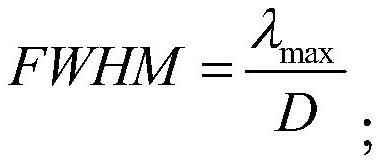Patents
Literature
53 results about "Airy disk" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
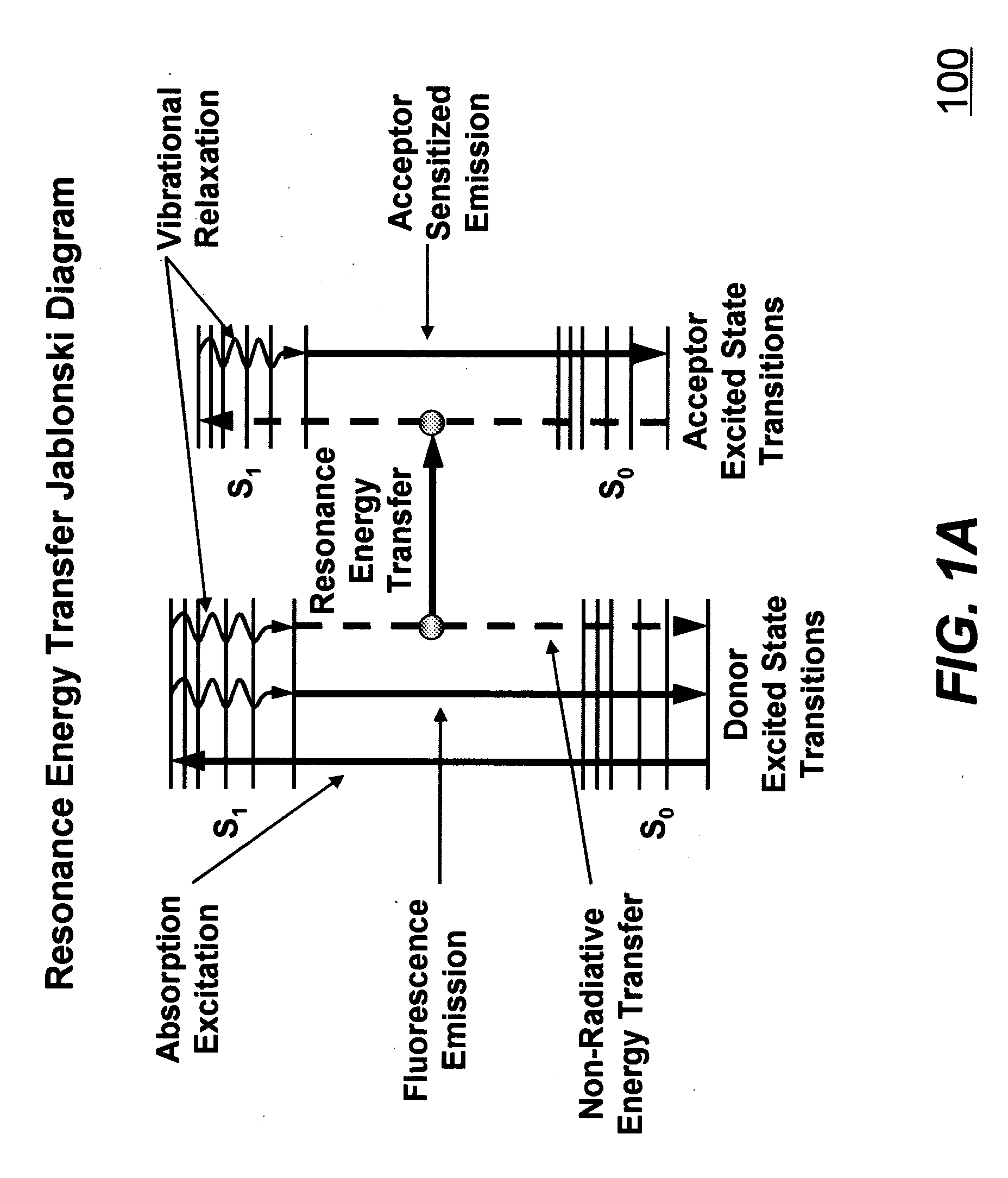
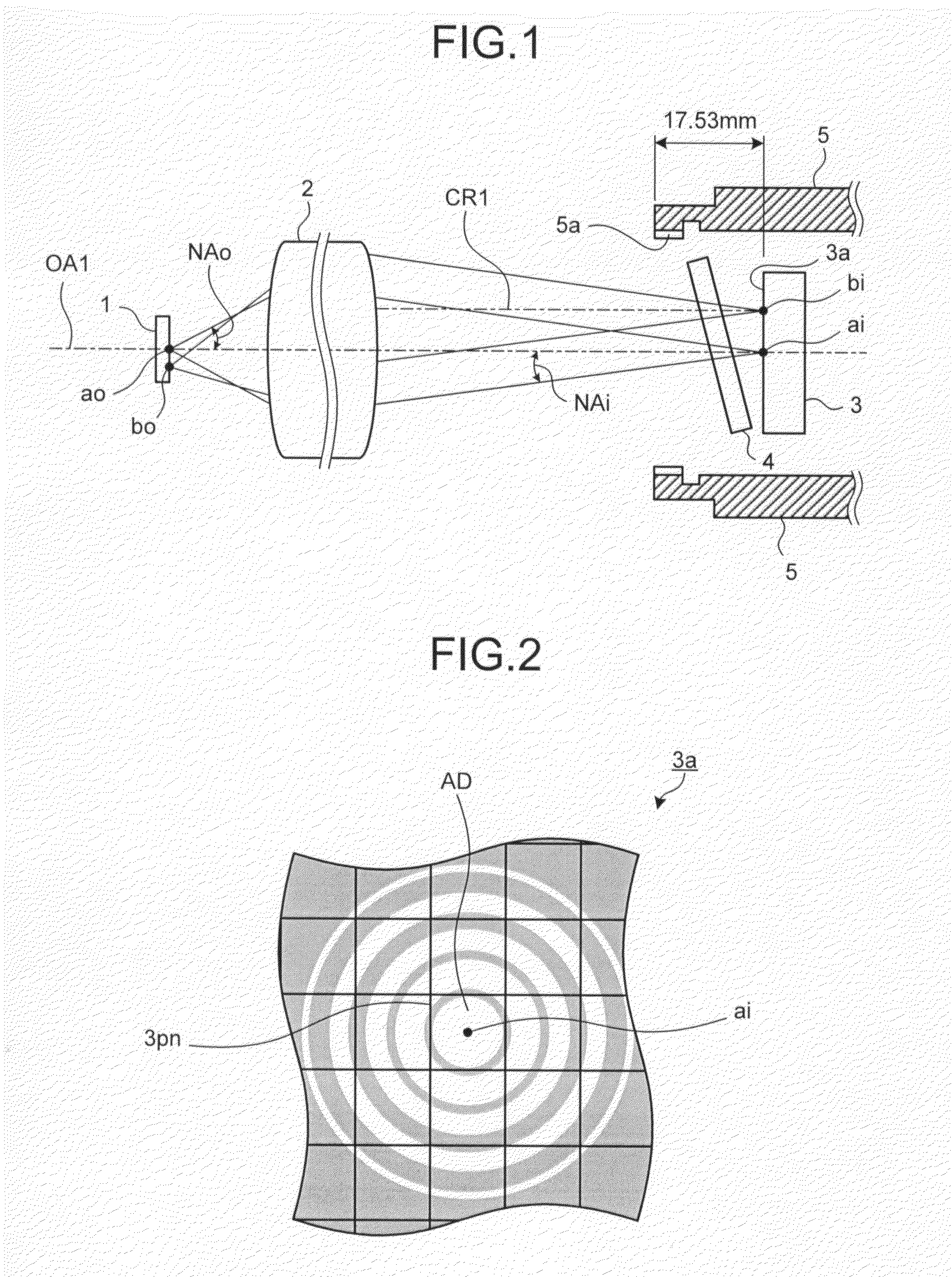
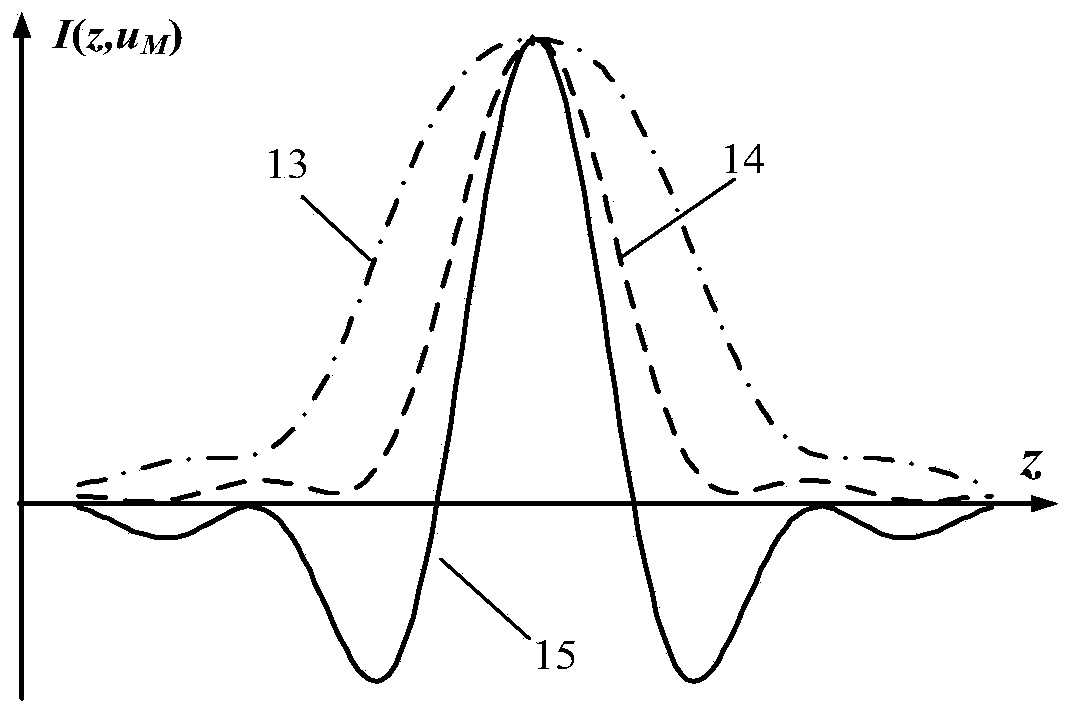
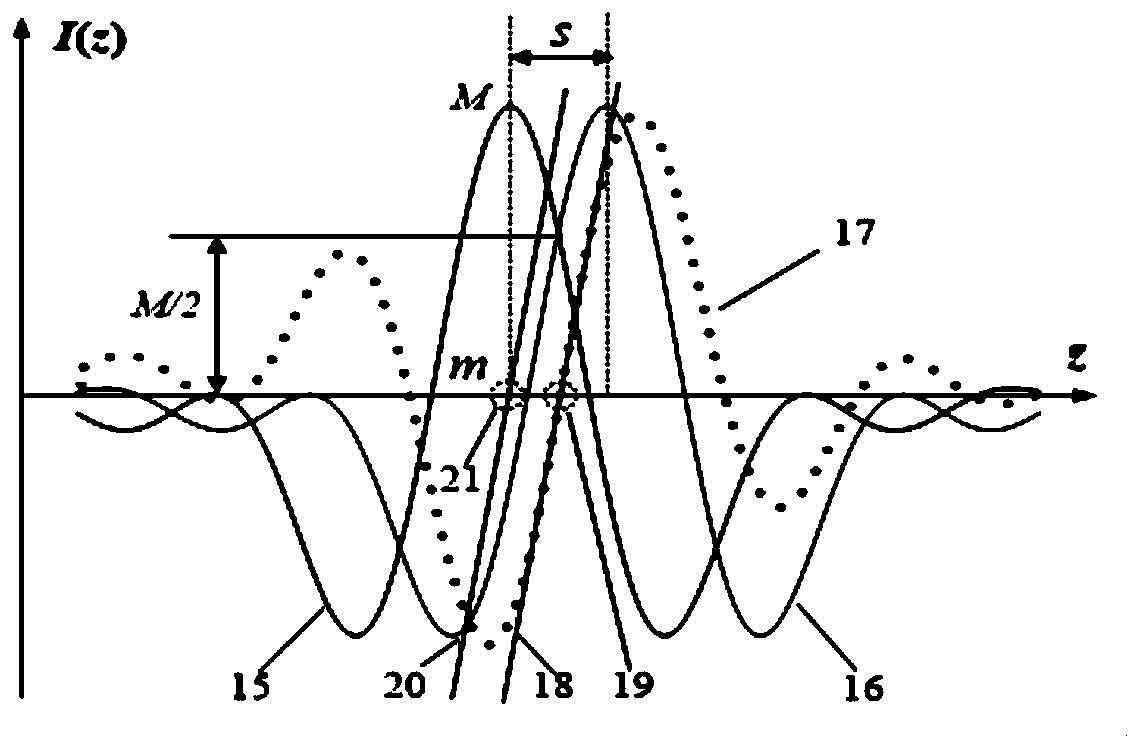
In optics, the Airy disk (or Airy disc) and Airy pattern are descriptions of the best-focused spot of light that a perfect lens with a circular aperture can make, limited by the diffraction of light. The Airy disk is of importance in physics, optics, and astronomy.
