Patents
Literature
417 results about "Ion transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ion transfer. a method of transporting chemicals across a membrane by using an electric current as a driving force.
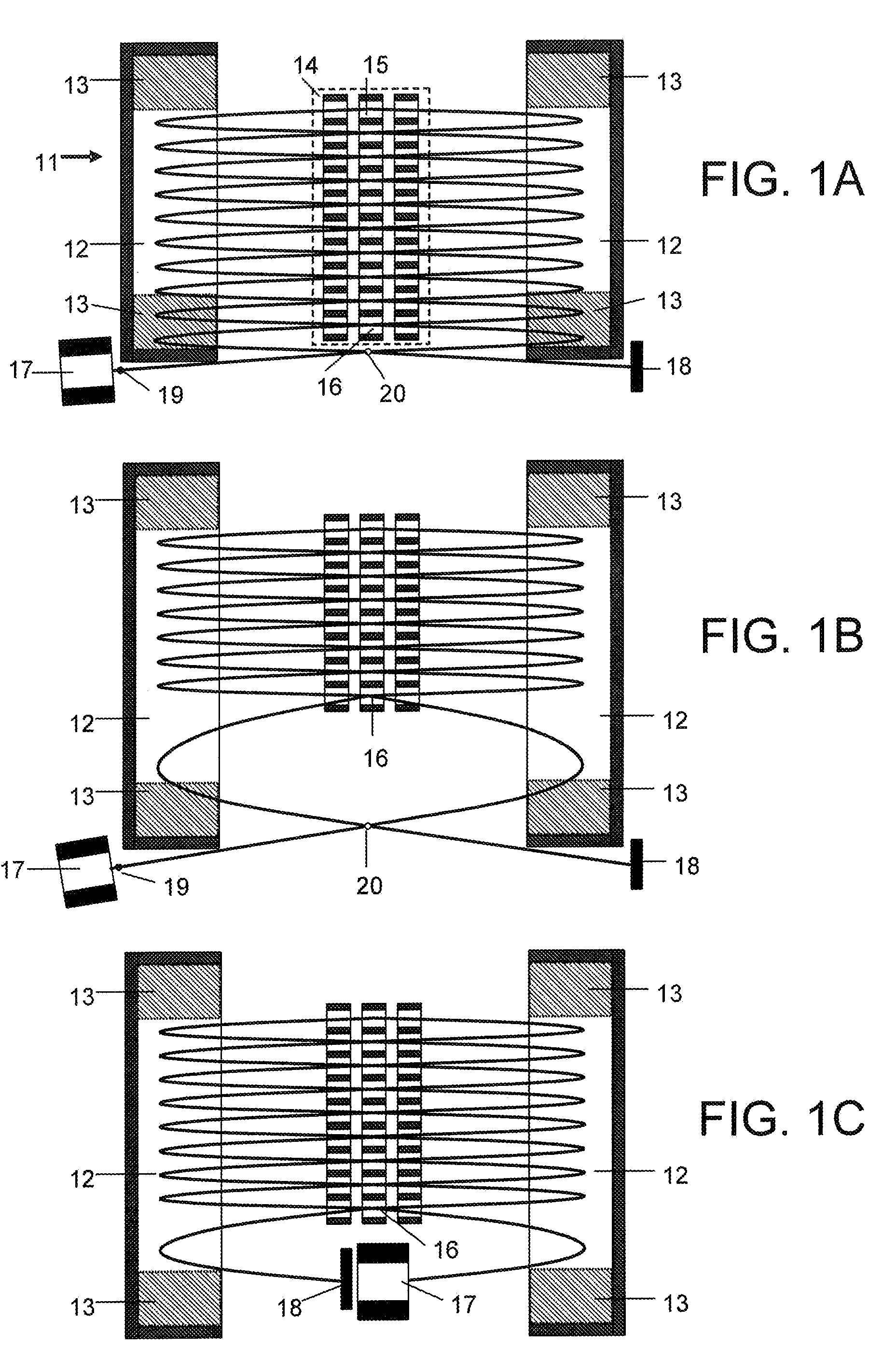
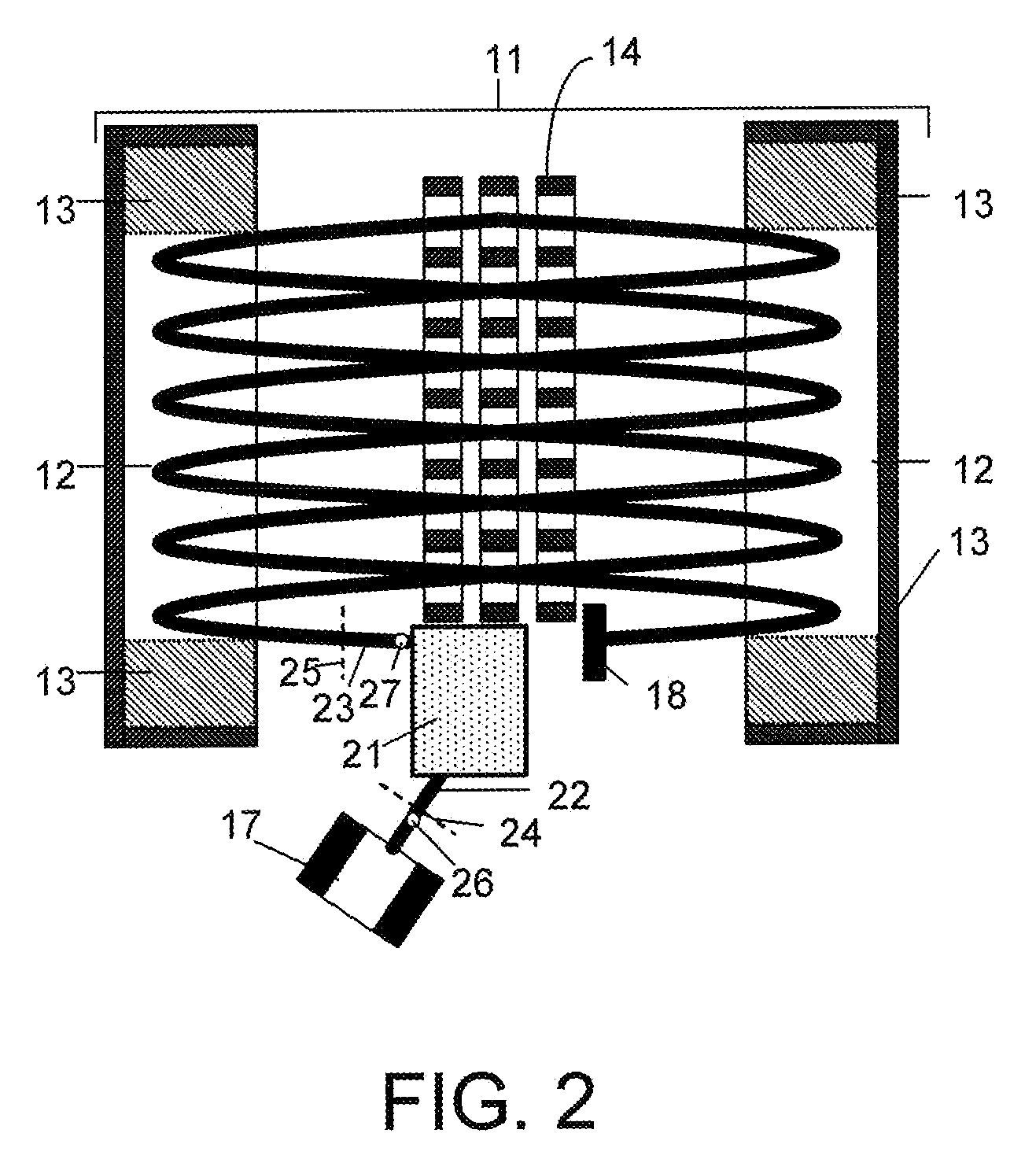
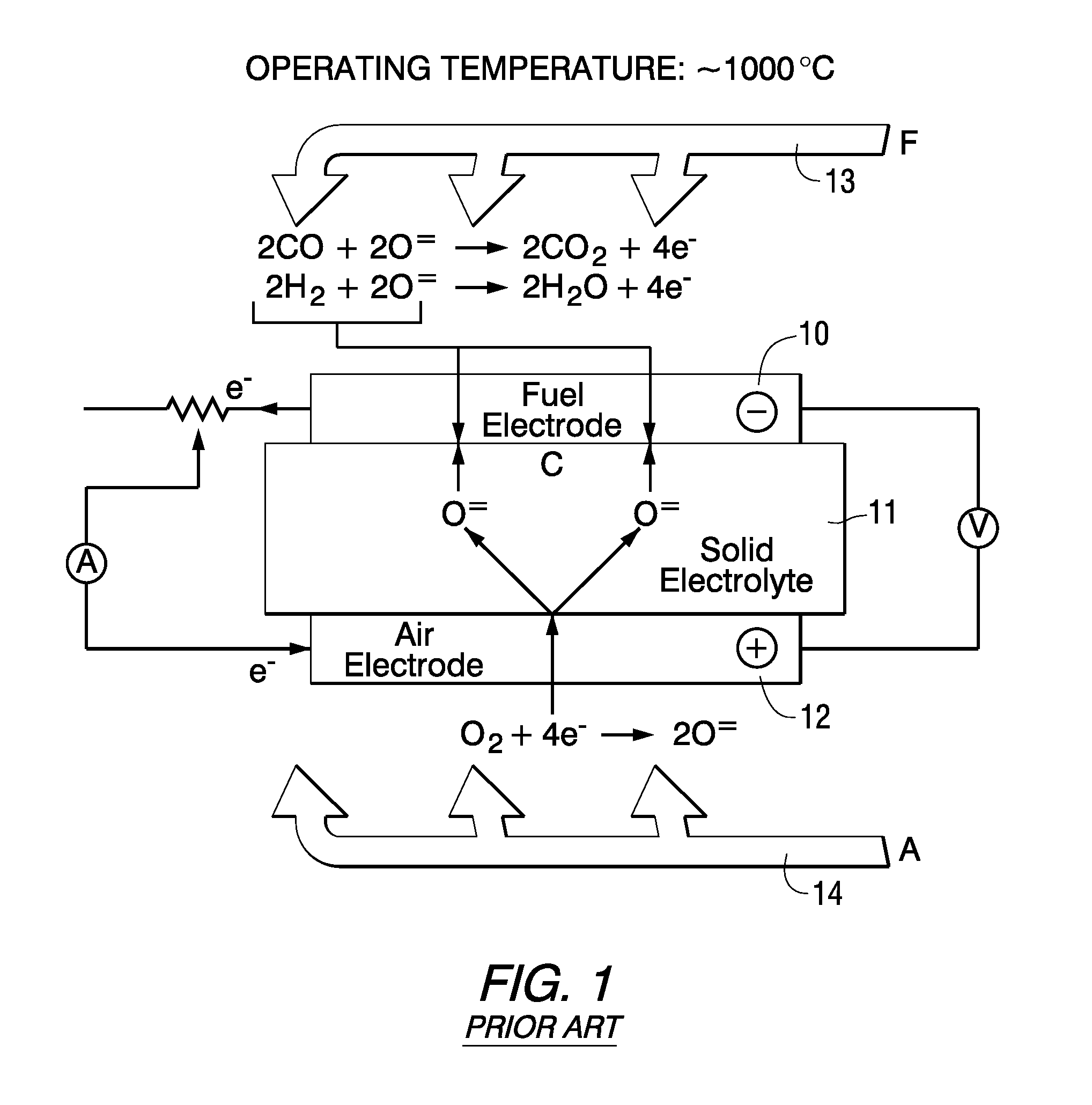
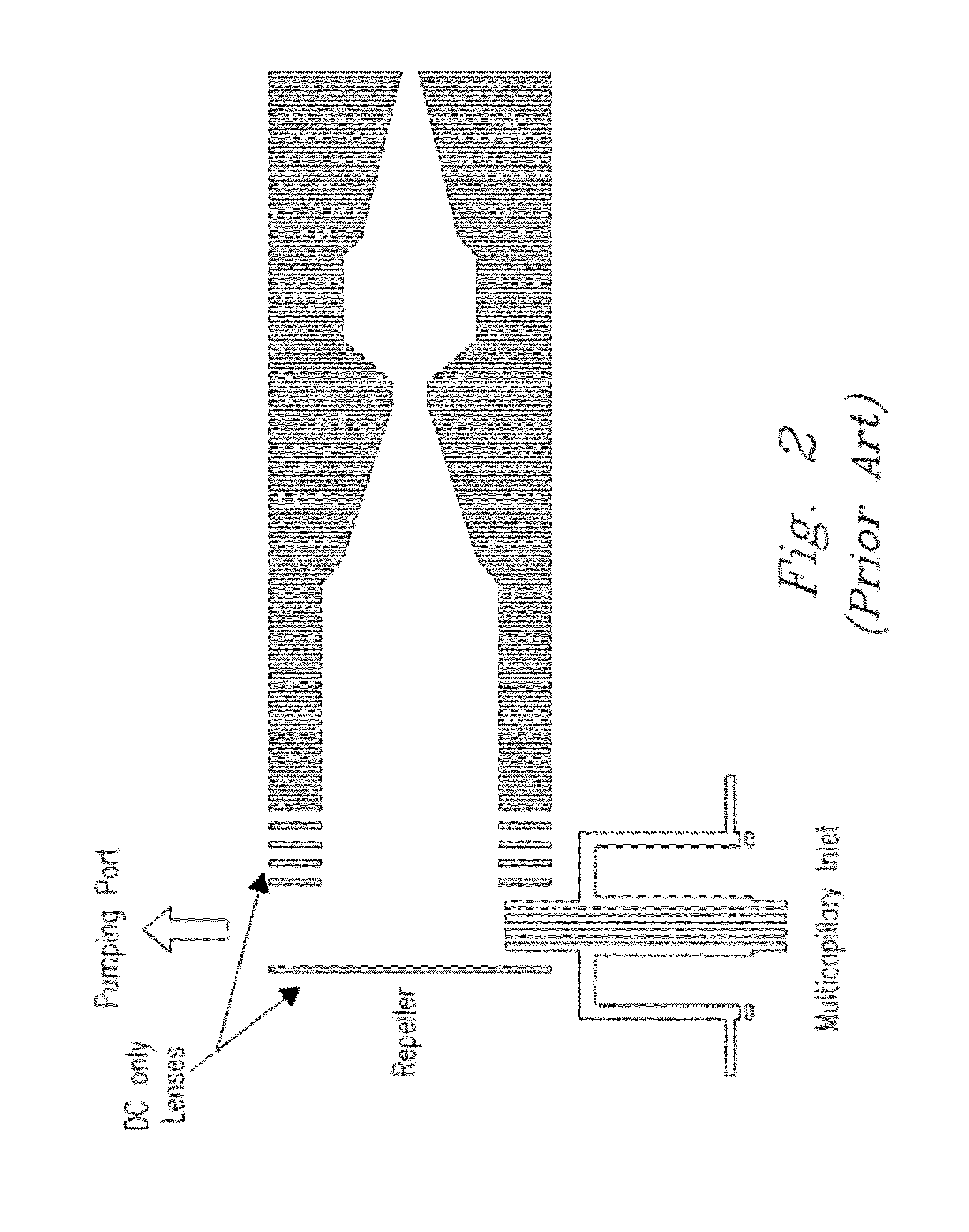
Low pollution power generation system with ion transfer membrane air separation
InactiveUS6945029B2Nitrogen oxideReduce electricity demandSolidificationLiquefactionPollutionCombustion products
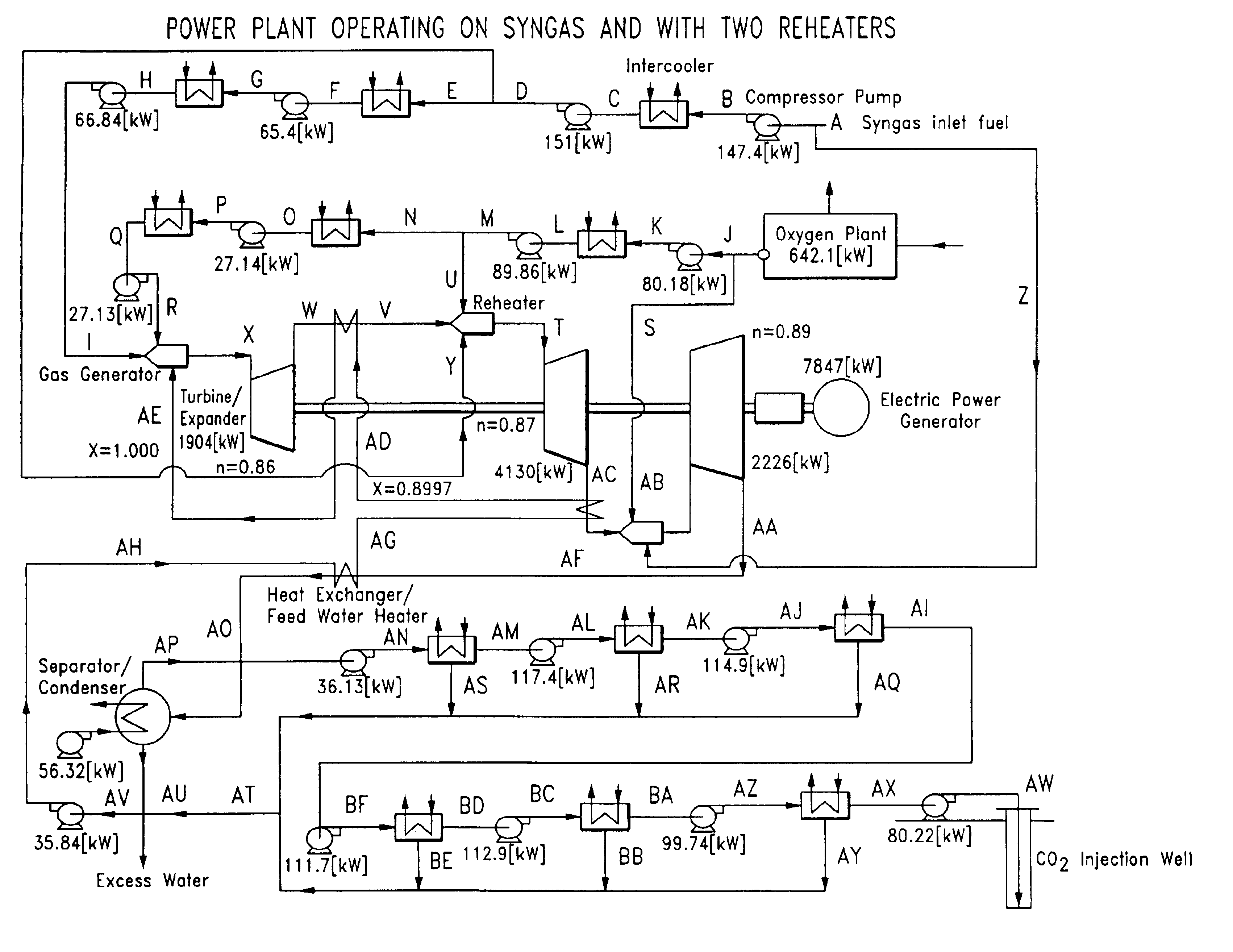
A low or no pollution power generation system is provided. The system has an air separator to collect oxygen. A gas generator is provided with inputs for the oxygen and a hydrocarbon fuel. The fuel and oxygen are combusted within the gas generator, forming water and carbon dioxide. Water or other diluents are also delivered into the gas generator to control temperature of the combustion products. The combustion products are then expanded through at least one turbine or other expander to deliver output power. The combustion products are then passed through a separator where the steam is condensed. A portion of the water is discharged and the remainder is routed back to the gas generator as diluent. The carbon dioxide can be conditioned for sequestration. The system can be optimized by adding multiple expanders, reheaters and water diluent preheaters, and by preheating air for an ion transfer membrane oxygen separation.
Owner:CLEAN ENERGY SYST
Multi-reflecting time-of-flight mass spectrometer with isochronous curved ion interface
ActiveUS20060214100A1Time-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryIon transfer
The present invention relates generally to a multi-reflecting time-of-flight mass spectrometer (MR TOF MS). To improve mass resolving power of a planar MR TOF MS, a spatially isochronous and curved interface may be used for ion transfer in and out of the MR TOF analyzer. One embodiment comprises a planar grid-free MR TOF MS with periodic lenses in the field-free space, a linear ion trap for converting ion flow into pulses and a C-shaped isochronous interface made of electrostatic sectors. The interface allows transferring ions around the edges and fringing fields of the ion mirrors without introducing significant time spread. The interface may also provide energy filtering of ion packets. The non-correlated turn-around time of ion trap converter may be reduced by using a delayed ion extraction from the ion trap and excessive ion energy is filtered in the curved interface.
