Patents
Literature
32results about How to "Large fill factor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
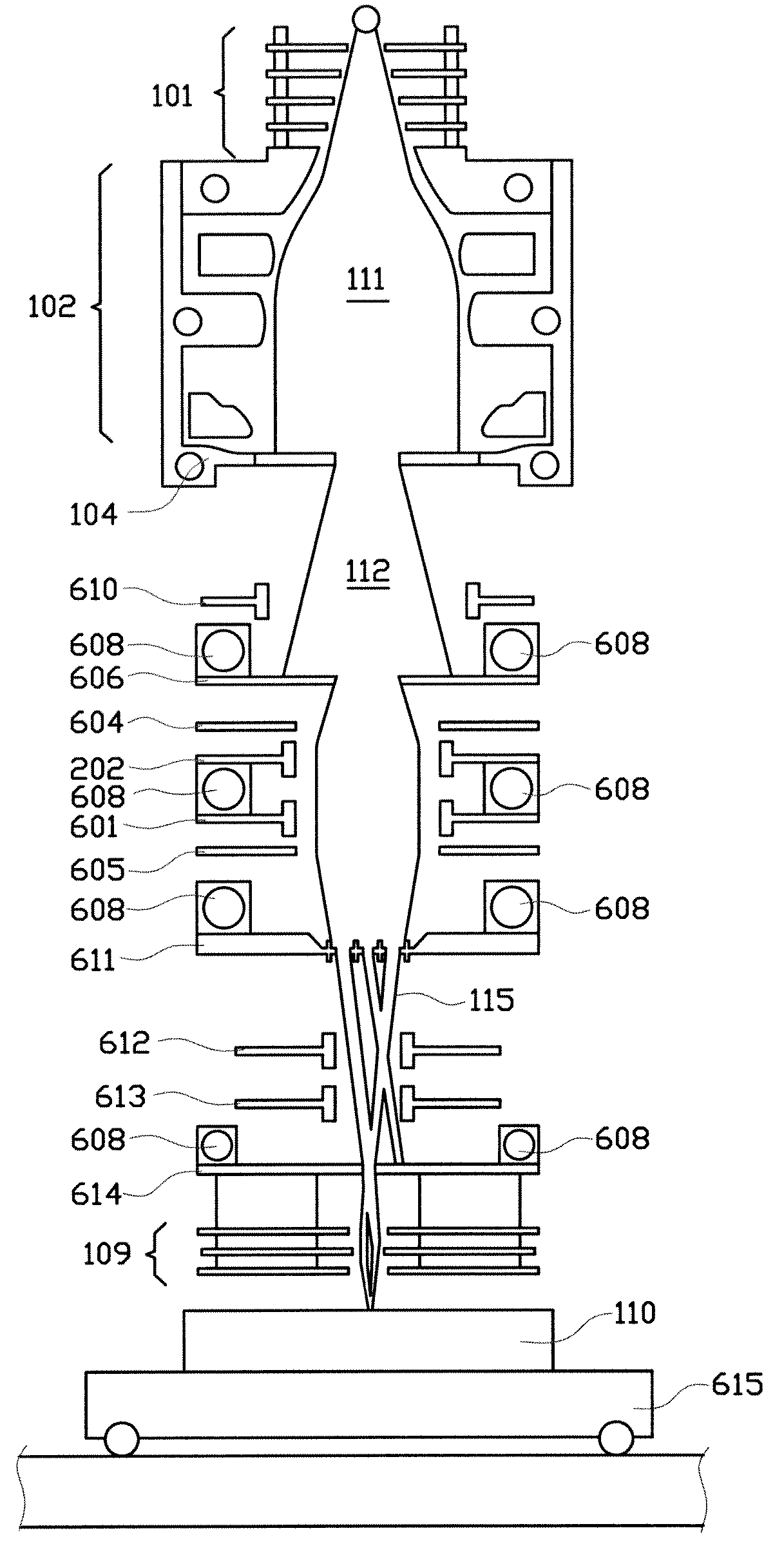
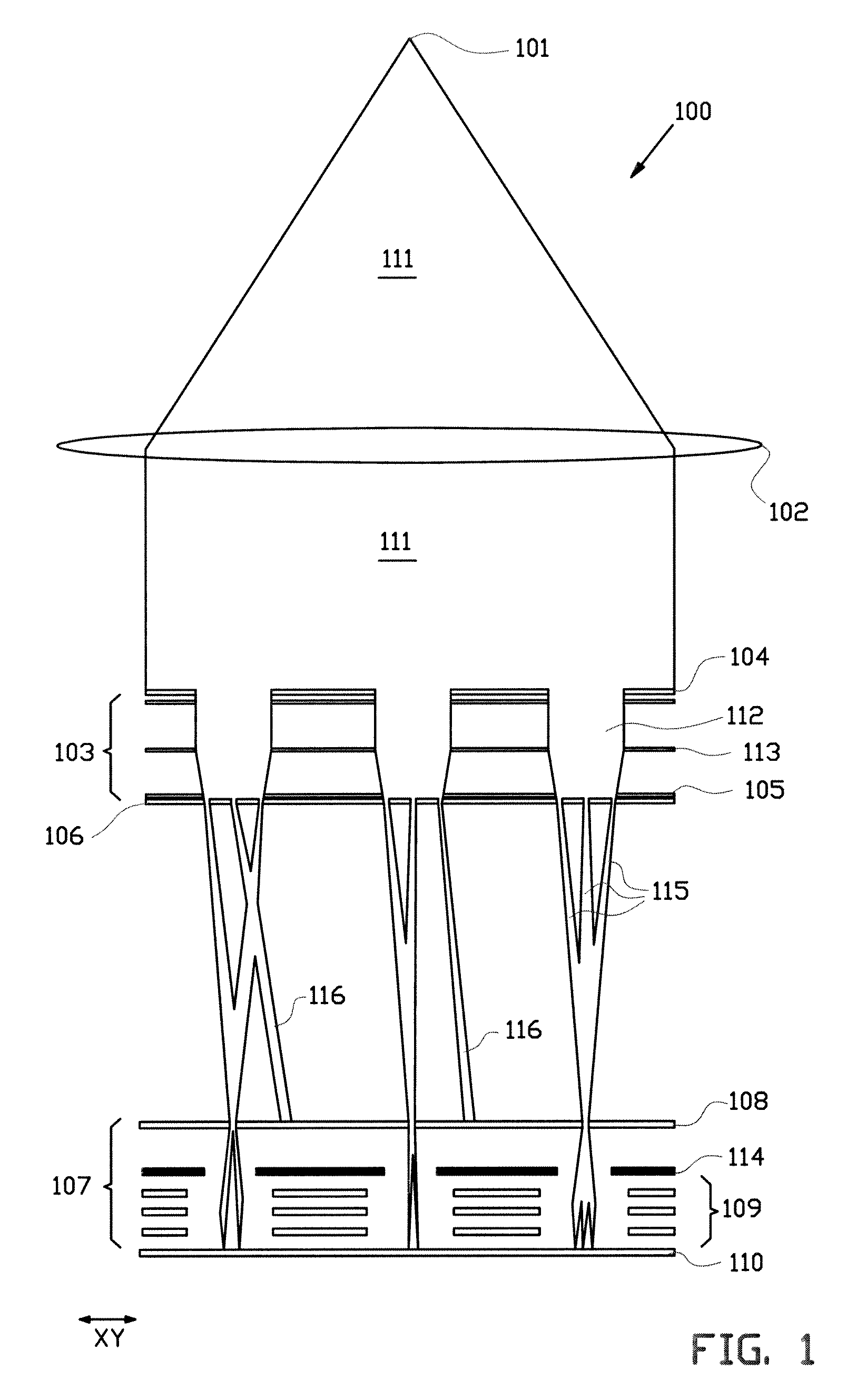
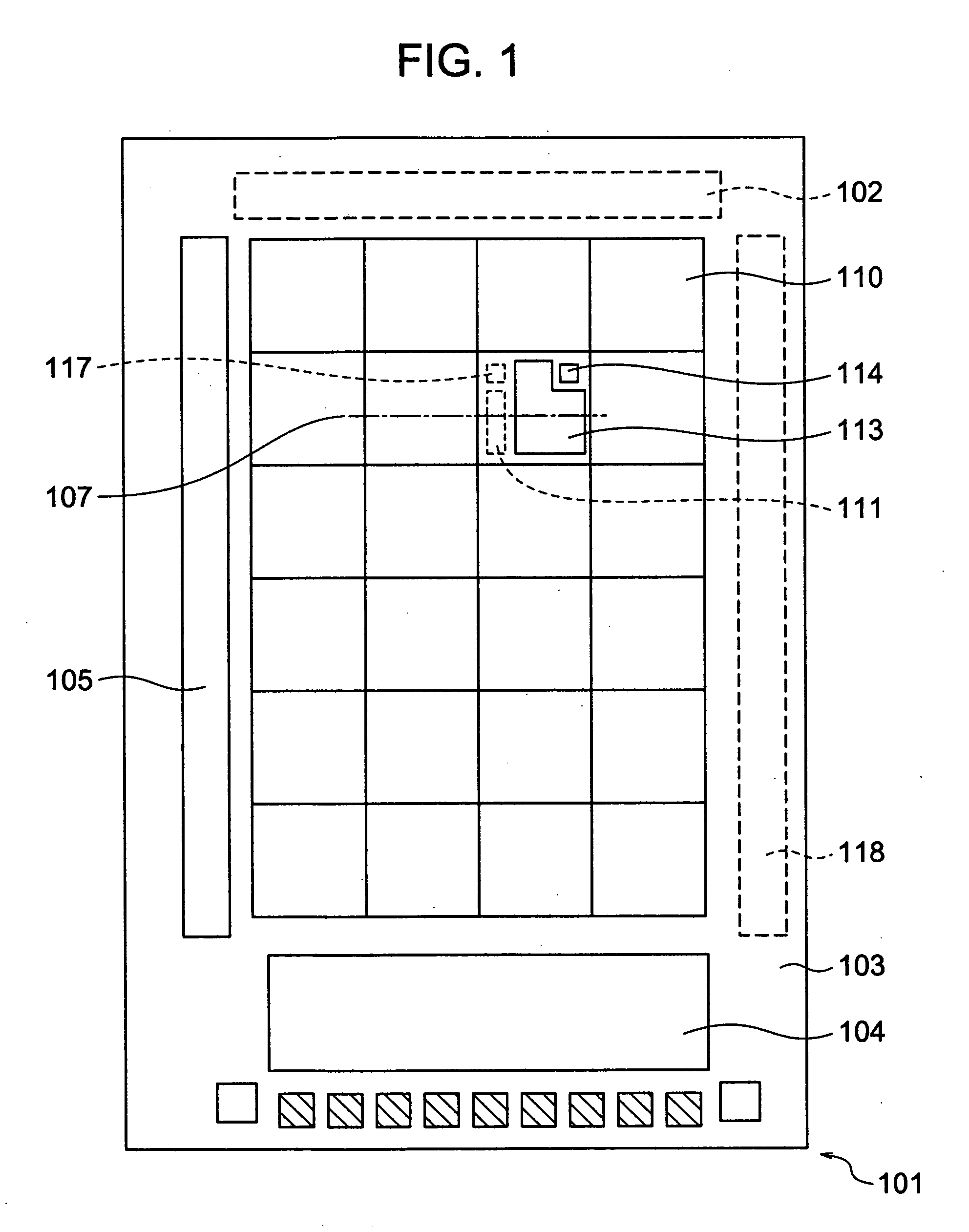
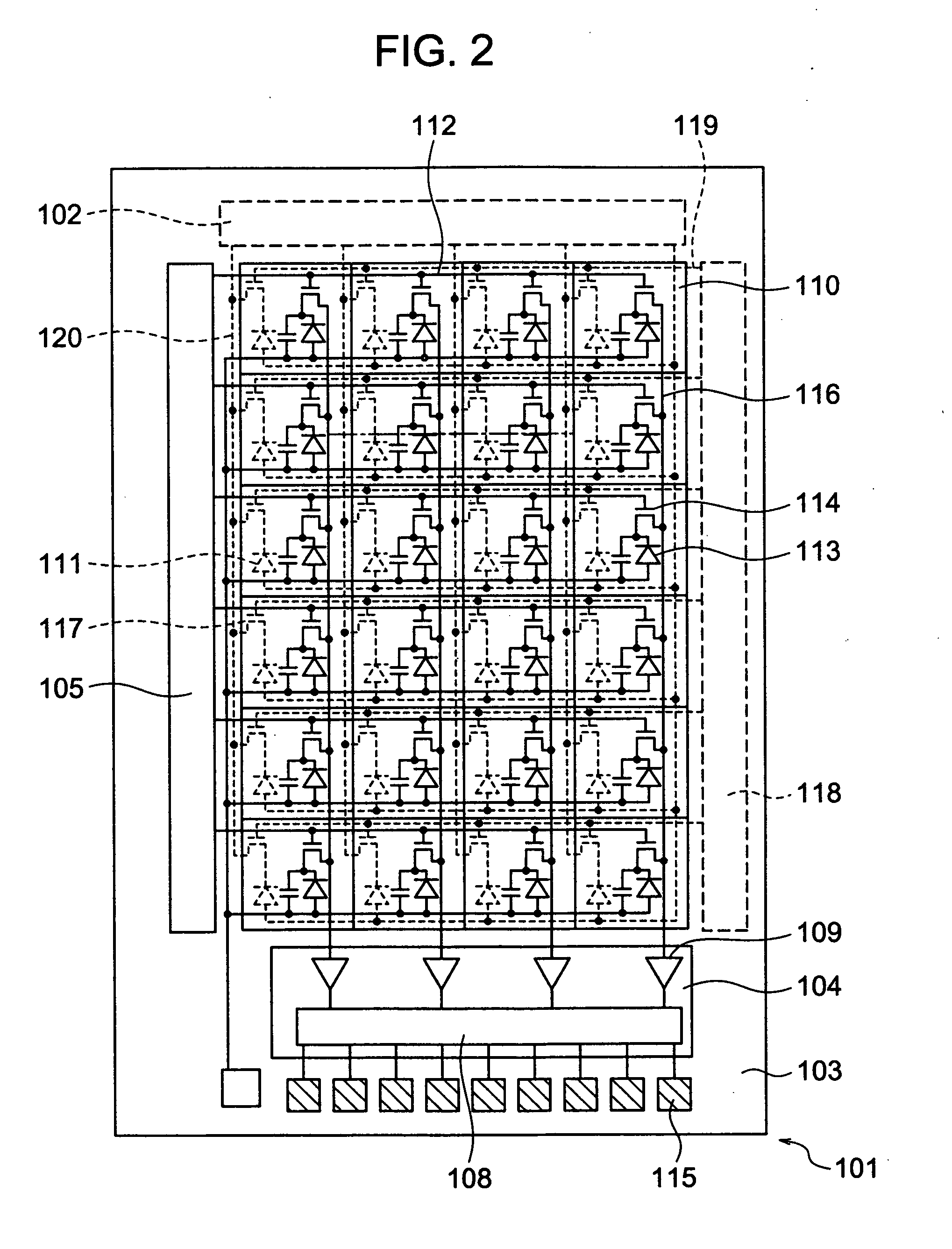
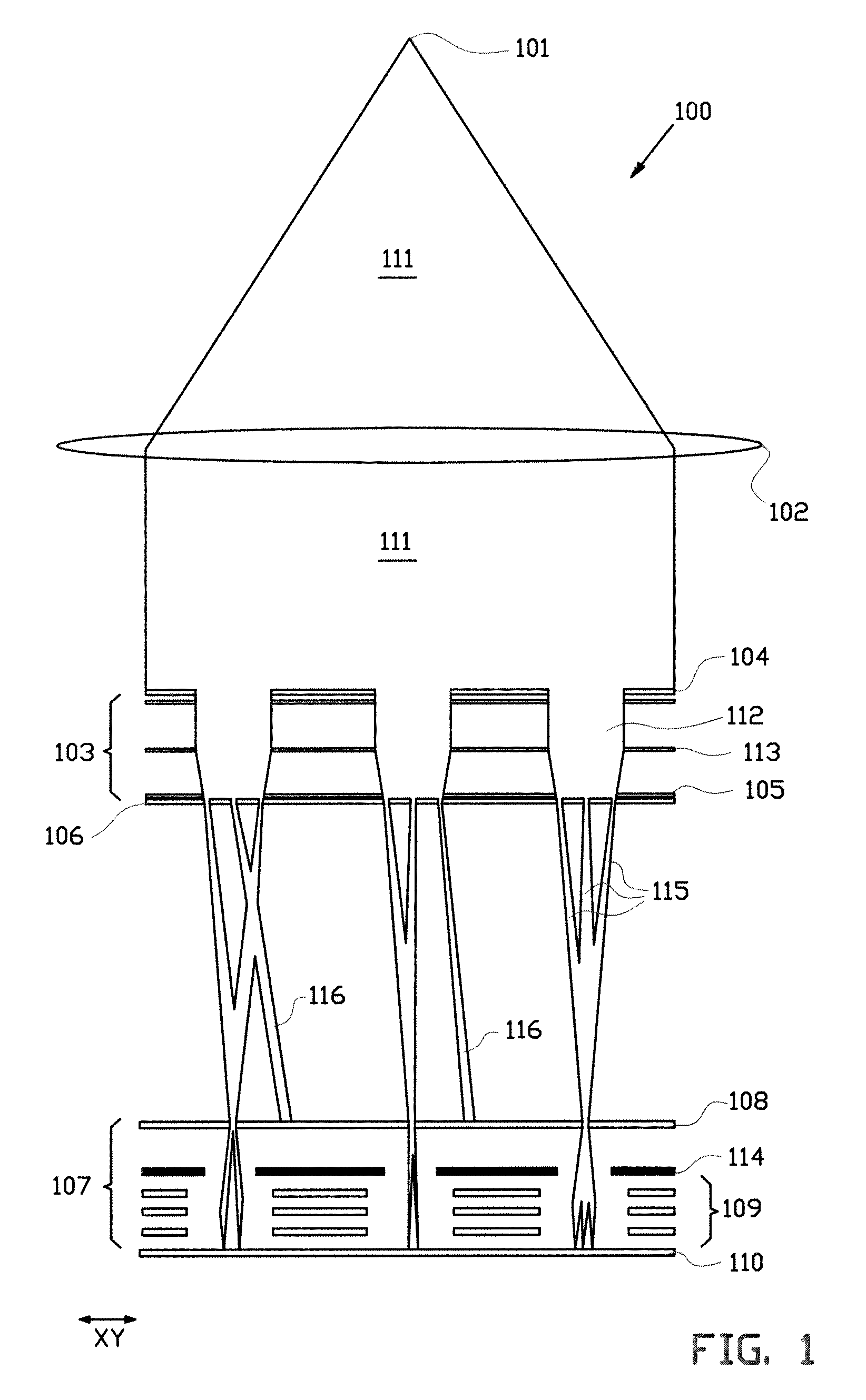
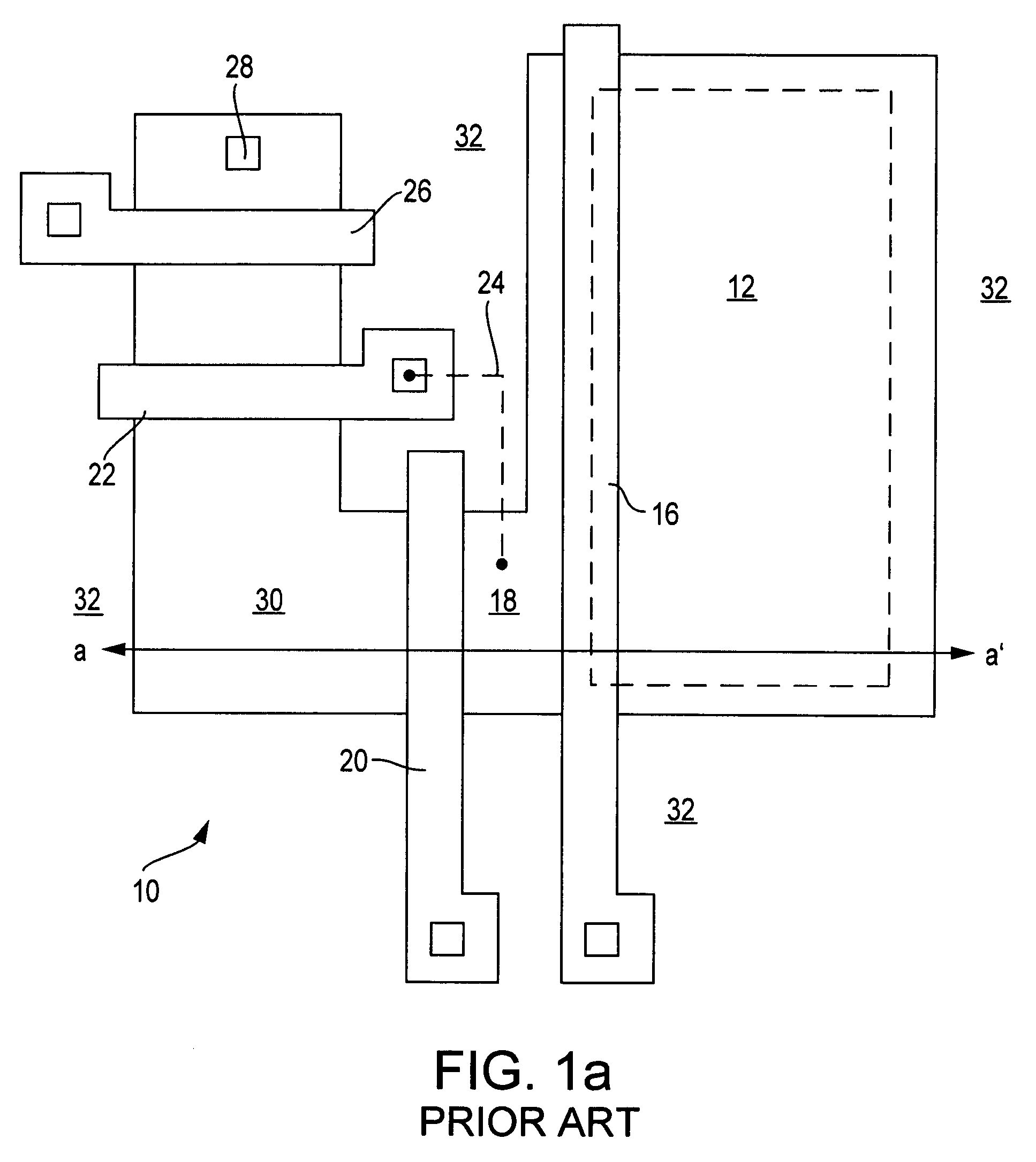
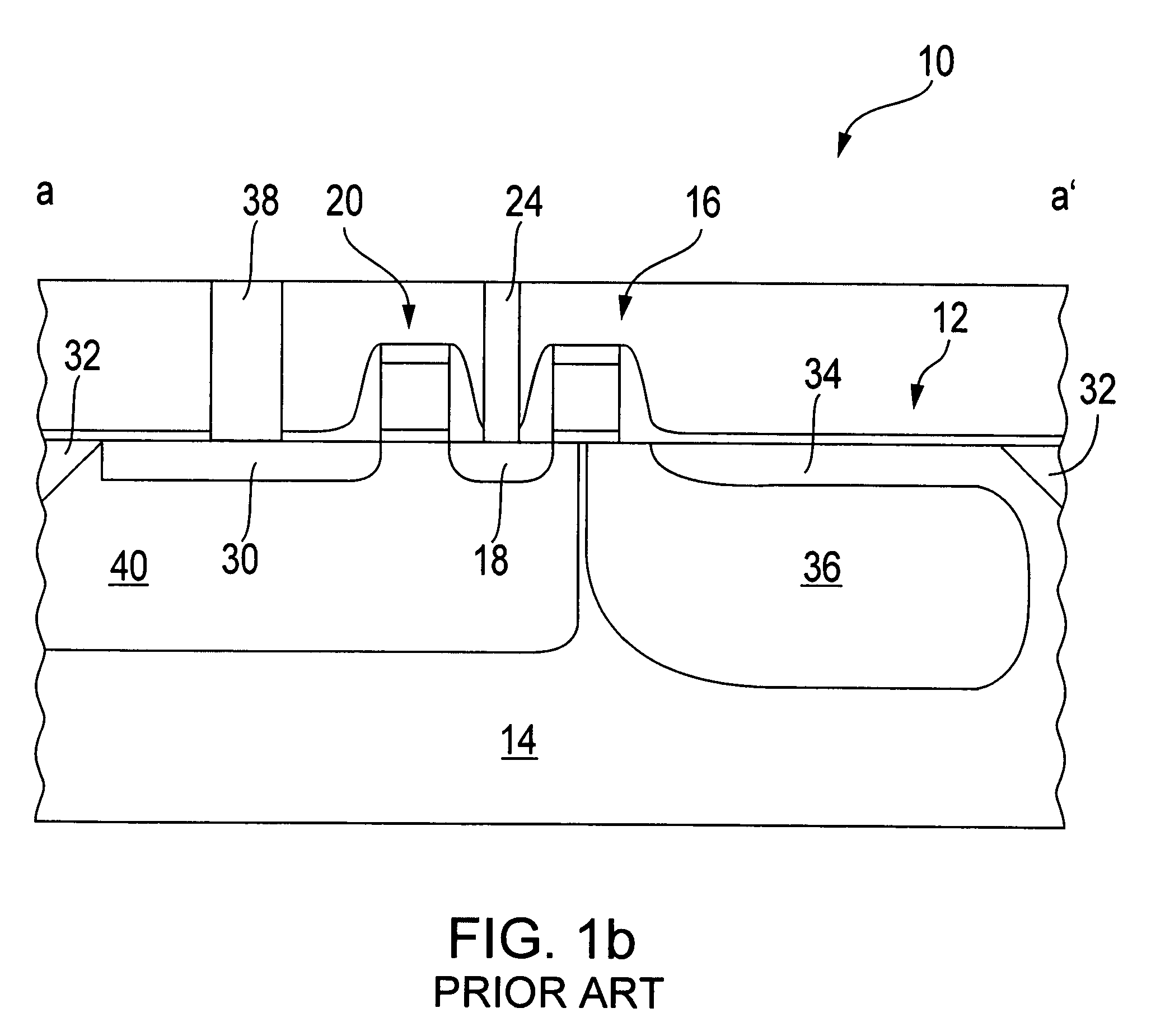
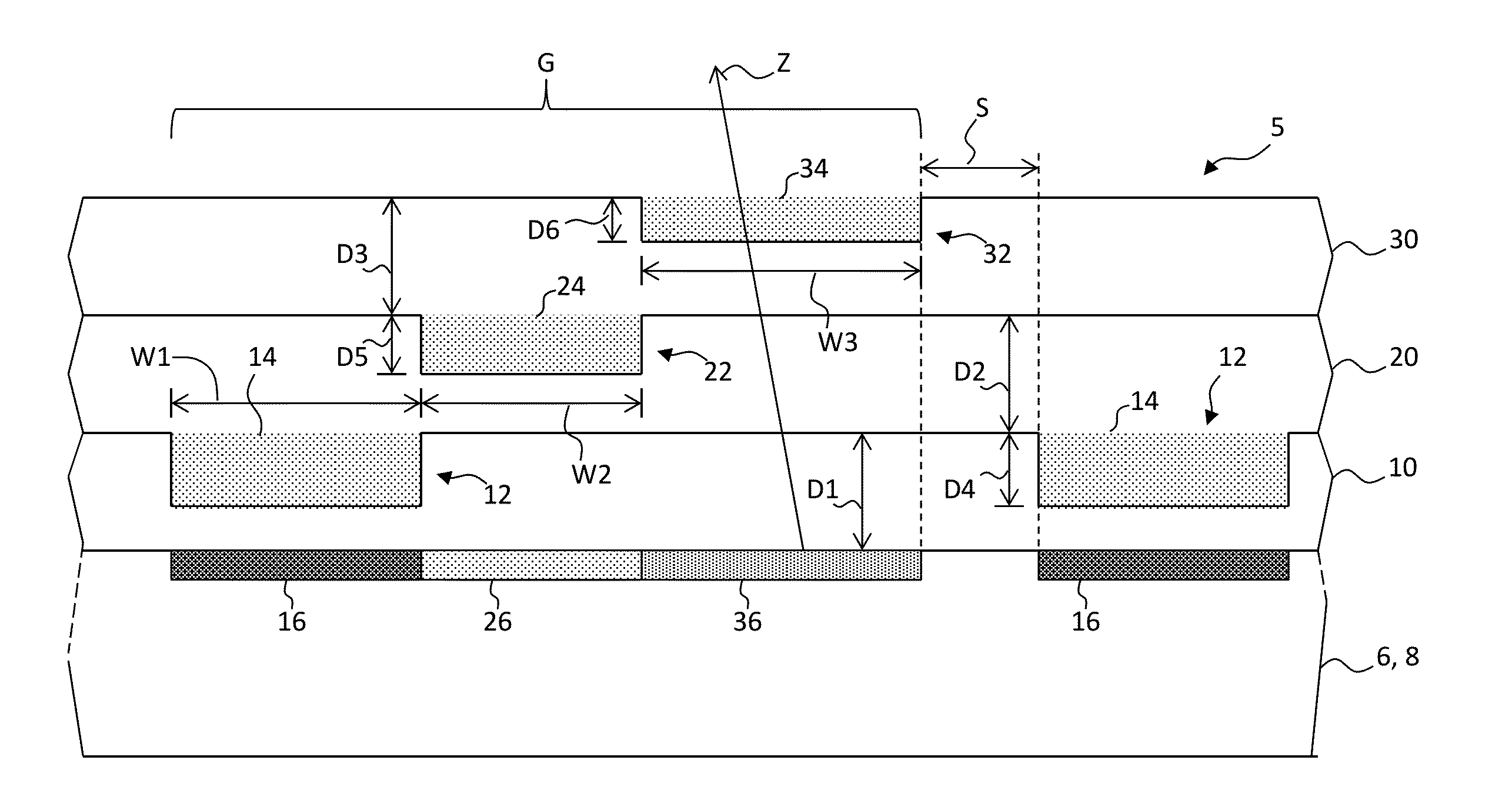
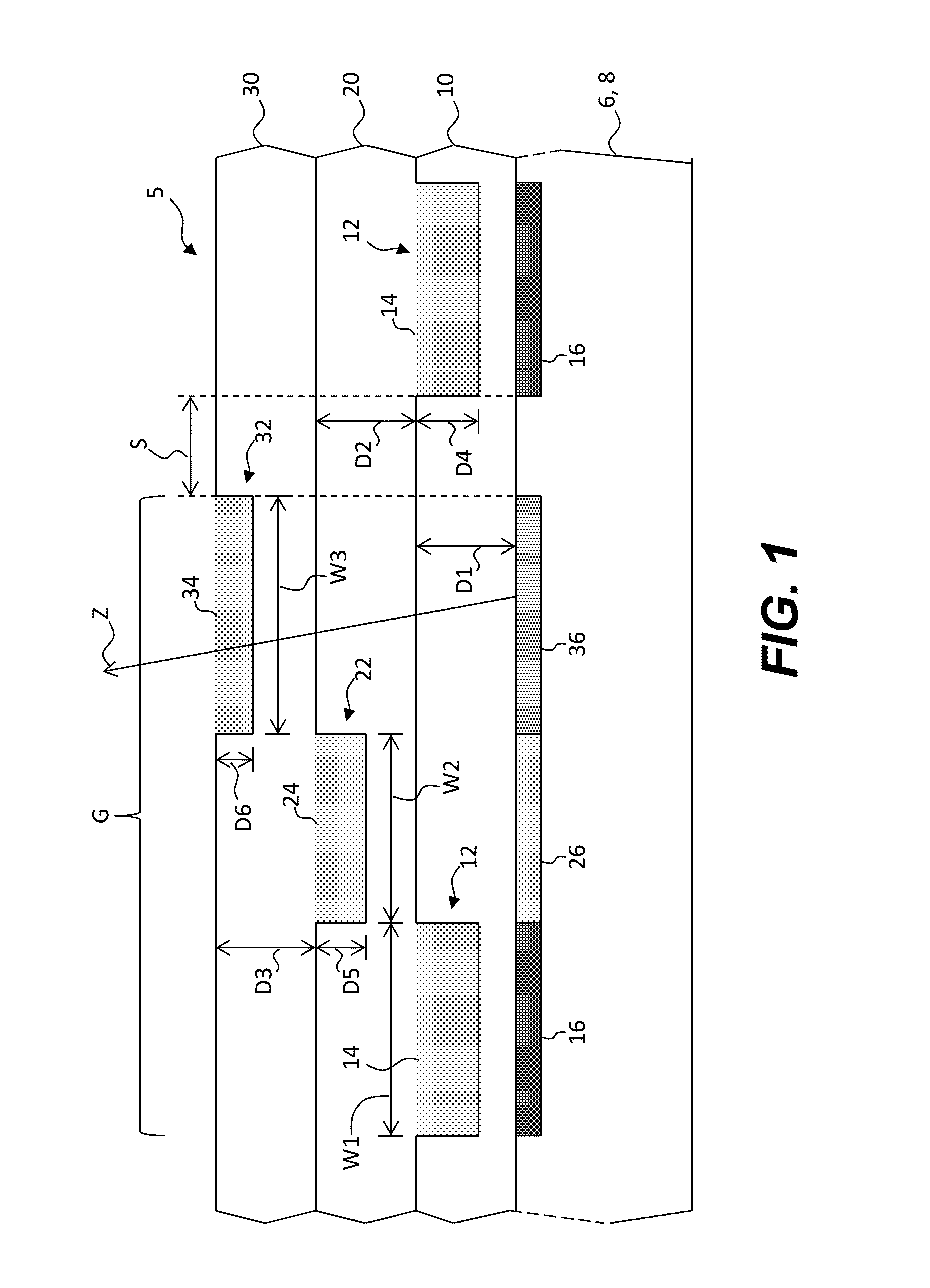
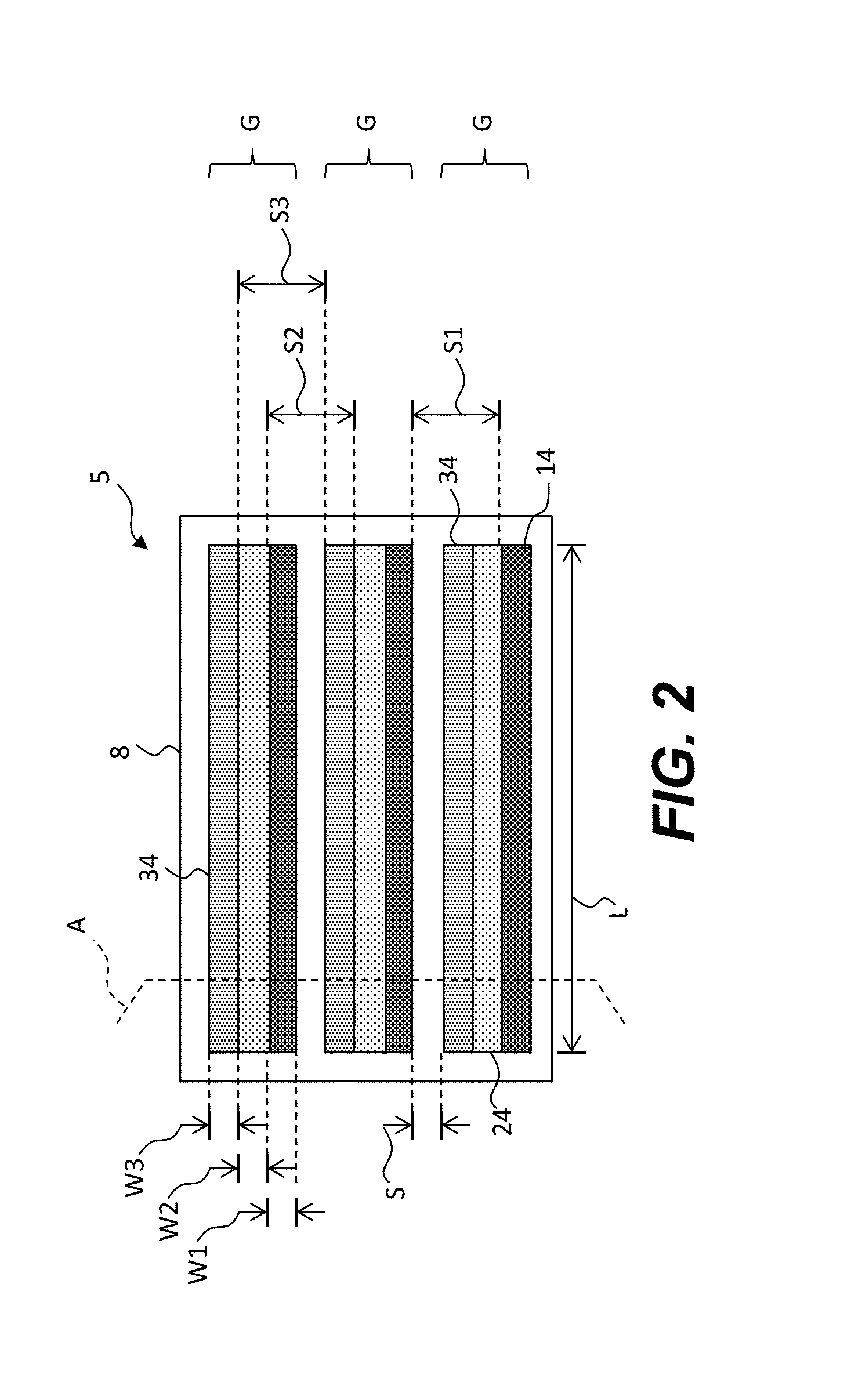
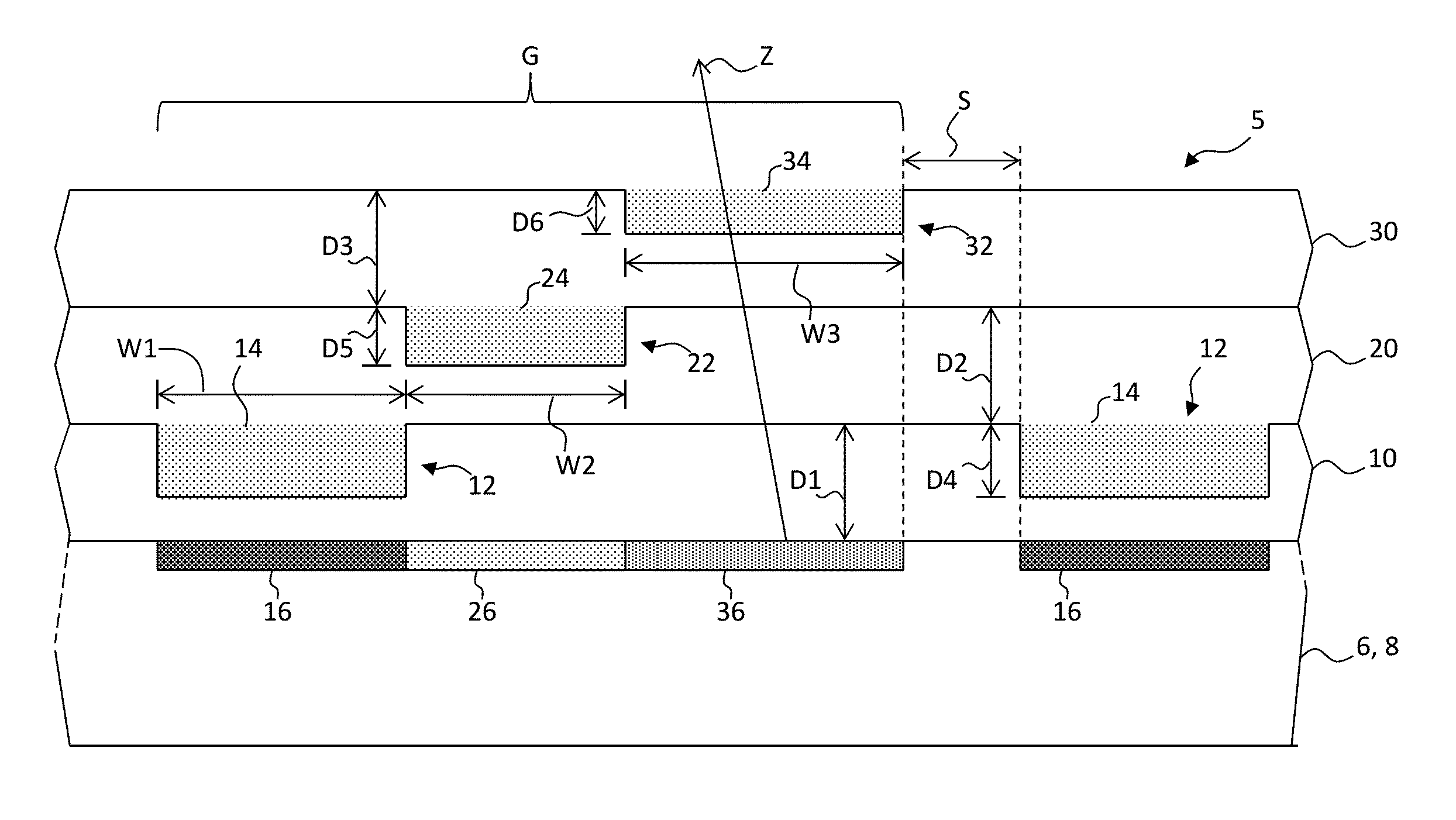
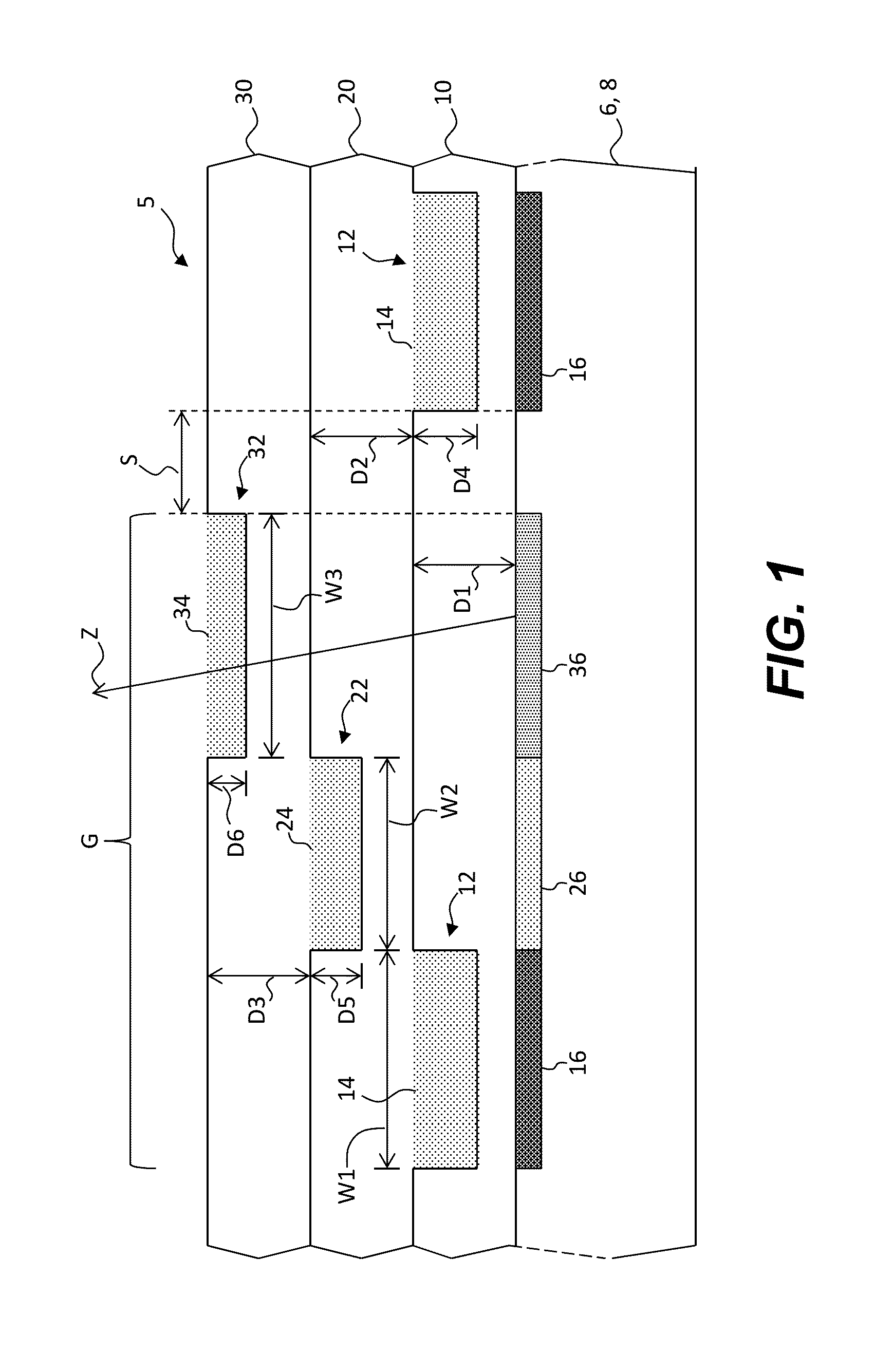
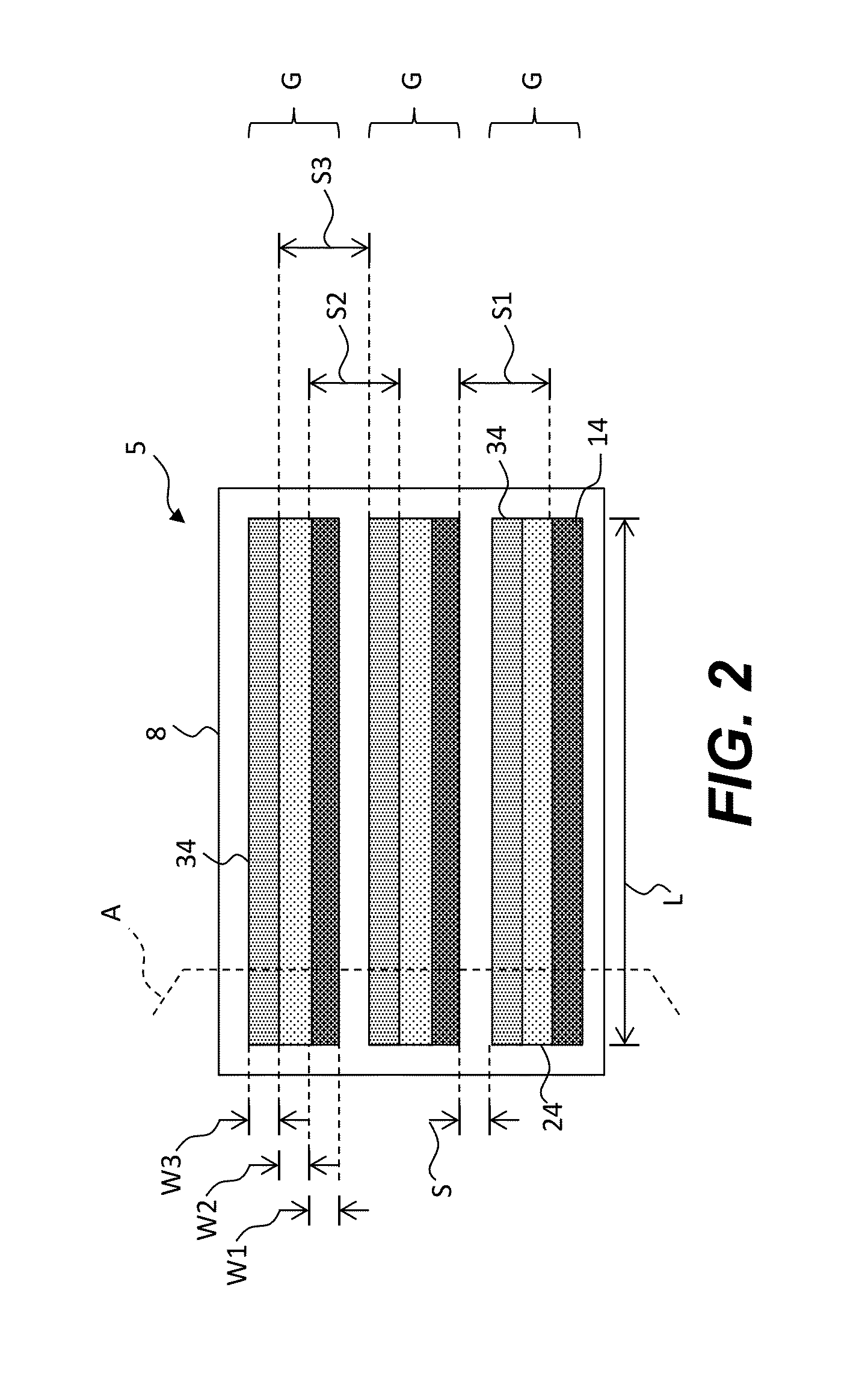
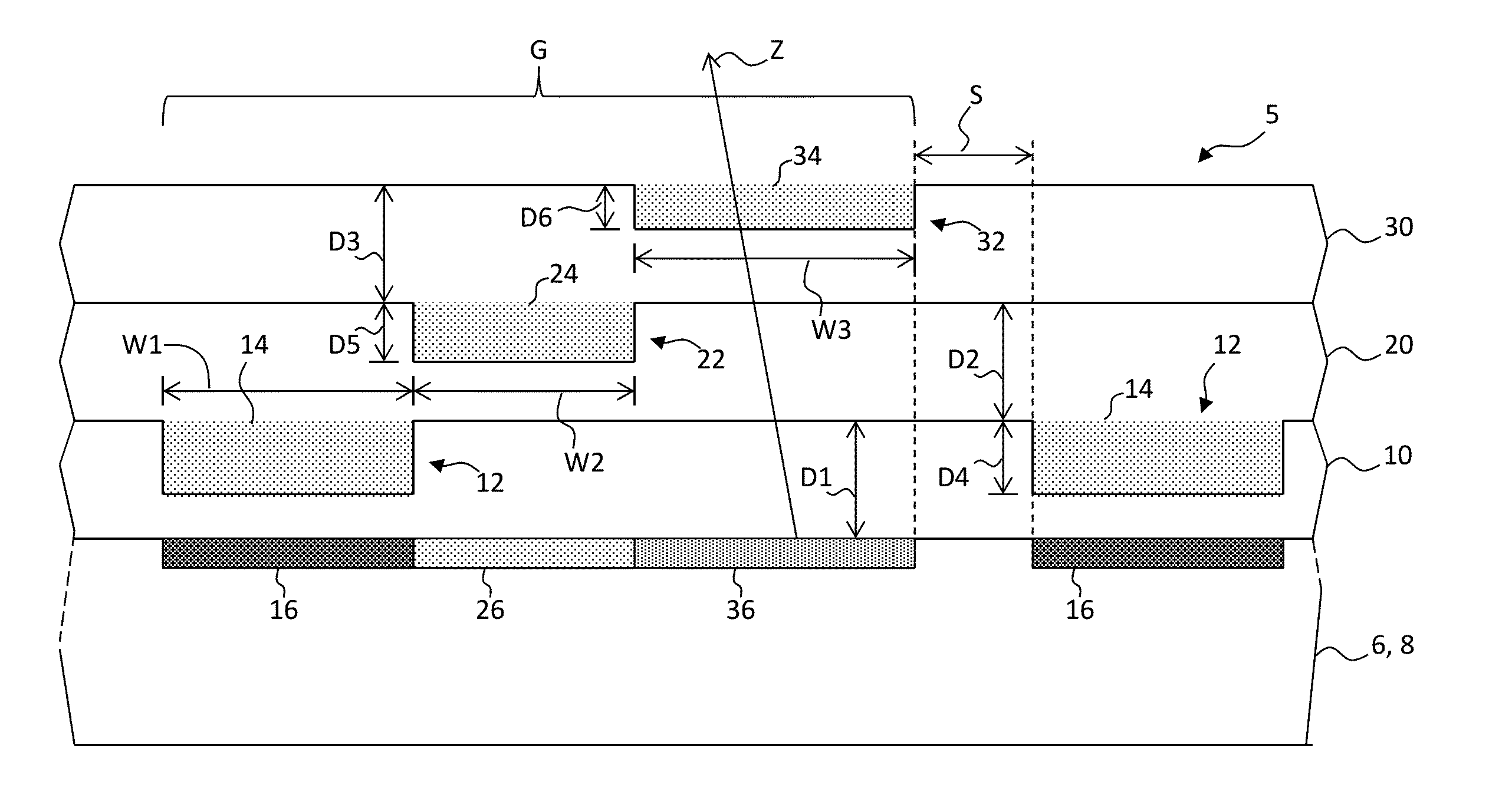
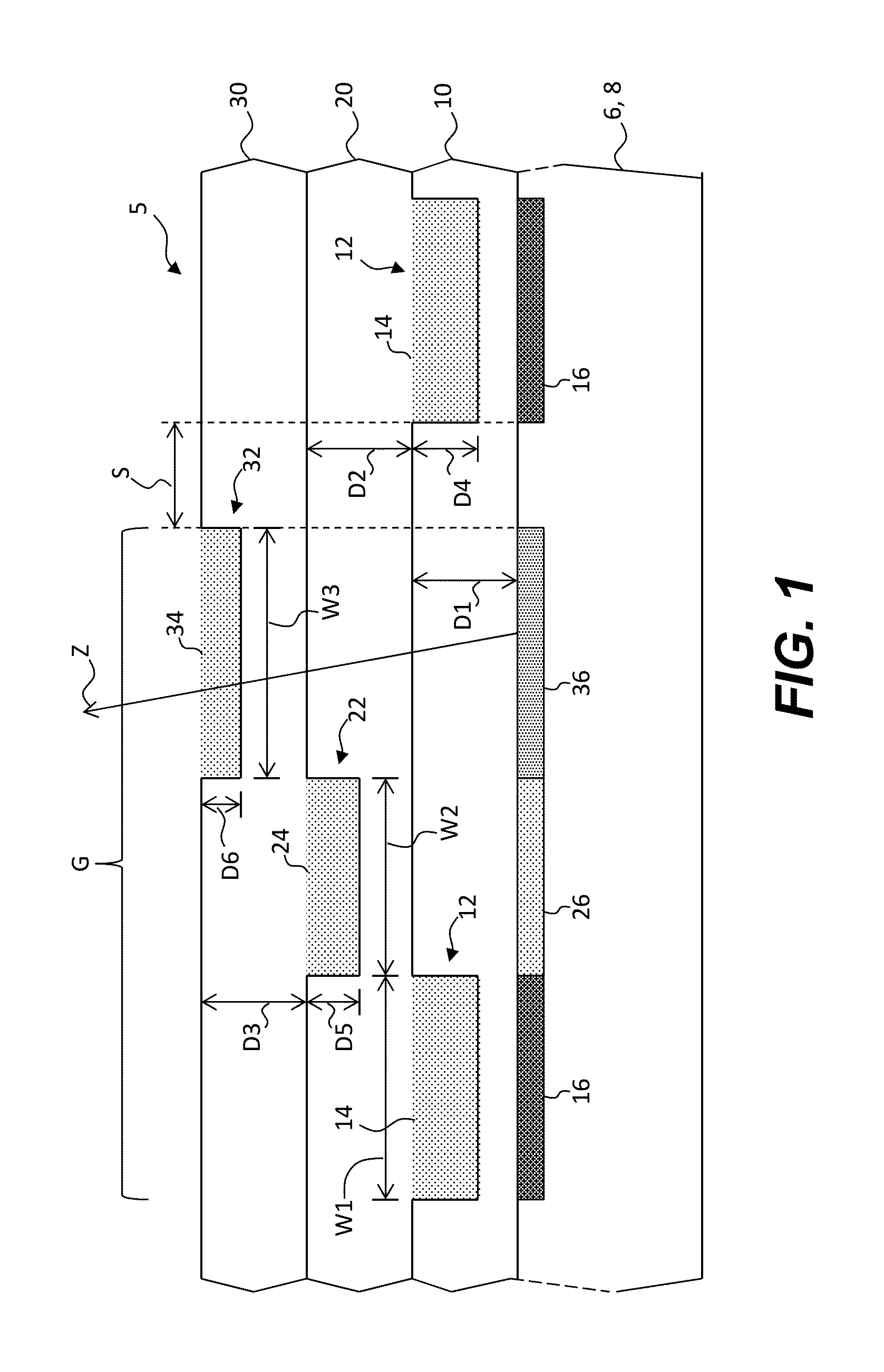
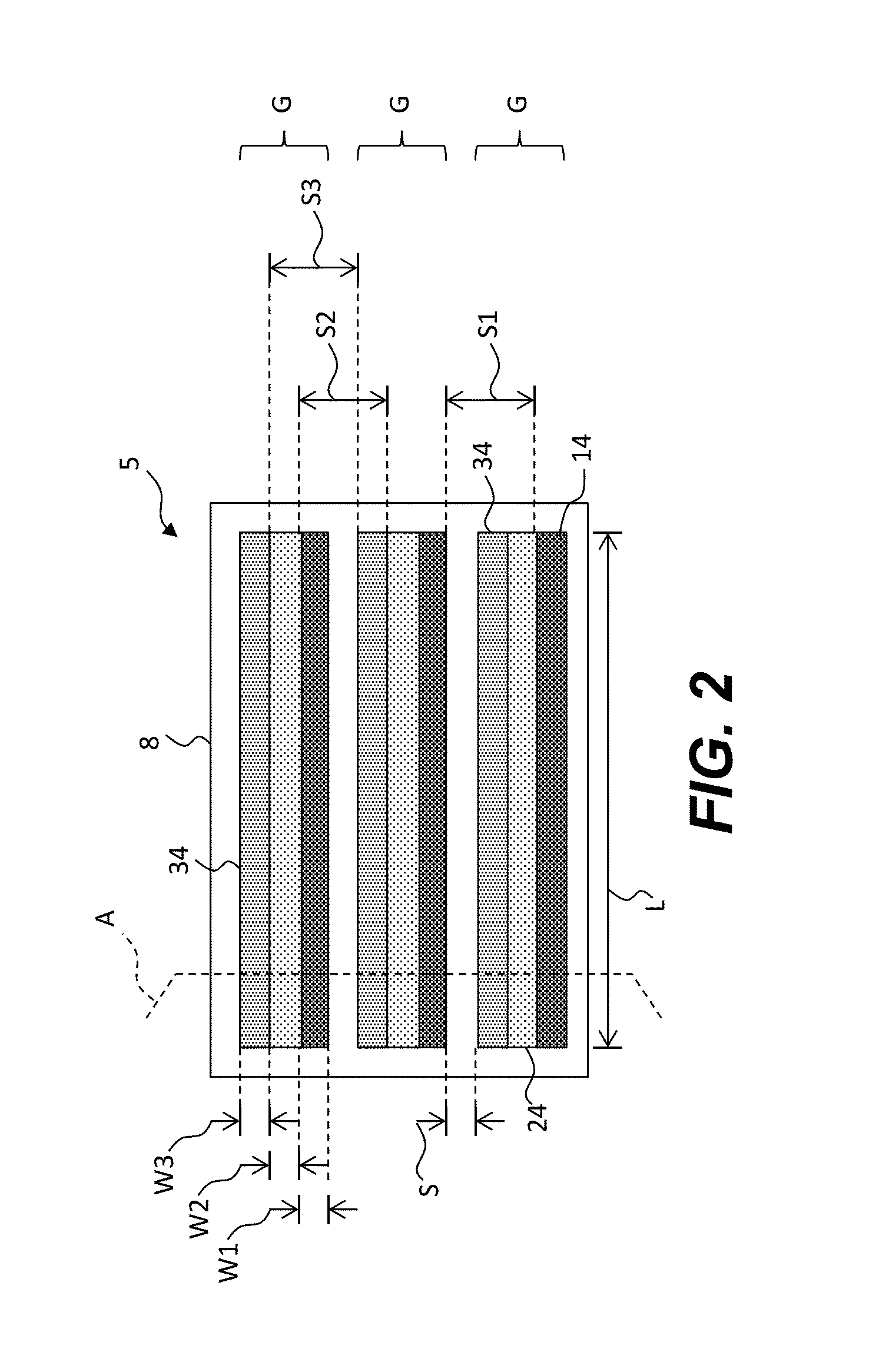
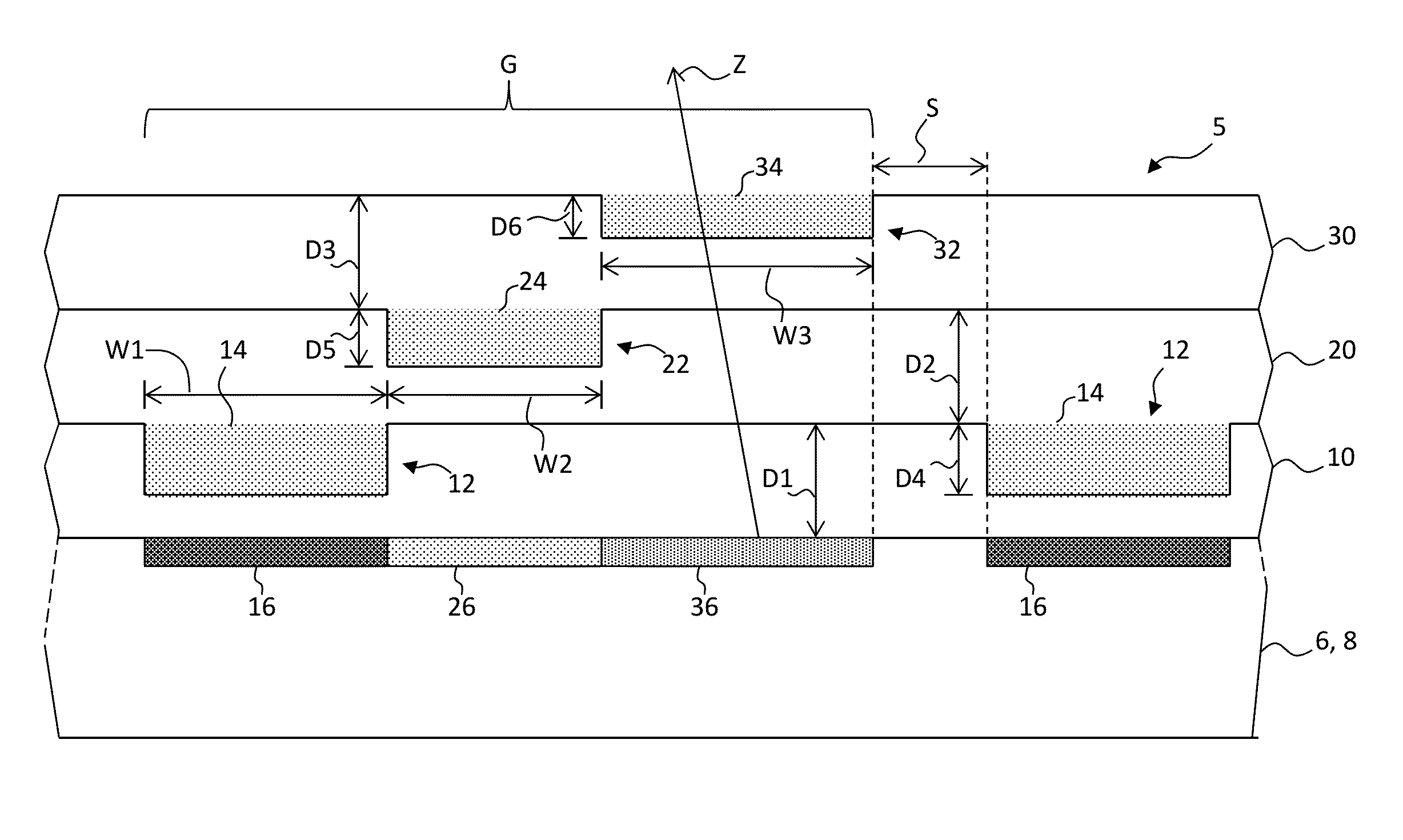
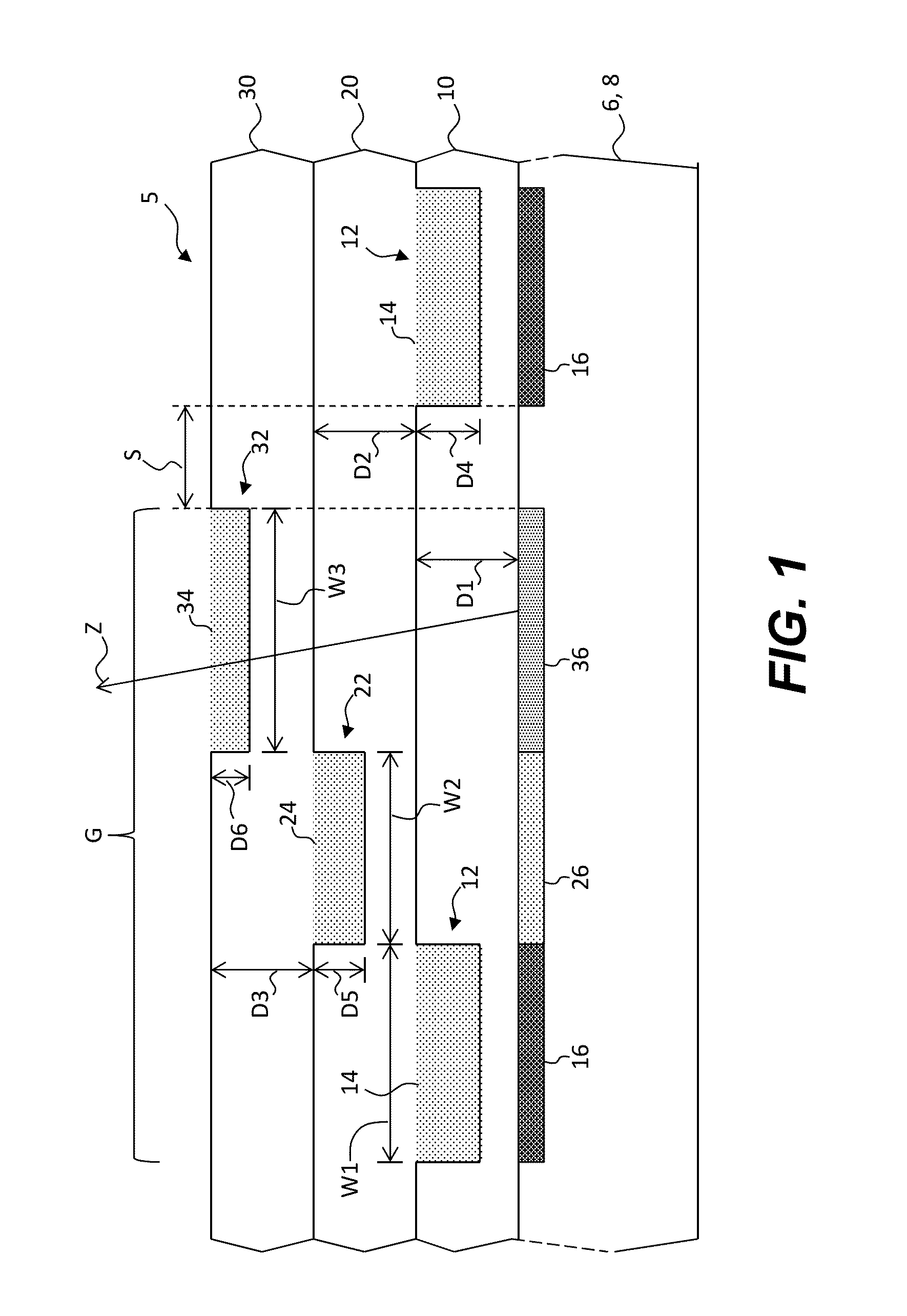
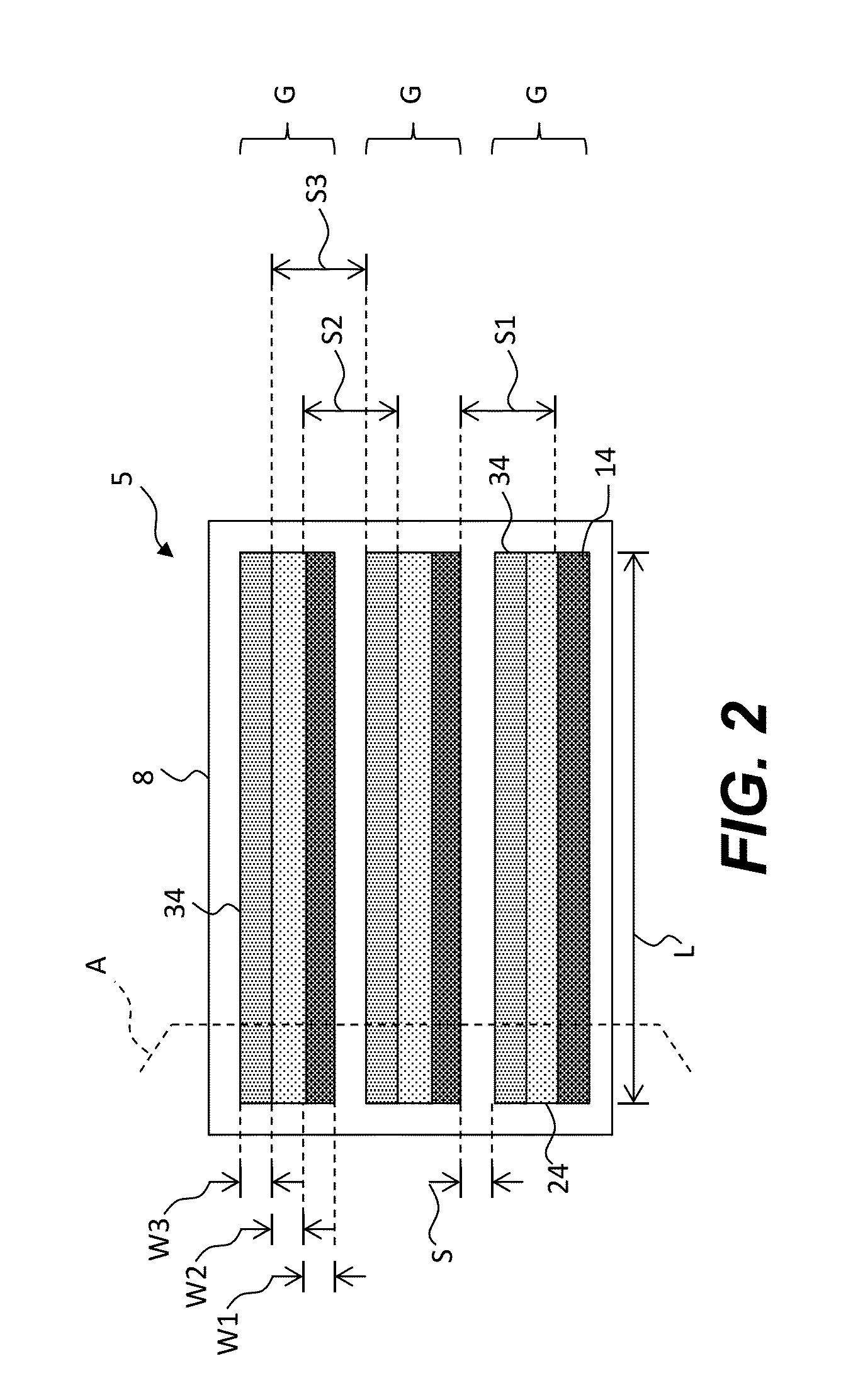
Charged particle system comprising a manipulator device for manipulation of one or more charged particle beams
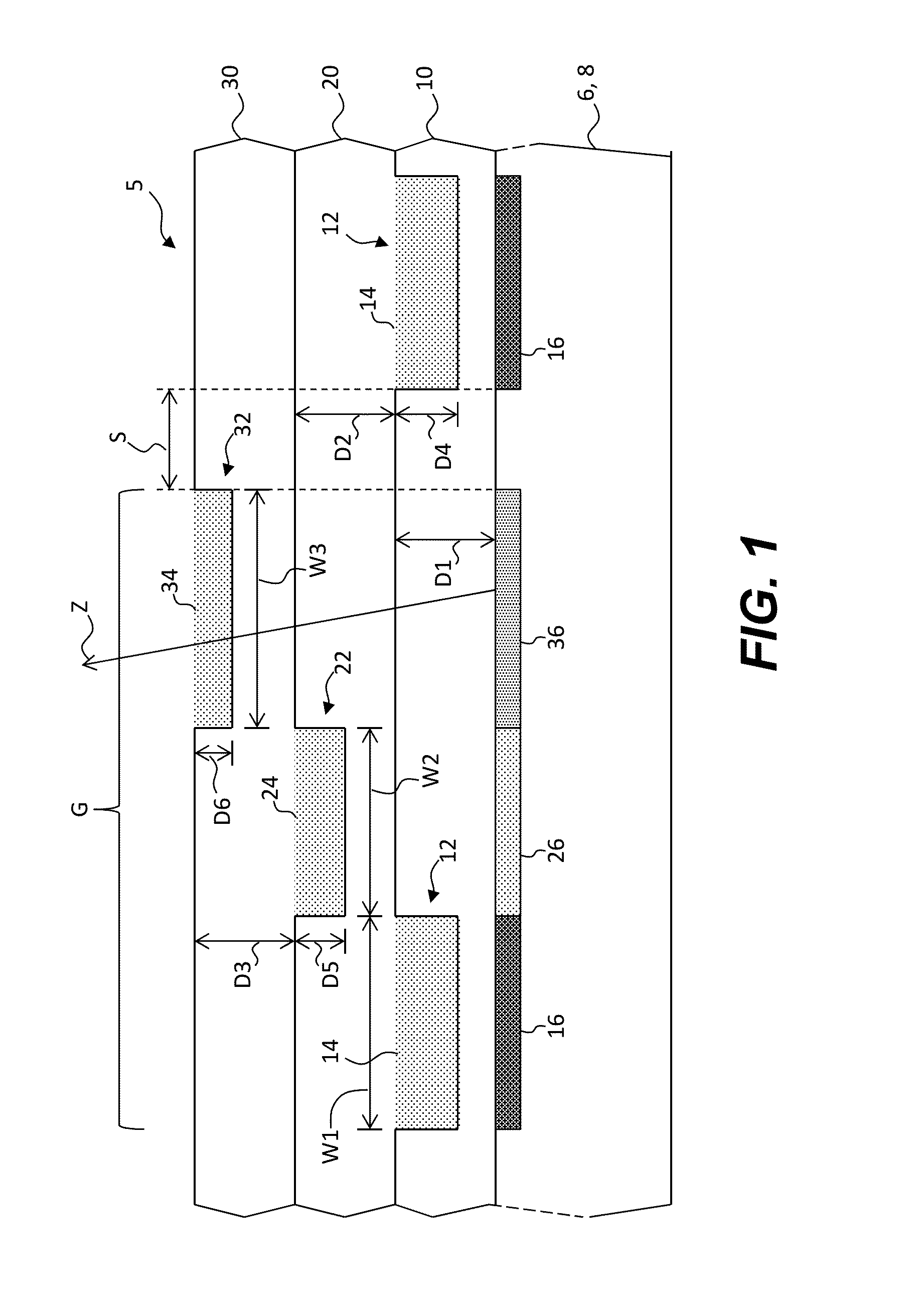
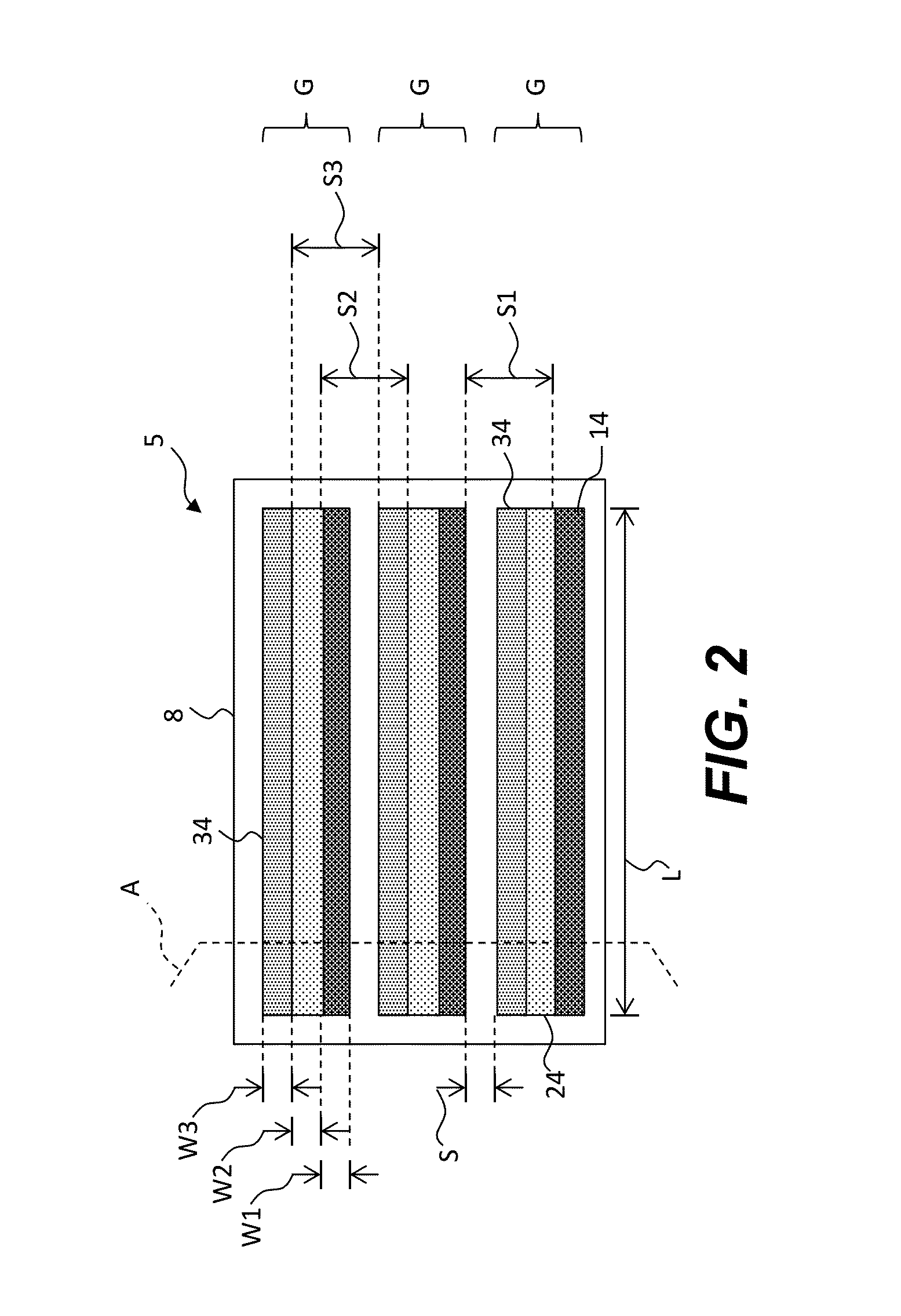
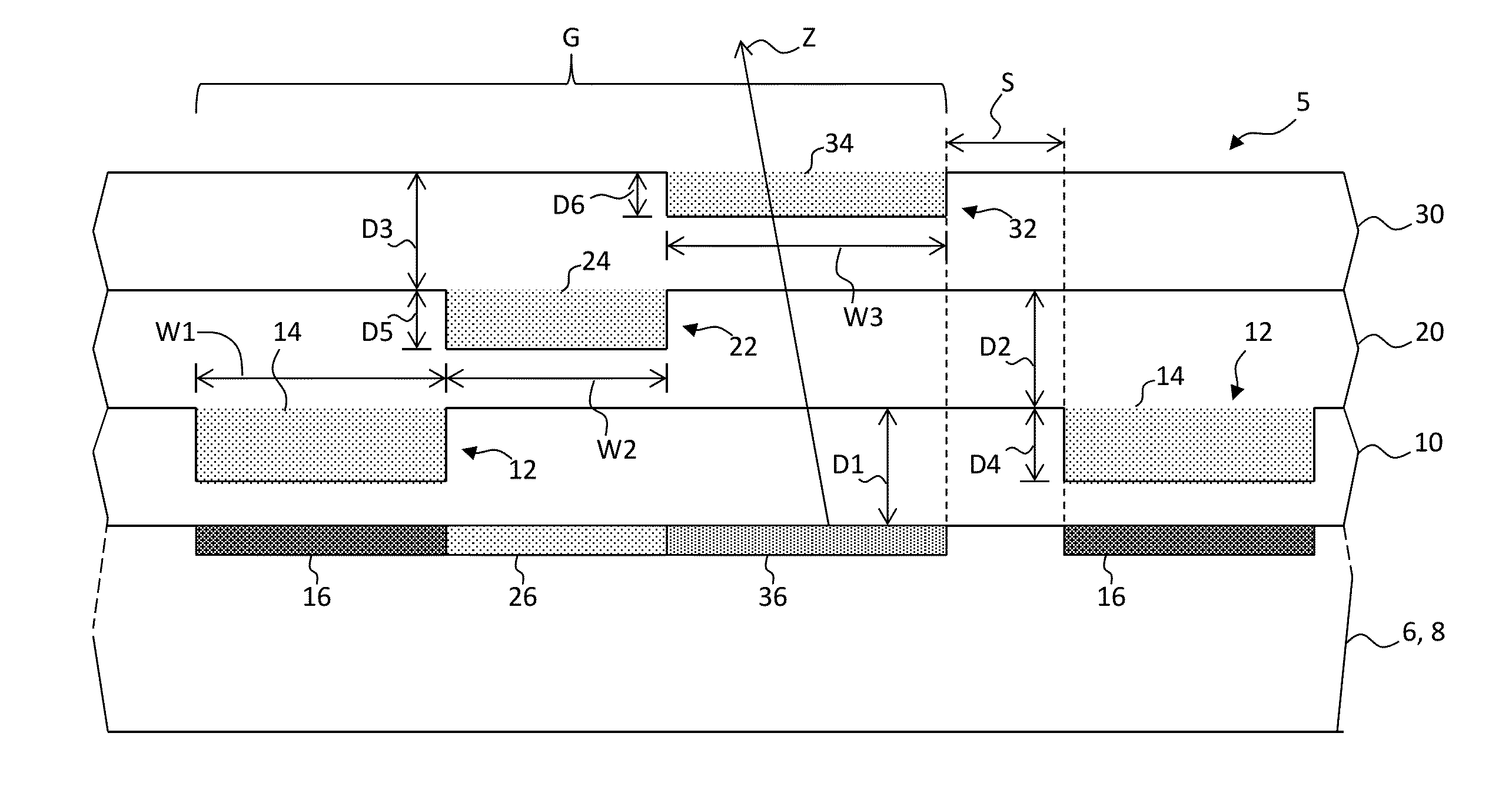
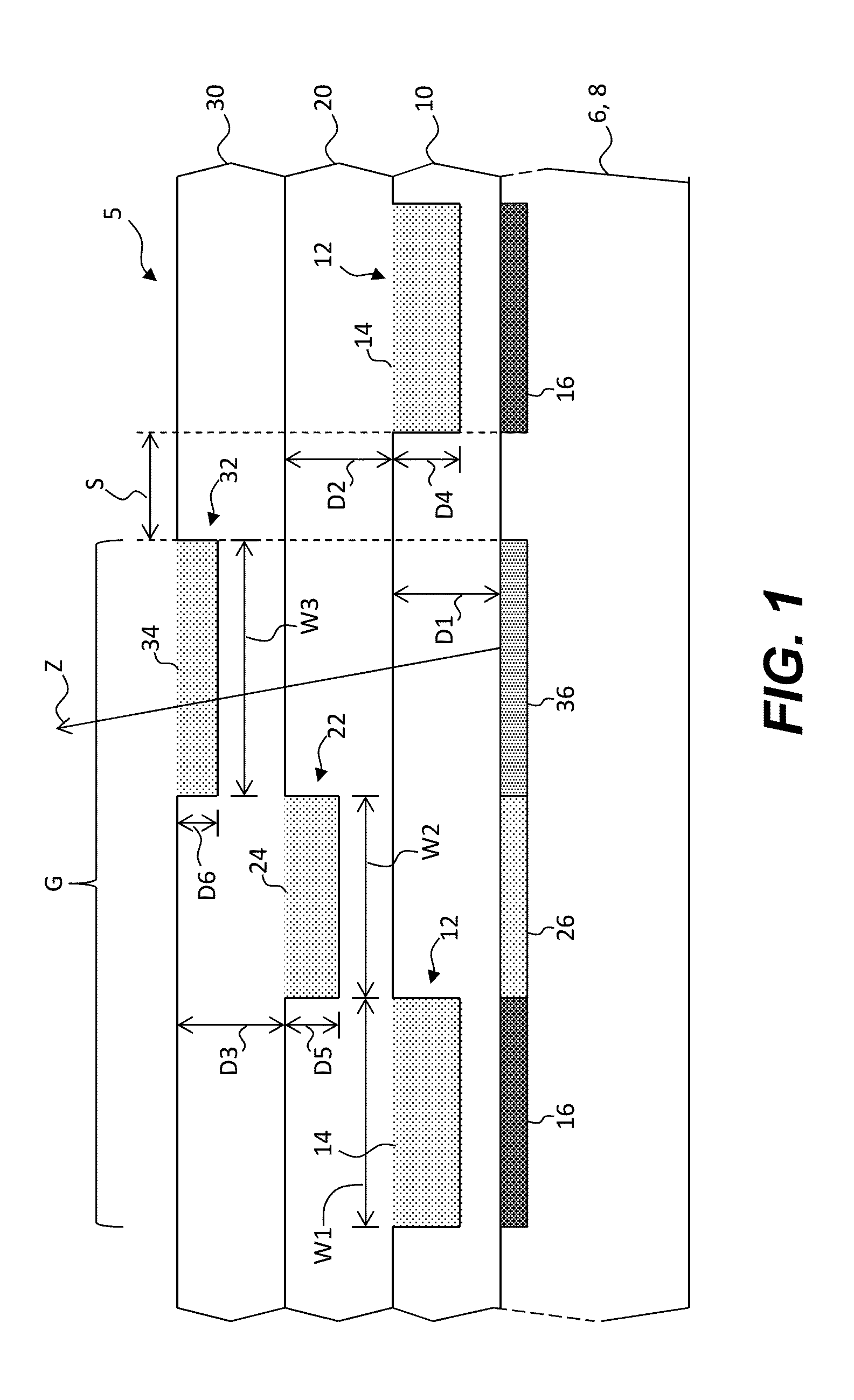
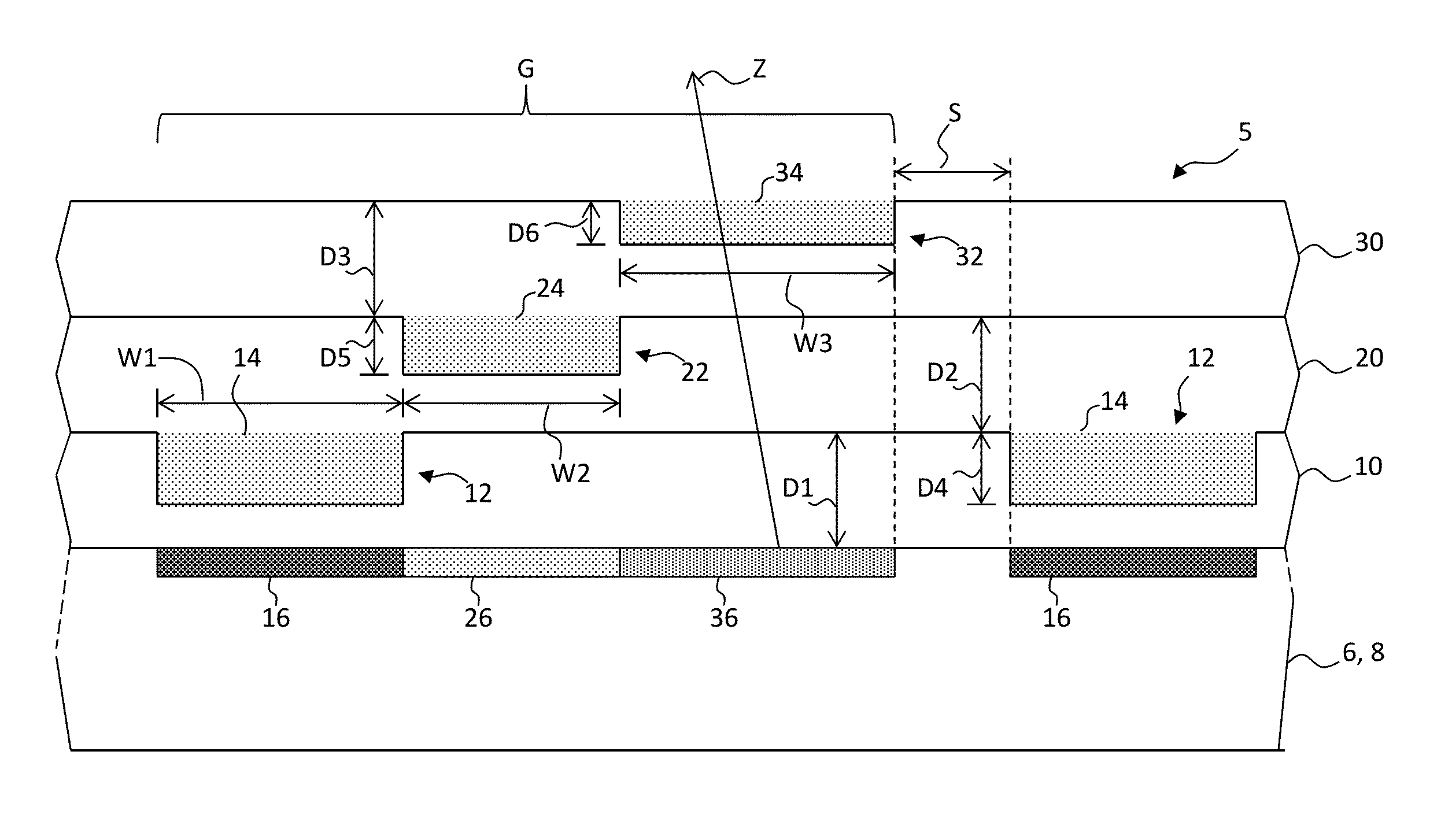
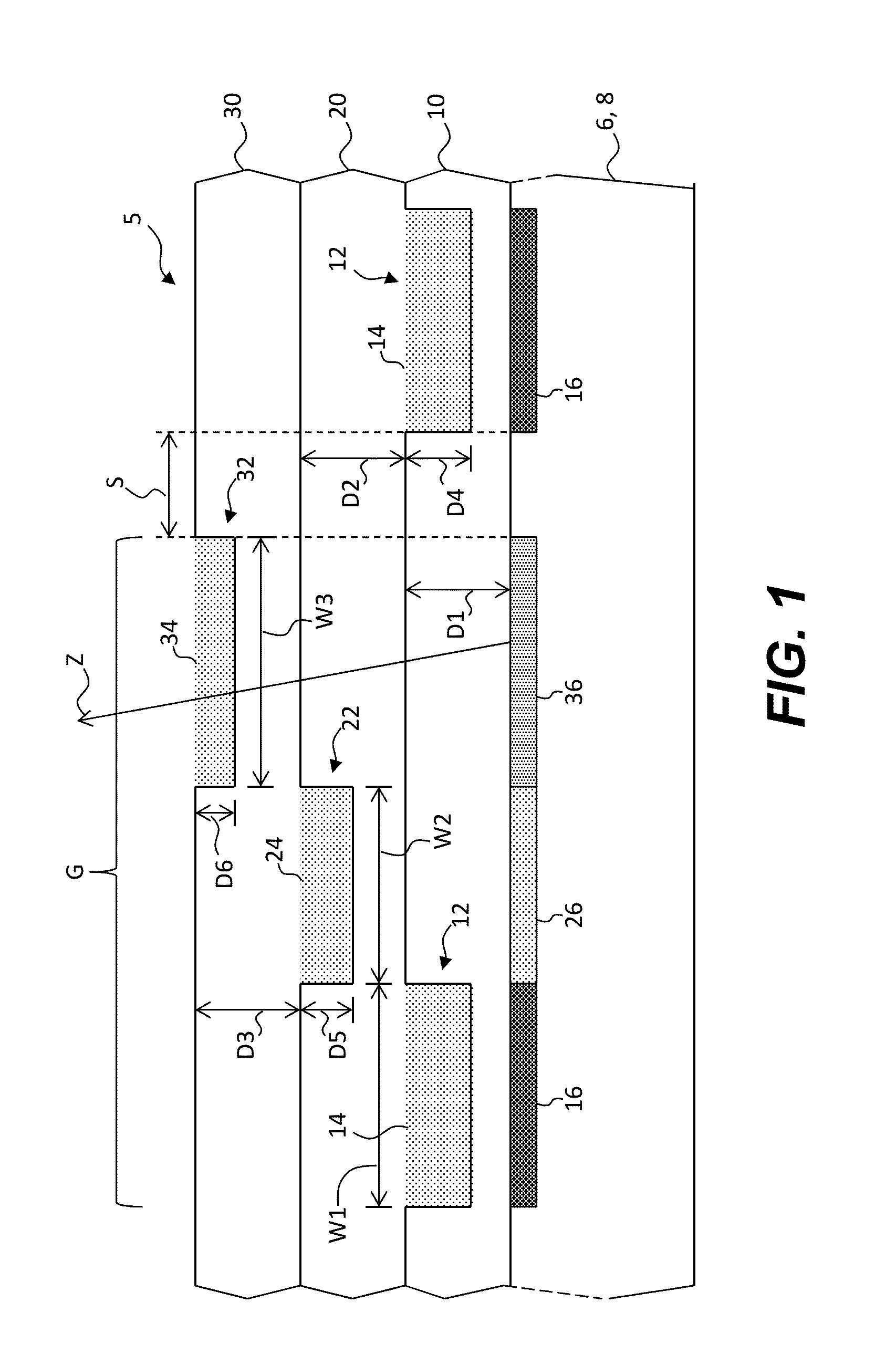
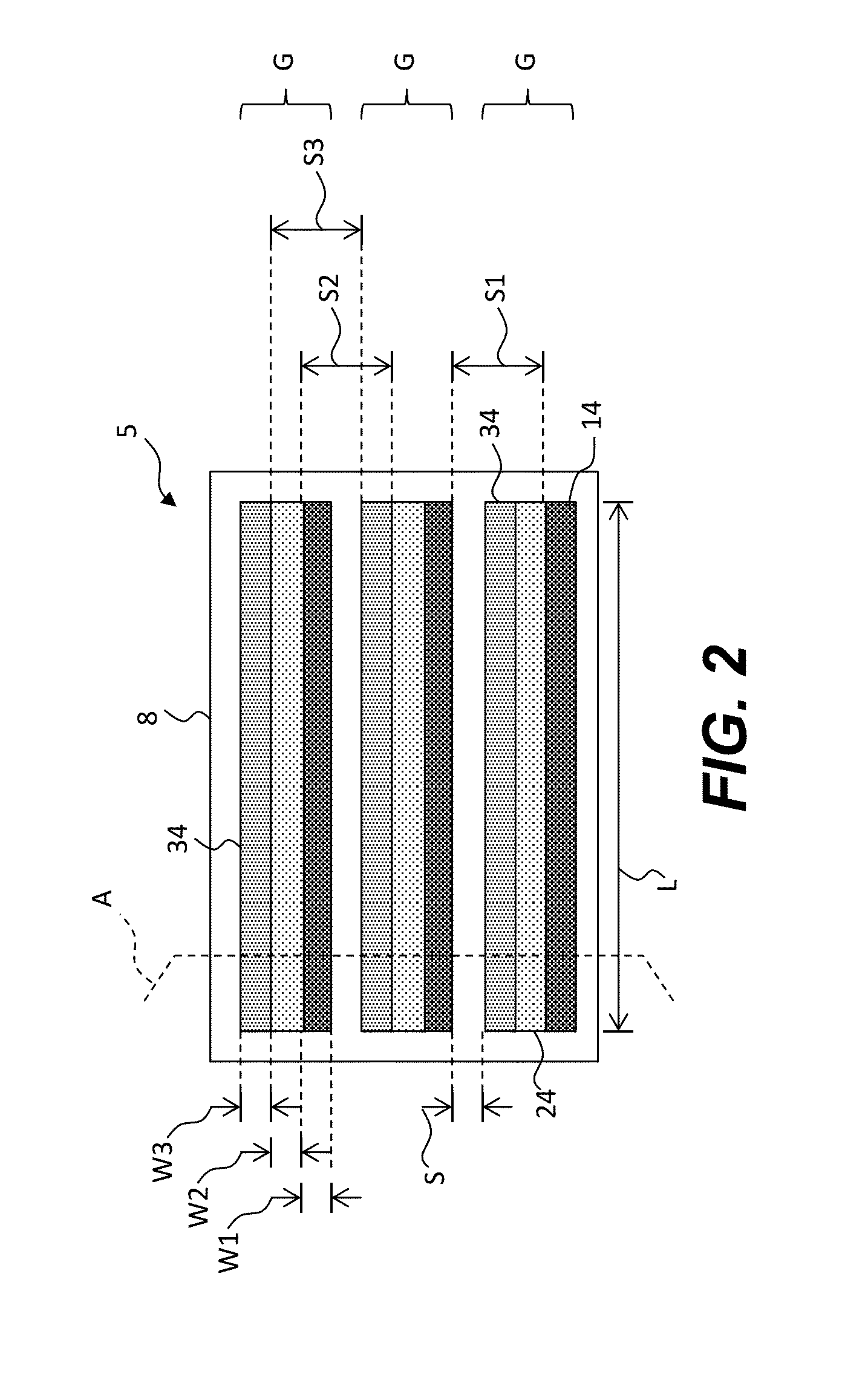
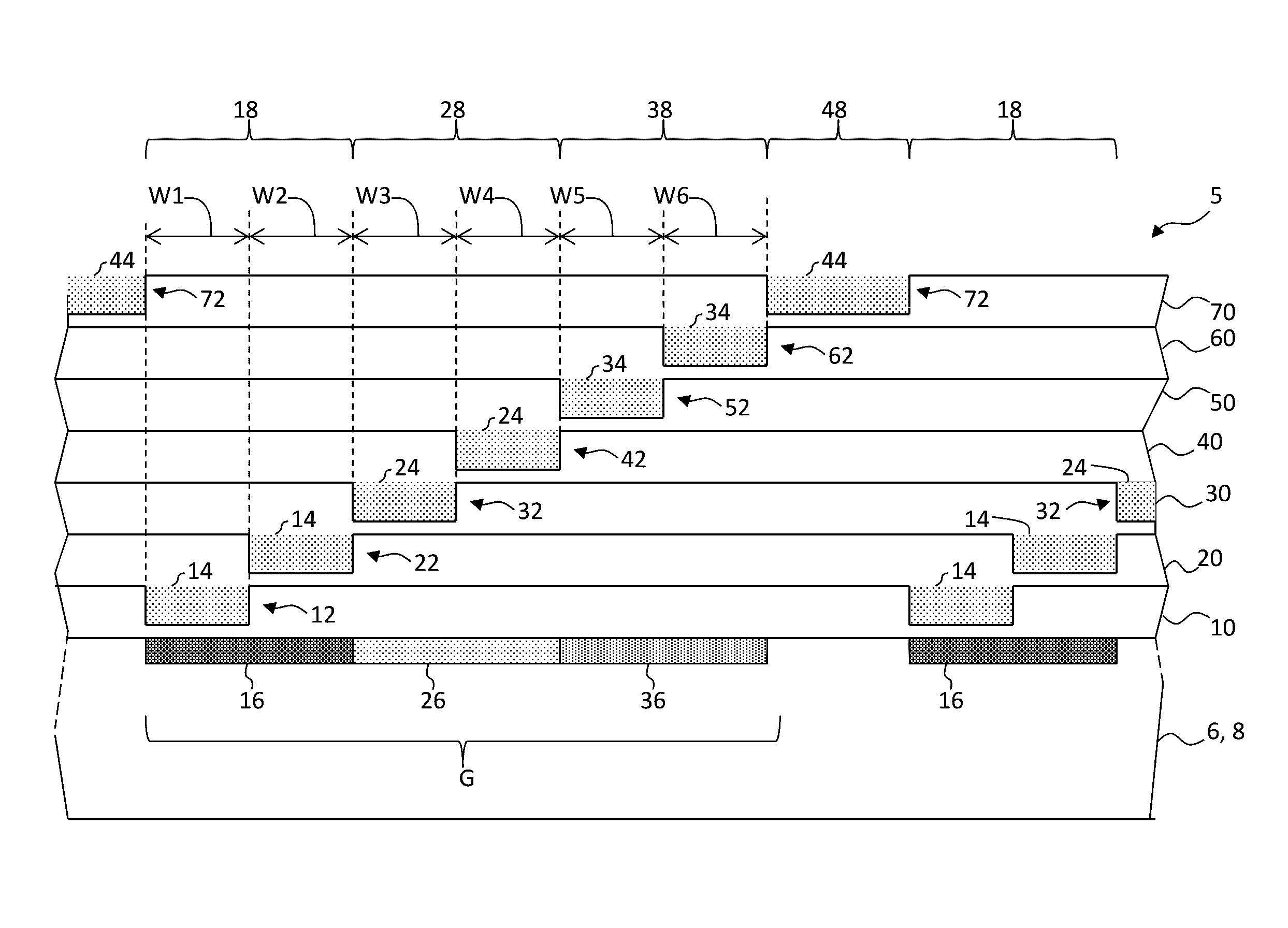
ActiveUS20120273690A1Not easy to produceImprove balanceOptical radiation measurementParticle separator tubesLithographic artistPlanar substrate
The invention relates to a charged particle system such as a multi beam lithography system, comprising a manipulator device for manipulation of one or more charged particle beams, wherein the manipulator device comprises at least one through opening in the plane of the planar substrate for passing at least one charged particle beam there through. Each through opening is provided with electrodes arranged in a first set of multiple first electrodes