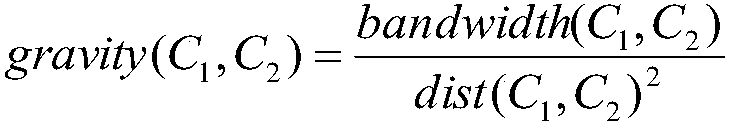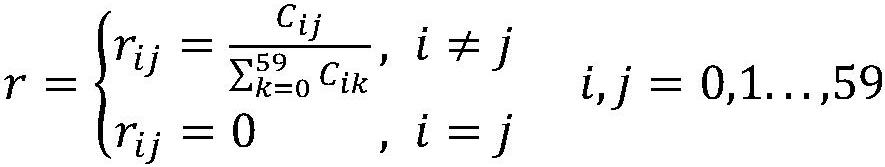Patents
Literature
47 results about "Disjoint-set" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computer science, a disjoint-set data structure (also called a union–find data structure or merge–find set) is a data structure that tracks a set of elements partitioned into a number of disjoint (non-overlapping) subsets. It provides near-constant-time operations (bounded by the inverse Ackermann function) to add new sets, to merge existing sets, and to determine whether elements are in the same set. In addition to many other uses (see the Applications section), disjoint-sets play a key role in Kruskal's algorithm for finding the minimum spanning tree of a graph.
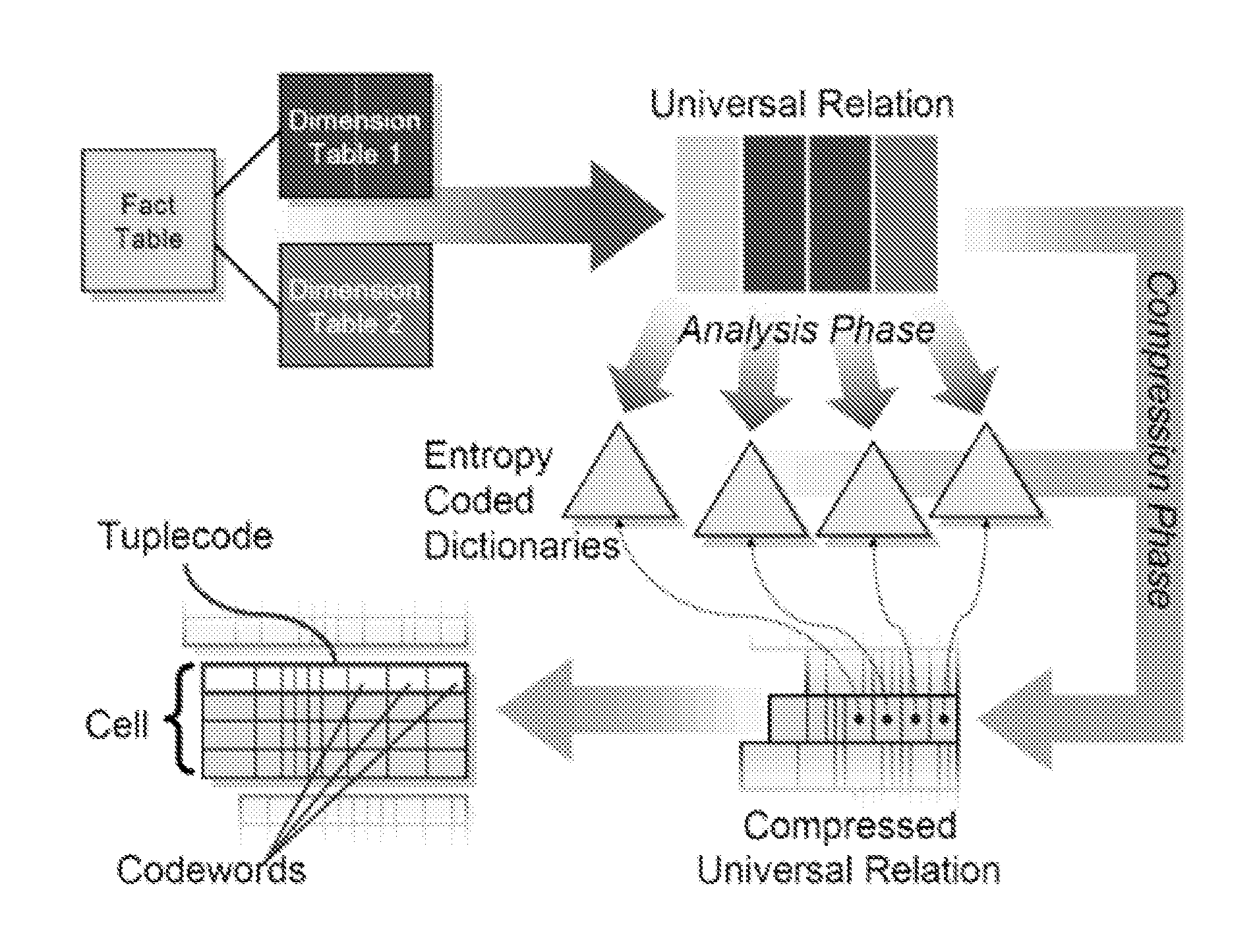
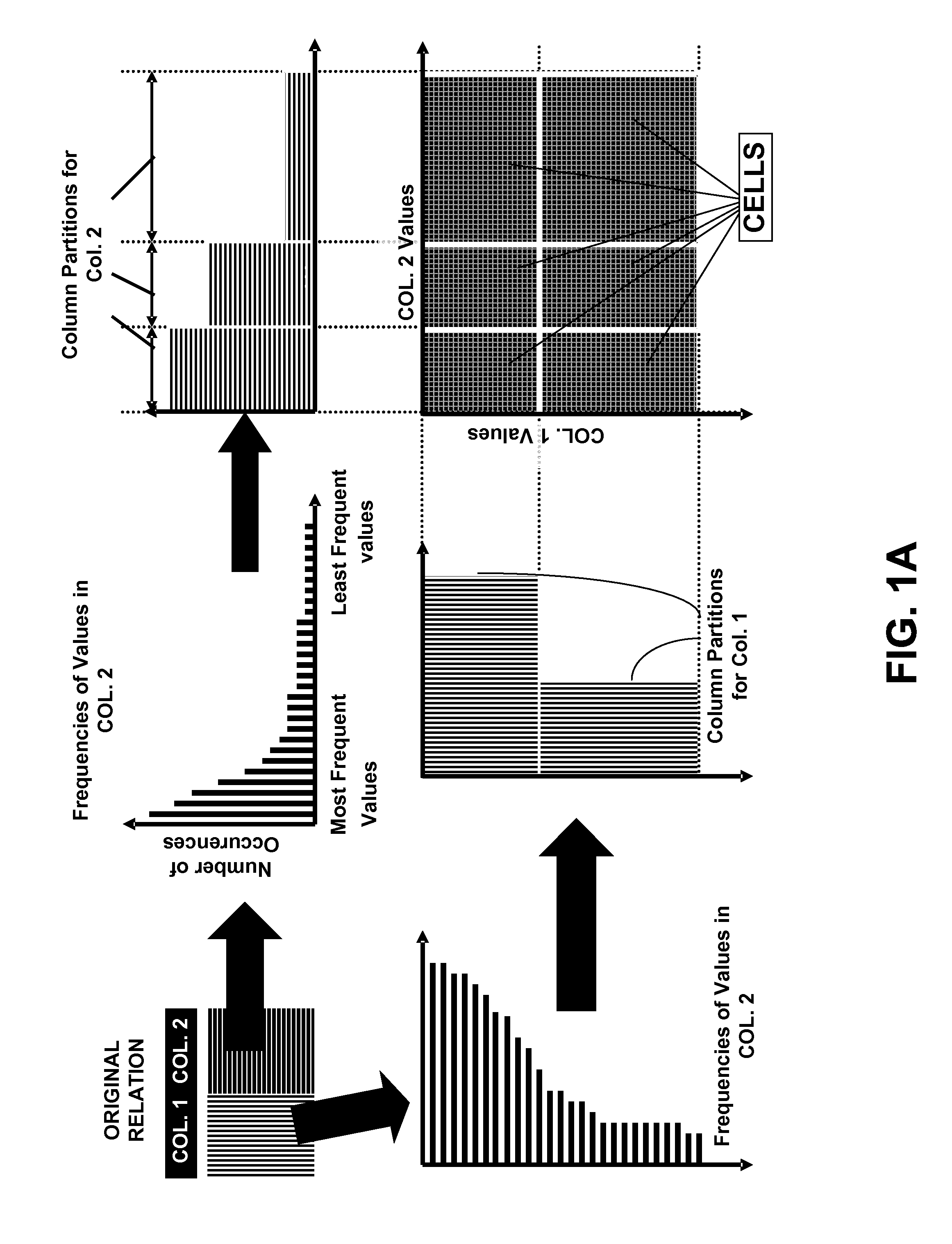
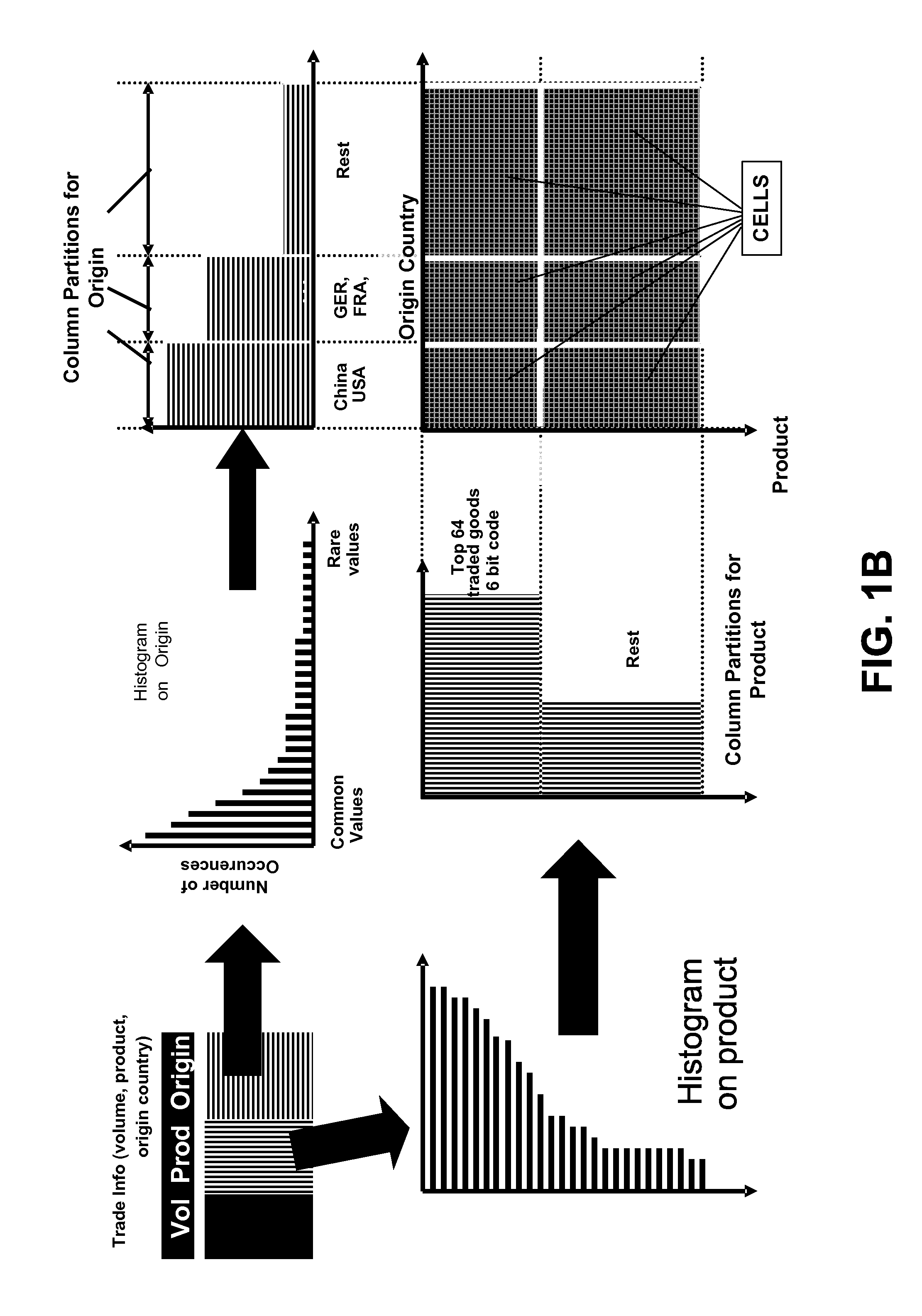
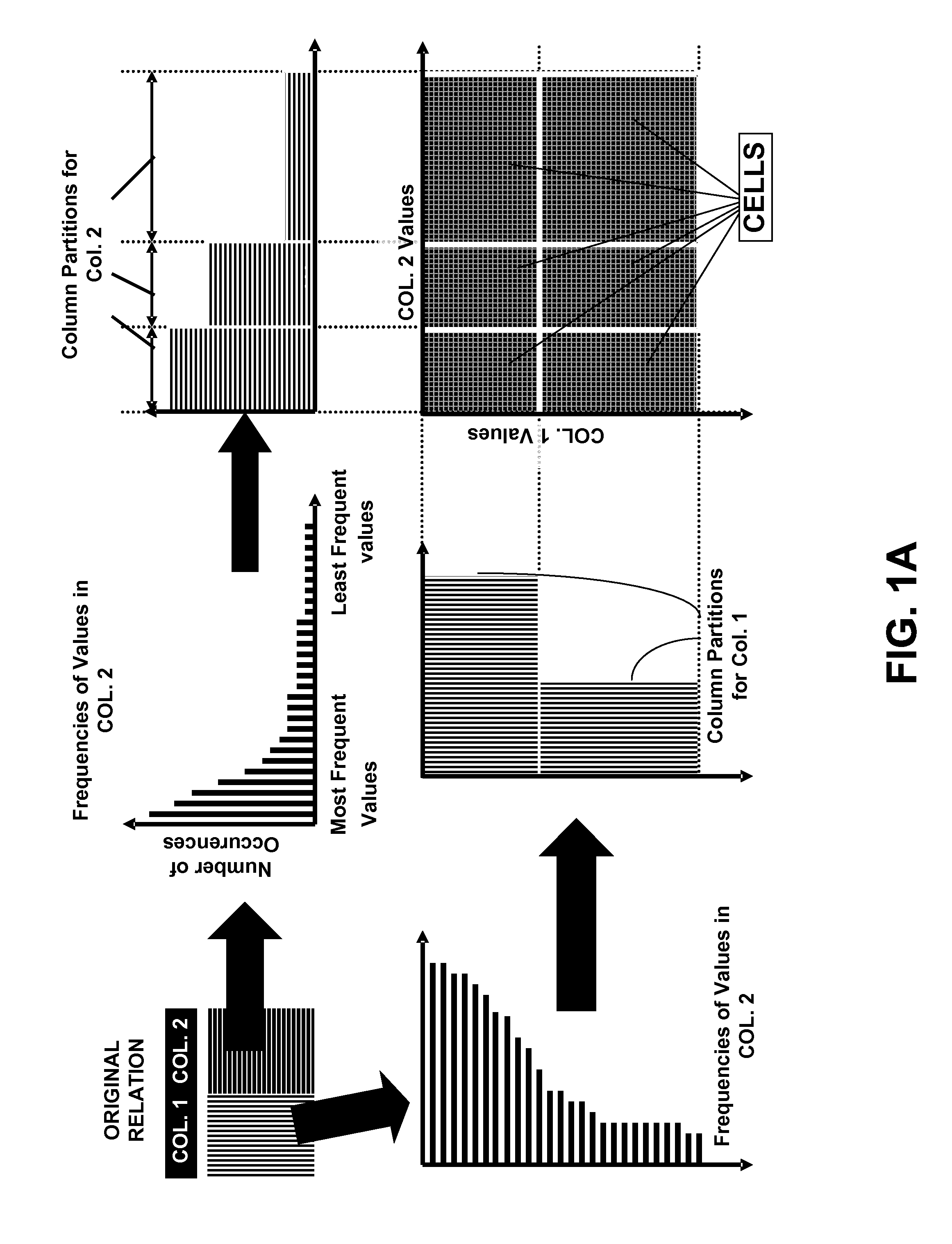
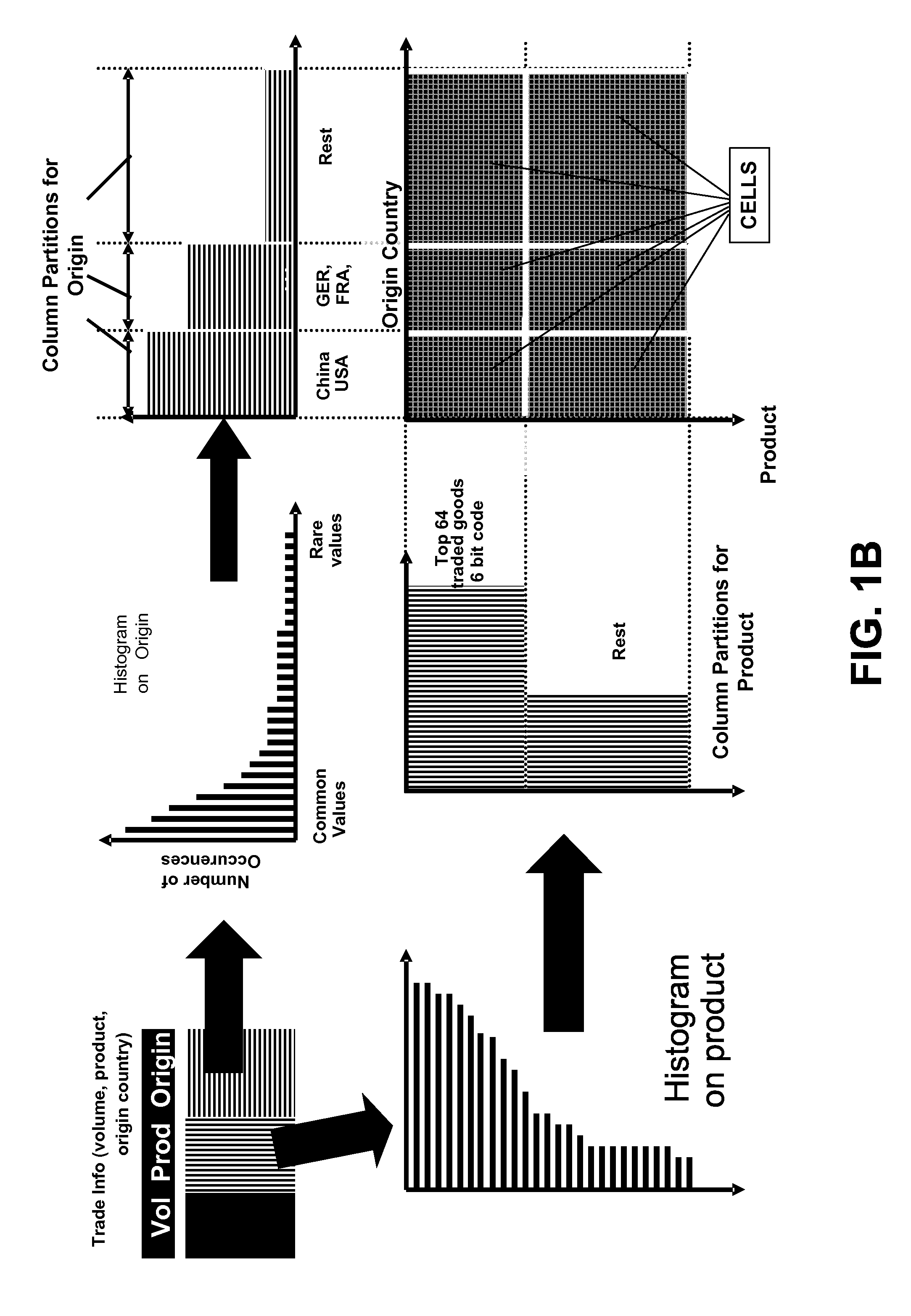
Frequency partitioning: entropy compression with fixed size fields
InactiveUS20090254521A1Improve query performanceAvoiding I/O bottleneckDigital data processing detailsCode conversionPattern recognitionDisjoint-set
Owner:IBM CORP
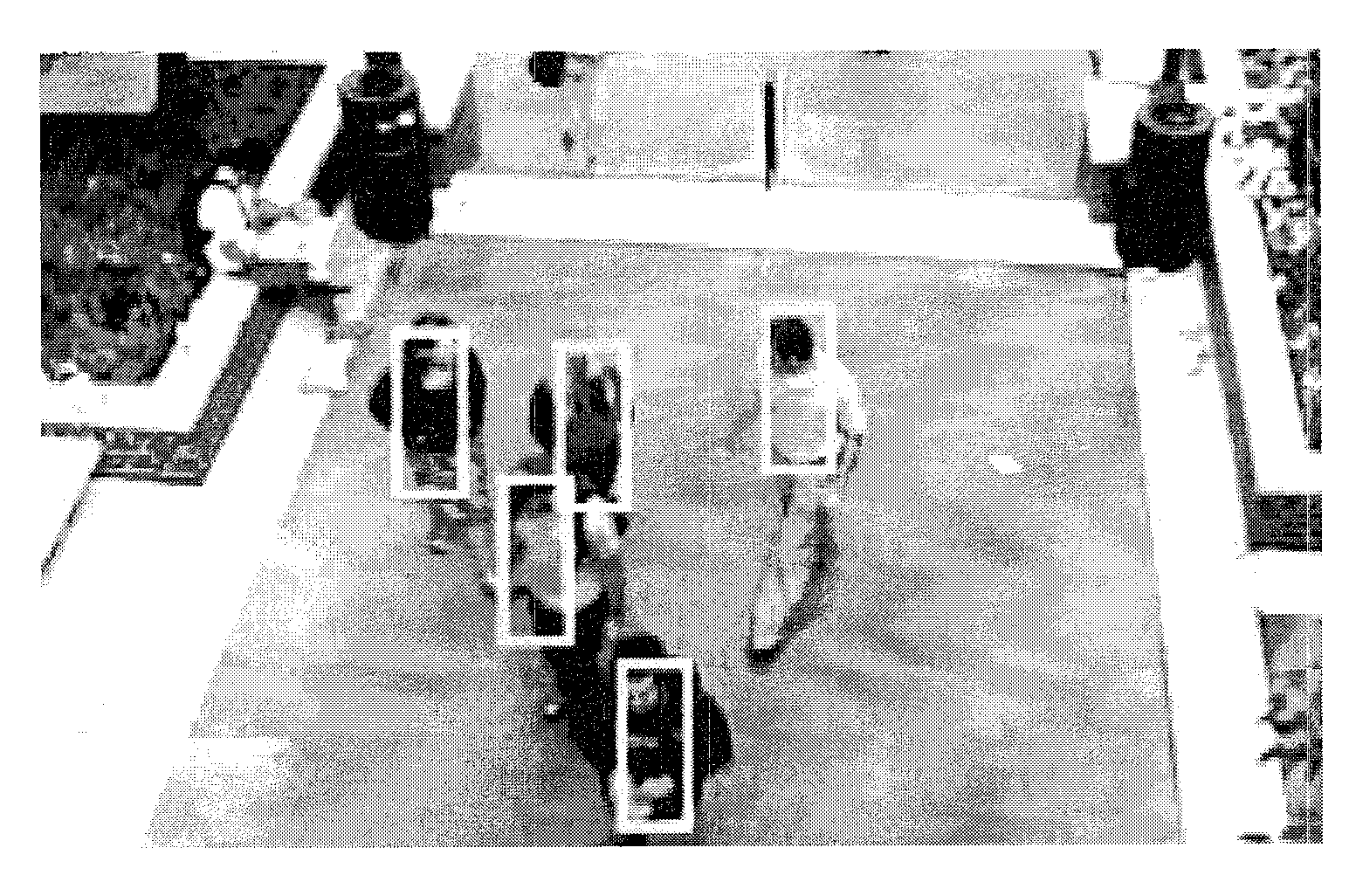
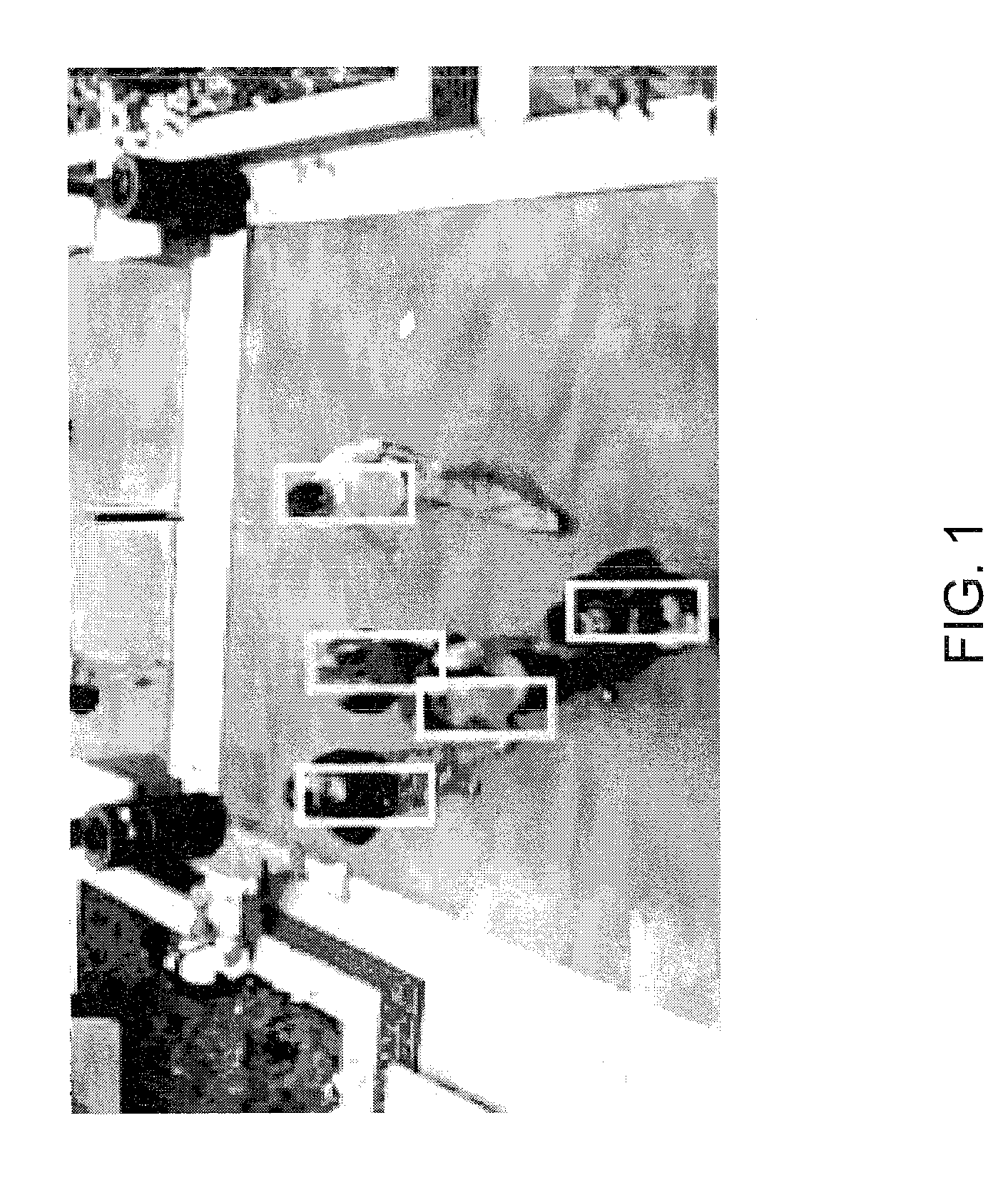
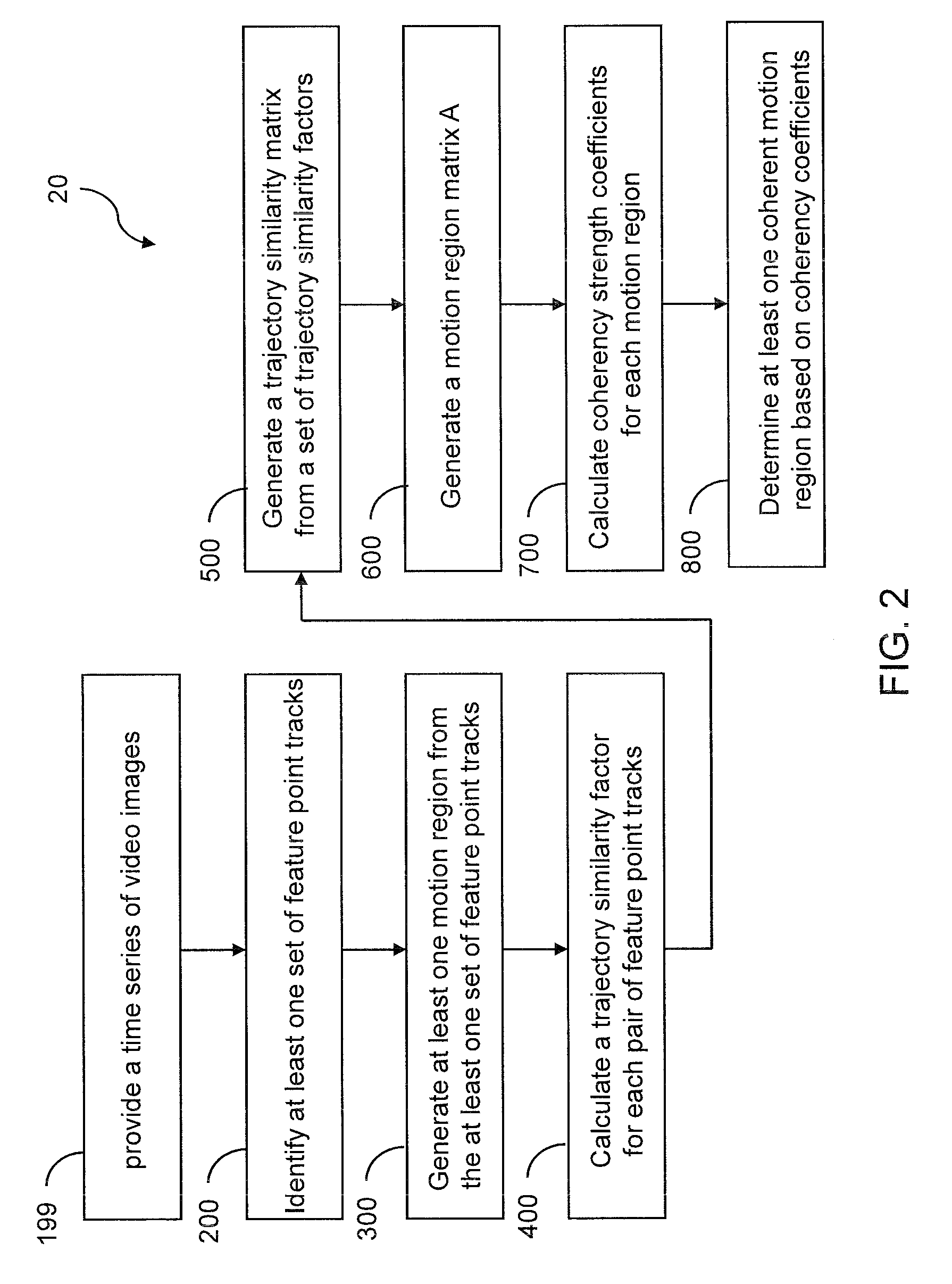
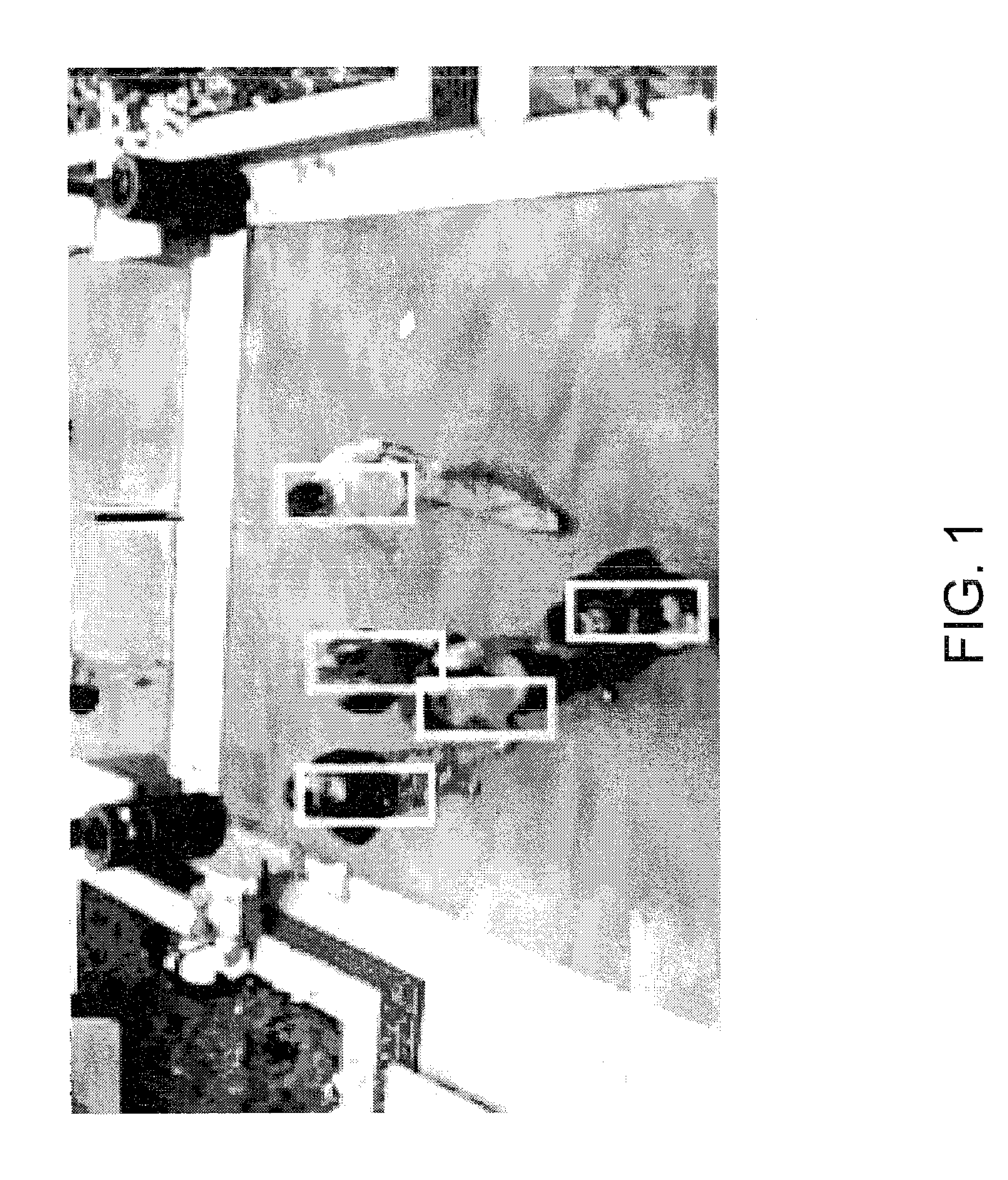
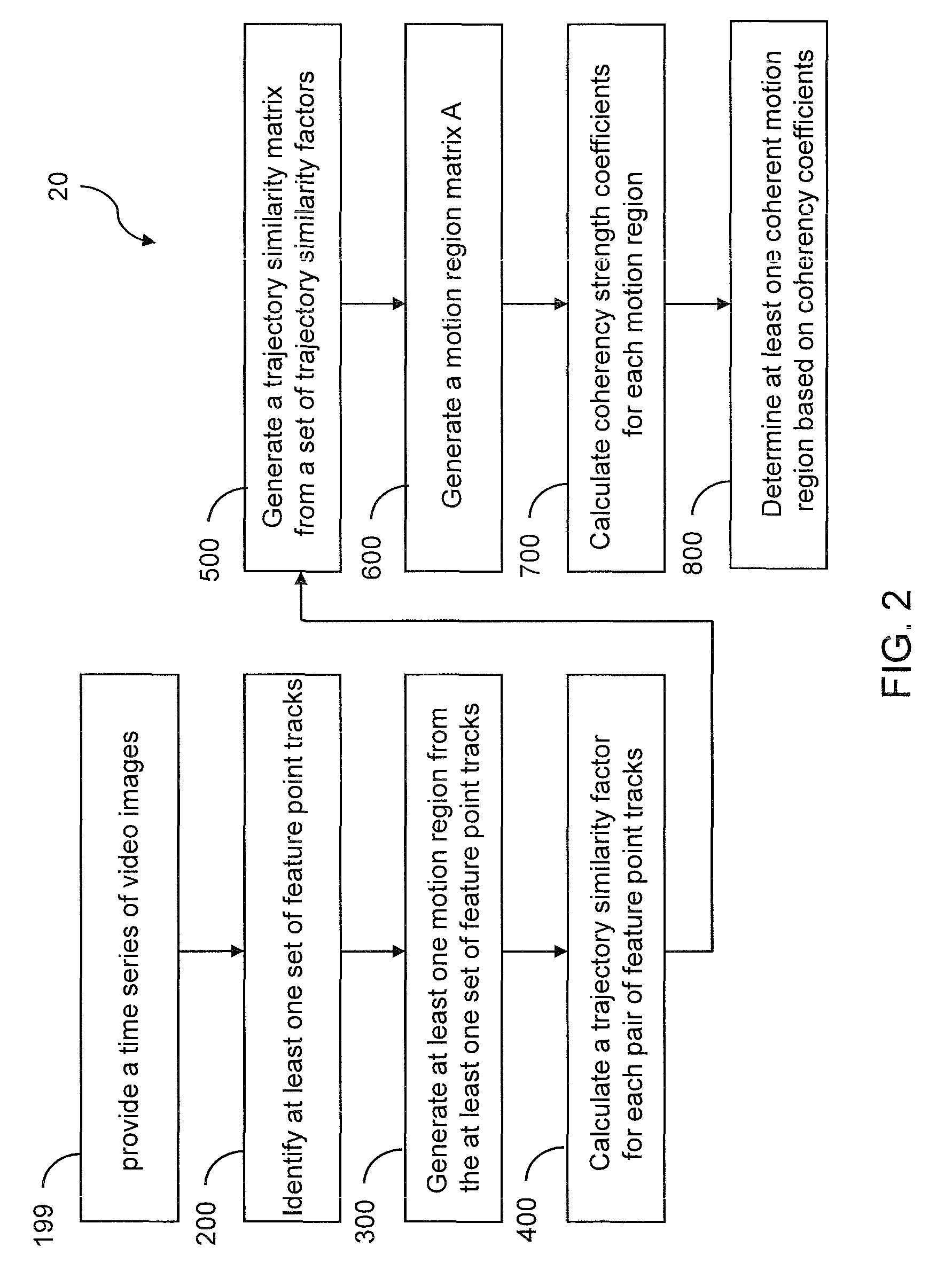
Detecting multiple moving objects in crowded environments with coherent motion regions
ActiveUS20100322474A1Minimise measureRobust to noisy or short point tracksImage enhancementTelevision system detailsThree-dimensional spaceDisjoint-set
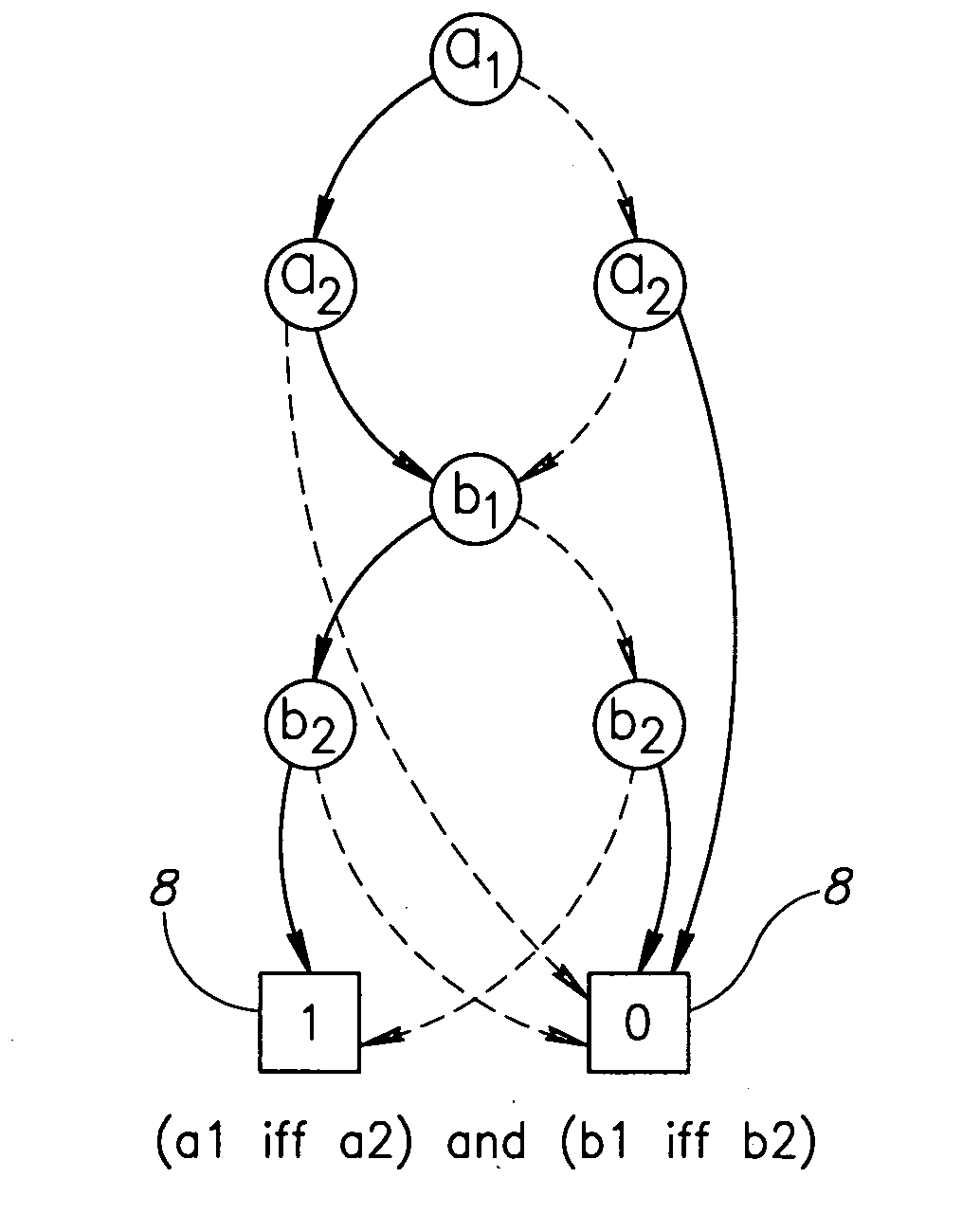
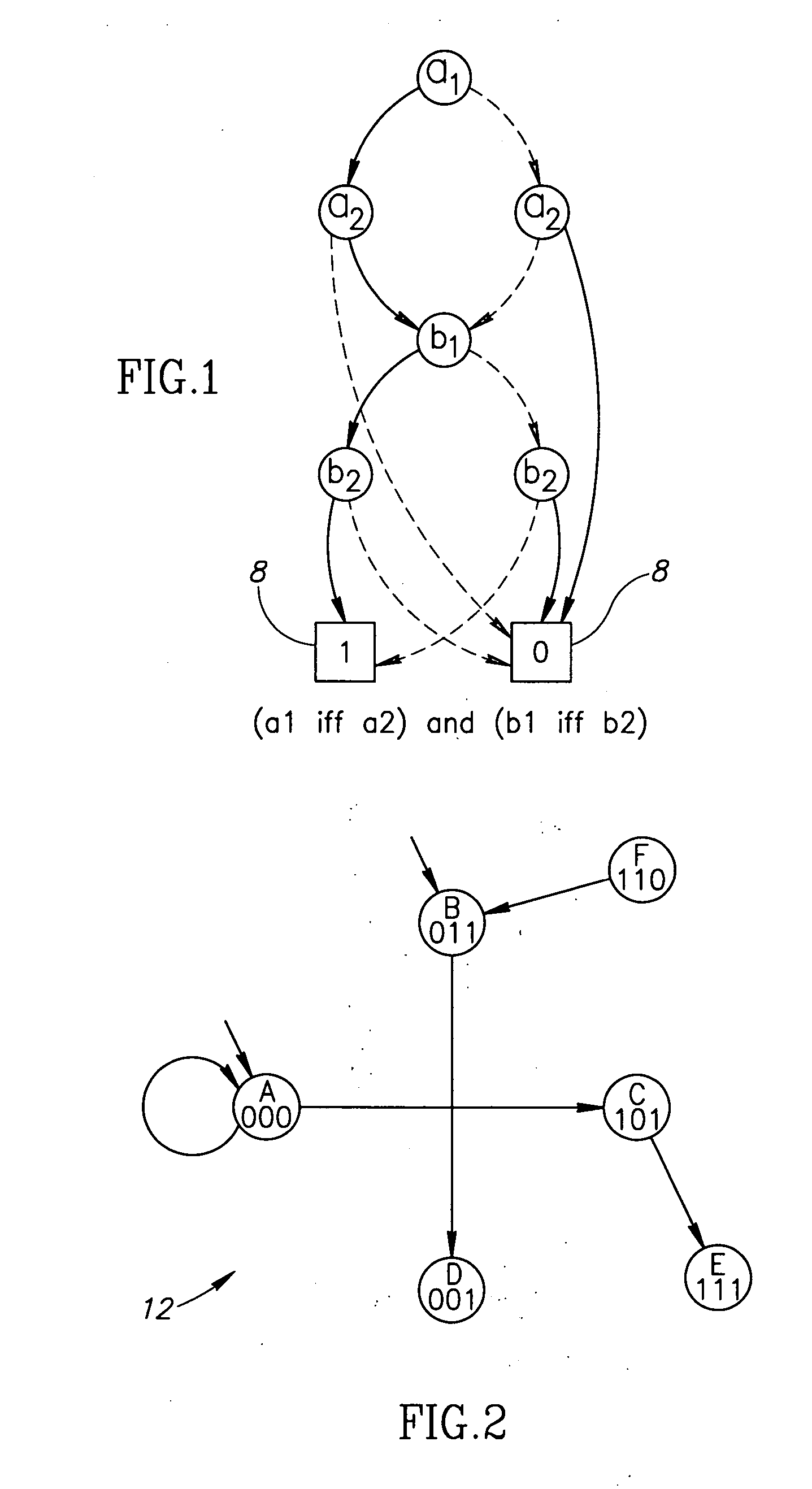
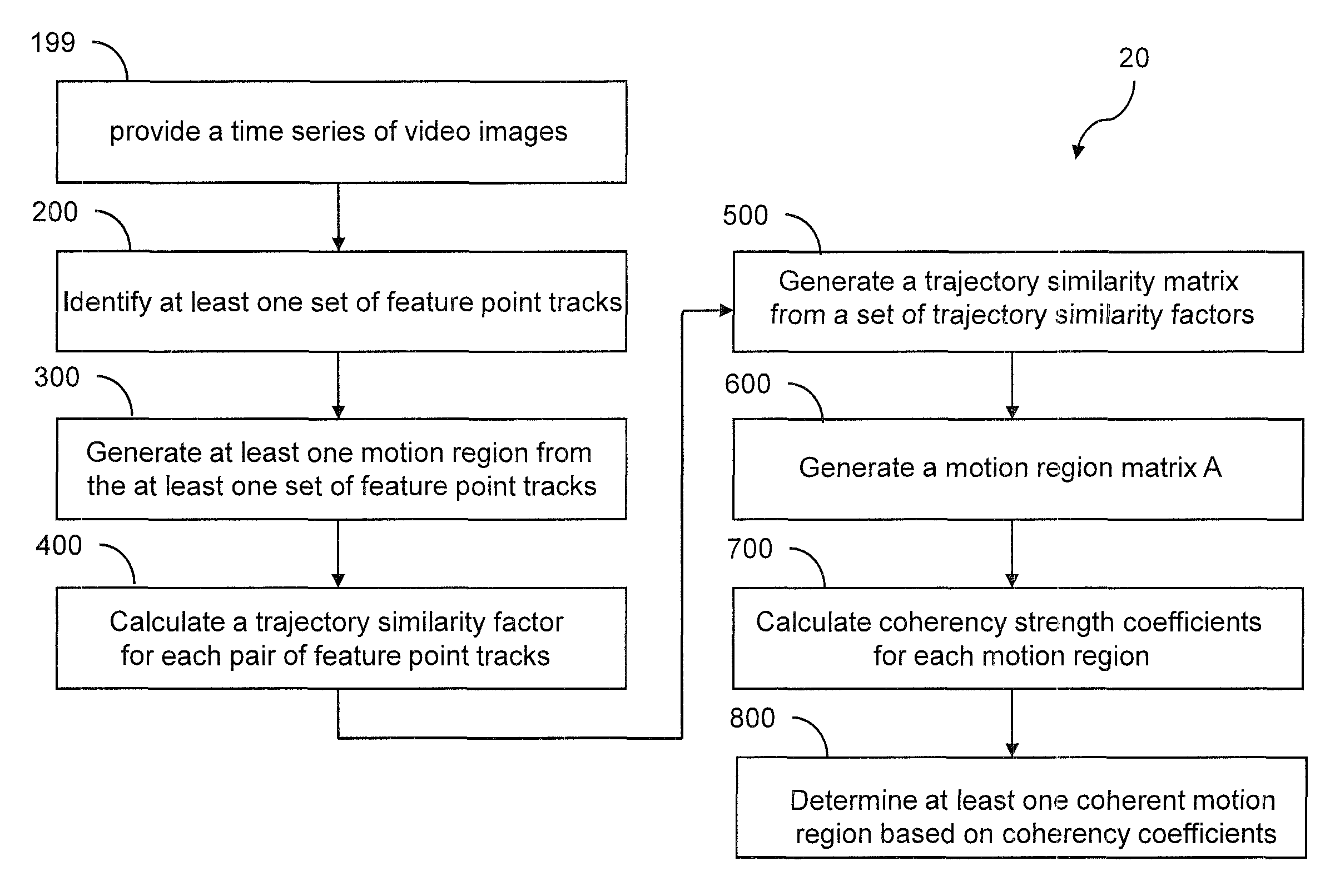
