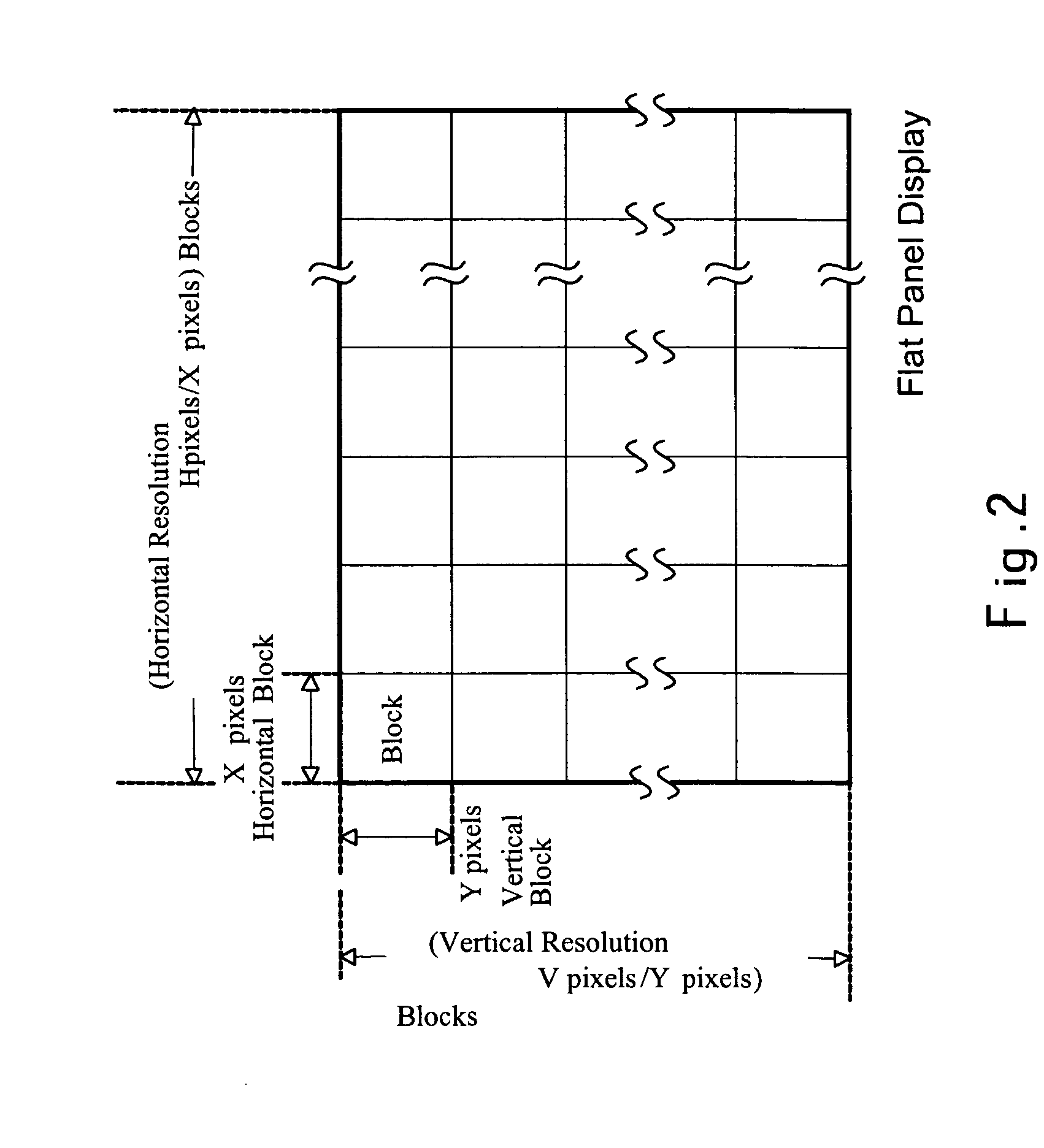
A method for displaying multiple-view auto-stereoscopic images without using stereoscopic glasses is disclosed in the invention. The multiple-view stereoscopic images are directly sent to the stereoscopic image synthesizer (or a software simulated by computer), and after the synthesizer has been informed about the view number and the horizontal and vertical display resolutions of the screen, the stereoscopic image synthesizing processing can be performed. Finally, the synthesized result will be displayed on the flat panel display. With the laminated lenticular lens vertically slanted at an angle of about 9.4623 degrees the viewer can watch the stereoscopic images on the display without wearing stereoscopic glasses.
Owner:I ART
Soft aperture correction for lenticular screens
An apparatus including an autostereoscopic image selection device having a plurality of lenticules is provided. The autostereoscopic image selection device has an opaque material applied thereto in gaps between the plurality of lenticules. The opaque material is applied to the autostereoscopic image selection device in a soft aperturing manner, the soft aperturing manner comprising applying the opaque material such that the opaque material is tapered from the gaps over the plurality of lenticules. The opaque material can be applied in accordance with a windowing function.
Owner:REAID INC
Autostereoscopic image output device
ActiveUS20110001803A1Good view-distributionGood image pixel structureSteroscopic systemsAutostereogram3d image
