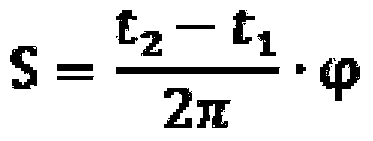Patents
Literature
40 results about "Segmented mirror" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
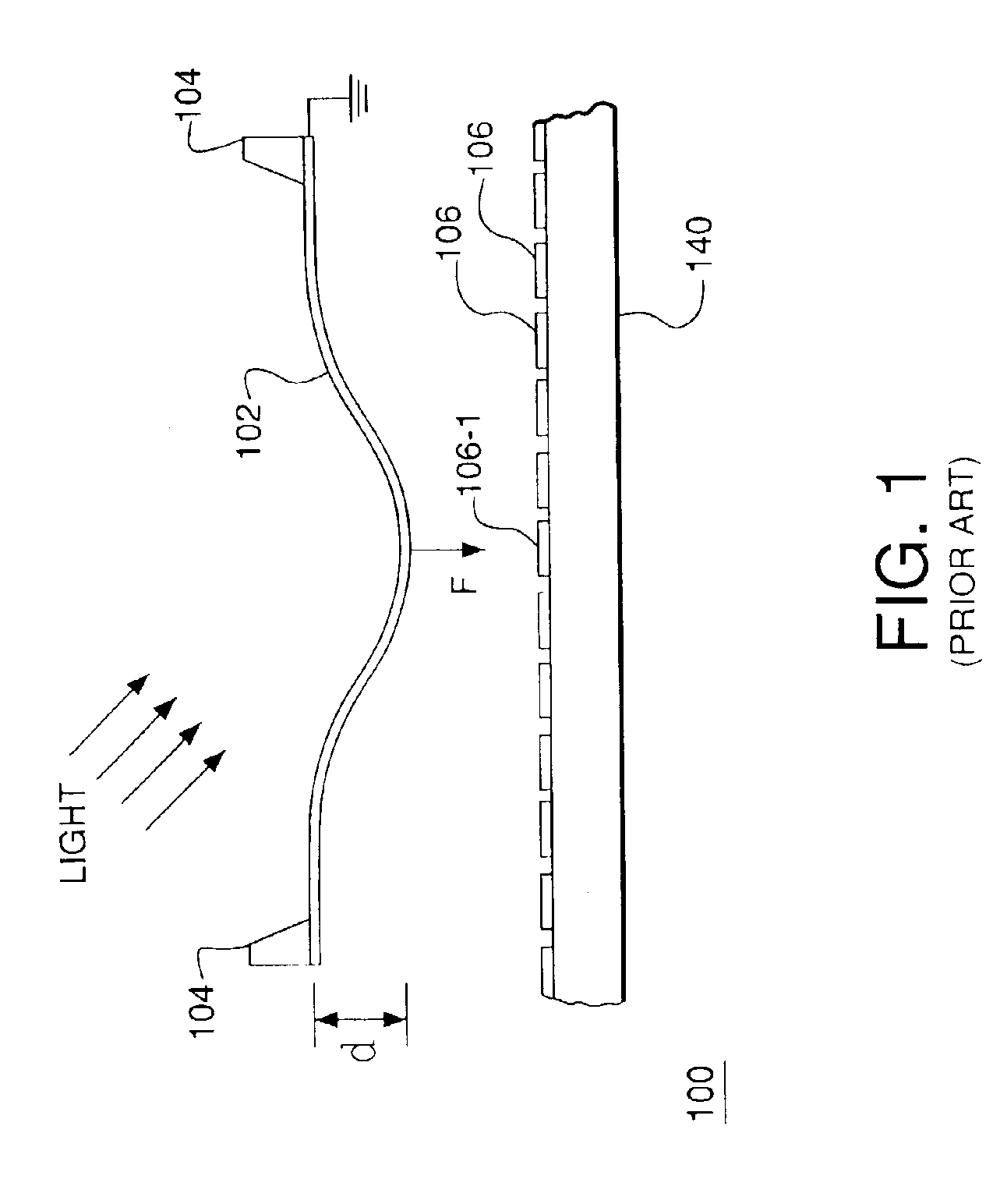
A segmented mirror is an array of smaller mirrors designed to act as segments of a single large curved mirror. The segments can be either spherical or asymmetric (if they are part of a larger parabolic reflector). They are used as objectives for large reflecting telescopes. To function, all the mirror segments have to be polished to a precise shape and actively aligned by a computer-controlled active optics system using actuators built into the mirror support cell. The concept and necessary technologies were initially developed under the leadership of Dr. Jerry Nelson at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and University of California during the 1980s, and have since spread worldwide to the point that essentially all future large optical telescopes plan to use segmented mirrors.
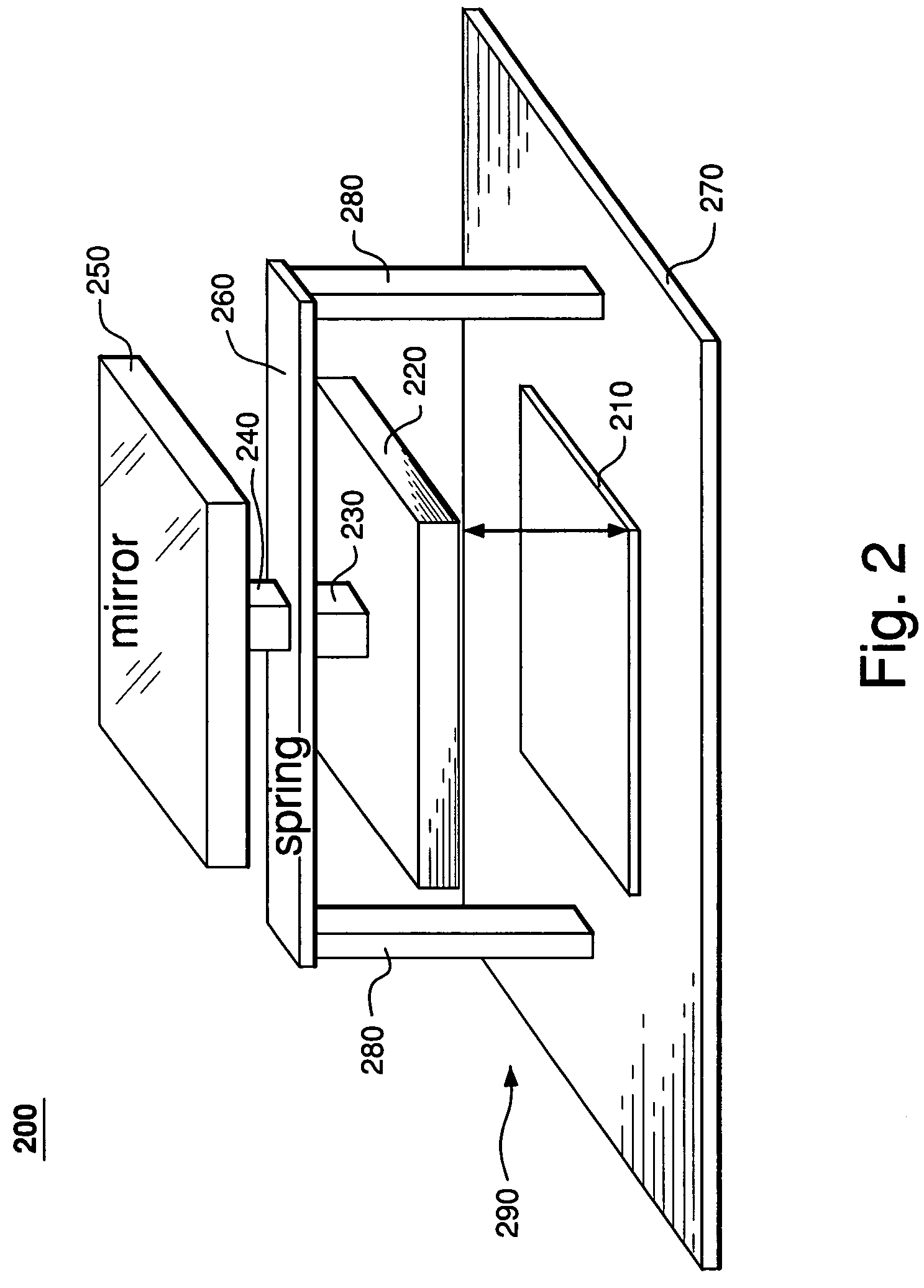
Deformable segmented MEMS mirror
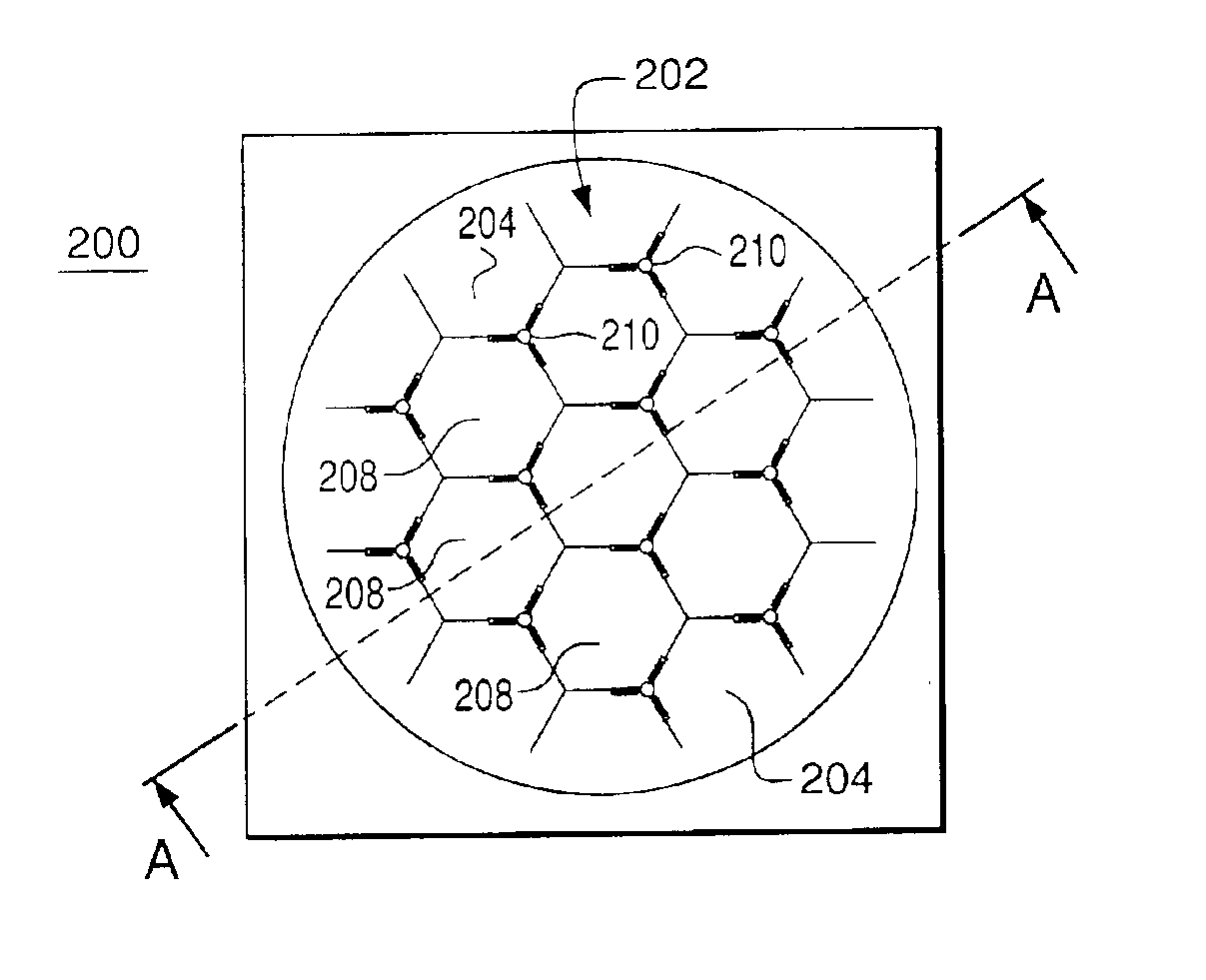
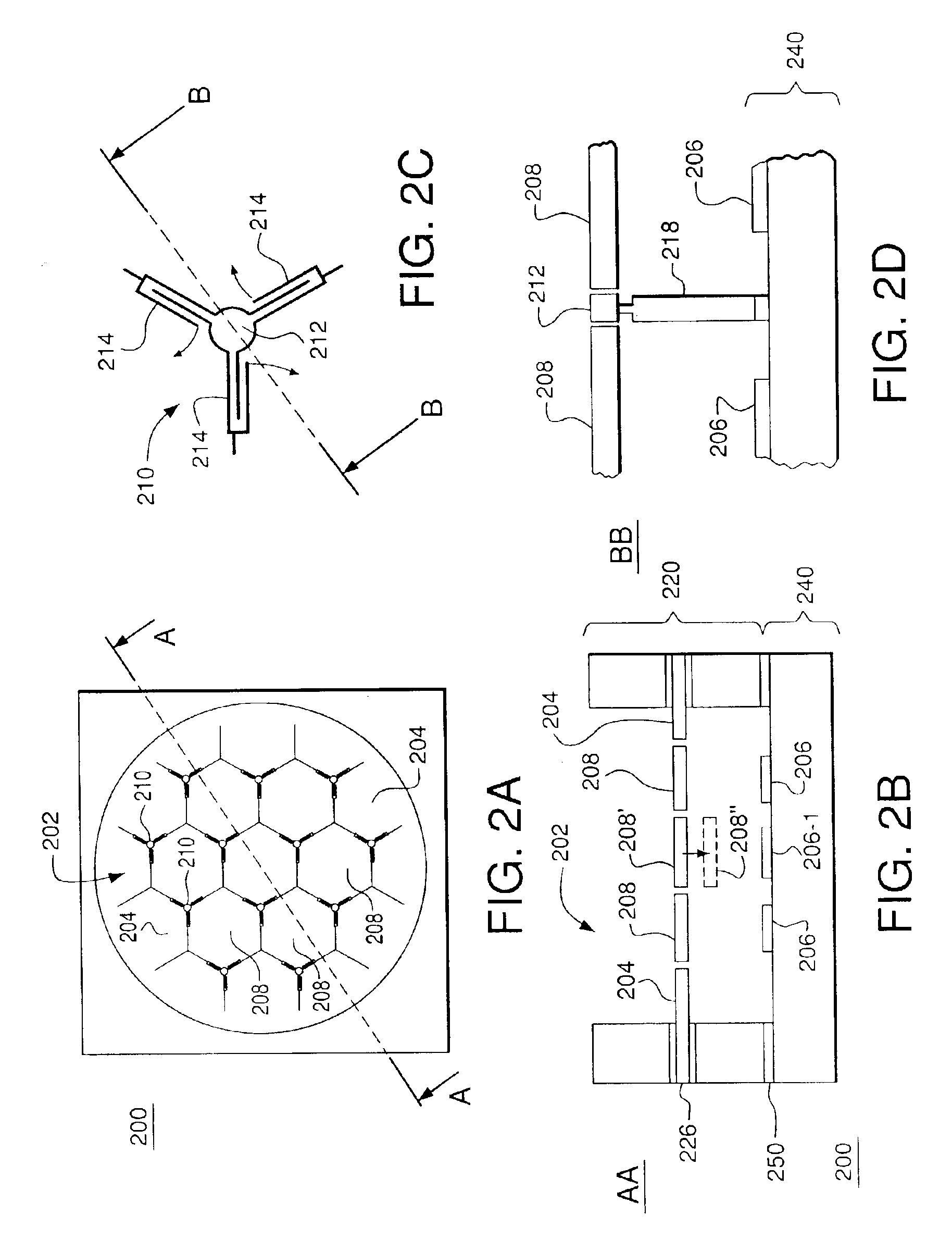
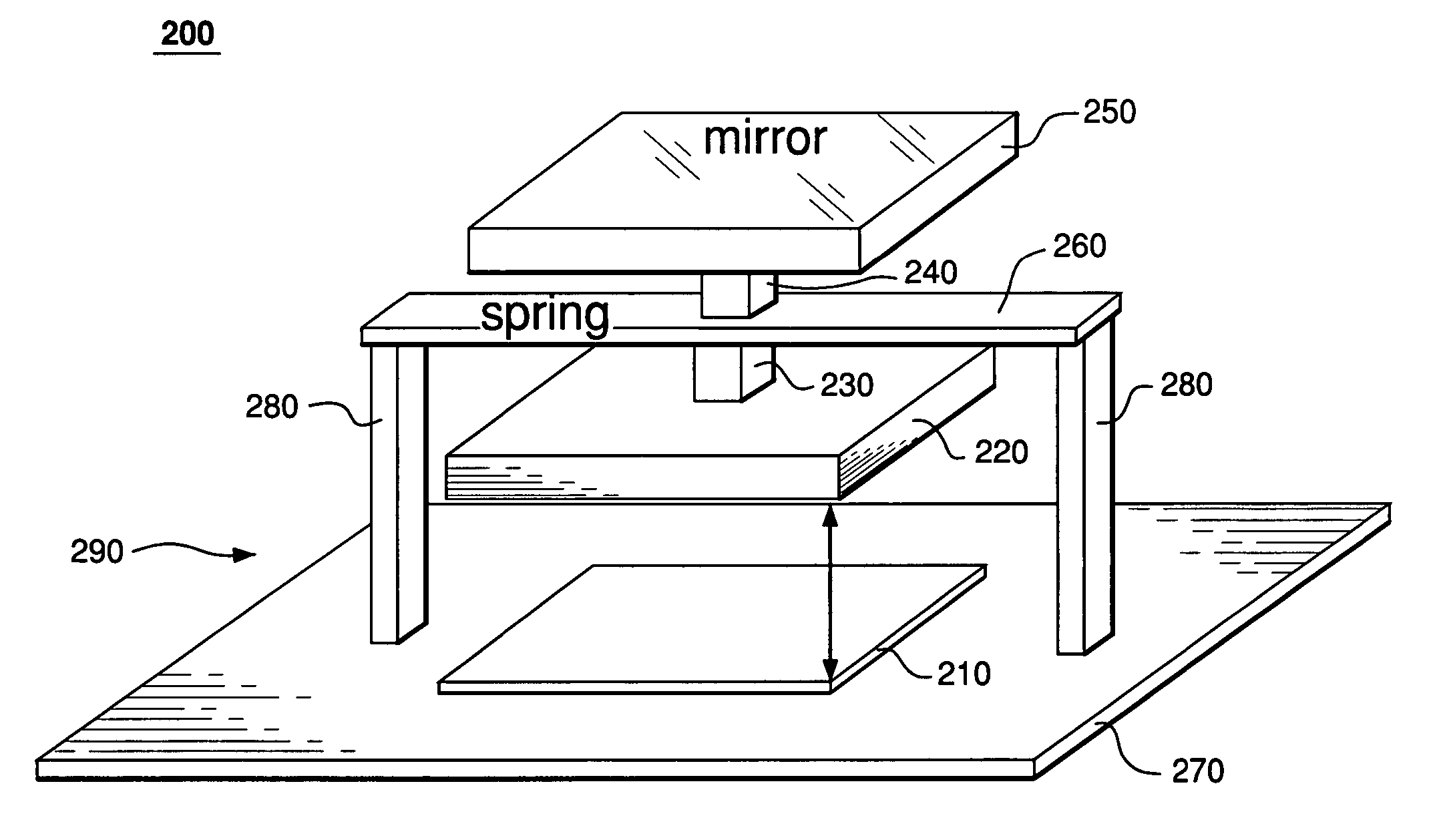
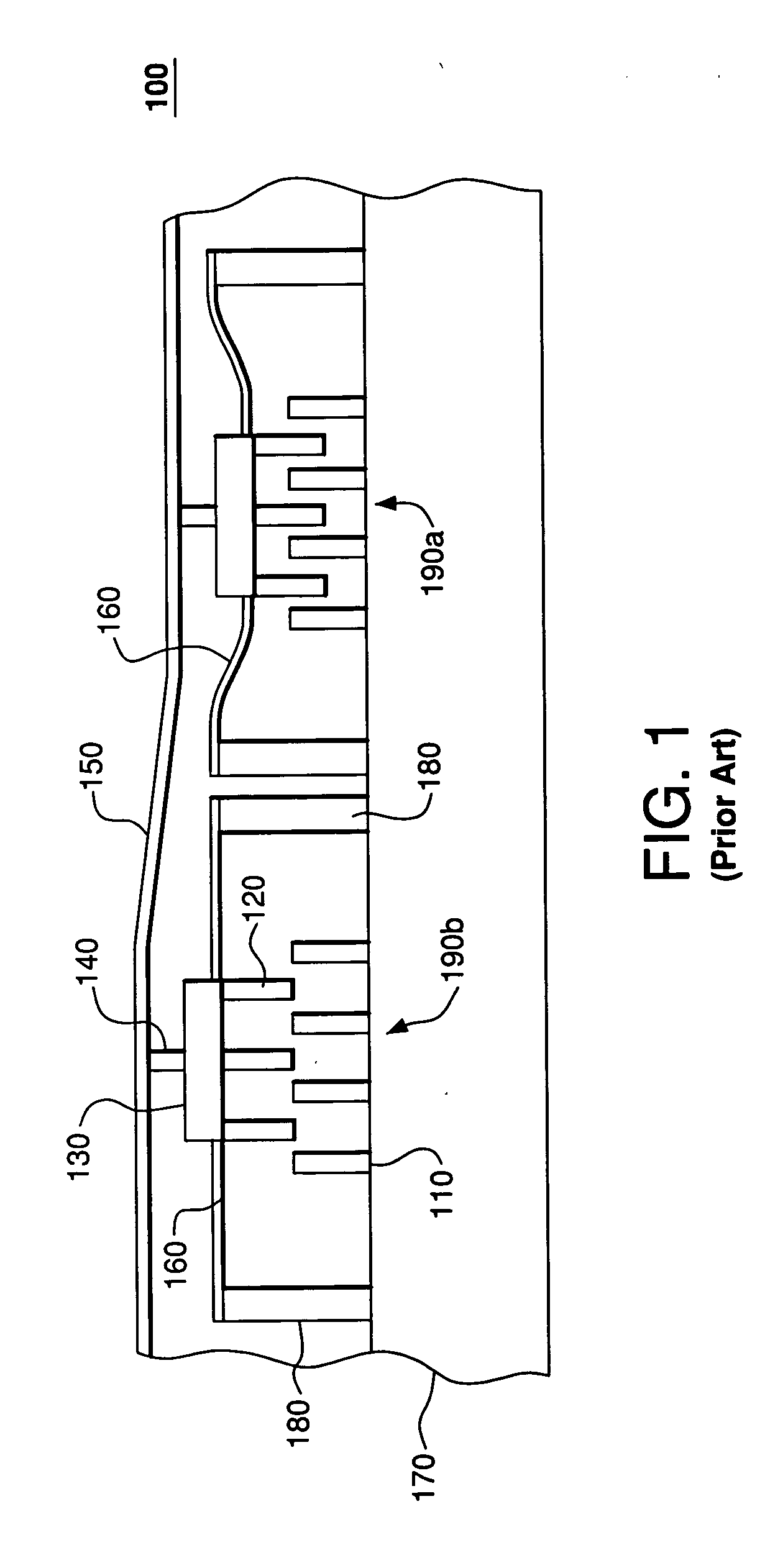
A MEMS device having a deformable segmented mirror. The mirror includes a plurality of movable segments supported on a substrate using spring vertices, each vertex having a fixed plate and one or more springs. In a representative embodiment, three springs support each movable segment, where each spring connects the movable segment to a different spring vertex. The MEMS device also has a plurality of electrodes, each of which can be individually biased. A movable segment moves in response to a voltage applied to an electrode located beneath that segment while the deformed springs attached to the segment provide a restoring force. Due to the fixed plates, motion of each movable segment is substantially decoupled from that of the adjacent segments, which makes the shape of the segmented mirror relatively easy to control. In addition, segments in a deformable mirror of the invention can be displaced by a distance that is significantly larger than the maximum deformation amplitude for a membrane mirror of the prior art. The MEMS device can be fabricated using two silicon-on-insulator (SOI) wafers and an etch fabrication technique.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Segmented MEMS mirror for adaptive optics or maskless lithography
ActiveUS20060126151A1Less stringent requirementsLarge lengthOptical elementsParallel plateDevice form
An apparatus having a plurality of arrayed MEMS devices, each device having a parallel-plate actuator and a reflective plate, both of which are mechanically coupled to a flexible beam attached between two anchors. Advantageously, the use of parallel-plate actuators in the apparatus alleviates stringent requirements for the alignment of lithographic masks employed in the fabrication process. In one embodiment, each flexible beam has a relatively small thickness and a relatively large length to effect a relatively large displacement range for the corresponding reflective plate. Movable electrodes of different parallel-plate actuators are configured to act as an electrical shield for the flexible beams, which reduces inter-device crosstalk in the apparatus. Reflective plates of different MEMS devices form a segmented mirror, which is suitable for adaptive-optics and / or maskless lithography applications.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
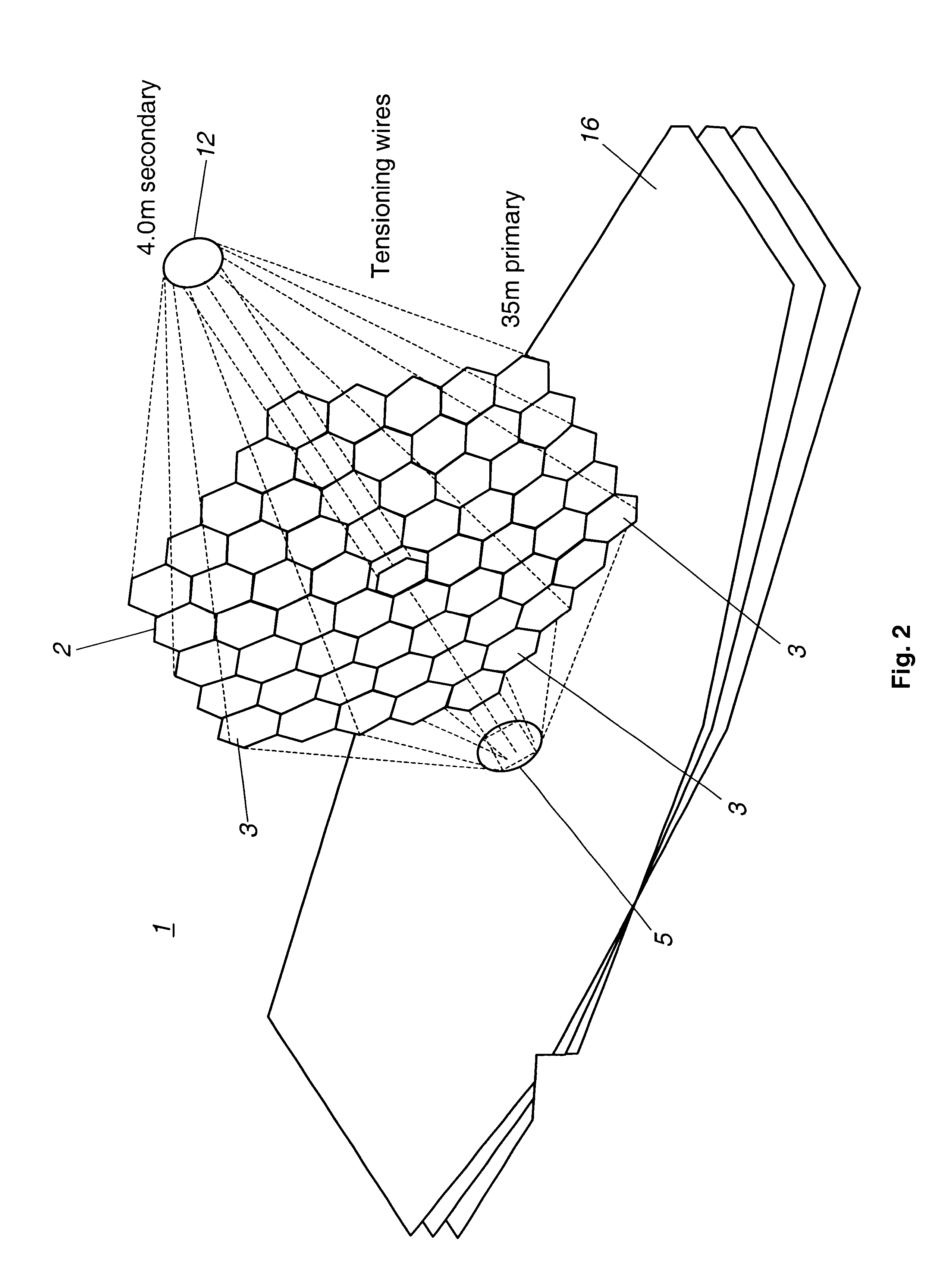