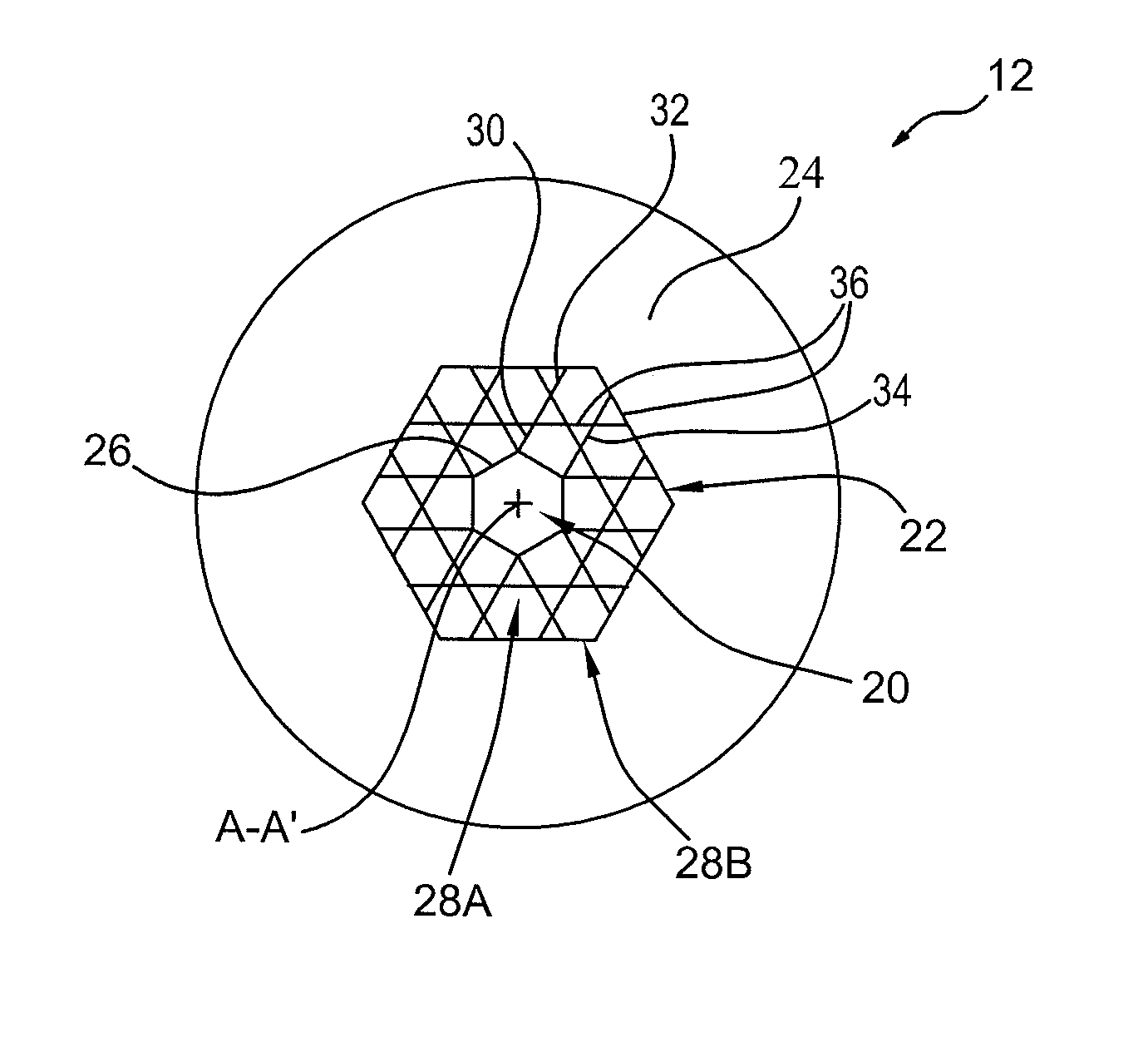
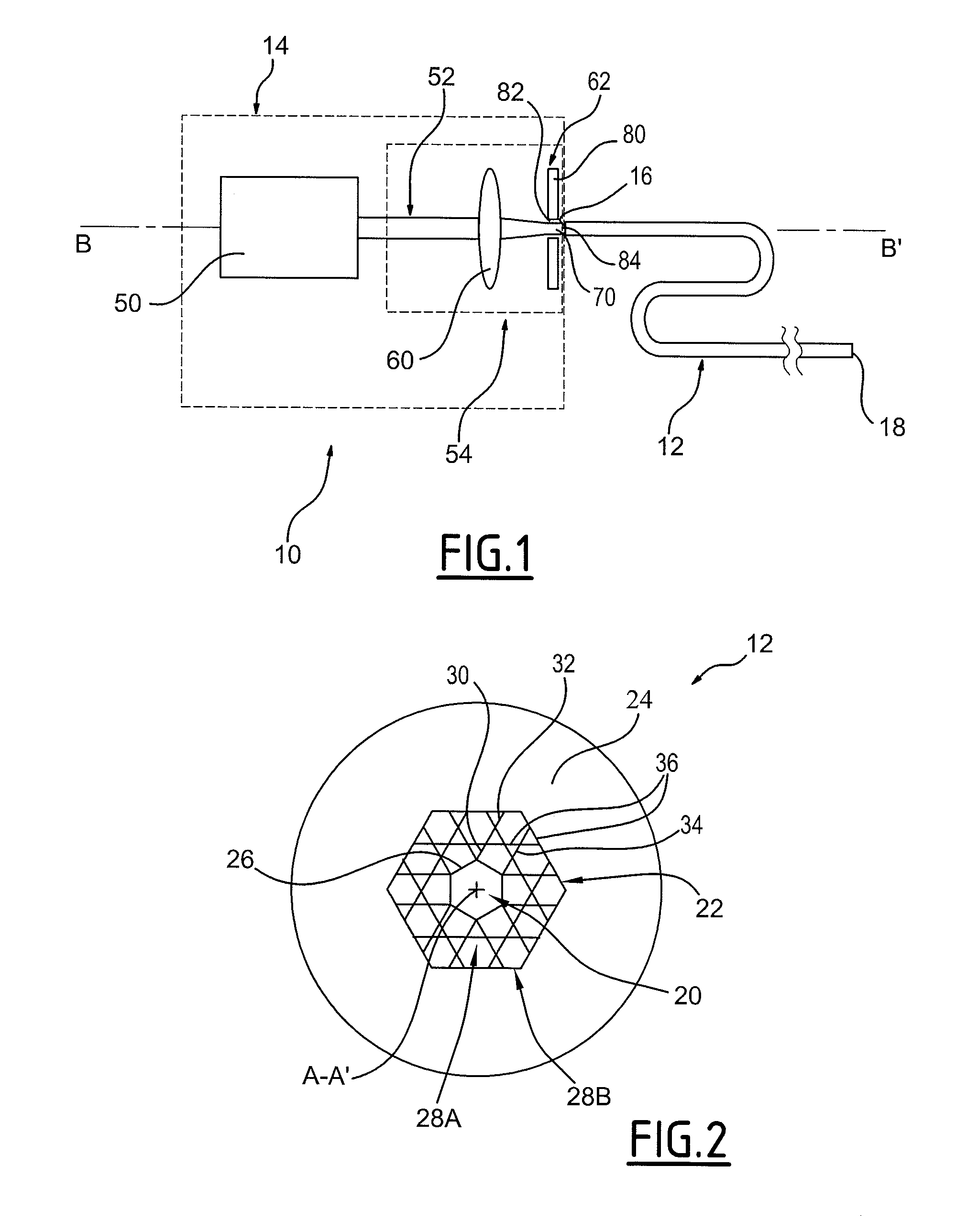
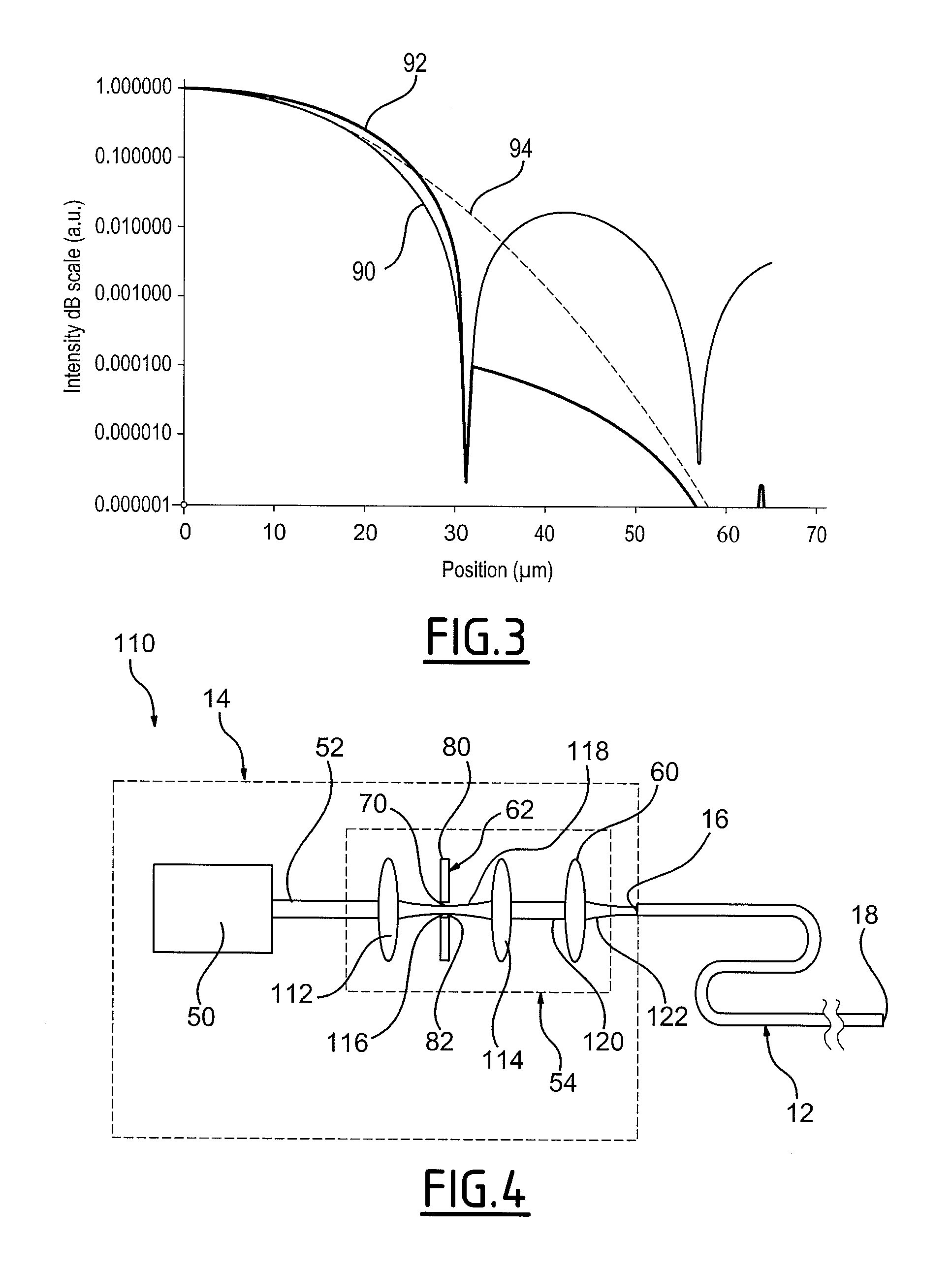
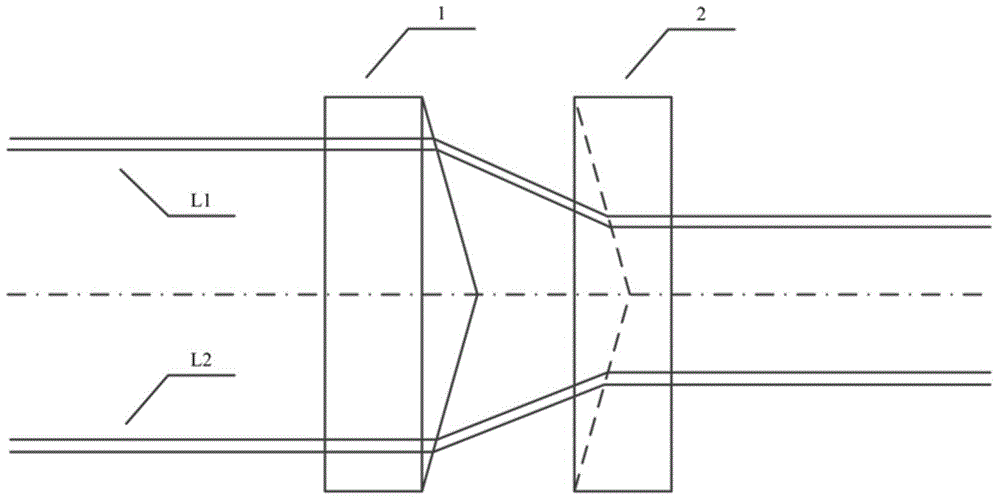
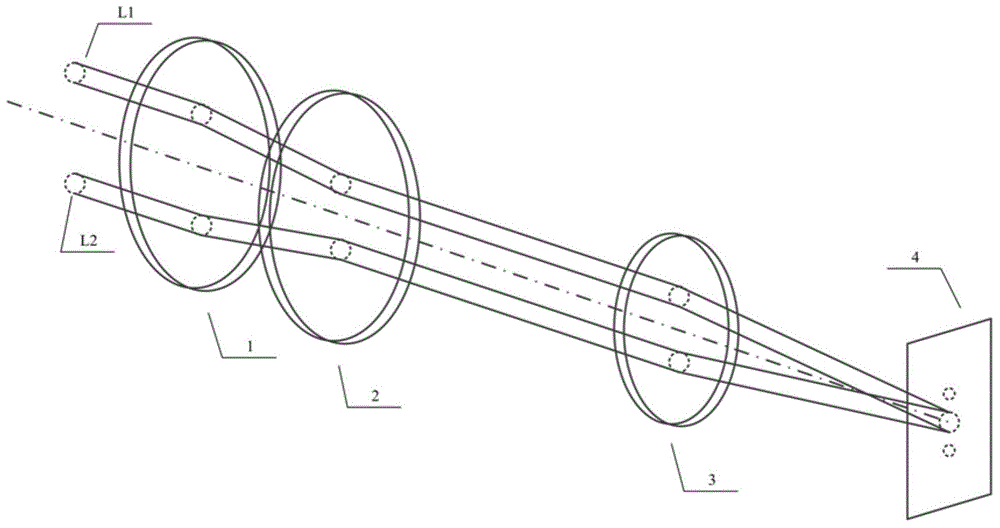
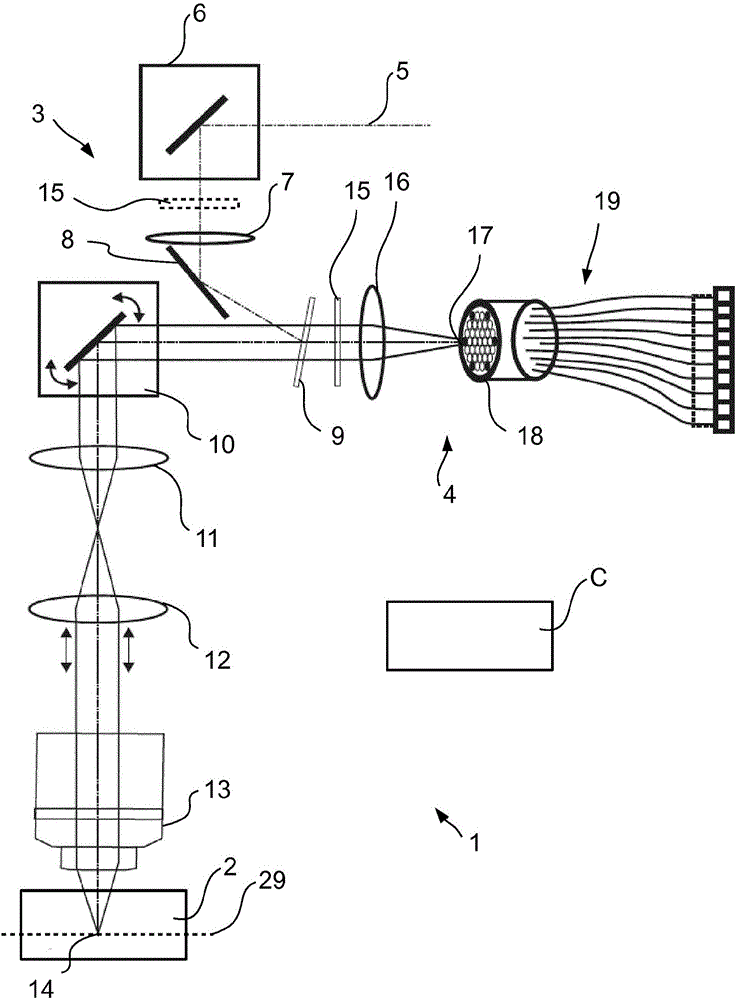
Device for transmitting light energy and associated transmission method
InactiveUS20130022060A1High energyHighly robustLaser using scattering effectsOptical light guidesLight energyLight beam
A device is provided that includes an optical fiber and an assembly illuminating the optical fiber capable of illuminating the optical fiber at an upstream end. The optical fiber includes a hollow core and an anti-resonant annular cladding arranged around the hollow core. The illuminating assembly generates a focused beam of Airy spot shape for injection into the input of the optical fiber.