Owner:LECO CORPORATION
Patch clamp apparatus and technique having high throughput and low fluid volume requirements
InactiveUS6063260ALow sample volume requirementLower the volumeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAutosamplerIon transfer
PCT No. PCT / EP95 / 02204 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 25, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 25, 1997 PCT Filed Jun. 7, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 13721 PCT Pub. Date May 9, 1996Apparatus for carrying out patch clamp technique utilized in studying the effect of certain materials on ion transfer channels in biological tissue, and more particularly patch clamp apparatus utilizing an autosampler, such as those utilized with HPLC apparatus, to provide high throughput, is disclosed. The invention additionally includes novel microperfusion chamber assemblies capable of utilizing only small amounts of material to be tested and only small amounts of liquid carrier, thereby enabling many tests to be completed in a short period of time. The invention more broadly relates to a novel electrophysiology drug handling and application set up for screening of chemical substances while providing high throughput and requiring only low volume of solutions and samples to be tested. The invention also comprises several novel procedures for utilizing the apparatus of the invention.
Owner:SOPHION BIOSCI
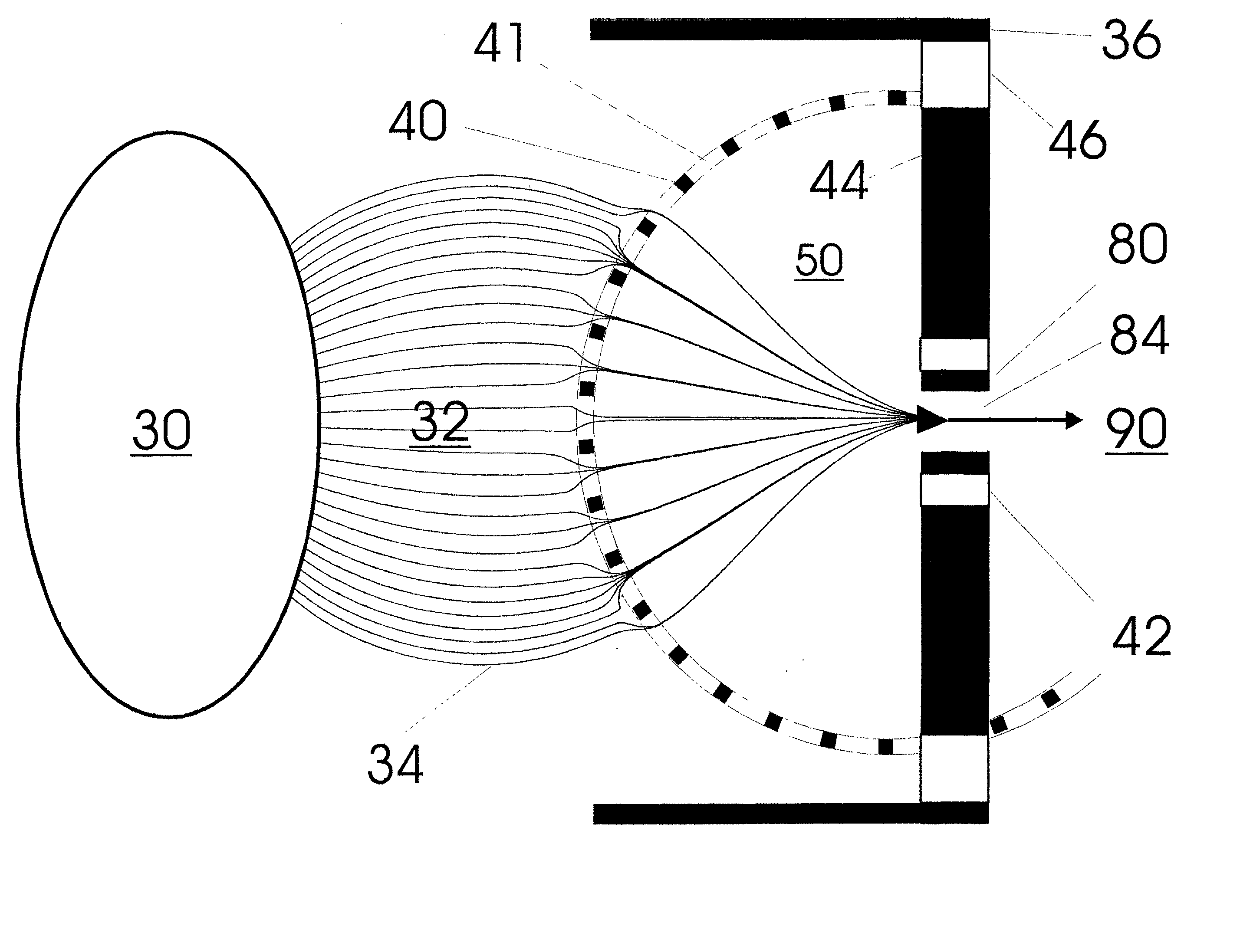
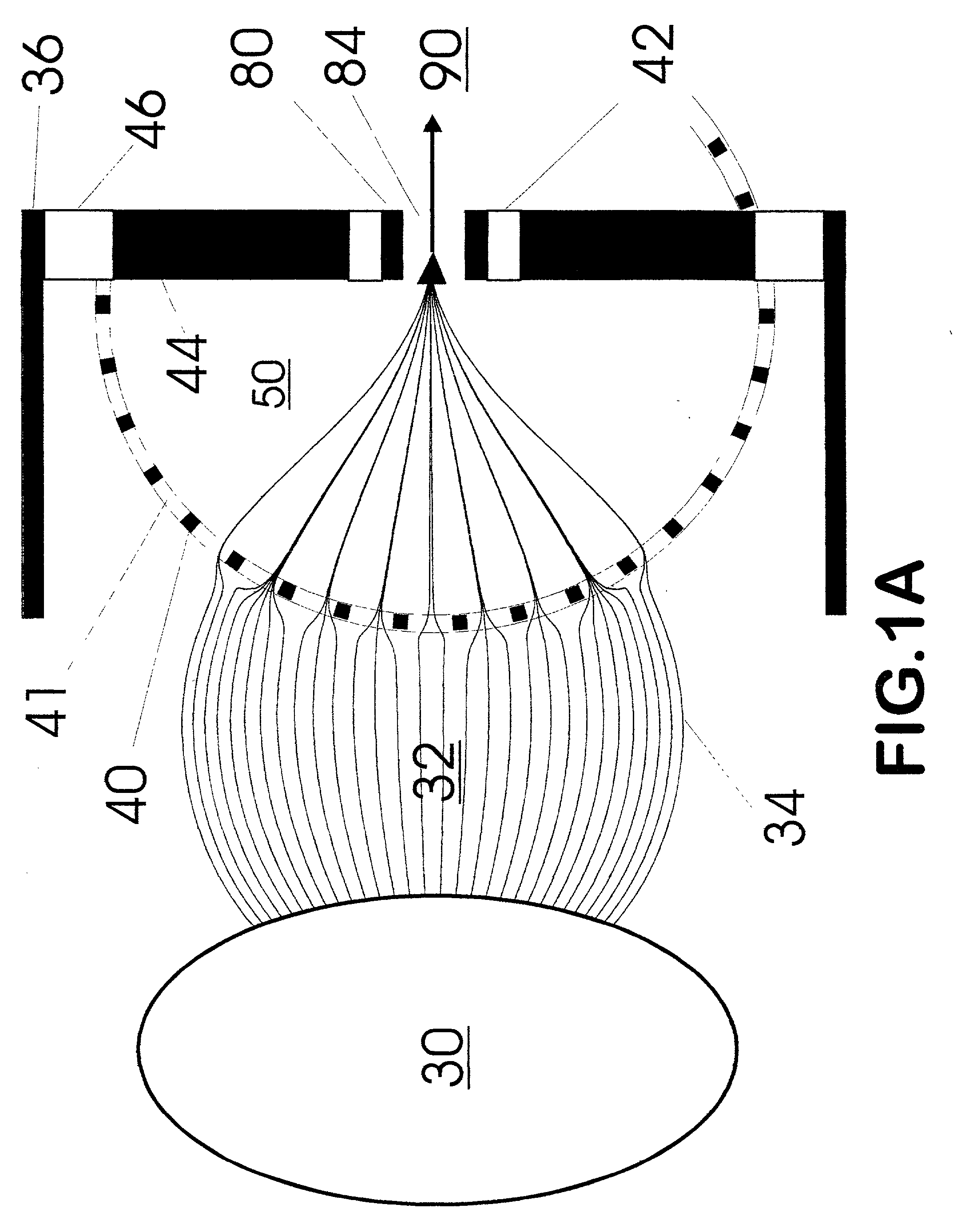
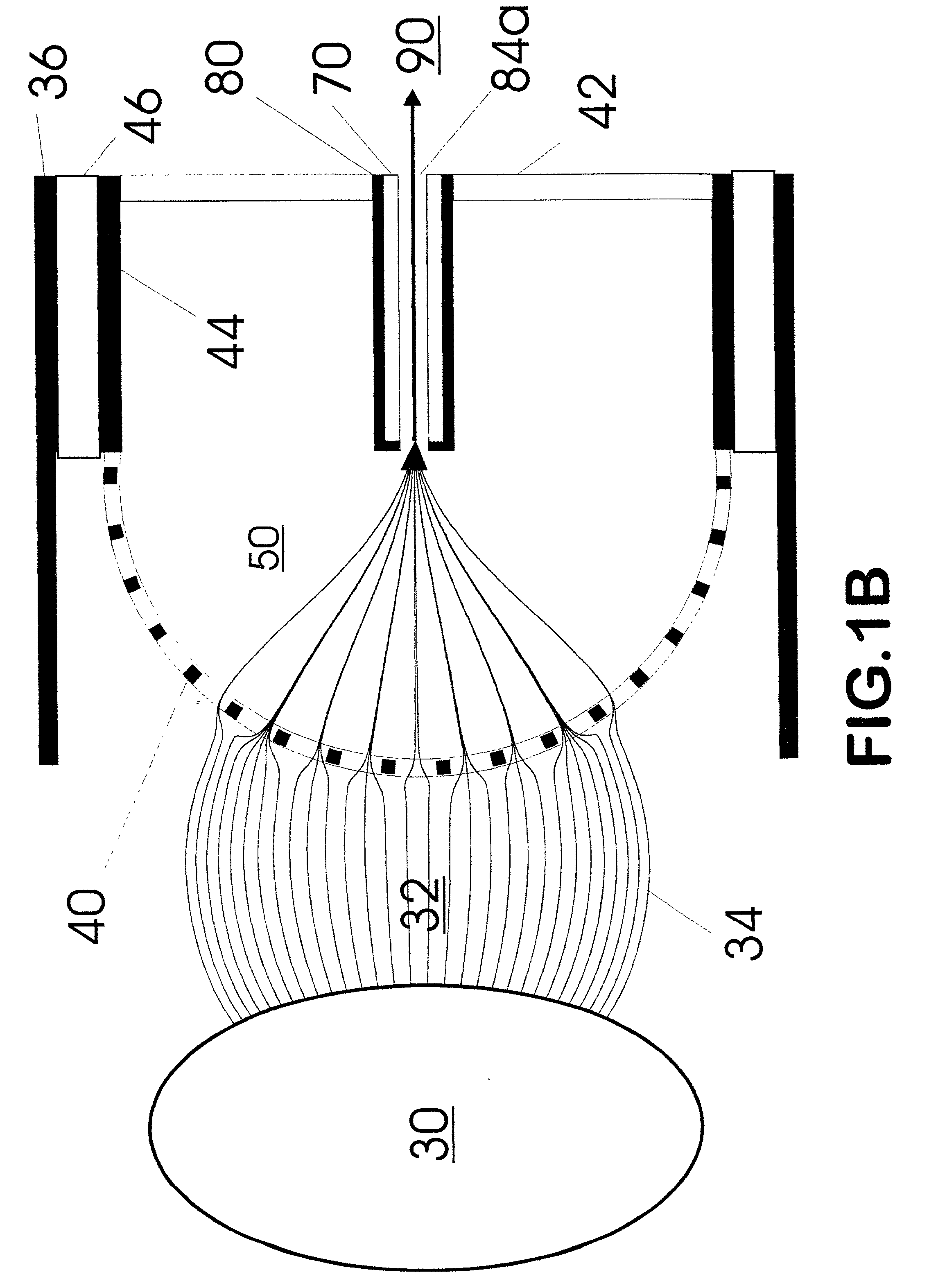
Apparatus and method for focusing ions and charged particles at atmospheric pressure
InactiveUS6744041B2Samples introduction/extractionIsotope separationInductively coupled plasmaElectrospray
Improvements have been made for collection and focusing of ions generated from atmospheric pressure sources such as electrospray, atmospheric pressure chemical ionization, inductively coupled plasma, discharge, photoionization and atmospheric pressure matrix assisted laser desorption ionization. A high transmission electro-optical surface is placed between the source regions and the focusing regions to optimize the field geometries and strengths in each respective region. Compression ratios of greater than 5000 are capable of transferring virtually all ions from large volume dispersive ion regions into ion beam cross-sections of less than 1 mm. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when coupled to atmospheric pressure ionization sources.
