Patents
Literature
99results about How to "Reduce junction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
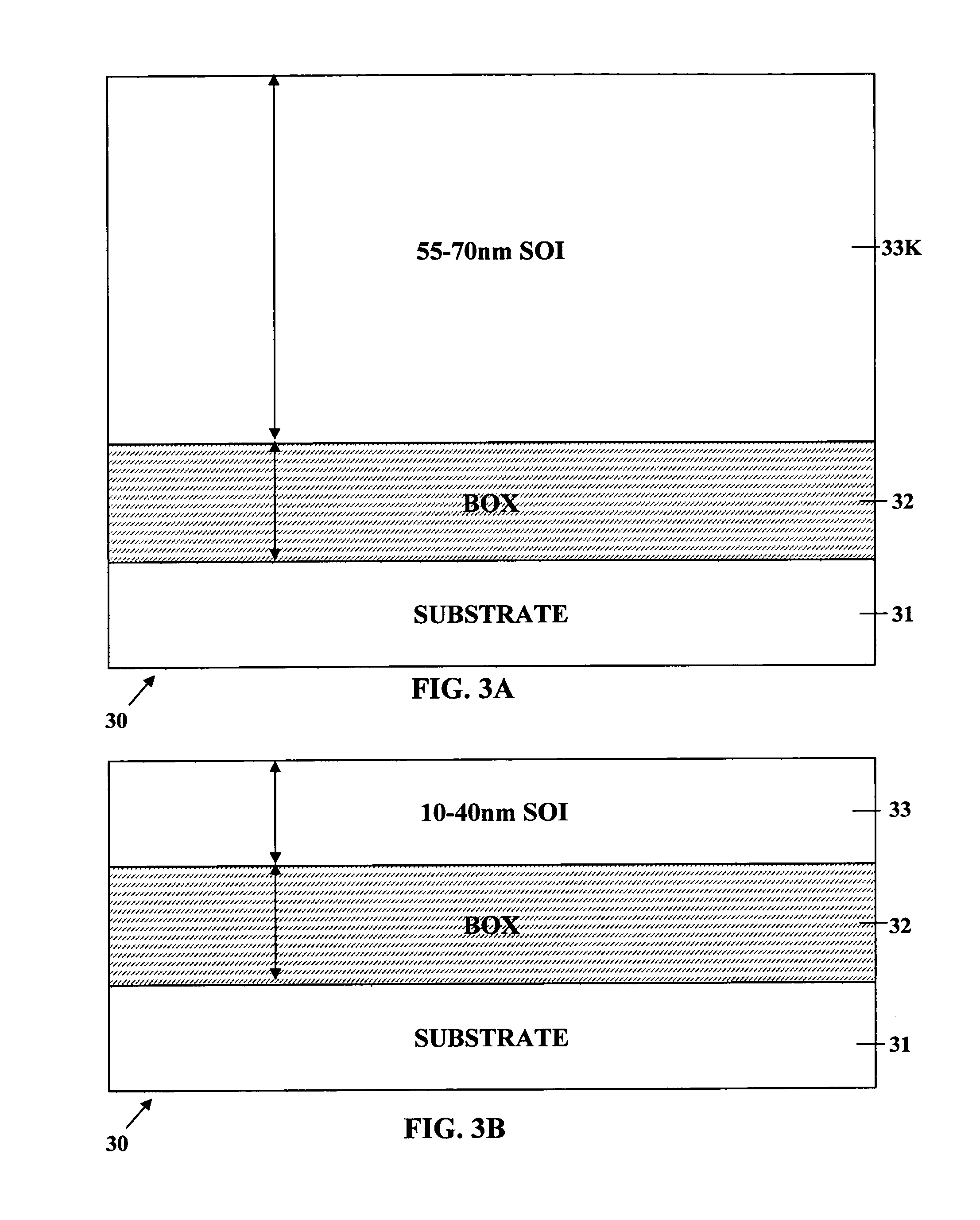
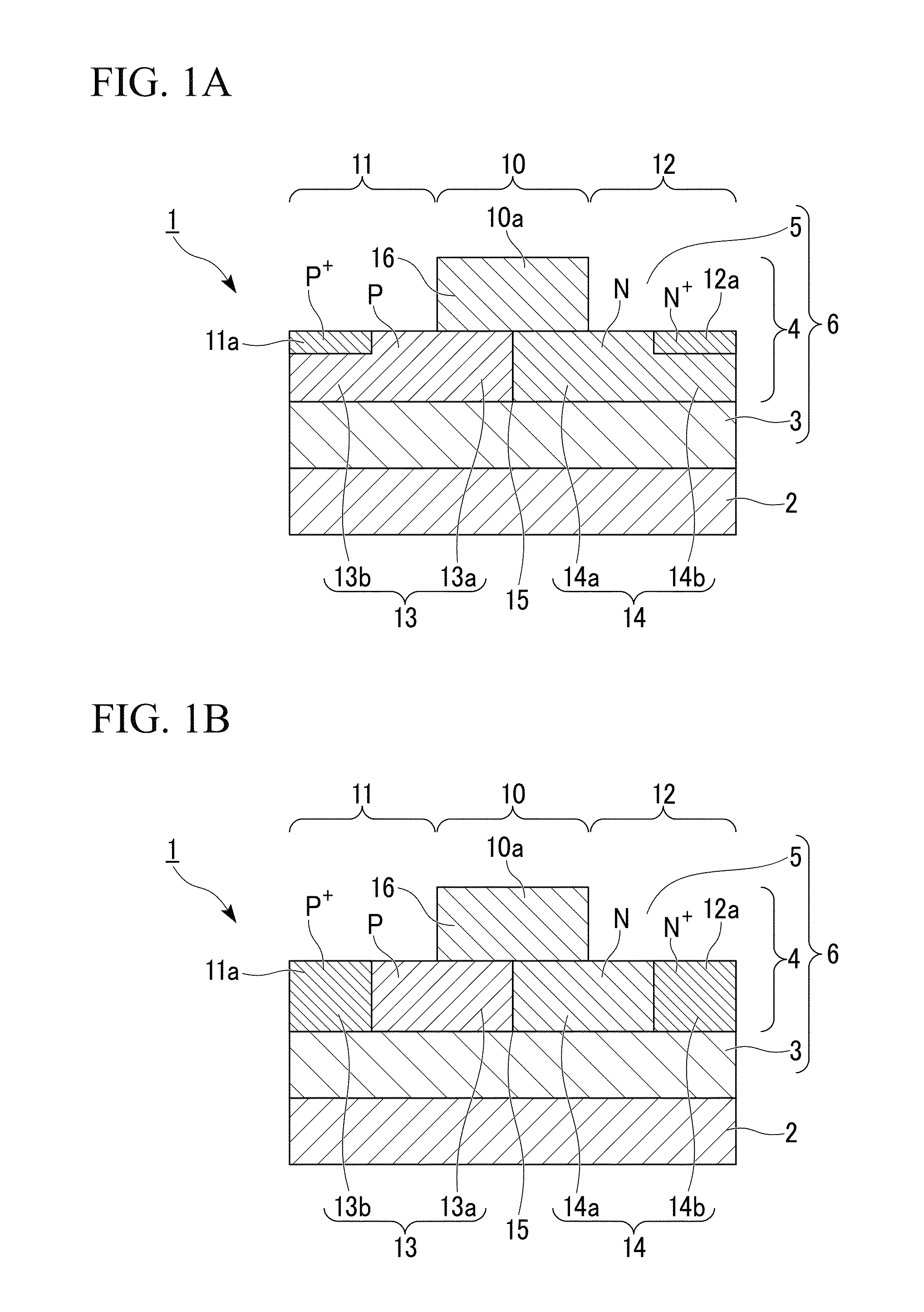
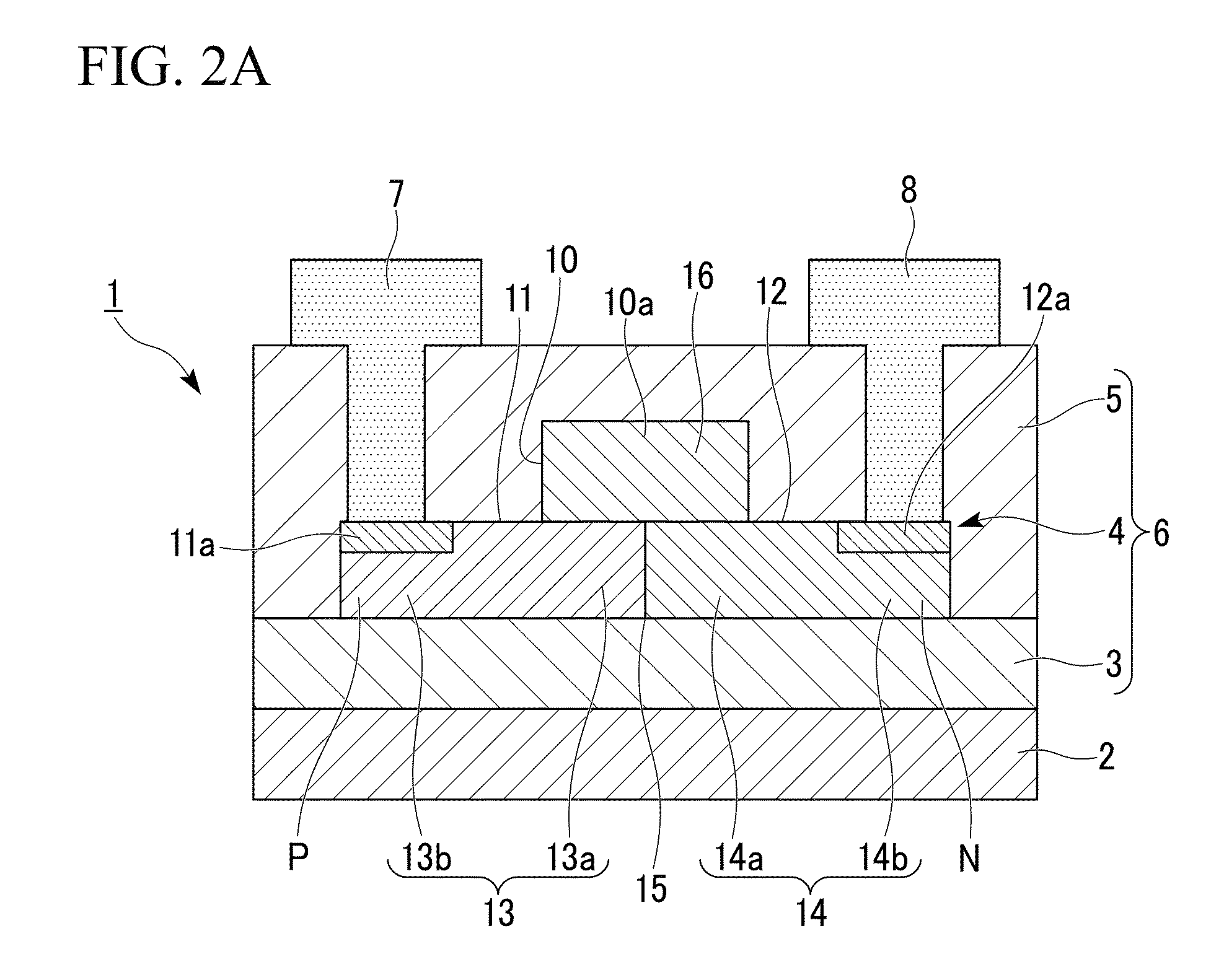
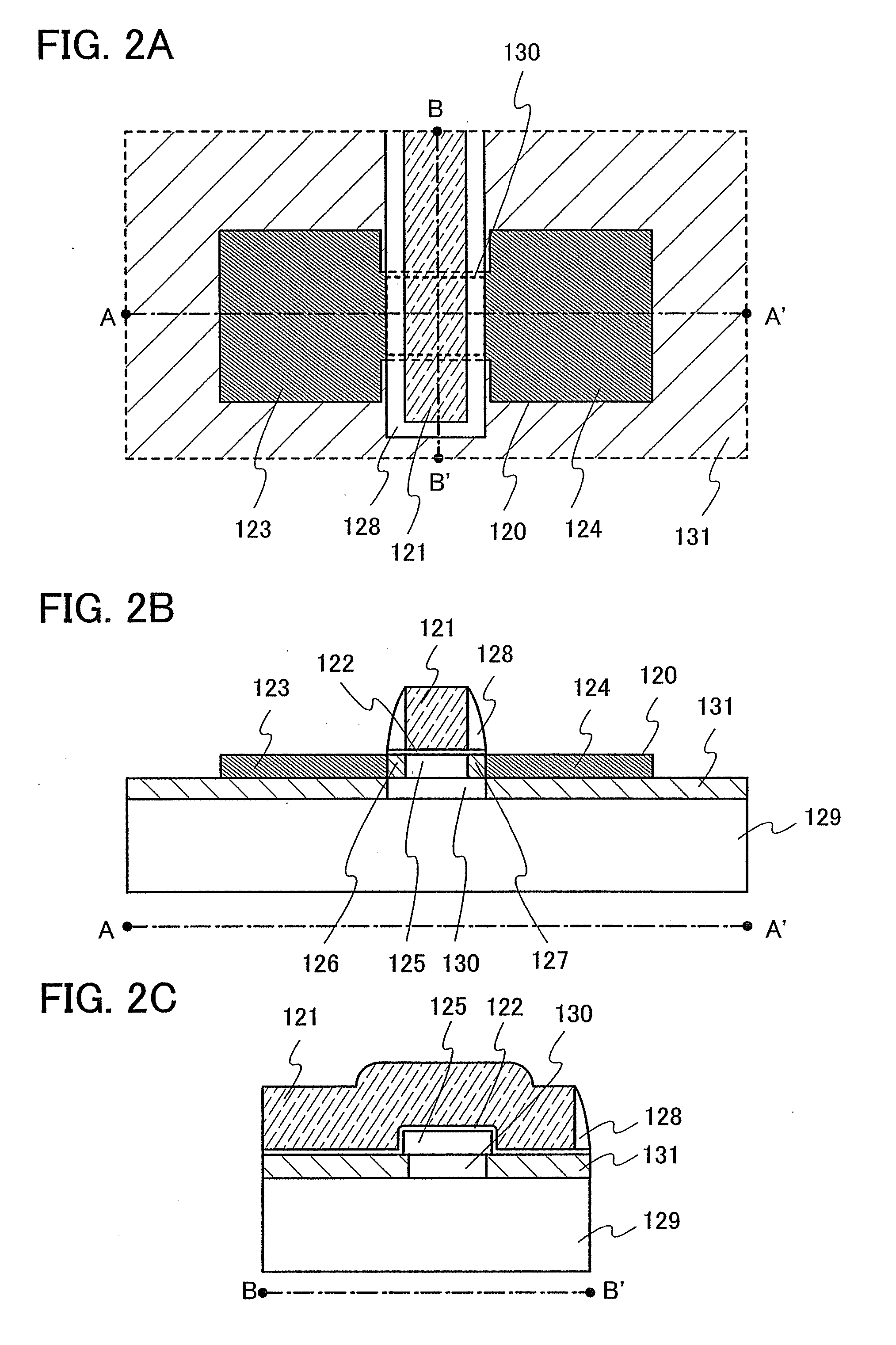
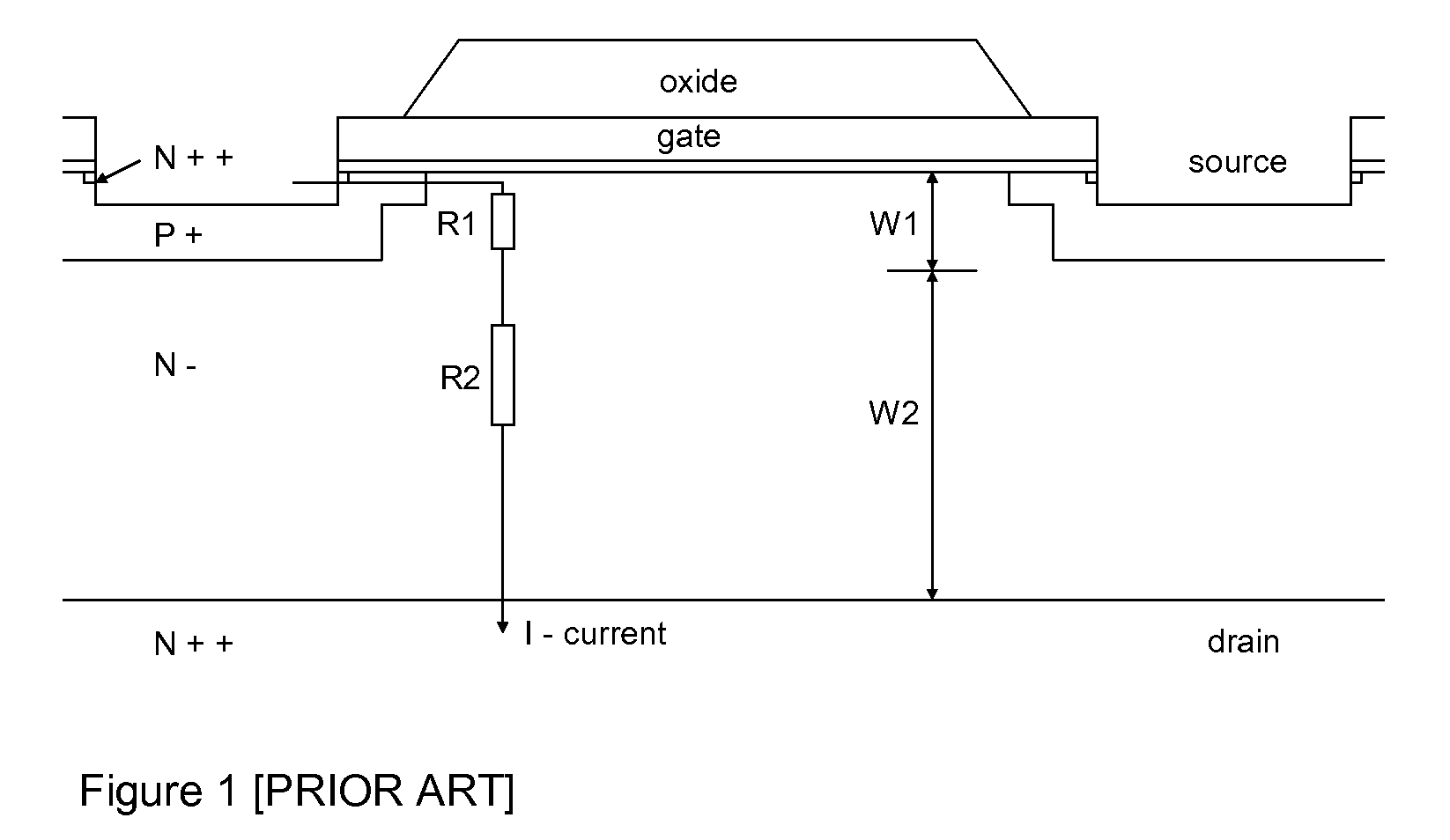
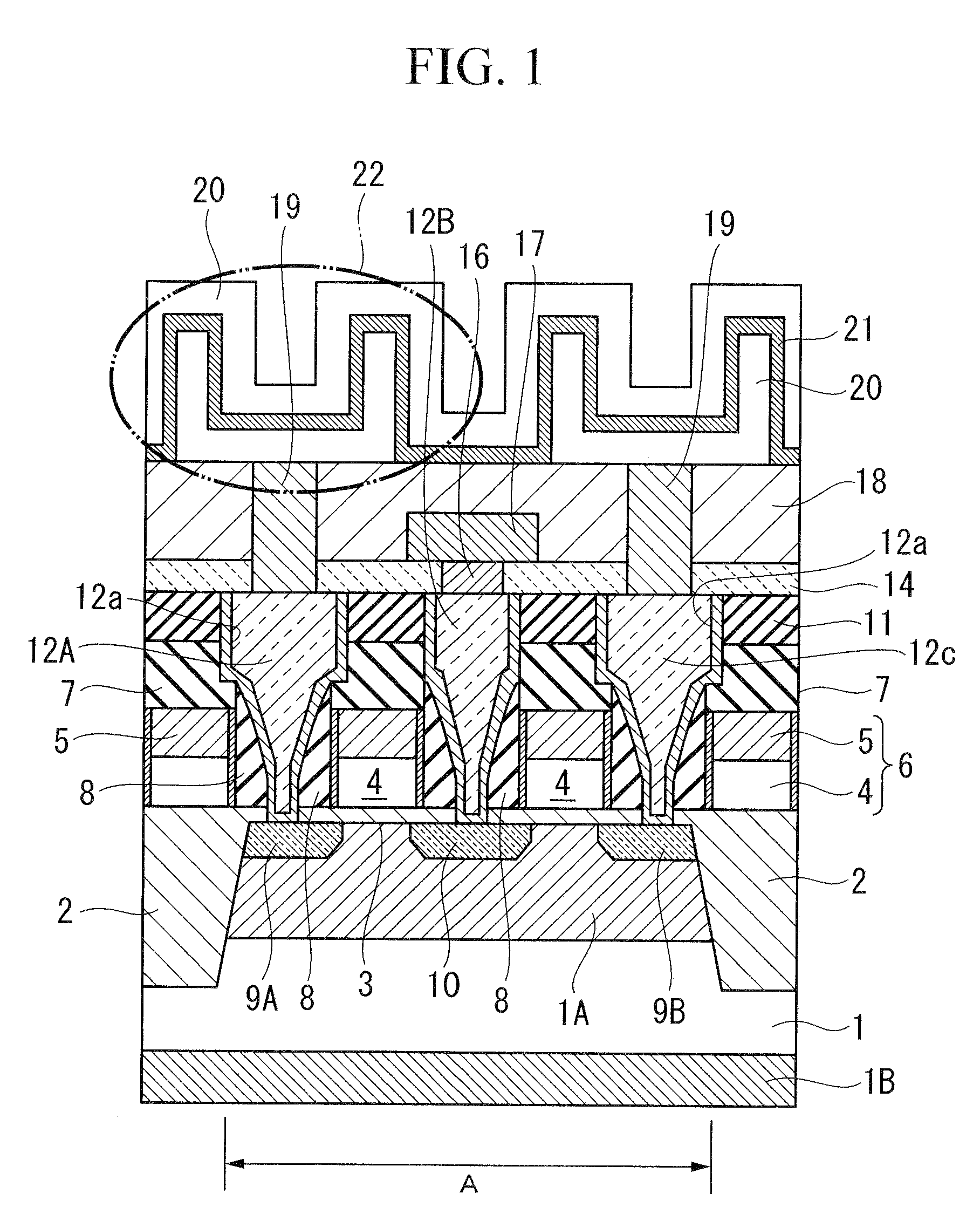
Ultra-thin body super-steep retrograde well (SSRW) FET devices
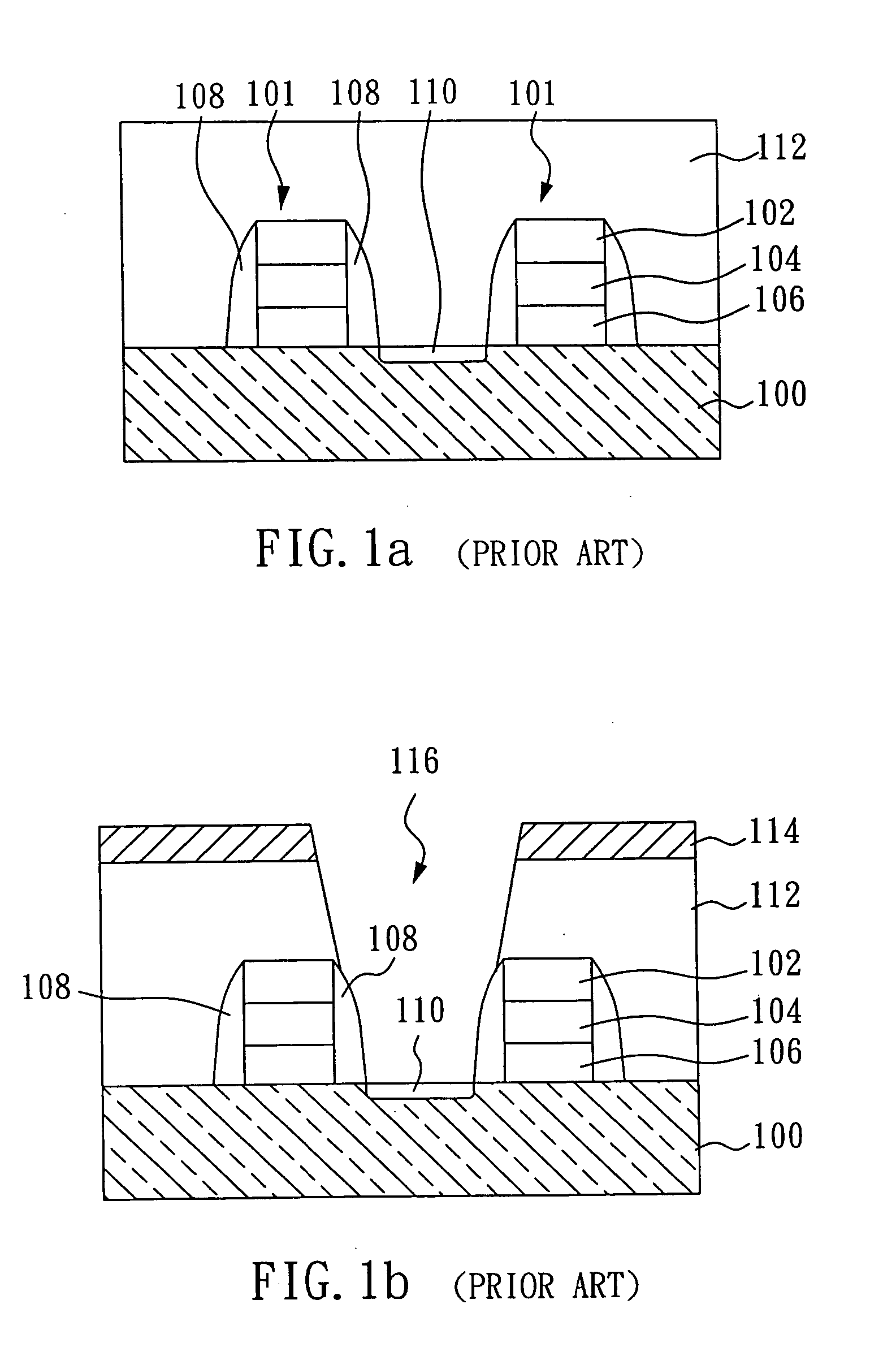
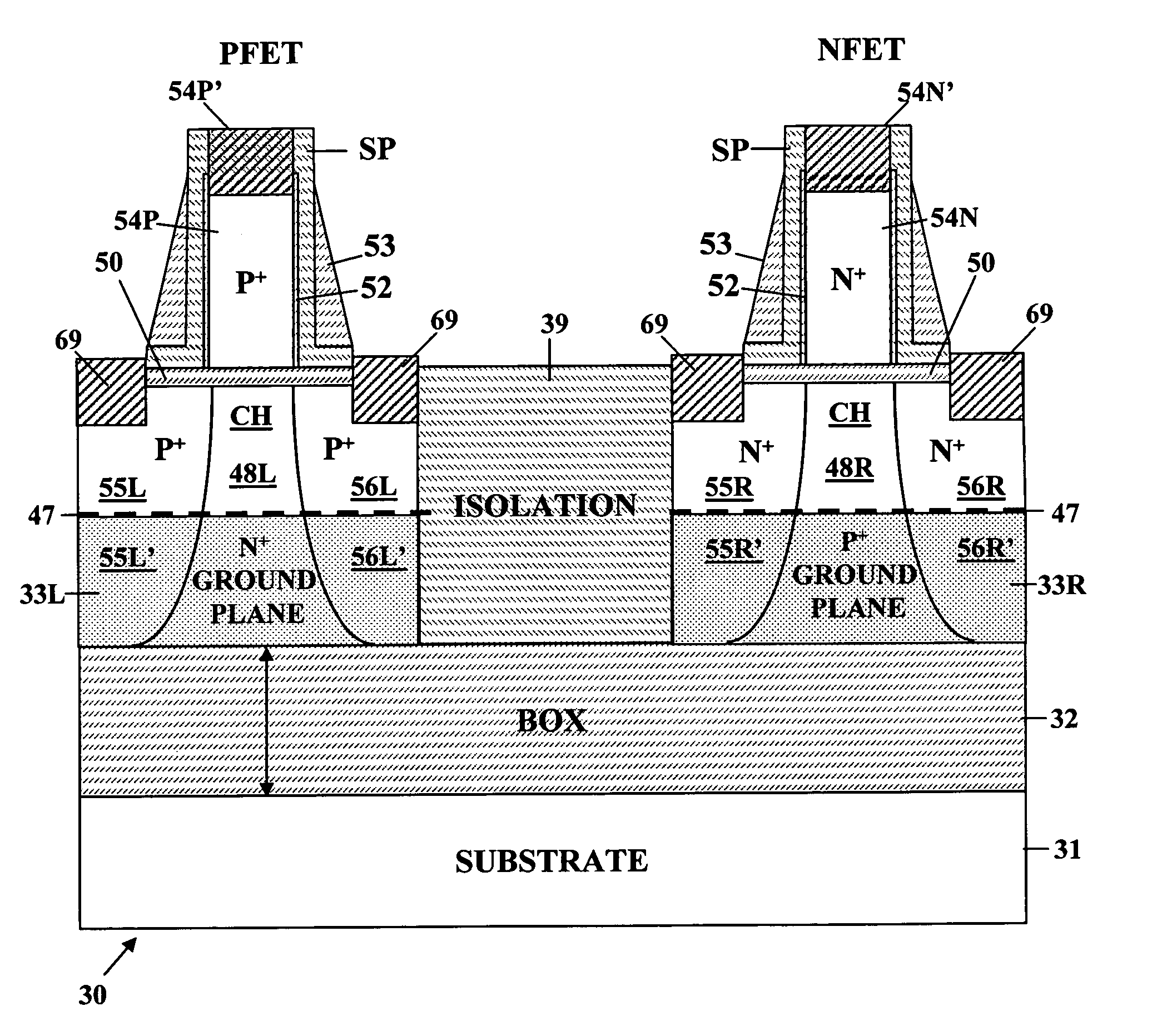
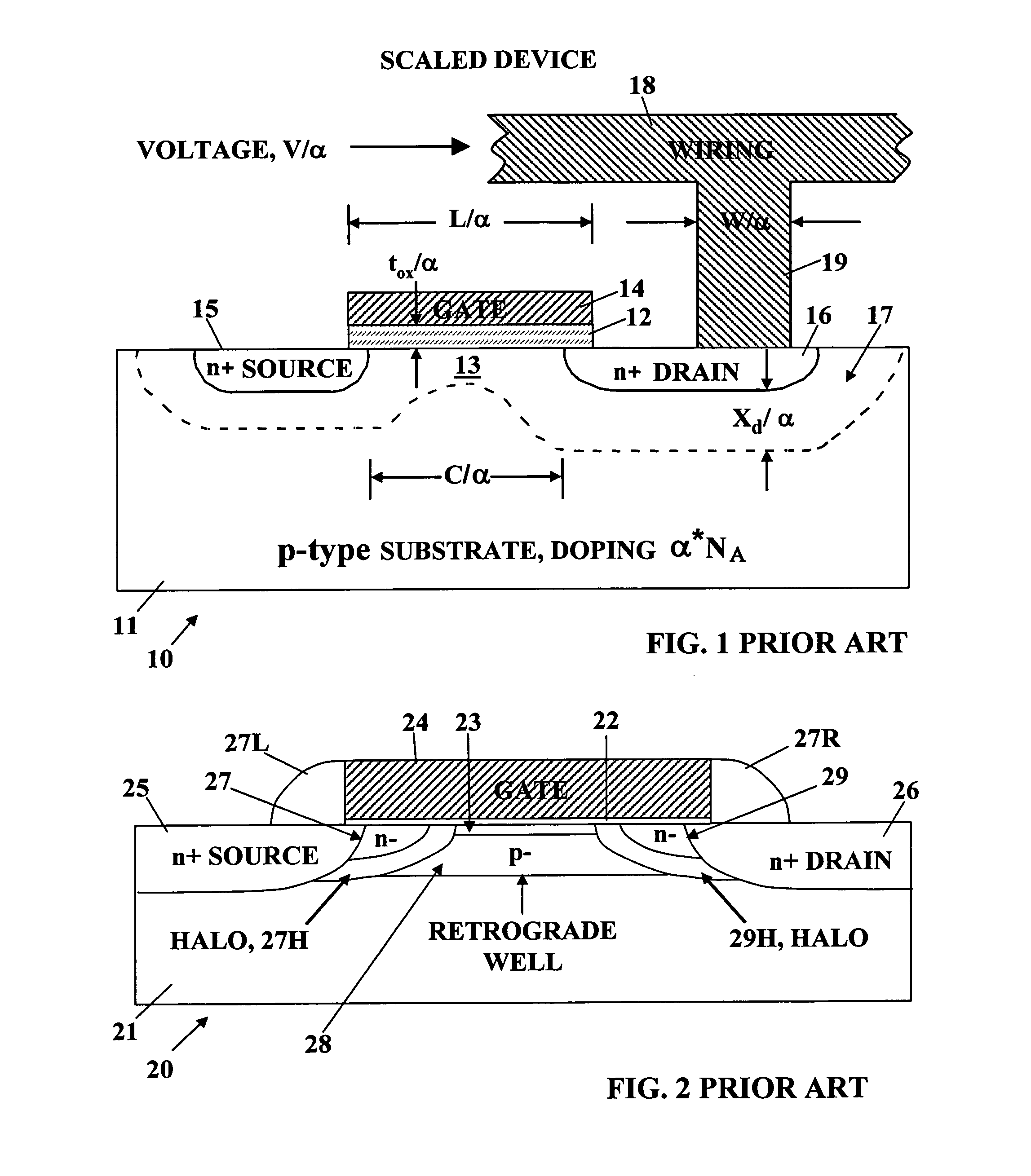
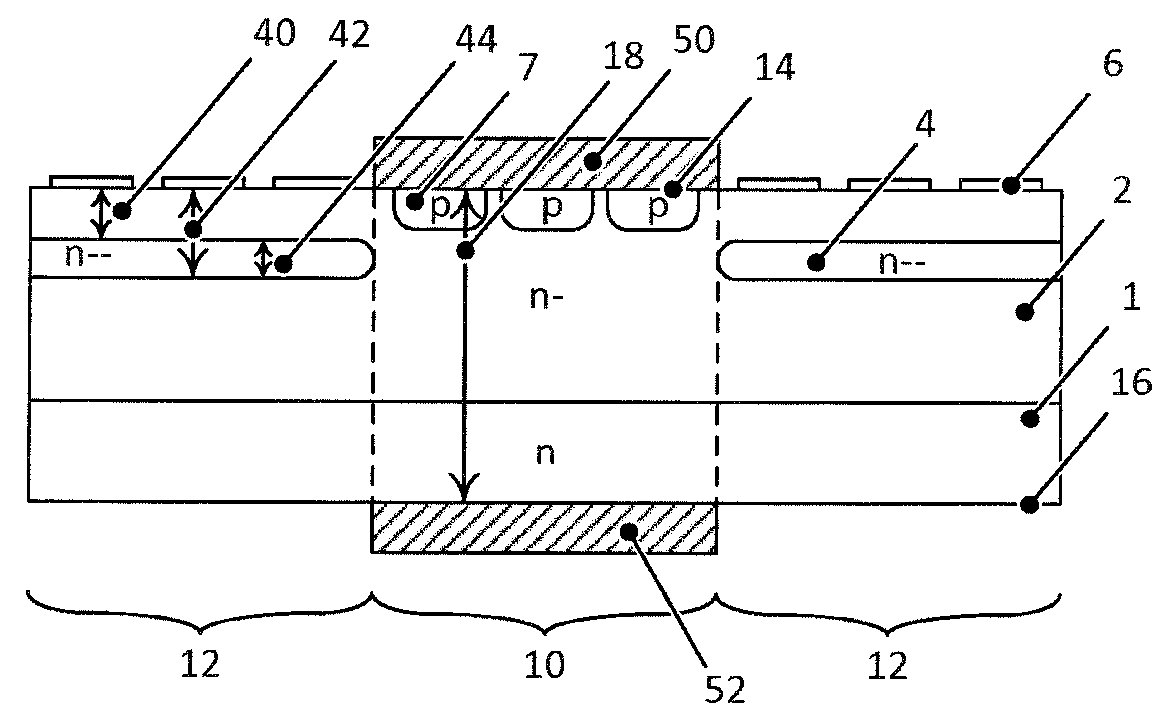
ActiveUS20060022270A1Minimize space-charge related fluctuationReduce capacitanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantGround plane
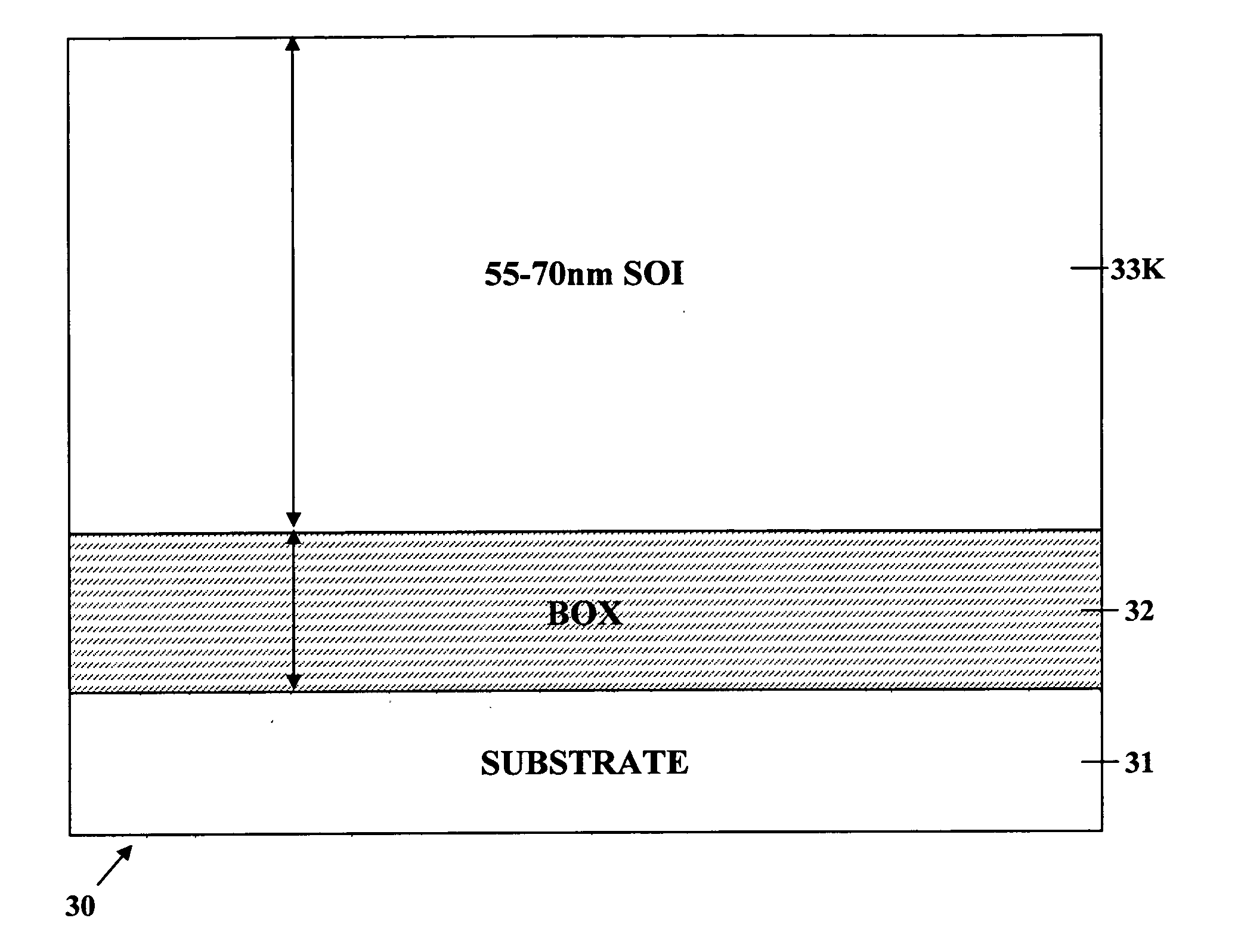
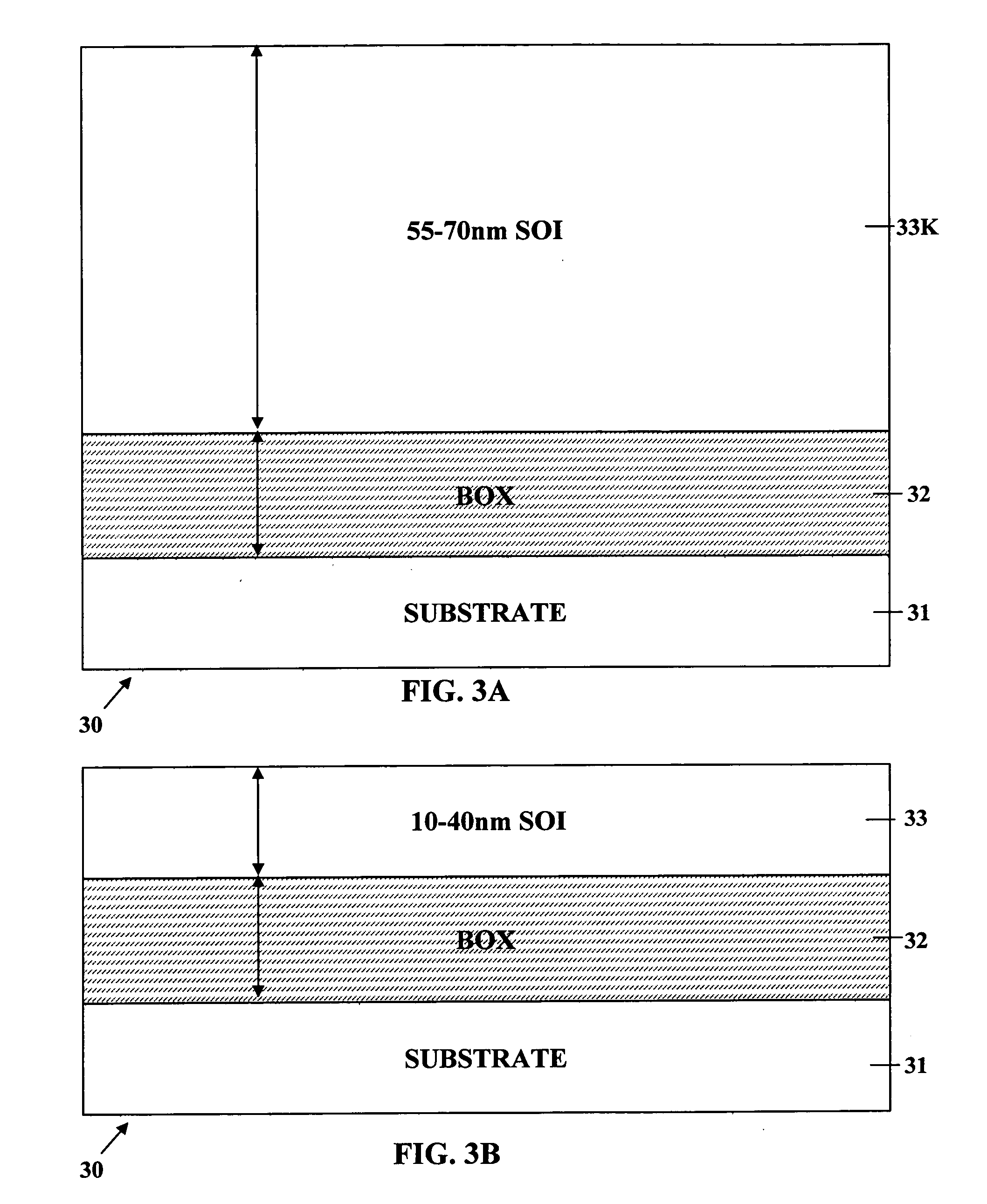
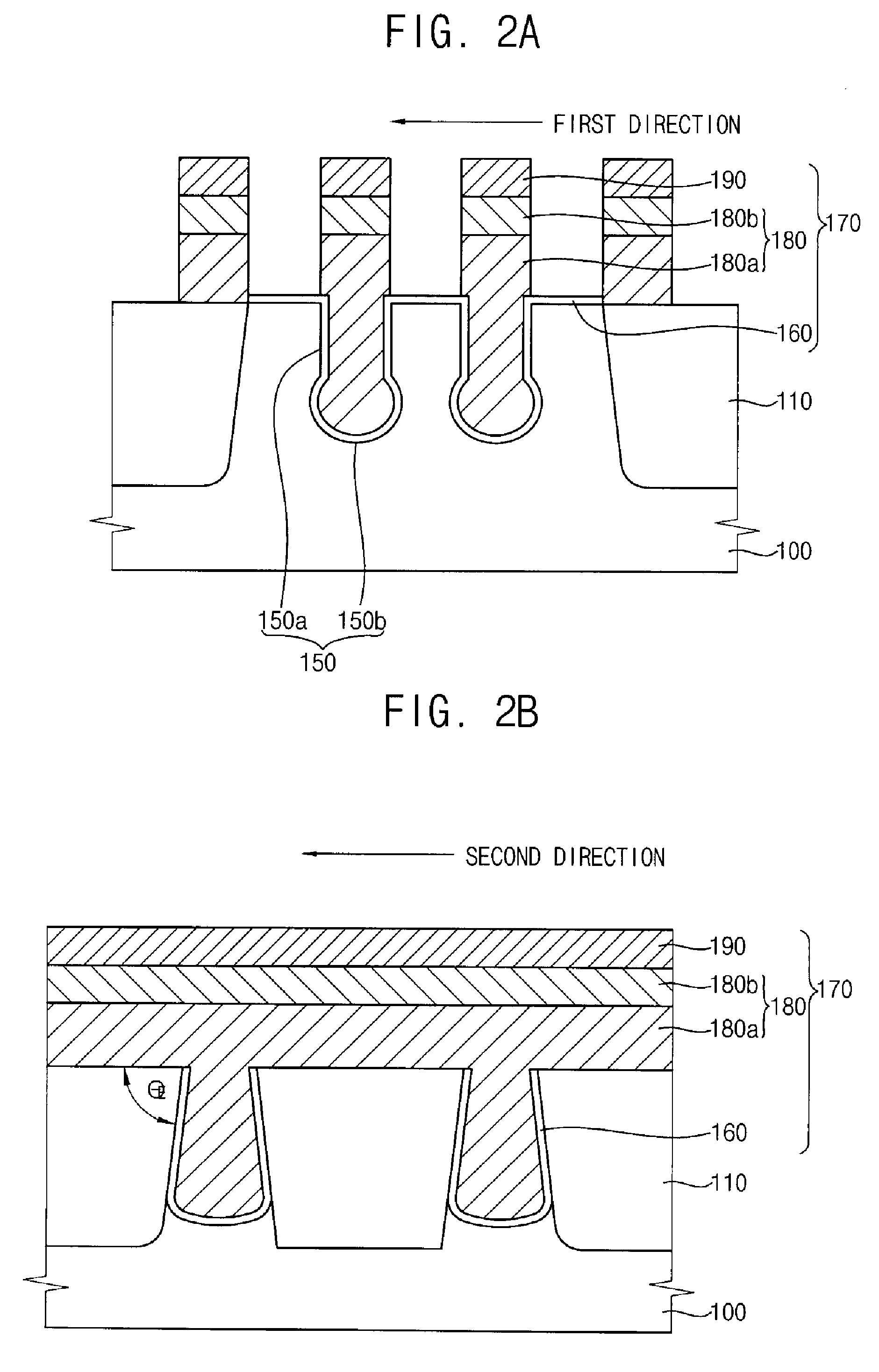
A method of manufacture of a Super Steep Retrograde Well Field Effect Transistor device starts with an SOI layer formed on a substrate, e.g. a buried oxide layer. Thin the SOI layer to form an ultra-thin SOI layer. Form an isolation trench separating the SOI layer into N and P ground plane regions. Dope the N and P ground plane regions formed from the SOI layer with high levels of N-type and P-type dopant. Form semiconductor channel regions above the N and P ground plane regions. Form FET source and drain regions and gate electrode stacks above the channel regions. Optionally form a diffusion retarding layer between the SOI ground plane regions and the channel regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method for forming self-aligned contact in semiconductor device
ActiveUS20050239282A1Prevent short-circuitingRule out the possibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialEngineering
A method for forming a self-aligned contact on a semiconductor substrate provided with a plurality of field-effect transistors. The method comprises the steps of forming a first insulating layer comprising a nitride along a profile of a gate structure and a junction region, forming a temporary layer comprising a doped oxide on the first insulating layer, removing a portion of the temporary layer by performing a selective etch of the oxide with a mask while leaving a plug portion of the temporary layer over the junction region, forming a second insulating layer comprising an undoped oxide in a region where the portion of the temporary layer is removed, removing the plug portion by performing a selective etch of the undoped oxide to form a contact hole, removing a portion of the first insulating layer at a bottom of the contact hole, and forming a conductive contact in the contact hole.
