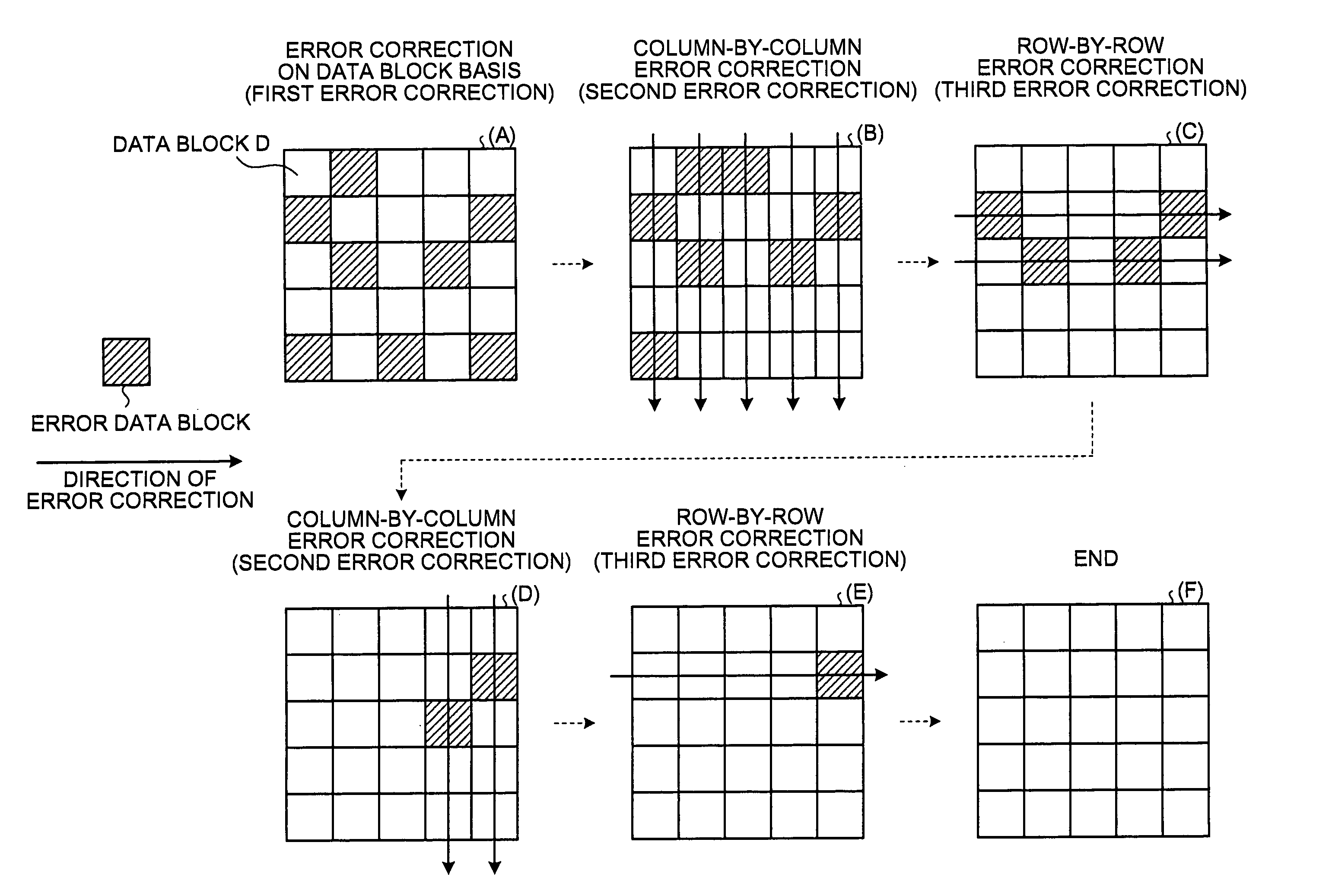
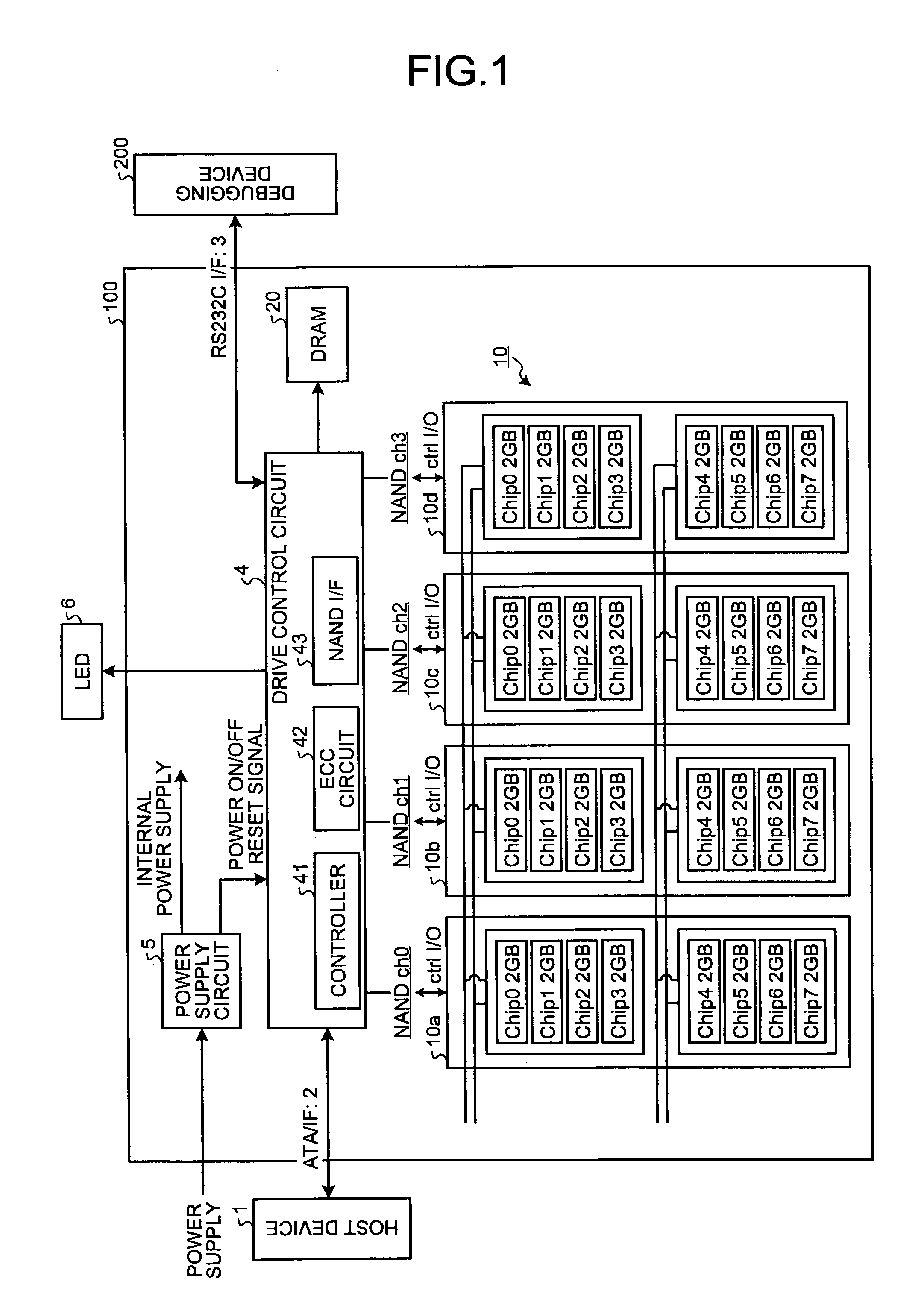
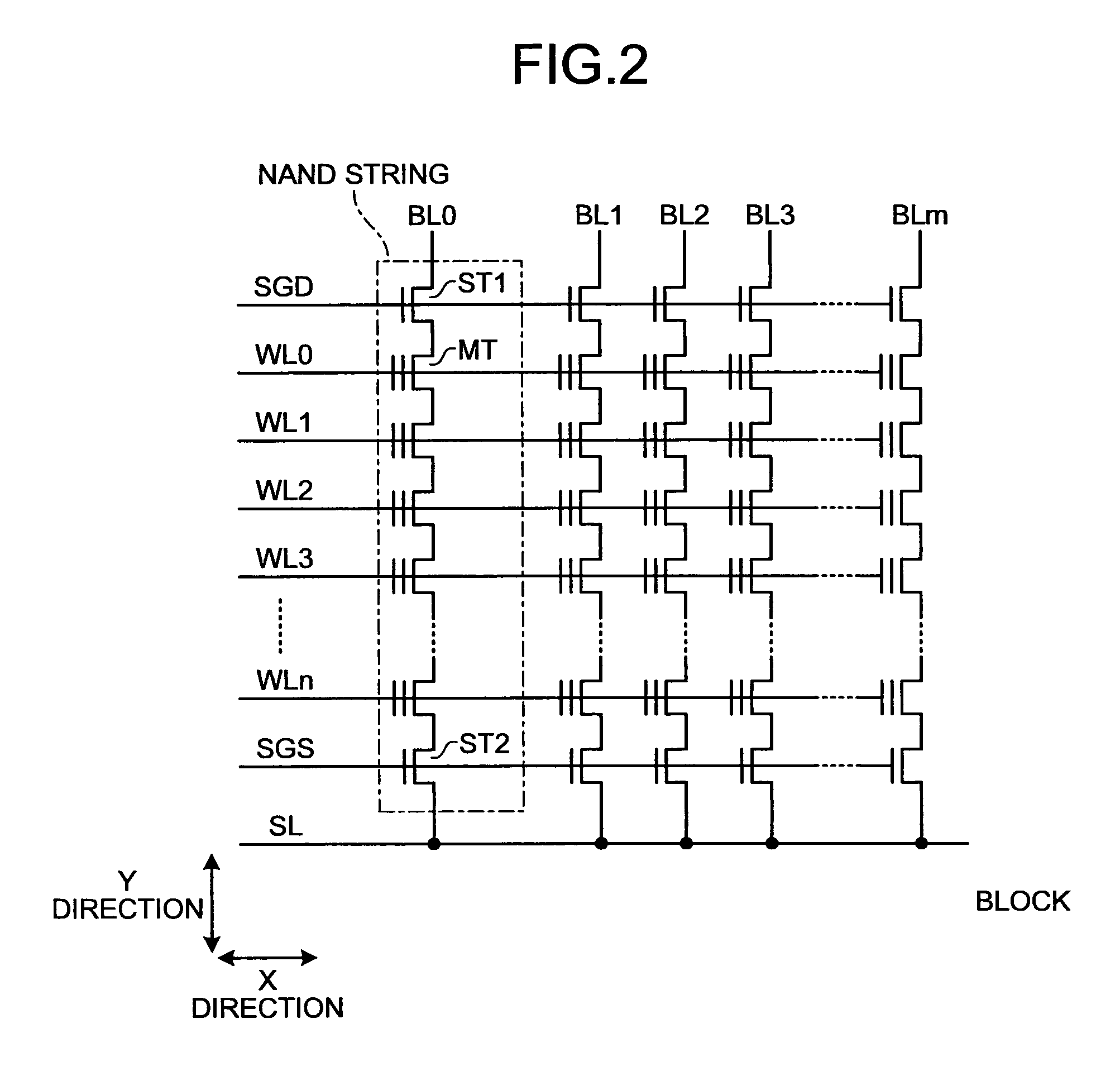
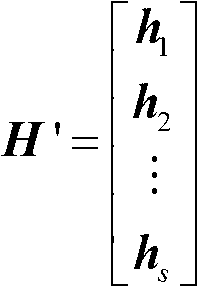Patents
Literature
188 results about "Hamming code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunication, Hamming codes are a family of linear error-correcting codes. Hamming codes can detect up to two-bit errors or correct one-bit errors without detection of uncorrected errors. By contrast, the simple parity code cannot correct errors, and can detect only an odd number of bits in error. Hamming codes are perfect codes, that is, they achieve the highest possible rate for codes with their block length and minimum distance of three. Richard W. Hamming invented Hamming codes in 1950 as a way of automatically correcting errors introduced by punched card readers. In his original paper, Hamming elaborated his general idea, but specifically focused on the Hamming(7,4) code which adds three parity bits to four bits of data.
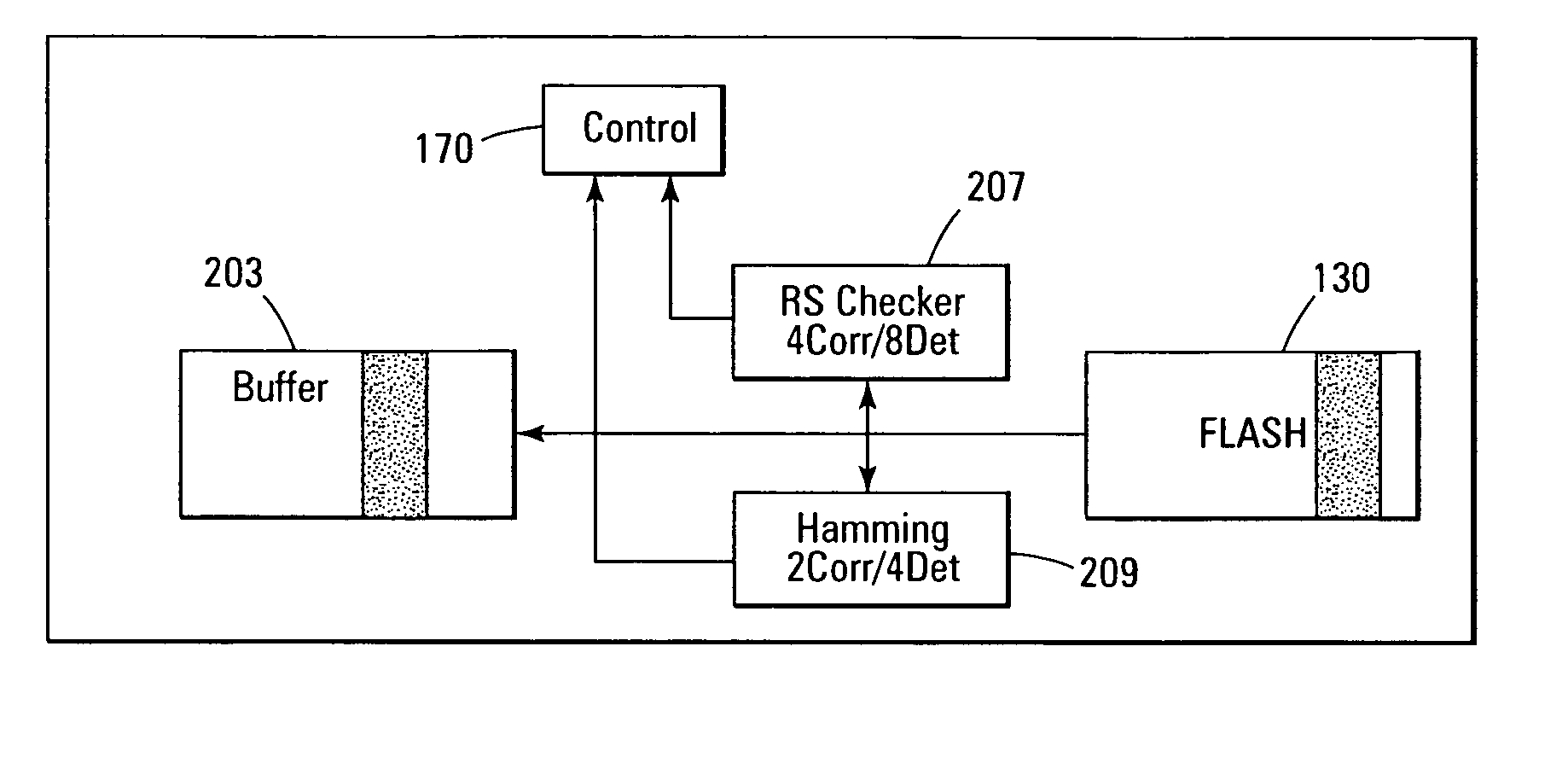
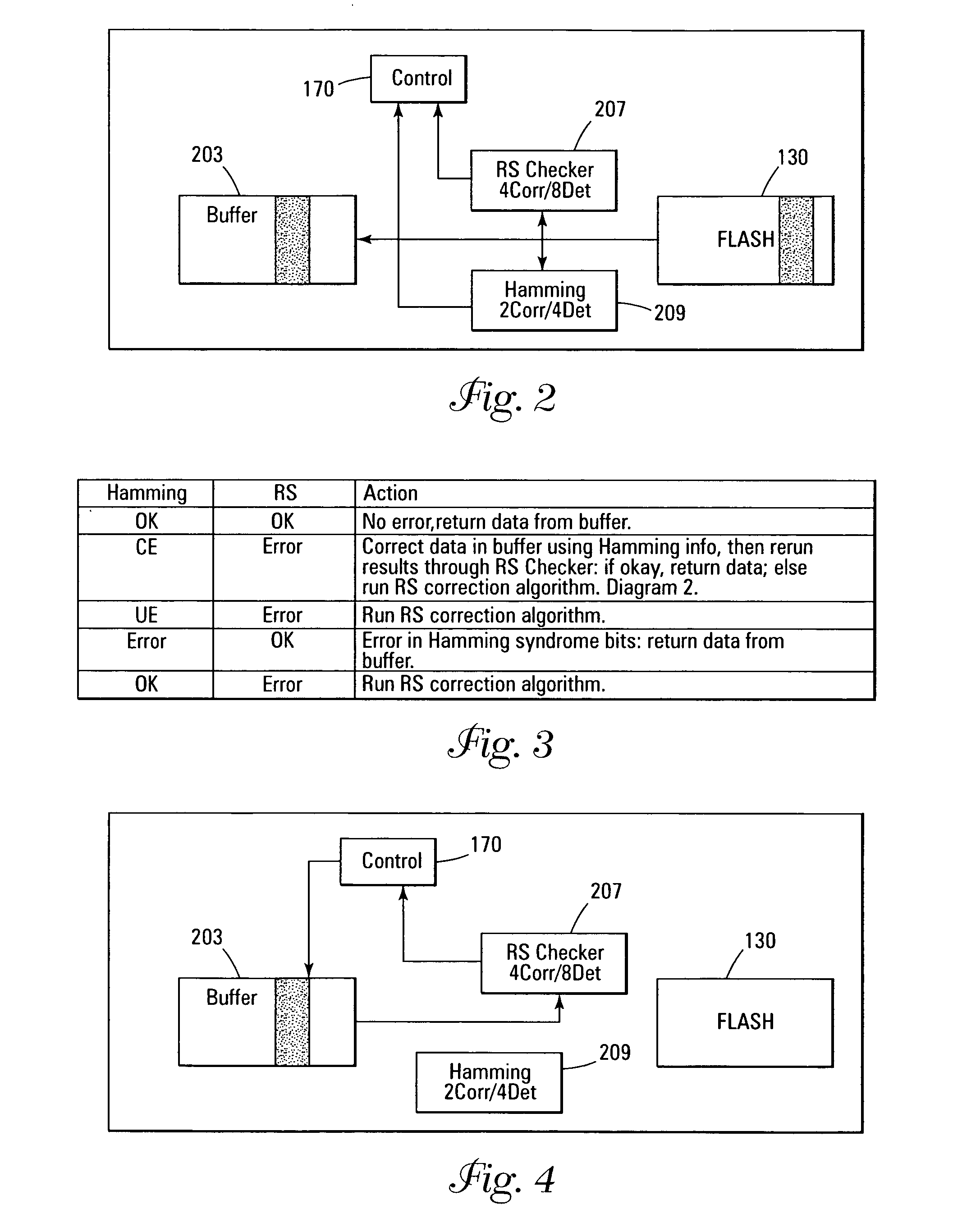
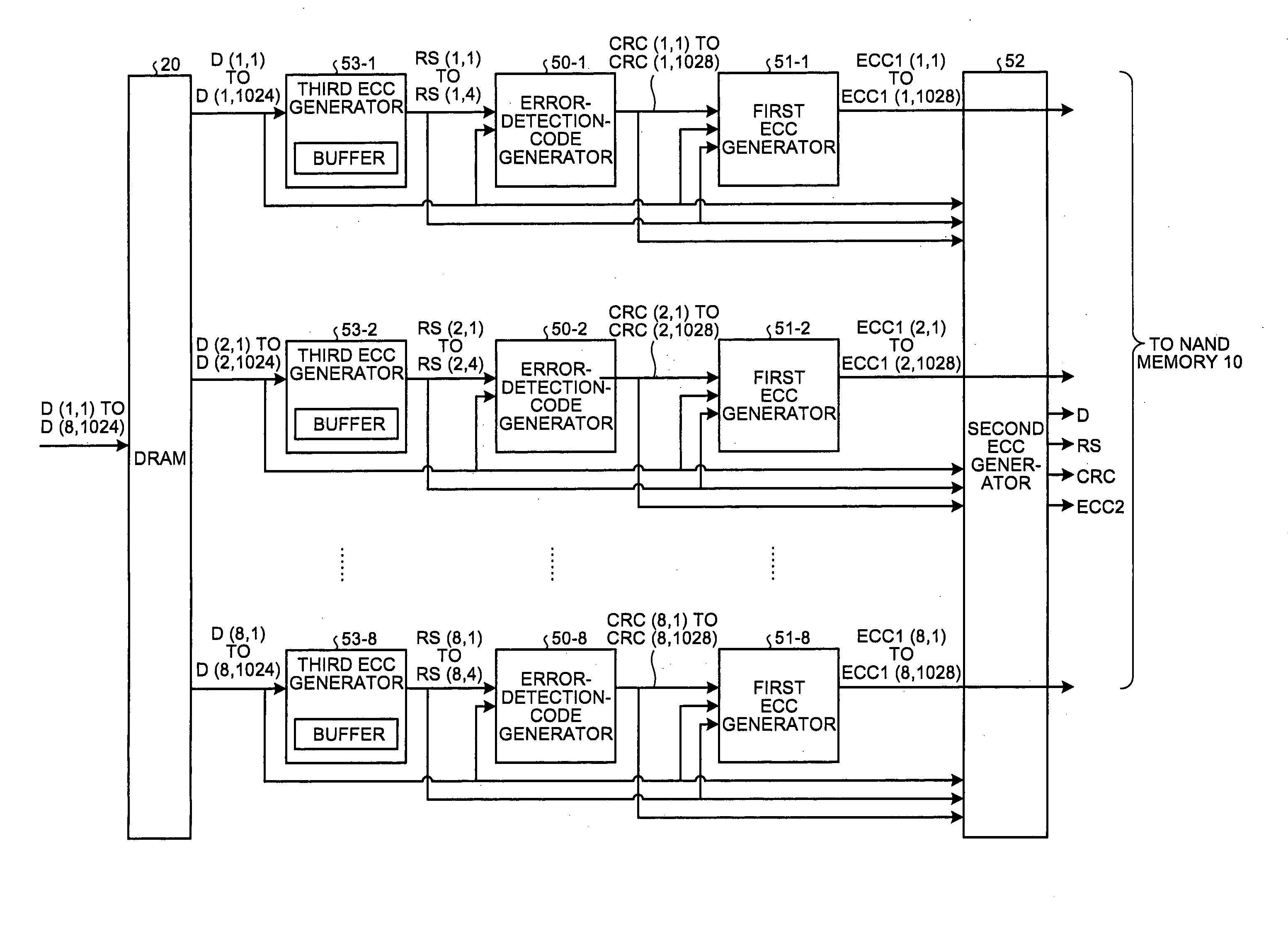
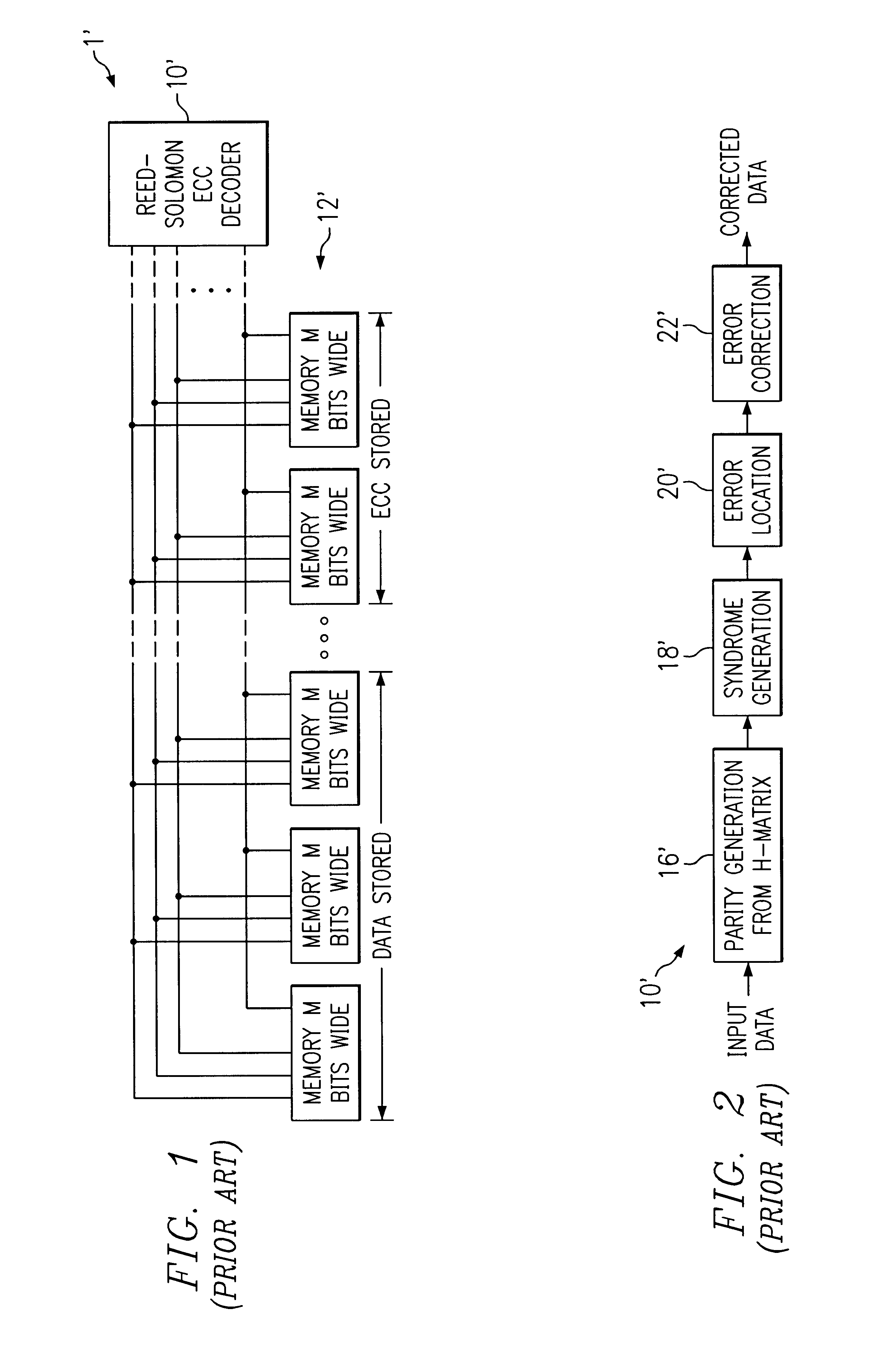
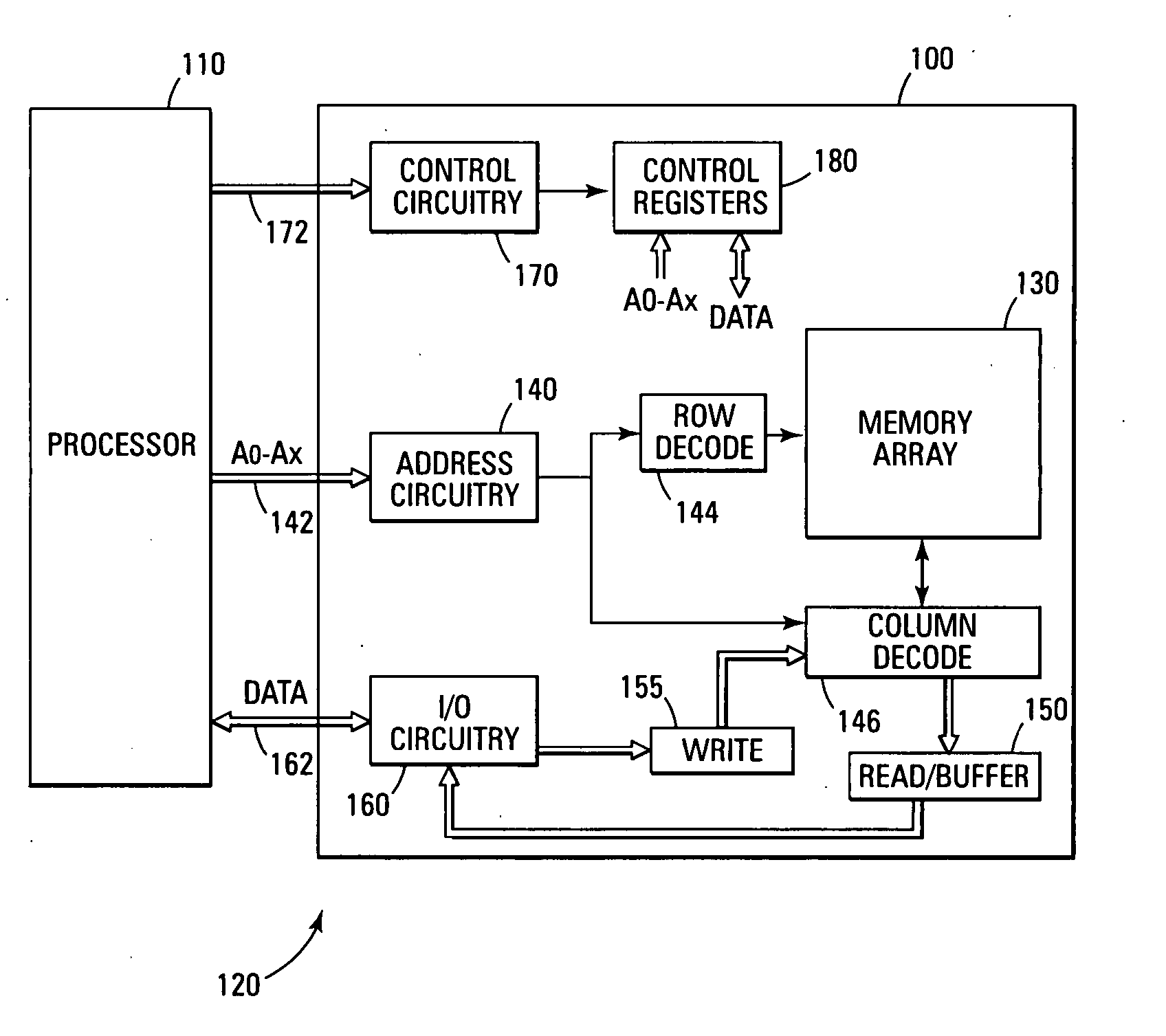
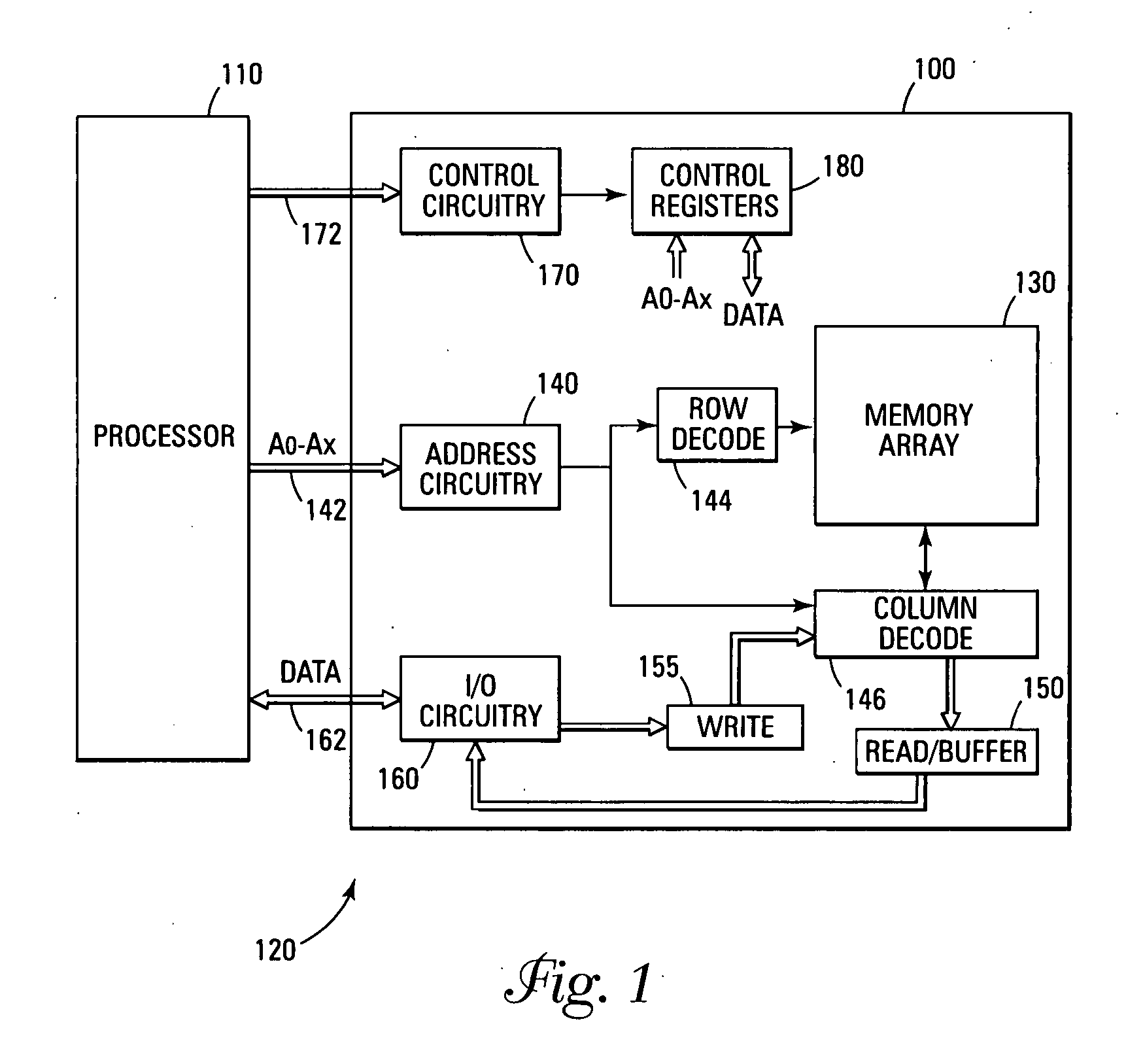
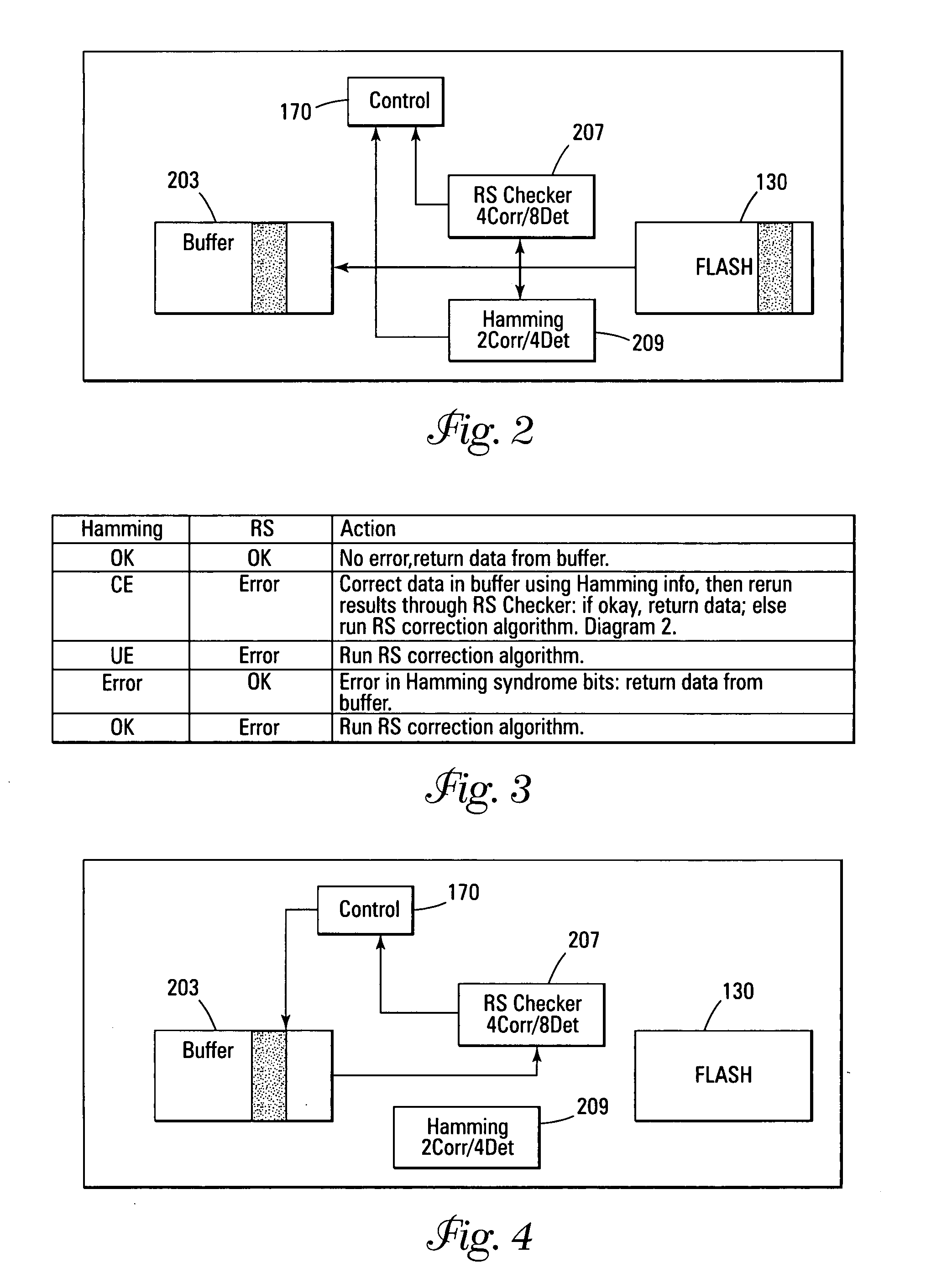
Error detection and correction scheme for a memory device
ActiveUS20050172207A1Code conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresHamming codeCorrection code
Data is read from a memory array. Before being stored in a data buffer, a Hamming code detection operation and a Reed-Solomon code detection operation are operated in parallel to determine if the data word has any errors. The results of the parallel detection operations are communicated to a controller circuit. If an error is present that can be corrected by the Hamming code correction operation, this is performed and the Reed-Solomon code detection operation is performed on the corrected word. If the error is uncorrectable by the Hamming code, the Reed-Solomon code correction operation is performed on the word.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
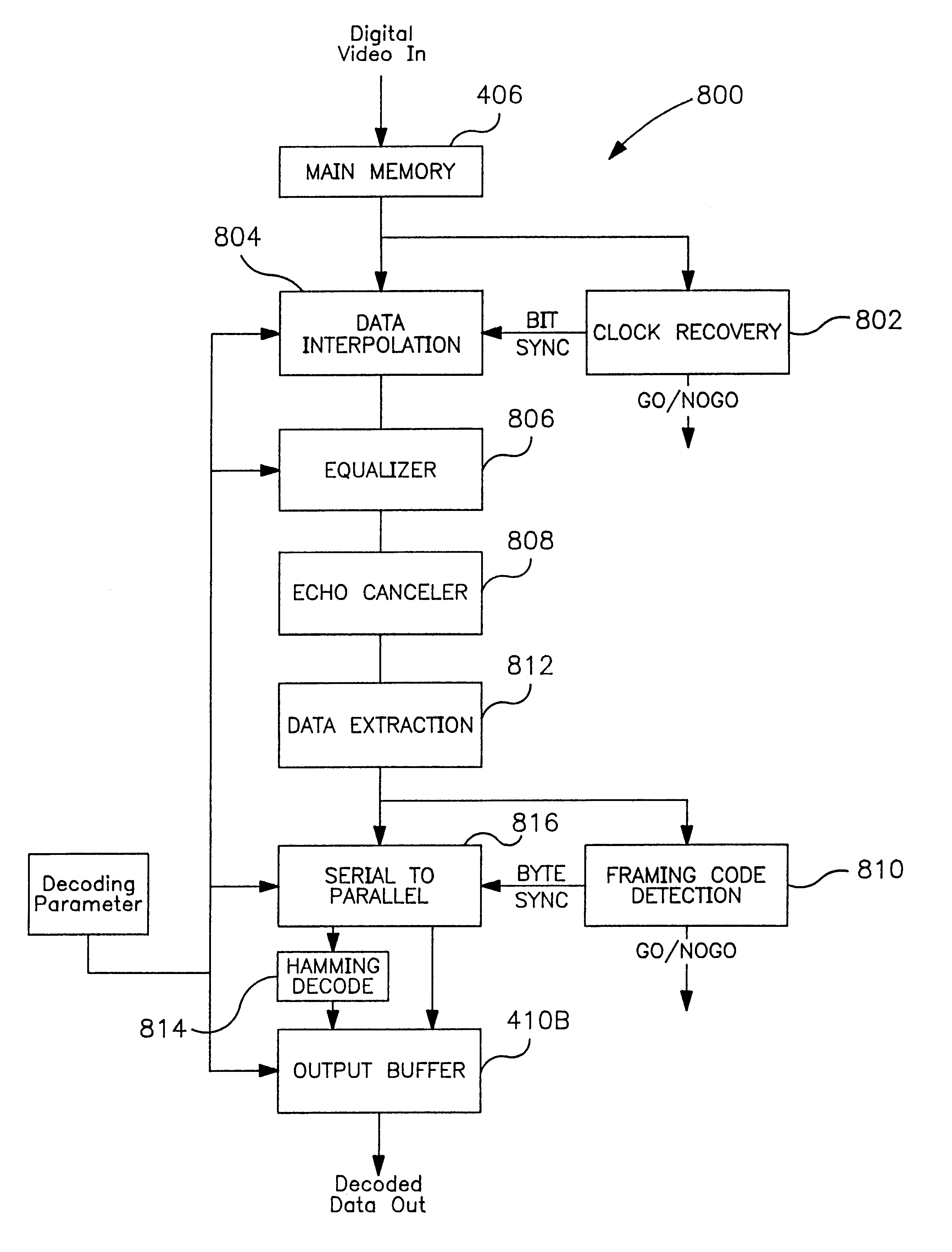
Method and system for decoding data in a signal
InactiveUS6239843B1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesHamming codeClosed captioning
A decoding system comprises a software-oriented implementation of the decoding process for extracting binary teletext and closed caption data from a signal. The decoder system according to one embodiment includes a processing unit which implements both a closed caption module and a teletext module. The decoder system calls the closed caption module to detect a clock synchronization signal associated with closed caption data. Upon finding the clock synchronization signal, the closed caption module synchronizes to the signal, identifies a framing code, and extracts the closed caption data. Similarly, the decoder system may call the teletext module for the teletext lines, which also synchronizes using a teletext clock synchronization signal. When the clock synchronization signal is detected, the teletext module interpolates the incoming data to reconstruct the data signal. The data signal is then processed to normalize the amplitude and reduce the "ghost" effects of signal echoes prior to the slicing of the data signal. The data is also suitably subjected to Hamming code error detection to ensure the accuracy of the data.
