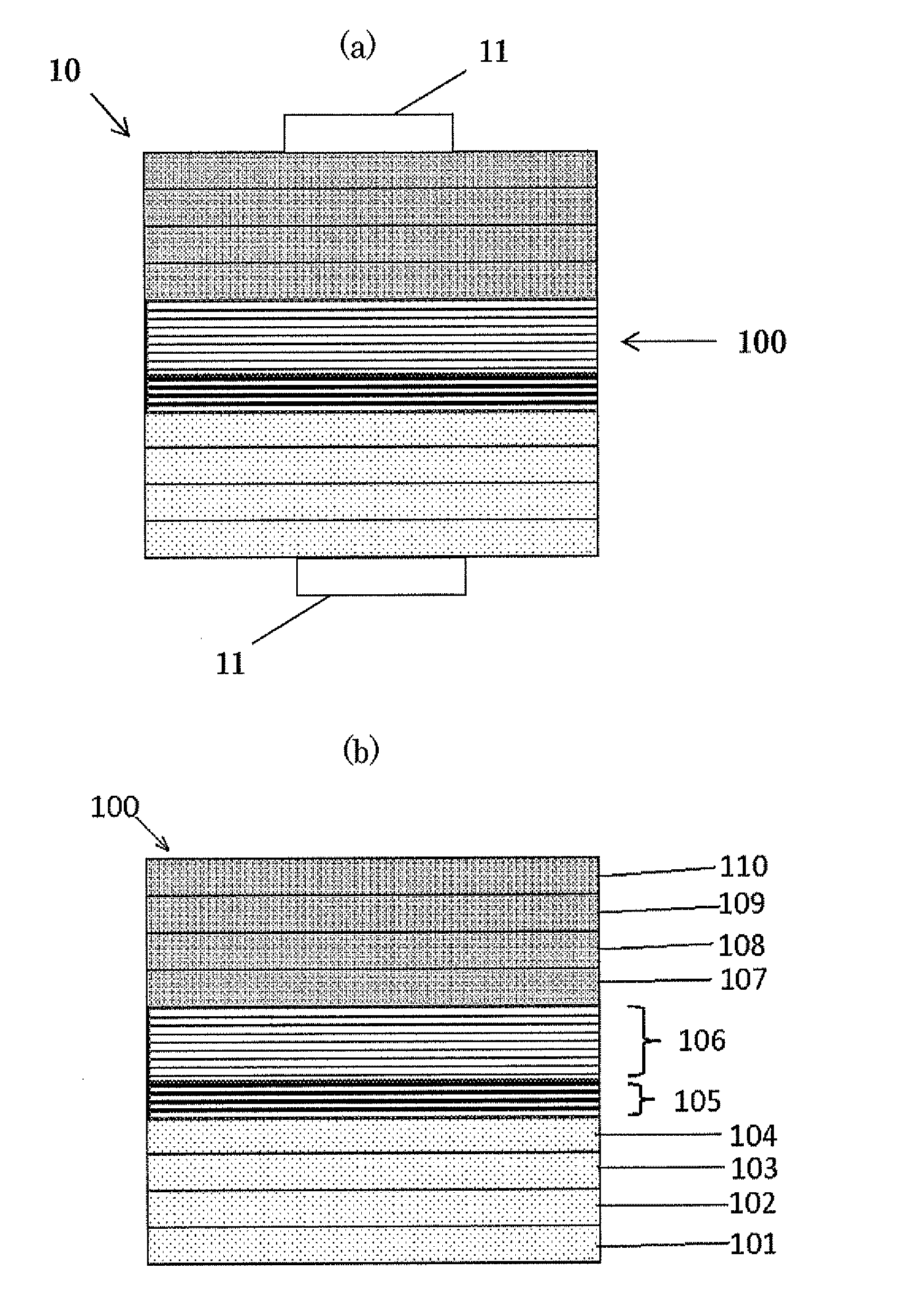
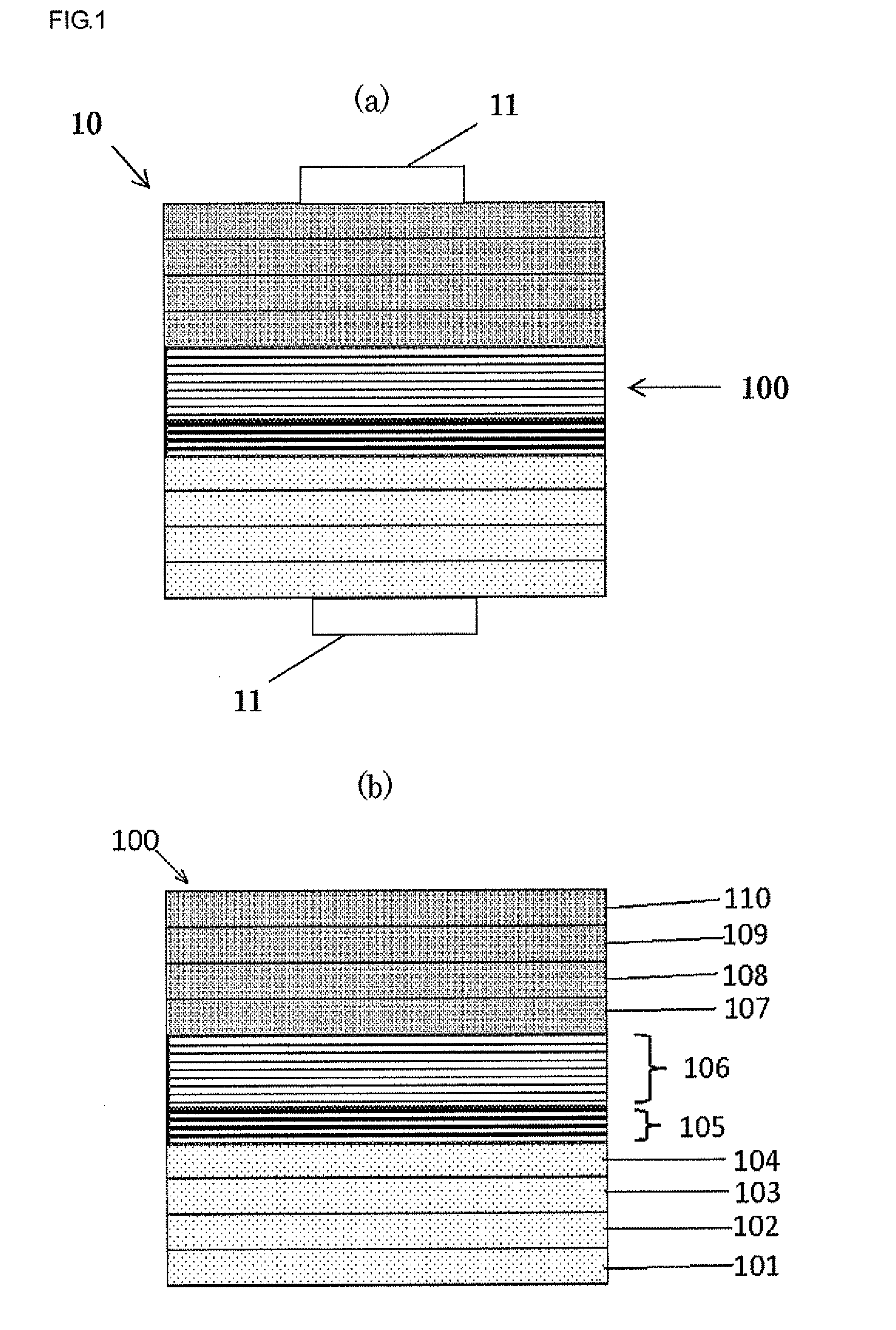
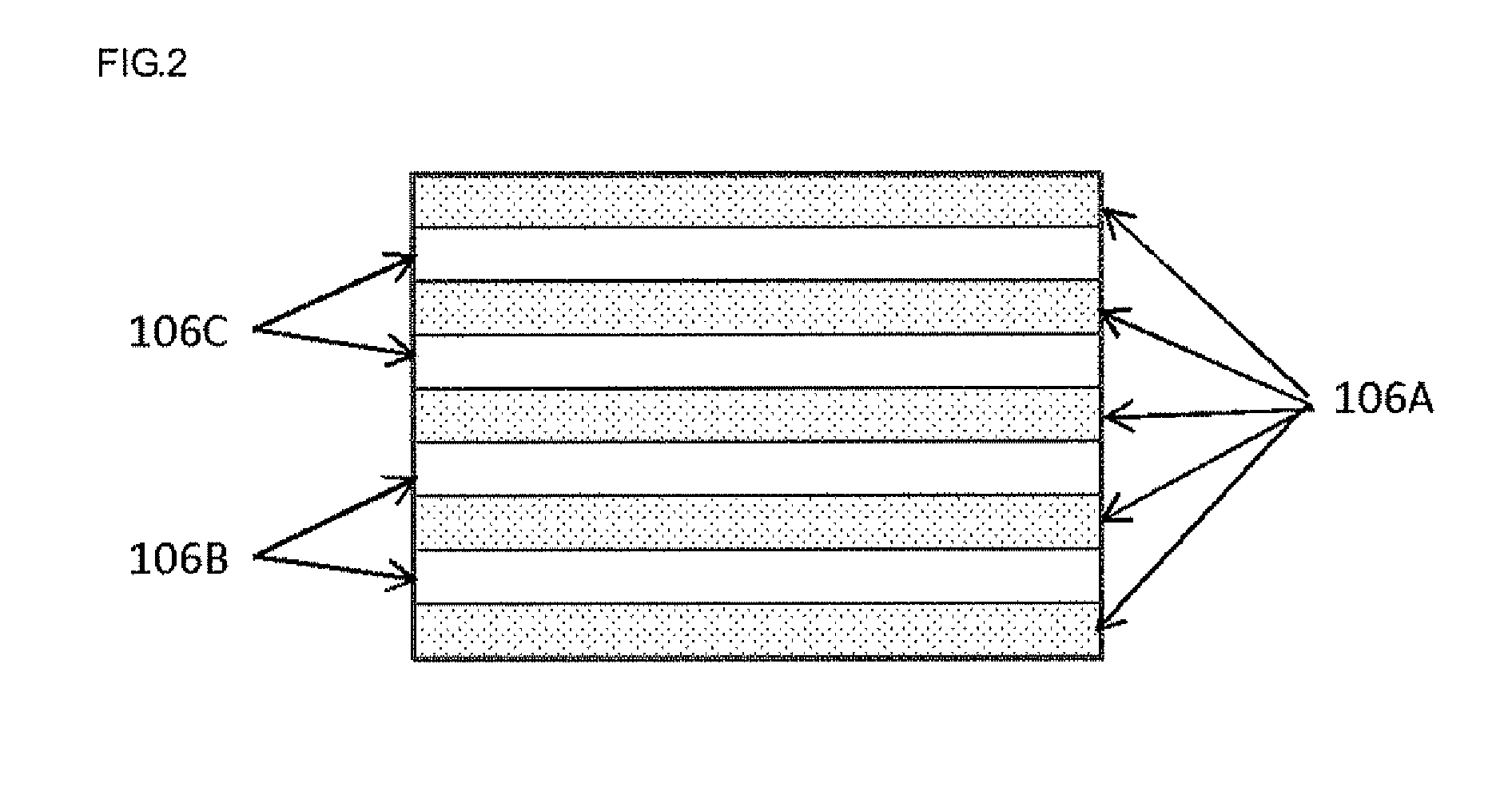
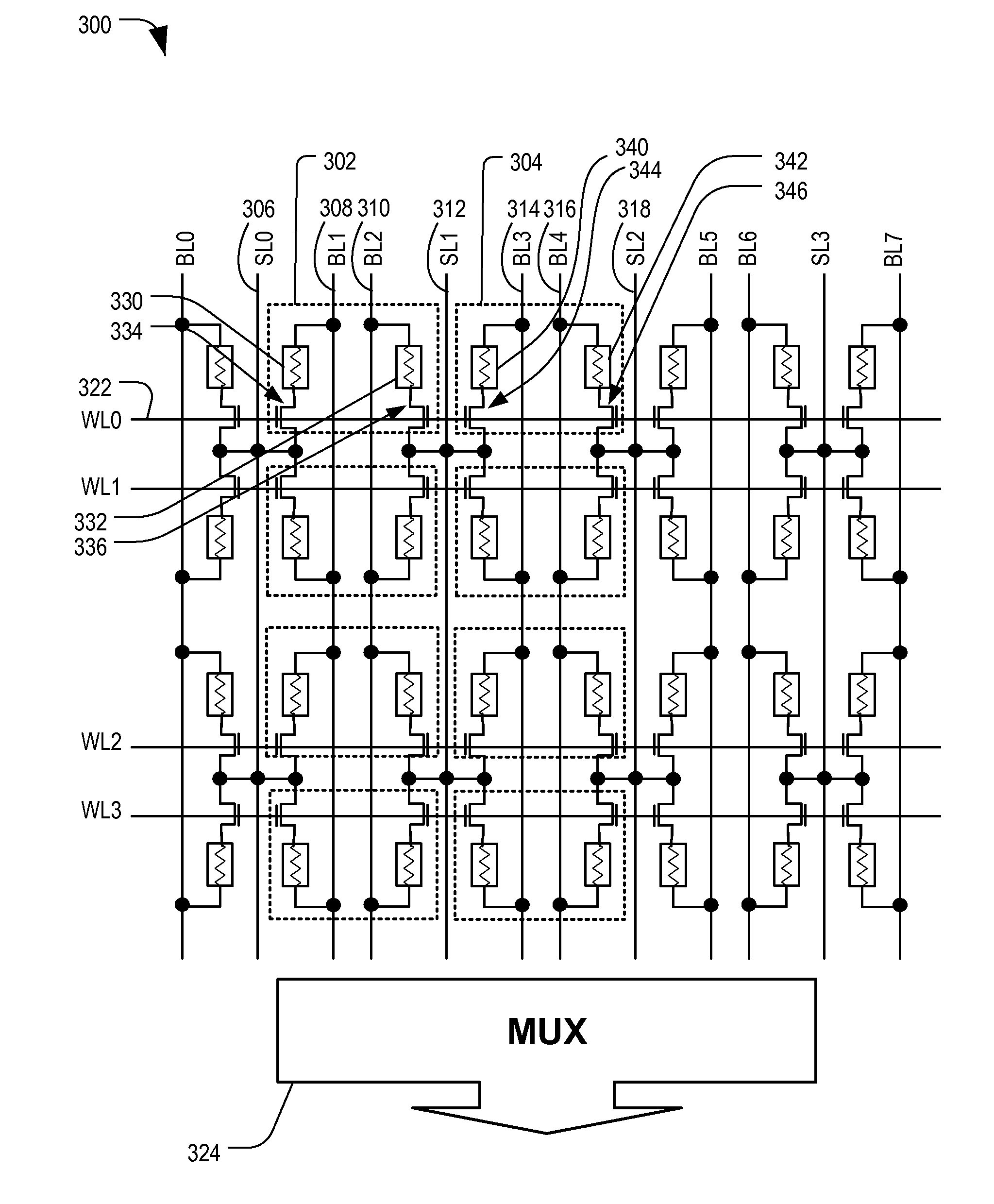
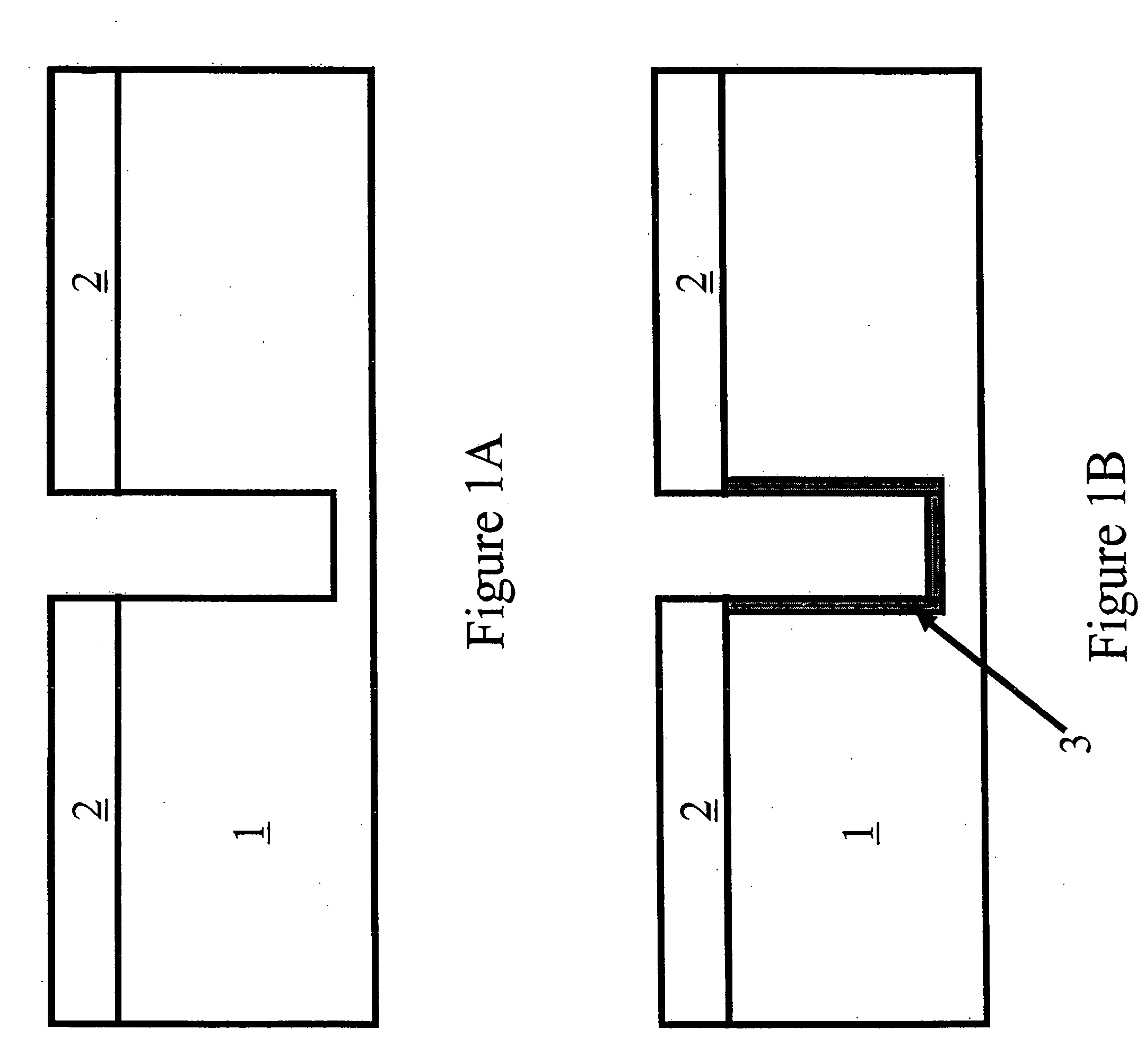
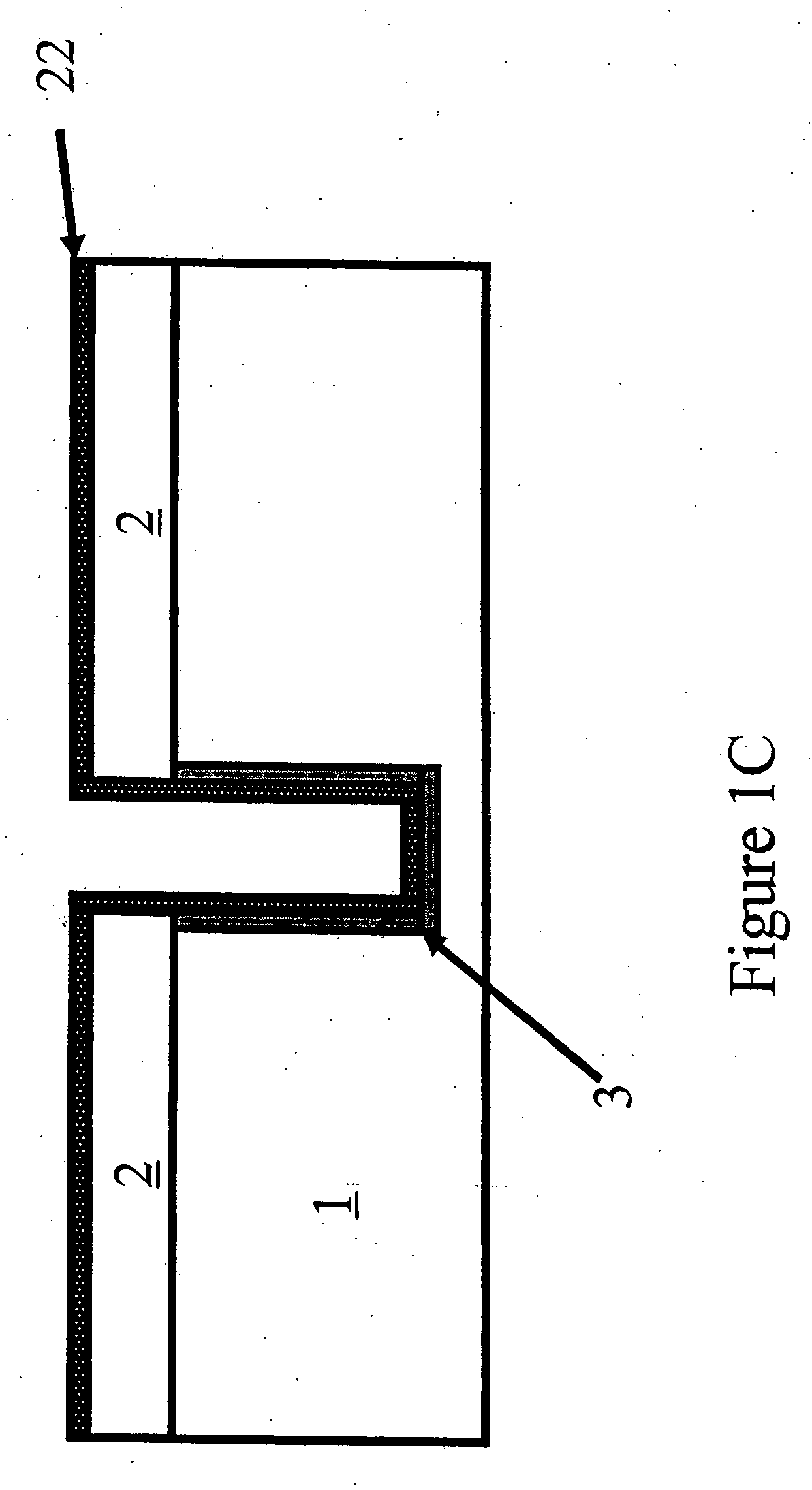
Patents
Literature
86results about How to "Reduce device area" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Improved on/off ratio for non-volatile memory device and method
ActiveUS20120012806A1Quick switchWide rangeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBulk negative resistance effect devicesSwitched currentEngineering
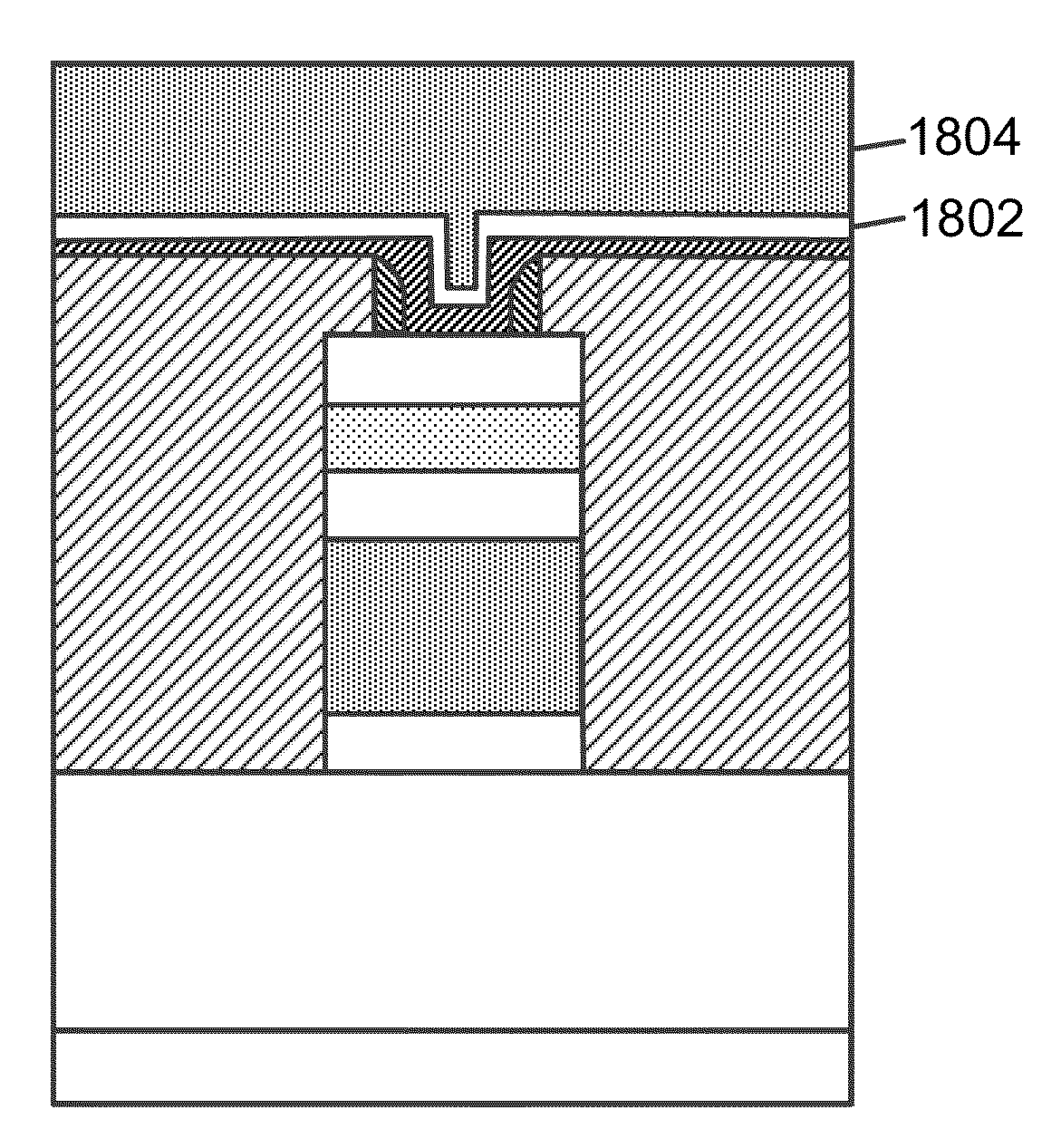
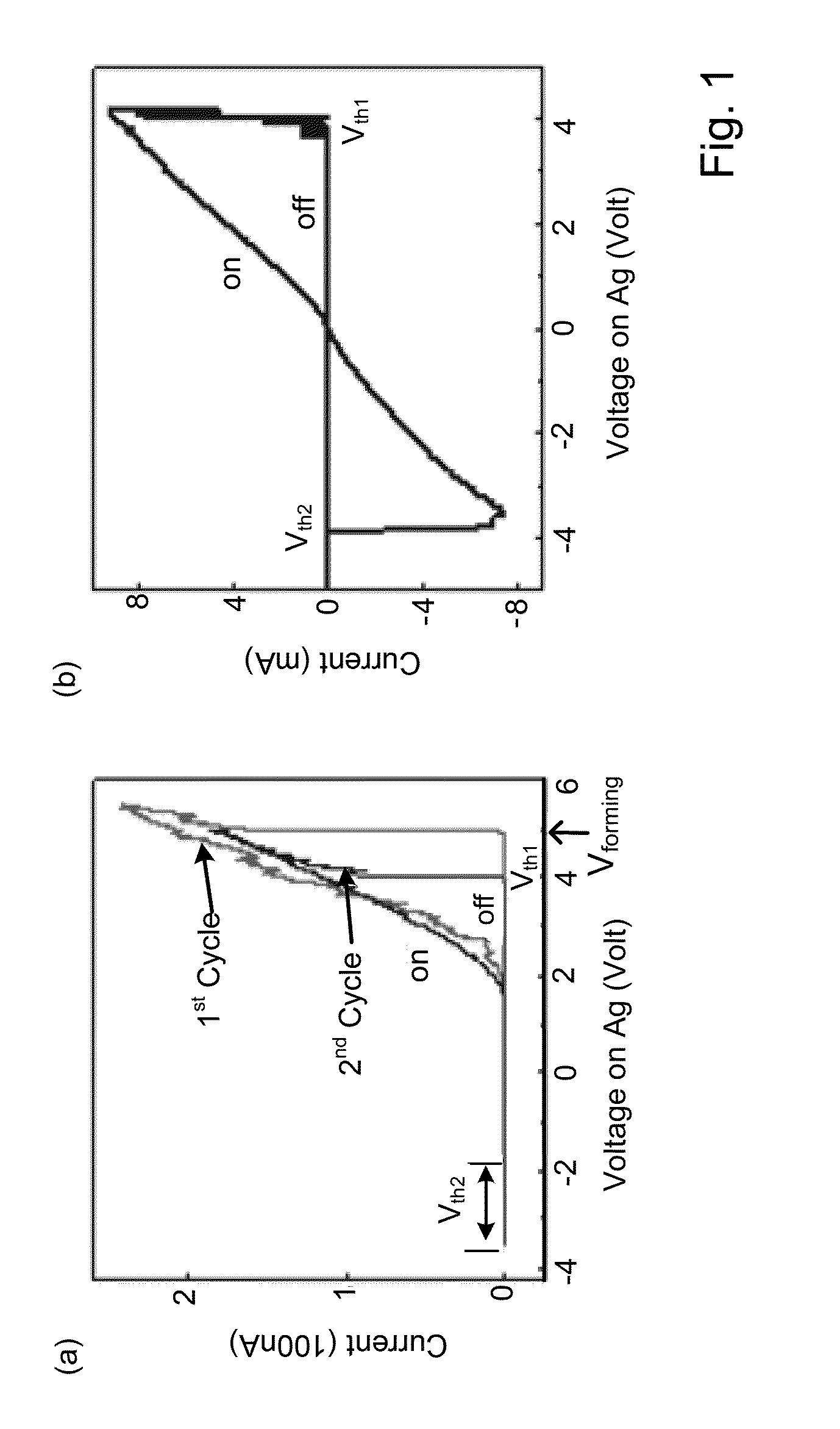
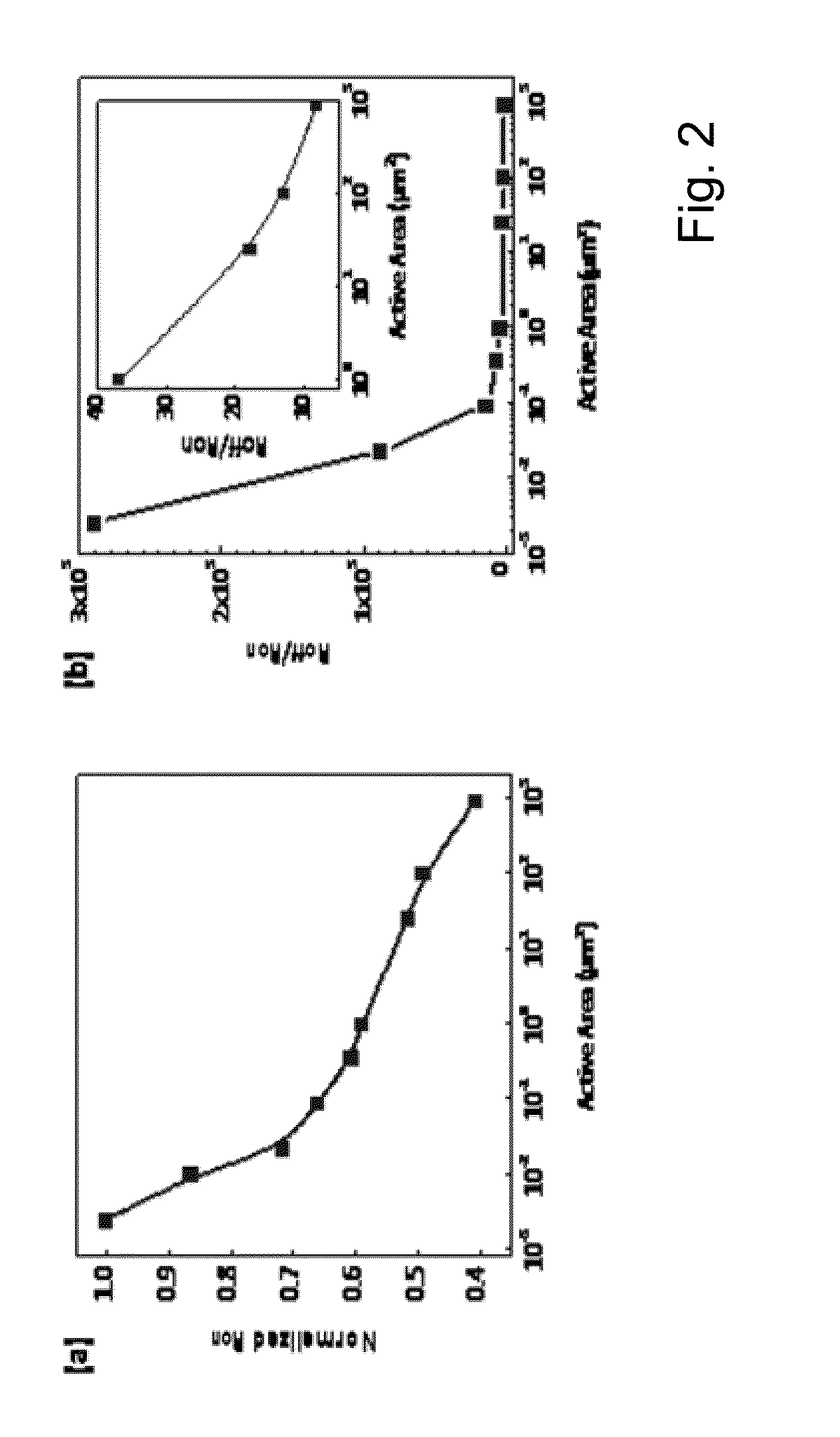
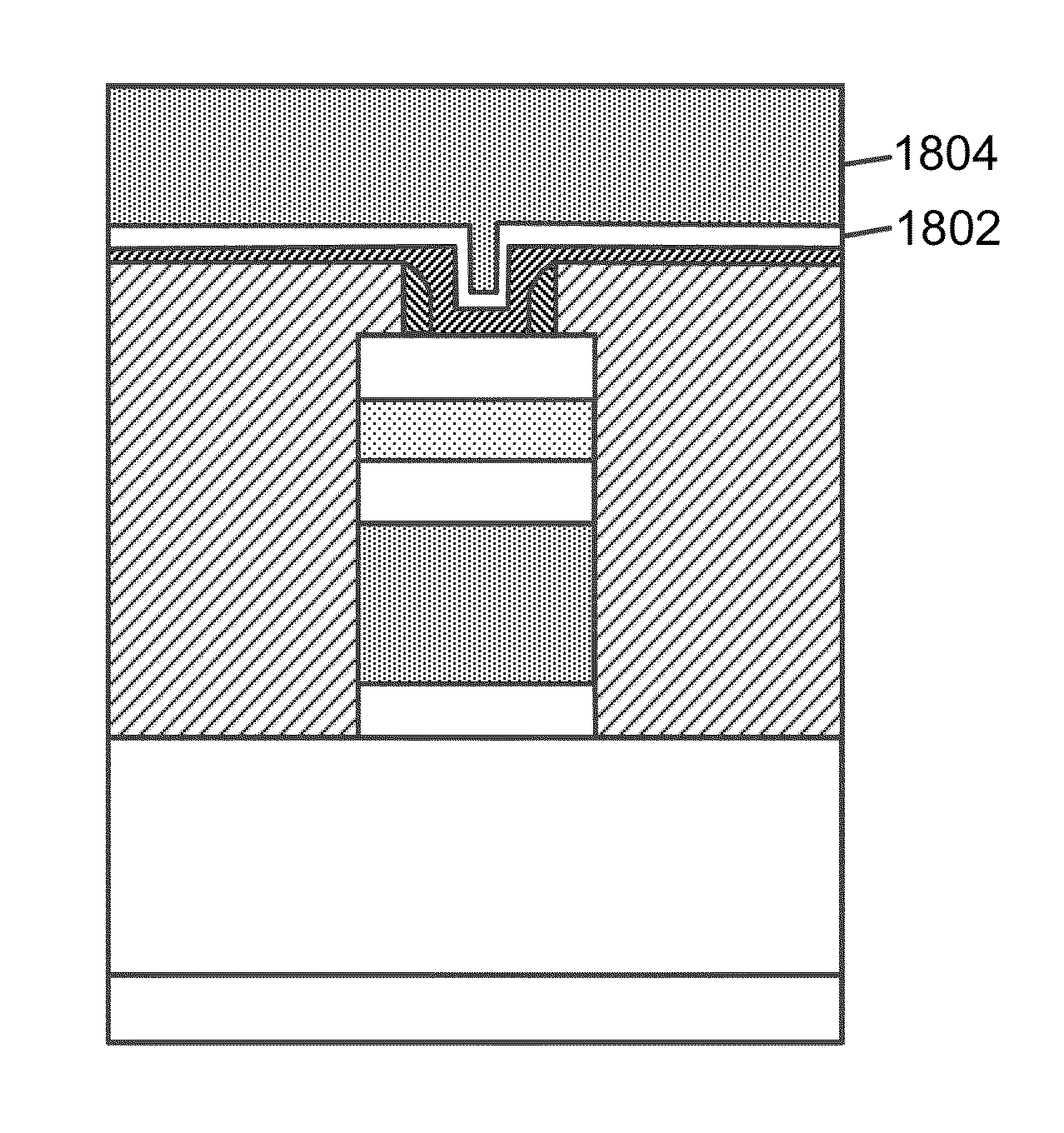
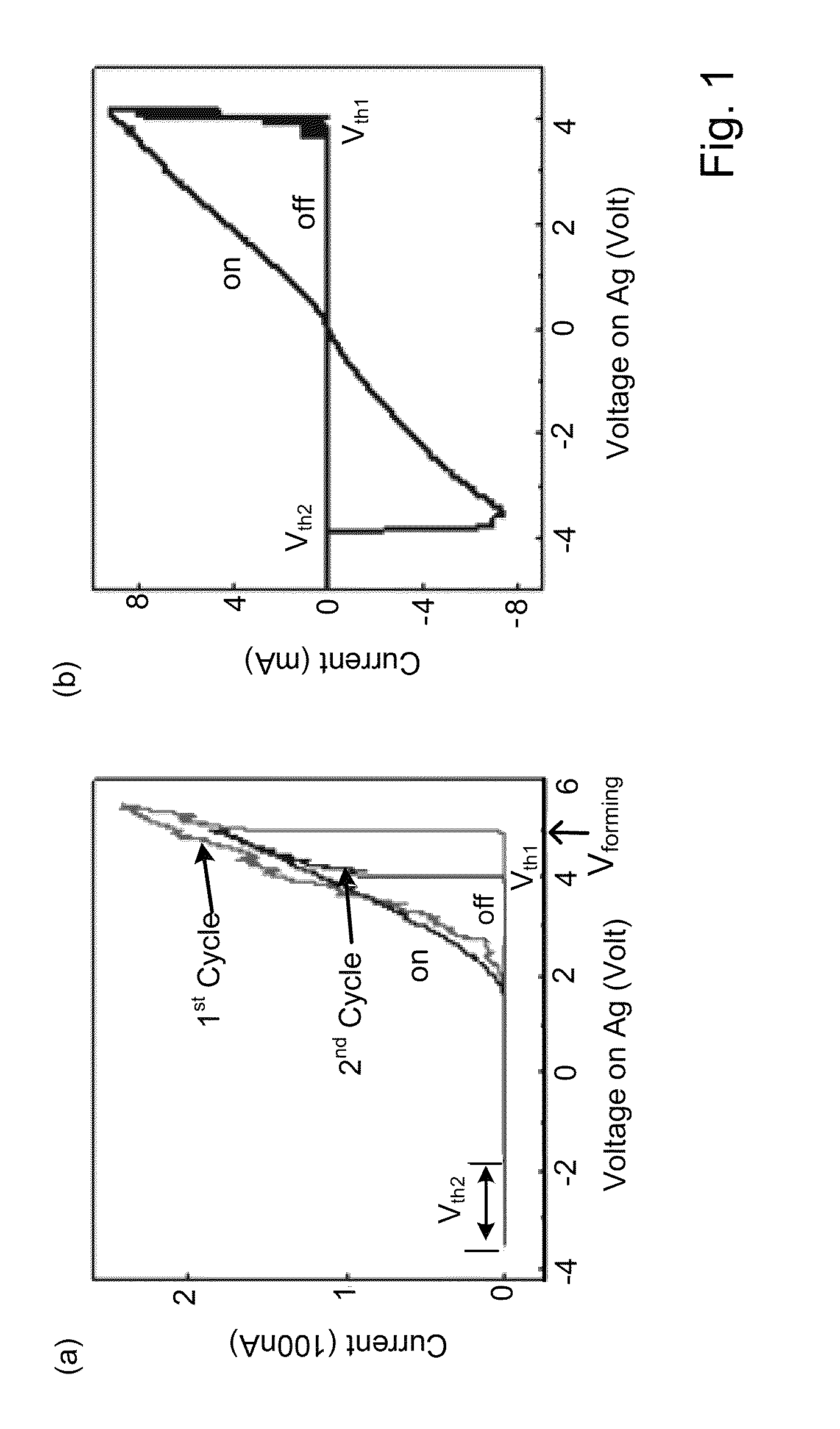
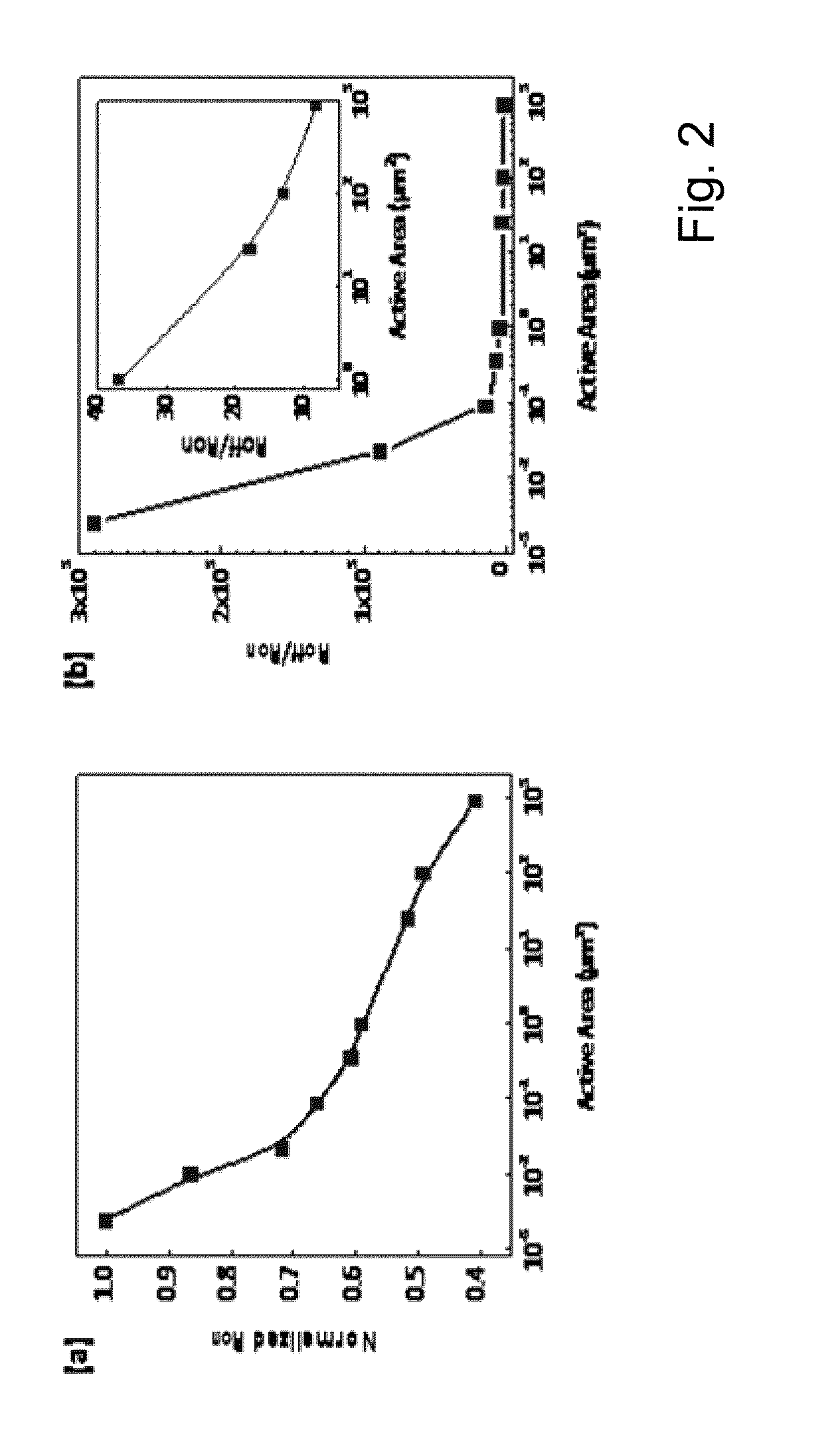
This application describes a method of forming a switching device. The method includes forming a first dielectric material overlying a surface region of a substrate. A bottom wiring material is formed overlying the first dielectric material and a switching material is deposited overlying the bottom wiring material. The bottom wiring material and the switching material is subjected to a first patterning and etching process to form a first structure having a top surface region and a side region. The first structure includes at least a bottom wiring structure and a switching element having a top surface region including an exposed region of the switching element. A second dielectric material is formed overlying at least the first structure including the exposed region of the switching element. The method forms a first opening region in a portion of the second dielectric layer to expose a portion of the top surface region of the switching element. A dielectric side wall structure is formed overlying a side region of the first opening region. A top wiring material including a conductive material is formed overlying at lease the top surface region of the switching element such that the conductive material is in direct contact with the switching element. The side wall spacer reduces a contact area for the switching element and the conductive material and thus a reduced active device area for the switching device. In a specific embodiment, the reduced area provides for an increase in device ON / OFF current ratio.
Owner:CROSSBAR INC
On/off ratio for non-volatile memory device and method
ActiveUS8168506B2Improve switching characteristicsLow yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBulk negative resistance effect devicesPower flowConductive materials
This application describes a method of forming a switching device. The method includes forming a first dielectric material overlying a surface region of a substrate. A bottom wiring material is formed overlying the first dielectric material and a switching material is deposited overlying the bottom wiring material. The bottom wiring material and the switching material is subjected to a first patterning and etching process to form a first structure having a top surface region and a side region. The first structure includes at least a bottom wiring structure and a switching element having a top surface region including an exposed region of the switching element. A second dielectric material is formed overlying at least the first structure including the exposed region of the switching element. The method forms a first opening region in a portion of the second dielectric layer to expose a portion of the top surface region of the switching element. A dielectric side wall structure is formed overlying a side region of the first opening region. A top wiring material including a conductive material is formed overlying at lease the top surface region of the switching element such that the conductive material is in direct contact with the switching element. The side wall spacer reduces a contact area for the switching element and the conductive material and thus a reduced active device area for the switching device. In a specific embodiment, the reduced area provides for an increase in device ON / OFF current ratio.
Owner:CROSSBAR INC
