Patents
Literature
281 results about "Lateral offset" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The lateral offset to obstruction is defined as the distance from the edge of traveled way, shoulder, or other designated point to a vertical roadside element.
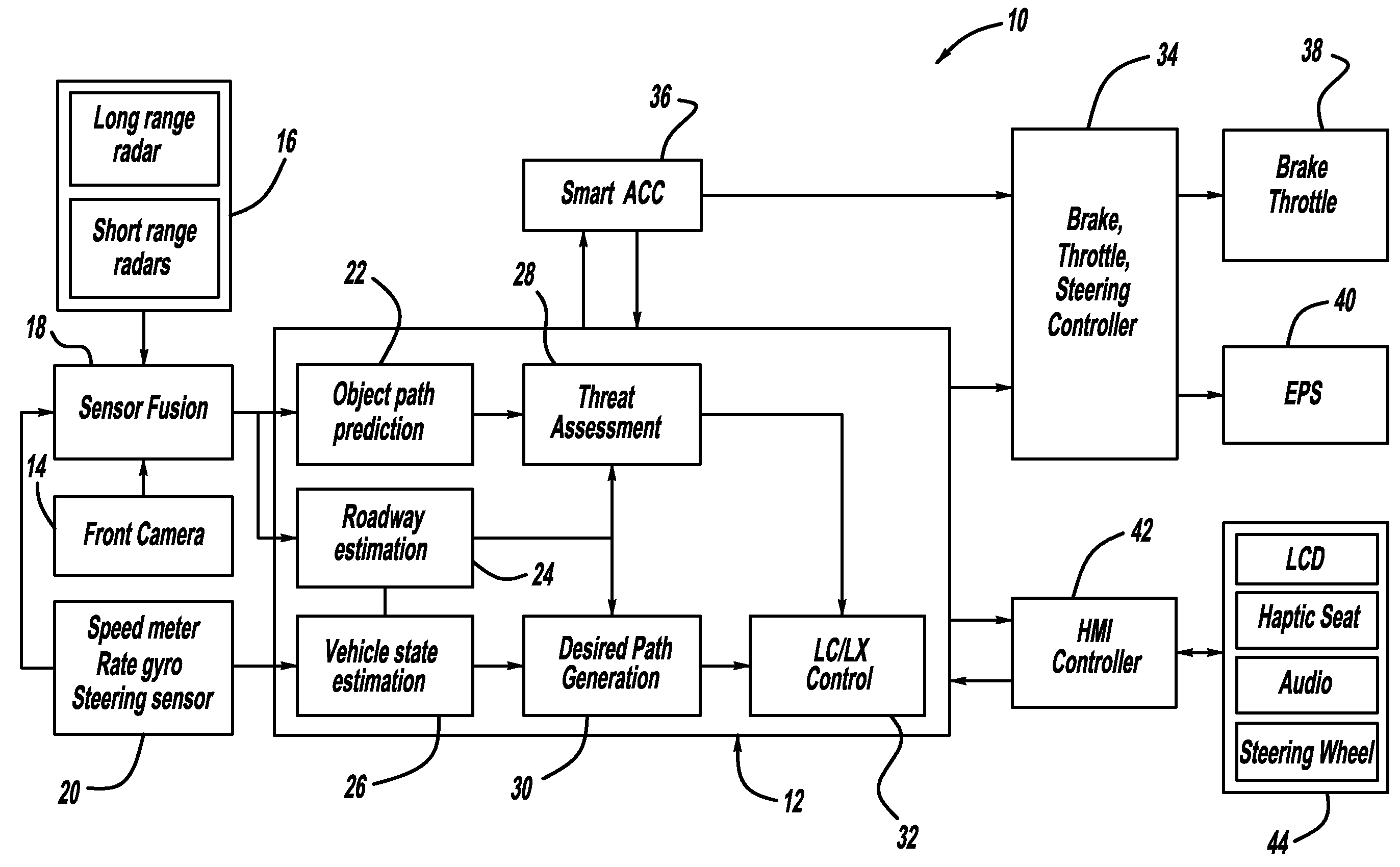
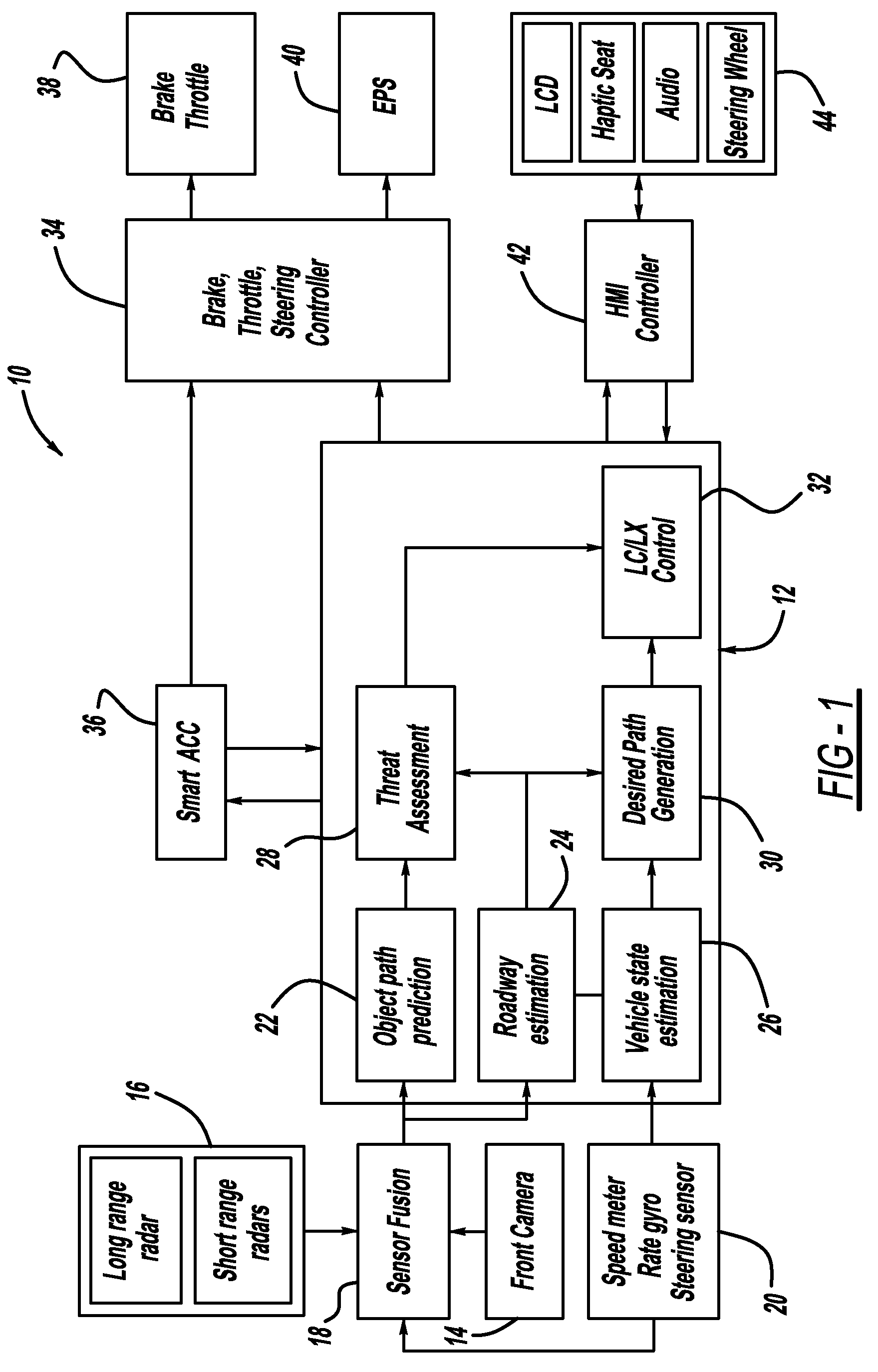
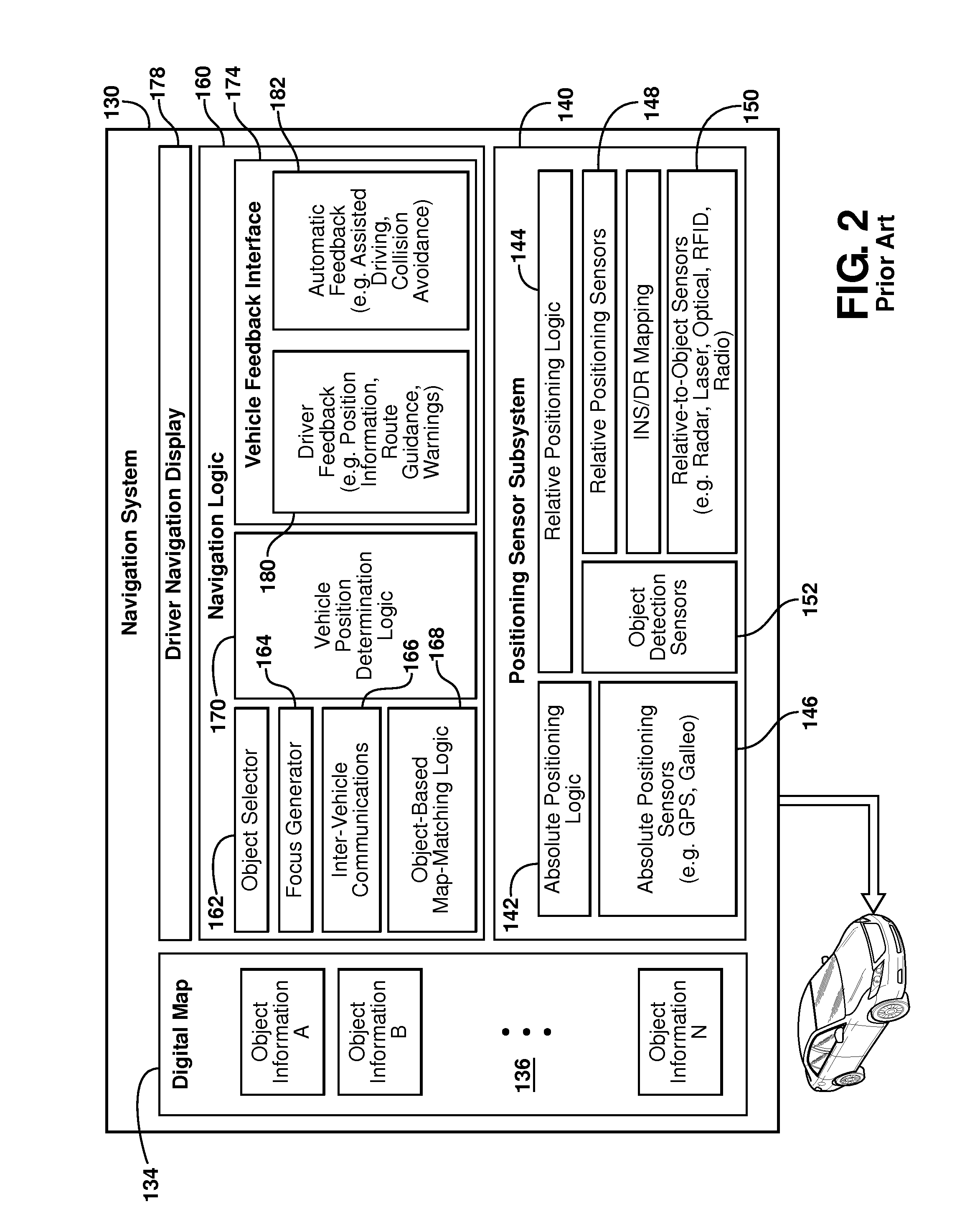
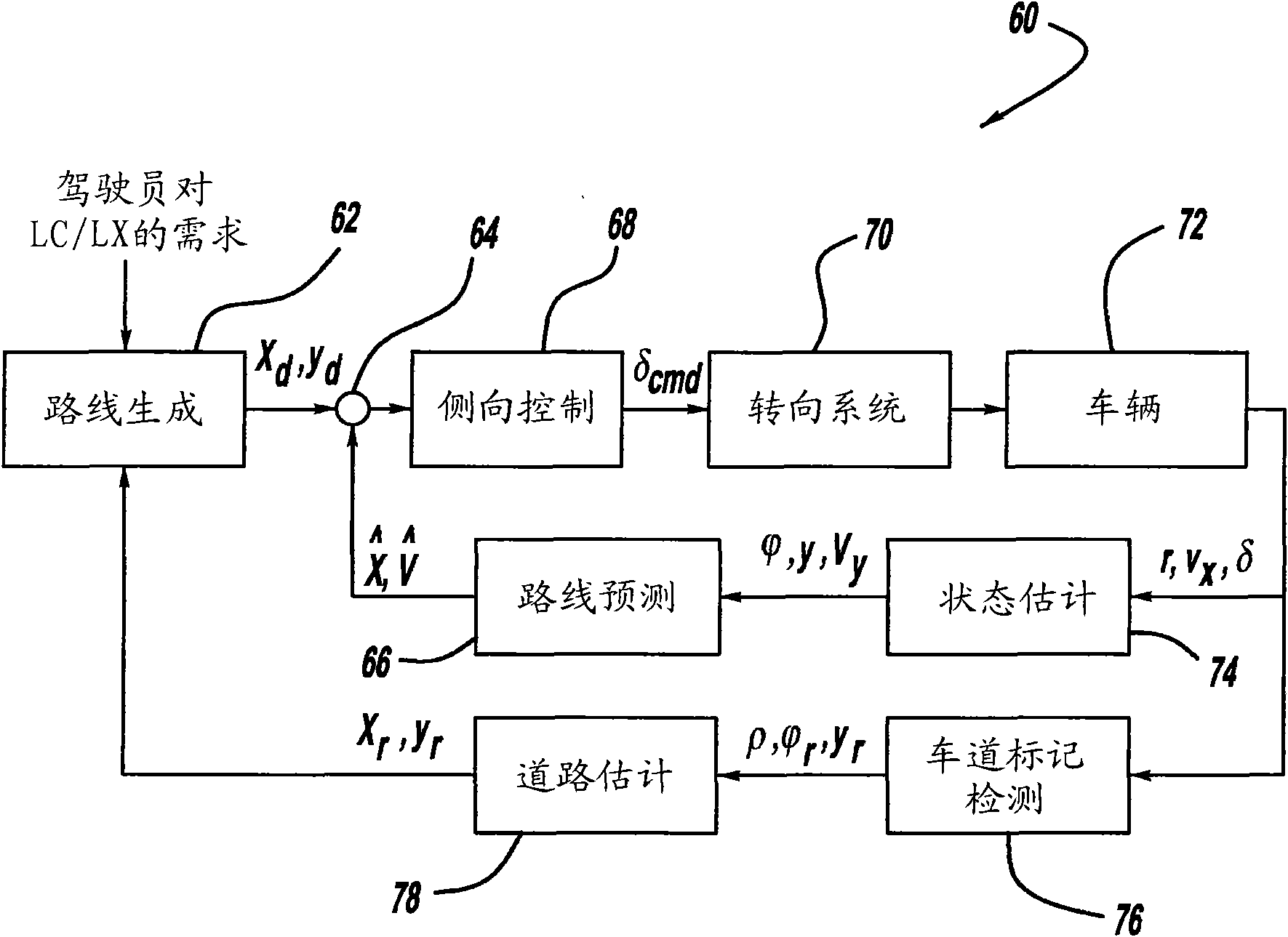
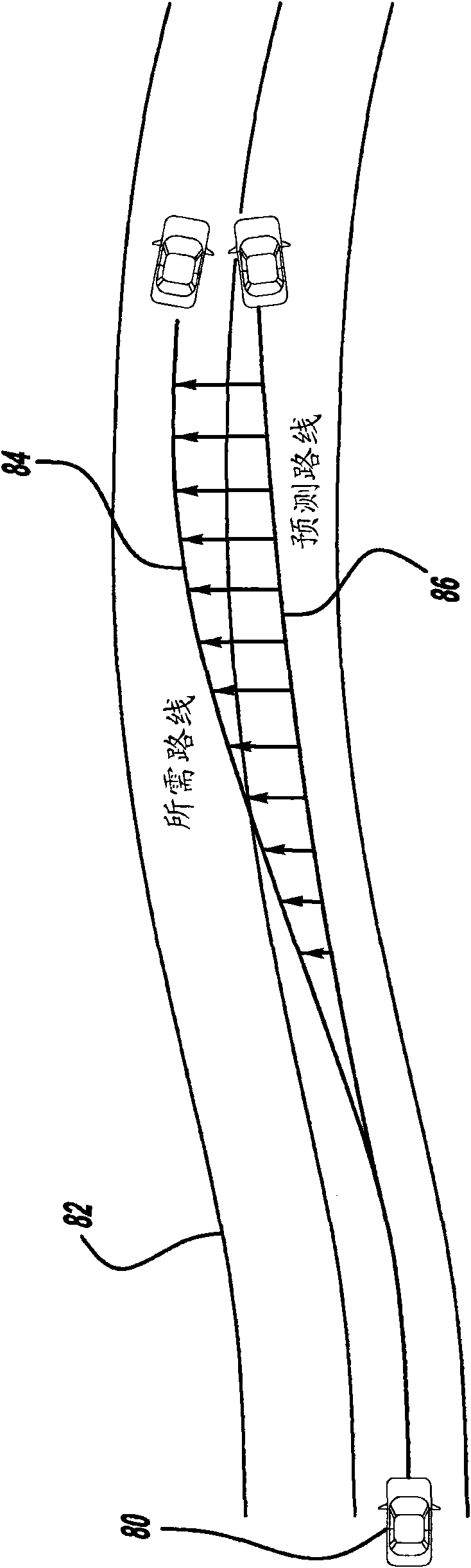
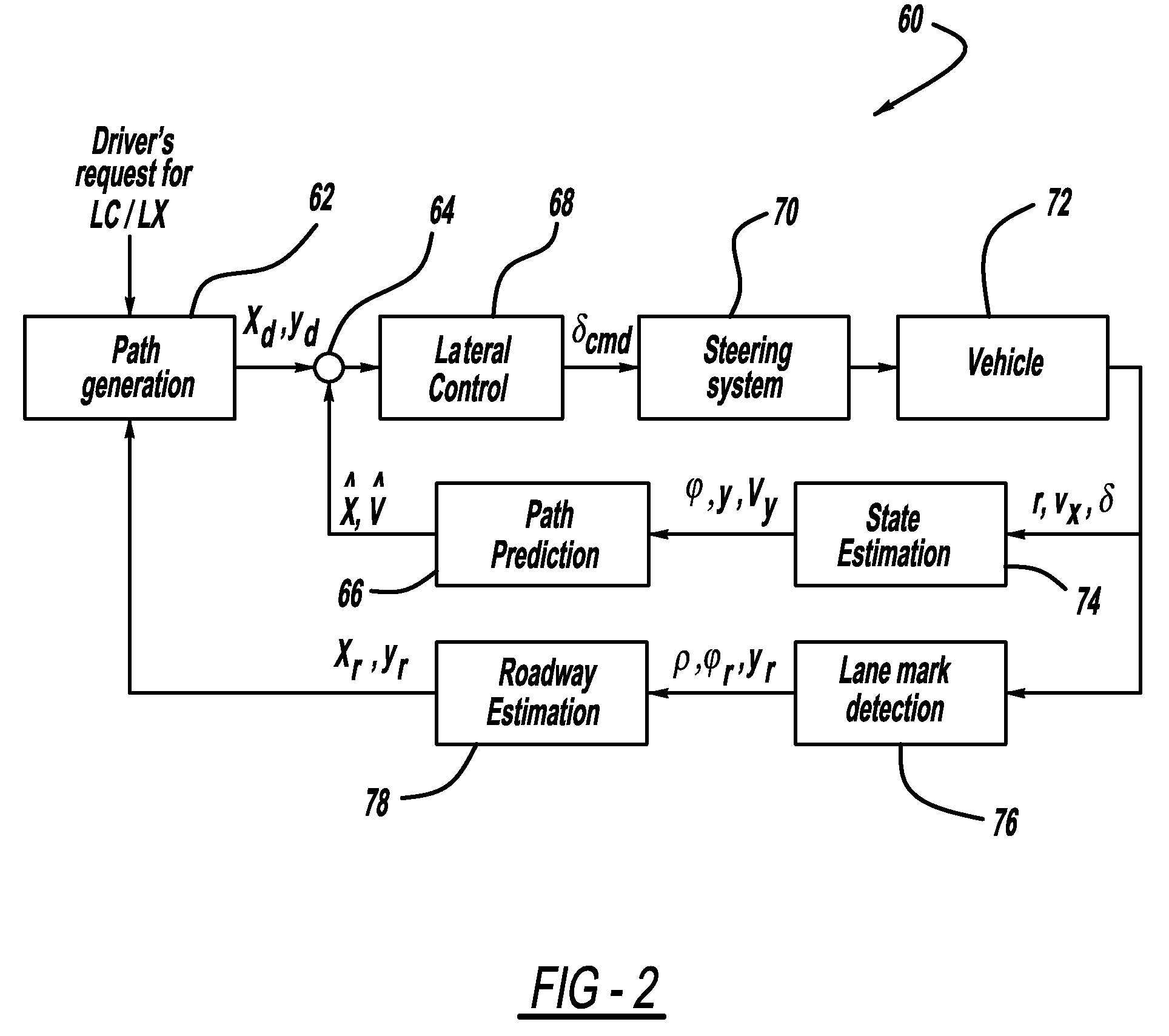
Model based predictive control for automated lane centering/changing control systems
ActiveUS20100228420A1Minimize error valueDigital data processing detailsAnti-collision systemsVehicle dynamicsCompletion time
A system and method for providing steering control for lane changing and lane centering purposes in an autonomous or semi-autonomous vehicle system. A vehicle vision system calculates roadway lane marking information, such as lateral offset, yaw angle and roadway curvature with respect to the vehicle's centered coordinate system. The roadway is then modeled as a second order polynomial equation. The method then predicts roadway lateral position and yaw angle over a pre-defined lane change completion time using a vehicle dynamic model. The method then compares a predicted vehicle path with a desired vehicle path to generate an error value, and calculates a steering angle command to minimize the error value, where the steering angle command is calculated as a function of vehicle lateral position, vehicle lateral speed, vehicle yaw rate and vehicle yaw angle. The steering angle command is then sent to the vehicle steering system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
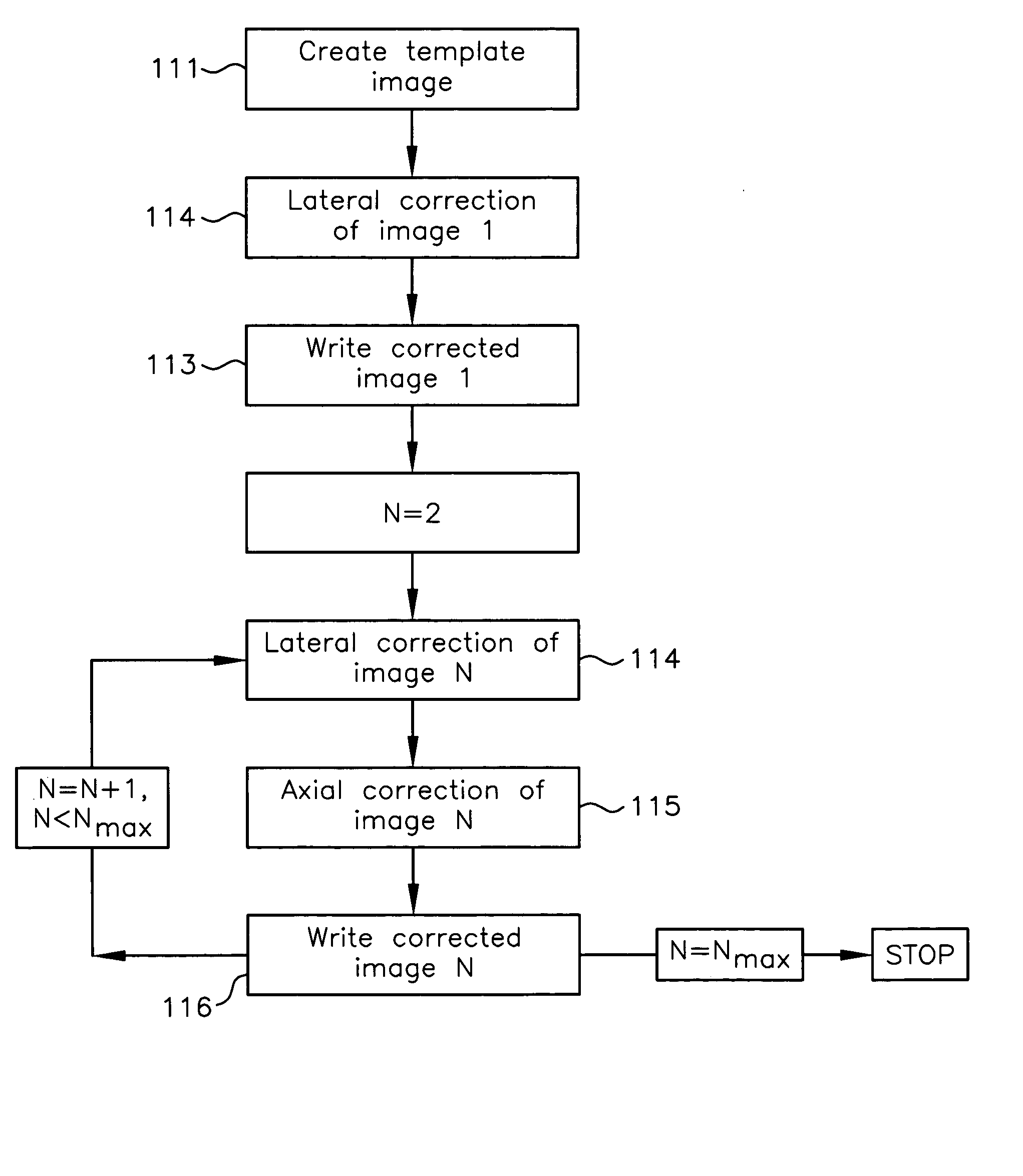
Method for correction of relative object-detector motion between successive views
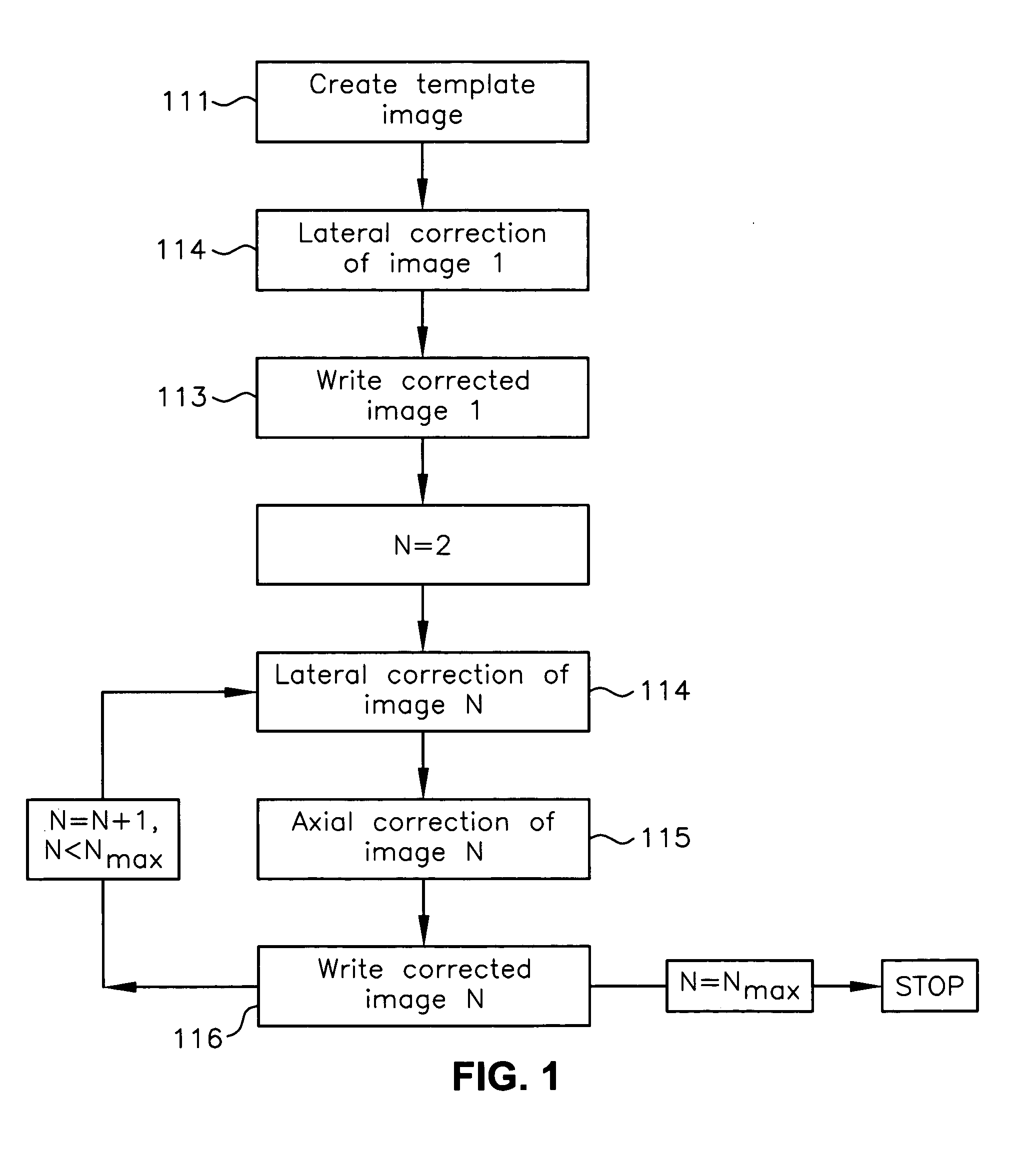
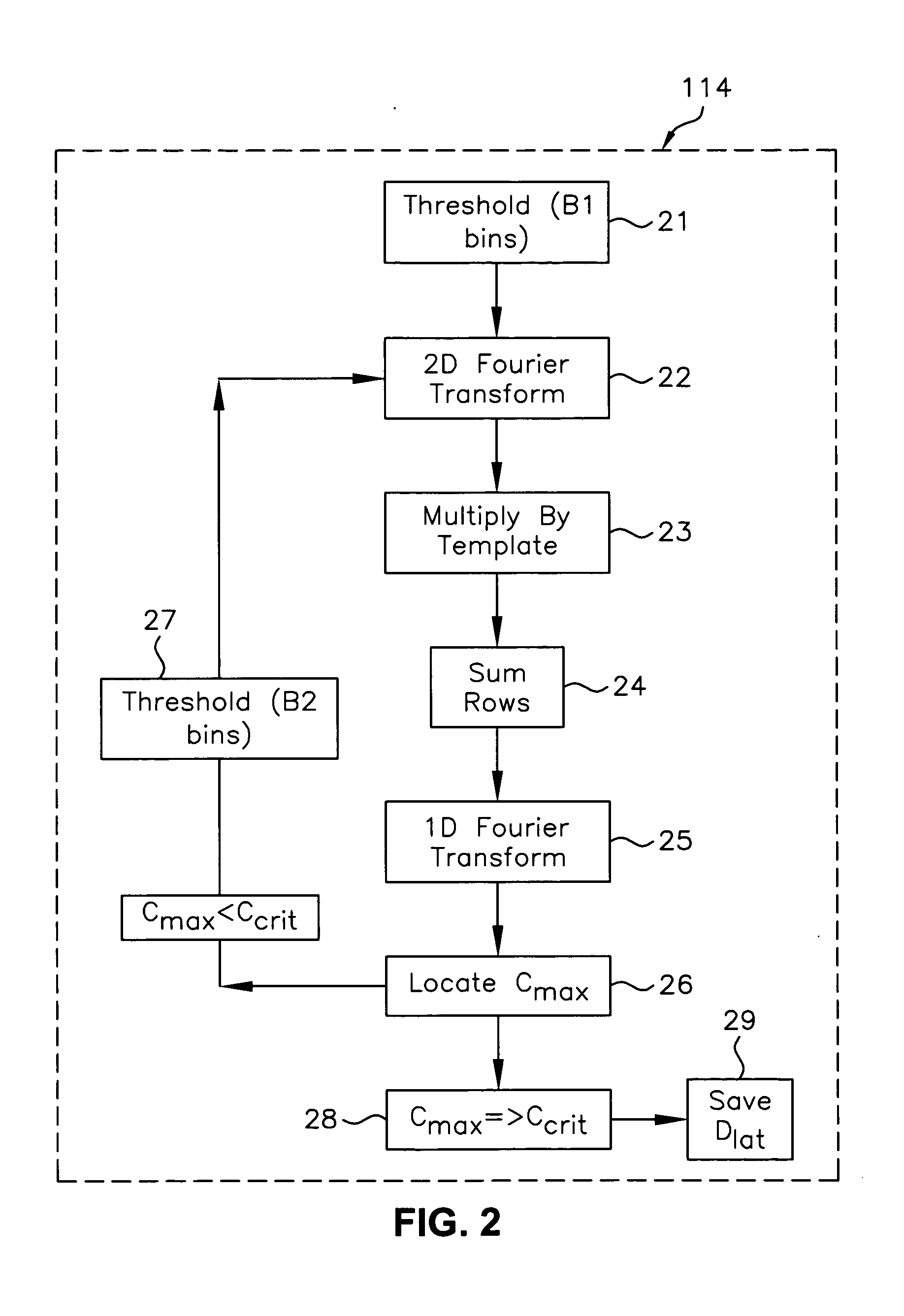
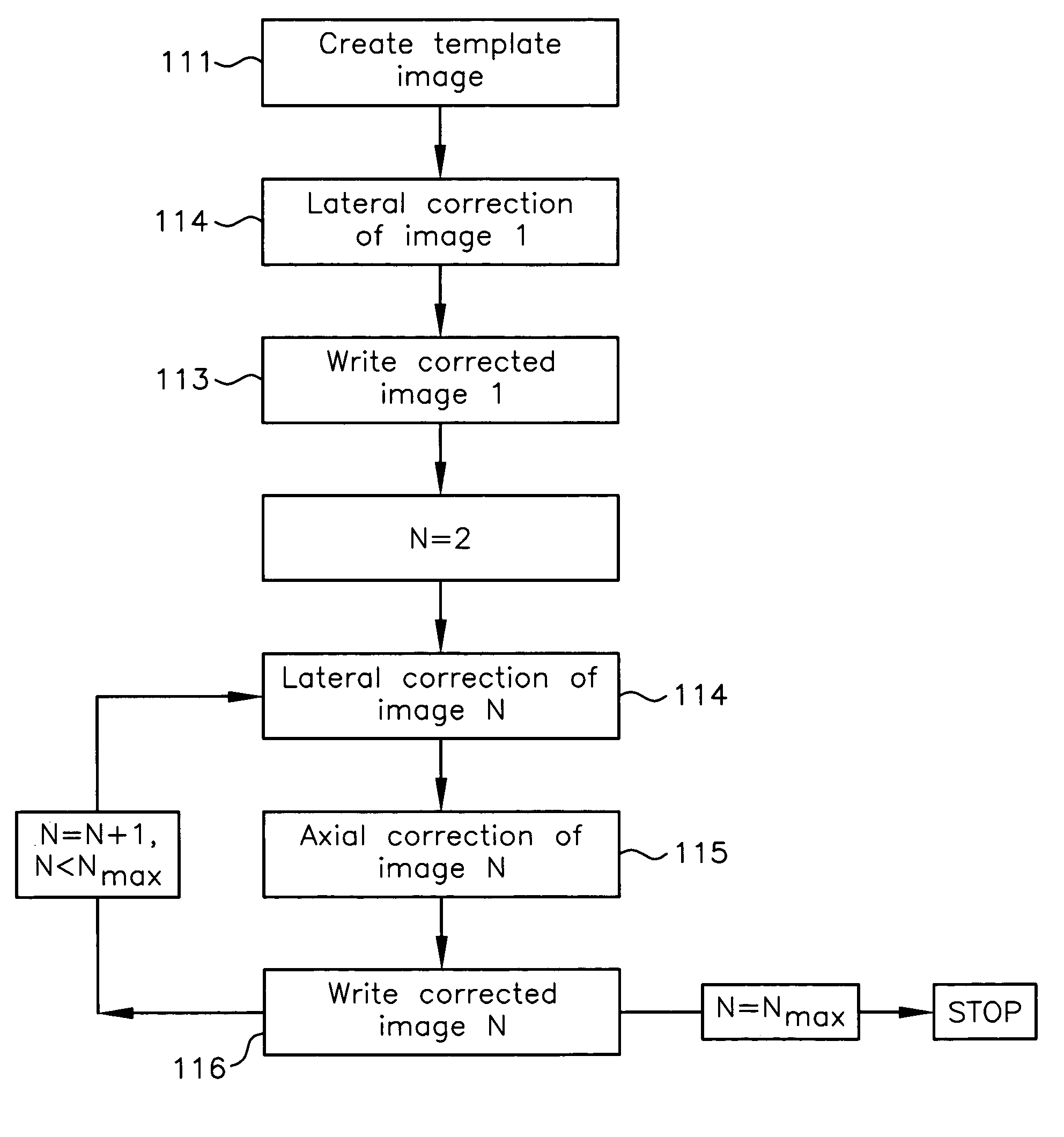
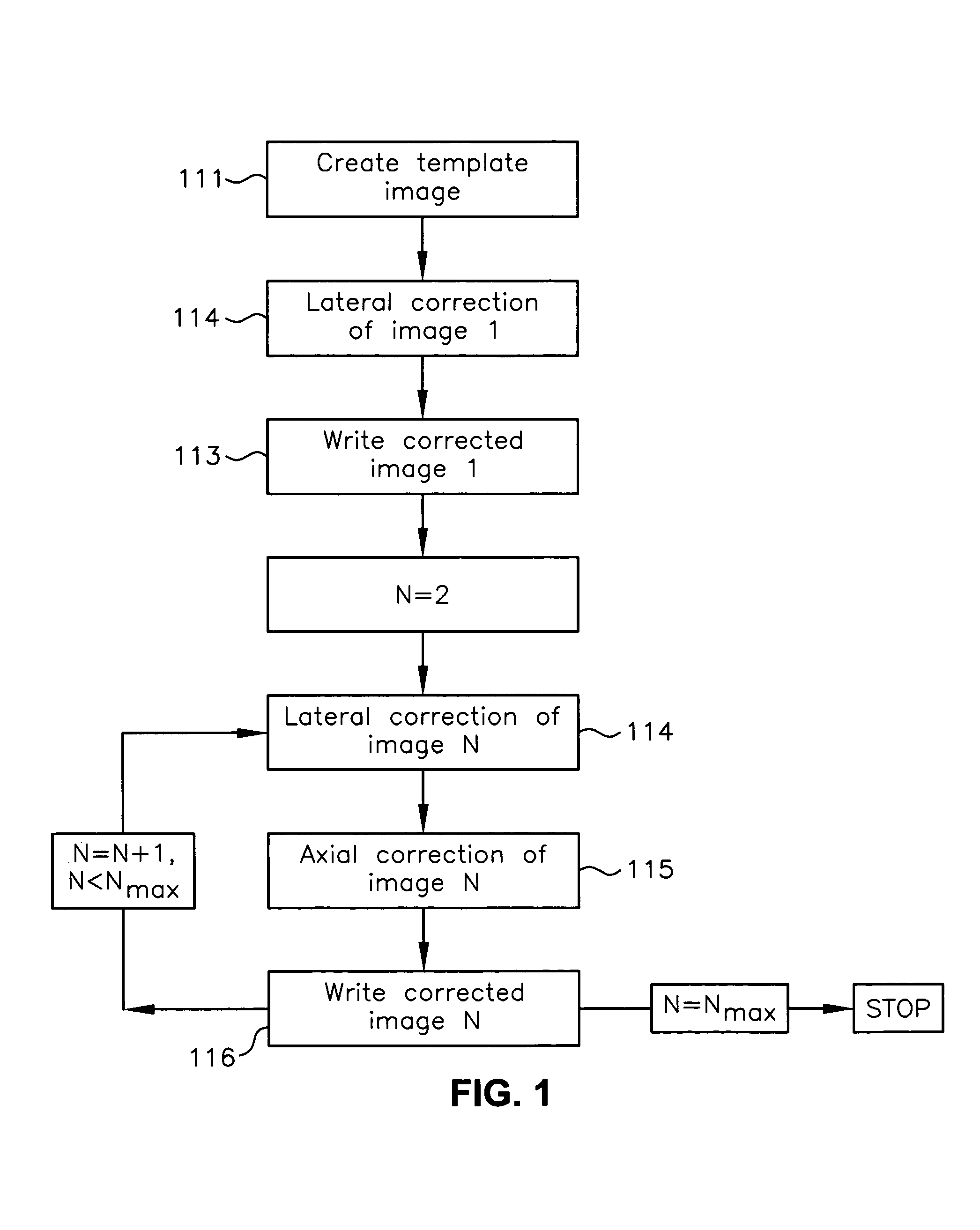
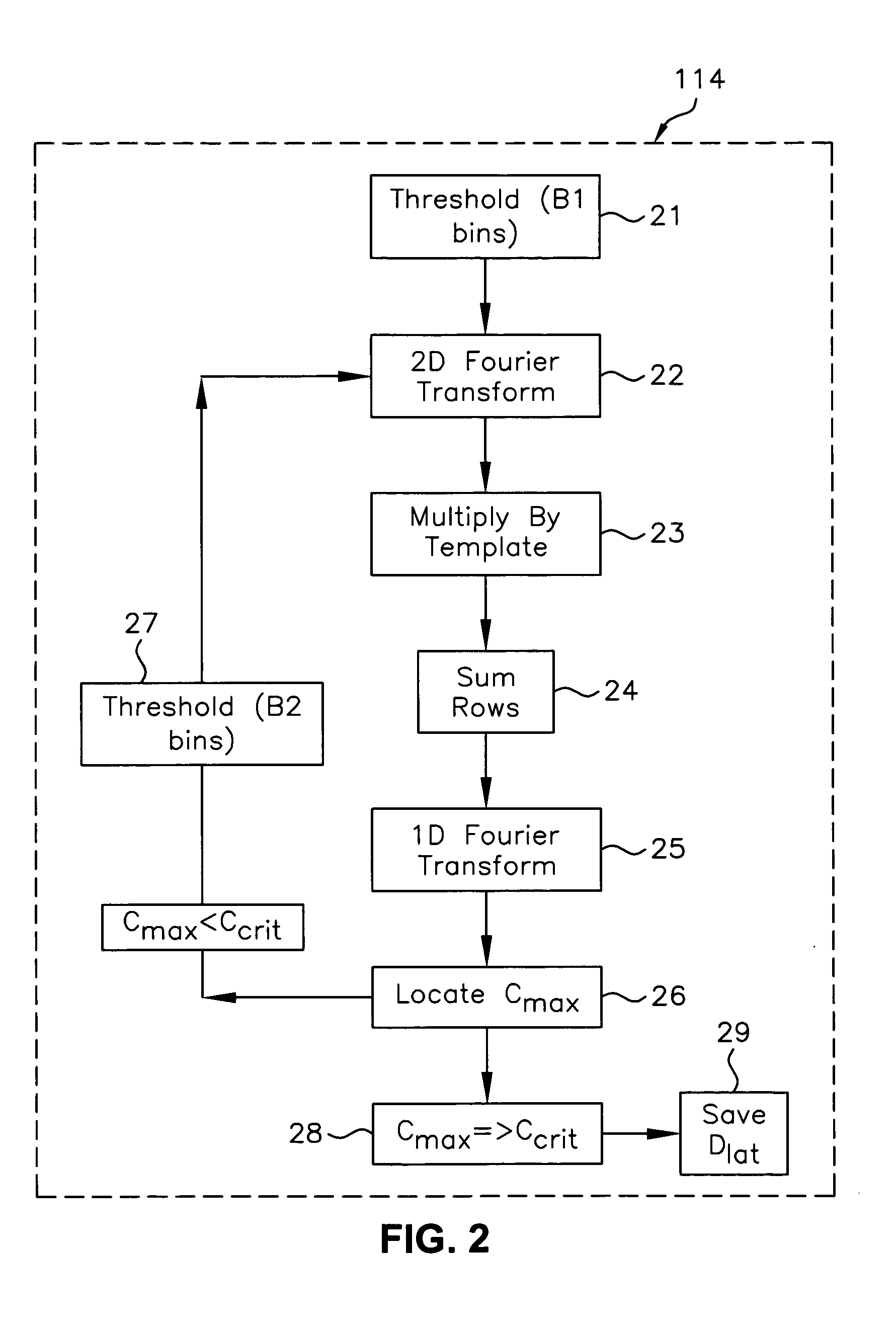
Registration correction for optical tomographic imaging in three dimensions. An object of interest is illuminated to produce an image. A lateral offset correction value is determined for the image. An axial offset correction value is determined for the image. The lateral offset correction value and the axial offset correction value are applied to the image to produce a corrected file image.