Owner:WAVO CORP
NAND flash memory device with ecc protected reserved area for non-volatile storage of redundancy data
InactiveUS20080065937A1Reduces silicon area requirementMeet cutting requirementsError detection/correctionStatic storageHamming codeArray element
Basic redundancy information is non-volatily stored in a reserved area of an addressable area of a memory array, and is copied to volatile storage therein at every power-on of the memory device. The unpredictable though statistically inevitable presence of failed array elements in such a reserved area of the memory array corrupts the basic redundancy information established during the test-on wafer (EWS) phase of the fabrication process. This increases the number of rejects, and lowers the yield of the fabrication process. This problem is addressed by writing the basic redundancy data in the reserved area of the array with an ECC technique using a certain error correction code. The error correction code may be chosen among majority codes 3, 5, 7, 15 and the like, or the Hamming code for 1, 2, 3 or more errors, as a function of the fail probability of a memory cell as determined by the EWS phase during fabrication.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
Systems and processes for fast encoding of hamming codes
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
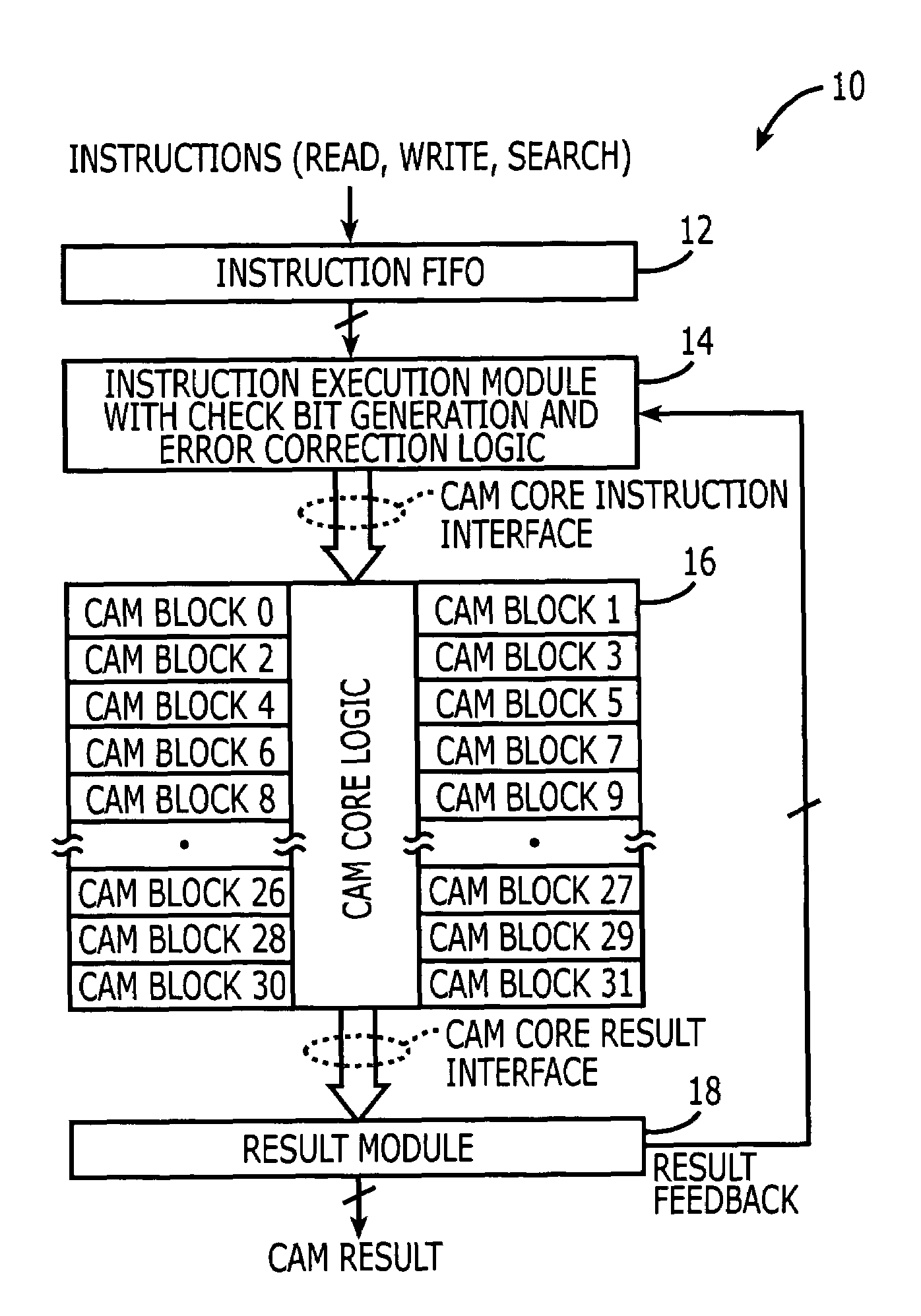
Content addressable memory (CAM) devices having multi-block error detection logic and entry selective error correction logic therein
Search engine devices include a content addressable memory (CAM) core having a plurality of CAM array blocks therein and a control circuit that is electrically coupled to the CAM core. The control circuit is configured to support internal error detection and correction operations using modified Hamming code words. These operations are performed without significant impact on the compare bandwidth of the search engine device, even when operations to read entries from the CAM core are performed as foreground operations that may block concurrent search operations. The control circuit may perform the error detection and correction operations by issuing multiple read instructions. These instructions include a first instruction (e.g., error check instruction) to read at least a first entry into the CAM core for the purpose of error detection and then, in response to detecting the first entry as erroneous, issuing a second instruction to read the first entry from the CAM core. The entry is then corrected and written back into the CAM core.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
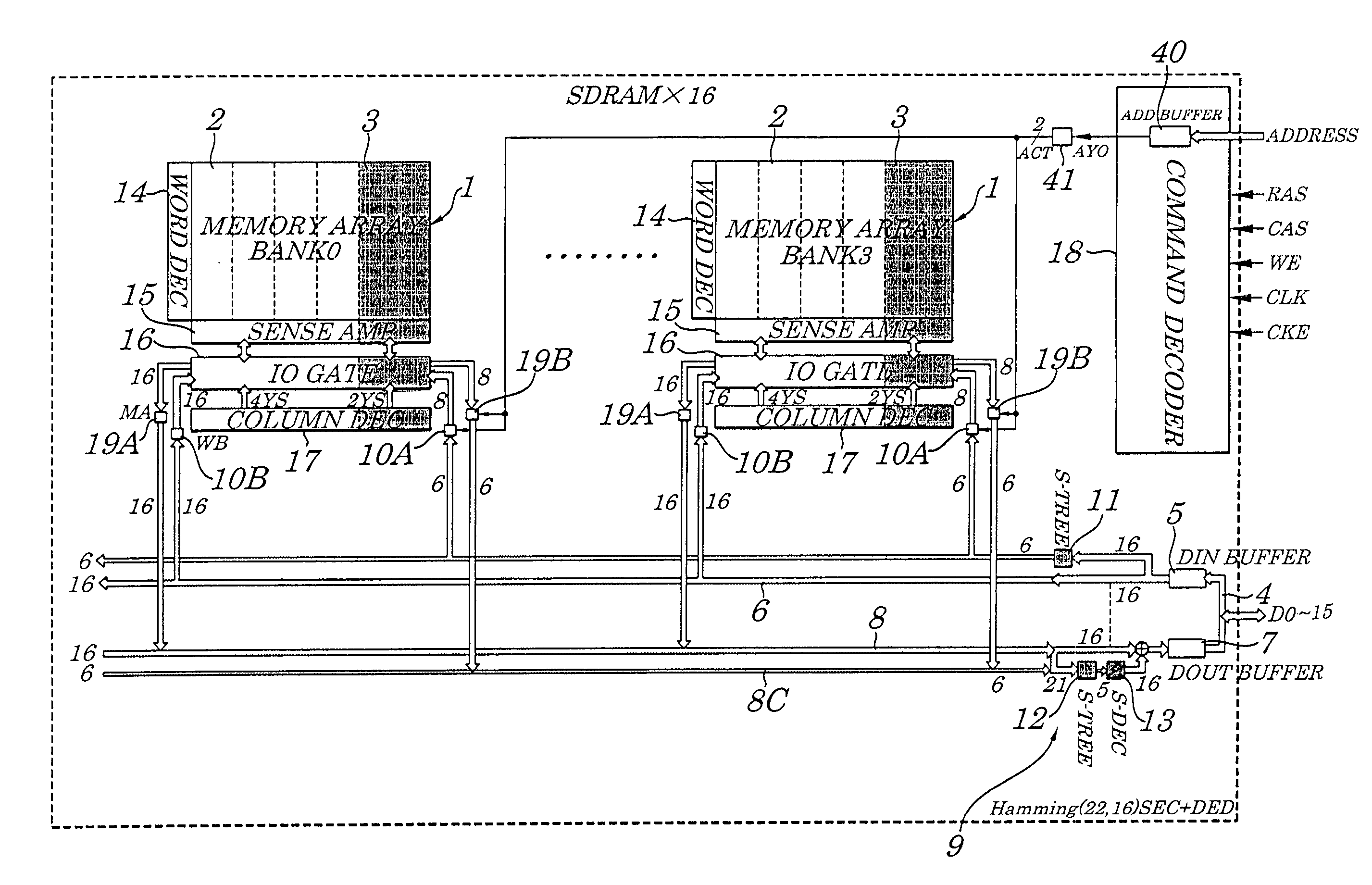
Semiconductor memory device provided with error correcting code circuitry
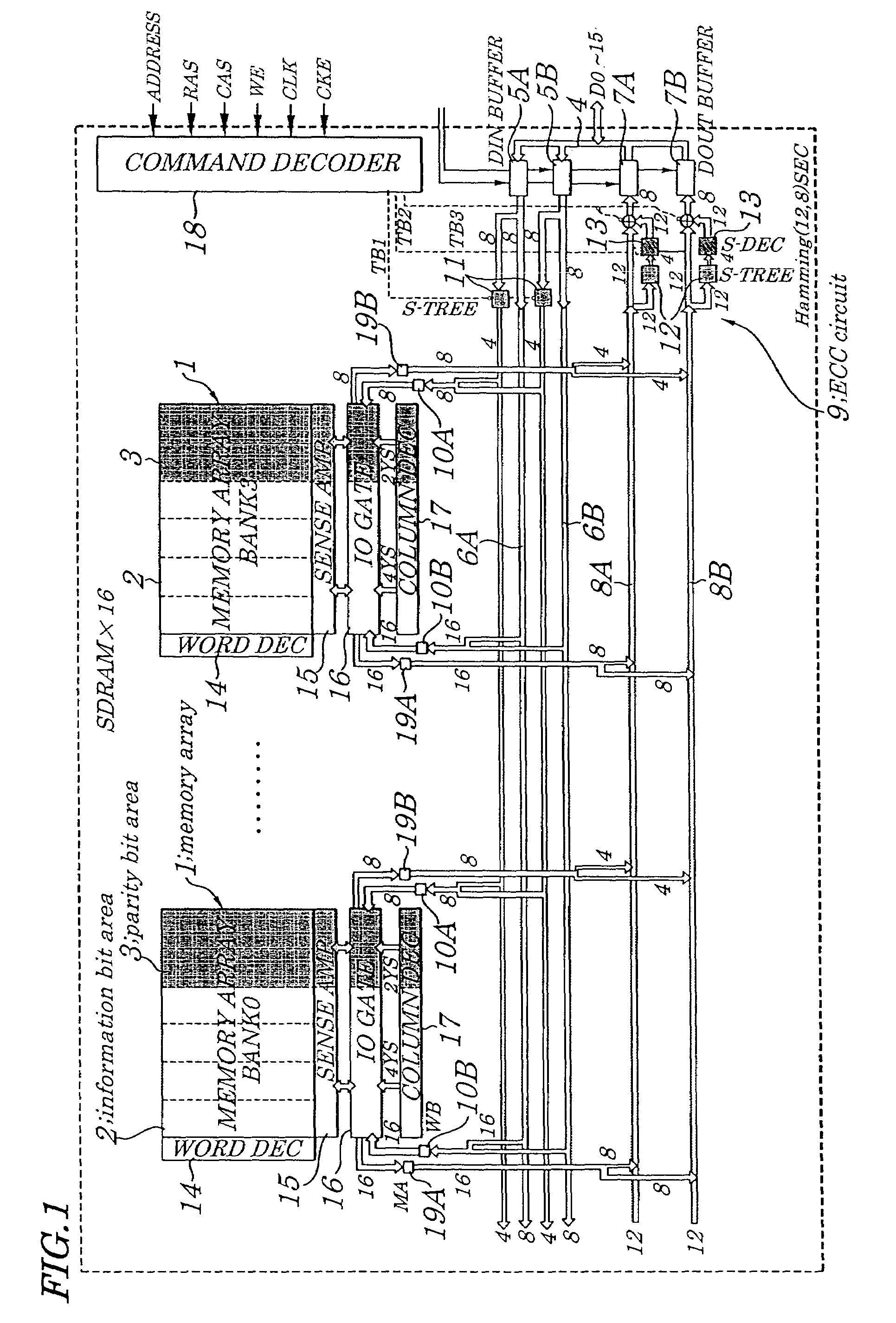
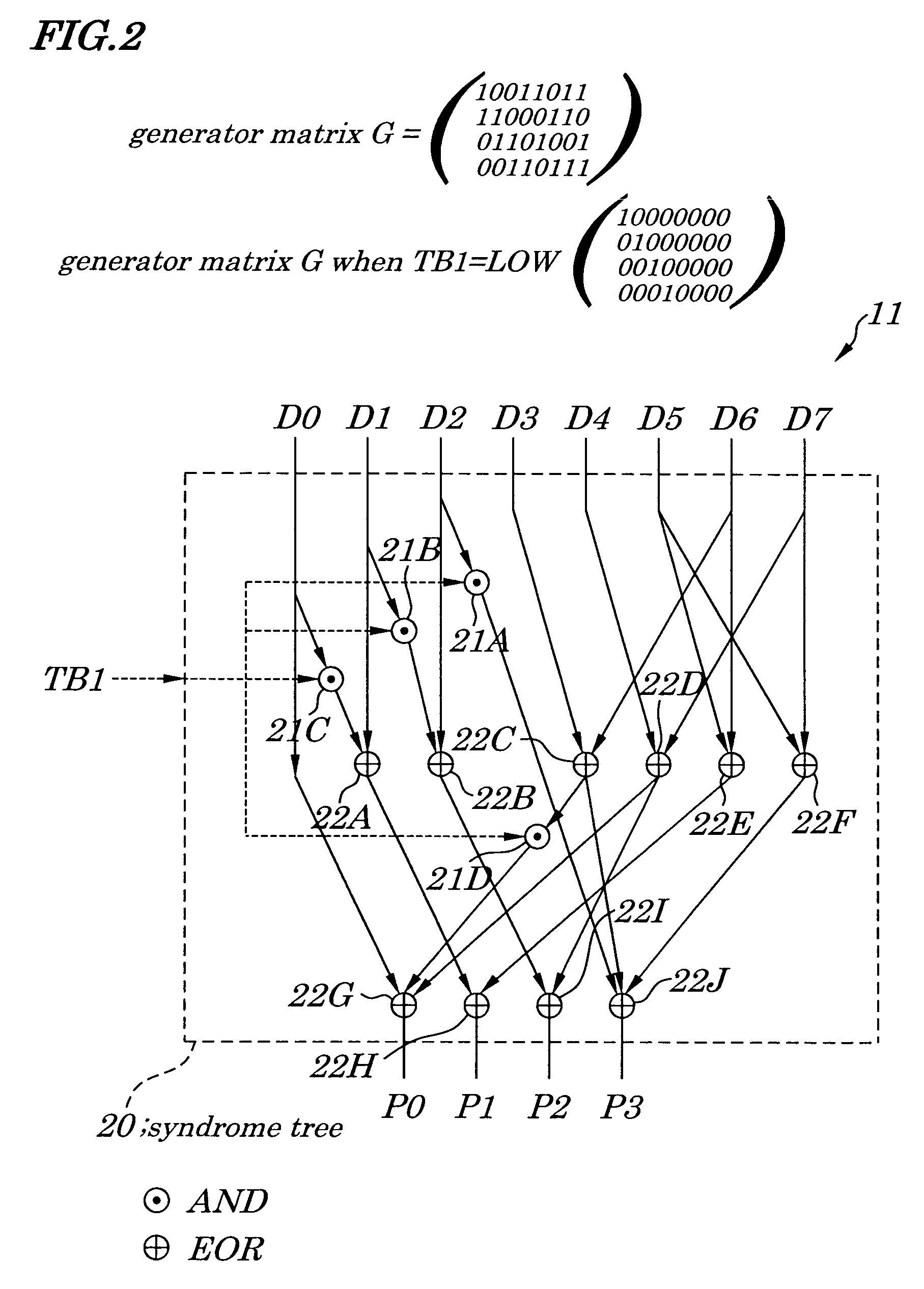
ActiveUS7225390B2Effective correctionReduce error rateCode conversionDigital storageHamming codeError location
