Patents
Literature
38results about How to "Improve ESD tolerance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
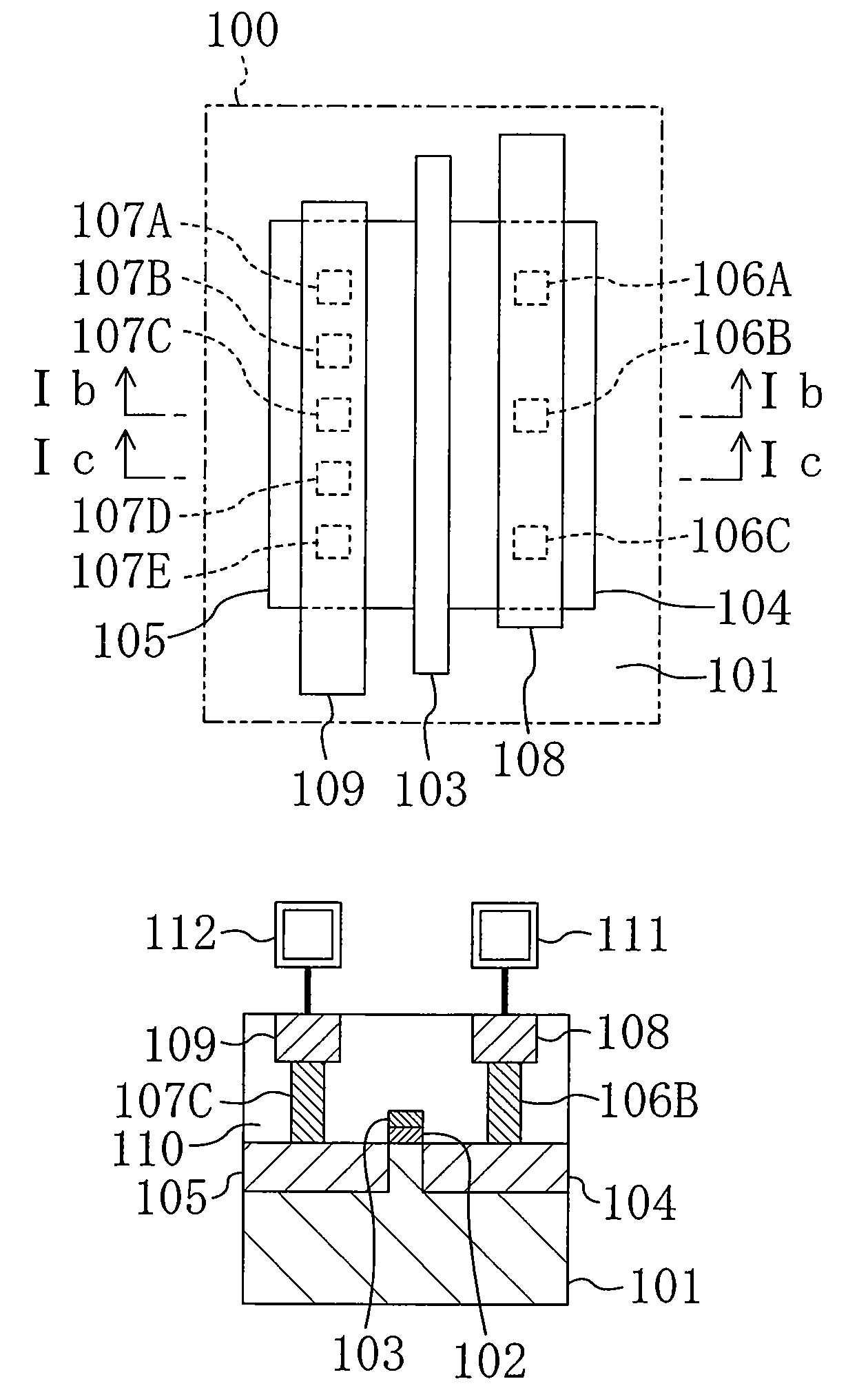
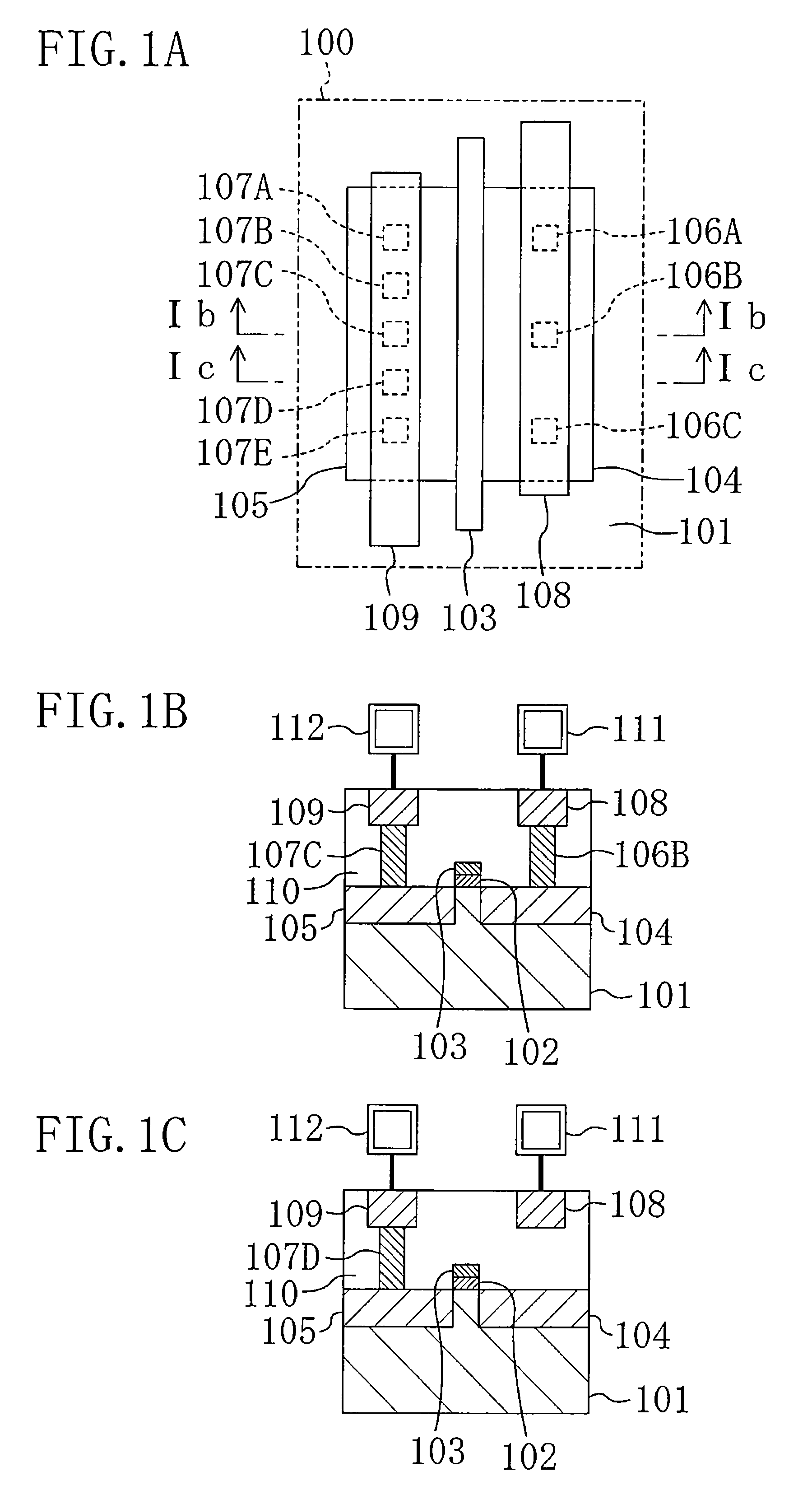
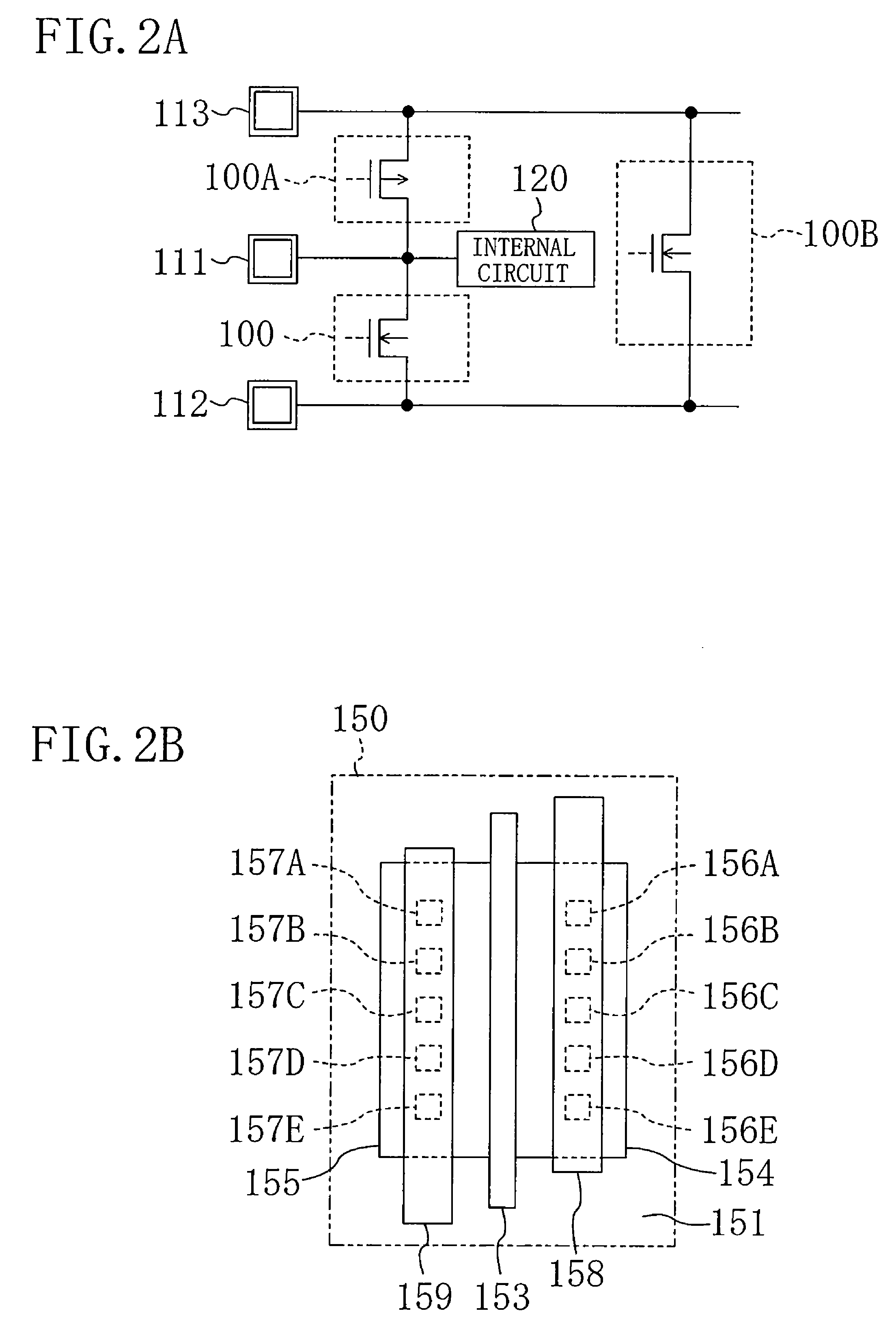
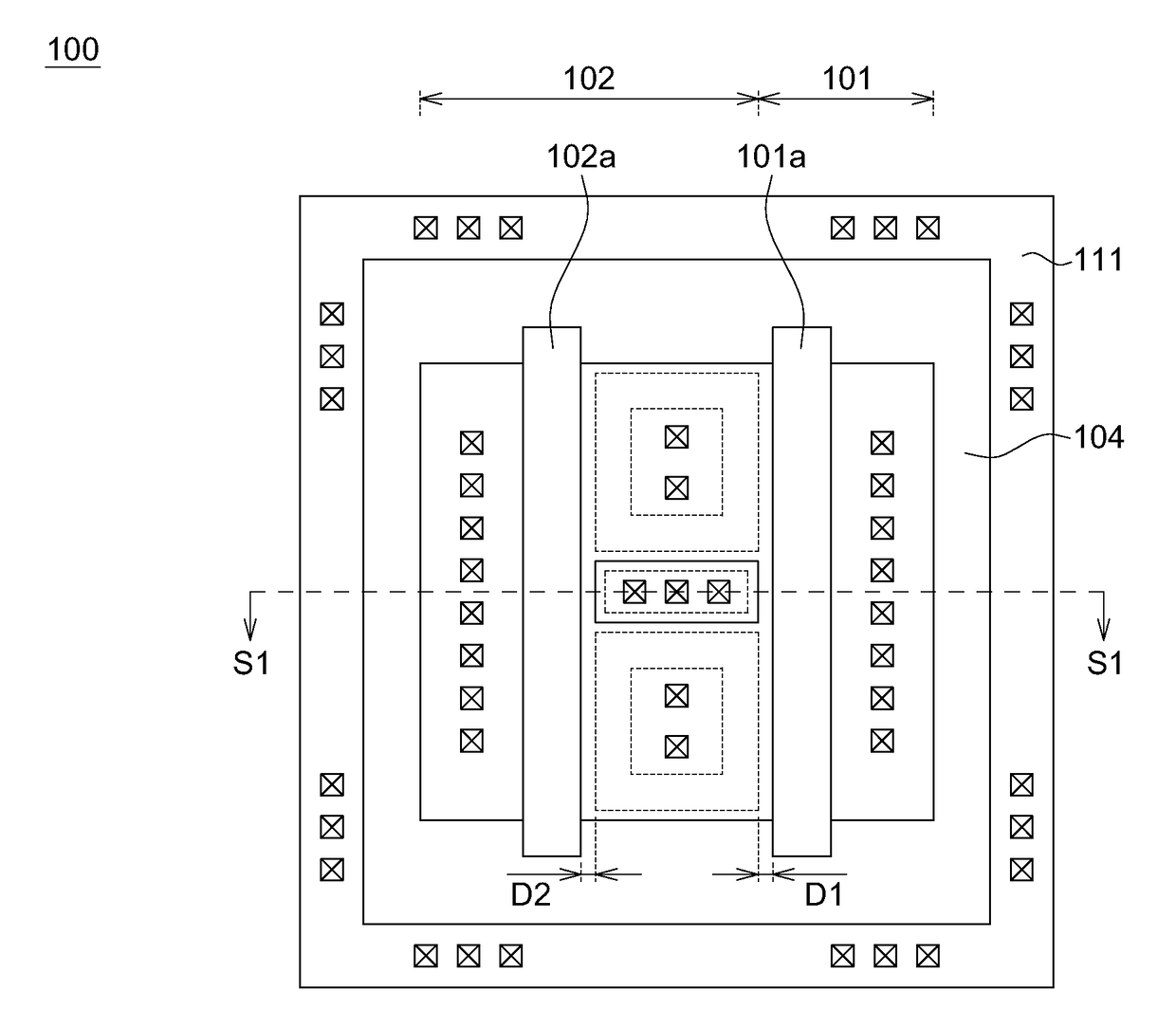
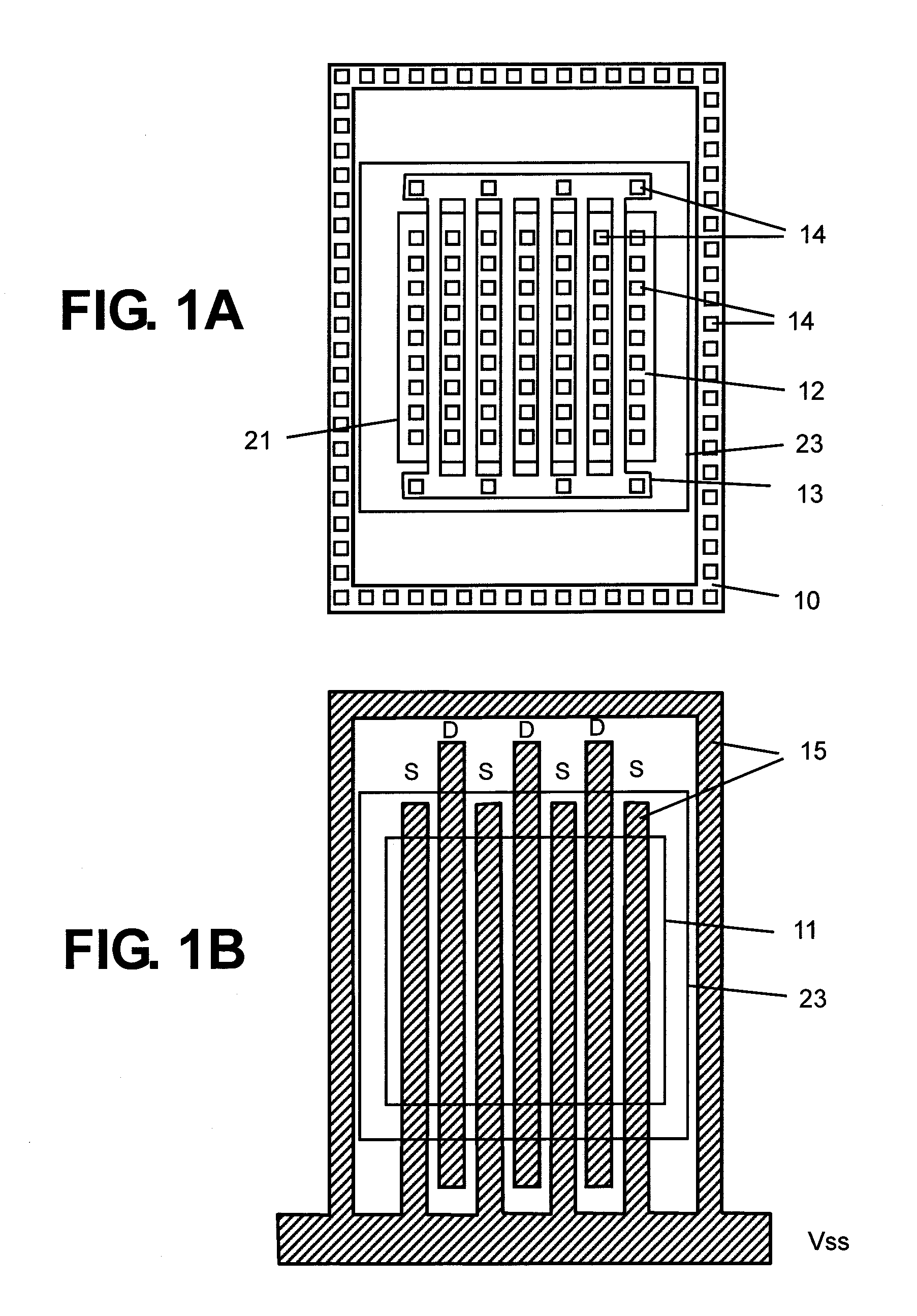
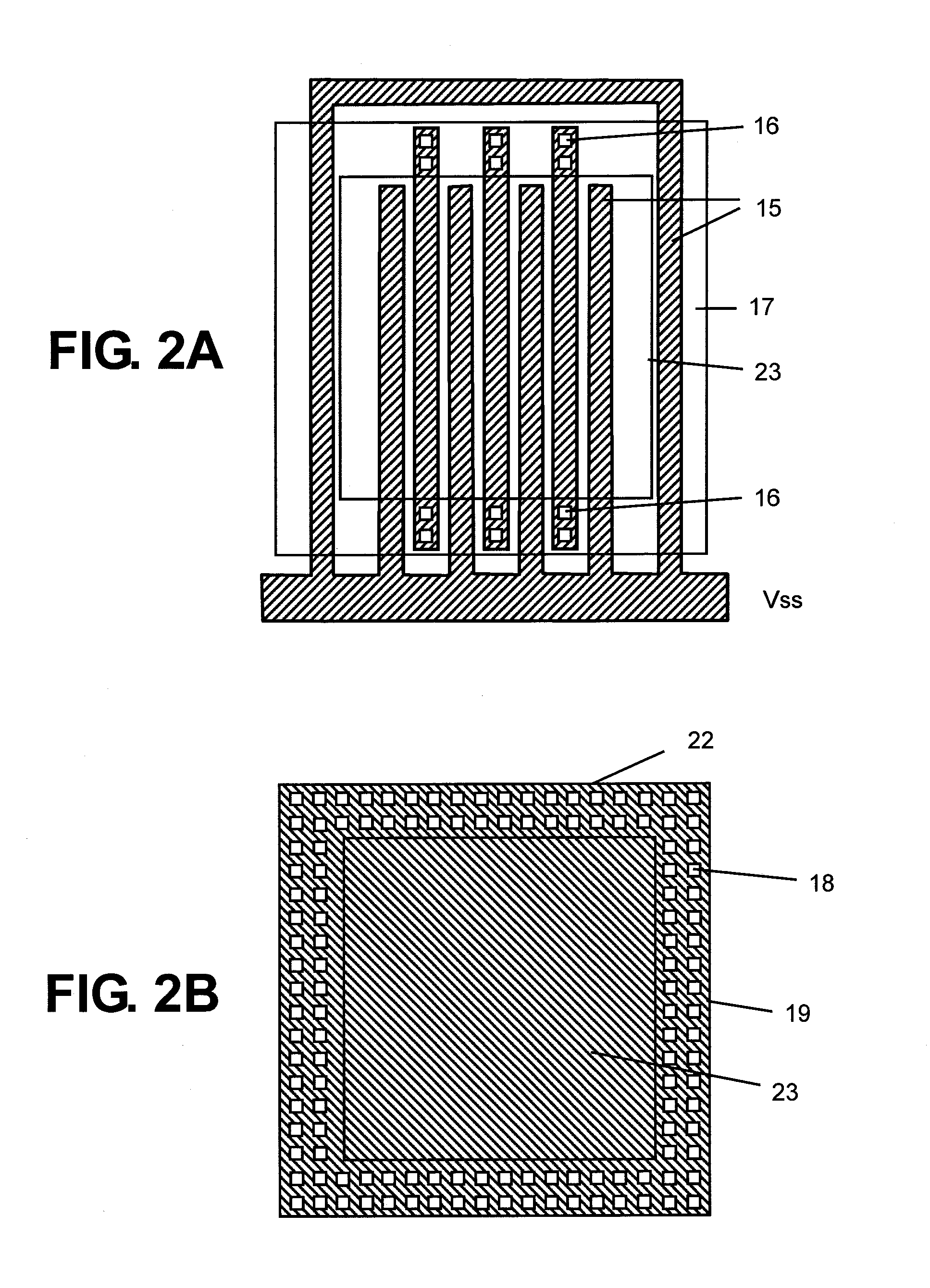
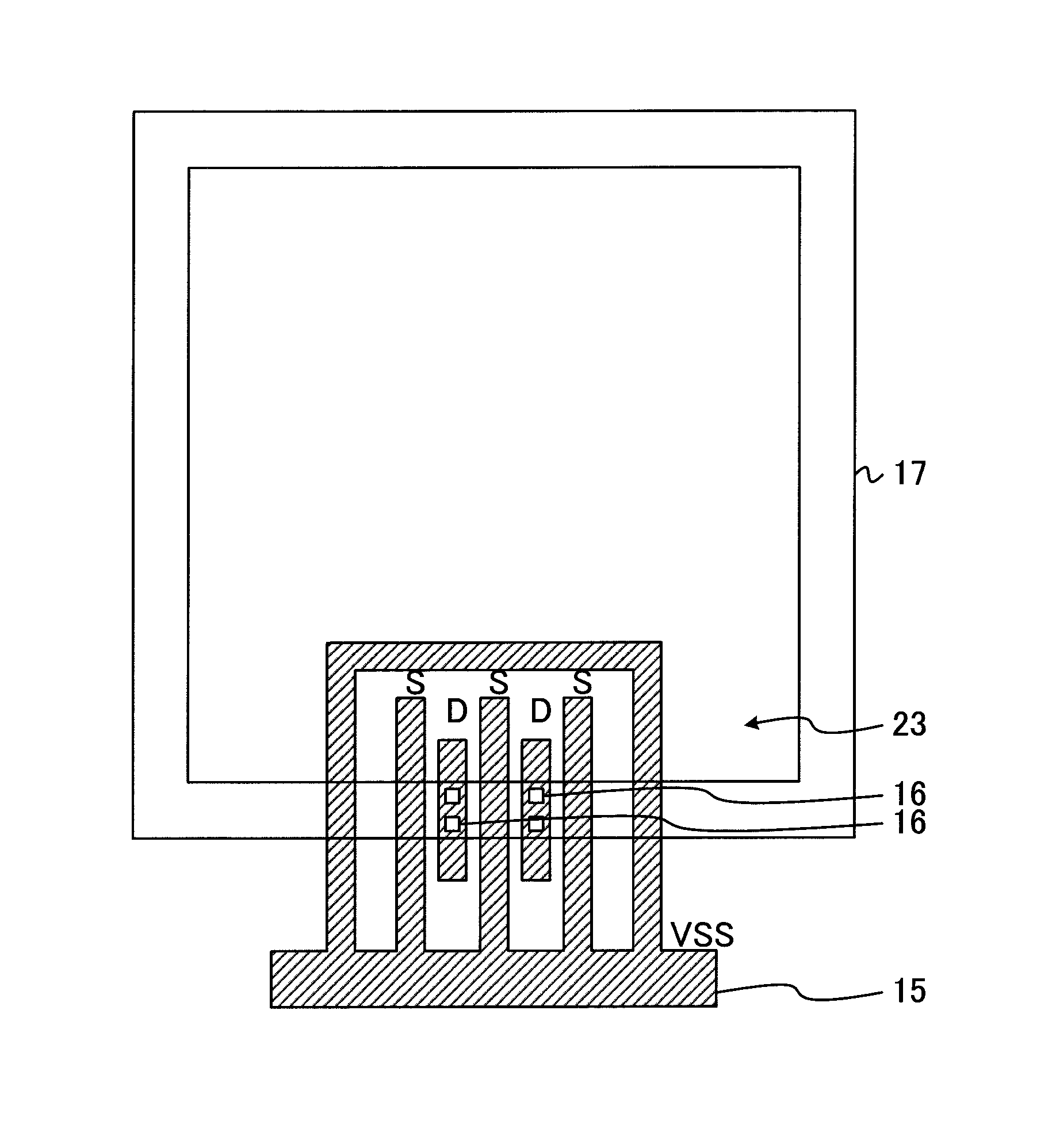
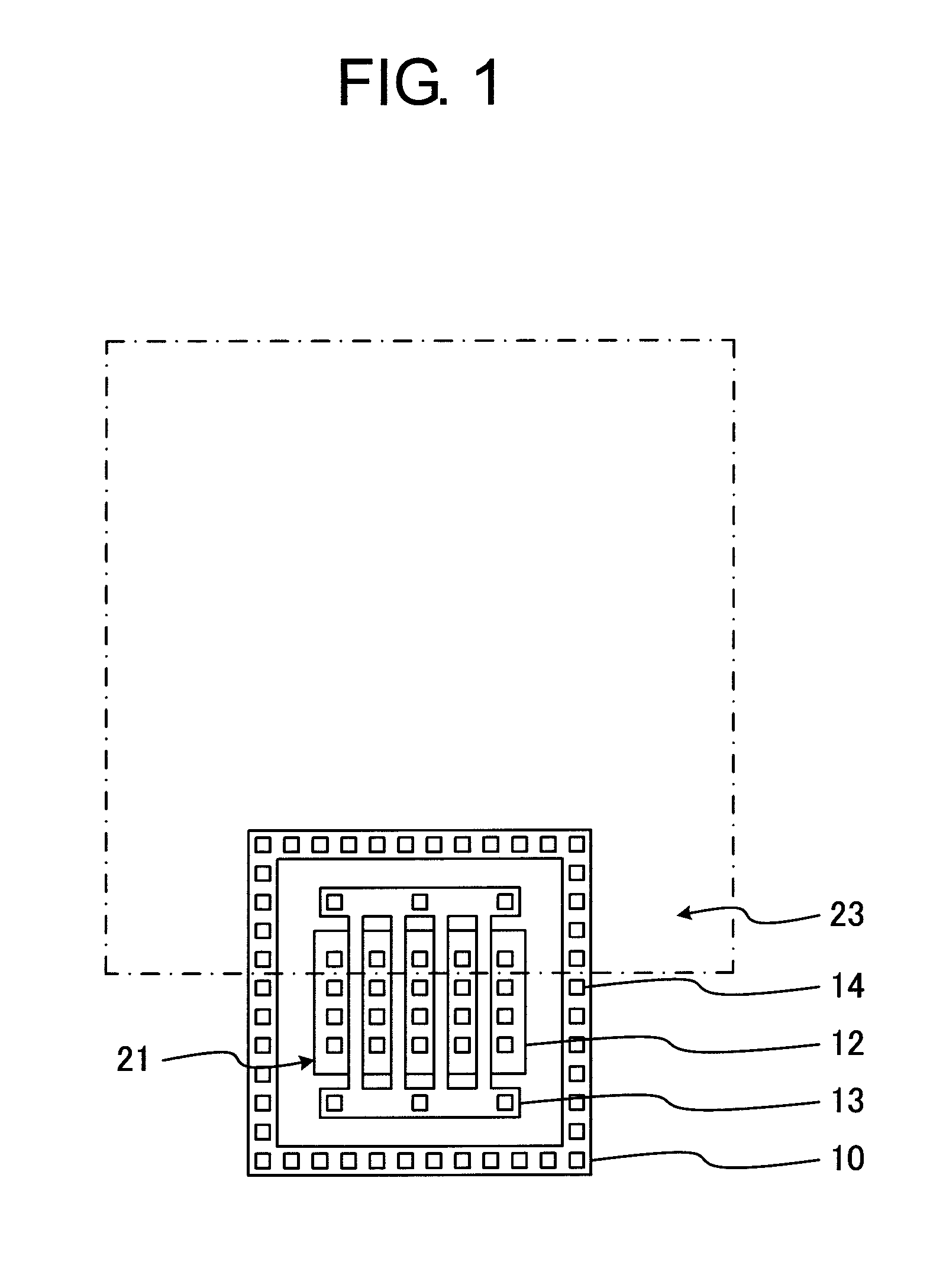
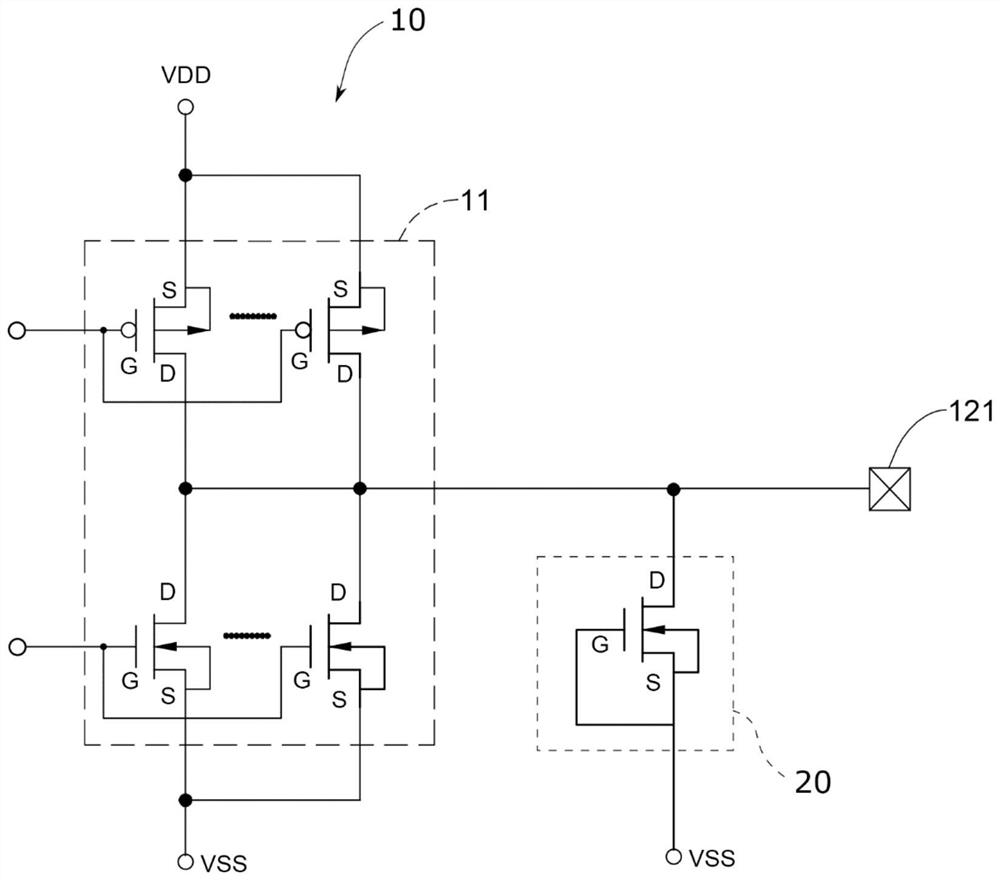
ESD protection for integrated circuits
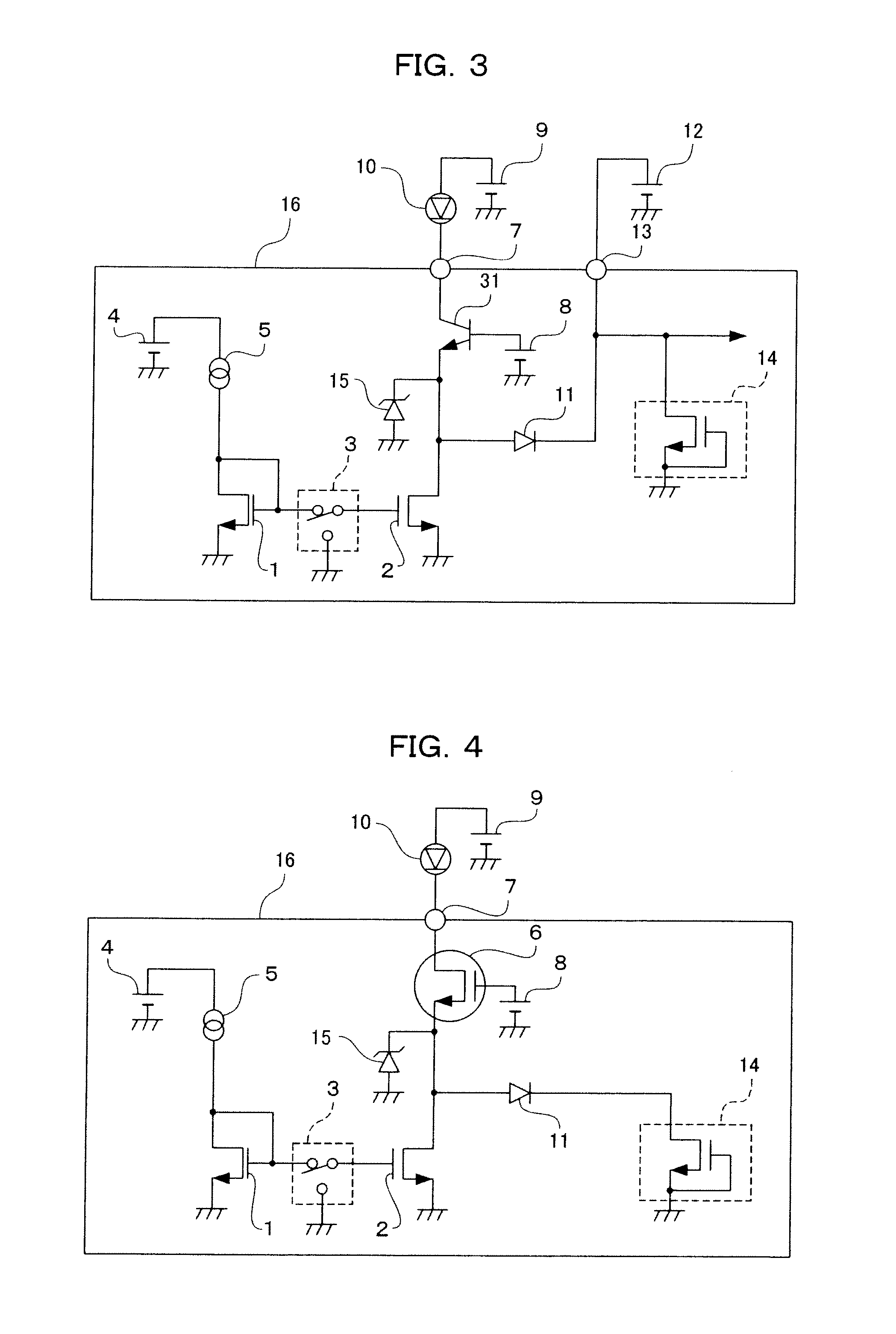
InactiveUS20050275027A1Improve ESD toleranceSimple structureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCMOSMOSFET
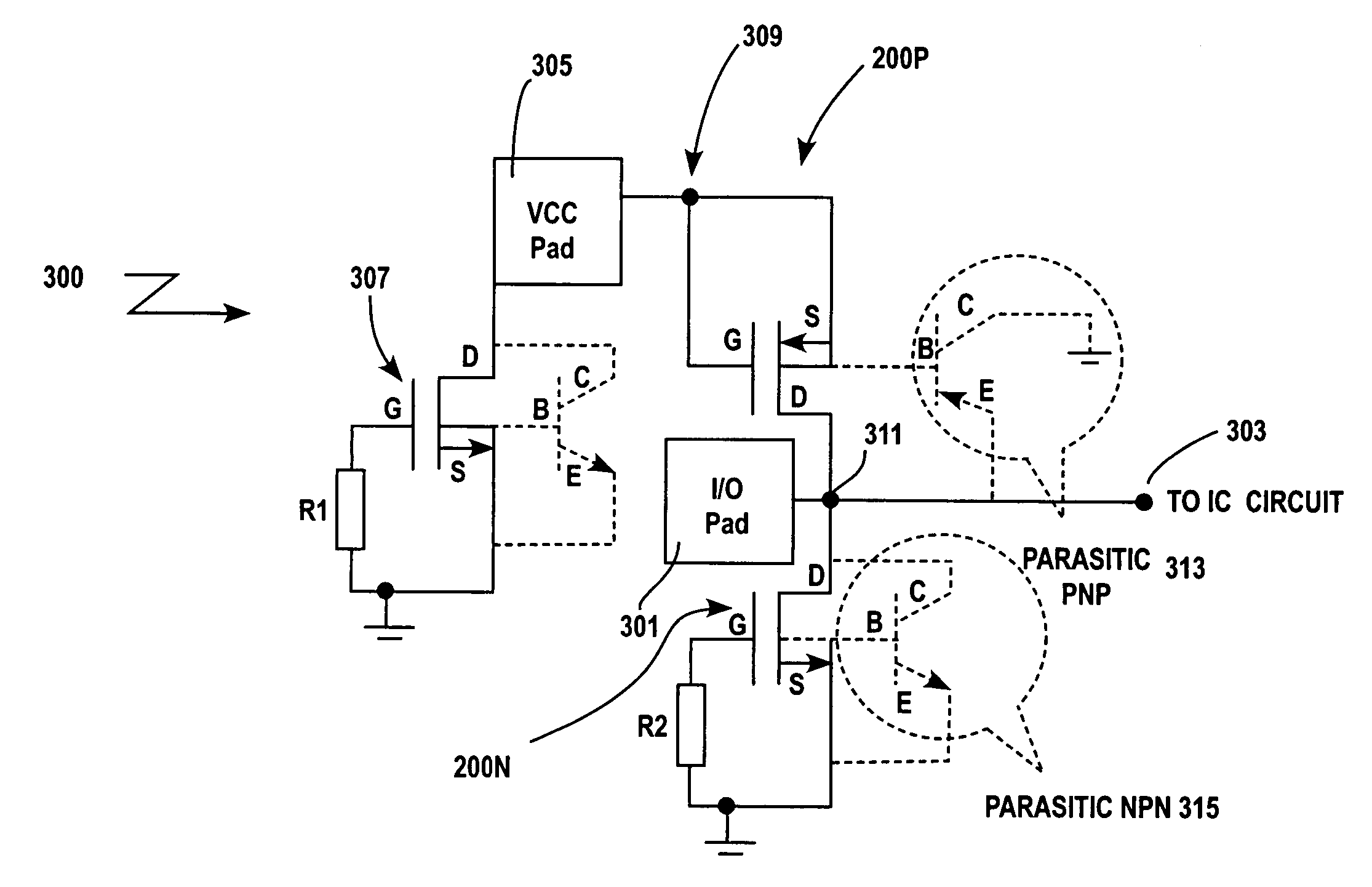
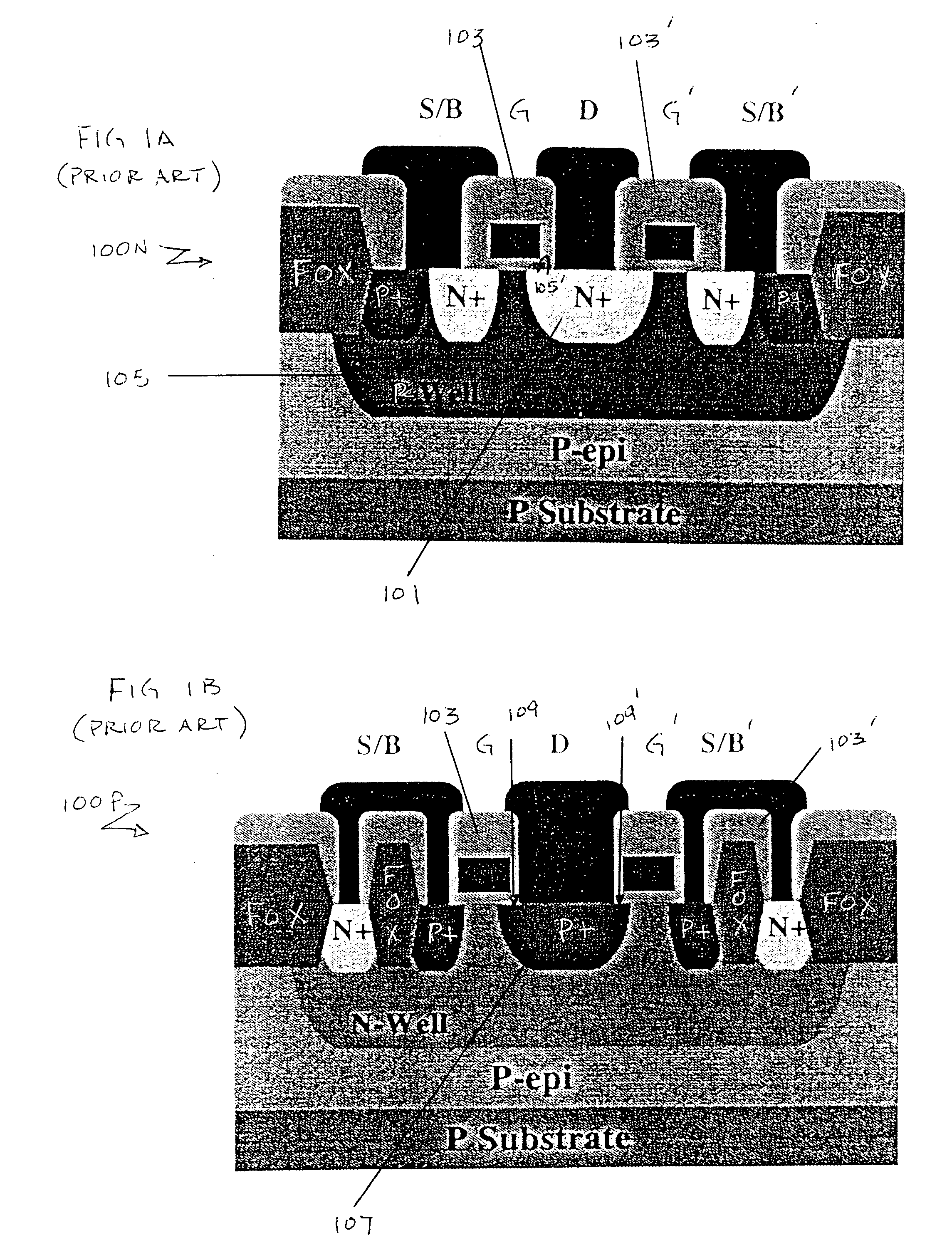
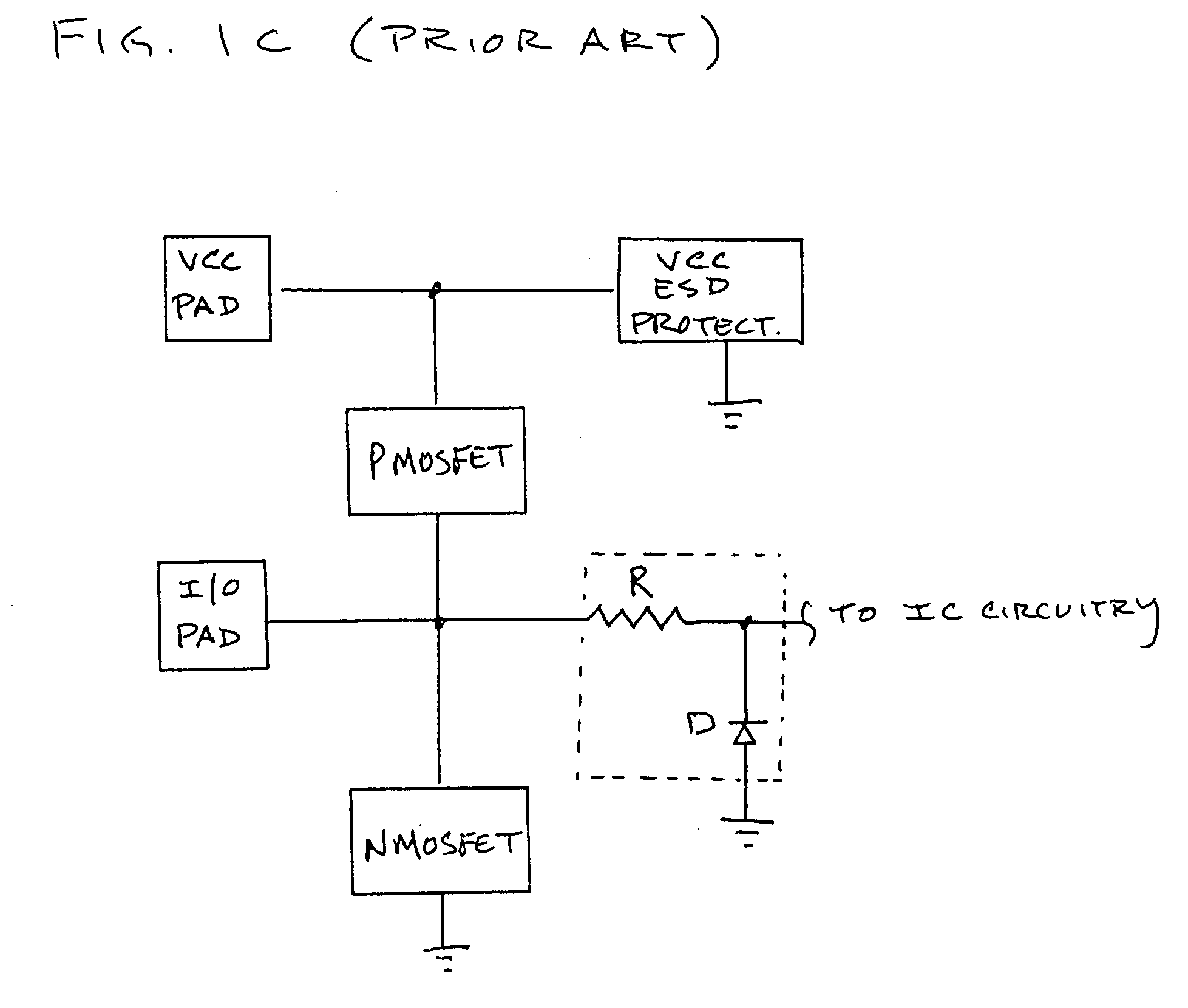
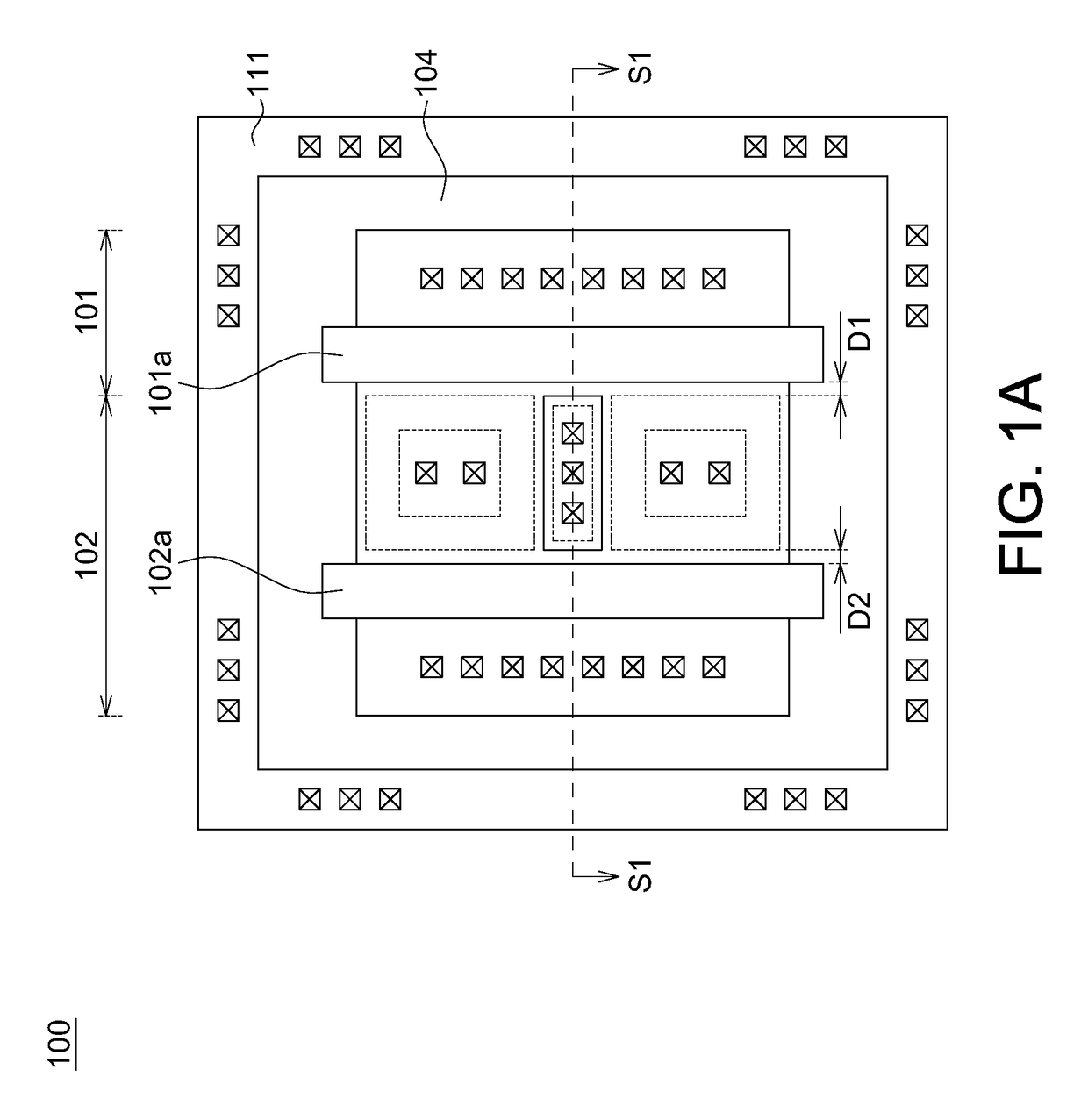
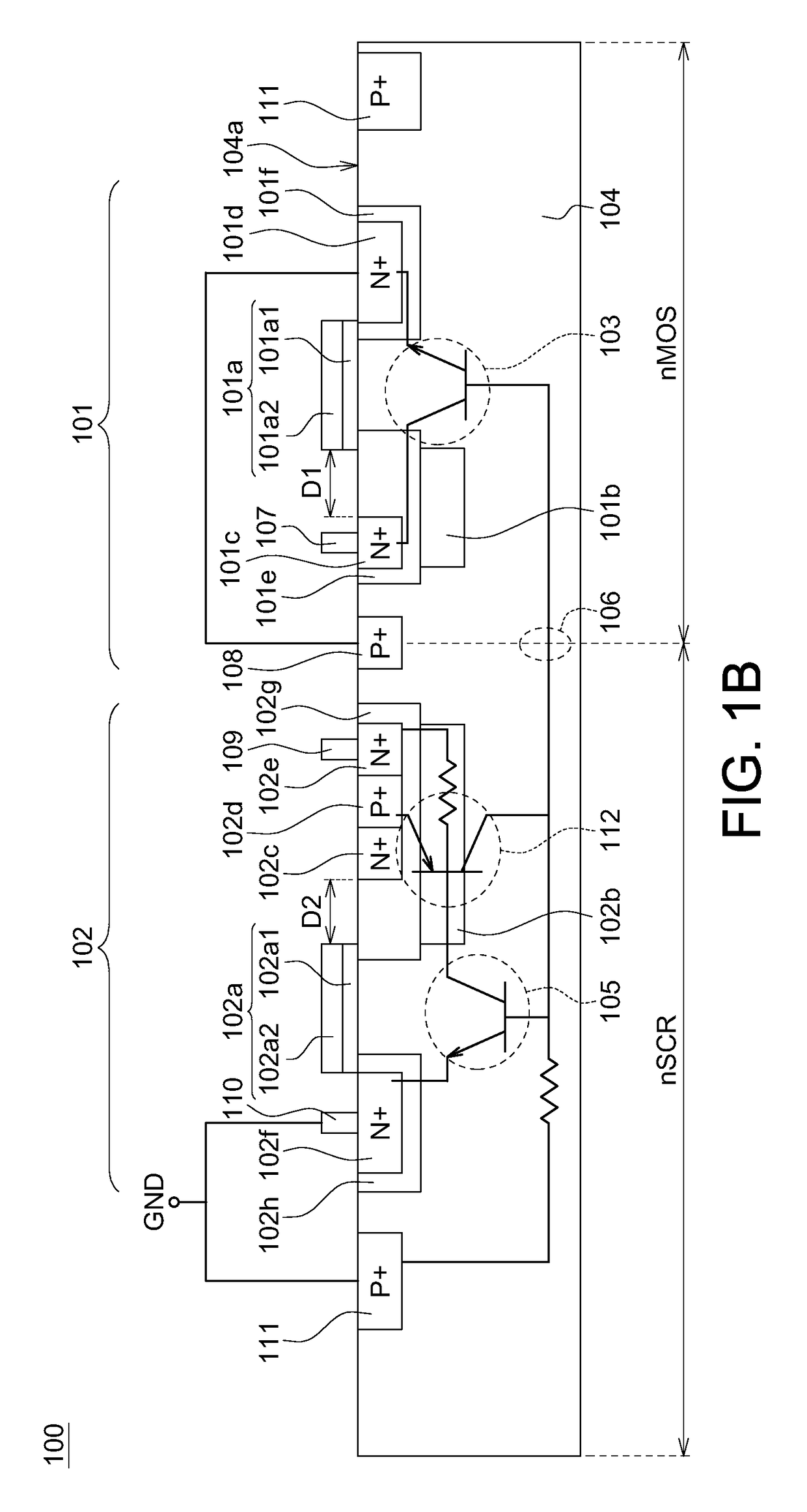
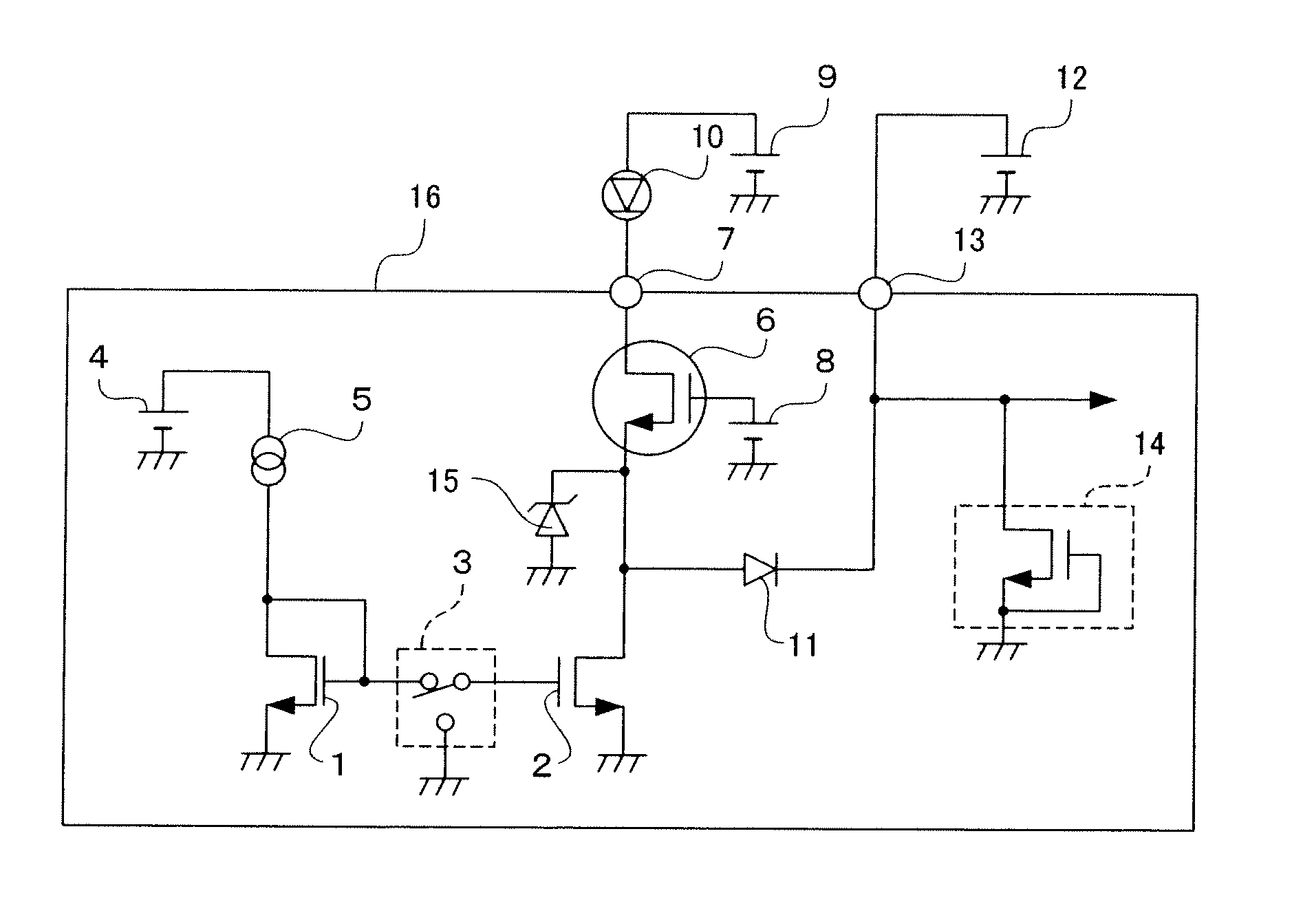
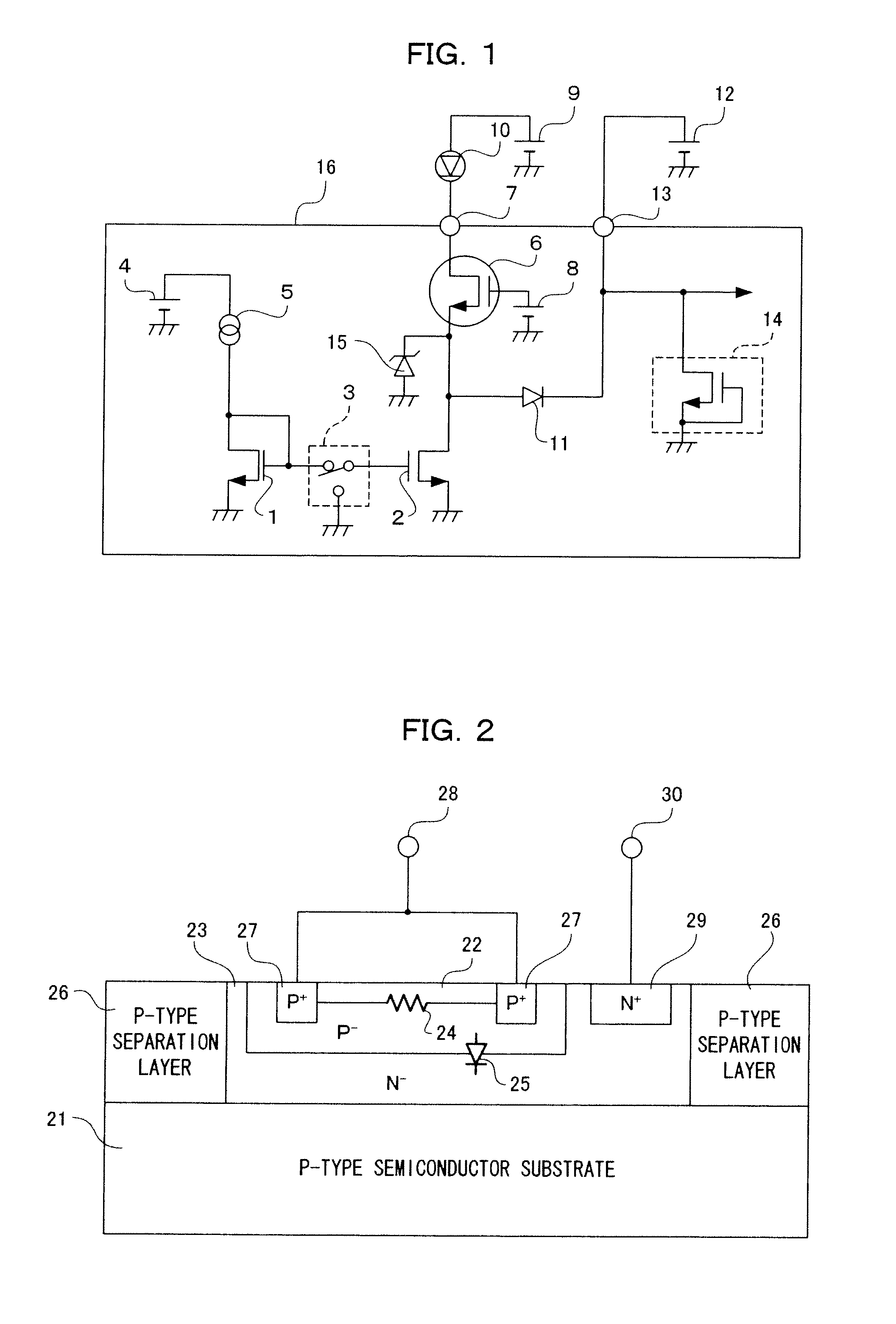
Electrostatic discharge protection for integrated circuits, particularly for enhancing electrostatic discharge protection performance for Input-output cells and power supply clamps used in CMOS and BiCMOS IC technologies is described. A P-type, implantation region, or layer, referred to as “P-deep,” in both N-MOSFET and P-MOSFET devices is provided to enhance electrostatic discharge protection performance. Parasitic transistor gain is enhanced by providing the P-deep region subposing the drain contact. Exemplary embodiments for N-type and P-type MOSFETs, MOSFETs with surface diodes, MOSFETS with SCRs, and push-pull Input-output CMOS circuits are described.
Owner:MICREL
Device for ESD protection circuit
