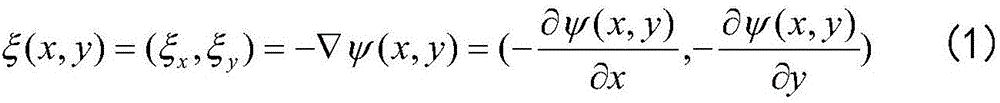Patents
Literature
70 results about "Very-large-scale integration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Very large-scale integration (VLSI) is the process of creating an integrated circuit (IC) by combining millions of MOS transistors onto a single chip. VLSI began in the 1970s when MOS integrated circuit chips were widely adopted, enabling complex semiconductor and telecommunication technologies to be developed. The microprocessor and memory chips are VLSI devices. Before the introduction of VLSI technology, most ICs had a limited set of functions they could perform. An electronic circuit might consist of a CPU, ROM, RAM and other glue logic. VLSI lets IC designers add all of these into one chip.
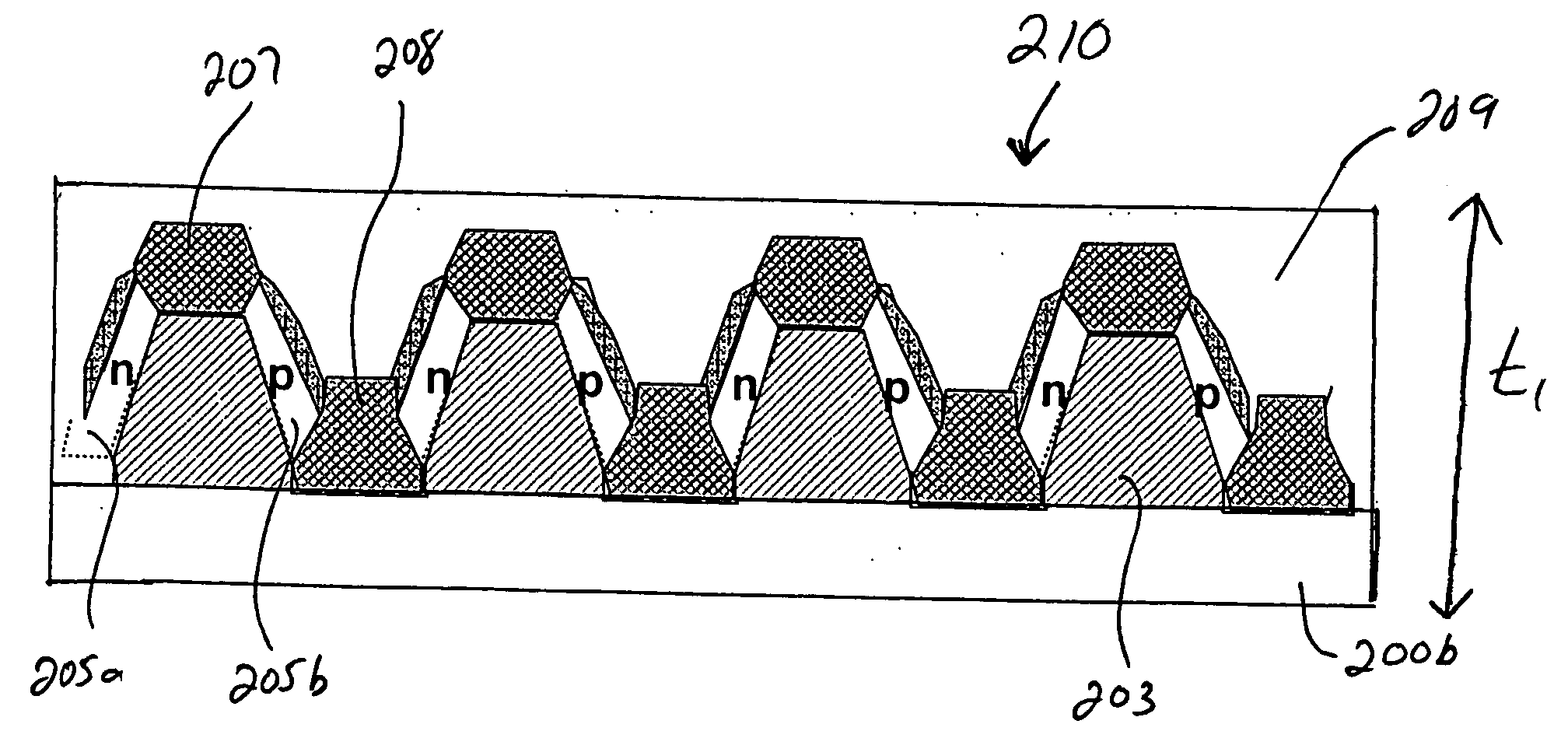
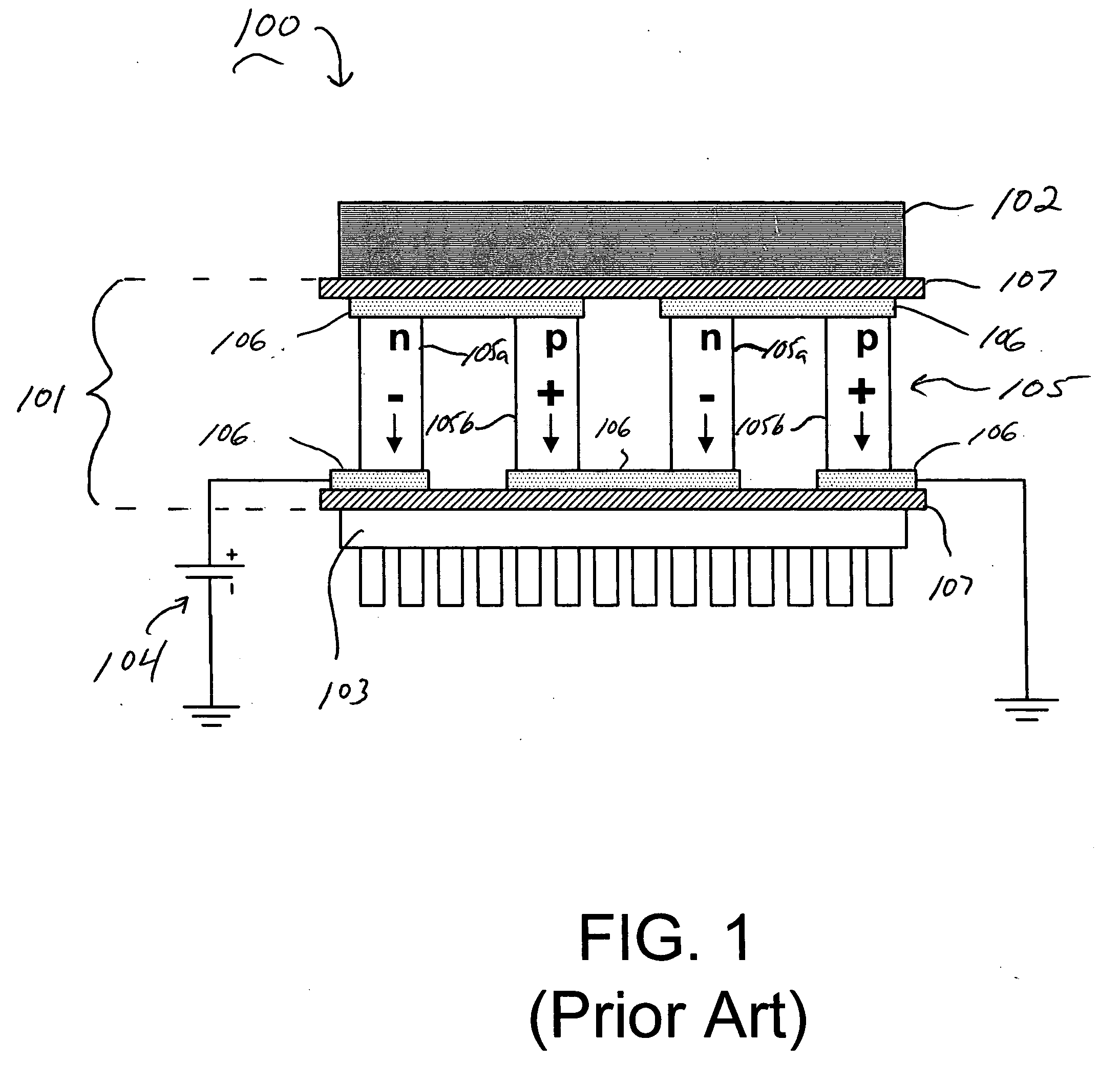
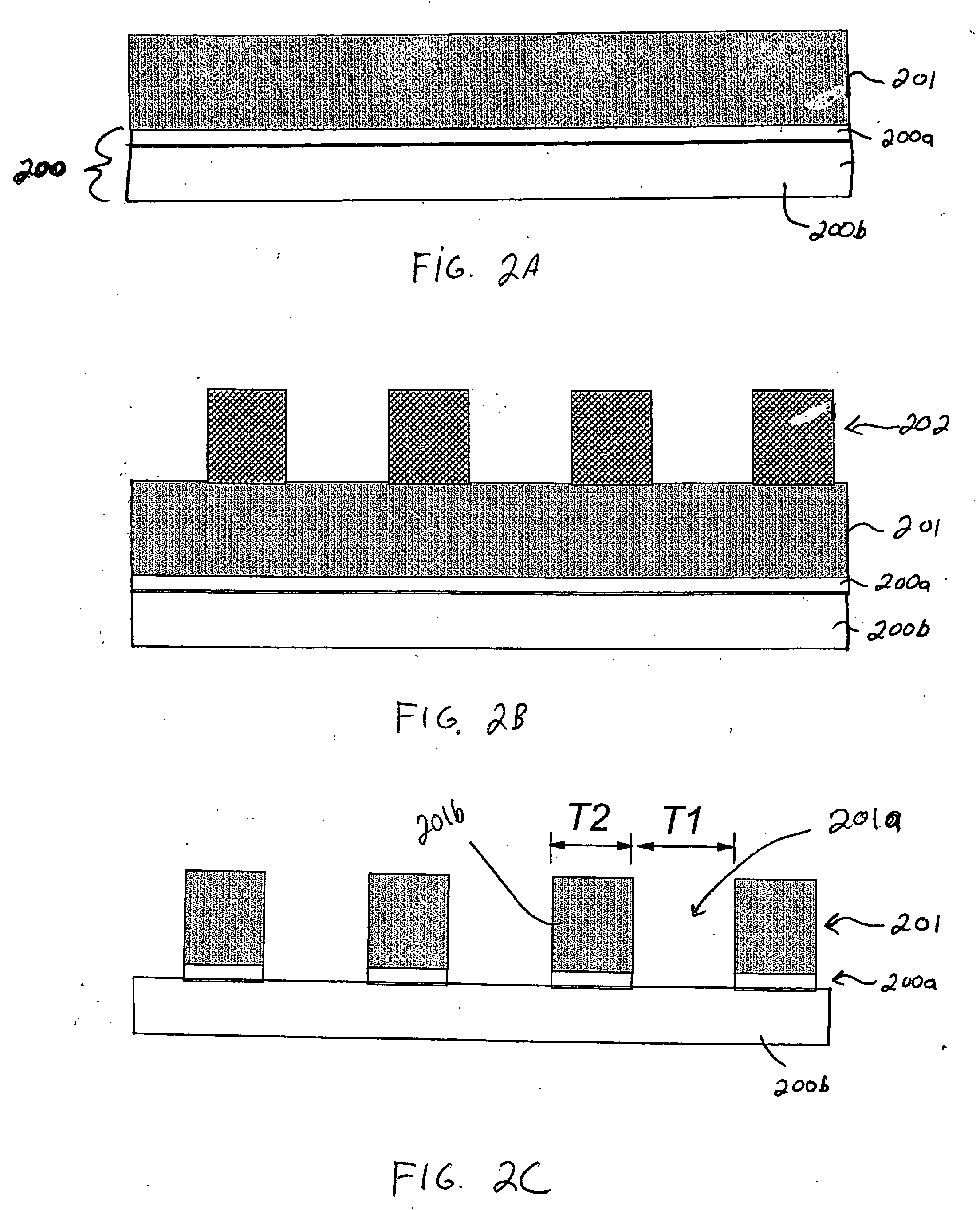
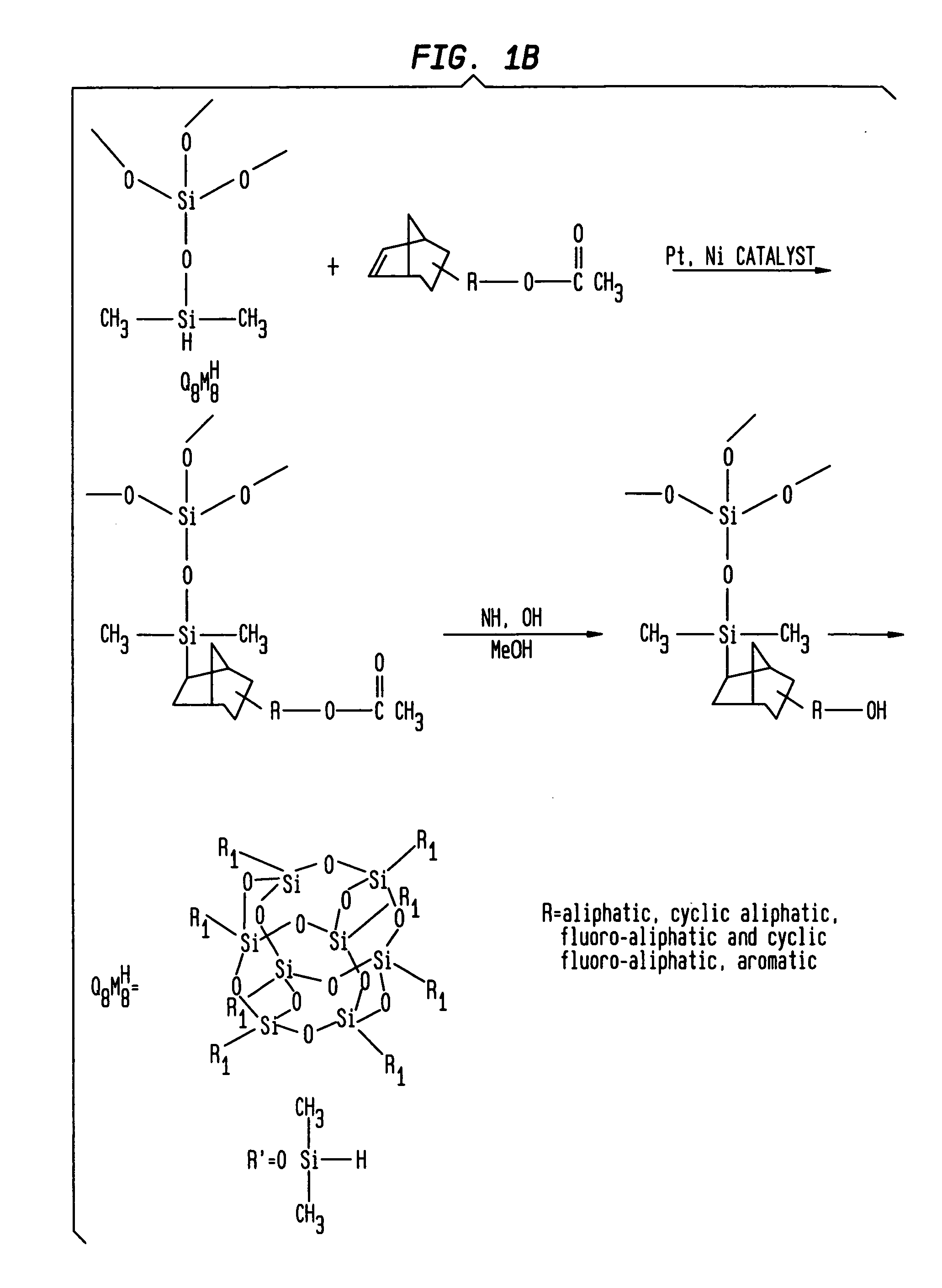
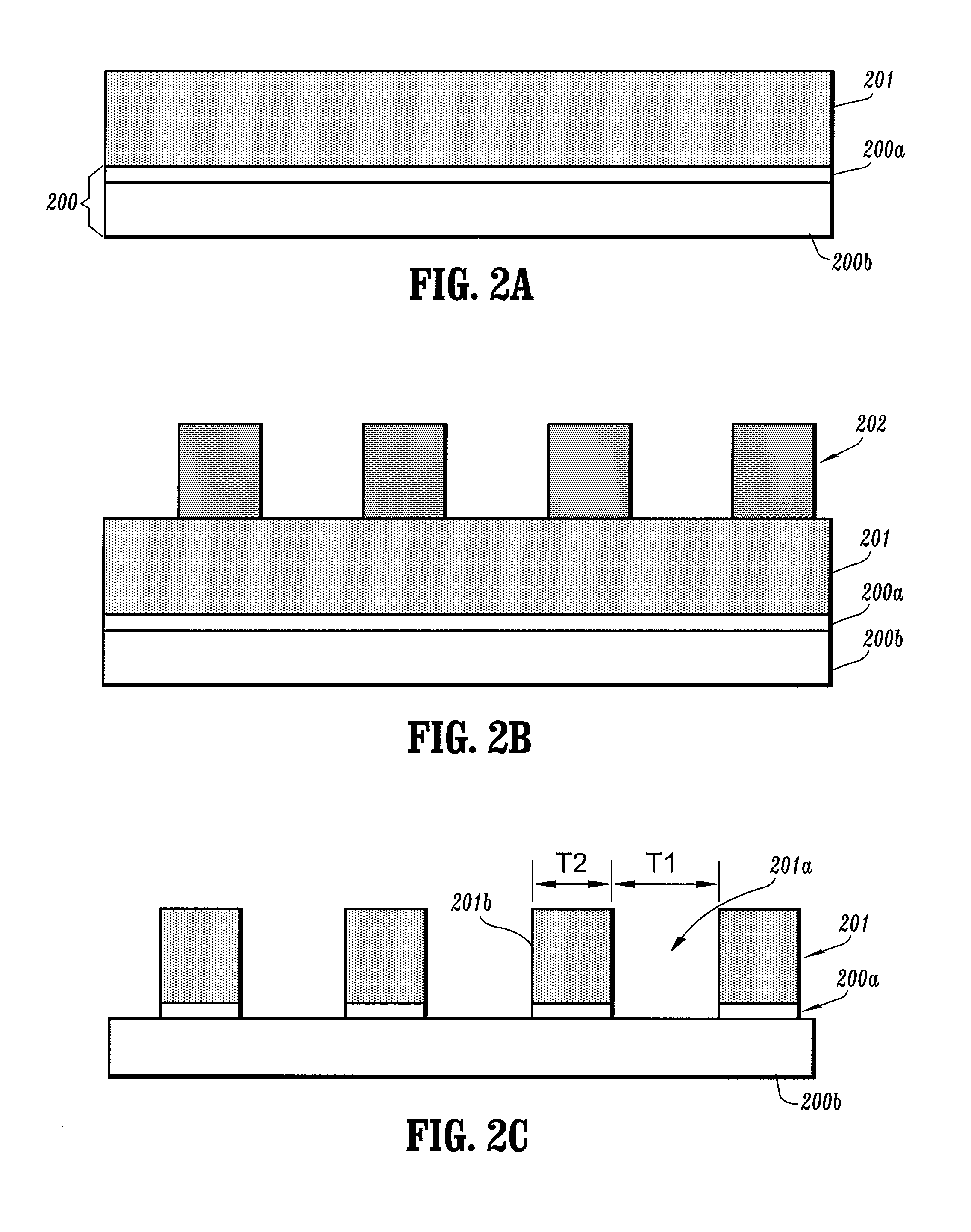
Integrated thermoelectric cooling devices and methods for fabricating same
ActiveUS20060102223A1Reduced dimensionIncrease heatThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric coolingHigh density
Semiconductor integrated thermoelectric devices are provided, which are formed having high-density arrays of thermoelectric (TE) elements using semiconductor thin-film and VLSI (very large scale integration) fabrication processes. Thermoelectric devices can be either separately formed and bonded to semiconductor chips, or integrally formed within the non-active surface of semiconductor chips, for example.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Patternable low dielectric constant materials and their use in ULSI interconnection
InactiveUS20060105181A1Low dielectric constantReduce complexityPhotosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInterconnectionVery-large-scale integration
The present invention relates to ultra-large scale integrated (ULSI) interconnect structures, and more particularly to patternable low dielectric constant (low-k) materials suitable for use in ULSI interconnect structures. The patternable low-k dielectrics disclosed herein are functionalized polymers that having one or more acid-sensitive imageable functional groups.