A semiconductor synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) device capable of correcting bits having a low error rate in a Pause Refresh Tail distribution and of reducing a data holding current by lengthening a refresh period so that the refresh period exceeds a period for a Pause Refresh real power. The semiconductor memory device is made up of a 16-bit SDRAM having a Hamming Code and including an ECC (Error Correcting Code) circuit made up of an encoding circuit controlled by a first test signal to output a parity bit corresponding to an information bit, a decoding circuit controlled by second test signal to output an error location detecting signal indicating an error bit in codeword, and an error correcting circuit controlled by a third test signal to input an error location detecting signal and to output an error bit in a reverse manner.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Forward error correction encoding for multiple link transmission capatible with 64b/66b scrambling
InactiveUS20080109707A1Reduce overheadCorrection errorError detection/correctionCode conversionHamming codeHigh bandwidth
Owner:IBM CORP
Forward error correction encoding for multiple link transmission compatible with 64B/66B scrambling
InactiveUS7996747B2Reduce overheadEasy to correctError detection/correctionCode conversionHamming codeHigh bandwidth
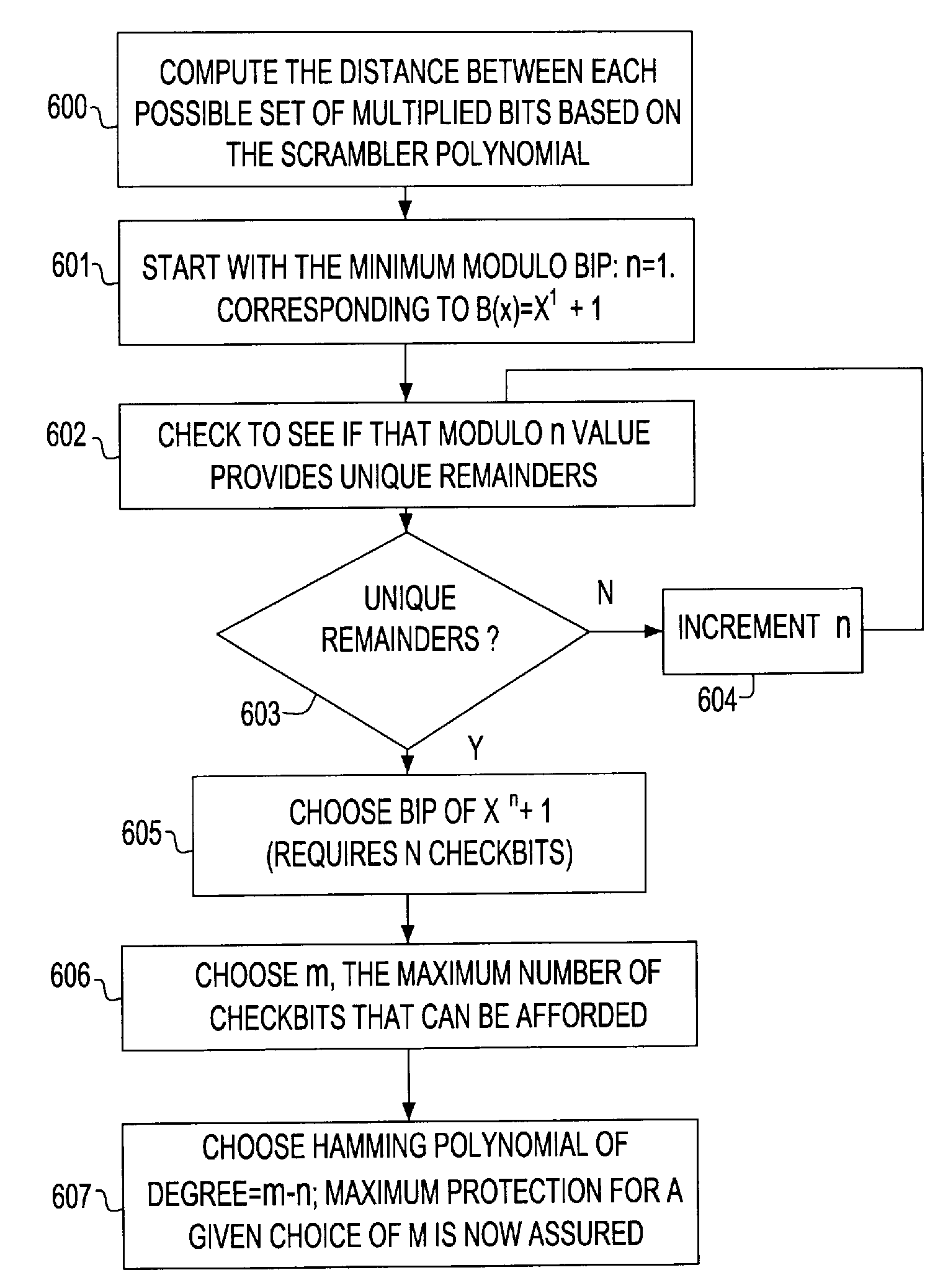
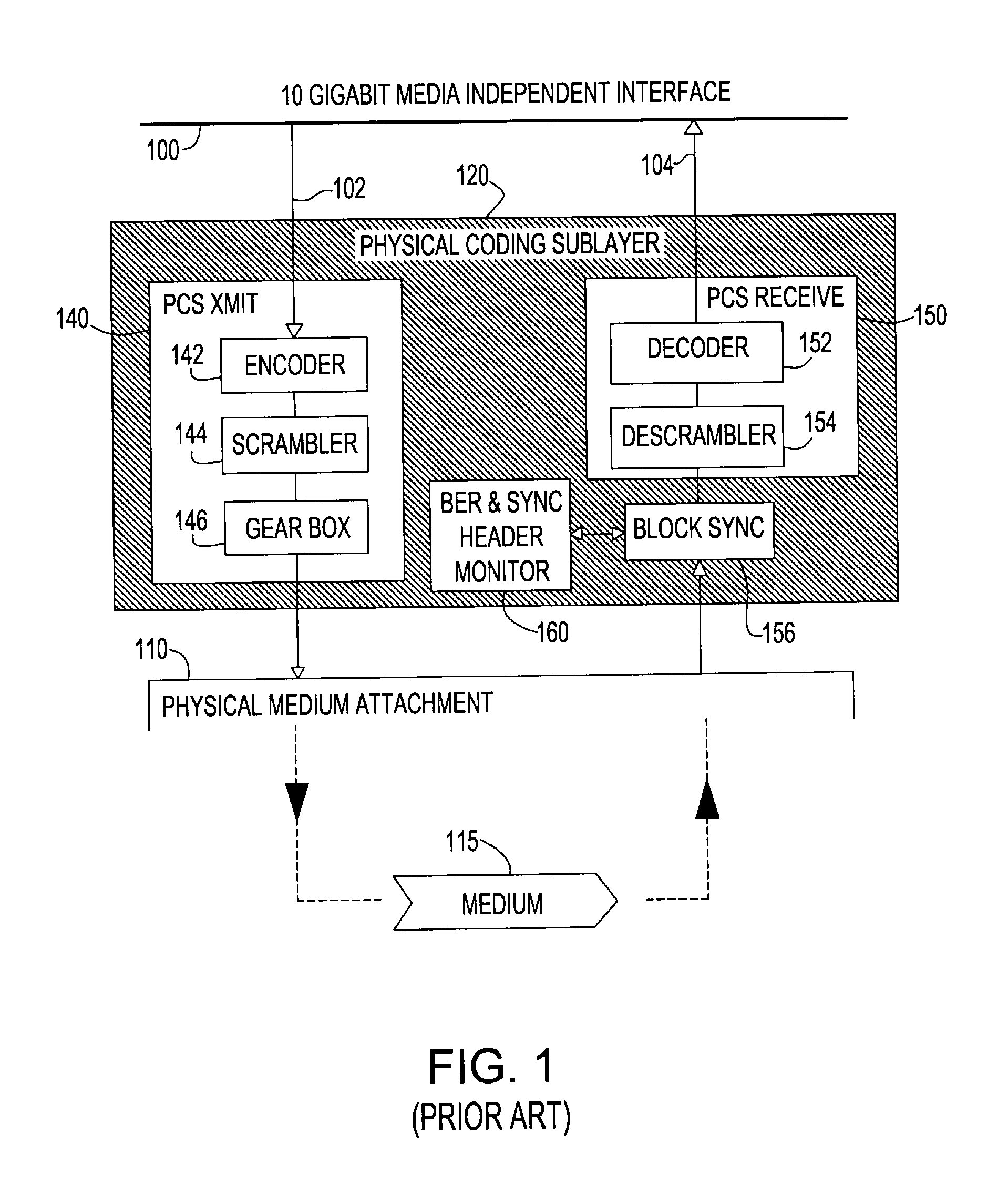
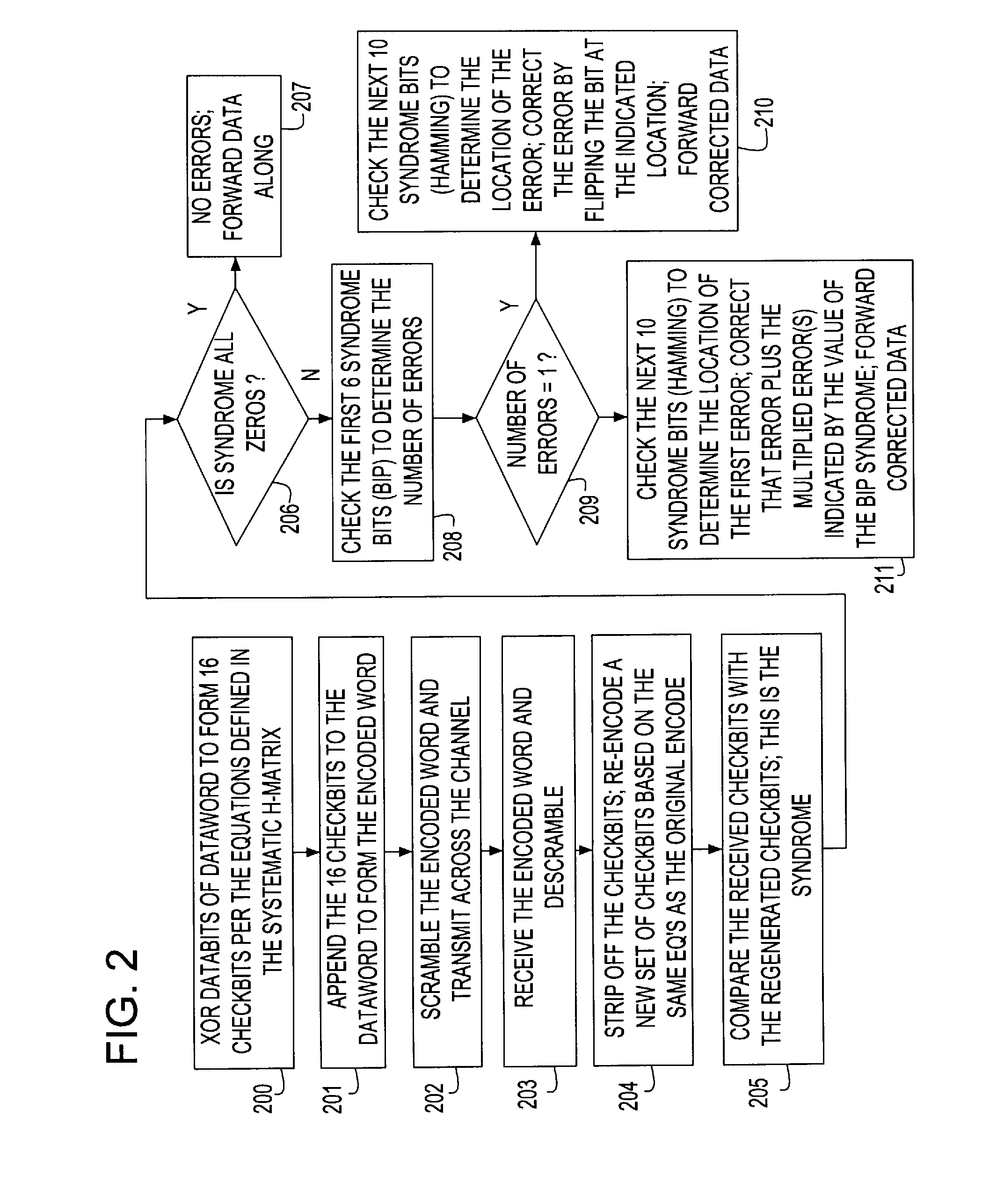
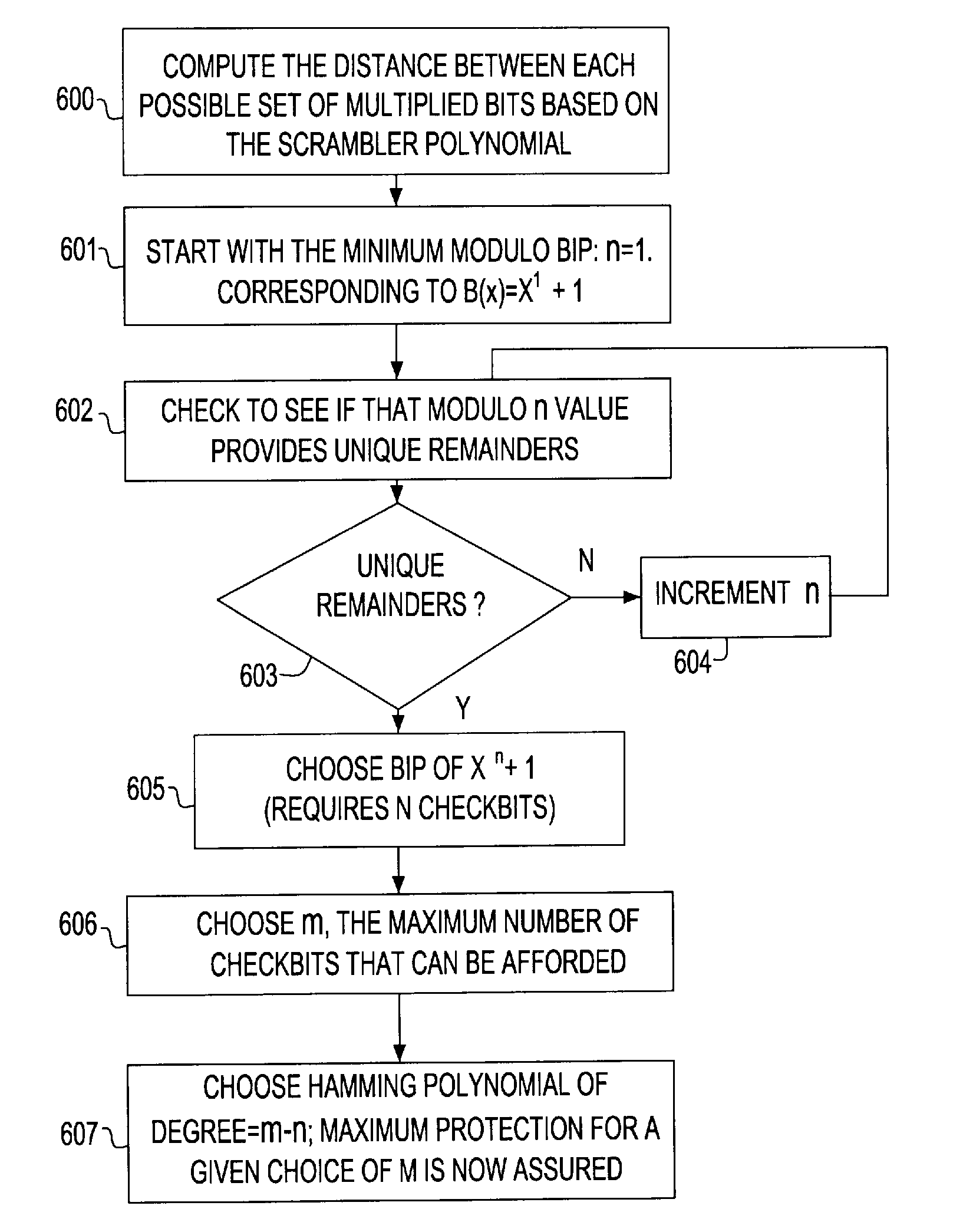
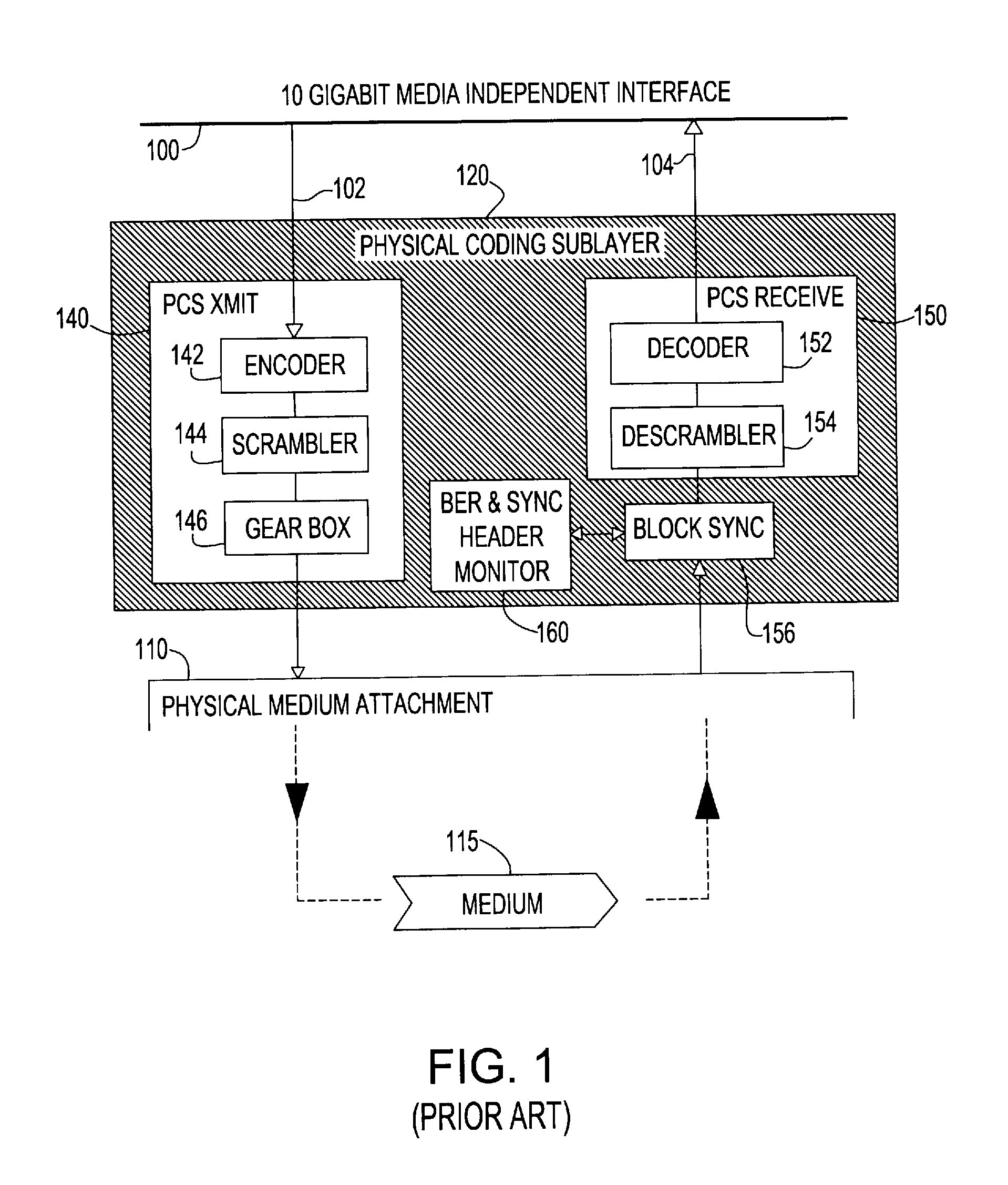
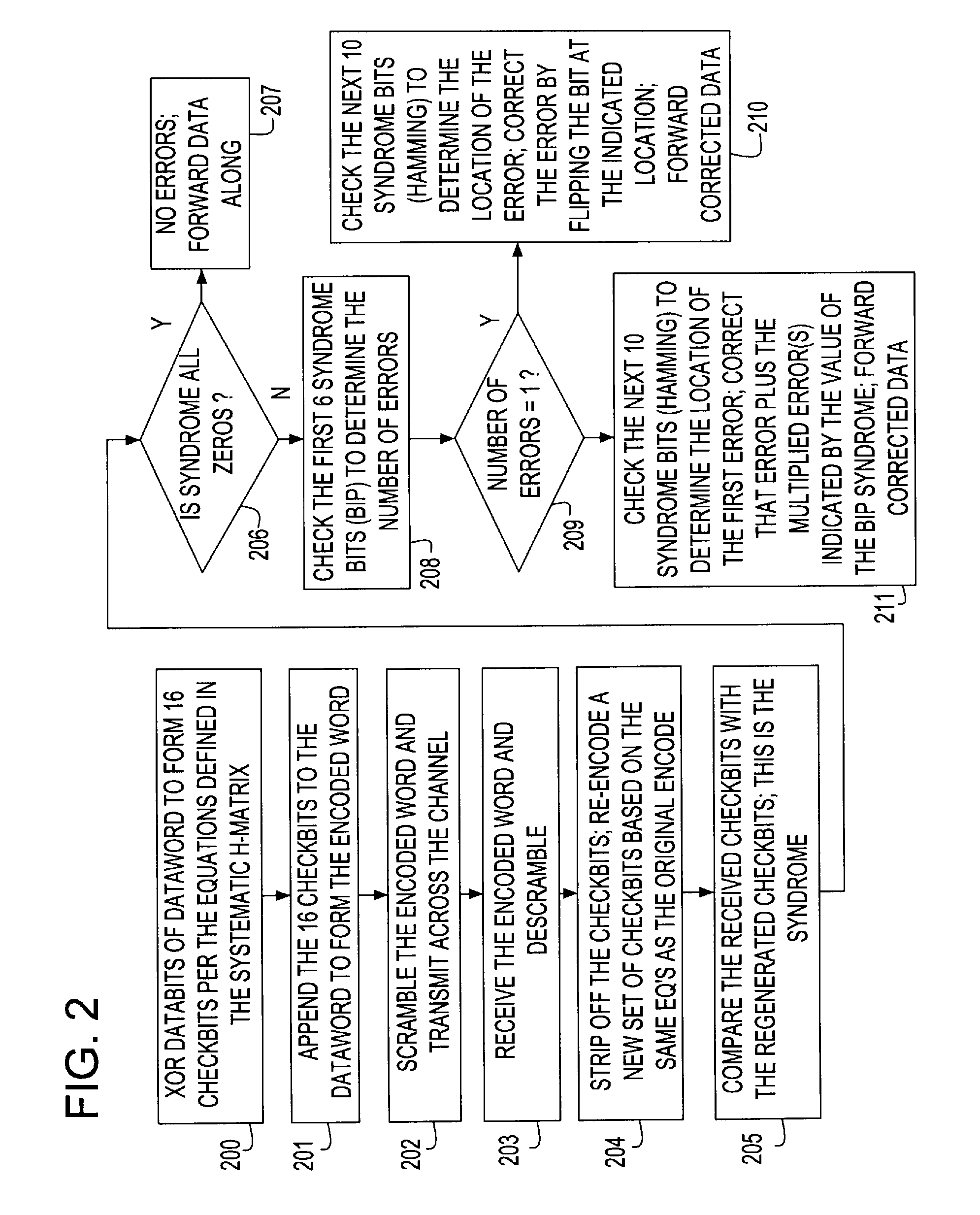
A Forward Error Correction (FEC) code compatible with the self-synchronized scrambler used by the 64B / 66B encoding standard for transmission on Serializer / Deserializer (SerDes) communications channel links. The FEC code allows encoding and decoding to occur before and after scrambling, respectively, so as to preserve the properties of the scrambling operation on the transmitted signal. The code allows the correction of any single transmission error in spite of the multiplication by three of all transmission errors due to the 64B / 66B scrambling process. A Hamming code is combined with a Bit Interleaved Parity code of degree n (BIP-n). These two codes provide for protection both for an error anywhere in the maximum length of the packet as well as for an error replicated two or three times by the descrambling process. All single bit errors, whether multiplied or not, have unique syndromes and are therefore easily correctable. In addition, the packet can be transported across multiple serial links for higher bandwidth applications without a degradation of the code efficiency. The Hamming code can be generated from any irreducible polynomial, such as H(x)=x10+x3+1. The BIP code is chosen to be of degree 6 to fit with 64B / 66B scrambling polynomial and is represented by B(x)=x6+1.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
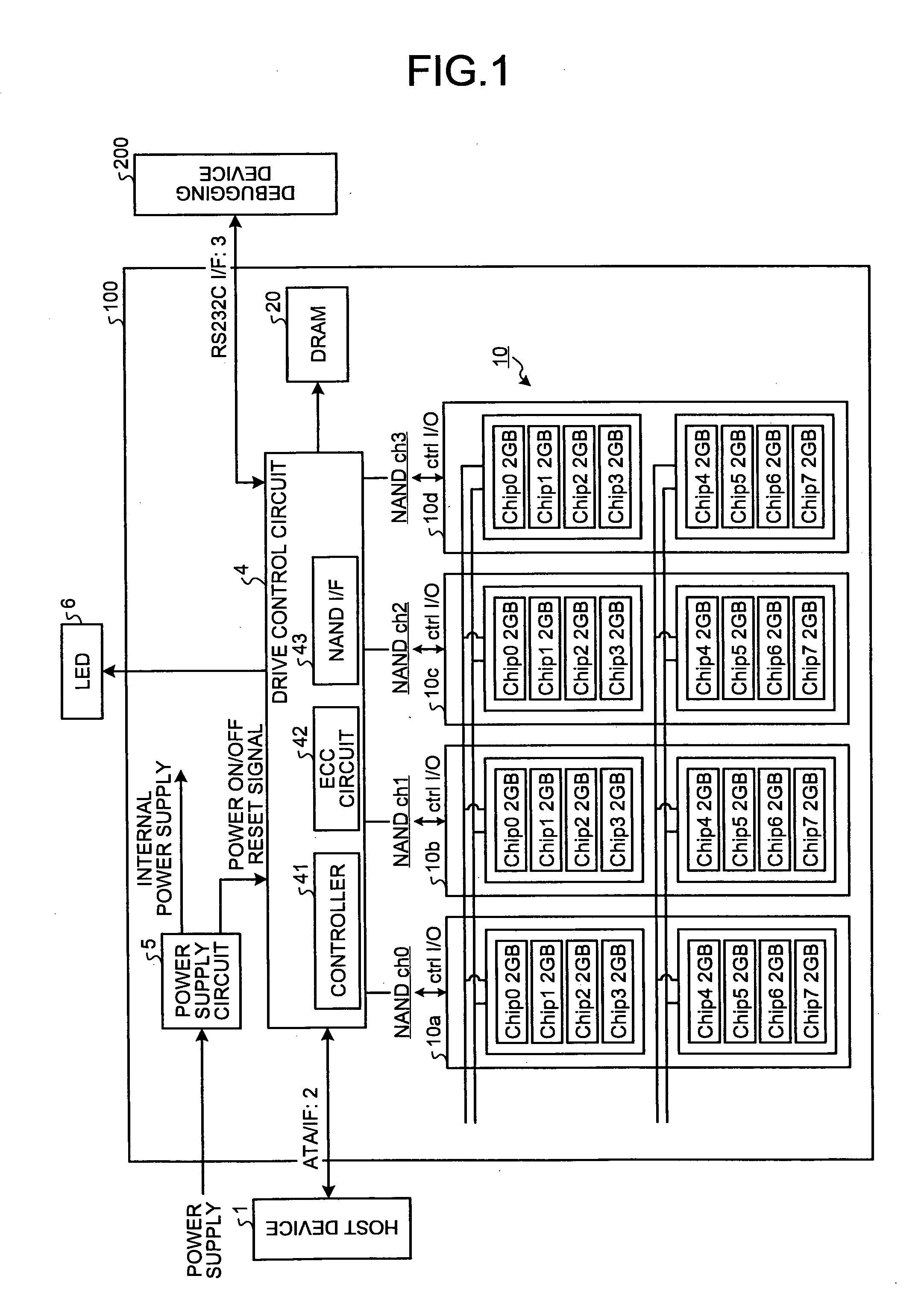
Semiconductor storage device, method of controlling the same, and error correction system
A semiconductor storage device, a method of controlling the same, and an error correction system allow reduction in power consumption and circuit scale without detriment to error correction capability. An error correction code (ECC) circuit of a solid state drive (SSD) performs first error correction on read data using a first error correction code (Hamming code), and further performs second error correction on the result of the first error correction using a second error correction code (BHC code). Furthermore, the ECC circuit performs third error correction on the result of the second error correction using a third error correction code (RS code).