along a first part of a perimeter of said through opening and in a second set of multiple second electrodes along a second part of said perimeter. An electronic control circuit is arranged for providing voltage differences the electrodes in dependence of a position of the first and second electrode along the perimeter of the through opening.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
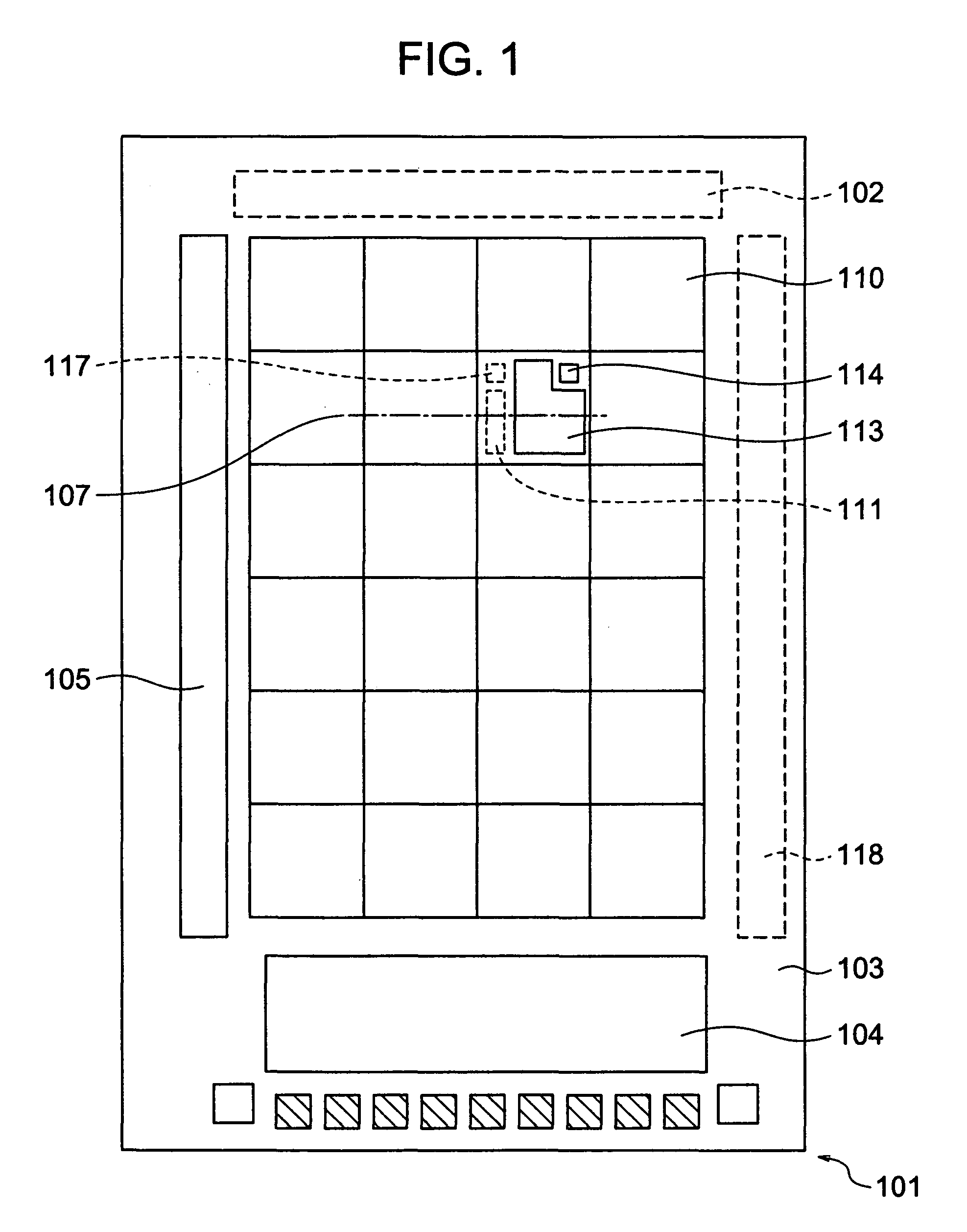
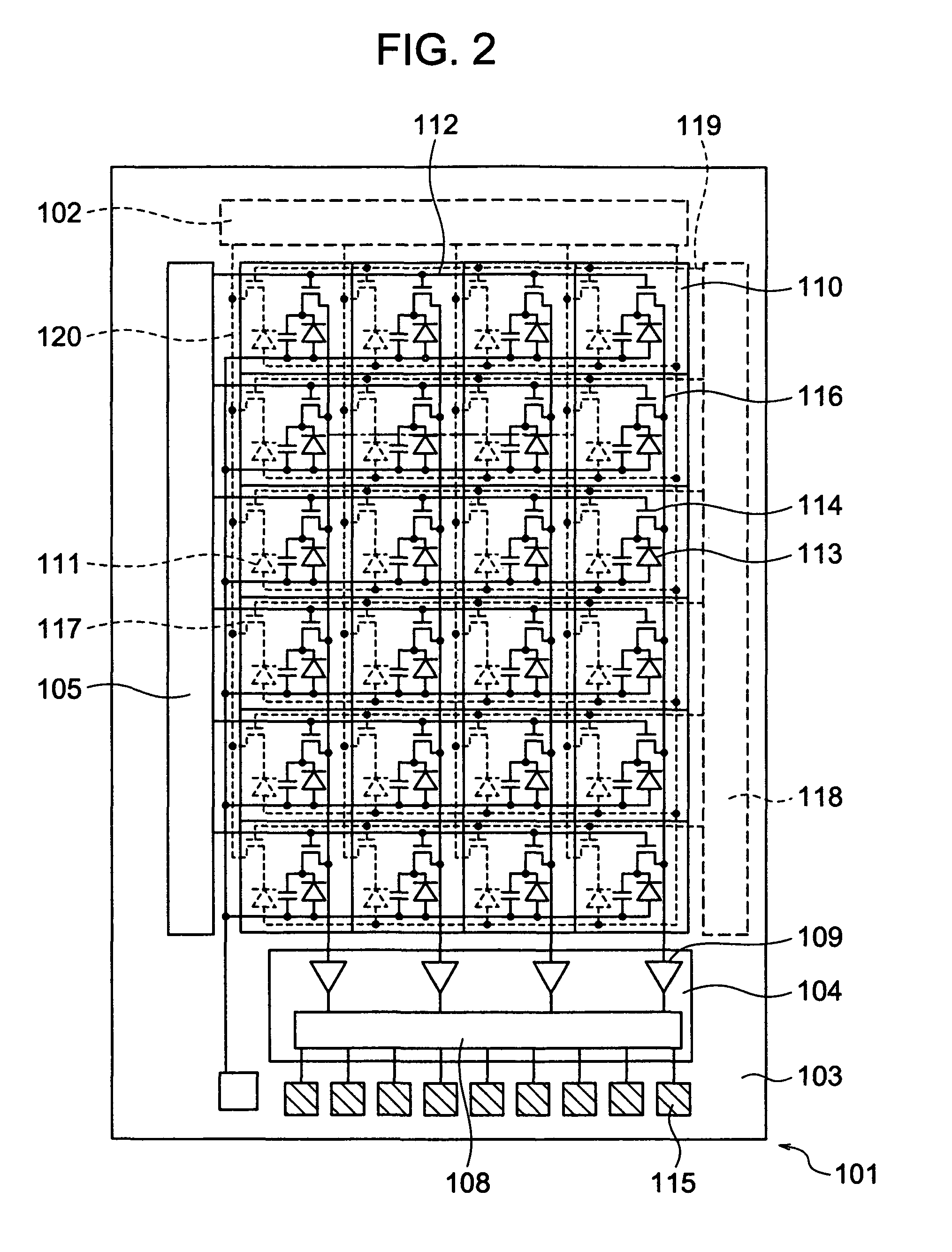
Imaging device and apparatus installed with the same
InactiveUS20080317303A1Good conditionEnhance the imageTelevision system detailsPerson identificationDirect radiationLength wave
An imaging device includes a light source layer having imaging light source units for radiating the imaging light containing a first wavelength on an object to be imaged, a detection layer having detection elements for detecting the light of the first wavelength radiated from the light source units, and a light-blocking unit interposed between the light source layer and the detection layer. The light source layer is held between the detection layer and the object to be imaged. The light-blocking unit is arranged in such a manner as to block the direct radiation of at least part of the light radiated from the light source units to the detection elements.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
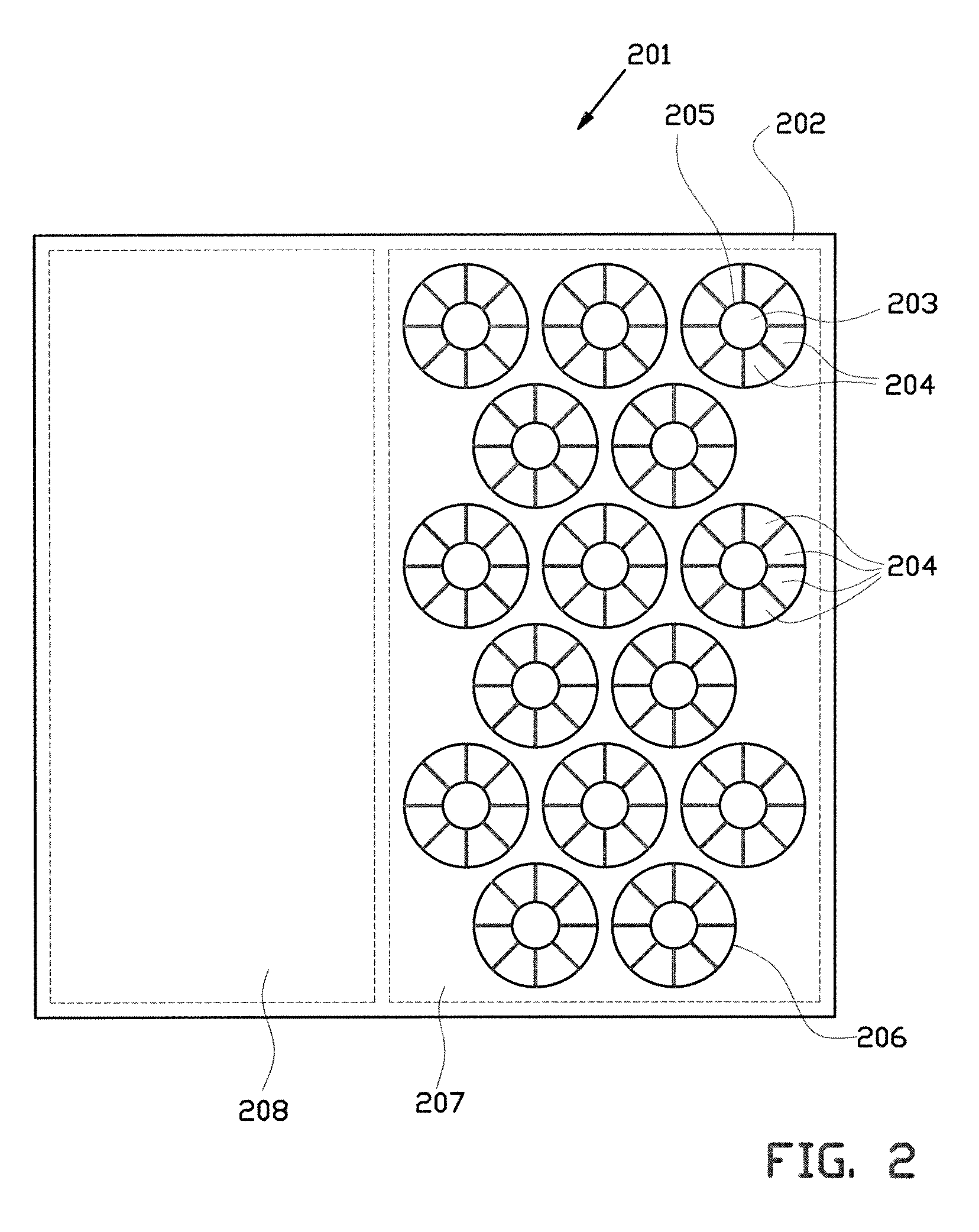
Photodiode array and method of making the same
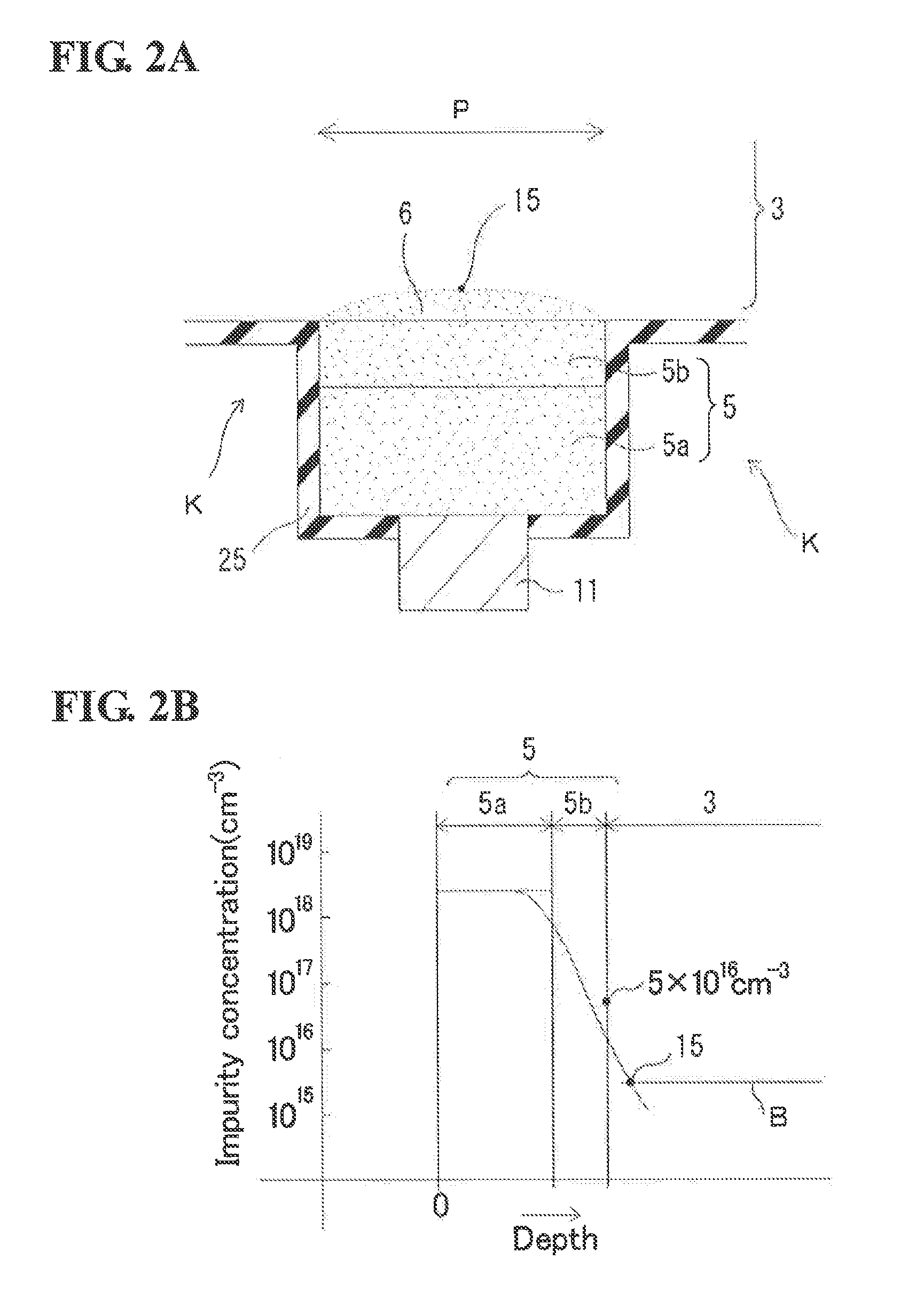
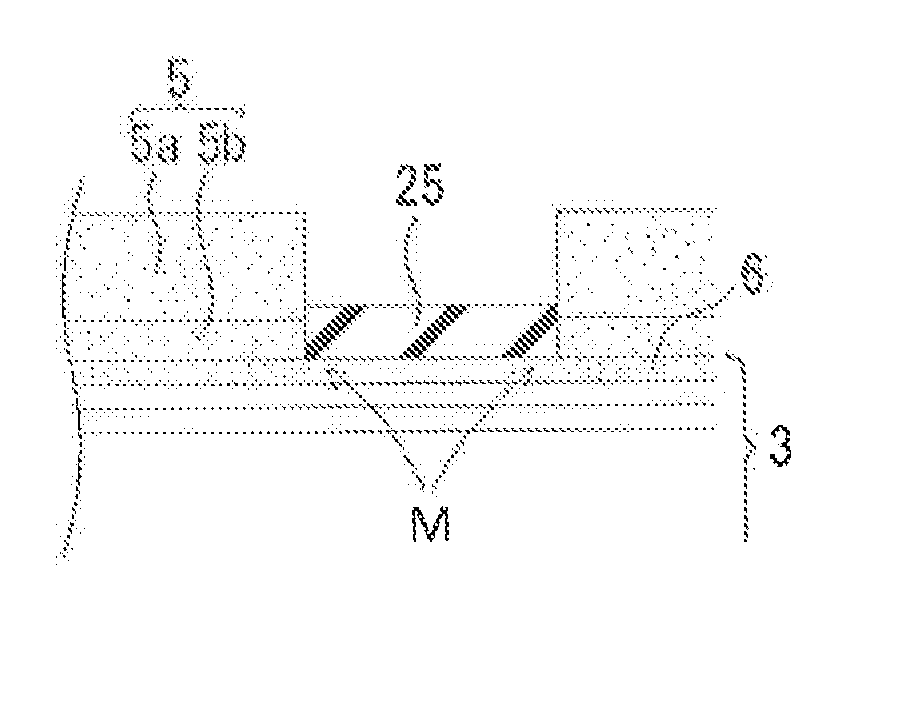
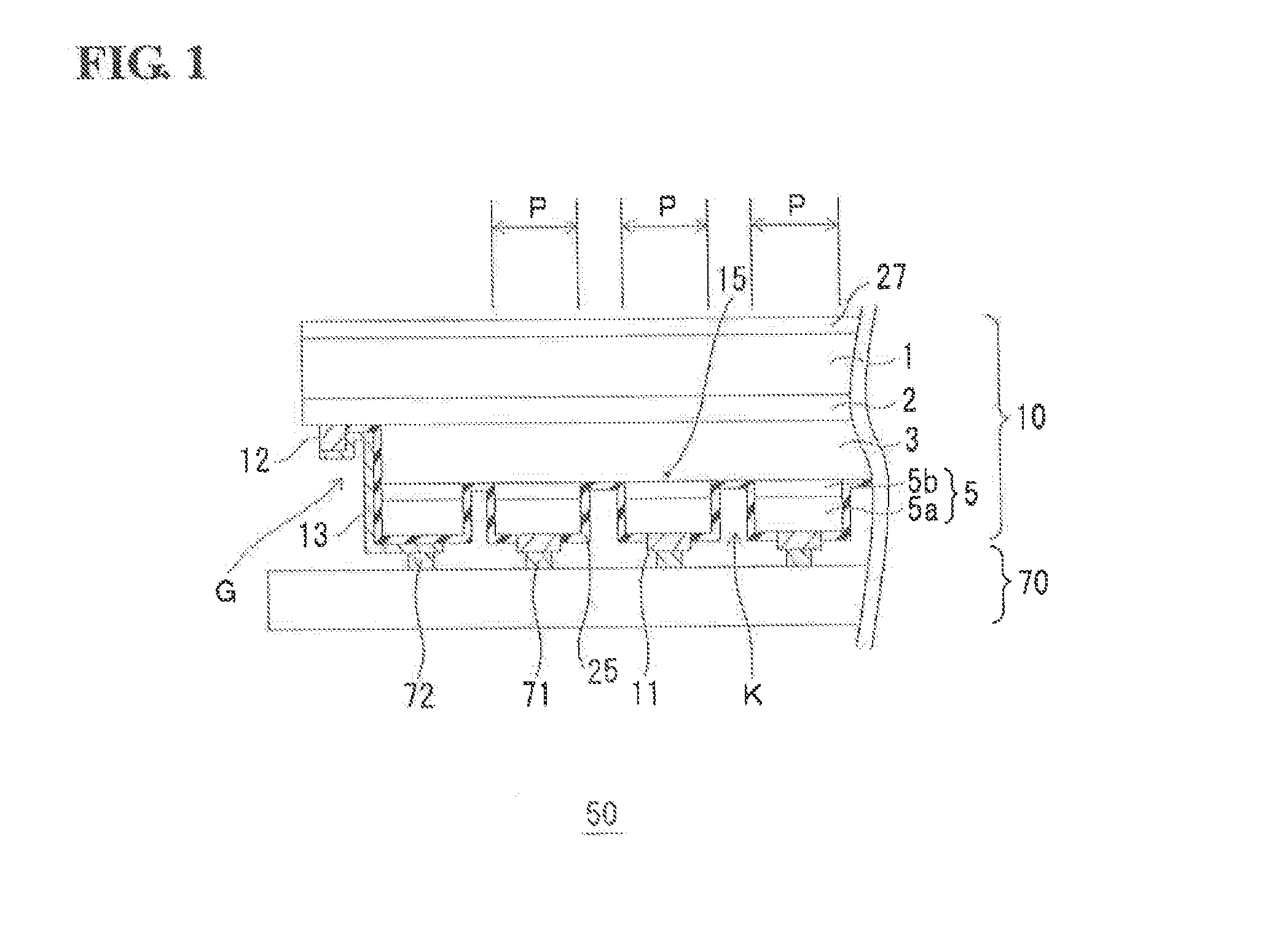
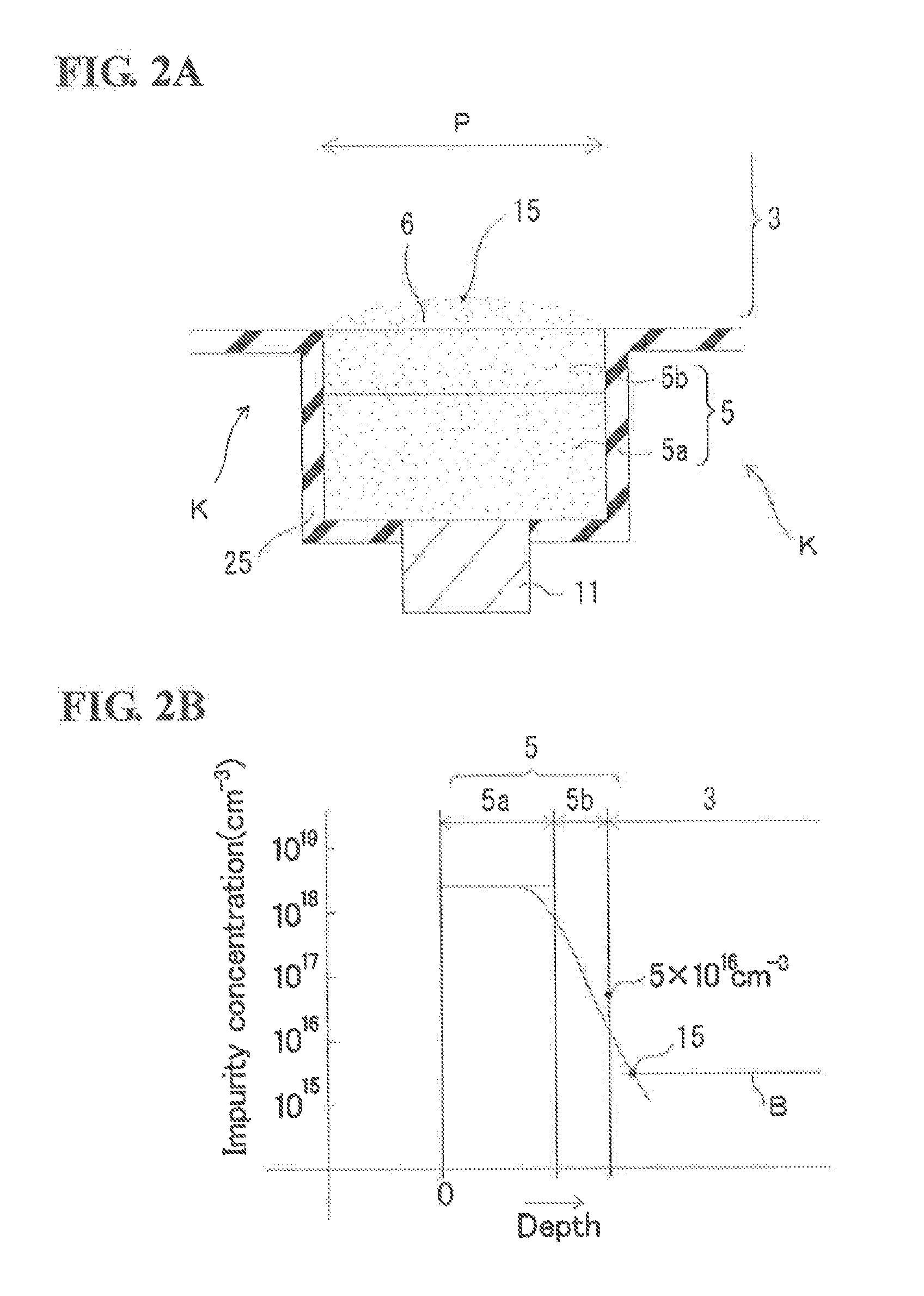
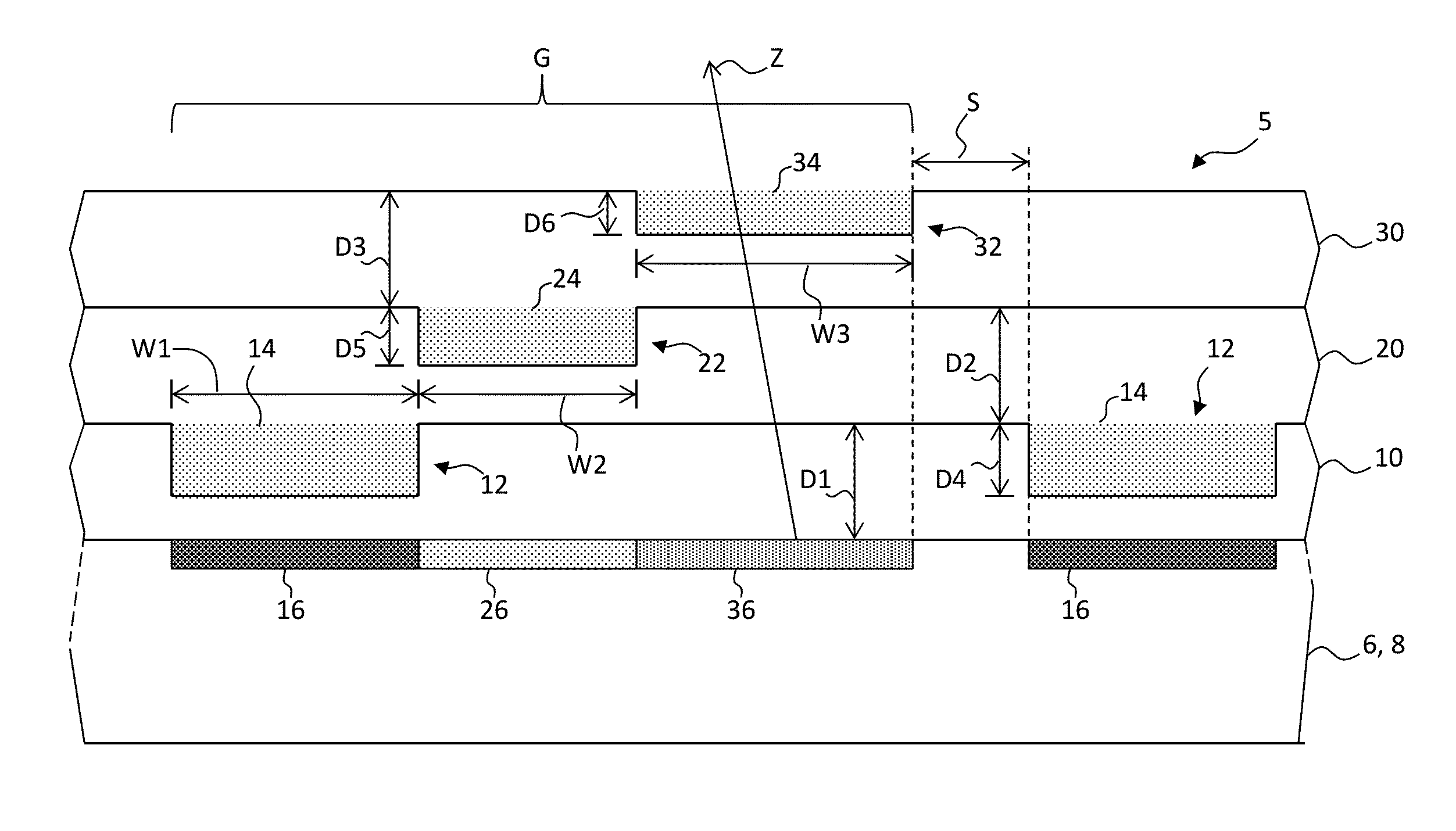
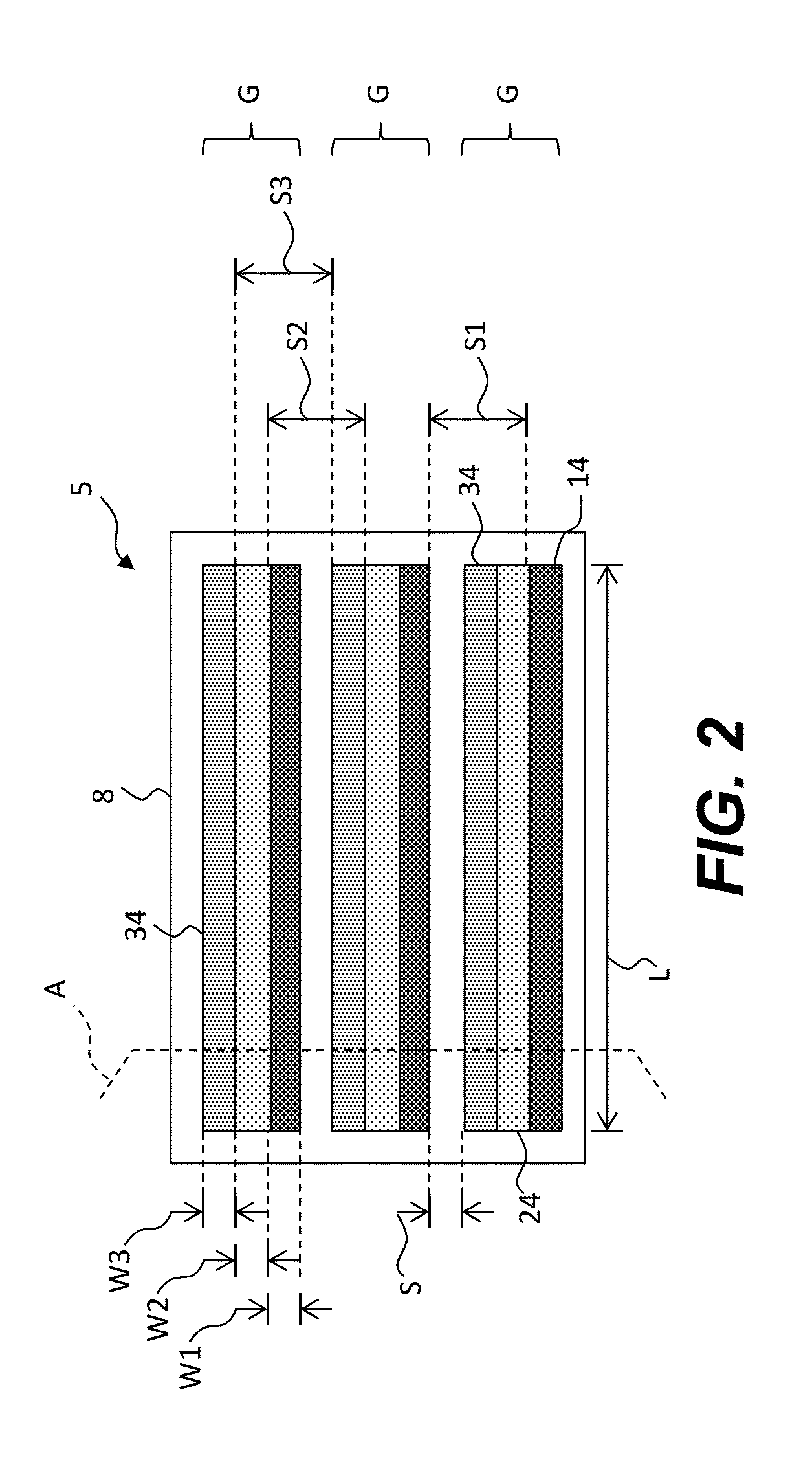
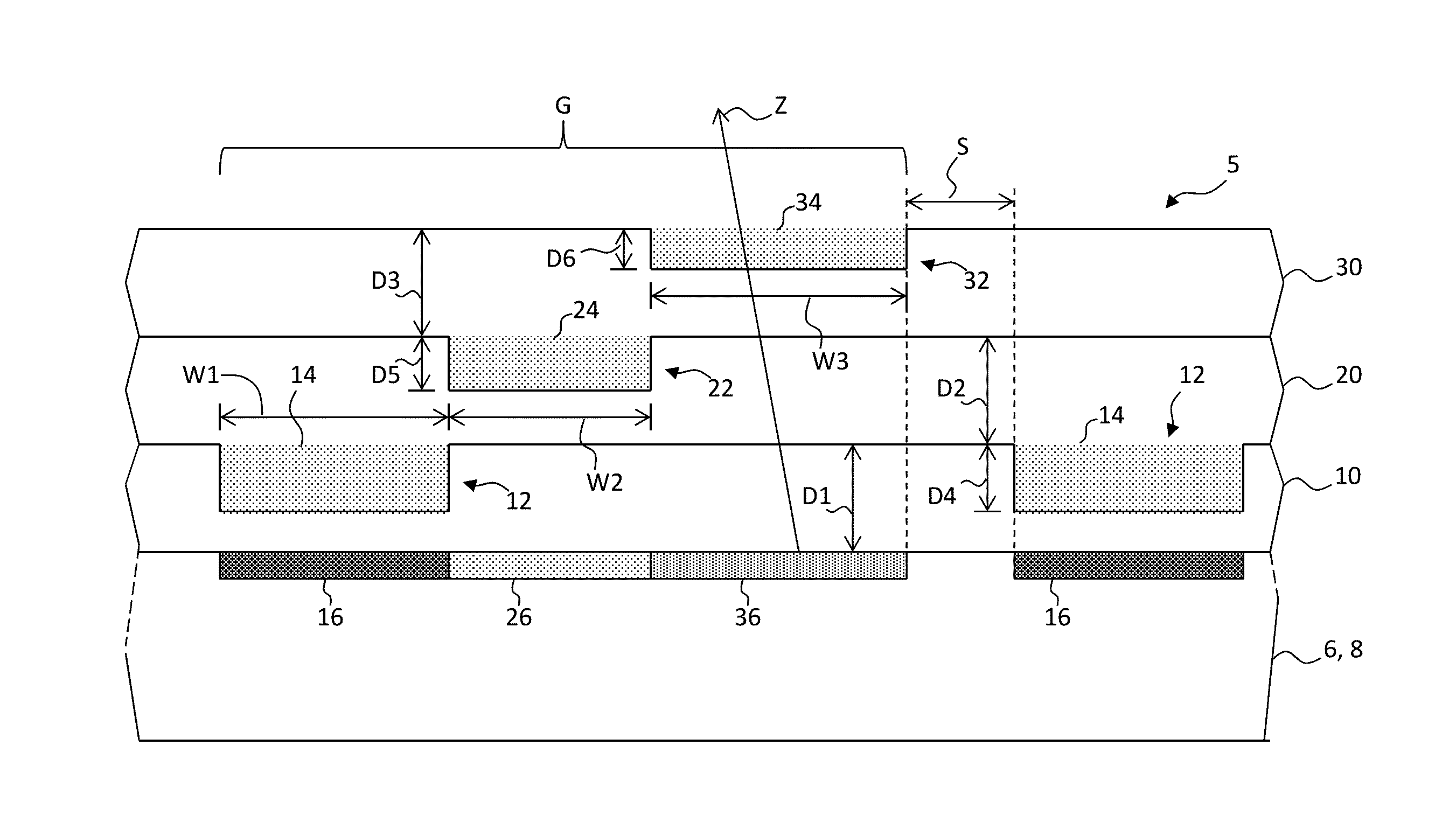
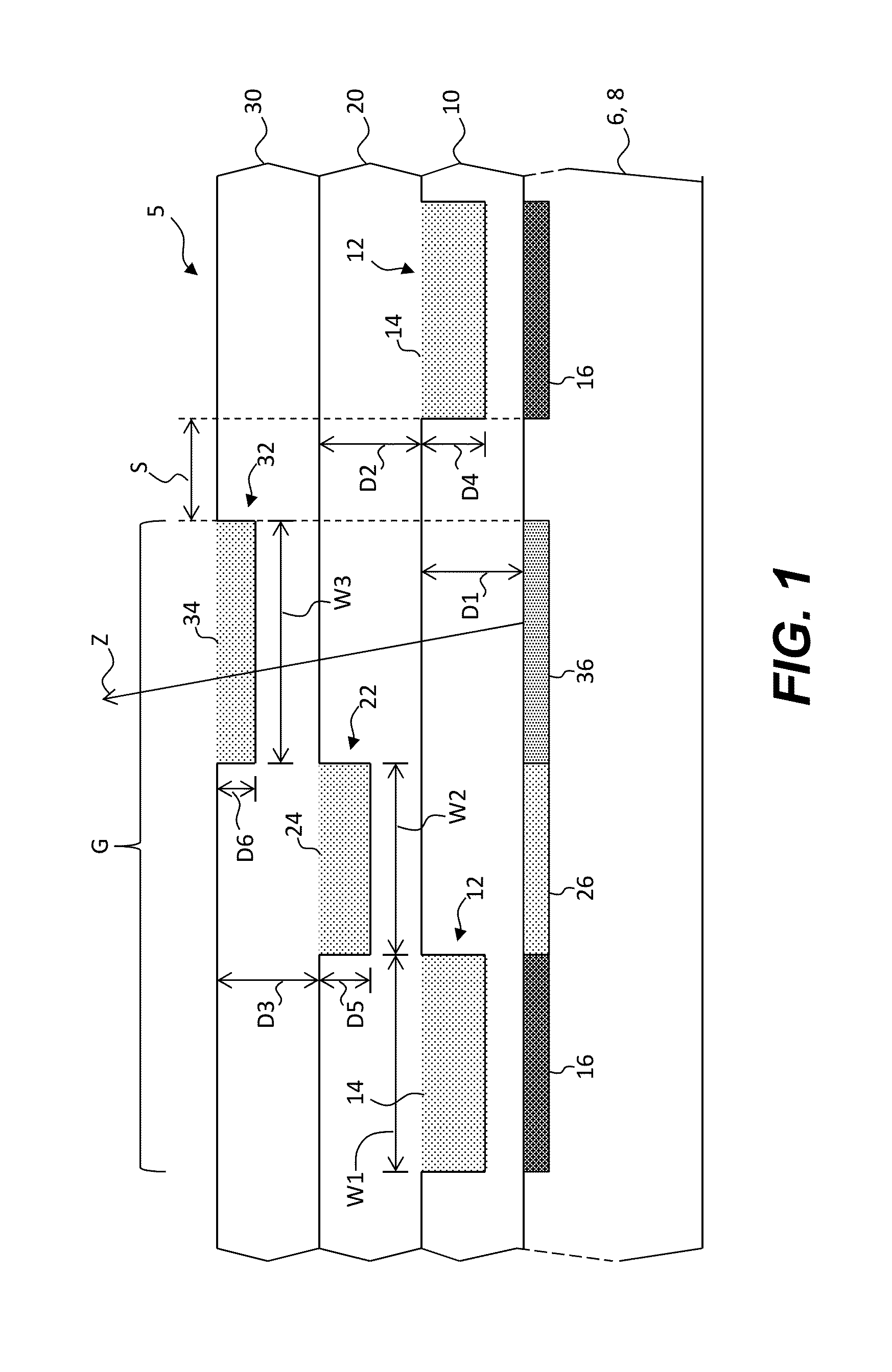
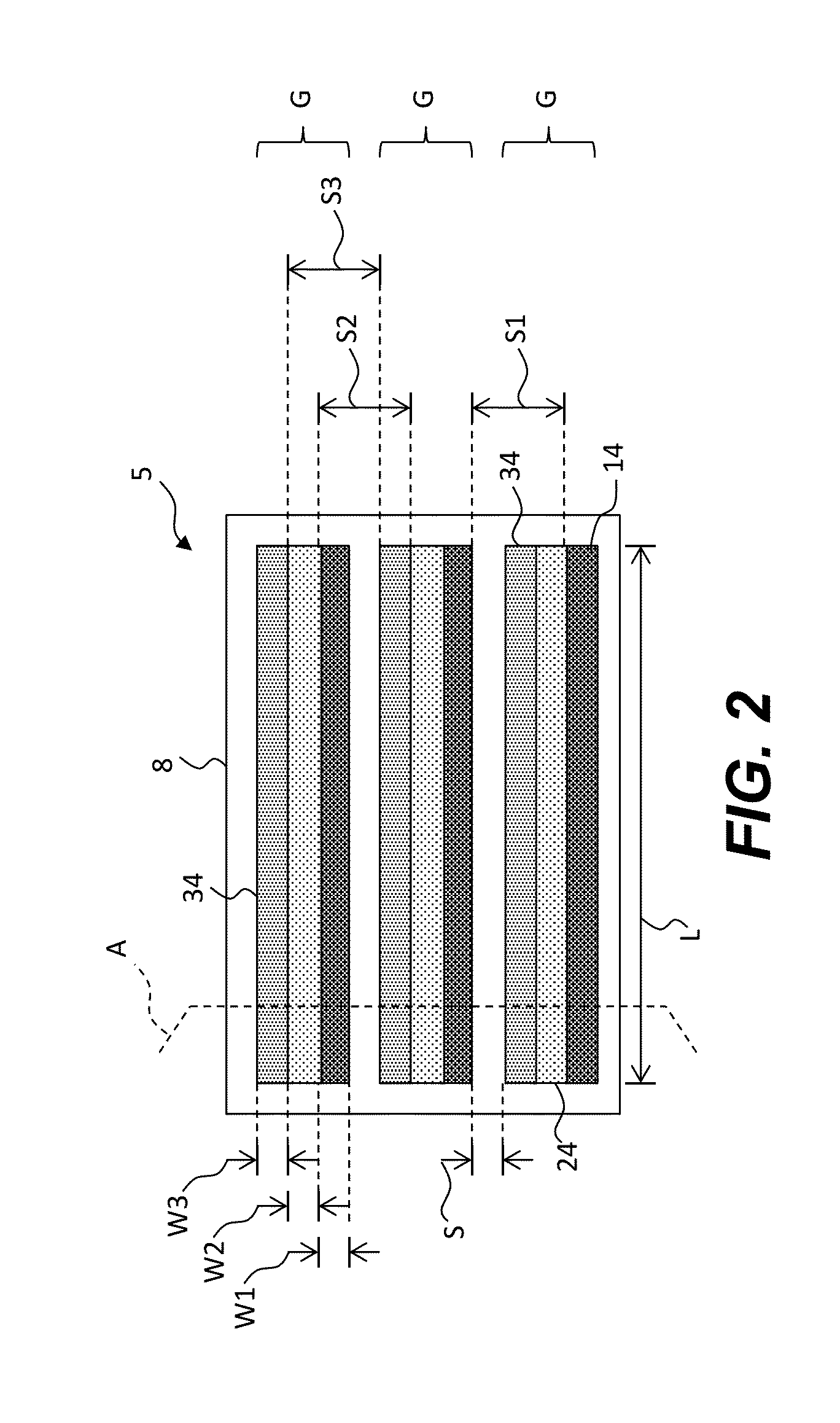
ActiveUS6853046B2Large fill factorImprove fill factorPhotometry using reference valueSolid-state devicesPhotodiodeSemiconductor
