Patents
Literature
429 results about "Error location" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
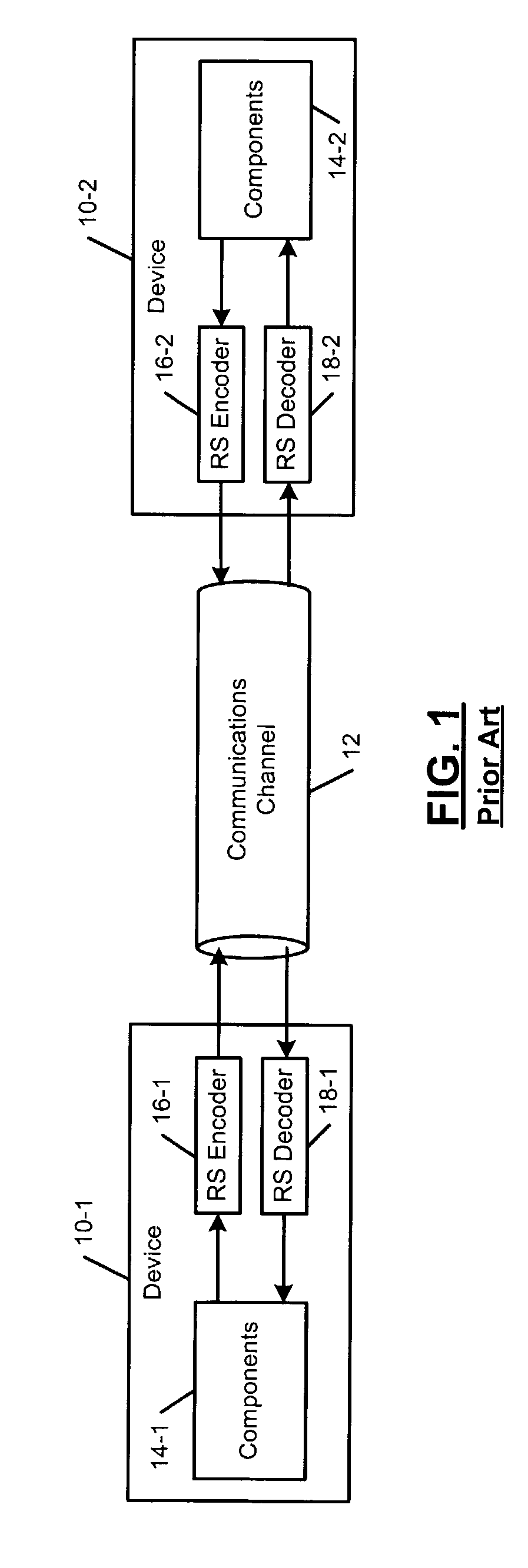
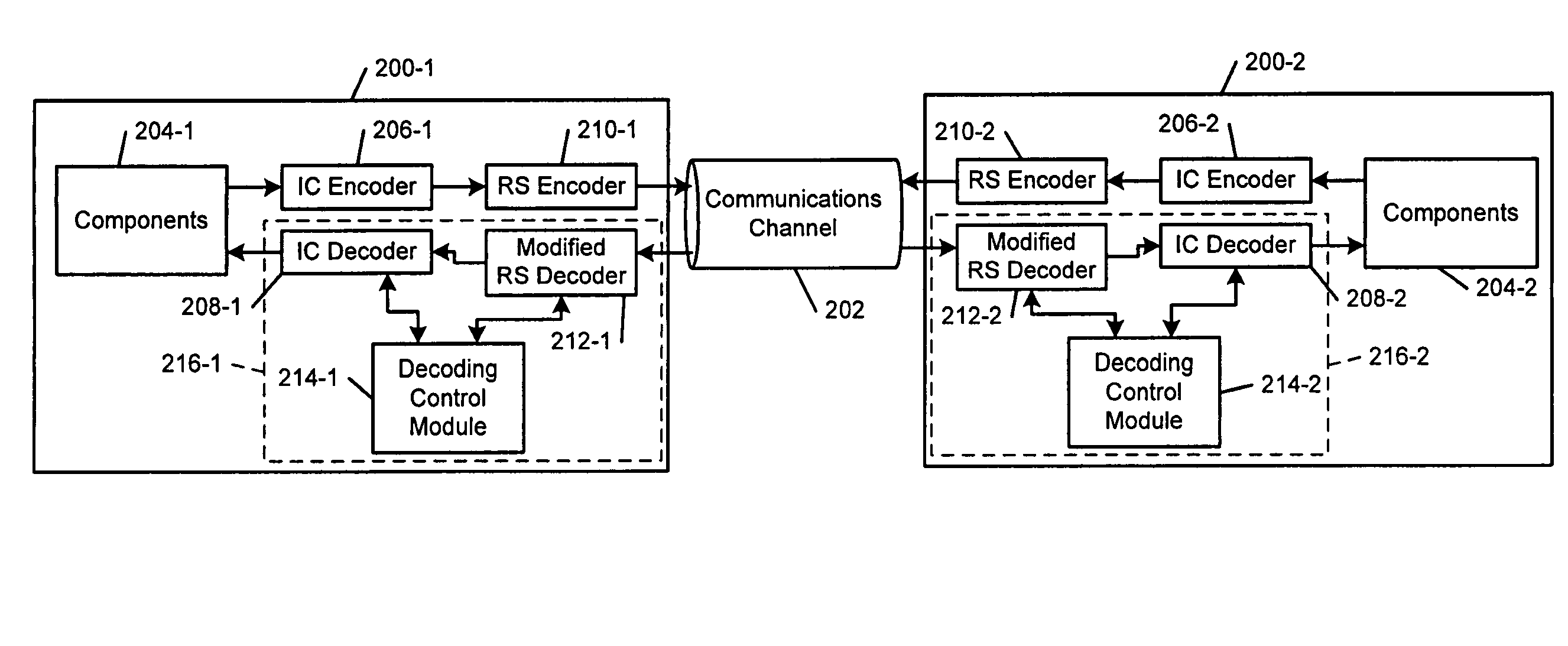
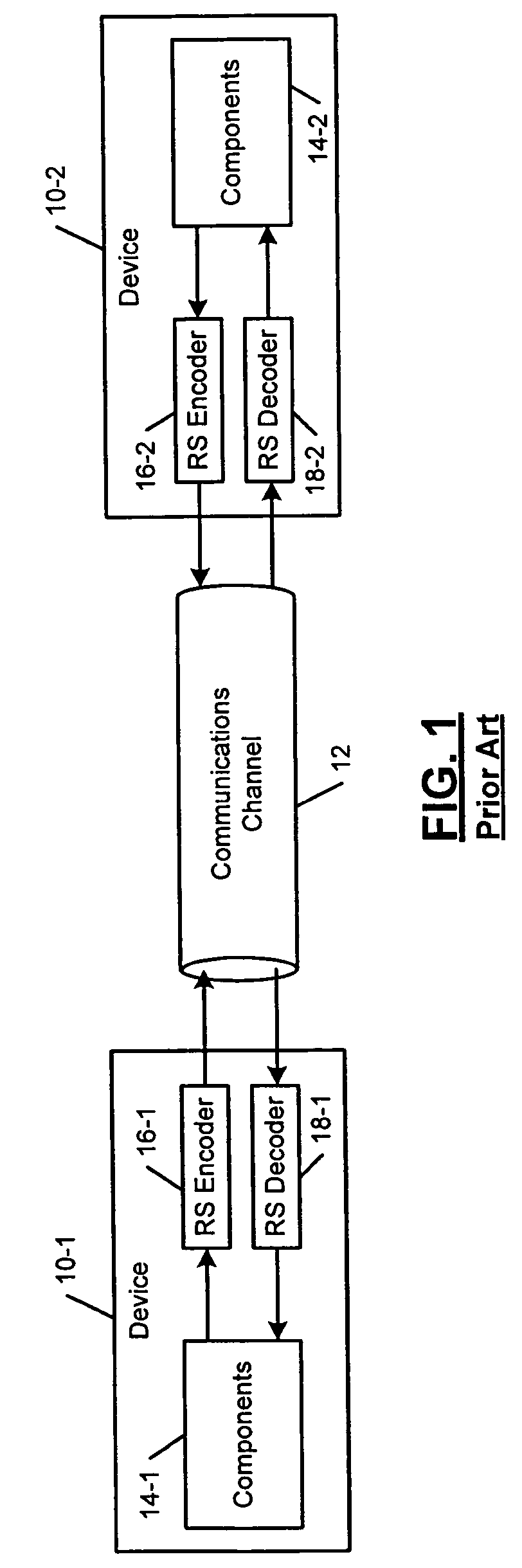
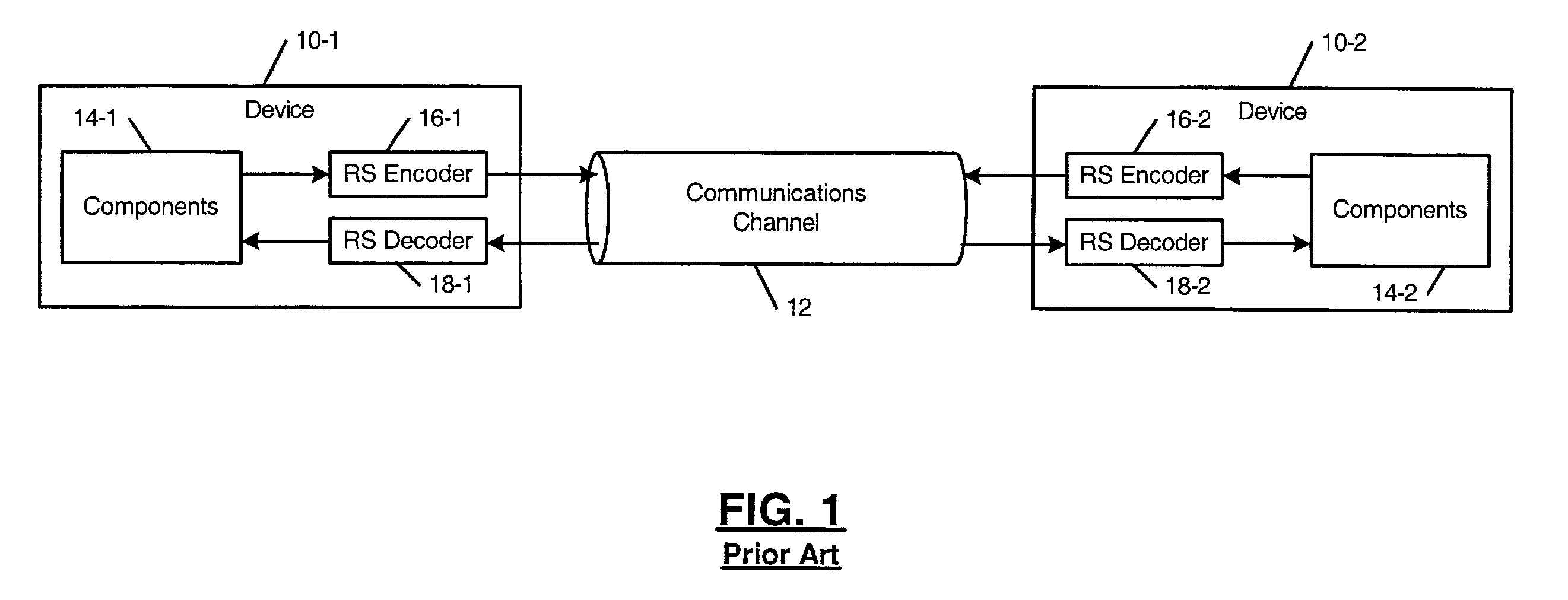
Techniques for detecting and correcting errors using multiple interleave erasure pointers
InactiveUS20050229069A1Correction capabilityTransmission systemsCode conversionBlock codeError location
Techniques for detecting and correcting burst errors in data bytes formed in a two-level block code structure. A second level decoder uses block level check bytes to detect columns in a two-level block code structure that contain error bytes. The second level decoder generates erasure pointers that identify columns in the two-level block structure effected by burst errors. A first level decoder then uses codeword check bytes to correct all of the bytes in the columns identified by the erasure pointers. The first level decoder is freed to use all of the codeword check bytes only for error byte value calculations. The first level decoder does not need to use any of the codeword check bytes for error location calculations, because the erasure pointers generated by the second level decoder provide all of the necessary error locations. This techniques doubles the error correction capability of the first level decoder.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV +1
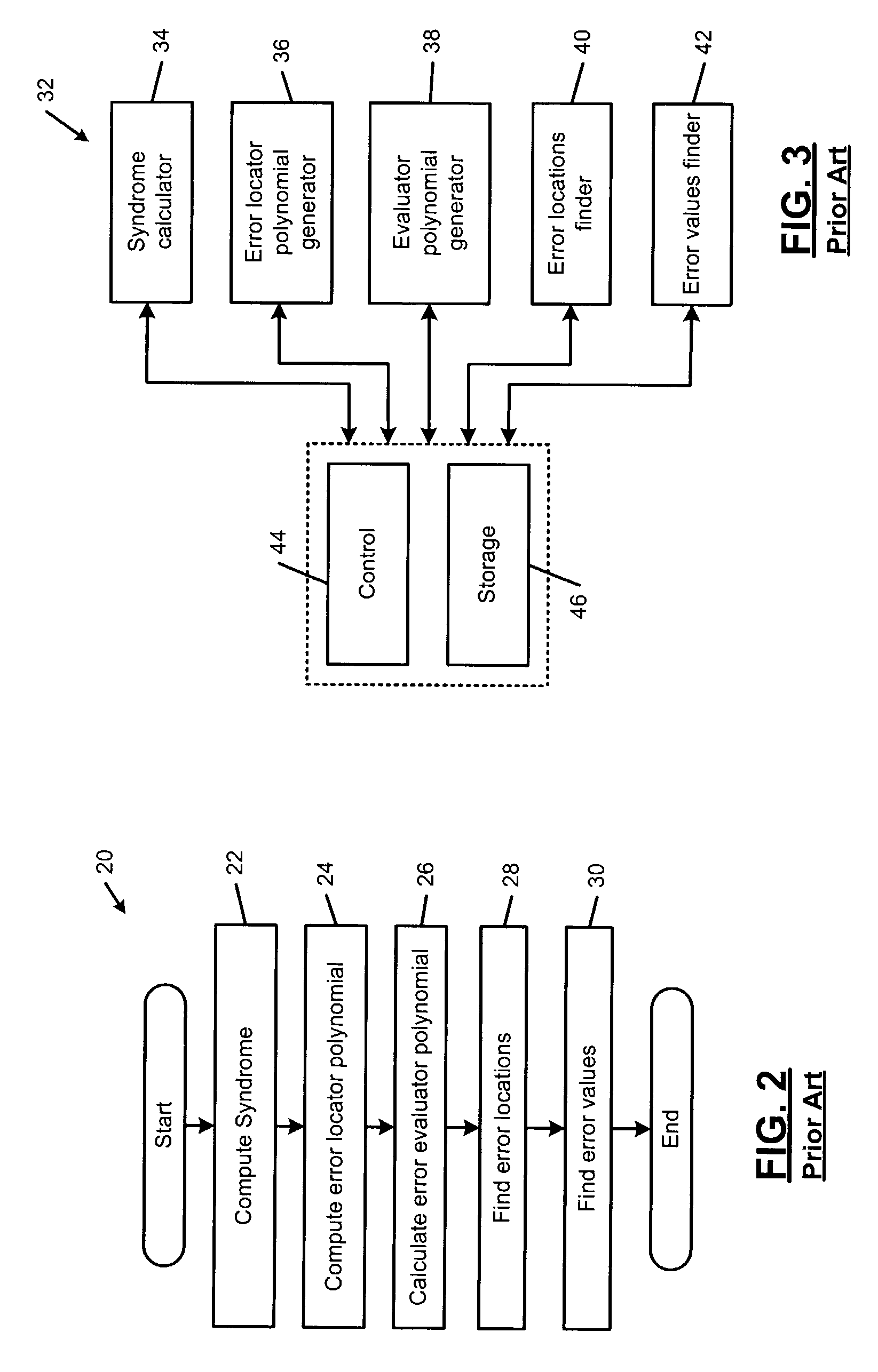
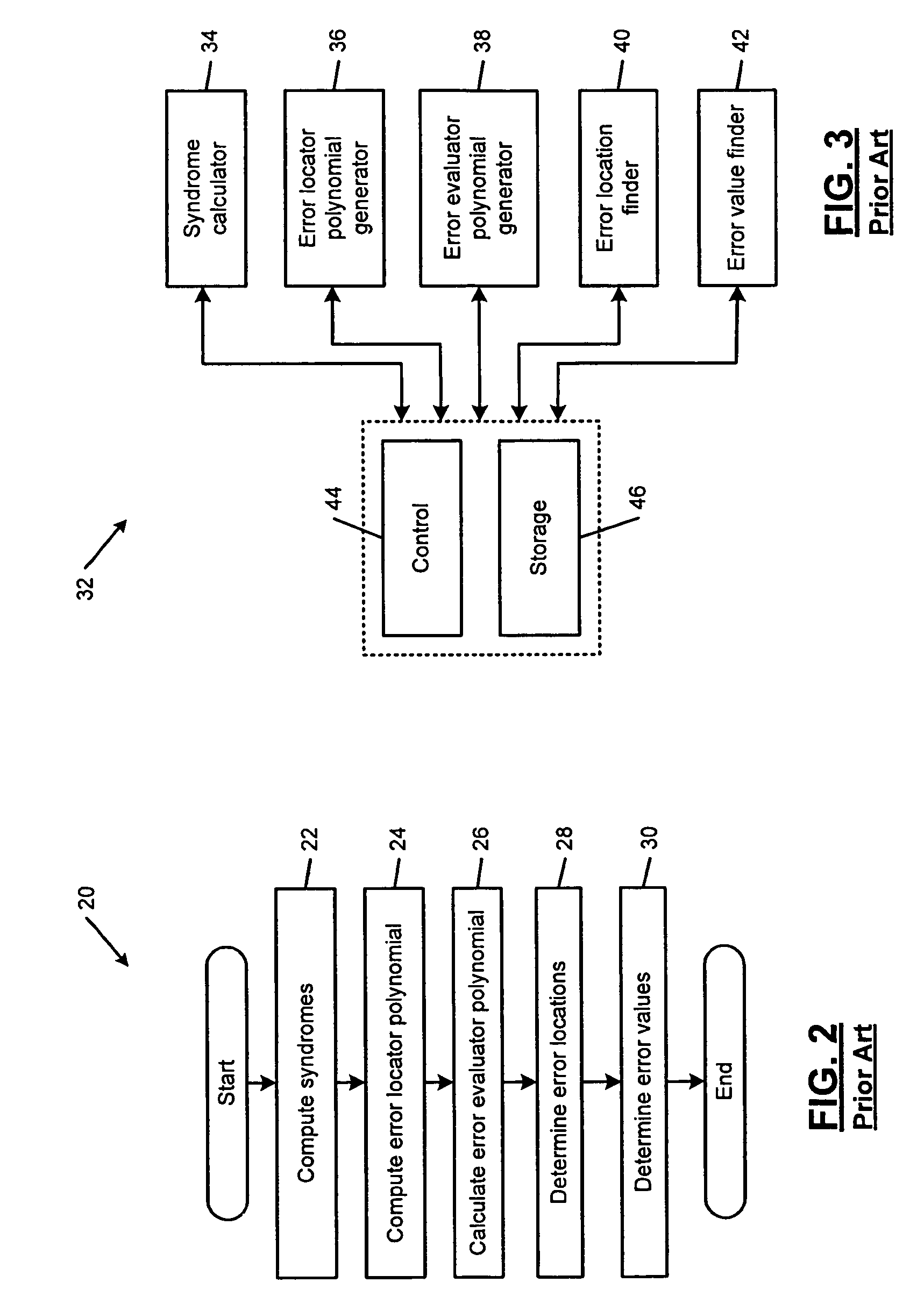
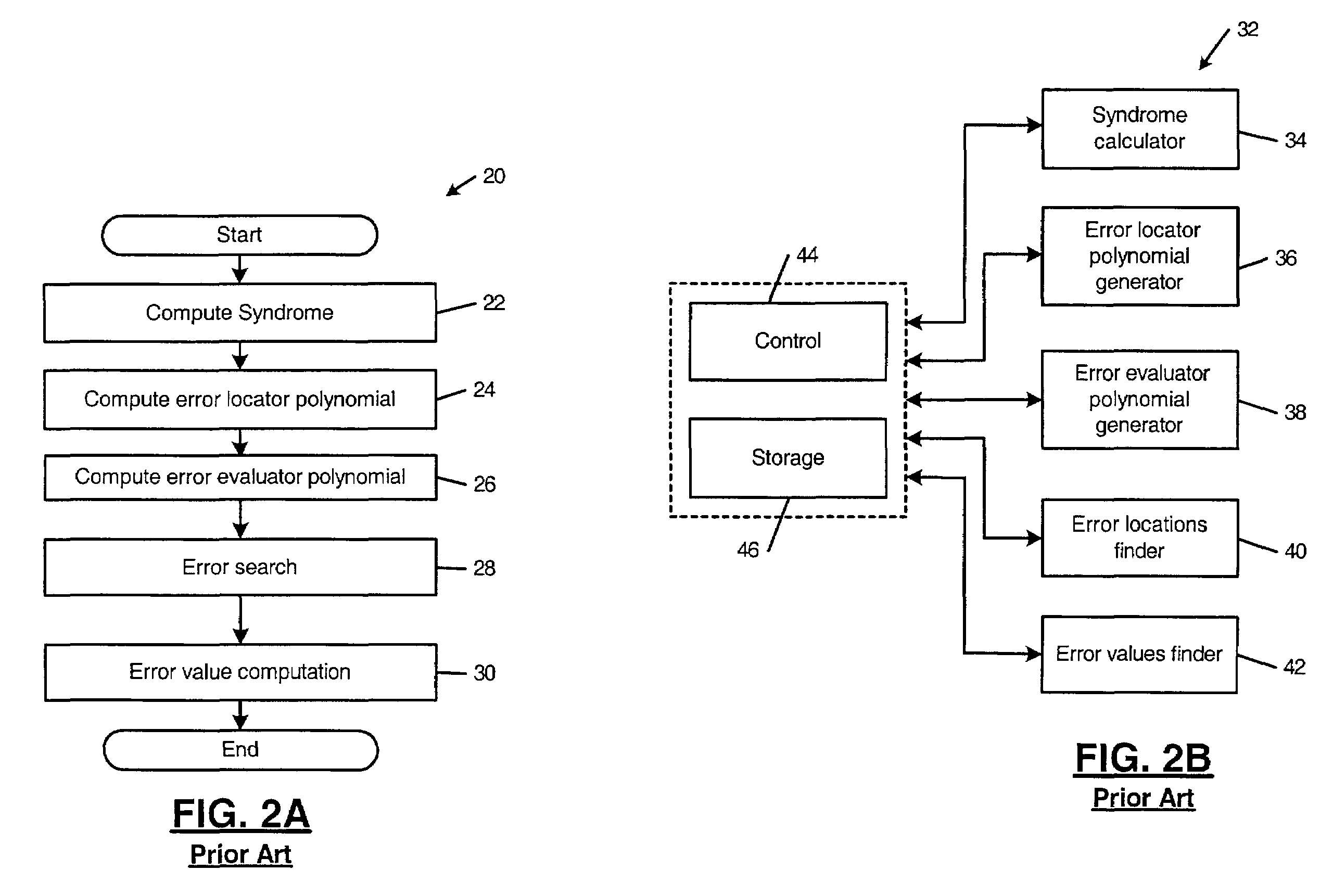
Error evaluator for inversionless Berlekamp-Massey algorithm in Reed-Solomon decoders
ActiveUS7010739B1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionError locationReed solomon decoder
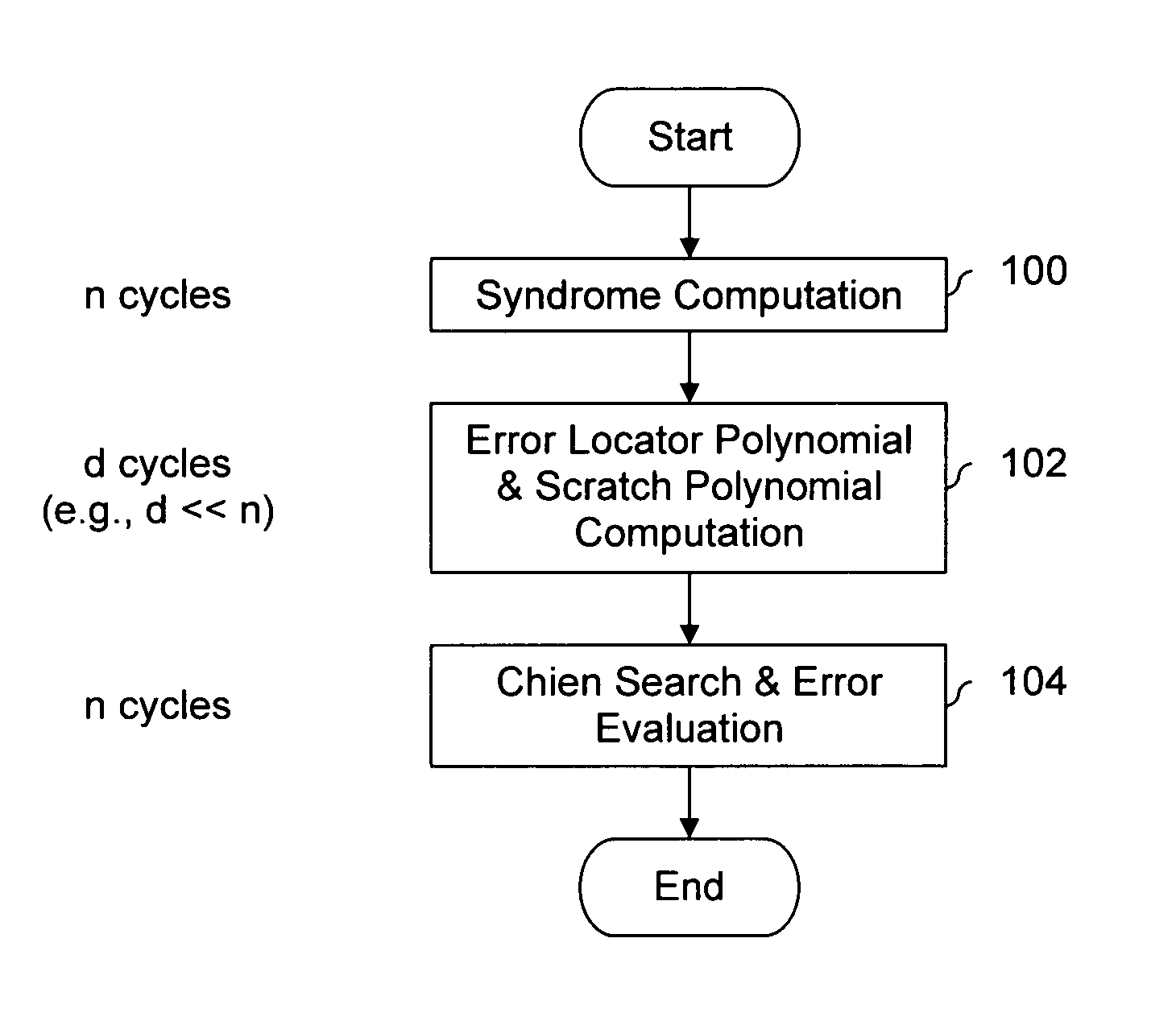
An error correcting Reed-Solomon decoder includes a syndrome calculator that calculates syndrome values. An error locator polynomial generator communicates with the syndrome calculator and generates an error locator polynomial. An error location finder communicates with at least one of the syndrome calculator and the error locator polynomial generator and generates error locations. An error values finder communicates with at least one of the syndrome calculator, the error location finder and the error locator polynomial generator and generates error values using an error value relationship that is not based on the traditional error evaluator polynomial. The error locator polynomial generator is an inversionless Berlekamp-Massey algorithm (iBMA), which calculates an error locator polynomial and a scratch polynomial. The error value relationship is based on the error locator polynomial and the scratch polynomial.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
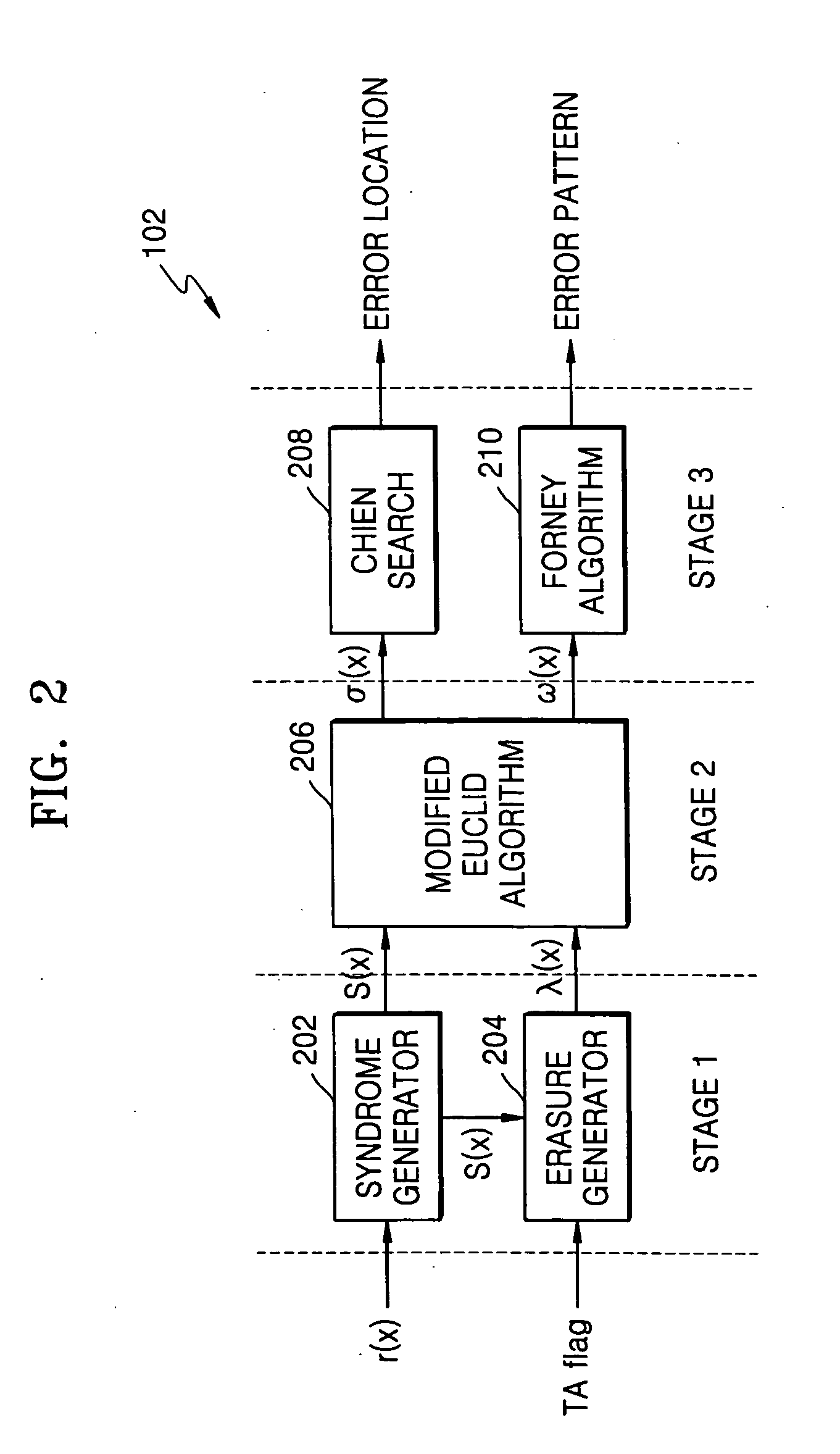
Forward Chien search type Reed-Solomon decoder circuit
ActiveUS20050172208A1Reduce aggregation timeShorten the timeCode conversionCyclic codesError locationReed solomon decoder
A Reed-Solomon decoder includes a Chien search circuit to receive an error location polynomial function, performs Chien search, and finds an error location; a Forney algorithm circuit to receives an error pattern polynomial function and find an error pattern; and, a seed generator circuit to indicates a seed value corresponding to a codeword length for the input data. A Chien search is performed to obtain and outputs exponential terms related to variables for the polynomials, wherein the Chien search is performed in the same computational direction as an order for the input data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
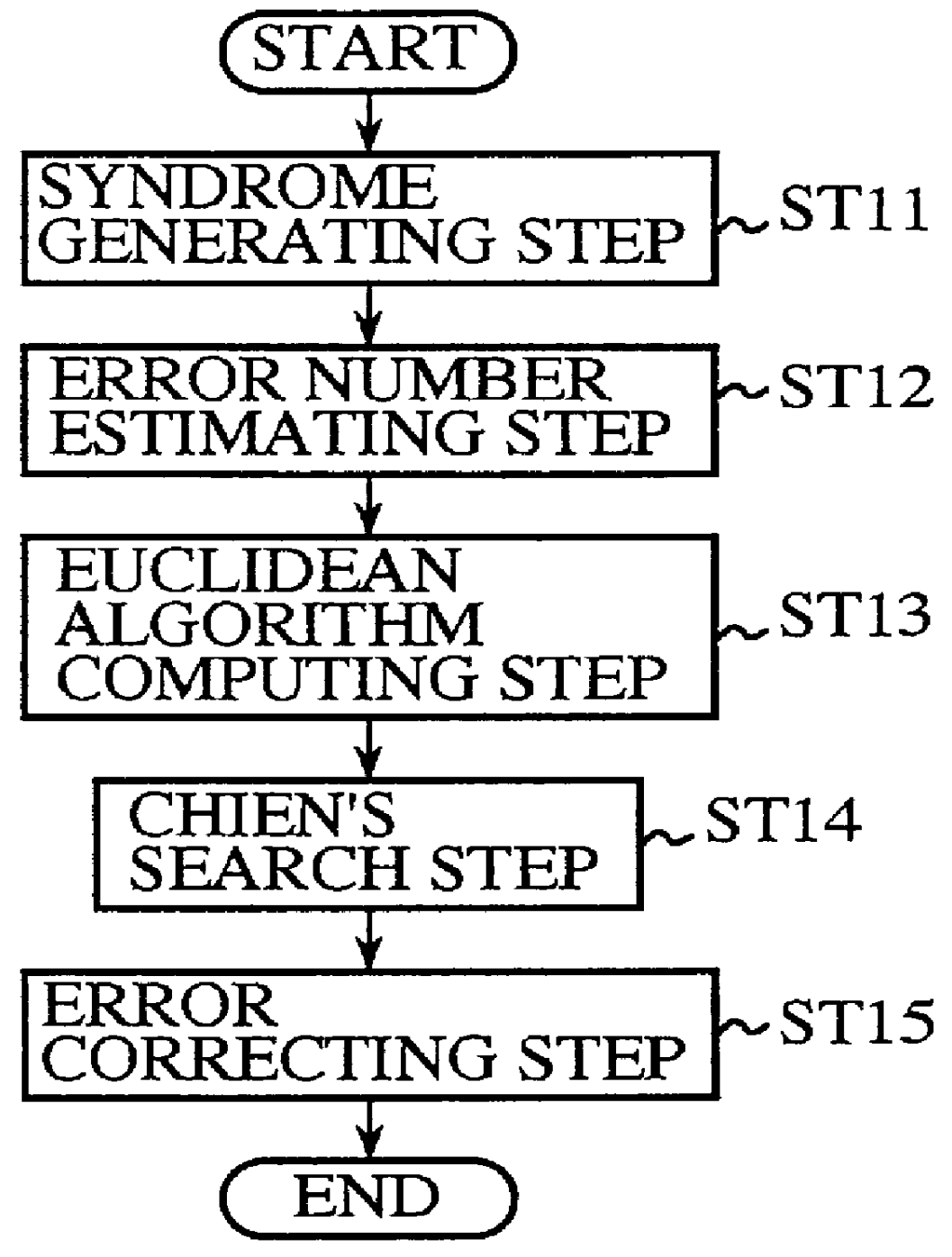
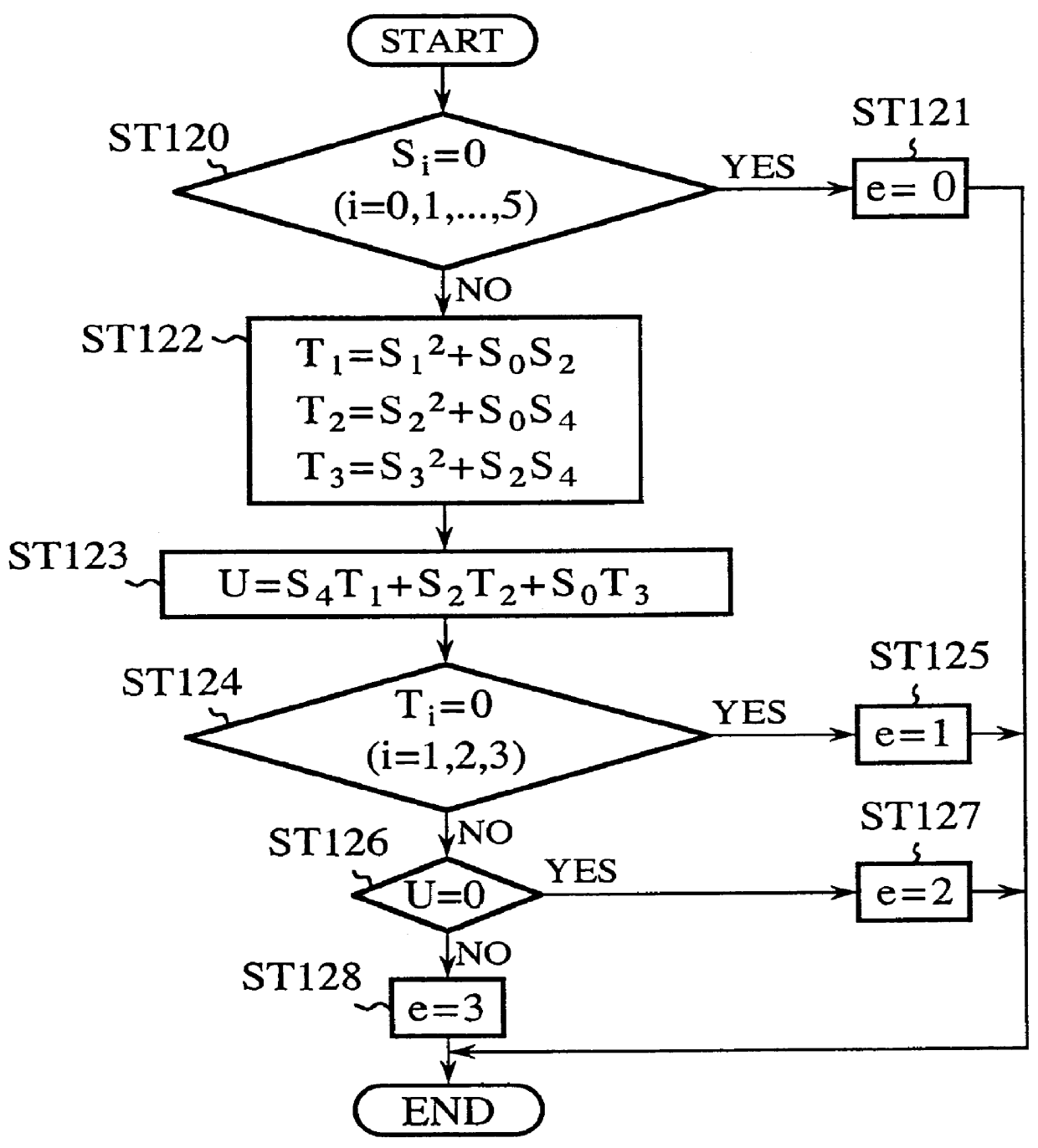
Error correcting decoding apparatus of extended Reed-Solomon code, and error correcting apparatus of singly or doubly extended Reed-Solomon codes