Owner:VISIONGATE
Speckle-image-based optical position transducer having improved mounting and directional sensitivities
InactiveUS6642506B1Reduce sensitivityAvoid smearingSlide gaugesMaterial analysis by optical meansImage detectionRelative motion
A speckle readhead includes a light source that outputs light towards an optically rough surface. Light scattered from this surface contains speckles. The scattered light is imaged onto an image detector, captured and stored. Subsequently, a second image is captured and stored. The two images are repeatedly compared at different offsets in a displacement direction. The comparison having the highest value indicates the amount of displacement between the readhead and the surface that occurred between taking the two images. An optical system of the readhead includes a lens and an aperture. The aperture can be round, with a diameter chosen so that the average size of the speckles is approximately equal to, or larger than, the dimensions of the elements of the image detector. The dimension of the aperture in a direction perpendicular to the direction of displacement can be reduced. Thus, the imaged speckles in that direction will be greater than the dimension of the image detector elements in that direction. Such a readhead is relatively insensitive to lateral offsets. The lens can be a cylindrical lens that magnifies the relative motion along the direction of displacement but does not magnify relative motions in the direction perpendicular to the direction of displacement. The optical system can also be telecentric. Thus, the readhead is relatively insensitive to both separation and relative motions between the readhead and the surface. The light source can be modulated to prevent smearing the speckles across the image detector. The light source can be strobed to freeze the image.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
CAS modular body reference and limb position measurement system
InactiveUS20060015018A1Surgical navigation systemsDiagnostic markersThree-dimensional spaceSacroiliac joint
A surgical bone reference assembly for communication with a CAS system, comprises a bone anchor fastenable to a bone element, an adjustable support and a trackable member that is located and tracked in three dimensional space by the CAS system. The support is removably fastenable to the bone anchor member and permits variable positioning relative to the bone anchor member. The support is intra-operatively detachable from and re-fastenable to the bone anchor member. A method of using a CT-free CAS system for determining a change in position of an un-tracked target limb is also provided. The method comprises engaging the trackable bone reference member to another bone element, locating and digitizing a landmark on the target limb, digitizing the landmark again following joint reduction, and determining at least one of a post-joint reduction limb length discrepancy and a target limb medio-lateral offset.
Owner:ORTHOSOFT
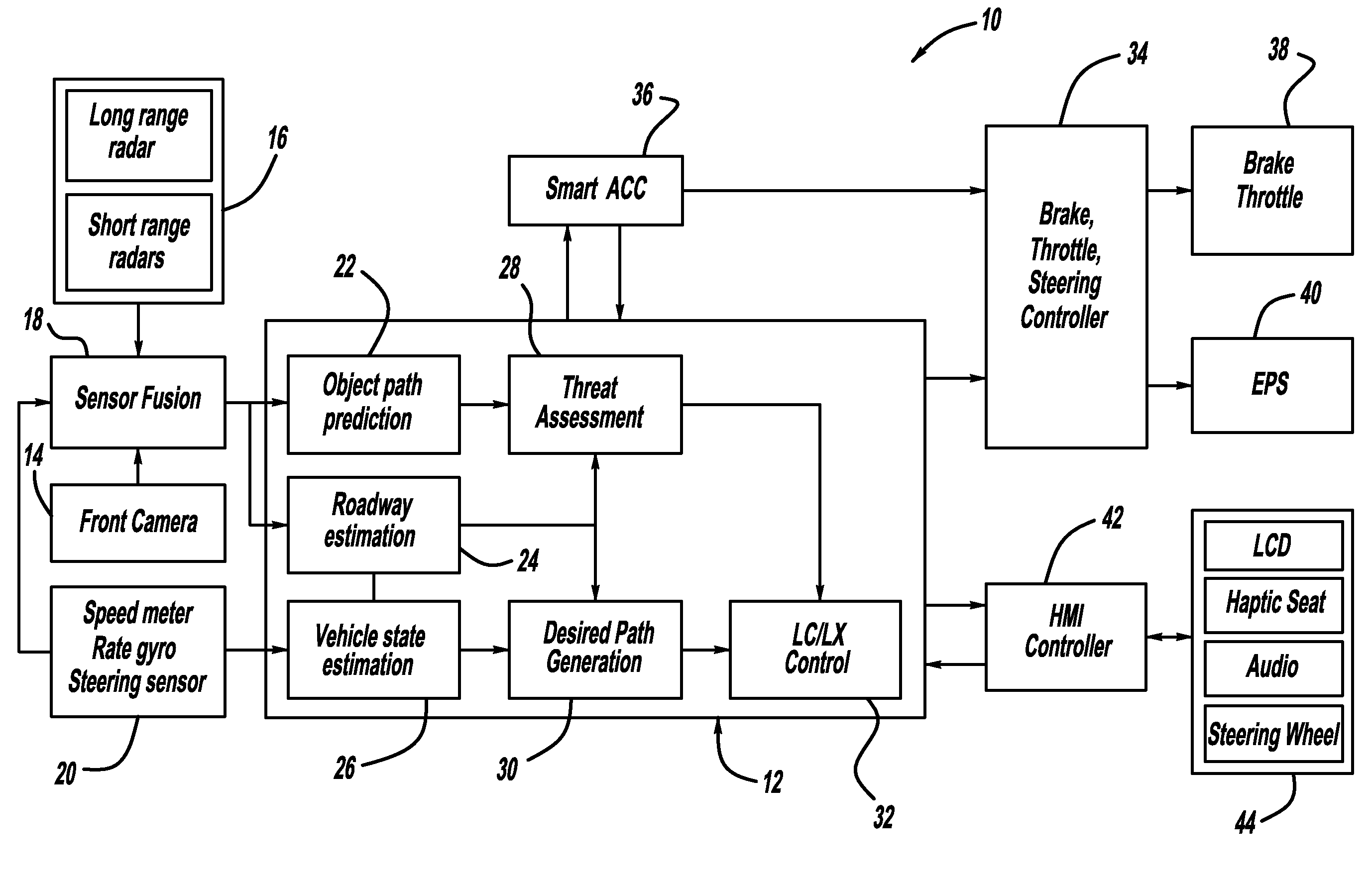
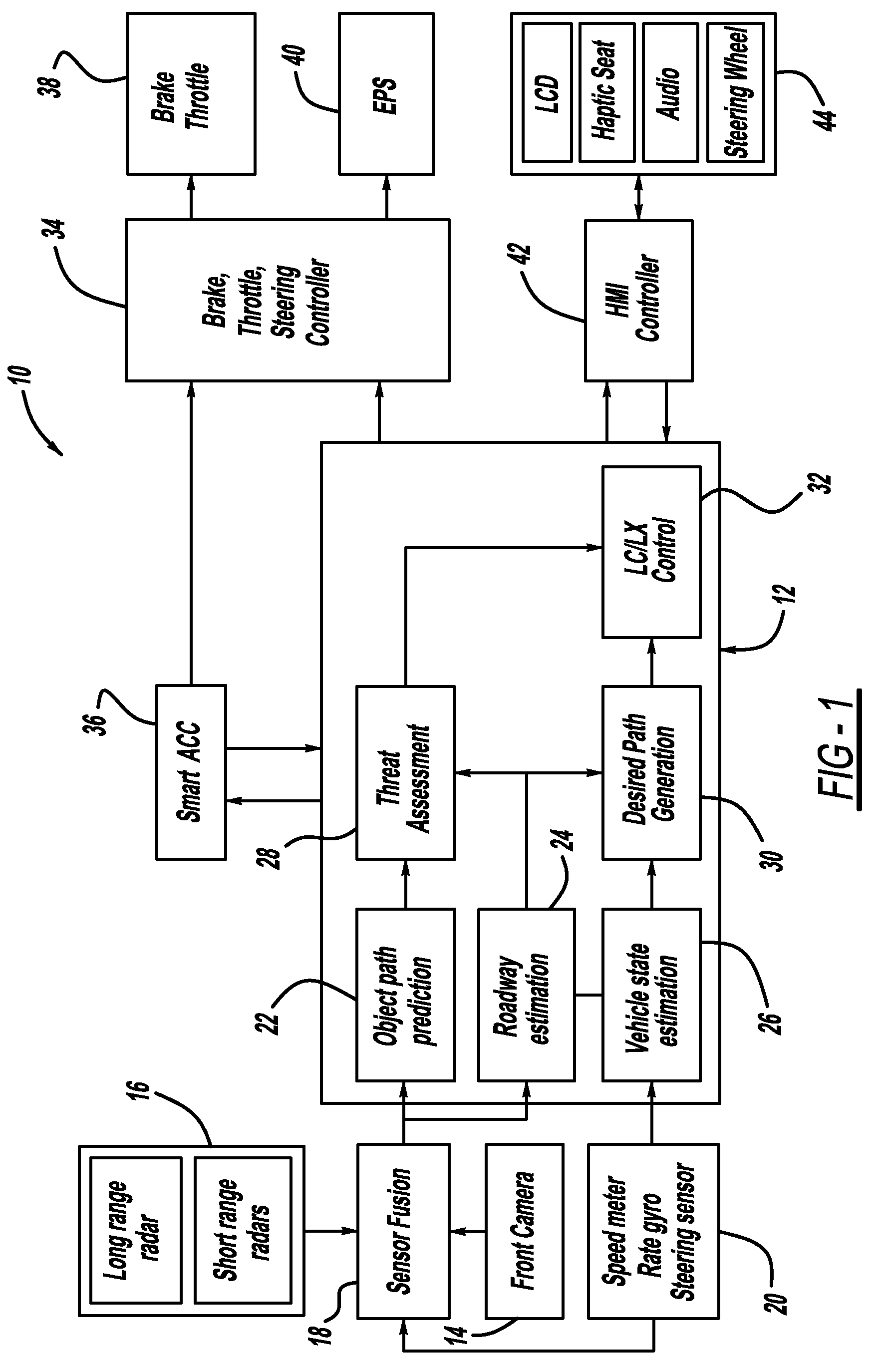
Systems, methods and devices for adaptive steering control of automotive vehicles
ActiveUS20090299573A1Steering driverSteering evenDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsMobile vehicleDriver/operator
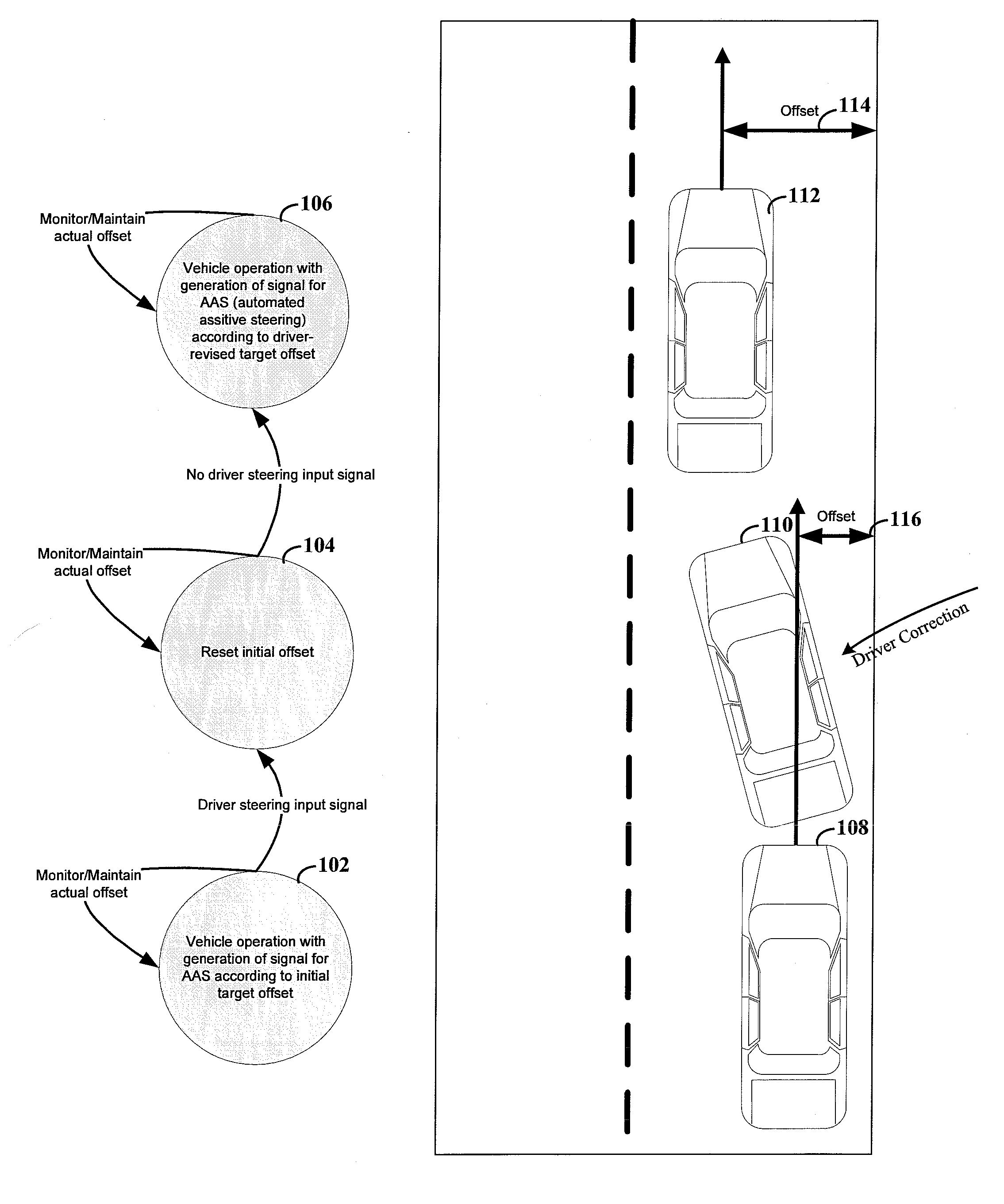
A variety of methods, systems, devices and arrangements are implemented for automated assistance for a driver. One such method relates to a synergistic combination of automation and human control for a motor vehicle traveling on a lane, thereby allowing human-based decisions to be supplement (or be supplemented by) automated decisions. Specific aspects facilitate maintenance of the vehicle on the lane. The vehicle is automatically steered towards a lateral offset within the vehicle lane. Steering input from the driver results in changes to this lateral offset. This modification of the lateral offset can be used to allow the driver to follow any trajectory parallel to the road, including trajectories where the vehicle is not centered within the lane.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
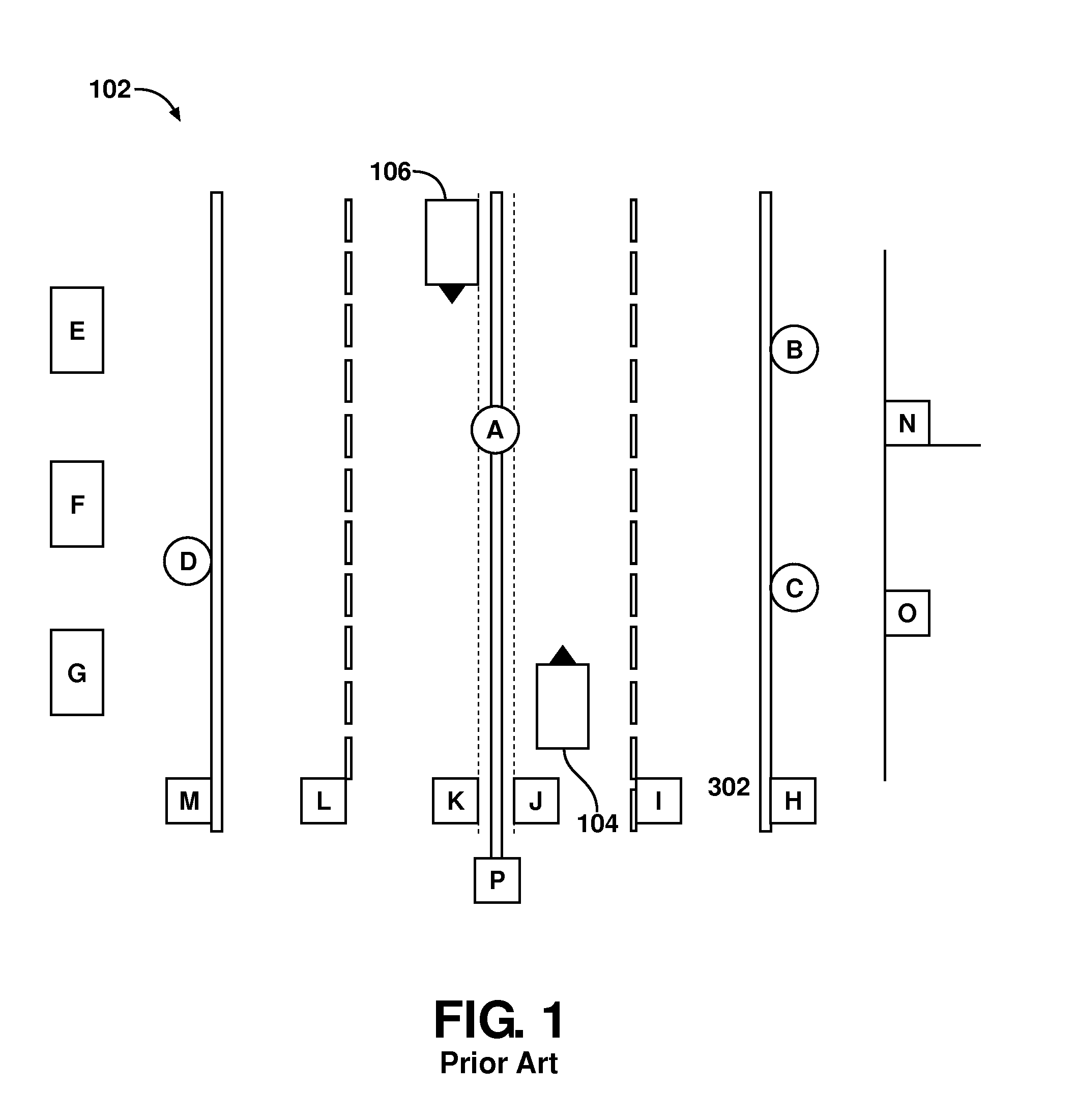
System and method for vehicle navigation using lateral offsets
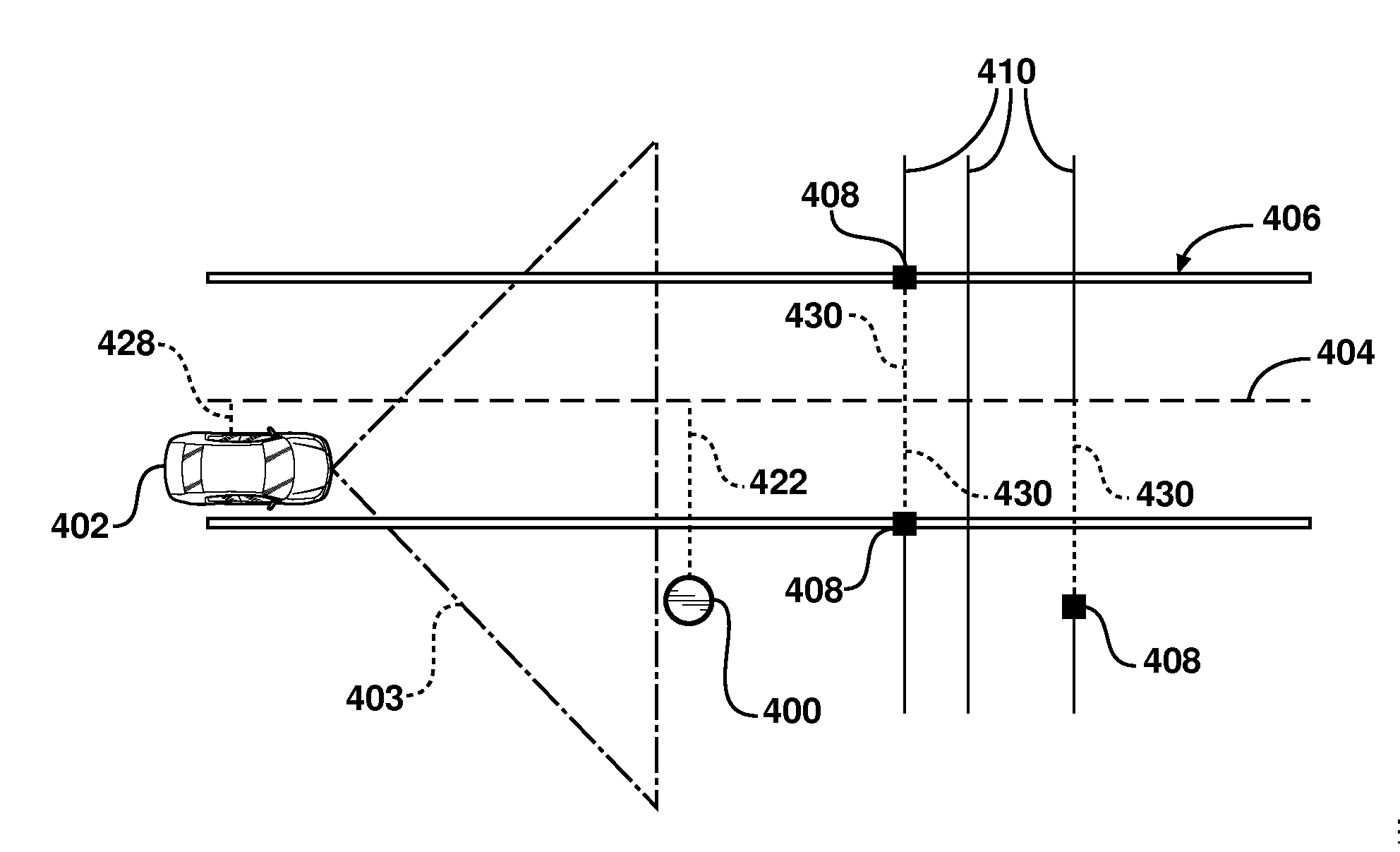
ActiveUS20120271540A1Enhanced driver assistance featureSimple calculationInstruments for road network navigationAnti-collision systemsRadarLaser scanning
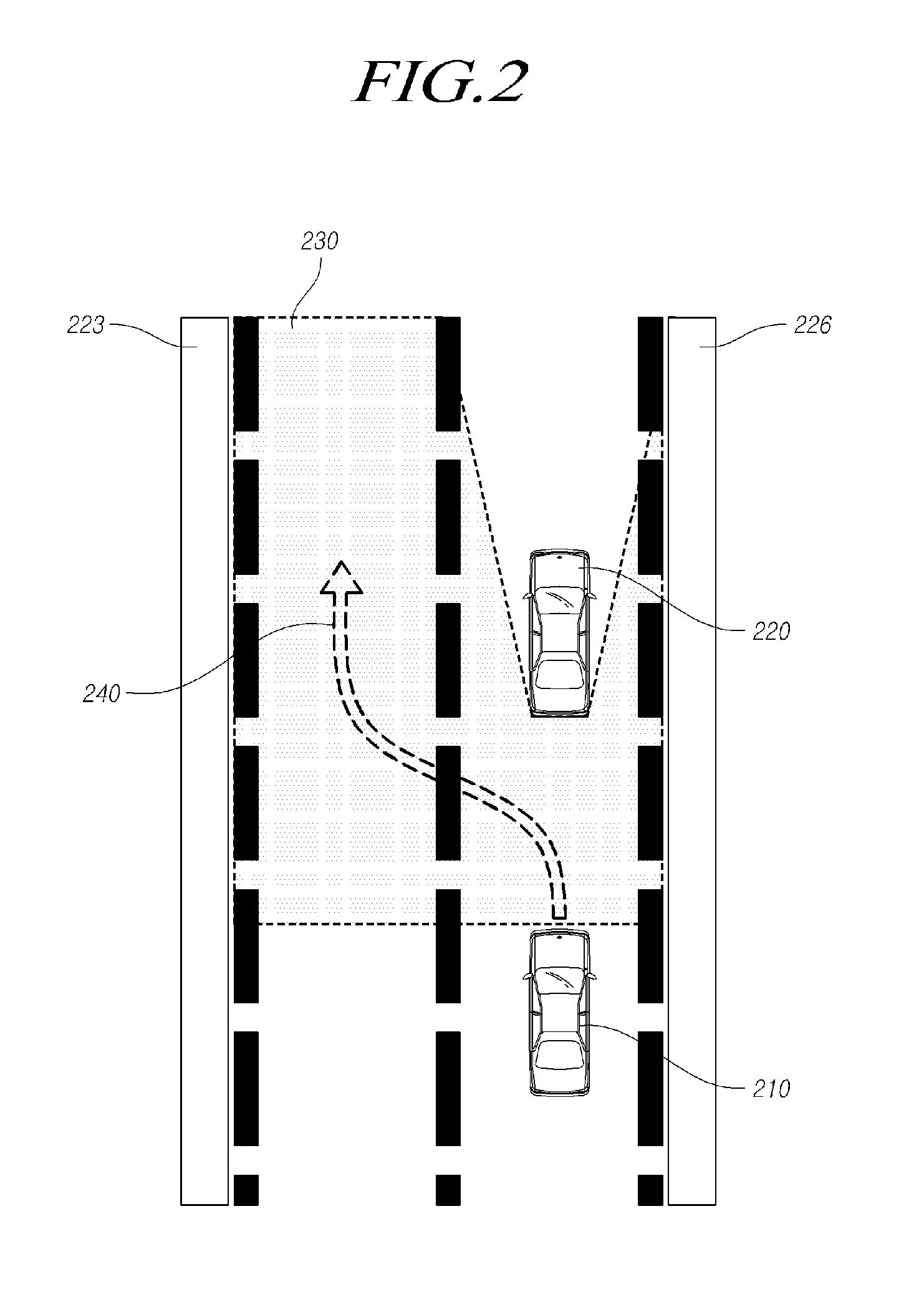
A navigation system for use in a vehicle (402). The system includes an absolute position sensor, such as GPS, in addition to one or more additional sensors, such as a camera, laser scanner, or radar. The system further comprises a digital map or database that includes records for at least some of the vehicle's surrounding objects (400). These records can include relative positional attributes with respect to a reference axis (404). As the vehicle (402) moves, sensors sense the presence of at least some of these objects (400), and measure the vehicle's relative position to those objects. This information is used to determine the vehicle's instantaneous lateral offset (428) relative to the reference axis (404), and support features such as enhanced driving directions, collision avoidance, or automatic assisted driving. The system also allows new objects (408, 414) to be attributed using relative positioning, and thereby factored into the enhanced navigation features.