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
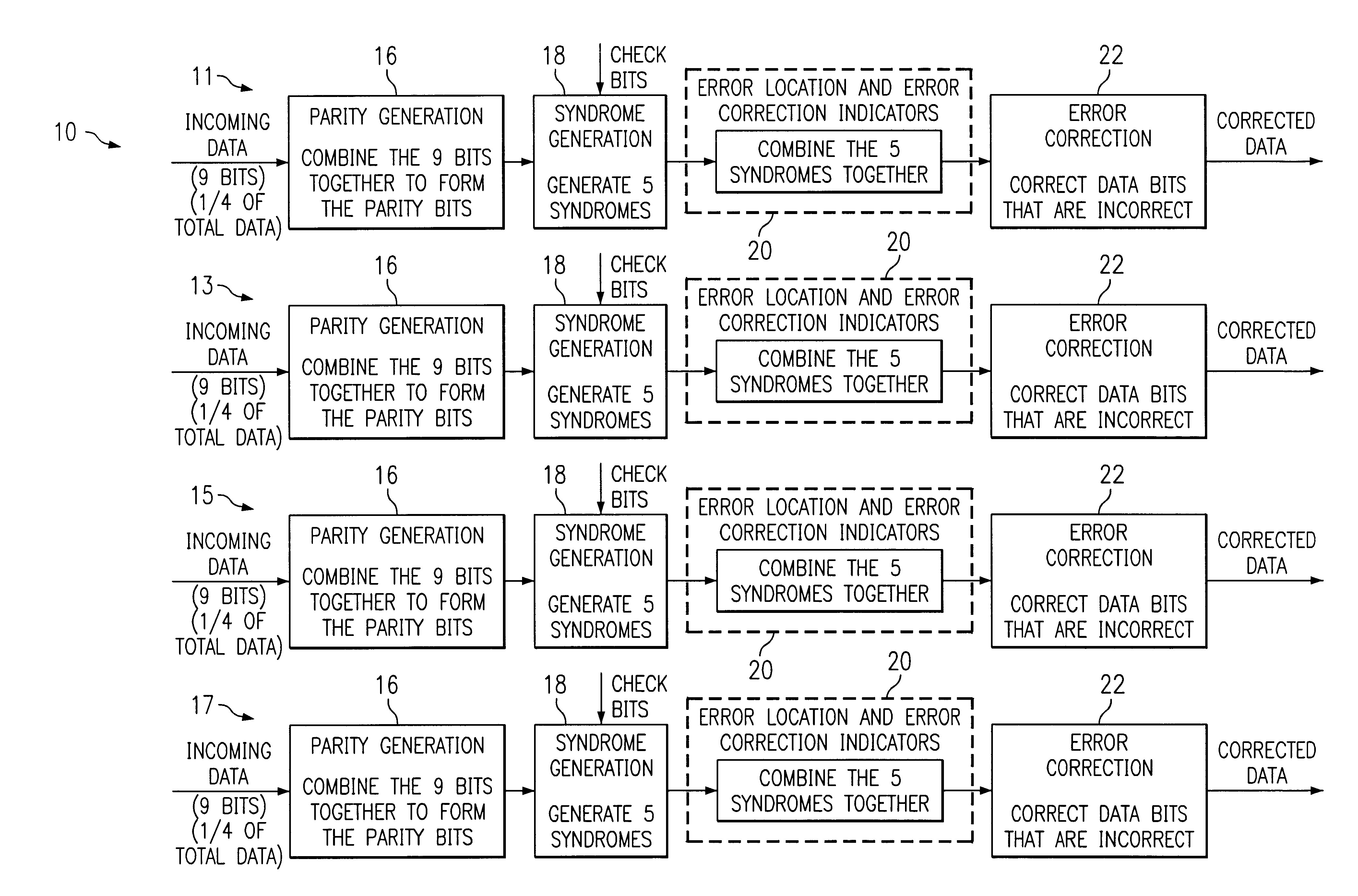
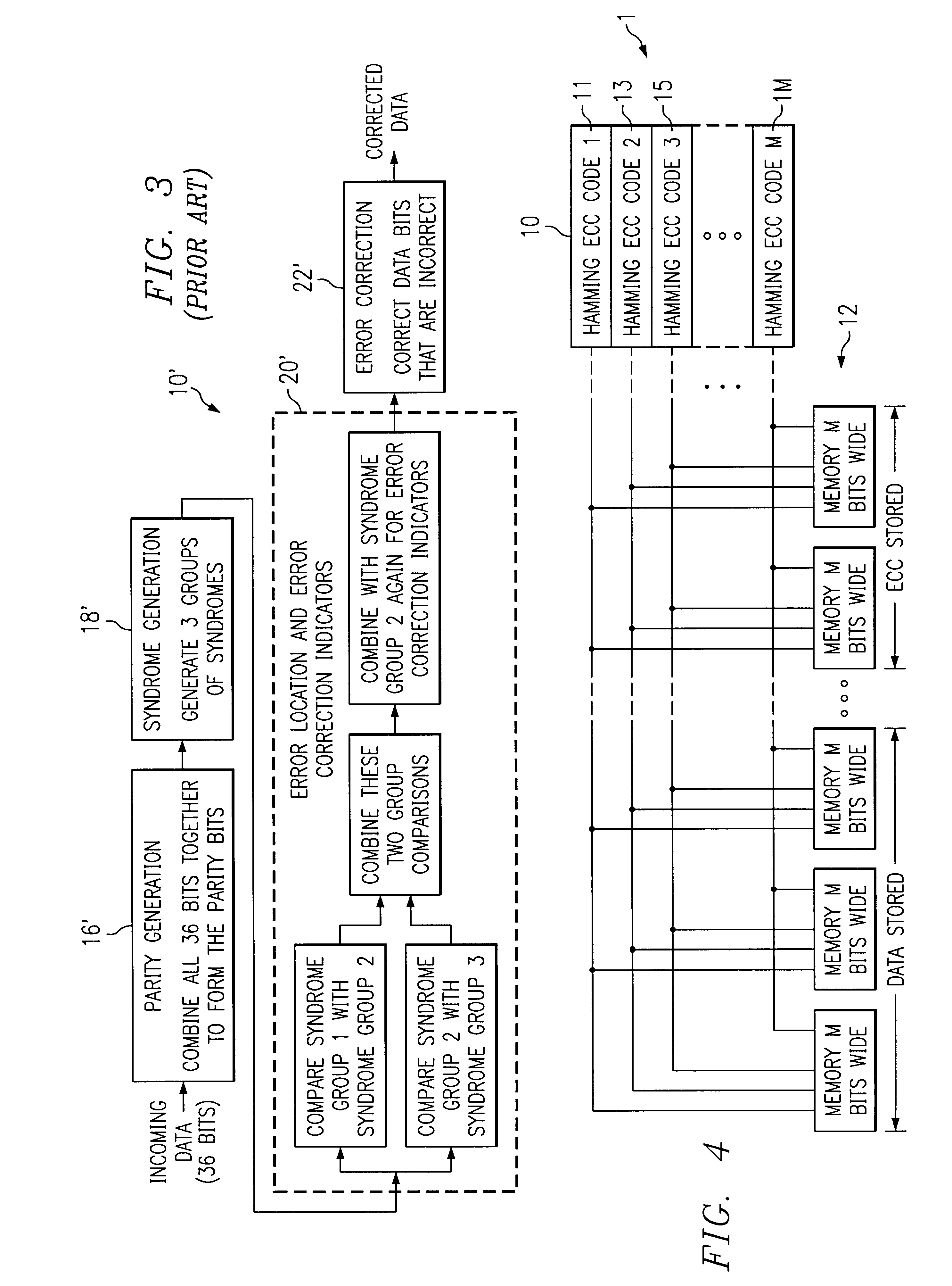
Multi-bit error correction system
InactiveUS6367046B1Error correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionHamming codeComputer module
An improved multi-bit error correction system. The inventive error correcting system performs a fast error correction operation on individual bits within multi-bit modules. In a specific implementation, the invention uses Hamming codes and divides an n times m bit data word into m modules, with each module having n bits. Next, the ith bits of each module are combined to form a set of parity bits. Syndrome bits are generated from the parity bits and used to locate errors in the bits and provide an indication of same. Finally, errors in the bits are corrected in a conventional manner to provide corrected data bits.
Owner:IBM CORP
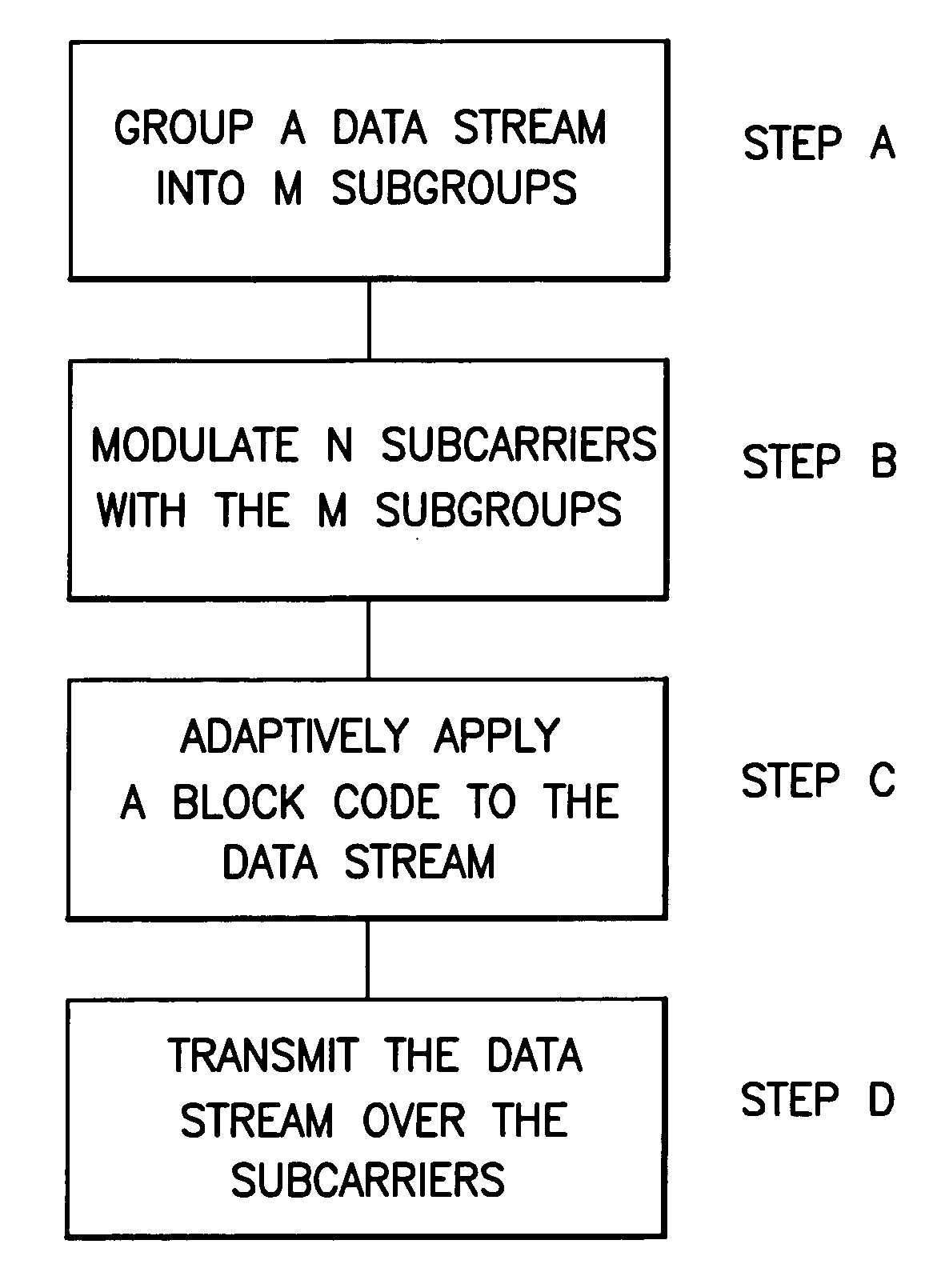
Adaptive multilevel block coded modulation for OFDM systems
InactiveUS20070019753A1Multiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsError correction/detection using block single space codingHamming codeData stream
A method includes grouping a data stream into a first plurality of subgroups, modulating a plurality of subcarriers with the first plurality of subgroups, adaptively applying a block code to said data stream comprising a repetition code, a Hamming code, and a plurality of uncoded bits based upon a channel characteristic of each of said plurality of subcarriers, and transmitting the data stream on the plurality of subcarriers.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
System and method for image search through images of multi-task portal vehicles
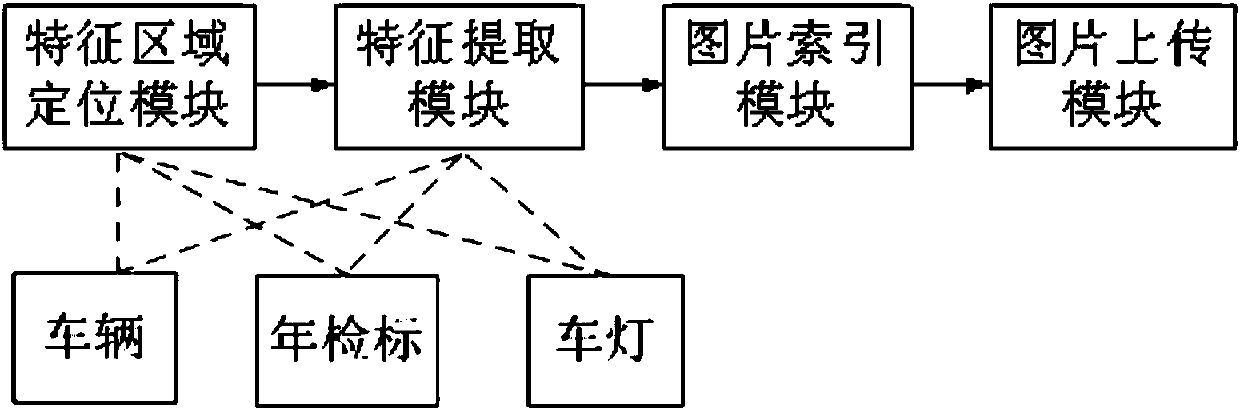
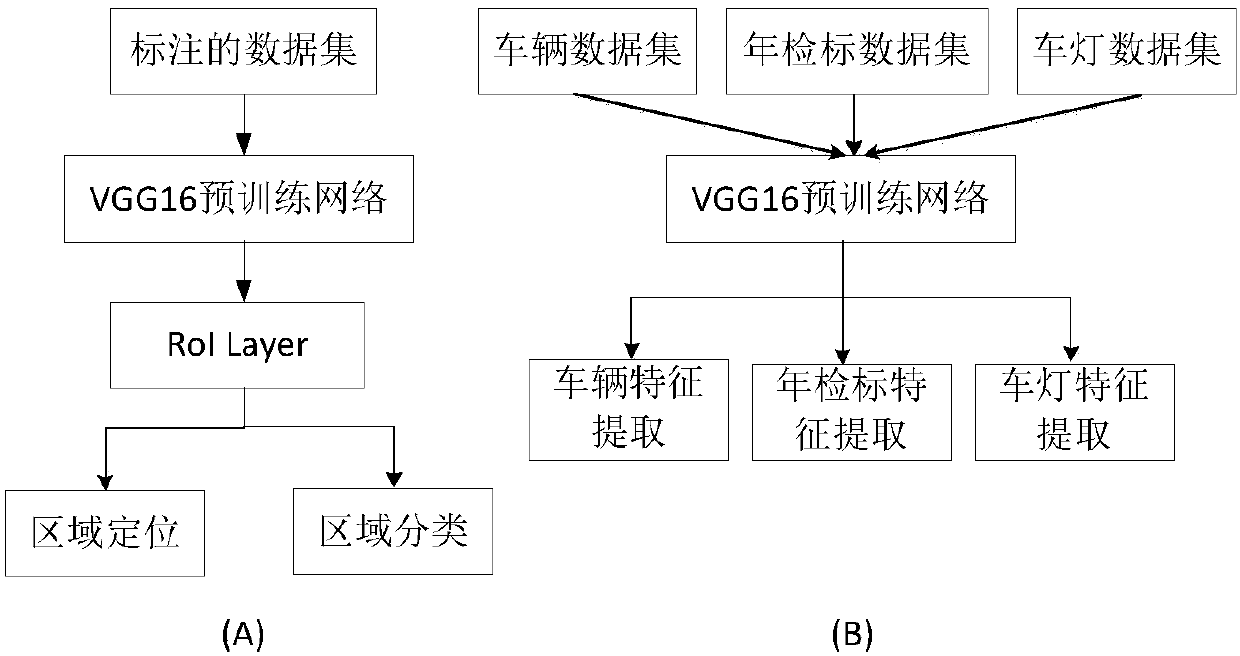
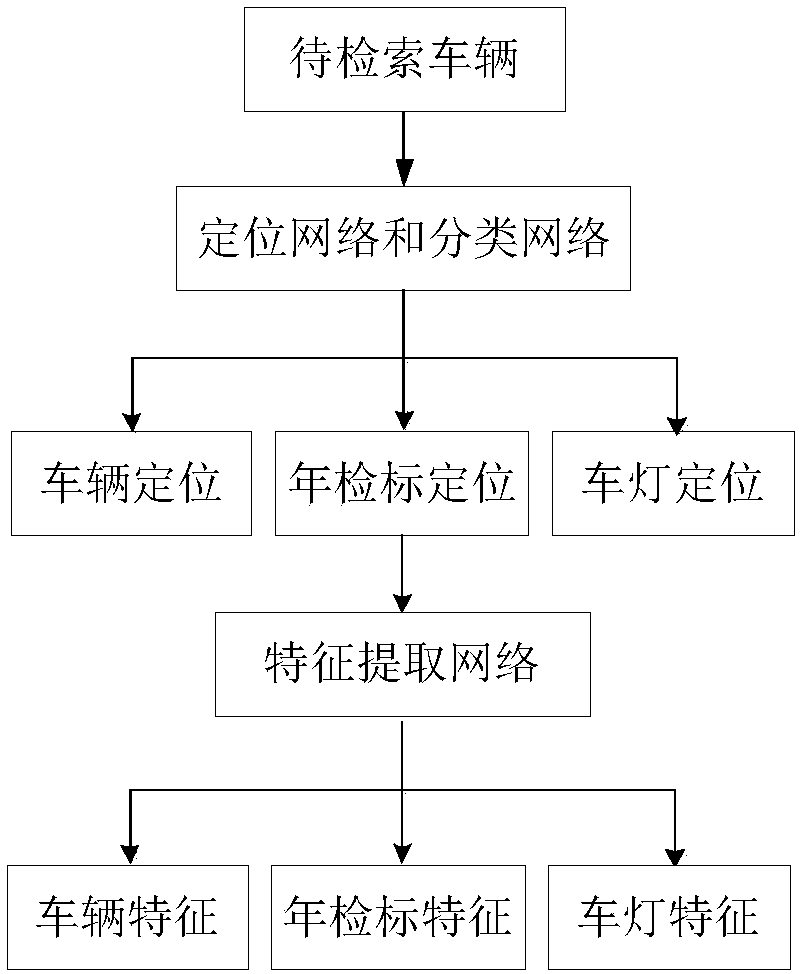
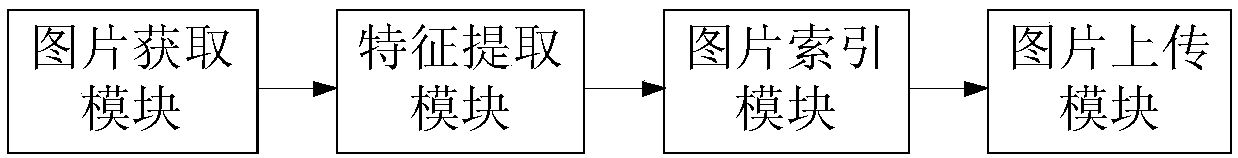
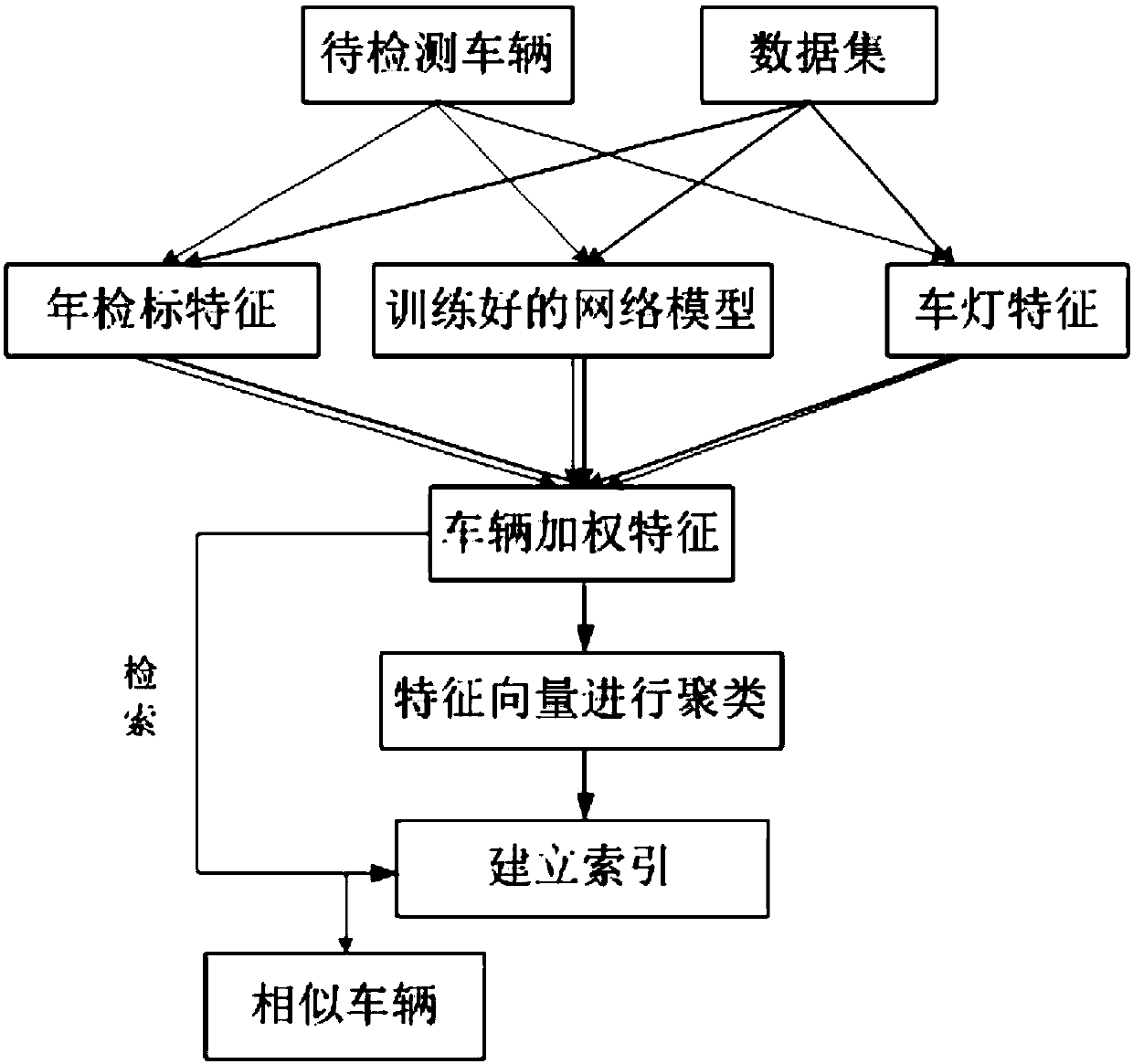
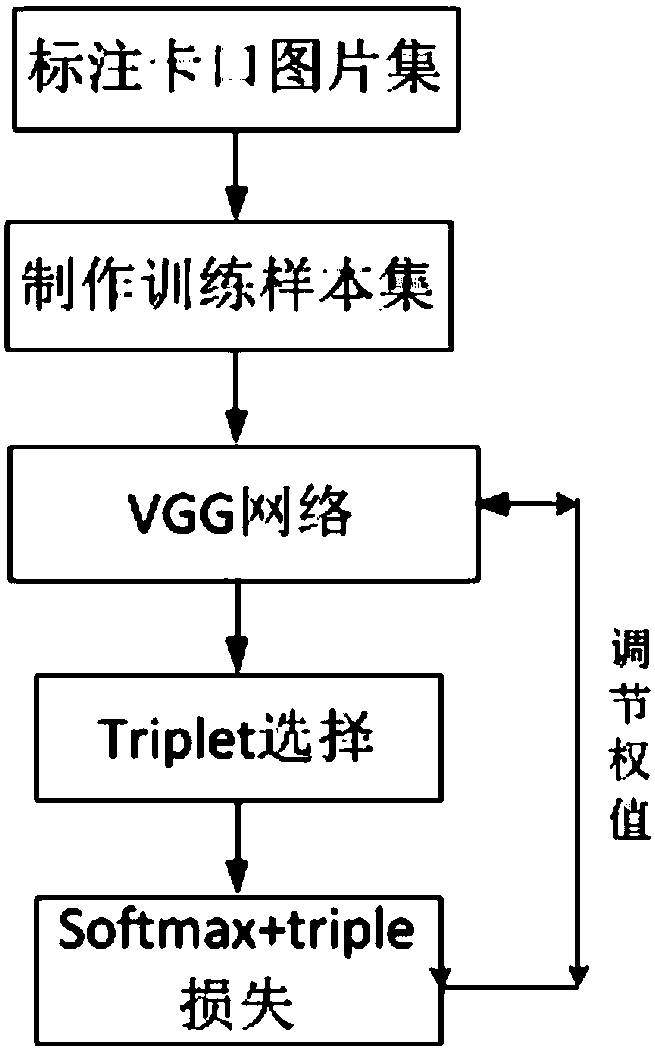
ActiveCN108171136AStrong semantic expression abilityEasy to classifyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsFeature vectorNerve network
The invention relates to a system and a method for image search through images of multi-task portal vehicles. According to the method, a deep neural network is utilized to establish a multi-task positioning network and a multi-task feature extraction network; the positioning network is trained based on an improved edge box detection technology and cascaded loss functions; positioning and feature detection are performed on vehicles, annual inspection signs and lamps in portal vehicle images, and global features and local features are combined; a softmax loss function and a triad loss function are adopted for network training; and finally local feature vectors are subjected to weighting combination, and global feature vectors of the last full-connection layer of the neural network are utilized to serve as vehicle features for retrieval, wherein an improved k-means algorithm is adopted to find a K class in retrieval, and then an SVM is utilized to form a Hash function for Hamming coding.In this way, retrieval speed is increased, and storage space is saved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG YINJIANG RES INST
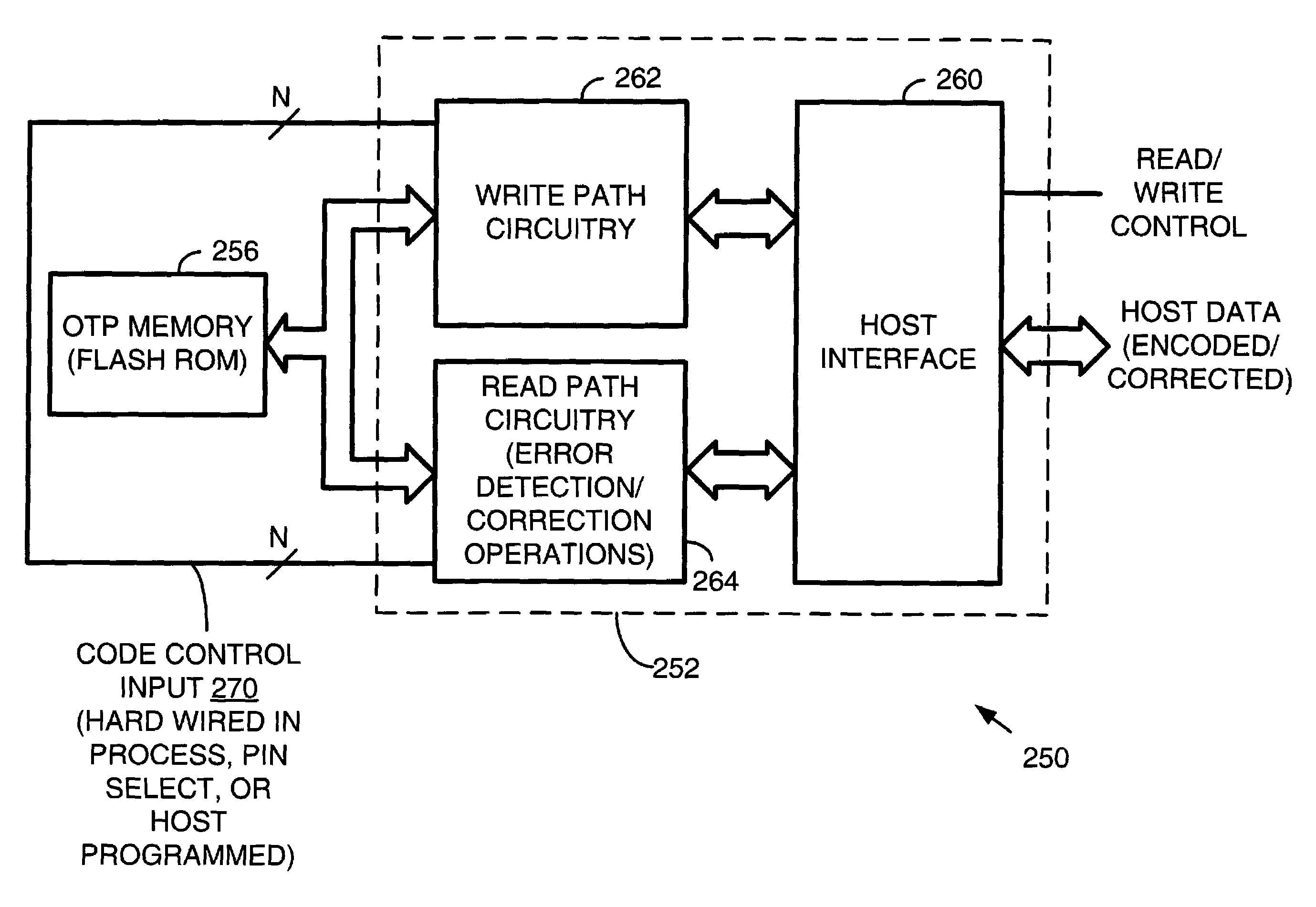
Variable Hamming error correction for a one-time-programmable-ROM
InactiveUS7003713B2Improve reliabilityEasy to migrateError identificationStatic storageHamming codeCommunications system
A one-time-programmable (OTP) module includes OTP memory and OTP input / output (I / O) that performs error correction operations. The OTP module may be used in a data communications system. The error correction operations operate according to one of a plurality of supported coding schemes. In one embodiment, the error correction operations are based upon Hamming code operations. The coding scheme employed by the error correction operations is set by a code control input. The code control input is chosen based upon the inherent quality of the OTP memory. The OTP module may thus be incorporated into any of a variety of processes, each of which has its own OTP memory quality.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