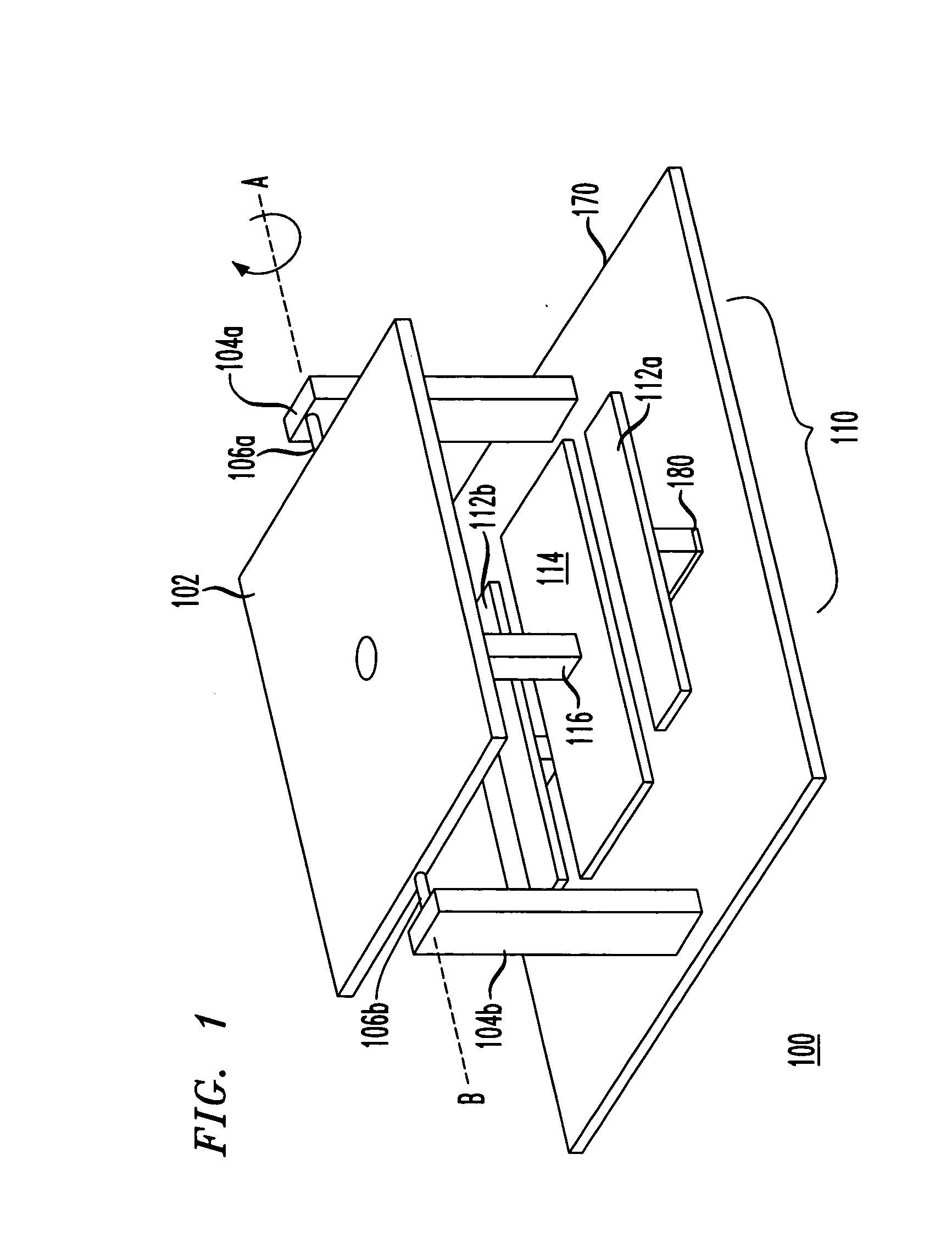
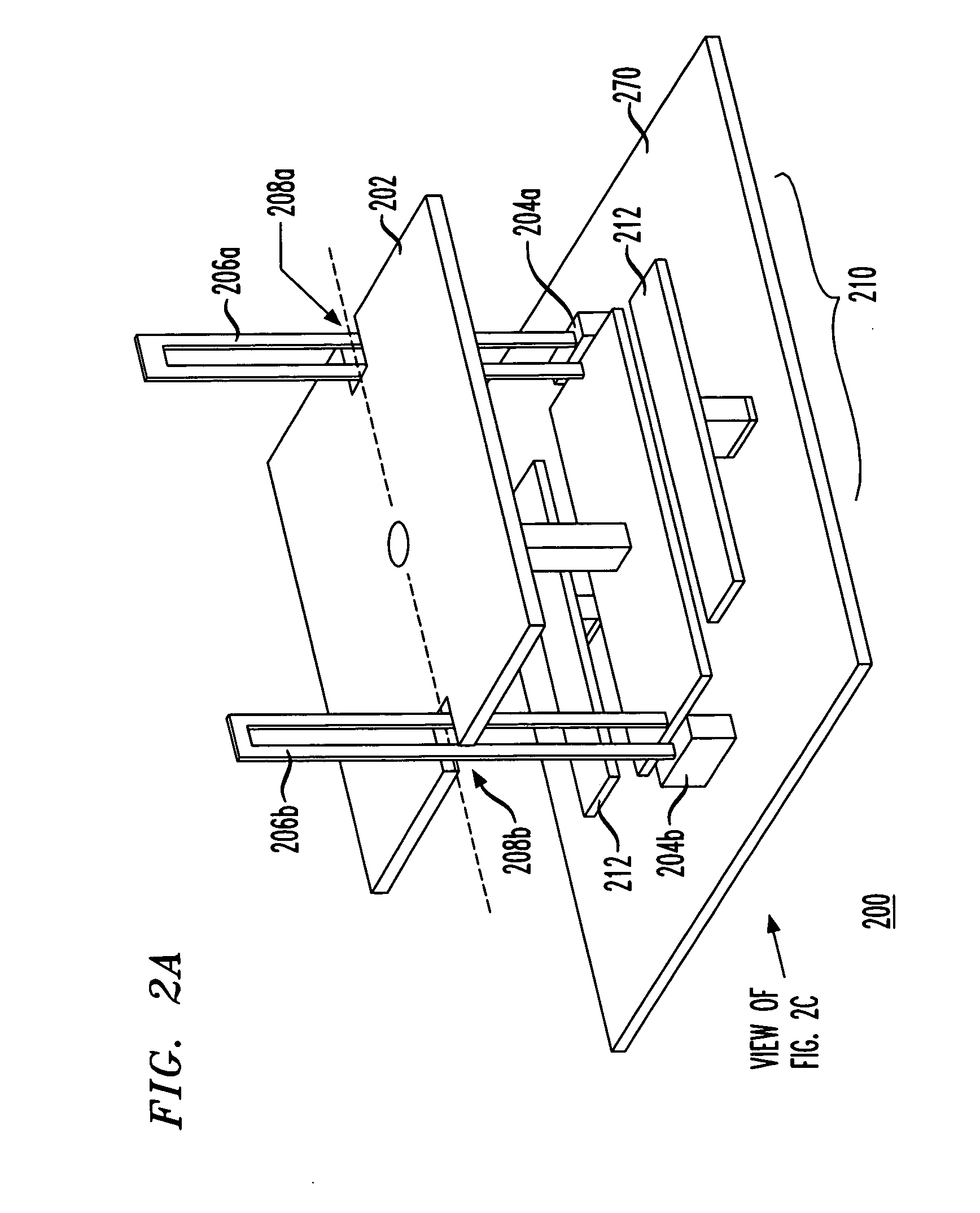
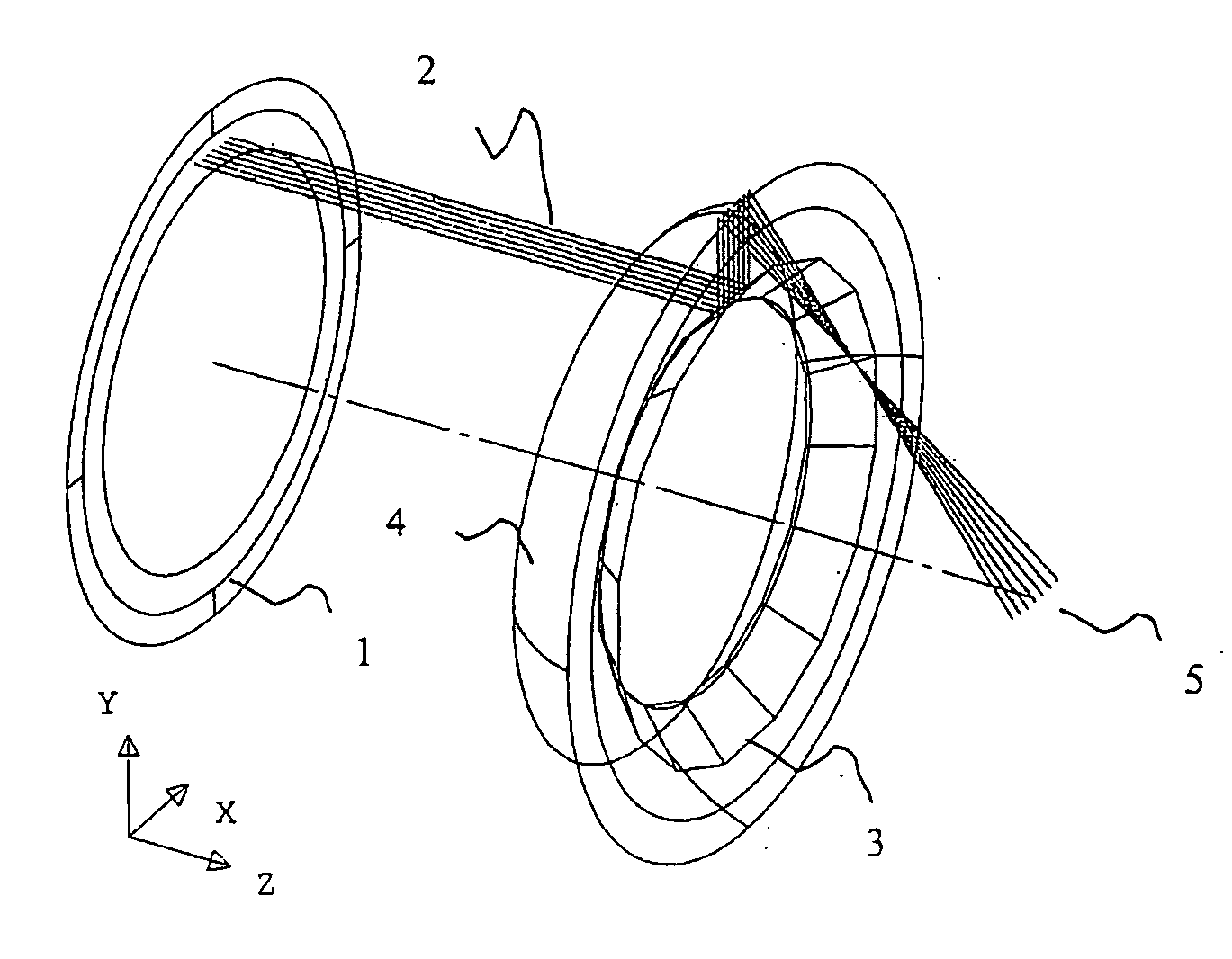
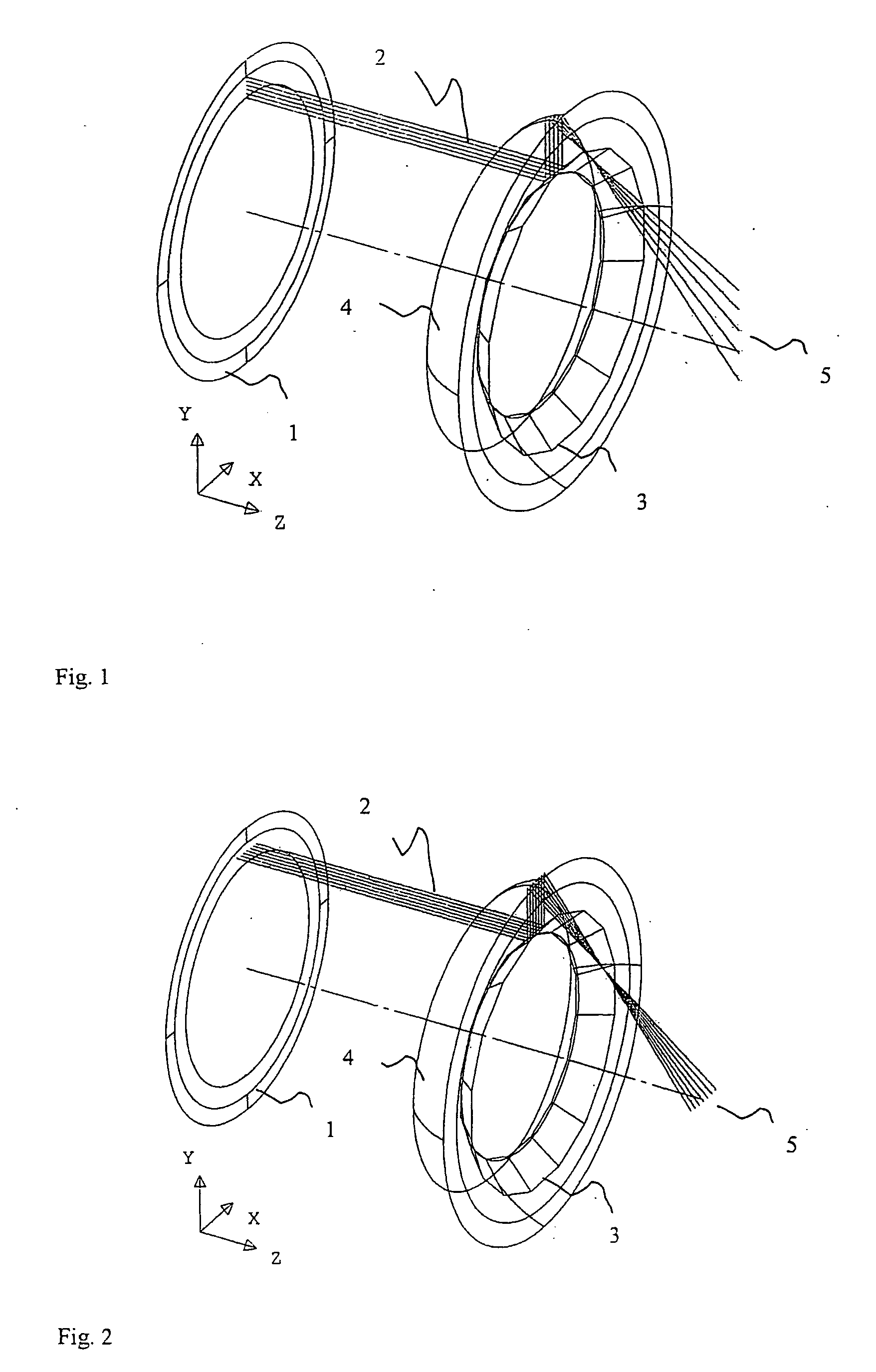
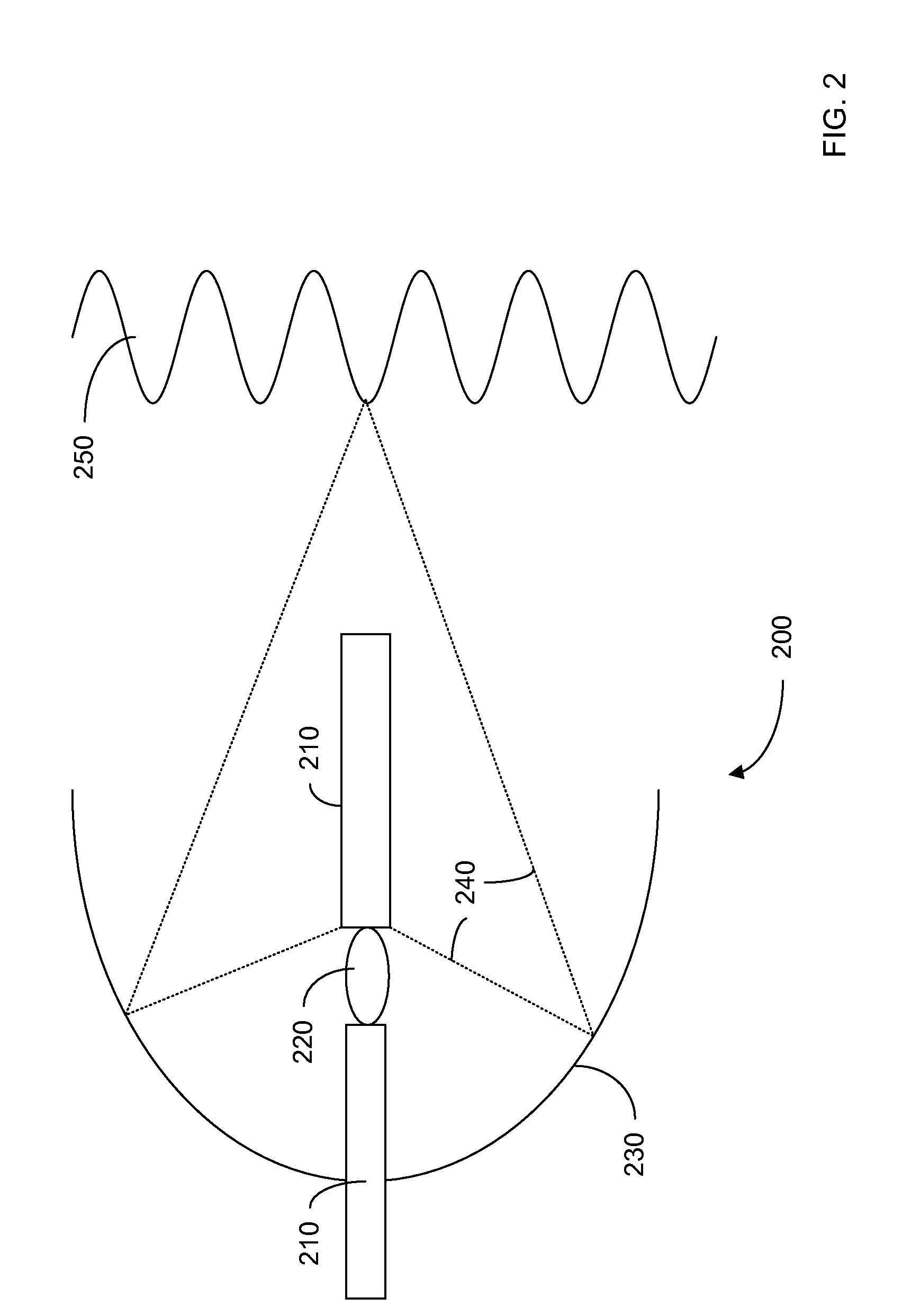
Optical telescope system with discontinuous pupil corrector and segmented primary mirror with spherical segments
InactiveUS6226121B1Inexpensive techniqueImproved and low-cost and high qualityMirrorsMicroscopesExit pupilPupil
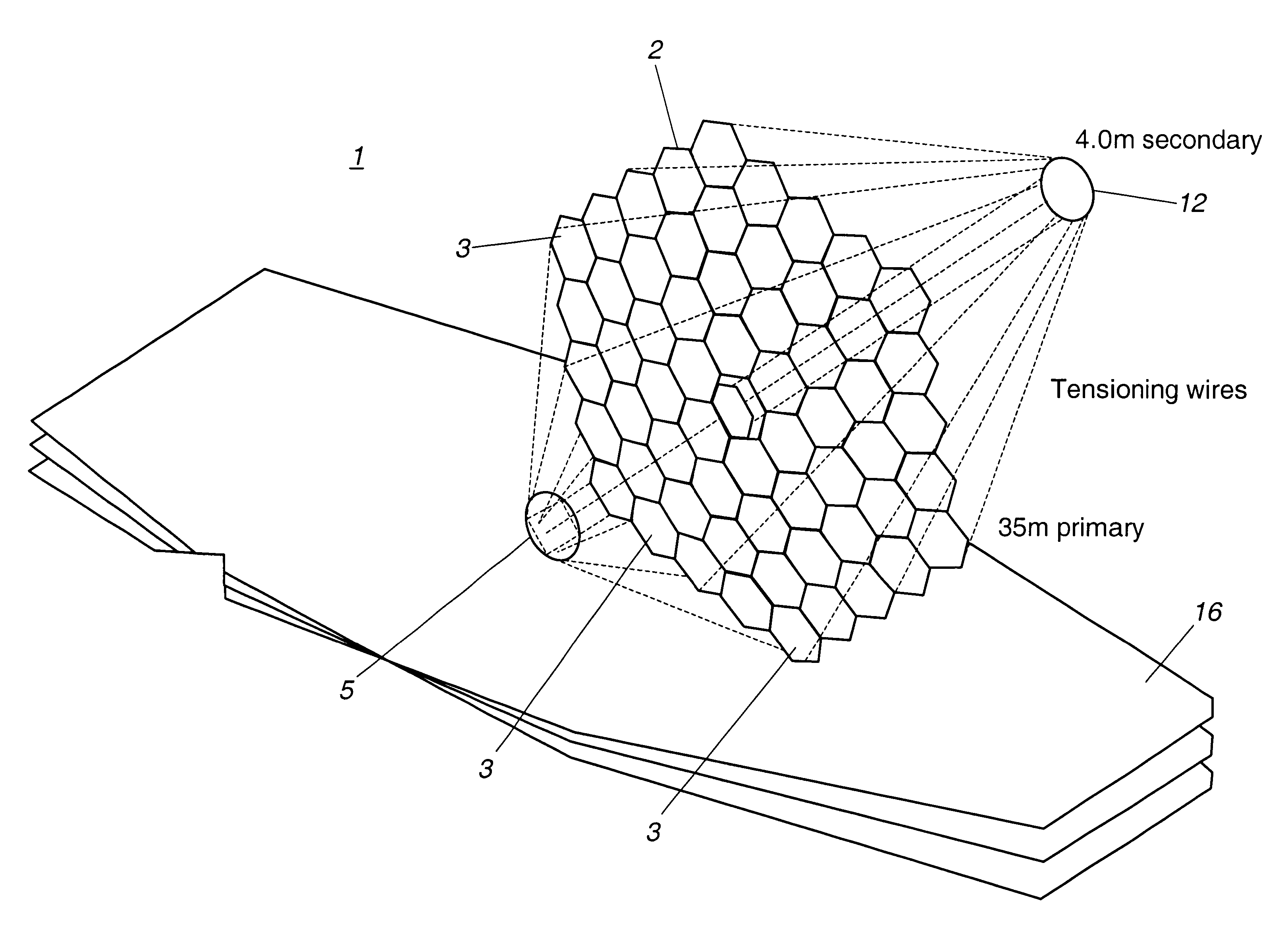
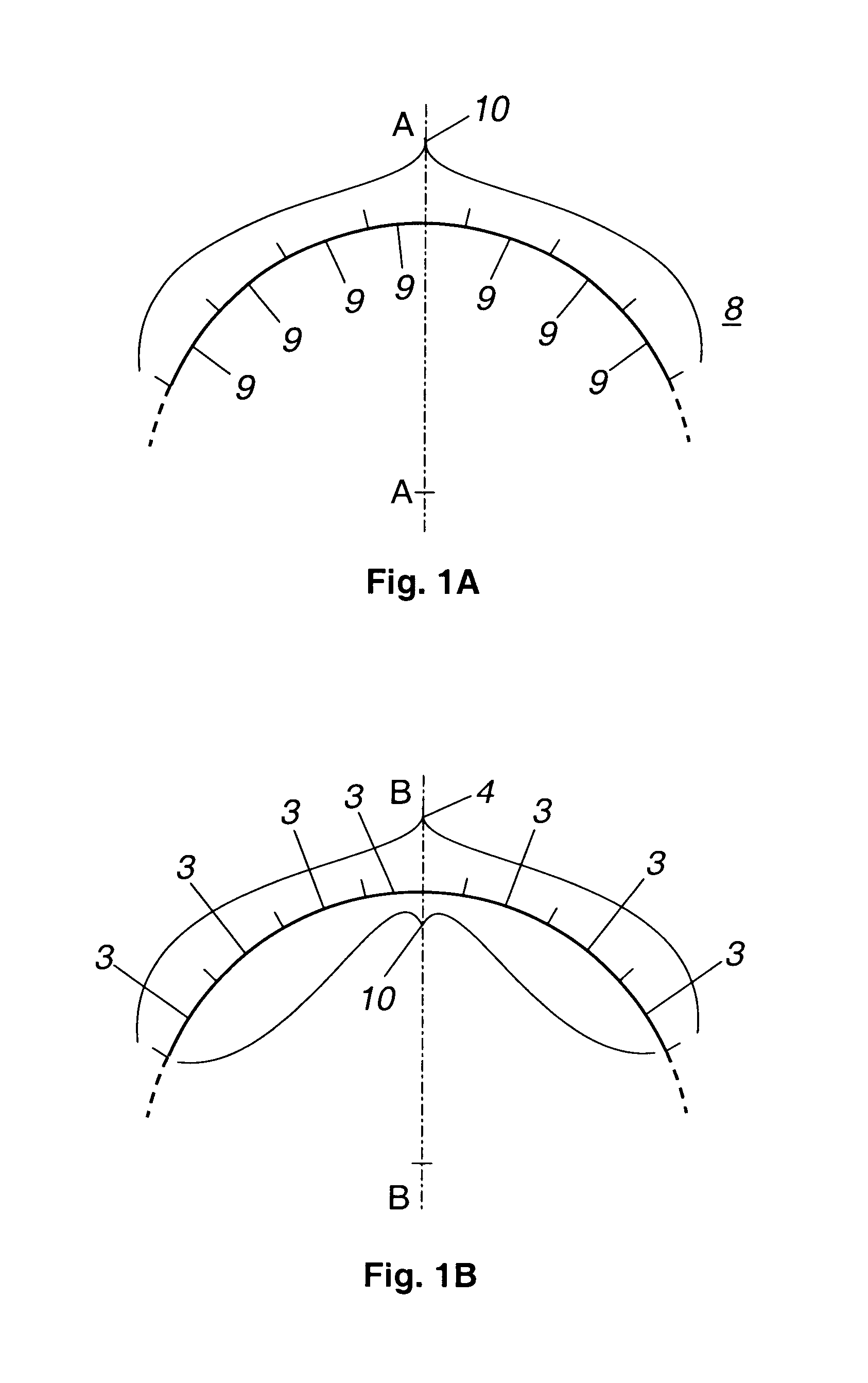
A large, low cost and high quality optical telescope system (1) includes a segmented primary mirror (2) having a plurality of spherical mirror segments (3) arranged in a non-spherical shape (4), a parabolic shape in the disclosed embodiment, so that the rays incident upon the individual spherical mirror segments stay separated at an exit pupil (5) of the system, allowing for correction of aberrations. A discontinuous pupil corrector in the form of a segmented mirror (7) having a plurality of aspheric correction terms in it, is located at the exit pupil for correction of aberrations introduced from respective ones of the plurality of spherical mirror segments of the primary mirror. The discontinuous pupil corrector preferably is a segmented deformable mirror. The telescope system and related method can achieve diffraction limited performance for very large systems. The disclosed embodiment is a 35 meter aperture, deployable space telescope system. Inexpensive replication techniques can be used for making the spherical primary mirror segments.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
MEMS hierarchically-dimensioned optical mirrors and methods for manufacture thereof
MEMS hierarchically-dimensioned optical mirrors, each comprising a substrate, a plurality of spacers disposed on the substrate, a plurality of piezoelectric / electrostrictive cantilever microactuators disposed on the plurality of spacers, and a monolithic deformable mirror or a segmented mirror array disposed on the plurality of the cantilever assemblies, having significantly improved overall device performances owing to the use of the cantilever microactuators based on relaxor ferroelectric single crystal materials and / or other piezoelectric / electrostrictive materials, are disclosed along with methods of manufacturing such devices.
Owner:WU XINGTAO
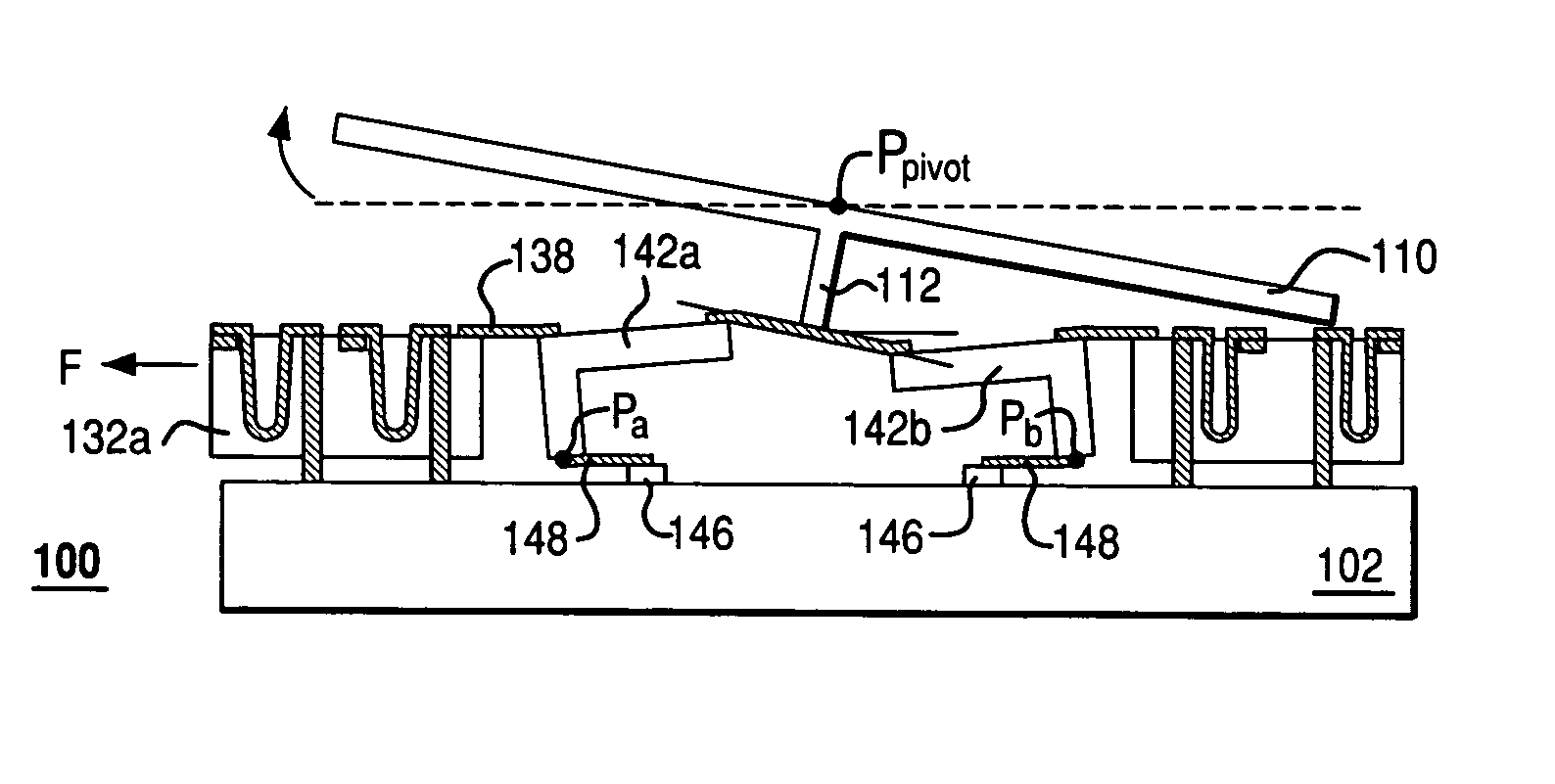
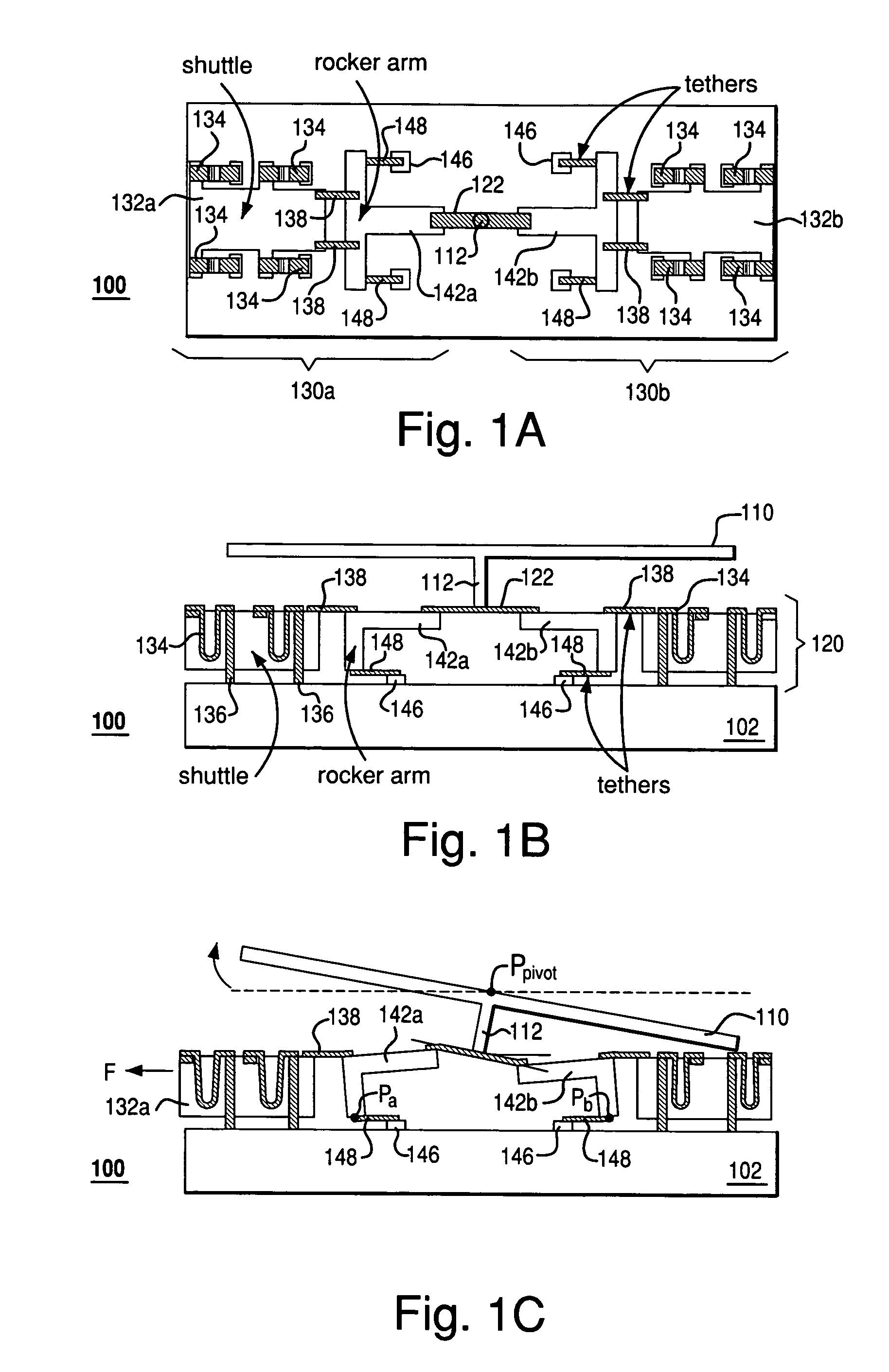
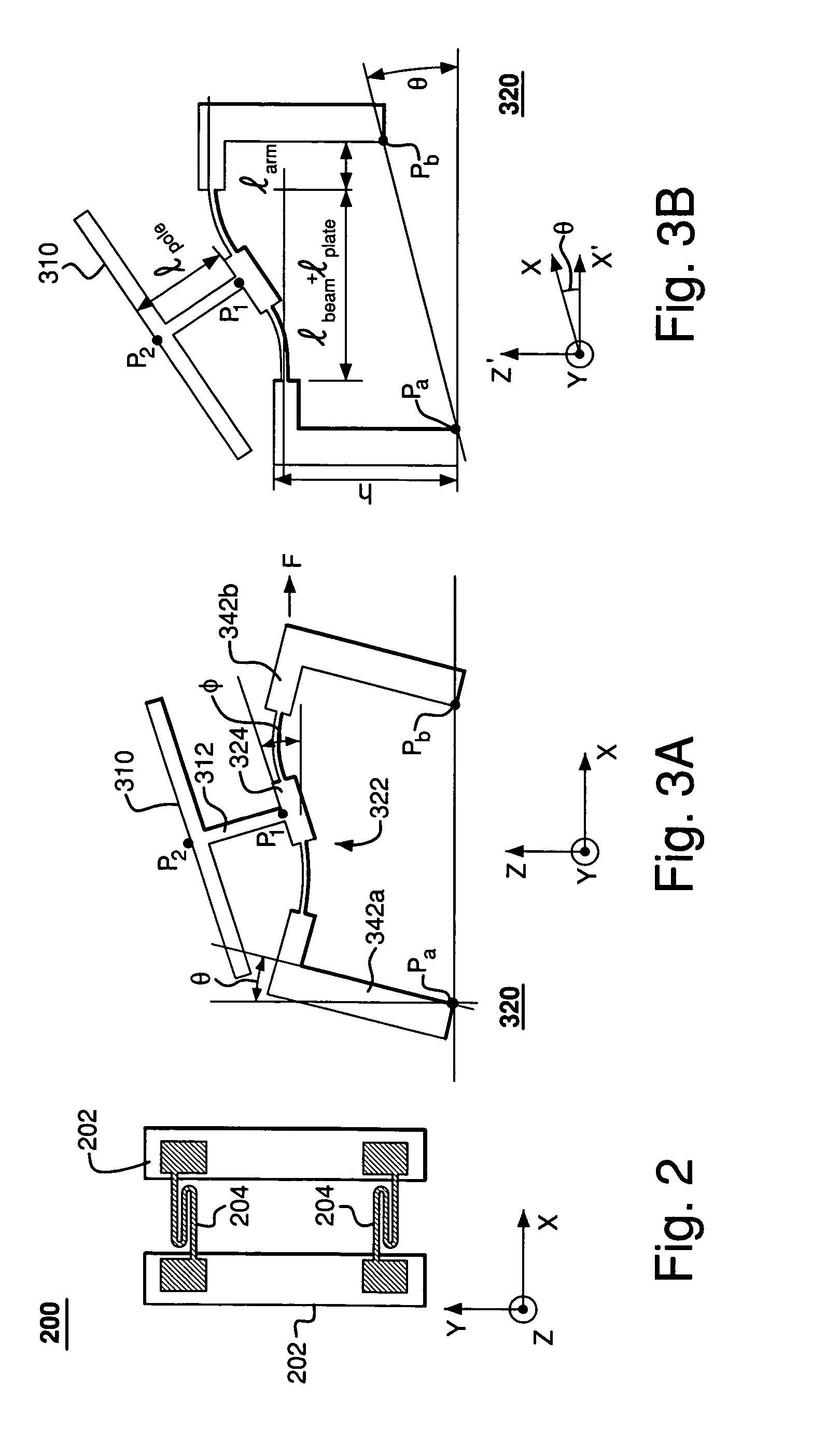
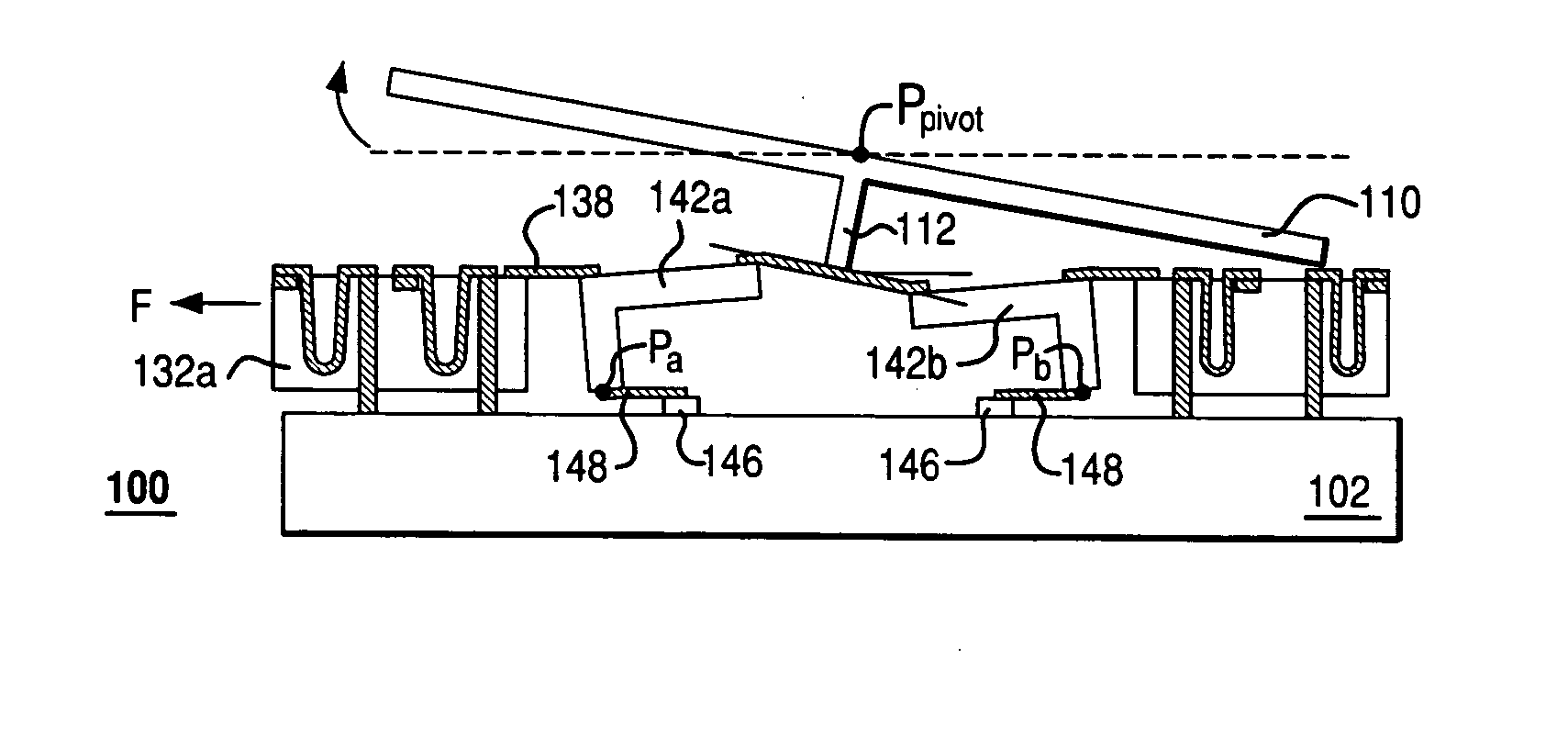
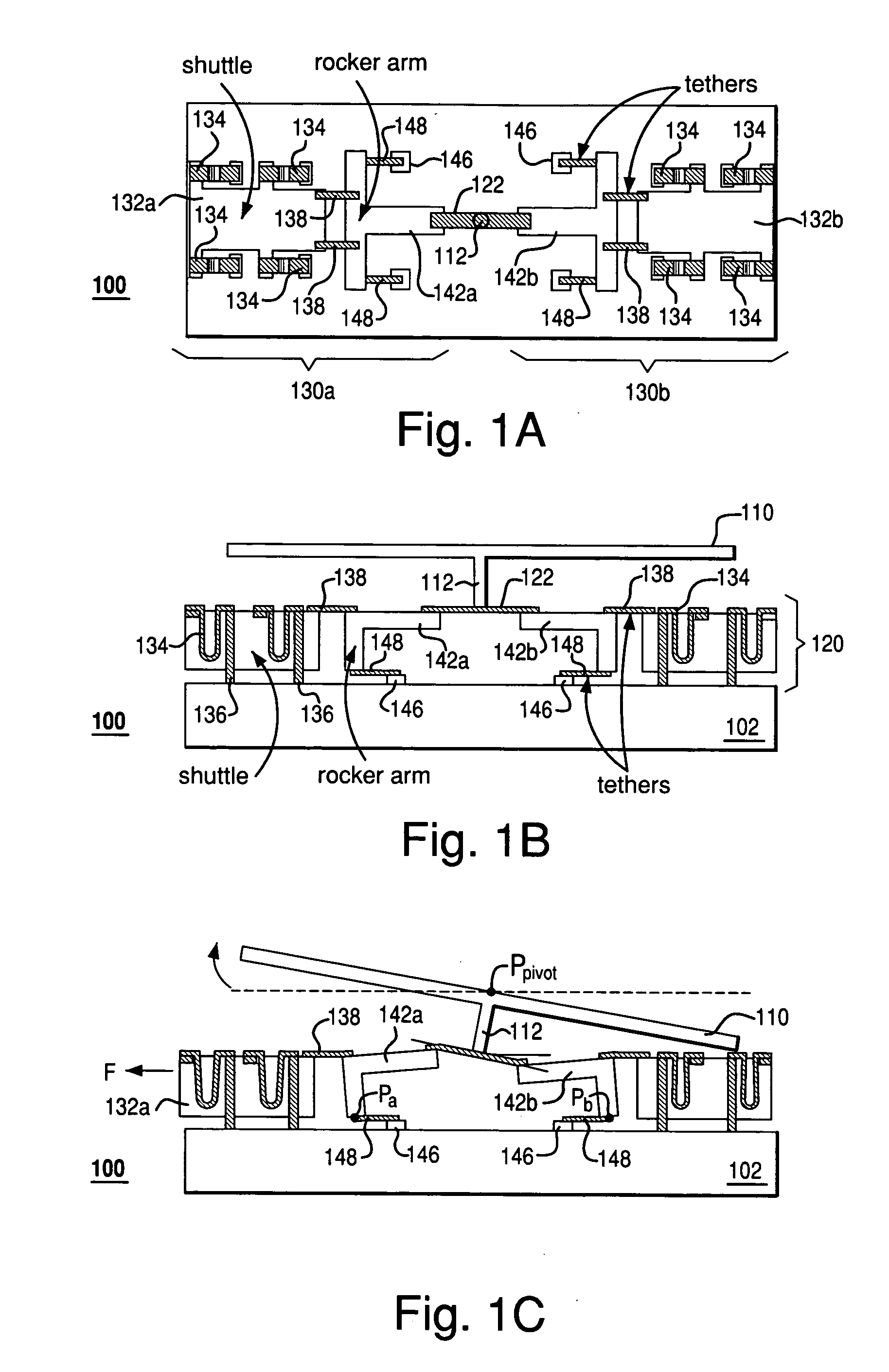
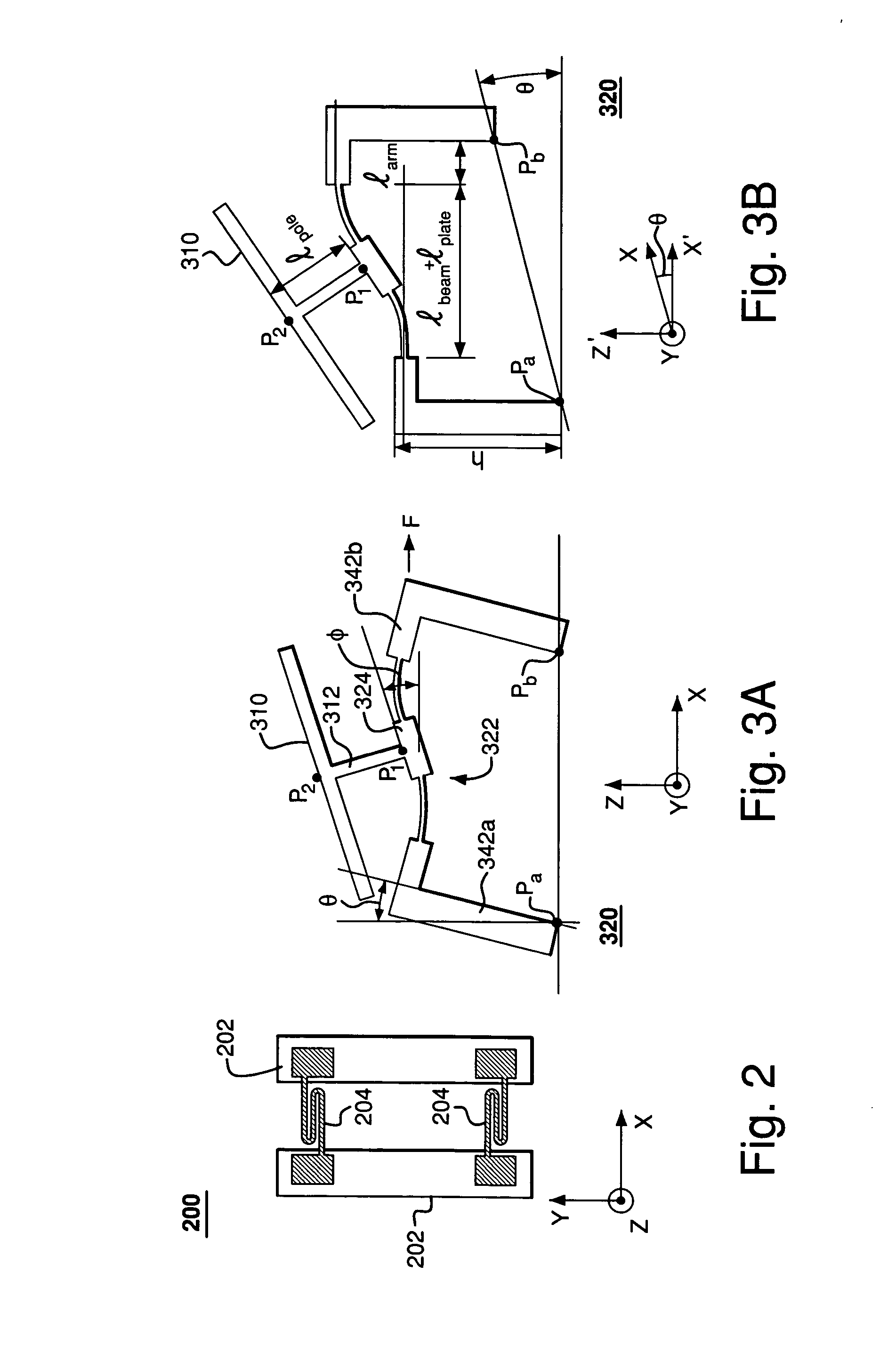
Rocker-arm actuator for a segmented mirror
InactiveUS7355317B2Reduces potential physical interferenceLarge fill factorElectrostatic motorsOptical elementsFill factorActuator
A MEMS device having a movable plate supported on a substrate by a support structure that is hidden under the plate and yet which can be implemented to enable rotation of the plate with respect to the substrate about a rotation axis lying at the plate surface. As a result, the support structure does not take up any area within the plane of the plate, while enabling rotation of the plate, during which the plate does not substantially move sideways. The latter property reduces potential physical interference between neighboring plates in an arrayed MEMS device and enables implementation of a segmented mirror having relatively narrow gaps between adjacent segments and, thus, a relatively large fill factor, e.g., at least 98%.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
MEMS device for an adaptive optics mirror