Owner:TOMTOM POLSKA
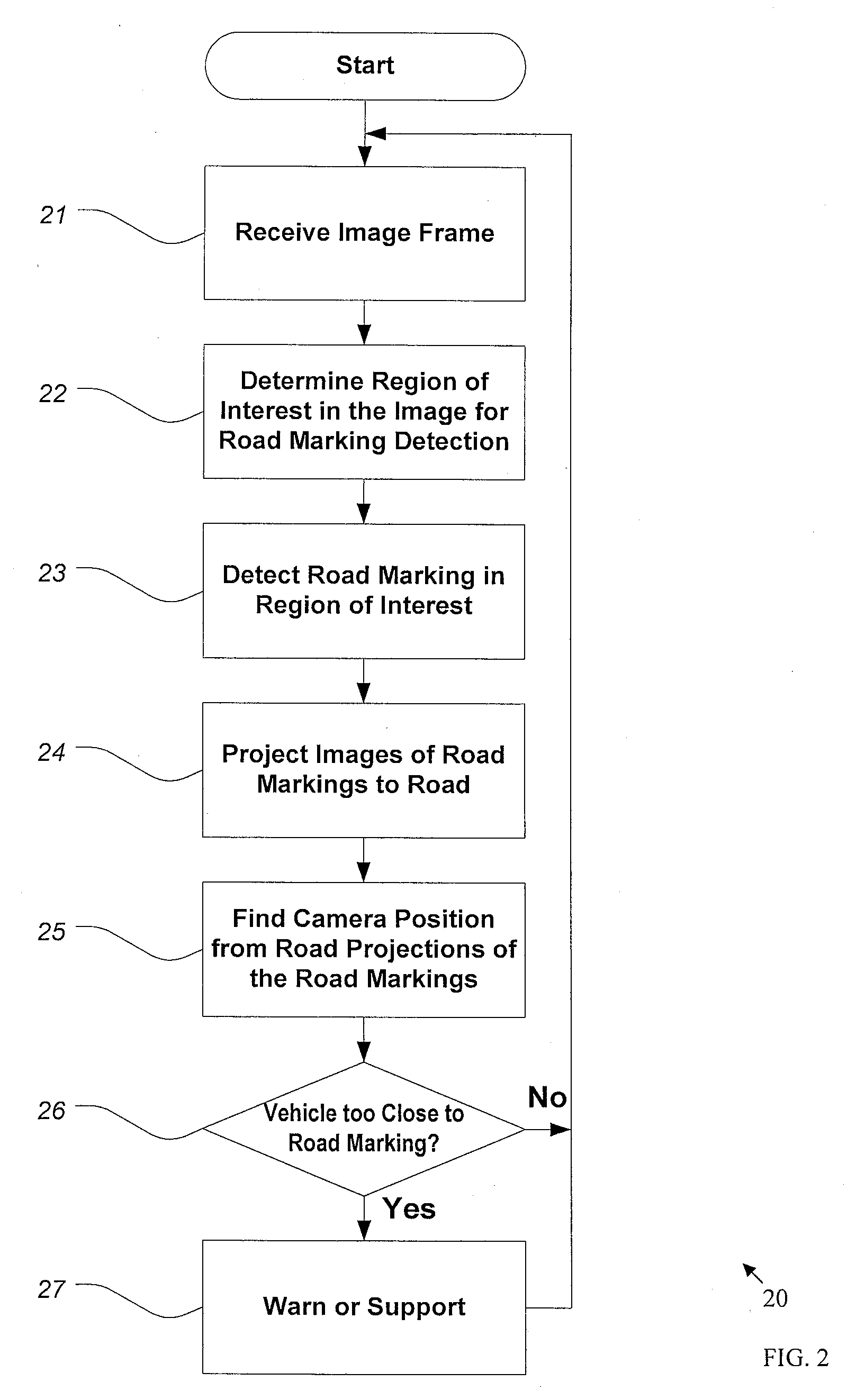
Method and system for video-based road characterization, lane detection and departure prevention
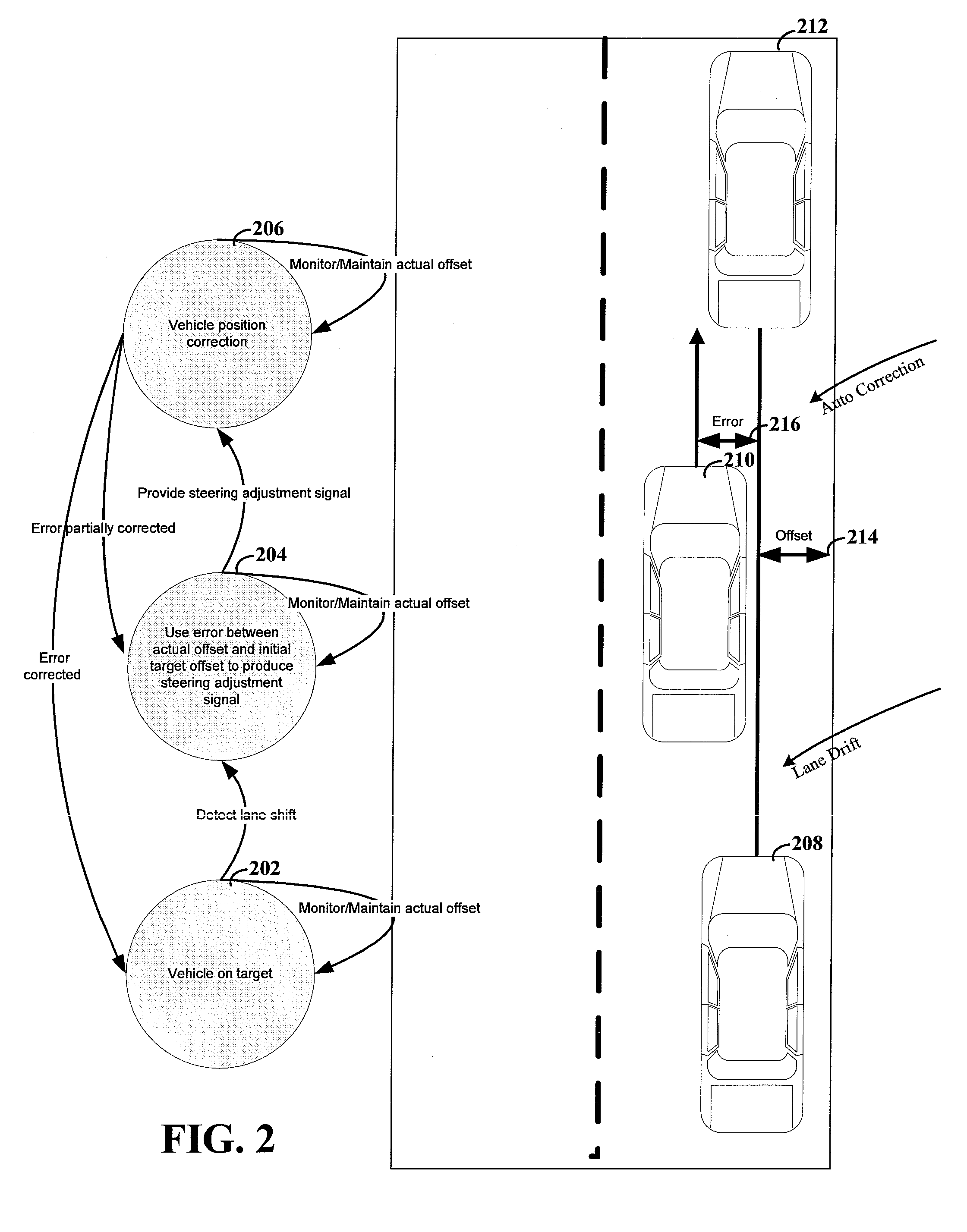
A method and system for video-based road departure warning for a vehicle on a road, is provided. Road departure warning involves receiving an image of a road in front of the vehicle from a video imager, and detecting one or more road markings in the image corresponding to markings on the road. Then, analyzing the characteristics of an image region beyond the detected markings to determine a rating for drivability of the road corresponding to said image region, and detecting the lateral offset of the vehicle relative to the markings on the road based on the detected road markings. A warning signal is generated as function of said lateral offset and said rating.
Owner:VALEO SCHALTER & SENSOREN
Integrated Automotive System, Pop Up Nozzle Assembly and Remote Control Method for Cleaning a Wide Angle Image Sensors Exterior Surface
ActiveUS20150138357A1Promote effectiveTelevision system detailsSpray nozzlesCamera lensRemote control
A pop-up external lens washing system has an extendable aiming fixture configured to aim a lens cleaning spray at an external lens which is exposed to the elements and apt to become soiled with debris. The extendable nozzle assembly is configured to be aimed toward the external lens by the extended aiming fixture during the washing operation only and has at least one laterally offset washing nozzle projecting from the aiming fixture to a spray washing fluid toward the external lens surface, spraying at a shallow, glancing spray aiming angle to impinge upon and wash the lens external surface.
Owner:DLHBOWLES INC
Presentation of Objects in Stereoscopic 3D Displays
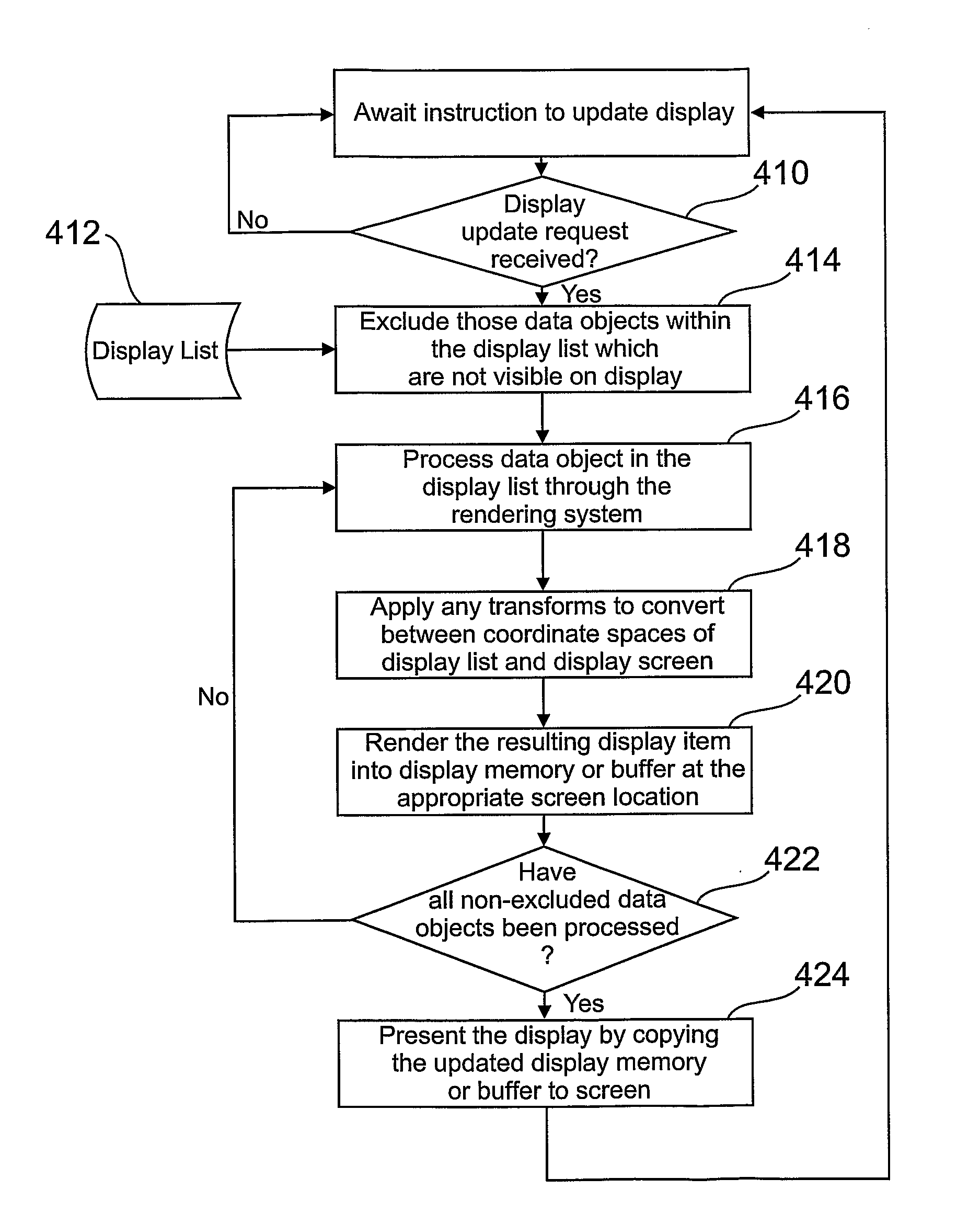
InactiveUS20110050687A1Good effectCathode-ray tube indicatorsExecution for user interfacesData processing systemComputer graphics (images)
A data processing system includes a rendering system adapted to process data objects to render display frames for presentation via a visual display screen. The display frames include 2D display items corresponding to the data objects, each display item having a 2D screen location within the display frame defined by reference to an X / Y display plane. The rendering system renders stereoscopic 3D views of display frames by rendering left- and right-eye views of the display frames. The left- and right-eye views of the display frames are rendered by processing the data objects corresponding to the 2D display items such that respective left- and right-eye copies of the 2D display items are included in the left- and right-eye views. A set of 3D effects rules is provided that specify relationships between stereoscopic 3D effects and parameters associated with the data objects corresponding to the 2D display items. The stereoscopic 3D effects include lateral offsets in the X-direction of the X / Y display plane to be applied when rendering left- and right-eye copies of display items at respective screen locations, such that selected 2D display items may be perceived by a viewer as being displaced along a Z-axis perpendicular to said X / Y plane. Corresponding computer-implemented methods and computer program products are also included.
