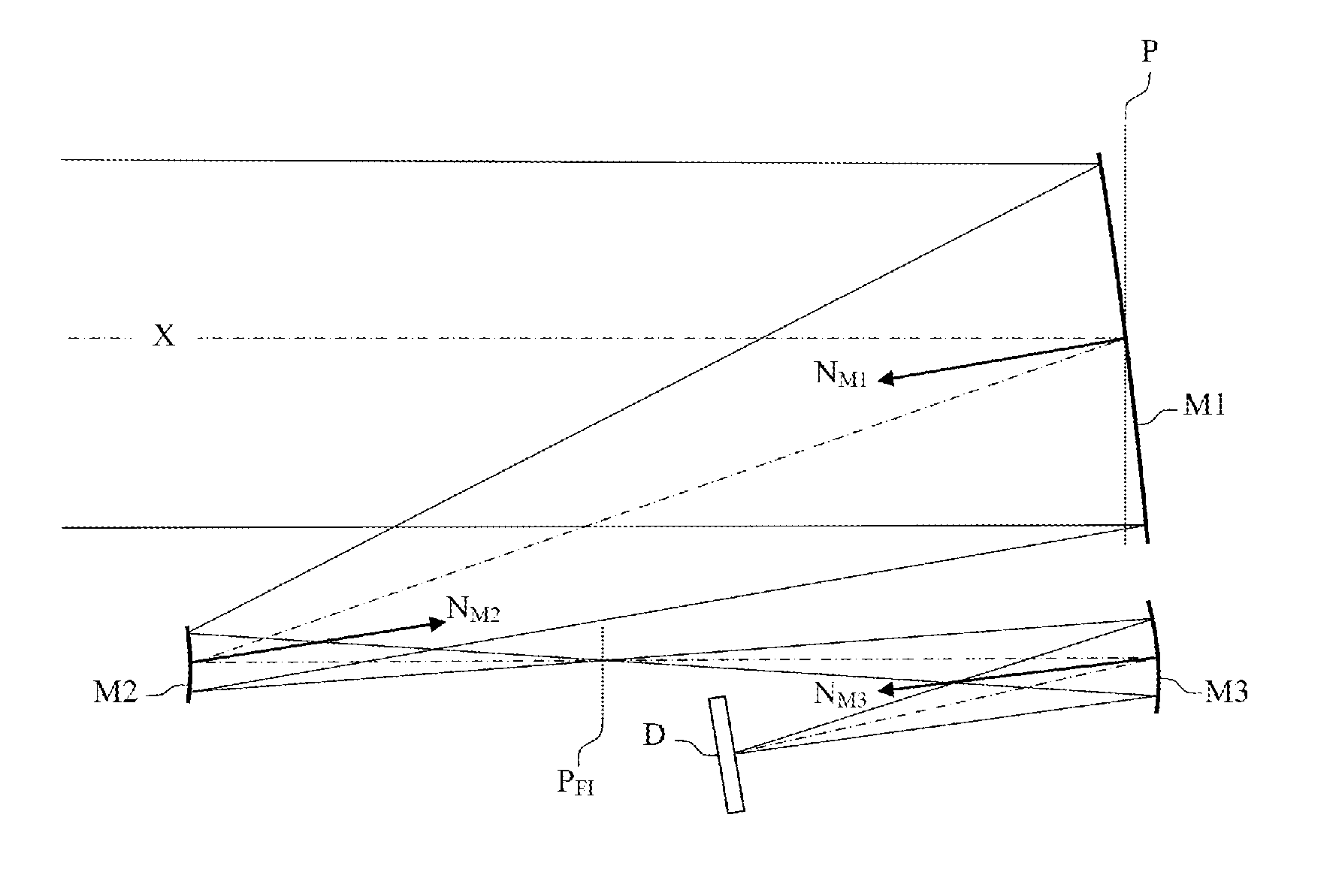
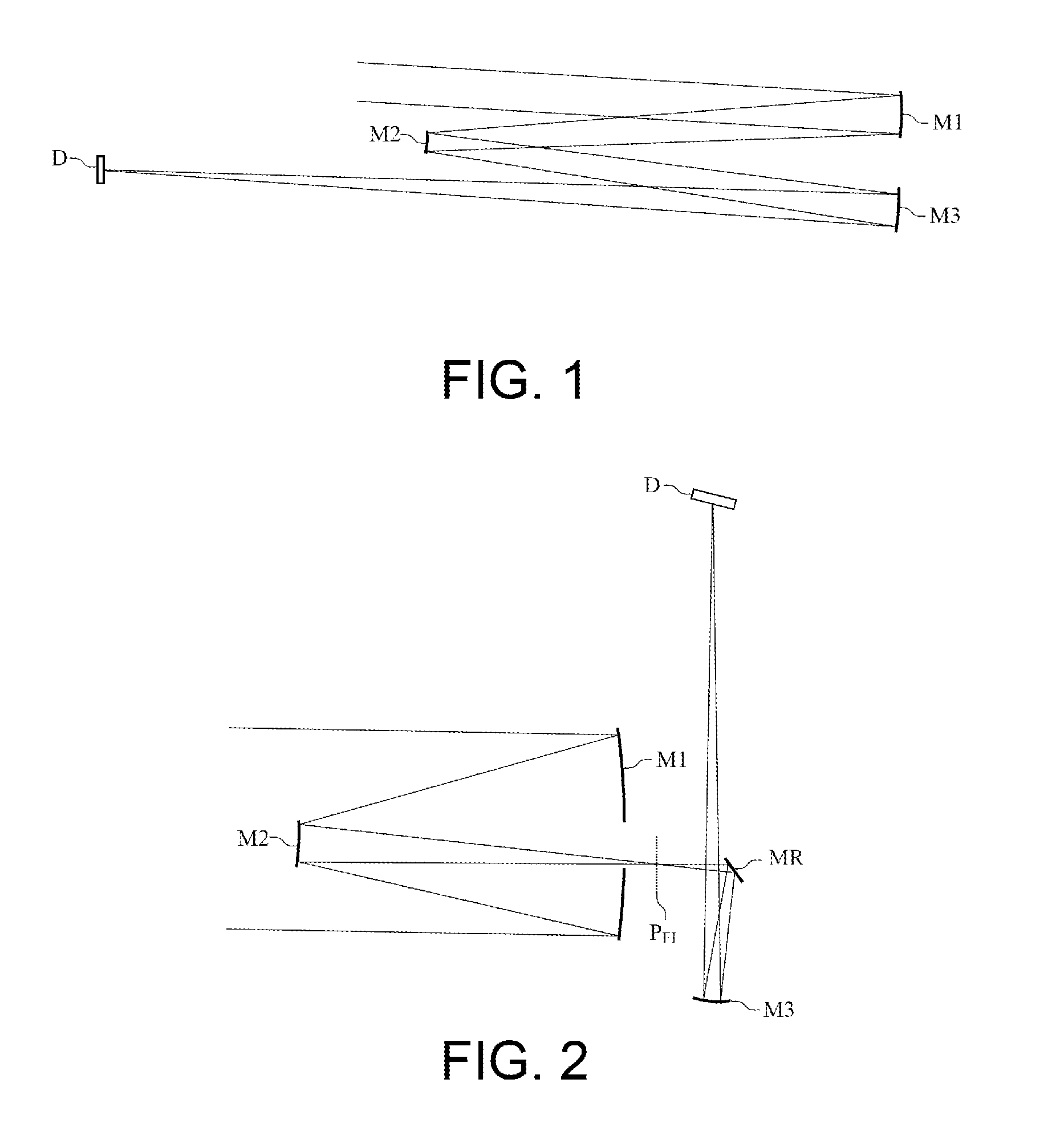
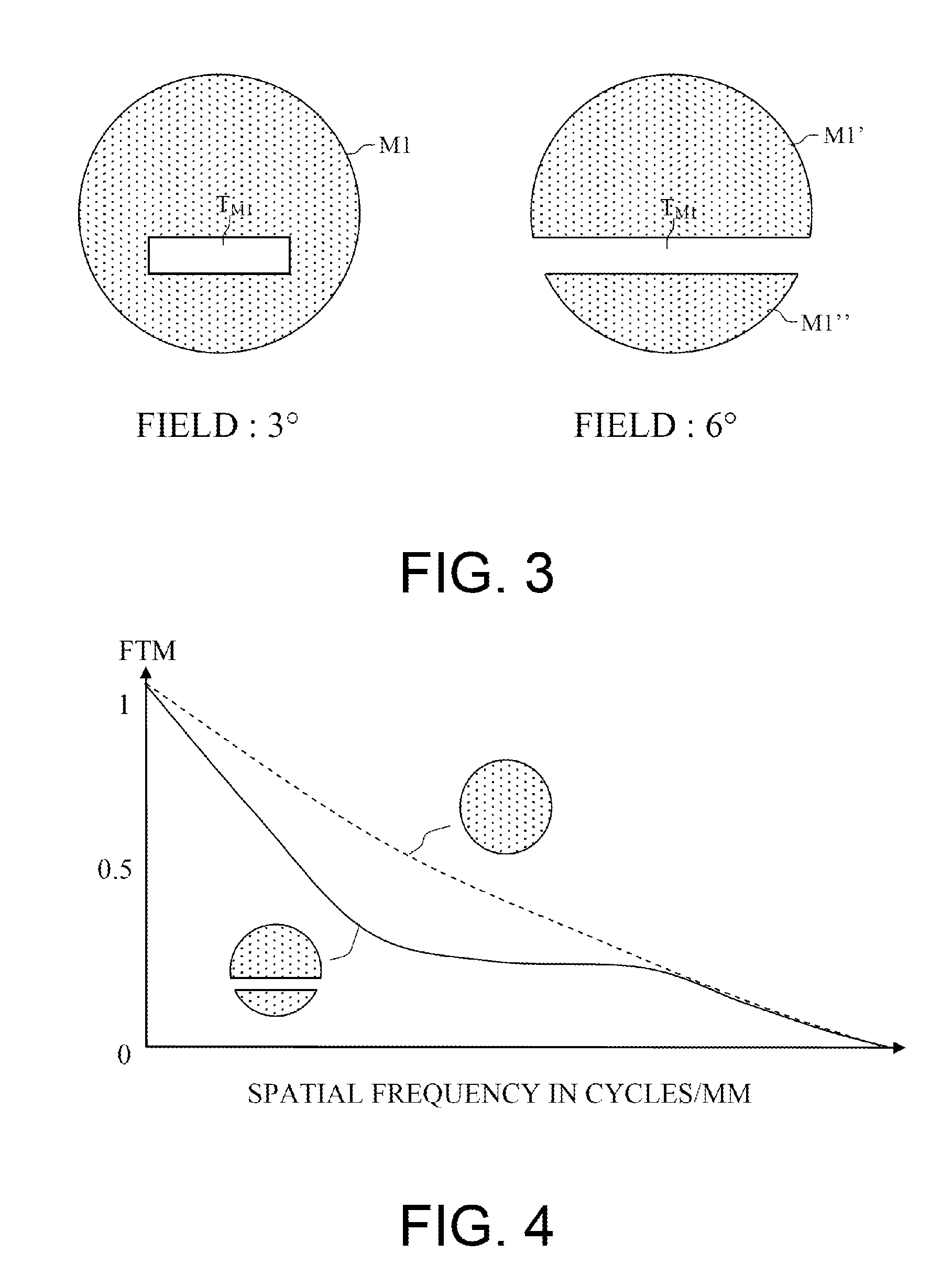
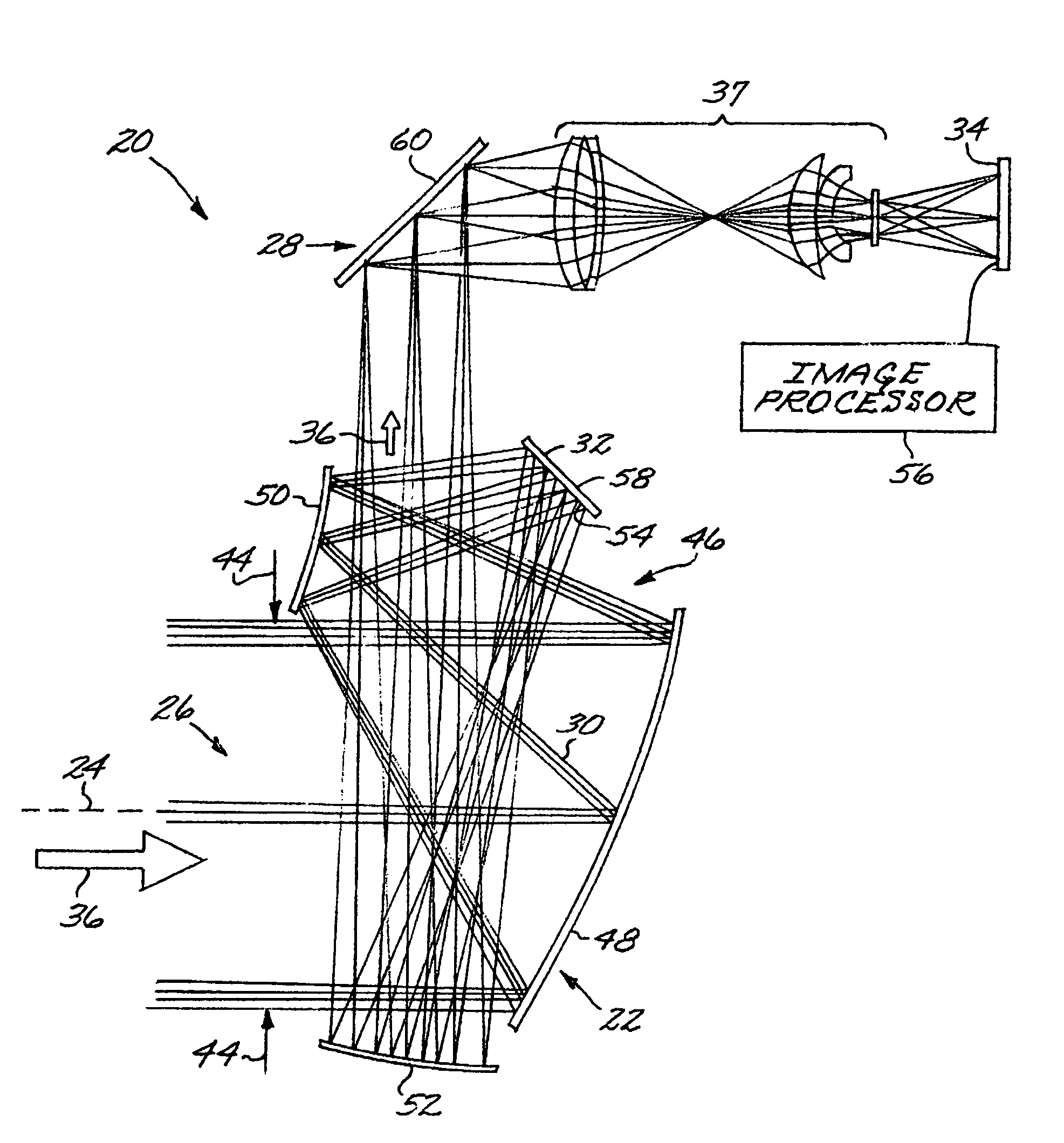
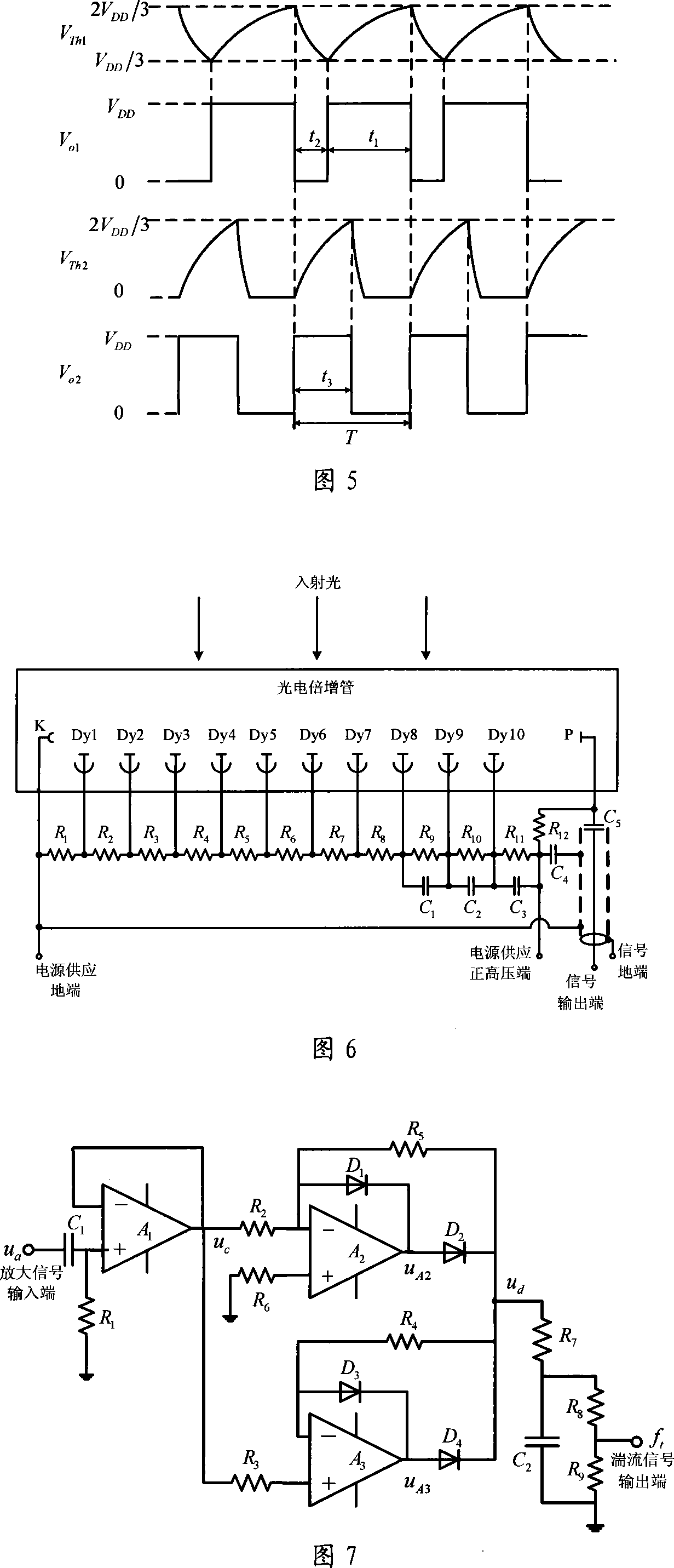
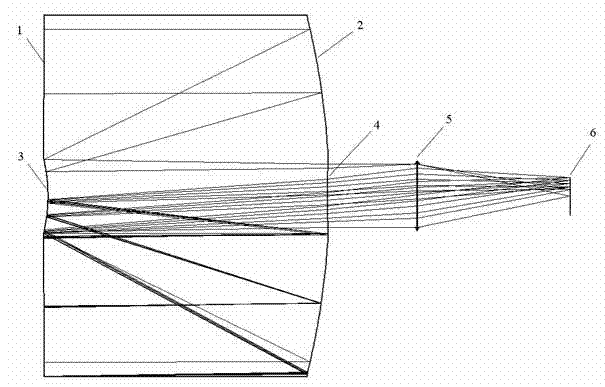
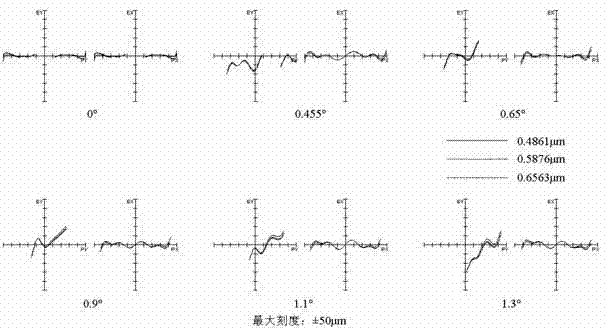
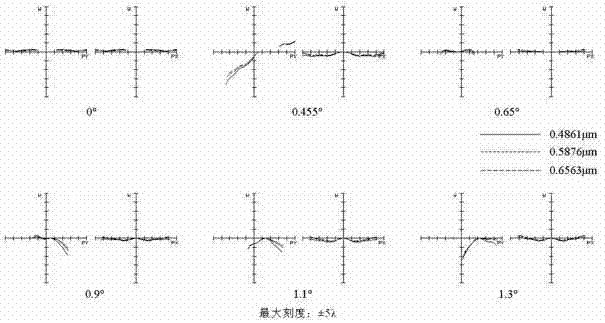
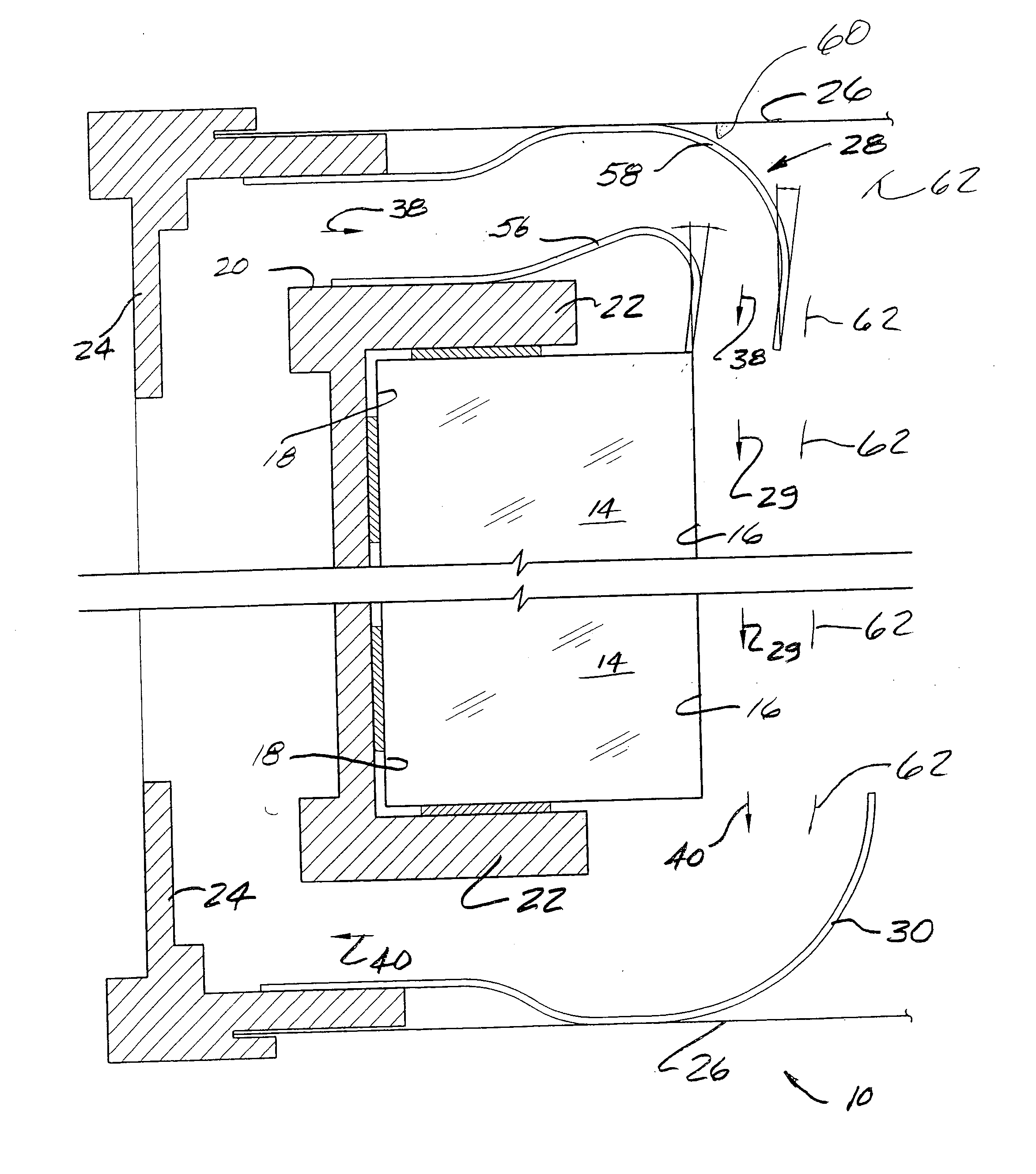
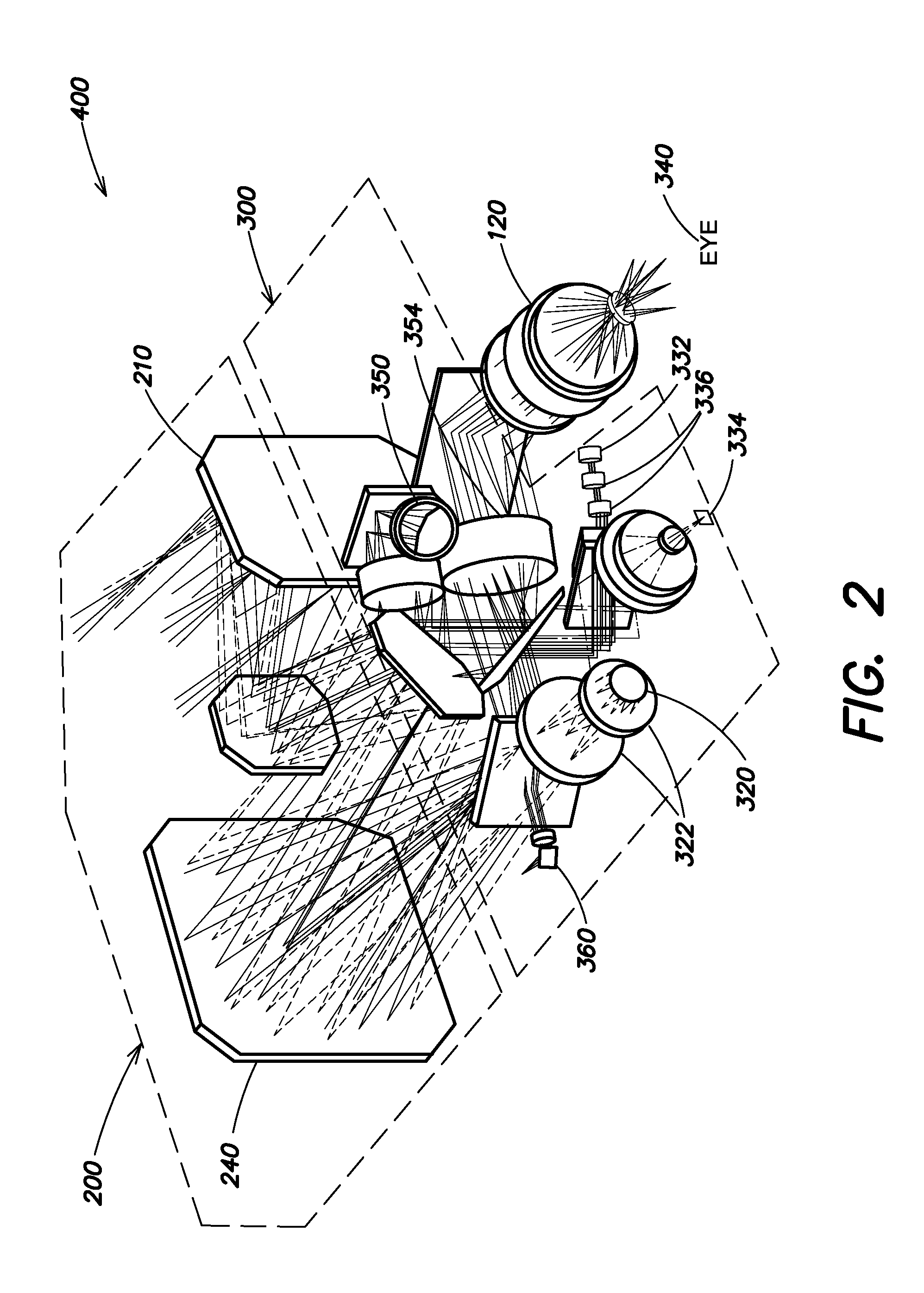
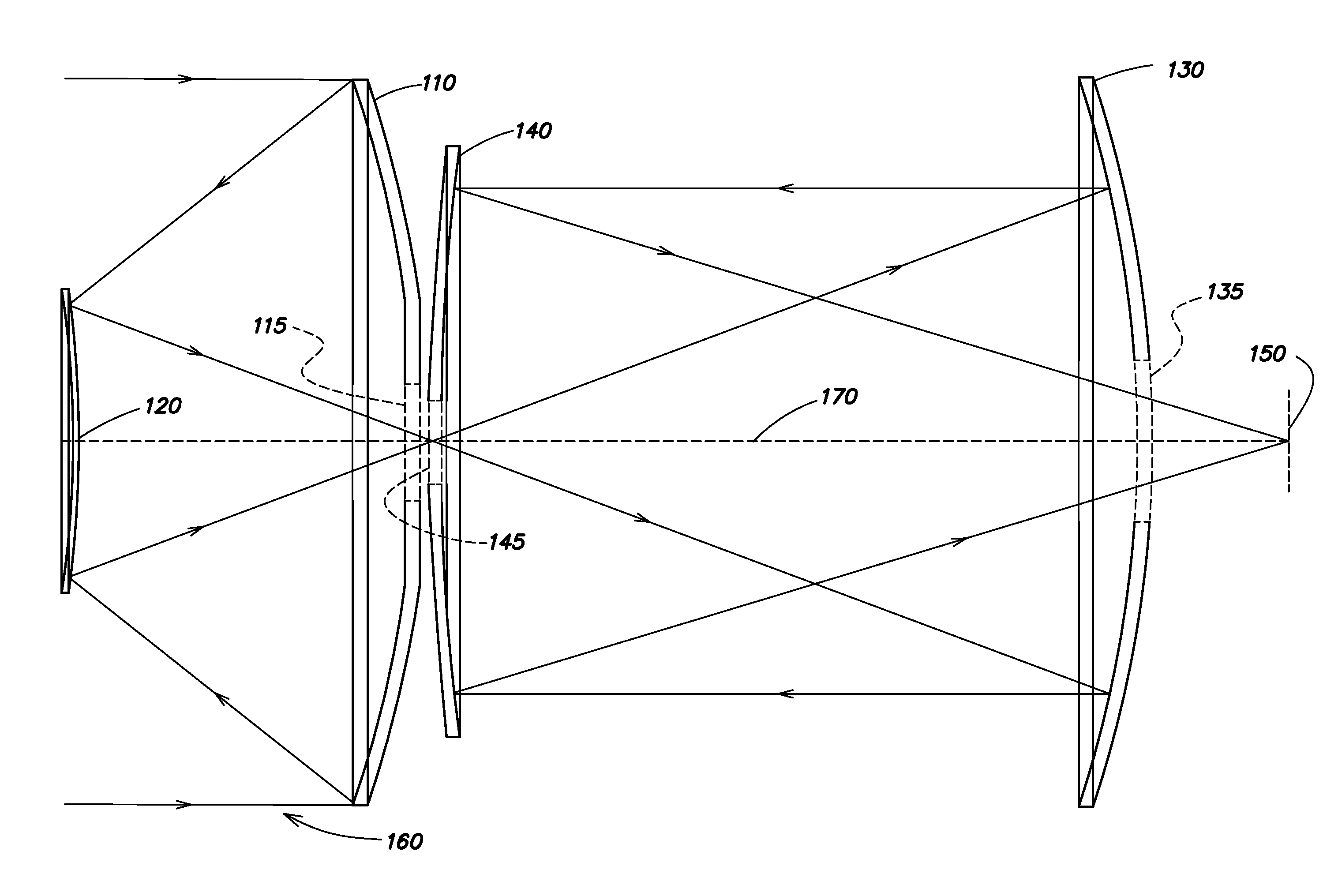
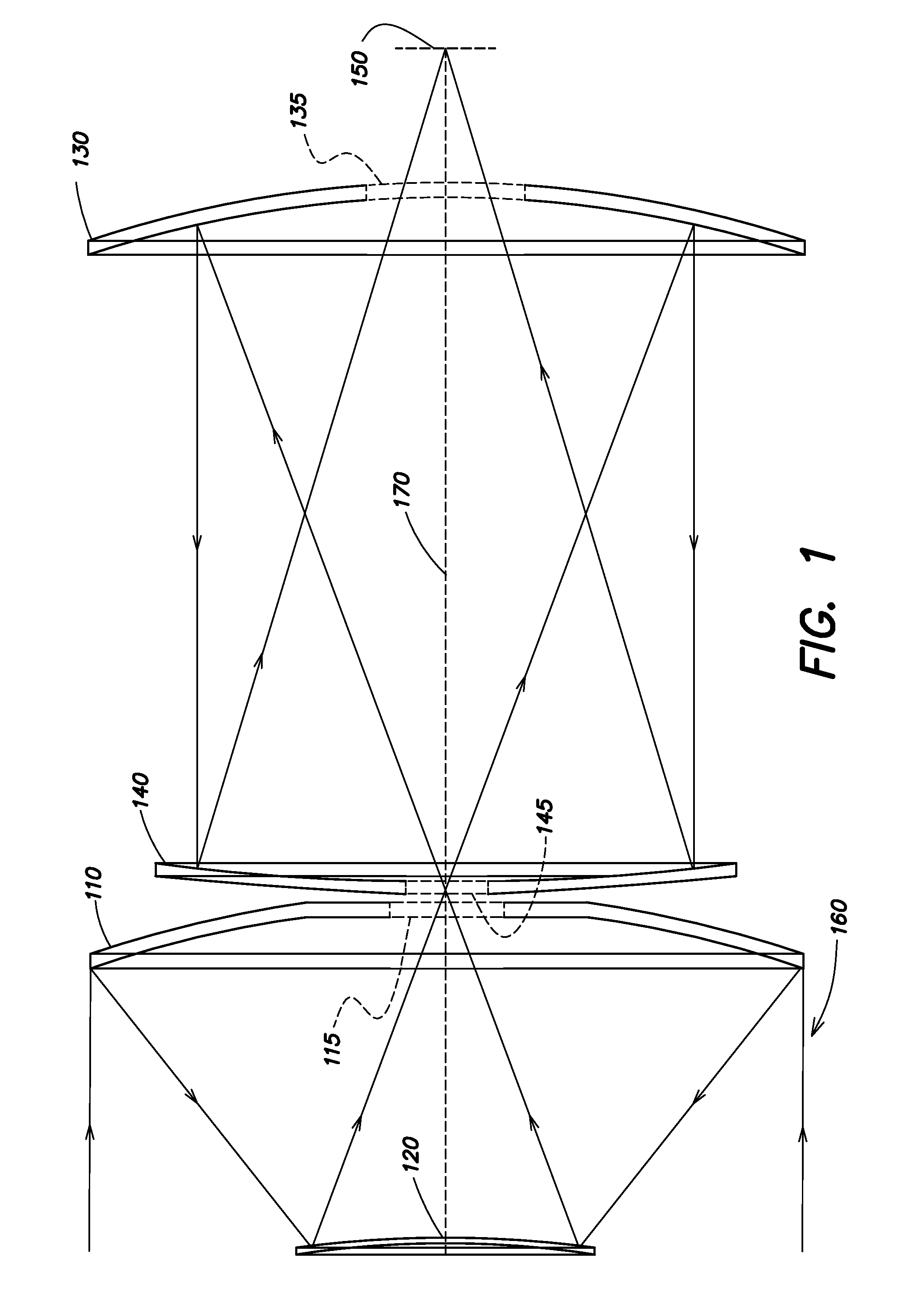
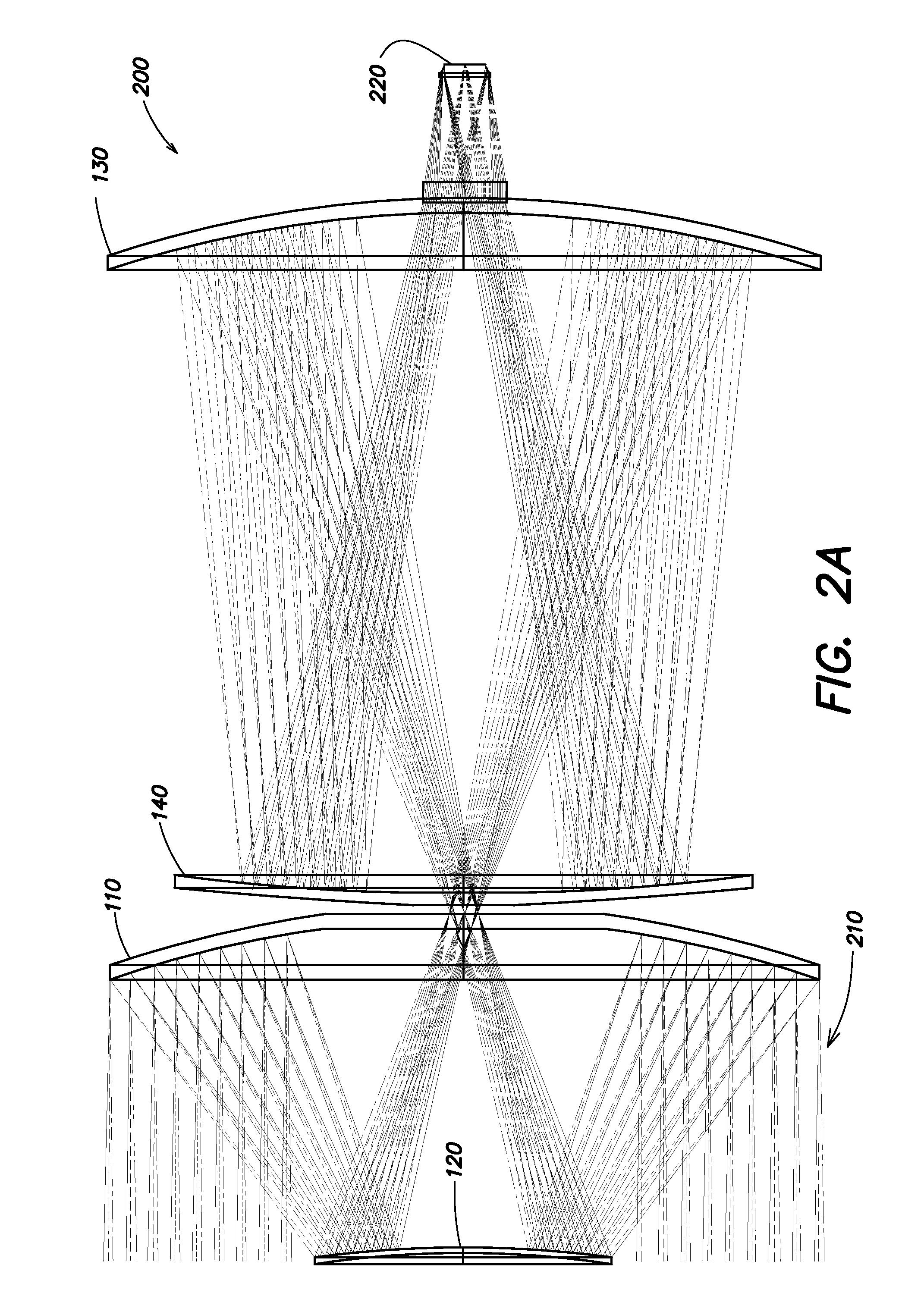
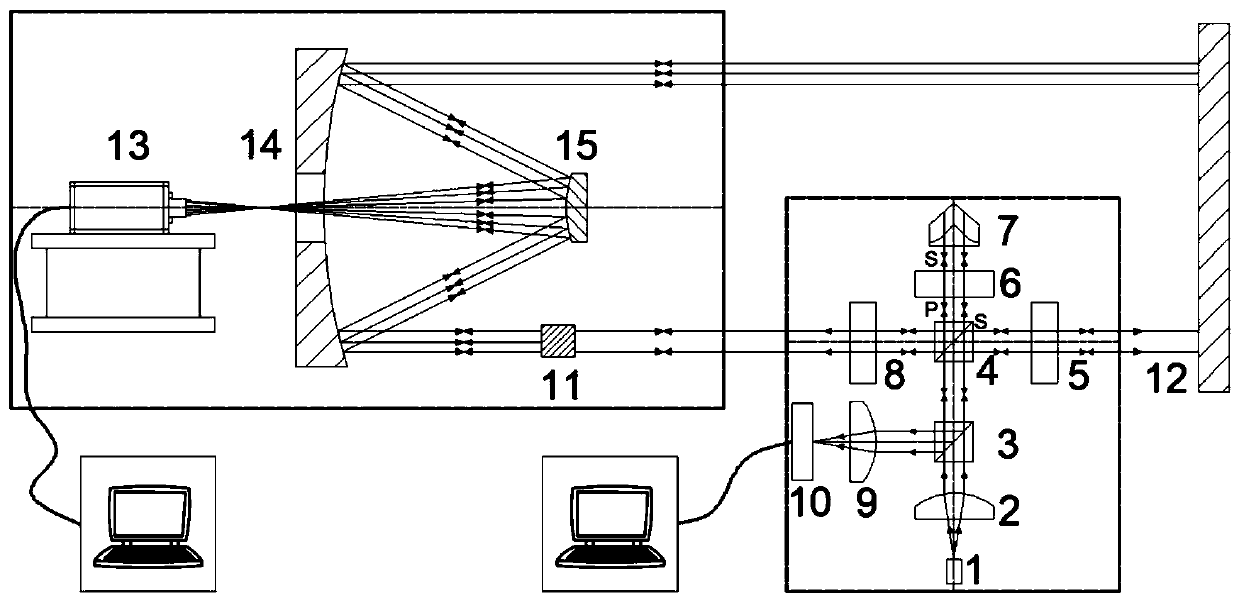
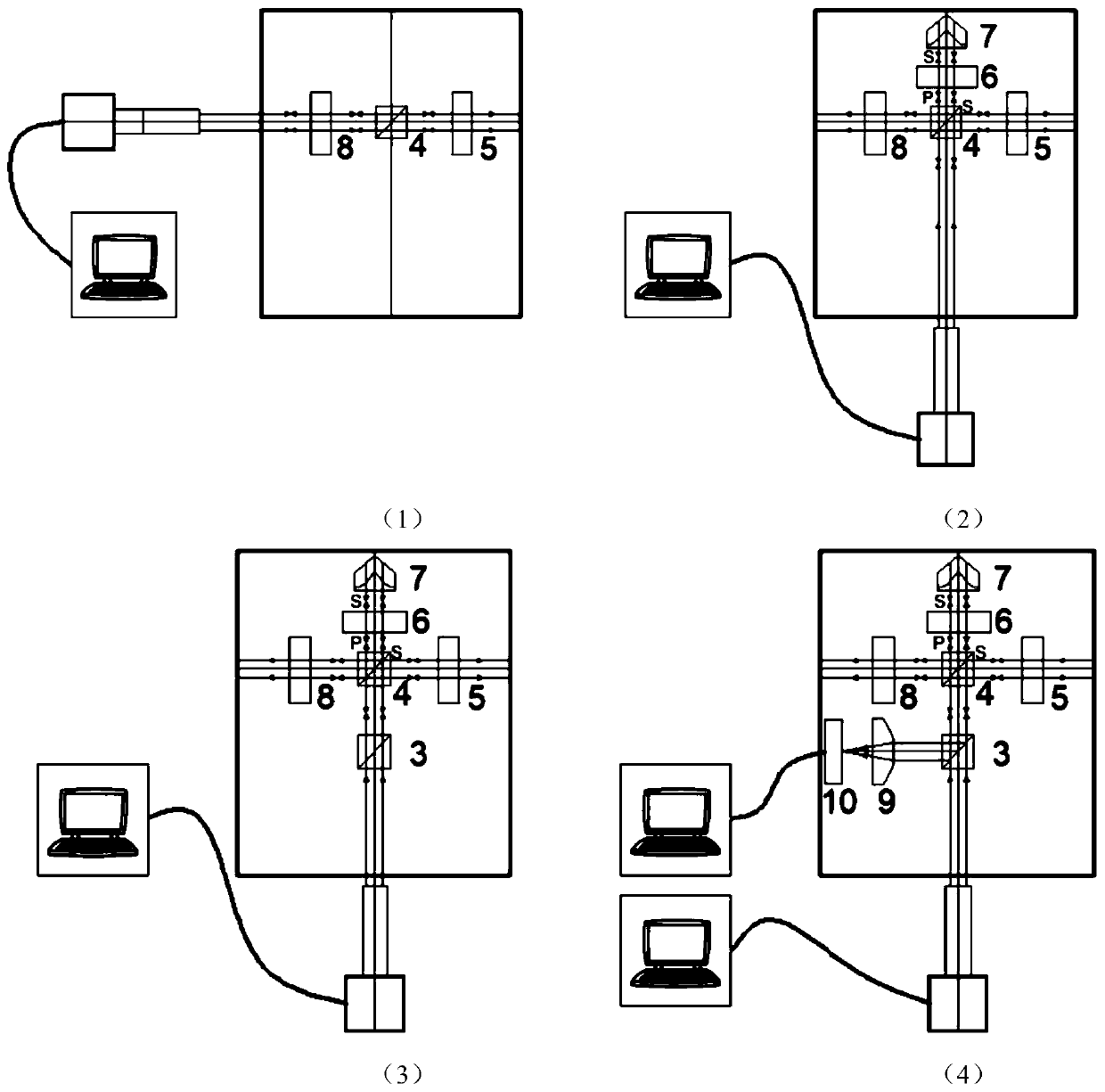
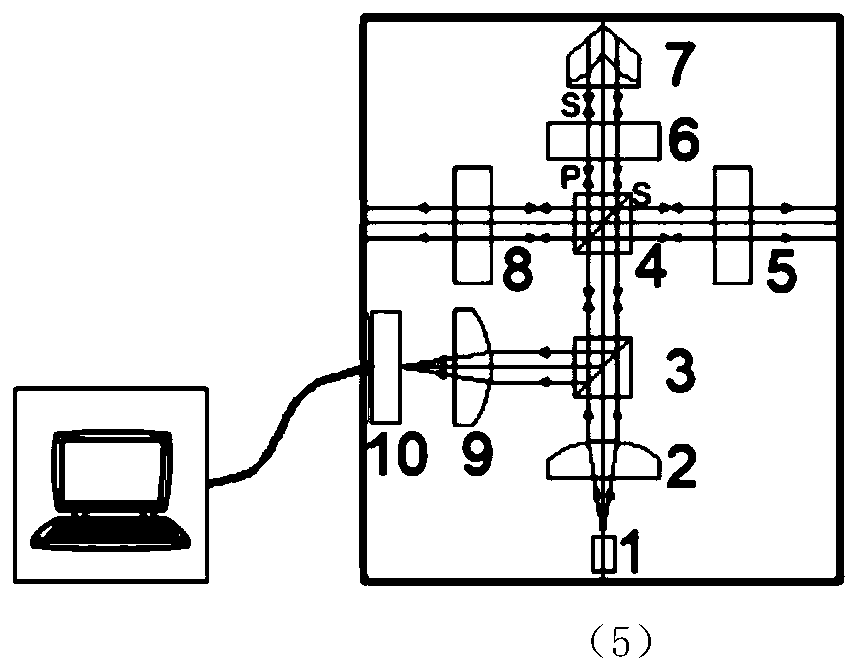
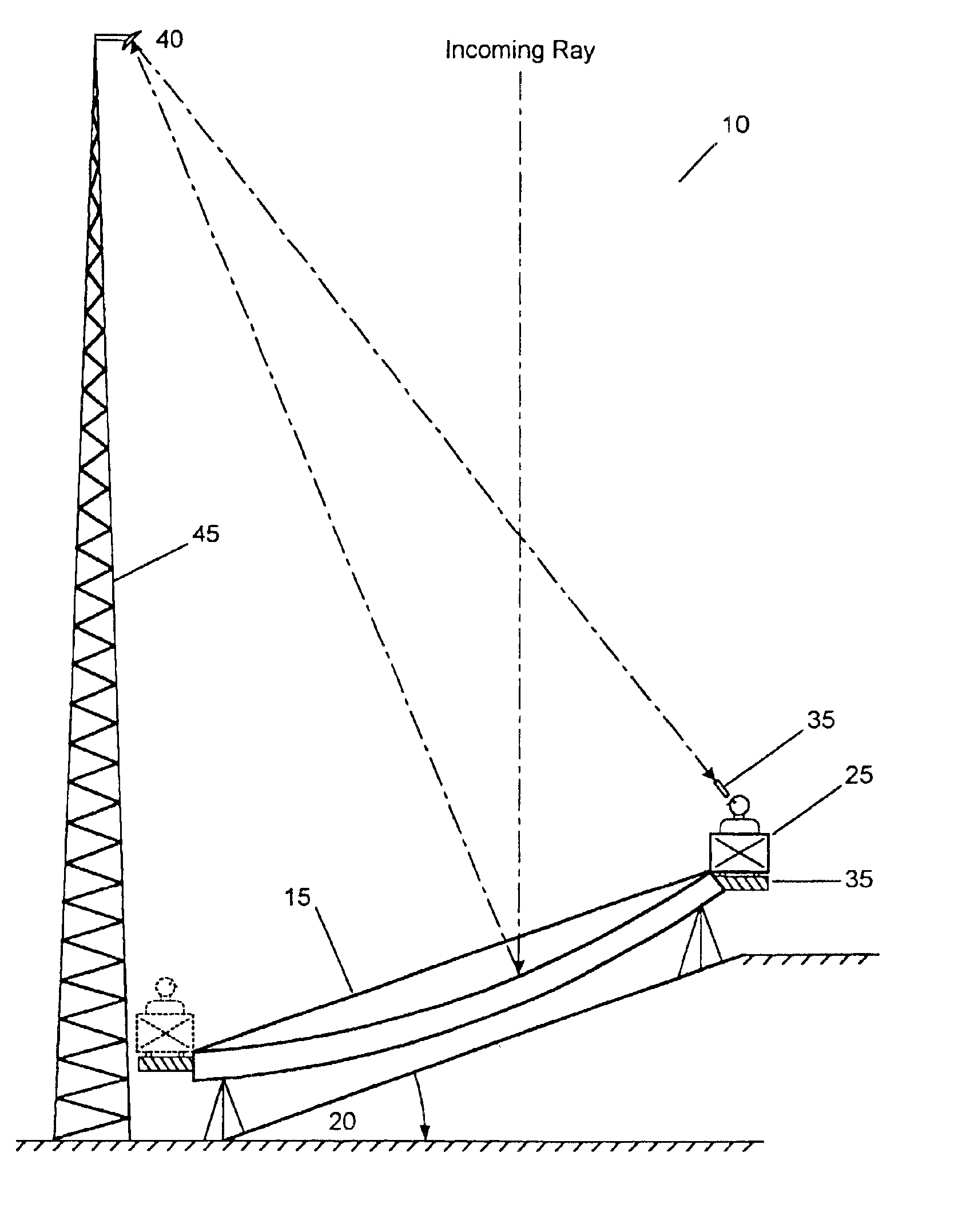
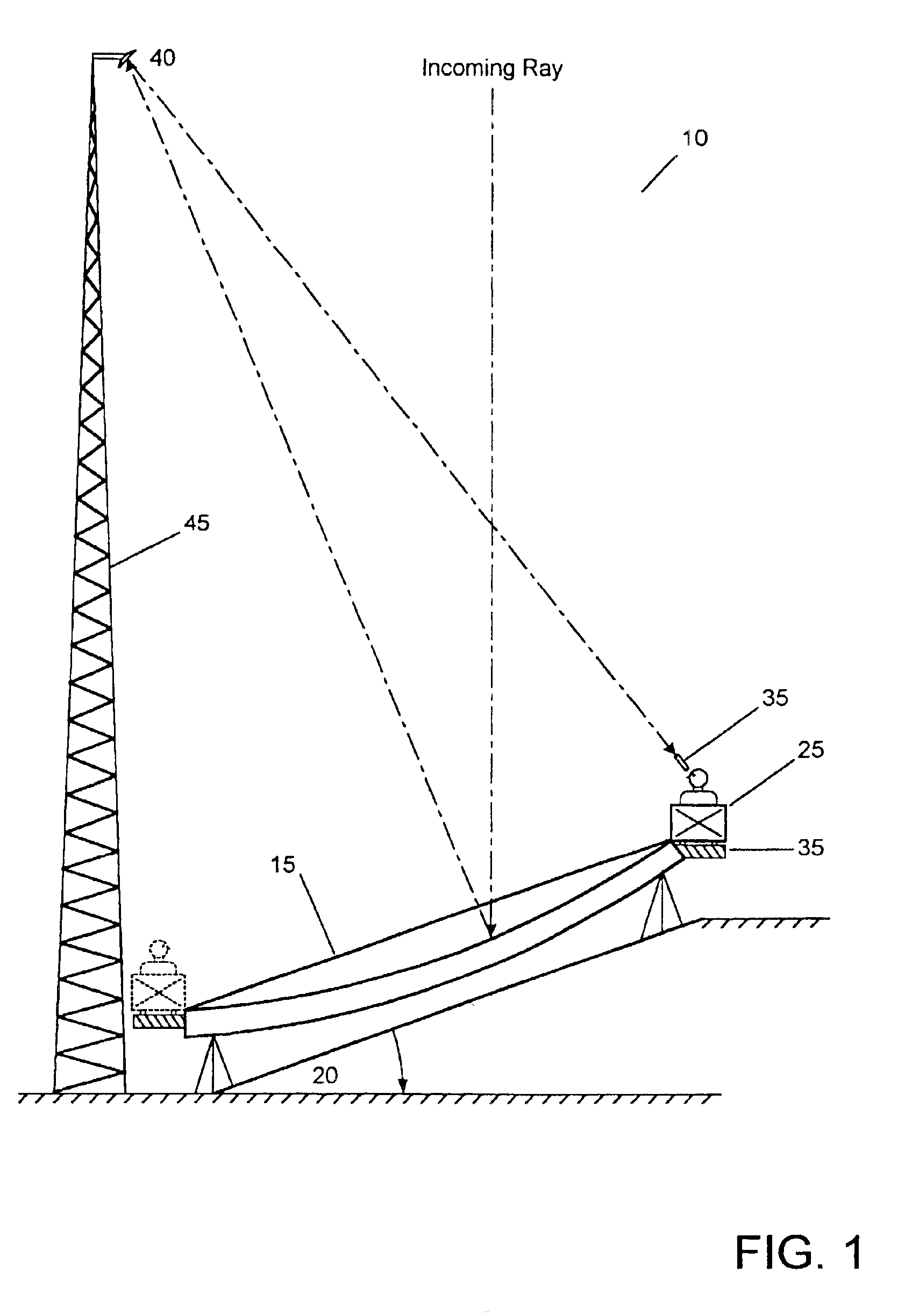
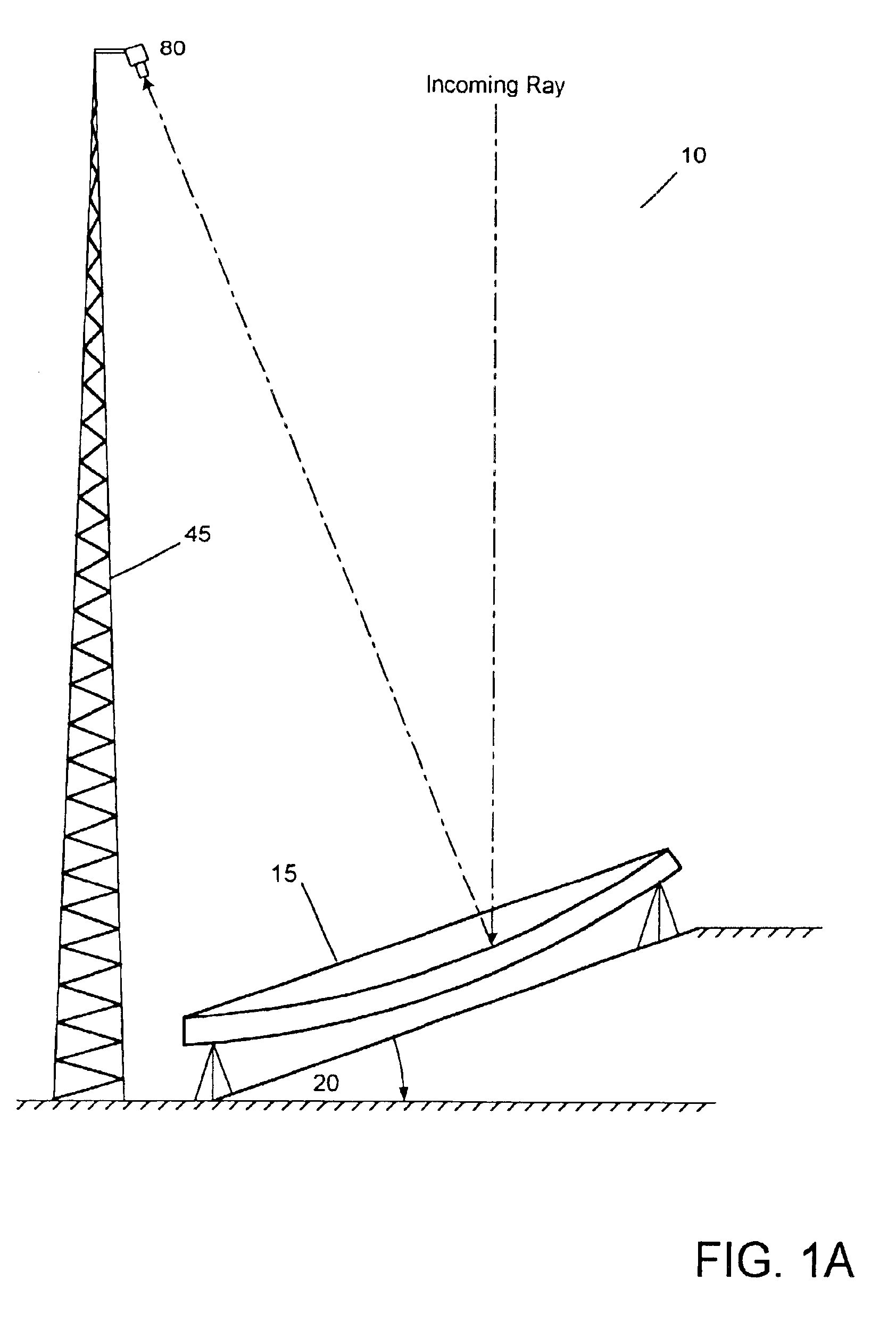
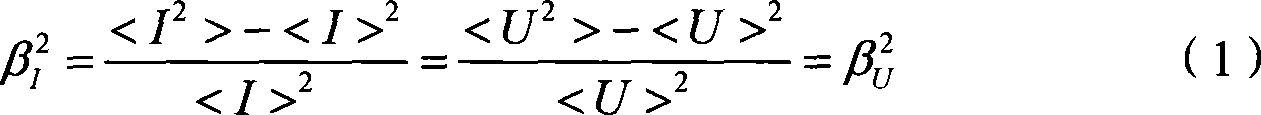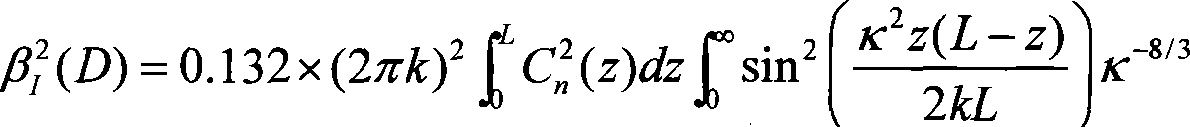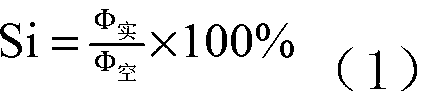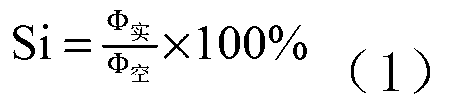Patents
