Patents
Literature
37 results about "Channel conductivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
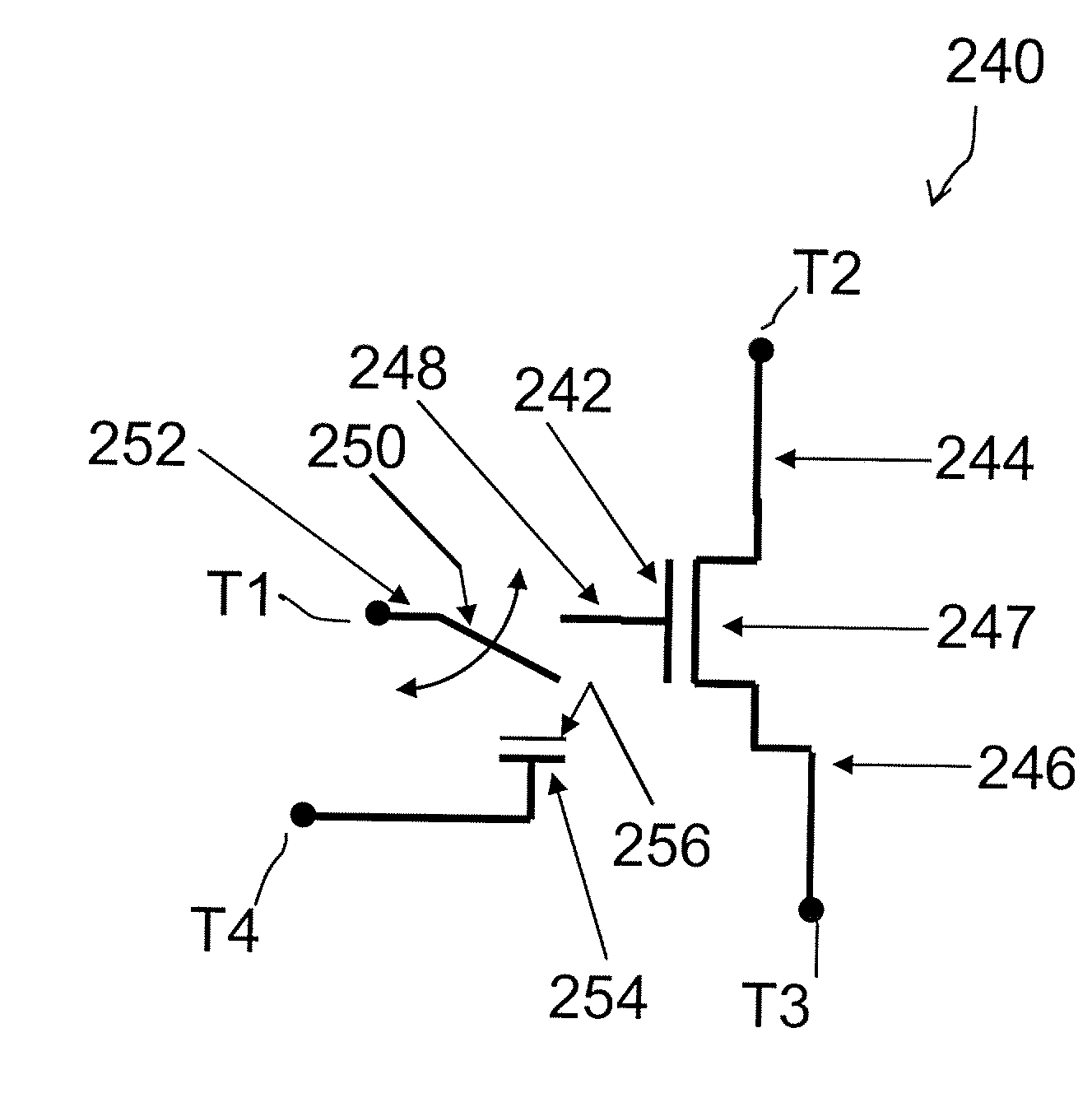
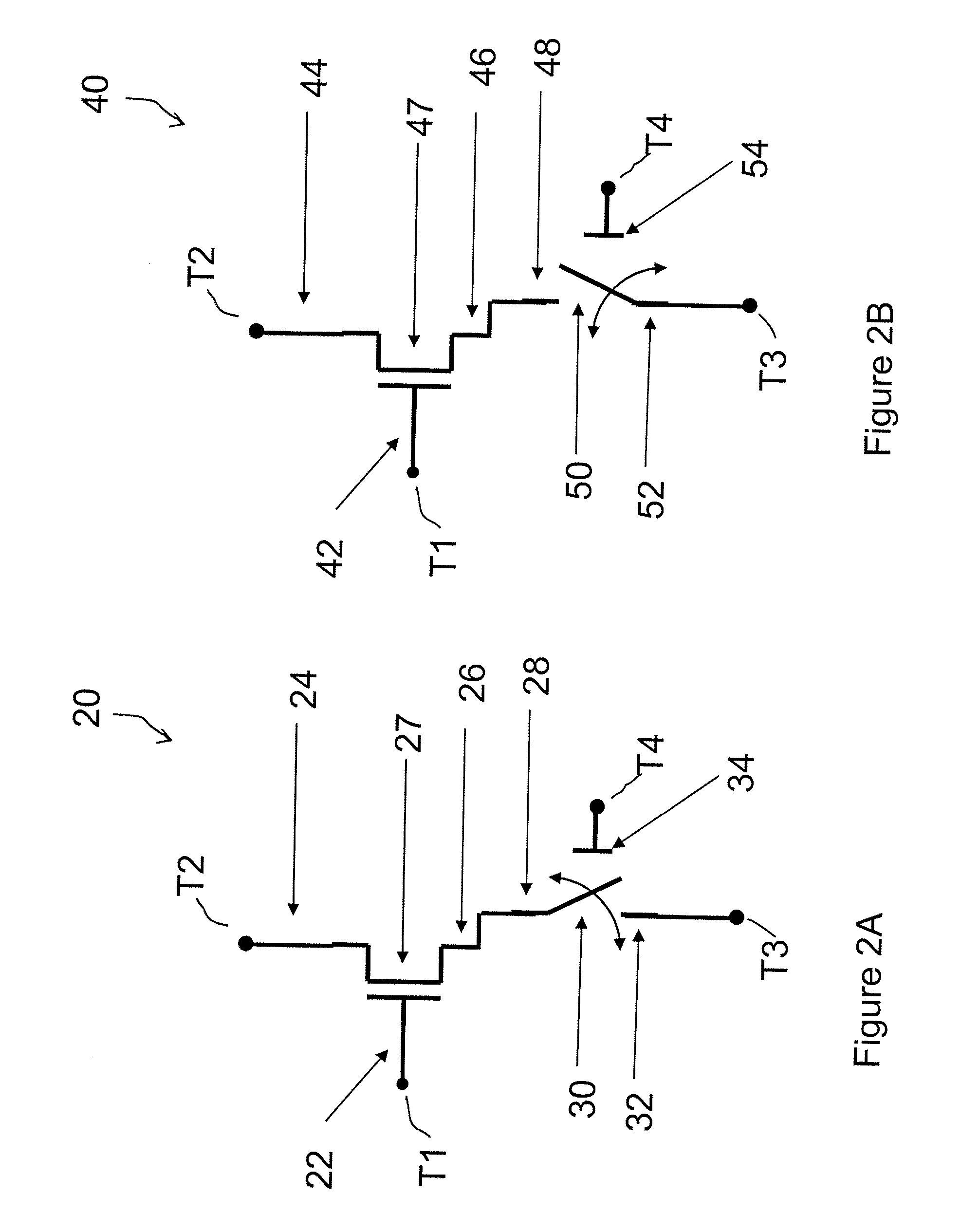
Field effect devices having a drain controlled via a nanotube switching element
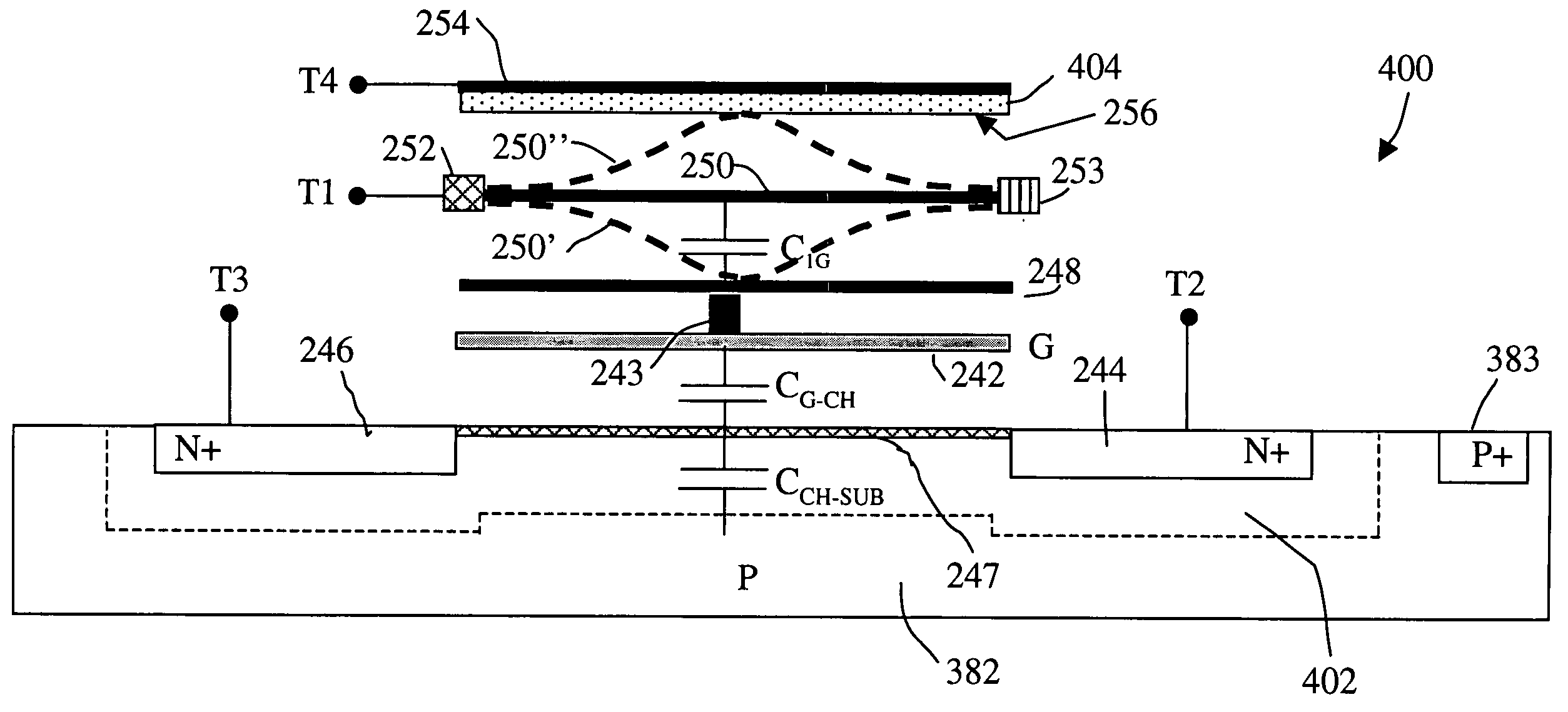
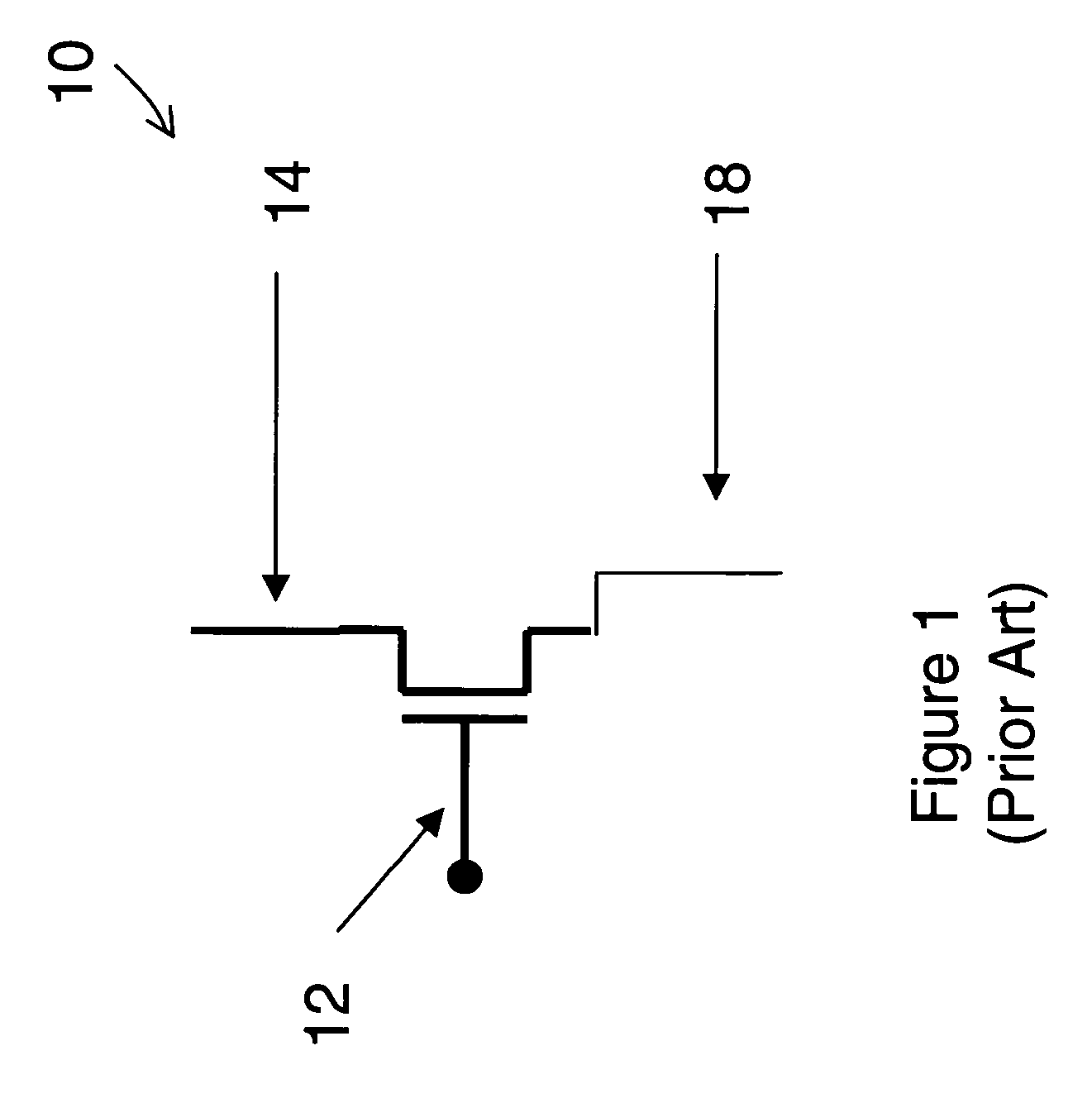
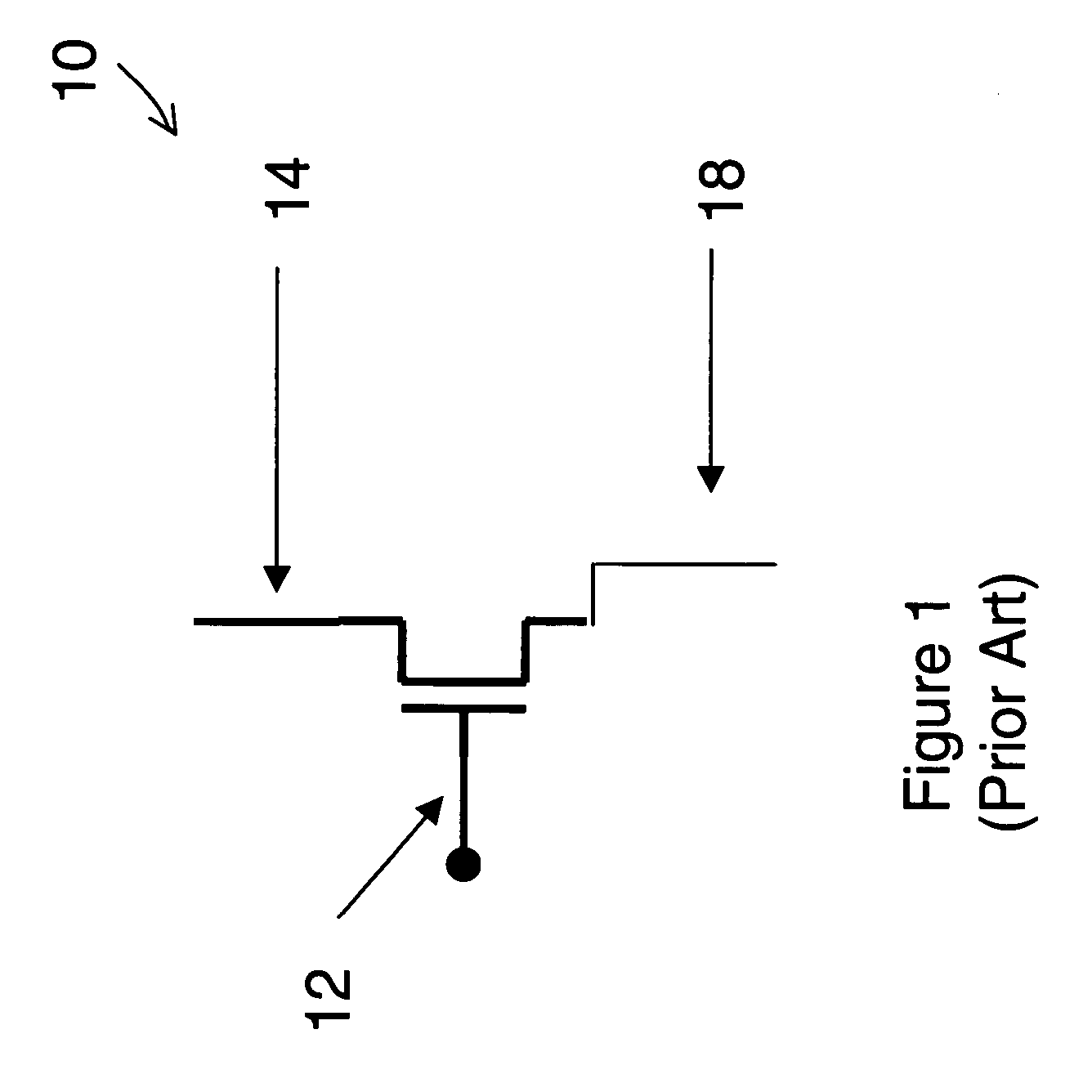
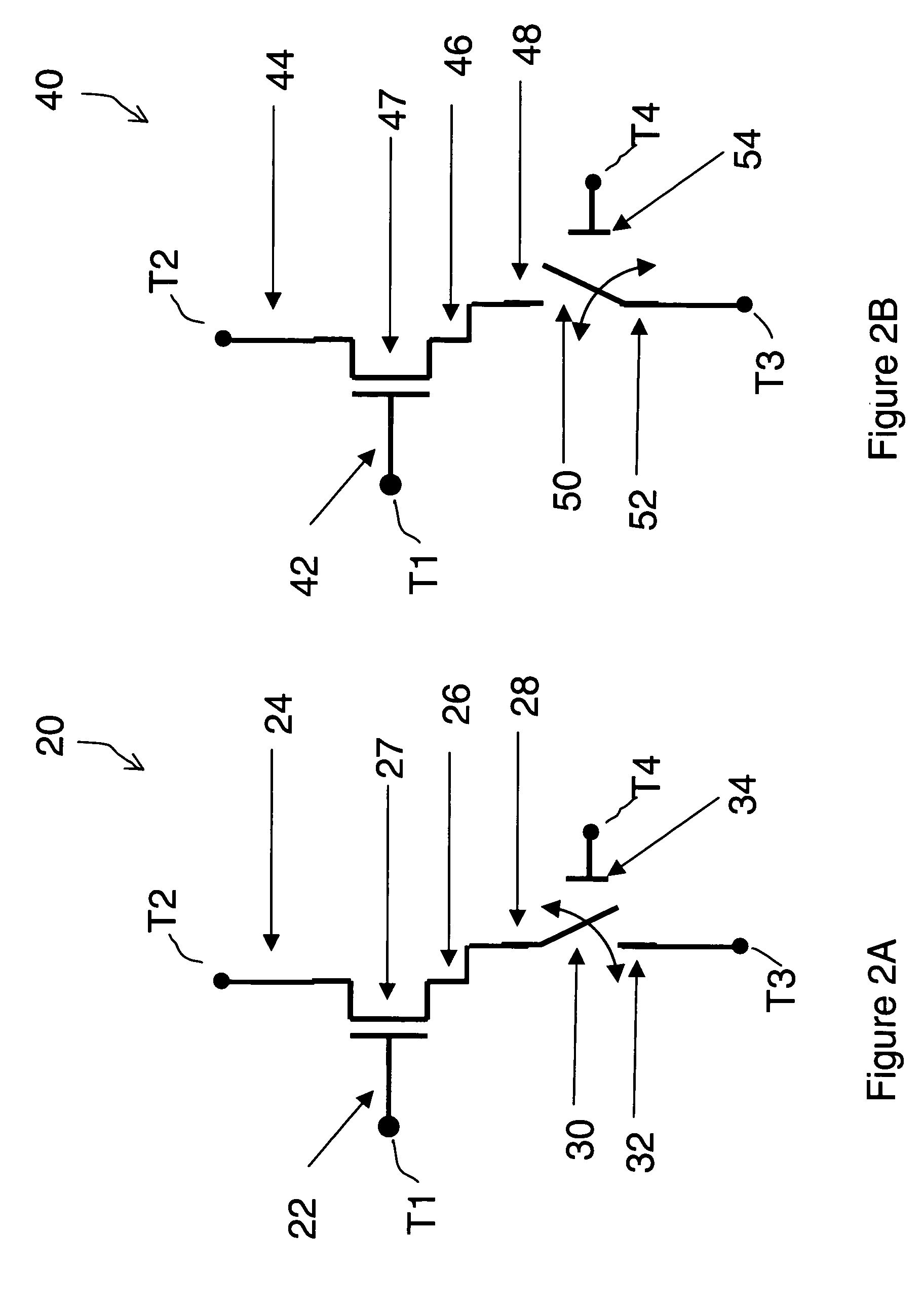
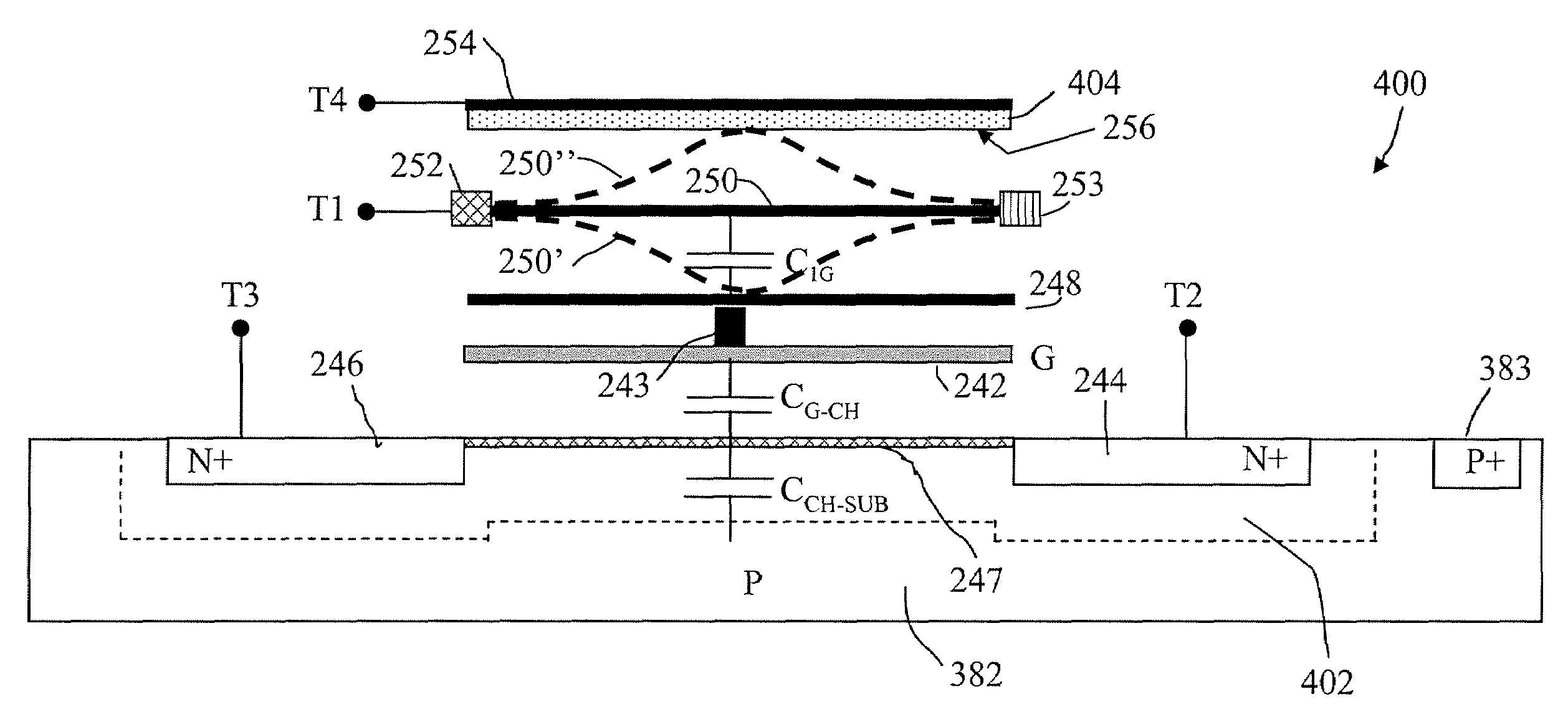
Field effect devices having a drain controlled via a nanotube switching element. Under one embodiment, a field effect device includes a source region and a drain region of a first semiconductor type and a channel region disposed therebetween of a second semiconductor type. The source region is connected to a corresponding terminal. A gate structure is disposed over the channel region and connected to a corresponding terminal. A nanotube switching element is responsive to a first control terminal and a second control terminal and is electrically positioned in series between the drain region and a terminal corresponding to the drain region. The nanotube switching element is electromechanically operable to one of an open and closed state to thereby open or close an electrical communication path between the drain region and its corresponding terminal. When the nanotube switching element is in the closed state, the channel conductivity and operation of the device is responsive to electrical stimulus at the terminals corresponding to the source and drain regions and the gate structure.