Owner:PICSEL INT LIMITED A MALTA
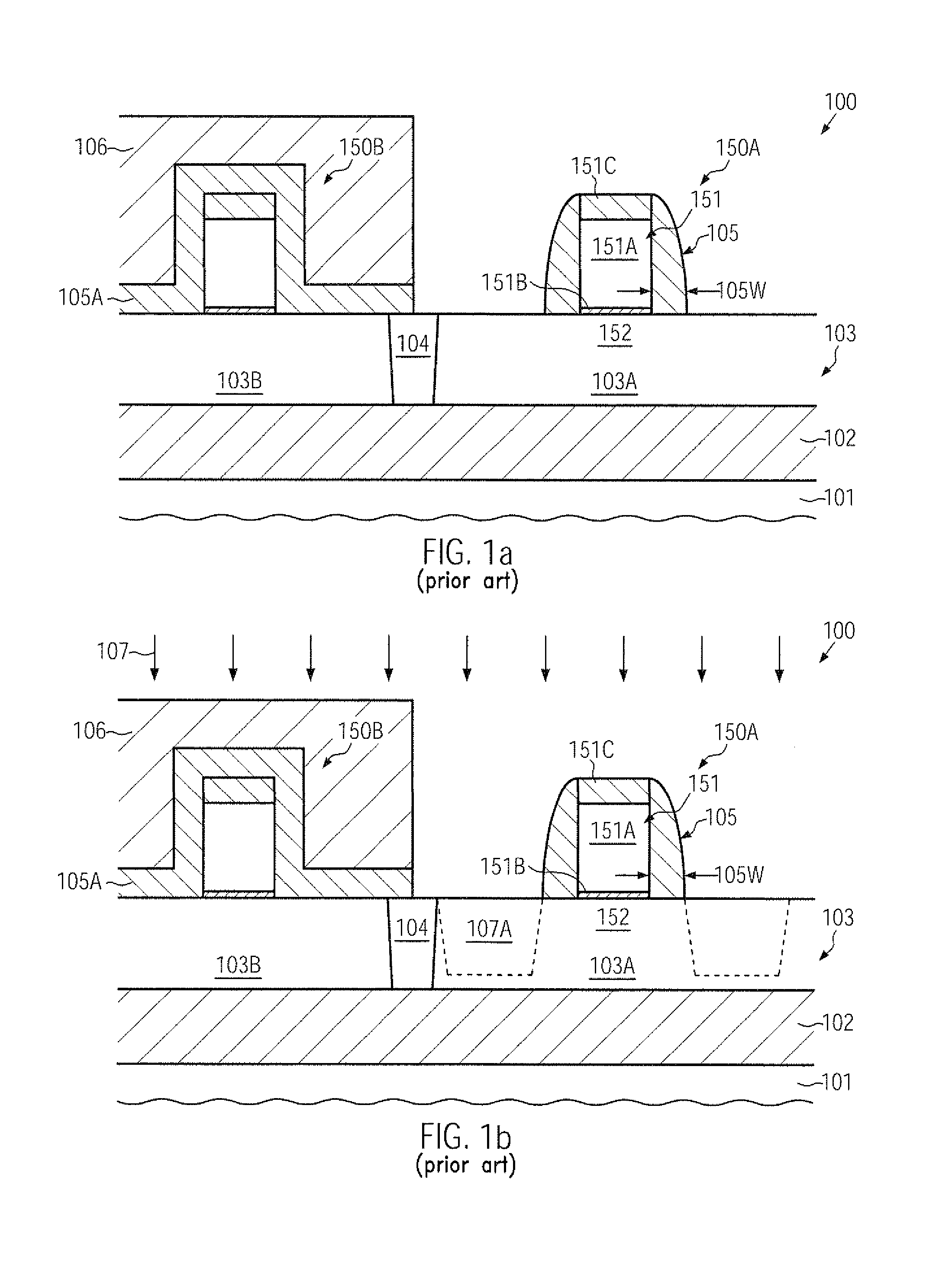
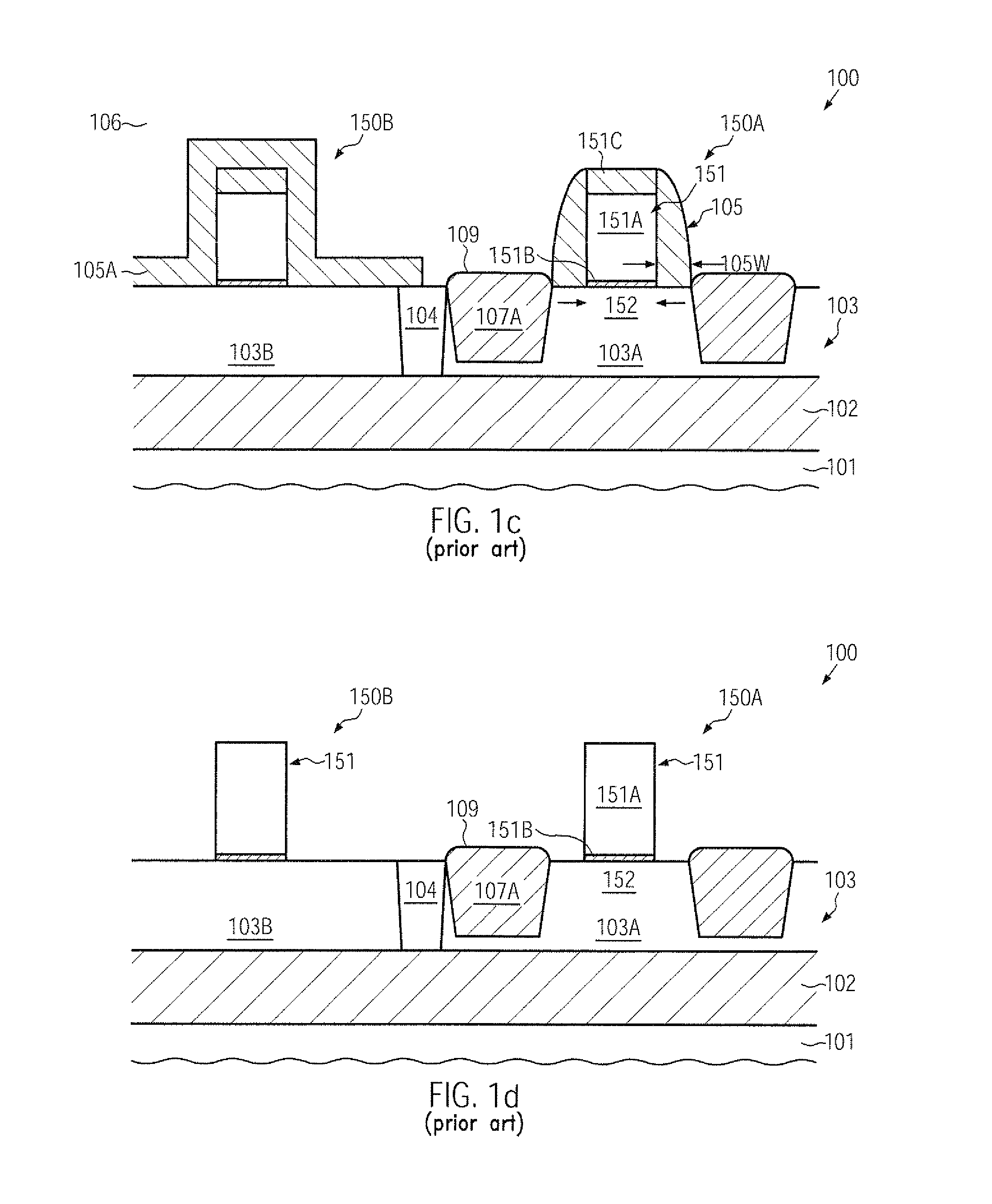
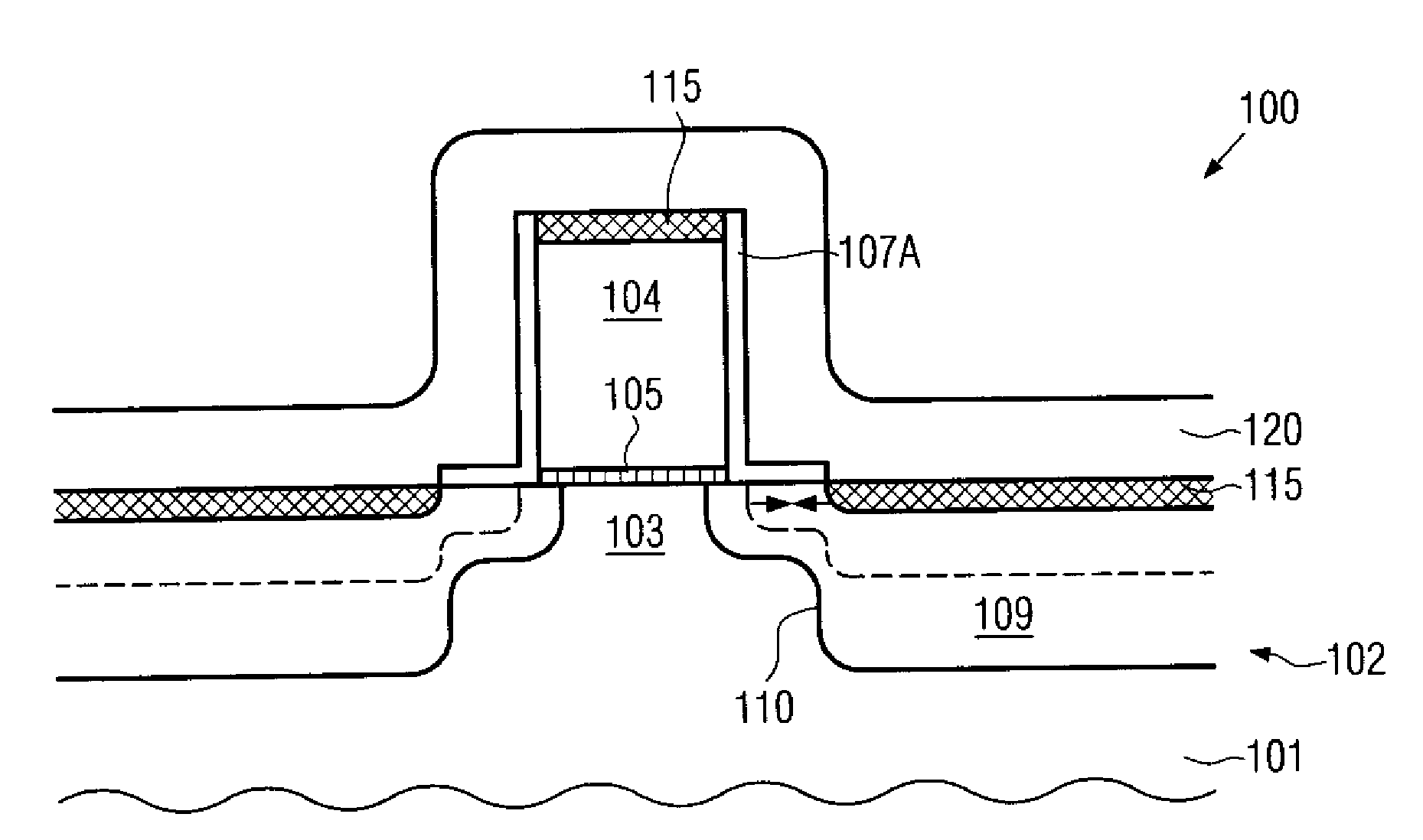
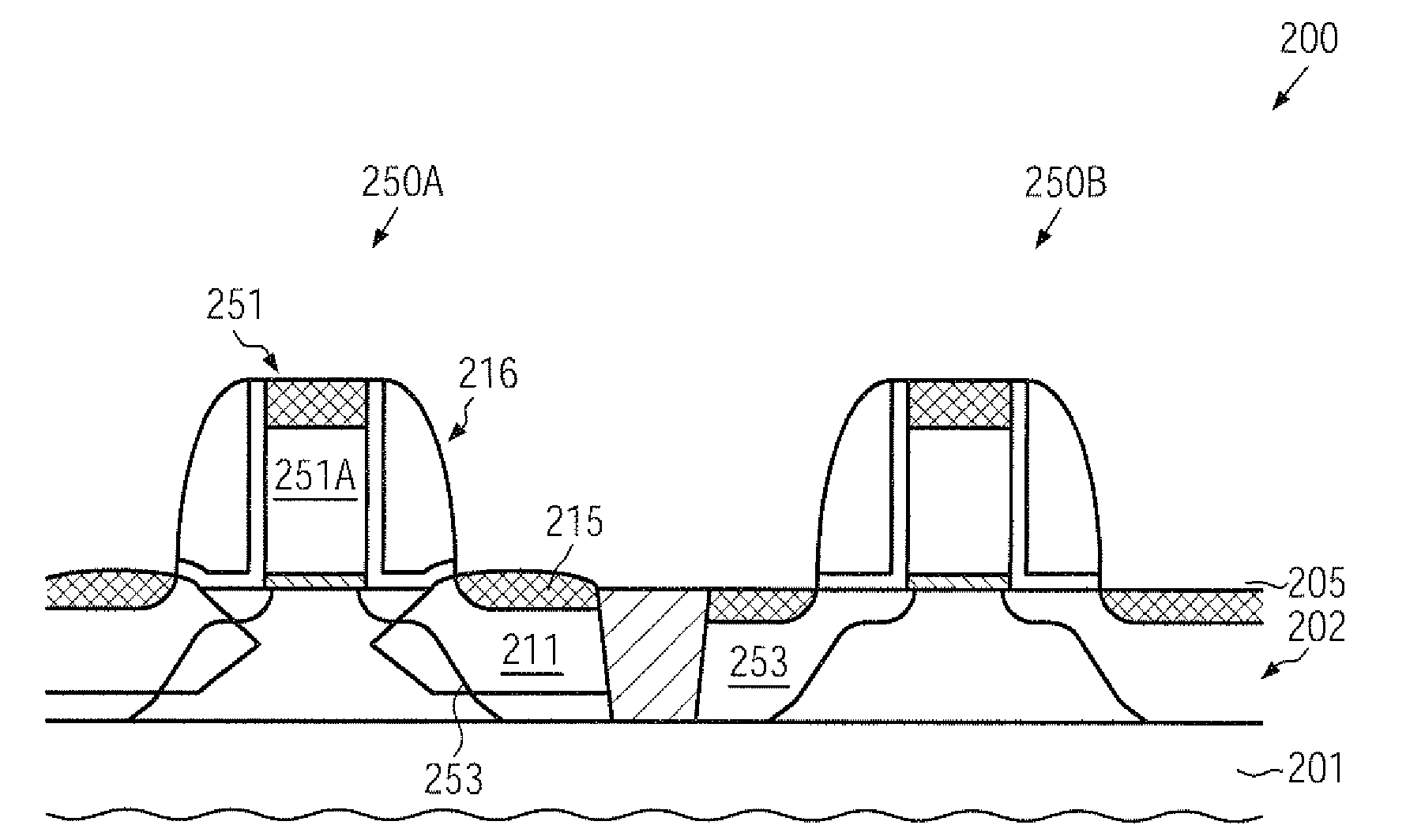
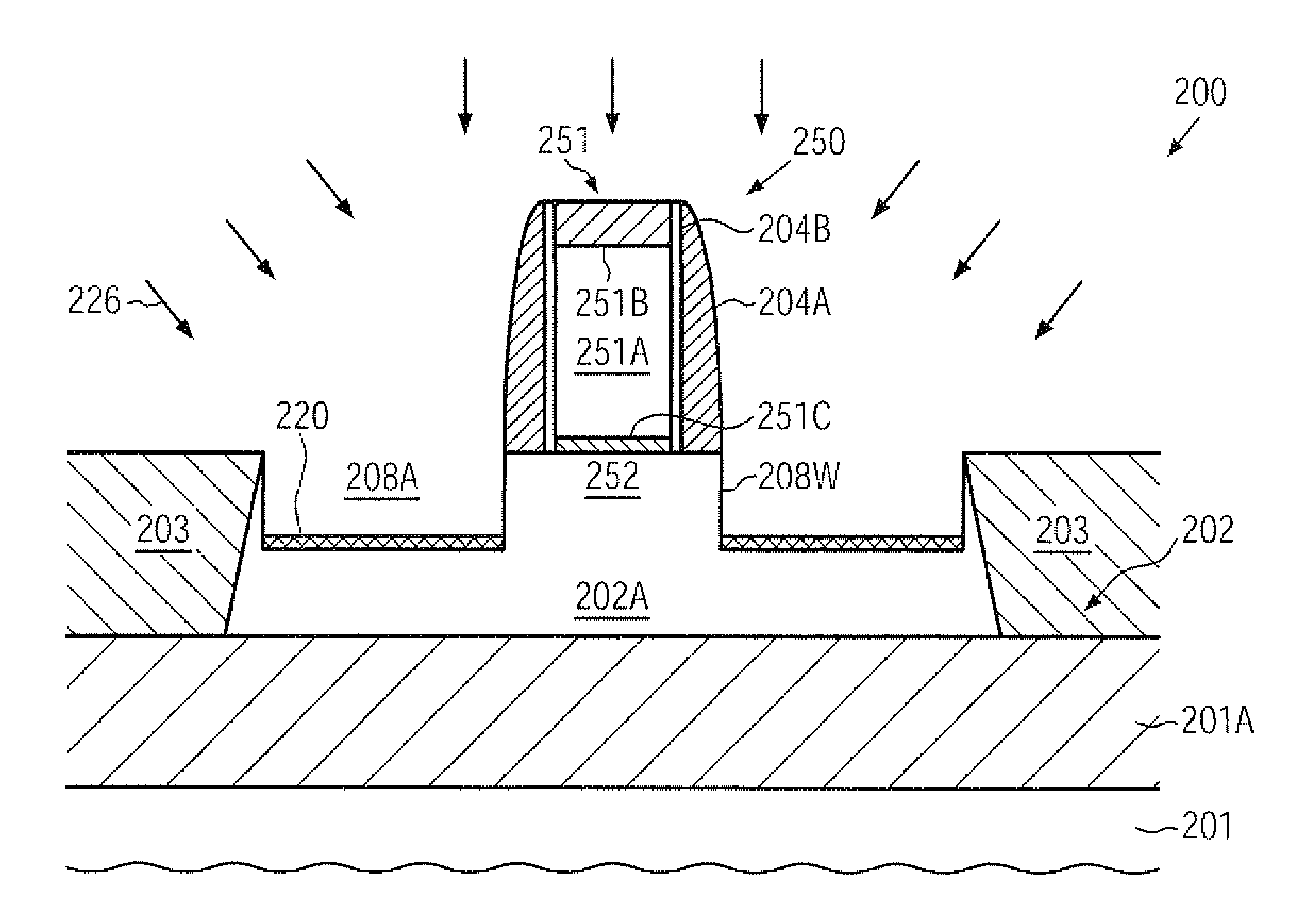
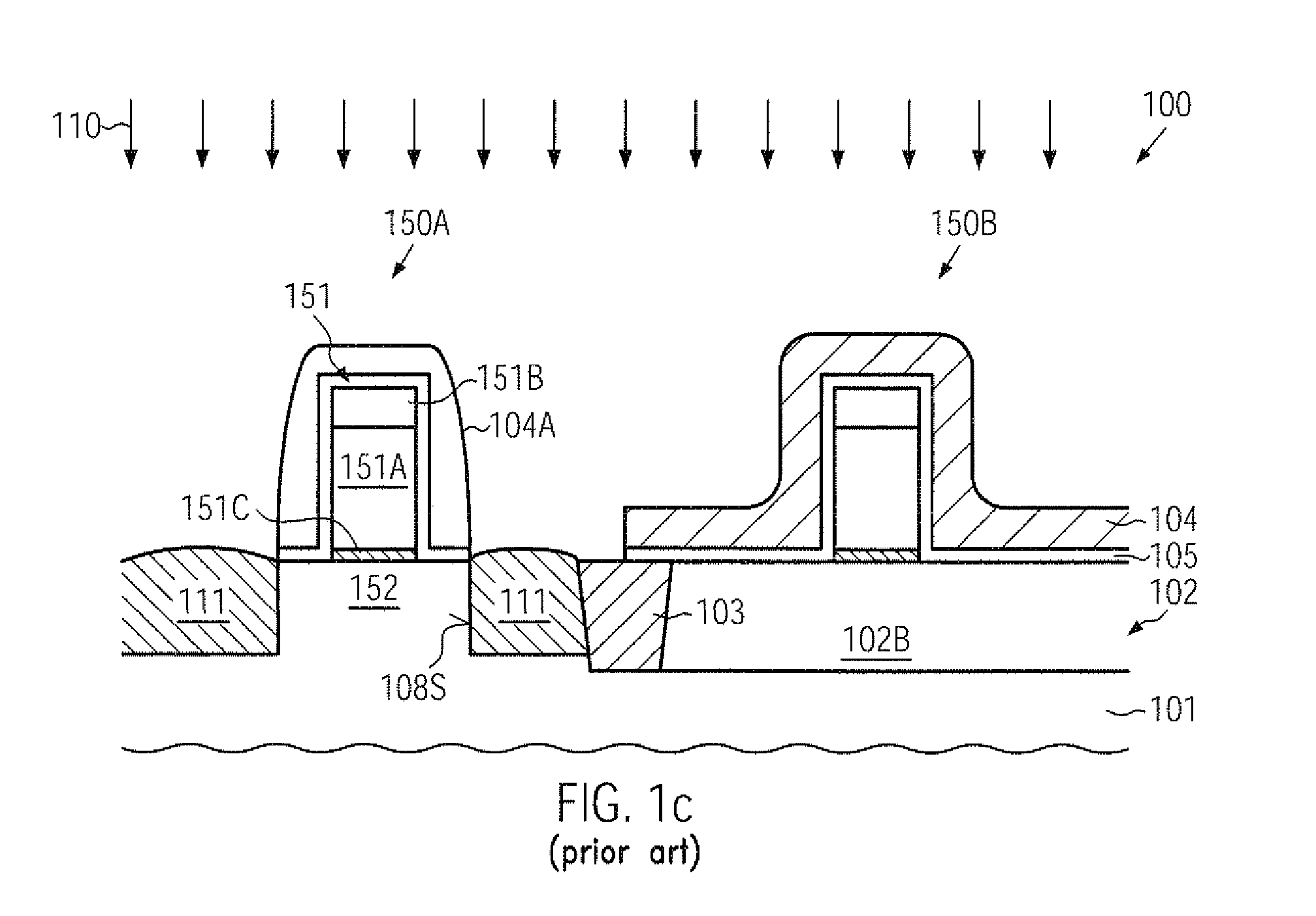
Transistor with an embedded strain-inducing material having a gradually shaped configuration
ActiveUS20120223363A1Improve controllabilityIncrease flexibilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor alloysAlloy
Owner:CHENGDU HAIGUANG MICROELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
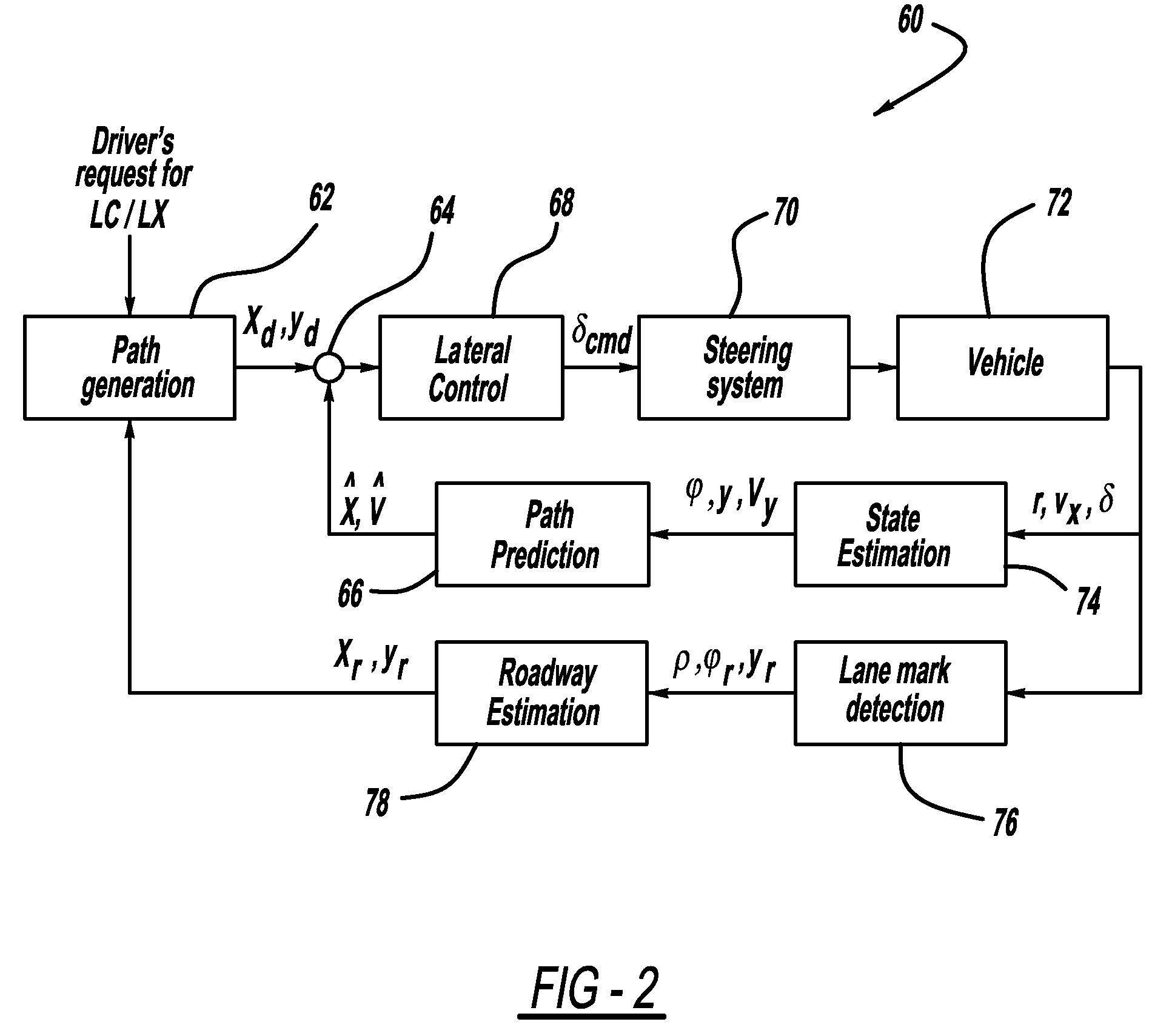
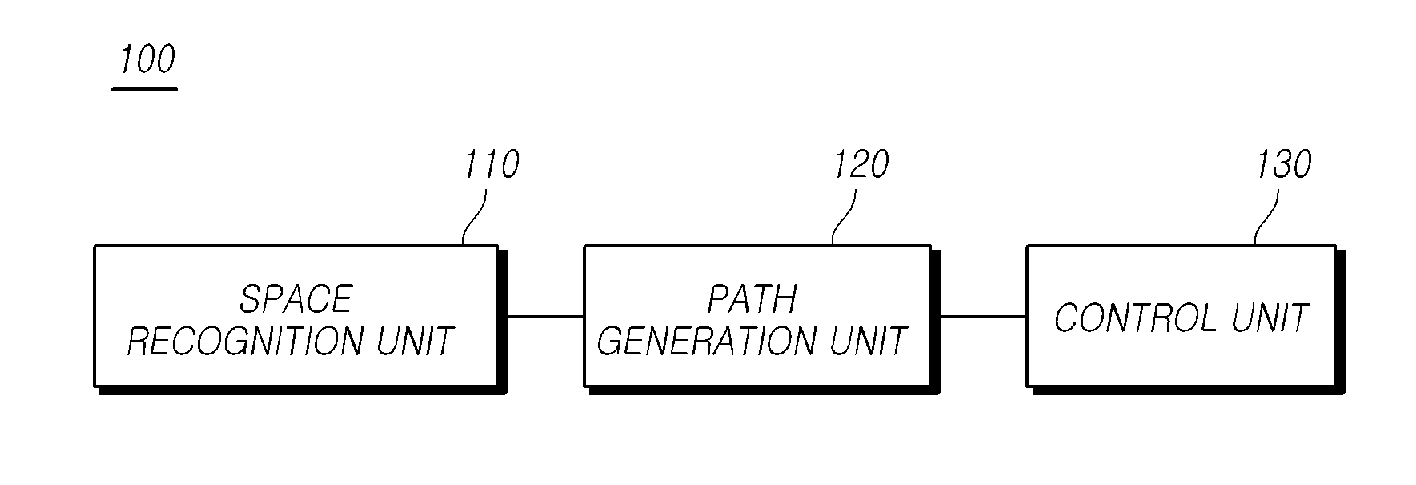
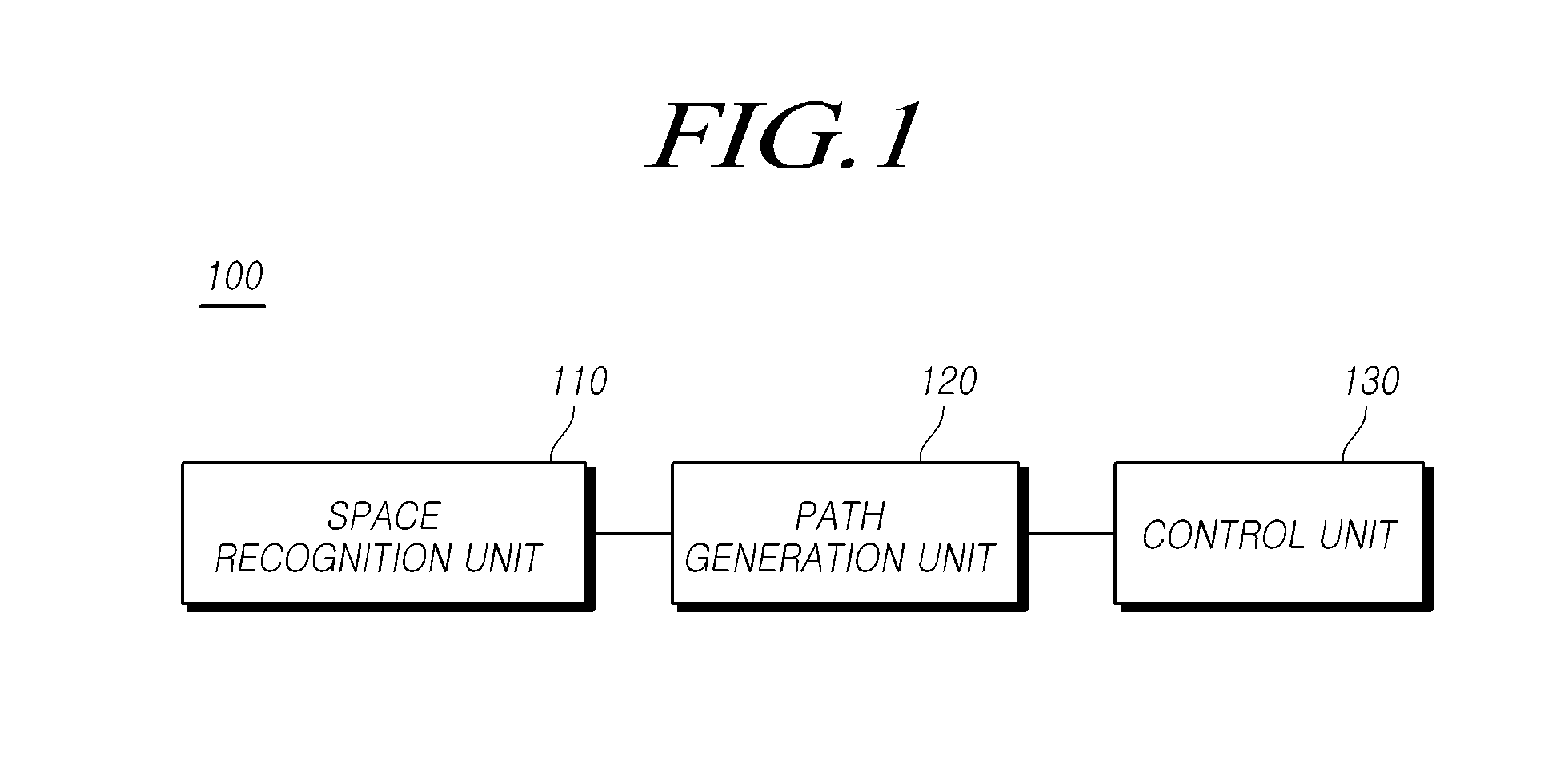
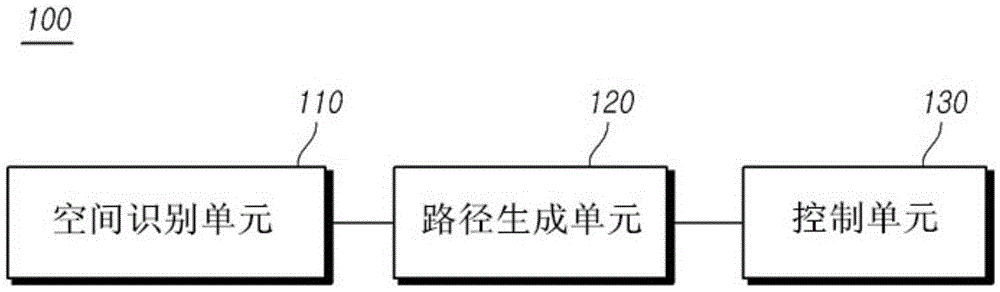
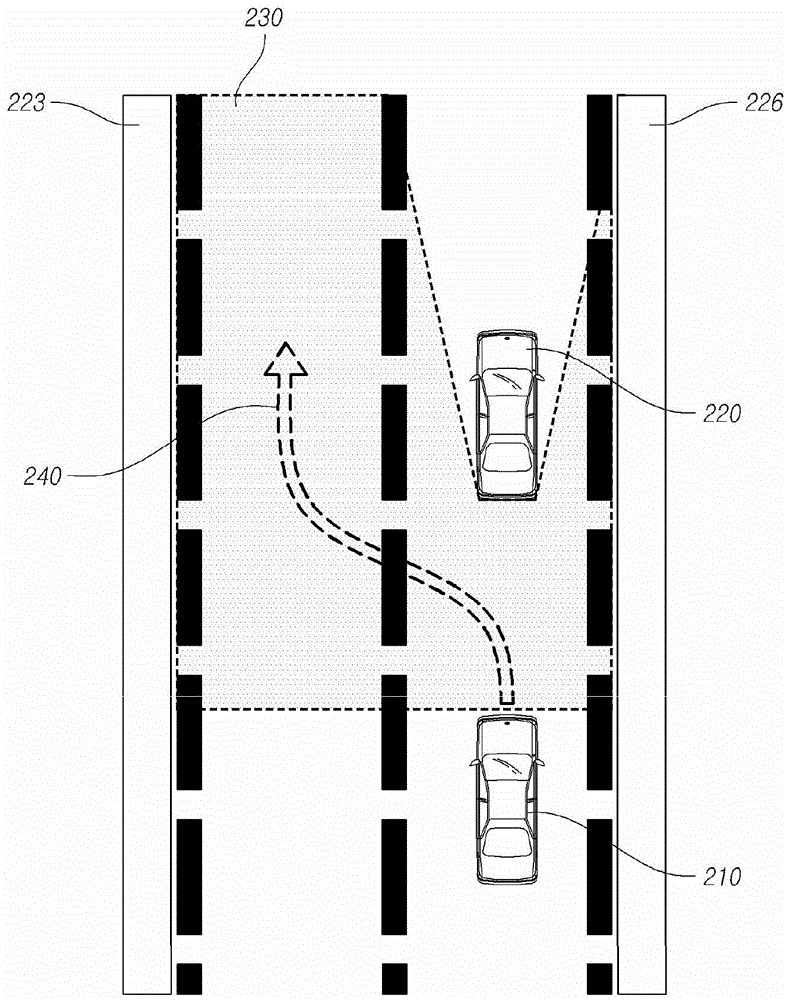
Lane change control device and control method
ActiveUS20160185388A1Provide securityTelevision system detailsVehicle fittingsSteering anglePath generation
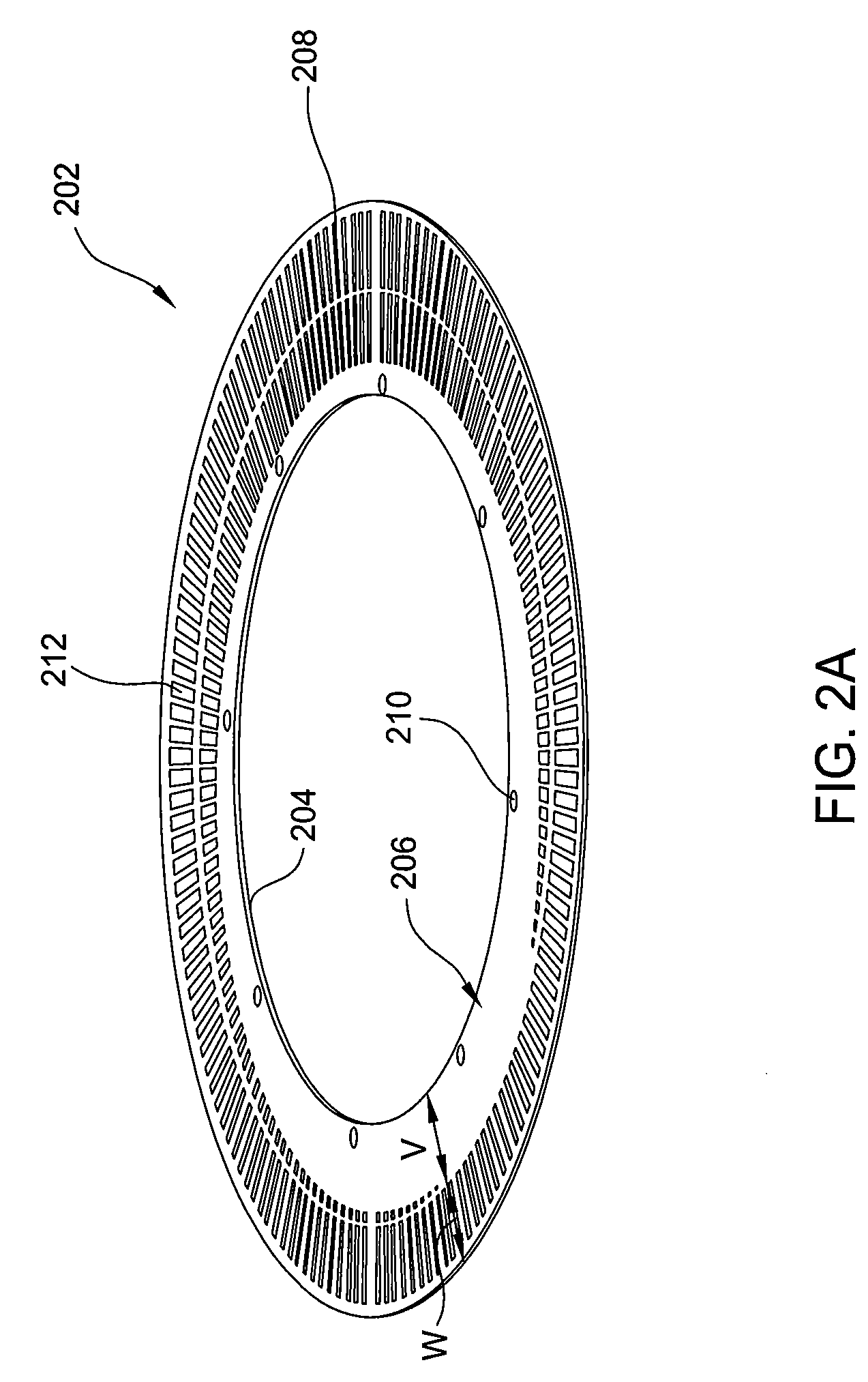
The present disclosure relates to an automatic lane change control of a vehicle is possible using a lane change control device including: a space recognition unit that detects a front object using a camera sensor of a vehicle, recognizes an empty space, and determines a target position, within the empty space on the basis of a lane modeling equation determined from a lateral offset, the vehicle's traveling velocity (V), and a lane change request time (t); a path generation unit that generates a path for moving from a current vehicle position to the target position; and a control unit that performs a lane change control that controls at least one of the vehicle's steering angle and a vehicle velocity such that the vehicle moves to the target position along the path.
Owner:HL KLEMOVE CORP
Driverless vehicle guidance system and method
InactiveUS6971464B2Prevent false detectionAutomatic initiationsNon-mechanical steering controlMagnetic markerEngineering
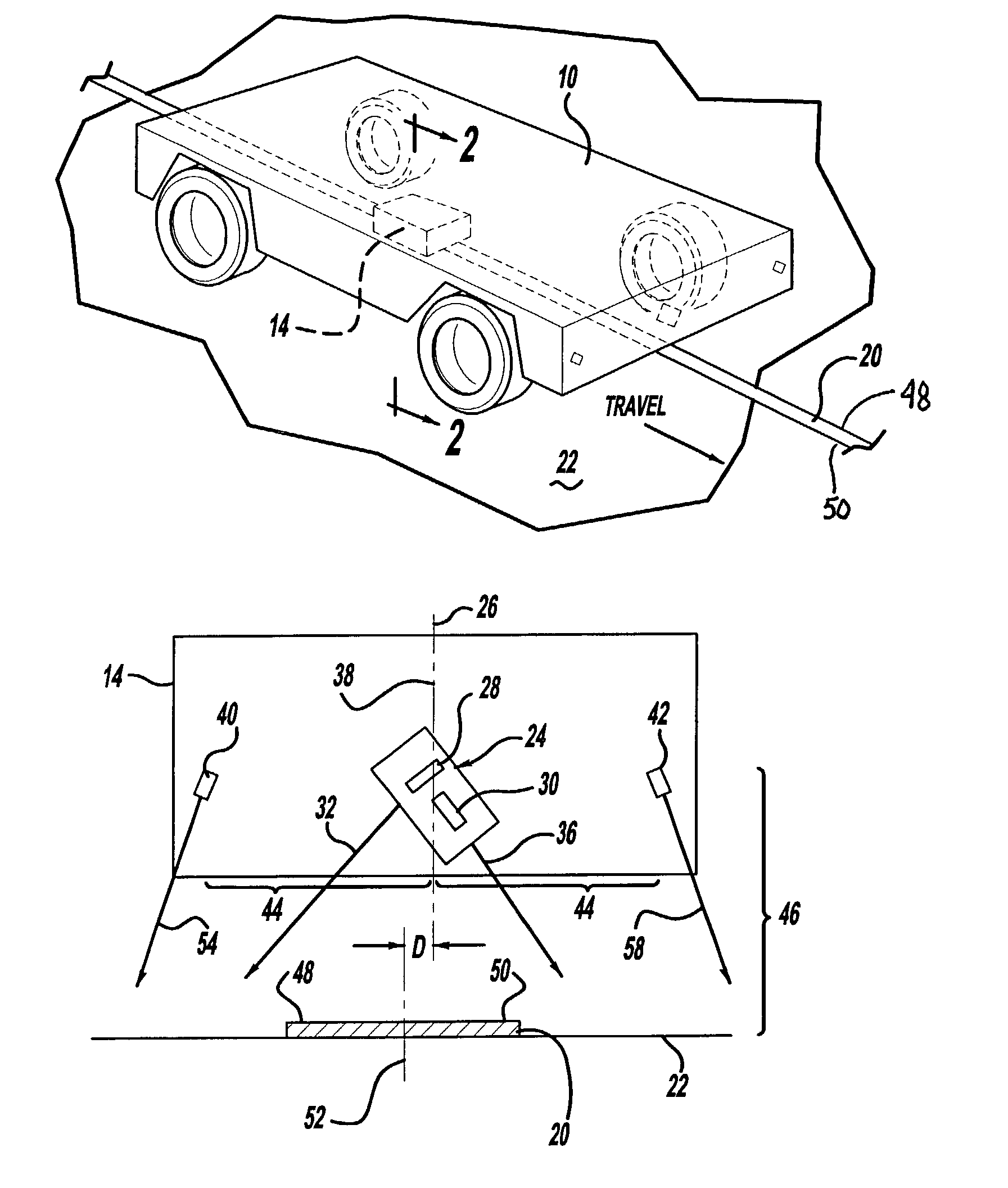
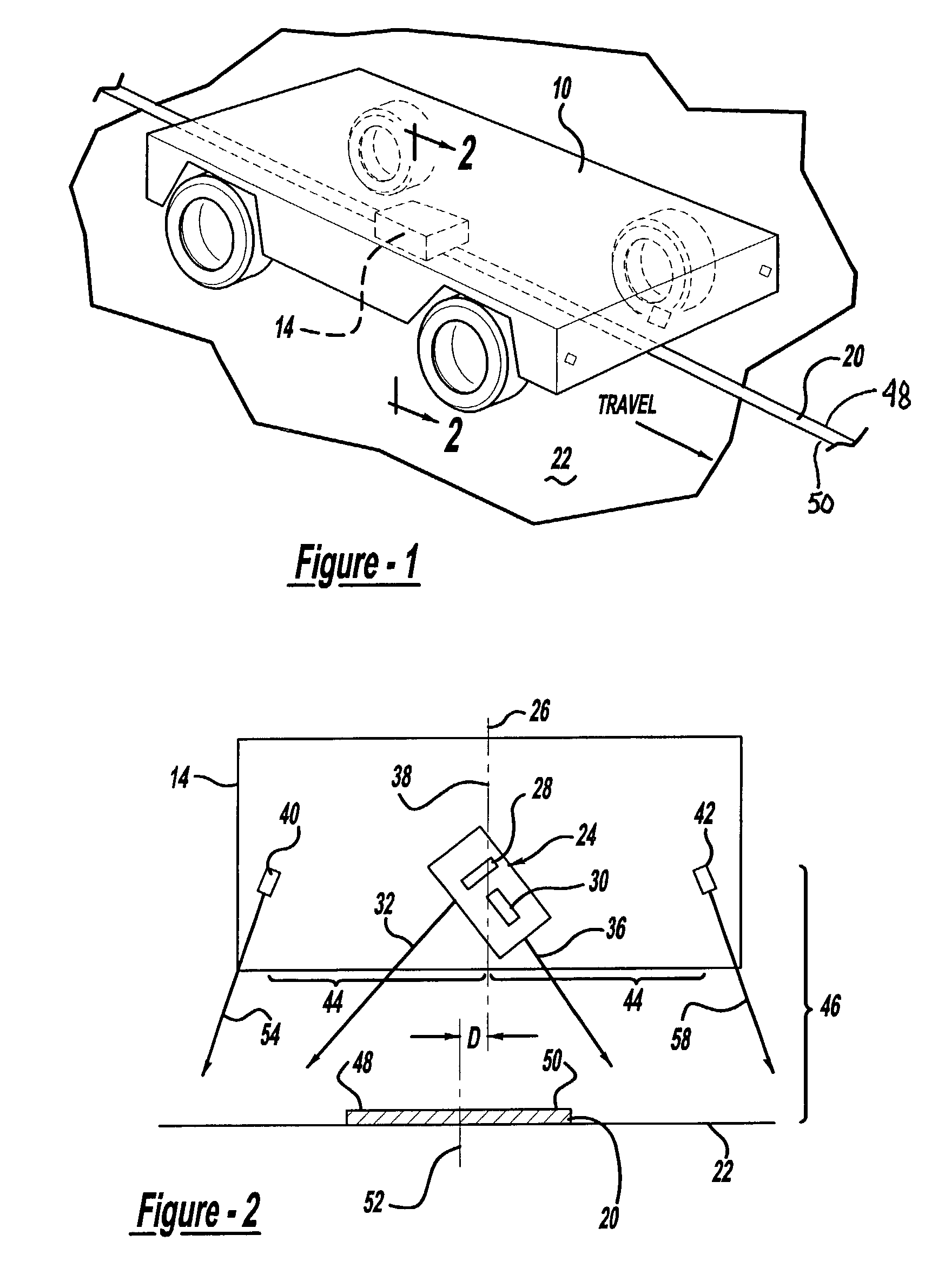
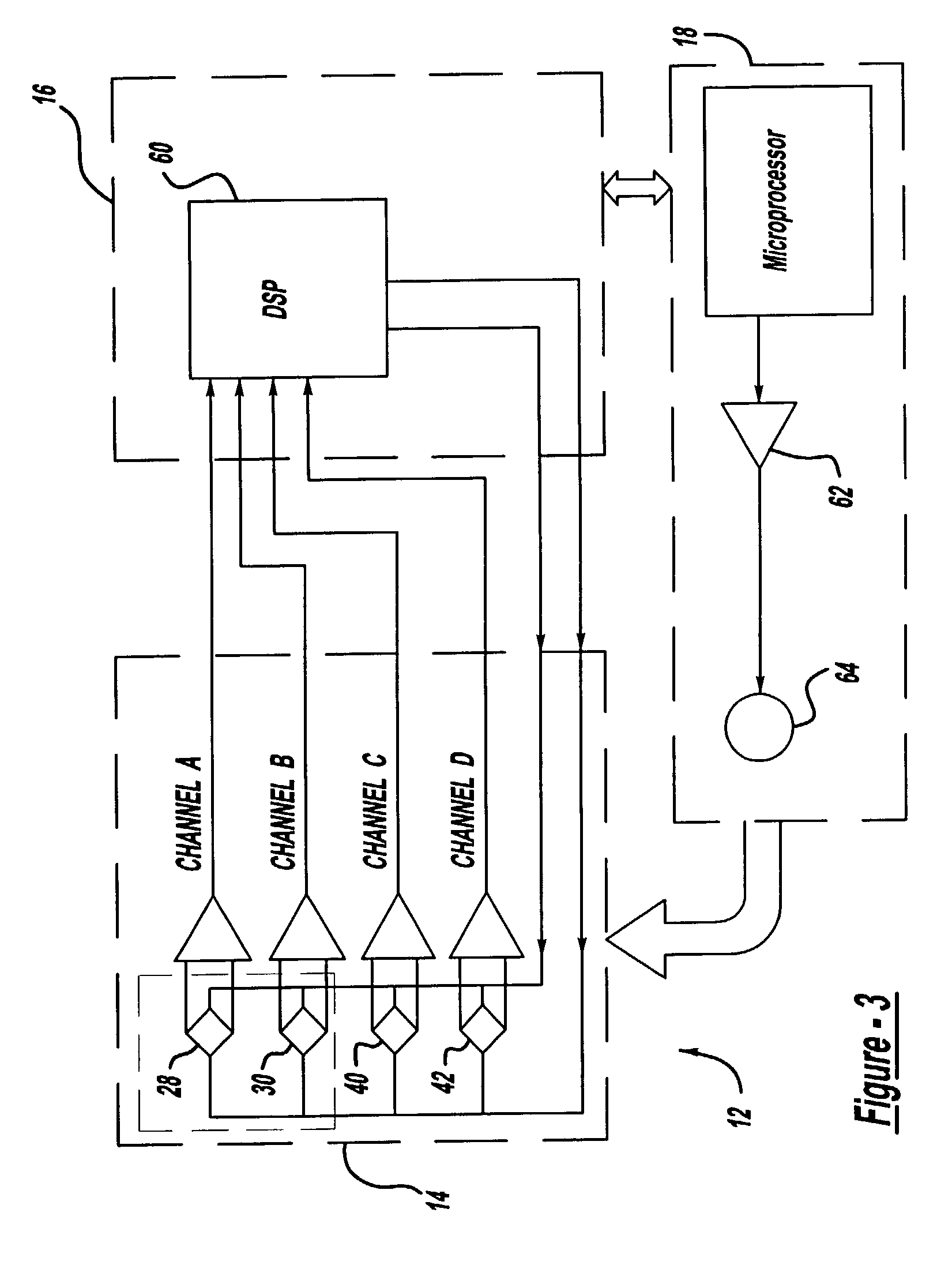
A vehicle guidance system for guiding a vehicle along a magnetic marker including a first magnetic sensor having a sensing axis, the first sensor measuring a first magnetic field. A second magnetic sensor has a sensing axis, the second sensor measuring a second magnetic field. The sensing axis of the second magnetic sensor crosses the sensing axis of the first magnetic sensor at a vehicle guide point. A processor is configured to receive data representative of the magnetic field measured by the first and second sensors and to calculate a lateral offset between the guide point and the magnetic marker based upon the measured magnetic fields. A method for guiding a vehicle in response to a marker having magnetic field is also disclosed. The steps of the method include measuring magnetic field strength proximate the marker, measuring ambient magnetic field strength remote from the marker, nulling the ambient magnetic field by removing the remote magnetic field strength from the proximate magnetic field strength, calculating a lateral displacement between the vehicle and the marker using the nulled magnetic field strength, and guiding the vehicle in response to the lateral displacement between the vehicle and the marker.