Literature
84 results about "Reflecting telescope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
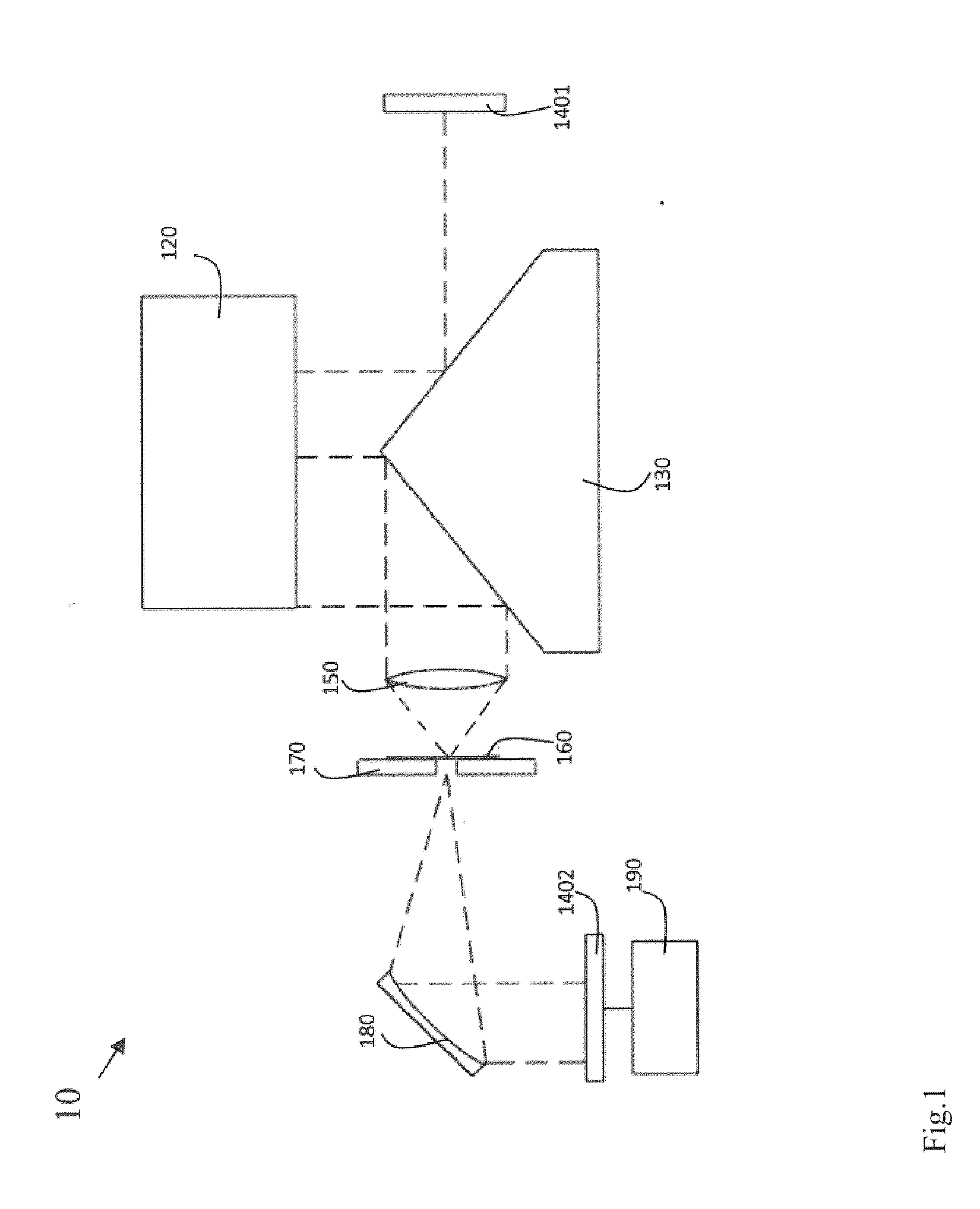
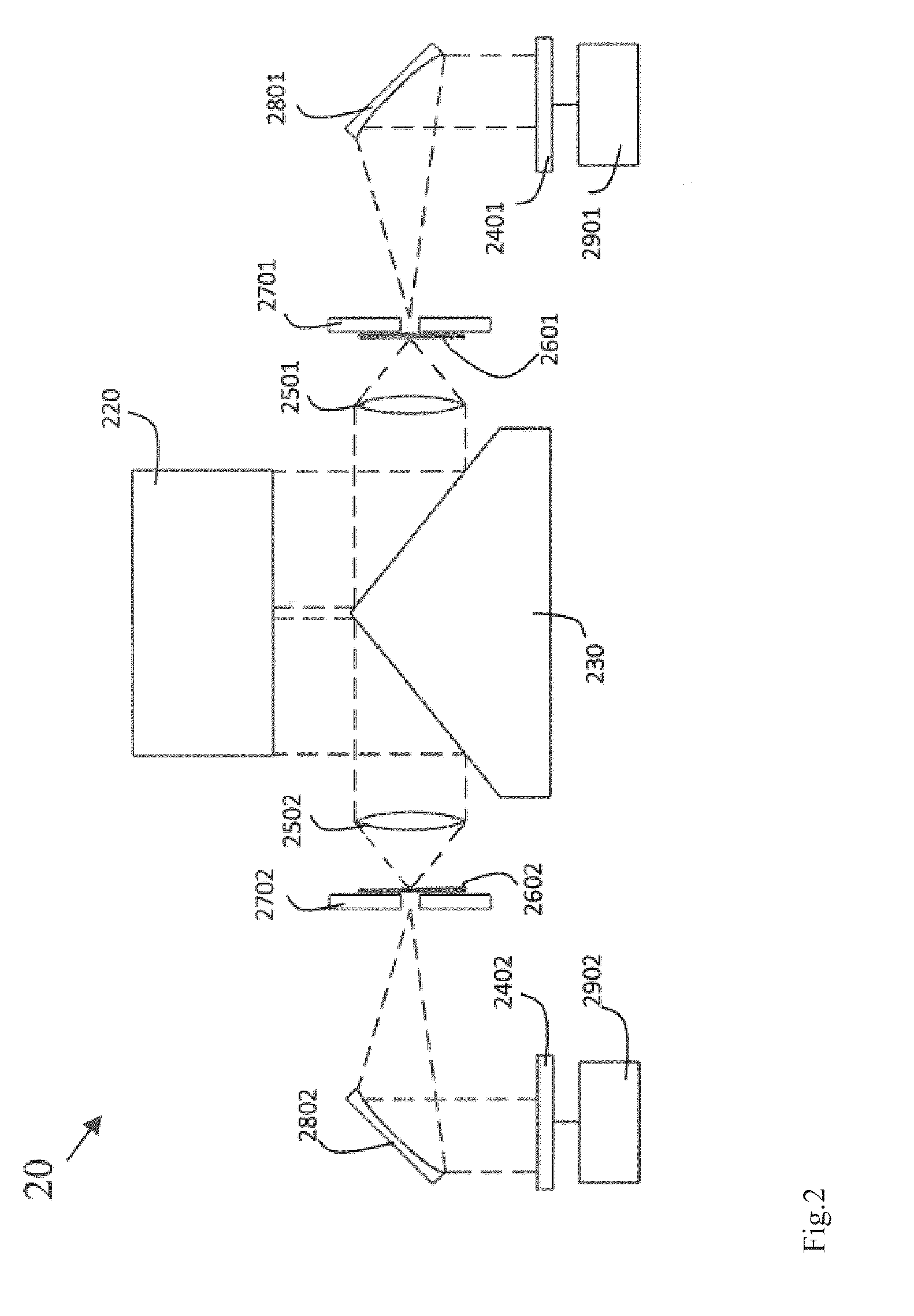
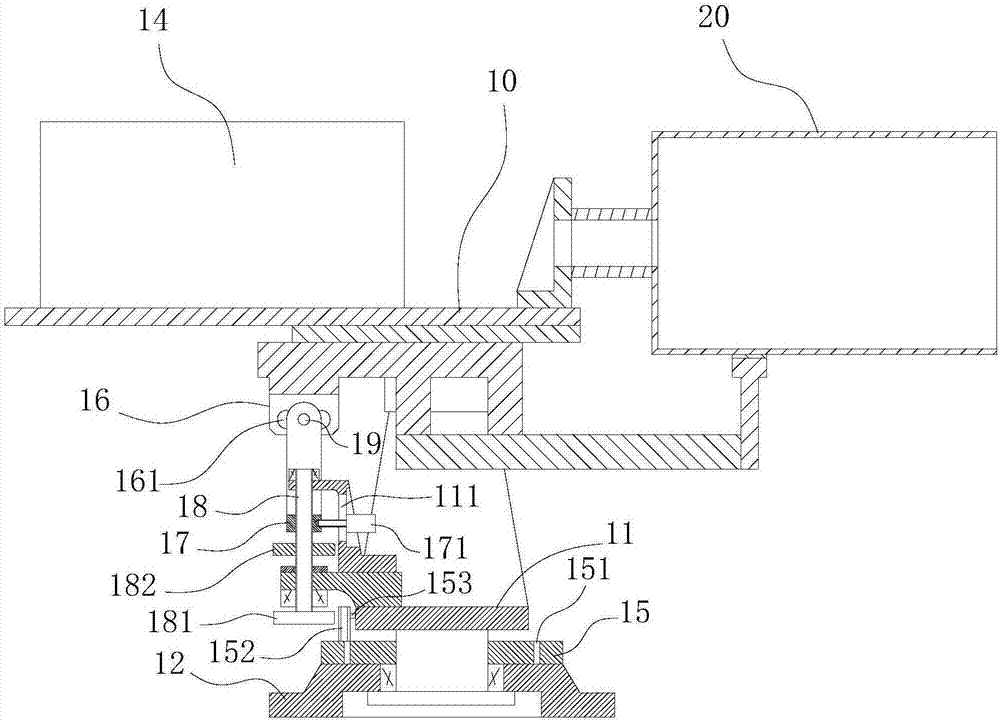
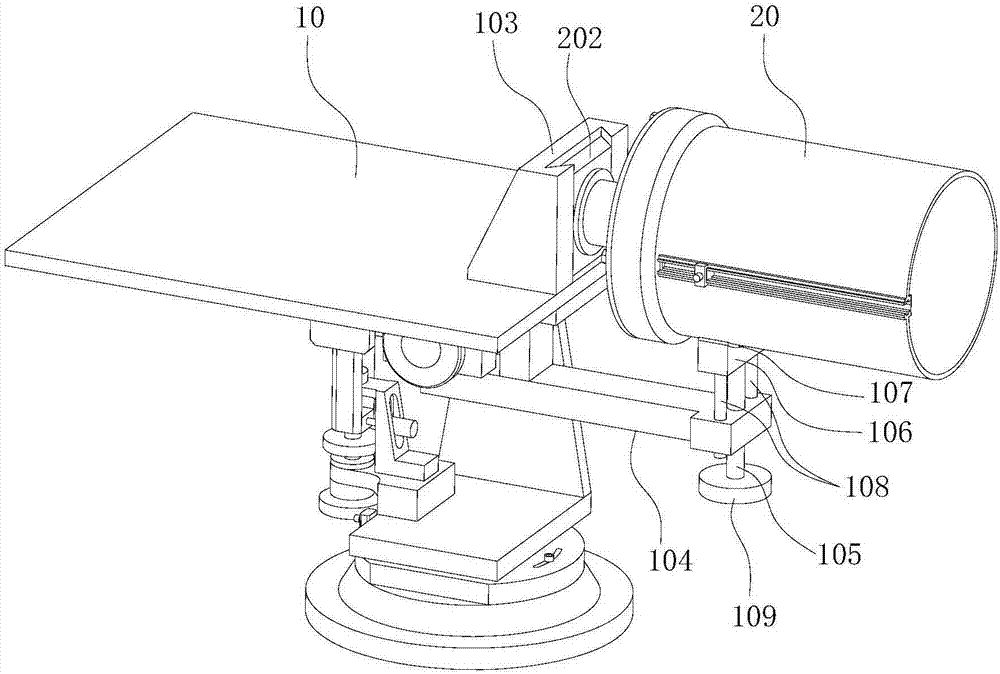
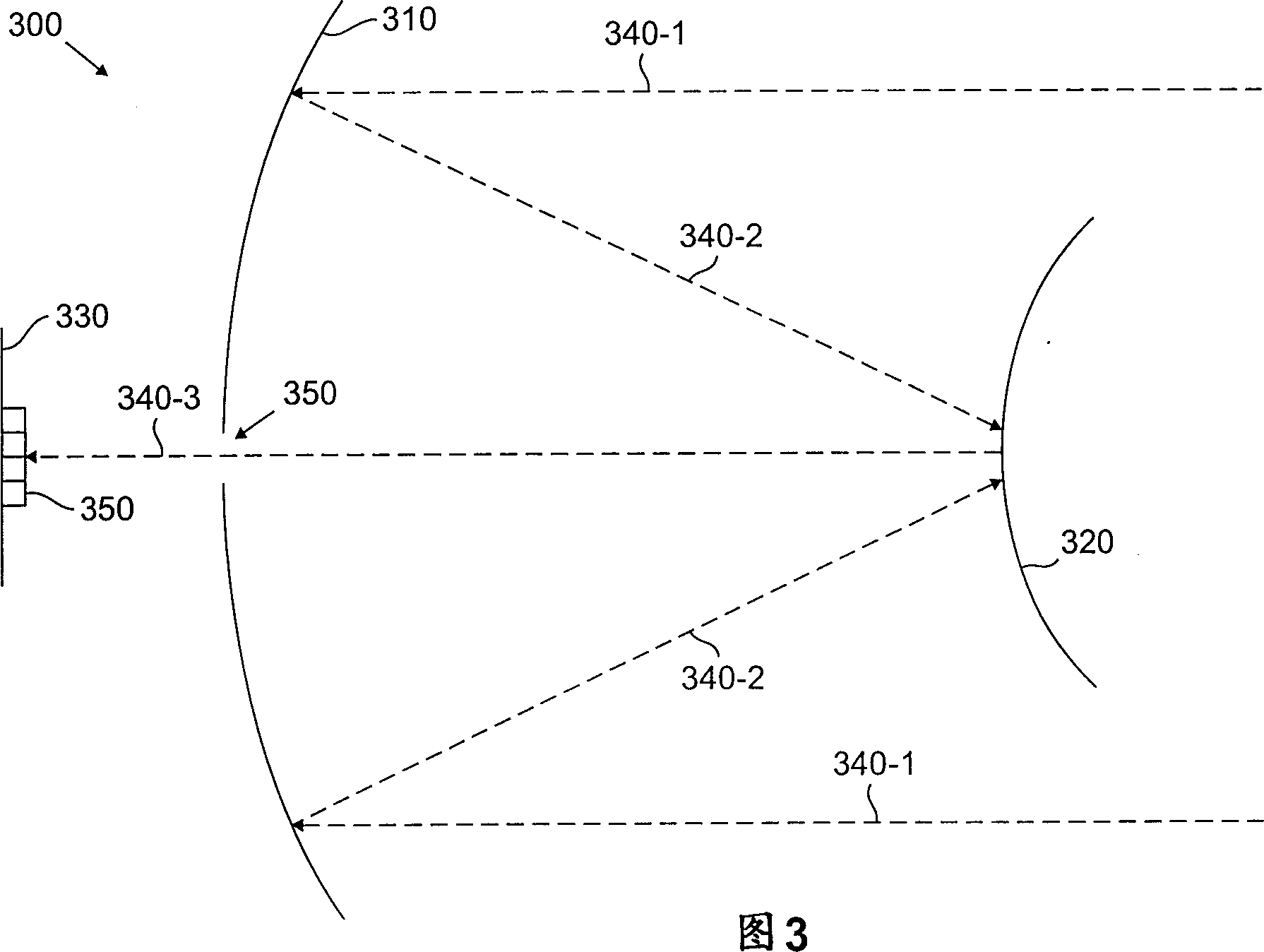
A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century, by Isaac Newton, as an alternative to the refracting telescope which, at that time, was a design that suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for very large diameter objectives. Almost all of the major telescopes used in astronomy research are reflectors. Reflecting telescopes come in many design variations and may employ extra optical elements to improve image quality or place the image in a mechanically advantageous position. Since reflecting telescopes use mirrors, the design is sometimes referred to as a "catoptric" telescope.