ActiveUS20050200938A1Small lateral displacementSmall surface areaInfluence generatorsMountingsFill factorOptoelectronics
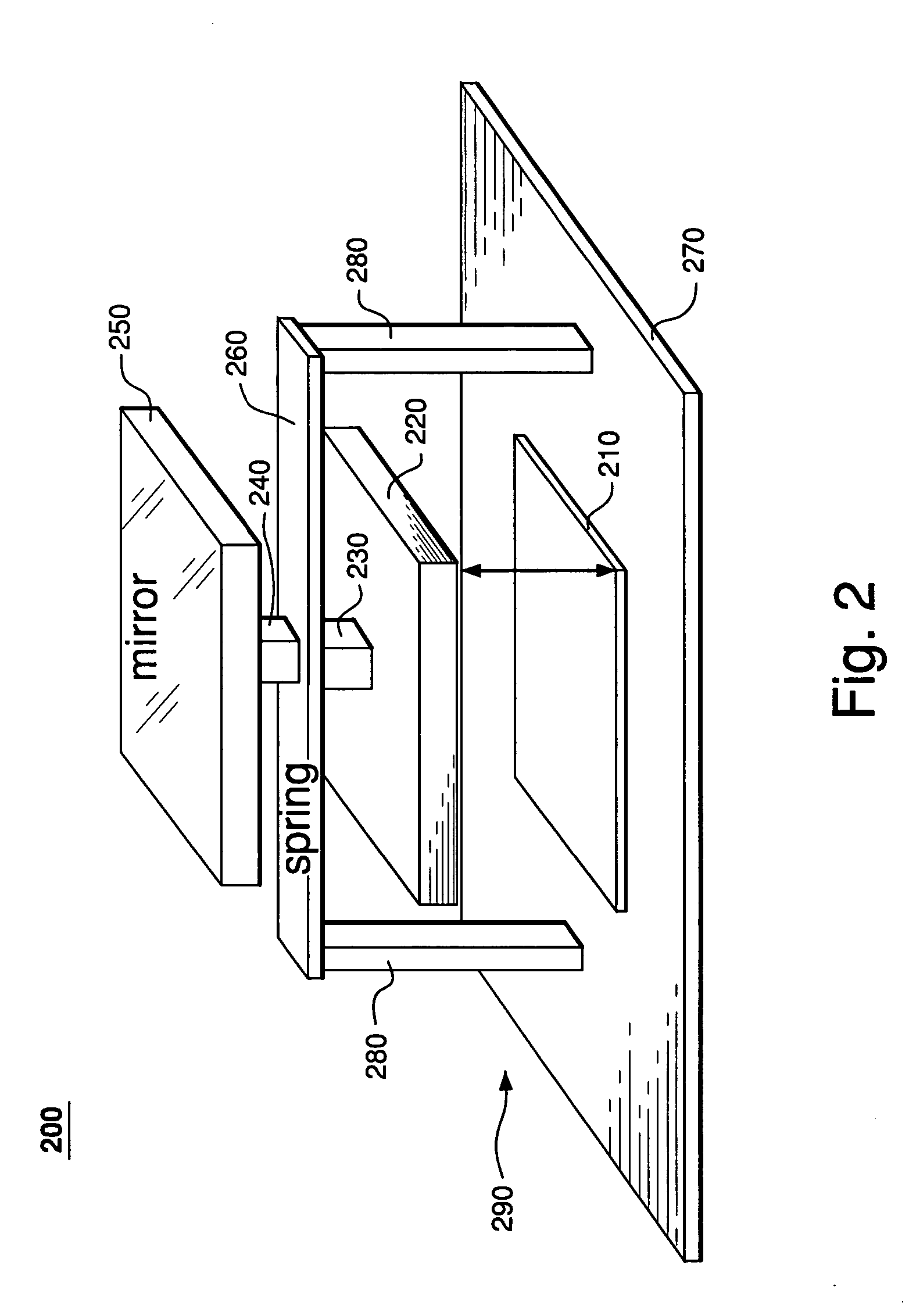
A MEMS device having a movable mirror pixel supported on a substrate and coupled to a motion actuator located between the mirror pixel and the substrate so as to enable rotation of the mirror pixel about an axis lying within the mirror plane. In one embodiment of the invention, the motion actuator has a movable electrode, on which the mirror pixel is mounted. The movable electrode is supported on the substrate by a pair of upright springs, each having two parallel segments joined at one end of the spring and disjoint at the other end. One disjoint segment end is coupled to the substrate, while the other disjoint segment end is coupled to the movable electrode. The end of the upright spring corresponding to the joined segment ends points away from the substrate such that (i) the spring body protrudes through a narrow slot in the mirror pixel and (ii) the mirror plane lies at about the mid-point of the spring. Advantageously, a mirror pixel of the invention enables implementation of a segmented mirror with tightly spaced mirror pixels providing a fill factor higher than about 98%.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Darkfield illumination system
Owner:CARL ZEISS JENA GMBH
Rocker-arm actuator for a segmented mirror
InactiveUS20060220492A1Reduces potential physical interferenceLarge fill factorElectrostatic motorsOptical elementsFill factorEngineering
A MEMS device having a movable plate supported on a substrate by a support structure that is hidden under the plate and yet which can be implemented to enable rotation of the plate with respect to the substrate about a rotation axis lying at the plate surface. As a result, the support structure does not take up any area within the plane of the plate, while enabling rotation of the plate, during which the plate does not substantially move sideways. The latter property reduces potential physical interference between neighboring plates in an arrayed MEMS device and enables implementation of a segmented mirror having relatively narrow gaps between adjacent segments and, thus, a relatively large fill factor, e.g., at least 98%.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
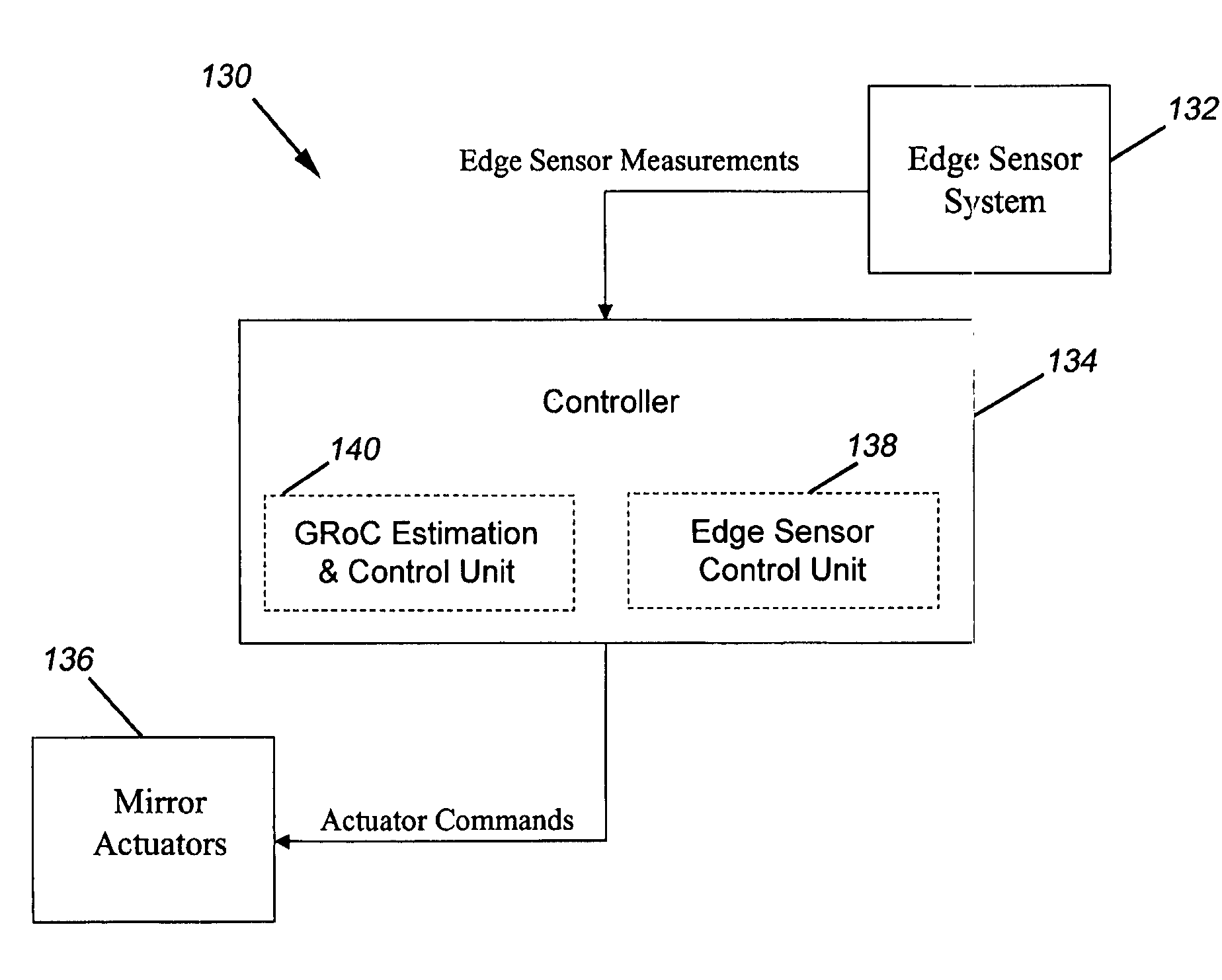
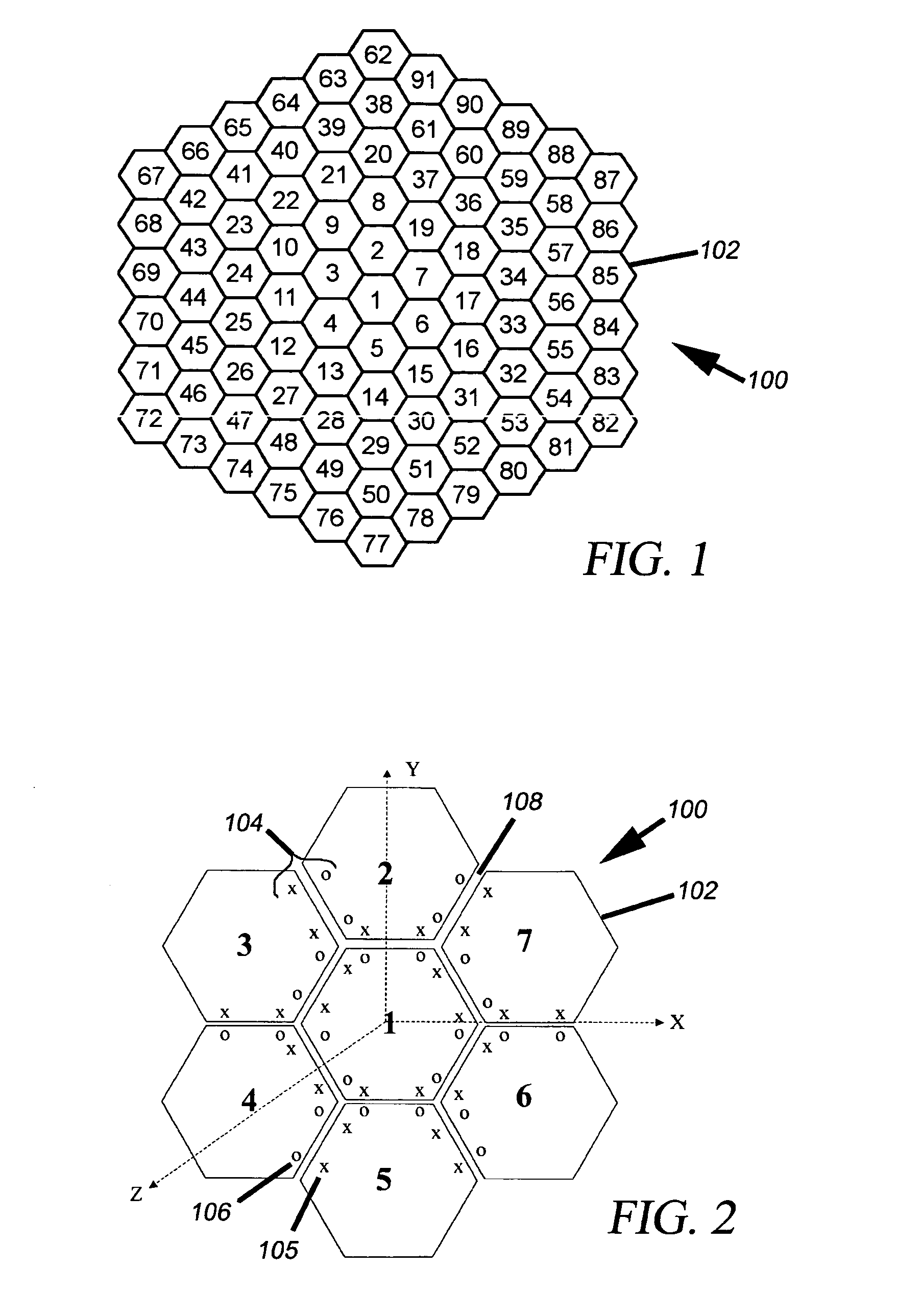
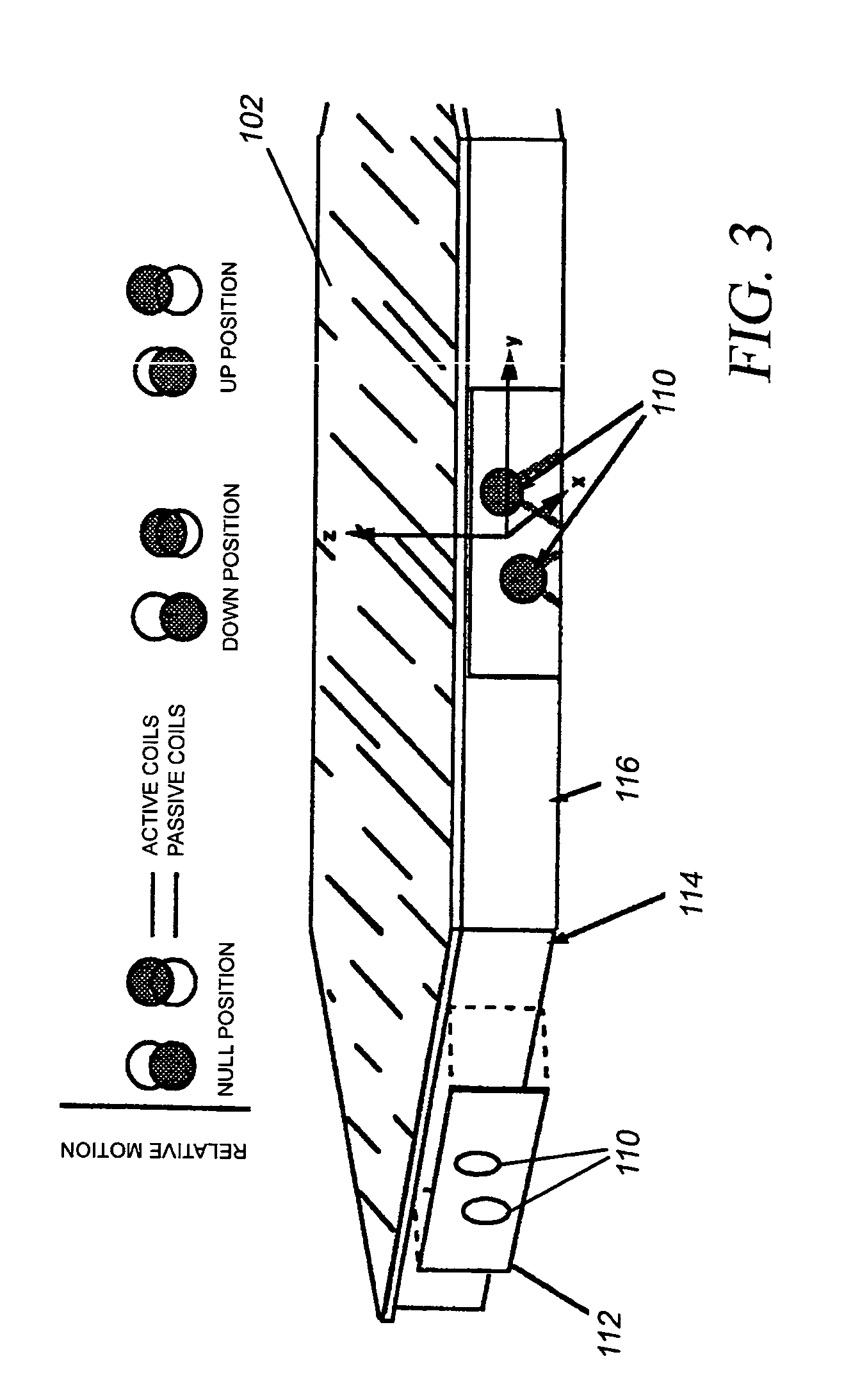
Global radius of curvature estimation and control system for segmented mirrors
InactiveUS7050161B1Reduce errorsError introduced by removing the predetermined boundary conditions is decreasedMirrorsUsing optical meansControl systemOptimal control
An apparatus controls positions of plural mirror segments in a segmented mirror with an edge sensor system and a controller. Current mirror segment edge sensor measurements and edge sensor reference measurements are compared with calculated edge sensor bias measurements representing a global radius of curvature. Accumulated prior actuator commands output from an edge sensor control unit are combined with an estimator matrix to form the edge sensor bias measurements. An optimal control matrix unit then accumulates the plurality of edge sensor error signals calculated by the summation unit and outputs the corresponding plurality of actuator commands. The plural mirror actuators respond to the actuator commands by moving respective positions of the mirror segments. A predetermined number of boundary conditions, corresponding to a plurality of hexagonal mirror locations, are removed to afford mathematical matrix calculation.
