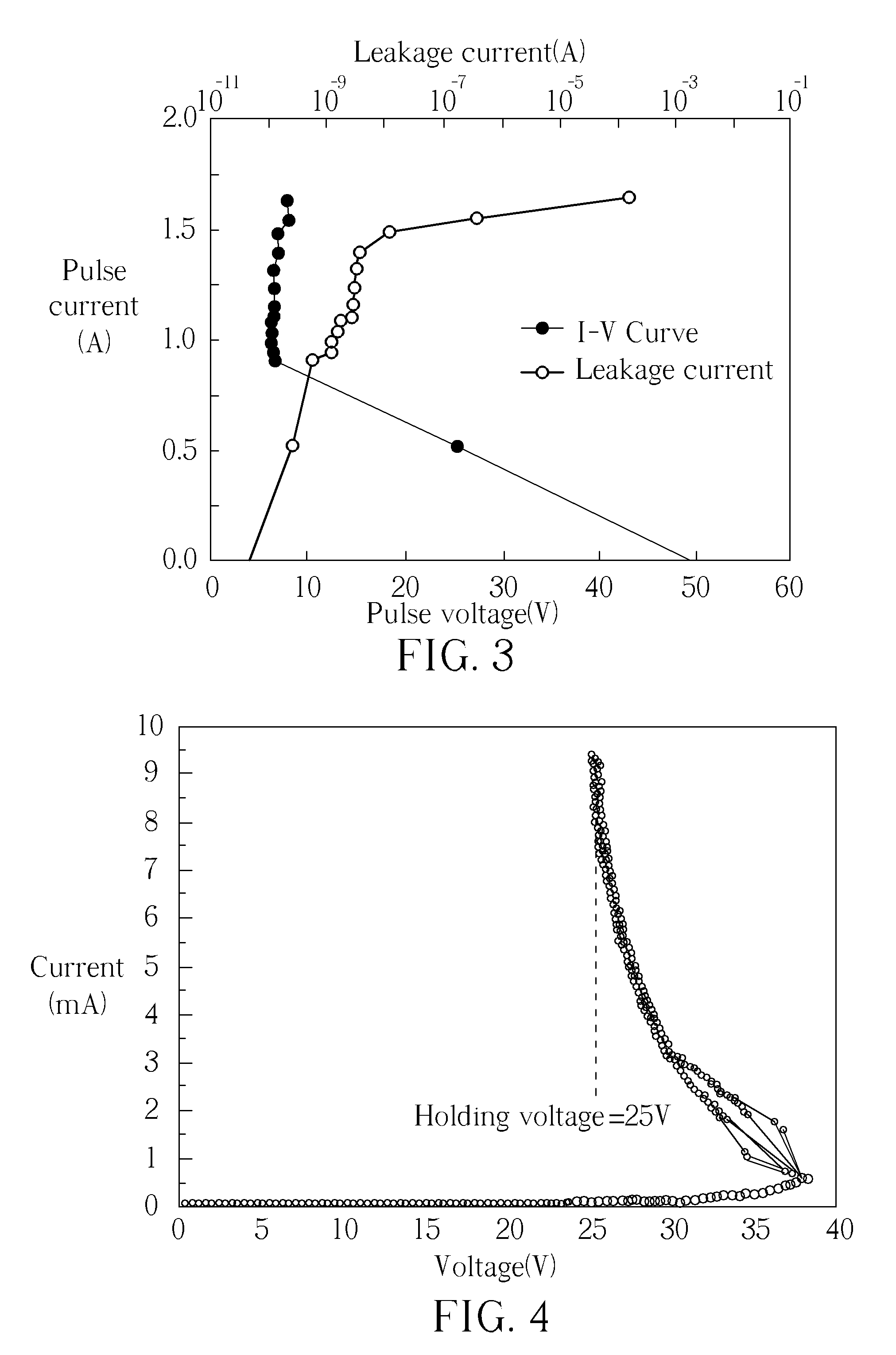
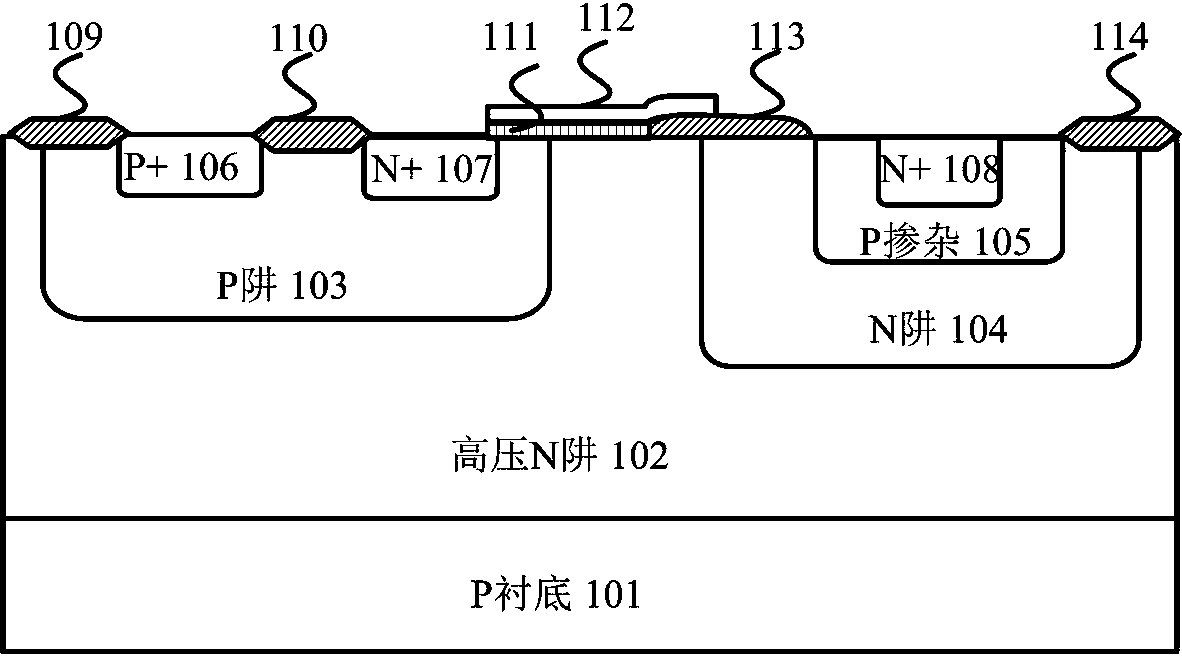
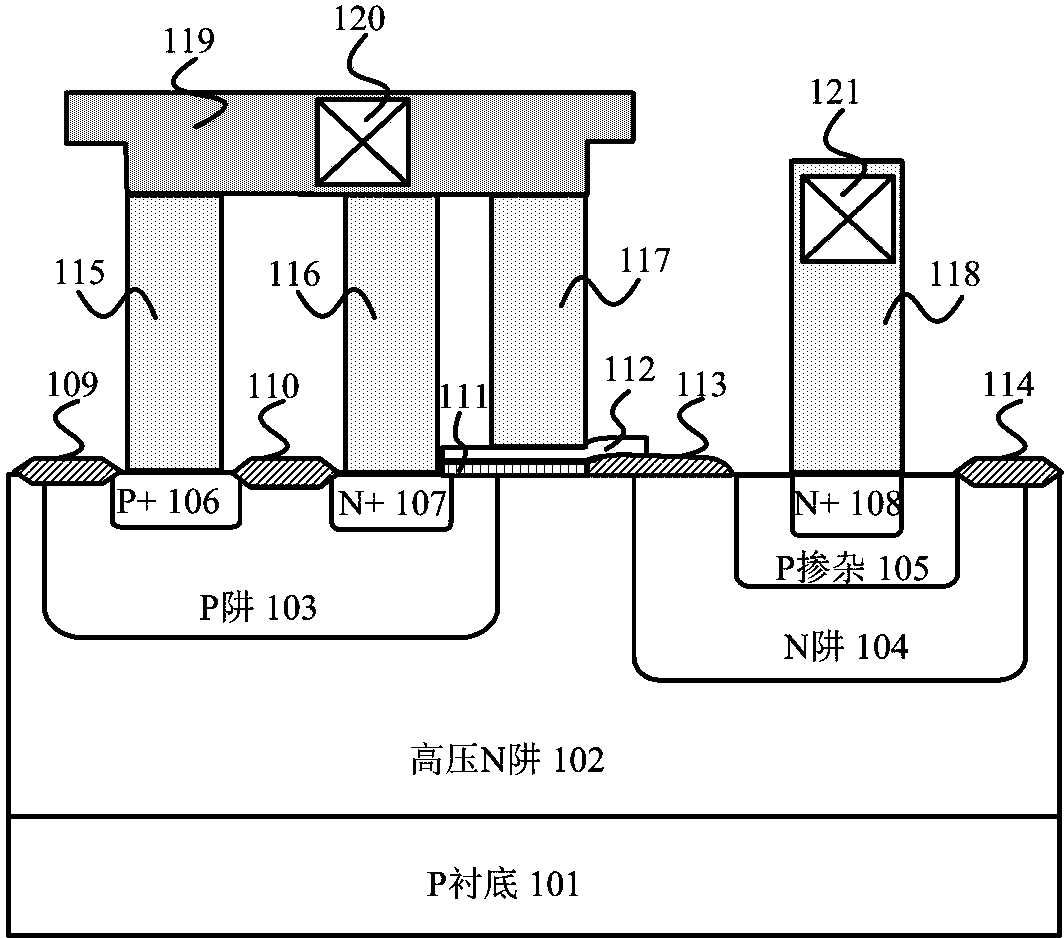
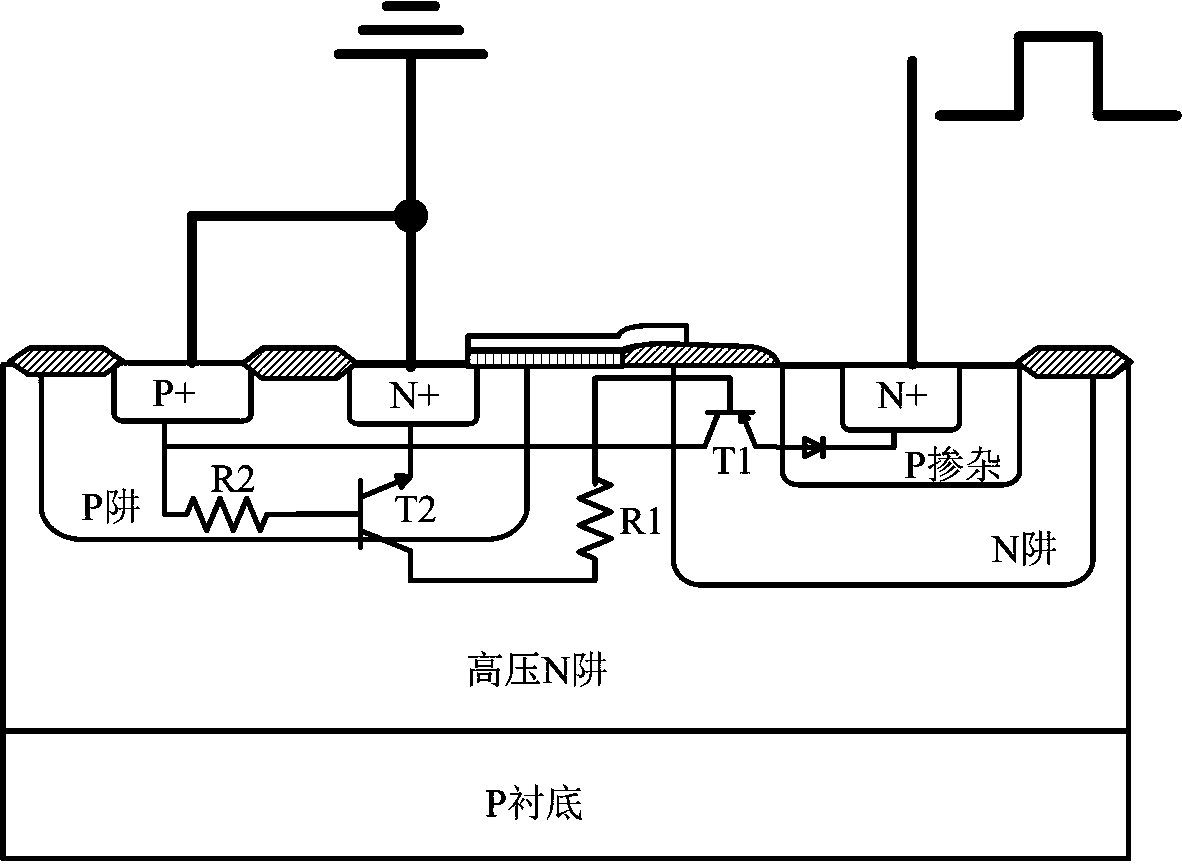
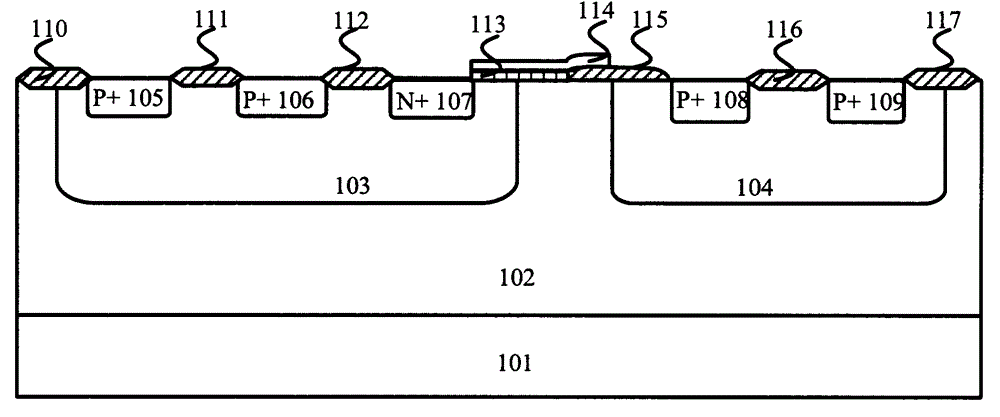
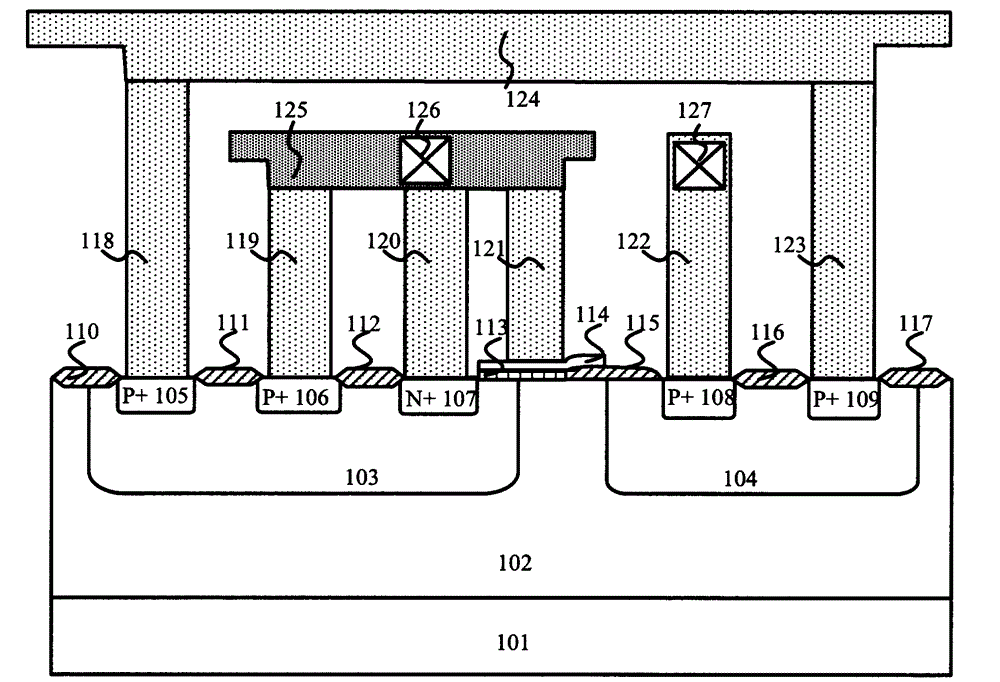
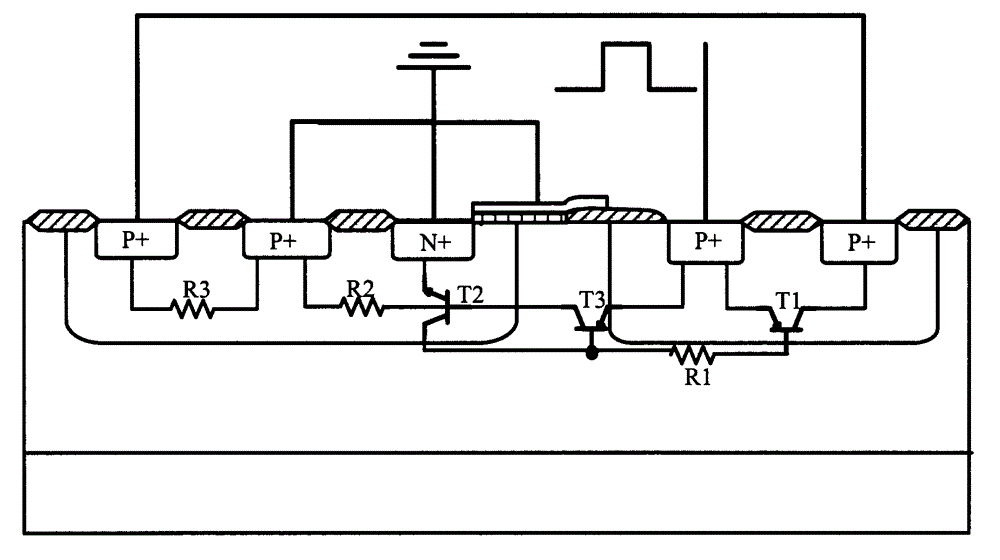
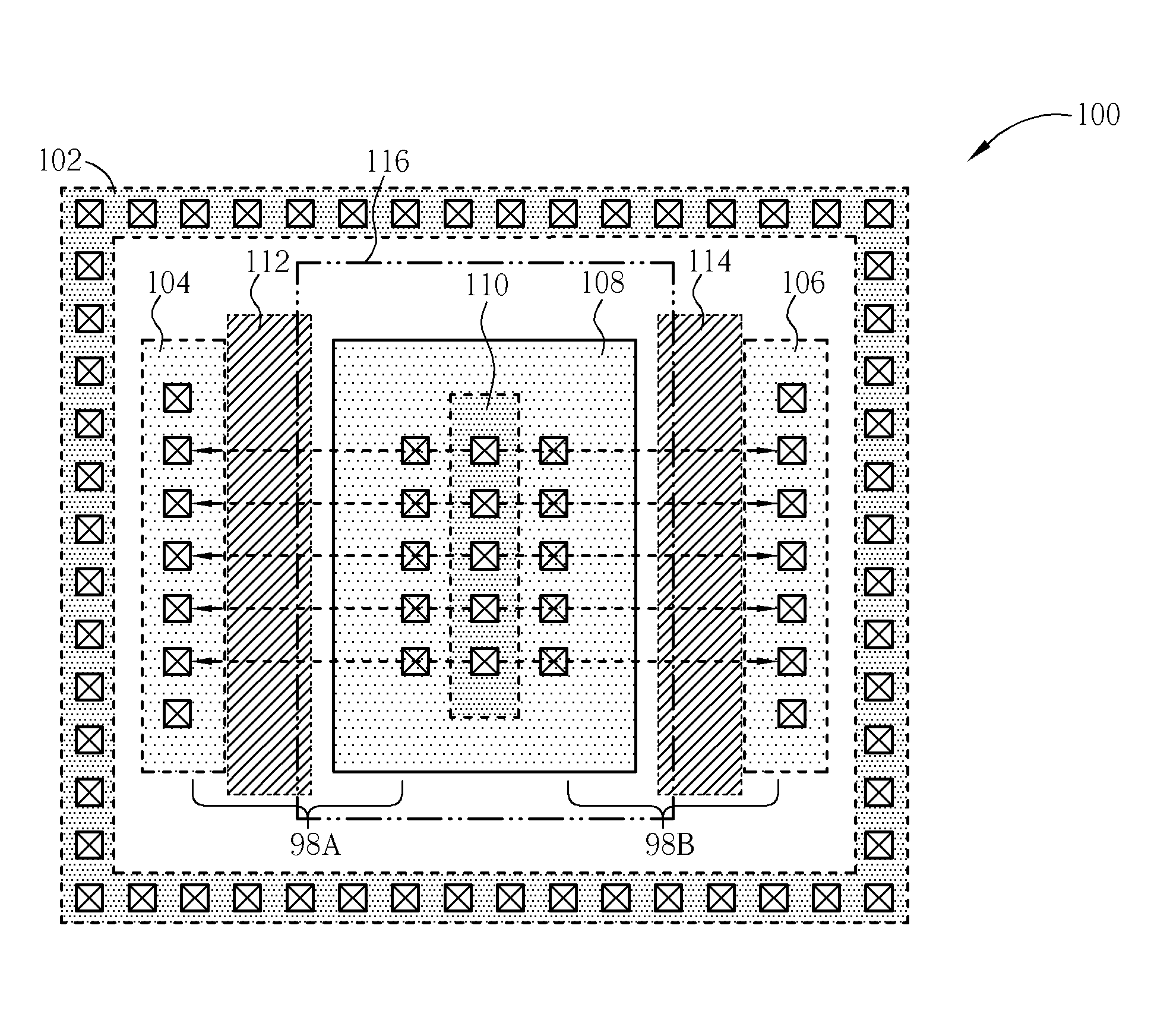
Patents
Literature
63results about How to "Enhanced ESD robustness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
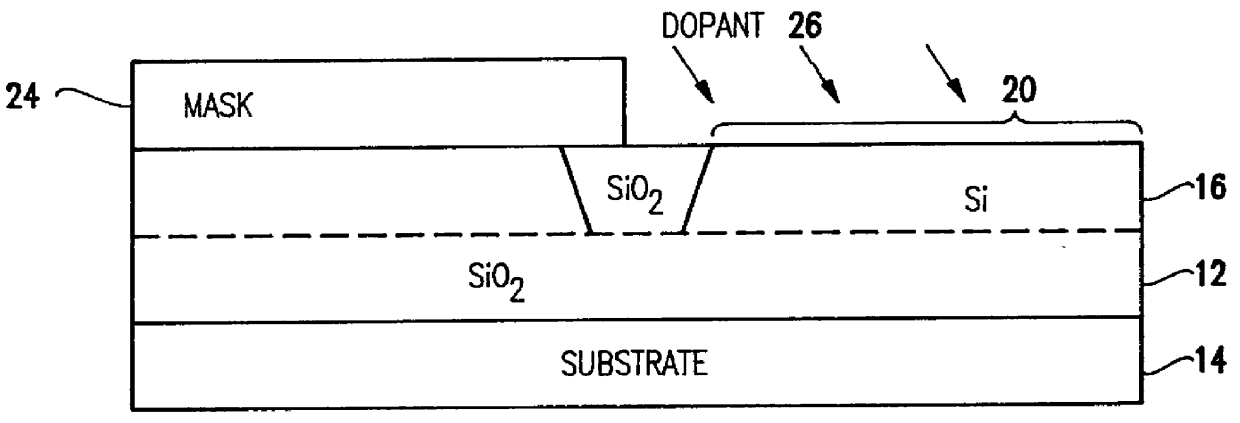
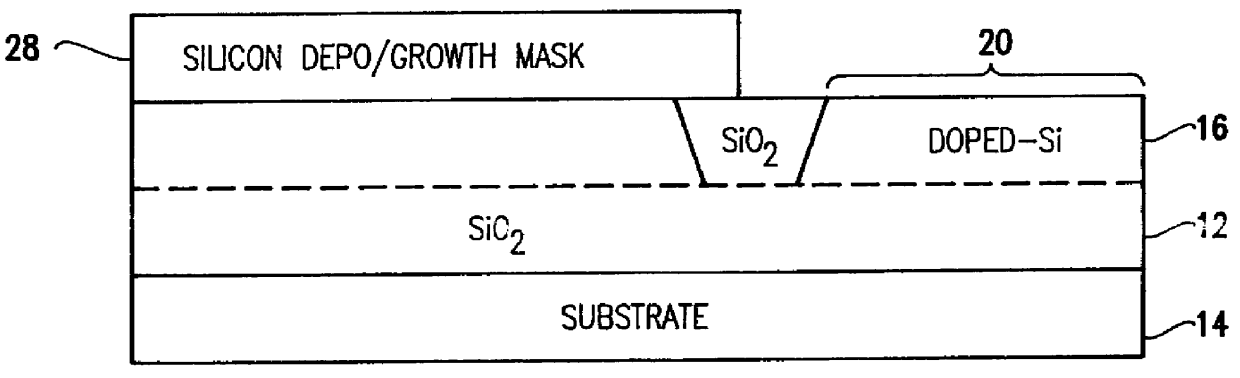
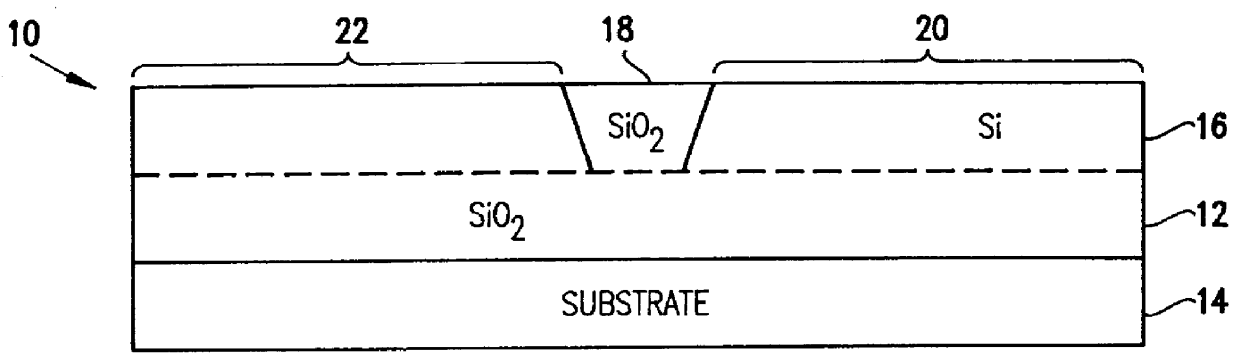
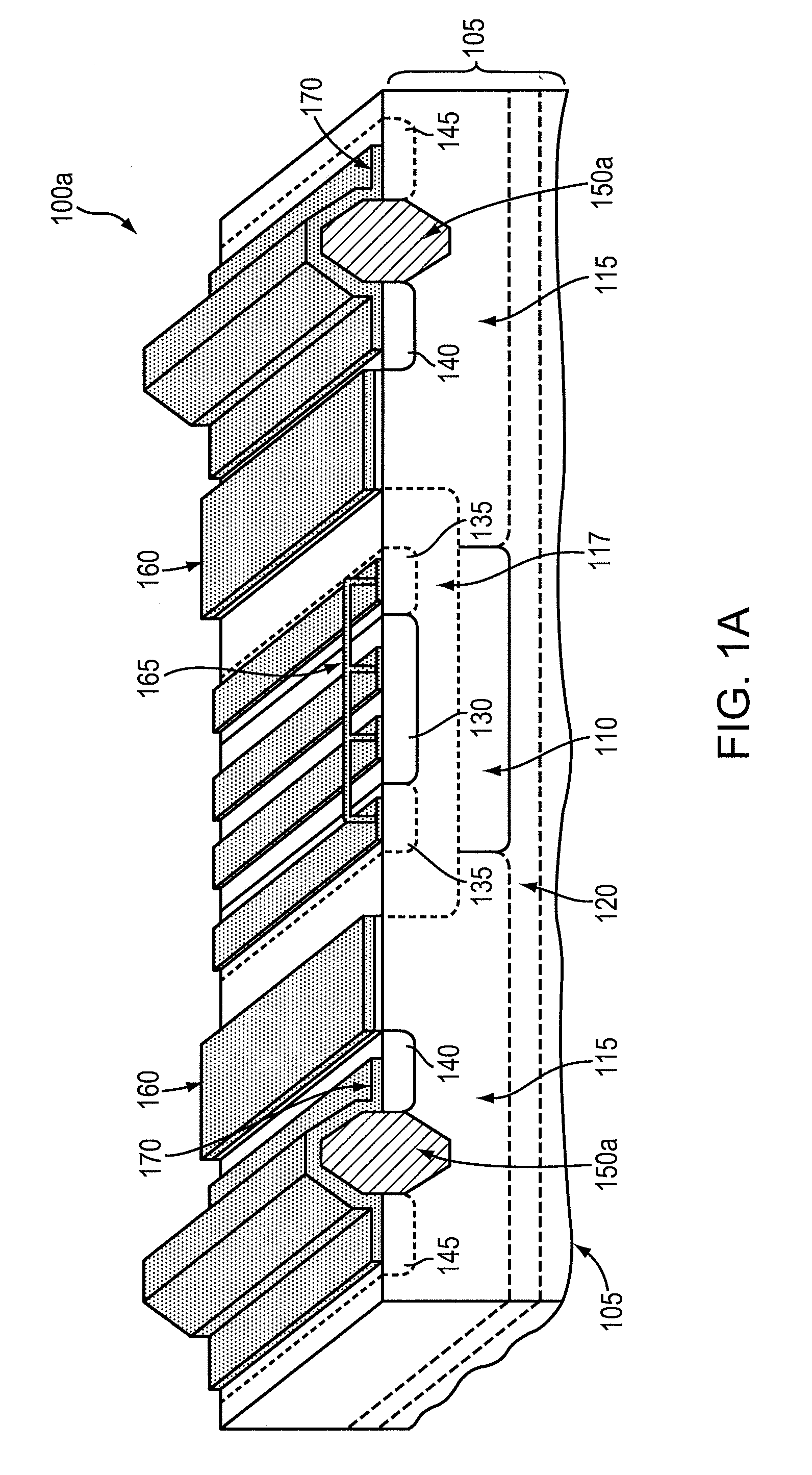
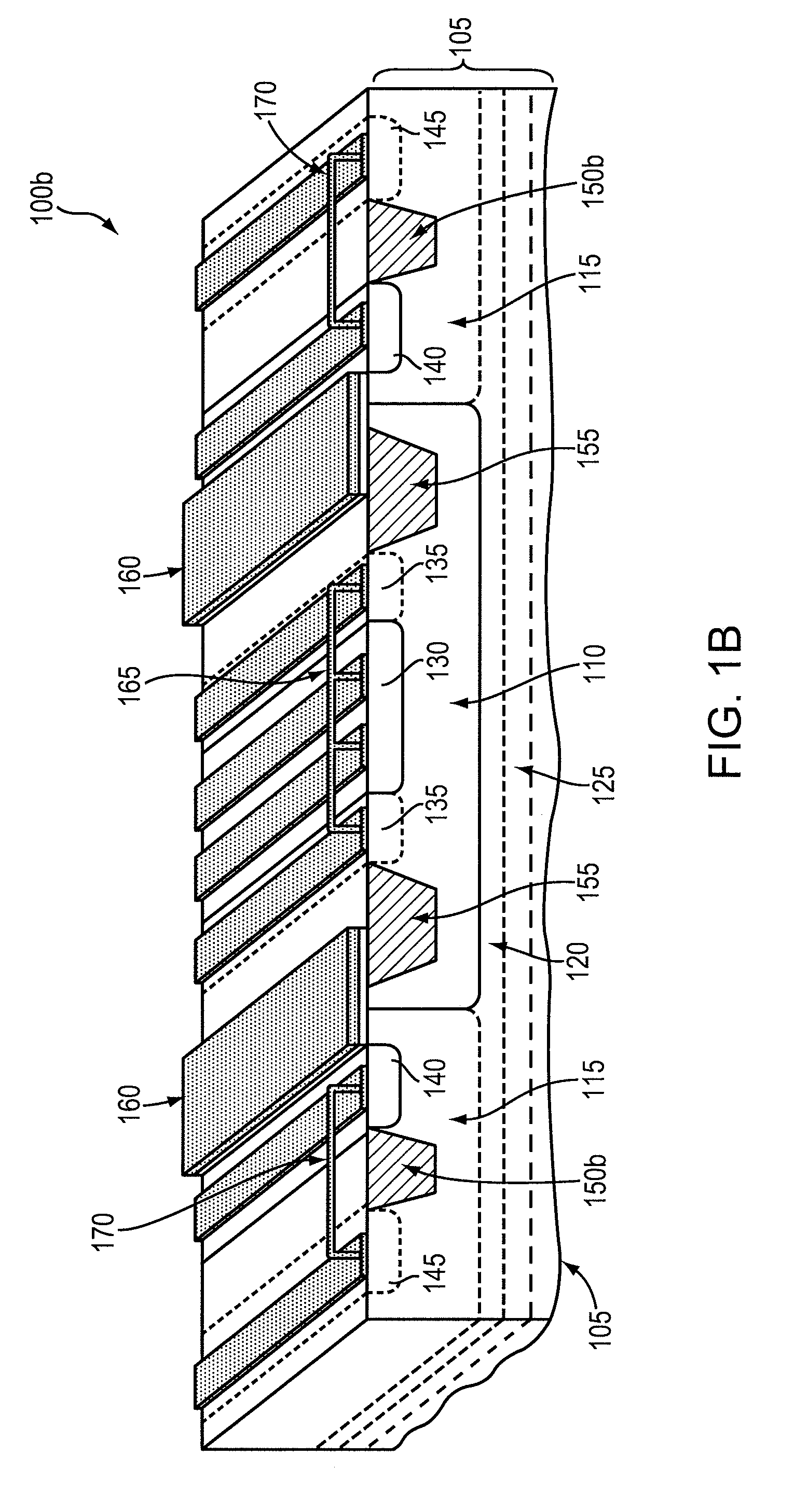
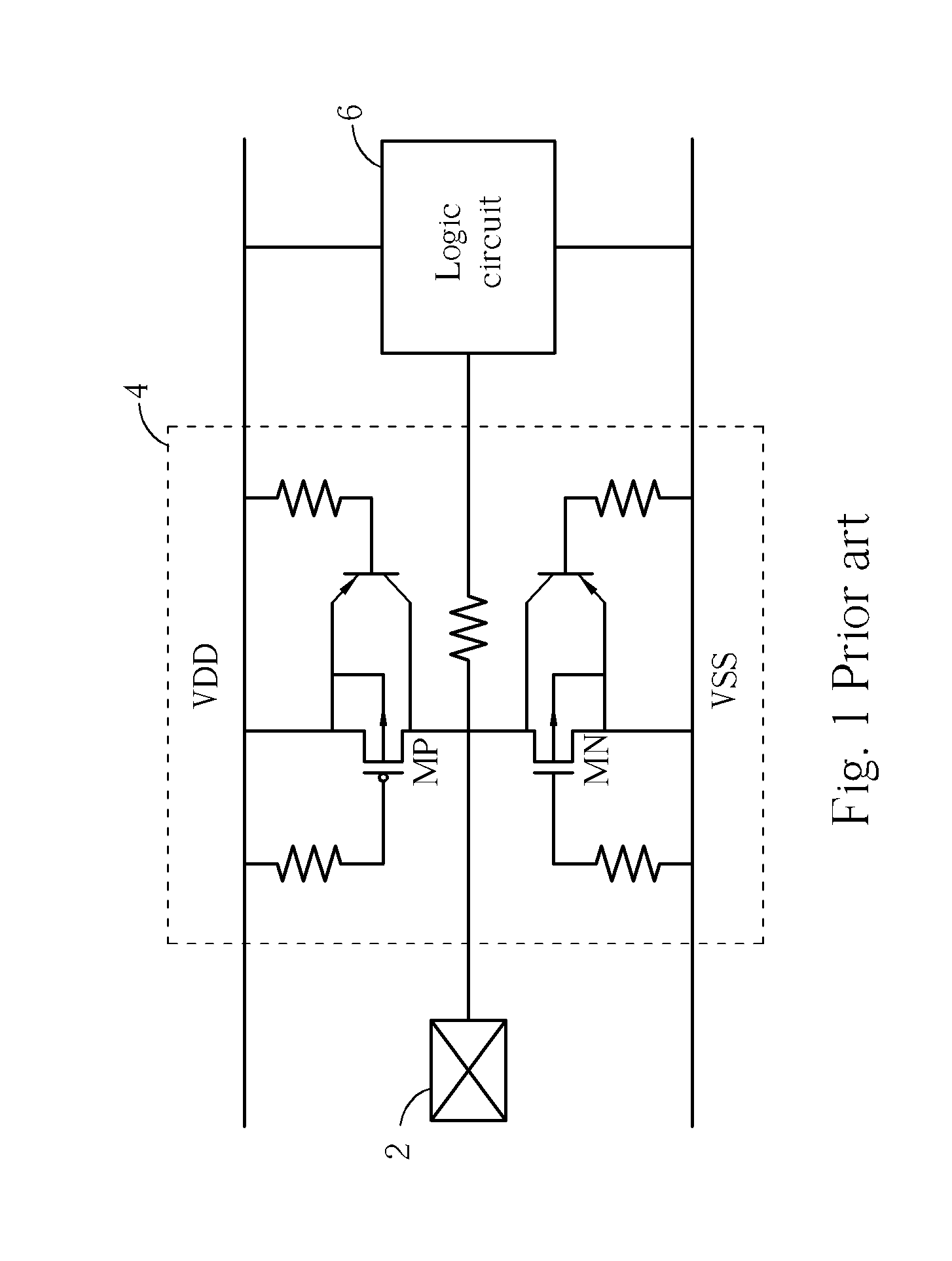
Silicon-on-insulator and CMOS-on-SOI double film fabrication process with a coplanar silicon and isolation layer and adding a second silicon layer on one region
InactiveUS6096584AHigher power-to-failure thresholdImprove protectionTransistorSolid-state devicesIsolation layerElectronic component
Silicon is formed at selected locations on a silicon-insulator (SOI) substrate during fabrication of selected electronic components, including resistors, capacitors, and diodes. The silicon location is defined using a patterned, removable mask, and the silicon may be applied by deposition or growth and may take the form of polysilicon or crystalline silicon. Electrostatic discharge (ESD) characteristics of the SOI device is significantly improved by having a thick double layer of silicon in selected regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