Intraocular lens
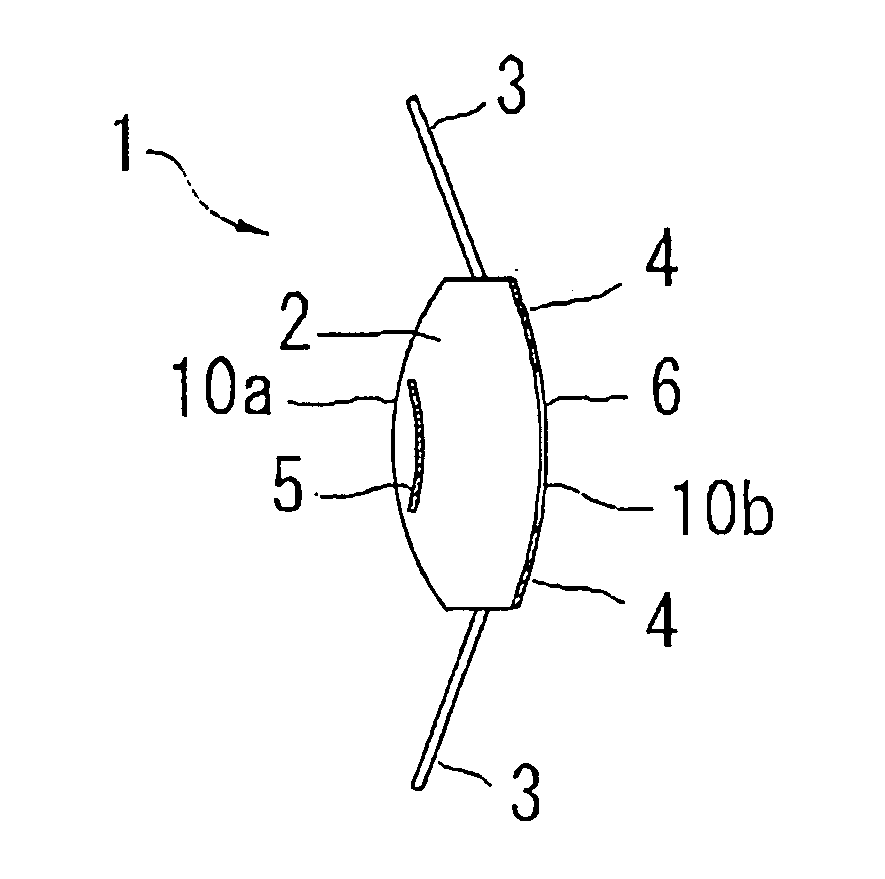
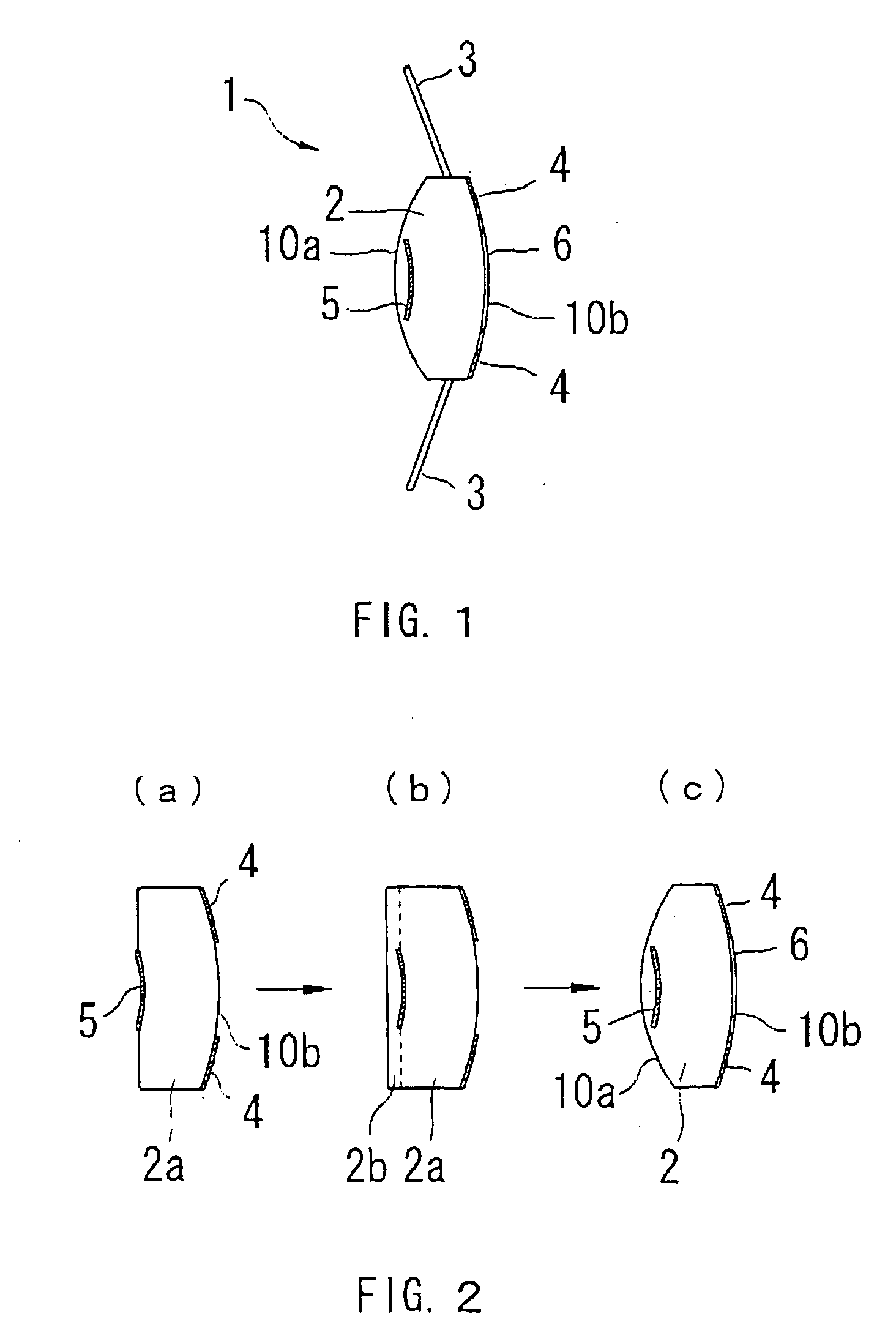
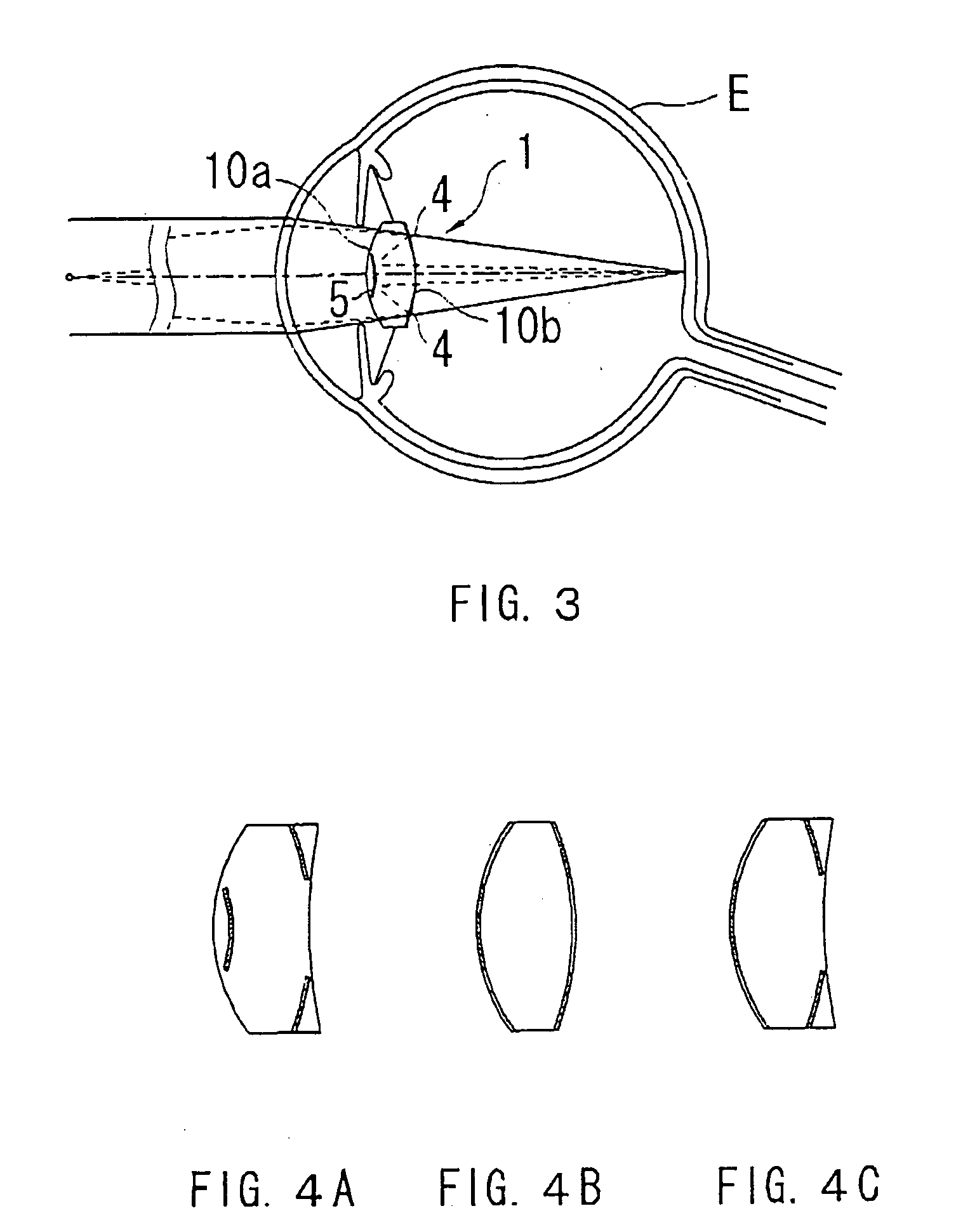
An intraocular lens for amblyopia designed in consideration of normalizing vision as well as magnifying vision, is provided with an optical part having predetermined refractive power, which includes front and rear side refractive surfaces, a supporting part for supporting the optical part within the eye, a first reflecting part formed at a rear surface side of the optical part for reflecting an incident light bundle, which has passed through the front surface of the optical part, toward the front surface, and a second reflecting part formed at a front surface side of the optical part for reflecting the incident light bundle, which has been reflected by the first one, toward the rear surface, wherein the first and second reflecting parts form a reflecting telescopic system which forms a magnified image on a retina, and at least one of them has a property of transmitting a part of the light bundle.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Confocal scanning and optical coherence tomograph based on self-adaptive optical technology
ActiveCN101869466AImproving Resolution in Longitudinal Sectional ImagingIncreased imaging resolution in transverse slicesPhase-affecting property measurementsEye diagnosticsReflecting telescopeImage detection
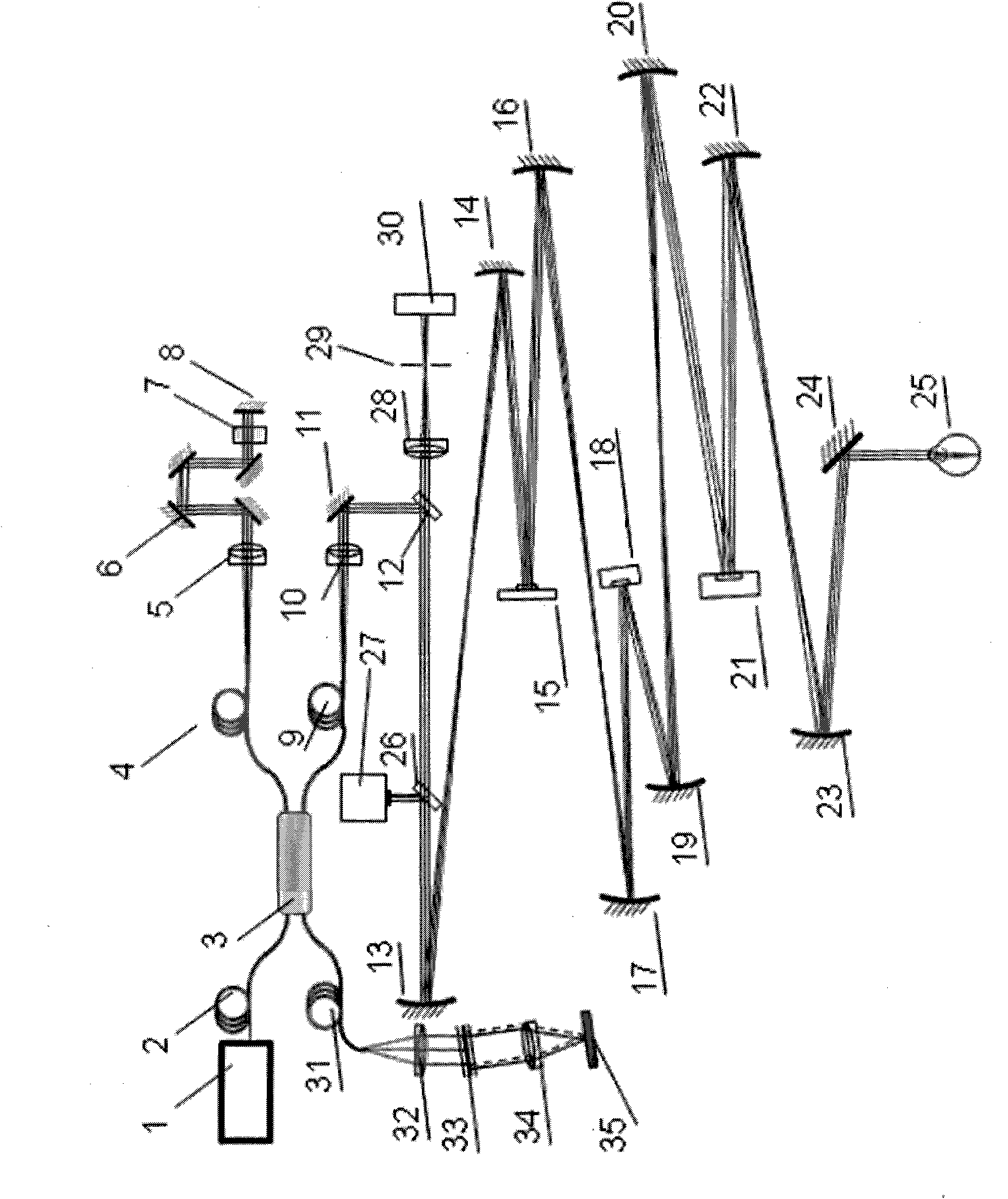
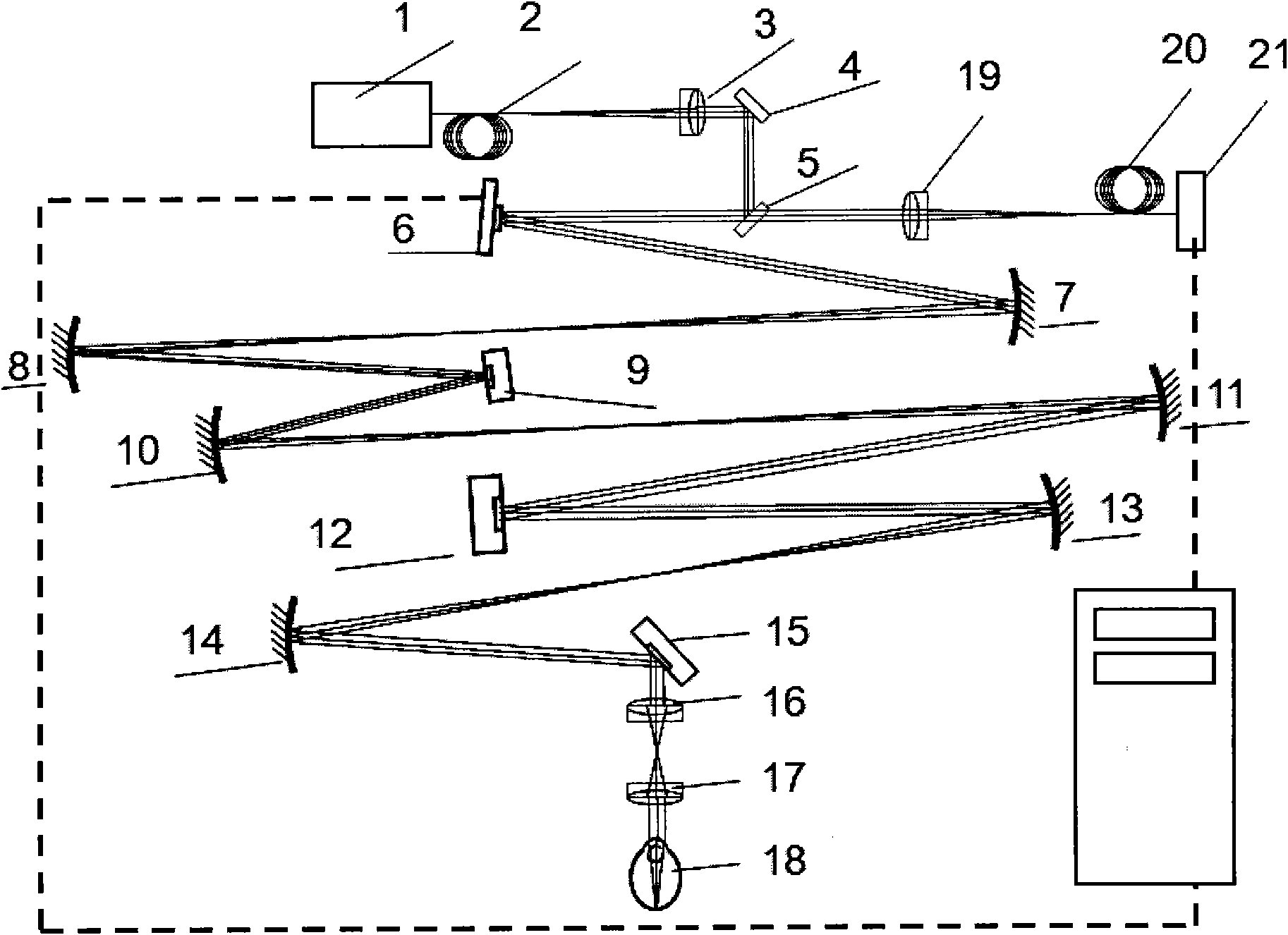
A confocal scanning and optical coherence tomograph based on self-adaptive optical technology comprises a light source component, a scanning and lighting light path component, an aberration detection and correction component, a confocal imaging detection component, a reference arm component and an optical coherence tomography detection component, wherein the components are linked by optical fiber and / or spherical reflecting telescopes; one part of low-coherent light emitted by the light source component enters into the reference arm component and then returns along the original path and the other part enters into the samples to be detected through the aberration detection and correction component and the scanning and lighting light path component in sequence and then returns from the samples to be detected along the original path; one part of the returning light is reflected to the aberration detection and correction component by a spectroscope and the other part is transmitted to another spectroscope and then is split into two parts, one part enters into the confocal imaging detection component and the other part enters into the optical coherence tomography detection component after being coupled with the light returning from the reference arm component. The tomograph can realize high-resolution three-dimensional imaging of the objects to be detected.