Owner:NASA
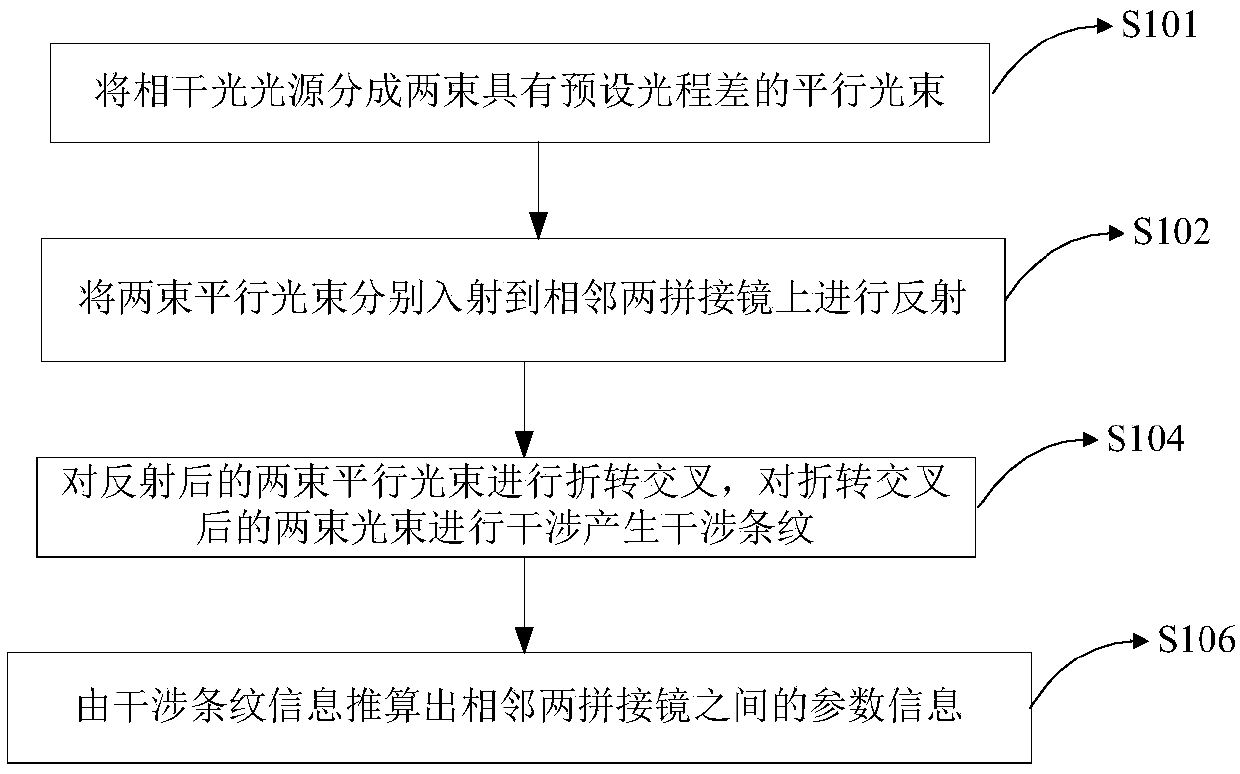
Adjacent segmented mirror detection method and detection system
ActiveCN109556513ASolve temperature problemsSolve Humidity ProblemsUsing optical meansLight beamOptoelectronics
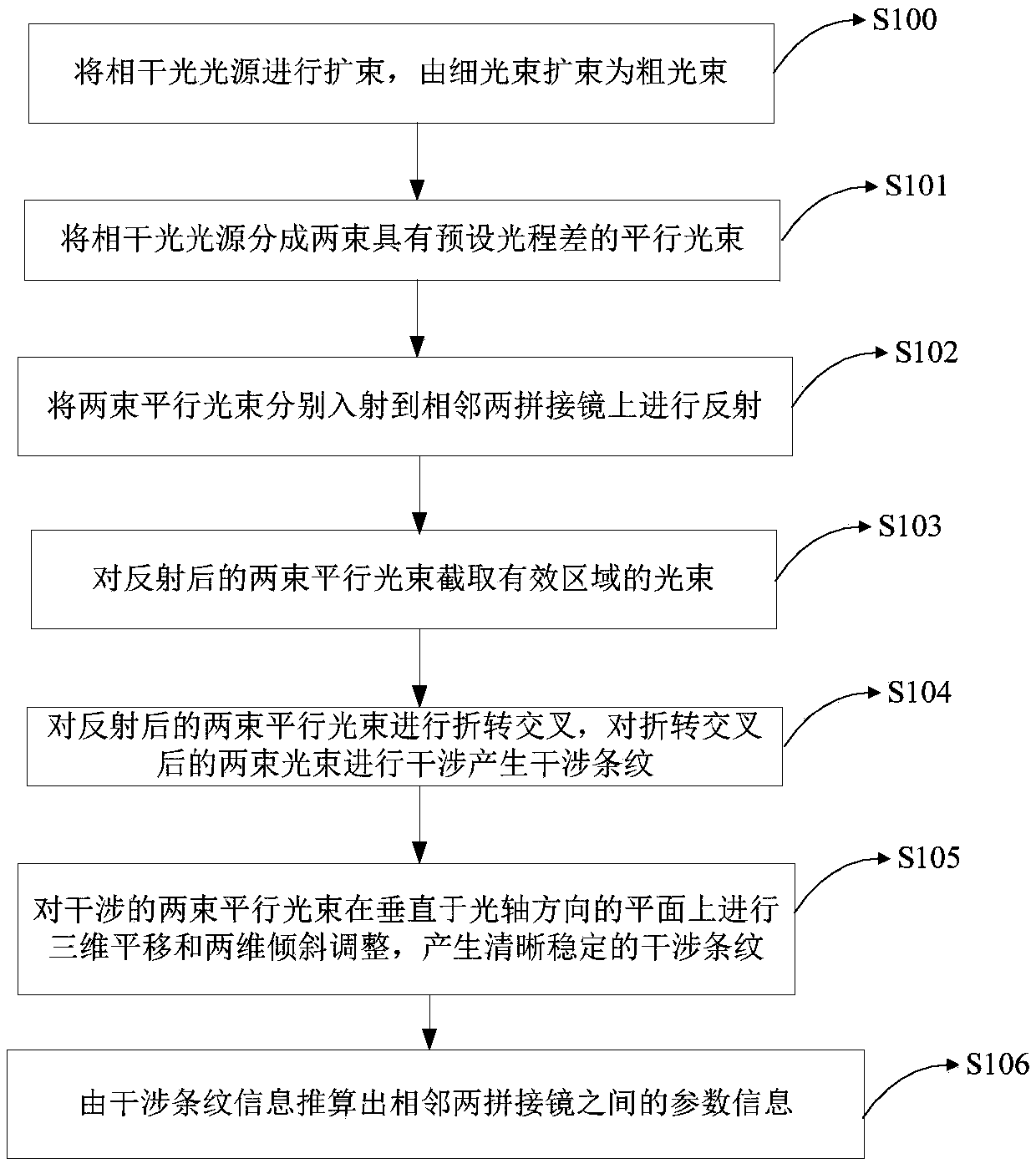
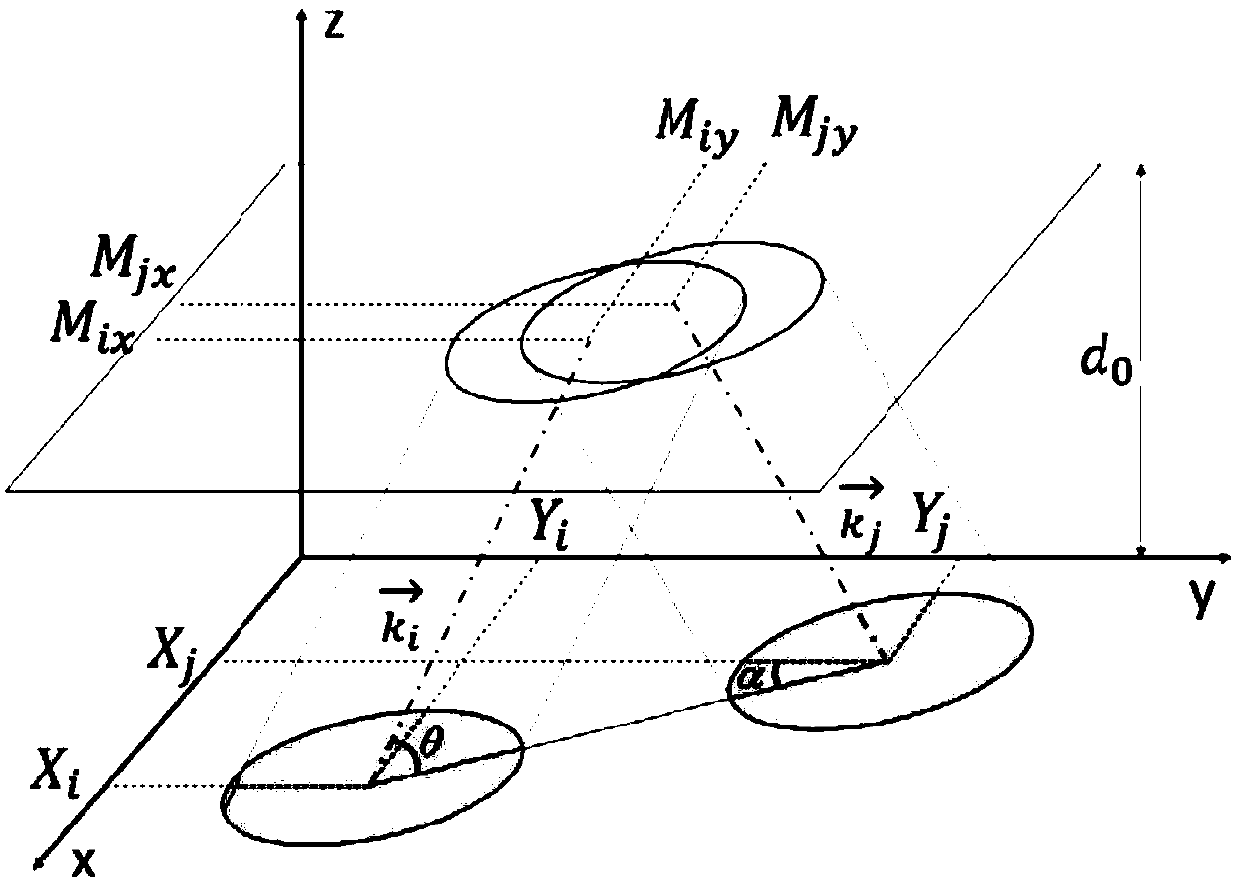
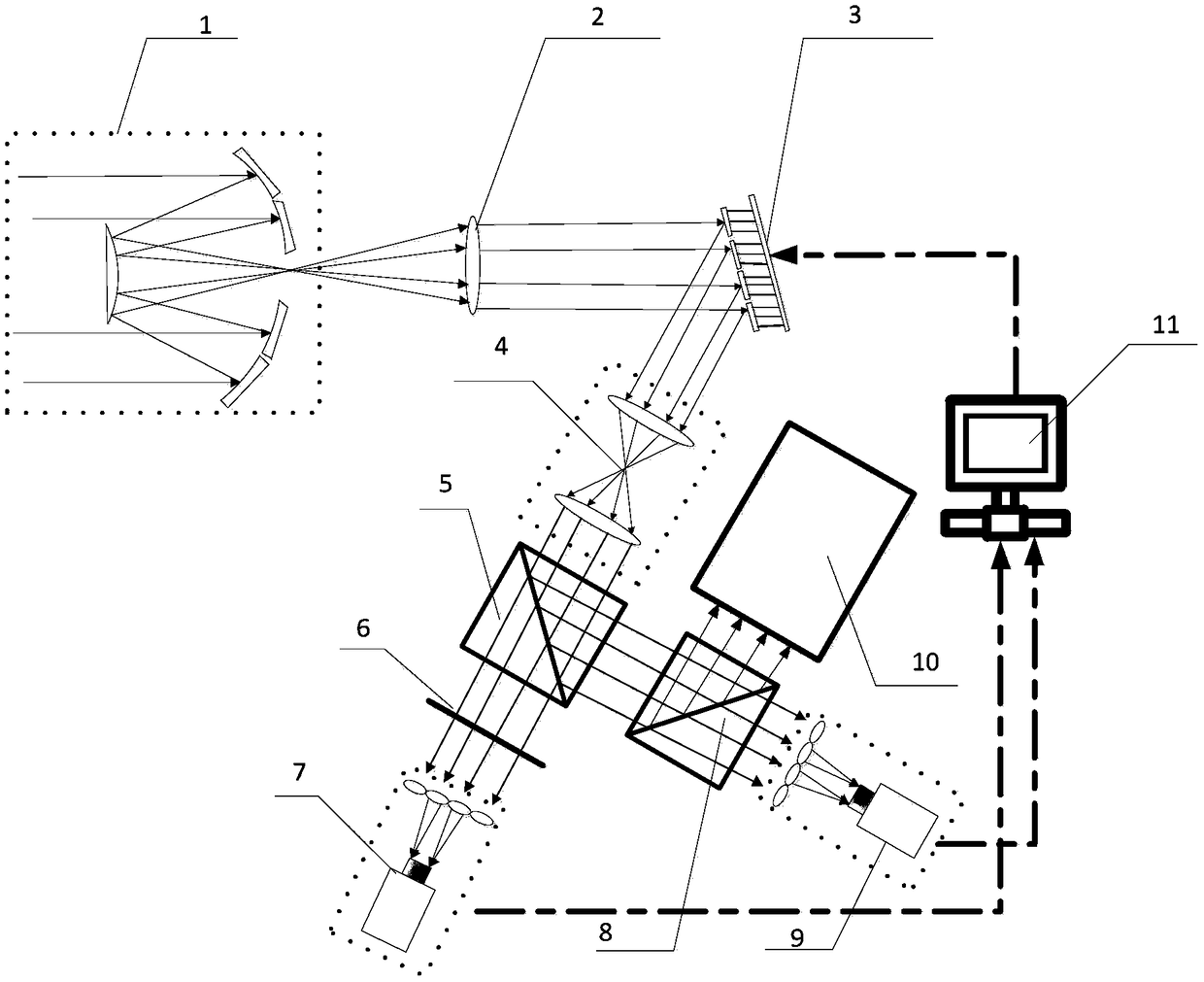
The invention relates to the field of optics, in particular to an adjacent segmented mirror detection method and detection system. The method and system comprise the following steps of: dividing the coherent light source into two parallel light beams having a predetermined optical path difference; enabling the two parallel light beams to be respectively incident on the two adjacent segmented mirrors for reflection; folding and crossing the two parallel light beams after reflection, and interfering the two light beams after the folding and crossing to generate interference fringes; and calculating the parameter information between two adjacent segmented mirrors according to the interference fringe information. Compared with an existing edge sensor detection method, the method is higher in precision, convenient to detach and maintain and free of being affected by environmental temperature, humidity, dust and the like. Moreover, the method is easy to operate during the adjustment process,and solves the problem that the traditional edge sensor is susceptible to environmental temperature, humidity, dust and the like. The method is suitable for segmented telescope mirrors that require high-precision confocal co-alignment. The structure is simple, the feasibility is strong, the installation is convenient, and the unit integration function is provided.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel co-phase detection method and device for segmented telescope
ActiveCN108827596AQuickly adjust the piston errorHigh precisionTesting optical propertiesBeam splitterControl system
A novel co-phase detection method and device for a segmented telescope are provided. The device comprises a segmented mirror telescope, a collimating lens, a segmented deformable mirror, a 4f system,a first beam splitter, a second beam splitter, a segmented mirror MASK, a Shaker-Hartmann wavefront detector, an imaging system and a control system. A white-light (400nm to 700nm) incoherent patternand a white-light ideal Airy disk pattern are used as a template, a segmented mirror piston error is calculated by using a cross-correlation algorithm, and the segmented mirror piston error is quicklyadjusted by adjusting the segmented deformable mirror. The detection method and a photoelectric detection system have unlimited ranges and high precision and quickly detect and adjust the piston error without increasing the complexity of an existing detection system.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
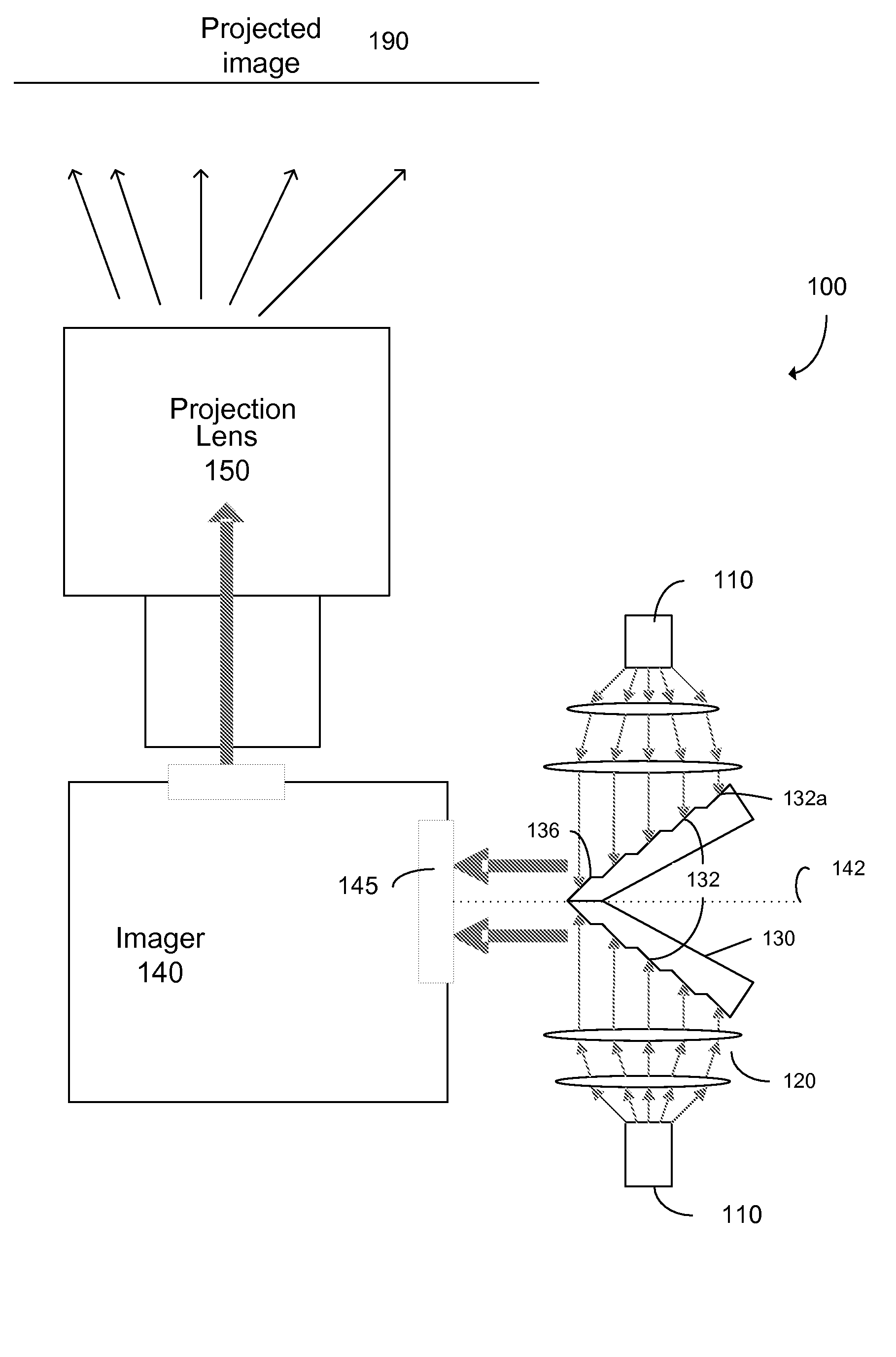
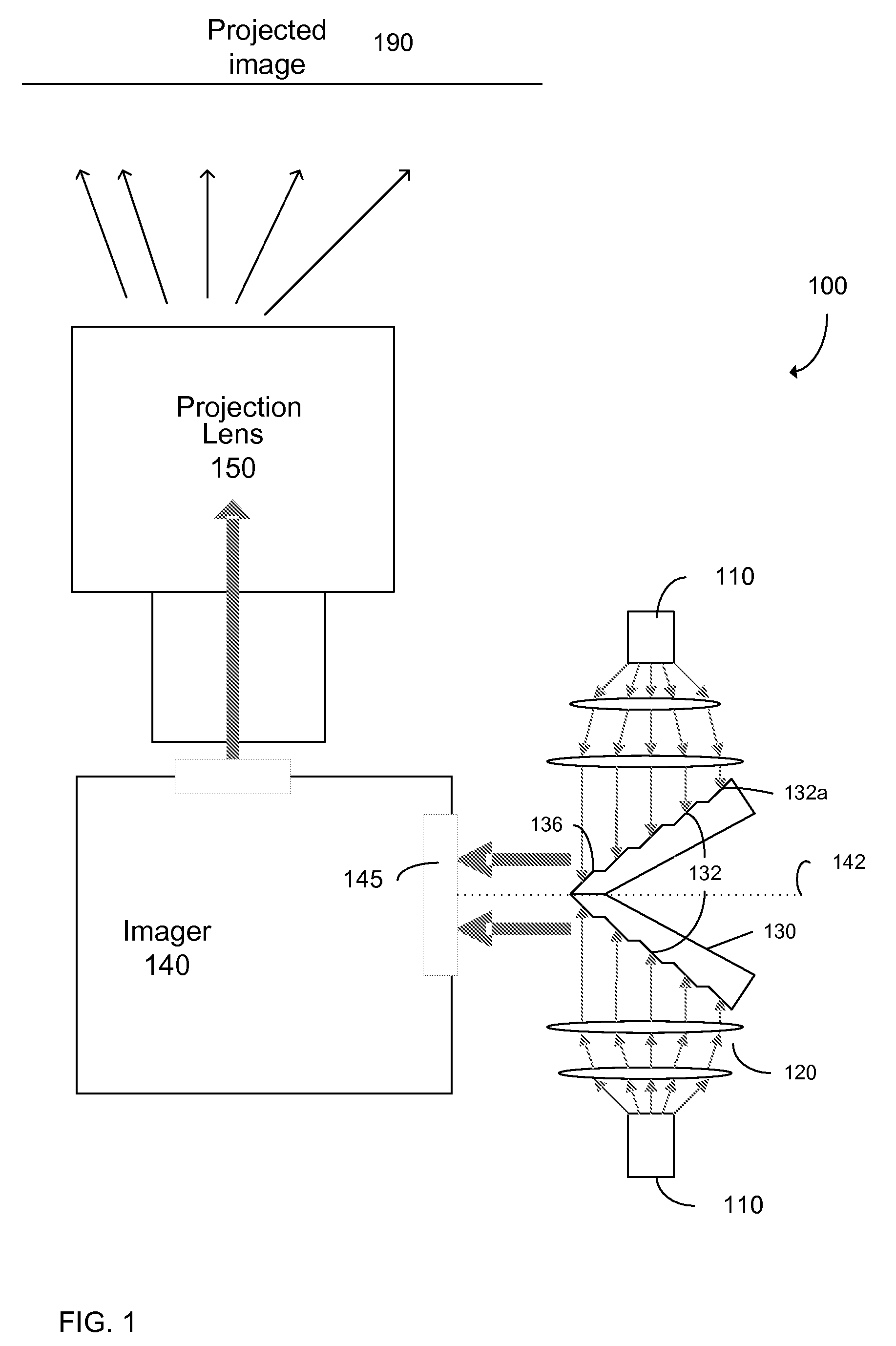
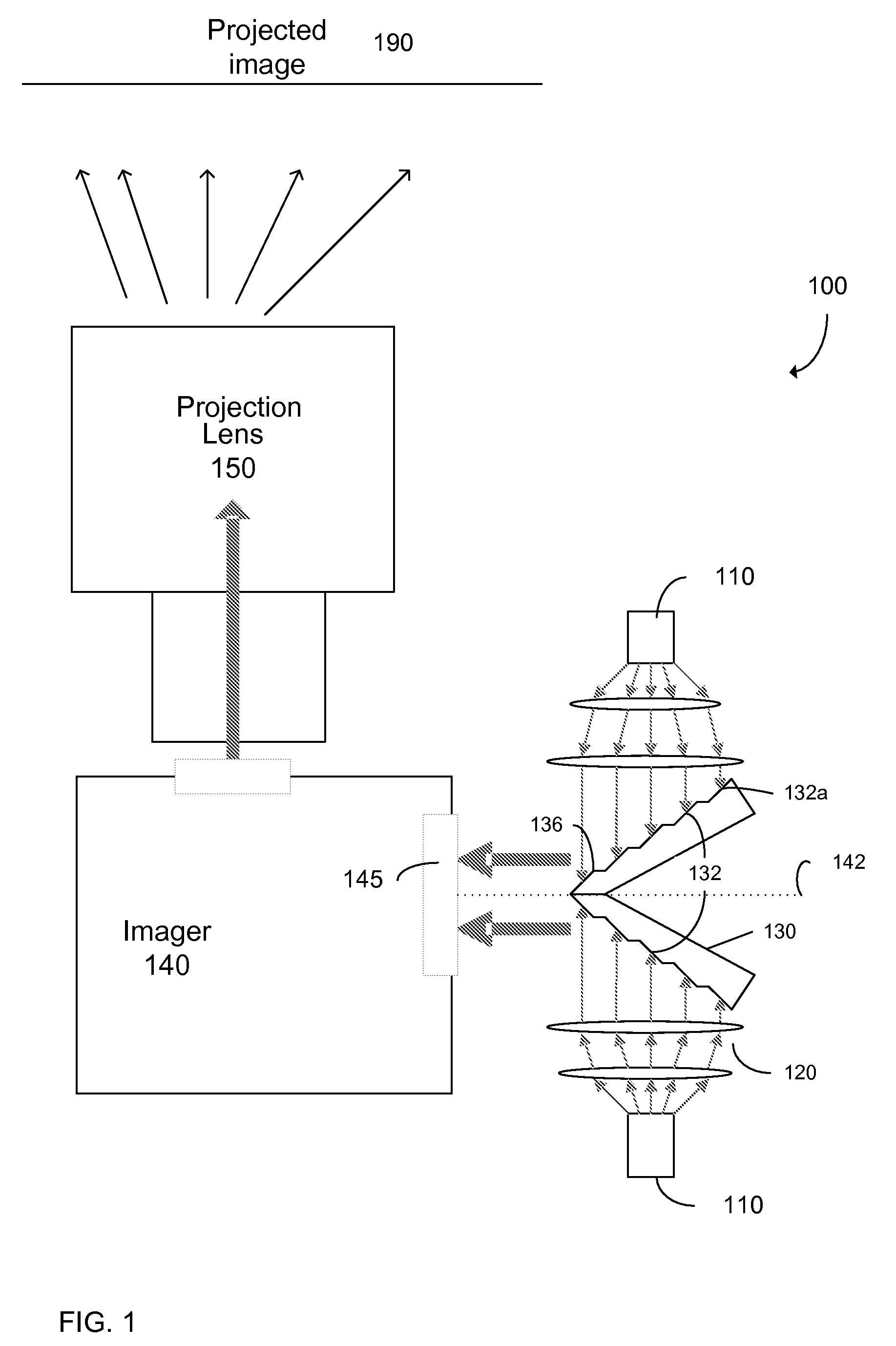
High intensity image projector using sectional mirror
ActiveUS20100110390A1Increase light intensityIncrease brightnessProjectorsColor television detailsHigh intensityPupil
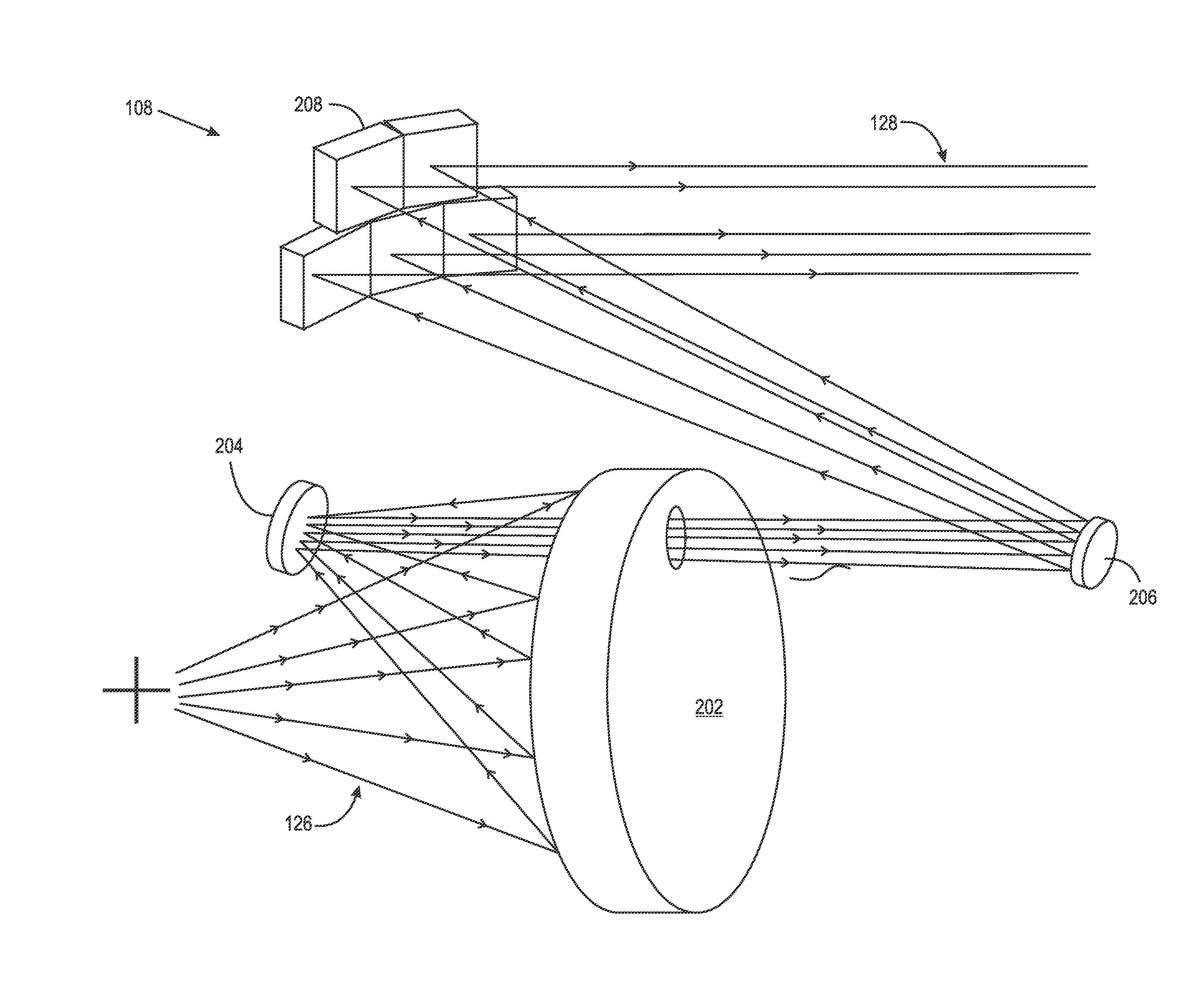
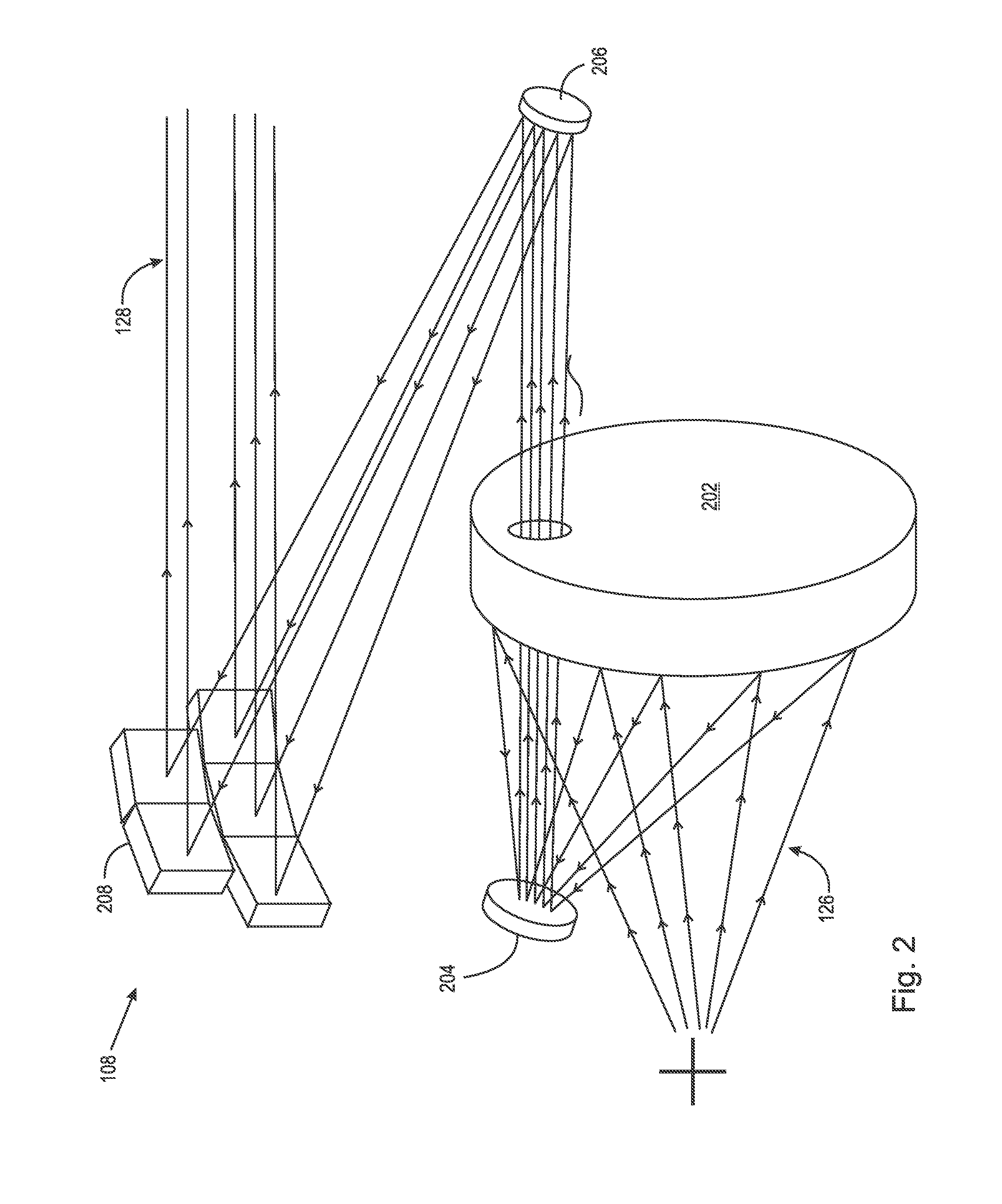
Image projectors with increased light intensity and methods for providing brighter images are provided. Image projectors, described herein, can provide the brightness while still providing any or all of compactness, low power consumption, and long lifetime. To increase brightness, sectional mirrors are used to respectively compress the light from two light sources into a single pupil (e.g. an aperture) of an imaging device. The compression can be accomplished by regions (e.g. sections) of the mirror having different angles with respect to the pupil. Relatively little light may be lost in the compression since minima for a light intensity pattern from a light source may occur between the regions that reflect the light.