Magnetoresistive effect element and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20060220084A1High integrationErroneous readingTransistorNanoinformaticsPhysicsMagnetoresistance
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
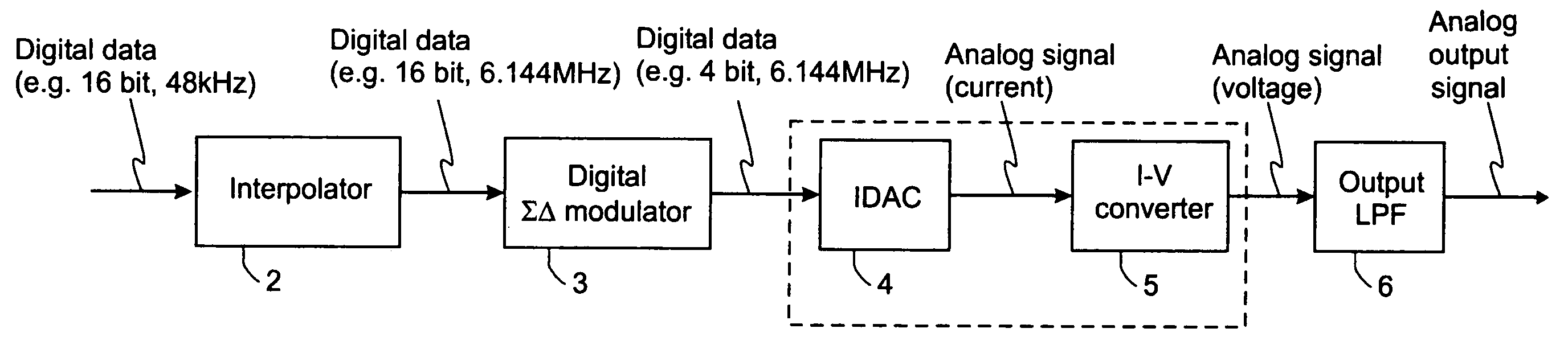
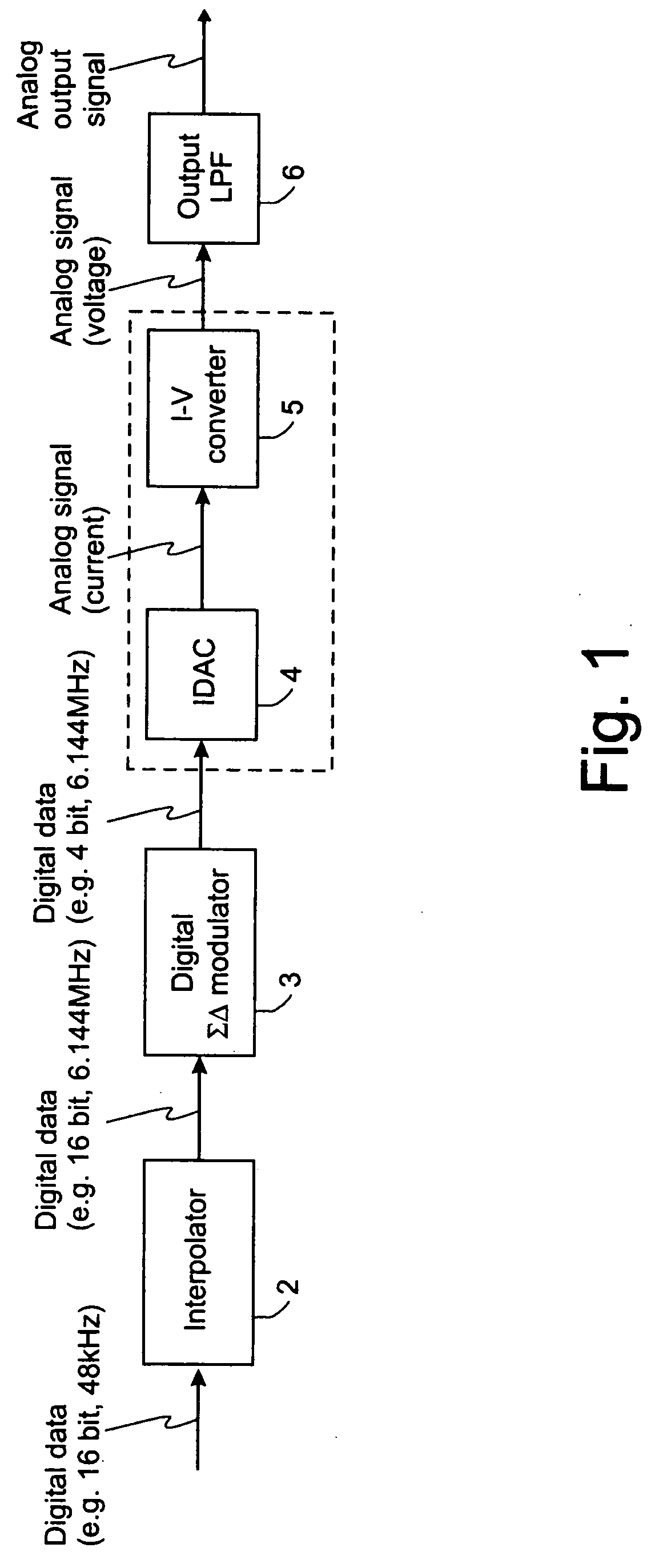
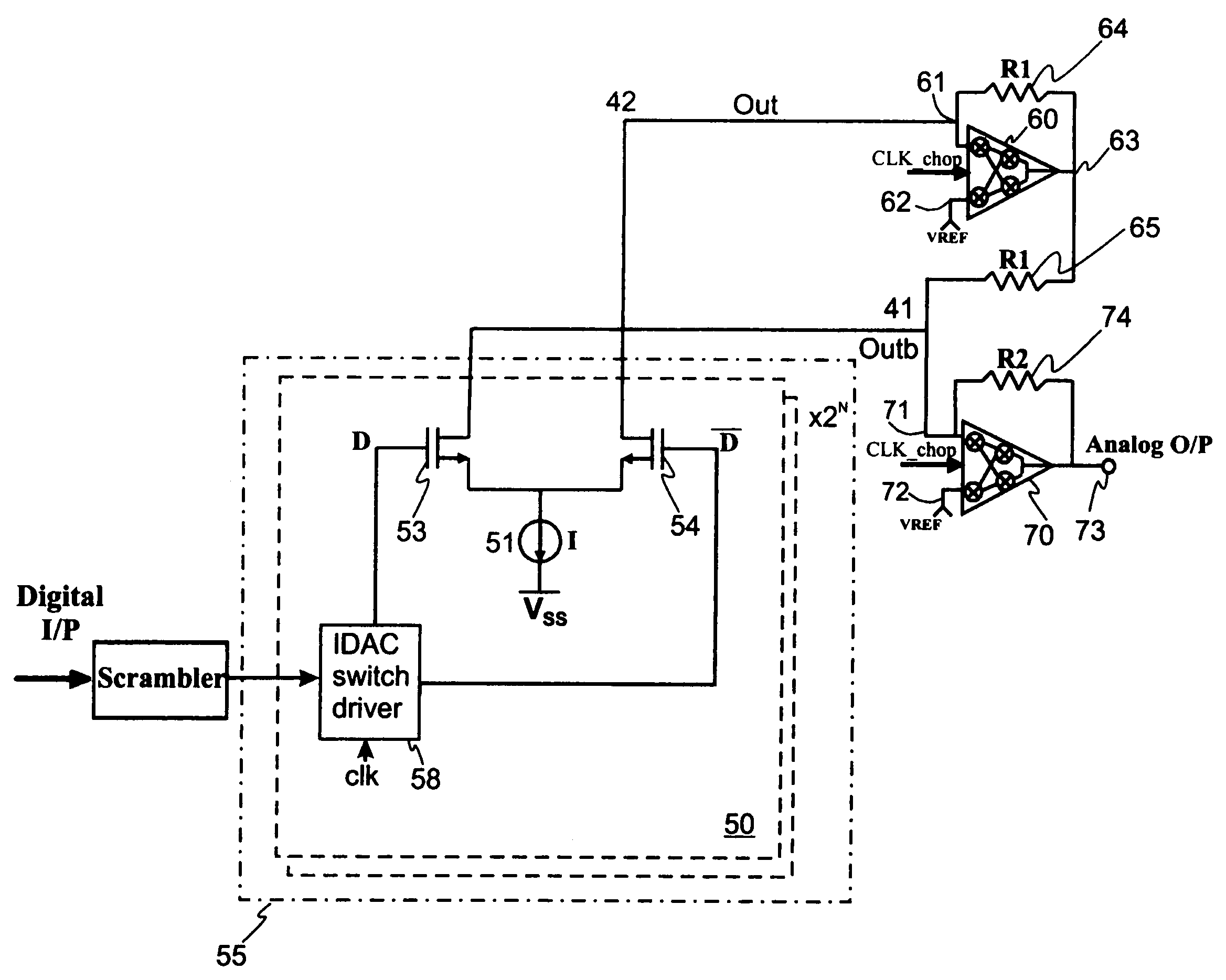
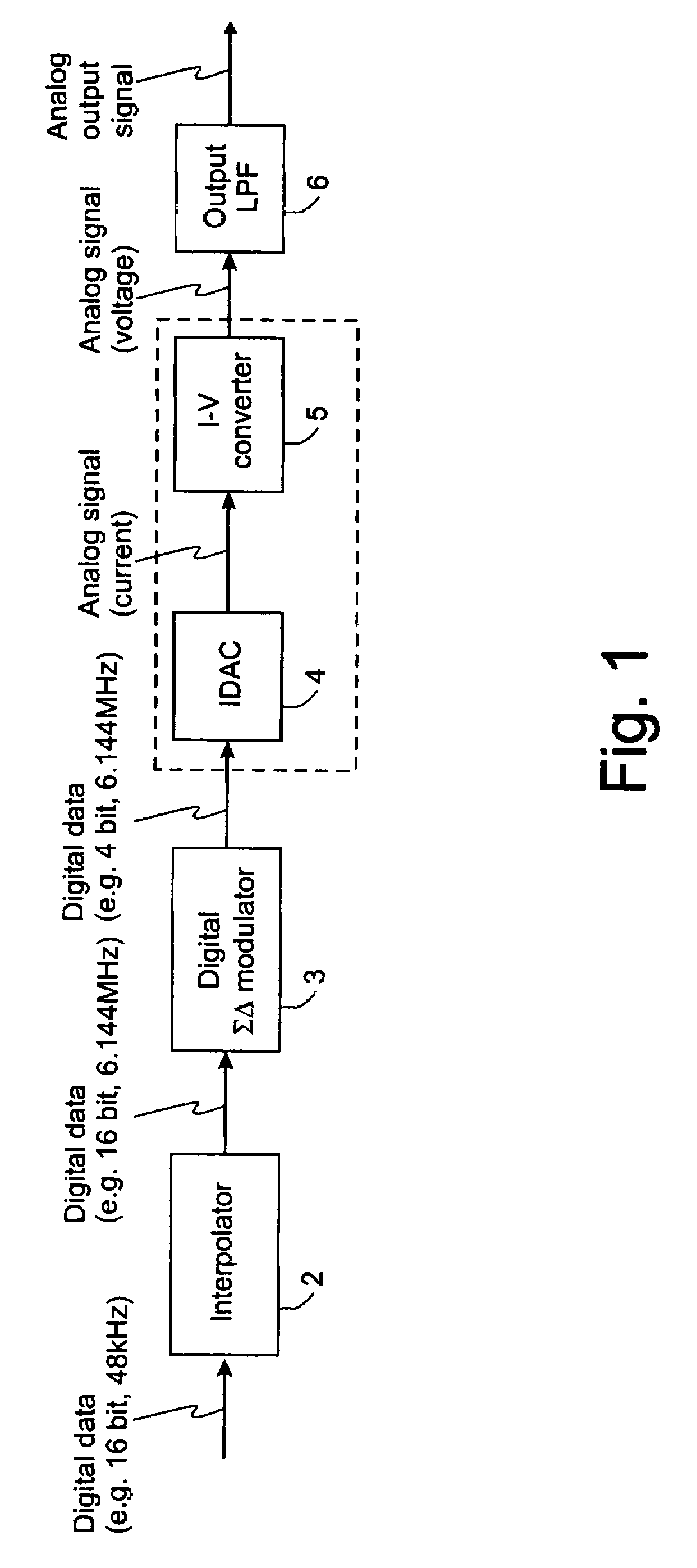
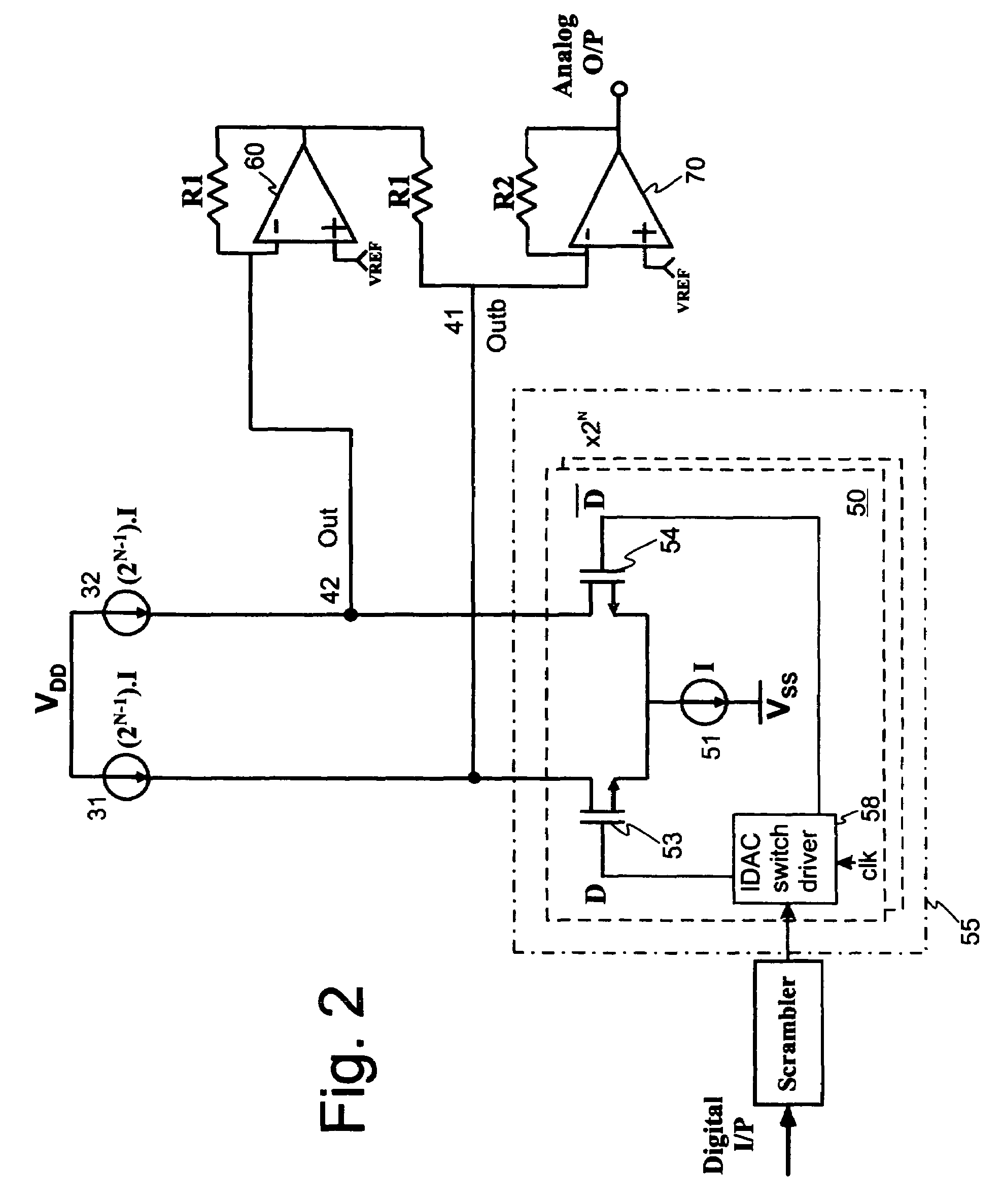
Continuous-time-sigma-delta DAC using chopper stabalisation
ActiveUS20060139193A1Reduce flicker noiseRemove flicker noiseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionVoltage converterGreek letter sigma
A sigma-delta digital-to-analog converter comprises a current digital-to-analog converter (IDAC) stage which generates a current depending on an input digital signal. An output current-to-voltage converter converts the generated signal to a voltage on a continuous-time basis. The amplifier used in the output current-to-voltage converter is chopper-stabilized. The converter can be single bit or multi-bit. The IDAC stage can be implemented with a pair of branches, a first branch comprising a first biasing current source and a second branch comprising a second biasing current source. The biasing current sources can be chopper-stabilized by connecting the bias current sources to the output current-to-voltage converter by a set of switches. The switches connect the biasing current sources to the output current-to-voltage converter in a first configuration and a second, reversed, configuration. This modulates flicker noise contributed by the bias current sources to the chopping frequency. from where it can be removed by filtering downstream of the current-to-voltage converter.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Bond pad with integrated transient over-voltage protection
ActiveUS8222698B2Small footprintTriggered quicklyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringTransistor
In various embodiments, the invention relates to bond pad structures including planar transistor structures operable as over-voltage clamps.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Thin film transistor device with high symmetry
InactiveUS20070215942A1High symmetryIncreased complexitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGrain boundaryCircuit design
A thin film transistor device with high symmetry is disclosed, in which the symmetrical structure of transistor is utilized to enable currents flowing in the channels of each transistor formed on a polysilicon film of a specific crystallization direction to pass the same amount of grain boundaries, thereby improving the uniformity of electrical characteristics of the device. By the thin film transistor device of the invention, not only the freedom of circuit design is increased, but also the circuit area of a TFT device occupied is reduced.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
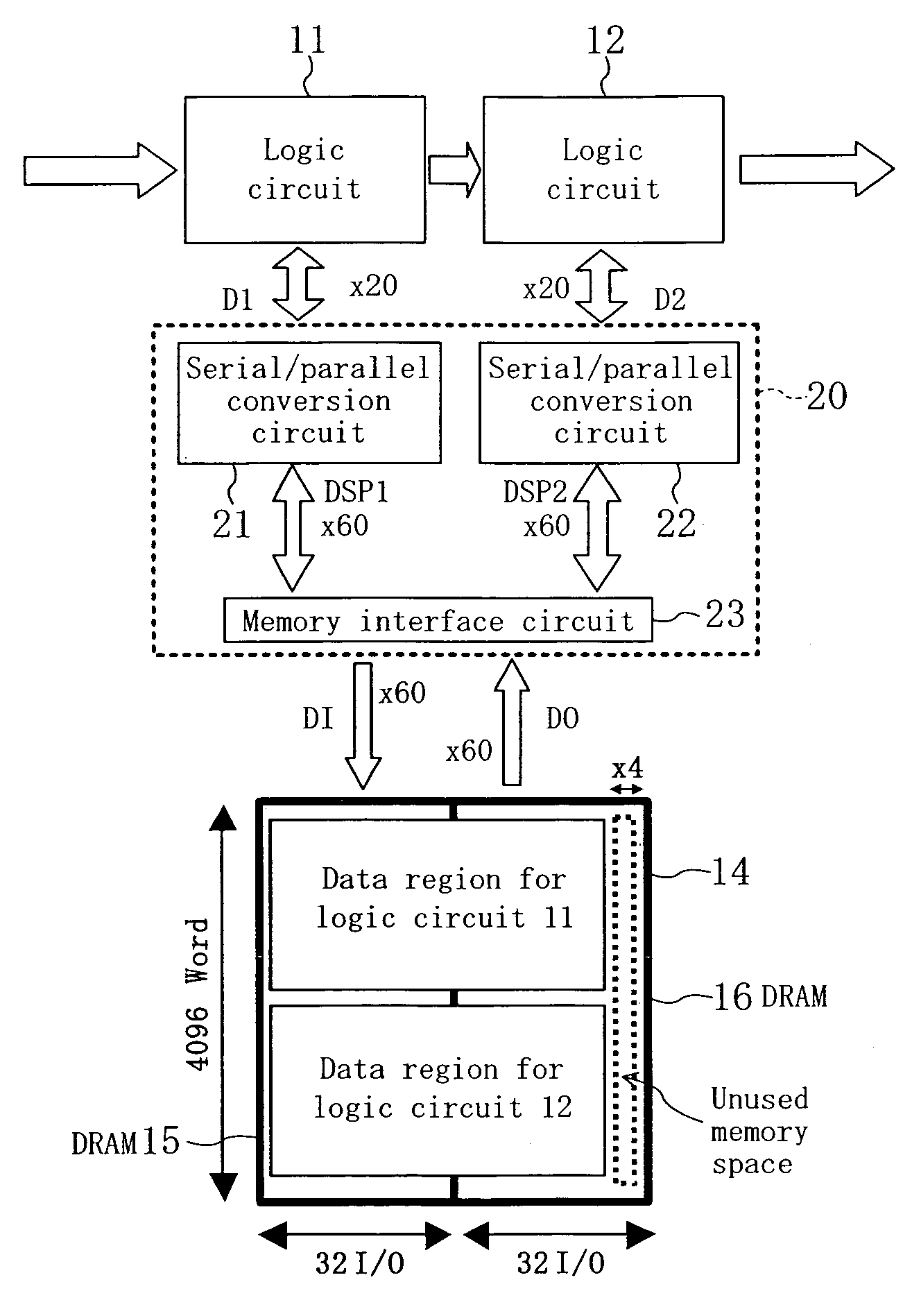
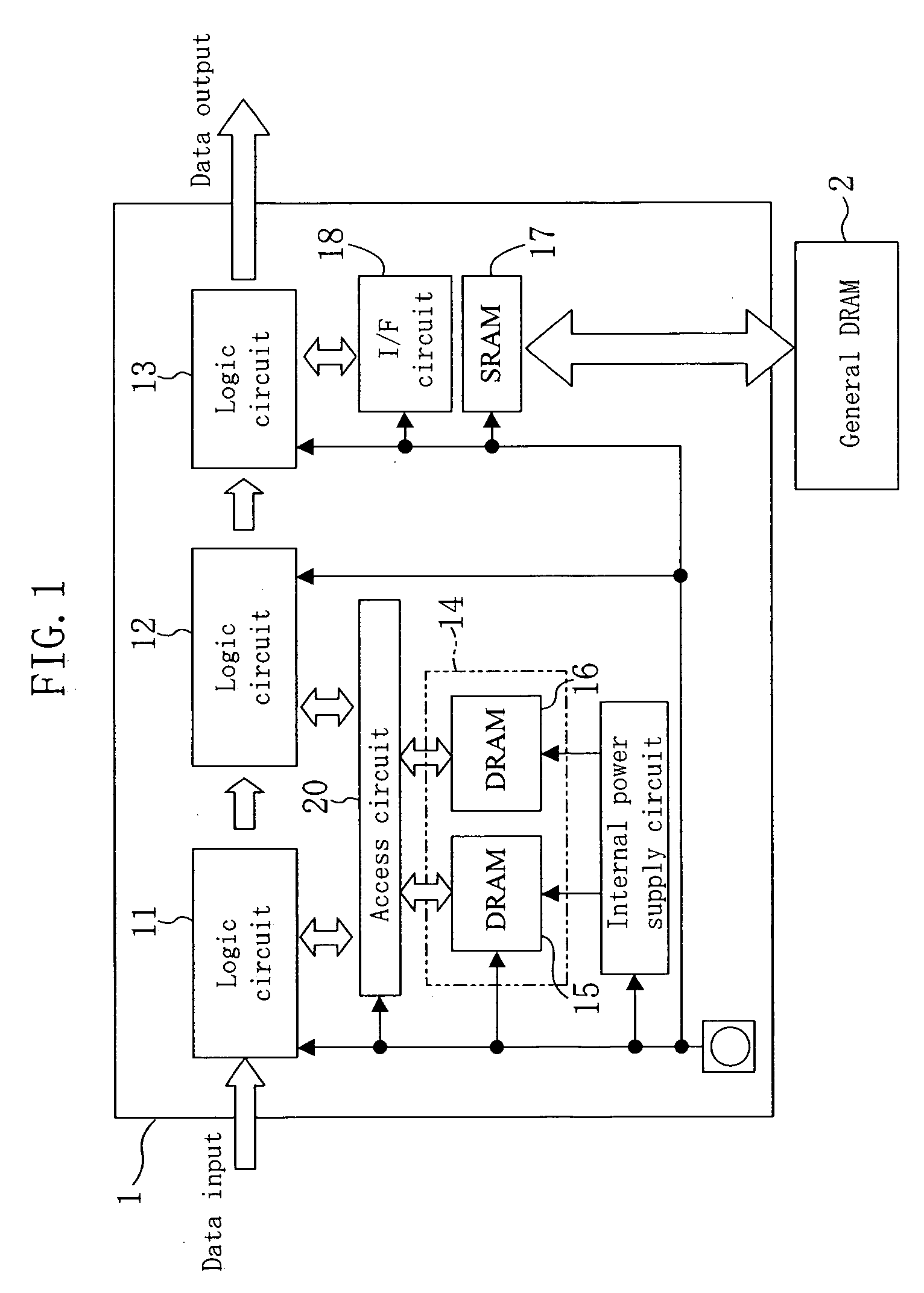
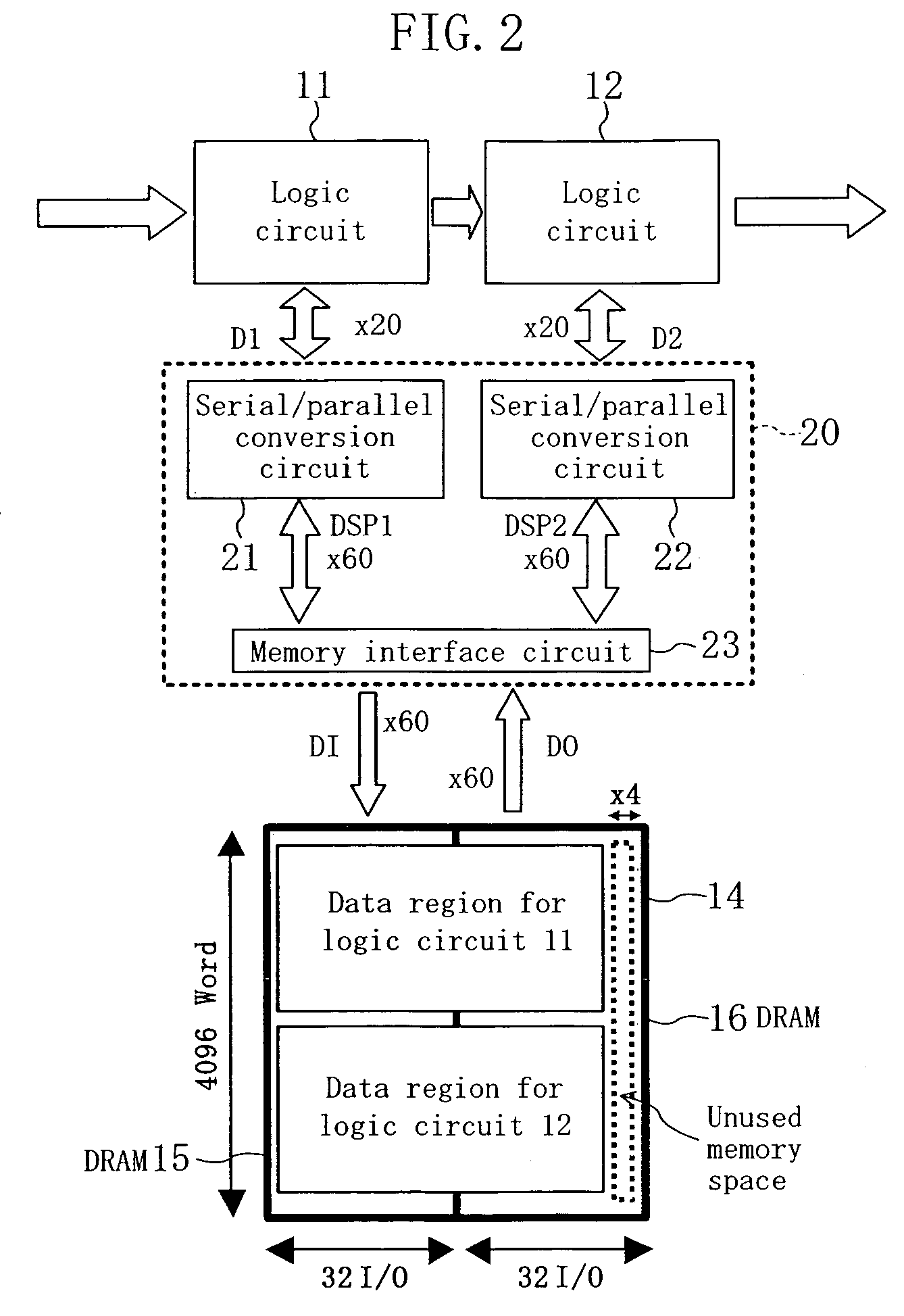
Semiconductor integrated circuit device having a common DRAM block accessed by a plurality of logic circuits
ActiveUS6990043B2Lower capability requirementsReduce areaMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageHemt circuitsComputer science
A plurality of logic circuits access a DRAM block by way of an access circuit. The operation clock for the DRAM block is set at a higher frequency than the system clock for the logic circuits. Outputs of a first bit width from the logic circuits are subjected to serial / parallel conversion into data of a second bit width and the data is written into the DRAM block.
Owner:CETUS TECH INC
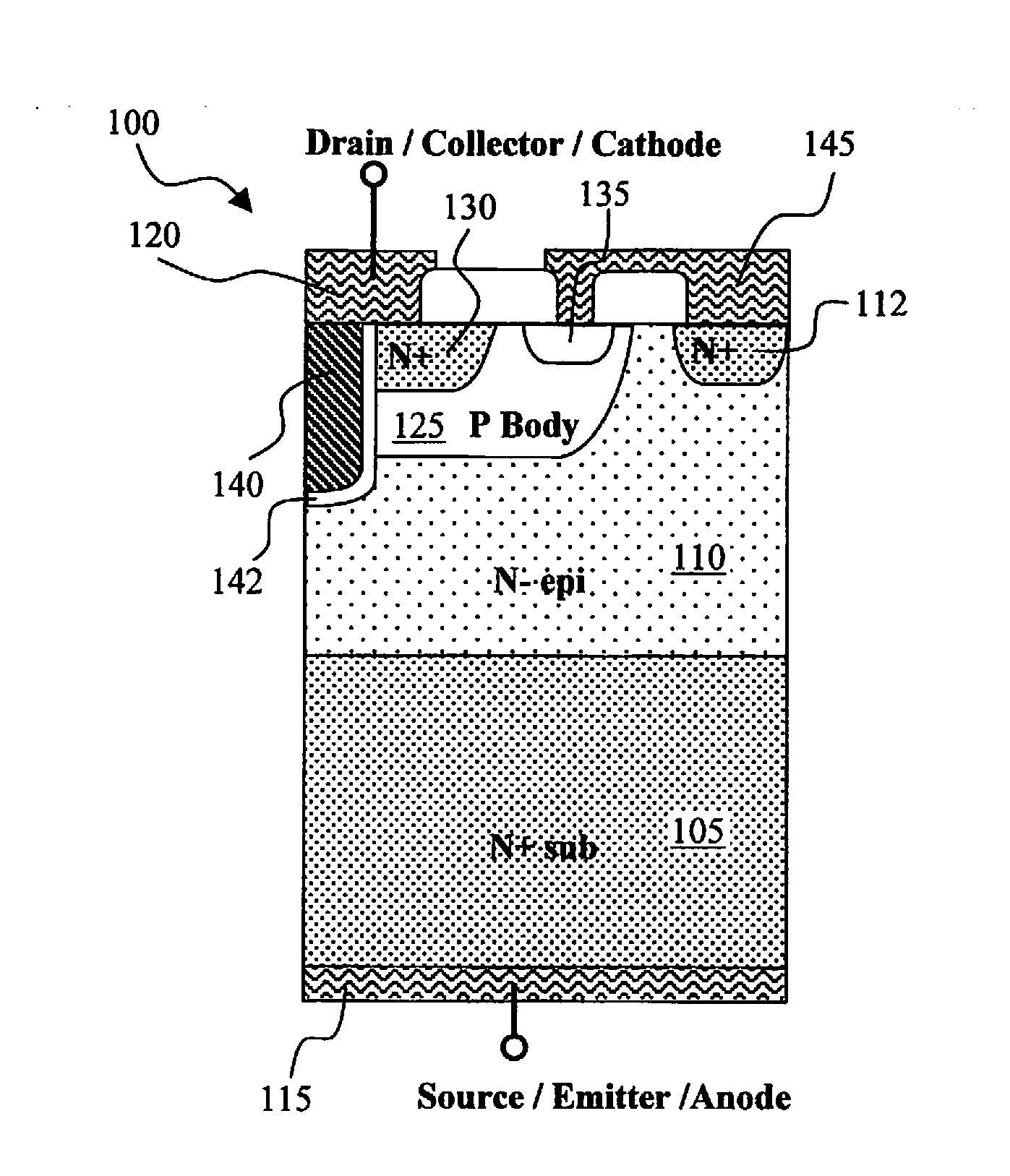
Bottom source NMOS triggered zener clamp for configuring an ultra-low voltage transient voltage suppressor (TVS)
ActiveUS20100321840A1Easy clampingReduce voltageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETBody contact