Owner:SUZHOU MICROCLEAR MEDICAL INSTR
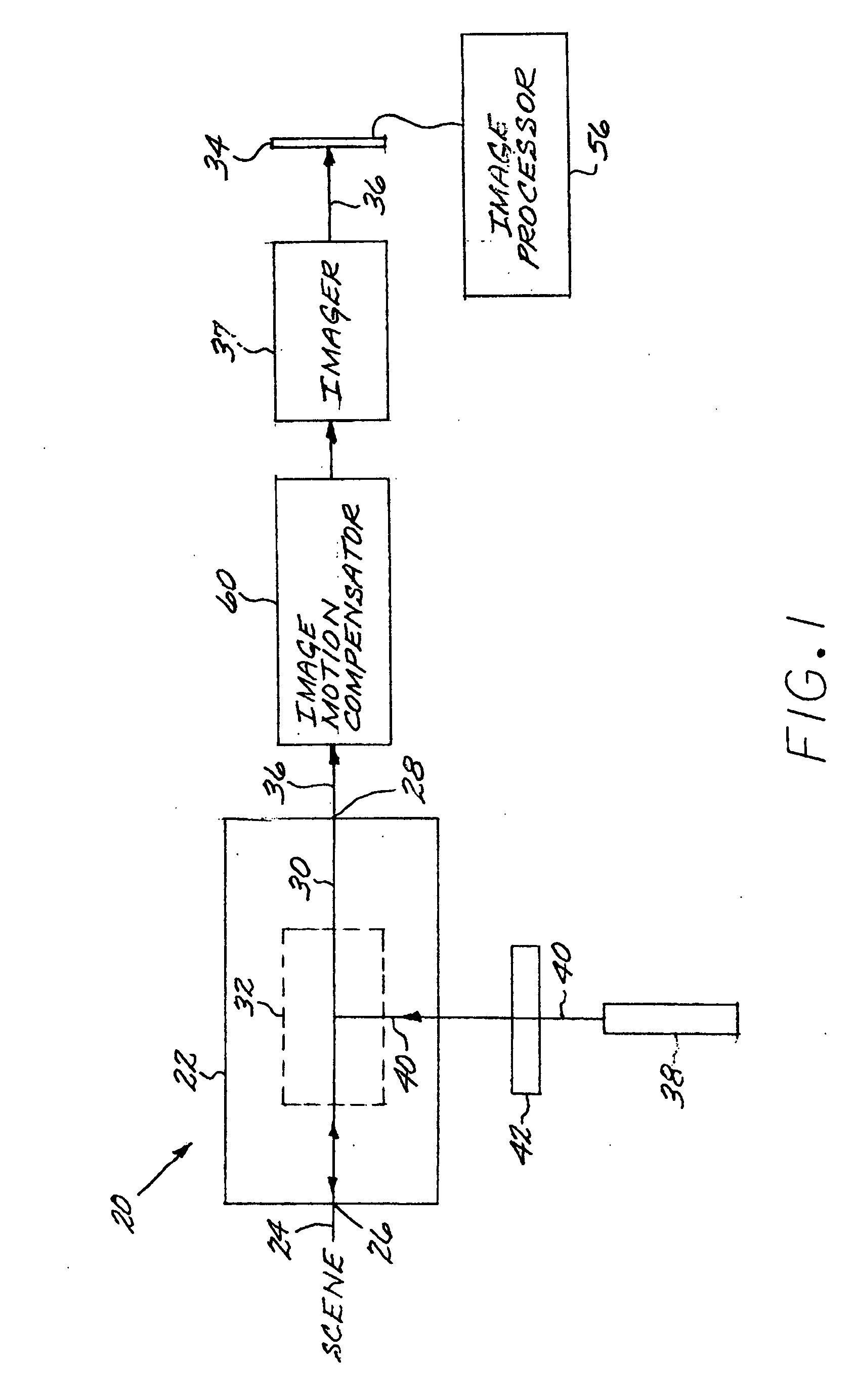
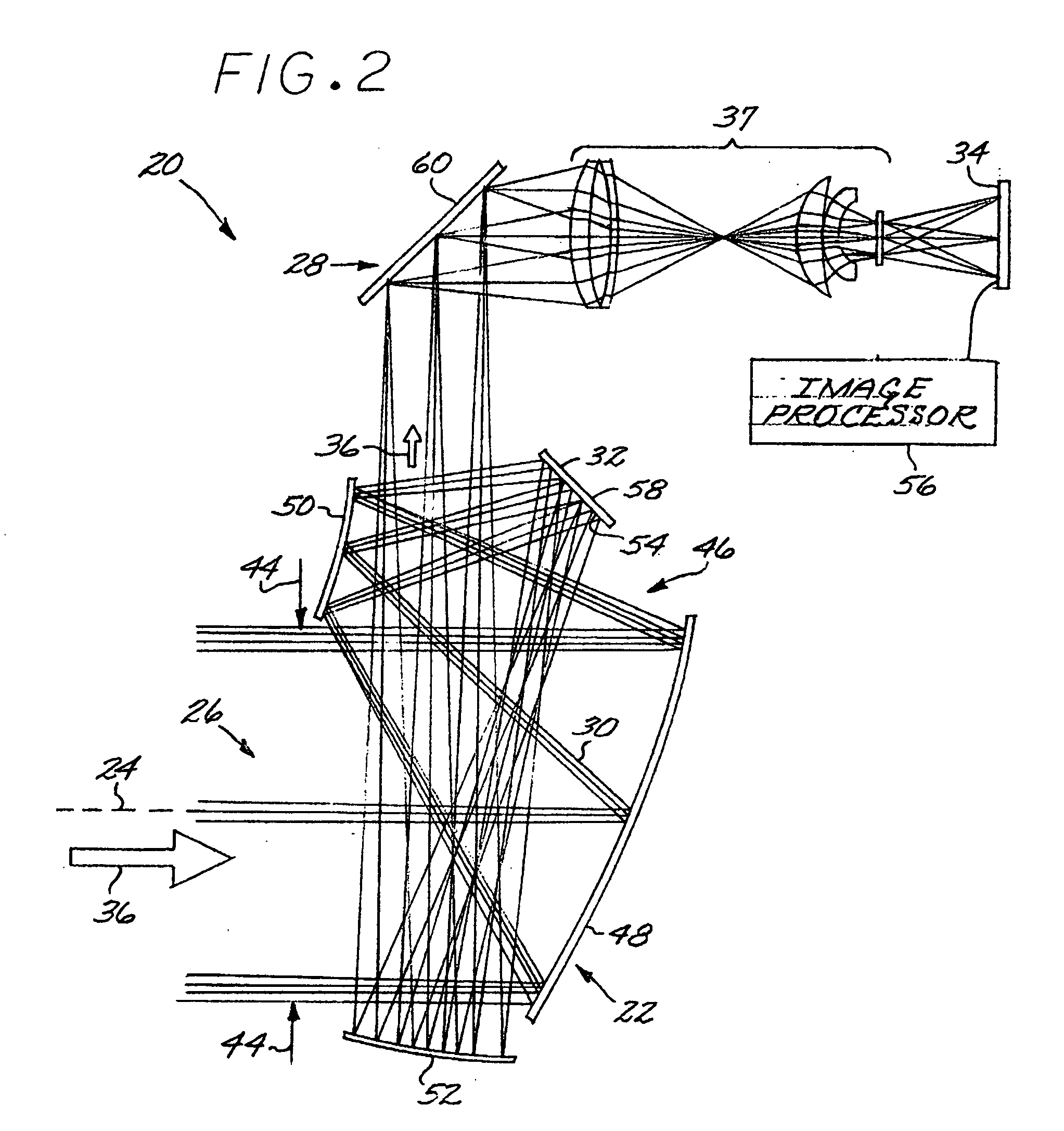
Imaging optical system including a telescope and an uncooled warm-stop structure
ActiveUS6969840B1Facilitating rapid cooldownReduce adverse effectsRadiation pyrometryMirrorsReflecting telescopeLight beam
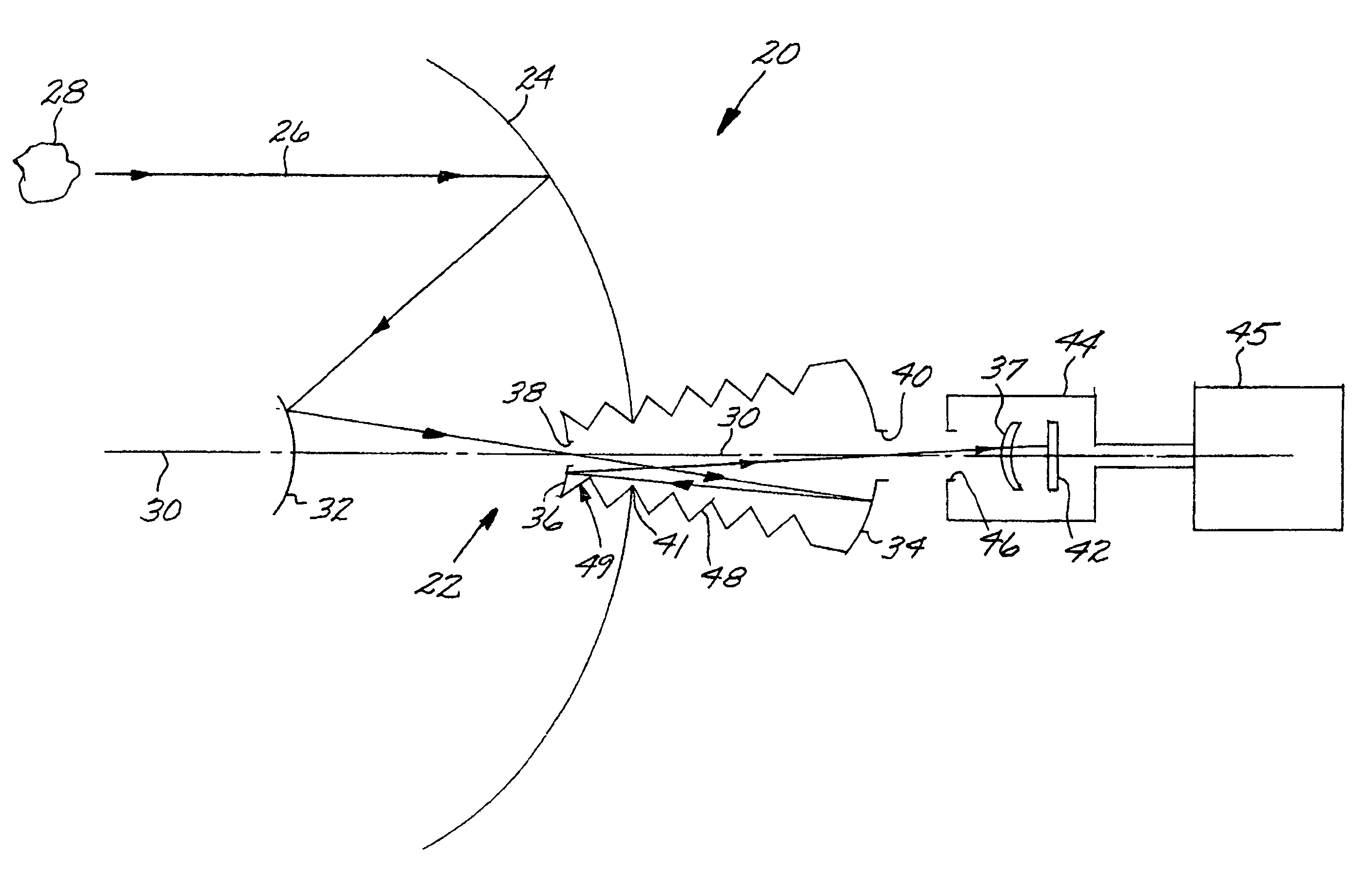
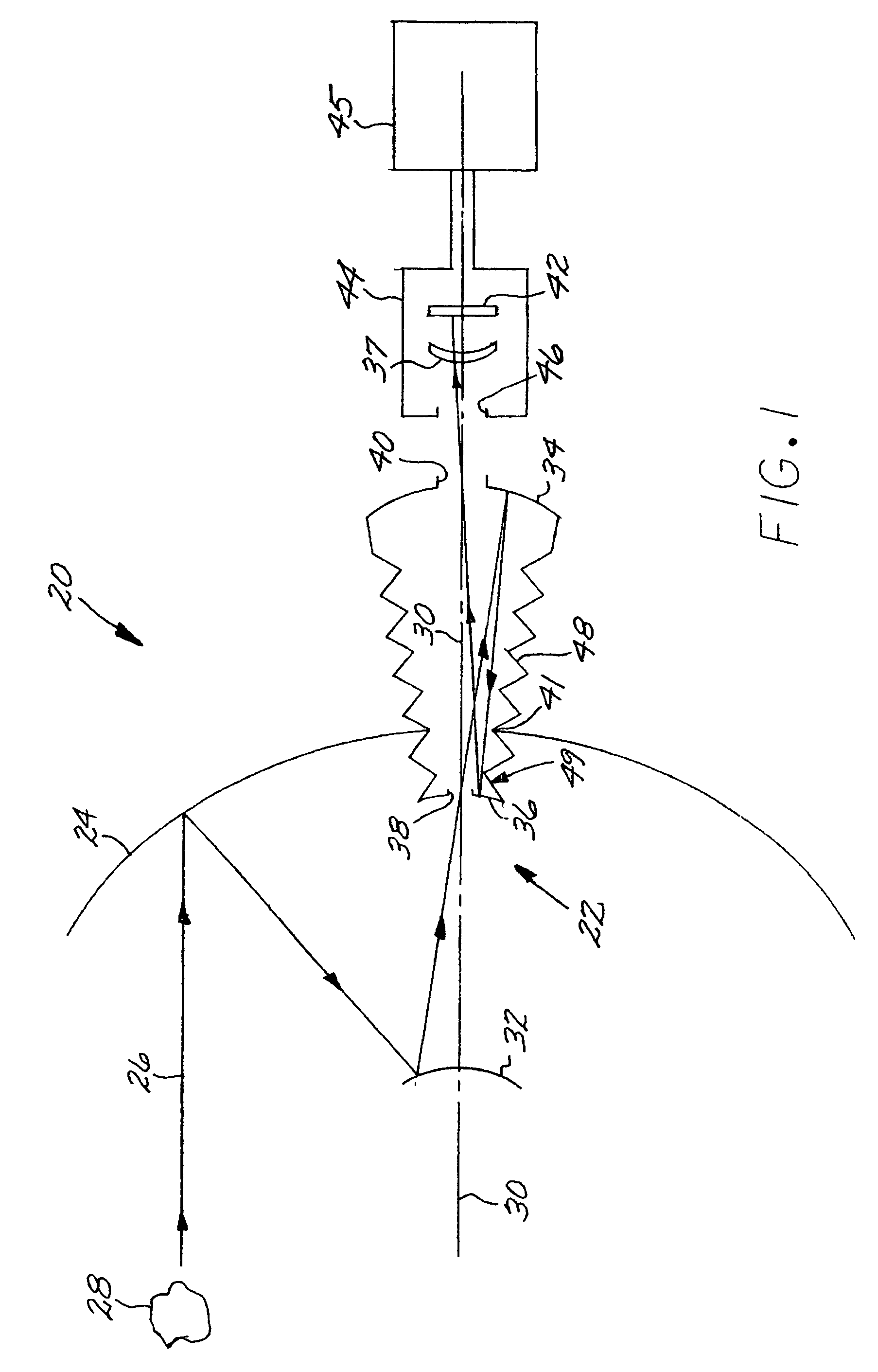
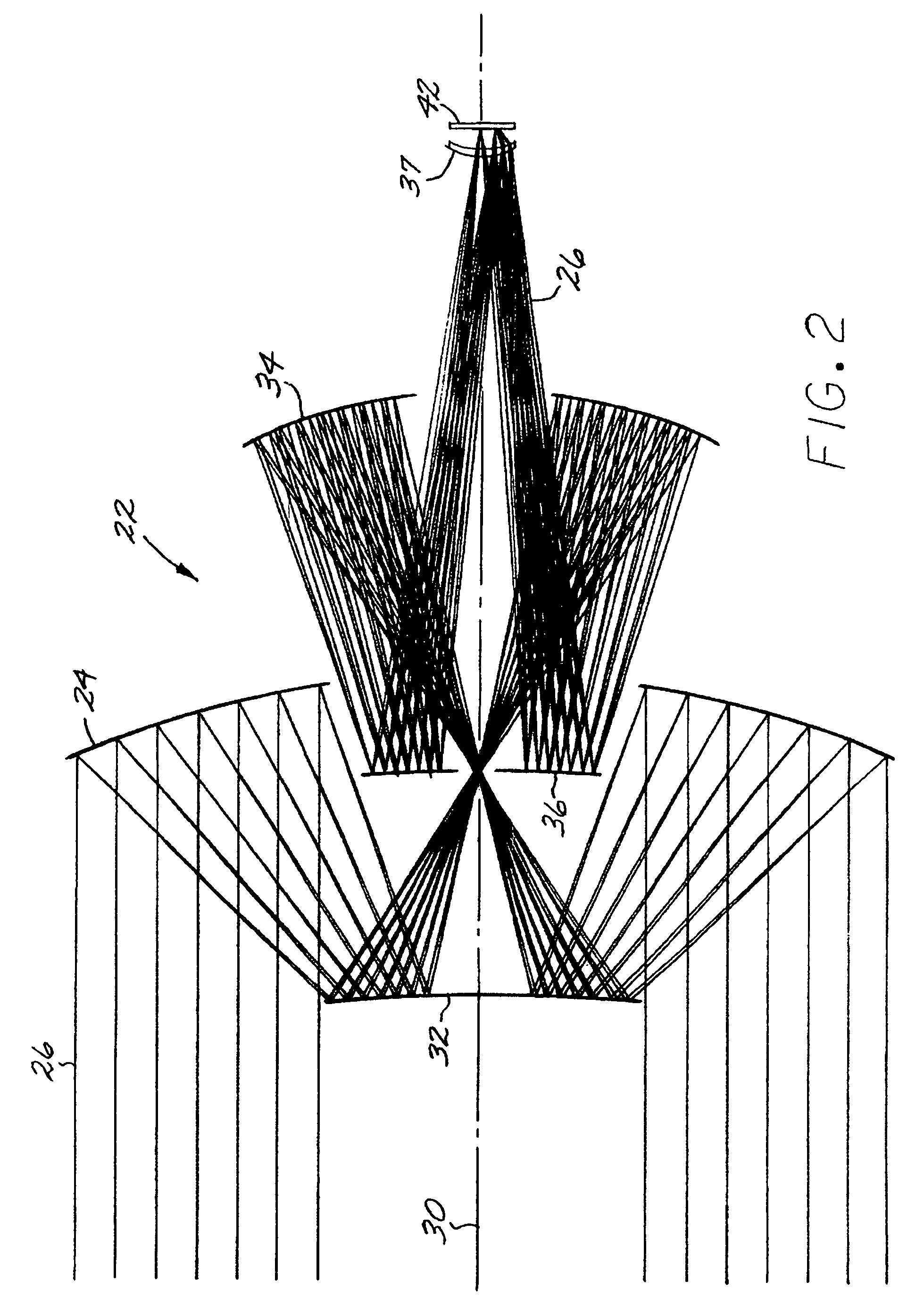
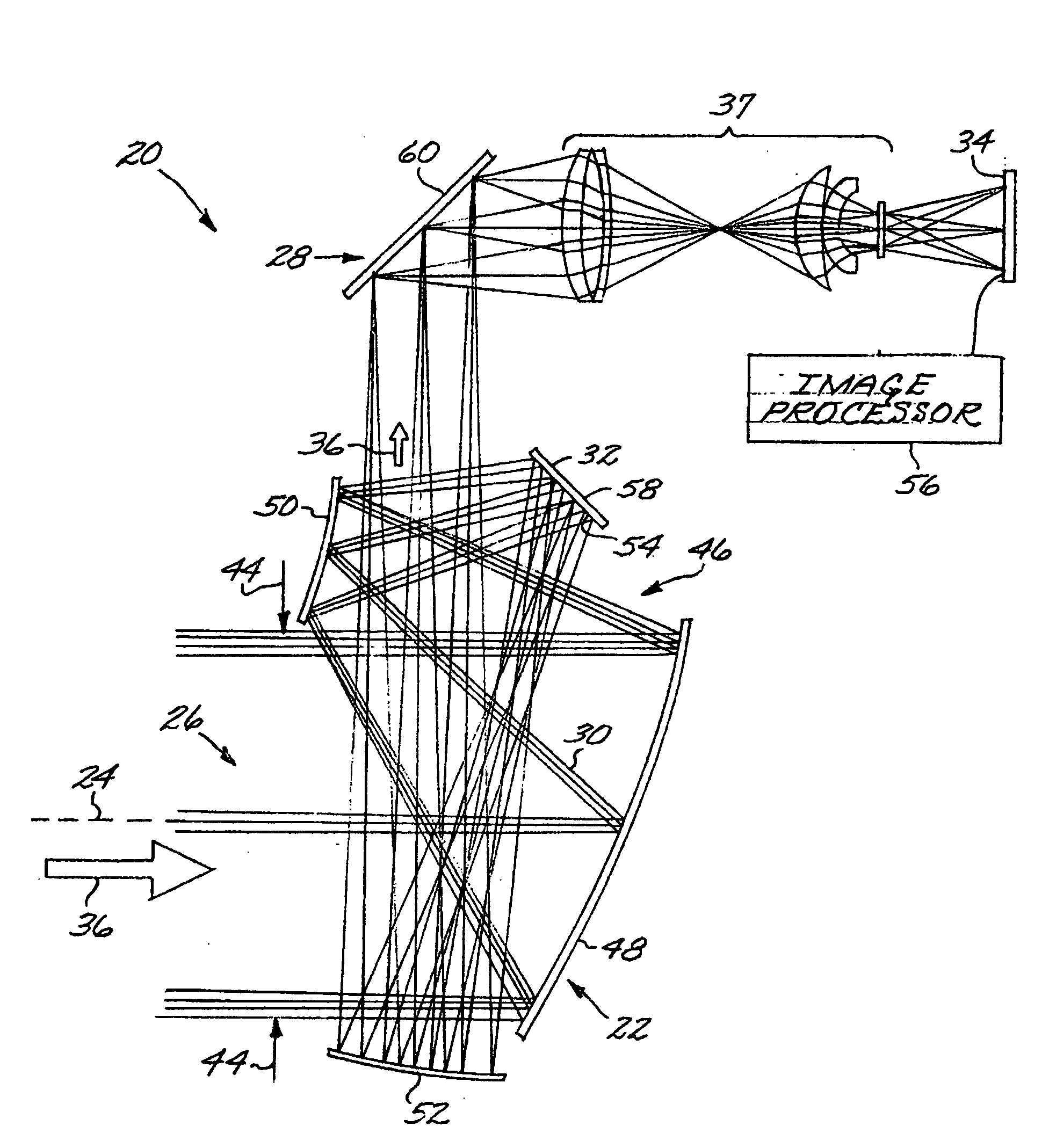
An all-reflective telescope has, in order, a positive-optical-power primary mirror, a negative-optical-power secondary mirror, a positive-optical-power tertiary mirror, a negative-optical-power quaternary mirror, and a positive-optical-power field lens. The mirrors and lens are axisymmetric about a beam axis. The light beam is incident upon an infrared detector after reflecting from the quaternary mirror. A cooling housing encloses the detector and the field lens, but does not enclose any of the mirrors. An uncooled warm-stop structure outside of the cooling housing but in a field of view of the detector is formed as a plurality of facets with reflective surfaces oriented to reflect a view of an interior of the cooling housing back to the interior of the cooling housing.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Device for automatic correcting telescope astigmatic aberration using telescope second lens
InactiveCN1987547AFast executionImprove performanceGenetic modelsOptical elementsReflecting telescopeBeam splitter
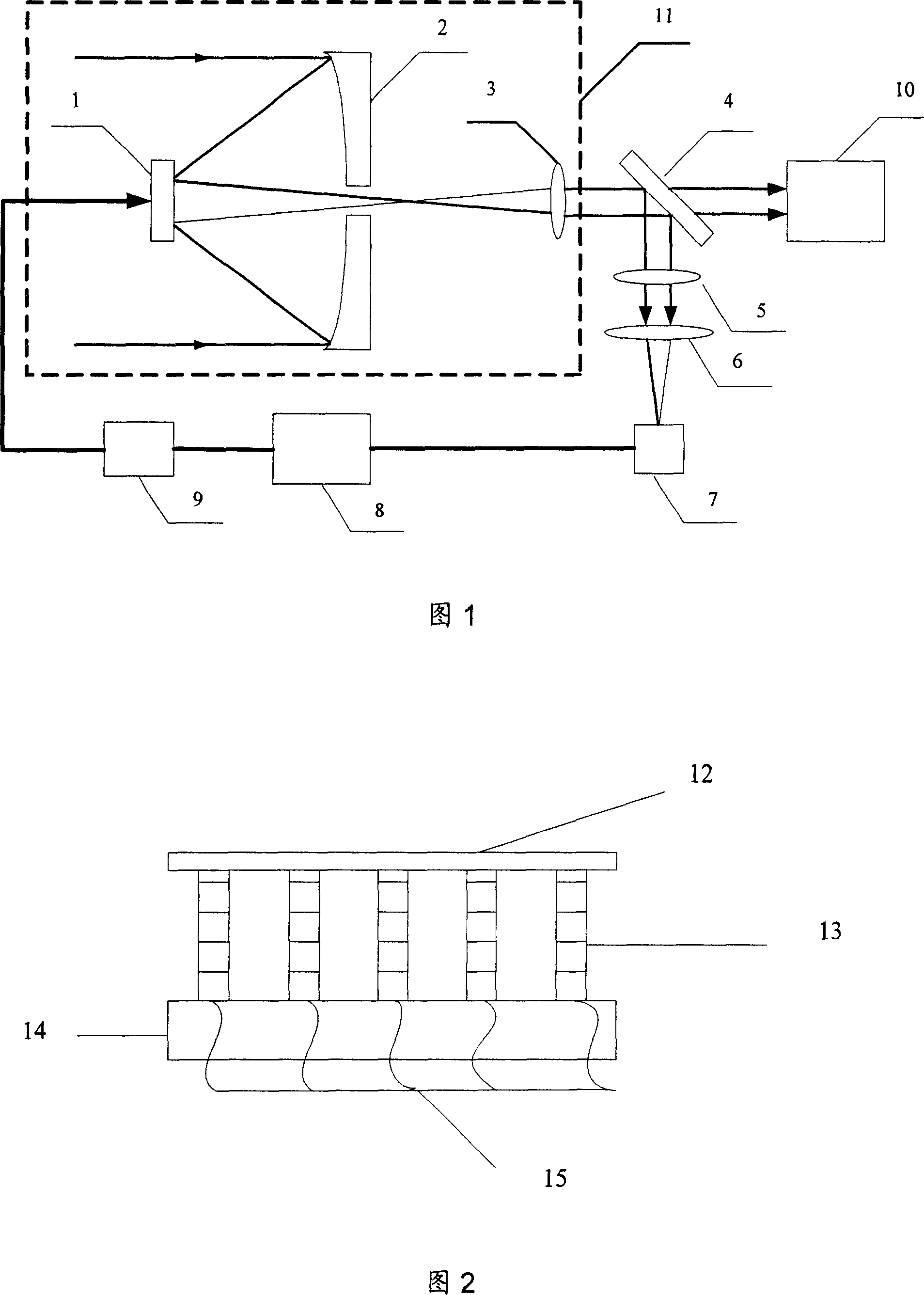
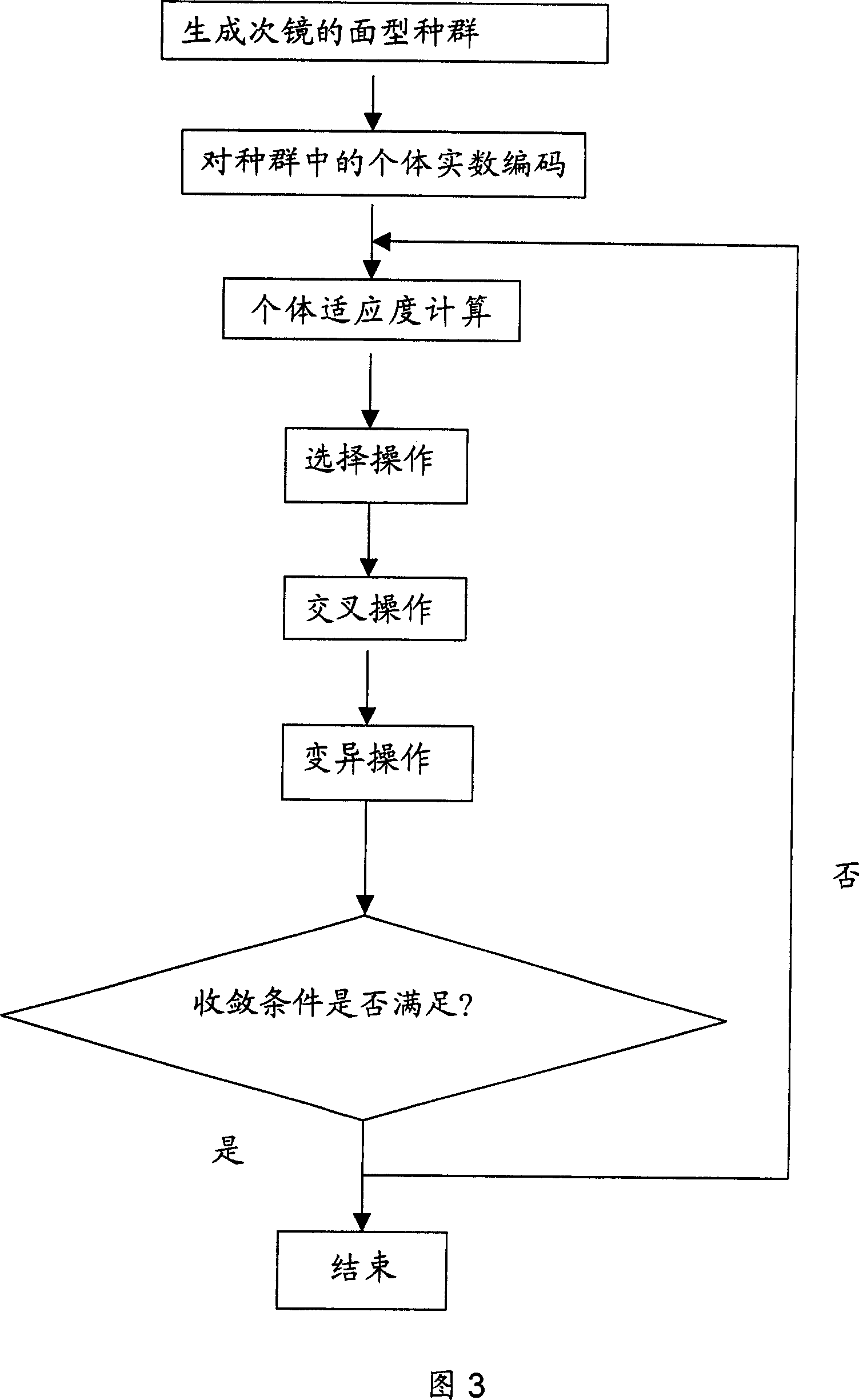
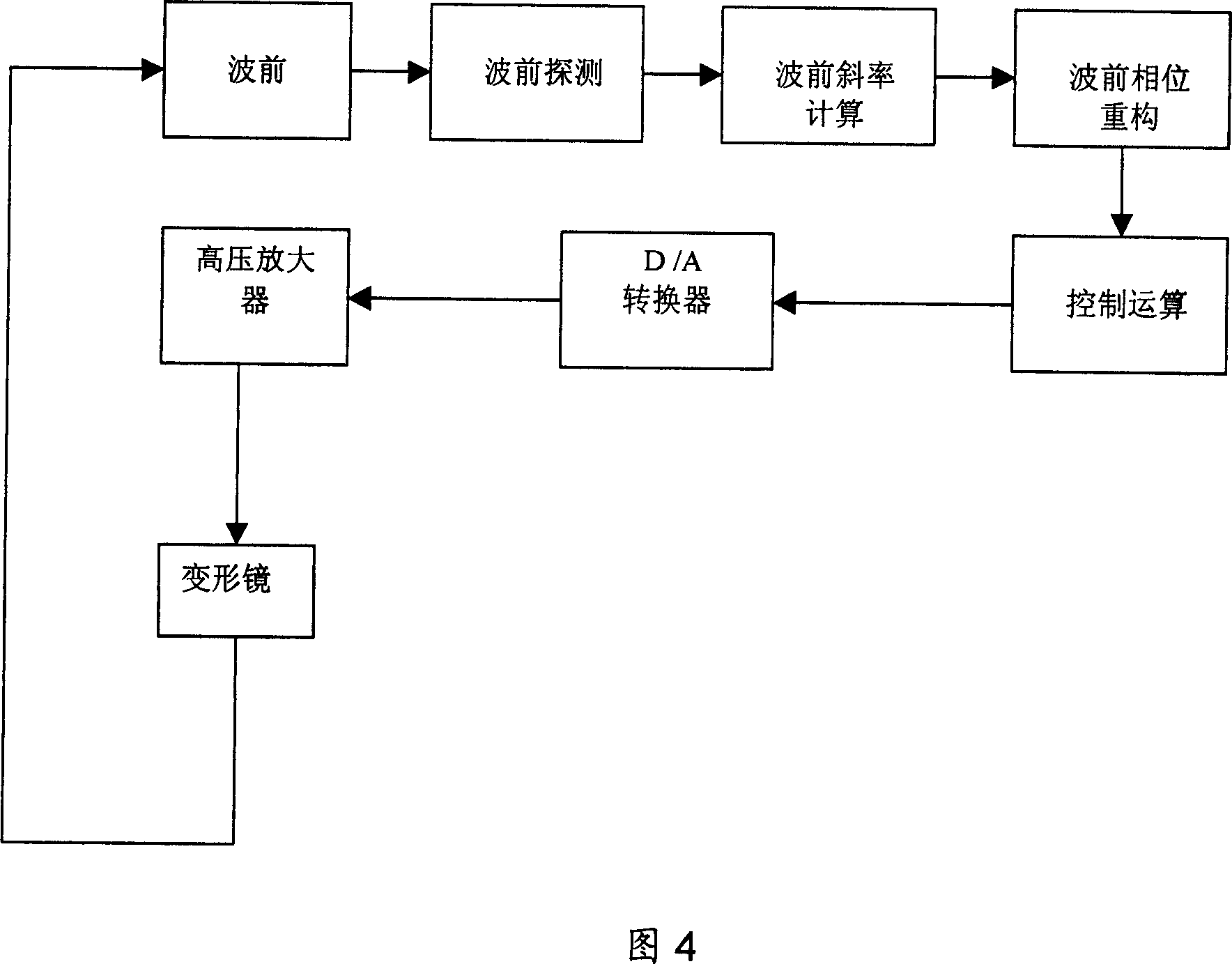
The device is mainly composed of reflecting telescope system, beam splitter, variable density attenuation disc, high voltage amplifier, CCD camera, data acquisition system, industrial control computer, and software control system based on genetic algorithm. Using secondary mirror of the reflecting telescope being as wave front phase corrector, the invention can adjust alignment between primary mirror and secondary mirror of the reflecting telescope automatically under condition of not introducing additional part of aberrational correction. The invention can corrects static and quasi-static aberration of the reflecting telescope as well as aberration brought by each optical part self in selfadaption. Advantage are: compact structure, simple control, and easy of implementation. The invention reduces system error of reflecting telescope imaging greatly, raises imaging capability of the telescope.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Common-aperture optical system incorporating a light sensor and a light source
ActiveUS20080186568A1Avoid misalignmentLight weightWave based measurement systemsSighting devicesReflecting telescopeBeam splitter
A common-aperture optical system includes a reflective telescope having a common boresight, an entrance pupil, an exit pupil, and a beam path extending from the entrance pupil to and beyond the exit pupil. A beam splitter intersects the beam path so that the beam path is incident upon the beam splitter. A light sensor is positioned to receive an input light beam traveling along the beam path after the beam path intersects the beam splitter and passes the exit pupil of the reflective telescope. A light source produces an output light beam incident upon the beam splitter and positioned to inject the output light beam into an inverse of the beam path and toward the entrance pupil of the reflective telescope. A diverger corrects at least one of the input light beam and the output light beam.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
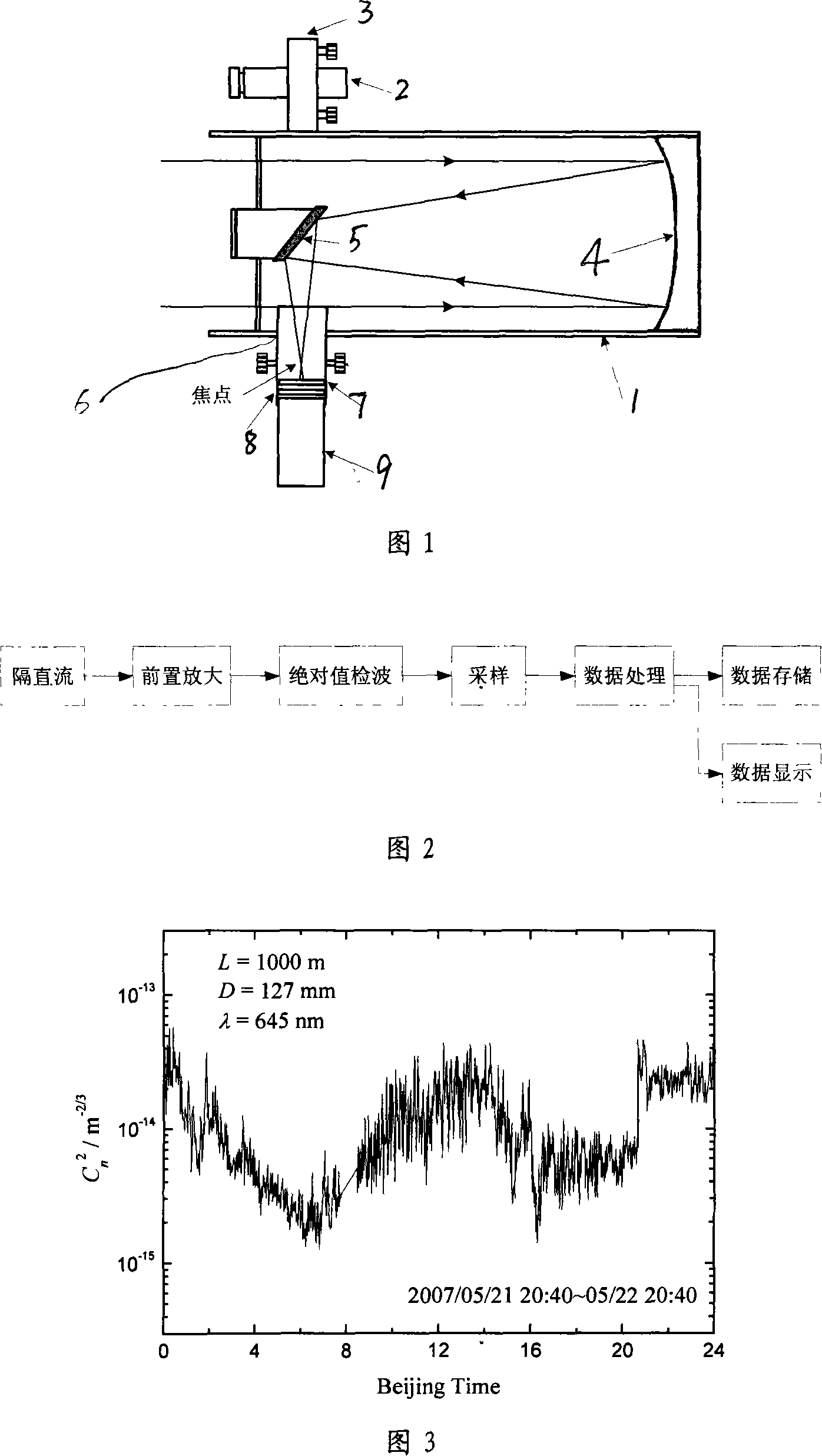
Large-caliber laser isotope scanner and method for measuring structure constant atmosphere index of refraction
InactiveCN101109702AAvoid saturationImprove signal-to-noise ratioPhase-affecting property measurementsReflecting telescopePlane mirror
The invention discloses a laser flasher with big diameter for measuring the structure constant of atmospheric refractivity as well as the method for that. The laser flasher comprises two opposite-arranged reflecting telescopes and lasers on the lens cones. The incident lights reach to the secondary plane mirror after being reflected by a main parabolic mirror in the lens cones, pass the openings, attenuating pieces and narrow-band interference filters on the lens cones, and then are converged on a photoelectric detector. At transmission test, two arrangements are placed at the two ends of the transmission path; the emitting system at one end of the path gives out modulated laser signals, after being transmitted by a turbulent atmosphere, the light signals are collected by the telescope at anther end, and go through photoelectric conversion by the photoelectric multiplier near to the focus; then the electric signals enter into a built-in control system for demodulation, sampling, processing, saving and displaying. The invention is of high accuracy and improves the accuracy in the measurements.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
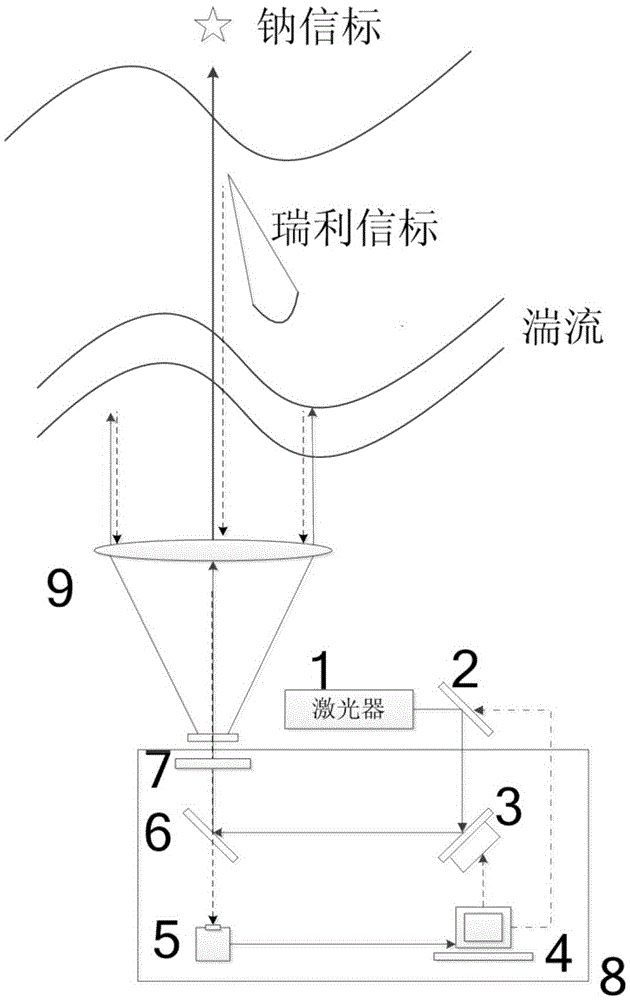
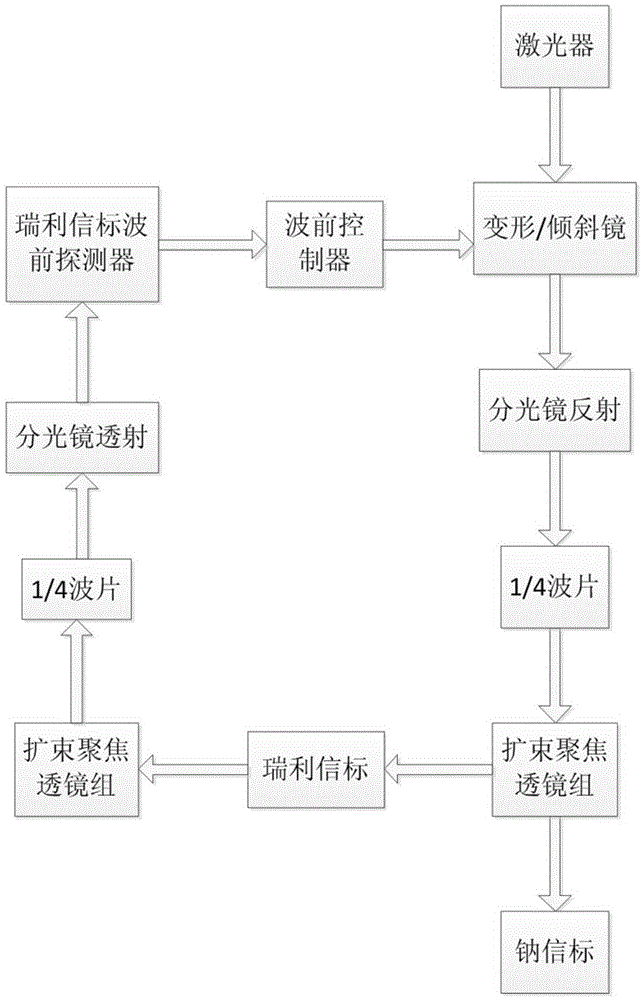
Co-aperture emission and correction telescope combining Rayleigh beacon and sodium beacon
ActiveCN105629457ASmall spotCorrecting for wavefront distortionTelescopesReflecting telescopeLight spot
The invention relates to a co-aperture emission and correction telescope combining the Rayleigh beacon and the sodium beacon. The telescope is formed by a sodium yellow-light laser, a beacon upstream light beam real-time compensation system and an emission telescope. The sodium yellow-light laser gives out laser of 589 nm so as to form the sodium beacon in a sodium layer in high-altitude excitation atmosphere of about 90 km, and generate the Rayleigh beacon in low altitude lower than 25 km. A low-density deformable reflection mirror and an inclining reflection mirror in the real-time compensation system carry out pre-correction on beacon upstream light beams, thereby achieving optimization of sodium beacon light spot shapes excited in the high-altitude atmosphere. The real-time light beam compensation system is mainly formed by the deformable reflection mirror, the inclining reflection mirror, a light splitting mechanism, a Rayleigh beacon wavefront detector and a wavefront controller. In this way, problems of expansion of sodium beacon shapes and inaccuracy of wavefront detection caused by poor observation address conditions and quite low observation angles of a telescope are solved and the telescope is characterized by compact structure, wide application range and easy achievement.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