An autostereoscopic image output device comprises an image panel having an array of image pixels (5) defining an image, the image pixels being arranged in rows and columns. An array of parallel lenticular elements (11) is positioned over the image panel, the lenticular elements having optical focal axes that are slanted at an angle (φ) to the image pixel columns. The image output device is operable in first and second modes, with the image panel and lenticular element array rotated by 90 degrees between the modes, thereby providing a landscape mode of operation and a portrait mode of operation, the slant angle φ in the landscape mode satisfies: 1≧tan φ≧1 / 2. This enables a 3D image device to be used in both the landscape and the portrait mode, while maintaining a good view-distribution and image pixel structure.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for autostereoscopic display
InactiveUS6972744B1Improve finenessImprove perceptionCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage data processingAutostereogramViewpoints
The invention relates to a method of autostereoscopically displaying an N-viewpoint image on a screen having display pixels disposed in rows and columns, each display pixel presenting p>1 color points, corresponding to first, second, . . . , and pth color components, in which method the pixels of an autostereoscopic image to be displayed are displayed by distributing in space the p color points of each pixel amongst the color points of corresponding color components in p different display pixels, the method of the invention starting from a “high definition” autostereoscopic image presenting at least as many pixels having p color points as the N viewpoint image has color points to generate a said autostereoscopic image to be displayed in which each pixel is a color point of the corresponding color component of p different pixels in the high definition autostereoscopic image.