Owner:MEGGITT FRANCE
Method and system for far-field microscopy to exceeding diffraction-limit resolution
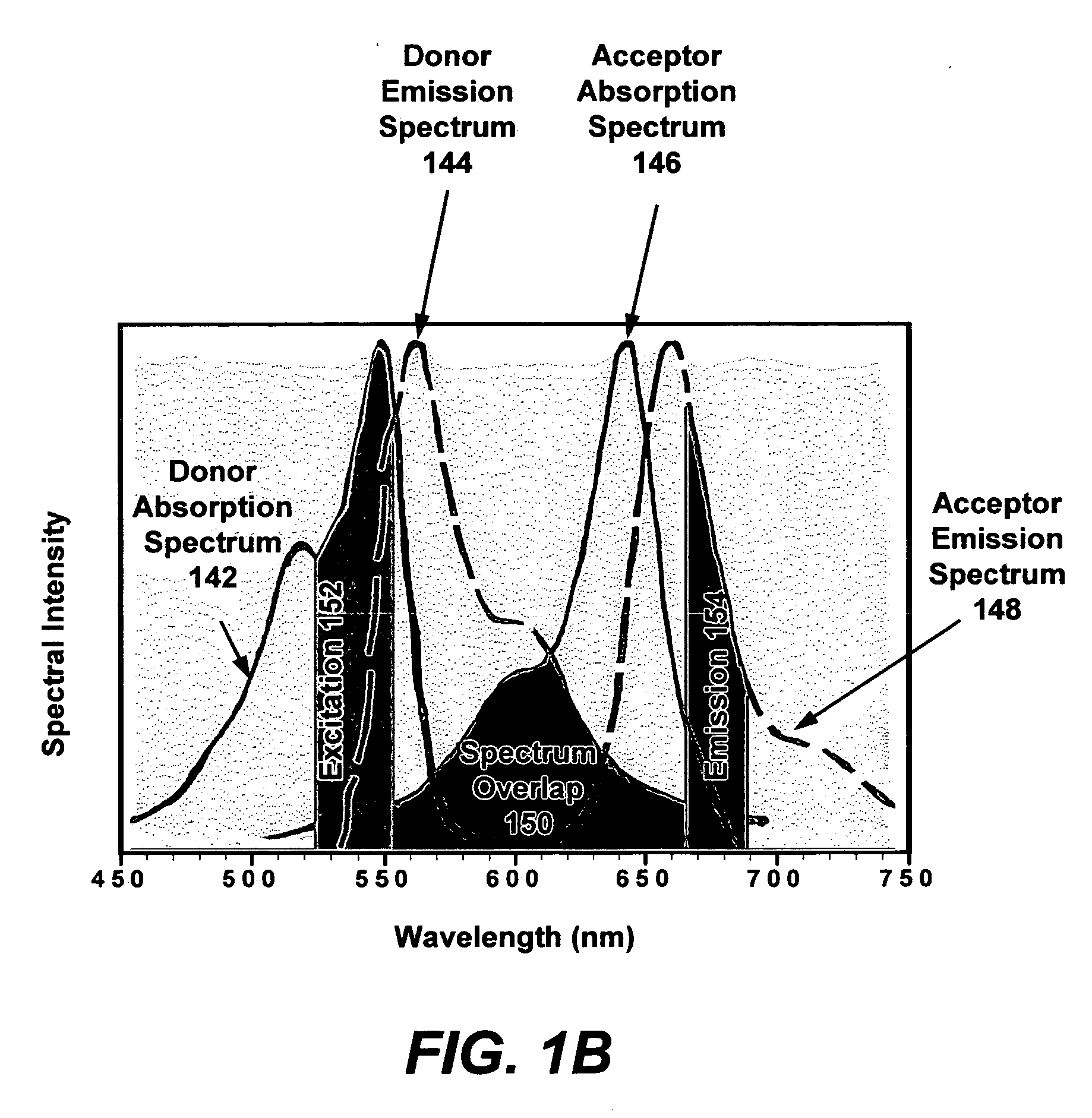
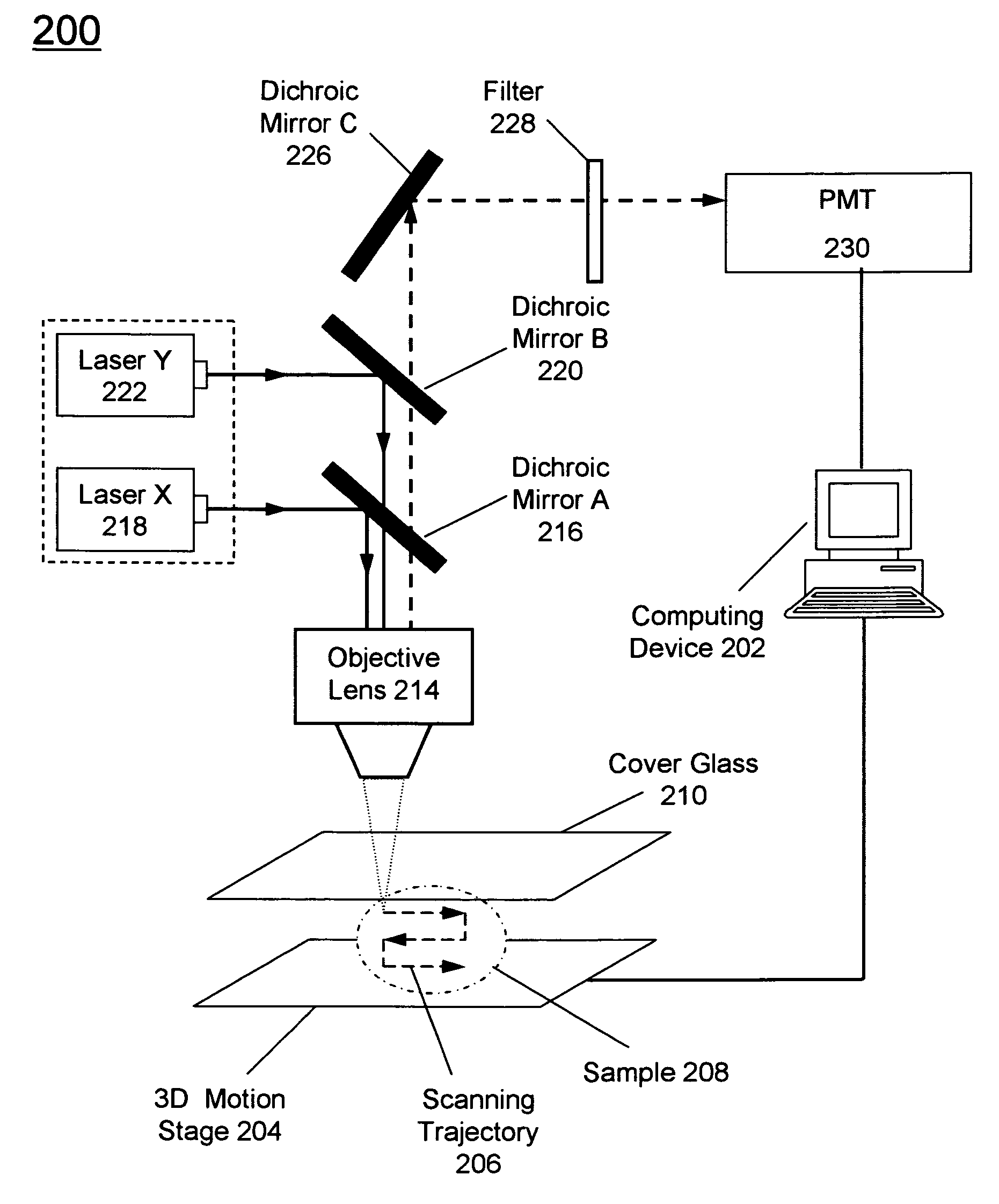
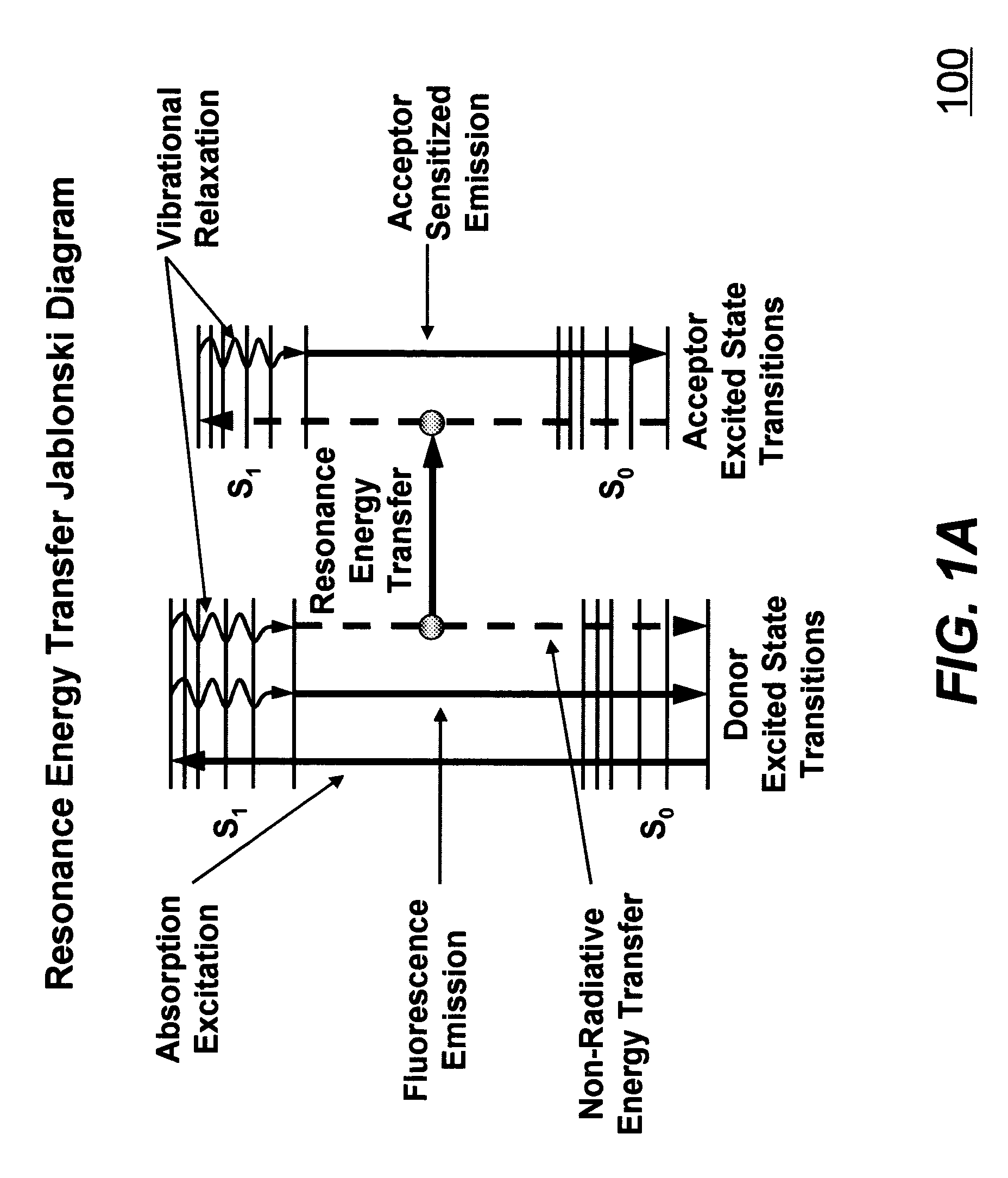
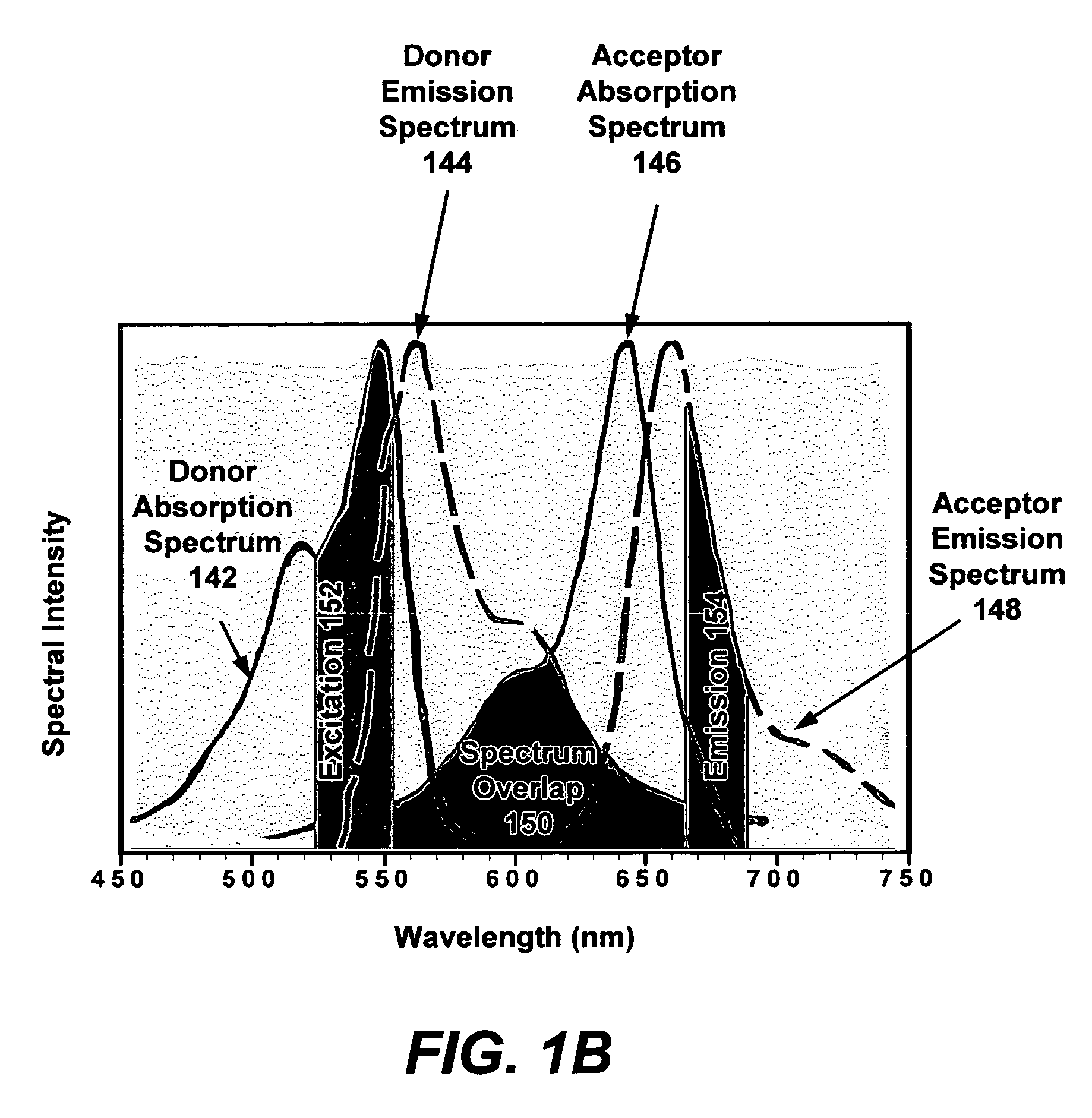
The bio-sample (e.g., a live cell) is labeled with a proper number of nanoparticles. Each nanoparticle is pre-co-doped with a controlled ratio of fluorophore donors and acceptors. Two laser pulses are applied to the bio-sample. The first laser pulse has a center wavelength near the peak of absorption spectrum of acceptors. The intensity of first laser pulse is adjusted such that FRET saturation occurs near the center of the focal spot. The focal spot of the first laser pulse is a diffraction-limited Airy disk that has the highest laser intensity in the center of the focal spot. The second laser has a center wavelength in the emission spectrum of acceptors and with a uniform intensity distribution throughout the focal spot. The fluorescence emission from acceptors after two laser pulses is from an area that is smaller than the diffraction-limited focal spot. Hence, a higher than diffraction-limit resolution is achieved.
Owner:LASER MICROTECH
Low-Light Specimen Image Pickup Unit and Low-Light Specimen Image Pickup Apparatus
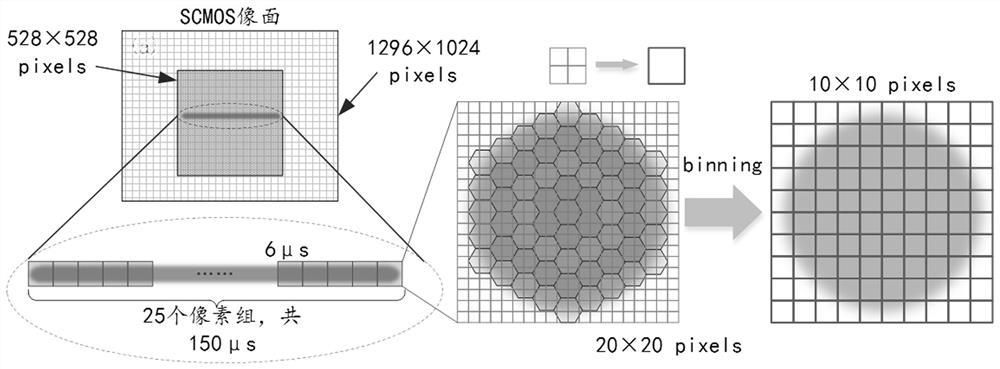
In order to be able to take an image of a specimen emitting low light in a short exposure time by a cooled CCD at about 0° C., a low-light specimen image pickup unit has an imaging optical system forming a specimen image of a specimen having a point light source emitting a low light, and the low-light specimen image pickup unit further has an image pickup unit having a plurality of pixels receiving incident light, for taking an image corresponding to the specimen image. In the low-light specimen image pickup unit, the imaging optical system is telecentric to a side of the specimen image of the imaging optical system, and condenses the low light emitted from the point light source to form an Airy disk of a size which is substantially the same as a pixel of the pixels, or which is smaller than the pixel. Here, the pixel receives the low light emitted from the point light source.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Method and system for far-field microscopy to exceeding diffraction-limit resolution
The bio-sample (e.g., a live cell) is labeled with a proper number of nanoparticles. Each nanoparticle is pre-co-doped with a controlled ratio of fluorophore donors and acceptors. Two laser pulses are applied to the bio-sample. The first laser pulse has a center wavelength near the peak of absorption spectrum of acceptors. The intensity of first laser pulse is adjusted such that FRET saturation occurs near the center of the focal spot. The focal spot of the first laser pulse is a diffraction-limited Airy disk that has the highest laser intensity in the center of the focal spot. The second laser has a center wavelength in the emission spectrum of acceptors and with a uniform intensity distribution throughout the focal spot. The fluorescence emission from acceptors after two laser pulses is from an area that is smaller than the diffraction-limited focal spot. Hence, a higher than diffraction-limit resolution is achieved.