A low voltage transient voltage suppressing (TVS) device supported on a semiconductor substrate supporting an epitaxial layer thereon. The TVS device further includes a bottom-source metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (BS-MOSFET) comprises a trench gate surrounded by a drain region encompassed in a body region disposed near a top surface of the semiconductor substrate wherein the drain region interfaces with the body region constituting a junction diode and the drain region encompassed in the body region on top of the epitaxial layer constituting a bipolar transistor with a top electrode disposed on the top surface of the semiconductor functioning as a drain / collector terminal and a bottom electrode disposed on a bottom surface of the semiconductor substrate functioning as a source / emitter electrode. The body regions further comprises a surface body contact region electrically connected to a body-to-source short-connection thus connecting the body region to the bottom electrode functioning as the source / emitter terminal. The gate may be shorted to the drain for configuring the BS-MOSFET transistor into a two terminal device with a gate-to-source voltage equal to a drain-to-source voltage. The drain / collector / cathode terminal disposed on top of the trench gate turns on the BS-MOSFET upon application of a threshold voltage of the BS-MOSFET thus triggering the bipolar transistor for clamping and suppressing a transient voltage substantially near a threshold voltage of the BS-MOSFET.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
Light-emitting device
The present invention provides a light-emitting device manufactured with use of a compound semiconductor substrate comprising at least: a p-type cladding layer; a multiple-active layer portion in which three or more active layers made of (AlxGa1-x)yIn1-yP (0≦x≦0.6, 0.4≦y≦0.6) and two or more barrier layers having a higher Al content rate x than the active layers are alternately laminated; and an n-type cladding layer, wherein the barrier layer on a side close to the p-type cladding layer has a smaller band gap than that of the barrier layer on a side close to the n-type cladding layer in the barrier layers, and the compound semiconductor substrate has a superlattice barrier layer between the multiple-active layer portion and the n-type cladding layer or in the n-type cladding layer. As a result, the light-emitting device having long life duration, low resistance, and high light-emitting efficiency (especially internal quantum efficiency) can be provided.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
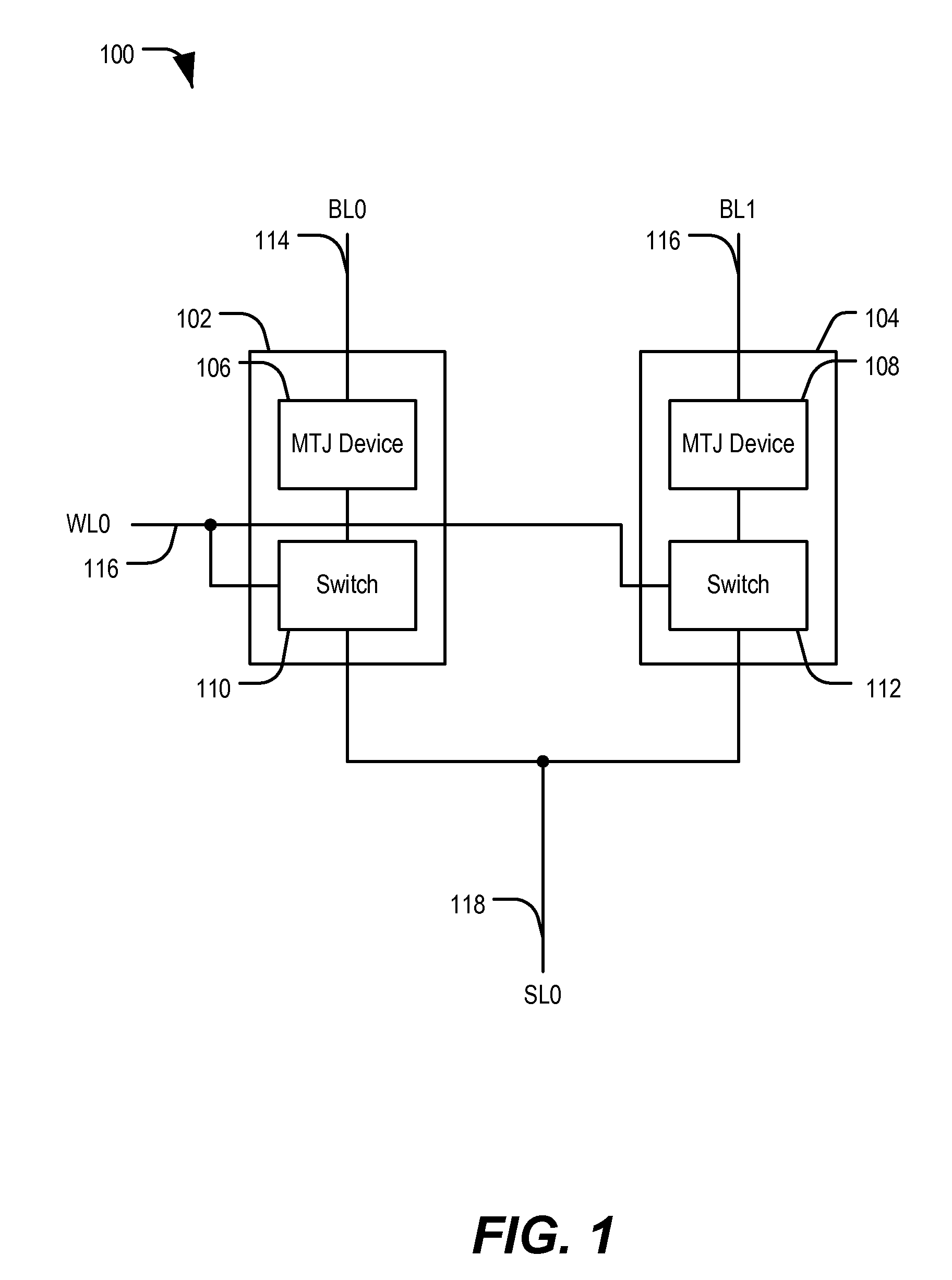
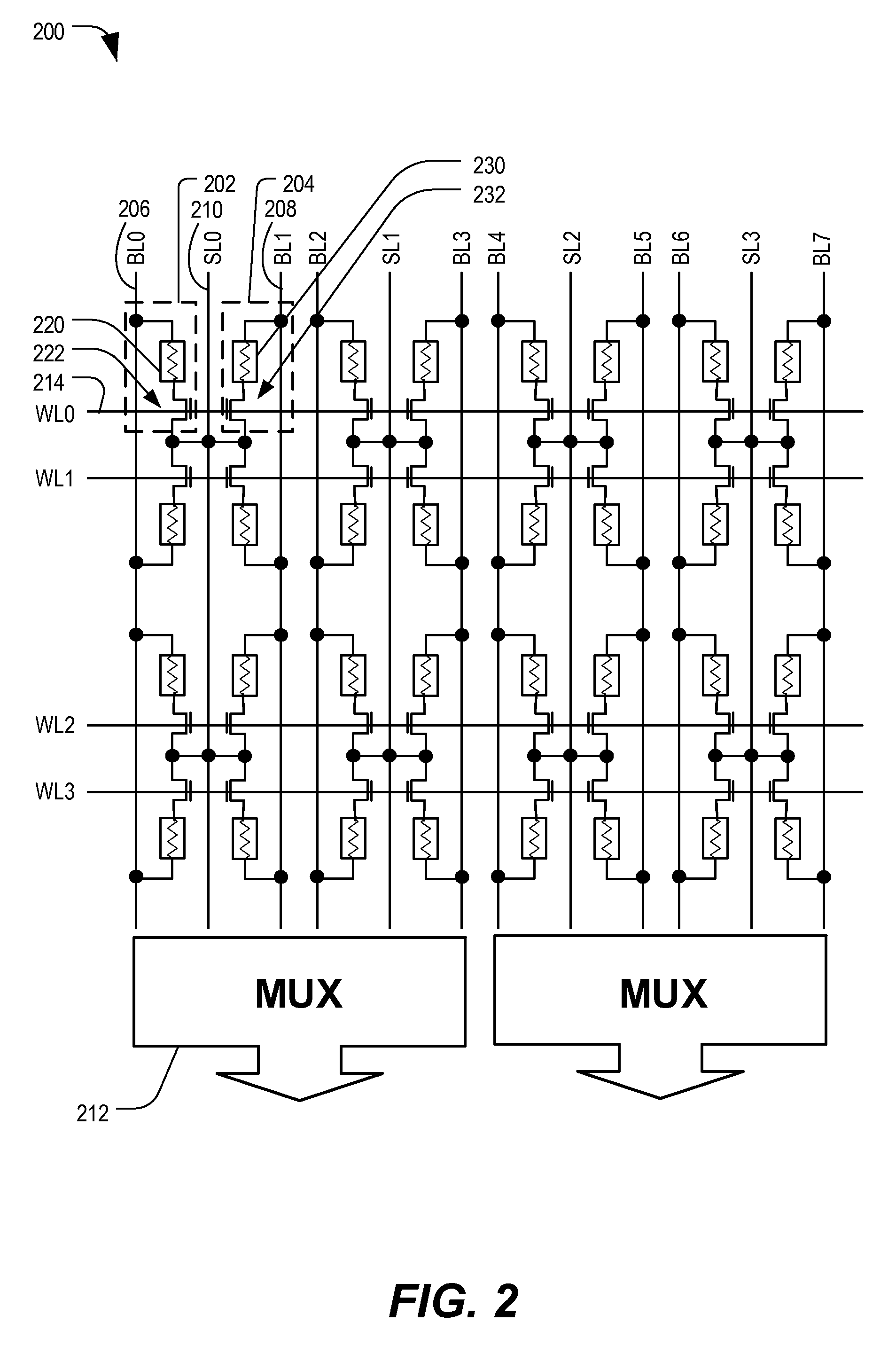
MRAM device with shared source line
In a particular embodiment, a memory device includes a first memory cell and a second memory cell. The memory device also includes a first bit line associated with the first memory cell and a second bit line associated with the second memory cell. The memory device also includes a source line coupled to the first memory cell and coupled to the second memory cell.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
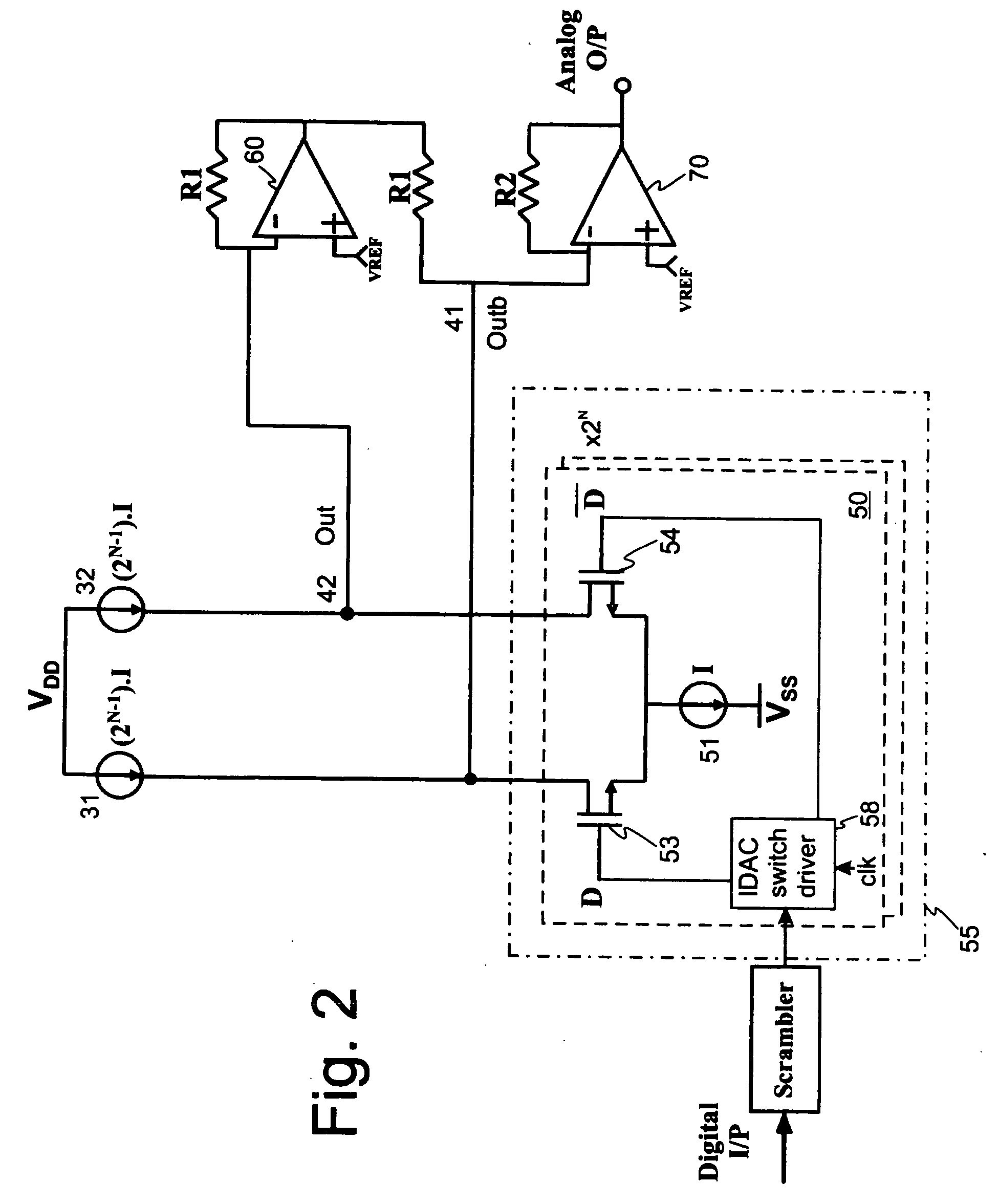
Continuous-time-sigma-delta DAC using chopper stabalization
ActiveUS7205920B2Improve performanceReduce die areaElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionVoltage converterAudio power amplifier
A sigma-delta digital-to-analog converter comprises a current digital-to-analog converter (IDAC) stage which generates a current depending on an input digital signal. An output current-to-voltage converter converts the generated signal to a voltage on a continuous-time basis. The amplifier used in the output current-to-voltage converter is chopper-stabilized. The converter can be single bit or multi-bit. The IDAC stage can be implemented with a pair of branches, a first branch comprising a first biasing current source and a second branch comprising a second biasing current source. The biasing current sources can be chopper-stabilized by connecting the bias current sources to the output current-to-voltage converter by a set of switches. The switches connect the biasing current sources to the output current-to-voltage converter in a first configuration and a second, reversed, configuration. This modulates flicker noise contributed by the bias current sources to the chopping frequency. from where it can be removed by filtering downstream of the current-to-voltage converter.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