Owner:ALIOSCOPY +1
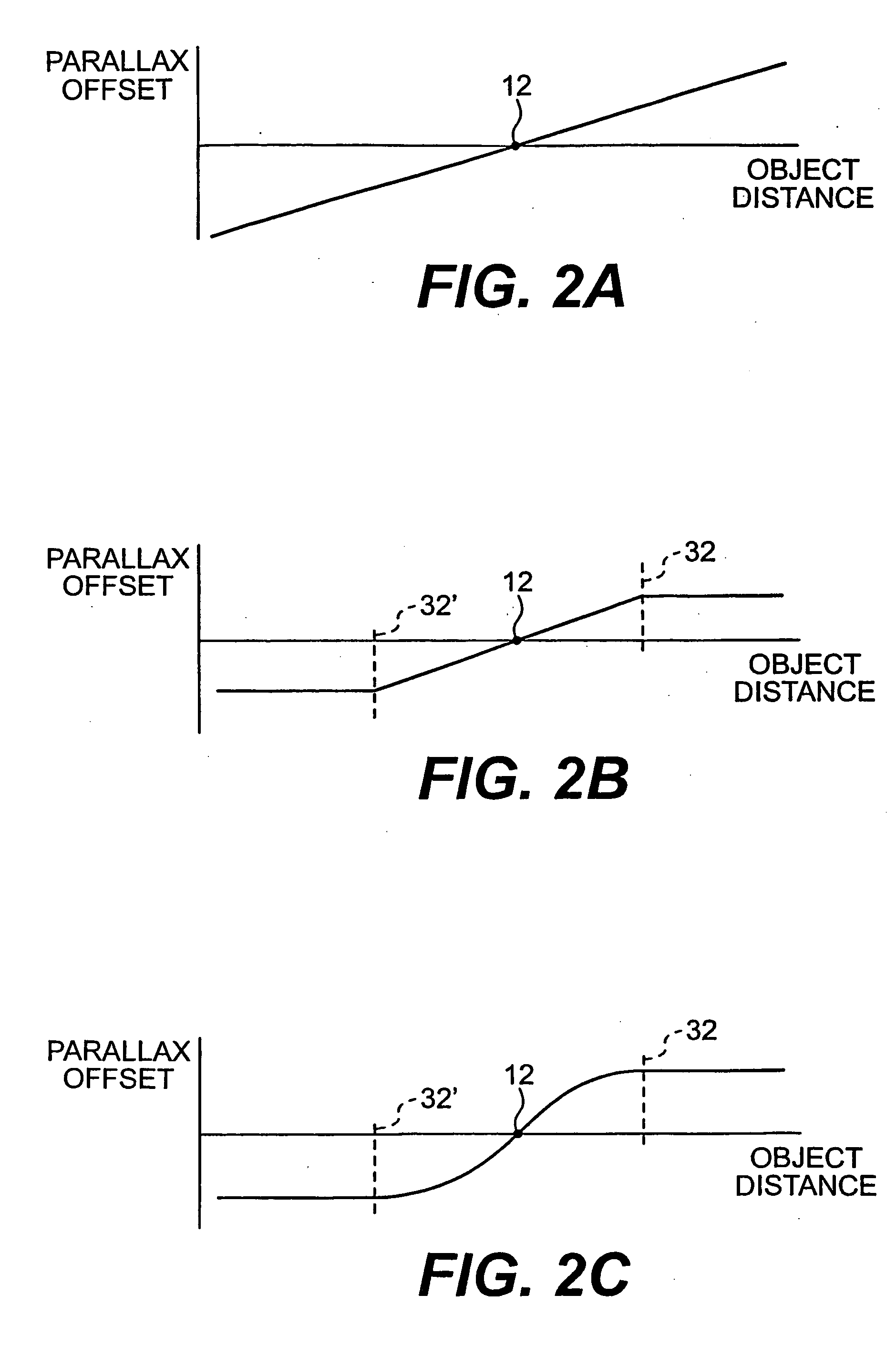
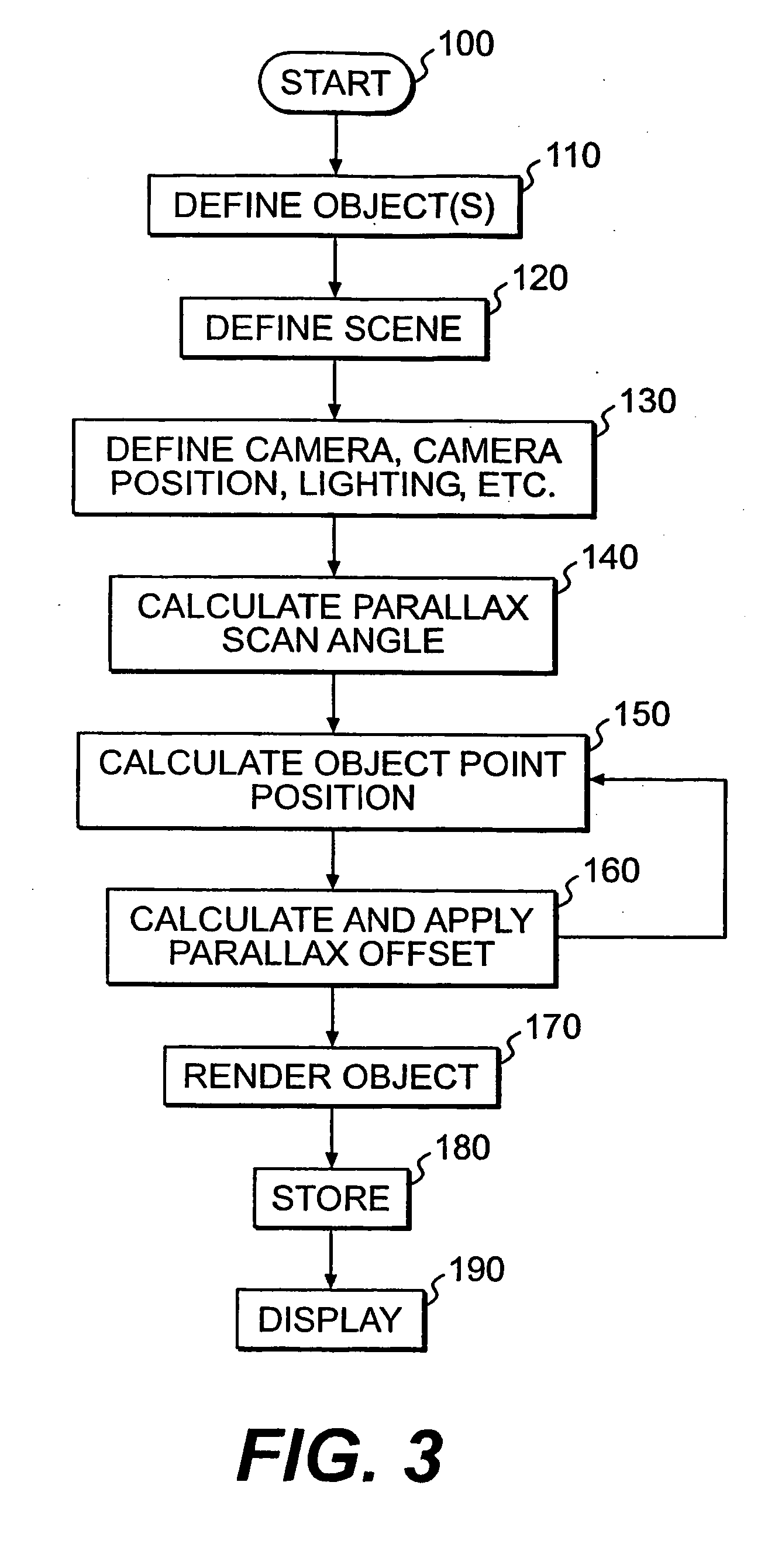
Parallax scanning through scene object position manipulation
ActiveUS7463257B2Character and pattern recognitionSteroscopic systemsAutostereogramParallax scanning
Owner:VISION III IMAGING
Stereoscopic display unit
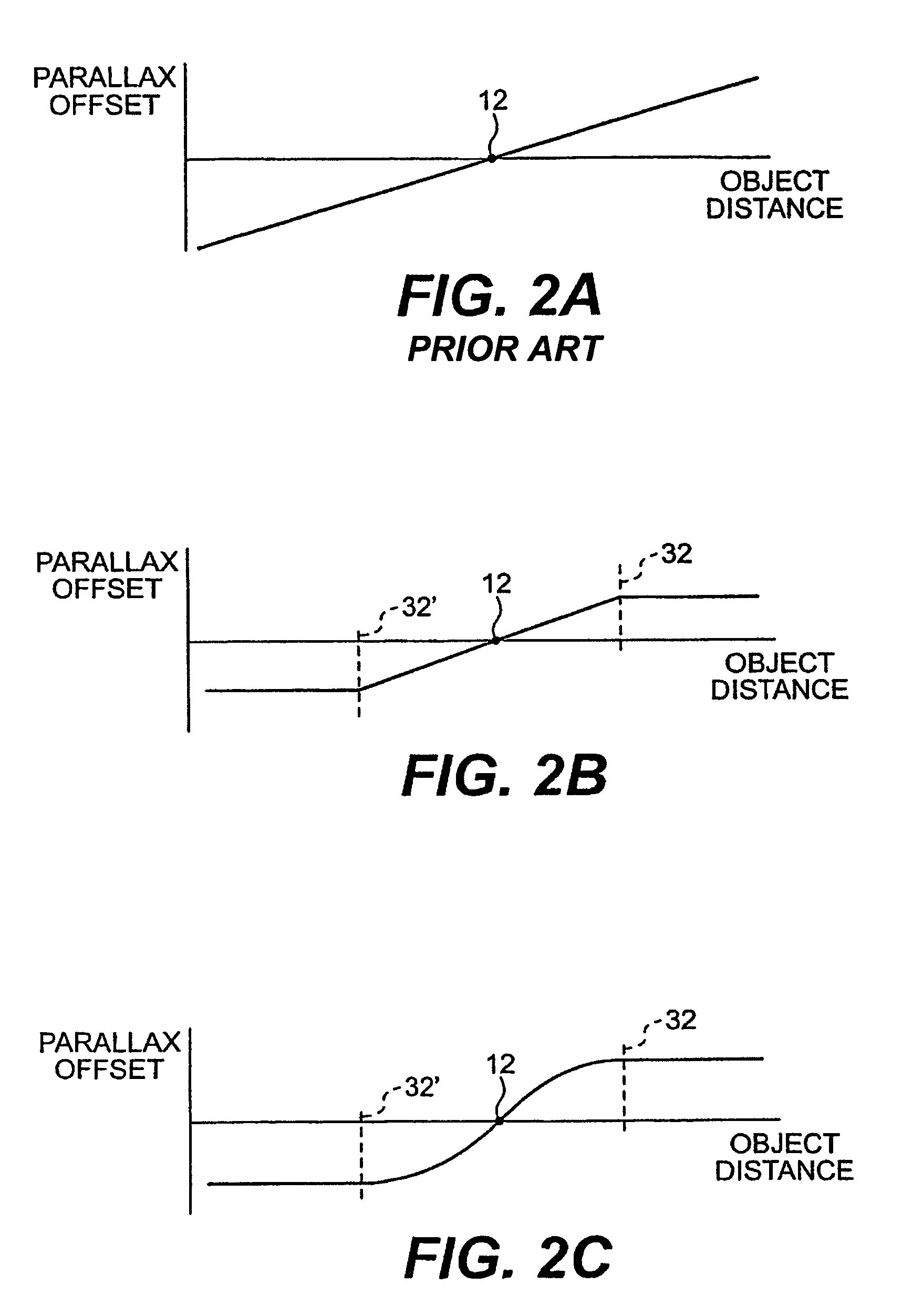
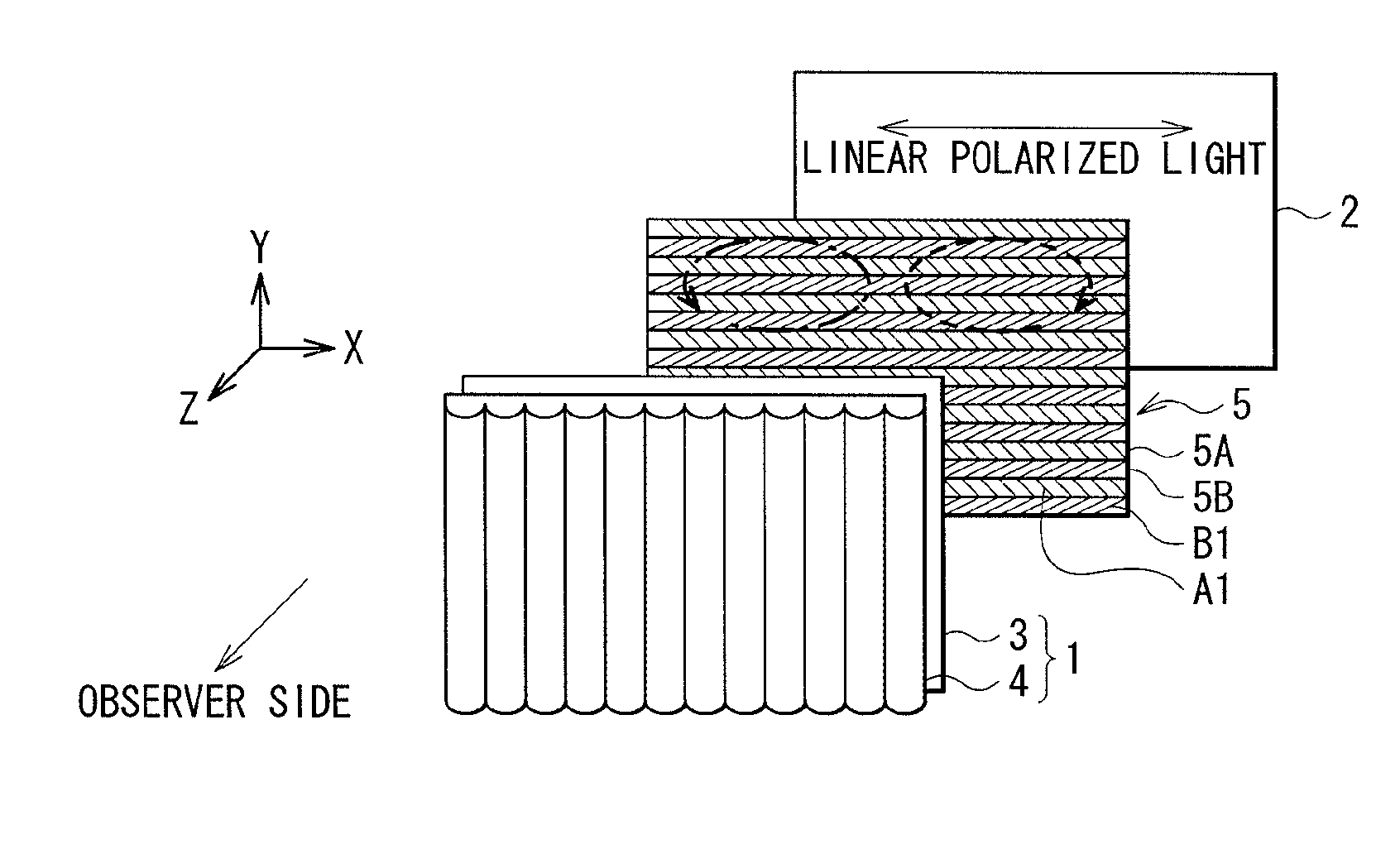
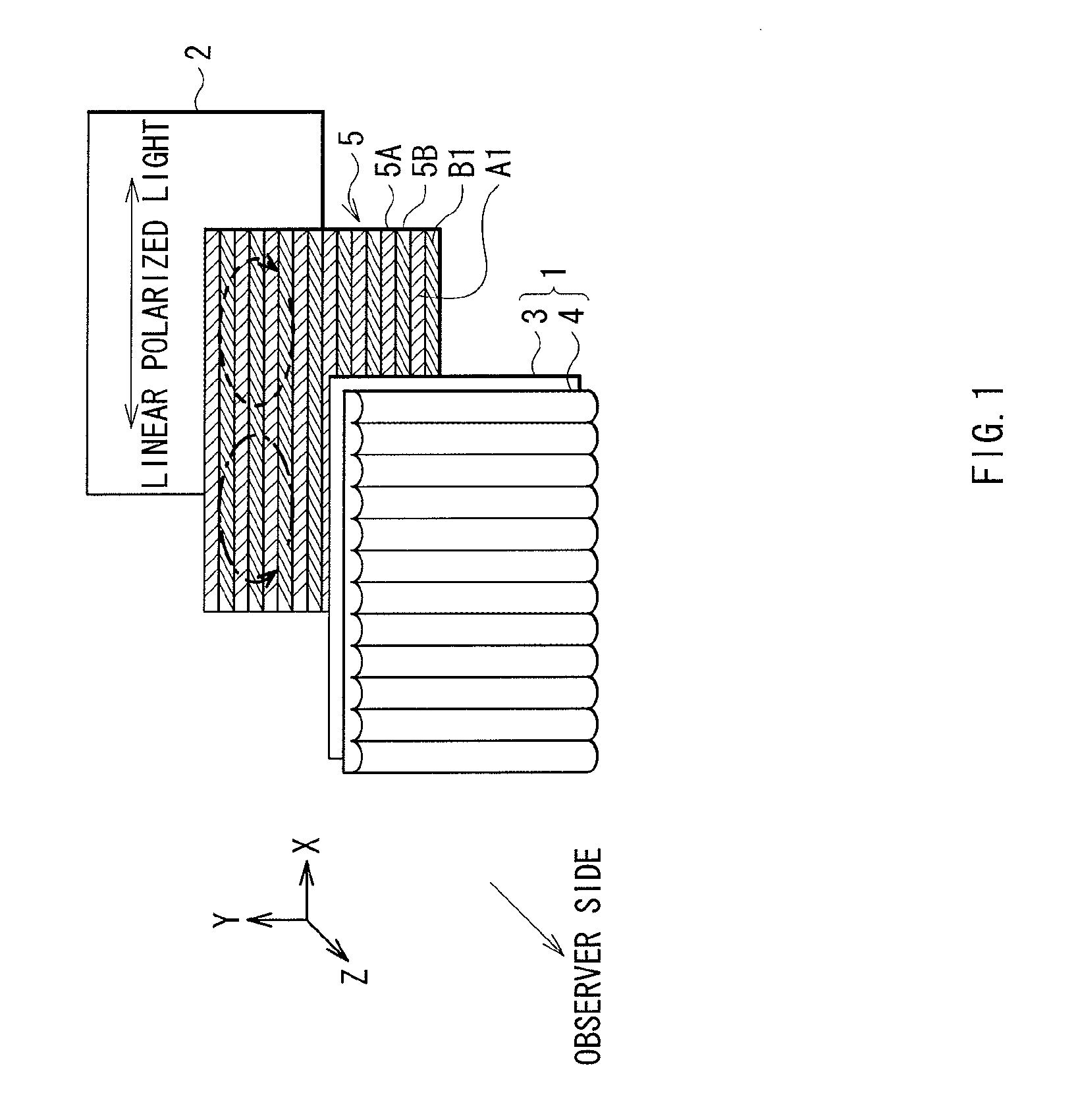
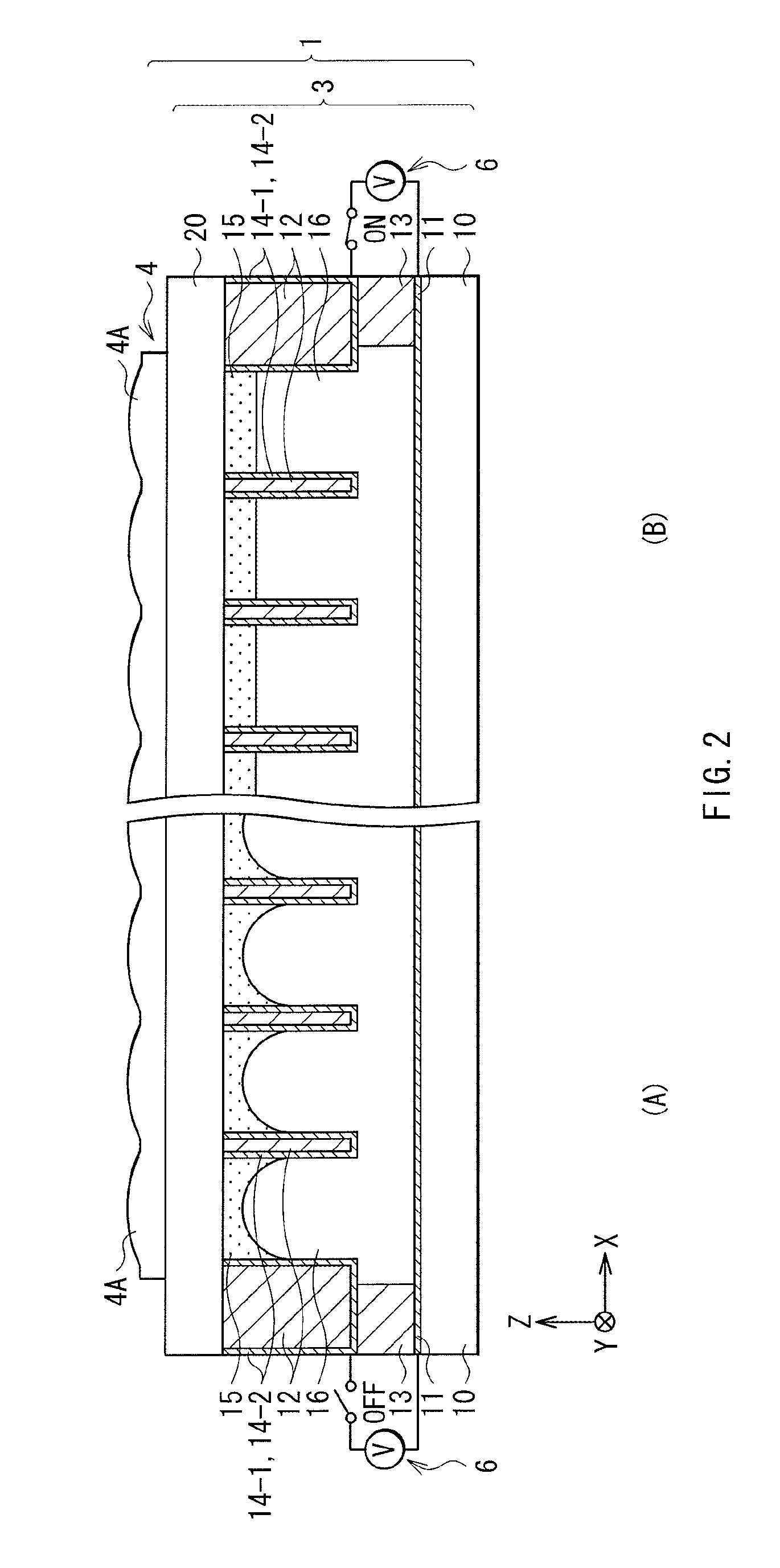
InactiveUS20110122128A1Small rangeDistance limitedSteroscopic systems3D-image renderingAutostereogramComputer science
Embodiments of the invention provide an image display device that is switchable between a two-dimensional display mode, a three-dimensional display mode enabling non-autostereoscopic image display, and a three-dimensional display mode enabling autostereoscopic image display. In one embodiment, the image display device comprises a display panel operable to transmit light corresponding to image data; a polarization state conversion section comprising a first polarization segment for converting light transmitted by the display device to a first polarization state, and a second polarization segment for converting light transmitted by the display device to a second polarization state; and an optical separation element that is placed, via application of a voltage, in an on state in which light transmitted by the display panel is refracted or an off state in which light transmitted by the display panel is not refracted.