A LDNMOS device for an ESD protection circuit including a P-type substrate and an N-type deep well region is provided. The P-type substrate includes a first area and a second area. The N-type deep well region is in the first and second areas of the P-type substrate. The LDNMOS device further includes a gate electrode disposed on the P-type substrate between the first and second areas, a P-type implanted region disposed in the first area of the P-type substrate, an N-type grade region disposed in the N-type deep well region of the first area, an N-type first doped region disposed in the N-type grade region, a P-type body region disposed in the N-type deep well region of the second area, an N-type second doped region disposed in the P-type body region, and a P-type doped region disposed in the P-type body region and adjacent to the N-type second doped region.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor apparatus and manufacturing method thereof
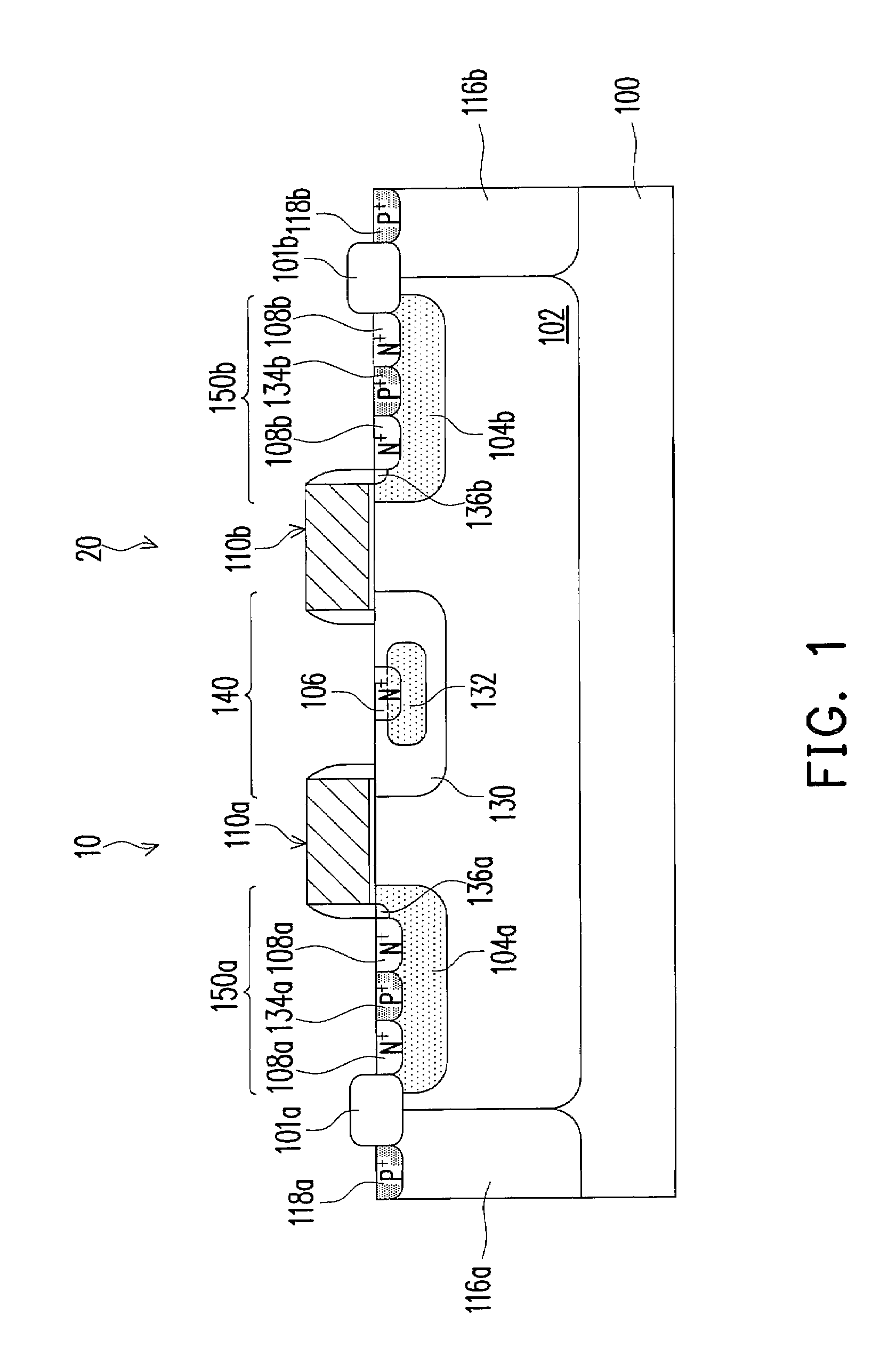
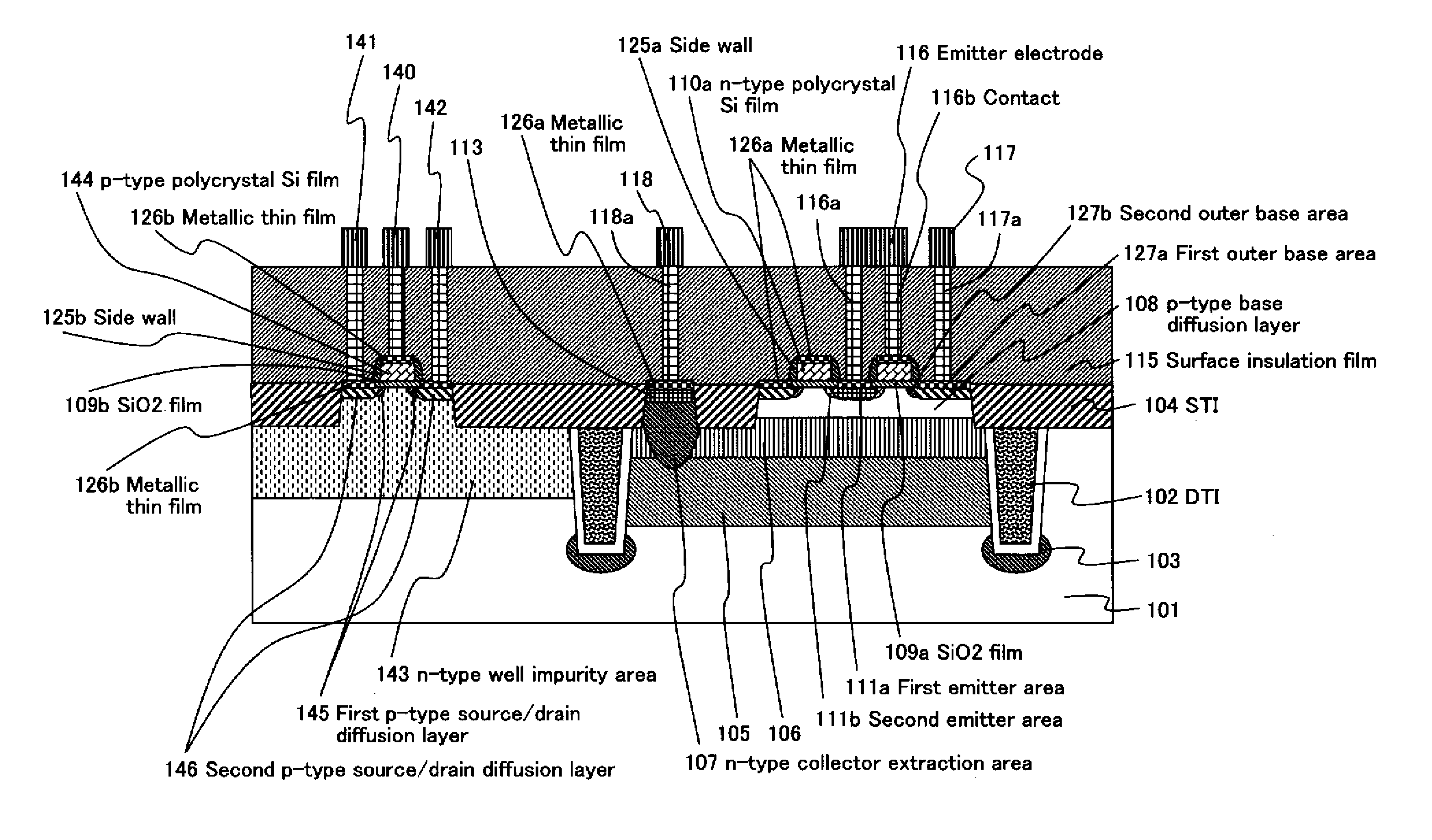
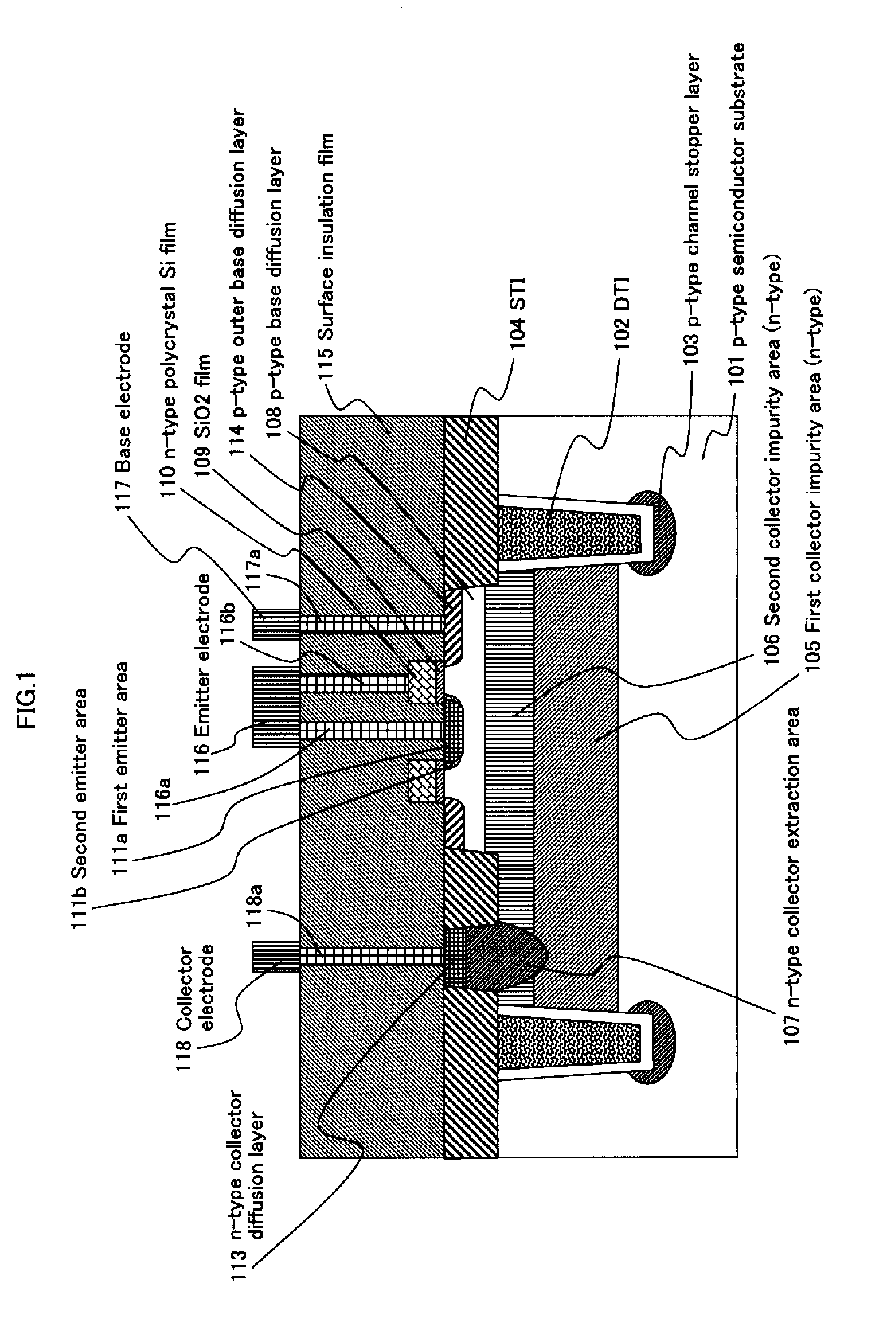
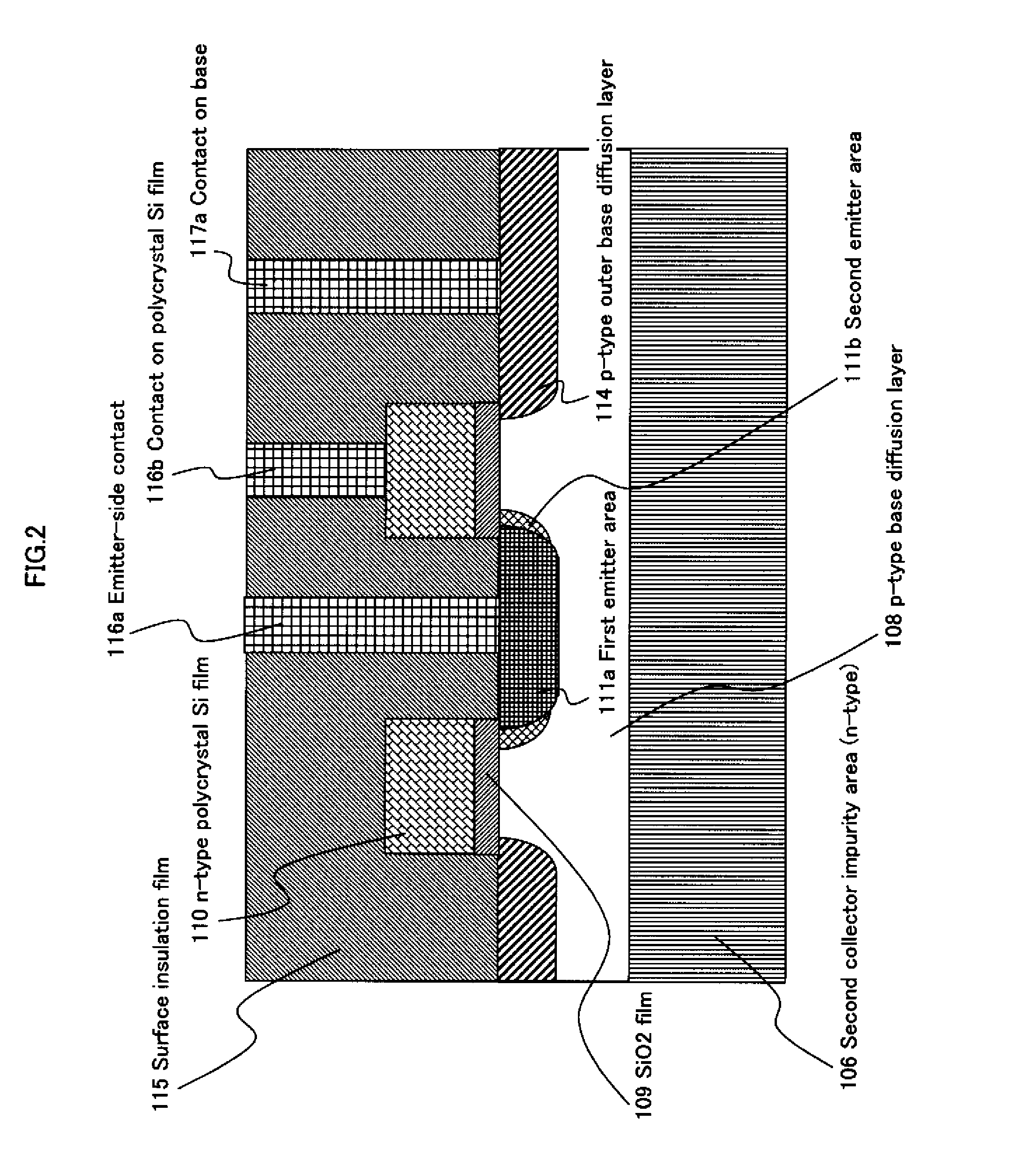
InactiveUS20110127615A1Reduce leakage currentReduce electric field strengthTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical field strengthImpurity ions
A high-performance semiconductor apparatus which can be easily introduced into the MOS process, reduces the leakage current (electric field strength) between the emitter and the base, and is insusceptible to noise or surge voltage, and a manufacturing method of the semiconductor apparatus. The emitter 111 is formed by performing the ion implantation twice by using the conductive film (109) as a mask. The second emitter area (111b) is formed by ion implantation of a low impurity density impurity ion, and the first emitter area (111a) is formed by ion implantation of a high impurity density impurity ion. As a result, the low impurity density second emitter area is formed in the circumference of the emitter 111, which lowers the electric field strength, and reduces the leakage current. Also the conductive film is connected with the emitter electrode (116), which makes the apparatus insusceptible to noise.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Semiconductor device