Coherent motion regions extend in time as well as space, enforcing consistency in detected objects over long time periods and making the algorithm robust to noisy or short point tracks. As a result of enforcing the constraint that selected coherent motion regions contain disjoint sets of tracks defined in a three-dimensional space including a time dimension. An algorithm operates directly on raw, unconditioned low-level feature point tracks, and minimizes a global measure of the coherent motion regions. At least one discrete moving object is identified in a time series of video images based on the trajectory similarity factors, which is a measure of a maximum distance between a pair of feature point tracks.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
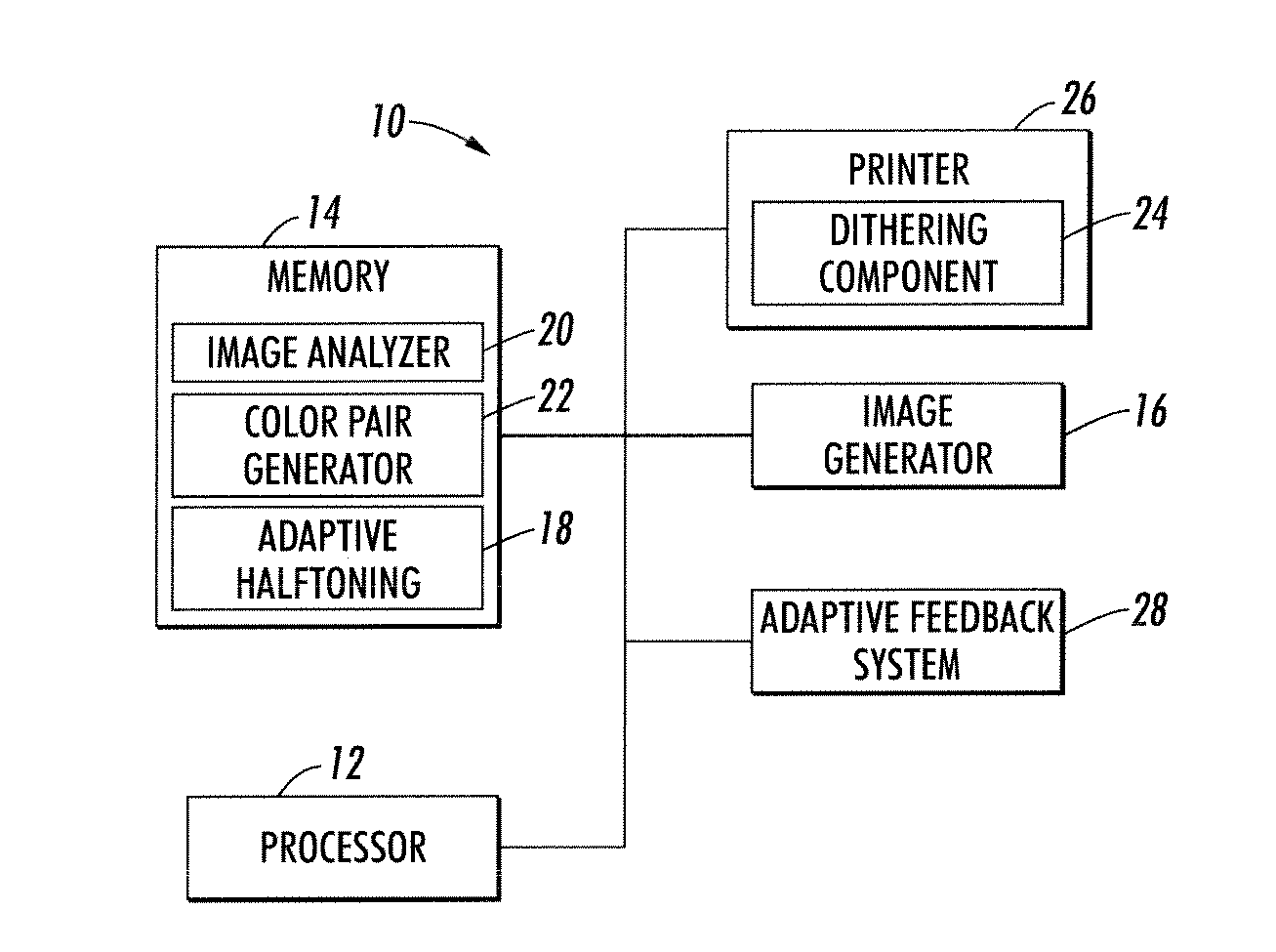
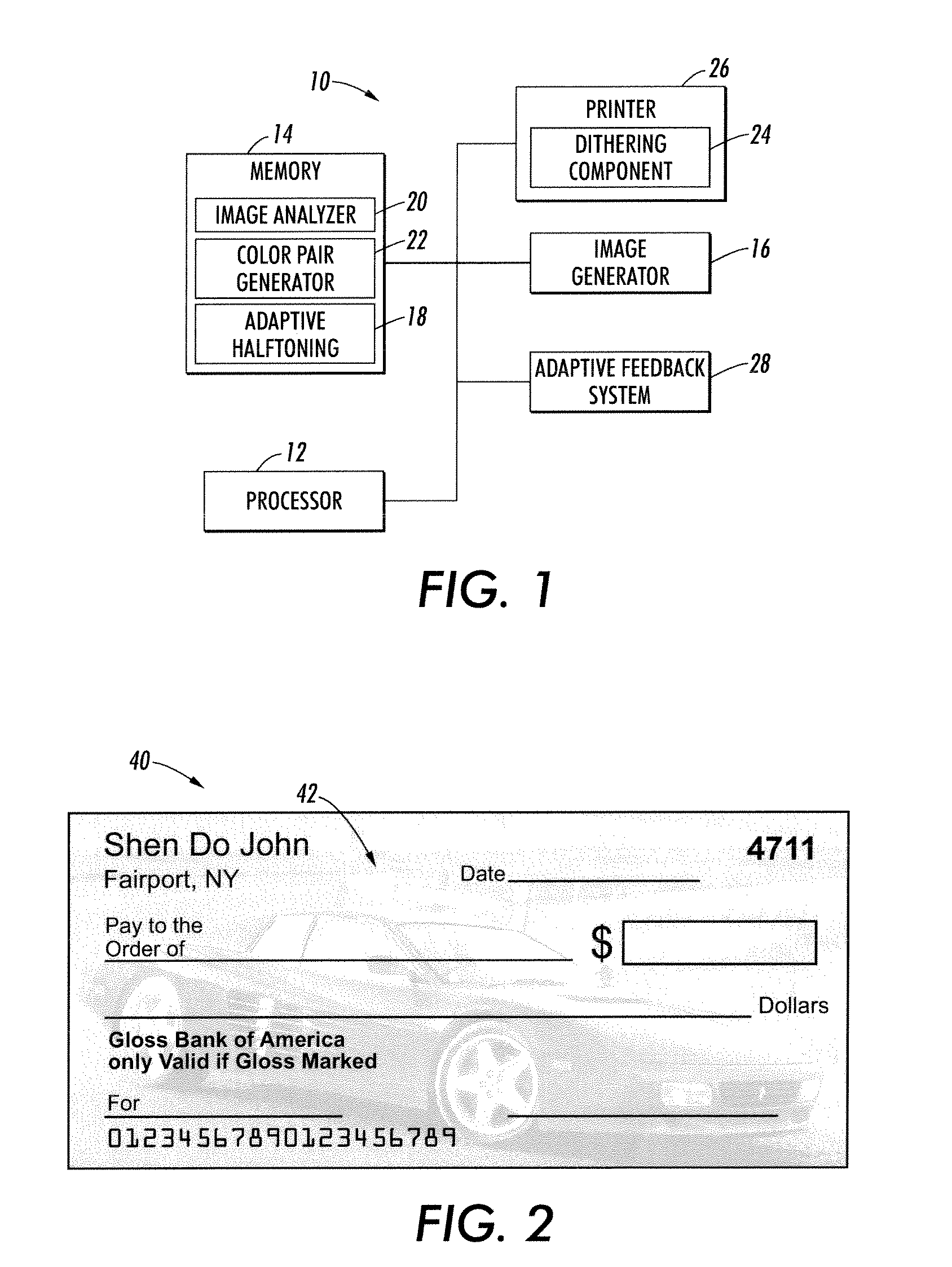
UV fluorescence encoded background images using adaptive halftoning into disjoint sets
InactiveUS20100157377A1Facilitate printing UV-fluorescent watermarksImprove securityPattern printingCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionFluorescence
Systems and methods are described that facilitate generating a background image with a UV-fluorescent watermark for printing on a document. A binary watermark mask is generated to separate the background image into the UV-active and the UV-dull regions. Based on the assigned binary value of the watermark mask, each pixel is assigned a UV-active or UV-dull color using an adaptive halftoning technique, in order to generate a binary UV-active image and a binary UV-dull image. A binary watermarked background image is generated by combining the binary UV-active and UV-dull images, and is printed on a document. The UV-active and UV-dull colors have different UV intensities under UV light, but are indistinguishable under normal lighting conditions. In this manner, the background image is visible when exposed to visible light, and the UV-fluorescent watermark is visible when exposed to UV light.
