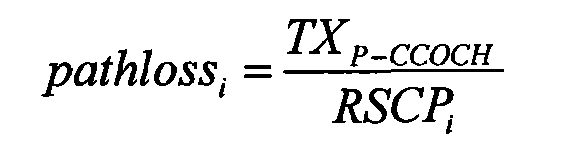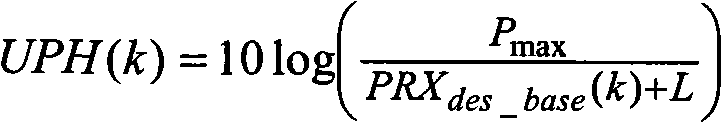Patents
Literature
332 results about "High-Speed Uplink Packet Access" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
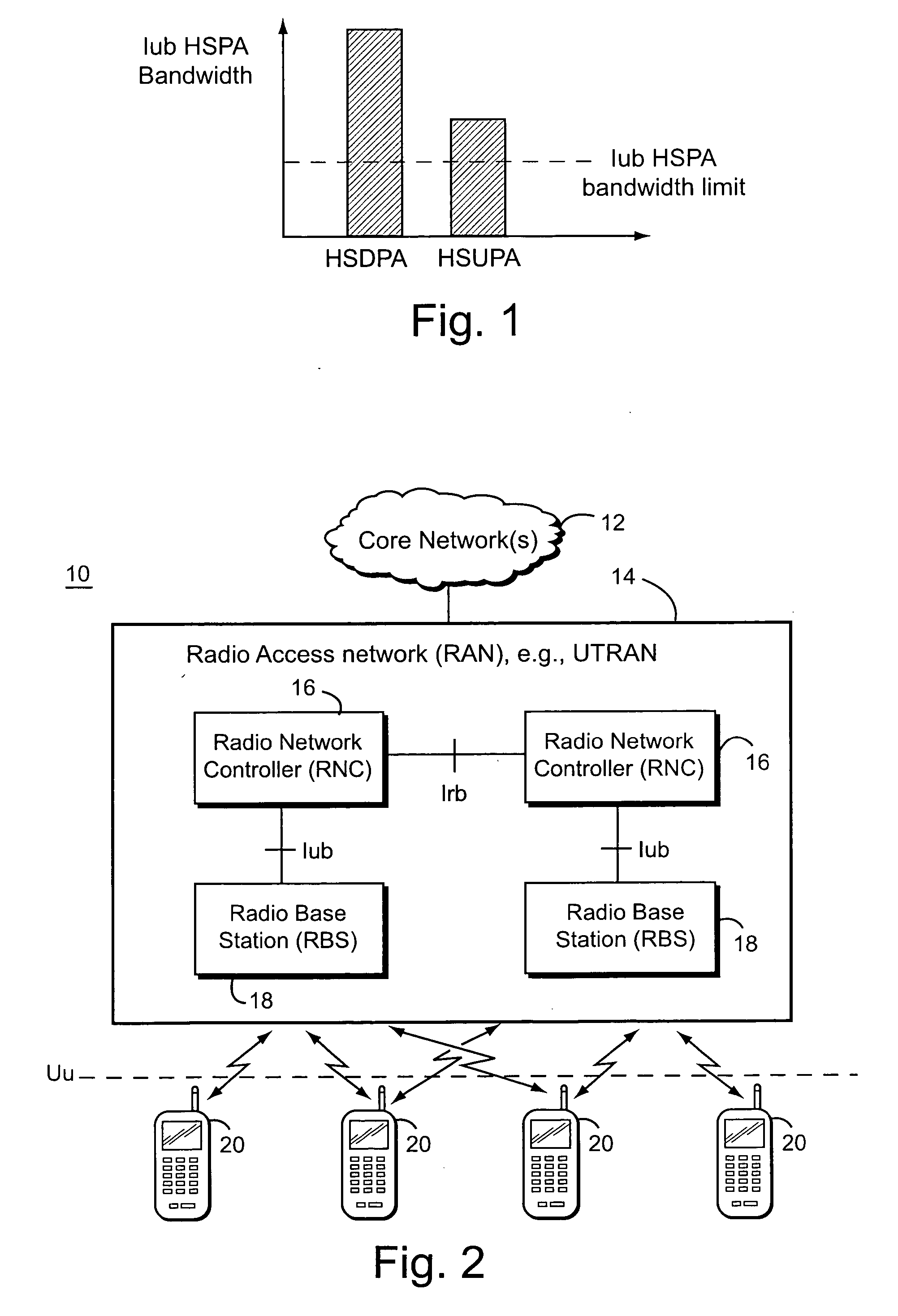
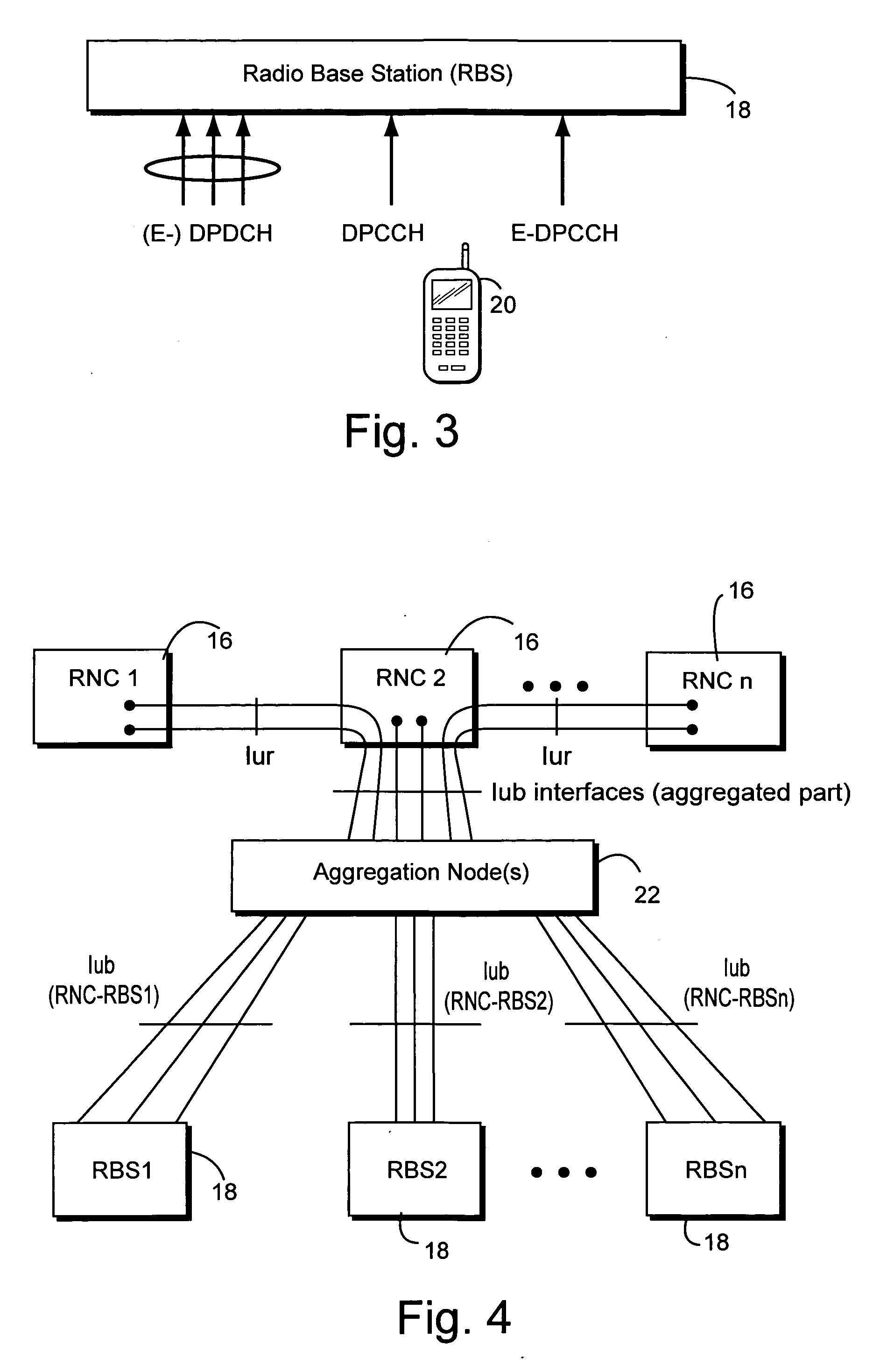
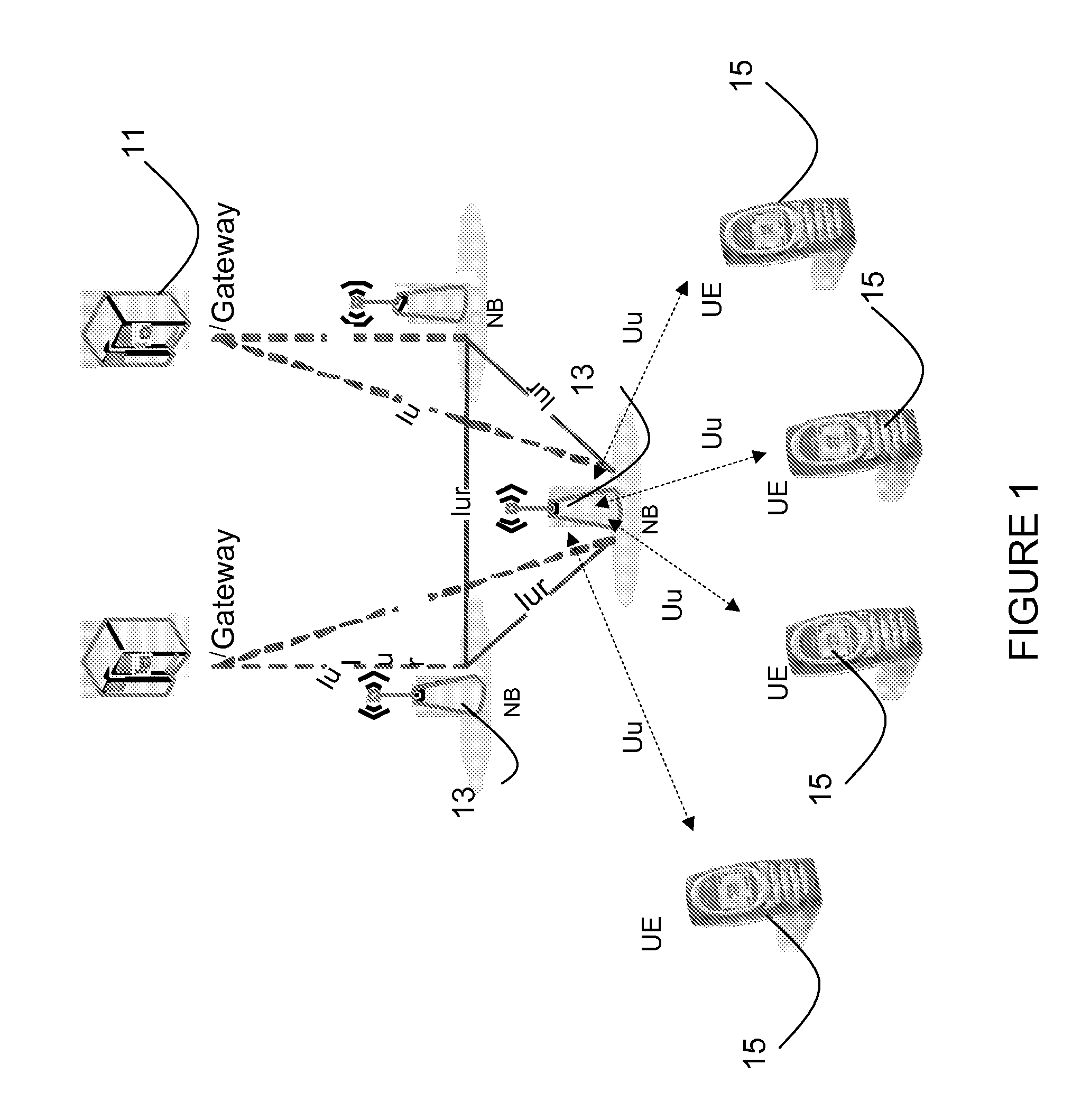
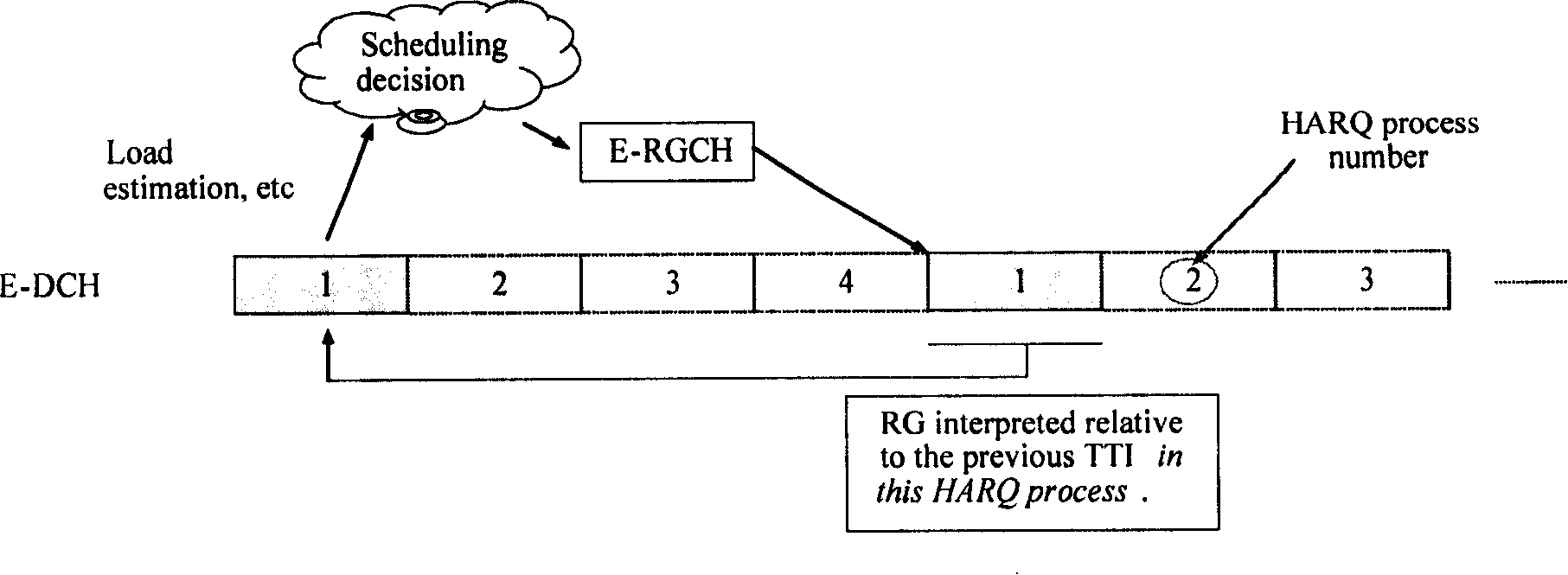
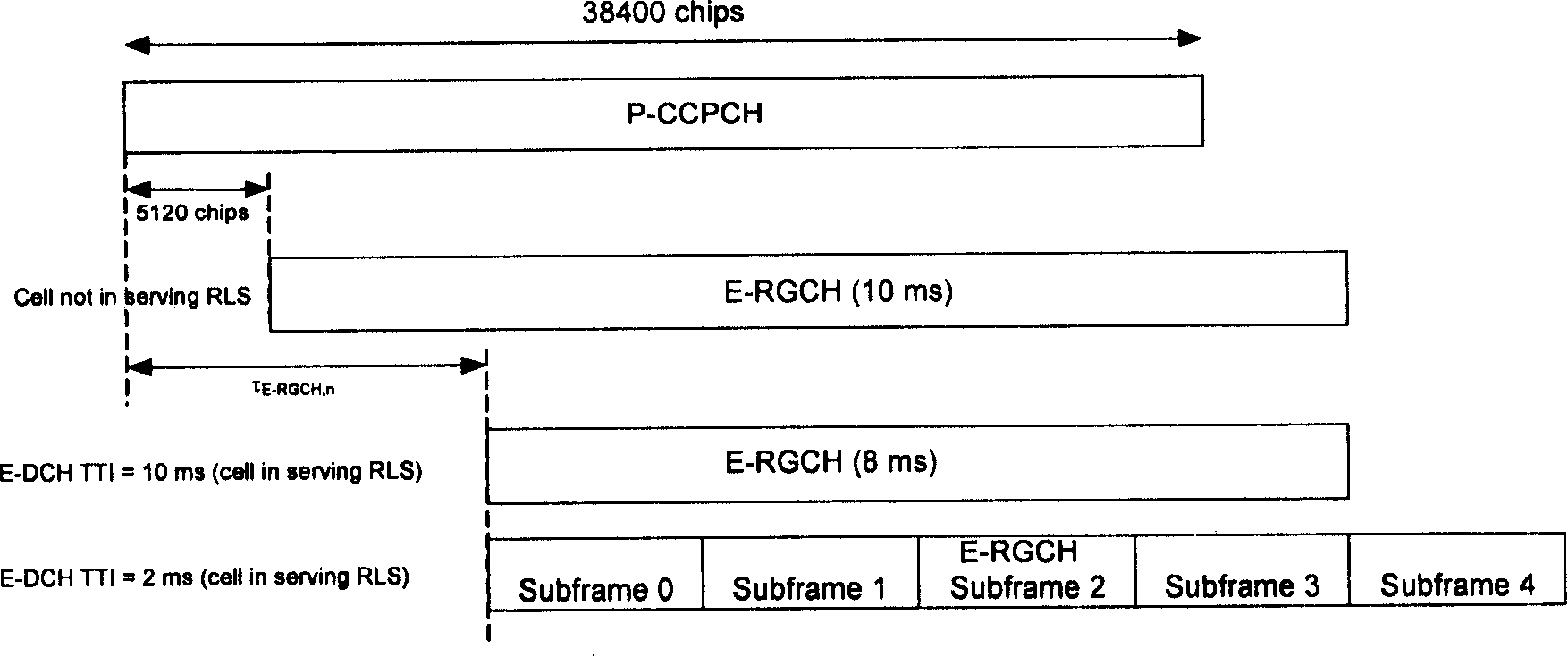
High-Speed Uplink Packet Access is a 3G mobile telephony protocol in the HSPA family with up-link speeds up to 5.76 Mbit/s. The name HSUPA was created by Nokia. The official 3GPP name for 'HSUPA' is Enhanced Uplink. The specifications for HSUPA are included in Universal Mobile Telecommunications System Release 6 standard published by 3GPP. – "The technical purpose of the Enhanced Uplink feature is to improve the performance of uplink dedicated transport channels, i.e. to increase capacity and throughput and reduce delay."
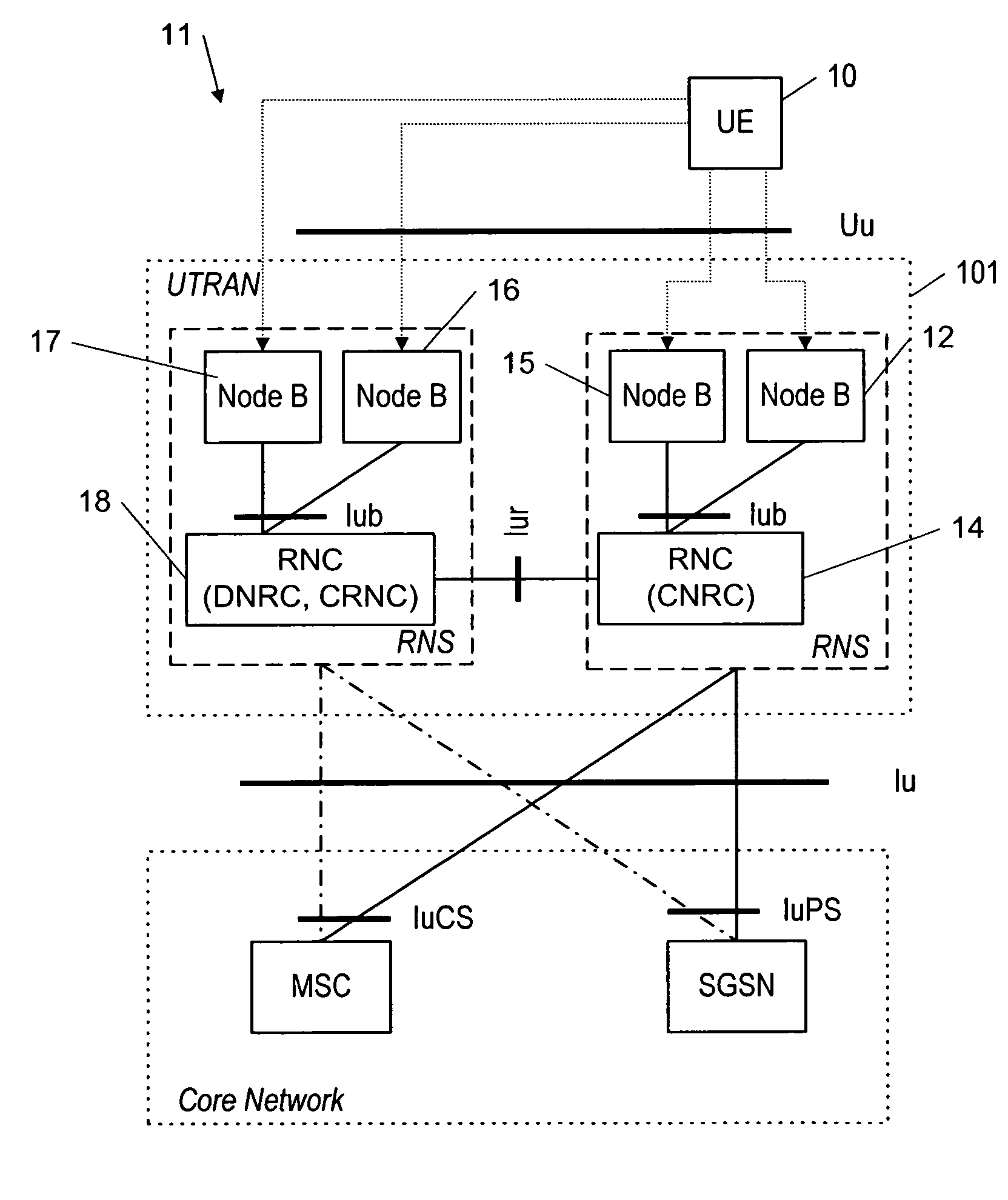
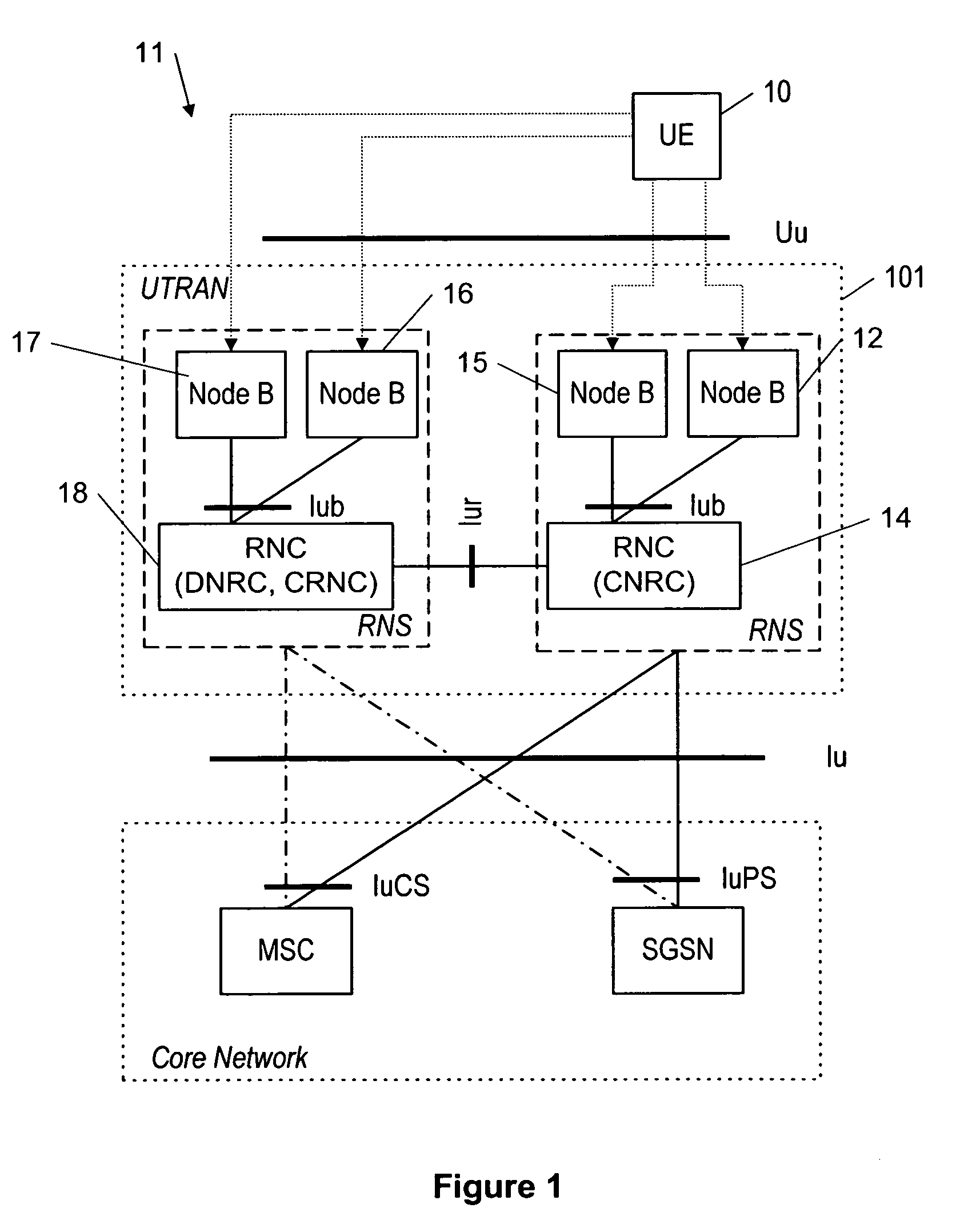
System and method for downlink signaling for high speed uplink packet access
ActiveUS20060056355A1Power managementNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemTransmitter
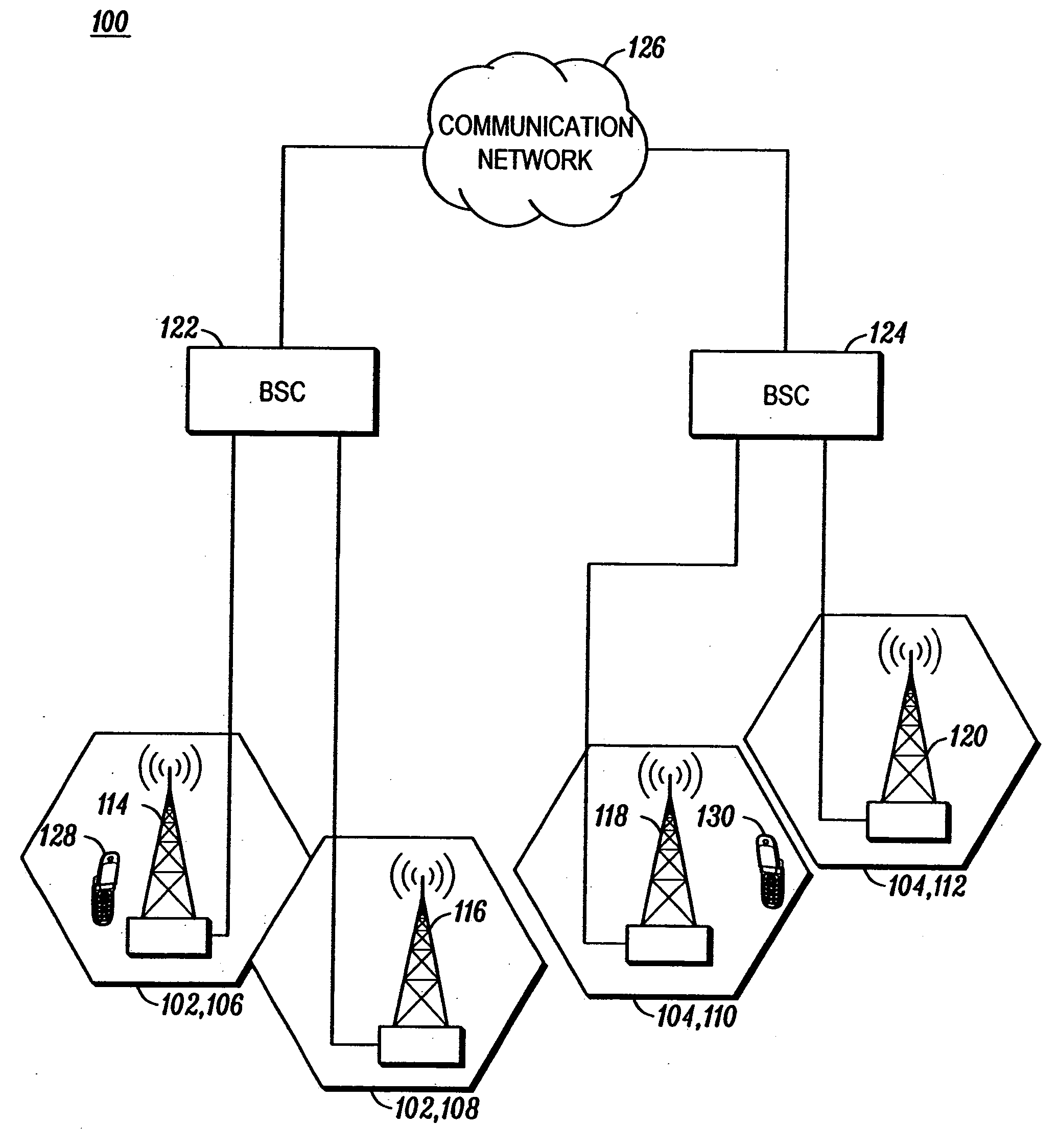
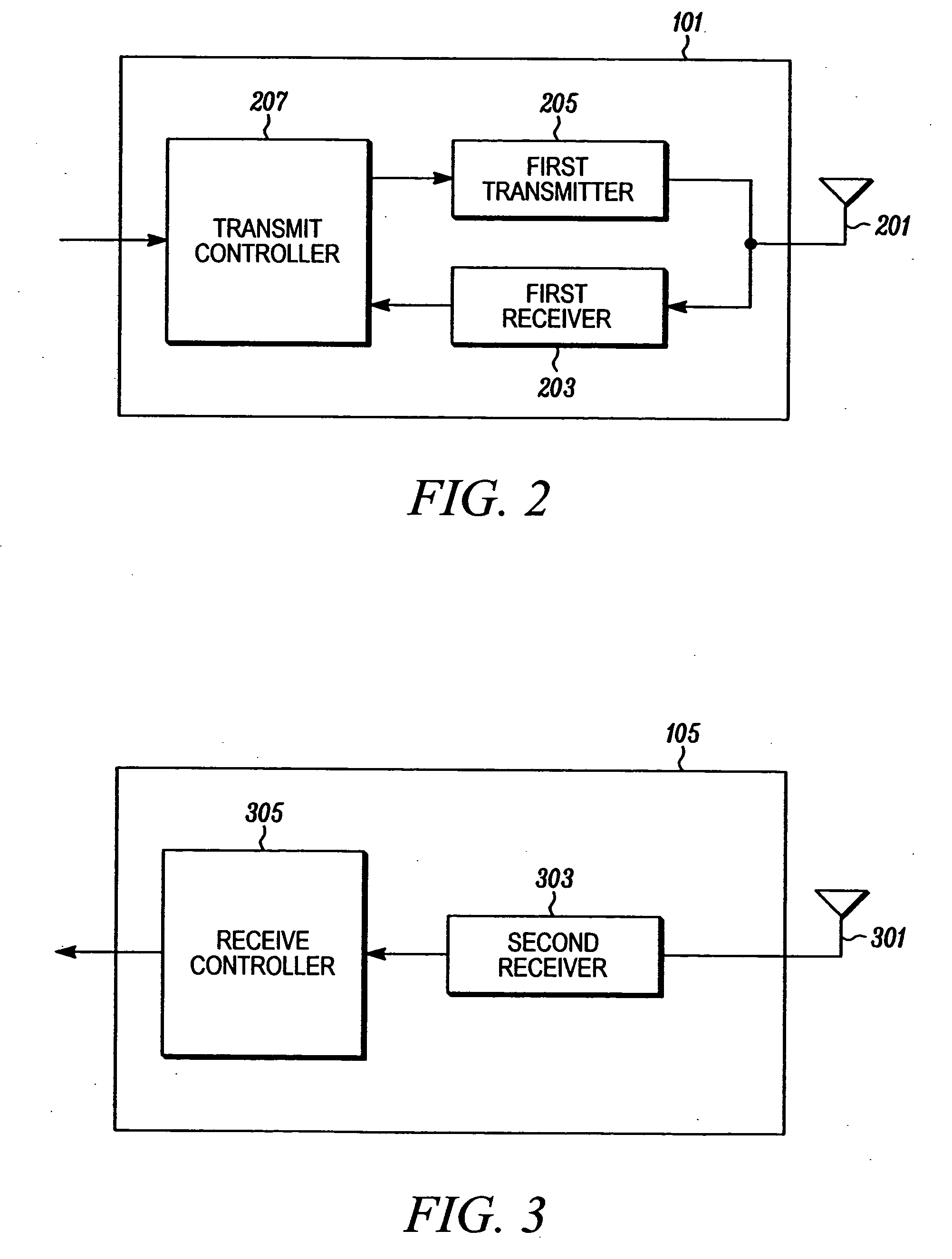
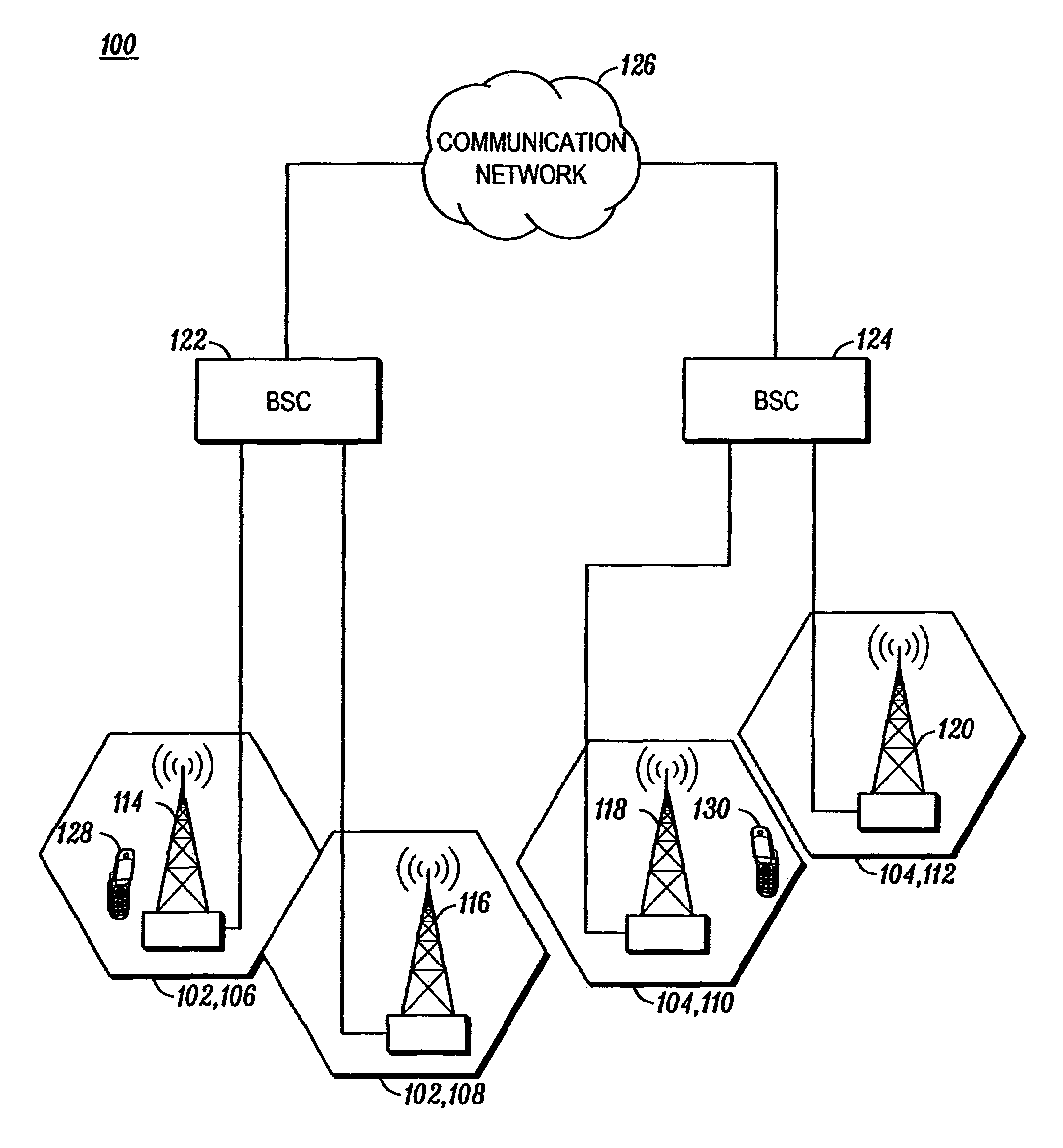
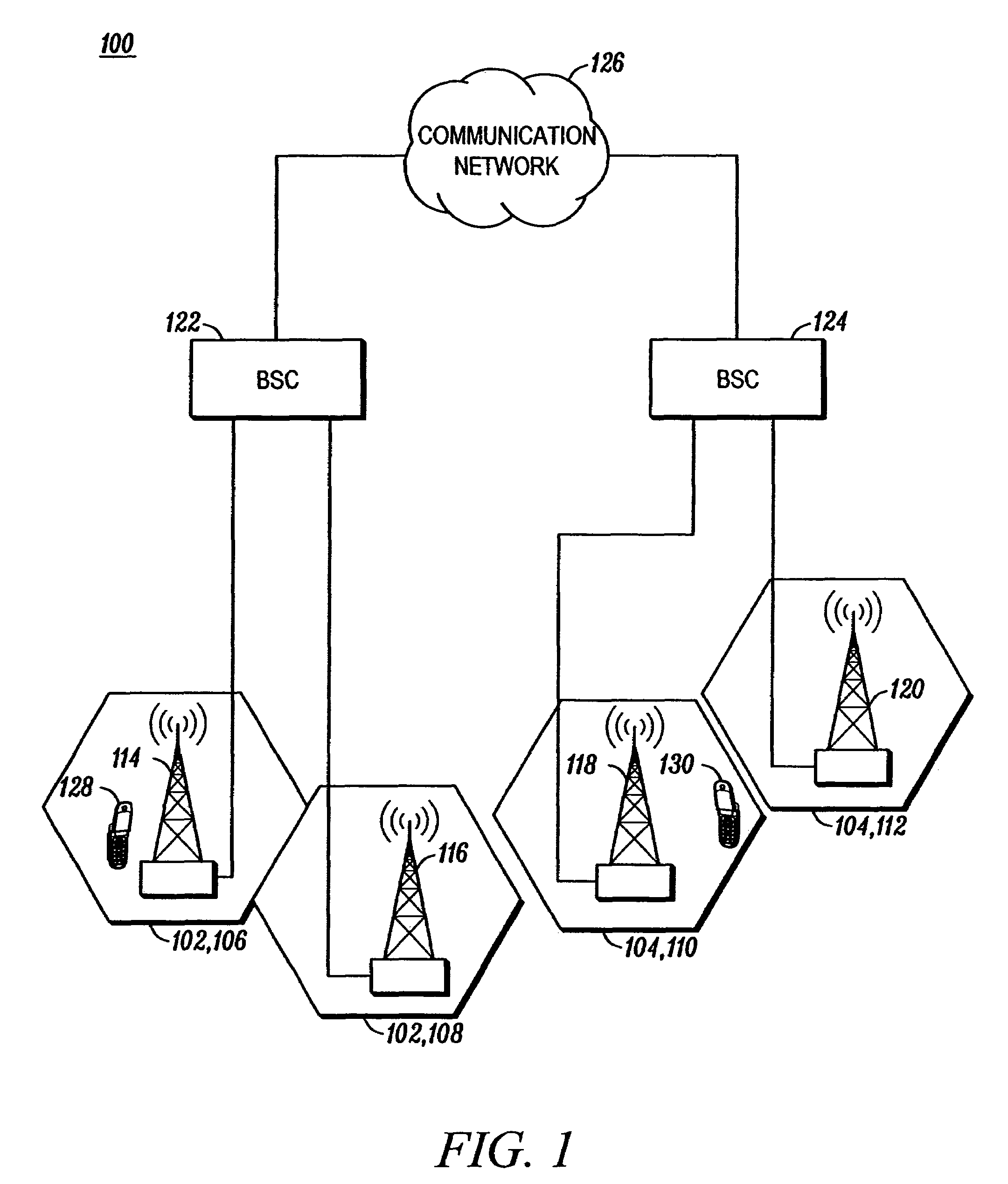
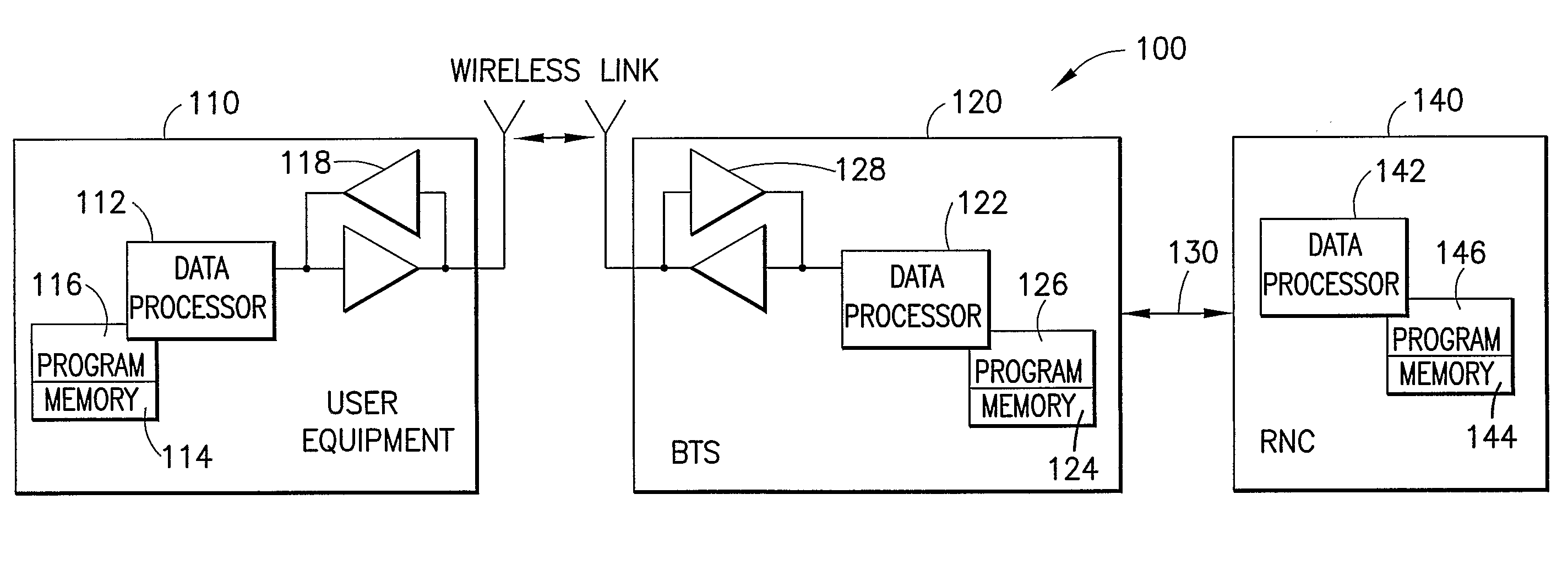
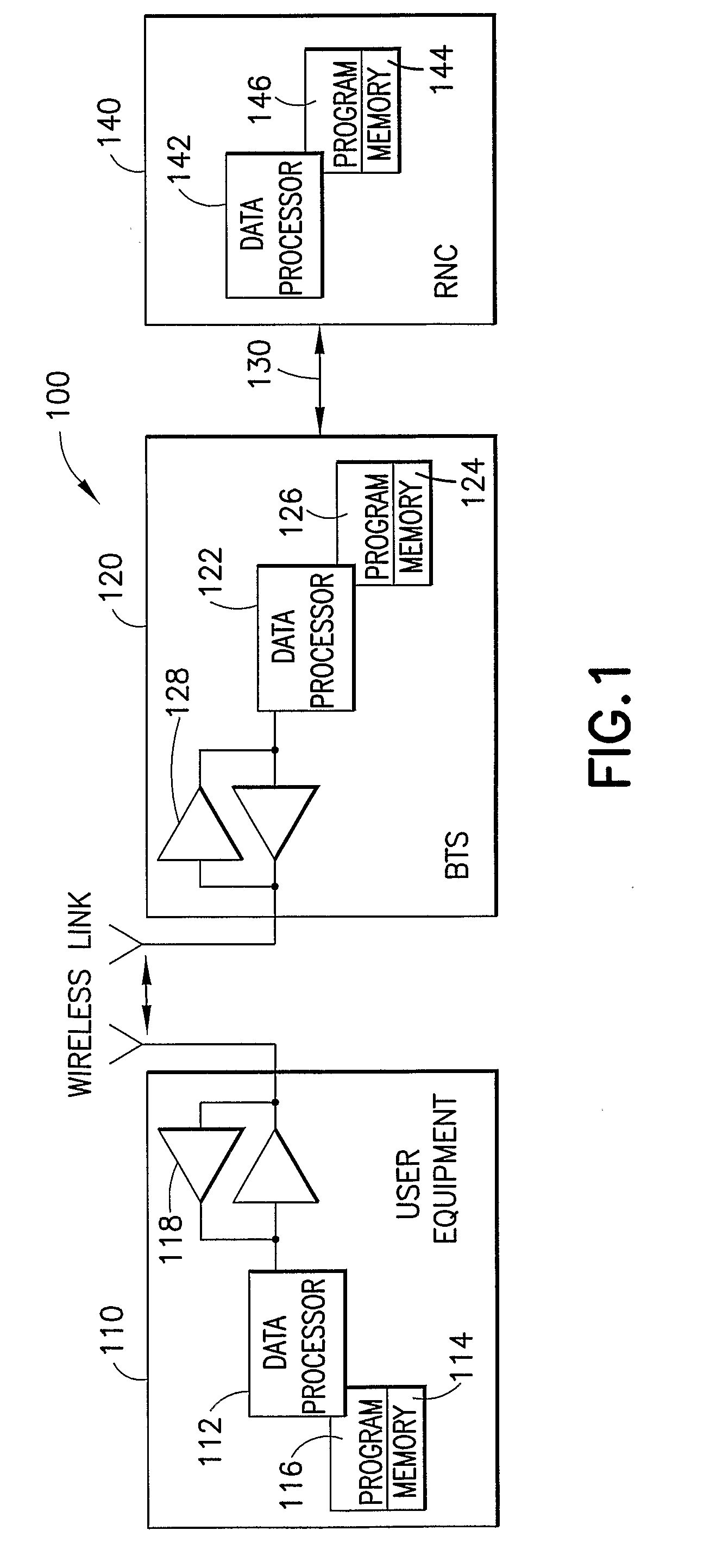
A wireless communication system (100) and method for providing high speed uplink packet access from user equipment (128, 130) to a base station (114, 116, 118, 120). Each of the user equipment (128, 130) and the base station (114, 116, 118, 120) includes a transmitter (1106, 1206), a receiver (1104, 1204), and a controller (1108, 1208) coupled to the transmitter and the receiver. Data packets are transmitted from the user equipment (128, 130) to the base station (114, 116, 118, 120). Control information, corresponding to the data packets, is transmitted from the base station (114, 116, 118, 120) to the user equipment (128, 130). The control information includes an absolute grant channel indicator and / or channelization code(s) assigned to the user equipment (128, 130). The controller (1108) of the user equipment (128, 130) is configured to minimize a number of channelization code per scheduling active set cell to be monitored by the user equipment based on the absolute grant channel indicator and / or to utilize the channelization code(s) in response to handoff and / or entering an active channel state.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
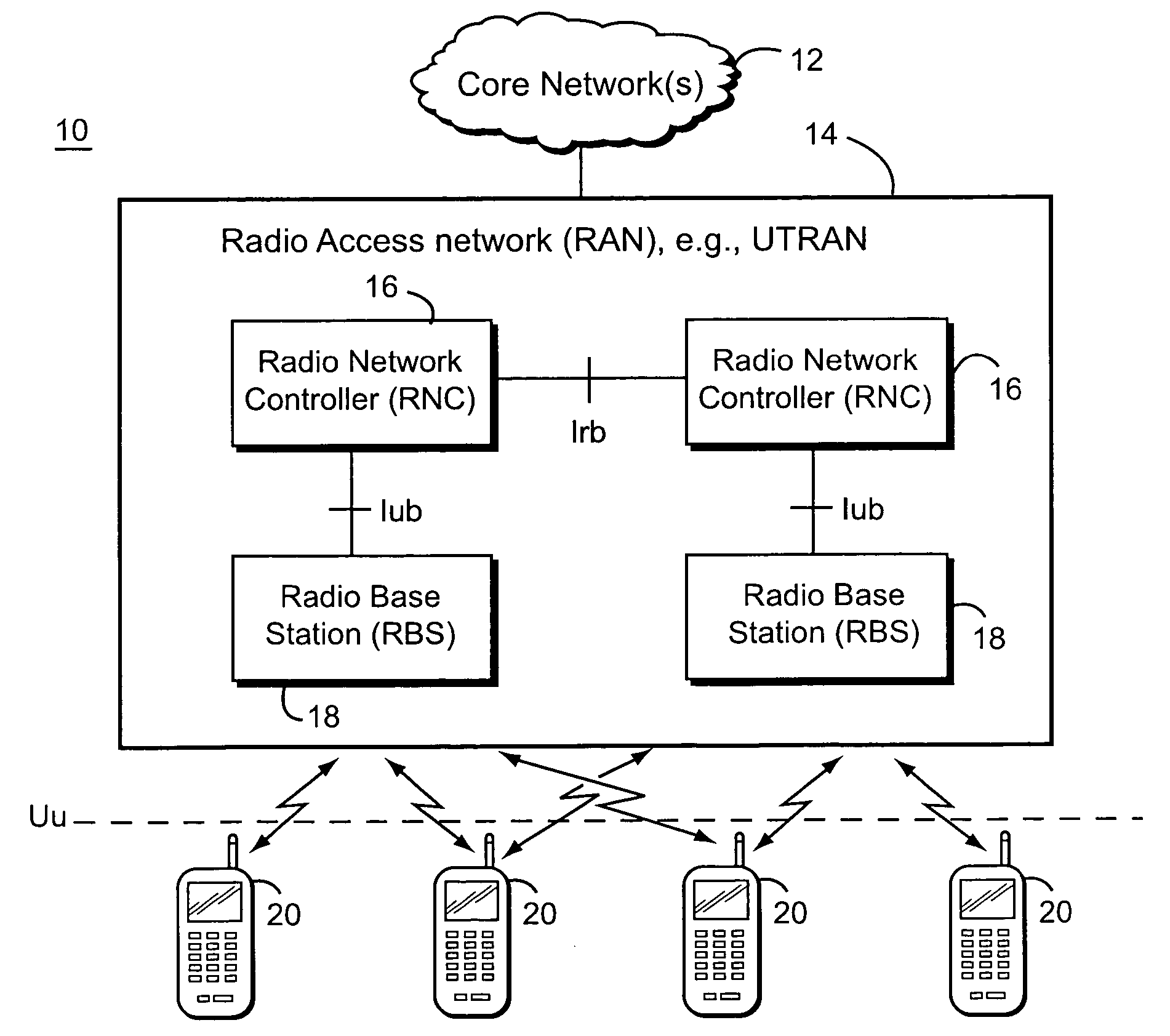
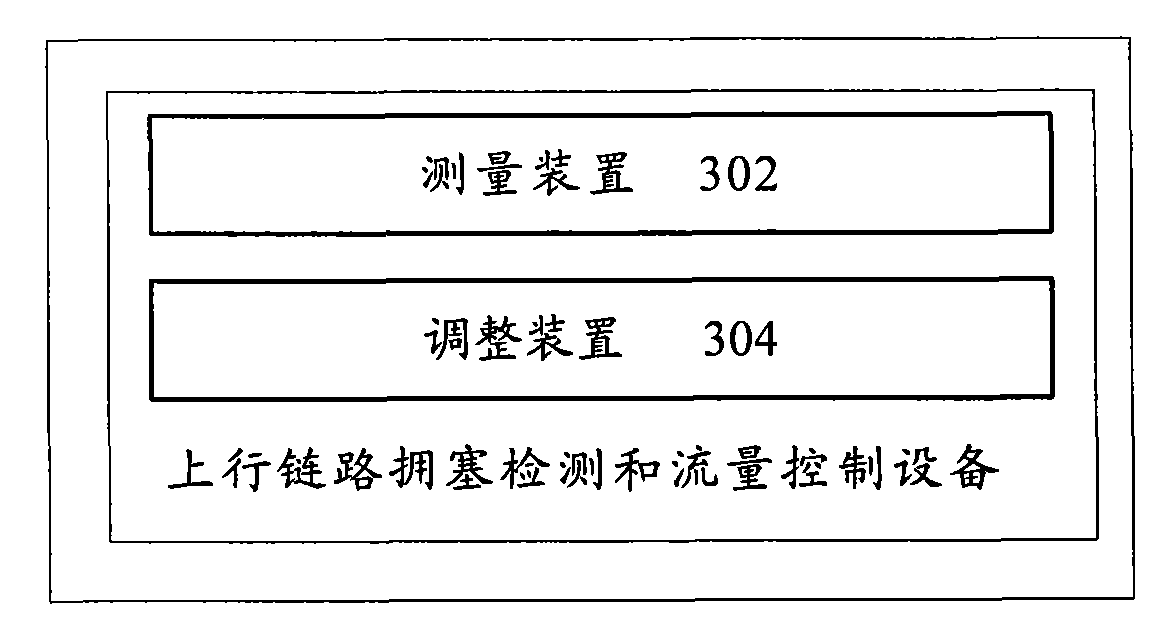
Uplink congestion detection and control between nodes in a radio access network
ActiveUS20060159016A1Reduce bit rate parameterReduce congestionError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementAccess networkCongestion detection
Congestion in a radio access network (RAN) associated with transporting uplink information originating from one or more mobile terminals is detected. That detected RAN congestion is reduced using any suitable technique (several examples are described) and may be implemented in one or more nodes in the RAN. One advantageous (but non-limiting) application is to a RAN that supports high speed uplink packet access (HSUPA) and / or one or more enhanced uplink dedicated channels (E-DCHs).