Owner:JERVIS B WEBB INT CO
Transistor having an embedded tensile strain layer with reduced offset to the gate electrode and a method for forming the same
ActiveUS20070254461A1Increase strainIncrease flexibilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTensile strainSalicide
By incorporating carbon by means of ion implantation and a subsequent flash-based or laser-based anneal process, strained silicon / carbon material with tensile strain may be positioned in close proximity to the channel region, thereby enhancing the strain-inducing mechanism. The carbon implantation may be preceded by a pre-amorphization implantation, for instance on the basis of silicon. Moreover, by removing a spacer structure used for forming deep drain and source regions, the degree of lateral offset of the strained silicon / carbon material with respect to the gate electrode may be determined substantially independently from other process requirements. Moreover, an additional sidewall spacer used for forming metal silicide regions may be provided with reduced permittivity, thereby additionally contributing to an overall performance enhancement.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
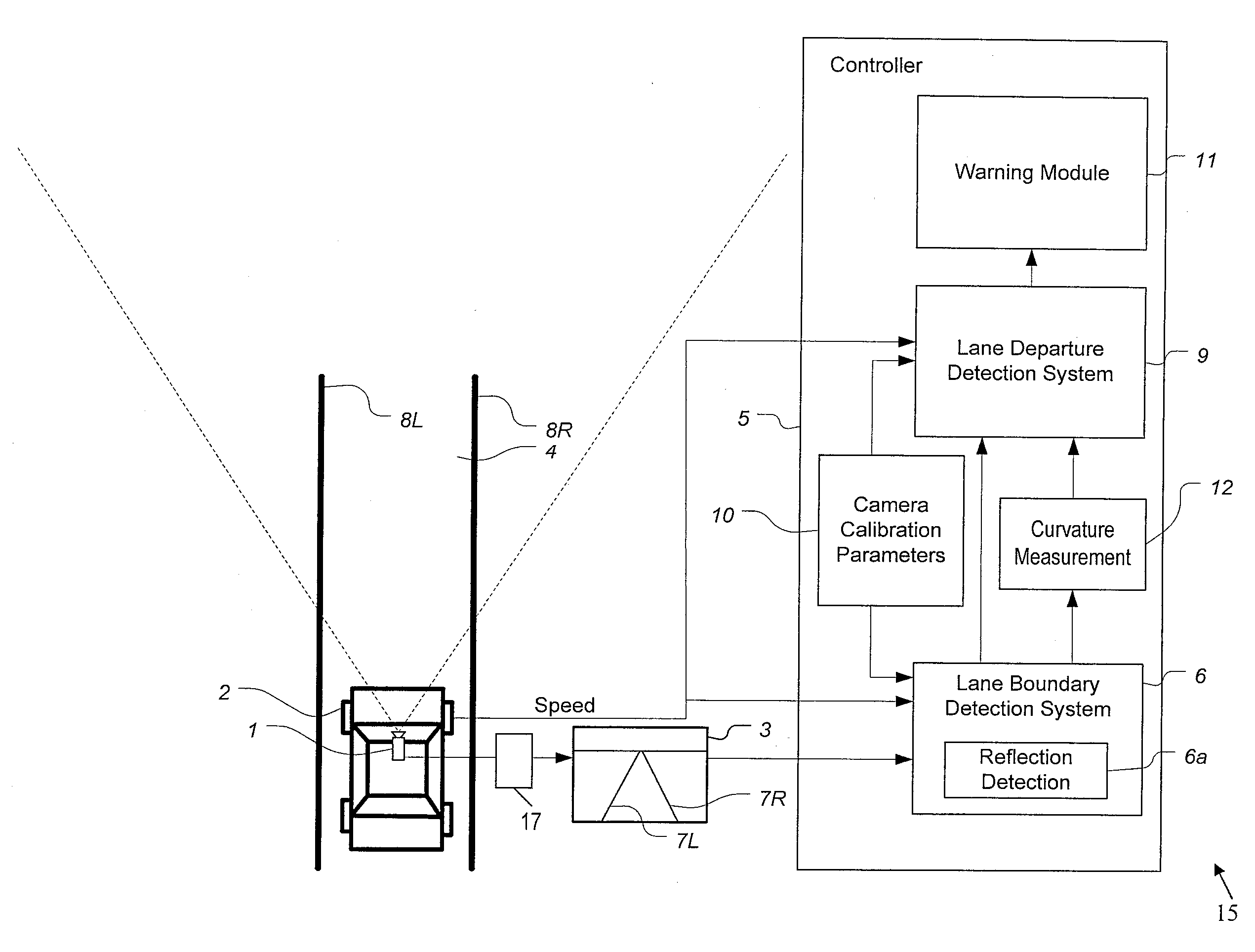
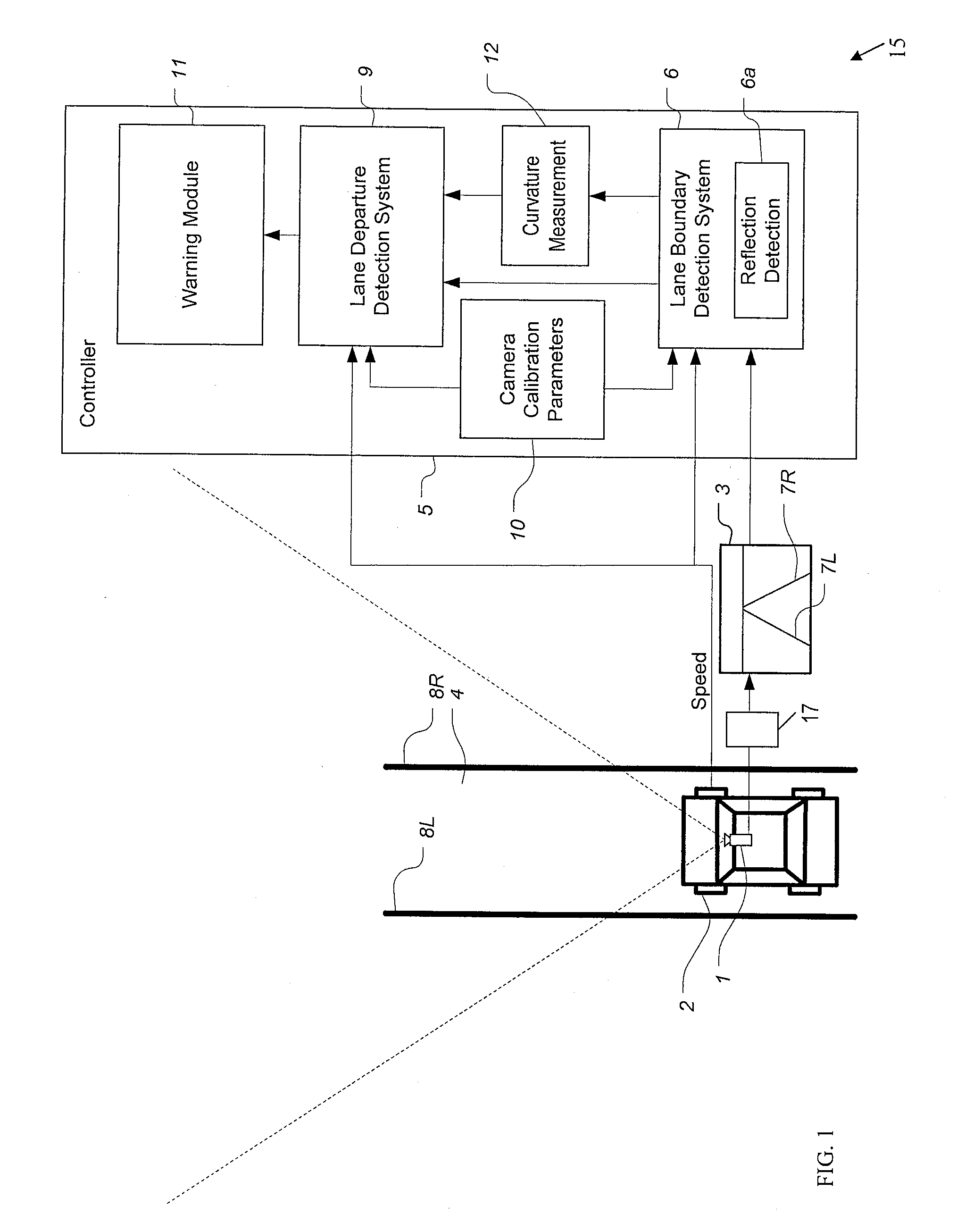
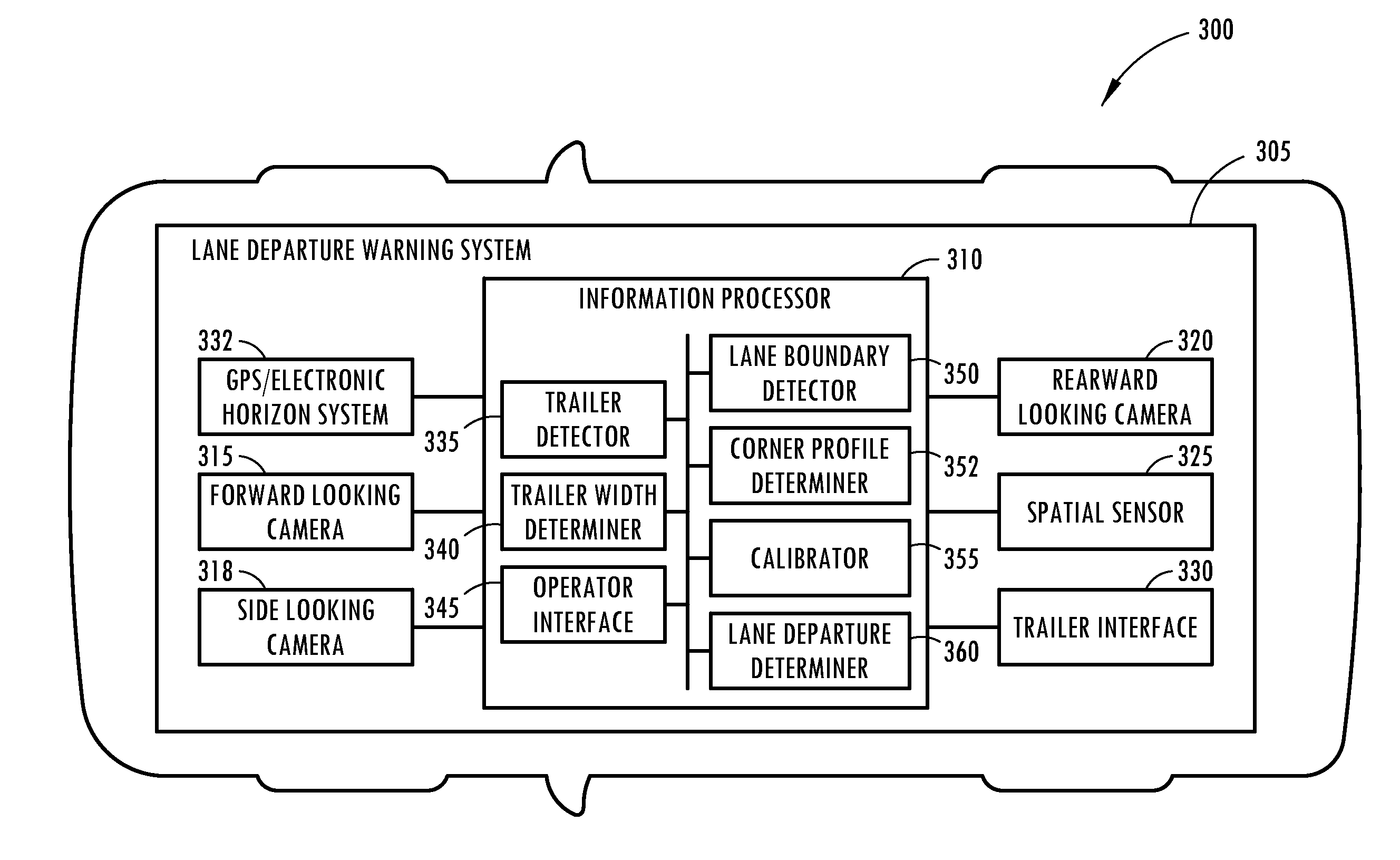
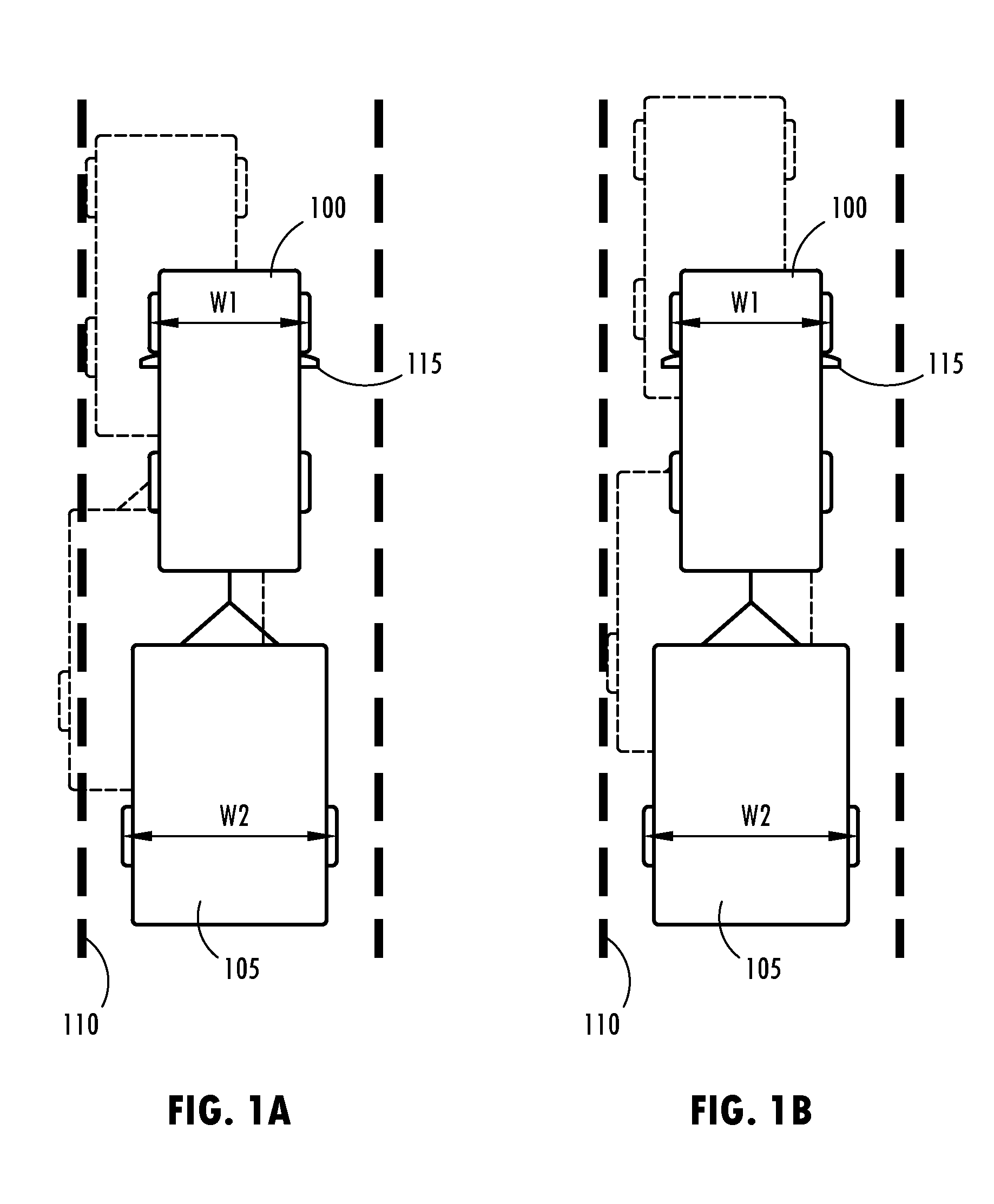
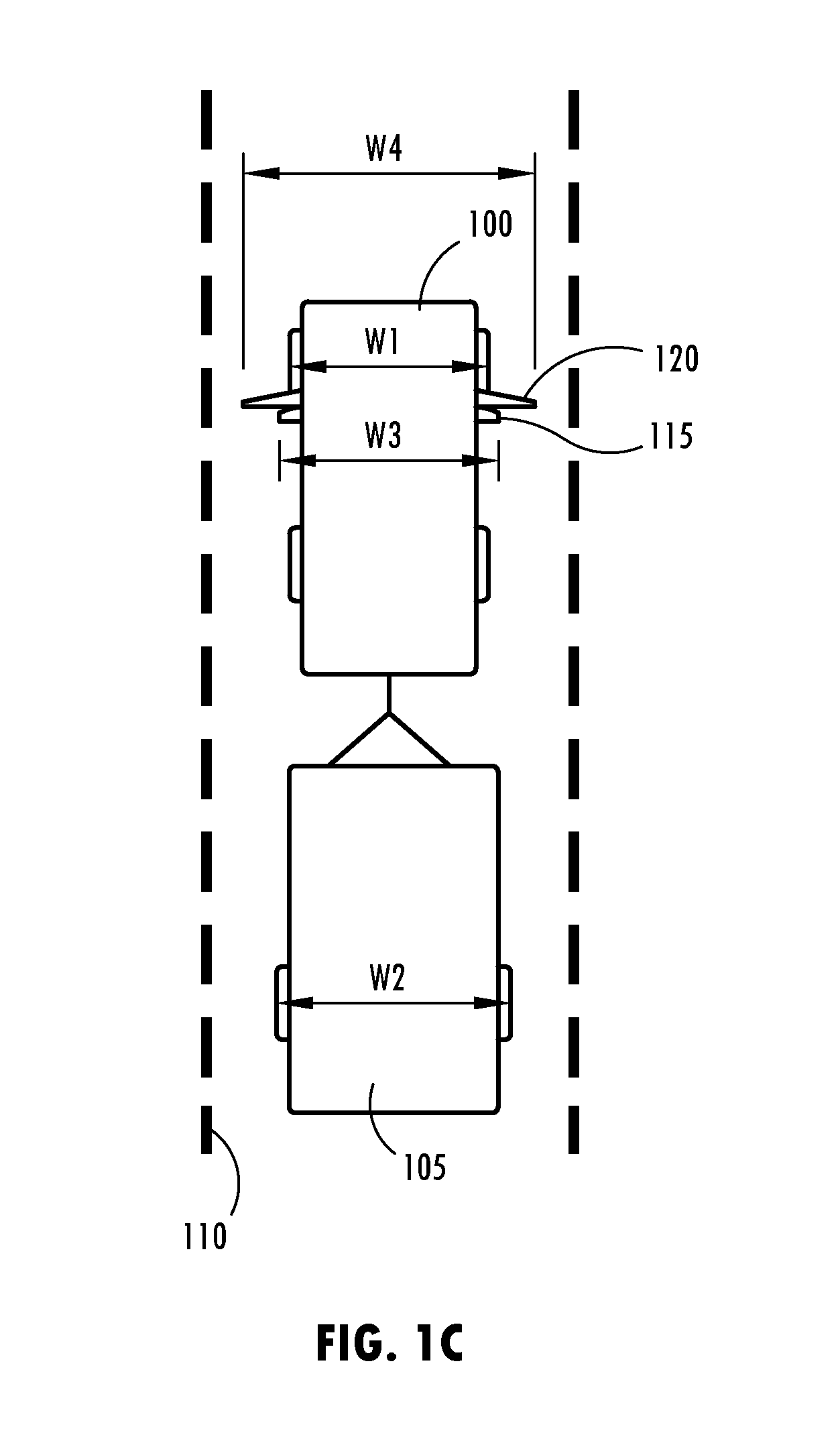
Trailer lane departure warning system
ActiveUS20140176716A1Reducing lateral offsetReducing the lateral offsetRoad vehicles traffic controlCharacter and pattern recognitionLane departure warning systemEngineering
A lane departure warning system has a trailer detector for detecting that a trailer is attached to a vehicle, a lane boundary detector for detecting a position of a lane boundary on a roadway over which the vehicle is travelling, and an information processor including a calibrator for generating calibration parameters used in determining an unintended lane departure event with respect to the lane boundary. The information processor initiates a process for allowing an operator to provide trailer width information when the trailer detector indicates that the vehicle is towing a trailer. The lane departure warning system also includes a sensor for detecting a hitch angle between the vehicle and the trailer. A controller determines a lateral offset of the trailer relative to the vehicle based on the hitch angle and a length of the trailer for generating a warning signal when the lateral offset crosses the lane boundary.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Lane Change Control Device And Control Method
ActiveCN105752081AProvide securityVehicle fittingsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementSteering anglePath generation
The present disclosure relates to a technology for changing lane in which a vehicle is driving, in particular to a lane change control device. The lane change control device comprises a space recognition unit that detects a front object by using a camera sensor of the vehicle, recognizes an empty space in which the front object does not exists, and determines a target position, within the empty space on the basis of a lane modeling equation determined from a lateral offset, the vehicle's traveling velocity (V), and a lane change request time (t), wherein the lateral offset is the distance between the center of the camera sensor and the center of the adjacent lane; a path generation unit that generates a path for moving from a current vehicle position to the target position; and a control unit that performs a lane change control that controls at least one of the vehicle's steering angle and a vehicle velocity such that the vehicle moves to the target position along the path. By the lane change control device, the automatic lane change control of the vehicle can be realized possibly.
Owner:HL KLEMOVE CORP
Total-internal-reflection fiber optic interface modules with different optical paths and assemblies using same
ActiveUS20130259419A1Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideFiberTotal internal reflection
Fiber optic interface modules and assemblies using same are disclosed, wherein the module includes first and second lenses formed therein that utilize total-internal reflection within the module body. The first and second lenses define first and second optical paths of different lengths. The module may operably support first and second optical fibers so that they are optically coupled to surfaces of the first and second lenses. The first and second lenses are designed to provide predetermined tolerances for lateral offsets relative to first and second active photo-devices while maintaining respective first and second coupling efficiencies between the active photo-devices and the corresponding first and second optical fibers.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
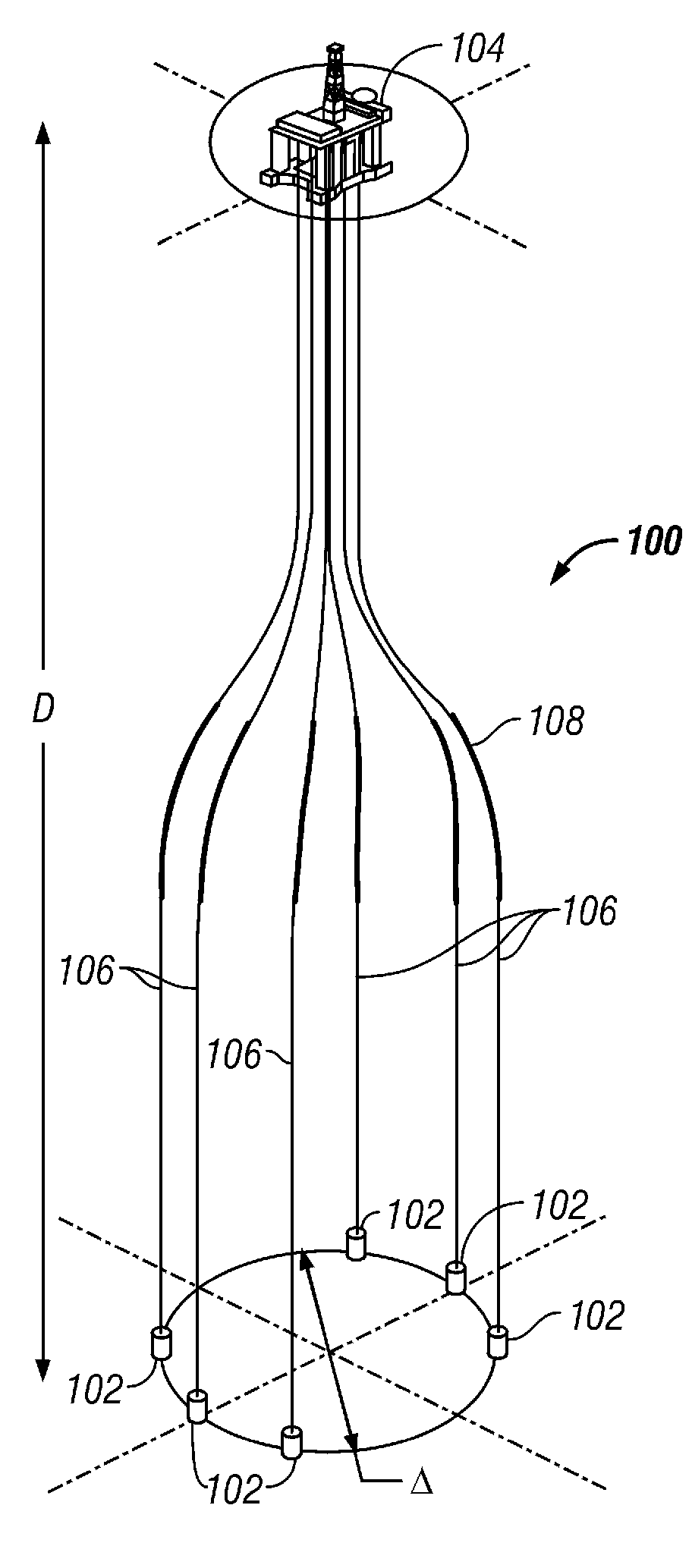
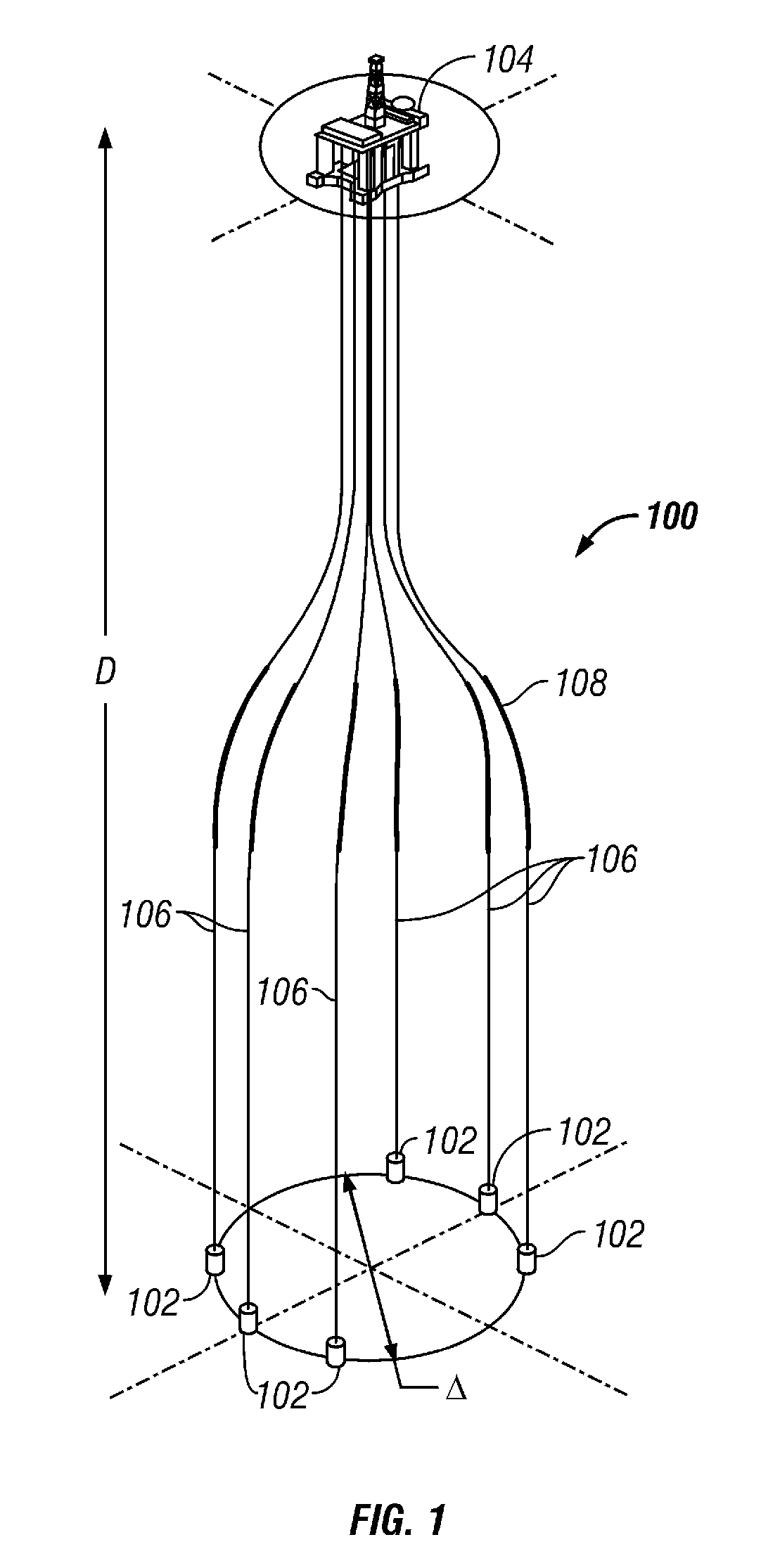
Subsea well communications apparatus and method using variable tension large offset risers
Disclosed are compliant variable tension risers (106) to connect deep-water subsea wellheads (102) to a single floating platform (104) in wet tree or dry try systems. The variable tension risers (106) allow several subsea wellheads (102), in water depths from 1220 to 3050 meters, at lateral offsets from one-tenth to twice the depth or more, to tie back to a single floating platform (104). Also disclosed are methods to counter buoyancy and install variable tension risers using a weighted chain ballast line (228, 230).