Owner:SHEEHAN EDWARD W +1
Multi-reflecting time-of-flight mass spectrometer with isochronous curved ion interface
ActiveUS7326925B2Time-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryTime-of-flight mass spectrometry
The present invention relates generally to a multi-reflecting time-of-flight mass spectrometer (MR TOF MS). To improve mass resolving power of a planar MR TOF MS, a spatially isochronous and curved interface may be used for ion transfer in and out of the MR TOF analyzer. One embodiment comprises a planar grid-free MR TOF MS with periodic lenses in the field-free space, a linear ion trap for converting ion flow into pulses and a C-shaped isochronous interface made of electrostatic sectors. The interface allows transferring ions around the edges and fringing fields of the ion mirrors without introducing significant time spread. The interface may also provide energy filtering of ion packets. The non-correlated turn-around time of ion trap converter may be reduced by using a delayed ion extraction from the ion trap and excessive ion energy is filtered in the curved interface.
Owner:LECO CORPORATION
High throughput systems and methods for parallel sample analysis
Systems and methods for analyzing multiple samples in parallel using mass spectrometry preferably coupled with fluid phase separation techniques are provided. A modular mass spectrometer includes a vacuum enclosure, multiple sample inlets, multiple common vacuum pumping elements, and multiple mass analysis modules disposed substantially within the enclosure, with each module preferably including a mass analyzer and a transducer. In one embodiment, the modules mate with the vacuum enclosure to define multiple sequential vacuum regions, with each vacuum region having an associated common vacuum pumping element. At least one multi-pole ion transfer optic element is preferably associated with each module. Fluid phase separation devices may include microfluidic devices utilizing chromatographic, electrophoretic, or other separation methods.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Secondary battery with auxiliary electrode
ActiveUS20090208834A1Weight and volumeImprove safety and reliabilityPrimary cell to battery groupingFinal product manufactureElectrolysisIon transfer
The present invention includes three-dimensional secondary battery cells comprising an electrolyte, a cathode, an anode, and an auxiliary electrode. The cathode, the anode, and the auxiliary electrode have a surface in contact with the electrolyte. The anode and the cathode are electrolytically coupled. The auxiliary electrode is electrolytically coupled and electrically coupled to at least one of the anode or the cathode. Electrically coupled means directly or indirectly connected in series by wires, traces or other connecting elements. The average distance between the surface of the auxiliary electrode and the surface of the coupled cathode or the coupled anode is between about 1 micron and about 10,000 microns. The average distance means the average of the shortest path for ion transfer from every point on the coupled cathode or anode to the auxiliary electrode.
Owner:MICROAZURE INC +1
Method and apparatus for ion manipulation using mesh in a radio frequency field
ActiveUS20110192969A1Better wayEasy to buildTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationIon chromatographyDesorption