A photodiode array comprises a semiconductor substrate formed with an array of a plurality of pn junction type photodiodes on a light incident surface side, the surface opposite from the incident surface in the semiconductor substrate being made of a (100) plane; a through hole, formed in an area held between the photodiodes, penetrating through the semiconductor substrate from the incident surface side to the opposite surface side; and a conductive layer extending from the incident surface to the opposite surface by way of a wall surface of the through hole; the through hole being formed by connecting a vertical hole part formed substantially perpendicular to the incident surface on the incident surface side, and a pyramidal hole part formed like a quadrangular pyramid on the opposite surface side to each other within the semiconductor substrate; the pyramidal hole part having a wall surface formed as a (111) plane.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Number resolving superconducting nanowire photon detector on multiple surfaces of a substrate
ActiveUS8577430B1Highly efficient number resolving capabilityIncrease the number ofSuperconductor detailsMachines/enginesElectricityNanowire
A superconducting nanowire photon detector apparatus comprising detection, insulating, and substrate layers. The insulating layer provides electrical isolation of a plurality of individual detector elements from the interconnection network fabricated on the substrate layer except where electrical interconnection between the inputs and outputs of each detector element and the interconnection network is intended.
Owner:AIR FORCE RES LAB RIJ
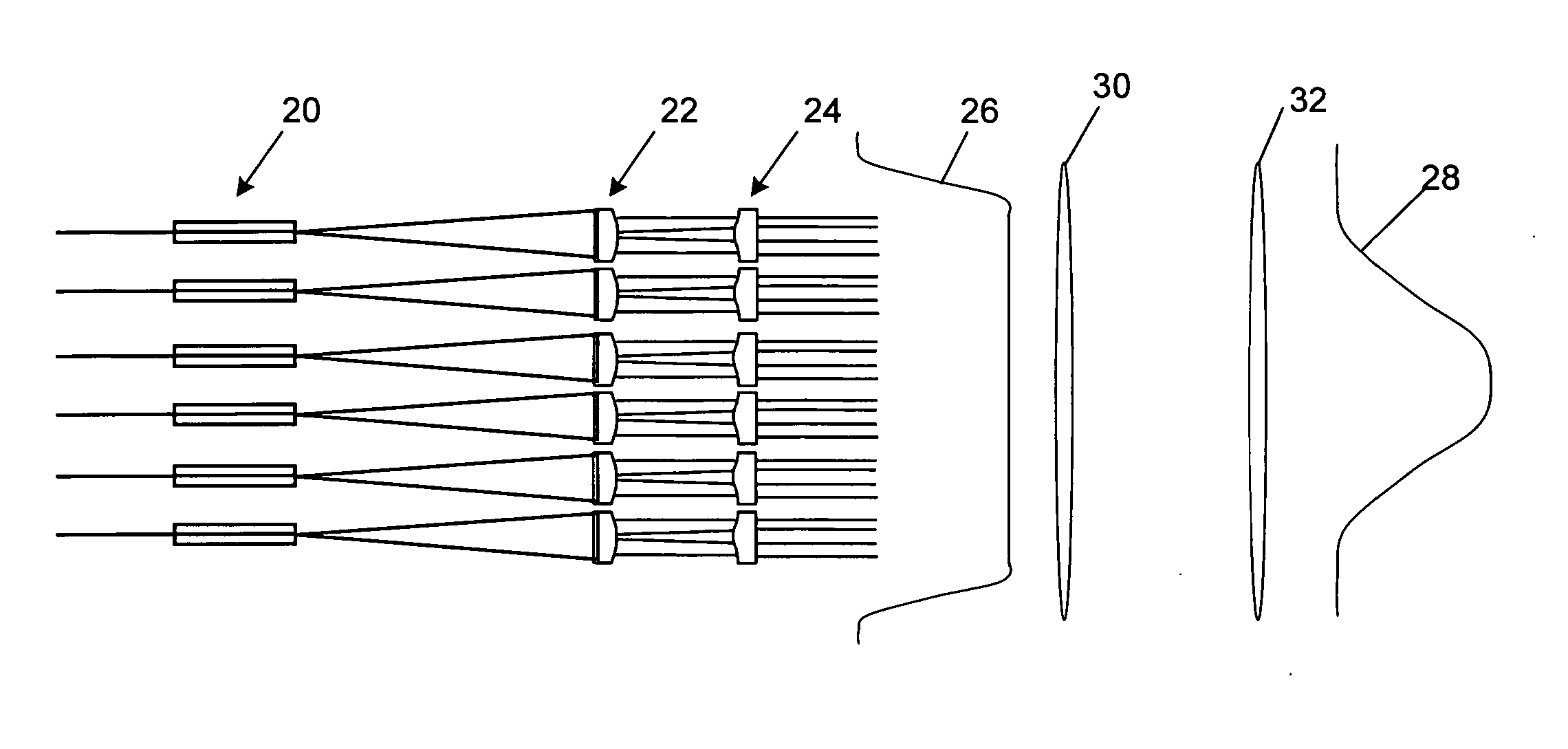
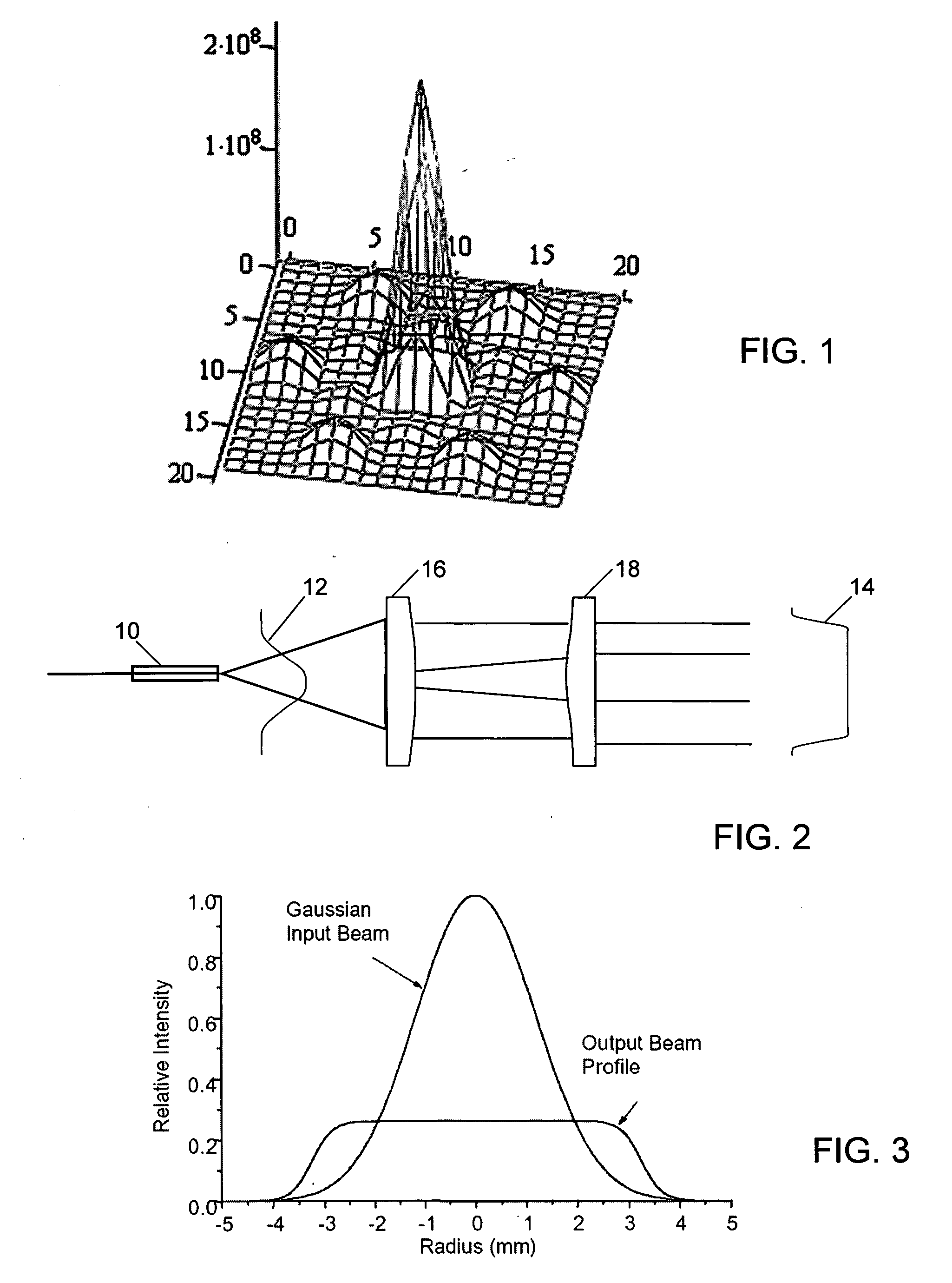
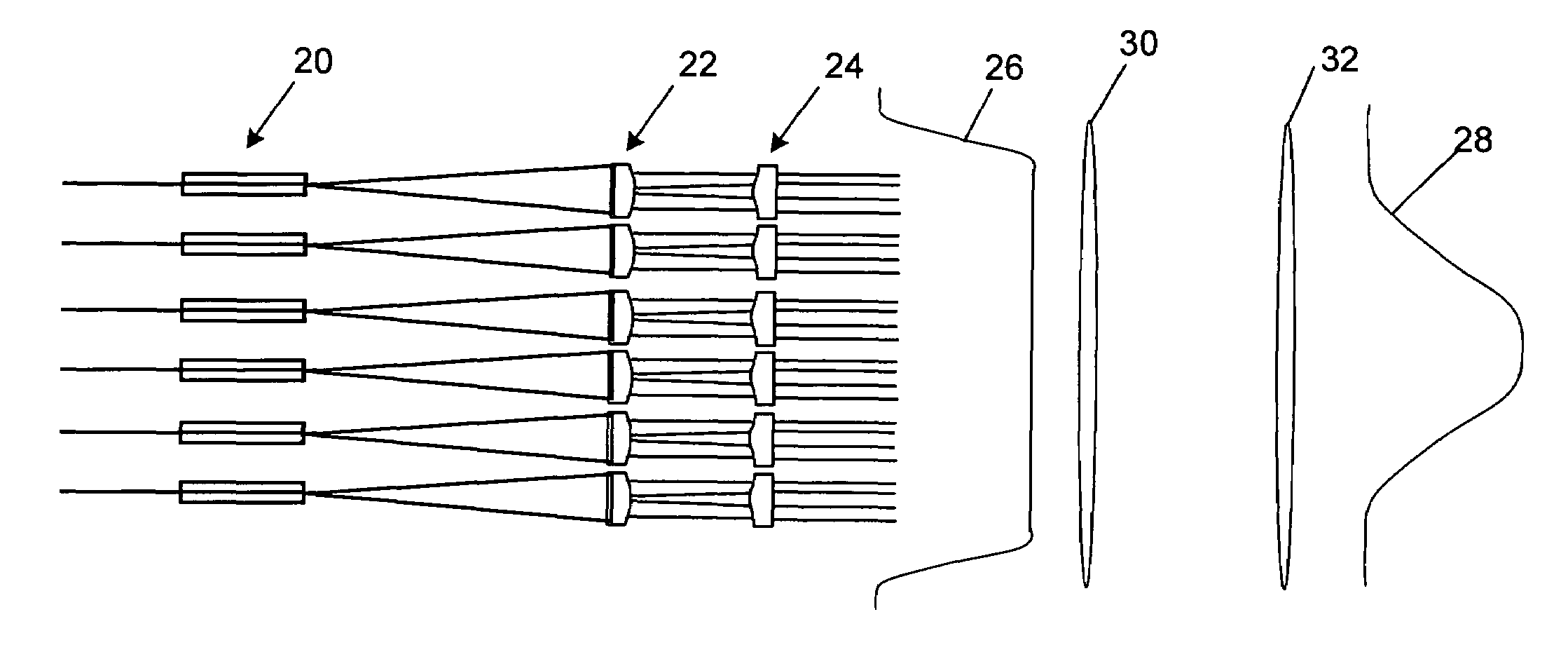
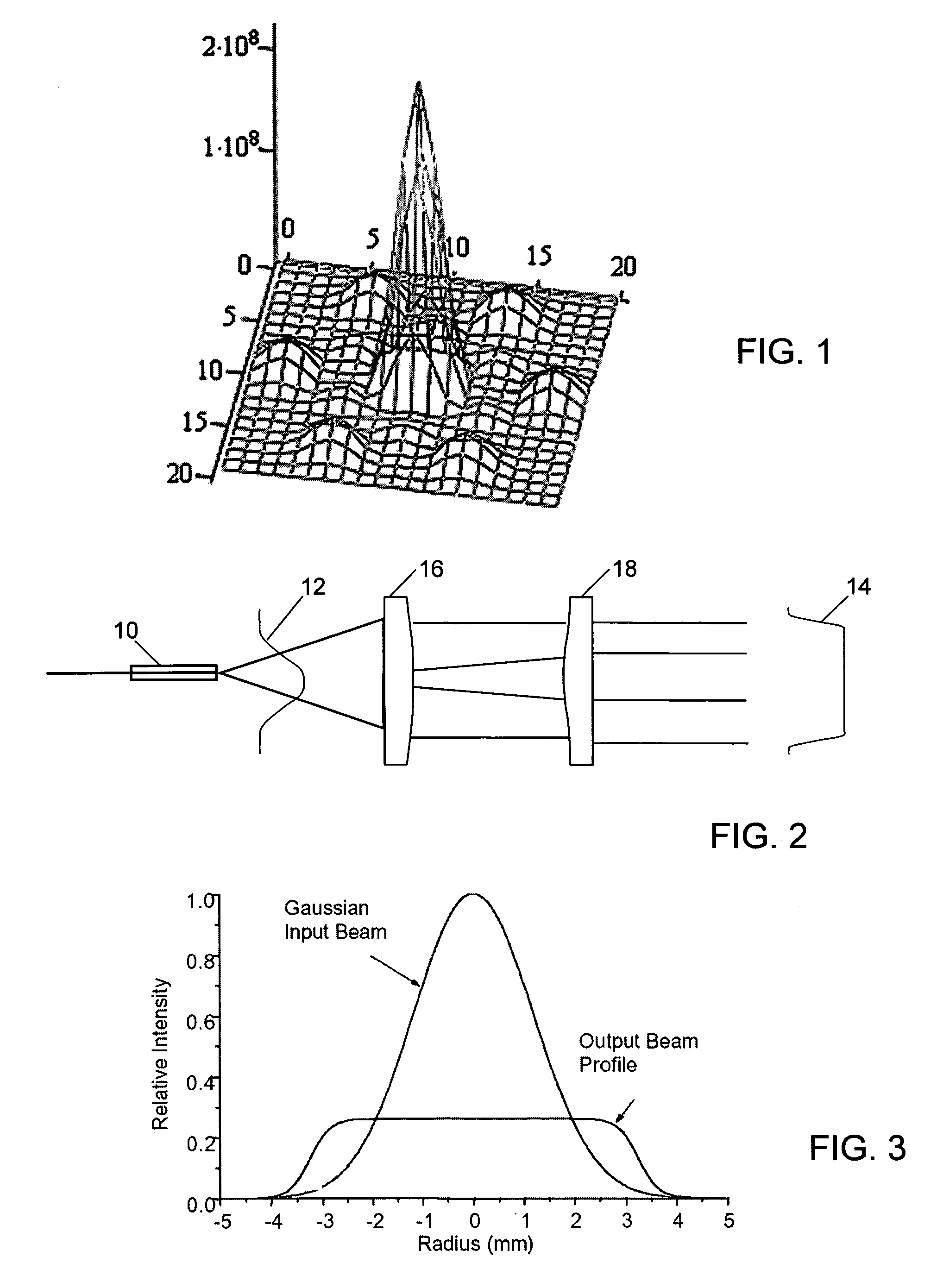
Method and apparatus for optimizing the target intensity distribution transmitted from a fiber coupled array