Owner:AURIGA INNOVATIONS INC
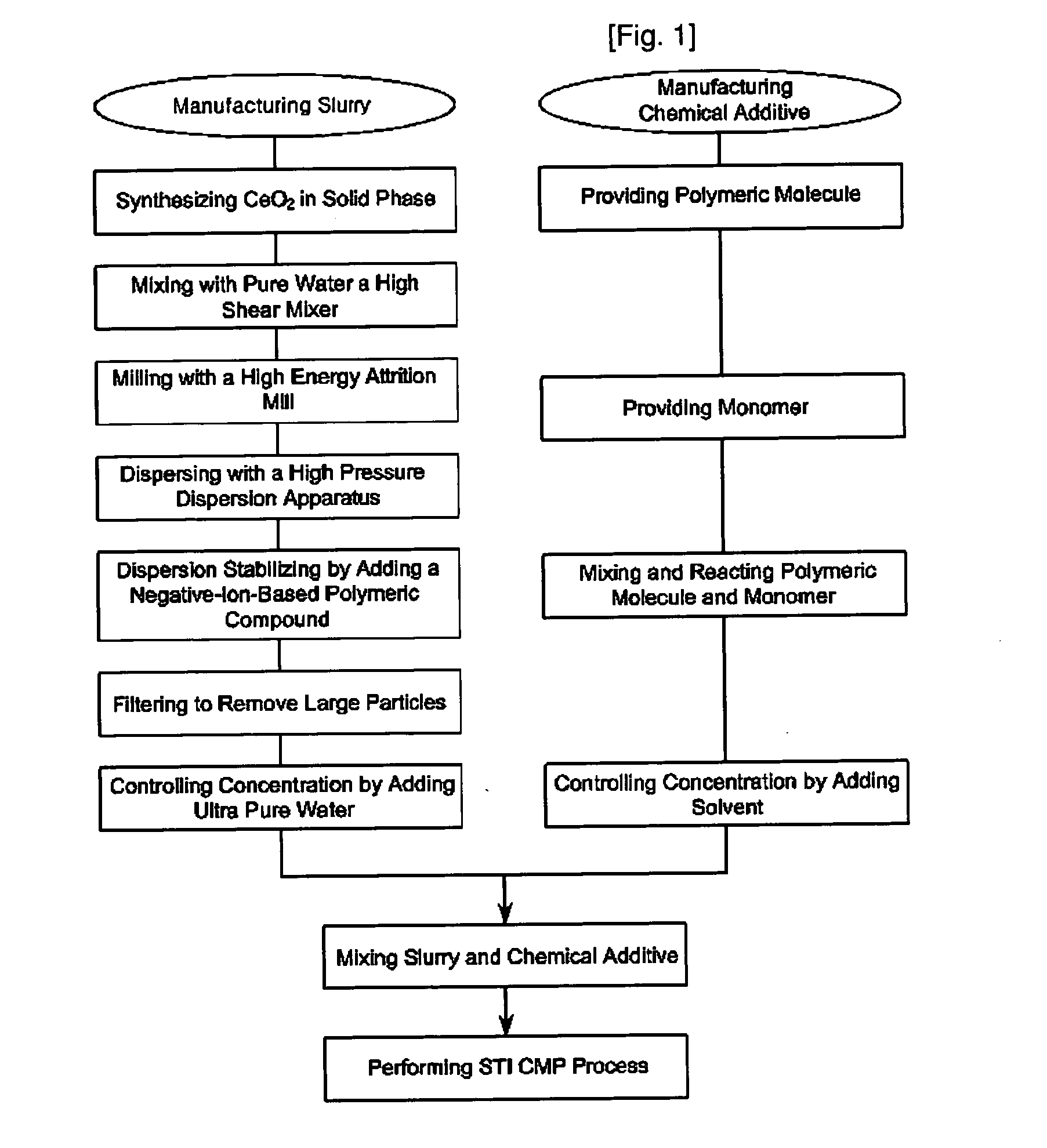
Ceria abrasive for cmp
InactiveUS20060207188A1High selectivityPolishing propertyPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesCompound (substance)Slurry
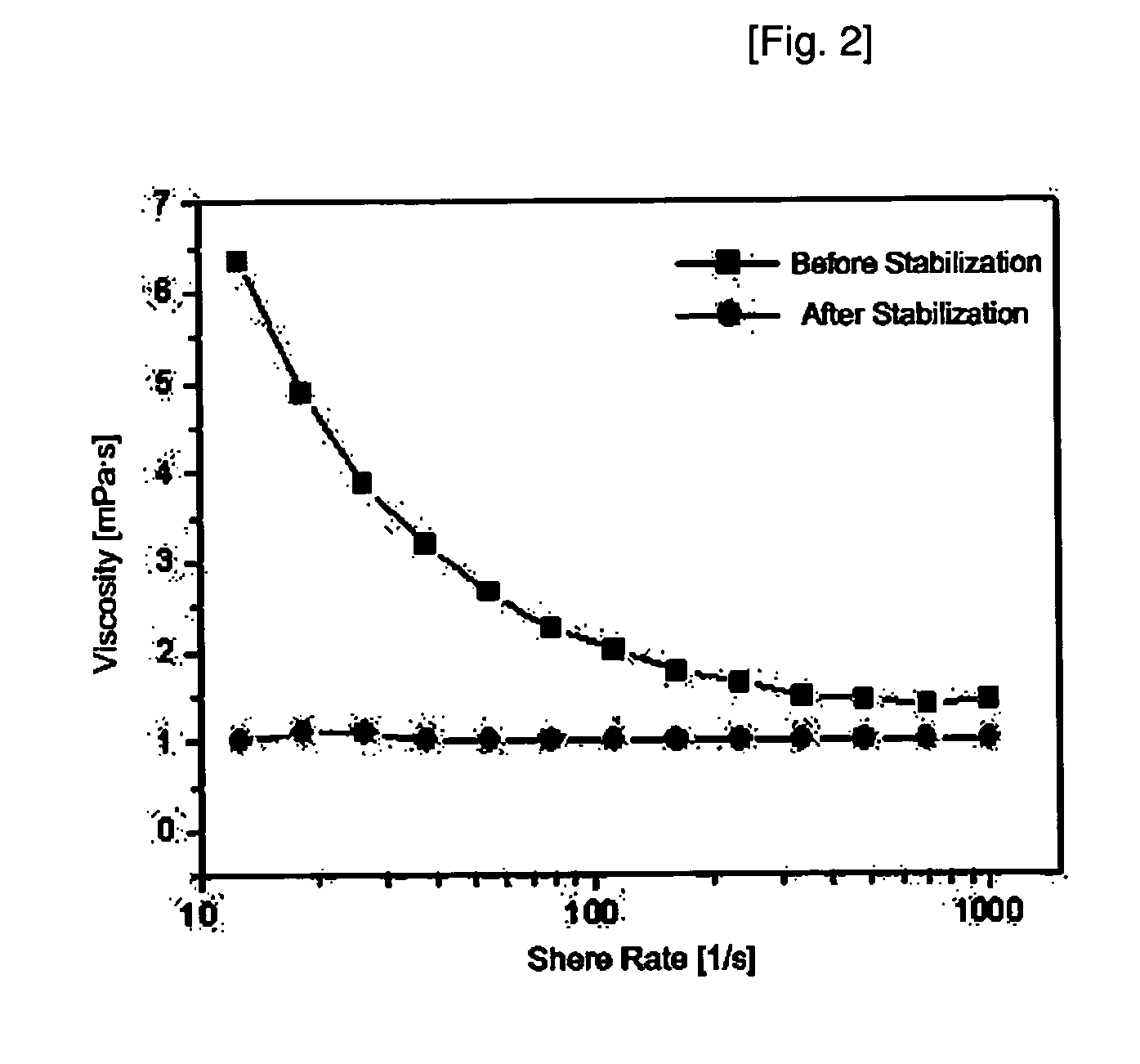
The present invention relates to a CMP abrasive comprising a ceria slurry and a chemical additive having two or more functional groups by mixing and synthesizing a polymeric molecule and a monomer. Also, the present invention relates to a method for a manufacturing CMP abrasive by providing a ceria slurry, manufacturing a chemical additive having two or more functional groups by mixing and synthesizing of the polymeric molecule and the monomer in a reactor, and mixing said slurry and said chemical additive. Therefore, when the abrasive according to the present invention is used as an STI CMP abrasive, it is possible to apply the abrasive to the patterning process required in the very large scale integration semiconductor process. Furthermore, the CMP abrasive of the present invention has a superior removal rate, superior polishing selectivity, superior within wafer non-uniformity (WIWNU), and minimized occurrence of micro scratches.
Owner:K C TECH +1
Method and apparatus for synchronized clock distribution
A method and apparatus are described which eliminate the clock skew problems associated with routing clock signals throughout a circuit. Particularly well suited for Very Large Scale Integration ("VLSI") chips, the method and apparatus provide a resonator which is distributed across the circuit. This allows the clock to be accessed at a variety of locations without any propagation delay between the access points. The method for distributing a single, distributed clock signal to a plurality of clock connection points in a circuit comprises two steps. The first step is to generate the clock signal, such that the clock signal is available at a plurality of clock source points without propagation delay. The second step is to couple the plurality of clock source points to the plurality of clock connection points in the circuit.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Integrated thermoelectric cooling devices and methods for fabricating same
ActiveUS7544883B2Reduced dimensionIncrease heatThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric coolingHigh density
Semiconductor integrated thermoelectric devices are provided, which are formed having high-density arrays of thermoelectric (TE) elements using semiconductor thin-film and VLSI (very large scale integration) fabrication processes. Thermoelectric devices can be either separately formed and bonded to semiconductor chips, or integrally formed within the non-active surface of semiconductor chips, for example.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Semiconductor devices having nanochannels confined by nanometer-spaced electrodes
InactiveUS20120256281A1Easily addressableMicrobiological testing/measurementSolid-state devicesVery-large-scale integrationNanometre
Semiconductor devices having integrated nanochannels confined by nanometer spaced electrodes, and VLSI (very large scale integration) planar fabrication methods for making the devices. A semiconductor device includes a bulk substrate and a first metal layer formed on the bulk substrate, wherein the first metal layer comprises a first electrode. A nanochannel is formed over the first metal layer, and extends in a longitudinal direction in parallel with a plane of the bulk substrate. A second metal layer is formed over the nanochannel, wherein the second metal layer comprises a second electrode. A top wall of the nanochannel is defined at least in part by a surface of the second electrode and a bottom wall of the nanochannel is defined by a surface of the first electrode.
Owner:IBM CORP
Low frequency notch filter integrated circuit
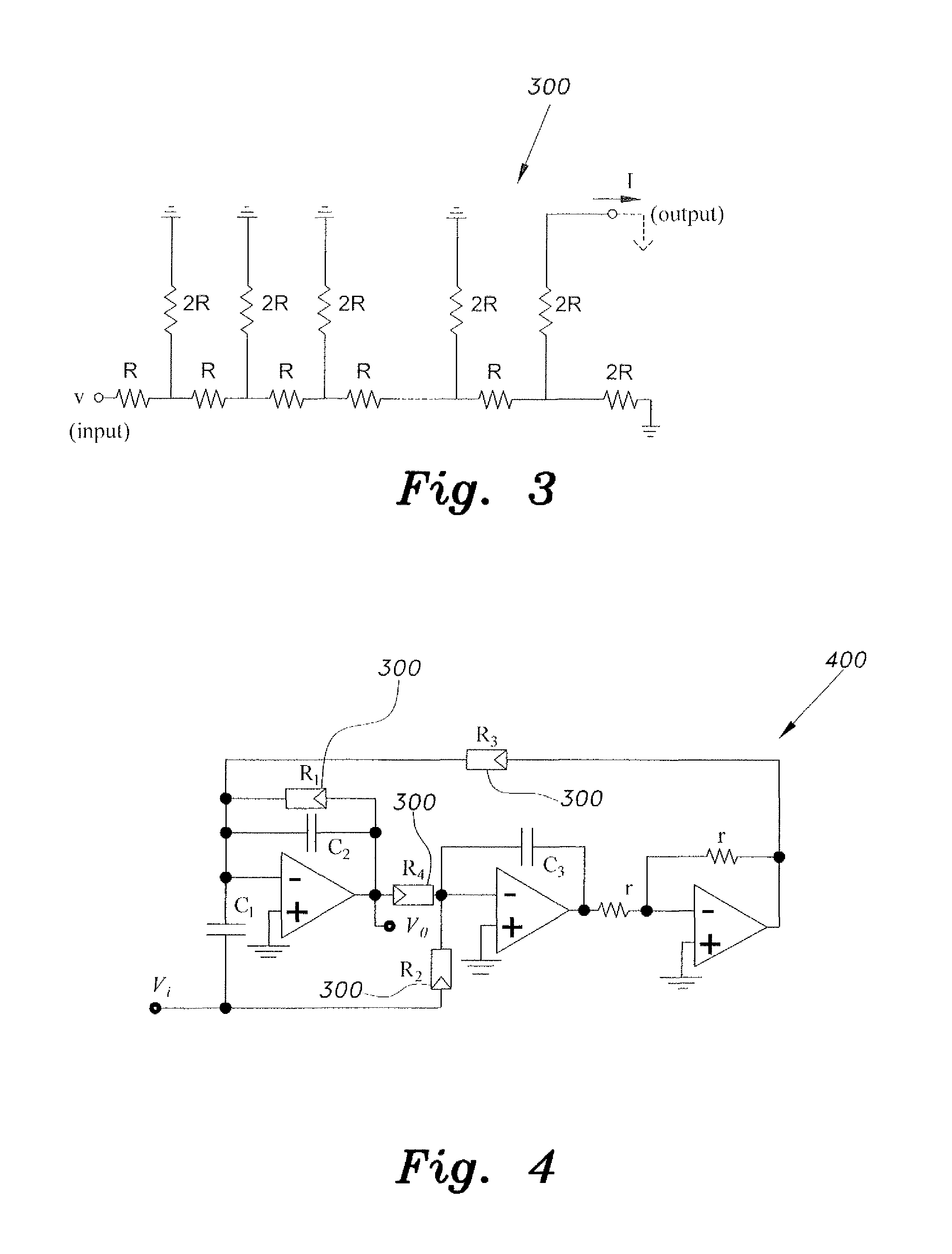
InactiveUS8436679B1Reduce areaPromotes its utilizationActive element networkOscillations generatorsIntegratorAudio power amplifier
The low frequency notch filter integrated circuit is implemented in a relatively small silicon area and with high linearity, thereby promoting the utilization of very large-scale integration (VLSI) techniques in biomedical instrumentation. The filter circuit utilizes R-2R ladders providing area saving of approximately 120:1. R-2R ladders function as digitally programmable resistors in a biquad configured Operational Amplifier filter circuit. Integrator loop topologies are used in the filter circuit. The preferred topology utilizes a Tow-Thomas circuit, which can be designed for the prerequisite gain and Q independently selecting two resistors. In addition, the three op amps in the Tow-Thomas topology have their non-inverting input grounded, and therefore their inverting inputs will be held ideally at virtual ground. These feature permits the use of op amps with small common mode input range.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS +1
VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) structural design method of parallel pipeline deblocking filter
InactiveCN101883285AImprove video qualityEliminate blockingTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationExternal storageFiltration
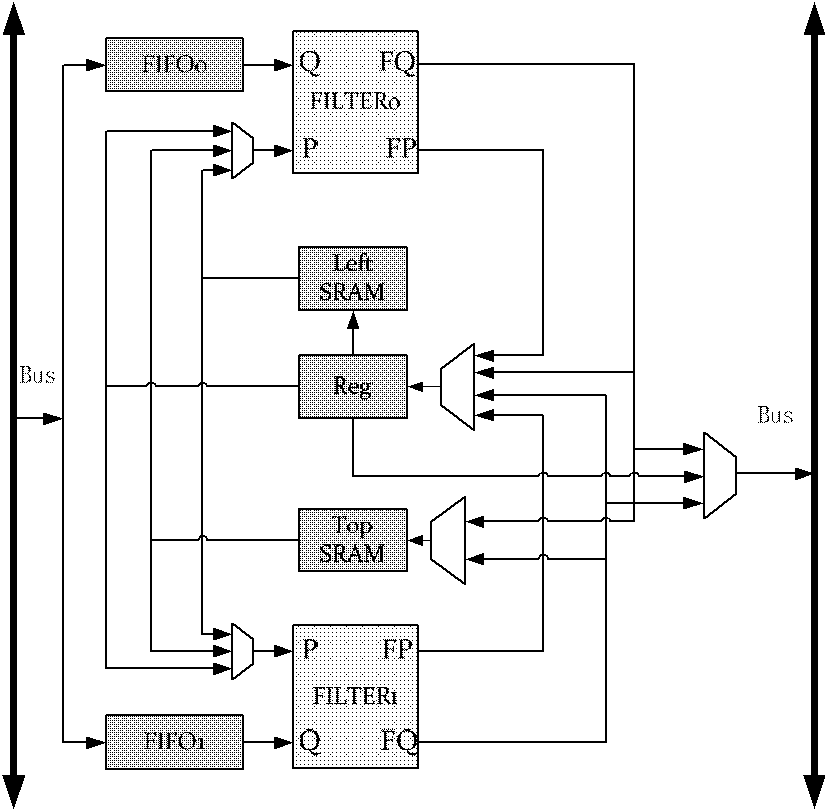
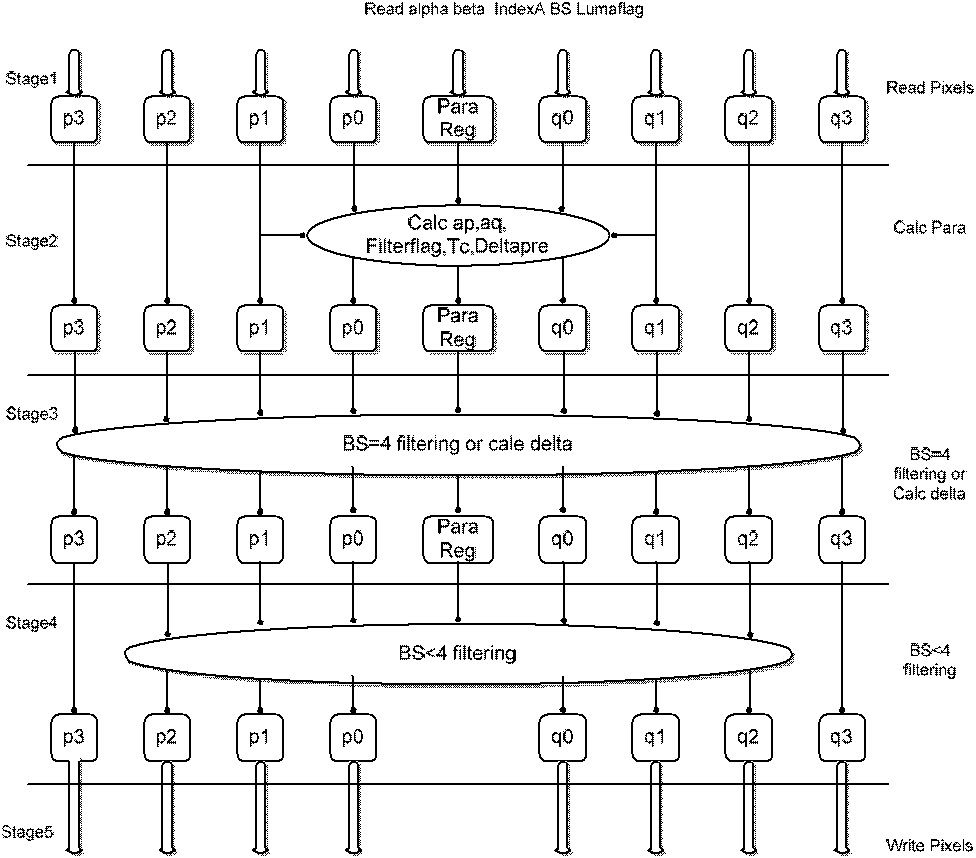
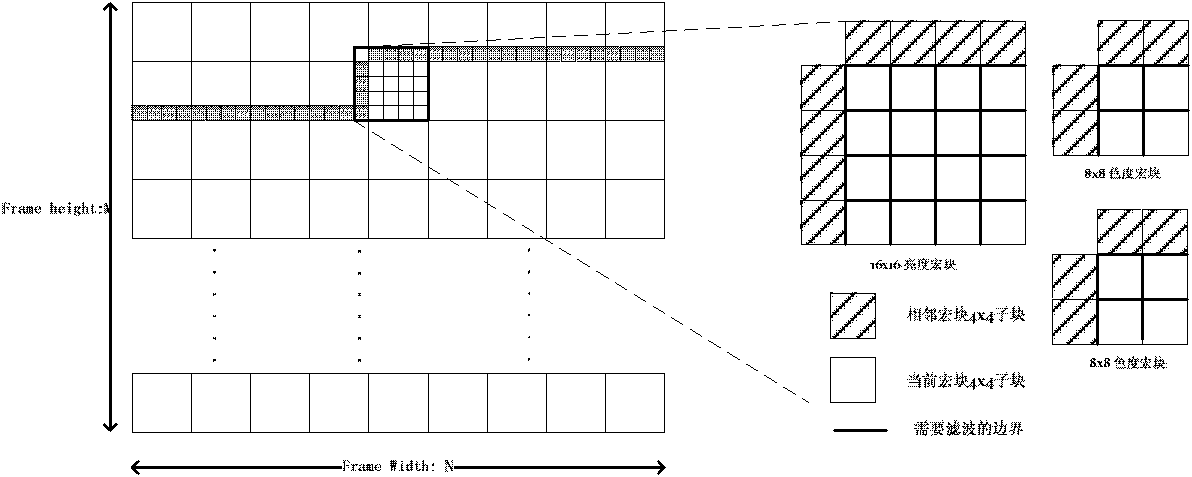
The invention discloses a VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) structural design method oriented to an ultrahigh-definition real-time deblocking filter by adopting a boundary filter based on a five-level pipeline. The method optimizes a mixed filtration order and data output to avoid the stalled waiting of the pipeline, improves the performance of the pipeline, increases the throughput by approximate double in comparison with a single filter design by adopting the parallel double-boundary filter structure, optimizes a storage strategy, a buffer mechanism and the filtration order, develops the on-chip temporary storage of filtration intermediate results for complexing, and lowers the bandwidth requirement for external storage and the requirement for intermediate storage.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
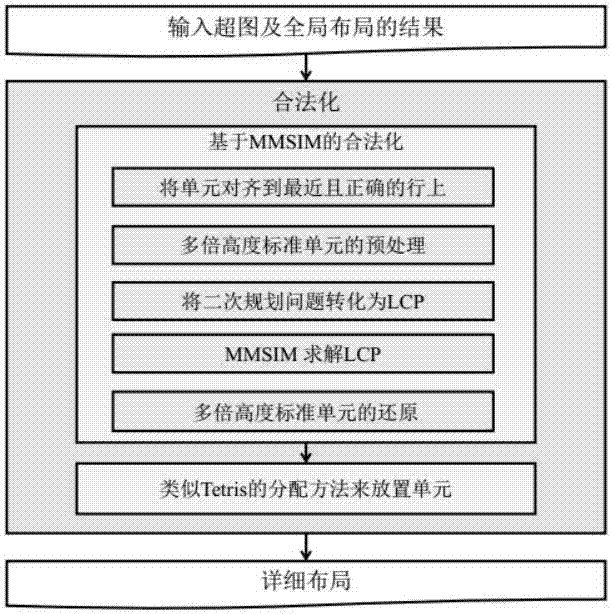
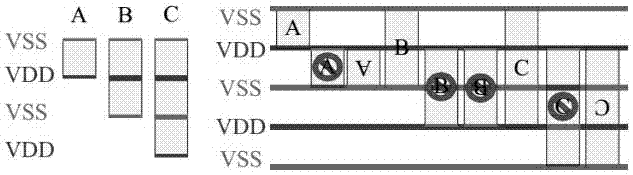
Legalized method used for mixed height standard cell circuit design
InactiveCN106971042ALegalization problem solvingLegalization issues meetCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsVery-large-scale integrationDecomposition
The invention relates to a legalized method used for mixed height standard cell circuit design. The technical scheme of the method comprises the following key points: (1) according to a cell position sequence obtained according to a global layout, carrying out relaxation on the right boundary constraint of a layout area, and converting a legalization problem of a mixed height standard cell into a corresponding LCP (Linear Complementary Problem), wherein the legalization problem can be effectively solved by an existing optimization method; (2) carrying out decomposition on a matrix in the converted LCP in a proper way, and using MMSIM (Matrix MultiSplitting Iterative Method) to solve the converted LCP, wherein the proper matrix decomposition meets MMSIM convergence requirements, and meanwhile, calculation time is greatly quickened; and (3) by use of the method, simultaneously optimizing all cells instead of optimizing cells one by one, and considering the legalization problem from a global perspective. An experiment result indicates that an efficient and practical legalization result (especially for a large-scale living example) can be provided, and the requirement of a mixed height standard cell legalization stage of existing VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) can be met.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus in locating clock gating opportunities within a very large scale integration chip design
InactiveUS20070250798A1Detecting faulty computer hardwareDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareVery-large-scale integration
A computer implemented method, apparatus, and computer usable program code for generating statistics for a set of components in a computer chip. An exemplary computer implemented method includes identifying the set of components in the computer chip. The set of components include those components which are not clock gated. The exemplary method also includes generating statistics for the set of components. The statistics are related to clock gating testing to identify whether one or more components of the set of components can be clock gated.