Owner:KELLOGG BROWN & ROOT LLC
Model based predictive control for automated lane centering/changing control systems
A system and method for providing steering control for lane changing and lane centering purposes in an autonomous or semi-autonomous vehicle system. A vehicle vision system calculates roadway lane marking information, such as lateral offset, yaw angle and roadway curvature with respect to the vehicle's centered coordinate system. The roadway is then modeled as a second order polynomial equation. The method then predicts roadway lateral position and yaw angle over a pre-defined lane change completion time using a vehicle dynamic model. The method then compares a predicted vehicle path with a desired vehicle path to generate an error value, and calculates a steering angle command to minimize the error value, where the steering angle command is calculated as a function of vehicle lateral position, vehicle lateral speed, vehicle yaw rate and vehicle yaw angle. The steering angle command is then sent to the vehicle steering system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Model based predictive control for automated lane centering/changing control systems
ActiveUS8190330B2Digital data processing detailsAnti-collision systemsVehicle dynamicsCompletion time
A system and method for providing steering control for lane changing and lane centering purposes in an autonomous or semi-autonomous vehicle system. A vehicle vision system calculates roadway lane marking information, such as lateral offset, yaw angle and roadway curvature with respect to the vehicle's centered coordinate system. The roadway is then modeled as a second order polynomial equation. The method then predicts roadway lateral position and yaw angle over a pre-defined lane change completion time using a vehicle dynamic model. The method then compares a predicted vehicle path with a desired vehicle path to generate an error value, and calculates a steering angle command to minimize the error value, where the steering angle command is calculated as a function of vehicle lateral position, vehicle lateral speed, vehicle yaw rate and vehicle yaw angle. The steering angle command is then sent to the vehicle steering system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
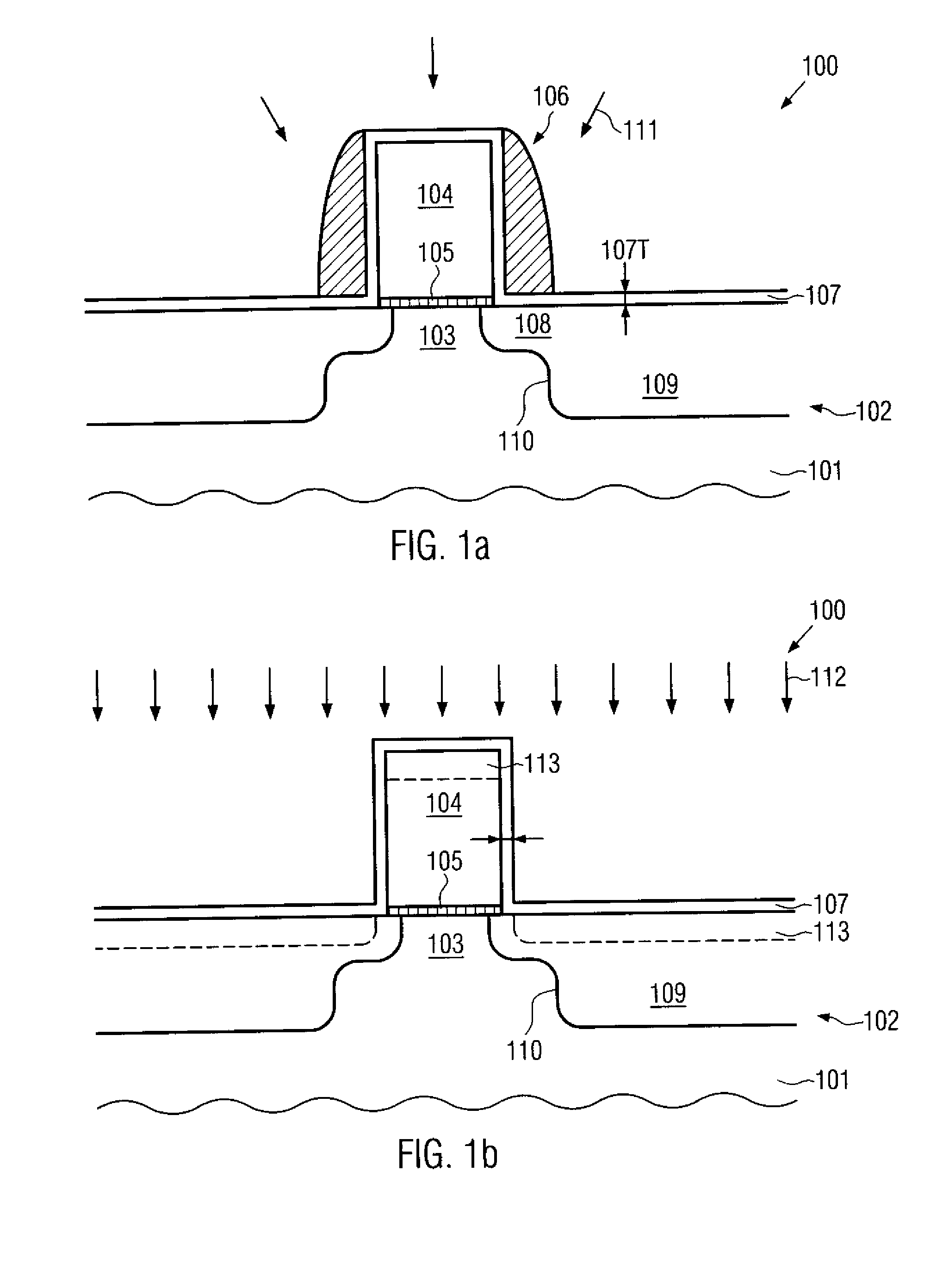
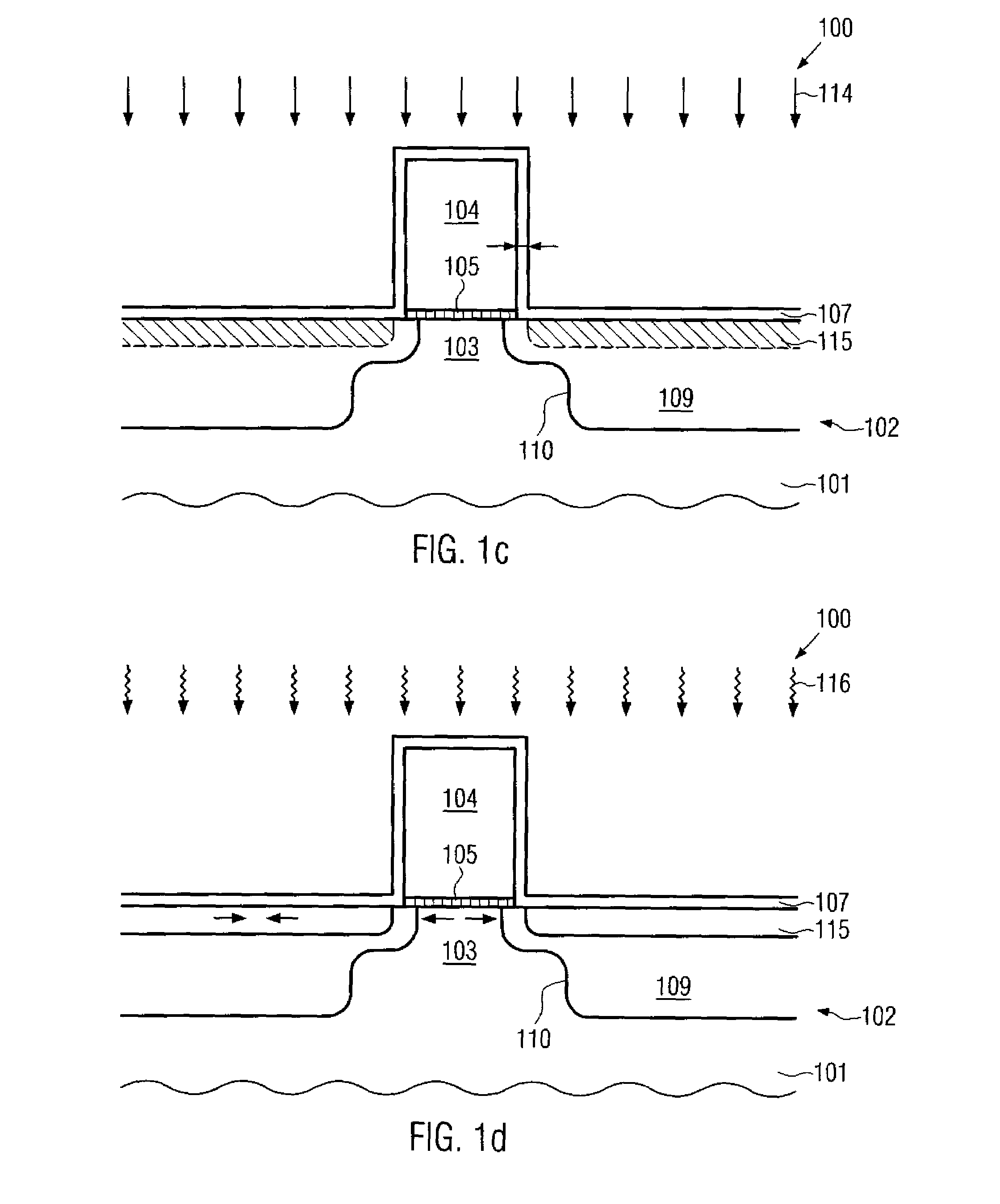
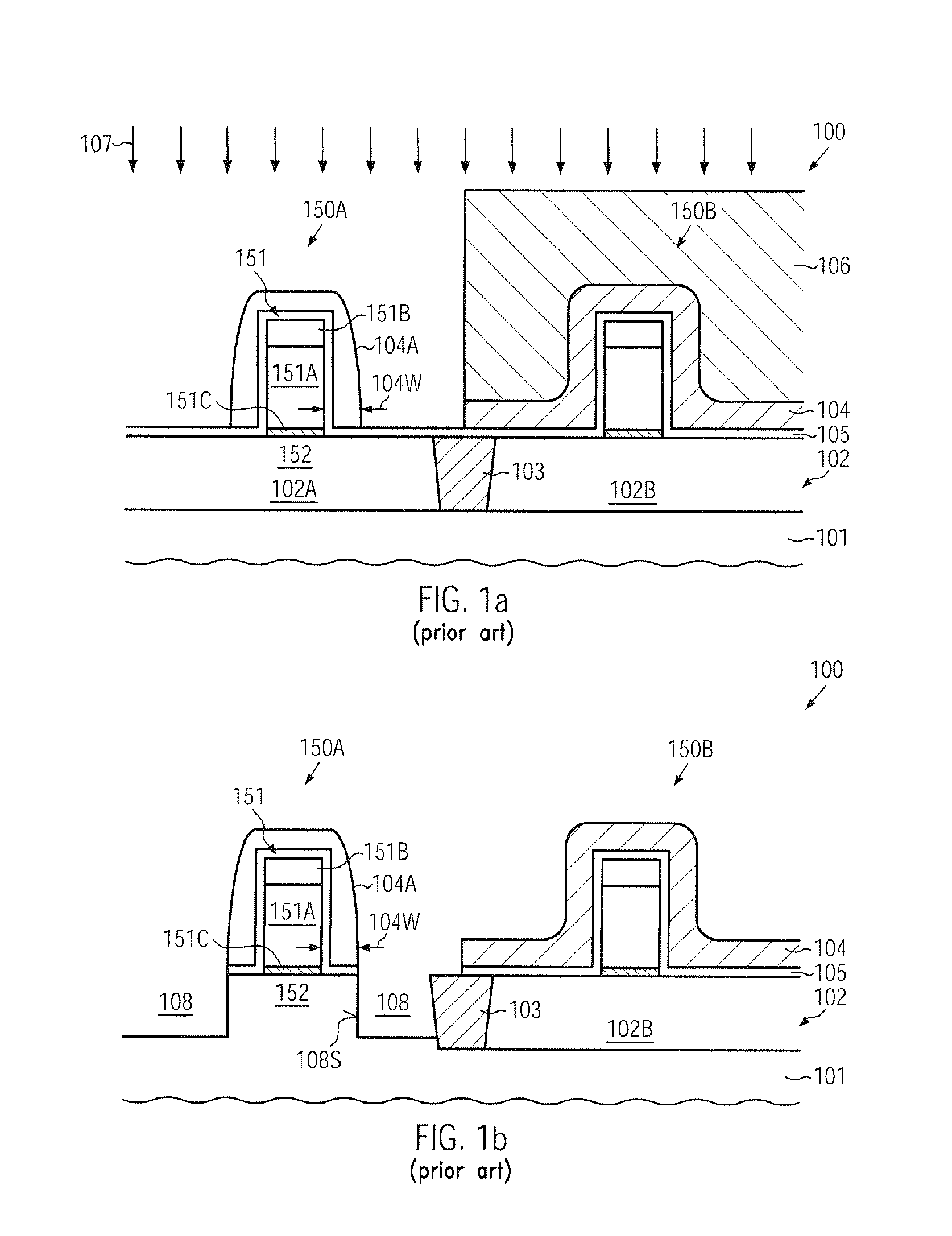
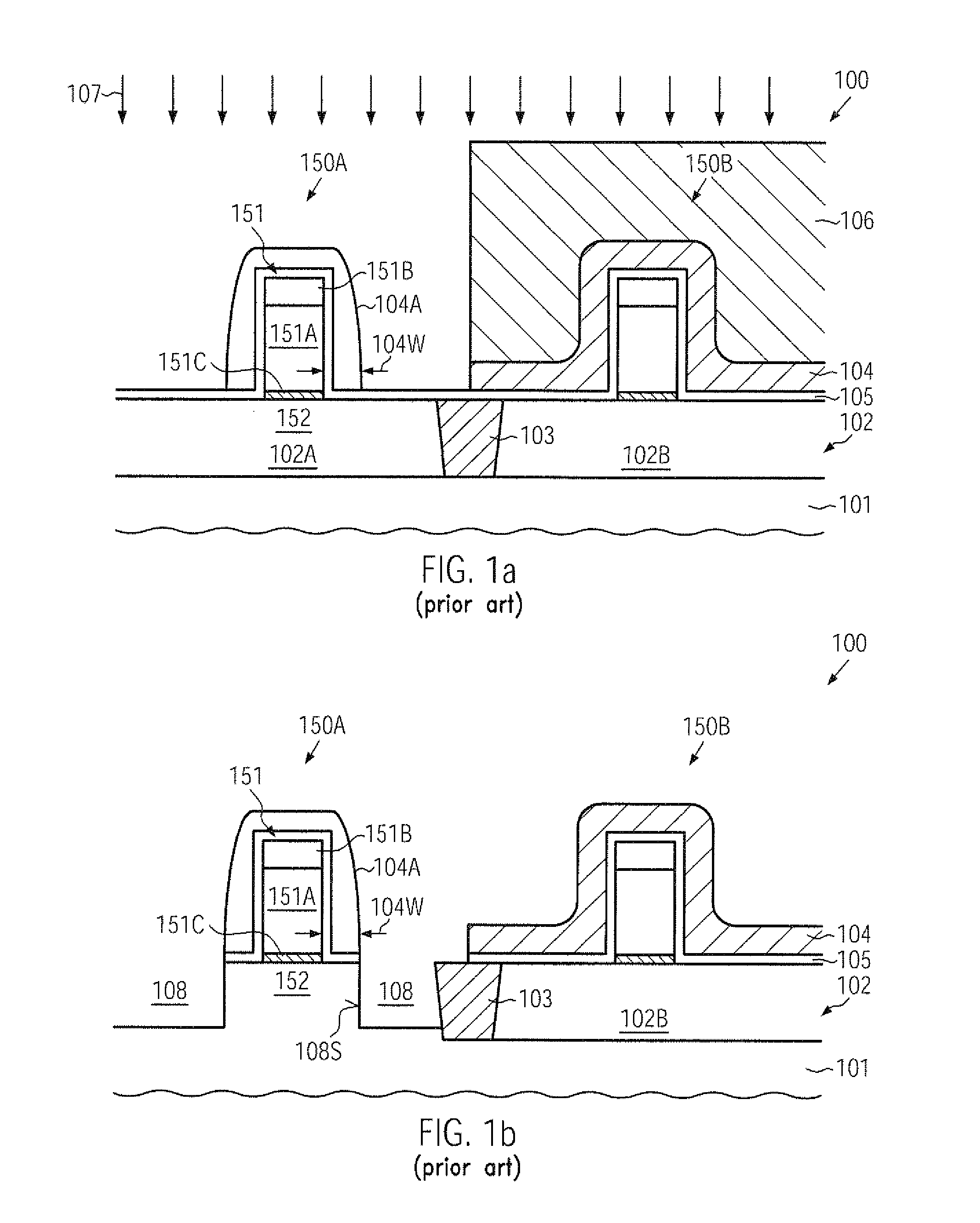
Transistor with embedded si/ge material having reduced offset to the channel region
ActiveUS20100078689A1Prevent backflowIncrease flexibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsSemiconductor alloys
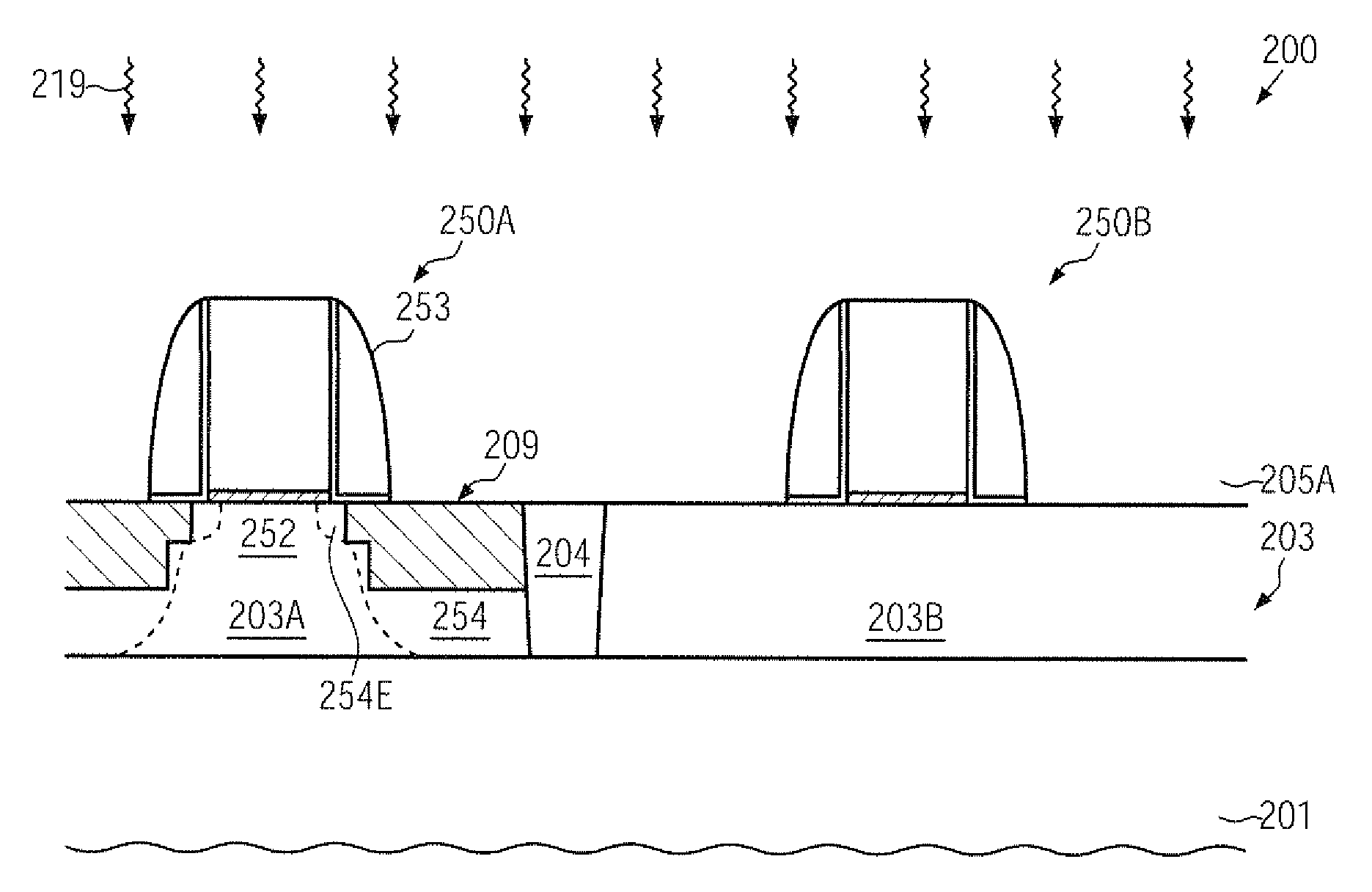
A strain-inducing semiconductor alloy may be formed on the basis of cavities which may have a non-rectangular shape, which may be maintained even during corresponding high temperature treatments by providing an appropriate protection layer, such as a silicon dioxide material. Consequently, a lateral offset of the strain-inducing semiconductor material may be reduced, while nevertheless providing a sufficient thickness of corresponding offset spacers during the cavity etch process, thereby preserving gate electrode integrity. For instance, P-channel transistors may have a silicon / germanium alloy with a hexagonal shape, thereby significantly enhancing the overall strain transfer efficiency.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
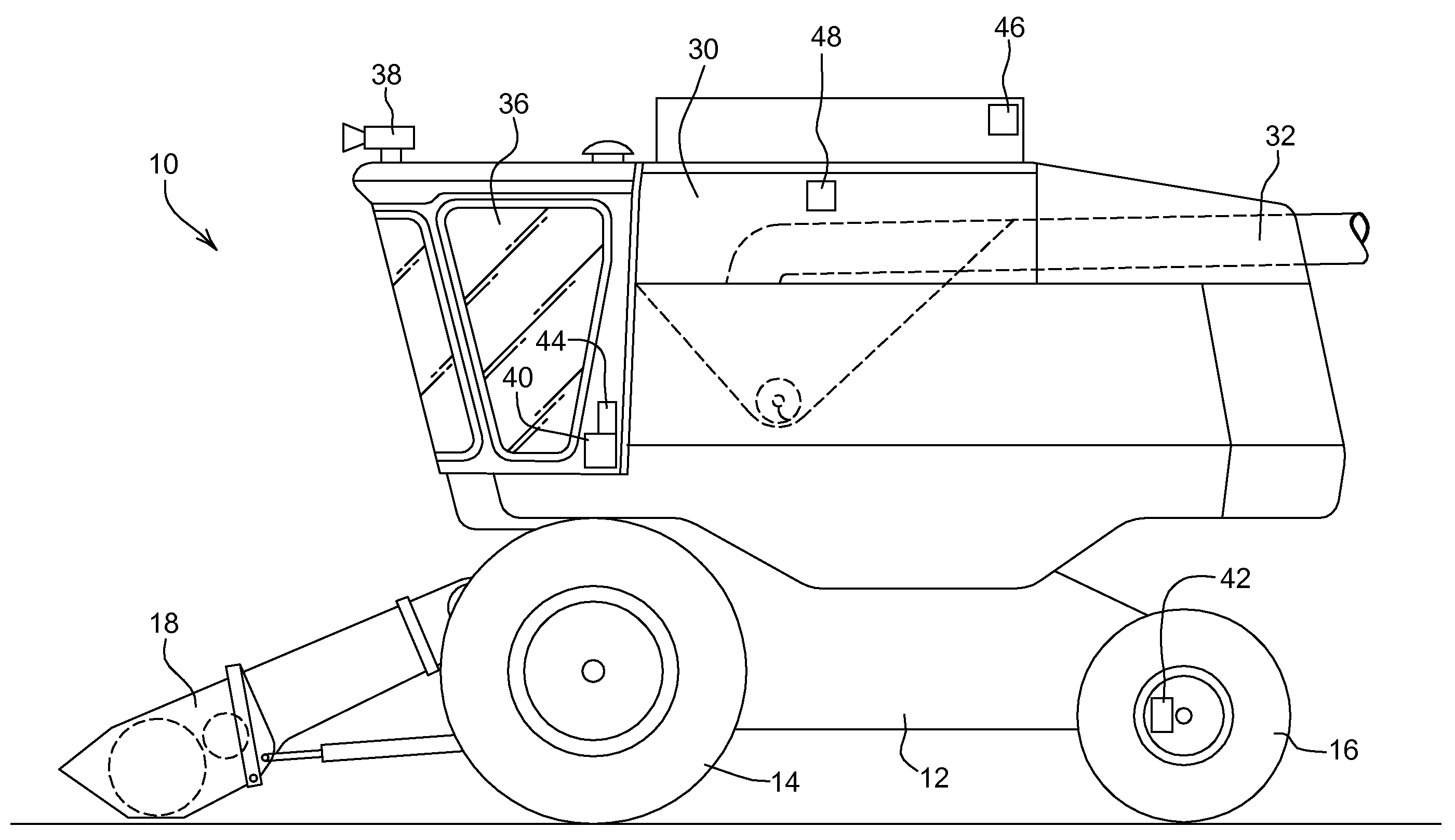
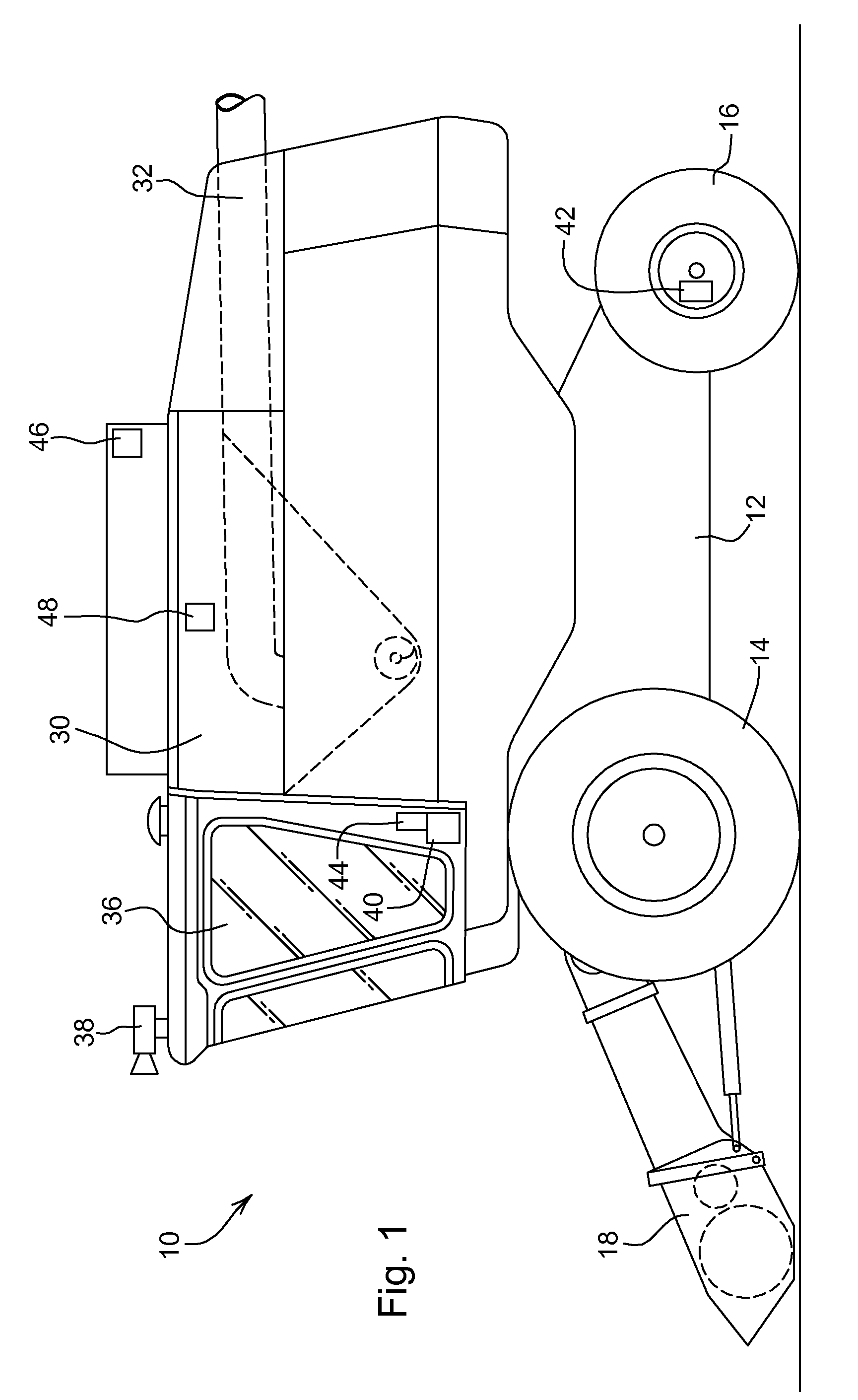
Automatic steering system and method for a work vehicle with feedback gain dependent on a sensed payload
ActiveUS20080275609A1Improve performanceImprove stabilityDigital data processing detailsOptical signallingAutomatic steeringControl signal
An automatic steering system for a work vehicle comprises a position sensor for detecting a position of the vehicle, a memory for storing information about a nominal path of the vehicle and a control unit coupled to the position sensor, to the memory and to a steering actuator for steering the vehicle. The control submits control signals to the steering actuator that depend upon a feedback gain and a lateral offset between the actual position and the nominal path. The feedback gain depends upon a sensed payload of the vehicle.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Subsea well communications apparatus and method using variable tension large offset risers
Disclosed are compliant variable tension risers (106) to connect deep-water subsea wellheads (102) to a single floating platform (104) in wet tree or dry try systems. The variable tension risers (106) allow several subsea wellheads (102), in water depths from 1220 to 3050 meters, at lateral offsets from one-tenth to twice the depth or more, to tie back to a single floating platform (104). Also disclosed are methods to counter buoyancy and install variable tension risers using a weighted chain ballast line (228, 230).
Owner:KELLOGG BROWN & ROOT LLC
Transistor comprising an embedded semiconductor alloy in drain and source regions extending under the gate electrode
InactiveUS20100219474A1Maintain integrityAvoid contactSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor alloysEngineering
A strain-inducing semiconductor alloy may be formed on the basis of cavities that may extend deeply below the gate electrode structure, which may be accomplished by using a sequence of two etch processes. In a first etch process, the cavity may be formed on the basis of a well-defined lateral offset to ensure integrity of the gate electrode structure and, in a subsequent etch process, the cavity may be increased in a lateral direction while nevertheless reliably preserving a portion of the channel region. Consequently, the strain-inducing efficiency may be increased by appropriately positioning the strain-inducing material immediately below the channel region without compromising integrity of the gate electrode structure.
Owner:ALSEPHINA INNOVATIONS INC
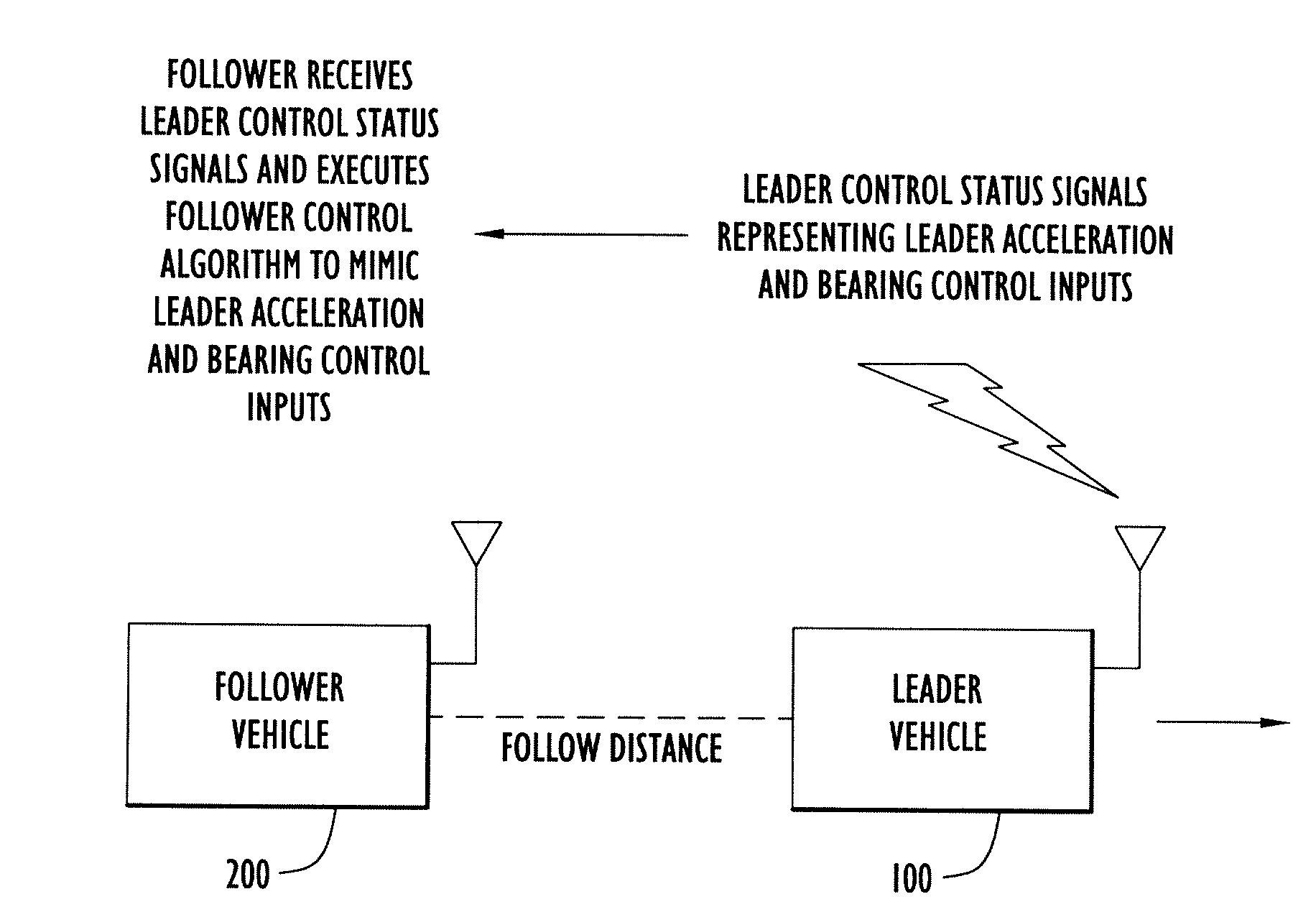
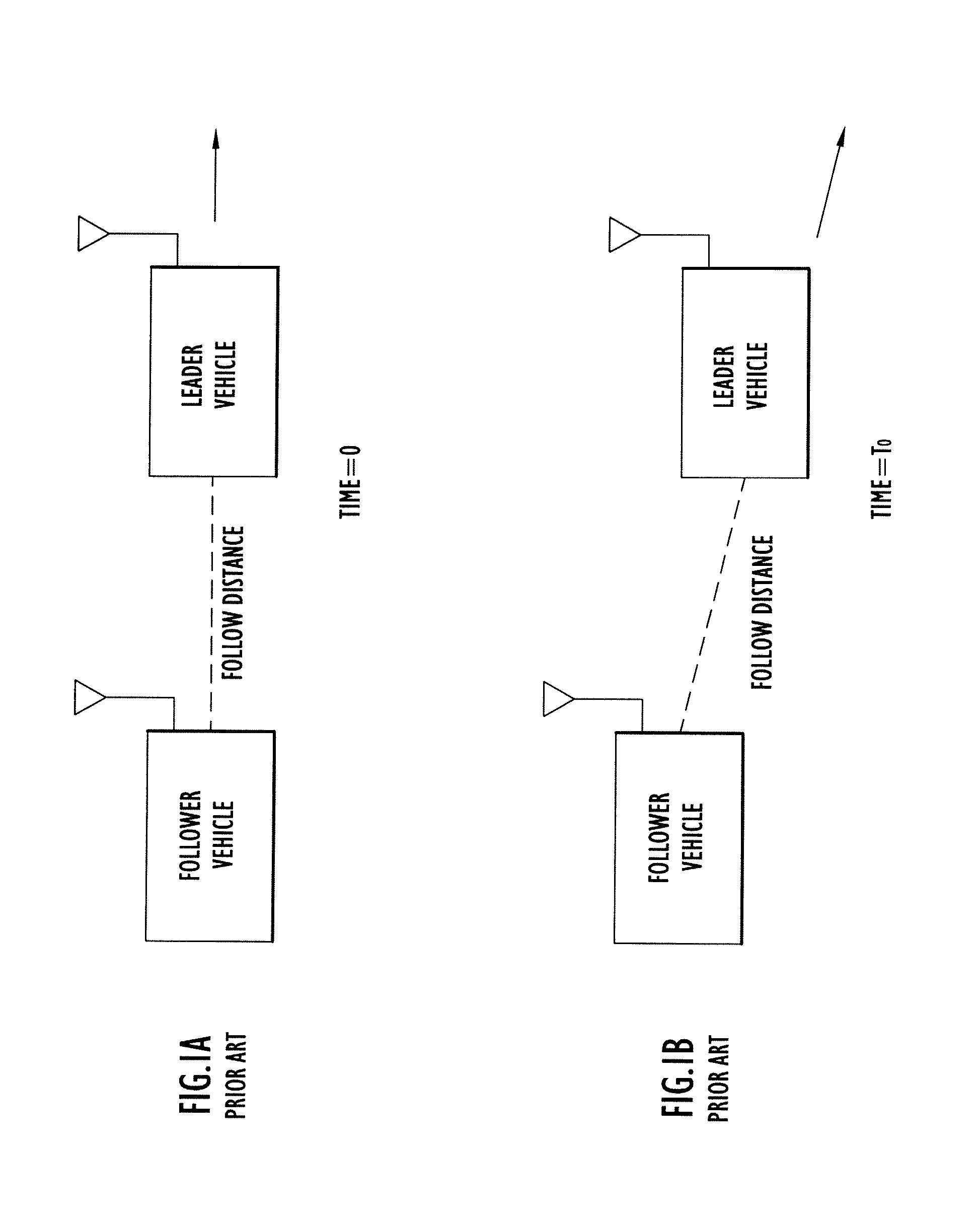
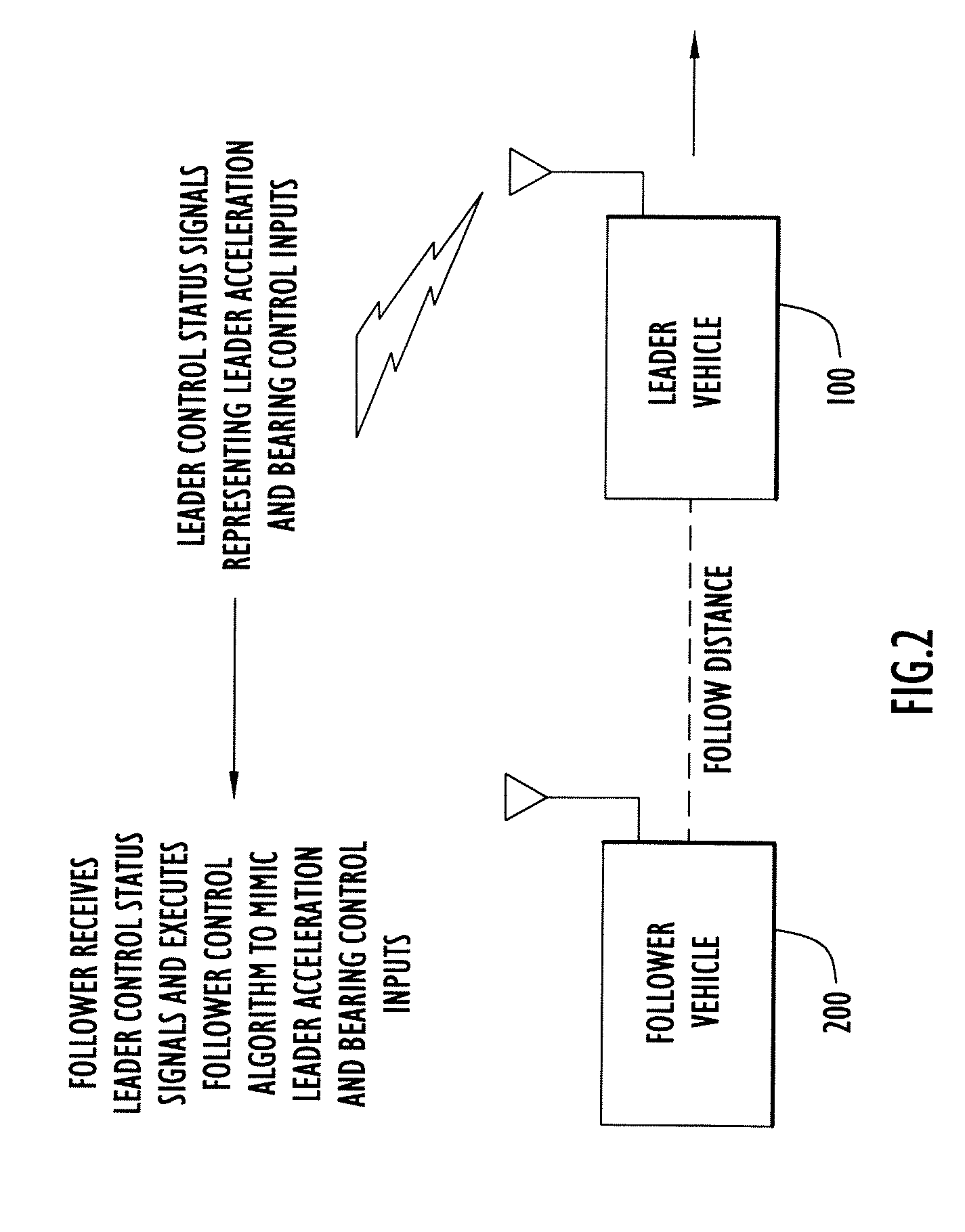
Close-Spaced Leader-Follower Navigation Using Control Mimic
ActiveUS20110224844A1Slow update rateDigital data processing detailsVehicle position/course/altitude controlAutomatic controlAcceleration control
A method is provided for automatically controlling a first vehicle (follower vehicle) that is to follow a second vehicle (leader vehicle) in a desired manner with respect to movement of the second vehicle. In the follower vehicle, bearing and acceleration control inputs are generated based on data representing bearing and acceleration control inputs made at the leader vehicle and a position of the follower vehicle relative to the leader vehicle so as to mimic in the follower vehicle the bearing and acceleration control inputs made in the leader vehicle. Adjustments may be made to the control inputs applied in the follower vehicle based on deviation between the velocity of the follower vehicle and velocity of the leader velocity, and on deviation between estimated (actual) follow distance and lateral offset and target follow distance and lateral offset between the follower vehicle and the leader vehicle.