Owner:XEROX CORP
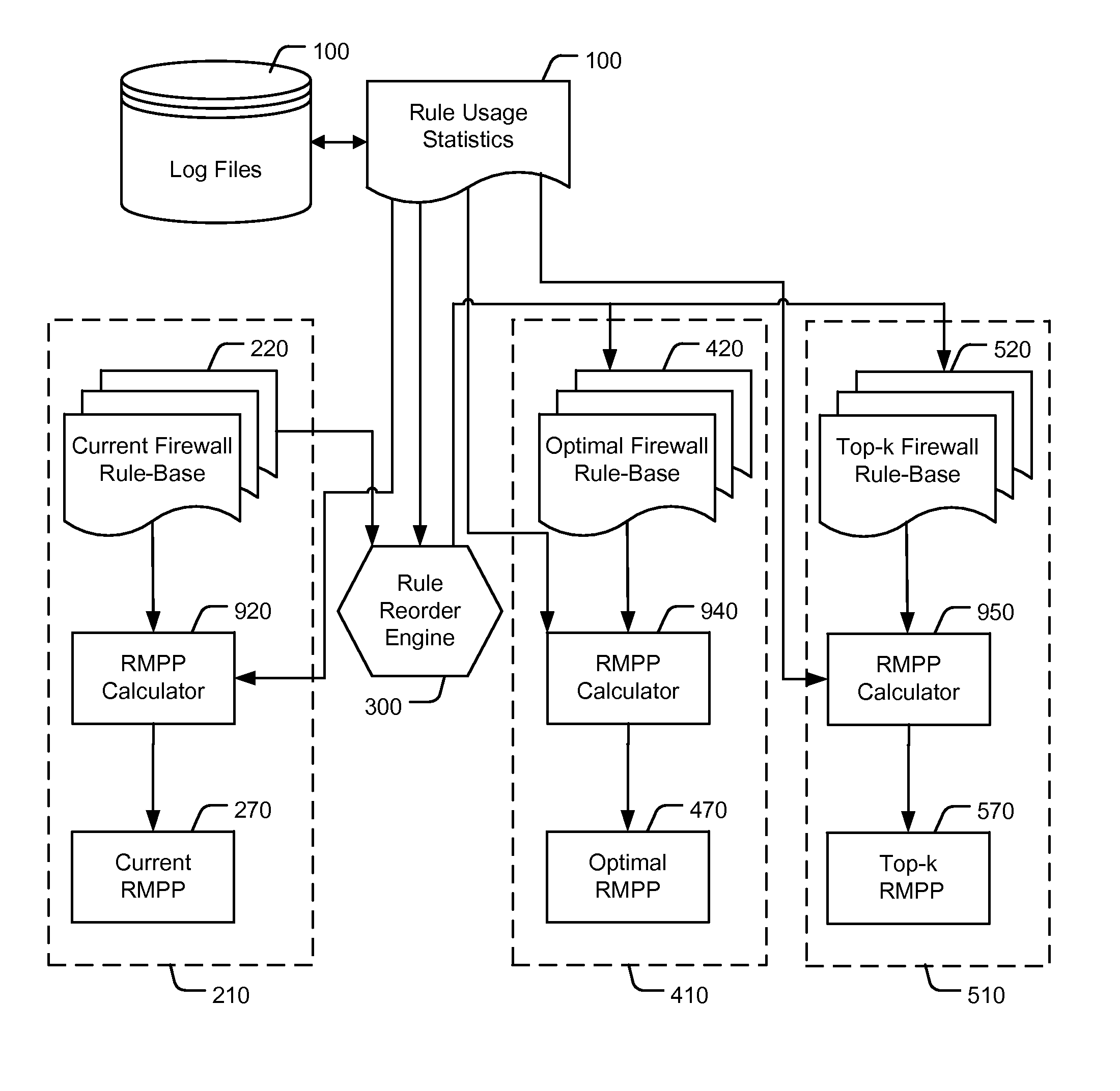
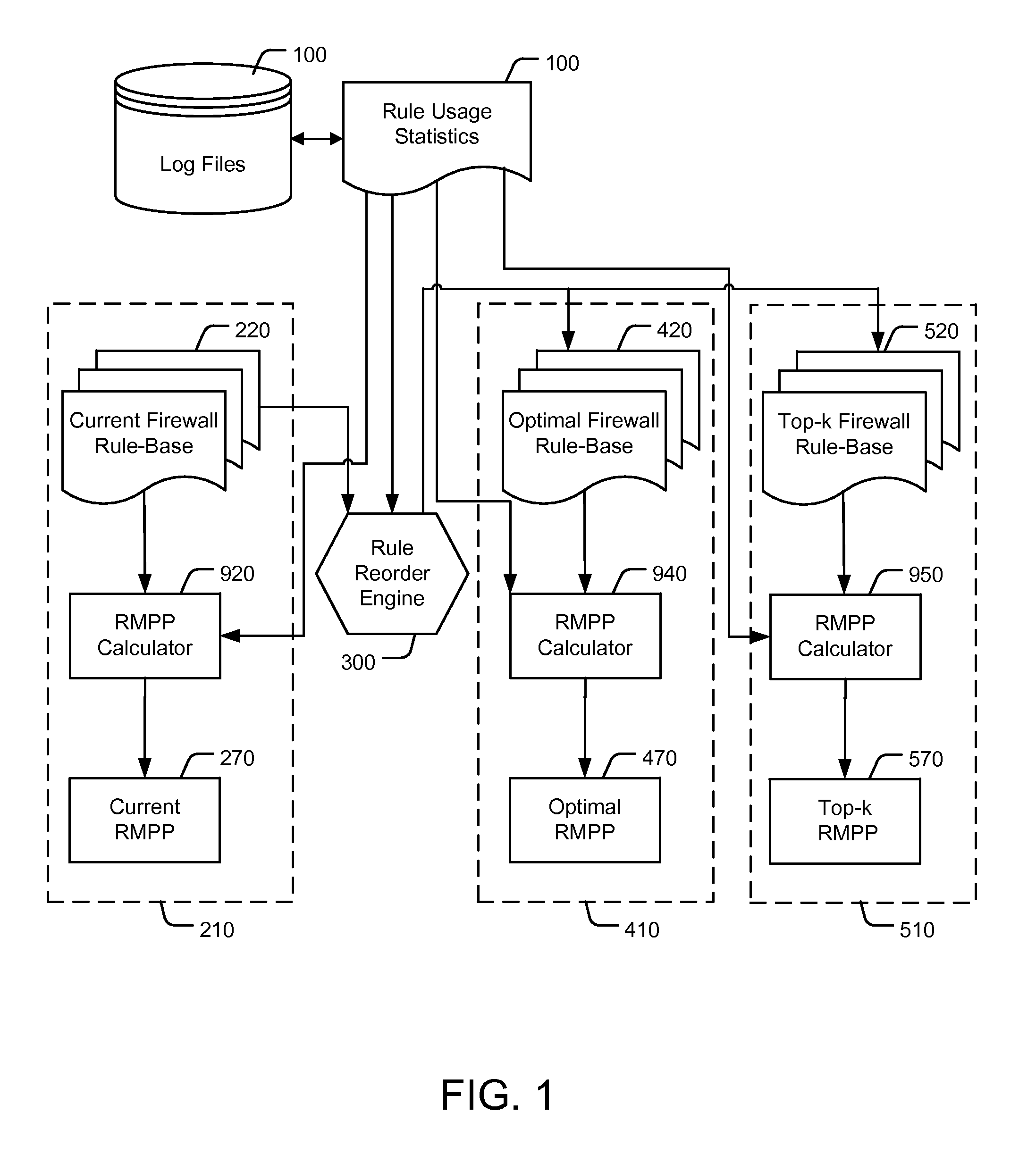
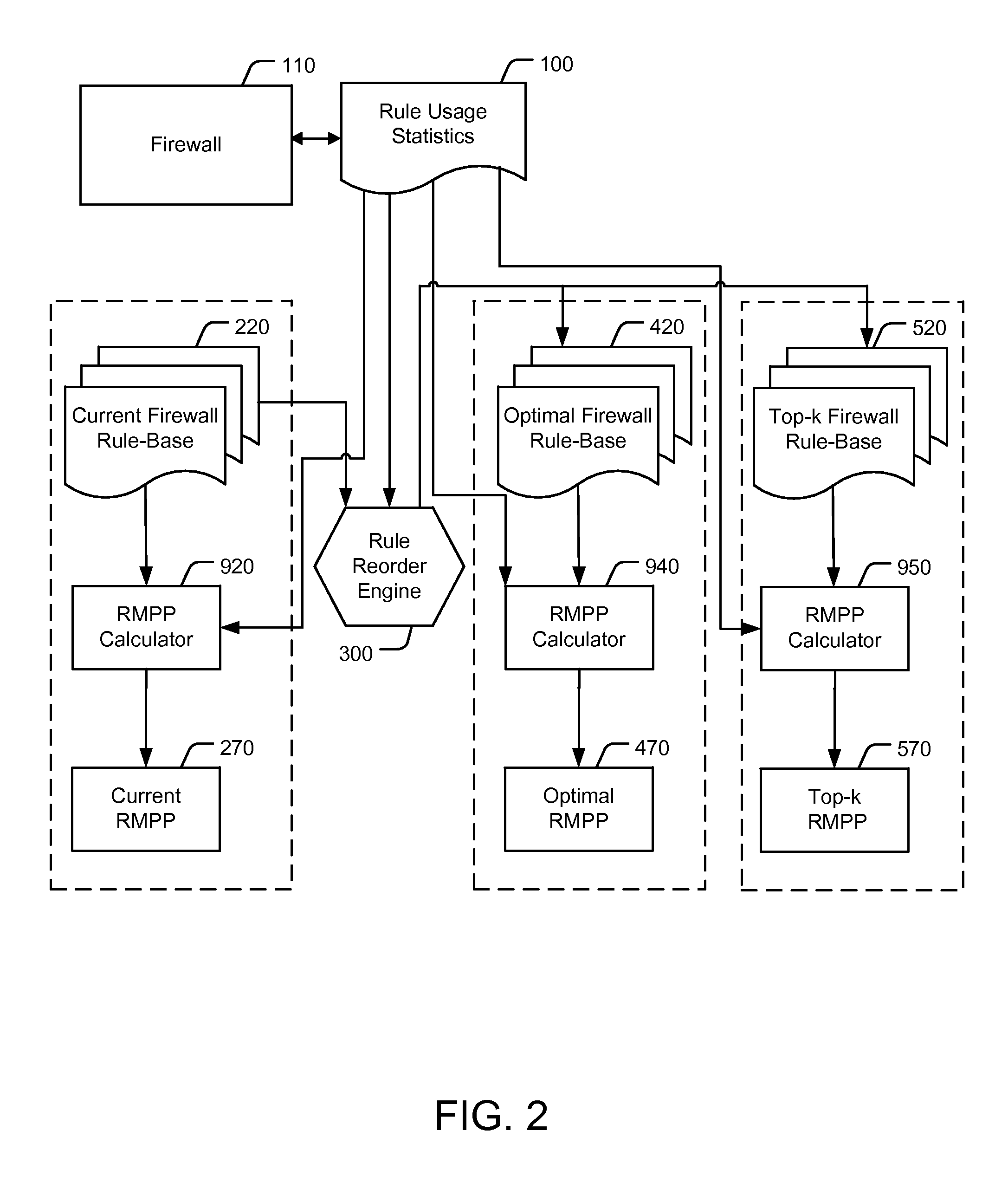
Reordering a firewall rule base according to usage statistics
ActiveUS8418240B2Reduce processReduction of the RMPPComputer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionDisjoint-set
A computer implemented method of reducing central processing unit (CPU) usage of a firewall by safe reordering a current firewall's rule-base exhibiting N rules. The method comprising: receiving rule usage statistics exhibiting usage frequency of each rule on the current firewall's rule-base; calculating a rules matched per packet (RMPP) parameter, being a summation of products of each rule identifier and the corresponding usage frequency for all the N rules; determining an alternative order of the rule base by repositioning rules, wherein the repositioned rules perform the same action on the firewall, or wherein the repositioned rules act on disjoint sets of network connections, and wherein the repositioning results in a reduction of the RMPP of the reordered rule base, thereby reducing the CPU usage of the firewall in implementing the alternative order of rules.
Owner:ALGORITHMIC SECURITY ISRAEL
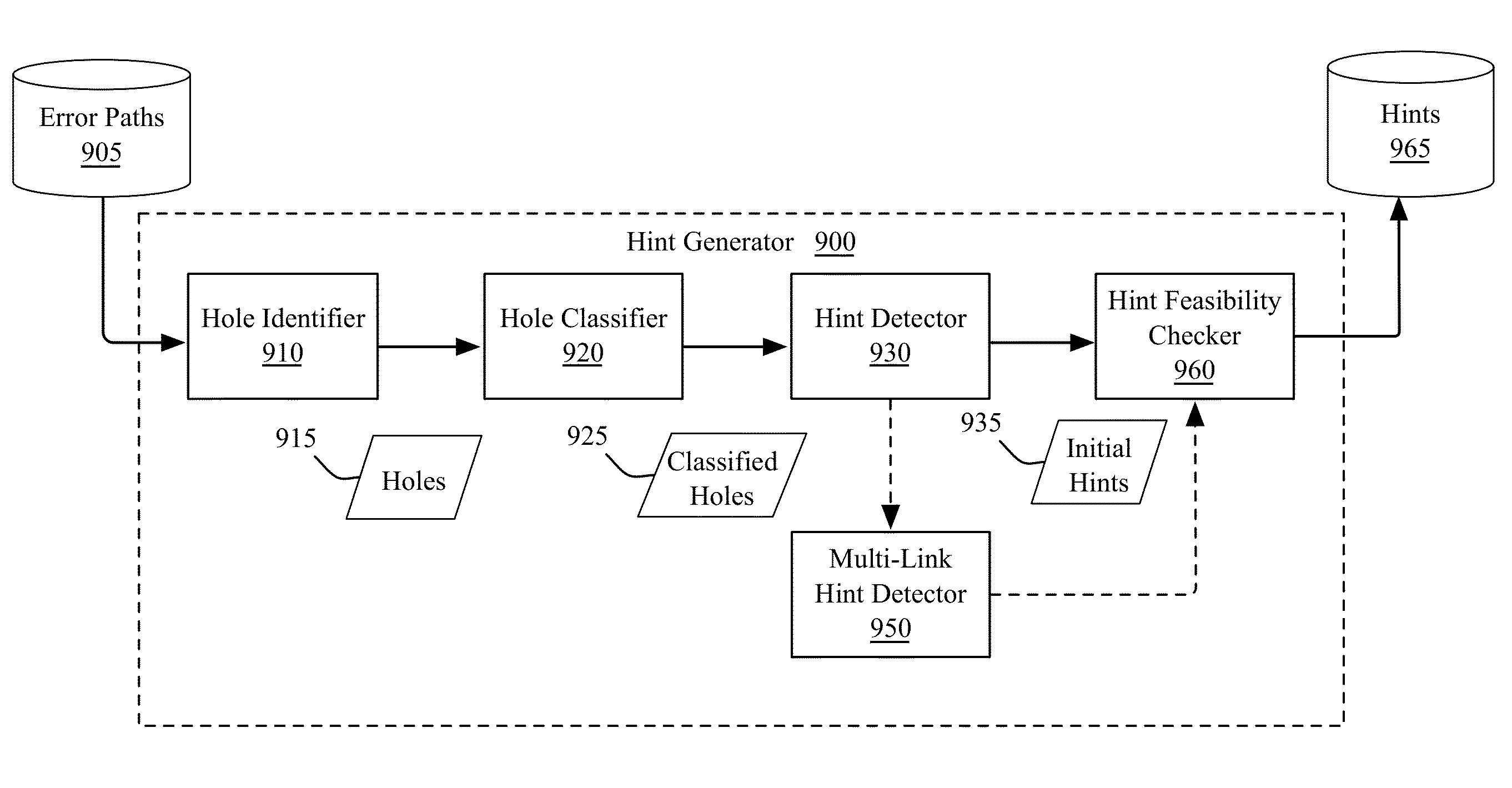
Method and apparatus for fixing double patterning color-seeding violations
InactiveUS8661371B1Eliminate violationsCAD circuit designOriginals for photomechanical treatmentDisjoint-setComputer science
A method for displaying layout-fixing hints for resolving color-seeding violations in an IC design layout. The method receives a set of error paths within a disjoint set of shapes. For each error path, the method performs an analysis on the error path to identify a set of layout-fixing hints that eliminates the color-seeding violation on the error path and does not introduce any new color-seeding violation. The method displays the set of identified hints for each error path in order to aid a user to resolve the color-seeding violations. The method displays each identified layout-fixing hint as a set of moving instructions. The set of moving instructions provides a set of indications of a distance by which a shape or an edge of the shape needs to be moved in order to resolve a color-seeding violation.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Frequency partitioning: entropy compression with fixed size fields
InactiveUS7827187B2Improve query performanceEasy to compressDigital data processing detailsCode conversionDisjoint-setComputational physics
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
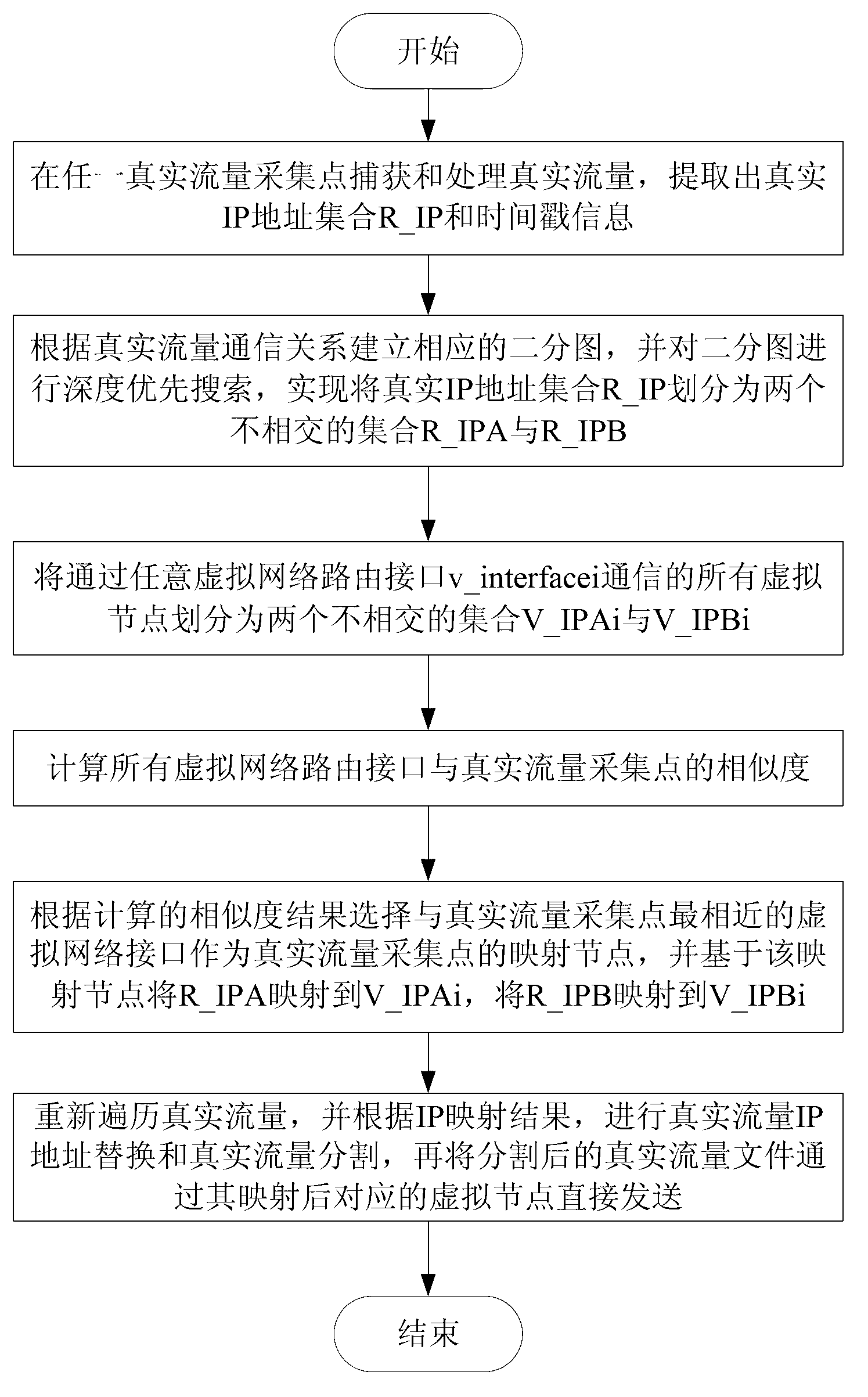
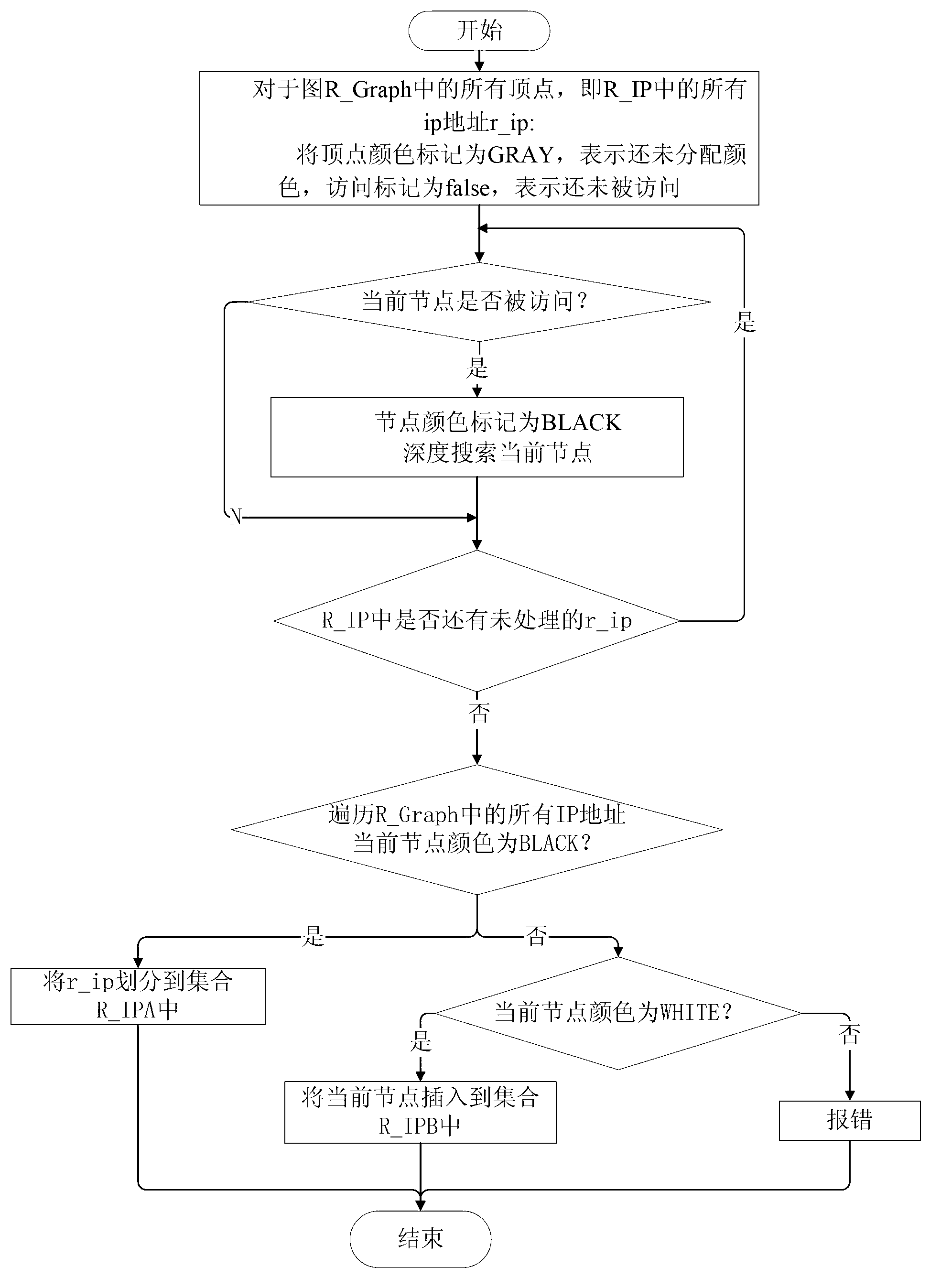
Traffic playback method and system for virtual network
ActiveCN103326900APerfect flow systemHigh degree of simulationData switching networksTraffic capacityDepth-first search
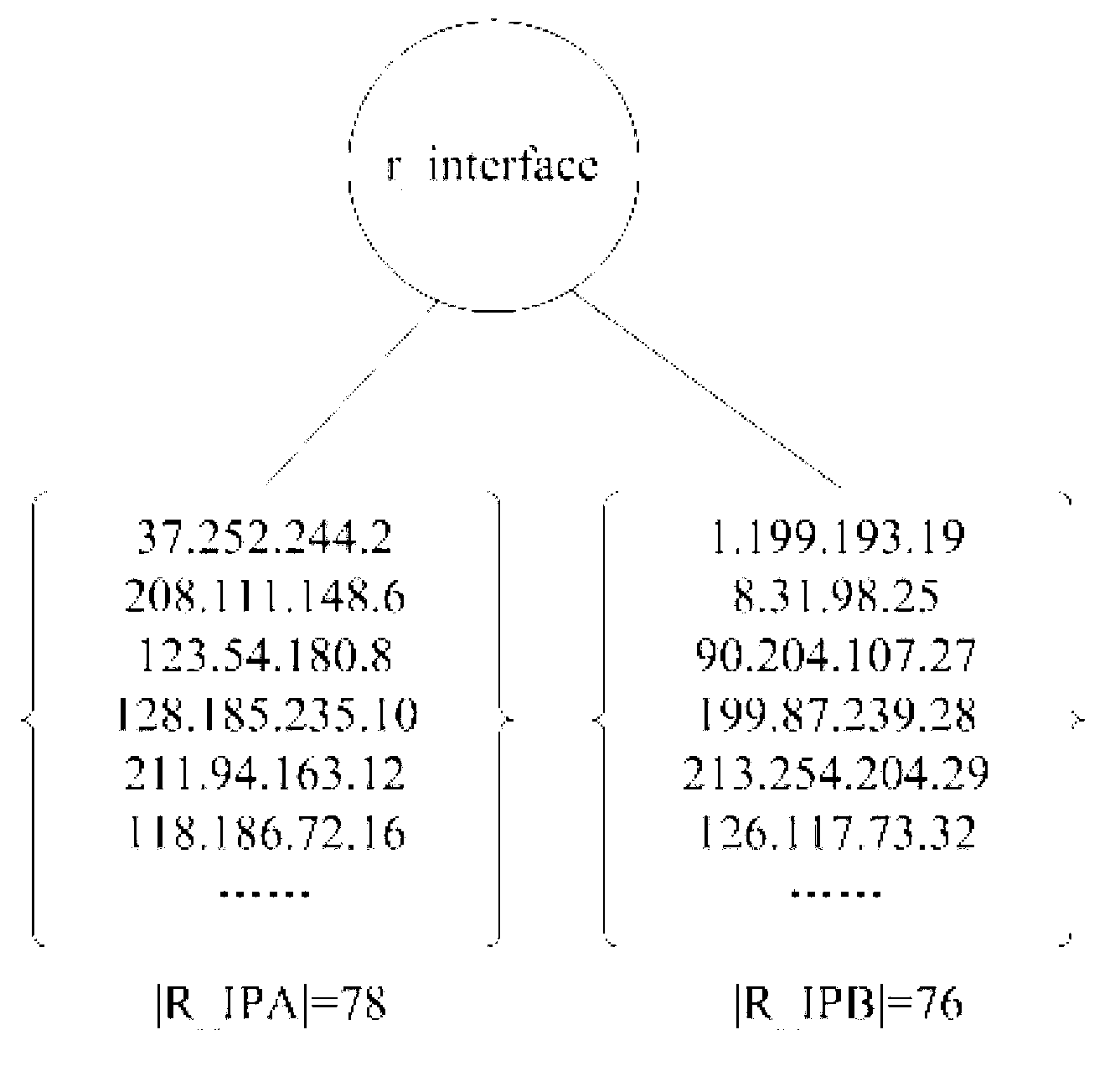