Owner:SONY CORP
Autostereoscopic imaging device and system comprising it
InactiveUS6574042B2Blocking phenomenonColor television detailsStereoscopic photographyAutostereogramViewpoints
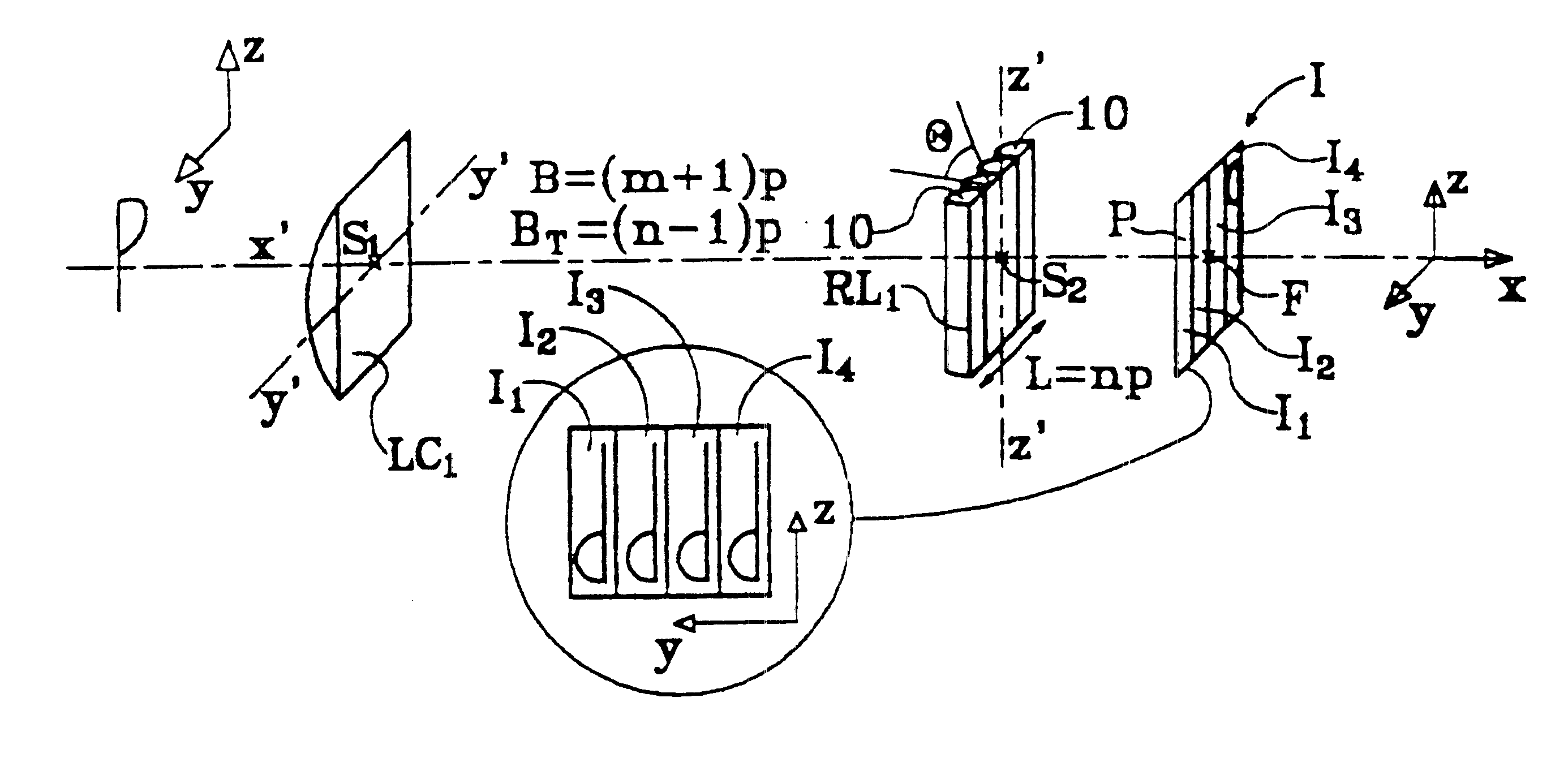
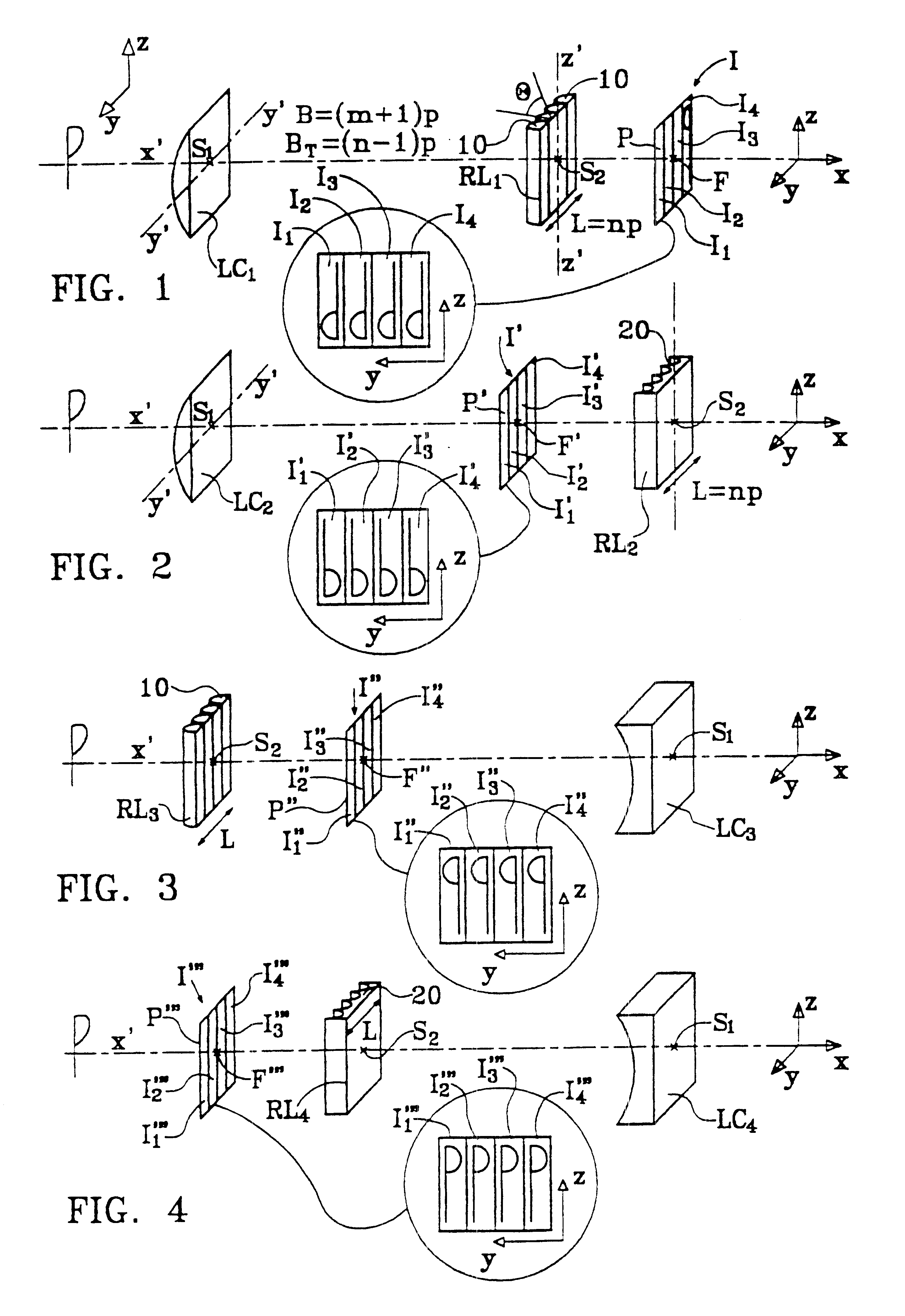
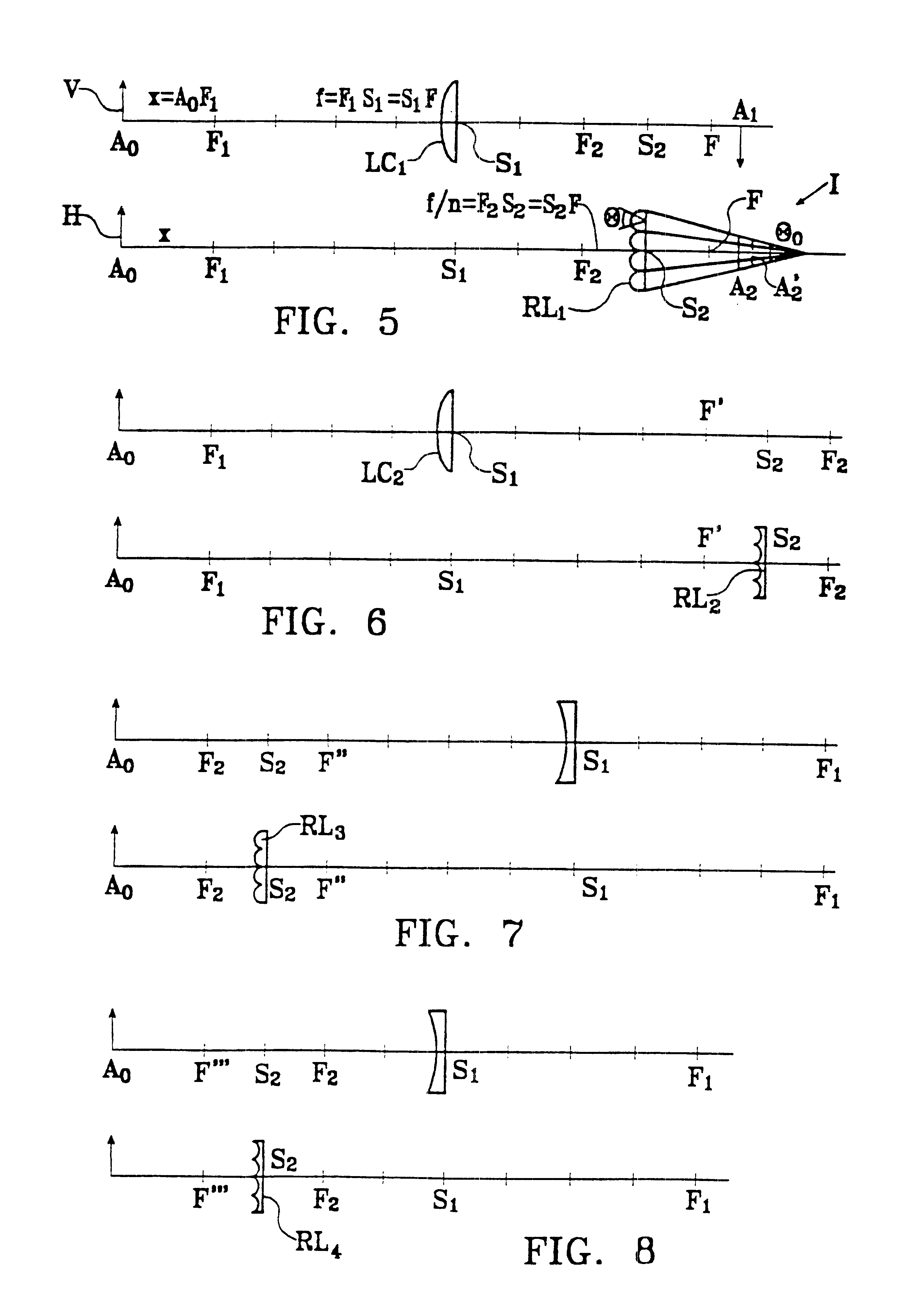
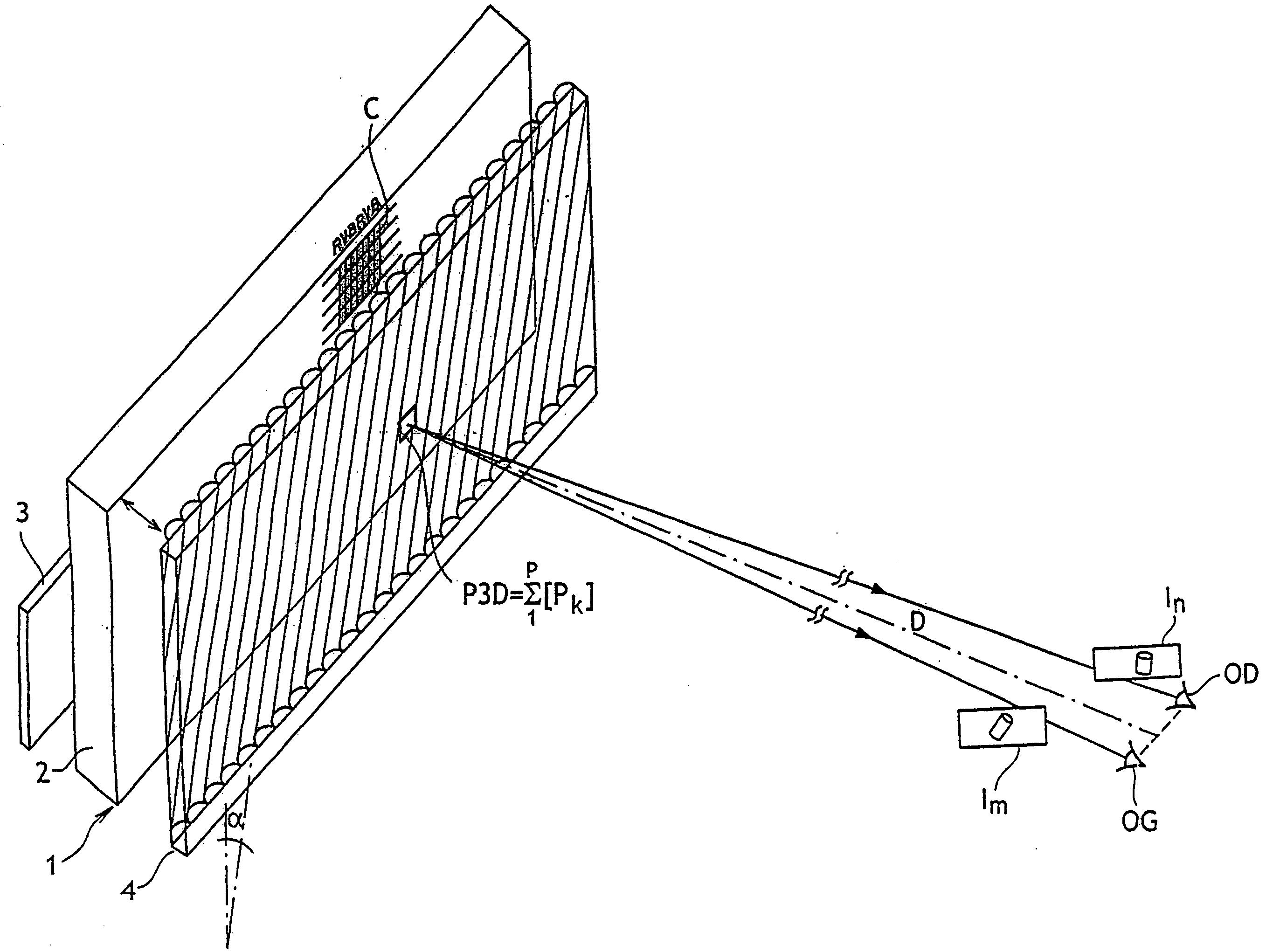
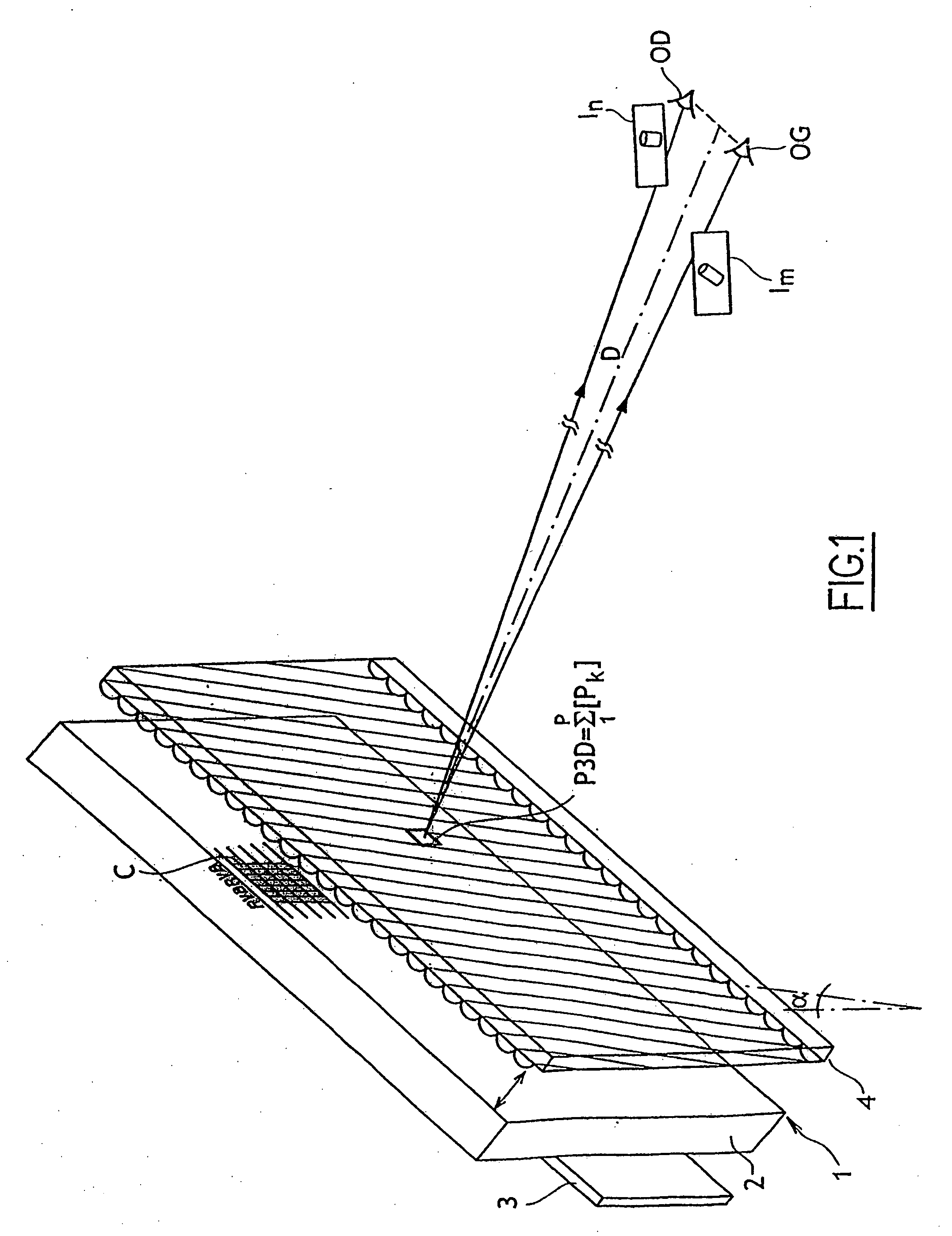
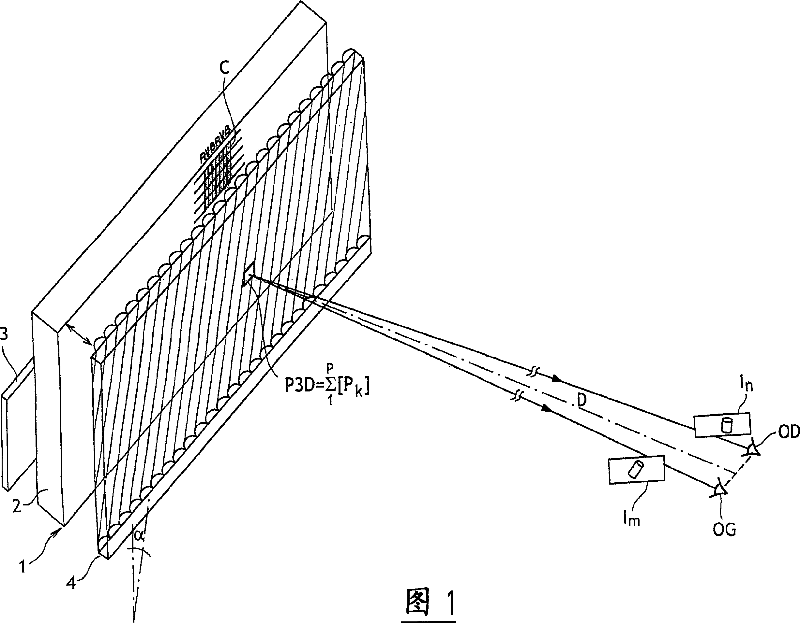
A device for forming an autostereoscopic image having n viewpoints, the device including a lens array (RL1) comprising cylindrical lens (10) having longitudinal axes parallel to a direction (zz') perpendicular to an optical axis (x'x) of the device. The device includes a cylindrical optical assembly whose longitudinal axis is perpendicular to zz' and to xx'. The lens array (RL1) comprises n cylindrical lens (10). The lens array (RL1) and the cylindrical optical assembly (LC1) share a common focusing plane (P) corresponding to a focusing distance DELTA. The absolute value of the ratio between the focal length of the cylindrical optical assembly and that of the lens array is substantially equal to n. Also provided is projection device implementing said image-forming device, and a projector projecting n flat elementary images, and a screen fitted with at least a projection array.
Owner:ALIOSCOPY
Parallax scanning through scene object position manipulation
One aspect of the invention includes and method of generating virtual autostereoscopic images using a computer. The method may include defining at least one object in a virtual three-dimensional space and defining a virtual point of view. Images may be generated by simulating a parallax scanning motion of the at least one object. The generated images and be displayed and stored.
Owner:VISION III IMAGING
Stereoscopic flat panel display with synchronized backlight, polarization control panel, and liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20110210964A1Quick displayCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsAutostereogramLiquid-crystal display
An enhanced liquid crystal display design is provided having relatively fast response time particularly useful in high speed or highly intense applications, such as stereoscopic or autostereoscopic image display. The liquid crystal display device is configured to display stereoscopic images, and comprises an LCD panel and control electronics configured to drive the LCD panel to a desired 10 stereoscopic display state. The control electronics are configured to employ transient phase switching and overdrive the LCD panel to a desired state to enable relatively rapid display of stereoscopic images.