Owner:NANTERO
Field effect devices having a gate controlled via a nanotube switching element
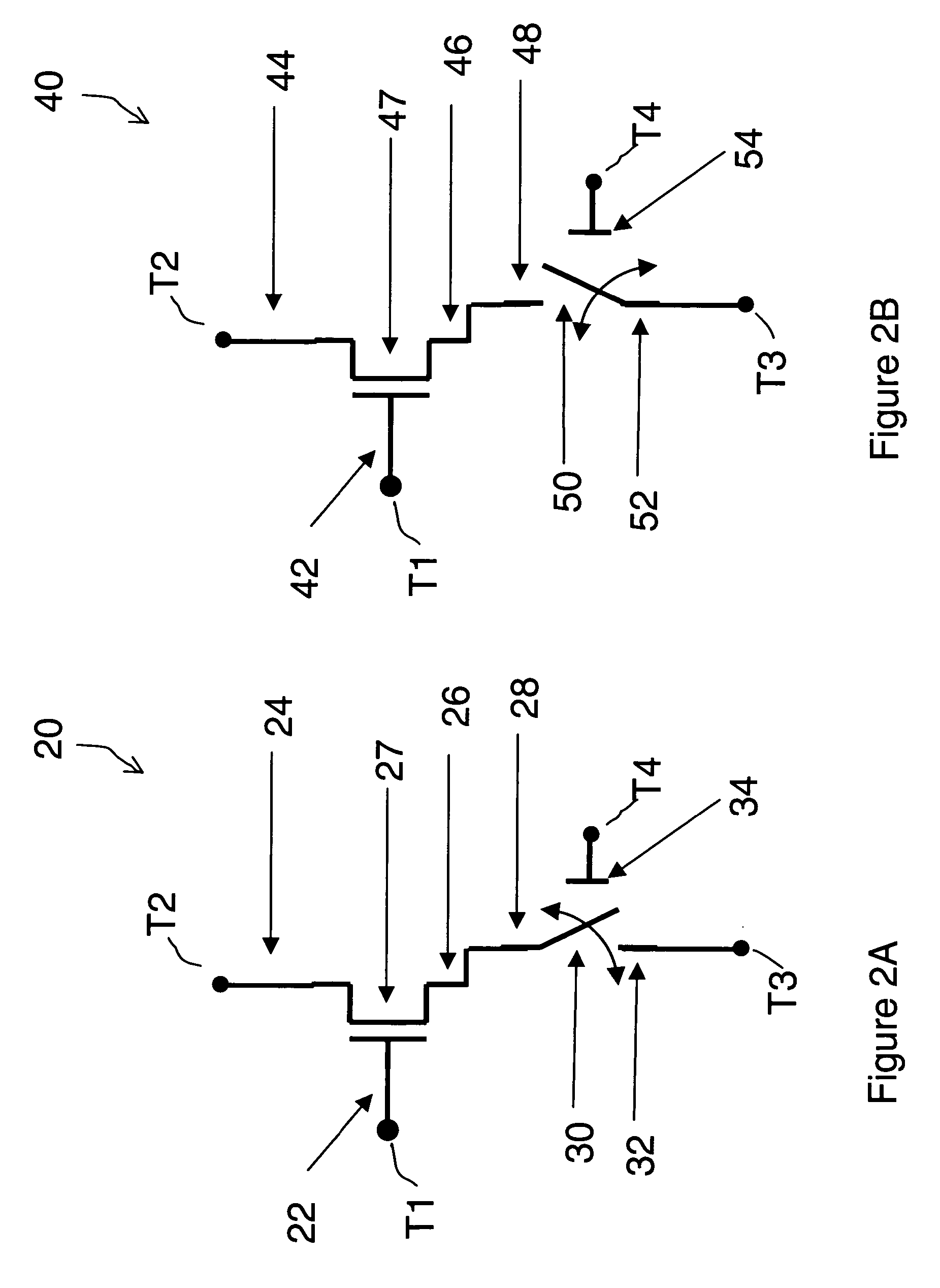
Field effect devices having a gate controlled via a nanotube switching element. Under one embodiment, a non-volatile transistor device includes a source region and a drain region of a first semiconductor type of material and each in electrical communication with a respective terminal. A channel region of a second semiconductor type of material is disposed between the source and drain region. A gate structure is disposed over an insulator over the channel region and has a corresponding terminal. A nanotube switching element is responsive to a first control terminal and a second control terminal and is electrically positioned in series between the gate structure and the terminal corresponding to the gate structure. The nanotube switching element is electromechanically operable to one of an open and closed state to thereby open or close an electrical communication path between the gate structure and its corresponding terminal. When the nanotube switching element is in the closed state, the channel conductivity and operation of the device is responsive to electrical stimulus at the terminals corresponding to the source and drain regions and the gate structure.
Owner:NANTERO
Field effect devices having a source controlled via a nanotube switching element
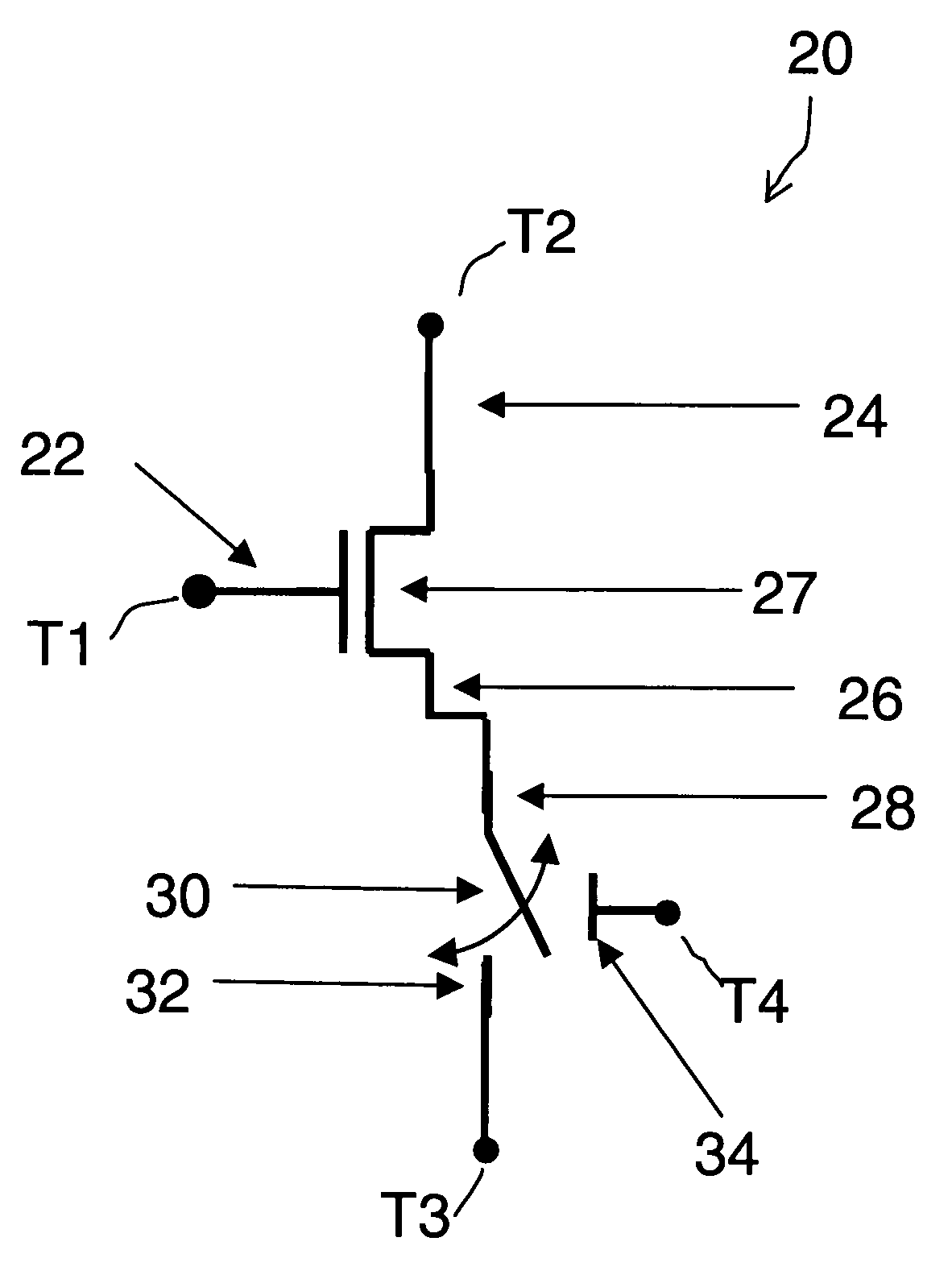
Field effect devices having a source controlled via a nanotube switching element. Under one embodiment, a field effect device includes a source region and a drain region of a first semiconductor type and a channel region disposed therebetween of a second semiconductor type. The drain region is connected to a corresponding terminal. A gate structure is disposed over the channel region and connected to a corresponding terminal. A nanotube switching element is responsive to a first control terminal and a second control terminal and is electrically positioned in series between the source region and a terminal corresponding to the source region. The nanotube switching element is electromechanically operable to one of an open and closed state to thereby open or close an electrical communication path between the source region and its corresponding terminal. When the nanotube switching element is in the closed state, the channel conductivity and operation of the device is responsive to electrical stimulus at the terminals corresponding to the source and drain regions and the gate structure.
Owner:NANTERO
HFET with low access resistance
InactiveUS20130032860A1SpecificEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceAccess resistance
A novel semiconductor power transistor is presented. The semiconductor structure is simple and is based on a Hetero-structure FET structure, where the access regions have been eliminated so as to effectively obtain a lower specific on-resistance, and a higher control on the transport properties of the device, drastically reducing the dispersion phenomena associated with these regions. The present invention can be realized both with polar and non-polar (or semi-polar) materials, without requiring delta doping implantation. It can be fabricated as an enhancement or depletion mode device with much higher control on the device threshold voltage with respect to state-of-the-art HFET devices, and achieving superior RF switching performance. Furthermore, due to the absence of access regions, enhancement mode devices can be realized without discontinuity in the channel conductivity, which results in an even lower on-resistance.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method of forming stress-relaxed SiGe buffer layer
InactiveUS20050196925A1Small thicknessLow densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETConstant composition
Provided is a method of forming a stress-relaxed SiGe buffer layer on a silicon substrate using a reduced pressure chemical vapor deposition (RPCVD) technique. The method includes: forming a graded composition layer having a predetermined germanium composition gradient on a silicon substrate; forming and thermally annealing a first constant composition layer having a predetermined germanium composition on the graded composition layer; removing the first constant composition layer by a predetermined thickness to planarize a surface; and forming a second constant composition layer on the first constant composition layer to form a SiGe buffer layer having the graded composition layer and the constant composition layer. A strained silicon or SiGe channel can be formed in a silicon-based MOSFET device or a MODFET device by forming the stress-relaxed SiGe buffer layer that has a relatively thin thickness, a low surface dislocation density, and a surface roughness similar to bulk silicon, and thus a device having excellent channel conductivity and high frequency characteristics can be manufactured.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
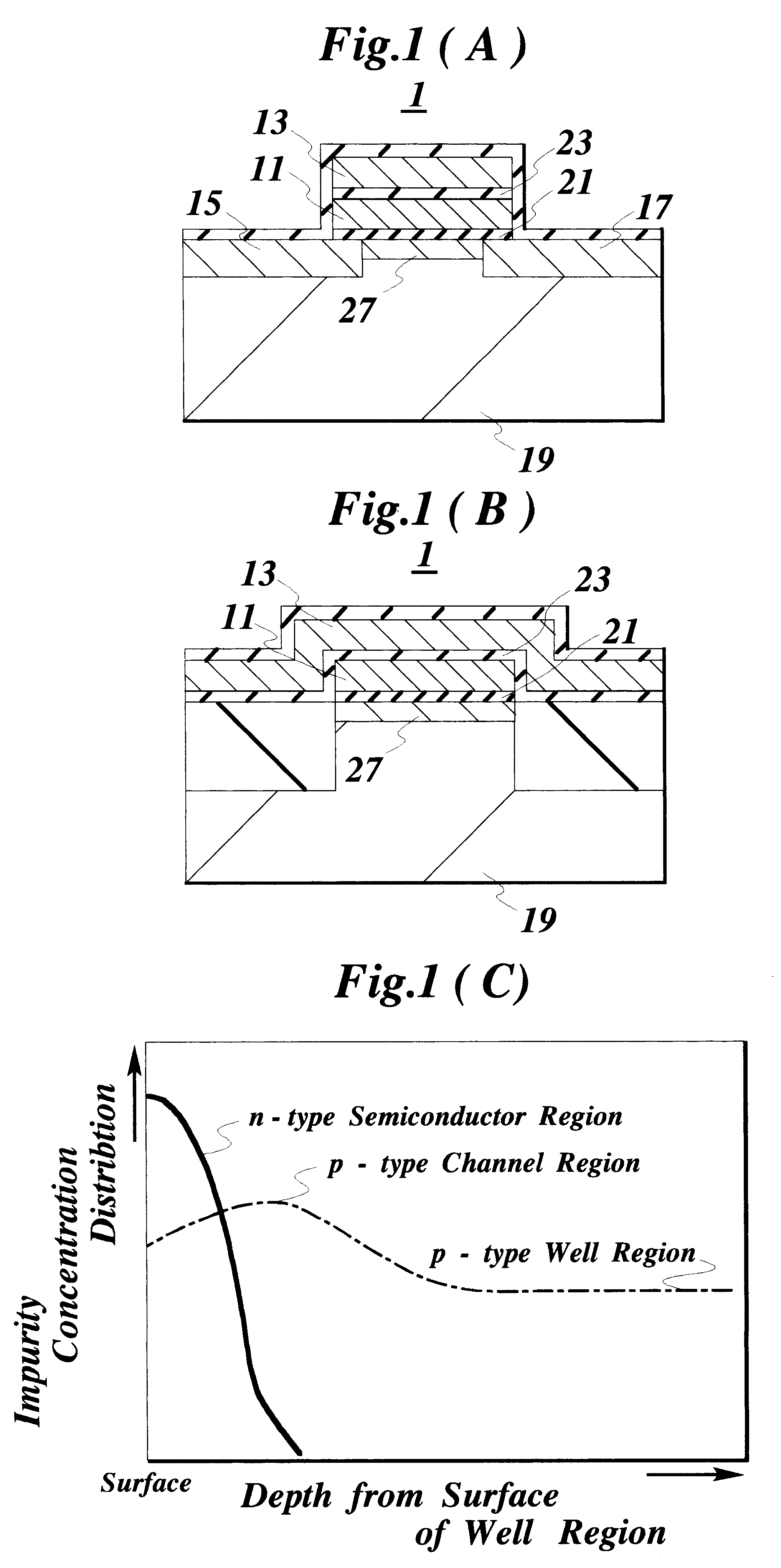
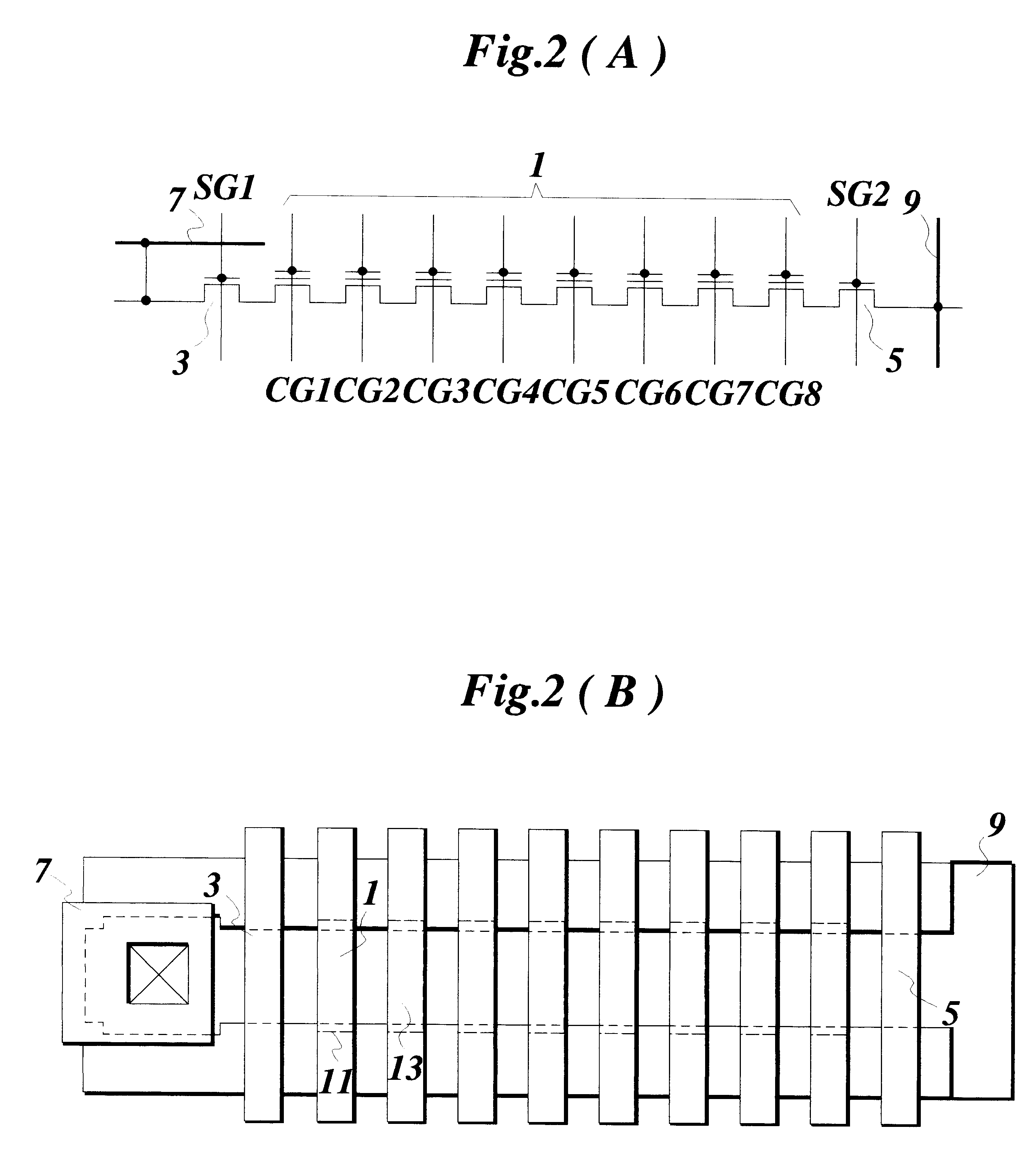
Erasable and programmable nonvolatile semiconductor memory, semiconductor integrated circuit device having the semiconductor memory and method of manufacturing the semiconductor memory
InactiveUS6222224B1Improve reliabilityReduced strengthTransistorSolid-state devicesChannel conductivitySemiconductor
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory has memory cells (1) each having an insulated-gate FET that has an information storage part. A semiconductor region (27) is formed at the surface of a channel region of each memory cell. The semiconductor region has the same conductivity type as a channel conductivity type and functions to decrease the strength of an electric field at the surface of the channel region. If the insulated-gate FET is of an n-channel type, the semiconductor region is of an n-type. The semiconductor region suppresses threshold voltage variations among the insulated-gate FETs of the memory cells and prevents soft-writing in the memory cells.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Field effect devices having a gate controlled via a nanotube switching element
Field effect devices having a gate controlled via a nanotube switching element. Under one embodiment, a non-volatile transistor device includes a source region and a drain region of a first semiconductor type of material and each in electrical communication with a respective terminal. A channel region of a second semiconductor type of material is disposed between the source and drain region. A gate structure is disposed over an insulator over the channel region and has a corresponding terminal. A nanotube switching element is responsive to a first control terminal and a second control terminal and is electrically positioned in series between the gate structure and the terminal corresponding to the gate structure. The nanotube switching element is electromechanically operable to one of an open and closed state to thereby open or close an electrical communication path between the gate structure and its corresponding terminal. When the nanotube switching element is in the closed state, the channel conductivity and operation of the device is responsive to electrical stimulus at the terminals corresponding to the source and drain regions and the gate structure.