ActiveUS20070217740A1Improve energy efficiencyHigh energyCoupling light guidesLensHigh power lasersFill factor
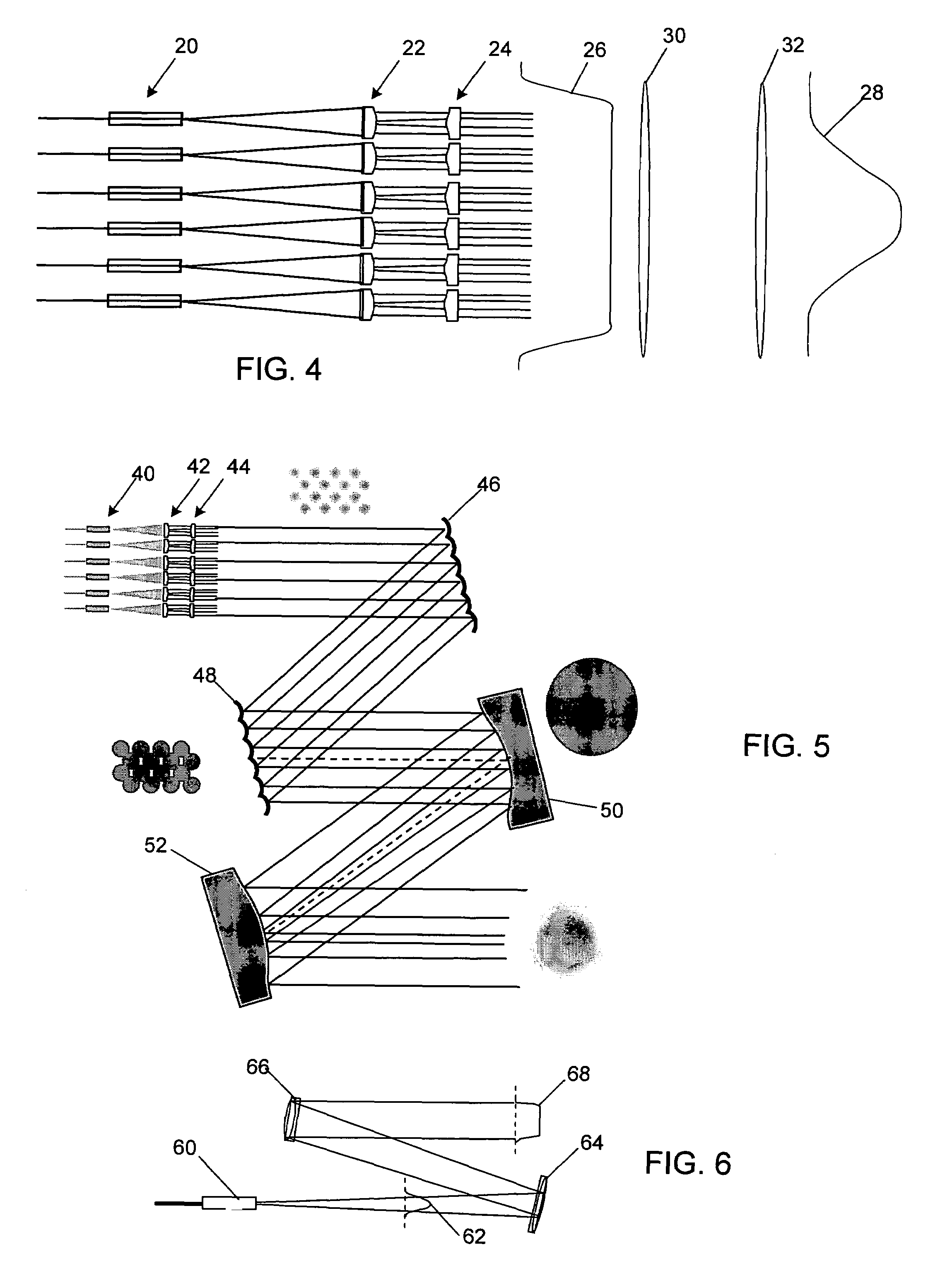
Encircled far field energy is substantially increased by modifying the near field energy distribution of radiation from each fiber in an emitting array. Each beamlet output from a fiber is modified to have a generally uniform cross-sectional energy distribution, using a pair of aspheric optical elements selected for that purpose. The optical elements may be refractive or reflective. The modified beamlets combine to form a composite output beam with a generally uniform energy distribution. Preferably, the composite beam is subject to an array-wide inverse transformation to a near-Gaussian distribution, further enhancing the encircled far field energy and providing a more efficient high power laser source. Further gains in efficiency are achieved by selecting a fiber bundle pattern, lens array pattern and lens shape that together result in a high fill factor.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Charged particle system comprising a manipulator device for manipulation of one or more charged particle beams
ActiveUS8618496B2Improve accuracyImprove fill factorOptical radiation measurementParticle separator tubesLithographic artistPlanar substrate
A charged particle system such as a multi beam lithography system. A manipulator device manipulates one or more charged particle beams. The manipulator device includes at least one through opening in the plane of the planar substrate for passing at least one charged particle. Each through opening is provided with electrodes arranged in a first set of multiple first electrodes along a first part of a perimeter of the through opening and in a second set of multiple second electrodes along a second part of the perimeter. An electronic control circuit is arranged for providing voltage differences the electrodes in dependence of a position of the first and second electrode along the perimeter of the through opening.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