Owner:REAID INC
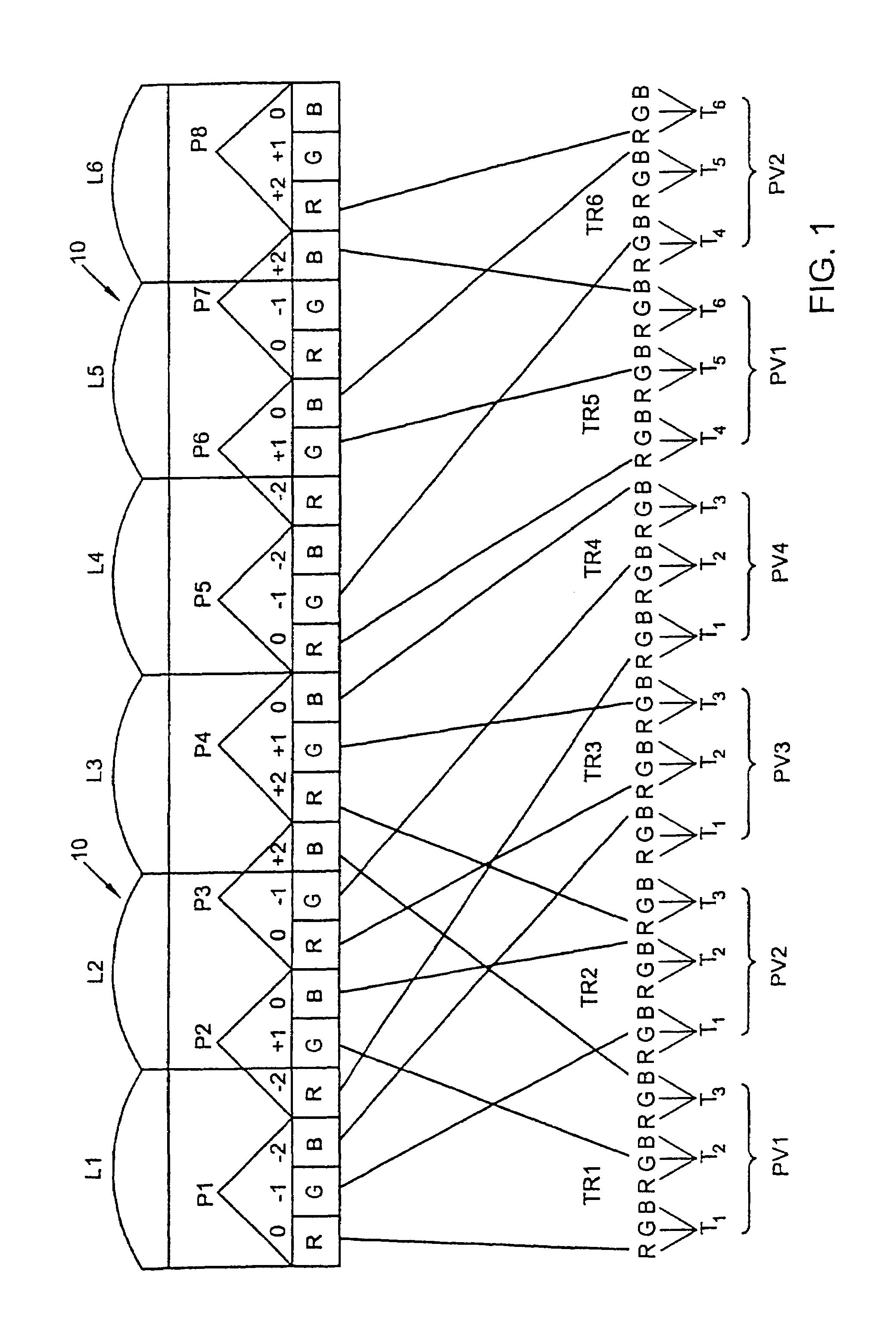
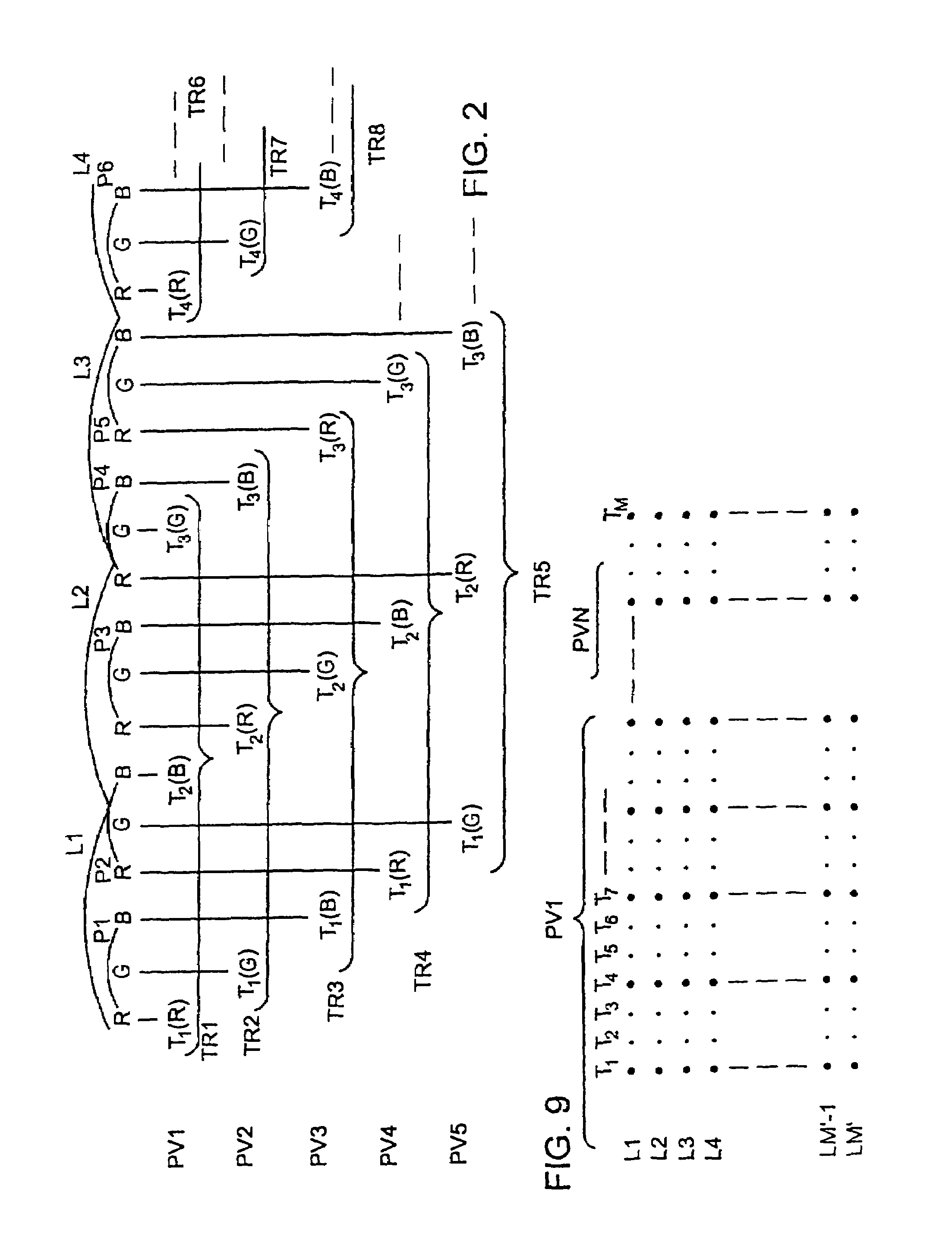
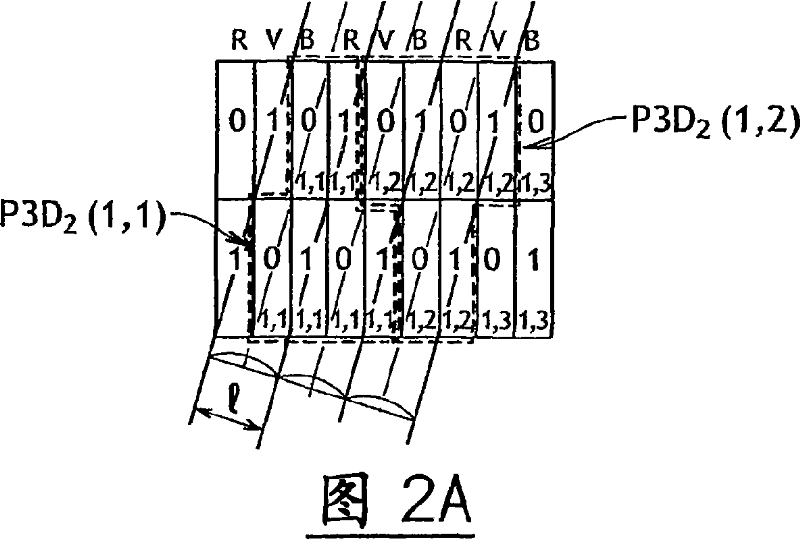
Lenticular Autostereoscopic Display Device and Method, and Associated Autostereoscopic Image Synthesising Method
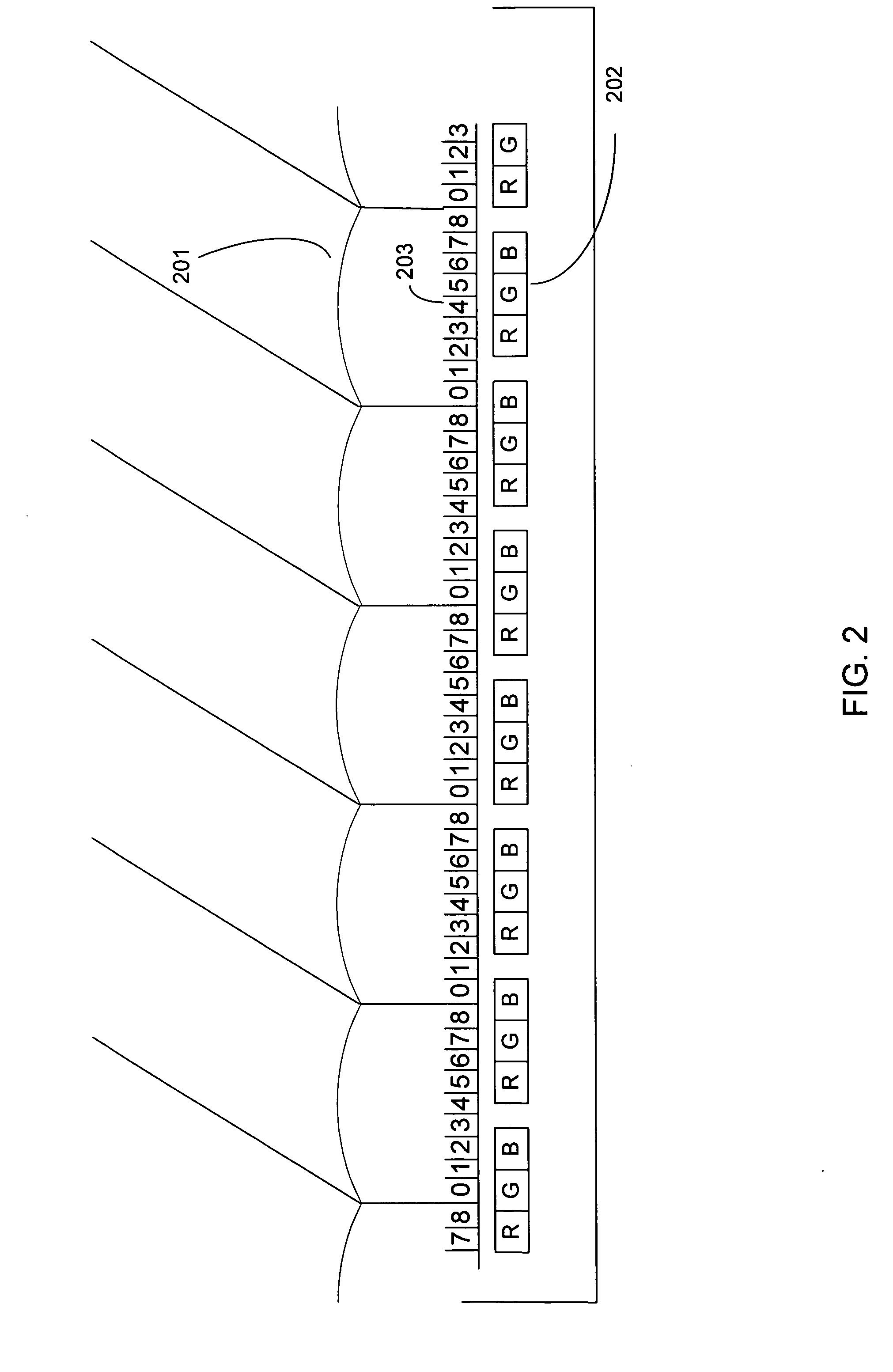
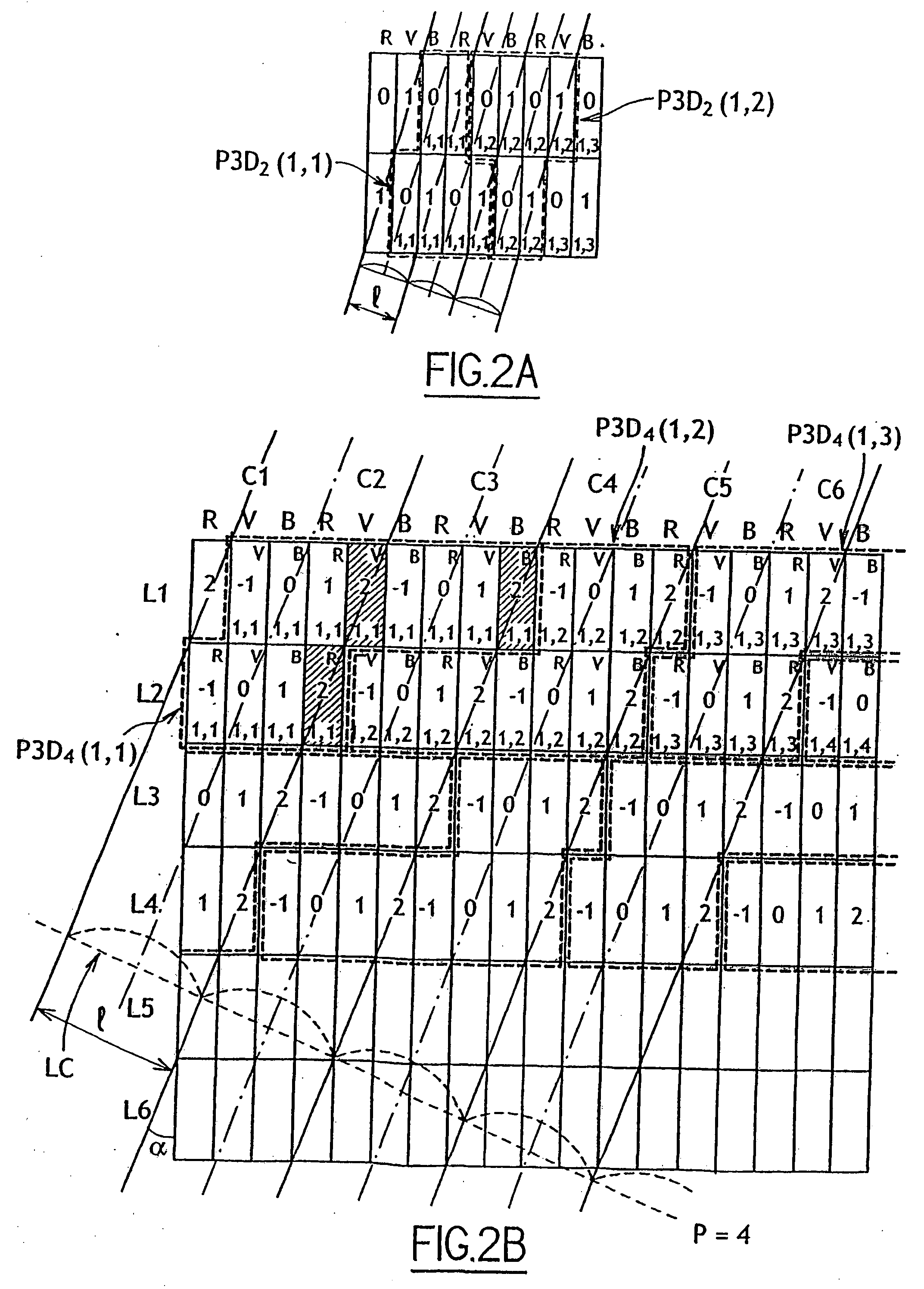
An autostereoscopic display device includes a matrix display screen and a lenticular array arranged in front of the display screen. The lenticular array is adapted to receive and optically process a raster image transmitted by the display screen, with the raster image being encoded in order to integrate a plurality P of viewpoints of a same scene. The display screen includes a matrix of screen pixels, each of which includes three color cells organized in rows and columns laid out so as to form columns of a same color within the screen. The image transmitted by the display screen comprises a set of three-dimensional pixels, each integrating the plurality P of viewpoints of an image pixel of the scene, and each three-dimensional pixel occupying 3×P color cells in two adjacent rows within the screen.
Owner:ARTISTIC IMAGES
Method for auto-stereoscopic image display with a wavelength filter array