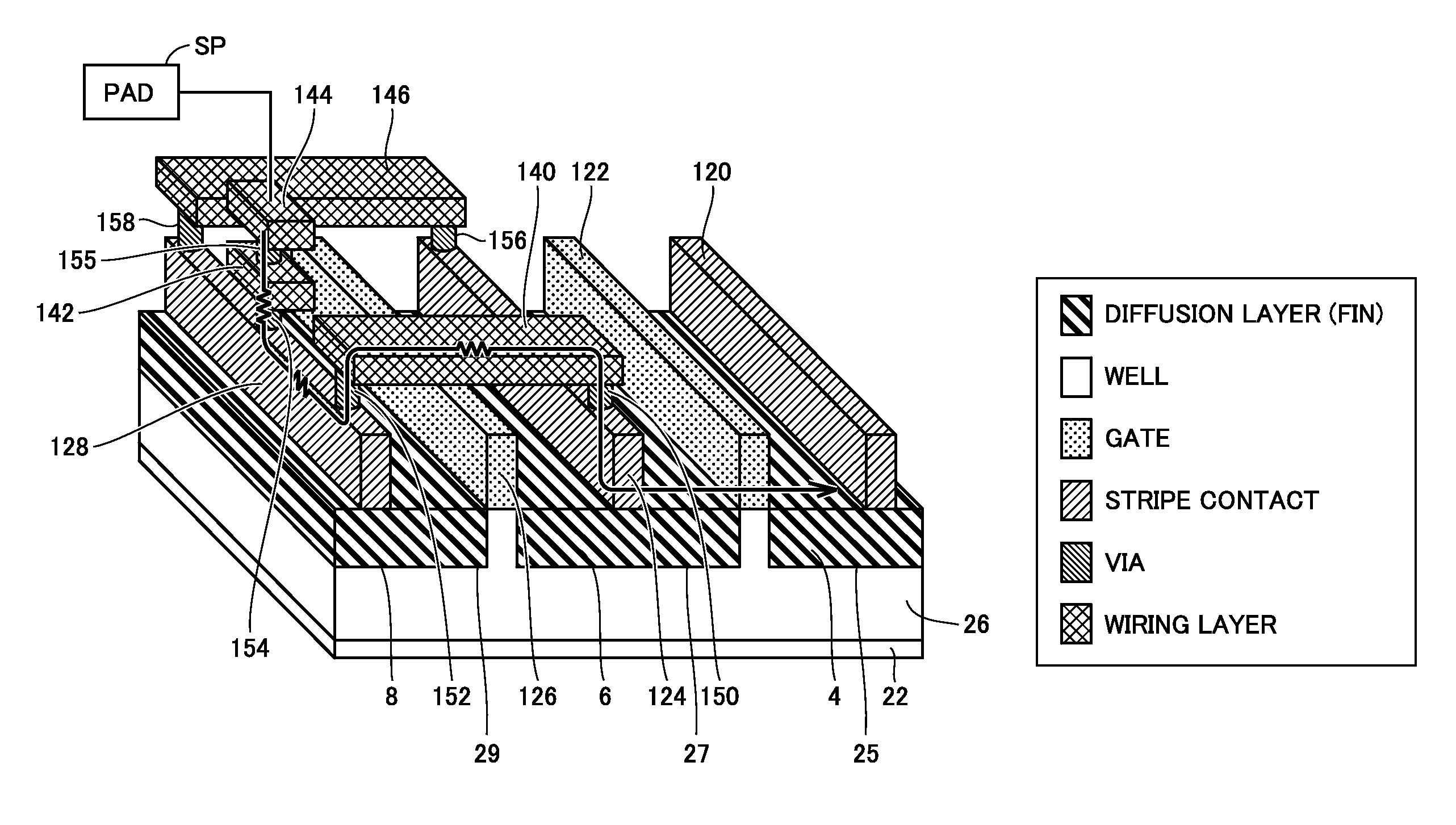
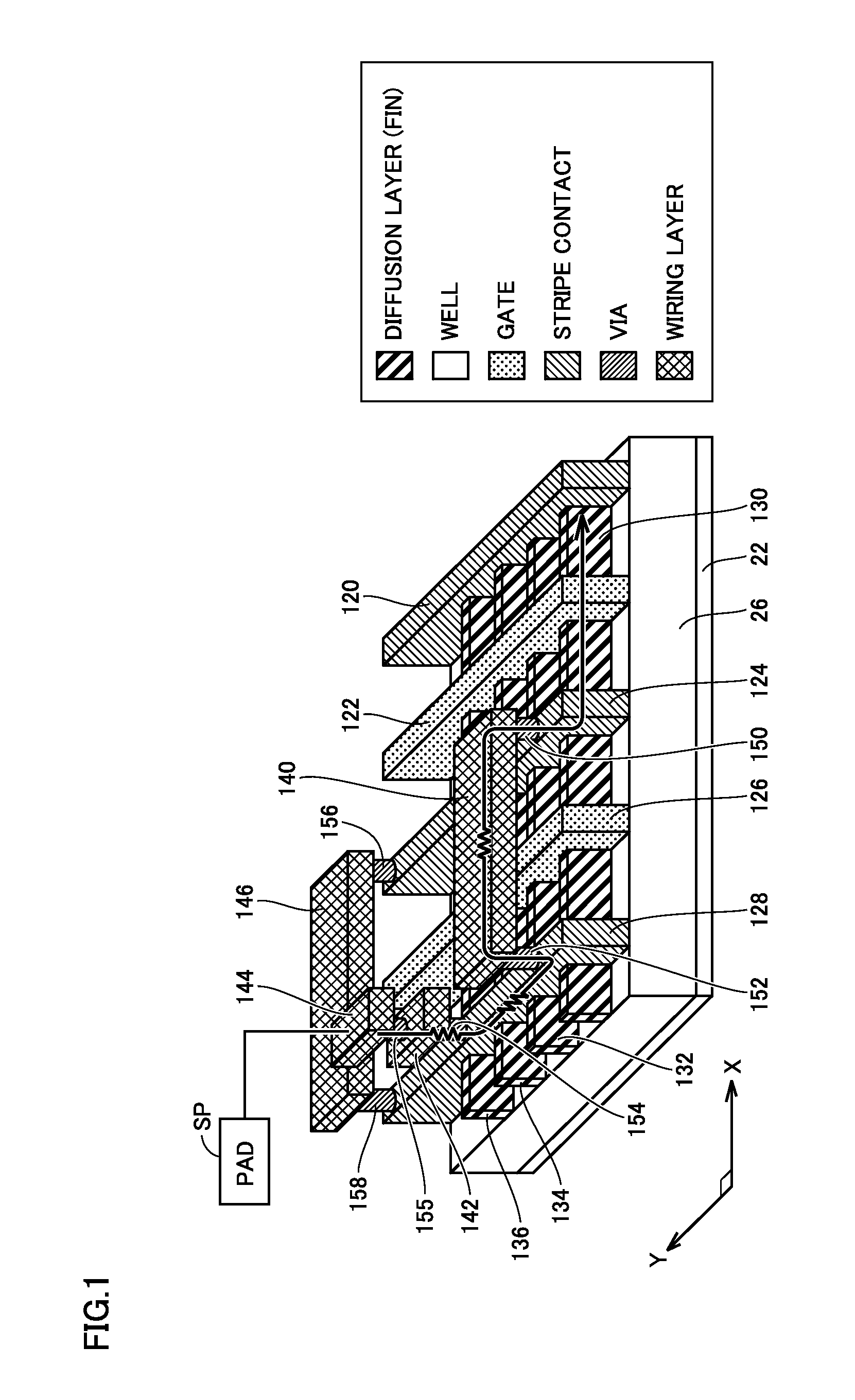
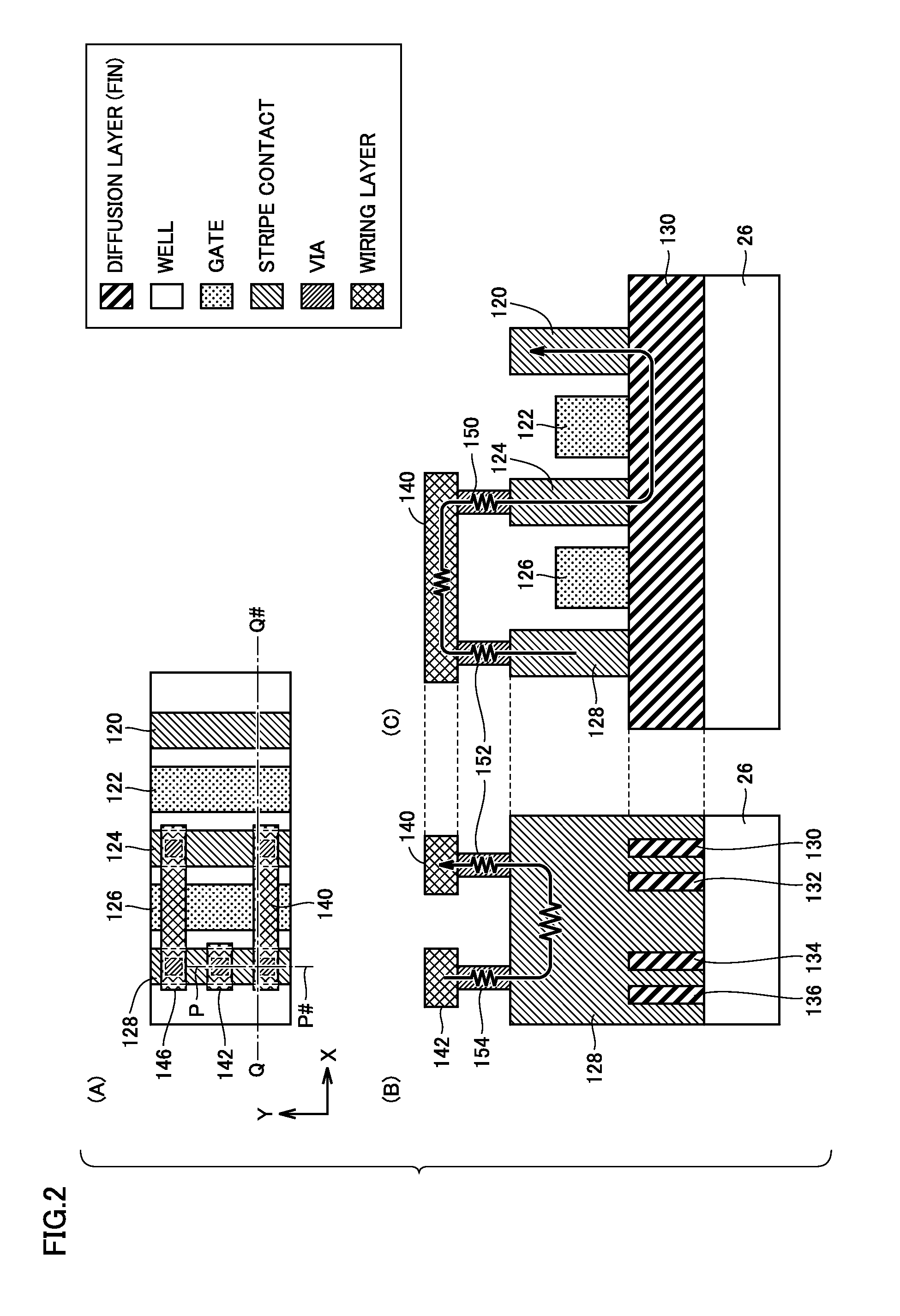
ActiveUS20160064373A1Improve ESD toleranceSimple wayTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor
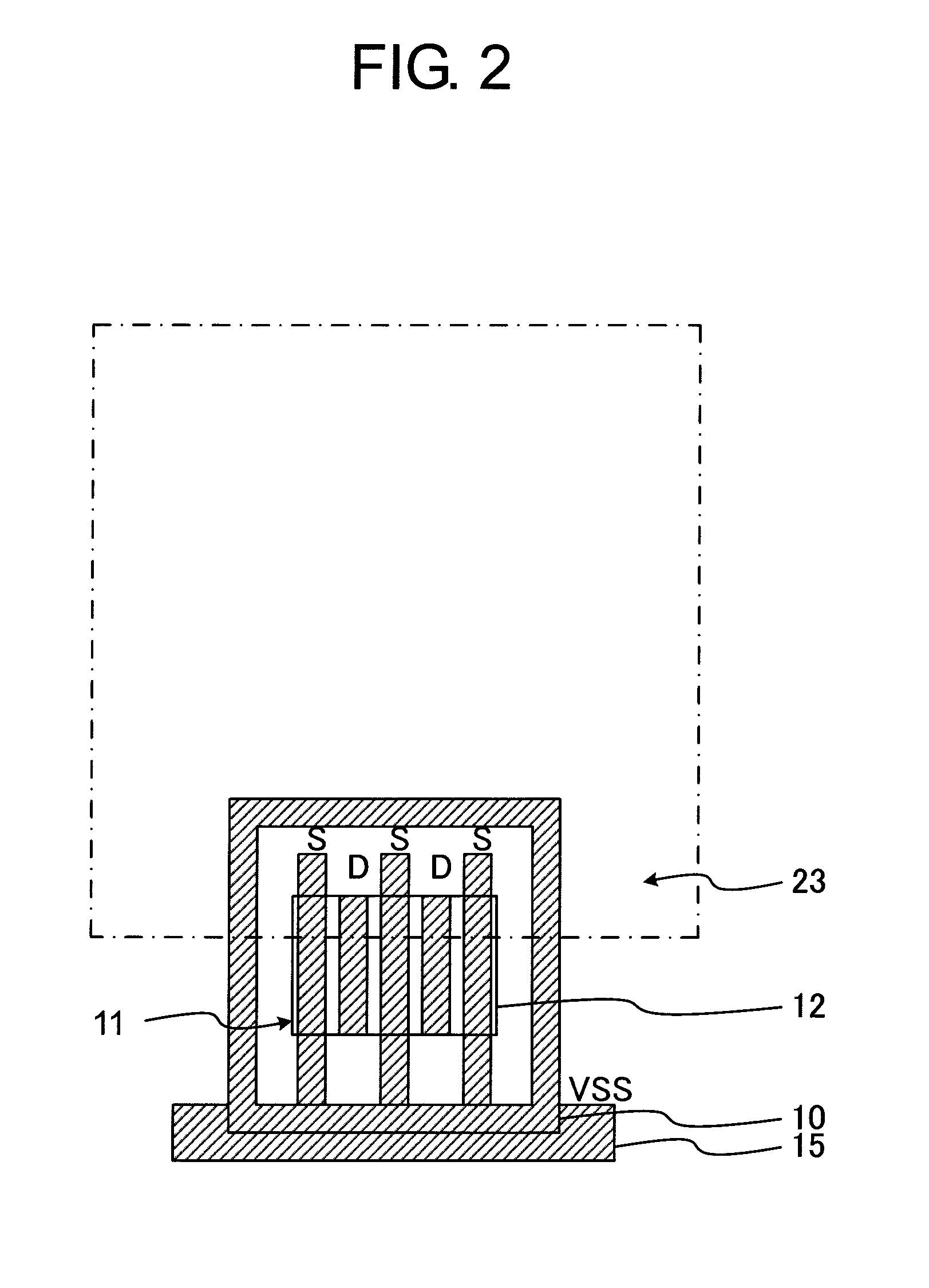
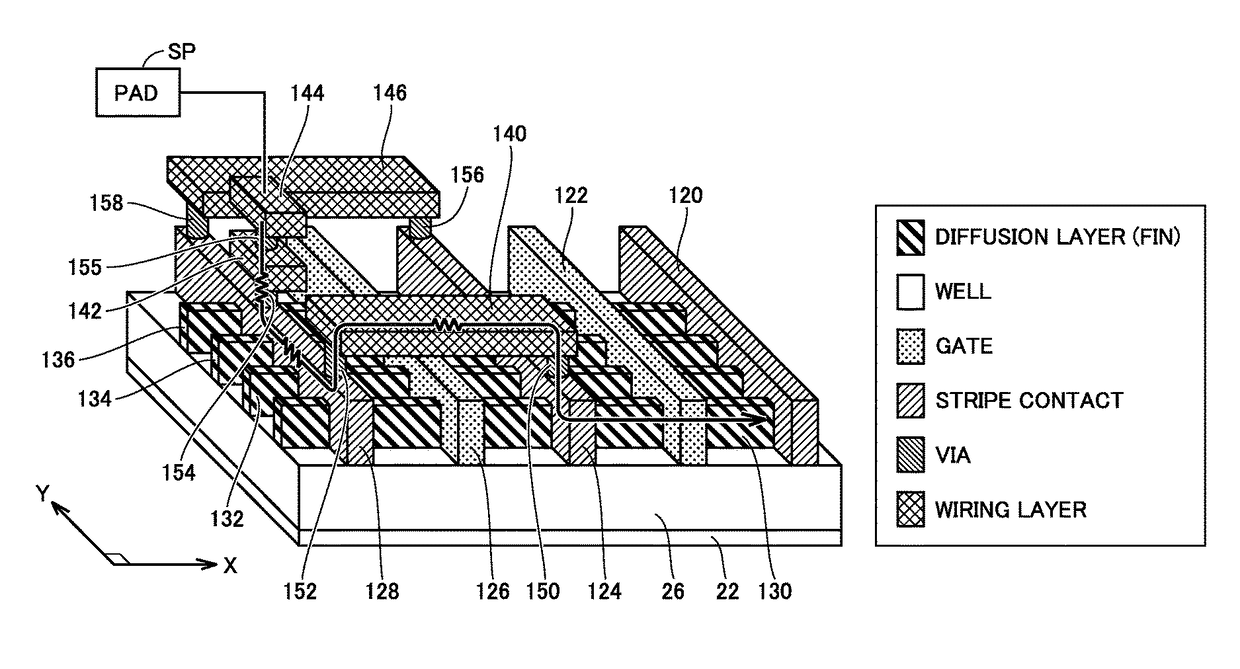
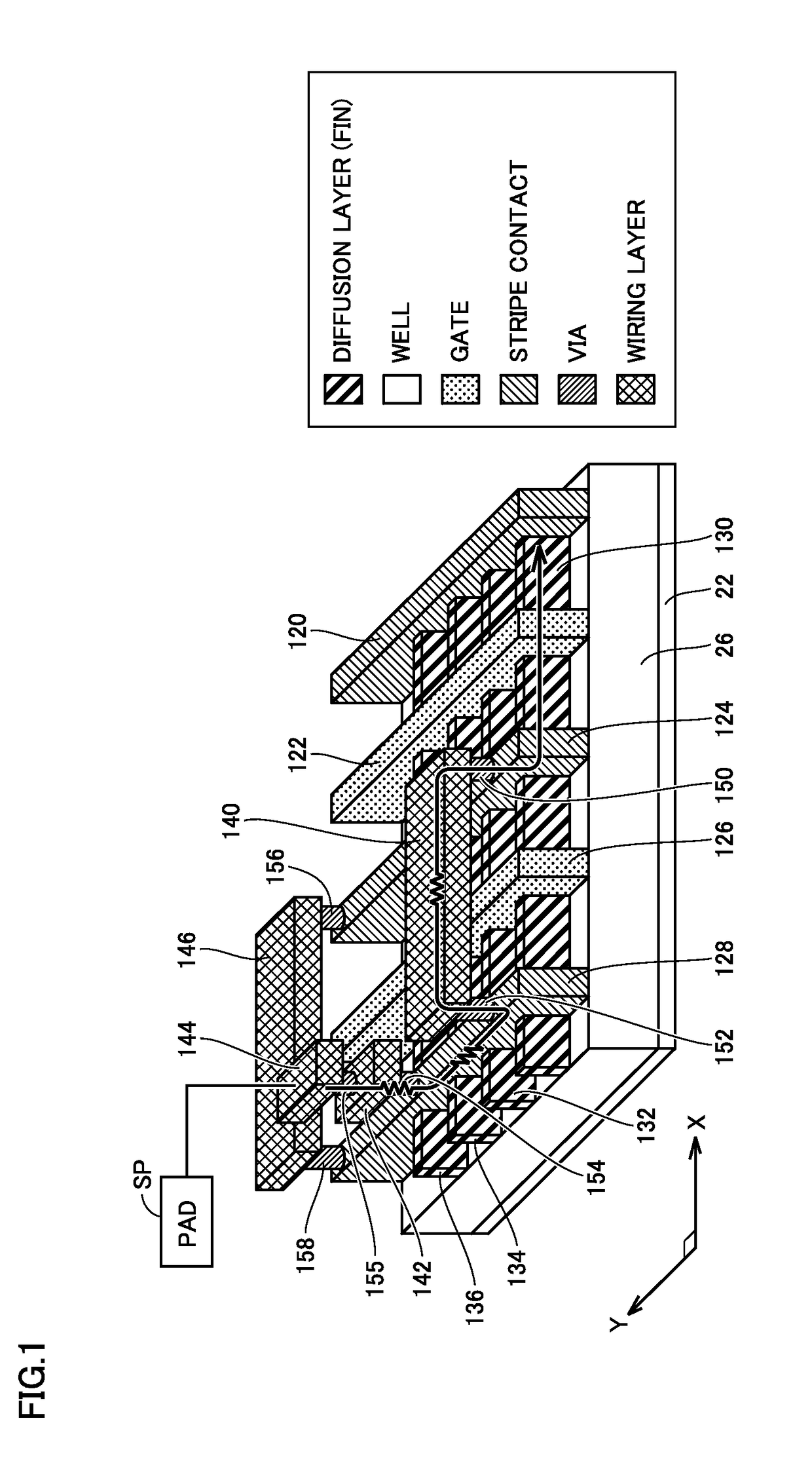
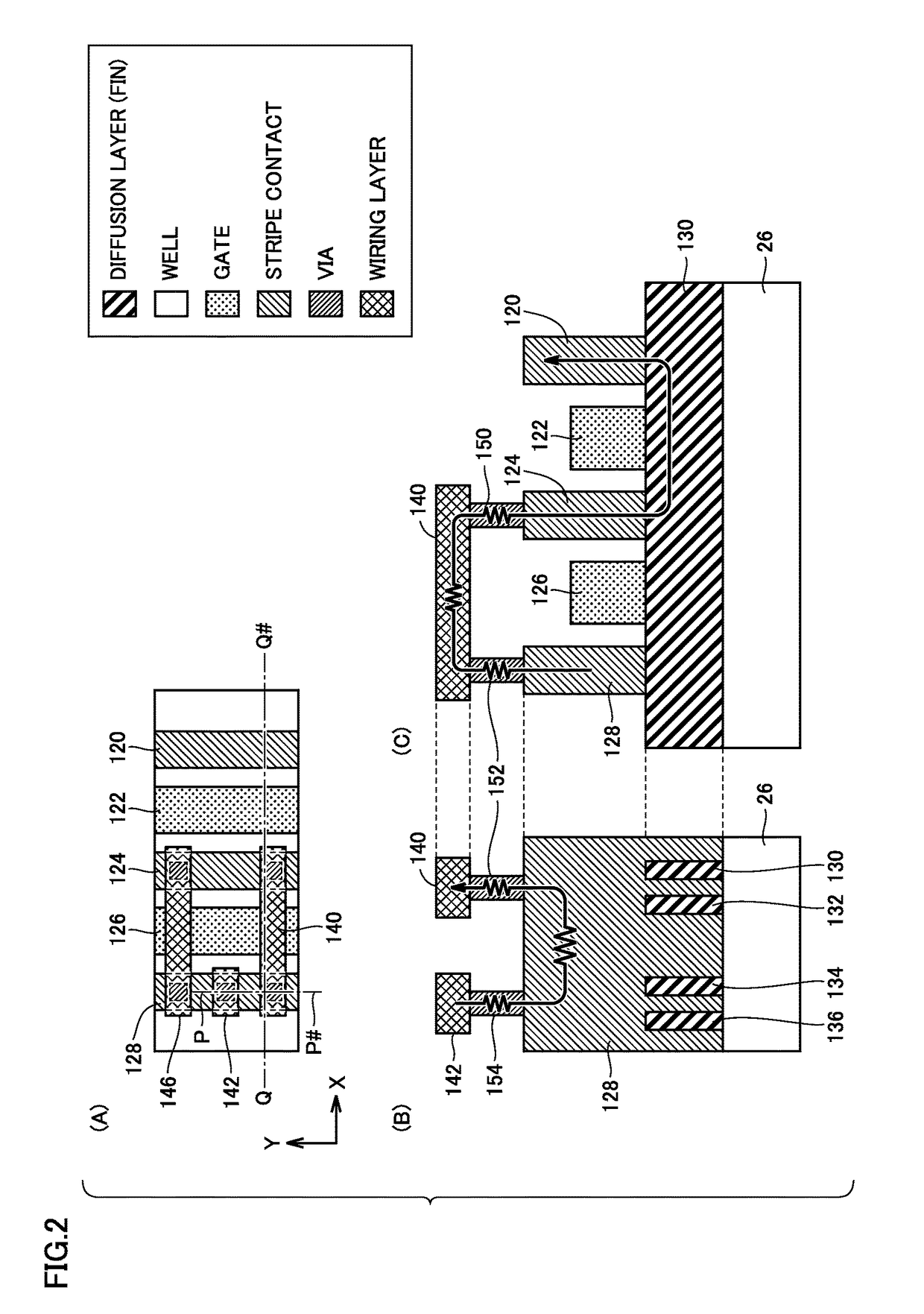
A semiconductor device includes a plurality of gate electrodes, and a plurality of stripe contacts, each formed alternately with each of the gate electrodes along a length direction of the gate electrodes. A conductive transistor with a reference potential applied to one of the stripe contacts forming one of a source and a drain is formed. One of the gate electrodes adjacent to one of the stripe contacts forming the other of the source and the drain is used as a first dummy gate electrode. The semiconductor device further includes a metal extending over the first dummy gate electrode to electrically connect together the stripe contacts formed on opposing sides of the first dummy gate electrode, and a pad connected to one of the stripe contacts formed on opposing sides of the first dummy gate electrode, which is provided across the first dummy gate electrode from the conductive transistor.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
ESD protection devices and methods to reduce trigger voltage
InactiveUS6858900B2Lower breakdown voltageReduce voltageTransistorThyristorP–n junctionBreakdown voltage
ESD protection devices and methods of forming them are provided in this invention. By employing the thin gate oxide fabricated by a dual gate oxide process and breakdown-enhanced layers, ESD protection devices with a lower trigger voltage are provided. The NMOS structure for ESD protection