Owner:PROJECTIONDESIGN
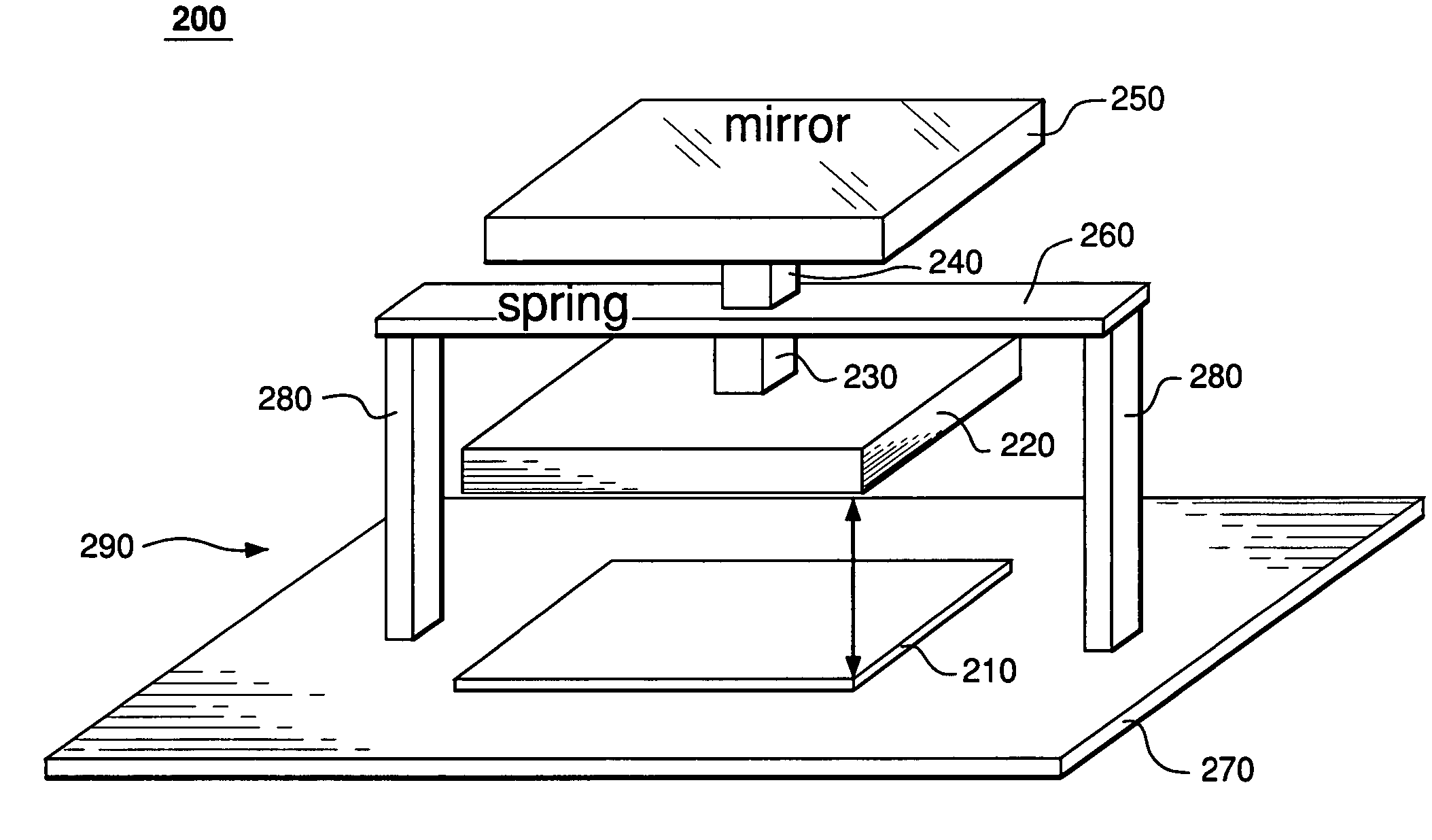
Reflector device
ActiveUS20060221473A1Suppress self weight deformationImprove accuracyMirrorsTelescopesPhysicsReference cell
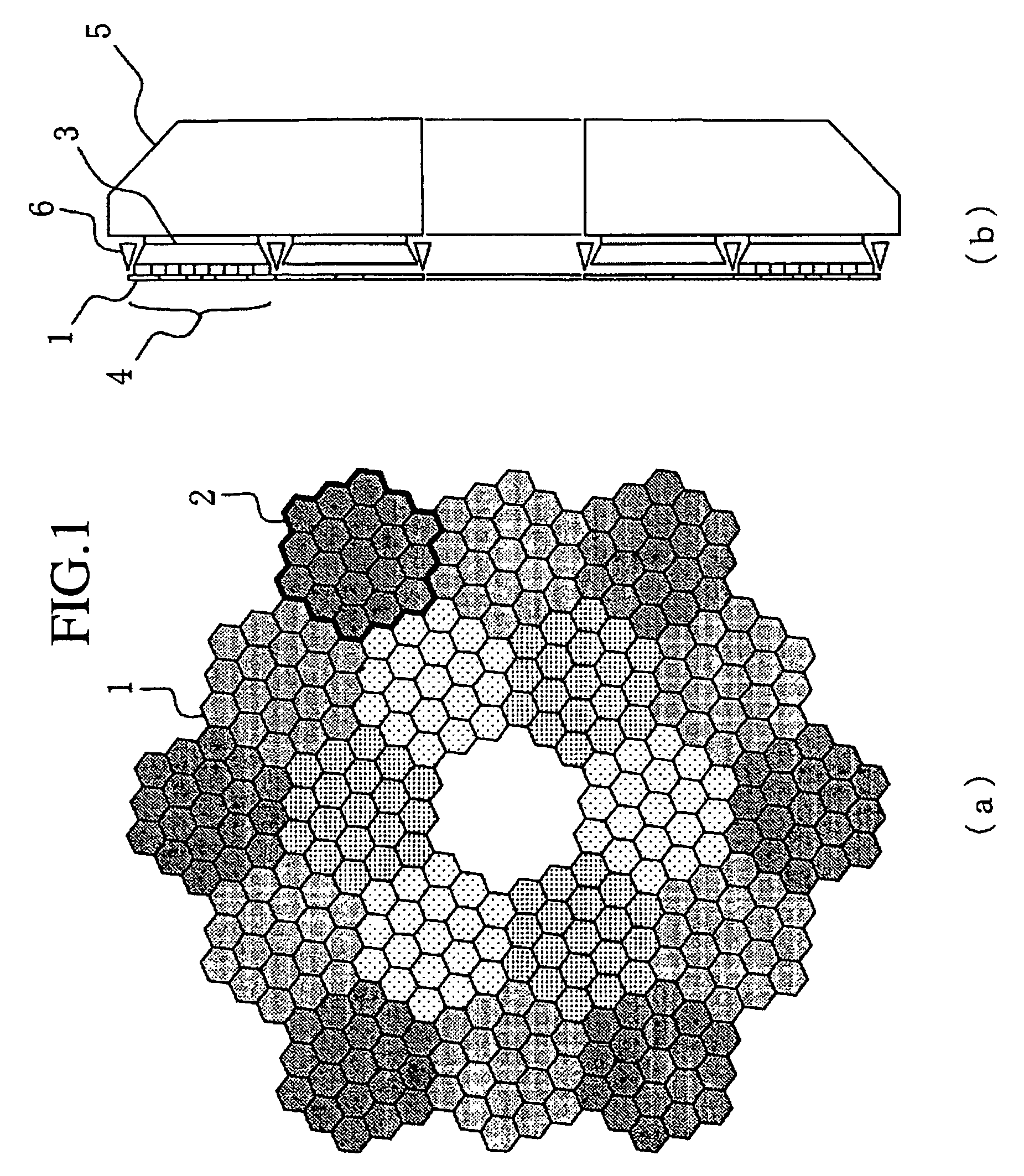
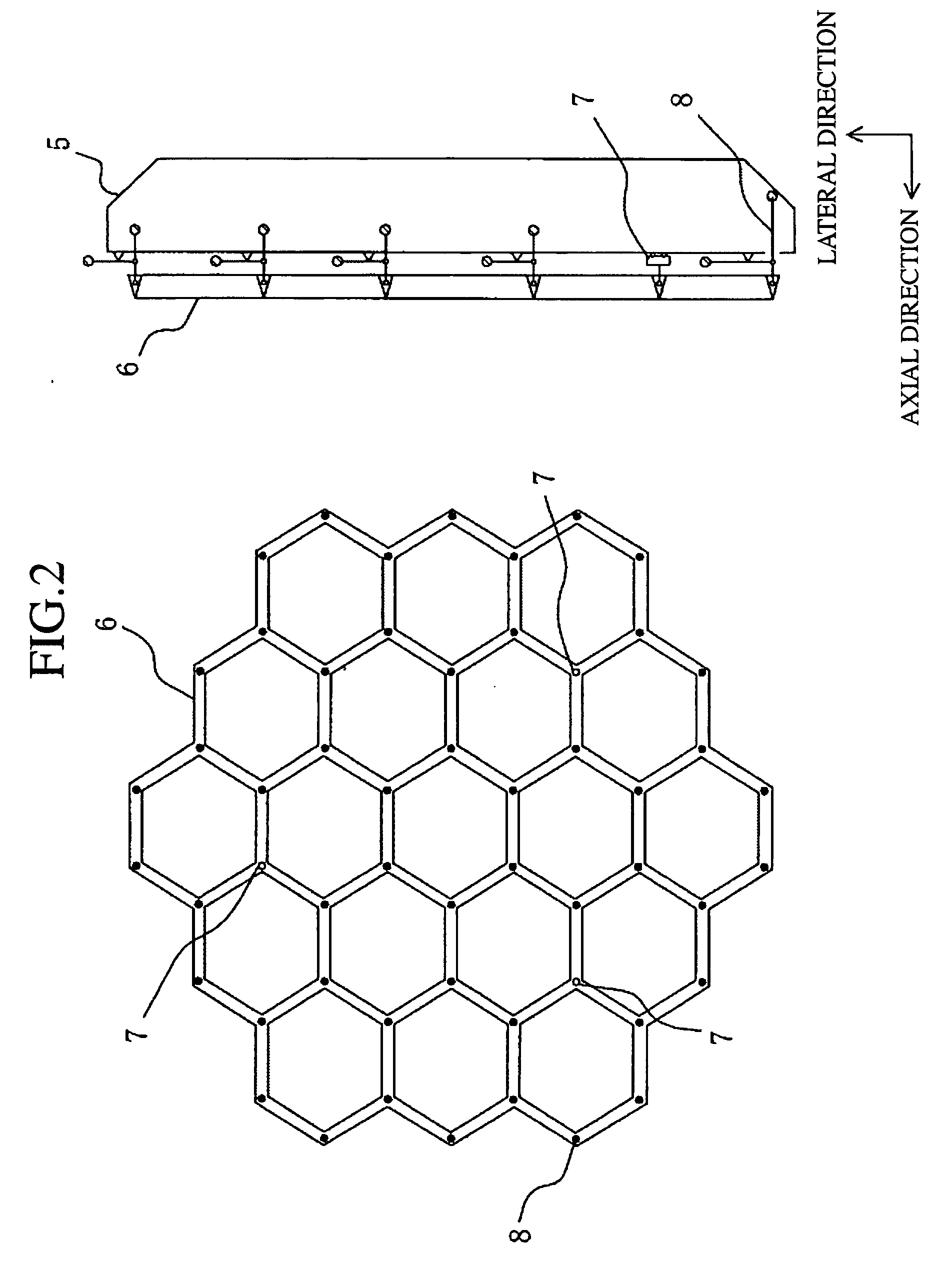
In a reflecting mirror, a plurality of segmented mirrors are grouped into a plurality of groups of a cluster, and are supported by a plurality of sub mirror cells. The plurality of sub mirror cells are supported by a mirror cell, and all the segmented mirrors are supported by the mirror cell. A reference cell is supported by a plurality of force support mechanisms disposed in the mirror cell with the reference cell being nearly in a weightlessness state. Projections and depressions are prevented from occurring in an axial direction of the reflecting mirror due to a self weight deformation, and the reference cell can be used as a reference surface for control of the positions of the plurality of segmented mirrors and those of the plurality of cluster mirrors in the axial direction of the reflecting mirror.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
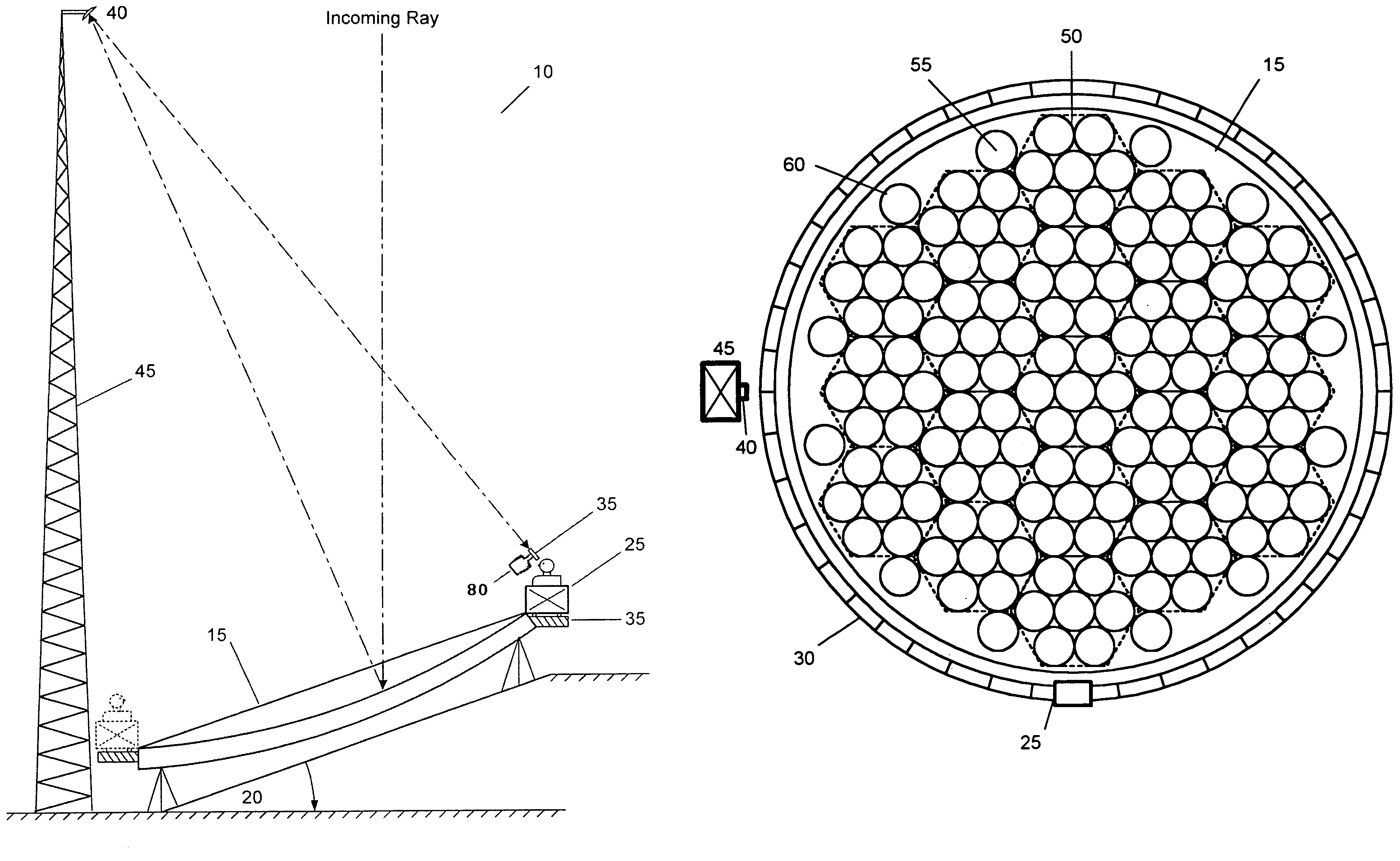
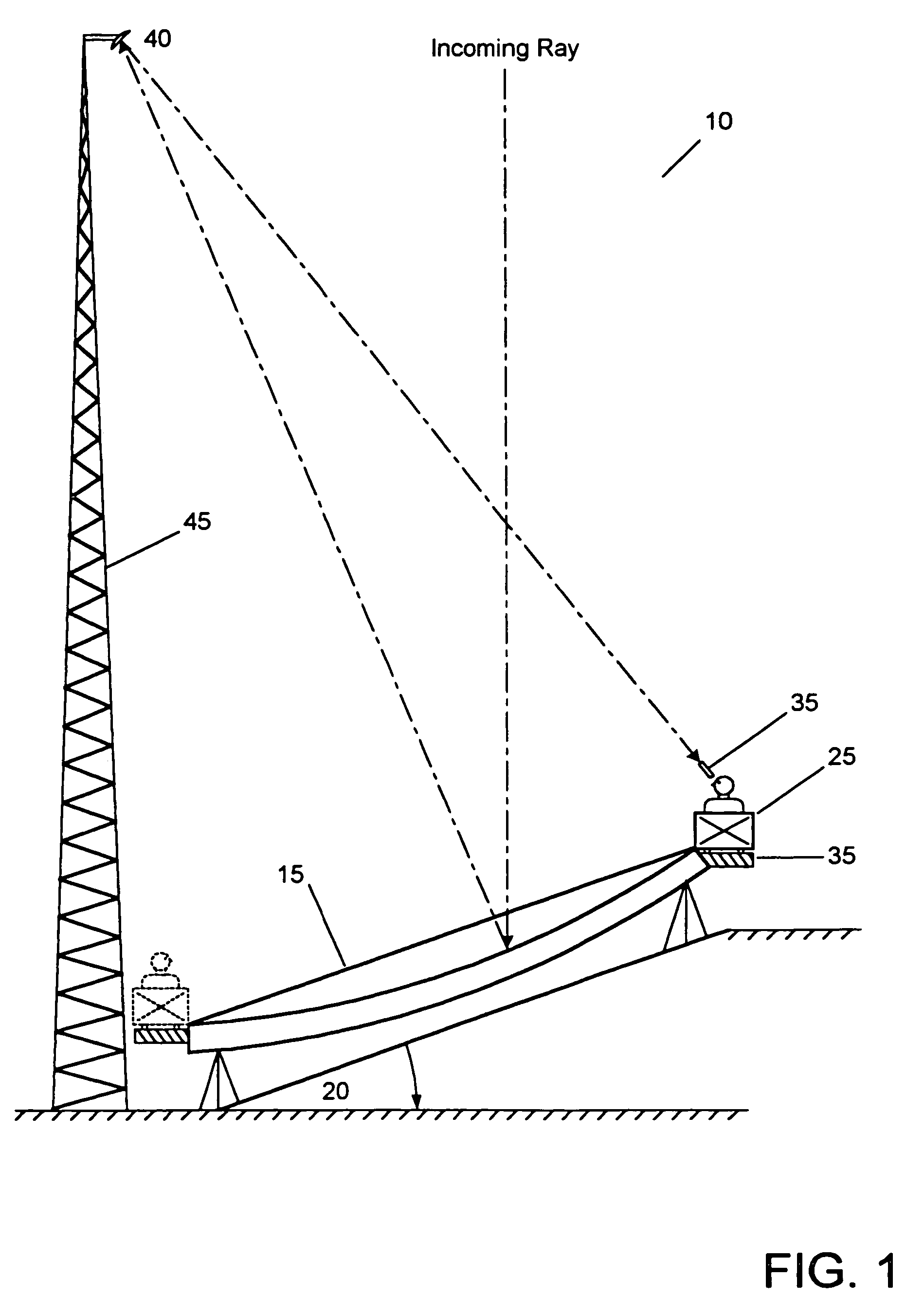
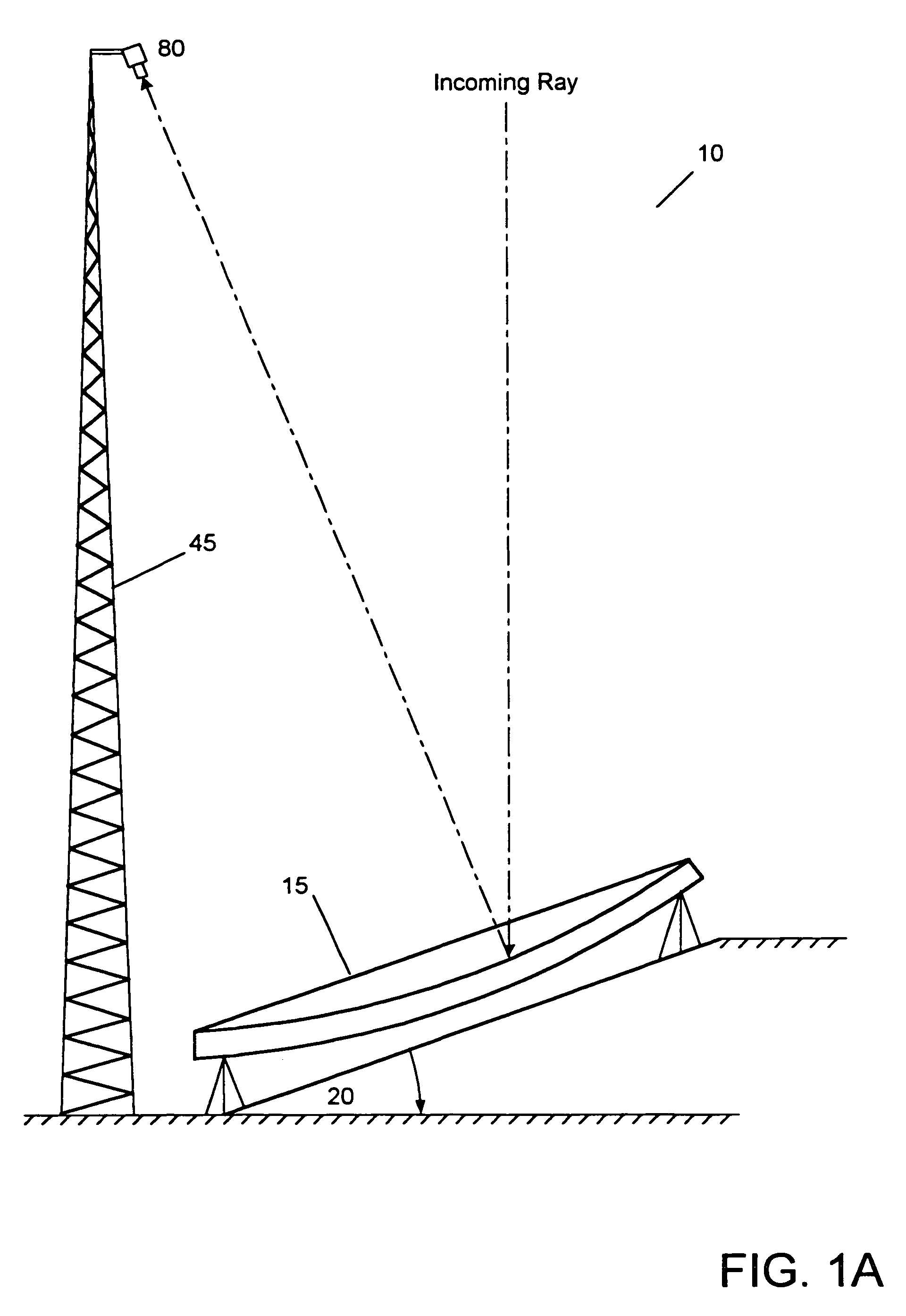
Compound telescope with a stationary primary objective mirror having movable collectors
The present invention relates to a novel land based reflecting telescope having a stationary, equatorially mounted, segmented mirror comprised of a plurality of movable mirrored collectors. These movable collectors are arranged in hexagonal groups to form a multiple mirrored reflector, which comprises the stationary compound telescope. A secondary mirror mounted atop a tower at the focal point directs the image toward the observation cart. Observers ride the periphery of the stationary mirror at a rate of one revolution per day. A retractable air supported hypalon cover protects the large primary mirror structure.
Owner:POPIL NICHOLAS B
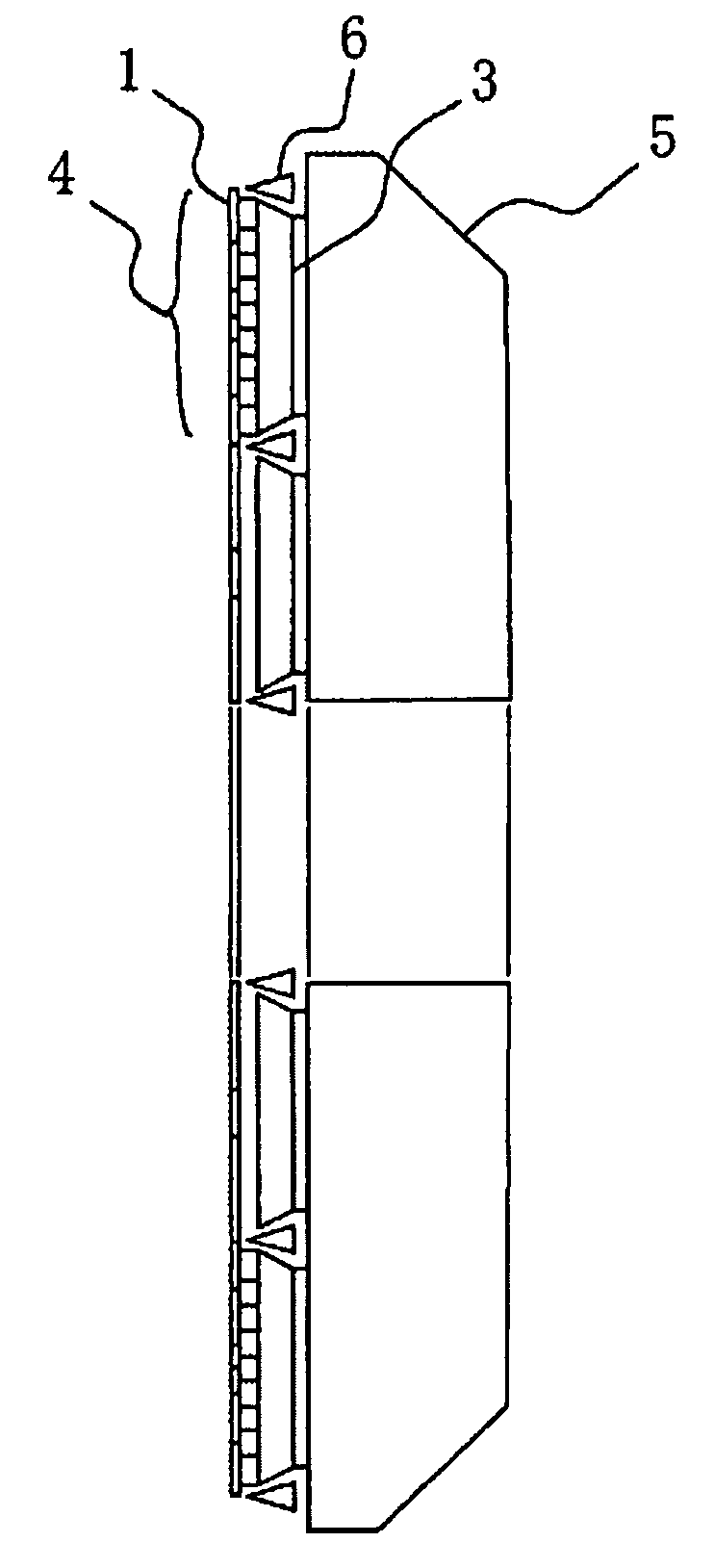
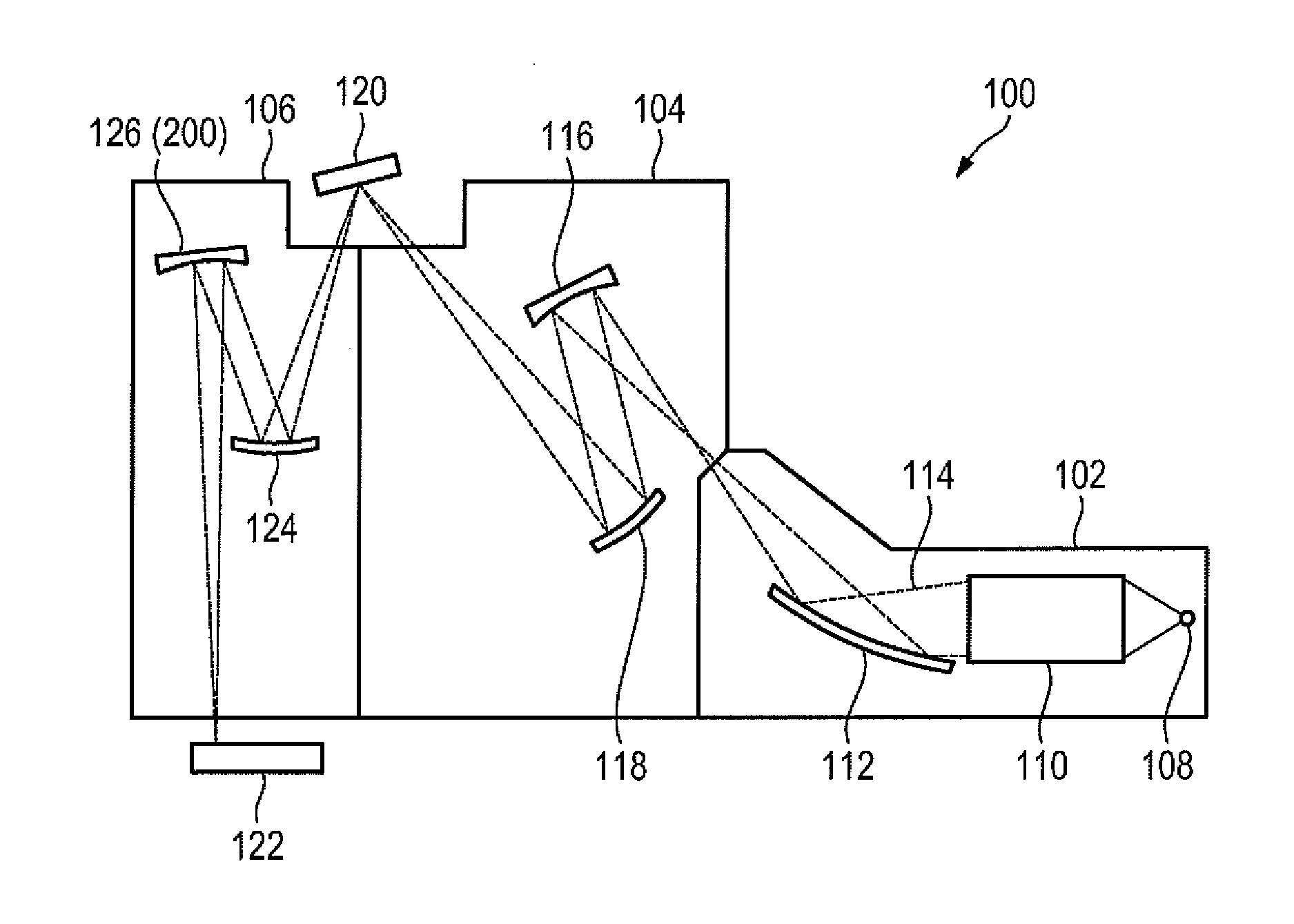
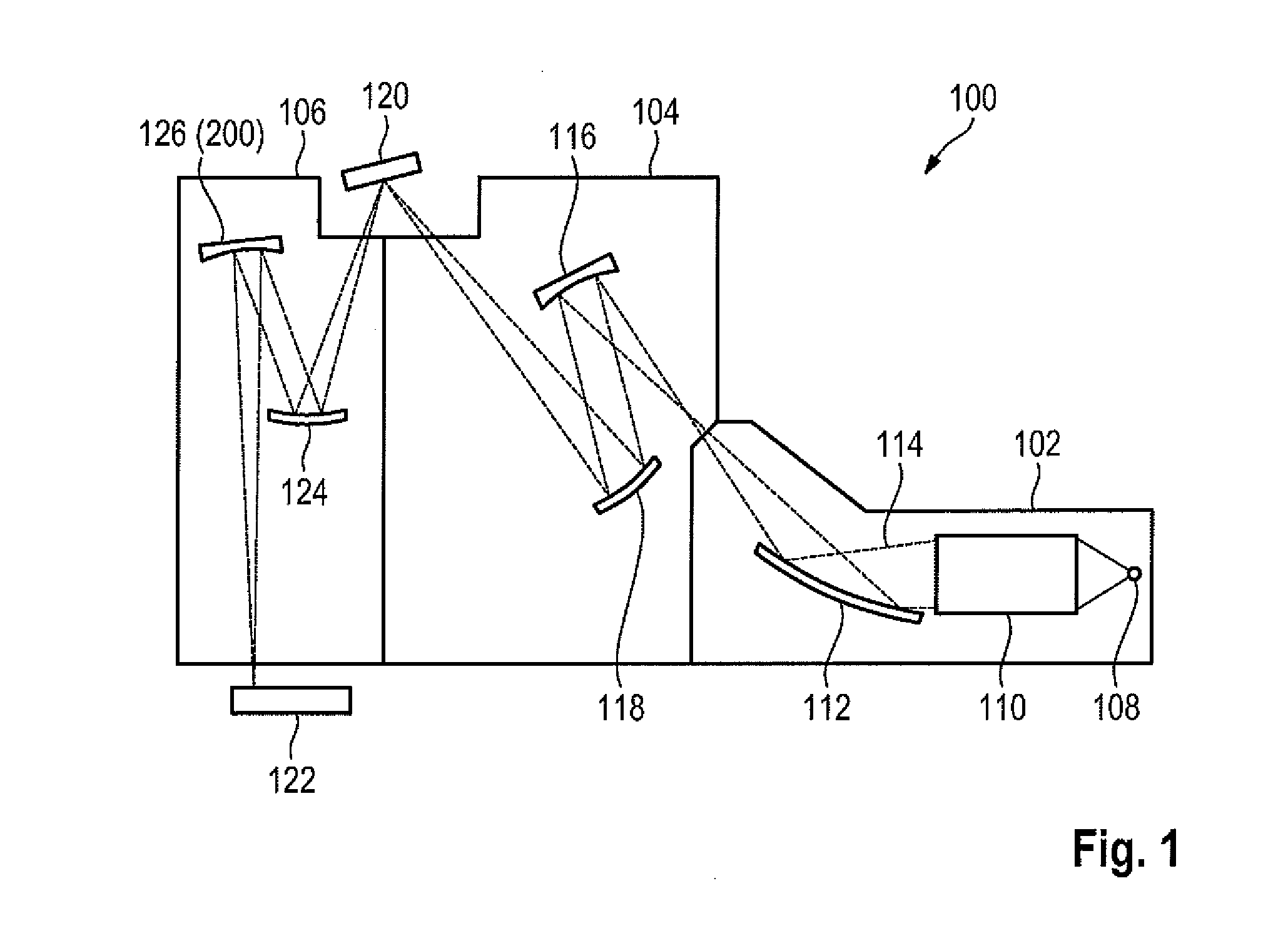
Segmented mirror apparatus for imaging and method of using the same
ActiveUS9448343B2Less distortionEasy to handleMirrorsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationCatoptricsPhotomask
Owner:KLA CORP
Precision micrometric displacement actuator used under polar region low-temperature environment
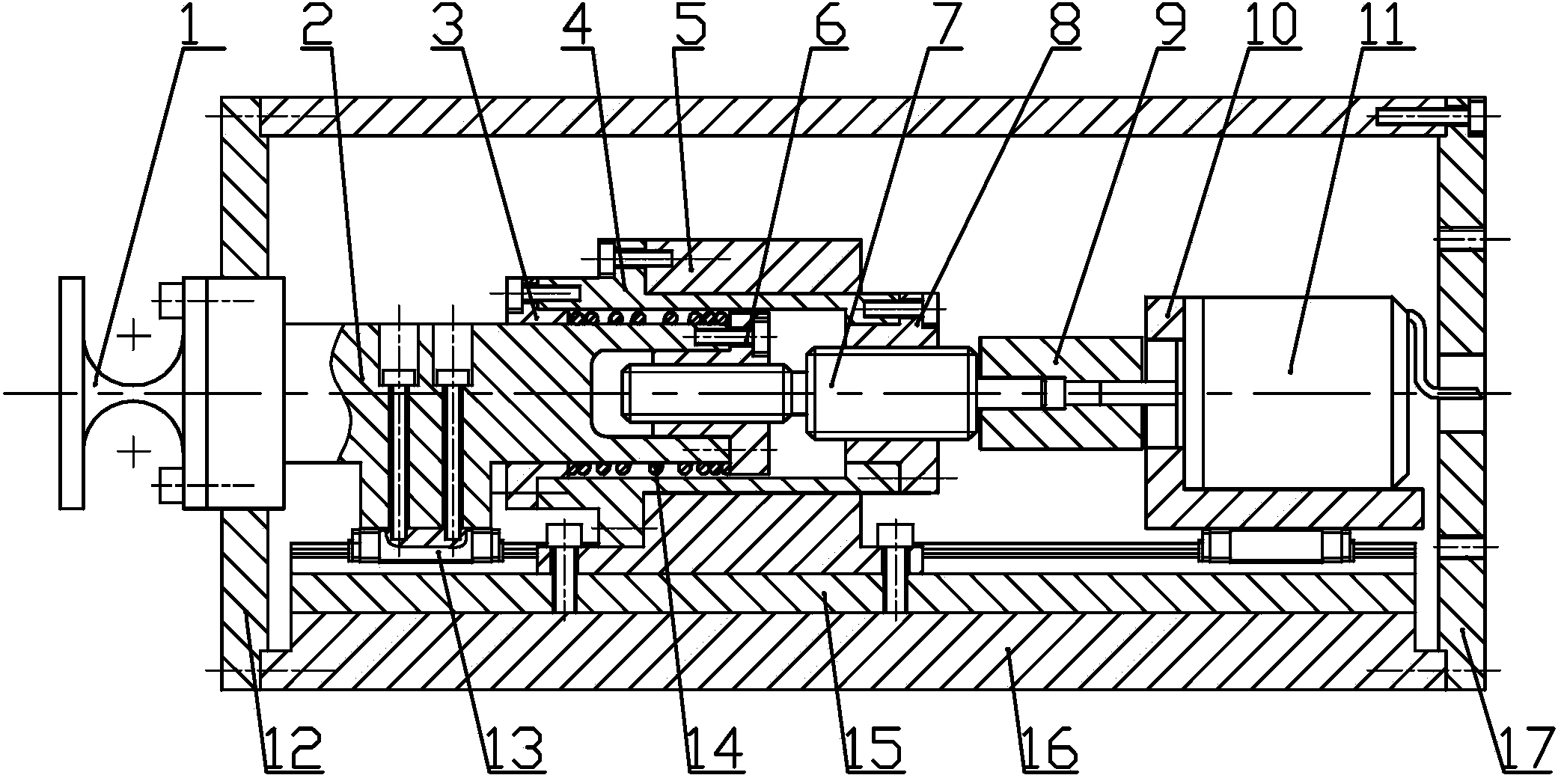