An error correcting decoding apparatus of an extended RS code capable of solving a problem of a conventional method in that Euclidean algorithm or Berlekamp-Massey algorithms must be performed twice in the worst case because of complicated algorithm, and this results in a delay of decoding. The present apparatus generates a syndrome from a received word, estimates the number of errors having occurred in the received word, computes error-locator polynomials and error-value polynomials while changing the initial values and ending condition of the Euclidean algorithm computation in accordance with the number of errors estimated, computes error locations and error values by performing Chien's search on these polynomials, and carries out the error correction on the basis of the error locations and error values. This makes it possible to achieve decoding by performing the Euclidean algorithm computation only once.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
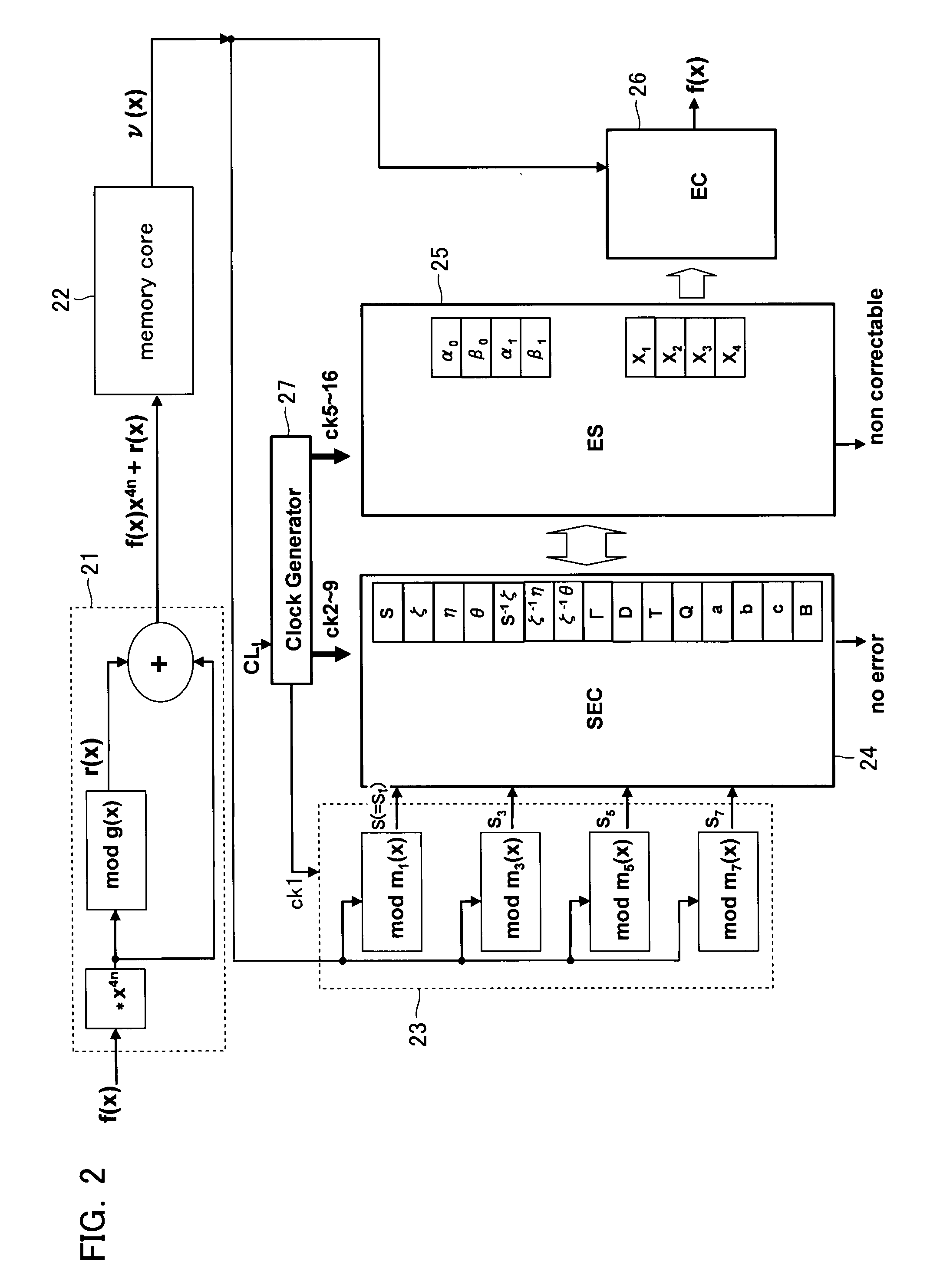
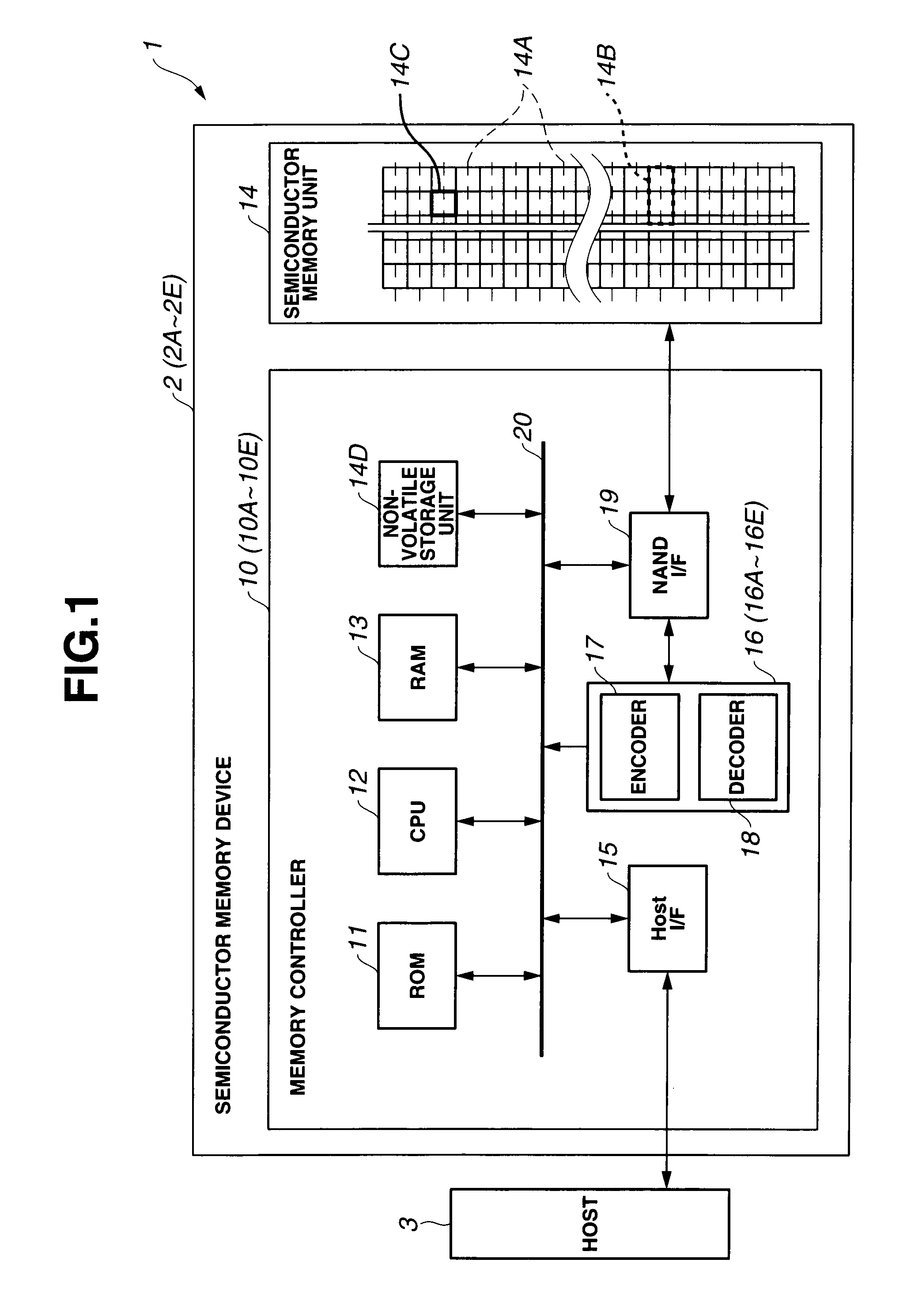
Data error detection and correction in non-volatile memory devices
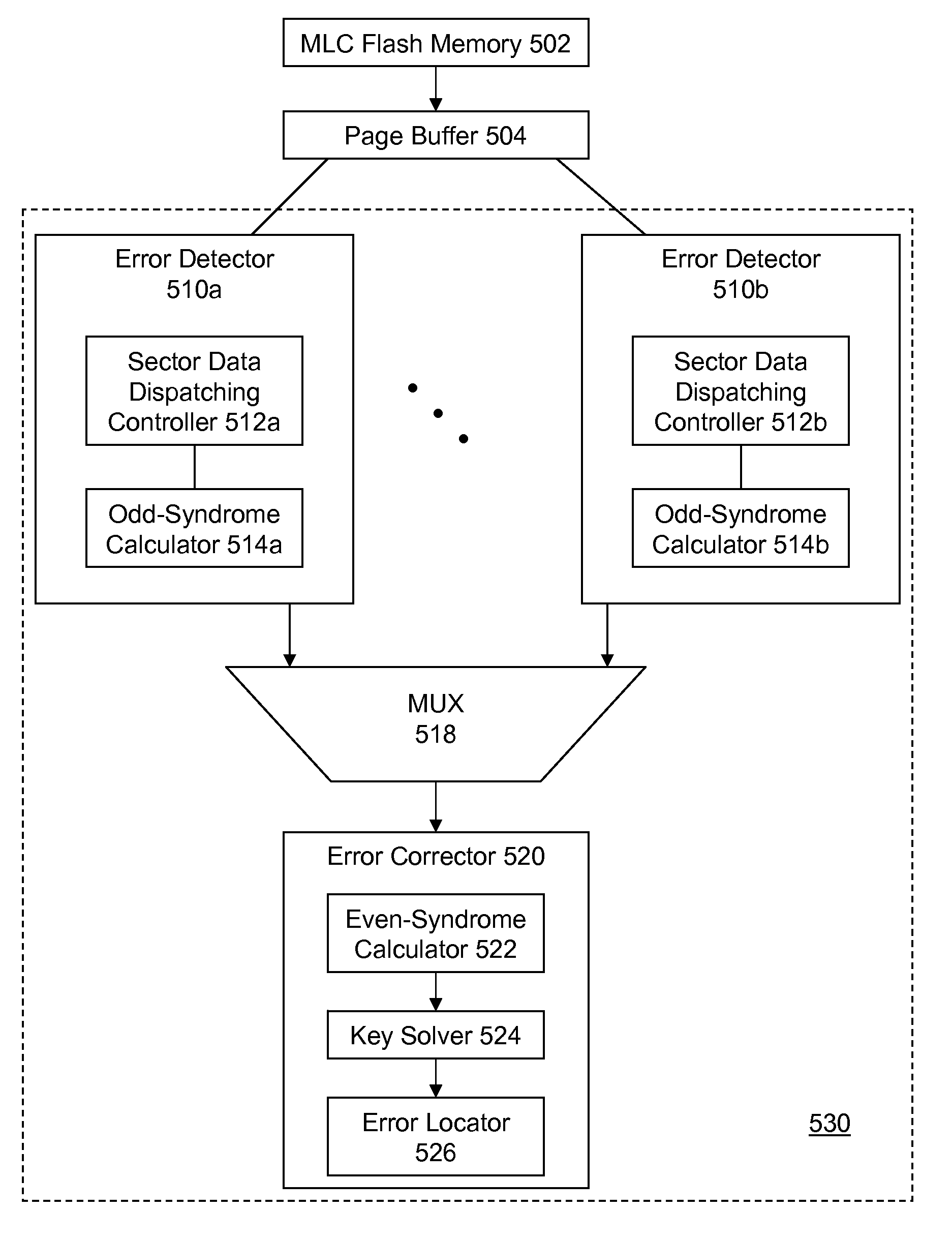
Data error detection and correction in non-volatile memory devices are disclosed. Data error detection and correction can be performed with software, hardware or a combination of both. Generally an error corrector is referred to as an ECC (error correction code). One of the most relevant codes using in non-volatile memory devices is based on BCH (Bose, Ray-Chaudhuri, Hocquenghem) code. In order to correct reasonable number (e.g., up to 8-bit (eight-bit)) of random errors in a chunk of data (e.g., a codeword of 4200-bit with 4096-bit information data), a BCH(4200,4096,8) is used in GF(213). ECC comprises encoder and decoder. The decoder further comprises a plurality of error detectors and one error corrector. The plurality of error decoders is configured for calculating odd terms of syndrome polynomial for multiple channels in parallel, while the error corrector is configured for sequentially calculating even terms of syndrome polynomial, key solver and error location.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
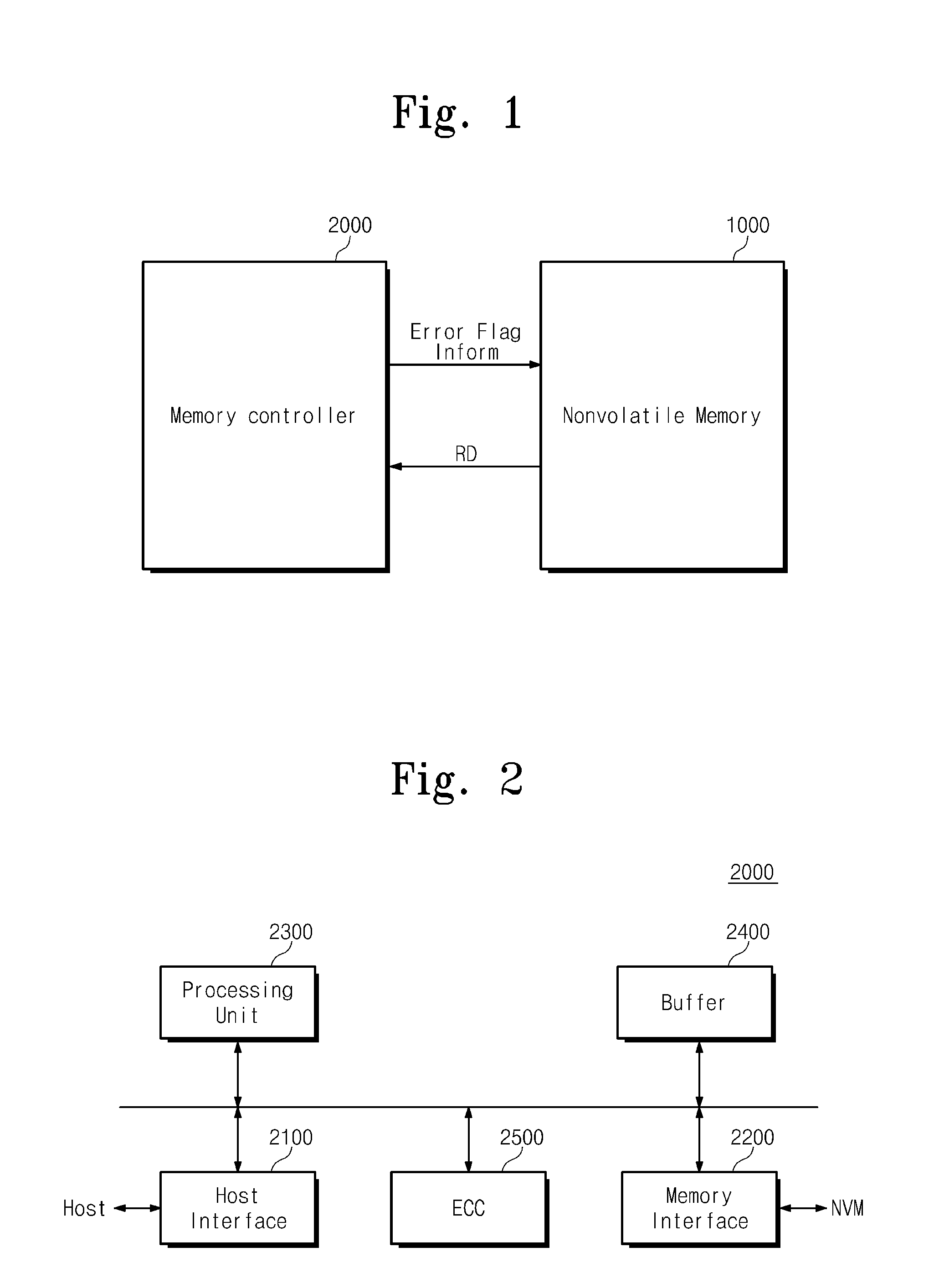
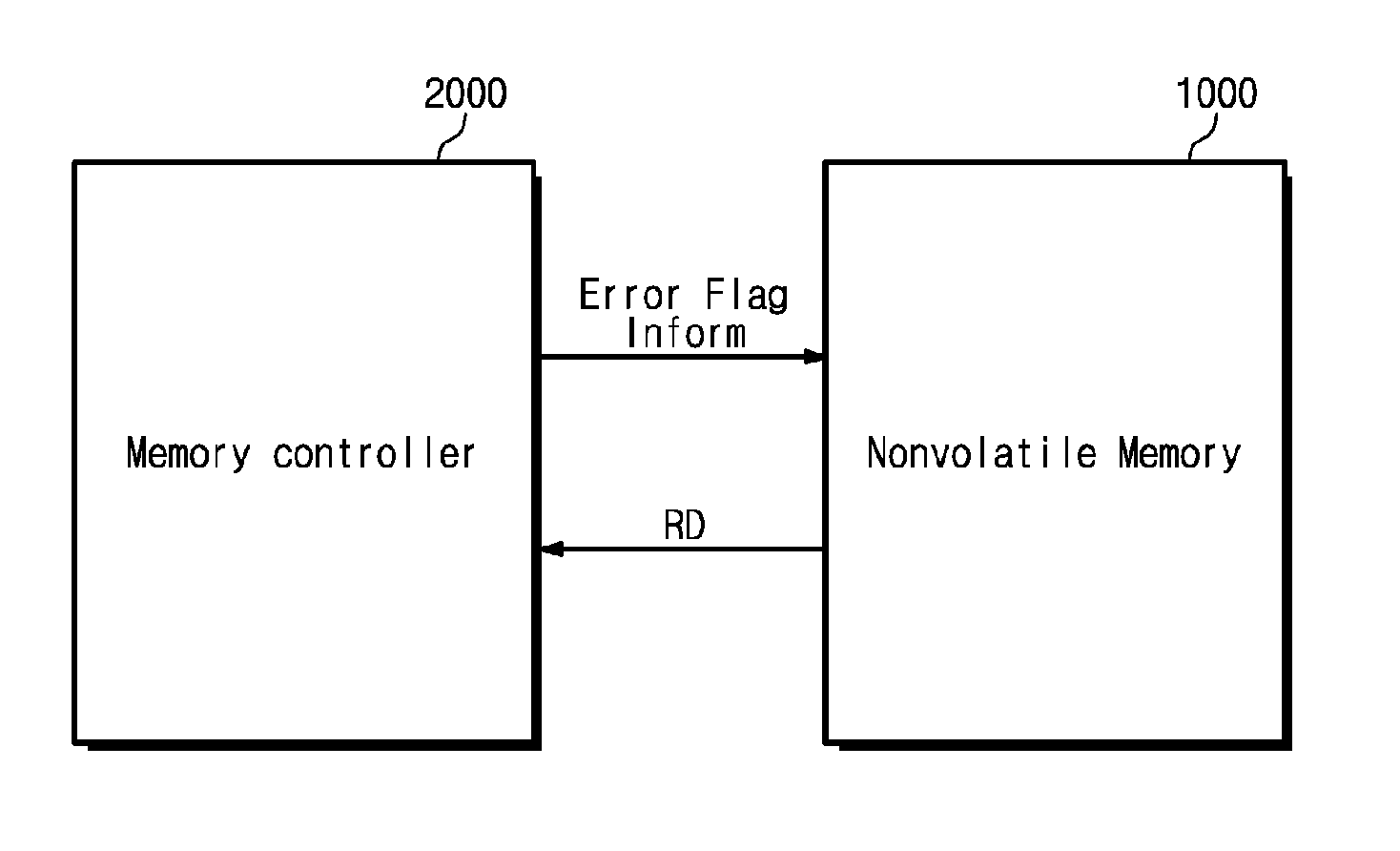
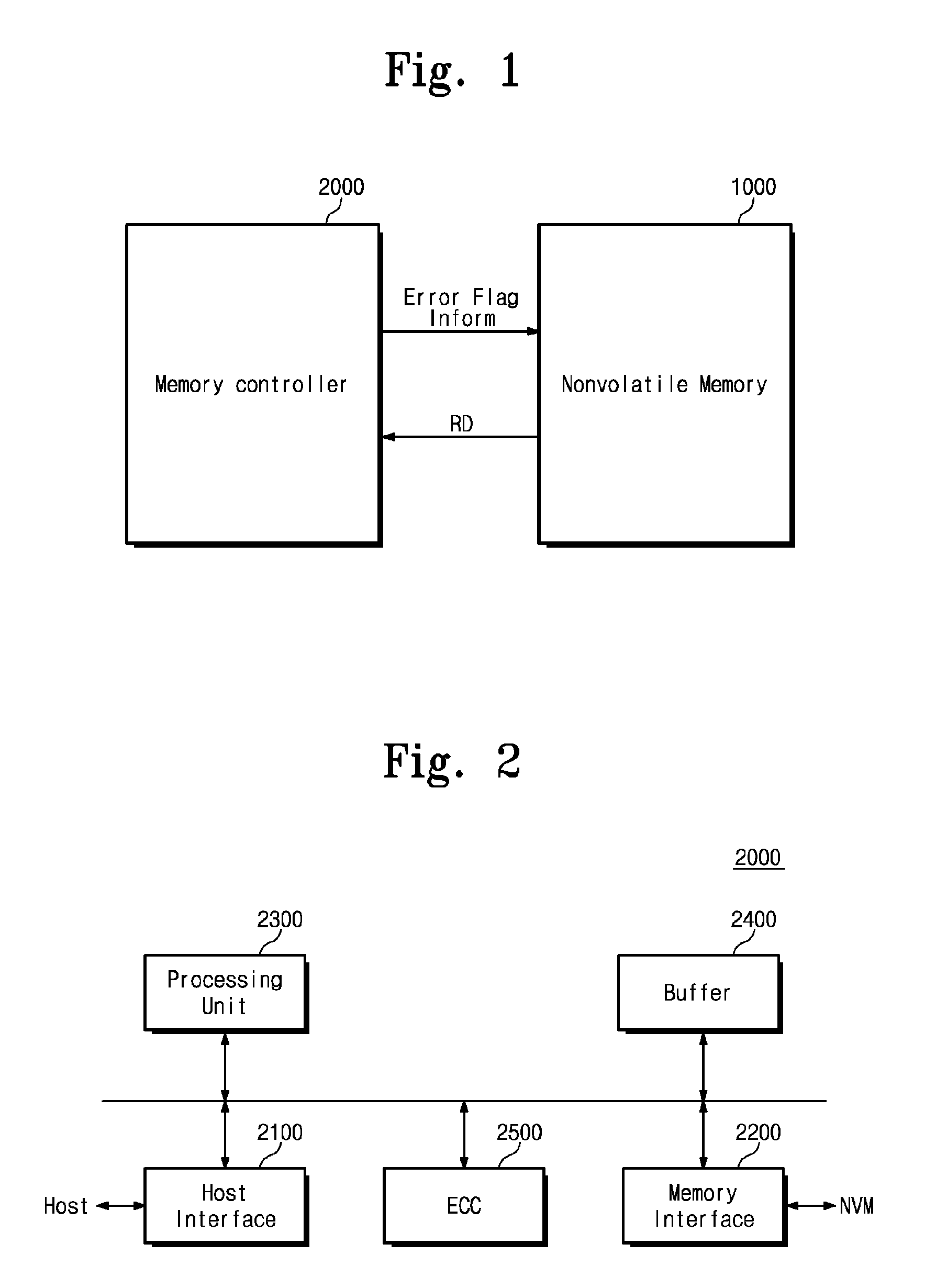
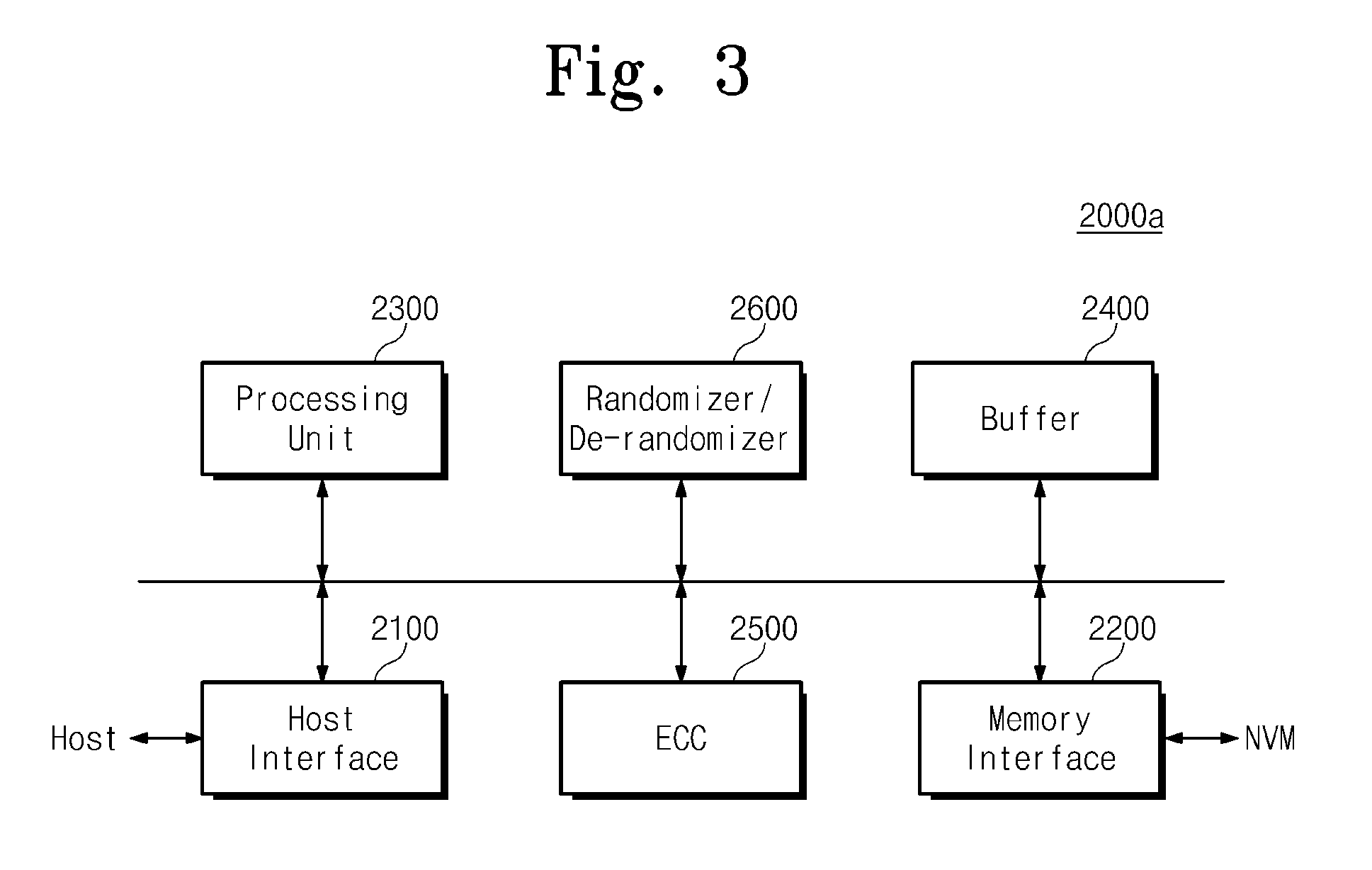
Memory system and operating method thereof
A memory system includes a nonvolatile memory device and a memory controller configured to control the nonvolatile memory device and configured to provide the nonvolatile memory device with error flag information including error location information of an error of data read from the nonvolatile memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
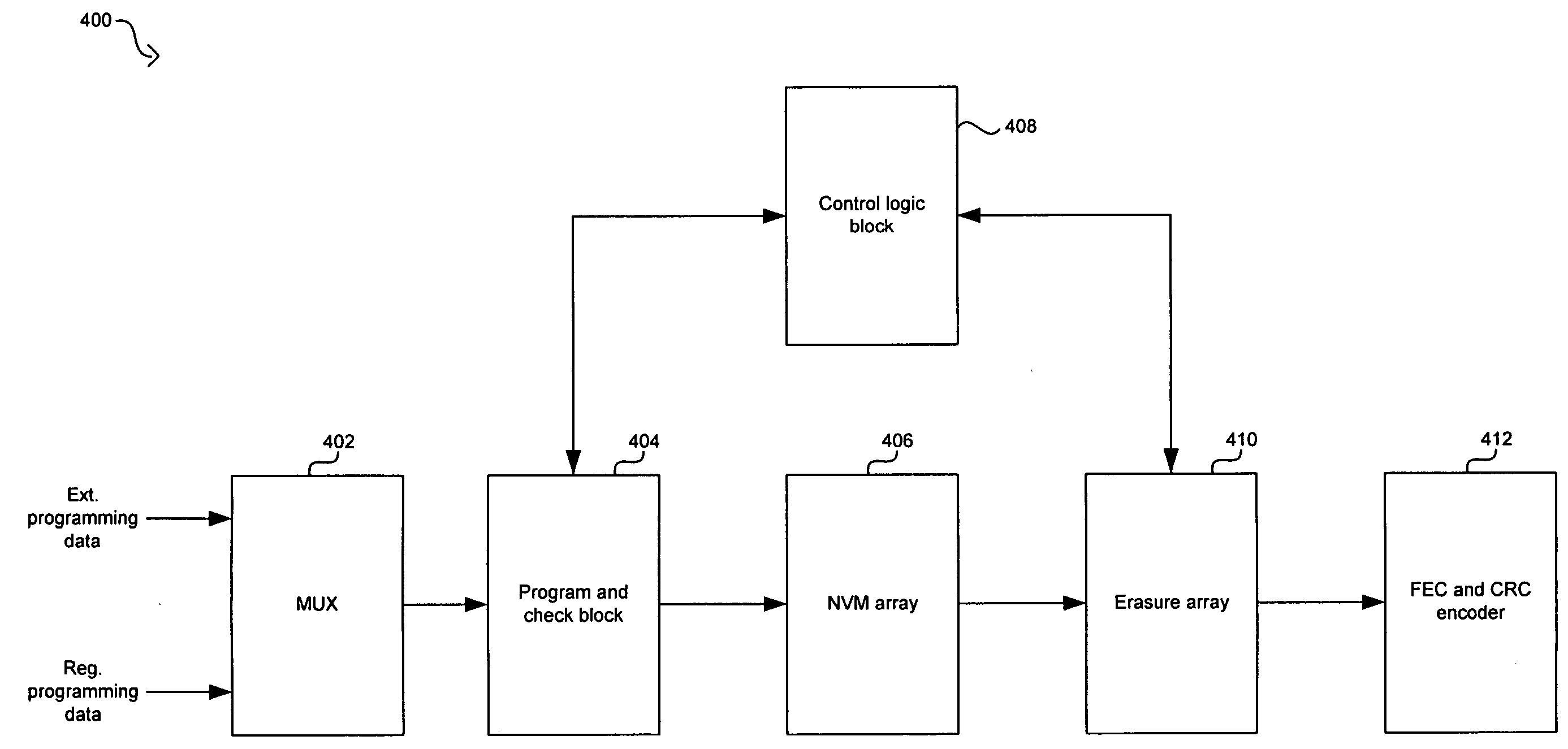
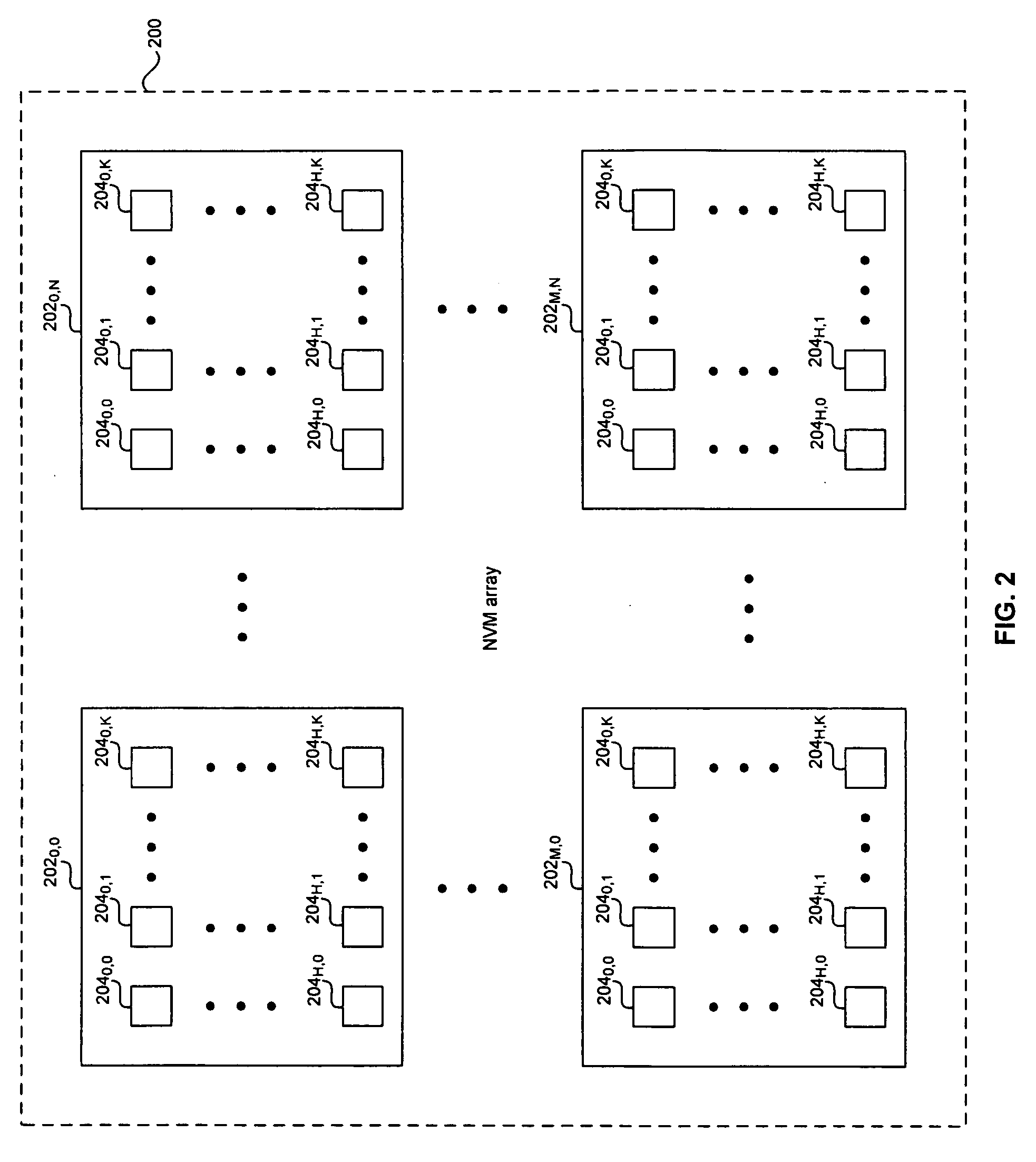
Method and system for a non-volatile memory with multiple bits error correction and detection for improving production yield
ActiveUS20070124647A1Improve production yieldError detection/correctionCode conversionProduction rateError location
A method and system for a non-volatile memory (NVM) with multiple bits error correction and detection for improving production yield are provided. Forward error correction (FEC) operations and cyclic redundancy check (CRC) operations may be utilized in an NVM array integrated in a chip to correct errors in memory elements and detect remaining errors respectively. When remaining errors are detected, the memory element may be substituted by redundant memory elements in the NVM array. An erasure operation in the FEC may be utilized to correct errors when the error location is known. The NVM array may be partitioned into classes that may each have specified FEC operations and a specified priority to substitute memory elements by redundant memory elements. The FEC and CRC operations may be utilized to protect secure information stored in the NVM array by disabling the chip when errors are detected while reading the secure information.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