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
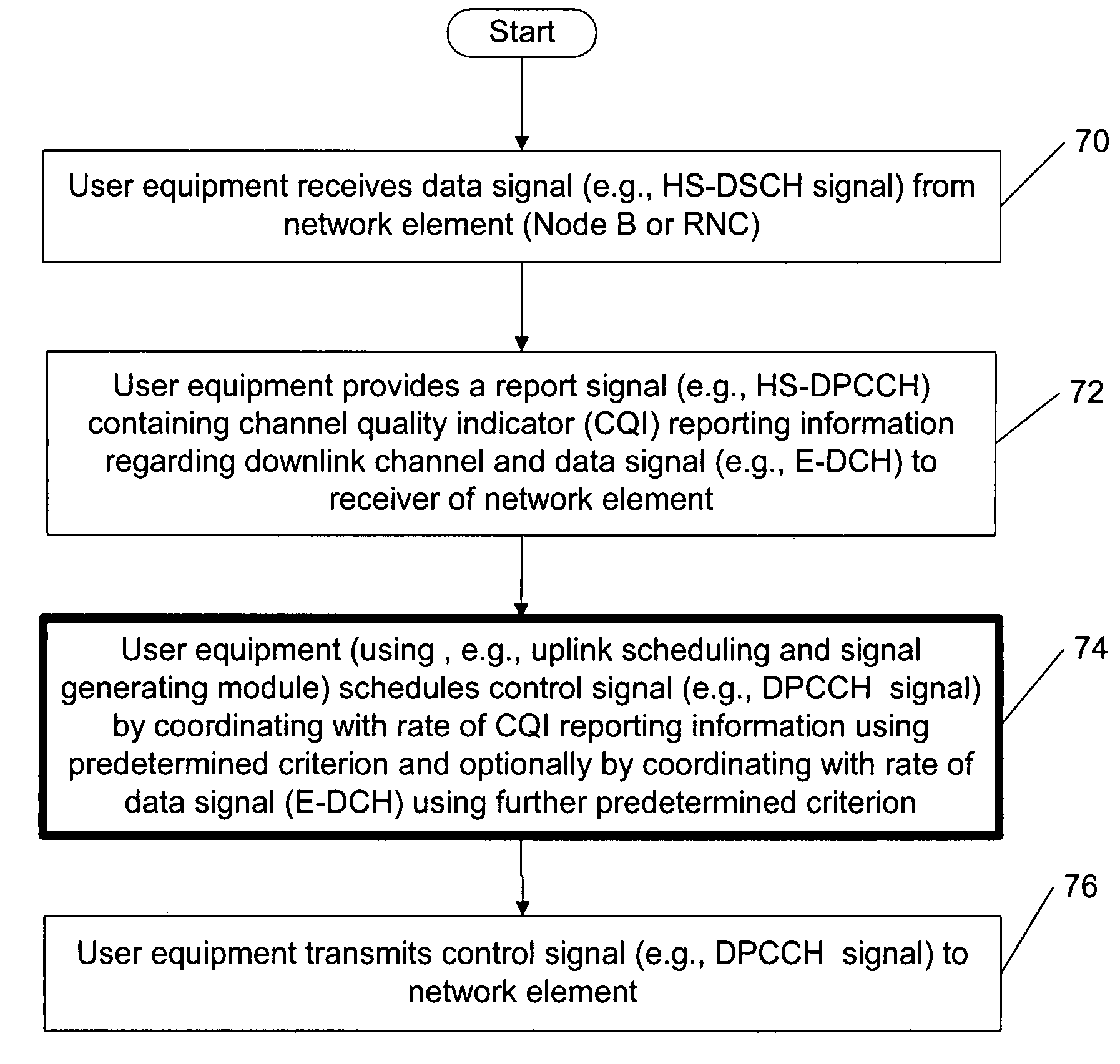
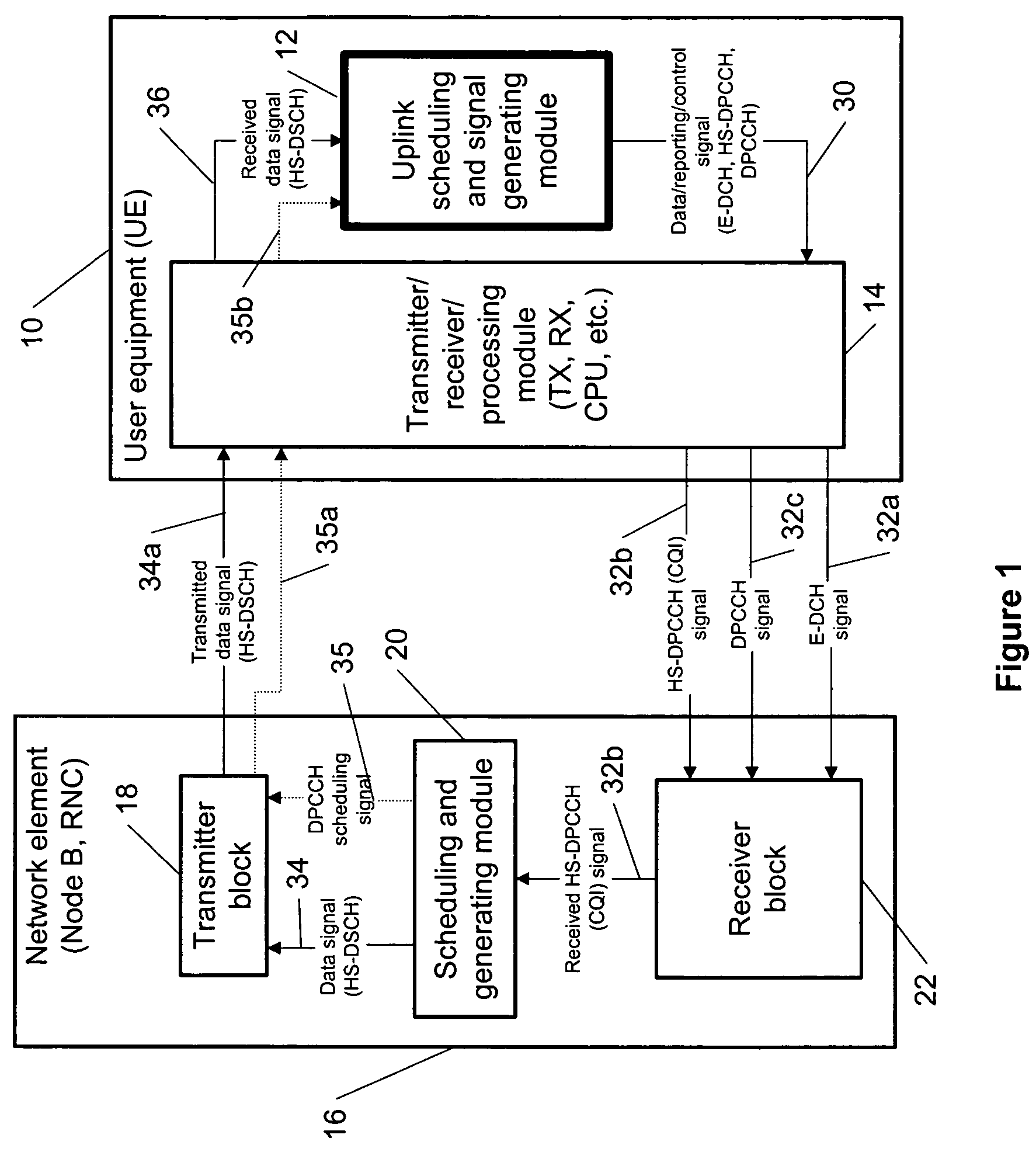
Coordinating uplink control channel gating with channel quality indicator reporting
ActiveUS20070030828A1Network traffic/resource managementConnection managementTelecommunicationsDPCCH
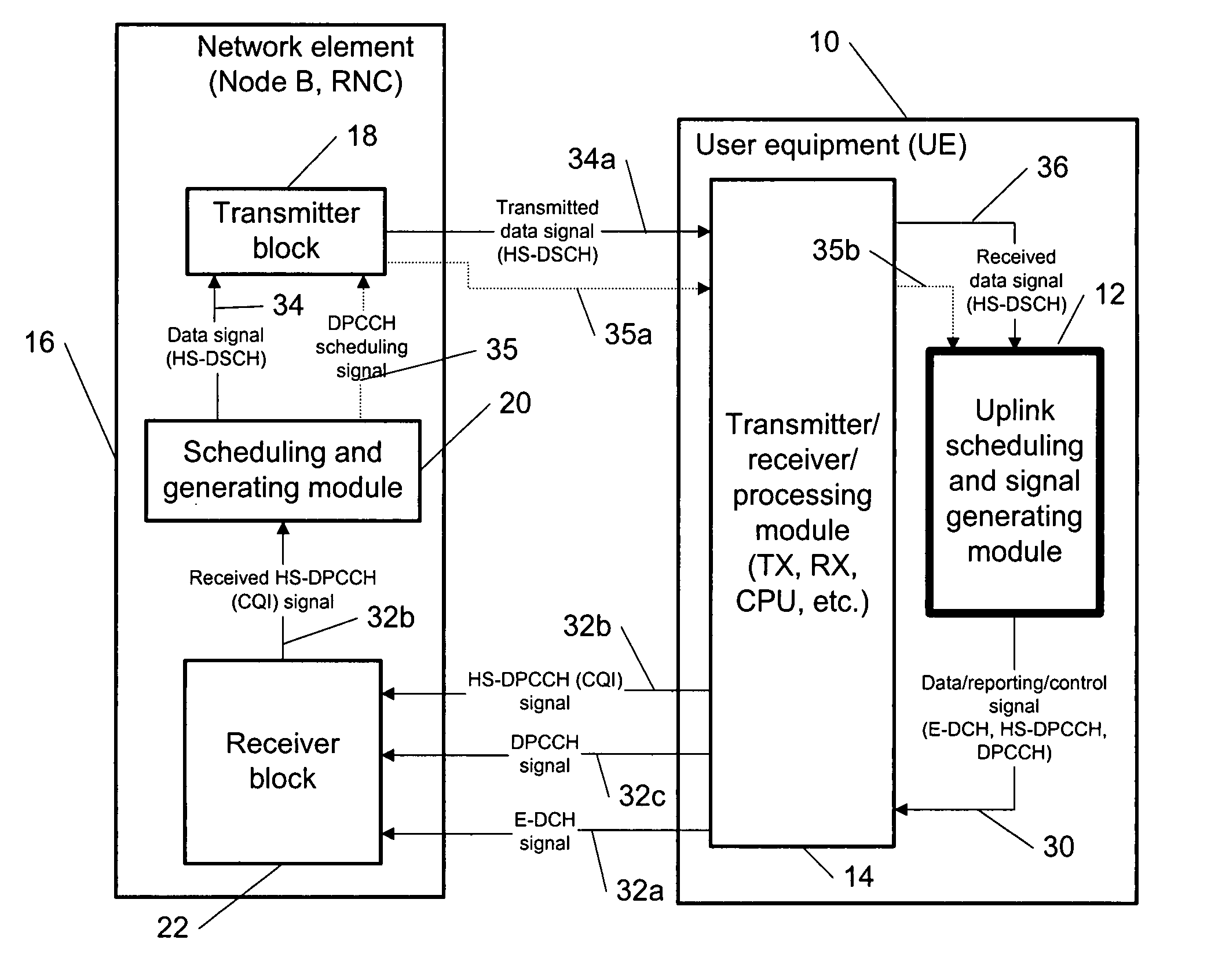
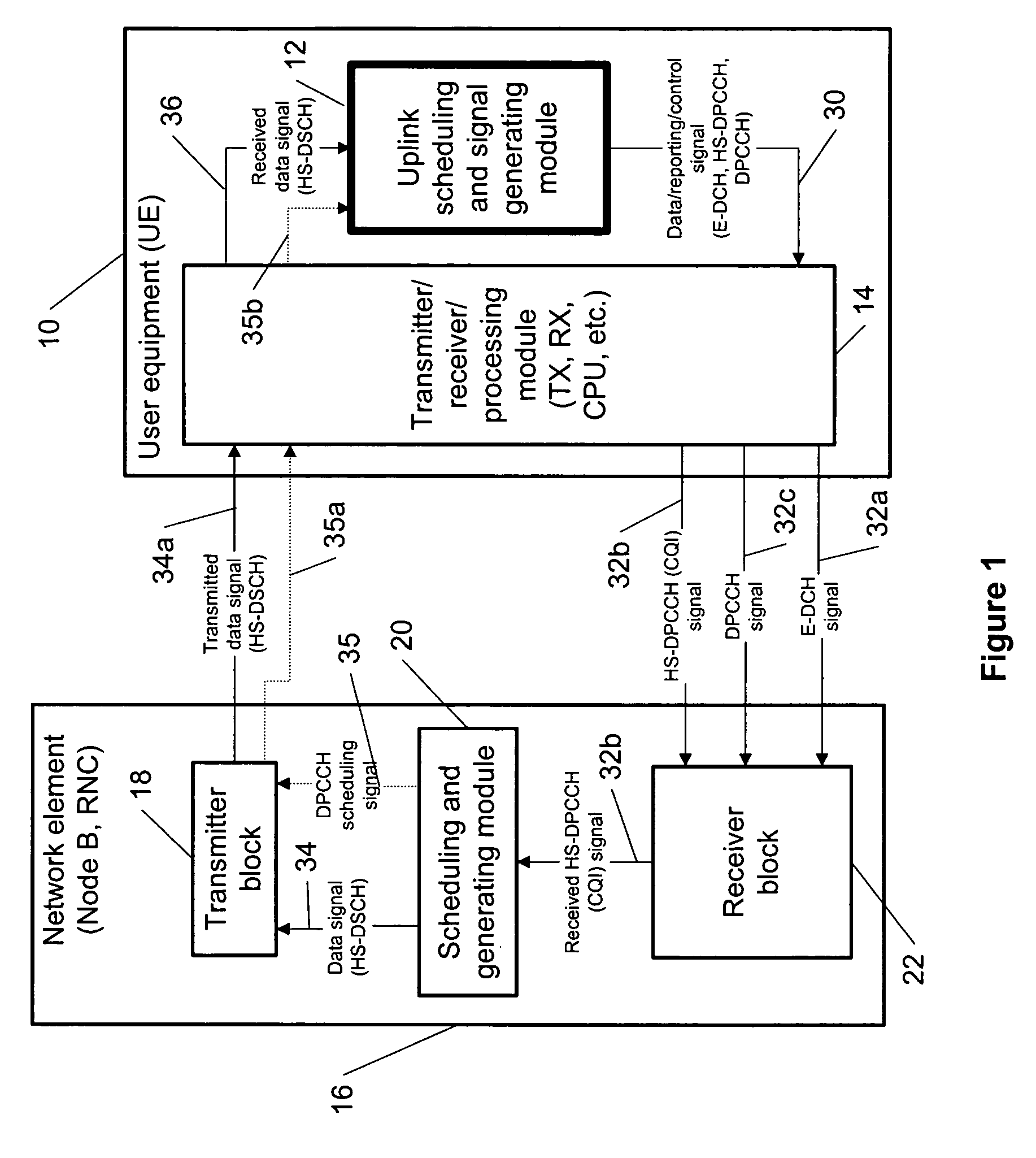
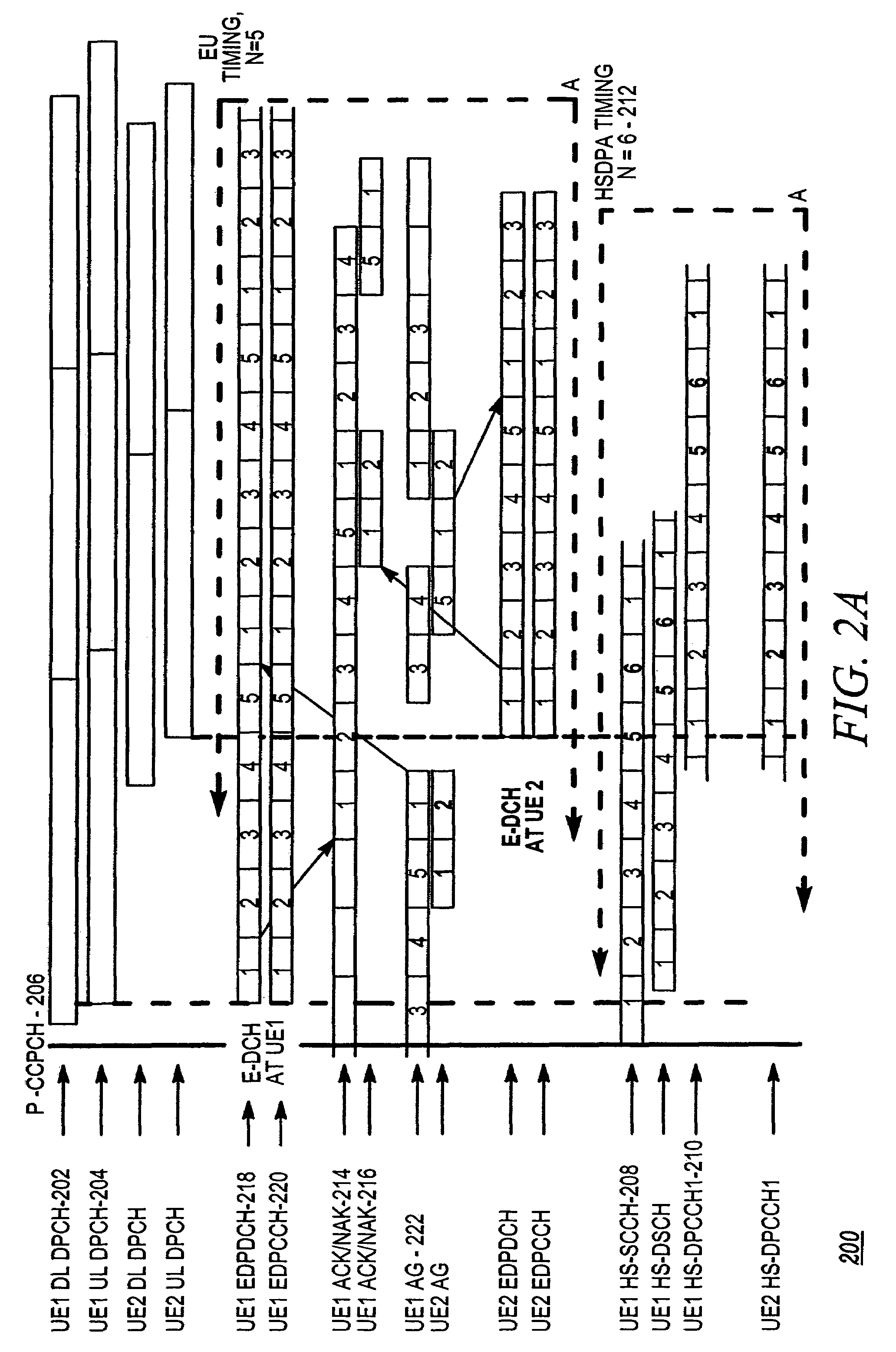
The specification and drawings present a new method, system, apparatus and software product for coordinating gating of an uplink (UL) control channel, e.g., a dedicated physical control channel (DPCCH), with UL reporting in regard to a downlink channel using, e.g., high speed uplink packet access (HSDPA) channel quality indicator (CQI) reporting.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Uplink congestion detection and control between nodes in a radio access network
InactiveUS20100232293A1High rateReduce rateError preventionTransmission systemsAccess networkRadio access network
Congestion in a radio access network (RAN) associated with transporting uplink information originating from one or more mobile terminals is detected. That detected RAN congestion is reduced using any suitable technique (several examples are described) and may be implemented in one or more nodes in the RAN. One advantageous (but non-limiting) application is to a RAN that supports high speed uplink packet access (HSUPA) and / or one or more enhanced uplink dedicated channels (E-DCHs).
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Uplink congestion detection and control between nodes in a radio access network
ActiveUS7724656B2High rateReduce rateError preventionTransmission systemsAccess networkCongestion detection
Congestion in a radio access network (RAN) associated with transporting uplink information originating from one or more mobile terminals is detected. That detected RAN congestion is reduced using any suitable technique (several examples are described) and may be implemented in one or more nodes in the RAN. One advantageous (but non-limiting) application is to a RAN that supports high speed uplink packet access (HSUPA) and / or one or more enhanced uplink dedicated channels (E-DCHs).
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
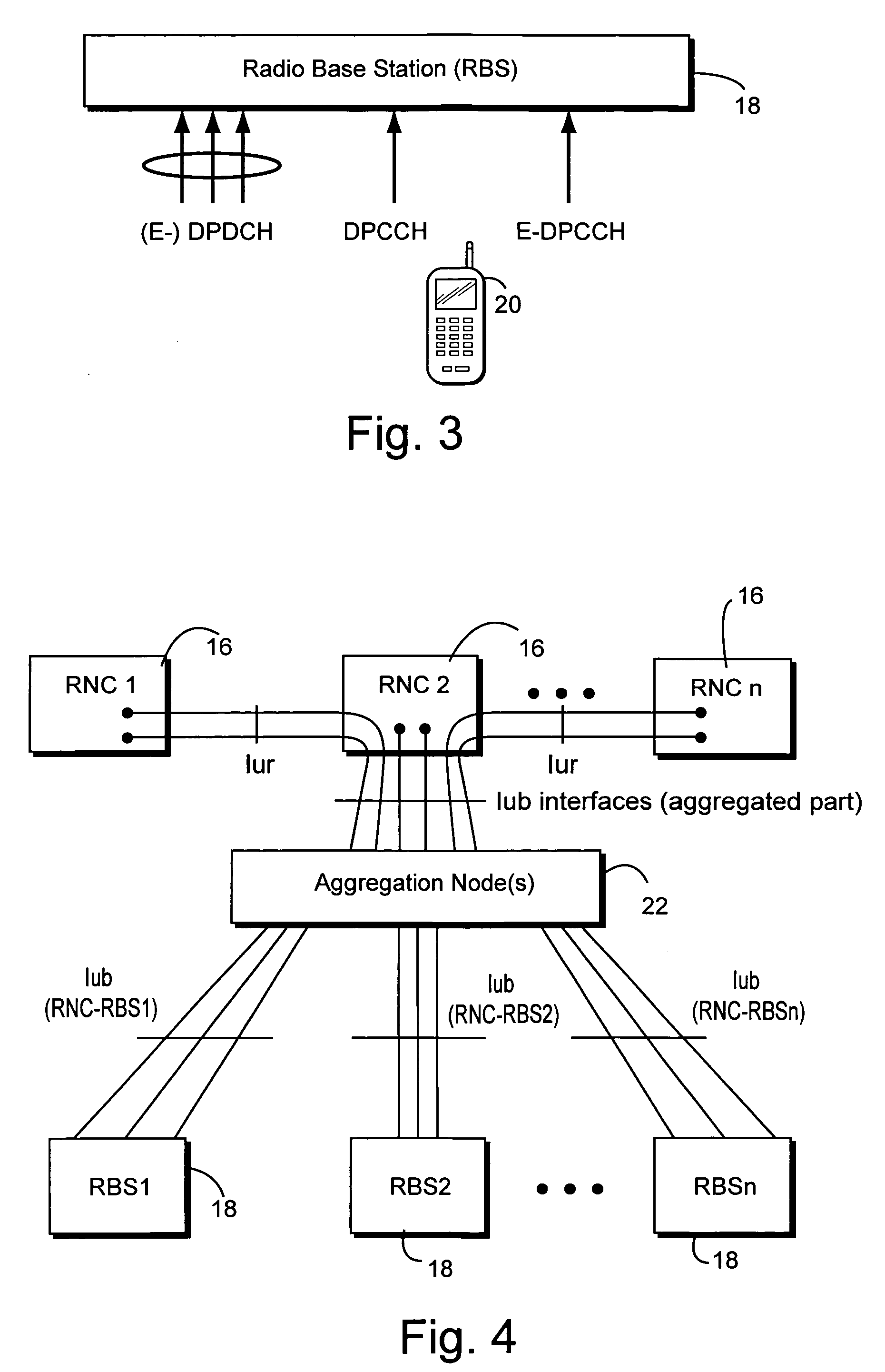
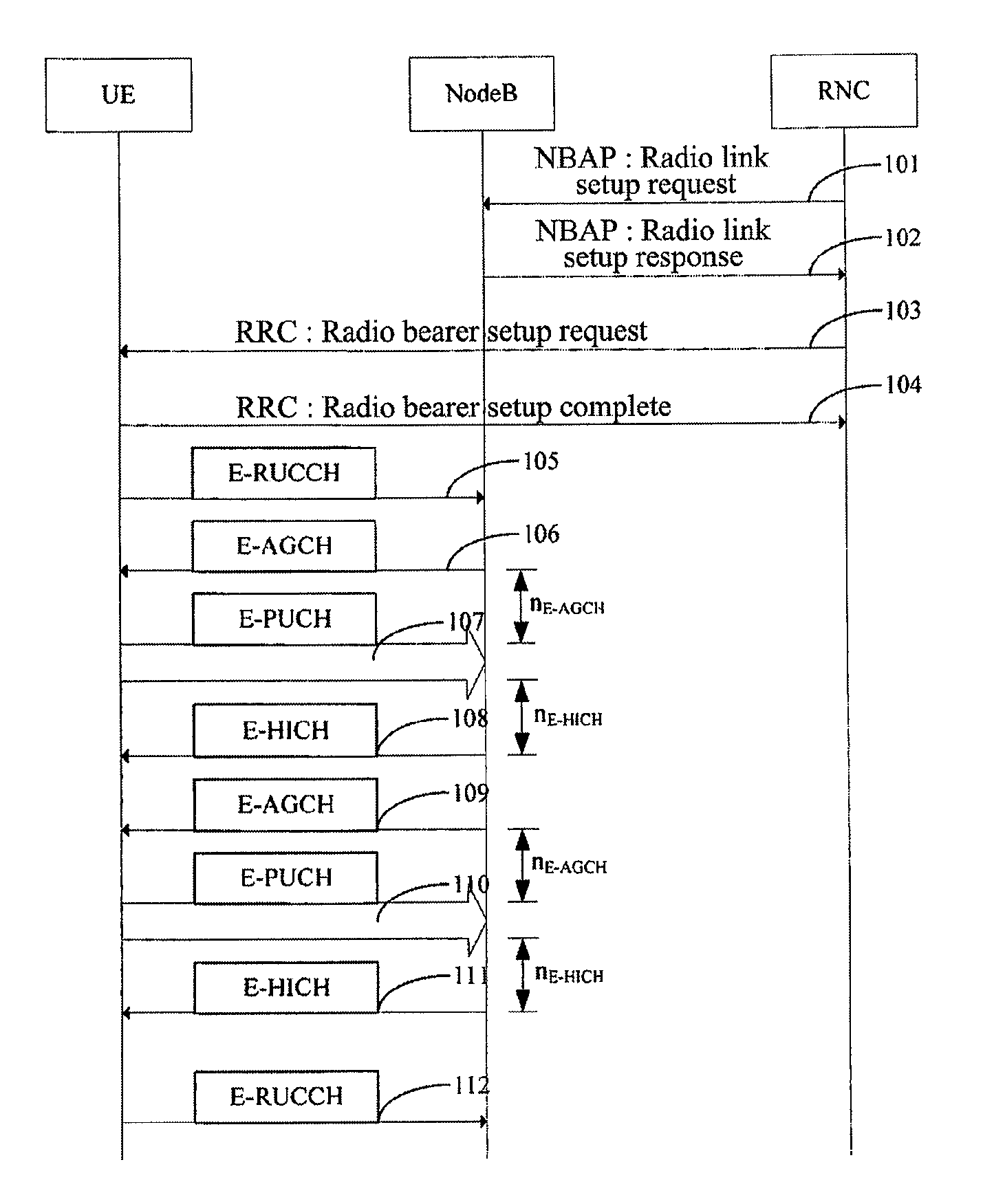
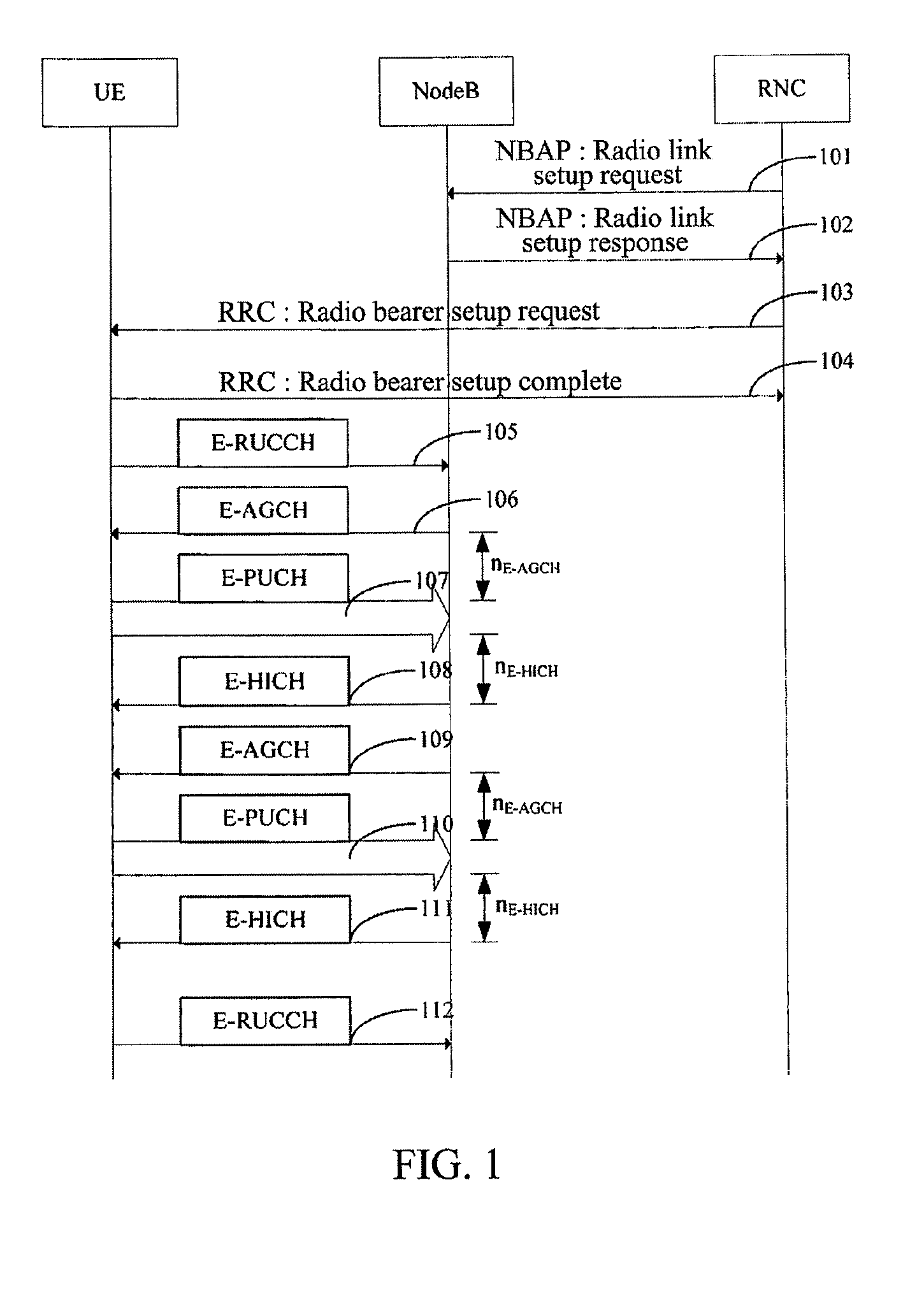
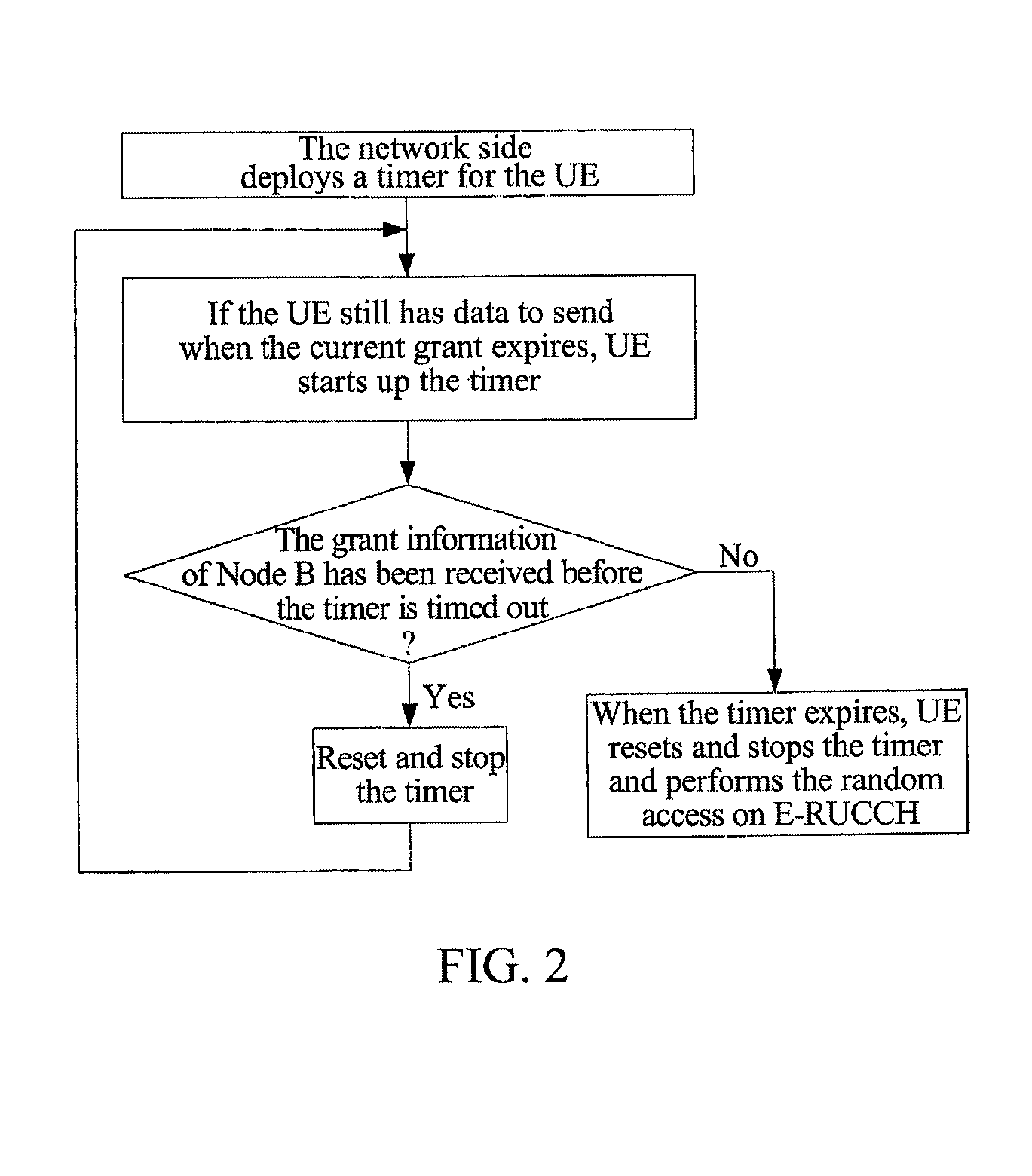
TD-SCDMA System and a Method for Controlling HSUPA Random Access Thereof
InactiveUS20100165953A1Avoiding invalid random accessImprove system efficiencyNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionTime delaysDelayed time
The present invention provides a time division synchronous code division multiple access (TD-SCDMA) system for controlling enhanced uplink random access, including user equipment (UE), node B and serving radio network controller. The present invention also provides a method for controlling the enhanced uplink random access in a time division synchronous code division multiple access system, including: in high speed uplink packet access scheduling service of time division synchronous code division multiple access system, the higher layer of network side deploys a timer at the user equipment side; if the user equipment still needs to transmit data when the current available grant expires, it starts up the timer which is used as the delay time of initiating the enhanced uplink random access. According to the ability of the network side in controlling E-DCH resources, the present invention can be used to control the time delay that UE initiates the enhanced uplink random access after one grant expires, so as to avoid invalid random access; meanwhile the present invention provides a reliable mechanism for the enhanced uplink random access. By using the method of this invention, system resources can be reasonably utilized, thereby greatly improving the system efficiency.