InactiveUS20040245440A1Quality improvementHigh image densityRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansAutostereogramWavelength filter
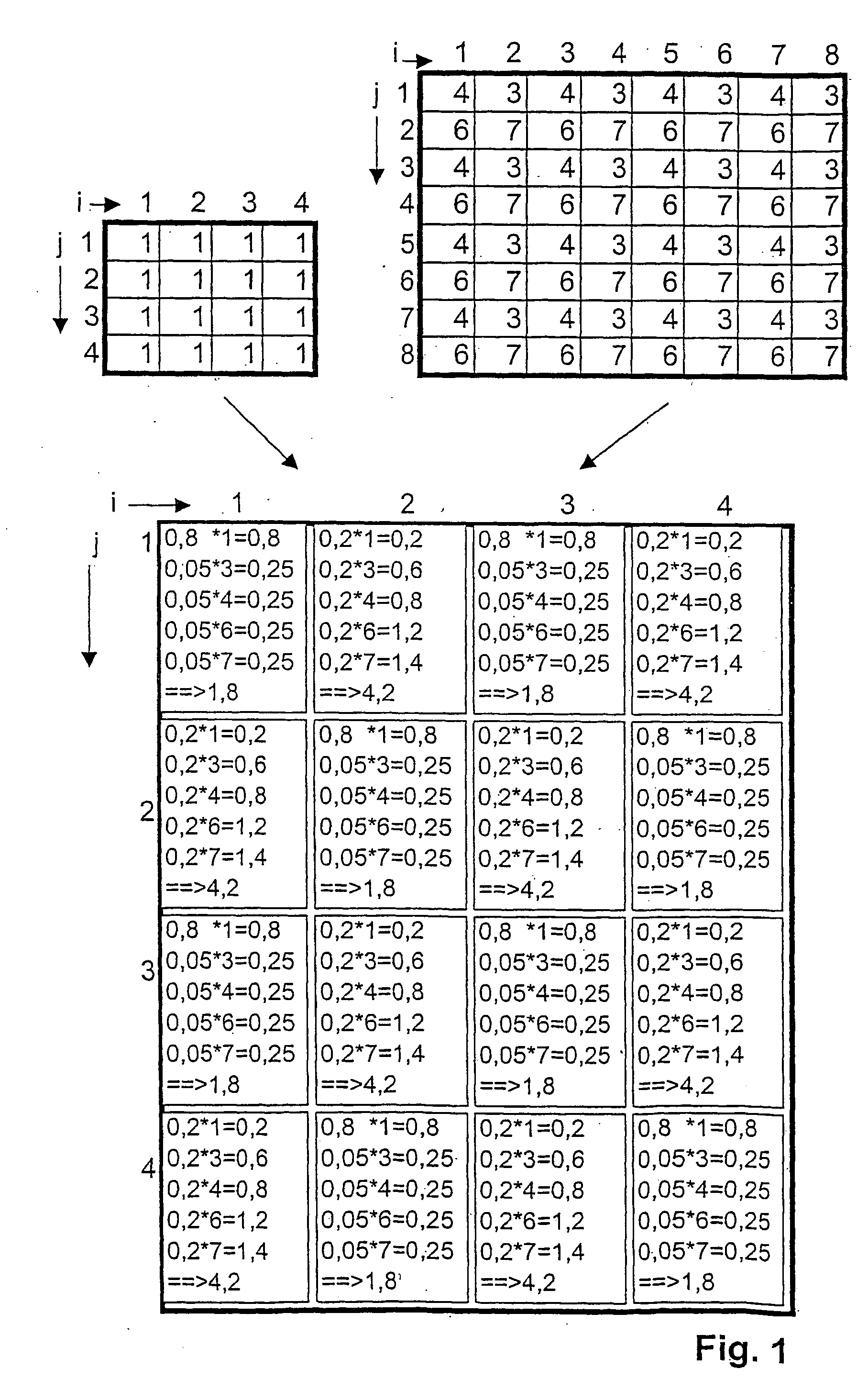
The invention relates to a method of spatial visualization of a scene or an object, in which several views of the scene or object are decomposed into bits of partial information, which are made optically visible by image rendering elements, and in which neighbored image rendering elements emit light of different wavelengths or wavelength ranges, and in which propagation directions for the light are given by means of wavelength filters in such a way that an observer will see predominantly bits of partial information of a first selection of views with one eye and predominantly bits of partial information of a second selection with the other eye. The invention is intended to improve the quality of spatial visualization. In such a method, at least one image rendering element is simultaneously allocated bits of partial information from at least two different views, the allocation being made in such a way that the wavelength of the partial information is always equal to the wavelength, or lies in the wavelength range, of the light emitted by the allocated image rendering element.