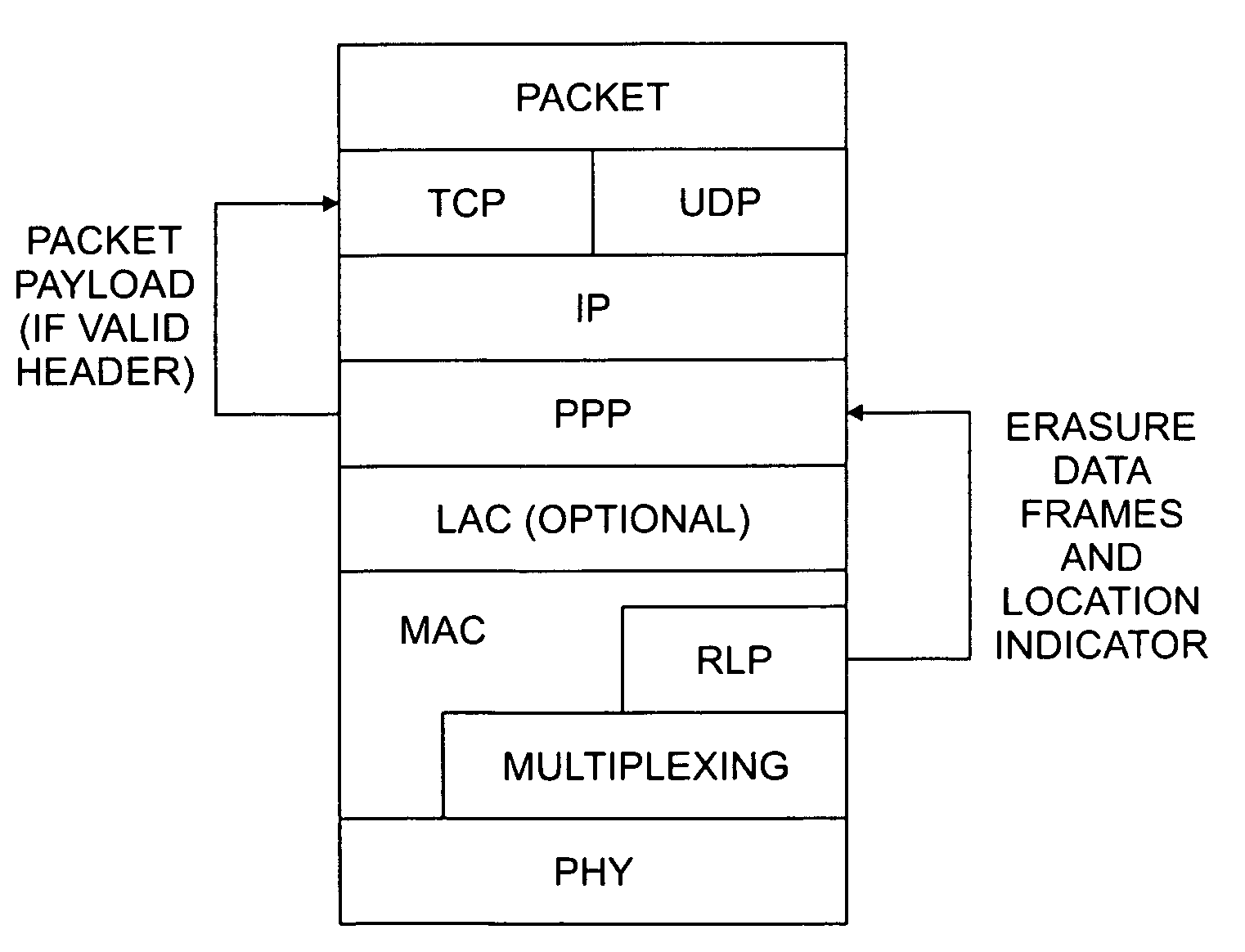
Radio link protocol (RLP)/point-to-point protocol (PPP) design that passes corrupted data and error location information among layers in a wireless data transmission protocol
InactiveUS7031257B1Reduces or avoids unnecessary packet discardingImprove performanceError preventionTransmission systemsPoint-to-Point ProtocolError location
A radio link protocol (RLP) / point-to-point protocol (PPP) design is disclosed for wireless multimedia packet networks that passes corrupted packet data and error location information among OSI layers. The RLP layer provides erasure data frames and optionally error location indicators to the PPP layer. When the PPP layer has access to the erasure data frames, the data frames can be padded with a predefined value, such as all zeroes “0” to prevent error propagation from one data frame (or octet) to the following data frames (or octets). When the PPP layer has access to the error location information, the PPP layer can detect if the PPP packet header is corrupted. When a valid header is detected, the PPP layer forwards the packet payload to the higher layers (TCP, UDP) whether or not the payload is properly received. Thus, the application has access to all the usable information, so the application can determine whether and how to utilize the information. The RLP / PPP design of the present invention allows packets with partially corrupted payloads to still be forwarded to the UDP layer and then to the application layer.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Semiconductor memory device provided with error correcting code circuitry
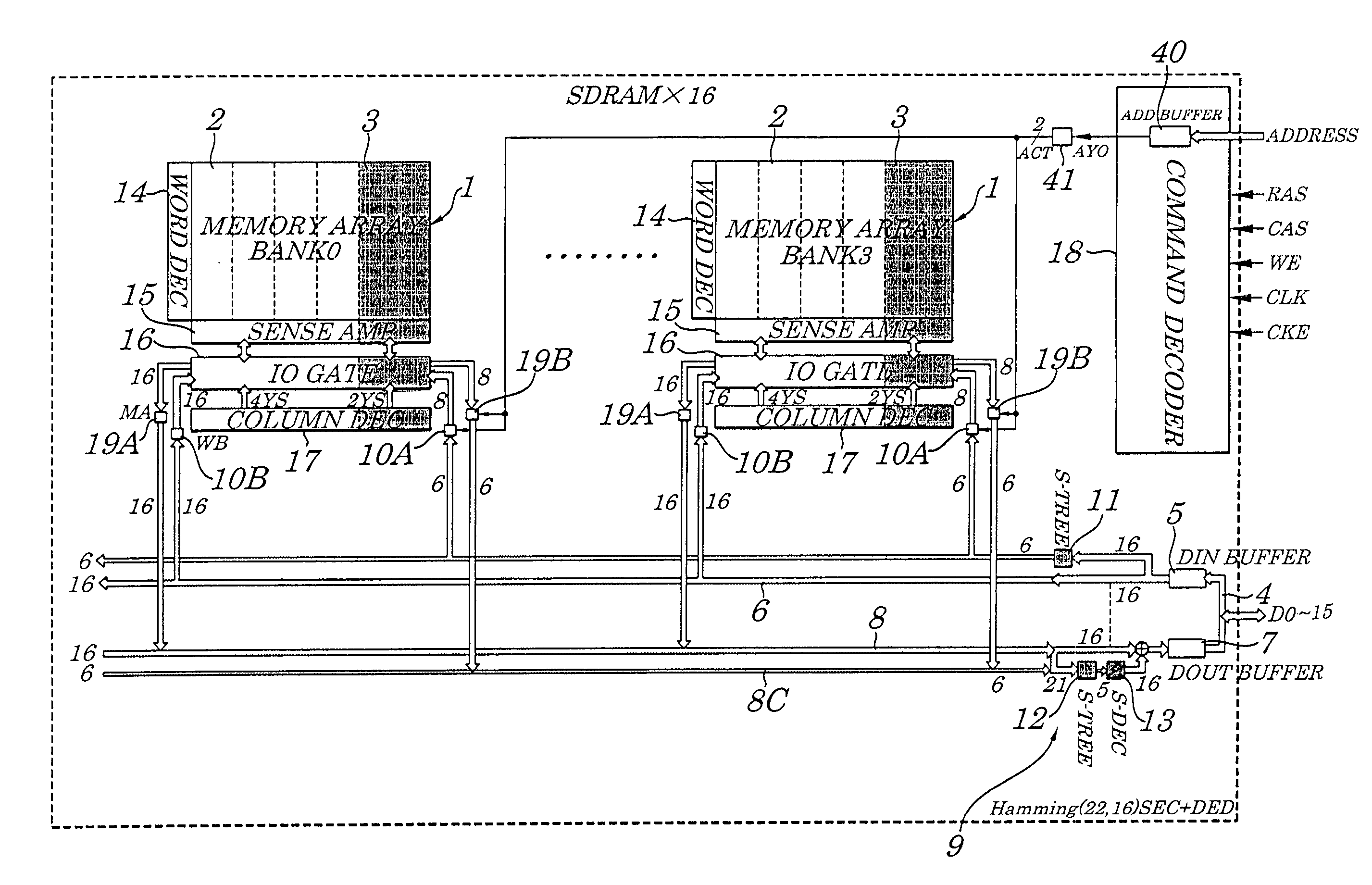
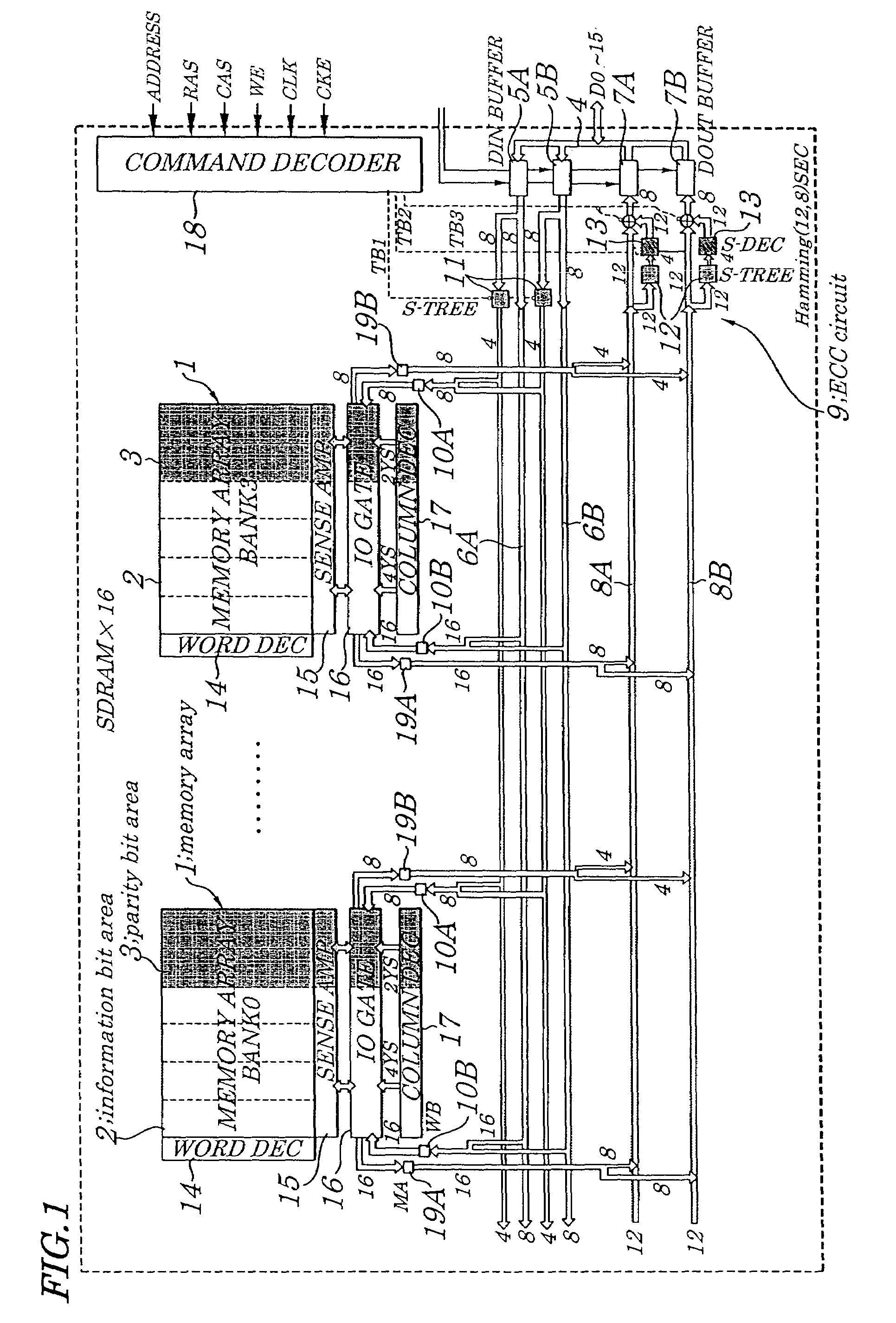
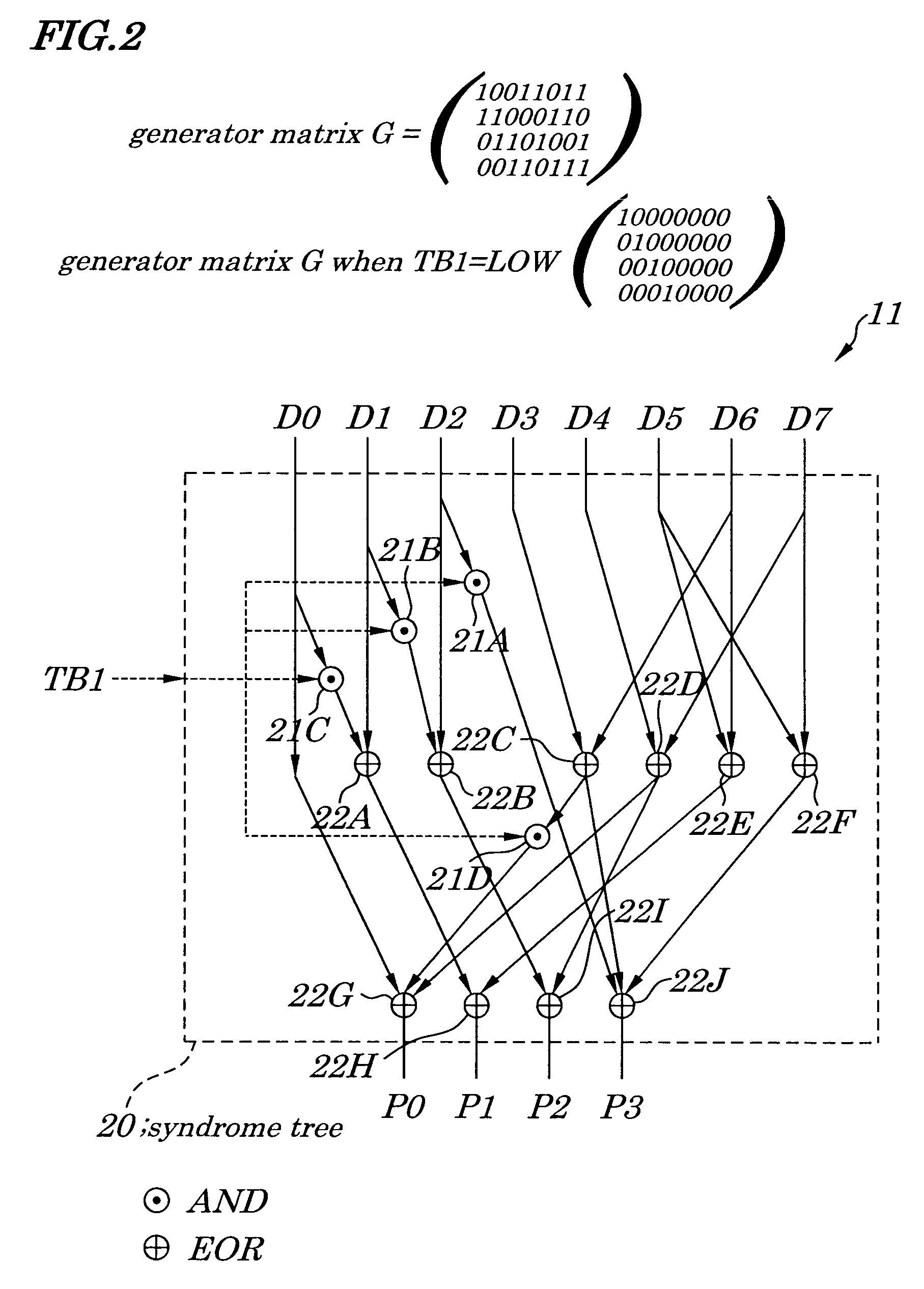
ActiveUS7225390B2Effective correctionReduce error rateCode conversionDigital storageHamming codeError location
A semiconductor synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) device capable of correcting bits having a low error rate in a Pause Refresh Tail distribution and of reducing a data holding current by lengthening a refresh period so that the refresh period exceeds a period for a Pause Refresh real power. The semiconductor memory device is made up of a 16-bit SDRAM having a Hamming Code and including an ECC (Error Correcting Code) circuit made up of an encoding circuit controlled by a first test signal to output a parity bit corresponding to an information bit, a decoding circuit controlled by second test signal to output an error location detecting signal indicating an error bit in codeword, and an error correcting circuit controlled by a third test signal to input an error location detecting signal and to output an error bit in a reverse manner.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
K nearest fuzzy clustering WLAN indoor locating method based on REE-P
InactiveCN101639527AEliminate the effects ofEfficient screeningPosition fixationWireless commuication servicesPattern recognitionError location
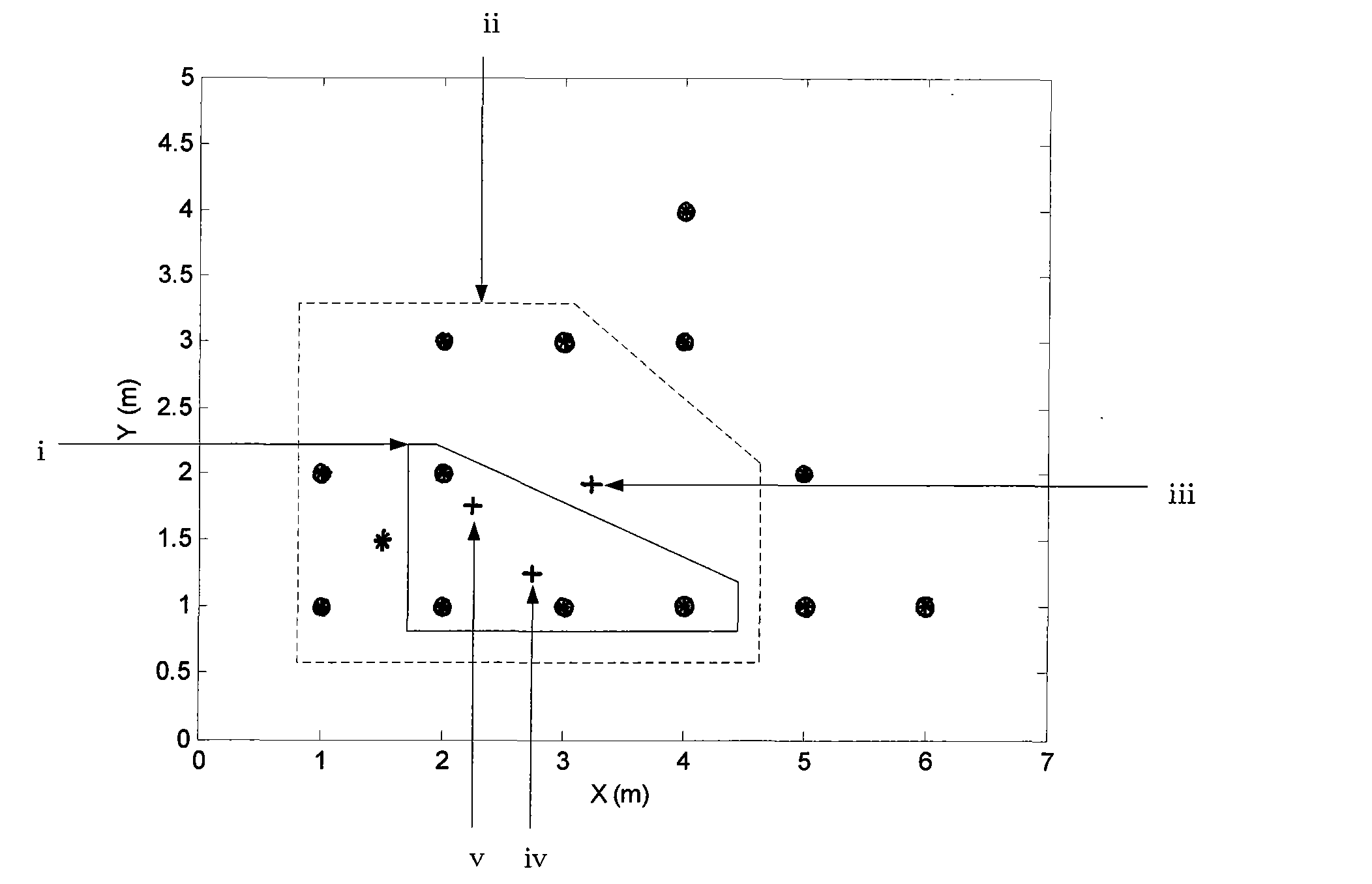
The invention provides a K nearest fuzzy clustering WLAN indoor locating method based on REE-P, relating to the indoor locating method in the field of identification. The method comprises the following steps of: 1. measuring and recording a RSS signal received by an user terminal at a point to be located; 2. ensuring K reference points which are most similar to the signal characteristic of the point to be located with a K nearest method; 3. classifying the RSS value of the selected reference points with a fuzzy clustering algorithm, computing the square of the difference between component in each clustering center vector and the RSS value from corresponding AP, accumulating the values in the clustering, and selecting one with the lowest sum; 4. reusing the fuzzy clustering algorithm to classify the positions of all the reference points and select the reference points which have the most same reference points as that selected from step 3; and 5. taking the sum of the reference points from step 3 and step 4, and taking the average coordinate of the reference points to be taken as the position of the point to be located. The method solves the problem of error location caused by the reference points of the K nearest method, and is used for identifying the position.