Ion manipulation systems include ion repulsion by an RF field penetrating through a mesh. Another comprises trapping ions in a symmetric RF field around a mesh. The system uses macroscopic parts, or readily available fine meshes, or miniaturized devices made by MEMS, or flexible PCB methods. One application is ion transfer from gaseous ion sources with focusing at intermediate and elevated gas pressures. Another application is the formation of pulsed ion packets for TOF MS within trap array. Such trapping is preferably accompanied by pulsed switching of RF field and by gas pulses, preferably formed by pulsed vapor desorption. Ion guidance, ion flow manipulation, trapping, preparation of pulsed ion packets, confining ions during fragmentation or exposure to ion to particle reactions and for mass separation are disclosed. Ion chromatography employs an ion passage within a gas flow and through a set of multiple traps with a mass dependent well depth.
Owner:LECO CORPORATION
Hydrographical rechargeable lithium or sodium ion battery
InactiveCN101154745ALow costGuaranteed cycle performanceAlkaline accumulatorsCell electrodesPower batteryIon transfer
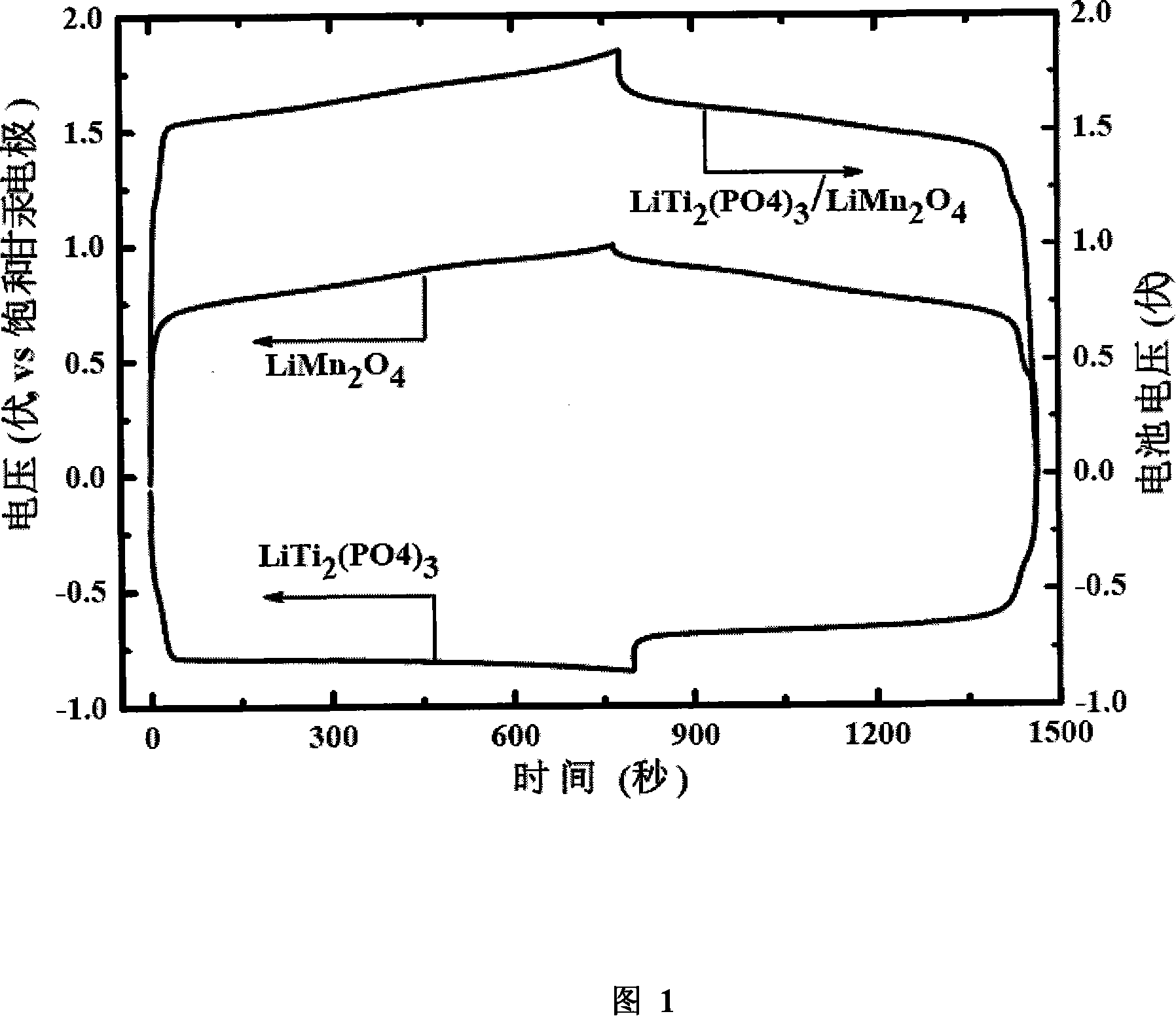
The invention belongs to electrochemical technical field, in particular to a novel high performance water system lithium ion battery. The invention adopts an ion embedding in-out mechanism used by an organic system lithium ion battery in an energy storage element which uses a water solution as an electrolyte. The embedding-in reaction ion mainly includes lithium ion composite and sodium ion composite. In the invention, the positive pole adopts a material containing the positive ion embedding-in composite while the negative pole adopts a shell structure material of LiTi2(PO4)3; the electrolyte adopts a water system electrolyte of the positive ion. The electric charging and discharging process only relates to the ion transfer between the two electrodes, and the invention can still has the characteristic of a rocking-chair type organic system lithium ion battery; the invention is of long cycling service life, big power, safety, low cost and no pollution, and is particularly suitable to be used as an ideal power battery of electric vehicle.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
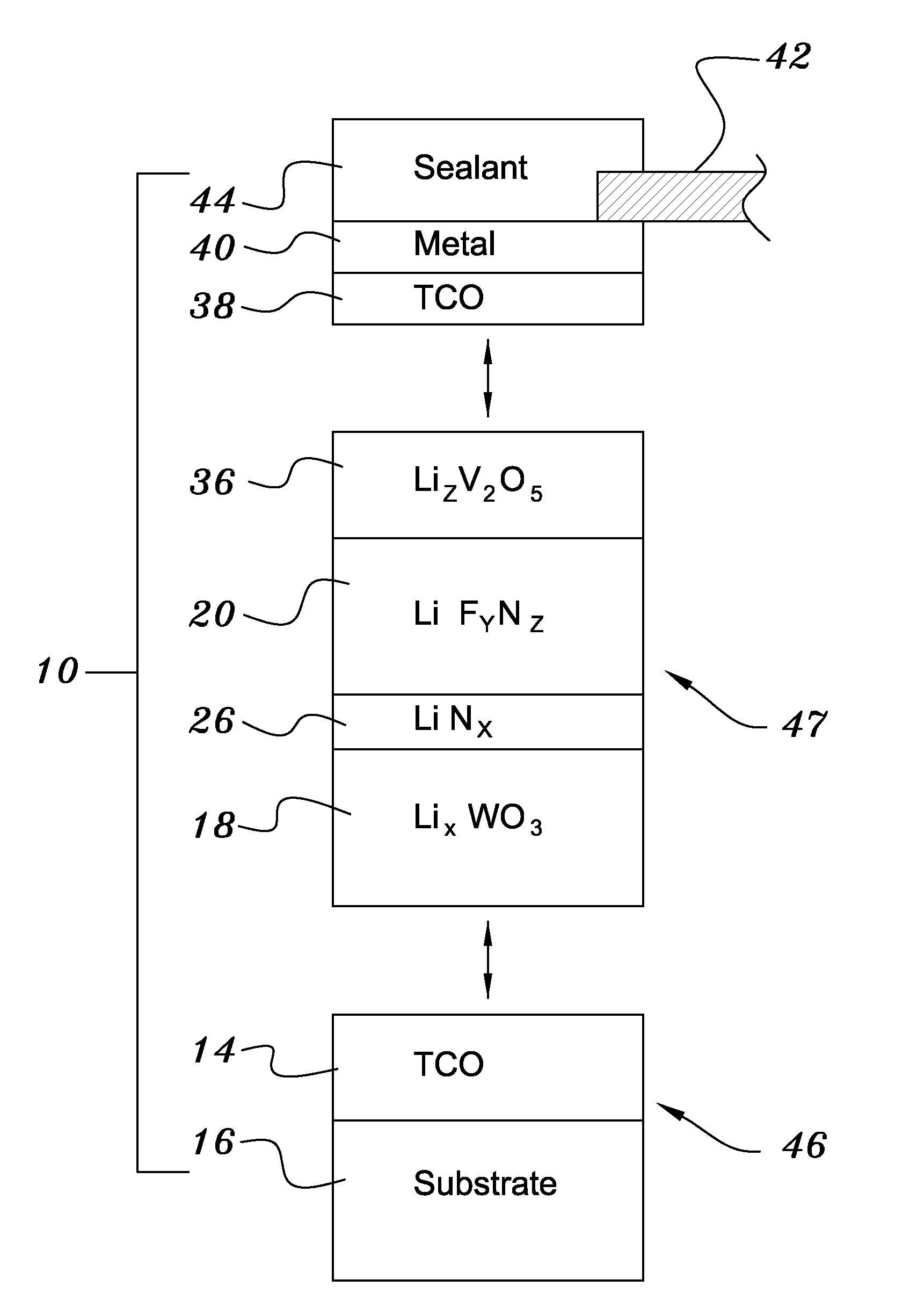
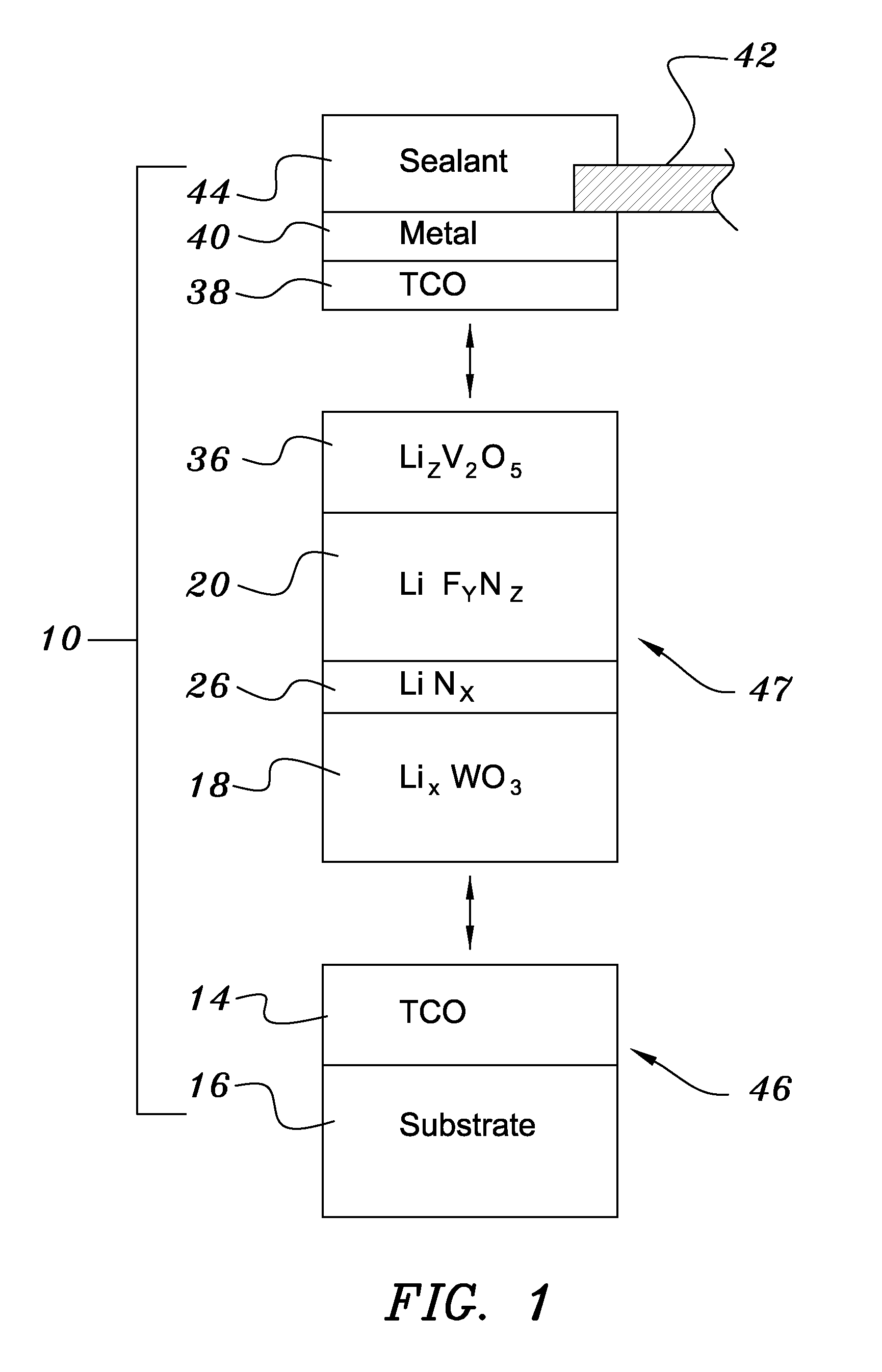
Electrochromic Device with Self-forming Ion transfer Layer and Lithium Fluoro-Nitride Electrolyte
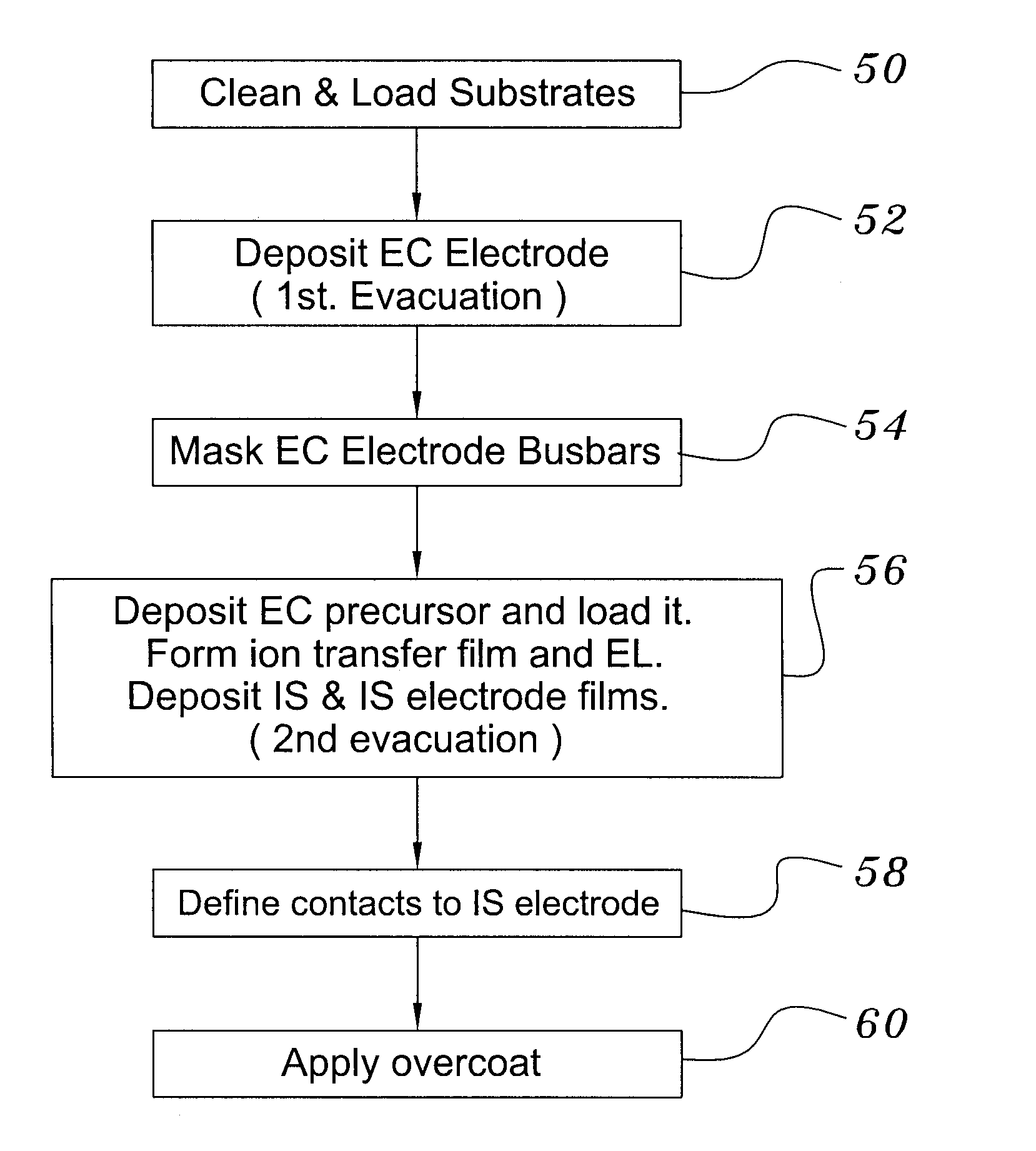
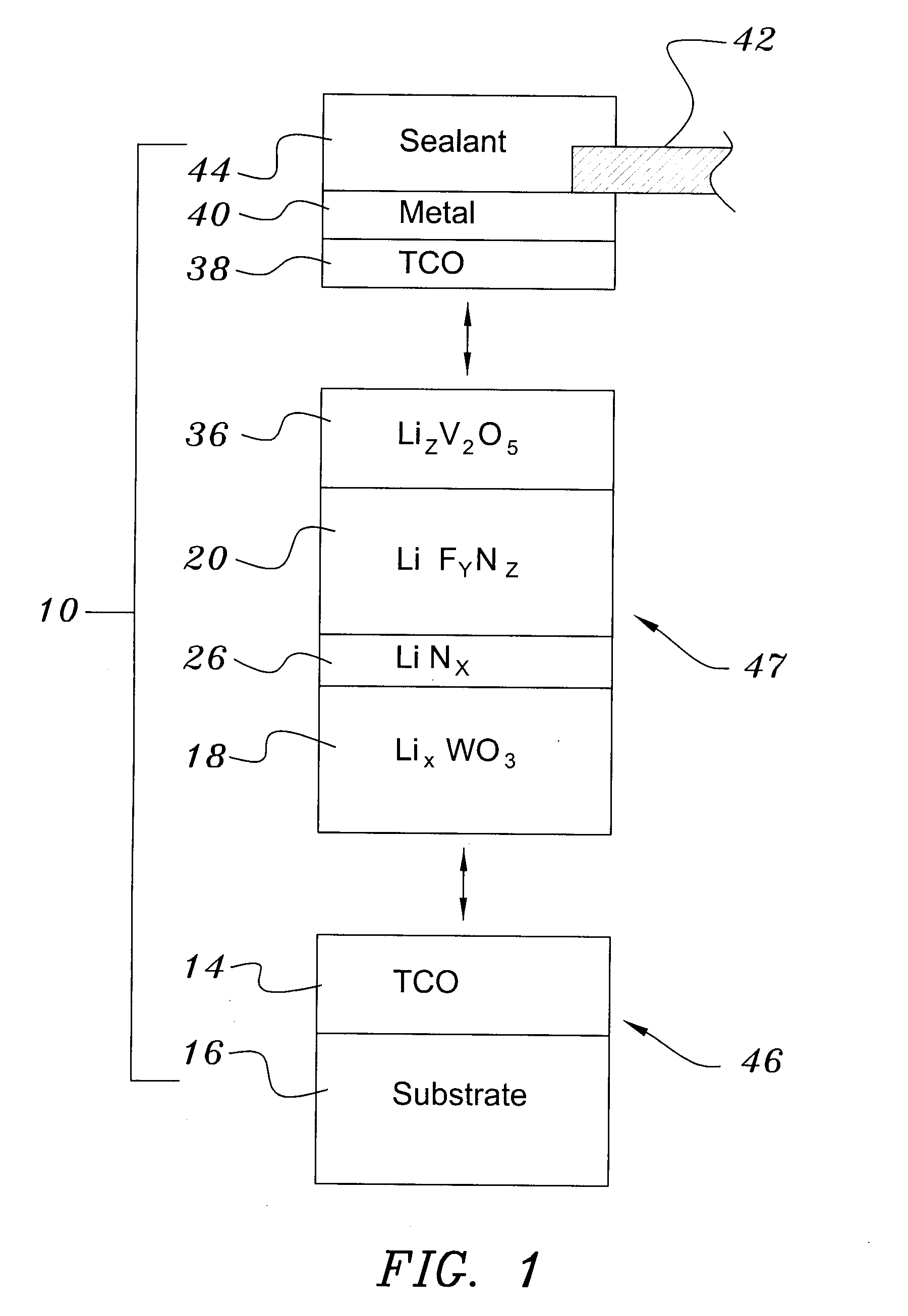
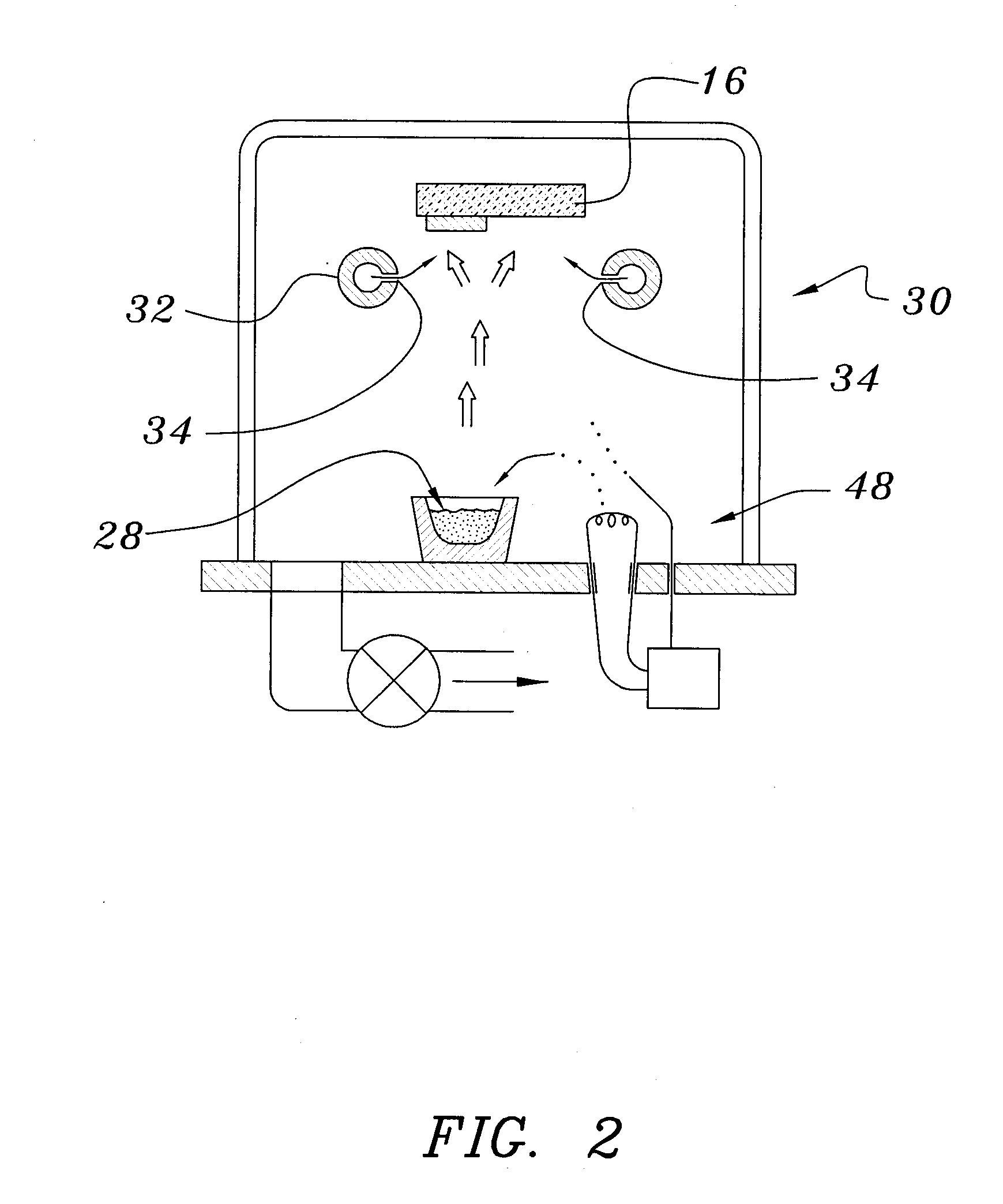
ActiveUS20070292606A1Solve many processesReduce usageCoatingsSpecial surfacesEvaporationElectrochromism
A method of preparing an electrochromic device involves forming multiple layers of selected materials on a substrate in a vacuum processing chamber. A first of these layers is an electrode layer deposited directly on the substrate and used for making contact to a subsequently deposited precursor film, preferably tungsten oxide, from which an electrochromic layer is formed by lithium loading in the presence of ionized nitrogen. This not only forms the electrochromic layer by diffusion of the lithium into the tungsten oxide, but also forms a thin lithium nitride ion transfer layer on the then exposed surface. Subsequently, a lithium fluoro-nitride electrolyte layer is formed on the ion transfer layer by evaporation from a lithium fluoride source in the presence of ionized nitrogen. An ion storage layer, which may be a vanadium oxide and a transparent second electrode layer are subsequently vacuum deposited.