Owner:NANTERO
Power device and method for fabricating thereof
InactiveUS20170345921A1Increased effective gate widthIncrease widthSemiconductor devicesWave structureGate oxide
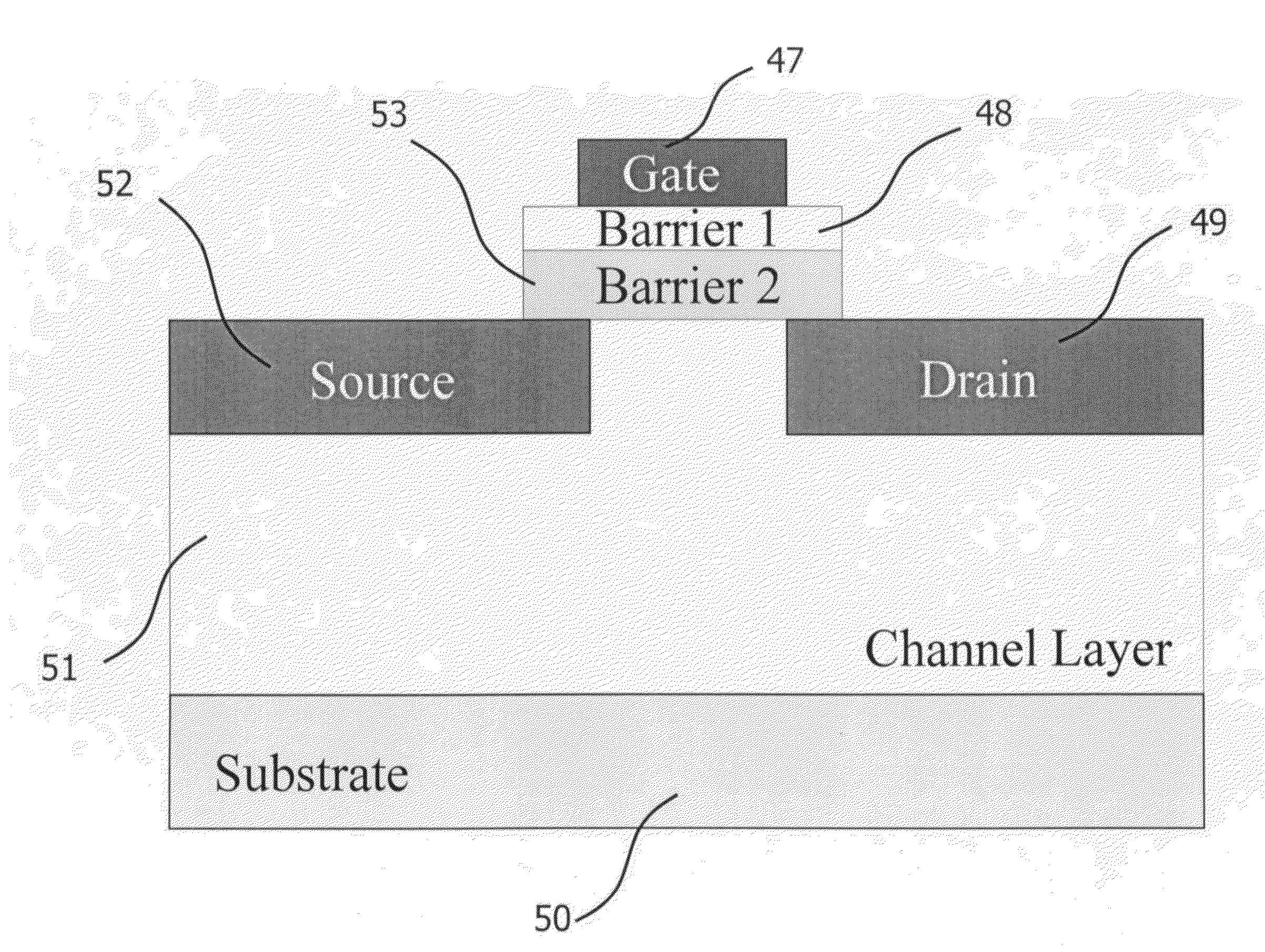
A power device having a patterned three-dimensional gate geometry is fabricated and described. The power device achieved increased effective gate width and increased channel conductivity per unit length. It includes at least a channel layer, a barrier layer, a dielectric layer, a gate disposed on the dielectric layer, dielectric layer disposed on the barrier layer and the channel layer, respectively. Gate includes protruding sections and extending sections directly contacting the dielectric layer. Dielectric layer includes a repeating rectangular-wave structure. The dielectric layer forms a gate oxide directly contacting trenches of channel layer. Alternatively, gate oxide can be disposed directly on a p-doped GaN filled region which includes an alternating repeating rectangular-wave structure.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20060255406A1Reduce device areaDistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialHemt circuits
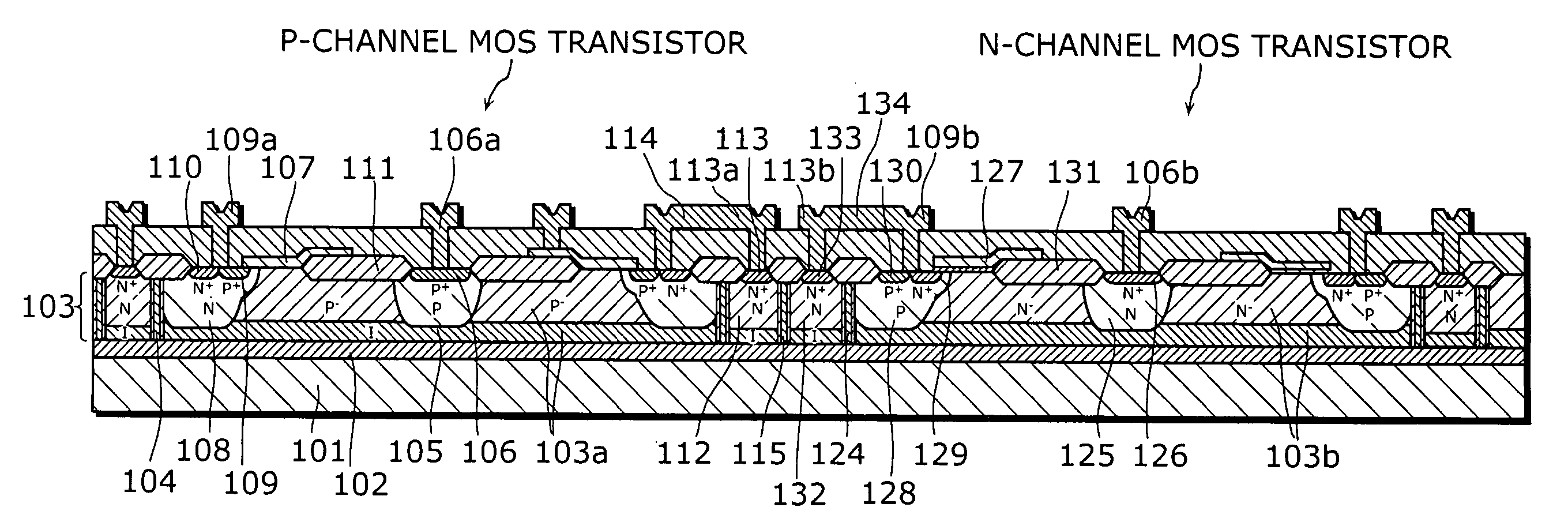
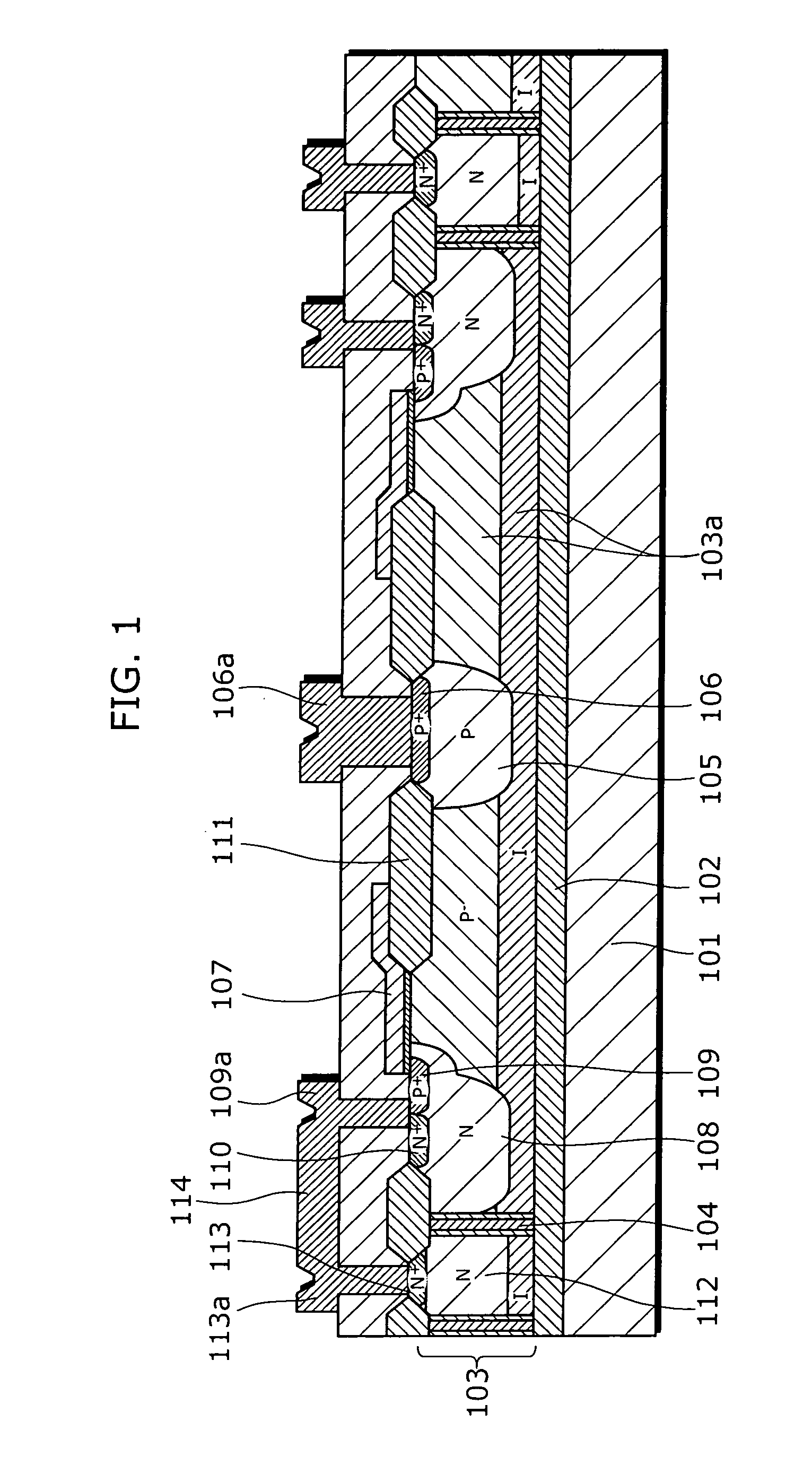
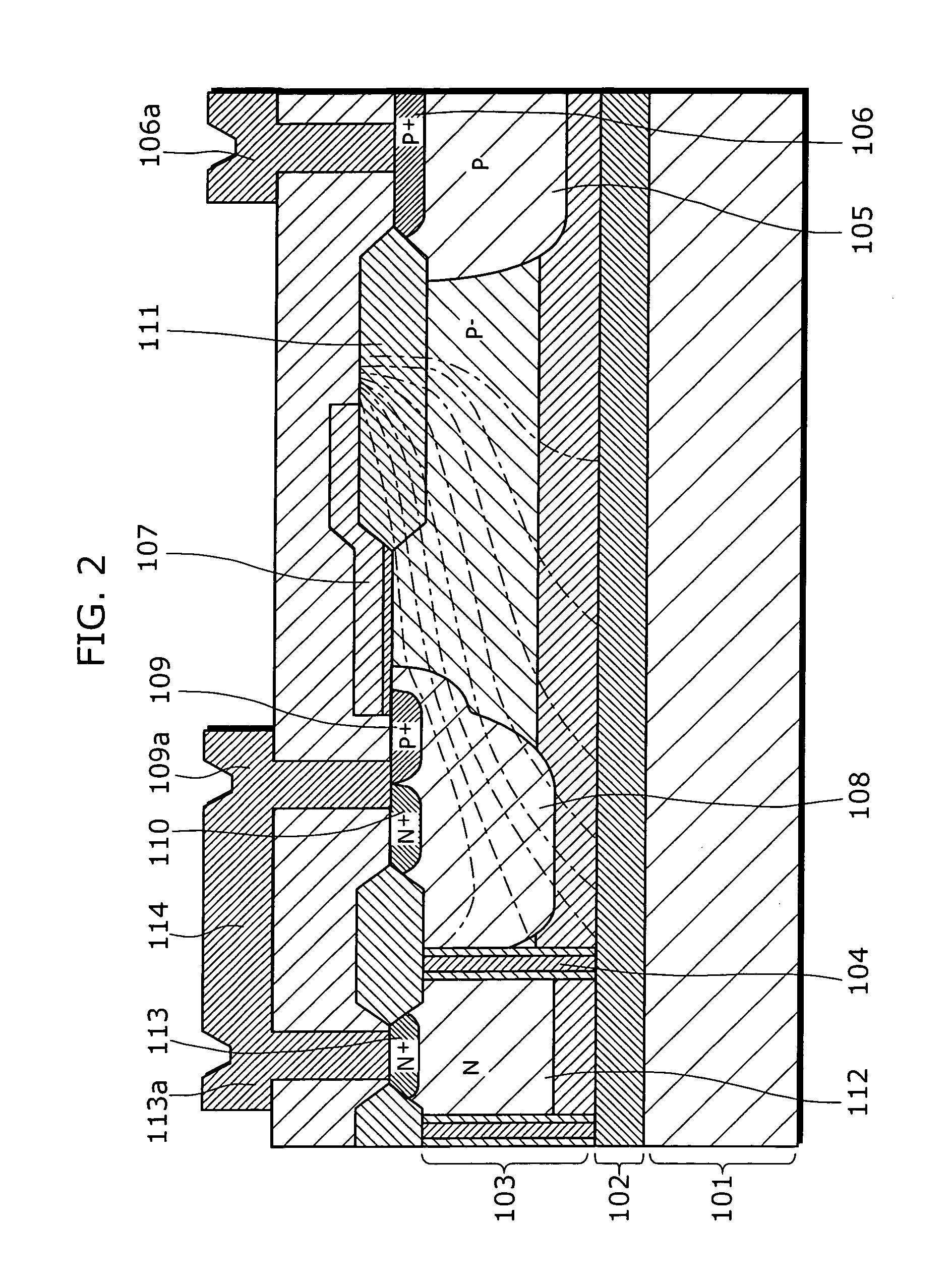
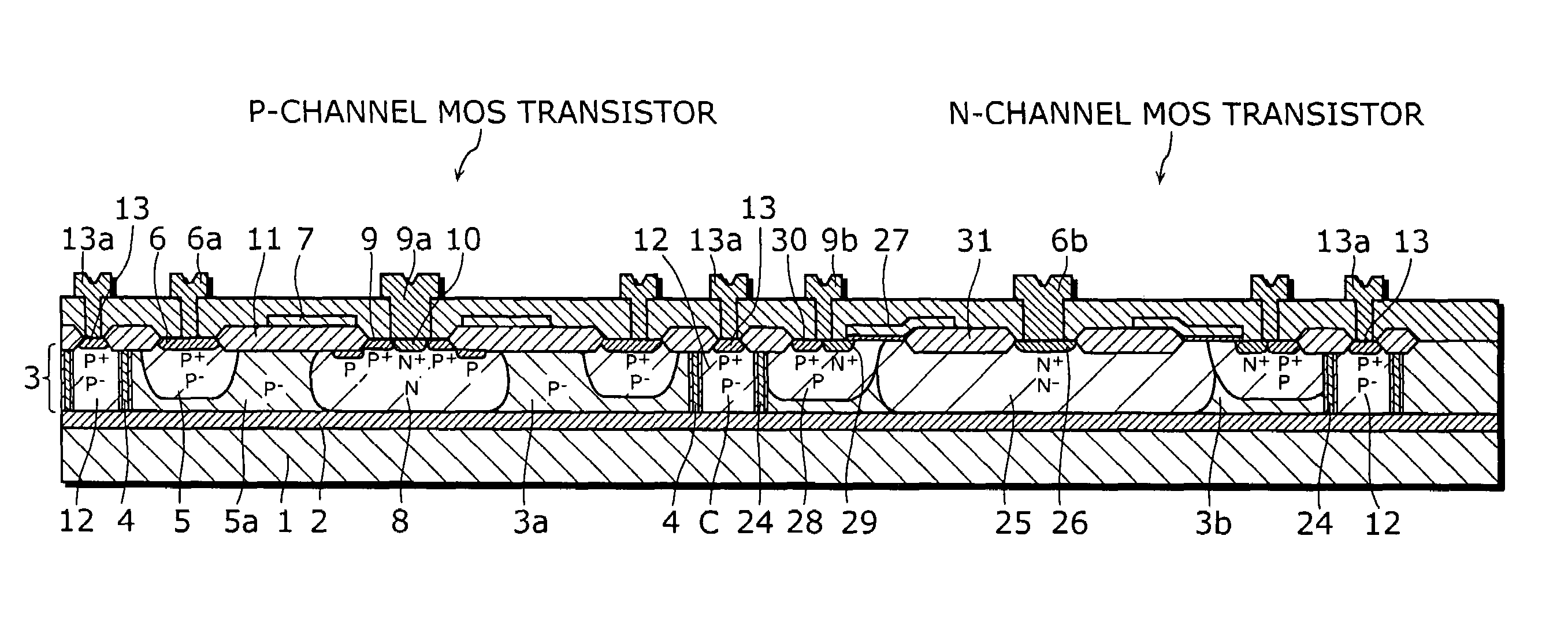
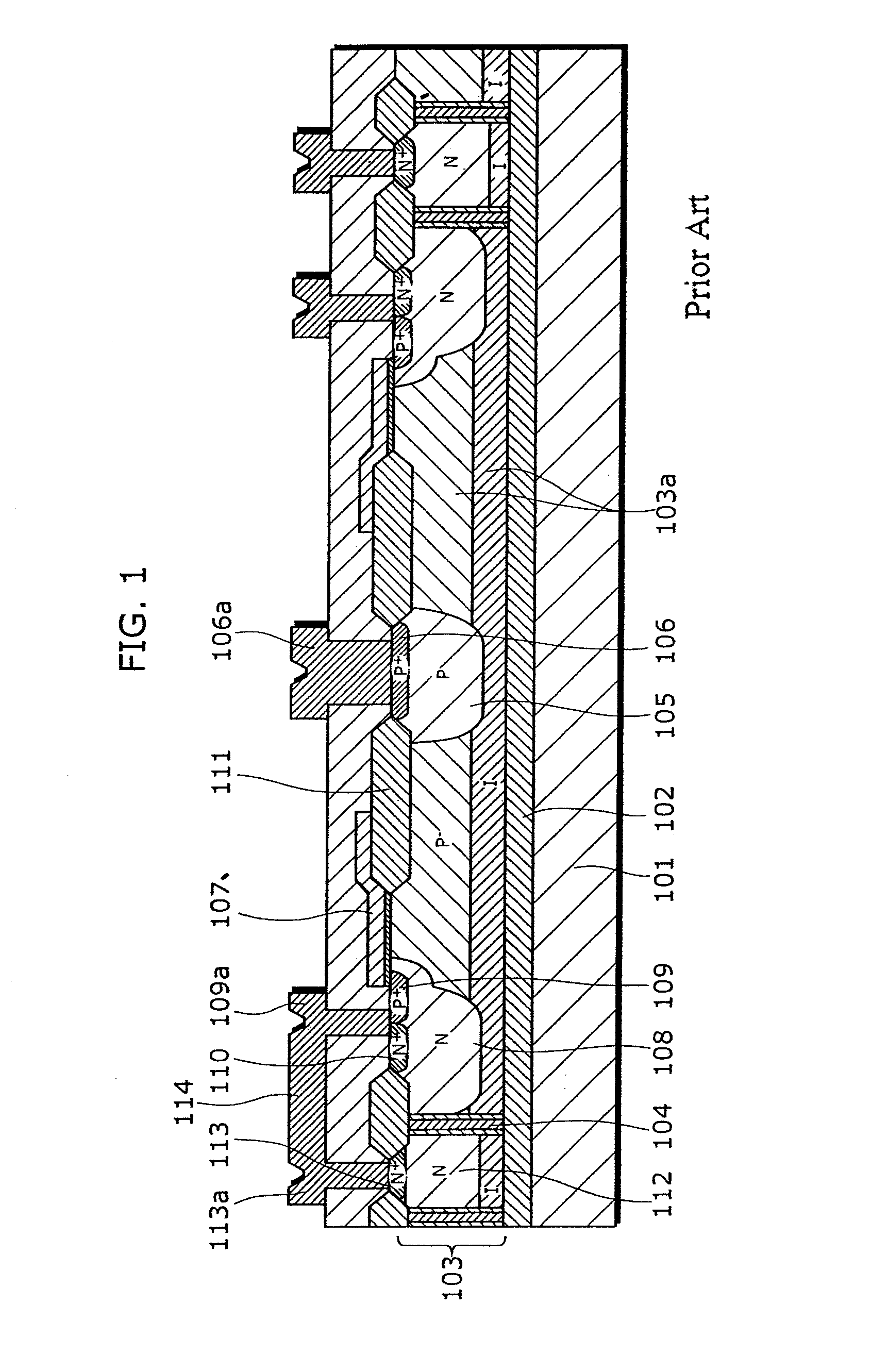
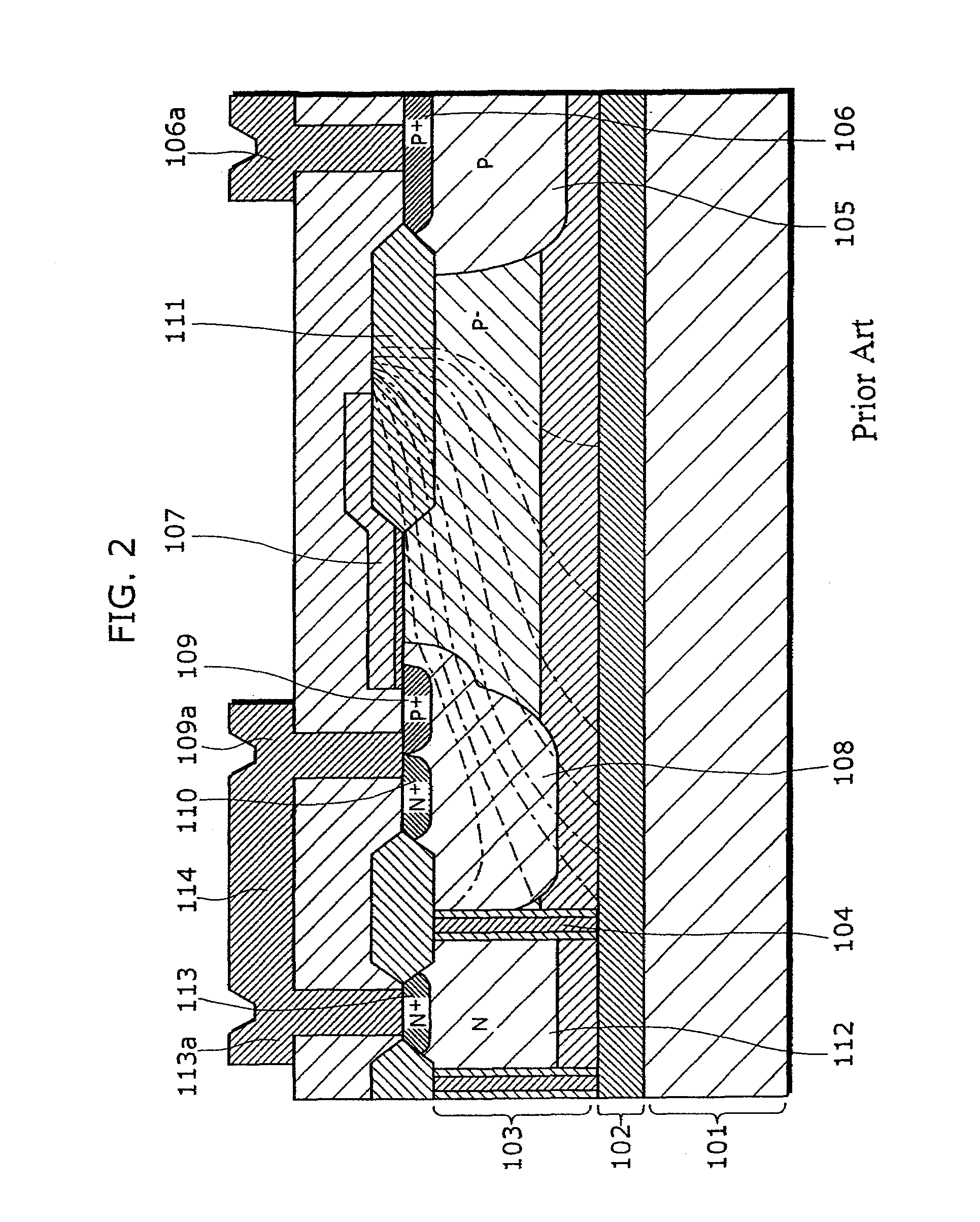
An object of the present invention is to provide a semiconductor device which enables to reduce the device area, while securing the breakdown voltage between the drain and the source of each MOS transistor for the semiconductor device including plural MOS transistors, which are arrayed adjacently each other, with different types of channel conductivity. The semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate, a buried oxide film and a semiconductor layer, and furthermore the semiconductor layer has an island-like semiconductor layer, in which a MOS transistor is formed, the MOS transistor has a source region, and a drain region that is positioned in the periphery of the source region, an island-like semiconductor layer, in which a MOS transistor is formed, the MOS transistor has a drain region, and a source region is that is positioned in the periphery of the drain region, an isolation trench which isolates the former island-like semiconductor layer from other portions of the semiconductor layer, an isolation trench which isolates the latter island-like semiconductor layer from other portions of the semiconductor layer, and a buffer region, in which the electric potential is fixed to the lowest electric potential in a circuit, which prevents an electrical interference occurred between transistors.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
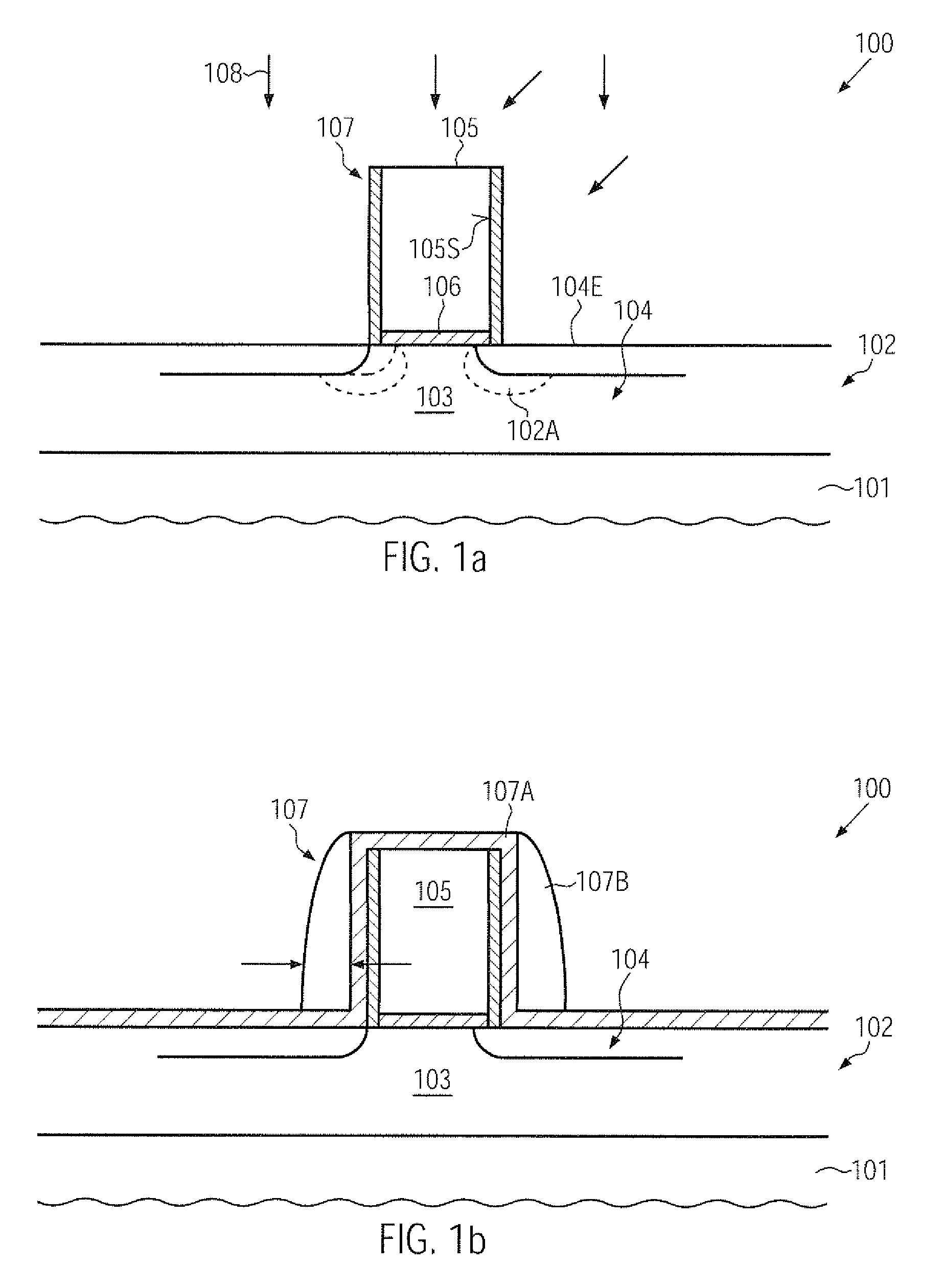
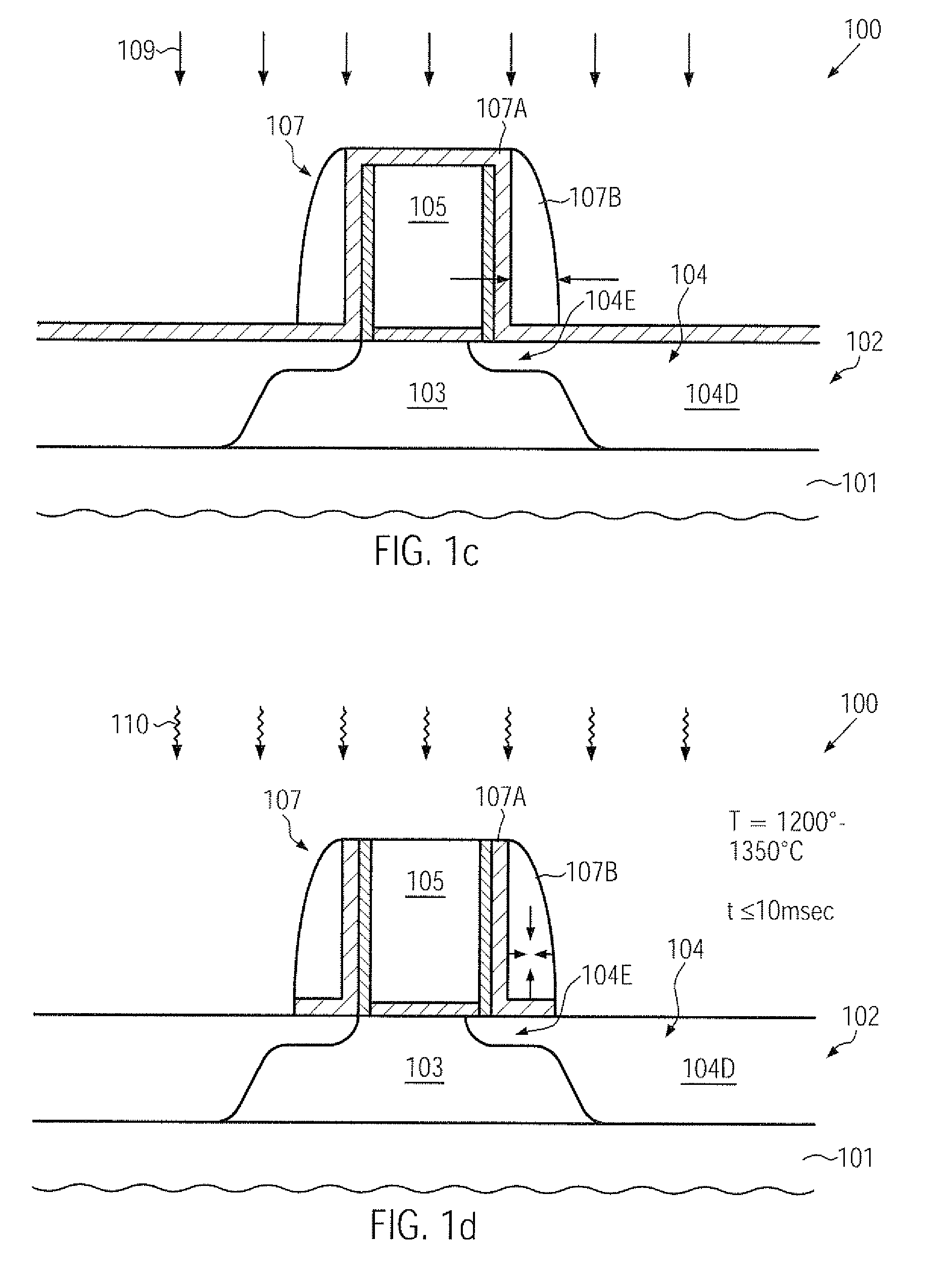
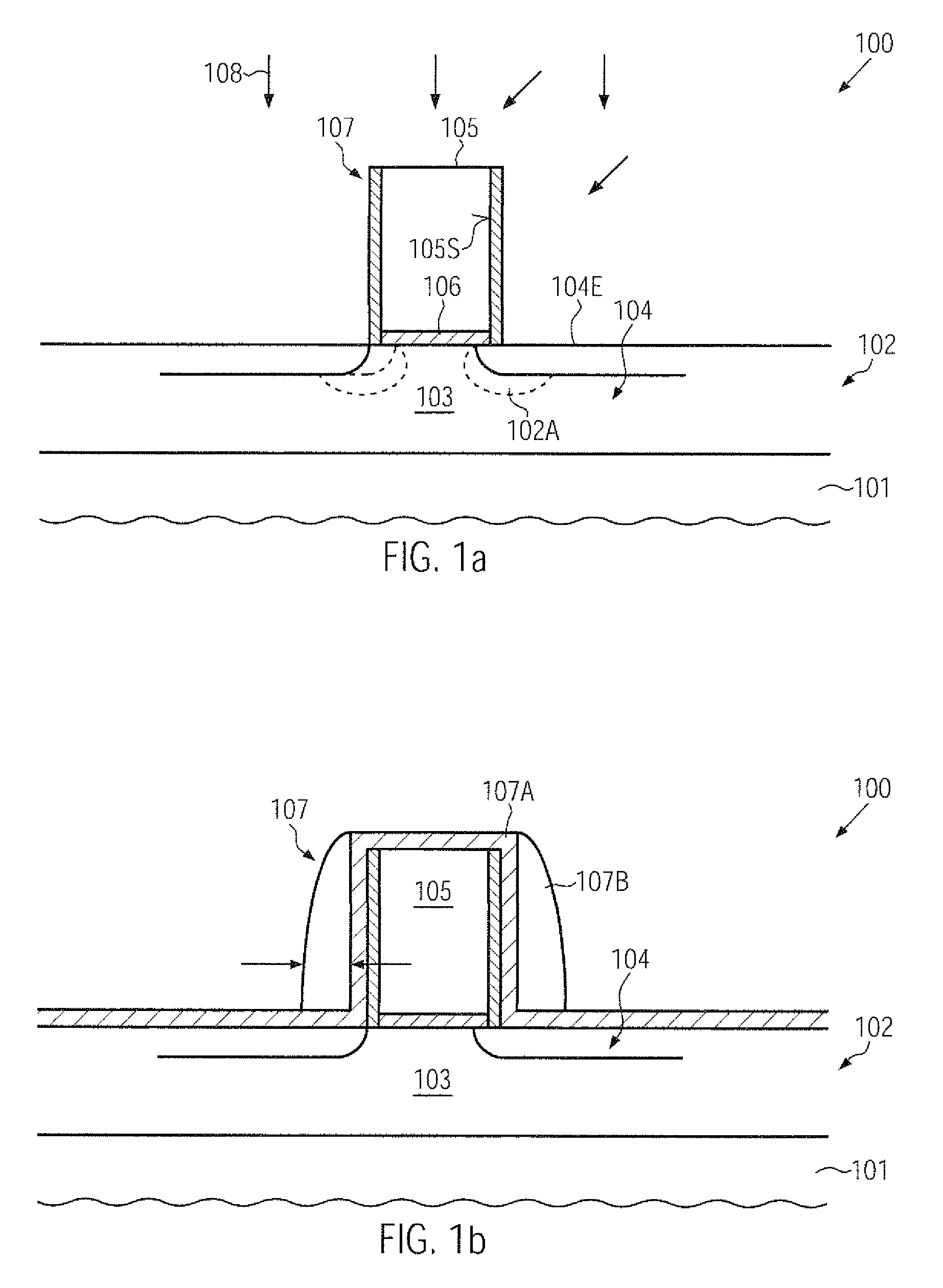
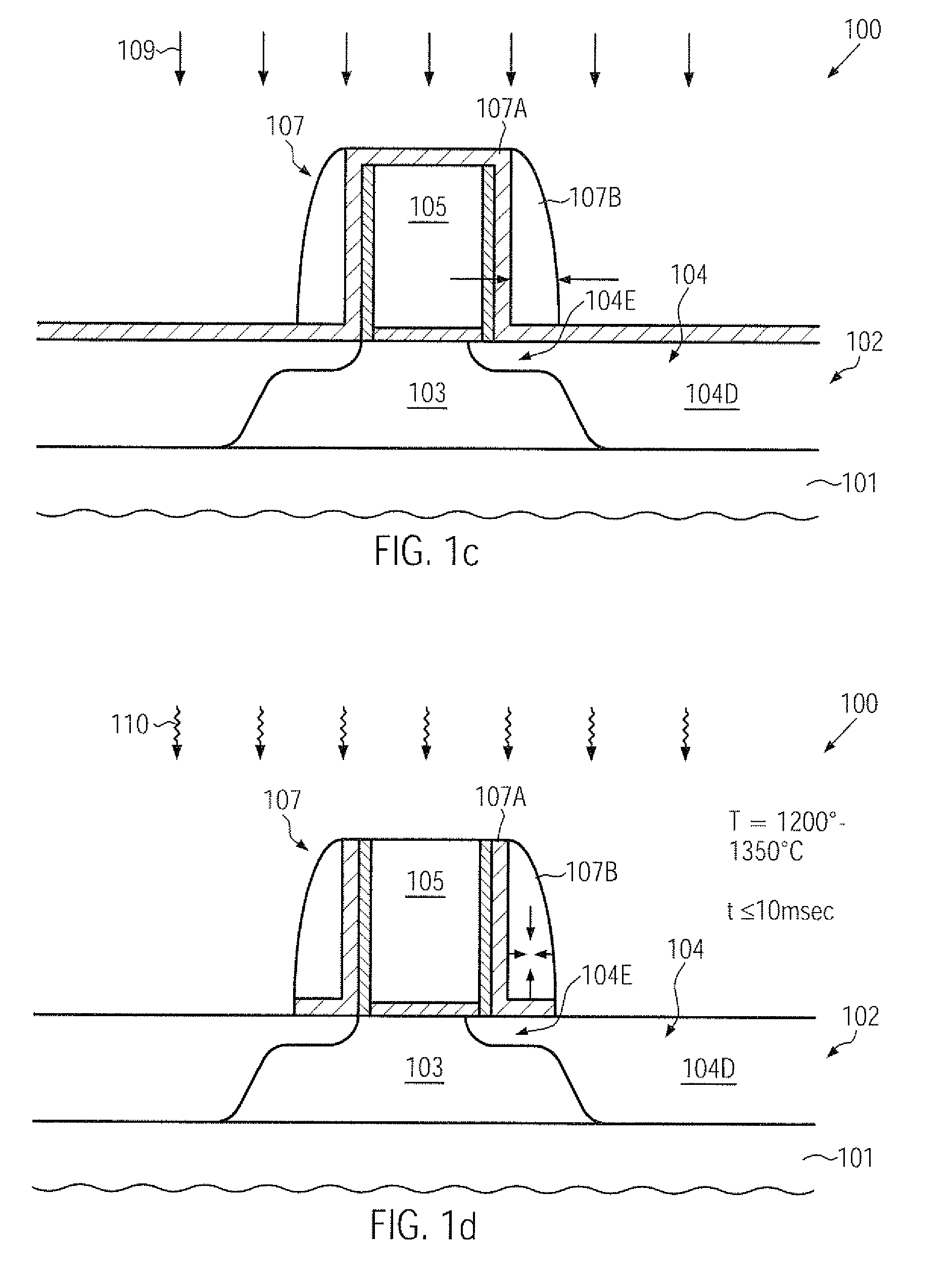
Technique for enhancing dopant profile and channel conductivity by millisecond anneal processes
ActiveUS20110121398A1Enhanced strain conditionReduced transistor dimensionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTensile strainDopant
During the fabrication of advanced transistors, significant dopant diffusion may be suppressed by performing a millisecond anneal process after completing the basic transistor configuration, wherein a stress memorization technique may also be obtained by forming a strain-inducing area within a sidewall spacer structure. Due to the corresponding void formation in the spacer structure, a high tensile strain component may be obtained in the adjacent channel region.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
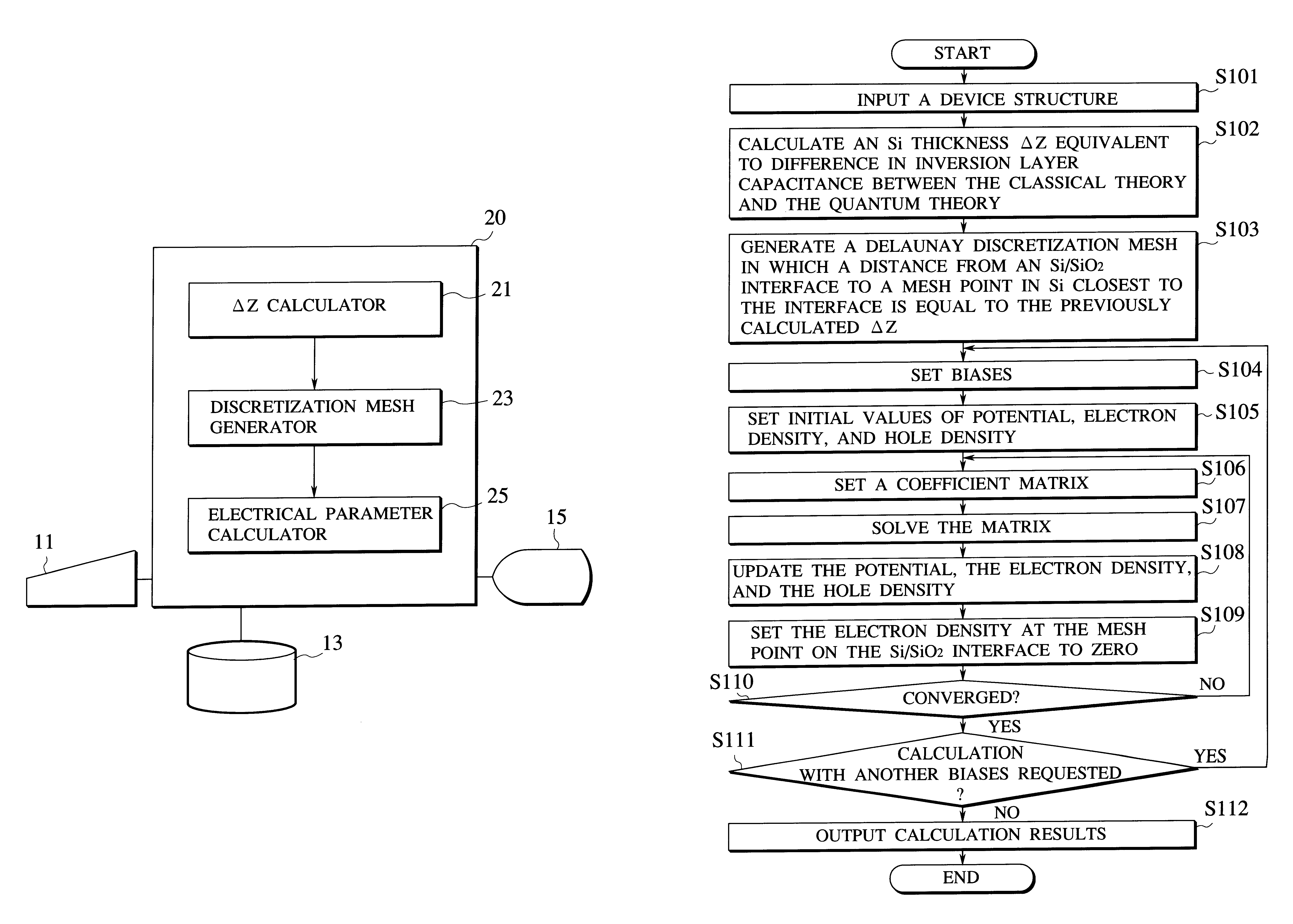
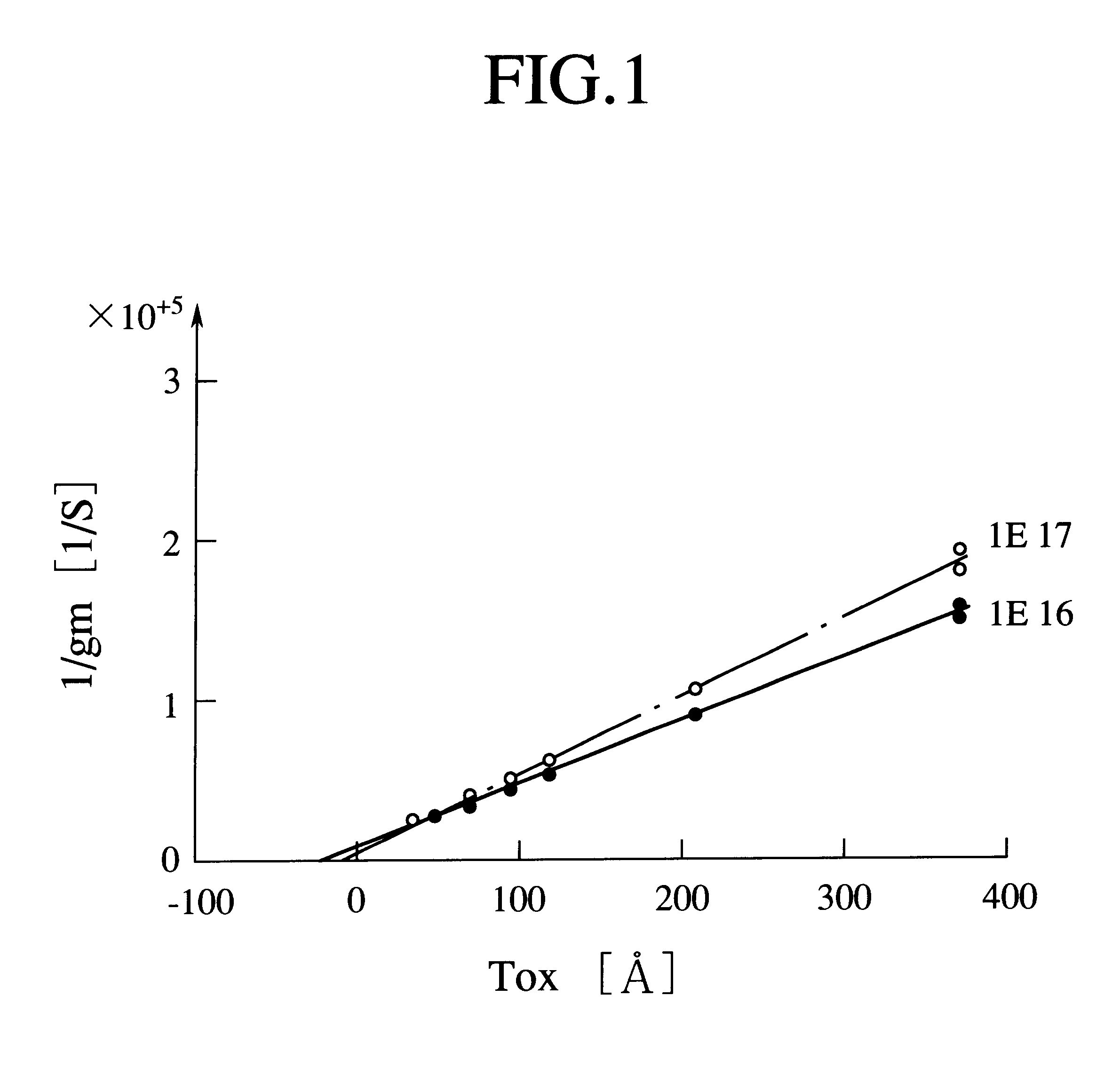
Electrical parameter evaluation system, electrical parameter evaluation method, and computer-readable recording medium for recording electrical parameter evaluation program
InactiveUS6195790B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputation using non-denominational number representationCapacitanceChannel conductivity
A DELTAZ calculator calculates difference between an inversion layer capacitance by a classical theory and an inversion layer capacitance by a quantum theory, calculates DELTAZ which is a thickness of a semiconductor substrate equivalent to the difference in inversion layer capacitance. A discretization mesh generator generates a Delaunay discretization mesh for a structure of the semiconductor device to be evaluated. An electrical parameter calculator calculates electrical parameters of the semiconductor device under constraint that a charge density of channel conductivity type of the semiconductor device is set to zero at discretization mesh points of the discretization mesh on an interface between an insulating film and the semiconductor substrate and at discretization mesh points of the discretization mesh in the semiconductor substrate which are located within a distance less than the stored DELTAZ from the interface between the insulating film and the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEMORY CORP
Field effect devices having a gate controlled via a nanotube switching element
Field effect devices having a gate controlled via a nanotube switching element. Under one embodiment, a non-volatile transistor device includes a source region and a drain region of a first semiconductor type of material and each in electrical communication with a respective terminal. A channel region of a second semiconductor type of material is disposed between the source and drain region. A gate structure is disposed over an insulator over the channel region and has a corresponding terminal. A nanotube switching element is responsive to a first control terminal and a second control terminal and is electrically positioned in series between the gate structure and the terminal corresponding to the gate structure. The nanotube switching element is electromechanically operable to one of an open and closed state to thereby open or close an electrical communication path between the gate structure and its corresponding terminal. When the nanotube switching element is in the closed state, the channel conductivity and operation of the device is responsive to electrical stimulus at the terminals corresponding to the source and drain regions and the gate structure.