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
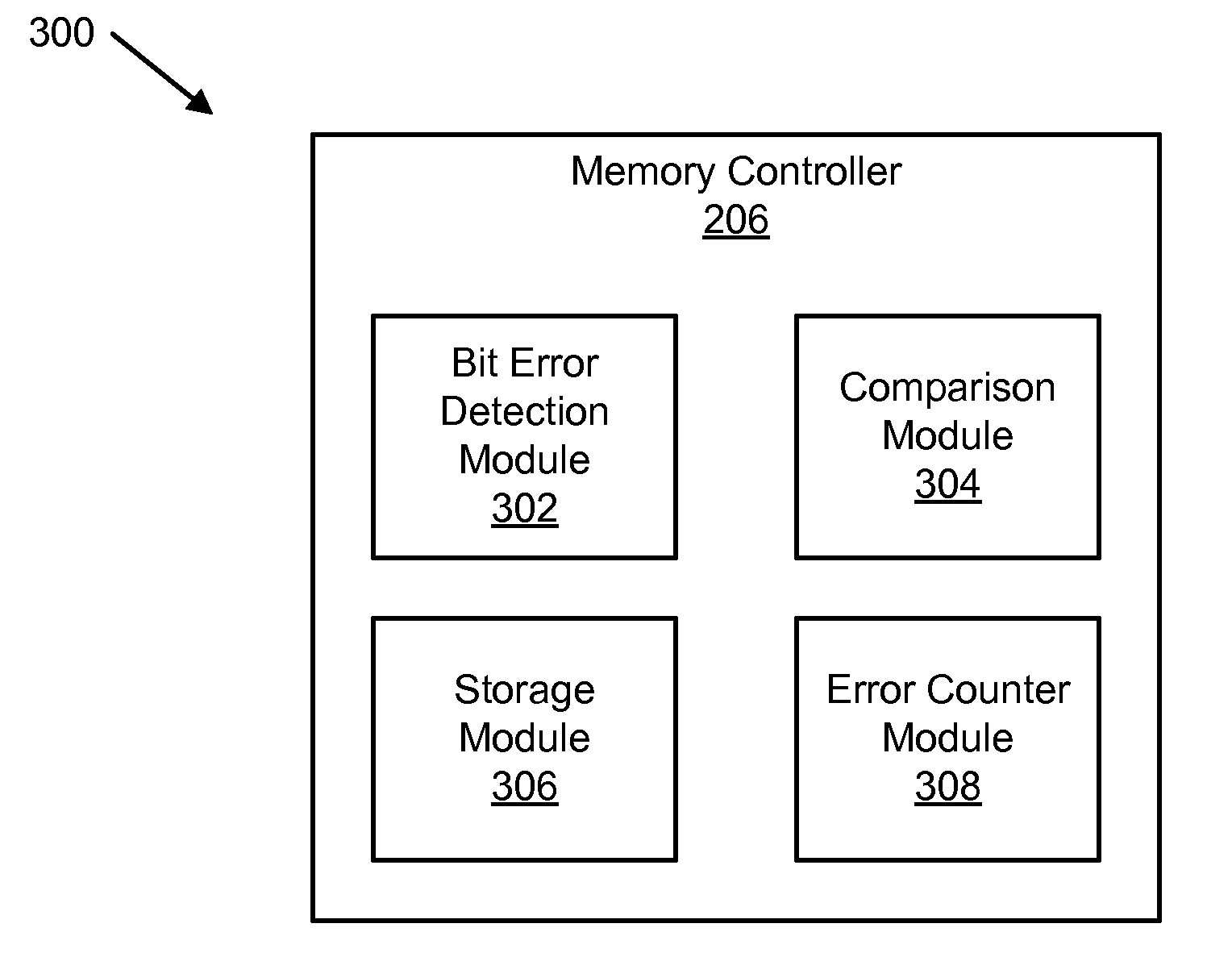
Apparatus and method for distinguishing temporary and permanent errors in memory modules
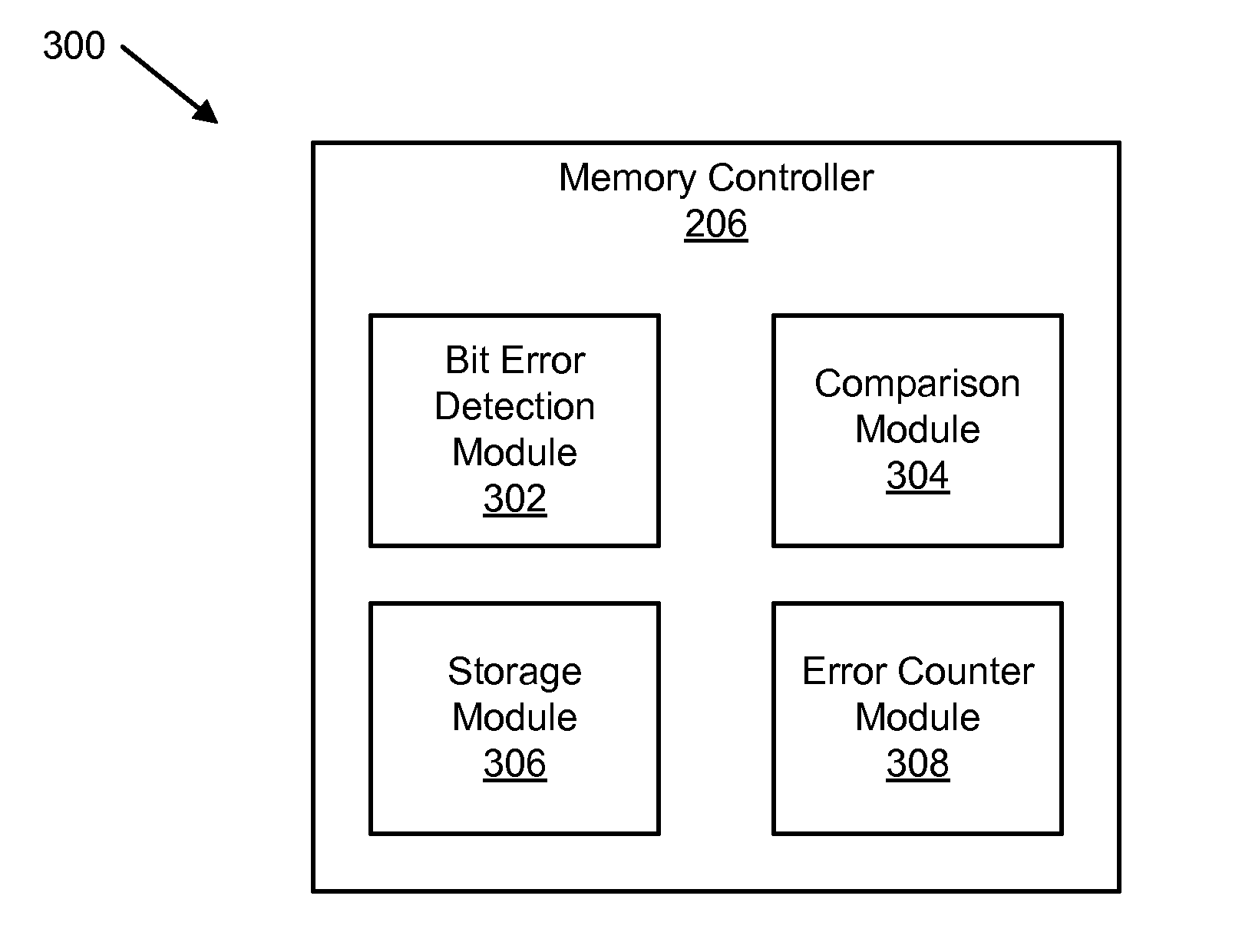
An apparatus and method are disclosed for distinguishing correctable bit errors in memory. A bit error detection module detects a correctable bit error in a memory in response to a READ operation. The correctable bit error is correctable using error-correcting code. The READ operation is generated during normal operation. A comparison module compares an error location indicator with a stored error location indicator. The error location indicator includes a memory location of the correctable bit error. The stored error location indicator corresponds to a previously stored error location indicator of a previous correctable bit error. A storage module stores the error location indicator if the comparison module determines that the error location indicator differs from a stored error location indicator. An error counter module increases an error counter corresponding to the error location indicator if the comparison module determines that the error location indicator matches a stored error location indicator.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus for system decoder and method for error correction of packet data
InactiveUS7131048B2Precise positioningReduce the burden onError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsFir systemComputer hardware
When a non-error-resilient application decoder receives a data stream containing syntax error due to transmission errors, such as packet losses in wireless communication, an application decoder cannot usually continue decoding the stream data anymore. According to the present invention, the data stream containing syntax error along with error correction data generated by error-detectable transmission system is inputted into an error correction part before inputted into the application decoder. The error correction part detects the error position in the data stream using the error detection data, corrects the syntax error in the stream data, and generates a stream data which is possible to be decoded by the application decoder. As a result, the data stream containing syntax error can continue decoding or be decoded in better quality by a non-error-resilient application decoder, without adding any error correcting function in the existing application decoder.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
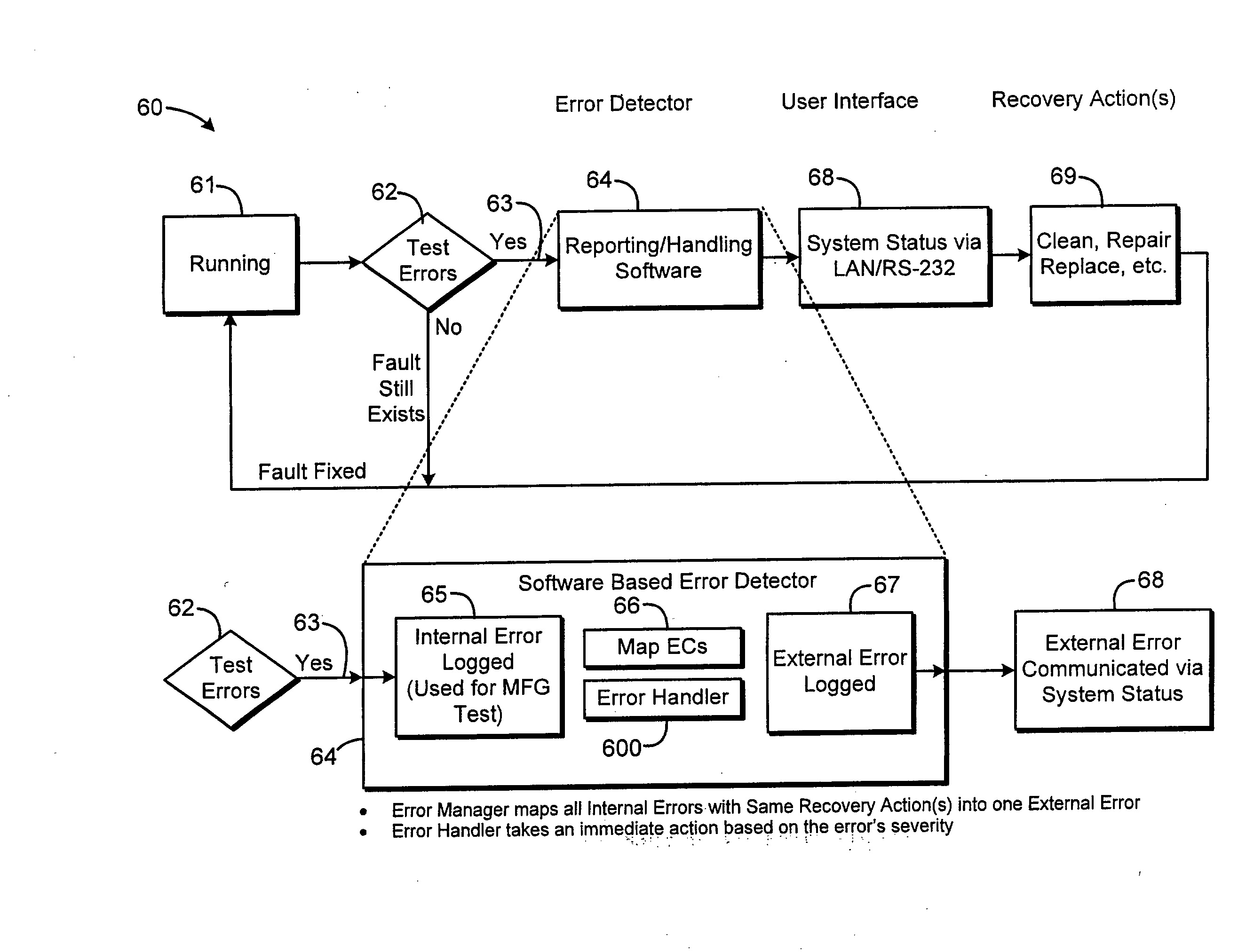
System and Method of Reporting Error Codes in an Electronically Controlled Device
A method of reporting errors in an electronically controlled device, comprises generating a first bit field representative of a severity of an internal error, generating a second bit field representative of a location of the internal error; and generating a third bit field representative of a cause of the internal error. The method also comprises structuring an internal error code, wherein the internal error code includes the first, second, and third bit fields.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Apparatus and method for distinguishing single bit errors in memory modules