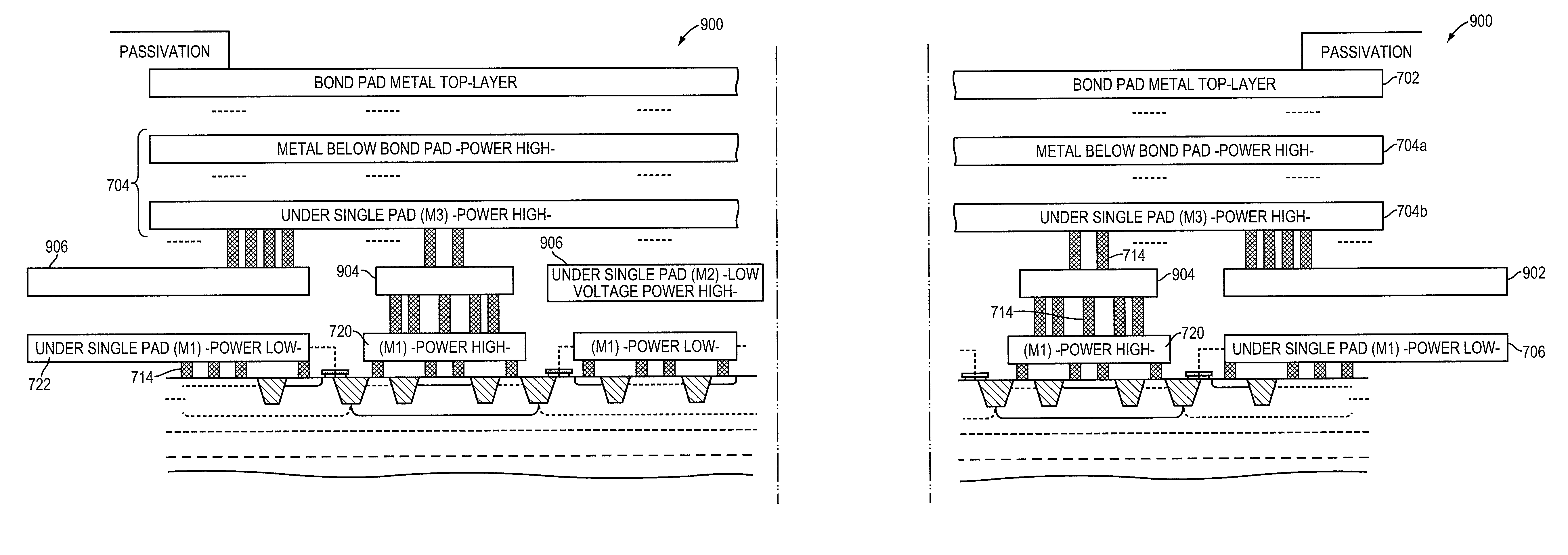
Bond pad with integrated transient over-voltage protection
ActiveUS8222698B2Small footprintTriggered quicklyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringTransistor
In various embodiments, the invention relates to bond pad structures including planar transistor structures operable as over-voltage clamps.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
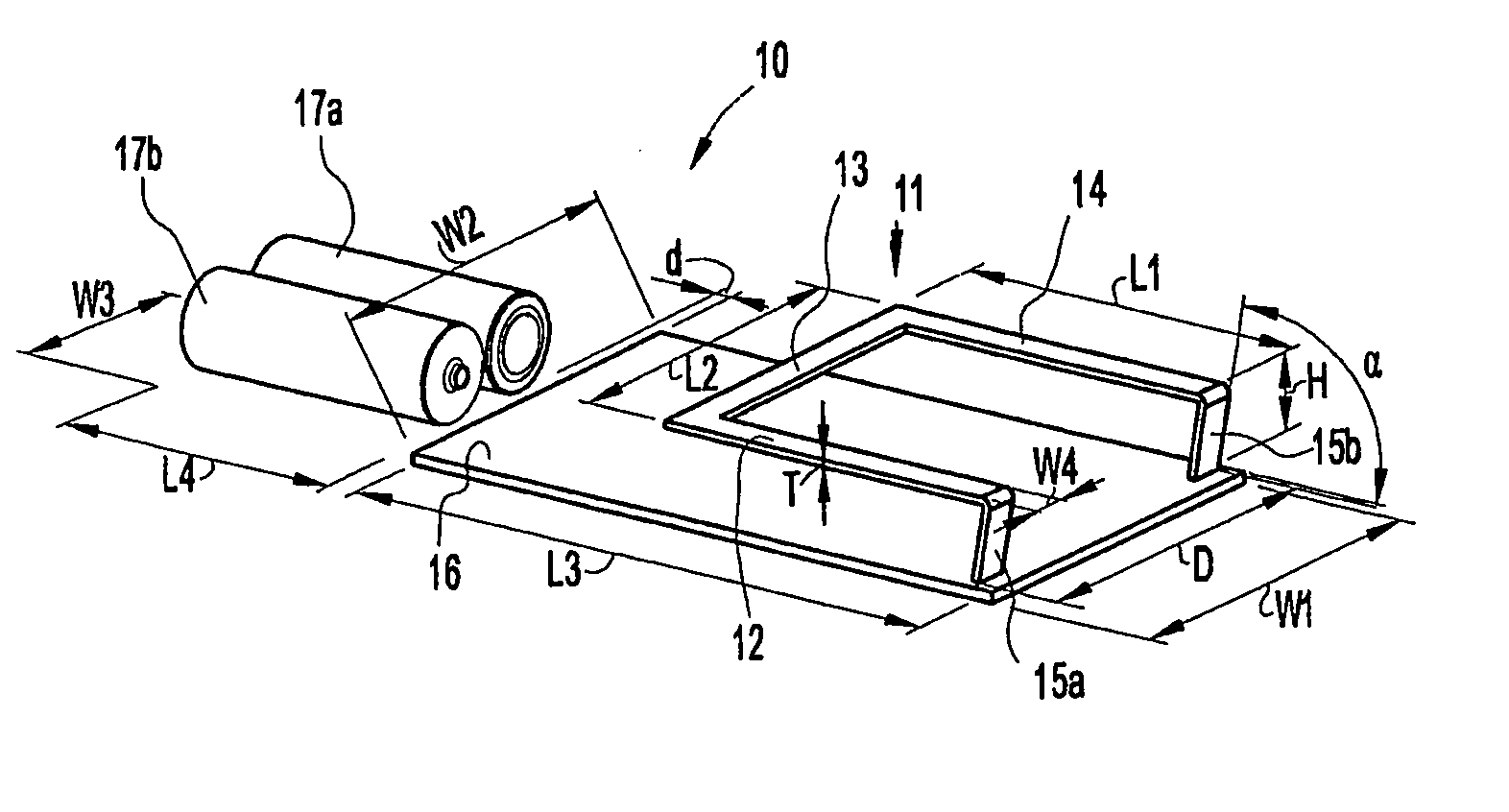
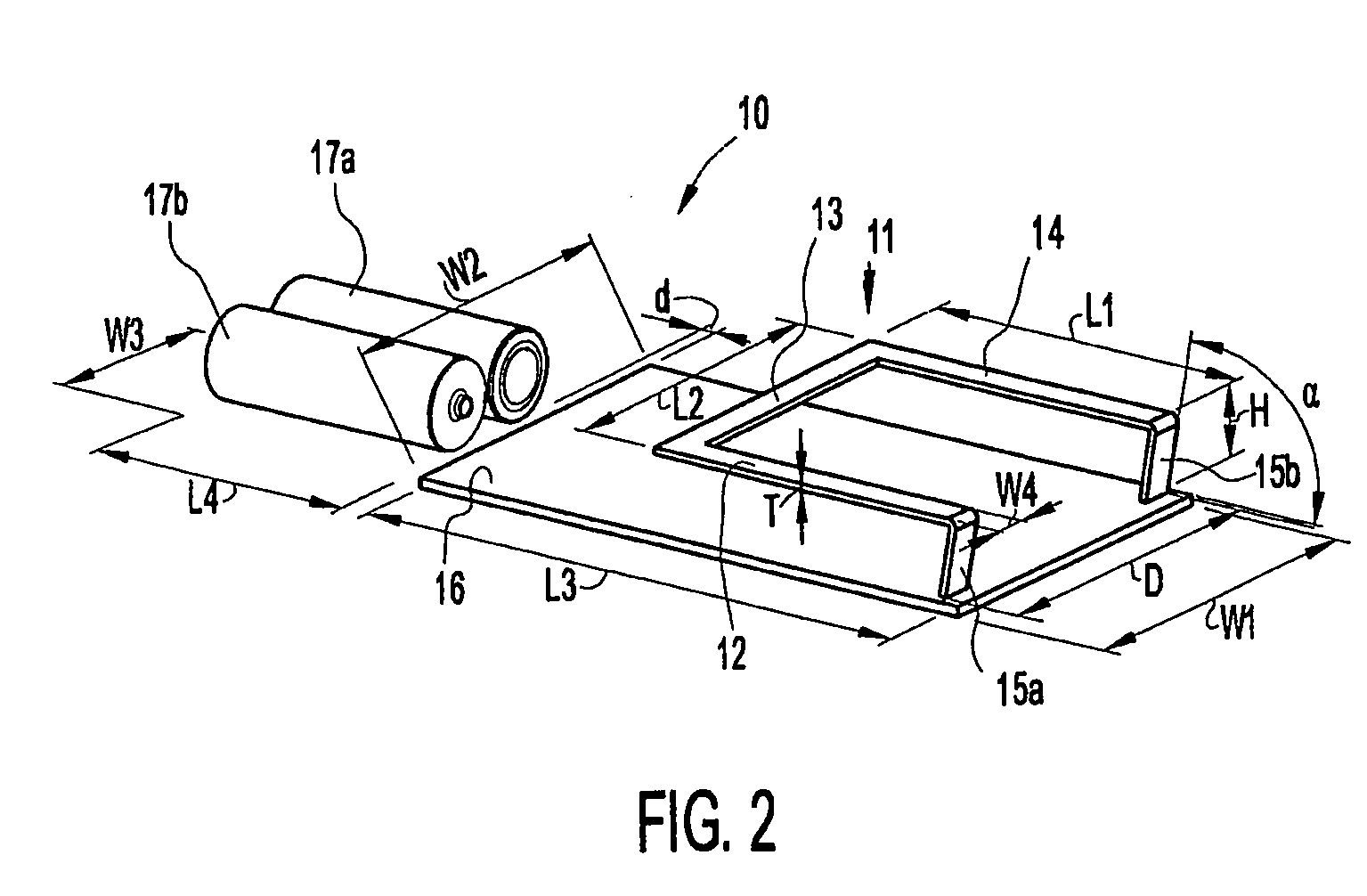
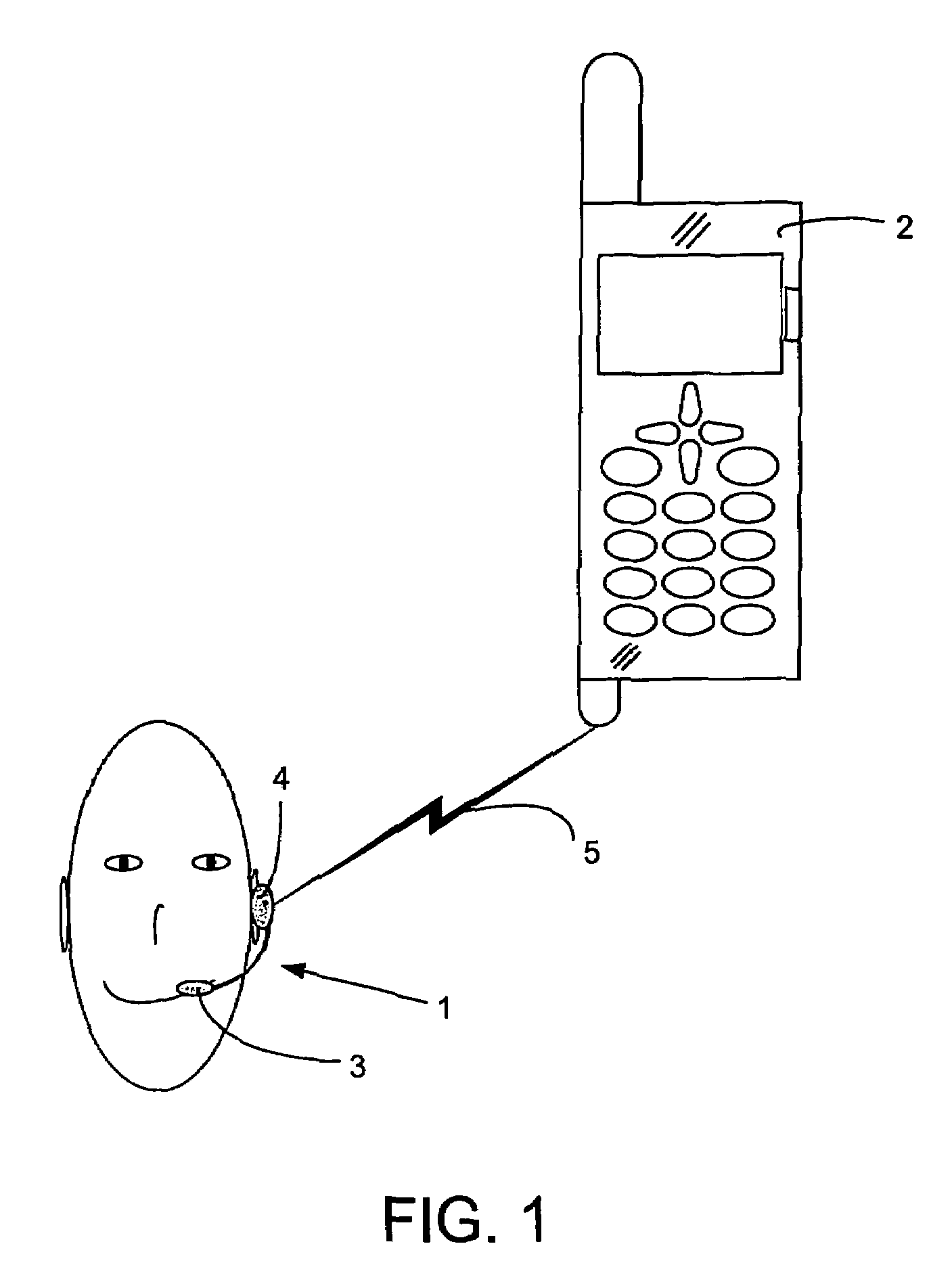
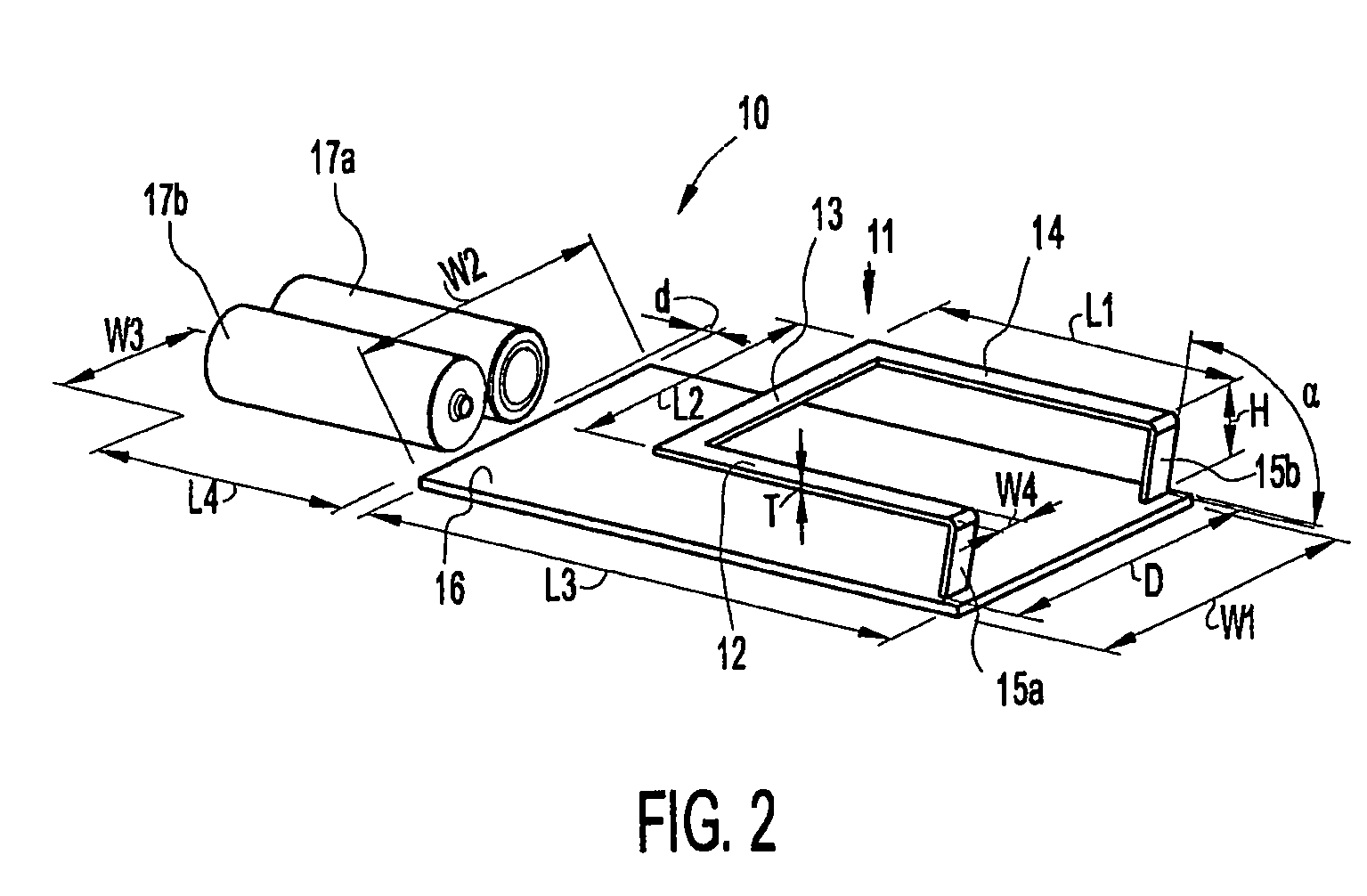
Wideband antena device with extended ground plane in a portable device
InactiveUS20060109182A1Effective bandwidthEnhanced ESD robustnessResonant long antennasAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringGround plane
An antenna device for a portable device has an antenna loop of conducting material to be connected to radio circuitry in the portable device. The antenna loop is positioned opposite a ground plane of a PCB. Also, the antenna device also comprises at least one battery, which is positioned in the extension of a first side of the PCB, and acts as an extension of the ground plane of the PCB.