Owner:IBM CORP
Circuit for realizing direct two dimension discrete small wave change
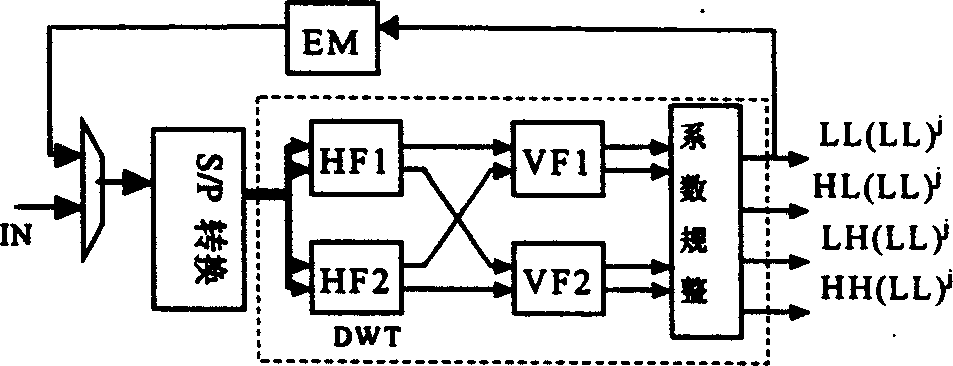
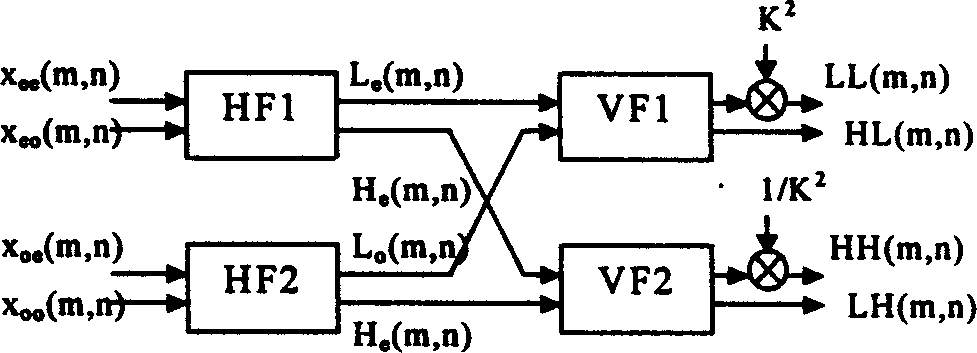
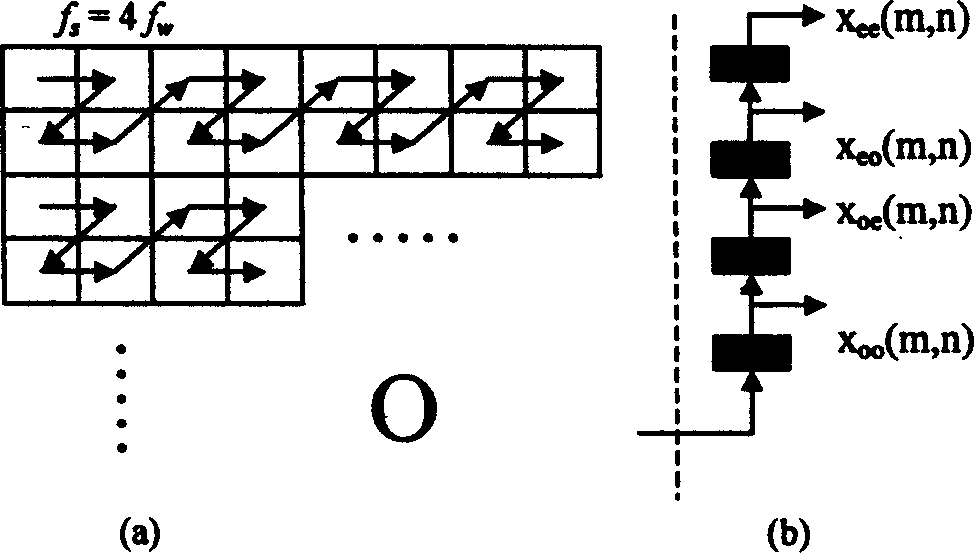
InactiveCN1588451AReduce power consumptionReduce control complexityImage codingData seriesExternal storage
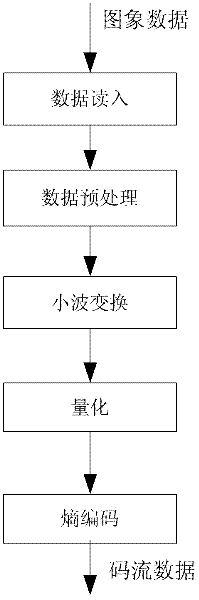
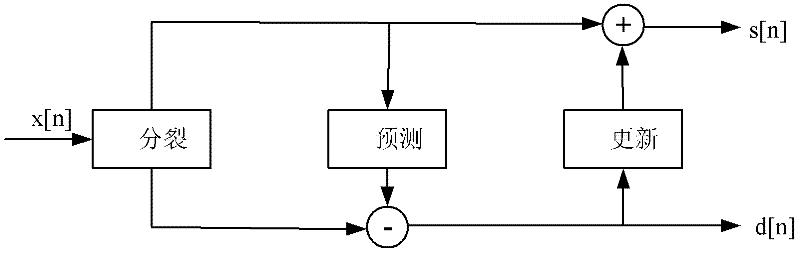
The invention is a circuit for realizing direction two-dimension discrete wavelet transition, which belongs to image data processing technology field, especially relates to hardware realization of direct two-dimension discrete wavelet transition. The aim is to decrease hardware cost and system delay, and it can be applied to very large scale integration circuit structure design of high speed and low power direct two-dimension discrete wavelet transition of all limit length filters, the invention includes selector, data series and parallel converting interface circuit, primary converting circuit which are connected in order electrically; the primary converting circuit is 4 input and 4 output structure, includes the first parallel filter and the second parallel filter, the first vertical filter and the second vertical filter connected to them and output coefficient regulating unit, the parallel and vertical filters are 2 input and 2 output structure, the first vertical filter and the second vertical filter output is connected to the output coefficient regulating unit; one output electric signal of the output coefficient regulating unit is connected to an external memory, the latter is outputted to one input end of the selector.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Two-dimensional photon crystal power separator
InactiveCN1609641ACoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionPhotonic crystal structureWaveguide
The present invention relates to one kind of 2D photon crystal power separator capable of being used in integrated optical path and operating to several light wave signals simultaneously. It includes one input waveguide, several output waveguides and coupling area of the 2D photon crystal power separator to connect the input waveguide and the output waveguides. The coupling area has input connected to the input waveguide and output connected to the output waveguides via bending waveguide. Altering the length of the middle coupling area can realize the 1X2, 1X3, 1X4 and 1X5 power separation of light signal, and perform the filtering and selective output of light signal in different wavelength. The present invention is based on 2D silicon base photon crystal structure, so that the present invention has the advantages of small size, low loss, simple making process and other advantages, and is suitable for new generation of large scale light integration and light communication.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Connection flux statistical information extraction method and VLSI structure
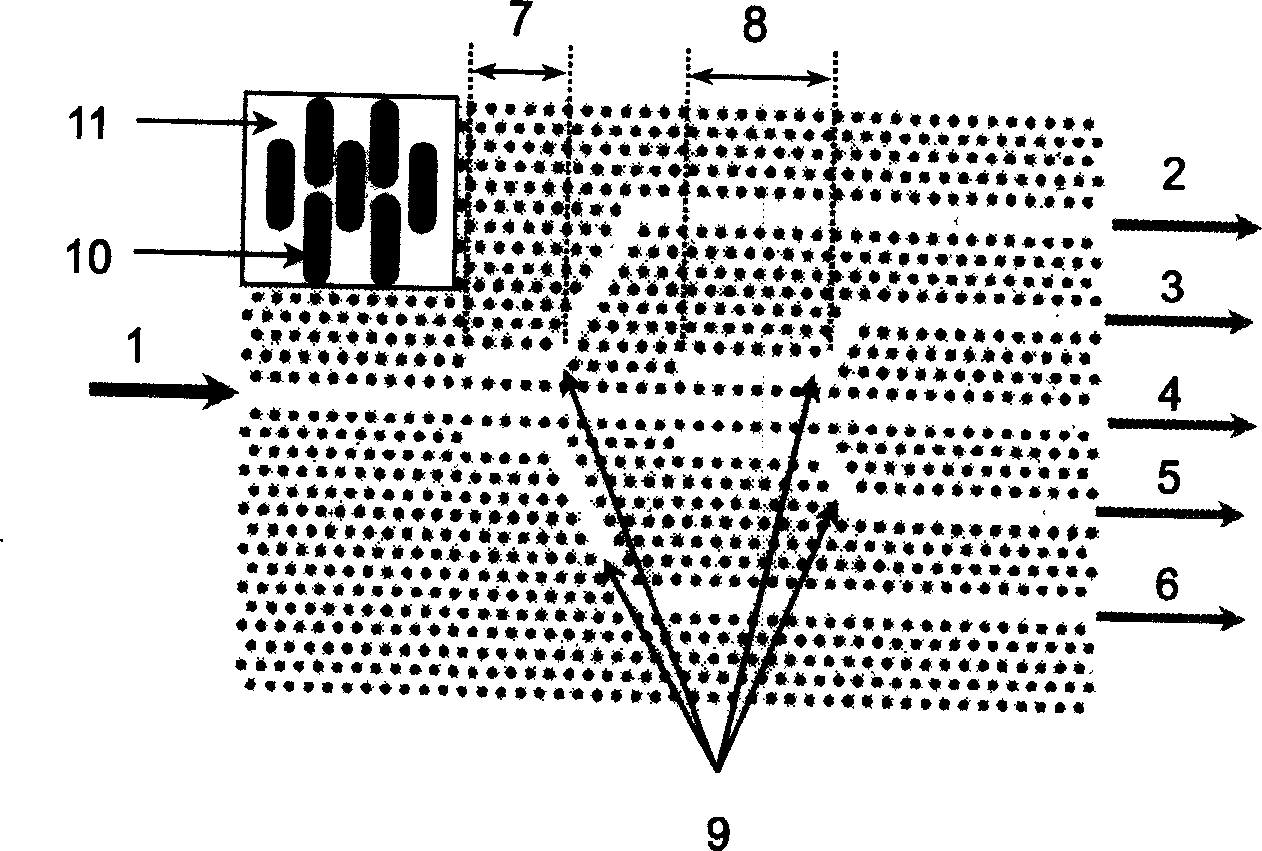
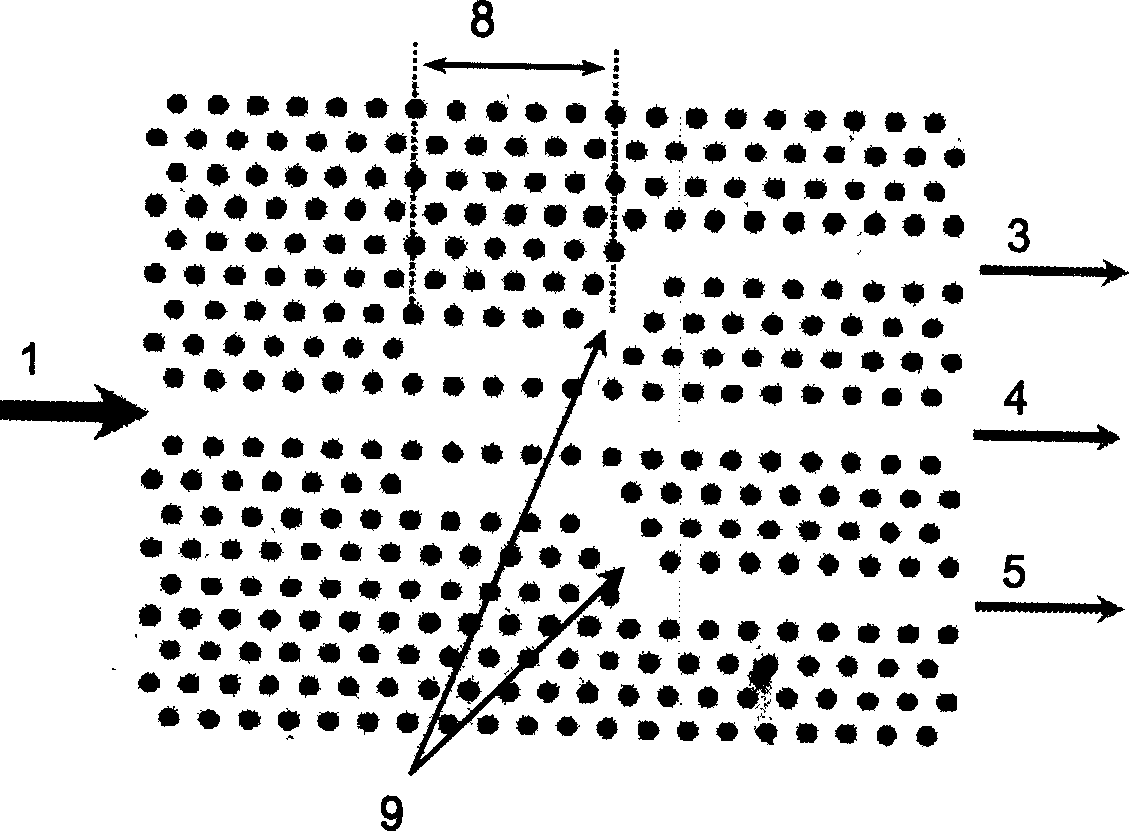
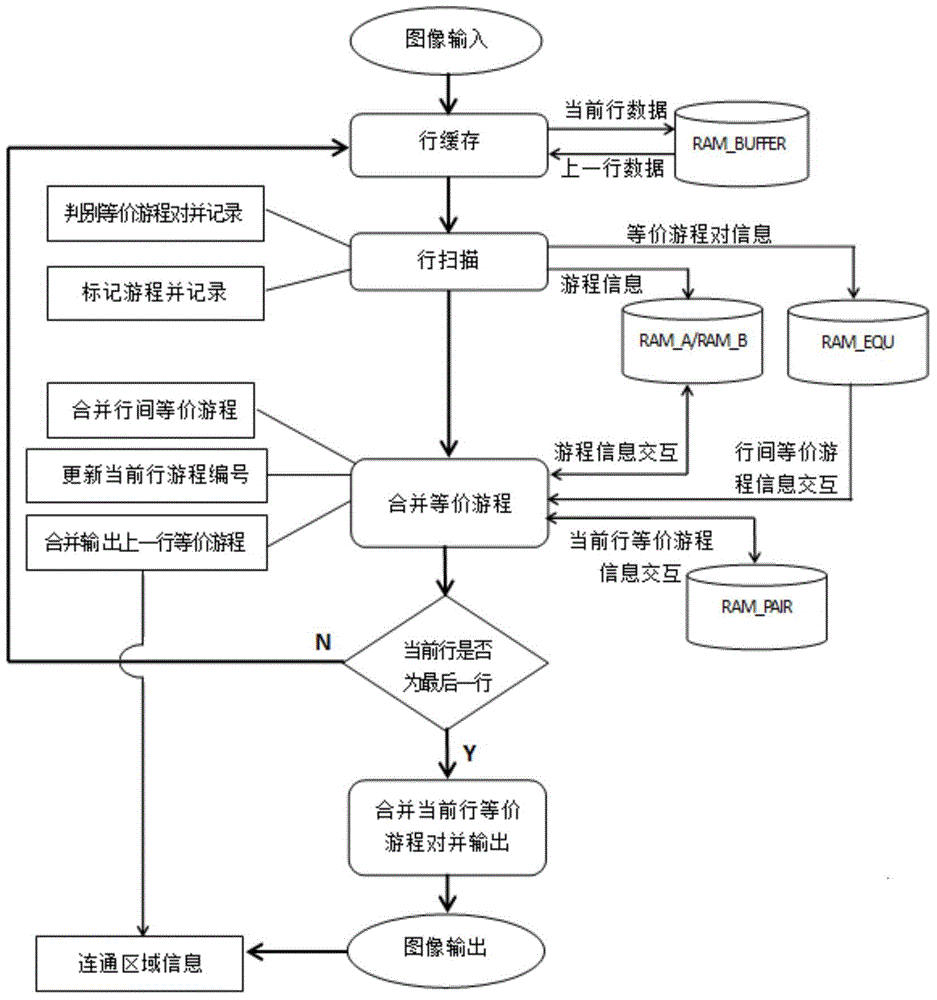
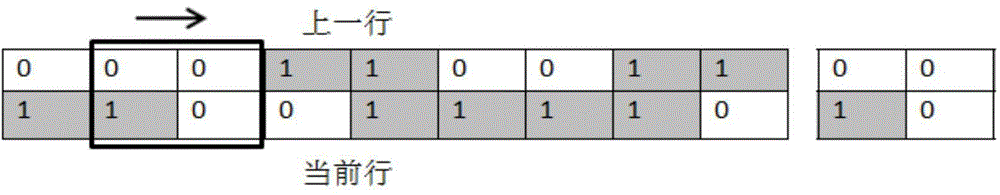
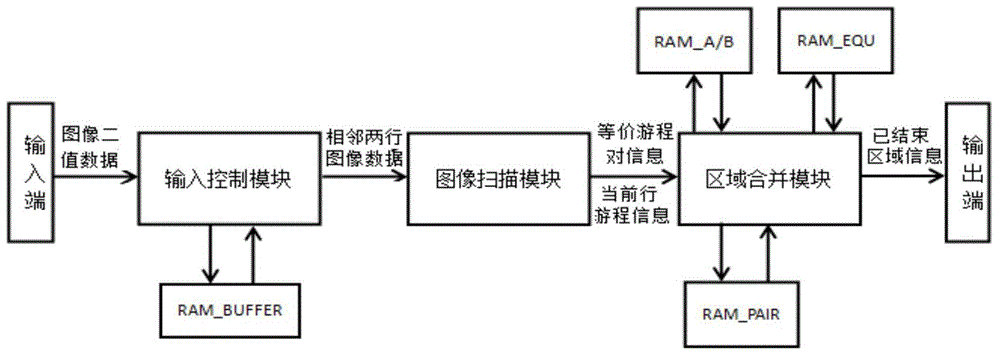
ActiveCN104680531AAvoid recordingSave memory spaceImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmResource consumption
The invention discloses a connection flux statistical information extraction method and a VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) structure. The connection flux statistical information extraction method comprises the following steps: simultaneously scanning two adjacent rows of a binary image; judging whether a connected area exists between the current row and the previous row; if yes, merging the area, connected with the current row, in the previous row into the current row according to an equivalent run pair merging rule; meanwhile, marking the area, not connected with the current row, in the previous row as an ended area, and outputting the information of the ended area; then updating the run number of the connected area in the current row; when the current row is the last one, according to the equivalent run pair merging rule, merging the connected area in the current row, then marking the merged and obtained area as the ended area, and outputting the information of the ended area, so as to obtain the connection flux statistical information. The connection flux statistical information extraction method disclosed by the invention can quickly process the binary image and extract the connection flux statistical information of the binary image, and is low in hardware resource consumption.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
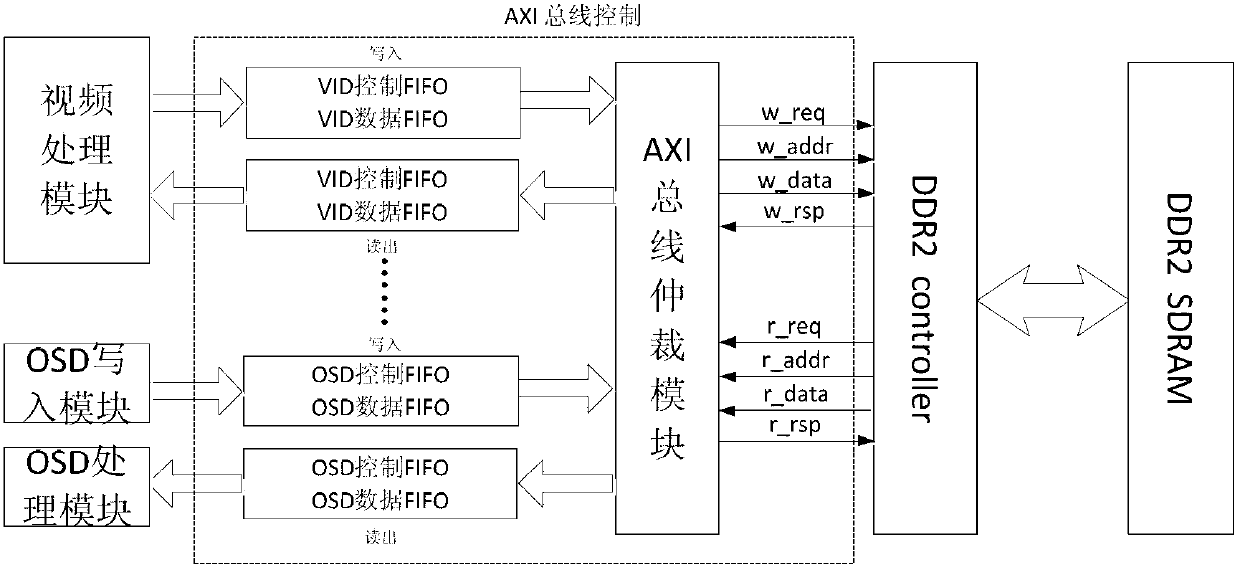
On screen display (OSD) control display method and device based on advanced extensible interface (AXI) bus protocol
InactiveCN103139509AReduce volumeLow costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVideo memoryVery-large-scale integration