Owner:NANTERO
Contactless mask programmable ROM
InactiveUS7227232B2High equipment integrationTransistorSolid-state devicesMask ROMChannel conductivity
A contactless Mask ROM is described, comprising a plurality of MOS-type memory cells. The memory cells include a plurality of first memory cells and a plurality of second memory cells. The first memory cells have a first channel conductivity so that they are depletion-mode MOS transistors, and the second memory cells have a second channel conductivity so that they are enhanced-mode MOS transistors. In the contactless Mask ROM, a memory cell shares two diffusions with two adjacent memory cells that are aligned with the memory cell along a first direction.
Owner:SOLID STATE SYST
Technique for enhancing dopant profile and channel conductivity by millisecond anneal processes
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Method for determining microfluid channel conductivity
ActiveCN105547686AReduce the difficulty of manufacturing processDetection time is shortMachine part testingMicro nanoHigh resolution imaging
The invention discloses a method for determining microfluid channel conductivity, belonging to the micro-nano field. The method comprises steps of filling a tracking reagent in a microfluid channel and performing cooling solidification, adopting a focused ion beam etching technology to obtain cross sections at different positions inside the microfluid channel, and observing the cross section of the microfluid channel through a high-resolution scanning electronic microscope to determine the conductivity of the microfluid channel.The invention lowers the manufacture technology difficulty, reduces the detection time, simplifies the detection process, and improves the flexibility and accuracy through the interception of the cross section and high resolution imaging of the scanning electronic microscopic.The invention is an appropriate method for determining microfluid channel conductivity.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Shiftable large-range capacitive coupling type non-contact conductivity measuring device and method
ActiveCN111044581ALarge measuring rangeSmall measurement requirementsMaterial resistanceCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
The invention relates to a shiftable large-range capacitive coupling type non-contact conductivity measuring device and a shiftable large-range capacitive coupling type non-contact conductivity measuring method. The measuring device comprises an insulation measurement pipeline, an excitation electrode module, a receiving electrode module, an alternating current excitation source, a voltage detection module and a control unit, wherein the receiving electrode module comprises at least two receiving electrodes; the excitation electrode module comprises at least two excitation electrodes, the number of the excitation electrodes is the same as that of the receiving electrodes, the measuring device further comprises an excitation electrode analog switch and a receiving electrode analog switch, the receiving electrode analog switch is connected with the control unit and the voltage detection module, and the excitation electrode analog switch is connected with the control unit; and the controlunit sequentially performs gear shifting measurement or directly outputs the conductivity value of the solution in the insulation measurement pipeline according to the voltage value output by means of the voltage detection module according to a certain method. Compared with the prior art, the shiftable large-range capacitive coupling type non-contact conductivity measuring method has the advantages of high detection sensitivity, large measurement range and the like, and can be applied to multi-channel conductivity detection occasions.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Special pH measurement device for electric generator inner cooling water system and working method thereof
The invention discloses a special pH measurement device for an electric generator inner cooling water system and a working method thereof. The device comprises a flowmeter, a conductivity flow cell, ahydrogen conductivity flow cell, a degassed hydrogen conductivity flow cell, a flow regulation valve, a multi-channel conductivity table, a PLC control panel, a color-changing cation exchange column,a carbon dioxide remover and an electric regeneration cation exchanger, wherein the flow regulation valve and the flowmeter are mounted on a sampling pipeline which is led out from a water outlet pipeline of the electric generator inner cooling water cooler, moreover, the flow regulation valve and the flowmeter, the conductivity flow cell, the electric regeneration cation exchanger, the color-changing cation exchange column, the hydrogen conductivity flow cell, the carbon dioxide remover and the degassed hydrogen conductivity flow cell are connected orderly according to a water flowing direction; the conductivity flow cell, the hydrogen conductivity flow cell and the degassed hydrogen conductivity flow cell are respectively connected with the multi-channel conductivity table, and the multi-channel conductivity table is connected with the PLC control panel. The device and the method provided by the invention have wide range of application, and can be used for both a stator cooling water system and a double-water inner cooling system.