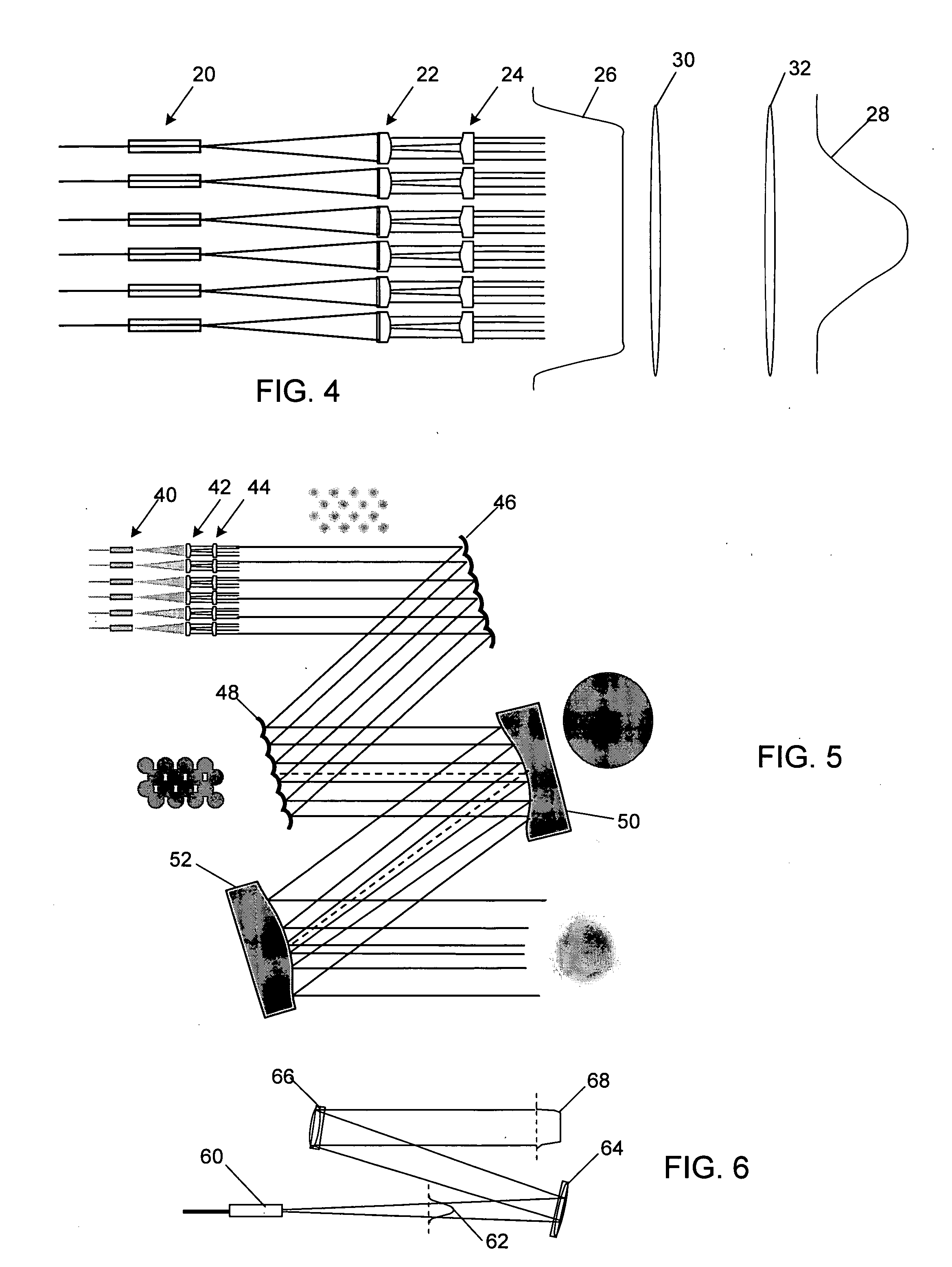
Method and apparatus for optimizing the target intensity distribution transmitted from a fiber coupled array
ActiveUS7283702B2High energyImprove fill factorCoupling light guidesLensHigh power lasersOptoelectronics
Encircled far field energy is substantially increased by modifying the near field energy distribution of radiation from each fiber in an emitting array. Each beamlet output from a fiber is modified to have a generally uniform cross-sectional energy distribution, using a pair of aspheric optical elements selected for that purpose. The optical elements may be refractive or reflective. The modified beamlets combine to form a composite output beam with a generally uniform energy distribution. Preferably, the composite beam is subject to an array-wide inverse transformation to a near-Gaussian distribution, further enhancing the encircled far field energy and providing a more efficient high power laser source. Further gains in efficiency are achieved by selecting a fiber bundle pattern, lens array pattern and lens shape that together result in a high fill factor.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Assembly to perform imaging on rodents
InactiveUS20120330130A1Eliminate remaining animal movementLarge fill factorRespiratory masksAnimal housingNon destructiveEngineering
An imaging device for imaging an anaesthetized animal such as a rodent (rats or mice or other animals), with the device having a split array coil capable of providing at least two channels for use in a restraining assembly with animal bed for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) the animal in real-time in a non-destructive manner.
