Finite field multiplier based on binary tree structure
A binary tree and finite field technology, applied in the field of finite field multipliers, can solve problems such as speed, area, and power consumption that cannot meet the requirements, and achieve obvious speed advantages, simple structure, and widely used effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The preferred embodiments of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
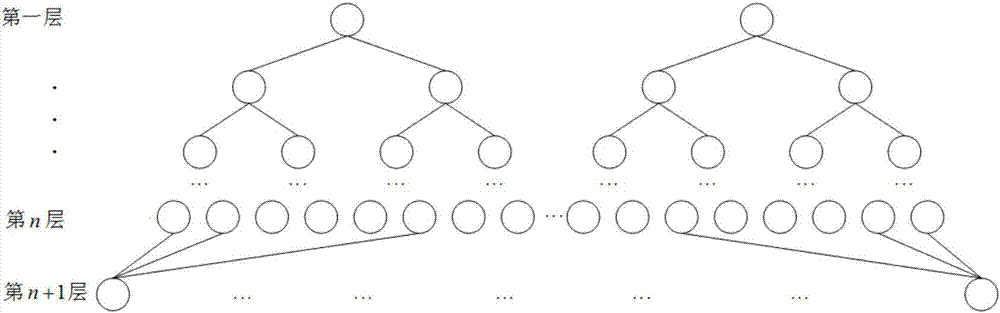
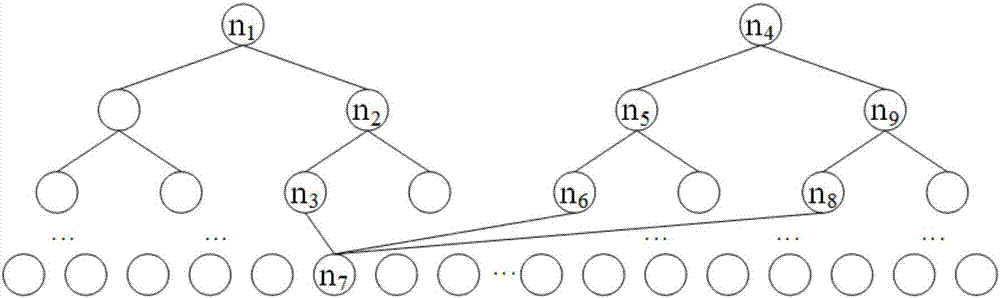
[0025] Such as figure 1 with figure 2 As shown, this example provides a finite field multiplier based on a binary tree structure, including:
[0026] Input port for entering the finite field GF(2 n ) operand a(x) and operand b(x);
[0027] The output port is used to output the multiplication result c(x) of the operand a(x) and the operand b(x);
[0028] And, the binary tree structure, used to execute GF(2 of operand a(x) and operand b(x) n ) multiplication;
[0029] Among them, the binary tree structure includes n+1 layers, from top to bottom, the first layer to the nth layer includes a left binary tree and a right binary tree, and the bottom layer is the n+1th layer; each node of the n+1th layer is connected to Three specific nodes of the nth layer are connected.
[0030] In the left binary tree and the right binary tree ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com