Owner:HUADIAN ELECTRIC POWER SCI INST CO LTD
Contactless mask programmable rom
ActiveUS20050127454A1High equipment integrationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMask ROMChannel conductivity
A contactless Mask ROM is described, comprising a plurality of MOS-type memory cells. The memory cells include a plurality of first memory cells and a plurality of second memory cells. The first memory cells have a first channel conductivity so that they are depletion-mode MOS transistors, and the second memory cells have a second channel conductivity so that they are enhanced-mode MOS transistors. In the contactless Mask ROM, a memory cell shares two diffusions with two adjacent memory cells that are aligned with the memory cell along a first direction.
Owner:SOLID STATE SYST
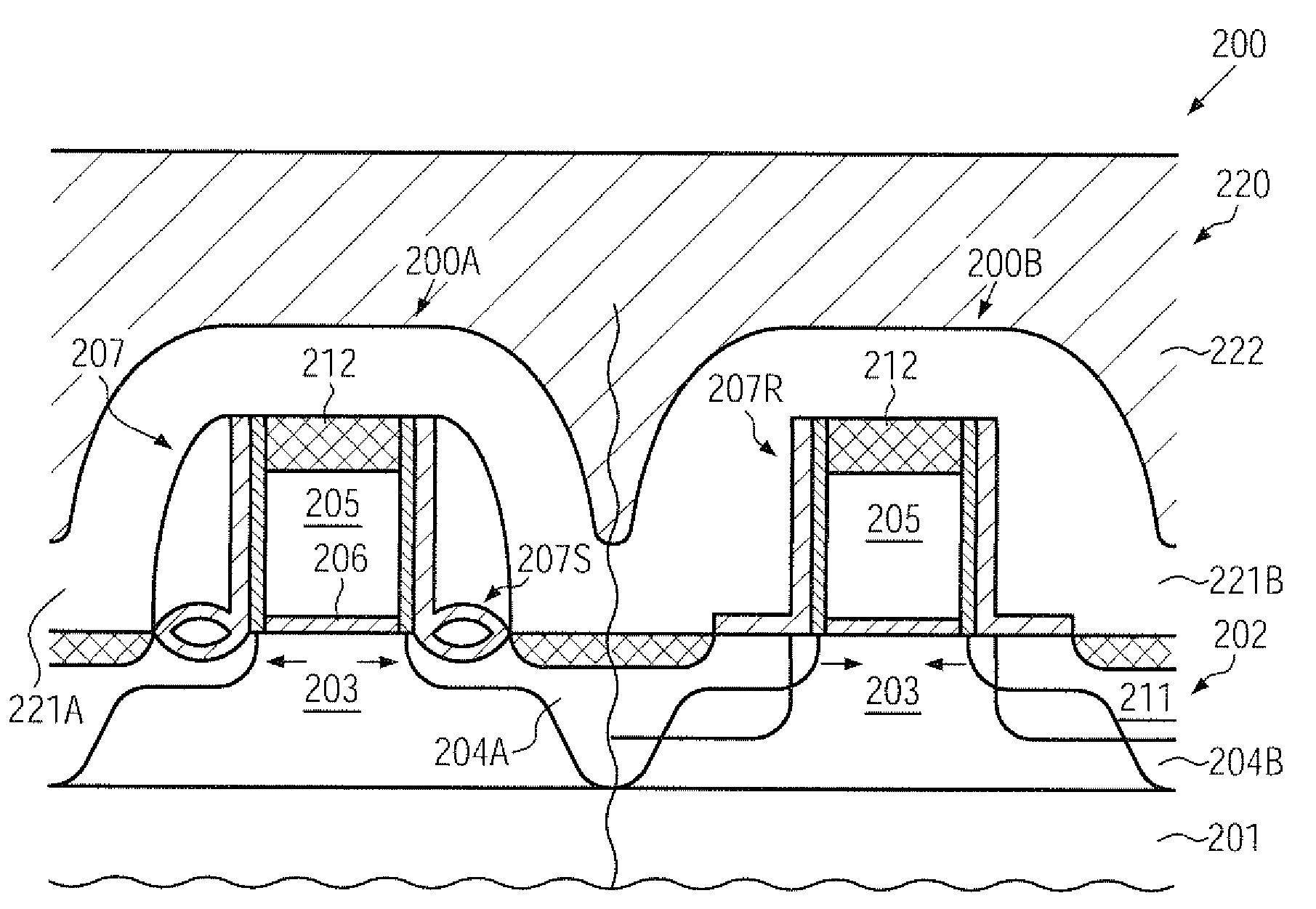
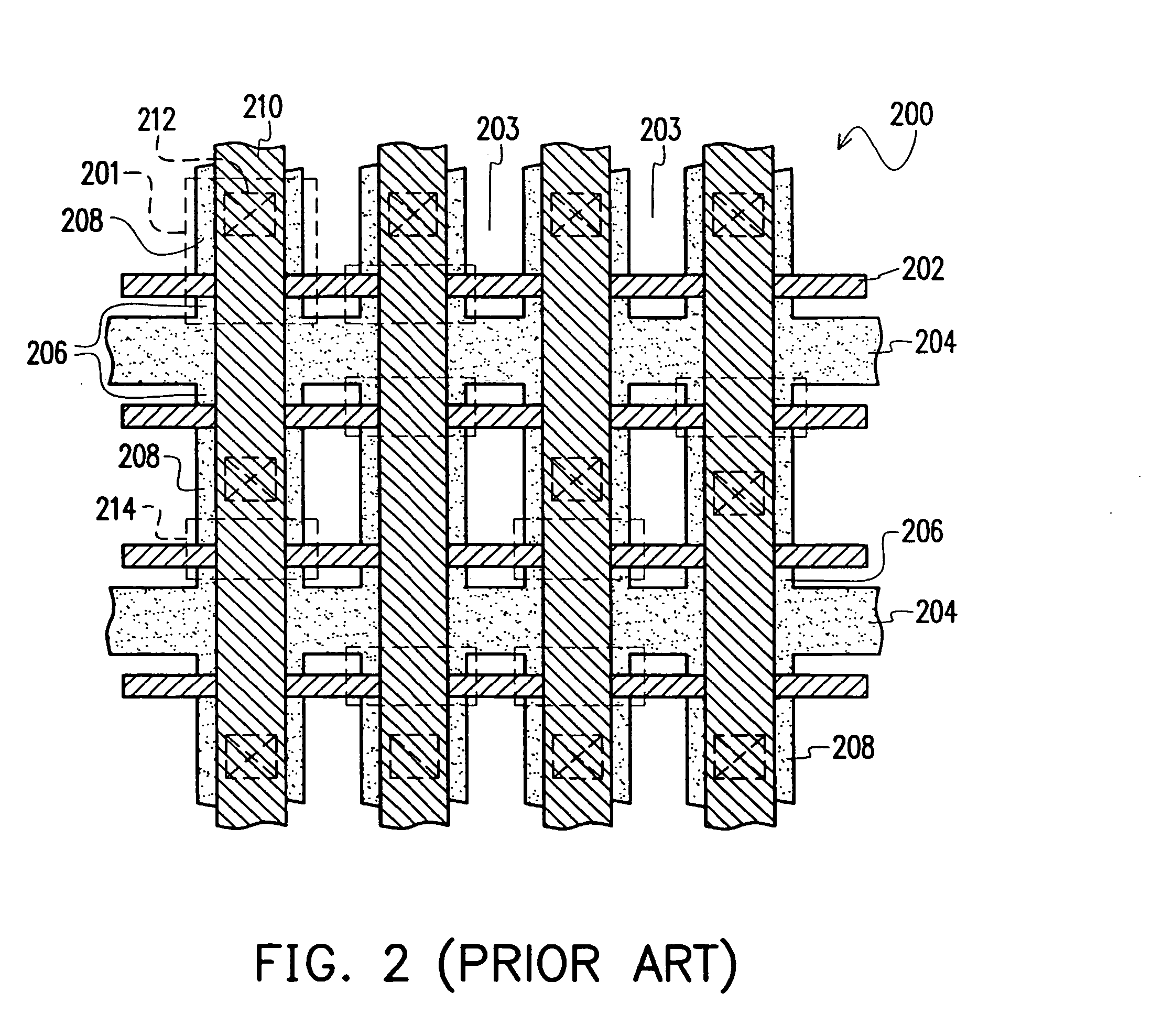
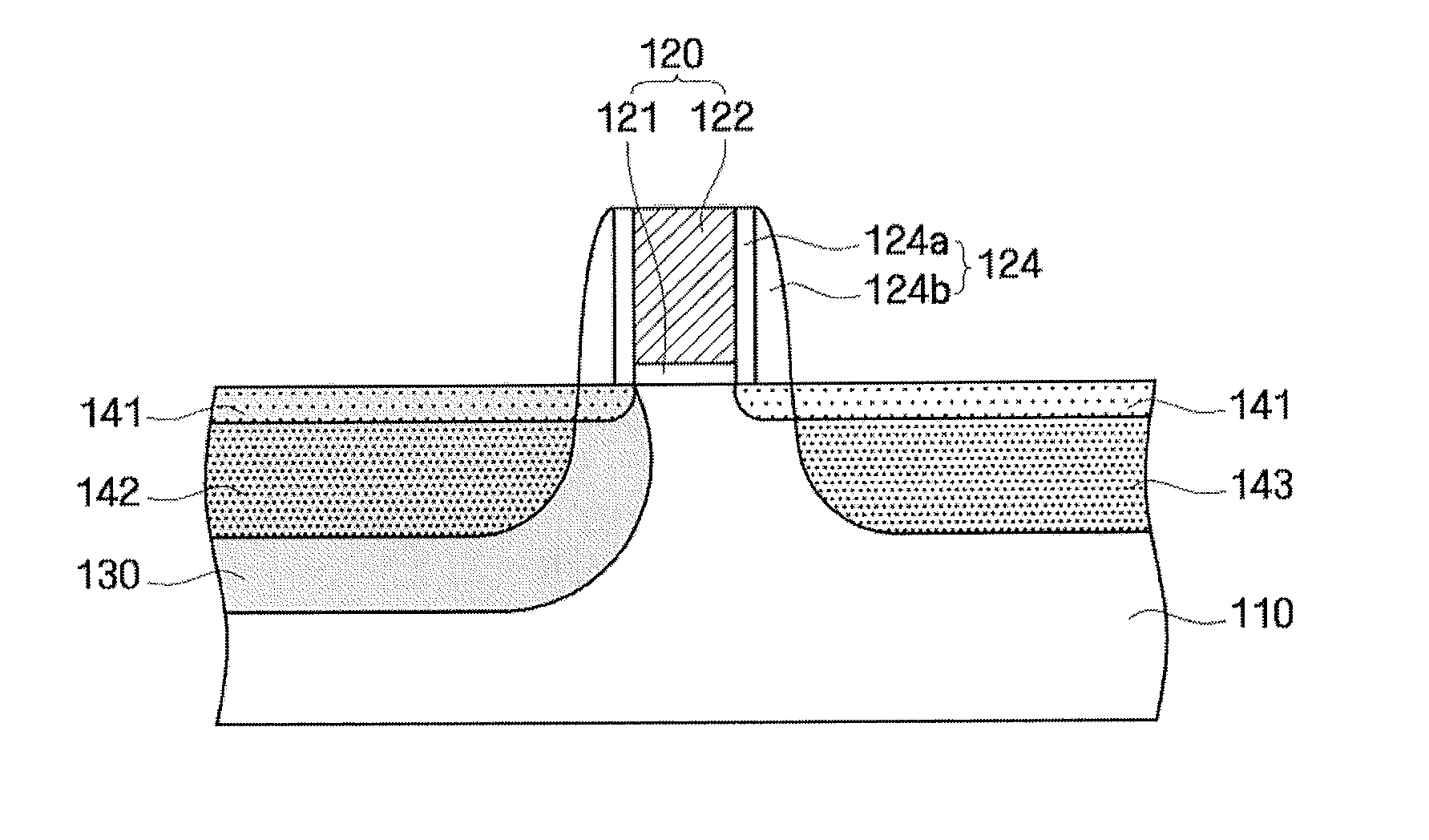
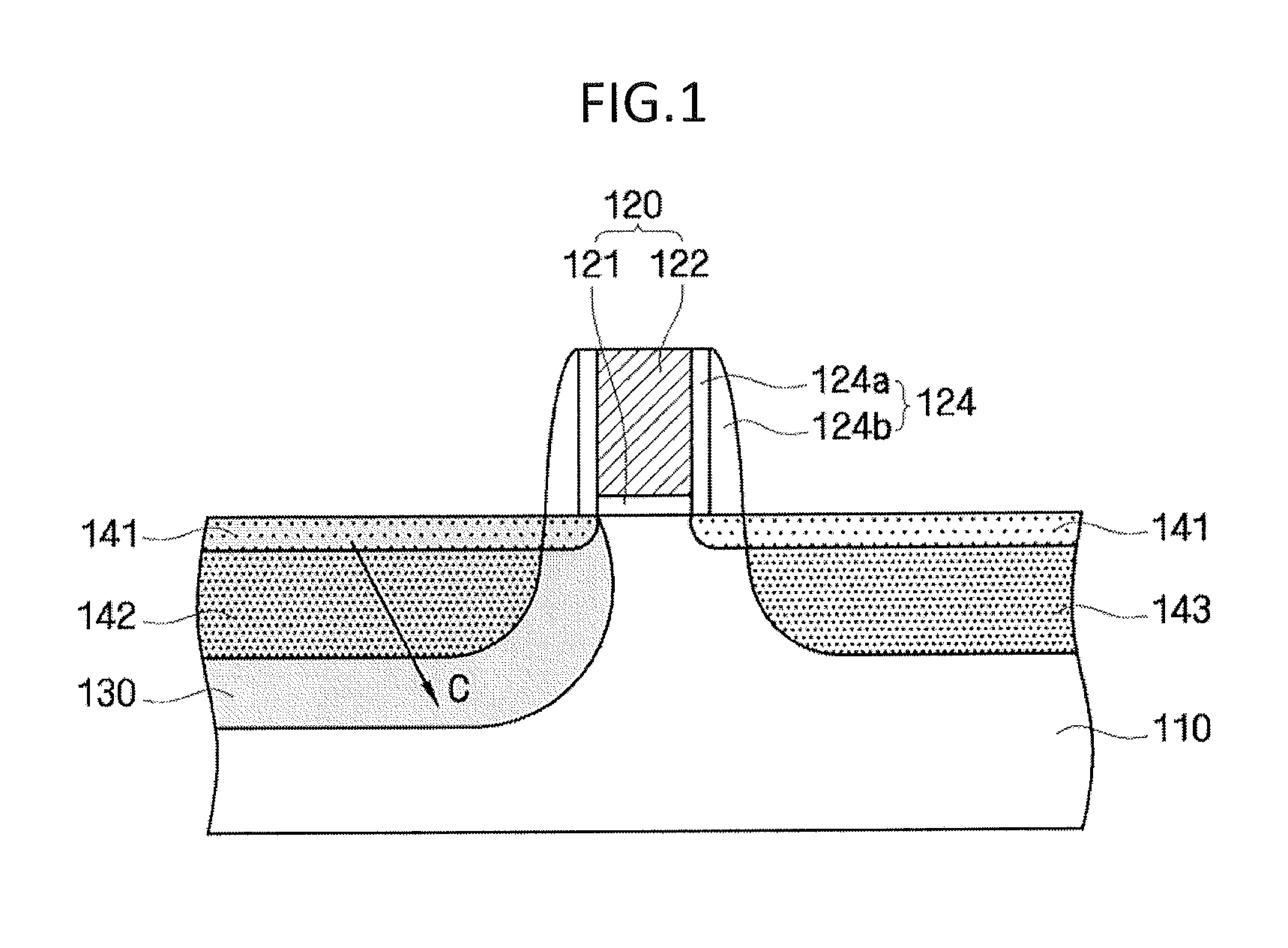
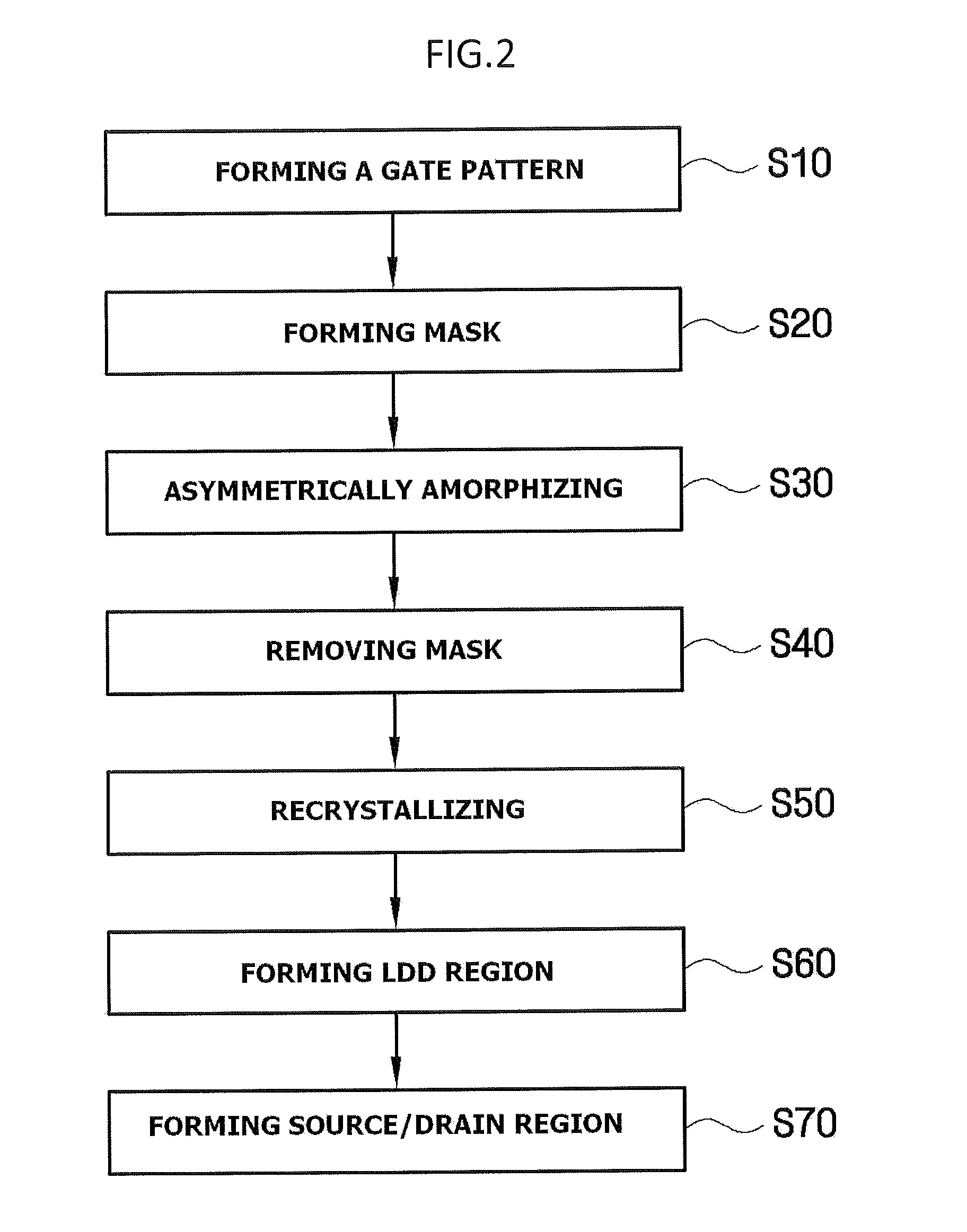
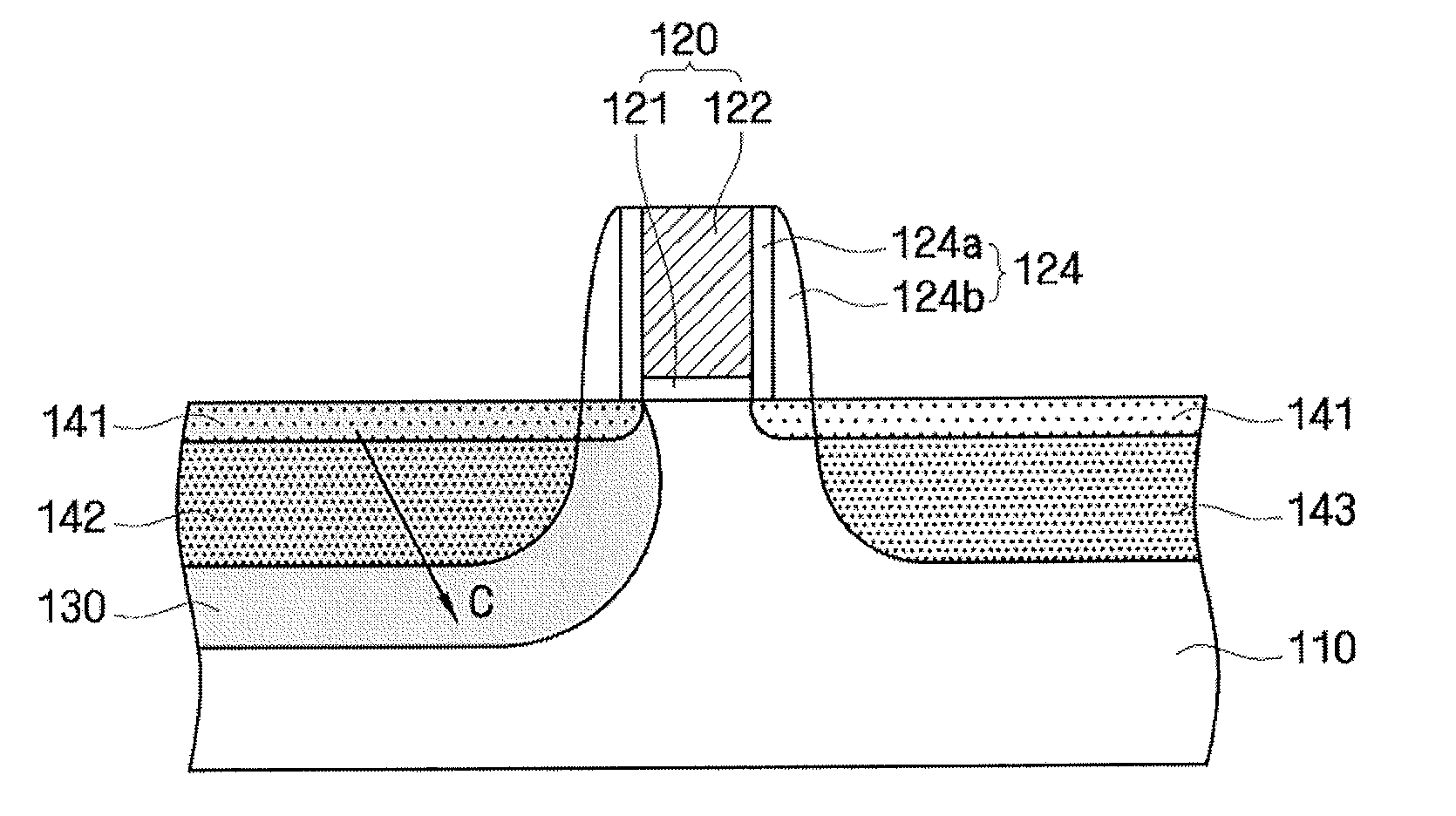
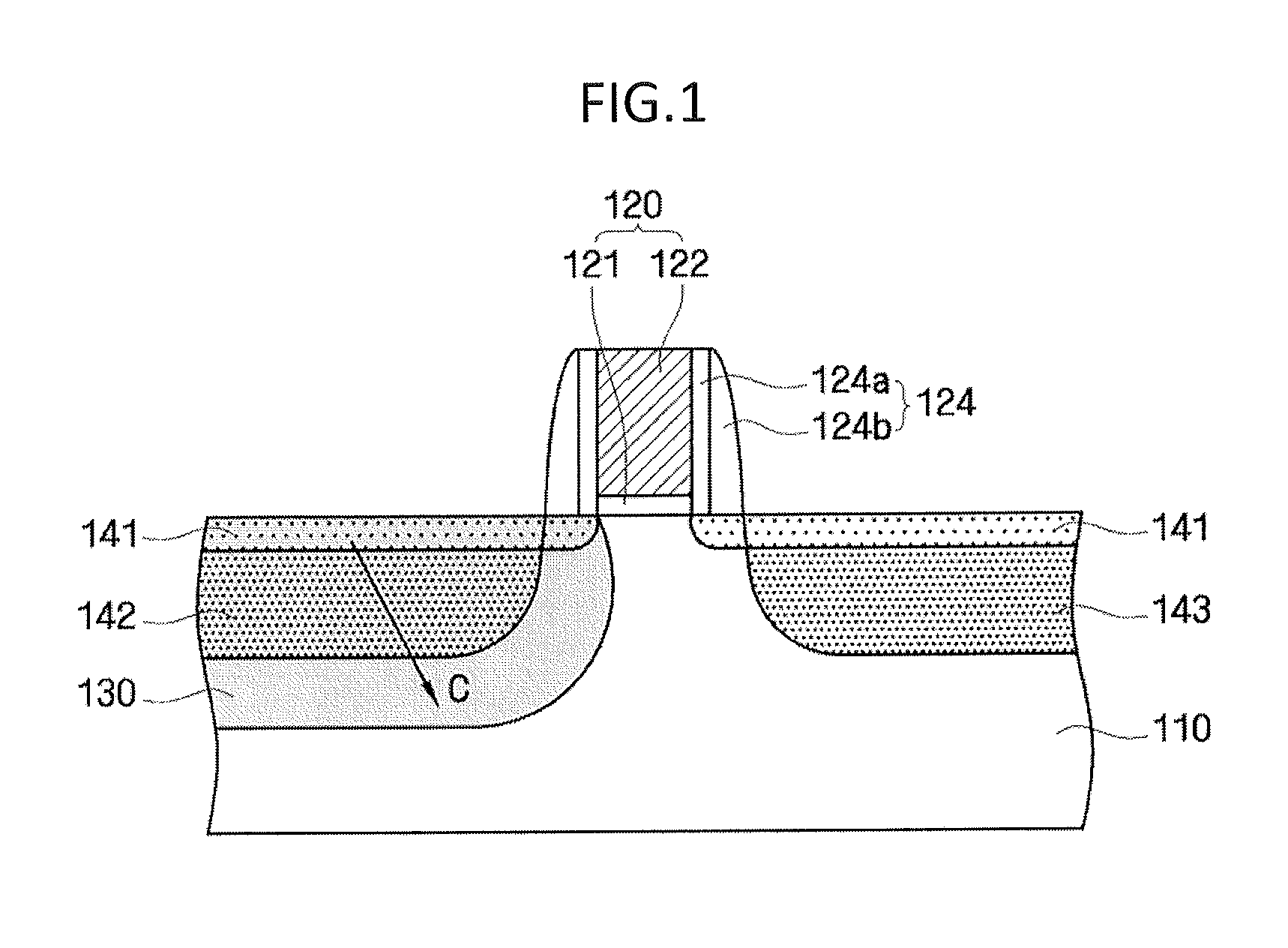
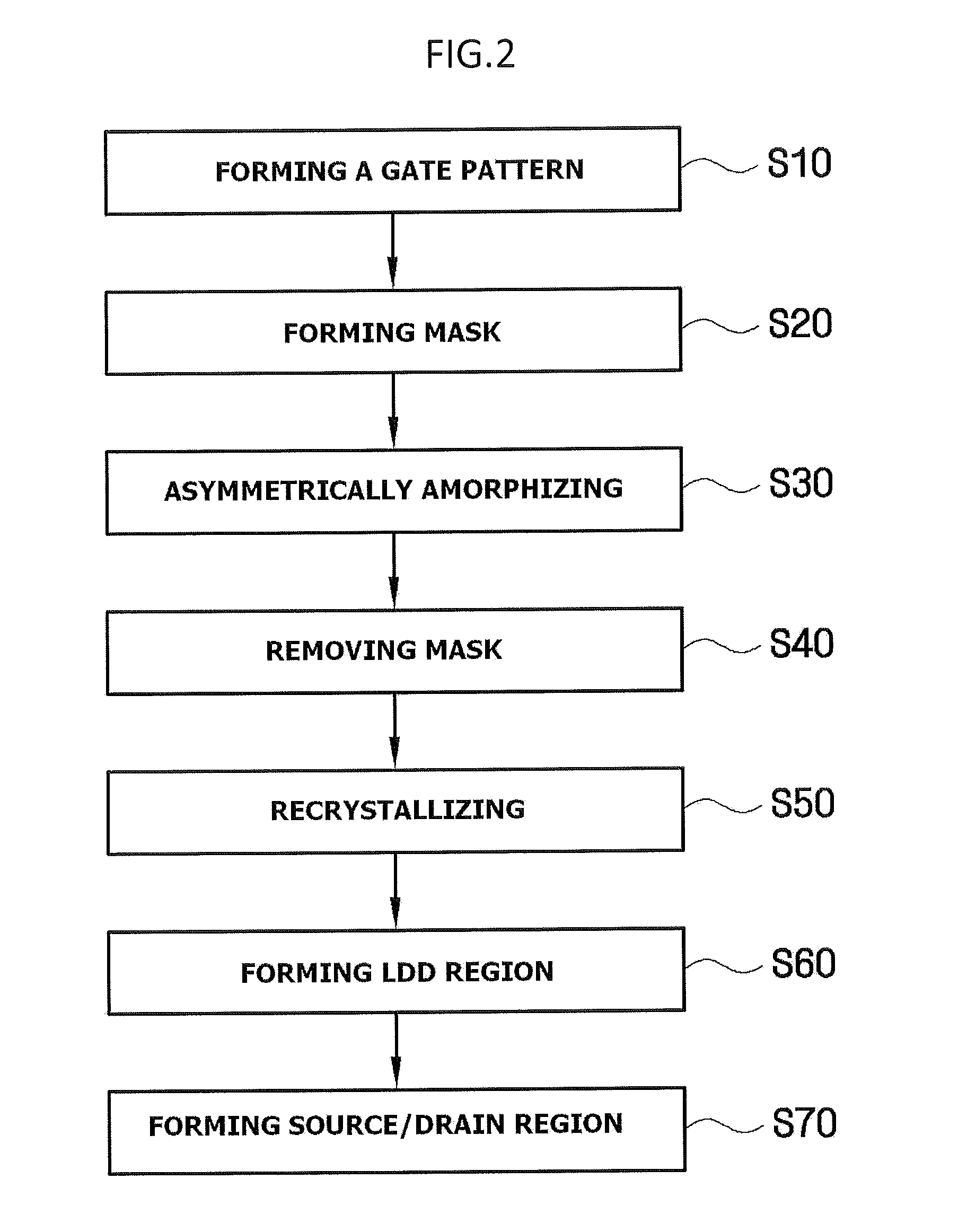
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20120108023A1High carrier mobilityIncrease pressureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialStacking fault
A semiconductor device is formed with a gate pattern formed on a substrate, and a recrystallized region having a stacking fault defect in the substrate at one side of the gate pattern. The semiconductor device can have a reduced leakage current and improved channel conductivity.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
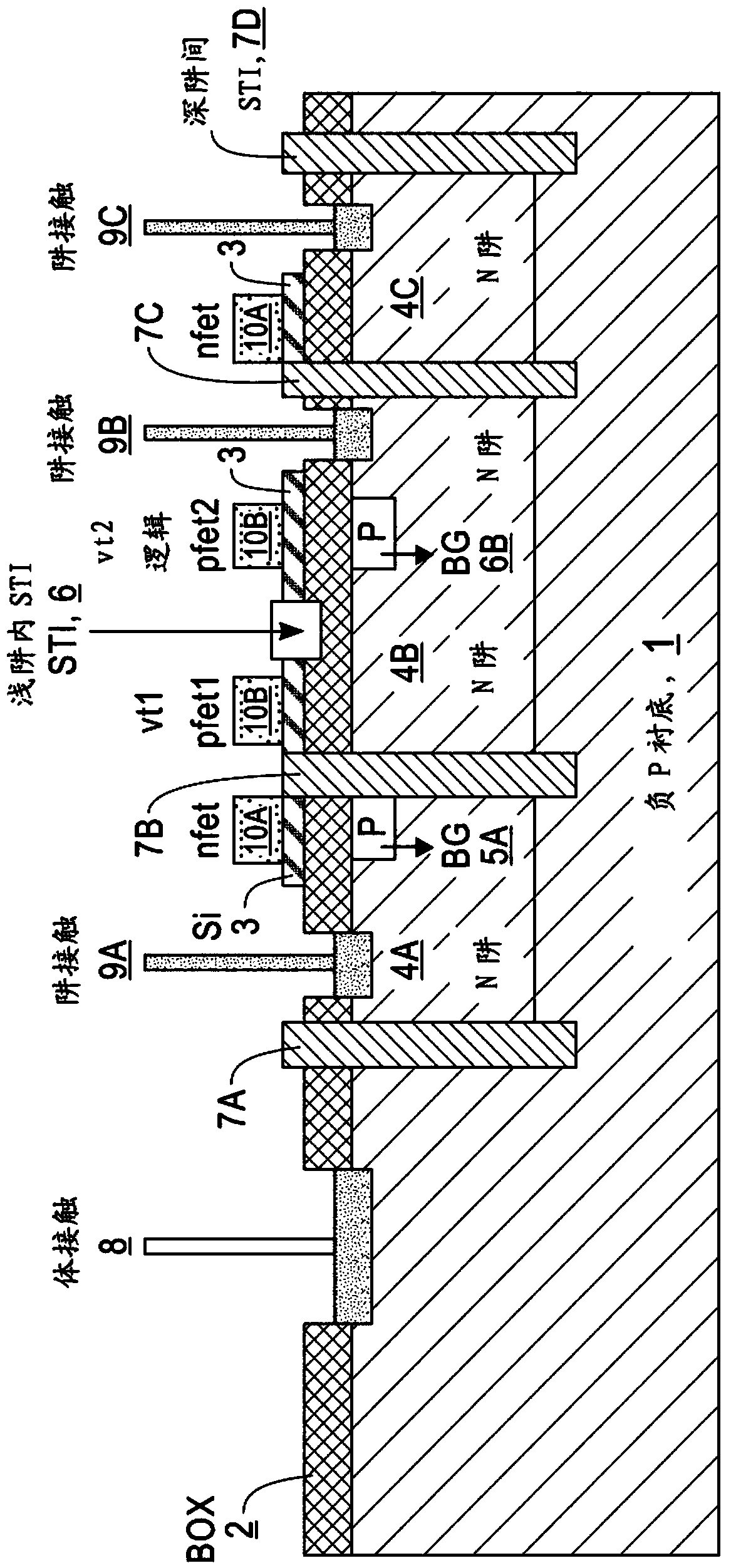
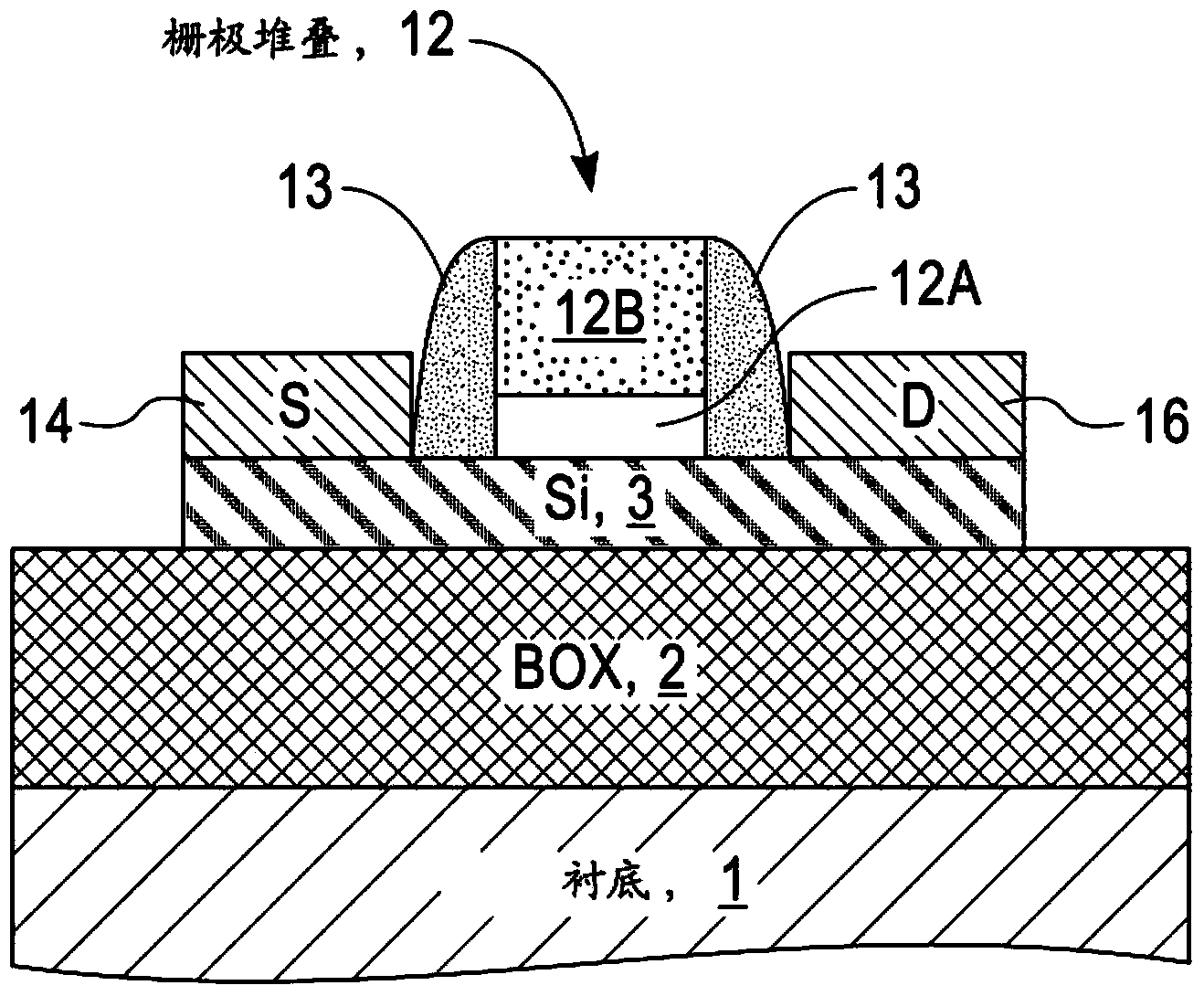
Improved structure for cmos etsoi with multiple threshold voltages and active well bias capability
