Bilateral misplaced differential confocal ultra-large curvature radius measurement method
A differential confocal and radius measurement technology, which is applied to measuring devices, instruments, and optical devices, can solve the problems of low precision in fixed focus, difficult precision length measurement, and long measurement optical path, so as to eliminate common mode noise and improve The effect of measurement accuracy and high-precision measurement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
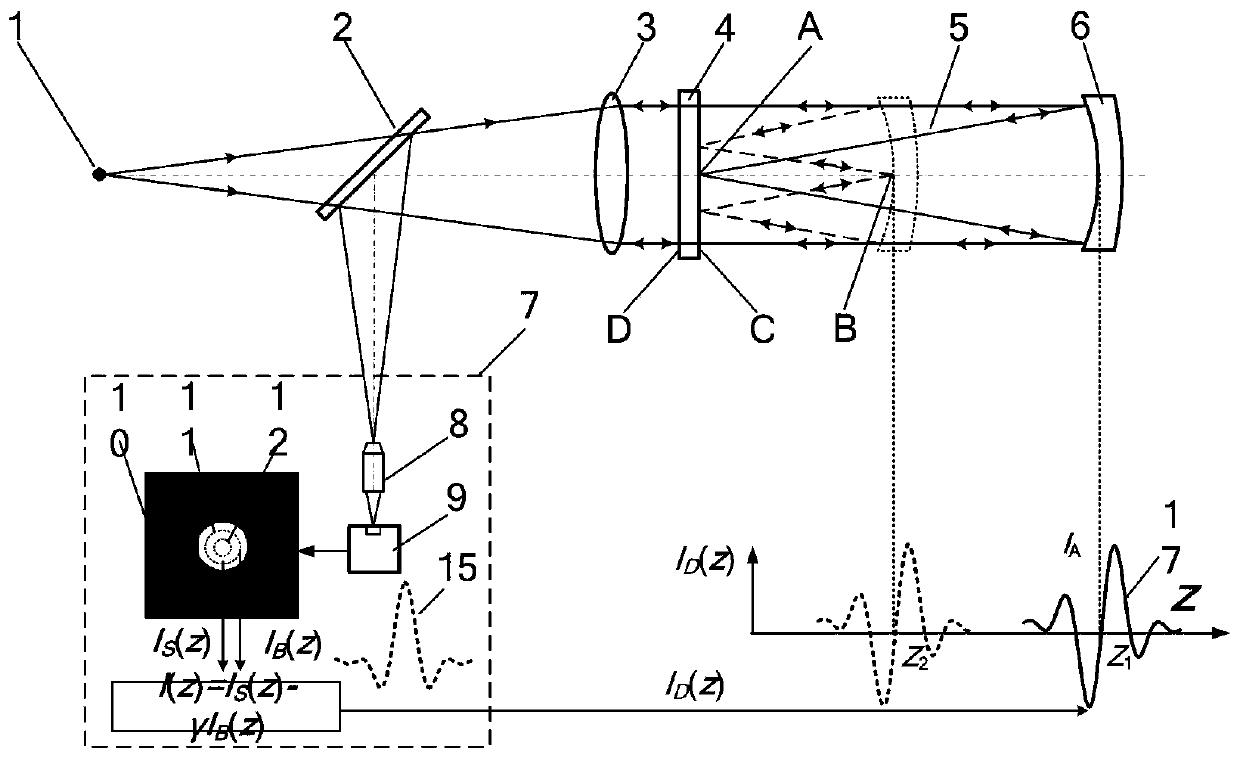
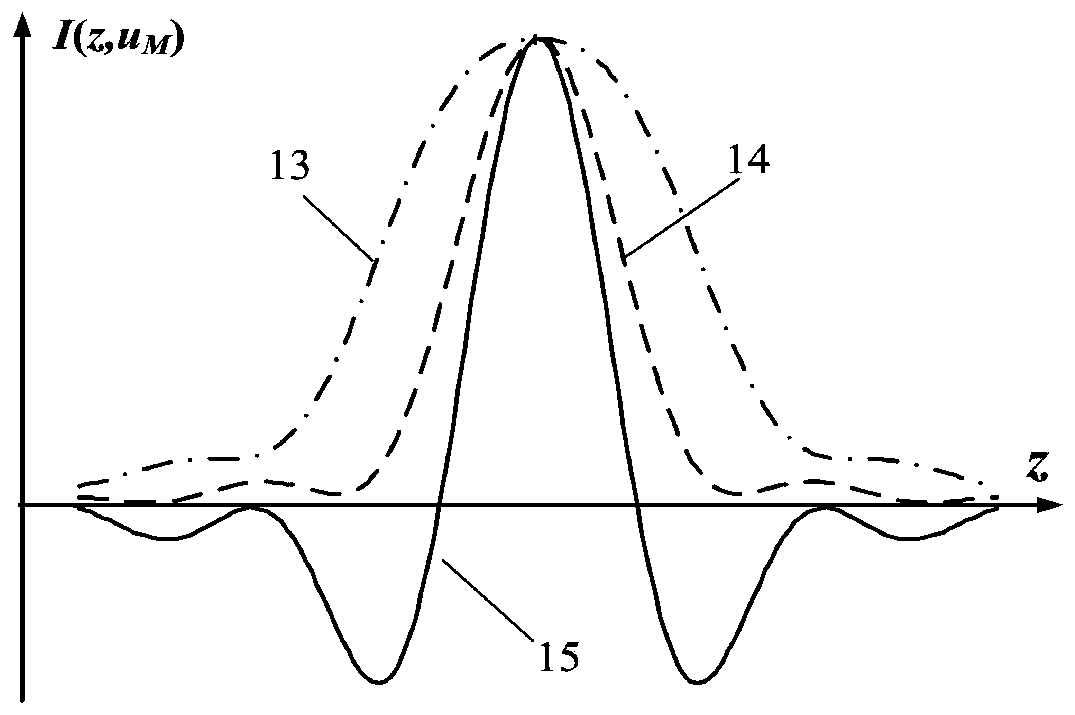
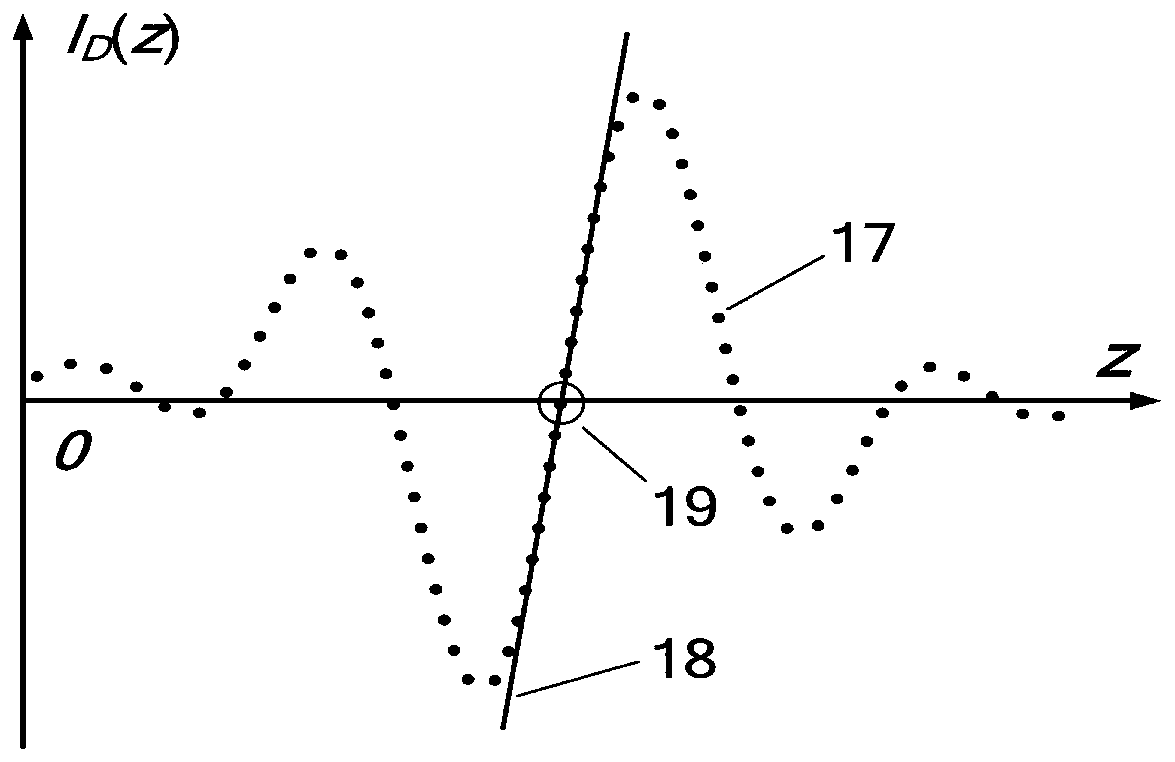
[0049] When the spherical element 6 to be tested is a concave lens with a diameter of D=150mm, the measurement of the super large radius of curvature of the bilateral misalignment differential confocal is shown in the attached Figure 5 As shown, the measurement steps of the bilateral dislocation differential confocal ultra-large radius of curvature measurement method are:
[0050] a) Start the measurement software of the main control computer 23, turn on the laser 28, and the light emitted by the laser 28 passes through the microscope objective lens 29 and the pinhole 30 to form a point light source 1. The light emitted by the point light source 1 passes through the beam splitter 2 , the collimating lens and the parallel flat crystal 4 and then irradiates on the spherical element 6 to be tested.
[0051] b) if figure 1 , adjust the measured spherical element 6 so that it has the same optical axis as the parallel flat crystal 4 and the collimator lens 3, so that the parallel ...
Embodiment 2
[0061]When the spherical element 6 to be tested is a concave lens with a diameter of D=150mm, the measurement of the super large radius of curvature of the bilateral misalignment differential confocal is shown in the attached Figure 6 As shown, the measurement steps of the bilateral dislocation differential confocal ultra-large radius of curvature measurement method are:
[0062] a) Start the measurement software of the main control computer 23, turn on the laser 28, and the light emitted by the laser 28 passes through the microscope objective lens 29 and the pinhole 30 to form a point light source 1. The light emitted by the point light source (1) passes through the beam splitter 2, the collimator lens 3 and the parallel flat crystal 4, and then irradiates on the spherical element 6 to be tested.
[0063] b) Adjust the measured spherical element 6 so that it has the same optical axis as the parallel flat crystal 4 and the collimator lens 3, so that the parallel light beam em...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com