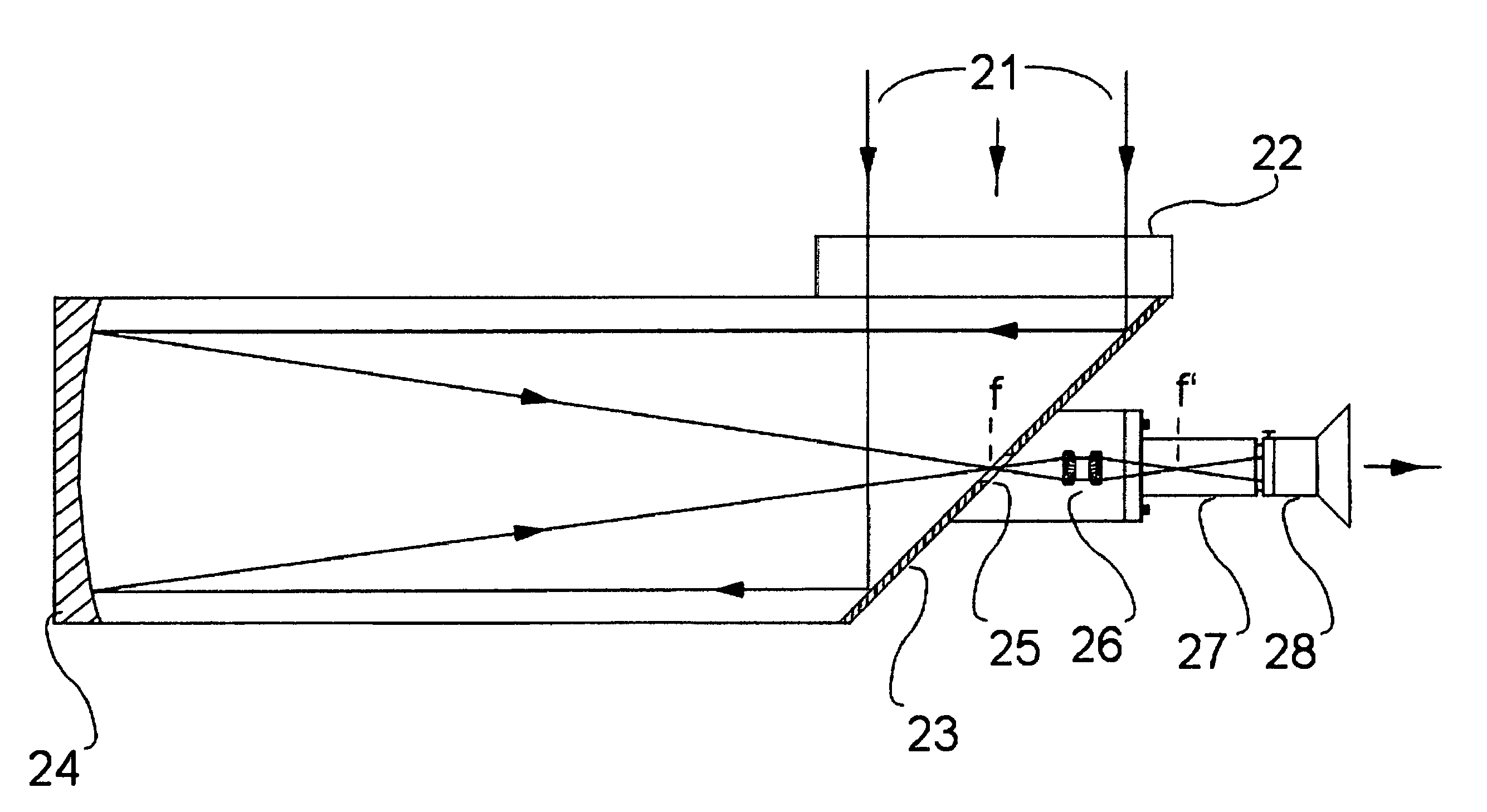
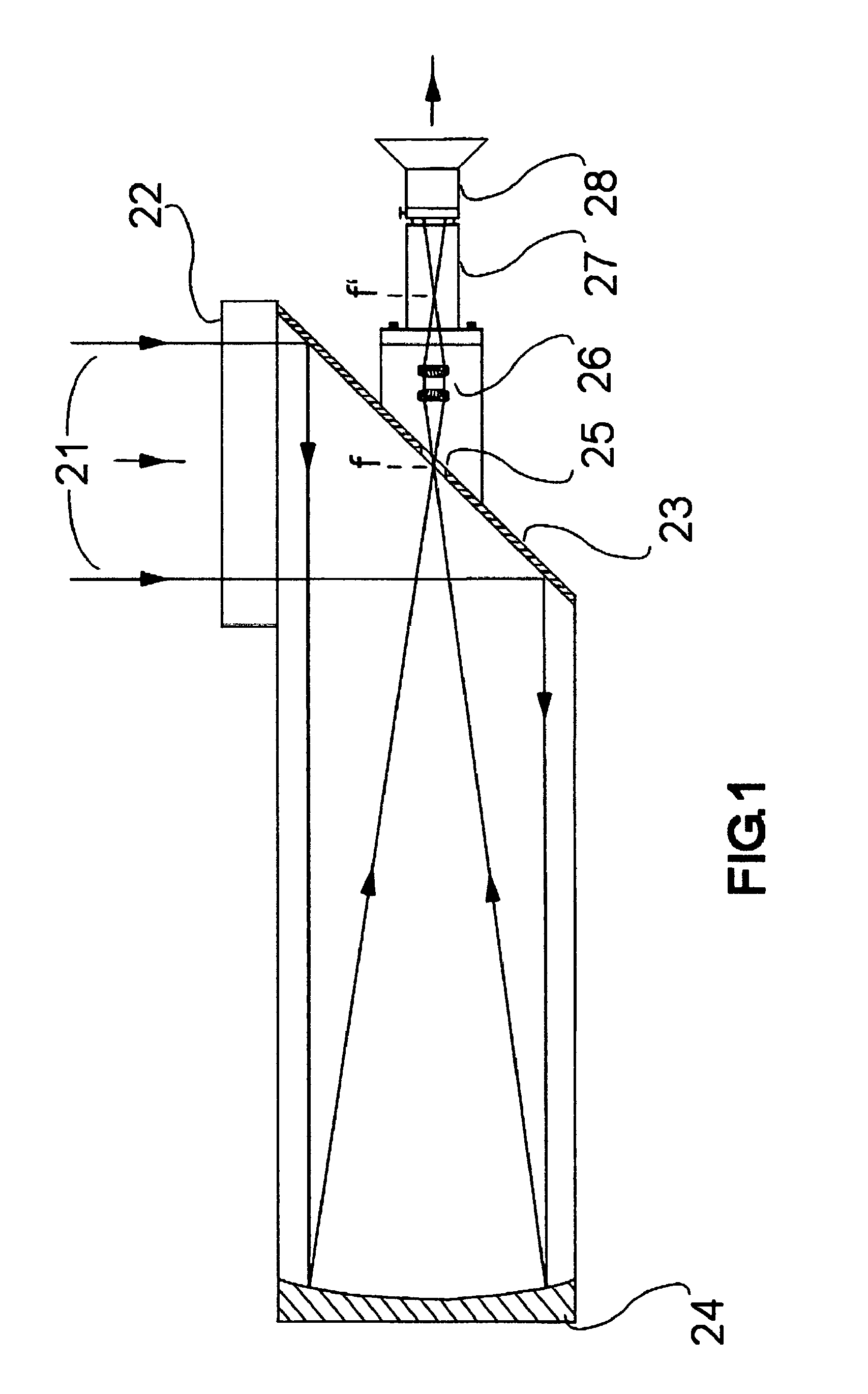
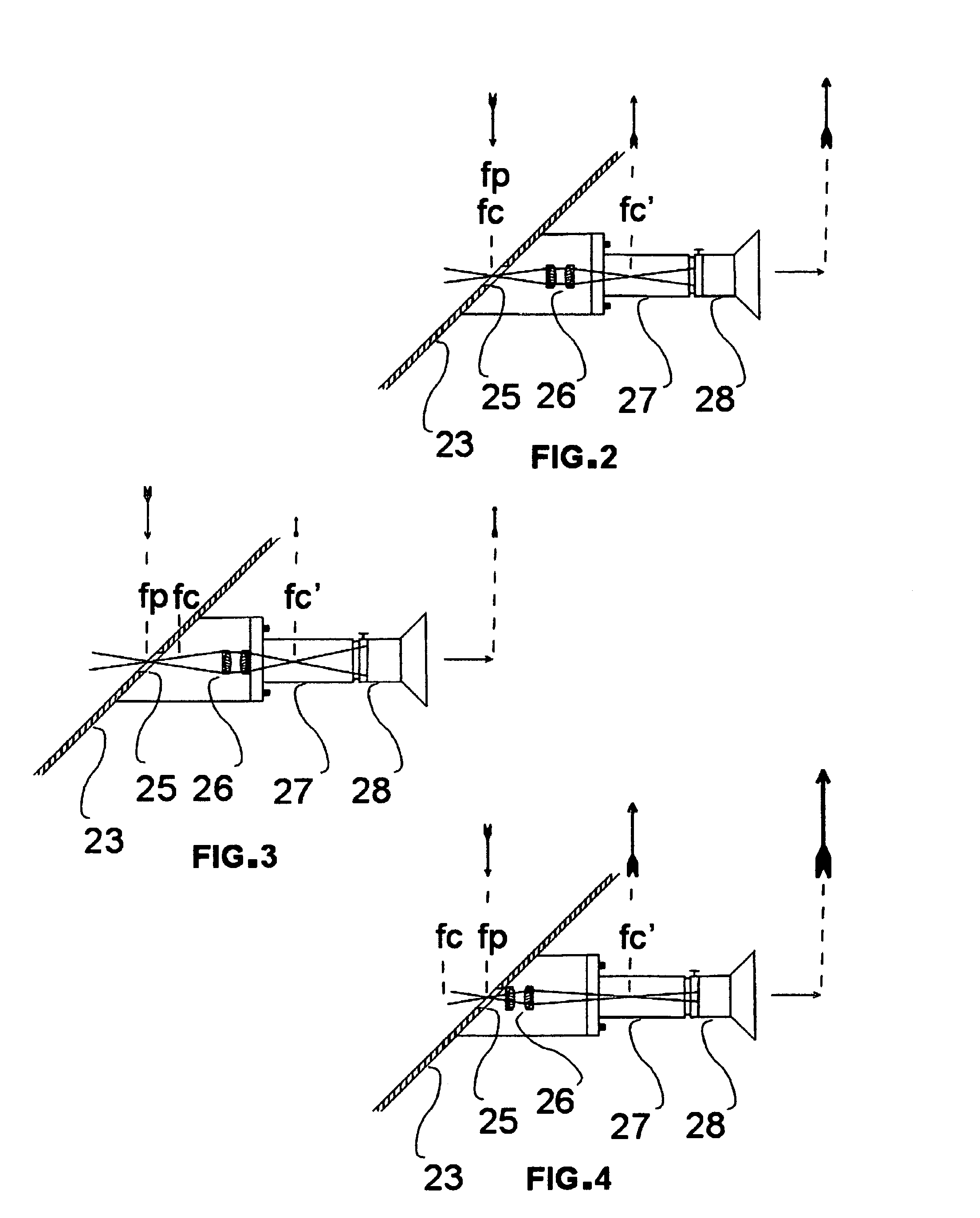
Camera System and Method for Observing Objects at Great Distances, in Particular for Monitoring Target Objects at Night, in Mist, Dust or Rain
InactiveUS20140009611A1High NIR sensitivityGood color contrastTelevision system detailsSighting devicesReflecting telescopeMultispectral image
A camera system and a method for the observation of objects at a large distance at night or through mist, dust, or rain, at an observation distance of 30 to 40 km, includes a pivotable target tracking mirror, a concave primary mirror with a long range, and a convex secondary mirror, which together form a reflecting telescope. The camera system also includes a Barlow lens system, an IR-sensitive image sensor arranged in the image plane of the reflecting telescope, a controllable high-speed shutter system for the image sensor, controllable IR illuminator to illuminate the object being observed by IR illumination pulses of multiple different colors, and a control device that coordinates control of the IR illuminator and of the high-speed shutter system in order to detect multispectral images captured by means of the image sensor according to a gated viewing technique.
Owner:EADS DEUT GMBH
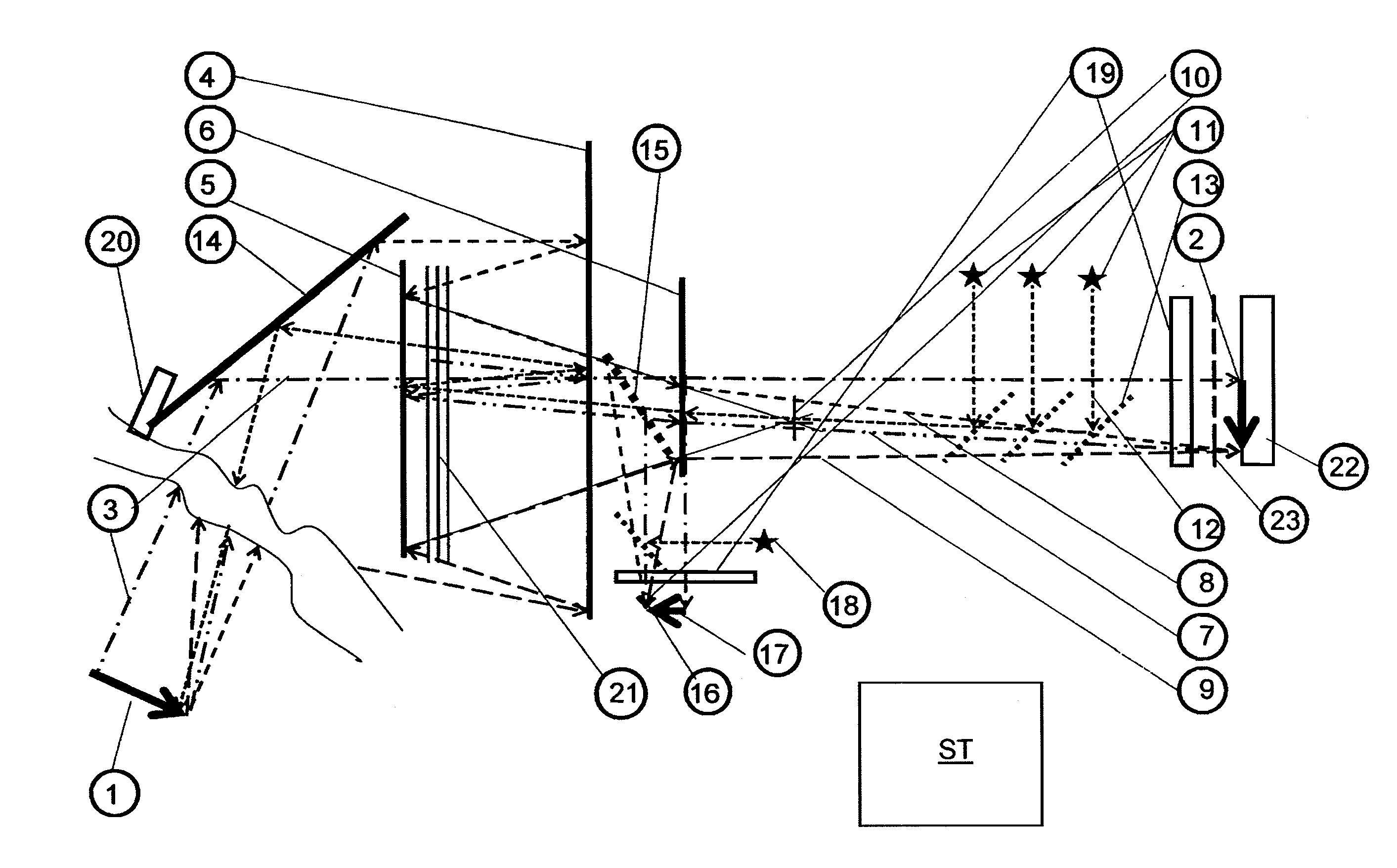
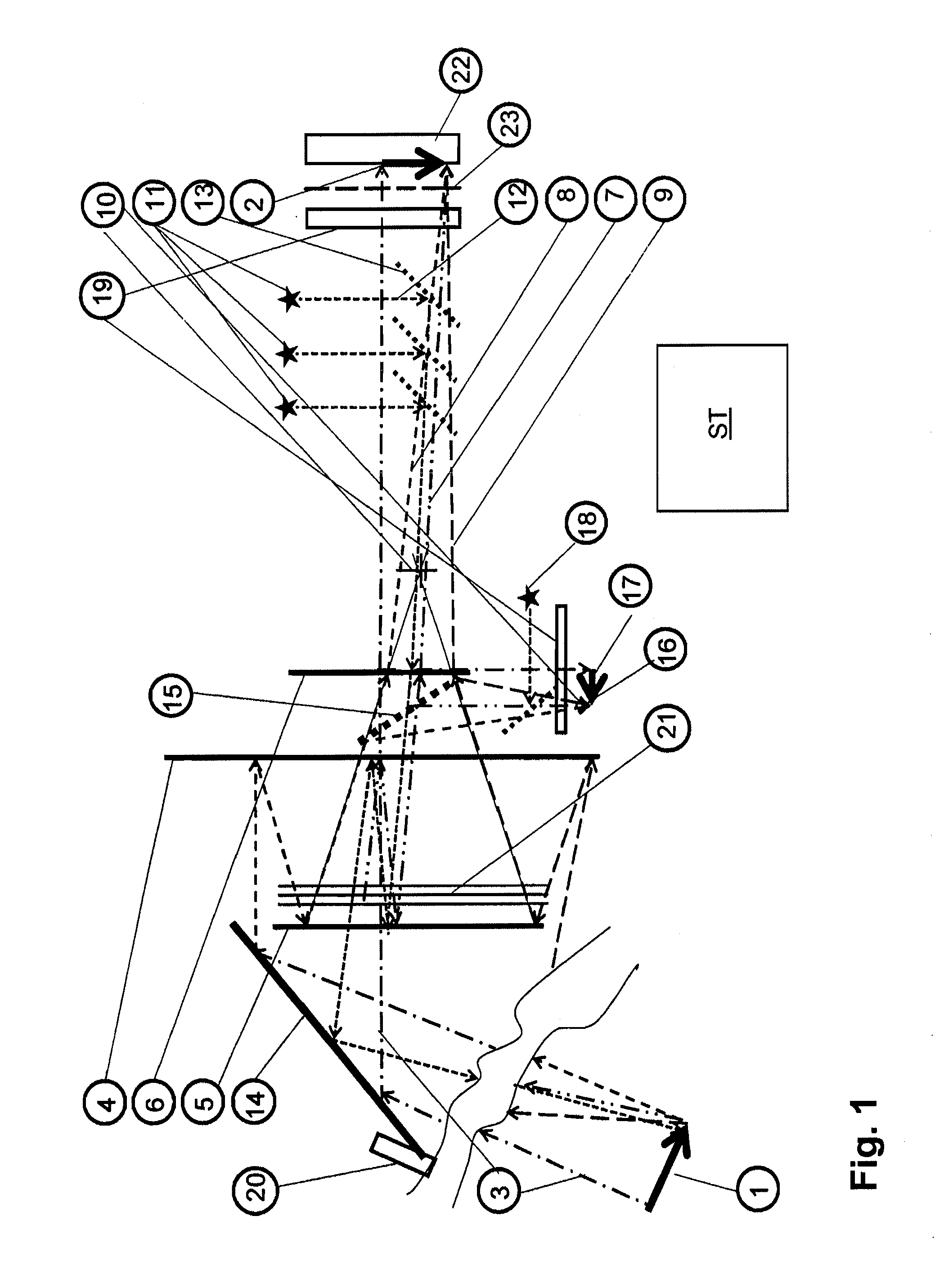
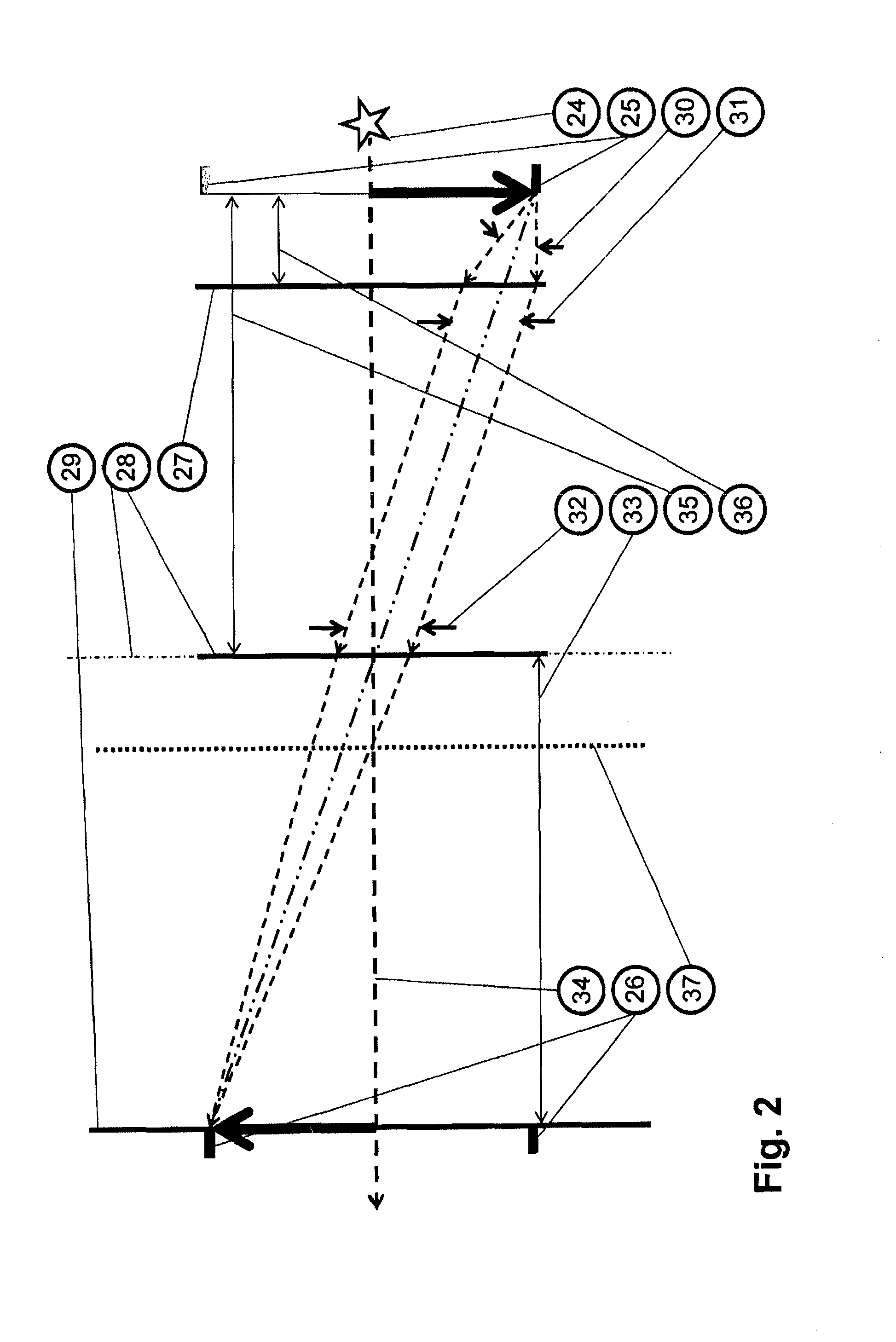
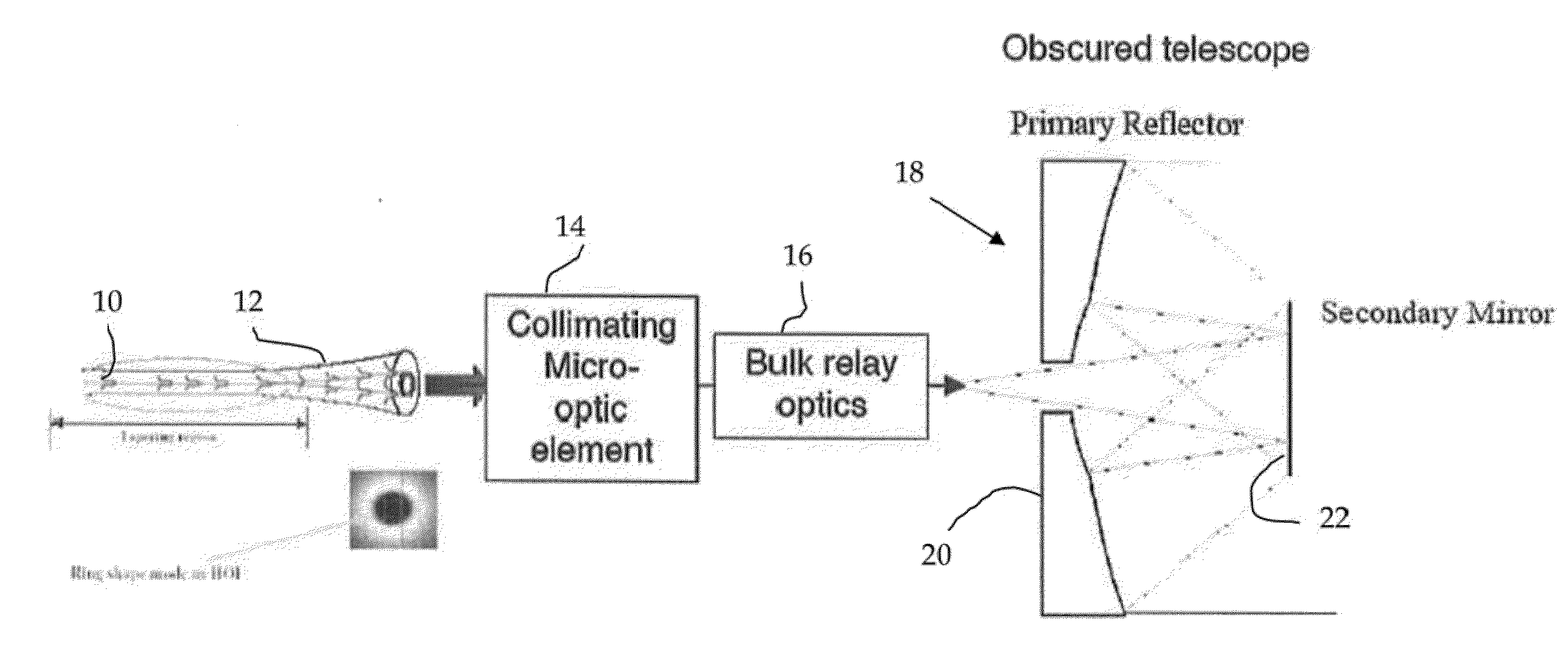
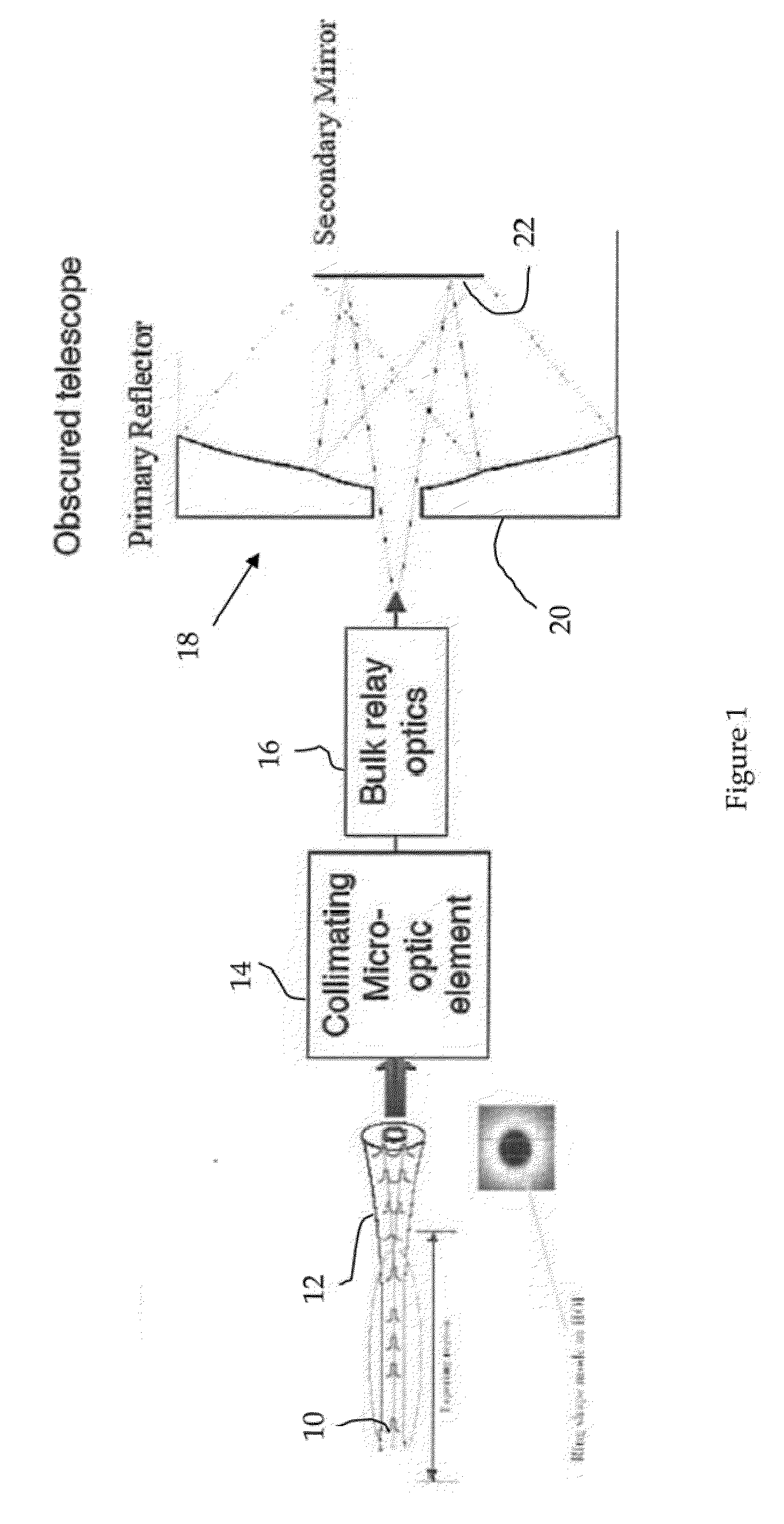
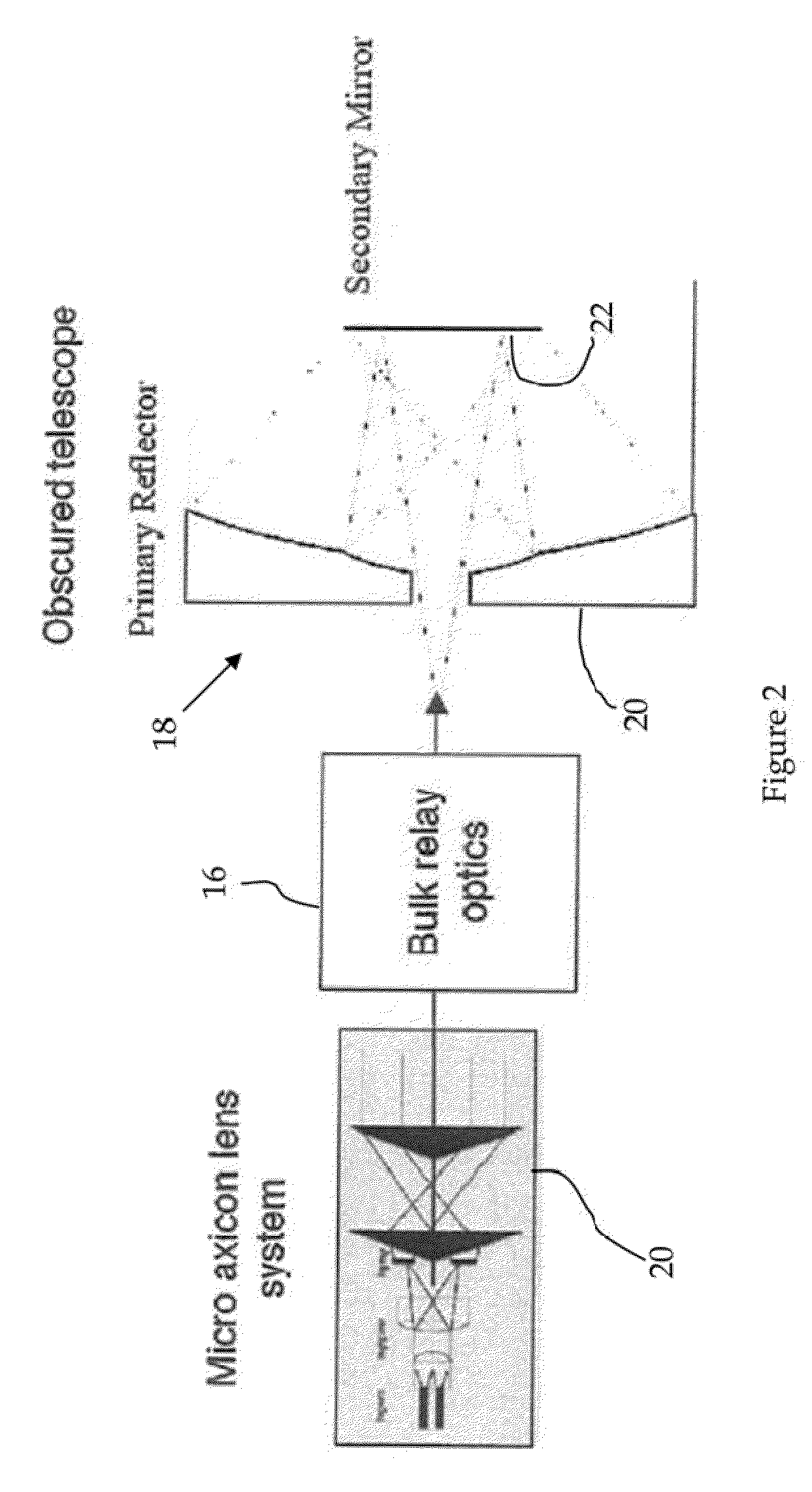
Low loss laser transmission through telescopes with mirror obscurations
The invention provides micro-optical and fiber based solutions to the problem of reflective telescopes with secondary or tertiary obscurations, and further, it ameliorates secondary or tertiary obscurations in compact reflective fiber-coupled telescopes configured as optical transmitters. One solution uses a custom hollow optical fiber and lens system to generate an annular beam that would not be obscured by the telescope secondary obscuration. Another solution uses a fiber coupled micro-axicon lens assembly to achieve the same result.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Efficient measuring system and method for transmittance of reflecting telescoping system
InactiveCN103308282AImprove the measurement effectEfficient measurementTesting optical propertiesTest efficiencyReflecting telescope
The invention provides an efficient measuring system and method for transmittance of a reflecting telescoping system. An aligning system is disposed on an emergent light path of a light source system. A star point unit is disposed between the light source system and the aligning system and located on a focal plane of the light source system. A rotary light beam axis folding system is disposed on an emergent light path of the aligning system. The reflecting telescoping system to be measured is disposed on an emergent light path of the rotary light beam axis folding system. The output end of the reflecting telescoping system to be measured is connected with a spectrum collecting system. The method includes: spatially translating aligning light beams through the rotary light beam axis folding system and then transmitting the same into the spectrum collecting system. The measuring system bypasses the special structure, with spoke ribs, of a reflecting telescoping system secondary scope, transmittance can be measured in areas among the spoke ribs, and transmittance of the whole caliber range of the telescoping system can be comprehensively measured after circular rotation.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Aberration compensation fundus microscope based on automatic optimization algorithm
InactiveCN102008289AIncrease the imaging range of the imaging functionImproving the imaging range of the imaging functionOthalmoscopesReflecting telescopeImaging quality
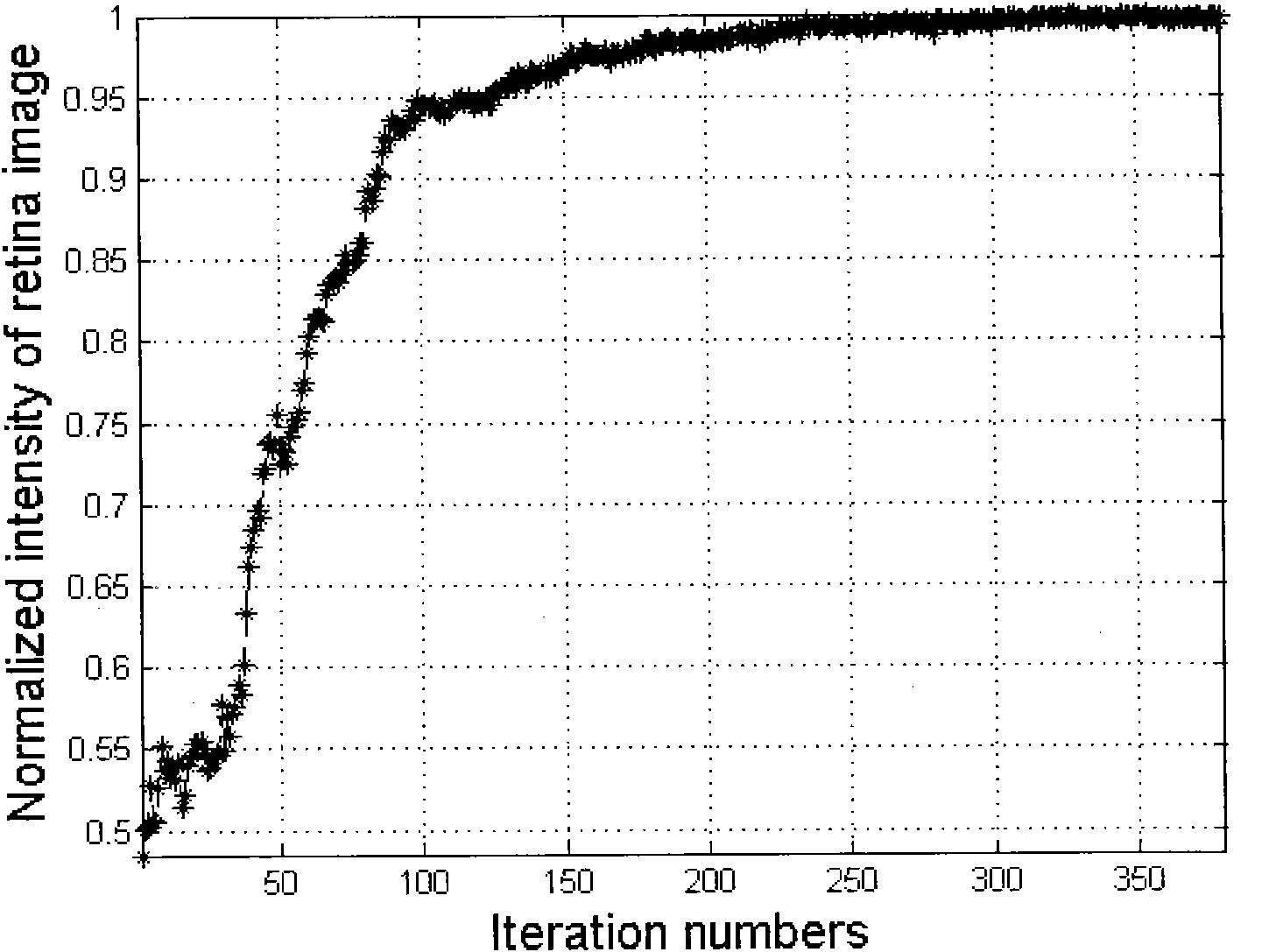
The invention discloses an aberration compensation fundus microscope based on an automatic optimization algorithm. The aberration compensation fundus microscope comprises a light source module, an aberration compensation module, a two-dimensional imaging and scanning module, a wide-field-of-view scanning module and an optical fiber receiving module, wherein, the two-dimensional imaging and scanning module is connected with the wide-field-of-view scanning module through a spherical reflecting telescope system; the optical fiber receiving module is placed at a terminal of a returning optical path of the microscope system and is behind a spectroscope; the illuminating light emitted from the light source module successively passes through the two-dimensional imaging and scanning module and the wide-field-of-view scanning module and then enters eyes; and the diffuse signal light from fundus retina of eyes returns along the original optical path, aberration correction is carried out on the light through an aberration correction module by the automatic optimization algorithm, and then the light enters the optical fiber receiving module through the spectroscope for signal detection. The aberration compensation fundus microscope greatly reduces the cost and the control difficulty of the traditional aberration compensation system, solves the synchronous imaging difficulty in the case of high resolution and wide view field, and greatly improves the imaging view field and the imaging quality of the traditional fundus imaging instrument.