The invention provides a precision micrometric displacement actuator used under a polar region low-temperature environment, and relates to the precision micrometric displacement actuator. The precision micrometric displacement actuator solves the problem a supporting and adjusting mechanism suitable for a large-scale segmented mirror telescope under the polar region low-temperature environment does not exist at present. A base plate is mounted in a shell, a rolling linear guide rail is mounted on the base plate, and a left end cap and a right end cap are arranged at the two ends of the shell in a covering mode respectively. A flexible shaft is mounted on a driving rod, a motor seat is mounted on the rolling linear guide rail, and a stepping motor is mounted on the motor seat. One end of a screw rod is connected with the stepping motor through an elastic coupler, a base is mounted on the base plate, and a sleeve is mounted in the base. A first nut is mounted at the left end of the driving rod, a second nut is mounted at the right end of the sleeve, and the other end of the screw rod is screwed on the second nut and the first nut. One end of the driving rod is inserted into the sleeve and is connected with the first nut, and the other end of the screw rod is connected with the flexible shaft. A shaft sleeve is arranged on the driving rod in a sleeved mode, and a pre-tightening spring is arranged on the driving rod in a sleeved mode and is compressed between the first nut and the shaft sleeve. The precision micrometric displacement actuator is used in the segmented mirror telescope.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
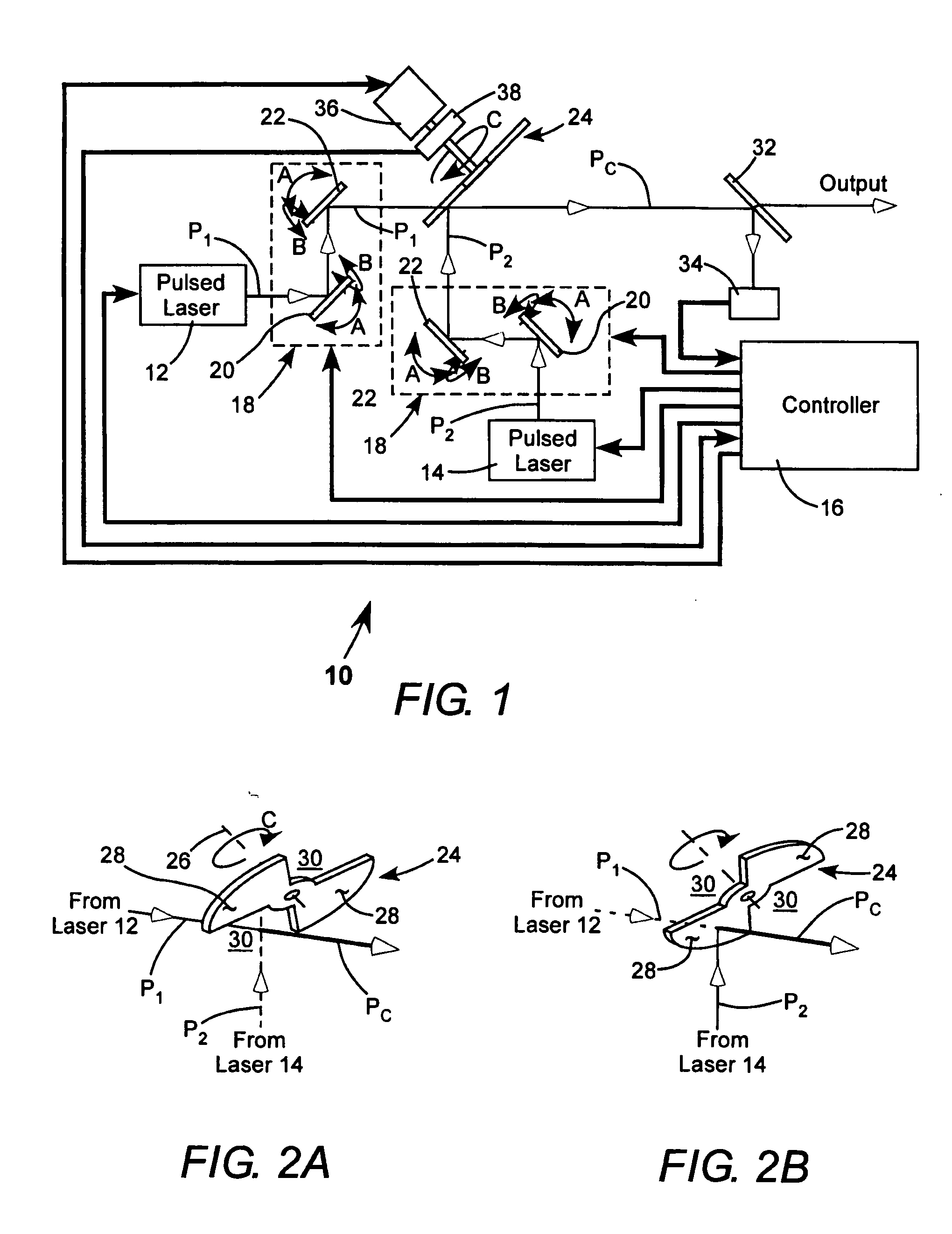
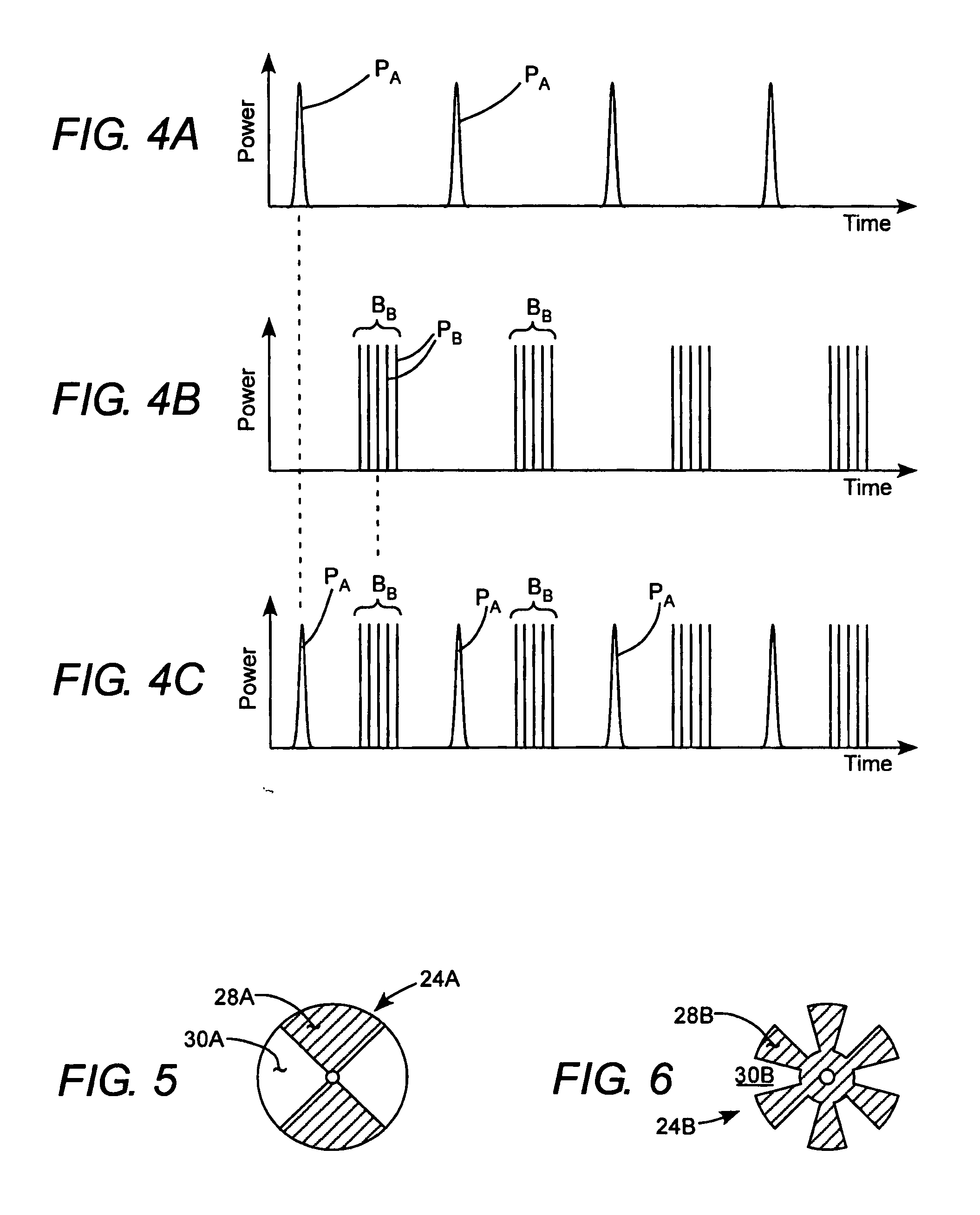
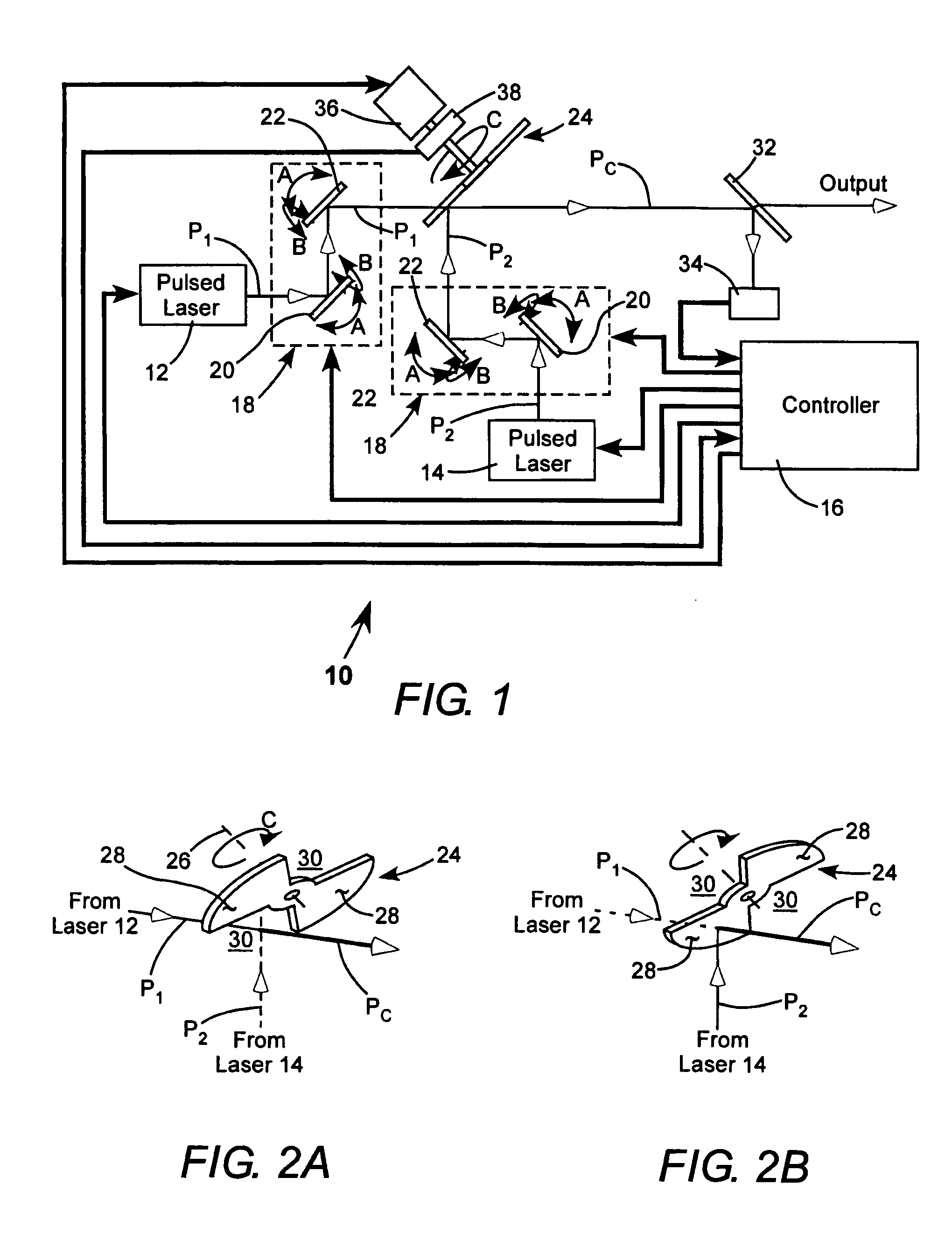
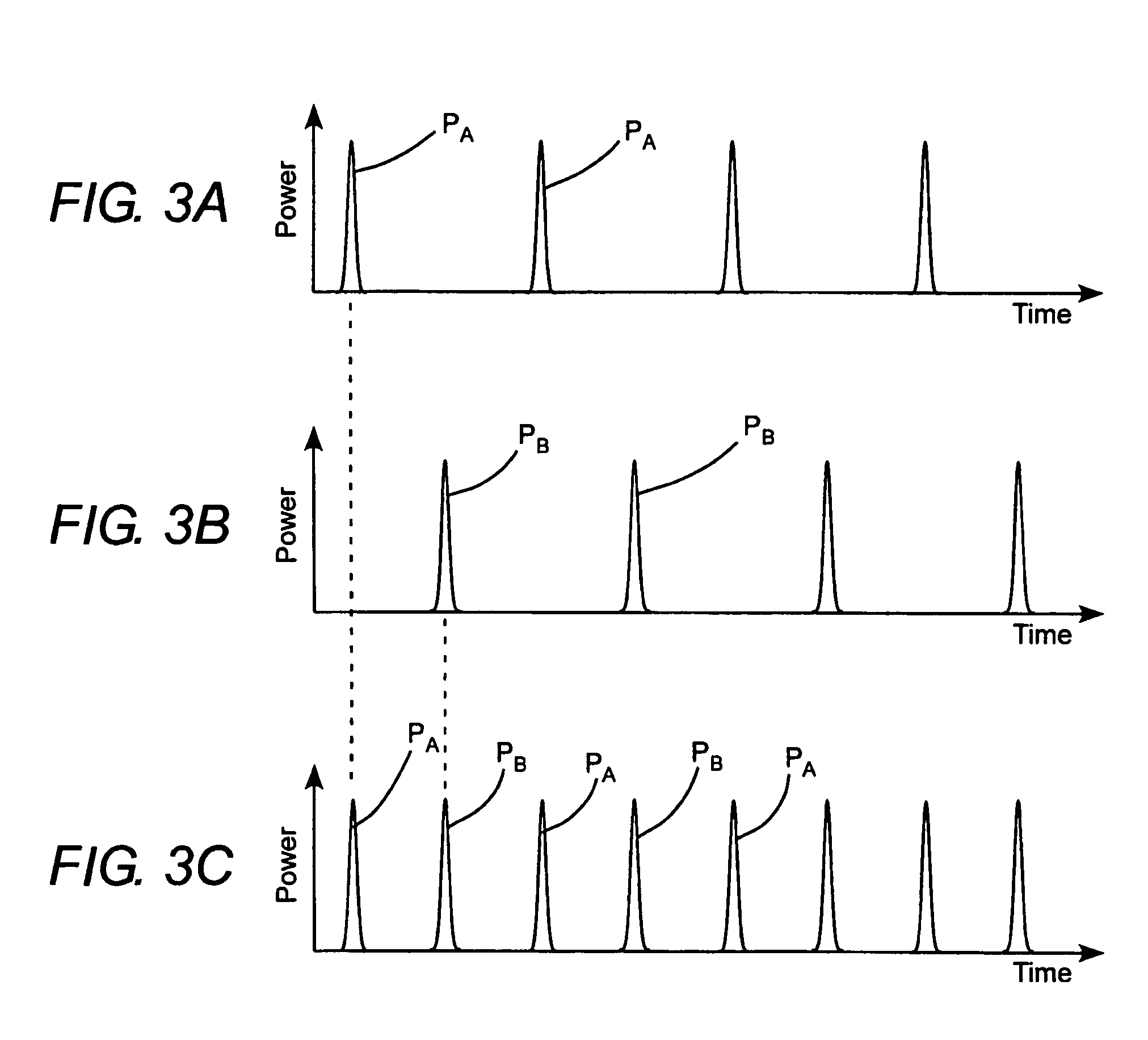
Apparatus for combining beams from repetitively pulsed lasers along a common path
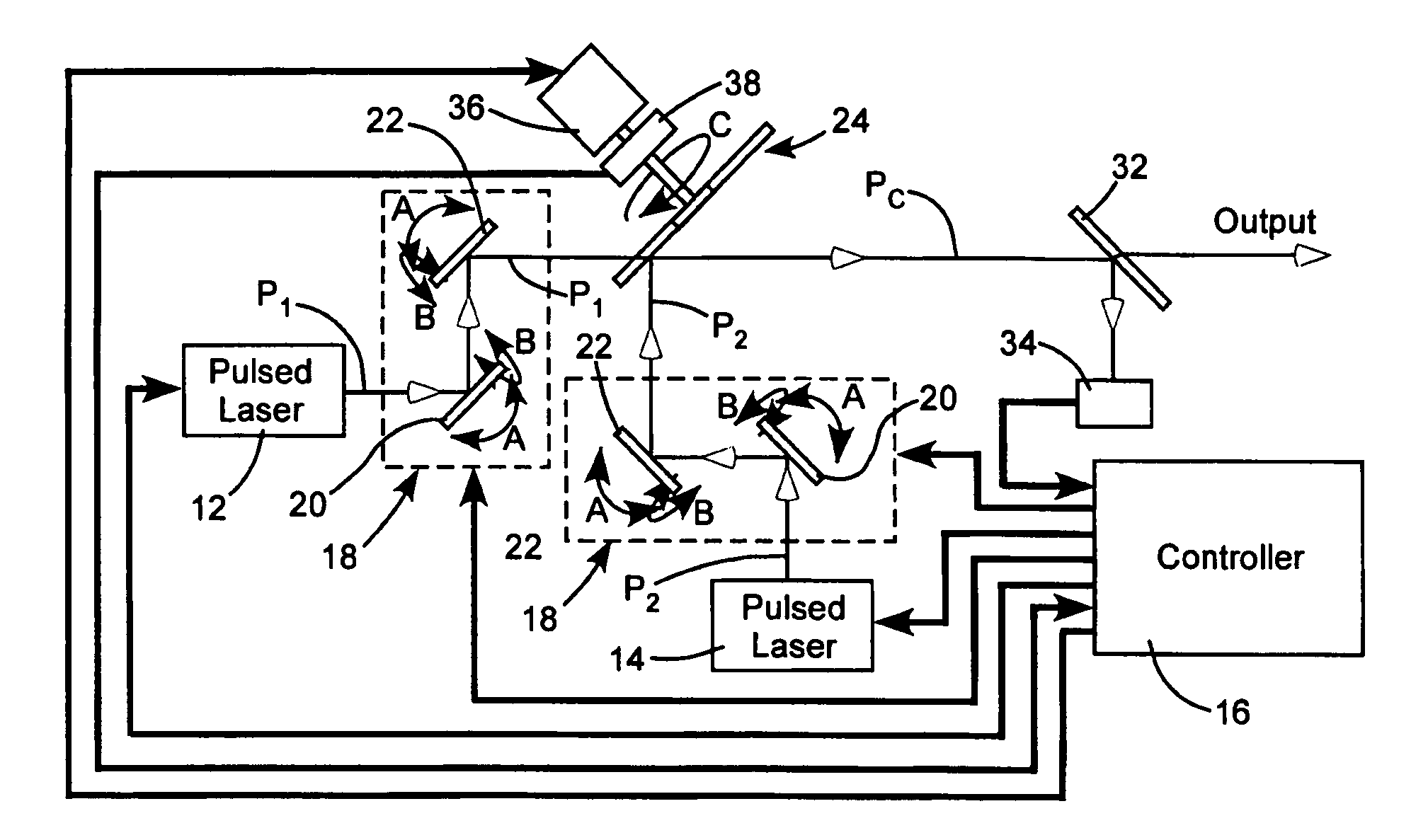
InactiveUS20060215725A1Optical resonator shape and constructionOptical devices for laserLight beamCommon path
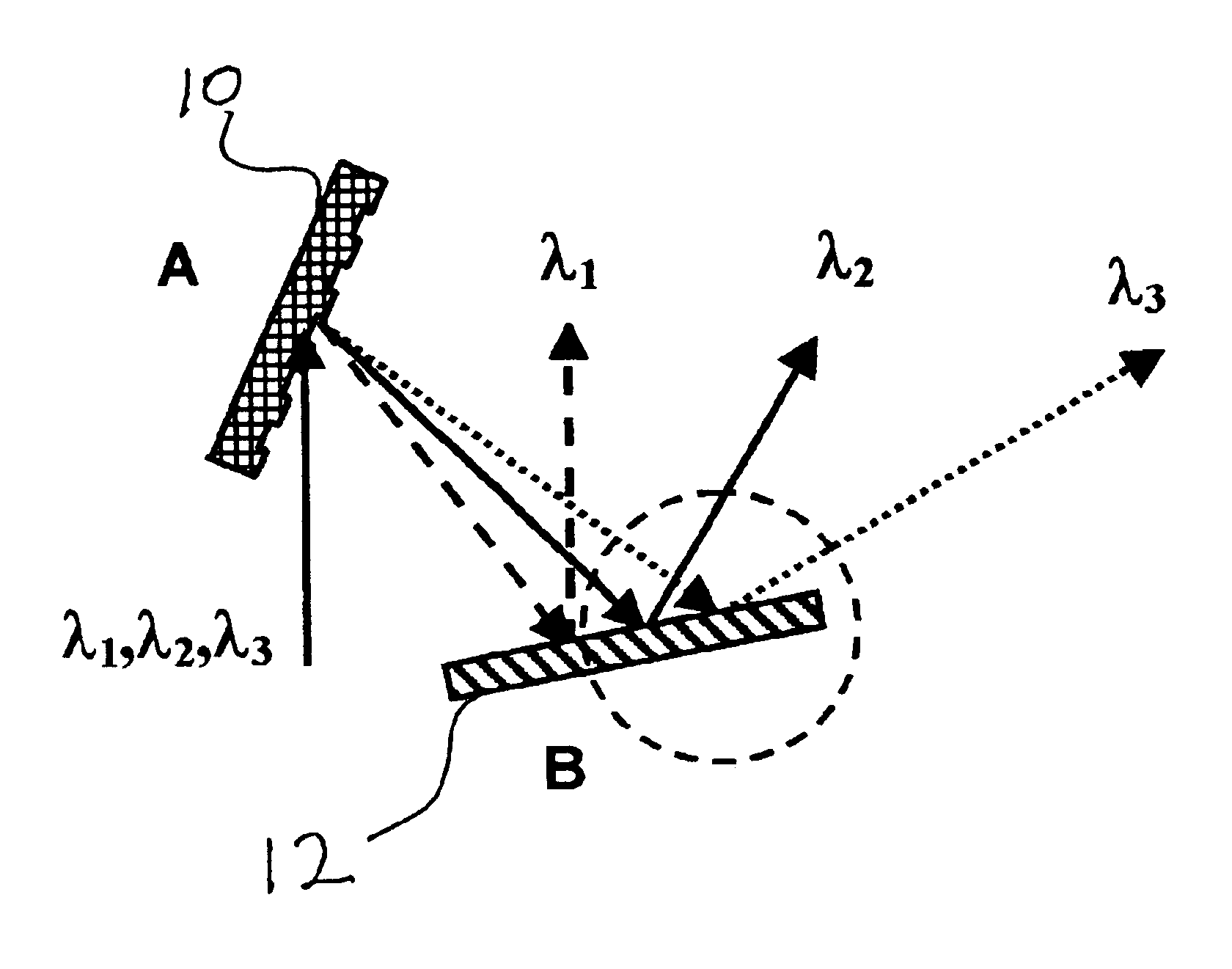
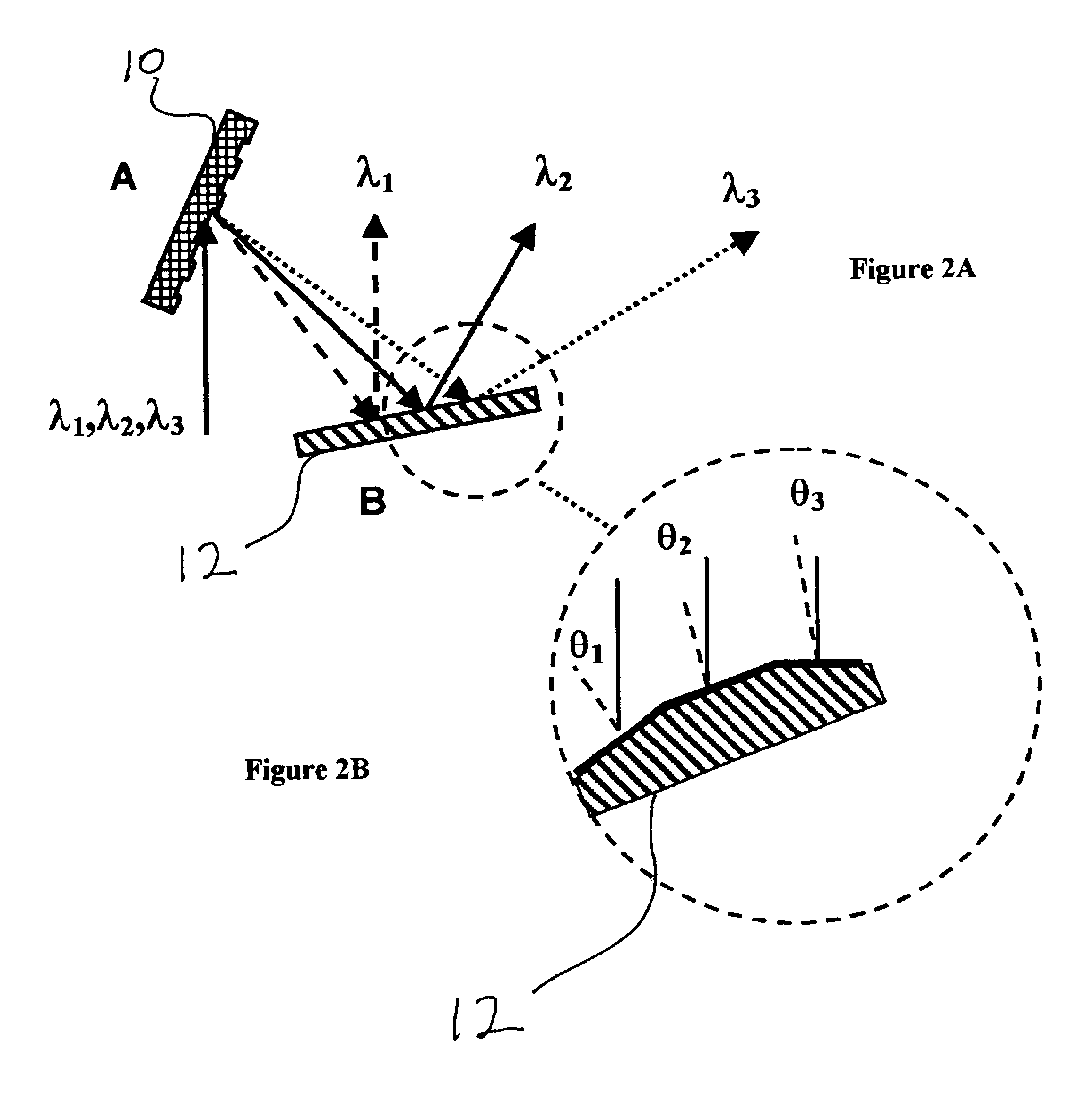
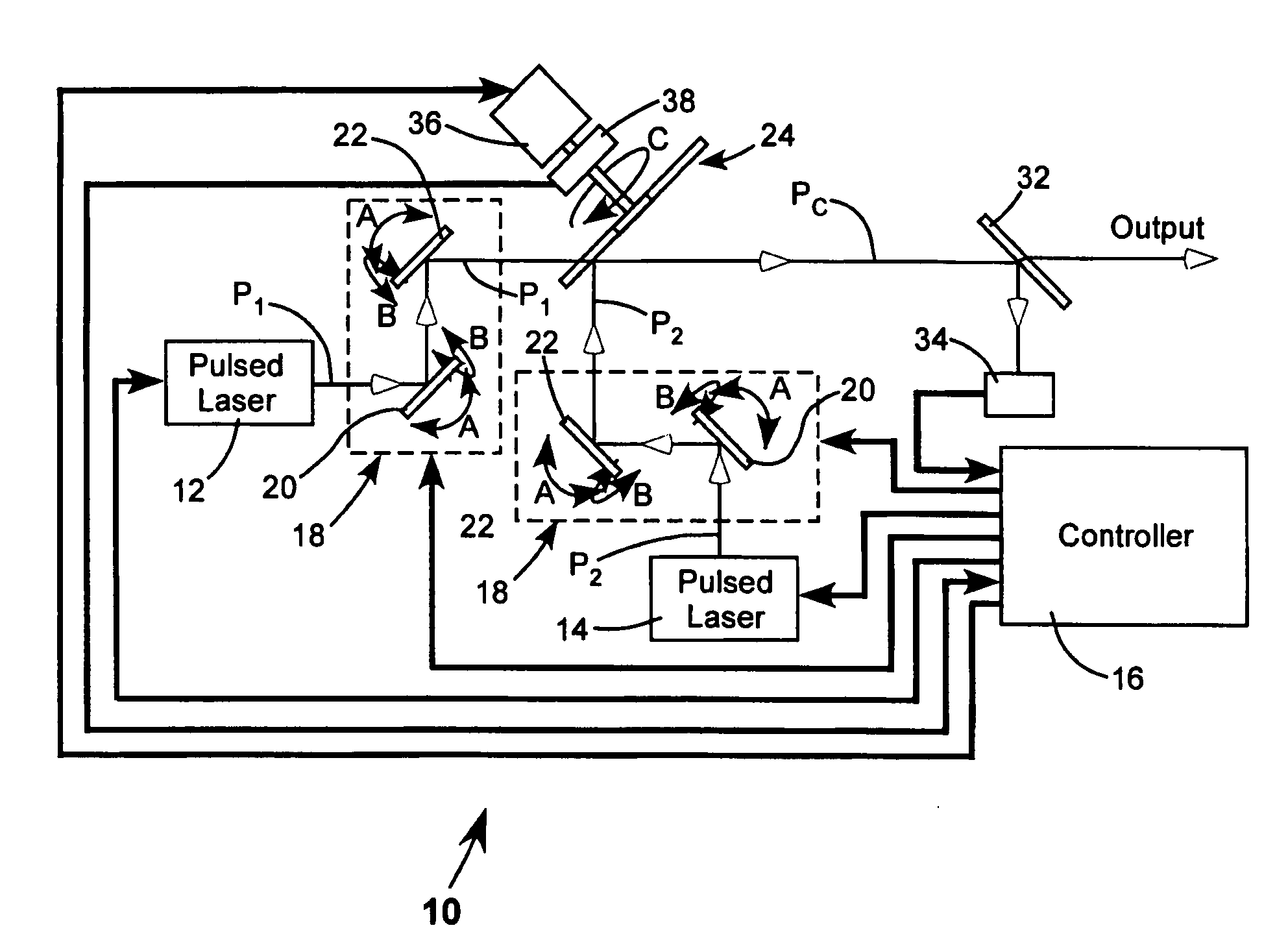
Two pulse sequences are delivered by two lasers. A rotating segmented mirror having one or more reflective areas and one or more transmissive areas is rotated synchronously with the delivery of the pulse sequences to transmit pulses from one sequence, and to reflect pulses from the other sequence at intervals.