Owner:NAN YA TECH
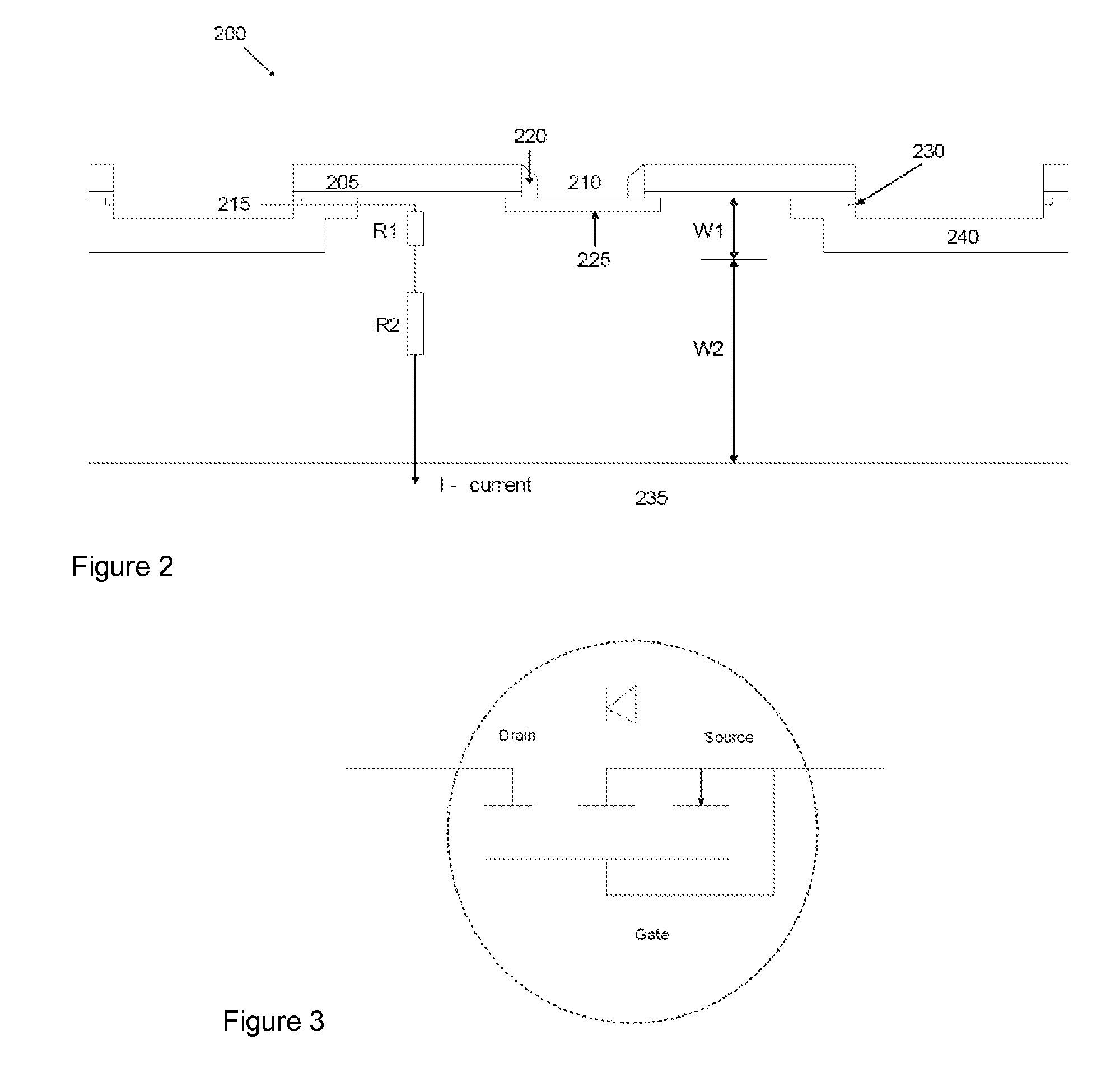
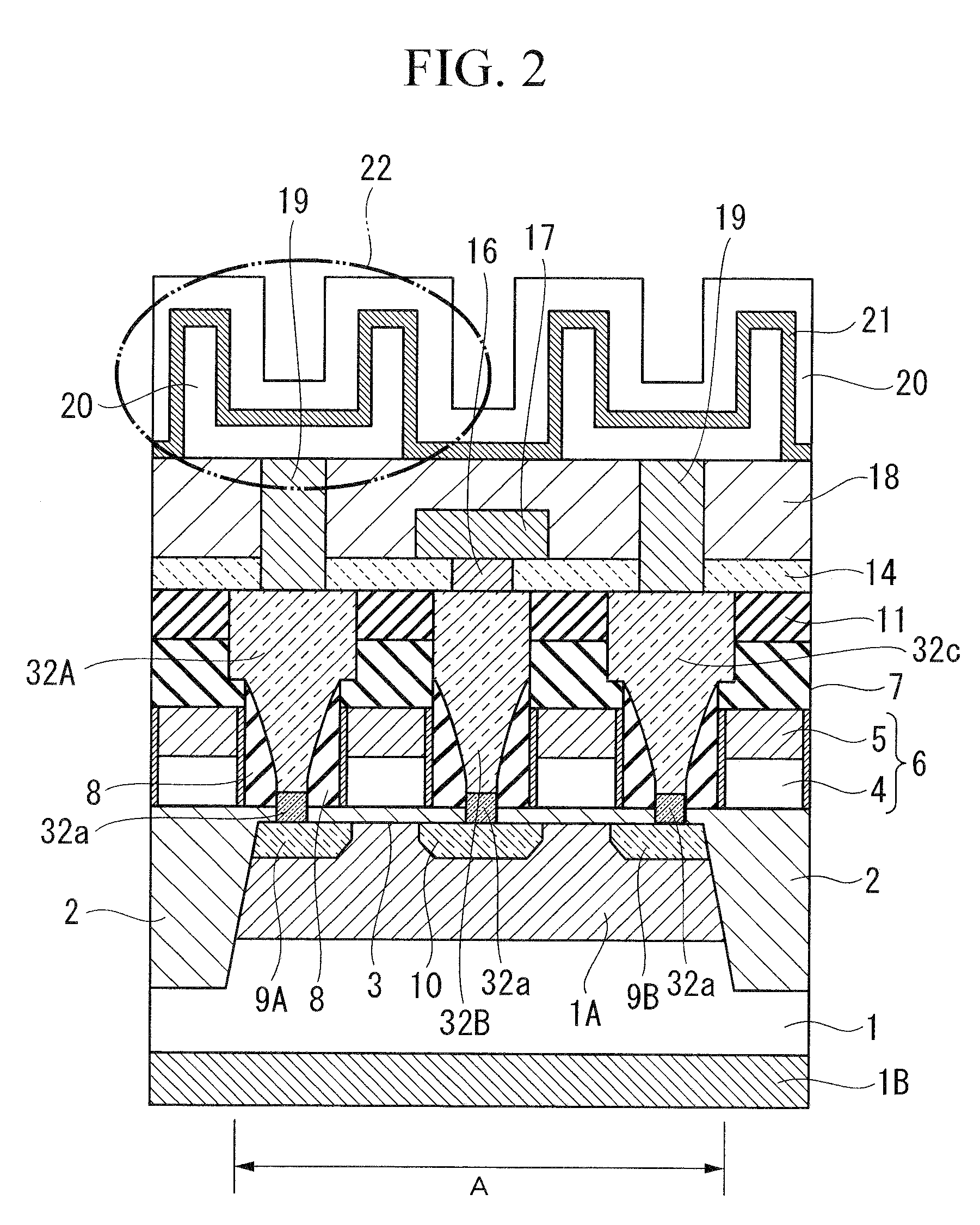
Ultra-thin body super-steep retrograde well (SSRW) FET devices
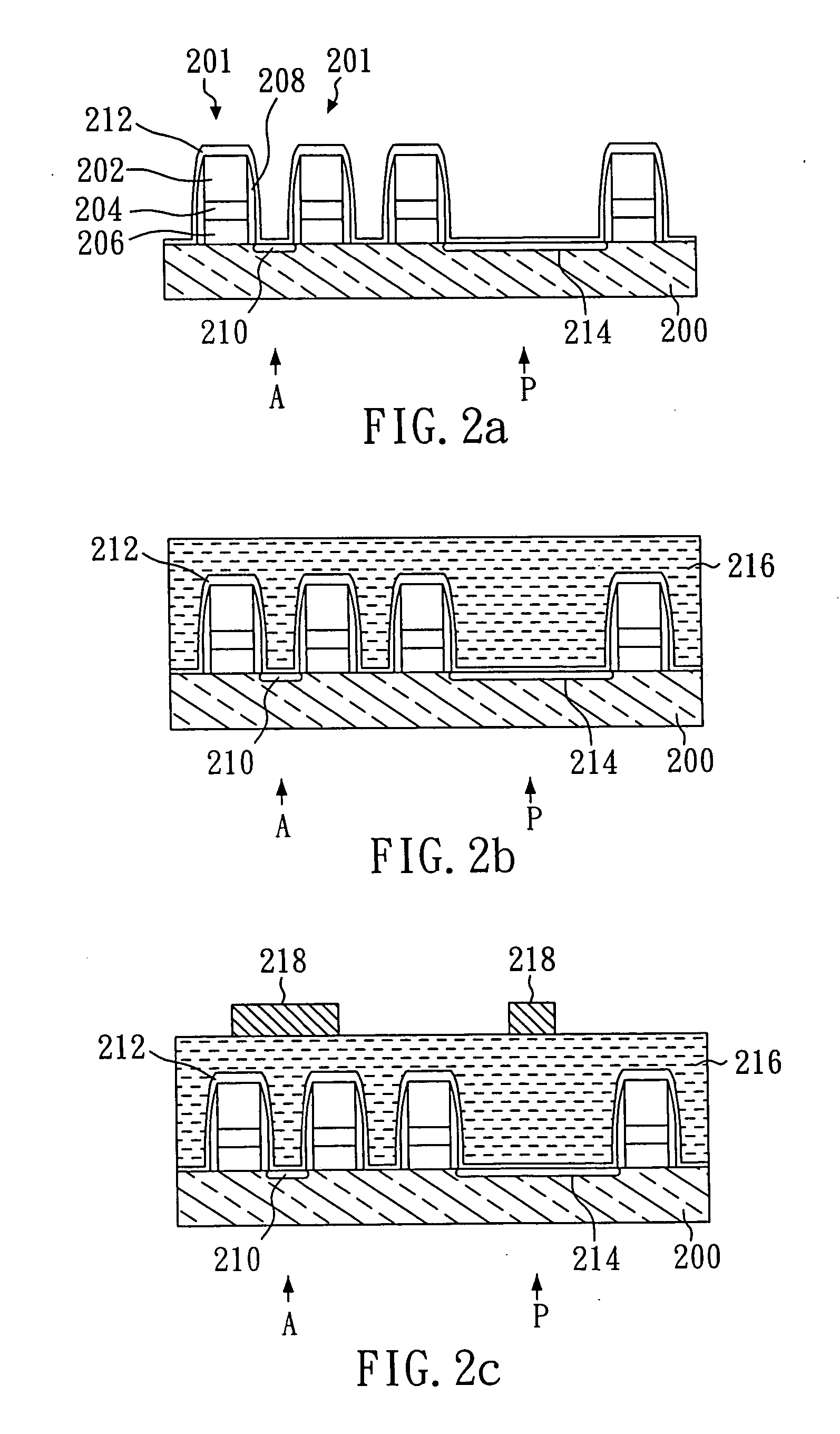
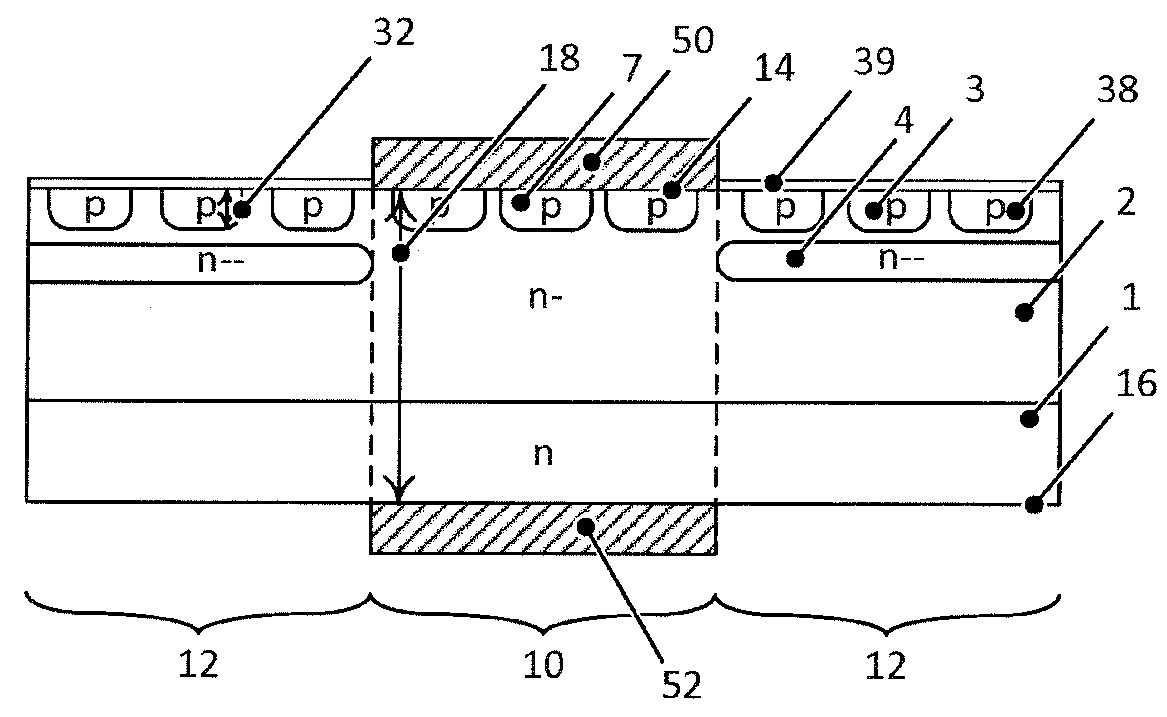
ActiveUS7002214B1Reduce capacitanceReduce junctionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantGround plane
A method of manufacture of a Super Steep Retrograde Well Field Effect Transistor device starts with an SOI layer formed on a substrate, e.g. a buried oxide layer. Thin the SOI layer to form an ultra-thin SOI layer. Form an isolation trench separating the SOI layer into N and P ground plane regions. Dope the N and P ground plane regions formed from the SOI layer with high levels of N-type and P-type dopant. Form semiconductor channel regions above the N and P ground plane regions. Form FET source and drain regions and gate electrode stacks above the channel regions. Optionally form a diffusion retarding layer between the SOI ground plane regions and the channel regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
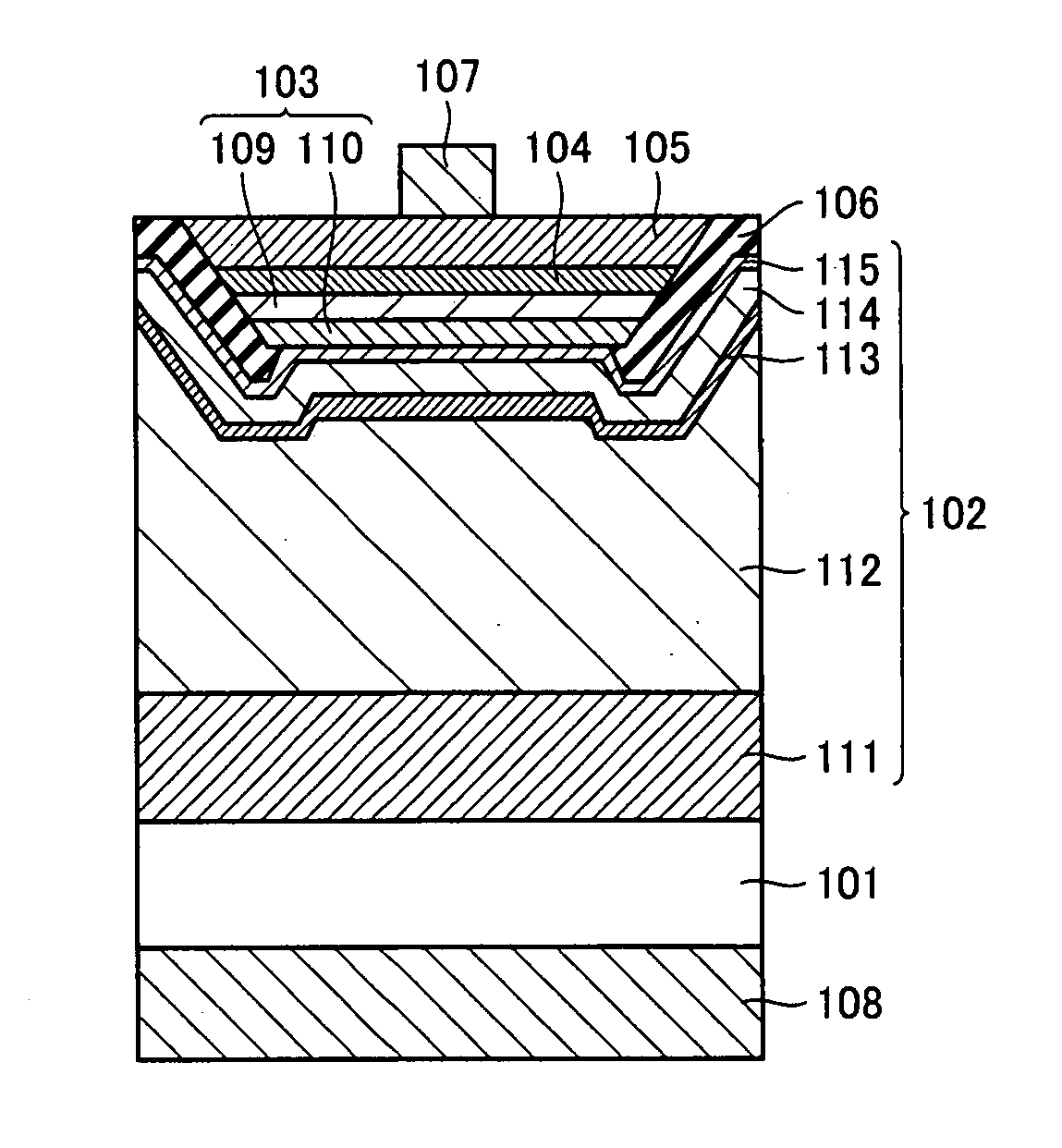
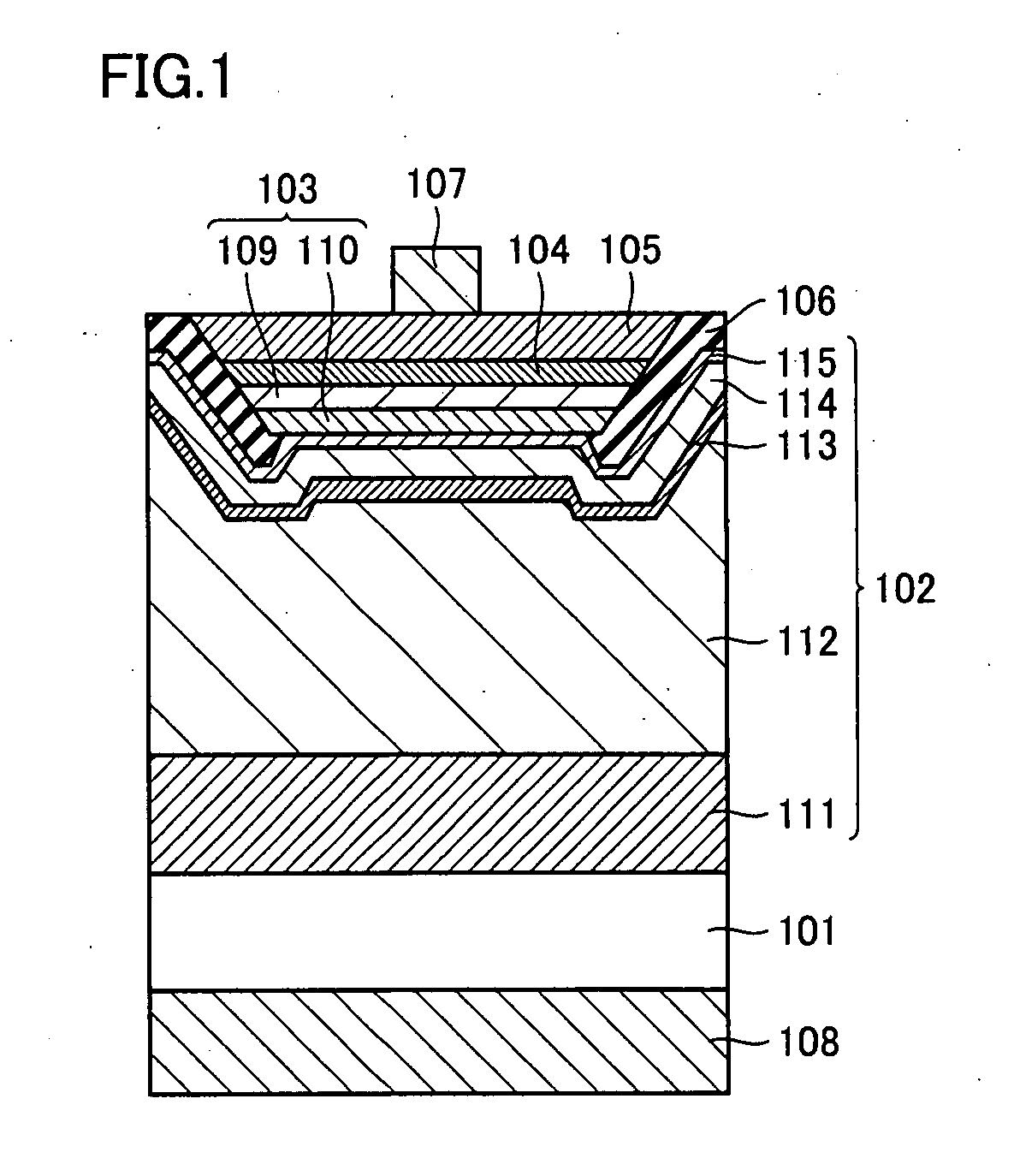
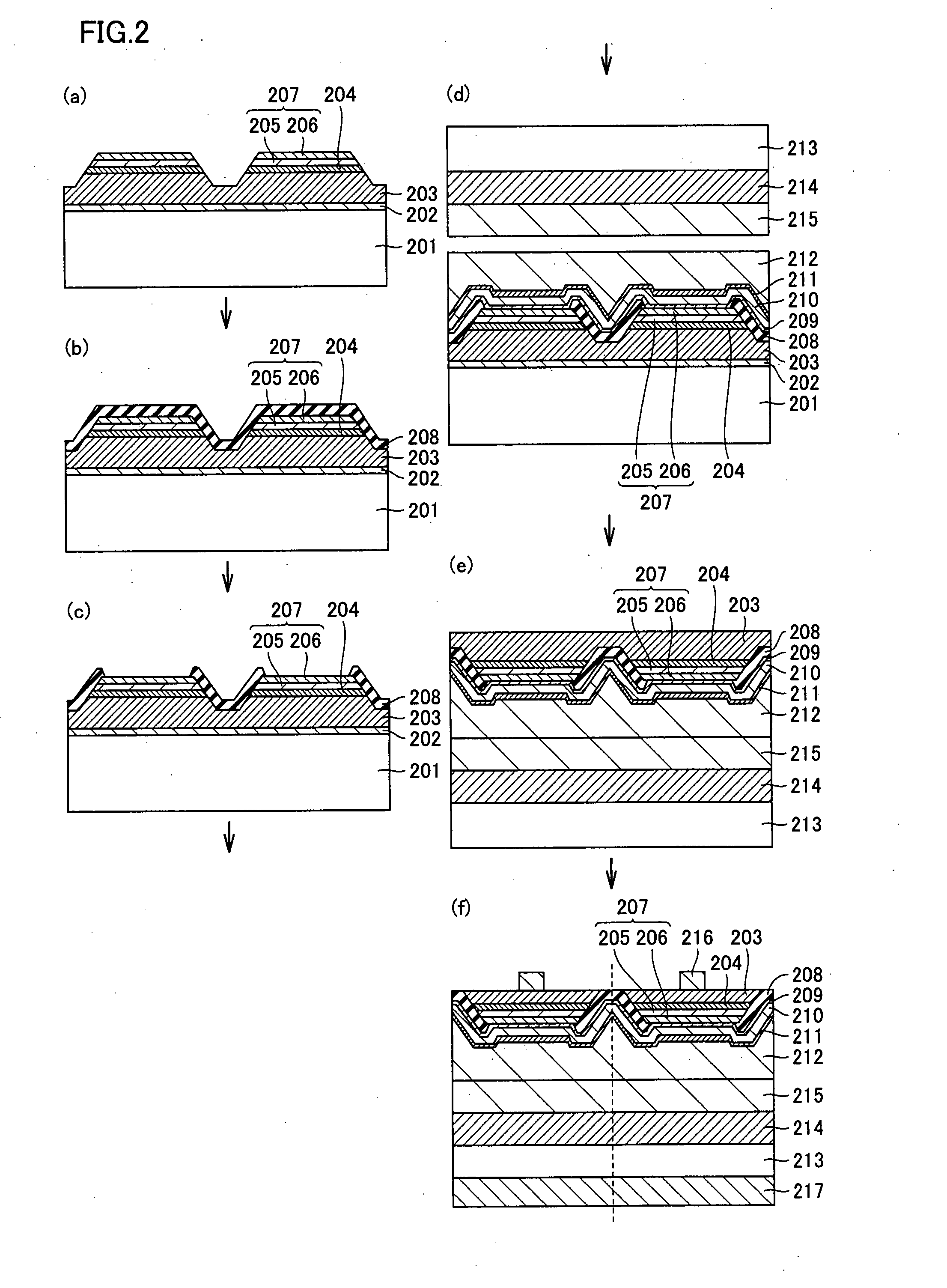
Nitride semiconductor light emitting device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080035949A1Increase productionReliable and reliableSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLight emitting deviceNitride semiconductors
A nitride semiconductor light emitting device includes a conductive substrate, a first metal layer, a second conductivity-type semiconductor layer, an emission layer, and a first conductivity-type semiconductor layer in this order. The nitride semiconductor light emitting device additionally has an insulating layer covering at least side surfaces of the second conductivity-type semiconductor layer, the emission layer and the first conductivity-type semiconductor layer. A method of manufacturing the same is provided. The nitride semiconductor light emitting device may further include a second metal layer. Thus, a reliable nitride semiconductor light emitting device and a method of manufacturing the same are provided in which short-circuit at the PN junction portion and current leak is reduced as compared with the conventional examples.
Owner:SHARP FUKUYAMA LASER CO LTD
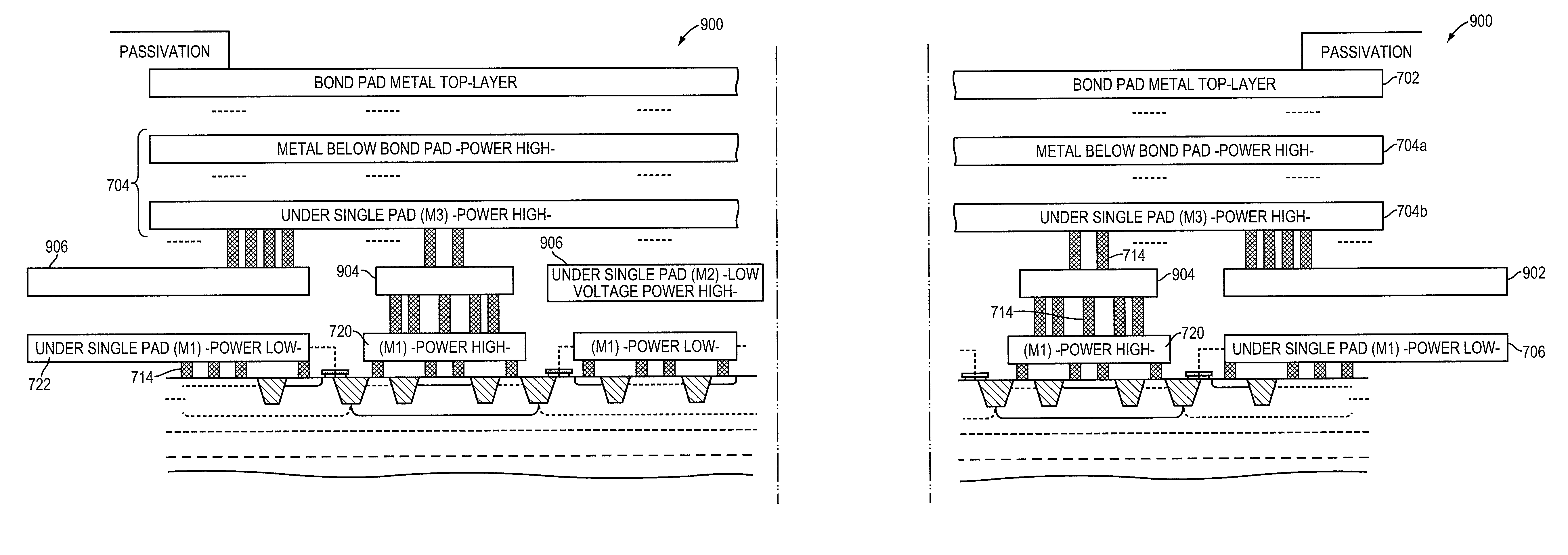
Bond pad with integrated transient over-voltage protection
ActiveUS8222698B2Small footprintTriggered quicklyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringTransistor
In various embodiments, the invention relates to bond pad structures including planar transistor structures operable as over-voltage clamps.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Optical element and mach-zehnder optical waveguide element
ActiveUS20140233878A1Increase changeEnlarge regionOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsEngineeringWaveguide
Provided is an optical element including an optical waveguide including a core formed from: a rib part; and a first and second slab parts sandwiching the rib part. The first slab part includes a P-type region, the second slab part includes an N-type region, the rib part includes a P-type region which is in contact with the P-type region provided in the first slab part, and an N-type region which is in contact with the N-type region provided in the second slab part. The rib part includes a top portion which is located above the first and second slab parts and includes an undoped region formed from at least one of an intrinsic region and a low-concentration doping region which is doped at a dopant concentration 1 / 10 or less of a dopant concentration in at least one of the adjacent P-type region and the adjacent N-type region.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
InactiveUS20080265323A1Reduce power consumptionCapacitance junction capacitance be reducedTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceDevice material
An object is to provide a semiconductor device in which, through a simpler process, junction capacitance and power consumption can be reduced more than a conventional semiconductor device, and a manufacturing method thereof. An insulating film including an opening is formed over a base substrate and a part of a bond substrate is transferred to the base substrate, with the insulating film interposed therebetween, whereby a semiconductor film including a cavity between the semiconductor film and the base substrate is formed over the base substrate. Then, a semiconductor device including a semiconductor element such as a transistor is manufactured using the semiconductor film. The transistor includes a cavity between the base substrate and the semiconductor film used as an active layer. One cavity may be provided or a plurality of cavities may be provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Adjustable Field Effect Rectifier
ActiveUS20090078962A1Function reliably and efficientlyFast recoveryThyristorMOSFETElectromagnetic interference
An Adjustable Field Effect Rectifier uses aspects of MOSFET structure together with an adjustment pocket or region to result in a device that functions reliably and efficiently at high voltages without significant negative resistance, while also permitting fast recovery and operation at high frequency without large electromagnetic interference.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Transistor having raised source and drain
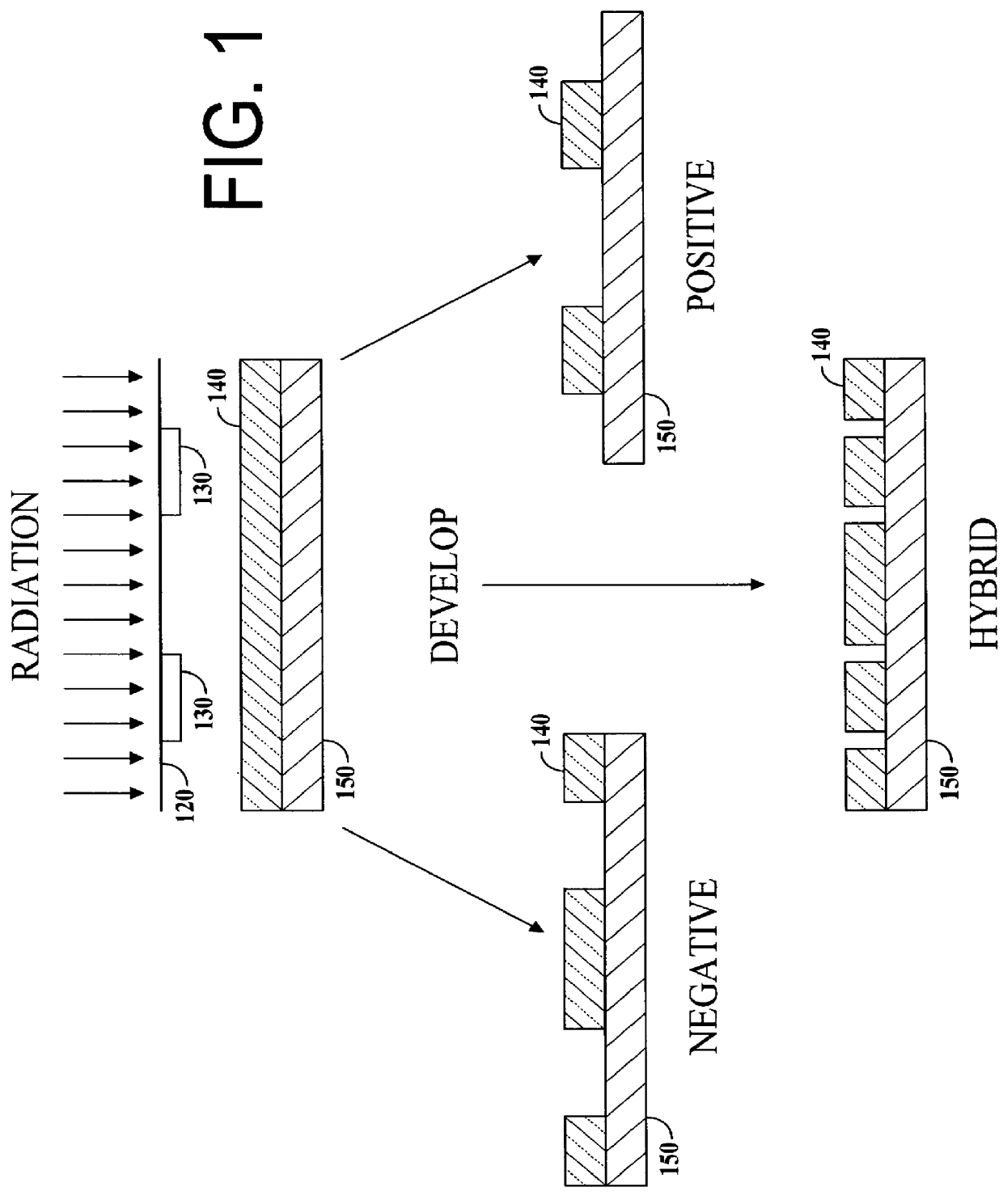
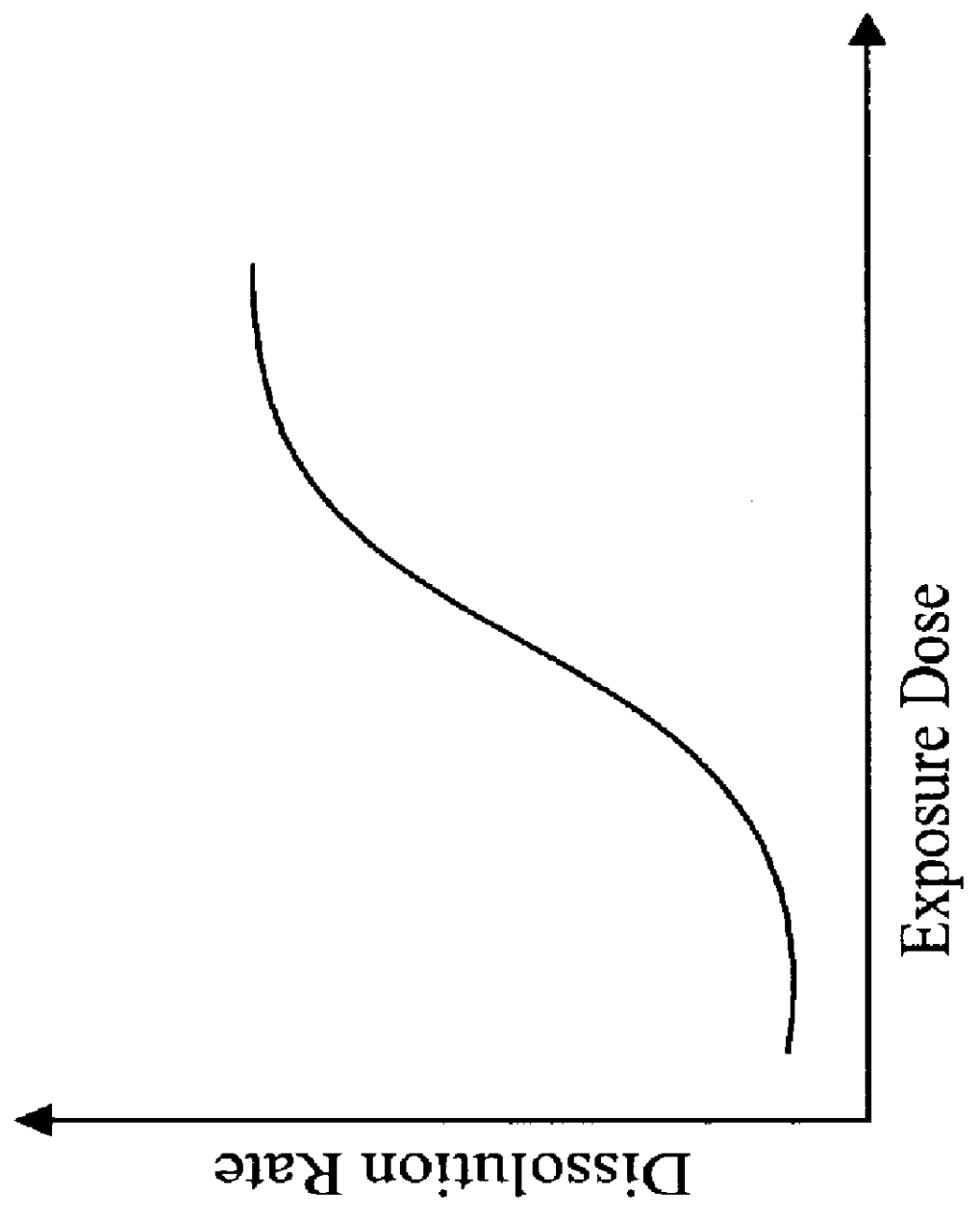
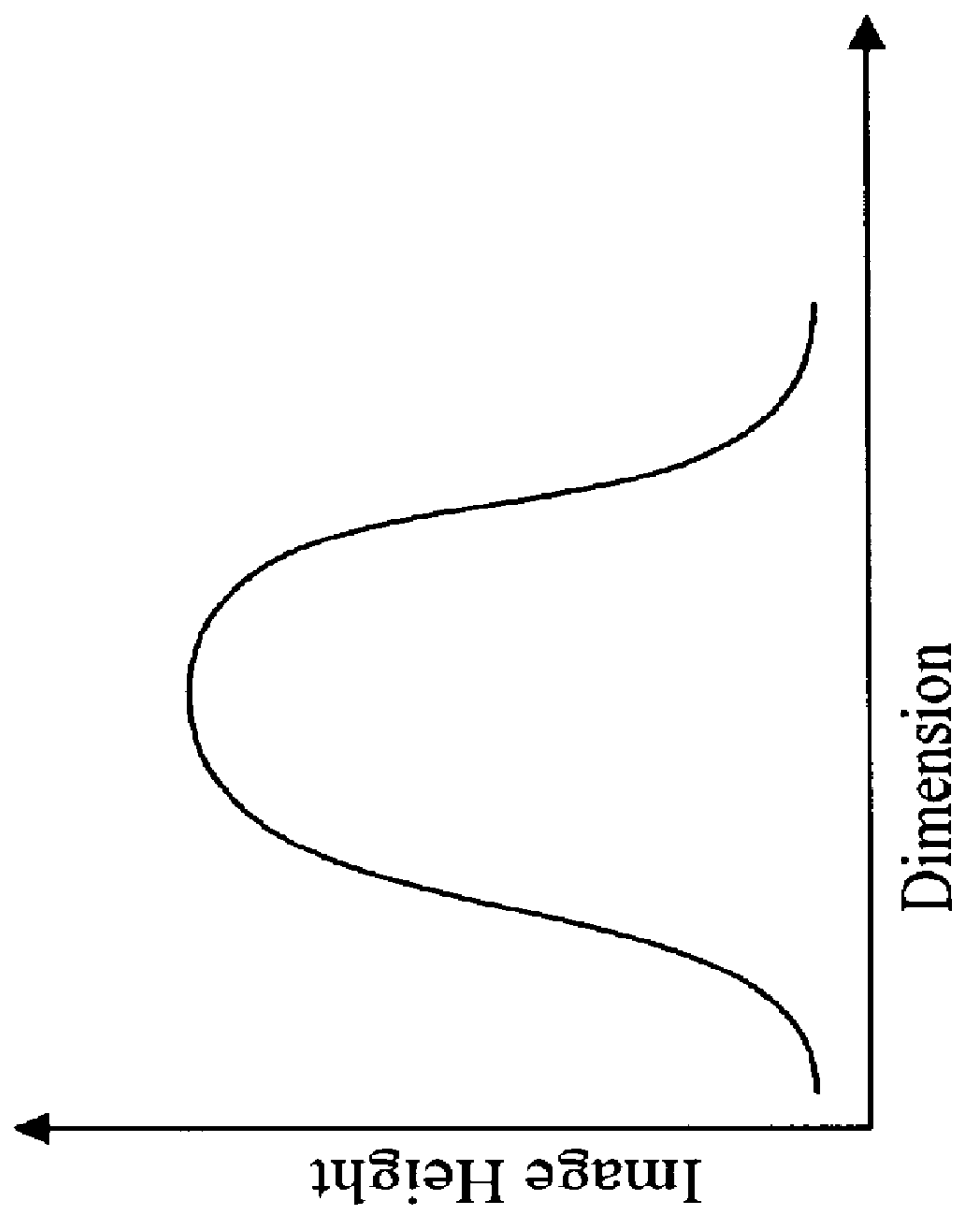
The preferred embodiment of the present invention provides a transistor structure and method for fabricating the same that overcomes the disadvantages of the prior art. In particular, the preferred structure and method results in lower leakage and junction capacitance by using raised source and drains which are partially isolated from the substrate by a dielectric layer. The raised source and drains are preferably fabricated from the same material layer used to form the transistor gate. The preferred method for fabricating the transistor uses hybrid resist to accurately pattern the gate material layer into regions for the gate, the source and the drain. The source and drain regions are then connected to the substrate by growing silicon. The preferred method thus results in an improved transistor structure while not requiring excessive fabrication steps.