according to the present invention has islands, a control gate and breakdown-enhanced layers. These islands as well as the breakdown-enhanced layers overlapping the drain region of the NMOS reduce the breakdown voltage of the PN junction in the drain region, thereby reducing the ESD trigger voltage and improving the ESD protection level of the NMOS. Furthermore, the invention is applicable to general integrated-circuit processes as well as various ESD protection devices.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
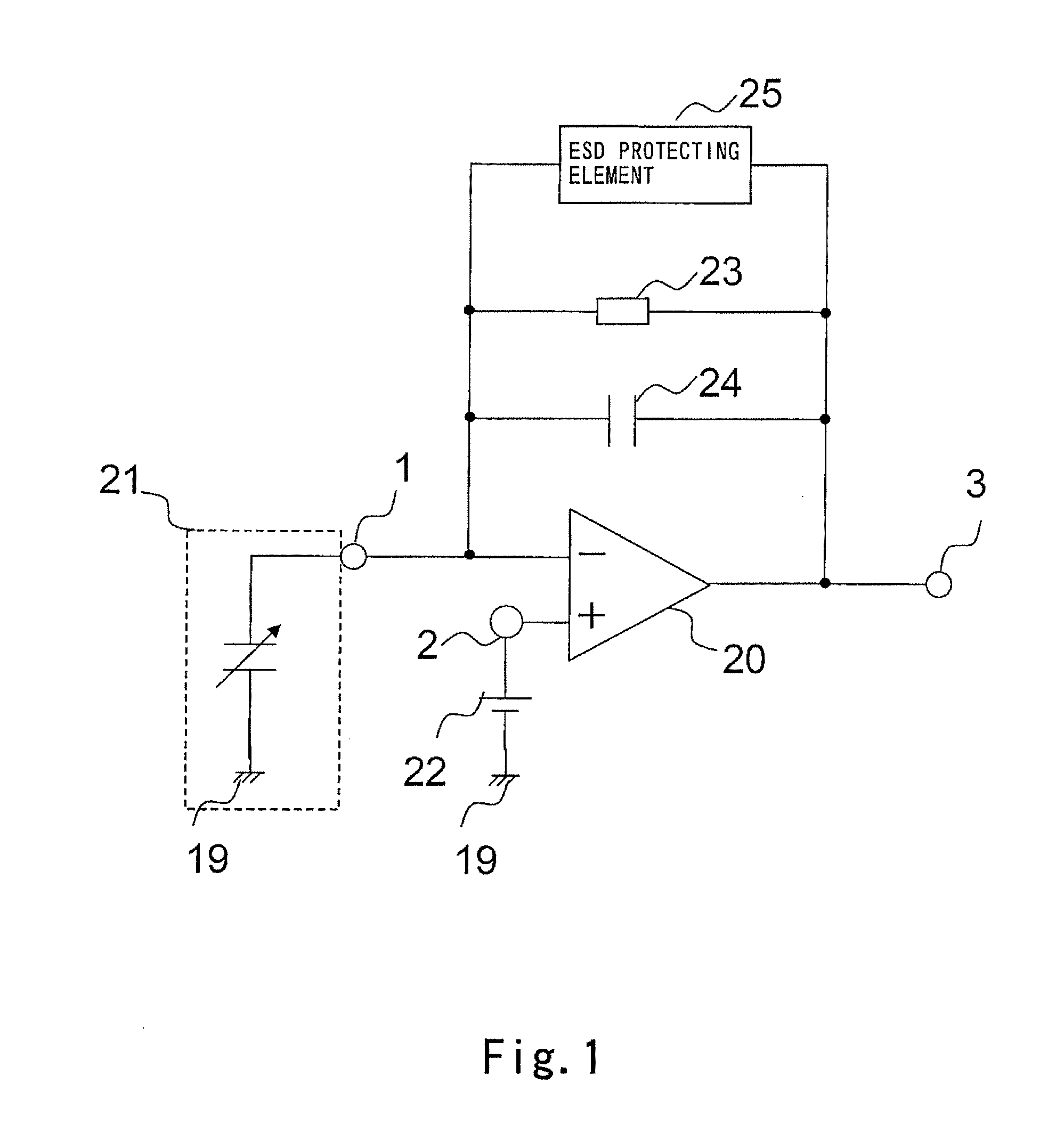
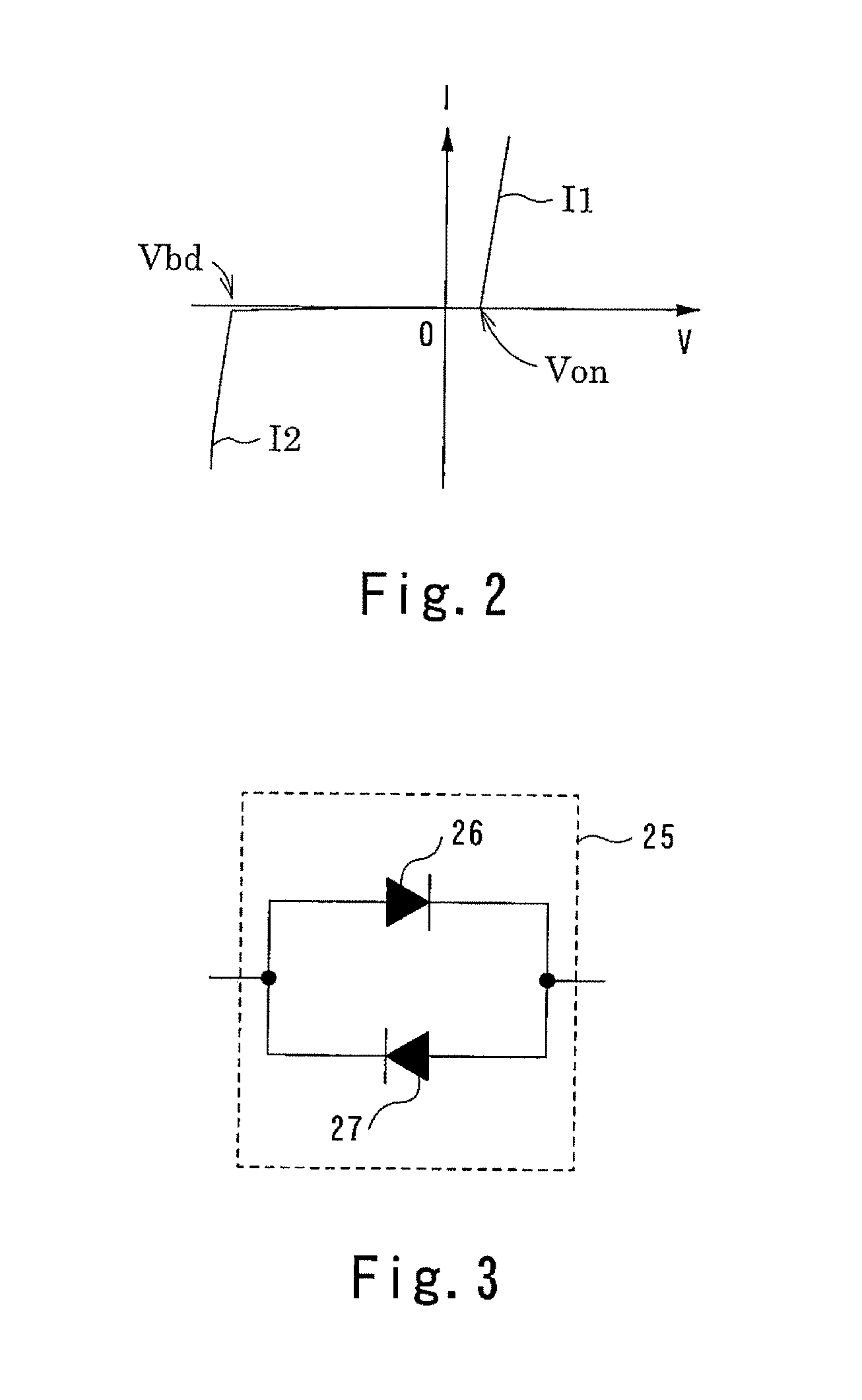
Amplifying device for condenser microphone
InactiveUS20120014541A1Improve ESD toleranceLow frequency amplifiersAmplifier protection circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierEngineering
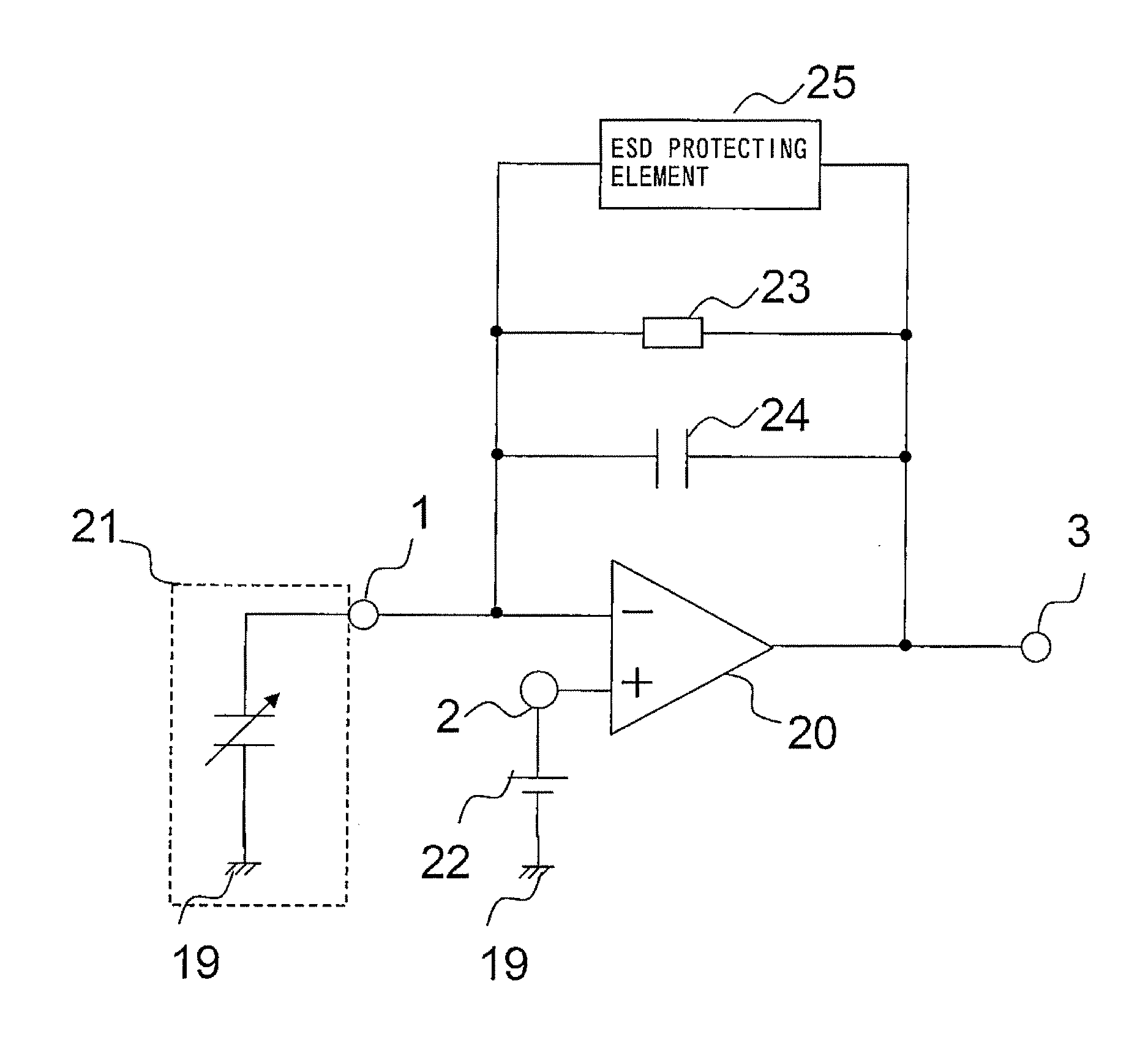
An amplifying device for a condenser-microphone according to the present invention includes: a differential amplifier (20) having an inverting input terminal (1) to which a sound pressure signal output from a condenser microphone (21) is input and a non-inverting input terminal (2) to which a dc bias voltage is applied; a capacitor (24) connected between an output terminal (3) of the differential amplifier (20) and the inverting input terminal (1) of the differential amplifier (20); a resistive element (23) connected, in parallel with the capacitor (24), between the output terminal (3) of the differential amplifier (20) and the inverting input terminal (1) of the differential amplifier (20); and an ESD protecting element (25) having bidirectional diode characteristics, the ESD protecting element (25) being connected, in parallel with the capacitor (24), between the output terminal (3) of the differential amplifier (20) and the inverting input terminal (1) of the differential amplifier (20).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Circuit and method for improving ESD tolerance and switching speed