Owner:COHERENT GMBH
Segmented MEMS mirror for adaptive optics or maskless lithography
An apparatus having a plurality of arrayed MEMS devices, each device having a parallel-plate actuator and a reflective plate, both of which are mechanically coupled to a flexible beam attached between two anchors. Advantageously, the use of parallel-plate actuators in the apparatus alleviates stringent requirements for the alignment of lithographic masks employed in the fabrication process. In one embodiment, each flexible beam has a relatively small thickness and a relatively large length to effect a relatively large displacement range for the corresponding reflective plate. Movable electrodes of different parallel-plate actuators are configured to act as an electrical shield for the flexible beams, which reduces inter-device crosstalk in the apparatus. Reflective plates of different MEMS devices form a segmented mirror, which is suitable for adaptive-optics and / or maskless lithography applications.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
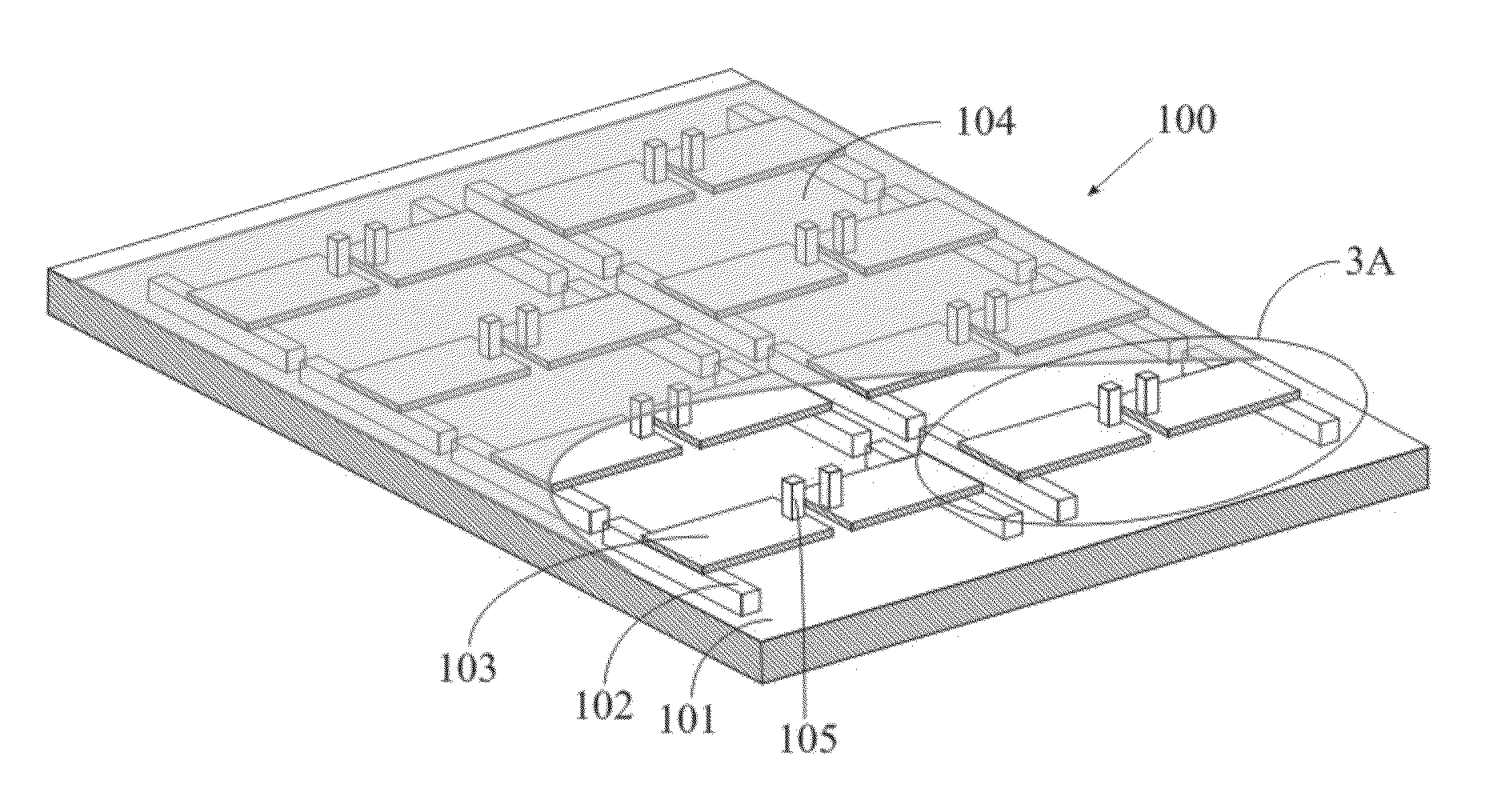
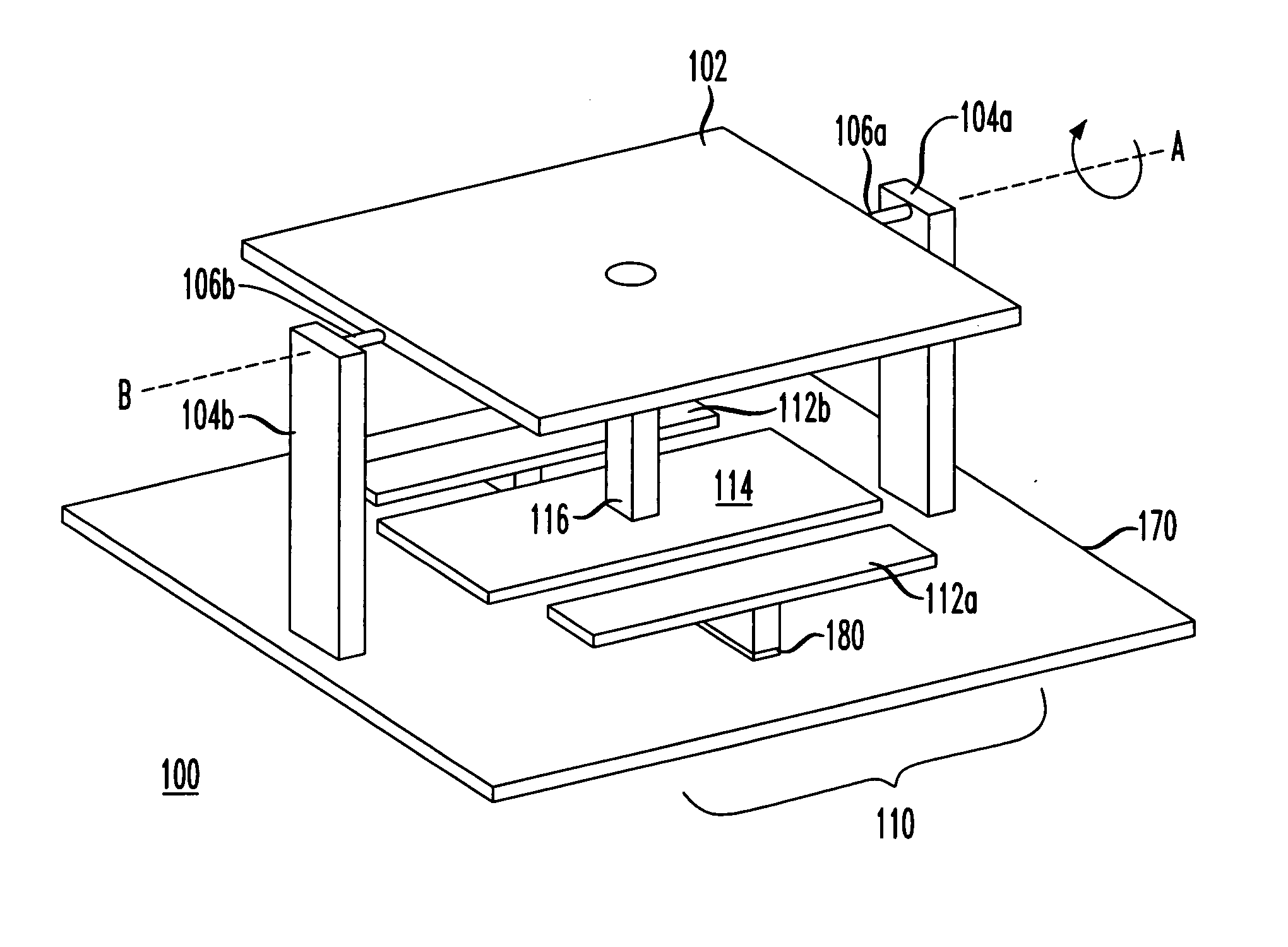
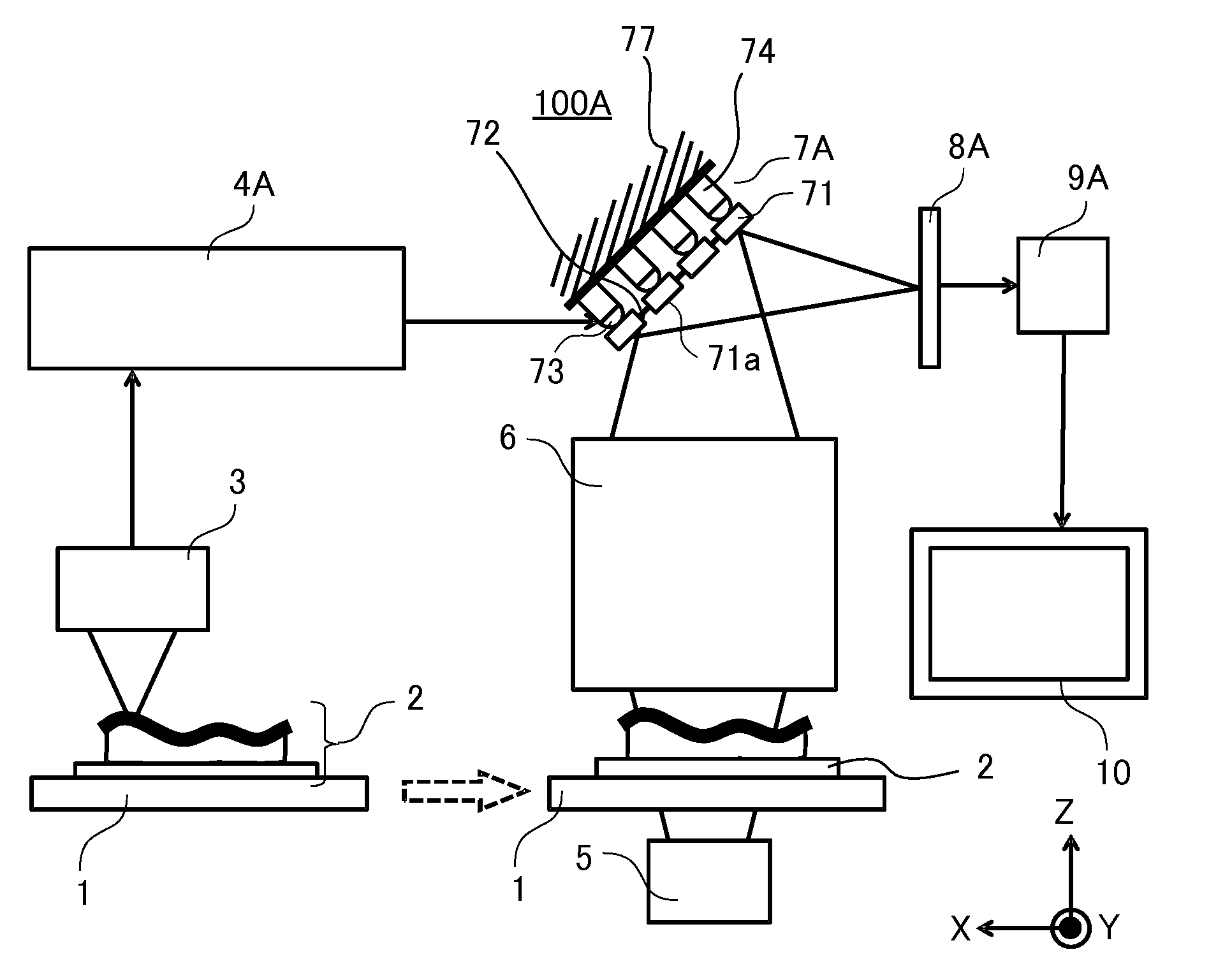
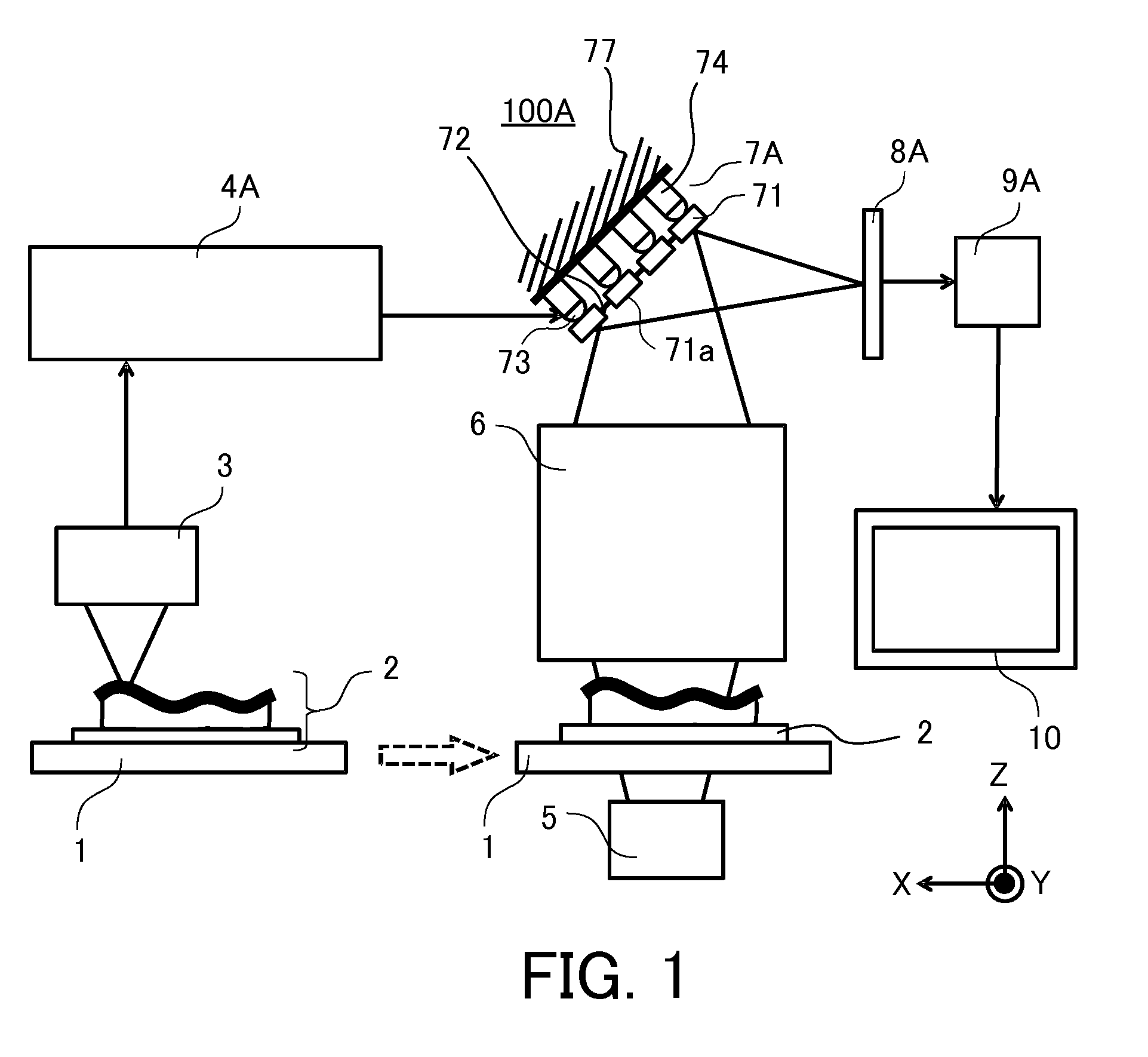
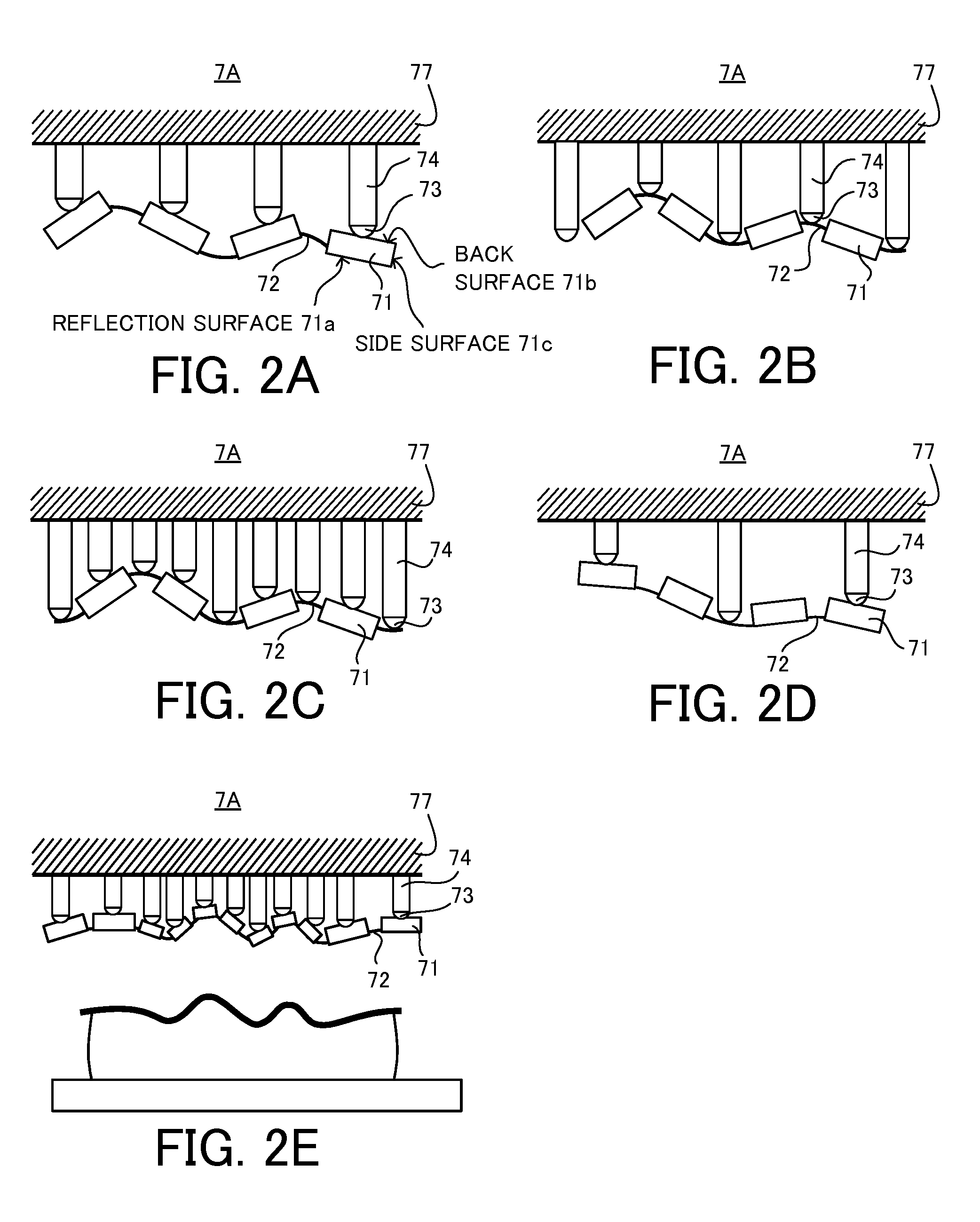
Mirror unit and image acquisition unit
A deformable mirror unit 7A including a plurality of segment mirrors 71 each having a surface 71a, a flexible member 72 configured to connect the plurality of segment mirrors 71 to each other, a driver 74 configured to apply a driving force to at least one of the segment mirror 71 and the flexible member 72 so as to change at least one of a position and a tilt of the reflection surface 71a of each of the plurality of segment mirrors 71, and a connector 73 configured to connect the driver 74 to at least one of the segment mirror 71 and the flexible member 72 and to be rotatable so as to change a light reflecting direction by the at least one reflection surface 71a is provided.
Owner:CANON KK
Segmented mirror apparatus for imaging and method of using the same
ActiveUS20140264051A1Less surface distortionEasy to installMirrorsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationCatoptricsPhotomask
An apparatus for inspecting a photomask, comprising an illumination source for generating a light which illuminates a target substrate, objective optics for receiving and projecting the light which is reflected from the target substrate, the objective optics includes a first mirror arranged to receive and reflect the light which is reflected from the target substrate, a second mirror which is arranged to receive and reflect the light which is reflected by the first mirror, a third mirror which is arranged to receive and reflect the light which is reflected by the second mirror, and a segmented mirror which is arranged to receive and reflect the light which is reflected by the third mirror. The segmented mirror includes at least two mirror segments. The apparatus further includes at least one sensor for detecting the light which is projected by the objective optics.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
High intensity image projector using sectional mirror
ActiveUS8235536B2Increase light intensityIncrease brightnessProjectorsColor television detailsPupilHigh intensity
Image projectors with increased light intensity and methods for providing brighter images are provided. Image projectors, described herein, can provide the brightness while still providing any or all of compactness, low power consumption, and long lifetime. To increase brightness, sectional mirrors are used to respectively compress the light from two light sources into a single pupil (e.g. an aperture) of an imaging device. The compression can be accomplished by regions (e.g. sections) of the mirror having different angles with respect to the pupil. Relatively little light may be lost in the compression since minima for a light intensity pattern from a light source may occur between the regions that reflect the light.
Owner:PROJECTIONDESIGN
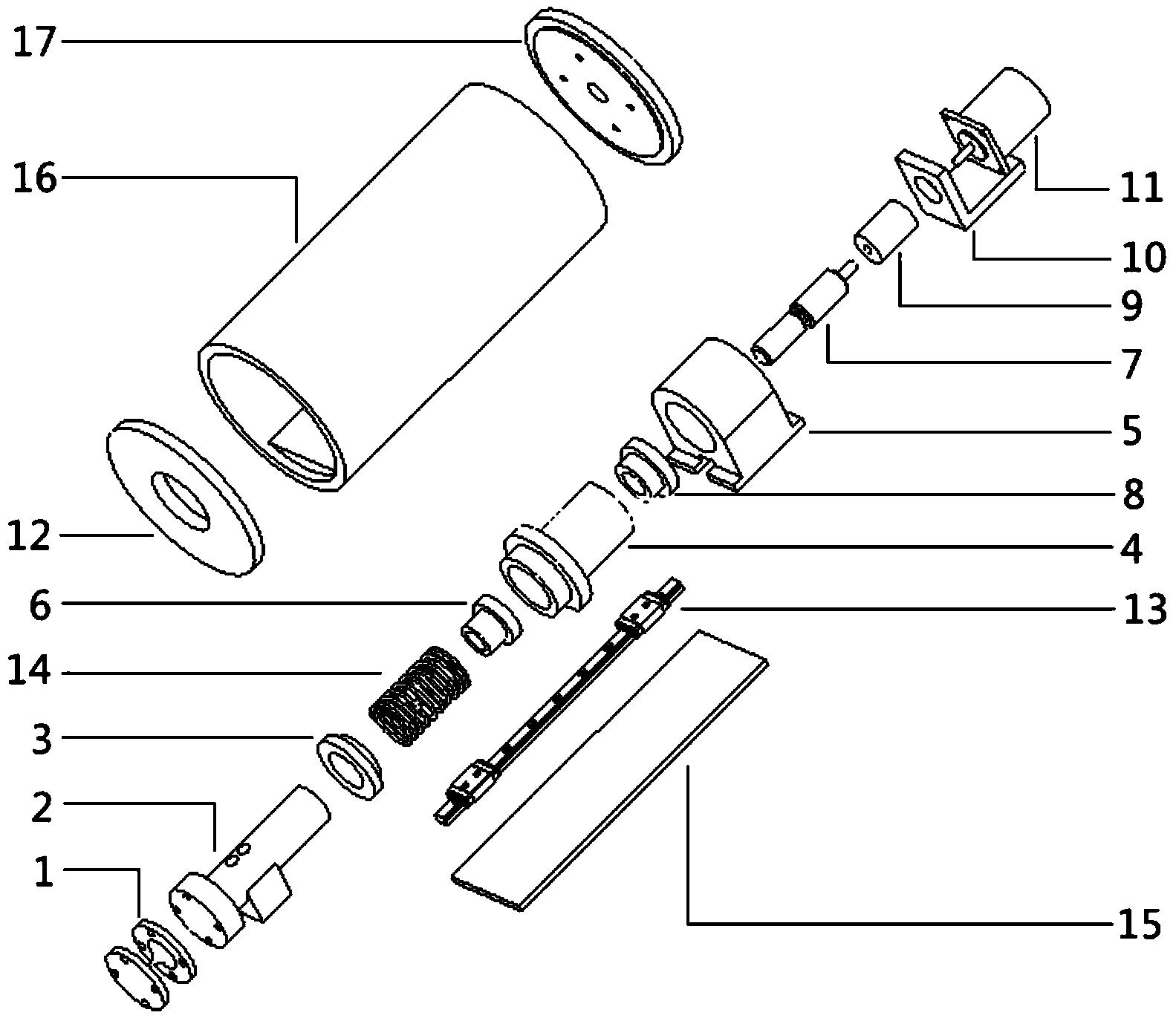
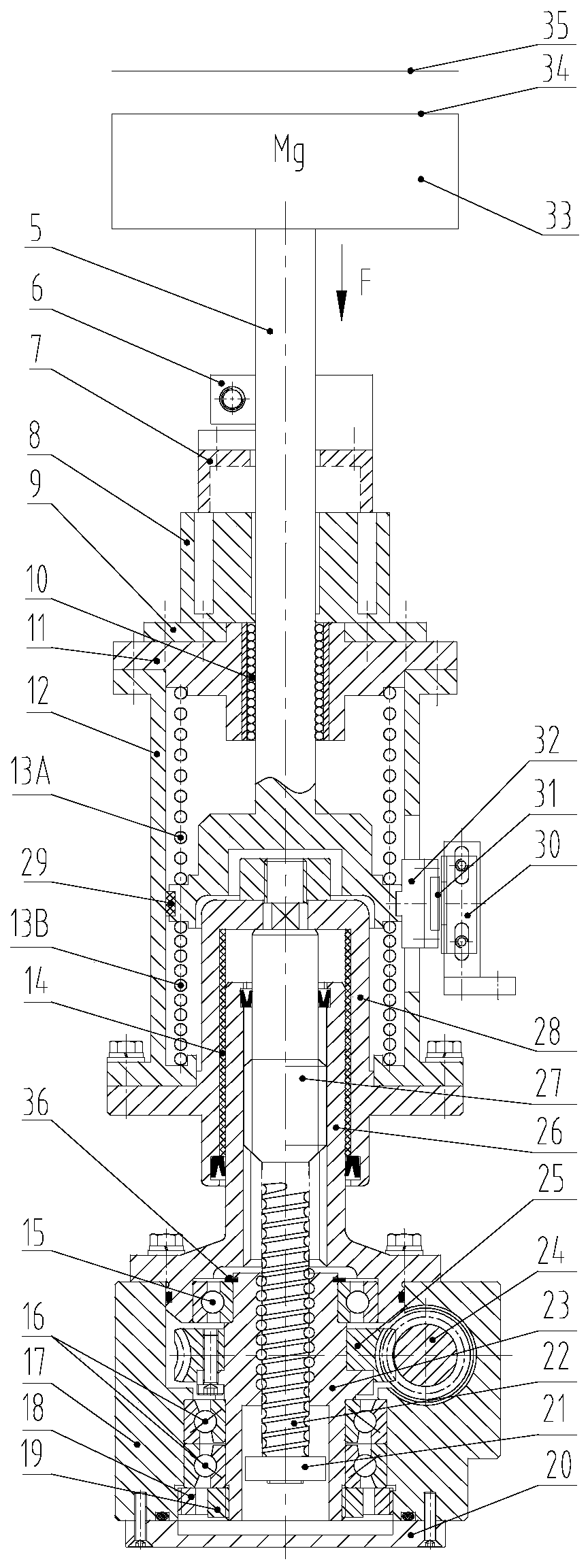
Nanoscale precise displacement actuator for large segmented mirror optical telescope
The invention discloses a nanoscale precise displacement actuator for a large segmented mirror optical telescope. Weight of sub-mirrors and a telescope assembly acts on an output shaft of a compression spring mechanism. A voice coil motor is on the compression spring mechanism and is coaxial with the output shaft. A mechanism composed of a worm gear pair, a ball screw pair and a spline pair is setunder the compression spring mechanism and is taken as a length telescopic device. The compression spring mechanism, the voice coil motor are the length telescopic device are coaxial with the outputshaft. The problem that the cost is high due to the fact that according to the same kind of lever type nanoscale precise displacement actuators, the output shafts swing, many joints are employed, thenumber of levers is high and processing is complex can be avoided. The nanoscale precise displacement actuator is relatively simple in structure and relatively low in production cost. A requirement ofthe large segmented mirror optical telescope for a great number of actuators can be satisfied.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ASTRONOMICAL OPTICS & TECH NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSE
Edge sensor for segmented mirror surface based on interference principle and working method thereof
ActiveCN110779443AClear principleCompact structureUsing optical meansWavefront sensorDigital imaging
The invention discloses an edge sensor for a segmented mirror surface based on an interference principle, and a working method thereof. The edge sensor is characterized in that: an optical flat or spherical lens is placed on a sub-mirror splicing seam of a measured segmented mirror surface, the front surface of the optical flat or spherical lens is completely anti-reflection, and the rear surfaceof the optical flat or spherical lens is provided with a coating film; a parallel light source is arranged on the other side of a sub-mirror of the measured segmented mirror surface and the optical flat or spherical lens, light rays vertically enter the optical flat or spherical lens by means of a semi-reflecting and semi-transmitting prism and then part of the light beam on the surface returns, the other part is reflected by the surface of the sub-mirror along an original path, the two beams of reflected light form interference fringes, the interference fringes enter a microscopic amplification imaging system by means of the semi-reflecting and semi-transmitting prism, and target surface receiving and digital imaging are carried out by means of a CCD or CMOS detector, namely, the splicingerror of the adjacent sub-mirrors can be handled. The edge sensor prevents starlight and wavefront sensors from occupying and wasting a limited high-imaging-quality field of view of an optical system, is low in price, stable in performance and not affected by environmental factors, and is suitable for detecting the splicing errors between the adjacent sub-mirrors of various optical segmented mirror surfaces.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ASTRONOMICAL OPTICS & TECH NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSE
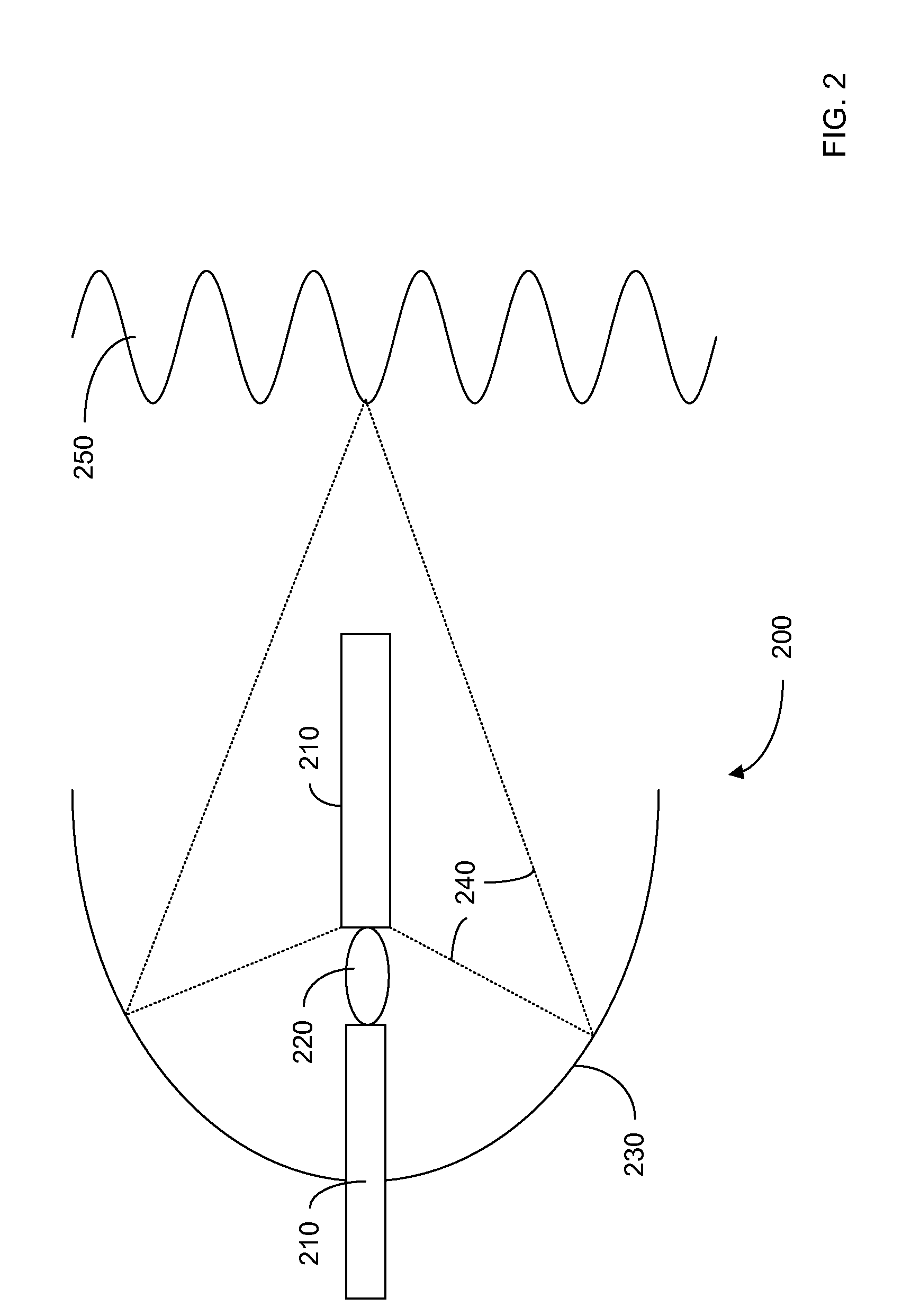
Wavelength separation elements for dense wavelength division multiplexing systems
InactiveUS6909822B2Simple designEasy to controlWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesGratingLength wave
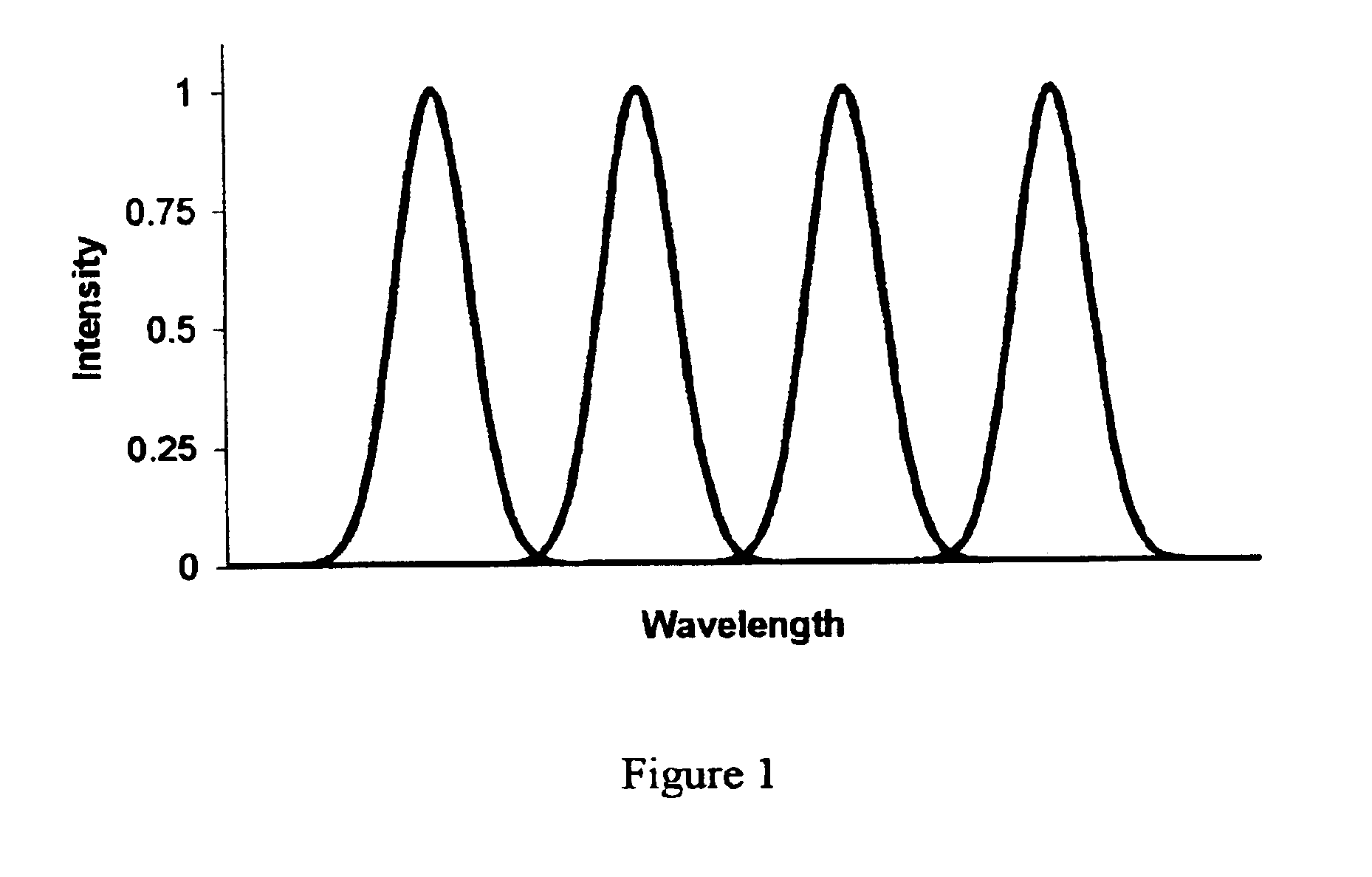
Systems are described that disperse the wavelength bands corresponding to the channel centers at a faster rate than the bandwidth of the channels themselves. An embodiment consists of a double element system including a grating, to create the initial separation, and a segmented mirror with multiple flat facets of different tilt, which reflect each spatially separated channel at a different angle. The size, position and angle of the facets are designed to match the spacing and position of individual channels of known wavelength and number that are diffracting from a grating with a predefined period, a set distance from this device. This system enables the individual channels to be re-imaged at some later point with a large separation between the channels, relative to their spatial size.