Owner:LASER MICROTECH
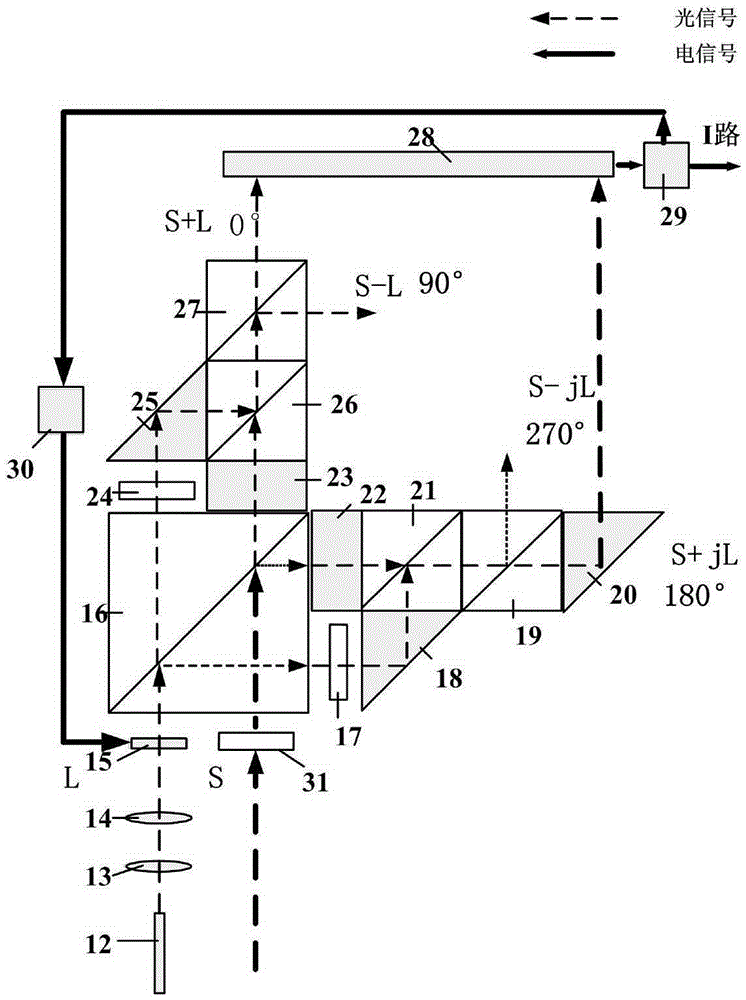
Spatial optical 90-degree mixer with high mixing efficiency
ActiveCN105353520AImprove the disadvantage of loss of signal light energyCompact structureOptical elementsBeam splitterLight spot
The invention discloses a free spatial optical 90-degree mixer device, belonging to the technical field of wireless communications. For solving the problems of the prior art, the device comprises a local oscillator laser, an expanded beam collimating lens, a positive lens, an electronic control polarizer, a first non-polarized beam splitter, a second non-polarized beam splitter, a third non-polarized beam splitter, a first polarized beam splitter, a second polarized beam splitter, a first right-angled reflecting prism, a second right-angled reflecting prism, a third right-angled reflecting prism, a first parallel flat plate, a second parallel flat plate, a first quarter wave plate, a second quarter wave plate, a balance detector, an electric power divider, an electronic control polarizer control circuit and a third quarter wave plate. Light spots of local oscillator light are converted into Airy disks by using the expanded beam collimating lens and the positive lens; the polarization state is controlled by the electronic control polarizer, the electric power divider, the electronic control polarizer control circuit and the third quarter wave plate, to realize consistent polarization state of the local oscillator light and signal light, so that the defect of loss of signal light energy in the original polarization control device is overcome.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
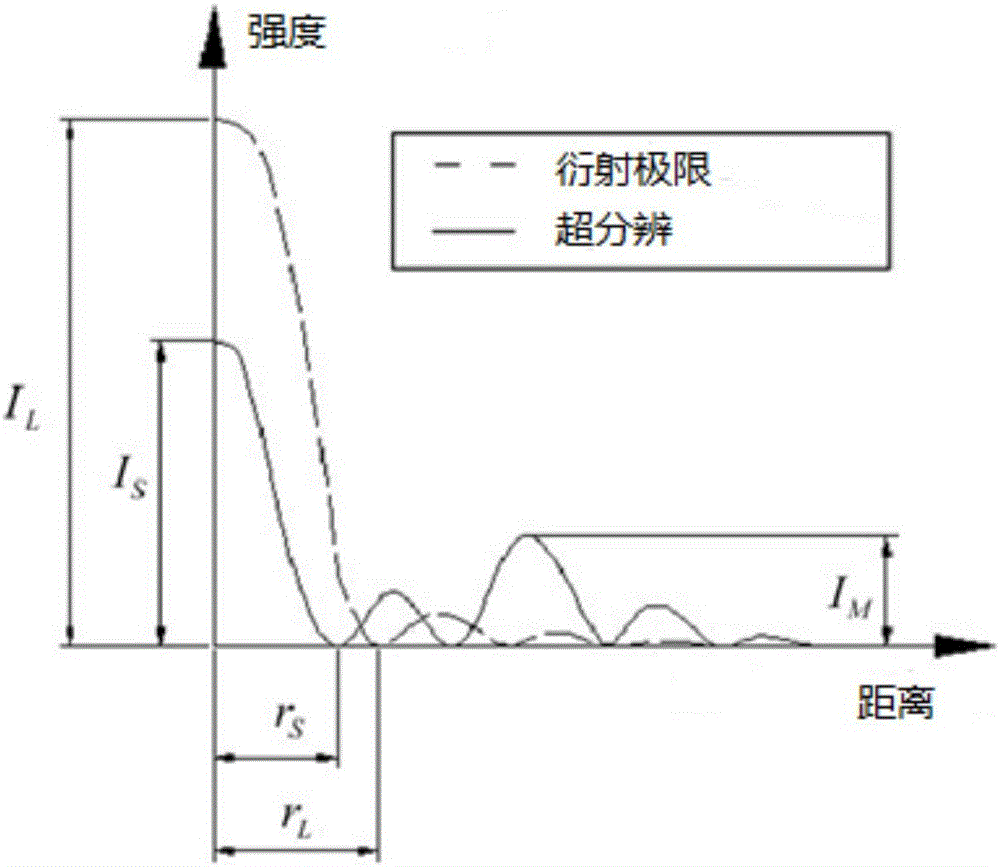
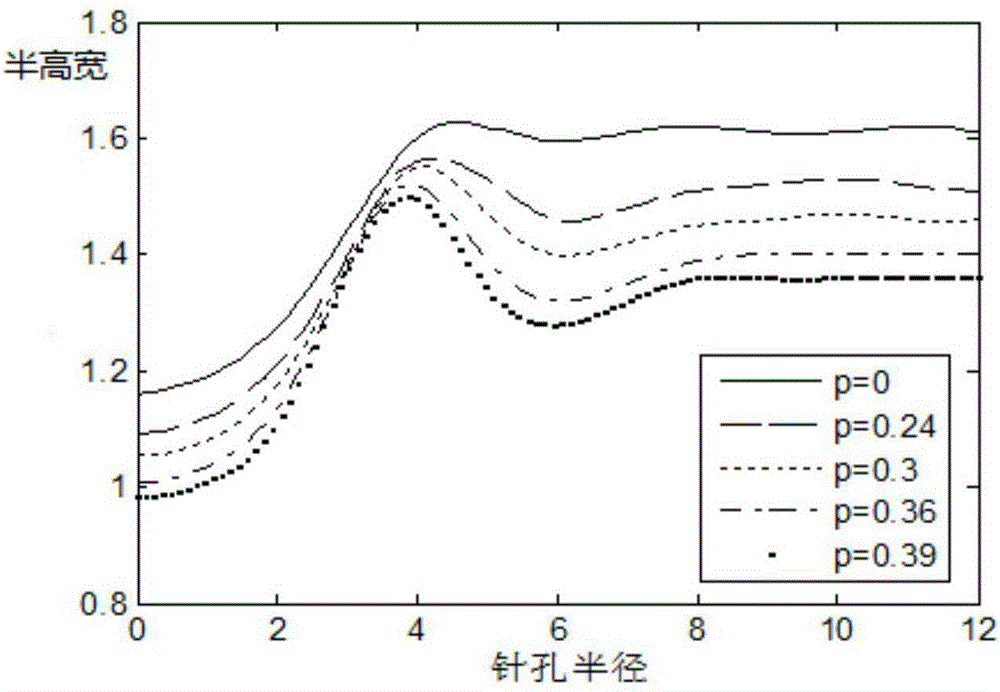
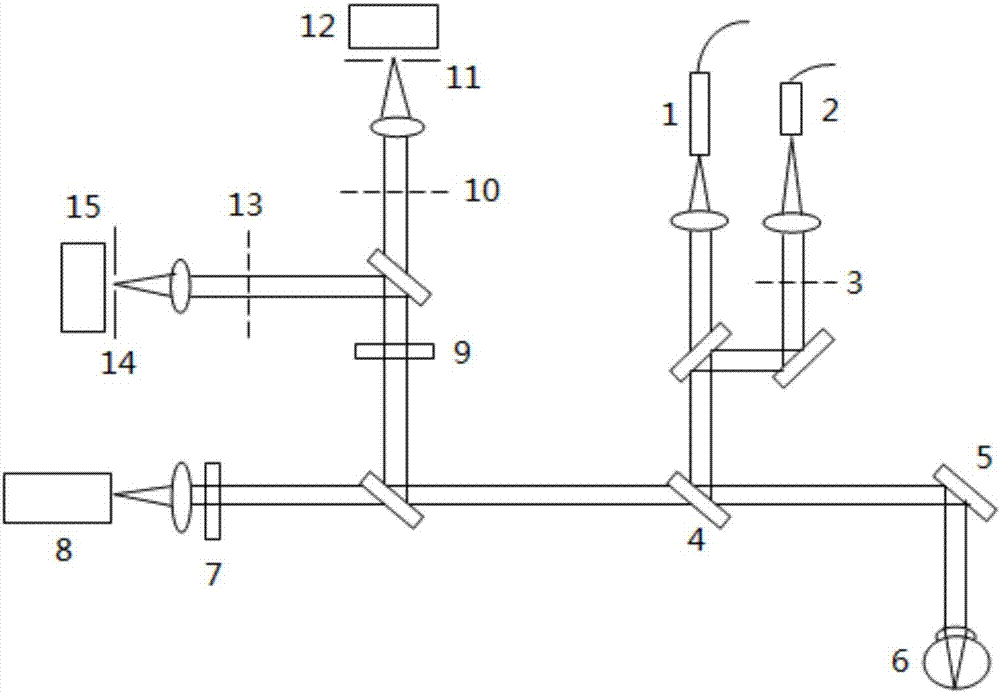
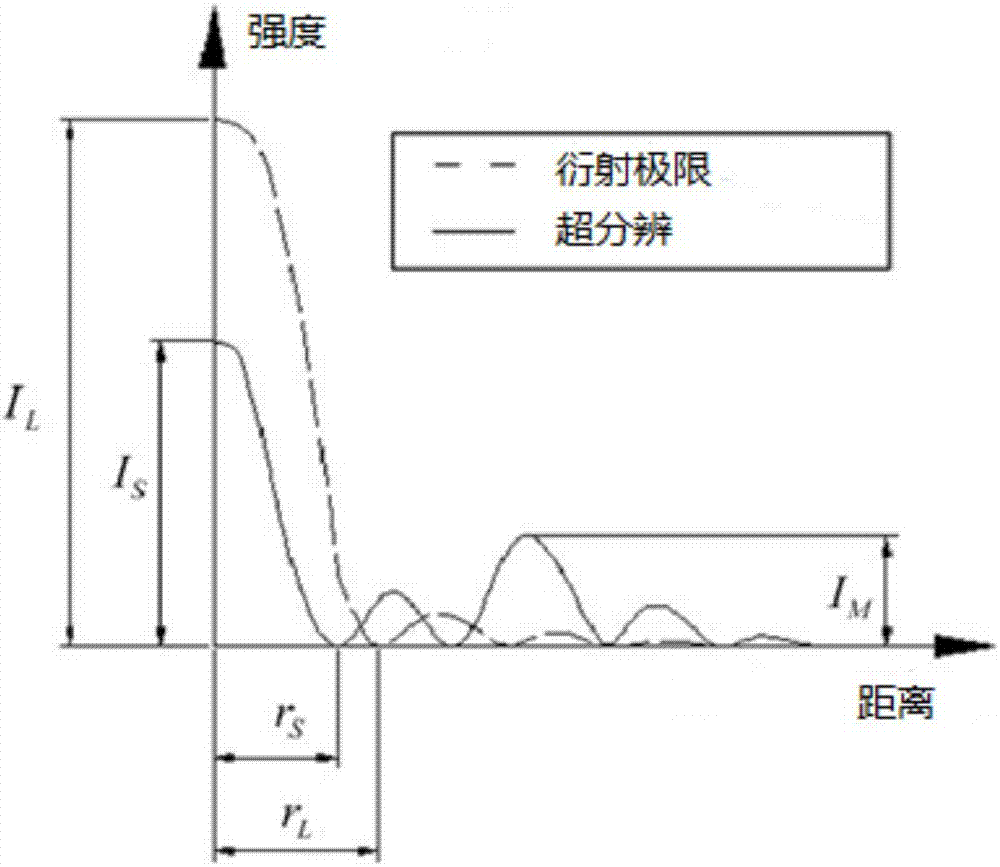
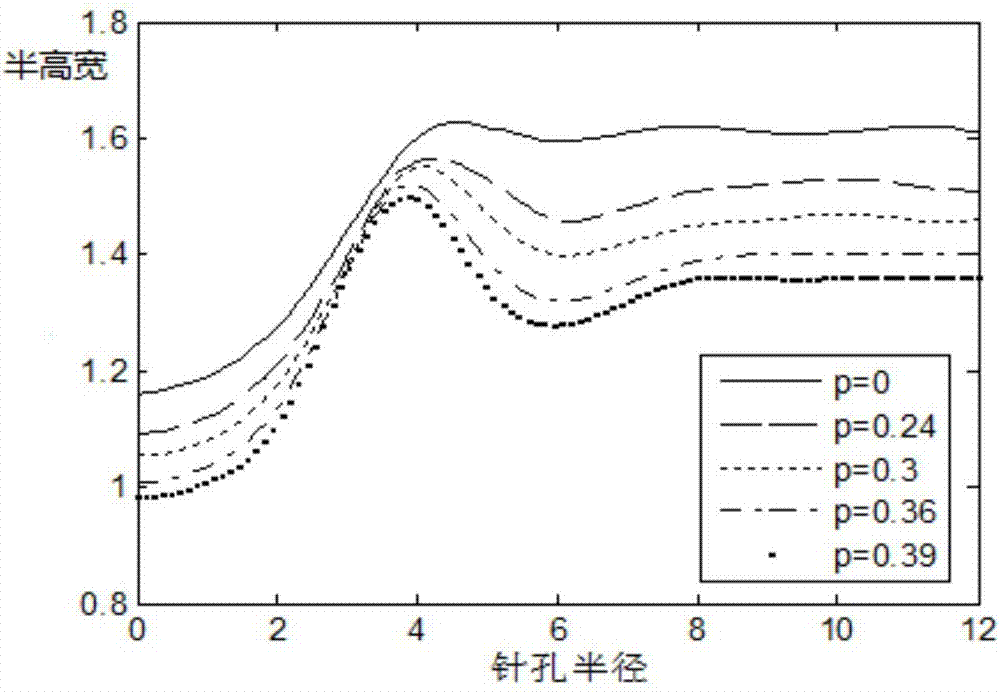
Super-resolution confocal ophthalmoscope based on optical pupil filter and dark field technique
The invention discloses a super-resolution confocal ophthalmoscope based on an optical pupil filter and a dark field technique. The super-resolution confocal ophthalmoscope is capable of accurately acquiring super-resolution dark field images of retinas of living human eyes in real time, and comprises a beacon light source, an imaging light source, an optical pupil filter, a two-dimensional scanning galvanometer, a Hartmann sensor, a deformable mirror, an optical filter and a photoelectric detection system. The beacon light source is used for correcting human eye aberrations; the imaging light source is used for acquiring human eye images. The operating method comprises the following steps: characterizing resolution according to Rayleigh criterion by using full width at half maximum, adding a two-zone type phase optical pupil filter at an illumination end, wherein the pinhole is equal to Airy disk size; allowing the pinhole to be equal to 1.5 times that of Airy disk size when the filter(s) is / are arranged at the imaging end or two ends, so that the diffraction limit condition can be realized when the transverse full width at half maximum is less than the pinhole of a general microscope equal to the Airy disk size, and the super-resolution image can be acquired at a super-resolution ratio. On the basis, the pinhole equal to the Airy disk size is translated by an Airy disk distance, the pinhole equal to 1.5 times that of the Airy disk size is subjected to central blocking or linear blocking, so that dark field imaging can be realized.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Imaging apparatus for low-light sample
An imaging apparatus for low-light sample comprises: an image-forming optical system which includes an objective lens and an image-forming lens and forms the sample image of an sample having a point light source, where the point light source emits weak light including fluorescence; an illumination optical system which radiates light from an illumination light source to the sample to make the sample emit fluorescence; and an image capturing means which includes a plurality of pixels and captures the image corresponding to the sample image. The illumination optical system radiates light from the illumination light source to the sample with the light not traveling via the objective lens, the image-forming optical system is approximately telecentric and is provided with a filter which is arranged between the objective lens and the image forming lens and wavelength-selectively extracts fluorescence from the sample, and the image-forming optical system is formed in such a way that the image-forming optical system collects weak light from the point light source to form airy disks the sizes of which are is approximately the same as or smaller than the sizes of the pixels.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Low-light specimen image pickup unit and low-light specimen image pickup apparatus
ActiveUS7630065B2Television system detailsColor/spectral properties measurementsOptoelectronicsPoint light source
In order to be able to take an image of a specimen emitting low light in a short exposure time by a cooled CCD at about 0° C., a low-light specimen image pickup unit has an imaging optical system forming a specimen image of a specimen having a point light source emitting a low light, and the low-light specimen image pickup unit further has an image pickup unit having a plurality of pixels receiving incident light, for taking an image corresponding to the specimen image. In the low-light specimen image pickup unit, the imaging optical system is telecentric to a side of the specimen image of the imaging optical system, and condenses the low light emitted from the point light source to form an Airy disk of a size which is substantially the same as a pixel of the pixels, or which is smaller than the pixel. Here, the pixel receives the low light emitted from the point light source.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Duty ratio adjusting device of two-dimensional (2D) large-scale laser beam array