Embodiments of systems, methods, and apparatus for improving ESD tolerance and switching time for semiconductor devices including metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) field effect transistors (FETs), and particularly to MOSFETs fabricated on semiconductor-on-insulator and silicon-on-sapphire substrates. Embodiments provide an improved FET structure having an accumulated charge sink (ACS) circuit, fast switching times, and improved ESD tolerance.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Semiconductor light emitting element
ActiveCN105428479AIncrease light emitting areaReduce migration rateSemiconductor devicesIsolation layerNitride
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductors, and particularly relates to a semiconductor light emitting element. The semiconductor light emitting element comprises a substrate, and a nitride buffer layer, an n-type layer, a shallow quantum well layer, a multiple quantum well layer and a p-type layer formed on the substrate sequentially. The semiconductor light emitting element is characterized in that a composite structure layer is also inserted between the shallow quantum well layer and the multiple quantum well layer; the composite structure layer at least comprises a p-type doped GaN layer, an n-type doped GaN layer, and an isolation layer located between the p-type doped GaN layer and the n-type doped GaN layer. The feature that p-type impurities in the composite structure layer are migrated to the shallow quantum well layer and the multiple quantum well layer is used, light emitting of the shallow quantum well layer and the composite structure layer is promoted while the light-emitting strength of the multiple quantum well layer is enhanced, the light outgoing area of the semiconductor element is increased, and the light-emitting strength is further enhanced.