Owner:ZTE CORP
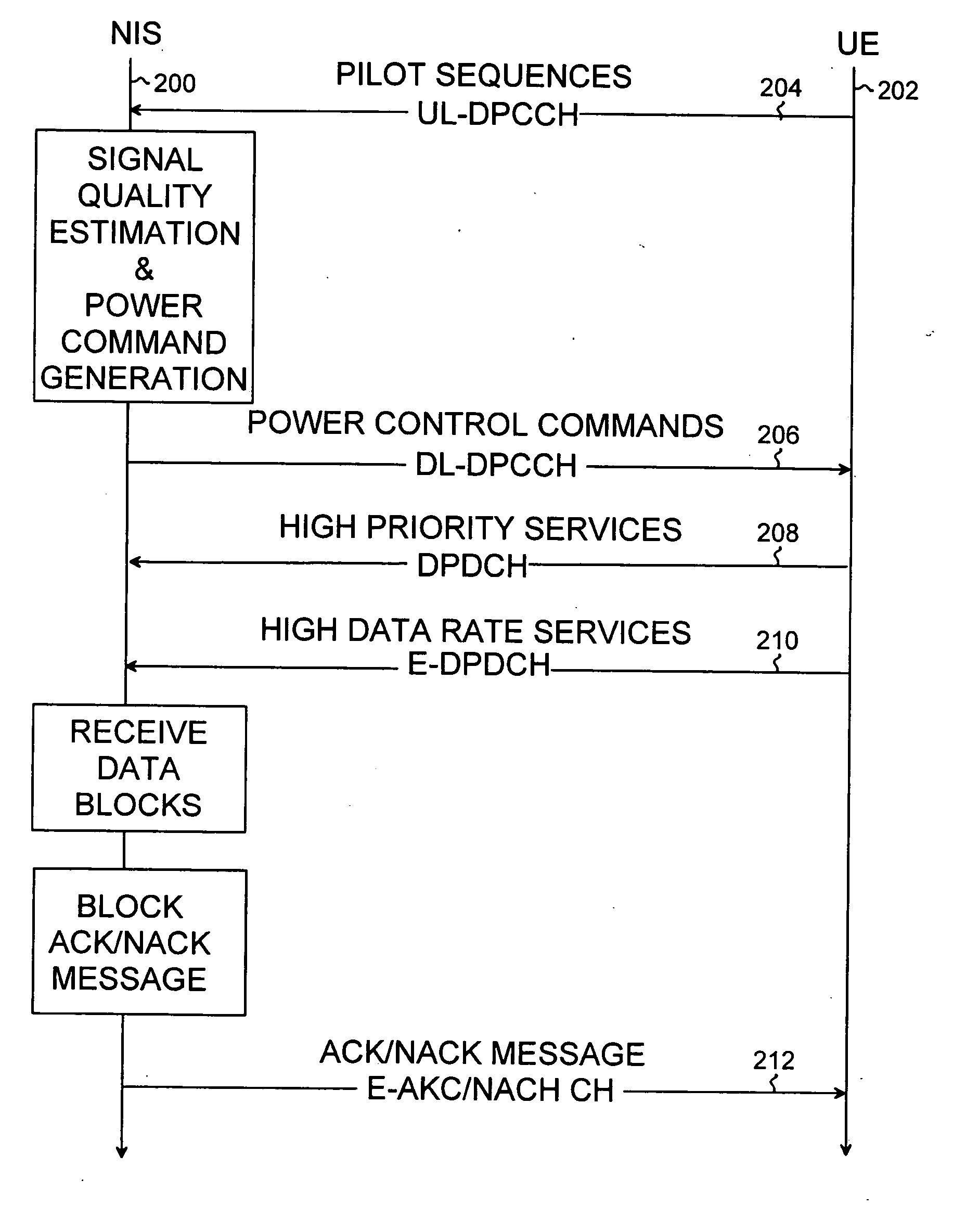
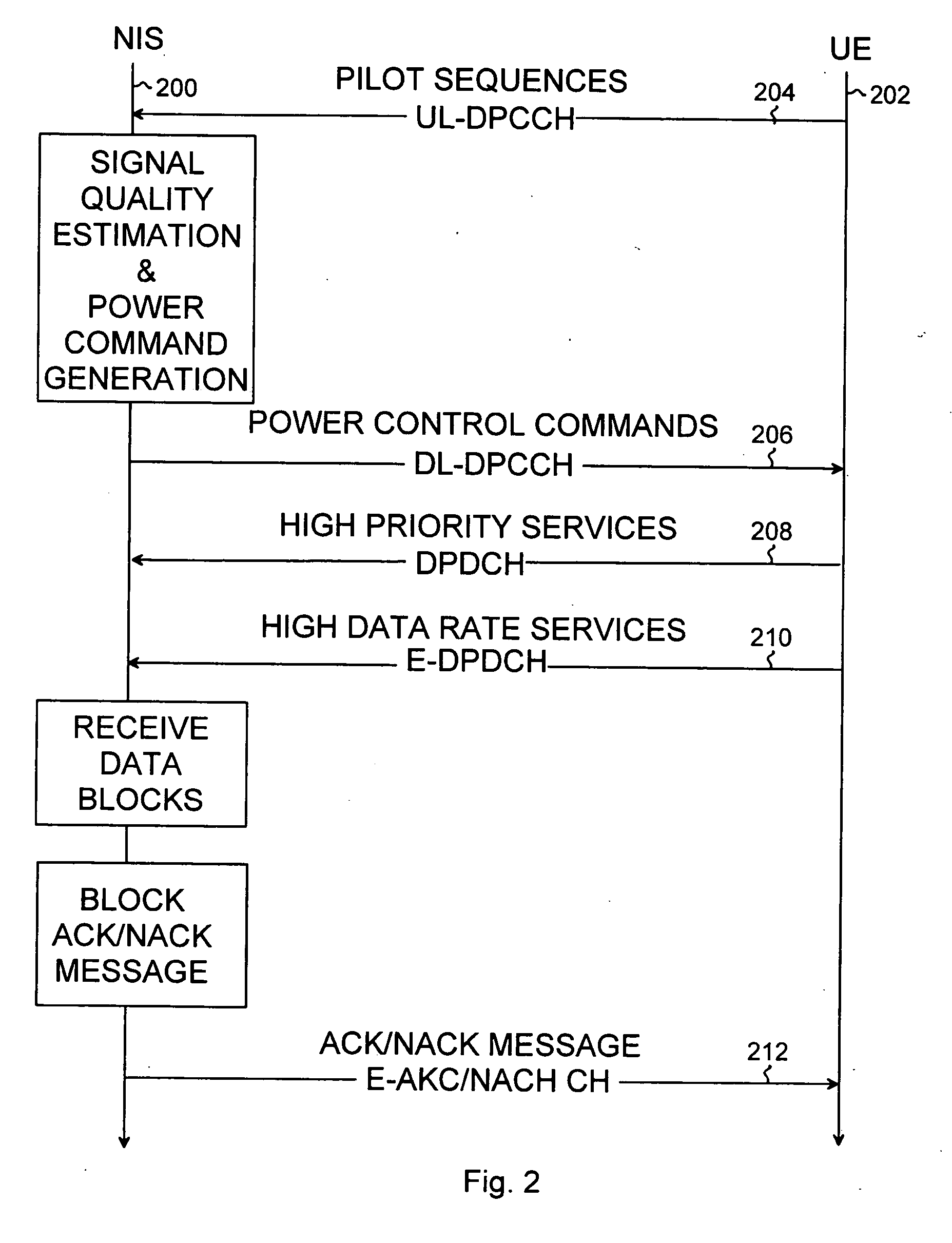
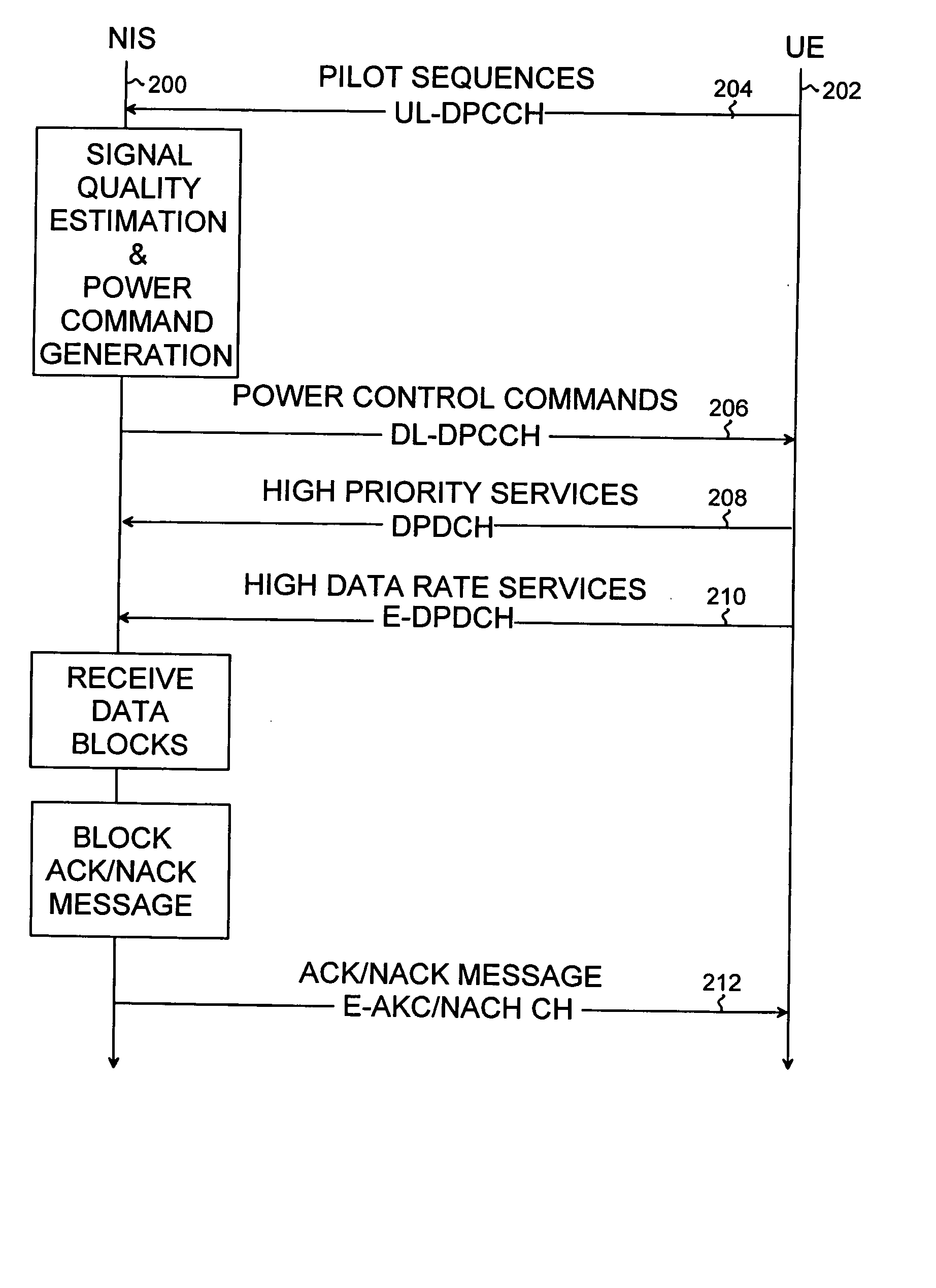
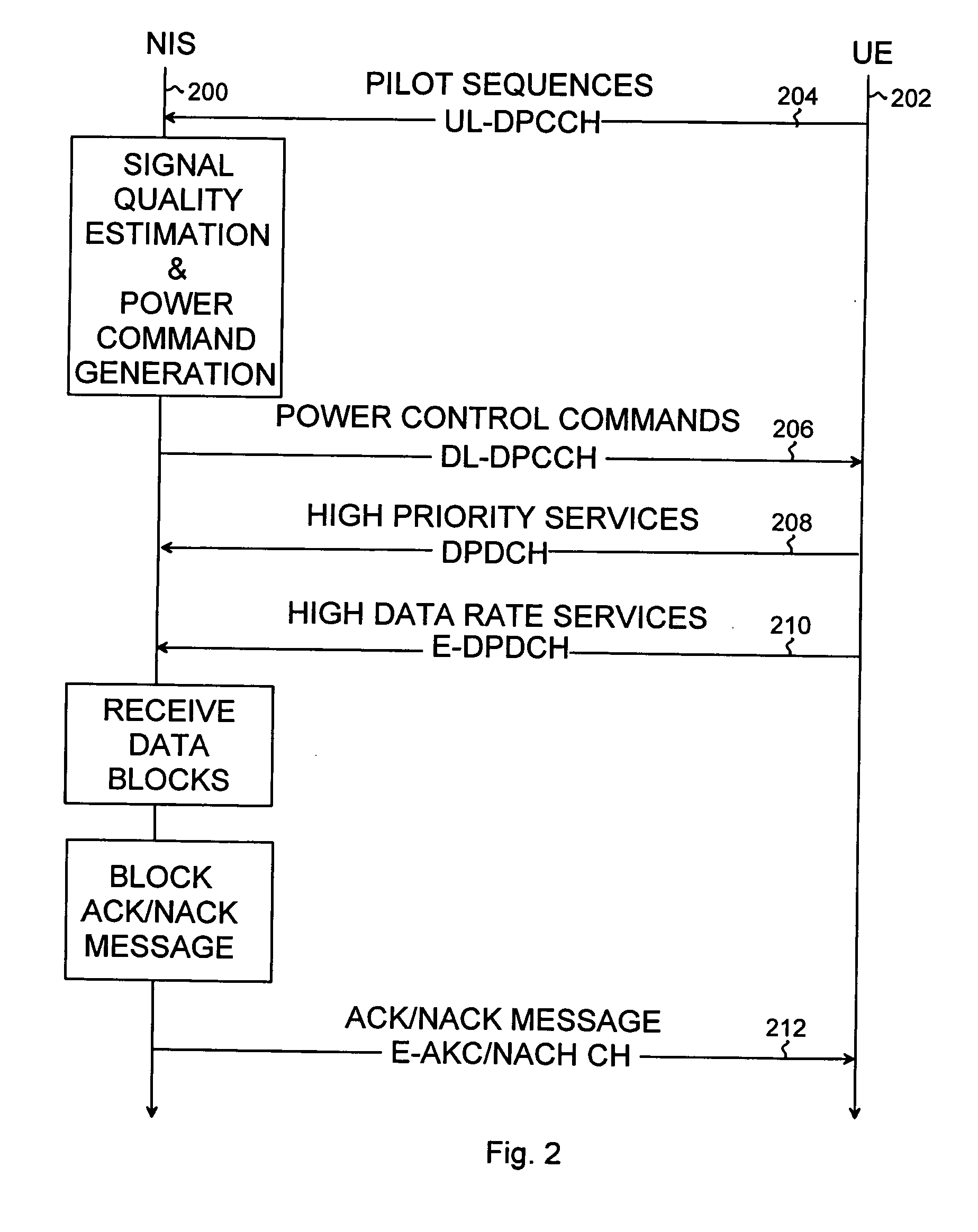
Radio resource control in HSUPA system
InactiveUS20060268789A1Simple methodFlexibility of power controlPower managementTransmission control/equalisingComputer networkPhysical control
Radio resource control in an HSUPA system is provided. The control procedure includes communicating data blocks between user equipment and a network infrastructure over a physical High Speed Uplink Packet Access channel, and communicating block information messages between the user equipment and the network infrastructure. The control procedure also includes adjusting a power offset value between the physical High Speed Uplink Packet Access channel and a Dedicated Physical Control Channel on the basis of at least one block information message.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Radio resource control in HSUPA system
InactiveUS20060034226A1Increase flexibilityPower managementTransmission control/equalisingComputer networkRadio Resource Control
A radio resource control in an HSUPA system is provided. The control procedure includes: communicating data blocks between user equipment and a network infrastructure over a physical High Speed Uplink Packet Access channel; communicating block acknowledgement messages between the user equipment and the network infrastructure, each block acknowledgement message indicating whether or not a data block was received successfully; and controlling transmission power of the physical HSUPA channel on the basis of at least one block acknowledgement message.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method and apparatus for uplink communication in a cellular communication system
InactiveUS20060056350A1Facilitate uplink communicationFacilitate data communicationNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsControl channelCellular communication systems
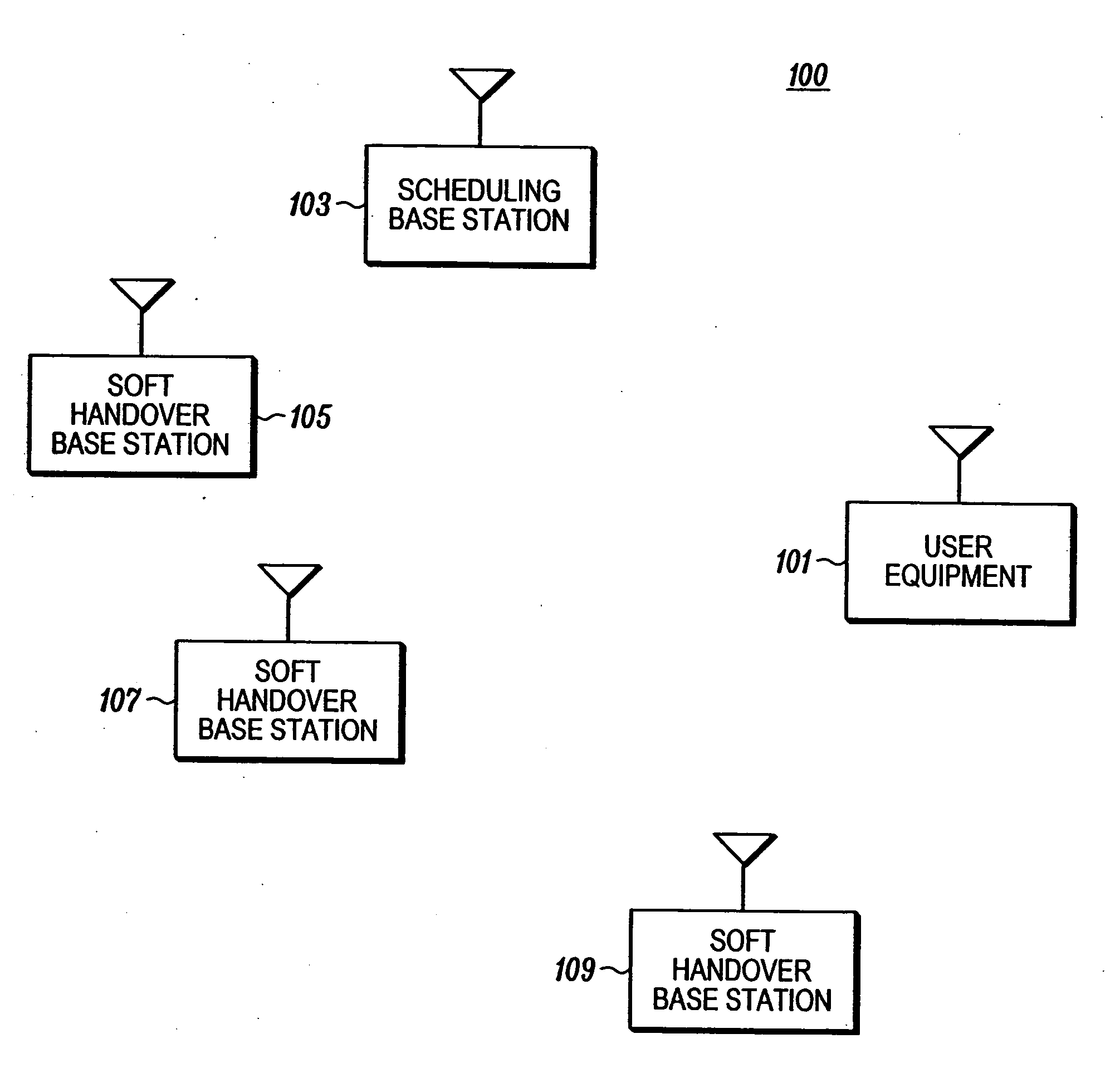
A cellular communication system (100) comprises a first base station (103) which schedules resource for a user equipment (101). When receiving a resource allocation message, the user equipment (101) transmits a first message comprising a transmit indication to a plurality of base stations (103-109) wherein the transmit indication is indicative of a subsequent transmission of a second message. The user equipment (101) then proceeds to determine a transmit format for the second message; and to transmit the second message to the plurality of base stations (103-109) using the transmit format. When receiving the transmit indication, the plurality of base stations (103-109) proceed to configure their receivers to receive the second message. The first message may be transmitted in a control channel and the second message may be transmitted in a user data channel. The invention is particularly applicable to a High Speed Uplink Packet Access HSUPA service in a UMTS cellular communication system and may facilitate soft handover.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