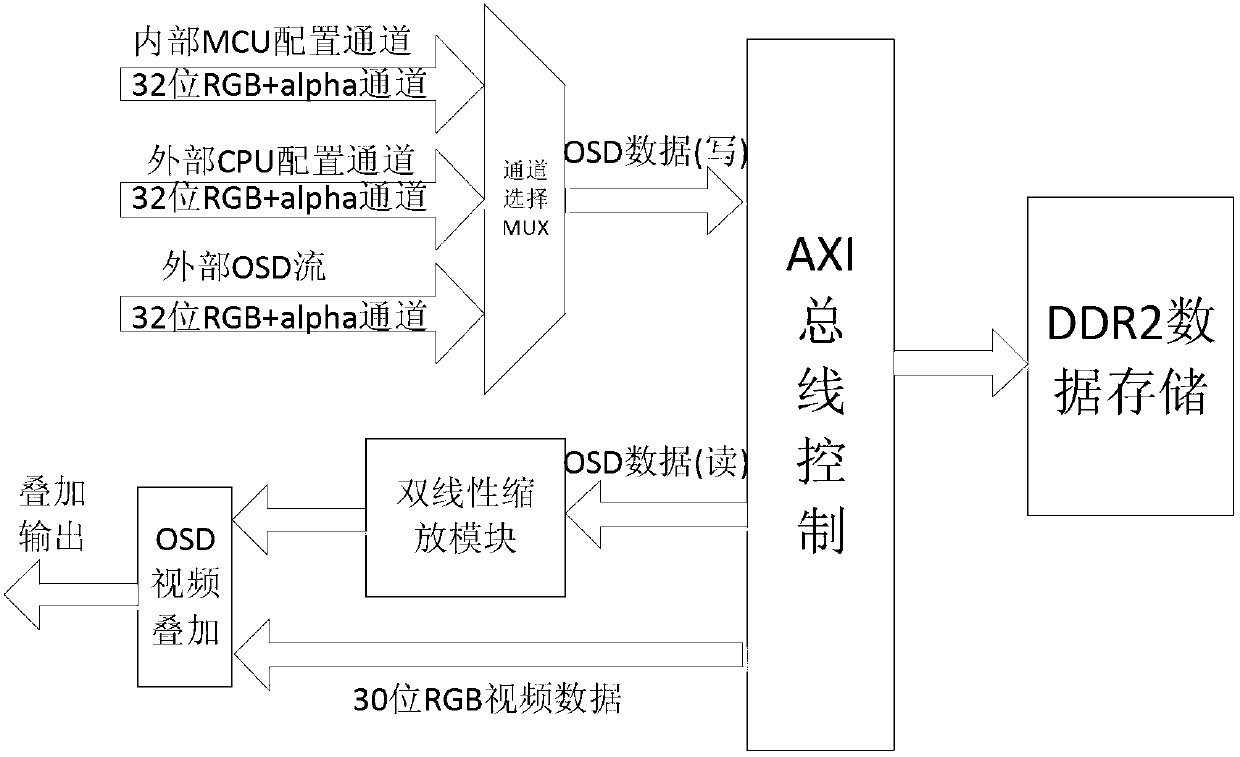
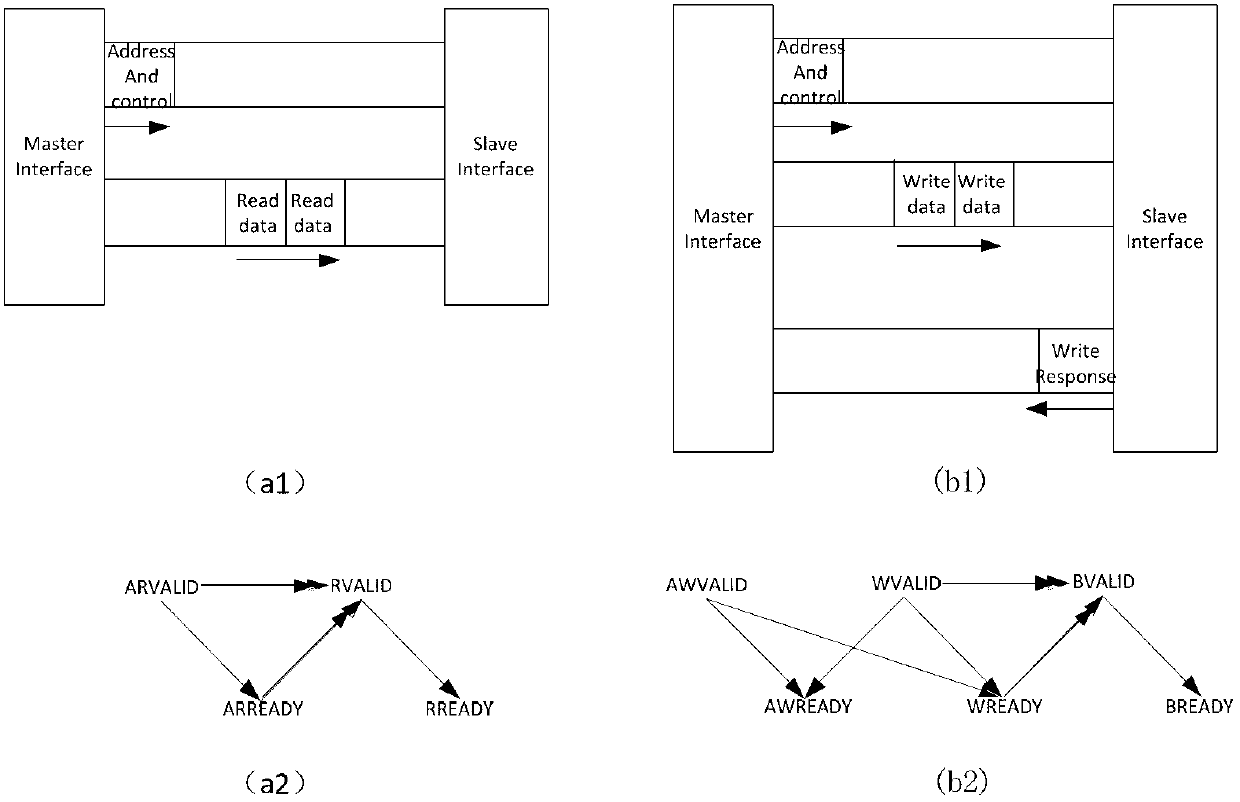
The invention discloses an on screen display (OSD) control display method and a device based on an advanced extensible interface (AXI) bus protocol. After OSD data is selected through an OSD data channel, flexible modification and display on an OSD map layer can be achieved by utilizing of read-write cache first input, first output (FIFO) and an advanced extensible interface (AXI) bus arbitration module, wherein video memory is shared by the OSD data, and at the same time, a path of video interfaces is arranged on the exterior so as to achieve the picture-in-picture effect. A bilinearity Scaler zoom module is used for carrying out zoom process on an OSD image with random proportions, and at last an OSD and video overlap module is utilized to achieve abundant and diversified display modes of the OSD. According to the OSD control display method and the device based on an AXI bus protocol, the design of very large scale integration (VLSI) is achieved, intensive study is carried out on key points in the VLSI, and code compiling and the function of the code compiling of a Verilog-hardware description language (HDL) are achieved on the basis of the intensive study on the key points in the VLSI.
Owner:西安创芯科技有限责任公司
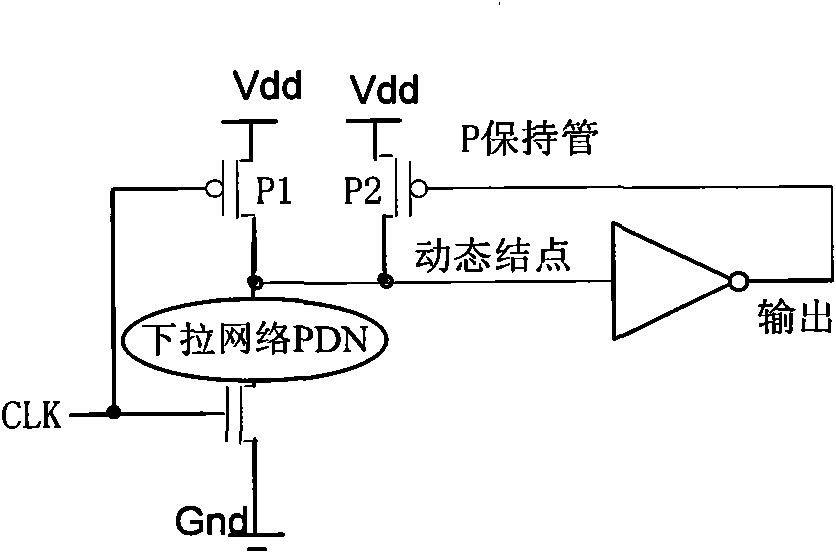
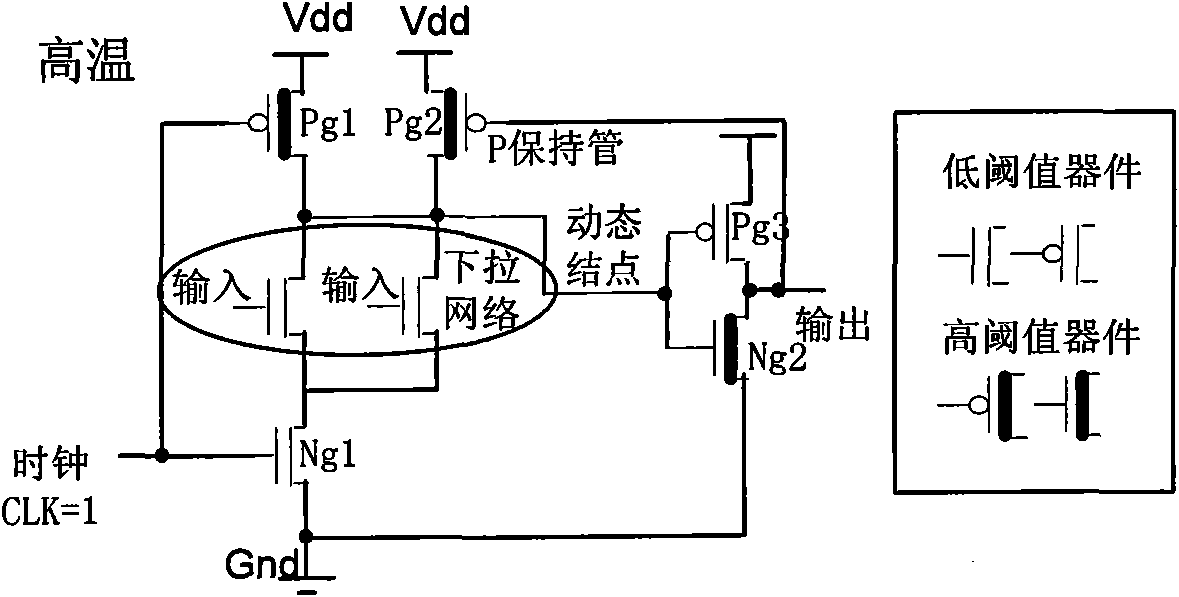
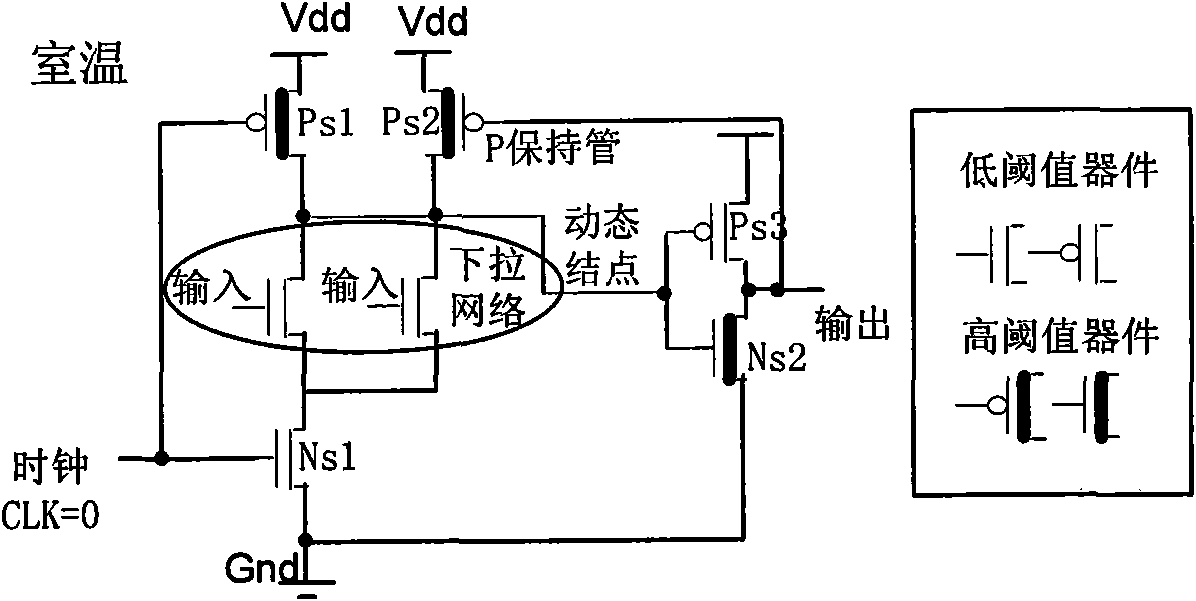
Dual-threshold domino circuit with optimal gate control vector used in low-power consumption VLSI (very large scale integration)
The invention relates to a dual-threshold domino circuit with an optimal gate control vector used in low-power consumption VLSI (very large scale integration), i.e., when the dual-threshold domino circuit is in a dormant state, leakage power consumption of the domino circuit is reduced by utilizing the optimal gate control vector. In the invention, after the dual-threshold domino circuit just enters the dormant state from an operating state, a chip is kept at unchanged high temperature owing to short time, and at the moment, the leakage power consumption can be effectively reduced by utilizing the gate control vector with a high-level input signal and a high-level clock signal; and after the dual-threshold domino circuit is changed into the dormant state from the operating state for a period of time, the temperature of the chip is reduced to room temperature, and at the moment, the leakage power consumption can be more effectively reduced by utilizing the gate control vector with a low-level input signal and a low-level clock signal.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Satisfiability problem-based manufacturable hot spot disconnecting and rerouting method
InactiveCN101894178AGeneration of controlTo avoidSpecial data processing applicationsVlsi physical designVery-large-scale integration
The invention relates to a satisfiability problem (SAT)-based manufacturable hot spot disconnecting and rerouting method which belongs to the very large scale integration (VLSI) physical design field. The method is characterized in that the topological structure constraint of hot spot and connectivity constraint of line networks are used as directions, SAT constraints are established in all the rerouted line networks in the region, the constraint problem is solved to route a plurality of line networks at the same time, and the generation of a new manufacturable hot spot can be effectively controlled. Meanwhile, as the method adopts the region-based disconnecting and rerouting strategy to ensure the efficiency; and the hot spot elimination ratio in the layout can be greatly increased through the dynamic marginal adjustment and the two-stage disconnecting and rerouting process involving offset. The experimental result proves that the method can fast and effectively eliminate the manufacturable hot spot in the layout; compared with the traditional disconnecting and rerouting algorithm aiming at the hot spot, the method has better convergence, and can more effectively avoid the generation of the new hot spot and ensure to find an existing and feasible rerouting scheme.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
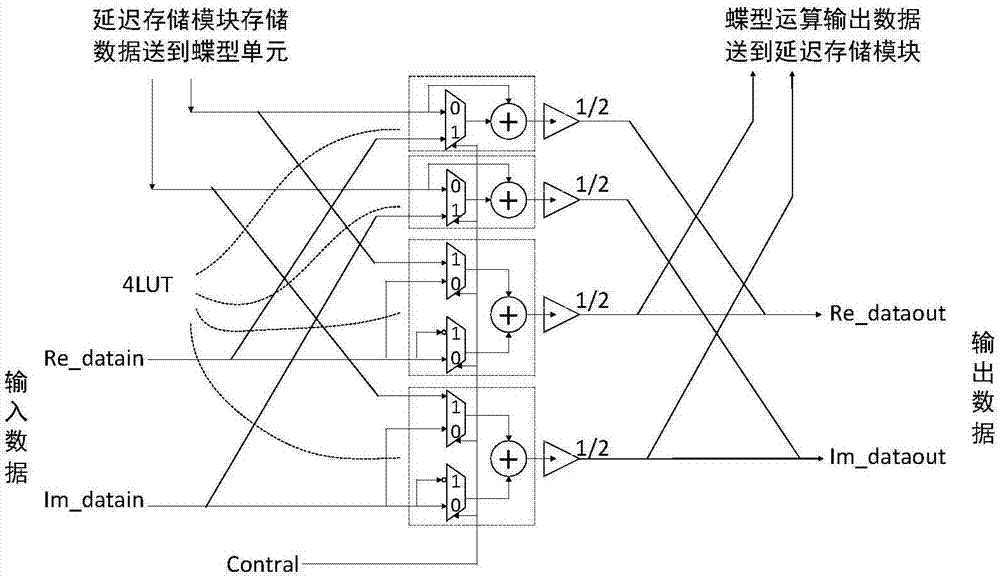
VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) design method of fast Fourier transform (FFT)
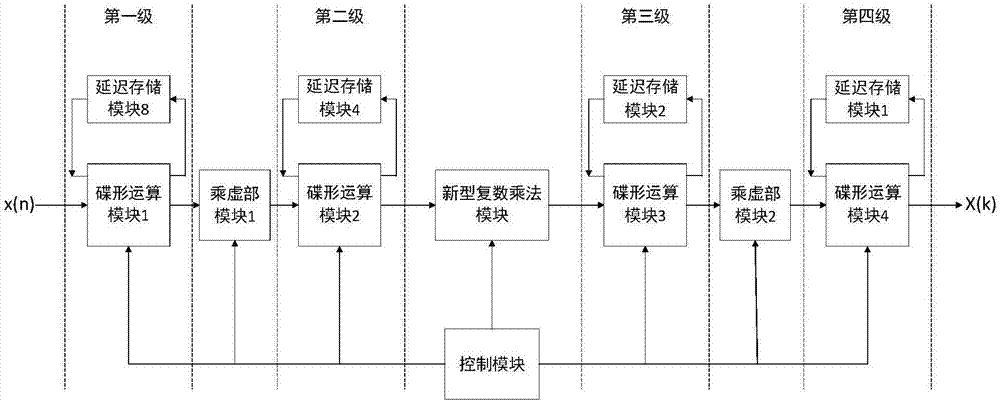
InactiveCN107544942ASolve the problem of hardware inefficiencyComplex mathematical operationsFast Fourier transformHardware architecture