A semiconductor substrate having a first type of conductivity and a top surface, a layer of oxide disposed over the top surface and a semiconductor layer disposed over the layer of oxide. A plurality of transistor devices are disposed upon the semiconductor layer. Each transistor device includes a channel between a source and a drain, where some transistor devices have a first type of channel conductivity and the remaining transistor devices have a second type of channel conductivity. A well region is formed adjacent to the top surface. The well region has a second type of conductivity. First trench isolation regions are between adjacent transistor devices that extend through the semiconductor layer. Second trench isolation regions are between adjacent transistor devices of opposite channel conductivity.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Molecular sensor based on virtual buried nanowire
ActiveCN104204789ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMaterial resistanceNanowireEngineering
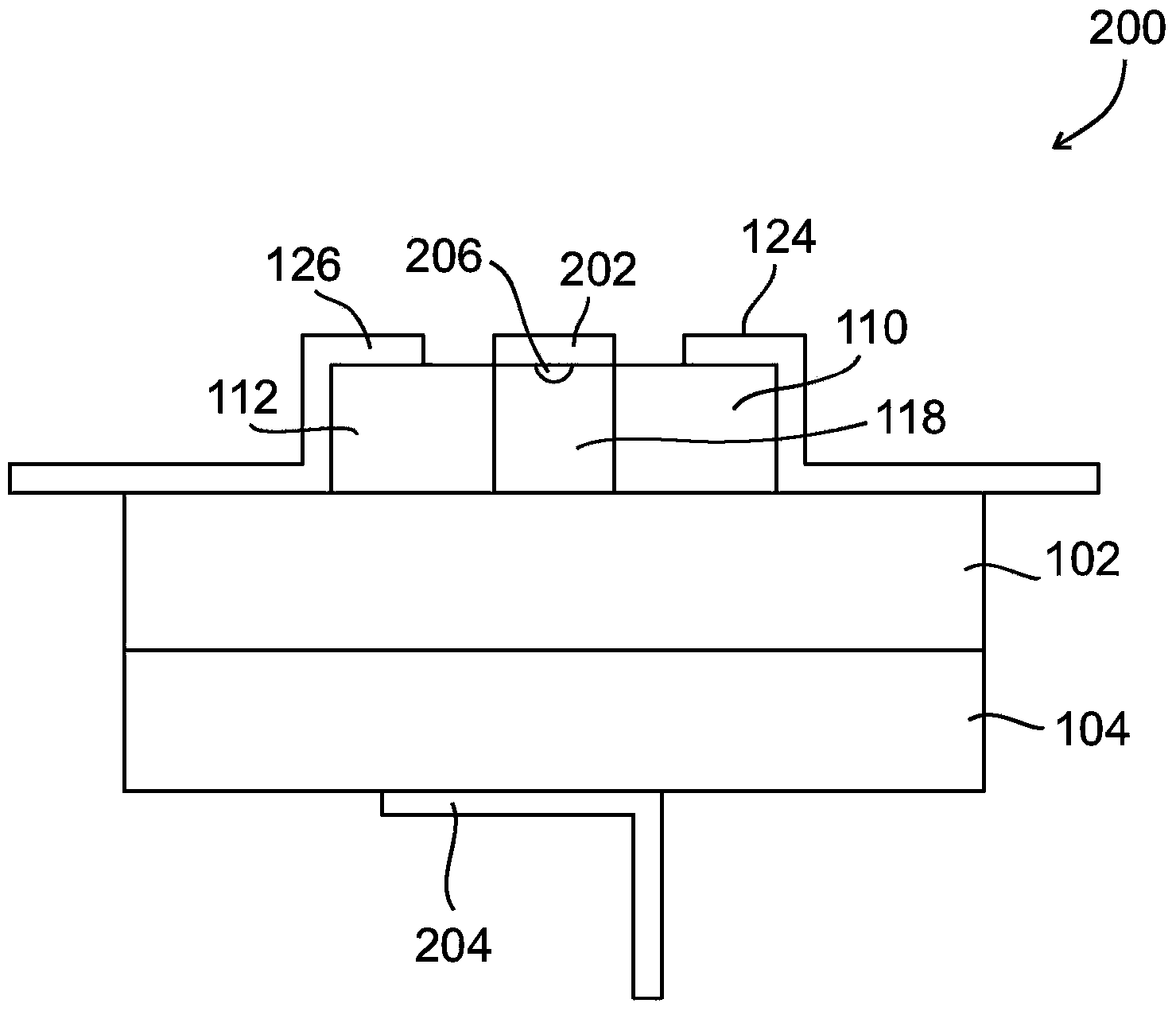
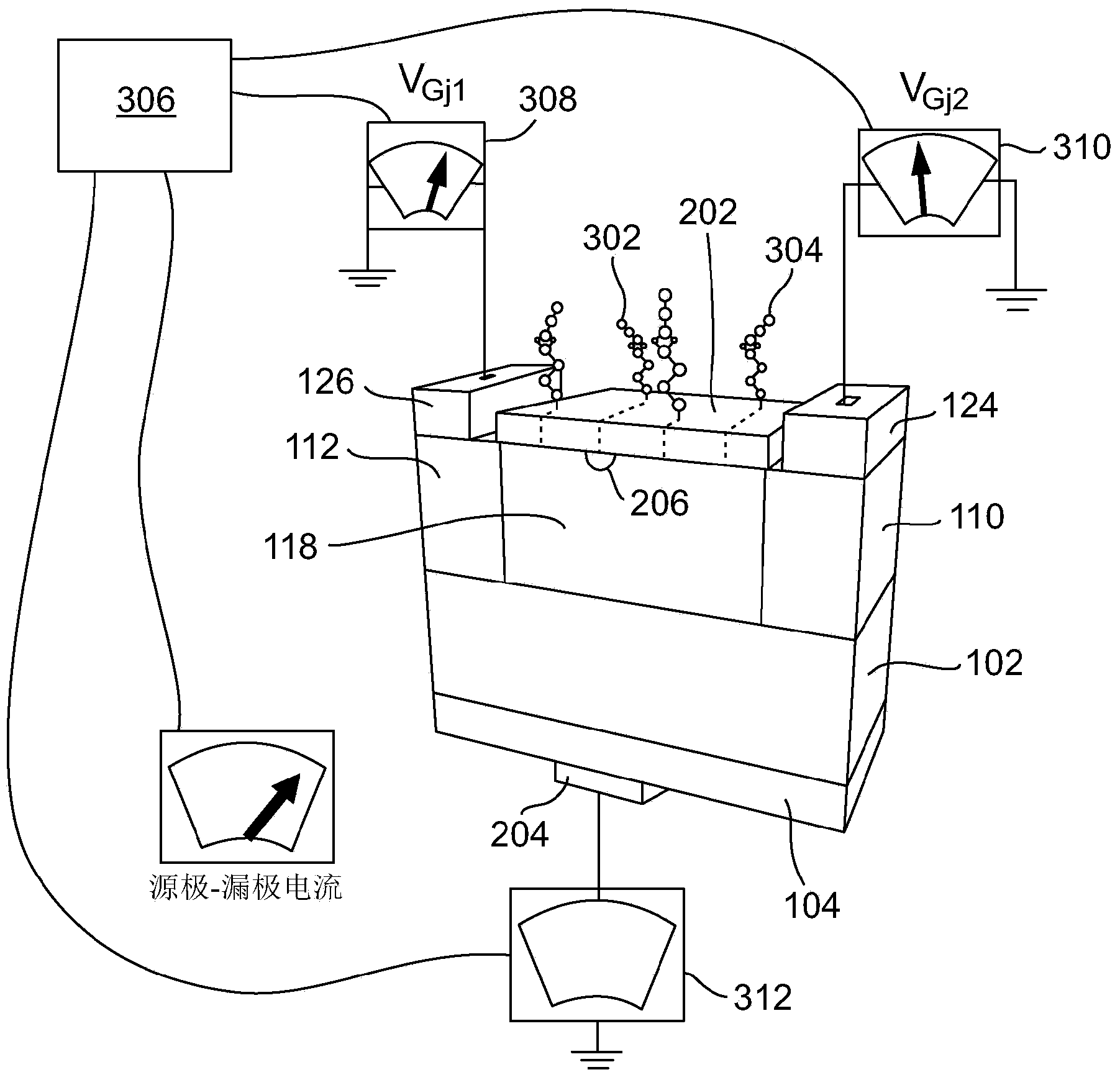
The present invention provides a method and a system based on a multi-gate filed effect transistor for sensing molecules in a gas or liquid sample. The said FET transistor comprises dual gate lateral electrodes (and optionally a back gate electrode) located on the two sides of an active region, and a sensing surface on top of the said active region. Appling voltages to the lateral gate electrodes, creates a conductive channel in the active region, wherein the width and the lateral position of the said channel can be controlled. Enhanced sensing sensitivity is achieved by measuring the channels conductivity at a plurality of positions in the lateral direction. The use of an array of the said FTE for electronic nose is also disclosed.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