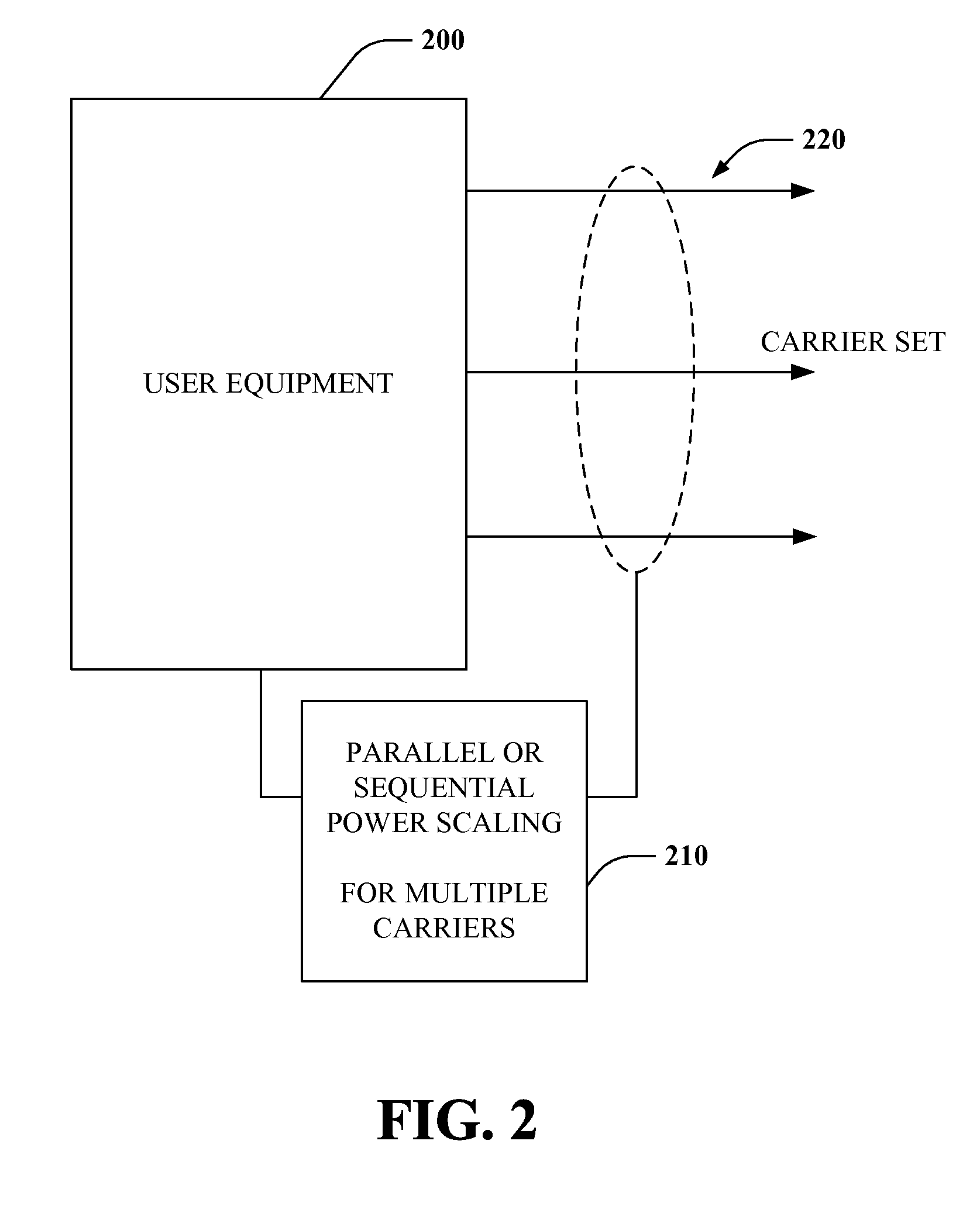
Control Signaling for Multiple Carrier High Speed Uplink Packet Access in Radio Frequency Communication Systems
Systems and methods for providing an efficient mechanism for transmitting information needed to receive a secondary carrier over an existing message protocol on a primary carrier for a multiple carrier capable communications terminal. The receiver terminal may receive, on a primary carrier, a message containing information including a timing offset and a cell identification for a secondary carrier, for example. The communications terminal may then correlate a receiver to receive the secondary carrier without the need for a separate synchronization signal on the secondary carrier. These embodiments result in additional efficiency in a communications system.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Closed-loop power control in multi-carrier high-speed uplink packet access
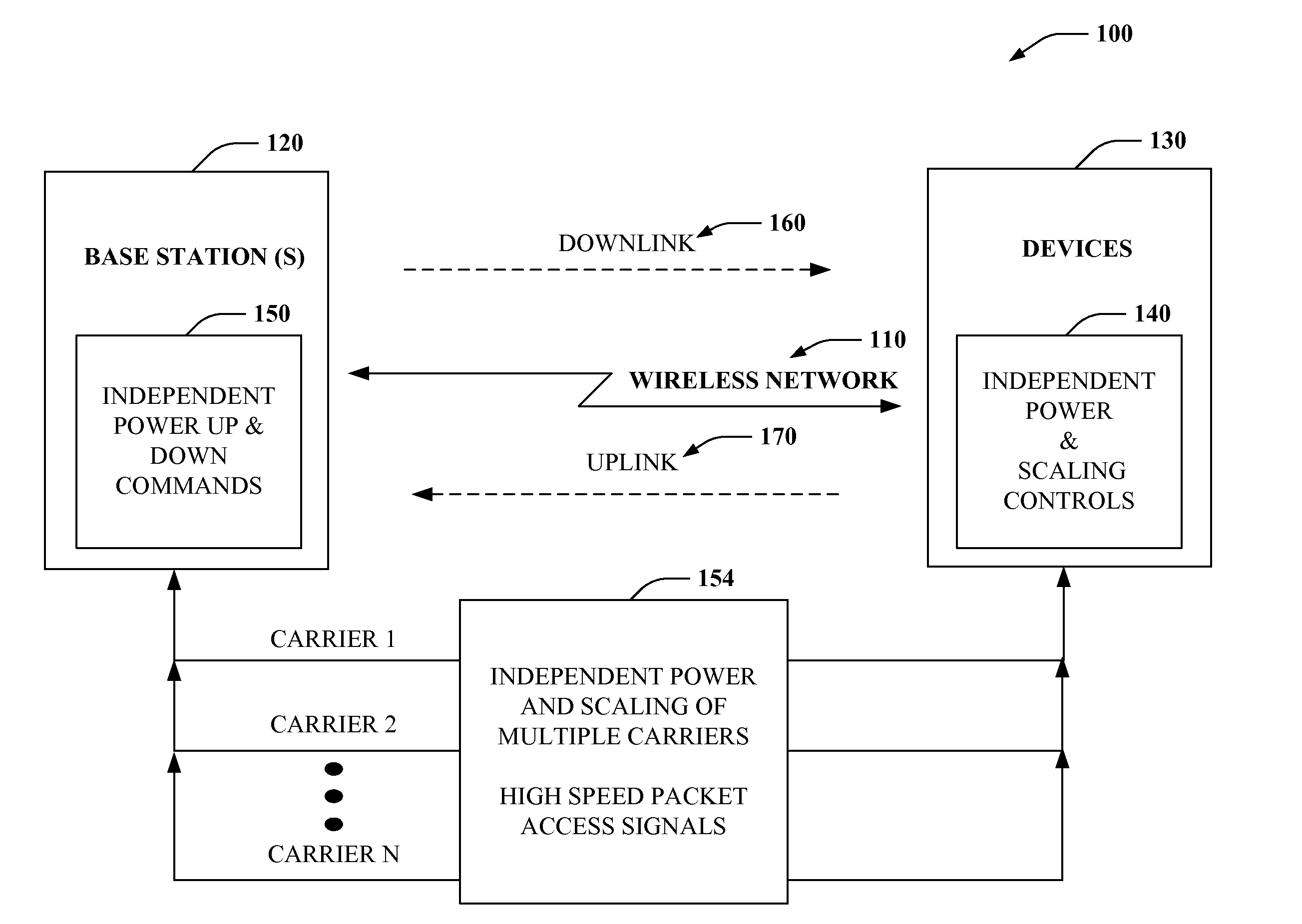
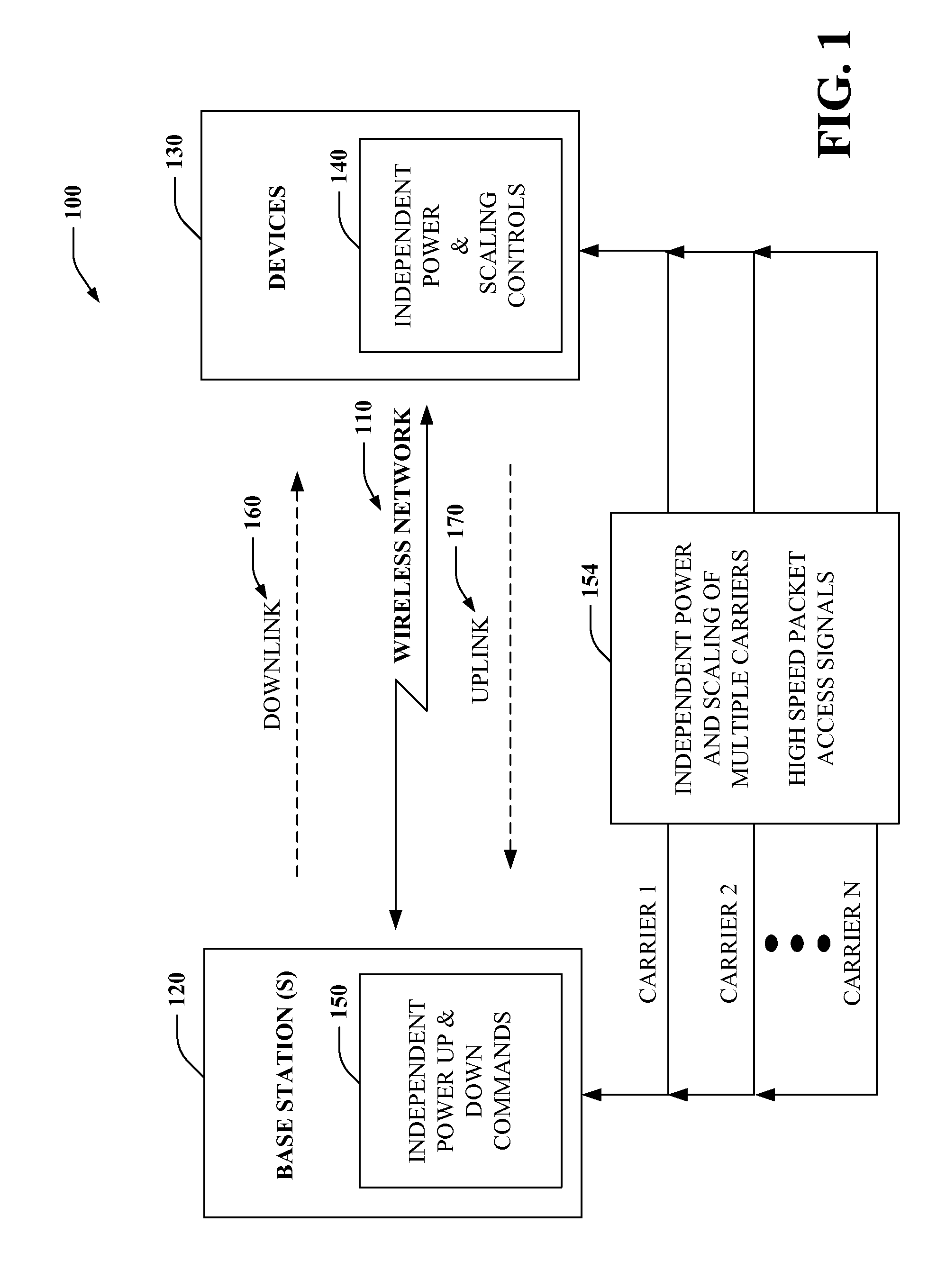
A method for wireless communications is provided. The method includes applying independent power controls to two or more carriers from a set of high speed packet access signals. The method includes monitoring power across the two or more carriers to determine power levels for the set of high speed packet access signals. The method also includes automatically adjusting at least one of the independent power controls in view of the determined power levels for the set of high speed packet access signals.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
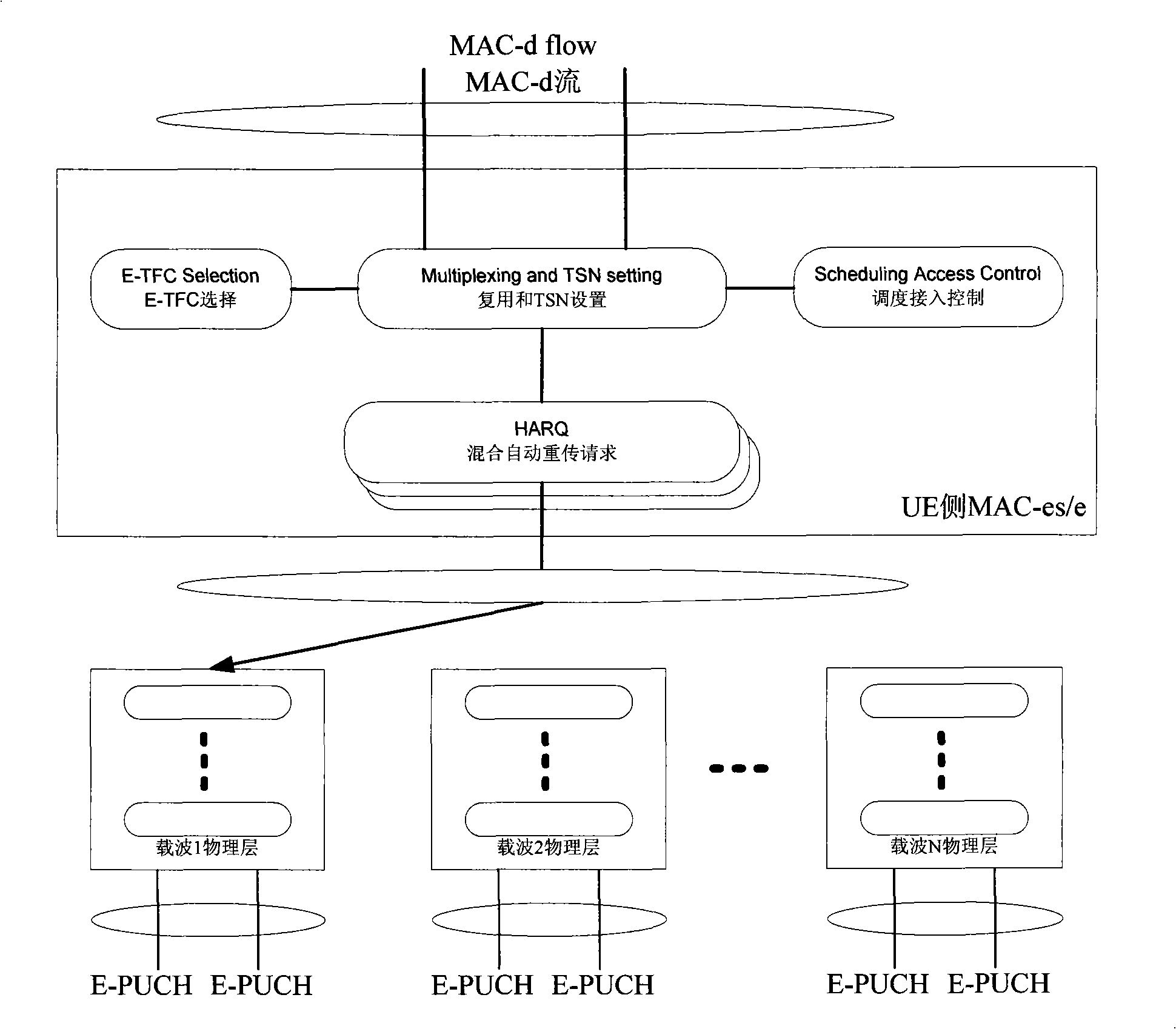
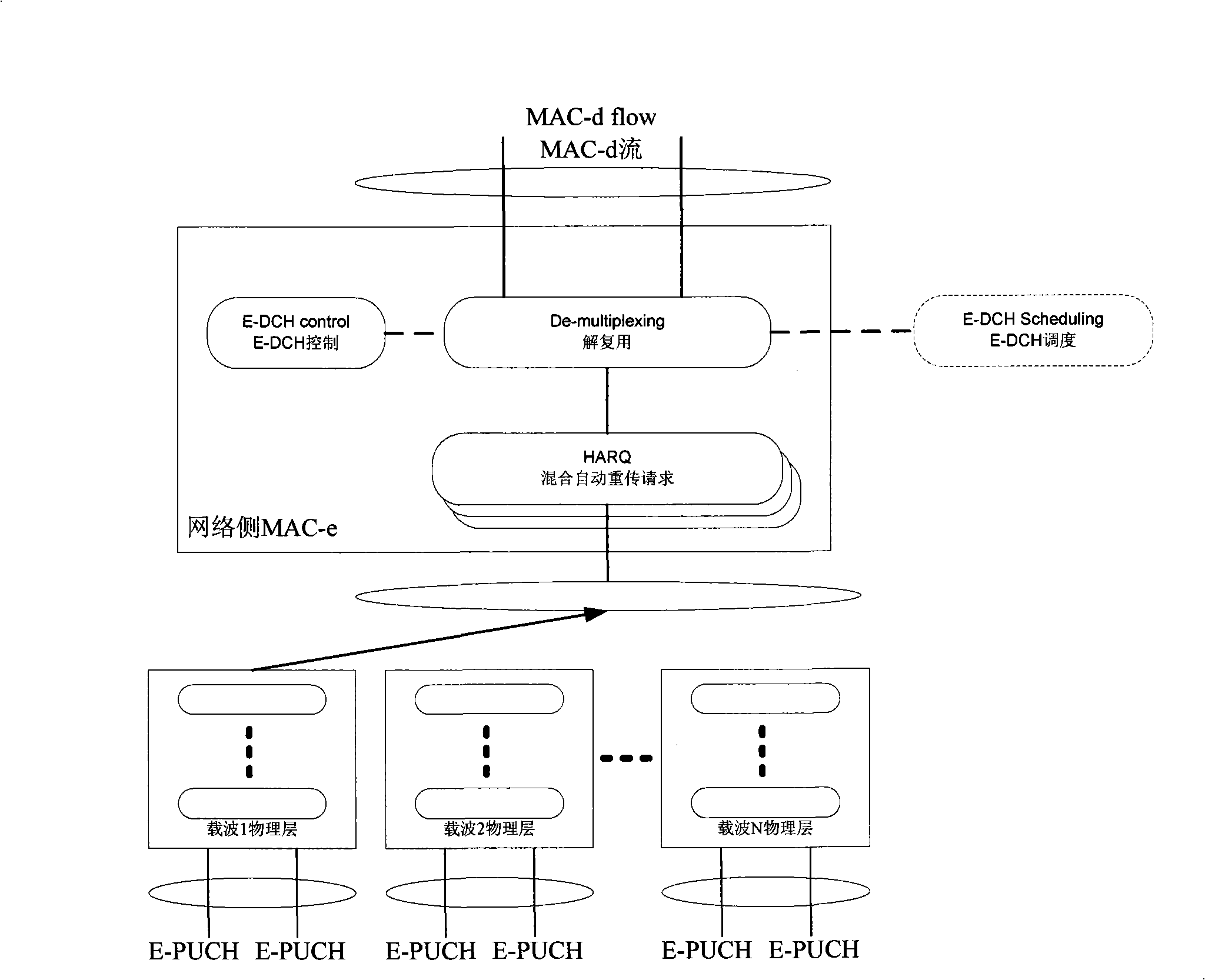
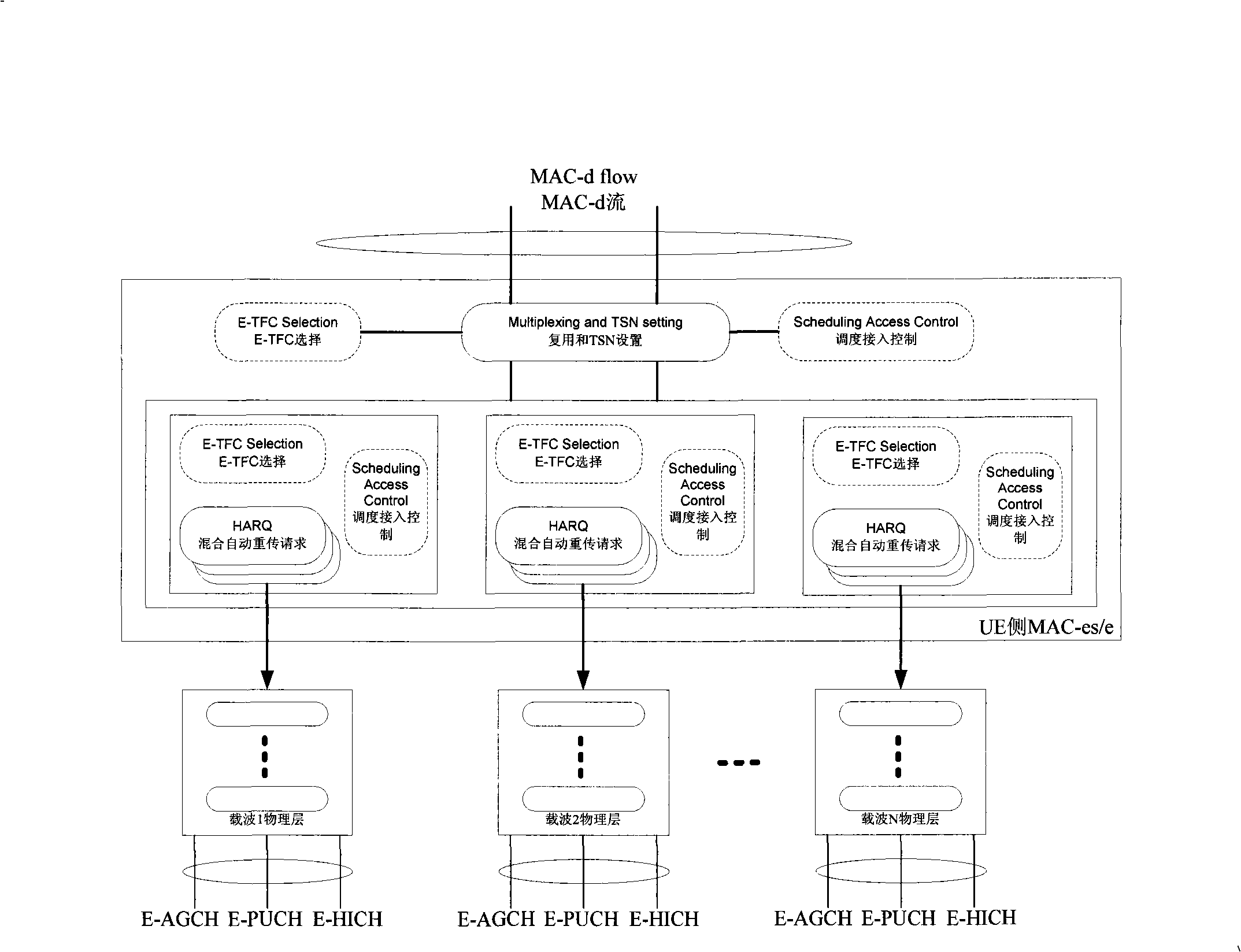
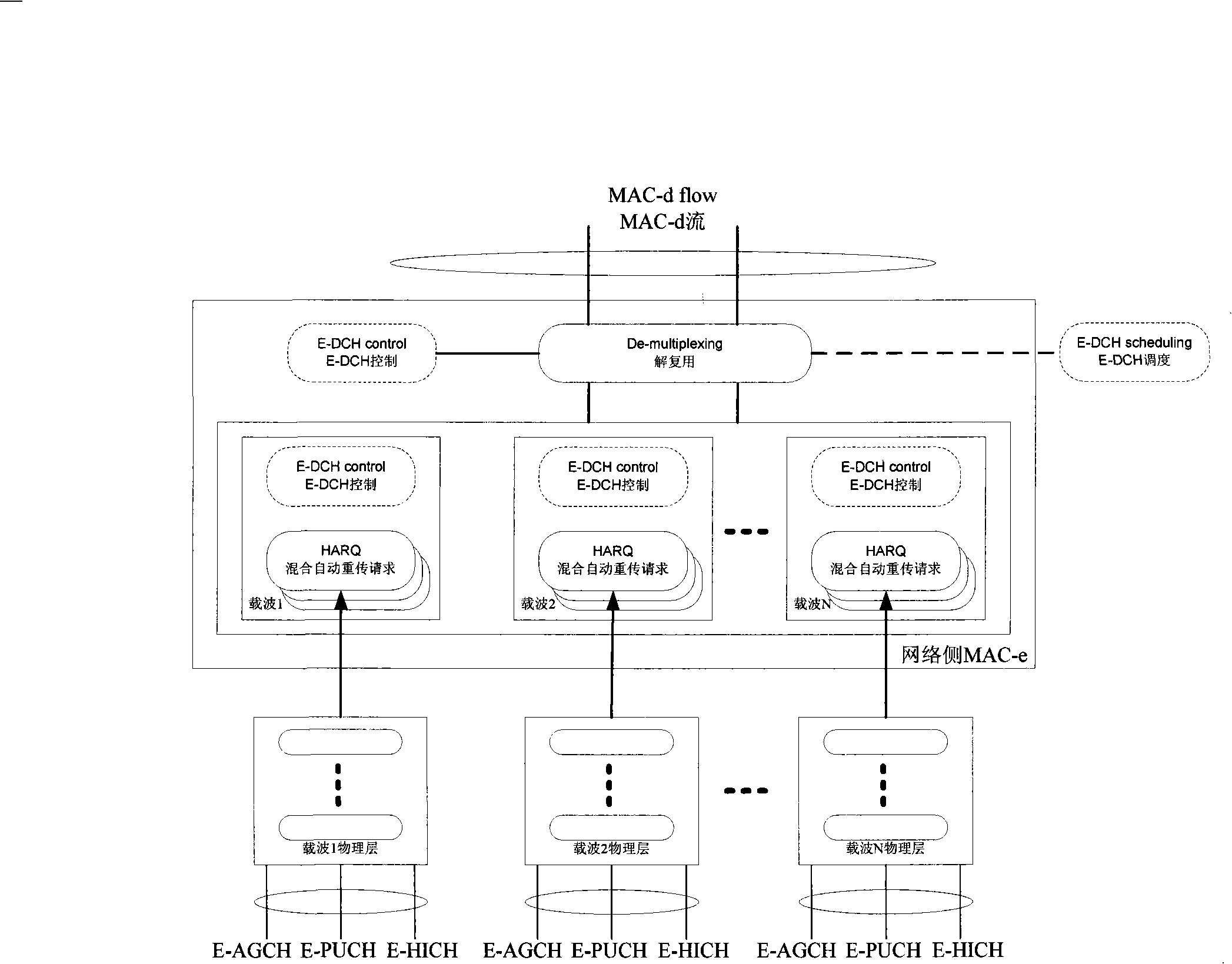
High-speed uplink packet access method of multi-carrier system
InactiveCN101335979ASolve the problem of low throughputImprove business service qualityError prevention/detection by using return channelRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsAccess methodCarrier signal
The invention relates to a high speed up link grouping access method of a multicarrier system, comprising: arranging E-AGCH, E-PUCH and E-HICH physical channel on one or a plurality of carriers; distributing useable E-AGCH, E-PUCH and E-HICH physical channel to for associate use on one or a plurality of carrier(s) through high level signaling; respectively building a MAC-e / MAC-es entity and a HARQ entity thereof and a course shared by each carrier at a network side and a terminal side, dynamically mapping the scheduling E-DCH transmitting data onto an E-PUCH physical channel of a carrier through the entity. The Node B dynamically schedules and authorizes the E-PUCH physical channel of the carrier to the terminal for E-DCH data transmission through E-AGCH carried with carrier indicating information. Receiving condition of E-DCH transmission on the carrier is fed back through the E-HICH physical channel.