Owner:苏州六六宏医疗器械有限公司 +1
Wavefront sensor, and lens meter and active optical reflecting telescope using the same
InactiveUS20010006210A1Photometry using reference valueOptical measurementsCamera lensReflecting telescope
A wavefront sensor includes a plurality of lenses disposed in the same plane, and an area sensor that receives a bundle of rays of light collected through each of the lenses as a luminous point. Each of the lenses comprises a plurality of concentric areas with different focal lengths, and the area sensor is located substantially halfway between a first position in which a plane wave forms an image after passing through one of the concentric areas with a minimum focal length, and a second position in which the plane wave forms an image after passing through another area with a maximum focal length. With the wavefront sensor thus arranged, the measurement can be always achieved with high accuracy without involving noticeable blurring of luminous points on the area sensor regardless of the wavefront shape of a light beam incident to the lenses.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Imaging Spectrometer
InactiveUS20110109903A1High resolutionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationChemical compositionReflecting telescope
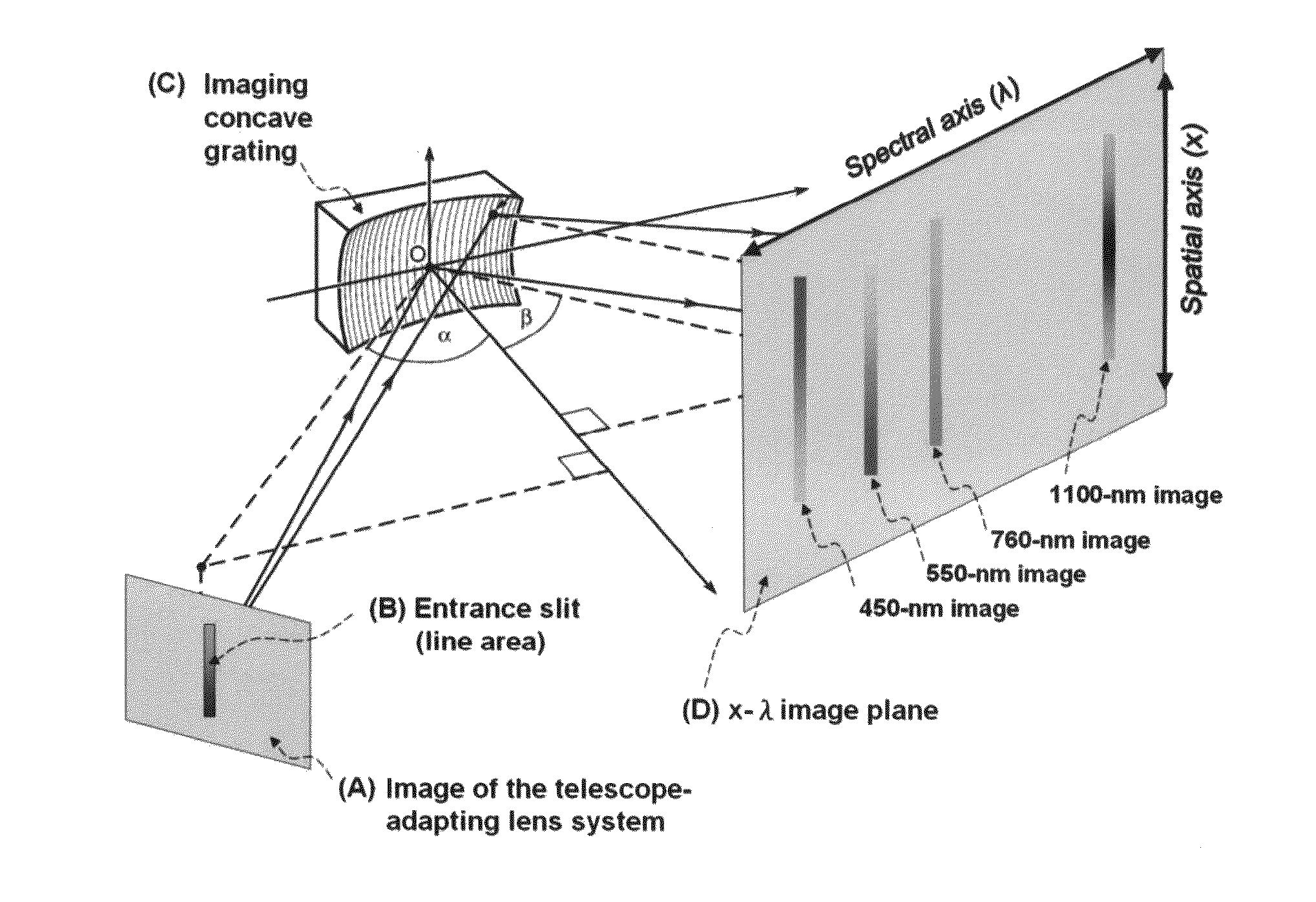
The present invention relates to an imaging device simultaneous records image and spectrum of an interested target utilizes spectral technology to acquire, process and exploit image data or spectrum data. The present invention allows for real time detection and identification of not only the traditional images but also the spectrum which shows the surface of the earth or reveals the chemical composition of the targeted tissue. The present invention includes a reflecting telescope, an imaging concave grating (ICG) system with spectrometer and a processor that performs spectral analysis on spectral data generated from the spectrometer.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Infrared transmitting device and infrared receiving device of atmospheric infrared detection equipment
PendingCN107064006AImprove efficiencyHigh precisionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationReflecting telescopeEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of atmospheric infrared detection equipment, and particularly relates to an infrared transmitting device and an infrared receiving device of the atmospheric infrared detection equipment. The overall pitching and left and right sweeping of the infrared detection equipment are achieved through a two-axis turntable. The equipment is simple in transmission structure, good in stability and high in adjustment precision, thus the installation and focusing efficiency and focusing precision of the infrared detection equipment are greatly improved. According to the equipment, a lens is installed on a movable support; the movable support is installed on a slider arranged on the barrel wall of a Casher reflection telescope; the position of the lens in the Casher reflection telescope can be adjusted in real time from the outside of the Casher reflection telescope; the operation is simple and convenient; the equipment assembly and maintenance efficiency are improved; the fast connection and positioning of the Casher reflection telescope and the turntable are achieved by using a dovetail type plug-in structure; the connecting structure is stable and reliable; the installation precision is high.
Owner:安徽星源环境科技有限公司
Six-degree-of-freedom secondary mirror regulating mechanism based on stacked piezoelectric blocks
InactiveCN104536126AHigh adjustment accuracyAchieve continuous motionTelescopesElectricityReflecting telescope
The invention belongs to the field of coaxial reflecting telescope regulating mechanisms and particularly relates to a six-degree-of-freedom secondary mirror regulating mechanism based on stacked piezoelectric blocks. The mechanism comprises a bottom plate, regulating units and a top platform used for carrying a secondary mirror, wherein the regulating units are arranged between the bottom plate and the top platform. The mechanism is characterized in that each regulating unit comprises a first combined flexible hinge, a lever amplifying device, a fixed frame, straight beam type flexible hinges, one stacked piezoelectric block and a second combined flexible hinge, wherein one end of the first combined flexible hinge is connected with the top platform, and the other end of the first combined flexible hinge is connected with the lever amplifying device; the lever amplifying device is connected with the fixed frame through the straight beam type flexible hinges; the stacked piezoelectric block is fixedly mounted in the fixed frame; one end of the second combined flexible hinge is connected with the fixed frame, and the other end of the second combined flexible hinge is connected with the bottom plate. By the adoption of the mechanism, the purposes of high-precision positioning of the secondary mirror and quick and active vibration isolation can be achieved.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Korsch-type compact three-mirror anastigmat telescope
ActiveUS20160341948A1Easy to correctBroaden the fieldTelescopesIntermediate imageReflecting telescope
A three-mirror anastigmat telescope comprises at least a concave first mirror, a convex second mirror and a concave third mirror, the three mirrors arranged so that the first mirror and the second mirror form, from an object at infinity, an intermediate image situated between the second mirror and the third mirror, the third mirror forming, from this intermediate image, a final image in the focal plane of the telescope. In the architecture of the telescope, at least the surface of the concave third mirror is a φ-polynomial surface.
Owner:THALES SA
Common-aperture optical system incorporating a light sensor and a light source
ActiveUS7545562B2Precise boresight alignmentMuch of lightWave based measurement systemsSighting devicesReflecting telescopeBeam splitter
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Transparent glass ceramic with low expansion coefficient and production method of product thereof
The invention discloses a transparent glass ceramic with low-expansion coefficient and a production method of a product thereof. The glass ceramic comprises the following components in percentage by weight: Li2O: 3.0-4.2%; A2lO3: 19.5-22.5%; SiO2: 60.0-68.0%; CaO: 0.4-3.5%; MgO: 0.0-1.0%; ZnO: 0.0-6.1%; BaO: 0.0-2.0%; B2O3: 0.0-2.5%; R2O: 0.3-0.7%; TiO2: 1.6-2.5%; ZrO2: 1.0-2.0%; P2O5: 0.5-5.0%; As2O3: 0.2-0.5%; Sb2O3: 0.3-0.6%; and NaCl: 0.3-0.6%. The transparent glass ceramic with low expansion coefficient prepared by the formula has high elastic modulus, is suitable for hot forming of super-thick super-large products, has the characteristic of no deformation of precision grinding, polishing and cold processing, and for example is suitable for blow molding of hot forming of thick products such as astronomical reflecting telescope mirror blanks with the weight of 4 tons, the diameter of 2.2 meters and the thickness of 0.35 meter, is suitable for hot forming and precision grinding coldprocessing of resonant cavity working bodies of cesium atomic clocks with no deformation, and is suitable for cutting, grinding and cold processing of ultrathin plates, or manufacturing of 5G mobilephone back plates of ultrathin and high-strength transparent glass ceramics by an overflow method and the like.
Owner:广东科迪微晶玻璃实业有限公司
Mod/demod method suitable for large caliber laser scintilloscope
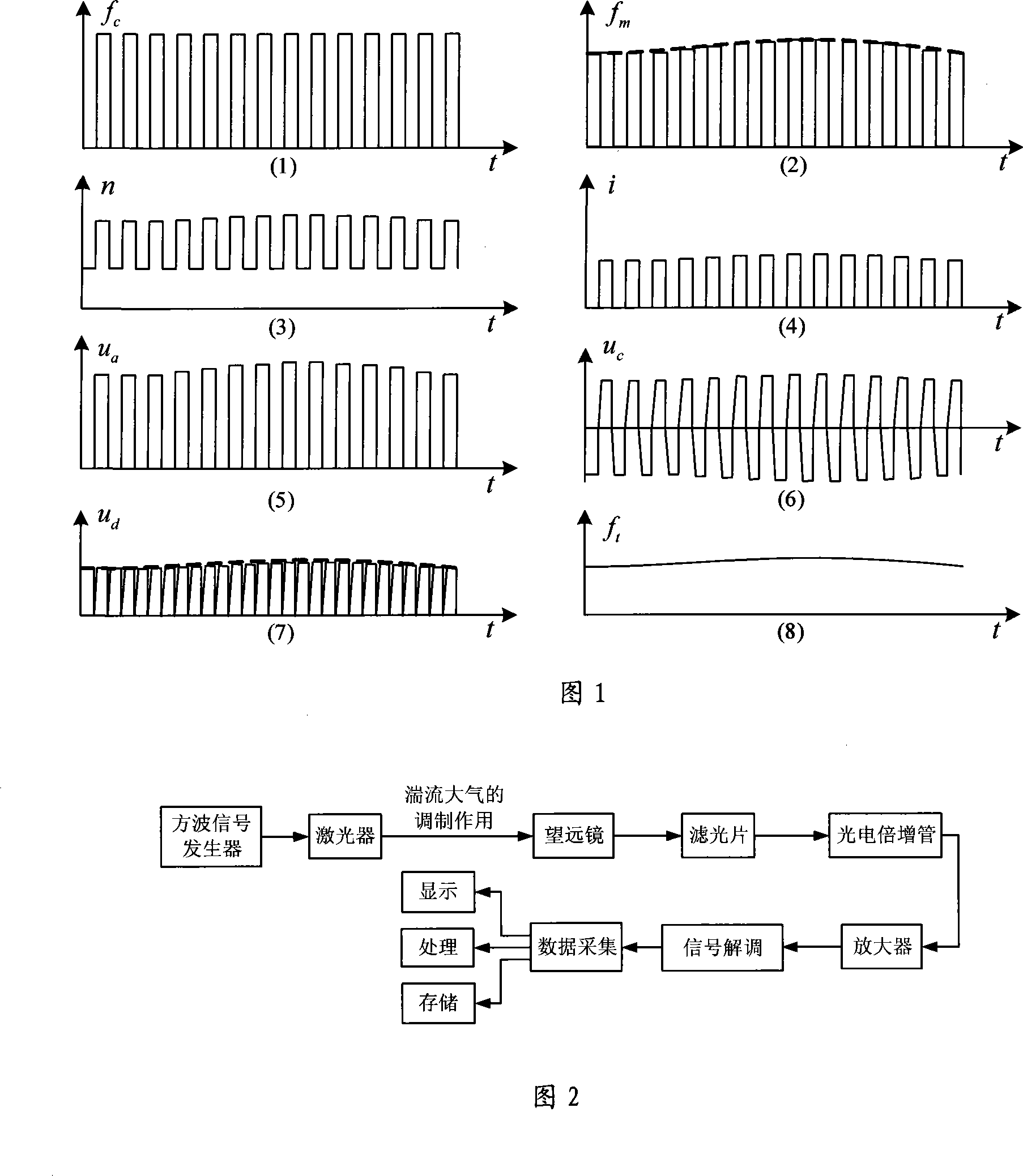
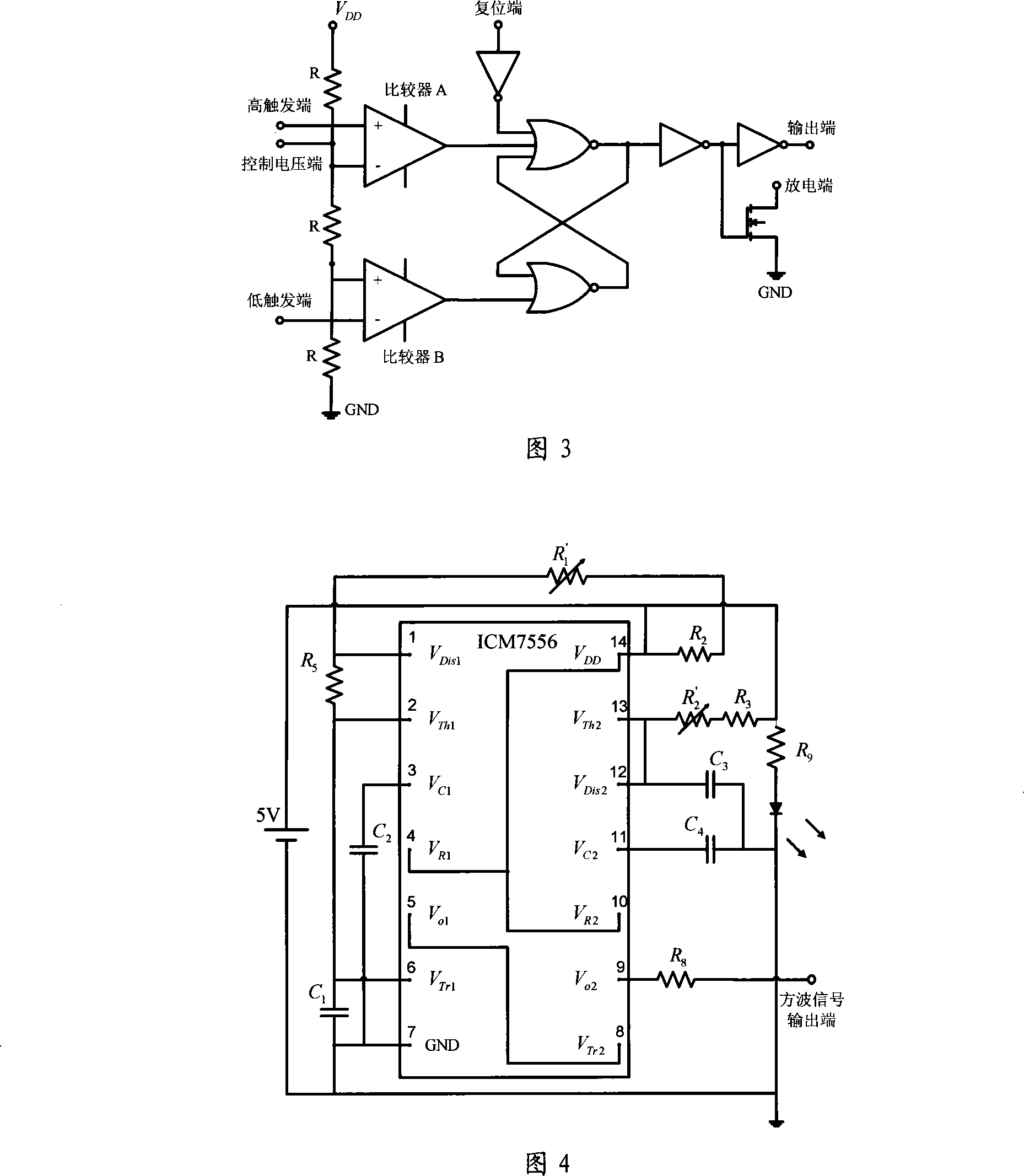
InactiveCN101162198AAvoid saturationEliminate background stray lightPhase-affecting property measurementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationCapacitanceLow-pass filter
The invention discloses a modulation and demodulation technique applicable to a heavy caliber laser isotope scanner. The heavy caliber laser isotope scanner is equipment used for measuring the structure constant of the atmospheric refractive index. Digital logic devices are used to compose a multi-resonant trigger circuit to output square signals with an adjustable frequency and a duty factor to control a laser to send out high-frequency carrier laser. when the carrier signals are transmitted through atmospheric turbulence, the turbulence modulates the amplitude of the carrier signals; a modulated wave is received by a reflecting telescope and is converted by a photomultiplier; background stray light and other direct current noise components are filtered out via a catholic grounding power supply circuit and by coordinating with a capacitance coupling signal output circuit; subsequently output direct current amplitude-modulated signals without the background are outputted after being amplified by a transconductance amplifier (TIA); the signals are coupled to AC square signals of plus-minus symmetry by a capacitance; DC signals only including high frequency peaks are obtained via an absolute value detector; a low-pass filter circuit with a very small RC time constant to filter out the high frequency peaks to accomplish signals demodulation and obtain turbulence pulsating signals. The application of modulation and demodulation technique improves the signal to noise ratio of the heavy caliber laser isotope scanner and the capacity of resisting disturbance and measuring accuracy of the device; therefore, the performance of the device is more stable. The method is also applicable to other fields where photomultipliers are used for feeble signals detection.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multilayer optical thin film and manufacturing method thereof
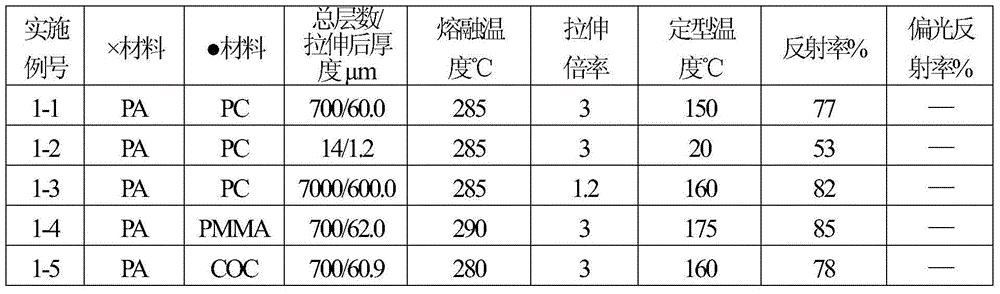
InactiveCN104459834AGood optical performancePolarization effect is obviousOptical elementsCompound aReflecting telescope
The invention discloses a multilayer optical thin film and a manufacturing method of the multilayer optical thin film. The multilayer optical thin film is characterized in that the thin film is formed by compounding one to 10,000 optical thin film units, and the thickness is 0.11 micron to 5,000 microns; each optical thin film unit is formed by compounding a layer of * material thin film and a layer of . material thin film, the thickness speciation of the * material thin films is 0.053 micron to one micron, and the thickness speciation of the . material thin films is 0.053 micron to one micron; the * material thin film and the . material thin film in the same optical thin film unit are different in refractive index. The multilayer optical thin film is manufactured in the mode of carrying out multilayer coextrusion through two extruders and then carrying out unidirectional or bidirectional stretching. The multilayer optical thin film has the functions of totally reflecting visible light and ultraviolet light, filtering 550nm green light and the like, and can be applied to manufacturing of building curtain wall reflecting thin films, automobile glass sticker thin films and reflecting telescopes.