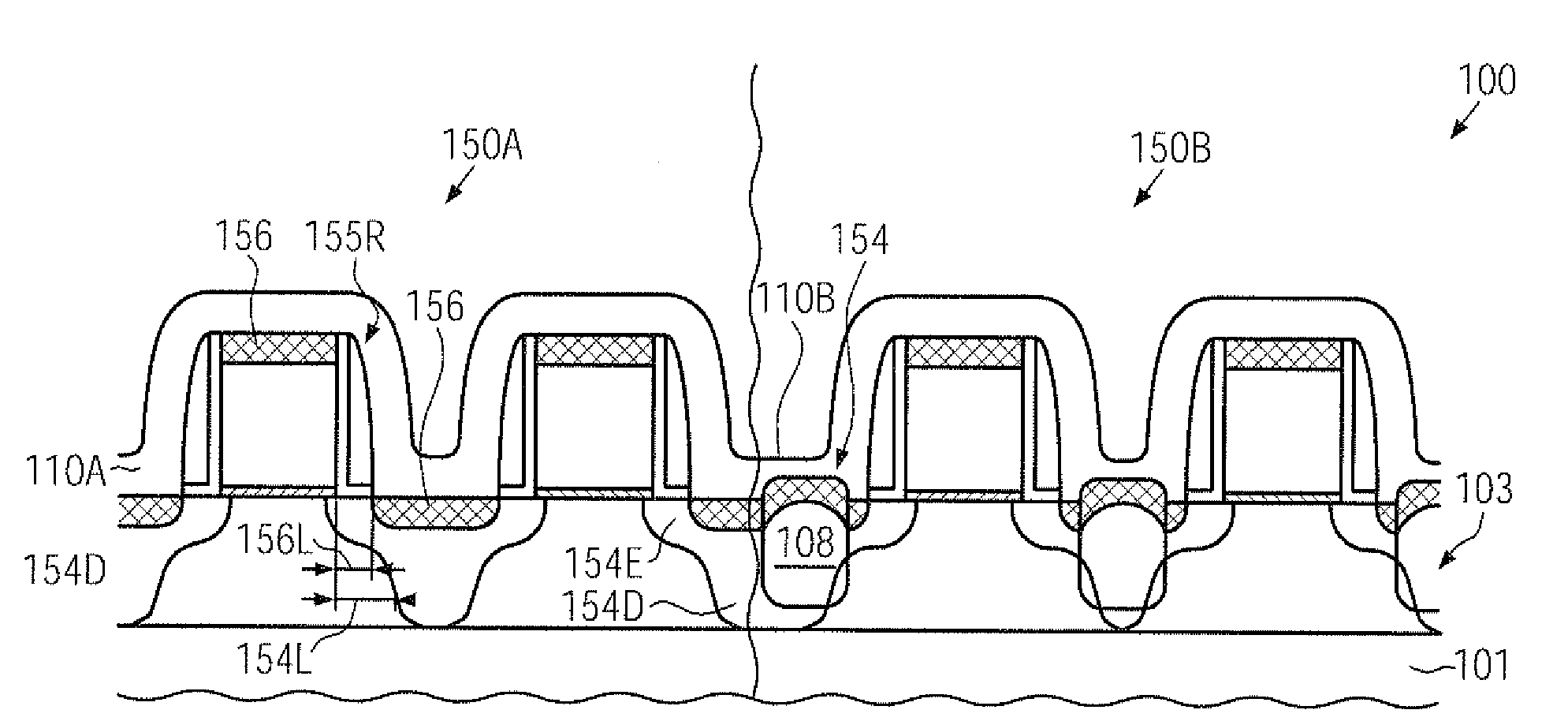
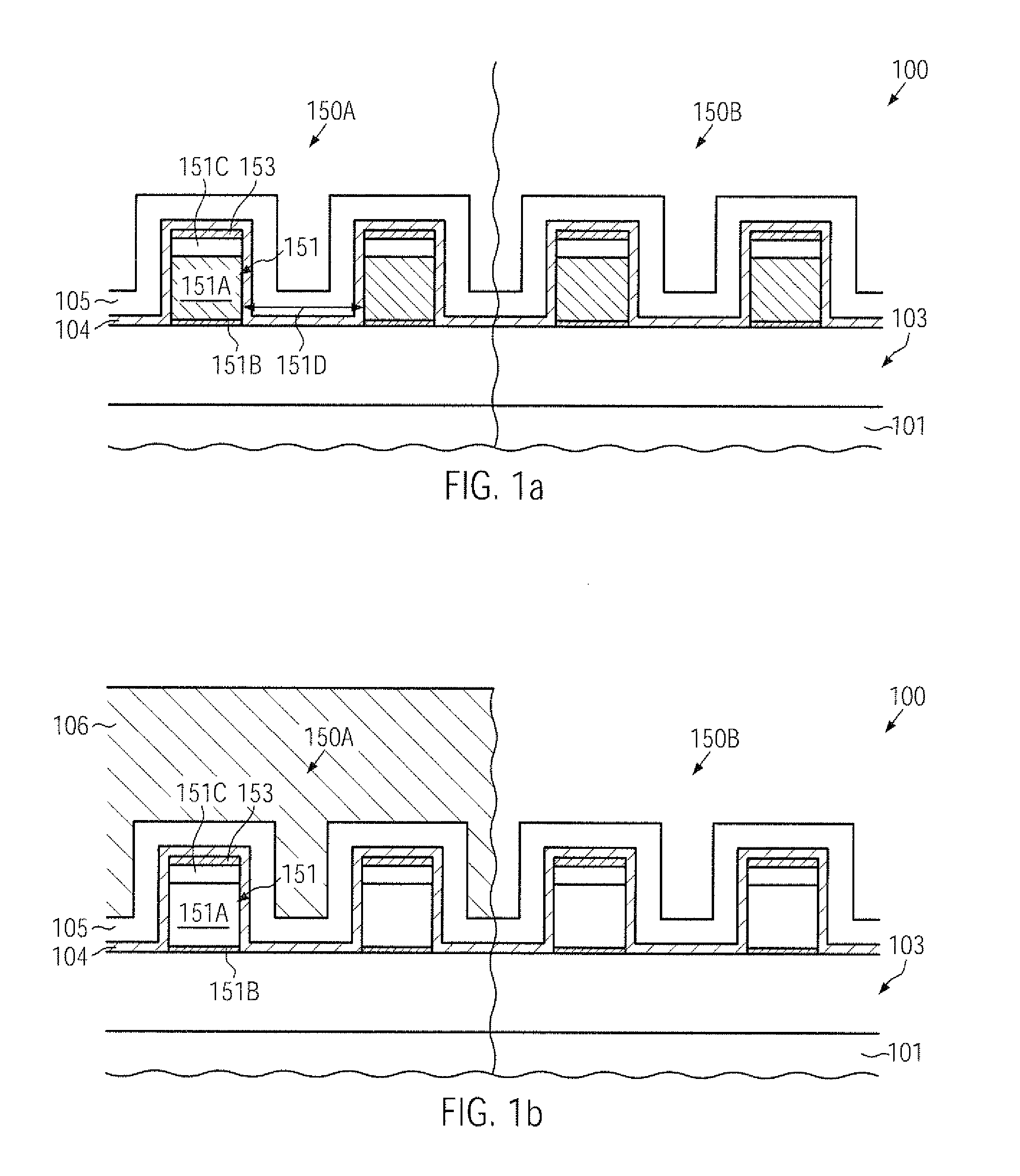
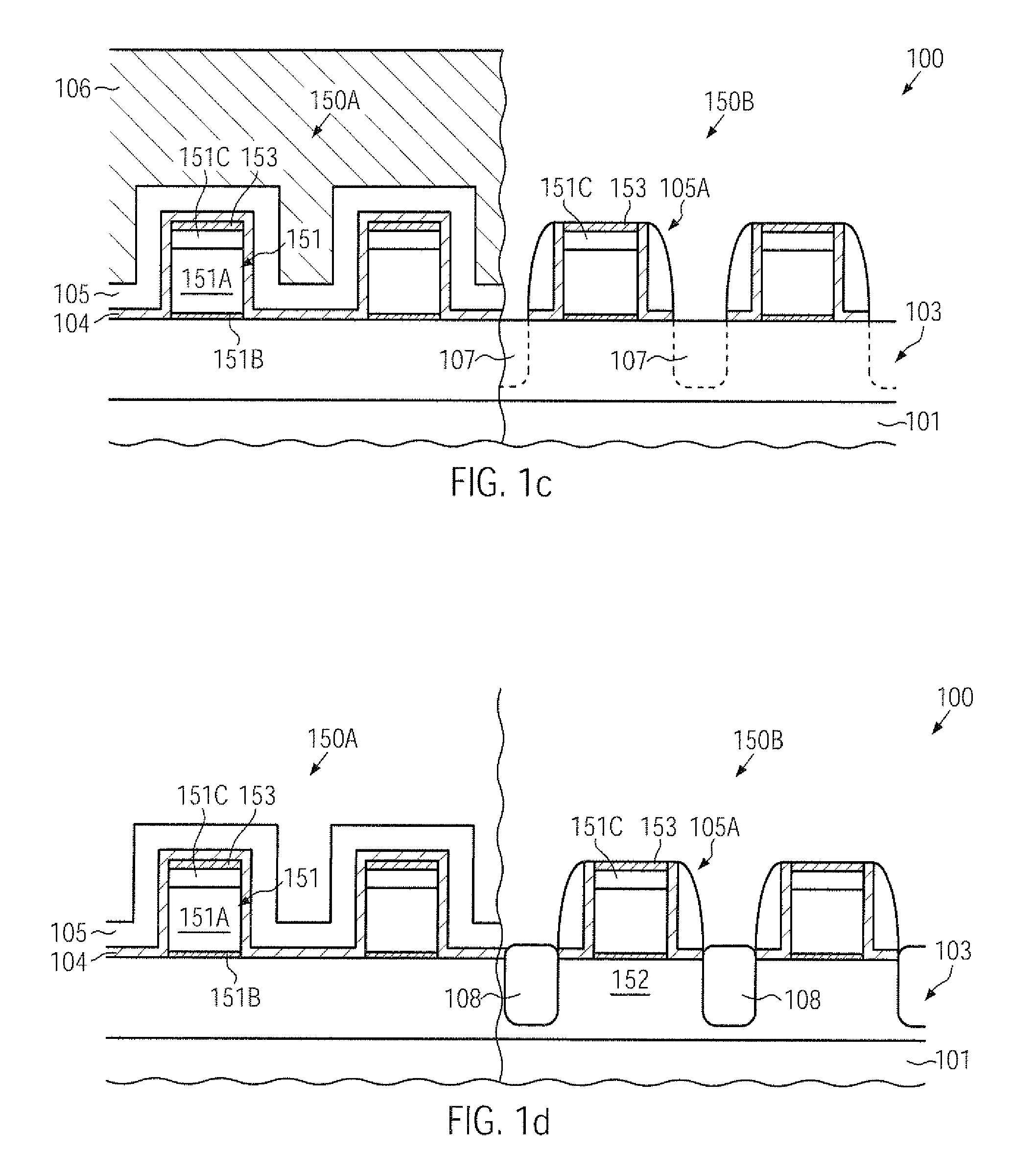
CMOS device comprising nmos transistors and pmos transistors having increased strain-inducing sources and closely spaced metal silicide regions
InactiveUS20100078735A1Reduce widthImprove controllabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSalicideMetal silicide
In a CMOS manufacturing process flow, a cap layer formed on top of a gate electrode material may be maintained throughout the entire implantation sequence for defining the drain and source regions and may be removed during an etch process in which the width of a sidewall spacer structure may be reduced so as to reduce a lateral offset of metal silicide regions and of a stressed dielectric material. Thus, overall enhanced transistor performance may be obtained while nevertheless providing a high degree of compatibility with existing CMOS process strategies.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
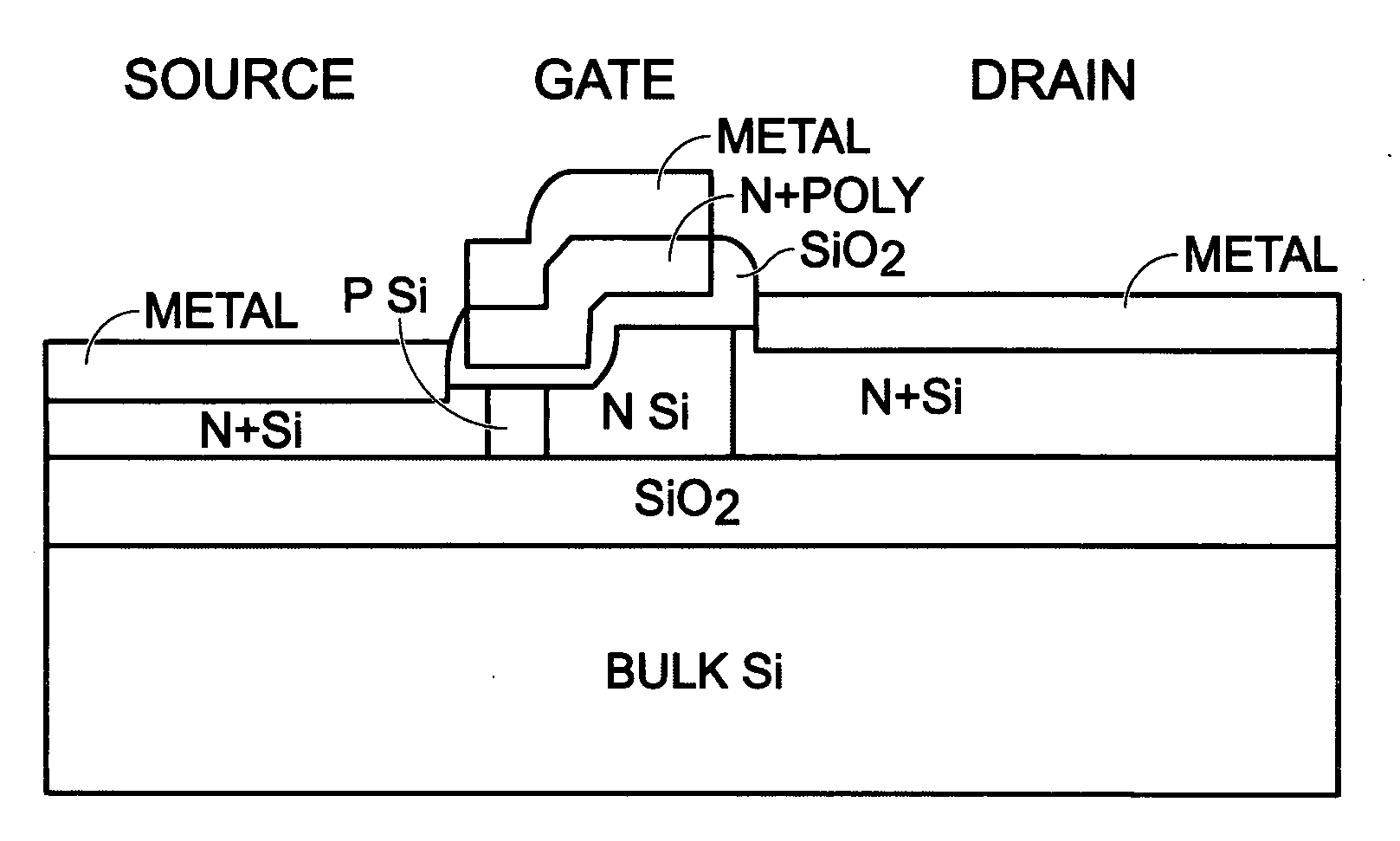
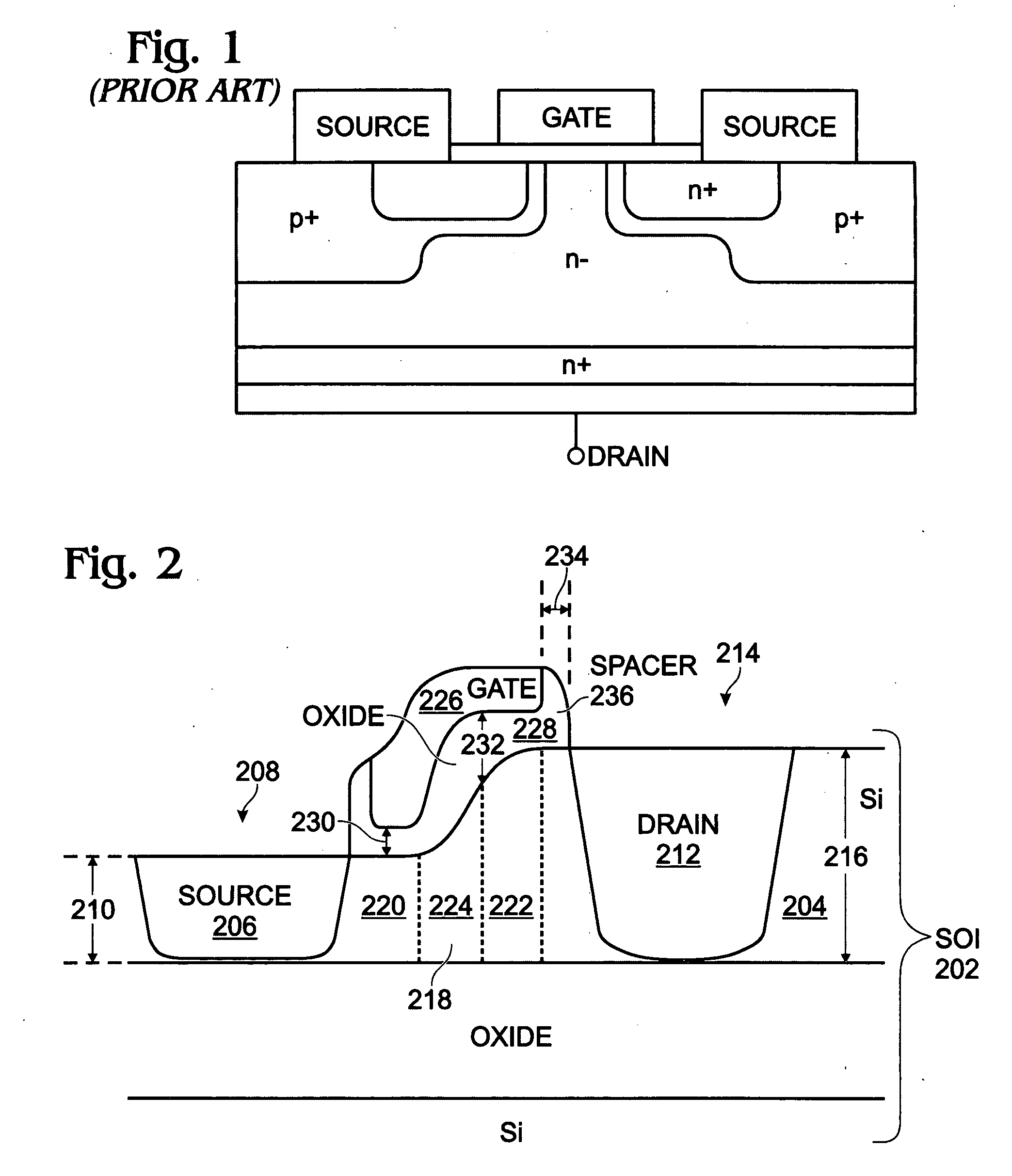
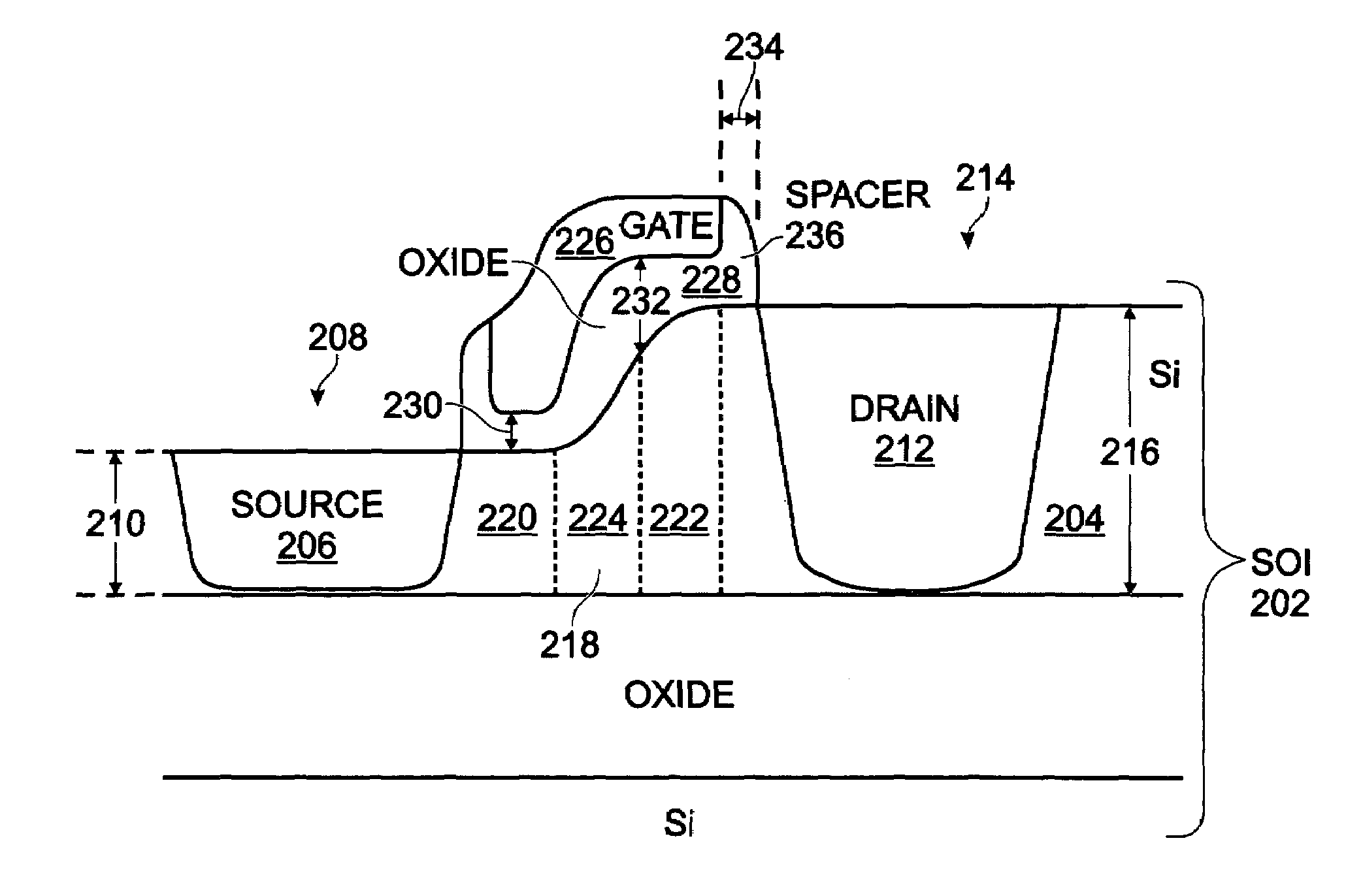
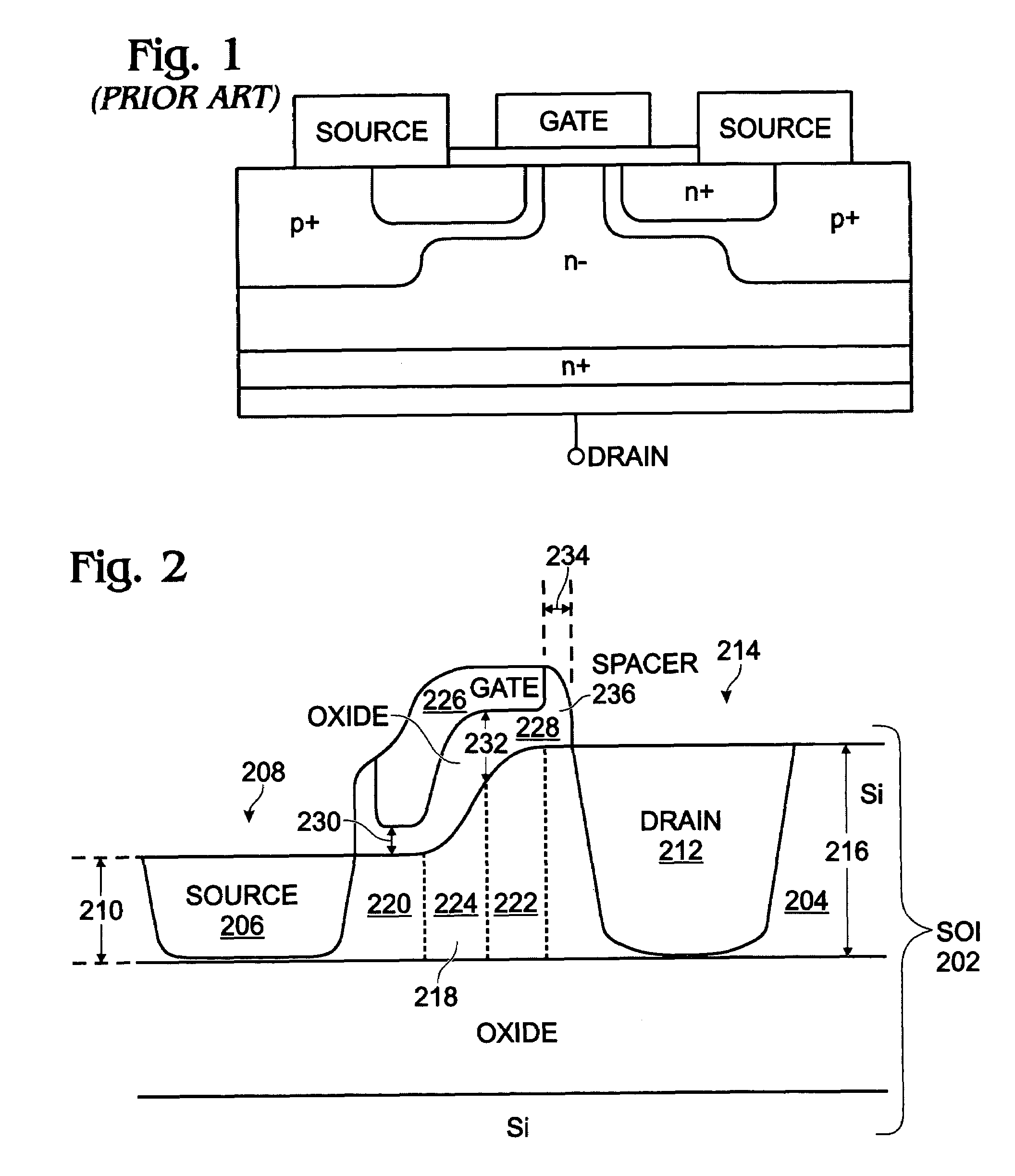
Thin silicon-on-insulator double-diffused metal oxide semiconductor transistor
InactiveUS20080290408A1Small parasitic capacitanceIncrease drive currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantSoi substrate
A method is provided for fabricating a silicon (Si)-on-insulator (SOI) double-diffused metal oxide semiconductor transistor (DMOST) with a stepped channel thickness. The method provides a SOI substrate with a Si top layer having a surface. A thinned area of the Si top layer is formed, and a source region is formed in the thinned Si top layer area. The drain region is formed in an un-thinned area of the Si top layer. The channel has a first thickness adjacent the source region with first-type dopant, and a second thickness, greater than the first thickness, adjacent the drain region. The channel also has a sloped thickness between the first and second thicknesses. The second and sloped thicknesses have a second-type dopant, opposite of the first-type dopant. A stepped gate overlies the channel.
Owner:SHARP KK
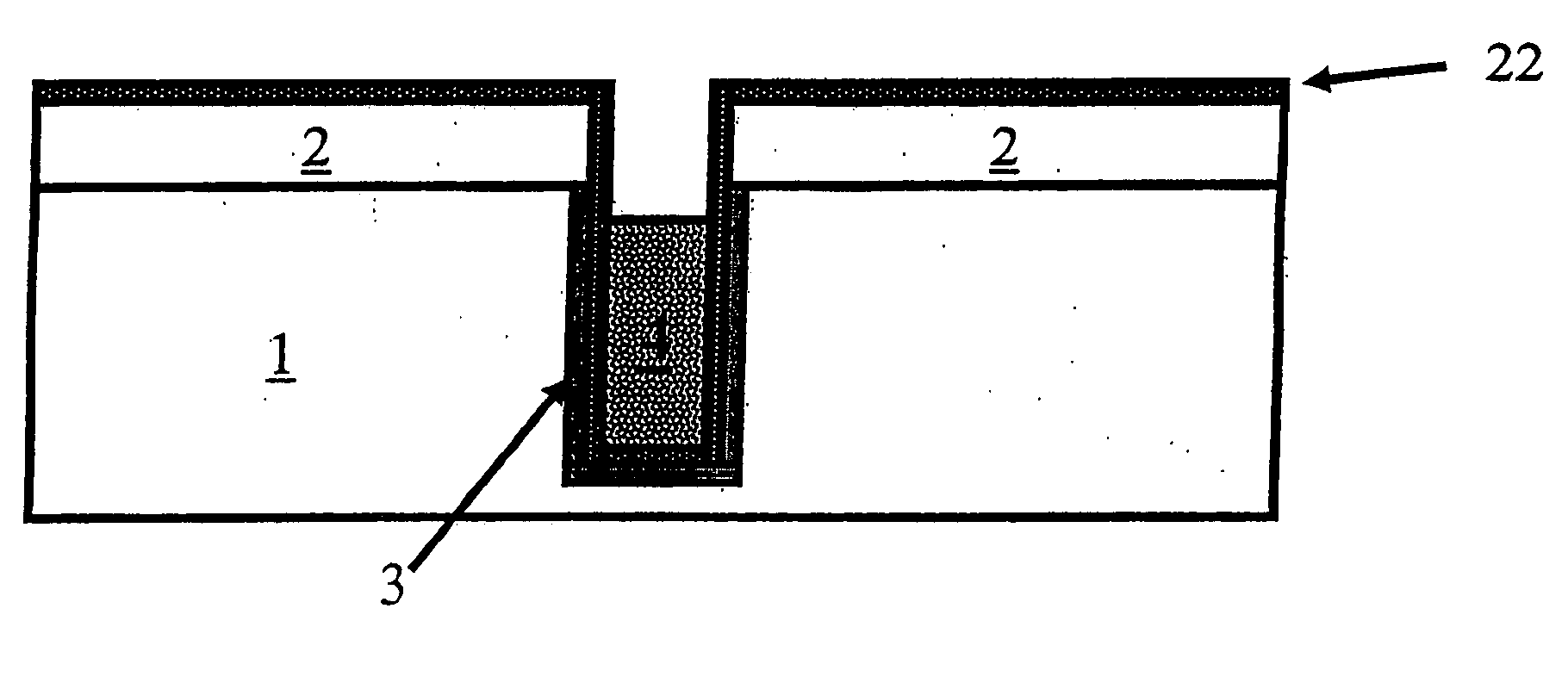
Formation of deep trench airgaps and related applications
ActiveUS20060258077A1Reduce widthReduce capacitanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringBiCMOS
A method for forming deep trench or via airgaps in a semiconductor substrate is disclosed comprising the steps of patterning a hole in the substrate, partly fill said hole with a sacrificial material (e.g. poly-Si), depositing spacers on the sidewalls of the unfilled part of the hole (e.g. TEOS) to narrow the opening, removing through said narrowed opening the remaining part of the sacrificial material (e.g. by isotropic etching) and finally sealing the opening of the airgap by depositing a conformal layer (TEOS) above the spacers. The method of forming an airgap is demonstrated successfully for use as deep trench isolation structures in BiCMOS devices.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Thin silicon-on-insulator double-diffused metal oxide semiconductor transistor
InactiveUS7598128B2Increase drive currentLower resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantSoi substrate
A method is provided for fabricating a silicon (Si)-on-insulator (SOI) double-diffused metal oxide semiconductor transistor (DMOST) with a stepped channel thickness. The method provides a SOI substrate with a Si top layer having a surface. A thinned area of the Si top layer is formed, and a source region is formed in the thinned Si top layer area. The drain region is formed in an un-thinned area of the Si top layer. The channel has a first thickness adjacent the source region with first-type dopant, and a second thickness, greater than the first thickness, adjacent the drain region. The channel also has a sloped thickness between the first and second thicknesses. The second and sloped thicknesses have a second-type dopant, opposite of the first-type dopant. A stepped gate overlies the channel.