Owner:GLOBAL INNOVATION AGGREGATORS LLC
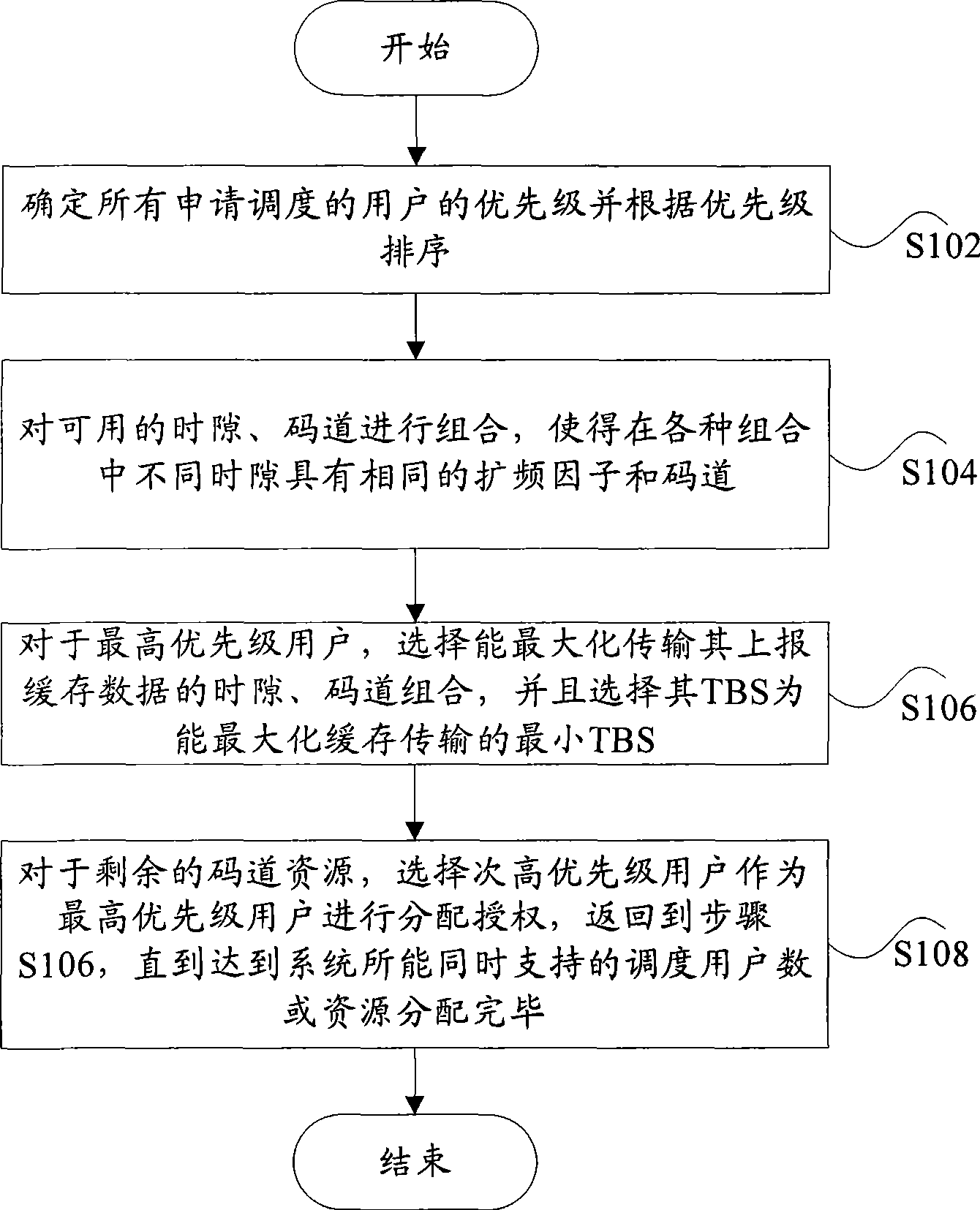
Method and system for scheduling medium access control layer of high speed ascending packet access
ActiveCN101378534AControl interferenceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationMedia access controlAuthorization
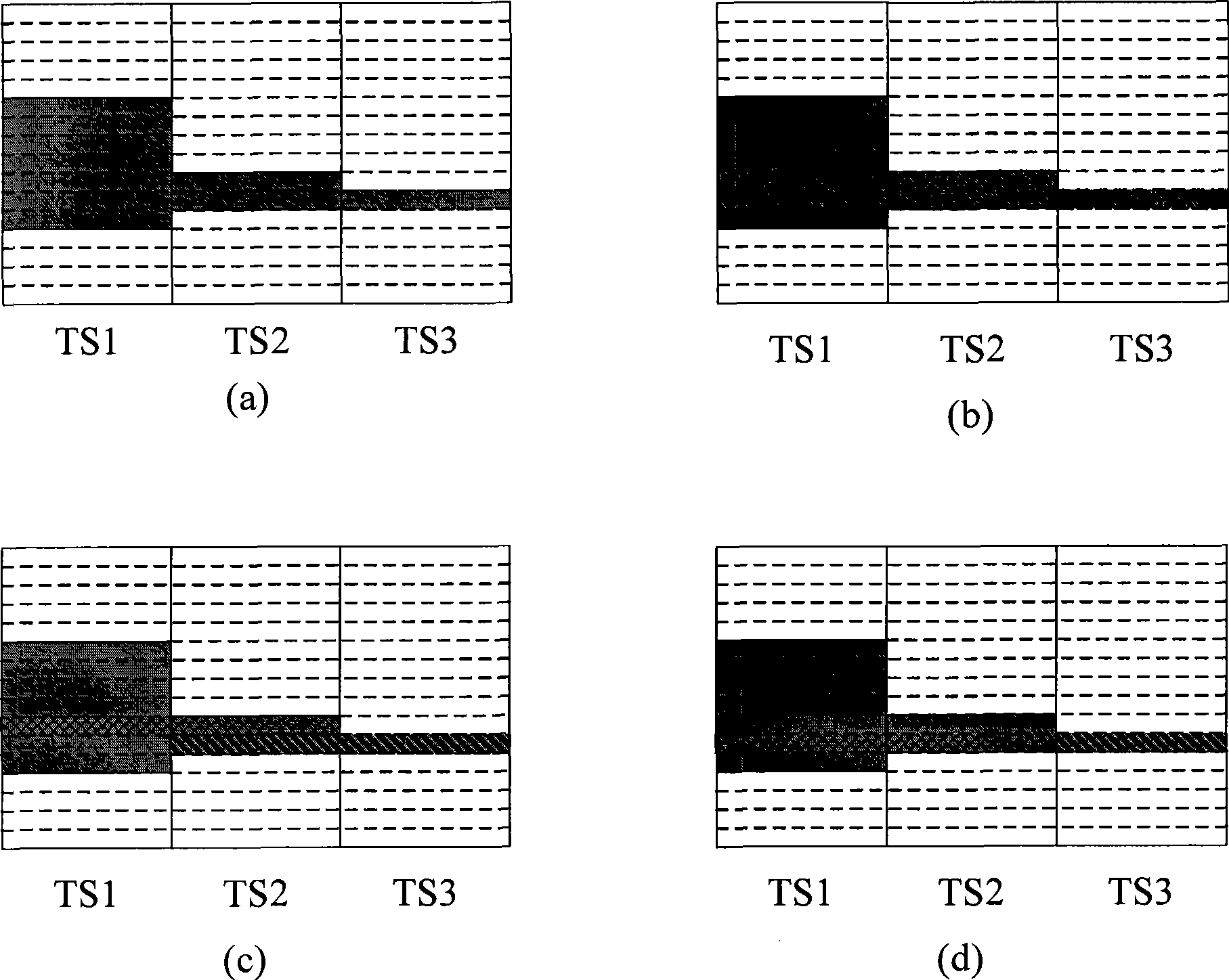
The invention provides a dispatching method for a media access control layer with high-speed uplink packet access and a system thereof. The method comprises the steps that: Step S102. the priority levels of users applying for dispatching are determined and ranking is carried out according to the priority levels; Step S104. combination is carried out to available slot times and code channels so as to cause various combinations to have the same spreading factor and code channel in different slot times; Step S106. the combination of slot times and code channels that can transmit reported caching data in a maximum manner is selected for users with the highest priority level and the minimum TBS that can cache transmission in a maximum manner is selected from the TBS of the users with the highest priority level; Step S108. as for the rest code channel resources, users with the priority level following the highest level are selected to be the users with the highest priority level to carry out authorization assignment, and Step S106 is carried out until that dispatching user number which the system can support simultaneously is achieved or resource allocation is finished.
Owner:ZTE CORP
High-speed uplink packet access method
InactiveCN101631333APerfect Scheduling RequestImprove the dynamic scheduling processWireless communicationTelecommunicationsCarrier signal
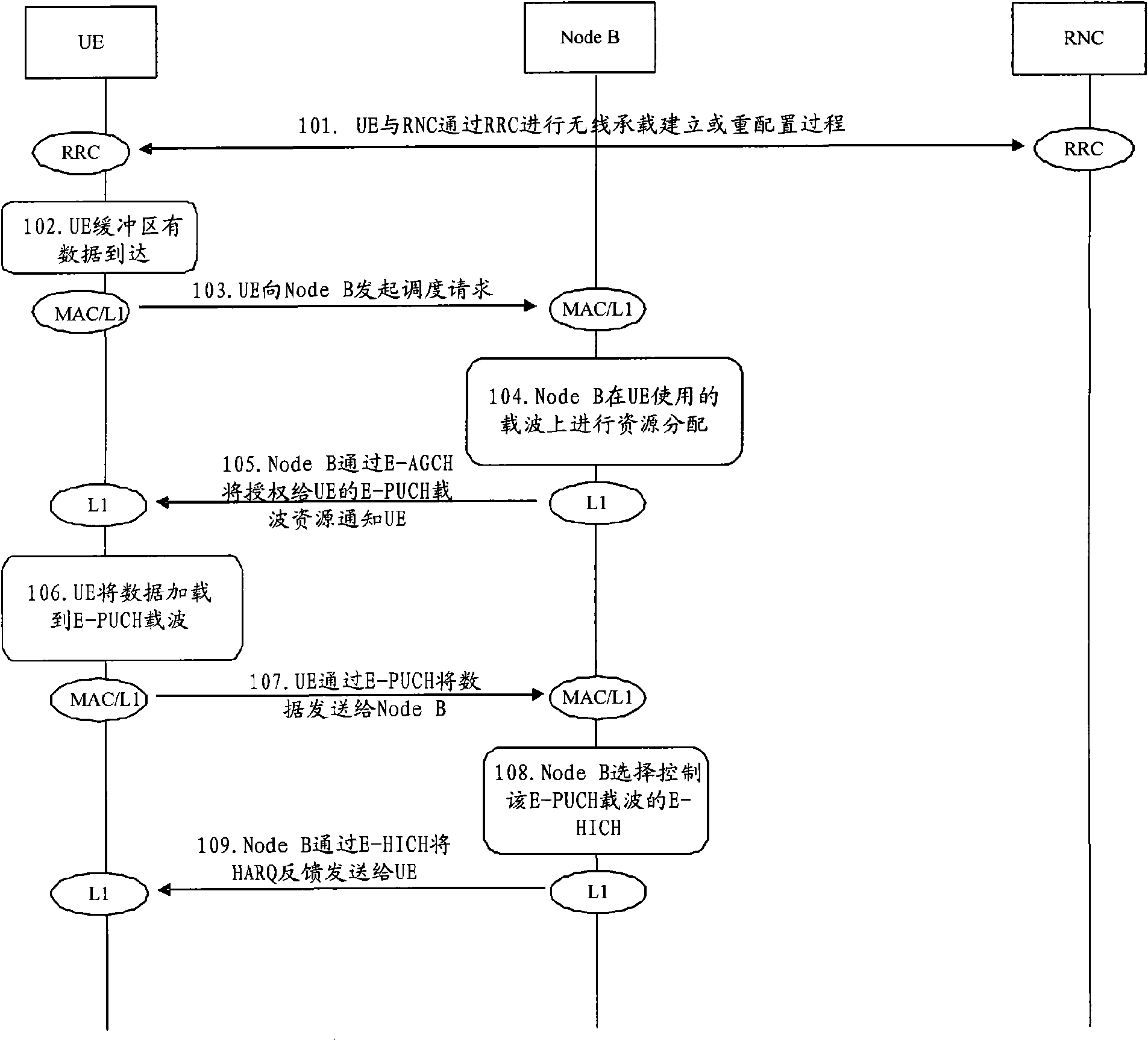
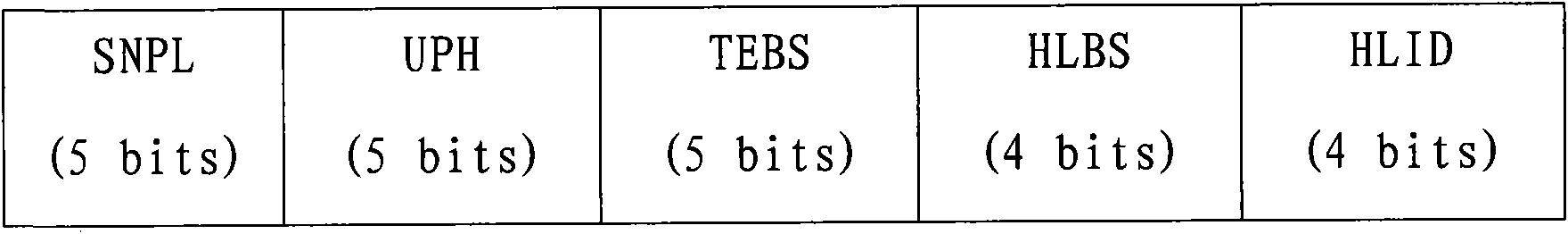
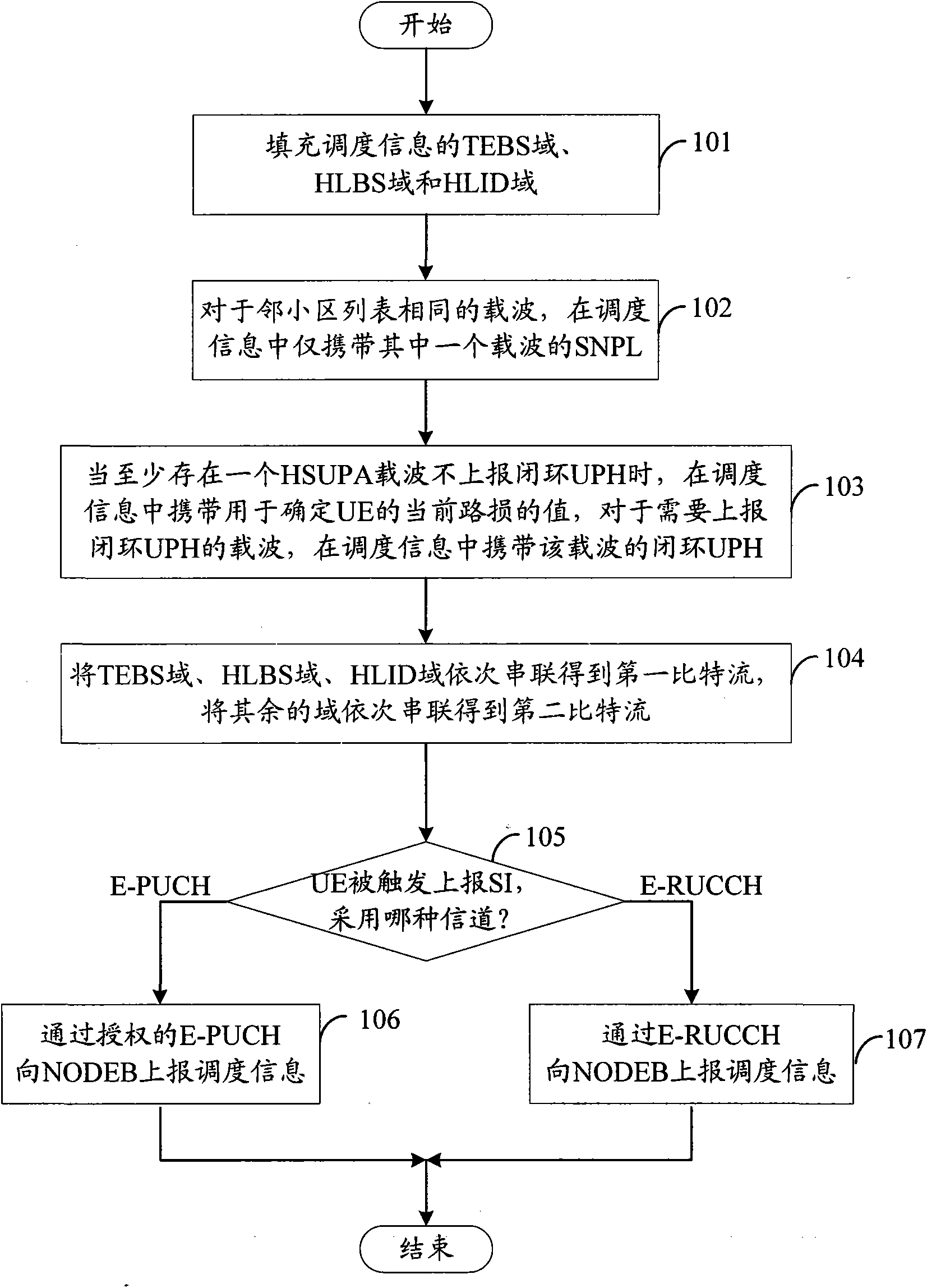
The invention provides a high-speed uplink packet access method comprising the following steps: reporting SI to a Node B by UE in a dispatching request; respectively reporting SNPL aiming at each HSUPA carrier wave in the SI; using a difference value between the total maximum transmitting power of the UE and all uplink carrier wave power which is planned to be used as UPH to report without dividing the UE; using a total data size in a UE buffer area as TEBS to report; using identify labels of logic channels with the highest priority level in logic channels with data to be transmitted of the UE as HLID to report; using a data amount as HLBS to report; and distributing resources by the Node B according to the information reported by the UE. The high-speed uplink packet access method completes the dispatching request and a dynamic dispatching process of multi-carrier HSUPA and realizes the transmission of the multi-carrier HSUPA.
Owner:北京万海云科技有限公司
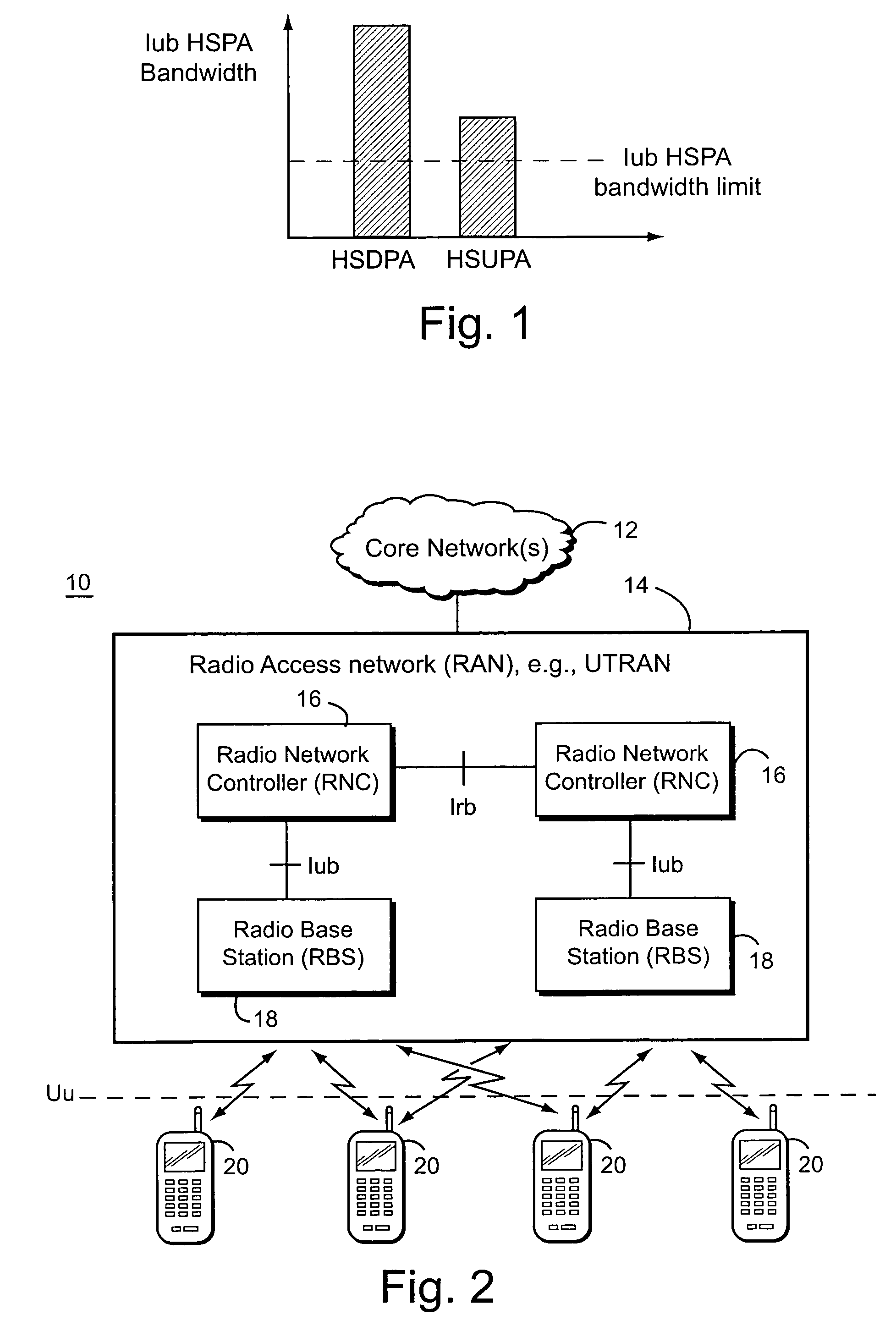
Data transmission controlling method, apparatus and system
InactiveCN101489263AReduce trafficHigh trafficNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmissionData transmissionBandwidth utilization
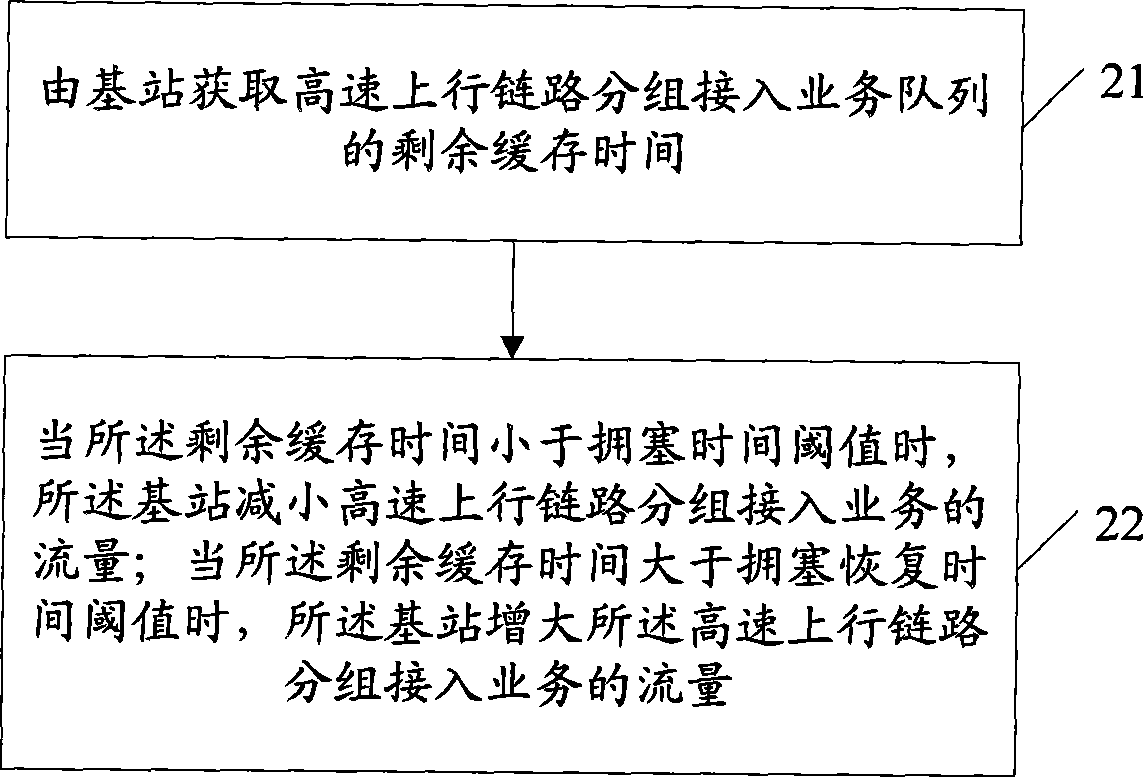
An embodiment of the invention discloses a data transmission control method, a device and a system thereof. The invention relates to the technical field of communication and is invented for increasing the usage factor of uplink bandwidth of transmission link between the base station controller and the base station. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the residual cache time of high speed uplink chain grouping access service queue; when the residual cache time is smaller than the congestion time threshold, reducing the flow of high speed uplink grouping access service; and when the residual cache time is larger than the congestion time threshold, increasing the flow of high speed uplink grouping access service. The embodiment of the invention is mainly applied for the uplink flow control technique of base station.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and device for determining cell throughput
ActiveCN101998476AEasy to planEasy to optimizeWireless communicationCommon control physical channelSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
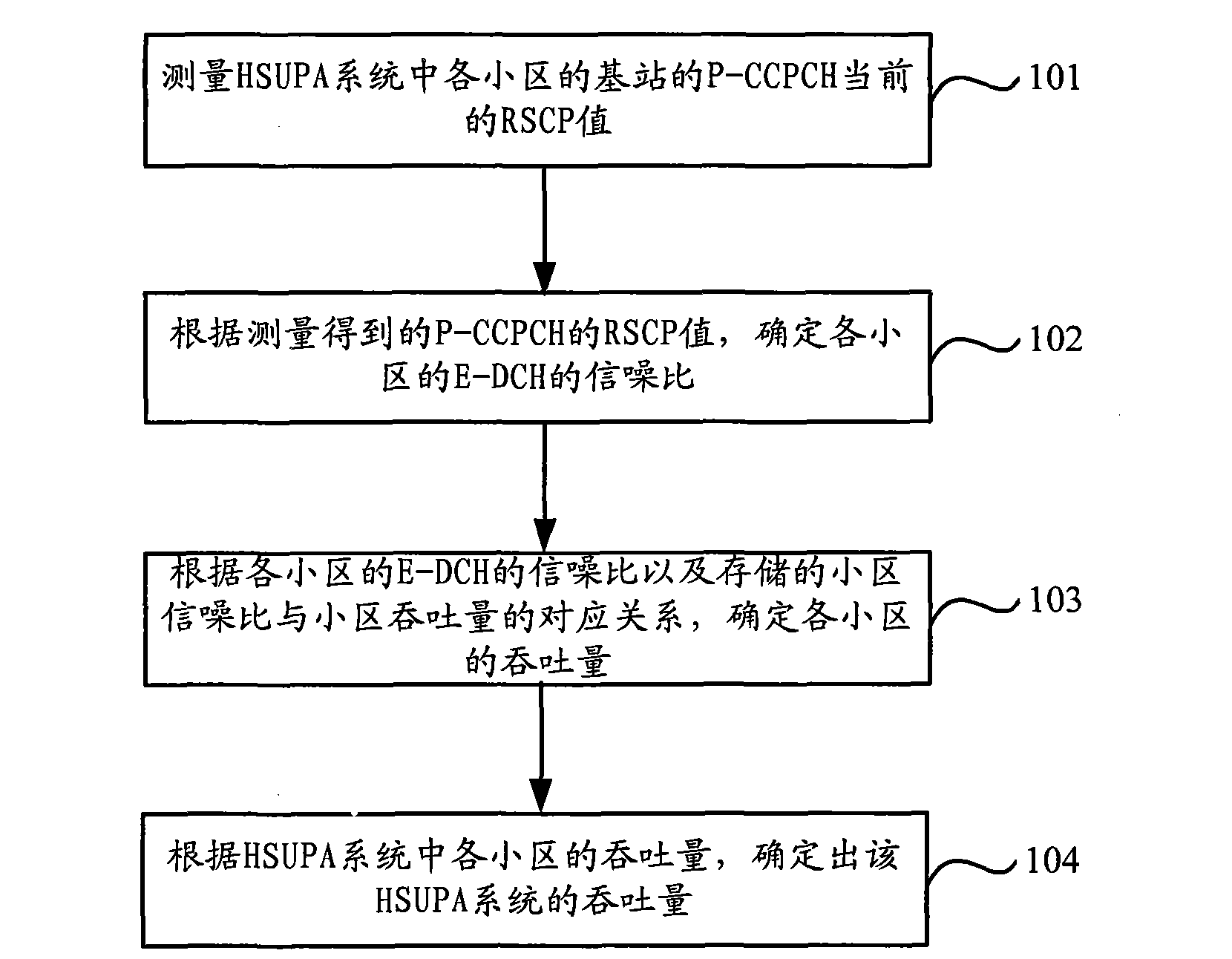
The invention discloses a method for determining cell throughput, which aims at solving the problem that the evaluation on the network performance of an HSUPA (High Speed Uplink Packet Access) system is inaccurate because the cell throughput is determined according to the static parameters and the throughput of the HSUPA system is determined according to the determined cell throughput in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring the current RSCP (Received Signal Code Power) value of a P-CCPCH (Primary Common Control Physical Channel) of each cell in the HSUPA system; and determining the throughput of each cell, wherein, for each cell, the E-DCH (Enhanced Dedicated Channel) signal to noise ratio of the cell is determined according to the RSCP value of the P-CCPCH of the cell and adjacent cells, and the throughput of the cell is determined according to the determined signal to noise ratio and the corresponding relationship between the preset cell signal to noise ratio and the cell throughput. When the technical scheme of the invention is adopted, the accuracy of the evaluation on the network performance of the HSUPA system can be improved. The invention is more favorable for the network planning and optimization.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP DESIGN INST
High speed uplink grouping accessing method for multi-carrier system
InactiveCN101330454AIncrease the peak upstream rateImprove business service qualityError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareCarrier signal
The invention relates to a high speed uplink packet access (HSUPA) method for a multicarrier system, which comprises allocating E-AGCH, E-PUCH and E-HICH physical channels on one or more carrier waves at the same time; allocating one or more E-PUCH physical channel carrier wave resources for a terminal, and allocating one or more E-AGCH and E-HICH physical channels on one or more carrier waves and correlating with the E-PUCH physical channel on the same carrier wave; constructing one MAC-e / MAC-es entity on the network side and on the terminal side respectively, wherein the entities share carrier waves but independently allocate a HARQ process; and dynamically mapping scheduled E-DCH transmitted data on one or more carrier waves; a Node B authorizes the correlated E-PUCH physical channels on one ore more carrier waves to the terminal via one or more E-AGCH dynamic scheduling authorizations for E-DCH data transmission; the Node B feeds back the reception state of the E-DCH transmitted data via one E-HICH physical channel on each carrier wave.