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for distinguishing correctable bit errors in memory. A bit error detection module detects a correctable bit error in memory. The correctable bit error is correctable using error-correcting code (“ECC”). A comparison module compares an error location indicator with a stored error location indicator. The error location indicator is a location of the correctable bit error. The stored error location indicator includes to at least one previously stored error location indicator of a previously detected correctable bit error. A storage module stores the error location indicator in response to the comparison module determining that the error location indicator differs from a stored error location indicator. A bit error counter module increases a random bit error counter if the comparison module determines that the error location indicator differs from a stored error location indicator and does not increase the random bit error counter otherwise.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Memory controller and operating method of memory controller
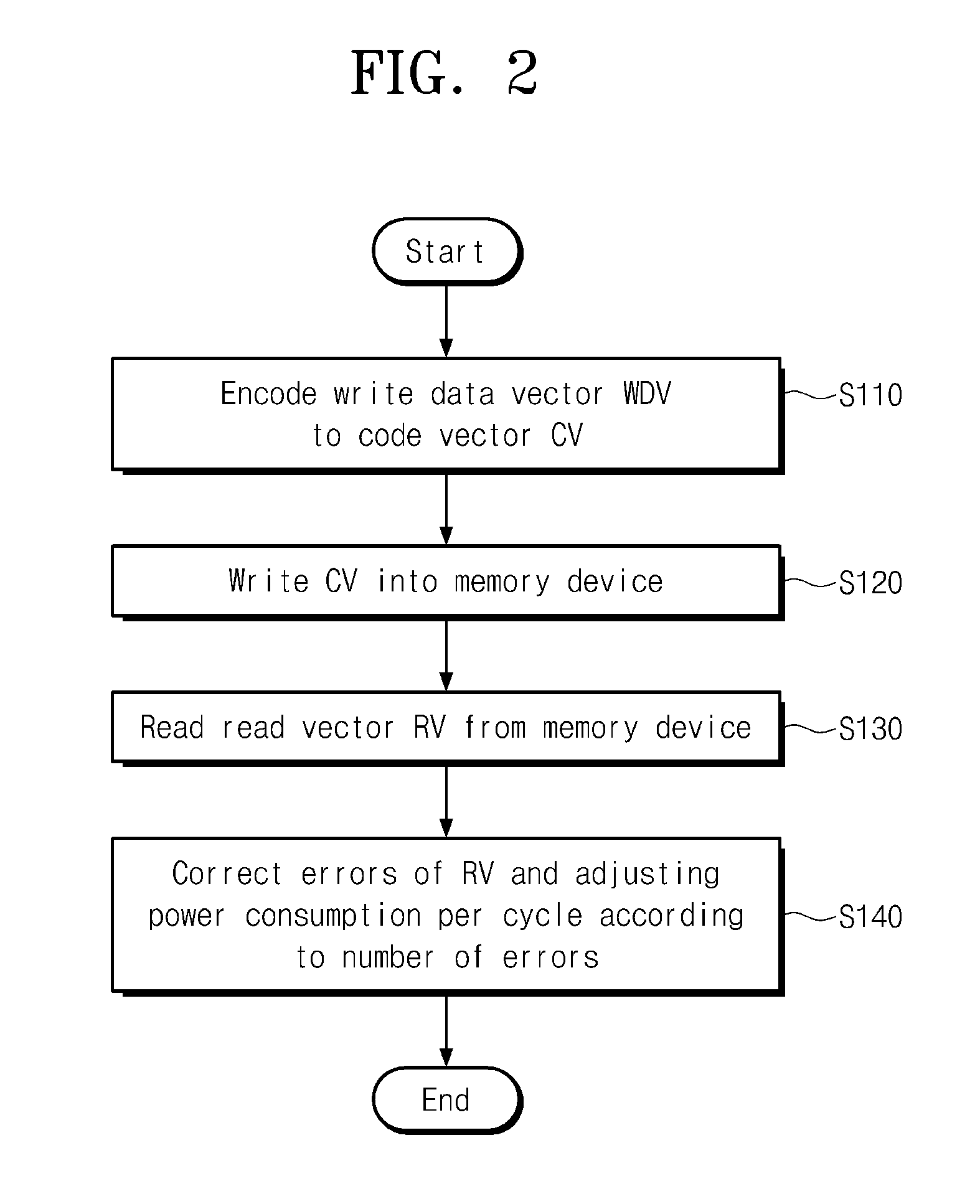
ActiveUS20120290901A1Reduce consumptionEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsError locationControl memory
A controller to control a memory system including a memory device. The controlling the memory system may include calculating an error location polynomial in a received read vector with a key equation solving unit of the memory system to read data from the memory device, estimating the number of errors in the received read vector with a control unit of the memory system according to at least one of the calculated error location polynomial and information on the error location polynomial, searching error locations of the received read vector according to the calculated error location polynomial with a chien search unit of the memory system with the control unit. A cycle-per power consumption of the chien search unit may be adjusted with the control unit. A maximum correction time may be adjusted according to the number of errors of the read vector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Data encryption and decryption method using a public key
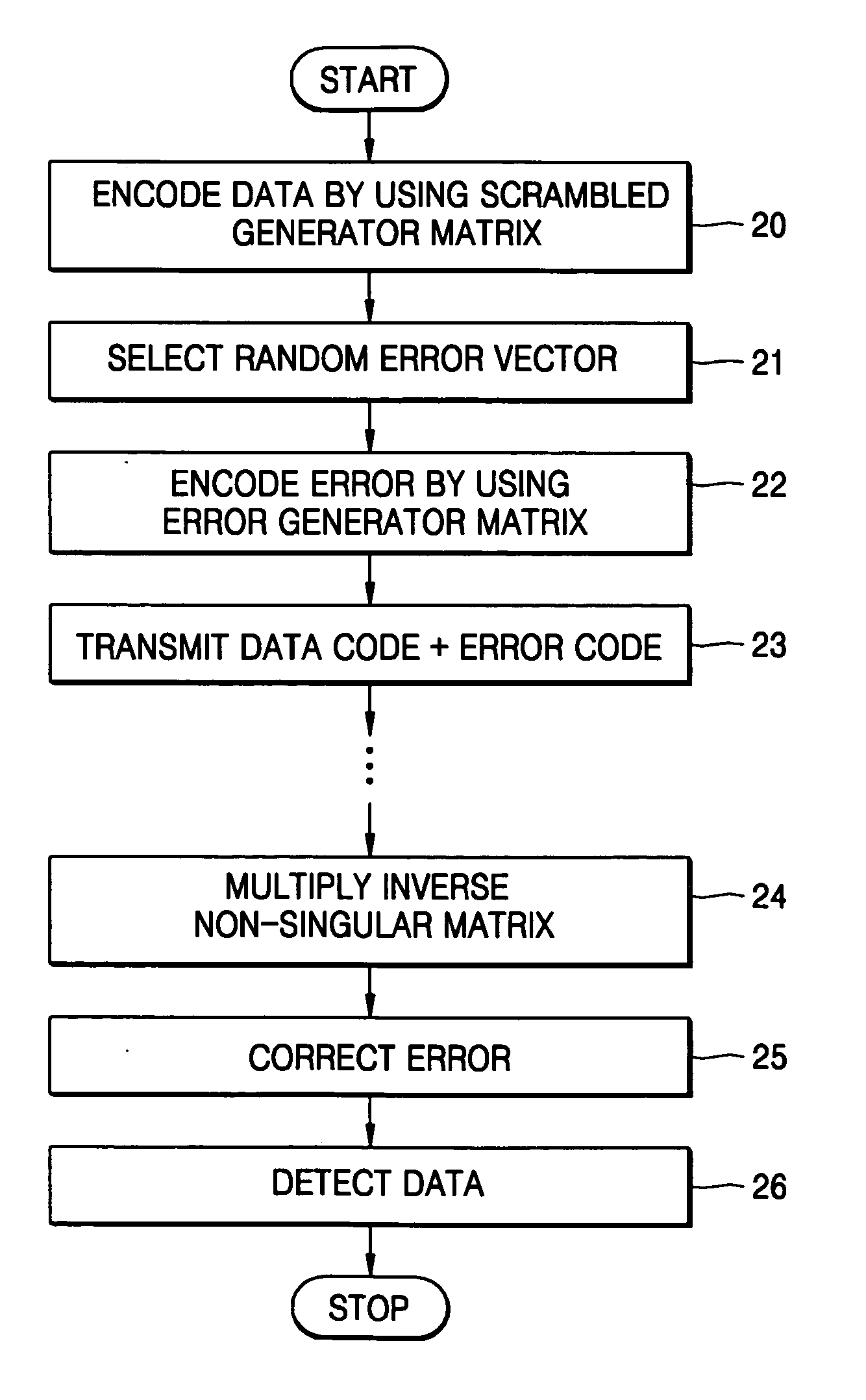
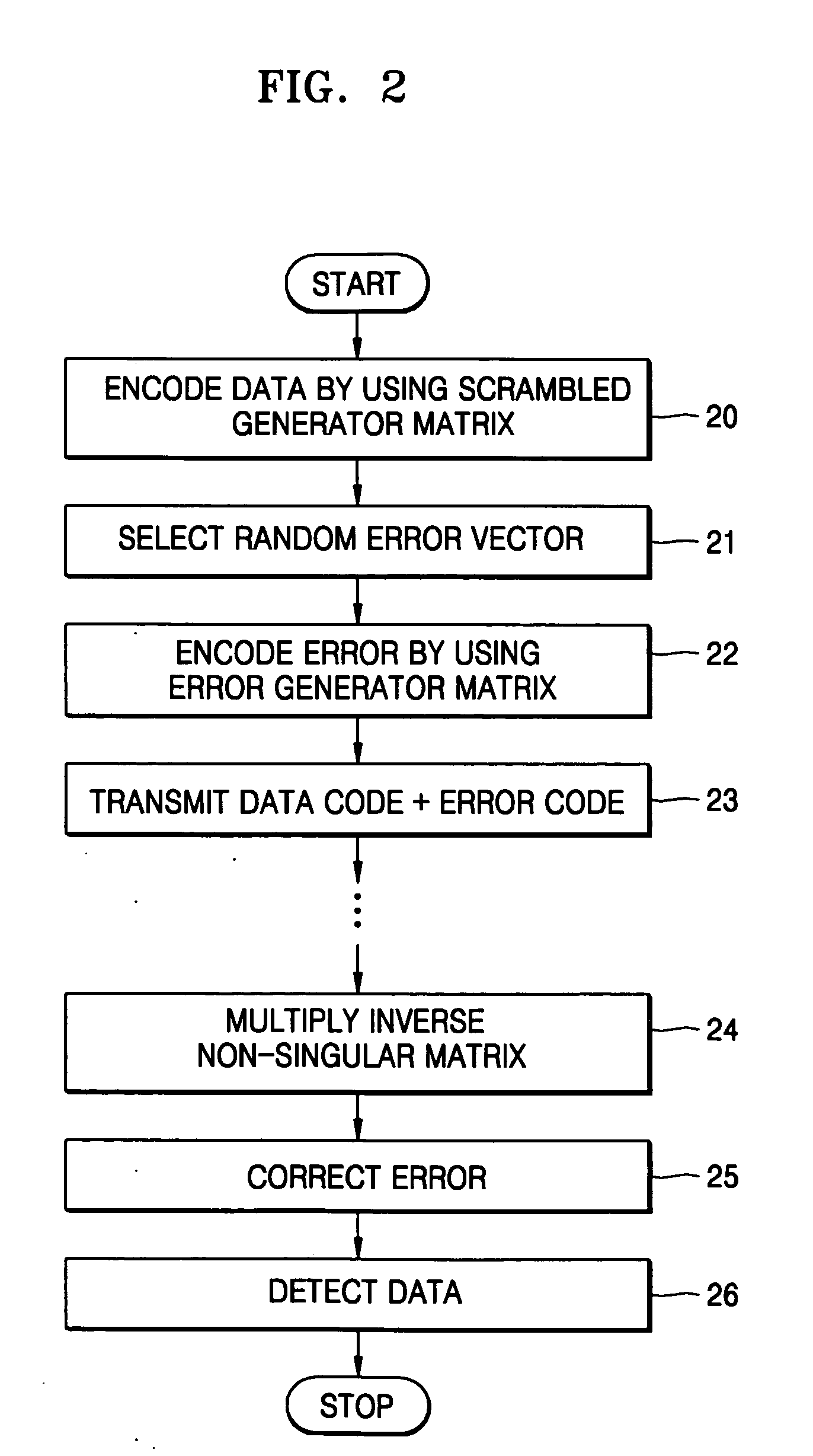
InactiveUS20050117745A1Small sizePublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationComputer hardwareCiphertext
A data encryption method using a public key includes encoding data into a first code using a first public key, selecting a predetermined error vector, encoding the selected error vector into a second code using a second public key, and generating a ciphertext by adding the first and second codes. A corresponding decryption method includes performing first decoding of the ciphertext using a first set of a plurality of secret keys, determining locations of errors in the result of the first decoding using a second set of the plurality of secret keys and declaring erasures to the locations, performing second decoding according to a predetermined decoding algorithm and correcting a predetermined number of errors and the declared erasures, and detecting data from a result of correcting the errors and erasures.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low complexity chien search in chase-type decoding of reed-solomon codes
Data is processed by obtaining a length of an error locator polynomial. It is determined whether the length of the error locator polynomial is greater than a threshold. In the event the length of the error locator polynomial is greater than the threshold, performance of a Chien search on the error locator polynomial is skipped. In the event the length of the error locator polynomial is less than or equal to than the threshold, the Chien search is performed on the error locator polynomial to determine one or more roots of the error locator polynomial, where the roots correspond to one or more error locations.