Owner:四川东方绝缘材料股份有限公司
Optical system for telescope
The invention discloses an optical system for a telescope. The optical system is an axisymmetric circular lens. According to the sequence of a light path, the front surface and the rear surface of the lens respectively comprise a circular aperture concentric with an optical axis and located in the centre of the lens and an annular aperture surrounding the circular aperture; and the surface shapes of the circular aperture and the annular aperture are axisymmetric aspheric surfaces or spherical surfaces. For the front surface of the lens, the central circular aperture of the front surface of the lens is a concave surface plated with an internal reflection film, and the annular aperture of the front surface of the lens is a convex surface plated with a reducing reflection film; and for the rear surface of the lens, the central circular aperture of the rear surface of the lens is a convex surface plated with a reducing reflection film, and the annular aperture of the rear surface of the lens is a concave surface plated with an internal reflection film. According to the invention, the telescope system on a single lens is realized, the number of the lens is reduced, material cost and processing cost are reduced, and the advantages of refracting telescopes and reflecting telescopes are reserved. With strong aberration correction ability, short light path, wide field, good image quality and convenience for carrying, the optical system is suitable for preparing glasses telescopes.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +1
Method and apparatus for improving image quality in a reflecting telescope
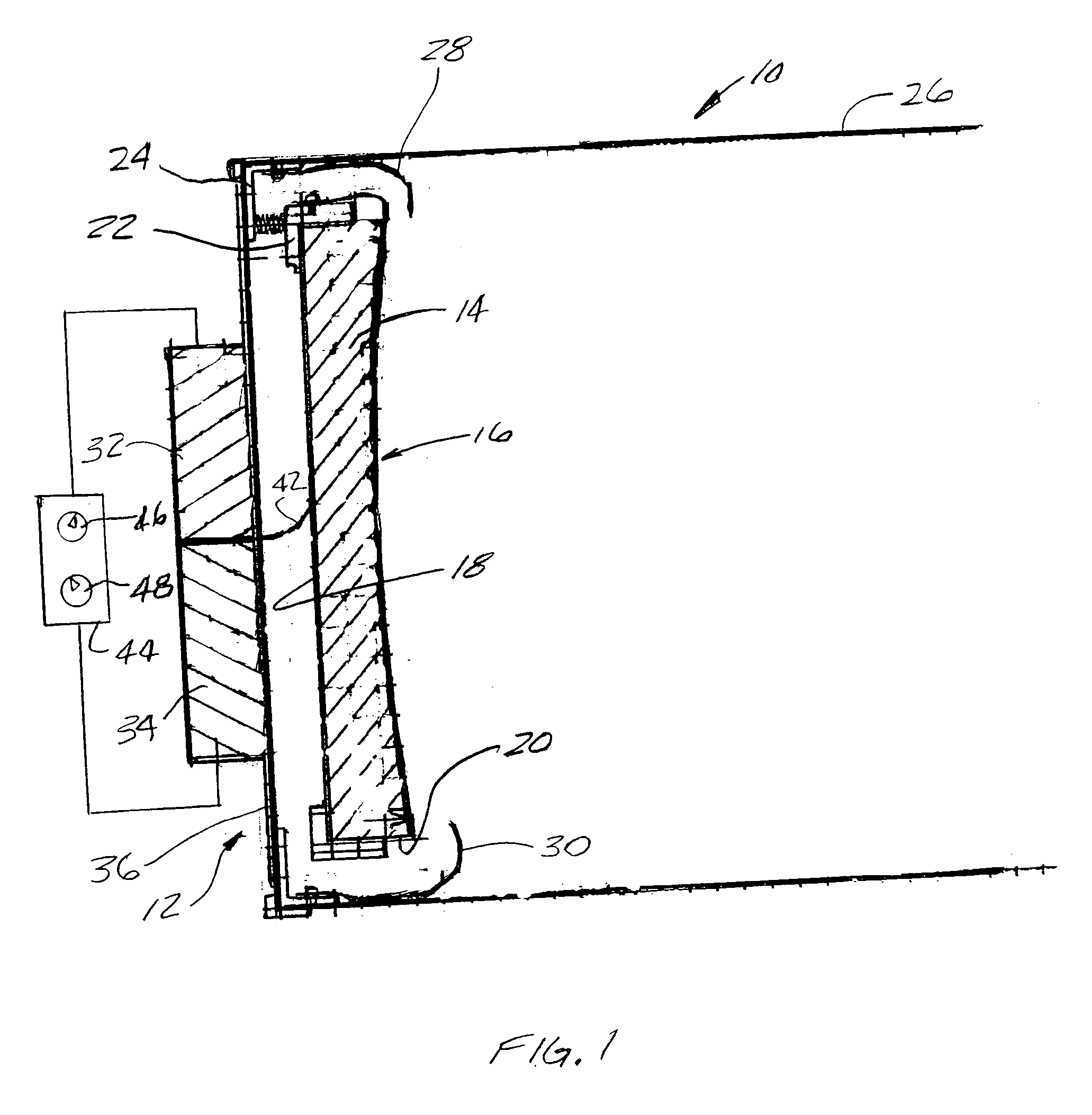
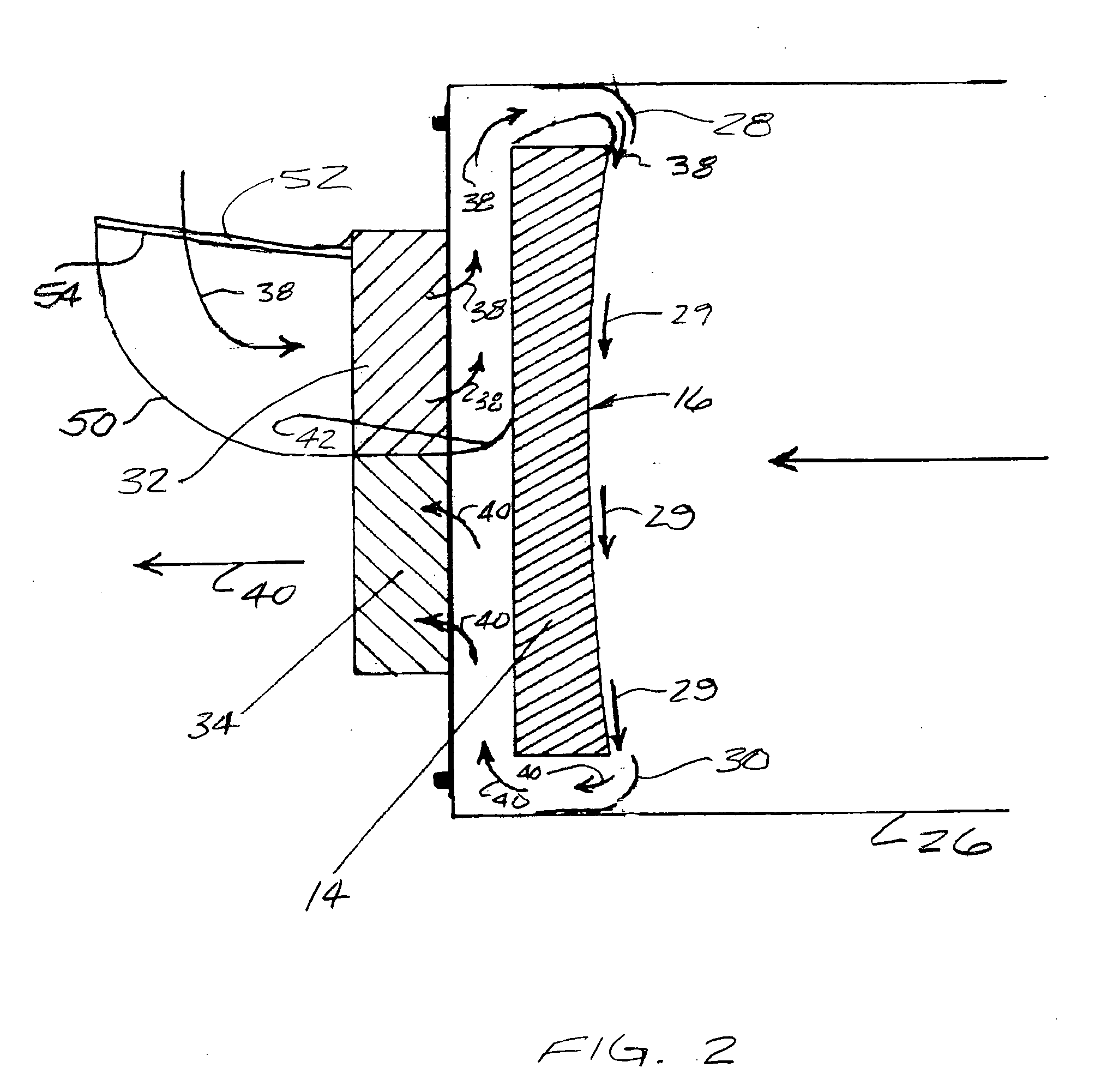
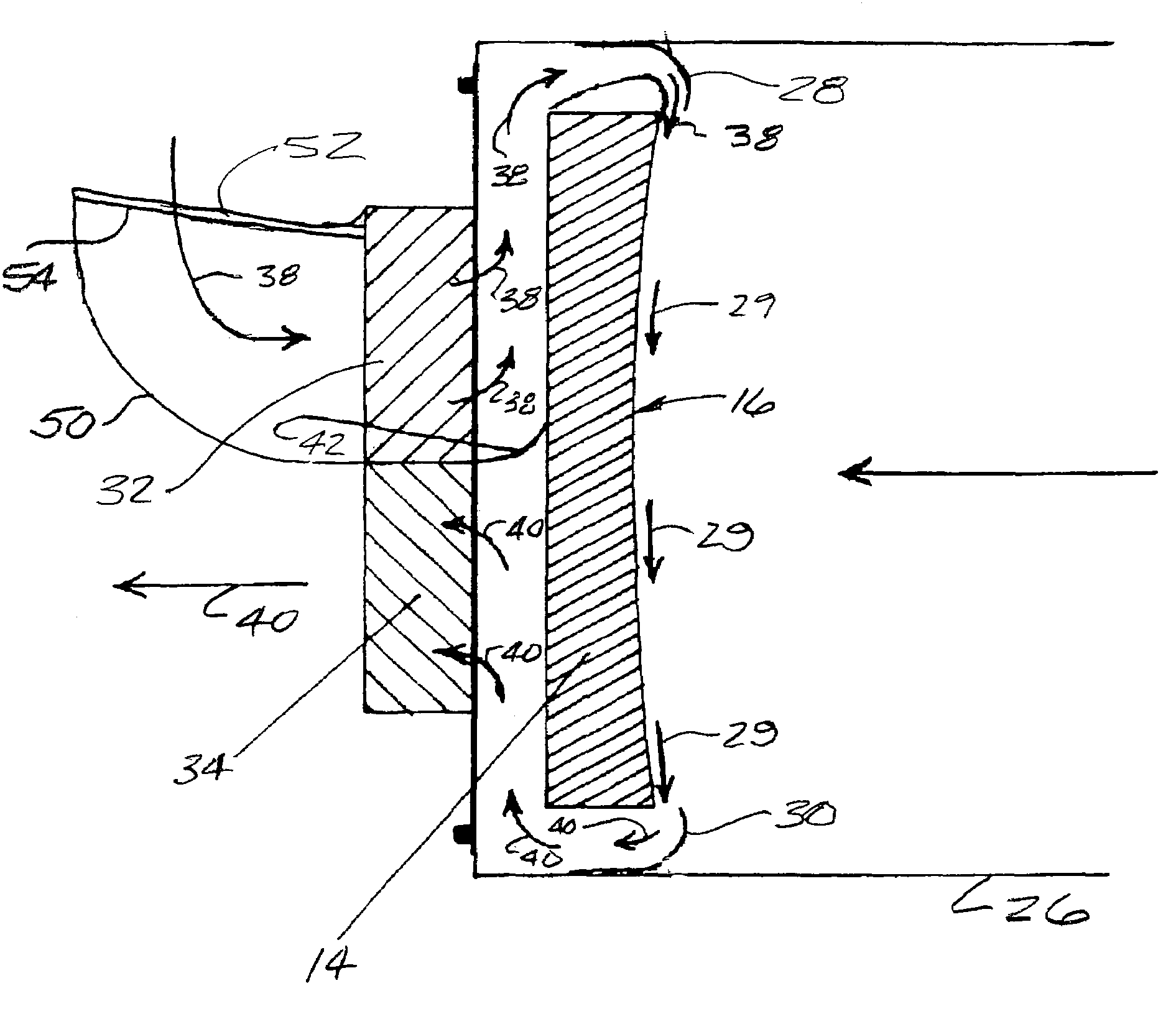
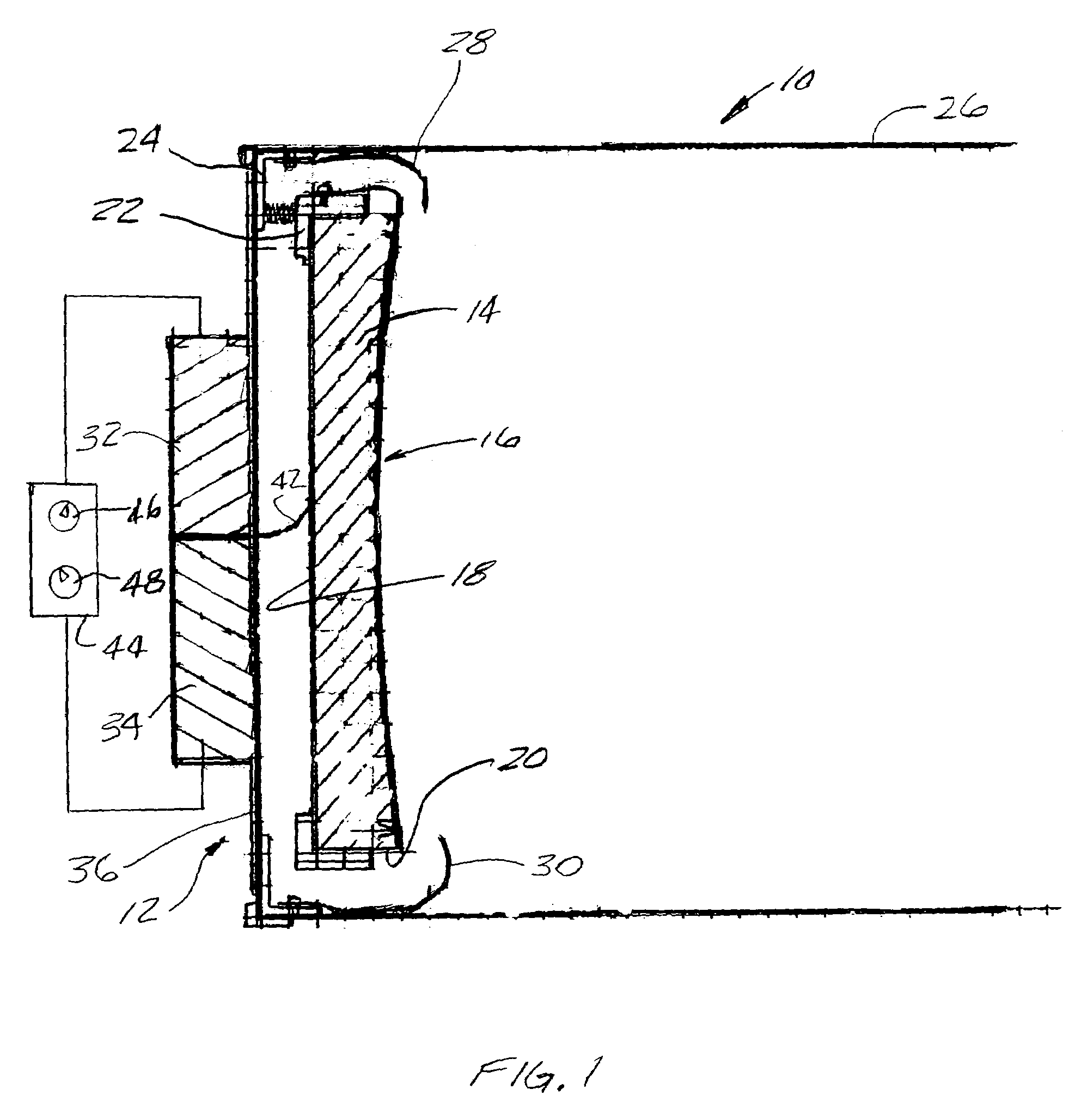
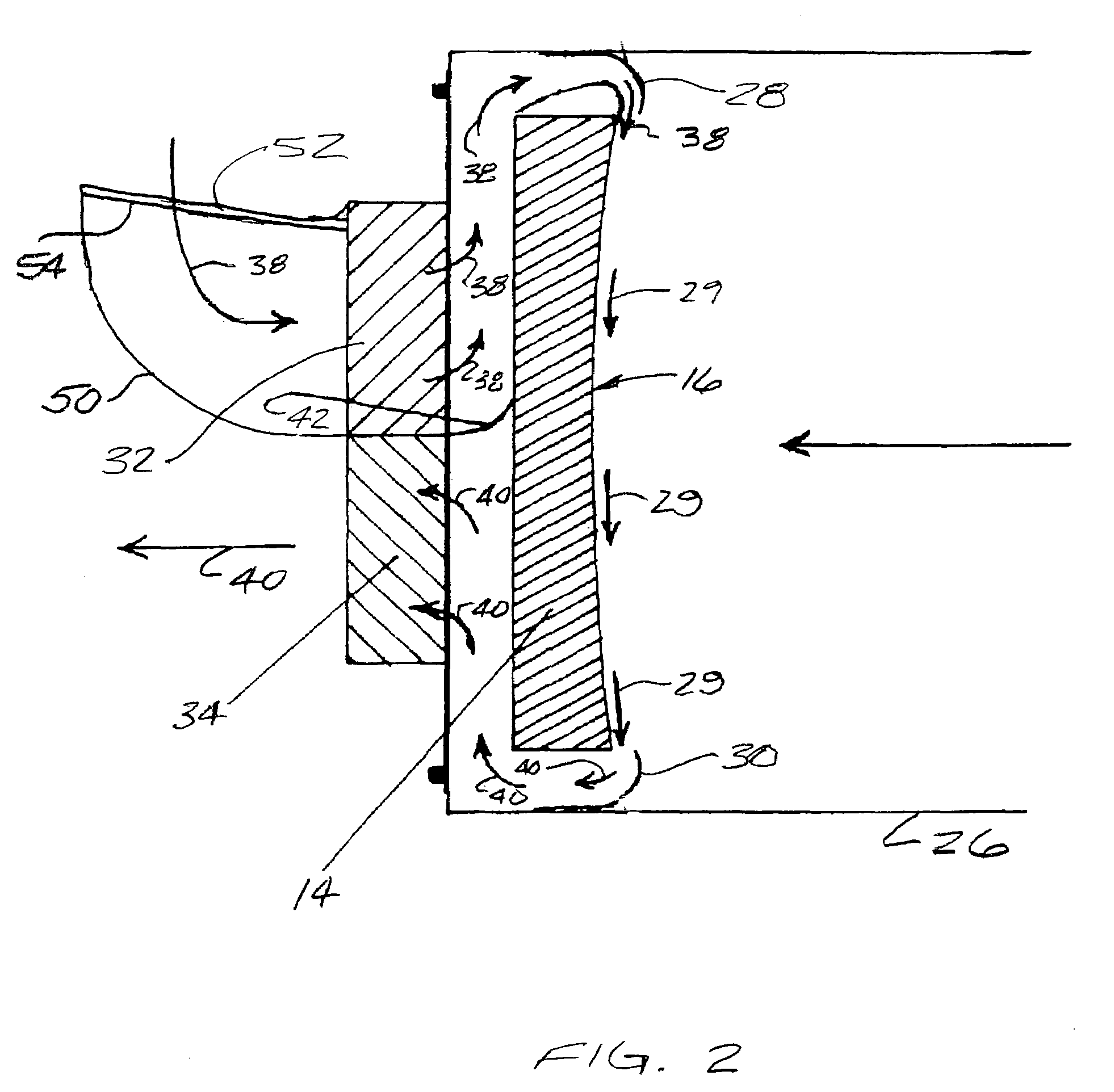
InactiveUS20070097500A1Effectively and efficiently sweep awayImprove clarityTelescopesMountingsReflecting telescopeImaging quality
A method and apparatus for improving image quality in a reflector-type telescope are provided, through utilization of one or more nozzles disposed about the periphery of a reflecting mirror of the telescope, for directing a flow of air from a backside of the mirror across a concave reflecting surface of the mirror, to thereby sweep away and / or preclude formation of image distorting thermal boundary layers, or other impediments to image quality, resulting from the mirror not being in thermal equilibrium with ambient air surrounding the mirror. Supply nozzles are provided around a portion of the periphery of the mirror, and exhaust pick-up nozzles are provided around another portion of the periphery of the mirror, to thereby cause a flow of air to closely adhere to the concave surface of the mirror.
Owner:WILLEY GERALD
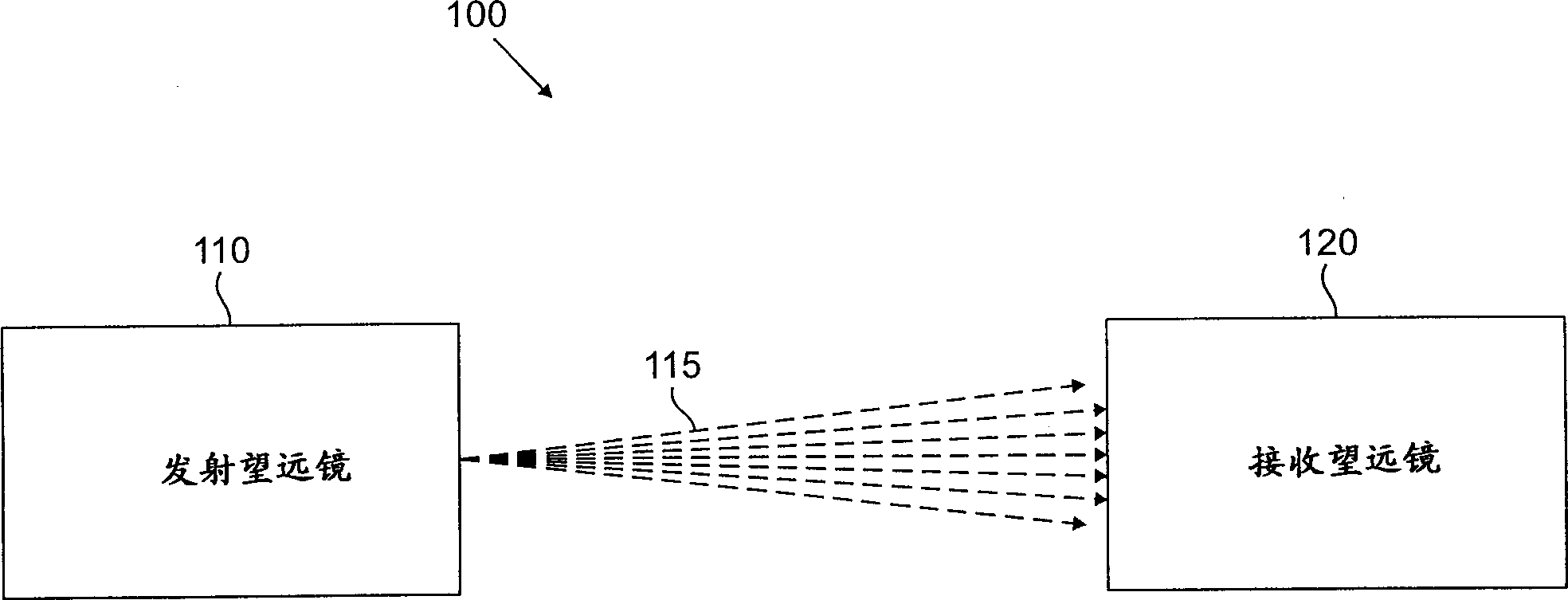
One-point-to-multipoint free space radio optical communication system
InactiveCN1347208AReduce manufacturing costReasonably preparedMirrorsSatellite communication transmissionFiberReflecting telescope
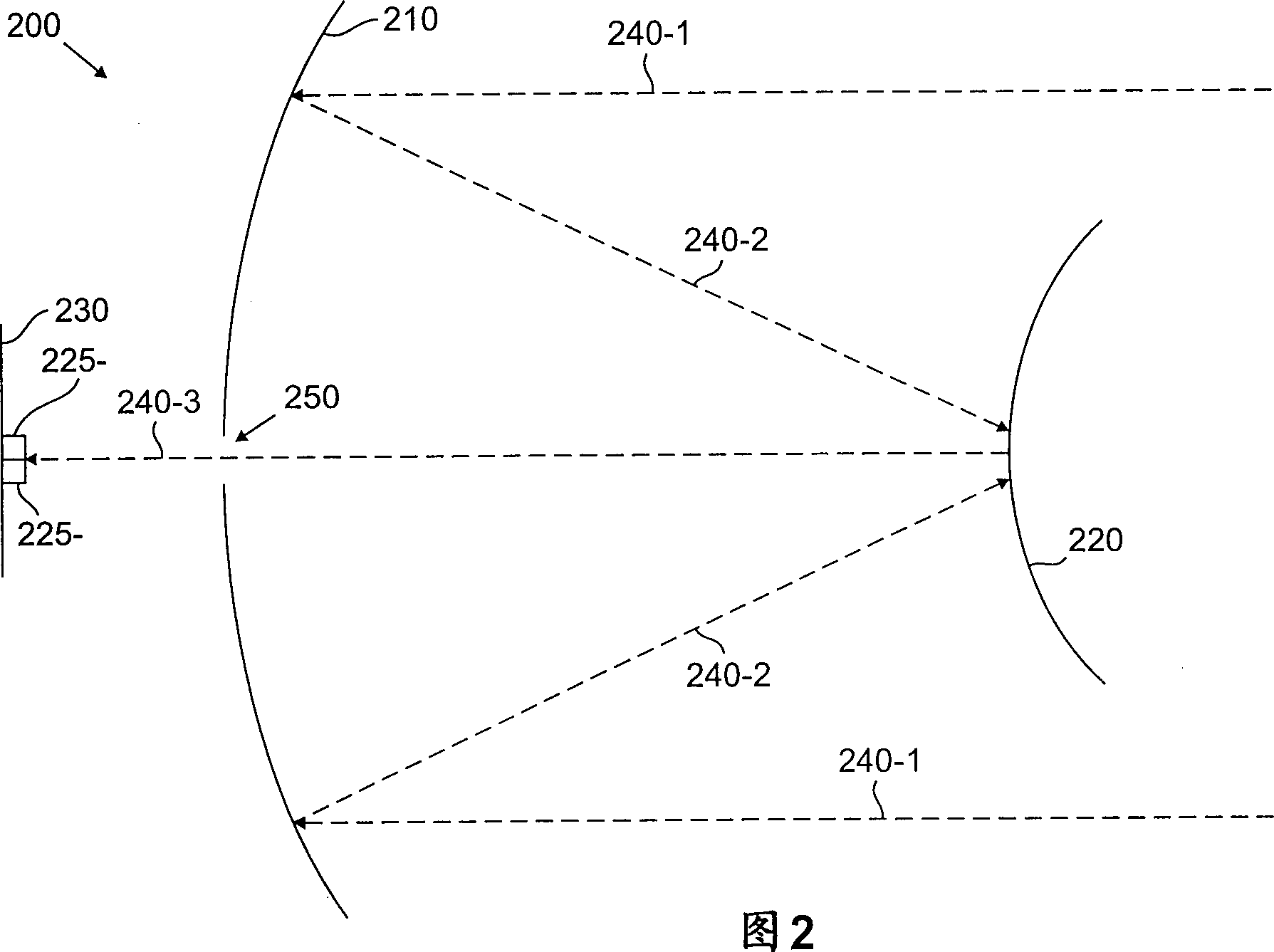
A free-space wireless optical communication system is disclosed that utilizes a telescope design having aspherical mirrors, such as a Ritchey-Chretien (RC) telescope. RC telescopes are characterized by a concave primary mirror and a convex secondary mirror each having a hyperbolic shape. The disclosed mirror configuration provides a larger focal plane that allows for automatic alignment between a transmitter and receiver with a stationary or fixed mirror design, further contributing to a lower fabrication cost. Among other benefits, the larger focal plane permits an n x n fiber array to be positioned in the focal plane of the RC optical telescope, thereby enabling point-to-multipoint communications with a single optical telescope. Each fiber in the n x n fiber array of a transmitting telescope can be focused on a different receiving telescope in a wireless optical communication system. In this manner, each fiber in the n x n fiber array sends optical energy over a distinct path to address a given receiving telescope.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Correct image zoomable reflecting telescope with near stationary eyepiece
ActiveUS20080037115A1Constant positionAccurate imagingMicroscopesTelescopesReflecting telescopePlane mirror
A correct image reflecting telescope with zoom capability comprised of a flat mirror, a parabolic primary mirror, and an image correcting system. The flat mirror reflects the incoming light from the telescope aperture into the parabolic primary mirror. The reflected light from the primary mirror passes back through a small centrally located opening in the flat aperture mirror and into an image correcting lens system. The image correcting system repositions the focal point of the primary mirror from a point in front of the flat aperture mirror to a point behind this mirror for observation with and eyepiece. The image correcting system makes the telescope useful in terrestrial as well as celestial applications and it can be moved with respect to the primary mirror such that a zoom feature results. This intrinsic zoom of the telescope allows an observer to use a single eyepiece in place of many, eliminates the need for an additional finder scope, and also makes the telescope useful in spotting scope applications. The eyepiece can remain at a stationary level for all observable directions.