Owner:ECLIPSE ENERGY SYST
Electrochromic device with self-forming ion transfer layer and lithium-fluoro-nitride electrolyte
ActiveUS7265891B1Solve many processesReduce usageElectrolytic capacitorsNon-linear opticsEvaporationElectrochromism
An electrochromic device is prepared by forming multiple layers of selected materials on a substrate in a vacuum processing chamber. A first of these layers is an electrode layer deposited directly on the substrate and used for making contact to a subsequently deposited precursor film, preferably tungsten oxide, from which an electrochromic layer is formed by lithium loading in the presence of ionized nitrogen. This not only forms the electrochromic layer by diffusion of the lithium into the tungsten oxide, but also forms a thin lithium nitride ion transfer layer on the then exposed surface. Subsequently, a lithium fluoro-nitride electrolyte layer is formed on the ion transfer layer by evaporation from a lithium fluoride source in the presence of ionized nitrogen. An ion storage layer, which may be a vanadium oxide and a transparent second electrode layer are subsequently vacuum deposited.
Owner:ECLIPSE ENERGY SYST
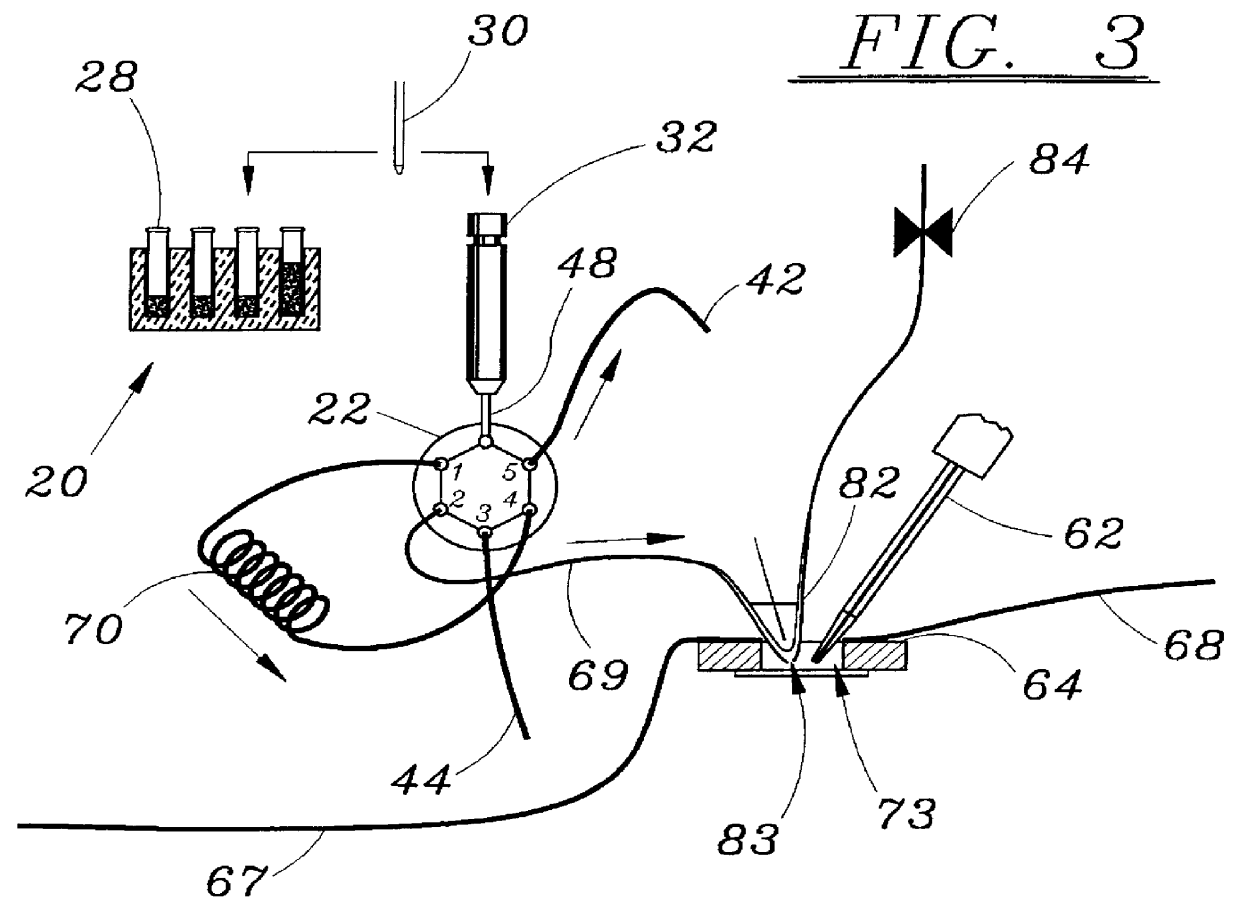
MALDI/LDI source
InactiveUS20070114437A1Efficient collectionParticle separator tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansAnalyteIon transfer
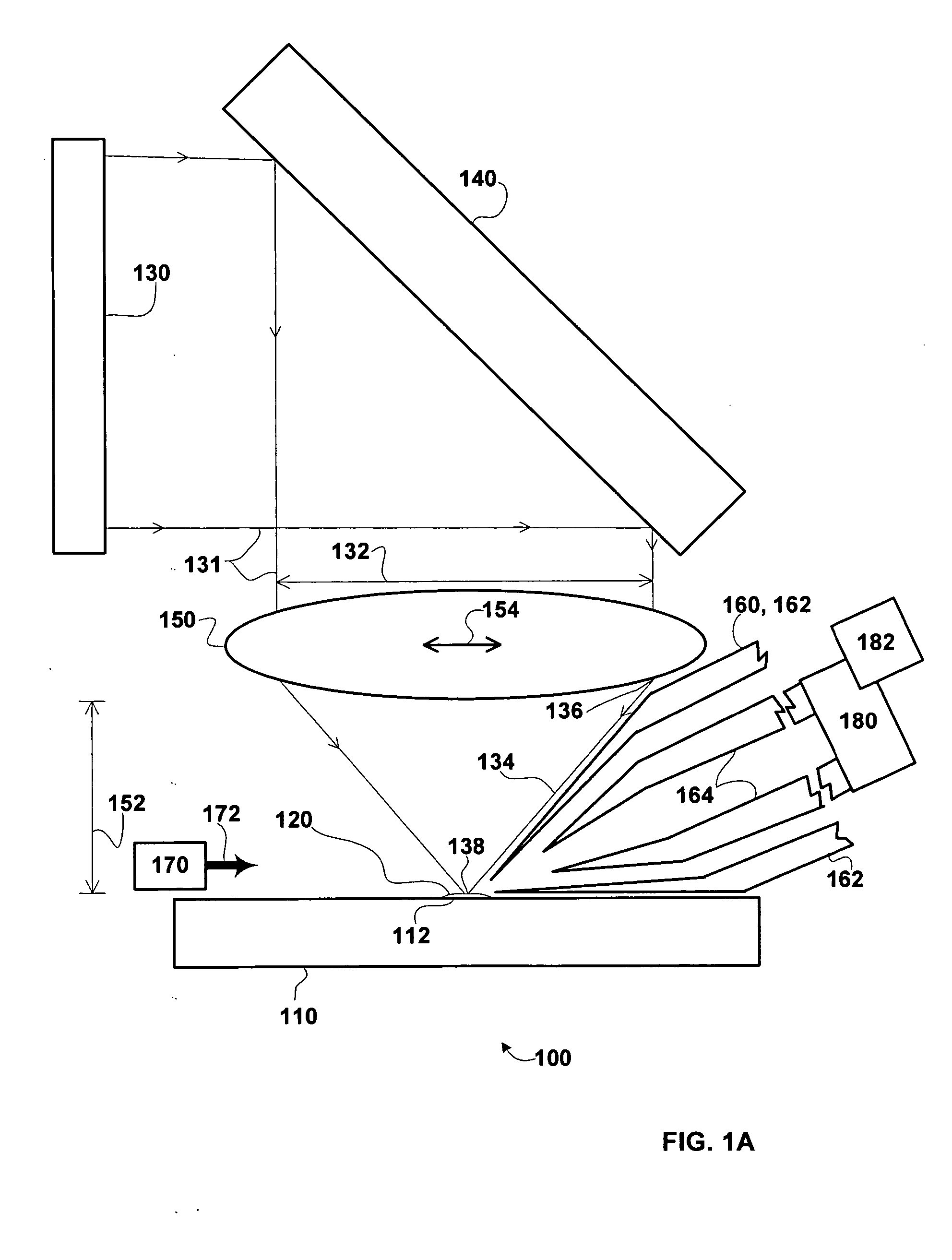
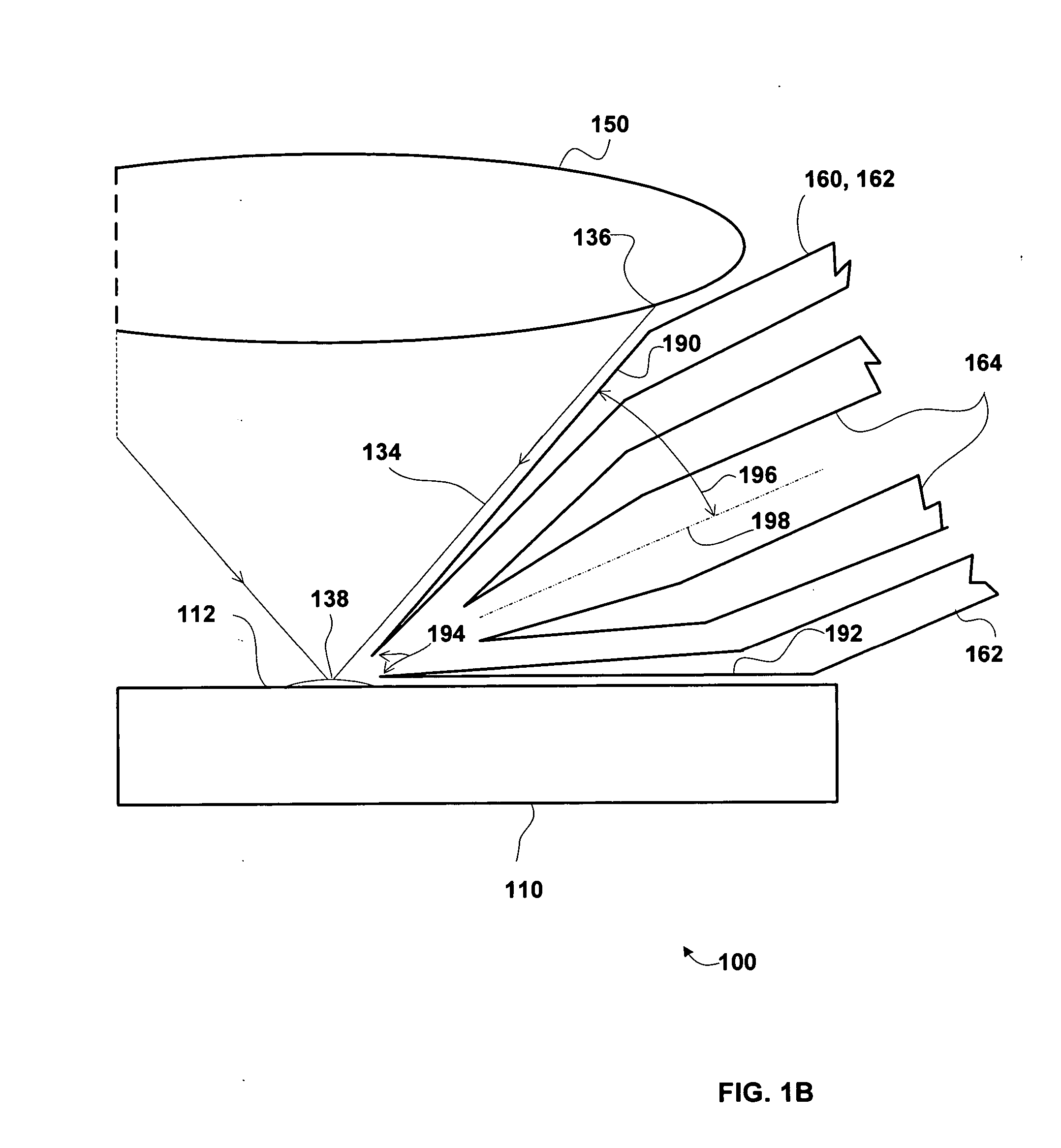