Owner:SONY CORP
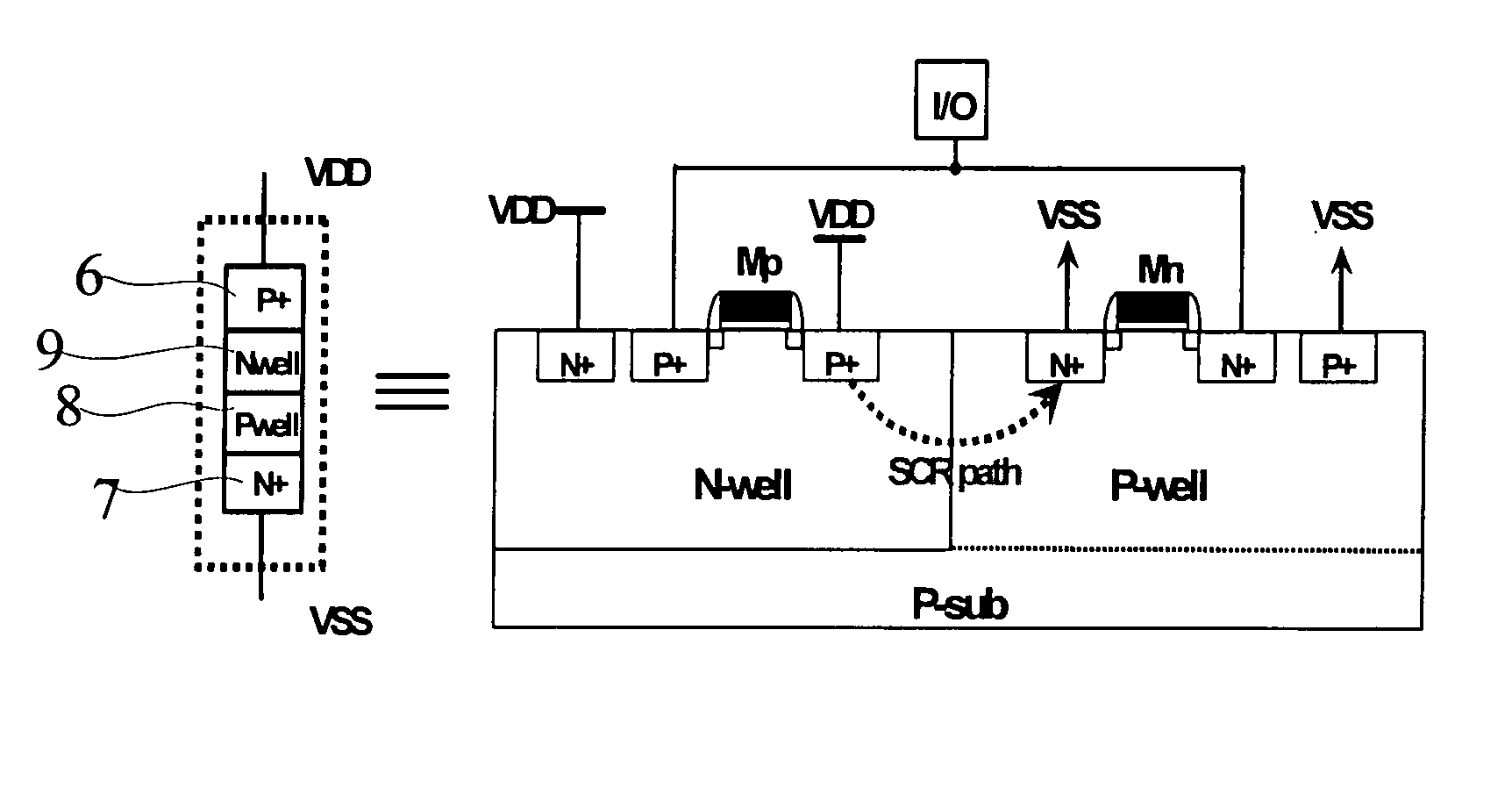
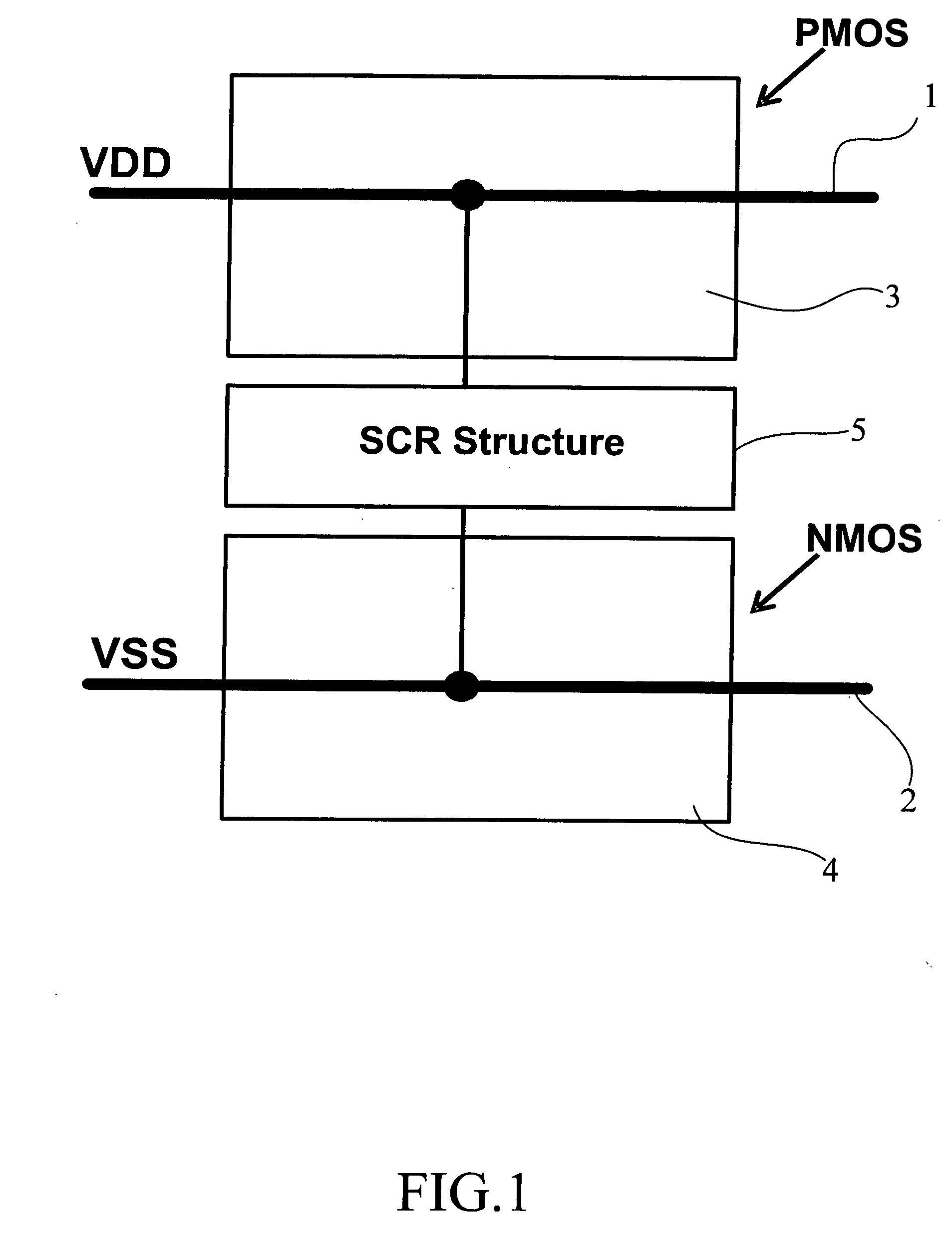
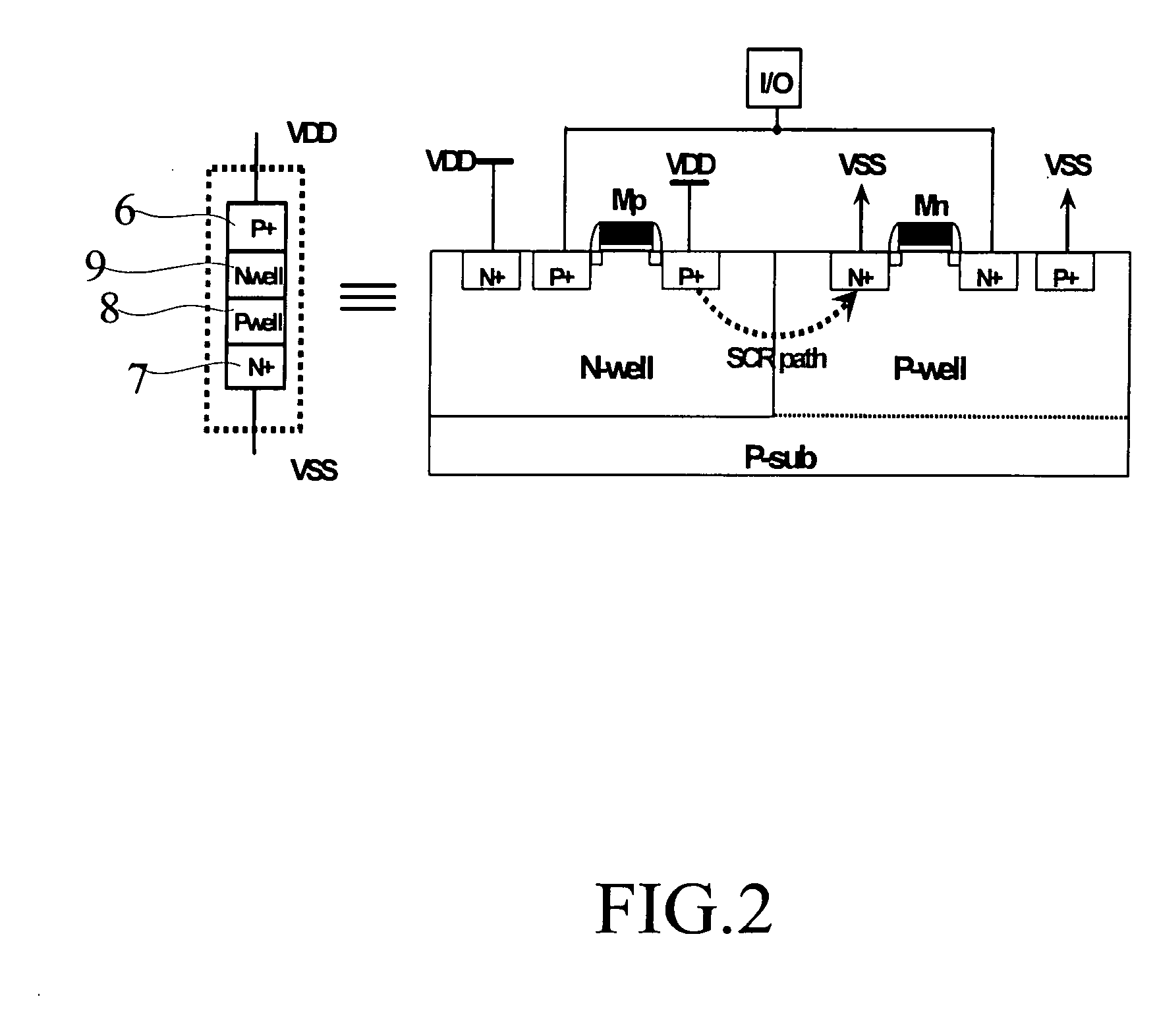
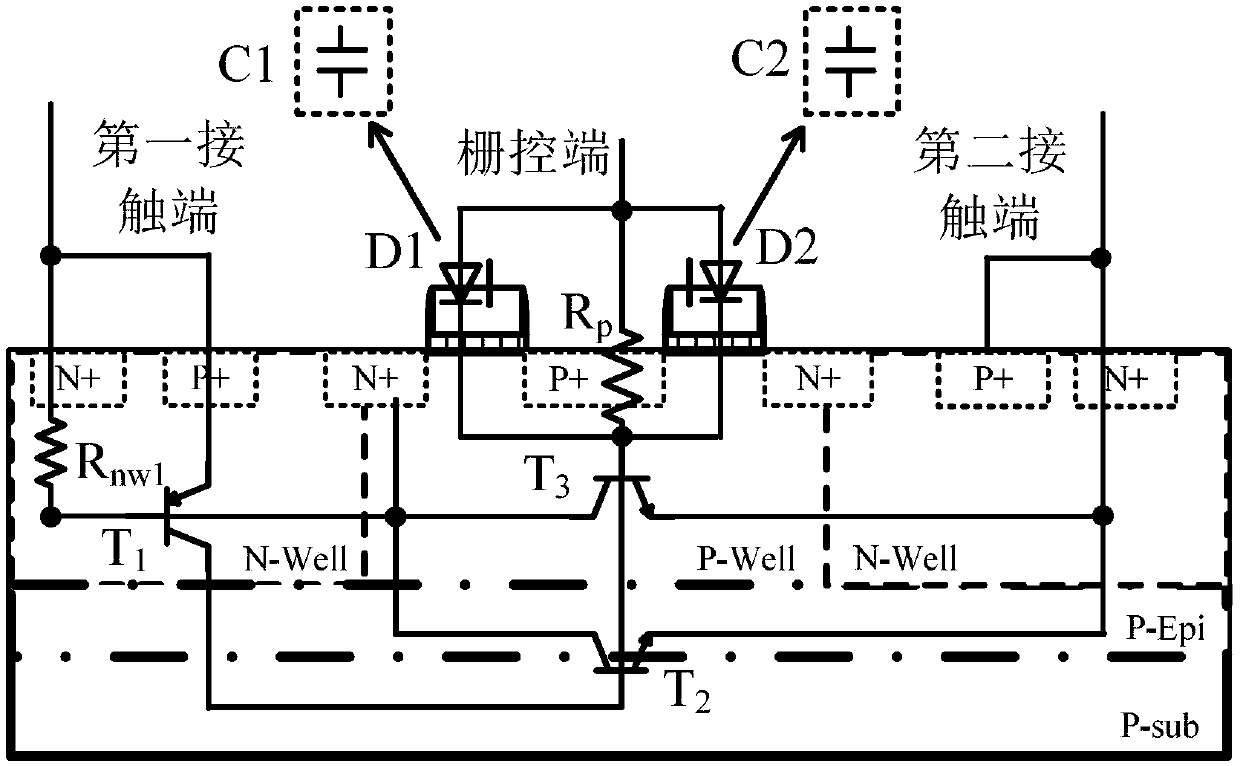
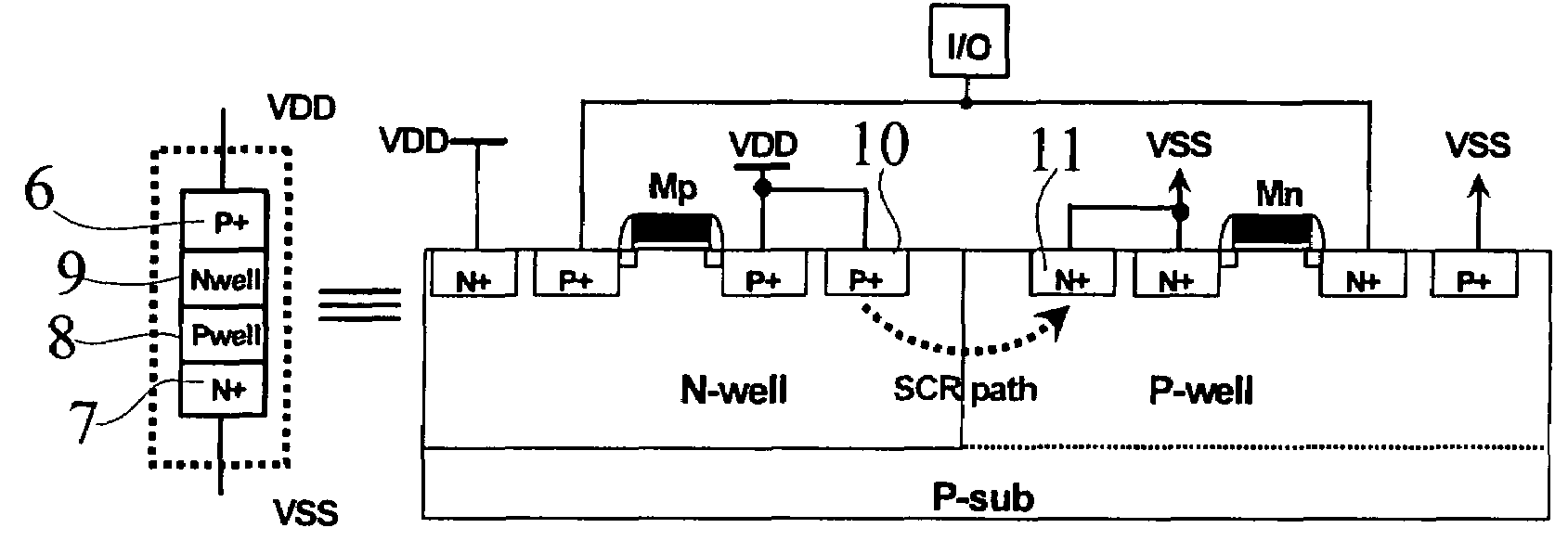
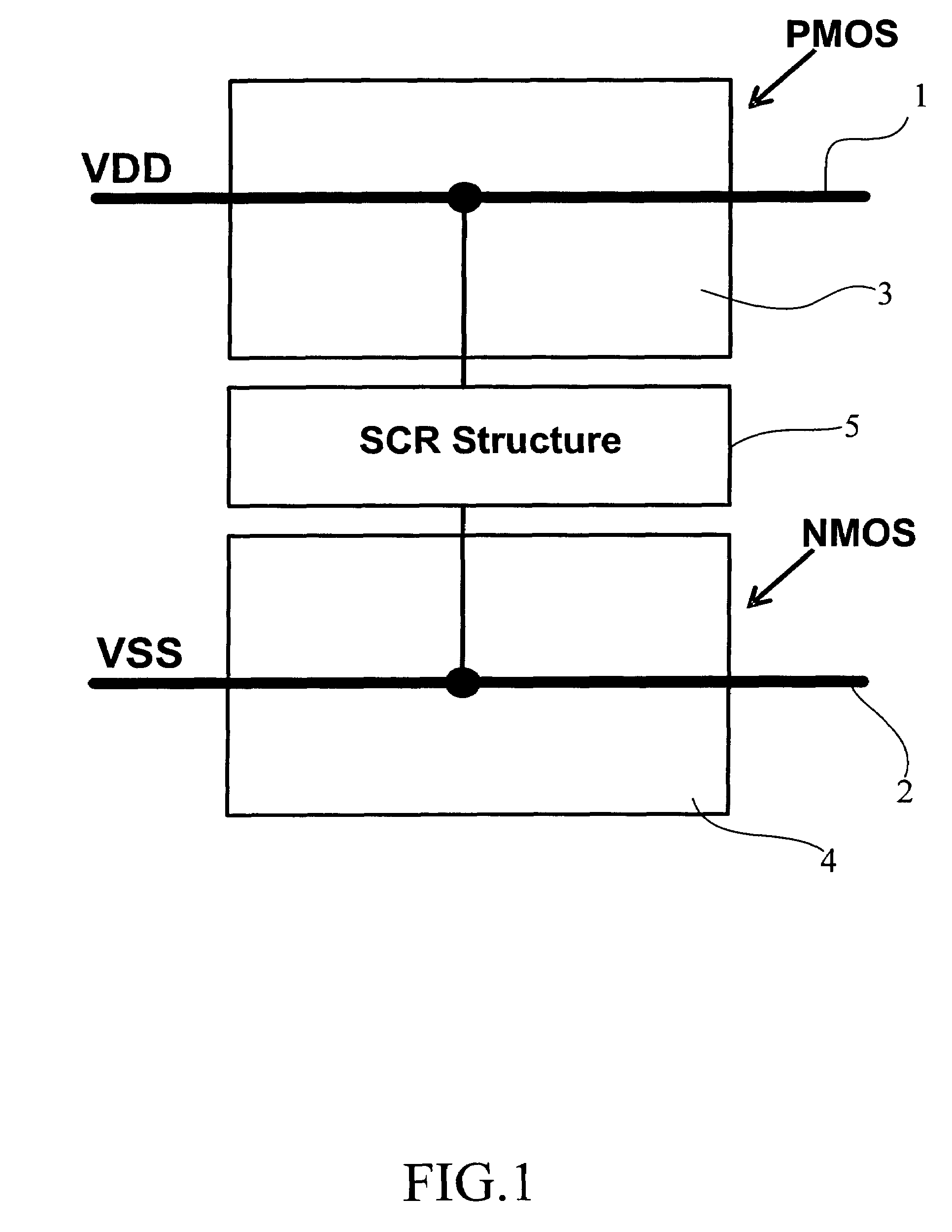
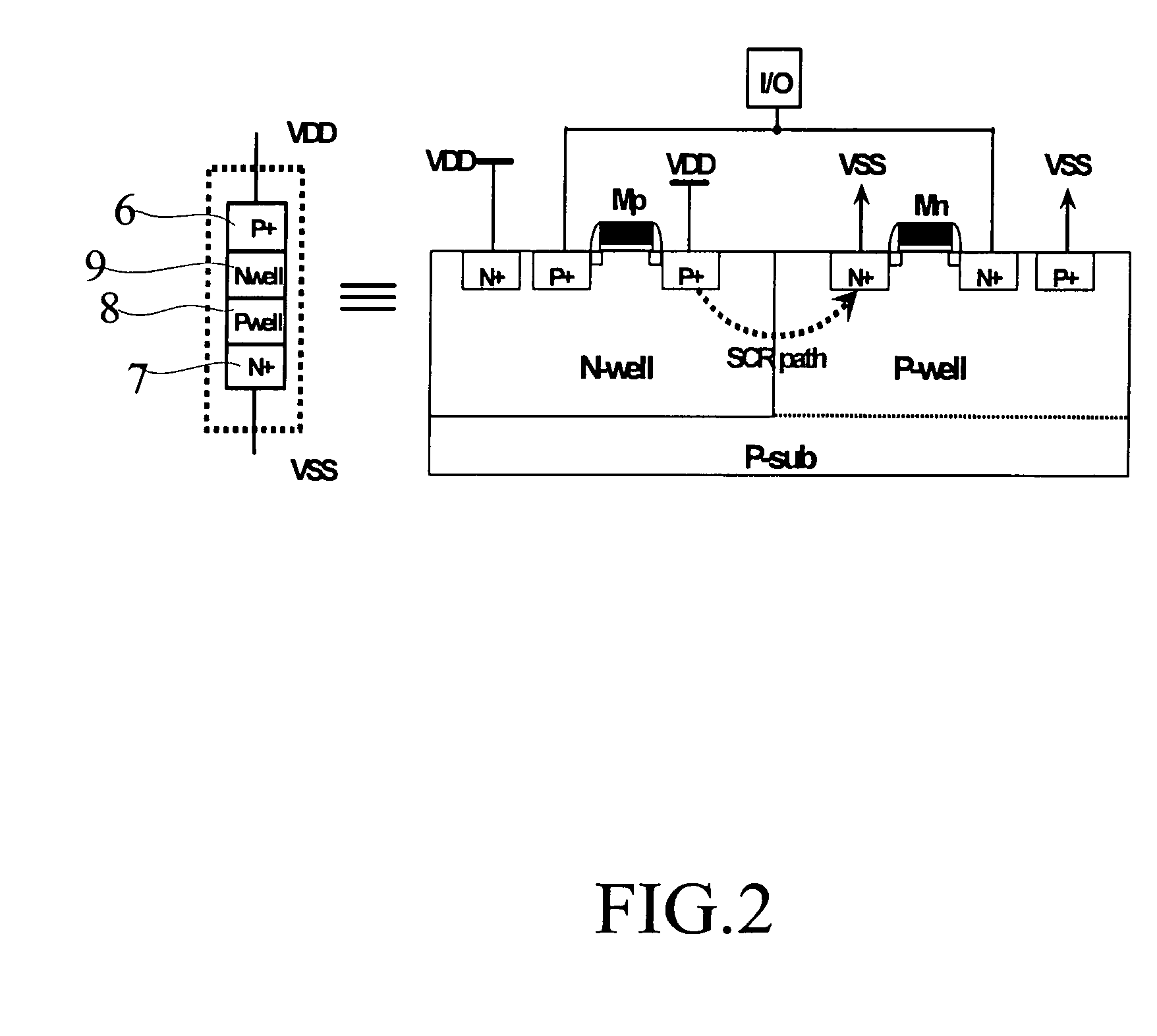
Silicon controlled rectifier for the electrostatic discharge protection
InactiveUS20050270710A1Reduce layout areaImprove robustnessTransistorThyristorSilicon-controlled rectifierFoundry
The present invention relates to an SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) for the ESD (electrostatic discharge) protection comprising two terminal electrodes of a first electrode and a second electrode, a PMOS, an NMOS and an SCR structure. By utilizing an embedded SCR, a whole-chip ESD protection circuit design can be obtained. The present invention is suitable for IC products, and for applications by IC design industries and IC foundry industries.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
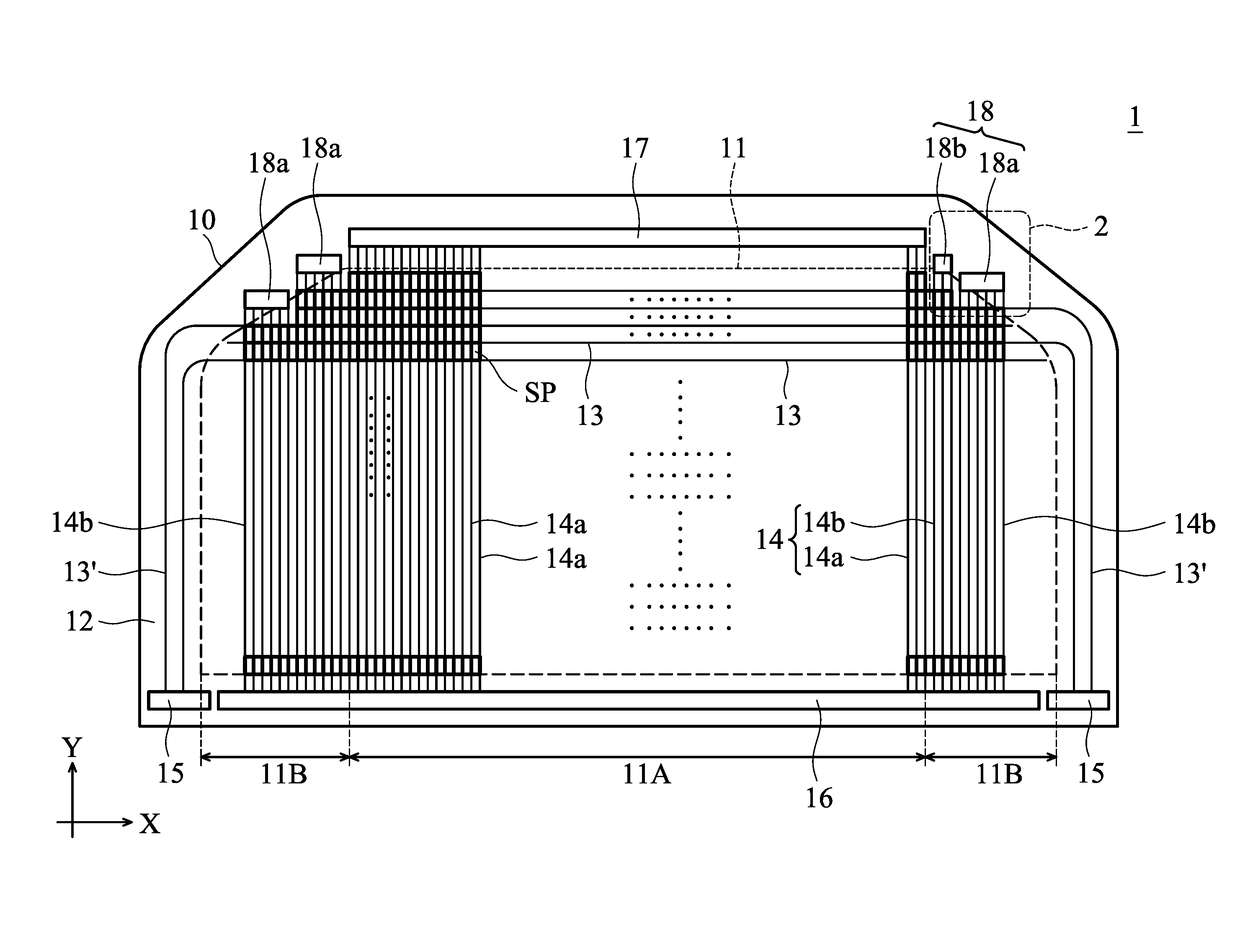
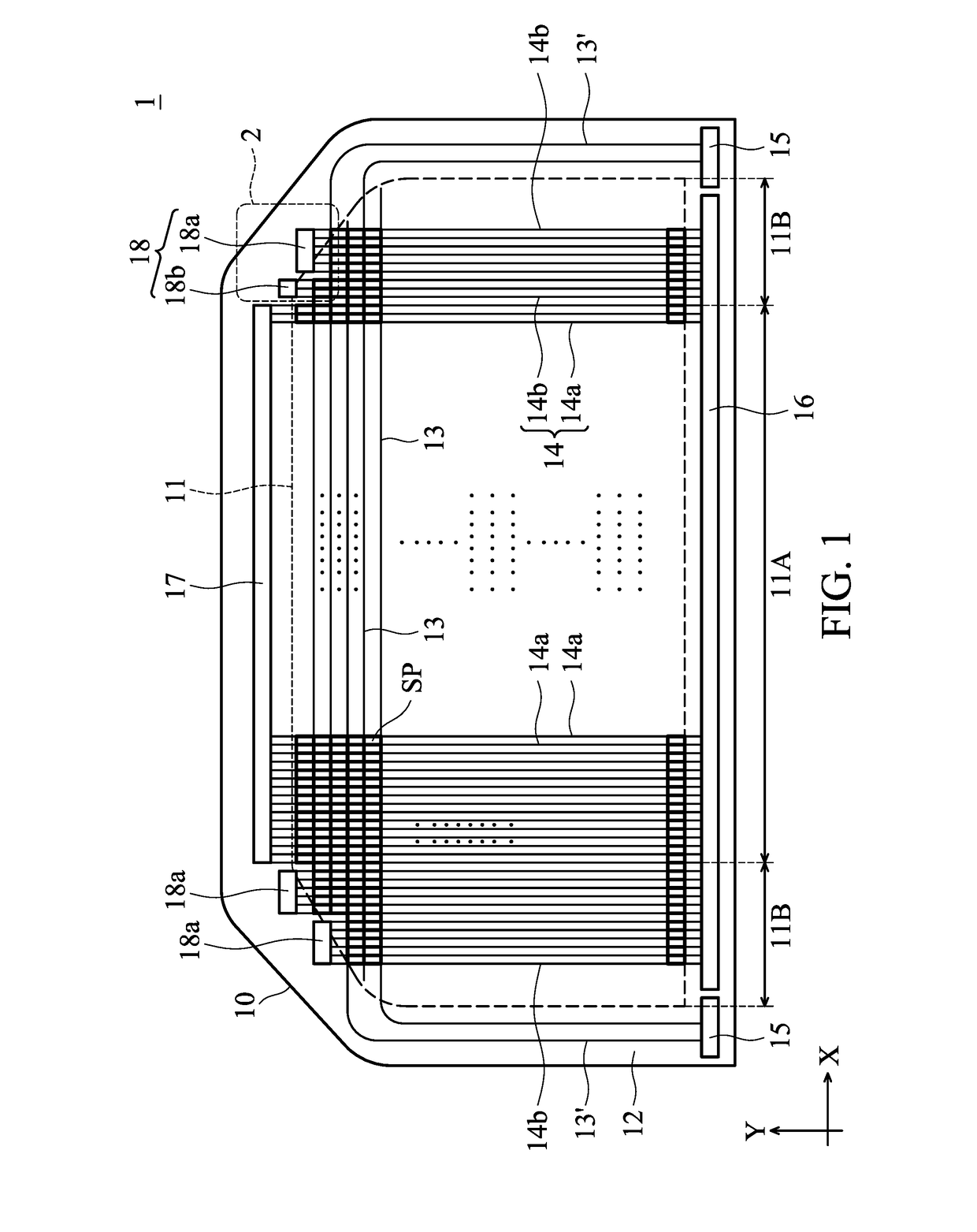
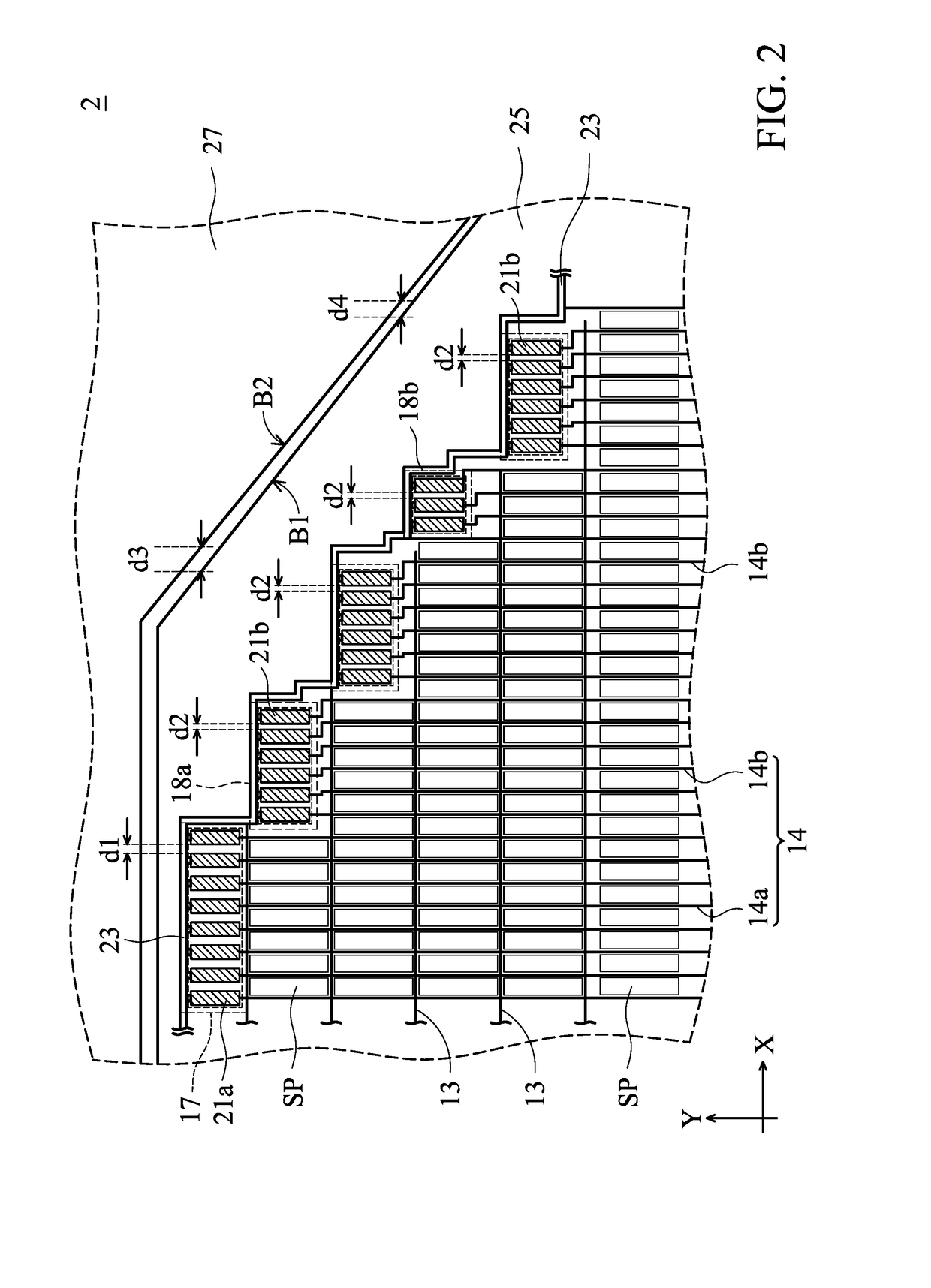
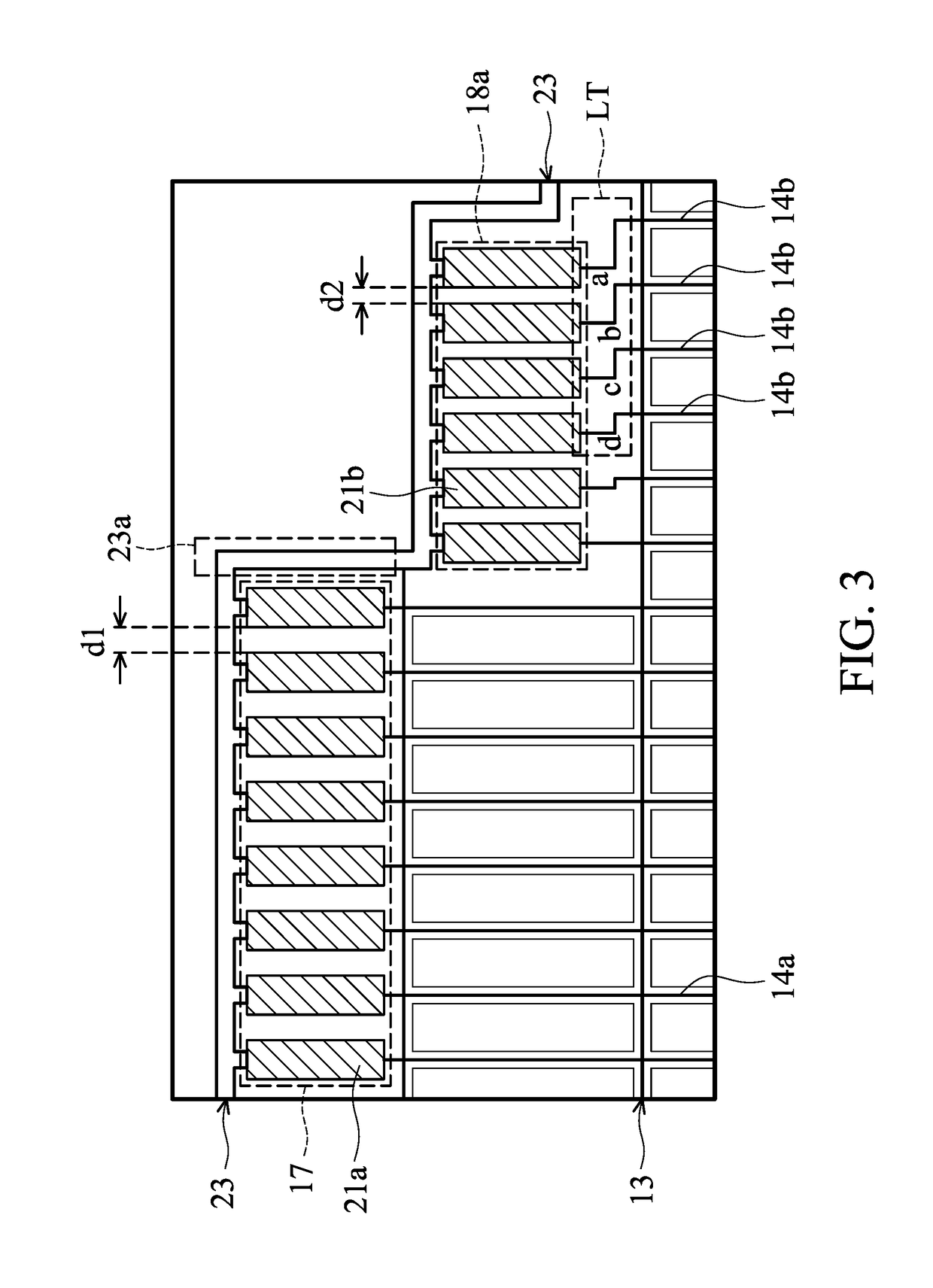
Display device
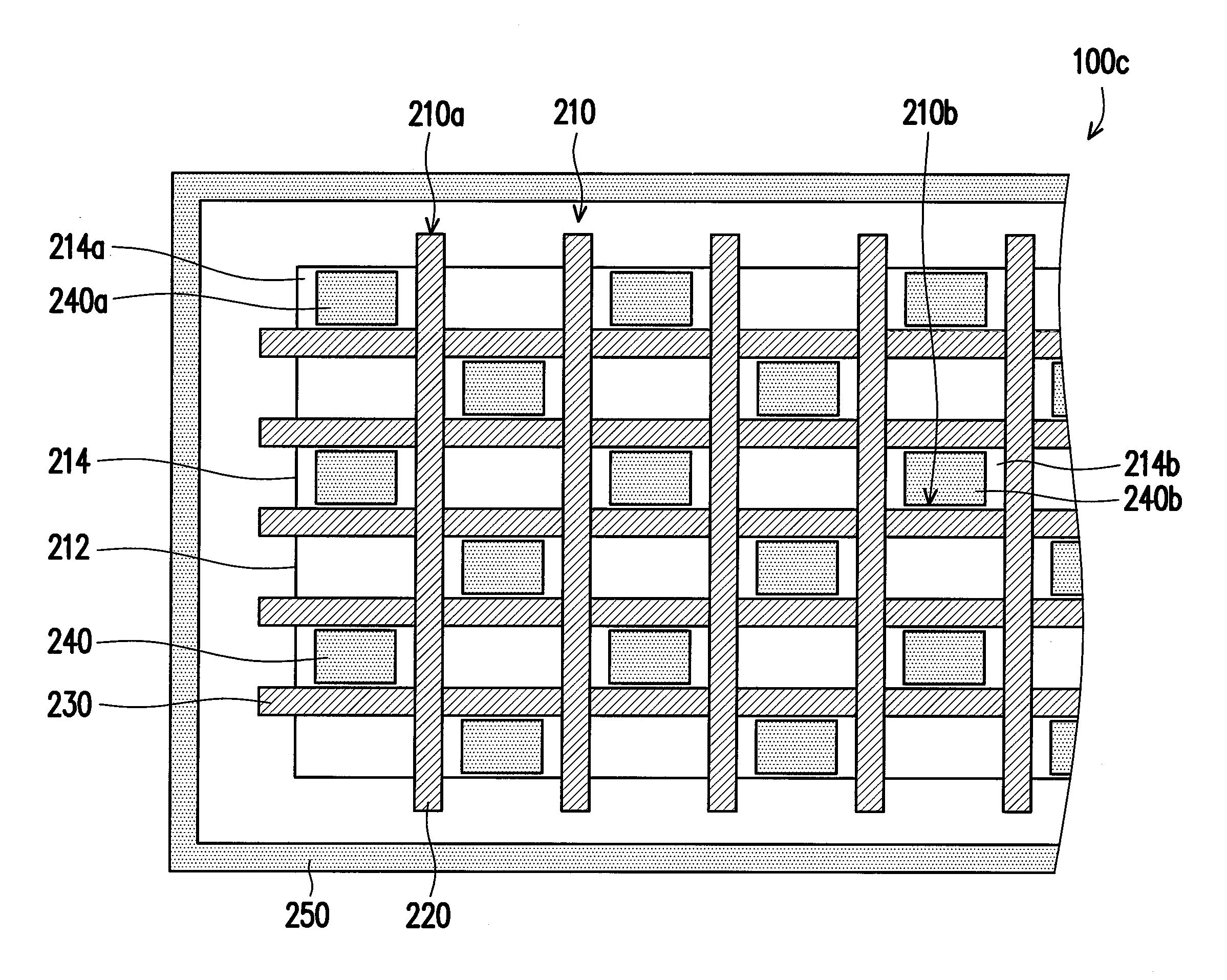
A display device that includes a substrate having a display region and an adjacent peripheral region is provided, including; a plurality of sub-pixels provided within the display region; a plurality of data lines electrically connected to the sub-pixels; and a first electronic circuit group and a second electronic circuit group provided in the peripheral region, connected to the corresponding data lines. The first electronic circuit group includes a plurality of first electronic circuits, and the second electronic circuit group includes a plurality of second electronic circuits. Two adjacent first electronic circuits are arranged with a first interval therebetween, and the first interval has a first width. Two adjacent second electronic circuits are arranged with a second interval therebetween, and the second interval has a second width. The first width and the second width are different.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
Electronic static discharge (ESD) protection device with bidirectional silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) structure embedded with interdigital N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS)
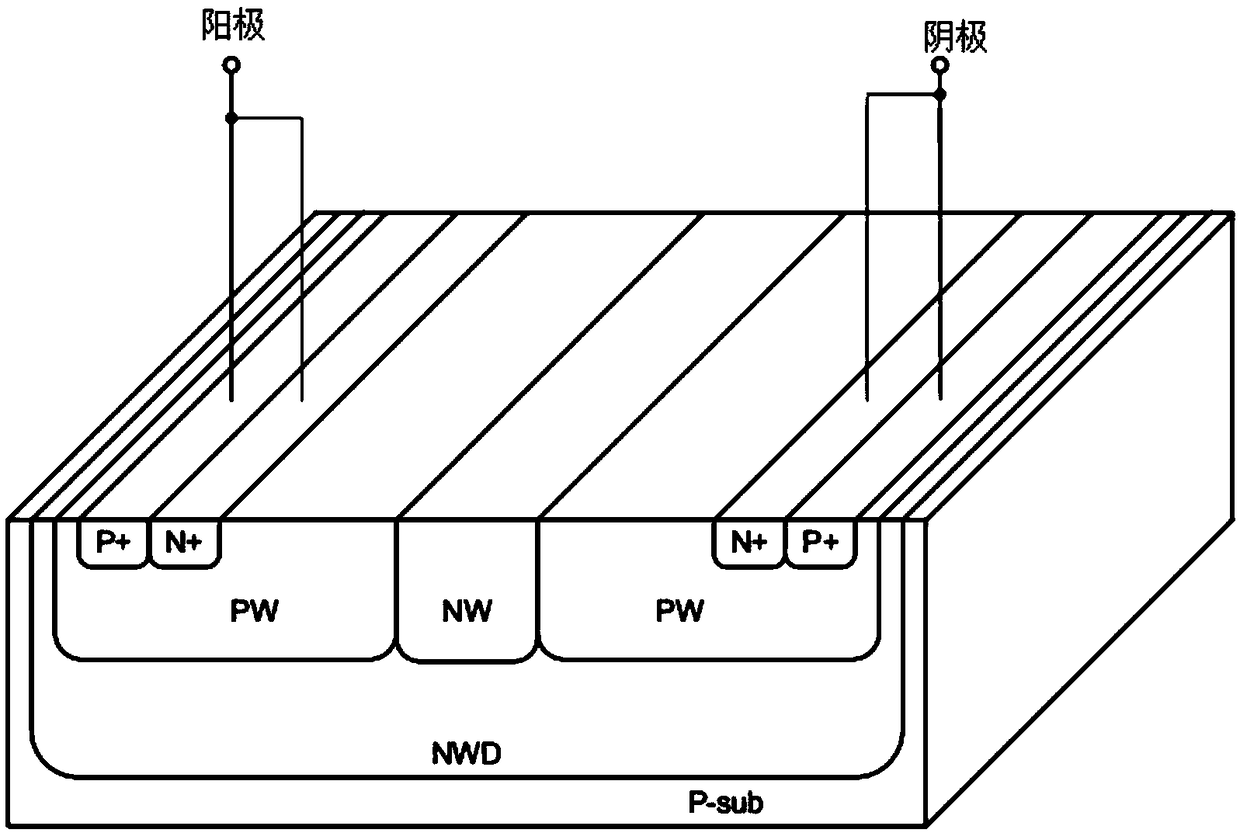
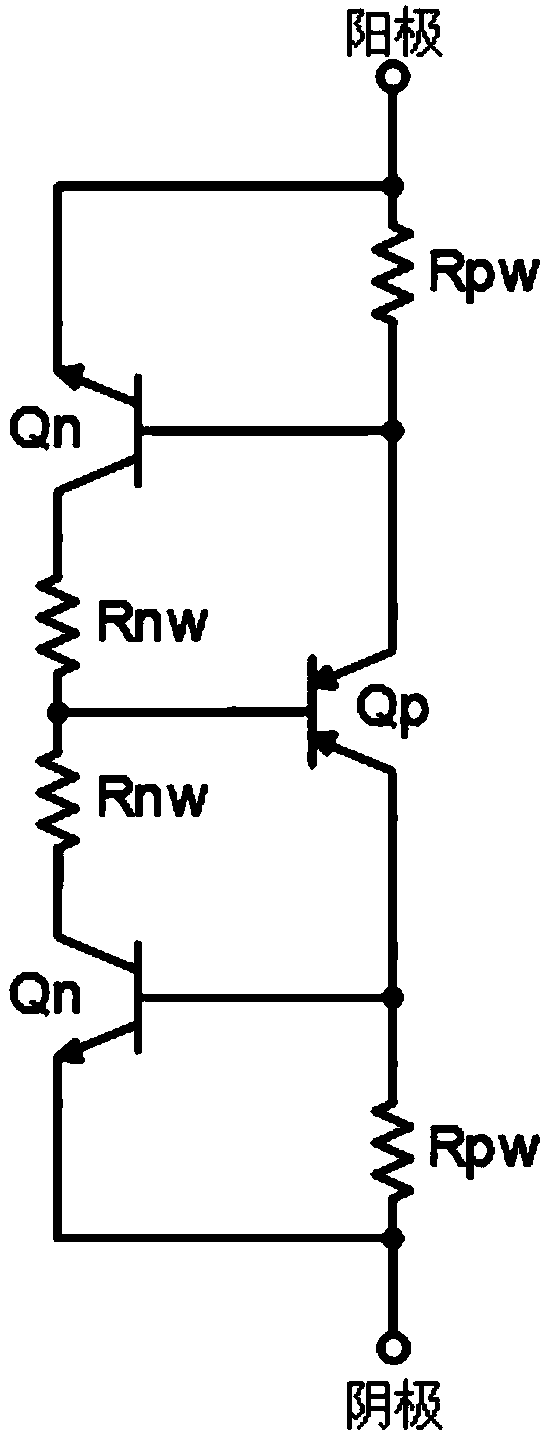
ActiveCN105428354AEnhanced ESD robustnessRealize two-way protectionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSilicon-controlled rectifierEngineering
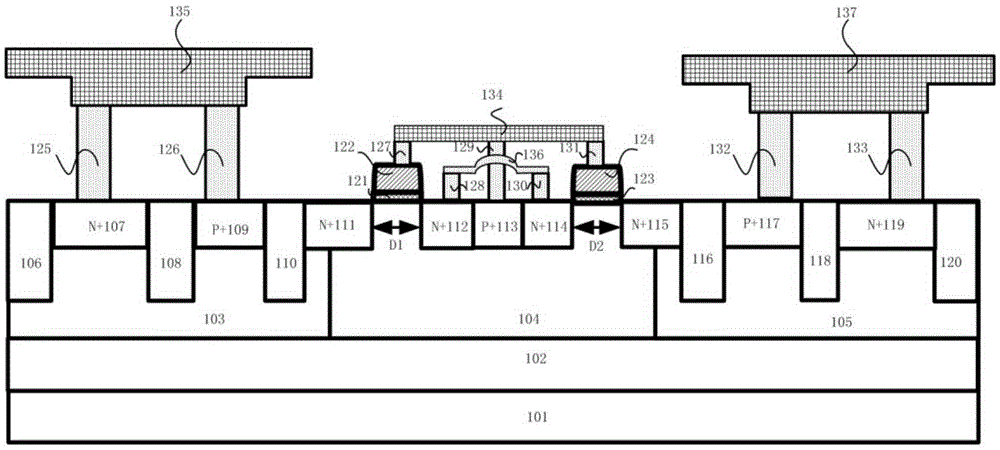
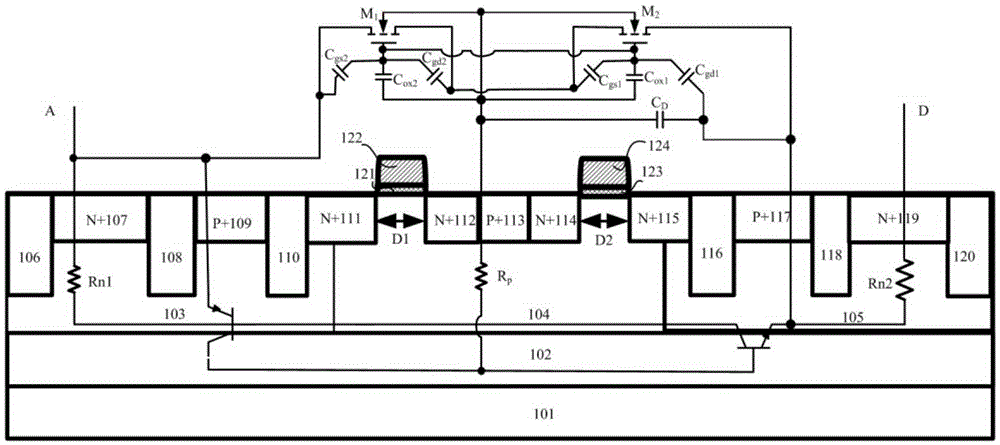
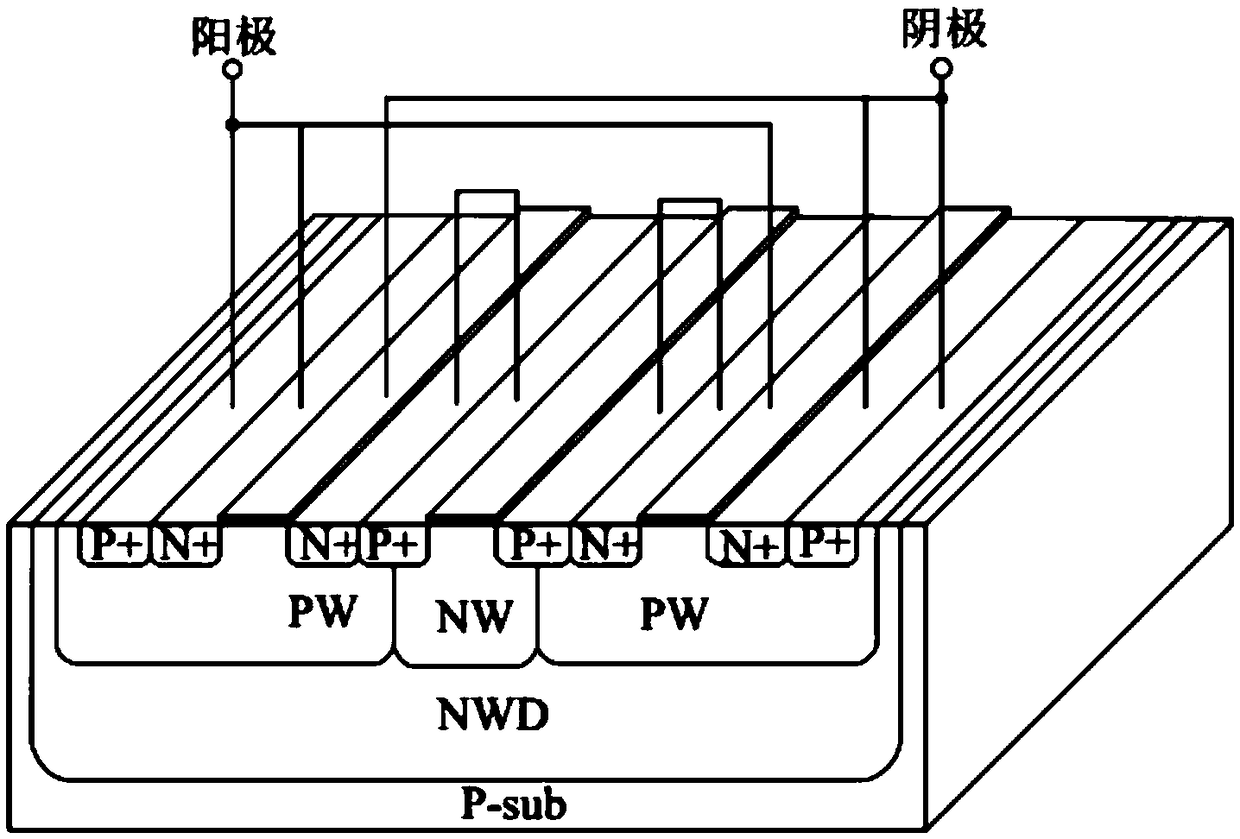