Owner:GLOBAL INNOVATION AGGREGATORS LLC
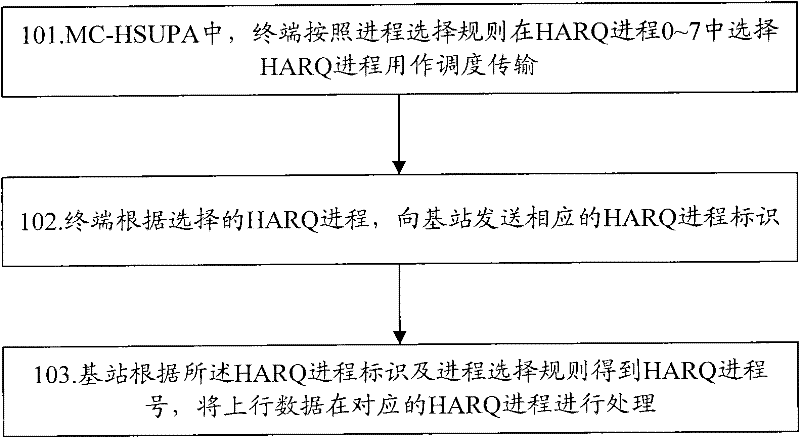
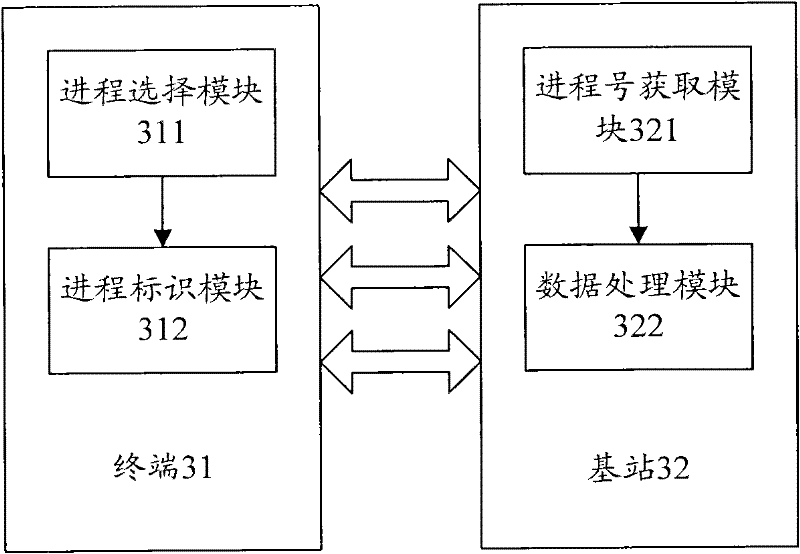
Hybrid automatic retransmission method, system and terminal in MC-HSUPA
ActiveCN102447547AEasy to handleIncrease flexibilityError prevention/detection by using return channelWireless communicationQuality of serviceComputer science
The invention discloses a hybrid automatic retransmission (HARQ) method in multi-carrier high speed uplink packet access (MC-HSUPA). In MC-HSUPA, a terminal selects HARQ process as scheduling transmission according to the process selecting rule and sends a corresponding HARQ process mark to a base station; the base station obtains HARQ process number according to the HARQ process mark and the process selecting rule and process uplink data at corresponding HARQ process. The invention discloses an HARQ system and terminal in MC-HSUPA at the same time. The proposal of the invention can make 4 HARQ scheduling processes owned by the terminal HARQ entity of the present MC-HSUPA expand to 8 scheduling processes to improve the processing performance of the MC-HSUPA terminal and the scheduling flexibility is improved to ensure the service quality and requirement.
Owner:盐城昊隆机械有限公司
Authorization allocating method and device of HSUPA (high speed uplink packet access) network
InactiveCN101742564AImprove satisfactionAvoid delay jitterNetwork traffic/resource managementSecurity arrangementAuthorizationEmbedded system
The invention discloses an authorization allocating method of an HSUPA (high speed uplink packet access) network. The method comprises the following steps that, Step 1, an HSUPA dispatcher allocates an authorization to a user terminal based on the service requirement of the user terminal; Step 2, the user terminal keeps the authorization until the service requirement of the user terminal changes, and the Step 1 is returned to; and the user terminal uses the authorization only when data packets need to be transmitted; and Step 3, the available load of a cell to be dispatched in a dispatching cycle is calculated based on a formula provided by the invention; and the HSUPA dispatcher can allocate the authorization to the user terminal in the cell to be dispatched more reasonably based on the calculated available load. The invention also provides a corresponding authorization allocating device of the HSUPA network. By using the method and the device, the delay of the authorization allocation existing in the HSUPA network can be avoided when a burst service occurs, thereby effectively avoiding the delay jitter of the user terminal.
Owner:ZTE CORP
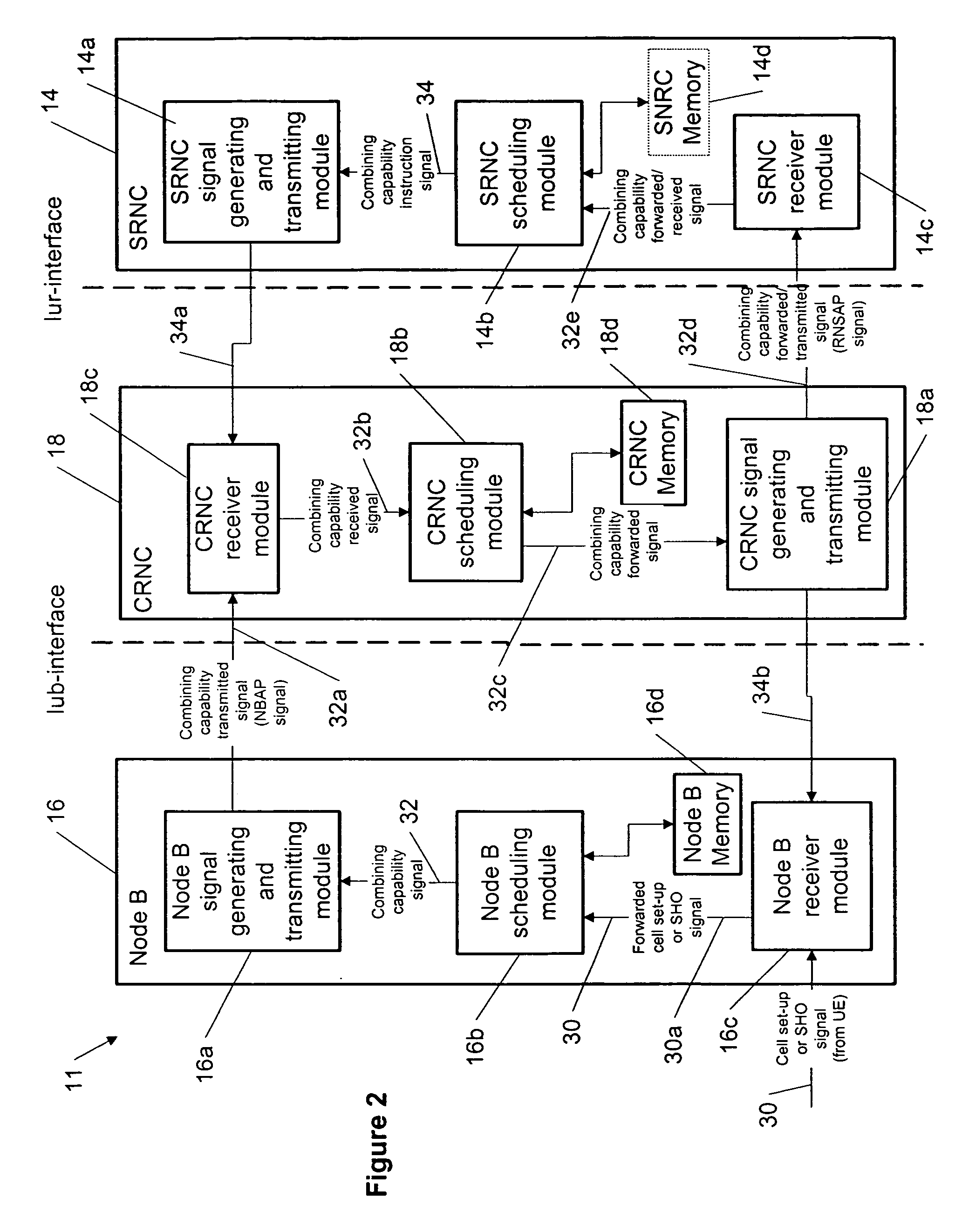
Signaling cell combining capabilities
InactiveUS20070104167A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesData packRadio networks
The specification and drawings present a new method, system, apparatus and software product for providing combining capability information of a Node B (supporting a cell to which a user equipment is set-up) to radio network controllers as related to HSUPA (High Speed Uplink Packet Access). The Node B can support among others, e.g., incremental redundancy (IR) combining and / or Chase combining. Furthermore, the combining capability information of the node B can be, e.g., for combining data received on an uplink enhanced dedicated channel (E-DCH).
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
System and method for downlink signaling for high speed uplink packet access
ActiveUS7693110B2Power managementNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemTransmitter
A wireless communication system (100) and method for providing high speed uplink packet access from user equipment (128, 130) to a base station (114, 116, 118, 120). Each of the user equipment (128, 130) and the base station (114, 116, 118, 120) includes a transmitter (1106, 1206), a receiver (1104, 1204), and a controller (1108, 1208) coupled to the transmitter and the receiver. Data packets are transmitted from the user equipment (128, 130) to the base station (114, 116, 118, 120). Control information, corresponding to the data packets, is transmitted from the base station (114, 116, 118, 120) to the user equipment (128, 130). The control information includes an absolute grant channel indicator and / or channelization code(s) assigned to the user equipment (128, 130). The controller (1108) of the user equipment (128, 130) is configured to minimize a number of channelization code per scheduling active set cell to be monitored by the user equipment based on the absolute grant channel indicator and / or to utilize the channelization code(s) in response to handoff and / or entering an active channel state.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
High-speed uplink packet access scheduling method and system
ActiveCN101212782ASimplify the scheduling processReduced processing power requirementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsStore-and-forward switching systemsAuthorizationDistributed computing
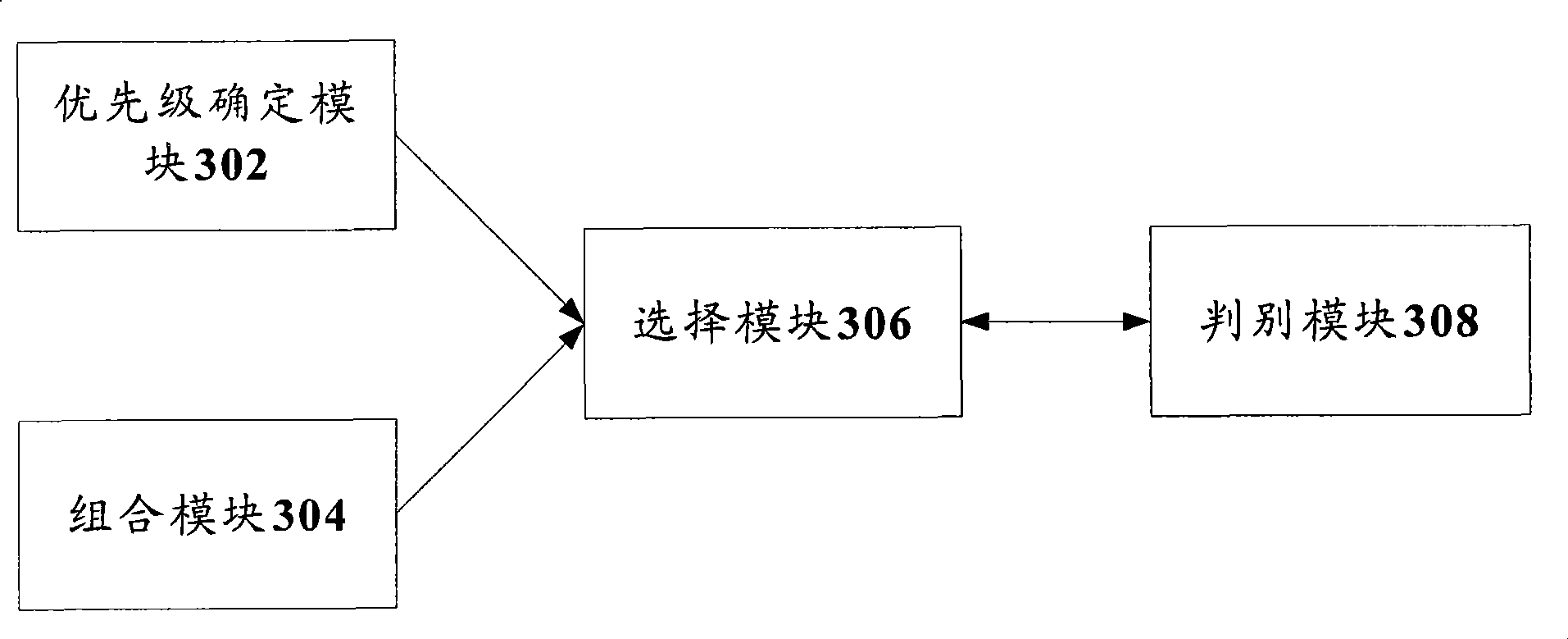
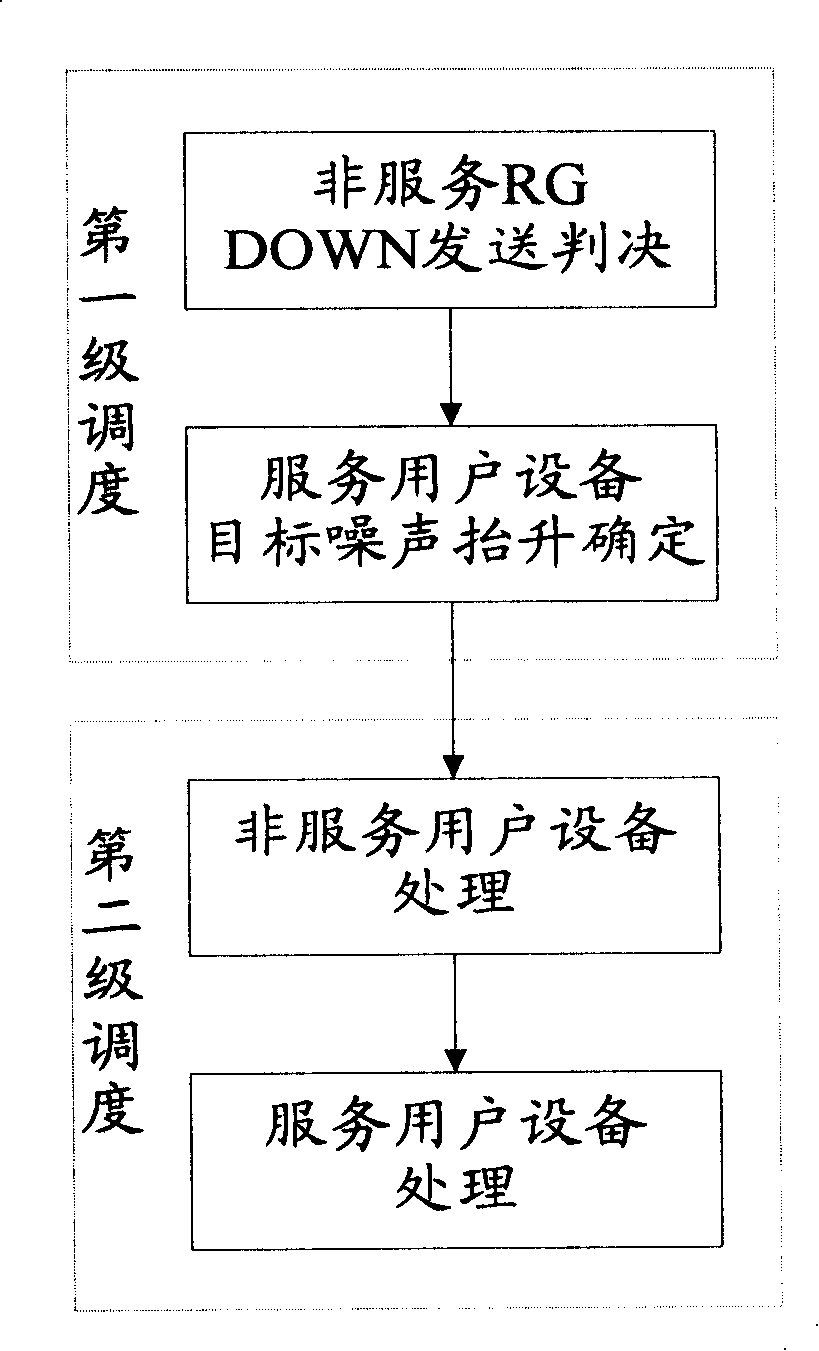
The invention discloses a dispatching method used for high speed upstream packet access and a system thereof. A first class dispatching, when a district is over-loaded and launching conditions are met, is used for determining UE required to launch non-service RG DOWN and sending information to a second class dispatcher, carrying out priority calculation and sorting to service UE, distributing the upstream load used for E-DCH between the service UE, determining target noise uplift resource to be distributed to each service UE, and sending information to a second class dispatcher. The second class dispatching, when non-service UE needs to launch RG DOWN, launches RG DOWN, estimates signal channel quality after the dispatching authorization comes into effect according to current information of the service UE and historical information, determines the specific authorization required to give to the service UE according to the target noise uplift distributed to the service UE, determines the authorization order demanded to launch, and launches dispatching order to the service UE. The dispatching method of the invention reduces complexity dispatcher and improves implementation efficiency of a dispatcher.
Owner:ZTE CORP
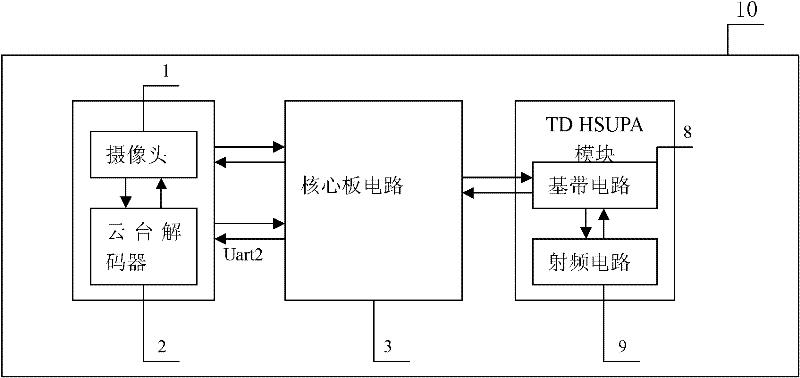
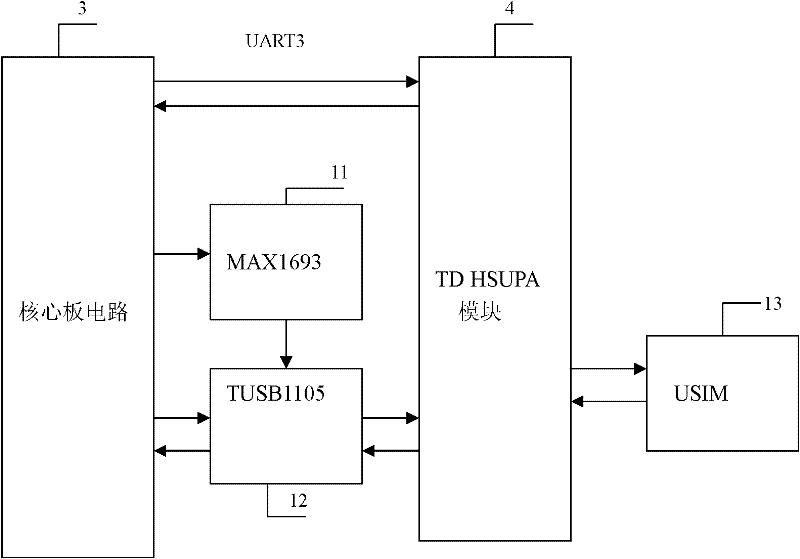
A video surveillance transmission device based on td-scdma network
InactiveCN102263935AIncrease the amount of informationLow costClosed circuit television systemsTransmissionVideo monitoringElectricity
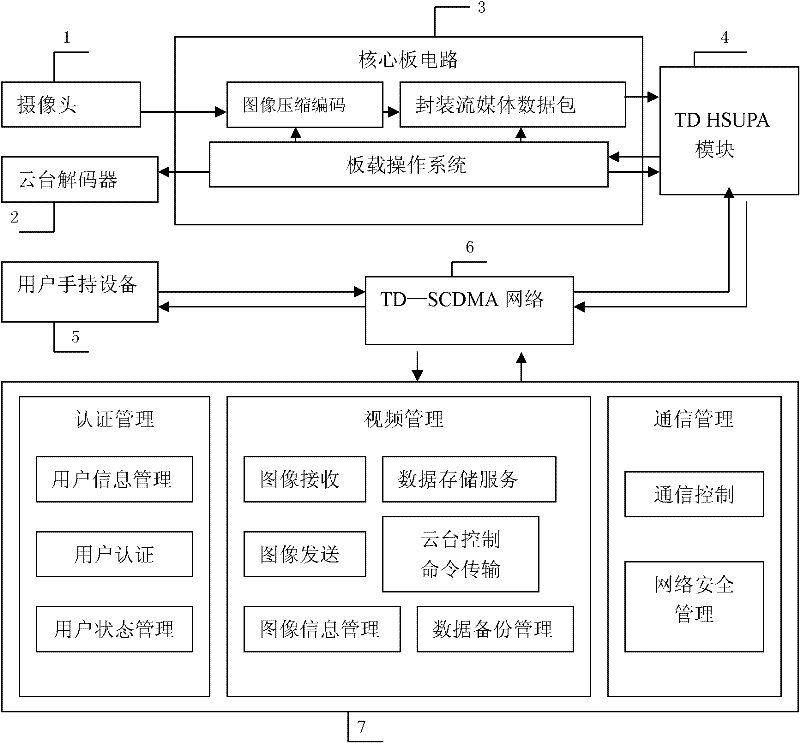
The invention relates to a video monitoring and transmission device based on the TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronization Code Division Multiple Access) network, belonging to the technical field of video information transmission equipment. The video monitoring and transmission device comprises a video data acquisition unit, a video monitoring center and a user handheld device, wherein the video data acquisition unit comprises a core board circuit and a TD HSUPA (Time Division High Speed Uplink Packet Access) module, the core board circuit is connected with a camera, a pan / tilt decoder and the TD HSUPA module, and the acquisition and the compression of video signals and the packaging of streaming media data can be realized; the video monitoring center provides service for the transmission, the storage and the forwarding of video data in the network, transmits the video data to the user handheld device and realizes real-time monitoring; and the user handheld device realizes field real-time monitoring and remote pan / tilt control through system play software installed on the user handheld device. The video monitoring and transmission device has quick video information transmission, high quality, low cost, good application prospect and environmental protection.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Coordinating uplink control channel gating with channel quality indicator reporting
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
HSUPA (High Speed Uplink Packet Access) scheduler and scheduling method by adopting MU MIMO (Multiple User Multiple Input Multiple Output) technology
ActiveCN102215588AImprove uplink throughputIncrease speedWireless communicationError prevention/detection by diversity receptionTD-SCDMAPeak value
The invention provides an HSUPA (High Speed Uplink Packet Access) scheduler and a scheduling method by adopting MU MIMO (Multiple User Multiple Input Multiple Output) technology, aiming to realize the scheduling of UE so as to share the resource except the resource occupied by the uplink channels scheduling E-PUCH (Enhanced Physical Uplink Channel) resource in MU MIMO mode or the uplink idle resource. The scheduling of the uplink channels out of the E-PUCH includes but not limited to: UL-DPCH (Uplink Dedicated Physical Channel), unscheduled E-PUCH, SPSE-PUCH, HS-SICH (High Speed Shared Information Channel), PRACH (Physical Random Access Channel) and E-RUCCH (E-DCH (Enhanced Dedicated Channel) Random-Access Uplink Control Channel). If the uplink channel types in the later TD-SCDMA (Time Division-Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access) system increase, the invention can be extended to apply to the increased uplink channels, namely the scheme can realize the scheduling of UE to multiplex uplink resources constituted by all uplink time slots in MU MIMO mode, so the uplink throughputs and the uplink peak rate of the HSUPA can be improved. The invention also provides a midamble shift in a default configuration mode to distribute the midamble shift for the HSUPA UEs which multiplex the same resource.