Owner:RAPID BIOMEDIZINISCHE GERATE RAPID BIOMEDICAL
Rocker-arm actuator for a segmented mirror
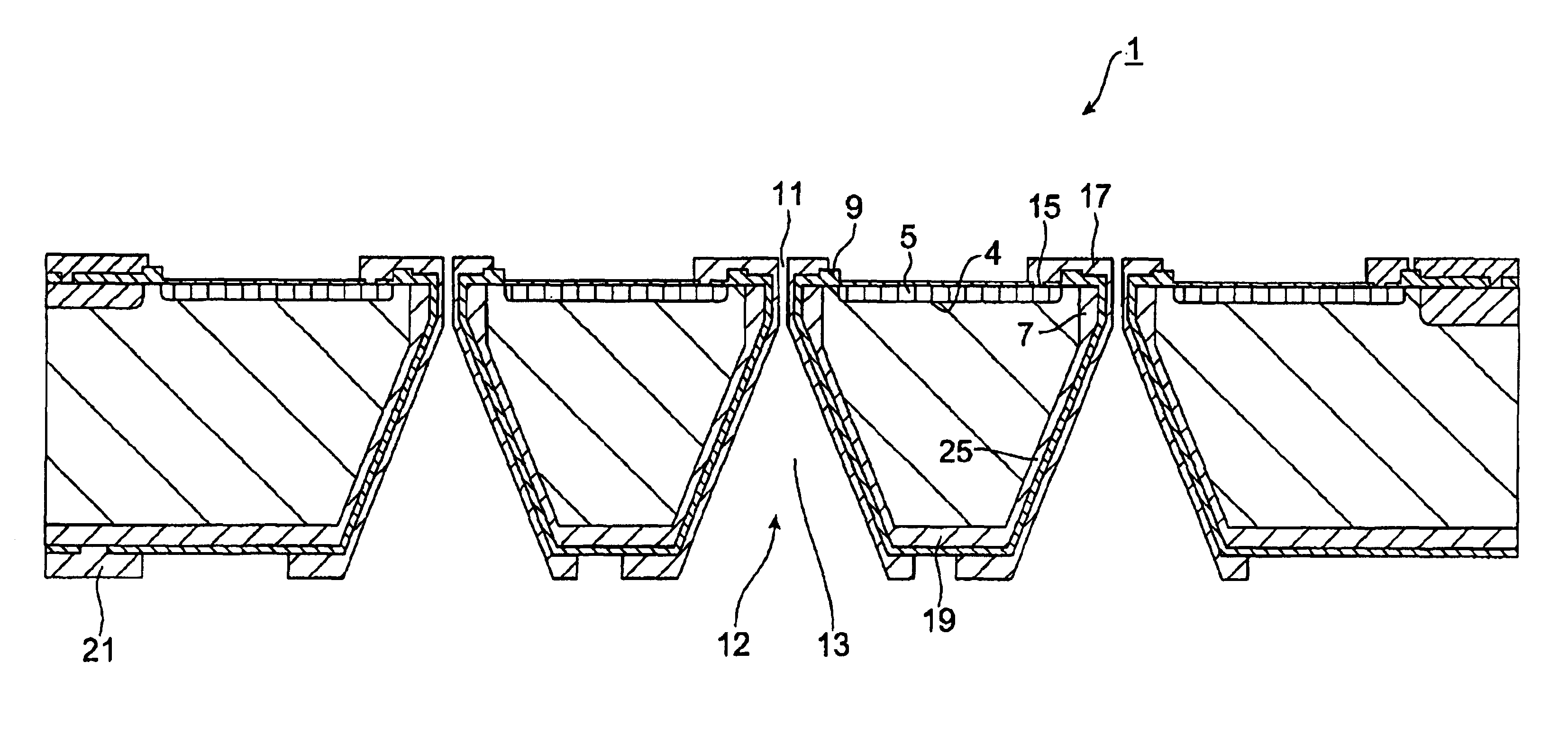
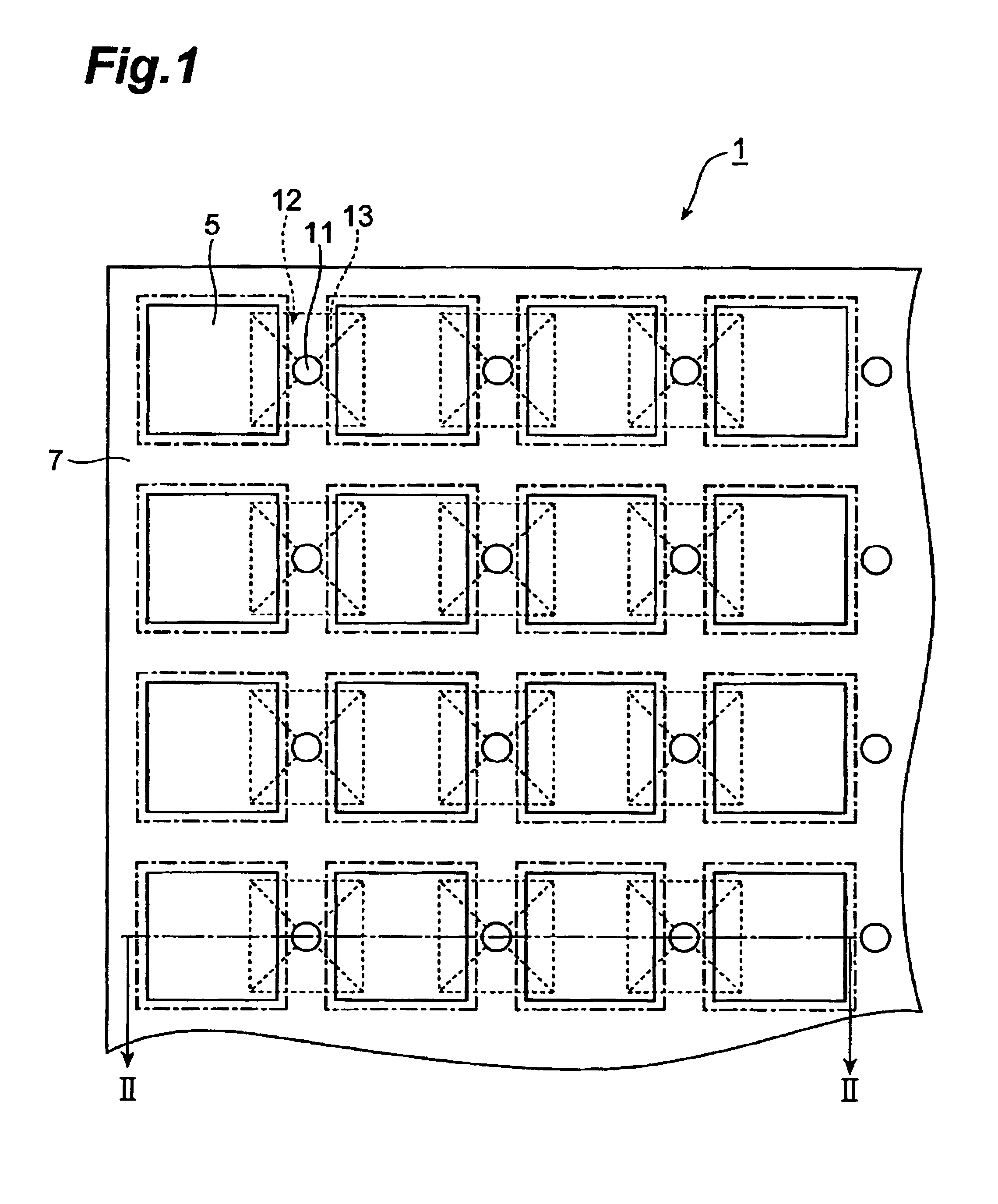
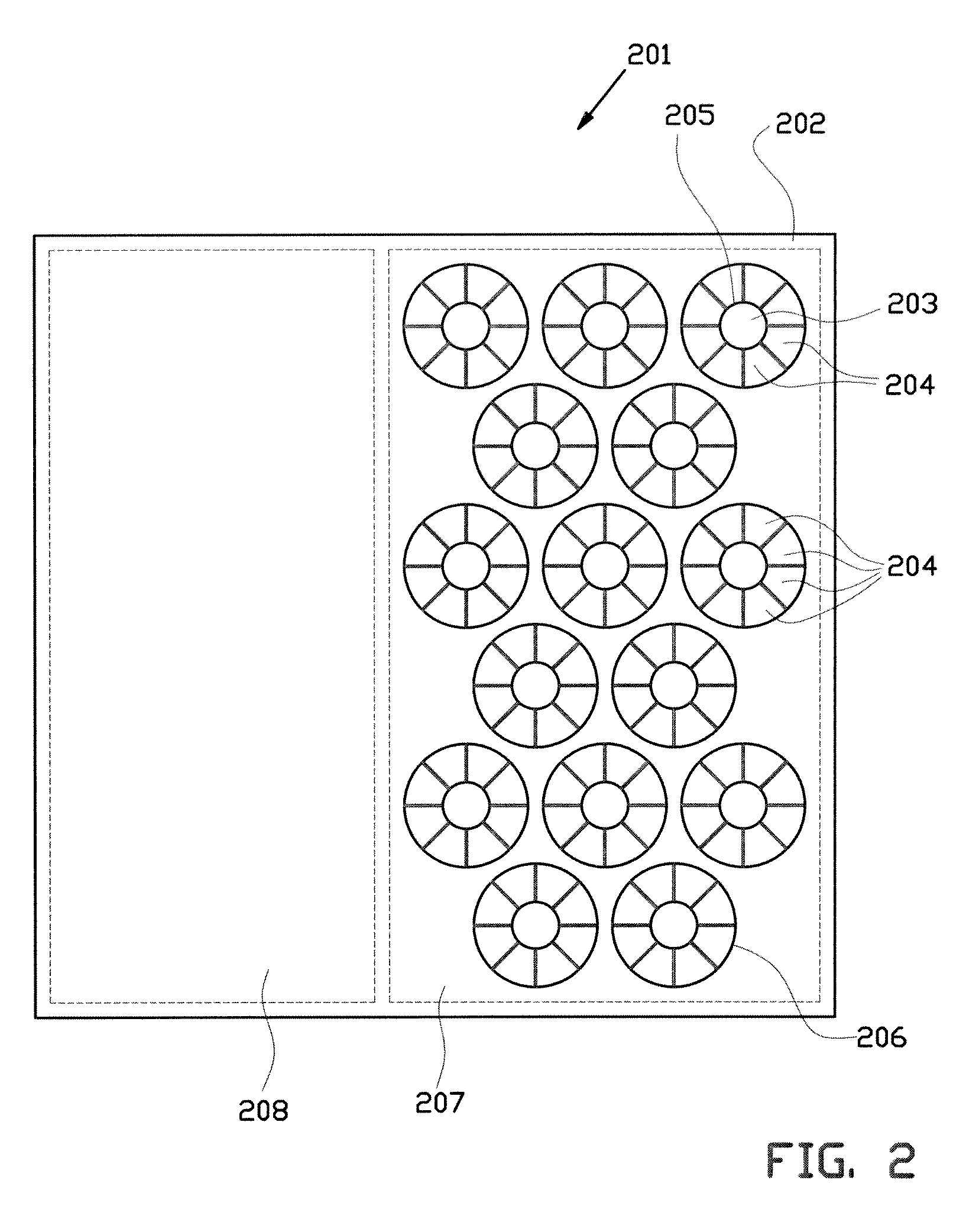
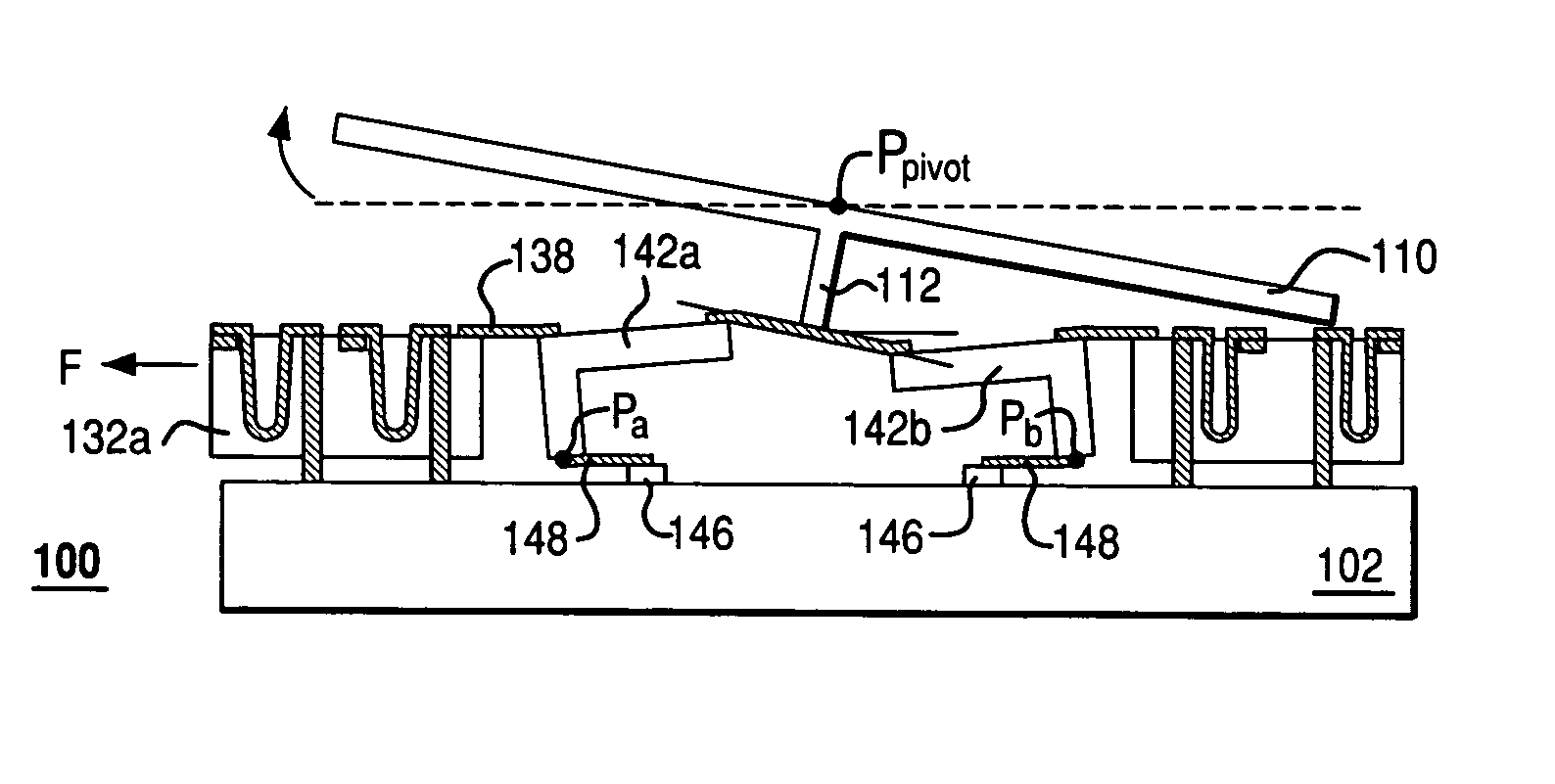
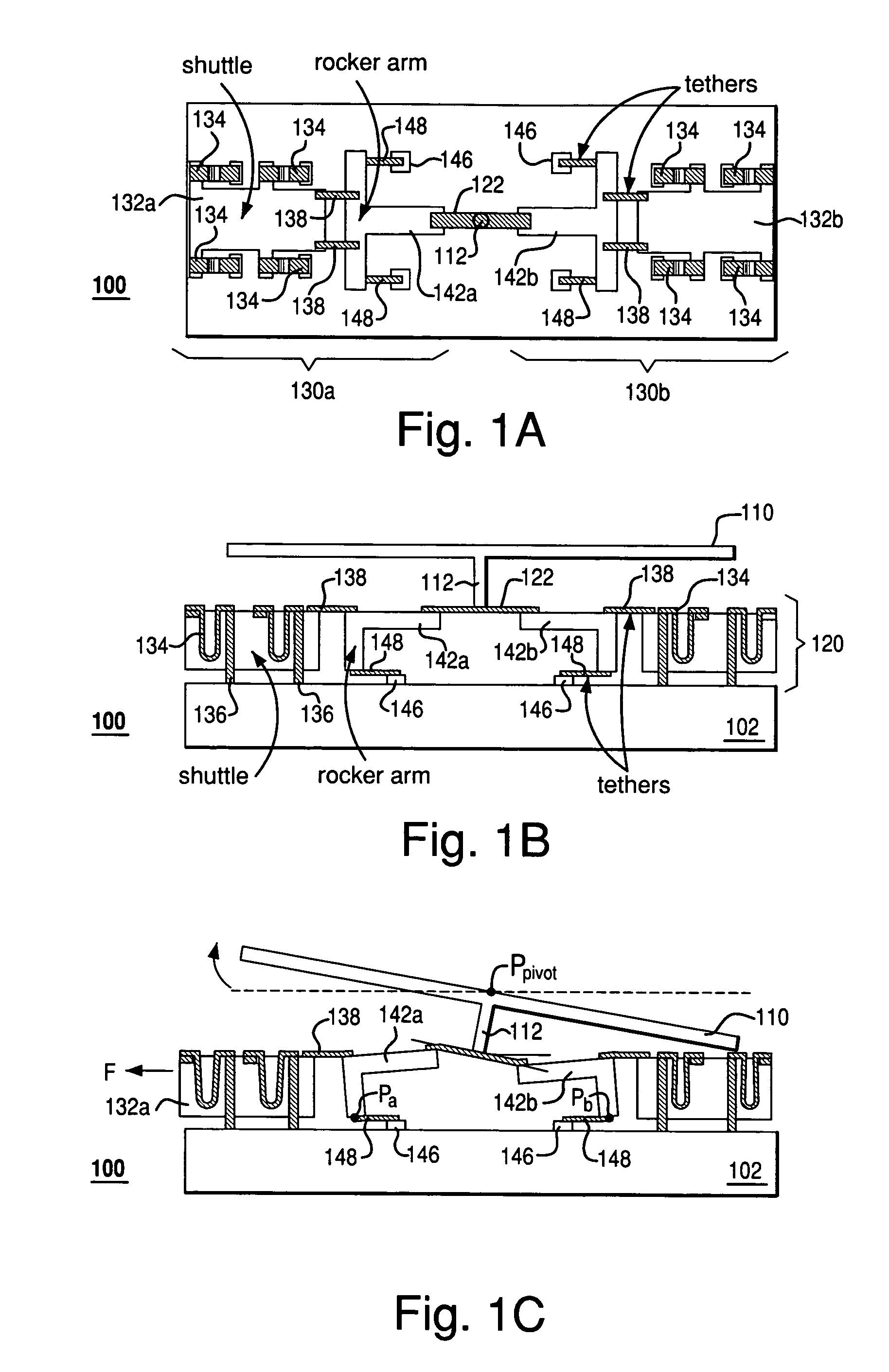
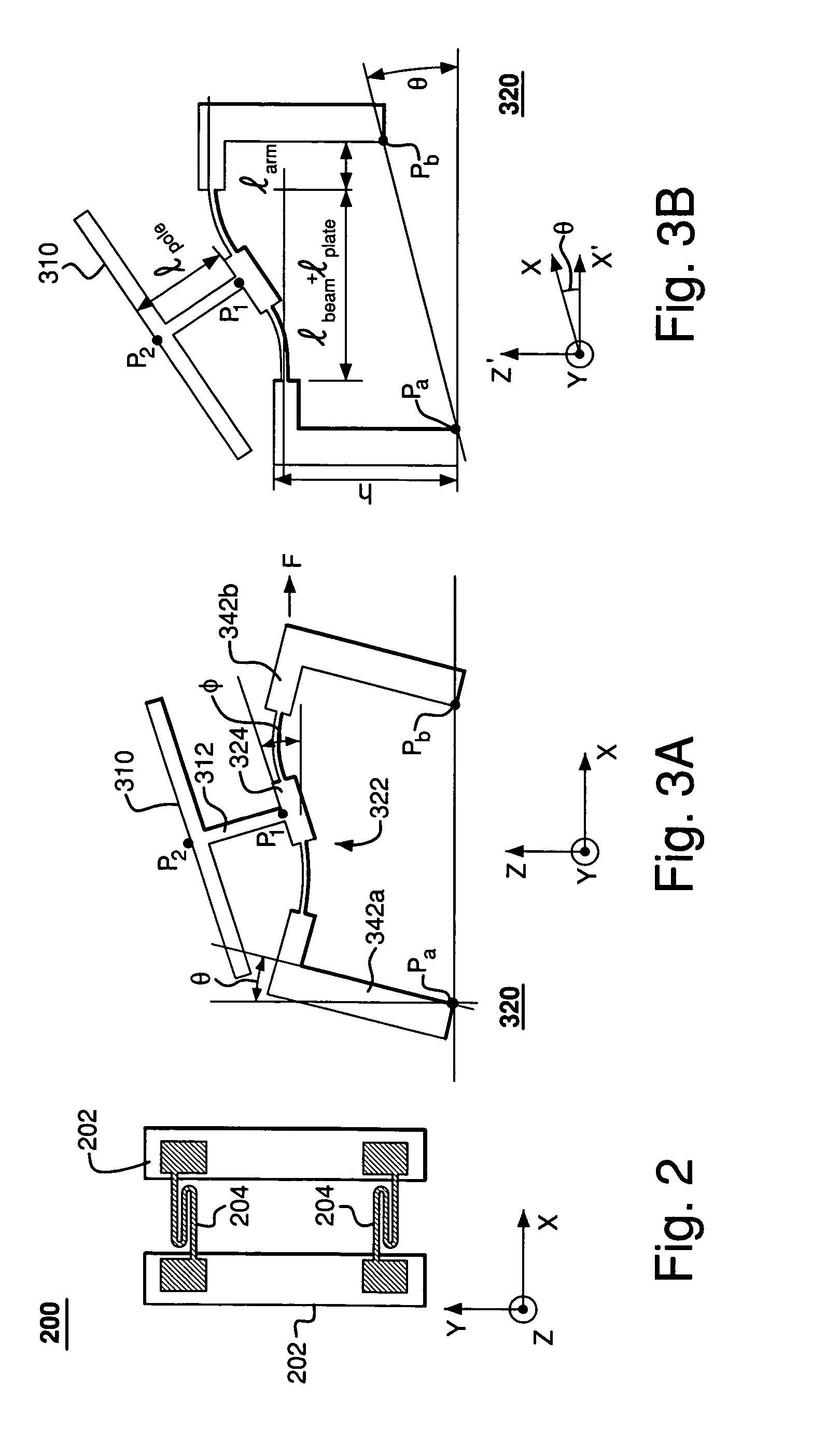
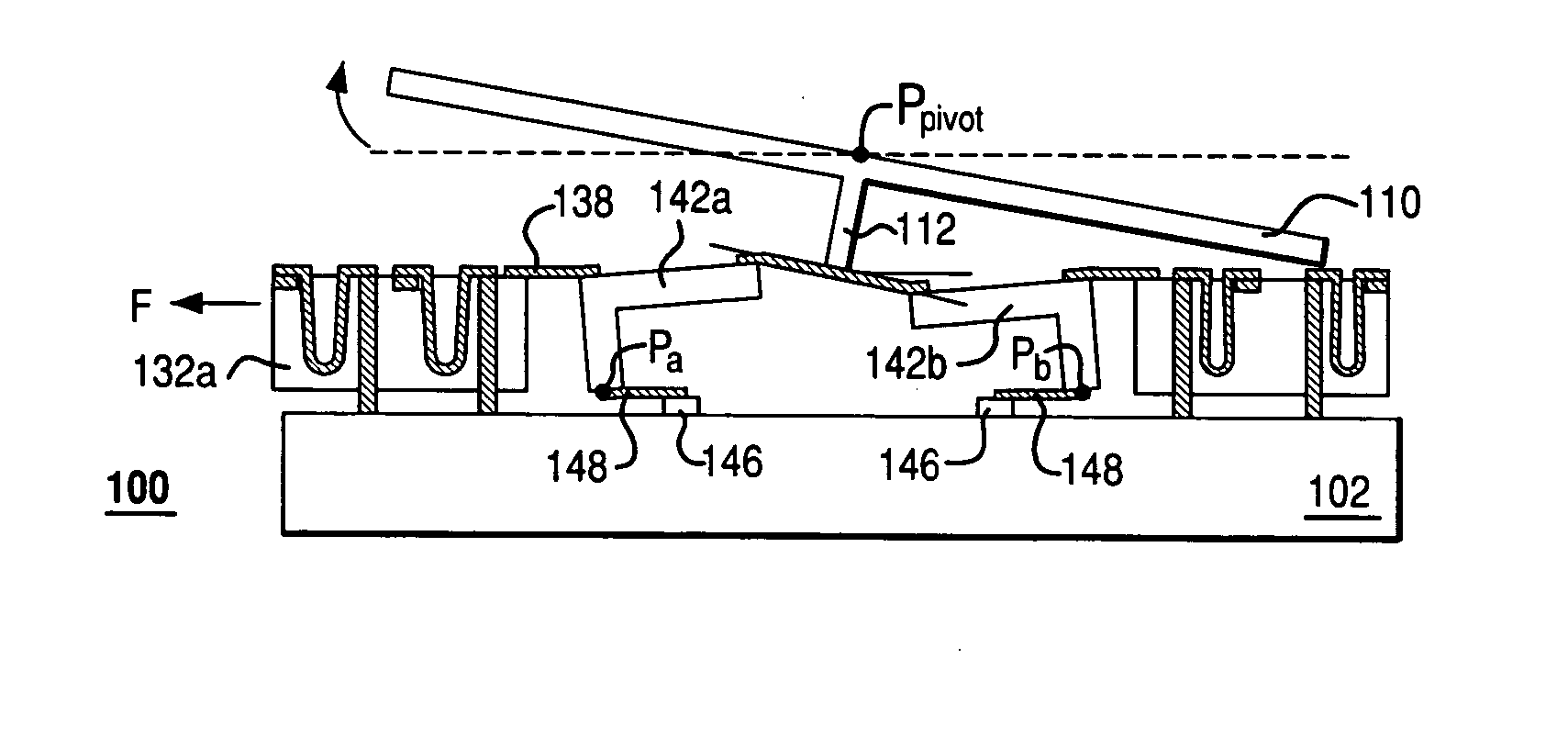
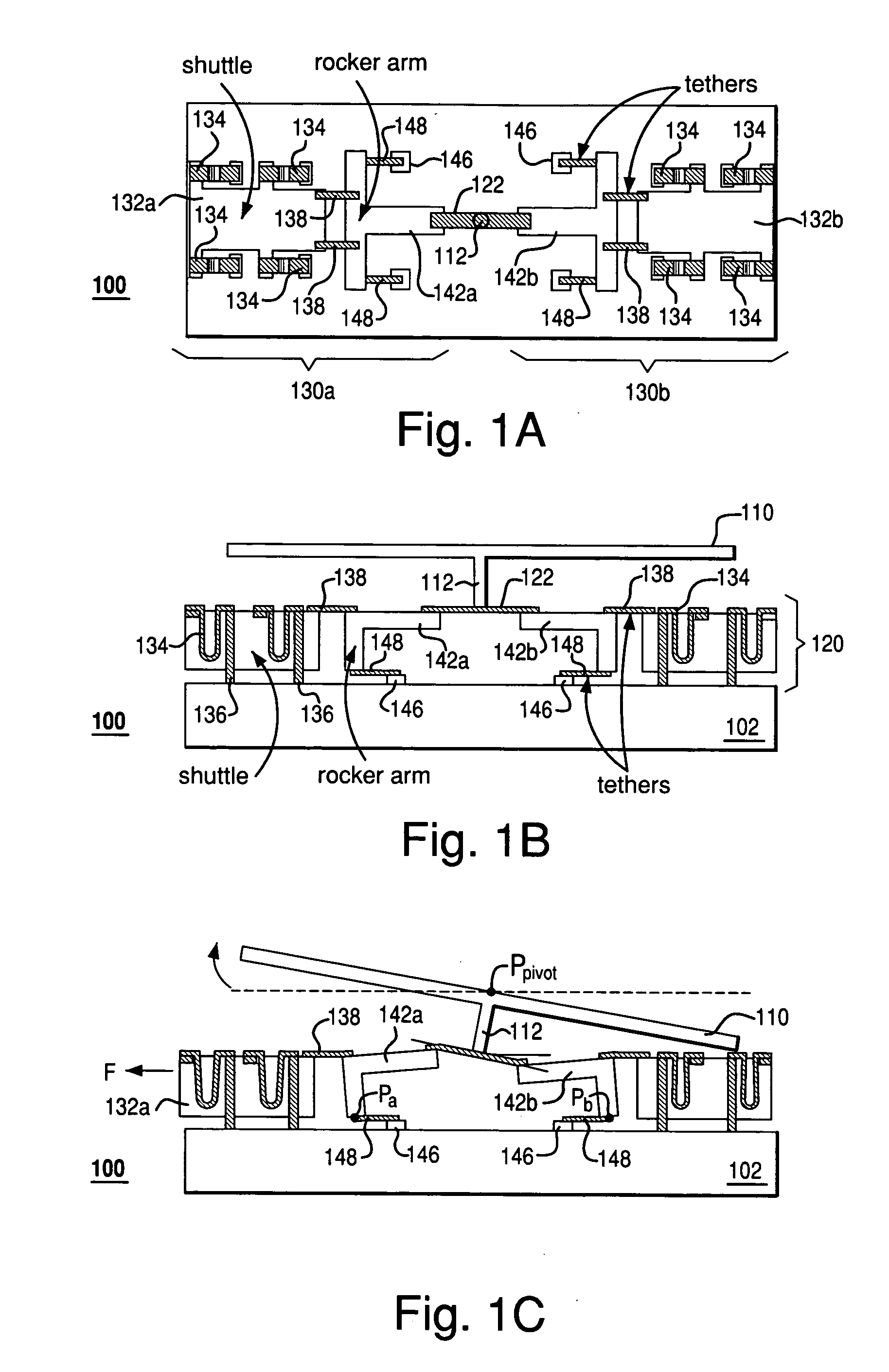
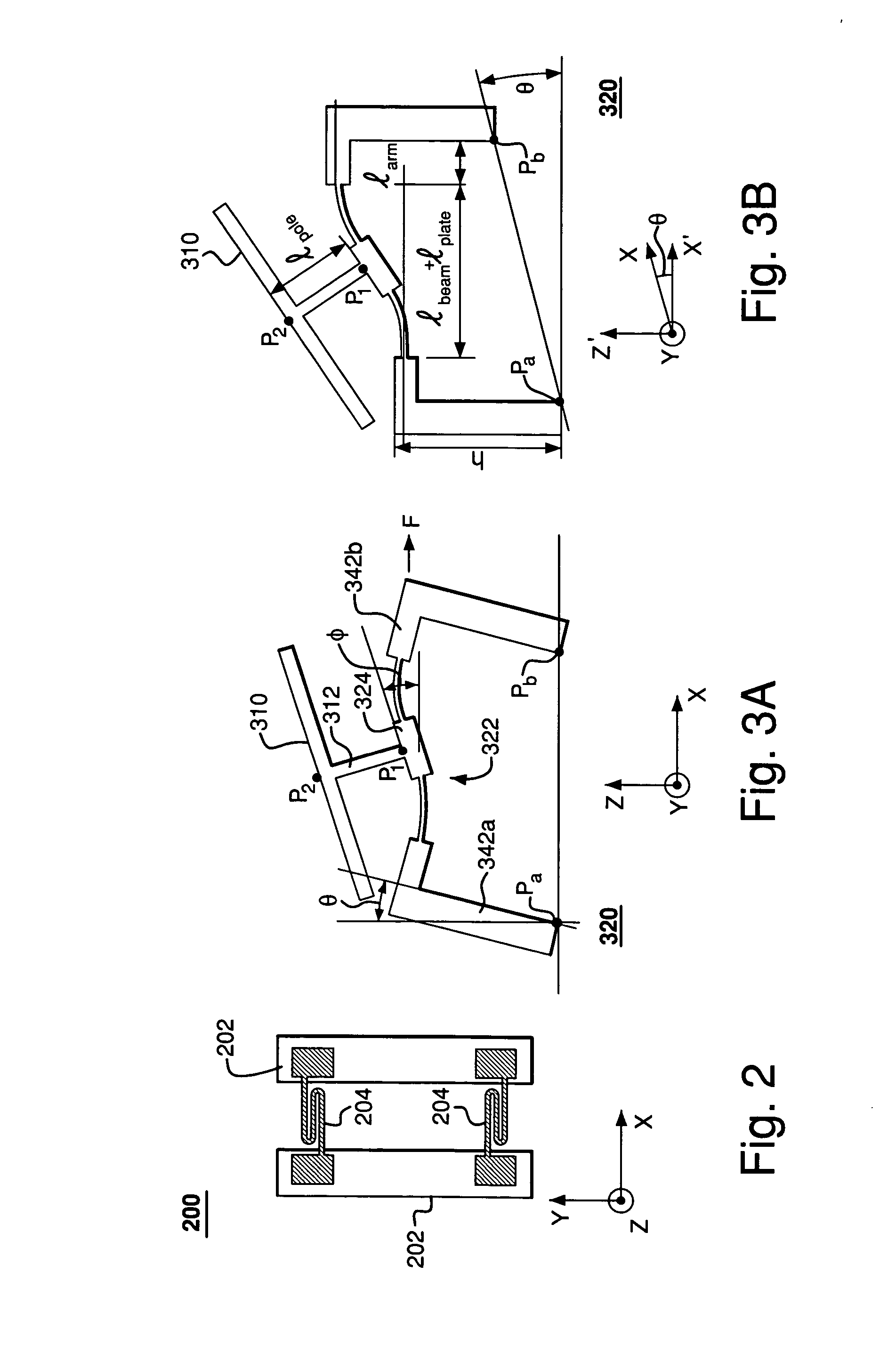
InactiveUS7355317B2Reduces potential physical interferenceLarge fill factorElectrostatic motorsOptical elementsFill factorActuator
A MEMS device having a movable plate supported on a substrate by a support structure that is hidden under the plate and yet which can be implemented to enable rotation of the plate with respect to the substrate about a rotation axis lying at the plate surface. As a result, the support structure does not take up any area within the plane of the plate, while enabling rotation of the plate, during which the plate does not substantially move sideways. The latter property reduces potential physical interference between neighboring plates in an arrayed MEMS device and enables implementation of a segmented mirror having relatively narrow gaps between adjacent segments and, thus, a relatively large fill factor, e.g., at least 98%.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
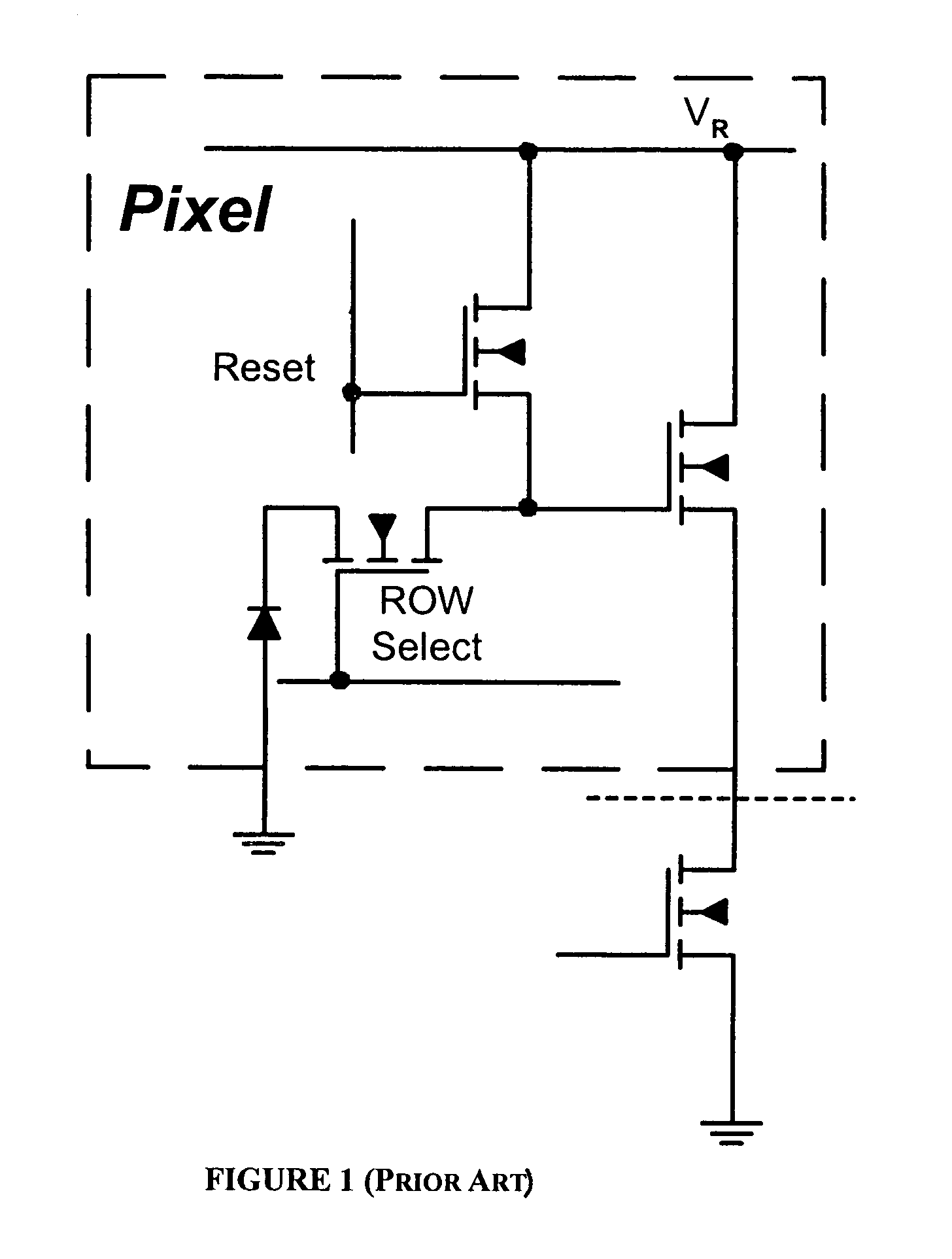
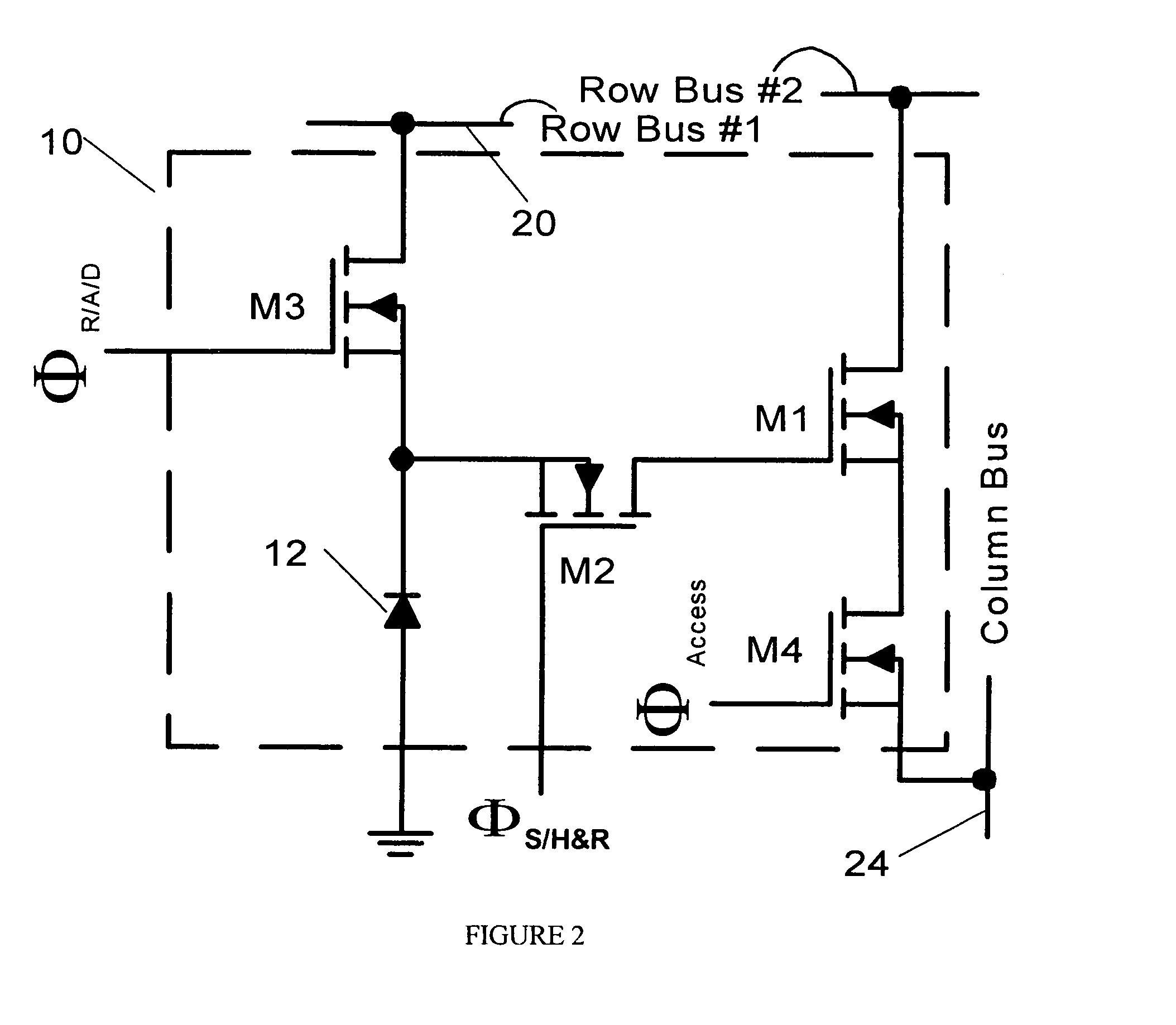
Compact active pixel with low-noise snapshot image formation
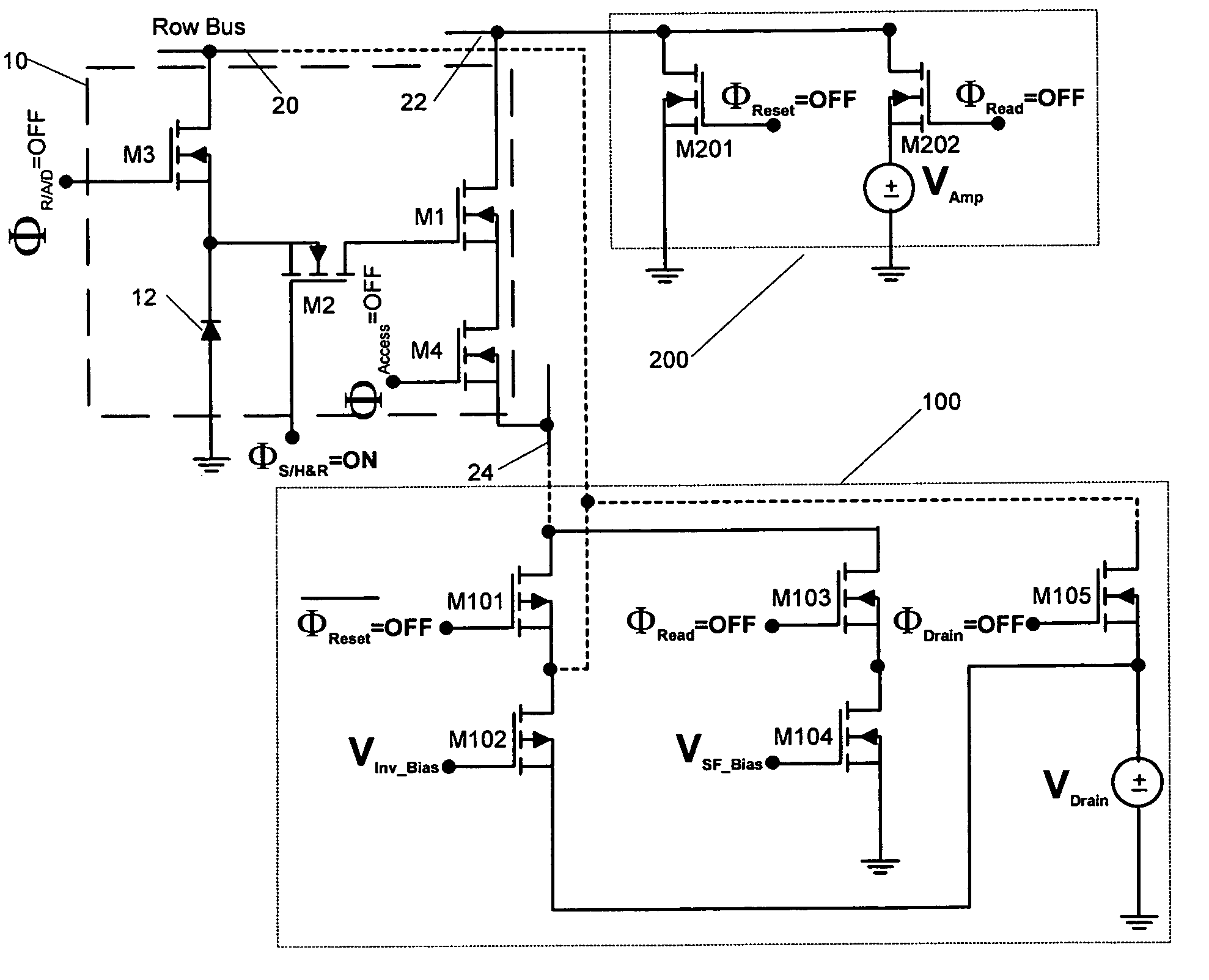
InactiveUS6965707B1Suppress noiseReduce noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMOSFETLow noise
A low-noise active pixel circuit is disclosed that efficiently suppresses reset (kTC) noise by using a compact preamplifier consisting of a photodetector and only four MOSFETs of identical polarity, in conjunction with ancillary circuits located on an imager's periphery. The supporting circuits help the simplified pixel circuit to synchronously acquire (i.e., take a snapshot) an image across an imaging array, read the signal with low noise, and efficiently reset the pixel with low noise.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
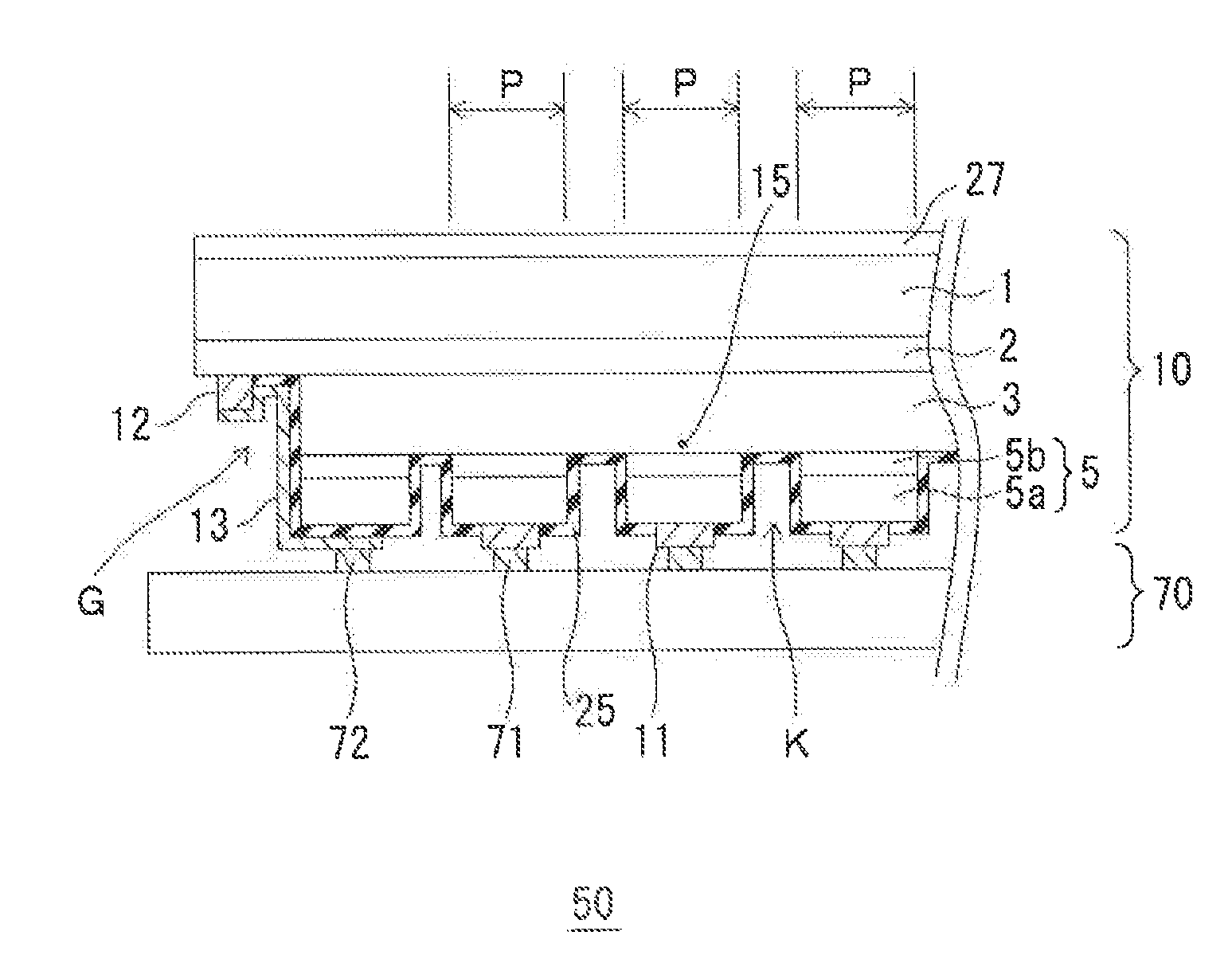
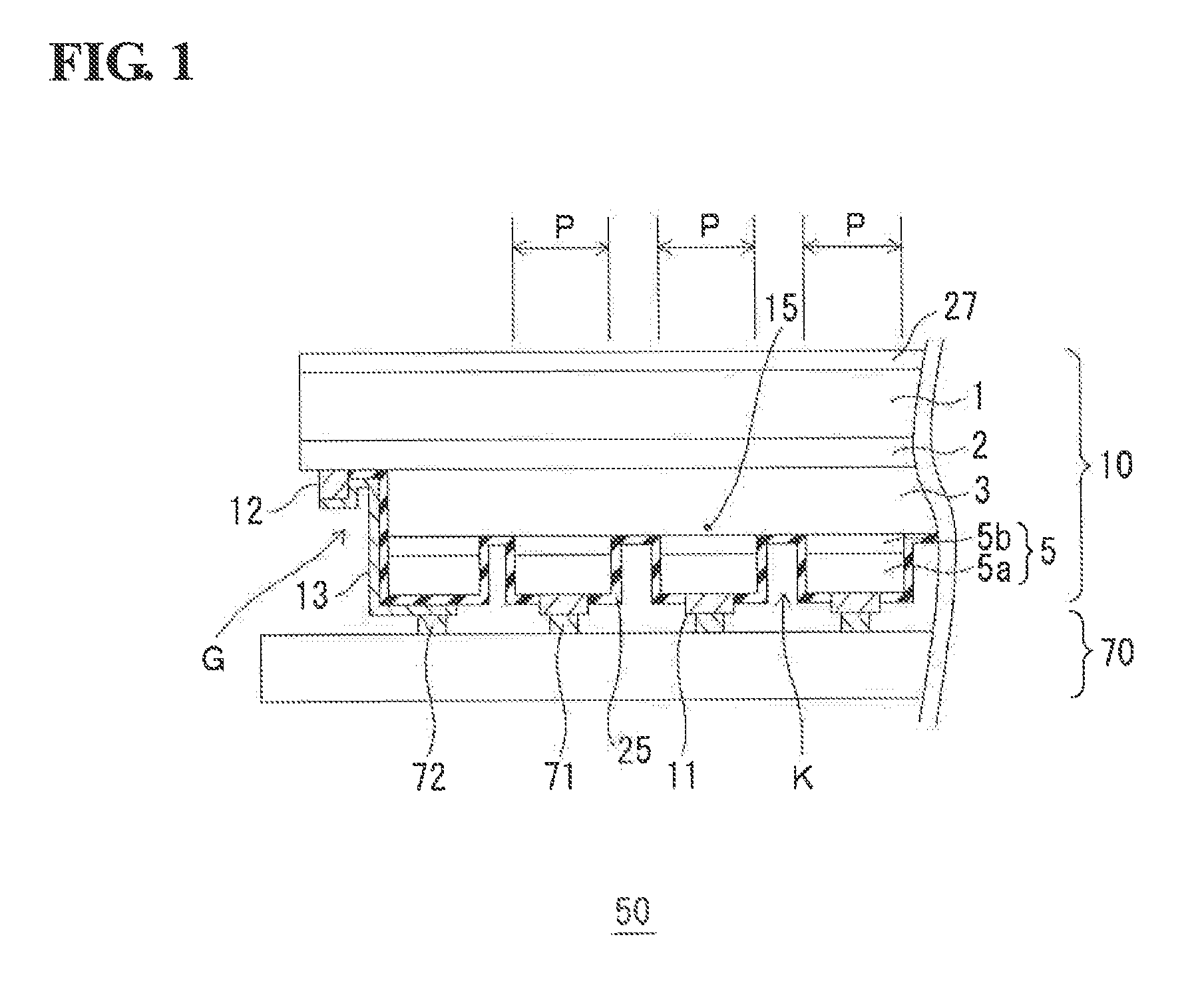
Light-receiving device and method for producing the same
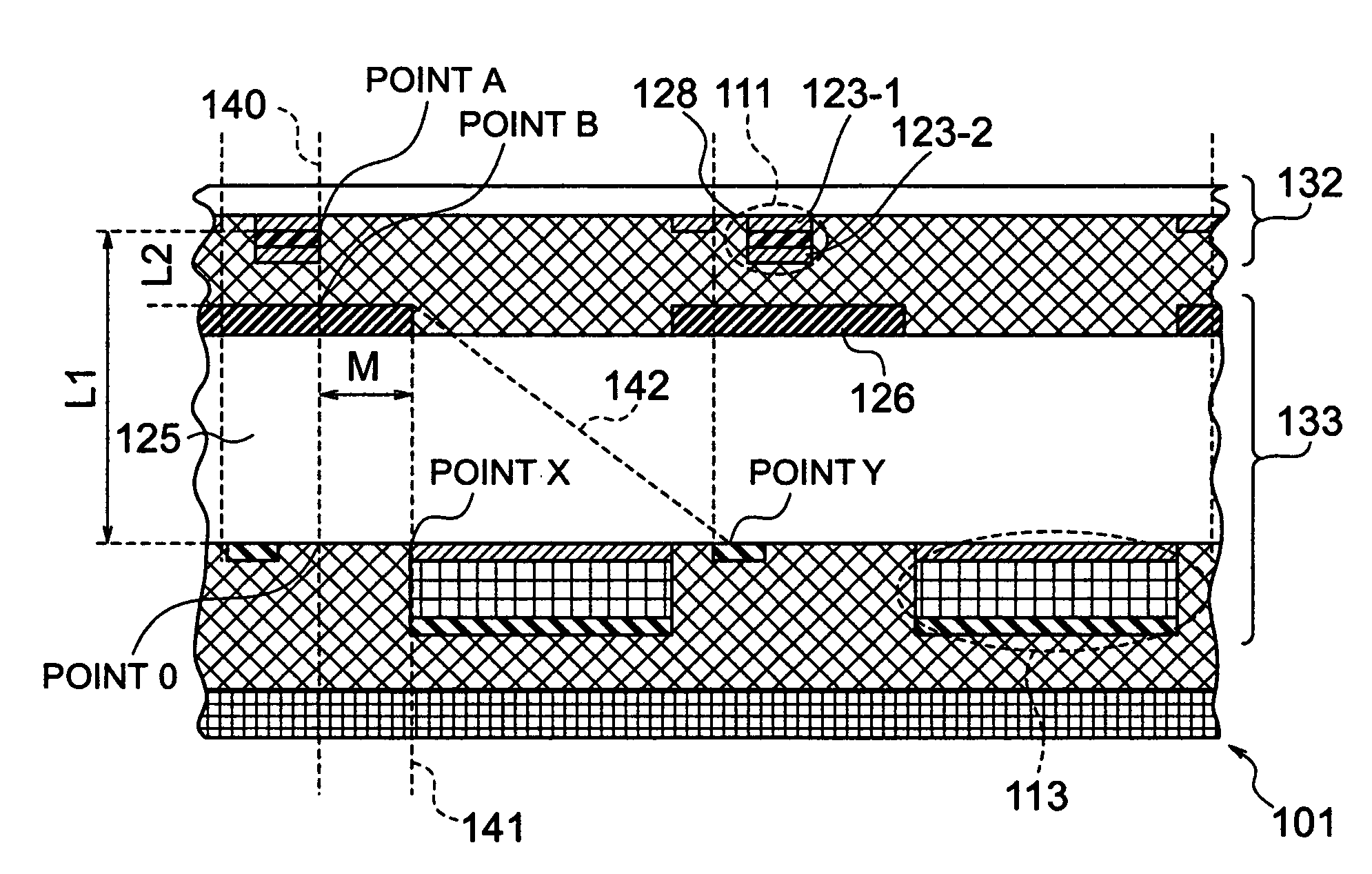
InactiveUS20140197373A1Increase in pixel pitch density is limitedIncrease productivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum wellP–n junction
A light-receiving device includes a light-receiving layer having an undoped multi-quantum well structure; a cap layer disposed on the light-receiving layer, the cap layer including a semiconductor layer doped with a p-type impurity; a mesa structure including the cap layer; a p-type region extending from the p-type semiconductor layer toward the light-receiving layer, the p-type region including the p-type impurity diffused from the semiconductor layer in the mesa structure; a p-n junction formed at an end of the p-type region; and an electrode disposed on the cap layer of the mesa structure. The mesa structure is defined by a trench surrounding the mesa. The trench has a bottom that reaches the vicinity of an upper surface of the light-receiving layer. The p-n junction is located in the light-receiving layer or at the boundary between the light-receiving layer and the cap layer disposed on the light-receiving layer.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Imaging device and apparatus installed with the same
InactiveUS7936983B2High detection sensitivityLarge fill factorTelevision system detailsPrintersLength waveDirect radiation
An imaging device includes a light source layer having imaging light source units for radiating the imaging light containing a first wavelength on an object to be imaged, a detection layer having detection elements for detecting the light of the first wavelength radiated from the light source units, and a light-blocking unit interposed between the light source layer and the detection layer. The light source layer is held between the detection layer and the object to be imaged. The light-blocking unit is arranged in such a manner as to block the direct radiation of at least part of the light radiated from the light source units to the detection elements.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Rocker-arm actuator for a segmented mirror
InactiveUS20060220492A1Reduces potential physical interferenceLarge fill factorElectrostatic motorsOptical elementsFill factorEngineering
A MEMS device having a movable plate supported on a substrate by a support structure that is hidden under the plate and yet which can be implemented to enable rotation of the plate with respect to the substrate about a rotation axis lying at the plate surface. As a result, the support structure does not take up any area within the plane of the plate, while enabling rotation of the plate, during which the plate does not substantially move sideways. The latter property reduces potential physical interference between neighboring plates in an arrayed MEMS device and enables implementation of a segmented mirror having relatively narrow gaps between adjacent segments and, thus, a relatively large fill factor, e.g., at least 98%.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