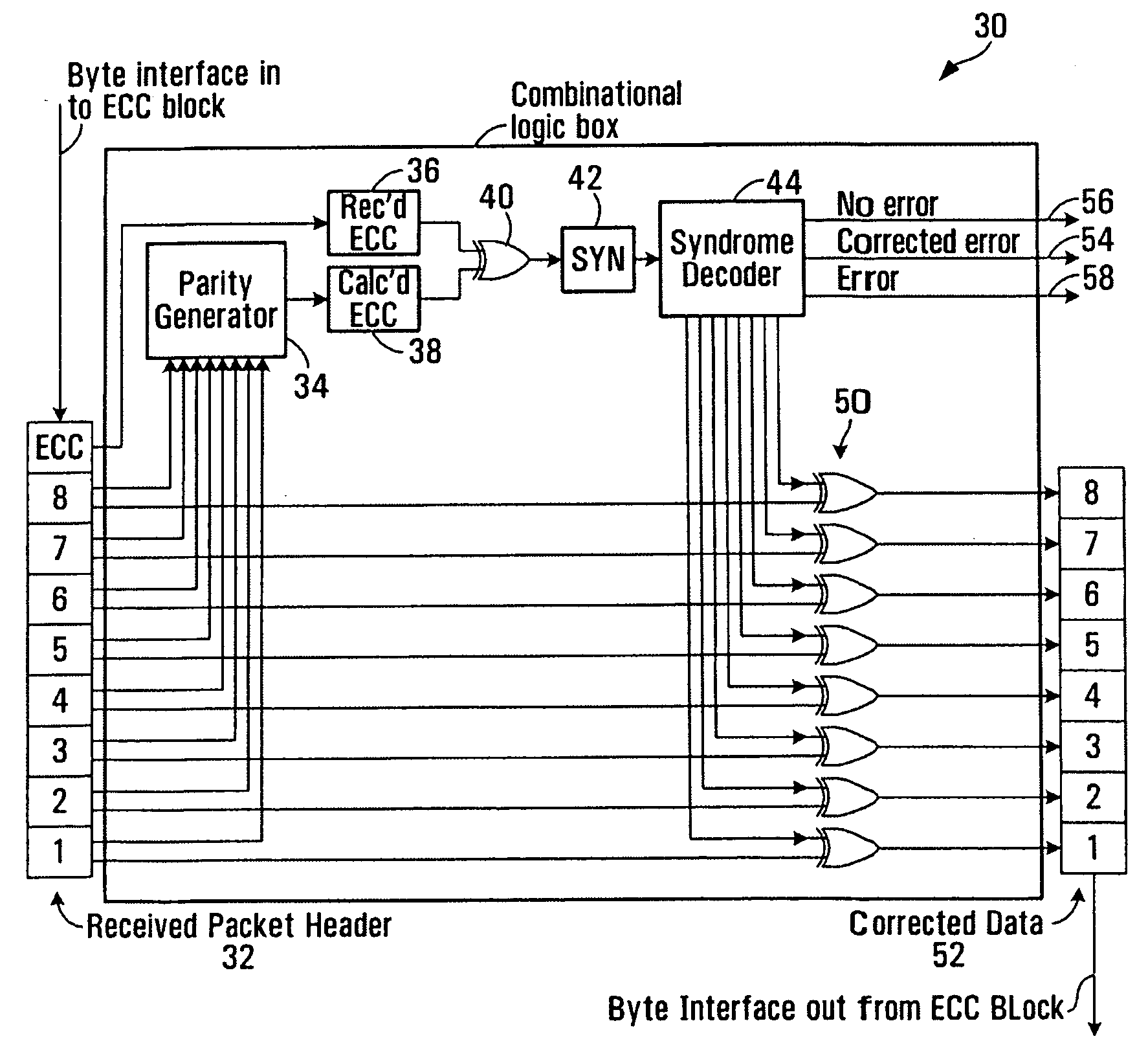
Method and apparatus for error management
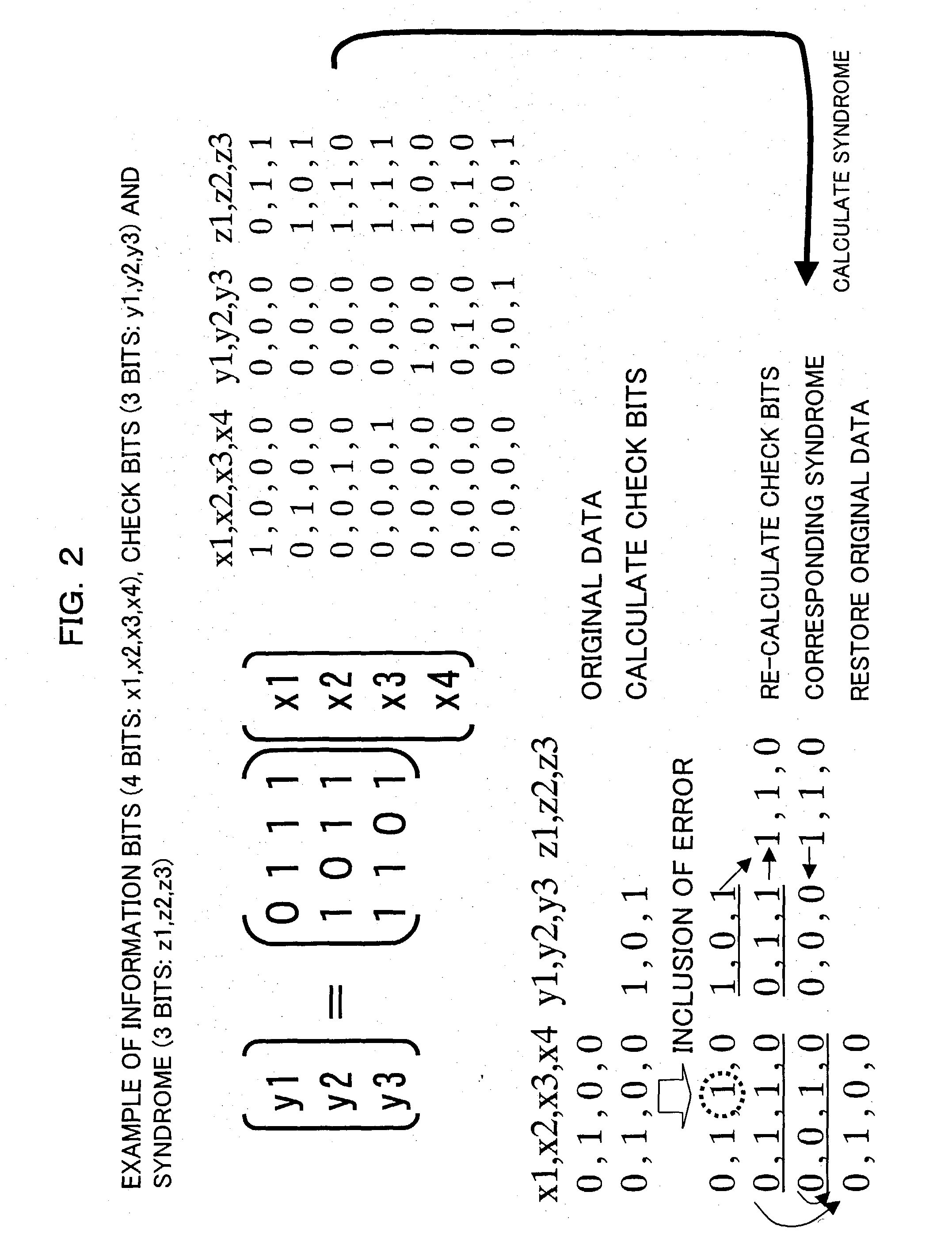
To derive a Hamming code to manage data errors a set of at least four parity bit positions is selected for parity bits which will protect a set of data bits (where each data bit has a data bit position in the data bit set). A syndrome is determined for each data bit position. This involves selecting a unique sub-set of at least three parity bit positions. The unique sub-set shares at least one parity bit position with at least one other unique sub-set of at least three parity bit positions. A parity bit value may then be calculated for each parity bit position based on the determined syndromes. The header of a packet may be provided with a word which defines the length of the packet and an error management code generated utilizing this word so that errors in the word may be detected and, possibly, corrected.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
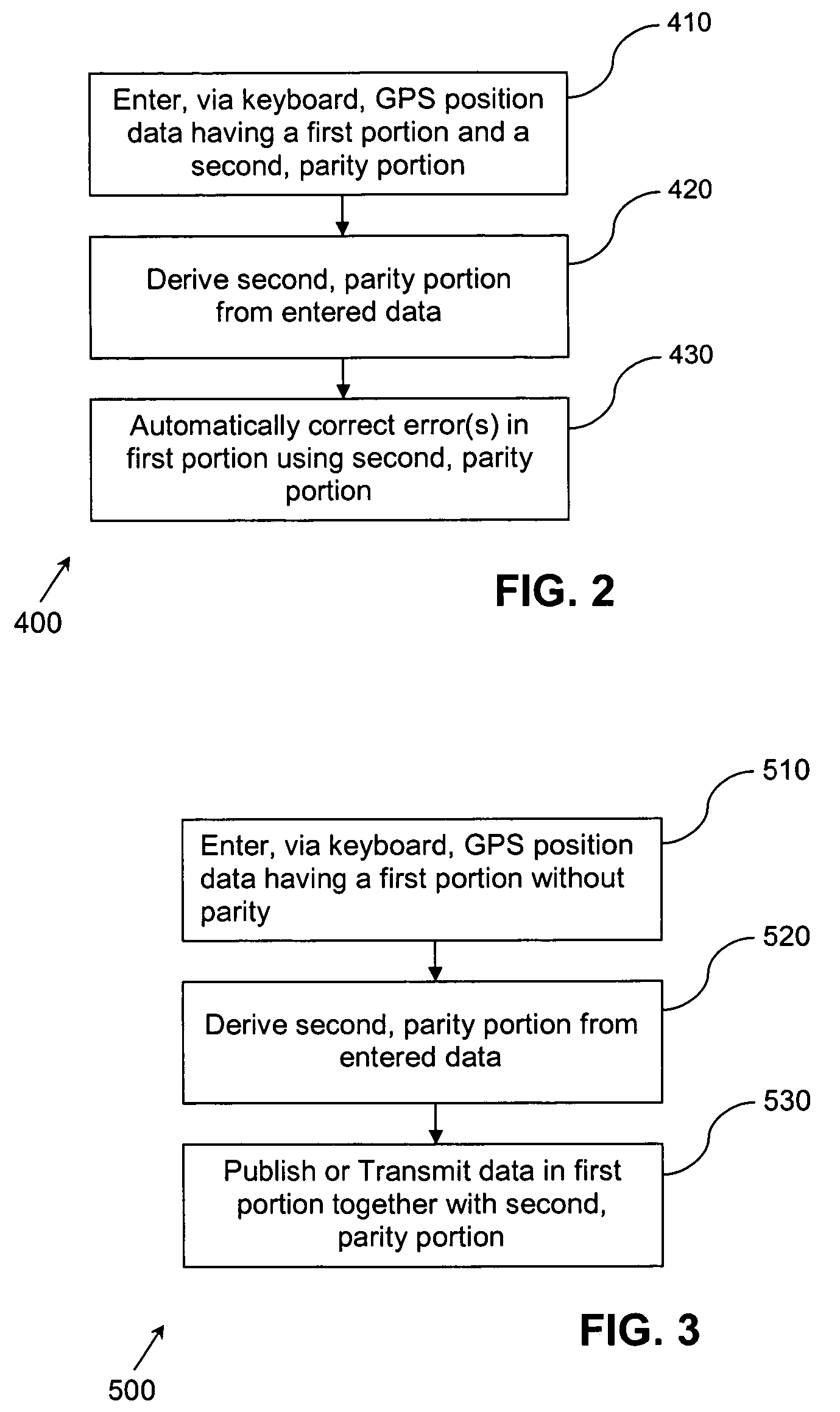
System and method for data entry
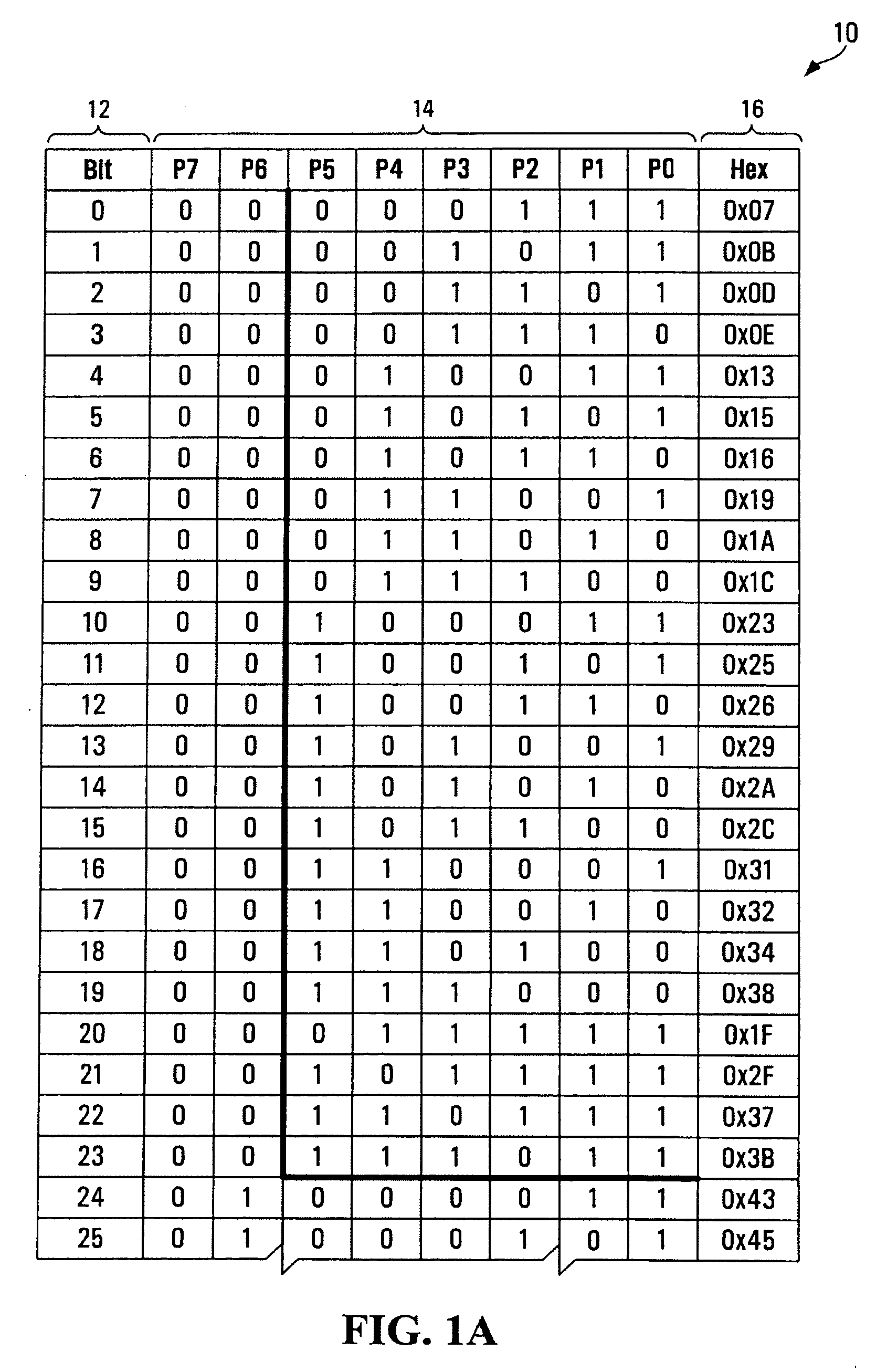
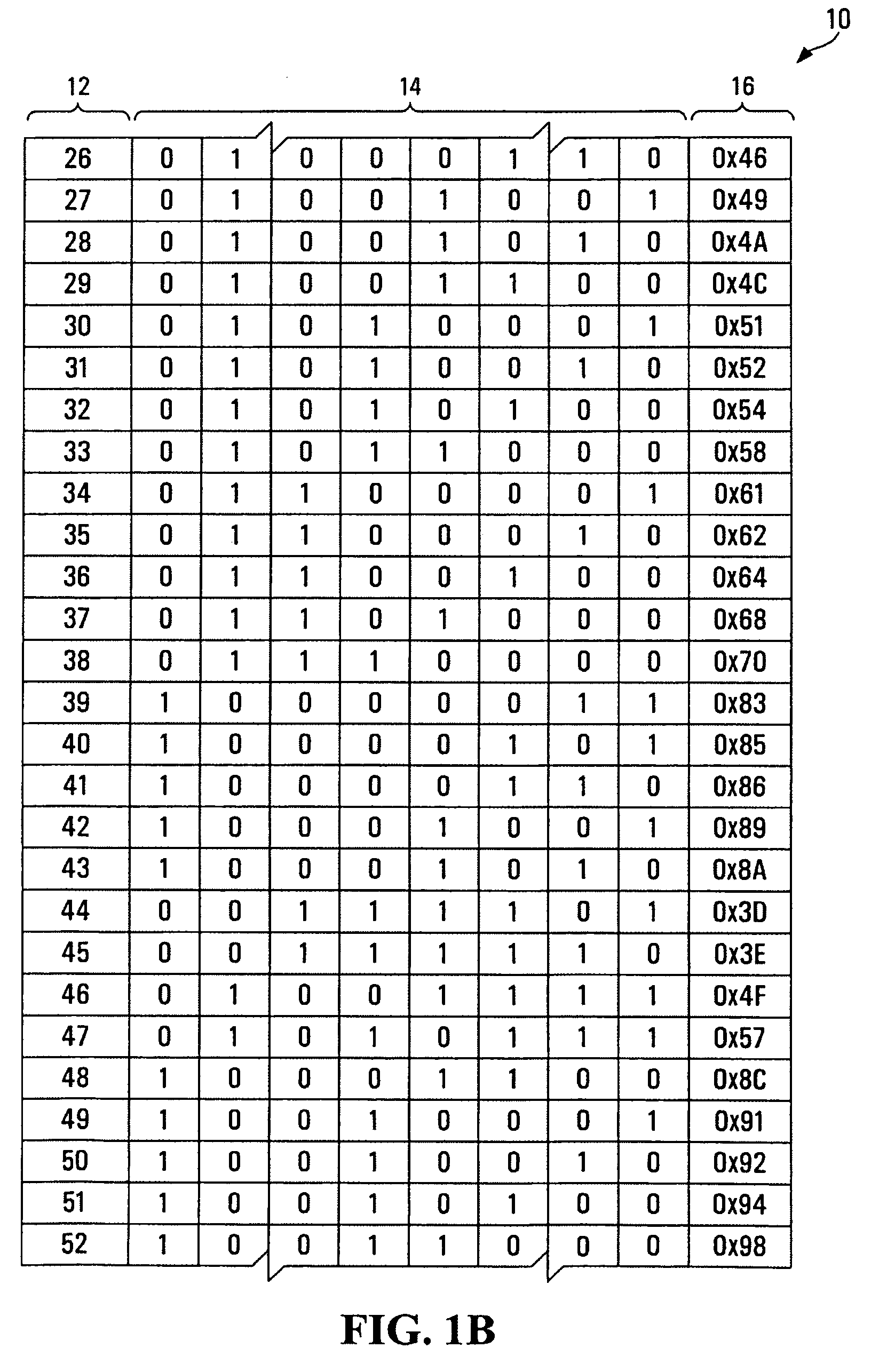
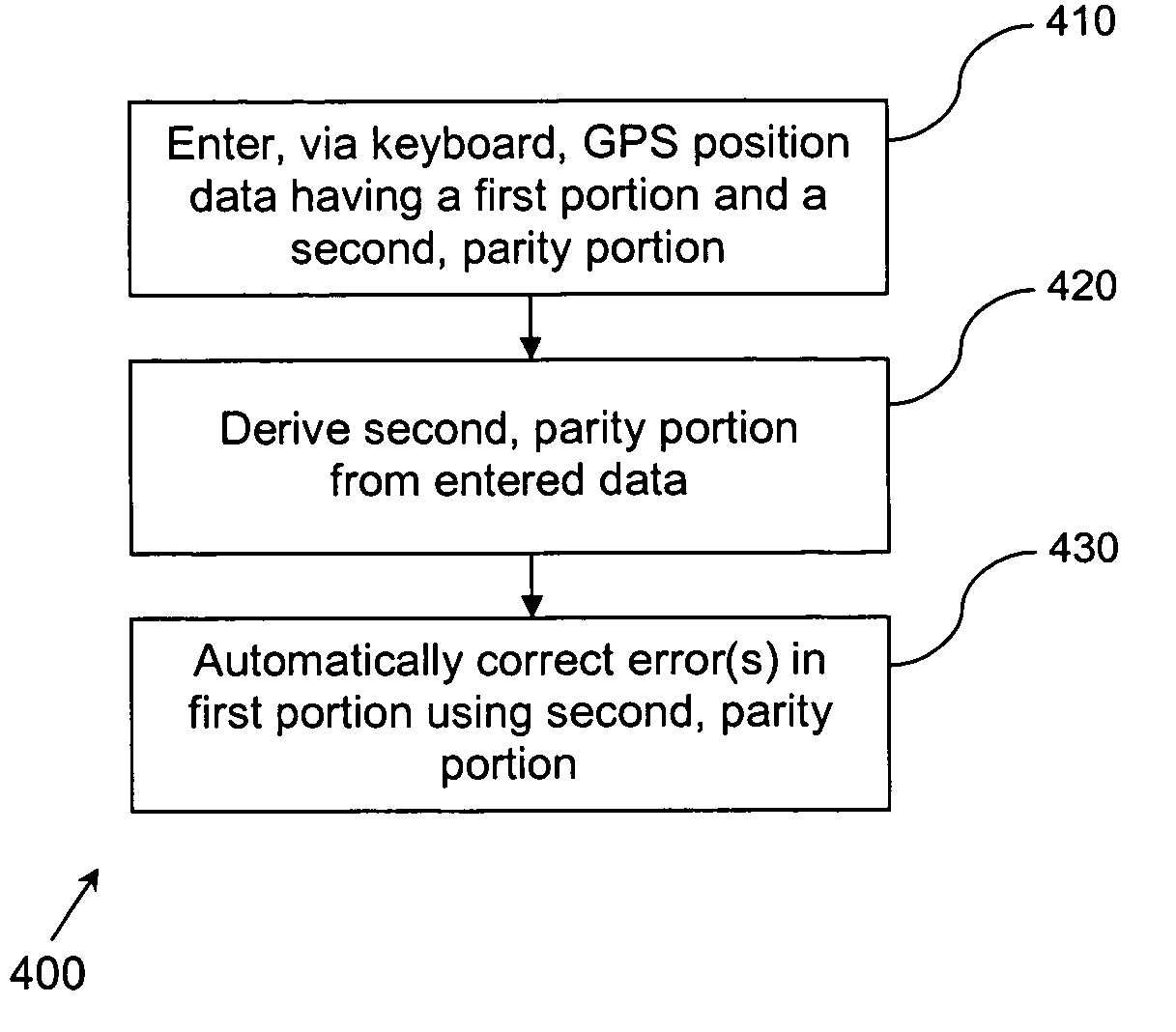
A system and method for data entry by an operator uses data containing a first component and a second component derived therefrom, wherein the second component has error detection and correction abilities therein. The second component of the entered data is used to detect and correct error in the data entered for the first component. The first and second components are preferably characters (e.g., representing GPS position information) entered via a data entry device, while the second component preferably comprises Hamming code. The detection and correction can be performed after data entry and again after signal transmission.
Owner:IBM CORP
Error detection and correction scheme for a memory device
ActiveUS20070162824A1Code conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresHamming codeCorrection code
Data is read from a memory array. Before being stored in a data buffer, a Hamming code detection operation and a Reed-Solomon code detection operation are operated in parallel to determine if the data word has any errors. The results of the parallel detection operations are communicated to a controller circuit. If an error is present that can be corrected by the Hamming code correction operation, this is performed and the Reed-Solomon code detection operation is performed on the corrected word. If the error is uncorrectable by the Hamming code, the Reed-Solomon code correction operation is performed on the word.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Encoding and decoding method and apparatus
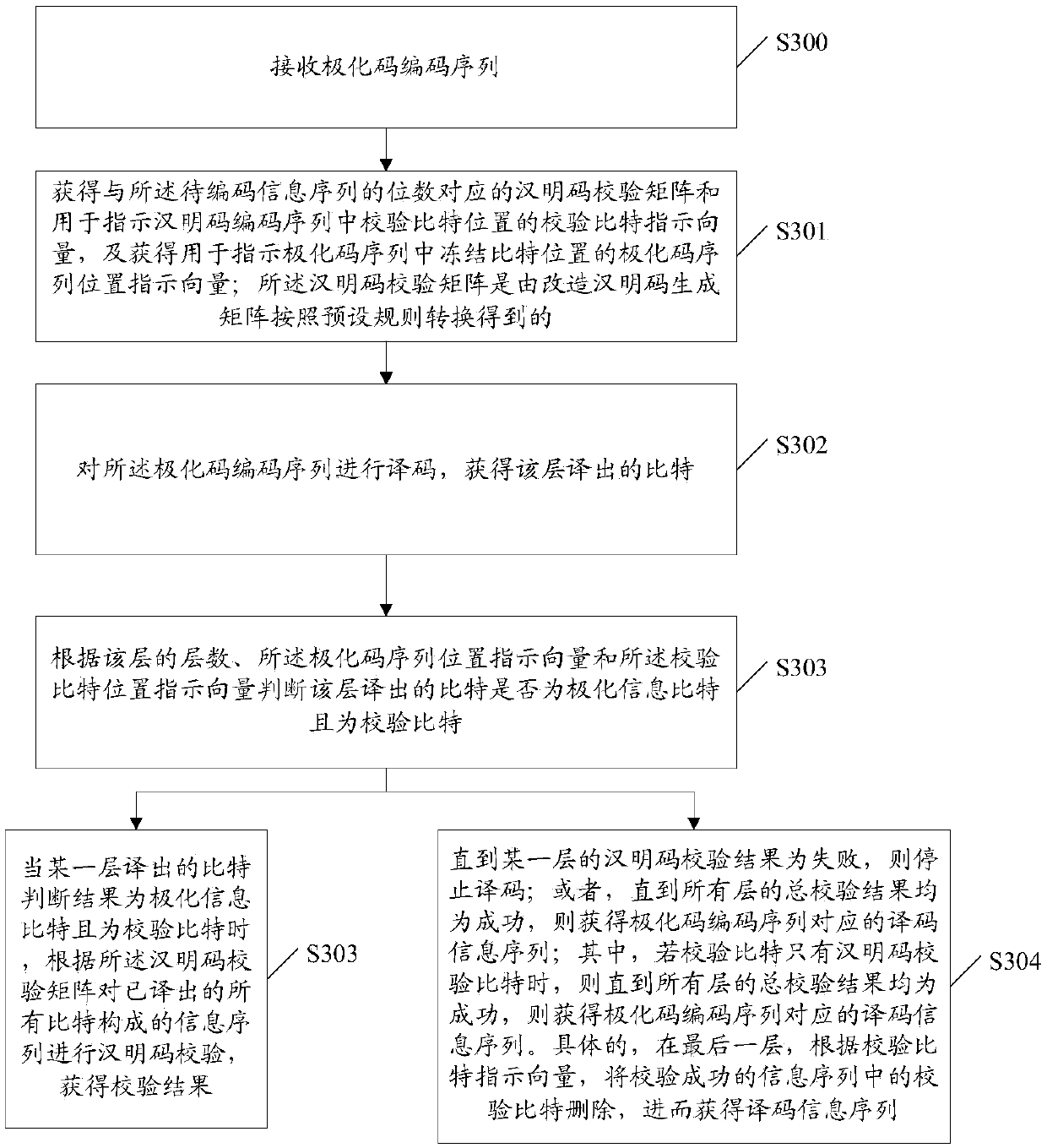
ActiveCN107612561AImprove error detection efficiencyError preventionError correction/detection using linear codesDecoding methodsHamming code
The invention discloses an encoding and decoding method and apparatus. In the encoding apparatus, a to-be-encoded information sequence is multiplied with a reformed Hamming code generation matrix obtained by inserting columns of corresponding check bits in the original Hamming code generation matrix in the columns of corresponding Hamming code information bits in the original Hamming code generation matrix to obtain a Hamming code encoding sequence, and the check bits in the Hamming code encoding sequence are dispersed in the Hamming code information bits, and polar code encoding is performedbased on a reformed polar code sequence. During decoding, layer-by-layer decoding is performed based on a serial decoding algorithm, once the bit decoded in each layer is the polar code information bit and is the check bit, Hamming code check is performed, the decoding is stopped in the case of check failure, thereby terminating the decoding in advance, and providing the error detection efficiencyof the decoding.