An electronic static discharge (ESD) protection device with a bidirectional silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) structure embedded with an interdigital N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) can be applied to an ESD protection circuit of an on-chip integrated circuit (IC) and mainly comprises a P substrate, a P epitaxial layer, a first N pit, a P pit, a second N pit, a first N+ injection region, a first P+ injection region, a second N+ injection region, a third N+ injection region, a second P+ injection region, a fourth N+ injection region, a fifth N+ injection region, a third P+ injection region, a sixth N+ injection region, a plurality of poly-silicon gates, a plurality of thin gate oxide layers and a plurality of shallow isolation grooves. On one hand, under the positive and negative ESD pulse effects, an ESD current discharge path with a symmetric structure and complete same electrical property exists in the device, the ESD current discharge ability of the device can be improved, and bidirectional protection of an ESD pulse is achieved; and on the other hand, the interdigital NMOS composed of an NMOS M<1> and an NMOS M<2> and a parasitic P pit resistor form a resistance-capacitance coupling current path, so that the ESD robustness of the device is enhanced, the current density in an SCR current conduction path is reduced, the conduction resistance of the SCR is increased, and the maintaining voltage is increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
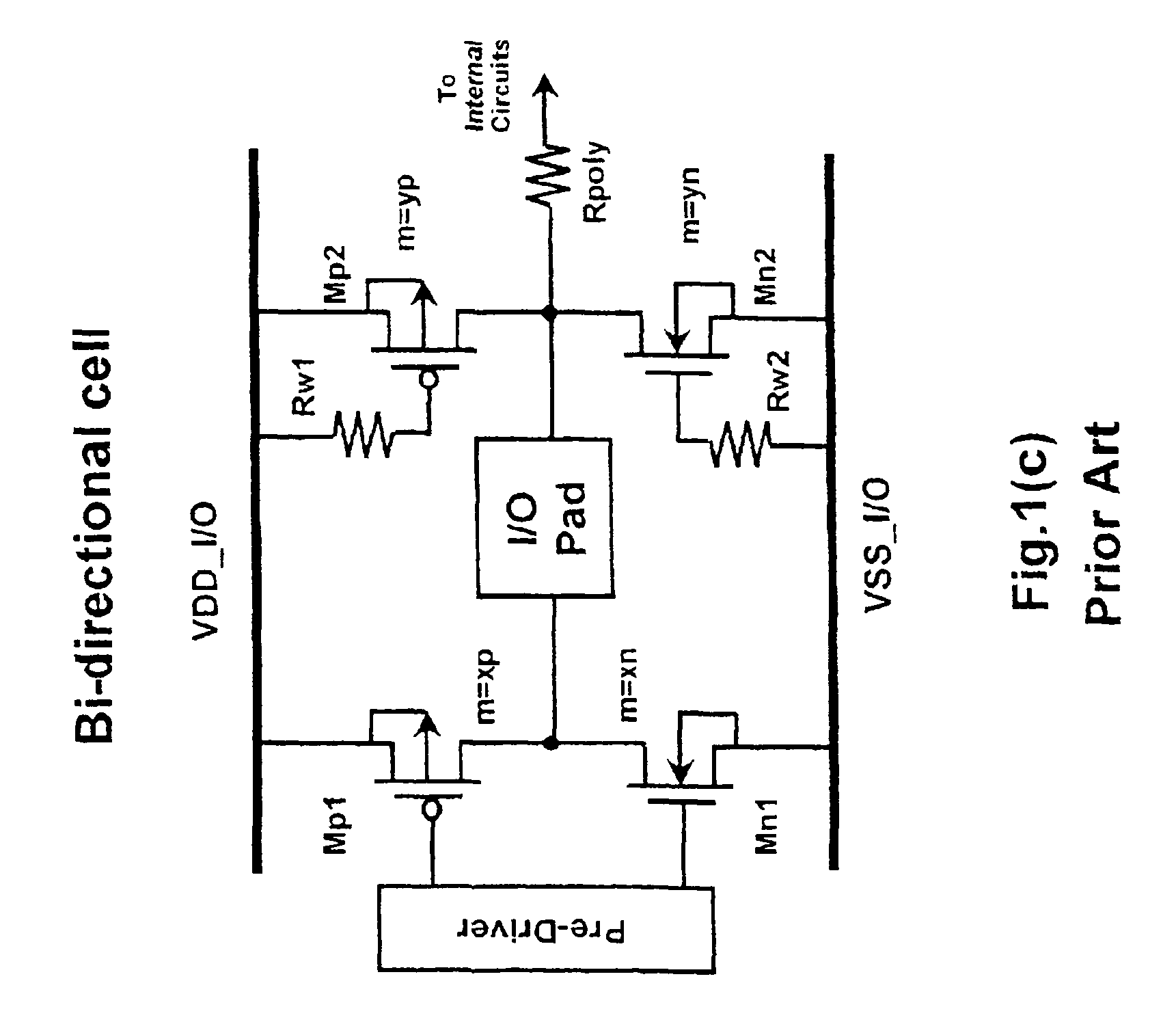
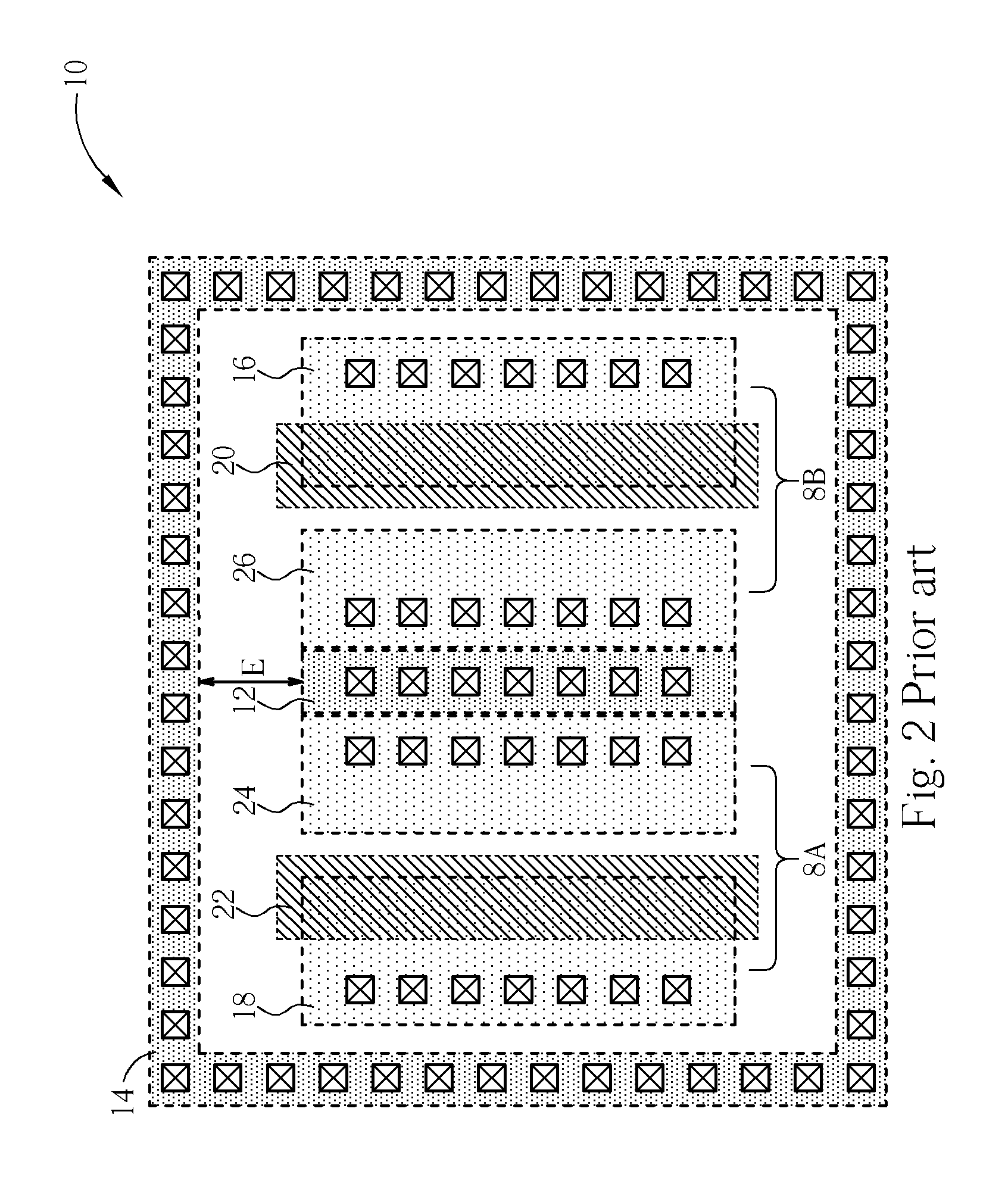
Input/output cell with robust electrostatic discharge protection
ActiveUS6849902B1Efficient conductionEnhanced ESD protectionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringSemiconductor
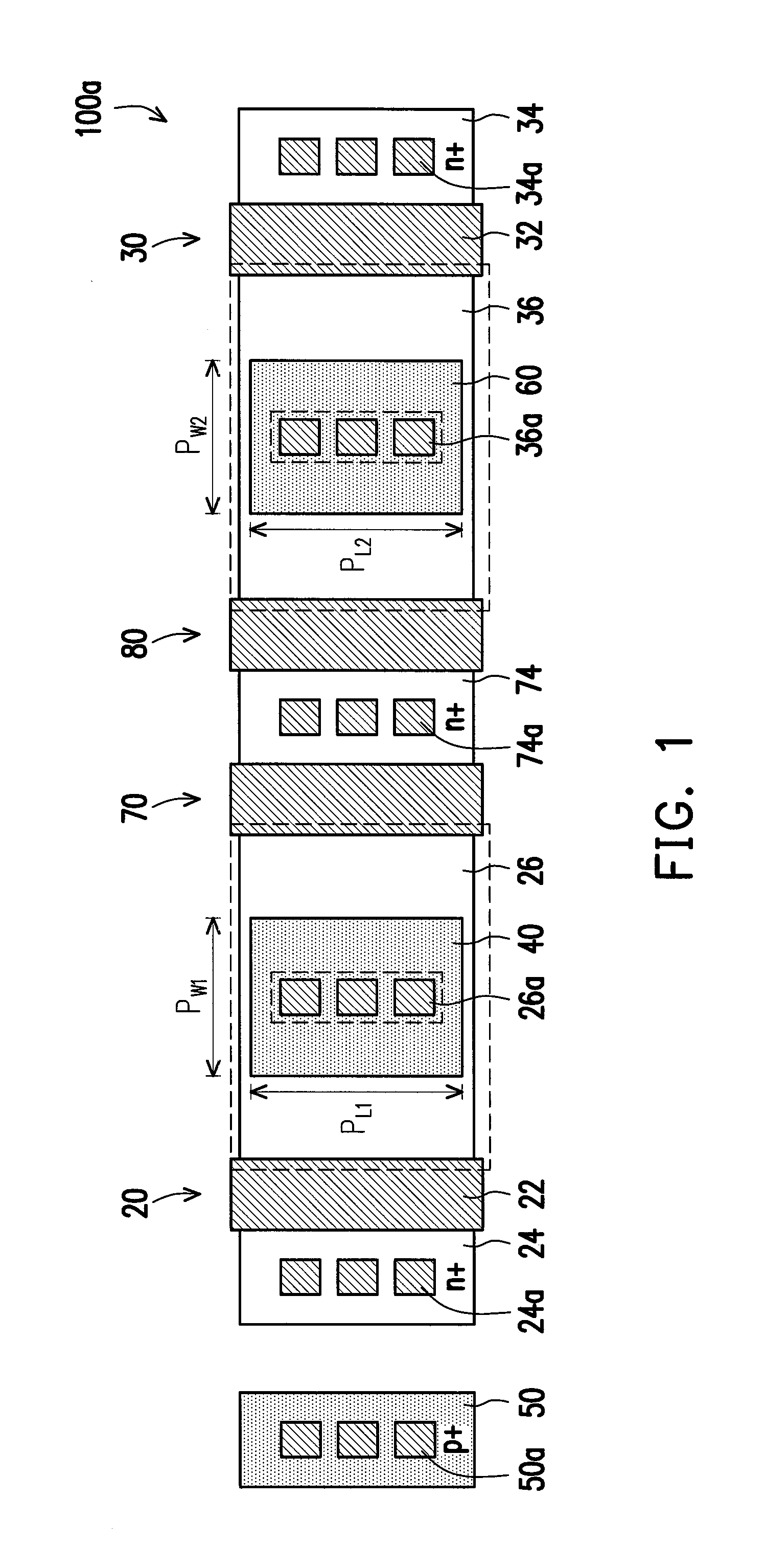
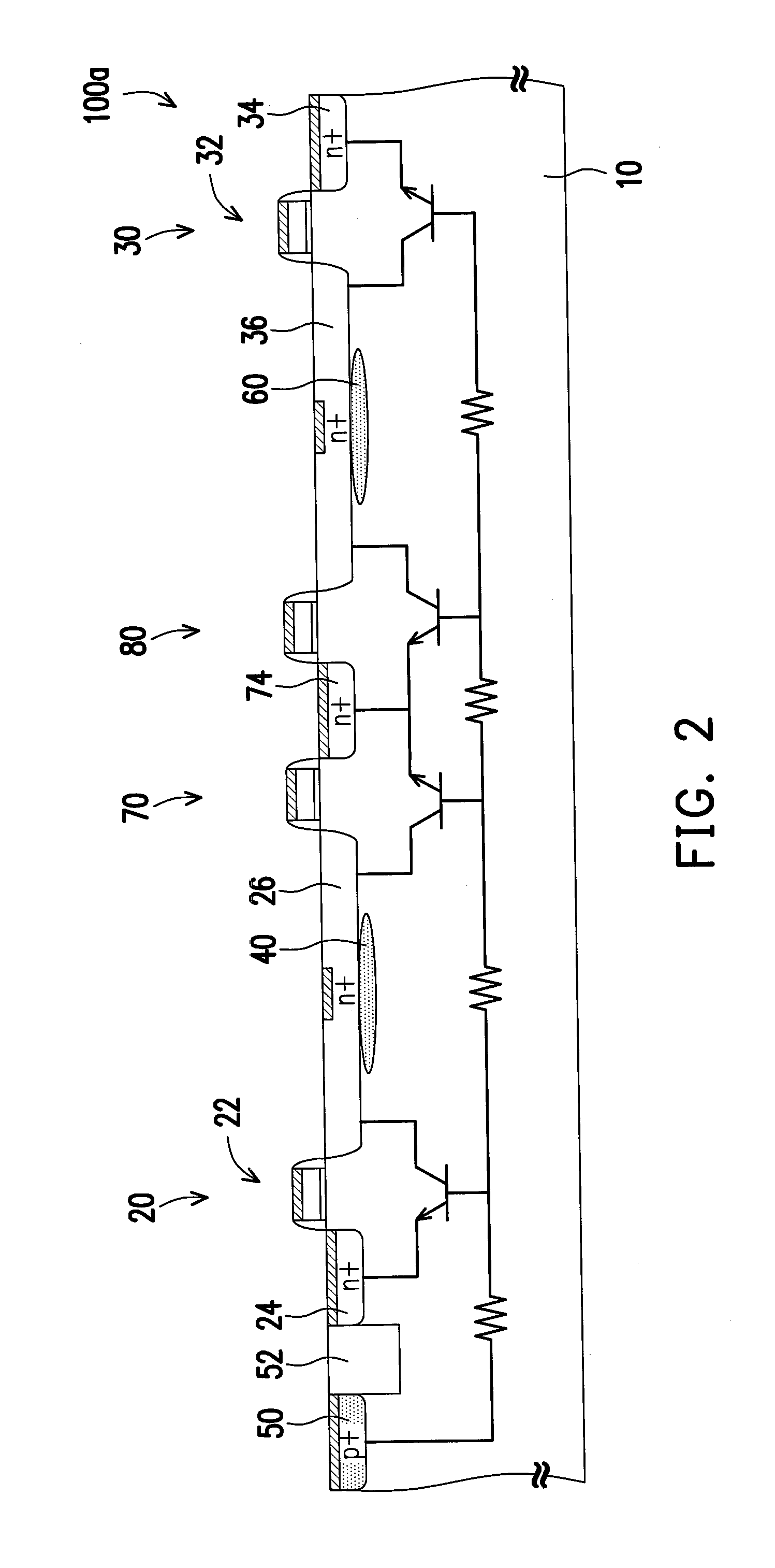
An electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection device with enhanced ESD robustness. The ESD protection device comprises a pad, a finger-type MOS, a well stripe and a doped segment. The pad is on a semiconductor substrate of a first-conductive type. The finger-type MOS is on the semiconductor substrate and comprises drain regions, source regions and channel regions. Each drain region is of a second-conductive type and is coupled to the pad. Each source region is of the second-conductive type and coupled to a power rail. Channel regions are formed on the semiconductor, substantially parallel to each other. Each channel region is located between one source region and one drain region. The well stripe is of the second-conductive type and formed on the semiconductor, in an angle to the channel regions. The doped segment is of the first-conductive type and in the well stripe. Furthermore, the doped segment is coupled to the pad.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Slider-level reader isolation measurement technique for advanced GMR heads
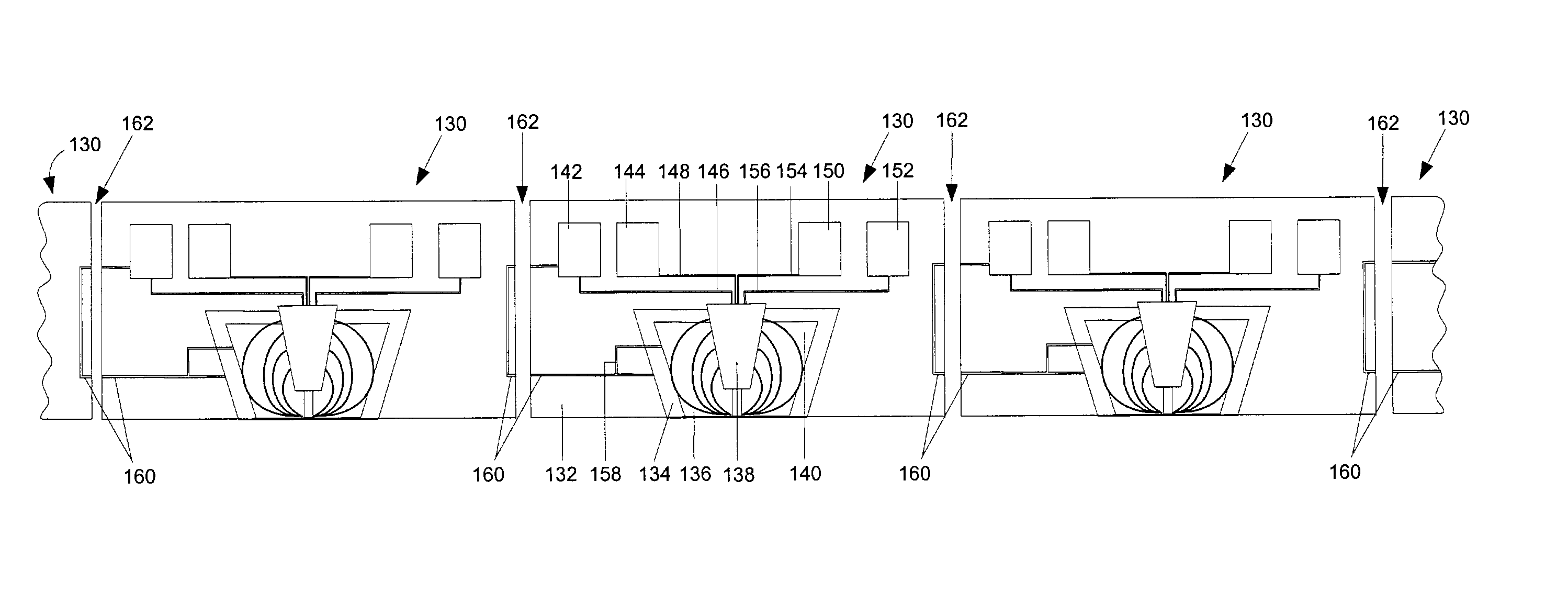
InactiveUS7151651B1Enhanced ESD robustnessReduce degradationRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsContact padEngineering