The invention relates to a VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) design method of a fast Fourier transform (FFT). An adopted 16-point FFT hardware architecture includes four improved butterfly computation modules, one complex-number multiplication module, four delay storage modules, two imaginary-part multiplication modules and one counter control module, and is divided into four levels. Each levelhas one of the improved butterfly computation modules and one of the delay storage modules. The complex-number multiplication module is located between the second level and the third level. One of theimaginary-part multiplication modules is located between the first level and the second level, and the other imaginary-part multiplication module is located between the third level and the fourth level. An effect of the counter control module is to control all the above modules to work normally. According to the improved butterfly computation modules, circuit structures that "adders are before selectors" in butterfly computation modules are improved into butterfly computation circuit structures that "the selectors are before the adders". Key-path delay of the improved butterfly computation circuit structures is unchanged.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Integrated Thermoelectric Cooling Devices and Methods for Fabricating Same
InactiveUS20090217961A1Reduced dimensionIncrease heatThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric coolingHigh density
Semiconductor integrated thermoelectric devices are provided, which are formed having high-density arrays of thermoelectric (TE) elements using semiconductor thin-film and VLSI (very large scale integration) fabrication processes. Thermoelectric devices can be either separately formed and bonded to semiconductor chips, or integrally formed within the non-active surface of semiconductor chips, for example.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
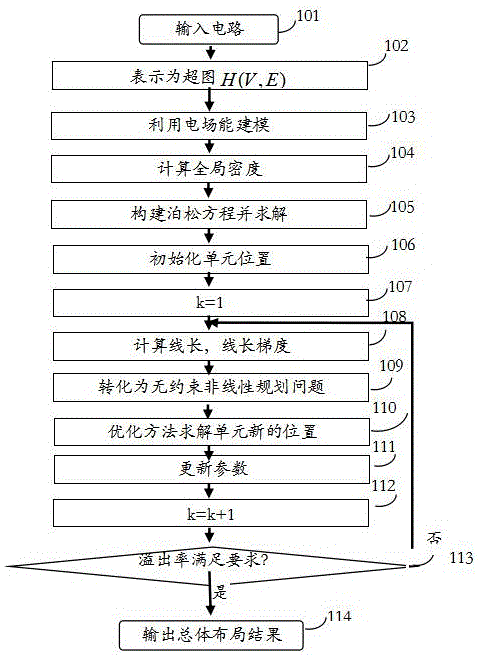
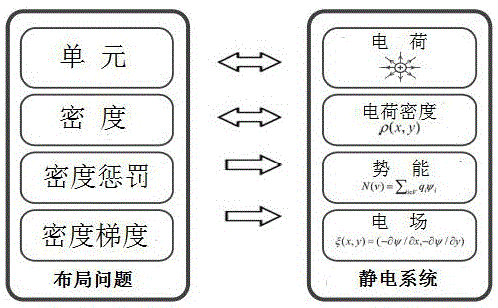
VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) standard unit placement method based on electric field energy modeling technology
ActiveCN107526860AAvoid errorsAvoid heavy calculationsSpecial data processing applicationsEnergy modelingVery-large-scale integration
The invention discloses a VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) standard unit placement method based on an electric field energy modeling technology. The method establishes the electric field energy model of a problem, and a global density function and an analytical solution of a Poisson equation are utilized to solve a VLSI standard unit global placement problem. The method has the technical key point that: (1) analogy is carried out on the placement problem and a static electricity system, a unit is taken as an electric charge, original density constraint is converted into zero potential energy constraint, a differential equation is constructed, an explicit expression is solved for the differential equation to more accurately describe the potential energy constraint, then, a penalty function method is adopted to convert the wire length target and the potential energy constraint of the VLSI global placement into an unrestraint nonlinear placement problem, and a proper optimization technology is selected for optimization; and (2) different from a situation that a method for evenly dividing bin is used for obtaining a discrete density function value, the method disclosed by the invention is characterized in that the global density expression of the unit and the overlapping constraint of a whole placement area is calculated so as to more accurately describe the distribution situation of the unit on the placement area.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
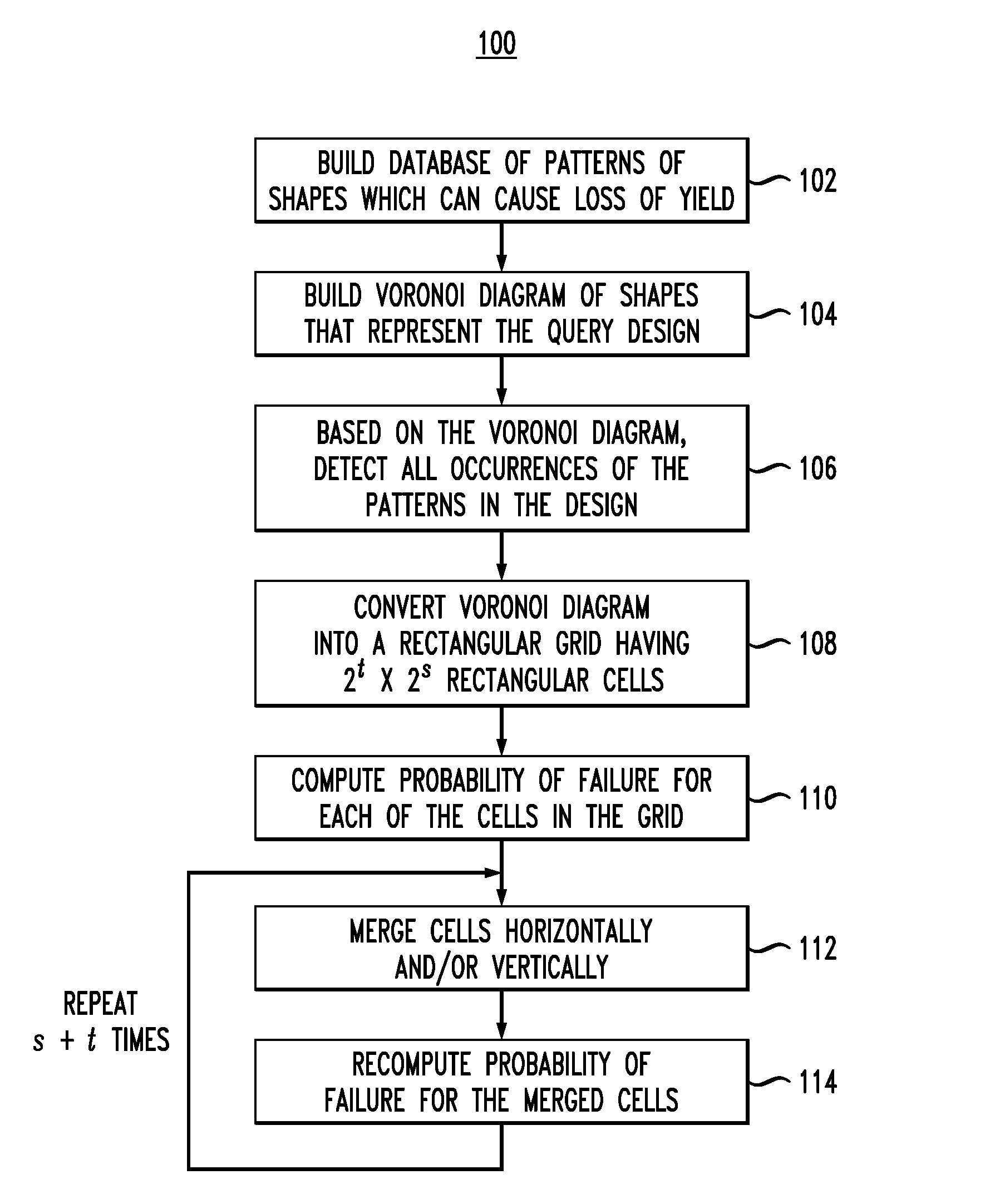
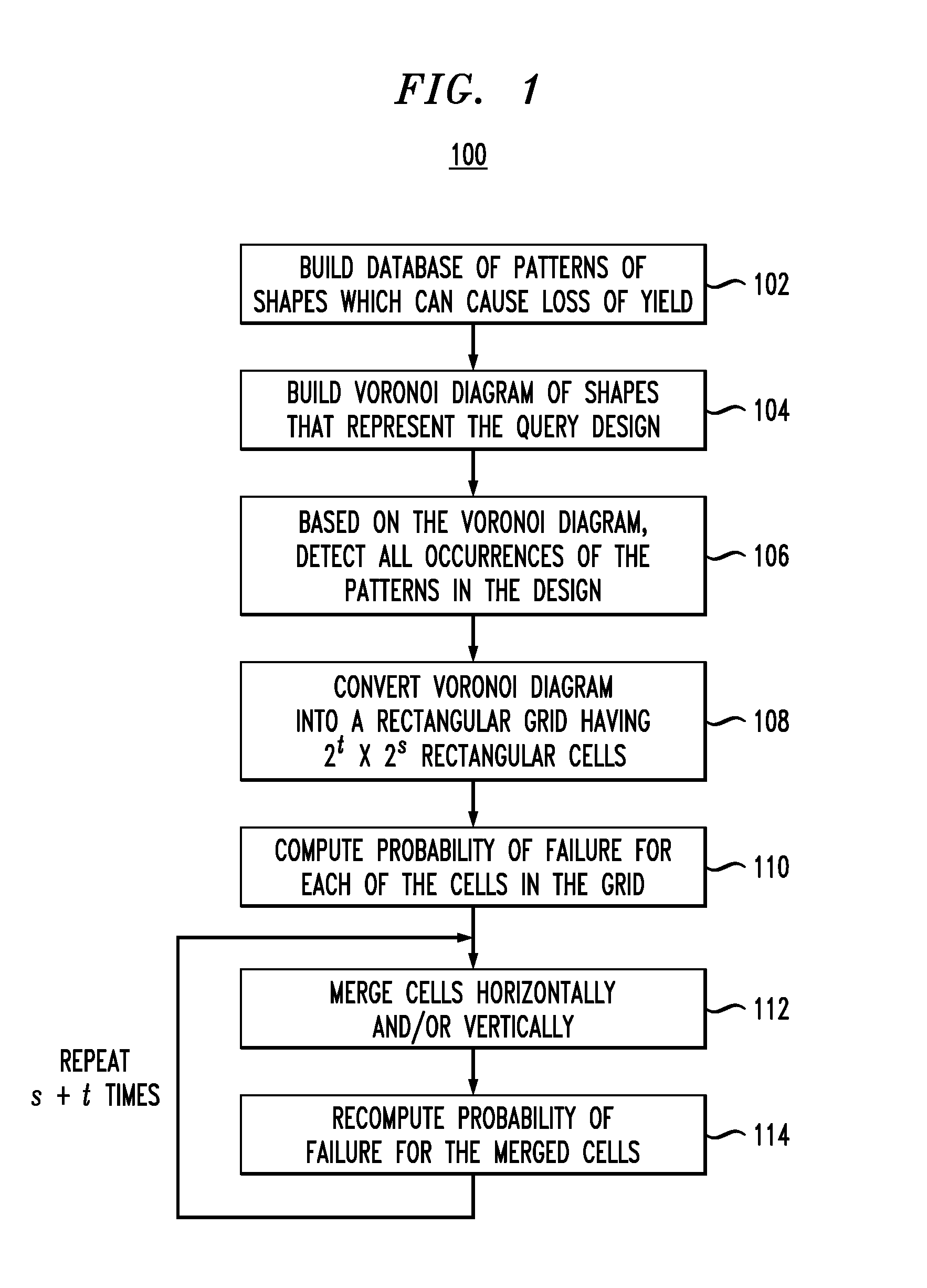
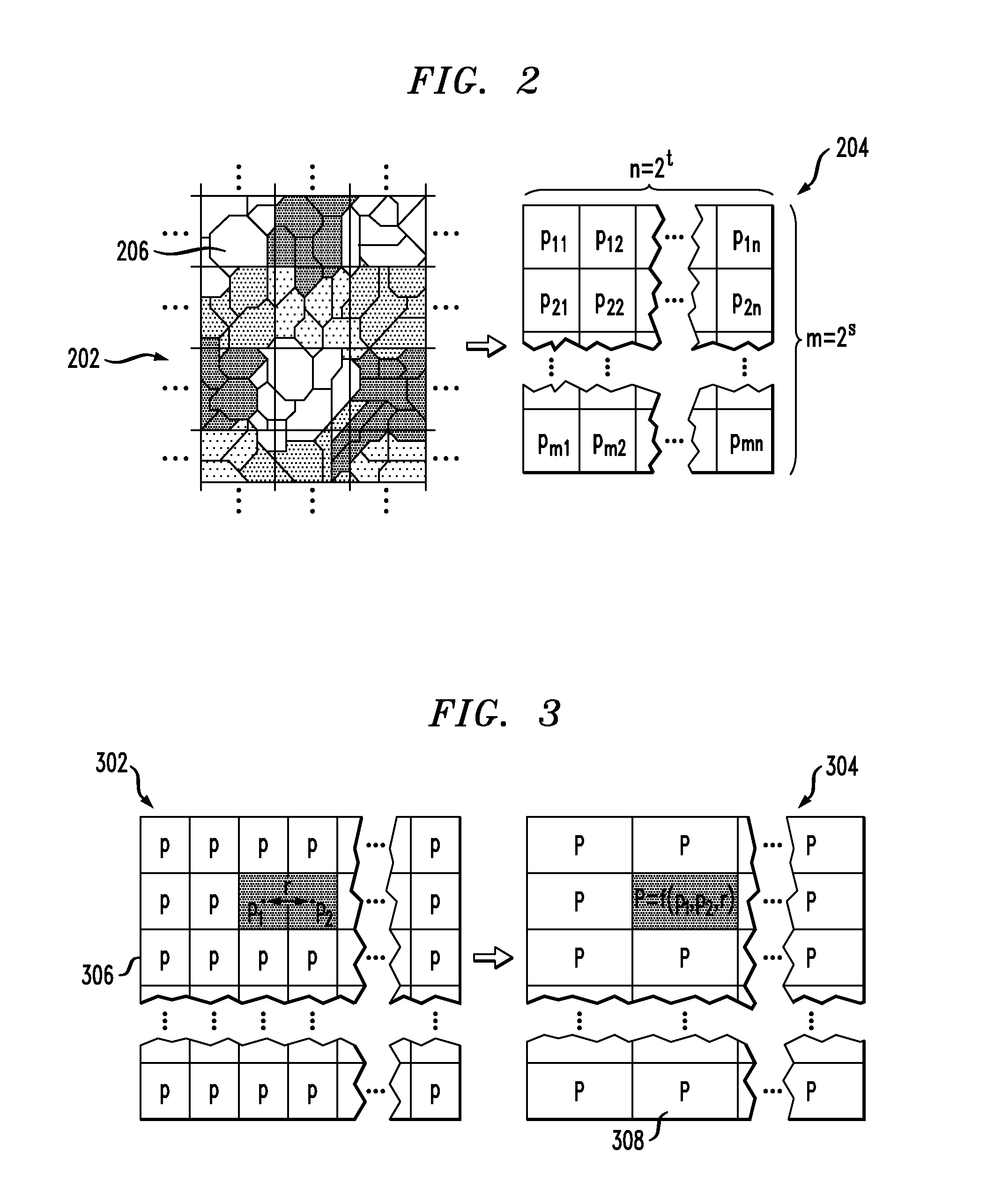
Spatial Correlation-Based Estimation of Yield of Integrated Circuits
ActiveUS20110219344A1Probabilistic CADSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSpatial correlationVery-large-scale integration
Techniques for estimating yield of an integrated circuit design, such as a very-large-scale integration (VLSI) design, are provided. In one aspect, a method for determining a probability of failure of a VLSI query design includes the following steps. A Voronoi diagram is built comprising a set of shapes that represent the design. The Voronoi diagram is converted into a rectangular grid comprising 2t×2s rectangular cells, wherein t and s are chosen so that one rectangular cell contains from about one to about five Voronoi cells. A probability of failure is computed for each of the cells in the grid. The cells in the grid are merged pairwise. A probability of failure for the merged cells is recomputed which accounts for a spatial correlation between the cells. The pairwise merge and recompute steps are performed s+t times to determine the probability of failure of the design.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
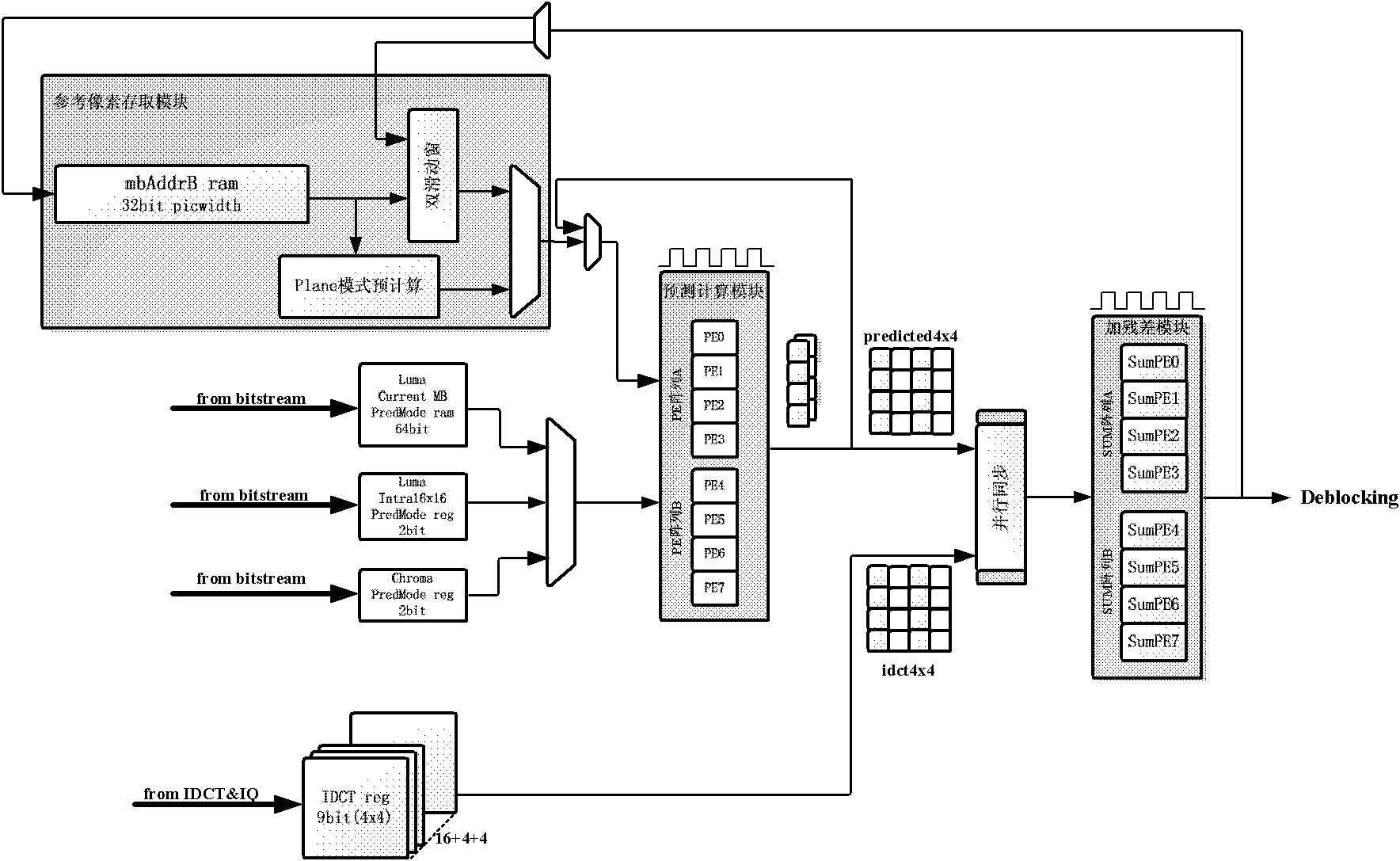
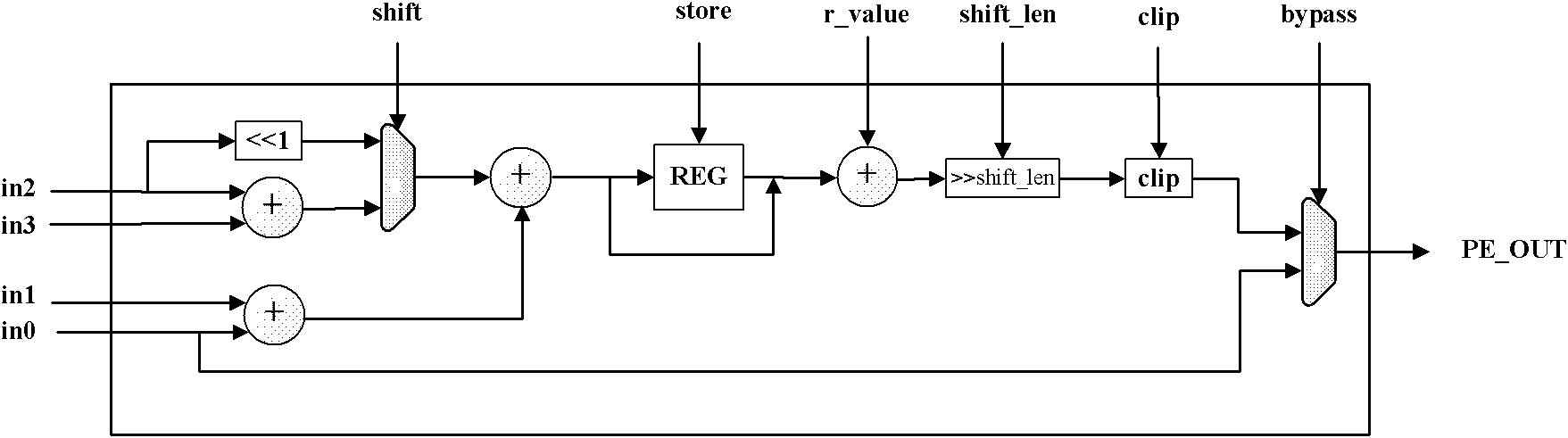
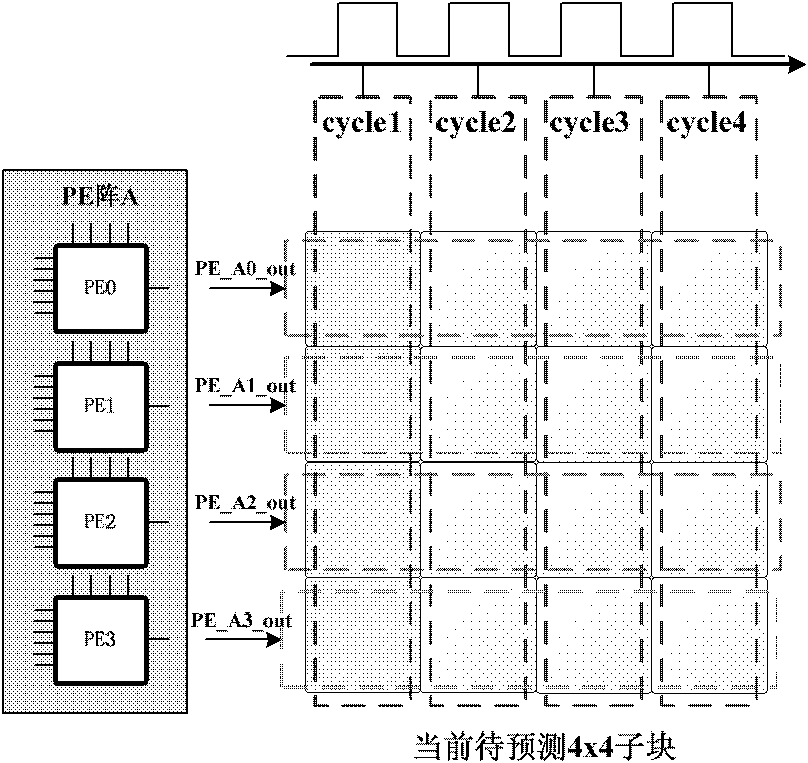
Very large-scale integration (VLSI) structural design method of parallel array-type intraframe prediction decoder