Owner:SK HYNIX MEMORY SOLUTIONS
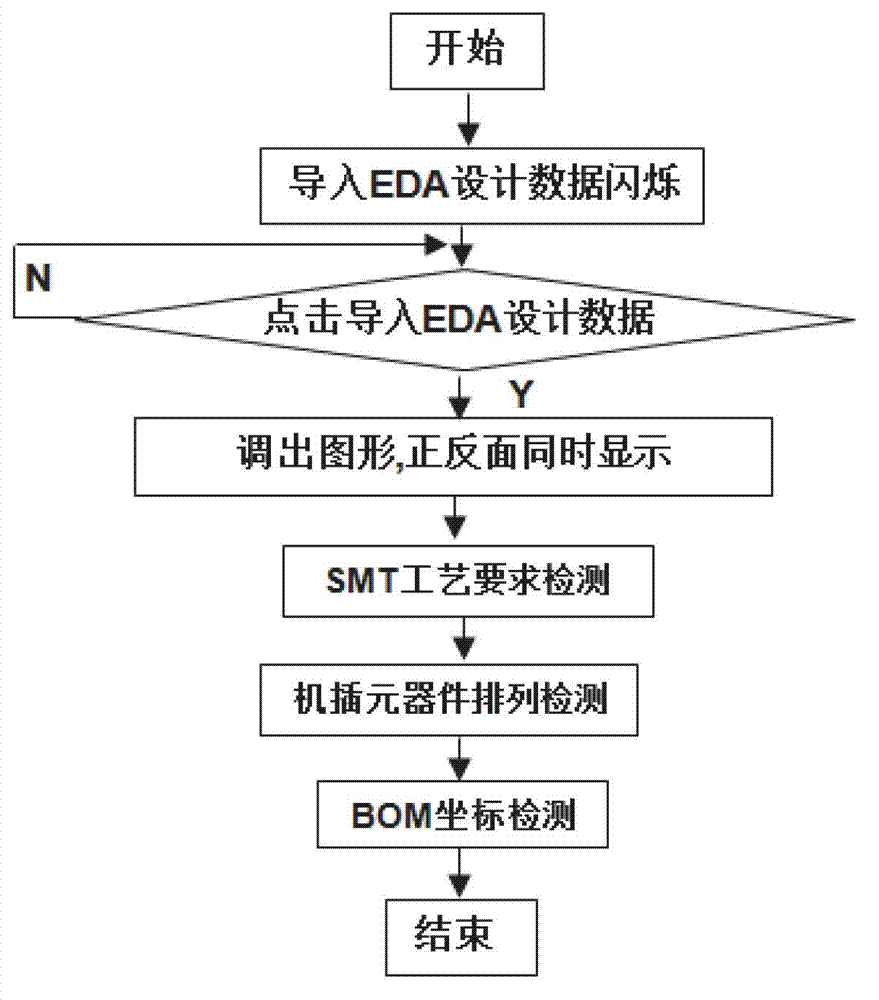
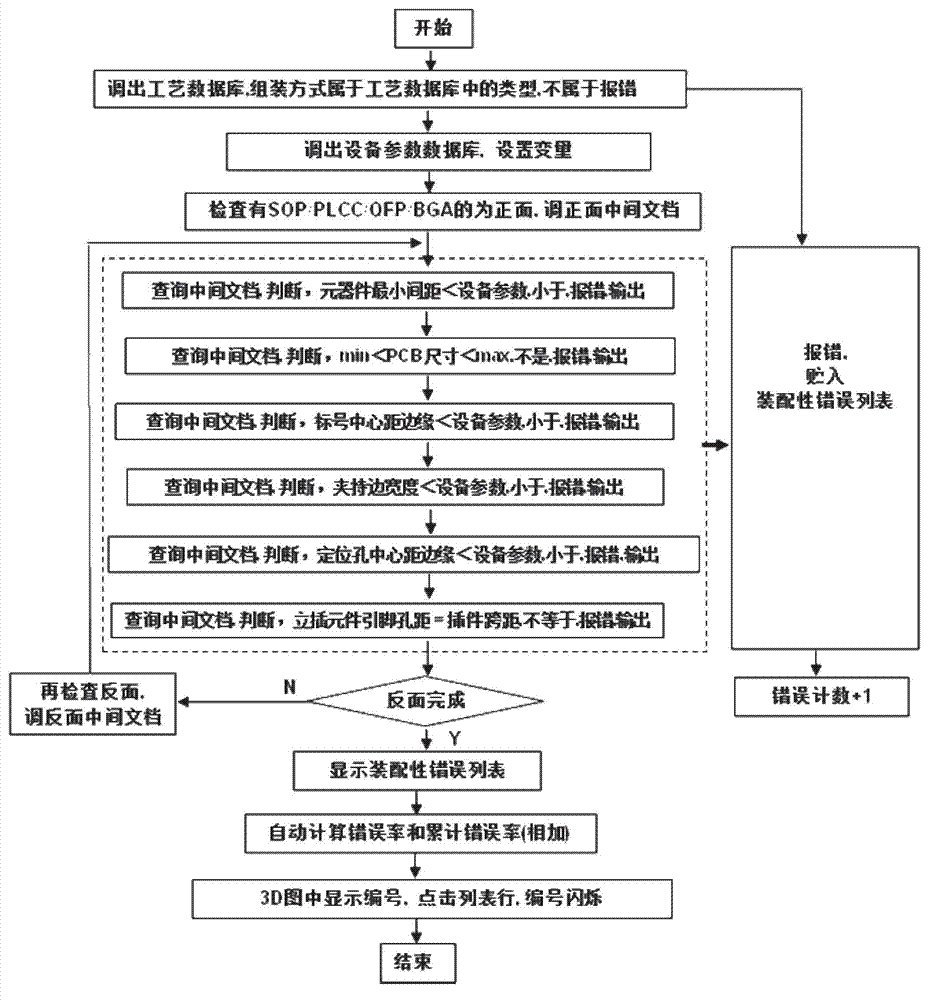
Visualization detection method of electronic product electronic design automation (EAD) design manufacturability
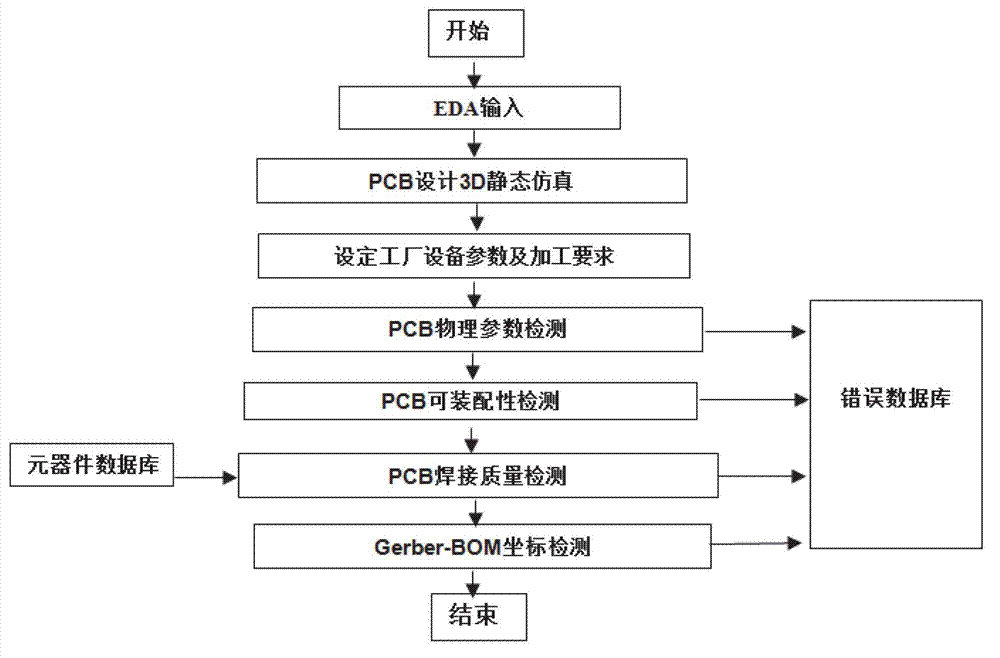
ActiveCN102930114AImprove efficiencyQuality improvementSpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingGraphics
The invention discloses a visualization detection method of electronic product electronic design automation (EDA) design manufacturability. Printed circuit board (PCB) three dimensional (3D) simulation of an EDA design document is conducted, PCBphysical parameter detection, PCB assembling ability, PCB welding quality detection and Gerber bill of material (BOM) coordinate detection are conducted in sequence, and specific error positions and types of former four steps of detection are displayed in visualization mode on a PCB 3D figure. On the basic of complete actual production experiences, the visualization detection method and a system of the EAD design manufacturability are developed according to international standard of information processing center (IPC), the PCB physical parameter detection, the PCB assembling ability, the PCB welding quality detection and the gerber BOM coordinate detection which are all designed by EDA are integrated, the various actual problems which are the contradictions of manufacture and design of PCB and are faced by enterprises are resolved, and efficiency and quality of electronic manufacture in particular to an original equipment manufacturer (OEM) are improved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU AUTOSMT INFORMATION TECH
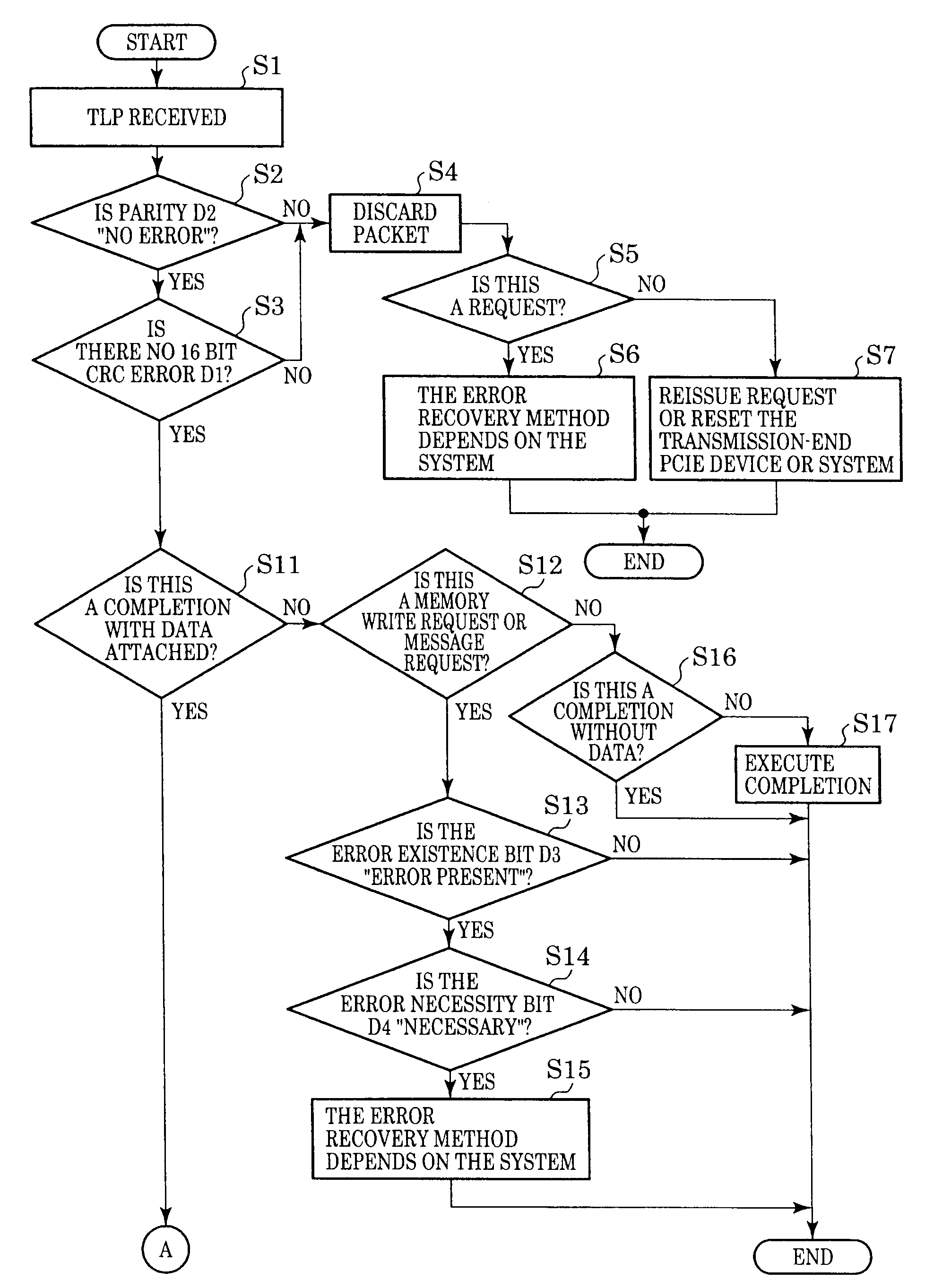
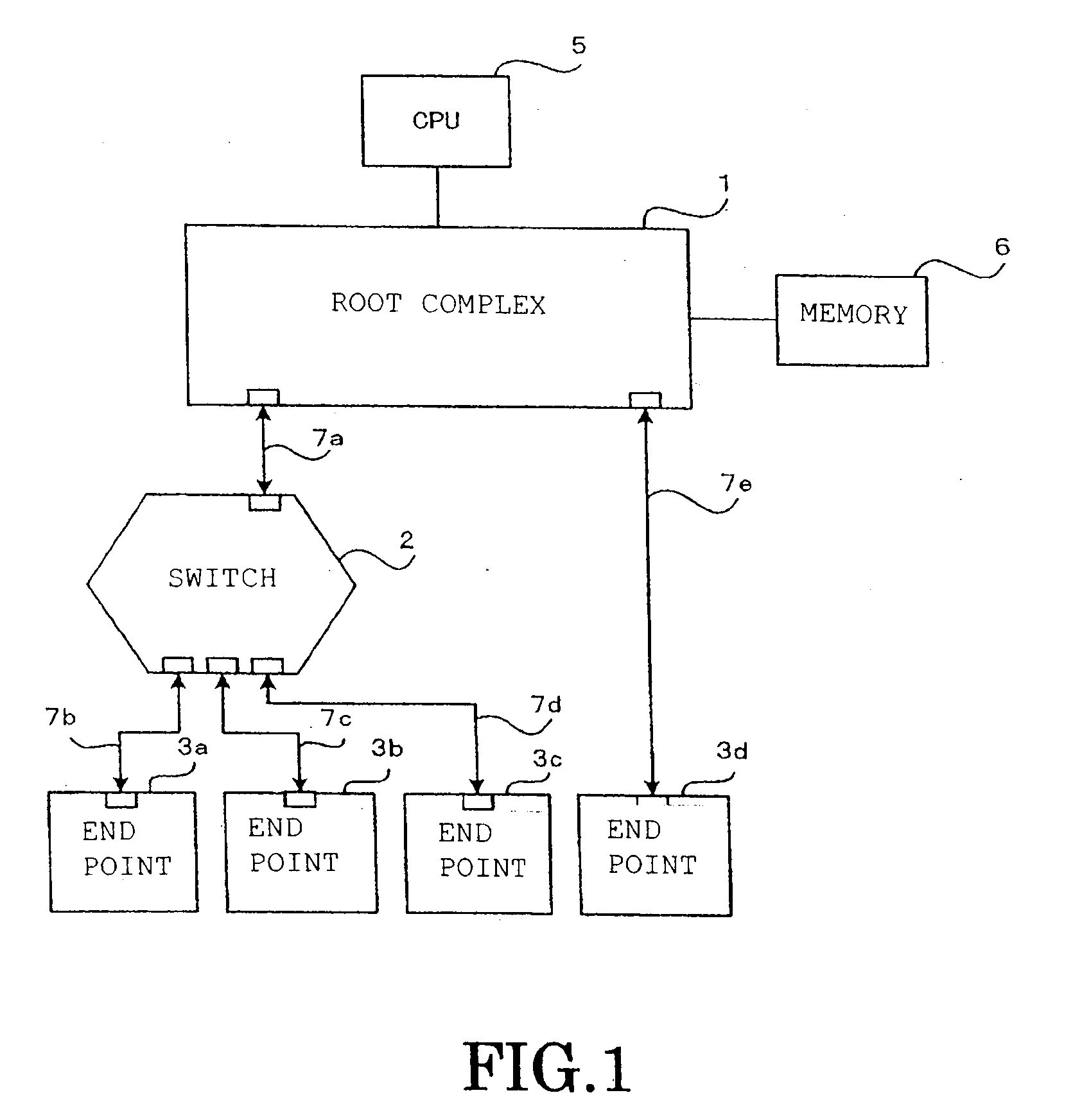
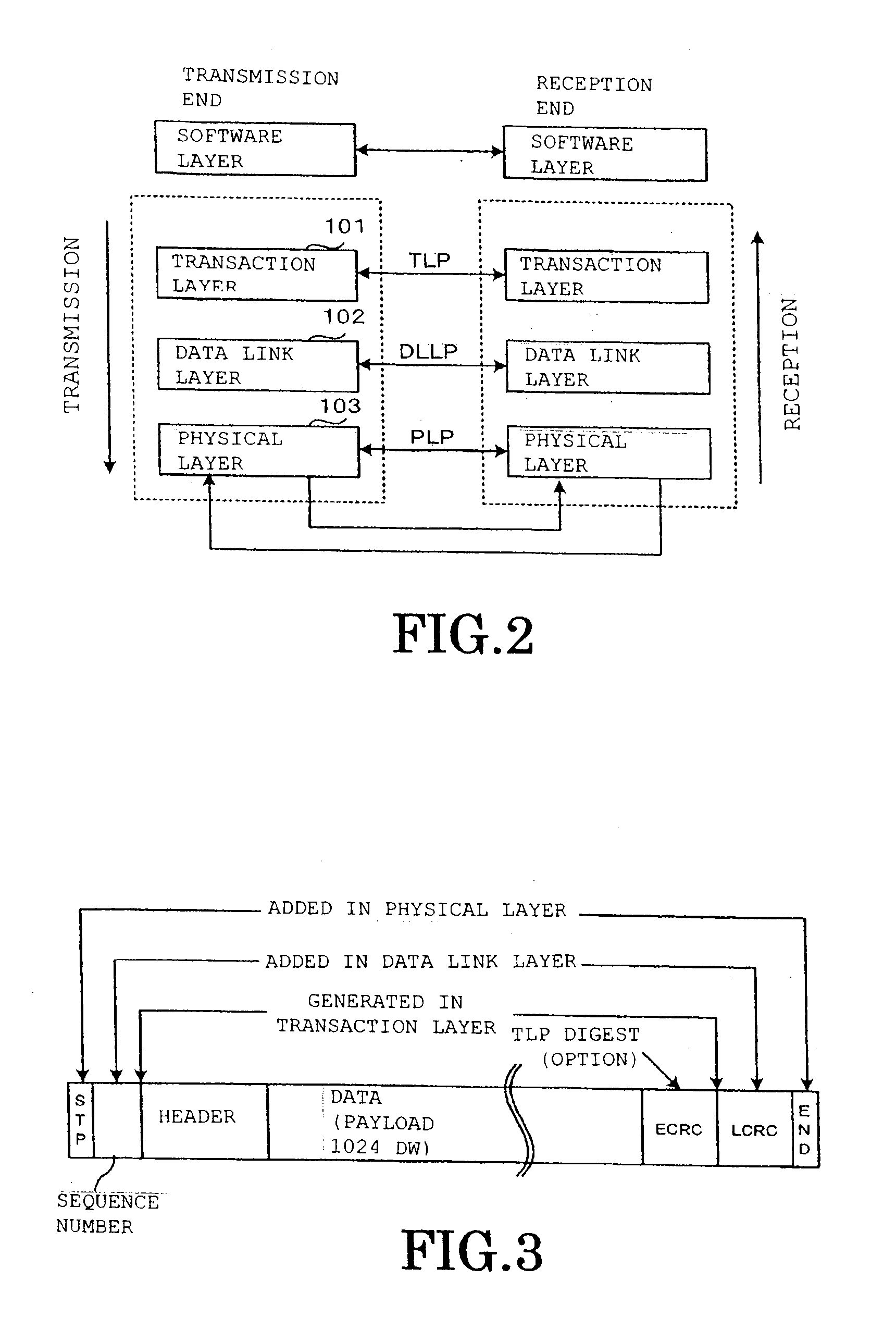
Pci.express communication system and communication method thereof
InactiveUS20100251055A1Reduce failure recovery timeImprove fault toleranceError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCommunications systemRoot complex
When a transaction layer circuit detects an error, error information in respect of transmission data is set in a TLP digest. The method includes: a step in which, at an endpoint (3a) that receives a memory read request transmitted by the root complex 1, if an error is detected during transmission of first data corresponding to the requested TLP, error information is set in the TLP digest and a completion with data attached is returned; a step in which the root complex (1) returns a memory read request based on the error information to the endpoint; a step in which the endpoint returns requested second data; and a step in which the root complex terminates the response after overwriting the error location of the first data that was held, with the second data.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Memory system and operating method thereof
A memory system includes a nonvolatile memory device and a memory controller configured to control the nonvolatile memory device and configured to provide the nonvolatile memory device with error flag information including error location information of an error of data read from the nonvolatile memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
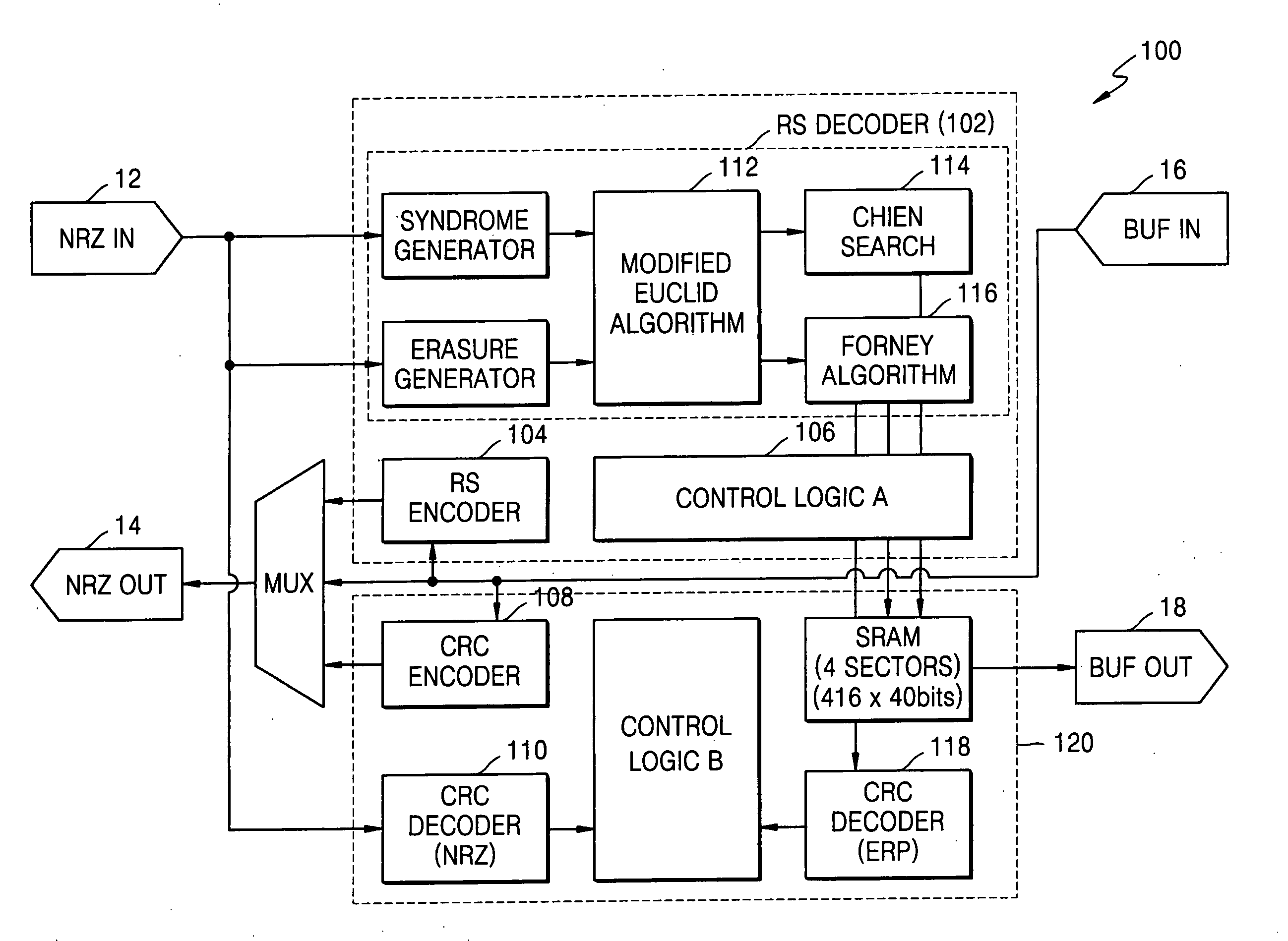
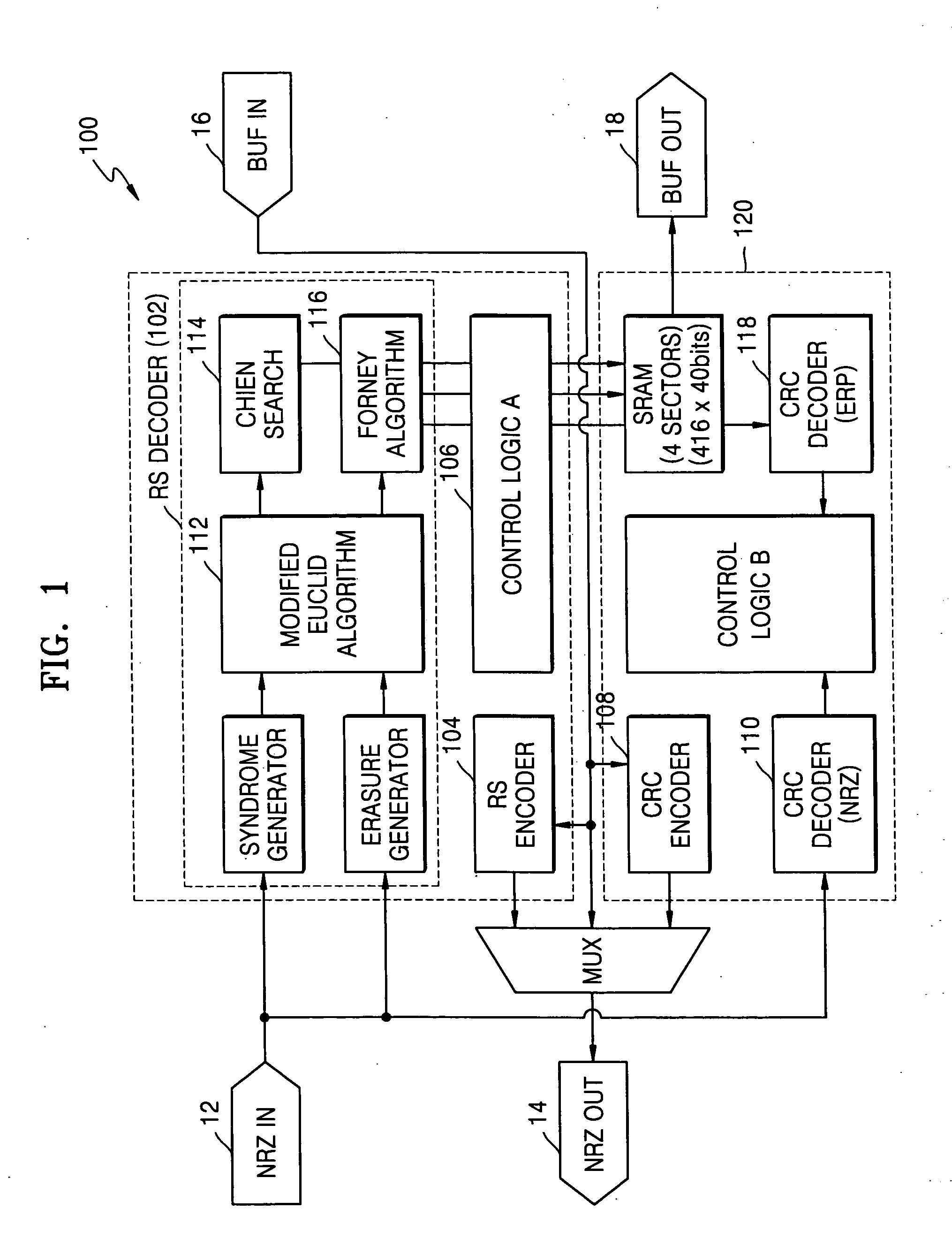
Decoding method for channel error correcting BCH code and RS code
ActiveCN101459431AReduce bit error rateAvoid the situation of "more correction and more error"Error preventionCyclic codesComputer hardwareCommunications system
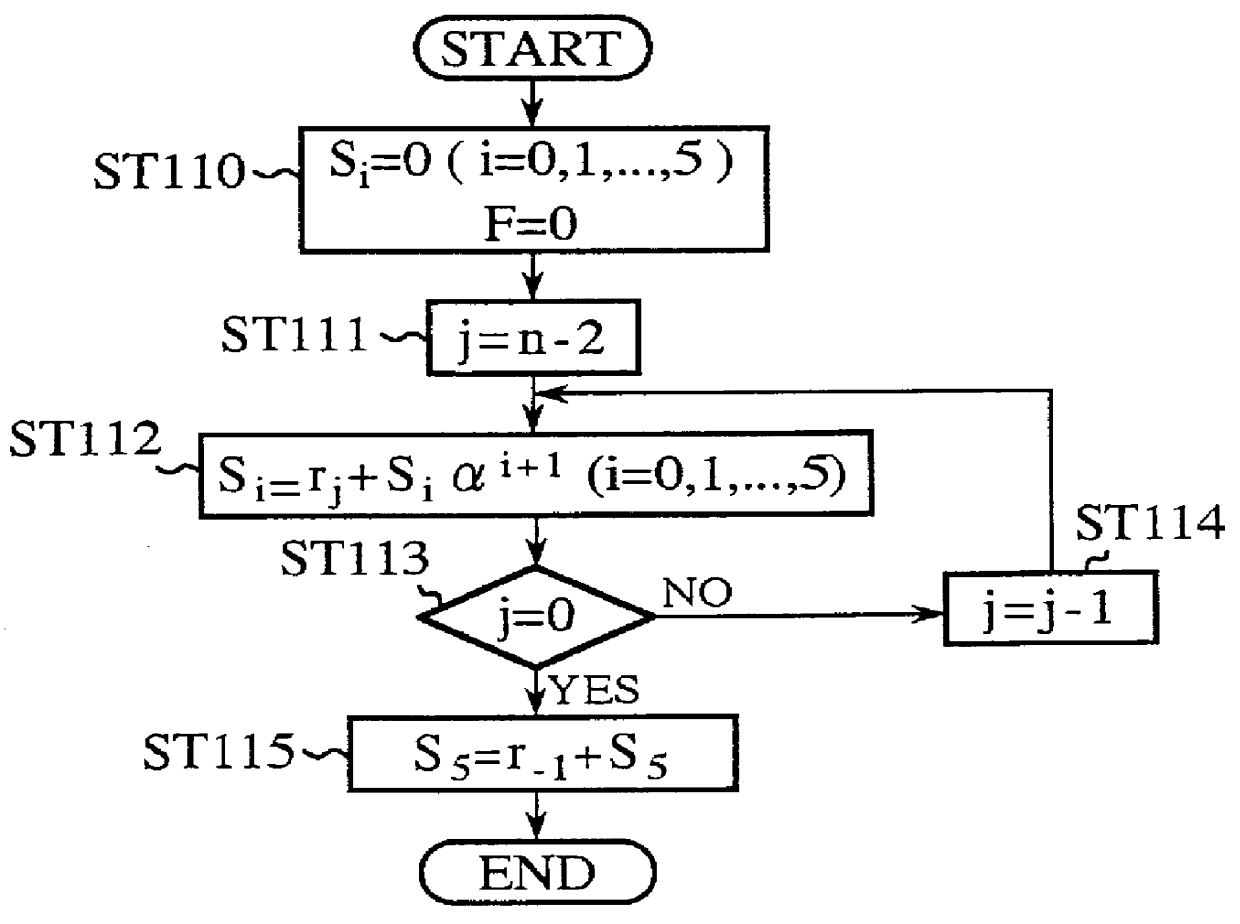
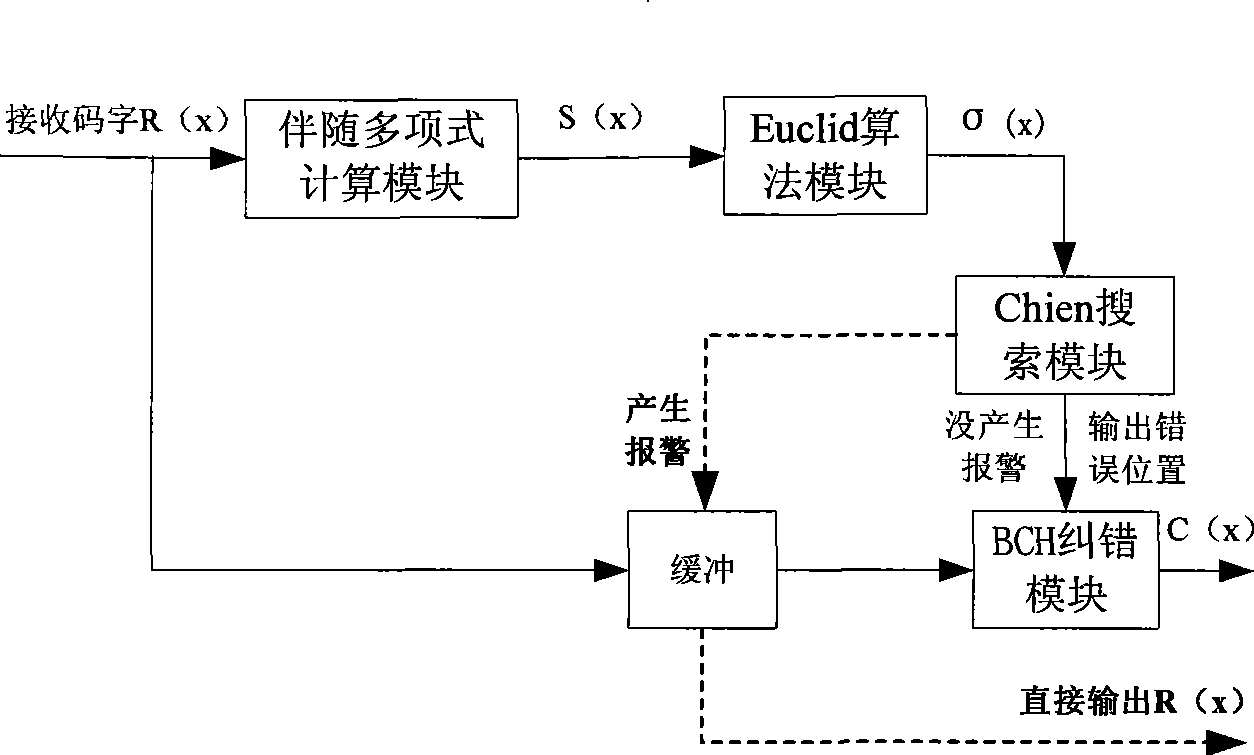
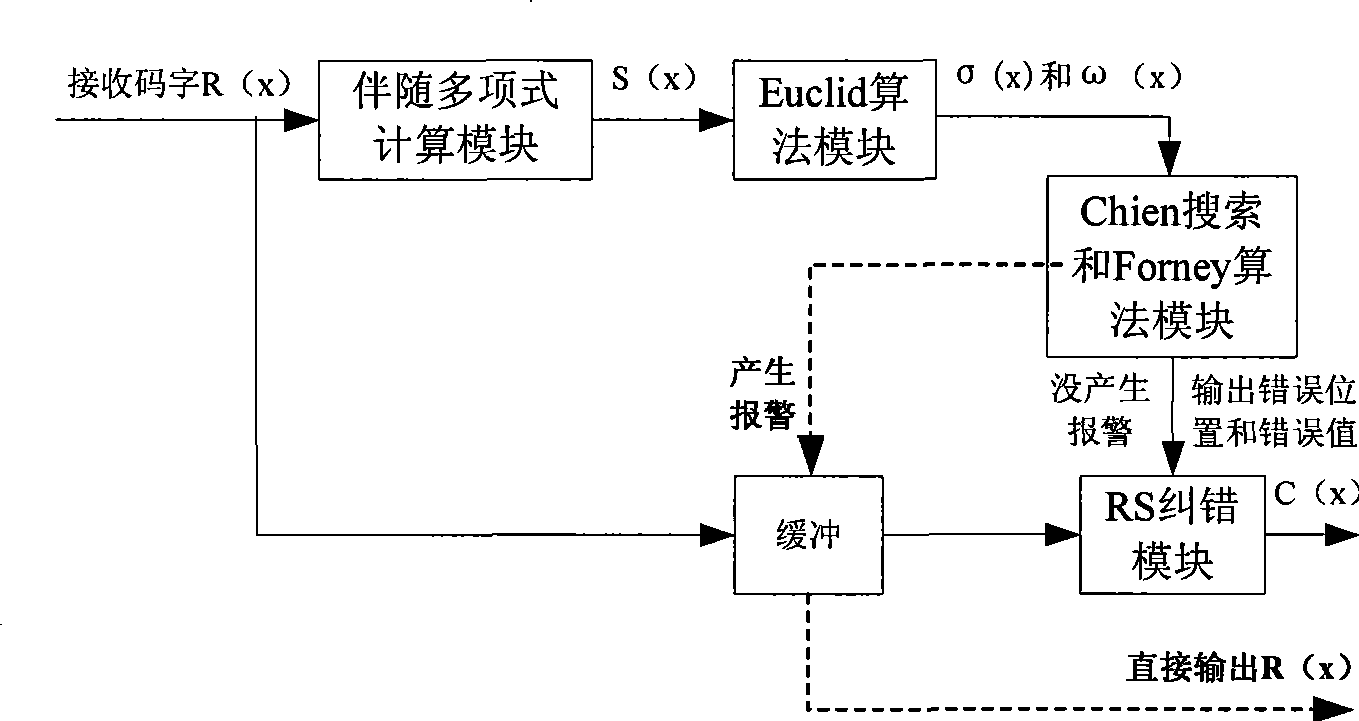
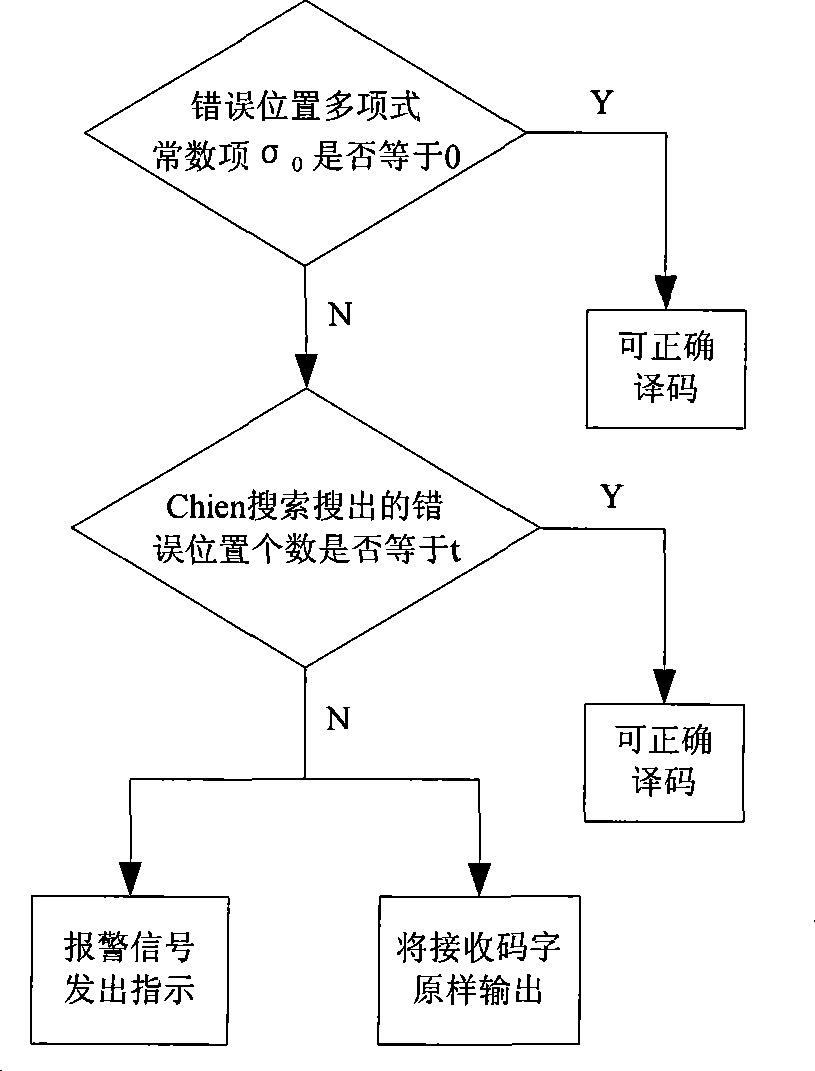