Owner:ANHUI SANAN OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS8035229B2Improve the immunityImprove ESD toleranceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsContact formationEngineering
Owner:PANNOVA SEMIC
Electrostatic discharge protection device with parasitic bipolar junction transistors
ActiveUS9640527B2Improve robustnessImprove toleranceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSilicon-controlled rectifierSilicon
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Insulated gate semiconductor device
ActiveUS20180166436A1Improve ESD toleranceEnsure sufficientTransistorSolid-state devicesZener diodeAnode
An insulated gate semiconductor device includes a main insulated gate transistor having a gate electrode controlling a main current, a current-detecting insulated gate transistor, which is disposed in parallel to a main insulated gate transistor, outputting a current on a proportional basis in size between the transistors to the main current flowing through the main insulated gate transistor, a temperature detecting diode formed integrally with these insulated gate transistors in a semiconductor substrate. Interposing an ESD tolerance Zener diode between an emitter electrode of the current-detecting insulated gate transistor and an anode electrode of the temperature detecting diode leads to securing the ESD tolerance for the current-detecting insulated gate transistor by using the temperature detecting diode.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveCN103681654AReduce widthImprove ESD toleranceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
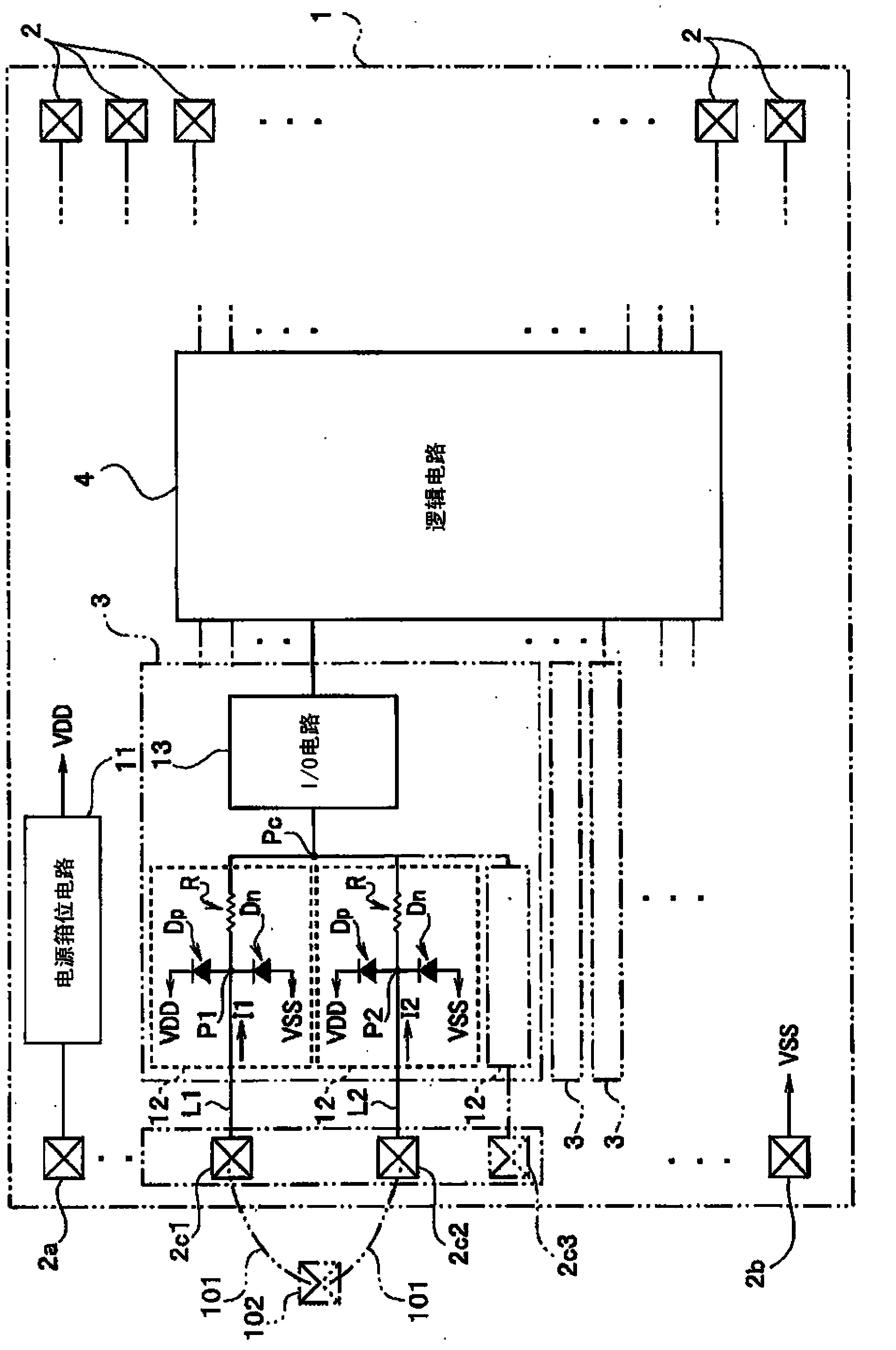
The invention provides a semiconductor device of ESD resistance while the width of the wiring pattern is not increased and the pin level of a chip of the semiconductor device is improved. A semiconductor device according to an embodiment includes a plurality of pads, a plurality of ESD protection circuits, each one of the ESD protection circuits being connected to a corresponding one of the plurality of pads, and an I / O circuit which is connected to a connection portion connecting output terminals of the plurality of ESD protection circuits to each other and which receives at least one input signal inputted into the plurality of pads.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
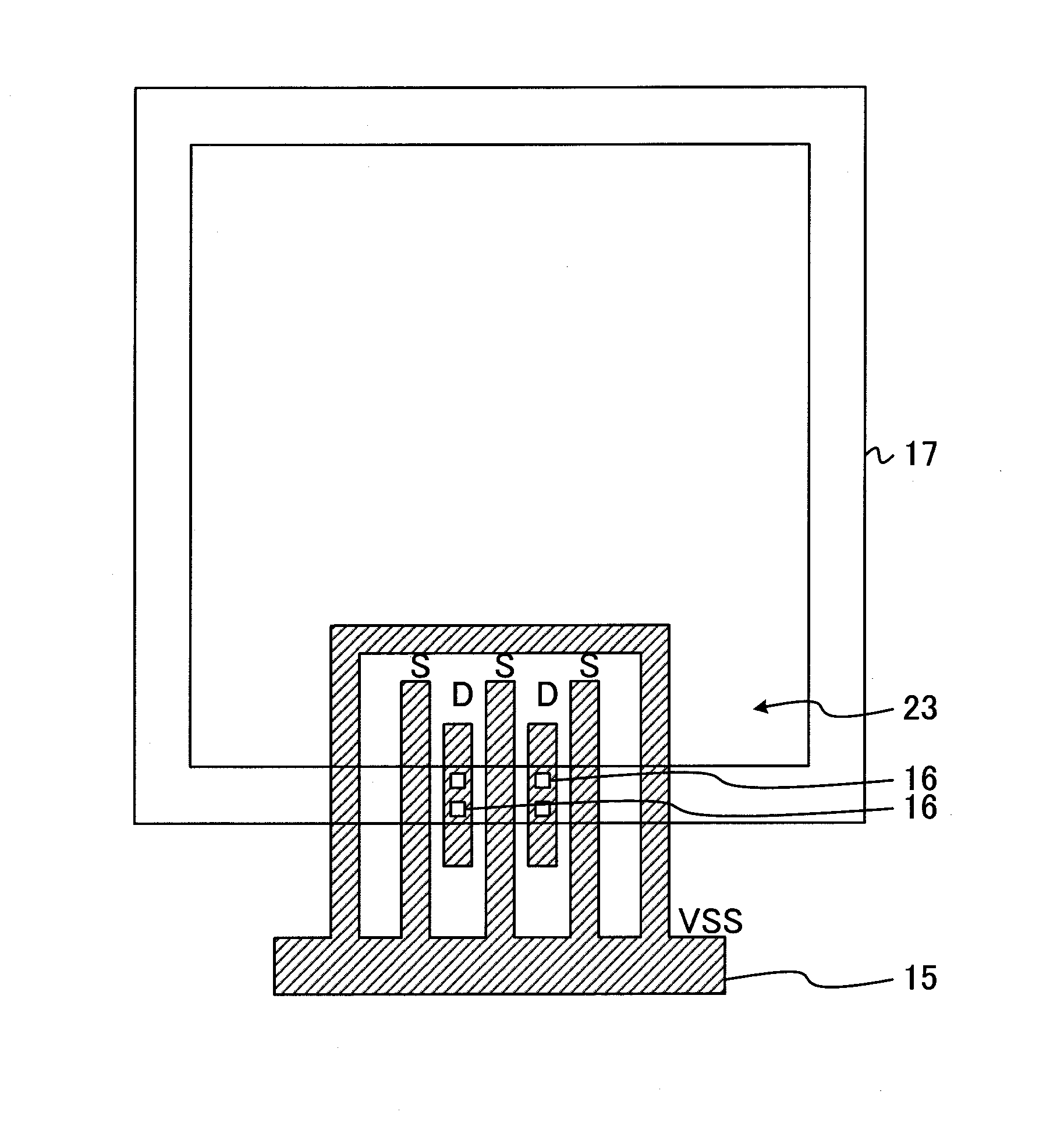
Semiconductor device
ActiveCN103794599AEasy to flow evenlyImprove ESD toleranceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical connectionSemiconductor
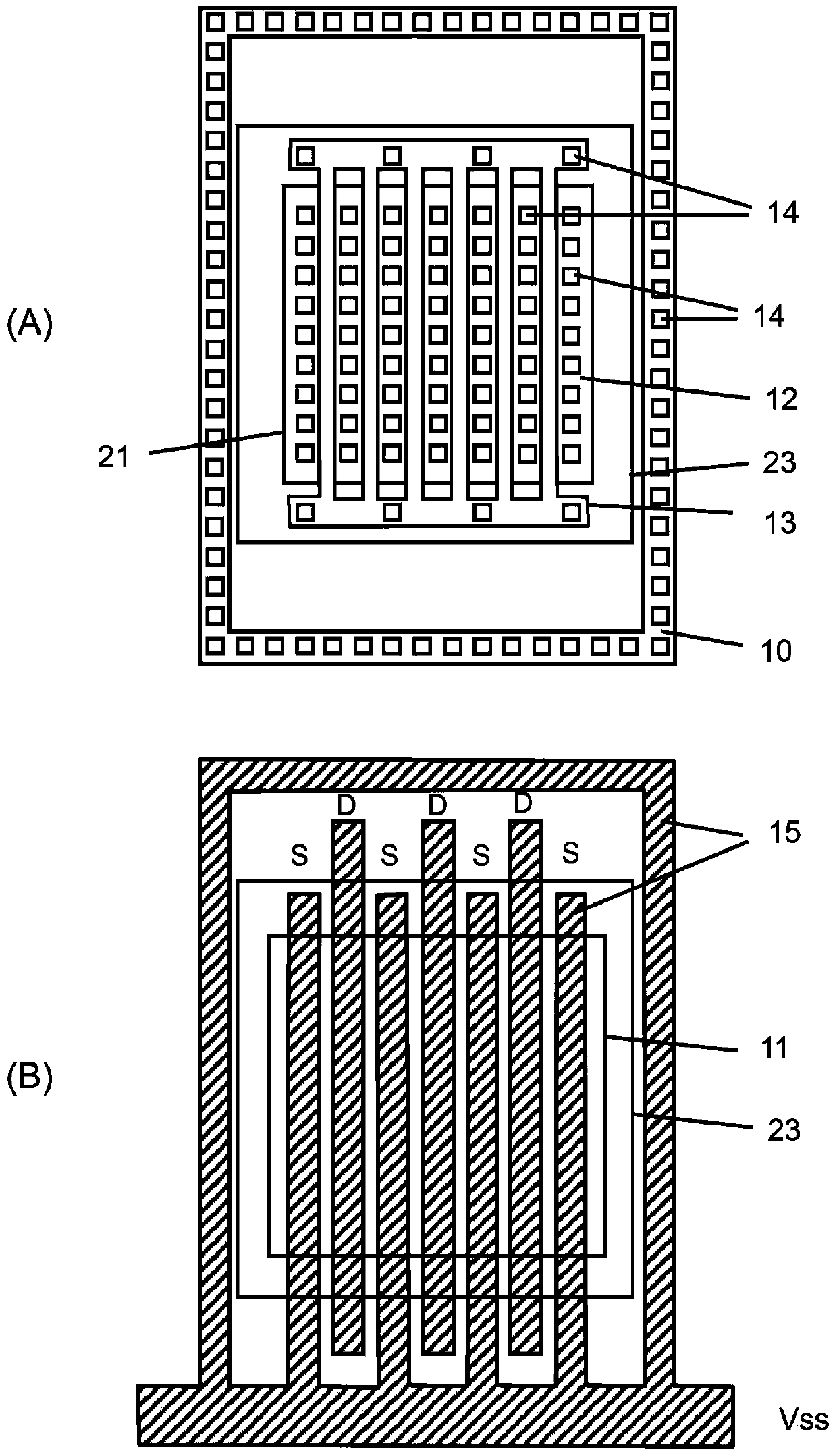
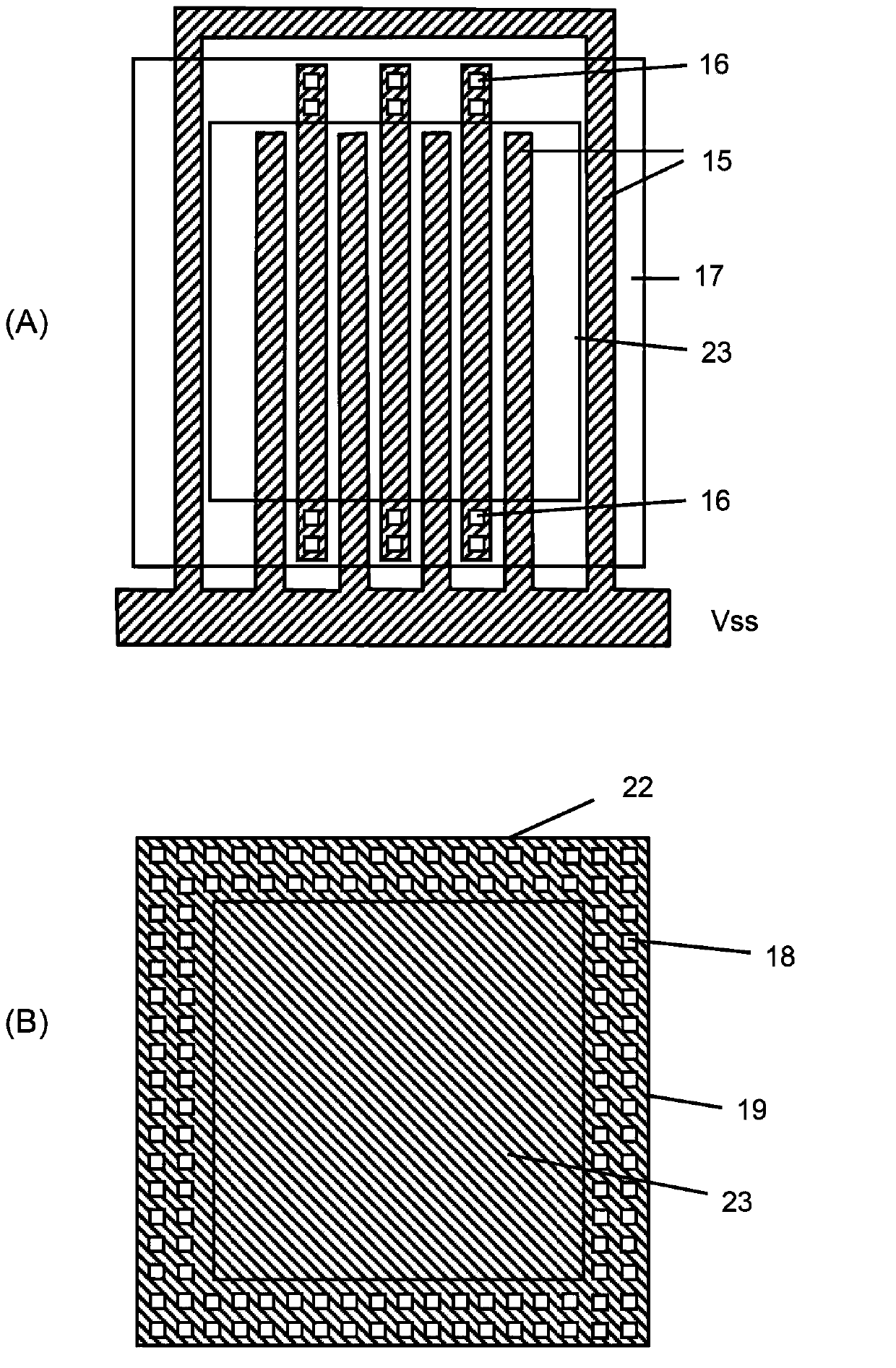
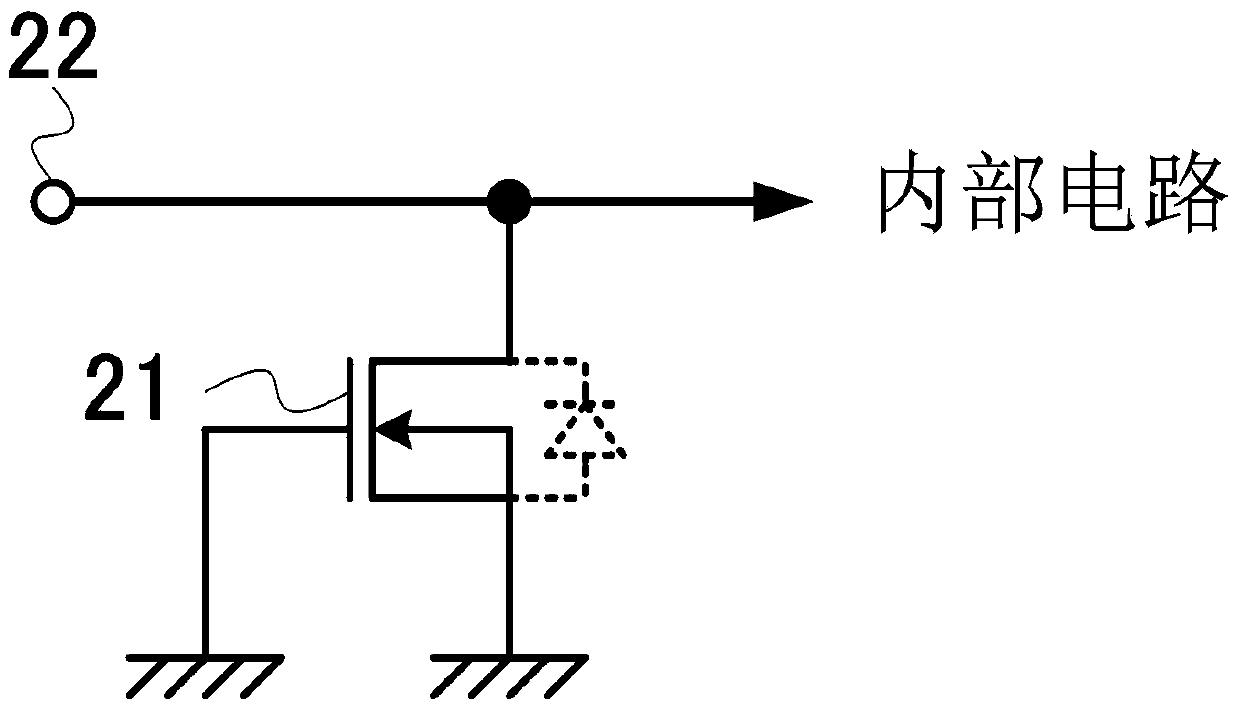
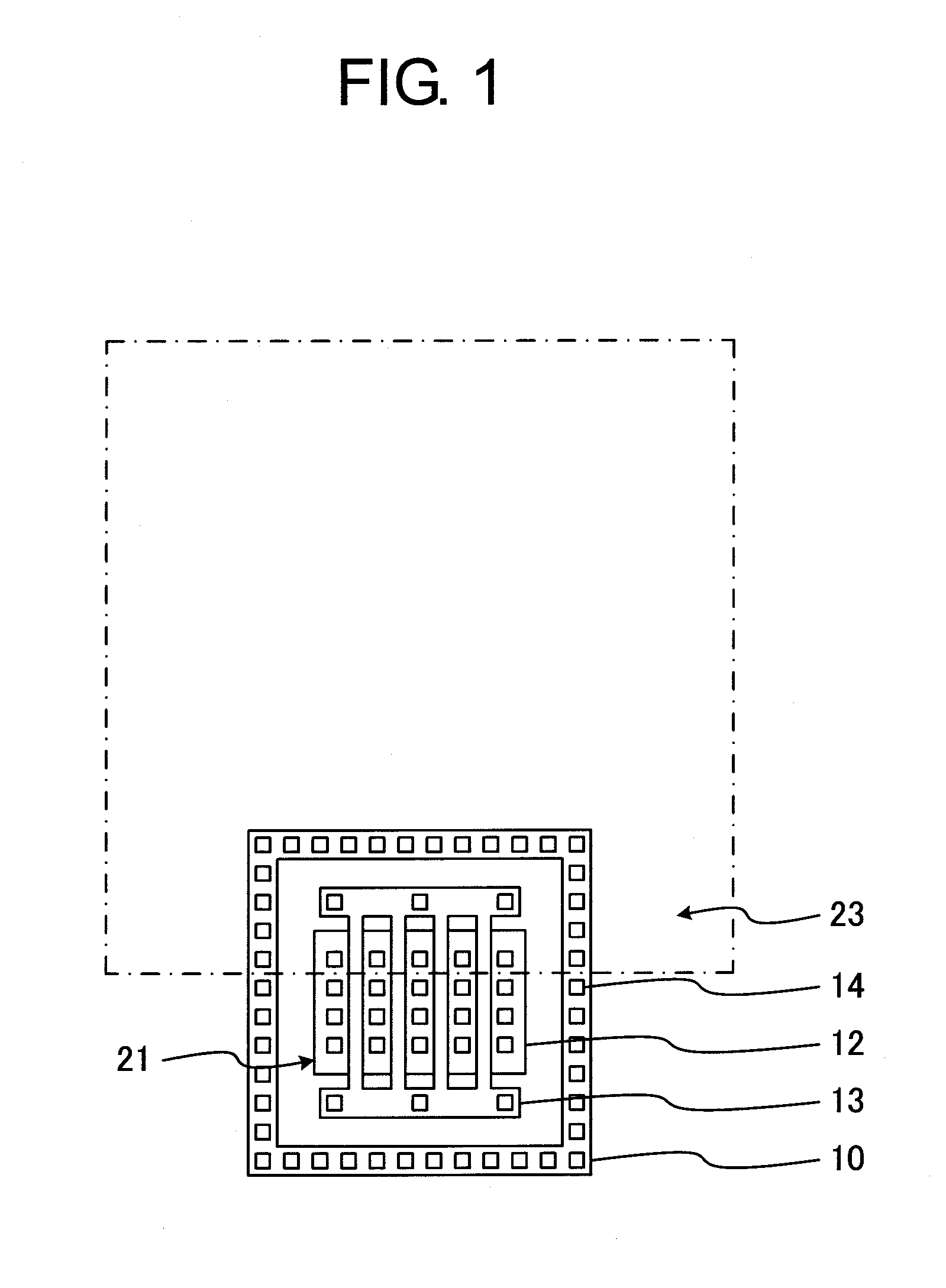
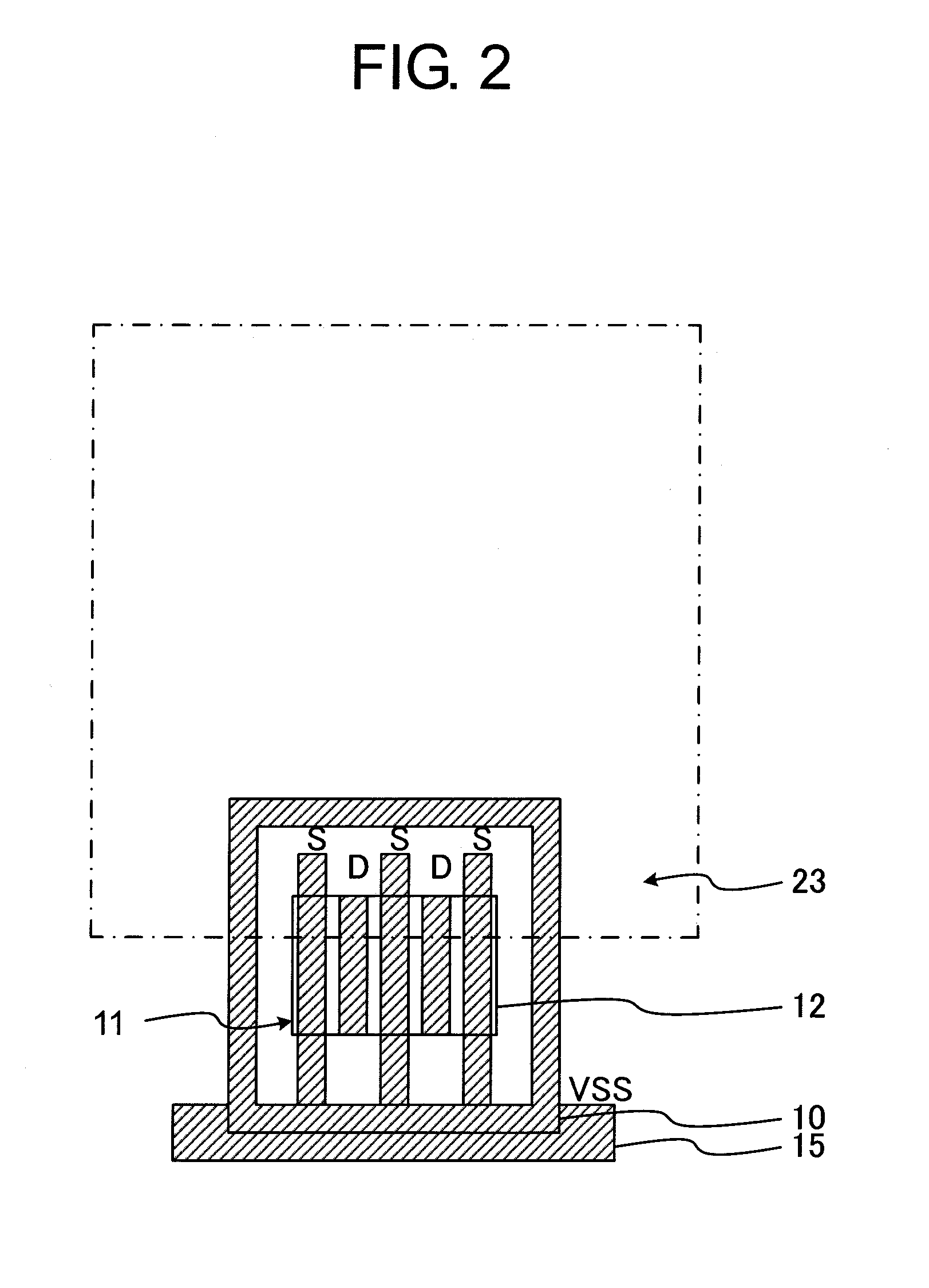
Provided is a semiconductor device having high ESD tolerance. A first via (16) is used for electrically connecting a pad (22) to a drain of an NMOS transistor of an ESD protective circuit. The first vias (16) are formed under the pad (22) only on one side of a rectangular ring-shaped intermediate metal film (17) and on another side thereof opposed to the one side. In other words, all the first vias (16) for establishing an electrical connection to the drains are present substantially directly under the pad (22). Consequently, a surge current caused by ESD and applied to the pad (22) is more likely to flow uniformly among all the drains. Then, respective channels of the NMOS transistor of the ESD protective circuit are more likely to uniformly operate, and hence the ESD tolerance of the semiconductor device is increased.