Owner:PERATON INC
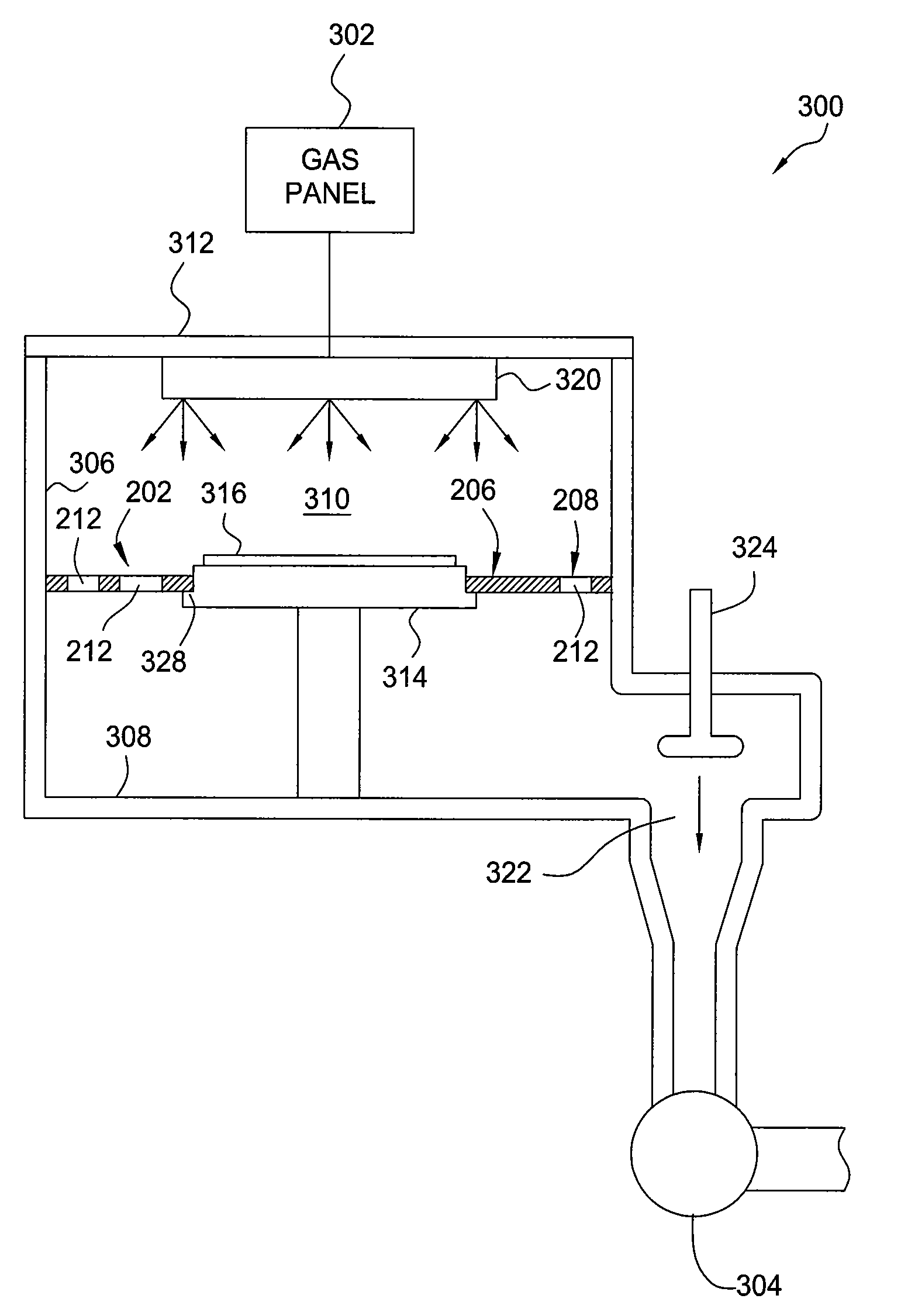
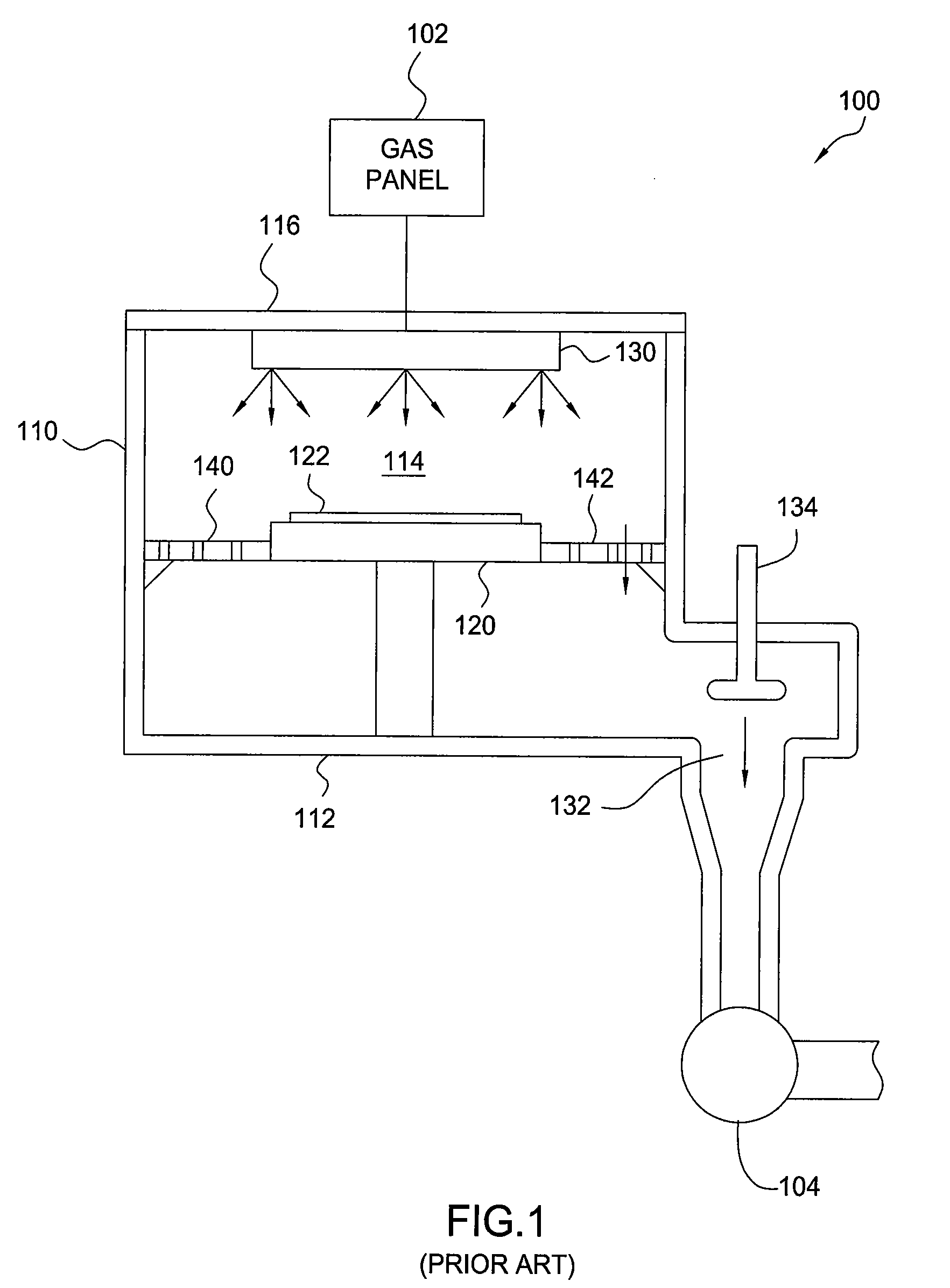
Gas flow equalizer plate suitable for use in a substrate process chamber
InactiveUS20090218043A1Improves airflow uniformityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFlow asymmetryProduct gas
A flow equalizer plate is provided for use in a substrate process chamber. The flow equalizer plate has an annular shape with a flow obstructing inner region, and a perforated outer region that permits the passage of a processing gas, but retains specific elements in the processing gas, such as active radicals or ions. The inner and outer regions have varying radial widths so as to balance a flow of processing gas over a surface of a substrate. In certain embodiments, the flow equalizer plate may be utilized to correct chamber flow asymmetries due to a lateral offset of an exhaust port relative to a center line of a substrate support between the process volume and the exhaust port.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for correction of relative object-detector motion between successive views
Motion correction for optical tomographic imaging in three dimensions. An object of interest is illuminated to produce an image. A lateral offset correction value is determined for the image. An axial offset correction value is determined for the image. The lateral offset correction value and the axial offset correction value are applied to the image to produce a corrected file image.
Owner:VISIONGATE
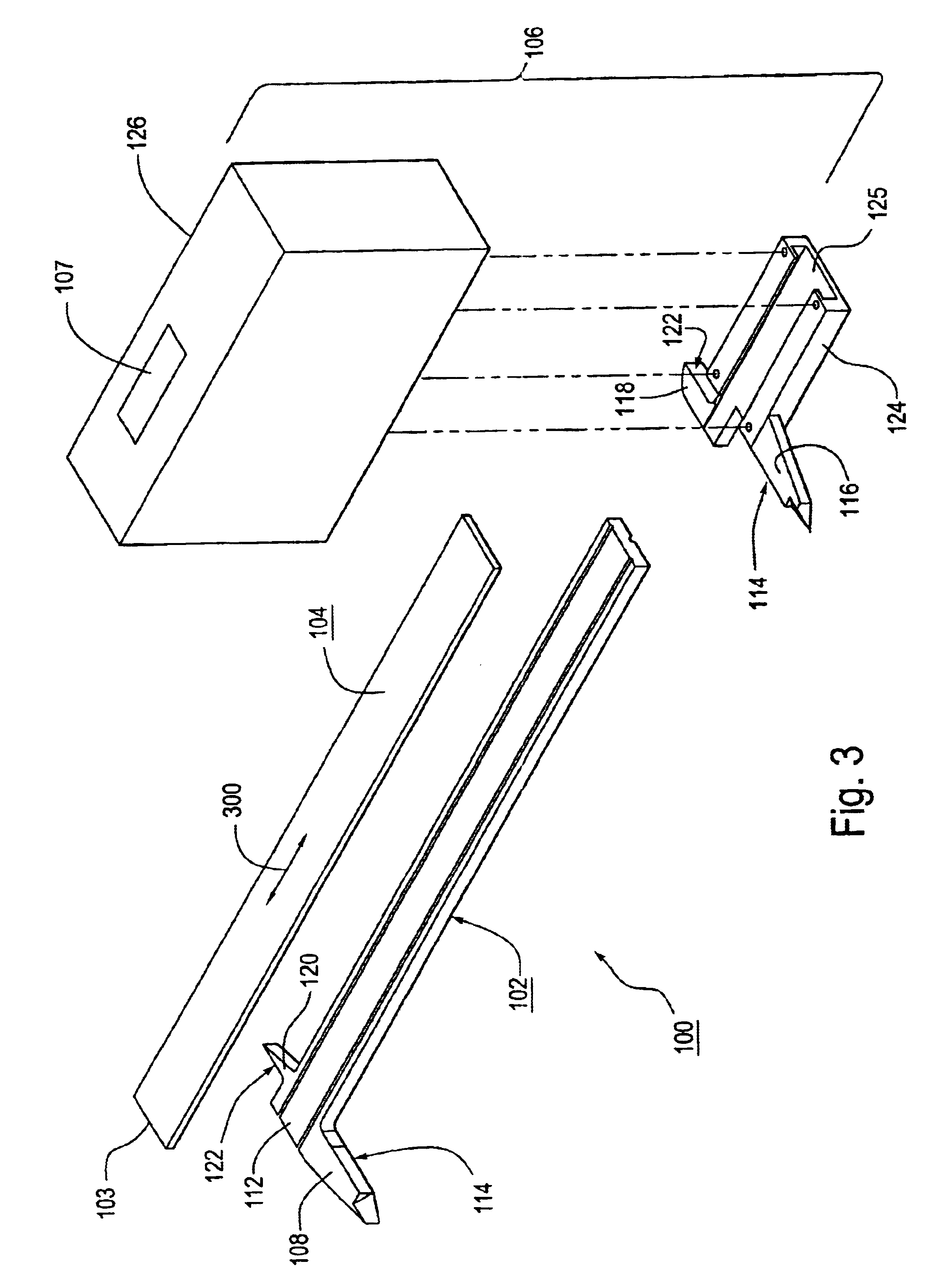
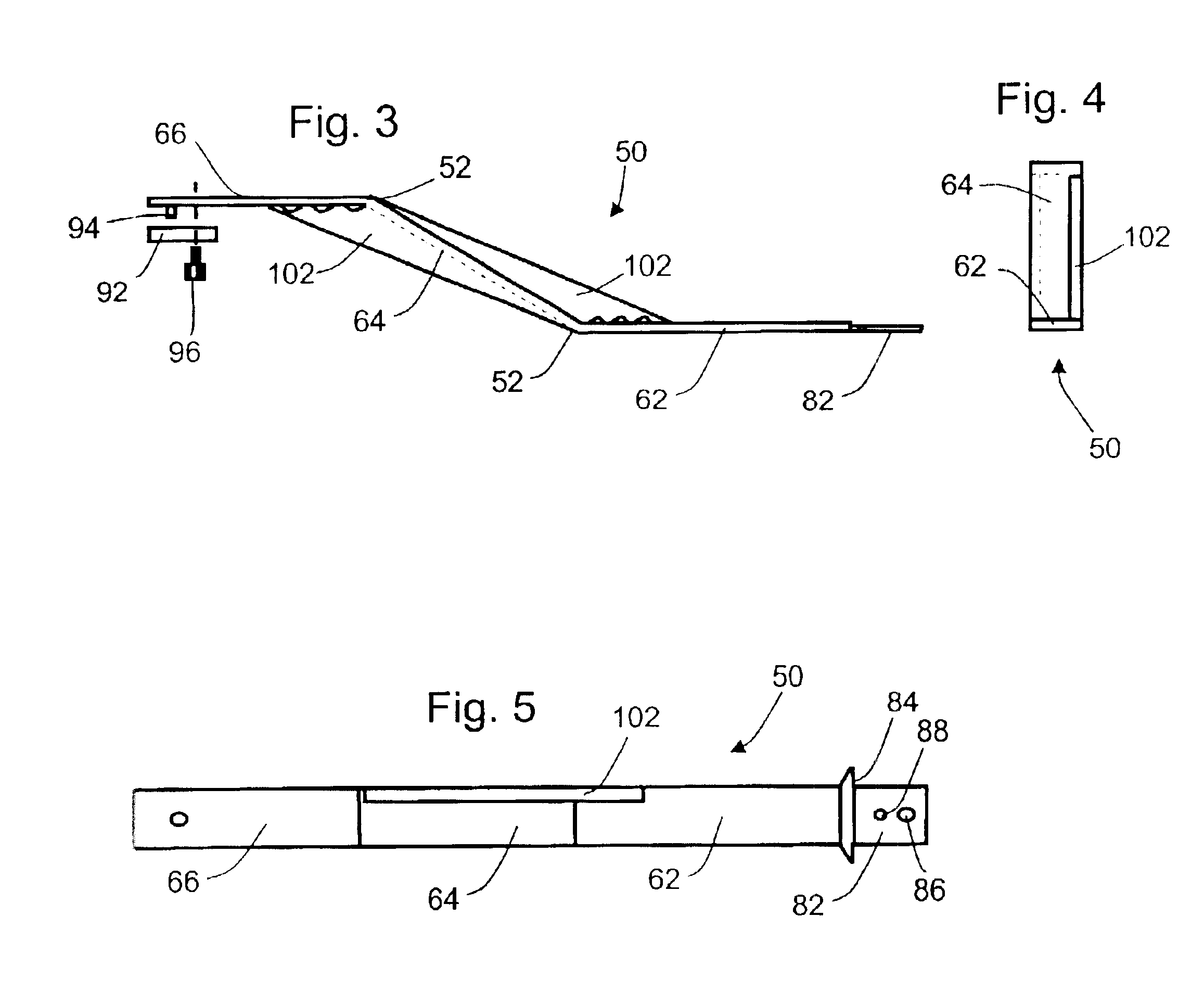
Reciprocating saw blade extension with lateral offset
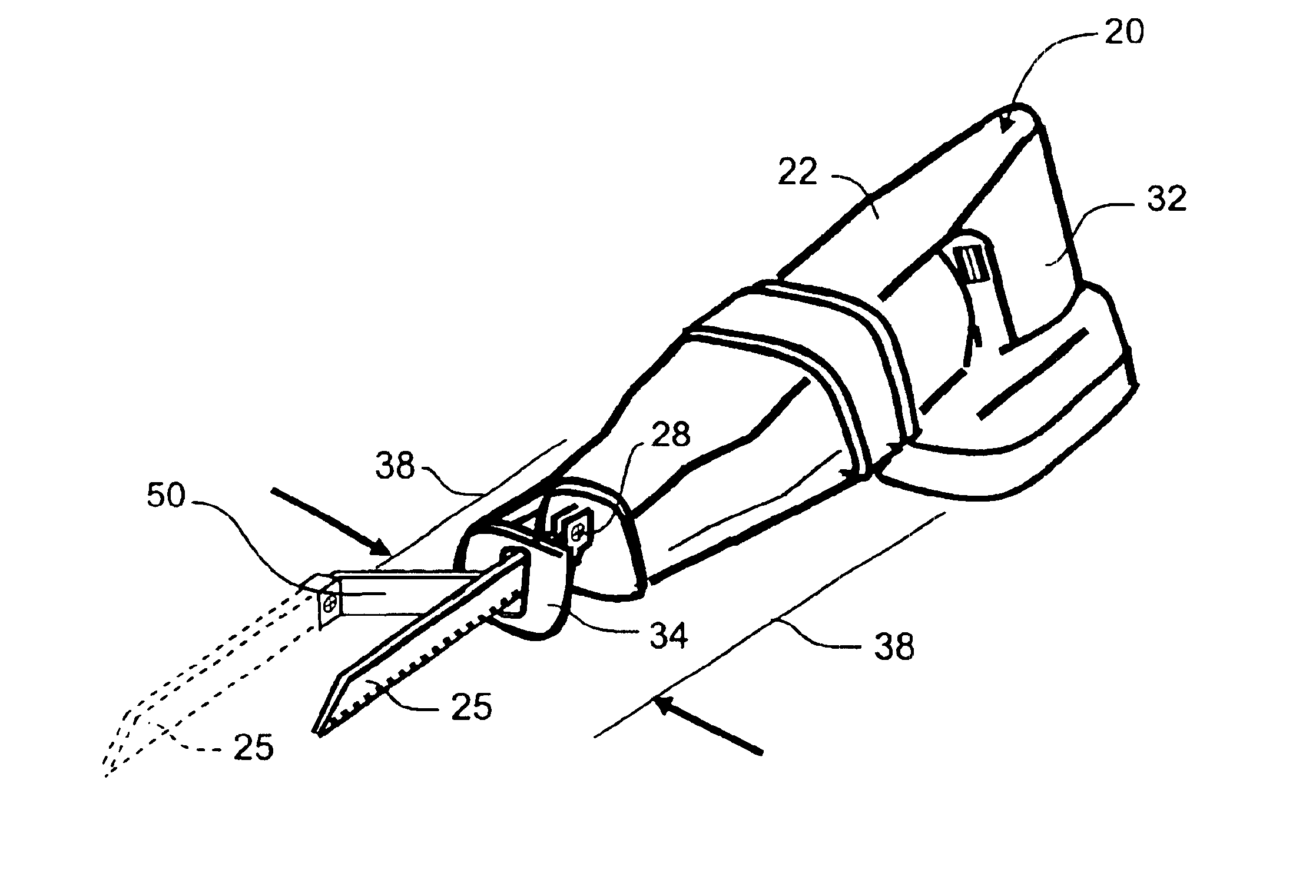
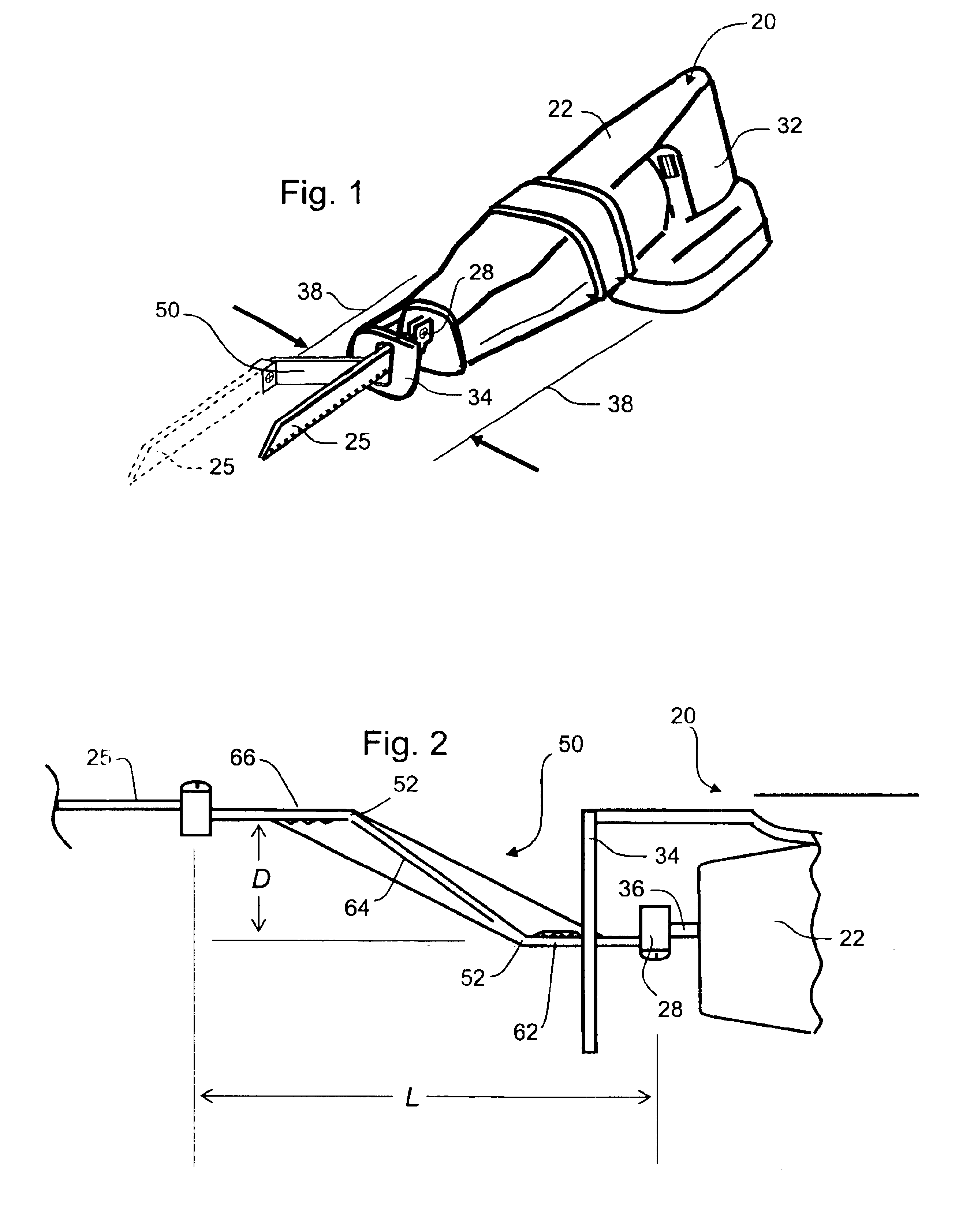
An extension is attachable to the driving shaft of a reciprocating blade tool such as a saber saw. The extension is attached to the drive shaft and the blade is attached to the end of the extension. The extension places the blade at a position spaced laterally and longitudinally from the nominal point of attachment of the blade to the driving shaft, the lateral spacing placing the new blade position approximately at the lateral outside edge of the tool housing, thereby permitting flush cuts. The extension can be formed of an integral strip or sheet having a proximal leg, an intermediate section and a distal leg, joined at equal and opposite obtuse angles. The angles are reinforced by two or more webs bent from the plane of the legs and attached, for example by welding, to the intermediate section.