Owner:WUHAN HONGXIN TECH DEV CO LTD
Fault-tolerant method of storage module of picosatellite based on FPGA
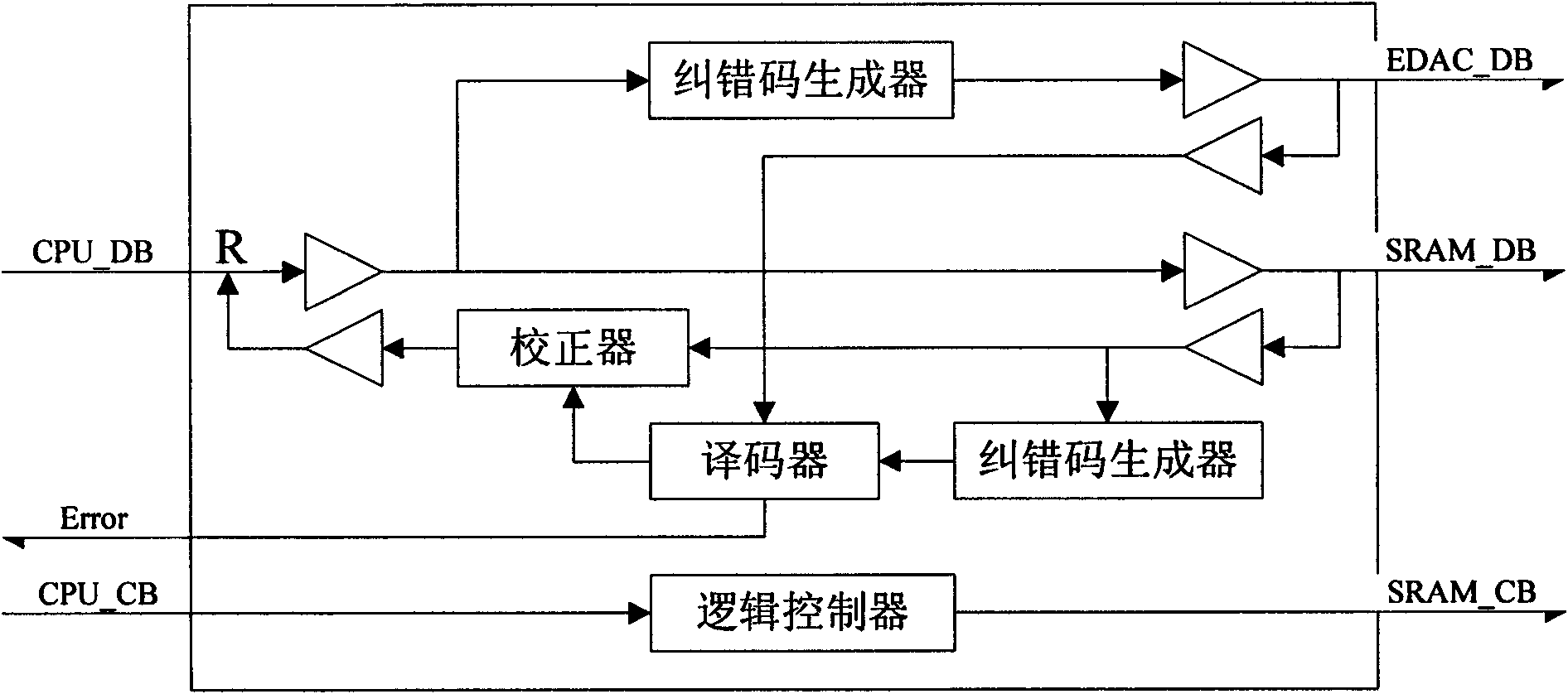
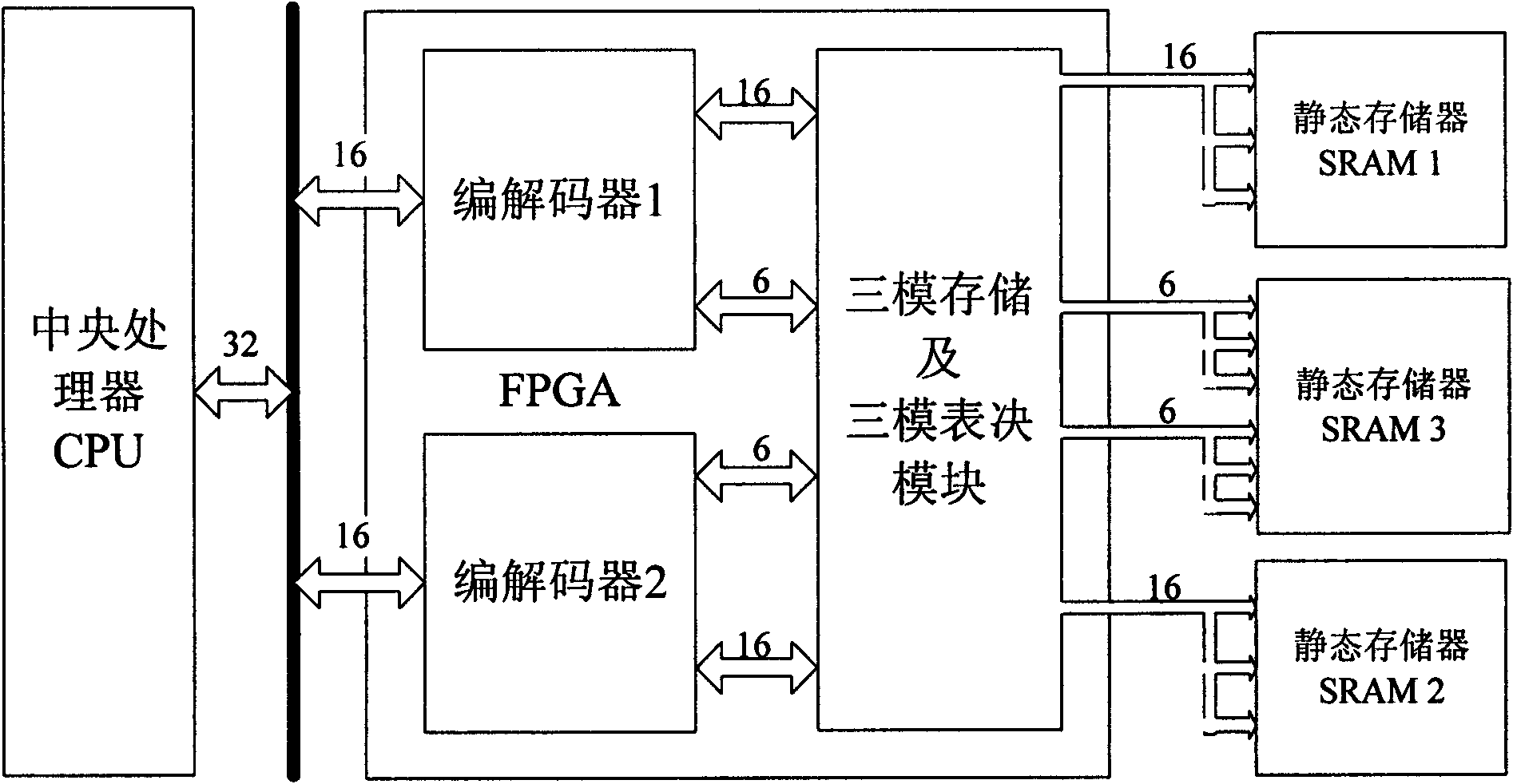
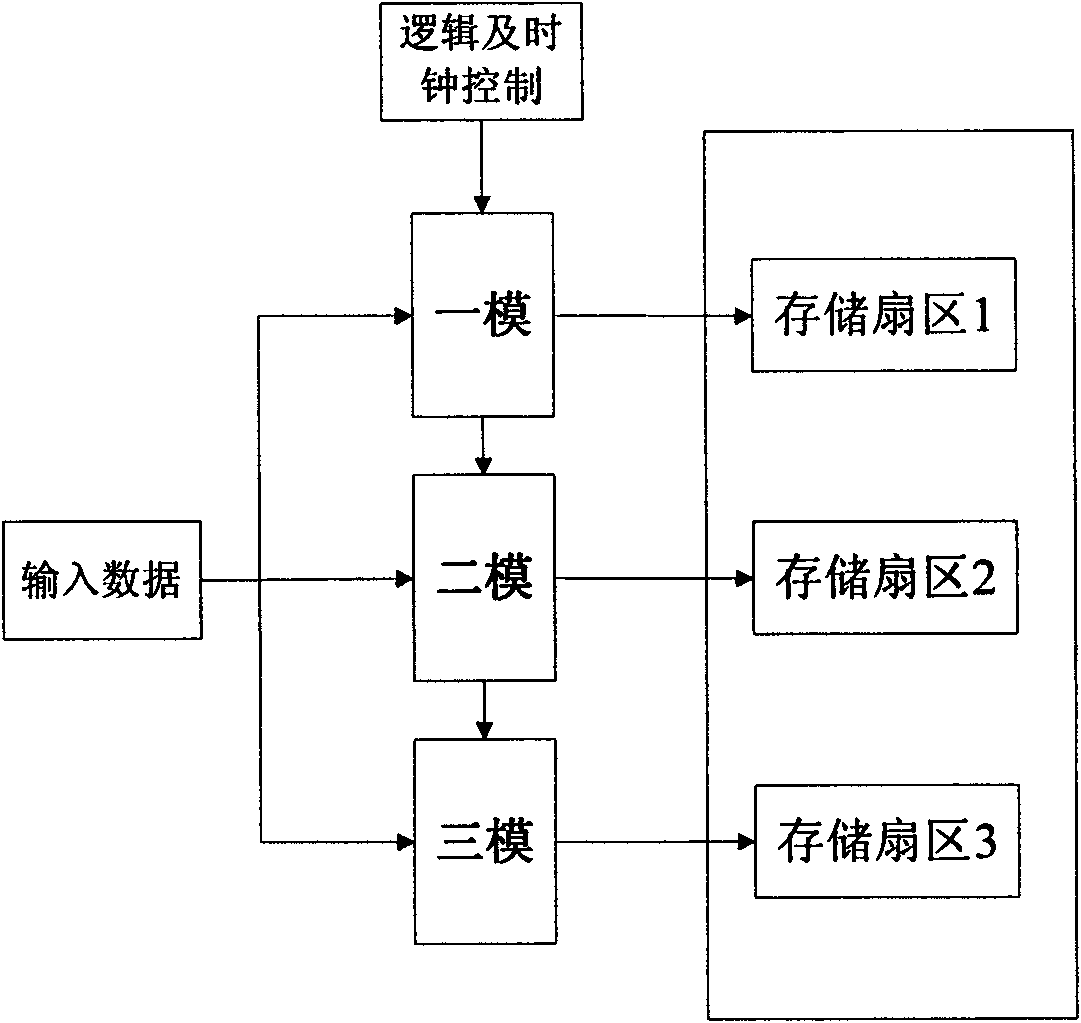
InactiveCN101615147AEnsure correct storageImprove reliabilityRedundant data error correctionHamming codeData needs
The invention discloses a fault-tolerant method of a storage module of a picosatellite based on FPGA. The fault-tolerant method comprises the following steps: a data bus divides data needing to be written into high-order data and low-order data, which are respectively transmitted to two same Hamming coding modules for processing the high-order data and low-order data so as to generate redundant data correspondingly; data and corresponding redundant data are respectively stored into three sectors in a static memory, and data in different sectors of same static memory is read when in reading data; comparison operation of '2 out of 3' is carried out according to bits so as to obtain read data which is transmitted to the corresponding Hamming coding modules; and the two Hamming coding modules respectively carry out comparison and correction to data and then output the data to a central processor. The method can lead the storage memory to realize 'SEC-DED', guarantee correct storage of check code, simultaneously adapt to important characteristics of light weight, small volume, low cost and short researching period well.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Semiconductor storage device, method of controlling the same, and error correction system
InactiveUS8086933B2Error detection/correctionRead-only memoriesHamming codeSemiconductor storage devices
A semiconductor storage device, a method of controlling the same, and an error correction system allow reduction in power consumption and circuit scale without detriment to error correction capability. An error correction code (ECC) circuit of a solid state drive (SSD) performs first error correction on read data using a first error correction code (Hamming code), and further performs second error correction on the result of the first error correction using a second error correction code (BHC code). Furthermore, the ECC circuit performs third error correction on the result of the second error correction using a third error correction code (RS code).
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Apparatus and method for diagnosing integrated circuit
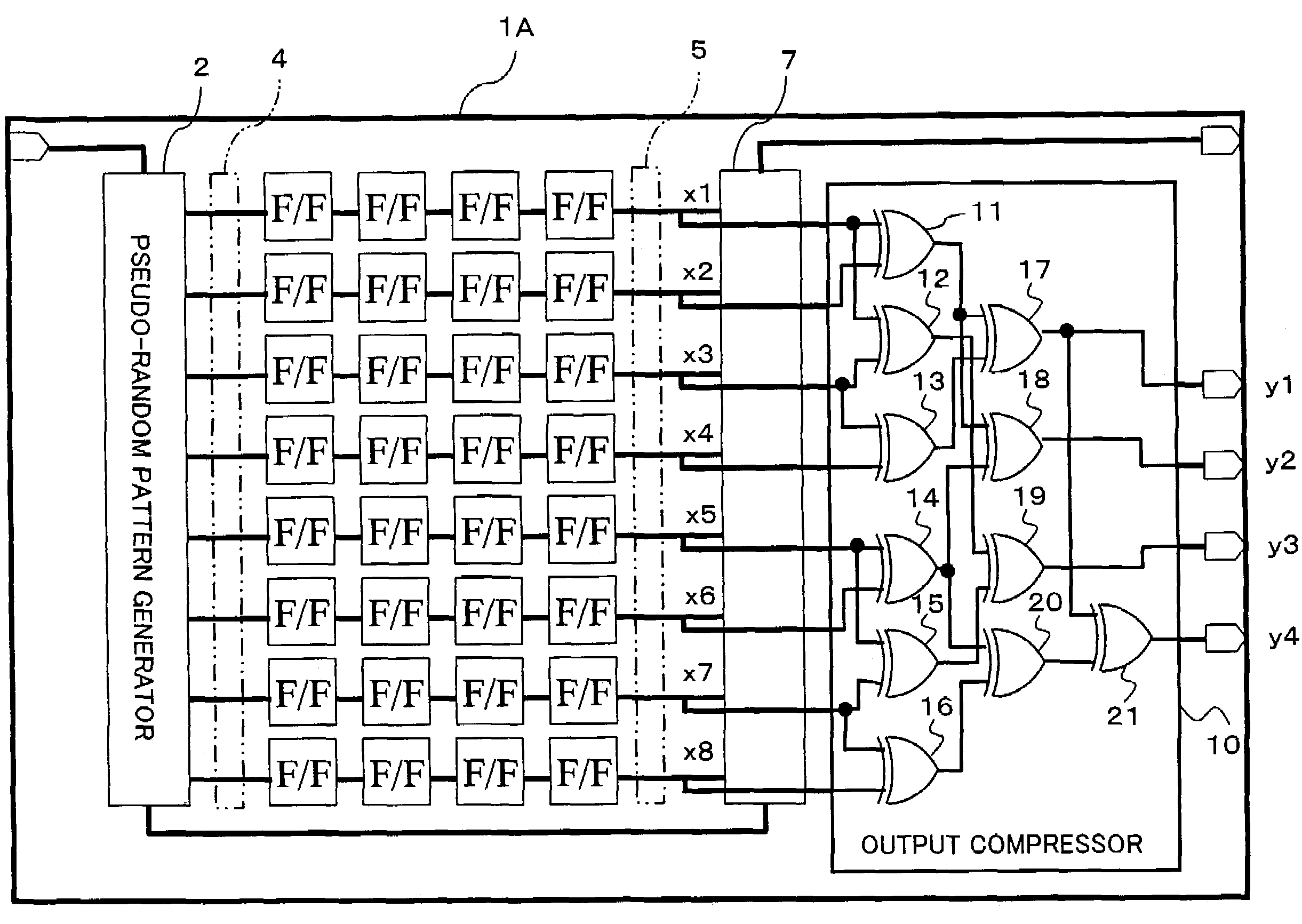
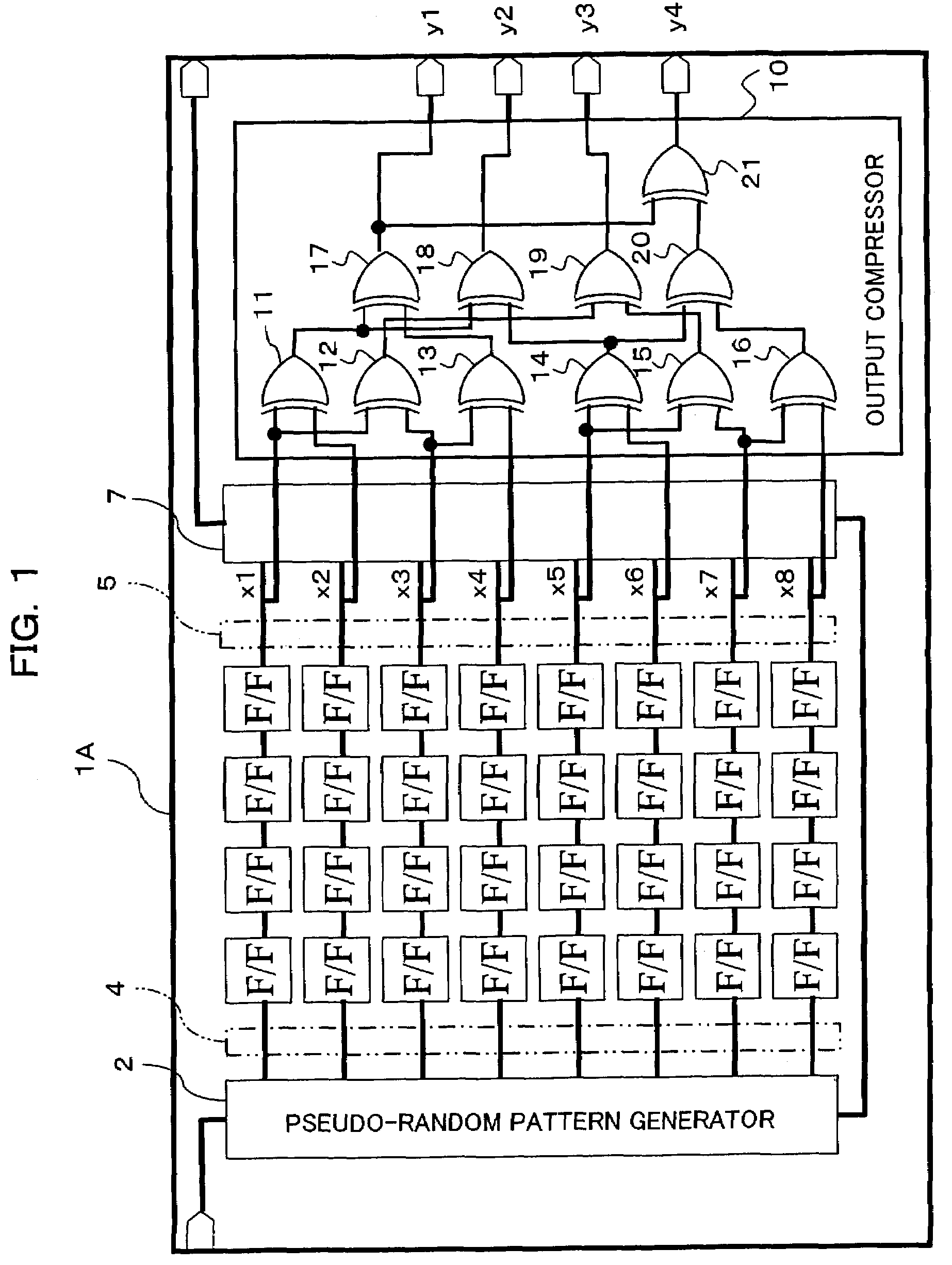
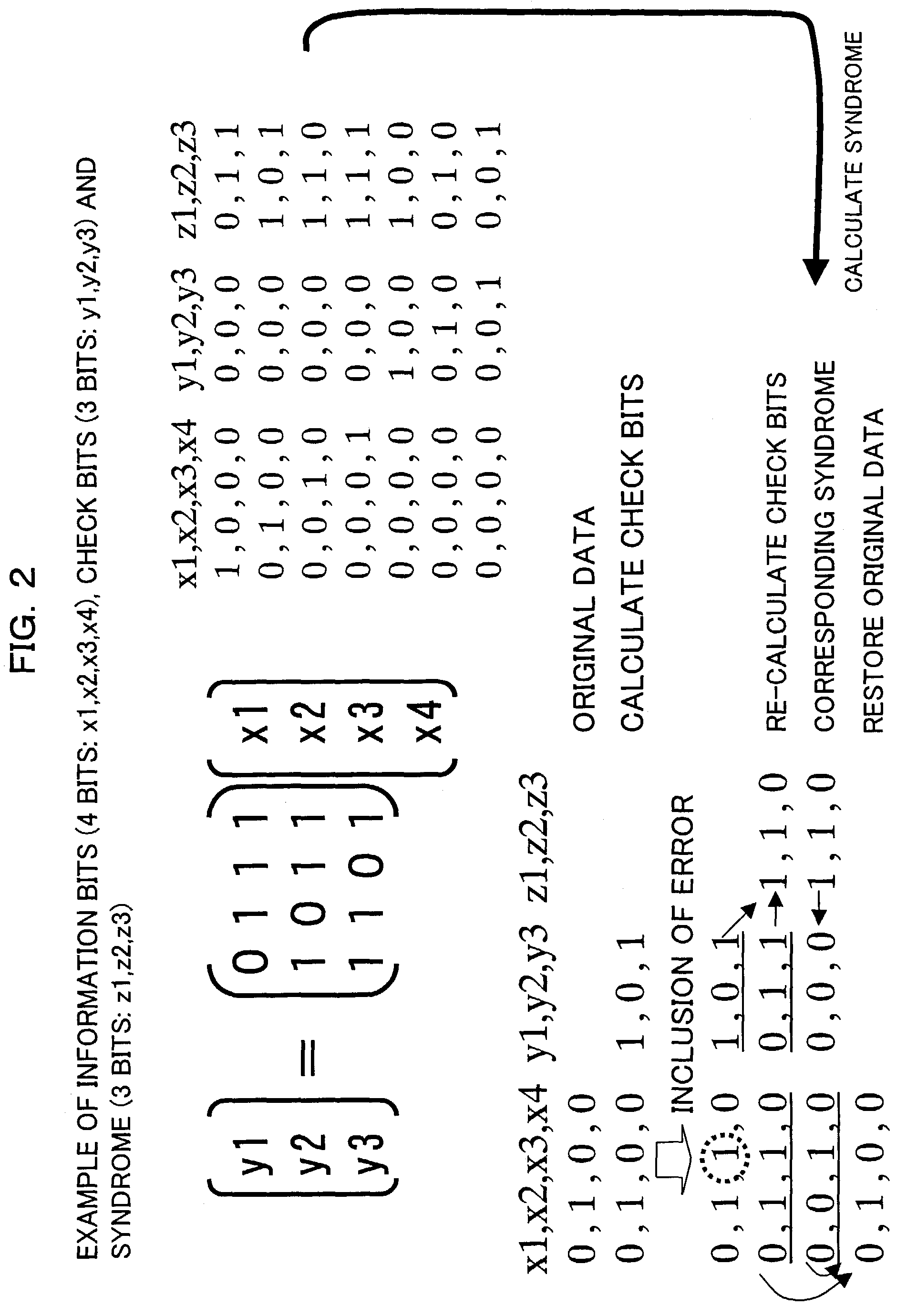
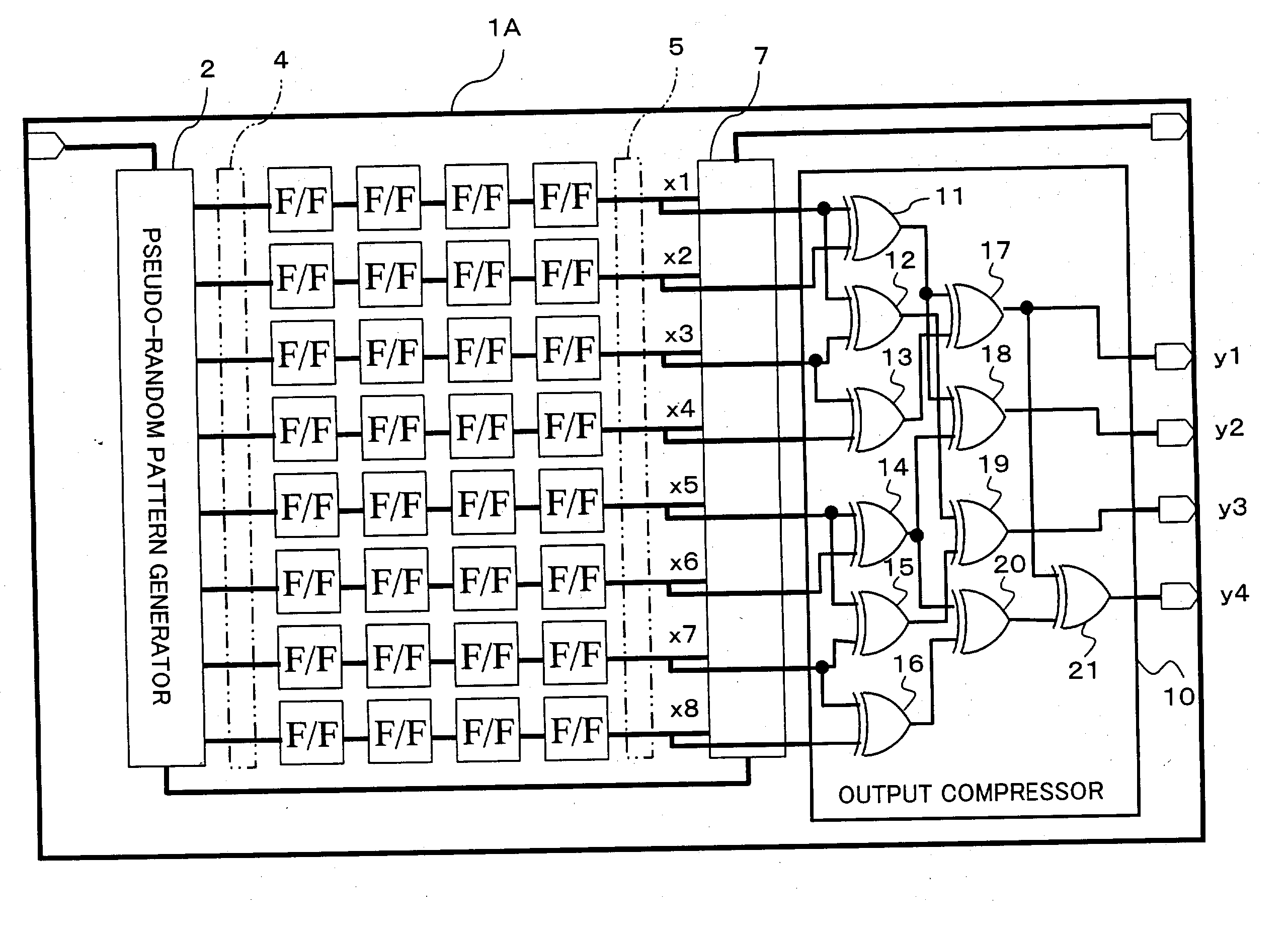
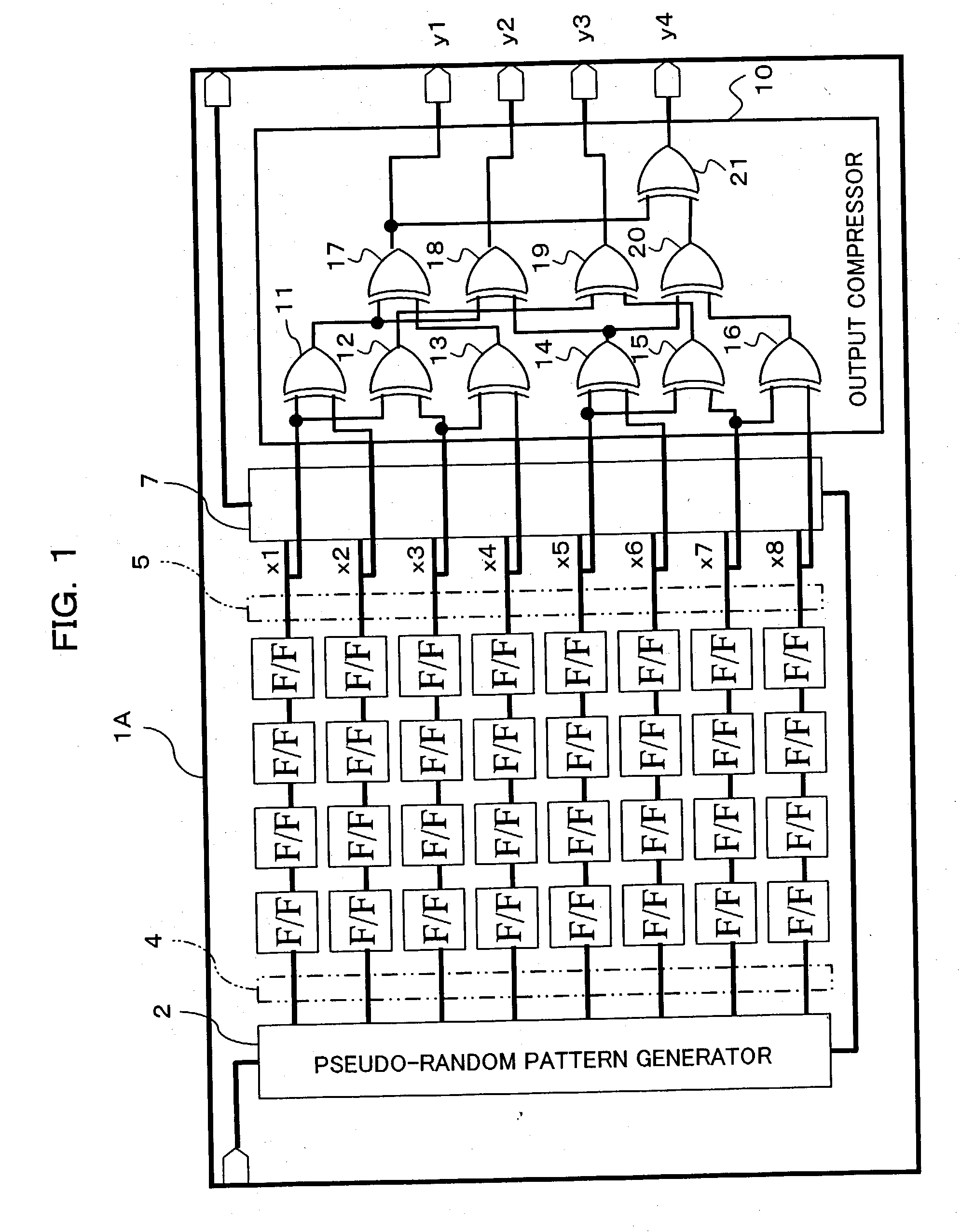
InactiveUS7337379B2Manufacturing failureAccurately specifiedElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionGraphicsShift register
An apparatus being able to not only detect a manufacturing defect of an integrated circuit but also specify a position at which the defect occurs even when outputs from scan paths are compressed and stored, or when the number of the scan paths is large. The apparatus has a pattern generator built in an integrated circuit to generate test patterns, a plurality of shift registers formed in parallel, into which the test patterns are shifted, and an output compressor for compressing a plurality of outputs shifted out from the shift registers with check bits of a Hamming code, and outputting them to the outside of the integrated circuit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Apparatus and method for diagnosing integrated circuit, and integrated circuit
InactiveUS20030229838A1Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionHamming codeShift register
An apparatus being able to not only detect a manufacturing defect of an integrated circuit but also specify a position at which the detect occurs even when outputs from scan paths are compressed and stored, or when the number of the scan paths is large. The apparatus has a pattern generator built in an integrated circuit to generate test patterns, a plurality of shift registers formed in parallel, into which the test patterns are shifted, and an output compressor for compressing a plurality of outputs shifted out from the shift registers with check bits of a Hamming code, and outputting them to the outside of the integrated circuit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Nand flash memory device with ecc protected reserved area for non volatile storage of redundancy data