Owner:IBM CORP
Adjustable field effect rectifier
ActiveUS8148748B2Improve performanceImproving reverse recovery characteristicThyristorMOSFETHigh voltage igbt
An Adjustable Field Effect Rectifier uses aspects of MOSFET structure together with an adjustment pocket or region to result in a device that functions reliably and efficiently at high voltages without significant negative resistance, while also permitting fast recovery and operation at high frequency without large electromagnetic interference.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Treatment of abnormal or excessive scars
InactiveUS20110130710A1Avoid communicationReduce junctionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderMedicineAtrophic scarring
Owner:BECKER DAVID LAWRENCE +2
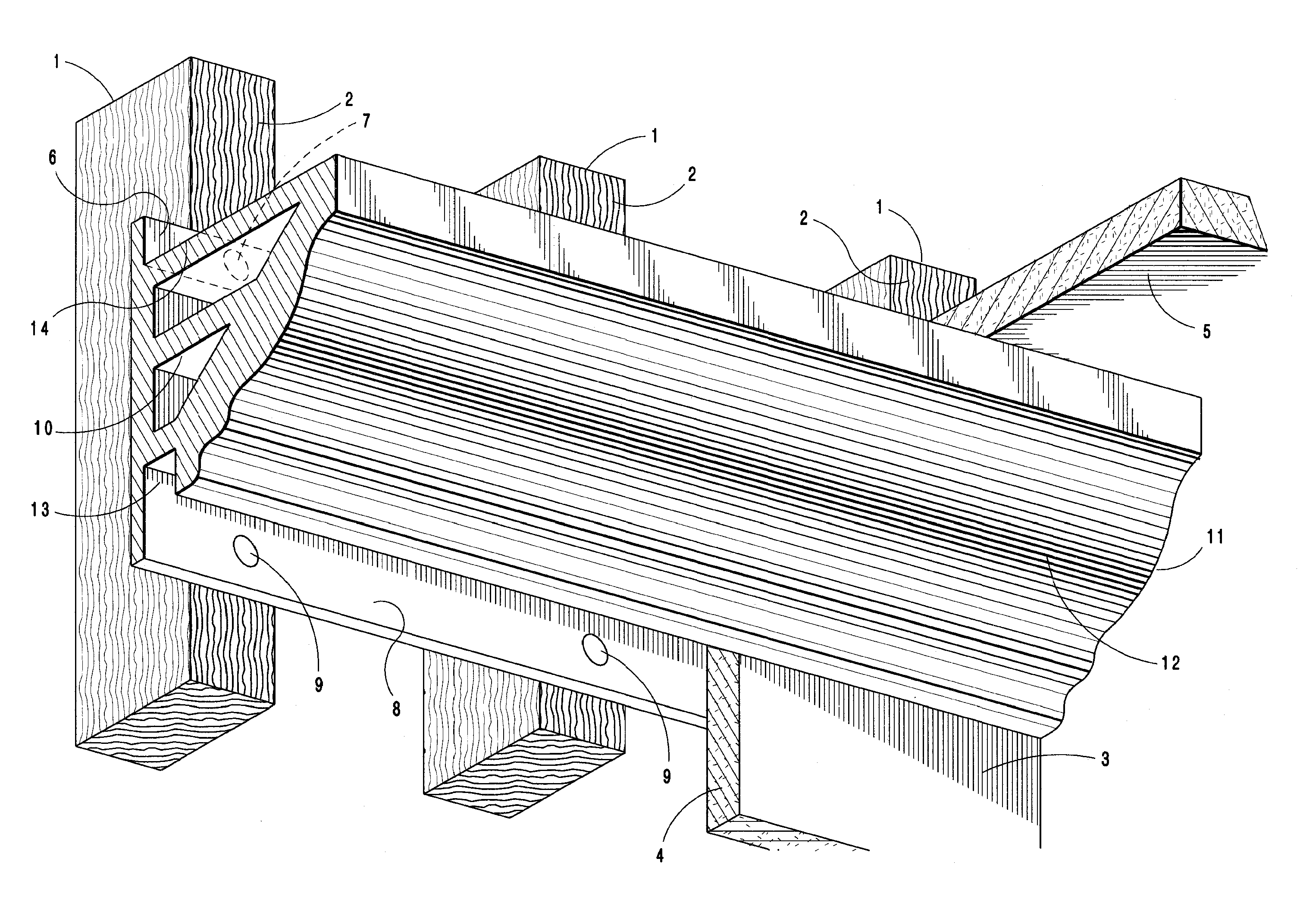
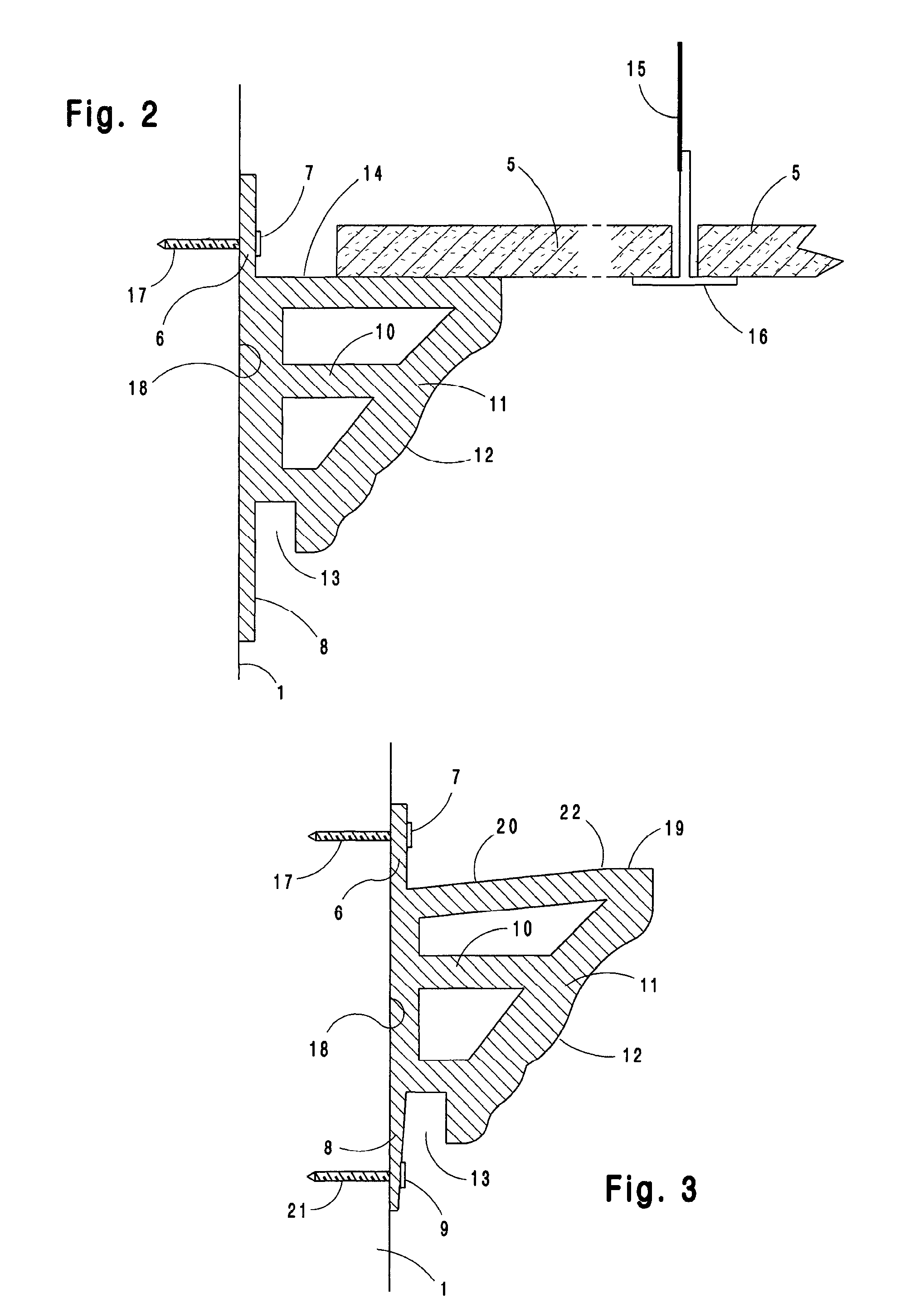
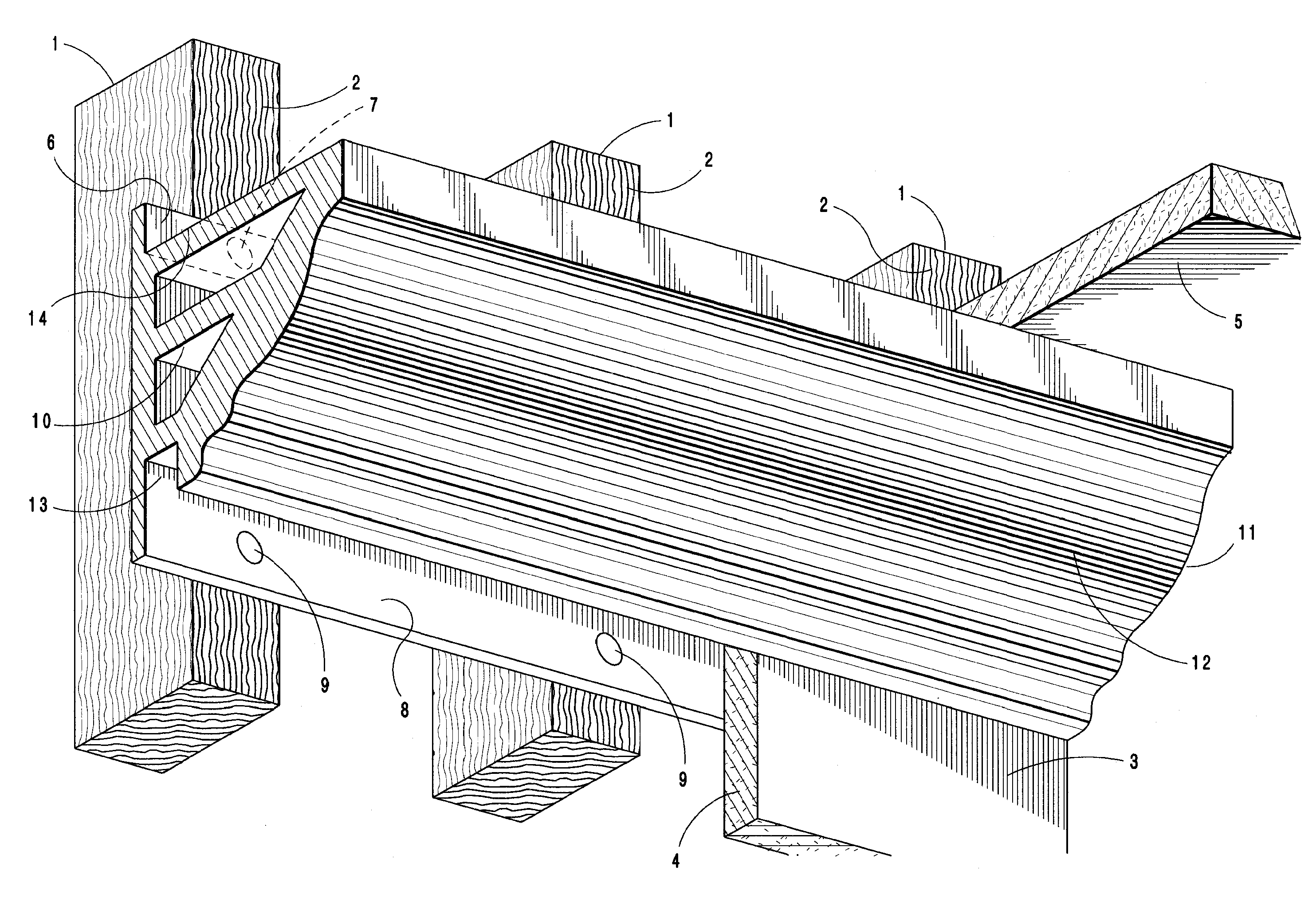
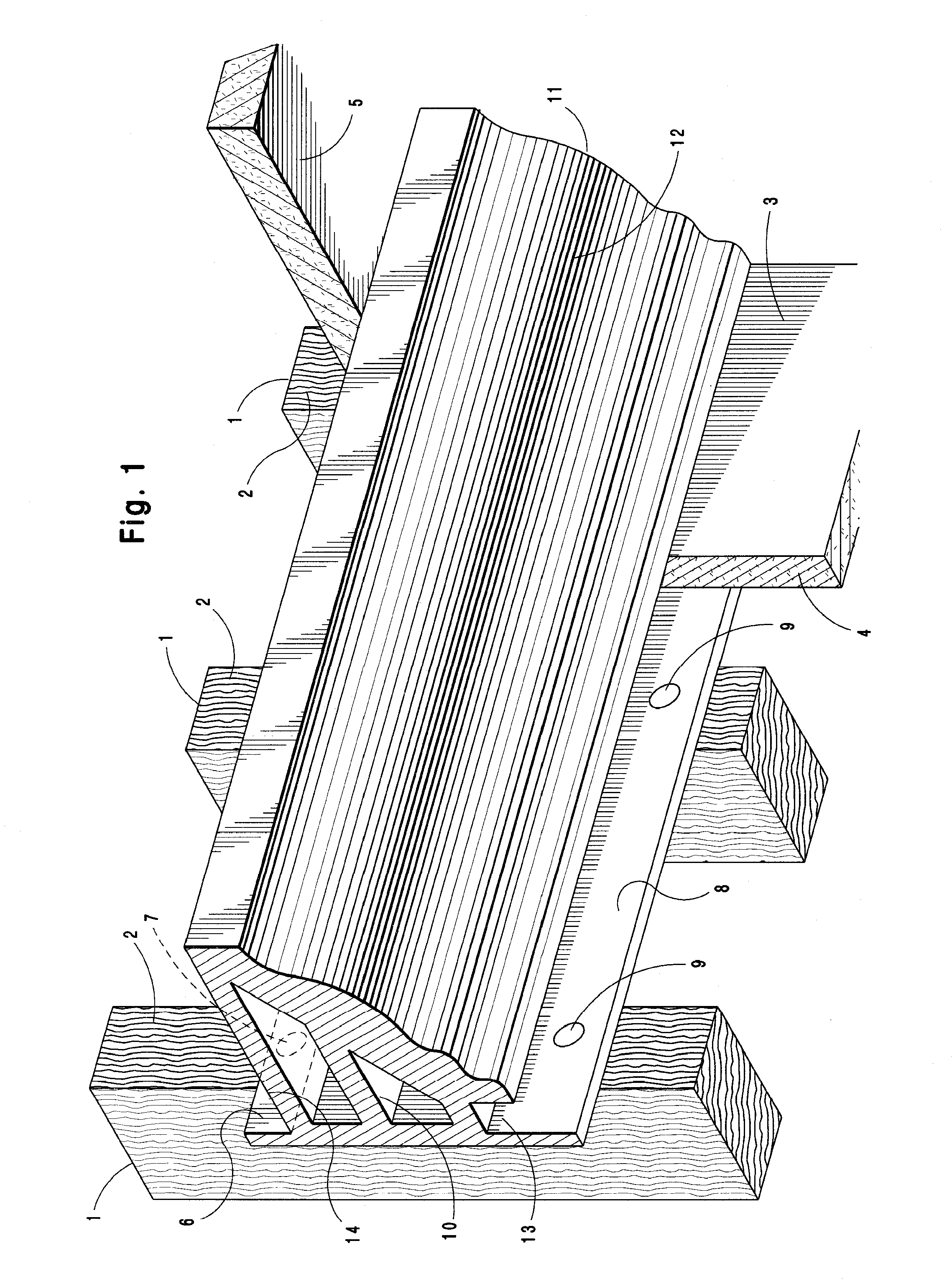
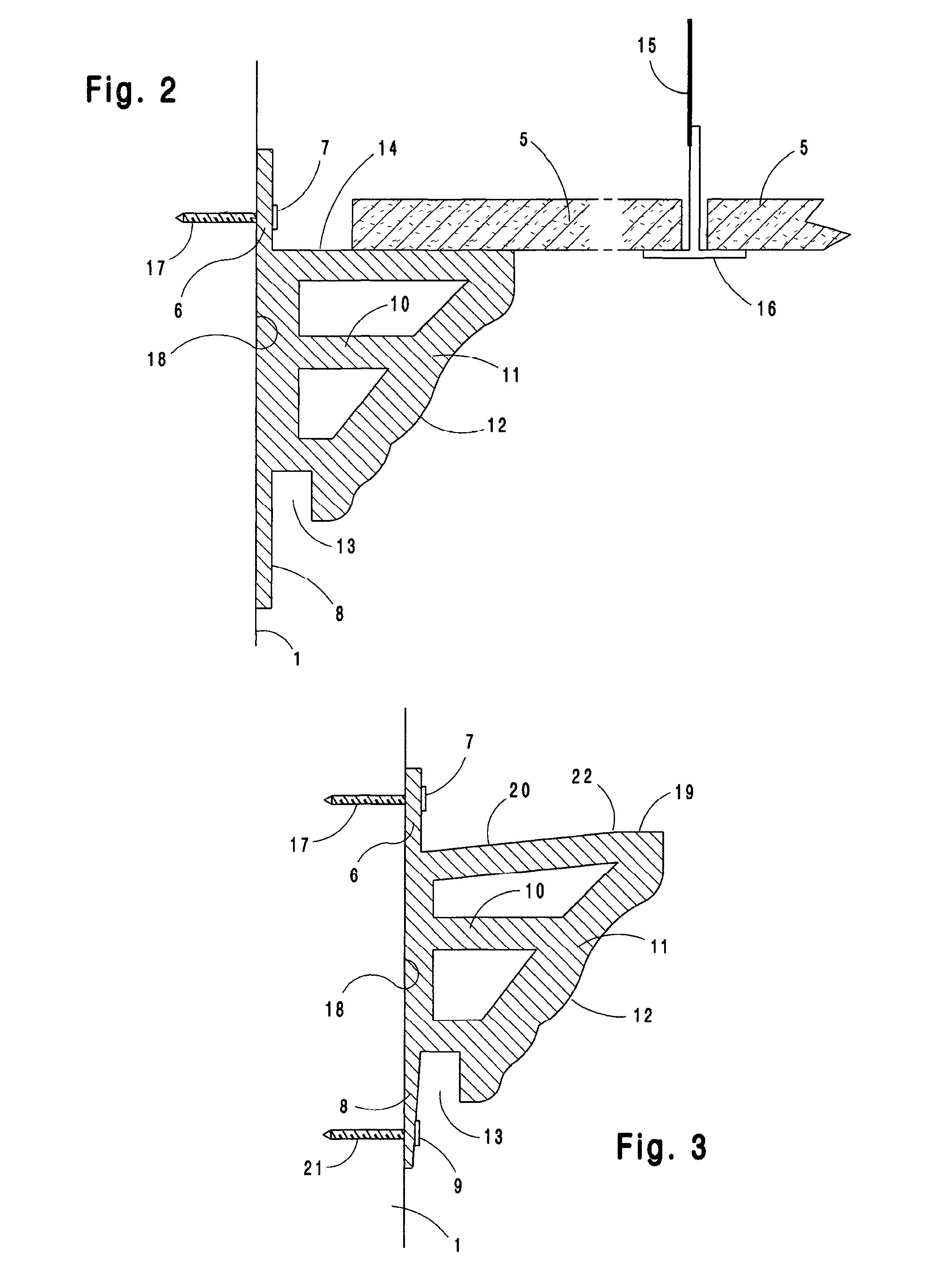
System and method for installation of decorative molding
A molding system for use in interior spaces at or near the top of a vertical wall having a decorative surface and a vertical mounting surface including an attachment flange used for fastening the molding section to the wall, said molding section having a center of mass which is spaced outwardly from the wall surface, and whereby the point of attachment of said molding to the wall is located at a vertically higher position on the molding section than the center of mass so that when secured to a wall the lower end of the molding section is continually urged towards the wall surface and is therefore maintained in continual contact with the wall surface.