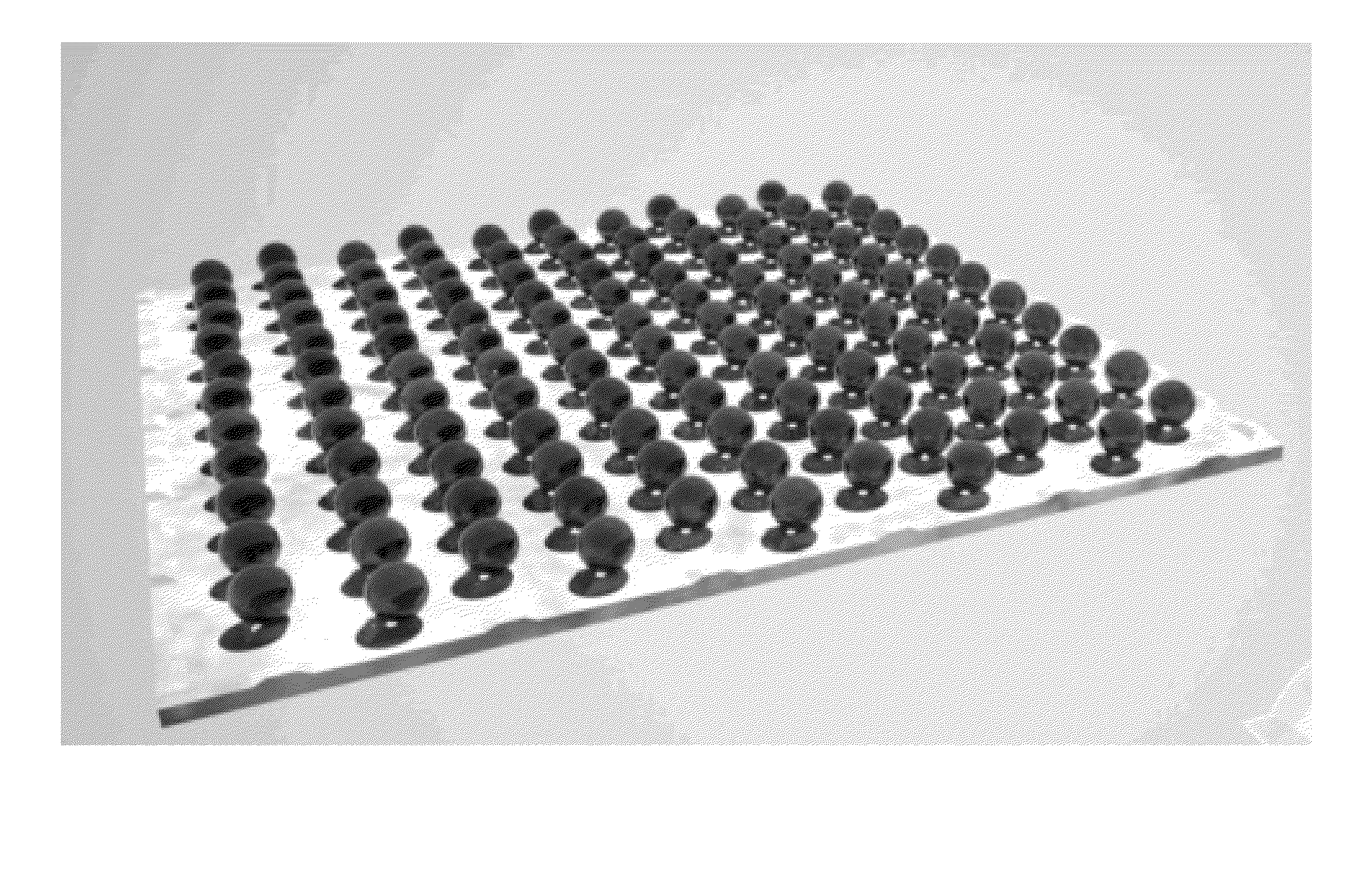
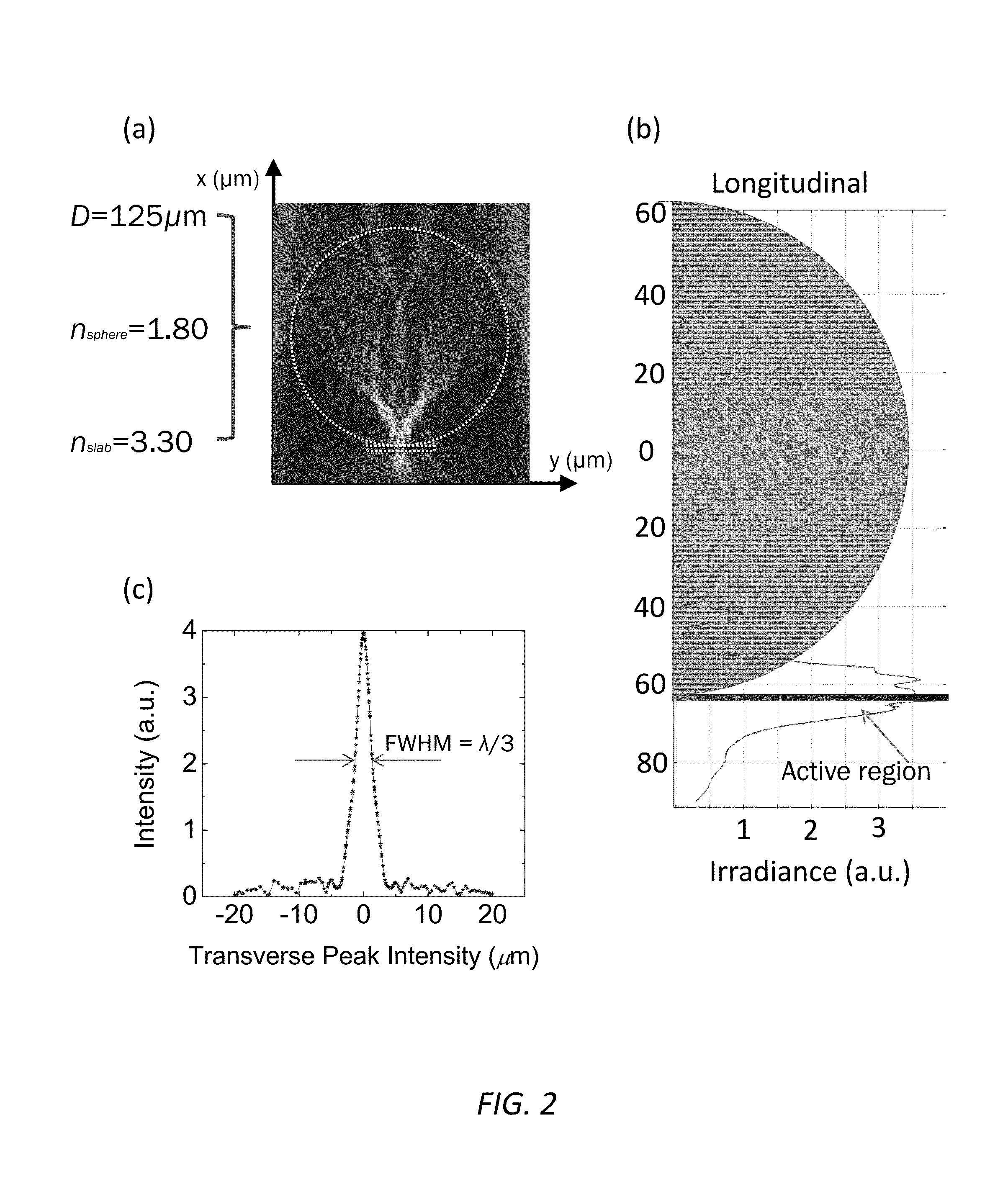
Photodetector focal plane array systems and methods
ActiveUS9362324B1Improve characteristicImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesPretreated surfacesPhotodetectorPhotovoltaic detectors
A photodetector focal plane array system, comprising: a substrate comprising a plurality of photosensitive regions; and a microcomponent disposed adjacent to each of the plurality of photosensitive regions operable for receiving incident radiation and directing a photonic nanojet into the associated photosensitive region. Optionally, each of the microcomponents comprises one of a microsphere and a microcylinder. Each of the microcomponents has a diameter of between between ˜λ and ˜100λ, where λ is the wavelength of the incident radiation. Each of the microcomponents is manufactured from a dielectric or semiconductor material. Each of the microcomponents has an index of refraction of between ˜1.4 and ˜3.5. Optionally, high-index components can be embedded in a lower index material. The microcomponents form an array of microcomponents disposed adjacent to the substrate.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +1
Detector of infrared radiation having a bi-material transducer
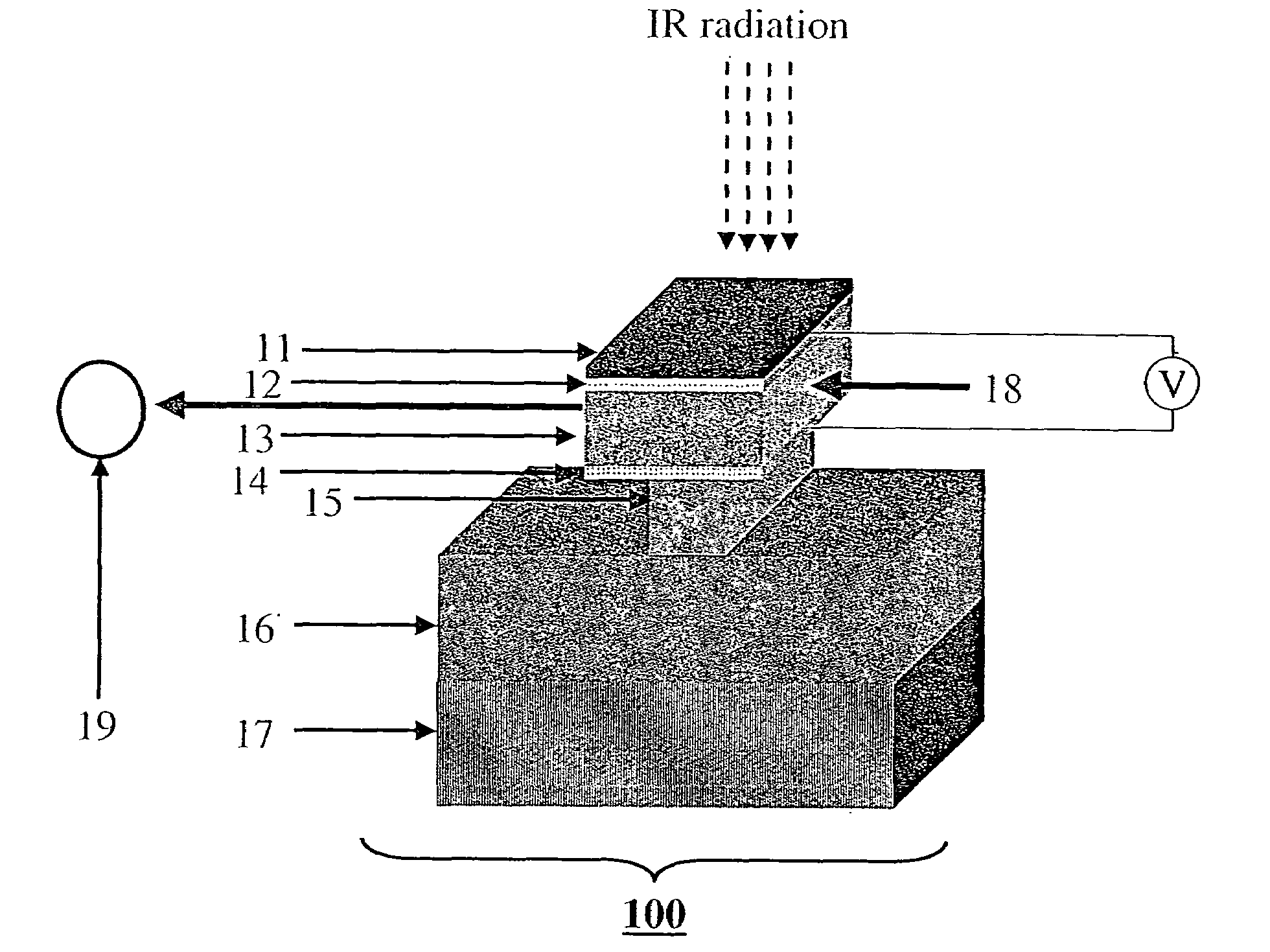
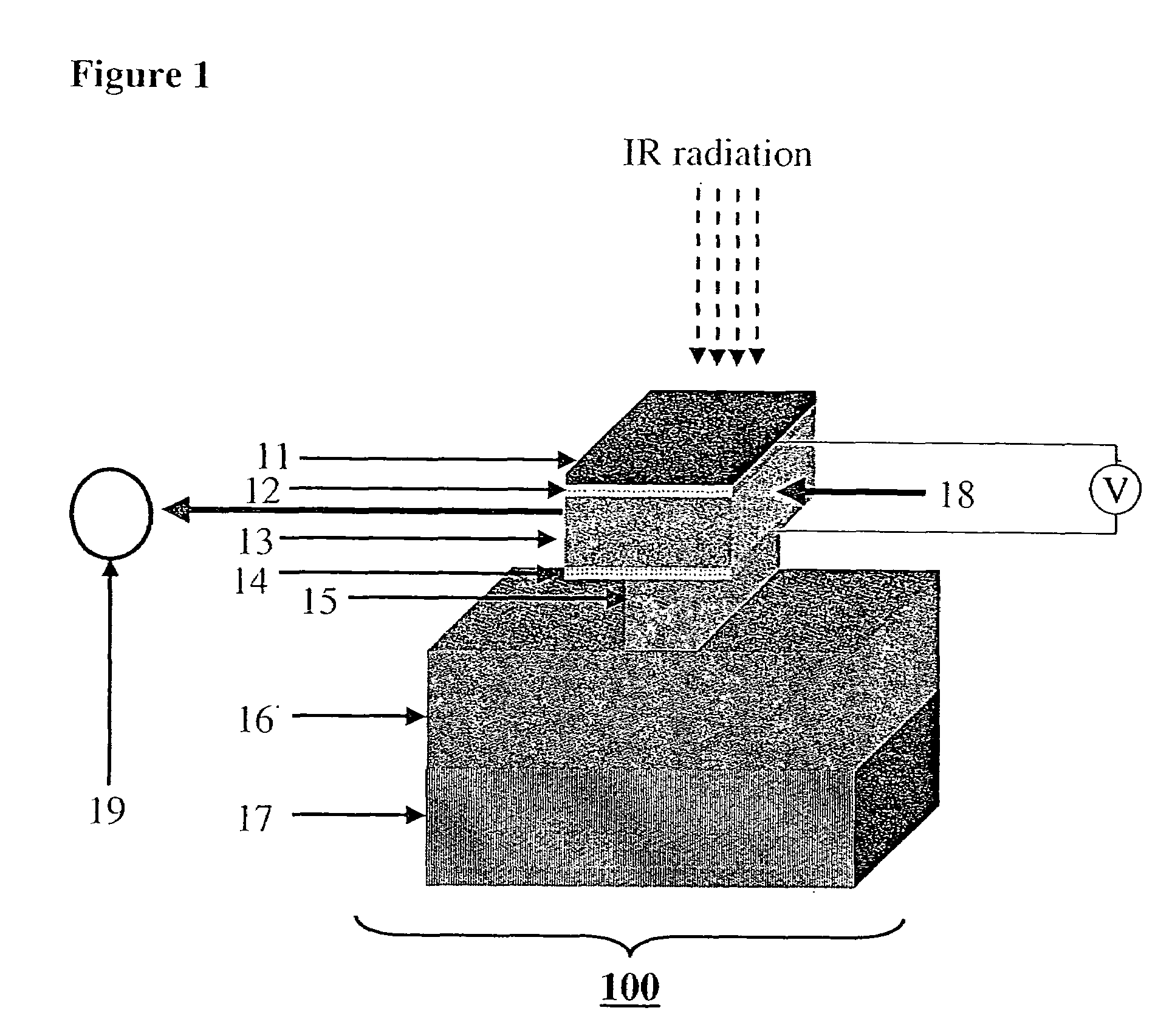
InactiveUS7580175B2Large fill factorCompensation for adverse effectsRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansOffset distanceTransducer
A representative embodiment of the invention provides an infrared (IR) detector having a movable plate supported at an offset distance from a substrate by a suspension arm. In response to a temperature difference between the plate and the substrate generated by the incident IR radiation, the suspension arm deforms and changes the offset distance for the plate. In one embodiment, the suspension arm has three rod-shaped bimorph transducers that lie within a plane that is parallel to the substrate. The transducers are also parallel to one another, with the transducer that is attached to an anchor of the suspension arm being located between the two transducers that are attached to the plate.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Electrically controlled tiltable microstructures
InactiveUS20070018065A1Large fill factorLarge angle tiltsStands/trestlesKitchen equipmentCouplingEngineering
Owner:TELEDYNE LICENSING
Thermal imaging system and method
InactiveUS7119334B2Increase thermal resistanceImprove performanceTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryRefractive indexThermal expansion
Systems and methods for thermal sensing and imaging using the electro-optic effect. A thermal detection system comprises a temperature sensing element that includes an electro-optic (EO) material layer having a length axis and characterized by a temperature dependent index of refraction, an electrical mechanism for inducing a chance in the index of refraction, a laser beam propagating lengthwise through EO layer for probing the refraction index change, and a light intensity meter for measuring a laser beam intensity change caused by the temperature dependent refraction index change. Thermal imaging is obtained by using a pixel array of such thermal sensing elements. The intensity reading may be done in either a cross-polarizer or a Mach Zehnder Interferometry reading configuration.
Owner:NAMAL TECH LTD
Image sensor with SOI substrate
ActiveUS7271025B2Large fill factorTotal current dropSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIncrease sizeFill factor
An imager pixel utilizing a silicon-on-insulator substrate, a photodiode in said substrate below the buried oxide, and a dual contact to said photodiode and methods of forming said imager pixel. The photodiode has an increased fill factor due to its increased size relative to the pixel.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
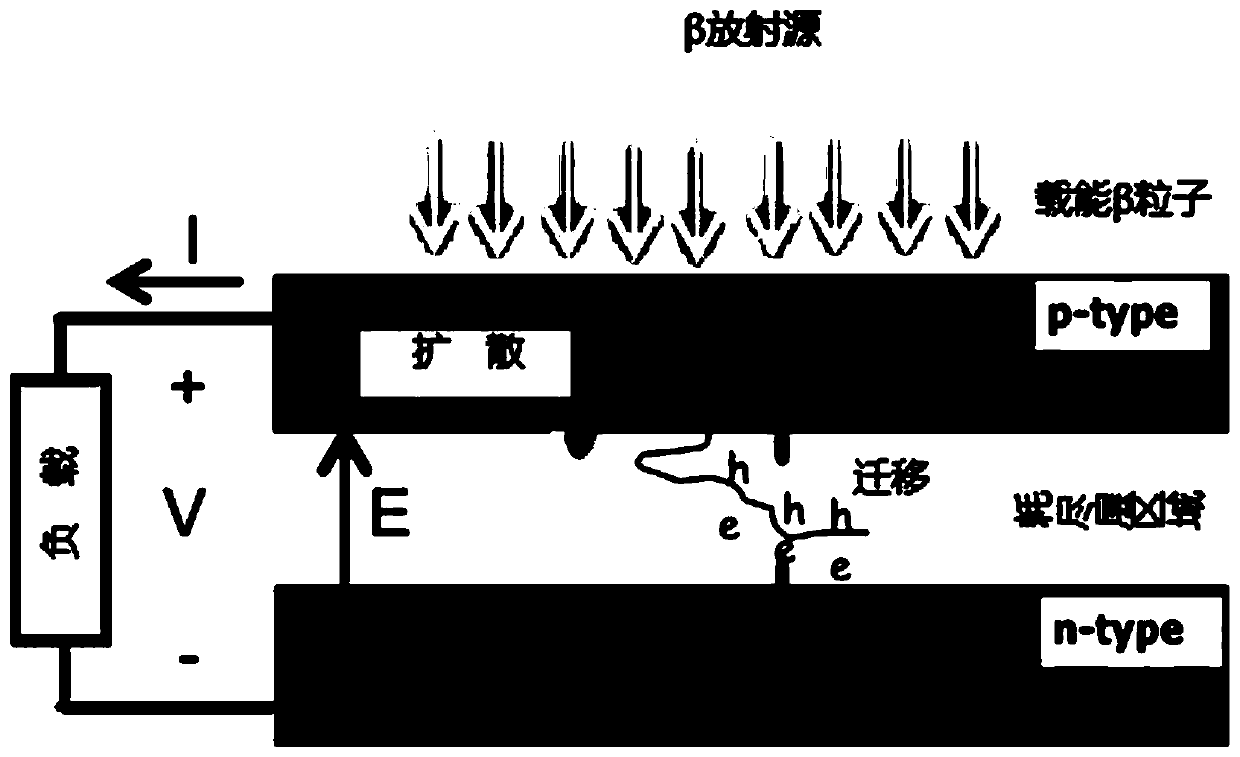
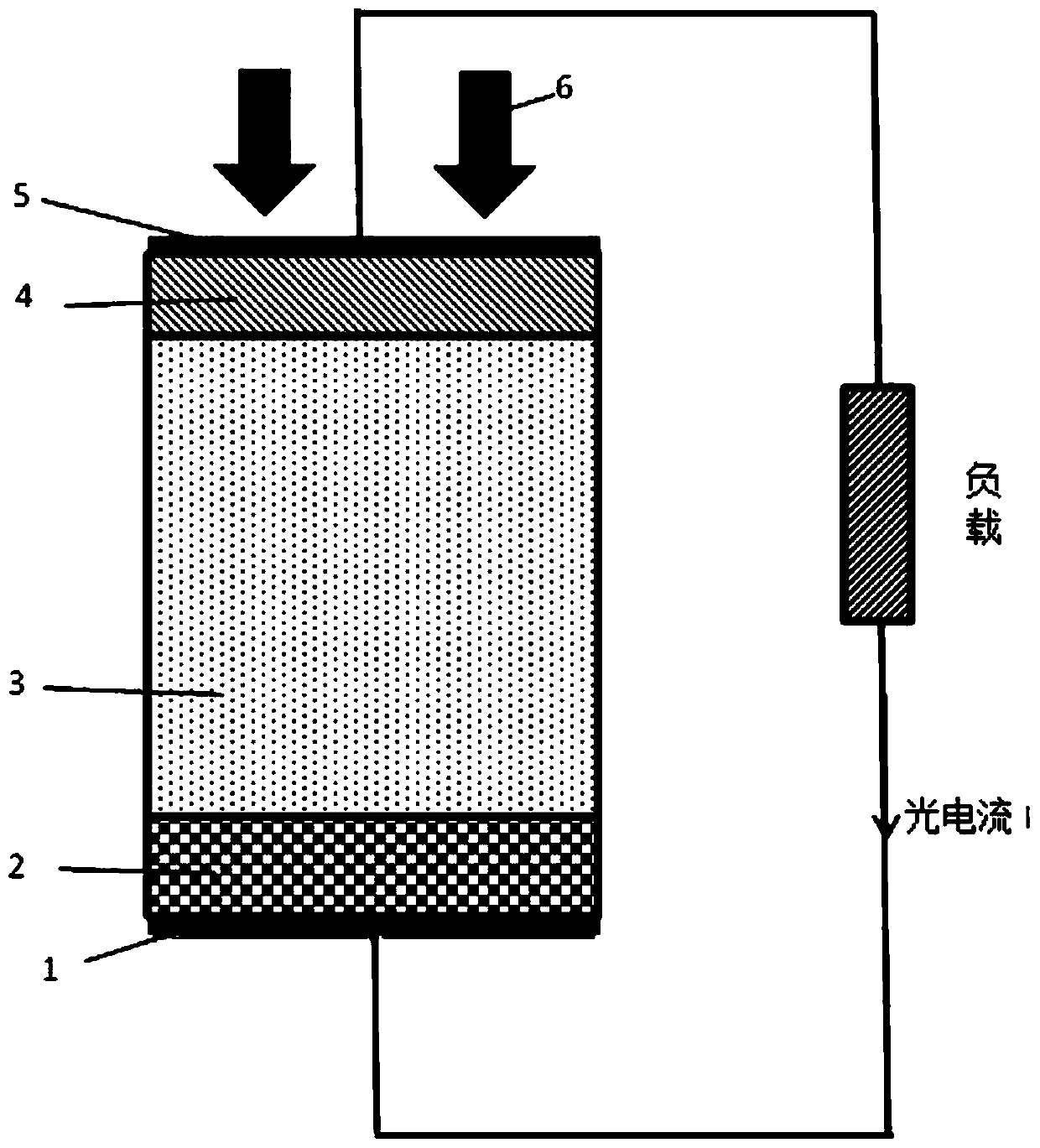
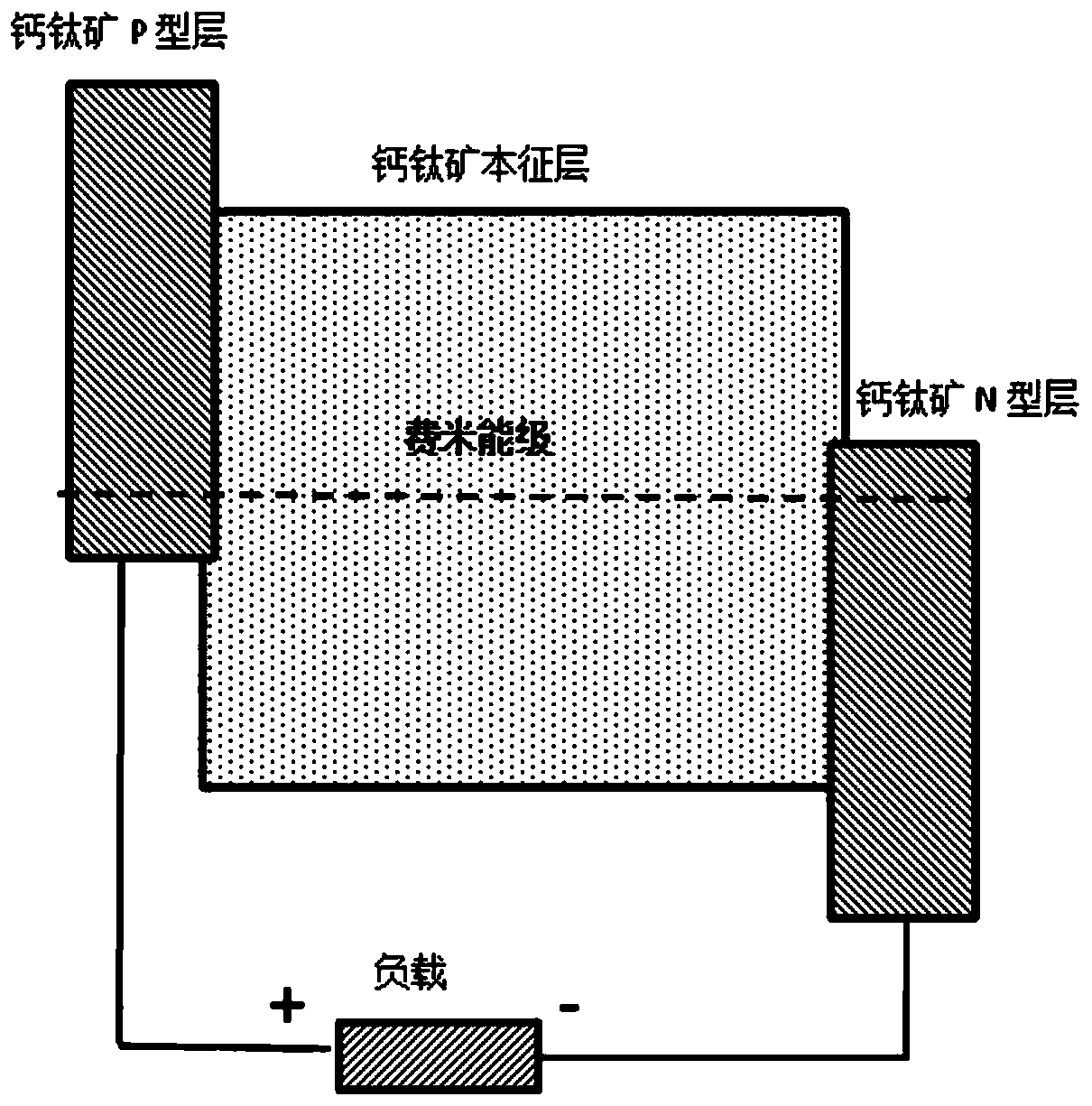
Radio-voltaic nuclear battery based on perovskite crystals
ActiveCN111261311AEfficient conversionPromote absorptionPhotovoltaic energy generationRadiation electrical energyElectrical batteryHigh energy