Owner:SHARP KK
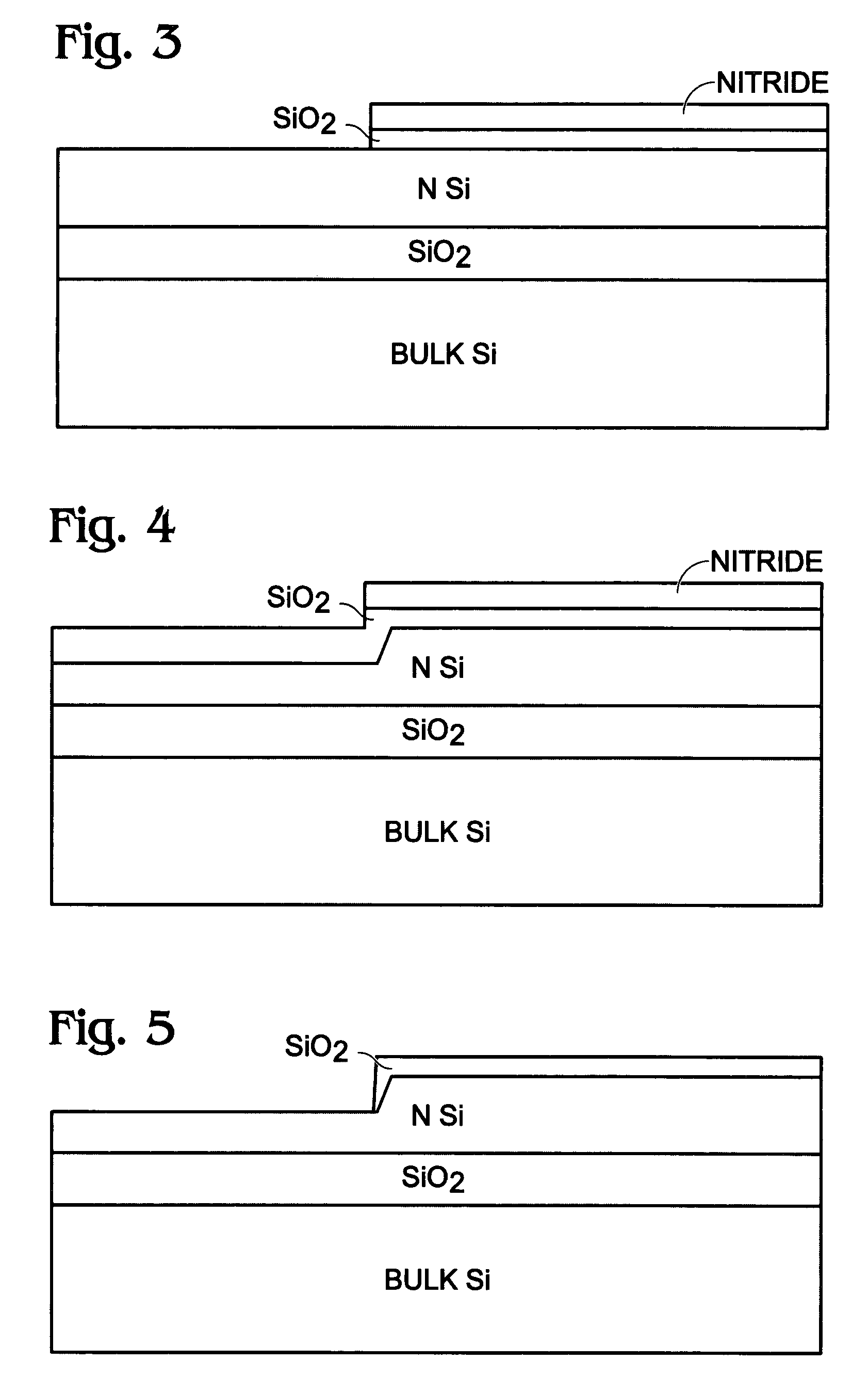
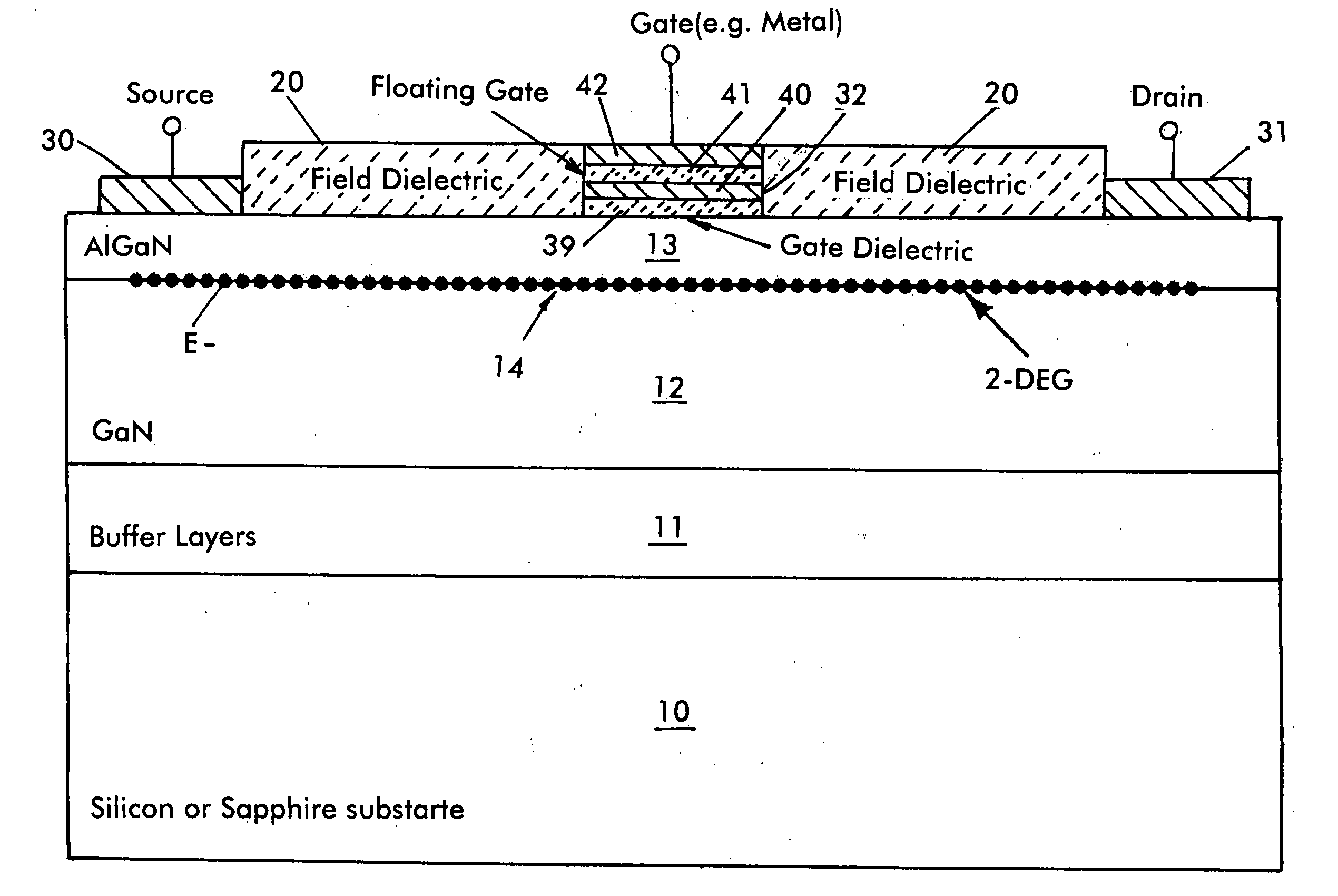
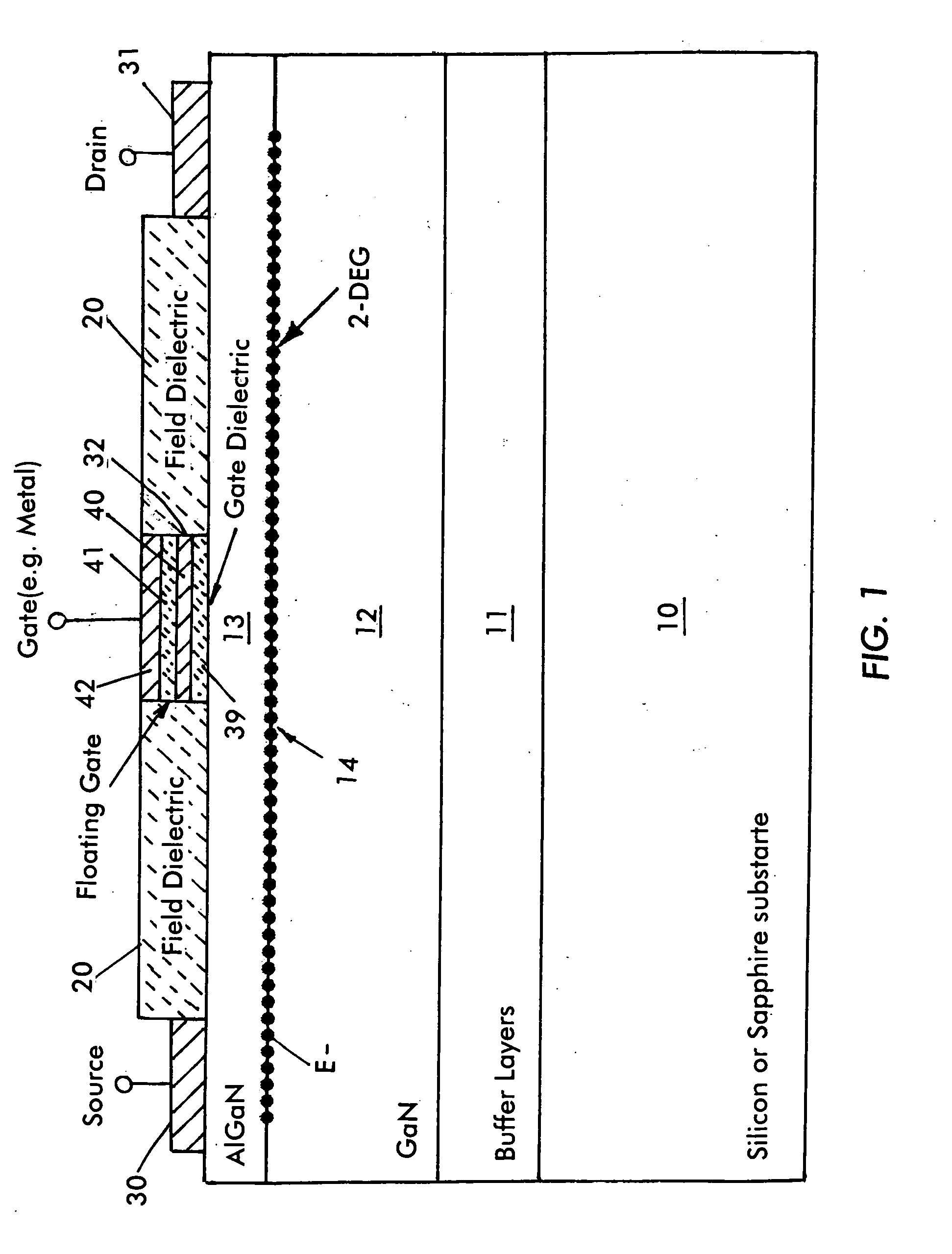
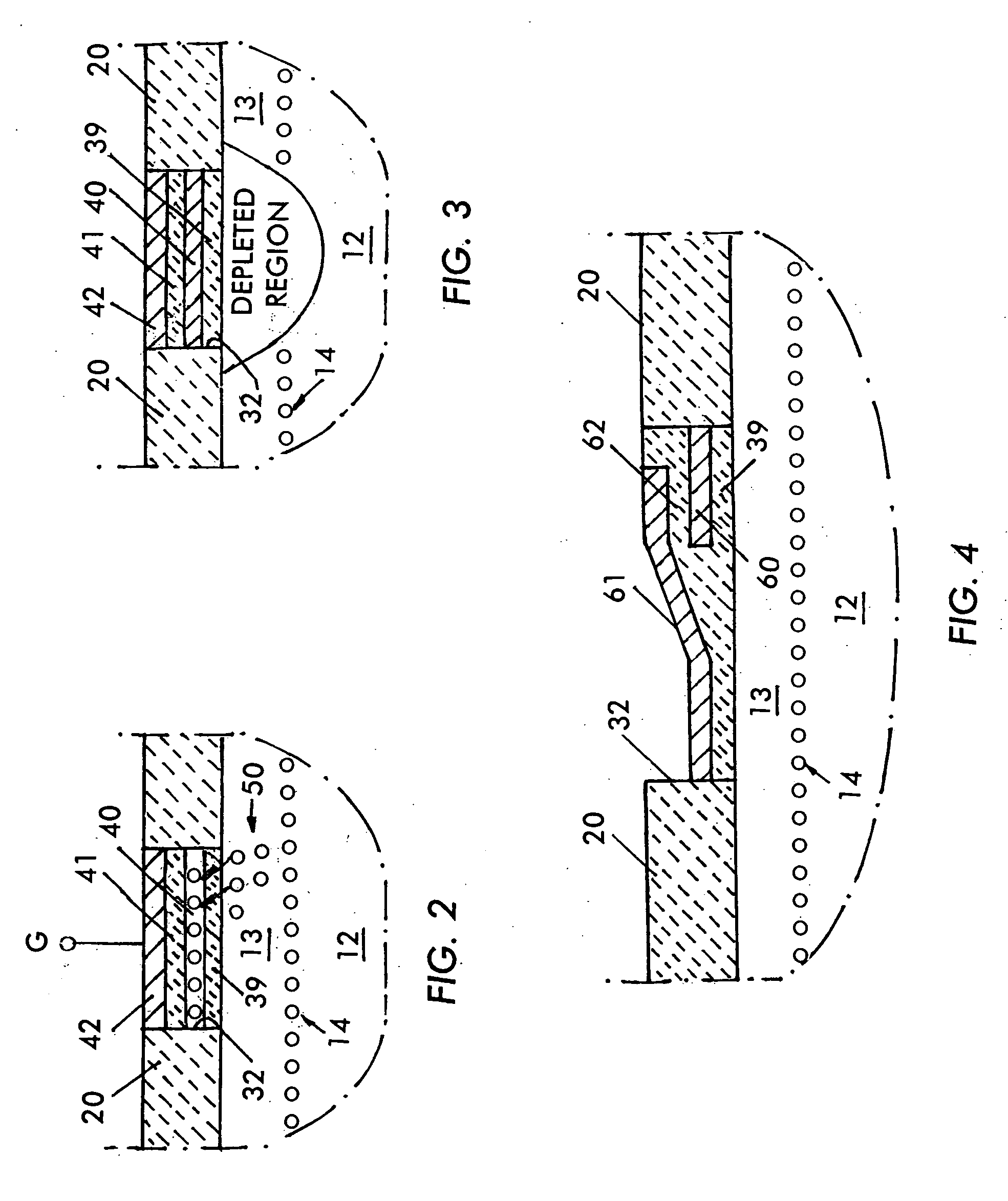
Enhancement mode iii-nitride device with floating gate and process for its manufacture
ActiveUS20100044751A1Reduce device areaImprove reliabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrideDielectric layer
An enhancement mode III-Nitride device has a floating gate spaced from a drain electrode which is programmed by charges injected into the floating gate to form a permanent depletion region which interrupts the 2-DEG layer beneath the floating gate. A conventional gate is formed atop the floating gate and is insulated therefrom by a further dielectric layer. The device is a normally off E mode device and is turned on by applying a positive voltage to the floating gate to modify the depletion layer and reinstate the 2-DEG layer. The device is formed by conventional semiconductor fabrication techniques.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Bottom source nmos triggered zener clamp for configuring an ultra-low voltage transient voltage suppressor (TVS)
ActiveUS20150084117A1Reduce leakageReduce device areaTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETLow voltage
A low voltage transient voltage suppressing (TVS) device supported on a semiconductor substrate supporting an epitaxial layer to form a bottom-source metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (BS-MOSFET) that comprises a trench gate surrounded by a drain region encompassed in a body region disposed near a top surface of the semiconductor substrate. The drain region interfaces with the body region constituting a junction diode. The drain region on top of the epitaxial layer constituting a bipolar transistor with a top electrode disposed on the top surface of the semiconductor functioning as a drain / collector terminal and a bottom electrode disposed on a bottom surface of the semiconductor substrate functioning as a source / emitter electrode. The body regions further comprises a surface body contact region electrically connected to a body-to-source short-connection thus connecting the body region to the bottom electrode functioning as the source / emitter terminal.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
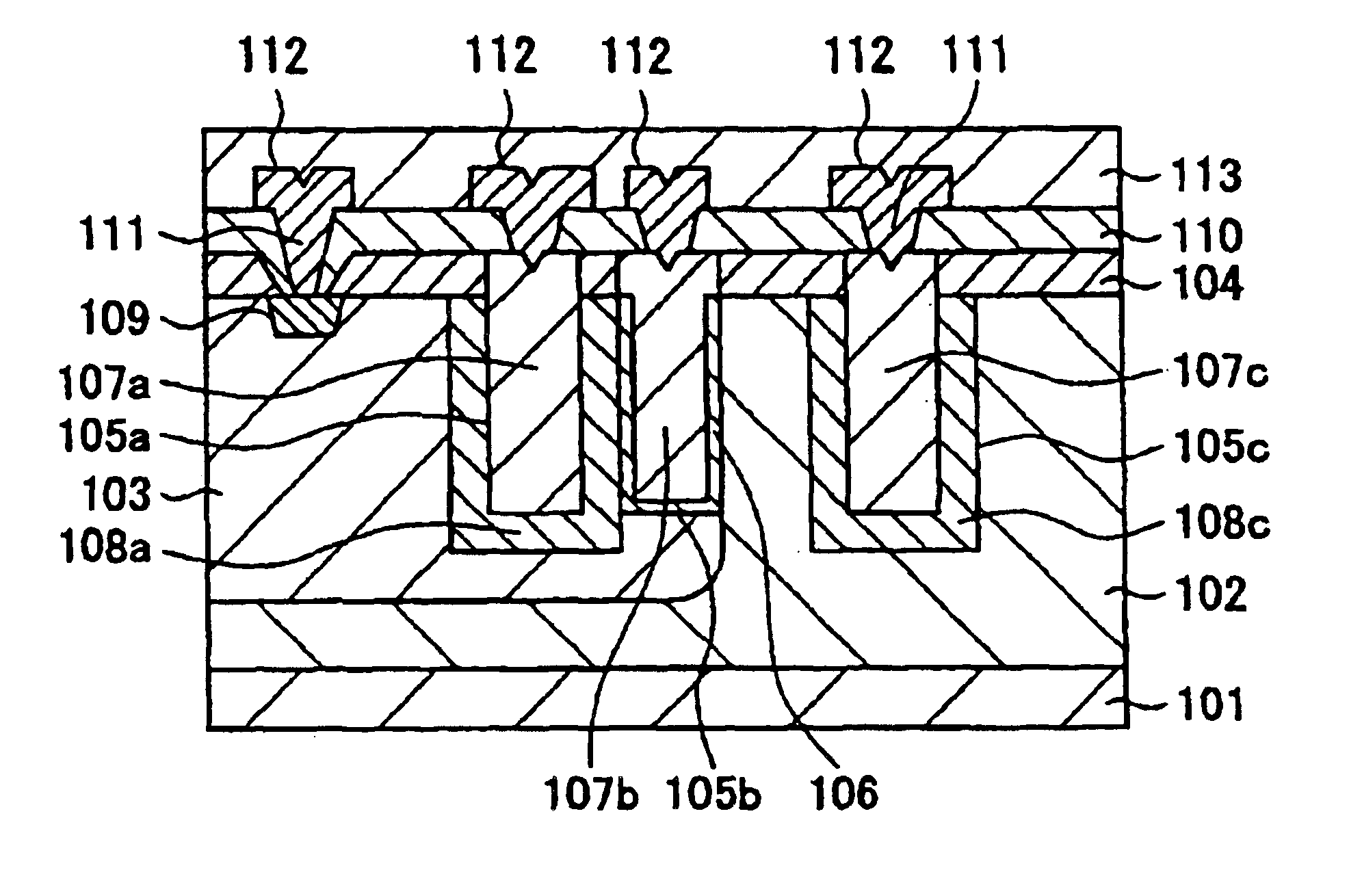
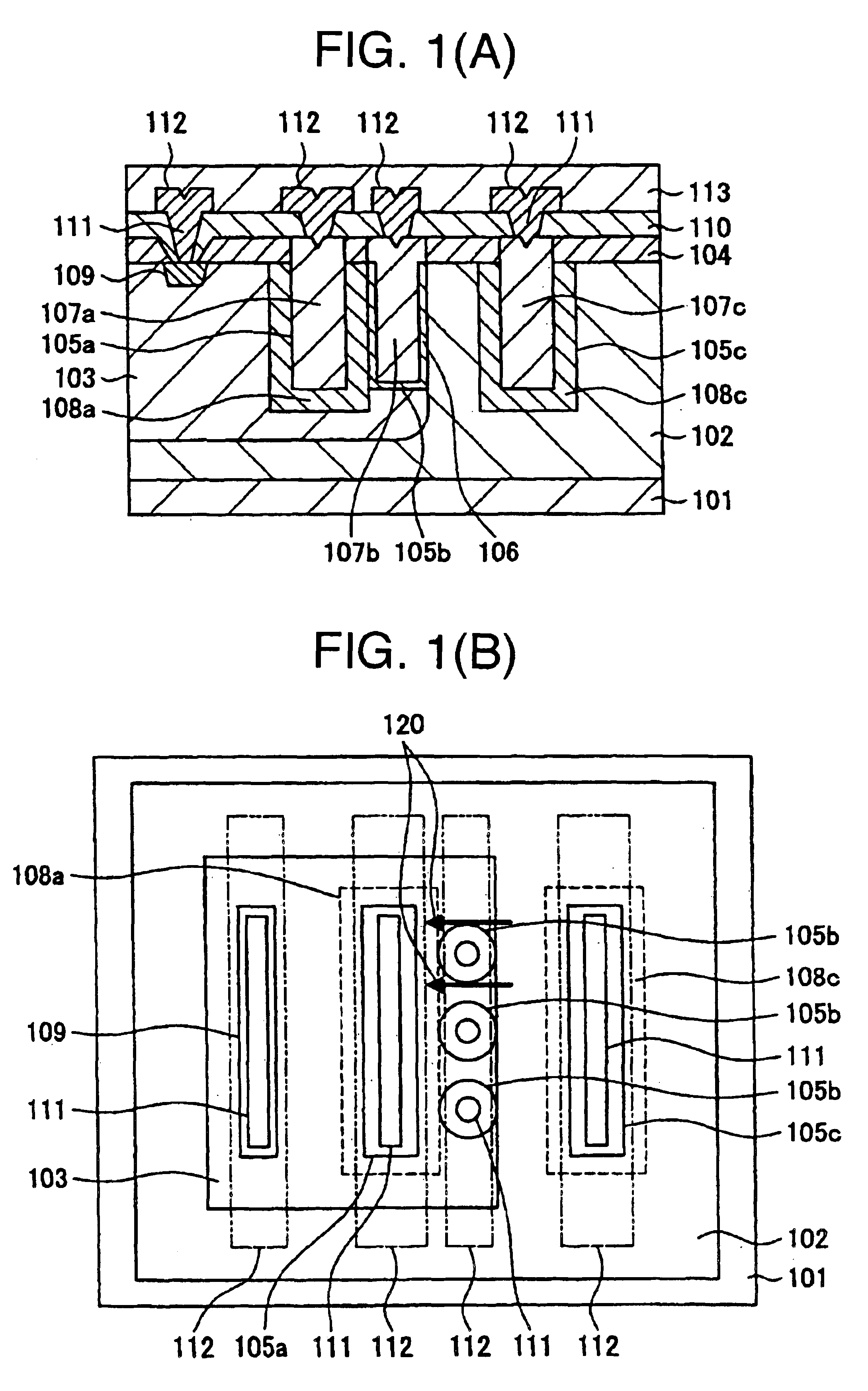
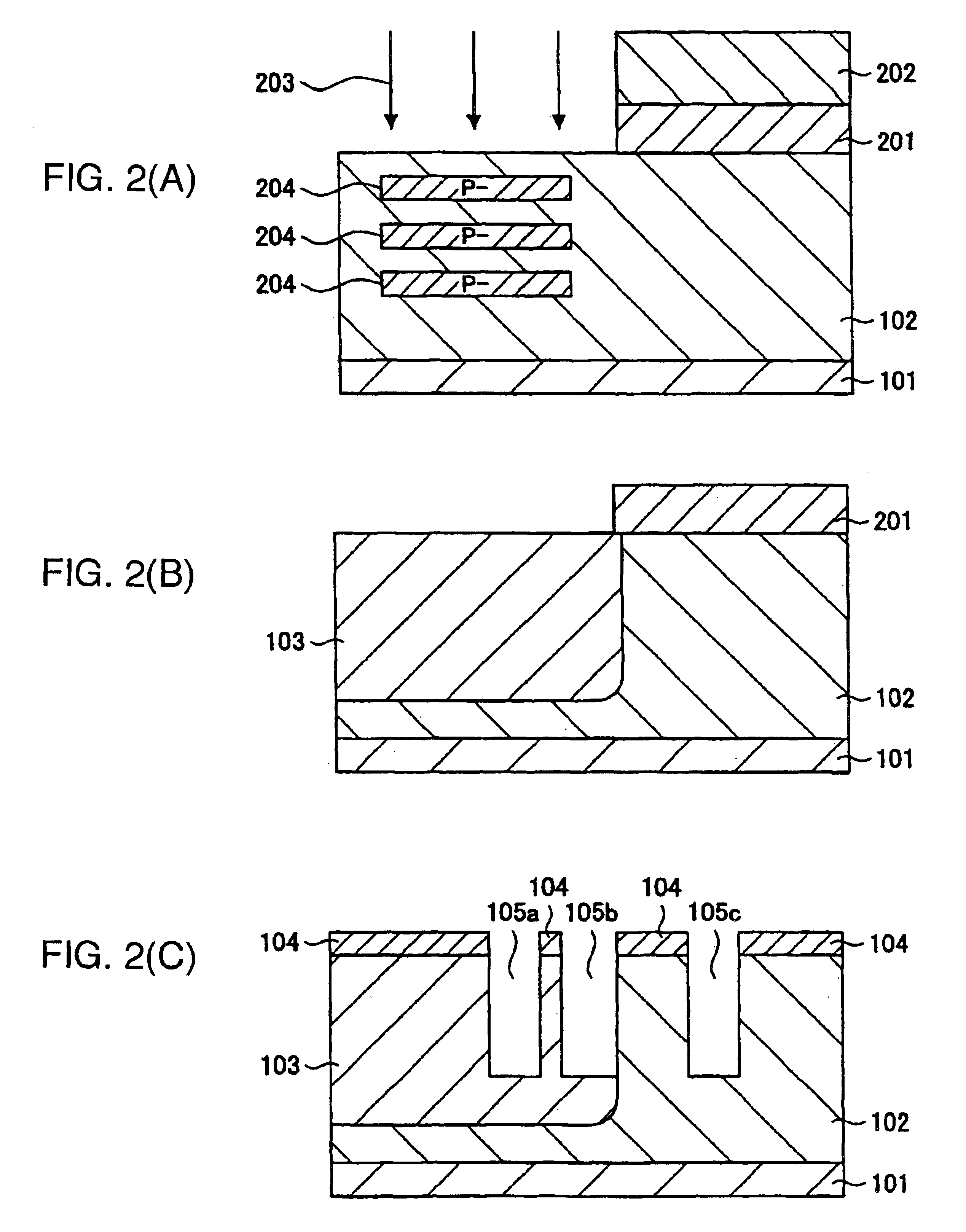
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20130270716A1Reduce device areaSimple manufacturing processSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
A semiconductor device including conductive lines configured to include first lines extending generally in parallel in a first direction and second lines extending generally in parallel in a second direction to intersect the first direction from the respective ends of the first lines and each second line having a width wider than the first line, and dummy patterns formed between the second lines.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
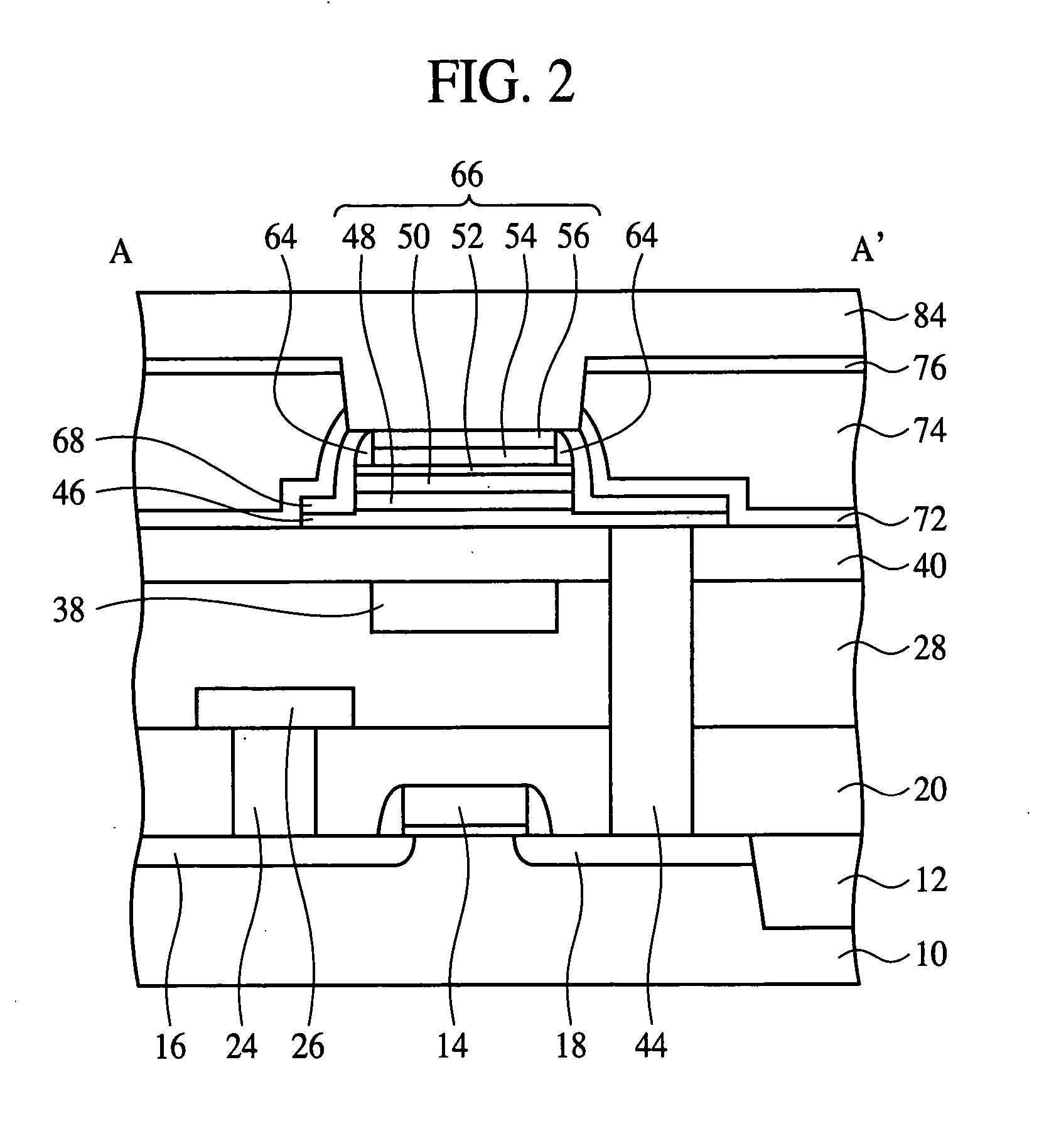
Semiconductor device
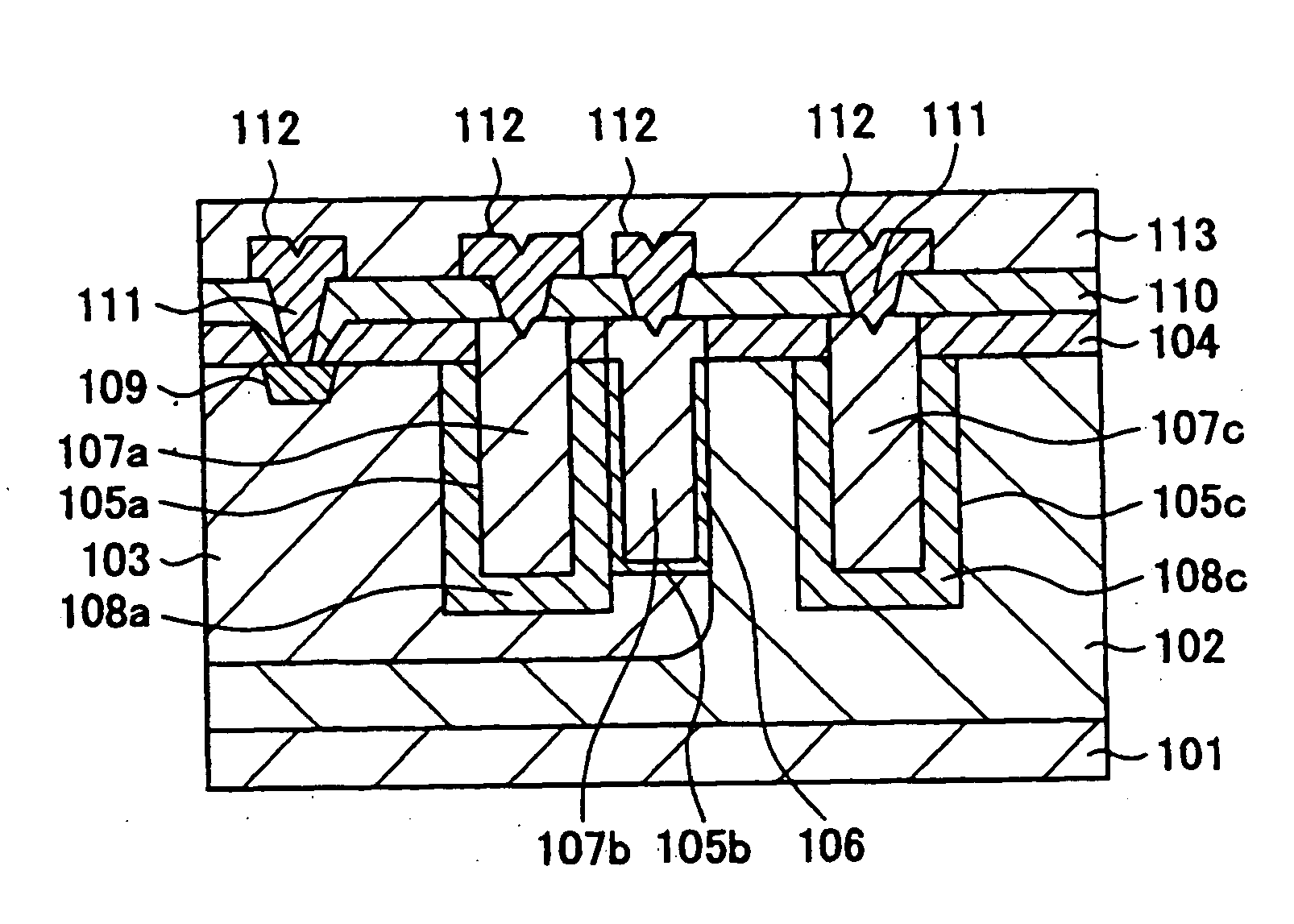
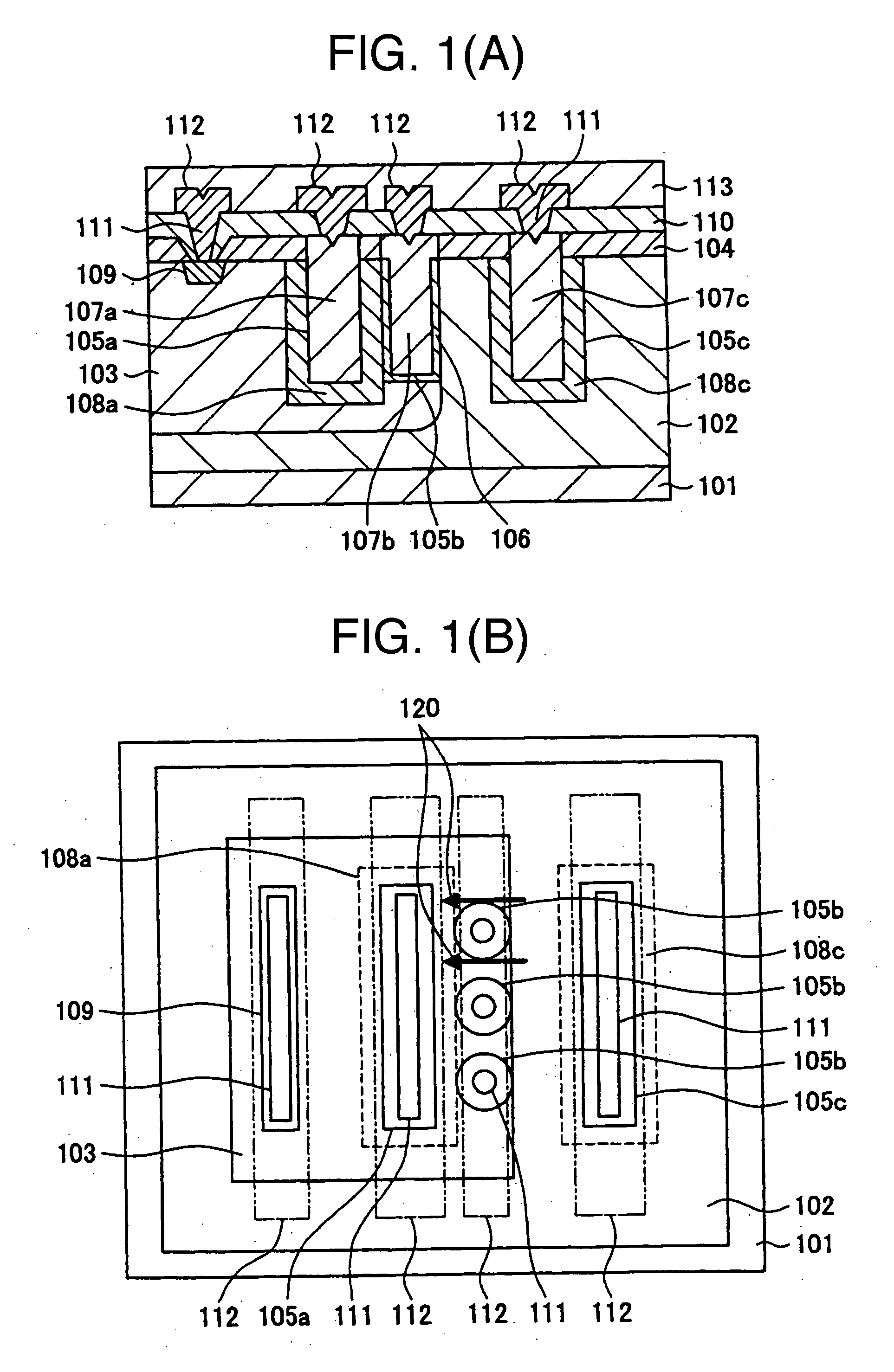
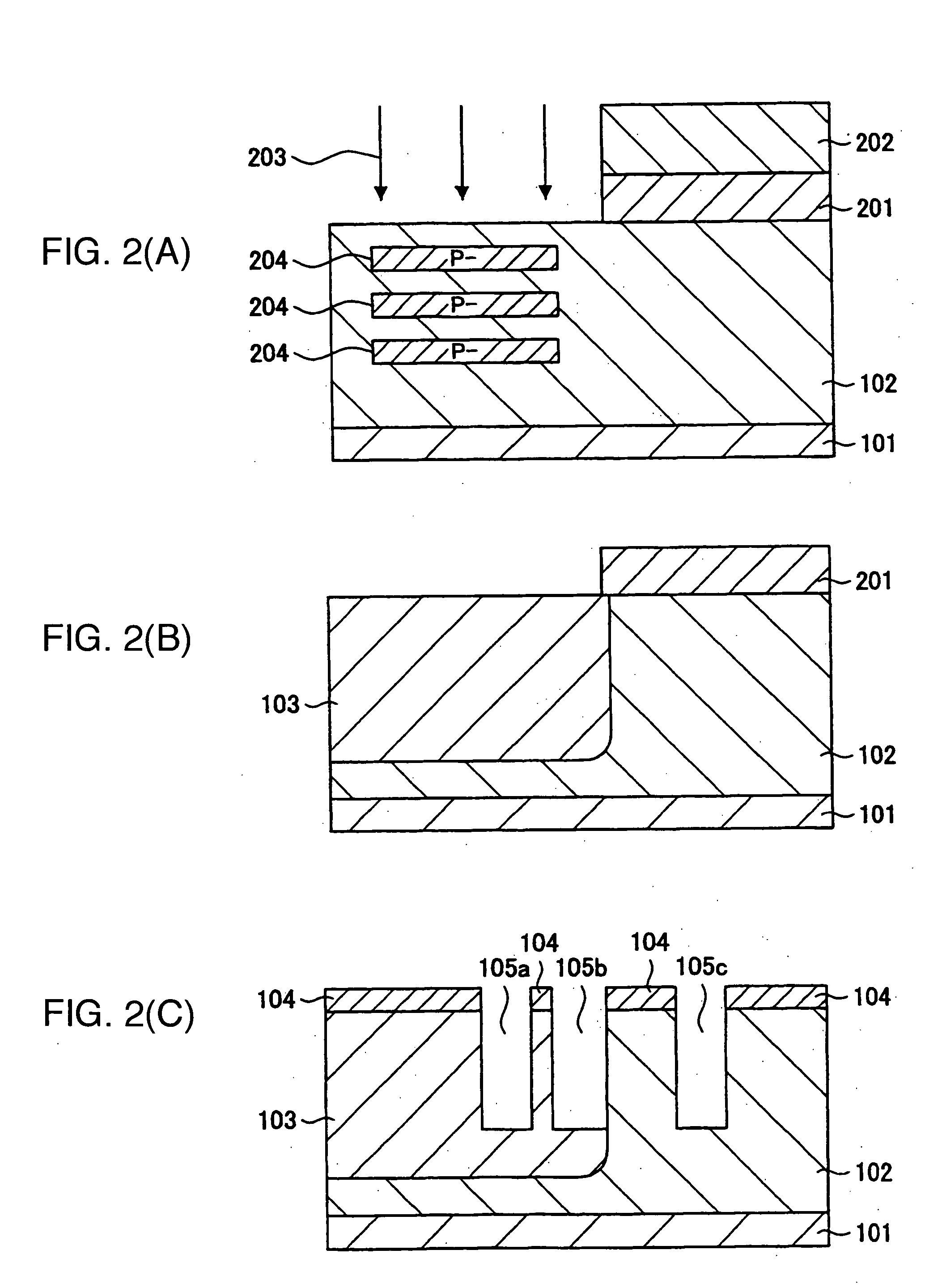
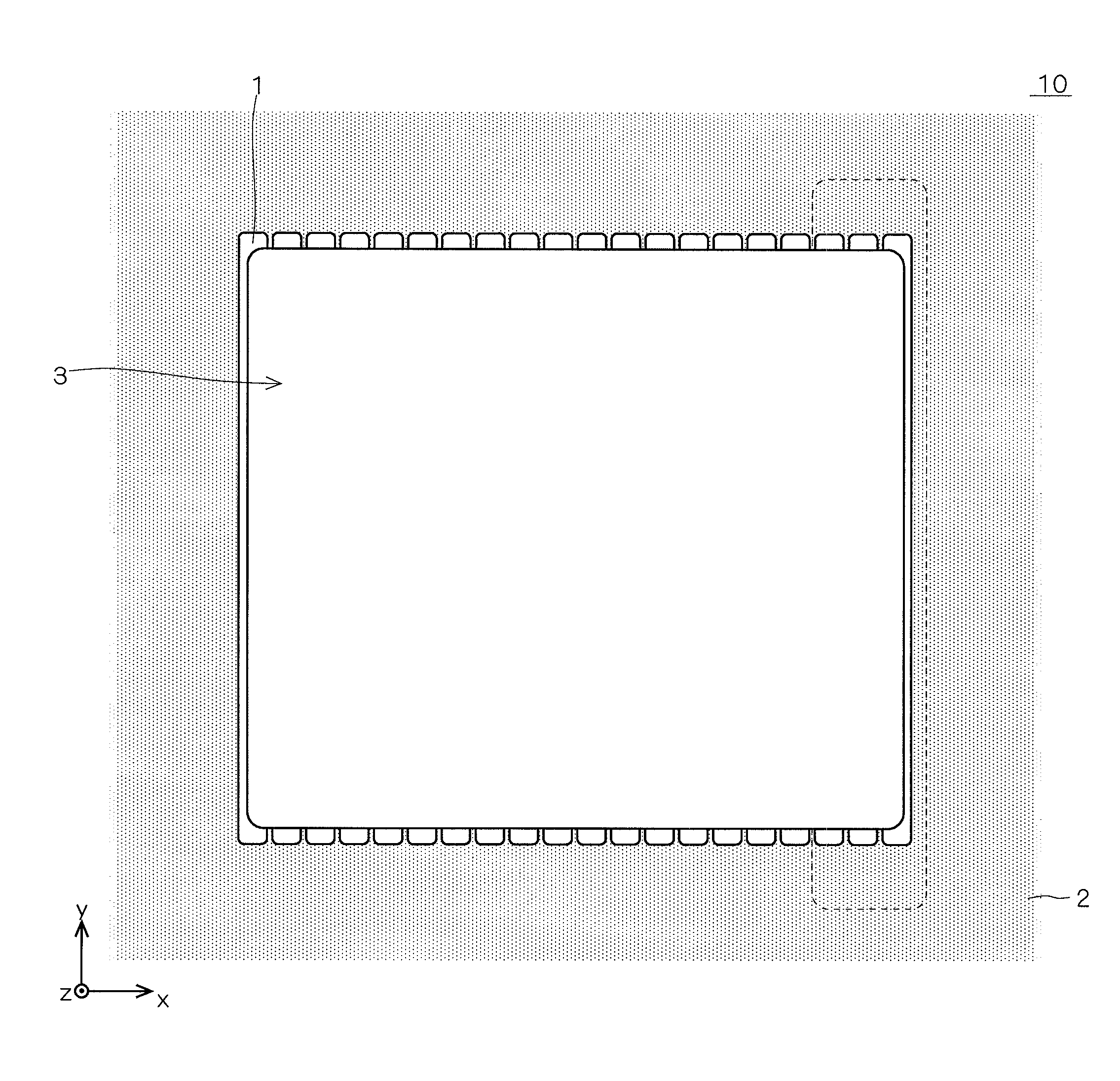
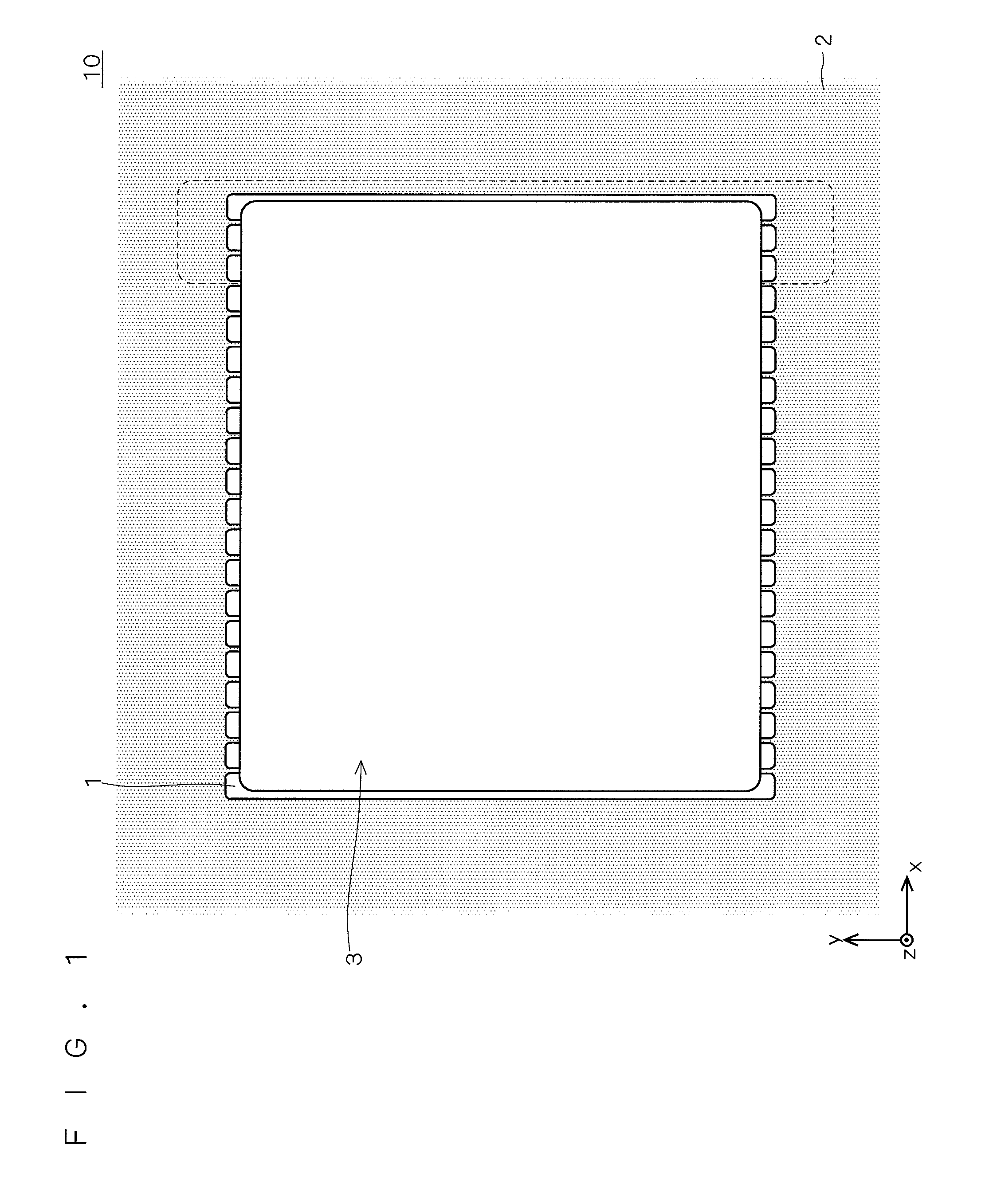
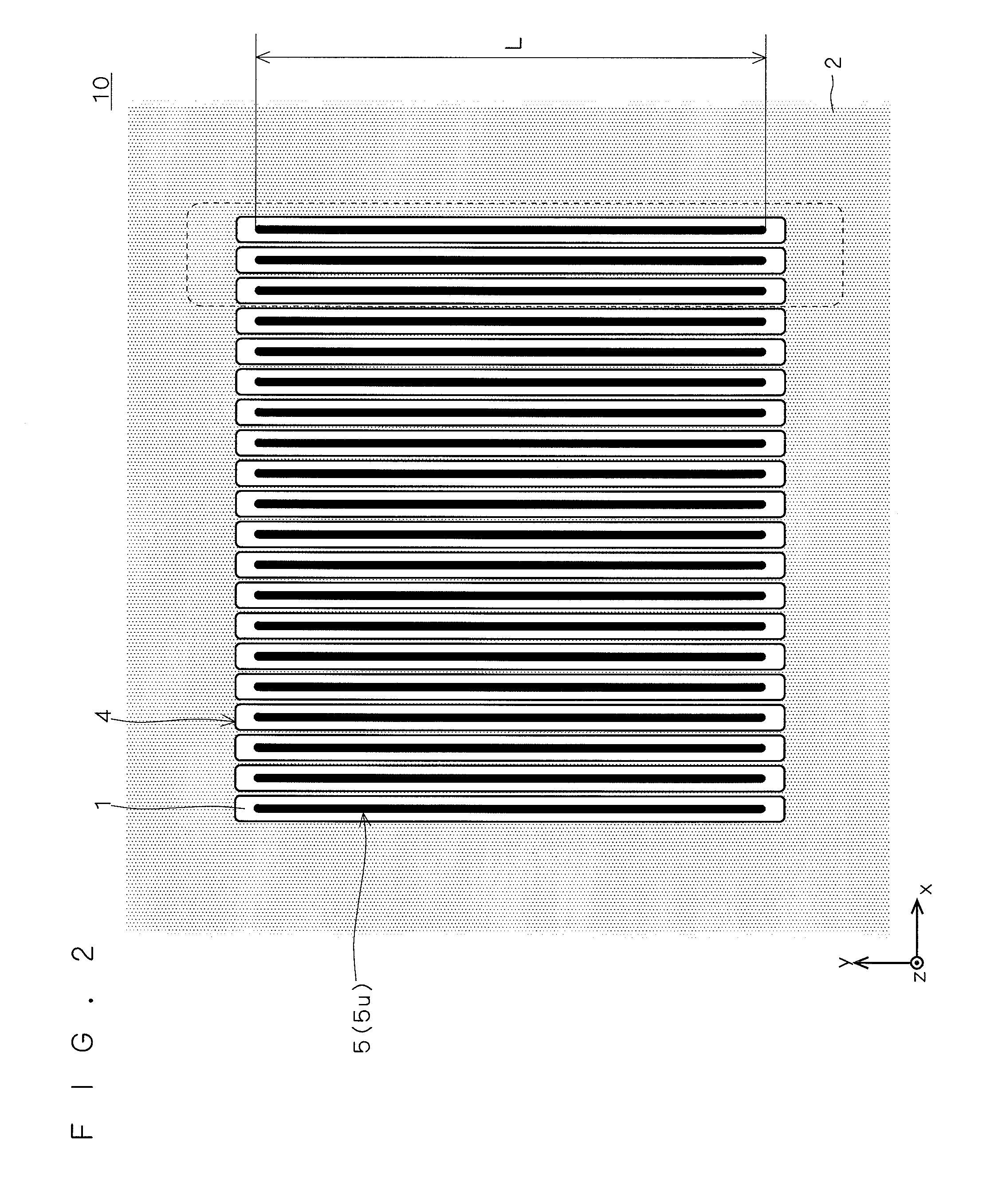
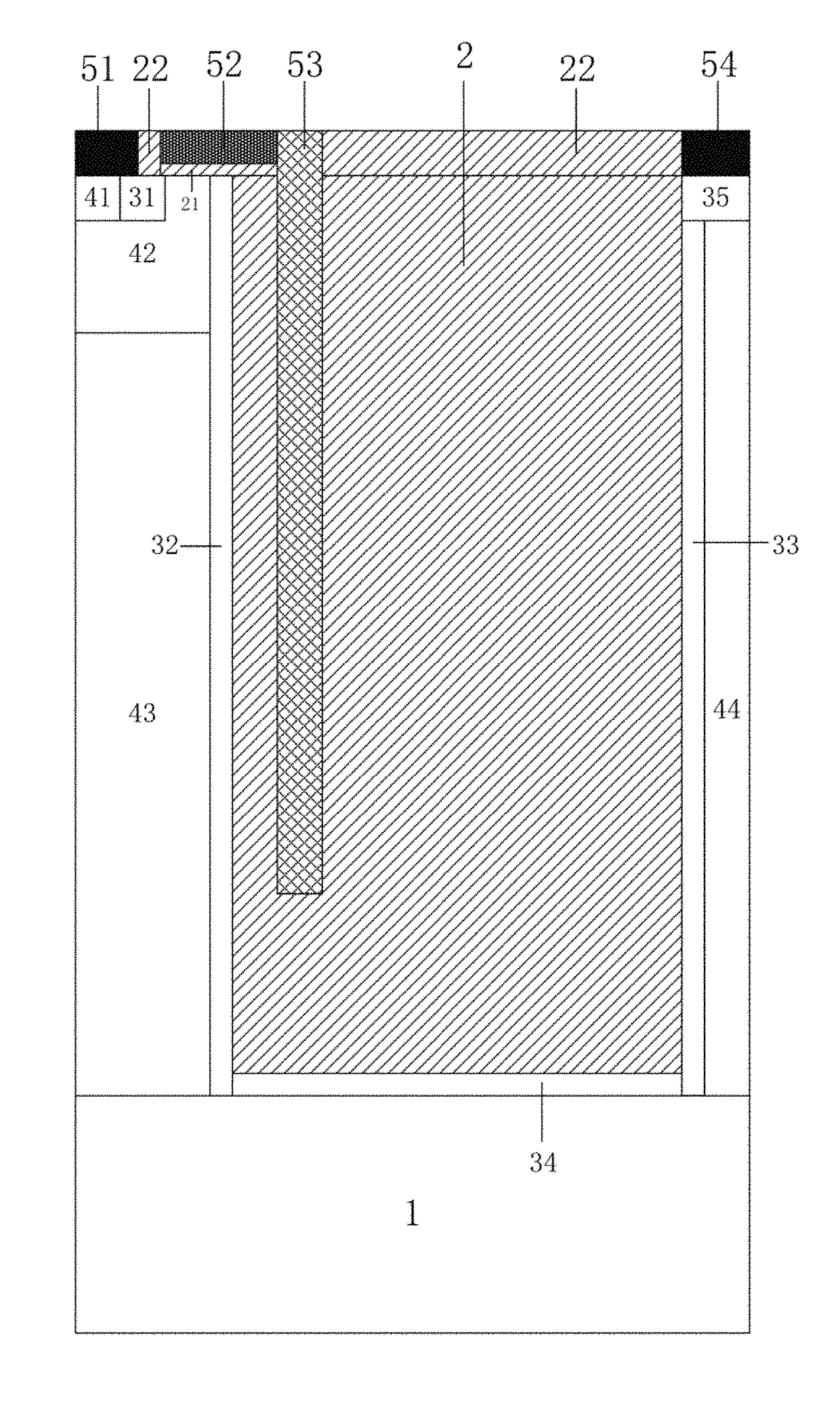