A read / write head for a disk drive having a shorting conductor from a shield of the read element to a conductor that runs from the write element to an external electrical contact pad. This allows for the measurement of the electrical isolation between the read sensor and the read shield via the external contact pads. Such a capability allows the electrical isolation to be measured both during the lapping process and subsequent to the heads being diced into separate sliders. This shorting conductor may be in the form of an internal shorting stud or in the form of an interim conductor that passes through the parting zone between adjacent heads. In the latter case, the shorting conductor is broken when the heads are diced so that a head of this embodiment can only be measured for electrical isolation prior to dicing.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Slider-level reader isolation measurement technique for advanced GMR heads
InactiveUS7042683B1Enhanced ESD robustnessReduce degradationRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsContact padEngineering
A read / write head for a disk drive having a shorting conductor from a shield of the read element to a conductor that runs from the write element to an external electrical contact pad. This allows for the measurement of the electrical isolation between the read sensor and the read shield via the external contact pads. Such a capability allows the electrical isolation to be measured both during the lapping process and subsequent to the heads being diced into separate sliders. This shorting conductor may be in the form of an internal shorting stud or in the form of an interim conductor that passes through the parting zone between adjacent heads. In the latter case, the shorting conductor is broken when the heads are diced so that a head of this embodiment can only be measured for electrical isolation prior to dicing.
Owner:MAXTOR
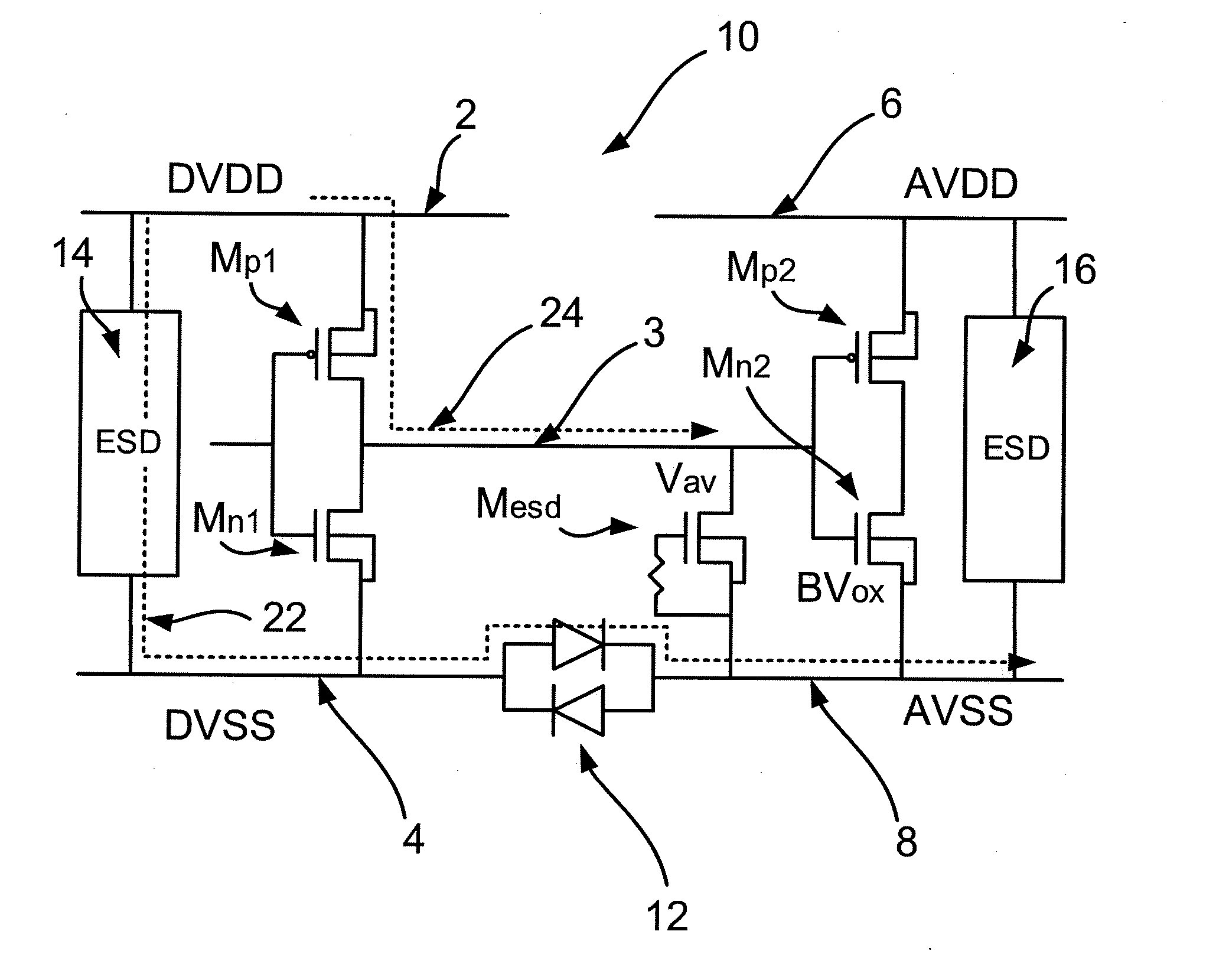
Semiconductor device comprising an ESD protection circuit
ActiveUS20160225758A1Delicate componentImprove robustnessTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceControl signal
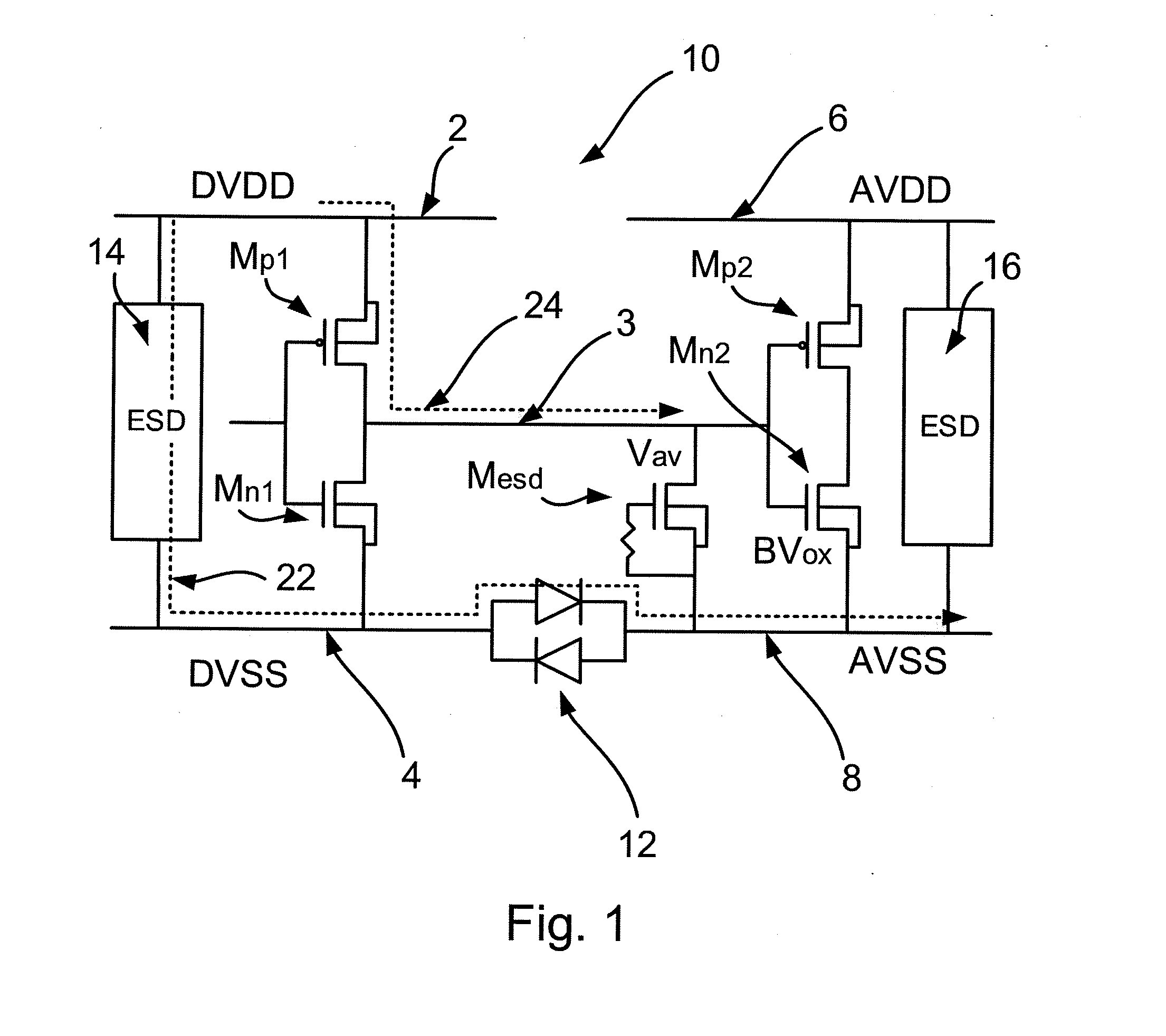
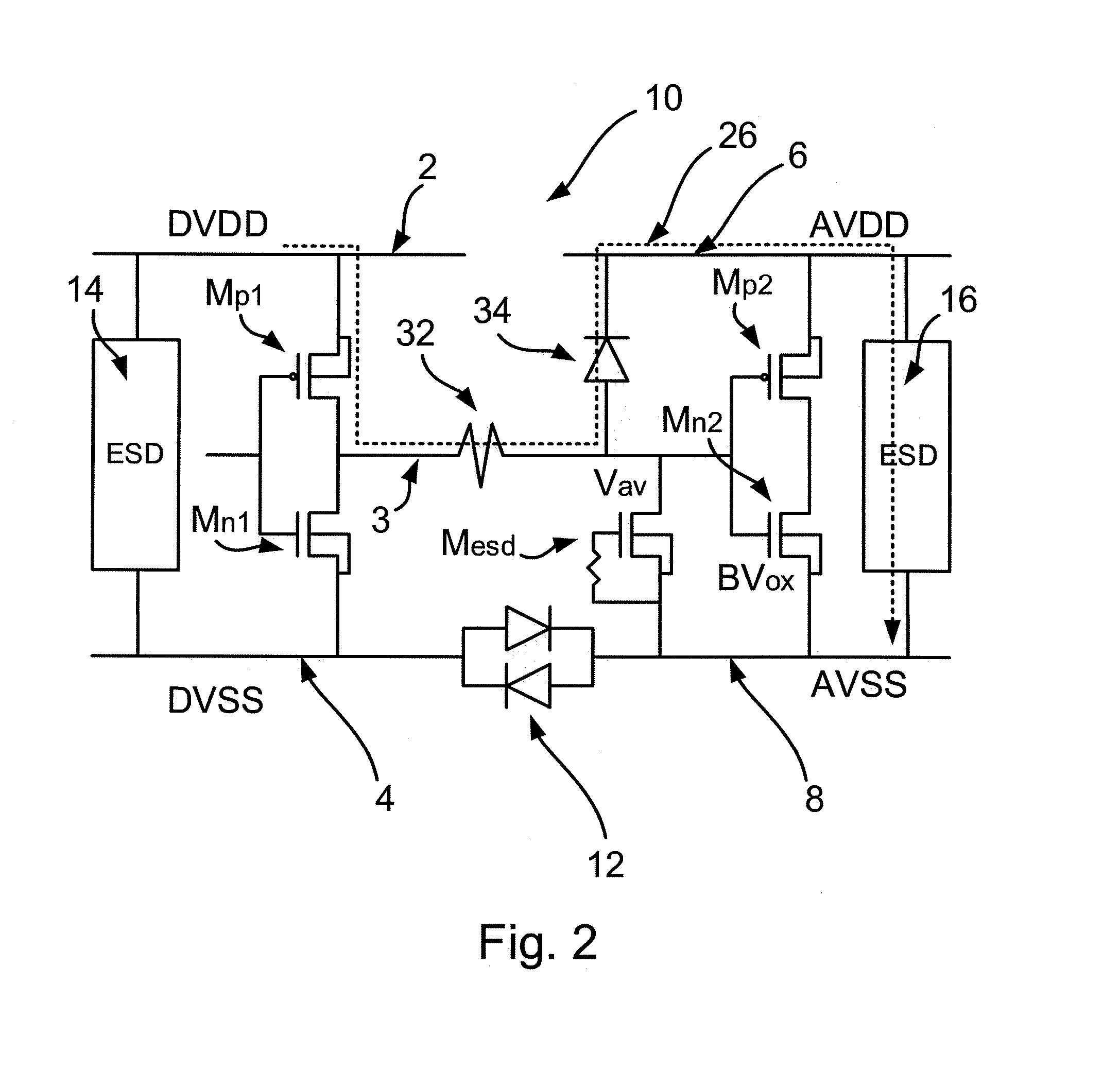
A semiconductor device and method. The device includes a first domain and a second domain each having a power rail and a ground rail. The device further includes a signal line connected between the first domain and the second domain. The device also includes an electrostatic discharge protection circuit for providing cross-domain ESD protection. The protection circuit includes a blocking transistor connected between the first domain power rail and the signal line. The protection circuit also includes a power rail clamp connected between the first domain power rail and the first domain ground rail. The power rail clamp is operable to apply a control signal to a gate of the blocking transistor to switch it on during normal operation and to switch it off during an ESD event. The power rail clamp is operable during the ESD event to conduct an ESD current.