Owner:SII SEMICONDUCTOR CORP
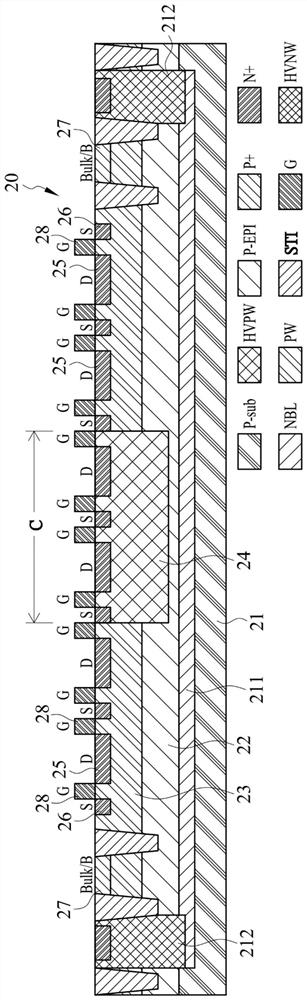
Semiconductor device
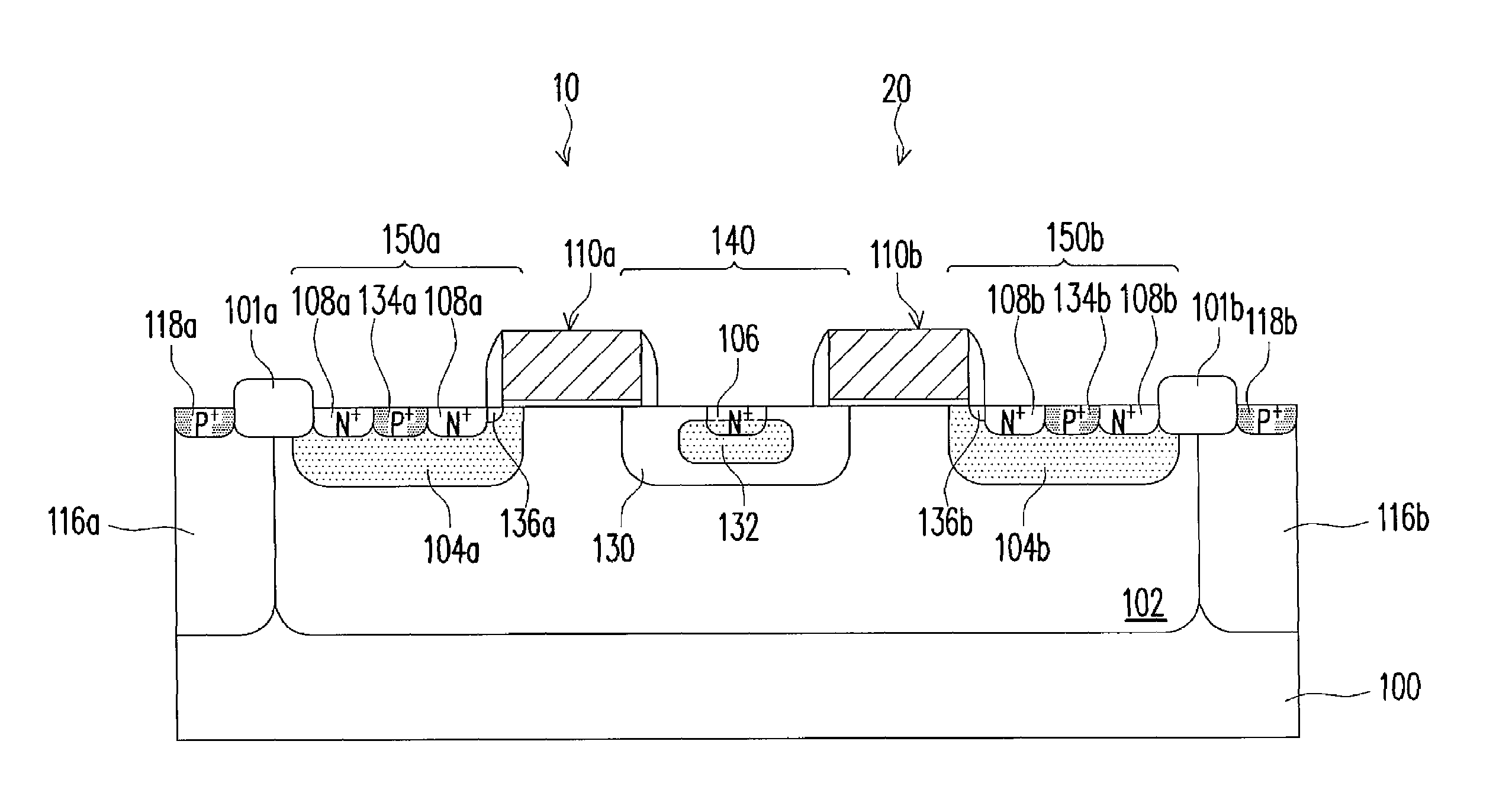
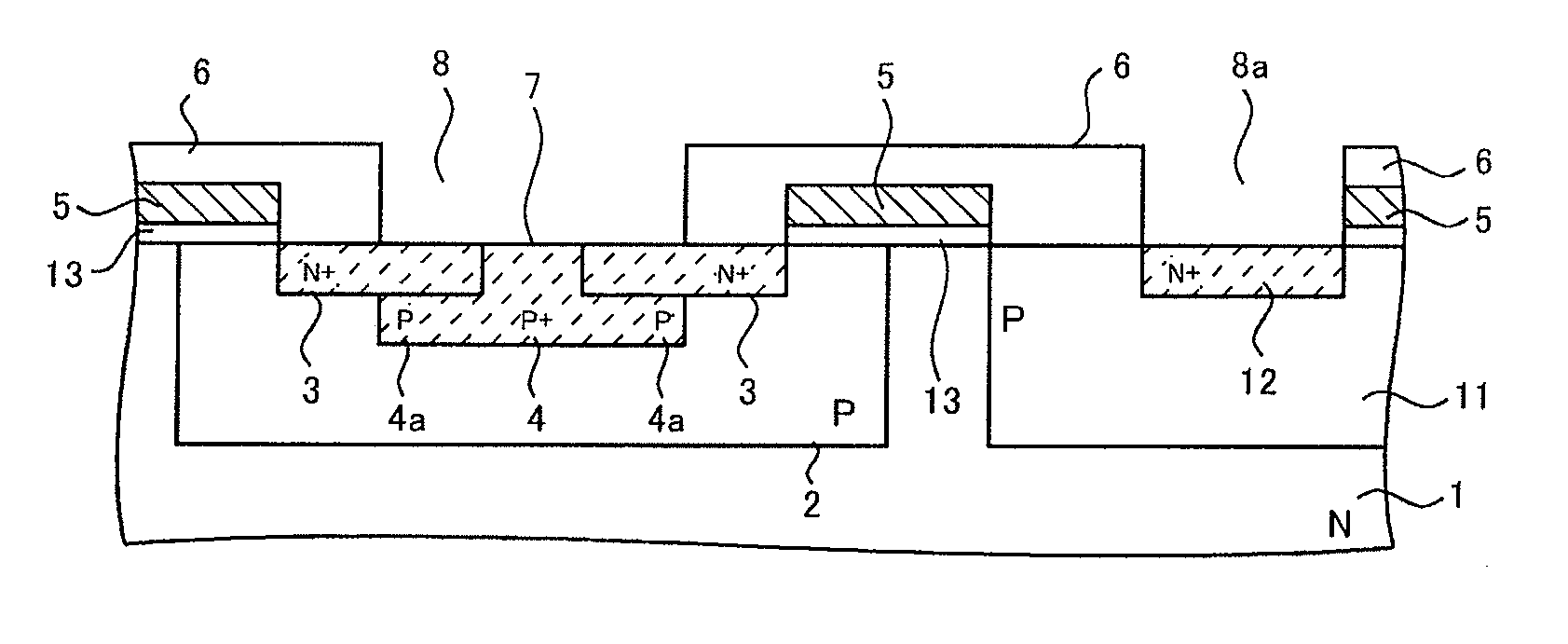
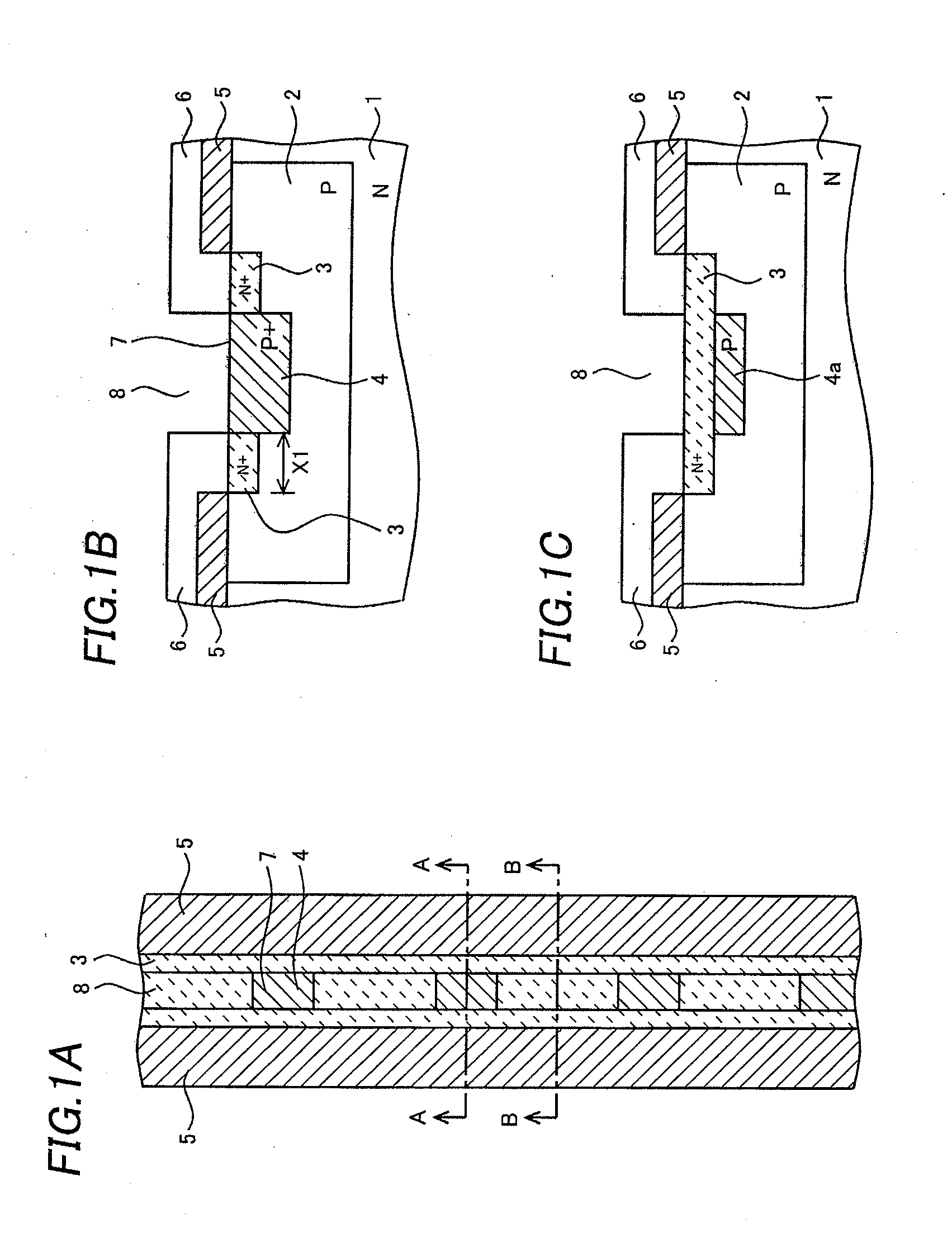
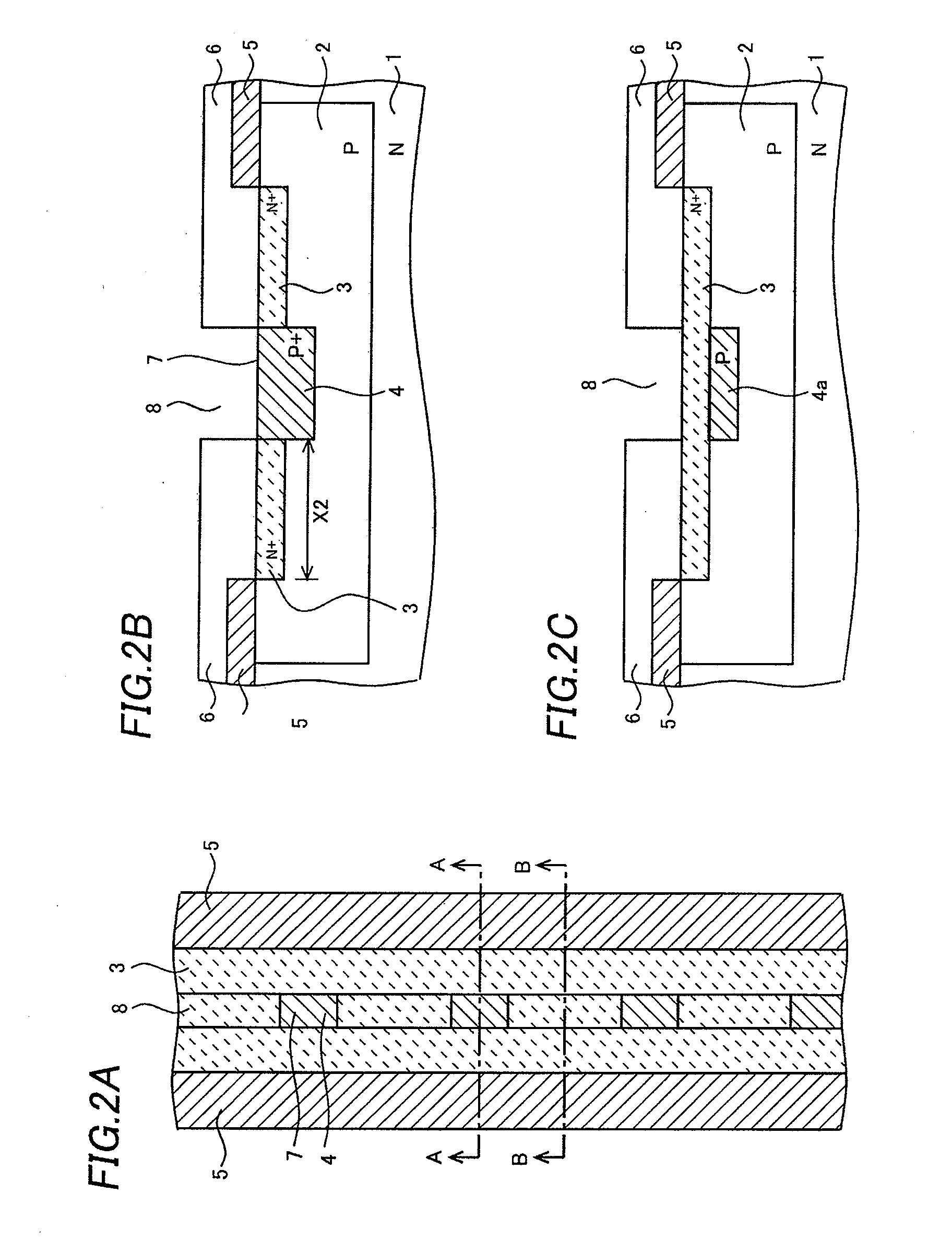
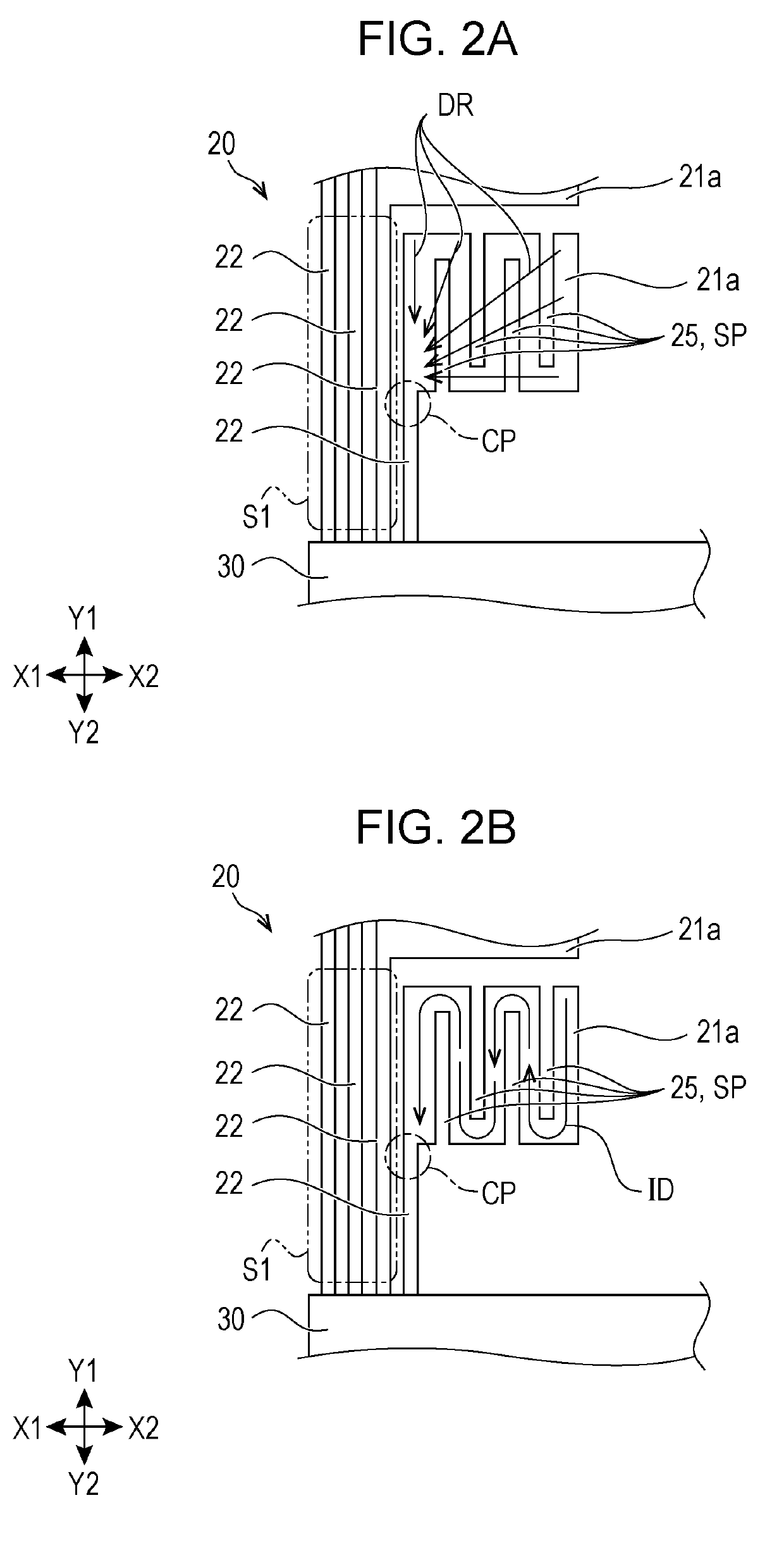
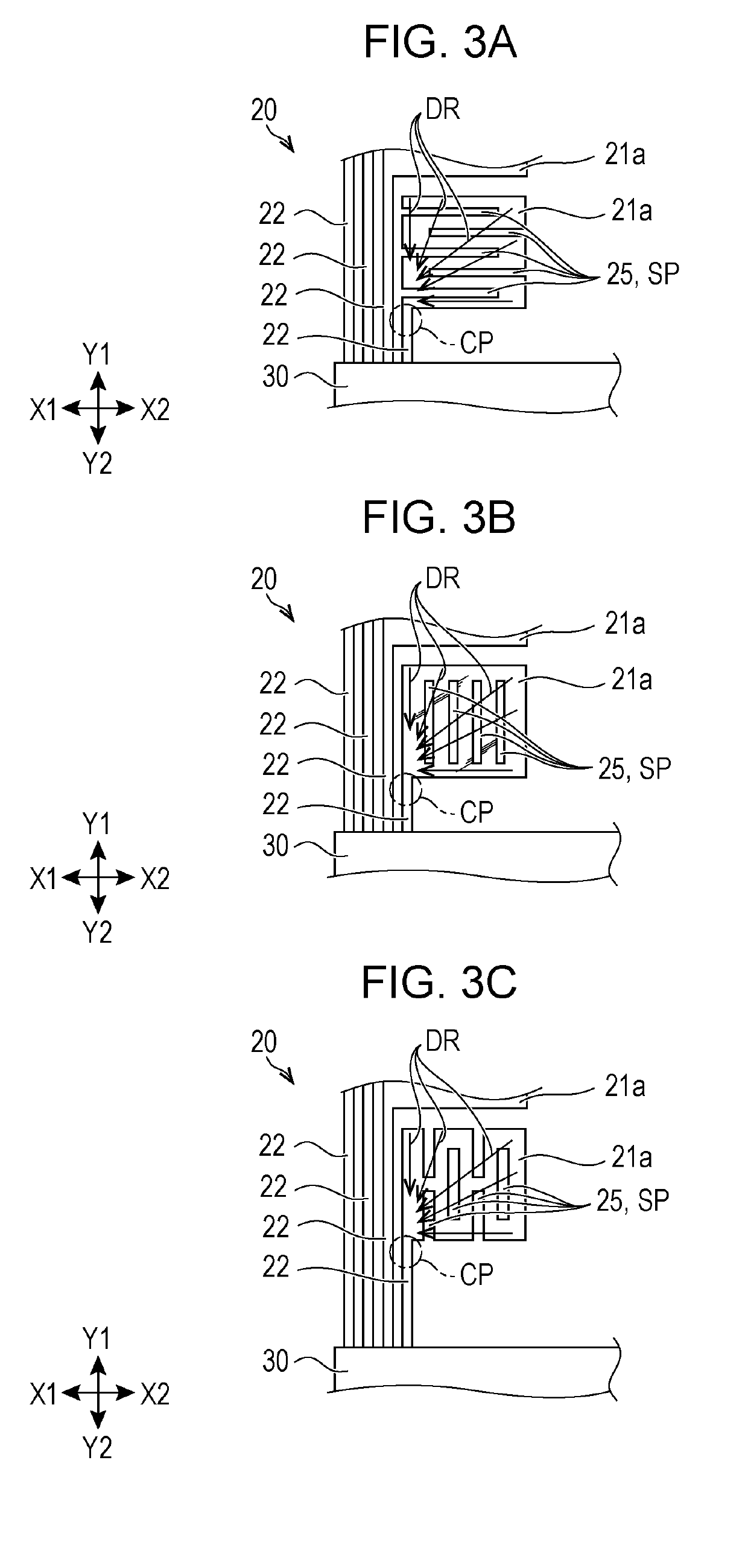
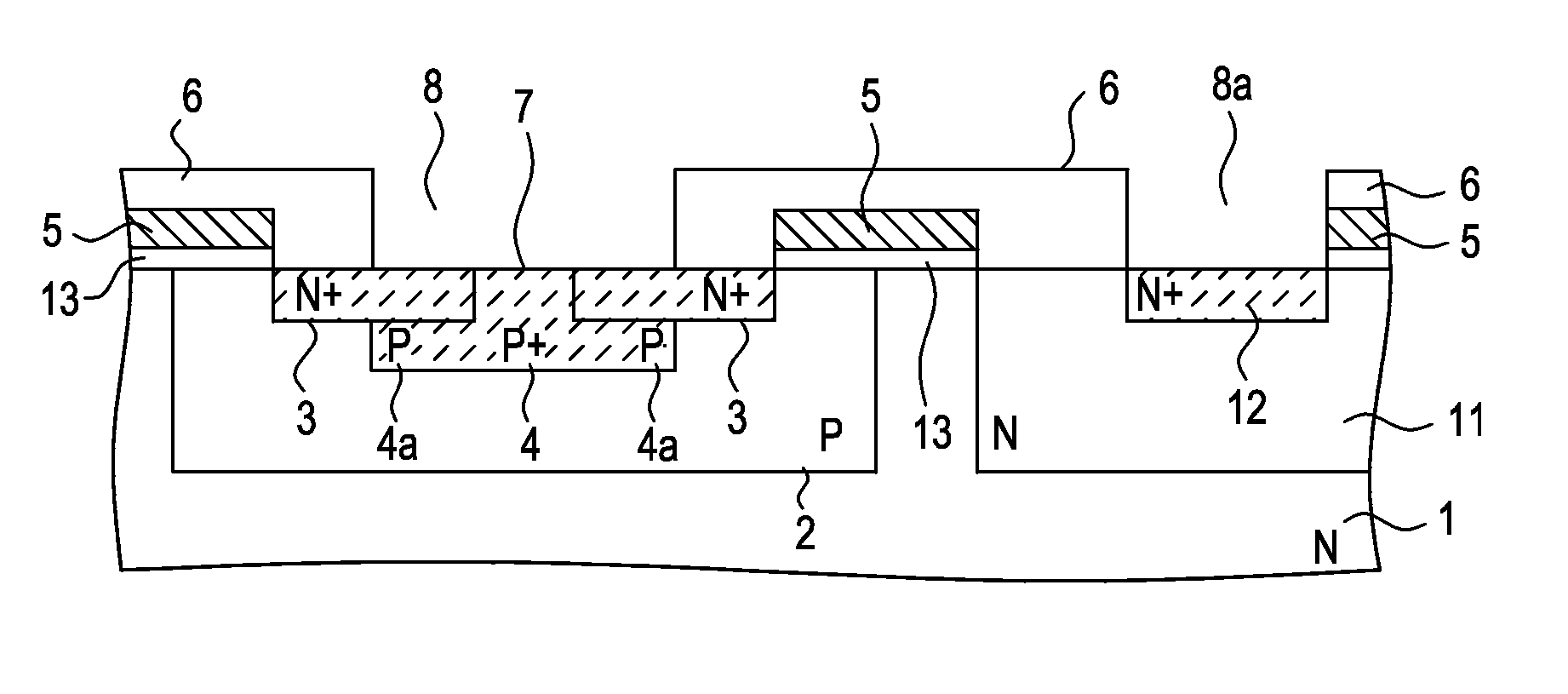
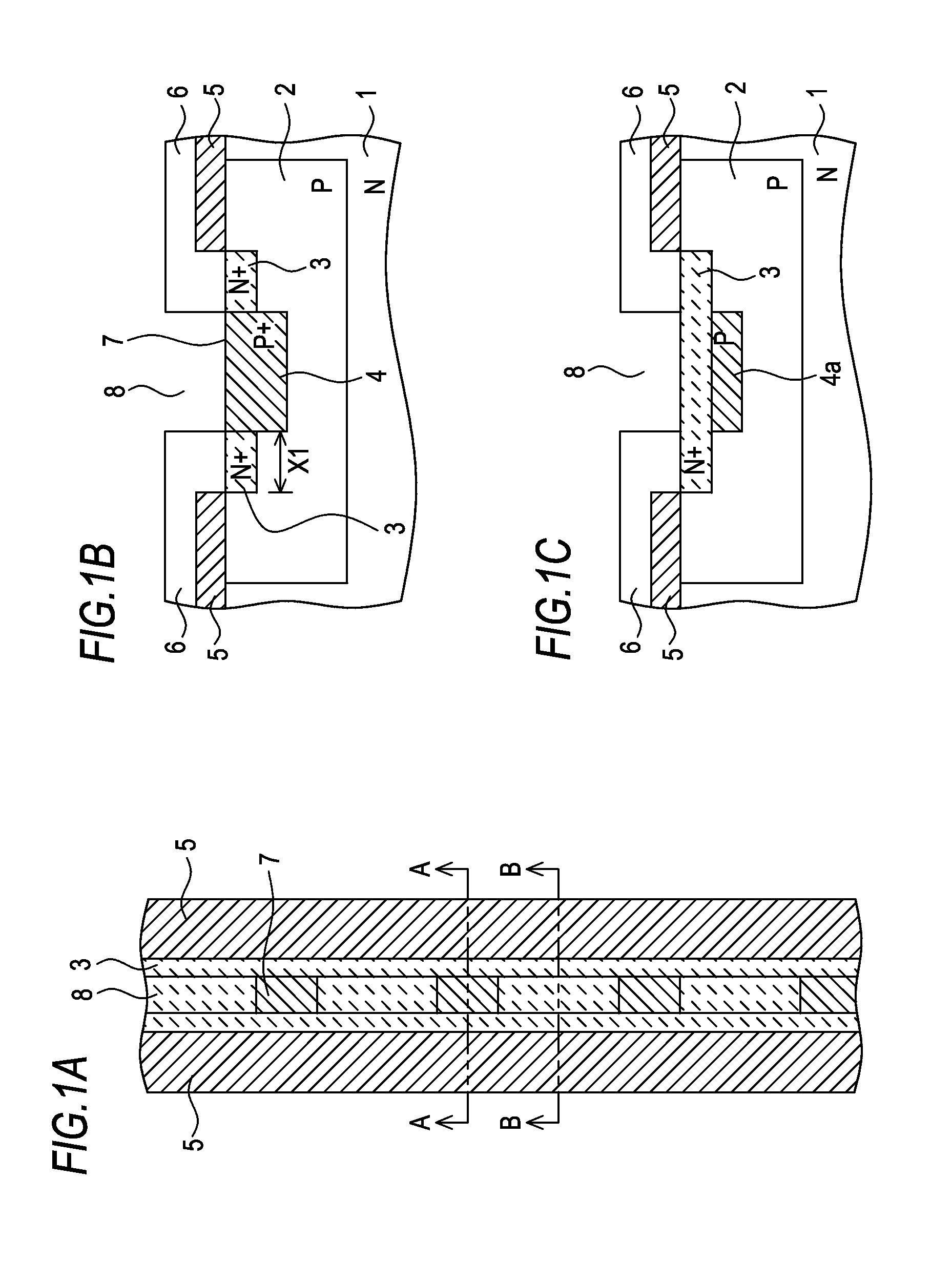
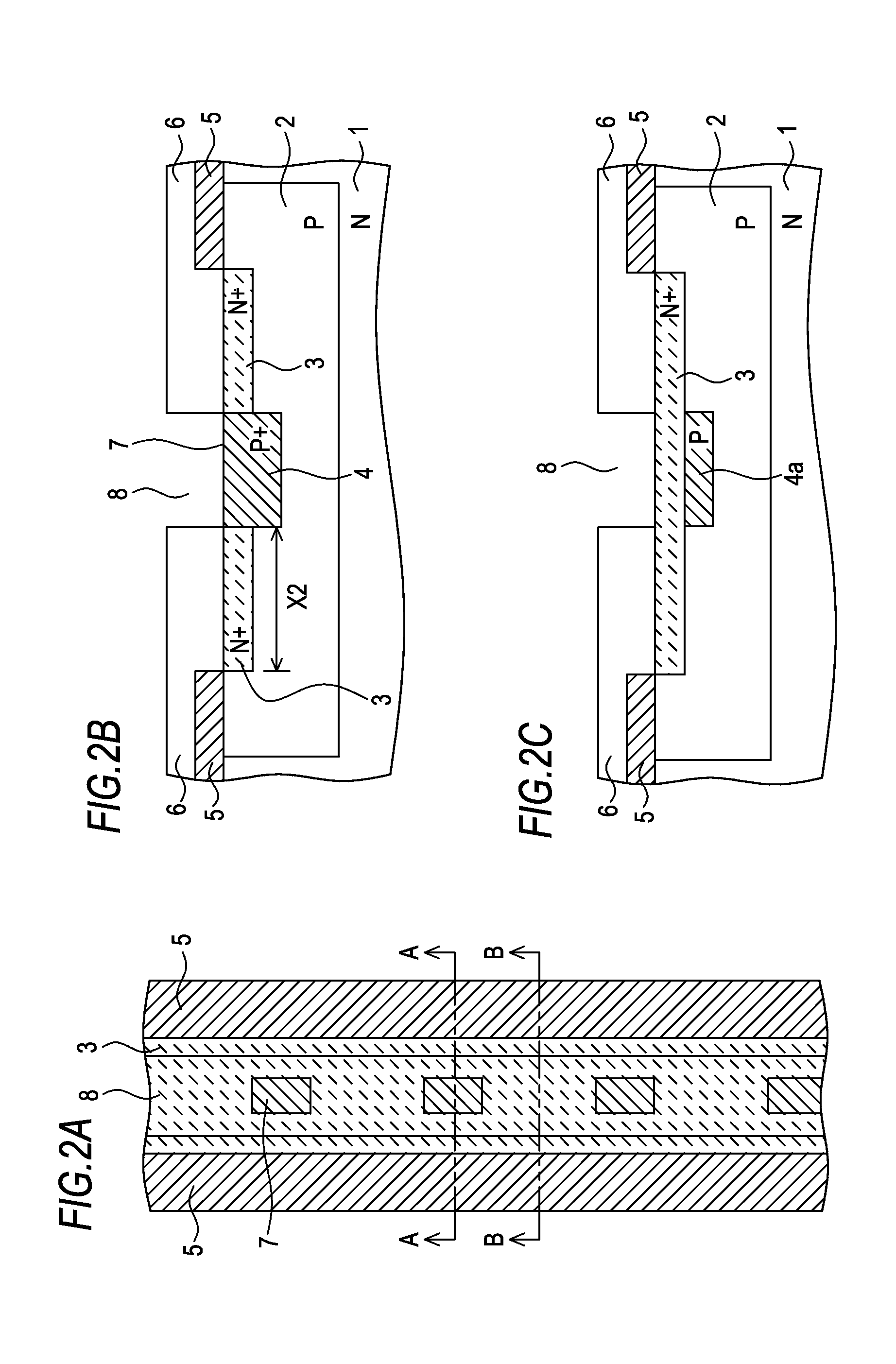
An ESD tolerance of an LDMOS transistor is improved. An N+ type source layer shaped in a ladder and having a plurality of openings in its center is formed in a surface of a P type base layer using a gate electrode and a resist mask. A P+ type contact layer is formed to be buried in the opening. At that time, a distance from an edge of the opening, that is an edge of the P+ type contact layer, to an edge of the N+ type source layer is set to a predetermined distance. The predetermined distance is equal to a distance at which an HBM+ESD tolerance of the LDMOS transistor, which increases as the distance increases, begins to saturate.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Capacitive sensor
InactiveUS10372280B2Sufficient ESD toleranceImprove ESD toleranceInsulated cablesElectrical equipmentPath lengthMetal nanowires
A capacitive sensor includes a base material provided with a pattern of a light-transmissive conductive film. The light-transmissive conductive film contains metal nanowires. The pattern includes a detection pattern formed of a plurality of detection electrodes arranged with intervals and a plurality of lead-out wirings linearly extending in a first direction from the corresponding ones of the plurality of the detection electrodes. At least one of the detection electrodes of the detection pattern includes a current path-setting section for elongating the linear path length of the current from the detection electrode toward the lead-out wiring.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
LDMOS (Laterally Diffused Metal Oxide Semiconductor) device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102931234AIncrease holding voltageImprove toleranceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLDMOSElectrostatic discharge
Owner:CSMC TECH FAB2 CO LTD
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) tolerance for a lateral double diffusion metal oxide semiconductor (LDMOS) transistor
An ESD tolerance of an LDMOS transistor is improved. An N+ type source layer shaped in a ladder and having a plurality of openings in its center is formed in a surface of a P type base layer using a gate electrode and a resist mask. A P+ type contact layer is formed to be buried in the opening. At that time, a distance from an edge of the opening, that is an edge of the P+ type contact layer, to an edge of the N+ type source layer is set to a predetermined distance. The predetermined distance is equal to a distance at which an HBM+ESD tolerance of the LDMOS transistor, which increases as the distance increases, begins to saturate.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
ldmos device and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN102931234BIncrease holding voltageImprove toleranceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLDMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
Owner:CSMC TECH FAB2 CO LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20140117451A1Esd tolerance be increaseImprove ESD toleranceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityPower semiconductor device
Provided is a semiconductor device having high ESD tolerance. A first via (16) is used for electrically connecting a pad (22) to a drain of an NMOS transistor of an ESD protective circuit. The first vias (16) are formed under the pad (22) only on one side of a rectangular ring-shaped intermediate metal film (17) and on another side thereof opposed to the one side. In other words, all the first vias (16) for establishing an electrical connection to the drains are present substantially directly under the pad (22). Consequently, a surge current caused by ESD and applied to the pad (22) is more likely to flow uniformly among all the drains. Then, respective channels of the NMOS transistor of the ESD protective circuit are more likely to uniformly operate, and hence the ESD tolerance of the semiconductor device is increased.
Owner:ABLIC INC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS9006831B2Improve ESD toleranceSpeed up the flowTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringSemiconductor
Provided is a semiconductor device having high ESD tolerance. A first via (16) is used for electrically connecting a pad to a drain of an NMOS transistor of an ESD protection circuit. The first via (16) is arranged directly above the drain and present substantially directly under the pad. Consequently, a surge current caused by ESD and applied to the pad is more likely to flow uniformly among all the drains. Then, respective channels of the NMOS transistor of the ESD protection circuit are more likely to uniformly operate, and hence the ESD tolerance of the semiconductor device increases.
Owner:ABLIC INC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS9640526B2Improve ESD toleranceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Electrostatic protection element layout structure with high electrostatic discharge tolerance
ActiveCN110620109AImprove ESD toleranceLower resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrostatic dischargeHigh energy
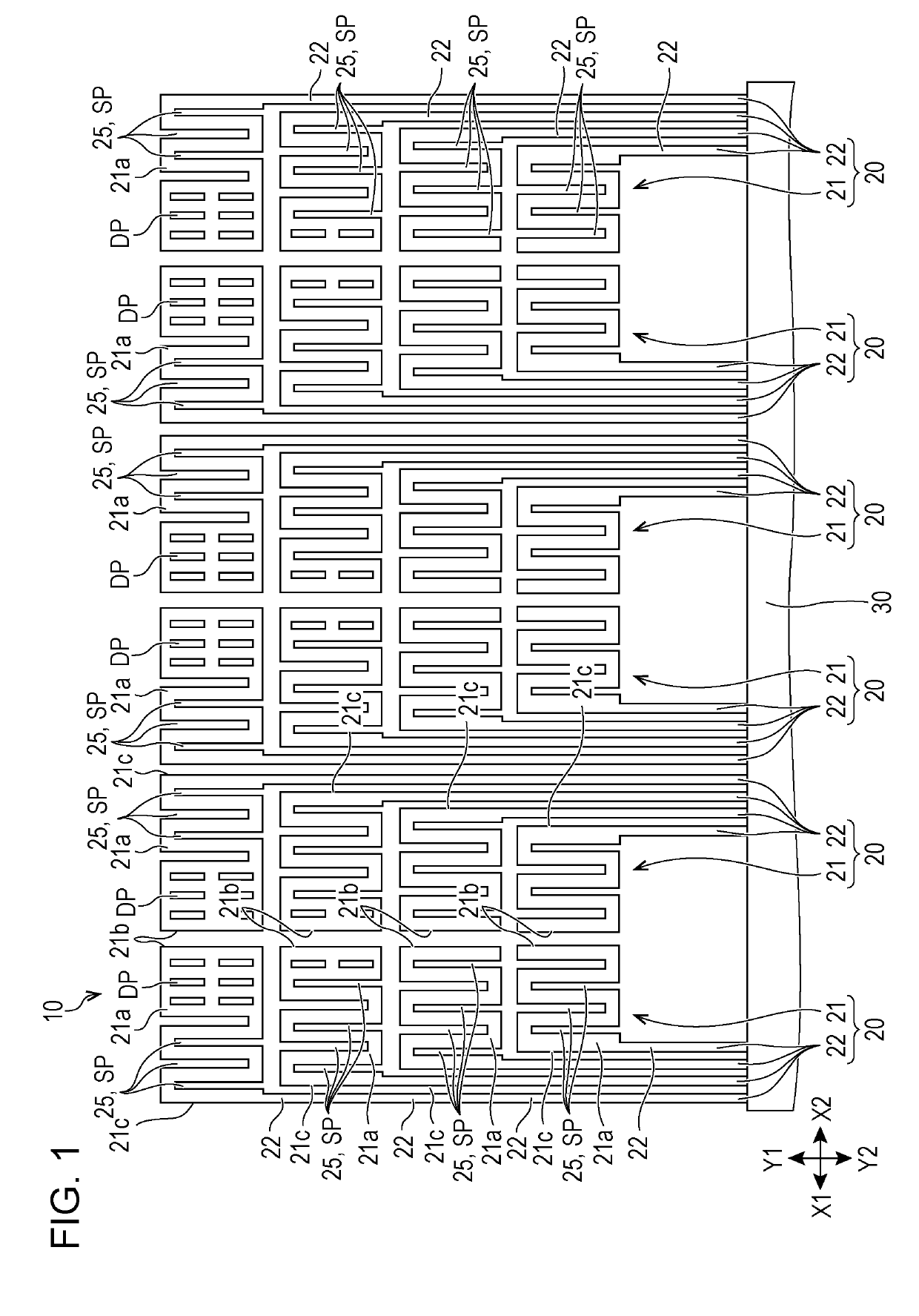
The invention discloses an electrostatic protection element layout structure with high electrostatic discharge tolerance. The structure comprises a plurality of NMOS transistors connected in parallel,wherein the NMOS transistors connected in parallel form an isolated NMOS multi-finger type semiconductor layout structure, a middle region of the isolated NMOS multi-finger semiconductor layout structure is a P-type doped region doped with high-energy P-type implanted ion concentration, so substrate resistance of the middle region is reduced. The structure is advantaged in that the total substrate resistance of the NMOS transistors corresponding to the middle region can be reduced, substrate resistance difference between the NMOS transistor corresponding to the middle region and the NMOS transistor corresponding to one of the NMOS transistors at two sides is reduced, so the NMOS transistors can be uniformly conducted, and the electrostatic discharge tolerance of the NMOS transistors is improved.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOG TECH INC
Electrostatic discharge preventing method for display and electrostatic discharge preventing device
ActiveCN1326241CImprove efficiencyImprove ESD toleranceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrostatic dischargeEngineering
A protective method and circuit distribution for electrostatic discharge of display device, which contains dividing a first input power line into plurality of second input power lines, setting an electrostatic protector around each second input power line for protecting from electrostatic discharge passing second power line, merging above mentioned second input power line into a third input power line.
Owner:TPO DISPLAY
Semiconductor element, semiconductor device, method for manufacturing semiconductor element, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveCN104518020AImprove ESD toleranceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