The invention discloses an encoding method of a channel error correcting code BCH code and an RS code, belonging to the digital communication field, which comprises calculating an adjoint polynomial S(x) through a received code R(x), solving the Berlekamp key equation through the Euclid algorithm to obtain an error location polynomial sigma (x), and correctly encoding if the constant term sigma 0 in the error location polynomial sigma (x) is zero, or calculating the error locations and the relative error values through the Chien search if the constant term sigma 0 in the error location polynomial sigma (x) is not equal to 0, and being able to correctly encode if the number of searched error locations is equal to the largest error correcting capability thereof, or sending a warning indication signal whose error number of receiving signals exceeds the largest error correcting capability, and outputting original receiving codes. The encoding method avoids the condition that the more errors are corrected, the more errors existing when the receiving code error number exceeds the largest error correcting capability of the channel error correcting code, thereby reducing the error code rate of the whole communication system.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
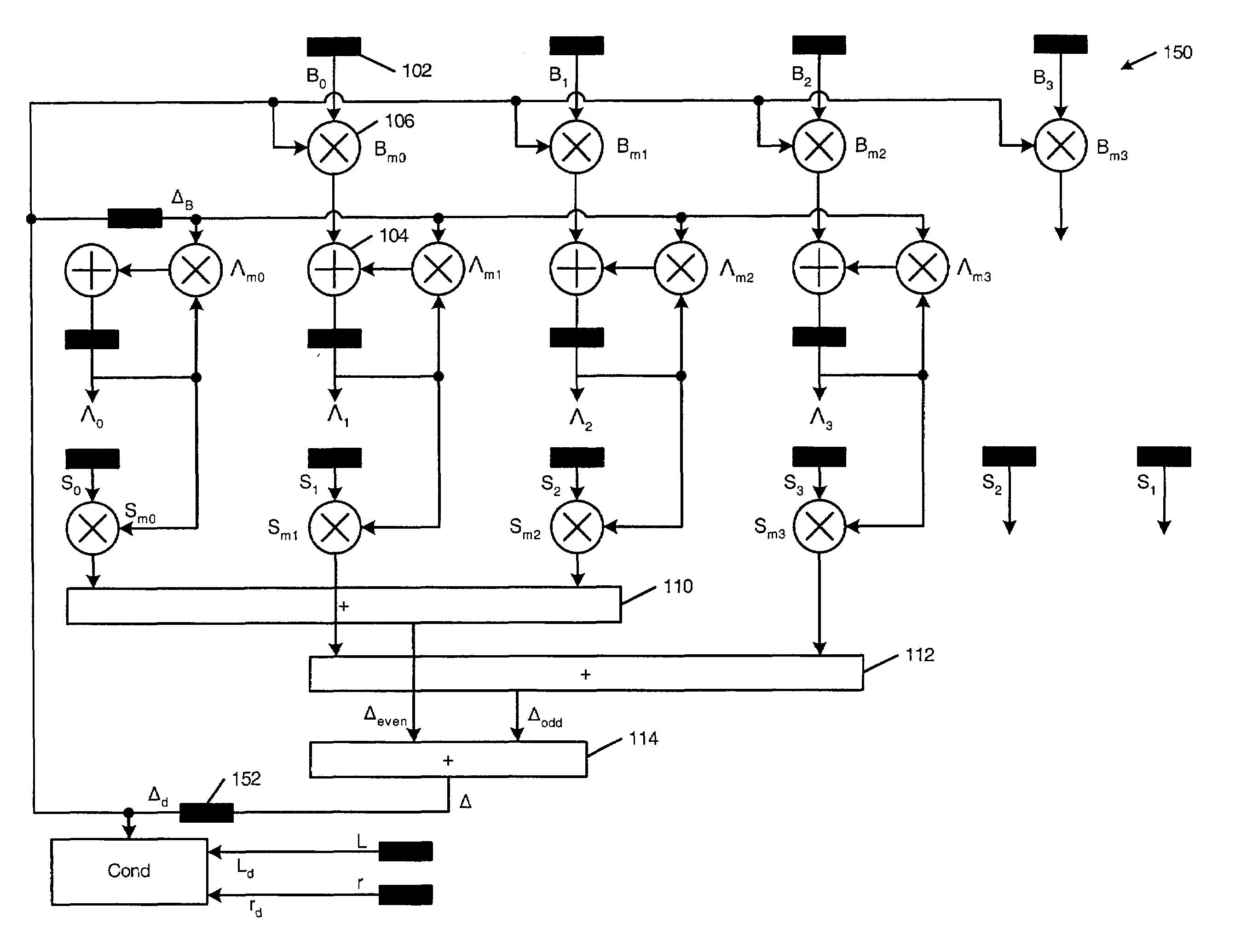
Optimized Reed-Solomon decoder
ActiveUS7788570B1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionError locationReed solomon decoder
A modified Reed-Solomon (RS) decoder comprises a syndrome calculation module that calculates a plurality of syndromes from a received codeword; a syndrome modification module that cyclically modifies the plurality of syndromes; an error correction module that selectively removes a set of error values from the received codeword at a set of error locations to create a corrected codeword; and a control module that determines whether the corrected codeword is valid, generates a success signal if the corrected codeword is valid, and selectively actuates the syndrome modification module if the corrected codeword is invalid.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Memory device with error correction system
There is disclosed a memory device with an error detection and correction system formed therein, the error detection and correction system being configured to detect and correct errors in read out data by use of a BCH code, wherein the error detection and correction system is 4-bit error correctable, and searches error locations in such a way as to: divide an error location searching biquadratic equation into two or more factor equations; convert the factor equations to have unknown parts and syndrome parts separated from each other for solving them; and compare indexes of the solution candidates with those of the syndromes, the corresponding relationships being previously obtained as a table, thereby obtaining error locations.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Error Correction in Multi-Valued (p,k) Codes
InactiveUS20080016432A1Rapidly detect and correct errorCode conversionCyclic codesCommunications systemError location
Methods, apparatus and systems for error correction of n-valued symbols in (p,k) codewords including Reed Solomon codes of p n-valued symbols with n>2 and k information symbols have been disclosed. Coders and decoders using a Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSR) are applied. An LFSR can be in Fibonacci or Galois configuration. Errors can be corrected by execution of an n-valued expression in a deterministic way. Error correcting methods using Galois arithmetic are disclosed. Methods using Cramer's rule are also disclosed. Deterministic error correction methods based on known symbols in error are provided, making first determining error magnitudes not necessary. An error location methods using up and down state tracking is provided. Methods and apparatus executing the methods with binary circuits are also disclosed. Systems using the error correcting methods, including communication systems and data storage systems are also provided.