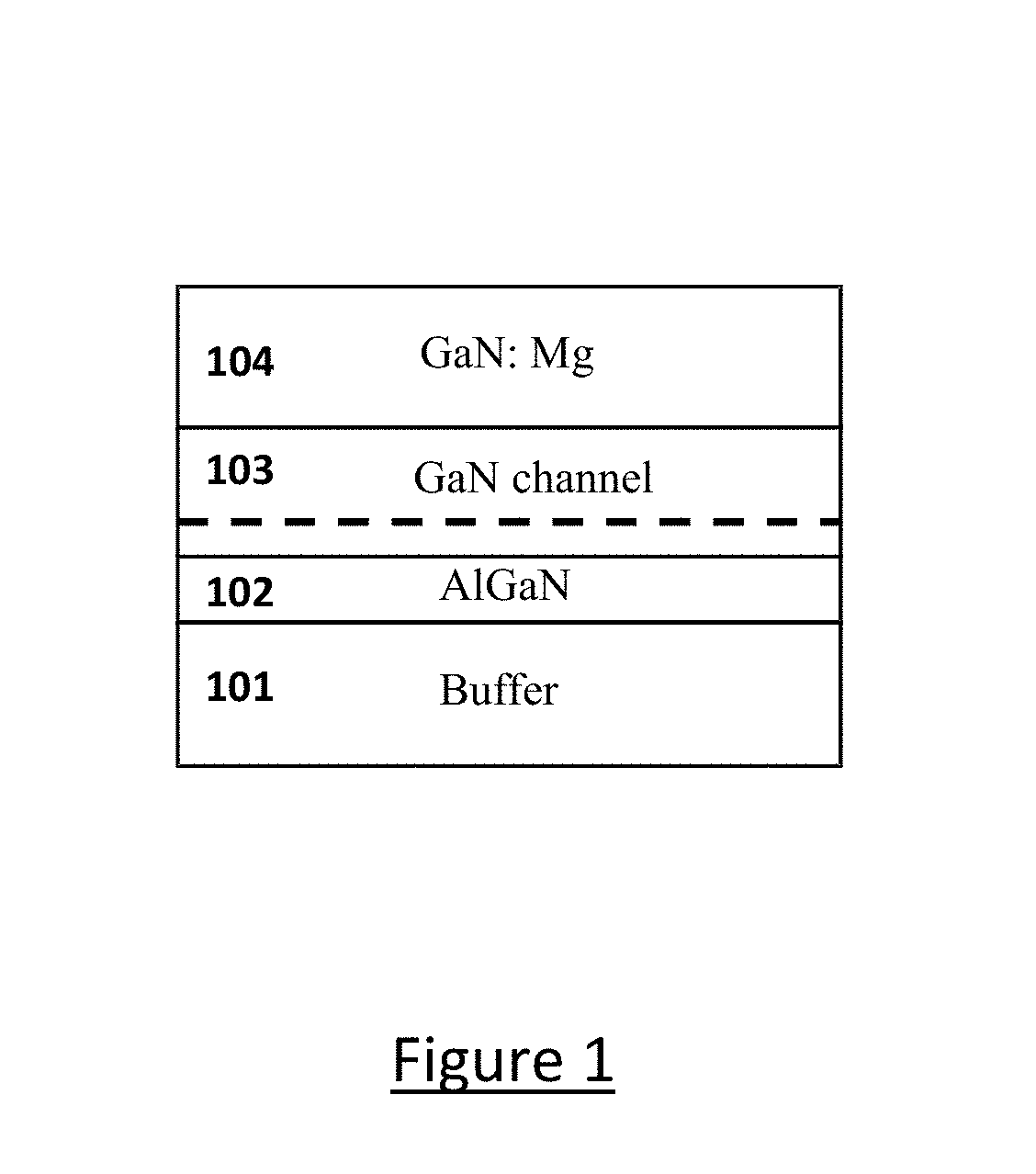
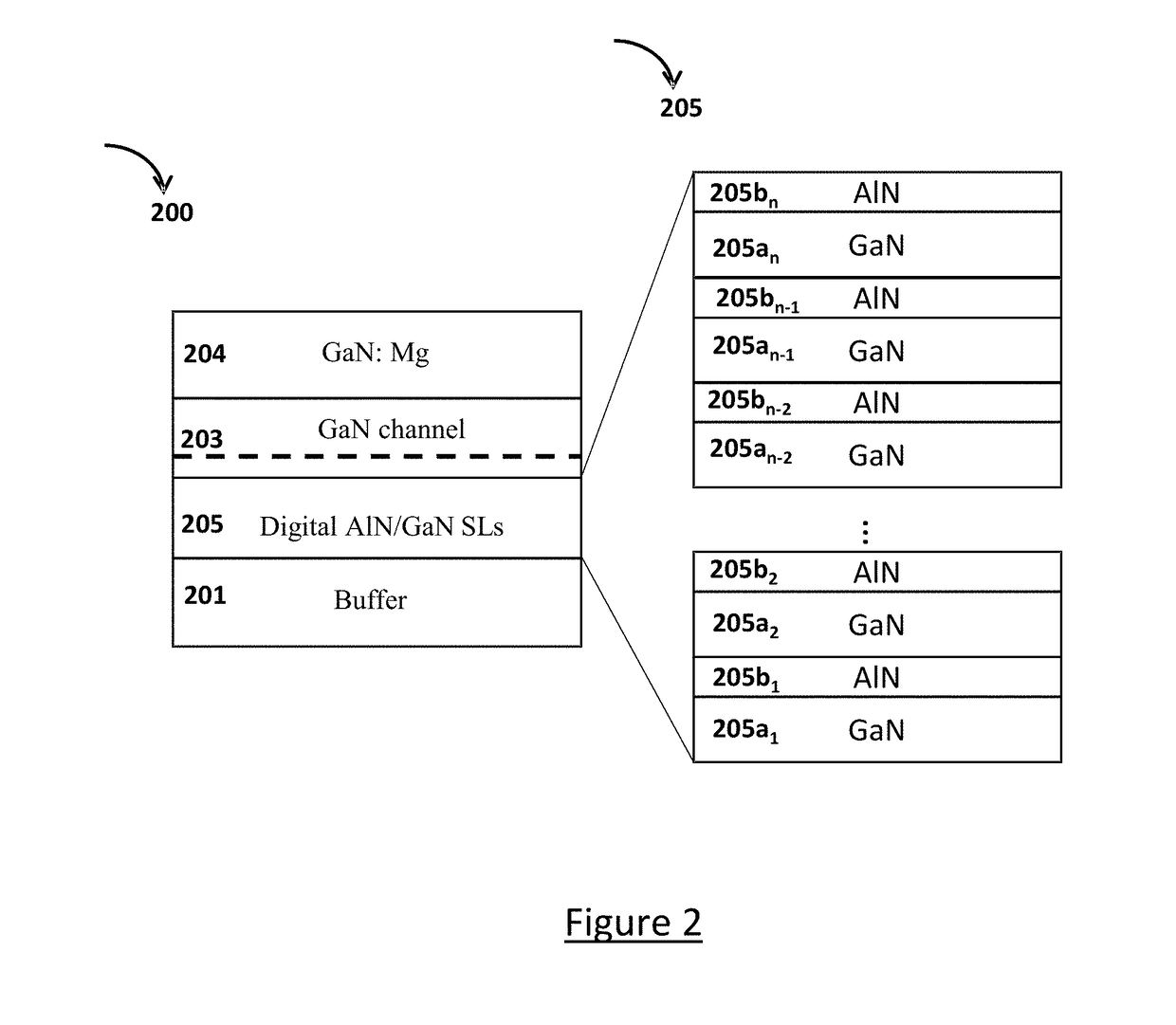
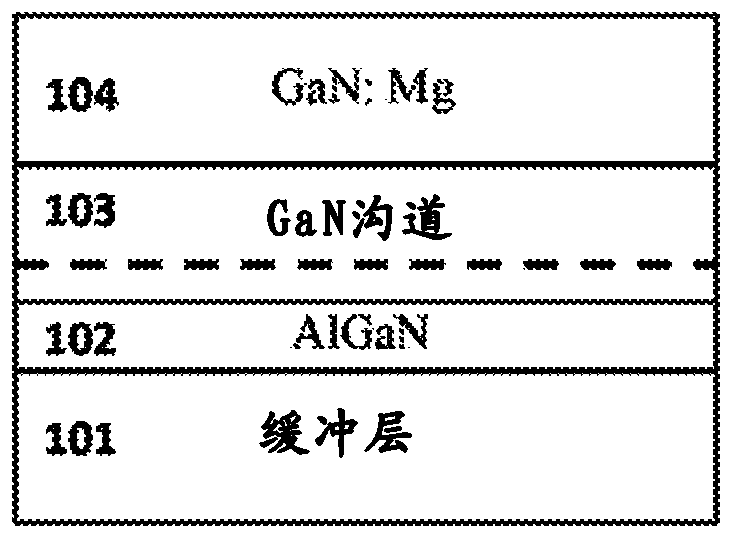
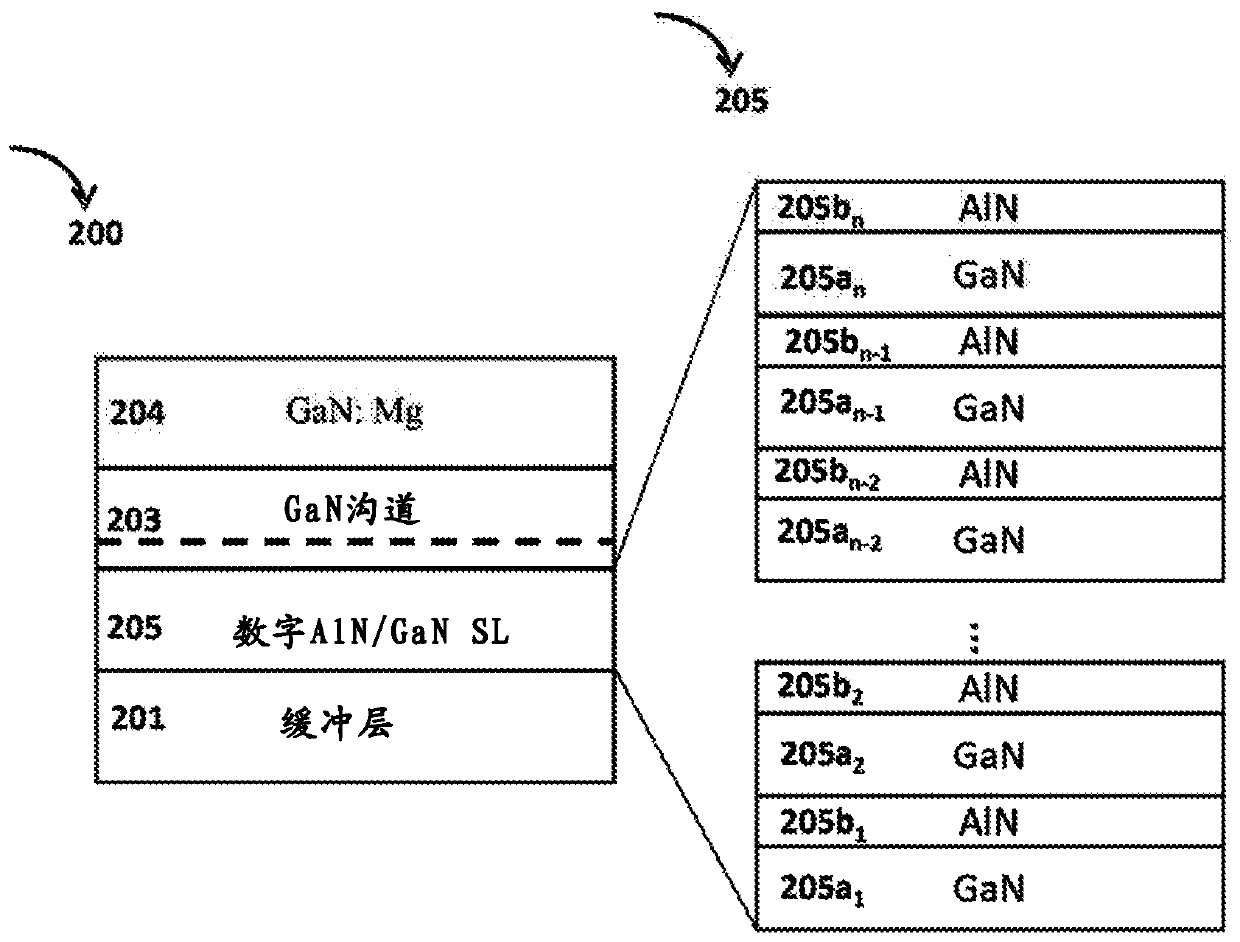
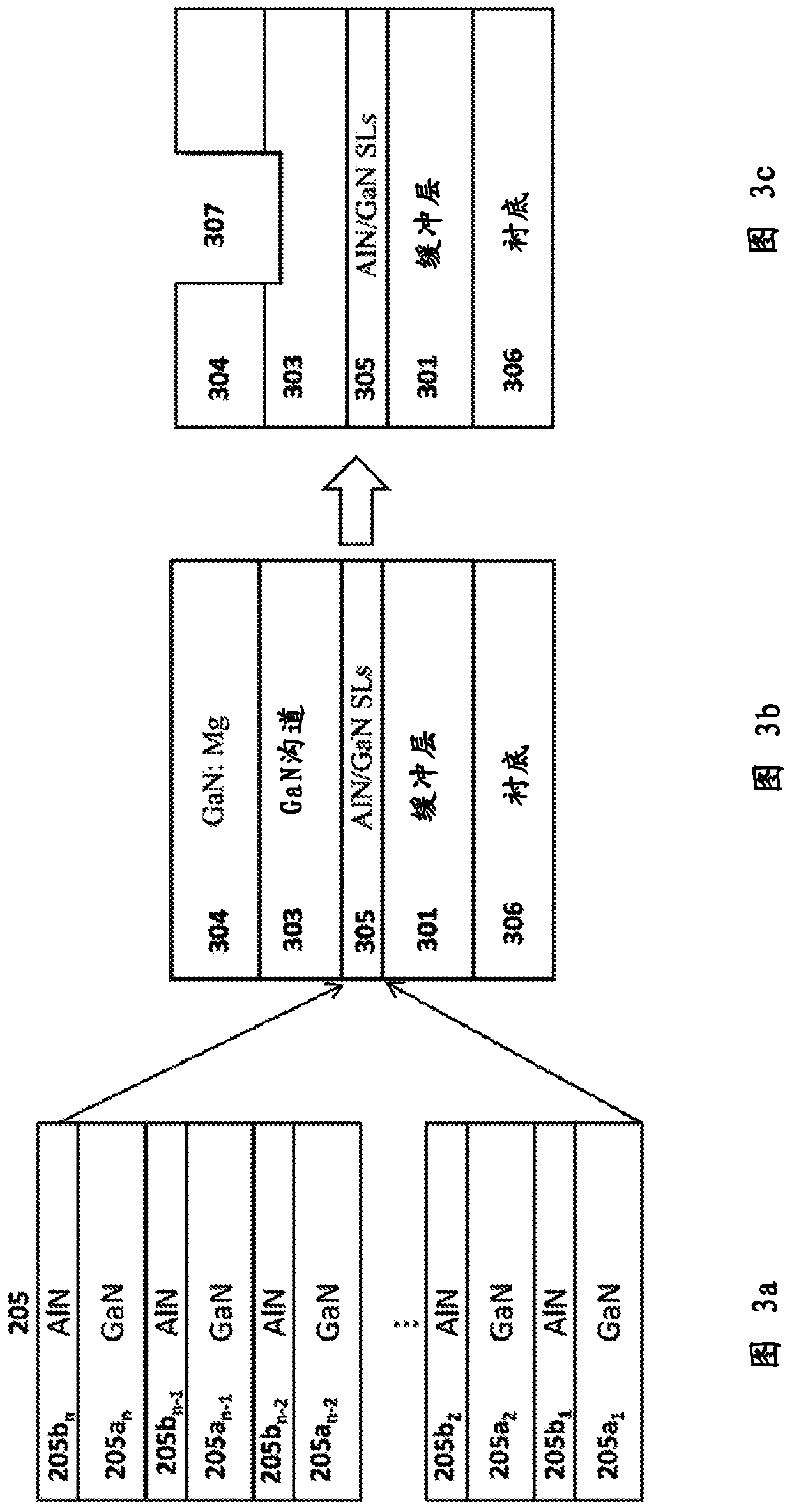
Digital alloy based back barrier for p-channel nitride transistors
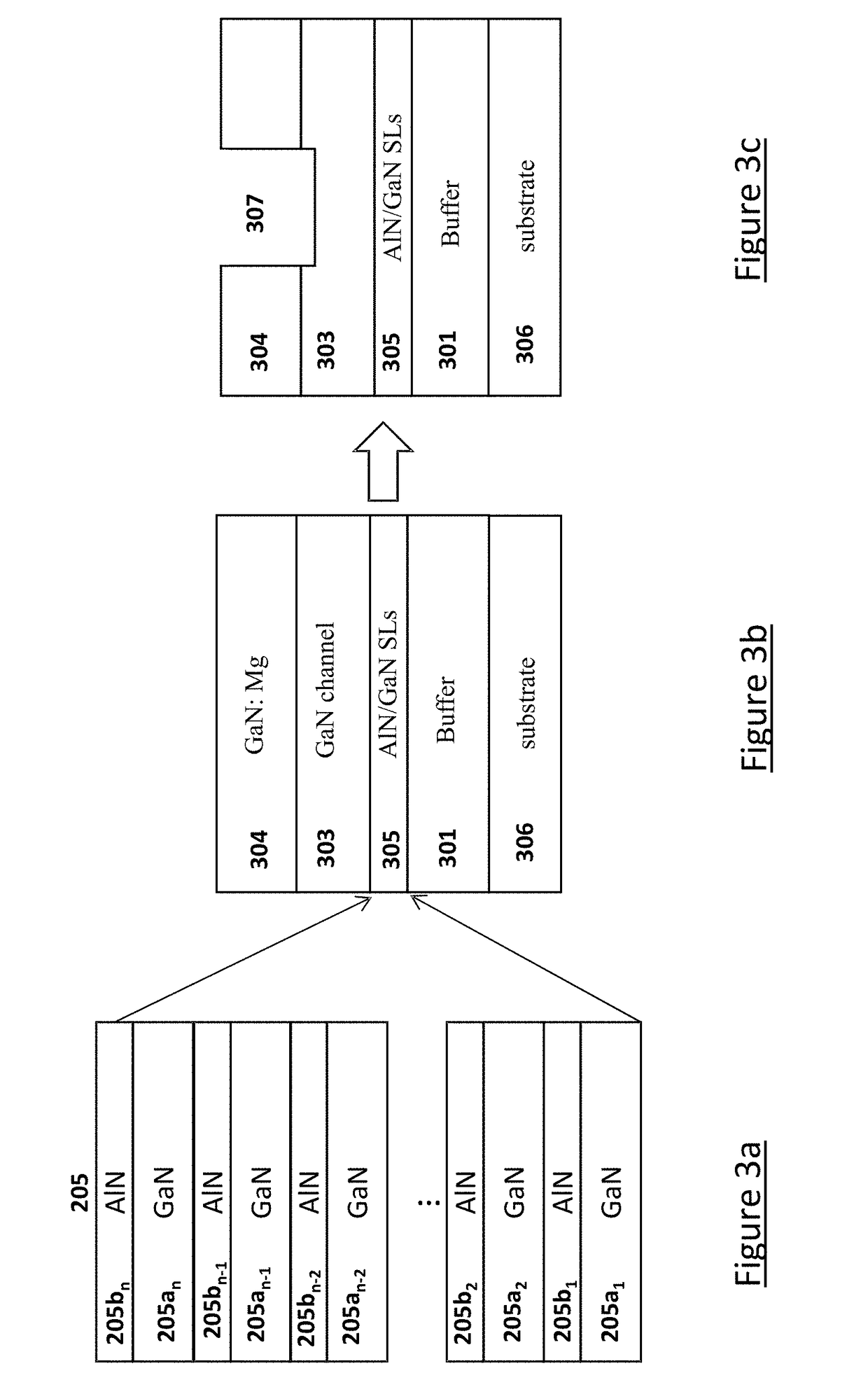
A III-nitride power handling device and the process of making the III-nitride power handling device are disclosed that use digital alloys as back barrier layer to mitigate the strain due to lattice mismatch between the channel layer and the back barrier layer and to provide increased channel conductivity. An embodiment discloses a GaN transistor using a superlattice binary digital alloy as back barrier comprising alternative layers of AlN and GaN. Other embodiments include using superlattice structures with layers of GaN and AlGaN as well as structures using AlGaN / AlGaN stackups that have different Aluminum concentrations. The disclosed device has substantially increased channel conductivity compared to traditional analog alloy back barrier devices.
Owner:HRL LAB
Measurement method for three-dimensional memory channel conductivity
The invention provides a measurement method for three-dimensional memory channel conductivity. Through combing a focusing ion beam machine and a nano-point needle table, the accuracy of the channel conductivity can be tested in advance before improving a peripheral circuit technique. The influence of poor problems of the peripheral control circuit on the three-dimensional memory channel conductivity in a traditional measurement method is solved, the test of the channel conductivity itself is realized, and the technical research and development cycle is shortened.