Owner:HOFFMAN JEREMY P +1
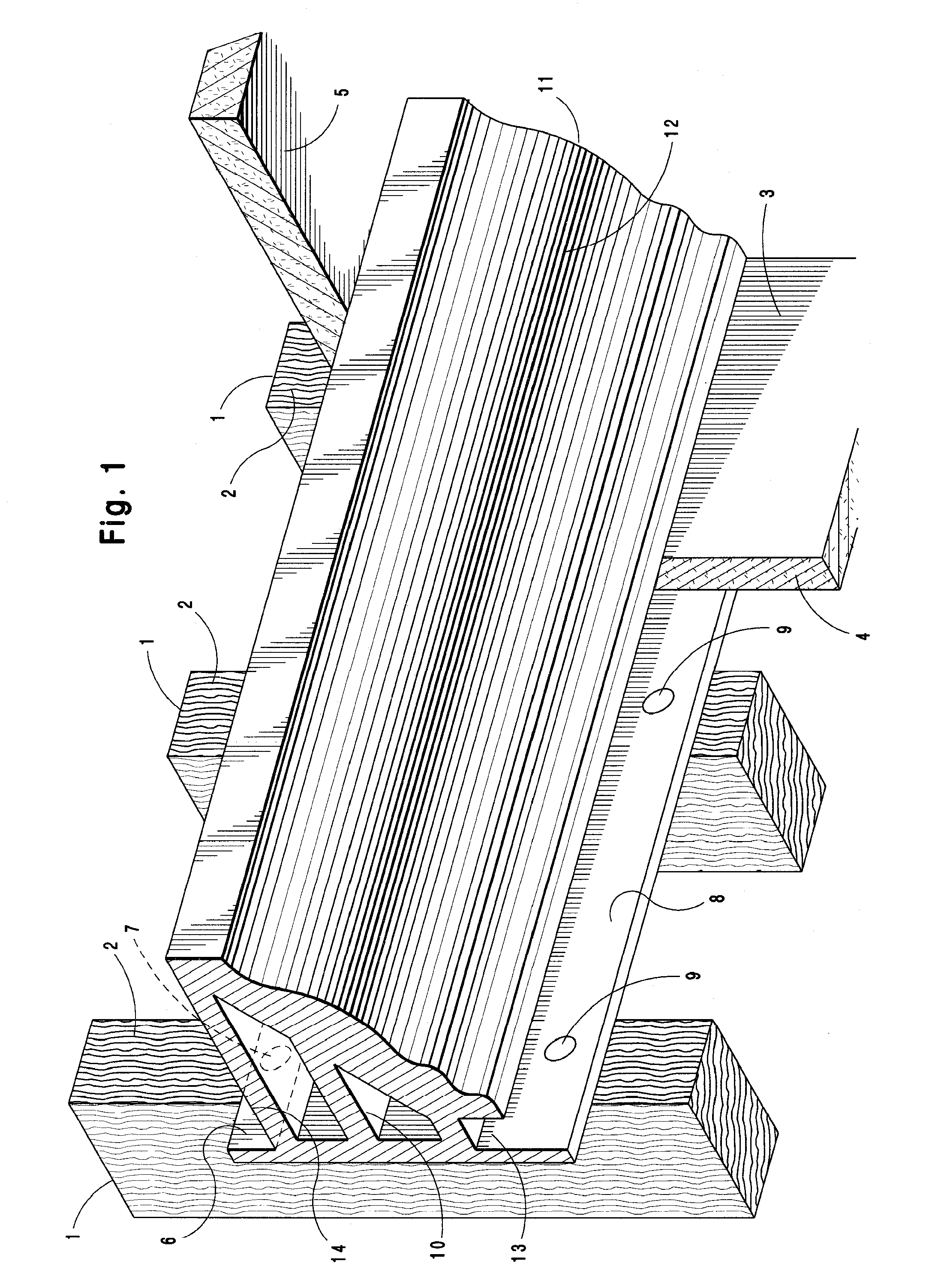
System and method for installation of decorative molding
ActiveUS7997043B1Improve rigidityAvoid assemblyCovering/liningsBuilding componentsInterior spaceEngineering
A molding system for use in interior spaces for use either with new construction or finished spaces, and in addition can be used with either a suspended ceiling or conventional ceiling, whereby the molding is incorporated with the wall and ceiling surfaces in such a manner that the joints with the ceiling and wall are plumb and being mounted such that the decorative molding surface of the molding can be installed in a finished form that does not require further finishing after installation.
Owner:MACMILLAN ROBERT +1
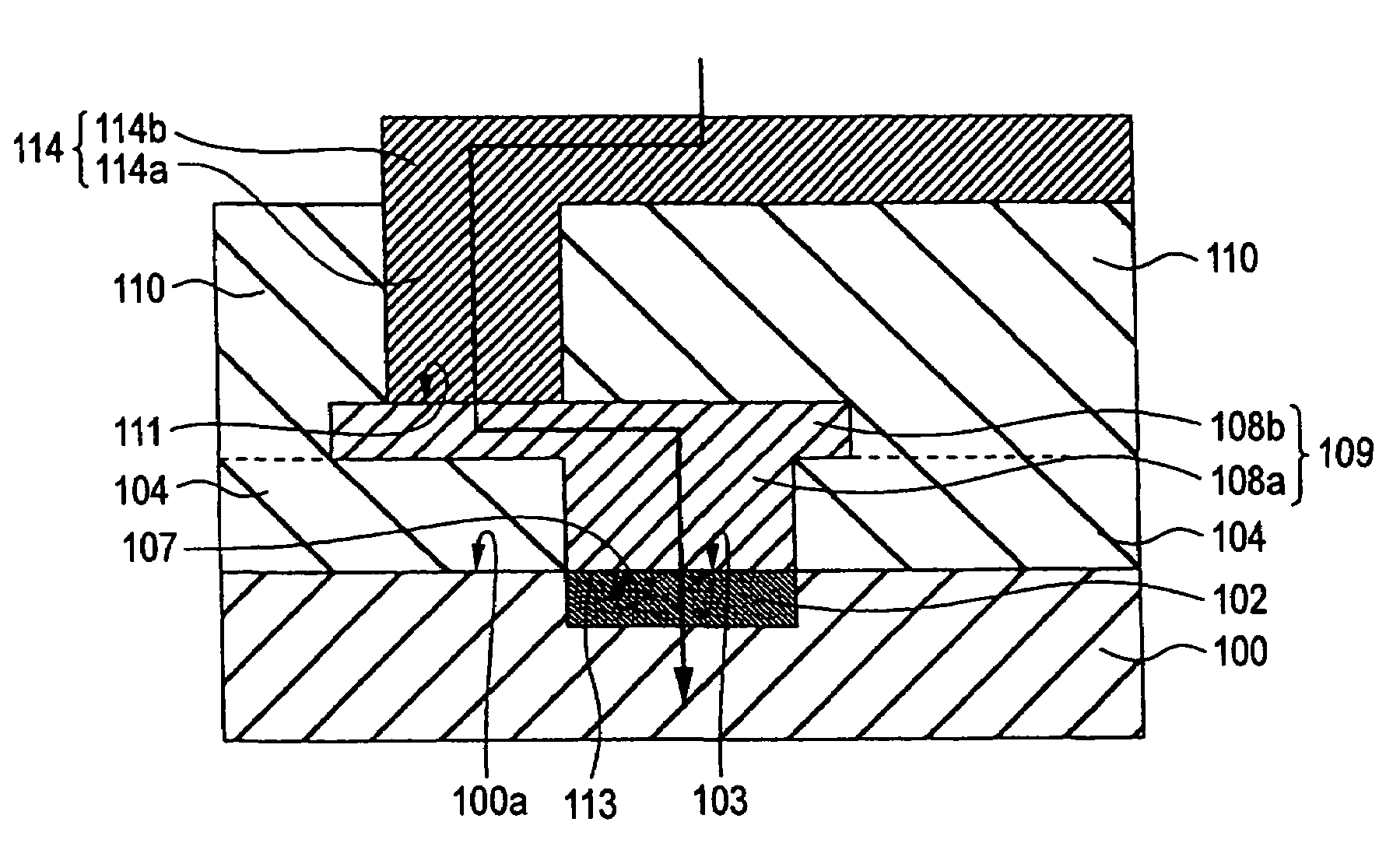
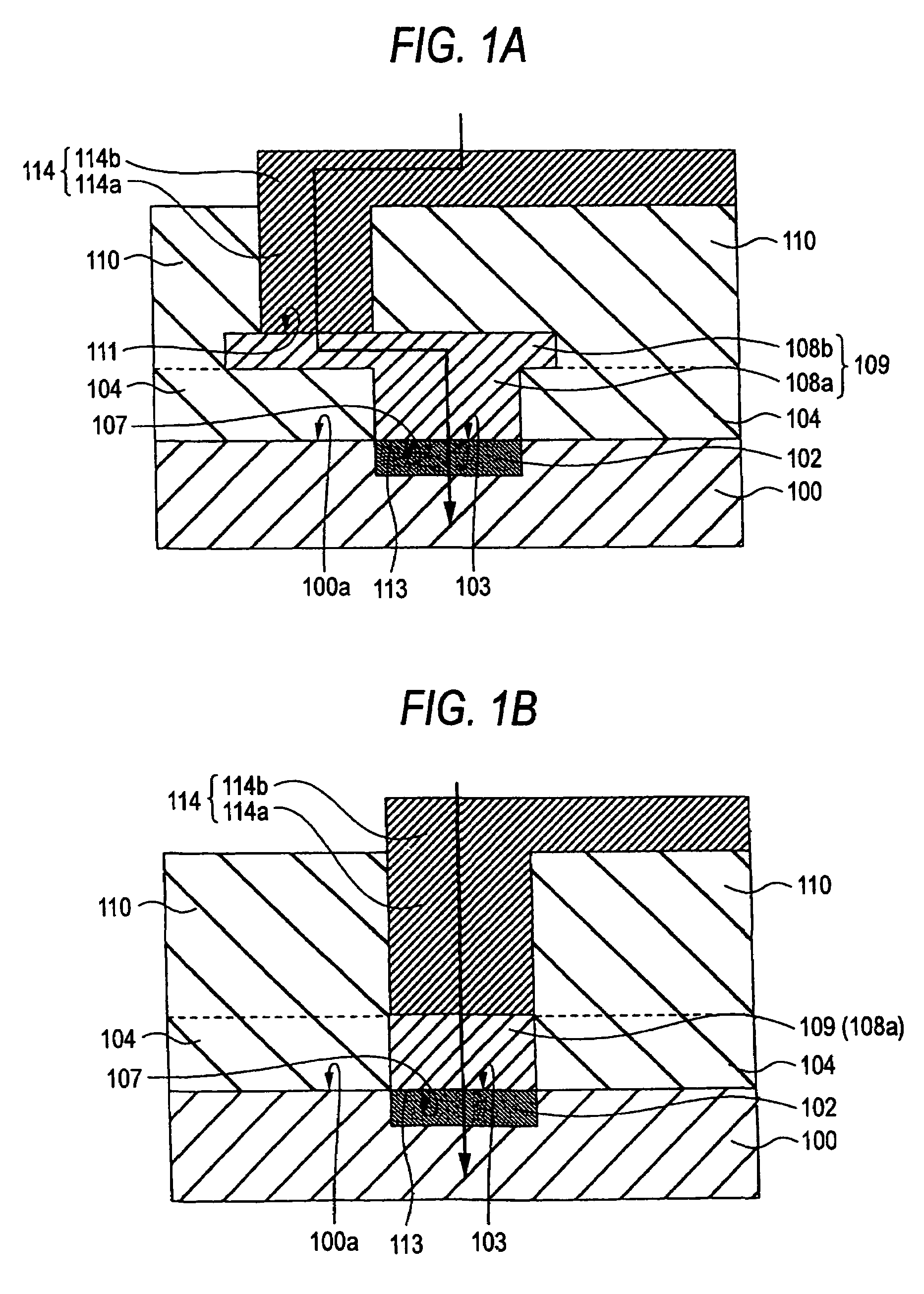
Semiconductor apparatus and manufacturing method thereof
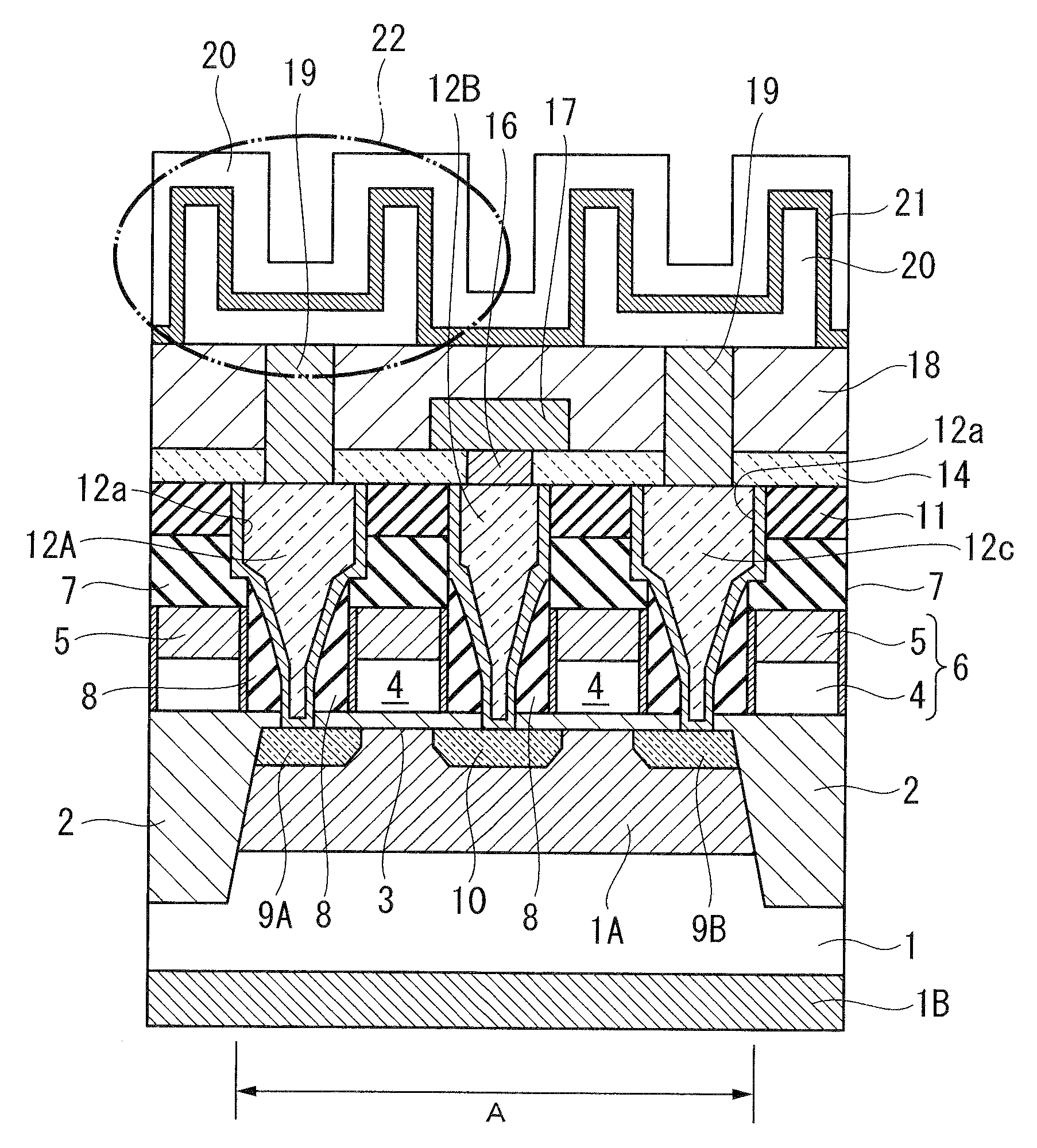
InactiveUS20110127615A1Reduce leakage currentReduce electric field strengthTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical field strengthImpurity ions
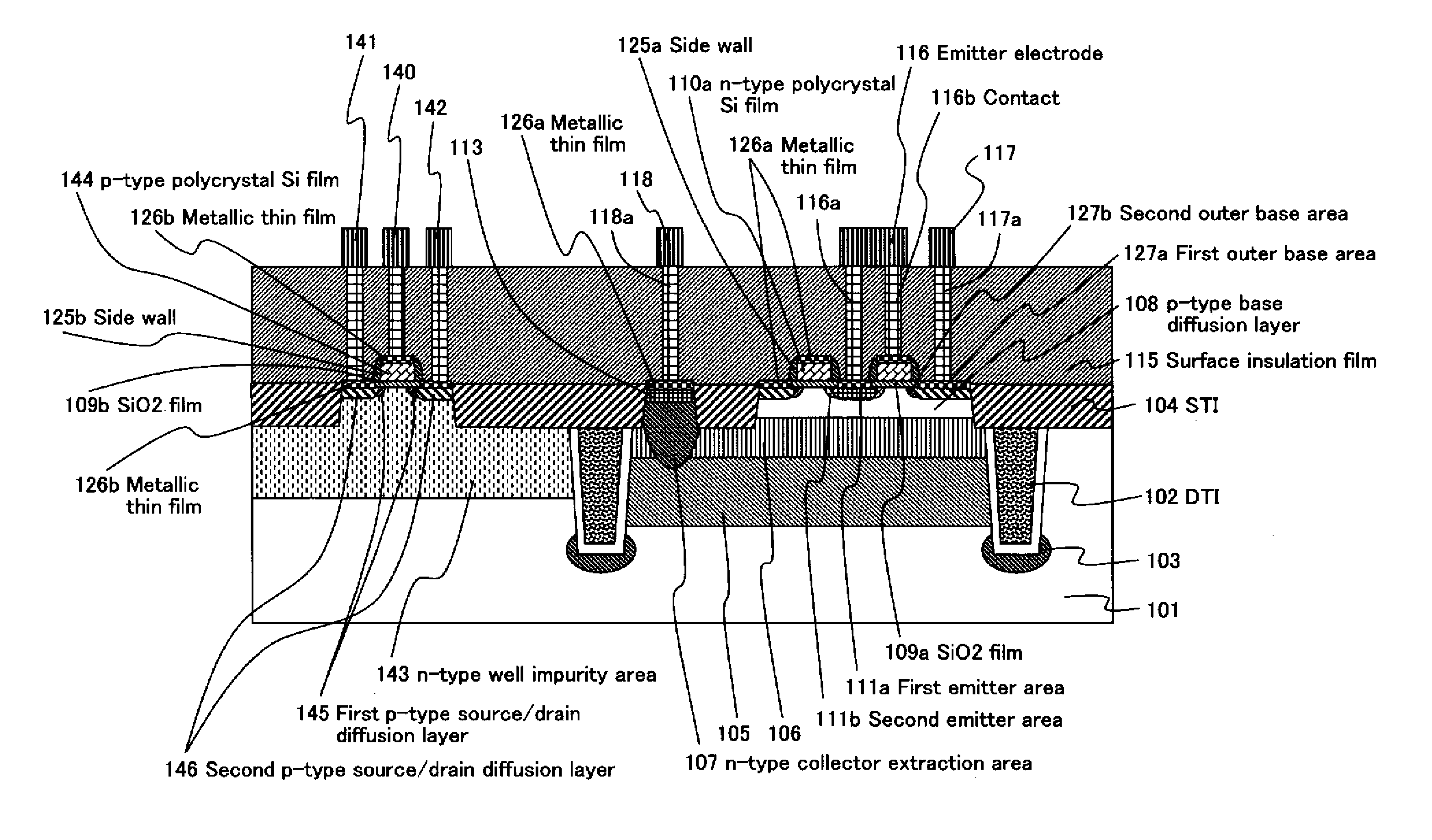
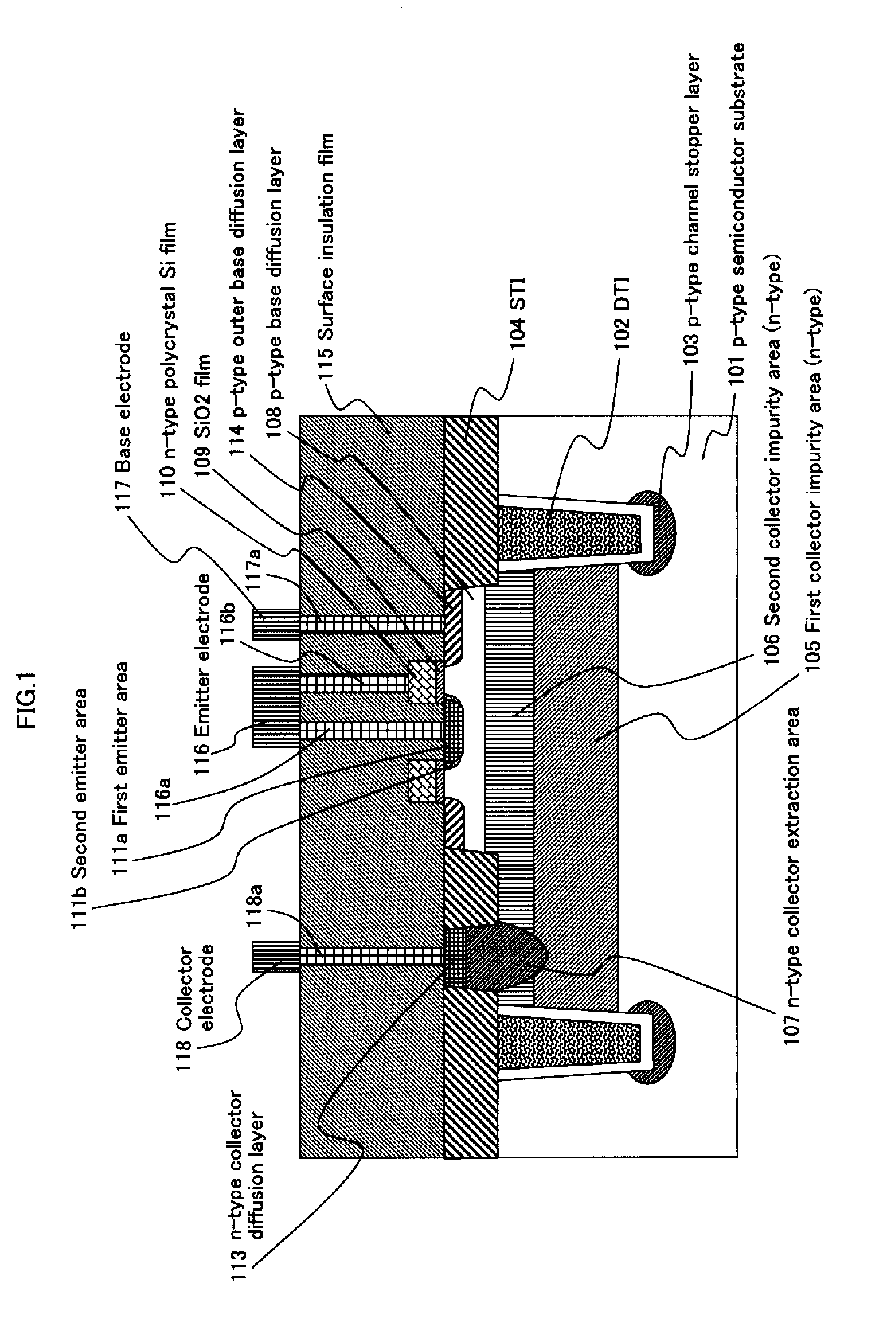
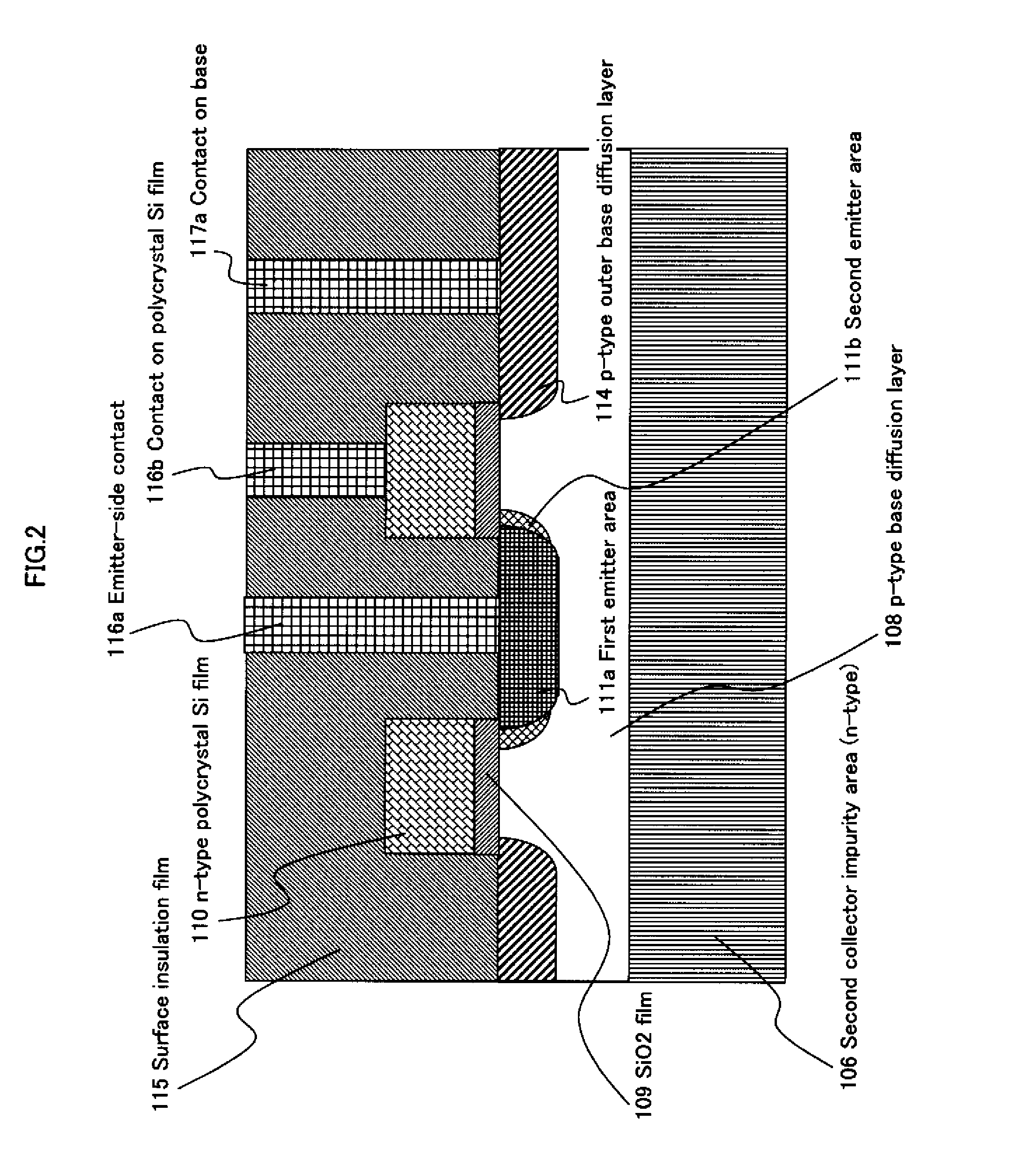
A high-performance semiconductor apparatus which can be easily introduced into the MOS process, reduces the leakage current (electric field strength) between the emitter and the base, and is insusceptible to noise or surge voltage, and a manufacturing method of the semiconductor apparatus. The emitter 111 is formed by performing the ion implantation twice by using the conductive film (109) as a mask. The second emitter area (111b) is formed by ion implantation of a low impurity density impurity ion, and the first emitter area (111a) is formed by ion implantation of a high impurity density impurity ion. As a result, the low impurity density second emitter area is formed in the circumference of the emitter 111, which lowers the electric field strength, and reduces the leakage current. Also the conductive film is connected with the emitter electrode (116), which makes the apparatus insusceptible to noise.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
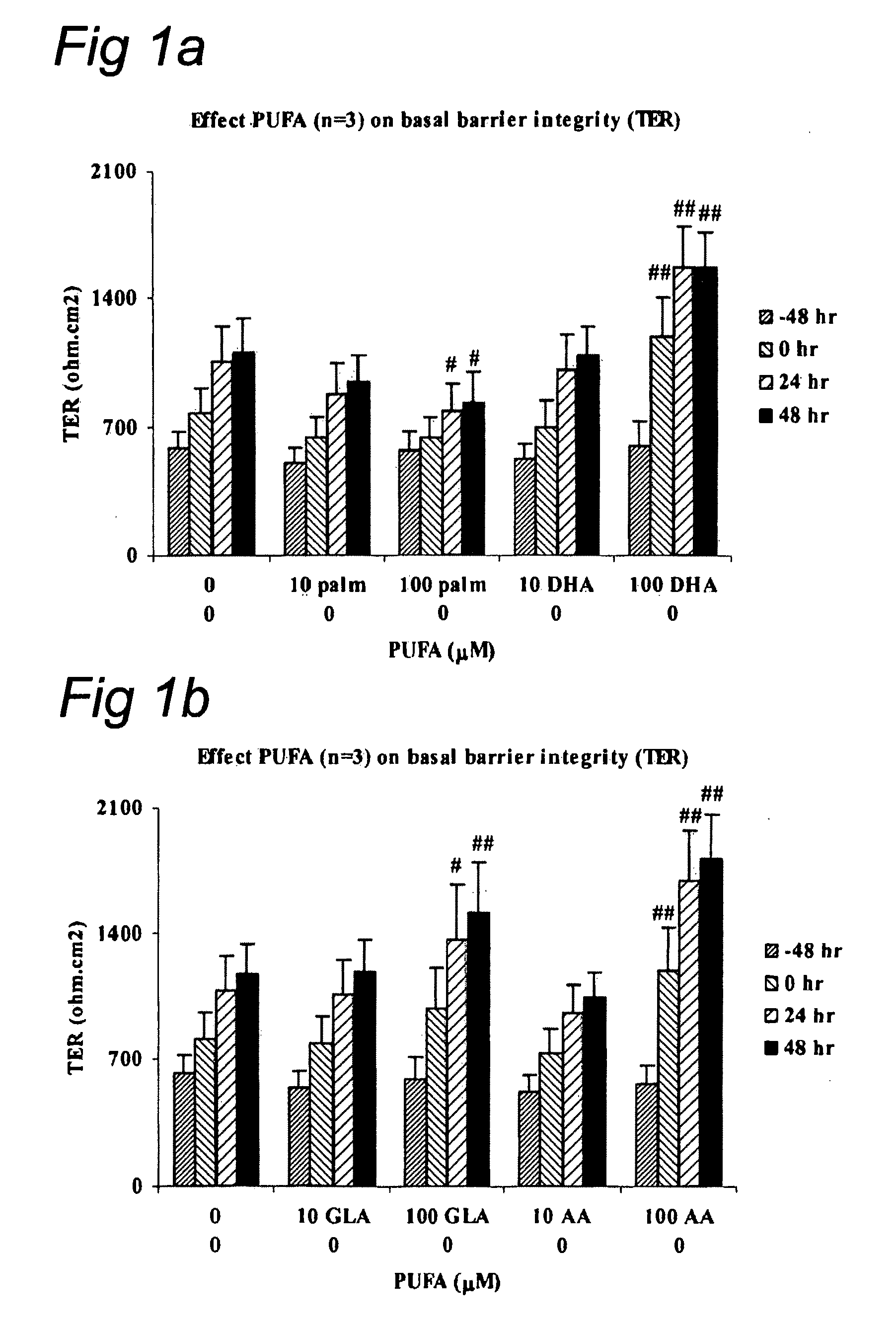
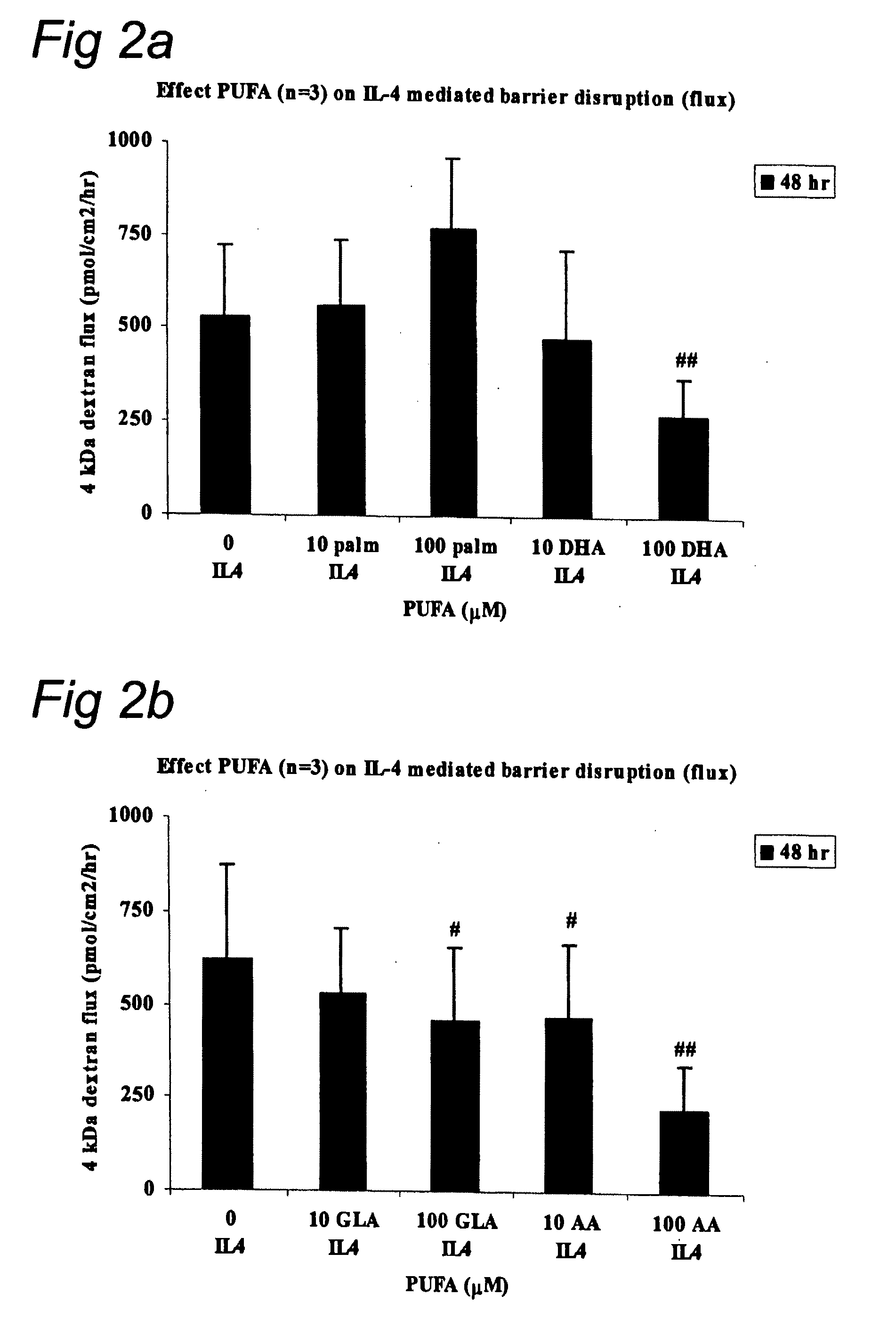
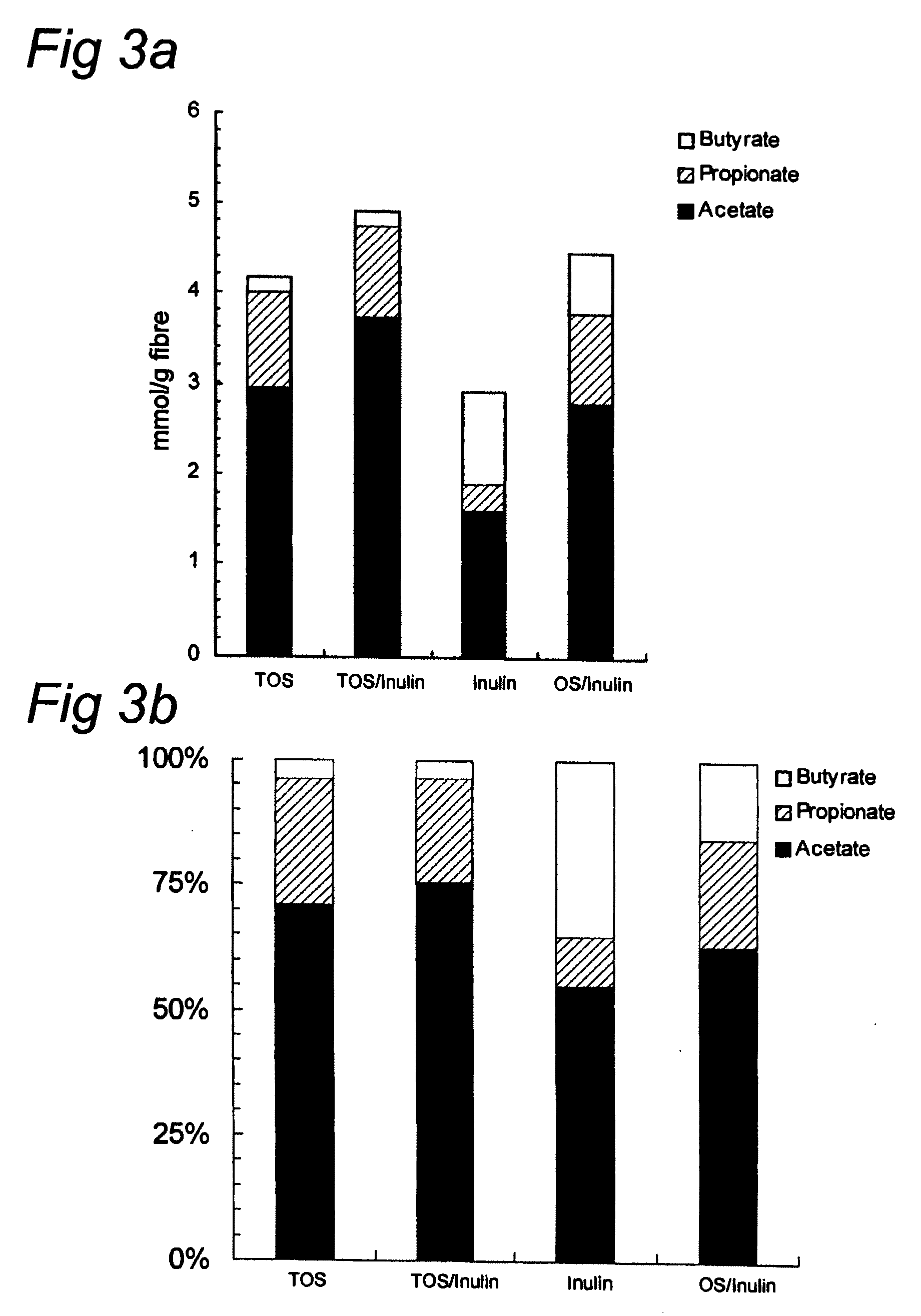
Barrier integrity in HIV patients
InactiveUS20100167982A1Reducing mucosal productionImproving intestinal integrityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDocosahexaenoic acidEicosapentaenoic acid
The invention concerns a method for stimulating intestinal barrier integrity in a patient infected with HIV by administering to said patient composition comprising: eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and arachidonic acid (ARA), and at least two distinct oligosaccharides.
Owner:NV NUTRICIA
Methods of forming asymmetric recesses and gate structures that fill such recesses and related methods of forming semiconductor devices that include such recesses and gate structures
InactiveUS7560359B2Improve featuresReduce leakage currentTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Gate-all-around field-effect-transistor devices and fabrication methods thereof
ActiveUS20190051729A1Reduce junctionLower threshold voltageNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorEngineering
A method for fabricating a gate-all-around field-effect-transistor device includes forming a plurality of first stacked structures, each including a first sacrificial layer and a first semiconductor layer; forming a first dummy gate structure across the first stacked structures and partially covering the top and the sidewall surfaces of each first stacked structure, and a first sidewall spacer on each sidewall surface of the first dummy gate structures; forming a first source / drain doped layer, and a dielectric structure exposing the top surfaces of the first dummy gate structure and each first sidewall spacer; removing the first dummy gate structure to form a first trench; removing a portion of the first sacrificial layer to form a first via which partially exposes the first source / drain doped layer; forming a first barrier layer on the first source / drain doped layer; and forming a first gate structure to fill the first trench and the first via.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Method for forming transistors with raised source and drains and device formed thereby
InactiveUS6100013AEnhanced transistor performanceOvercome limitationsTransistorDecorative surface effectsCapacitanceResist
