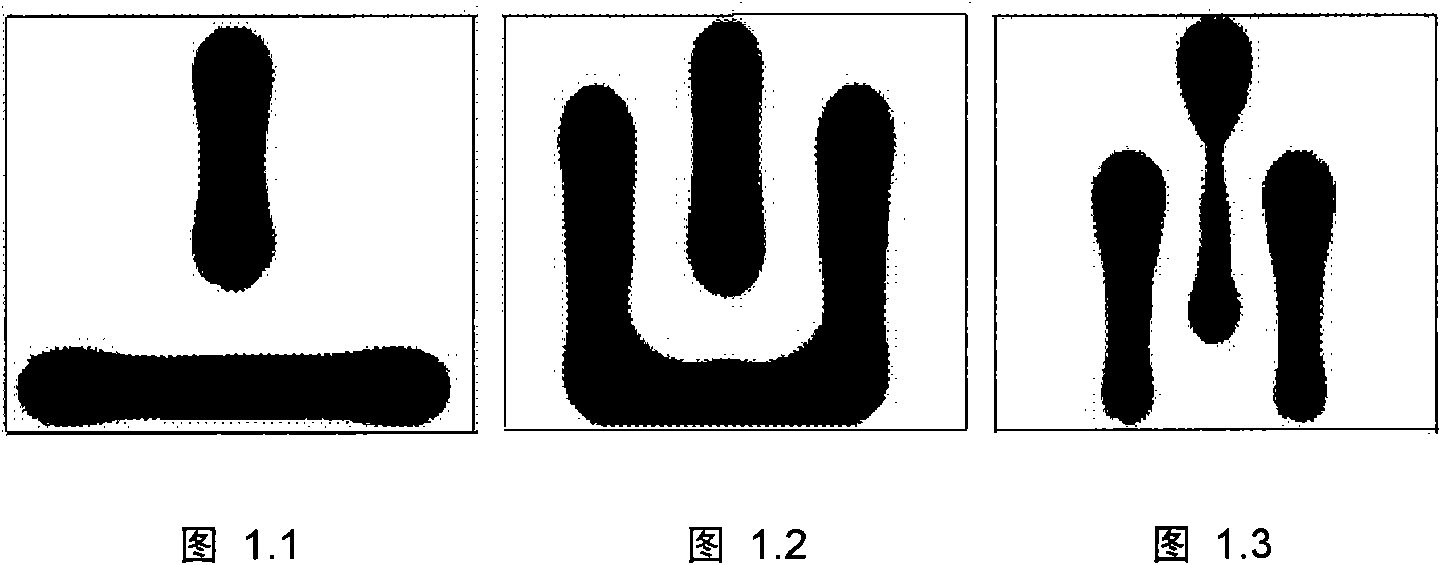
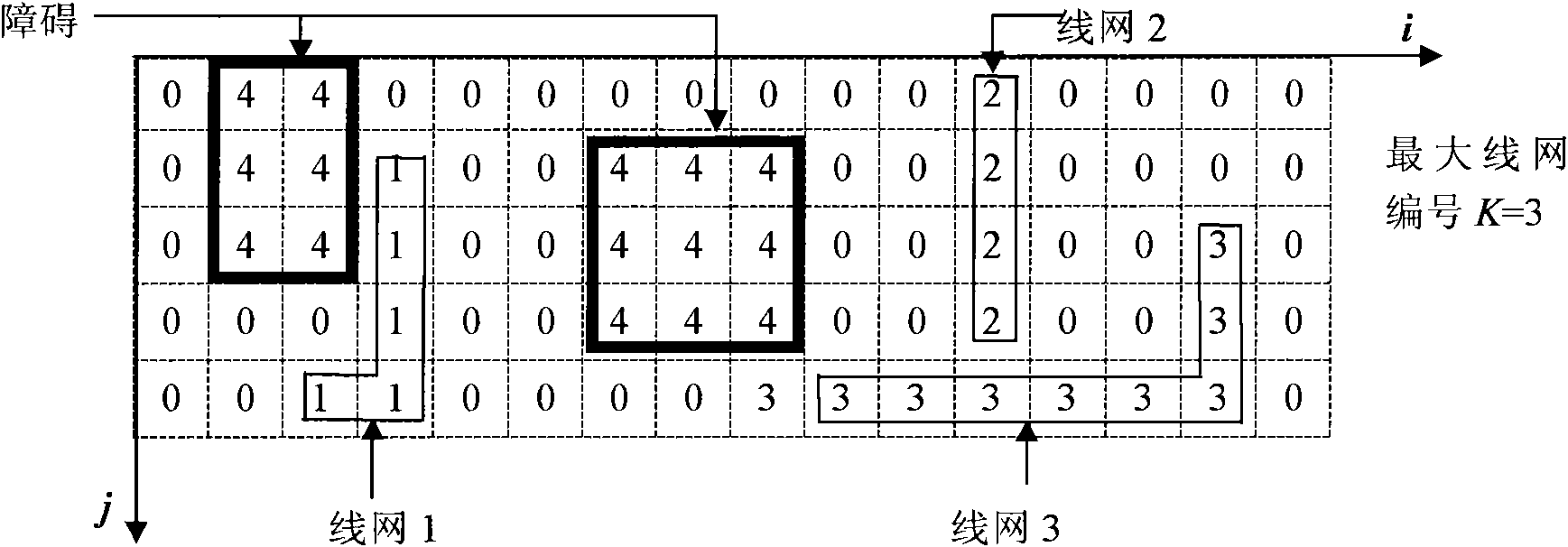
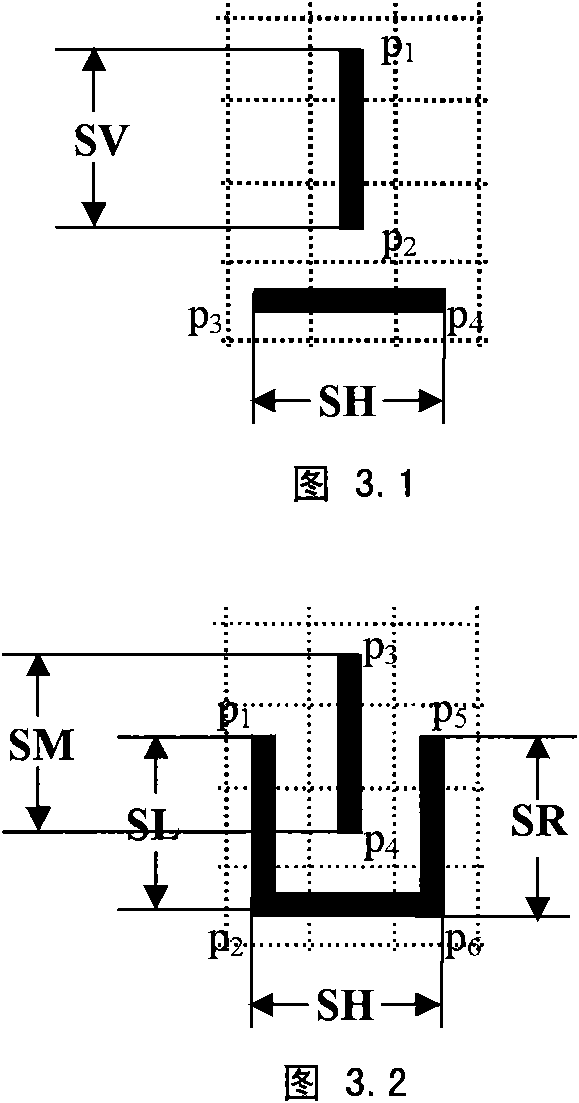
Satisfiability problem-based manufacturable hot spot disconnecting and rerouting method
A satisfying and manufacturable technology, applied in the field of manufacturability in physical design, can solve problems such as hotspot graphics are not easy to lithography, circuits cannot work properly, layout graphics, deformation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0161] This method has been developed and implemented in the UNIX environment using C++ language. The implemented program is based on the layout of the completed detailed wiring, by searching the hot program to count the number and location information of the hotspots in the layout, and finally a new layout with completely eliminated or greatly reduced hotspots is given as output.
[0162] The following describes the workflow of the program:
[0163] 1. Computer initialization.
[0164] The input of the program is the layout information of the detailed wiring and all the hotspot information contained in the layout, among which:
[0165] The layout is represented as a two-dimensional array [v i, j ] I×J To achieve, the size of the two-dimensional array is equal to the grid number I×J of the layout, and the grid v i, j The size of is equal to a set line spacing plus a set line width, i represents the row number of the grid, j represents the column number of the grid, i=1, 2,..., I, j...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com