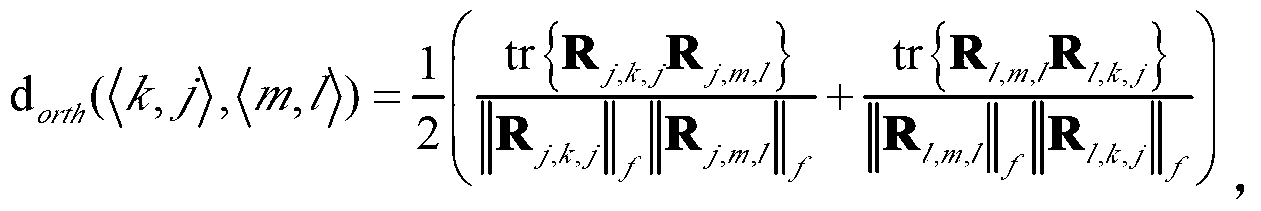Spatial-orthogonality-based large-scale MIMO (multiple input multiple output) system pilot frequency distribution method
A technology of system pilot frequency and distribution method, applied in baseband system components, transmission systems, digital transmission systems, etc., can solve problems such as the inability of the base station to distinguish signals, the limited spatial dimension of pilot signals, and pilot pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The present invention will be described below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
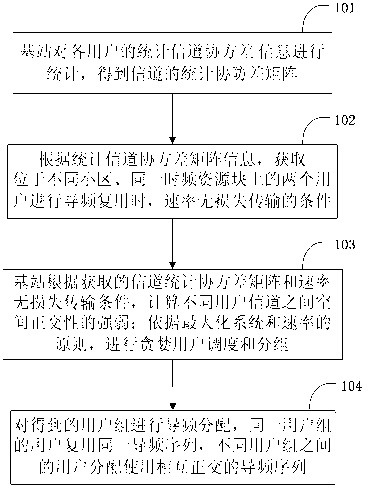
[0030] The example of the present invention provides a kind of large-scale MIMO system pilot allocation method based on spatial orthogonality, comprising the following steps:
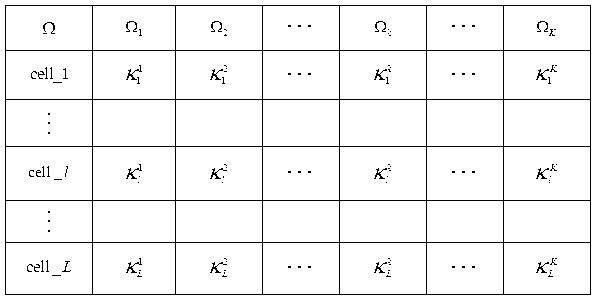
[0031] Step 1. Obtain the statistical covariance matrix information R of the channel from user k in cell l to the base station in cell j j,k,l ,j,l∈{1,…,L},k∈{1,…,K};
[0032] Step 2. According to the channel statistical covariance matrix information obtained in step 1, obtain the condition of rate lossless transmission when two users located in different cells and on the same time-frequency resource block perform pilot multiplexing;
[0033] Step 3. According to the channel statistical covariance matrix information obtained in step 1, the base stations of all cells compare and calculate the degree of spatial orthogonality between different user channels, and use the rate lossless transmission condition ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com