Owner:GENERAL ATOMICS
Apparatus for combining beams from repetitively pulsed lasers along a common path
InactiveUS7336691B2Optical resonator shape and constructionOptical devices for laserLight beamCommon path
Two pulse sequences are delivered by two lasers. A rotating segmented mirror having one or more reflective areas and one or more transmissive areas is rotated synchronously with the delivery of the pulse sequences to transmit pulses from one sequence, and to reflect pulses from the other sequence at intervals.
Owner:COHERENT GMBH
Sub-mirror assembling and disassembling device for segmented mirror of large astronomical telescope
InactiveCN105196274ALower center of gravityImprove stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsFiberSky
A Ssub-mirror assembling and disassembling deviceequipment for a segmented mirror of a large astronomical telescope is characterized in that a high-speed large-displacement robot and a minutesmall-displacement high-precision positioning robot form a series robot, the high-speed large-displacement robot adopts a hydraulic lifting and descending retractor device and is provided with two telescopic arms, the minutesmall-displacement high-accuracy positioning robot is mounted at the tail ends of the two telescopic arms, and adopts a motor lead screw device provided with a three-claw manipulator, and a vertical rotation device, a vertical lifting device, a horizontal adjustment device and a pitching mechanism are arranged between the three-claw manipulator and a manipulator chassis. The sub-mirror assembling and disassembling equipment makes up for the deficiency of the prior art, completely replaces original manpower for operation, realizes assembling and disassembling of sub mirrors of a primary mirror of an LAMOST (Large Sky Area Multi-object Fiber Spectroscopic Telescope), can meet the requirement of high-precision high-reliability mirror splicing of the primary mirror of the telescope, and meanwhile provides experience for mirror assembling of a large telescope in future.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ASTRONOMICAL OPTICS & TECH NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSE
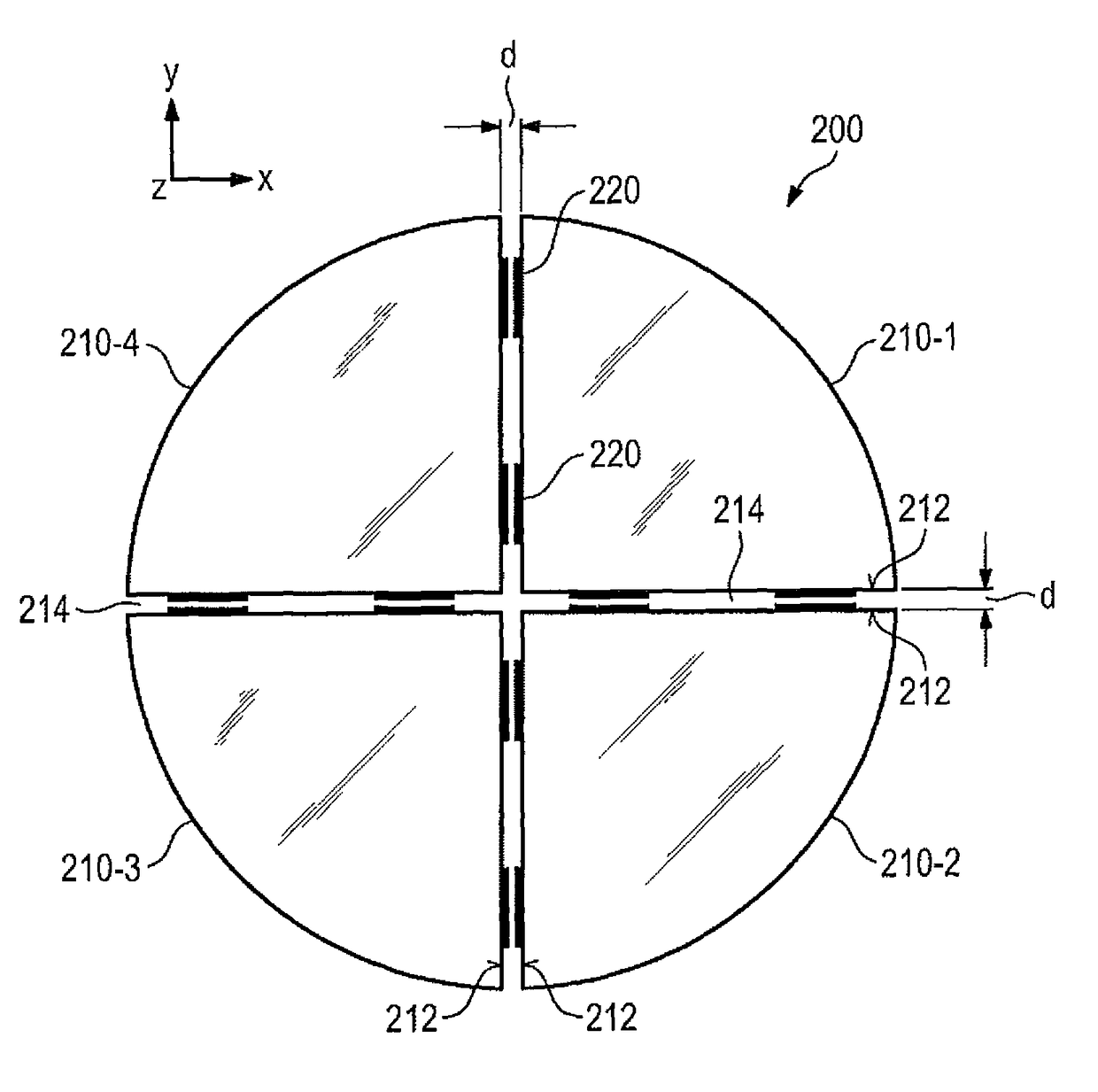
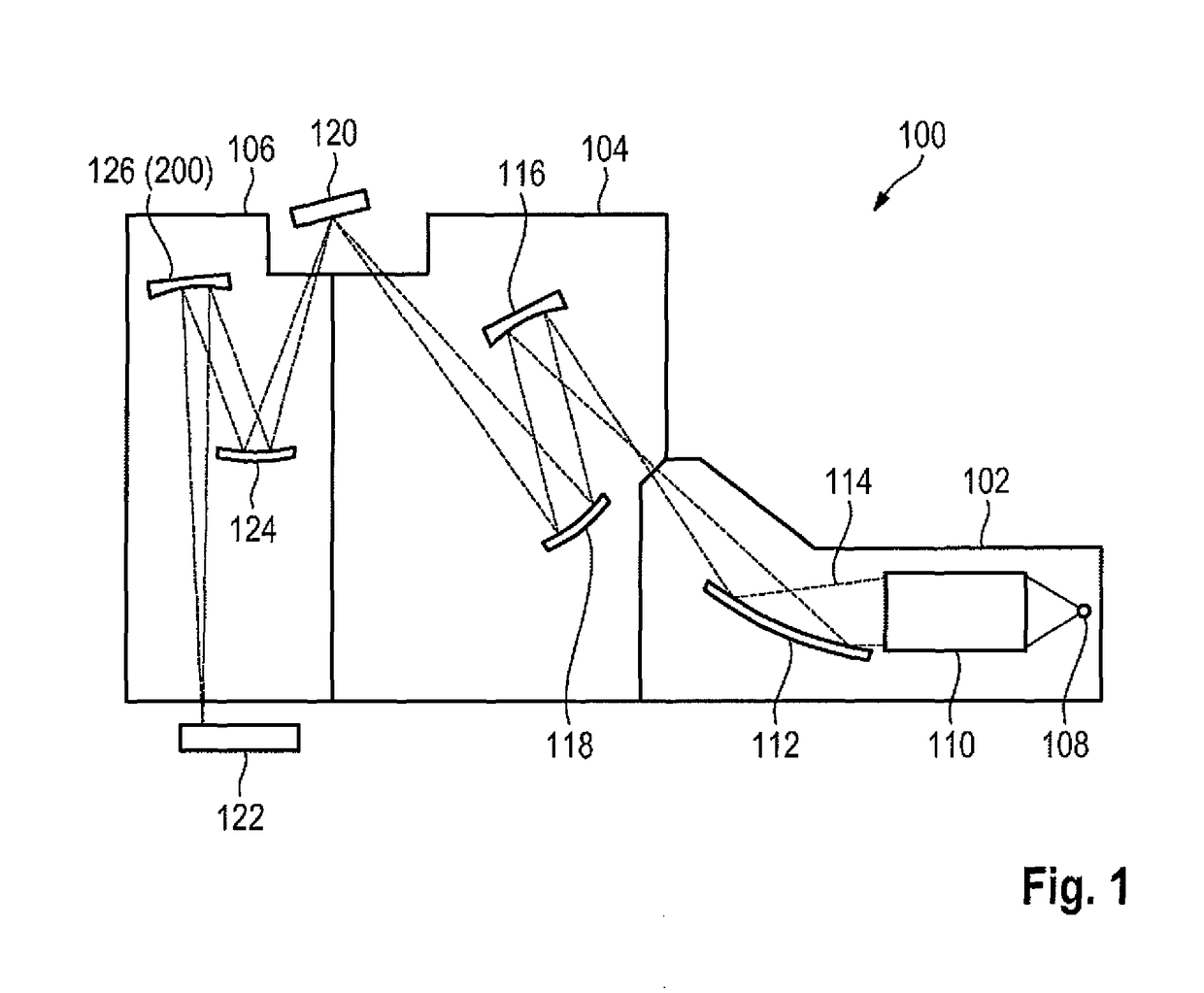
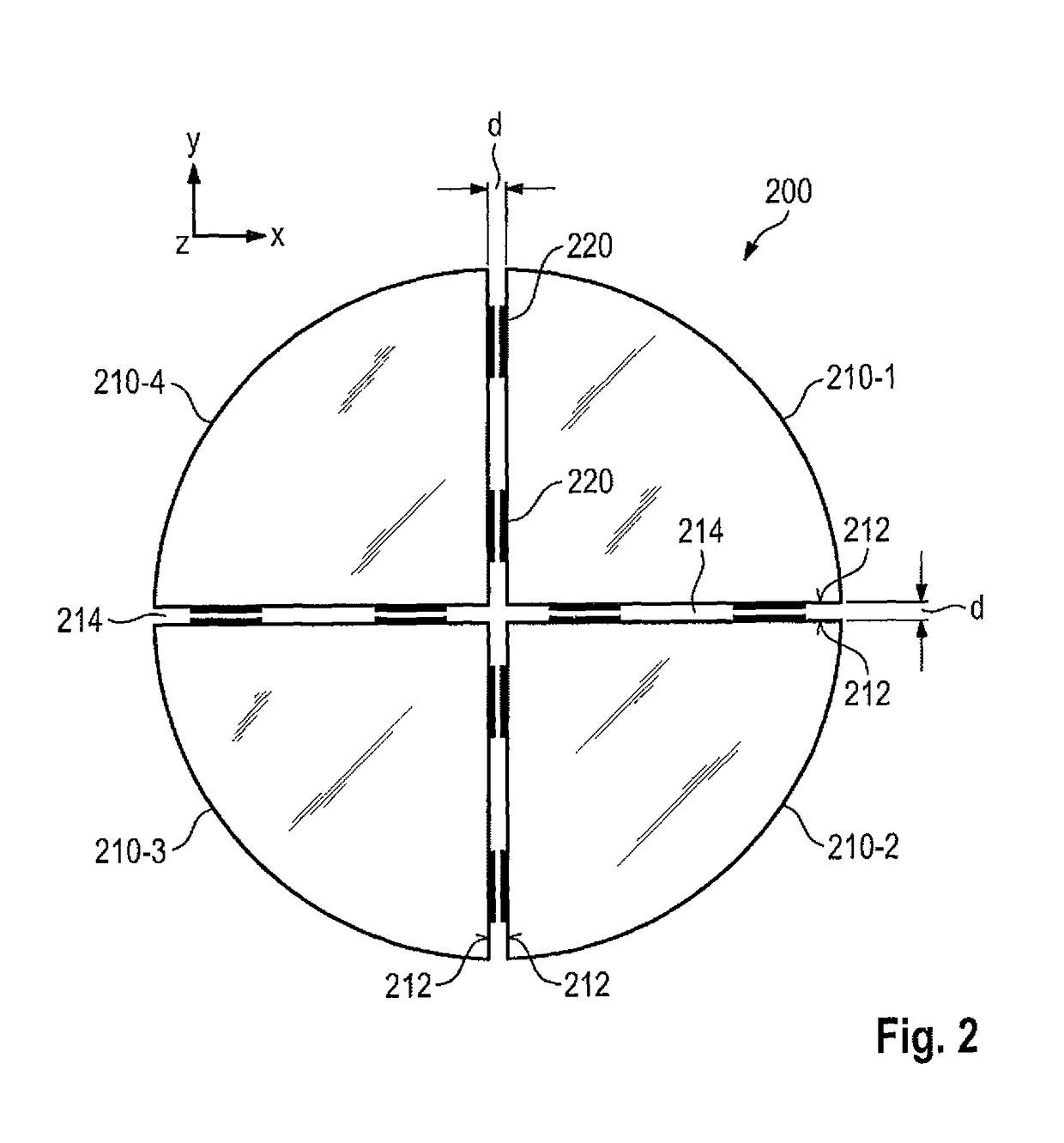
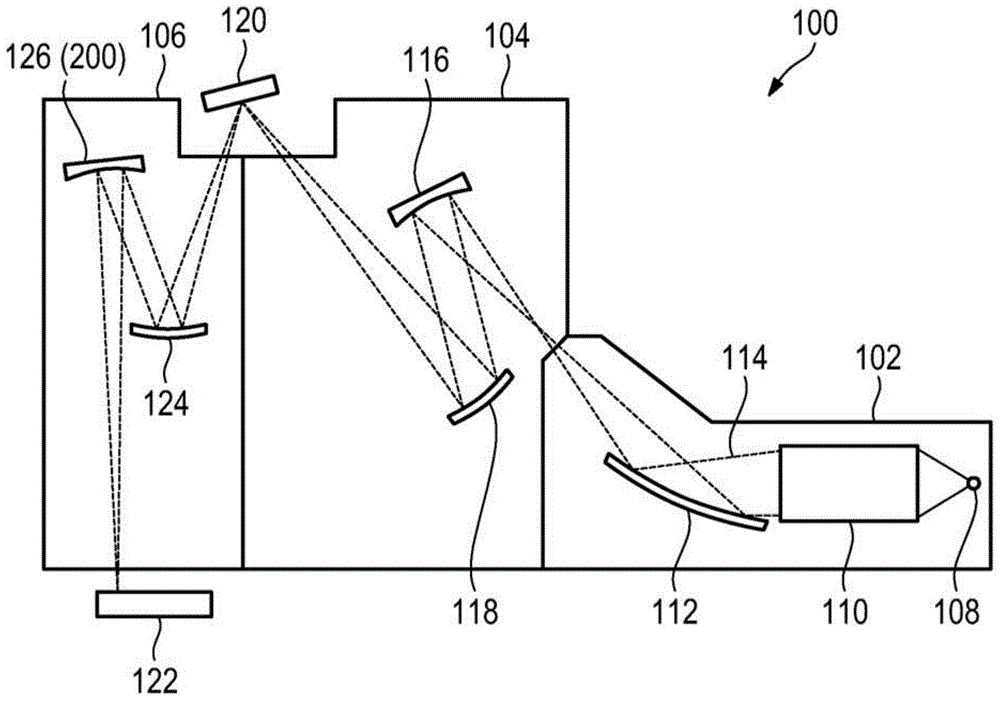
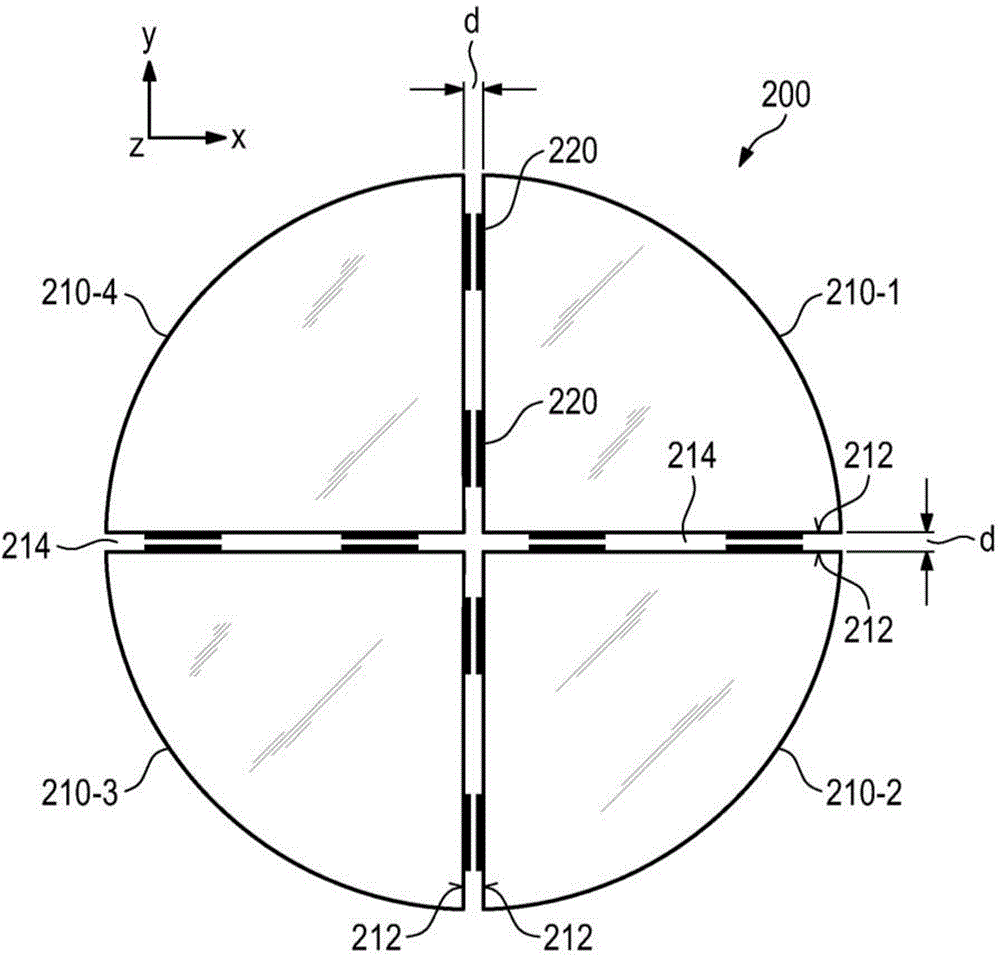
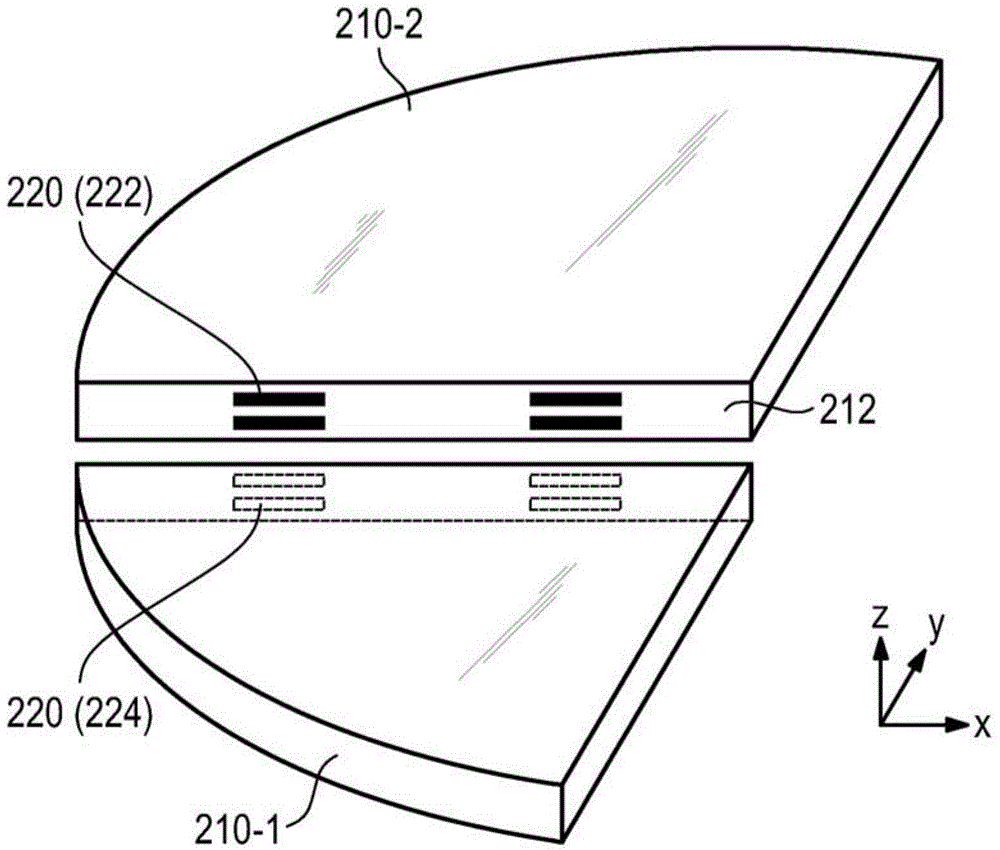
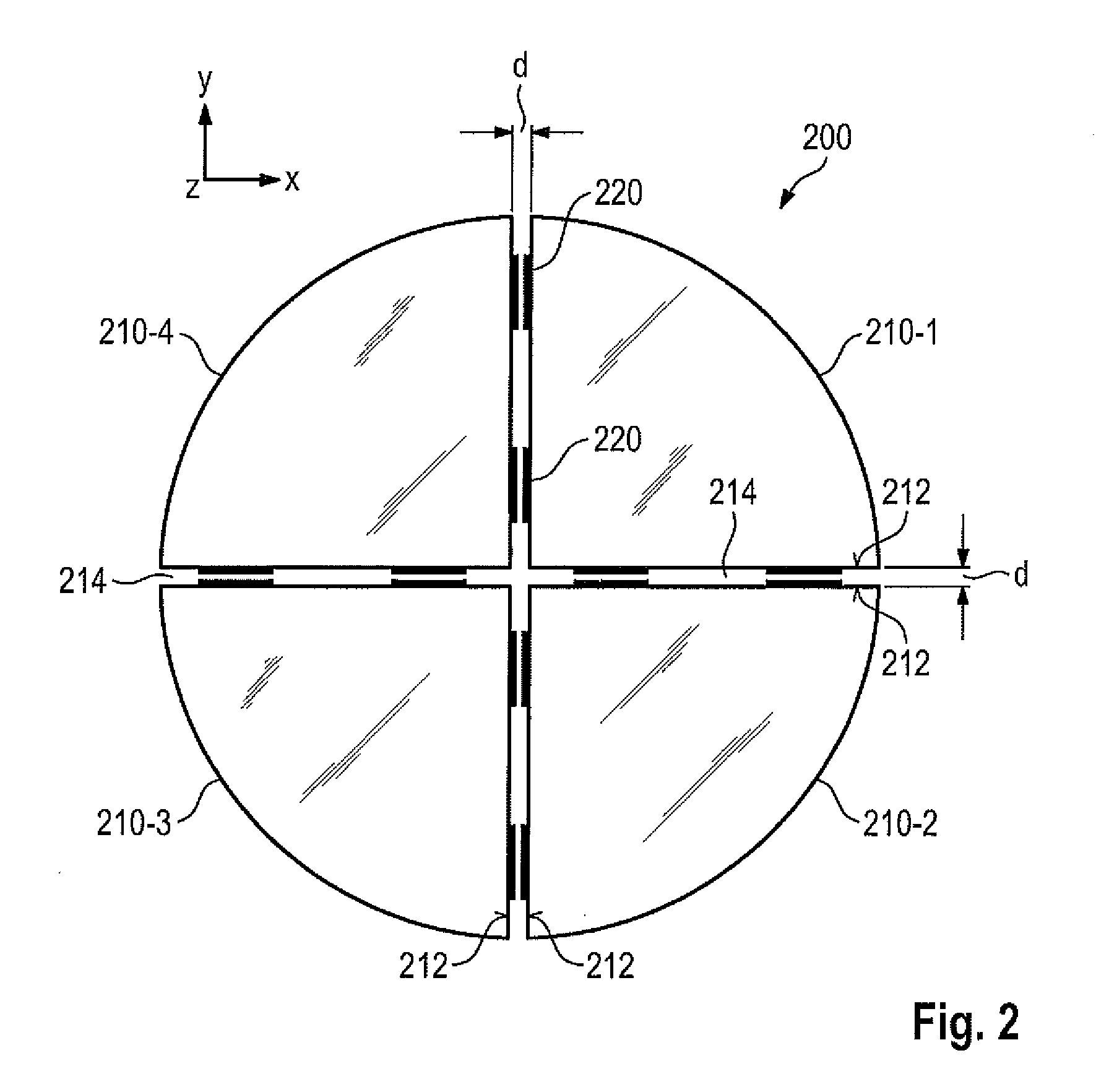
Lithography apparatus with segmented mirror
ActiveUS9846375B2Improve linearityVacuum gauge using gaseous frictional resistance variationUsing electrical meansLithographic artistPhotolithography
A lithography apparatus is disclosed, which comprises a mirror having at least two mirror segments which are joined together in such a way that an interspace is formed between the mirror segments, and a sensor for detecting the relative position of the mirror segments, wherein the sensor is arranged in the interspace between the mirror segments.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Lithography apparatus with segmented mirror
ActiveCN104428647APrecise position adjustmentSave spaceVacuum gauge using gaseous frictional resistance variationUsing electrical meansLithographic artistSegmented mirror
A lithography apparatus is disclosed, which comprises a mirror having at least two mirror segments which are joined together in such a way that an interspace is formed between the mirror segments, and a sensor for detecting the relative position of the mirror segments, wherein the sensor is arranged in the interspace between the mirror segments.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
In-ground telescope with a stationary primary objective mirror having movable collectors
InactiveUS7221504B2More stabilityThe equipment is bulkyTelescopesMountingsReflecting telescopeLand based
The present invention relates to a novel land based reflecting telescope having a stationary, equatorially mounted, segmented mirror comprised of a plurality of movable mirrored collectors. These movable collectors are arranged in hexagonal groups to form a multiple mirrored reflector, which comprises the stationary compound telescope. A secondary mirror mounted atop a tower at the focal point directs the image toward the observation cart. Observers ride the periphery of the stationary mirror at a rate of one revolution per day. A retractable air supported hypalon cover protects the large primary mirror structure.
Owner:POPIL NICHOLAS B
Lithography apparatus with segmented mirror
ActiveUS20150103327A1Improve linearityVacuum gauge using gaseous frictional resistance variationUsing electrical meansLithographic artistPhotolithography
A lithography apparatus is disclosed, which comprises a mirror having at least two mirror segments which are joined together in such a way that an interspace is formed between the mirror segments, and a sensor for detecting the relative position of the mirror segments, wherein the sensor is arranged in the interspace between the mirror segments.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com