Owner:TD TECH COMM TECH LTD
Apparatus, Method and Computer Program Product Providing Uplink Gain Factor for High Speed Uplink Packet Access
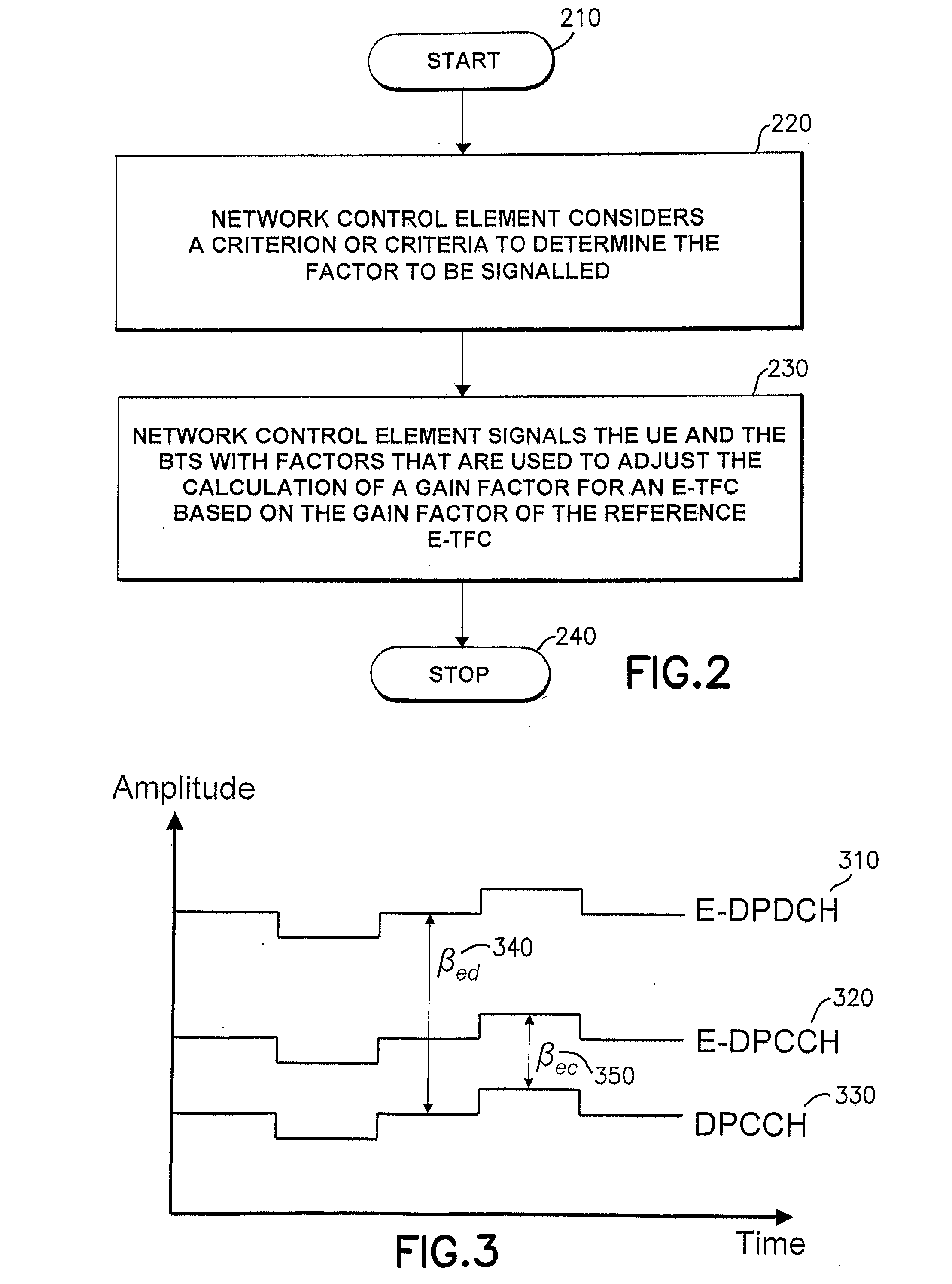
ActiveUS20110038305A1Increase system capacityPower managementWireless commuication servicesRadio networksControl signal
Apparatus, methods and computer program products operate a radio network controller in a wireless communications system to determine a factor to be used by user equipment operative in the wireless communications network to determine a gain factor for an E-TFC based on the gain factor of a reference E-TFC; and to signal the factor to the user equipment. The radio network controller may select the factor based on at least one criterion. In another aspect, apparatus, methods and computer program products operate user equipment to receive a factor from a wireless communications network, and to use the factor transmitted by the wireless communications network to determine a gain factor that relates a data signal to be transmitted by the user equipment in a data channel and a control signal transmitted by the electronic device in a control channel, where the control signal transmitted in the control channel carries information for use in receiving the data signal. In additional aspects, the user equipment is further configured to select a formula for use in determining the gain factor in dependence on signaling received from the wireless communications network.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method and device for congestion detection and flow control of uplink
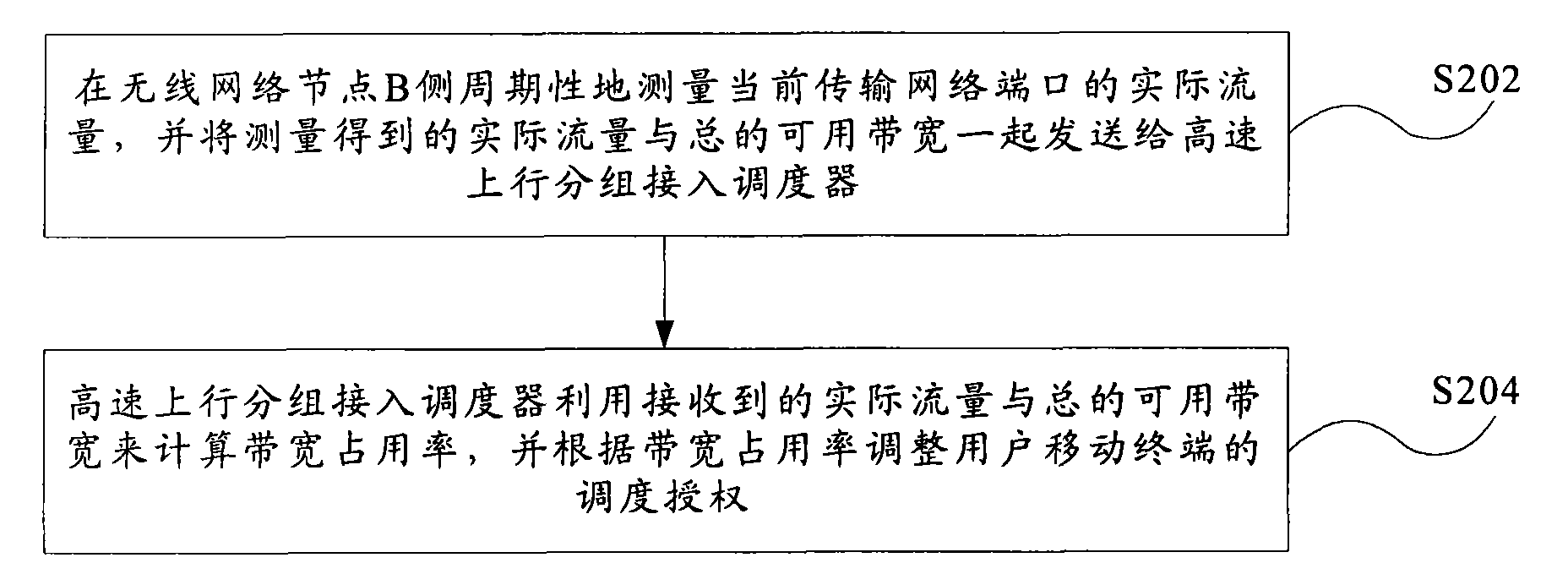
InactiveCN101594630AIncrease profitReduce lossNetwork traffic/resource managementCongestion detectionAuthorization
The invention discloses a method and a device for congestion detection and flow control of an uplink. The method for congestion detection and flow control of the uplink comprises that: step S202, actual flow of a current transmission network port is measured periodically on a B side of a wireless network node, and the actual flow obtained by the measurement and total available bandwidth are sent to a high-speed uplink packet access scheduler together; and step S204, the high-speed uplink packet access scheduler calculates bandwidth occupation rate by utilizing the received actual flow and the total available bandwidth, and adjusts scheduling authorization of a user mobile terminal according to the bandwidth occupation rate. The method and the device greatly shorten the time of responding and processing the congestion of Iub interface transmission bandwidth, and reduce the loss of signals and data caused by the congestion.
Owner:深圳市恒程汇文化科技有限公司
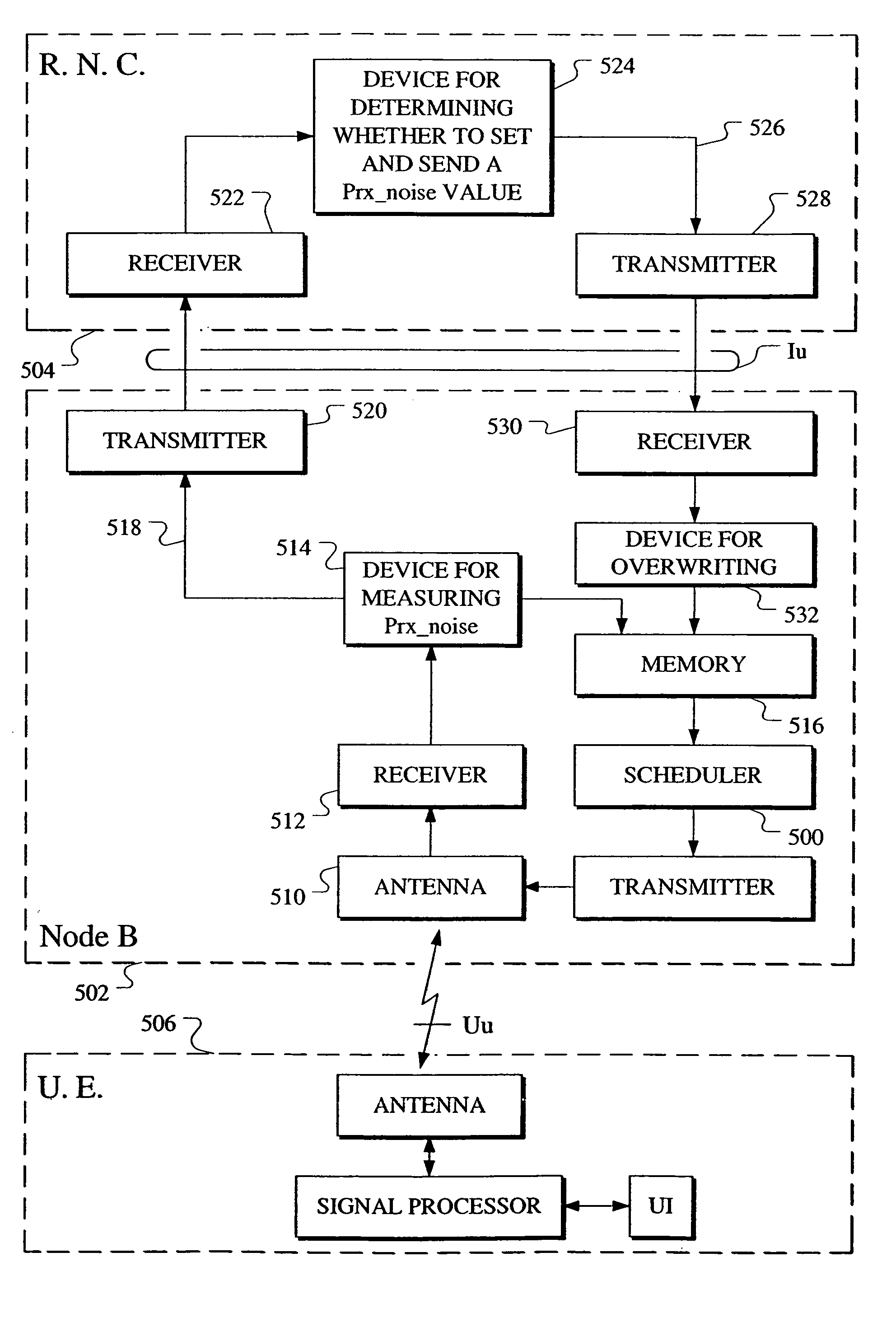
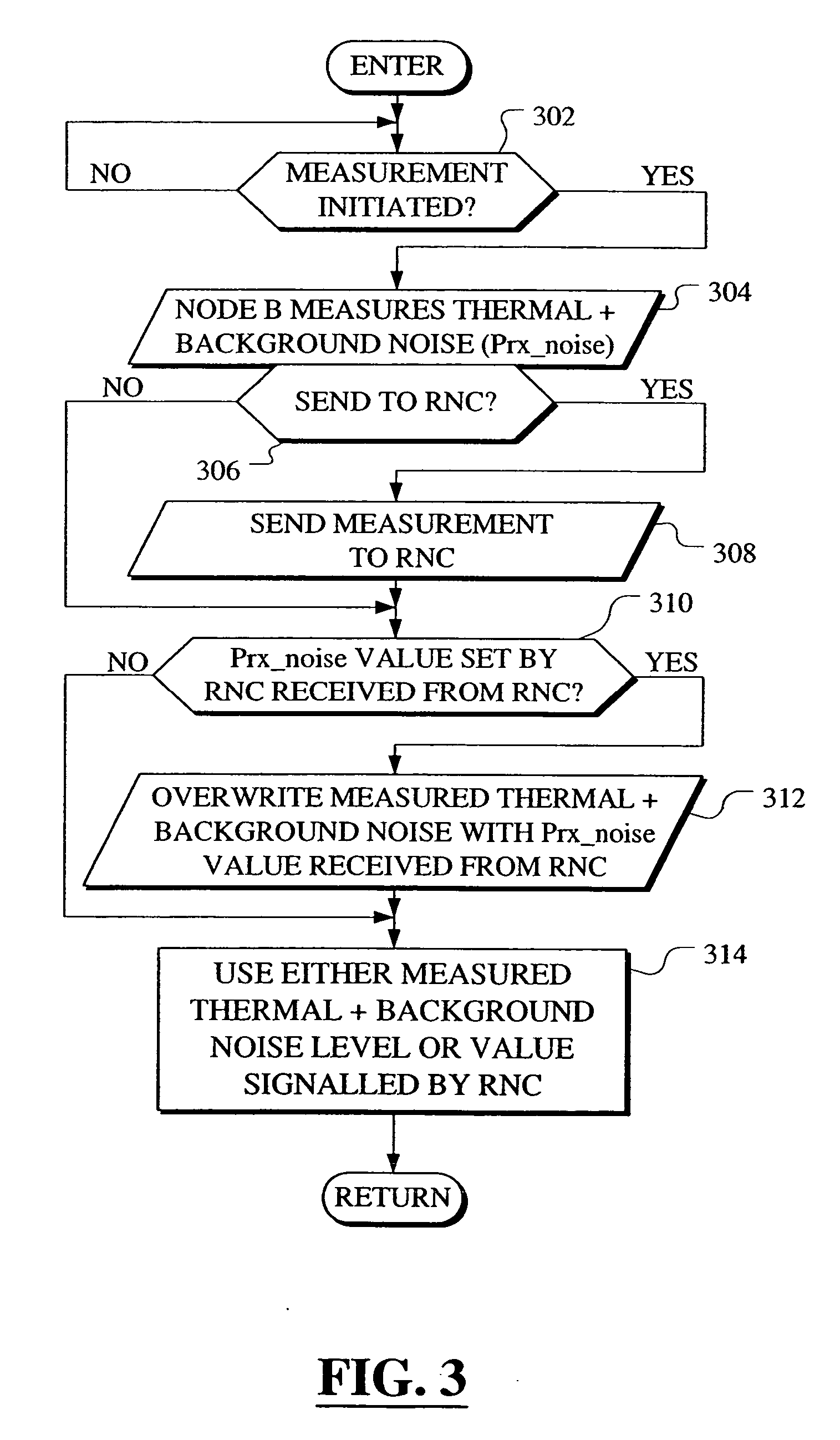
Noise level communication for high speed uplink packet access
ActiveUS20060178112A1Guaranteed usageTransmission monitoringWireless communicationNoise levelComputer science
A communication flow for HSUPA is shown that allows a NodeB to measure the thermal plus background noise level (Prx<sub2>—< / sub2>noise), and at the same time which also allows the RNC, according to its own (centralized) strategy, to overwrite the very same value that is then used in NodeB (de-centralized) scheduling.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method for reporting scheduling information
InactiveCN101959246AImprove compatibilityReduce the amount of informationNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunicationsClosed loop
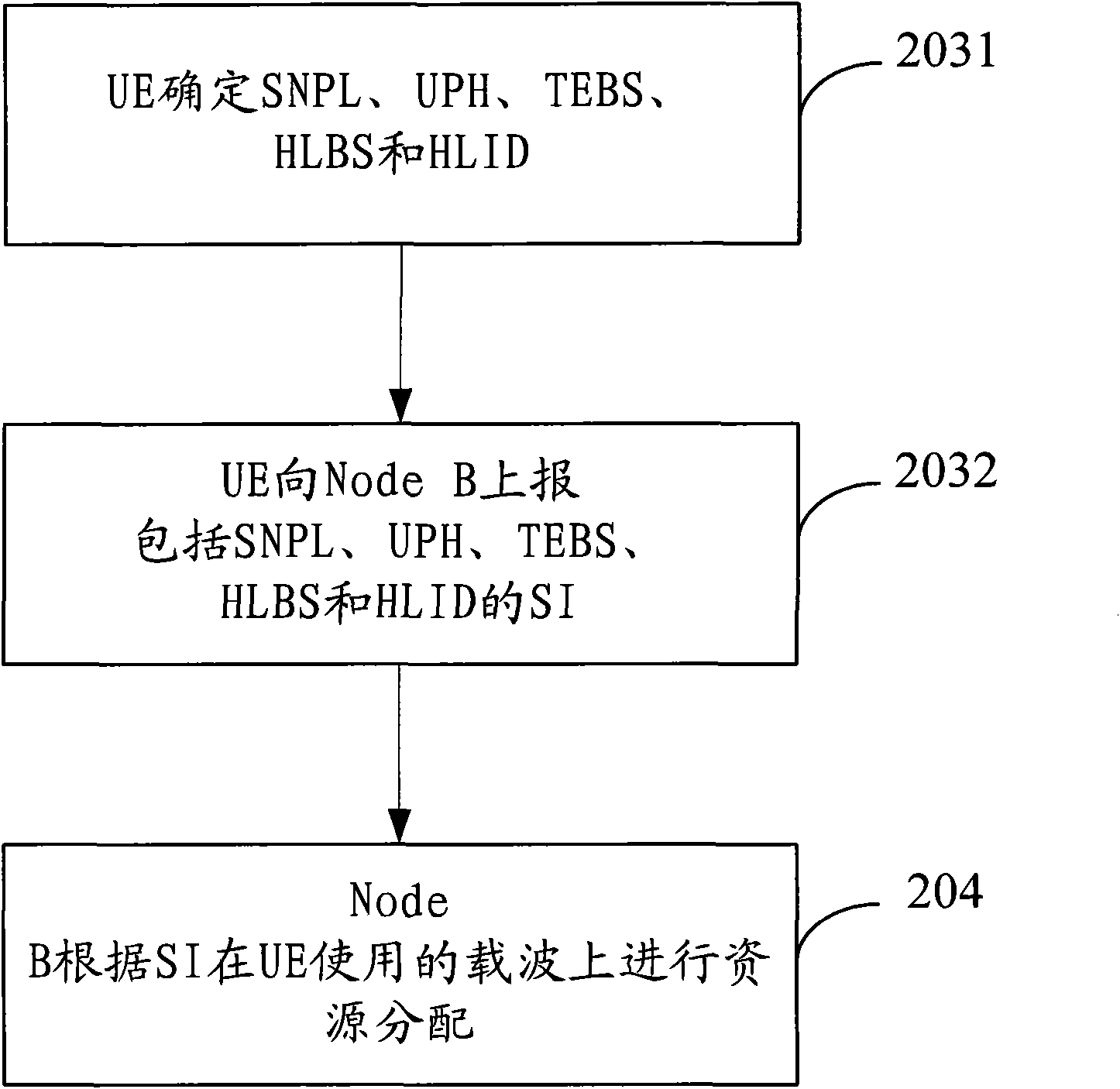
The invention discloses a method for reporting scheduling information, which is suitable for the condition that User equipment (UE) supports a multicarrier High Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA). In the method, the current path loss information of Total Enhanced Dedicated Channel (E-DCH) Buffer State (TEBS), High Priority Logic Channel Buffer State (HLBS), High Priority Logic Channel Identity (HLID), Service Cell and Neighborhood Cell Path Loss Information (SNPL), closed loop UE Power Allowance (UPH) or UE of the multicarrier HSUPA supported by the UE are filled in the scheduling information, and corresponding methods for reporting the scheduling information to the NODEB are provided aiming at the fact that whether the UE adopts an Enhanced Physical Uplink Channel (E-PUCH) or not so as to solve the problems that UE constructs and reports the scheduling information when the UE supports the multicarrier HSUPA.
Owner:TD TECH COMM TECH LTD
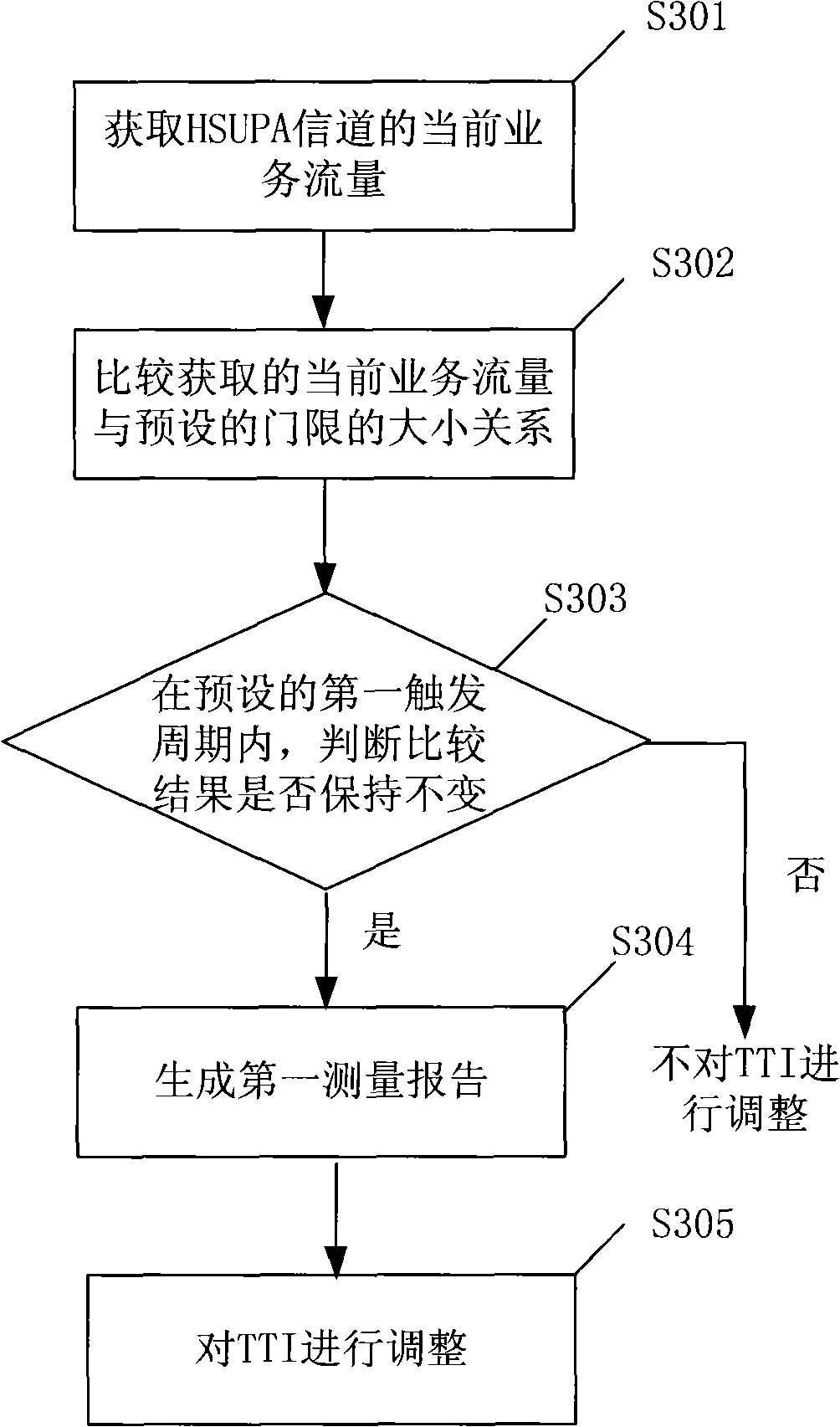
Method and device for adjusting transmission time interval
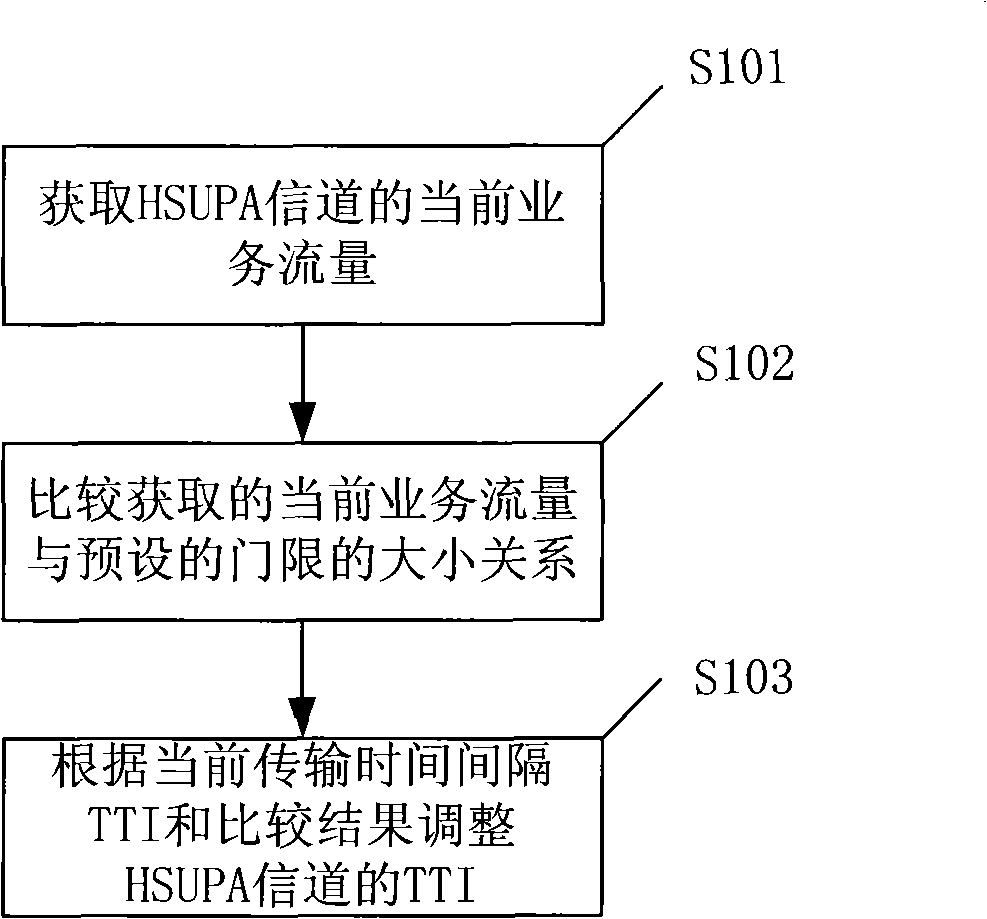
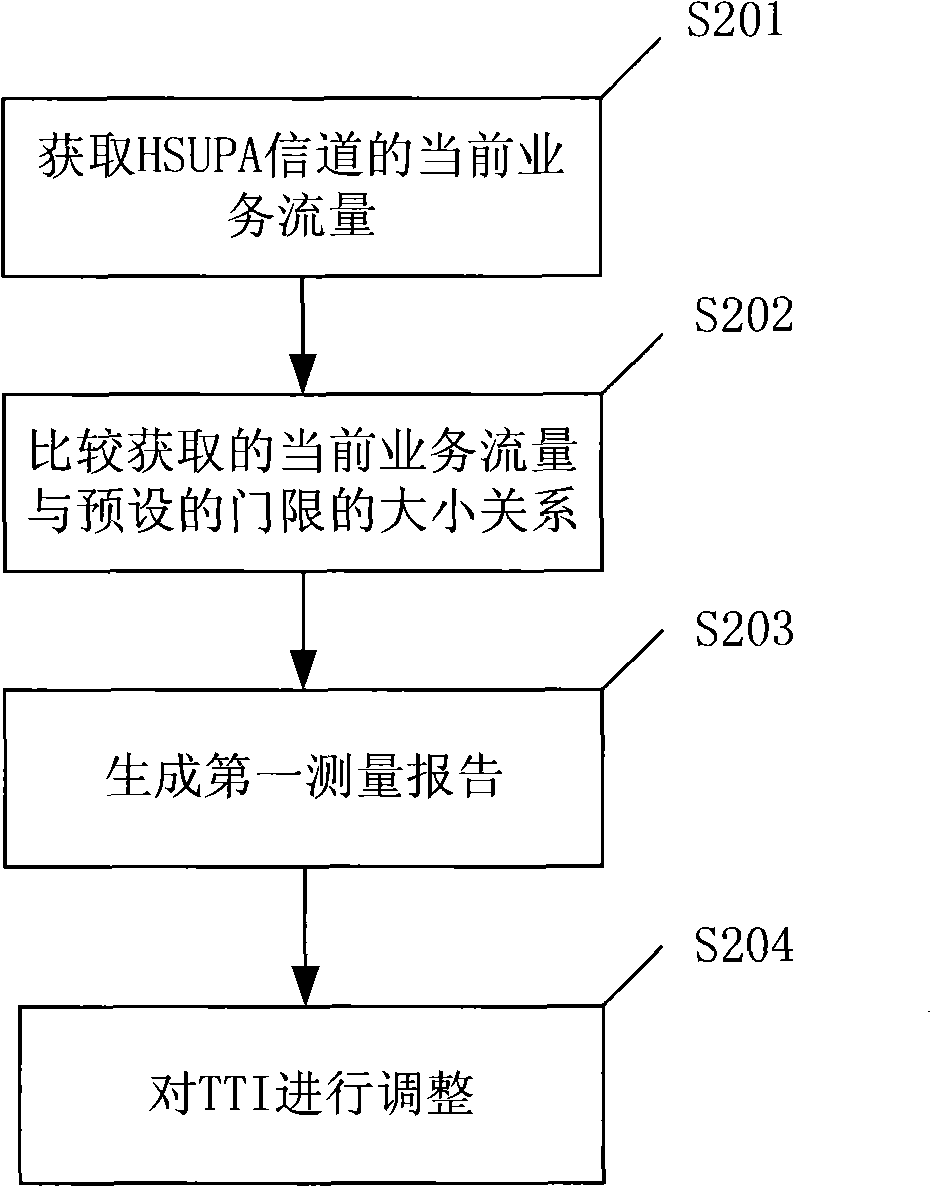
InactiveCN101572905AIncrease profitMeet the needs of data transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementService flowData transmission
The embodiment of the invention provides a method for adjusting transmission time interval TTI. The method mainly comprises the following steps: obtaining current service flow of a high-speed uplink packet access HUSPA channel; comparing the obtained current service flow with a predetermined threshold; and adjusting the TTI of the HUSPA channel according to the current TTI and the comparison result. The embodiment of the invention also provides a TTI adjusting device and a wireless network controller. The method, the TTI adjusting device and the wireless network controller can adjust the TTI of the HUSPA channel according to the actual service flow so that the TTI not only satisfies the need of data transmission but also can try to improve the channel resource utilization rate of a base station.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com