Owner:YANGTZE MEMORY TECH CO LTD
High-flux liquid conductivity measuring equipment
PendingCN109856195AAccurate placementPut in undisturbedMaterial resistanceMeasuring instrumentGround conductivity
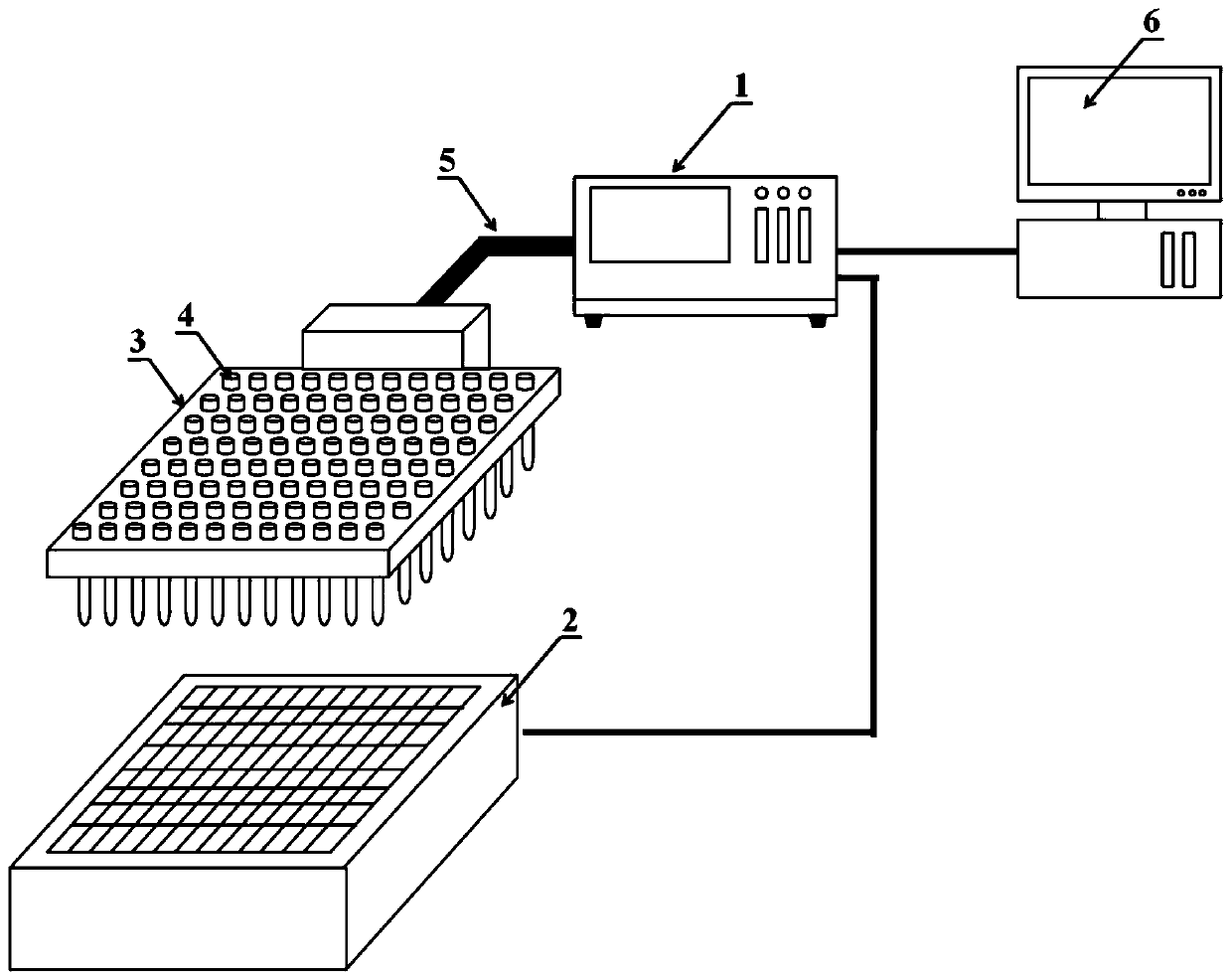
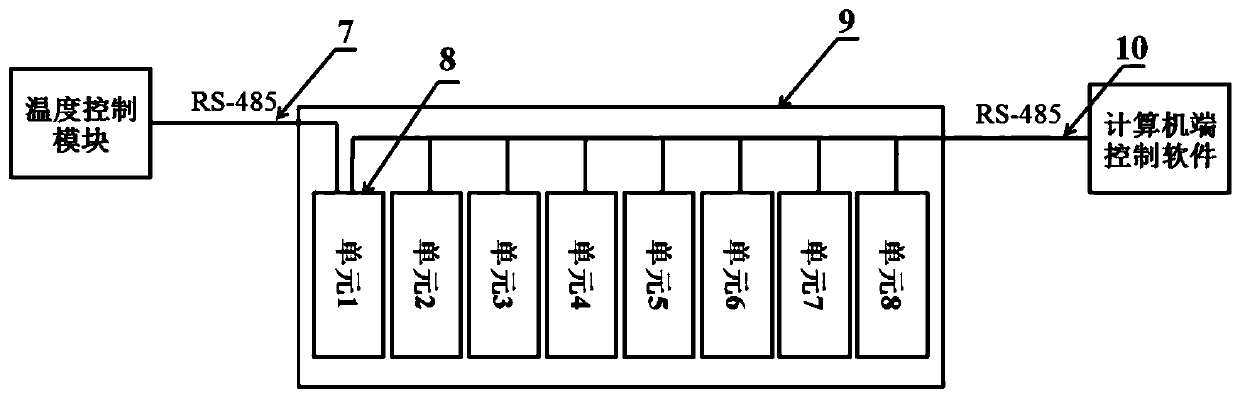
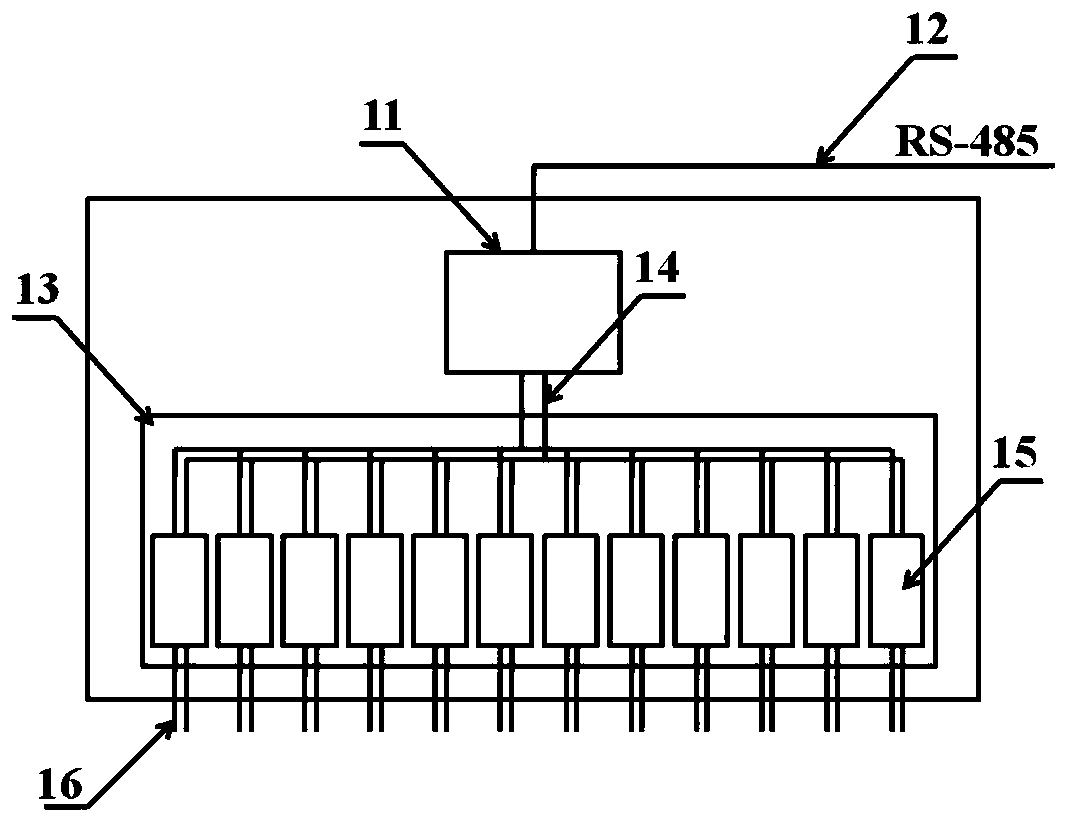
The invention relates to high-flux liquid conductivity measuring equipment, which belongs to the field of material testing devices and is used for carrying out high-flux measurement and monitoring onthe conductivity of a liquid at different temperatures. The equipment comprises a high-flux conductivity measuring instrument, a temperature control module, multi-channel conductivity measuring electrode clamps, conductivity measuring electrodes and computer side control software. The measuring equipment can realize high-flux measurement for the liquid conductivity, and is mainly applied but not limited to the measurement of electrolyte conductivity in the battery fields such as non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries, sodium-ion batteries and potassium-ion batteries. The measuring equipment is applicable to various laboratory environments as well as the measurement and online-monitoring for the conductivity of other liquids in the industrial field, can automatically complete the conductivity measurement and recording for a lot of liquid samples within a very short time, has sufficient accuracy and reliability, wide measurement range, good expandability and compatibility and can greatly improve the experimental efficiency. Meanwhile, the measuring equipment has the advantages of relatively low cost, compact structure and shape, easy maintenance and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Junction field effect transistor and preparation method thereof
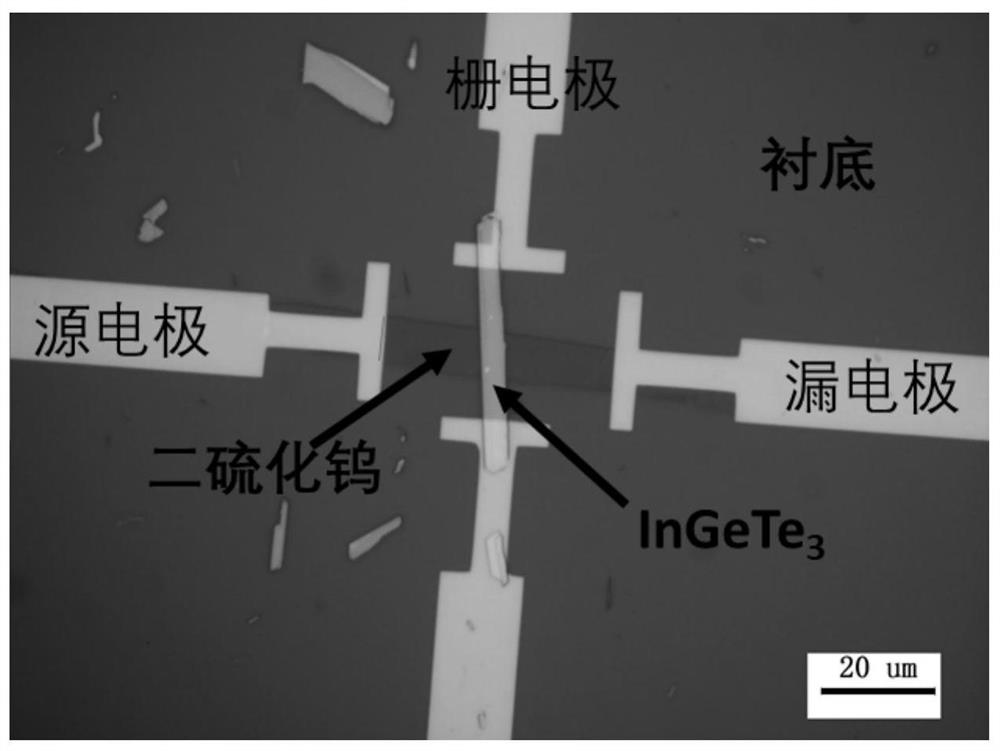
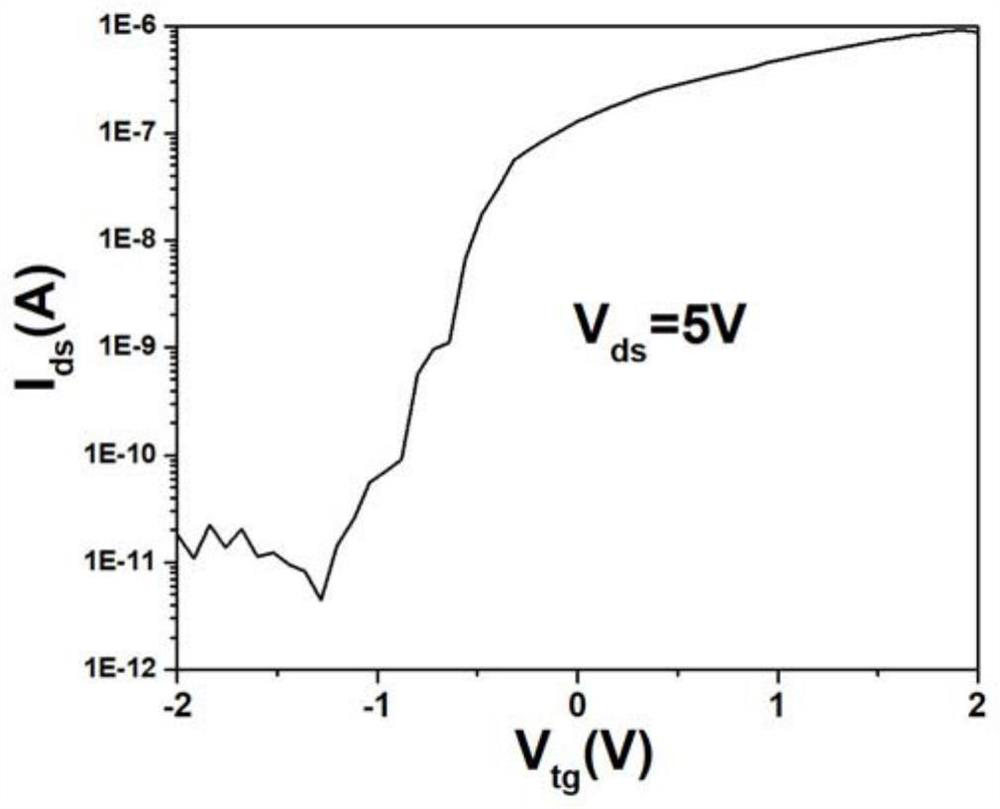
ActiveCN112447858AGuaranteed purityReduce the impactSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesThin membraneField effect
The invention discloses a junction field effect transistor and a preparation method thereof. The junction field effect transistor comprises a substrate, an N-type tungsten disulfide film, a P-type InGeTe3 film, a source electrode, a drain electrode and a top gate electrode, the N-type tungsten disulfide film is arranged on the surface of the substrate, the source electrode and the drain electrodeare arranged at the two ends of the surface of the N-type tungsten disulfide film, and the P-type InGeTe3 film is arranged on the surface of the N-type tungsten disulfide film; and the top gate electrode is arranged on the surface of the P-type InGeTe3 thin film and located between the source electrode and the drain electrode. According to the invention, WS2 and InGeTe3 are applied to the JFET, the width of a depletion region in the N-type tungsten disulfide thin film is realized by regulating and controlling the voltage of the P-type InGeTe3 thin film, the adjustment of channel conductivity is realized, the generation of interface defects is inhibited, the influence of the interface state on carrier transport is reduced, the sub-threshold swing of the device is reduced by virtue of the advantage of no complex dielectric engineering of the JFET, and the switching ratio and the current density are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Body tied intrinsic fet
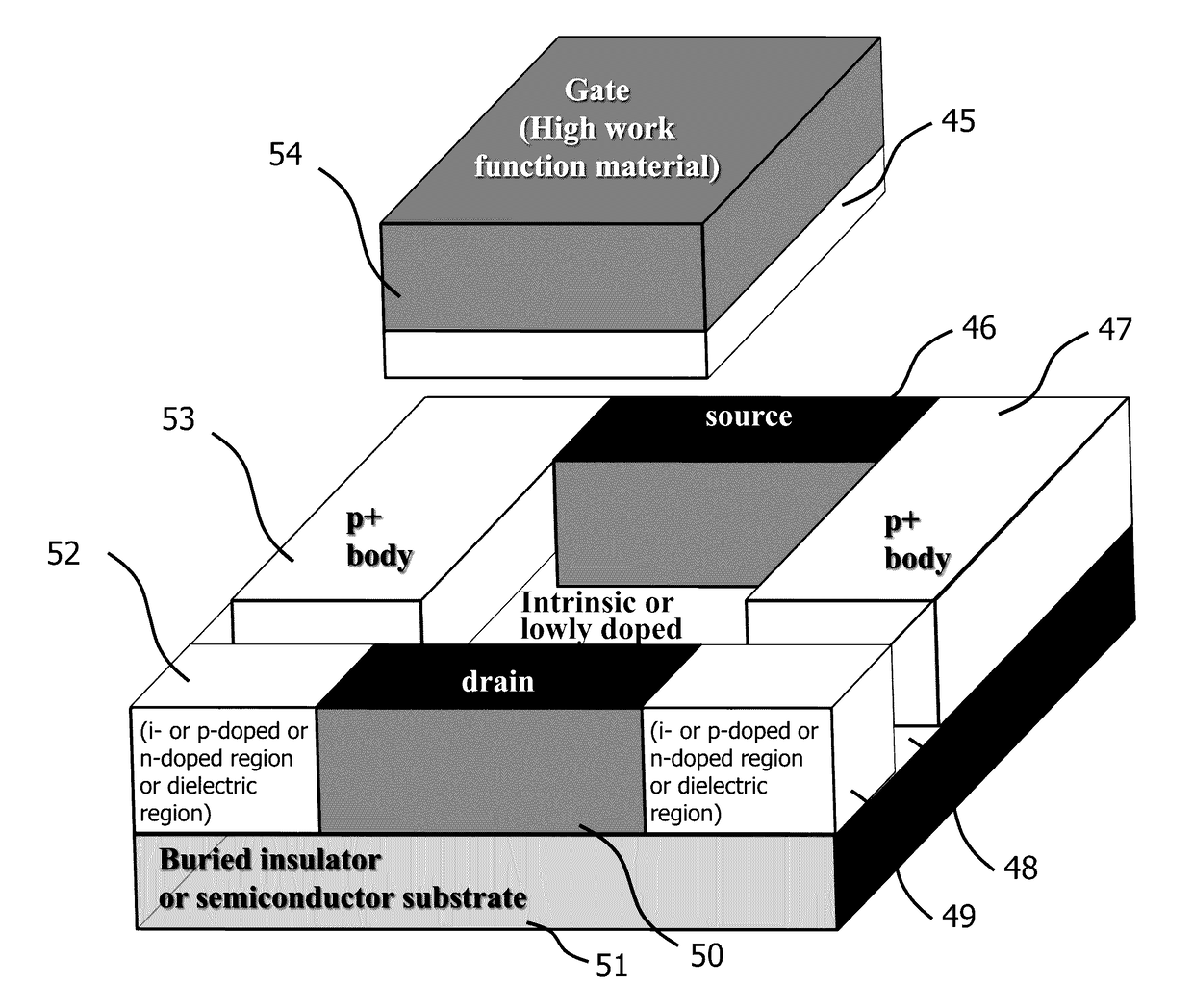
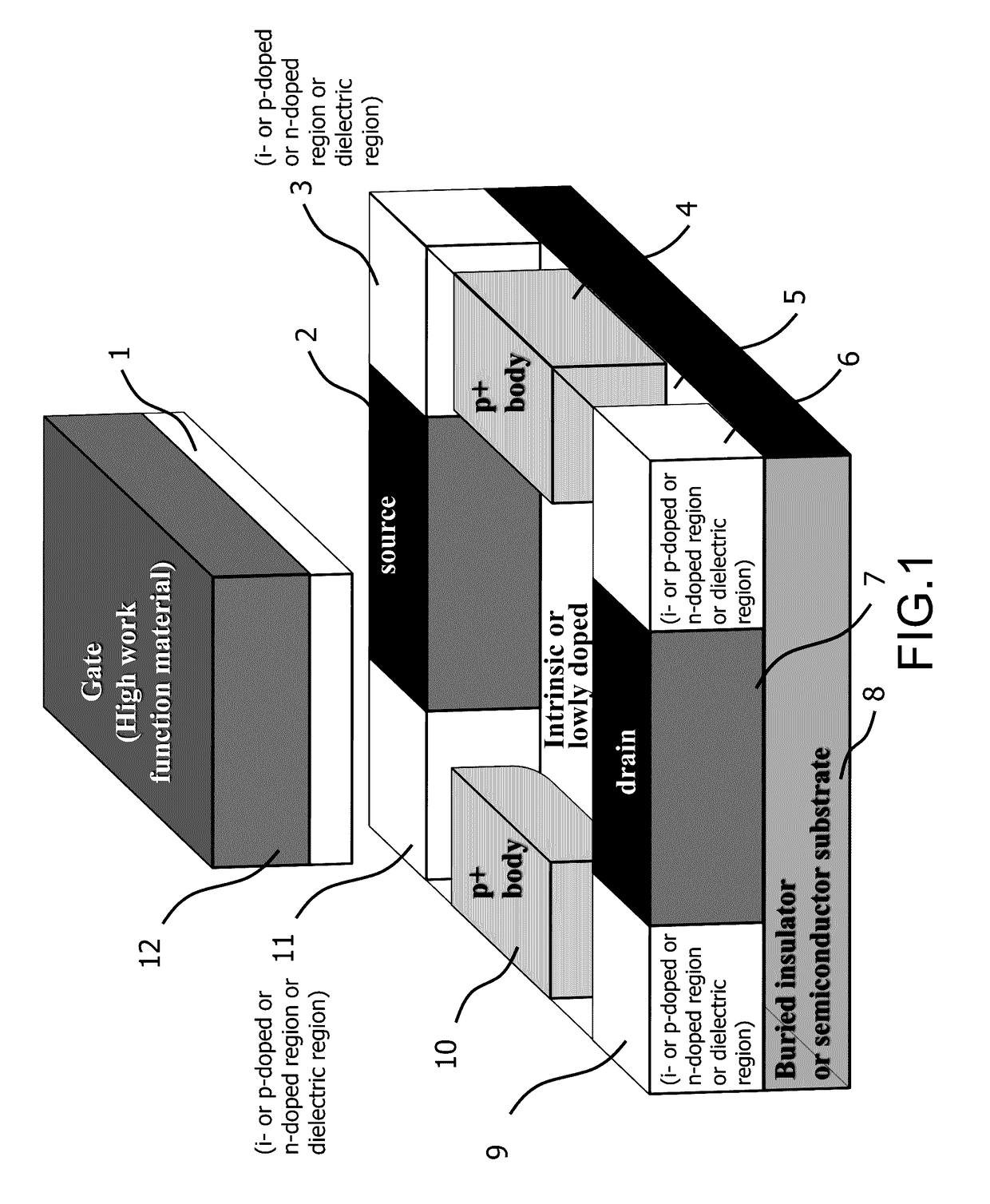
InactiveUS20170170276A1Reduces Random Dopant Fluctuation phenomenonReduce variation of threshold voltageTransistorMOSFETSemiconductor structure
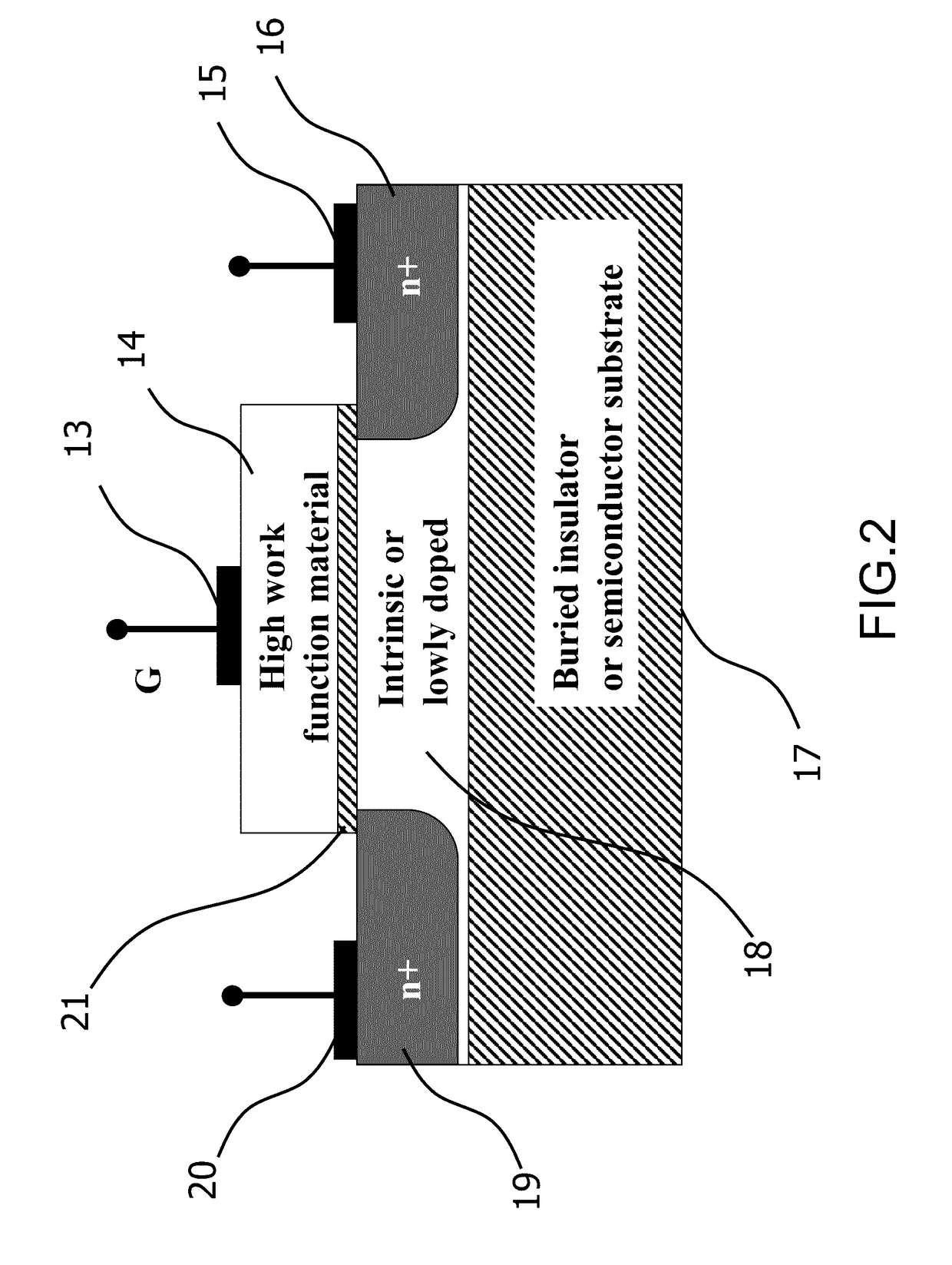
A novel semiconductor transistor is presented. The semiconductor structure has a MOSFET like structure, with the difference that the device channel is formed in an intrinsic region, so as to effectively decrease the impurity and surface scattering phenomena deriving from a high doping profile typical of conventional MOS devices. Due to the presence of the un-doped channel region, the proposed structure greatly reduces Random Doping Fluctuation (RDF) phenomena decreasing the threshold voltage variation between different devices. In order to control the threshold voltage of the device, a heavily doped poly-silicon or metallic gate is used. However, differently from standard CMOS devices, a high work-function metallic material, or a heavily p-doped poly-silicon layer, is used for an n-channel device and a low work-function metallic material, or heavily n-doped poly-silicon layer, is used for a p-channel FET. Doped or insulating regions are used to increase the control on the channel conductivity.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS8633078B2Reduce leakage currentImproved channel conductivityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialStacking fault
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for optimizing the channel conductivity of diamond material
InactiveCN107331701AImprove channel conduction abilityImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricHydrogen
The invention provides a method for optimizing the channel conductivity of a diamond material. The method comprises a first step of providing a diamond substrate; a second step of treating the surface of the diamond substrate with a hydrogen plasma to form a hydrogen plasma treatment layer; a third step of depositing a first oxide layer on the hydrogen plasma treatment layer; a fourth step of depositing a second oxide layer on the first oxide layer and photoetching a gate dielectric layer; a fifth step of growing a source / drain electrode metal on the device formed in the fourth step; and a sixth step of growing a gate electrode metal on the device formed in the fifth step. The method of the invention can improve the channel conductivity of the hydrogen-terminated diamond surface.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS7342283B2Avoid interferenceReduce device areaTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialHemt circuits
An object of the present invention is to provide a semiconductor device which enables to reduce the device area, while securing the breakdown voltage between the drain and the source of each MOS transistor for the semiconductor device including plural MOS transistors, which are arrayed adjacently each other, with different types of channel conductivity. The semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate, a buried oxide film and a semiconductor layer, and furthermore the semiconductor layer has an island-like semiconductor layer, in which a MOS transistor is formed, the MOS transistor has a source region, and a drain region that is positioned in the periphery of the source region, an island-like semiconductor layer, in which a MOS transistor is formed, the MOS transistor has a drain region, and a source region that is positioned in the periphery of the drain region, an isolation trench which isolates the former island-like semiconductor layer from other portions of the semiconductor layer, an isolation trench which isolates the latter island-like semiconductor layer from other portions of the semiconductor layer, and a buffer region, in which the electric potential is fixed to the lowest electric potential in a circuit, which prevents an electrical interference occurred between transistors.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Digital alloy based back barrier for p-channel nitride transistors
PendingCN111033750ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLattice mismatchEngineering
A III-nitride power handling device and the process of making the III-nitride power handling device are disclosed that use digital alloys as back barrier layer to mitigate the strain due to lattice mismatch between the channel layer and the back barrier layer and to provide increased channel conductivity. An embodiment discloses a GaN transistor using a superlattice binary digital alloy as back barrier comprising alternative layers of AlN and GaN. Other embodiments include using superlattice structures with layers of GaN and AlGaN as well as structures using AlGaN / AlGaN stackups that have different Aluminum concentrations. The disclosed device has substantially increased channel conductivity compared to traditional analog alloy back barrier devices.
Owner:HRL LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com