The invention relates to a traffic playback method and system for a virtual network. The traffic playback method includes a first step of capturing and processing real traffic, extracting a real IP address set R_IP, a second step of conducting depth-first search on a bipartite graph which is generated by real traffic communication relationships, dividing the real IP address set R_IP into two disjoint sets, namely, a set R_IPA and a set R_IPB, a third step of dividing all virtual nodes which are in communication through any virtual network routing interface v_interfacei into two disjoint sets, namely a set V_IPAi and a set V_IPBi, a fourth step of calculating similarities of all the virtual network routing interfaces and a real traffic collecting point, a fifth step of selecting a virtual network interface which is most similar to the real traffic collecting point to be used as a mapping node of the traffic collecting point, conducting IP address mapping based on the mapping mode, and a sixth step of traversing the real traffic again to achieve real traffic playback in the virtual network. When the traffic is played back in the virtual network through the traffic playback method and system for the virtual network, the real traffic communication environment is restored as good as possible, and the virtual network traffic system is improved.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Systems and methods for scheduling business and residential services in optical networks
ActiveUS8437355B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationDynamic bandwidth allocationTraffic capacity
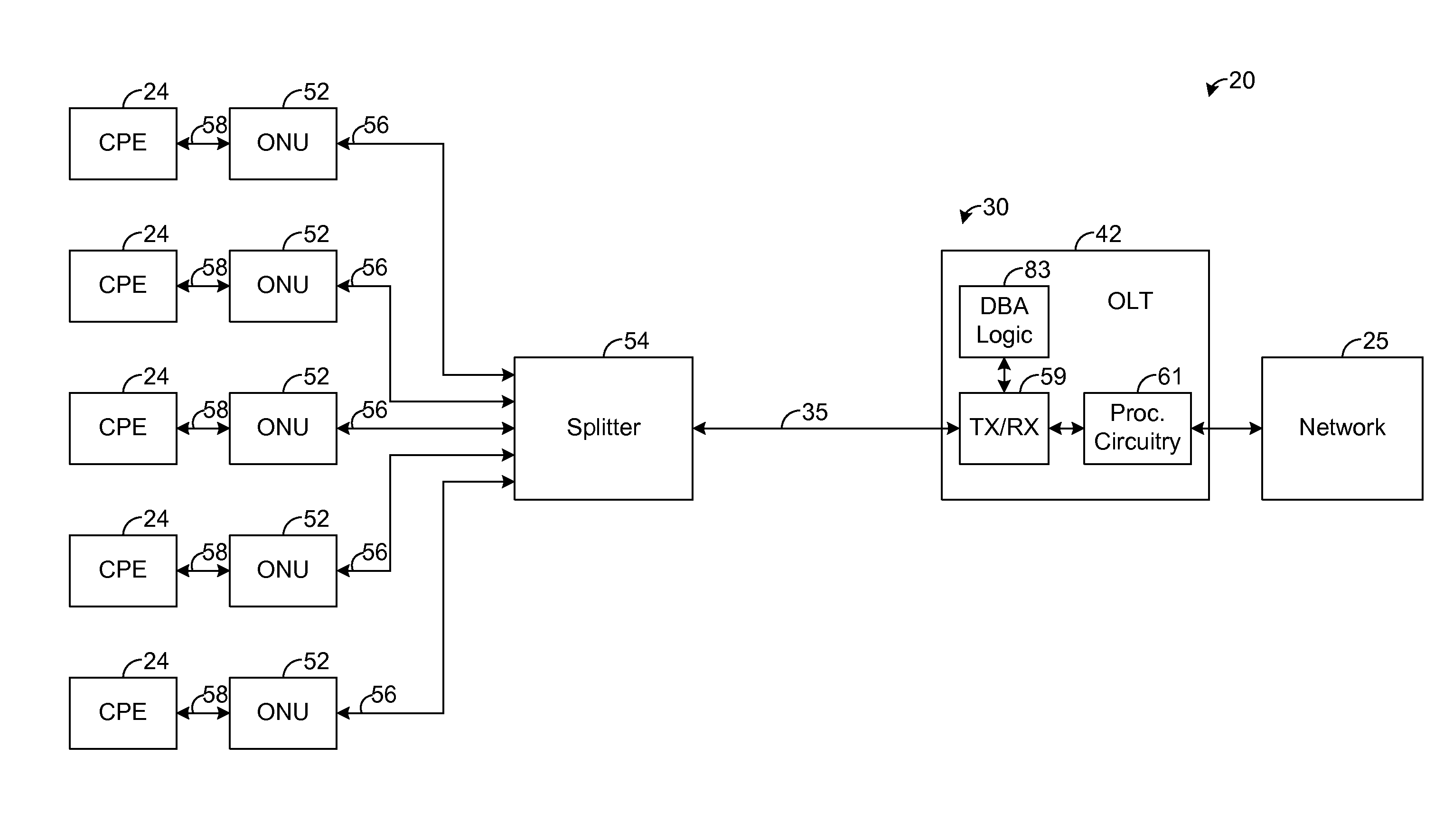
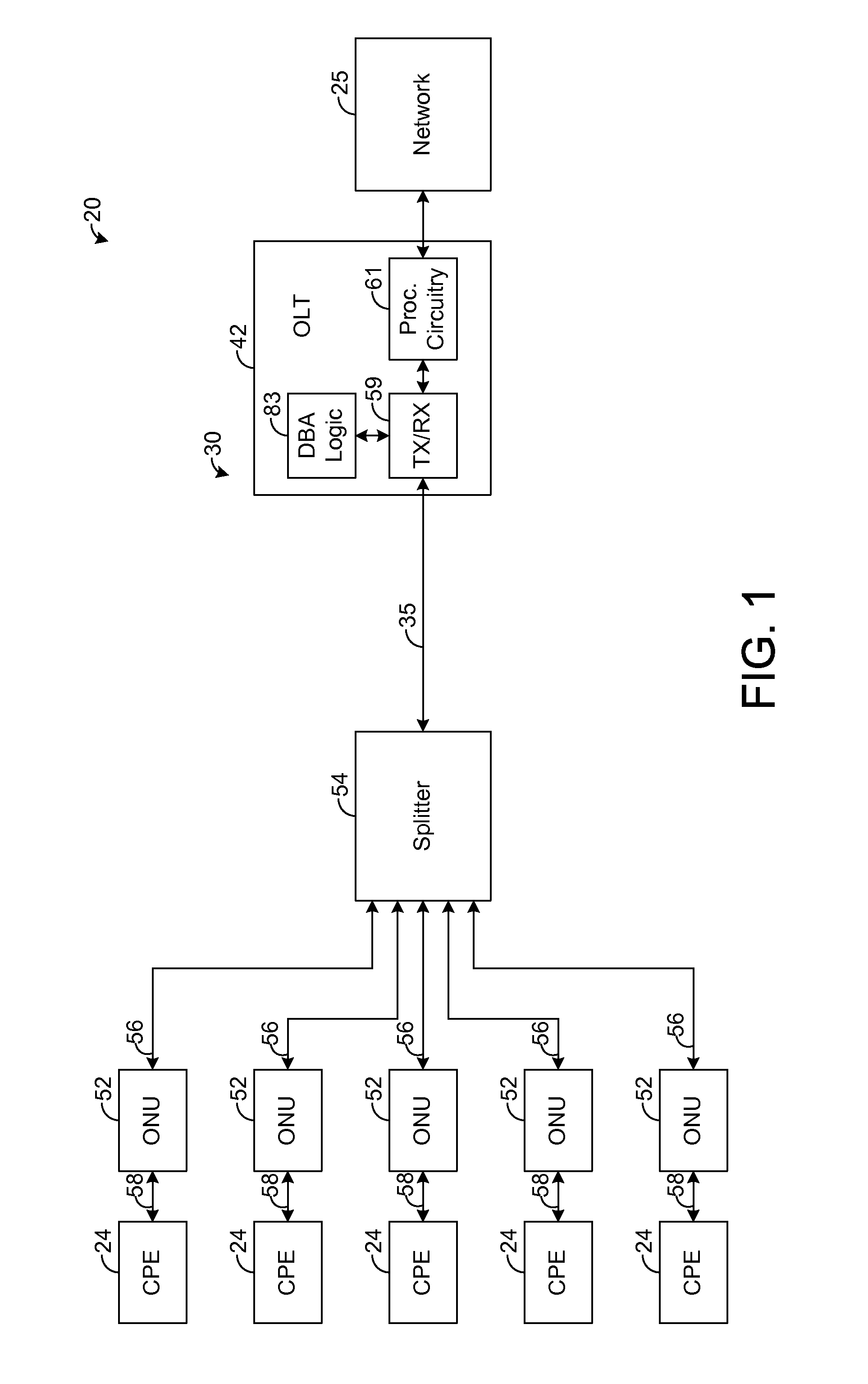
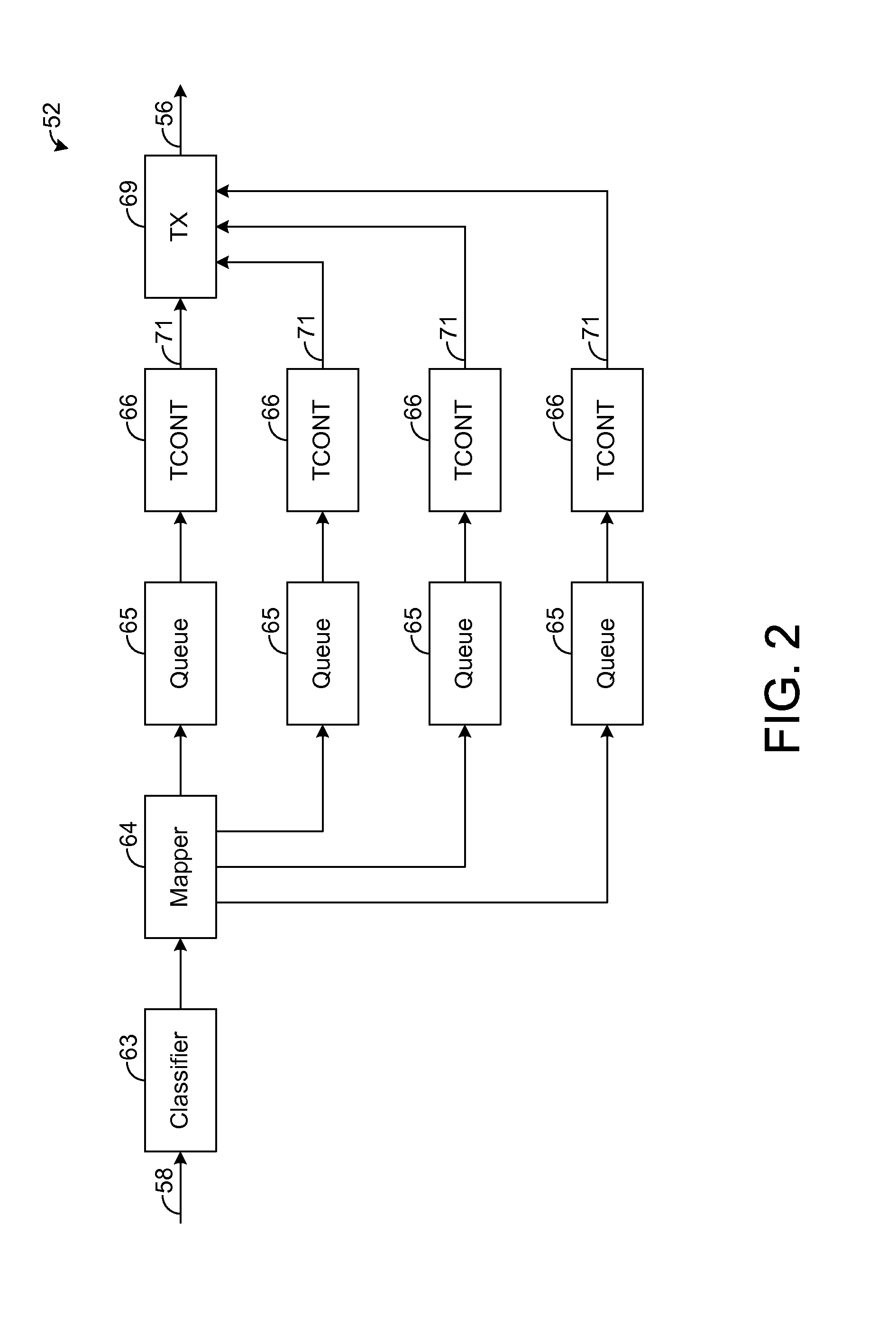
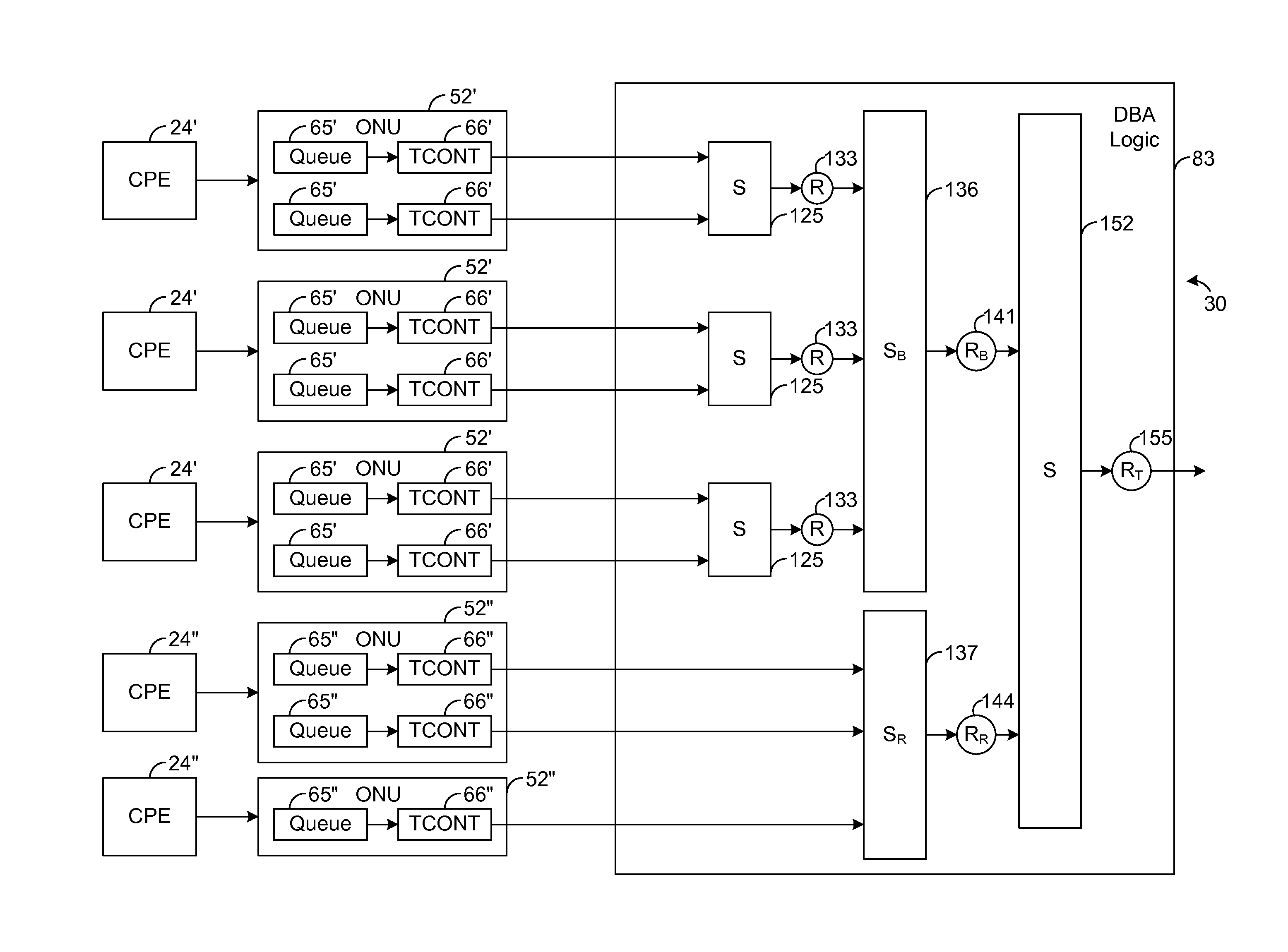
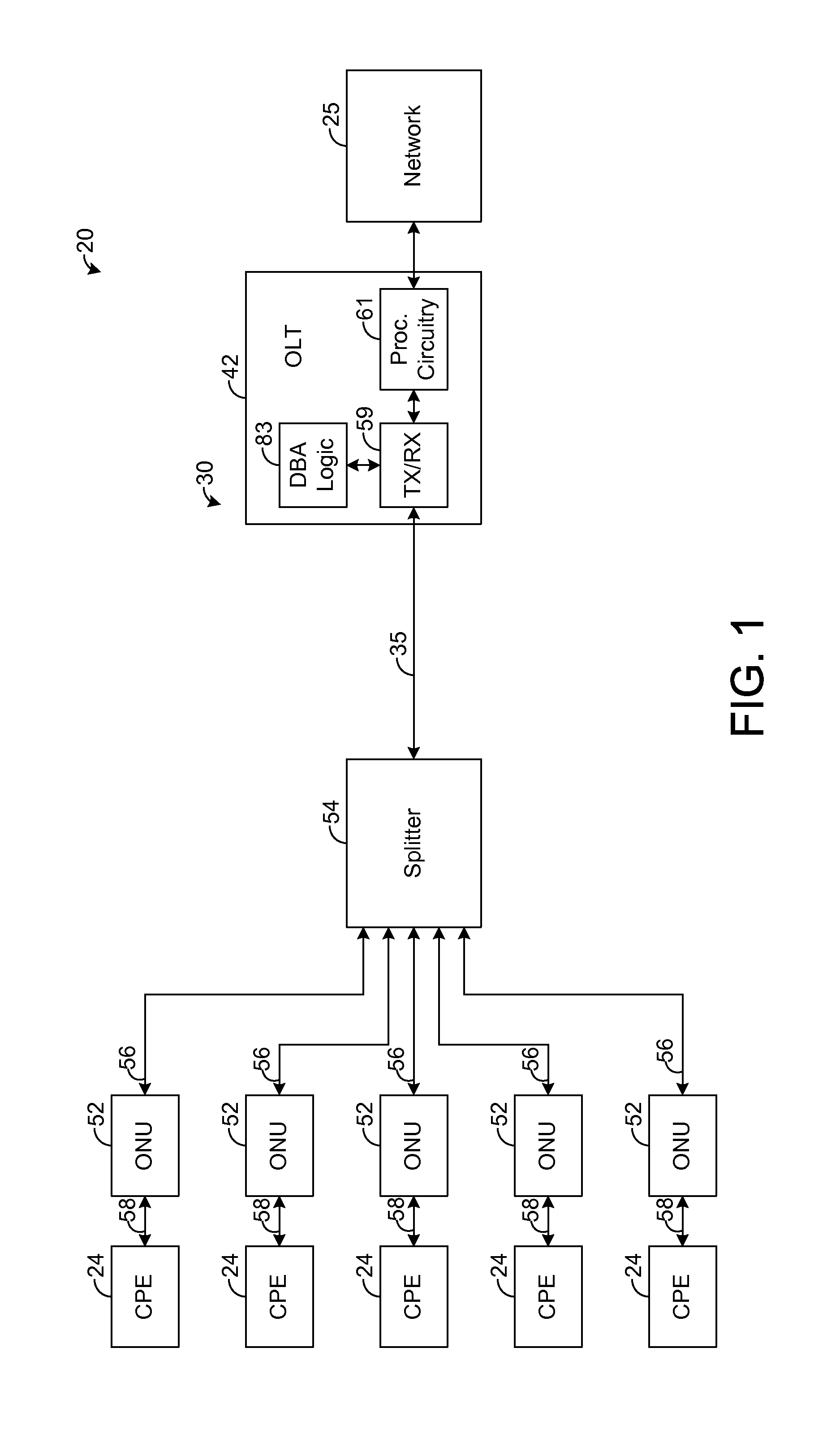
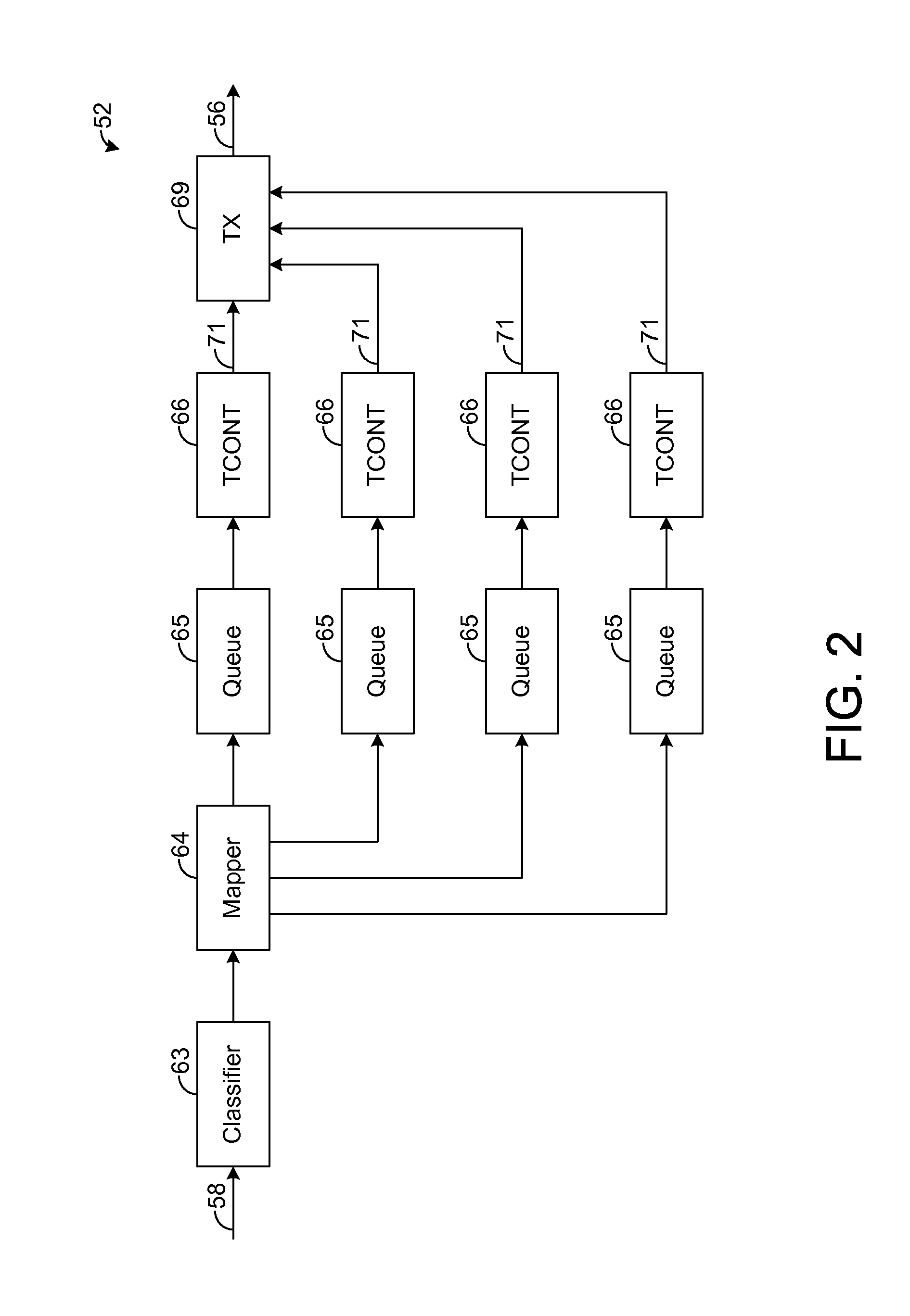
A passive optical network (PON) has an optical line termination (OLT) that terminates an optical fiber servicing a plurality of optical network units (ONUs). Each ONU has one or more traffic containers (TCONTs) addressable by the OLT. The PON dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA) implements a scheduling hierarchy, including several scheduling layers, such that disjoint sets of TCONTs can be grouped together, then disjoint sets of groups can be grouped, and so on. In such hierarchy, the residential traffic can be grouped separately from the business traffic. Further, within either the residential or business group, traffic may be grouped to define scheduling layers (“sub-groups”) within the residential or business group. Scheduling in one group or sub-group is performed independently of the scheduling in other groups or sub-groups, subject to the available bandwidth for each group. The scheduling may be controlled to allow the residential services to be oversubscribed while still ensuring compliance of service level performance metrics for the business services.