Owner:TERNARYLOGIC
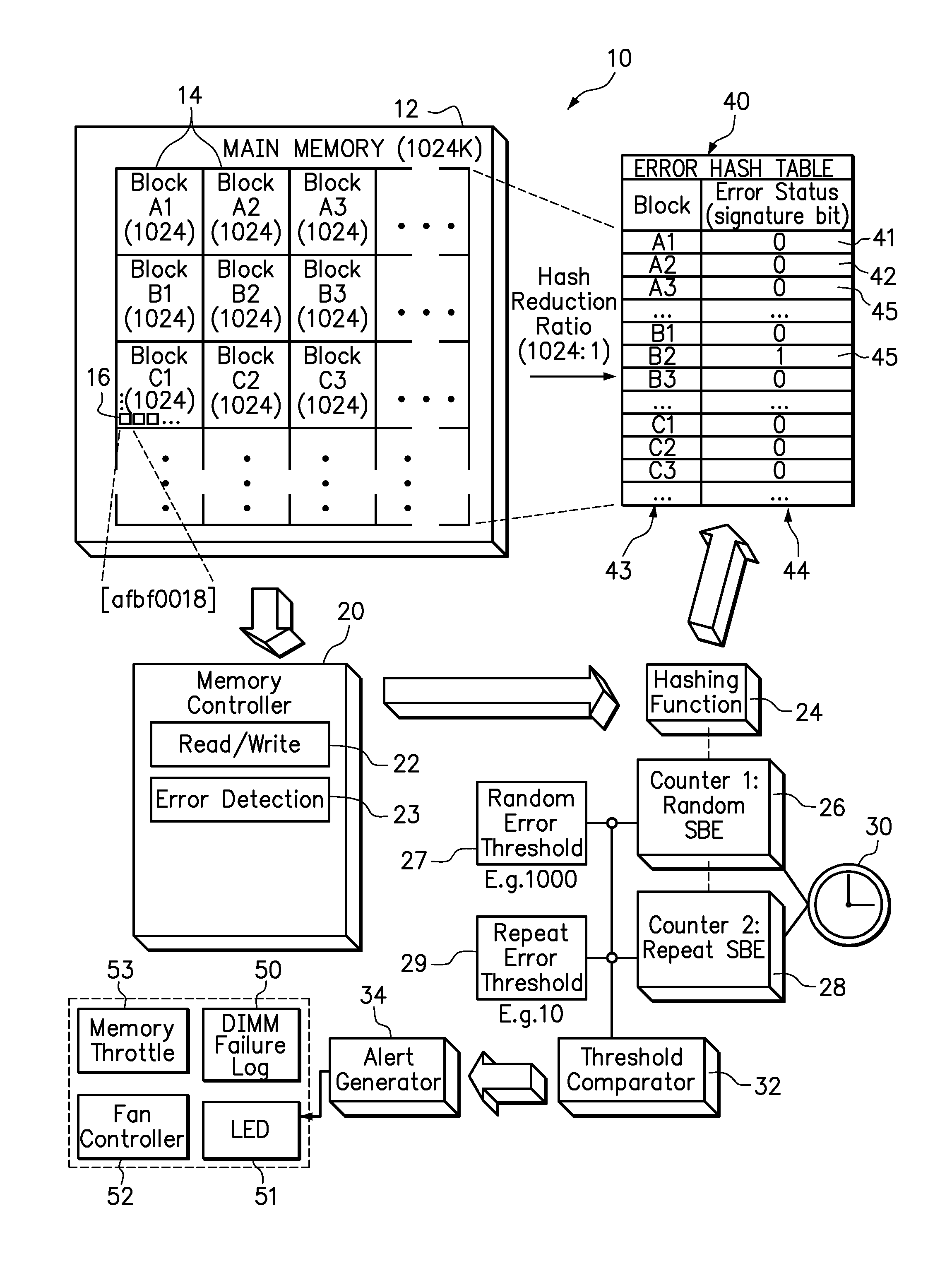
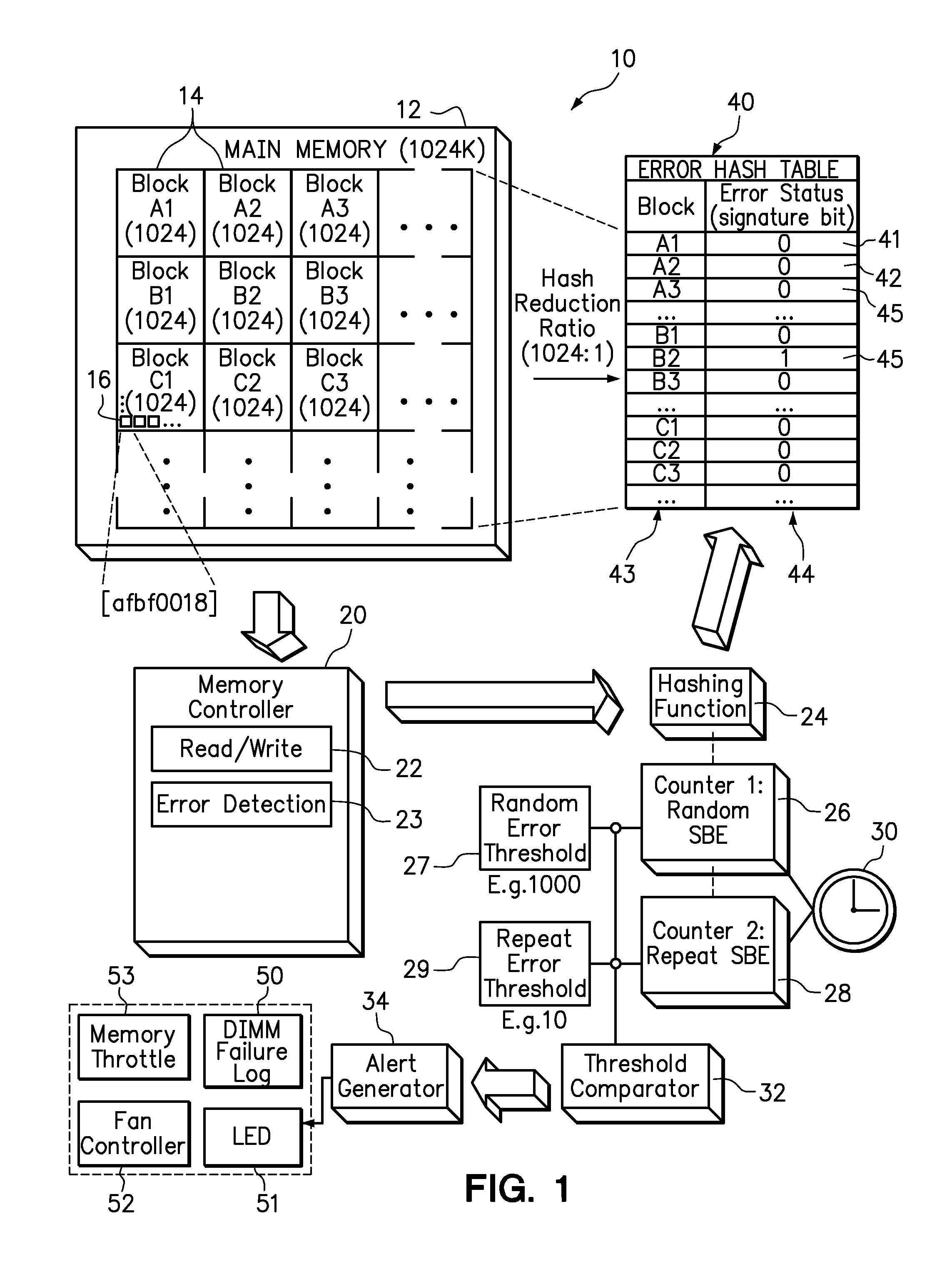
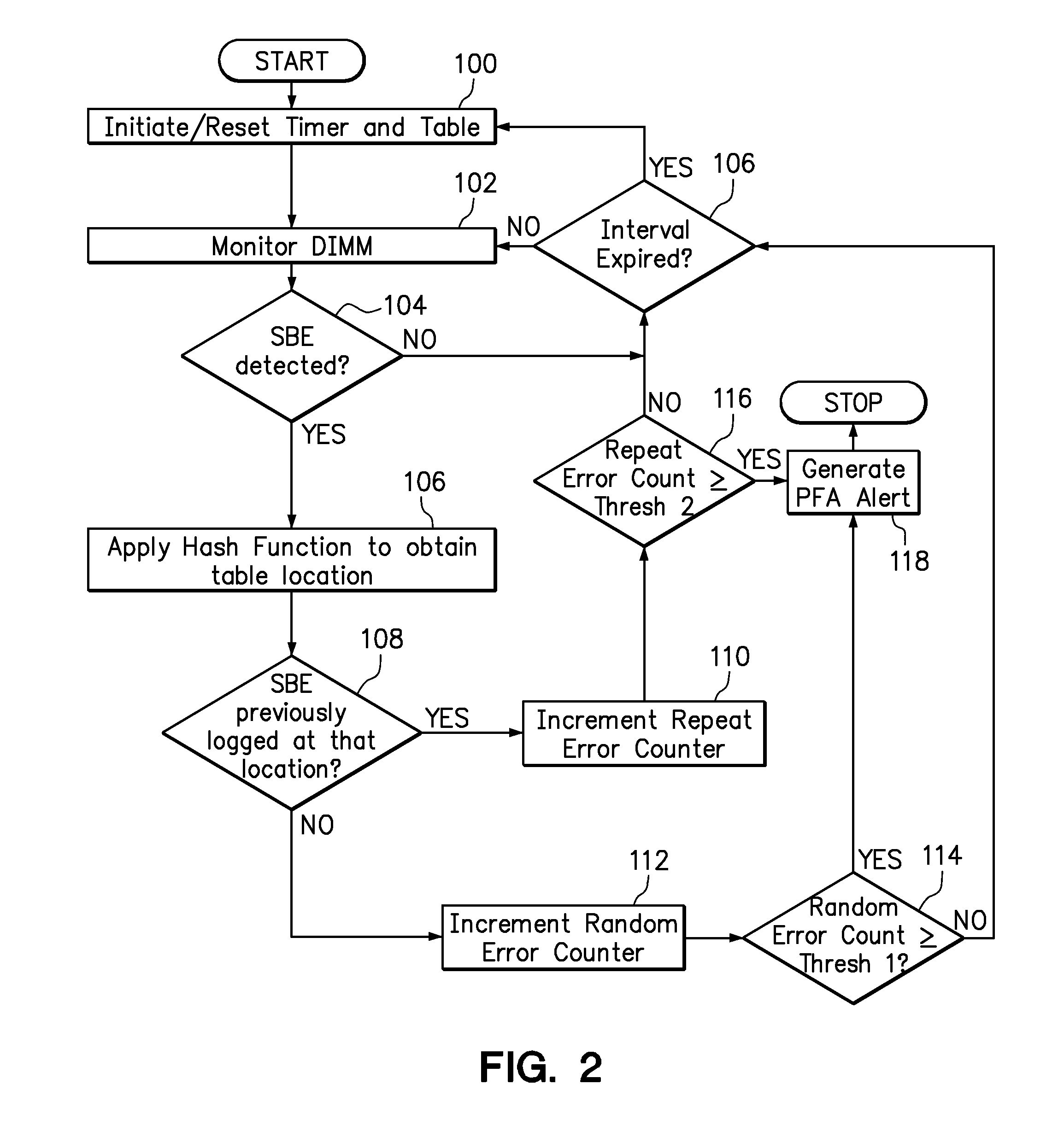
Use of hashing function to distinguish random and repeat errors in a memory system
ActiveUS20120072786A1Detecting faulty computer hardwareReliability/availability analysisMemory addressHash function
One embodiment provides an error detection method wherein single-bit errors in a memory module are detected and identified as being a random error or a repeat error. Each identified random error and each identified repeat error occurring in a time interval is counted. An alert is generated in response to a number of identified random errors reaching a random-error threshold or a number of identified repeat errors reaching a repeat-error threshold during the predefined interval. The repeat-error threshold is set lower than the random-error threshold. A hashing process may be applied to the memory address of each detected error to map the location of the error in the memory system to a corresponding location in an electronic table.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
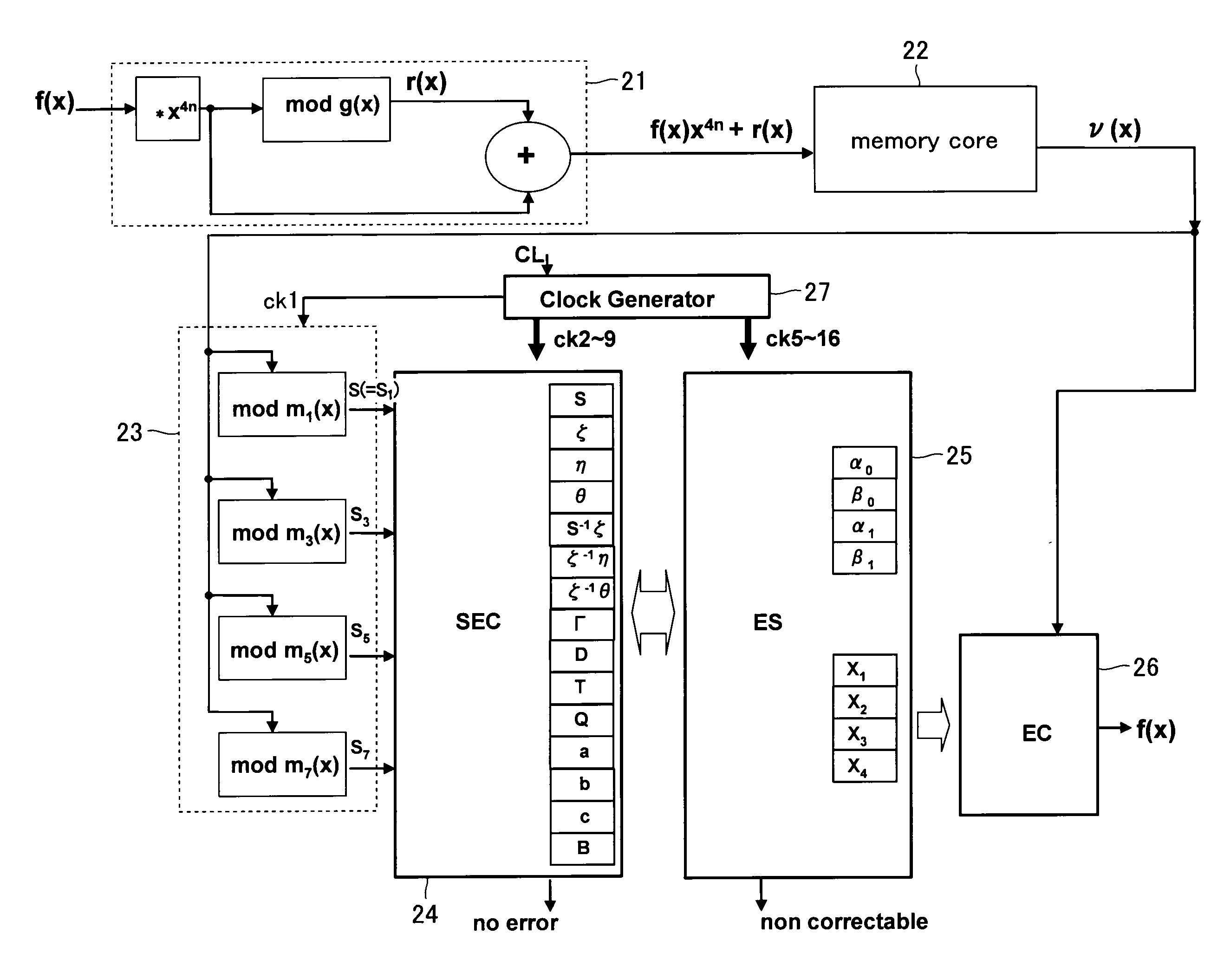
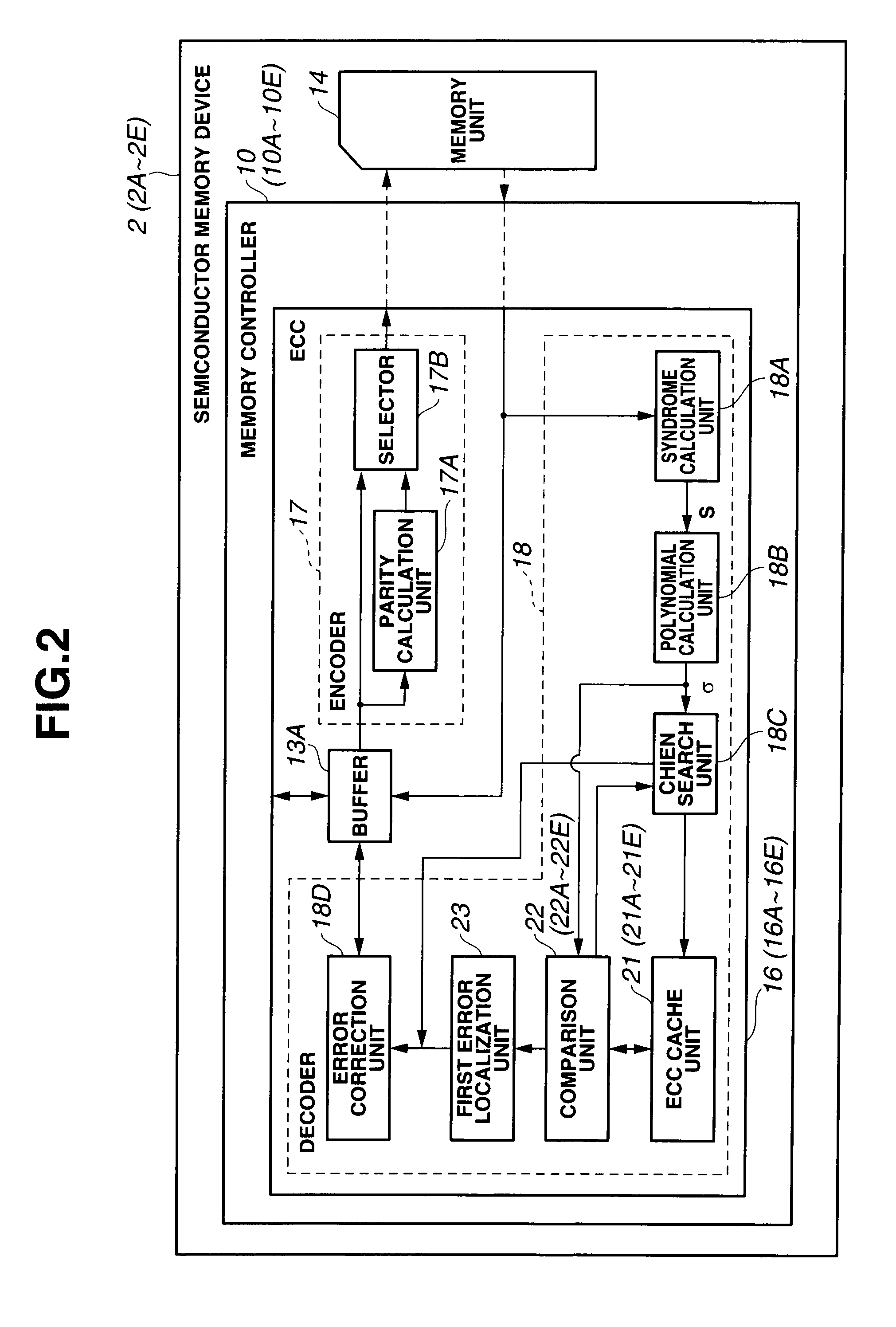
Error detector/corrector, memory controller, and semiconductor memory device
An error detector / corrector includes an ECC cache unit configured to store an error bit address which represents an error location by associating the error bit address with an error page address and a coefficient α of an error location polynomial; a comparison unit configured to check for a match by comparing new values with stored values, where the new values are an error page address detected by a syndrome calculation unit and a coefficient α of the error location polynomial calculated by a polynomial calculation unit while the stored values are an error page address and a coefficient α of the error location polynomial stored in the ECC cache unit; and a first error localization unit configured to identify a location of the error bit address stored in the ECC cache unit as the error location when the comparison unit determines that the compared values match.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Efficient high-speed Reed-Solomon decoder
A Reed-Solomon decoder includes an inversionless Berlekamp-Massey algorithm (iBMA) circuit with a pipelined feedback loop. An error locator polynomial generator generates error locator polynomial values. A scratch polynomial generator generates scratch polynomial values. A discrepancy generator generates discrepancy values based on the error locator polynomial values and the scratch polynomial values. Multipliers used to generate the discrepancy values are also used to generate the error locator polynomial to reduce circuit area. A first delay circuit delays the discrepancy values. A feedback loop feeds back the delayed discrepancy values to the error locator polynomial generator and the scratch polynomial generator. An error location finder circuit communicates with the iBMA circuit and identifies error locations. An error value computation circuit communicates with at least one of the error location finder circuit and the iBMA circuit and generates error values.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Techniques for detecting and correcting errors using multiple interleave erasure pointers
InactiveUS7231578B2Correction capabilityTransmission systemsBurst error correctionBlock codeError location
Techniques for detecting and correcting burst errors in data bytes formed in a two-level block code structure. A second level decoder uses block level check bytes to detect columns in a two-level block code structure that contain error bytes. The second level decoder generates erasure pointers that identify columns in the two-level block structure effected by burst errors. A first level decoder then uses codeword check bytes to correct all of the bytes in the columns identified by the erasure pointers. The first level decoder is freed to use all of the codeword check bytes only for error byte value calculations. The first level decoder does not need to use any of the codeword check bytes for error location calculations, because the erasure pointers generated by the second level decoder provide all of the necessary error locations. This techniques doubles the error correction capability of the first level decoder.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV +1
Method and apparatus for testing software
ActiveUS20070038898A1Enable detectionError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsComputer hardwareDiagnostic data
A state table includes a plurality of possible states of a computer system and the corresponding actions which produce transitions between source and target states. A set of test programs is stored, each test program performing an action in the state table. A test selects an action corresponding to the current state of the computer system; executes the test program which performs the selected action; determines the state of the computer system after the test program has executed; and compares the determined state to the state indicated in the state table as the target state to the selected action on the source state. When an error is found, instead of stopping execution, the test operations to be performed are dynamically reconfigured. Weightings are dynamically allocated to actions in the state table to create a weighted set, and selection of the next test is carried out using random selection over the weighted set. Thus, the continued testing is biased over time towards particular transitions and / or states near to the error location. This enables a tester to discover any other bugs in the same area and also to obtain further diagnostic data on the failure.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com