A MALDI / LDI source includes an ion collection device, e.g., a skimmer, orifice, mass analyzer, ion transfer optics and / or ion guide, configured for use with a short focal length lens with a large aperture. In some embodiments, the ion collection device includes an outer edge that can be disposed approximately parallel to a beam envelope between a lens and a focal point positioned at a MALDI / LDI sample. This configuration of the outer edge allows the ion collection device to be placed in close proximity to the focal point. This placement results in favorable collection efficiencies of laser desorbed analyte from the MALDI / LDI sample.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
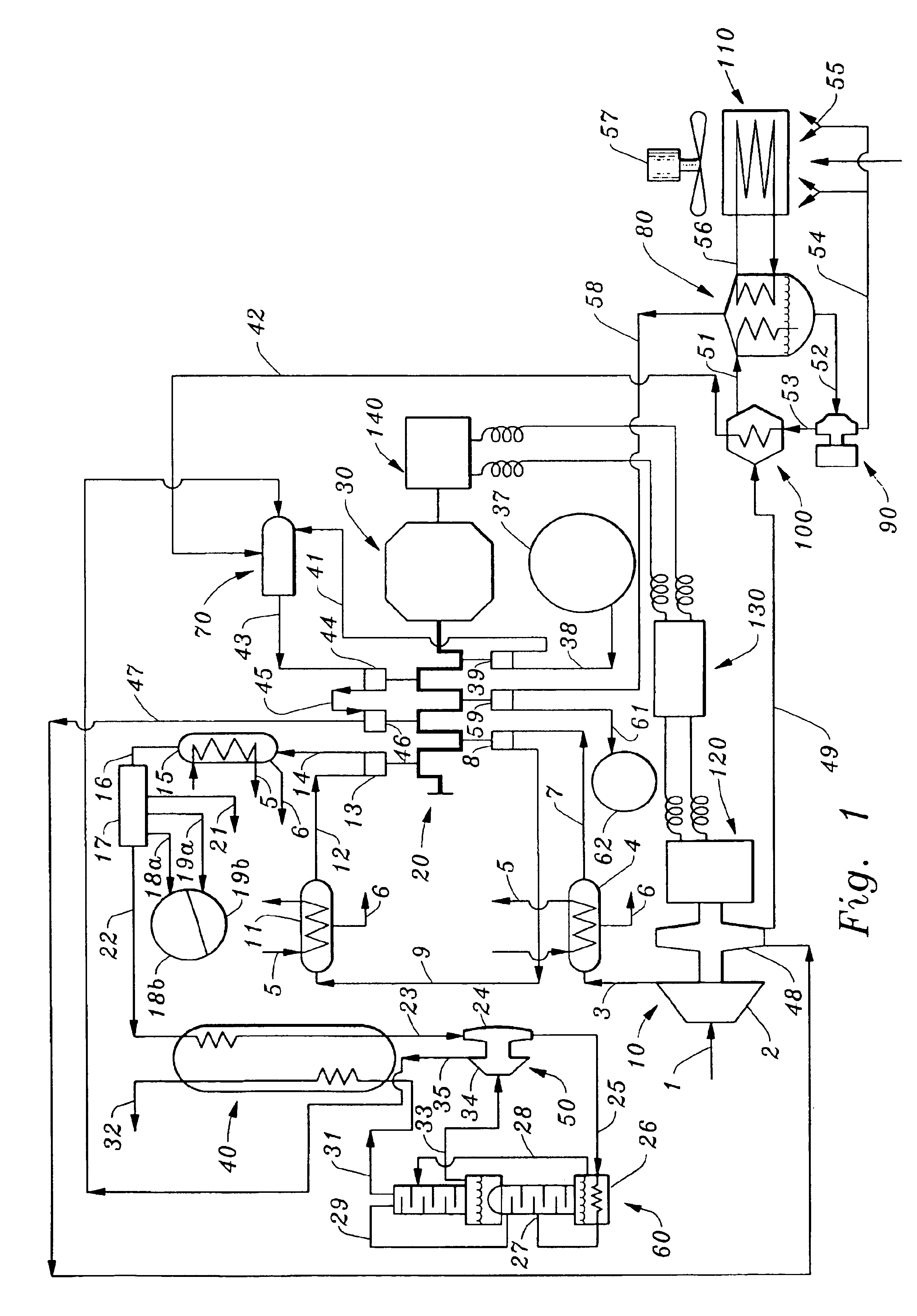
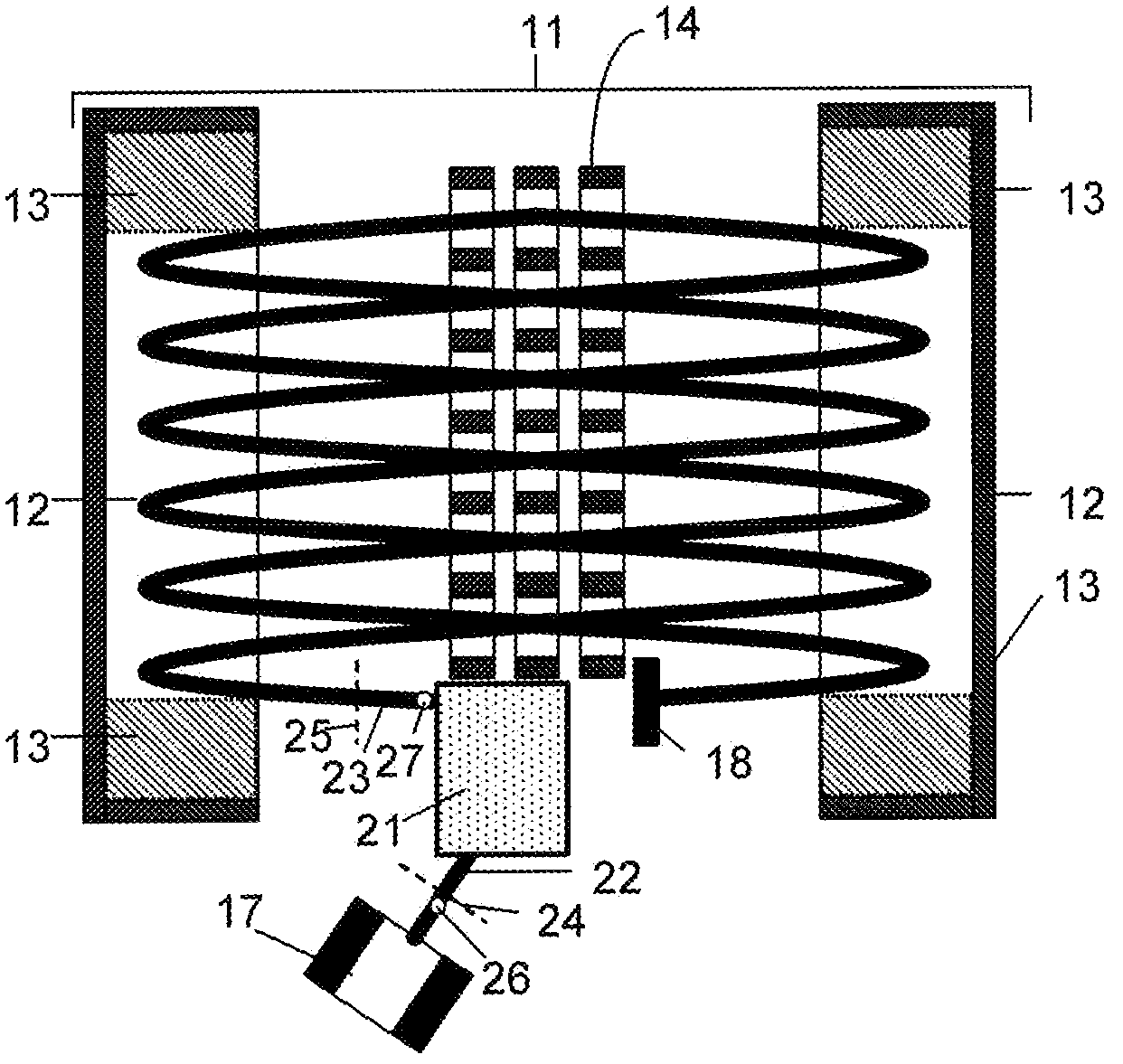
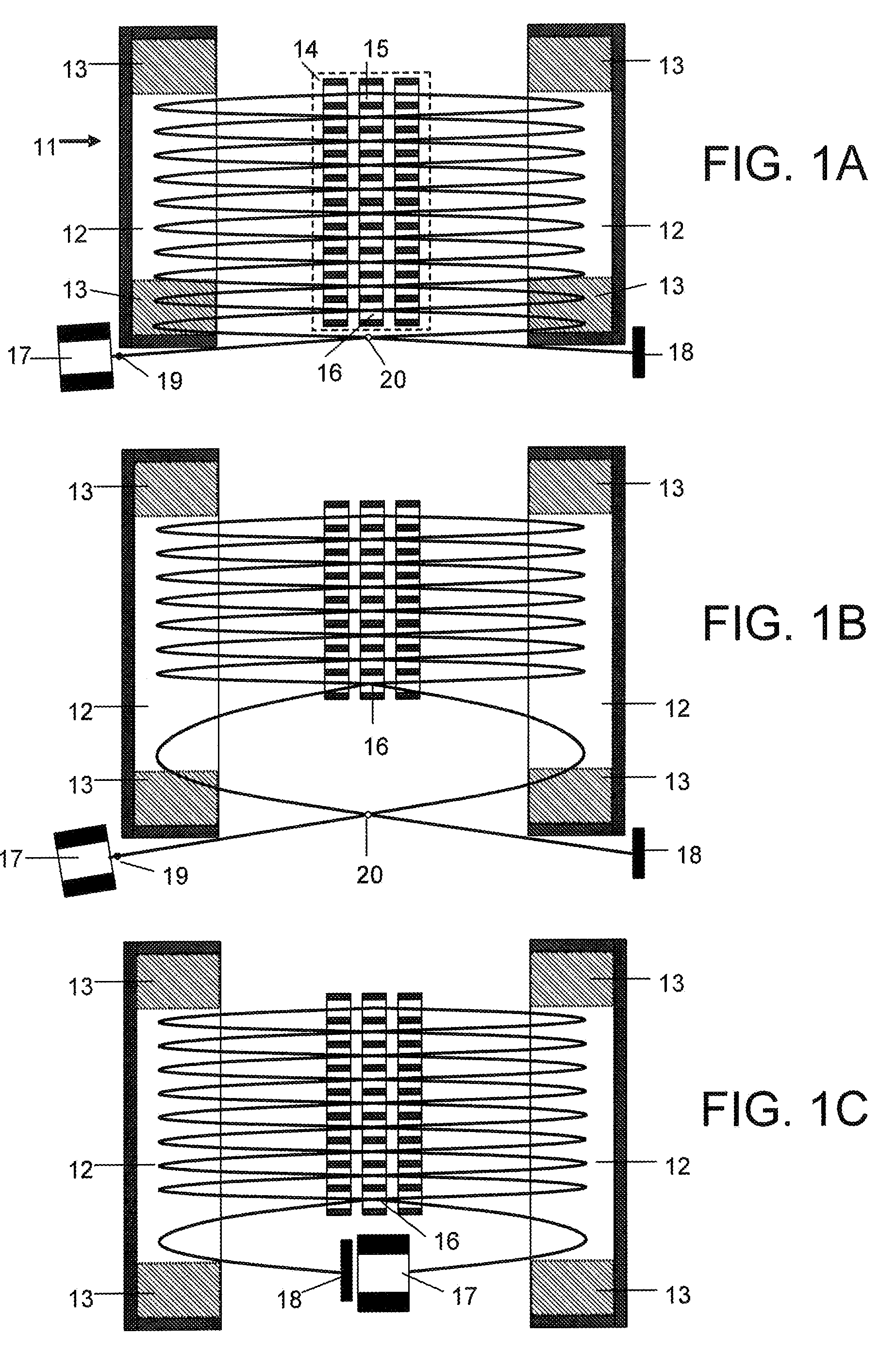
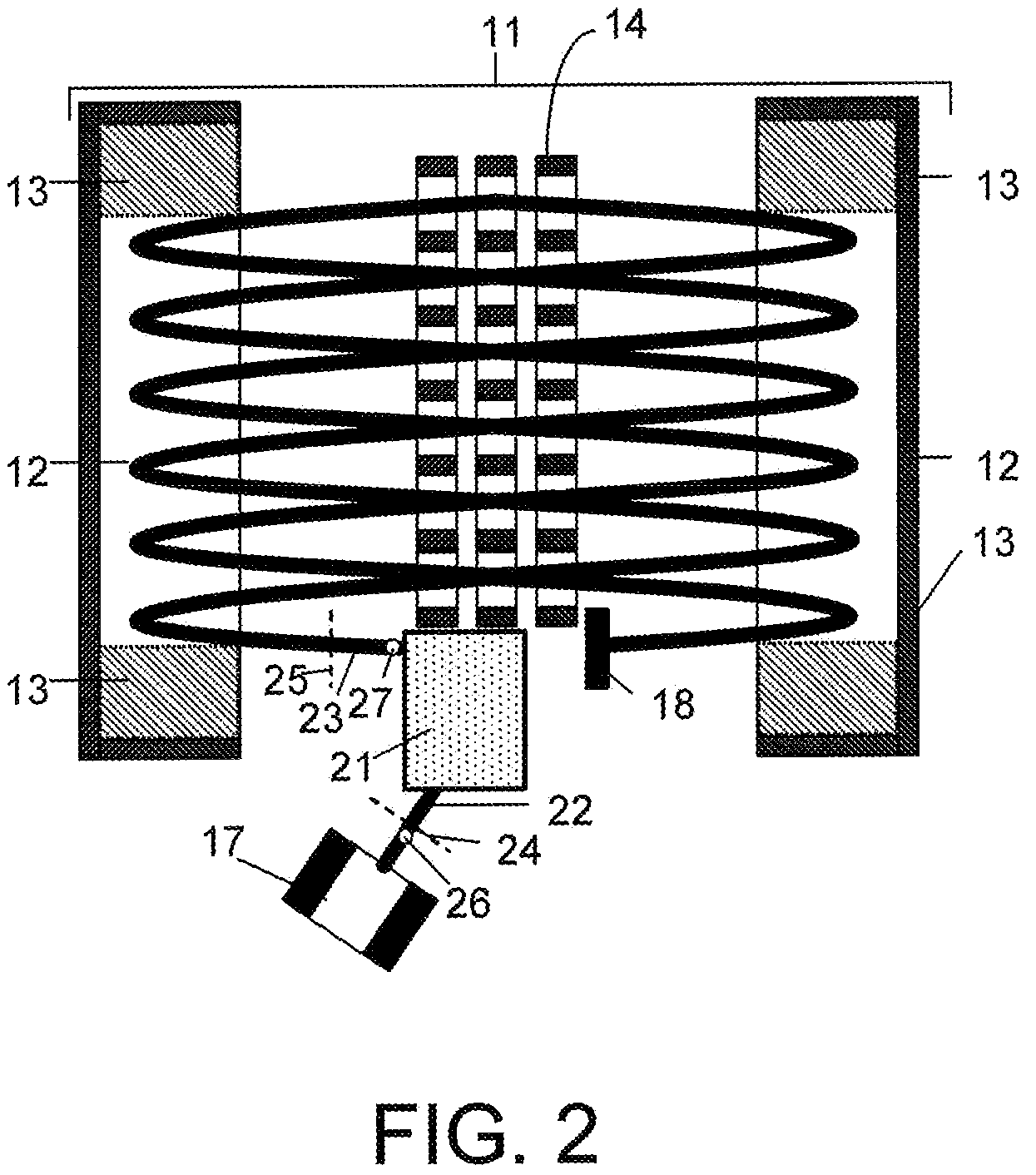
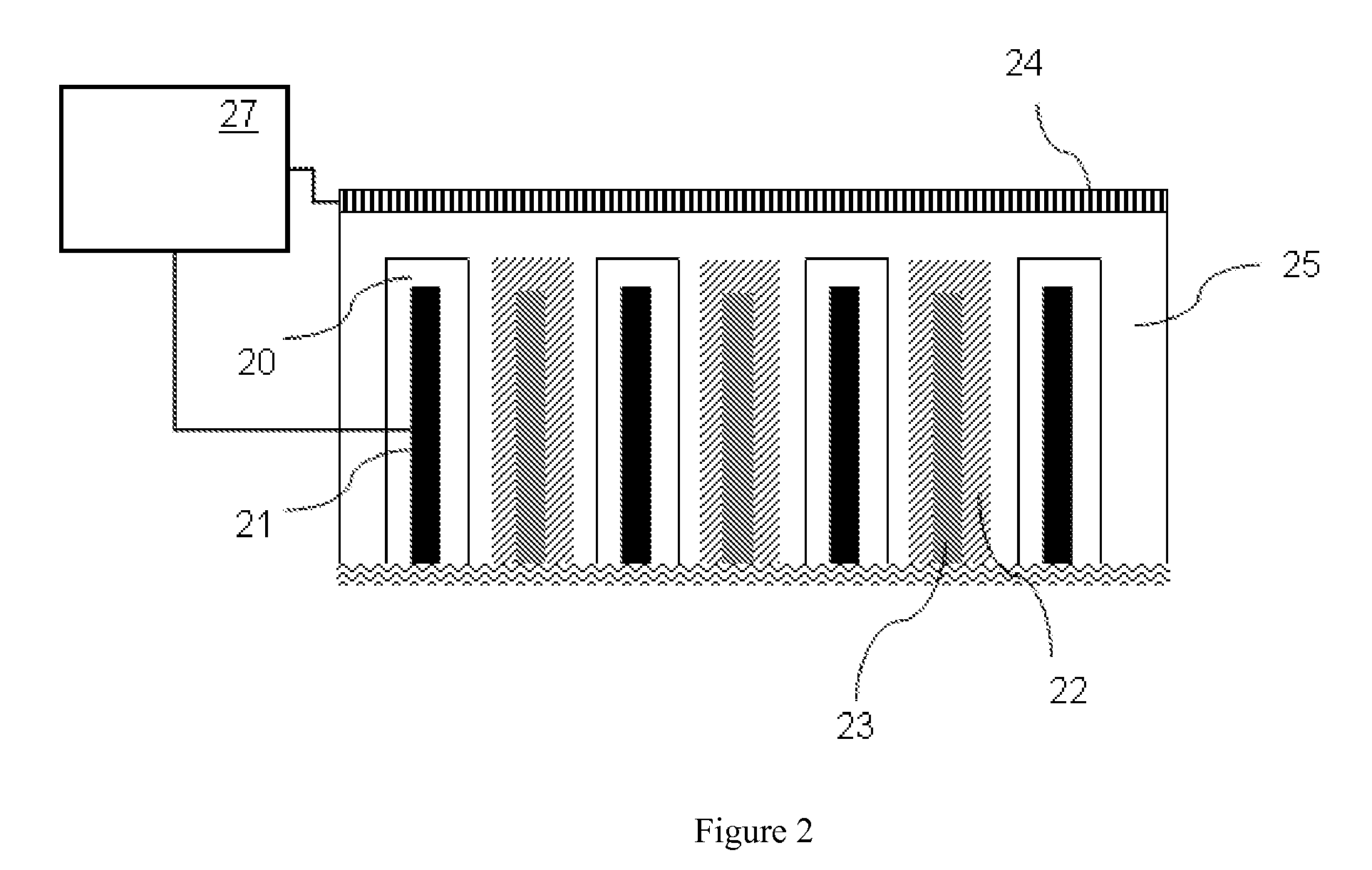
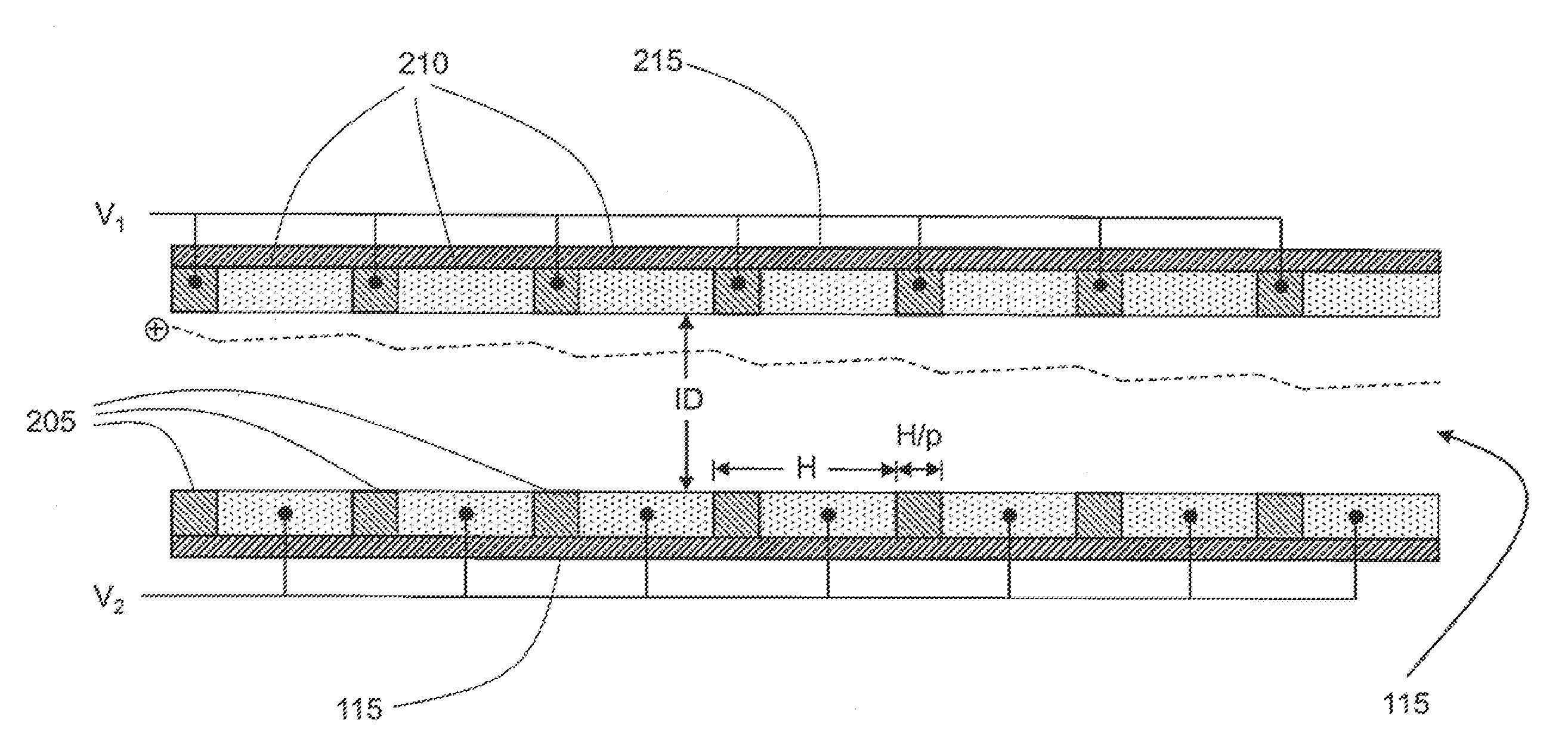
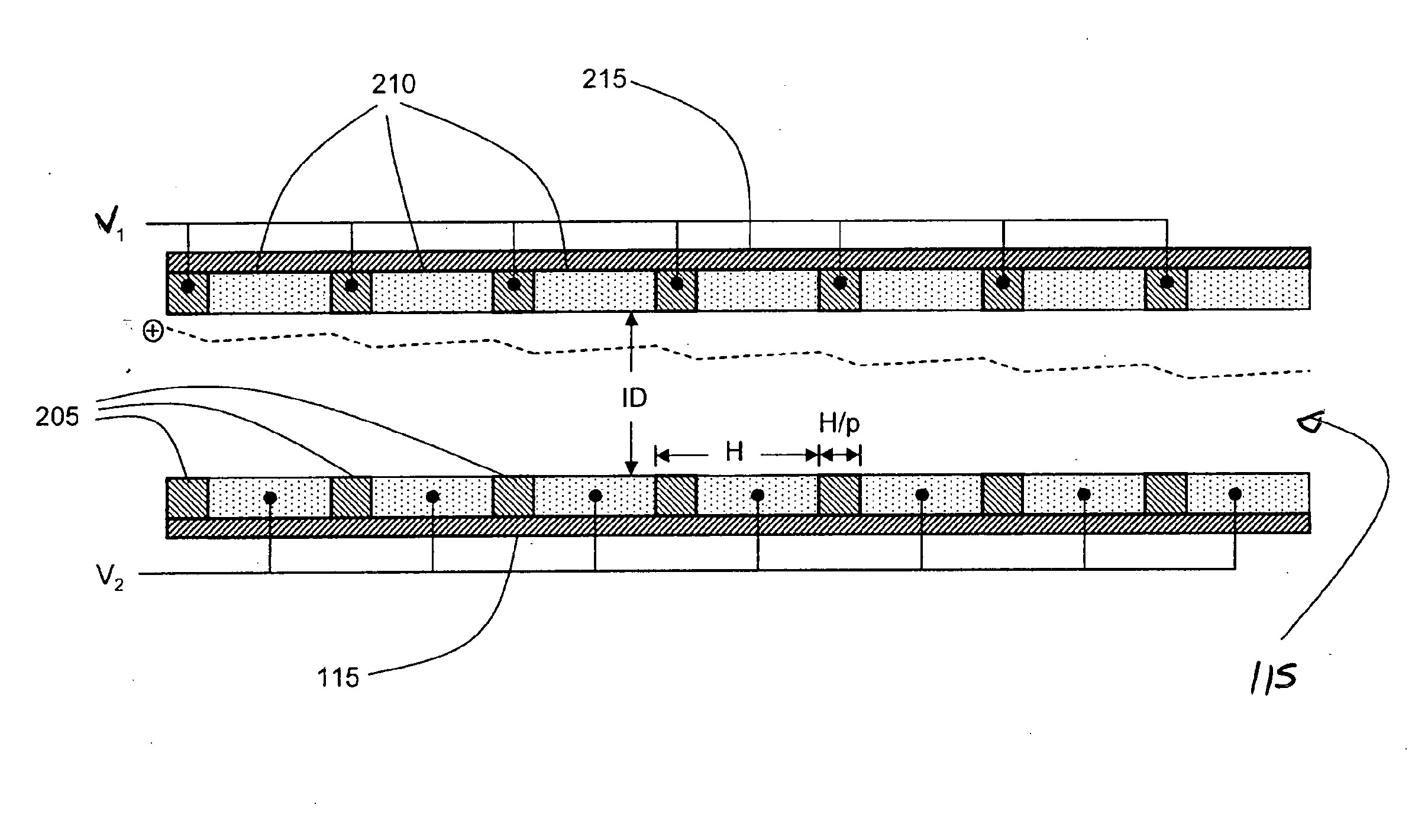
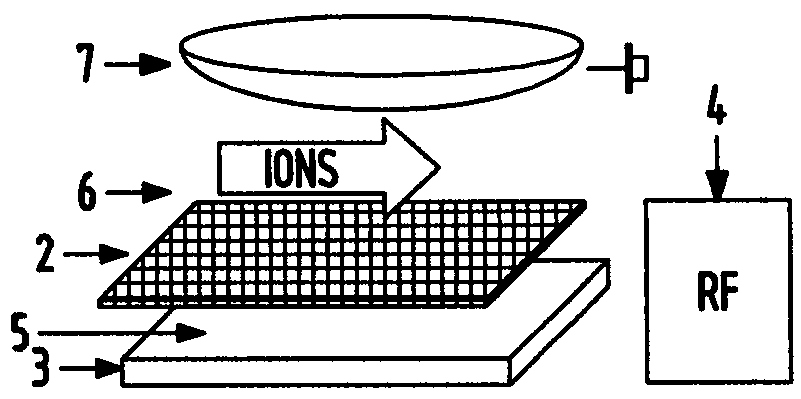
Ion transfer tube with spatially alternating DC fields
An ion transfer arrangement for transporting ions between higher and lower pressure regions of a mass spectrometer includes an electrode assembly (120) with a first plurality of ring electrodes (205) arranged in alternating relation with a second plurality of ring electrodes (210). The first plurality of ring electrodes (205) are narrower than the second plurality of ring electrodes (210) in a longitudinal direction, but the first plurality of ring electrodes have a relatively high magnitude voltage of a first polarity applied to them whereas the second plurality of ring electrodes (210) have a relatively lower magnitude voltage applied to them, of opposing polarity to that applied to the first set of ring electrodes (205). In this manner, ions passing through the ion transfer arrangement experience spatially alternating asymmetric electric fields that tend to focus ions away from the inner surface of the channel wall and towards the channel plane or axis of symmetry.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
Ionization source chamber and ion beam delivery system for mass spectrometry
InactiveUS6809312B1Time-of-flight spectrometersIon sources/gunsMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryIon transfer
The present invention is for an improved ionization source chamber and ion beam delivery system which includes a vacuum chamber and flange arrangement, for mounting the means for transferring sample ions from the port to a mass analyzer and for mounting the ion production means, respectively. The flange containing the ion production means may be attached to the vacuum chamber via a hinge such that the flange can open as a door to provide easy access to the ion transfer electrodes in the vacuum chamber. Further, a variety of different ion production means may be mounted on the flange of the ionization source chamber of the present invention. As a result, any ion production means may be used with the present invention by substituting a flange which includes the desired ion production means.
