Key equation solving circuit of read-solomon decoder
An equation solving and decoder technology is applied in the field of Reed-Solomon decoder key equation solving circuit, which can solve the problems of limiting the increase of the clock operating frequency of the decoder circuit and the length of the critical path.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
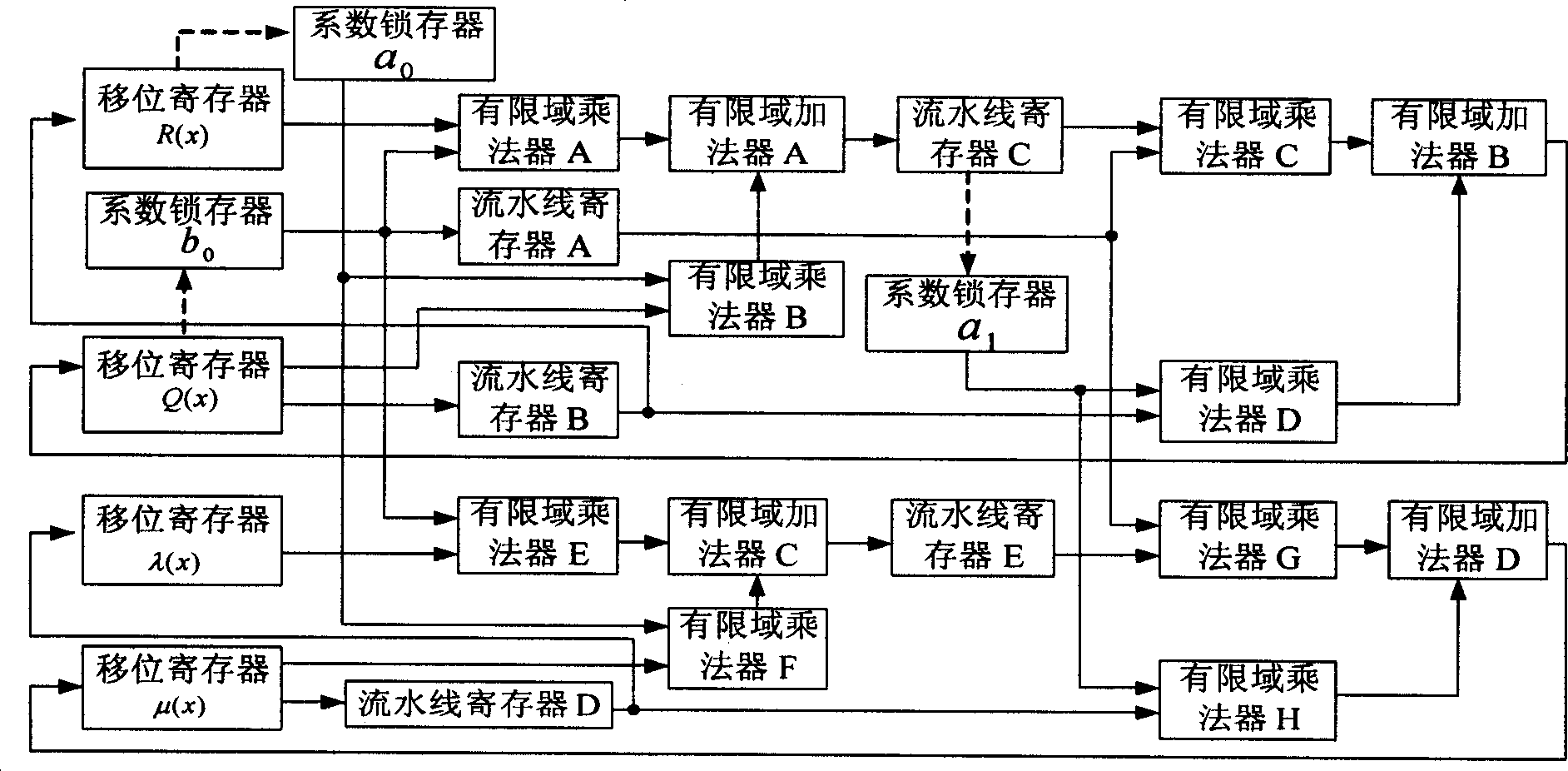
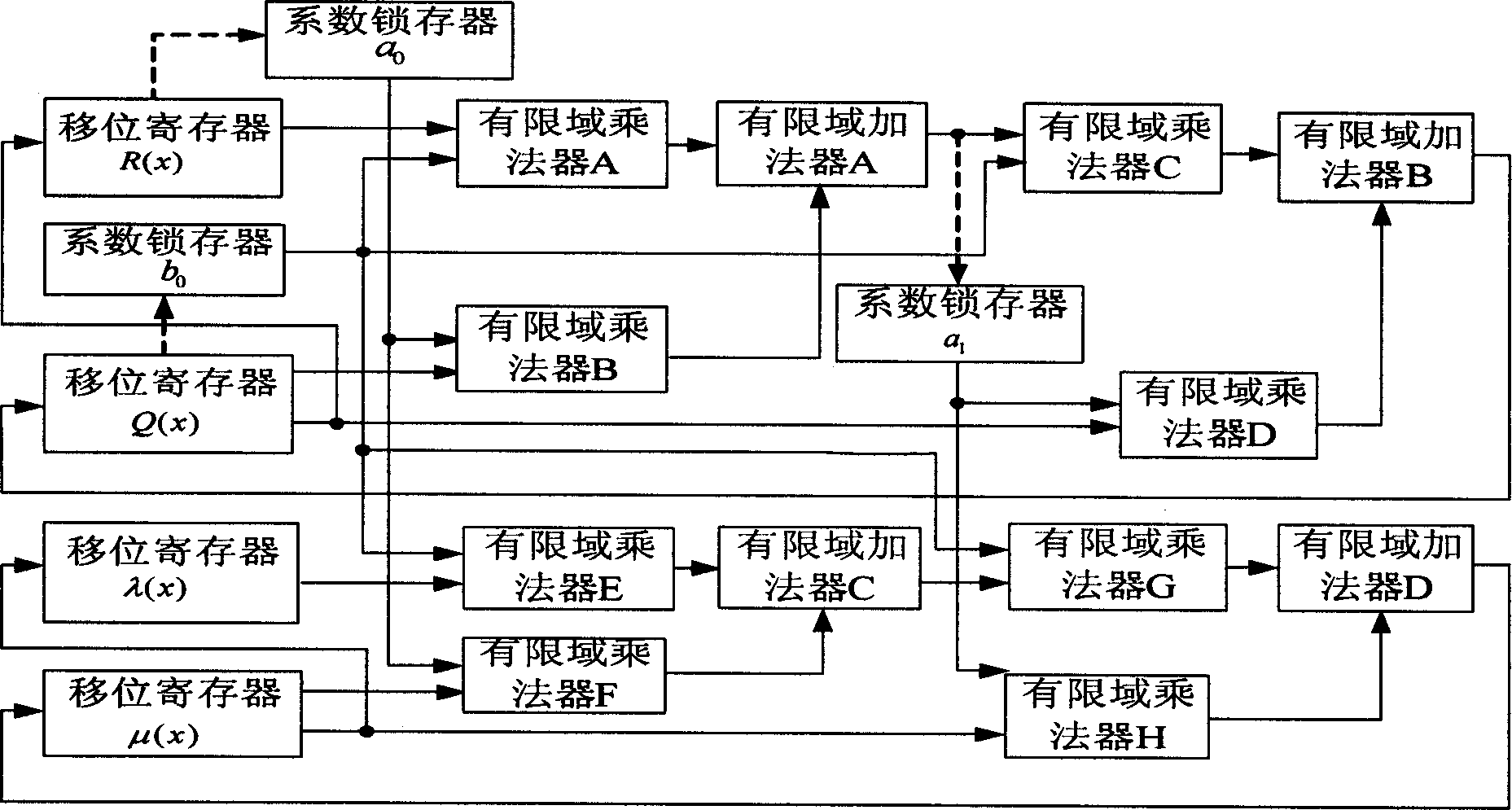
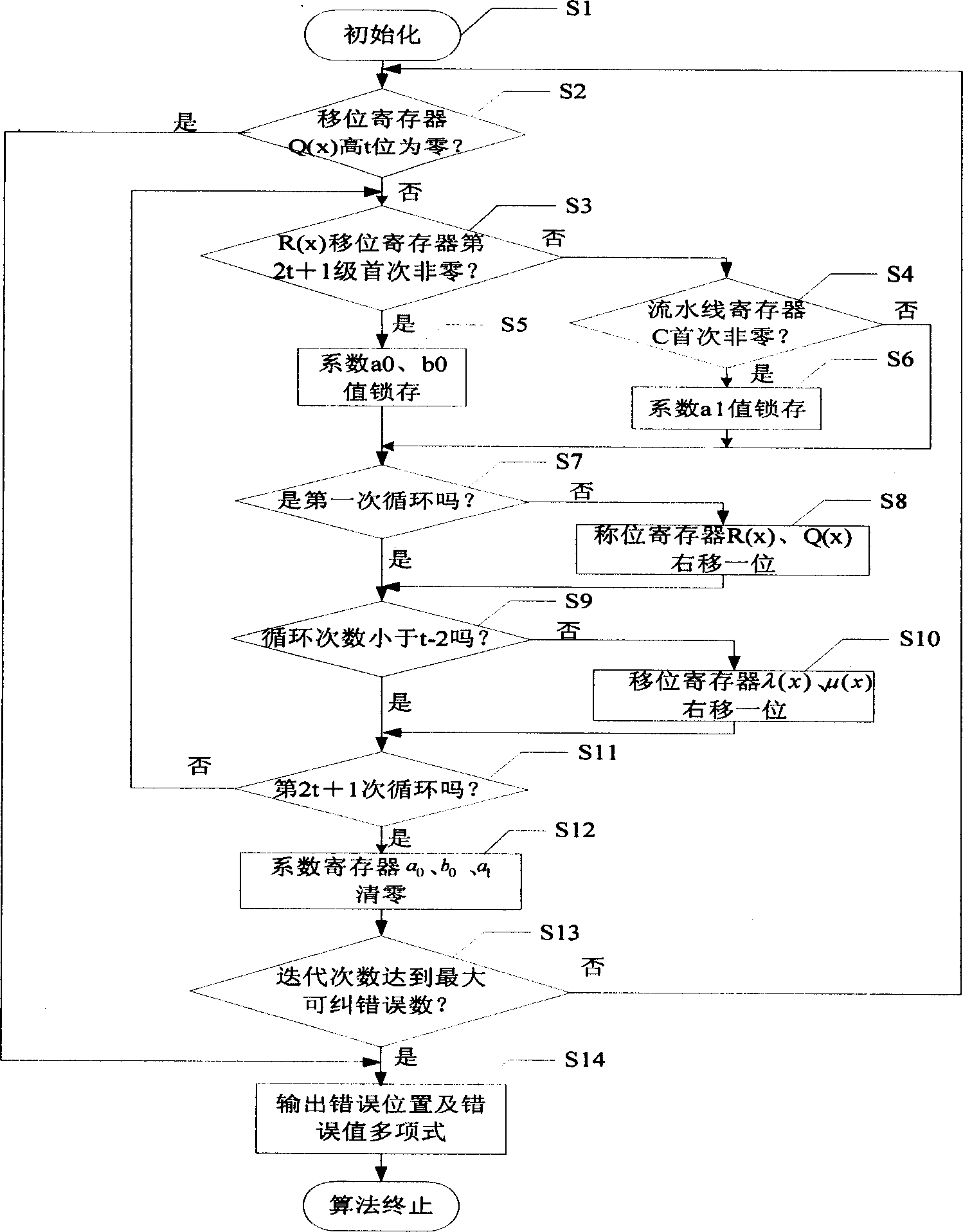
[0013] refer to figure 1 . The previous part completes the function of calculating the error value polynomial, and the following part calculates the error position polynomial. The circuit includes: R(x) shift register, Q(x) shift register, λ(x) shift register, μ(x) shift register, finite field multiplier A, finite field multiplier B, finite field Multiplier C, finite field multiplier D, finite field multiplier E, finite field multiplier F, finite field multiplier G, finite field multiplier H, finite field adder A, finite field adder B, finite field adder C. Finite field adder D. Coefficient a 0 Latch, Coefficient b 0 Latch, coefficient a 1 Latches. a 0 , b 0 Respectively R(x), Q(x) highest term coefficient, a 1 is the highest term coefficient of R(x) after an odd number of iterations of the key equation. Each stage of the shift register registers values as elements in a finite field.
[0014] The R(x) shift register is a 2t+1 stage right shift register. At the tim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com