According to one embodiment, a semiconductor element includes a first semiconductor layer, a second semiconductor layer, a first electrode, a second electrode, a control electrode, a pad unit, an insulating layer, and a conductor. The second semiconductor layer is provided on the first semiconductor layer. The first electrode is provided on the second semiconductor layer. The second electrode is provided on the second semiconductor layer. The control electrode is provided on the second semiconductor layer. The pad unit is provided on the second semiconductor layer. The pad unit is electrically connected to the control electrode. The insulating layer is provided on the second semiconductor layer. The insulating layer has an opening. The conductor is provided on the insulating layer. The conductor covers at least a part of the opening.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Electrostatic discharge protection circuit and deep submicron semiconductor component thereof
InactiveCN108231758AImprove ESD toleranceImproved ESD toleranceTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrostatic discharge protectionSemiconductor components
The invention discloses an electrostatic discharge protection circuit and a deep submicron semiconductor component thereof. A boundary between a heavily doped region corresponding to a drain electrodeof the deep submicron semiconductor component and an adjacent lightly doped region are pushed outwardly, so that a gap is formed between the boundary and the sidewall of the nearest grid insulating layer and the boundary is not aligned with the sidewall of the grid insulating layer. Thus, in the deep submicron semiconductor component, the drain electrode is not too close to a source electrode dueto smaller layout of a deep submicron technology, and the electrostatic discharge tolerance of the deep submicron semiconductor component is improved effectively.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOG TECH INC
ESD protection component layout structure with high ESD tolerance
ActiveCN110620109BImprove ESD toleranceLower resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh energyEngineering
The invention discloses a layout structure of an electrostatic protection element with high electrostatic discharge tolerance, which includes a plurality of parallel-connected NMOS transistors, and these parallel-connected NMOS transistors form an isolated NMOS multi-finger semiconductor layout structure; wherein the The middle region of the isolated NMOS multi-finger semiconductor layout structure is a P-type doped region doped with high-energy P-type implanted ion concentration, which reduces the substrate resistance of the middle region; thus, the corresponding The total substrate resistance of the NMOS transistor is reduced, and the substrate resistance difference between it and the NMOS transistor corresponding to one of the two sides is reduced, so that the NMOS transistor can be uniformly turned on, and the electrostatic discharge tolerance of the NMOS transistor is improved.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOG TECH INC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20140138762A1Improve ESD toleranceSpeed up the flowTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringSemiconductor
Provided is a semiconductor device having high ESD tolerance. A first via (16) is used for electrically connecting a pad to a drain of an NMOS transistor of an ESD protection circuit. The first via (16) is arranged directly above the drain and present substantially directly under the pad. Consequently, a surge current caused by ESD and applied to the pad is more likely to flow uniformly among all the drains. Then, respective channels of the NMOS transistor of the ESD protection circuit are more likely to uniformly operate, and hence the ESD tolerance of the semiconductor device increases.
Owner:ABLIC INC
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS7974056B2Improve pressure resistanceImprove response speedTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor
A semiconductor device which can achieve high breakdown voltage and high ESD tolerance of a current drive output terminal at the same time, and can quicken the response speed of a current flowing through the current drive output terminal. The inventive semiconductor device is provided, between the current drive output terminal and a first transistor or a low breakdown voltage element, with a second transistor having a breakdown voltage higher than that of the first transistor or that of the low breakdown voltage element. Furthermore, the inventive semiconductor device is provided with a diode having an anode connected with a path between the first transistor or the low breakdown voltage element and the second transistor, and a cathode connected with an ESD protection circuit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
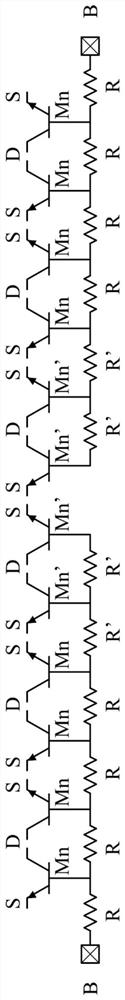
Transistor capable of boosting electro-static discharge tolerance and its layout method
InactiveCN100544000CImprove ESD toleranceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringGuard ring
Transistors and their layout methods that can improve electrostatic discharge tolerance. The layout method includes: defining the first conductive type guard ring area; defining the first elongated second conductive type diffusion area; defining the second elongated second conductive type diffusion area, wherein the first and second elongated second conductive type diffusion areas The two conductive type diffusion areas are not connected; the ring type second conductivity type diffusion area is defined between the first and second elongated second conductivity type diffusion areas; the first conductivity type is defined inside the ring type second conductivity type diffusion area Diffusion area; a first grid is defined between the first elongated second conductivity type diffusion area and the ring type second conductivity type diffusion area; A second grid is defined between the conductive diffusion regions. The first and second elongated second conductive type diffusion regions are arranged parallel to each other inside the first conductive type guard ring region, and the first and second elongated second conductive type diffusion regions are arranged on the first conductive type on opposite sides of the type guard ring area.
Owner:ILI TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Semiconductor light emitting element
ActiveCN105428479BIncrease light emitting areaReduce migration rateSemiconductor devicesIsolation layerNitride
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductors, and particularly relates to a semiconductor light emitting element. The semiconductor light emitting element comprises a substrate, and a nitride buffer layer, an n-type layer, a shallow quantum well layer, a multiple quantum well layer and a p-type layer formed on the substrate sequentially. The semiconductor light emitting element is characterized in that a composite structure layer is also inserted between the shallow quantum well layer and the multiple quantum well layer; the composite structure layer at least comprises a p-type doped GaN layer, an n-type doped GaN layer, and an isolation layer located between the p-type doped GaN layer and the n-type doped GaN layer. The feature that p-type impurities in the composite structure layer are migrated to the shallow quantum well layer and the multiple quantum well layer is used, light emitting of the shallow quantum well layer and the composite structure layer is promoted while the light-emitting strength of the multiple quantum well layer is enhanced, the light outgoing area of the semiconductor element is increased, and the light-emitting strength is further enhanced.
Owner:ANHUI SANAN OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com