Owner:PHOENIX 3D
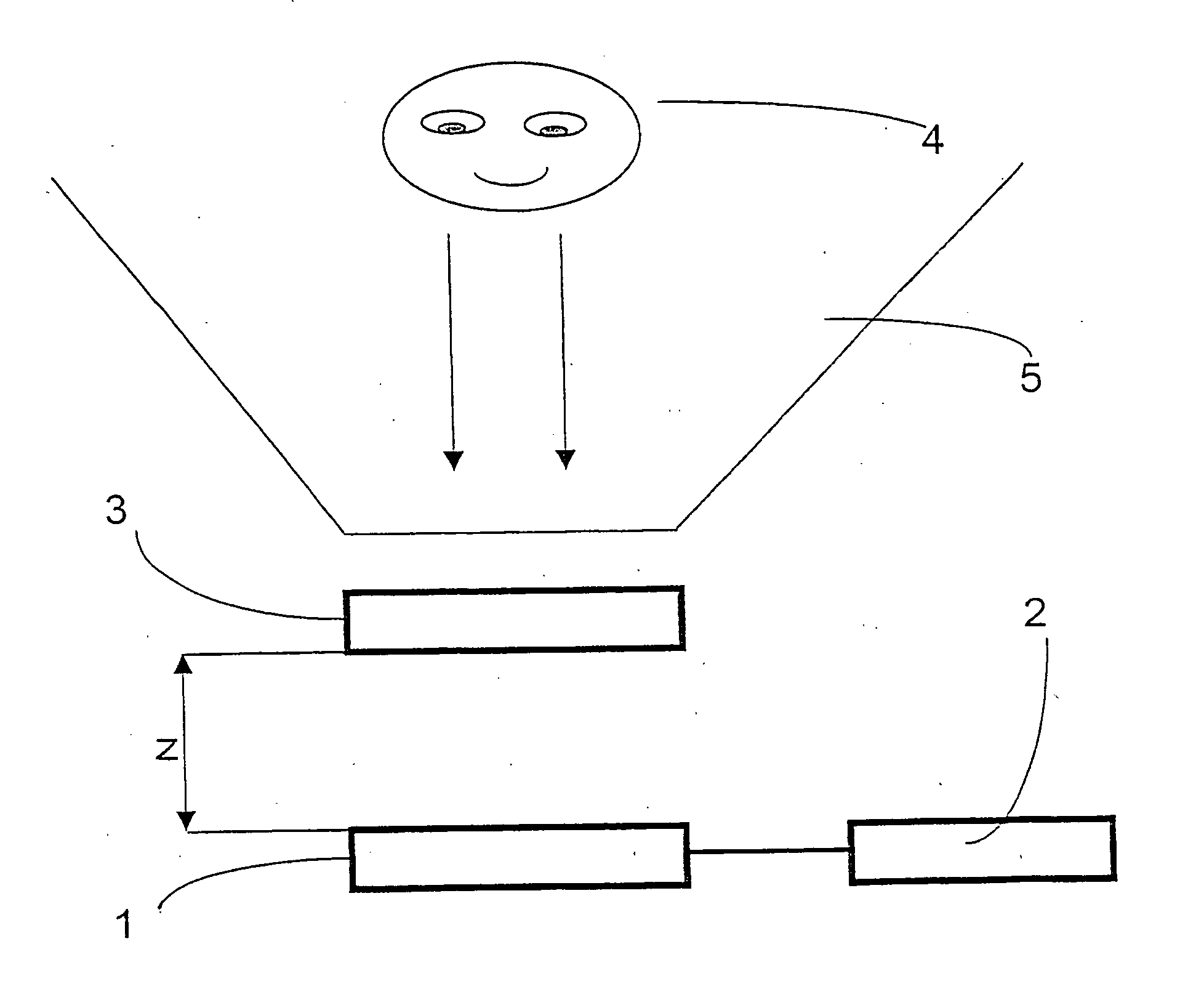
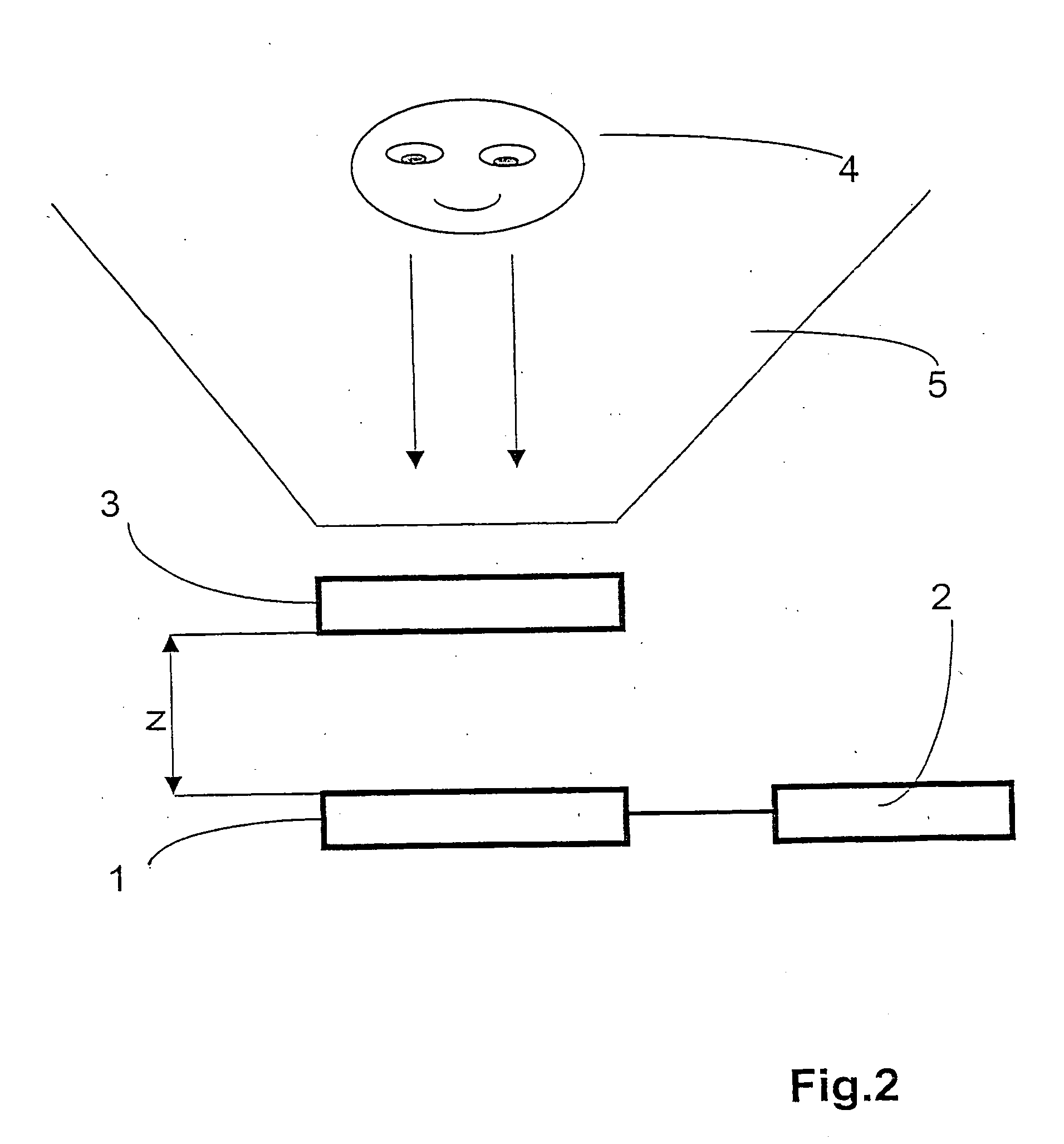
Display device
A one-pixel structure of a display panel included in an auto-stereoscopic image display device adopts an in-plane switching mode. Transparent counter electrodes that are not provided in a liquid crystal panel of a normal in-plane switching mode are formed correspondingly to pixel peripheral regions on a second transparent substrate side and, in 3-dimensional image display, a vertical electric field is forcibly generated between the transparent counter electrodes and the comb-shaped electrodes, which causes the liquid crystal molecules to rise to show black display in the pixel peripheral regions. In 2-dimensional image display, meanwhile, the transparent counter electrodes are set to be floating, and the display panel is caused to have a structure substantially equivalent to a structure in which the transparent counter electrodes are not provided, to thereby make the display in pixel peripheral regions identical to the display (brightness) in a pixel main region.
Owner:TRIVALE TECH LLC
Autostereoscopic image display and method for driving the same
ActiveUS20140125783A1Avoid flickeringCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsAutostereogramOptical axis
An autostereoscopic display and a method for driving the same are discussed. The autostereoscopic display according to an embodiment includes a display panel displaying data of a left eye image and data of a right eye image and a three-dimensional (3D) cell which is positioned on the display panel or is embedded in the display panel and separates optical axes of the left eye image and the right eye image. A frame rate of the 3D cell is greater than a frame rate of the display panel.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Moiré-based auto-stereoscopic watermarks
ActiveUS7706025B2Other printing matterPaper-money testing devicesAutostereogramComputer graphics (images)
Provided herein are teachings directed to the creation of moiré-based auto-stereoscopic watermarks in rendered images. By choosing different halftone structures, which differ by having different spatial frequencies for each of two delineated partitions in an image, it becomes possible to embed arbitrary binary patterns into printed documents as digital watermarks. The invisible watermarks become moiré auto-stereoscopic images when the prints are viewed through an overlaid transparency “decoder” suitably prepared by virtue of being rendered with a uniform halftone structure having the correct special frequency in relationship with the partition frequencies employed in the printed document.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Resolution For Autostereoscopic Video Displays
ActiveUS20170195580A1FocusTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAutostereogramStereoscopic video
A single pixel of a video display can display respective individual pixels of multiple views. In other words, a video display can include more views for an autostereoscopic image than the physical pixels of the video display would ordinarily support. The physical pixel is time-multiplexed in that the physical pixel displays a pixel of one view for a given time interval and a view multiplexer deflects the light from the physical pixel by a predetermined angle to make the pixel appear in a location corresponding to the pixel of the view. In another time interval, the physical pixel displays a pixel of a different view and the view multiplexer deflects light from the physical pixel by a different predetermined angle to make the pixel appear in a location corresponding to the pixel of the different view.
Owner:SOLIDDD
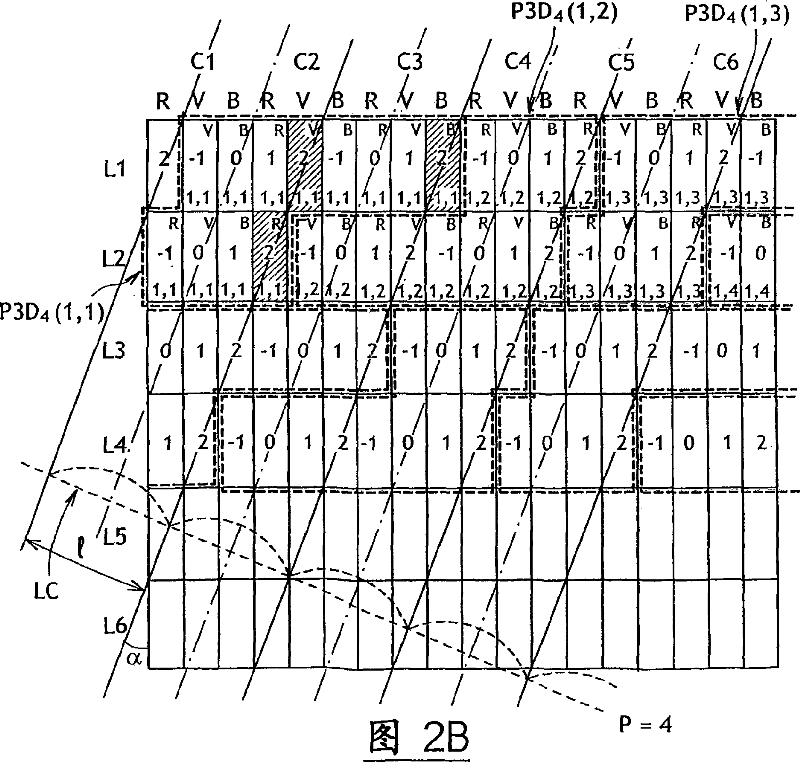
Lenticular autostereoscopic display and method and associated autostereoscopic image synthesising method
A autostereoscopic display device comprises a matrix display screen (2) and a lenticular array (4) which is disposed in front thereof and an lenticular axis inclined with respect to the vertical axis of said display screen (2), wherein said lenticular array (4) is arranged in such a way that it receives and optically processes a raster image transmitted by the display screen, said raster image is encoded for integrating a plurality (P) of viewing points of the same scene, the display screen comprises an array of image pixels each of which comprises three colour cells organised in rows and columns and disposed in such a way that columns of the same colour (R, V, B) are formed within the screen. The image emitted by the display screen (2) is formed by the assembly of three-dimensional pixels (P3D) each of which integrates the plurality (P) of viewing points of the scene pixel image and each three-dimensional pixel (P3D) occupies 3xP colour cells on two adjacent rows within the screen. Said invention is used, in particular for three-dimensional computer and TV set screens.
Owner:ARTISTIC IMAGES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com