Basic redundancy information is non-volatily stored in a reserved area of an addressable area of a memory array, and is copied to volatile storage therein at every power-on of the memory device. The unpredictable though statistically inevitable presence of failed array elements in such a reserved area of the memory array corrupts the basic redundancy information established during the test-on wafer (EWS) phase of the fabrication process. This increases the number of rejects, and lowers the yield of the fabrication process. This problem is addressed by writing the basic redundancy data in the reserved area of the array with an ECC technique using a certain error correction code. The error correction code may be chosen among majority codes 3, 5, 7, 15 and the like, or the Hamming code for 1, 2, 3 or more errors, as a function of the fail probability of a memory cell as determined by the EWS phase during fabrication.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
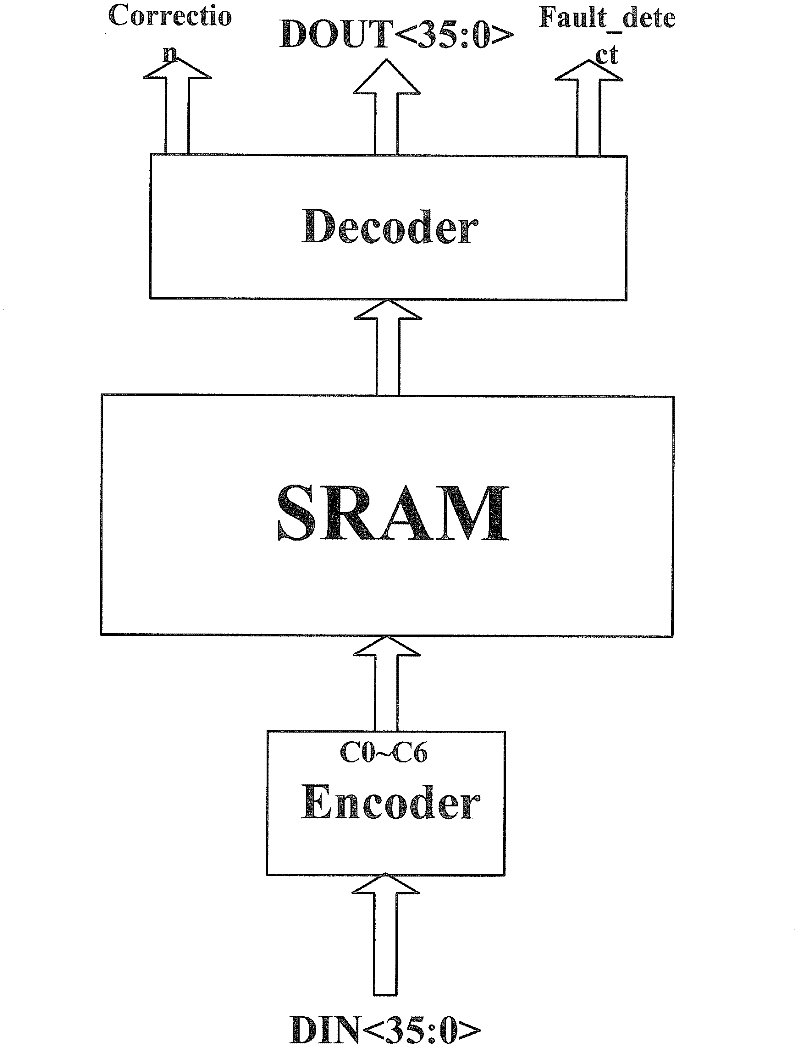
Hamming code based method for carrying out fault tolerance on static RAM multiple bit upset
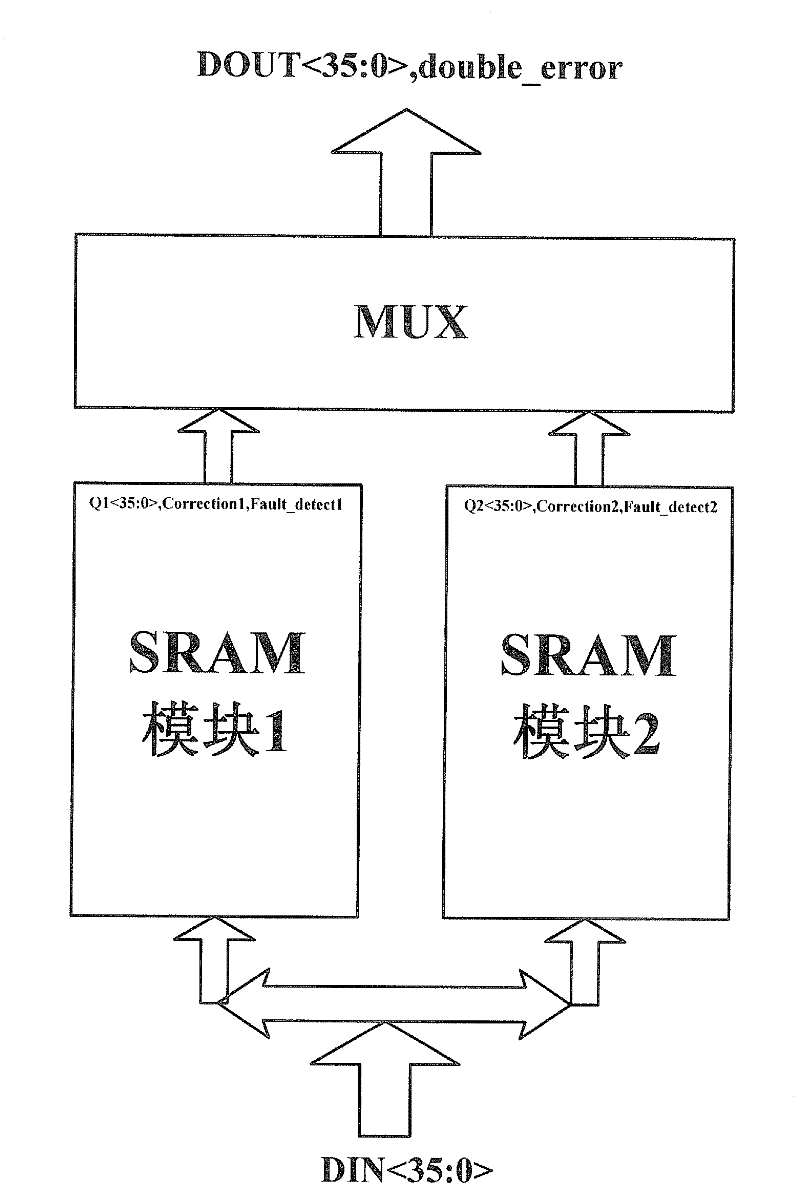
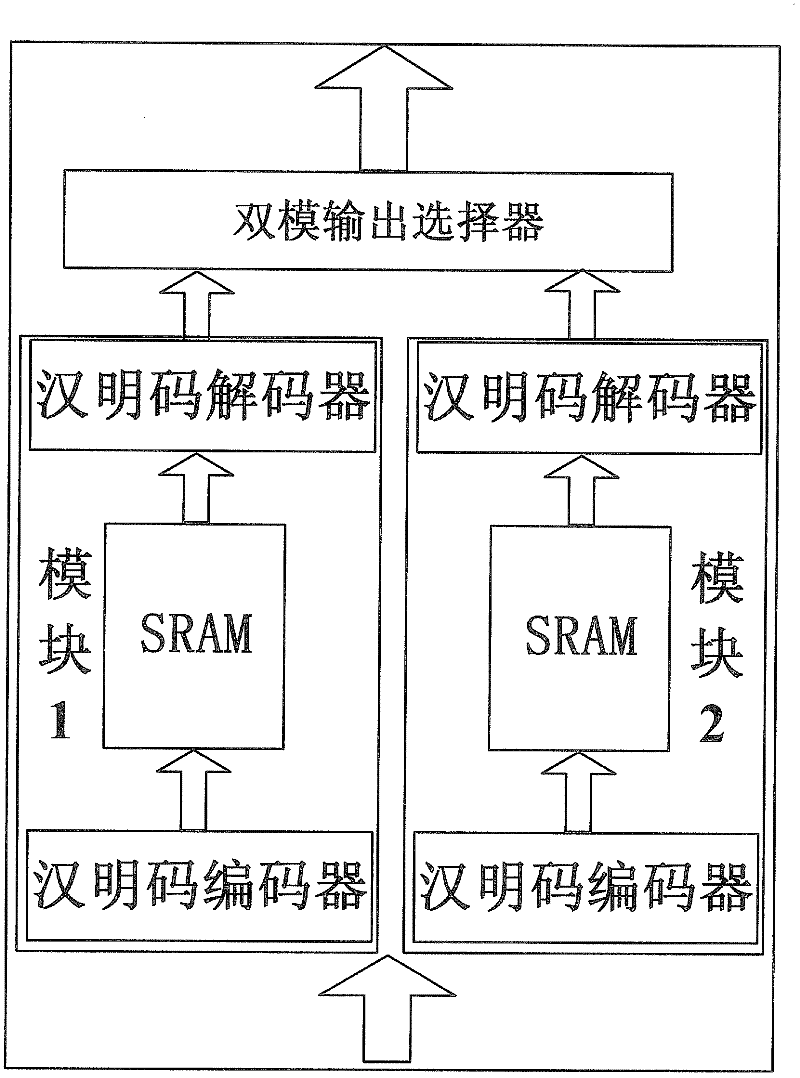
The invention discloses a Hamming code based method for carrying out fault tolerance on static RAM (random-access memory) multiple bit upset. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out coding and decoding on the static RAM by employing Hamming code; employing two identical static RAMs with Hamming code coding and decoding to realize parallel input and output; and connecting a dual mode output selection circuit on output terminals of the two static RAMs. The invention has certain tolerance on SRAM multiple bit upset caused by high energy particles; and as no refresh or update is required, a system speed is increased substantially.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Local feature and deep learning-based gateway vehicle retrieval system and method
ActiveCN108197538AStrong semantic expression abilityEasy to classifyCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsHamming codeFeature vector
The invention relates to a local feature and deep learning-based gateway vehicle retrieval system and method. According to the system and method, global features of vehicles are extracted by utilizinga deep neural network; a network model is trained by adoption of loss functions of softmax loss and triple loss; annual inspection mark features and vehicle lamp features are extracted to obtain local feature vectors; and finally the local feature vectors are weighted and combined, and global feature vectors of the last full-connection layer of the neural network are utilized to serve as vehiclefeatures to carry out retrieval. During the retrieval, an improved k-means algorithm is adopted to find K classes, and hash functions are formed by utilizing a SVM so as to carry out Hamming code encoding, so that the retrieval speed and the retrieval precision are improved and the storage space is saved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG YINJIANG RES INST
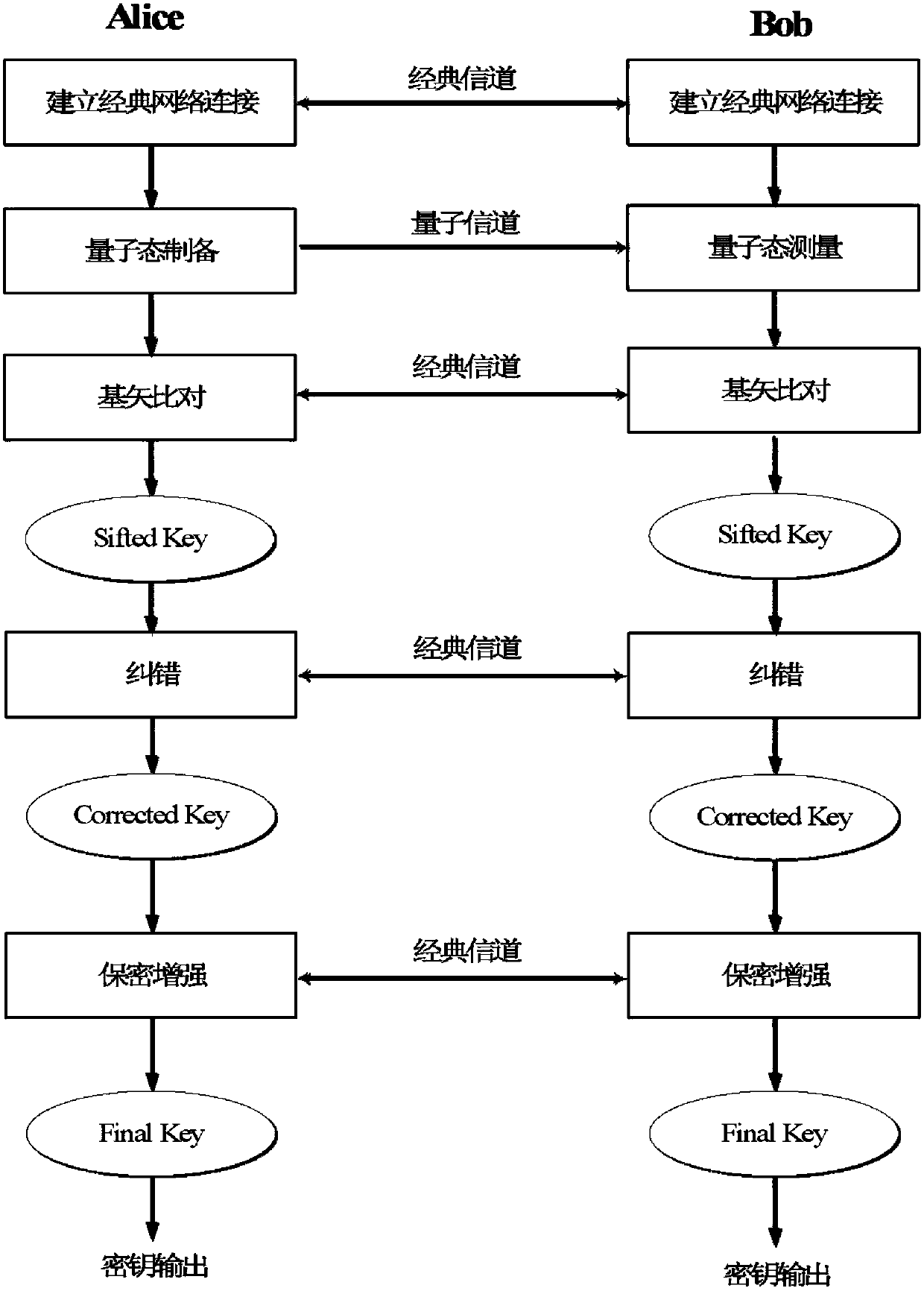
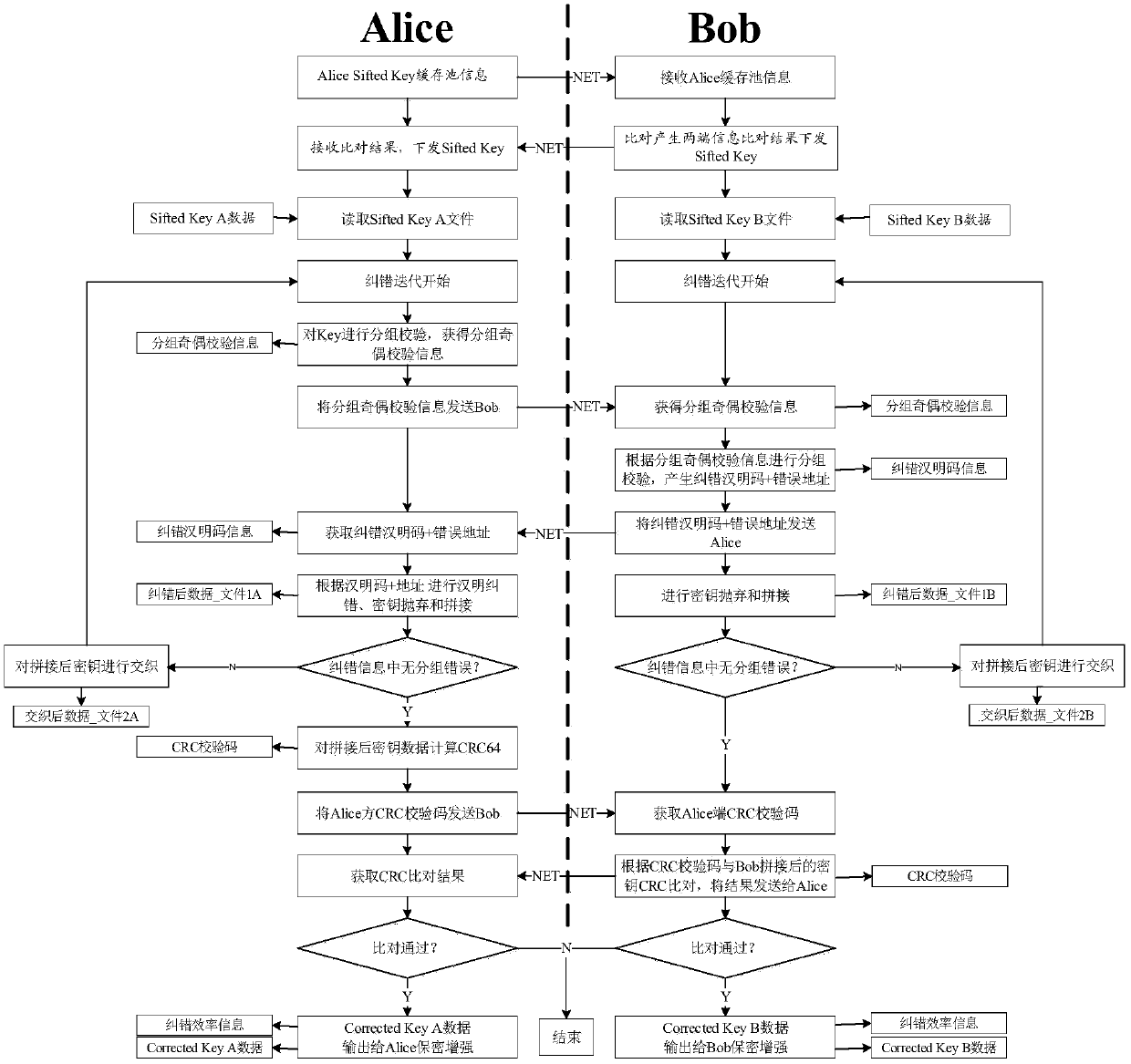
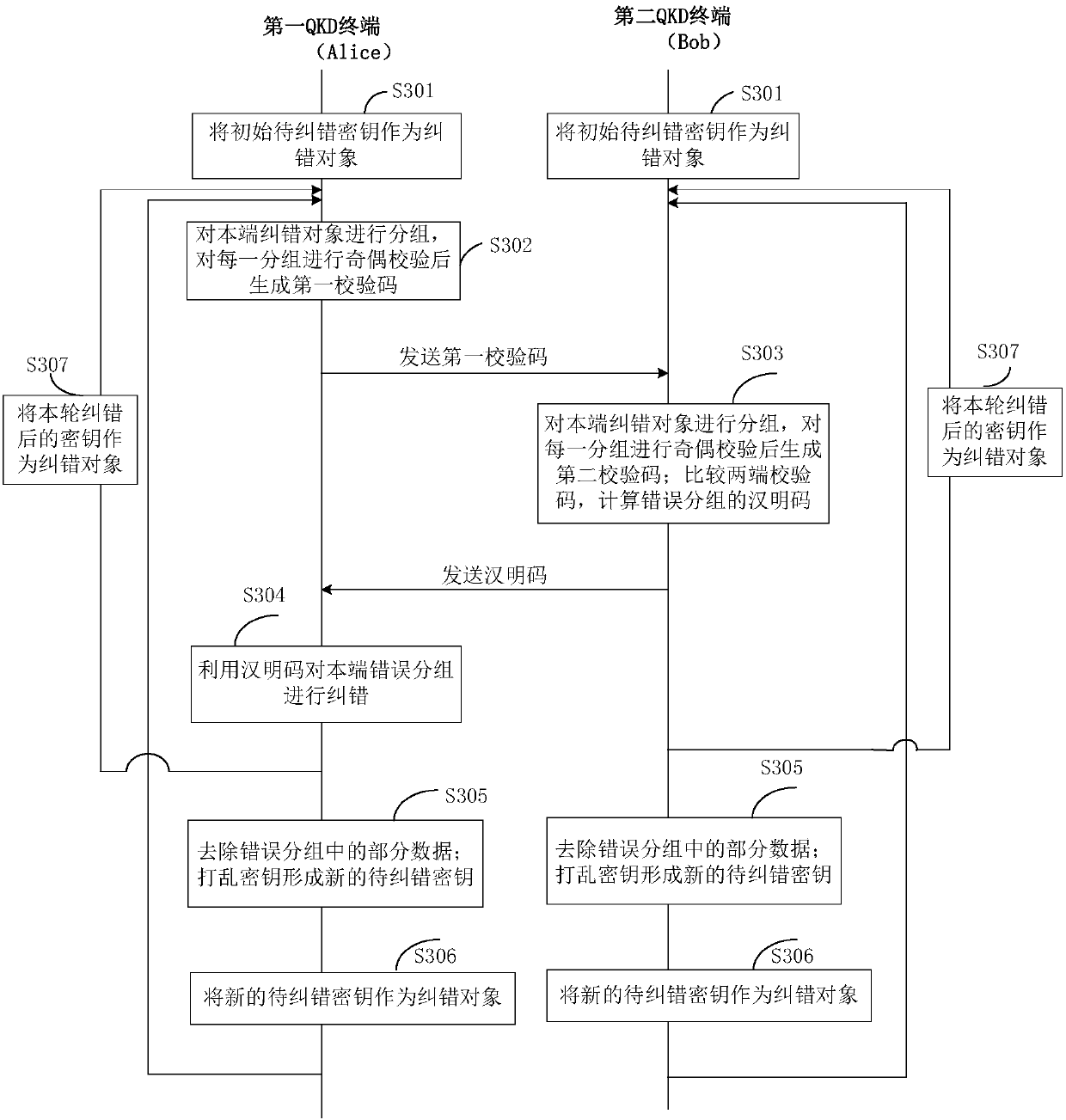
A key error correction method and a quantum key distribution system
ActiveCN109936445AReduce the number of interactionsReduce leakageKey distribution for secure communicationHamming codeComputer hardware
The invention discloses a key error correction method and a quantum key distribution system, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the error correction of a to-be-corrected key through employing a mode that parity check is combined with Hamming codes, specifically, enabling a first QKD terminal to divide the to-be-corrected key of a home terminal into at least two groups, and informinga second QKD terminal of the parity check code of each group; the second QKD terminal realizing the same group as the first QKD terminal for the to-be-corrected secret key of the home terminal, determining the parity check codes of each group, and determining which groups are inconsistent at two ends by comparing the parity check codes of the same group at the two ends; therefore, one end, namelythe first QKD terminal, can be subjected to grouped error correction through the Hamming code, so that one round of error correction is completed. According to the invention, the number of interactiontimes between two QKD devices can be greatly reduced, so that the error correction efficiency is improved, and the information leakage amount is reduced.