The preferred embodiment of the present invention provides a transistor structure and method for fabricating the same that overcomes the disadvantages of the prior art. In particular, the preferred structure and method results in lower leakage and junction capacitance by using raised source and drains which are partially isolated from the substrate by a dielectric layer. The raised source and drains are preferably fabricated from the same material layer used to form the transistor gate. The preferred method for fabricating the transistor uses hybrid resist to accurately pattern the gate material layer into regions for the gate, the source and the drain. The source and drain regions are then connected to the substrate by growing silicon. The preferred method thus results in an improved transistor structure while not requiring excessive fabrication steps.
Owner:IBM CORP
Semiconductor device and method of forming the same
ActiveUS20080230845A1Energy stabilityObtaining stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorDiffusion barrier
A semiconductor device may include, but is not limited to, a single crystal silicon diffusion layer, a polycrystal silicon conductor, and a diffusion barrier layer. The diffusion barrier layer separates the polycrystal silicon conductor from the single crystal silicon diffusion layer. The diffusion barrier layer prevents a diffusion of at least one of silicon-interstitial and silicon-vacancy between the single crystal silicon diffusion layer and the polycrystal silicon conductor.
Owner:HEFEI RELIANCE MEMORY LTD
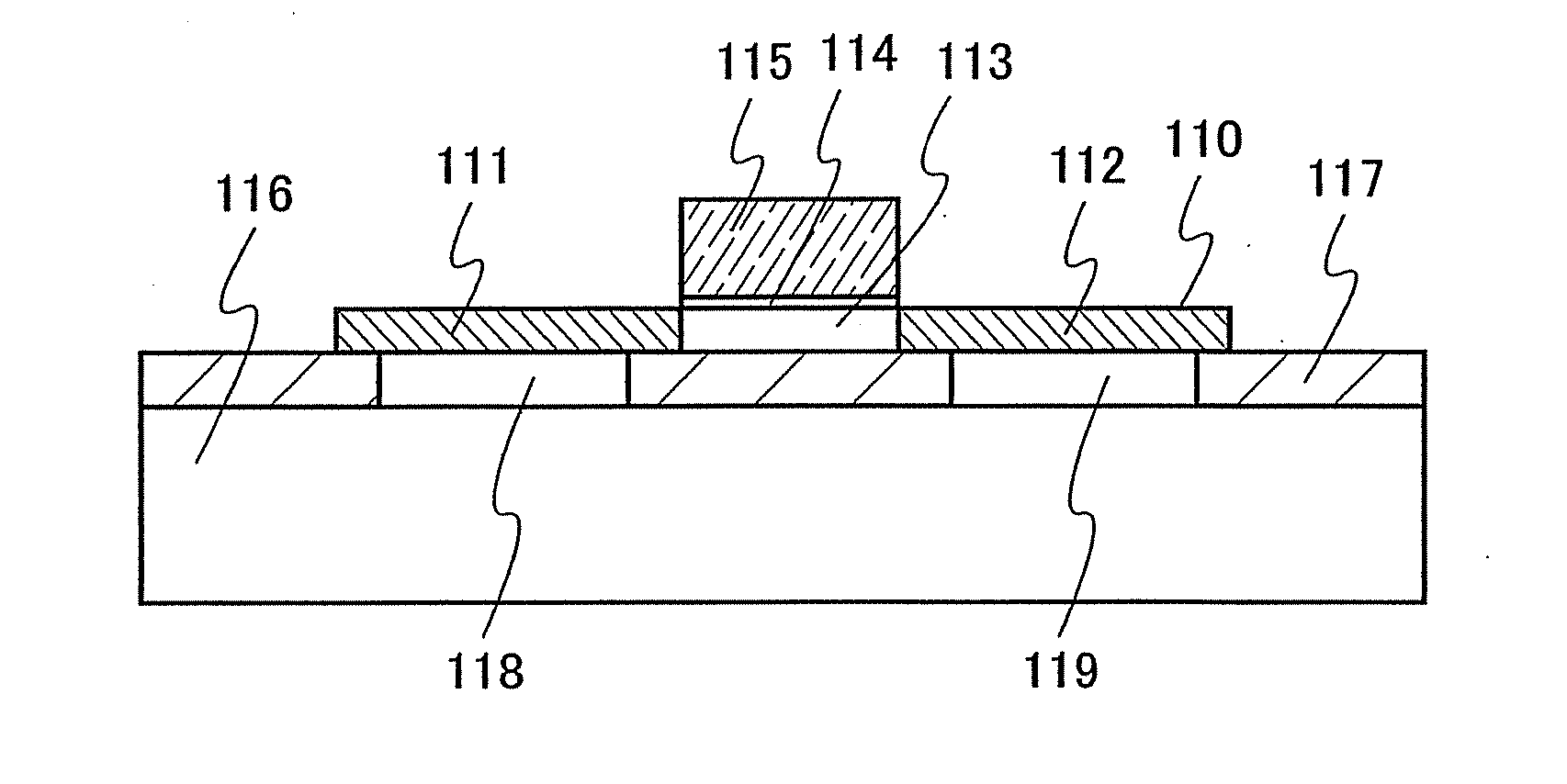
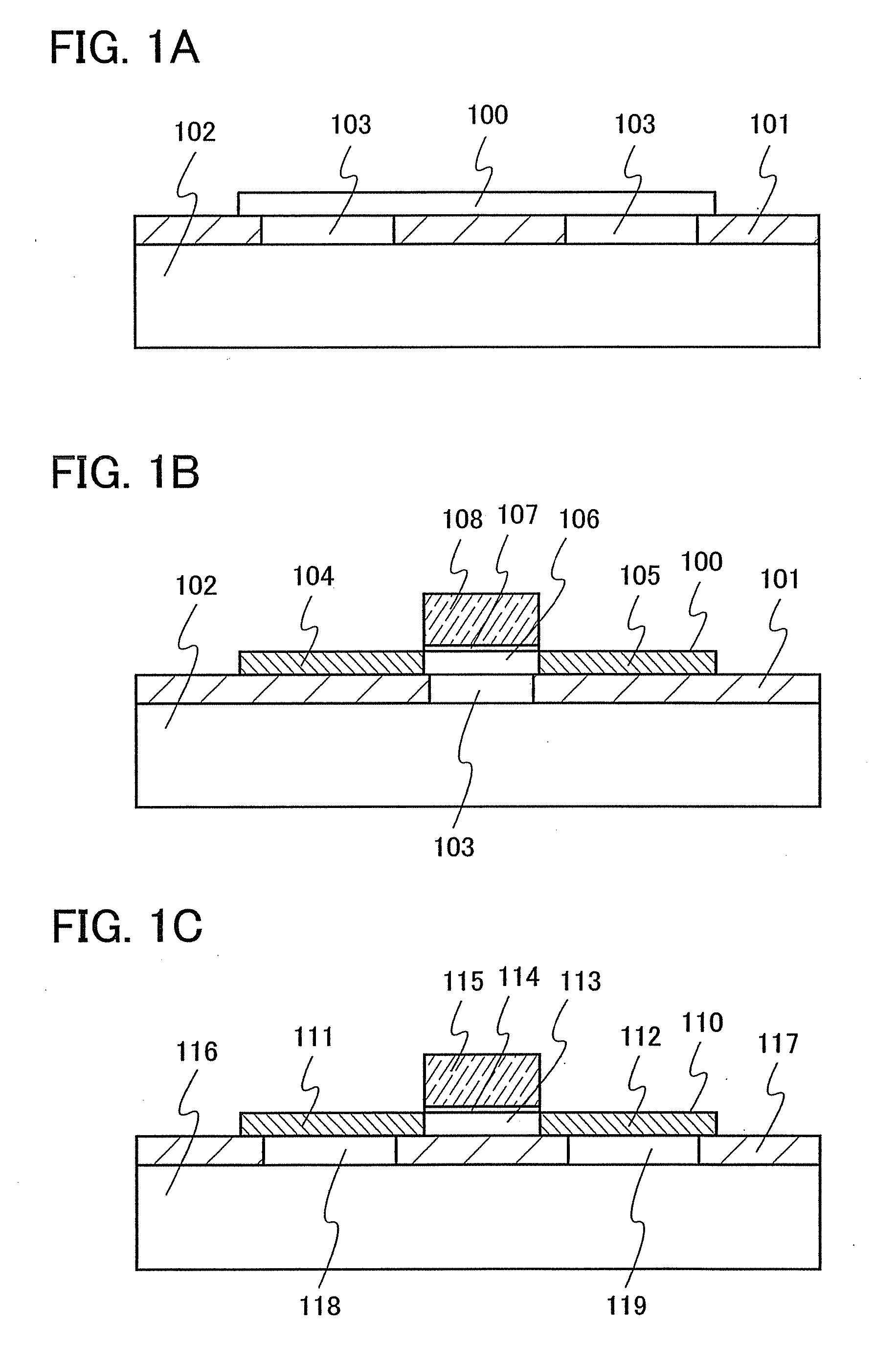
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS7309921B2Reduce junctionLimits flow directionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringImpurity
Leakage current generated in a PN junction diode is reduced, and charge-up current caused by plasma treatment in formation of wiring connected to the PN junction diode is controlled. An N+ region as a first conductive type impurity region provided in a Si substrate with an upper surface being exposed on one main surface of the Si substrate, a P+ polysilicon plug provided with a bottom being contacted with an upper surface of the N+ region, and wiring connected to a top of the P+ polysilicon plug are included.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7151034B2Improve featuresTotal current dropSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
The present invention discloses improved semiconductor device and method for manufacturing wherein one side of a source and drain region and a portion of a channel region are disposed on a buried oxide layer formed on a semiconductor substrate and the side of the source and drain region and another portion of the channel region are disposed on a Si epitaxial layer formed on a semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Double-patterned magneto-resistive random access memory (MRAM) for reducing magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) pitch for increased MRAM bit cell density
ActiveUS20190214554A1Reduce sizeFacilitates MTJsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
Double-patterned magneto-resistive random access memory (MRAM) for reducing magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) pitch for increased MRAM bit cell density is disclosed. In one aspect, to fabricate MTJs in an MRAM array with reduced MTJ row pitch, a first patterning process is performed to provide separation areas in an MTJ layer between what will become rows of fabricated MTJs, which facilitates MTJs in a given row sharing a common bottom electrode. This reduces the etch depth and etching time needed to etch the individual MTJs in a subsequent step, can reduce lateral projections of sidewalls of the MTJs, thereby relaxing the pitch between adjacent MTJs, and may allow an initial MTJ hard mask layer to be reduced in height. A subsequent second patterning process is performed to fabricate individual MTJs. Additional separation areas are etched between free layers of adjacent MTJs in a given row to fabricate the individual MTJs.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Electrical junction box
InactiveUS20140198467A1Downsize the printed circuit boardsDownsizing/densification of the electrical junction boxStacked spaced PCBsElectrical connection printed elementsElectricityElectrical junction
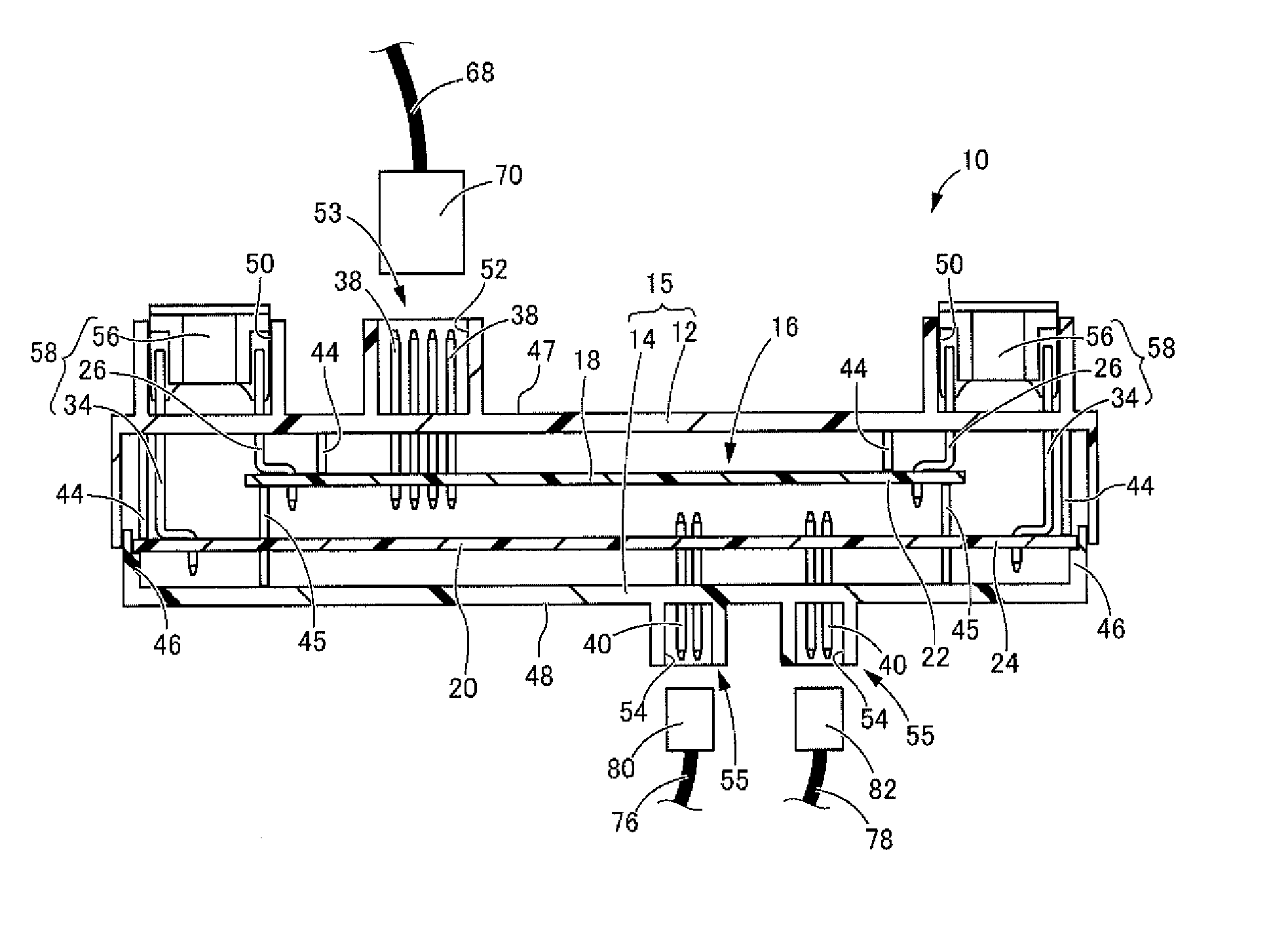
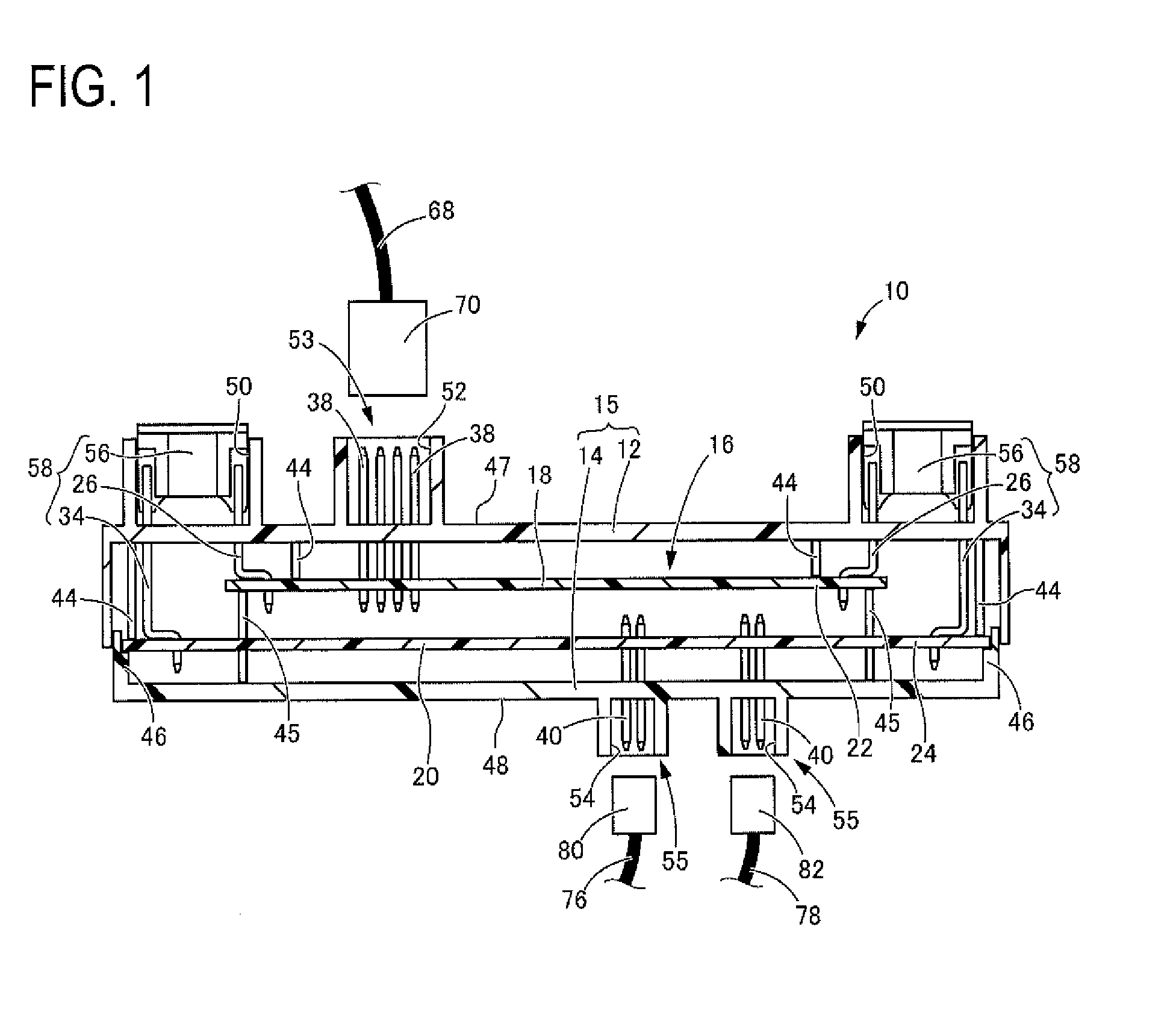
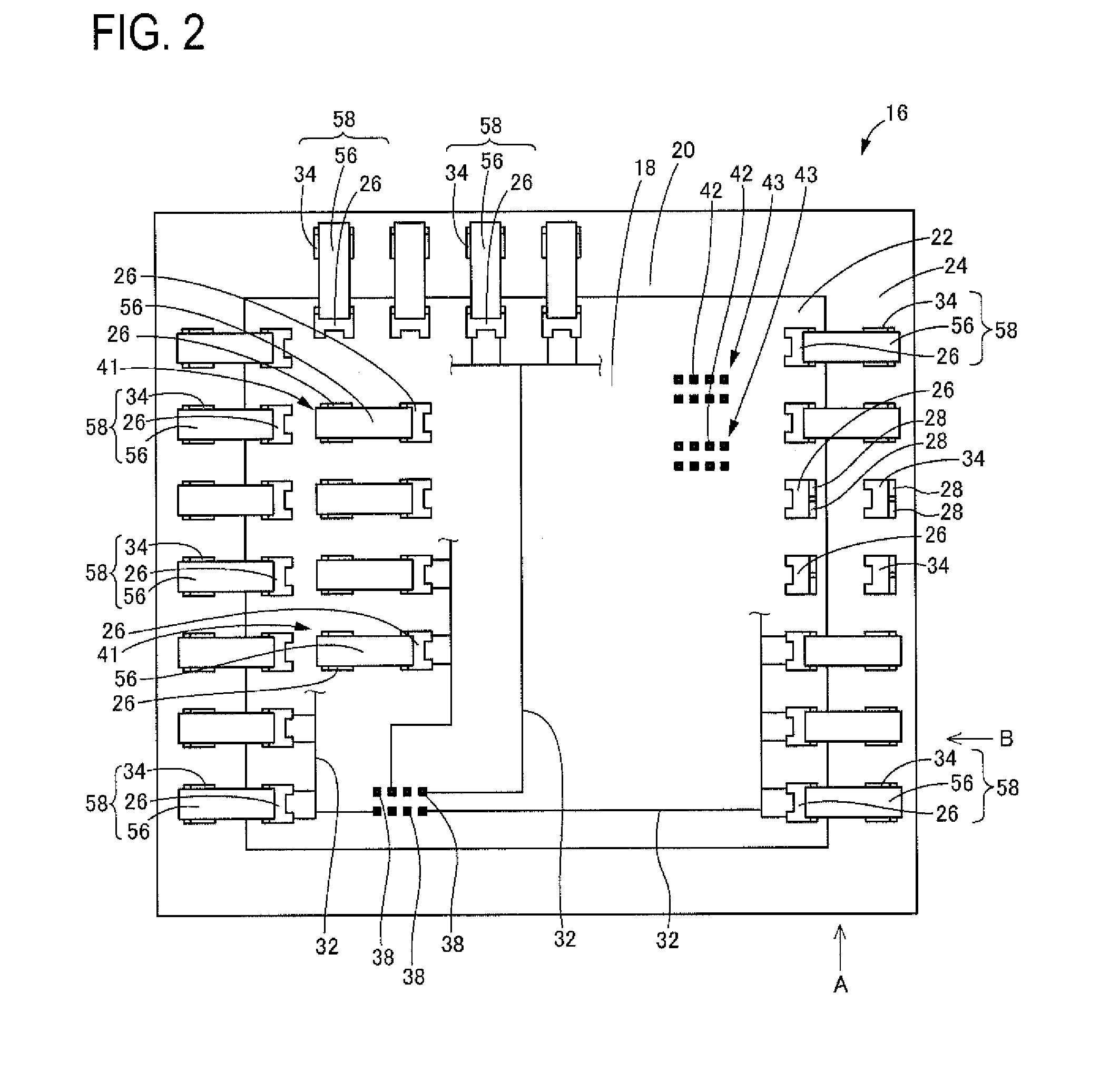
An electrical junction box is provided in which a printed circuit board is accommodated in a case so as to configure an internal circuit, the electrical junction box achieving downsizing / densification with high space efficiency and simplified routing of electric cables of connectors. As the internal circuit, a printed circuit board stack is used in which a first printed circuit board and a second printed circuit board are arranged so as to face each other. A power supply input connector that is to be mounted to a front wall-side connector mounting portion provided on a front wall of a case is connectable to the first printed circuit board, whereas an output connector that is to be mounted to a rear wall-side connector mounting portion provided on a rear wall of the case is connectable to the second printed circuit board.