ActiveUS20060255406A1Reduce device areaDistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialHemt circuits
An object of the present invention is to provide a semiconductor device which enables to reduce the device area, while securing the breakdown voltage between the drain and the source of each MOS transistor for the semiconductor device including plural MOS transistors, which are arrayed adjacently each other, with different types of channel conductivity. The semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate, a buried oxide film and a semiconductor layer, and furthermore the semiconductor layer has an island-like semiconductor layer, in which a MOS transistor is formed, the MOS transistor has a source region, and a drain region that is positioned in the periphery of the source region, an island-like semiconductor layer, in which a MOS transistor is formed, the MOS transistor has a drain region, and a source region is that is positioned in the periphery of the drain region, an isolation trench which isolates the former island-like semiconductor layer from other portions of the semiconductor layer, an isolation trench which isolates the latter island-like semiconductor layer from other portions of the semiconductor layer, and a buffer region, in which the electric potential is fixed to the lowest electric potential in a circuit, which prevents an electrical interference occurred between transistors.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
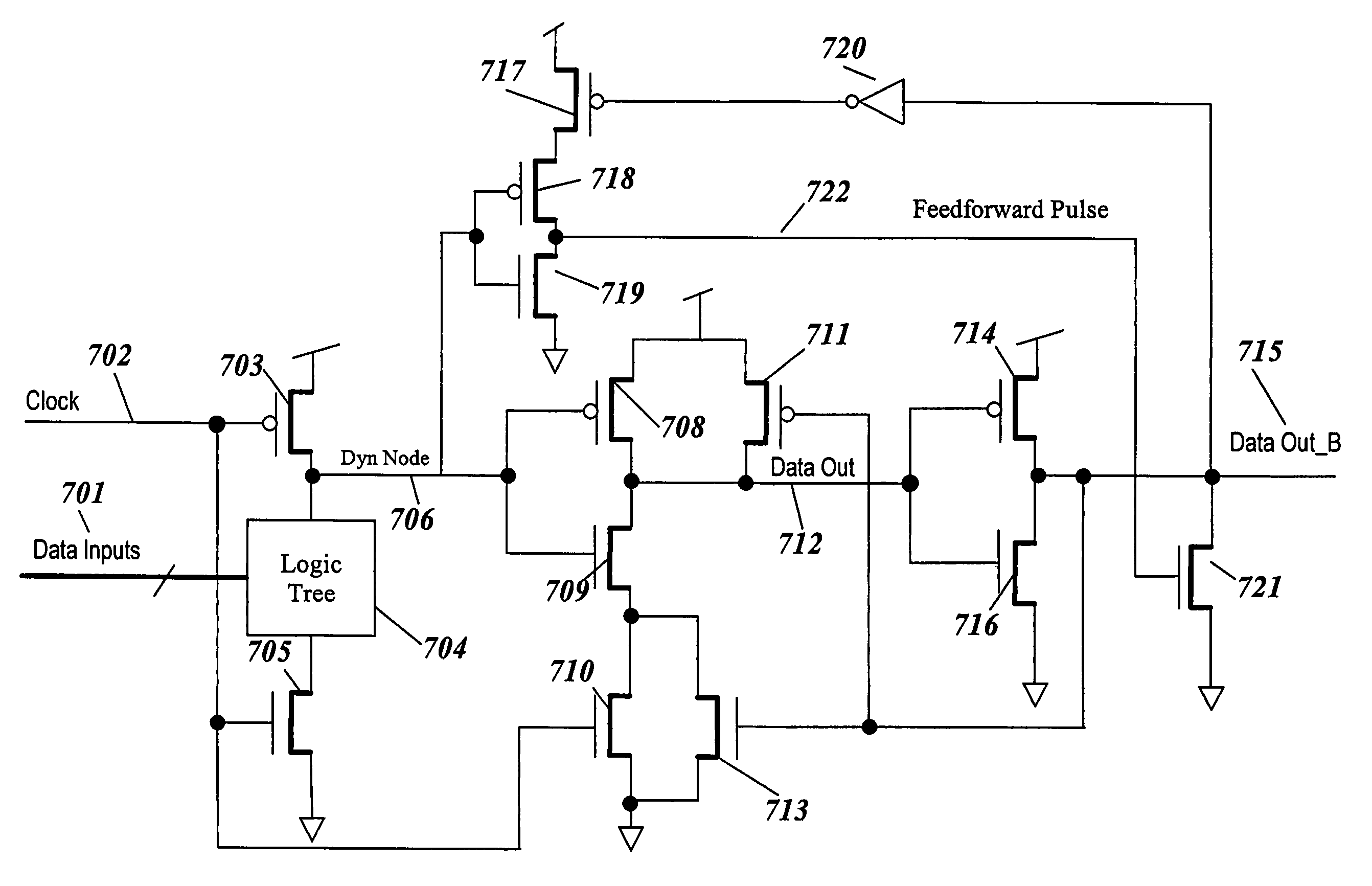
Feedforward limited switch dynamic logic circuit
InactiveUS6919739B2Reduce leakageReduce total powerLogic circuits characterised by logic functionElectric pulse generatorField-effect transistorSwitching power
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
A structure of a lateral diffusion mos transistor in widespread use as a power control device
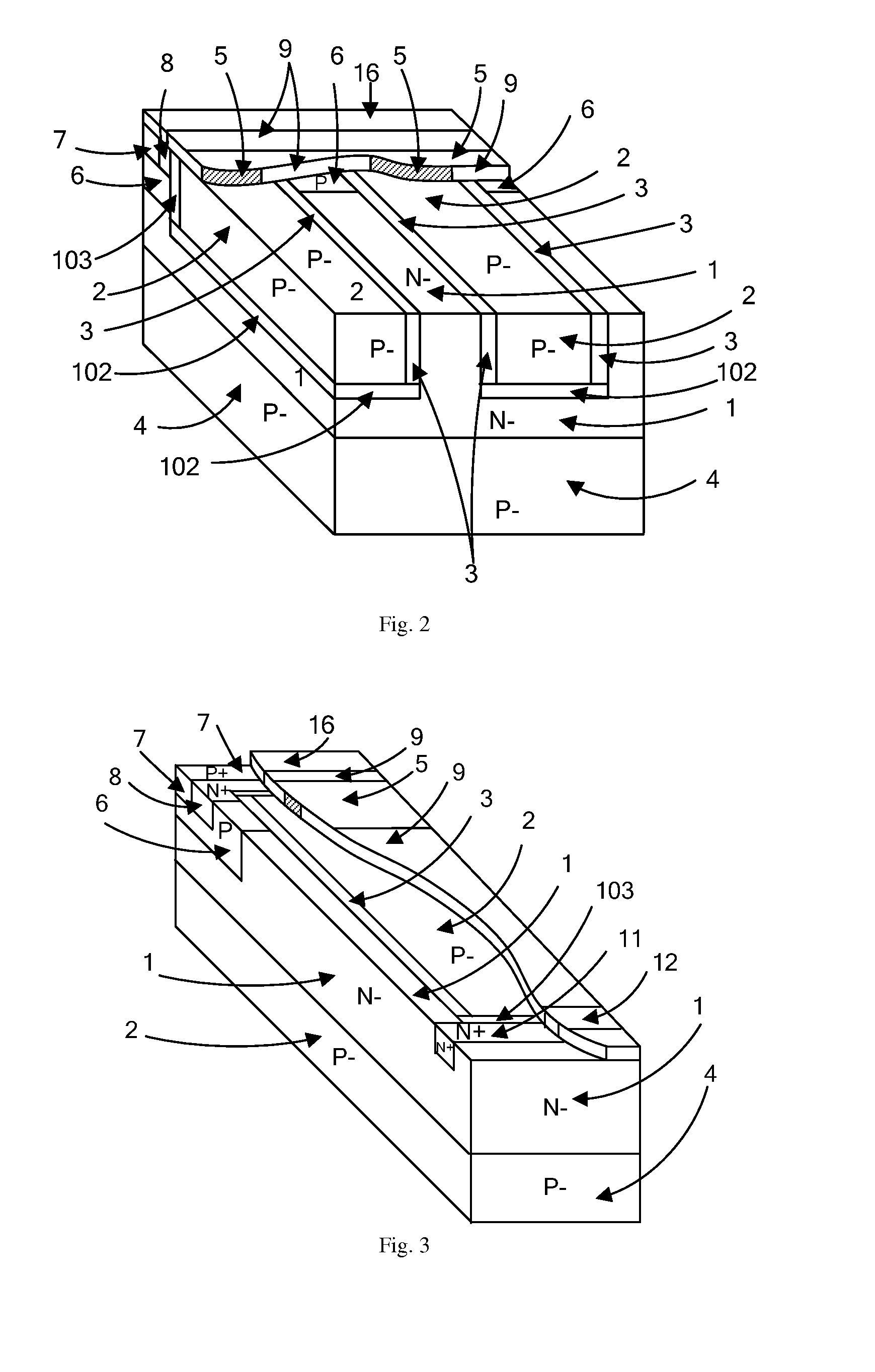
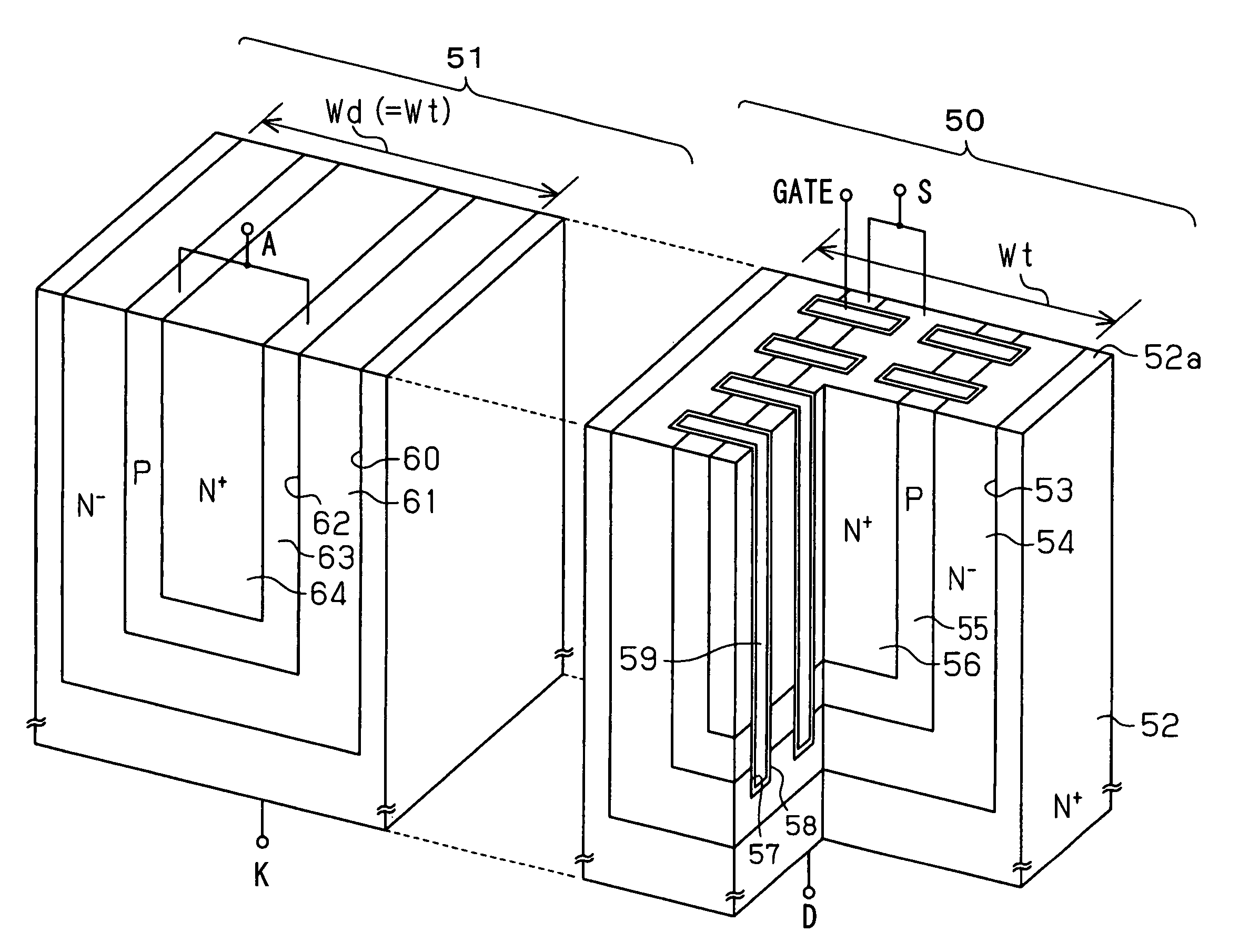
InactiveUS20050093060A1High currentShort pathTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialHigh pressure
There is provided a semiconductor device structured so as to be mounted jointly with other devices on one chip, and capable of controlling a large current in spite of a small device area while having small on-resistance, thereby enabling a high voltage resistance to be obtained. In the case of NLDMOS, the semiconductor device comprises an N well layer, formed on a p-type semiconductor substrate, a P well layer formed in the N well layer, a source electrode formed in a source trench cavity within the P well layer, a gate electrode formed in at least one of gate trench cavities within the P well layer, through the intermediary of an oxide film, and a drain electrode formed in a drain trench cavity within the N well layer, and further, N+ diffused layers are formed around the source trench cavity, the drain trench cavity, respectively.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
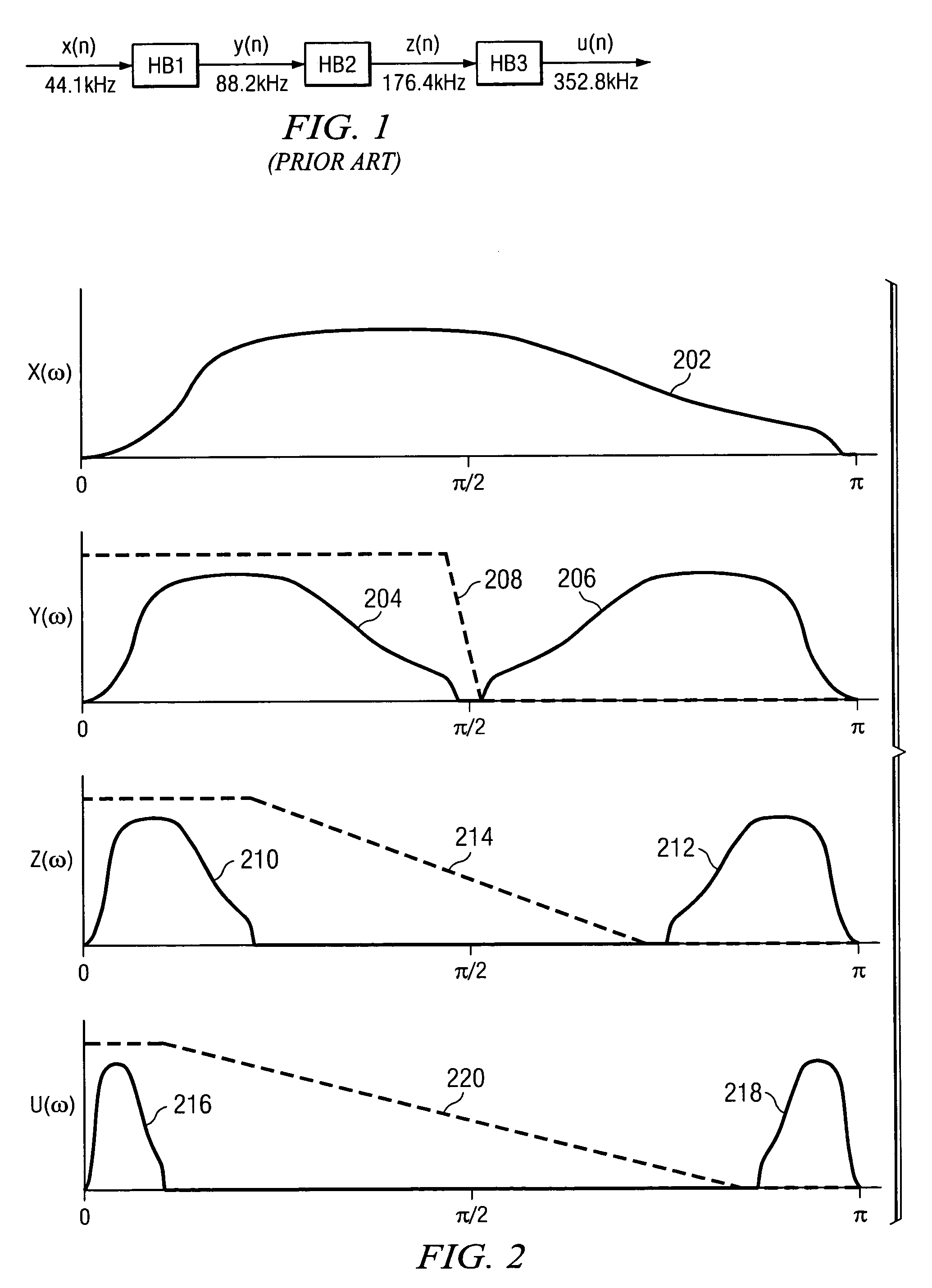
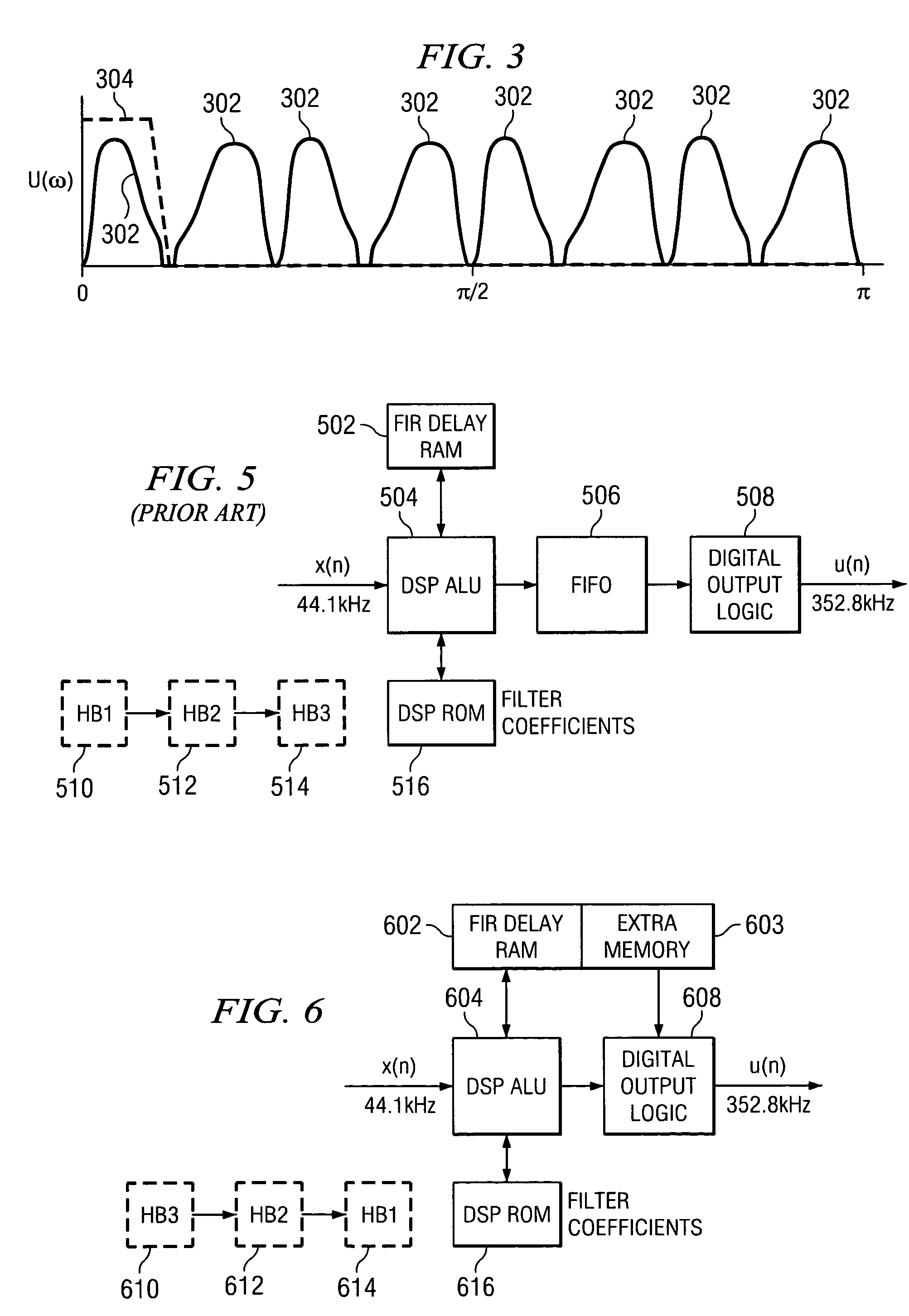
Method and apparatus for efficient multi-stage FIR filters
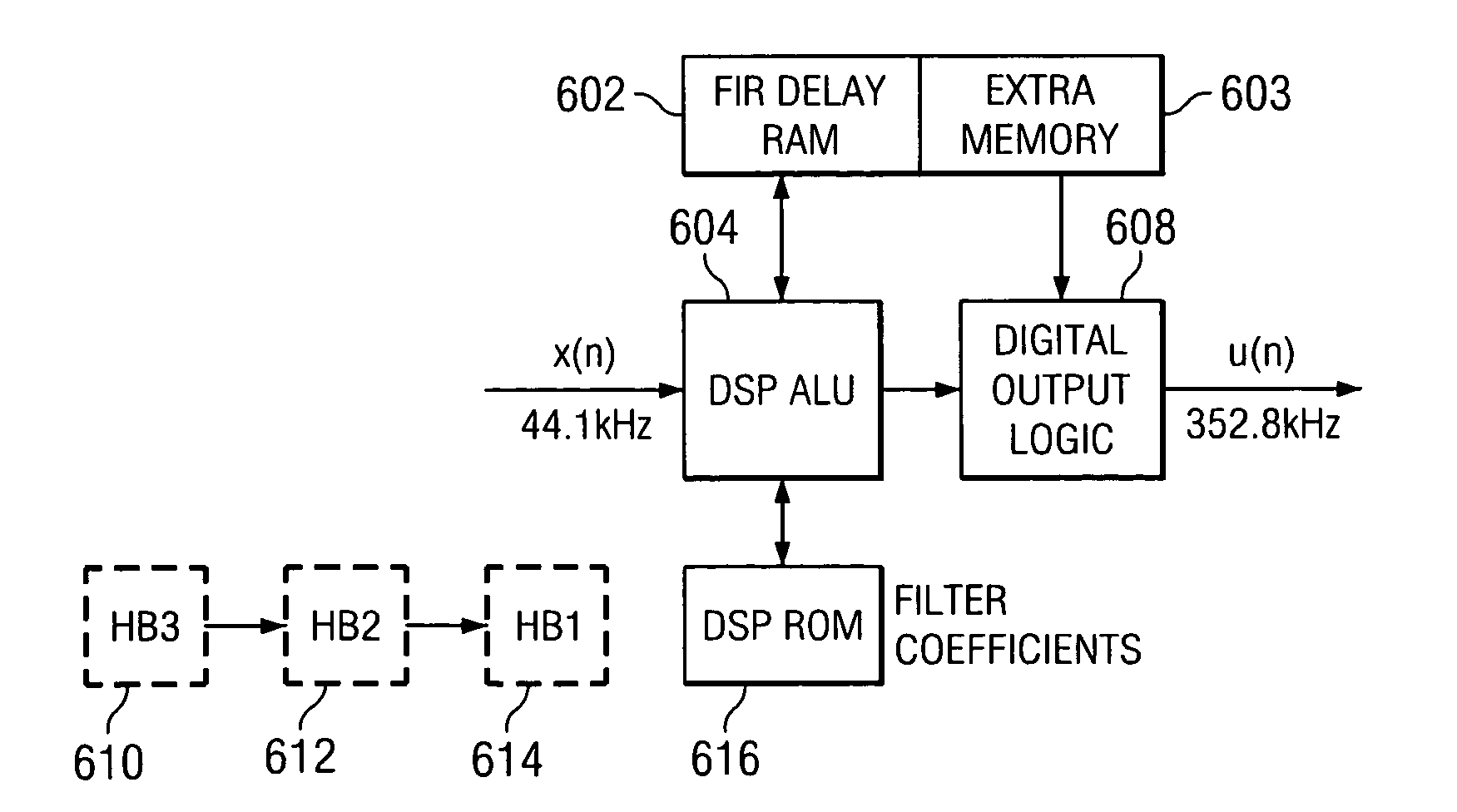
ActiveUS7492848B2Guaranteed independencePrecision productionMultiple-port networksDigital technique networkReverse orderRandom access memory
