Semiconductor light emitting element
A technology of light-emitting components and semiconductors, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as asymmetric distribution of electrons and holes, and achieve the effects of improving luminous efficiency, avoiding lattice quality, and increasing luminous intensity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
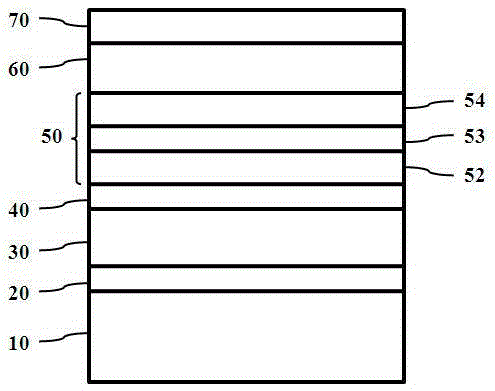
[0032] See attached figure 1 , a semiconductor element with a composite structure layer 50, comprising a substrate 10, and a nitride buffer layer 20, an n-type layer 30, a shallow quantum well layer 40, a multi-quantum well layer 60 and a p-type layer sequentially formed on the substrate 10 layer 70, and a composite structure layer 50 located between the shallow quantum well layer 40 and the multiple quantum well layer 60, wherein the substrate 10 is a sapphire flat substrate, a sapphire patterned substrate, a silicon nitride substrate, a GaN substrate , silicon substrate, glass substrate or metal substrate, the nitride buffer layer 20 is a single-layer structure or a superlattice structure, which is a binary or ternary structure composed of Ga, N, In, Al Or a quaternary structure; the p-type layer 70 is a Mg-doped GaN layer.
[0033] Continue to see attached figure 1 , in this embodiment, the composite structure layer 50 at least includes a p-type doped GaN layer 54, an n-t...
Embodiment 2
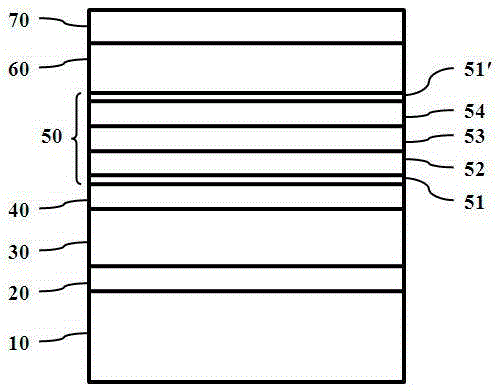
[0036] See attached figure 2 The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the composite structure layer 50 also includes a first electron blocking layer 51 adjacent to the shallow quantum well layer 40 and a second electron blocking layer 51' adjacent to the multi-quantum well layer 60, wherein, The materials of the first electron blocking layer 51 and the second electron blocking layer 51' are both AlGaN, and their thicknesses are the same or different. In this embodiment, the thicknesses of the electron blocking layer 51 and the second electron blocking layer 51' are preferably the same, and the preferred thickness range is Both are 400 angstroms to 600 angstroms.
[0037] Specifically, see the attached image 3 , the composite structure layer 50 from bottom to top is the first electron blocking layer 51, n-type doped GaN layer 52, Al x In y Ga 1-x-y N isolation layer 53, p-type doped GaN layer 54, and second electron blocking layer 51'; wherein, the ba...
Embodiment 3
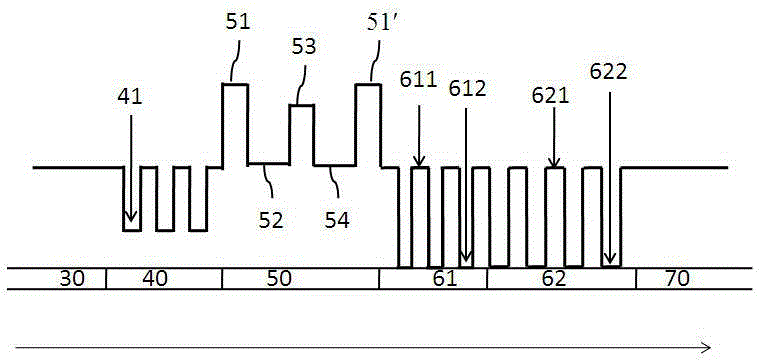
[0042] See attached Figure 4 The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the composite structure layer 50 at least includes a p-type doped GaN layer 54, an n-type doped GaN layer 52, and a layer between the p-type doped GaN layer 54 and the n-type doped GaN layer. The material between layers 52 is Al x In y Ga 1-x-y A periodic structure 50' composed of N isolation layers 53 alternately, a first electron blocking layer 51 adjacent to the shallow quantum well layer 40, and a second electron blocking layer 51' adjacent to the multi-quantum well layer 60, wherein the period of the periodic structure 50' The number is greater than or equal to 2, and each cycle includes n-type doped GaN layer 52, isolation layer 53, p-type doped GaN layer 54 and isolation layer 53, and the first electron blocking layer 51 and the second electron blocking layer 51' are rich in While collecting electrons in the composite structure layer 50, control the migration of the p-type i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com