Owner:QUANTUMCTEK
Error correcting method and apparatus
InactiveUS6728925B2Reduce transmission delayReduce in quantityCode conversionSingle error correctionComputer hardwareCoding block
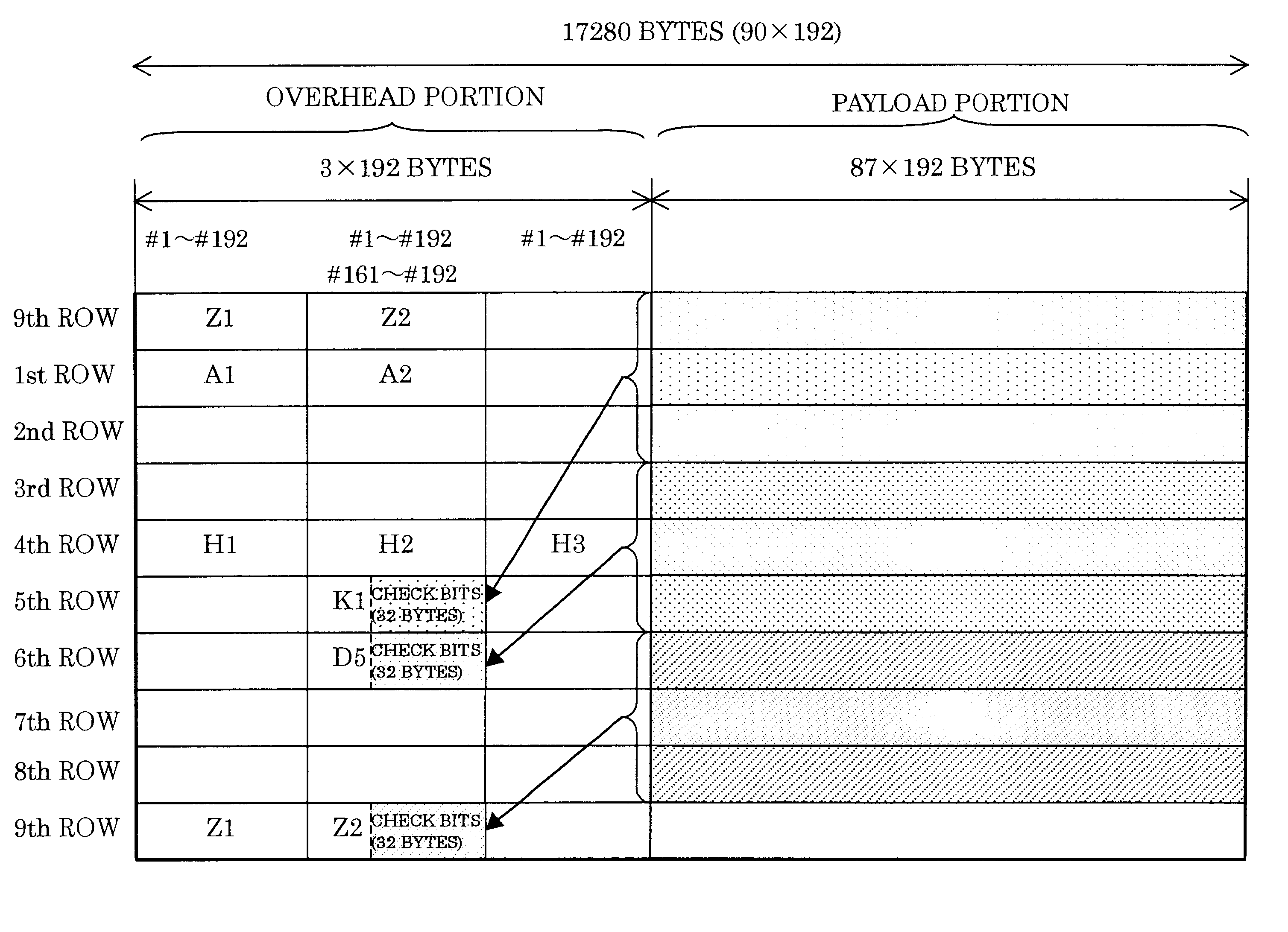
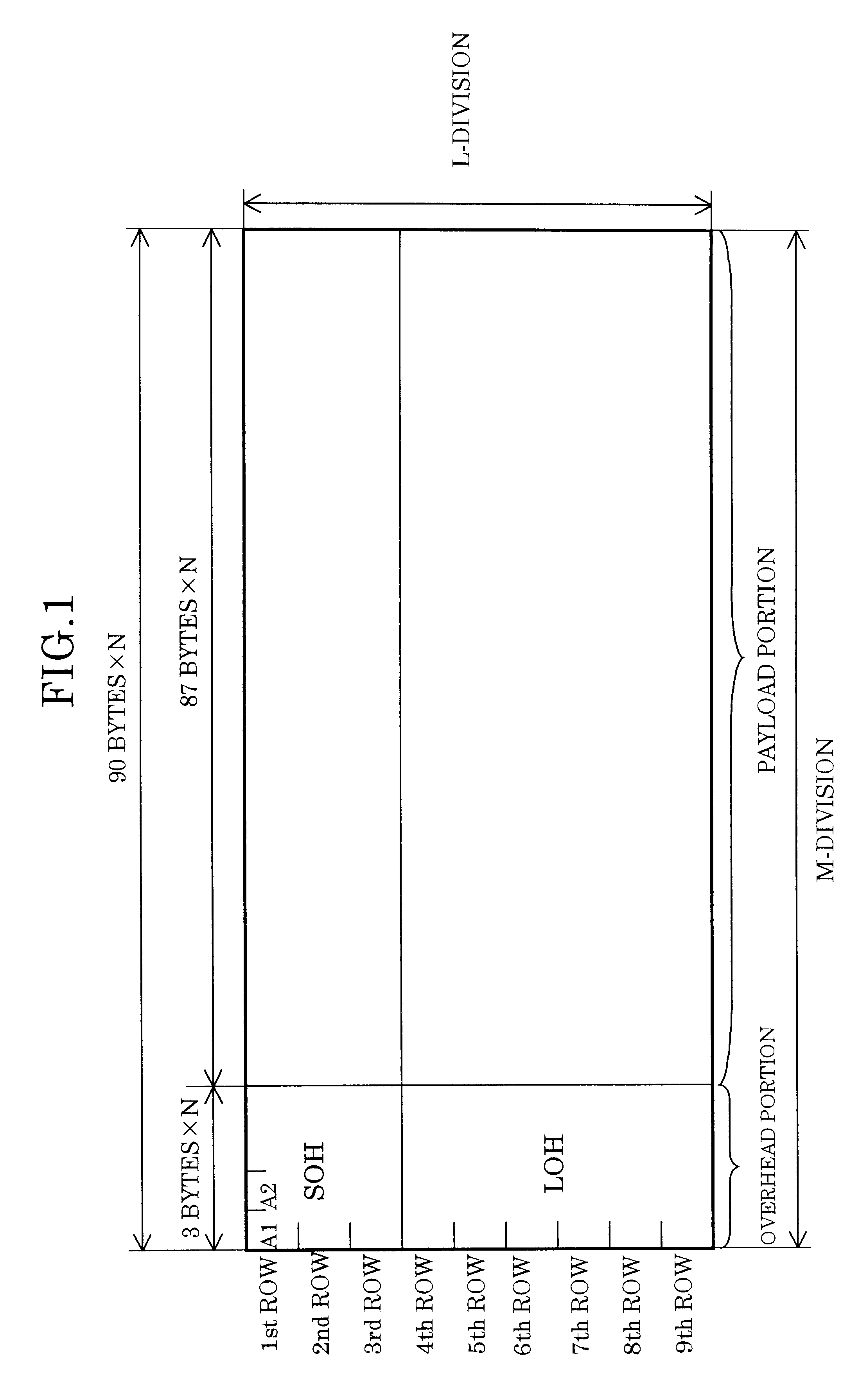
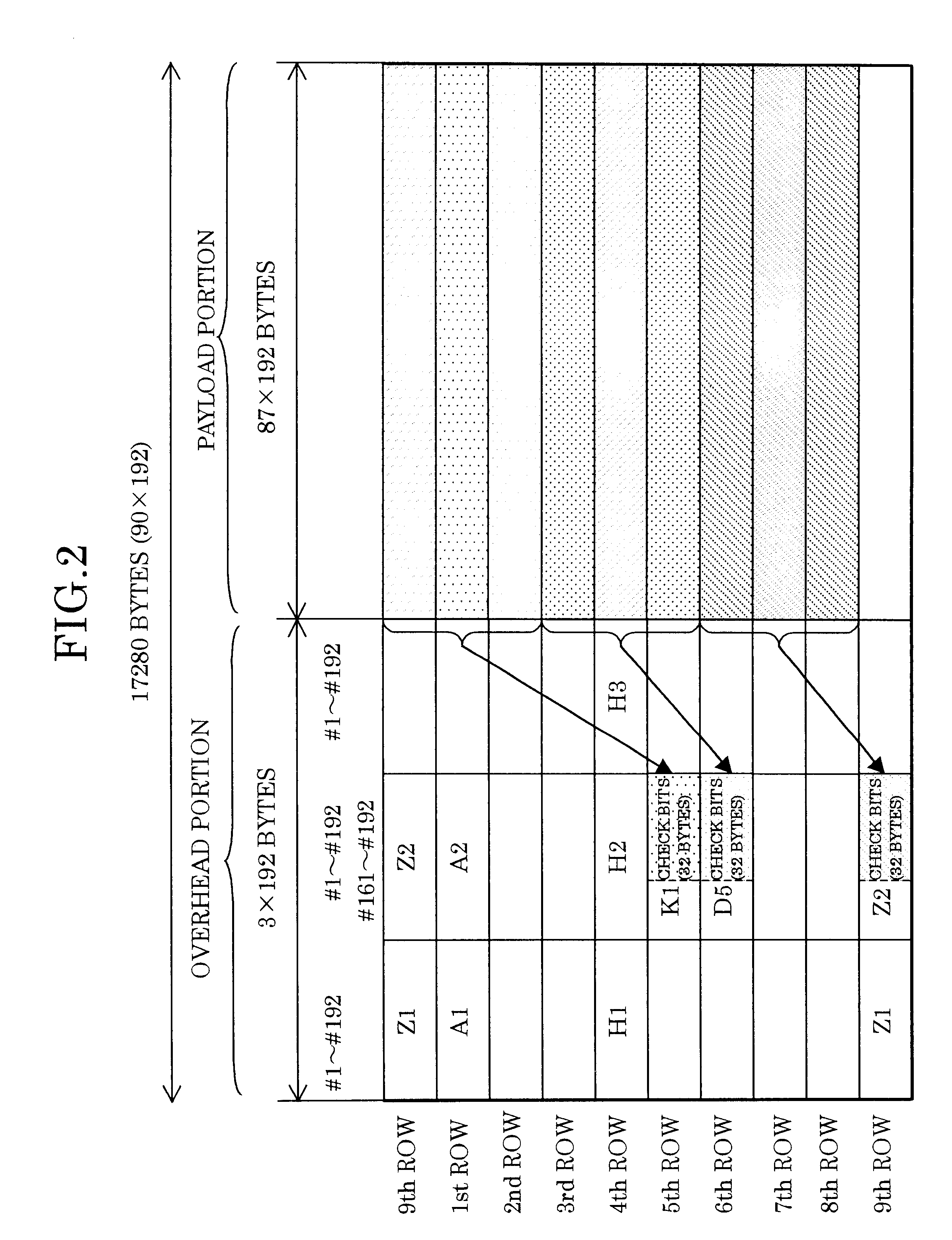
In an error correcting method and an apparatus therefor using Hamming codes, a frame regulated by a synchronous network is divided into L blocks in the direction of row. Preferably, information bits and check bits are allocated to a payload portion and non-defined bits of an LOH portion, respectively. More preferably, the information bits and the check bits are divided into M sub blocks to form a Hamming code block. In addition, a code error correcting means rearrange each Hamming code block per bit and further preferable, a syndrome register with a plurality of banks operates an error syndrome of the Hamming code block, and based on the operation result, the code error correction of the Hamming code block is performed by a bank switchover.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Maximum likelihood decoding for input streams containing known data
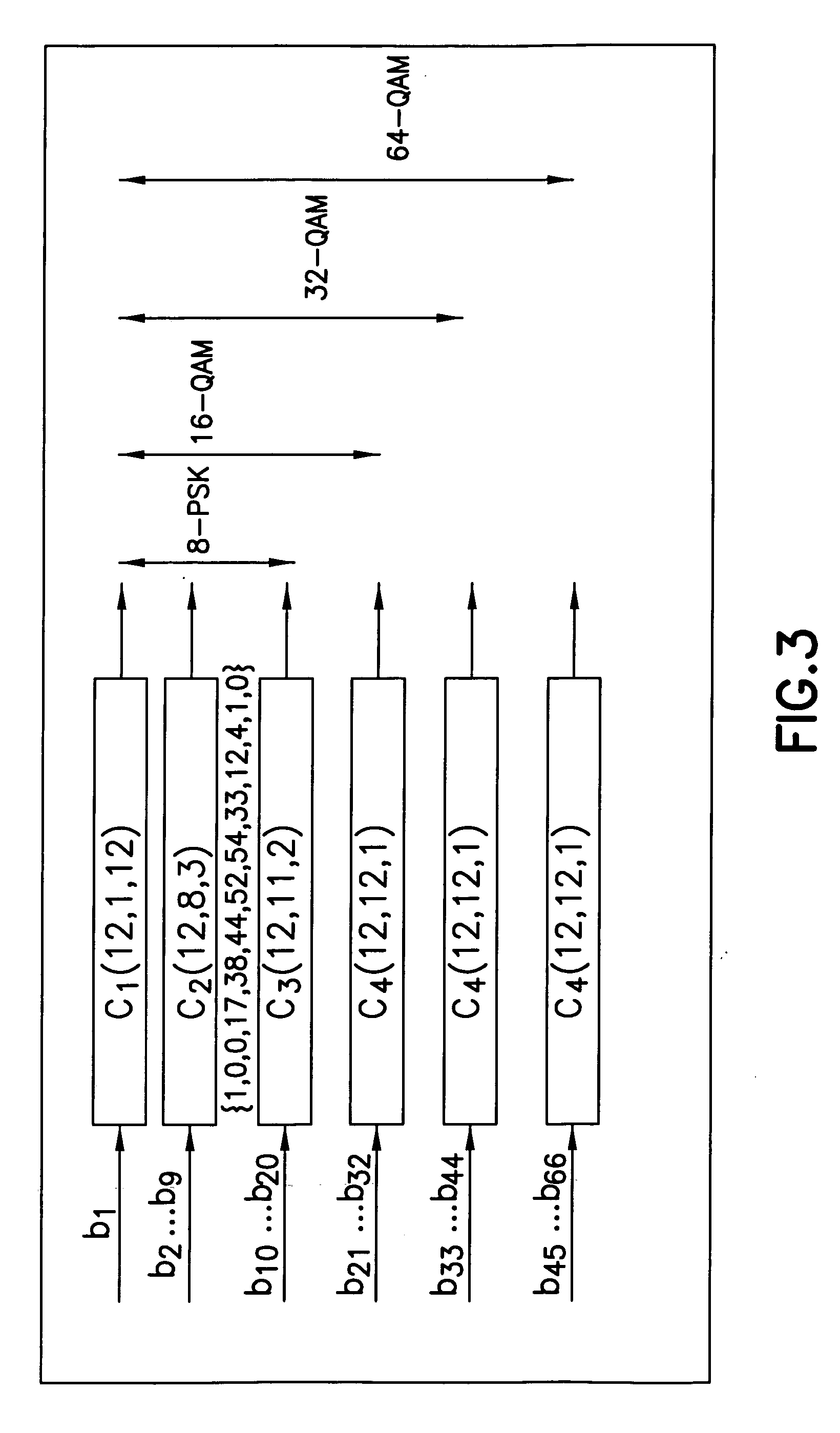
InactiveUS6950976B1Reduce total powerShorten the timeData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesHamming codeOn board
A method is described for decoding a signal in a noise environment using maximum likelihood soft decision decoding for input streams containing known data. ISI problems are ameliorated, and decoding is implemented by palmtop computers and devices of limited computational capability. Decoded signals make use of the (12, 8) Hamming Code for a MOBITEX application. A table with predetermined ISI values is downloaded from a host processor to an on-board DSP at runtime. Known information in the frame header is utilized to help determine unknown data. Decoding proceeds in one embodiment by finding codewords that minimize a sum corresponding to data values extracted from header information. Other tables generated for use contain soft decision information and FEC words. Minimizing data translation by using known data and other embodiments advantageously minimize computational resources required to decode data by maximum likelihood soft decision decoding.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Fault-tolerant asynchronous serial transceiver device based on field programmable gata array (FPGA)
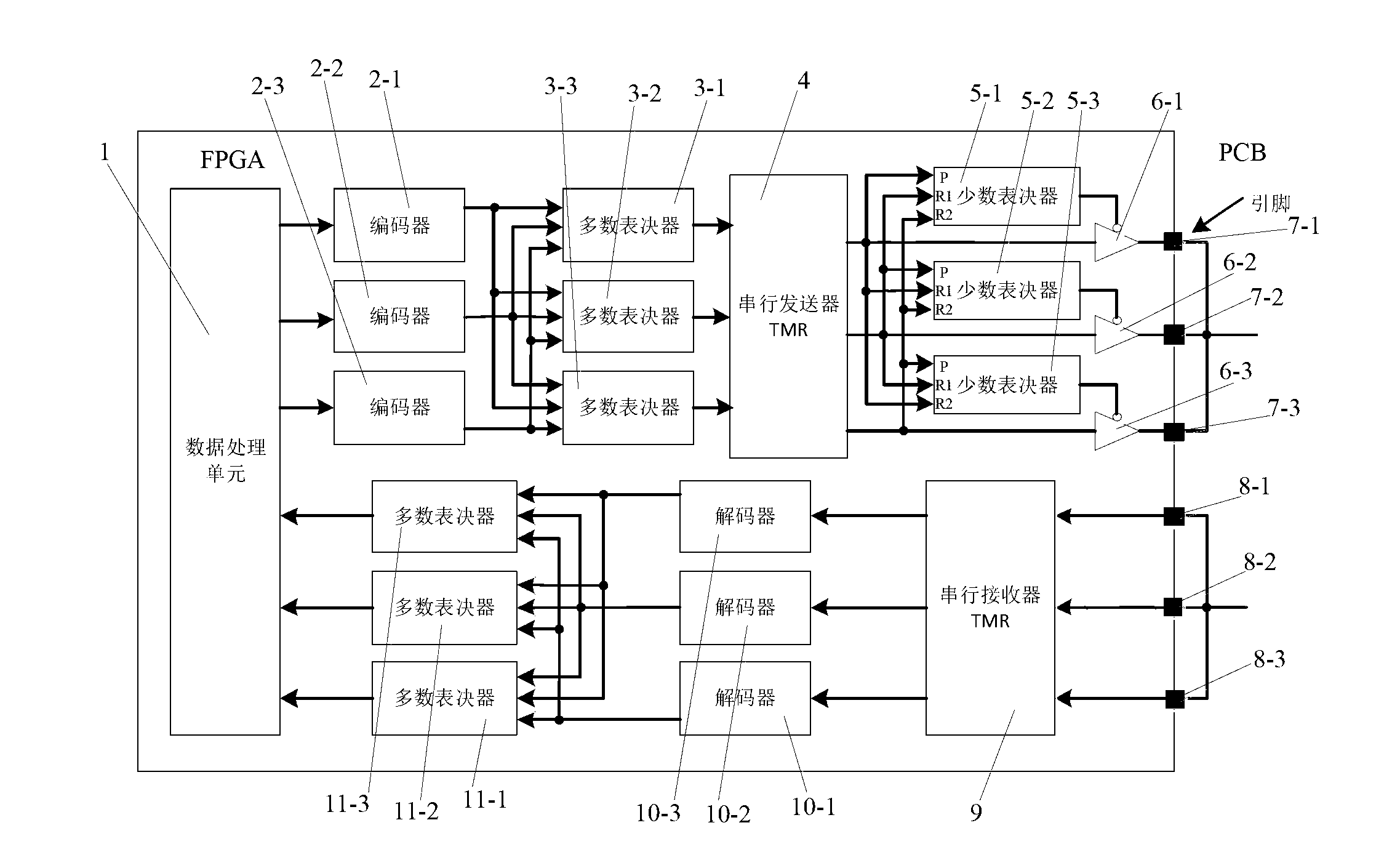
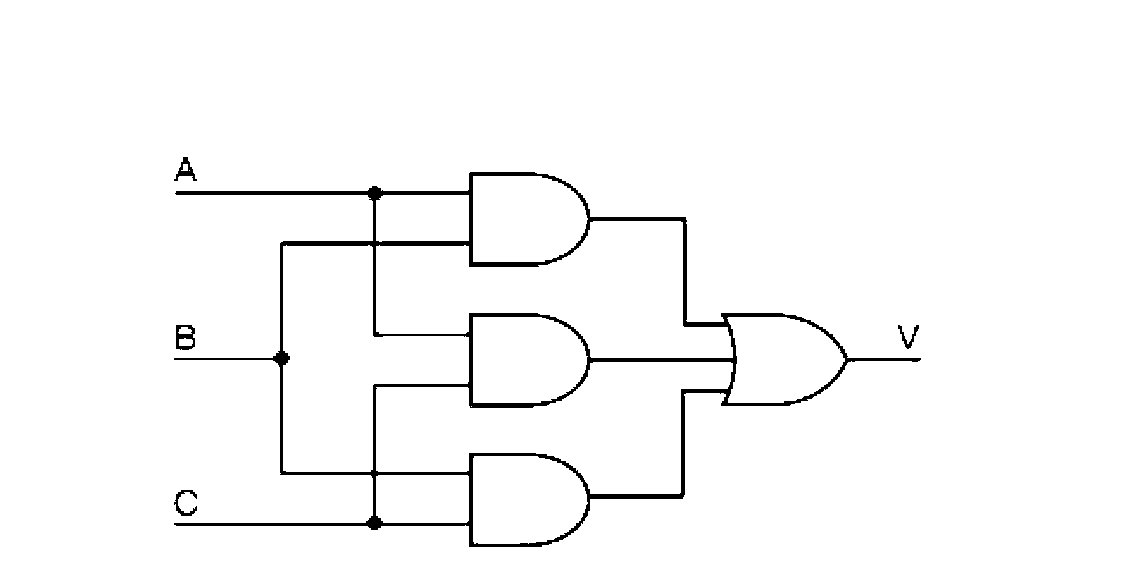
ActiveCN103176934AImprove toleranceAddressing Anti-Single Event EffectsElectric digital data processingHamming codeTransceiver
The invention provides a fault-tolerant asynchronous serial transceiver device based on a field programmable gata array (FPGA). The device comprises a data transmitter, a data receiver, an extended Hamming code encoder, an extended Hamming code decoder, a majority voter and a minority voter. Triple modular redundancy (TMR) processing is respectively conducted on all modules. As for the transmitter, firstly, to-be-sent data are sent to the extended Hamming code encoder by a data processing unit, encoded codons are sent to the majority voter by the encoder, the codons voted by the majority voter are sent to a serial transmitter, and parallel data are converted to serial data by the serial transmitter and are sent out. As for the receiver, serial input signals are input into the FPGA through a pin, serial-parallel converting of received data is achieved in the FPGA by a serial receiver, the serial data are converted to the parallel data by the serial receiver, and the parallel data are transmitted to the decoder.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
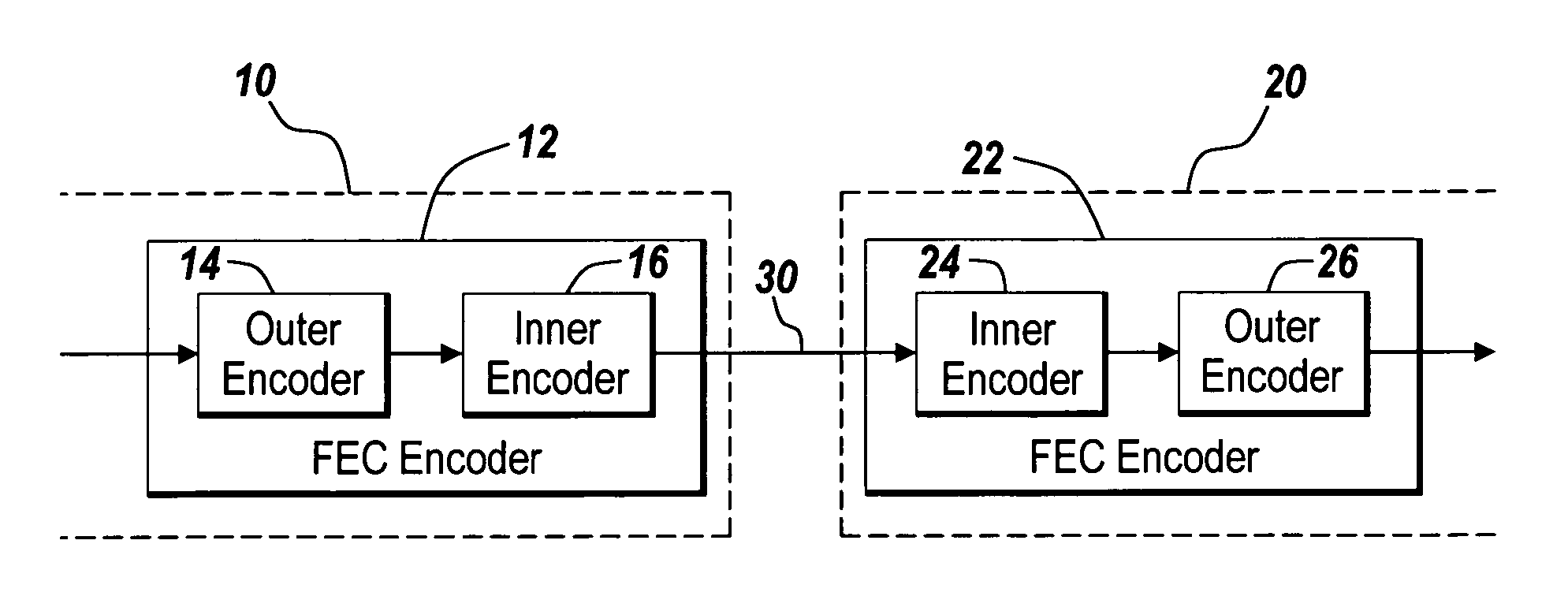
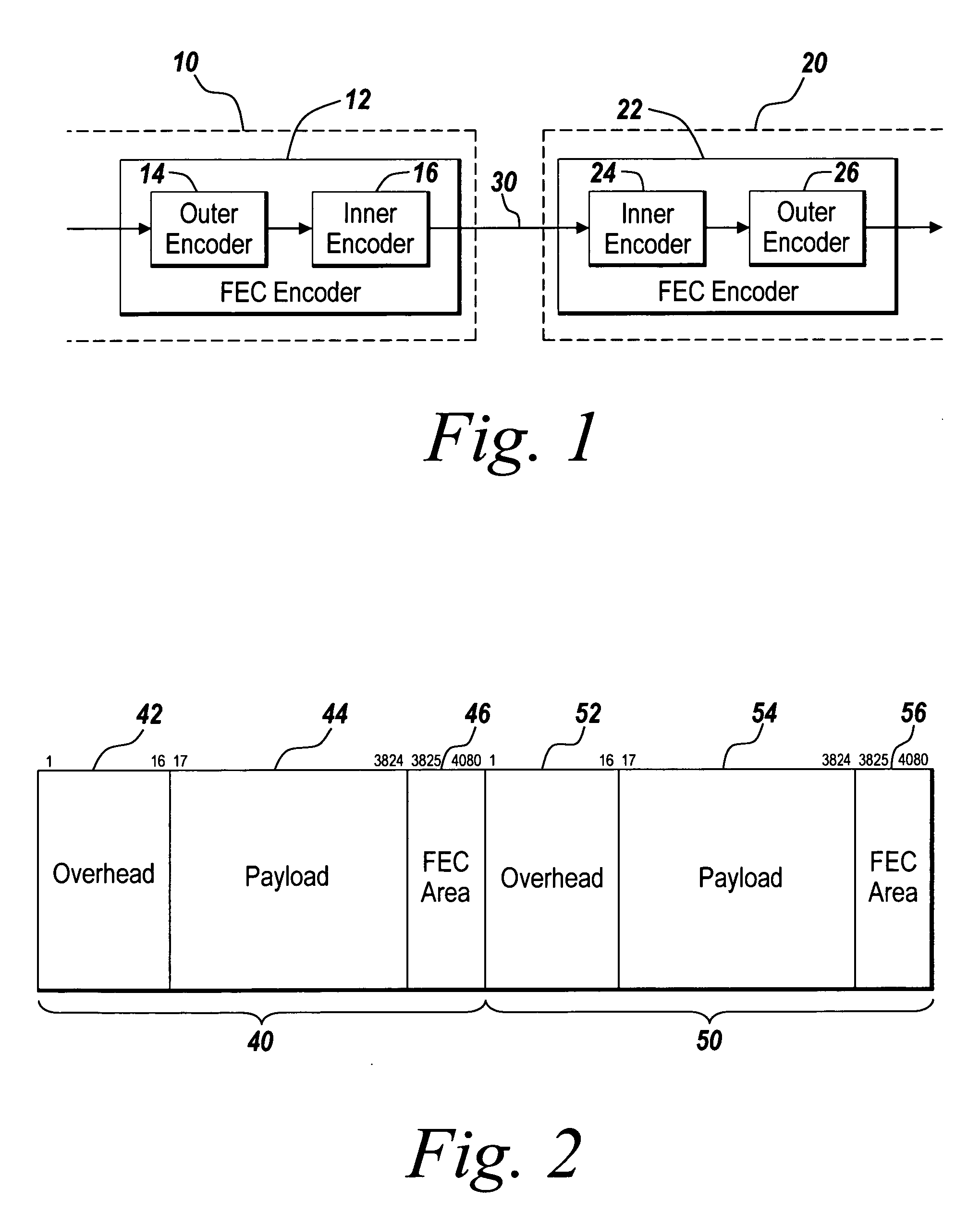
Fibre optic communications
An encoder and an encoding method are suitable for use in an optical communication system. A concatenated coding scheme is used, in which the source data are encoded by means of an outer encoder to produce outer encoded data, and the outer encoded data are encoded by means of an inner encoder to produce inner encoded data, which are transmitted over a communications medium, such as an optical fibre. The inner encoder acts to produce inner encoded data in a format which occupies the space occupied one or more (for example, two) frames as defined in a standard, in this case the ITU-T G.709 standard. The inner encoder forms a product code from two sets of codewords, for example Extended Hamming codes. More particularly, at least one of the two sets of codewords is a shortened code, in order that the inner encoded data exactly occupies a plurality of frames as defined in the standard.
Owner:PHYWORKS
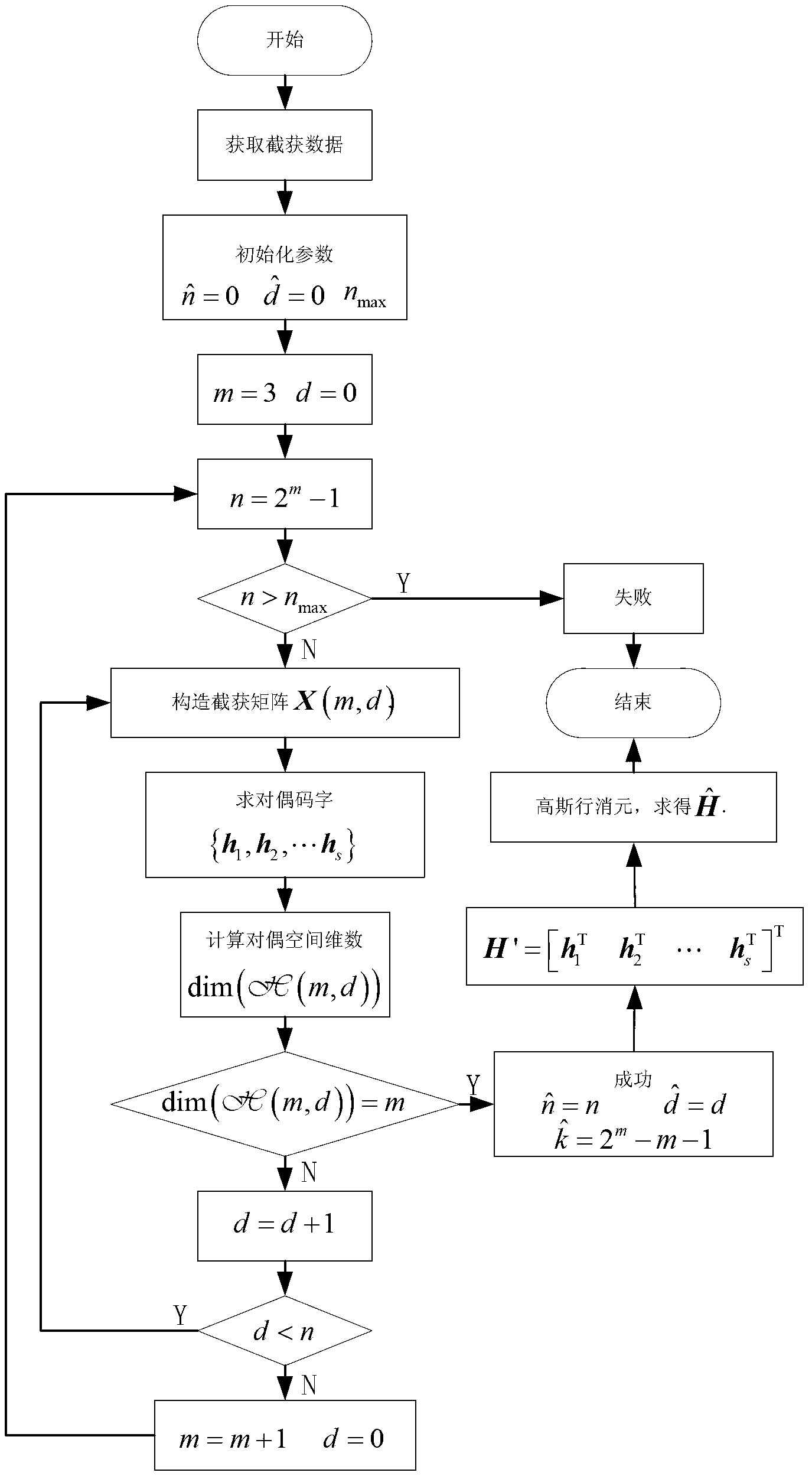
Blind identification method for coding parameter of hamming code
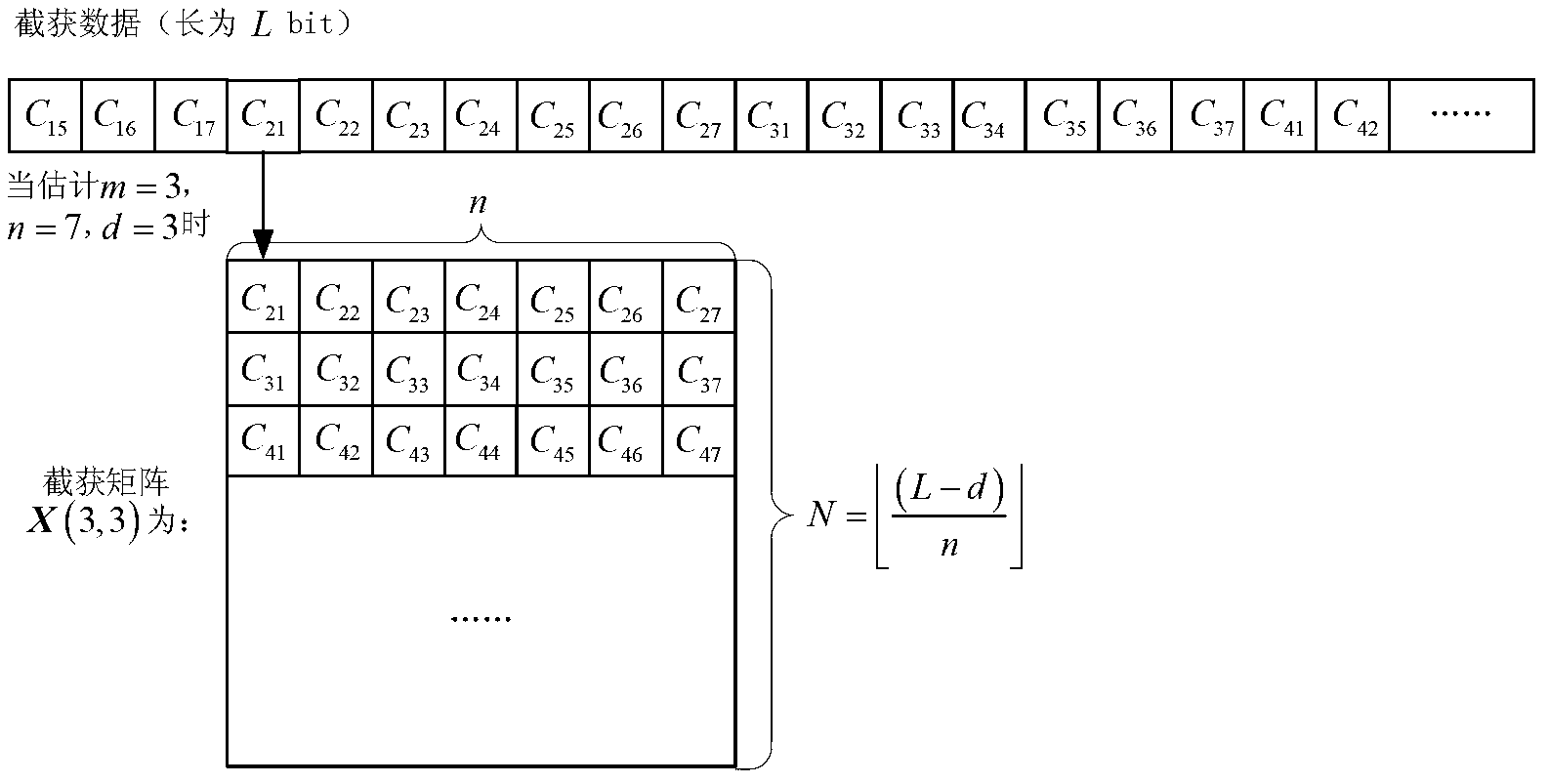
InactiveCN102710266ARealize blind recognitionImprove toleranceSingle error correctionProgramming languageCoding block
The invention provides a blind identification method for a coding parameter of a hamming code. The code length of the hamming code and a code block synchronization moment are estimated by judging the dimension number of a dual space of the hamming code, and information bit lengths in codewords are obtained by the code lengths of the codewords, the weight distribution properties of dual codes are used for exhaustive searching to find dual codewords, and a check matrix is obtained according to the dual codewords. The blind identification of the coding parameter of the hamming code is realized; and furthermore, the tolerance of the blind identification to an error code is improved by setting a proper threshold.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com