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
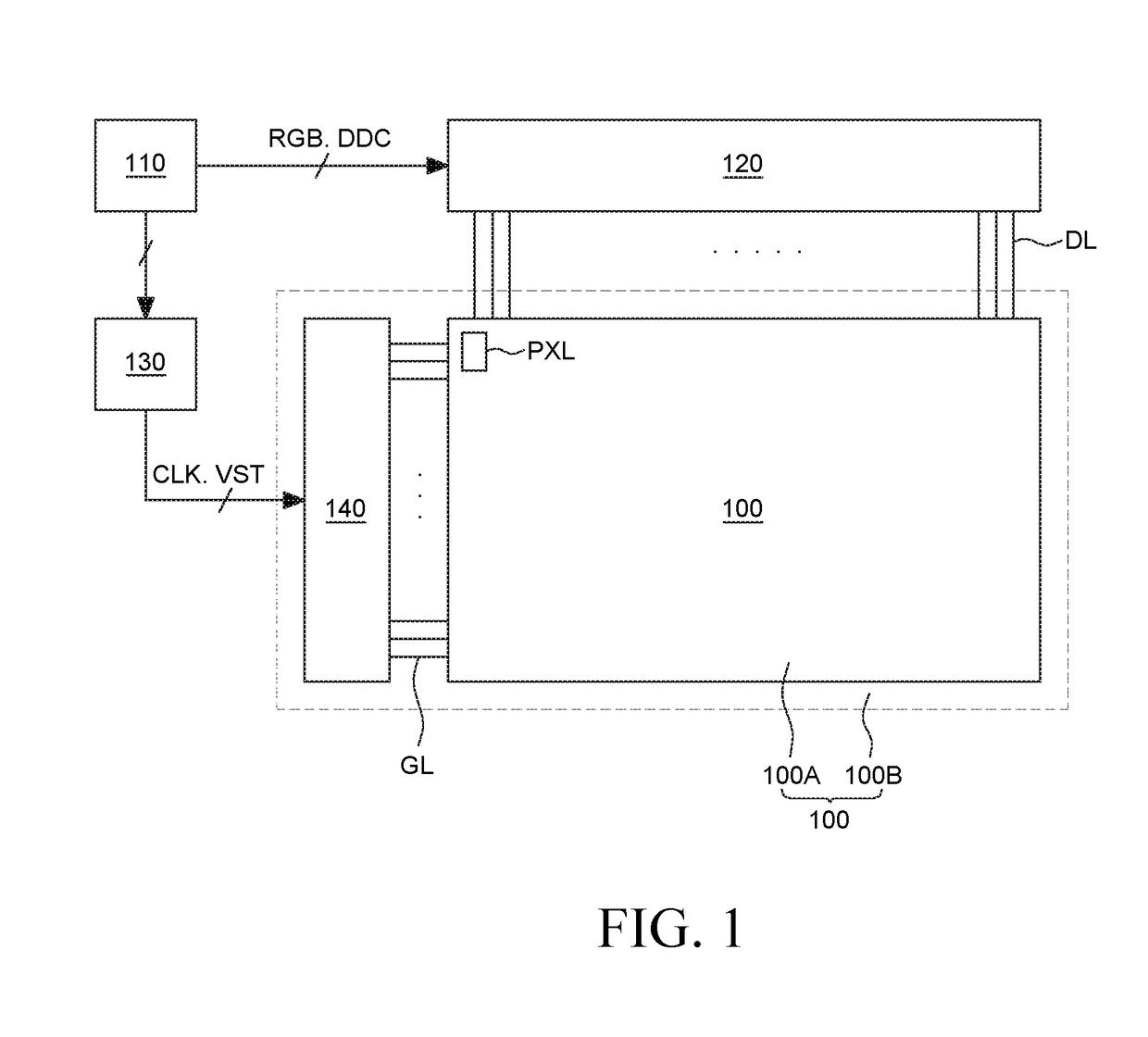
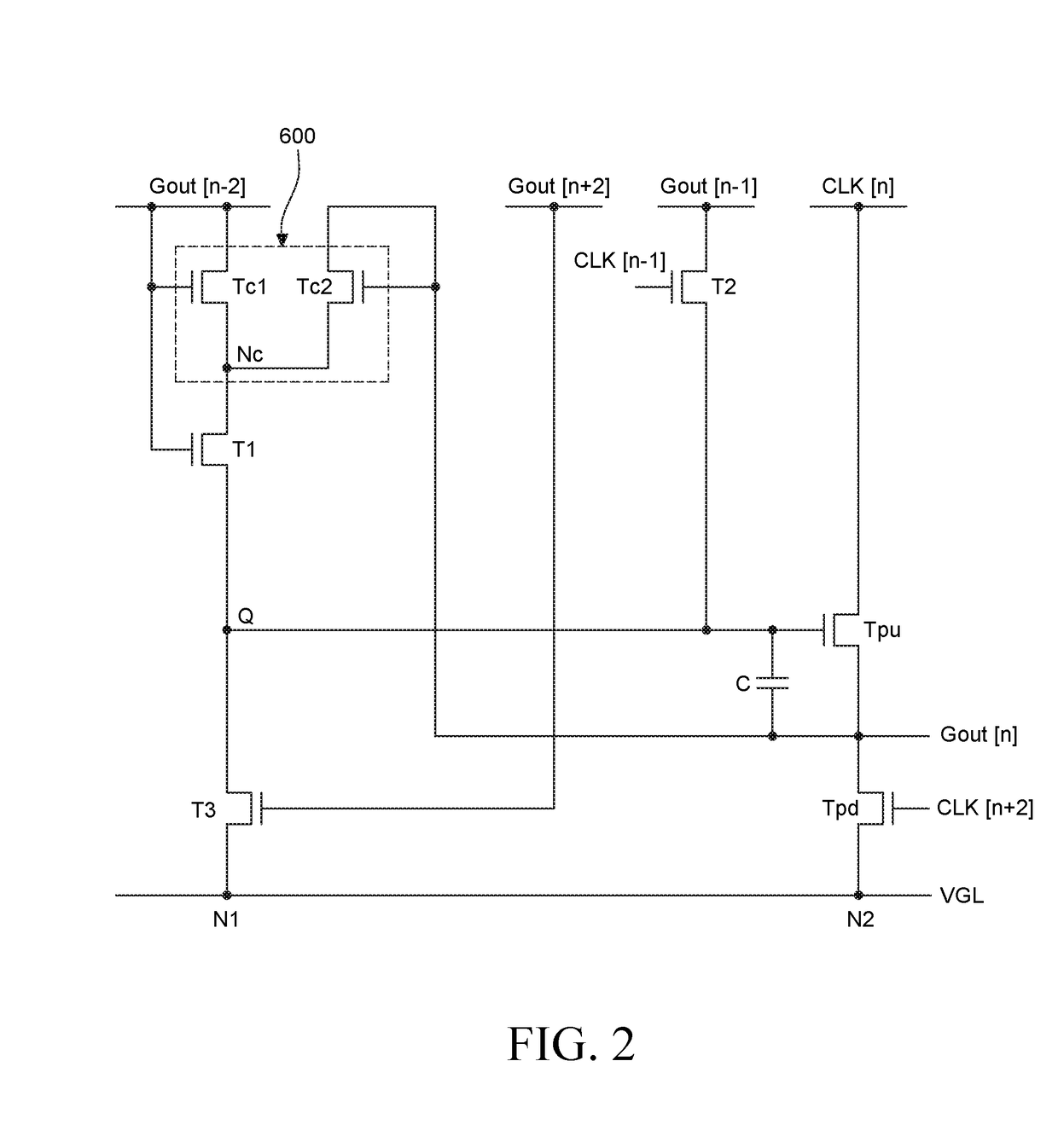
Gate driving circuit and display device using the same
ActiveUS20170316731A1Promote degradationReduced characteristicsStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerDisplay device
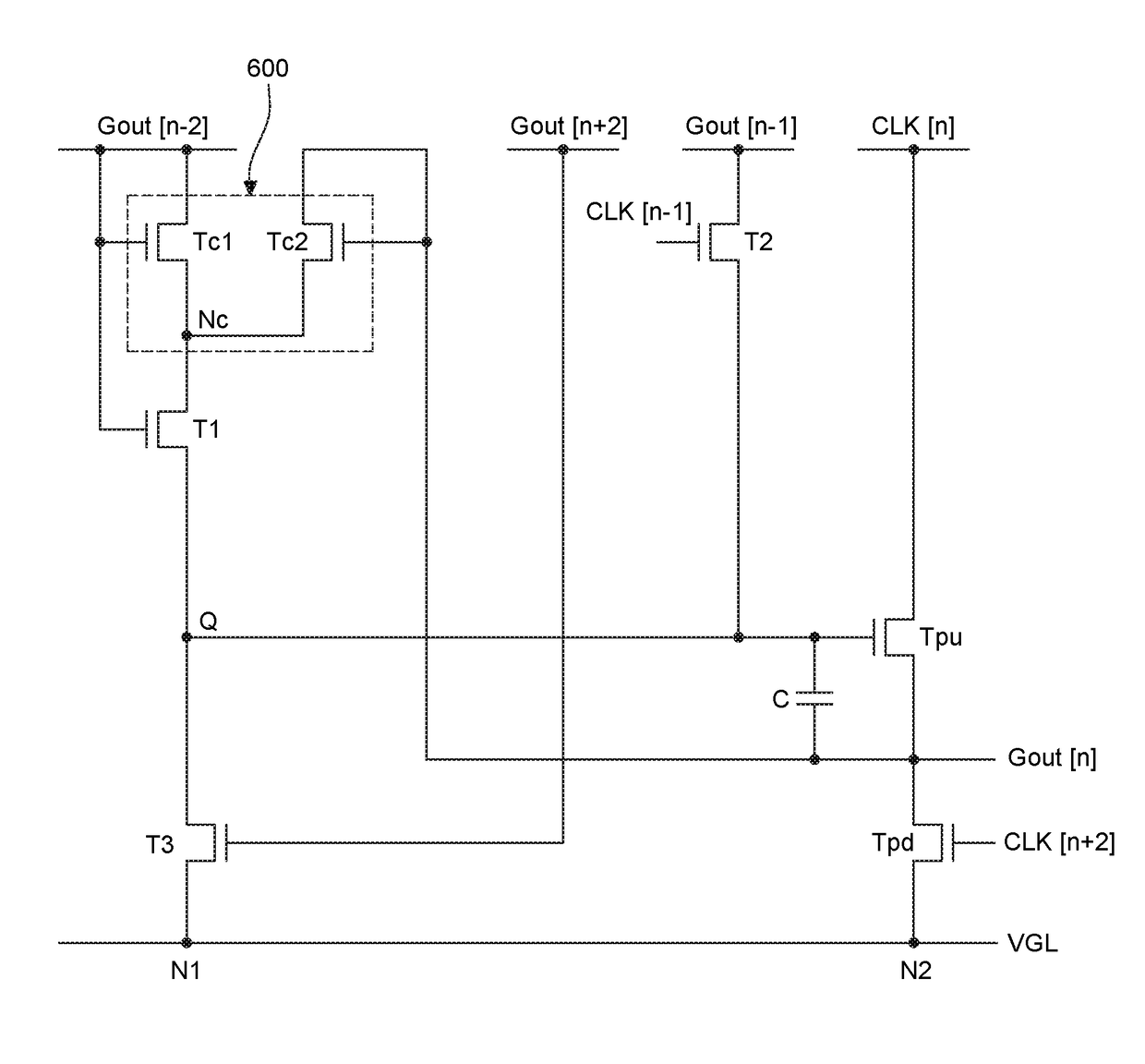
Agate driving circuit and a display device are disclosed. The gate driving circuit includes a shift register including a plurality of stages. Among the stages, an Nth stage includes a first transistor charging a Q node and a junction stress control circuit. A pull-up transistor using the Q node as a gate input controls an output signal of a stage output terminal. The junction stress control circuit includes a first, second, and third control transistors. The first control transistor, the second control transistor, the third control transistor, and the first transistor are connected to each other through a common node. The second control transistor adjusts junction stresses for the first control transistor and the first transistor by controlling a voltage of the common node. When the second control transistor is turned off, the third control transistor discharges the voltage of the common node.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
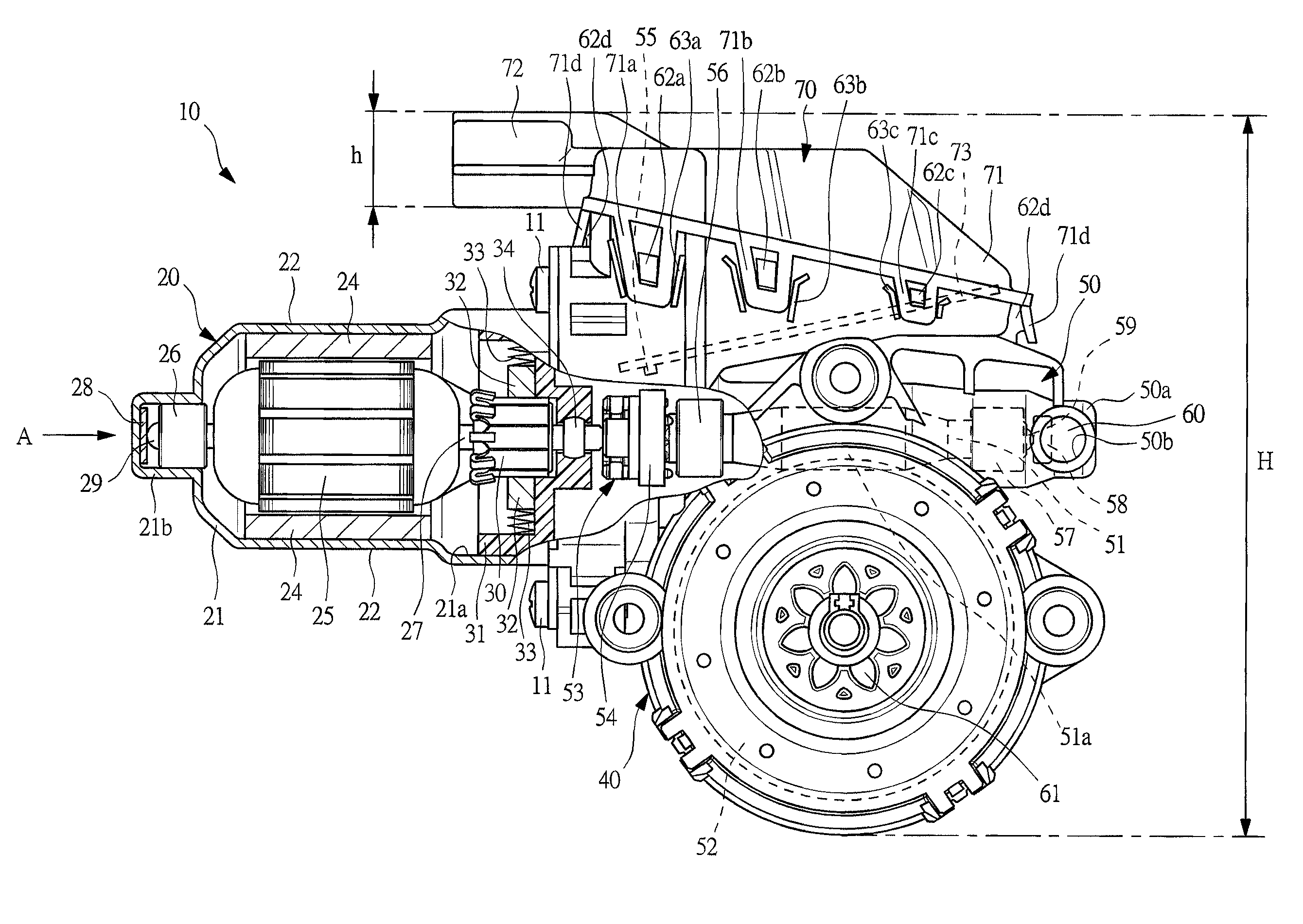
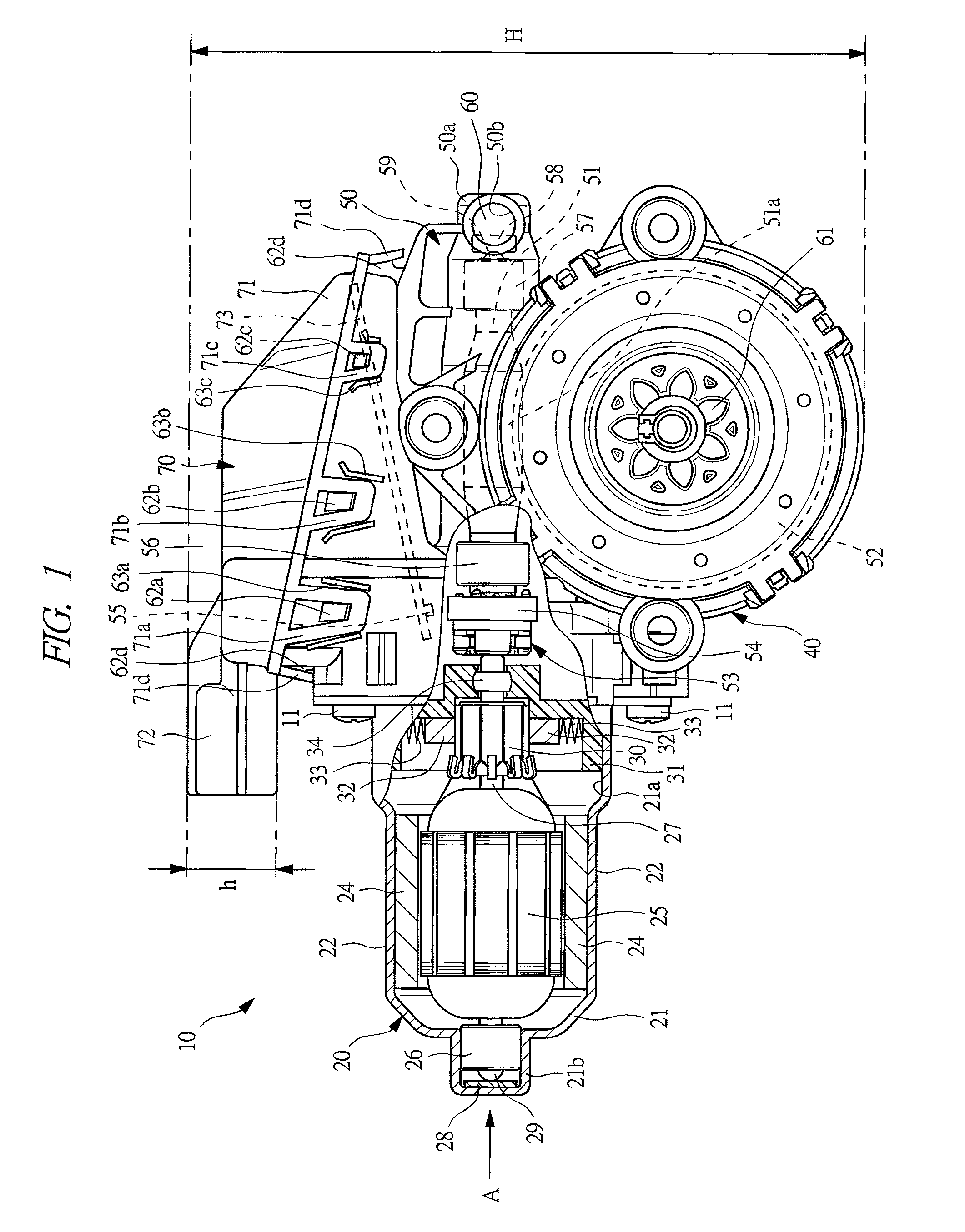
Motor with speed reduction mechanism
InactiveUS20120025643A1Guaranteed uptimeKeep for a long timeAssociation with control/drive circuitsCoupling device detailsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:MITSUBA CORP
ESD protection device and method for manufacturing the same
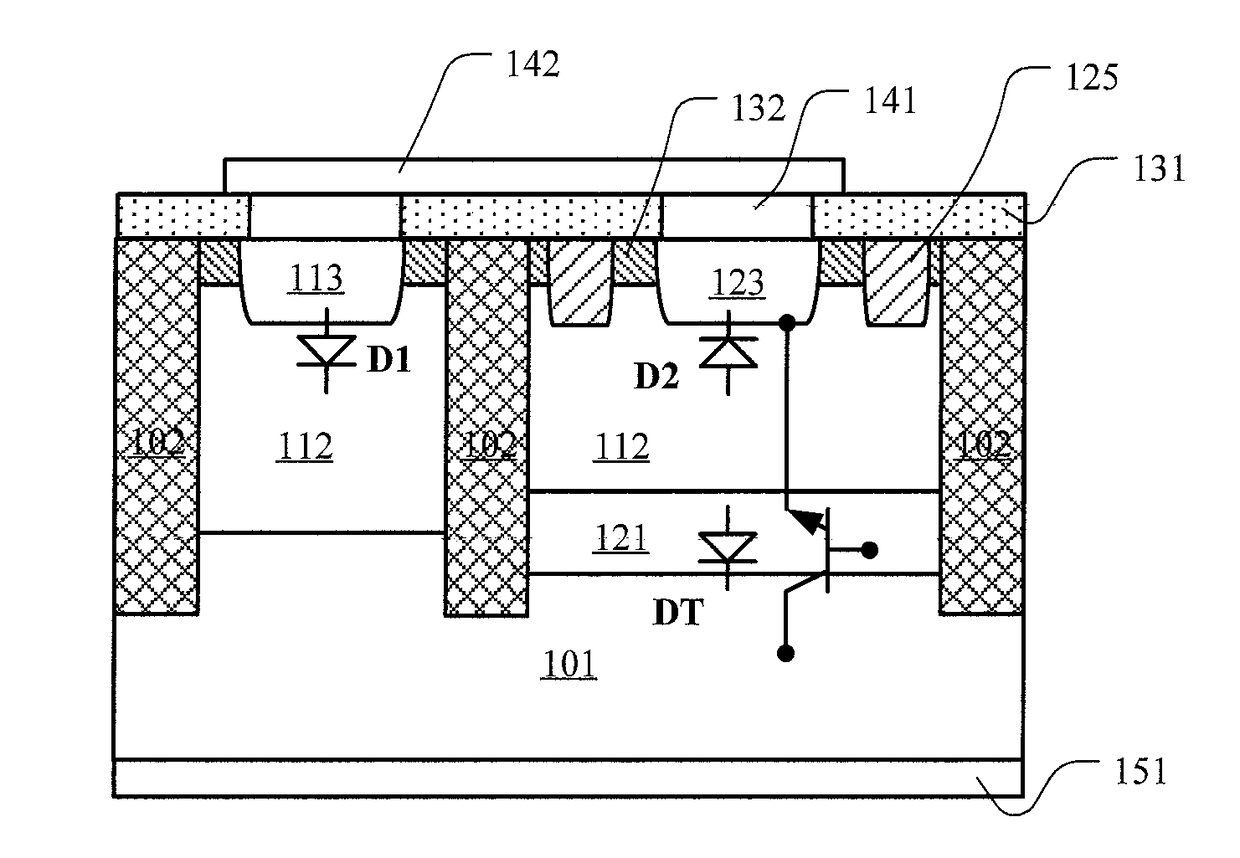
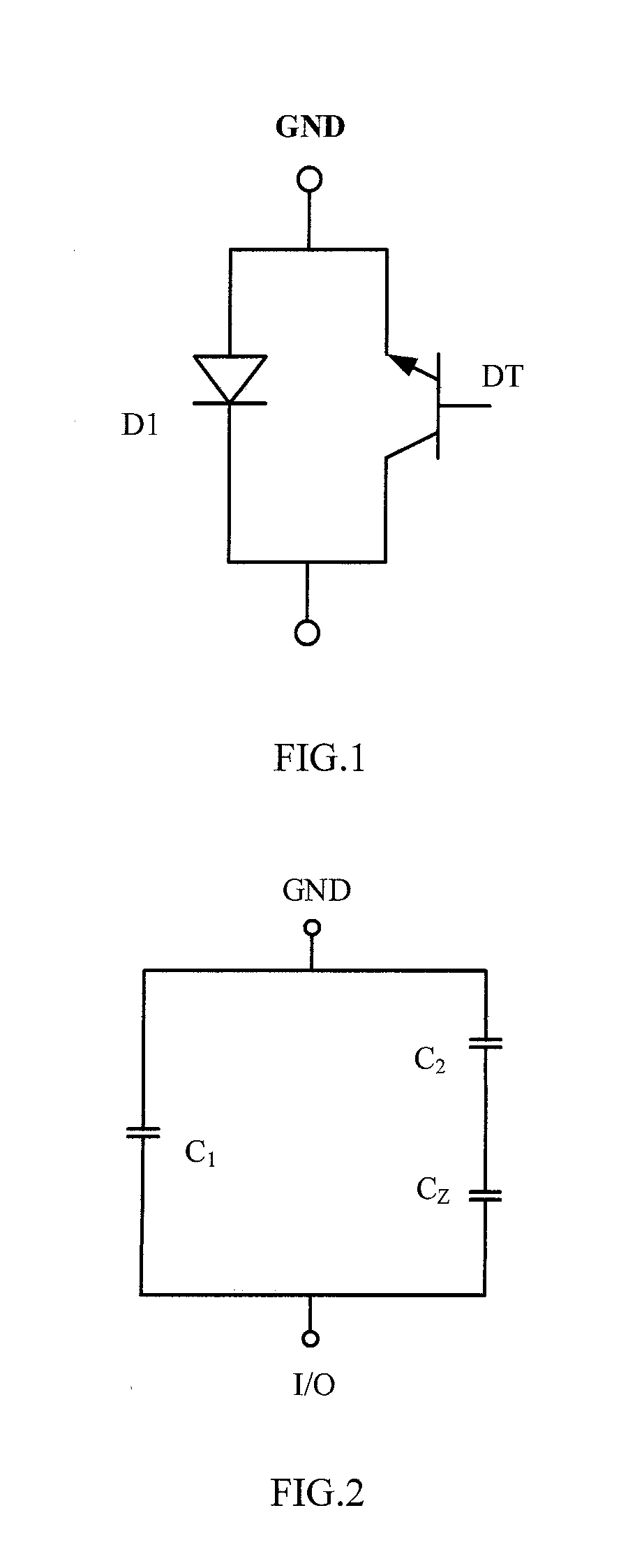
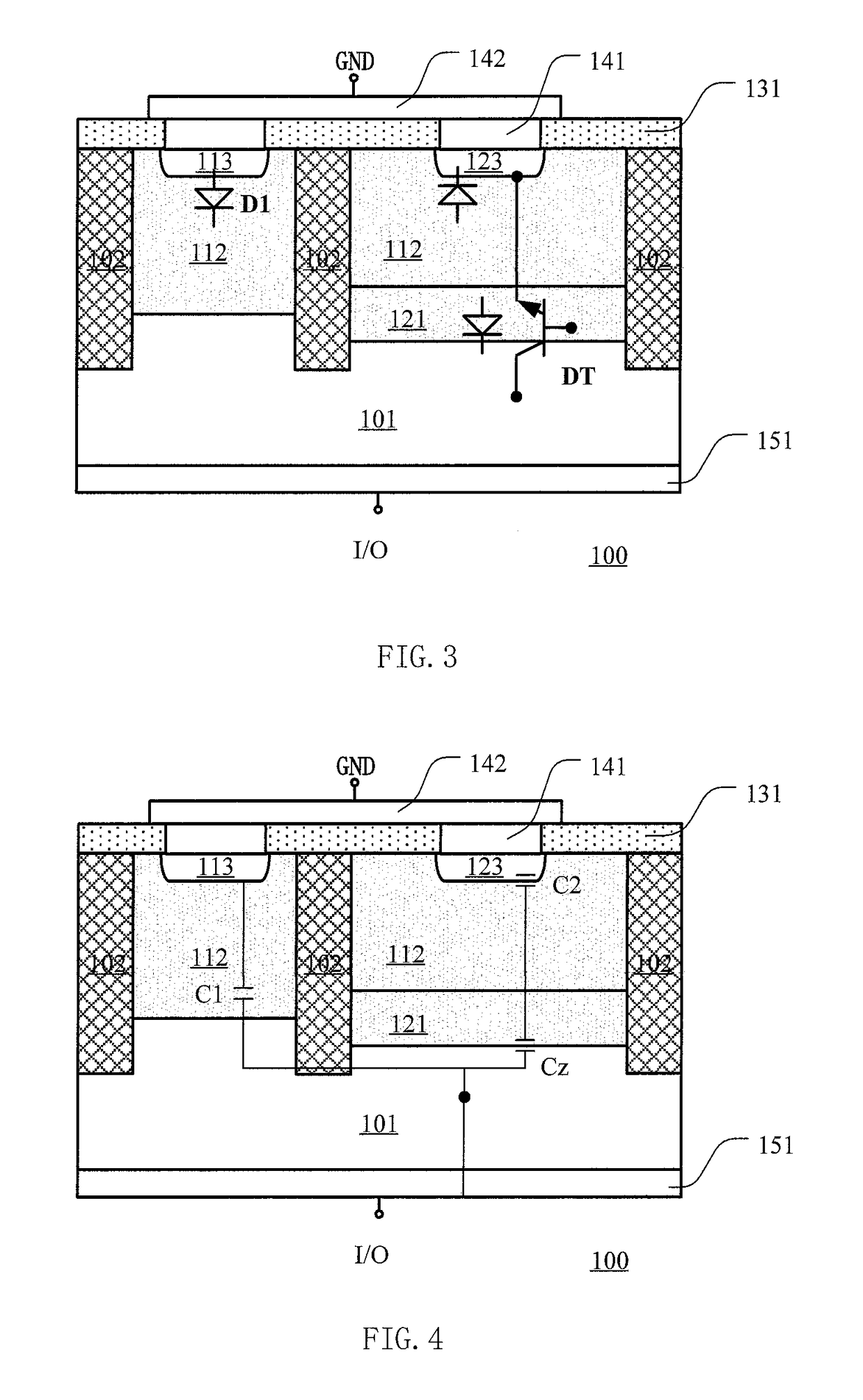
ActiveUS20180047717A1Junction capacitanceIncrease in junction capacitanceTransistorSolid-state devicesRectifier diodesParasitic capacitance
Disclosed is a method for manufacturing an ESD protection device. The ESD protection device includes a rectifier diode and an open-base bipolar transistor, the anode of the rectifier diode is the first doped region and the cathode of the rectifier diode is the semiconductor substrate, the emitter region, base region and collector region of the open-base bipolar transistor are the second doped region, the epitaxial semiconductor layer and semiconductor substrate, respectively, the first doped region and the second doped region extend through the doped region into the epitaxial semiconductor layer by a predetermined depth. The doped region can suppress the induced doped region around the second doped region, so that the parasitic capacitance of the open-base bipolar transistor is reduced and the response speed is improved.