Owner:ADTRAN
Wavelength and filter arrangement for WDM networks
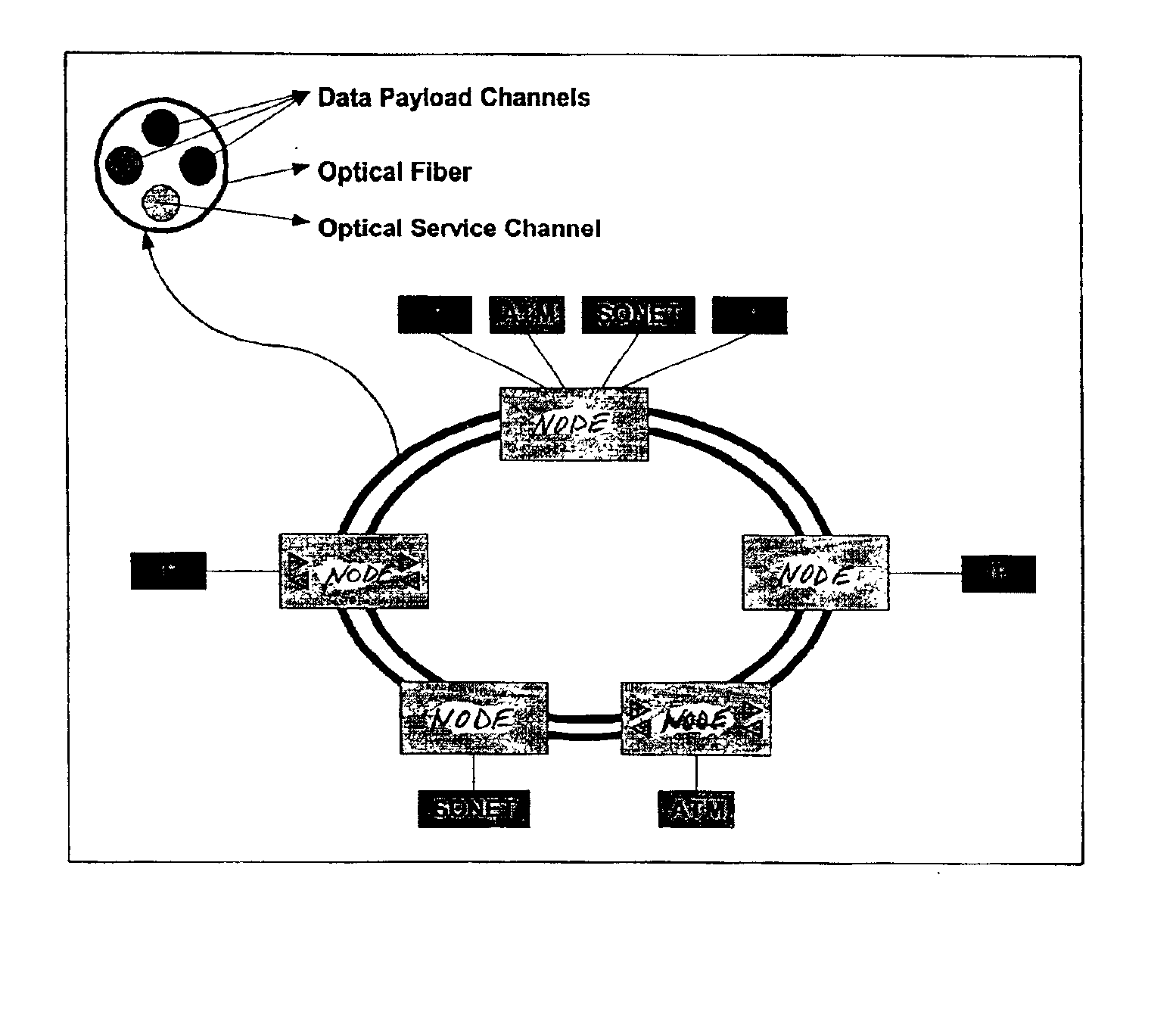
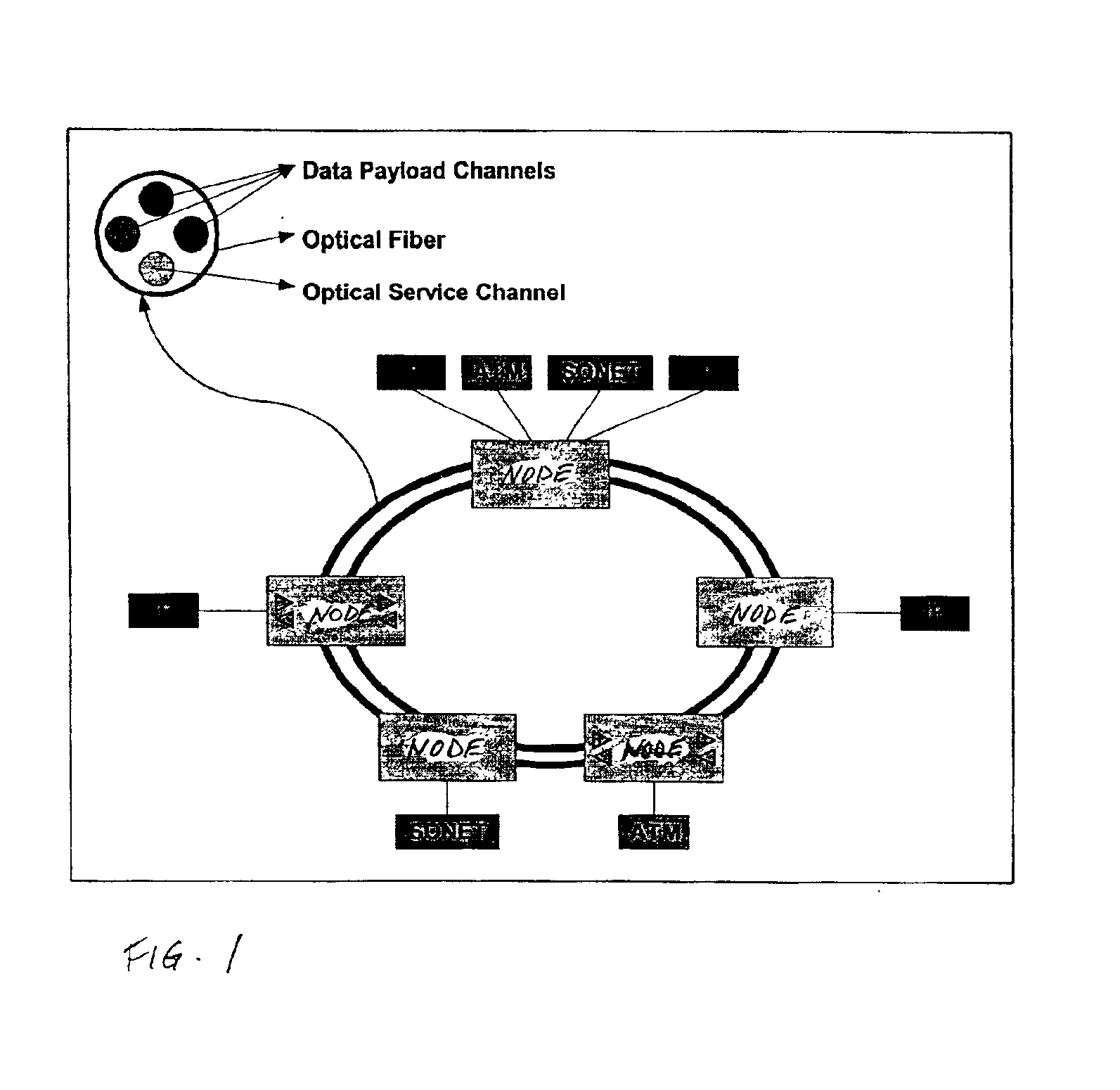
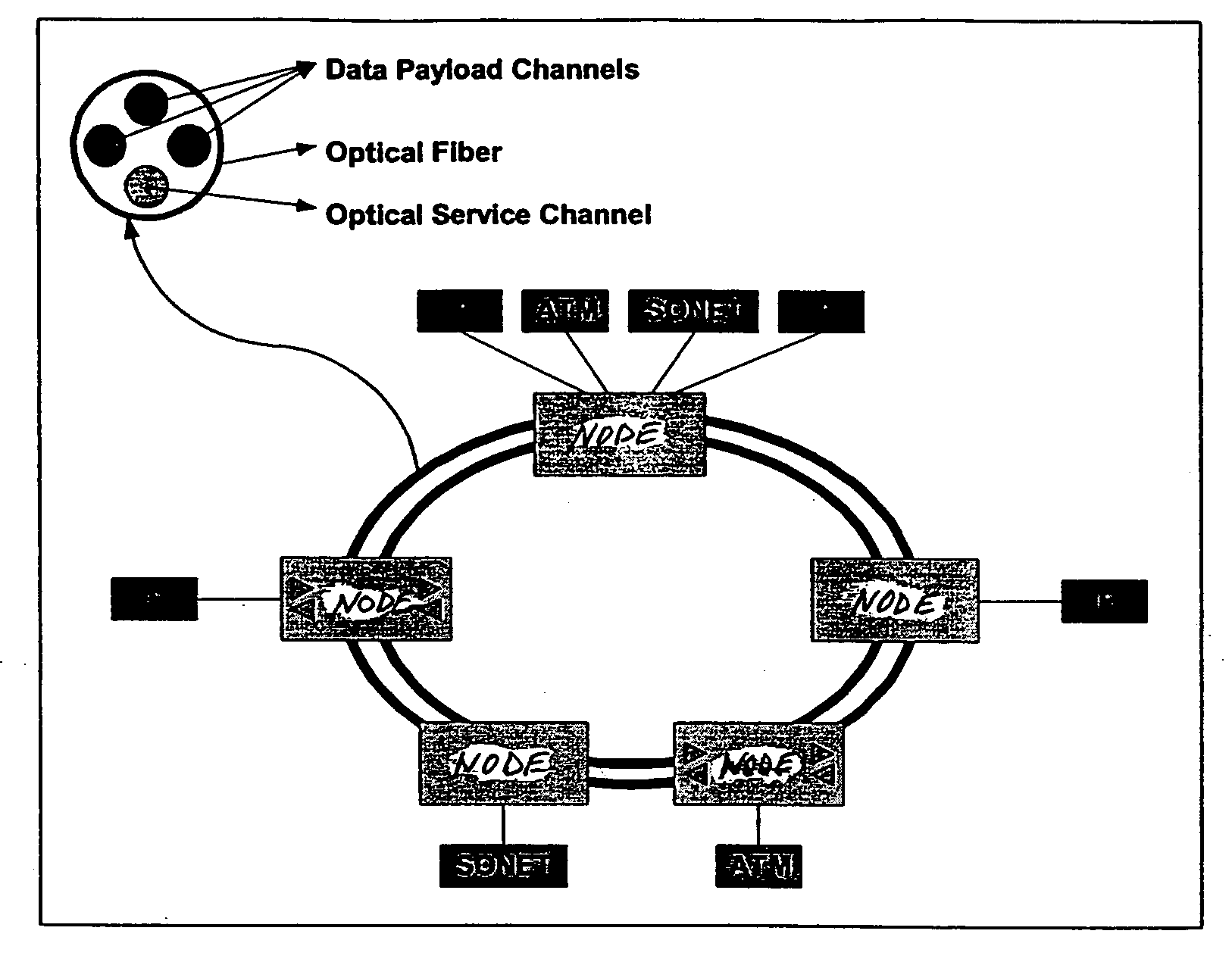
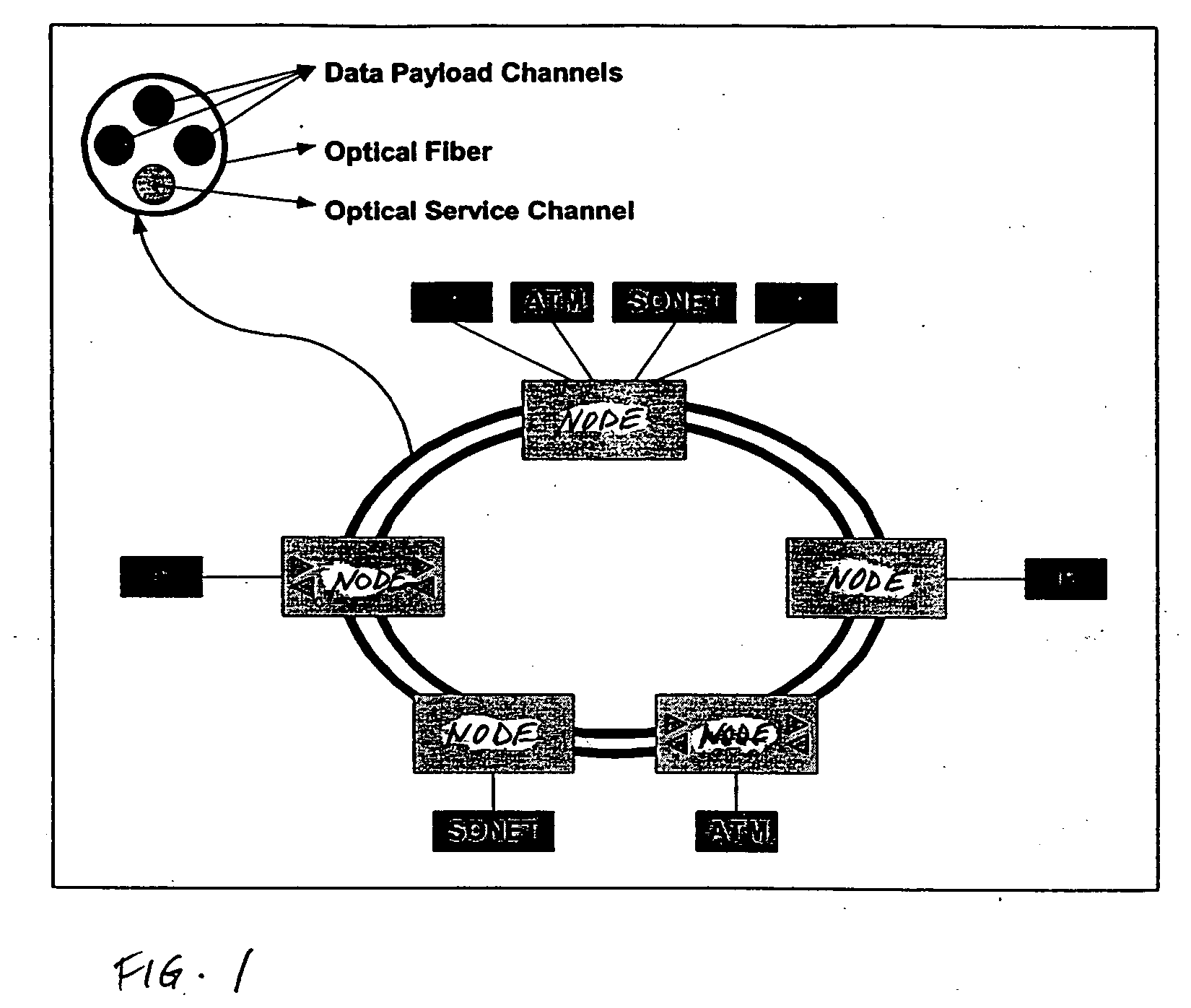
InactiveUS6885822B1Efficient wavelength managementEffective filteringLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberDisjoint-set
Owner:CIENA
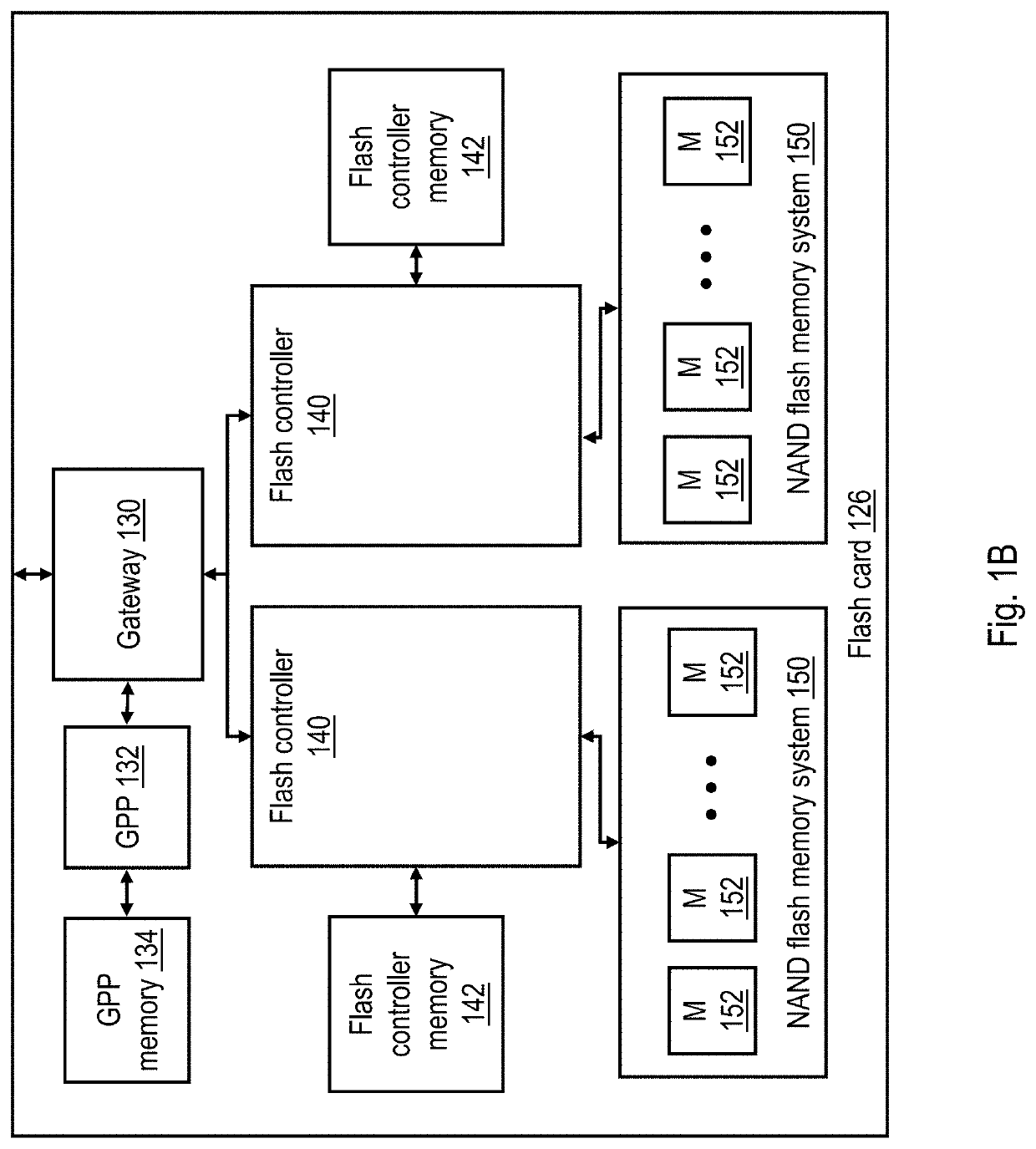
Background mitigation reads in a non-volatile memory system
ActiveUS20190391746A1Accurately reflectRemissionInput/output to record carriersDisjoint-setError mitigation
A controller of a non-volatile memory manages each of multiple disjoint sets of physical pages as a respective page group. The controller mitigates errors by repetitively performing background mitigation reads of each of the plurality of blocks including, in order, performing a background mitigation read of a first physical page in a first page group in a first block; prior to again performing a background mitigation read in the first block, performing a background mitigation read of a first physical page in a first page group in each other of the plurality of blocks; performing a background mitigation read of a first physical page in a second page group in the first block; and prior to again performing a background mitigation read in the first block, performing a background mitigation read of a first physical page in a second page group in each other of the plurality of blocks.
Owner:IBM CORP
Topology detection method based on cloud computing network
ActiveCN104158748ATopology detection implementationData switching networksDisjoint-setStructure of Management Information
The invention provides a topology detection method based on a cloud computing network. The topology detection method is suitable for detecting a network topology under the environment of the cloud computing network, and is used for detecting the topology from two separate layers, wherein the first layer of the topology comprises a router and a computing node; time delay is detected by sending a socket 'sandwich' pack; the second layer of the topology comprises the distribution of virtual machines under the computing node in the cloud computing environment. The method is used for detecting the communication time delay between the virtual machines with an MPI, and merging and clustering by adopting the disjoint-set data structure algorithm after corresponding calculation, so as to obtain the distribution of the virtual machines. Through the adoption of the method, the integral topological structure under the whole cloud computing network environment can be detected more completely.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
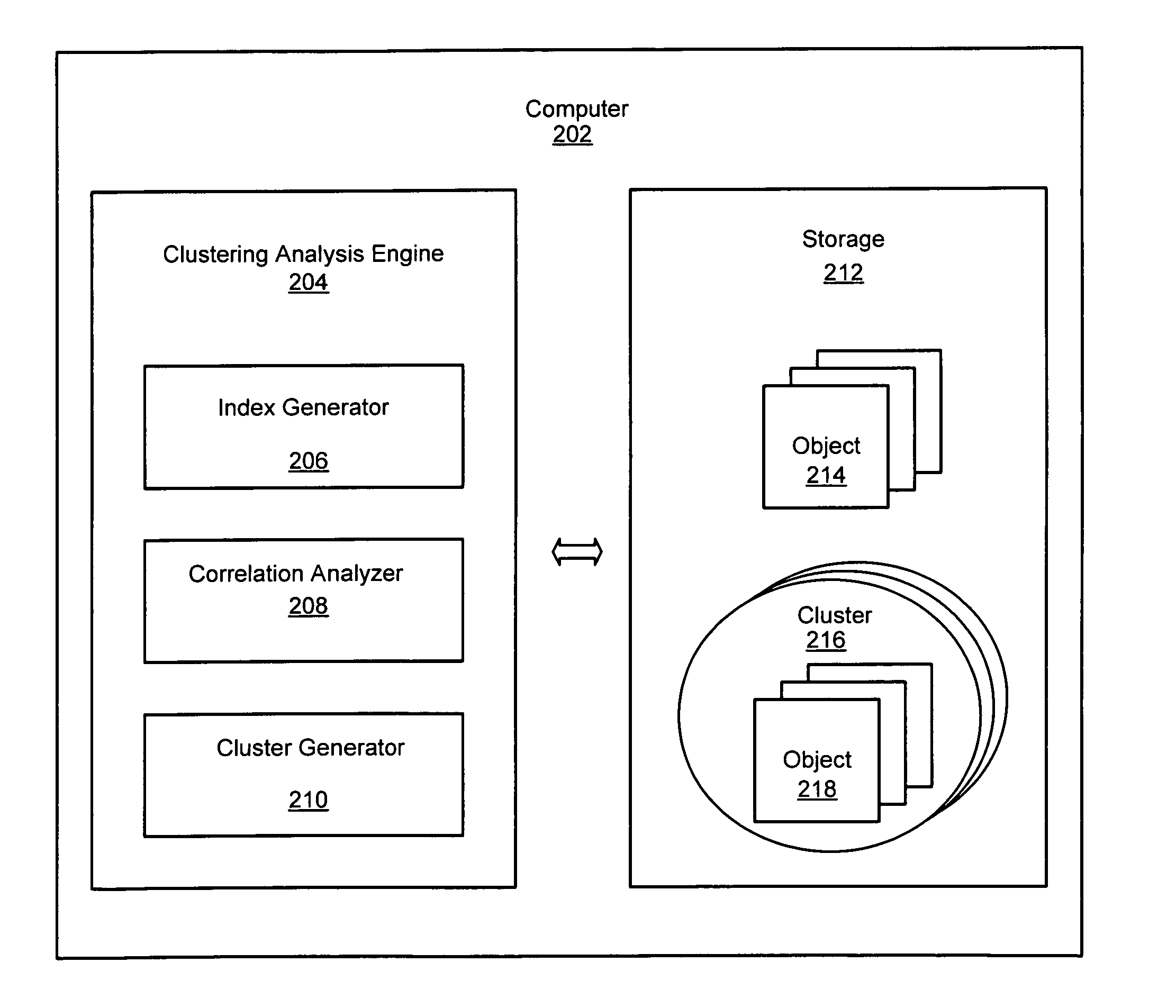
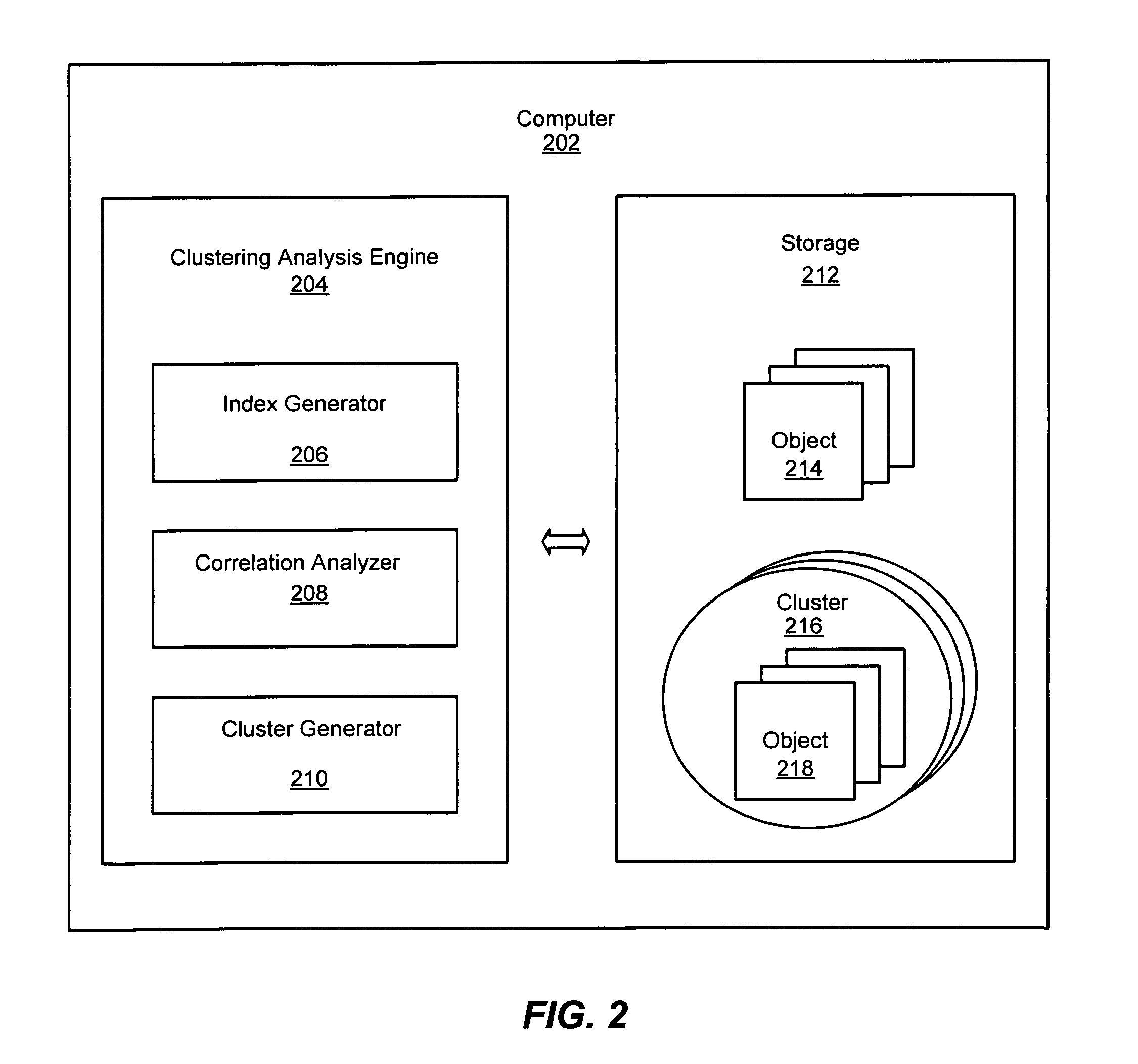
System and method for clustering using indexes
InactiveUS20080140707A1Efficiently findEfficient clusteringDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsDisjoint-setReverse index
An improved system and method is provided for clustering objects using indexes for a matrix representing a collection of objects. Objects to be clustered may be represented as a rectangular matrix. An index may be created for accessing the rows of the matrix and an inverted index may be created for accessing the columns of the matrix based upon the connectivity of the edges between rows and columns of the matrix. Each node represented by a row may be joined to a nearest node represented by another row to produce disjoint sets of nodes. The disjoint sets of nodes may represent clusters that may then be output for use by an application. Moreover, the objects to be clustered may be clusters of objects that may be correlated into a hierarchy of clusters of objects.