InactiveCN101902643ADecode real timeImprove decoding efficiencyTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationMultiplexingProduction line
The invention discloses a design method of a parallel array-type intraframe prediction decoder. By adopting an intraframe parallel array technique, the parallel decoding of the sub-macro-blocks is achieved, and the decoding efficiency of the intraframe macro-blocks is improved. By adopting a multi-prediction mode multiplexing technique, the intraframe prediction calculation units PE are realized.Four PE units in each sub-macro-block predict four pixels in parallel. By adopting a self-adapting production line technique, the prediction decoding of the self-adapting production line of the sub-macro-blocks in the PE array is achieved. By adopting a parallel prediction sequence technique, the prediction sequence of the parallel decoding is realized according to the dependency relationship of the reference pixels, and the data conflict is solved. By adopting a double-sliding window mechanism, the requirement of double PE arrays on the parallel decoding of the sub-macro-blocks is met, and the parallel synchronization of the PE arrays is coordinated. By the method, the requirements on the decoding of the high-definition and ultra-high-definition video can be satisfied; and the decoding efficiency and performances are improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Finite field multiplier based on RS (reed-solomon) code
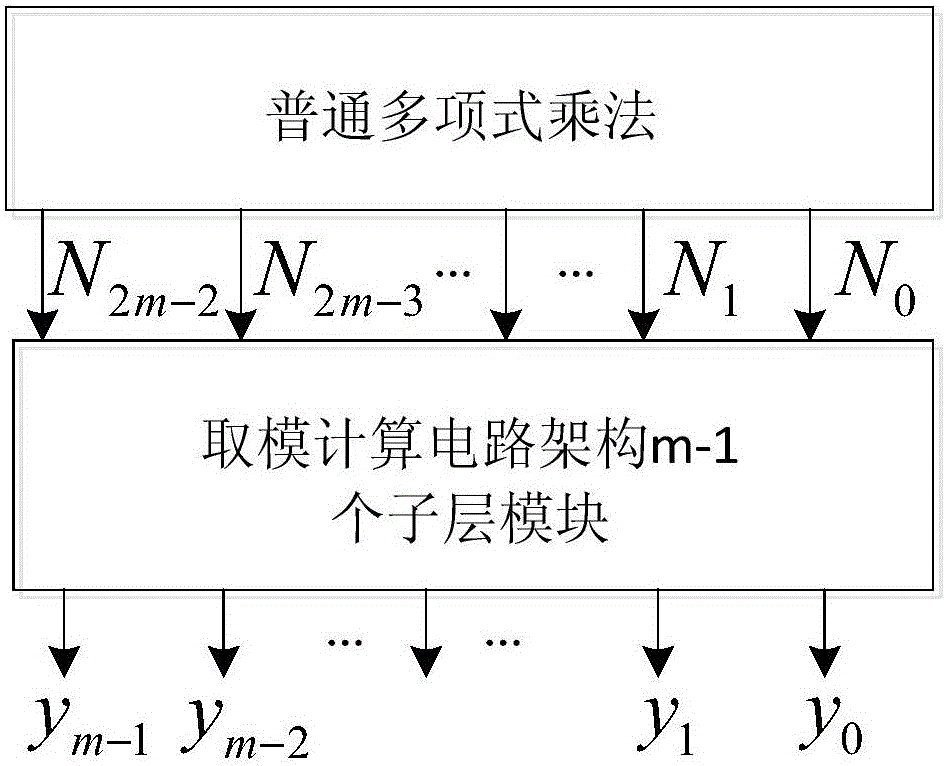
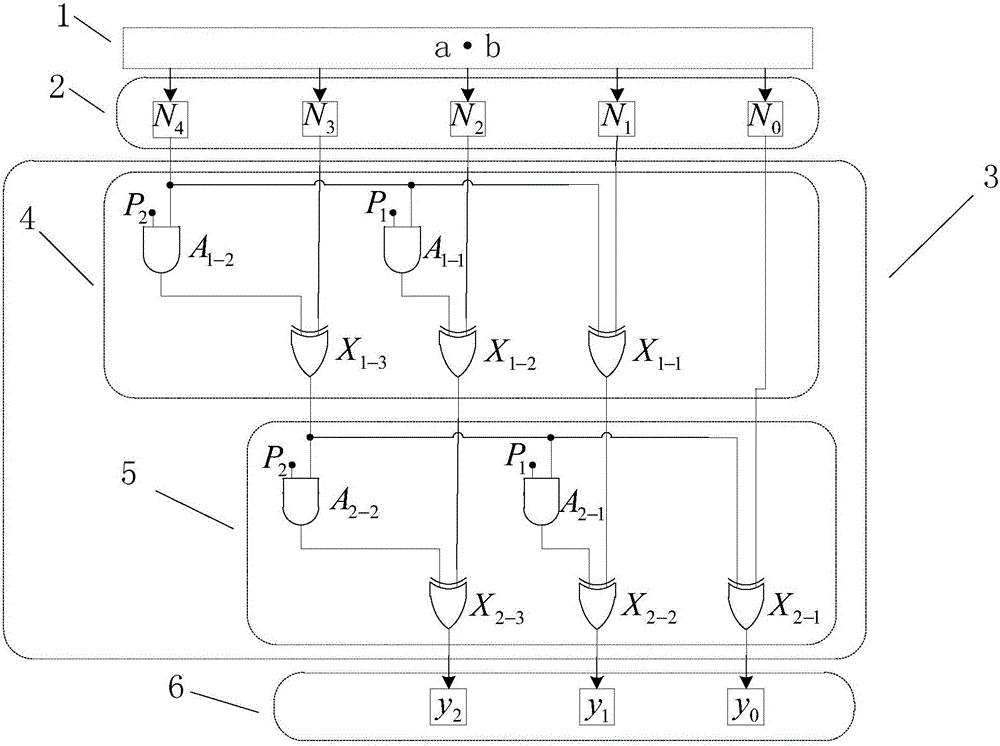
ActiveCN106201433ASatisfy the urgent need of easy-to-implement designSatisfy urgent needs that are easy to implementComputation using non-contact making devicesCommunications systemTheoretical computer science
The invention provides a finite field multiplier based on an RS (reed-solomon) code. The finite field multiplier based on the RS code is composed of two partial operations, firstly a common polynomial multiplication is carried out, and the obtained result is a polynomial with the highest order of 2m-2, wherein m is bit width of two finite field multipliers; and secondly, modular operation is carried out on the primitive polynomial p(x) by adopting the product polynomial, and the obtained remainder coefficient is namely final result of a finite field multiplication. The invention innovatively provides a two-step implementation method of the finite field multiplier. A modulus calculating circuit is composed of sublayers of the same structures, structure is regular, expansion is easy, engineering realization is applicable, the finite field multiplier with any bit width can be realized by regulating sublayers in a modulus obtaining circuit framework, and the finite field multiplier is especially applicable to error control code field such as application of the RS code and can meet urgent demand of easy implementation of VLSI (very large scale integration) design in a communication system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
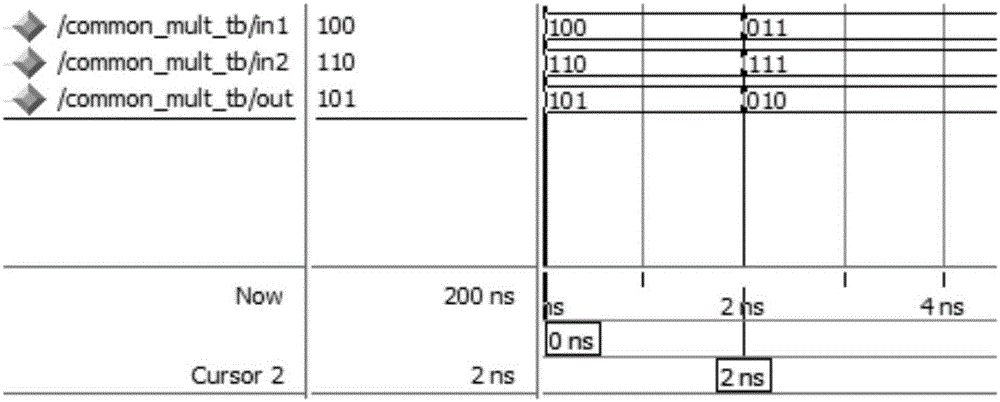
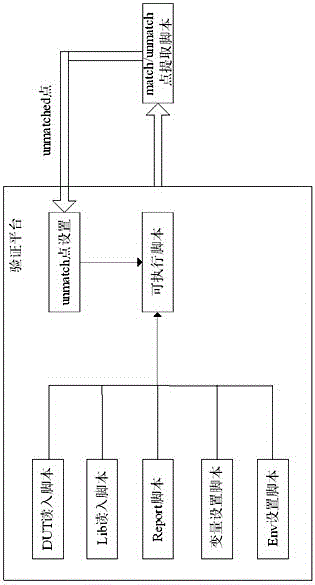
VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) formal verification platform and method
InactiveCN105893685ARealize processingFully automatedSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureSource code
The invention discloses a VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) formal verification platform and method. The verification platform comprises components including a variable setting script, a Lib reading script, a DUT reading script, an Env setting script and a Report setting script. The verification platform further comprises a match / unmatch point extraction subscript for processing an output result of the verification platform. The VLSI formal verification platform and method use perl to realize the processing of the result, realize the automatic iterative verification of unmatch points, respectively manage source codes Lib of all modules to be verified and greatly reduce the consumption of reading time.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
Wavelength-tunable laser system
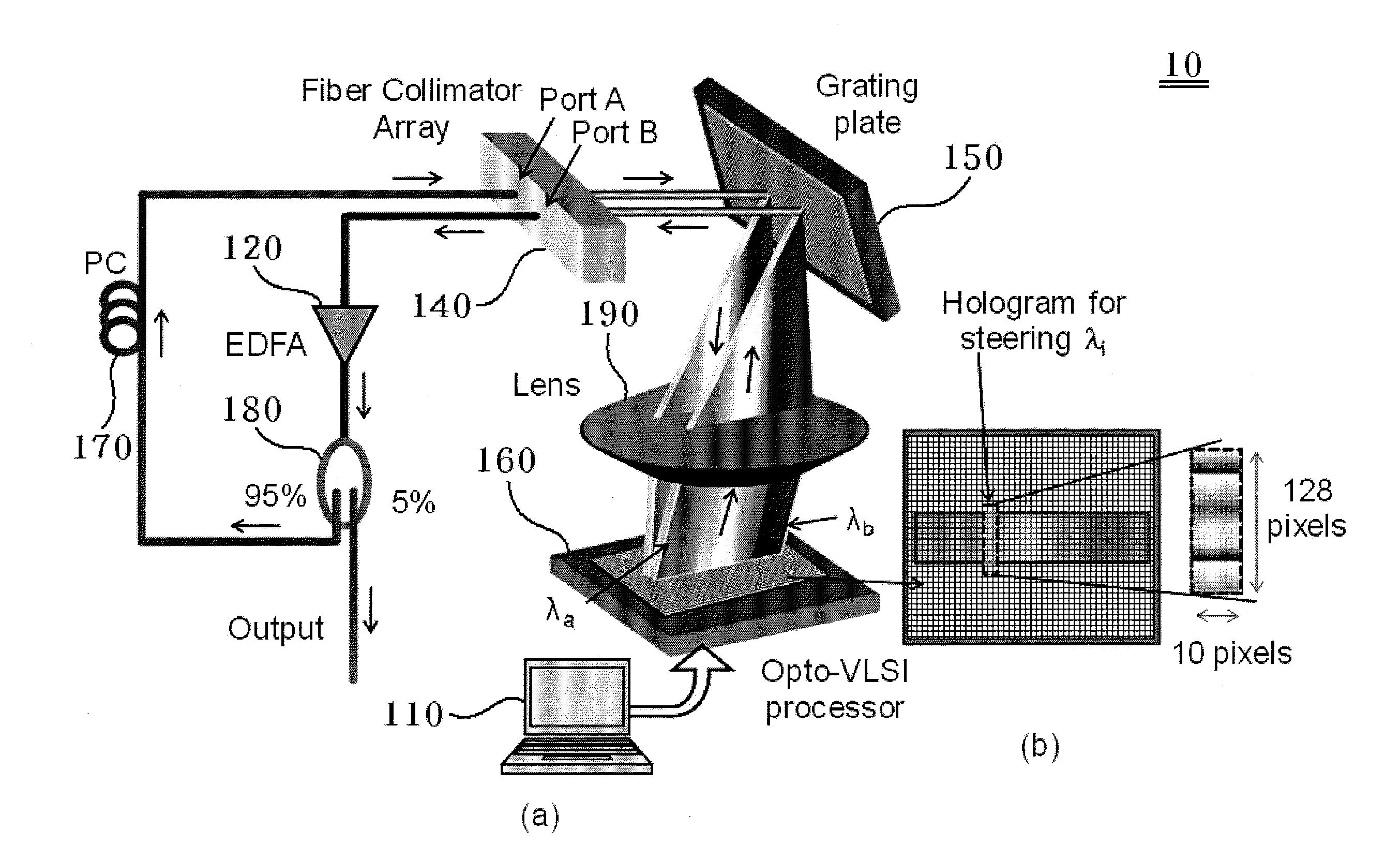
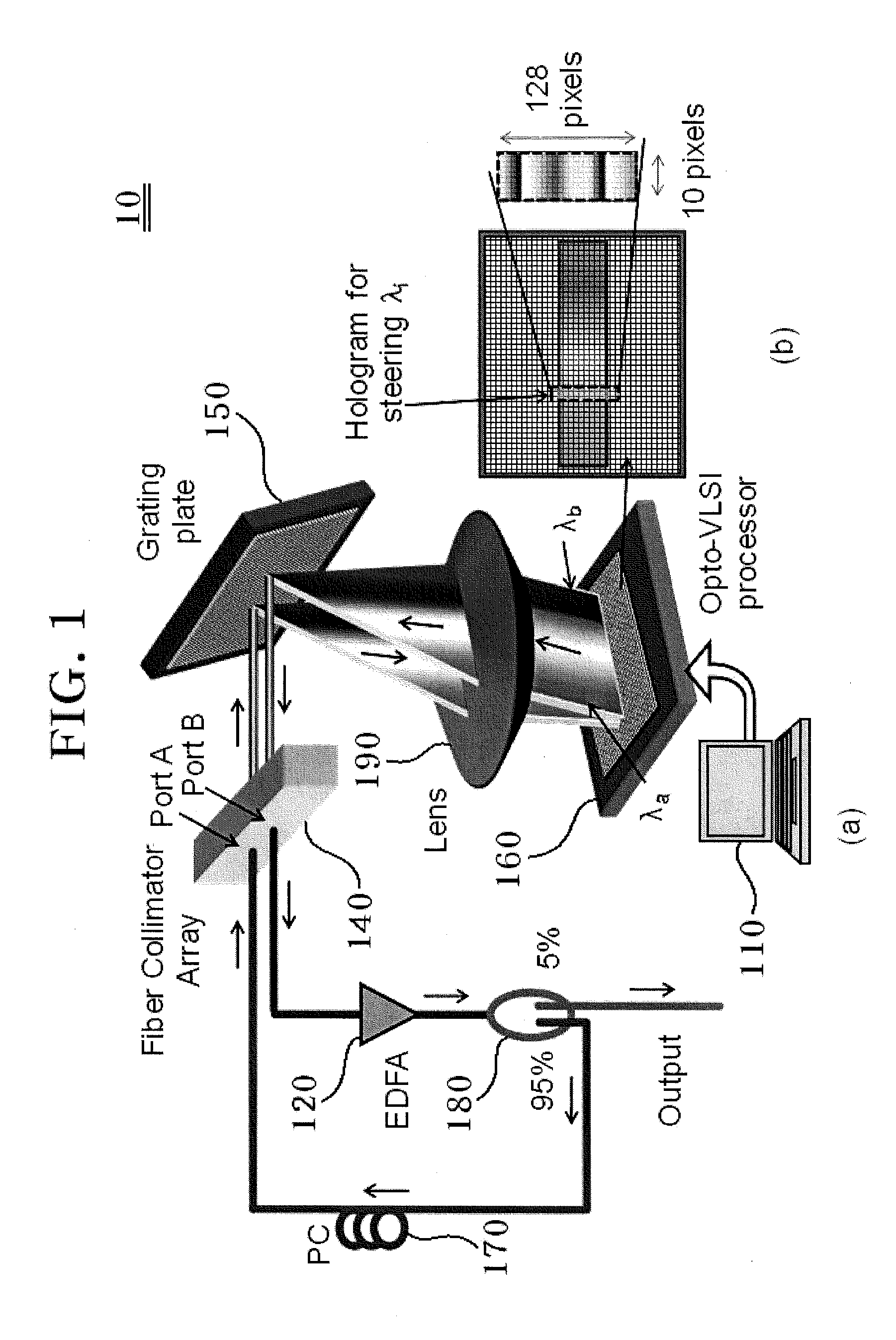
ActiveUS20120120466A1Small sizeImprove accuracyLaser detailsInstrumentsAudio power amplifierLength wave
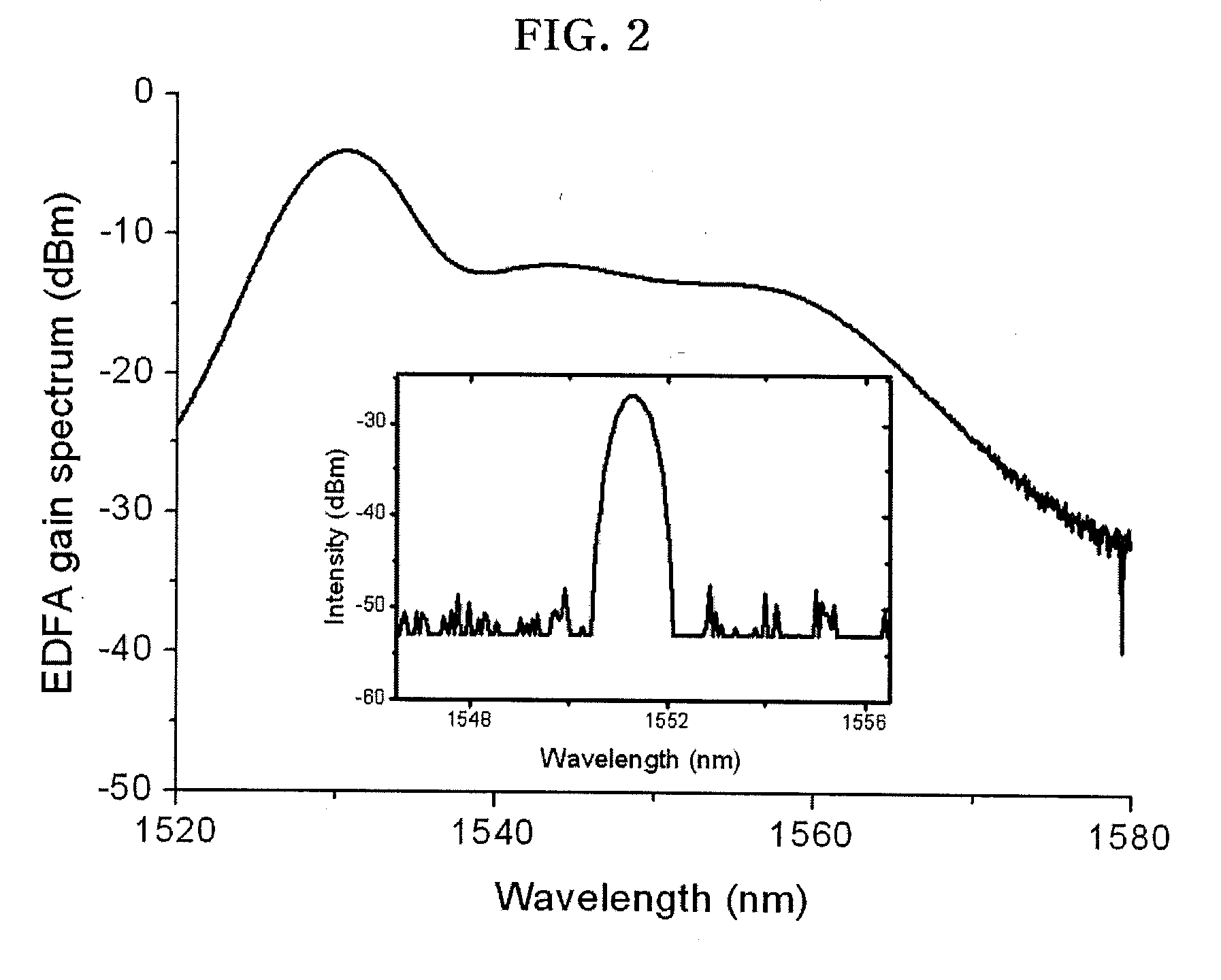
A wavelength-tunable laser system includes an optical fiber collimator array having at least two ports, an optical amplifier connected to one port of an optical fiber, an optical coupler for coupling light incident from the optical amplifier and transmitting the coupled light to another port, a diffraction grating plate for guiding each wavelength component of light incident from the optical fiber collimator array in a different direction, and an Opto-Very Large Scale Integration (Opto-VLSI) processor.
