Multi-point unmarked differential super-resolution imaging method and device
A super-resolution imaging and marking technology, which is applied in the field of optical engineering, can solve the problems of complex system structure, reduced imaging speed, and the single-frame exposure speed of area array detectors cannot be compared with single-photon detectors, so as to achieve the goal of improving imaging efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing.
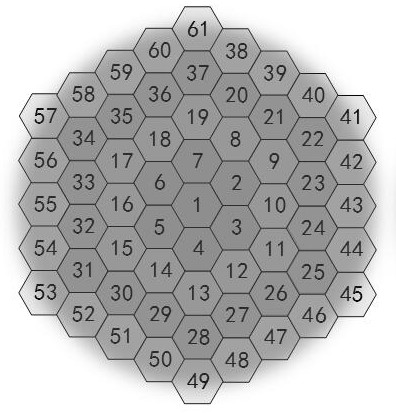
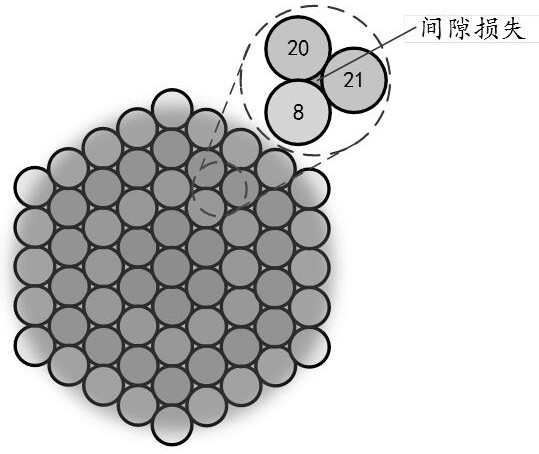
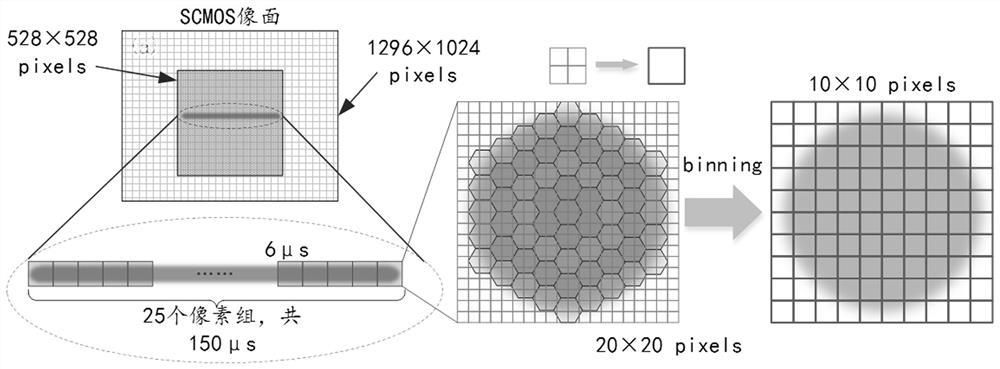
[0032] Airy disk subdivision is the process of using parallel detectors to subdivide the detected Airy disk and then reconstruct the image. Such as Figure 1a As shown, the more ideal number of parallel detectors, the better the imaging quality. Taking 61 detectors covering one Airy disk as an example, 61 images will be obtained at the same time in the end, and then one frame of image will be obtained after the image is translated and reorganized. Although this method does not break the diffraction limit, it greatly increases the proportion of high-frequency information, thereby obtaining resolution and signal-to-noise ratio beyond conventional confocal imaging. Although the more subdivisions, the better the imaging quality, but the more detectors are required. In practice, if a single photon counter is used as a detector, on the one hand, because there is no commercial p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com