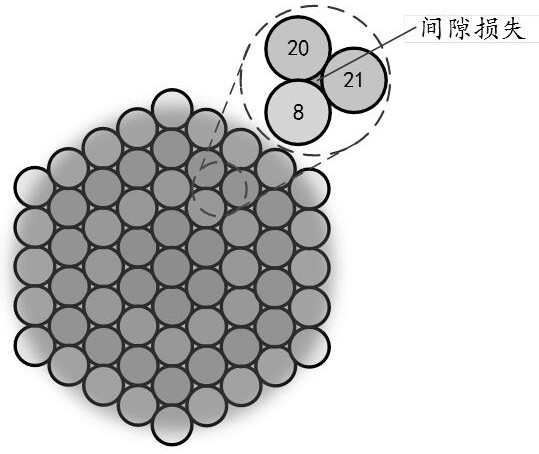
Provided is a duty ratio adjusting device of a 2D large-scale laser beam array. The device comprises a convex pyramid prism and a concave pyramid prism, wherein the convex pyramid prism and concave pyramid prism are arranged coaxially, the diameters of the two pyramid prisms are the same, the edge thickness of the two pyramid prisms are the same, and conical surfaces of the two pyramid prisms are complementary. The device can adjust the duty ratio of the 2D large-scale laser beam array, and further improve the brightness of far-field Airy points of coherent combination. The device has the advantages including wide duty-ratio adjustment range, convenient adjustment, simple and compact structure and high stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
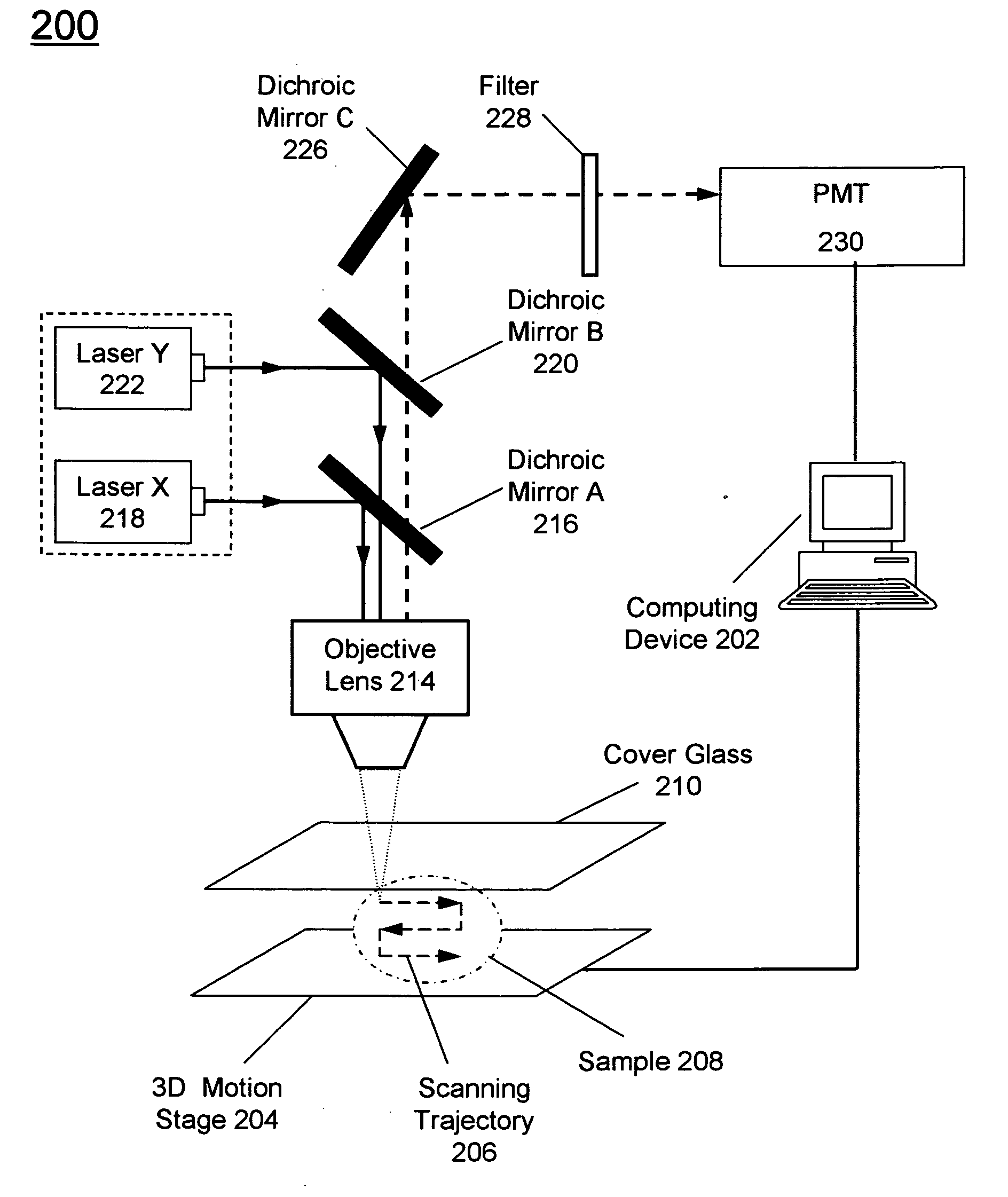
High-resolution scanning microscopy with discrimination between at least two wavelength ranges
ActiveUS20170227749A1Reduce adjustmentMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesSpatially resolvedTwo dimensional detector
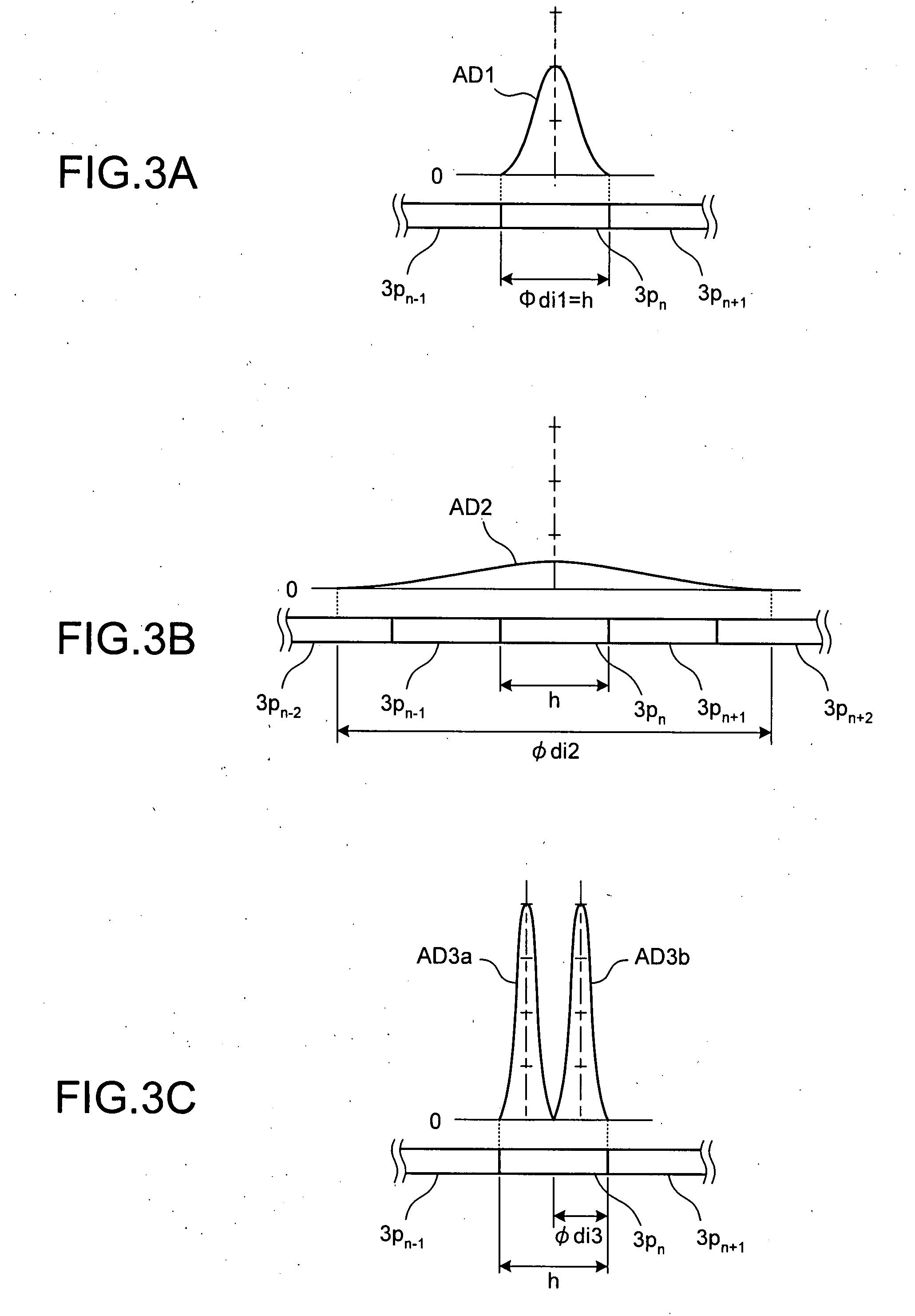
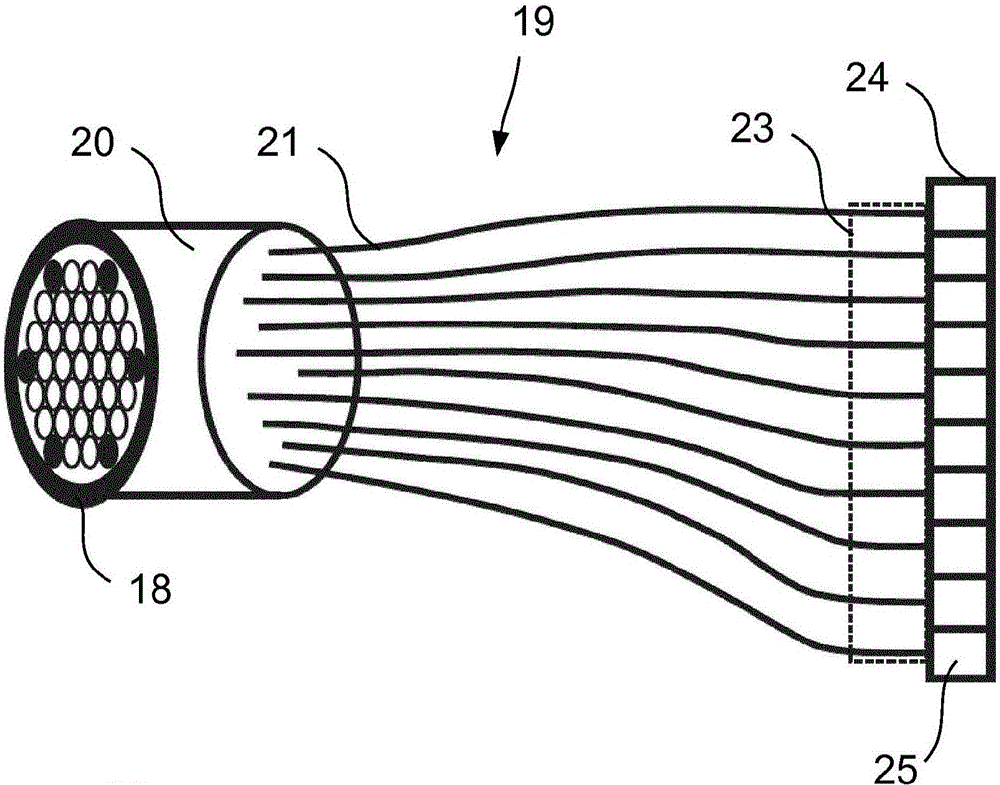
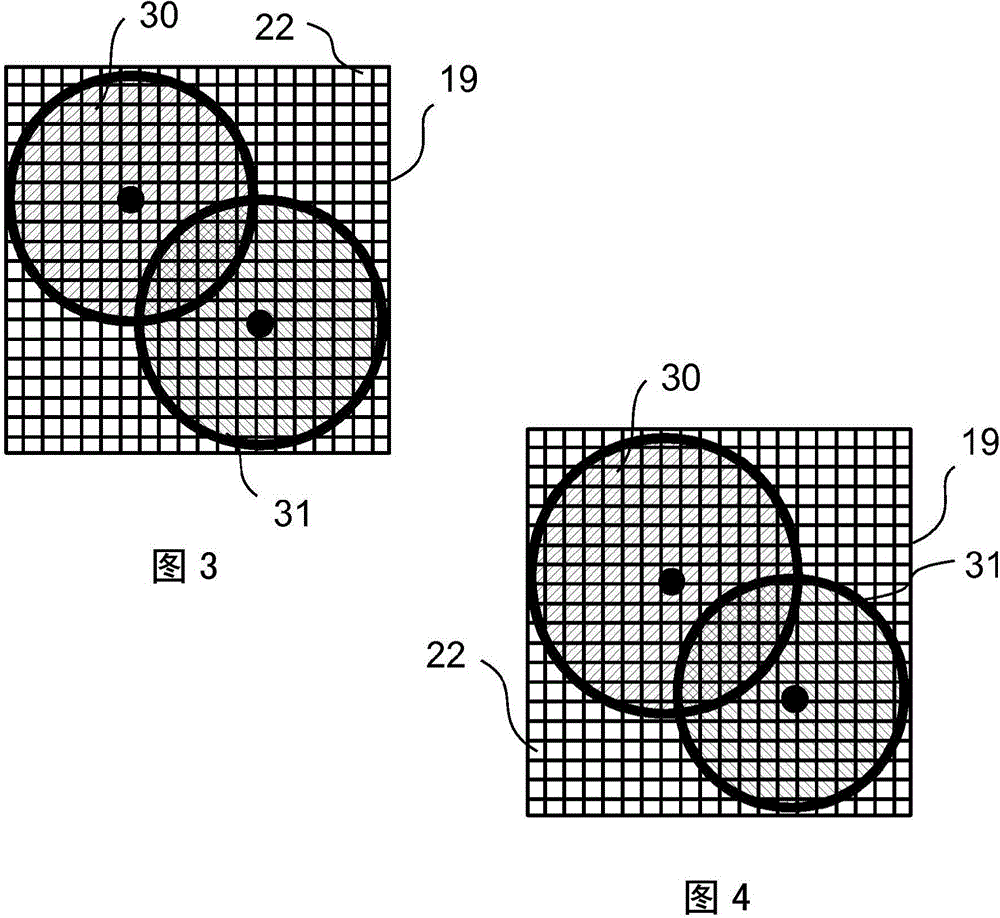
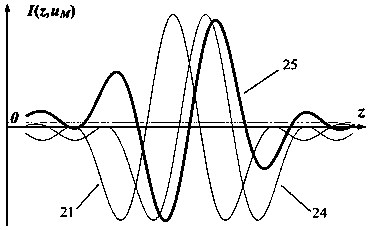
A microscopy high-resolution scanning method, including exciting a sample with illumination radiation focused at a point to form a diffraction-limited illumination spot so as to emit fluorescence radiation. The point is imaged in a diffraction image on a spatially resolving two-dimensional detector. The sample is scanned at scanning positions with increments that are smaller than half the diameter of the spot. An image of the sample with a resolution increased beyond a resolution limit of the image is generated from the data of the two-dimensional detector and the scanning positions. To discriminate between at least two predetermined wavelength ranges in the fluorescence radiation of the sample, Airy disks corresponding to the wavelength ranges are generated on the two-dimensional detector, the Airy disks being offset laterally from one another such that the diffraction image consists of the mutually offset Airy disks. The Airy disks are evaluated when generating the sample image.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Method for measuring bilateral dislocation differential confocal radius of curvature
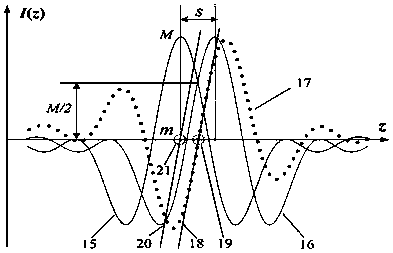
ActiveCN109990733AHigh sensitivityImprove signal-to-noise ratioUsing optical meansInterference resistanceComputer vision
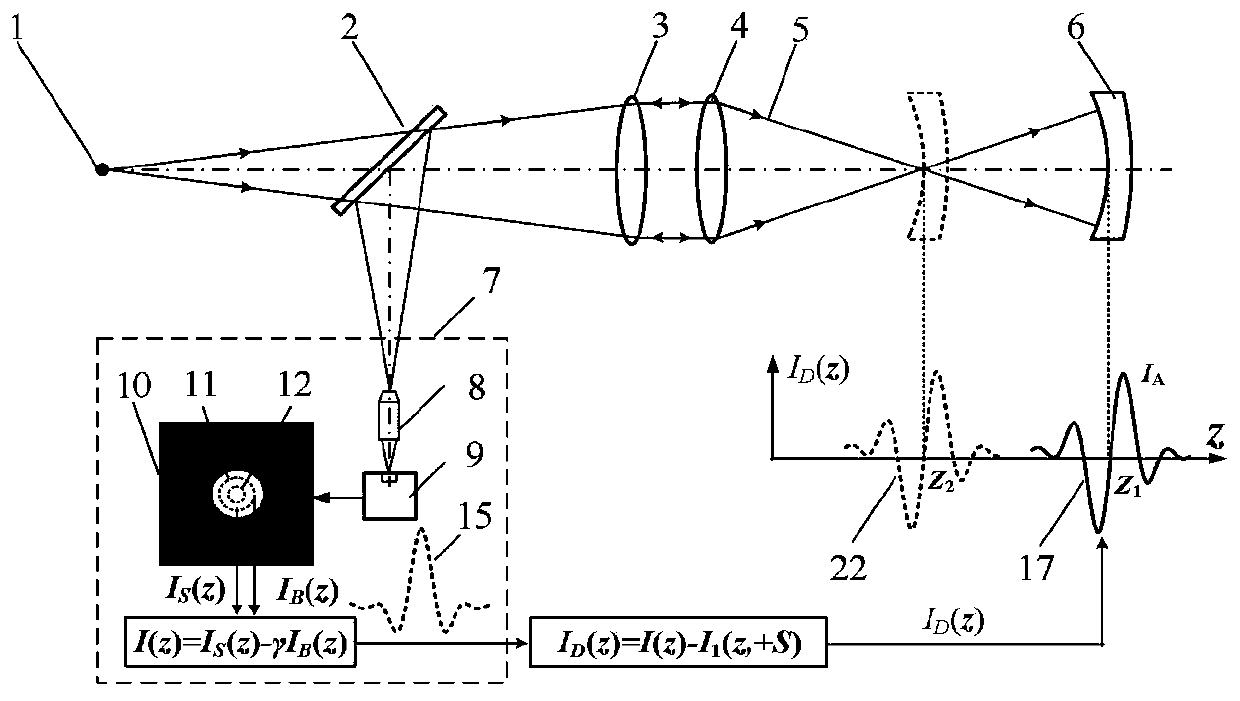
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical precision measurement and relates to a method for measuring a bilateral dislocation differential confocal radius of curvature. In a confocal measurement optical path system, the method comprises the following steps: firstly, in an airy disk image detected by a CCD, a large virtual pinhole detection area and a small virtual pinhole detection area are set through software, the two detected confocal characteristic curves are subjected to subtraction processing so as to sharpen the confocal characteristic curves, then, the sharpened confocalcharacteristic curves are subjected to bilateral dislocation differential subtraction processing to obtain an axial high-sensitivity differential confocal characteristic curve, and finally, the characteristic of accurate correspondence of the bilateral dislocation differential confocal characteristic curve zero point and the focal point of the confocal measurement system is used to carry out high-precision focus fixing and addressing on the "cat eye" and "confocal" positions of the measured sphere, so as to improve the focus fixing accuracy in the measurement of the spherical radius of curvature. Compared with the existing radius-of-curvature method, the method has the advantages of high measurement accuracy, strong environmental interference resistance, simple structure and the like and has wide application prospects in the technical field of optical precision measurement.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
High-resolution scanning microscopy with discrimination between at least two wavelength ranges
InactiveCN106662733AMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesSpatially resolvedTwo dimensional detector
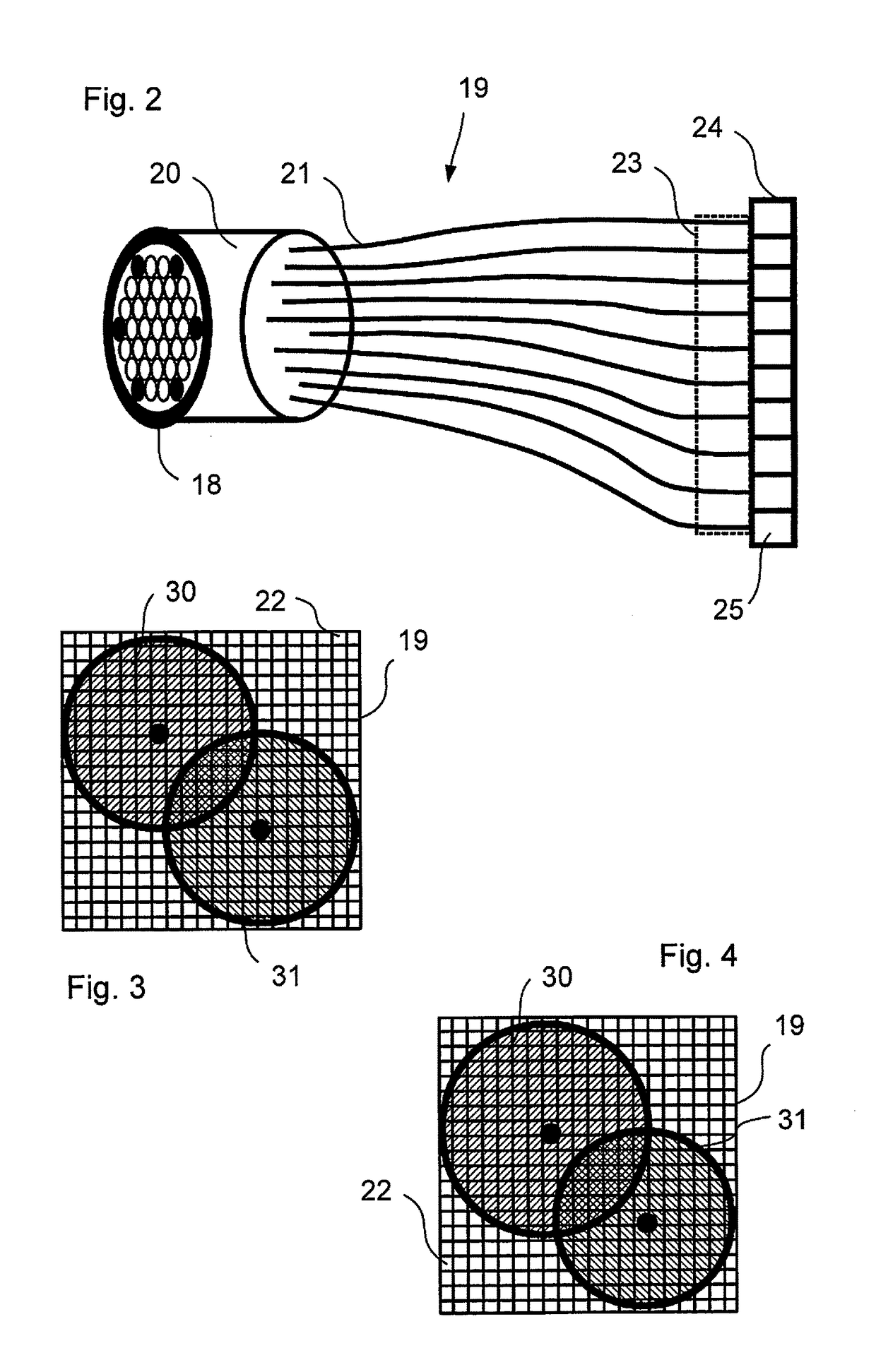
For the purposes of high-resolution scanning microscopy, a sample (2) is excited by illumination radiation (5) to emit fluorescence radiation in such a way that the illumination radiation (5) is focused at a point in or on the sample (2) to form a diffraction-limited illumination spot (14). The point is imaged in a diffraction image (17) on a spatially resolving two-dimensional detector (19) in a diffraction-limited fashion, wherein the two-dimensional detector (19) has a spatial resolution which resolves a diffraction structure of the diffraction image (17). The sample (2) is scanned by means of various scanning positions with an increment that is smaller than half the diameter of the illumination spot (14). An image of the sample (2) with a resolution that is increased beyond a resolution limit of the image is generated from the data of the two-dimensional detector (19) and from the scanning positions assigned to these data. For the purposes of discriminating between at least two predetermined wavelength ranges in the fluorescence radiation of the sample (2), a number of Airy disks (30-33) corresponding to the at least two predetermined wavelength ranges are generated on the two-dimensional detector (19), which Airy disks are offset laterally from one another such that the diffraction image (17) consists of the mutually offset Airy disks (30-33). The Airy disks (30-33) are evaluated when generating the image of the sample (2).