Owner:OATH INC
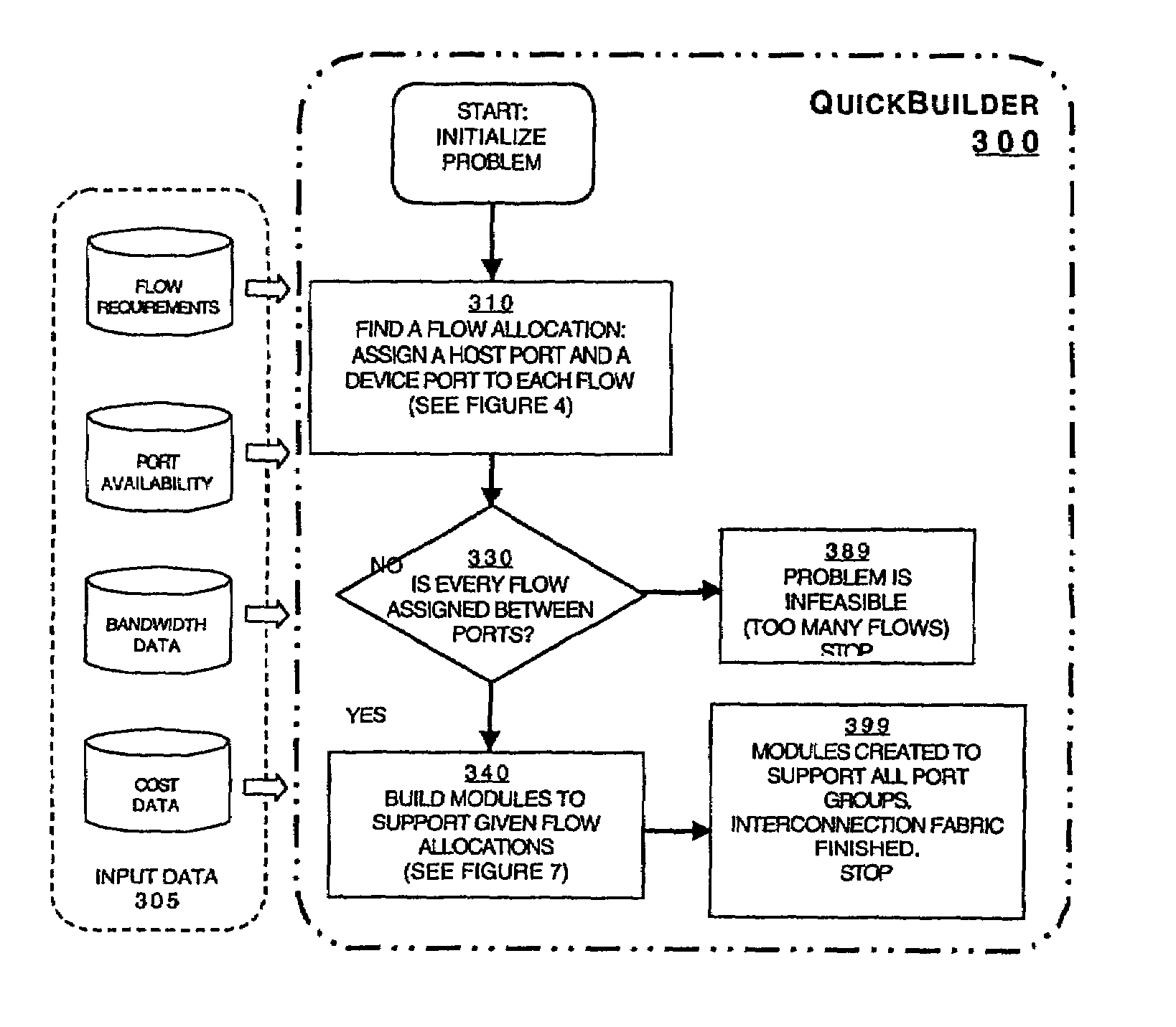
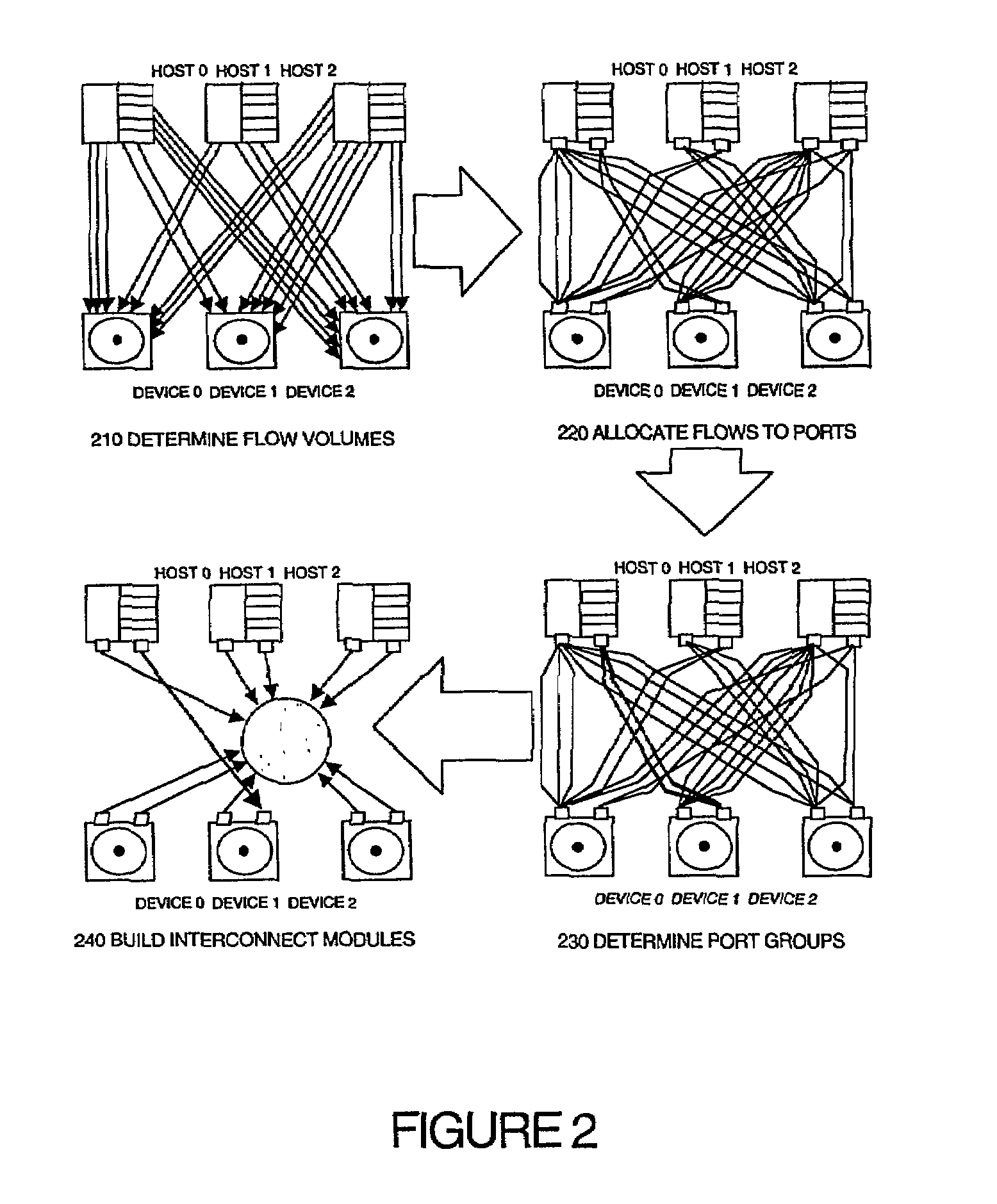
Module-building method for designing interconnect fabrics
ActiveUS7502839B2Improve automationCost-effective designDigital computer detailsData switching networksTraffic capacityDisjoint-set
Disclosed is a method for designing a network with a given set of network flow requirements, each flow requirement having a source, a destination and a bandwidth. The method comprises the steps of assigning each flow to a port on its associated source and destination, determining the partition of source and destination ports into port groups which are disjoint sets, and generating network modules to support the assignment of flows by using an appropriate interconnected combination of links, hubs and switches. The design of the module accounts for the relative costs of the links, hubs and switches and finds the allocation and subsequent module design that produces a cost effective interconnection fabric that supports all flow requirements.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
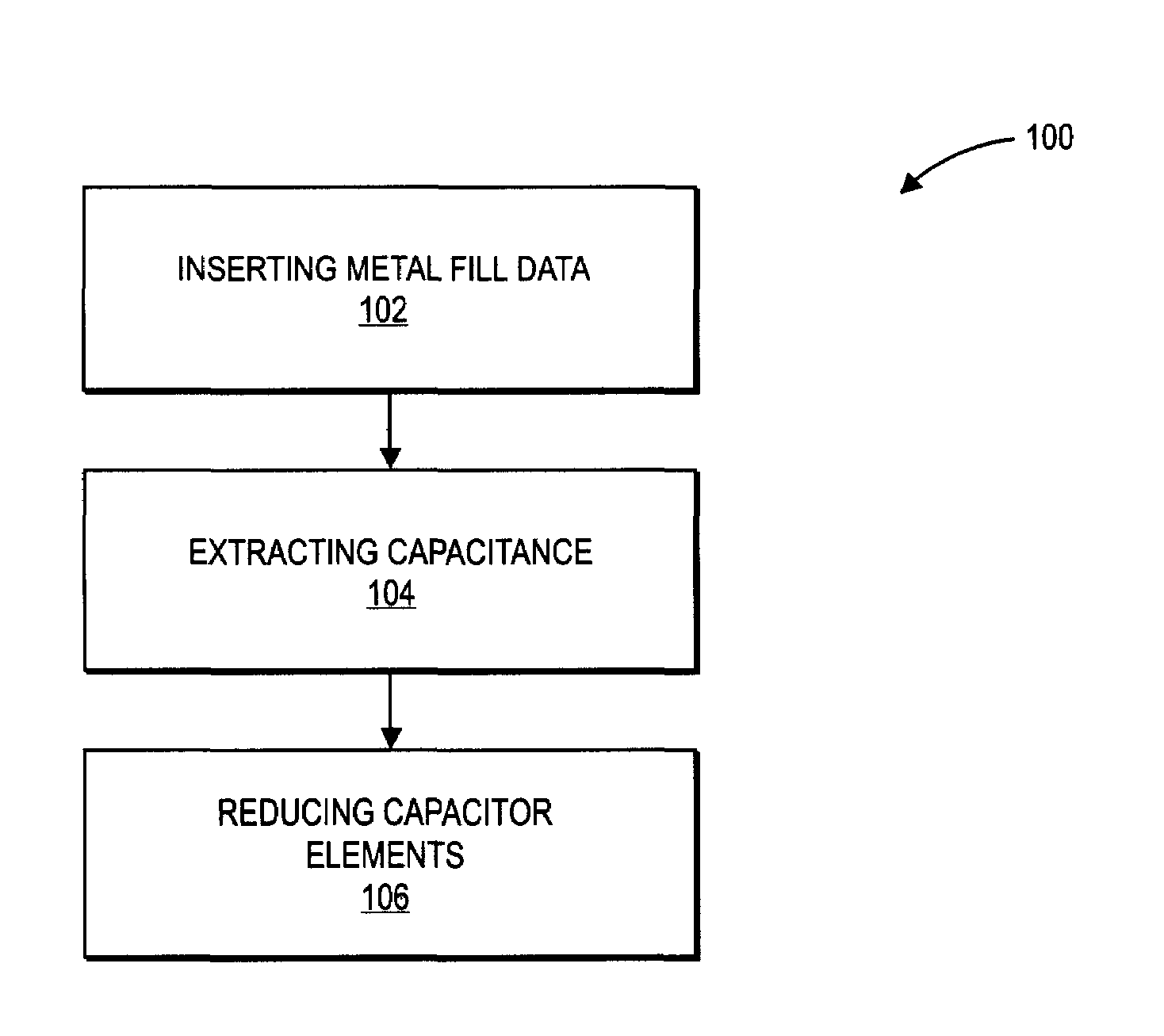
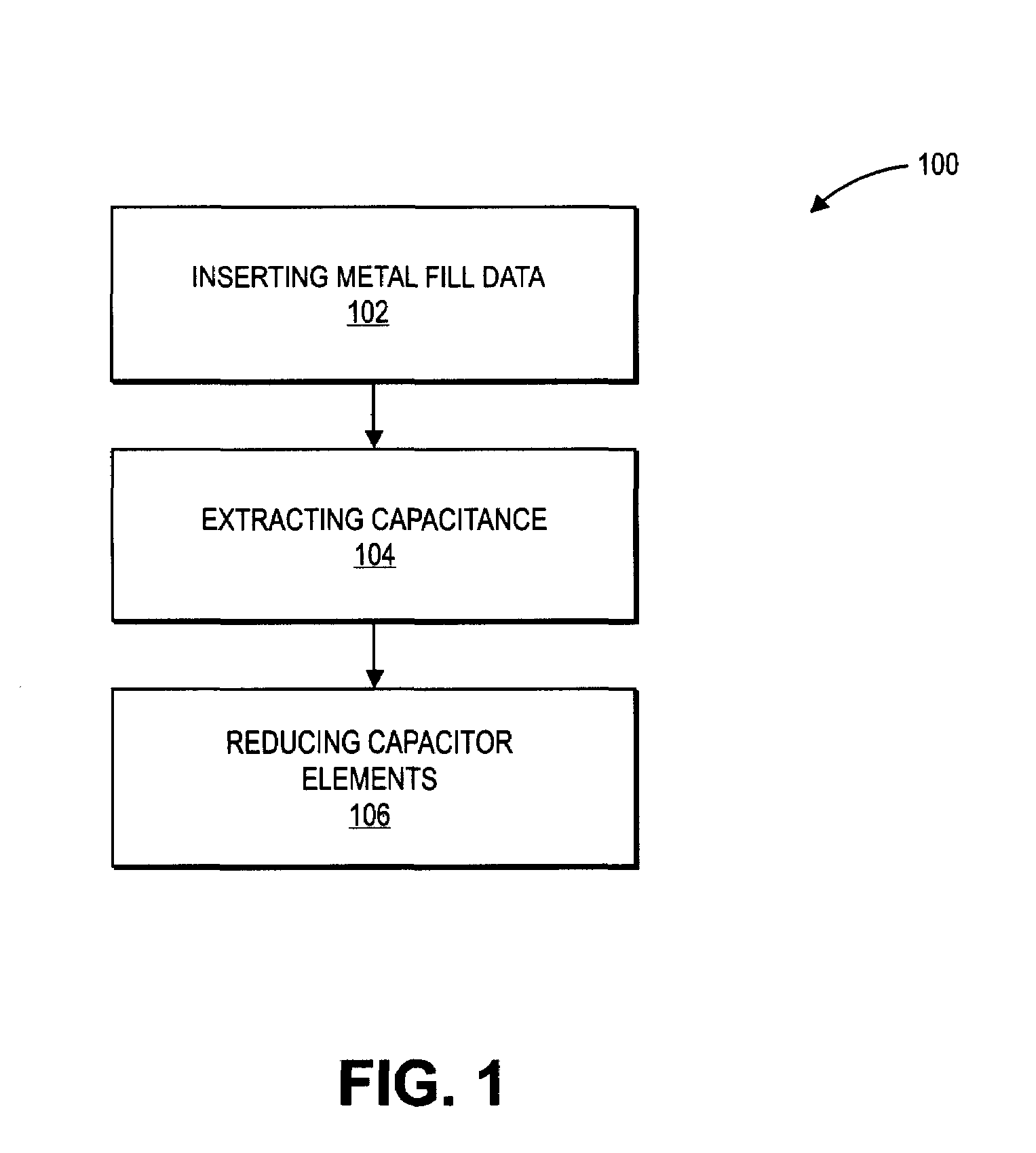
Extraction and reduction of capacitor elements using matrix operations
InactiveUS7350167B1Extract capacitanceComputation using non-denominational number representationCAD circuit designCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A method for extracting capacitance from a layout record includes solving a matrix equation to obtain a set of capacitors that account for metal fill while eliminating floaters. A method for extracting capacitance from a layout record includes partitioning floaters into disjoint sets, and converting a capacitance matrix into block-diagonal form by ordering conductors according to the disjoint sets.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Targeted rectangular conditioning
ActiveUS20190058502A1Improve the vectoring gainsData augmentationCross-talk reductionOrthogonal multiplexDisjoint-setData signal
A vectoring controller for configuring a vectoring processor that jointly processes DMT communication signals to be transmitted over, or received from, a plurality of N subscriber lines according to a vectoring matrix. In accordance with an embodiment, the vectoring controller is configured, for given ones of a plurality of tones, to enable the given tone for direct data communication over a first set of N−Mk targeted lines out of the plurality of N subscriber lines, and to disable the given tone for direct data communication over a second disjoint set of Mk supporting lines out of the plurality of N subscriber lines, Mk denoting a non-null positive integer. The vectoring controller is further configured to configure the vectoring matrix to use an available transmit or receive power at the given tone over the second set of Mk supporting lines for further enhancement of data signal gains at the given tone over the first set of N−Mk targeted lines.
Owner:NOKIA OF AMERICA CORP
Exponential storage system and method
A system records a sequence of frames of a video in circular buffers. Each buffer is configured to store the frames in a sequential order. Disjoint sets of frames are selected from the video. There is one set of frames for each buffer such that a first set selects a first fraction of the frames, each subsequent set of frames is a smaller fraction then a previous set of frames, and a last set of selected frames includes remaining frames. The sets of frames are stored sequentially in the corresponding buffers.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
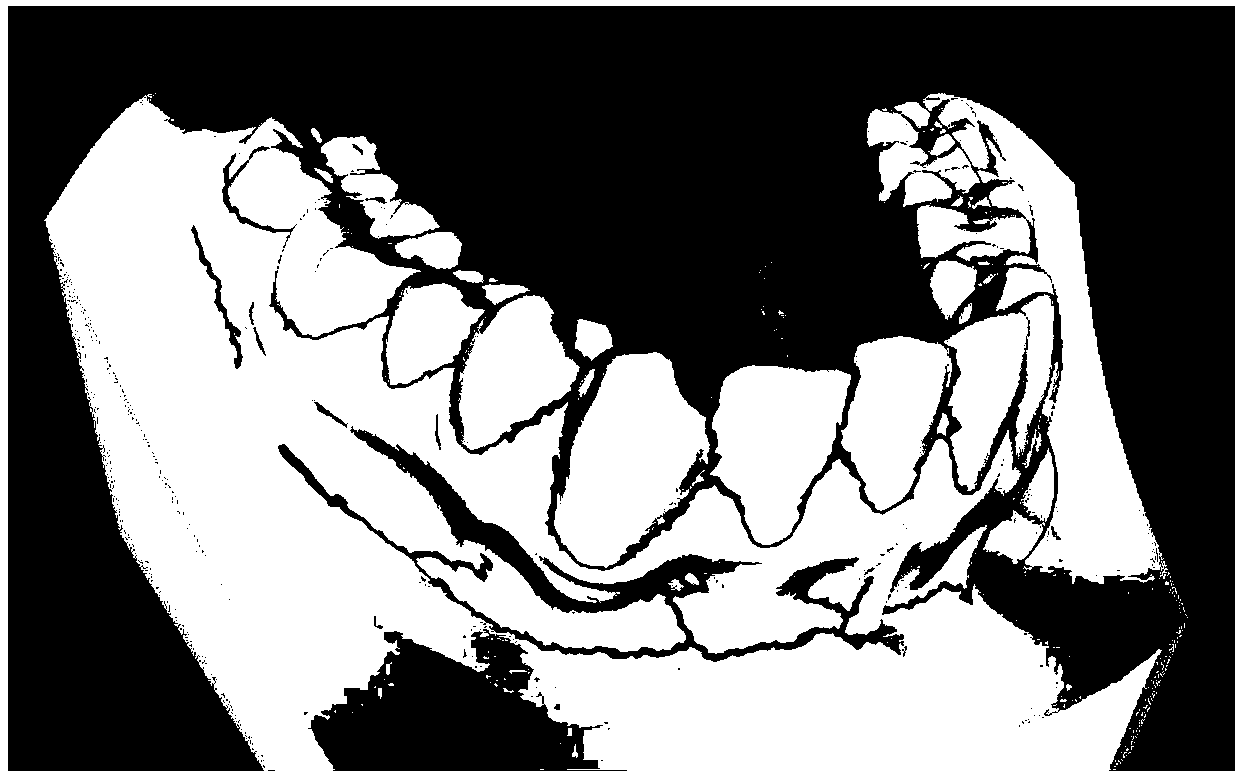
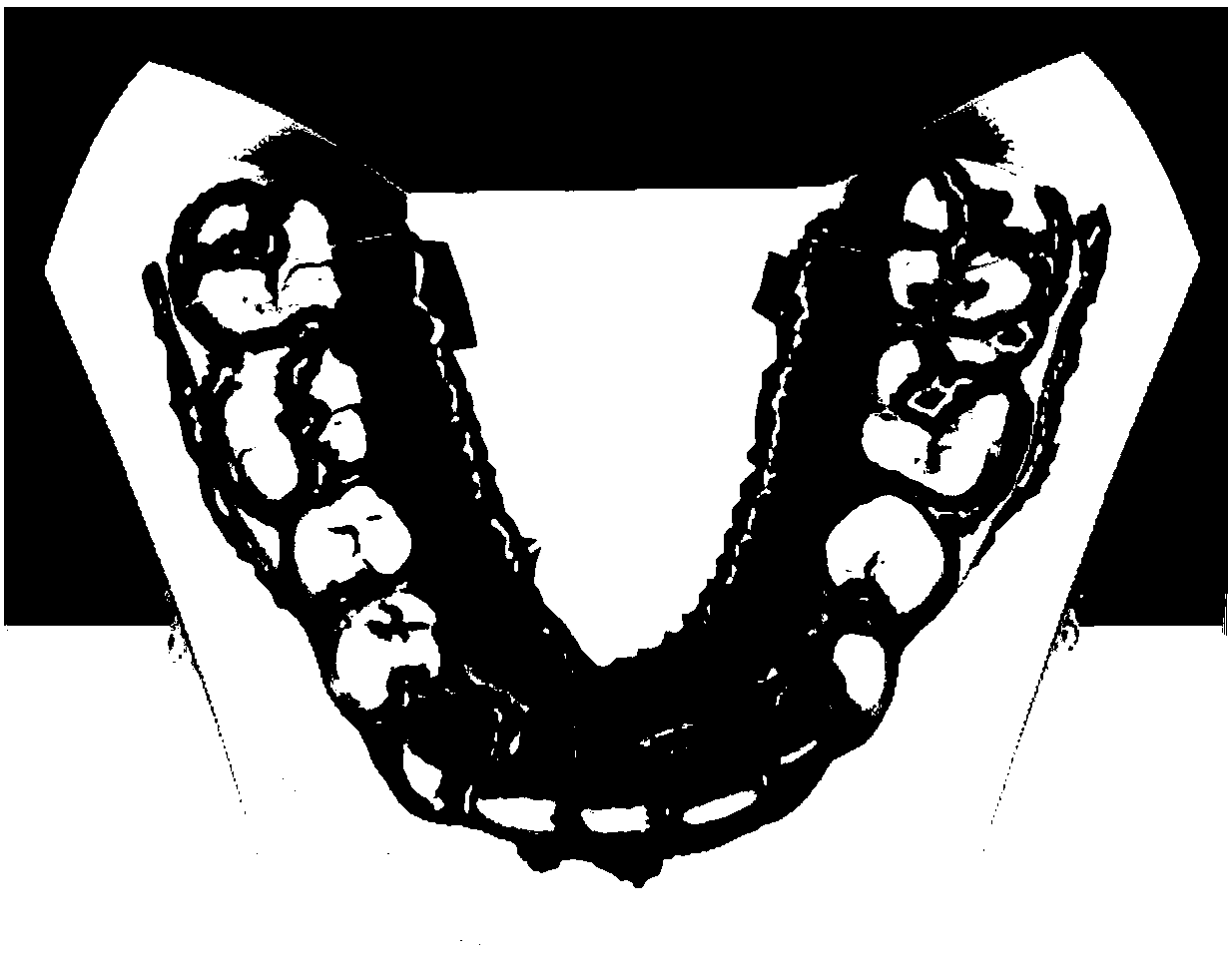
Automatic segmentation method of tooth three-dimensional network model
ActiveCN108364356AReduce work stressHigh degree of automationImage data processingAutomatic segmentationWorking pressure
The present invention provides an automatic segmentation method of a tooth three-dimensional network model. The method comprises four special functions and the steps of: automatic curvature thresholdselection operation, feature area skeletonizing operation, closing of feature area gaps by employing a distance field constraint method, and distribution of different colors for segmented disjoint sets. The algorithm comprises the steps of: initial feature area extraction, morphology operation, removal of redundant branches in the initial segmentation, closing of gaps in the feature skeleton, andprocessing of excessive segmentation. The automatic segmentation method of a tooth three-dimensional network model is high in degree of automation and only needs to input the quantity of teeth to completely segment each tooth in a tooth model so as to greatly relieve the medical workers' working pressure.
Owner:成都格登特科技有限公司
Symbolic model checking of generally asynchronous hardware
InactiveUS20060058989A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusCAD circuit designDisjoint-setModel checking
Owner:IBM CORP
Detecting multiple moving objects in crowded environments with coherent motion regions
ActiveUS8462987B2Minimise measureRobust to noisy or short point tracksImage enhancementTelevision system detailsThree-dimensional spaceDisjoint-set
Coherent motion regions extend in time as well as space, enforcing consistency in detected objects over long time periods and making the algorithm robust to noisy or short point tracks. As a result of enforcing the constraint that selected coherent motion regions contain disjoint sets of tracks defined in a three-dimensional space including a time dimension. An algorithm operates directly on raw, unconditioned low-level feature point tracks, and minimizes a global measure of the coherent motion regions. At least one discrete moving object is identified in a time series of video images based on the trajectory similarity factors, which is a measure of a maximum distance between a pair of feature point tracks.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
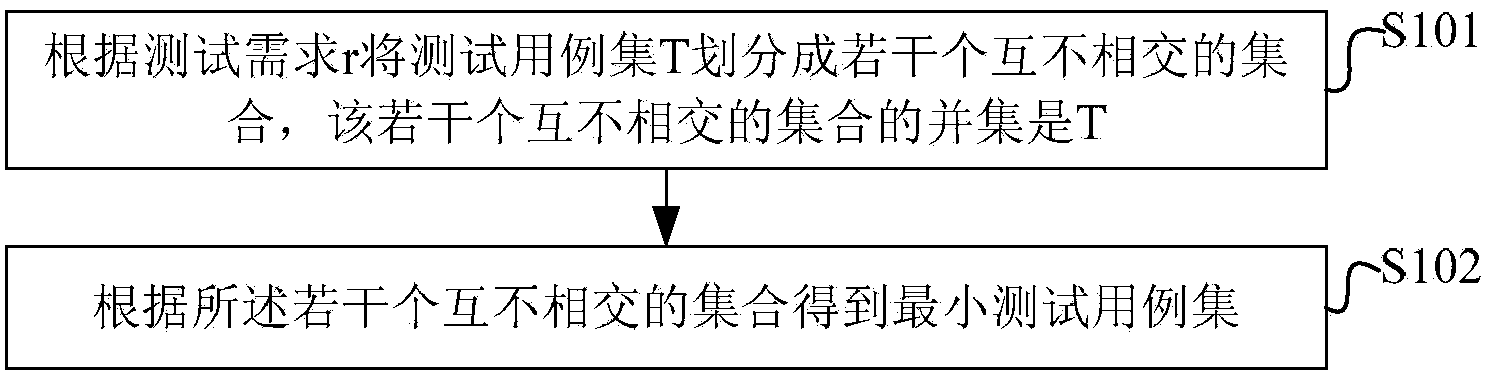
Generation method of minimum test case suite
InactiveCN104239204ASolve the simplification problemImprove test efficiencySoftware testing/debuggingTest efficiencyDisjoint-set
The invention discloses a generation method of a minimum test case suite and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps: according to the interrelation of a test requirement r, dividing a total test case suite T into a plurality of mutually disjoint sets, wherein the union set of the mutually disjoint sets is T; according to the mutually disjoint sets, obtaining the minimum test case suite. According to the method, the inherent minimum test case suite determined by all test requirements in a test target can be generated so as to fundamentally solve a test case suite simplification problem and improve test efficiency.