Owner:REALE GEORGE S +1
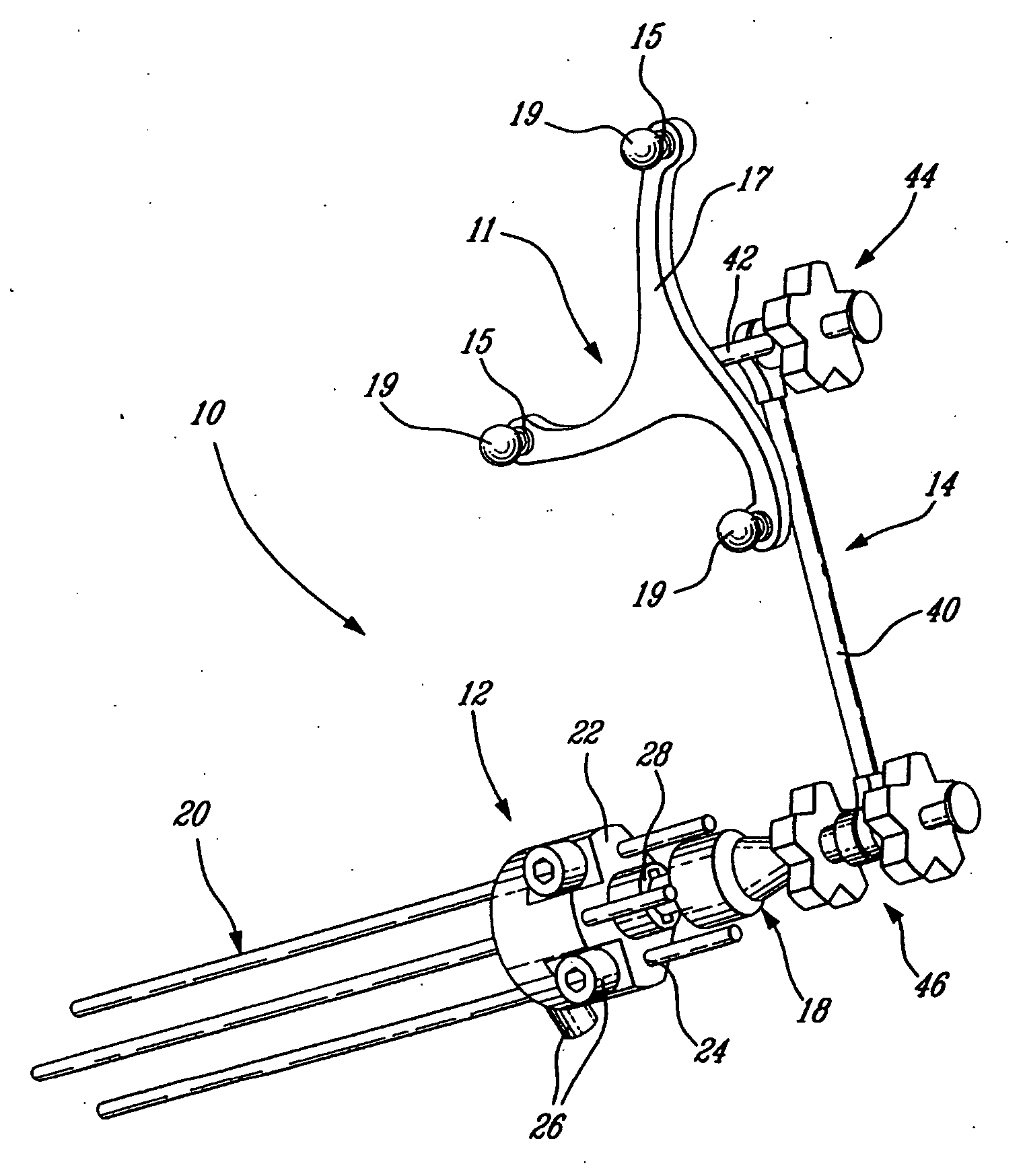
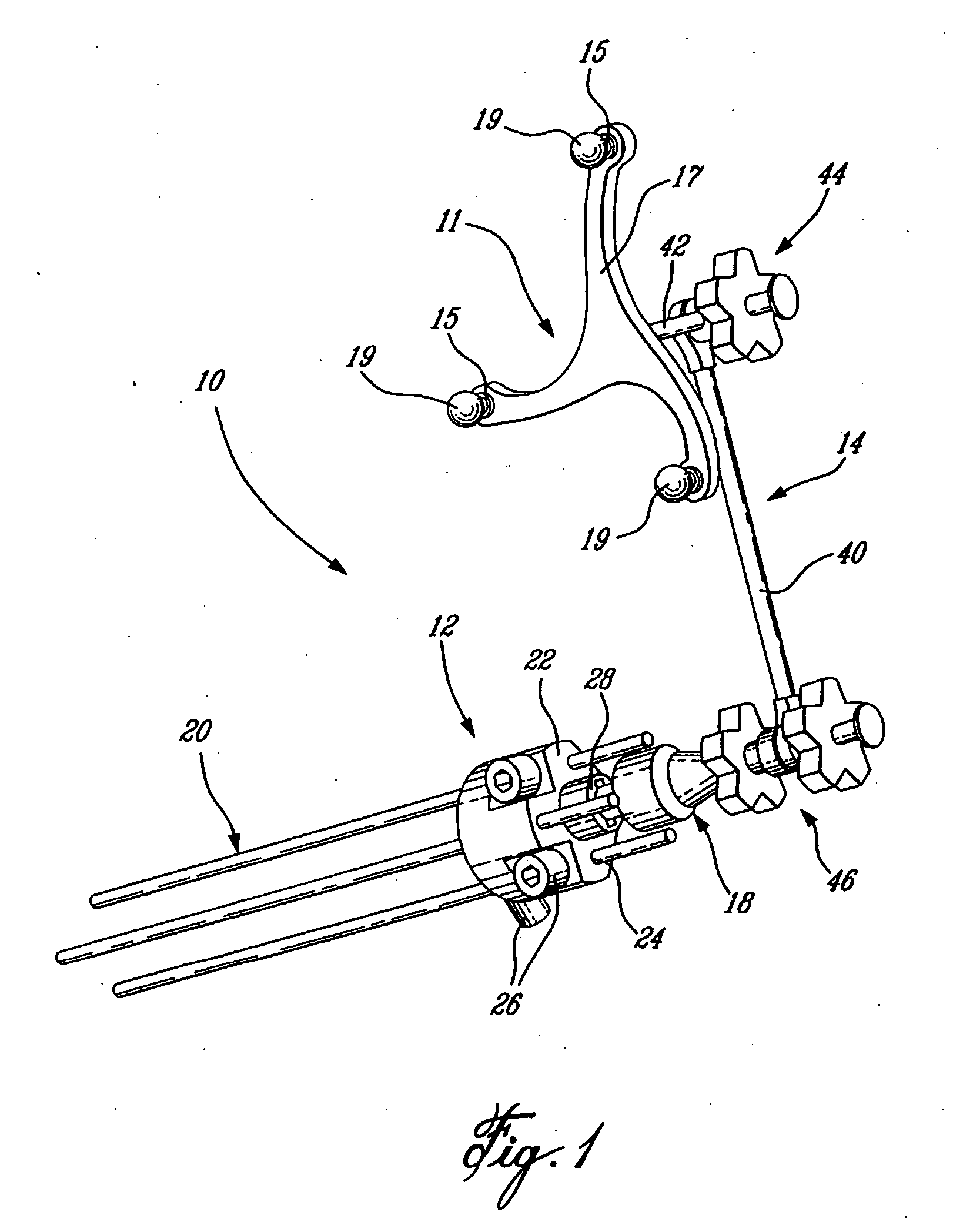
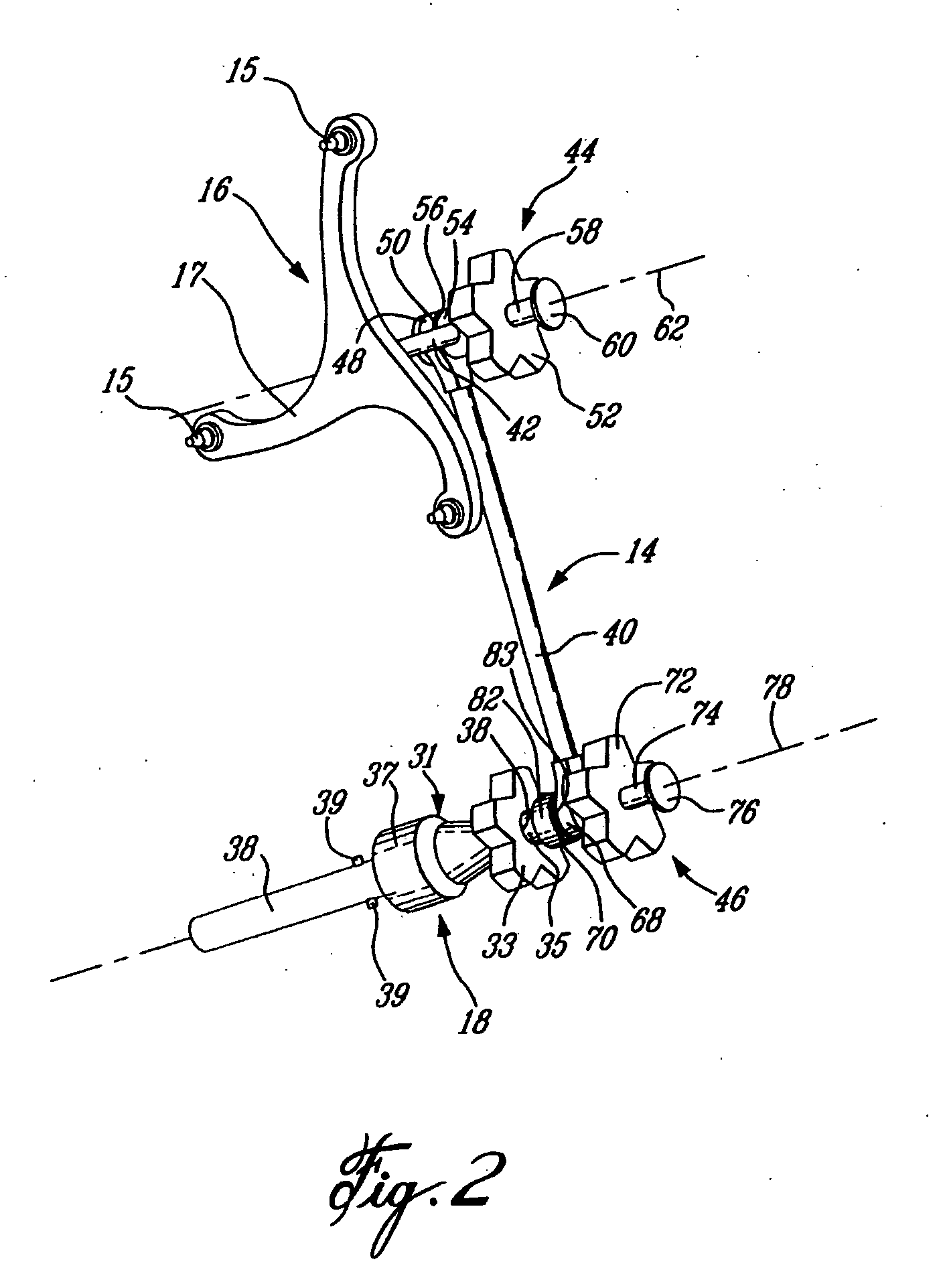
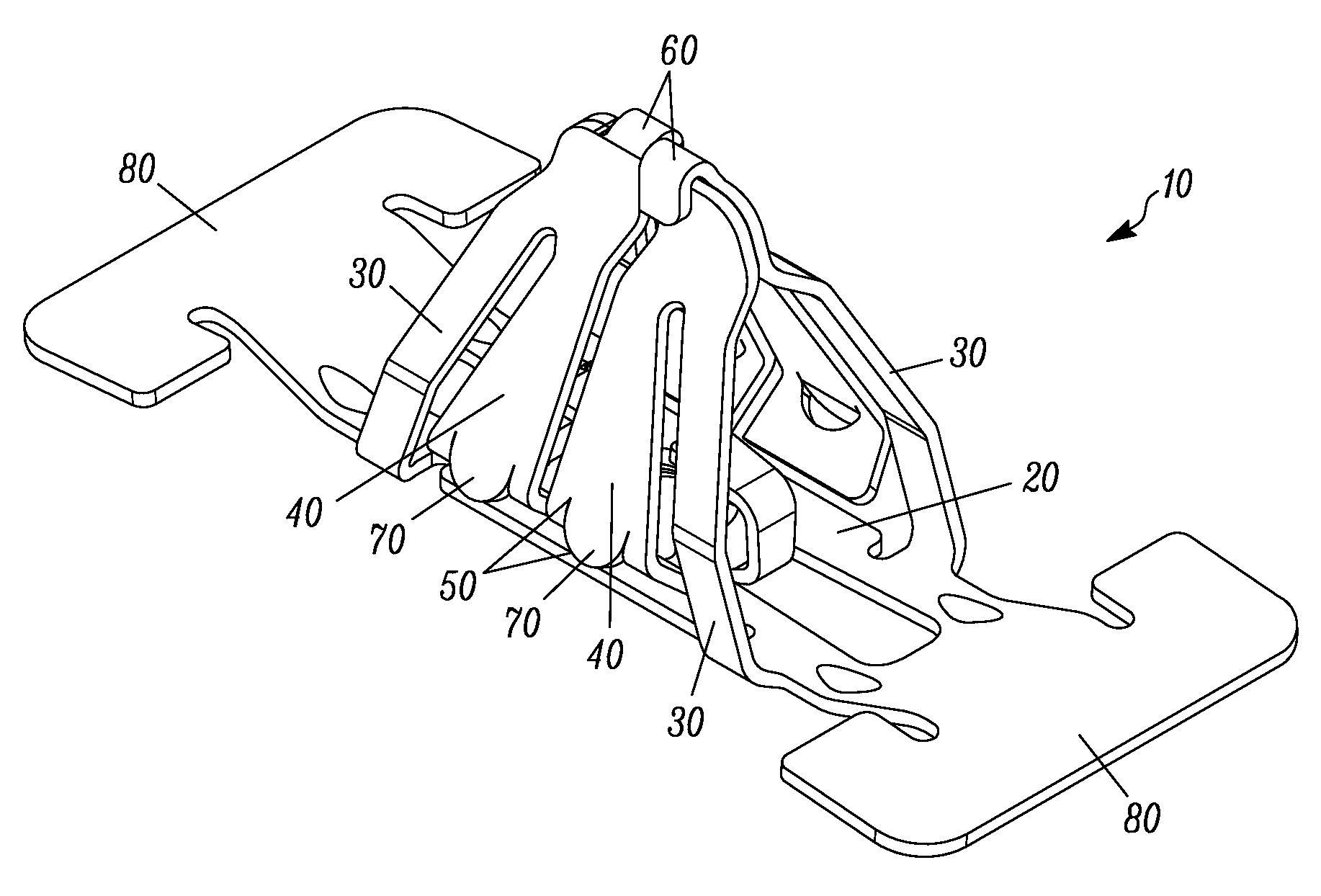
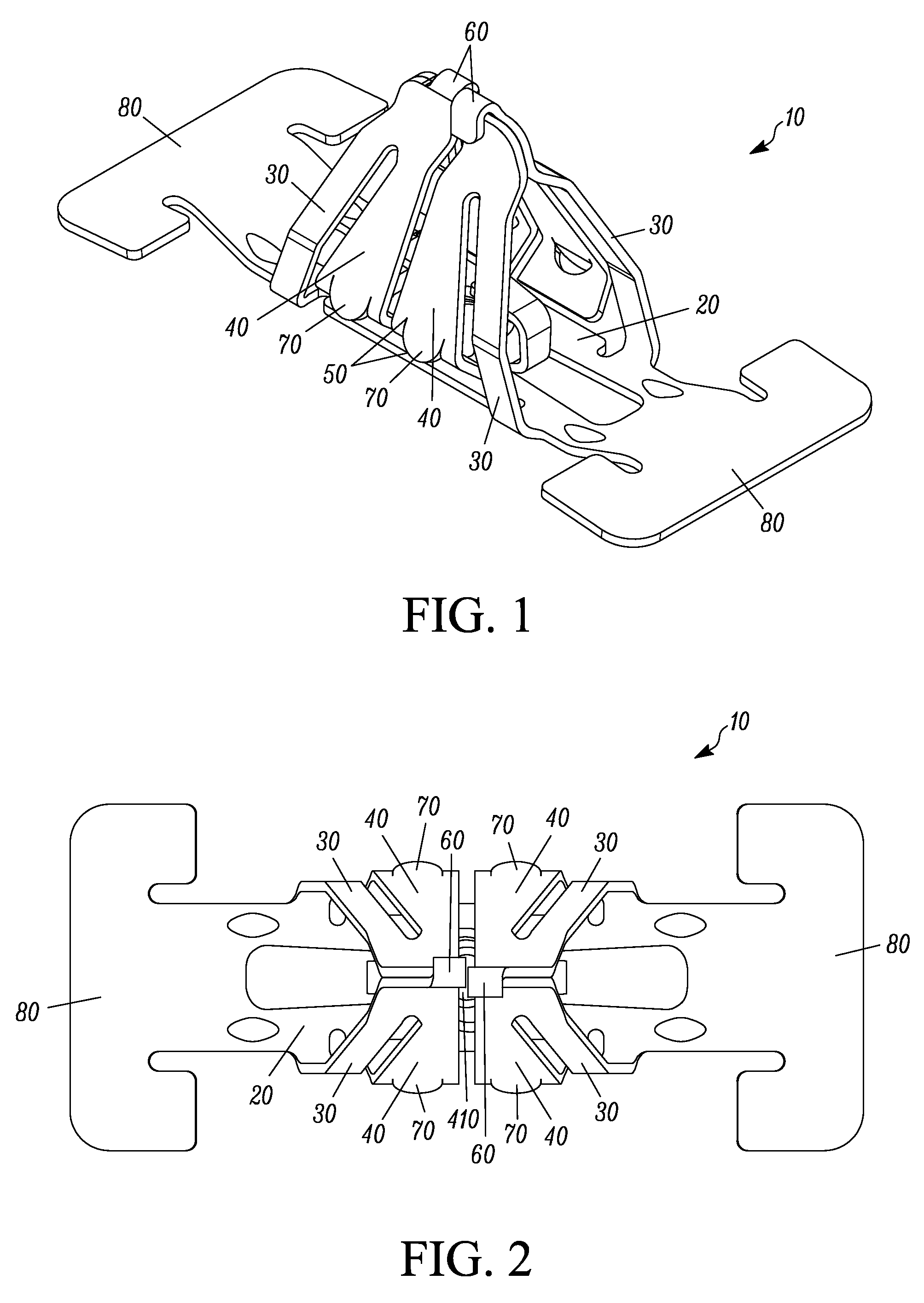
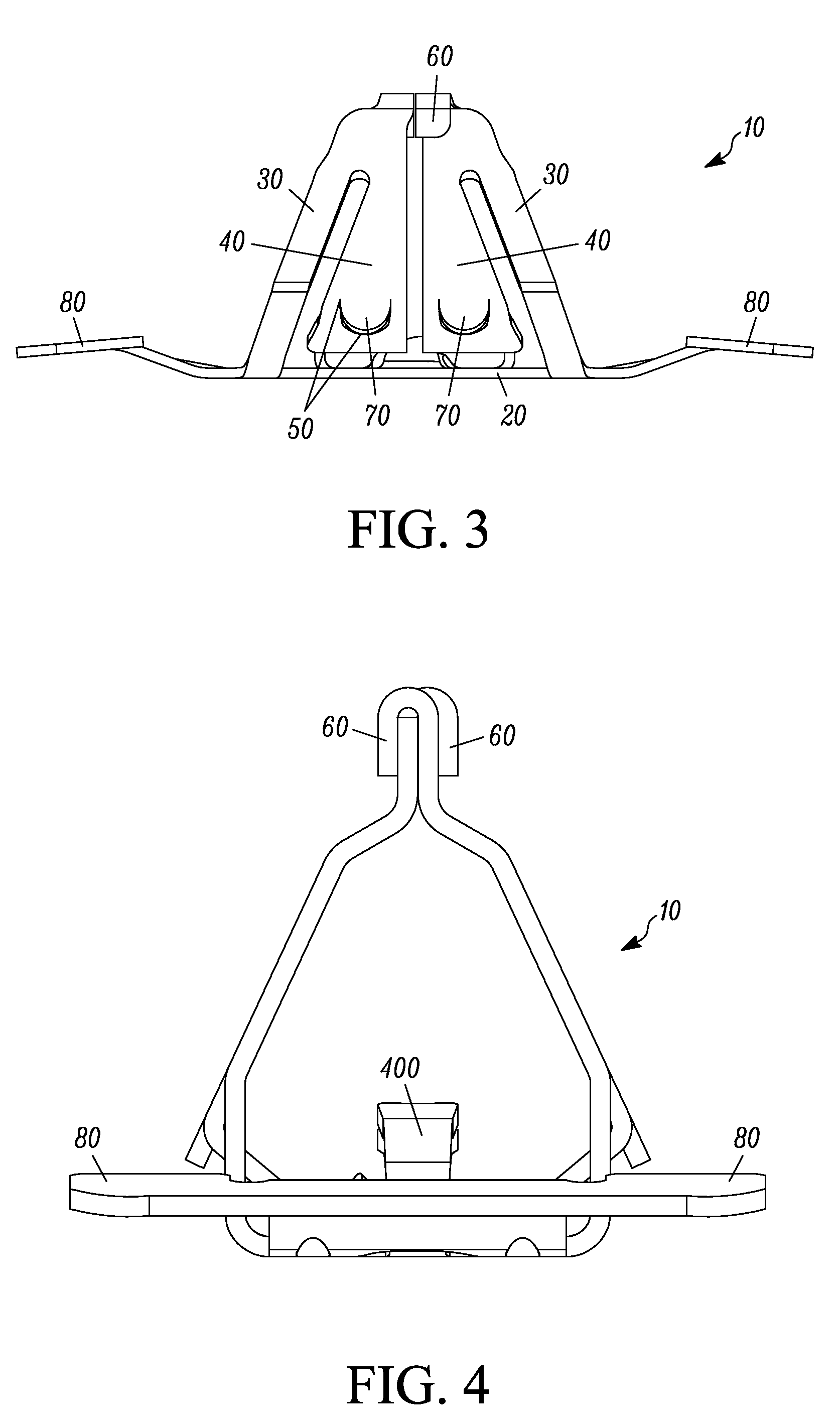
Continuously adaptive fastener clip
A fastener clip includes a base plate and a first and second pair of laterally offset legs extending from the base plate. At least one first wing extends from the first pair of laterally offset legs. The at least one first wing has an engagement region. At least one second wing extending from the second pair of laterally offset legs. The at least one second wing has an engagement region, such that a distance between the engagement regions and the base plate is operative to vary continuously according to a slot thickness. The fastener clip is operative for insertion into the slot defined in a first engagement structure, such as a vehicle chassis.
Owner:TERMAX CORP
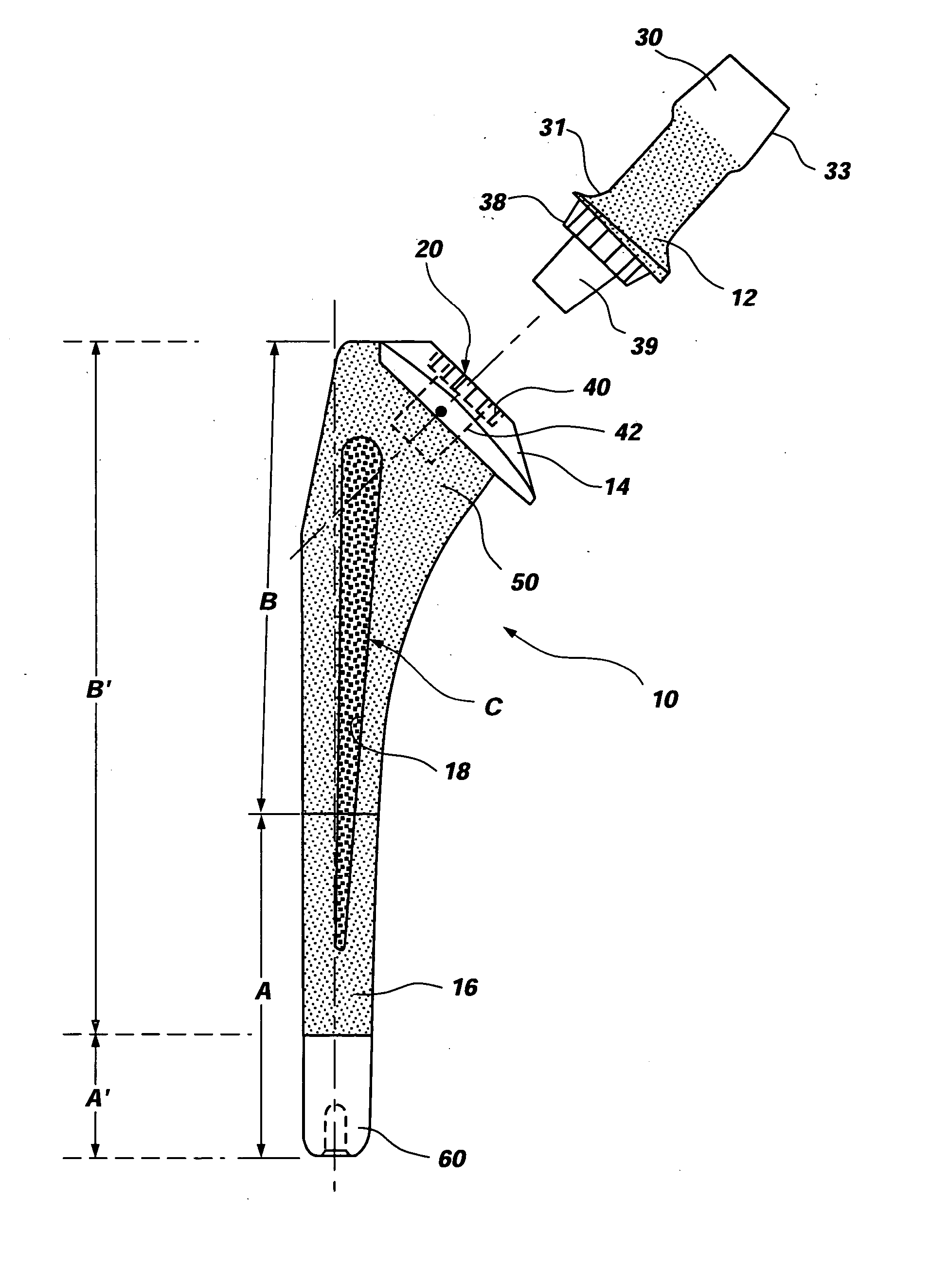
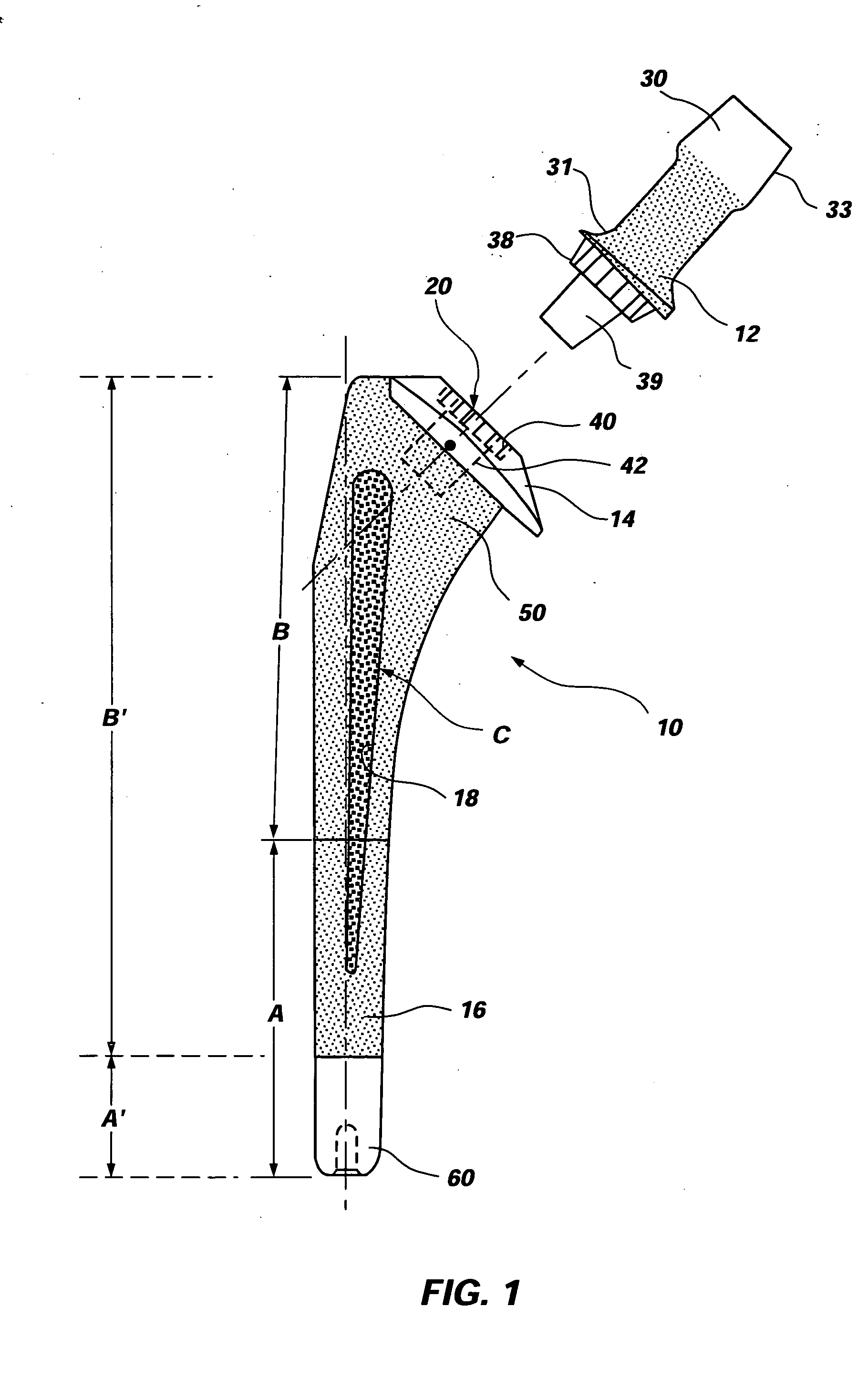
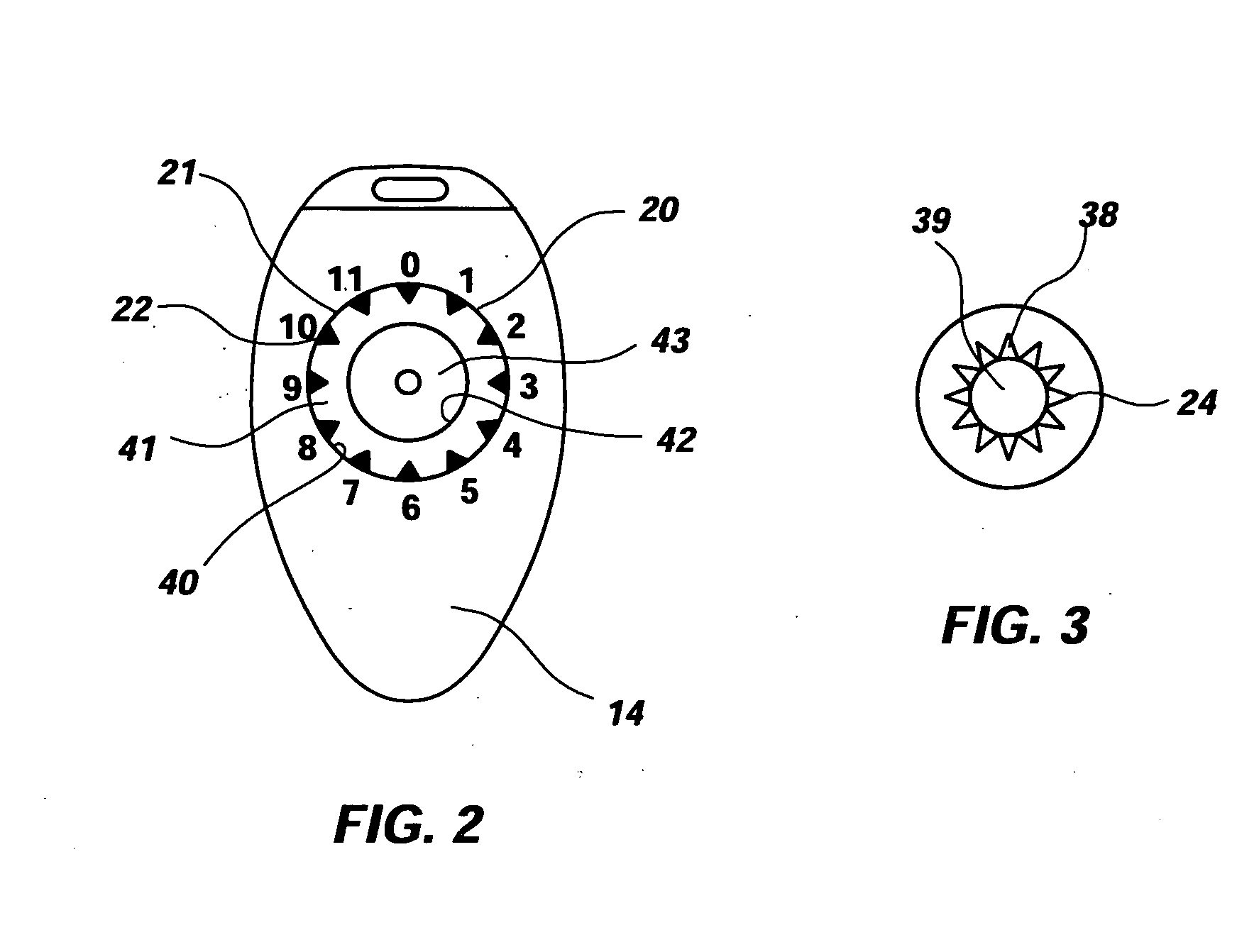
Differential porosity prosthetic hip system
A prosthetic femoral implant for use in a hip joint, as a ball and socket type joint, is disclosed. The implant includes a modular neck having a variety of adjustable positions to adjust the lateral offset and version angle of the femoral implant in relation to the femur. The implant further includes a broad, full collar for providing a compression force increasing the interdigitation between the interface of the bone, implant and cement. The implant also includes a stem having a depression having a roughened porous surface for resisting the increased torsional loads placed on the implant due to the increased lateral offset and version angle. The stem further comprises three distinct zones, each zone having its own roughened surface creating a tripartite differential porosity.
Owner:ENCORE MEDICAL ASSET CORP
Method and device for calculating a path which is laterally offset with respect to a reference path
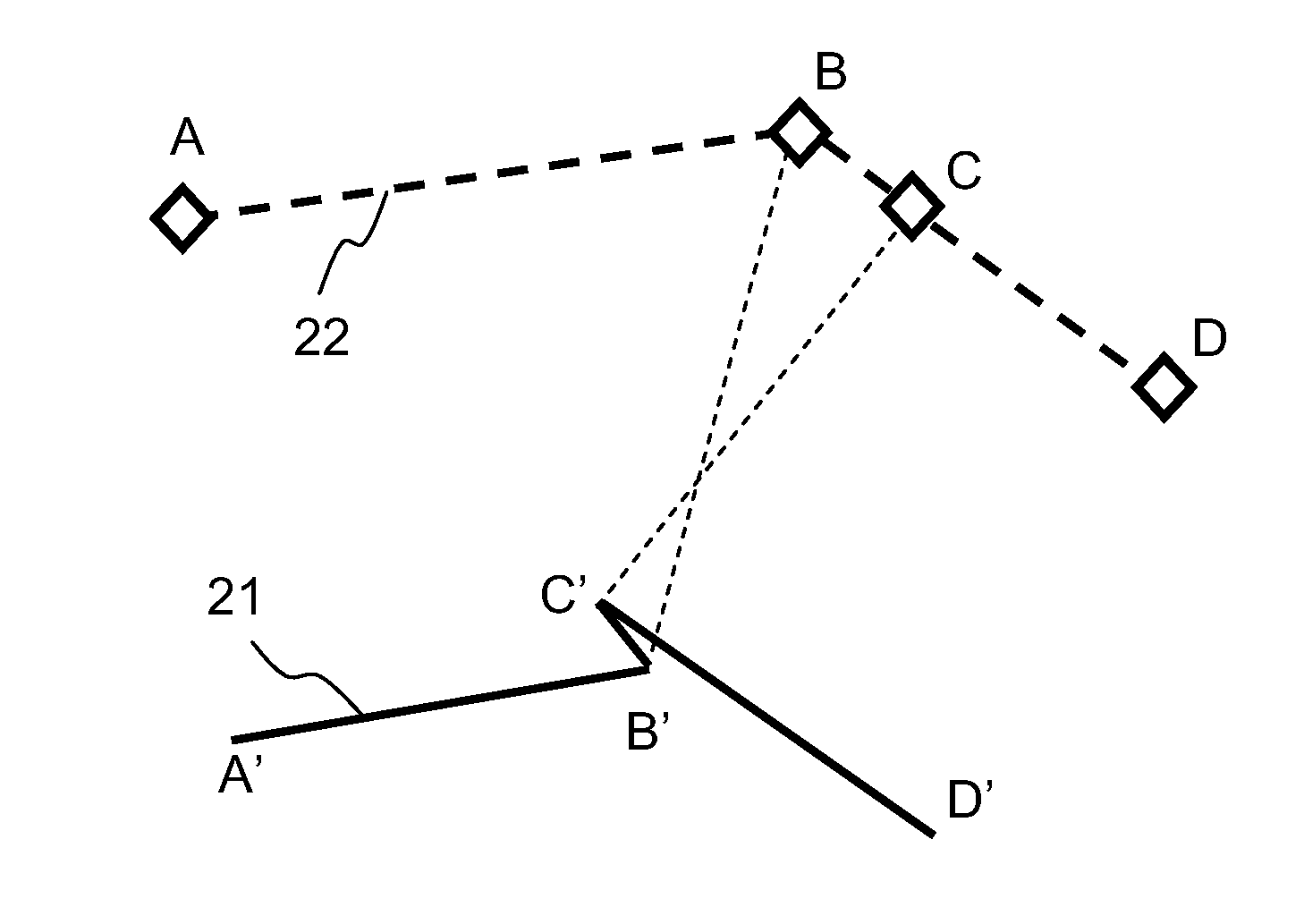
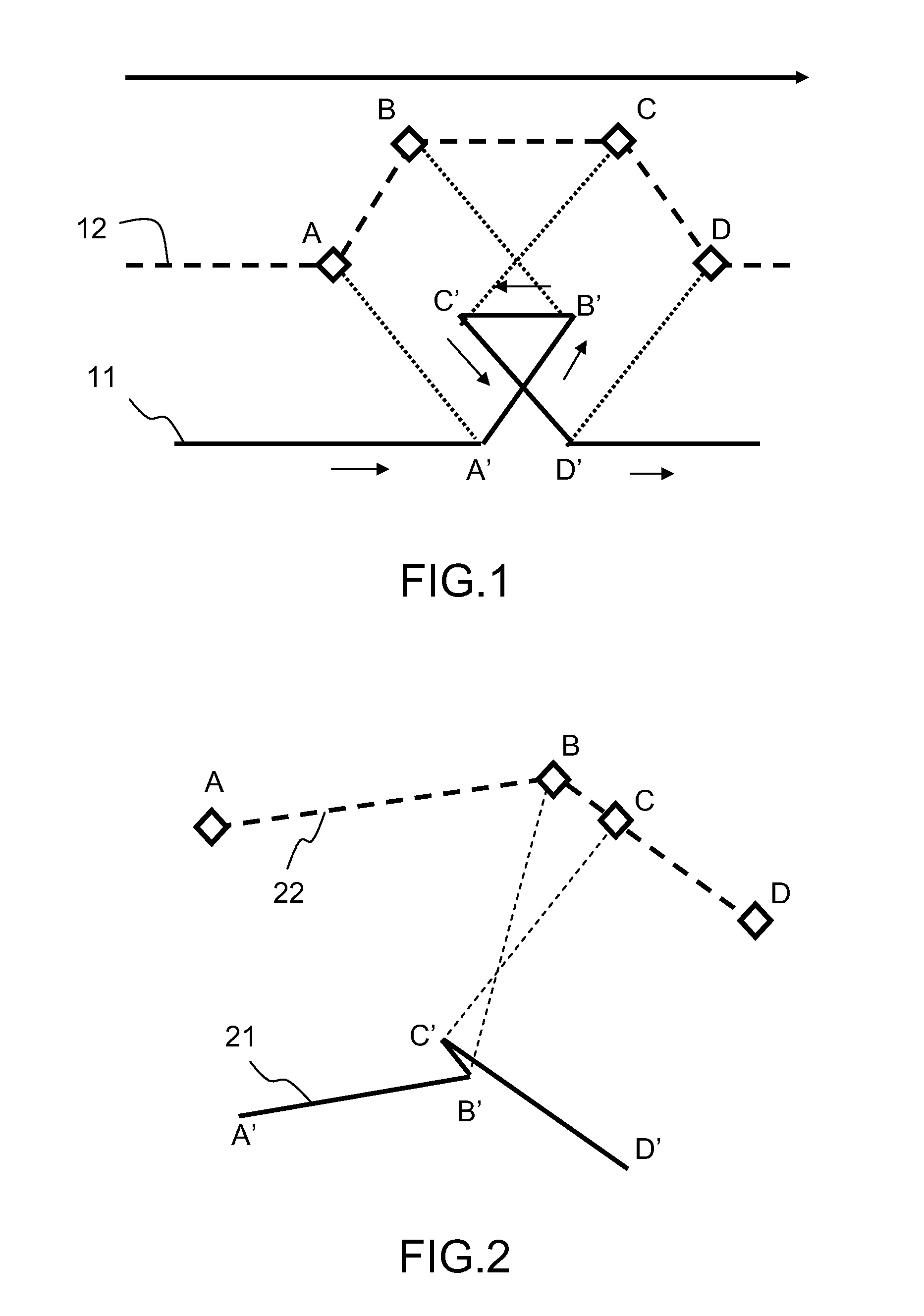
ActiveUS20080154490A1Possible to connectInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlLateral offsetAdjacent segment
The invention relates to a method of calculating a path which is offset laterally by a first distance with respect to a reference path, comprising the calculation of a flight plan which is offset with respect to a reference flight plan. The reference flight plan is defined on the basis of waypoints and of segments defining a reference path between the waypoints. Each segment has a start point and an end point making it possible to define a course corresponding to the direction of travel by an aircraft. The laterally offset flight plan is calculated on the basis of waypoints associated with the waypoints of the reference flight plan, called associated points and being situated at the intersection. The laterally offset flight path includes lines, parallel with the segments of the reference flight plan, offset by the first distance from the reference flight plan. It is further defined by the bisectrix of the angle formed by two adjacent segments at a waypoint belonging to the reference path. The method includes detection of the segments of the offset flight plan, whose direction of travel is reversed with respect to that of the corresponding segment belonging to the reference flight plan. The elementary paths are calculated, making it possible to connect the segments of the offset flight plan whose direction of travel is not reversed.
Owner:THALES SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com