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY LLC
Novel co-phase detection method and device for segmented telescope
ActiveCN108827596AQuickly adjust the piston errorHigh precisionTesting optical propertiesBeam splitterControl system
A novel co-phase detection method and device for a segmented telescope are provided. The device comprises a segmented mirror telescope, a collimating lens, a segmented deformable mirror, a 4f system,a first beam splitter, a second beam splitter, a segmented mirror MASK, a Shaker-Hartmann wavefront detector, an imaging system and a control system. A white-light (400nm to 700nm) incoherent patternand a white-light ideal Airy disk pattern are used as a template, a segmented mirror piston error is calculated by using a cross-correlation algorithm, and the segmented mirror piston error is quicklyadjusted by adjusting the segmented deformable mirror. The detection method and a photoelectric detection system have unlimited ranges and high precision and quickly detect and adjust the piston error without increasing the complexity of an existing detection system.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
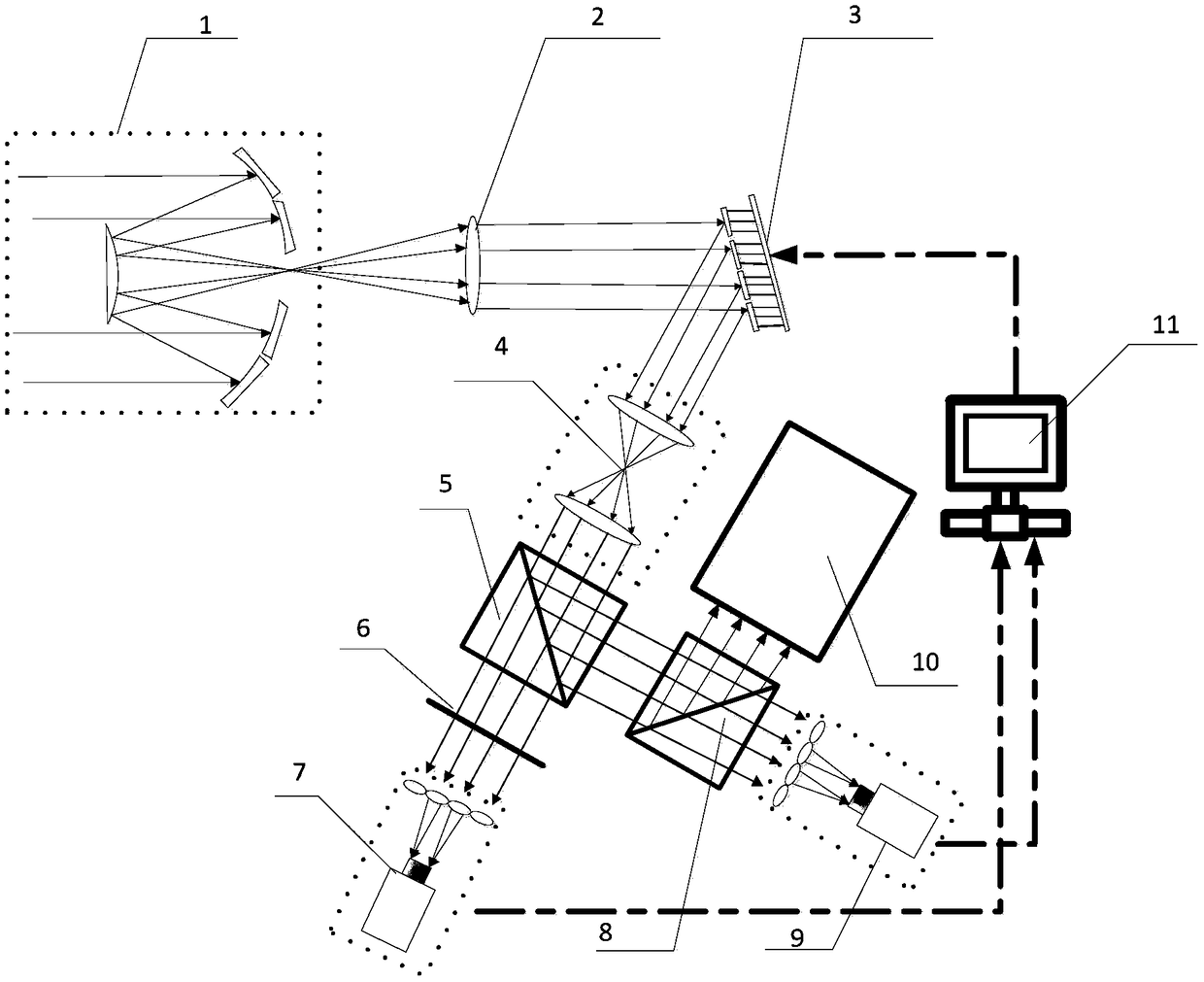
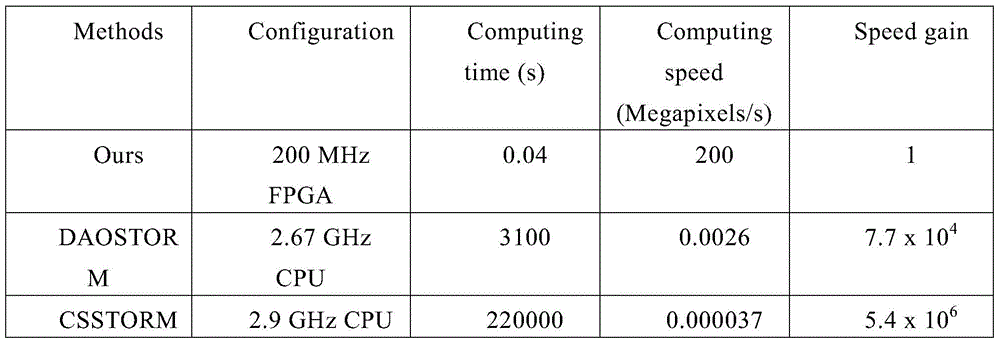
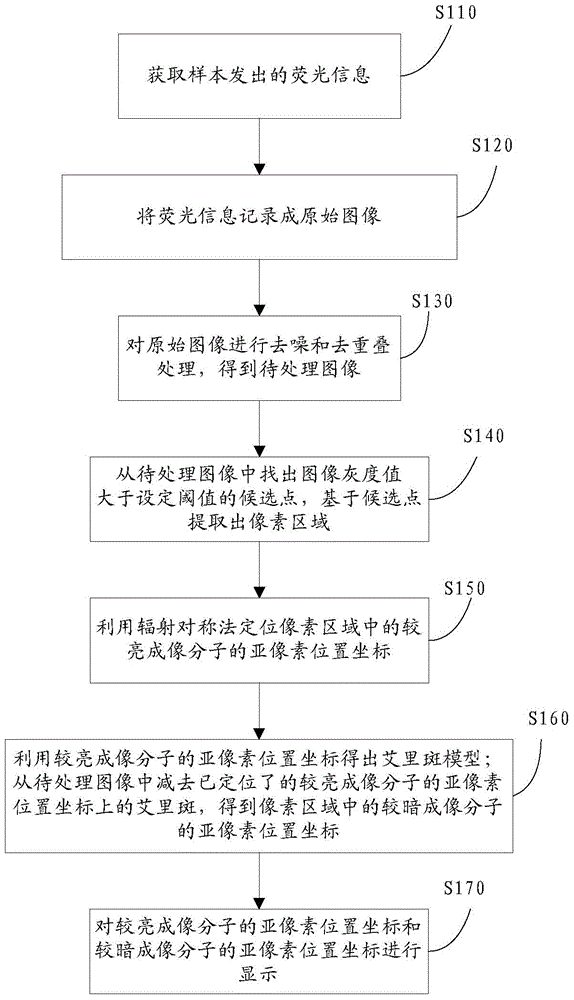
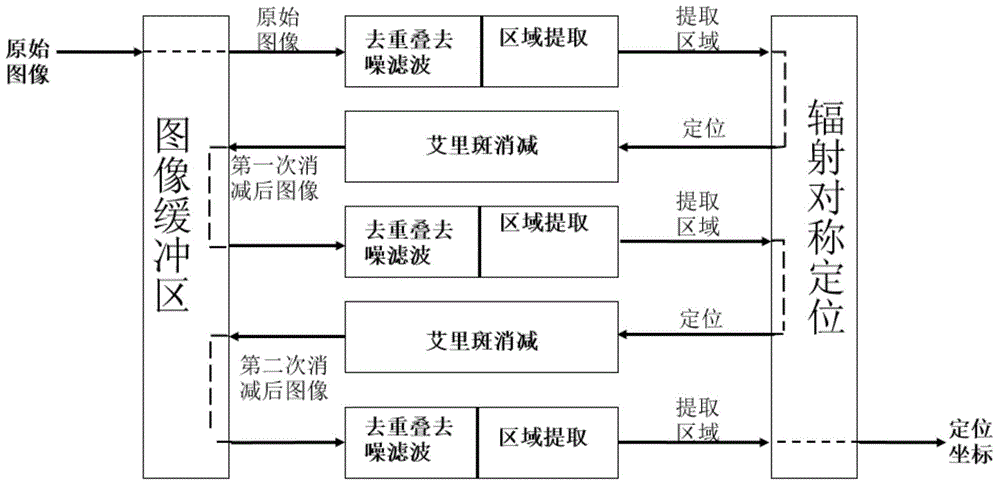
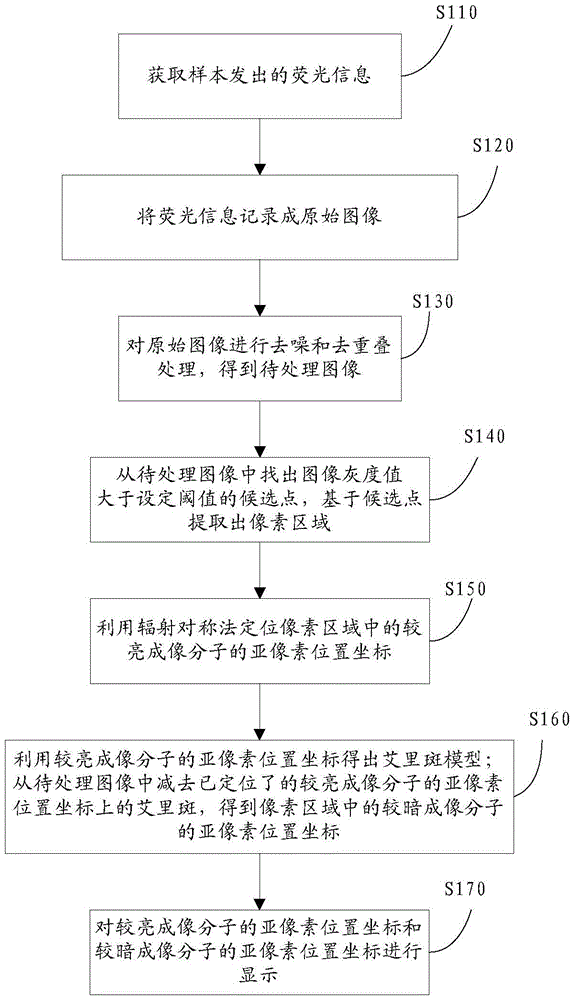
Method and system suitable for high-speed continuous super-resolution positioning and imaging
ActiveCN104062272AQuick analysisEasy to handleImage enhancementImage analysisImaging analysisImaging technique
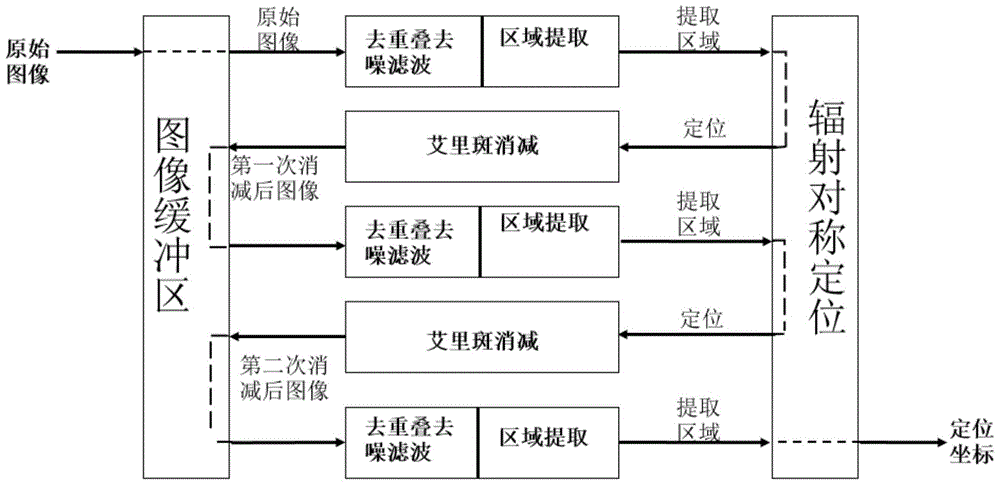
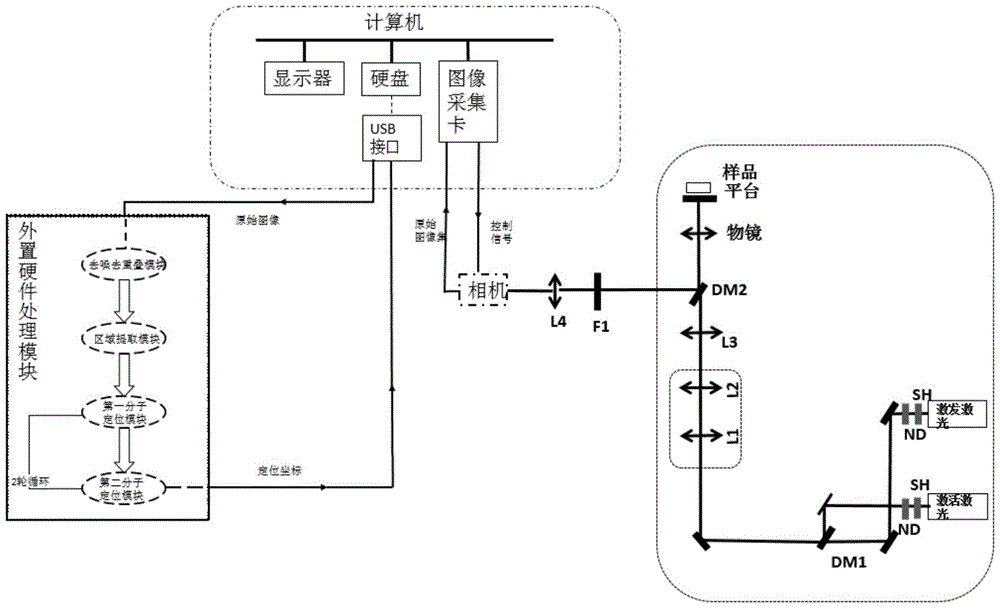
The invention relates to the technical field of super-resolution imaging, and discloses a method and a system suitable for high-speed continuous super-resolution positioning and imaging. The method comprises the steps of performing denoising and de-overlapping on an original acquired image to obtain an image to be processed; positioning a sub-pixel position coordinate of a brighter imaging molecule from the image to be processed by a radiation symmetric method, and obtaining an airy disk model on the sub-pixel position coordinate of the brighter imaging molecule; then subtracting the airy disk model on the sub-pixel position coordinate of the brighter imaging molecule by the image to be processed to obtain a sub-pixel position coordinate of a darker imaging molecule, and finally displaying the sub-pixel position coordinates of the imaging molecules to realize real-time quick analysis, processing and displaying on a super-resolution positioning image, so that the requirement on biological application on an image analysis speed is met.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Atmospheric stabilizer filter and method
A diffracting optical filter for use with telescopes provides a plurality of cells separated by opaque lines on an translucent substrate, the spacing of the cells proportionally spaced to match the Airy disk of a specific optical system for the telescope to aid observation through a turbulent atmosphere.