An interpolation filter without a FIFO memory is configured as a cascade arrangement of simpler interpolation sub-filters that are operated in reverse order. The interpolation sub-filter that produces the highest sampling frequency is operated first, followed by interpolation sub-filters that operate at successively lower sampling frequencies. Computational independence of the cascaded sub-filters is guaranteed by adding delays to sampled and filtered signals. Delays are implemented by operating each of the cascaded sub-filters using prior filtering results that are computed during a previous sampling interval. A small increment to random-access memory is required for storing the successively delayed signals. The digital signal processor performing the filtering process is stalled for one clock cycle at the time a filtered signal sample is outputted so that the outputted signal sample can be produced without a timing conflict.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Micro-piezoelectric driver for MEMS
InactiveCN1483660AShorten the lengthReduce device areaPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesFlexible microstructural devicesDeflection anglePiezoelectric composite
The miniature piezoelectric driver capable of producing deflection angle and vertical displacement for MEMS is characterized by that its structure is a kind of suspension folded piezoelectric composite multi-layer film elastic driving arm, it has at least two sections or more than two sections of parallel driving arms. The driving arms of two sides of suspension structure are connected with substrate. Every driving arm contains elastic layer and piezoelectric composite film on the elastic layer. When the driving voltages with opposite polarity are applied on the upper and lower electrodes of piezoelectric films on the adjacent parallel different driving arms, the parallel adjacent piezoelectric driving arms can produce opposite bend, and on the driving arm of middle portion positioned in the suspension structure the maximum vertical displacement or deflection angle can be produced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Transient voltage suppressor and fabrication method thereof
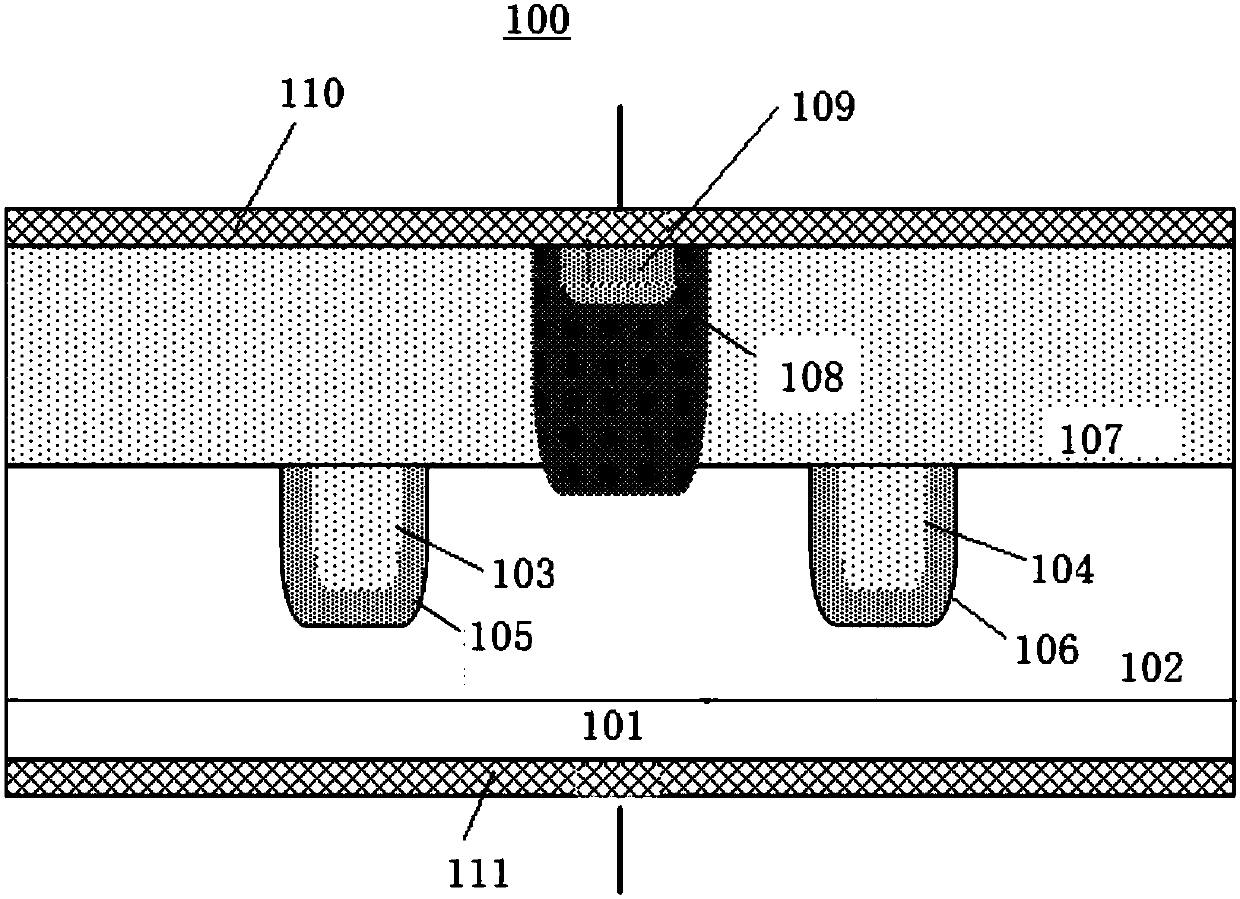
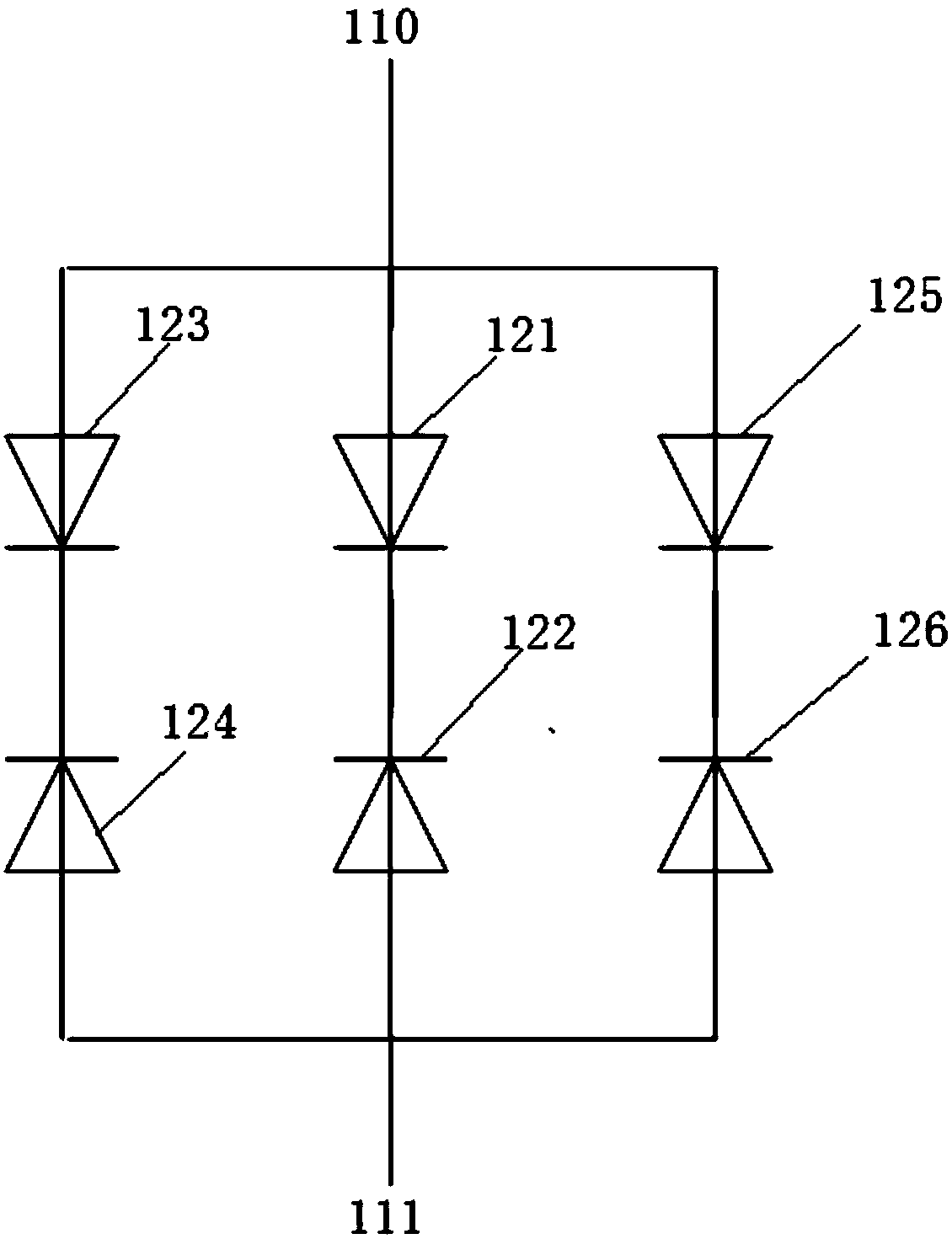
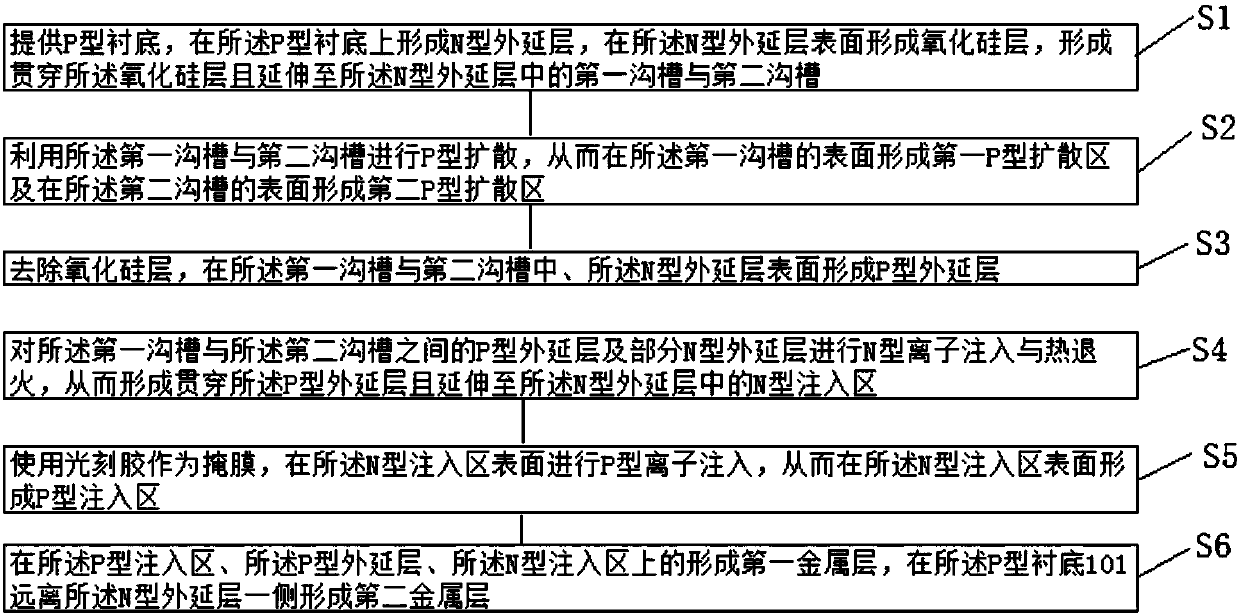
InactiveCN108054164AReduce device areaReduce process difficultySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransient voltage suppressorEngineering
The invention provides a transient voltage suppressor and a fabrication method thereof. The transient voltage suppressor comprises a P-type substrate, an N-type epitaxial layer, a first groove, a second groove, a first P-type diffusion region, a second P-type diffusion region, P-type epitaxial layers, an N-type injection region and a P-type injection region, wherein the N-type epitaxial layer is formed on the P-type substrate, the first groove and the second groove are formed in a surface of the N-type epitaxial layer, the first P-type diffusion region is formed on a surface of the first groove, the second P-type diffusion region is formed on a surface of the second groove, the P-type epitaxial layers are formed in the first groove and the second groove and on the N-type epitaxial layer, the N-type injection region penetrates through the P-type epitaxial layer and extends to the N-type epitaxial layer between the first groove and the second groove, and the P-type injection region is formed on a surface of the N-type injection region.