Owner:NANJING SILERGY SEMICON TECH CO LTD
Method for fabricating semiconductor device and semiconductor device using the same
ActiveUS20060003558A1Reduce leakage currentImproved PMOS device characteristicTransistorDecorative surface effectsCapacitanceIsolation layer
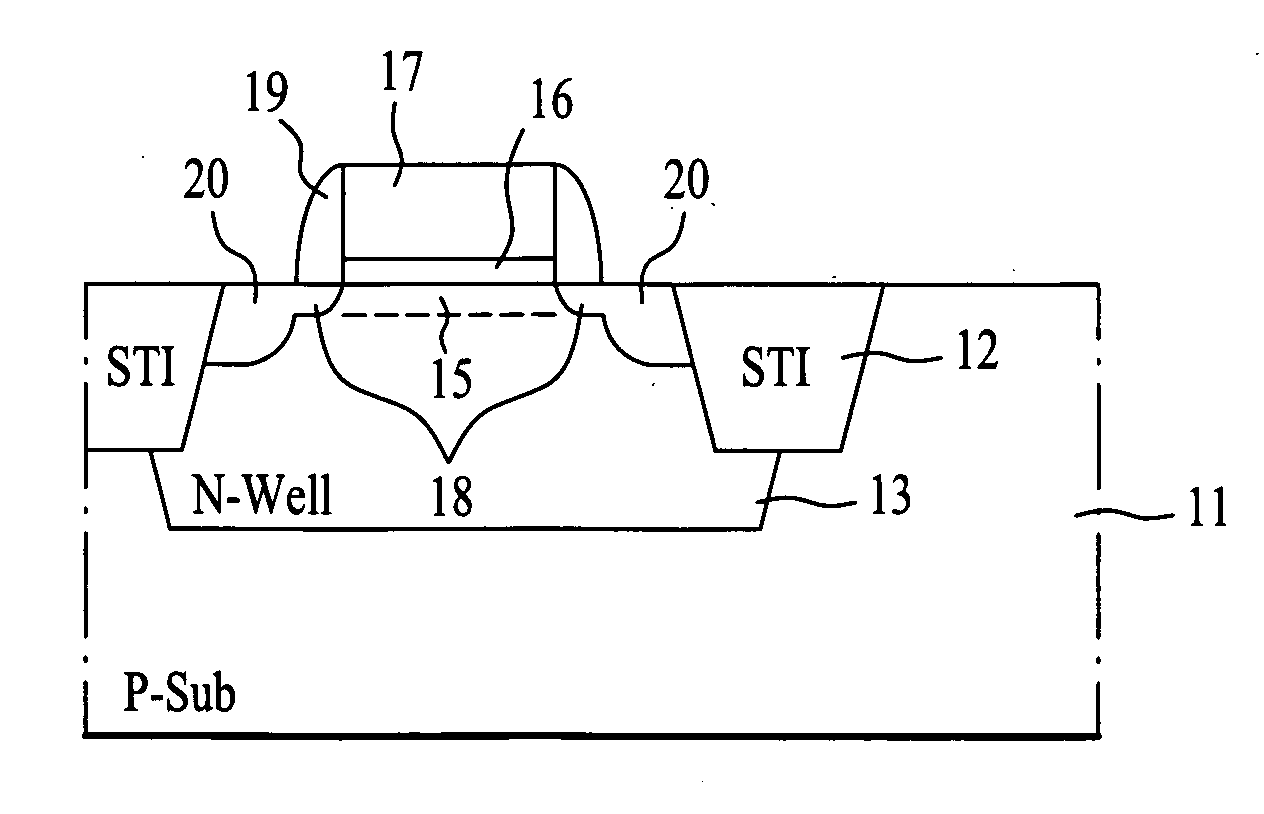
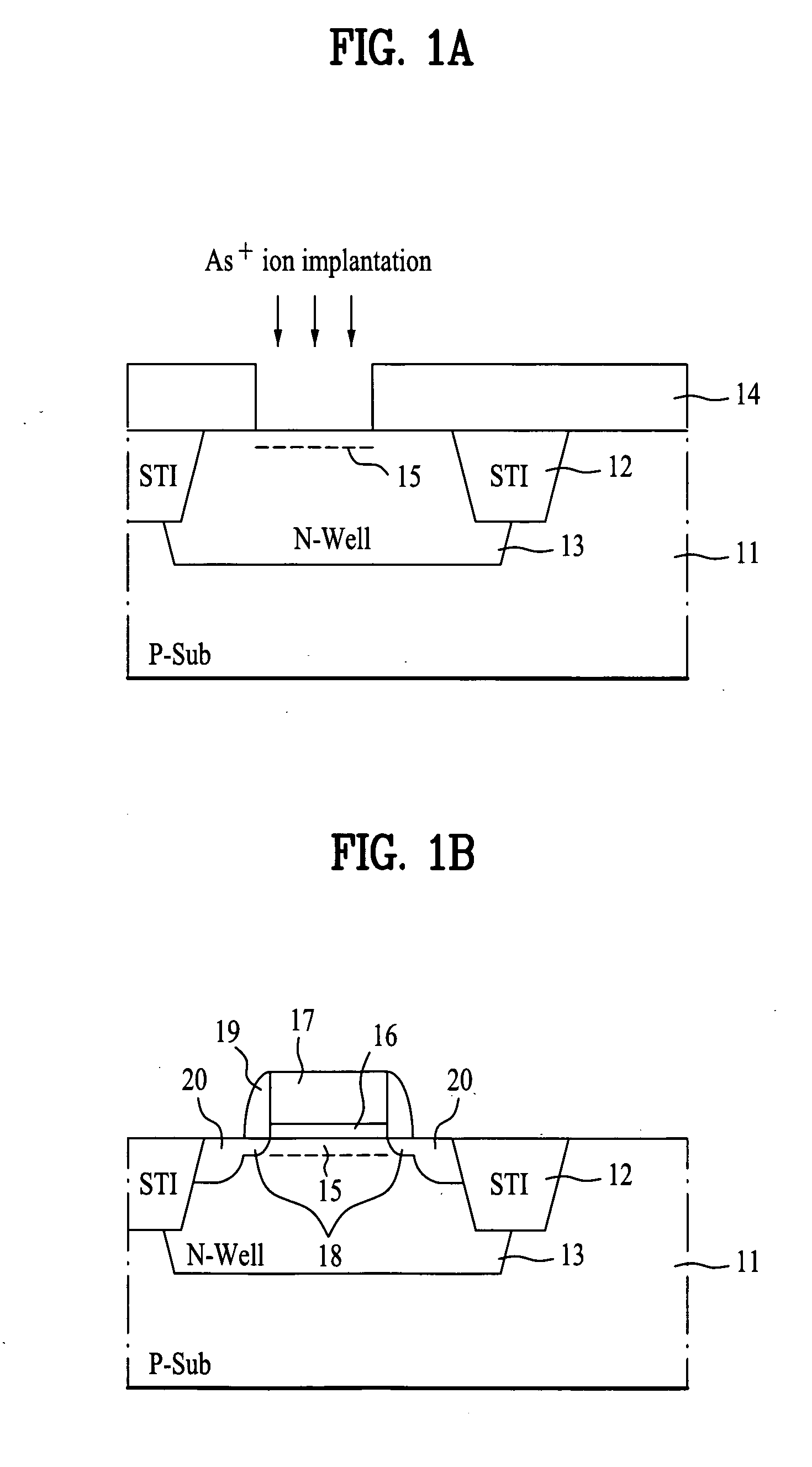
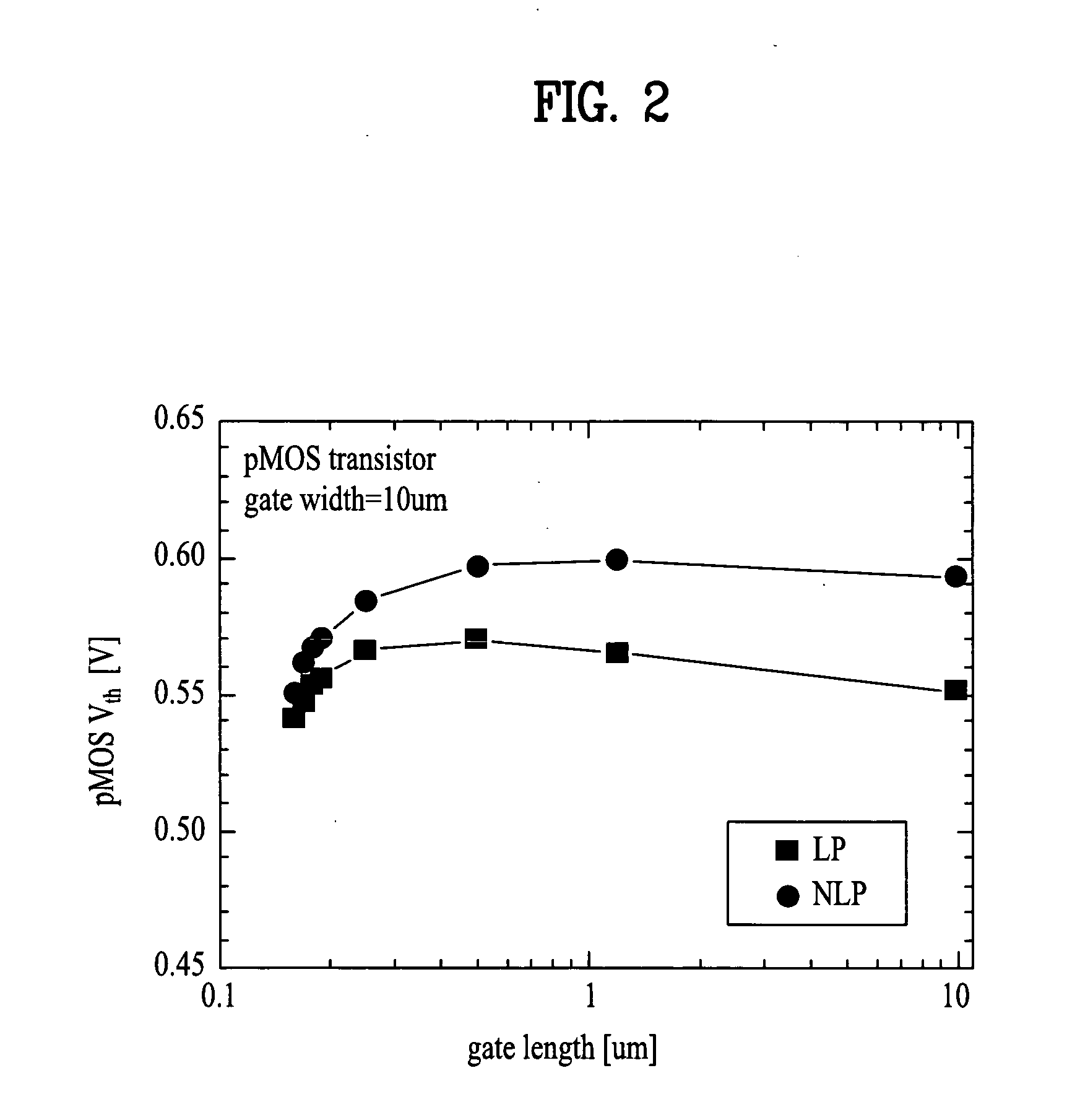
A method for fabricating a semiconductor device improves off-state leakage current and junction capacitance characteristics in a pMOS transistor. The method includes forming a device isolation layer defining an active area in a semiconductor substrate; and forming a channel ion implantation layer by an implantation of arsenic ions in a predetermined region of the active area of the semiconductor substrate at a predetermined density, the channel ion implantation layer having a predetermined doping profile according to the predetermined density of arsenic ion implantation. The implantation may be a low-density implantation of 1.0×1012 ˜10×1013 atoms / cm2 performed at an energy level of 10˜100 keV.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD +1
Treatment of surgical adhesions
InactiveUS20110144182A1Reduce adhesionReduce incidenceOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSurgical AdhesionsTreatment surgery
Connexin modulation for the treatment of surgical adhesions, and associated methods, compositions, and articles.
Owner:BECKER DAVID LAWRENCE +2
Method for manufacturing an edge termination for a silicon carbide power semiconductor device
ActiveUS20180108789A1Easy to manufactureEffective preventionSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceOptoelectronics
A method for manufacturing an edge termination structure for a silicon carbide power semiconductor device having a central region and an edge region is provided. The following manufacturing steps are performed: a) providing an n-doped silicon carbide substrate, b) epitaxially growing a silicon carbide n-doped drift layer on the substrate, which has a lower doping concentration than the substrate, c) creating at least one p-doped termination layer by implanting a second ion up to a maximum termination layer depth and annealing on the first main side, d) forming a doping reduction layer having a depth range, which doping reduction layer comprises at least one doping reduction region, wherein a depth of a doping concentration minimum of the doping reduction layer is greater than the maximum termination layer depth, wherein for the creation of each doping reduction region: implanting a first ion with an implantation energy in the drift layer at least in the edge region, wherein the first ion and the at least one implantation energy are chosen such that the doping reduction layer depth range is less than 10 μm, e) annealing the doping reduction layer, wherein step d) and e) are performed such that the doping concentration of the drift layer is reduced in the doping reduction layer.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
Nitride semiconductor light emitting device
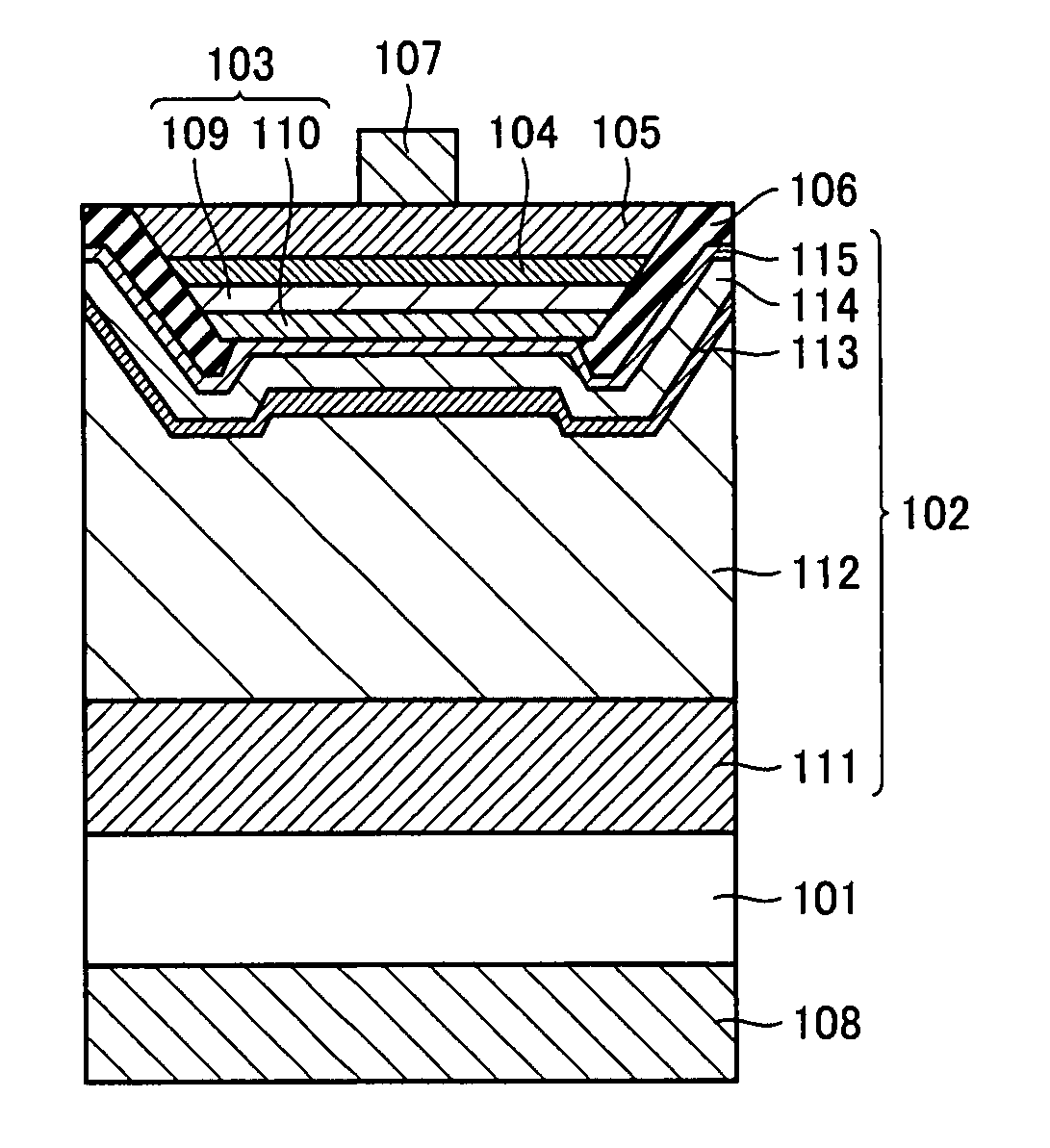
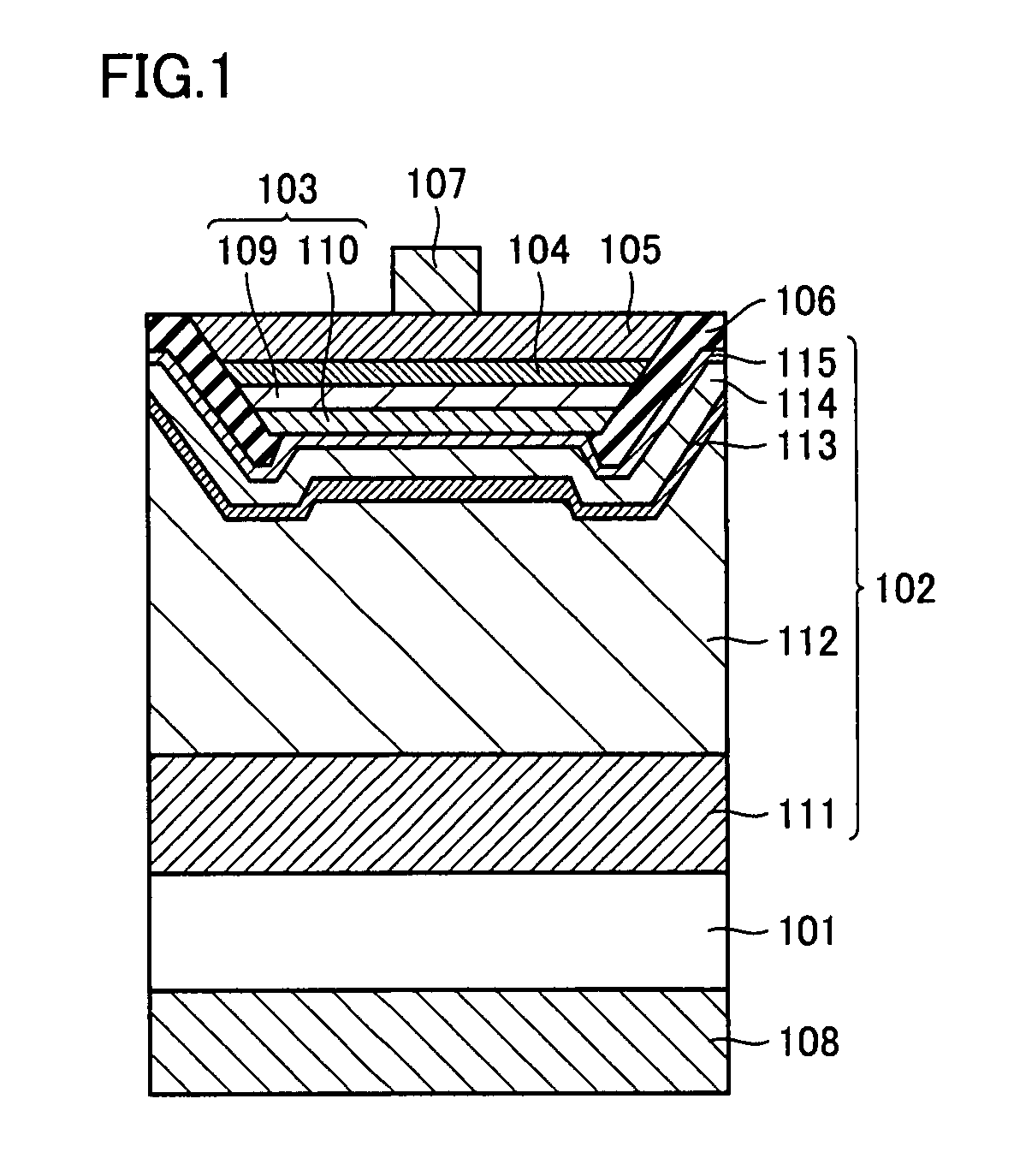
ActiveUS8324639B2Reduce junctionReduce leakageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLight emitting deviceNitride semiconductors
A nitride semiconductor light emitting device includes a conductive substrate, a first metal layer, a second conductivity-type semiconductor layer, an emission layer, and a first conductivity-type semiconductor layer in this order. The nitride semiconductor light emitting device additionally has an insulating layer covering at least side surfaces of the second conductivity-type semiconductor layer, the emission layer and the first conductivity-type semiconductor layer. A method of manufacturing the same is provided. The nitride semiconductor light emitting device may further include a second metal layer. Thus, a reliable nitride semiconductor light emitting device and a method of manufacturing the same are provided in which short-circuit at the PN junction portion and current leak is reduced as compared with the conventional examples.
Owner:SHARP FUKUYAMA LASER CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com