Owner:NXP BV
Bidirectional ESD protection anti-latch-up device of holosymmetric dual-grid-control-diode triggering SCR structure
ActiveCN107658295ALower the trigger voltageOpen fastSolid-state devicesDiodeCapacitanceHemt circuits
The invention discloses a bidirectional ESD protection anti-latch-up device of a holosymmetric dual-grid-control-diode triggering SCR structure, and the device can be used for improving the capabilityof an IC chip in resisting ESD. The device mainly consists of a P substrate, a P epitaxial part, a first N well, a P well, a second N well, a first N+ injection region, a first P+ injection region, asecond N+ injection region, a second P+ injection region, a third N+ injection region, a third P+ injection region, a fourth N+ injection region, a first polysilicon gate, a first thin gate oxide layer covering the first polysilicon gate, a second polysilicon gate, and a second thin gate oxide layer covering the second polysilicon gate. The device has a resistance-capacitance coupling auxiliary triggering path under the action of ESD stress, does not need an additional layout area, also can make the most of the advantages of low triggering voltage of a resistance-capacitance coupling circuitand the short start time, and shortens the voltage hysteresis amplitude of the device. In addition, the device also employs the conduction characteristics of the gate control diodes, improves the potential of a parasitic well resistor of the N well, and speeds up the starting of a current releasing path of the SCR structure. Moreover, the device has two ESD current releasing paths and a holosymmetric structure, facilitates the improvement of the ESD robustness of the device, and can achieve the bidirectional protection of ESD.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Silicon controlled rectifier for the electrostatic discharge protection
InactiveUS7542253B2Improve effectivelyReduce areaTransistorThyristorFoundrySilicon-controlled rectifier
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
High-voltage electronic static discharge (ESD) protection device with positive-negative (PN) junction auxiliary trigger silicon controlled rectifier-laterally diffused metal oxide semiconductor (SCR-LDMOS) structure
ActiveCN105742281AImprove ESD protection capabilityEnhanced ESD robustnessSolid-state devicesDiodeNegative feedbackLDMOS
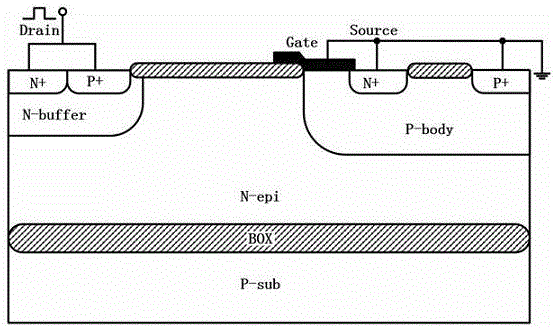
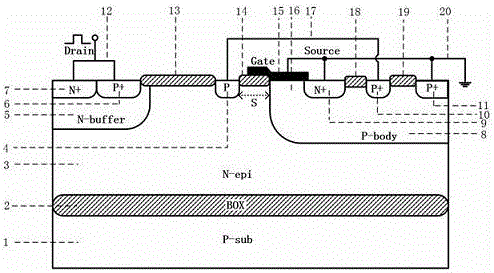
The invention discloses a high-voltage electronic static discharge (ESD) protection device with a positive-negative (PN) junction auxiliary trigger silicon controlled rectifier-laterally diffused metal oxide semiconductor (SCR-LDMOS) structure. The high-voltage ESD protection device comprises a P-type substrate, wherein a buried oxygen layer is arranged on the P-type substrate, a shift region is arranged on the buried oxygen layer, an N-buffer region, a P region and a P-body region are sequentially arranged on the shift region from left to right, a first drain heavily-doping N+ region and a first drain heavily-doping P+ region are sequentially arranged in the N-buffer region from left to right, a second source heavily-doping N+ region, a second source heavily-doping P+ region and a third source heavily-doping P+ region are sequentially arranged in the P-body region from left to right, and the P region and the second source heavily-doping P+ region are connected through a wire. When a drain of the ESD protection device encounters a positive ESD pulse, a reverse bias PN junction is used for helping improving the hole carrier concentration before trigger starting, and a trigger voltage V<t1> is reduced; and moreover, with the introduction of the reverse bias PN junction into the device, the positive and negative feedback effect of a parasitic SCR can be effectively prevented, thus, the maintaining voltage V<h> of the device can be effectively increased, and the latch-up effect of the device is prevented.
Owner:ANHUI LONGXINWEI TECH CO LTD
ESD protection device structure
ActiveUS20110042716A1Lower the trigger voltageEnhanced ESD robustnessTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPulse voltagePhysics
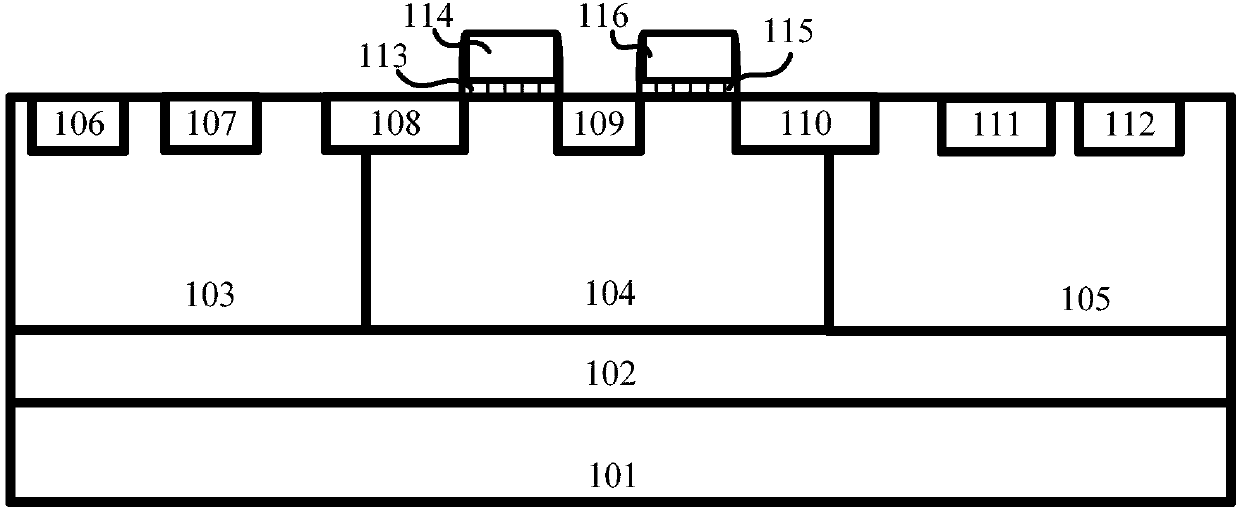
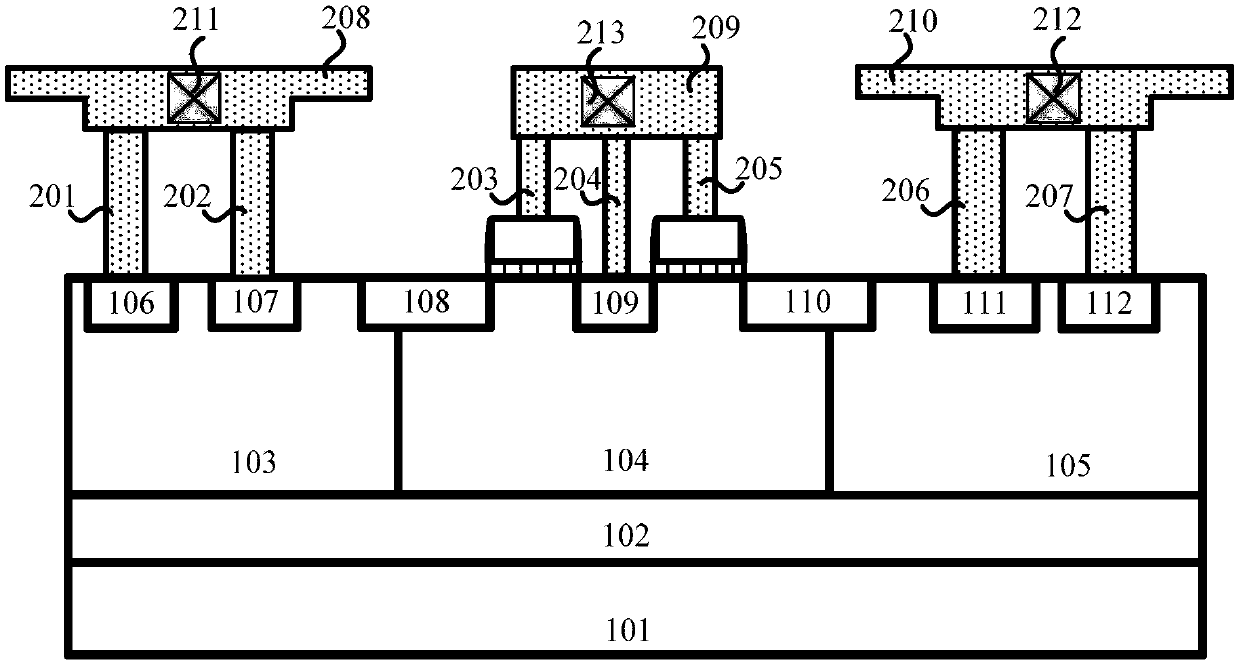
An ESD protection device structure includes a well having a first conductive type, a first doped region having a second conductive type disposed in the well, a second doped region having the first conductive type, and a third doped region having the second conductive type disposed in the well. The second doped region is disposed within the first doped region so as to form a vertical BJT, and the first doped region, the well and the third doped region forms a lateral BJT, so that pulse voltage that the ESD protection structure can tolerate can be raised.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
ESD protection component of LDMOS structure and with high maintaining voltage
ActiveCN103715233AImprove high pressure performanceInhibition of the Kirk effectTransistorHemt circuitsPolysilicon gate
An ESD protection component of an LDMOS structure and with high maintaining voltage can be used for an on-chip IC high-voltage ESD protection circuit and mainly comprises a P substrate, a high-voltage N trap, an N trap, a P trap, a P sink doping, a P+ injection region, a first N+ injection region, a second N+ injection region, a meal anode, a metal cathode, a polysilicon gate, a thin gate oxide layer and a plurality of field oxide isolation regions. According to the ESD protection component of the LDMOS structure, under the action of an high-voltage ESD, on one hand, a parasitic SCR current discharging path is formed by the P sink doping, the N trap, the high-voltage N trap, the P trap and the first N+ injection region, idle currents of the component are increased, and ESD robustness of the component is improved; on the other hand, by means of a biasing reversal PN junction formed between the second N+ injection region and the P sink doping, maintaining voltage of the component is improved and the latch-up-resistant capacity of the component is improved.
Owner:扬州市冠科科技有限公司
Electrostatic discharge protection semiconductor device
ActiveUS9653450B2Lower threshold voltageEnhanced ESD robustnessTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
An ESD protection semiconductor device includes a substrate, a gate set formed on the substrate, a source region and a drain region formed in the substrate respectively at two sides of the gate set, and at least a first doped region formed in the drain region. The source region and the drain region include a first conductivity type, and the first doped region includes a second conductivity type. The first conductivity type and the second conductivity type are complementary to each other. The first doped region is electrically connected to a ground potential.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
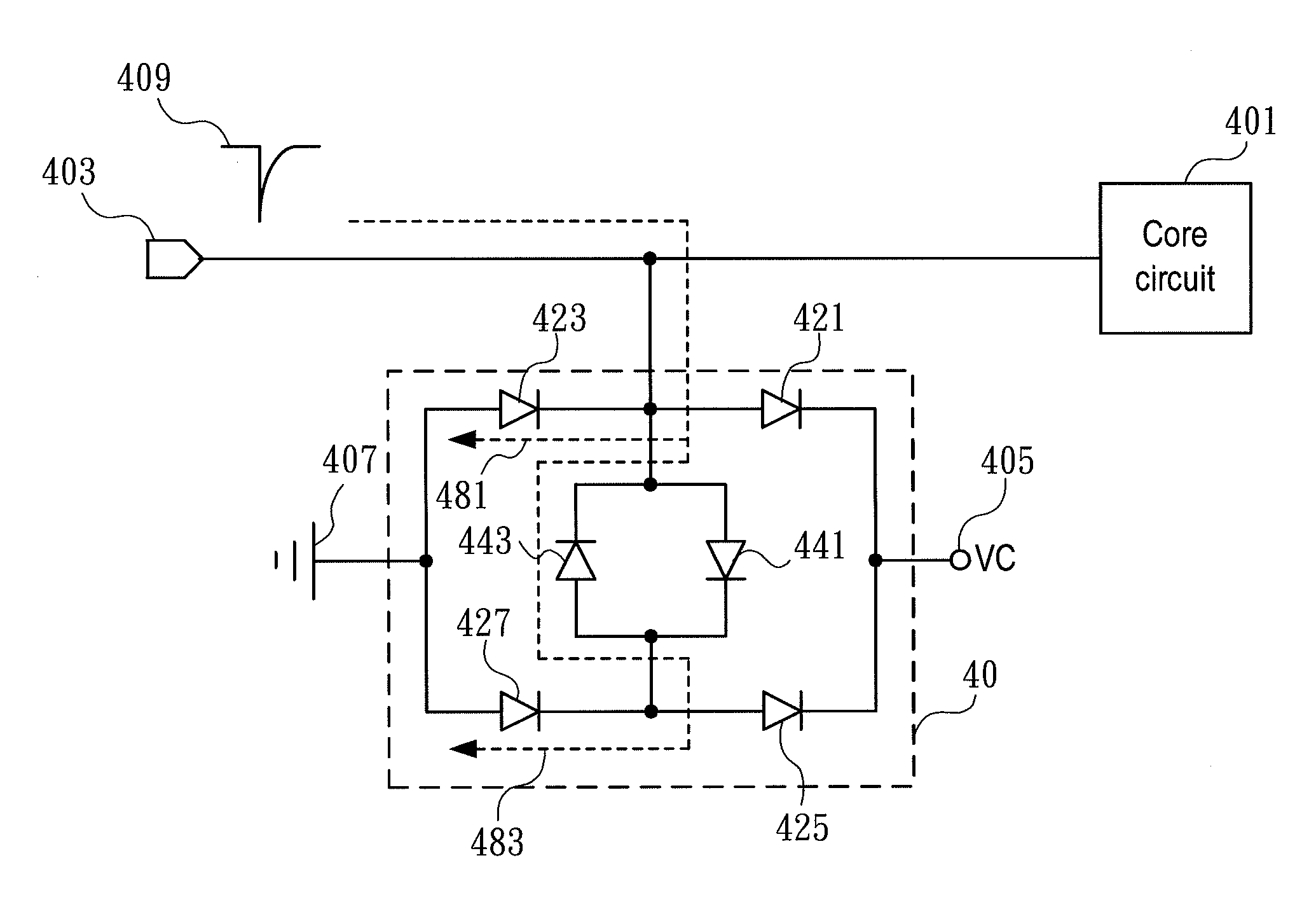
Low parasitic capacitance electrostatic discharge protection circuit
ActiveUS20110211285A1Enhanced ESD robustnessReduce parasitic capacitanceEmergency protective arrangement detailsOvervoltage protection resistorsParasitic capacitanceEngineering
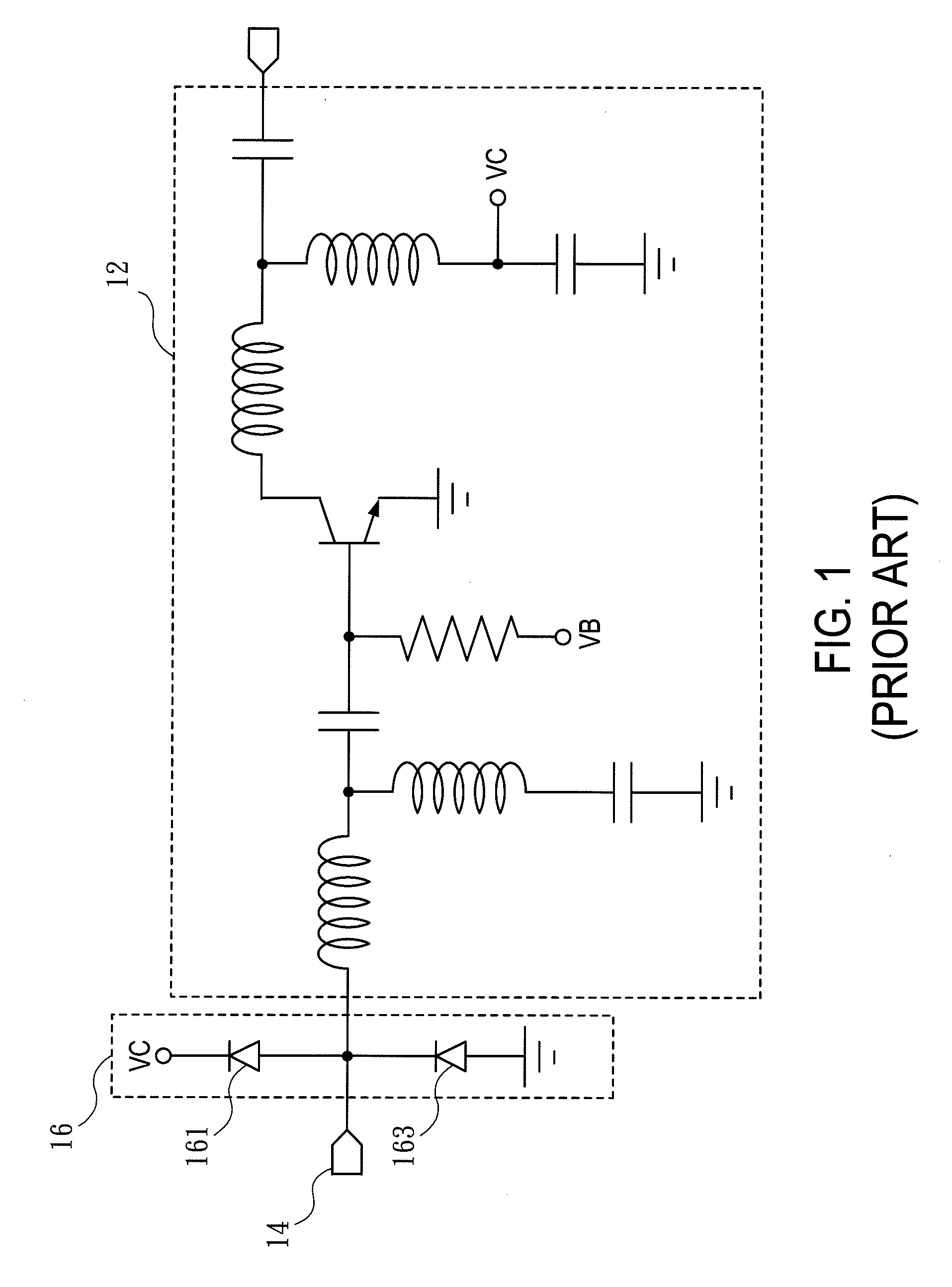
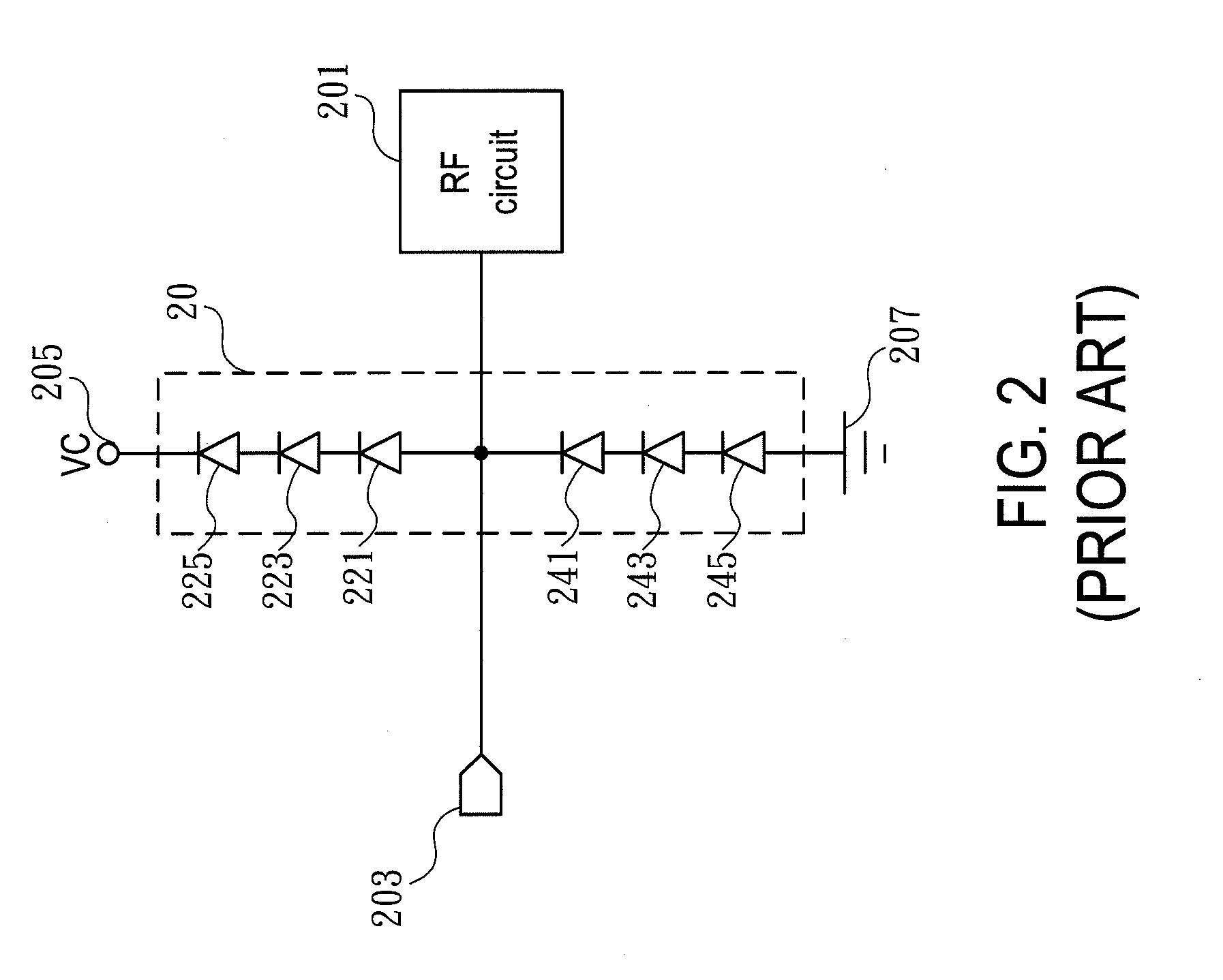
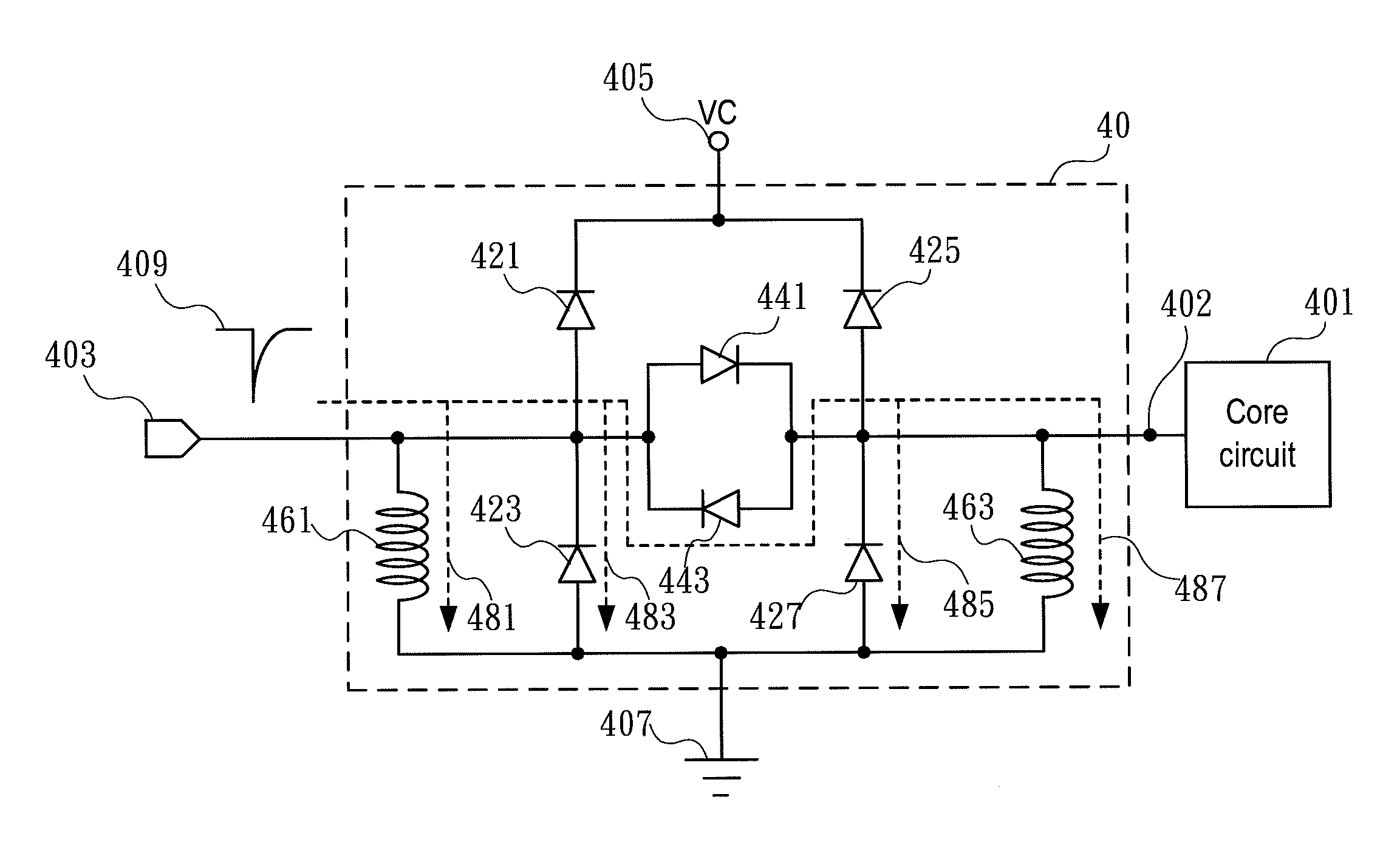
The present invention relates to an electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection circuit, and more particularly to a low parasitic capacitance electrostatic discharge protection circuit. An ESD protection circuit is established with the structure in accordance with the present invention comprising a plurality of discharging paths. The ESD protection circuit is connected to the input / output pad of a radio frequency (RF) core circuit. Such that, the RF core circuit with the ESD protection circuit of the present invention feature much higher ESD robustness. And the parasitic capacitance of the ESD protection is reduced because of the structure of the present invention.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
InactiveUS20100252911A1Enhanced ESD robustnessIncrease the areaSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
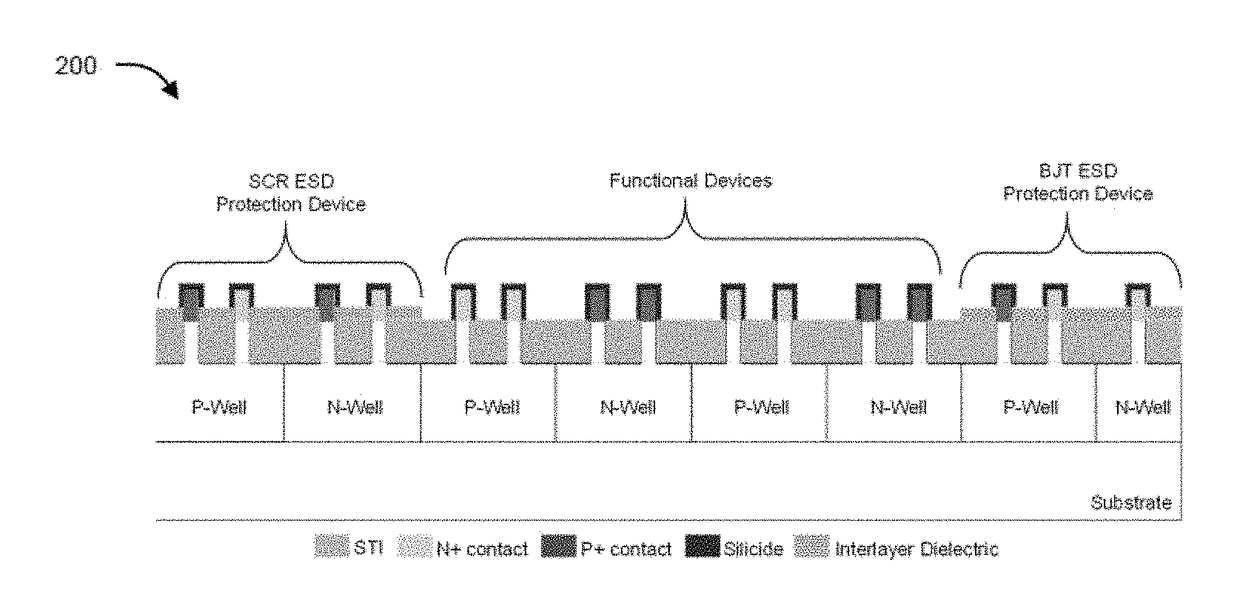
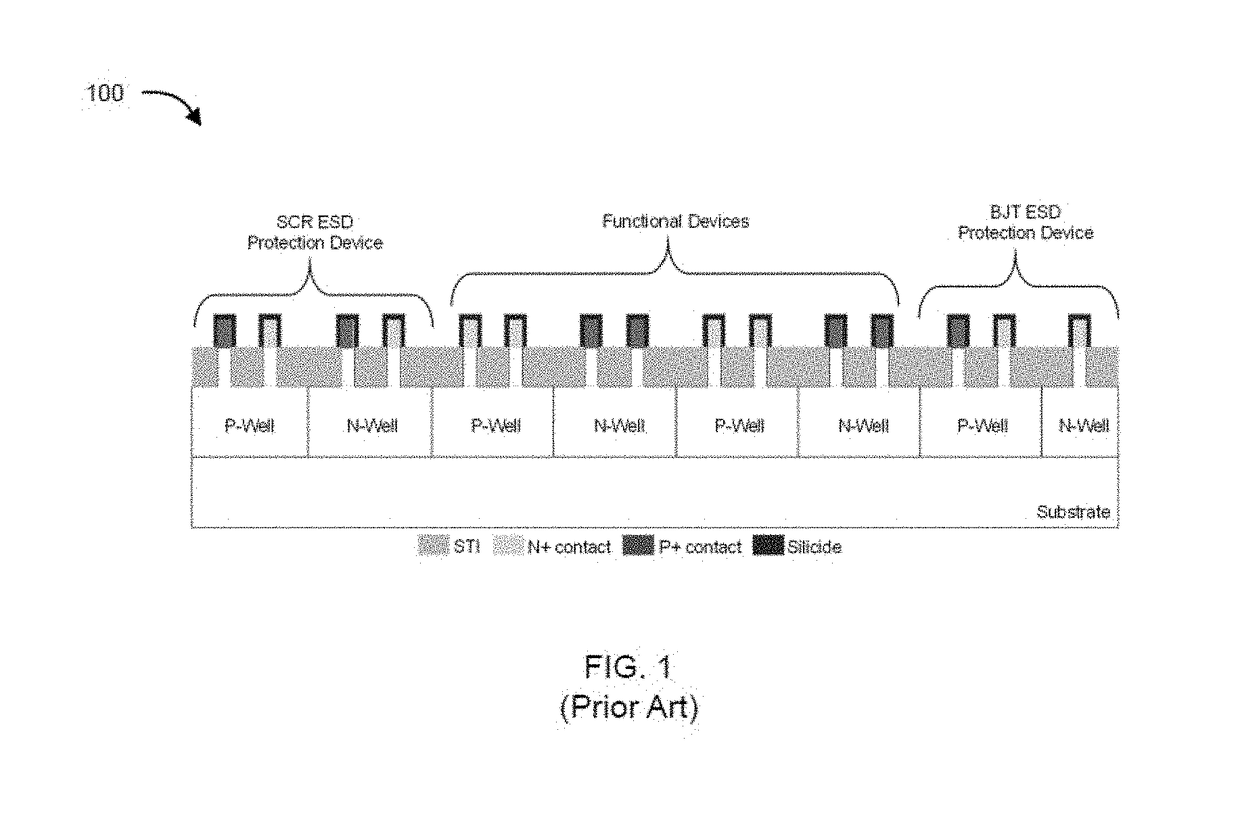
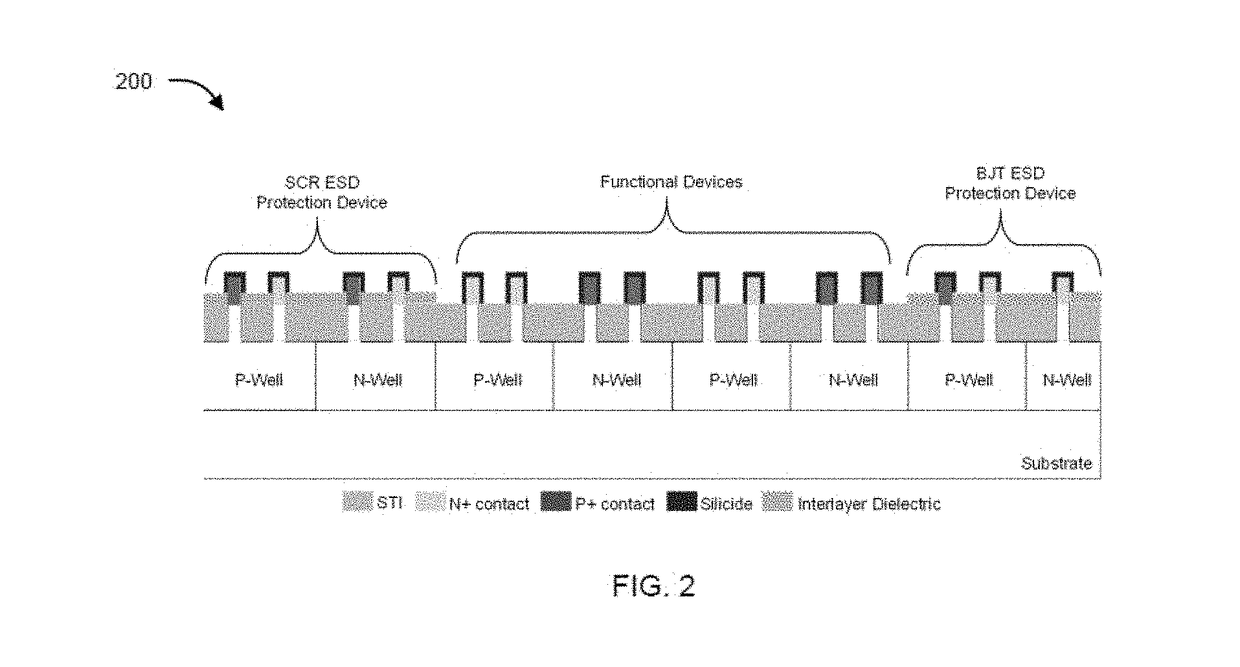