Owner:BARZIZA SAMUEL W
Multi-point unmarked differential super-resolution imaging method and device
ActiveCN114355621AFrame rate unchangedImproving Imaging EfficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesBeam splitterPhase mask
The invention discloses a multi-focus unmarked differential super-resolution imaging method and device based on an area array detector and Airy spot subdivision, light emitted by a laser is divided by a polarizing beam splitter into two beams of light with mutually vertical polarization directions, and the two beams of light are modulated by phase masks loaded by a left half screen and a right half screen of an SLM respectively; the two light beams are a solid light beam and a hollow light beam respectively; and then the solid light beam and the hollow light beam are combined, the combined light beam is divided into a first sub-light beam and a second sub-light beam, the first sub-light beam and the second sub-light beam respectively comprise the solid light beam and the hollow light beam, the first sub-light beam and the second sub-light beam enter a scanning galvanometer module at a certain angle and are focused by an objective lens to form a first focal spot combination and a second focal spot combination, and therefore four focal spots are formed on a focal plane. Based on a method of converting a time domain into a space domain, a single-point detector is replaced by an area array detector, and subdivision of more than 40 detectors can be carried out on Airy spot 4 at relatively low cost. And meanwhile, multi-focus excitation is adopted, so that the imaging efficiency of the system is further improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB +1
Transverse subtraction differential confocal ultra-long focal length measurement method
ActiveCN109990984ARealize high-precision measurementImprove capture accuracyOptical axis determinationLens position determinationComputer visionComputer science
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Bilateral misalignment differential confocal ultra-long focal length measurement method
ActiveCN109990983AHigh sensitivityImprove signal-to-noise ratioOptical axis determinationLens position determinationInterference resistanceMeasurement plane
The invention provides a bilateral misalignment differential confocal ultra-long focal length measurement method, and belongs to the technical field of optical precision measurement. According to thebilateral misalignment differential confocal ultra-long focal length measurement method disclosed by the invention, in a confocal measurement system, large and small virtual pinhole detection areas are set via software on an Airy disk image detected by a CCD, subtraction processing is performed on two confocal characteristic curves detected by the CCD to sharpen the confocal characteristic curves,then bilateral misalignment differential subtraction processing is performed on the confocal characteristic curves to obtain differential confocal characteristic curves with high axial sensitivity, and then zero points of the bilateral misalignment differential confocal characteristic curve and a focal point of the confocal measurement system accurately correspond to the characteristic to preformhigh-precision focusing positioning on position points of a mobile measurement plane mirror in ultra-long focal length measurement, so as to achieve the high-precision measurement of the ultra-long focal length. Compared with the existing ultra-long focal length measurement method, the bilateral misalignment differential confocal ultra-long focal length measurement method provided by the invention has the advantages of high measurement precision, high ambient interference resistance, simple structure and the like, thereby having a wide application prospect in the technical field of optical precision measurement.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for measuring axial clearances of bilateral dislocation differential confocal mirror groups
ActiveCN109883343AHigh sensitivityImprove signal-to-noise ratioUsing optical meansInterference resistanceMeasurement precision
The invention discloses a method for measuring axial clearances of bilateral dislocation differential confocal mirror groups, and belongs to the technical field of optical precision measurement. According to the method, a small virtual pinhole detection area and a small virtual pinhole detection area are firstly set on an Airy disk image detected by a CCD in a confocal measurement system, and subtraction is carried out on two detected confocal characteristic curves to sharpen the confocal characteristic curves; bilateral dislocation differential subtraction is carried out on the sharpened confocal characteristic curves to obtain axial high-sensitivity differential confocal characteristic curves; characteristics accurately corresponding to zero points of the bilateral dislocation differential confocal characteristic curves and a focus of the confocal measurement system are utilized to carry out high-precision focus fixing and locating on inner and outer peak positions of a measured mirror group; and finally ray tracing compensation calculation is carried out to accurately obtain an axial clearance of the measured mirror group. Compared with the existing mirror group clearance measurement methods, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of being high in measurement precision, strong in environment interference resistance and simple in structure, and has a wide application prospect in the technical field of optical precision measurement.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Atmospheric stabilizer filter and method
A diffracting optical filter for use with telescopes provides a plurality of cells separated by opaque lines on an translucent substrate, the spacing of the cells proportionally spaced to match the Airy disk of a specific optical system for the telescope to aid observation through a turbulent atmosphere.
Owner:BARZIZA SAMUEL W
Bilateral misplaced differential confocal ultra-large curvature radius measurement method
ActiveCN110068290ARealize high-precision measurementImprove capture accuracyUsing optical meansInterference resistanceComputer vision
The invention discloses a bilateral misplaced differential confocal ultra-large curvature radius measurement method, belonging to the technical field of optical precision measurement. According to themethod, in a confocal measurement system, firstly, large and small virtual pinhole detection areas are set through software on an airy disk image detected at CCD and two confocal characteristic curves detected by the CCD are sharpened through subtraction treatment, then, bilateral misplaced differential subtraction is executed for the sharpened confocal characteristic curve so as to obtain a high-sensitivity differential confocal characteristic curve; secondly, based on a null point of the bilateral misplaced differential confocal characteristic curve and a focal point of the confocal measurement system are accurately corresponding to the characteristics, high-precision focus-fixed locating is executed for each characteristic position point in ultra-large curvature radius measurement, andconsequently, high-precision measurement of ultralong focal length. Compared with the existing large curvature radius measurement method, the method provided by the invention has the advantages, suchas high precision, high environment interference resistance and simple structure, and has wide application foreground in the technical field of optical precision measurement.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for measuring ultra-large curvature radius through transverse subtraction and differential confocal processing
ActiveCN109945804ARealize high-precision measurementImprove capture accuracyUsing optical meansComputer scienceImage area
The invention discloses a method for measuring an ultra-large curvature radius through transverse subtraction and differential confocal processing and belongs to the technical field of optical precision detection. According to the method, in a confocal measurement system, firstly, a large and small virtual pinhole detection area (image area) is set through software on a CCD detected airy disk image through software, two confocal characteristic curves detected by a CCD are subjected to subtraction processing to sharpen the confocal characteristic curves, finally, all characteristic points in ultra-large curvature radius measurement are subjected to high-precision fixed focusing by use of the characteristic that a zero point of a transverse subtraction and differential confocal characteristic curve and a focus of the measurement system correspond to each other precisely, and further, high-precision measurement of the ultra-large curvature radius is realized. The method provides a brand-new technical way for high-precision measurement of the ultra-large curvature radius.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
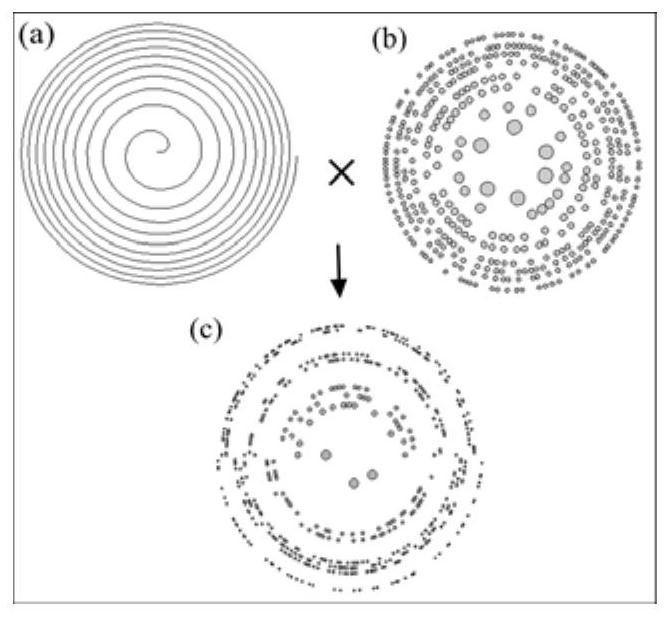
Design method of Fermat spiral Greek ladder photon sieve and its imaging optical path
The point spread function determines the imaging properties of the optical system, and different point spread functions can achieve different imaging results. By introducing the Fermat helix into the Greek ladder photon sieve, the Fermat helix modulates the distribution positions of the sieve holes in the Greek ladder photon sieve to obtain the Fermat helix Greek ladder photon sieve. Through the imaging optical path based on the Fermat spiral Greek ladder photon sieve to generate multiple focal points in the axial direction, the function of different point spread functions of the multi-focal plane of a single device is realized, including anisotropic Airy disk and vortex focus, which can be applied to coherence Focusing and imaging from X-ray to terahertz band in light field. The first and third focuses are anisotropic Airy disks, which can achieve different resolutions in different directions for the input object, which helps to improve the resolution of the object's interested direction; the second focus is the vortex focus, The vortex focus can be used for optical trapping. In addition, when used for imaging, the radial Hilbert transform can be realized based on the helical phase filter, and the edge enhancement of the amplitude and phase objects can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bilateral Displacement Differential Confocal Ultra-Large Curvature Radius Measurement Method
ActiveCN110068290BHigh sensitivityImprove signal-to-noise ratioUsing optical meansInterference resistanceConfocal
The invention discloses a bilateral misplaced differential confocal ultra-large curvature radius measurement method, belonging to the technical field of optical precision measurement. According to themethod, in a confocal measurement system, firstly, large and small virtual pinhole detection areas are set through software on an airy disk image detected at CCD and two confocal characteristic curves detected by the CCD are sharpened through subtraction treatment, then, bilateral misplaced differential subtraction is executed for the sharpened confocal characteristic curve so as to obtain a high-sensitivity differential confocal characteristic curve; secondly, based on a null point of the bilateral misplaced differential confocal characteristic curve and a focal point of the confocal measurement system are accurately corresponding to the characteristics, high-precision focus-fixed locating is executed for each characteristic position point in ultra-large curvature radius measurement, andconsequently, high-precision measurement of ultralong focal length. Compared with the existing large curvature radius measurement method, the method provided by the invention has the advantages, suchas high precision, high environment interference resistance and simple structure, and has wide application foreground in the technical field of optical precision measurement.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
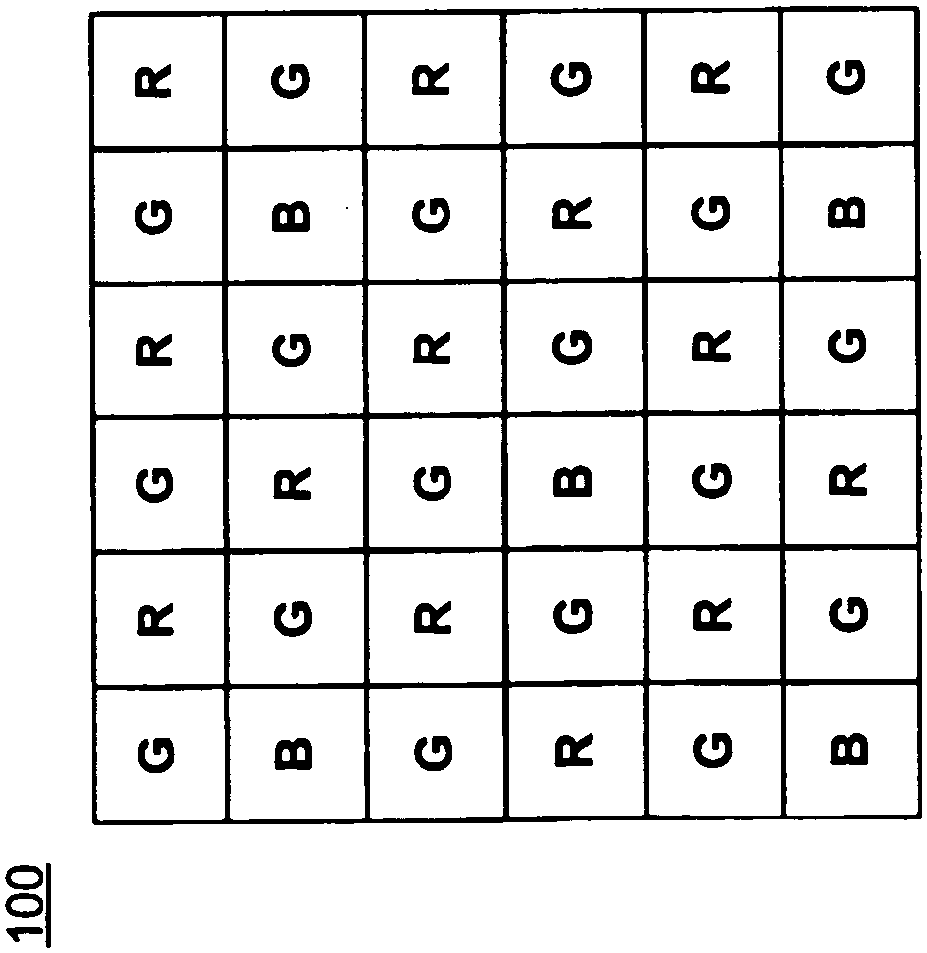
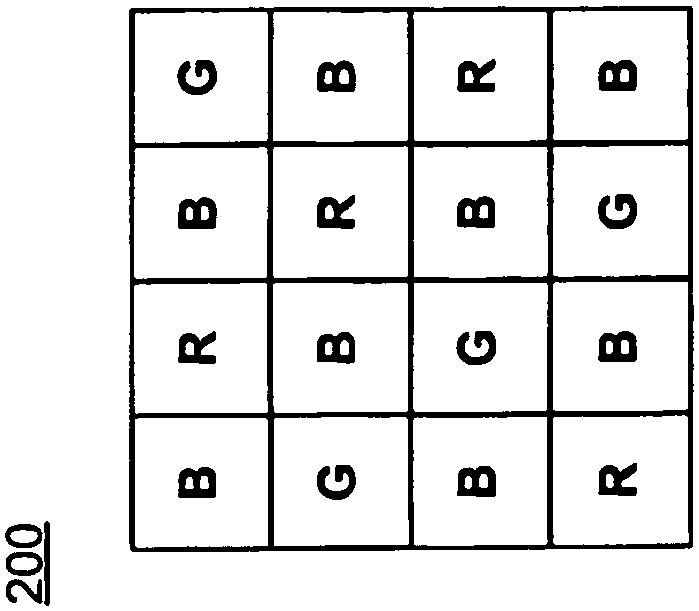
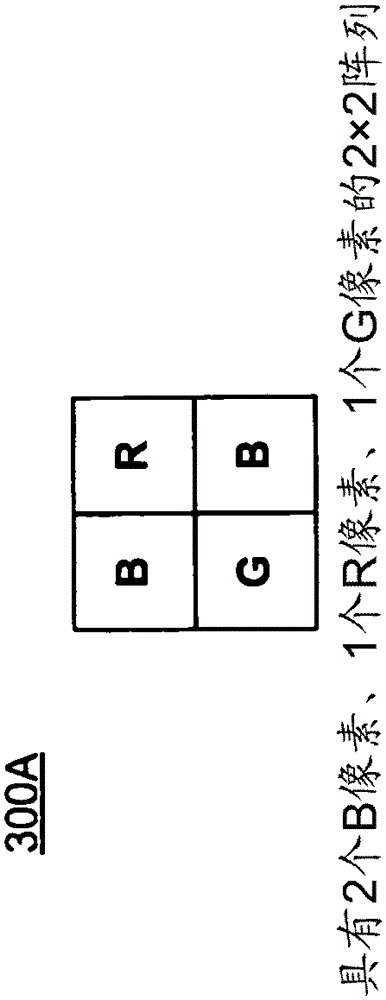
Color Filter and Demosaic Transformation Techniques for Digital Imaging
A color filter array or mosaic is provided for imaging a scene using diffraction limited optics. The distribution of color types in the color filter array is biased towards smaller wavelengths to avoid or reduce the loss of spatial resolution information at higher wavelengths caused by a greater degree of diffraction at higher wavelengths . Demosaicing methods for reconstructing partial or full color images from raw image data involve applying correction factors to take diffraction into account. The correction factor is based on pixel size and / or a measure of the degree of diffraction (eg Airy disk diameter for each wavelength in the color filter array).