Owner:DUBY DANTE
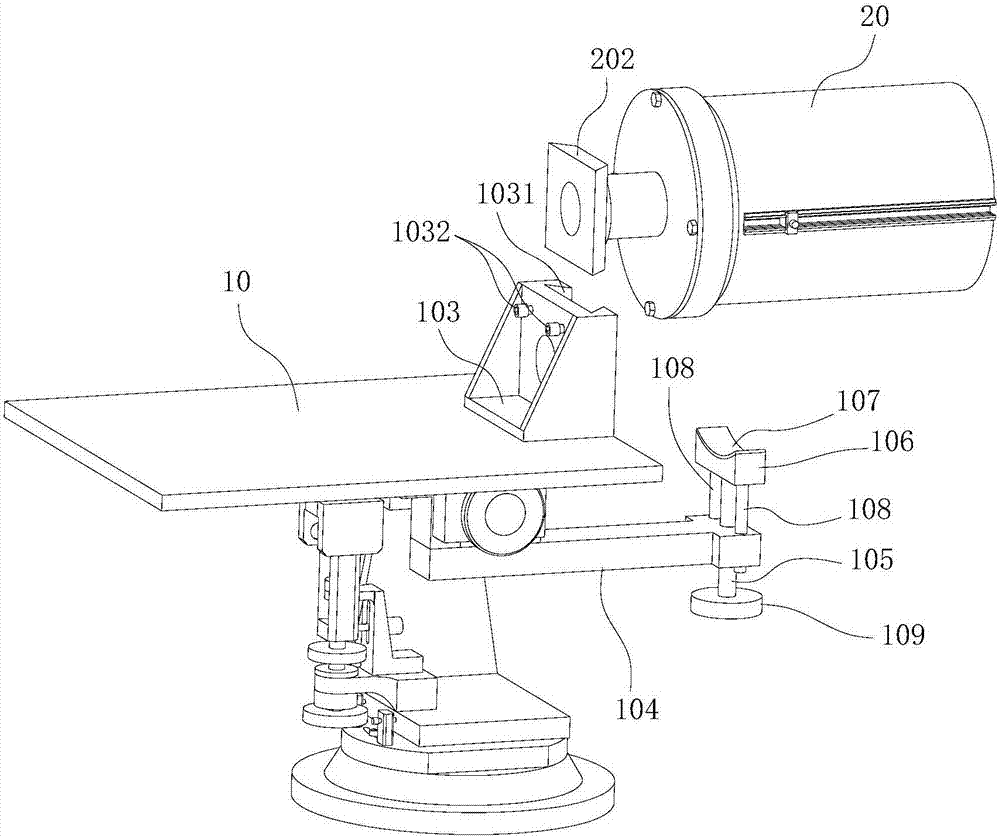
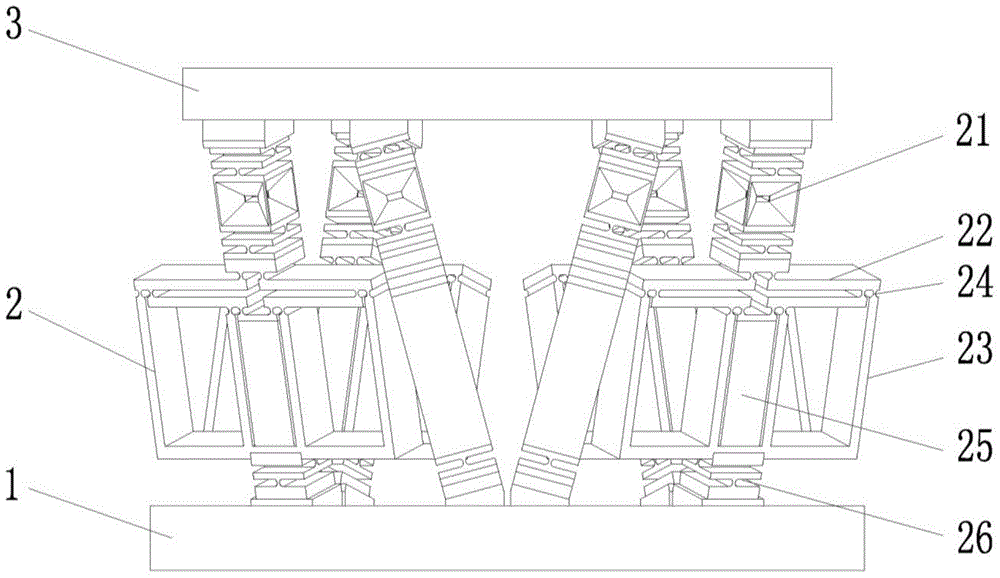
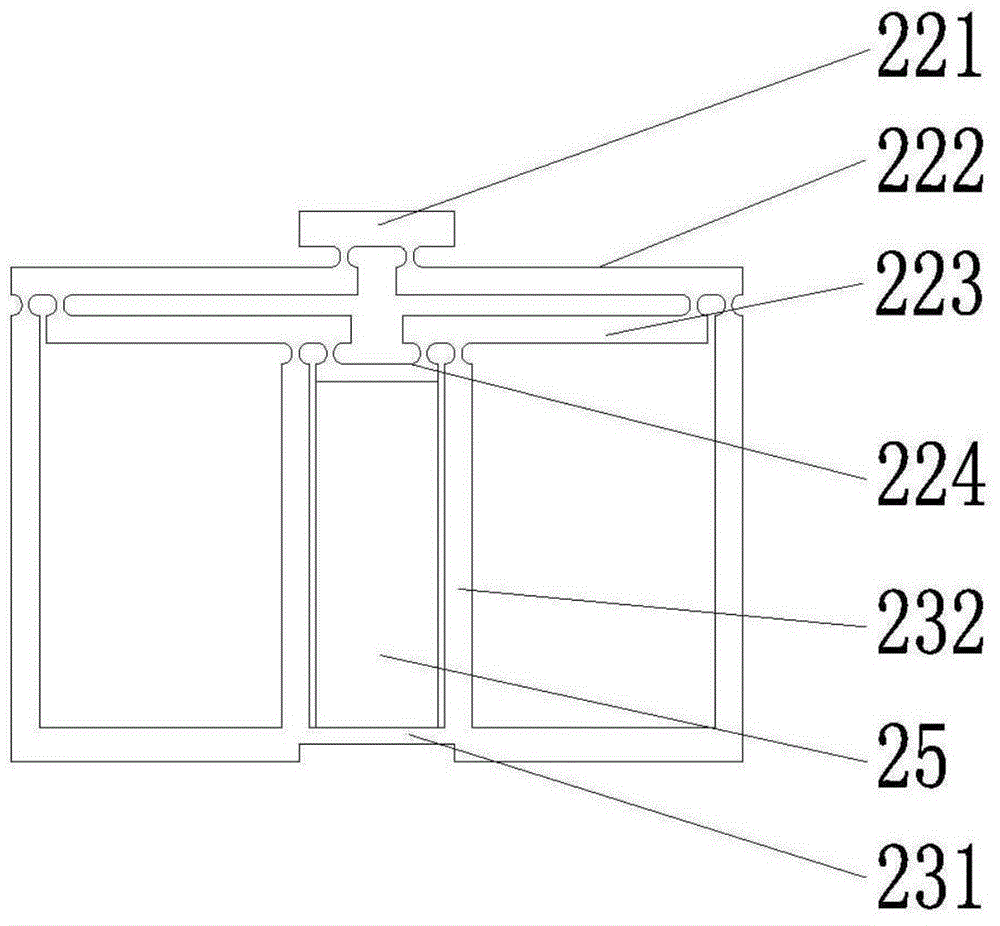
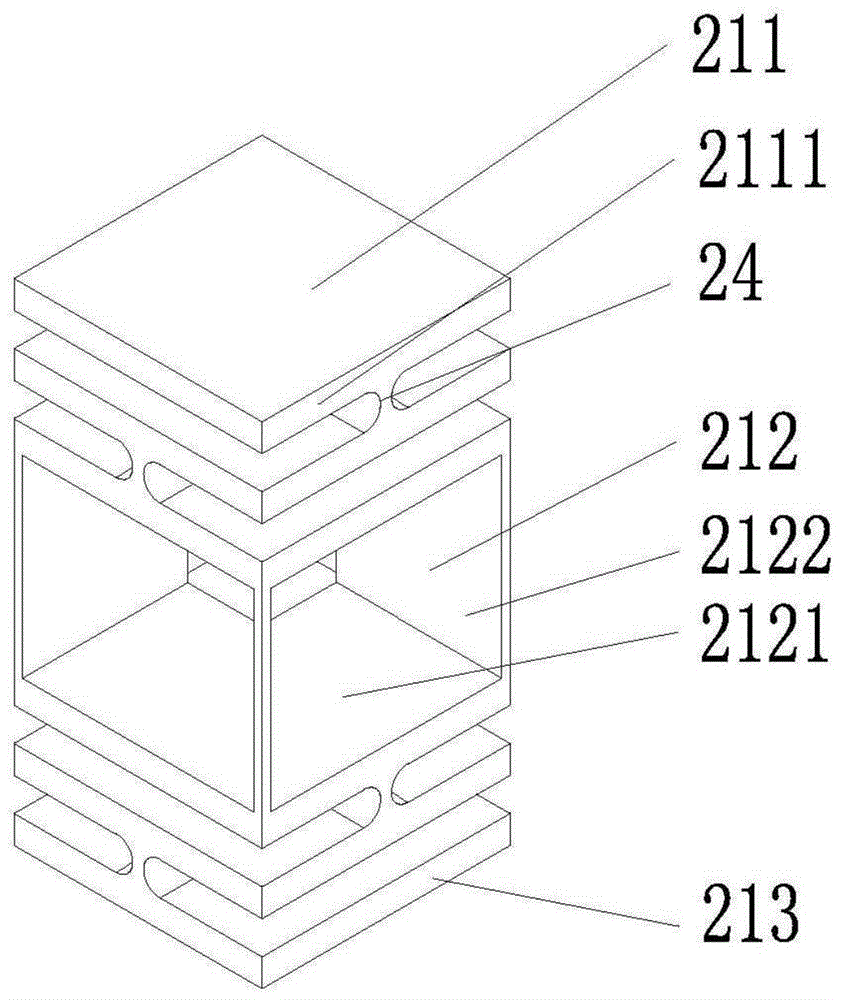
Multi-frequency telescope apparatus for celestial observations using reflecting telescope
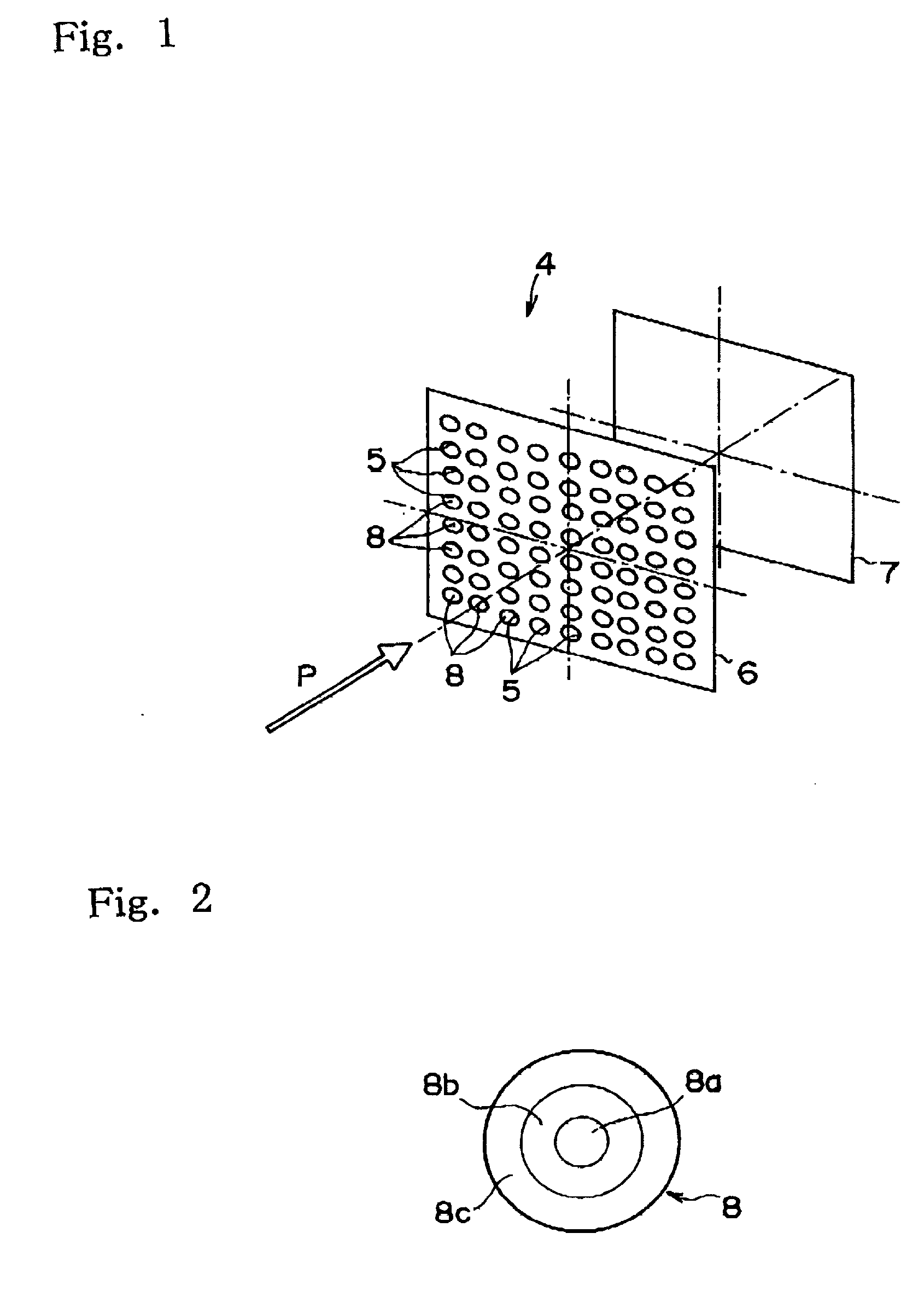
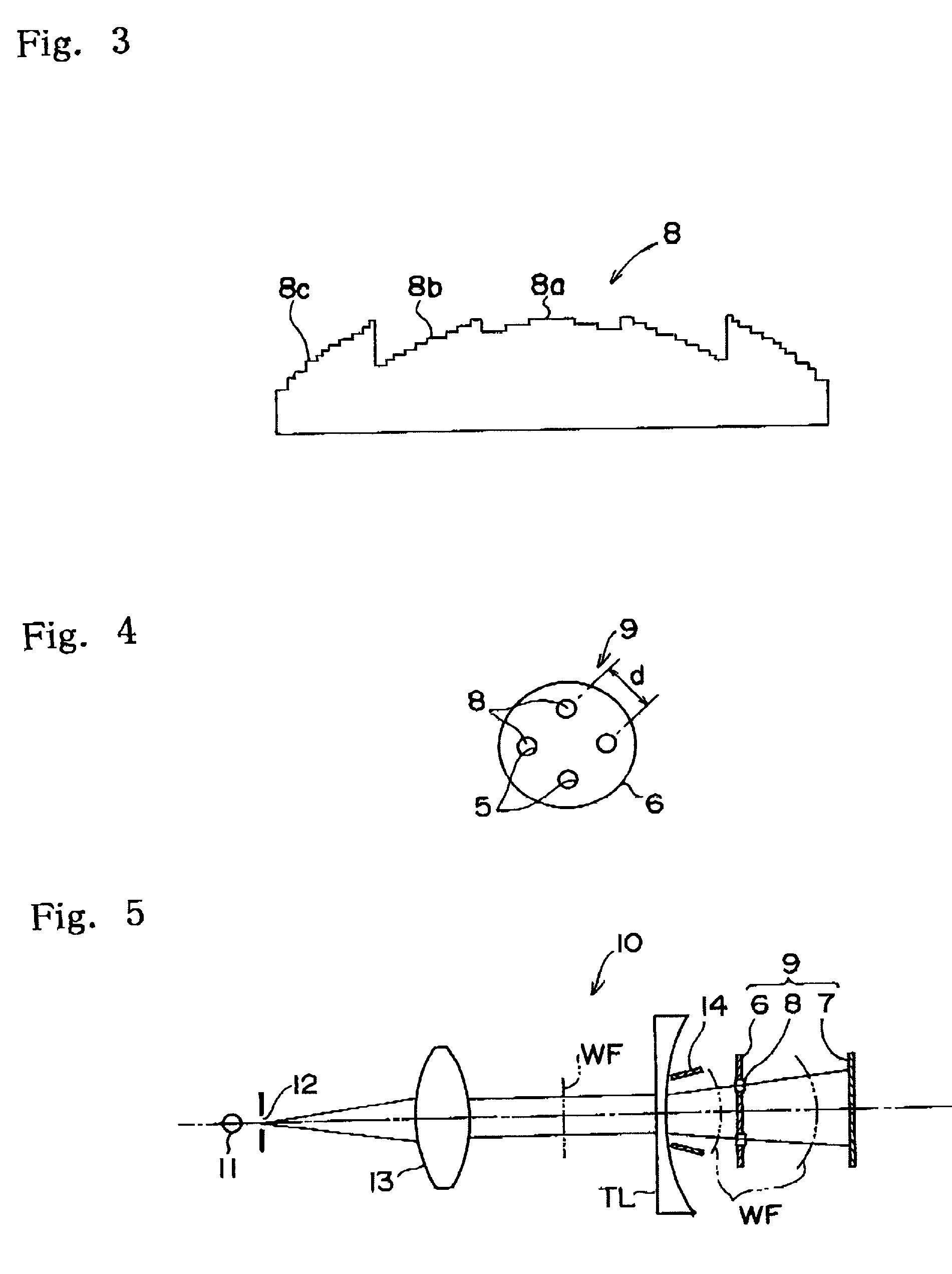
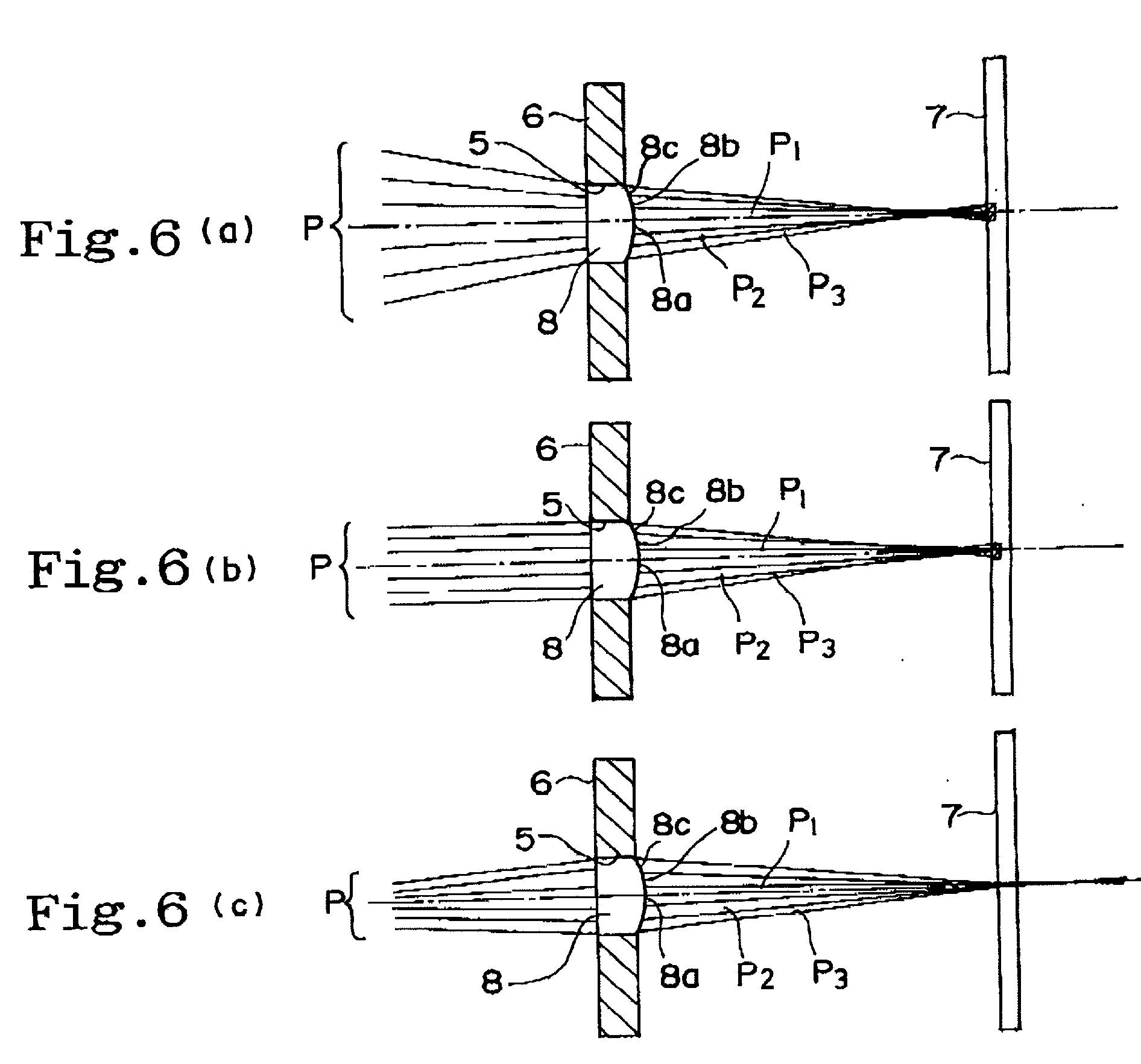
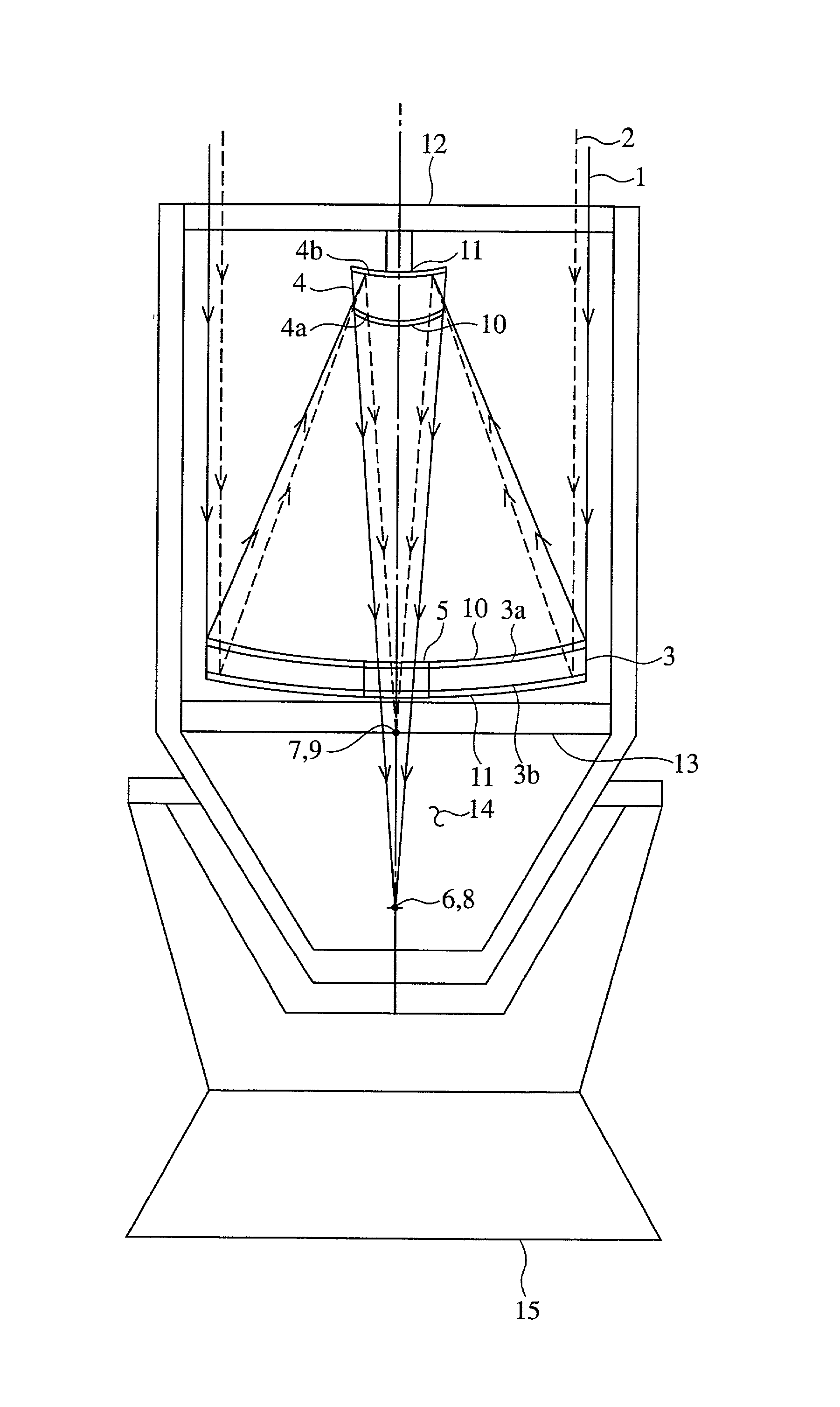
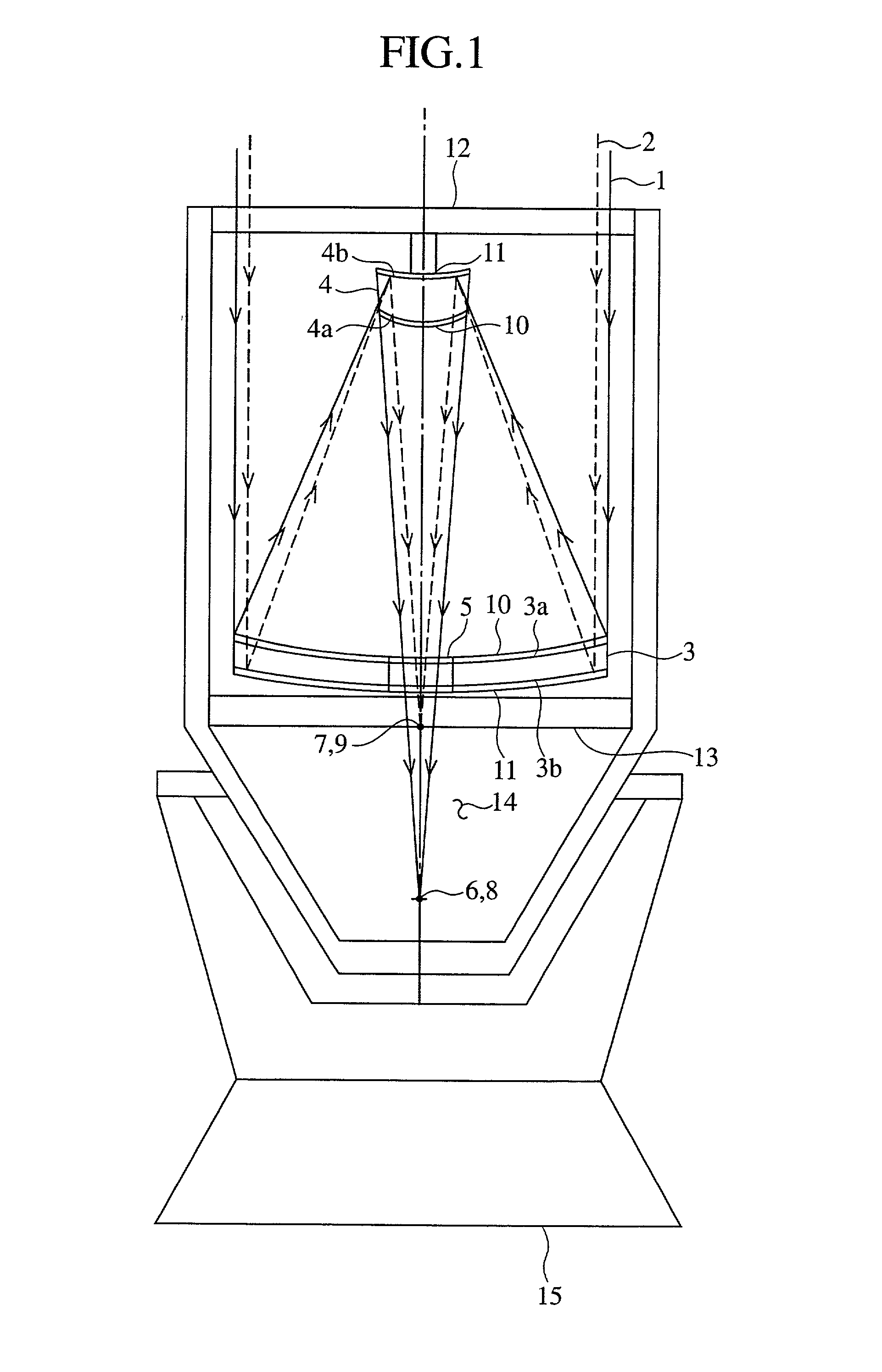
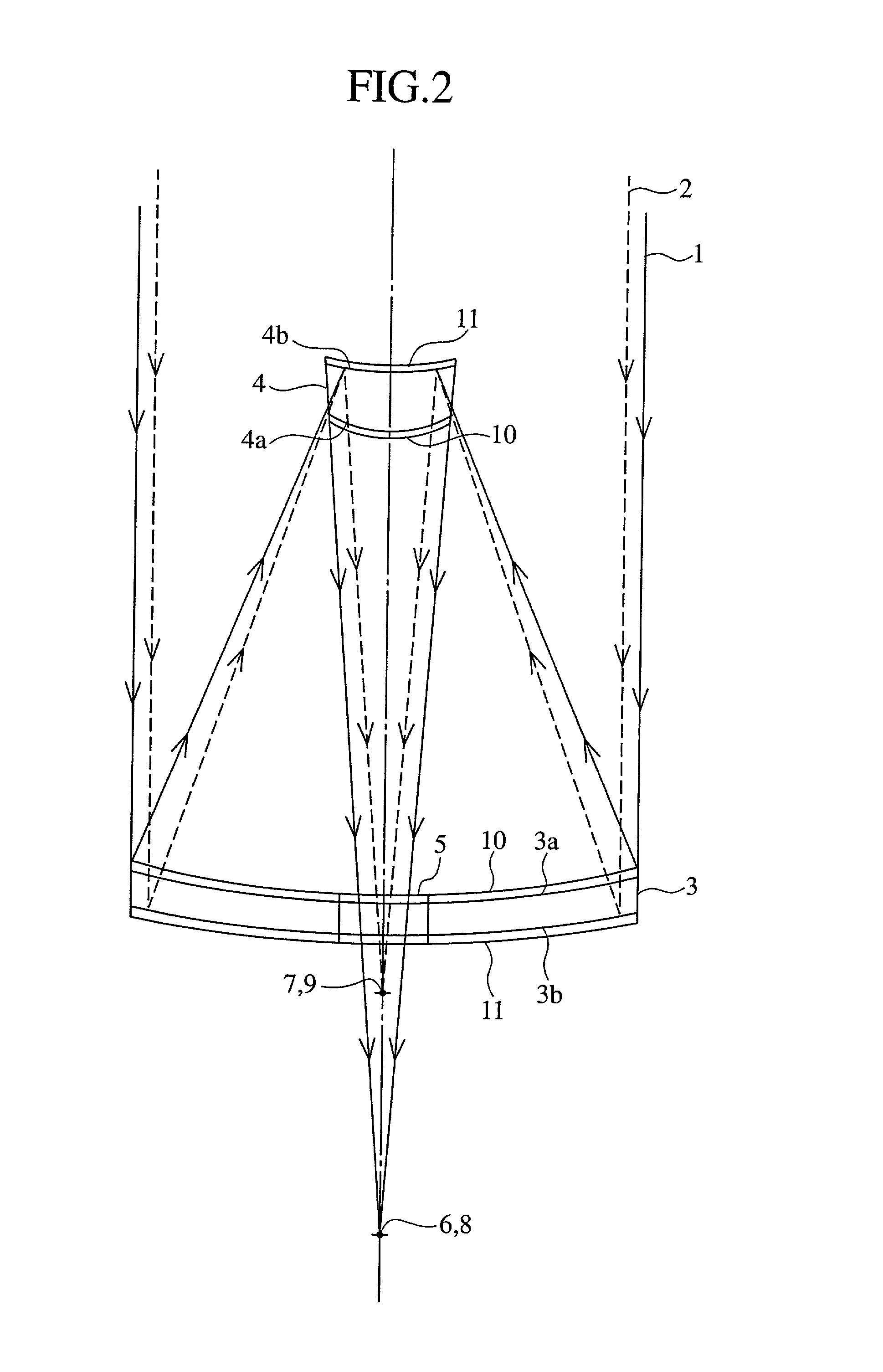
A telescope apparatus for celestial observations by a reflecting telescope which is provided with: a first reflecting mirror 3 having its surface 3a coated over the entire area thereof with a grid-like metallic film 10 that reflects radio waves 1 but permits the passage therethrough of infrared and visible rays 2 and having its back 3b coated over the entire area thereof with a full-face metallic film that reflects both of the radio waves 1 and the infrared and visible rays 2; and a second reflecting mirror 4 having its surface 4a coated over the entire area thereof with the grid-like metallic film 10 that reflects the radio waves 1 but permits the passage therethrough of the infrared and visible rays 2 and having its back 4b coated over the entire area thereof with the full-face metallic film 11 that reflects both of the radio waves 1 and the infrared and visible rays.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method and apparatus for improving image quality in a reflecting telescope
InactiveUS7374294B2Improve image qualityTight adhesionTelescopesMountingsReflecting telescopeImaging quality
A method and apparatus for improving image quality in a reflector-type telescope are provided, through utilization of one or more nozzles disposed about the periphery of a reflecting mirror of the telescope, for directing a flow of air from a backside of the mirror across a concave reflecting surface of the mirror, to thereby sweep away and / or preclude formation of image distorting thermal boundary layers, or other impediments to image quality, resulting from the mirror not being in thermal equilibrium with ambient air surrounding the mirror. Supply nozzles are provided around a portion of the periphery of the mirror, and exhaust pick-up nozzles are provided around another portion of the periphery of the mirror, to thereby cause a flow of air to closely adhere to the concave surface of the mirror.
Owner:WILLEY GERALD
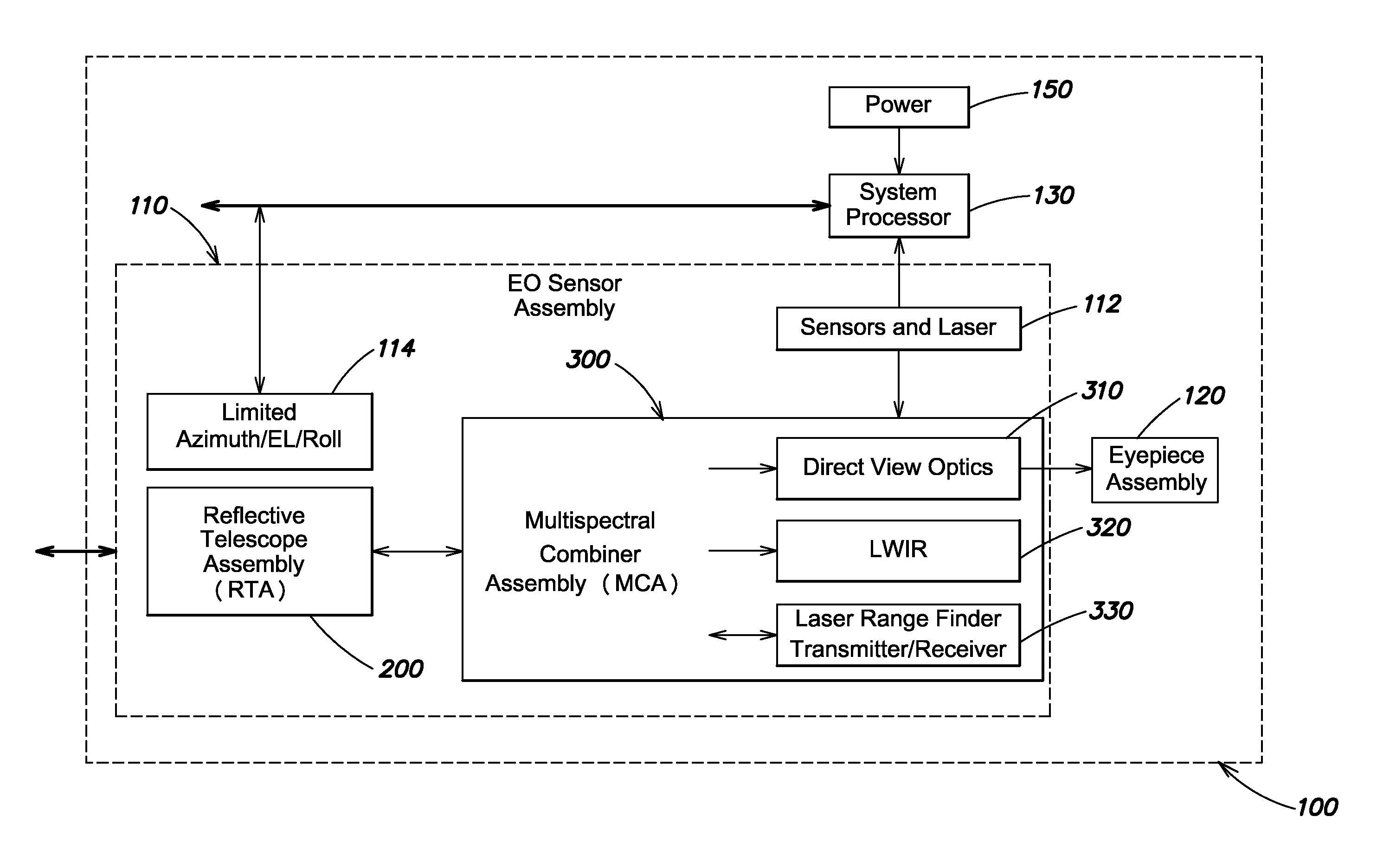
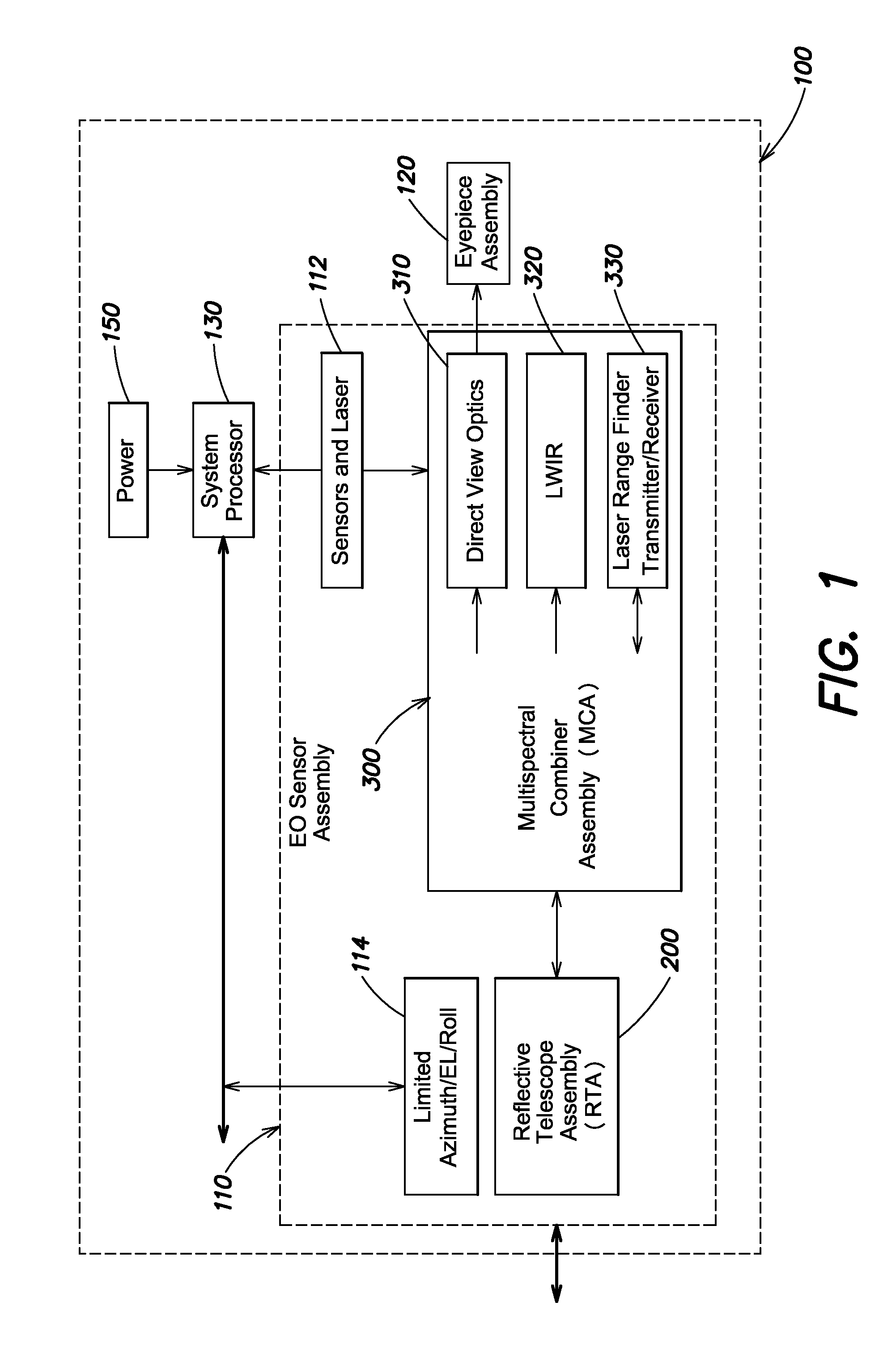
Optical configuration for a compact integrated day/night viewing and laser range finding system
ActiveUS20150253133A1Small sizeReduce weightOptical rangefindersSighting devicesReflecting telescopeEyepiece
A compact integrated optical system including an eyepiece, a reflective telescope, and a multi-spectral combiner optically coupled between the reflective telescope and the eyepiece, and configured to direct visible light received via the reflective telescope assembly along a direct view optical path to the eyepiece assembly. In one example, the multi-spectral combiner includes a display that displays a visual representation of the imagery of the viewed scene, and laser range-finder transceiver that transmits and receives a laser beam via the reflective telescope. A pair of beamsplitters is used to separate the imaging optical path from the direct view and laser range-finding optical paths. A blocking device is used to enable laser range-finding capability during daytime viewing of the imaging optical path imagery on the display. The reflective telescope provides a common aperture for the direct view optical path, an imaging optical path, and the laser range-finder transceiver.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Scanning telescope
ActiveUS20150177507A1Easy to useRadiation pyrometryDirection controllersReflecting telescopeOptical axis
A scanning telescope including an on-axis four-mirror reflective telescope configured to receive electromagnetic radiation through an optical aperture and to direct and focus the electromagnetic radiation onto an imaging detector, the on-axis four-mirror reflective telescope including a rear-most mirror configured to be movable over a range of angular tilt relative to an optical axis of the scanning telescope to scan a field of view of the imaging detector over a scan range. In one example, the rear-most scanning mirror is the tertiary mirror of the four-mirror reflective telescope, and all four mirrors are axisymmetric about the optical axis of the telescope.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Optical calibration device for reflecting telescope optical axis monitoring based on polarization and beam splitting
PendingCN110793756AAchieve registrationImprove test repeatabilityOptical axis determinationLens position determinationReflecting telescopeBeam splitting
The invention discloses an optical calibration device for reflecting telescope optical axis monitoring based on polarization and beam splitting. The device comprises an optical fiber light source, a collimating lens, a beam splitting prism, a polarization and beam splitting prism, a first parallel flat plate, a quarter-wave plate, a pyramid prism, a second parallel flat plate, a converging lens and a detector. In the optical calibration process of a telescope system, the polarization and beam splitting prism, the quarter-wave plate and the pyramid prism are adopted to generate two beams whichare collinear in opposite directions, and high-precision registration of the optical axis of the optically calibrated telescope system and the normal of an auxiliary standard plane mirror is realized.The device is used for a relative test and overcomes test precision problems brought by manual interpretation errors, a test environment and the like in a traditional optical axis absolute test. Besides, the reference optical axis and the test optical axis share the same optical path, the influence of vibration in the testing process is avoided, and therefore test efficiency and optical calibration efficiency are greatly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compound telescope with a stationary primary objective mirror having movable collectors
The present invention relates to a novel land based reflecting telescope having a stationary, equatorially mounted, segmented mirror comprised of a plurality of movable mirrored collectors. These movable collectors are arranged in hexagonal groups to form a multiple mirrored reflector, which comprises the stationary compound telescope. A secondary mirror mounted atop a tower at the focal point directs the image toward the observation cart. Observers ride the periphery of the stationary mirror at a rate of one revolution per day. A retractable air supported hypalon cover protects the large primary mirror structure.
Owner:POPIL NICHOLAS B
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com