Semiconductor devices and methods to enhance electrostatic discharge (ESD) robustness, latch-up, and hot carrier immunity
ActiveUS20180247929A1High latch-up immunityEnhanced life expectancyTransistorThyristorSalicideEngineering
The present disclosure relates to non-planar ESD protection devices. The present disclosure provides a device structure and method of fabricating the structure that is essentially immune to latch-up and possess high ESD robustness and reliability. In an aspect, the present disclosure provides a mixed silicidation and selective epitaxy (epi) FinFET processes for latch-up immunity together with ESD robustness, thereby allowing achievement of ESD efficient parasitic structures together with latch-up immune and reliable functional devices. The present disclosure provides a dual silicidation scheme where ESD protection element(s) have fins that are partially silicided, and functional devices have fins that are fully silicided. The present disclosure also provides a hybrid contact and junction profile scheme where ESD protection element(s) have fins that are partially silicided with or without deep junctions depending on their application, and functional devices have fins that are fully silicided with the silicide edge crossing the junction. On the other hand, a dual Epi scheme is implemented such that ESD protection elements have fins with Epi contact, and functional devices have fins that are fully silicided without Epi (raised S / D) contact.
Owner:INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE
Three-end compact and compound SCR device for whole-chip ESD protection
ActiveCN110190052AReduce conductance modulation effectFulfill protection needsTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSEngineering
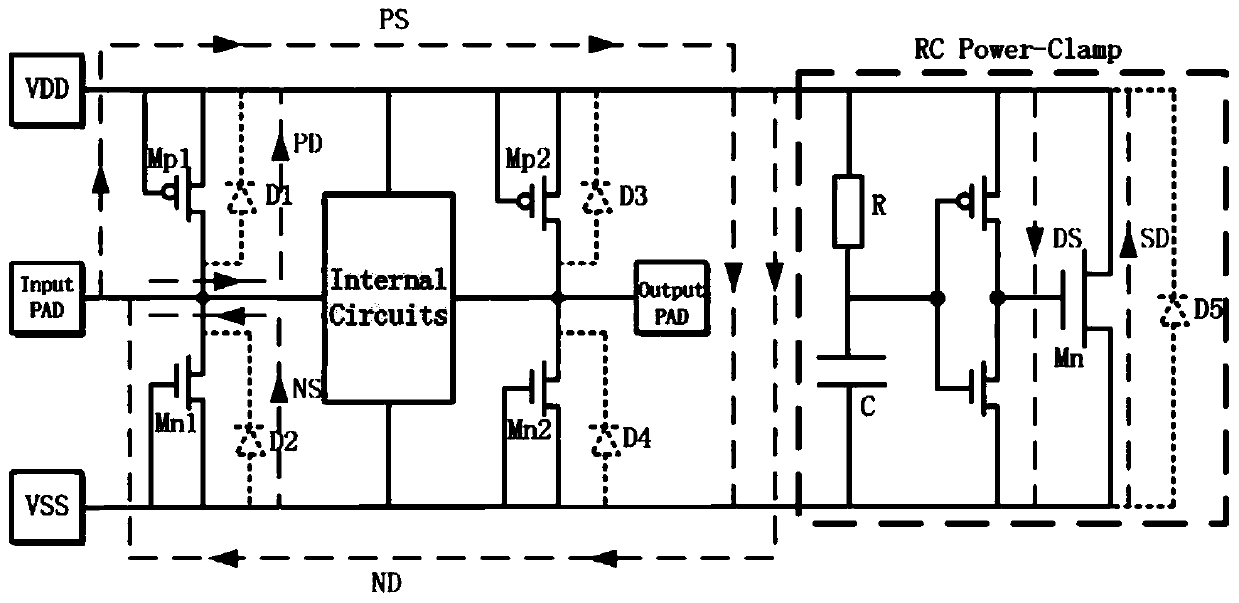
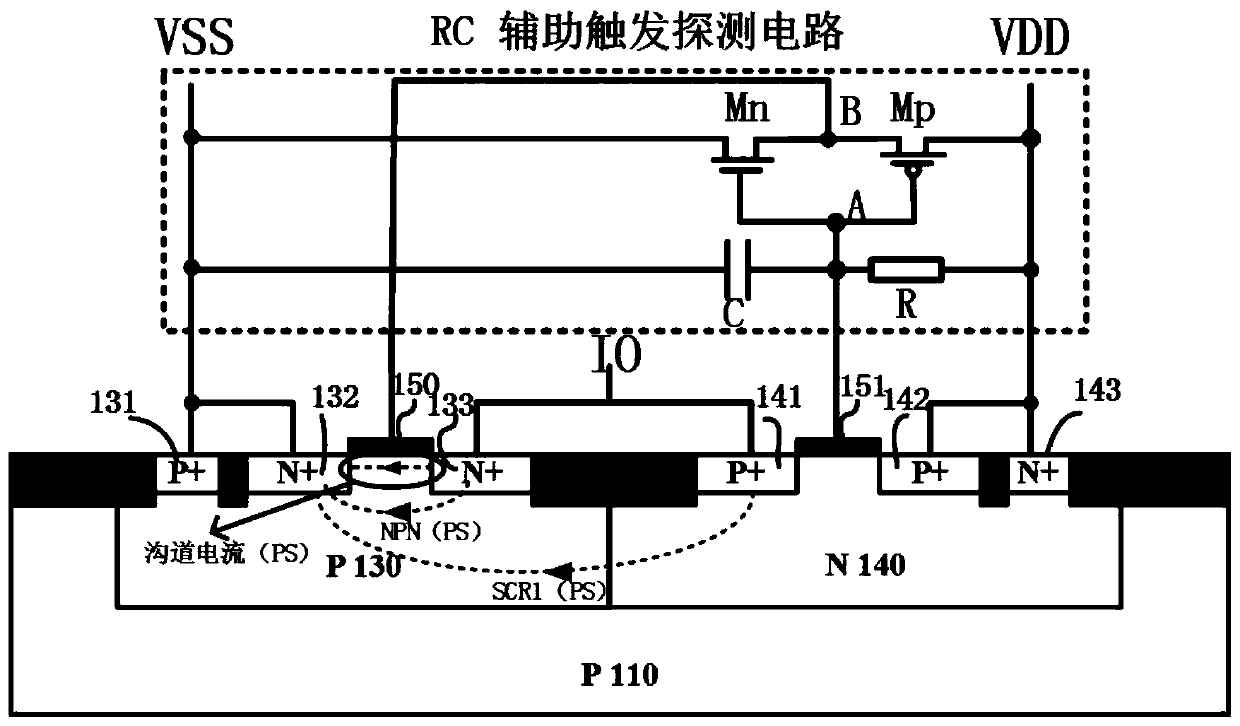
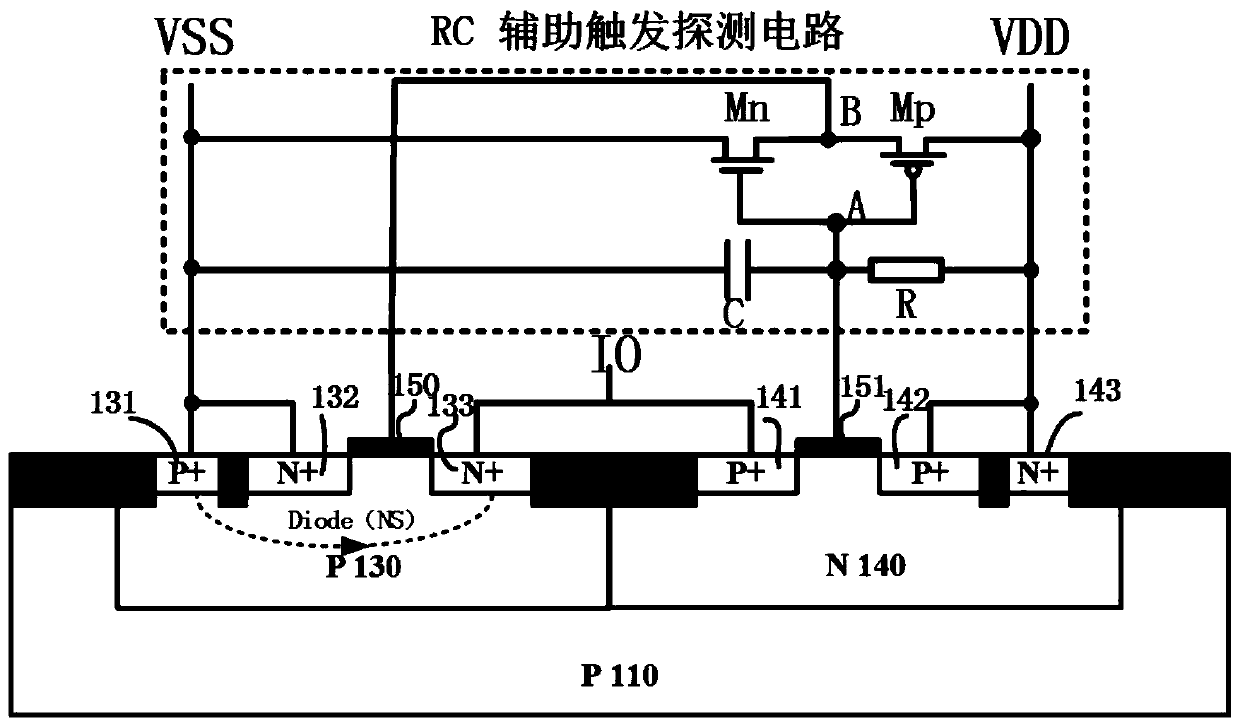
The present invention belongs to the technical field of electrons, especially relates to the design of an ESD (Electro-Static discharge) protection circuit, and especially provides a three-end compactand compound SCR device (CCSCR) for whole-chip ESD protection. The three-end compact and compound SCR device comprises a main discharge CCSCR and a RC auxiliary trigger detection circuit; the main discharge CCSCR is a three-end device, three parasitic SCR pathways are introduced on the basis of the CMOS device structure so that the whole-chip ESD protection with high robustness is achieved in a smaller territory area; the RC auxiliary trigger detection circuit is introduced to further reduce the triggering voltage of the device; and besides, the CCSCR can be taken as a two-end device to supply ESD protection between any one IO port and a power supply.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Wideband antenna device with extended ground plane in a portable device
InactiveUS7319433B2Effective bandwidthEnhanced ESD robustnessResonant long antennasAntenna supports/mountingsBroadbandGround plane
An antenna device for a portable device has an antenna loop of conducting material to be connected to radio circuitry in the portable device. The antenna loop is positioned opposite a ground plane of a PCB. Also, the antenna device also comprises at least one battery, which is positioned in the extension of a first side of the PCB, and acts as an extension of the ground plane of the PCB.
Owner:SONY CORP
Electrostatic protection device
ActiveCN108899313AEnhanced ESD robustnessIncrease holding voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringVoltage
The invention provides an electrostatic protection device comprising a substrate, wherein a deep N trap is arranged in the substrate, a first P trap, a first N trap and a second P trap are sequentially arranged in the deep N trap from left to right, a first P+ injection region, a first N+ injection region and a second N+ injection region are sequentially arranged in the first P trap from left to right, a third N+ injection region, a fourth N+ injection region and a fourth P+ injection region are sequentially arranged in the second P trap from left to right, the second P+ injection region is bridged between the first P trap and the first N trap, the third P+ injection region is bridged between the first N trap and the second P trap, the first P+ injection region and the first N+ injection region are both connected with an anode, and the fourth P+ injection region and the fourth N+ injection region are both connected with a cathode. According to the electrostatic protection device, the maintaining voltage can be improved, the trigger voltage is reduced, and the ESD robustness of the device is improved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Band-pass structure electrostatic discharge protection circuit
ActiveUS8482889B2Enhanced ESD robustnessImprove performanceEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentArrangements responsive to excess voltageBand-pass filterEngineering
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Electrostatic discharge protection structure
ActiveUS20150008529A1Improve robustnessEnhanced ESD robustnessTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectrostatic discharge protection
Provided is an electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection structure including a substrate, a pick-up region, a first MOS device, a second MOS device, a first doped region and a second doped region. The pick-up region is located in the substrate. The first MOS device has a first drain region of a first conductivity type located in the substrate. The second MOS device has a second drain region of the first conductivity type located in the substrate. The first drain region is closer to the pick up region than the second drain region is. The first doped region of a second conductivity type is located under the first doped region. The second doped region of the second conductivity type is located under the second doped region. The area and / or doping concentration of the first doped region is greater than that of the second doped region.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Bidirectional high-voltage ESD protection device of full-symmetric LDMOS triggered SCR structure
ActiveCN110880500AEnhanced ESD robustnessImprove pressure resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesDischarge efficiencyEngineering
The invention discloses a bidirectional high-voltage ESD protection device of a full-symmetric LDMOS triggered SCR structure, and belongs to the field of electrostatic discharge protection and surge resistance of integrated circuits. The protection device is mainly composed of a P substrate, a deep N well, a first P well, an N well, a second P well, a first P + injection region, a first N + injection region, a first polysilicon gate, a first thin gate oxide layer, a first field oxide isolation region, a second P + injection region, a second field oxide isolation region, a second polysilicon gate, a second thin gate oxide layer, a second N + injection region and a third P + injection region. The two NLDMOSs are embedded to form an auxiliary trigger SCR current path in which the on-state NLDMOS and the off-state NLDMOS are connected in series. The voltage withstanding capability of the device is improved, so that the device meets the ESD protection requirement of a high-voltage power supply domain, the ESD robustness of the device is enhanced, the discharge efficiency of the device in unit area is improved, the carrier concentration of a base region in a parasitic SCR structure is reduced, and the maintaining voltage of the device is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
ESD protection design with turn-on restraining method and structures
InactiveUSRE43215E1Improve the level ofEnhanced ESD robustnessTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrostatic dischargeTransistor
The present invention is directed to an electrostatic discharge (ESD) device with an improved ESD robustness for protecting output buffers in I / O cell libraries. The ESD device according to the present invention uses a novel I / O cell layout structure for implementing a turn-on restrained method that reduces the turn-on speed of an ESD guarded MOS transistor by adding a pick-up diffusion region and / or varying channel lengths in the layout structure.