Owner:YTEL PHOTONICS
Complementary logic gate device
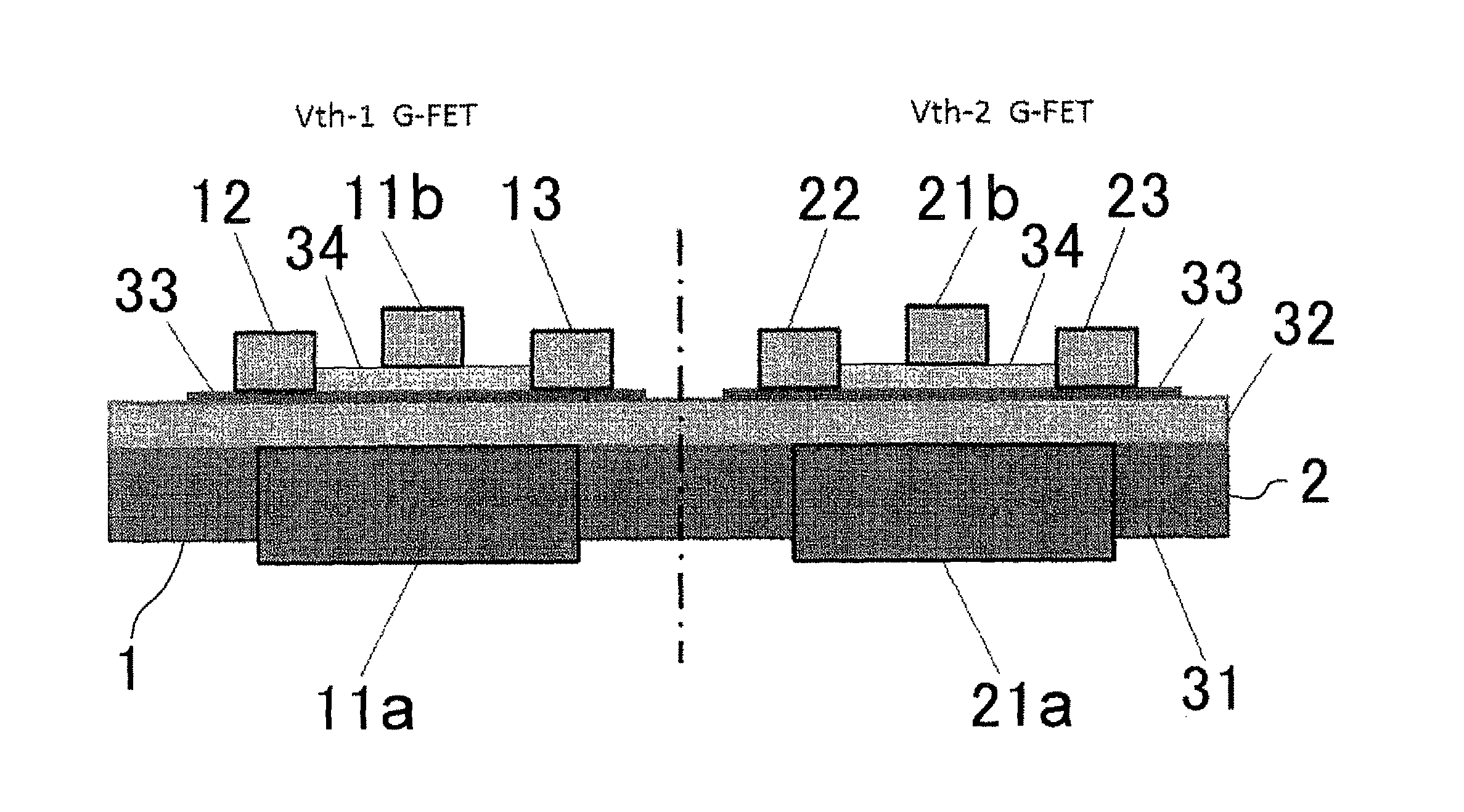
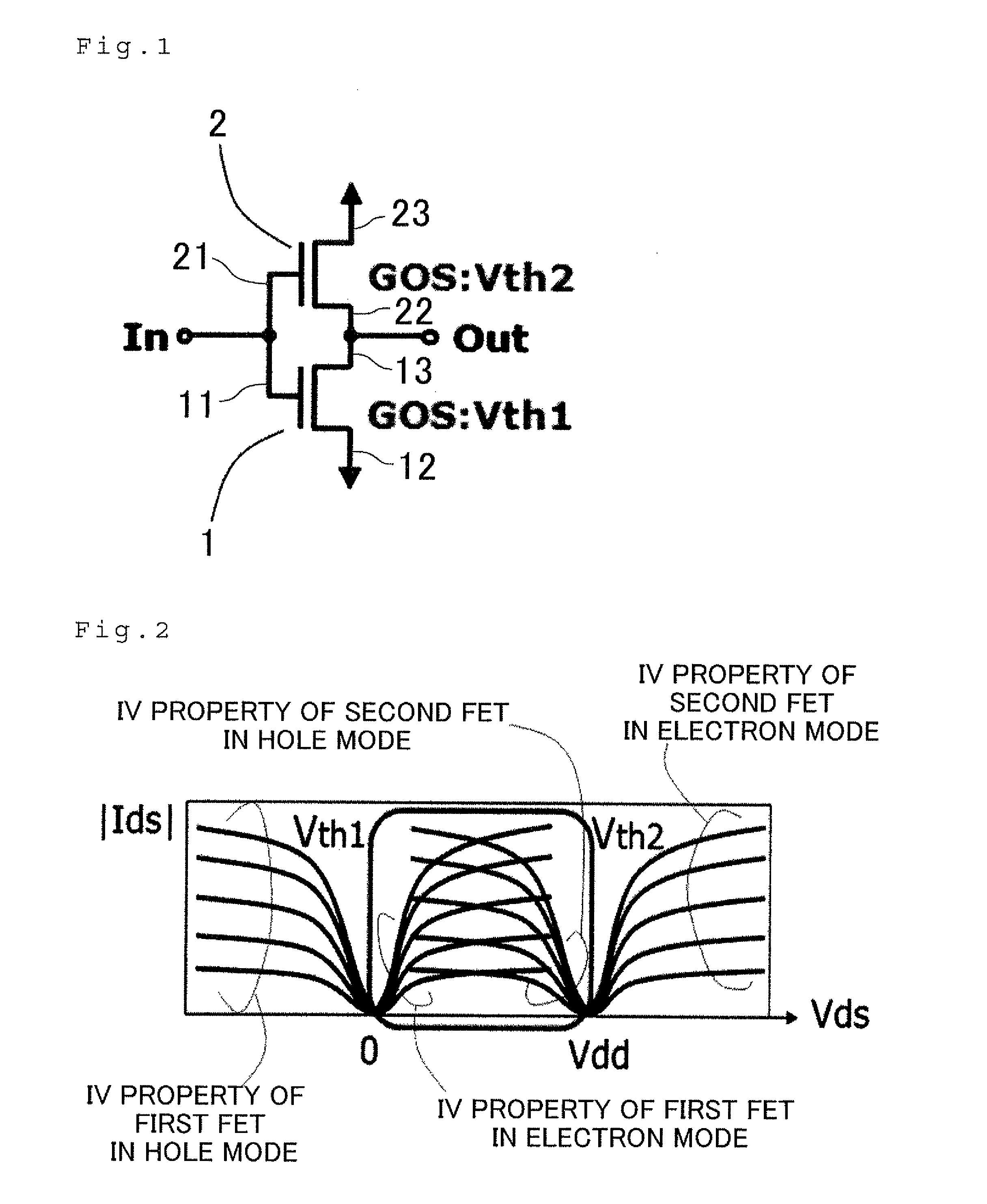
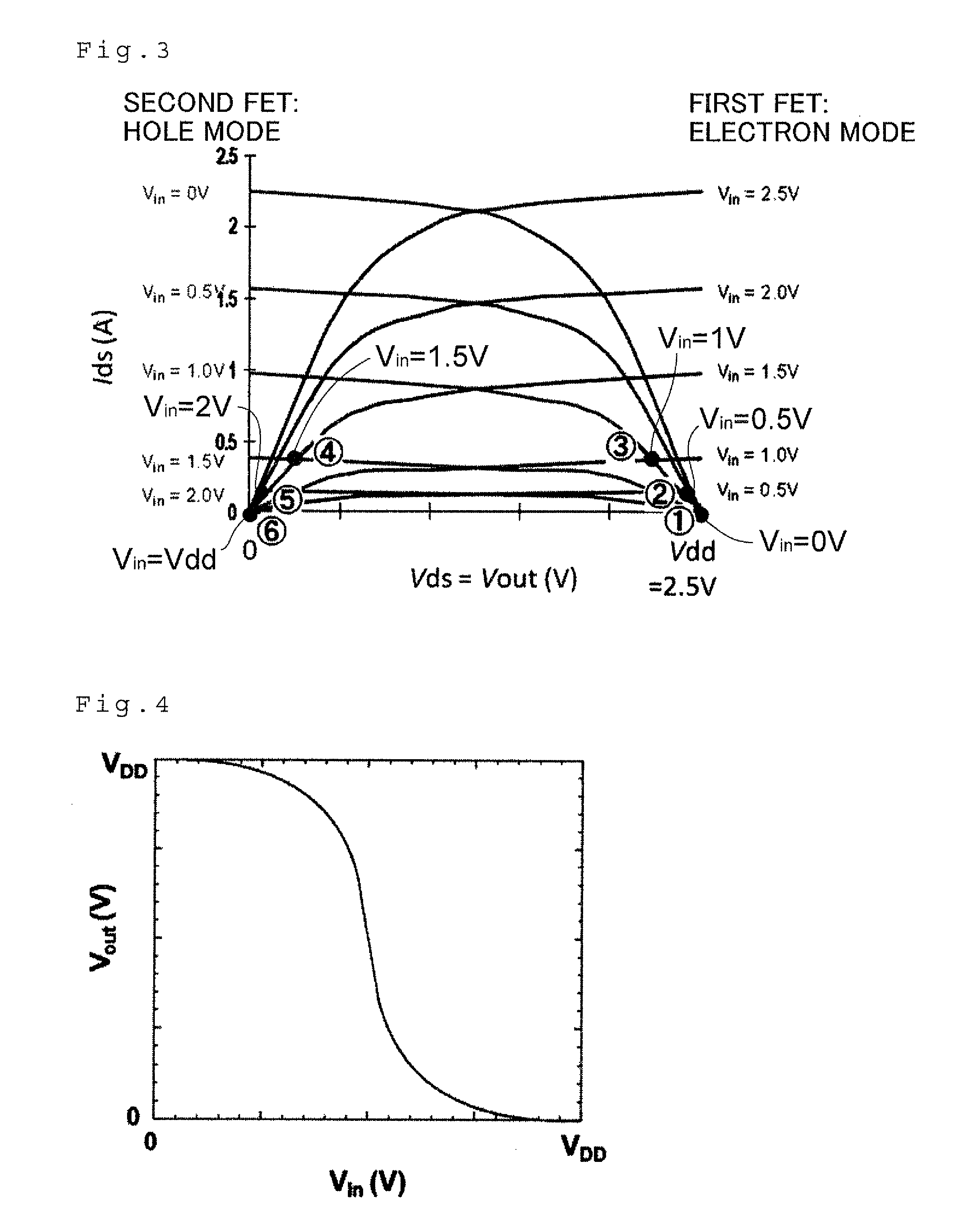
Provided is a complementary logical gate device represented by a silicon CMOS logical circuit among semiconductor integrated logical circuits which can effectively solve the problem of the speed performance limit of an ultra-large scale integration and an ultra-low power consumption type logical circuit. The complementary logical gate includes an electron running layer formed by grapheme without using an n-channel FET or a p-channel FET, has the ambipolar characteristic, and uses only two FET having different threshold values, i.e., a first FET and a second FET. The first FET has a gate electrode short-circuited to a gate electrode of the second FET so as to constitute an input terminal. The first FET has a source electrode set to a low potential. The first FET has a drain electrode connected to a source electrode of the second FET so as to constitute an output terminal. The second FET has a drain electrode set to a high potential.
Owner:OTSUJI TAIICHI +1
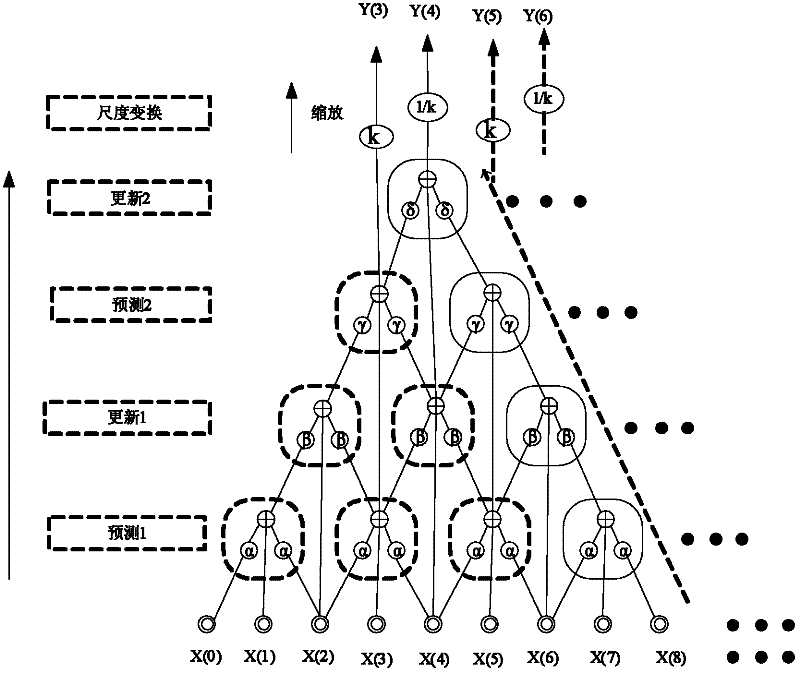
Method for realizing image compression based on folding flow line wavelet transformation
InactiveCN102510489AReduce areaReduce the numberTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationImage compressionSingle shot
The invention provides a method for realizing image compression based on folding flow line wavelet transformation, and particularly relates to a technology based on folding flow lines. The folding flow lines adopt a uniform architecture very large scale integration (VLSI) for the transformation of various wavelets, so that the resource consumption is reduced by structuring the shortest iterative calculation path for wavelet transformation, and the hardware utilization efficiency is improved by simplifying improving steps and adopting a single-shot input structure. An experiment result shows that for the same image, if the structure and a traditional long flow line structure are adopted for an experiment, the method is more excellent in resource consumption and hardware utilization rate.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
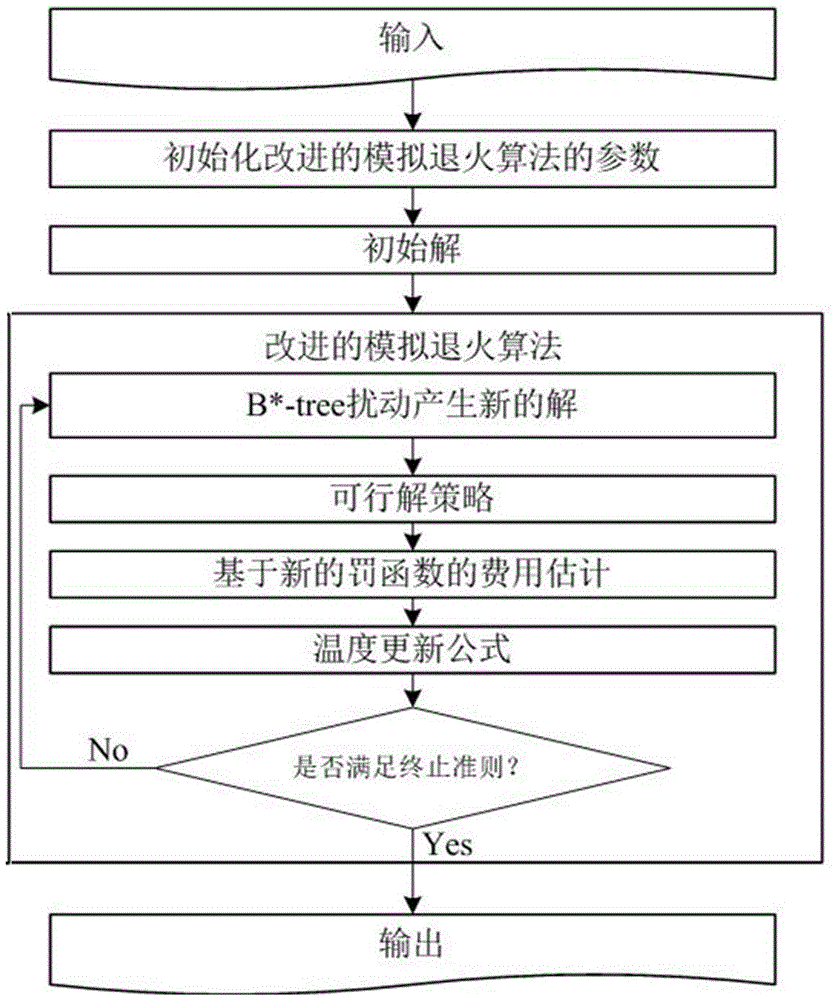
VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) layout design method for solving given border constraint
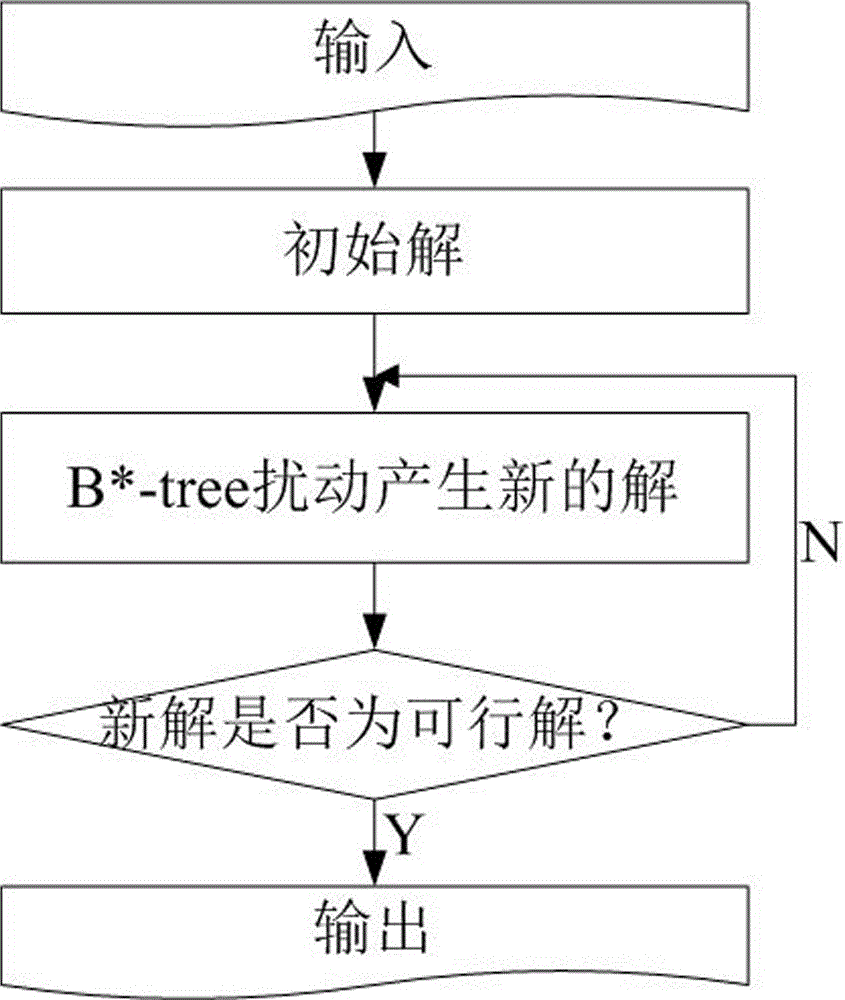
InactiveCN106777849ARestricted movementReduce the temperatureCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsRandomizationVery-large-scale integration
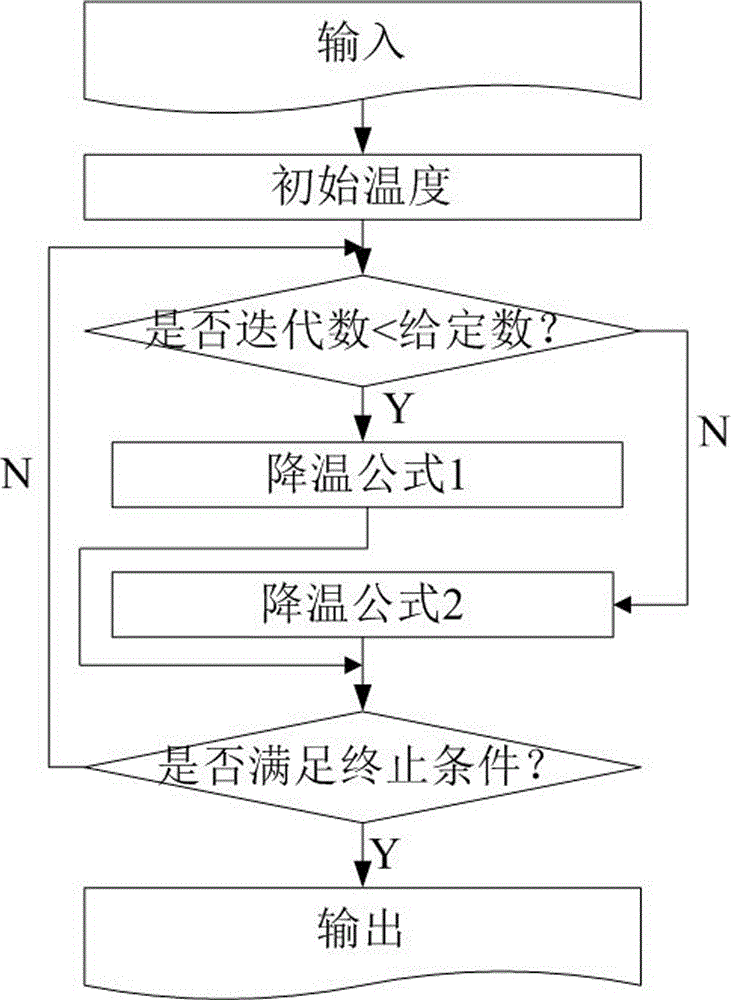
The invention relates to a VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) layout design method for solving a given border constraint. By adopting a strategy of randomization, a random initial layout is used as an initial solution of a hybrid simulated annealing algorithm. The border constraint is proposed as a violating penalty function of a target function. The violating penalty function introduces a length function considering each module over a given border based on an area function considering a minimum rectangle enclosing candidate layout results over the given border. Based on the hybrid simulated annealing algorithm, a feasible solution strategy is introduced. Solutions produced via a series B*-tree disturbance are feasible solutions, so that better solutions can be obtained from the algorithm. The optimal solution is searched by introducing the hybrid simulated annealing algorithm, and a new temperature update formula is adopted in the algorithm. The new temperature update formula shortens the time for solving the spatial search phase, and more time is used for searching the better solutions in the temperature rise phase, so that the probability of finding the optimal solution is improved.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