Owner:NANJING LISHUI HIGH-TECH VENTURE CAPITAL MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070228519A1Excellent propertyMaintain good propertiesTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectric fieldCathode electrode
A semiconductor device made of a group-III nitride semiconductor having excellent properties is provided. The semiconductor device has a horizontal diode structure of Schottky type or P—N junction type, or combined type thereof having a main conduction pathway in the horizontal direction in a conductive layer with unit anode portions and unit cathode electrodes being integrated adjacently to each other in the horizontal direction. The conductive layer is preferably formed by depositing a group-III nitride layer and generating a two-dimensional electron gas layer on the interface. Forming the conductive layer of the group-III nitride having high breakdown field allows the breakdown voltage to be kept high while the gap between electrodes is narrow, which achieves a semiconductor device having high output current per chip area. Further, an electrode pad layer provided on an insulation protecting layer relieves electric field concentration at a junction of each unit anode portion and each unit cathode electrode, which achieves higher breakdown voltage.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Lateral high-voltage device
InactiveUS10068965B1Small surface areaReduce the specific On-ResistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh pressureDielectric layer
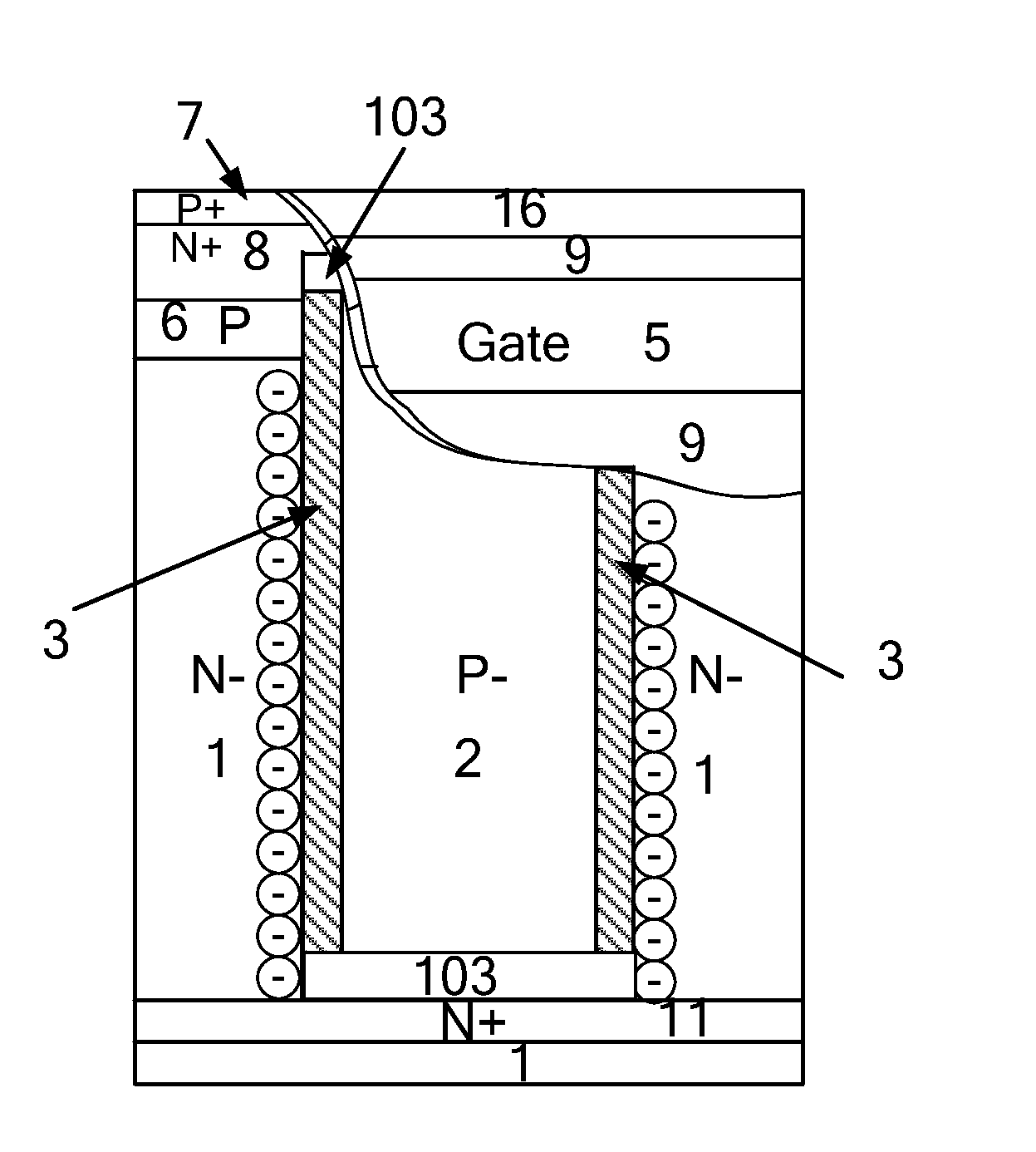
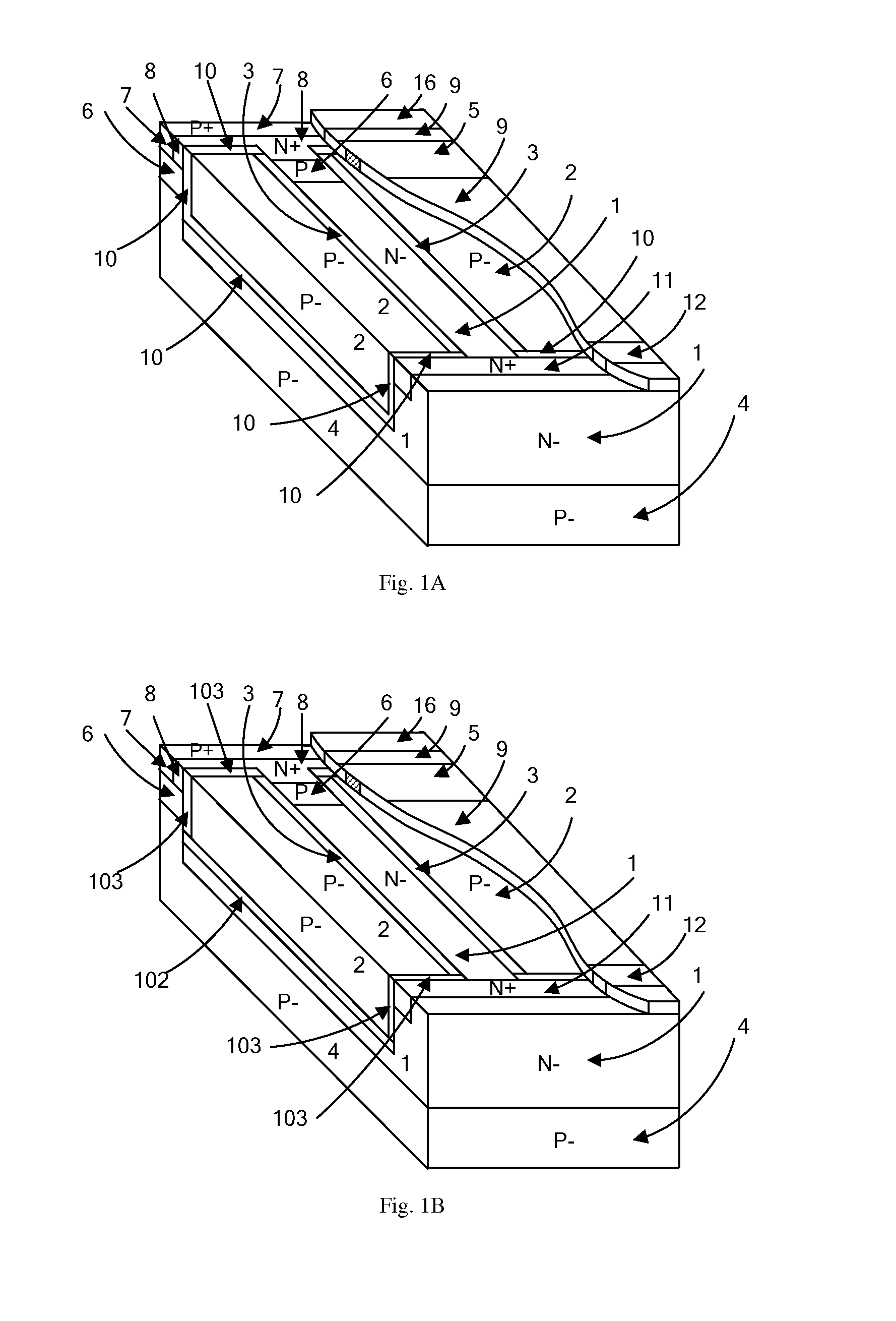
The present invention relates to a lateral high-voltage device. The device includes a dielectric trench region. A doping-overlapping structure with different doping types alternating mode is provided at least below, on a left side of, or on a right side of the dielectric trench region. The device also includes a dielectric layer, a body field plate, a polysilicon gate, a gate oxide layer, a first N-type heavy doping region, a second N-type heavy doping region, a P-type heavy doping region, a P-well region, the first N-type doping pillar, the second N-type doping pillar, the third N-type doping pillar, the first P-type doping pillar, and the second P-type doping pillar. The invention adopts a dielectric trench region in the drift region to keep the breakdown voltage BV of the device while reducing the surface area of the device, and effectively reducing the device's specific On-Resistance RON,sp.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Lateral power device having low specific on-resistance and using high-dielectric constant socket structure and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveUS20150333170A1Evenly distributedImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceOhmic contact
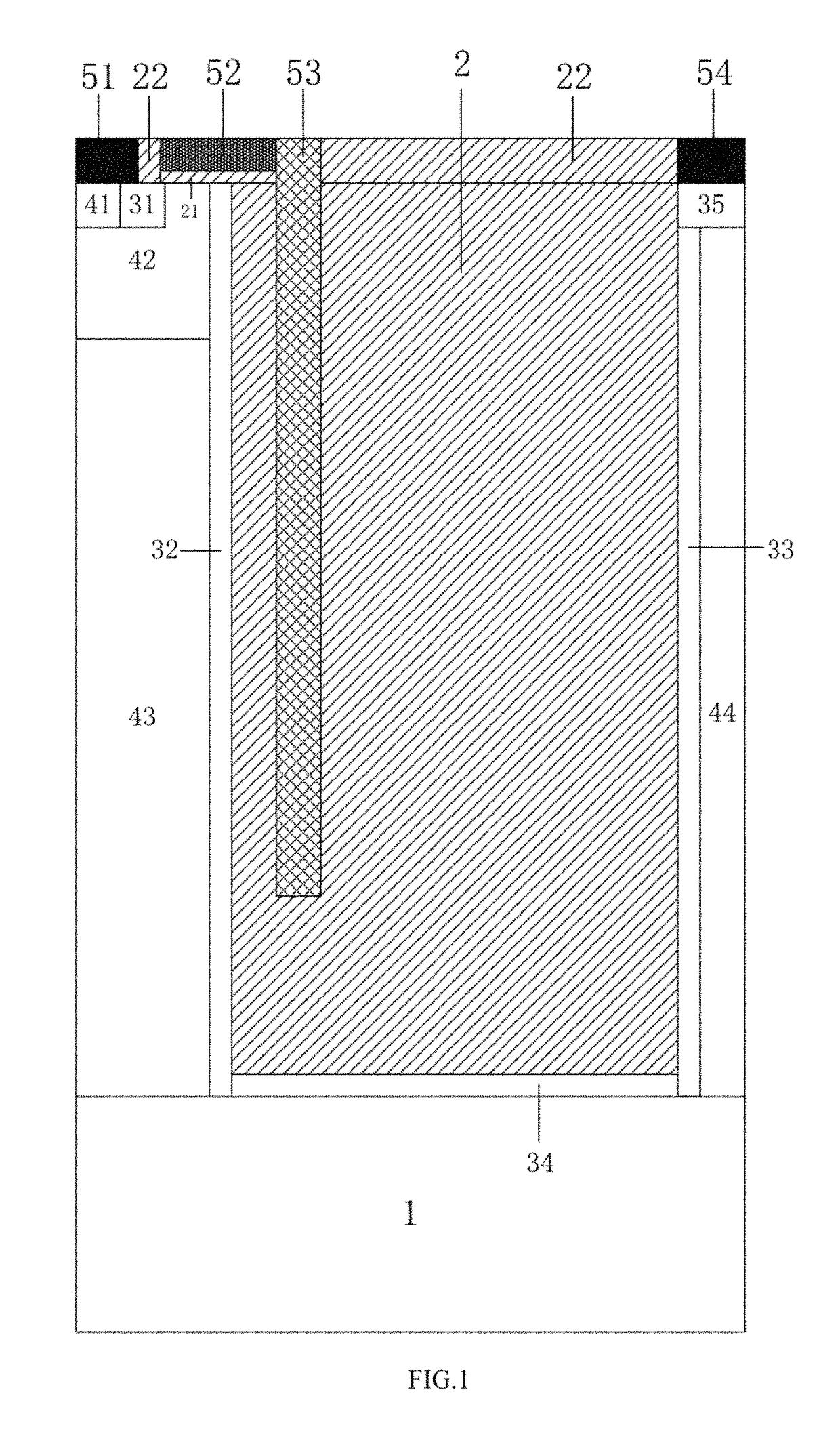
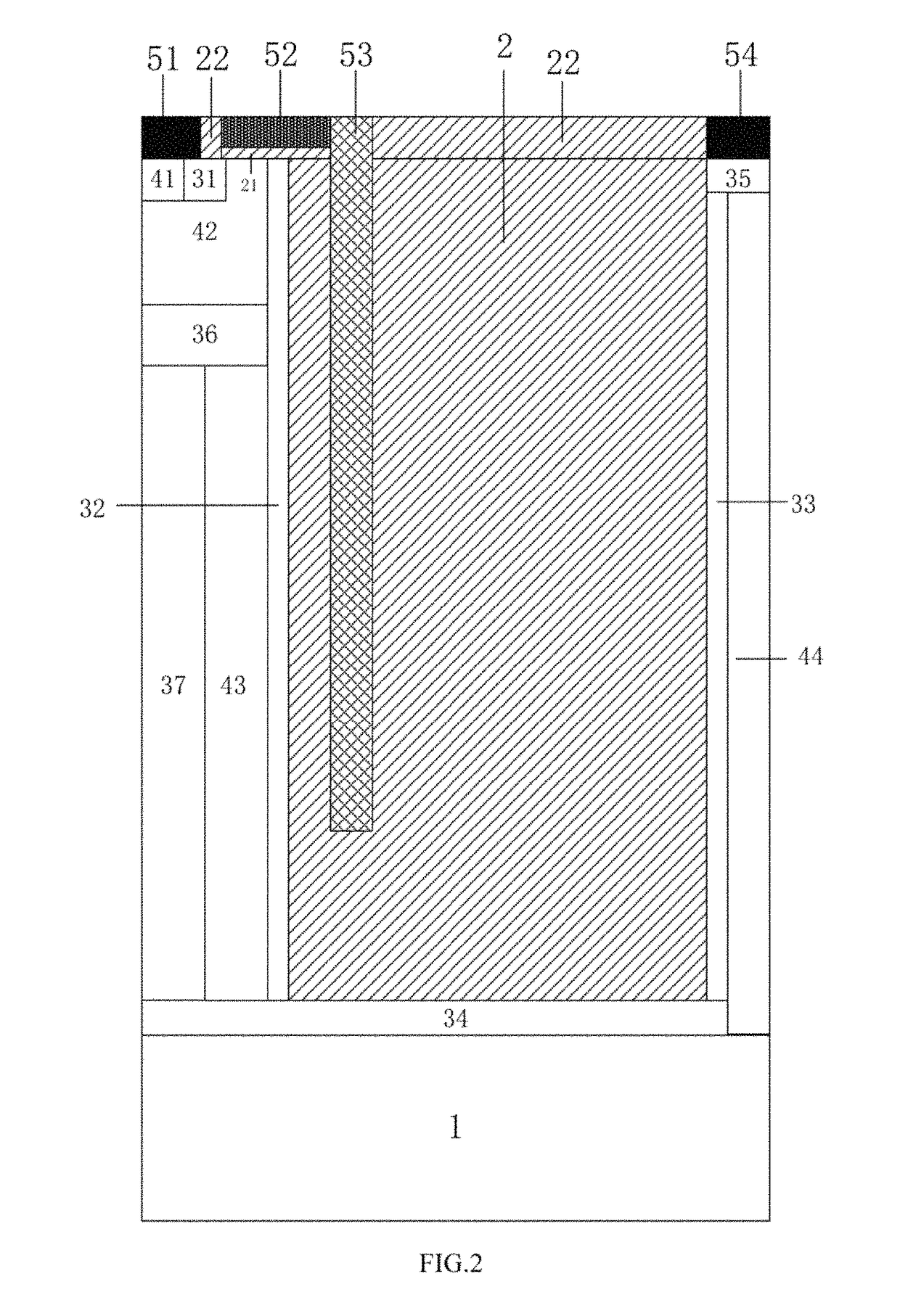
Provided is a lateral power device having low specific ON-resistance and using a high-dielectric constant socket structure and a manufacturing method therefor, which relate to semiconductor power devices. A source electrode (8) of the device is of a first conduction type, and a channel region (6), a silicon substrate (4) and an ohmic contact heavily-doped region are of a second conduction type; at least two isolation regions are arranged in an embedded manner in a drift region (1); between the isolation regions are the drift region (1) and the channel region (6); each isolation region extends from the source electrode (8) to a drain electrode (11); high-dielectric constant material strips (3) and first insulation dielectric layers (10) form boundaries of the bottoms and sidewalls of the isolation regions; the isolation regions are filled with a first filling material (2), a second insulation dielectric layer (9) is arranged on the upper surface of the drift region (1) and the upper surfaces of the isolation regions, and a gate electrode (5) directly contacts the first filling material (2) via holes on the second insulation dielectric layer (9); and a source electrode lead-out wire (16) and a drain electrode lead-out wire (12) directly contact the source electrode (8) and the drain electrode (11) respectively via the holes on the second insulation dielectric layer (9). The area of a power device can be greatly reduced on the premise of not reducing the withstand voltage and not increasing the specific ON-resistance.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Structure of a lateral diffusion MOS transistor in widespread use as a power control device
InactiveUS6921942B2High currentOn-resistance of the device can be further reducedTransistorSolid-state devicesInter layerEngineering
There is provided a semiconductor device structured so as to be mounted jointly with other devices on one chip, and capable of controlling a large current in spite of a small device area while having small on-resistance, thereby enabling a high voltage resistance to be obtained. In the case of NLDMOS, the semiconductor device comprises an N well layer, formed on a p-type semiconductor substrate, a P well layer formed in the N well layer, a source electrode formed in a source trench cavity within the P well layer, a gate electrode formed in at least one of gate trench cavities within the P well layer, through the intermediary of an oxide film, and a drain electrode formed in a drain trench cavity within the N well layer, and further, N+ diffused layers are formed, around the source trench cavity, the drain trench cavity, respectively.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
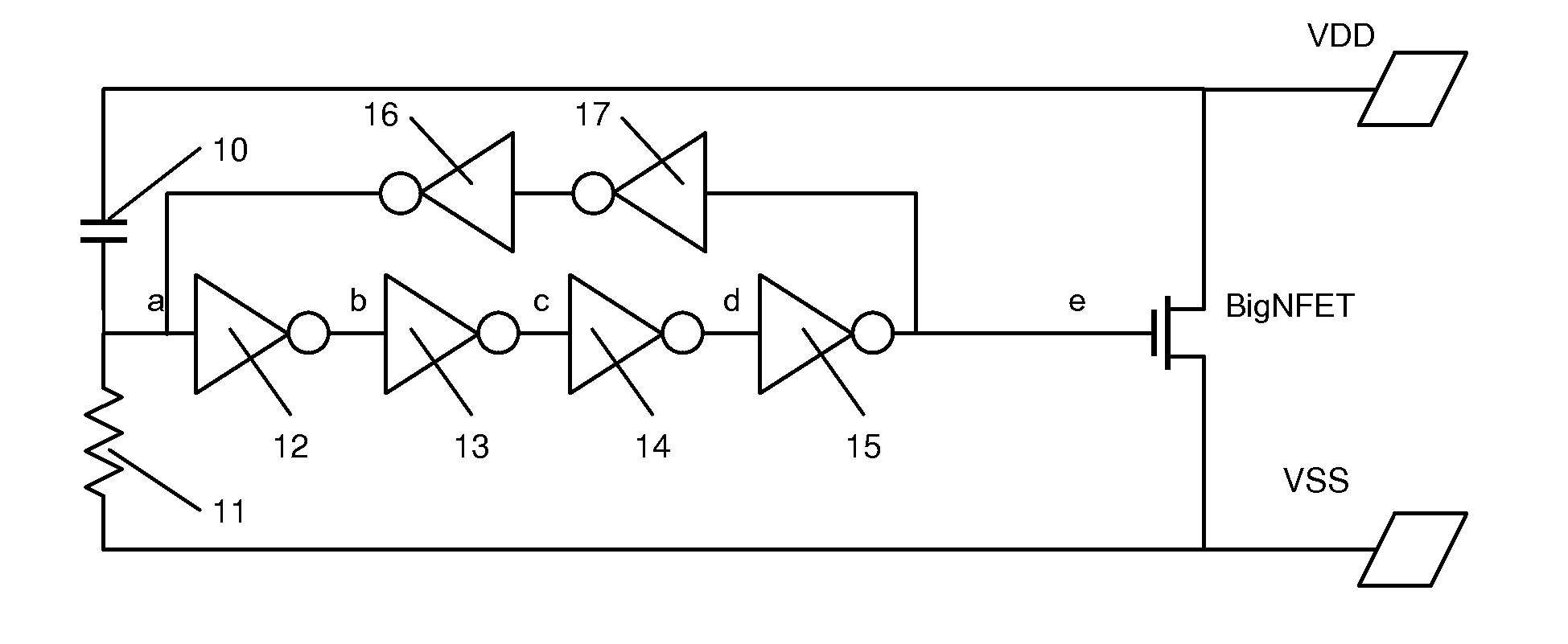
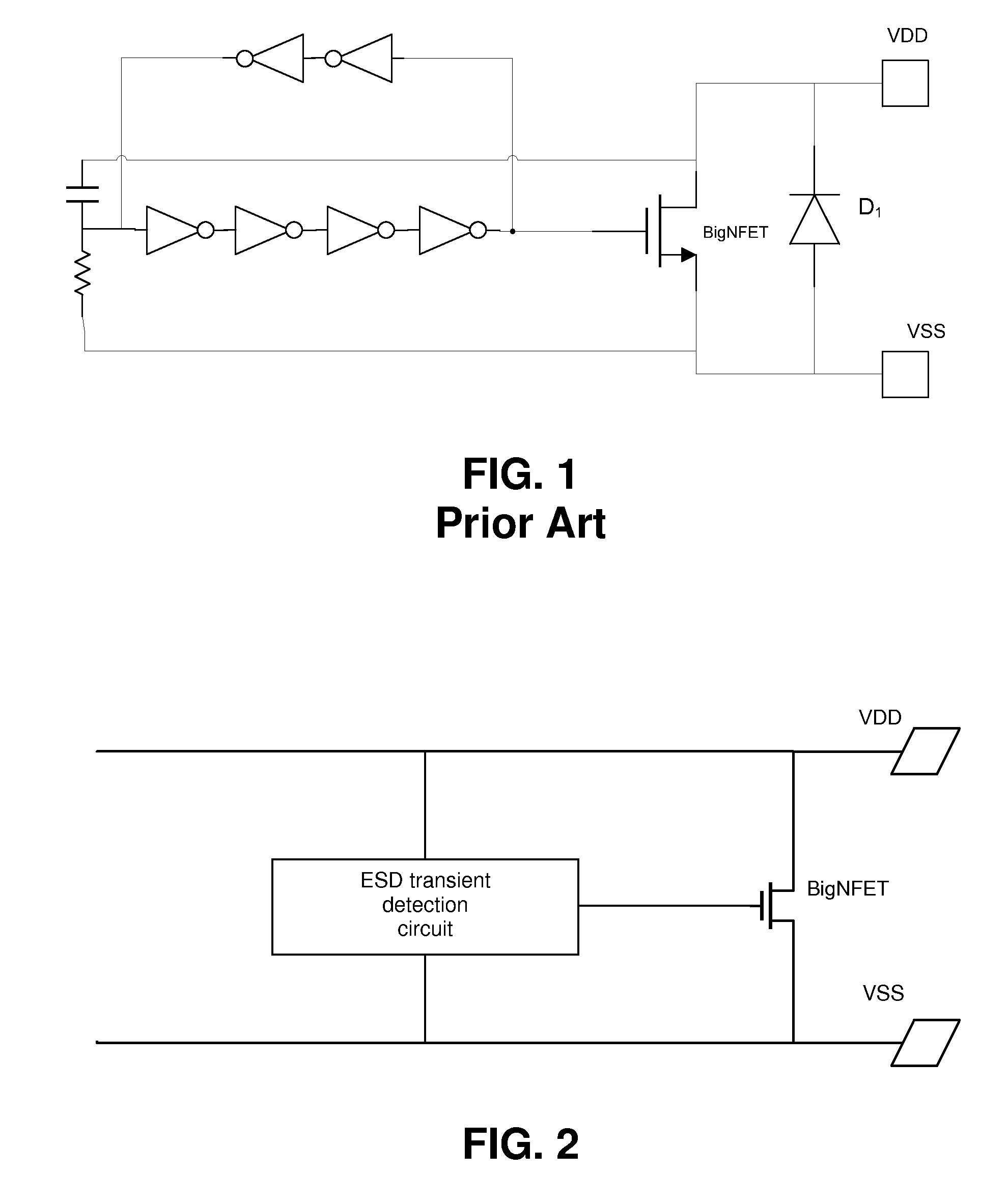
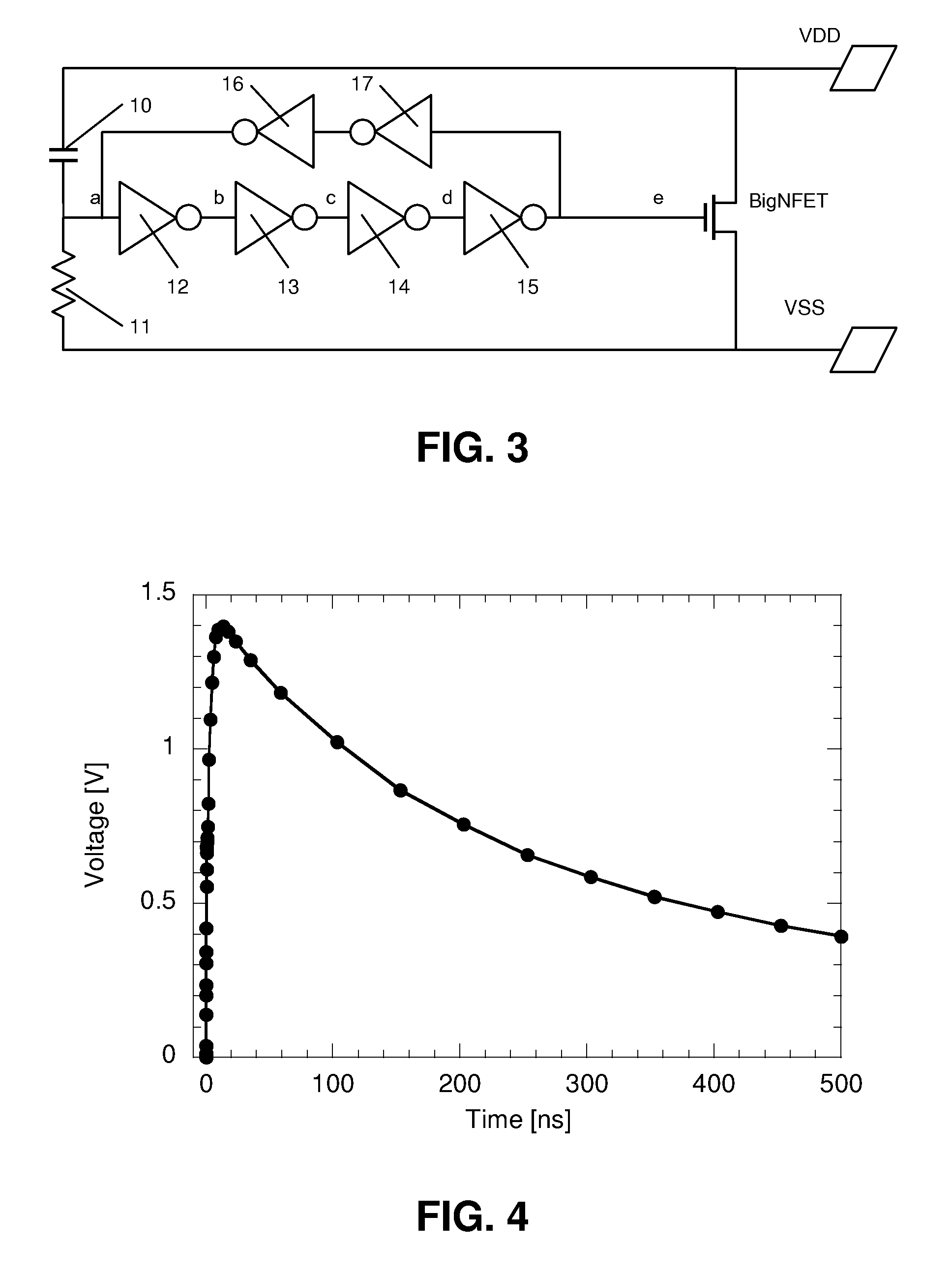
Bidirectional ESD Power Clamp
InactiveUS20100142105A1Easy to controlReduce device areaTransistorEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentSemiconductor structureEngineering
The disclosed method and device relates to a bidirectional ESD power clamp, comprising a semiconductor structure (BigNFET; BigPFET) having a conductive path connected between first and second nodes and having a triggering node via which the conductive path can be triggered. An ESD transient detection circuit is connected between the first and second nodes and to the triggering node and comprises a first part for detecting an occurrence of a first ESD transient on the first node. The semiconductor structure is provided on an insulator substrate, such that a parasitic conductive path between said first and second nodes via the substrate is avoided. The ESD transient detection circuit further comprises a second part for detecting an occurrence of a second ESD transient on the second node.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com