Owner:TRANSPACIFIC IP LTD
Electrostatic discharge protection semiconductor device
ActiveUS10008489B2Lower threshold voltageEnhanced ESD robustnessTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorElectrostatic discharge protection
An electrostatic discharge protection semiconductor device includes a substrate, a gate set positioned on the substrate, a source region and a drain region formed in the substrate respectively at two sides of the gate set, at least a first doped region formed in the drain region, and at least a second doped region formed in the substrate. The source region and the drain region include a first conductivity type, the first doped region and the second doped region include a second conductivity type, and the first conductivity and the second conductivity type are complementary to each other. The first doped region and the second doped region are electrically connected to each other.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
ESD protection device of IGBT structure and with high maintaining voltage
ActiveCN104485329AIncrease the secondary failure currentEnhanced ESD robustnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceHigh voltage
An ESD protection device of an IGBT structure and with a high maintaining voltage can be used in an on-chip IC high-voltage ESD protection circuit. The ESD protection device is mainly composed of a P substrate, a high-voltage N well, an N well, a P well, a first P+ injection region, a second P+ injection region, an N+ injection region, a third P+ injection region, a fourth P+ injection region, a metal anode, a metal cathode, a polycrystalline silicon gate, a thin gate oxide layer and a plurality of field oxide isolation regions. According to the ESD protection device of the IGBT structure, under the action of high-voltage ESD pulses, on one hand, a current discharge path with a PNPN structure is formed by the third P+ injection region, the N well, the high-voltage N well, the P well and the N+ injection region, thereby improving failure current of the device and enhancing ESD robustness of the device; and on the other hand, another current discharge path with a parasitic PNP triode and a parasitic resistor being connected in series is formed by the third P+ injection region, the N well, the fourth P+ injection region, the first P+ injection region, the P well and the second P+ injection region, thereby improving the maintaining voltage of the device and enhancing anti-latch capability of the device.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
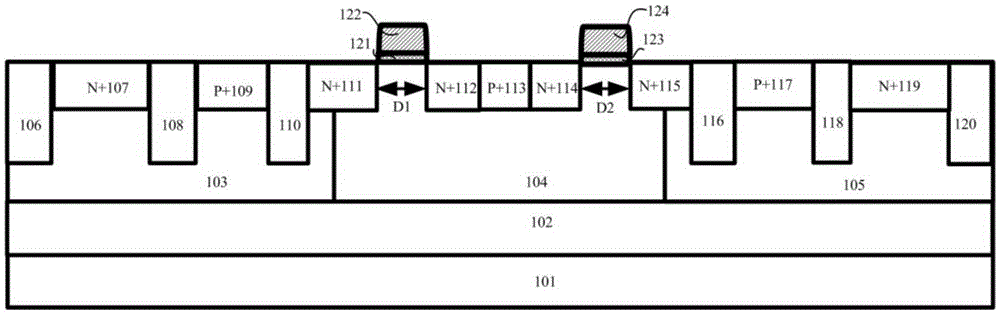
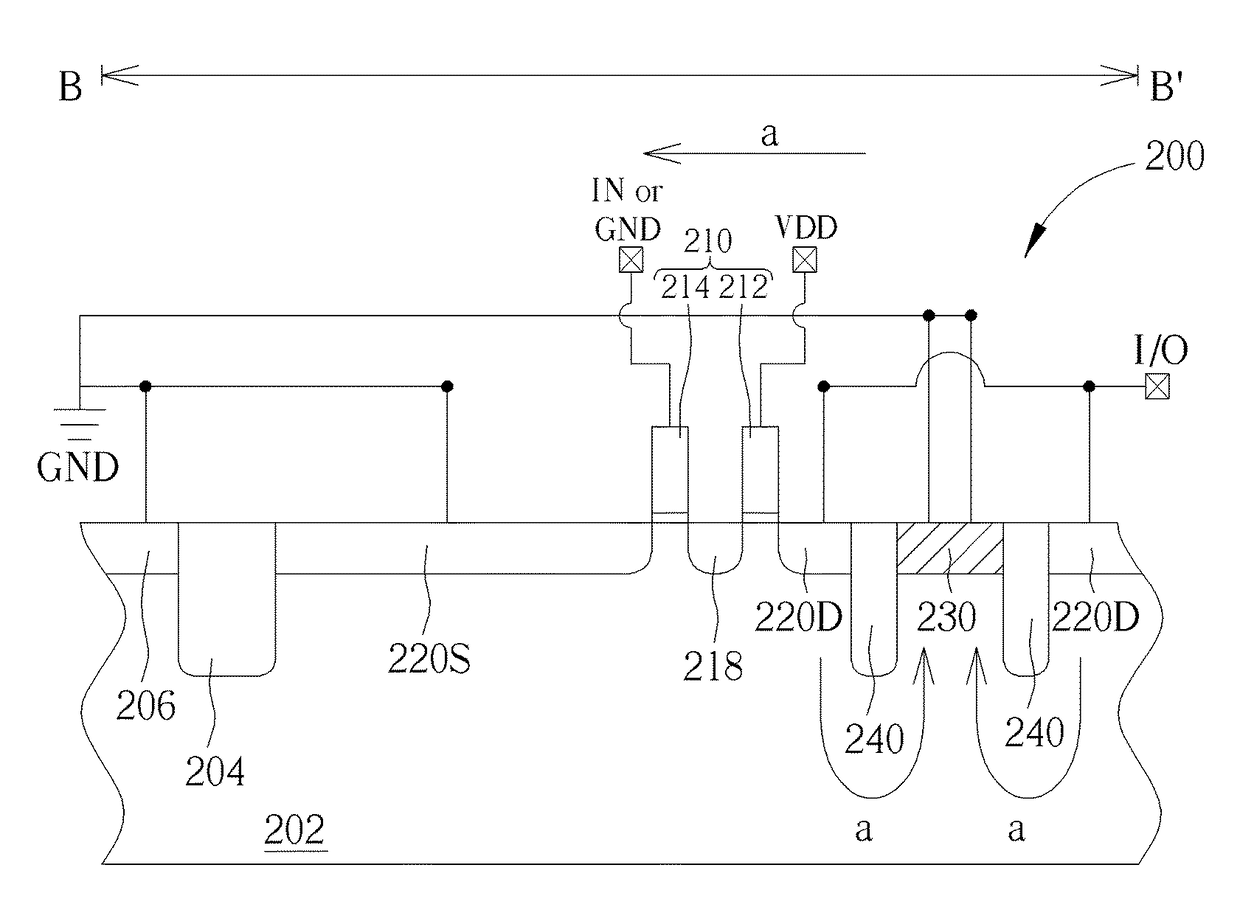
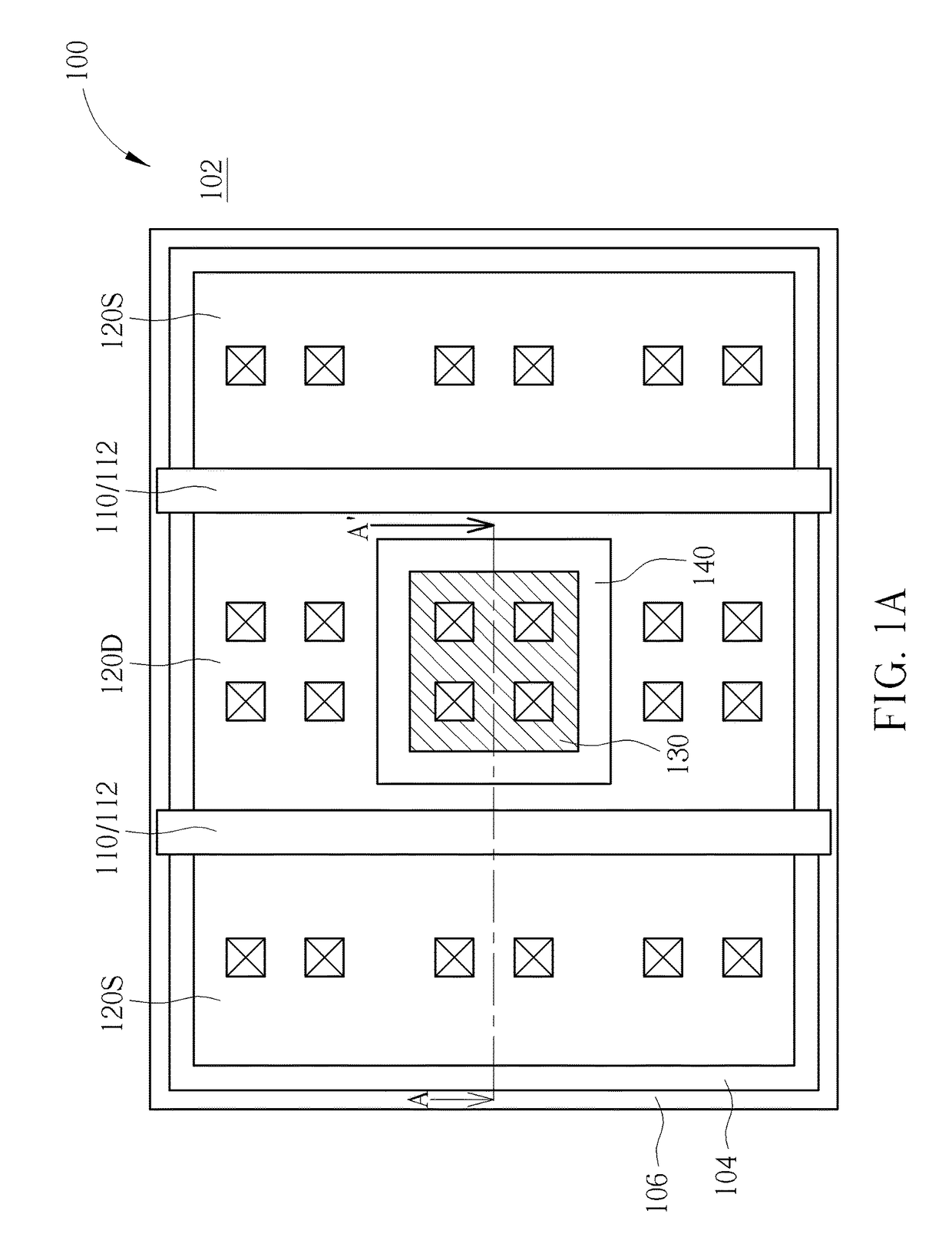
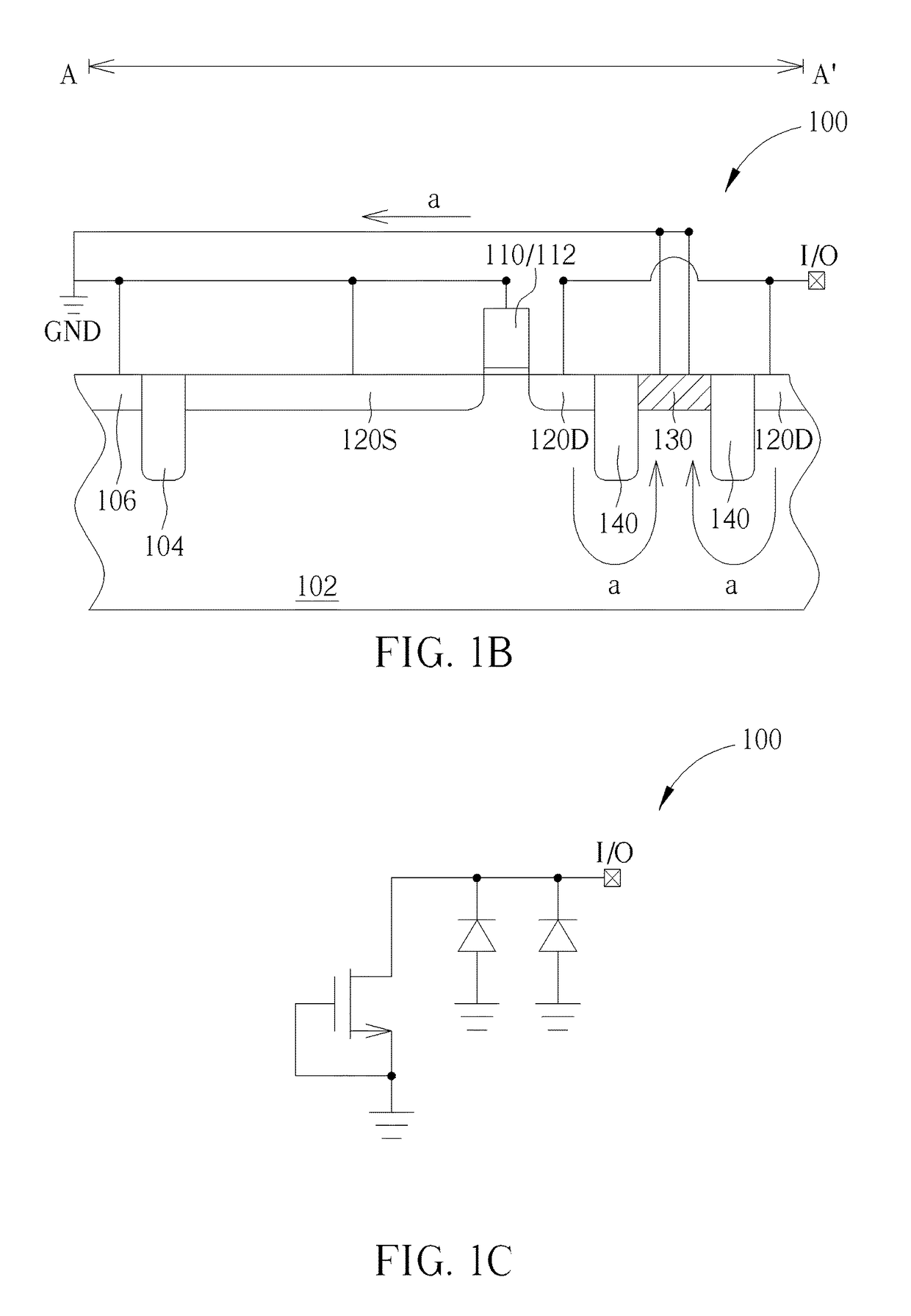
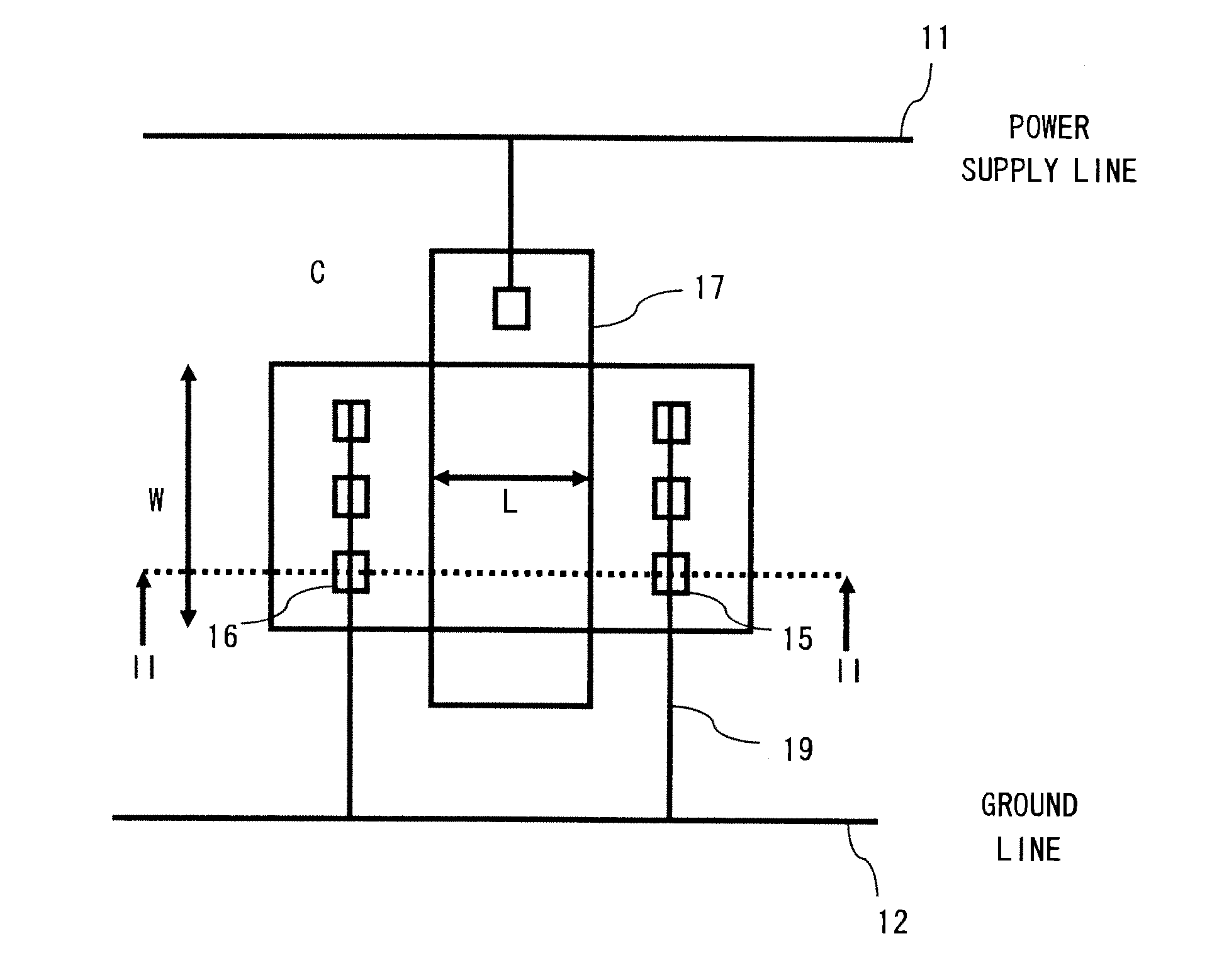
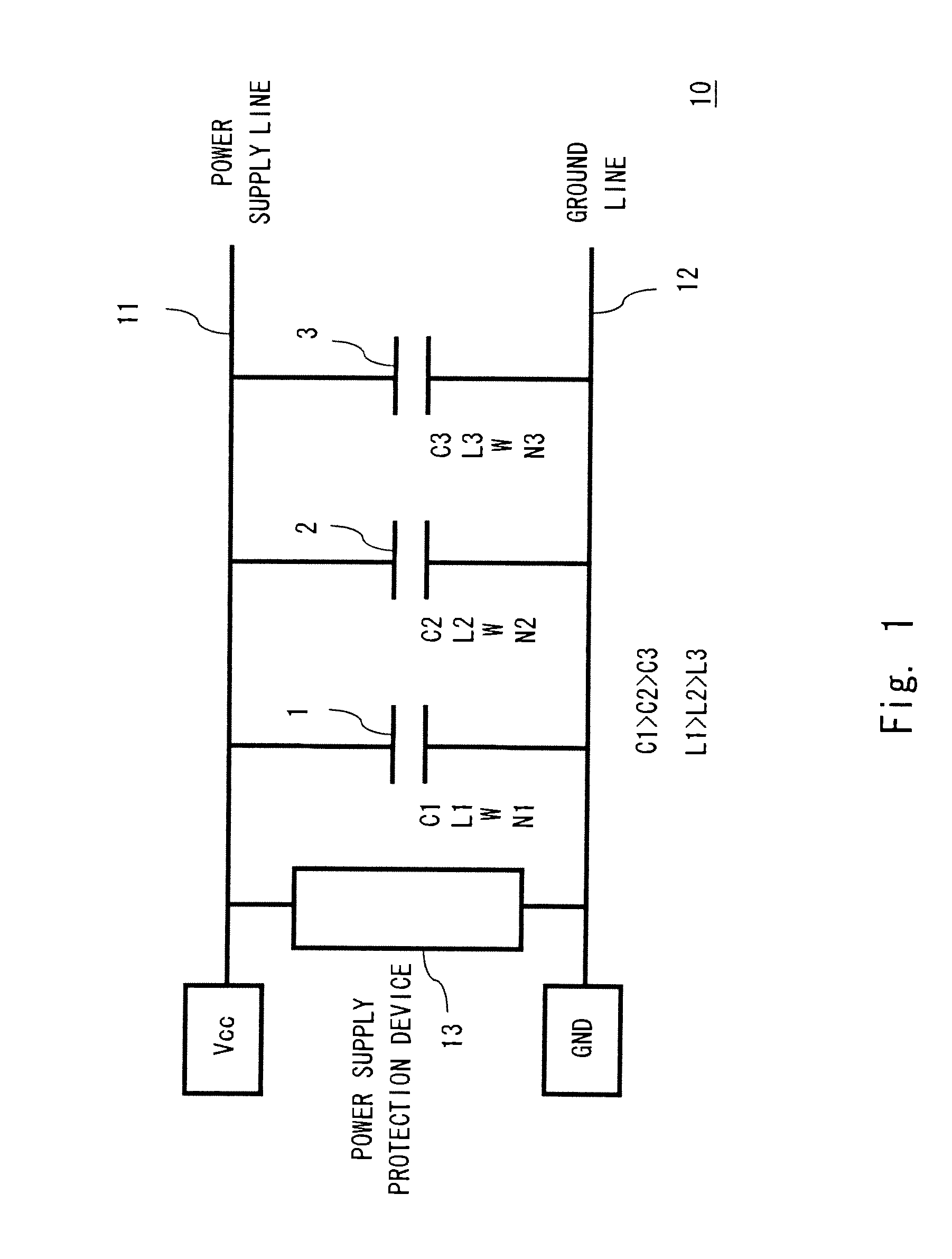
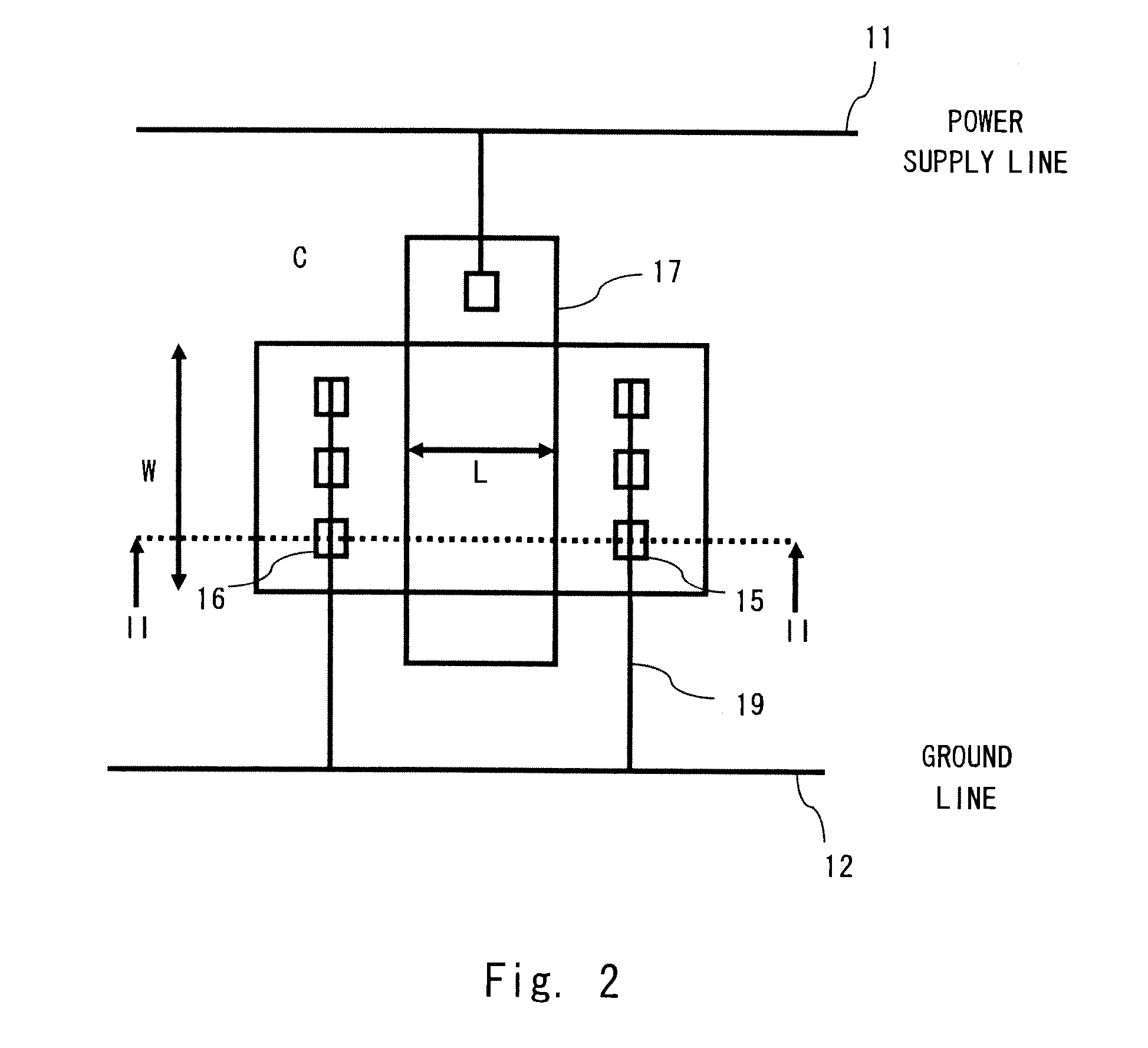
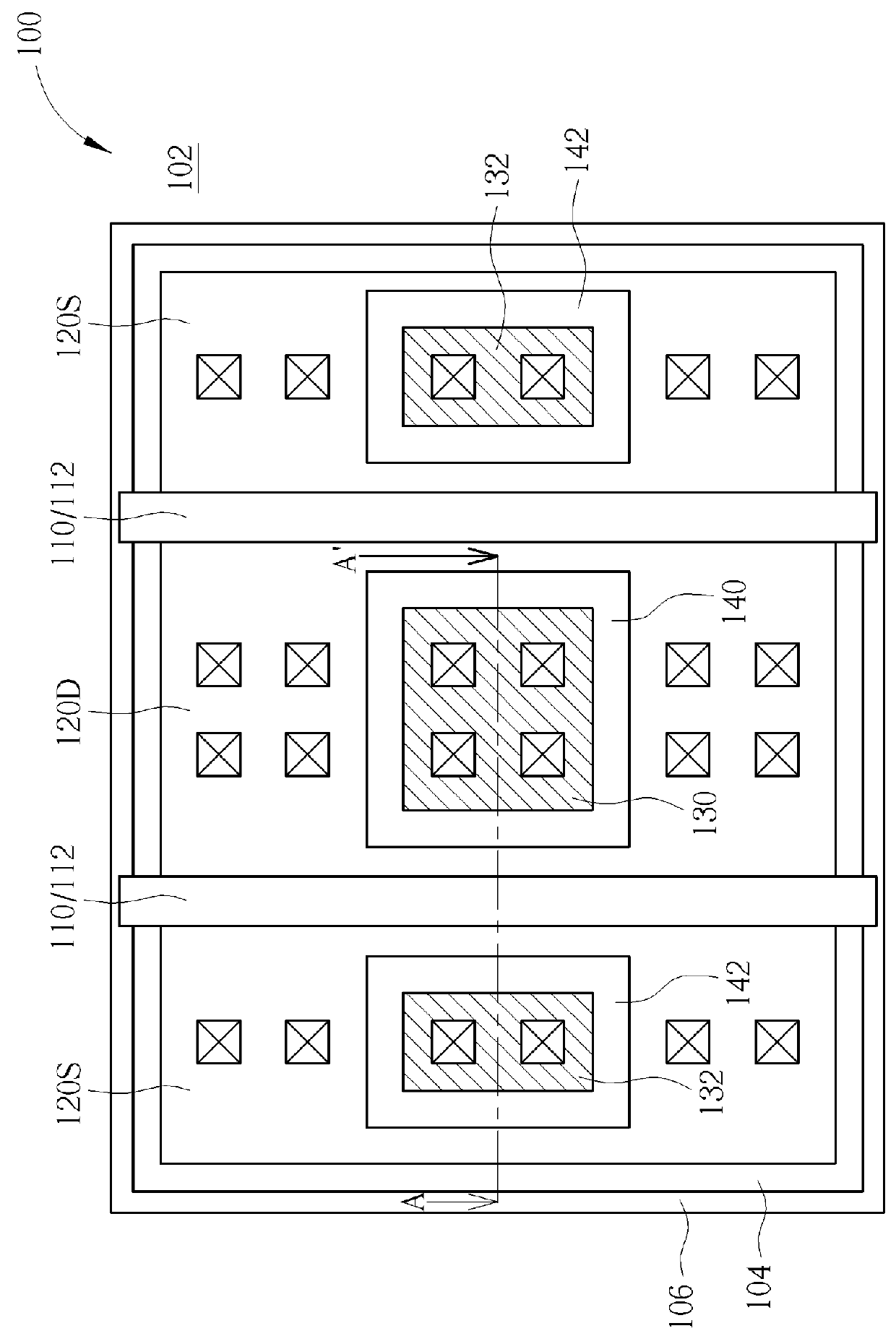
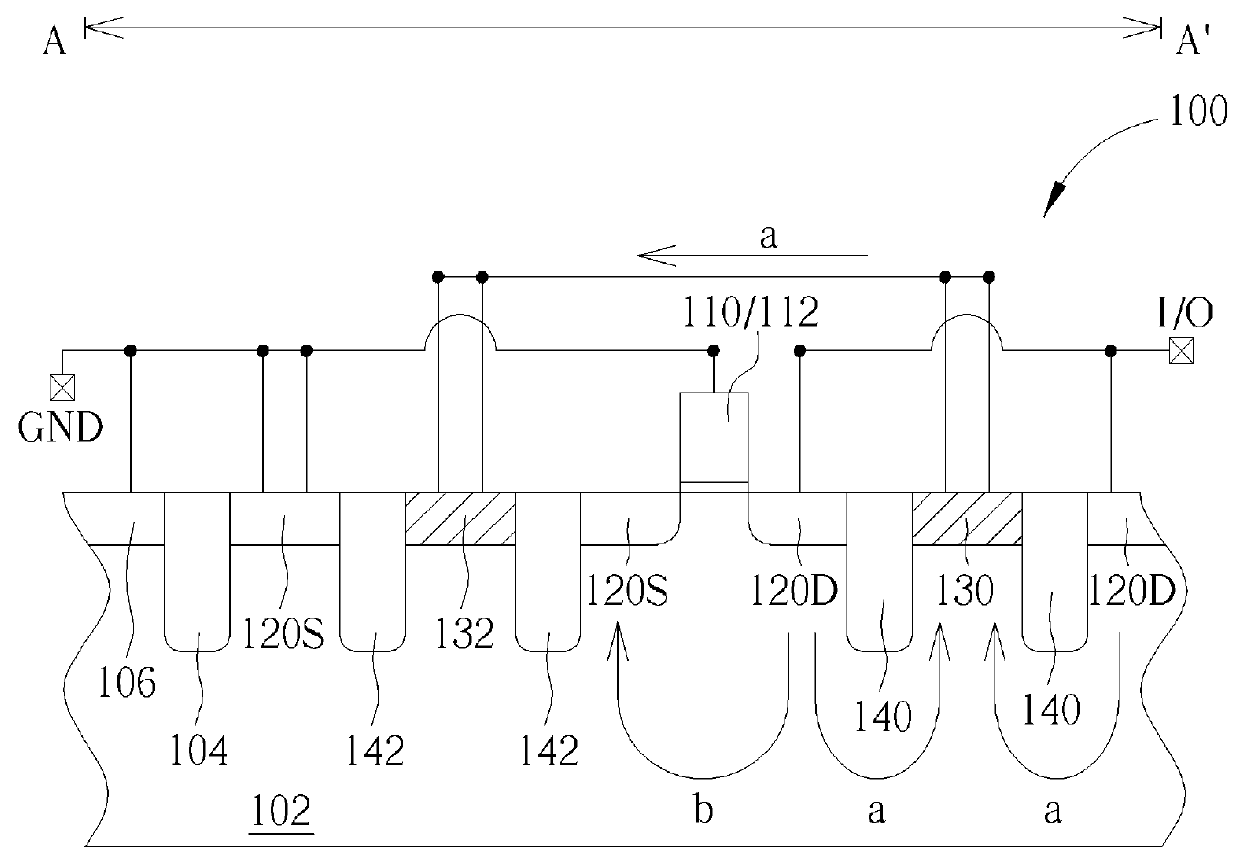
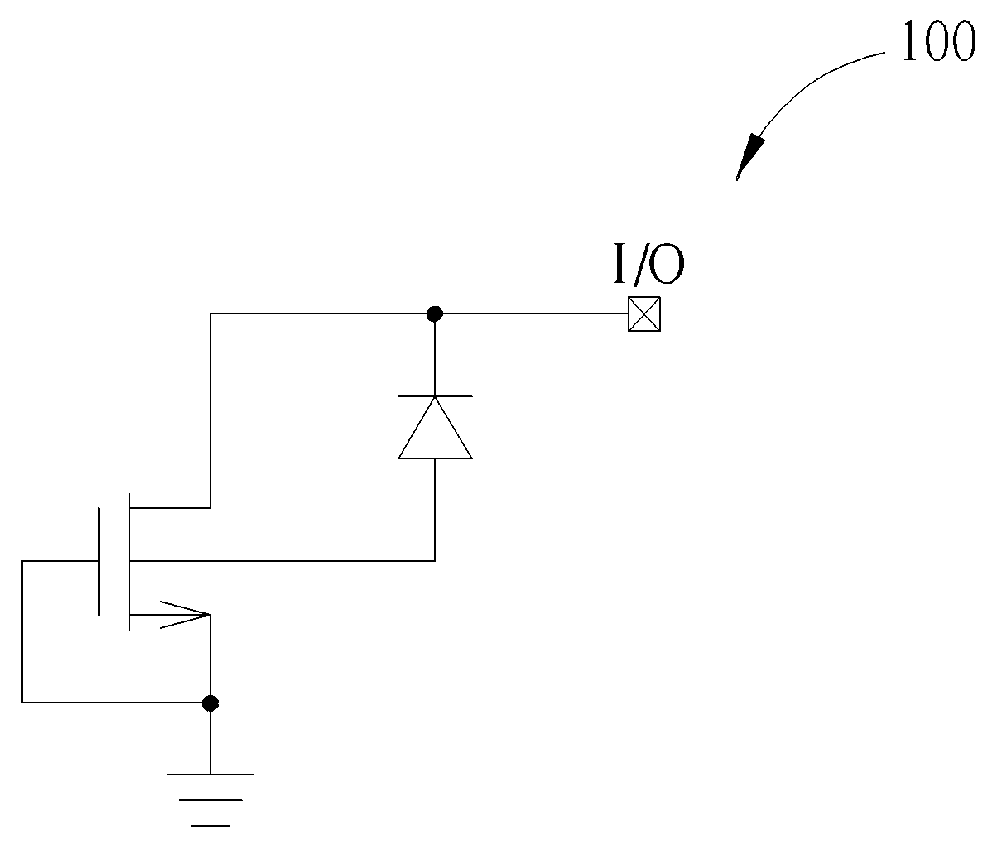
Transistor with increased ESD robustness and related layout method thereof
The invention relates to a layout method for a transistor with improved ESD robustness. The layout method includes defining a ring region from a first conductive type; defining a first and a second rectangular diffusion regions from a second conductive type, wherein the first and second rectangular diffusion regions are isolated from each other; defining a ring diffusion region of the second conductive type between the first and second rectangular diffusion regions; defining a first gate electrode between the first rectangular diffusion region of the second conductive type and the ring diffusion region of the second conductive region; and defining a second gate electrode between the second rectangular diffusion region of the second conductive type and the ring diffusion region of the second conductive type.
Owner:ILI TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Display device with different circuit groups
A display device that includes a substrate having a display region and an adjacent peripheral region is provided, including; a plurality of sub-pixels provided within the display region; a plurality of data lines electrically connected to the sub-pixels; and a first electronic circuit group and a second electronic circuit group provided in the peripheral region, connected to the corresponding data lines. The first electronic circuit group includes a plurality of first electronic circuits, and the second electronic circuit group includes a plurality of second electronic circuits. Two adjacent first electronic circuits are arranged with a first interval therebetween, and the first interval has a first width. Two adjacent second electronic circuits are arranged with a second interval therebetween, and the second interval has a second width. The first width and the second width are different.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com