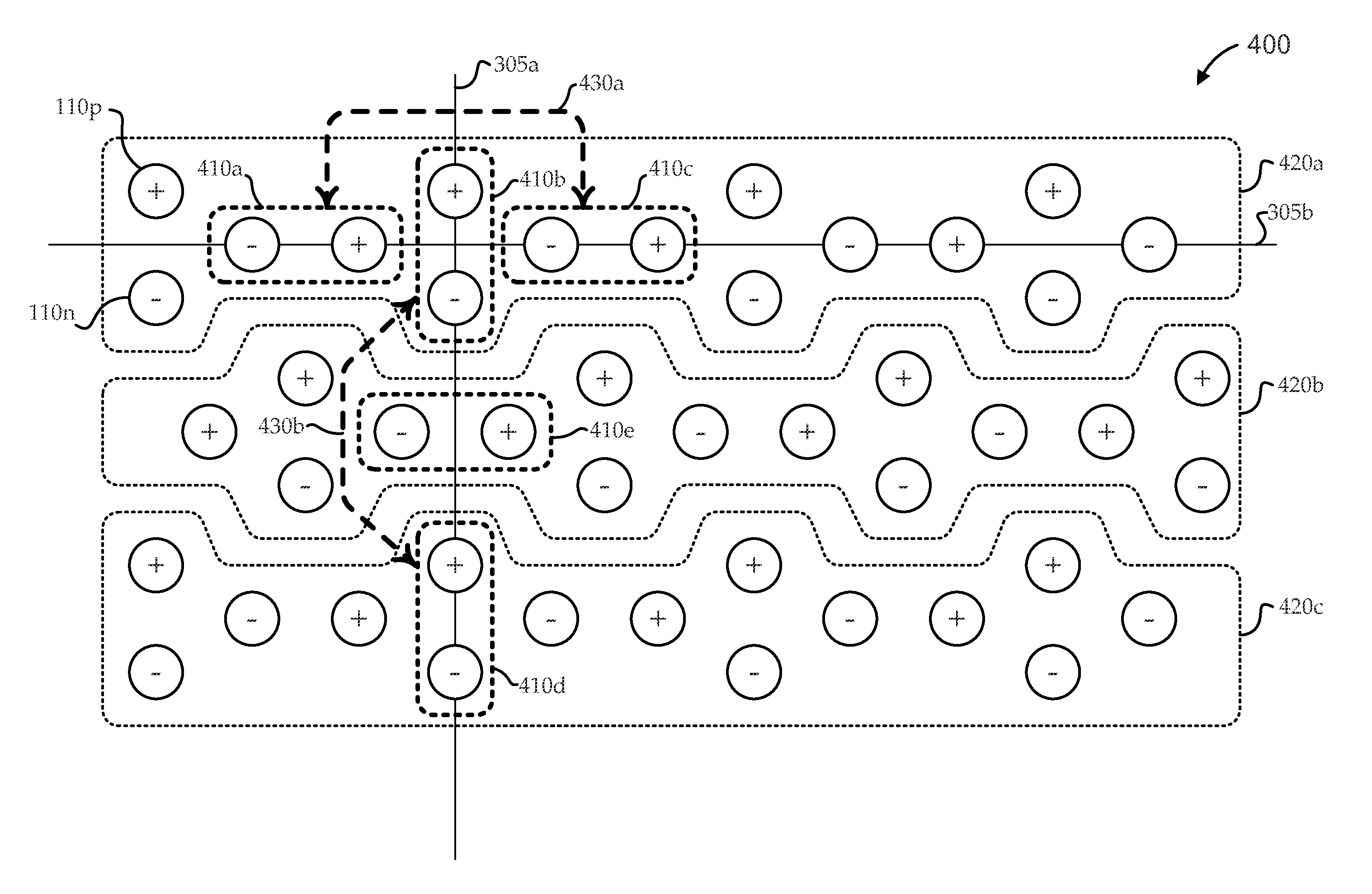
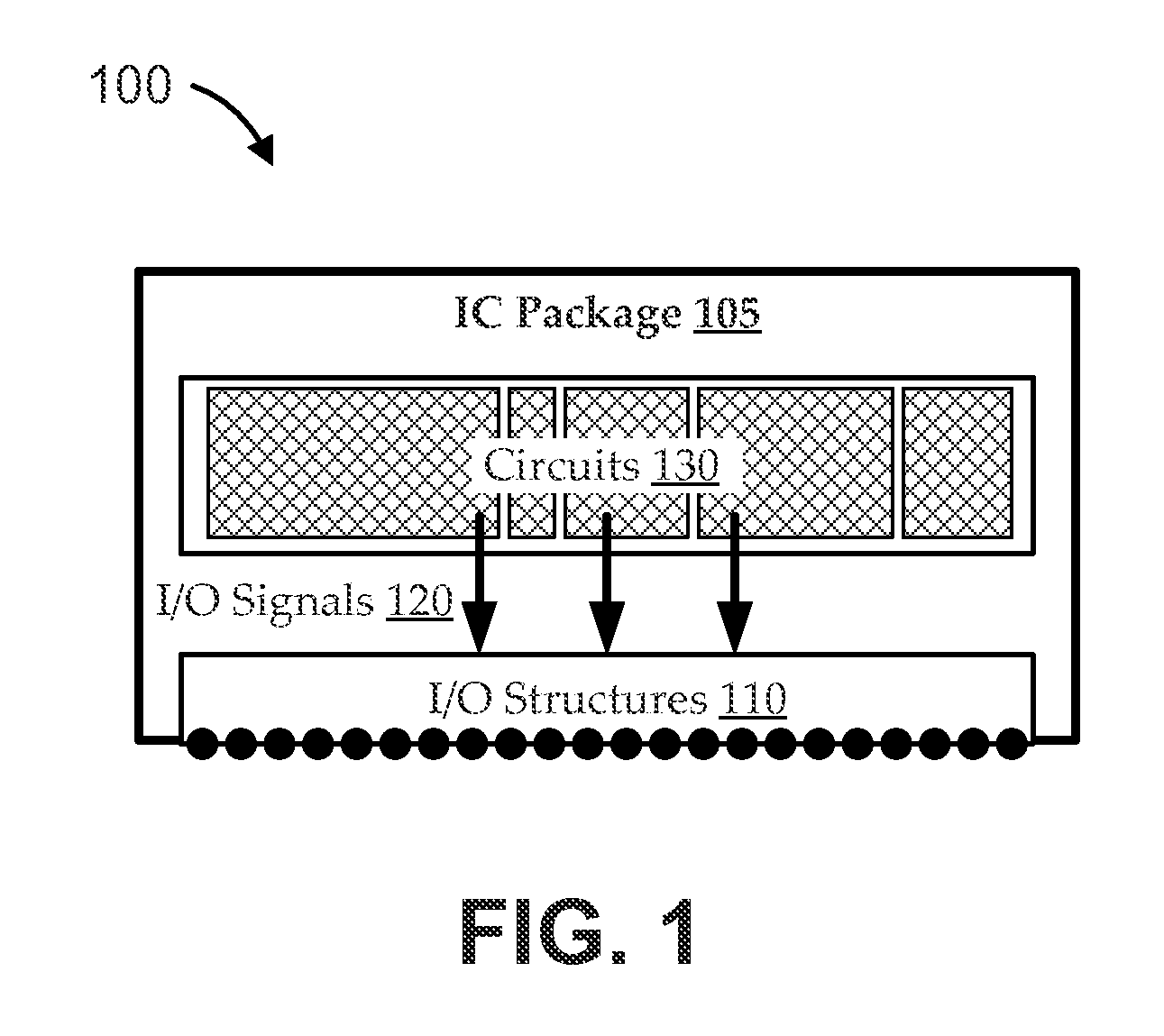
Low-noise arrangement for very-large-scale integration differential input/output structures
ActiveUS9543243B2Cancel noiseSuppress noiseSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLow noiseEngineering
Embodiments of the invention provide low-noise arrangements for very-large-scale integration (VLSI) differential input / output (I / O) structures (I / O pins, solder bumps, vias, etc.). Novel geometries are described for arranging differential pairs of I / O structures in perpendicular or near-perpendicular “quads.” The geometries effectively place one differential pair on or near the perpendicular bisector of its adjacent differential pair, such that field cancellation and differential reception can substantially eliminate noise without the need for added spacing or shields. By exploiting these effects, embodiments can suppress noise, independent of I / O structure spacing, and arbitrarily small spacings are permitted. Such arrangements can be extended into running chains, and even further into arrays of parallel chains. The parallel chains can be separated by supply structures (e.g., power supply bumps, or the like), and such supply structures can supply power to the I / O circuits of the IC, while also shielding adjacent chains from each other.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
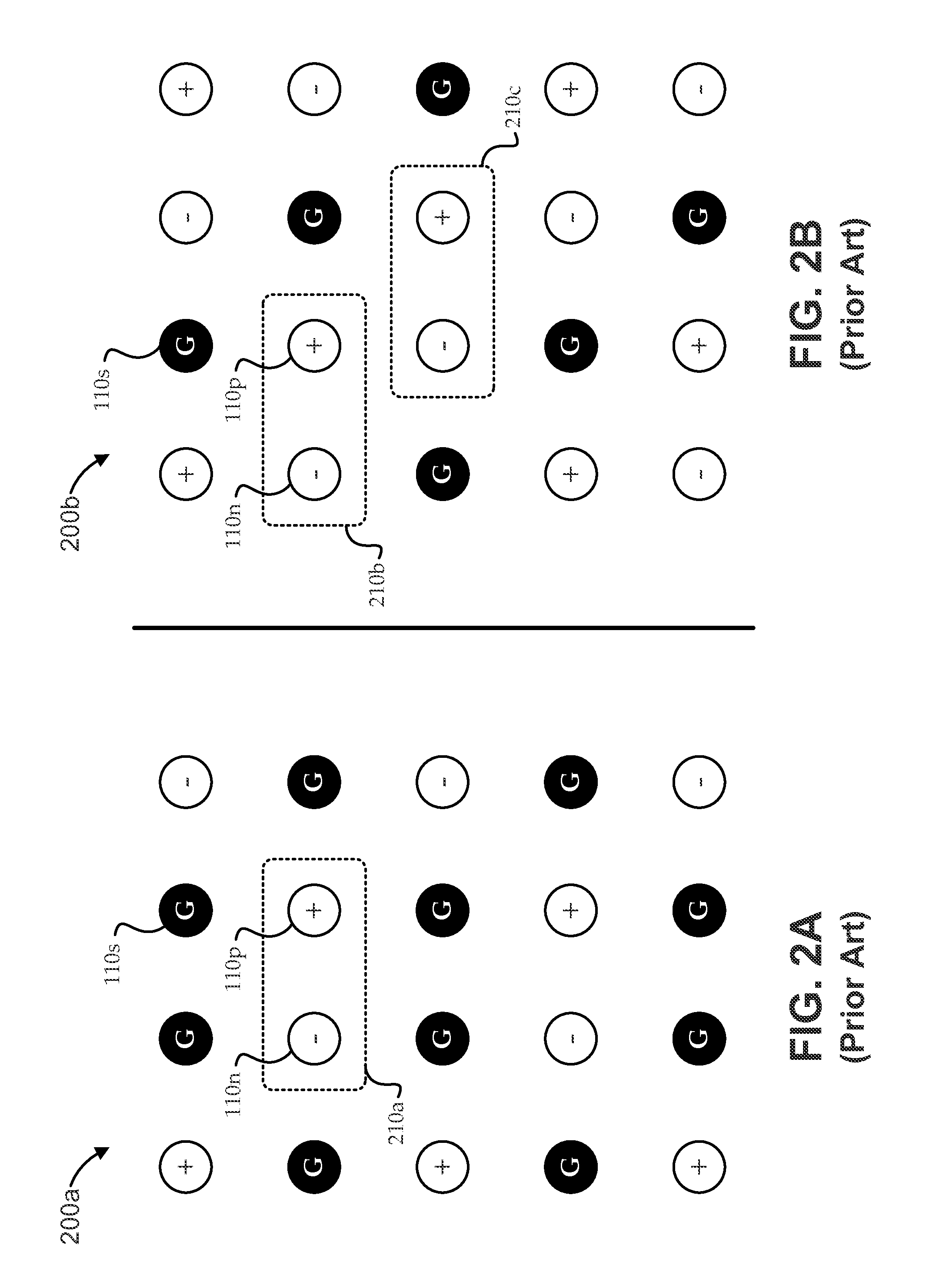
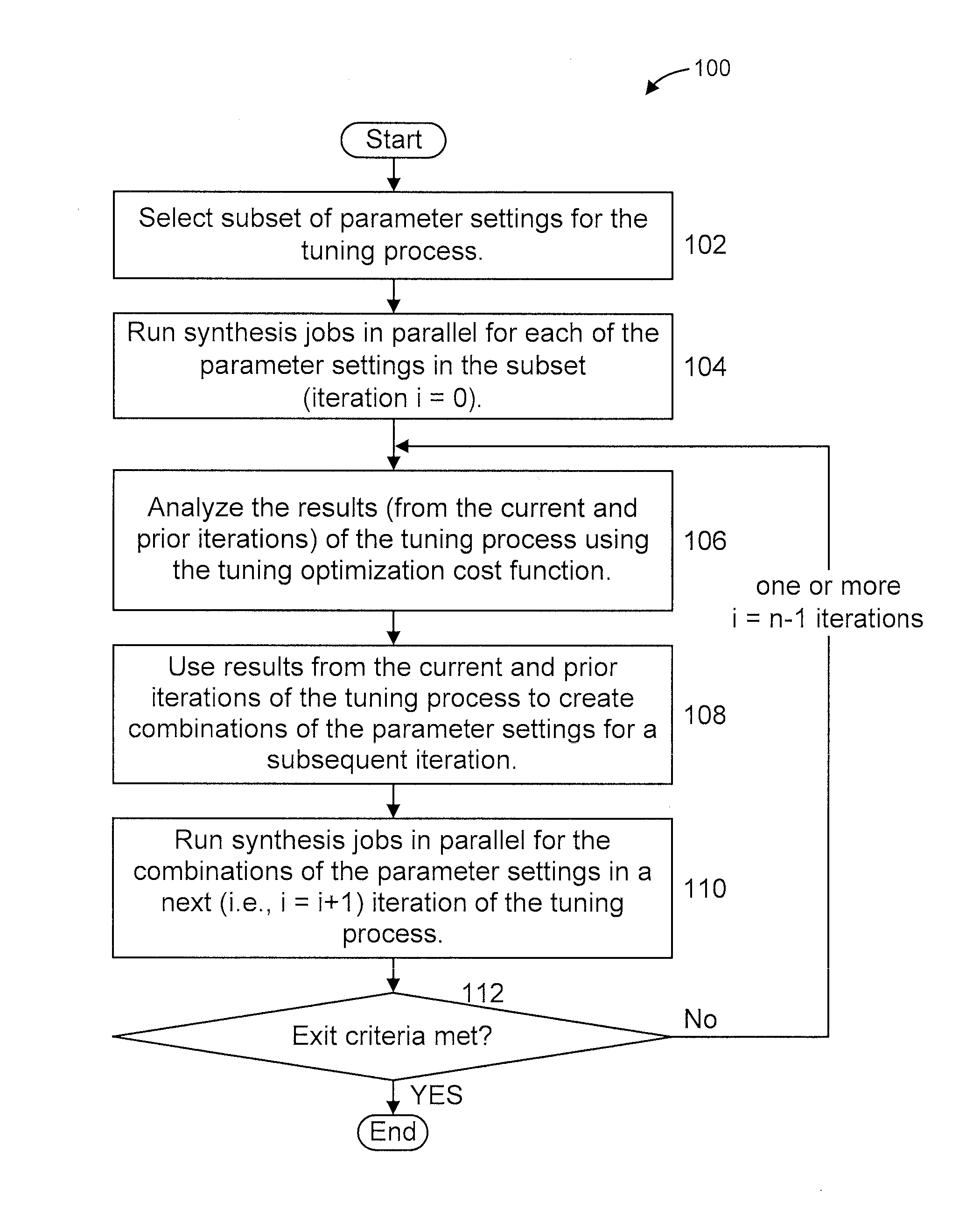
Enhanced parameter tuning for very-large-scale integration synthesis
InactiveUS20160147932A1Machine learningComputer aided designTheoretical computer scienceVery-large-scale integration
A method and system are provided for tuning parameters of a synthesis program for a design description. The method includes (a) ranking individual parameter impact by evaluating a design-cost function of each of the parameters. The method further includes (b) creating a set of possible parameter combinations that is ordered by an estimated-cost function. The method additionally includes (c) selecting, from the set of possible parameter combinations, top-k scenarios having best estimated costs to form a potential set, and running at least some of the top-k scenarios in parallel through the synthesis program. The method also includes (d) repeating steps (b)-(c) for one or more iterations until at least one of a maximum iteration limit is reached and an exit criterion is satisfied.
Owner:IBM CORP
VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) design method for two-dimensional discrete wavelet transform
InactiveCN106570272AImprove hardware efficiencyShorten critical path delaysCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsVery-large-scale integrationComputer science
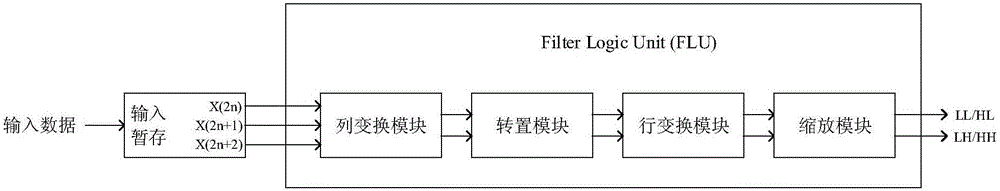
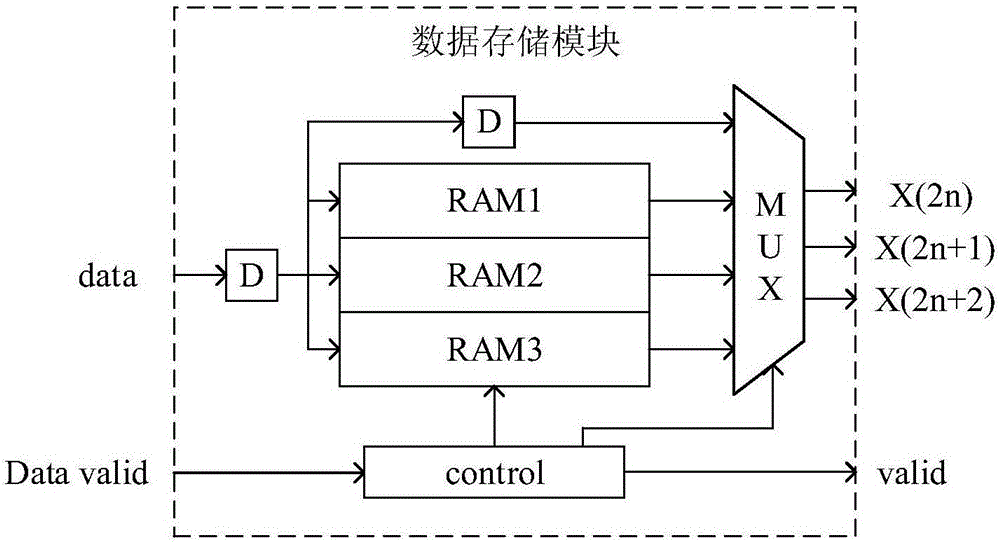
The invention relates to VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) design method for two-dimensional discrete wavelet transform. A discrete wavelet transform framework of nine seventh wavelet is employed and comprises an input data storage module, a line transform module, a transposition module, a row transform module and a zoom module, data firstly and sequentially enters the data storage module, then is sent to subsequent modules by the storage module for sequential processing and is finally output by the zoom module, all multiplication is substituted by shift operation of an addition and subtraction method, the line transform module employs a three-input wavelet transform calculation method, and the row transformer module uses a two-input calculation method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com