Owner:INSPUR BEIJING ELECTRONICS INFORMATION IND
Traffic management method for mobile robotics system
InactiveUS20180210459A1Lower requirementAvoid deadlockPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesRobotic systemsRobotics
The present invention provides a traffic management method for a mobile robotics system, including: step 1, defining the physical size of a mobile robot and the position of a point on a traveling path; step 2, for each point on the traveling path, obtaining profile information of the mobile robot on this point in combination with the physical size of the mobile robot, so as to further obtain the profile information of the mobile robots over the whole traveling path; step 3, with respect to a first path, calculating whether the profiles of the mobile robots on the first path and on a second path intersect, and if the profiles thereof intersect, then the first path and the second path are disjoint; step 4, calculating whether the profiles of the mobile robots on the first path and all other paths intersect, so as to further obtain the disjoint sets of all paths. The method of the present invention realizes full automation of the disjoint sets among the paths, avoids dead locks as a result of the configuration as much as possible, and solves the problems of error-prone disjoint sets and heavy workload in the manual configuration.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GUOZI ROBOT TECH
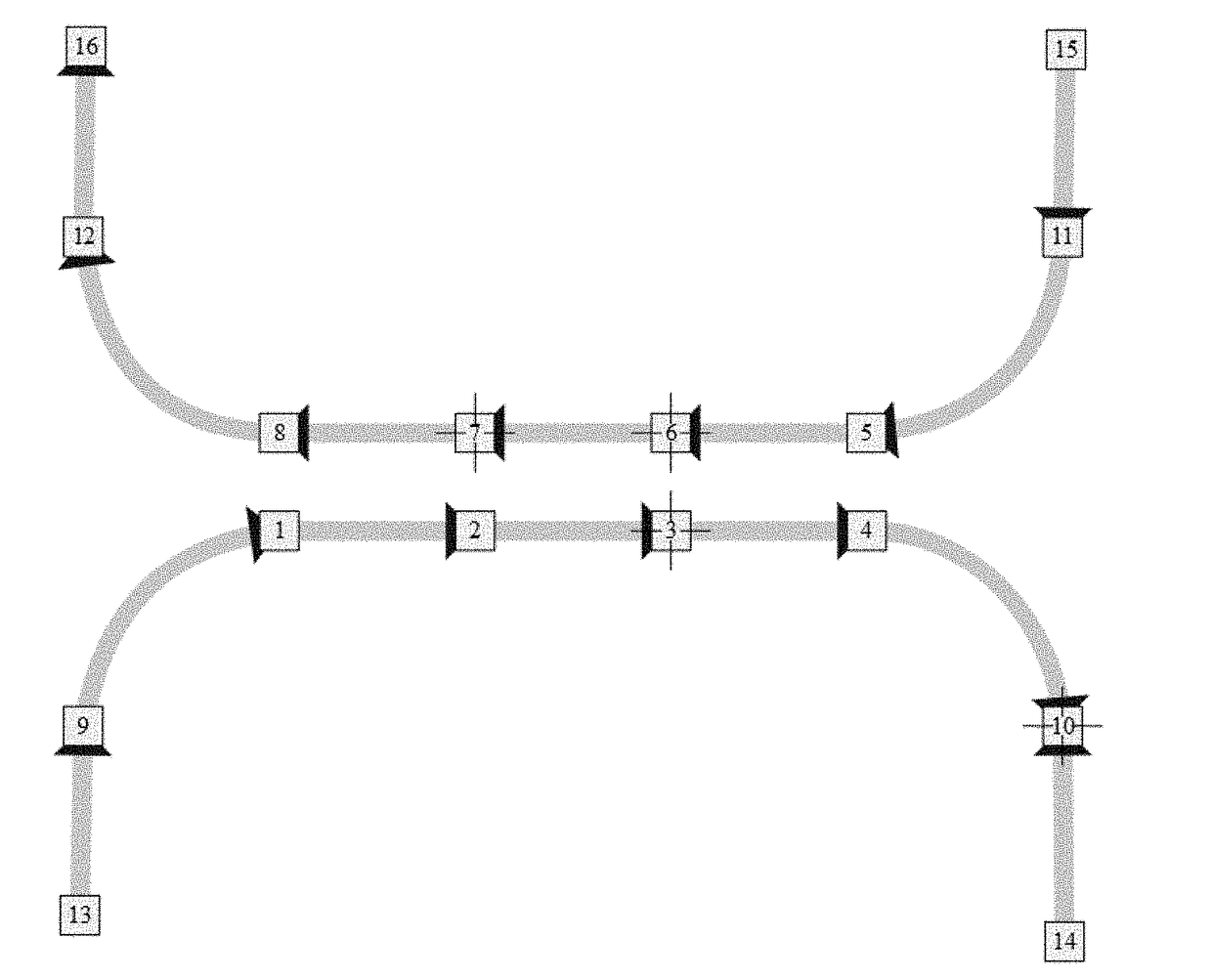
Traffic routing tree construction method based on geographic location
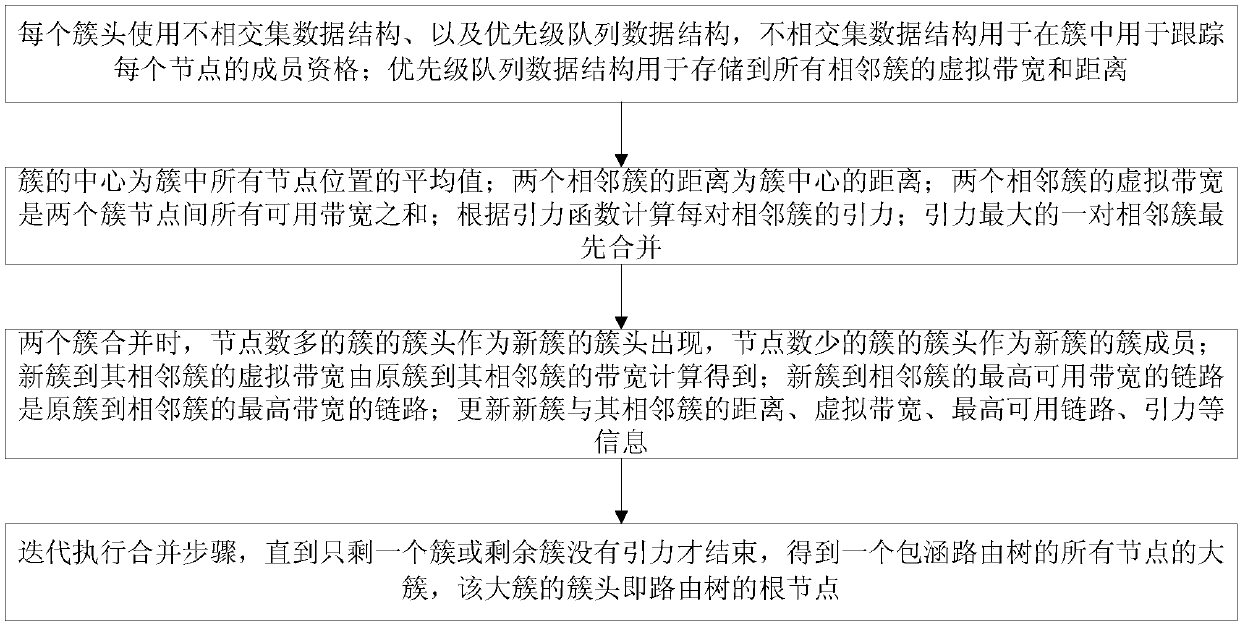
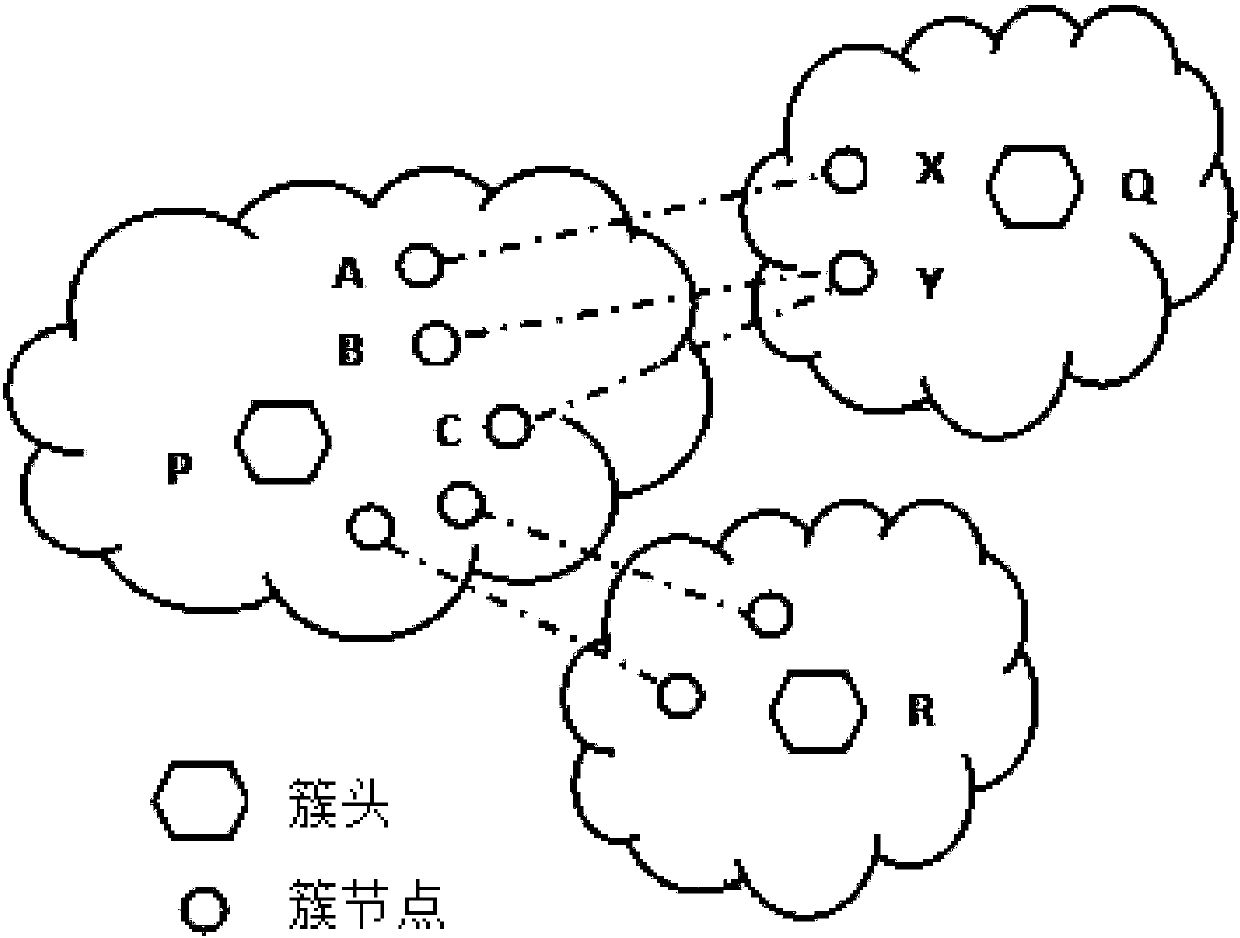
InactiveCN107911293AReduce complexityAvoid the problem of many conflicting packagesData switching networksNODALMassive gravity
The invention provides a traffic sensing routing tree construction method based on geographic location routing. The method comprises the steps that a disjoint set data structure is used to track the membership of each node in a cluster; a priority queue data structure is used to store virtual bandwidths and distances to all adjacent clusters; the virtual bandwidth of two adjacent clusters is the sum of all available bandwidths between two cluster nodes, and a pair of adjacent clusters with the maximum attraction are merged first; the cluster head of a cluster with many nodes appears as a new cluster head; the cluster center is the average of the locations of all nodes in the cluster; the virtual bandwidth of the new cluster to the adjacent cluster is calculated from the bandwidth of the original cluster to the adjacent cluster; the highest available bandwidth link from the new cluster to the adjacent cluster is the highest bandwidth link from the original cluster to the adjacent cluster; and until only one cluster left or the rest of the clusters have no attraction, the method ends, and a large cluster with all nodes of a routing tree is acquired, wherein the cluster head of the large cluster is the node of the routing tree root. According to the invention, location and traffic information are considered at the same time; the number of collision packets and the average path hops are reduced; and the average path throughput is increased.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
D2D network setup method based on scalable video streaming user quality of experience
ActiveCN108111991AIncrease capacityGuaranteed quality of experienceTransmissionMachine-to-machine/machine-type communication serviceDisjoint-setAdaptive video
The invention discloses a D2D network setup method based on scalable video streaming user quality of experience. D2D communication is organized into a spanning tree for transmitting scalable adaptivevideo streaming. In an initialization phase, a D2D network is organized into the spanning tree with acceptable user quality of experience and fairness. In a management phase, the service continuity isrespectively maintained under the condition that different devices arrive or depart. On the basis of a local search technology, according to the scheme, data structures of disjoint sets and the localsearch technology are combined, the reachable operation time is O [mn alpha (m, n)]. According to the scheme, the capacity of a service network can be improved, the quality of experience, fairness and continuity of the service are ensured, and a great number of users can be supported.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Flame simulating light-emitting devices and related methods
Lighting systems, devices, methods and apparatus for simulating a candle flame are disclosed. The systems and methods can employ spatially distributed, disjointed sets of light-emitting elements that are independently controlled (526) with randomized control signals to simulate a candle flame by forming spatially and temporally varying lighting effects. Further, the disjointed sets can be controlled (526) such that the total light intensity is essentially maintained. In addition, systems and methods can employ a transition probability model (508) to adjust intensities of light-emitting elements in a way that accurately mimics a candle flame.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Systems and methods for scheduling business and residential services in optical networks
ActiveUS20130251371A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic network arrangementsStructure of Management InformationDisjoint-set
A passive optical network (PON) has an optical line termination (OLT) that terminates an optical fiber servicing a plurality of optical network units (ONUs). Each ONU has one or more traffic containers (TCONTs) addressable by the OLT. The PON dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA) implements a scheduling hierarchy, including several scheduling layers, such that disjoint sets of TCONTs can be grouped together, then disjoint sets of groups can be grouped, and so on. In such hierarchy, the residential traffic can be grouped separately from the business traffic. Further, within either the residential or business group, traffic may be grouped to define scheduling layers (“sub-groups”) within the residential or business group. Scheduling in one group or sub-group is performed independently of the scheduling in other groups or sub-groups, subject to the available bandwidth for each group. The scheduling may be controlled to allow the residential services to be oversubscribed while still ensuring compliance of service level performance metrics for the business services.