The invention relates to a radio-voltaic nuclear battery based on perovskite crystals and a preparation method thereof. A nuclear battery structure sequentially comprises a radiation source, an anodeelectrode, a p-type perovskite layer, an intrinsic perovskite layer, an n-type perovskite layer and a cathode from top to bottom. In the nuclear battery structure, the radiation source emits high-energy particles such as beta particles, X rays and gamma rays, the high-energy particles are absorbed in the high-thickness intrinsic perovskite layer, and photo-induced electron / hole pairs are generatedthrough a photoelectric effect. The p-type perovskite layer, the intrinsic perovskite layer and the n-type perovskite layer form a PIN structure, and the PIN structure forms a depletion layer. Due toa built-in electric field of the depletion layer, photo-induced electrons / hole pairs generated by the high-energy particles are separated and drift towards the cathode and the anode respectively to form open-circuit voltage or short-circuit current.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Photodetector focal plane array systems and methods
ActiveUS20160190194A1Improve efficiencyHigh frequency responseSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic detectorsSemiconductor materials
A photodetector focal plane array system, comprising: a substrate comprising a plurality of photosensitive regions; and a microcomponent disposed adjacent to each of the plurality of photosensitive regions operable for receiving incident radiation and directing a photonic nanojet into the associated photosensitive region. Optionally, each of the microcomponents comprises one of a microsphere and a microcylinder. Each of the microcomponents has a diameter of between ˜λ and ˜100λ, where λ is the wavelength of the incident radiation. Each of the microcomponents is manufactured from a dielectric or semiconductor material. Each of the microcomponents has an index of refraction of between ˜1.4 and ˜3.5. Optionally, high-index components can be embedded in a lower index material. The microcomponents form an array of microcomponents disposed adjacent to the substrate.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +1
Light-receiving device and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20160155880A1Increase in pixel pitch density is limitedIncrease productivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum wellP–n junction
A light-receiving device includes a light-receiving layer having an undoped multi-quantum well structure; a cap layer disposed on the light-receiving layer, the cap layer including a semiconductor layer doped with a p-type impurity; a mesa structure including the cap layer; a p-type region extending from the p-type semiconductor layer toward the light-receiving layer, the p-type region including the p-type impurity diffused from the semiconductor layer in the mesa structure; a p-n junction formed at an end of the p-type region; and an electrode disposed on the cap layer of the mesa structure. The mesa structure is defined by a trench surrounding the mesa. The trench has a bottom that reaches the vicinity of an upper surface of the light-receiving layer. The p-n junction is located in the light-receiving layer or at the boundary between the light-receiving layer and the cap layer disposed on the light-receiving layer.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Ribbed large-format imprinting method
ActiveUS20160062005A1Improve uniformityIncrease in sizeLamination ancillary operationsMouldsEngineeringMicro cavities
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Stacked large-format imprinting method
InactiveUS20160062008A1Large fill factorIncrease in sizeLamination ancillary operationsMouldsChemistryMicro cavities
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Filled large-format imprinted structure
InactiveUS20160062003A1Improve uniformityIncrease in sizeOptical filtersPhotomechanical apparatusEngineeringMicro cavities
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Ribbed large-format imprinted structure
InactiveUS20160062176A1Improve uniformityIncrease in sizeLayered productsPhotomechanical apparatusEngineeringMicro cavities
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Multi-layer large-format imprinting method
InactiveUS20160062181A1Improve uniformityIncrease in sizeLamination ancillary operationsMouldsChemistryMicro cavities
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Filled large-format imprinting method
ActiveUS20160062004A1Improve uniformityIncrease in sizeLamination ancillary operationsMouldsBiomedical engineeringMicro cavities
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Stacked large-format imprinted structure
InactiveUS20160062007A1Improve uniformityIncrease in sizeLayered productsOptical filtersOptoelectronicsMicro cavities
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Multi-layer large-format imprinted structure
InactiveUS20160062006A1Improve uniformityIncrease in sizeOptical filtersPhotomechanical apparatusPhysicsMicro cavities
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Stacked large-format imprinted structure
InactiveUS9545000B2Large fill factorIncrease in sizeOptical filtersPhotomechanical apparatusPhysicsMicro cavities
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com