Owner:发明科学基金I有限责任公司
A Super-resolution Confocal Ophthalmoscope Based on Pupil Filter and Dark Field Technology
The invention discloses a super-resolution confocal ophthalmoscope based on an optical pupil filter and a dark field technique. The super-resolution confocal ophthalmoscope is capable of accurately acquiring super-resolution dark field images of retinas of living human eyes in real time, and comprises a beacon light source, an imaging light source, an optical pupil filter, a two-dimensional scanning galvanometer, a Hartmann sensor, a deformable mirror, an optical filter and a photoelectric detection system. The beacon light source is used for correcting human eye aberrations; the imaging light source is used for acquiring human eye images. The operating method comprises the following steps: characterizing resolution according to Rayleigh criterion by using full width at half maximum, adding a two-zone type phase optical pupil filter at an illumination end, wherein the pinhole is equal to Airy disk size; allowing the pinhole to be equal to 1.5 times that of Airy disk size when the filter(s) is / are arranged at the imaging end or two ends, so that the diffraction limit condition can be realized when the transverse full width at half maximum is less than the pinhole of a general microscope equal to the Airy disk size, and the super-resolution image can be acquired at a super-resolution ratio. On the basis, the pinhole equal to the Airy disk size is translated by an Airy disk distance, the pinhole equal to 1.5 times that of the Airy disk size is subjected to central blocking or linear blocking, so that dark field imaging can be realized.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
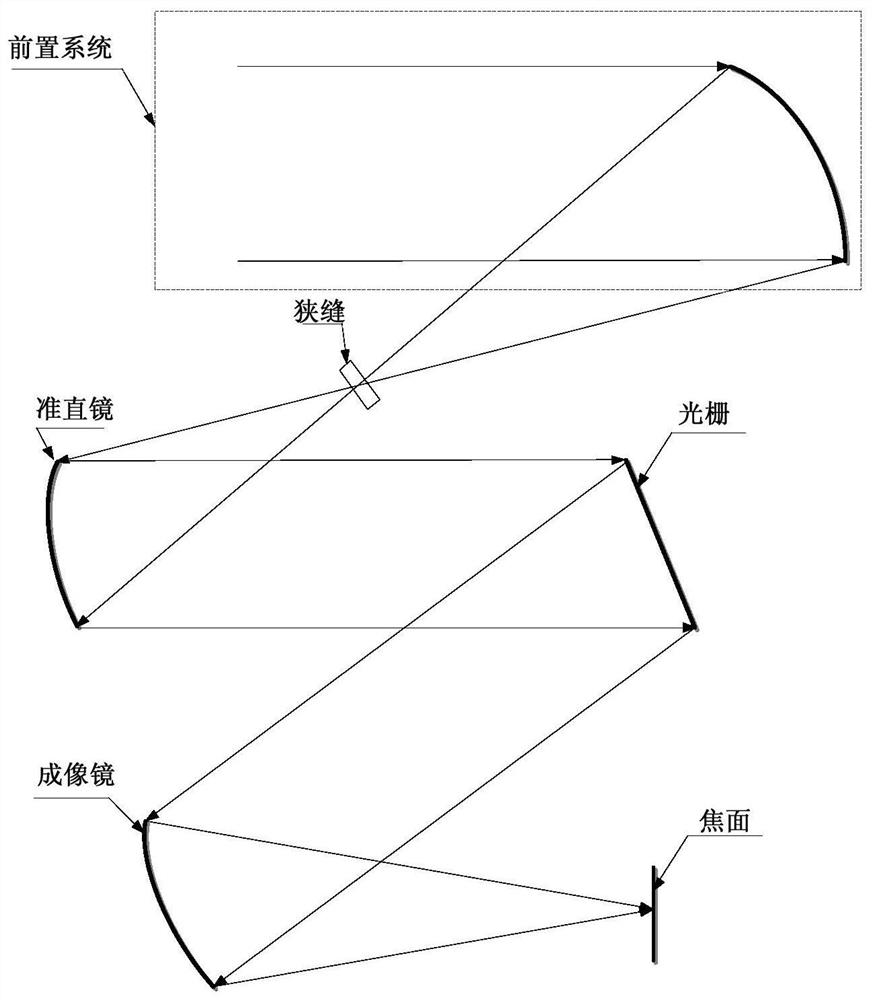
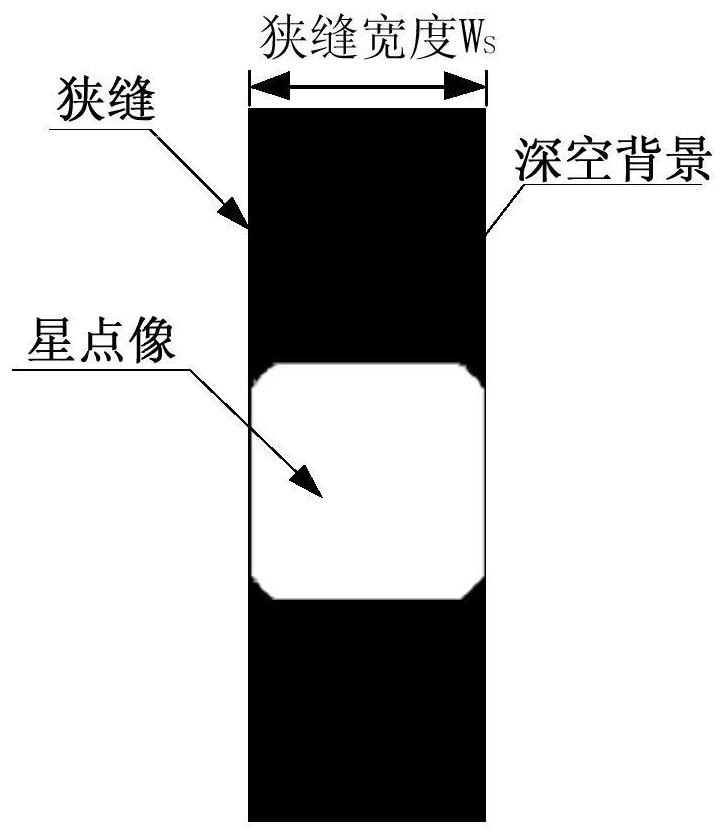
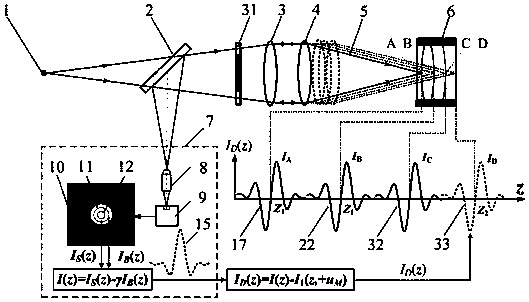
A Calculation Method of Focal Length and Slit Size of Optical System of Grating Spectrometer
ActiveCN111060287BEfficient designMeet the requirements of high-sensitivity detectionSpectrum investigationOptical axis determinationImaging qualityOptical spectrometer
The invention discloses a method for calculating the focal length and slit size of the optical system of a grating spectrometer. The method comprises the following steps: establishing an optical system of a space astronomical point source detection grating spectrometer so that the image quality of the optical system reaches the diffraction limit; Maximum wavelength λ max and the entrance pupil diameter D of the optical system to obtain the full width at half maximum FWHM of the star point image PSF at the slit; according to the full width at half maximum FWHM of the star point image PSF at the slit, the spectral sampling rate n and the pixel spacing p of the detector in the spectral direction to obtain the optical system The focal length f'; according to the wavelength maximum λ of the detection spectrum max and the entrance pupil diameter D of the optical system to obtain the size of the first dark ring of the Airy disk; according to the focal length f' of the optical system, the magnification δ of the optical system and the size of the first dark ring of the Airy disk, the width Ws of the slit is obtained. The invention determines the focal length and size of the optical system of the grating spectrometer for space astronomical detection, and can carry out the detailed design of the optical system of the grating spectrometer for space astronomical detection.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
A method and system suitable for high-speed continuous super-resolution positioning imaging
ActiveCN104062272BQuick analysisEasy to handleImage enhancementImage analysisImage denoisingImaging analysis
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Axial gap measurement method of bilateral misalignment differential confocal lens group
ActiveCN109883343BHigh sensitivityImprove signal-to-noise ratioUsing optical meansInterference resistanceConfocal
The invention discloses a method for measuring axial clearances of bilateral dislocation differential confocal mirror groups, and belongs to the technical field of optical precision measurement. According to the method, a small virtual pinhole detection area and a small virtual pinhole detection area are firstly set on an Airy disk image detected by a CCD in a confocal measurement system, and subtraction is carried out on two detected confocal characteristic curves to sharpen the confocal characteristic curves; bilateral dislocation differential subtraction is carried out on the sharpened confocal characteristic curves to obtain axial high-sensitivity differential confocal characteristic curves; characteristics accurately corresponding to zero points of the bilateral dislocation differential confocal characteristic curves and a focus of the confocal measurement system are utilized to carry out high-precision focus fixing and locating on inner and outer peak positions of a measured mirror group; and finally ray tracing compensation calculation is carried out to accurately obtain an axial clearance of the measured mirror group. Compared with the existing mirror group clearance measurement methods, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of being high in measurement precision, strong in environment interference resistance and simple in structure, and has a wide application prospect in the technical field of optical precision measurement.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
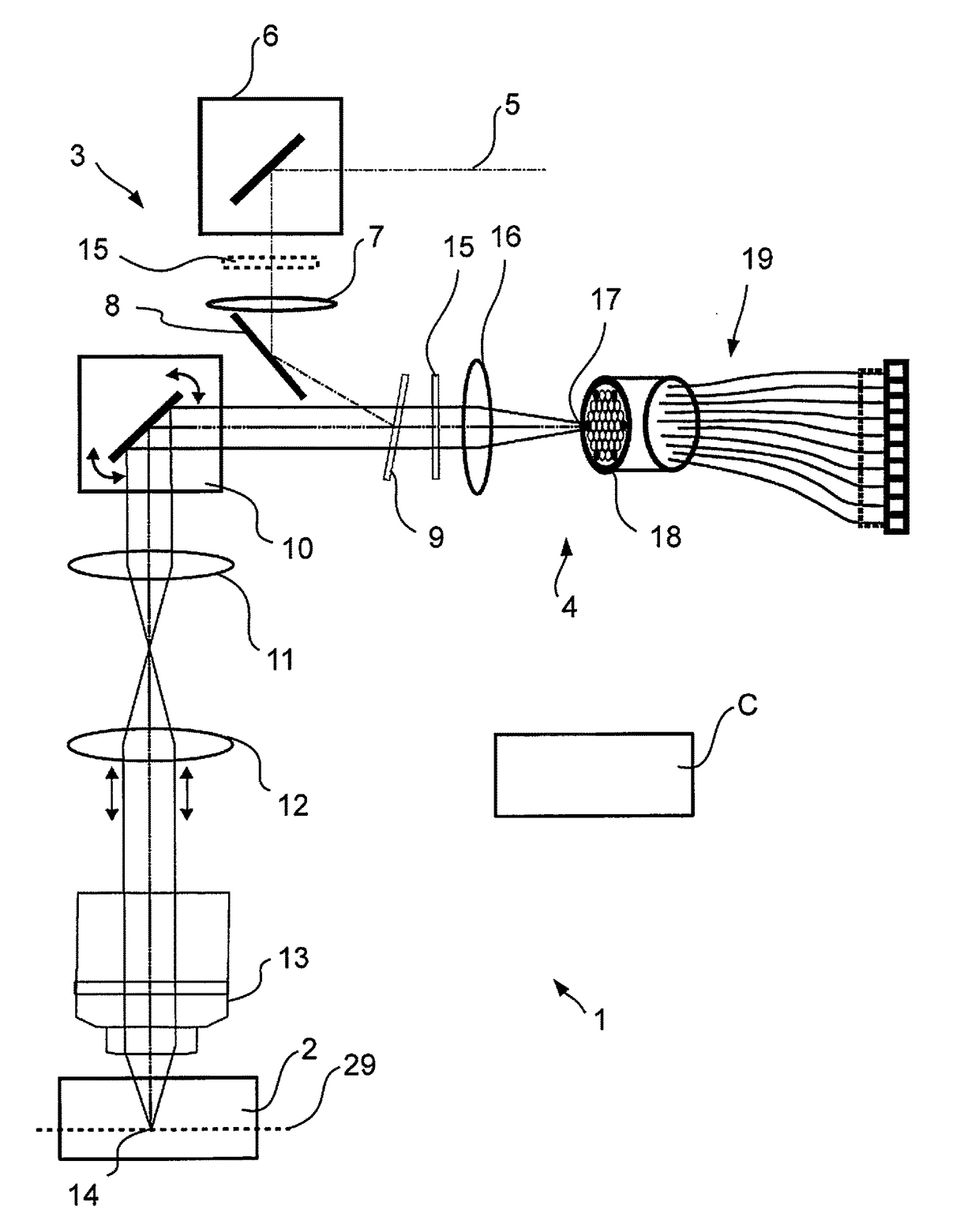
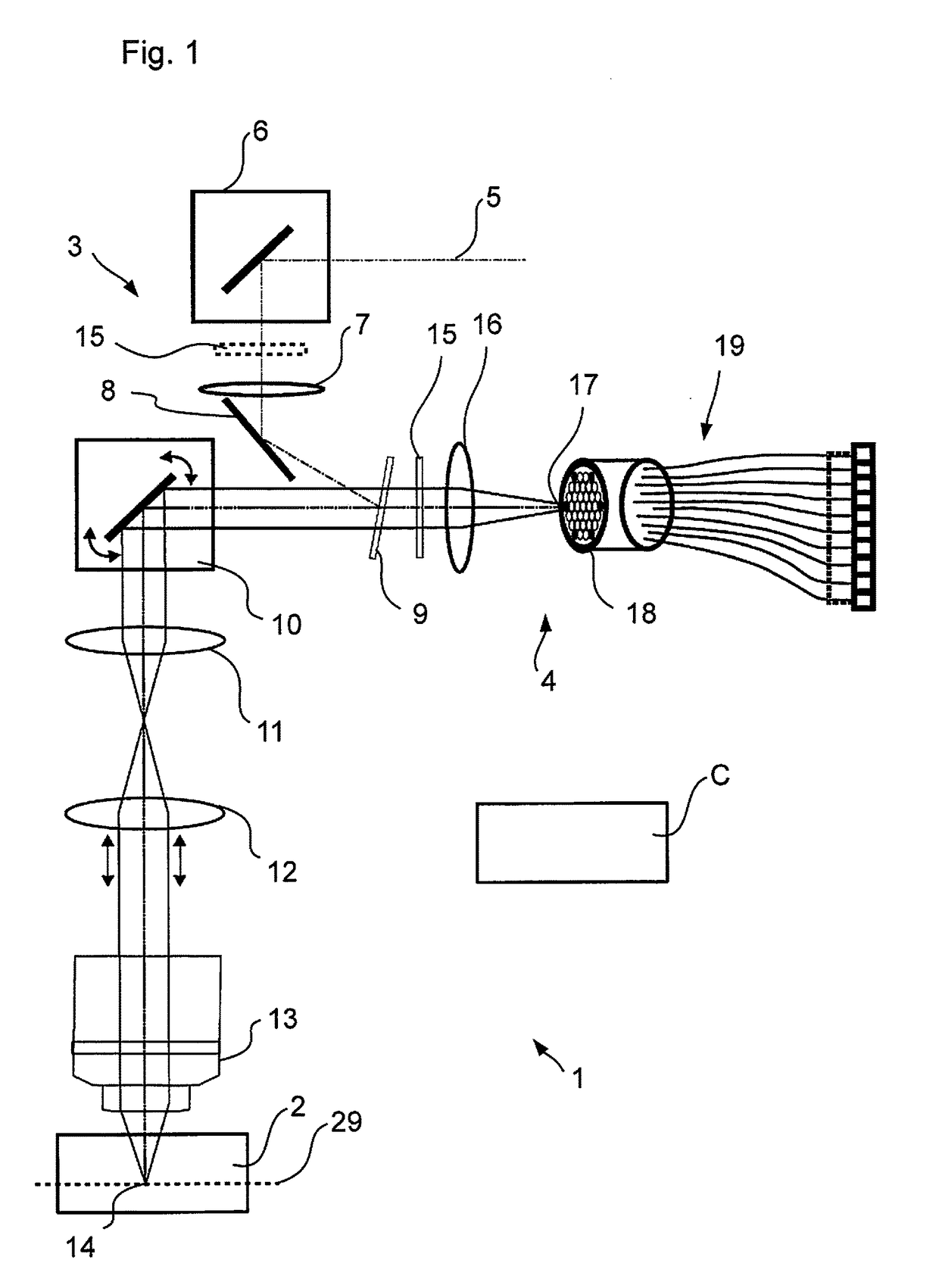
Light Microscopy and Microscopy Methods
The invention relates to an optical microscope having a sample plane on which a sample to be studied can be positioned, the optical microscope having a light source for emitting illumination light, and an optical imaging device for directing the illumination light into the sample plane. A device and a detector arrangement having a plurality of detector elements for detecting sample light from a sample. In this case, the distance between adjacent detector elements is smaller than the Airy disk produced by a point in the sample plane on the detector device. The optical microscope according to the invention is characterized in that a scanning device is provided with at least a first and a second optical device, the optics of which can be moved simultaneously in a common direction in order to generate illumination scanning movements in opposite directions to one another. and detecting the scanning motion, the first and the second optical device each having a plurality of optical elements arranged side by side, by means of which optical elements spaced apart from each other can be simultaneously studied, the first and the second optical device being arranged such that from the sample plane The optical path of the sample light towards the detector device and the optical path of the illumination light from the light source towards the sample plane both pass through the first optical device and only one of these two light paths passes through the second optical device and in order to achieve the opposite direction to the illumination scanning movement The direction of the detection scanning motion enables the sample light to be imaged non-invertedly and with an imaging ratio less than 1 by the scanning device.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com