Owner:ADTRAN
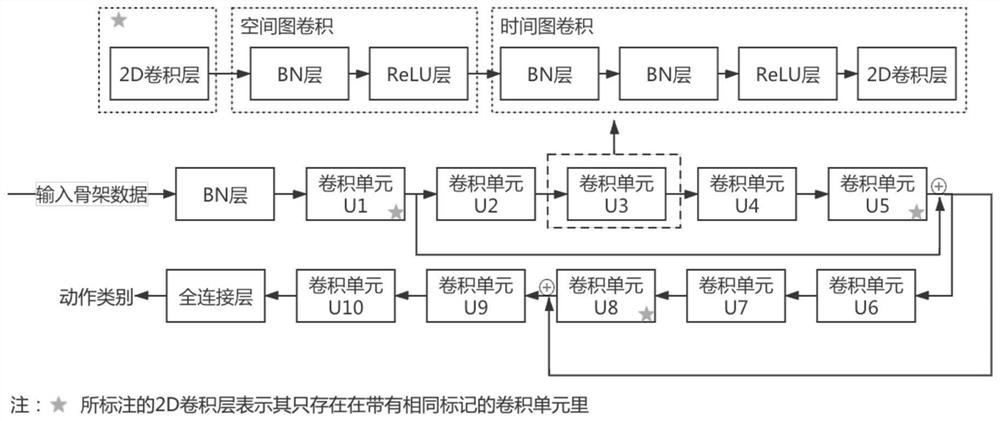
Two-stage behavior recognition fine classification method based on graph convolutional network
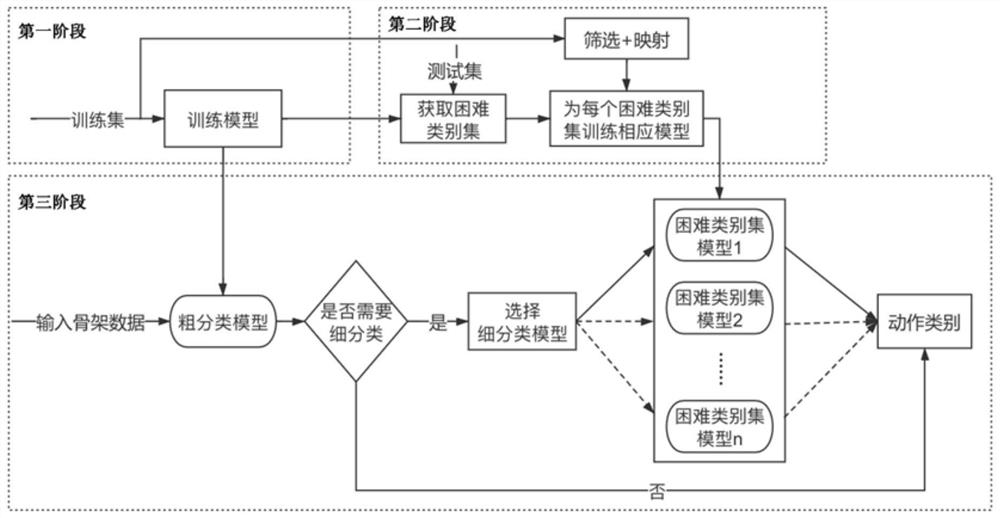
PendingCN113762175AFully excavatedImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setClassification methods
The invention discloses a two-stage behavior recognition fine classification method based on a graph convolutional network. According to the method, the accuracy of behavior recognition is improved mainly by reclassifying a difficult category set, and the method is divided into three stages: in the first stage, training a coarse classification model; in the second stage, acquiring difficult category sets and training difficult category set models, acquiring the difficult category sets by a confusion matrix of the rough classification model on the test set and a union-check set algorithm, and training the difficult category set models for the different difficult category sets; and in a third stage: during on-line inference, according to an inference result of the rough classification model, inputting the samples which need to be finely classified into the difficult category set model for re-classification. According to the method provided by the invention, aiming at the problem that a model is difficult to classify similar actions, the problem that the similar actions are difficult to classify is relieved to a certain extent by a rough classification-fine classification two-stage architecture, the accuracy of behavior recognition is improved, and a better result is obtained on a public data set.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
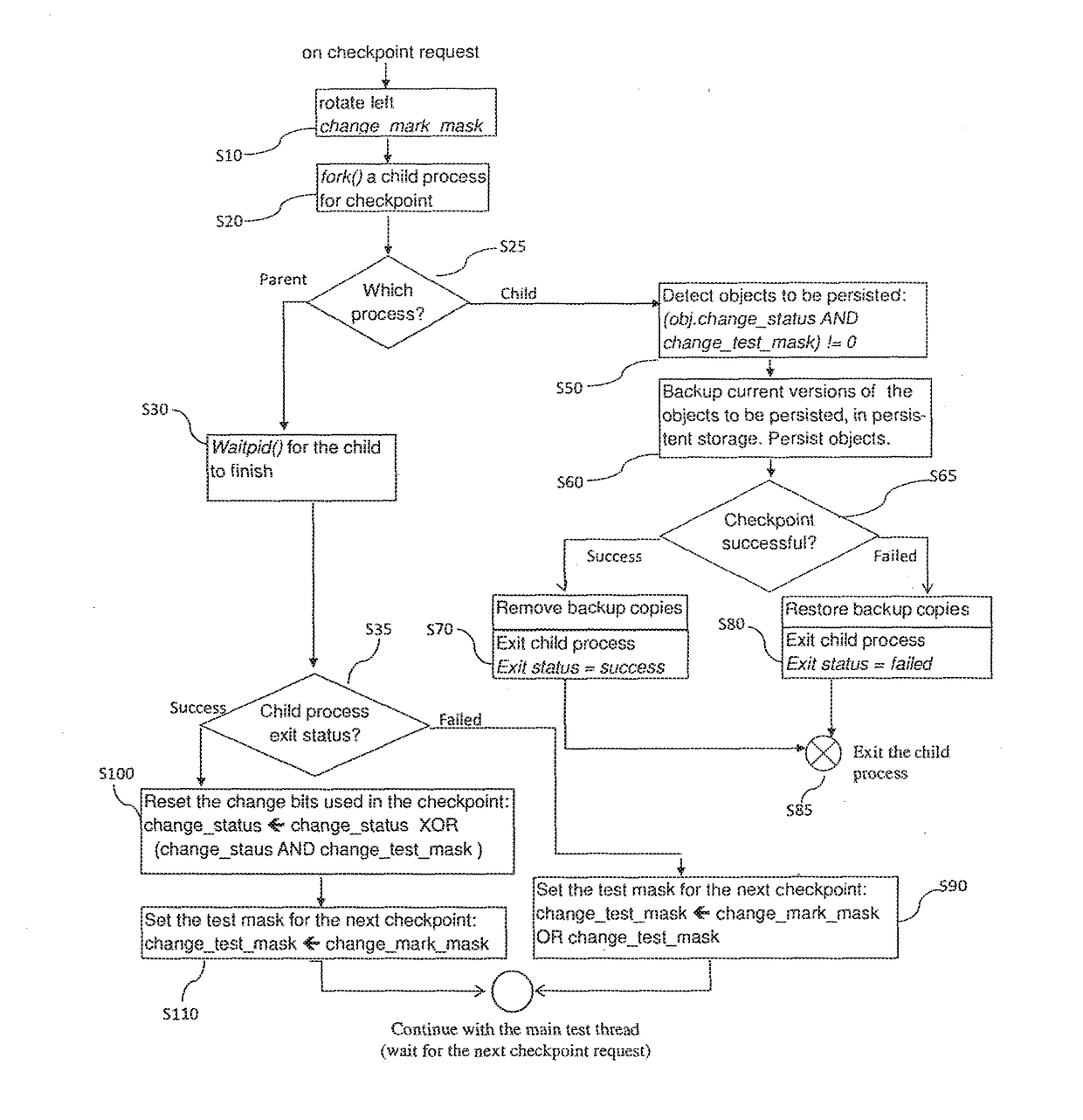
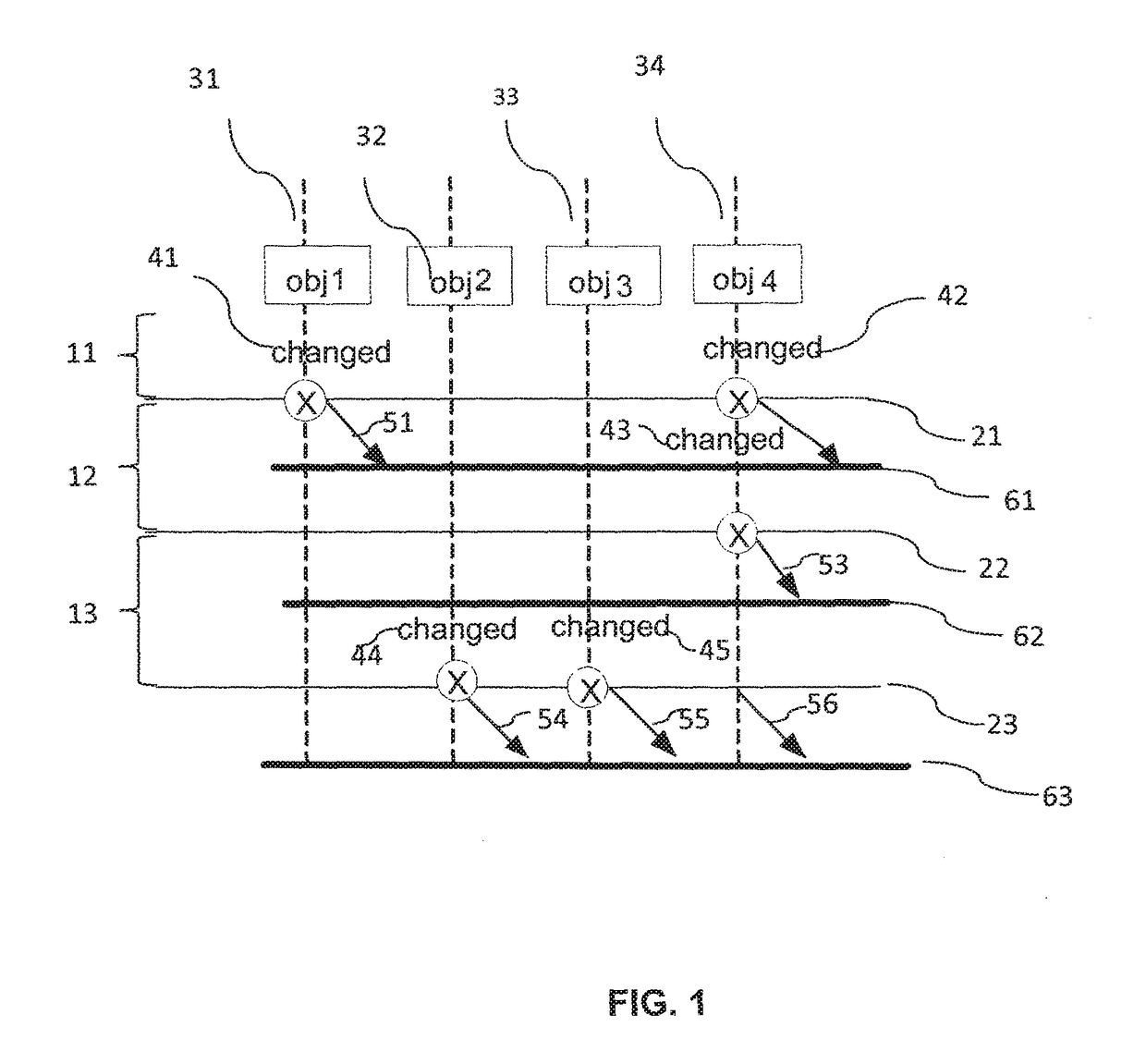
Method and Apparatus for Tracking Objects in a First Memory
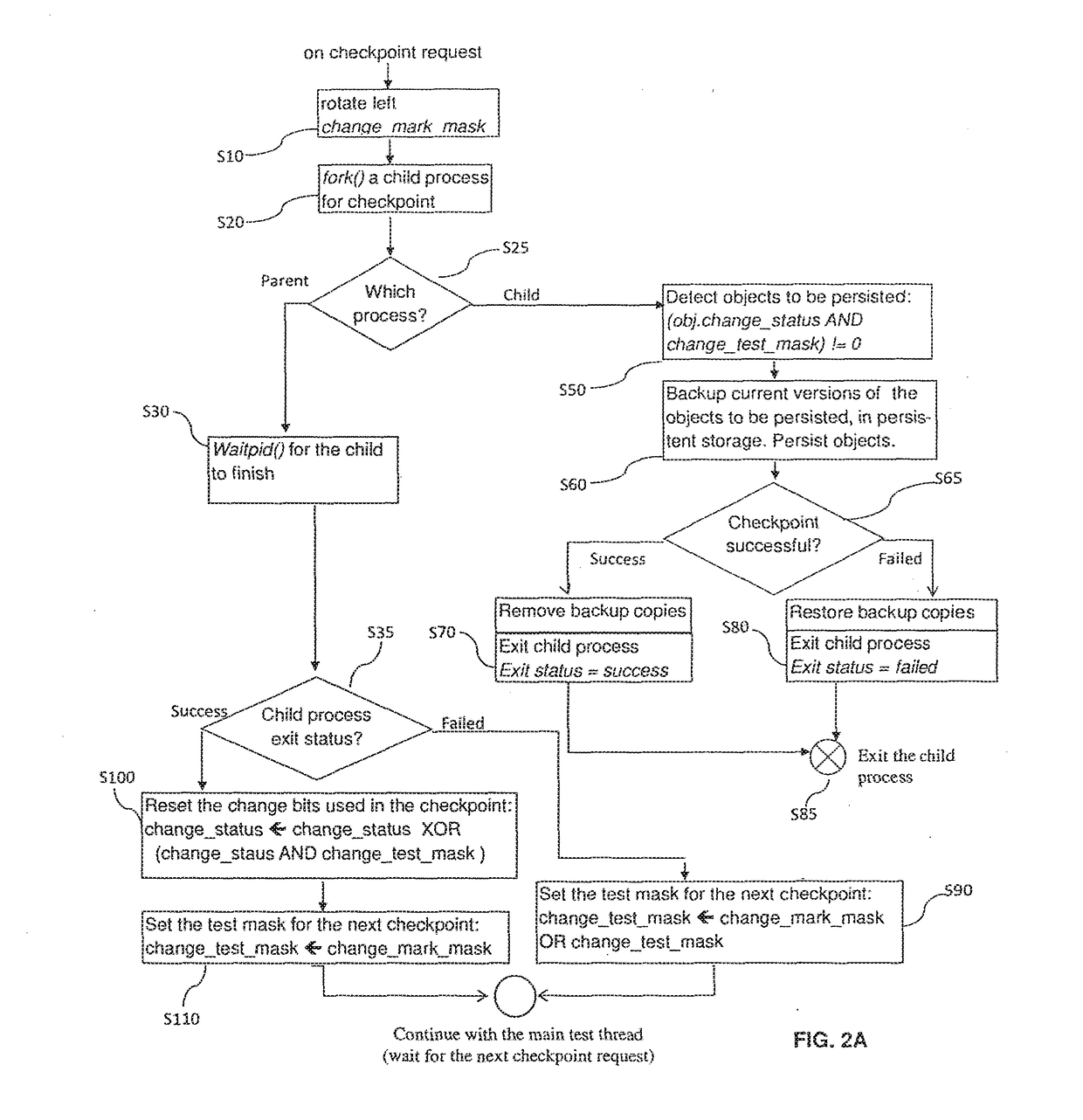
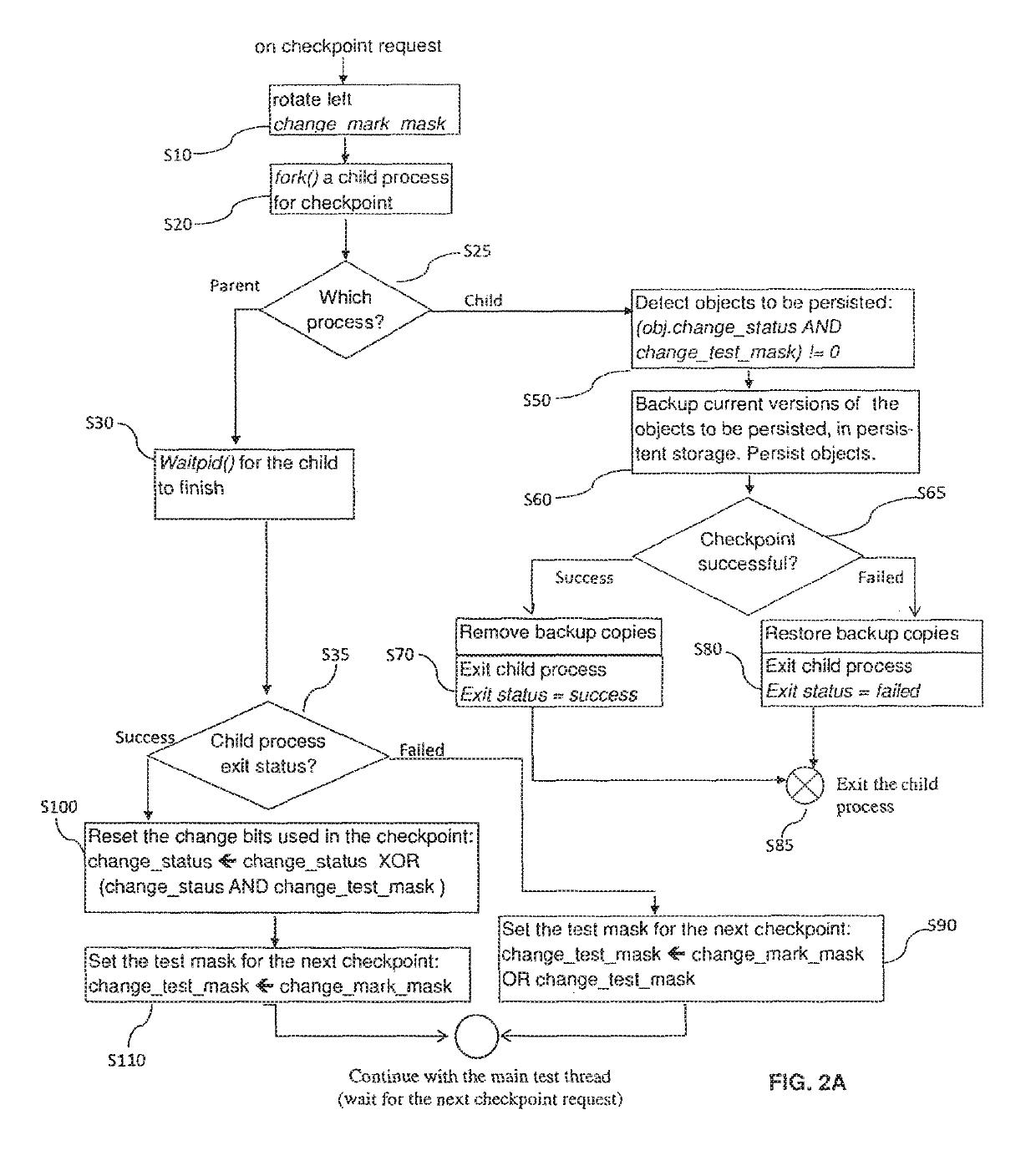
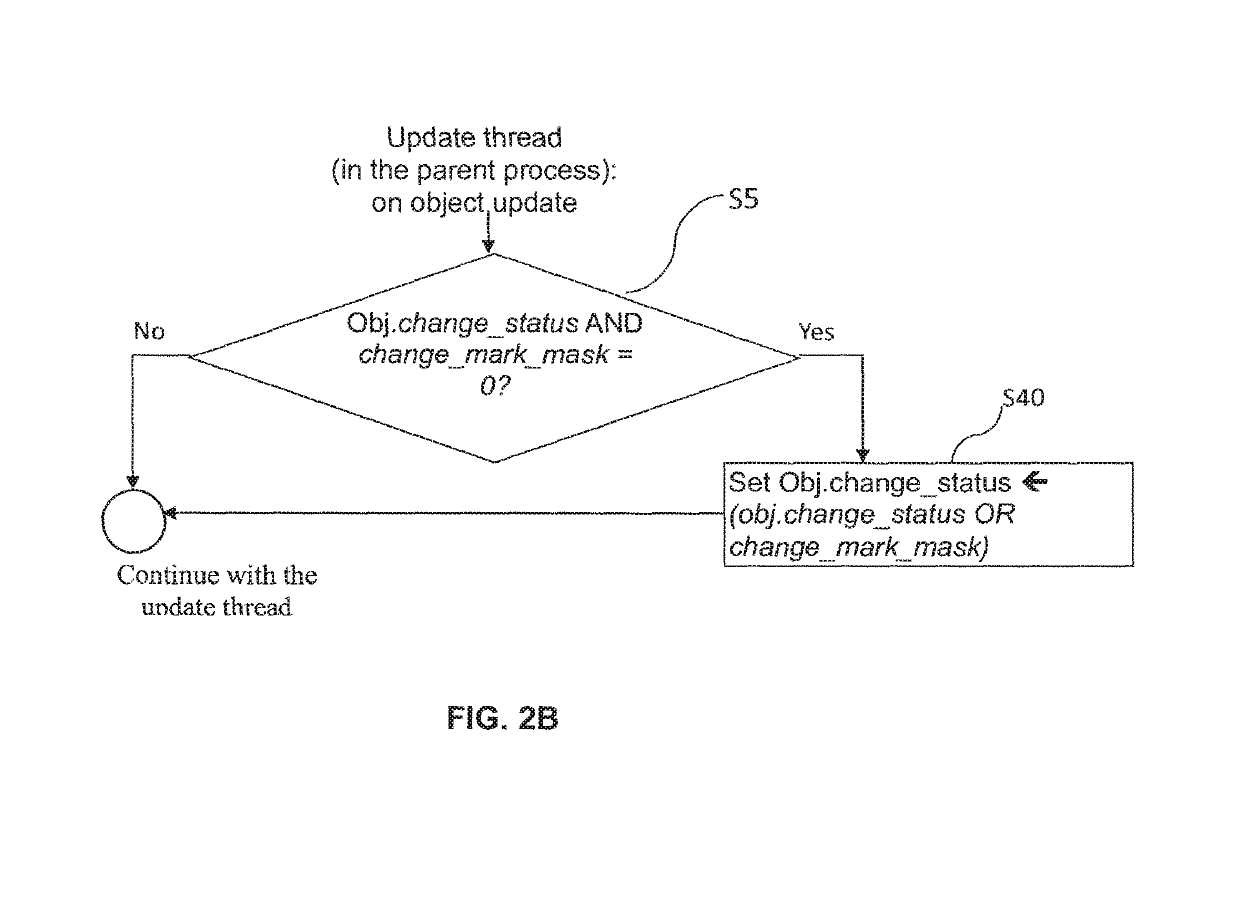
ActiveUS20180046548A1Prevent unauthorized accessEfficient implementationProgram initiation/switchingRedundant operation error correctionDisjoint-setCopying
A method for tracking objects in a first memory during a plurality of time intervals is provided, wherein the method comprises: updating, by one or more update threads, copying, by the one or more test threads, the one or more non-copied shadow objects to a second memory, determining, by the one or more test threads whether the step of copying the one or more non-copied shadow objects was successful, and updating, by the one or more test threads, the status variables of corresponding objects that correspond to the one or more non-copied shadow objects that were copied successfully, wherein subsequent bits of the status variables correspond to subsequent time intervals and wherein the one or more update threads and the one or more test threads operate on disjoint sets of bits of the status variables.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Wavelength and filter arrangement for WDM networks
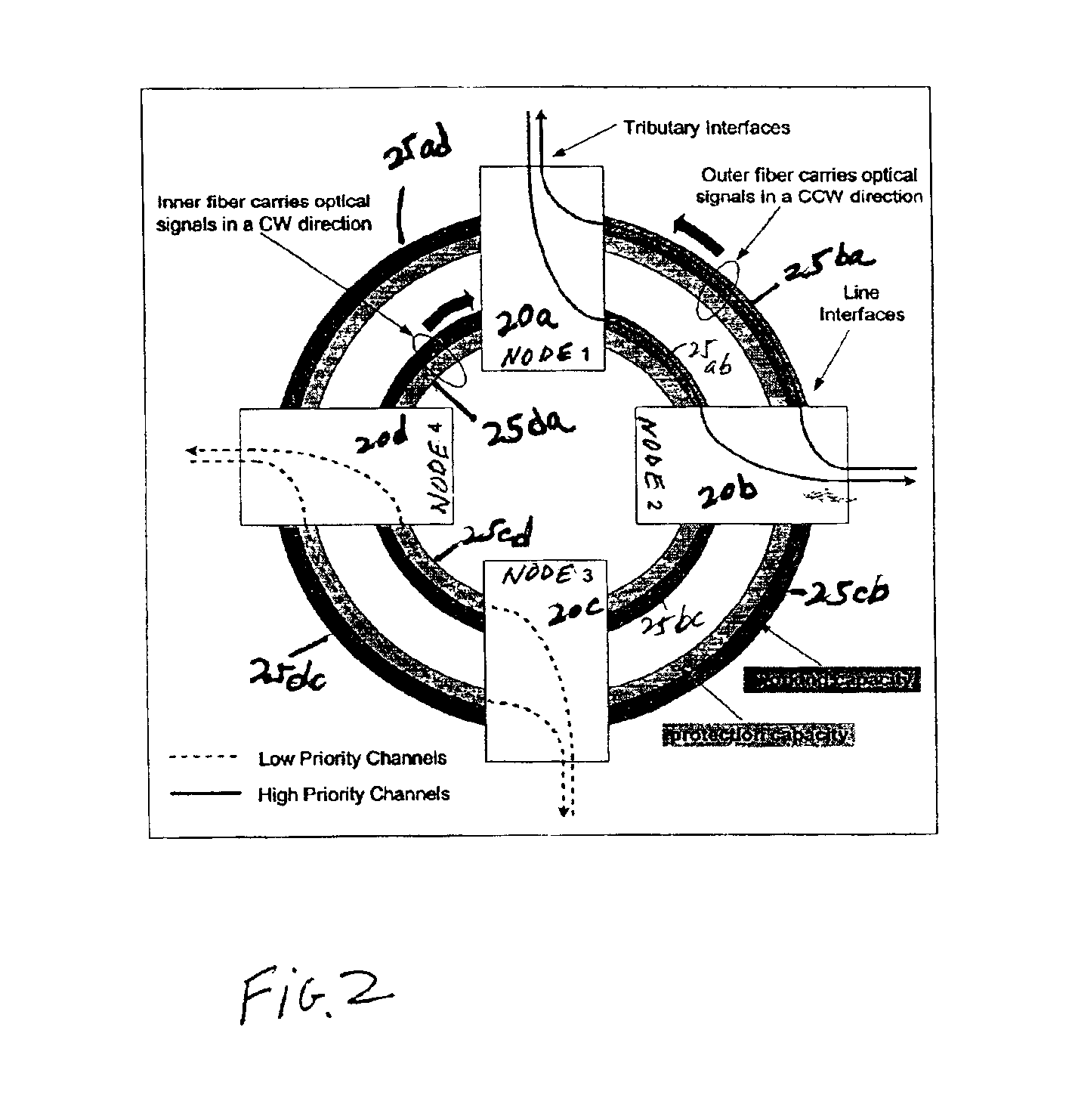
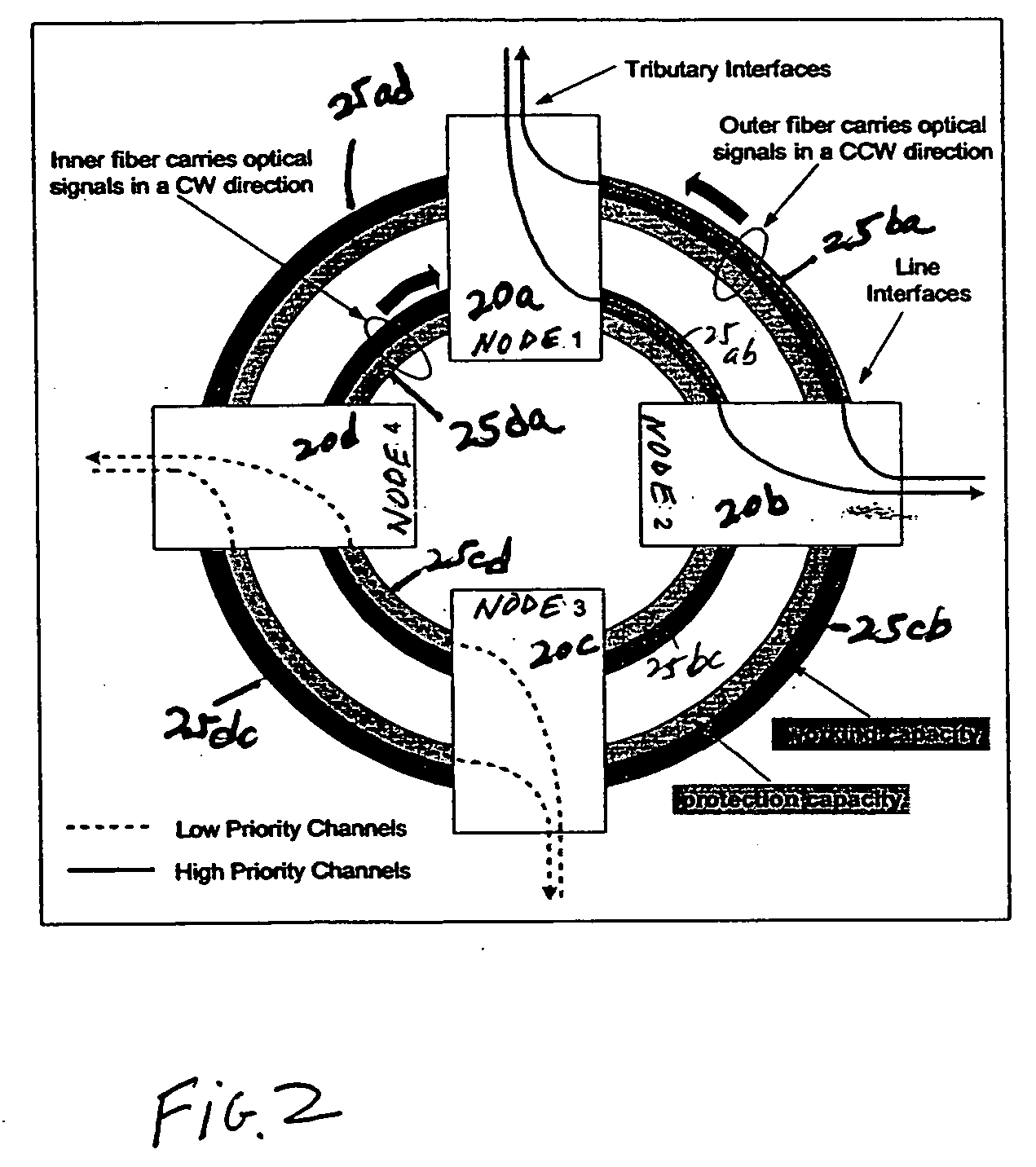
InactiveUS20050180746A1Eliminate crosstalkLess expensiveLaser detailsError preventionFiberDisjoint-set
In a ring having first and second adjacent nodes, and two fibers carrying information between the first and second nodes, the first fiber carries information in one direction, while the second fiber carries information in another direction. Each fiber includes wavelength capacity allocated to working and protection traffic. The working and protection wavelength capacities in the first fiber are respectively assigned to first and second disjoint sets of wavelengths, while the working and protection wavelength capacities in the second fiber are respectively assigned to the second and first disjoint sets of wavelengths.
Owner:CIENA
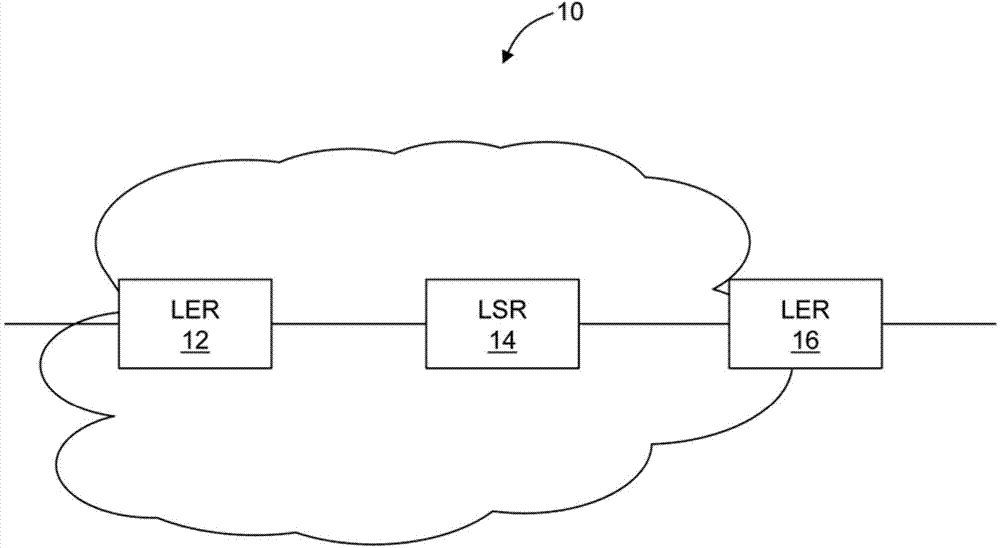
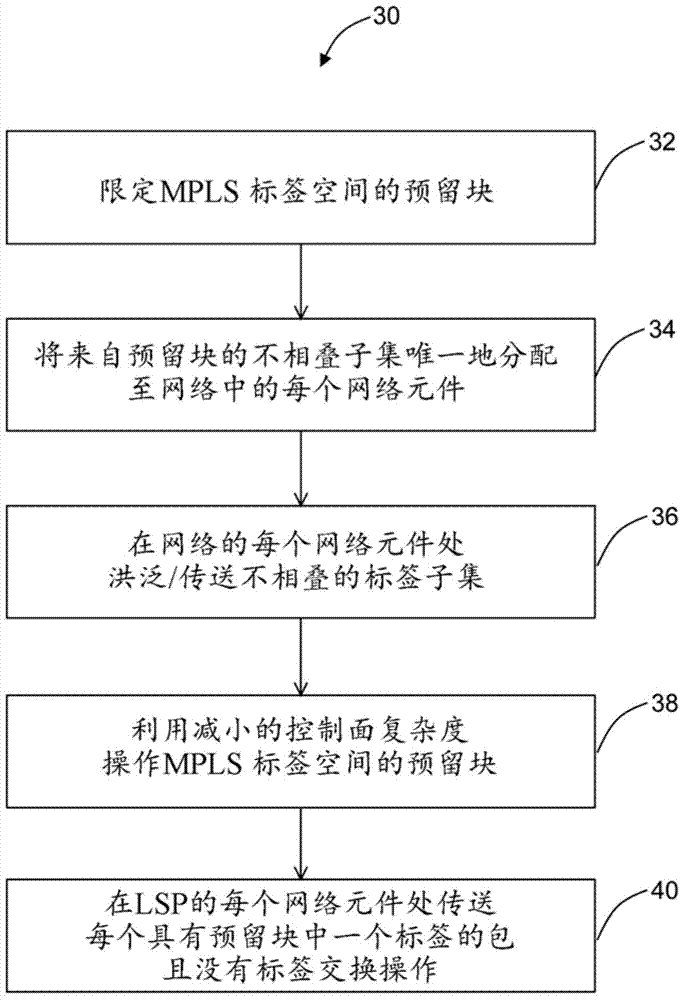
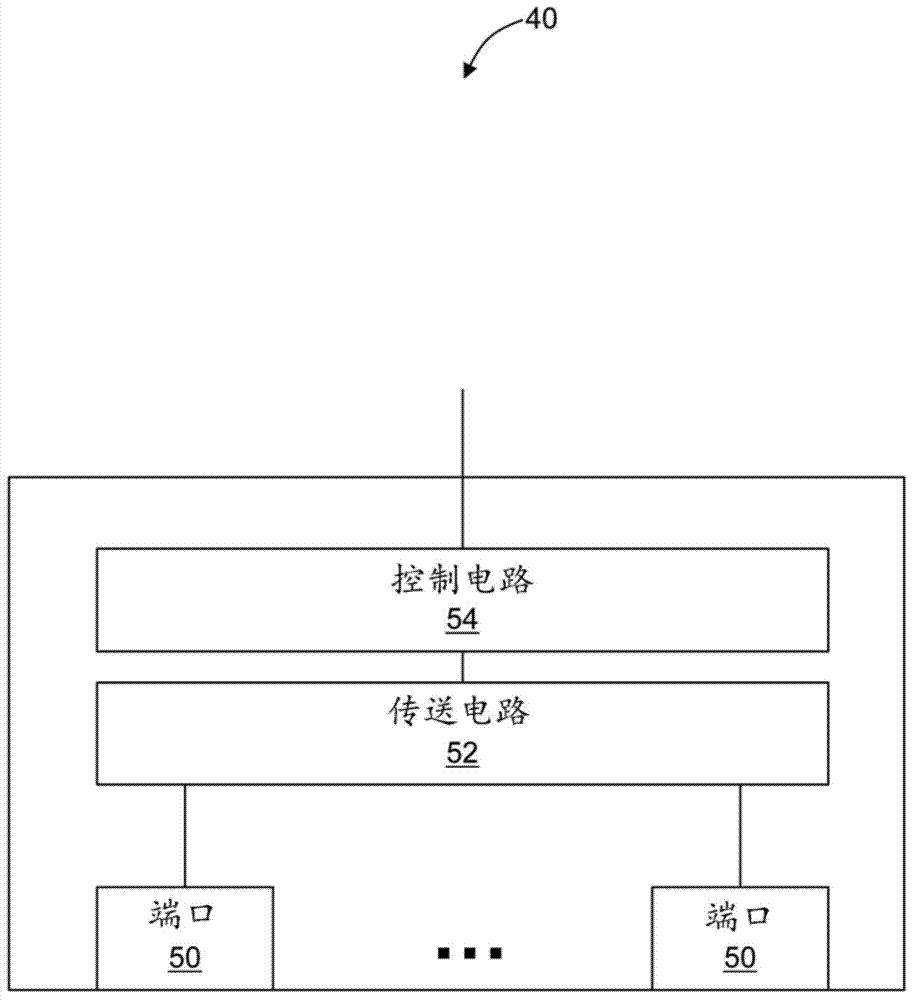
Reduced complexity multiprotocol label switching
A reduced complexity Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) method, 30, a MPLS network element, 40, and a MPLS network, 10, utilize an MPLS operating regime whereby disjoint sets of one or more MPLS labels are uniquely and specifically associated with just one switch, i.e. each switch node is assigned one or more non-overlapping labels from the RFC 3032 20 bit label space to bind to particular service end-points; which then enables these labels to embody the core properties of a destination address (DA) in the network sub-domain in which they are used. The central property is that these DA labels are constant for a given forwarding path across the entire sub-domain, remaining unchanged at any extends in the network. Once that is achieved, any and all hop-by-hop signaling protocols are unnecessary, since there is no need for label swapping, and the label-switching-node binding information can be flooded by interior routing protocols only.
Owner:希尔纳公司
Method and apparatus for tracking objects in a first memory
ActiveUS10503601B2Avoiding race condition and undeterministic behaviorPrevent unauthorized accessProgram initiation/switchingRedundant operation error correctionDisjoint-setObject storage
A method for tracking objects in a first memory during a plurality of time intervals is provided, wherein the method comprises: updating, by one or more update threads, copying, by the one or more test threads, the one or more non-copied shadow objects to a second memory, determining, by the one or more test threads whether the step of copying the one or more non-copied shadow objects was successful, and updating, by the one or more test threads, the status variables of corresponding objects that correspond to the one or more non-copied shadow objects that were copied successfully, wherein subsequent bits of the status variables correspond to subsequent time intervals and wherein the one or more update threads and the one or more test threads operate on disjoint sets of bits of the status variables.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com