Owner:BRUKER SCI LLC
Ion transfer from multipole ion guides into multipole ion guides and ion traps
InactiveUS6121607AReduce the overall diameterImprove ion transfer efficiencyStability-of-path spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionIon trap mass spectrometryReduced size
A multipole ion guide is configured to improve the transmission efficiency of ions which traverse the length of one ion guide and enter either another multipole ion guide such as a quadrupole mass analyzer or a three dimensional ion trap. The ion transfer multipole ion guide radial dimensions are reduced such that the pole assembly and an appropriately shaped exit lens can be positioned within a portion of the internal space defined by the larger radius second multipole ion guide poles. Ions exiting the first ion guide of reduced size find themselves inside the second ion guide close to the centerline. In this manner ions can be efficiently transferred from one ion guide to another, even for those ions with low kinetic energies. In a second embodiment of the invention, the exit region of a multipole ion guide is configured such that the multipole ion guide poles can be extended into a counterbore of a three dimensional ion trap end cap electrode. With this configuration, ions (including those with low kinetic energies) can be transferred into a three dimensional ion trap with increased trapping efficiency.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
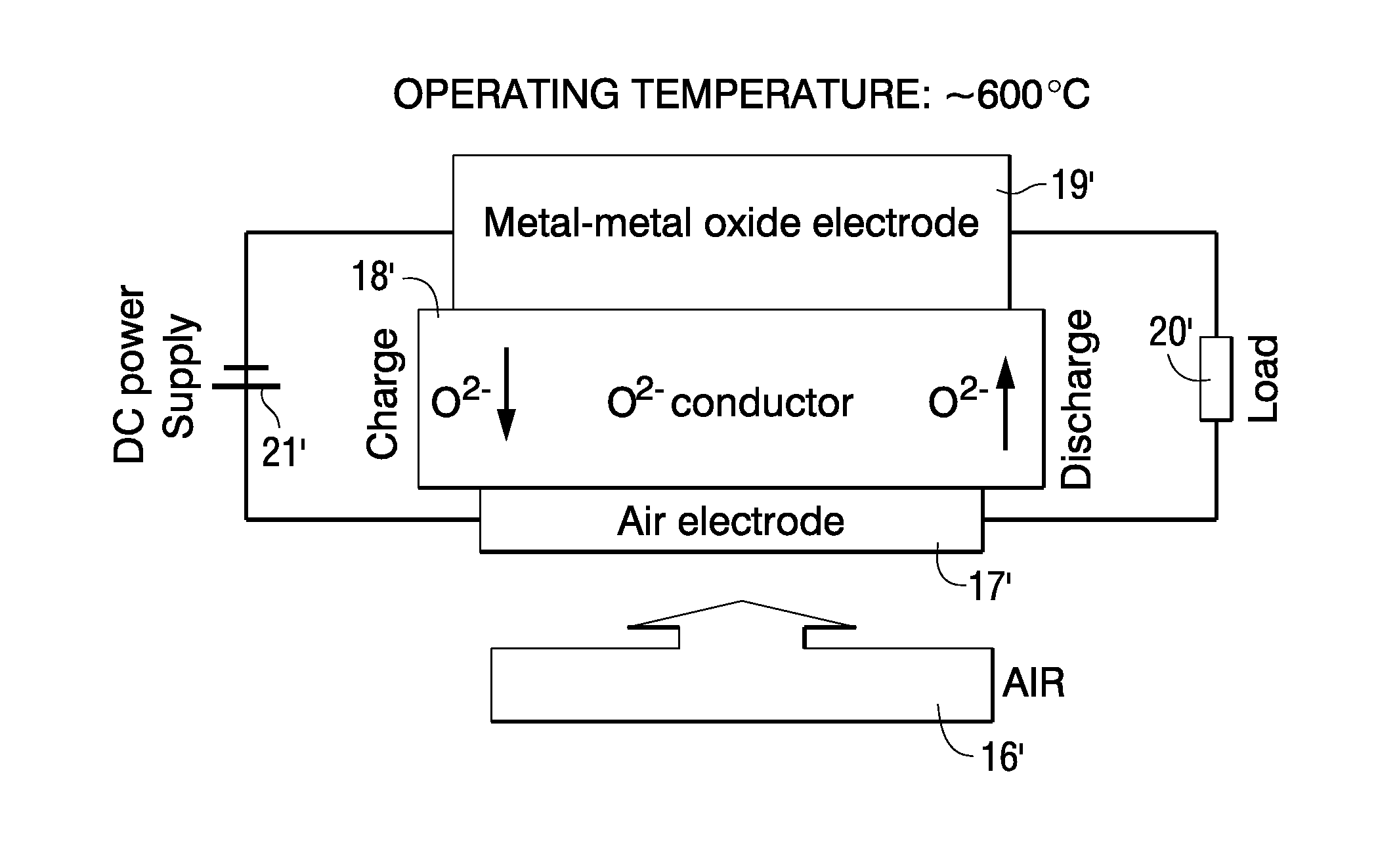
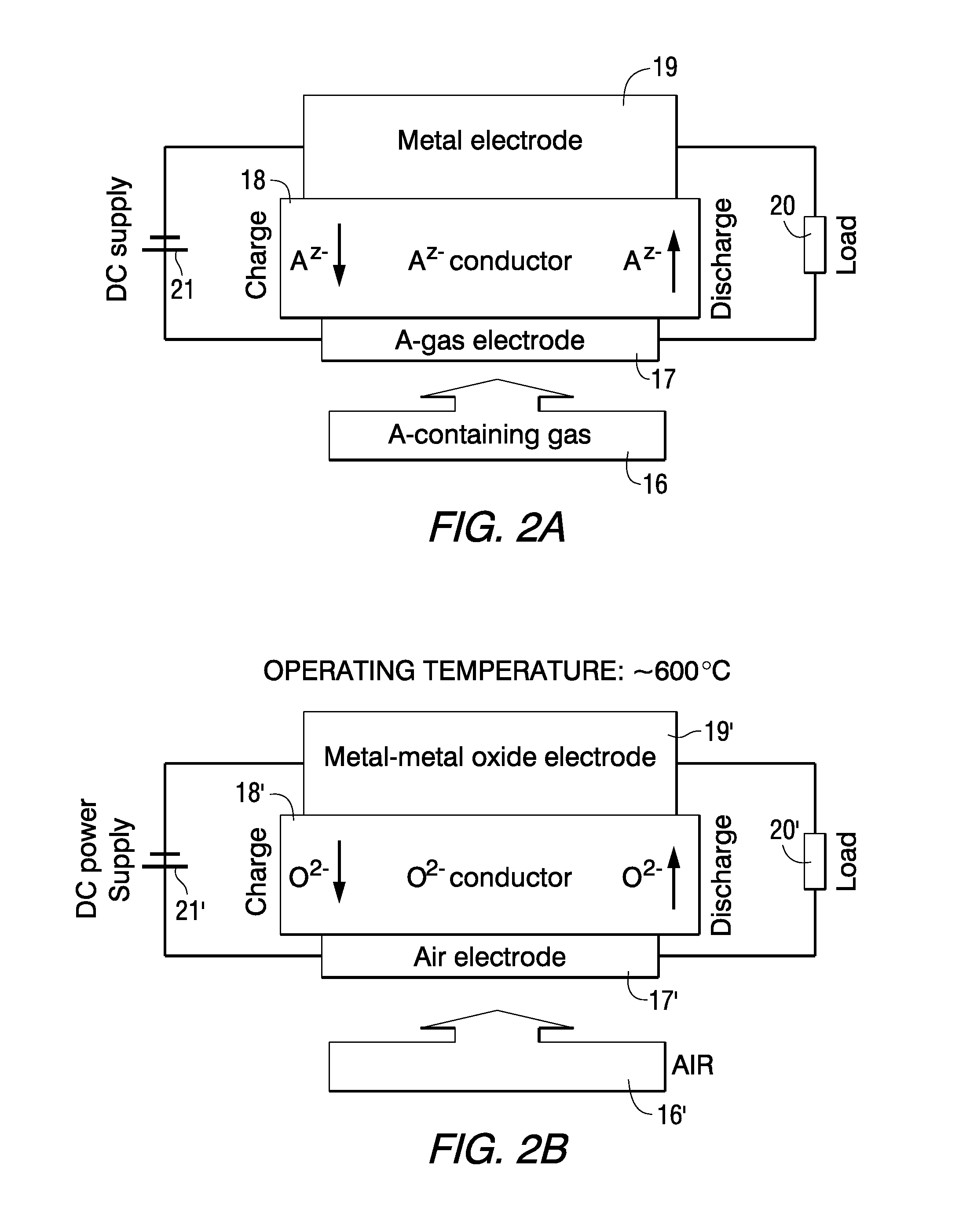
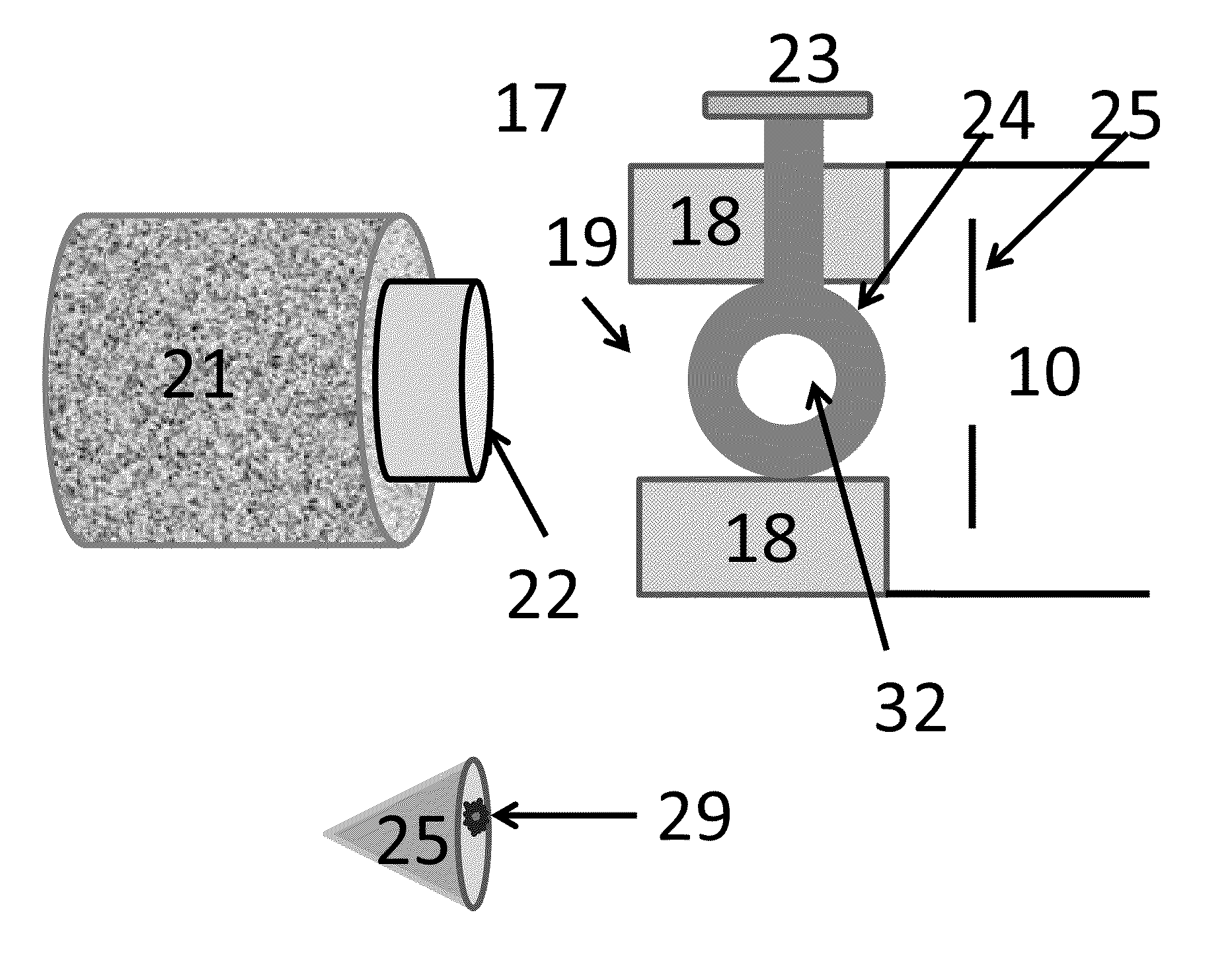
Electrical Storage Device Including Oxide-ion Battery Cell Bank and Module Configurations
InactiveUS20110033769A1Easy to operateFuel and primary cellsSolid electrolytesIon transferEngineering
A rechargeable electrical storage device is disclosed, where one embodiment utilizes an anion (“A”) conducting electrolyte (18) and ion transfer between two electrodes (17, 19) where one electrode is preferably a metal electrode 19 that contains a mixture of metal and metal oxide, so that during operation, oxide-ions shuttle between the two electrodes (17, 19) in charging and discharging modes and the metal electrode (19) serves as a reservoir of species relevant to anion “A”.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
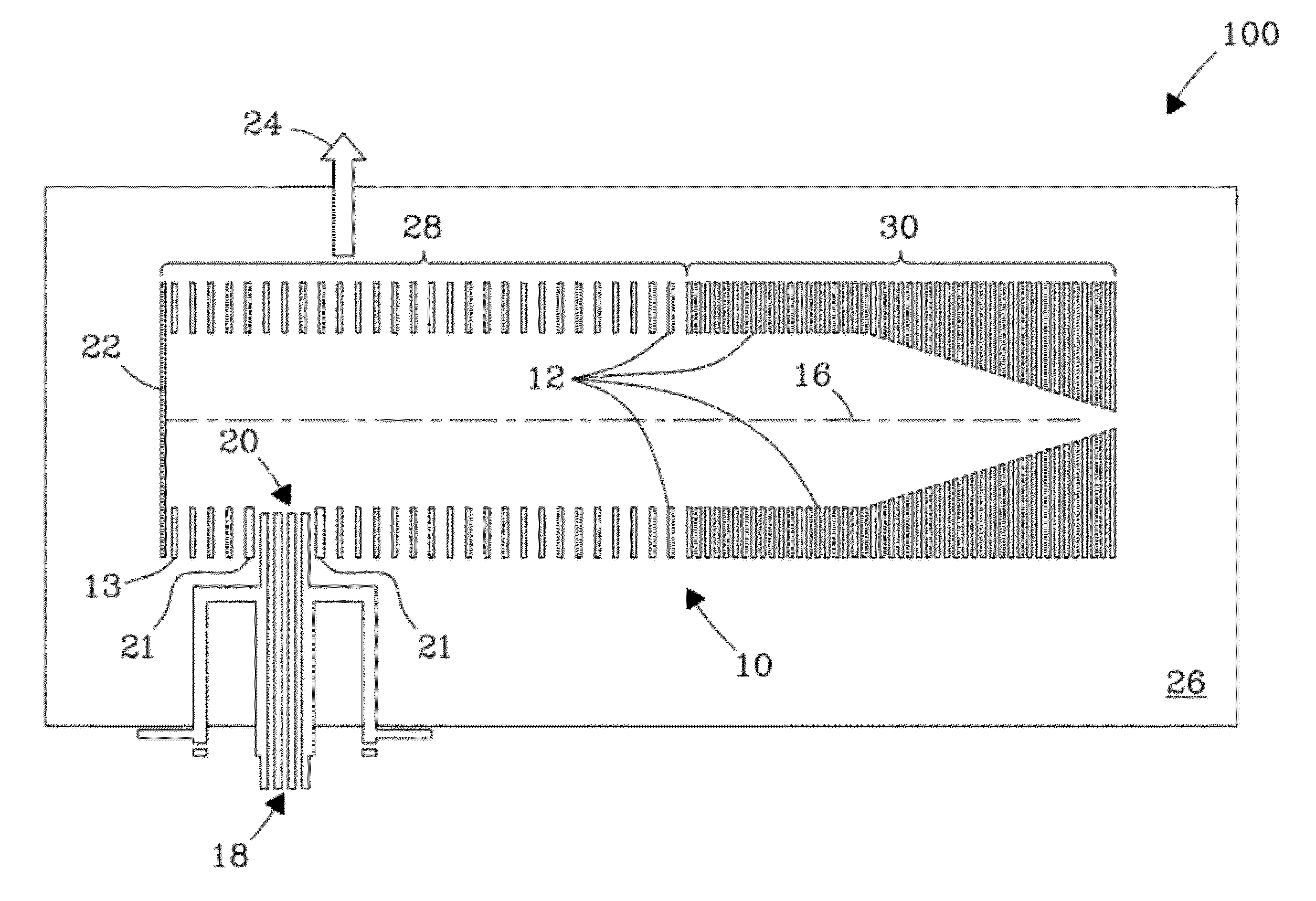
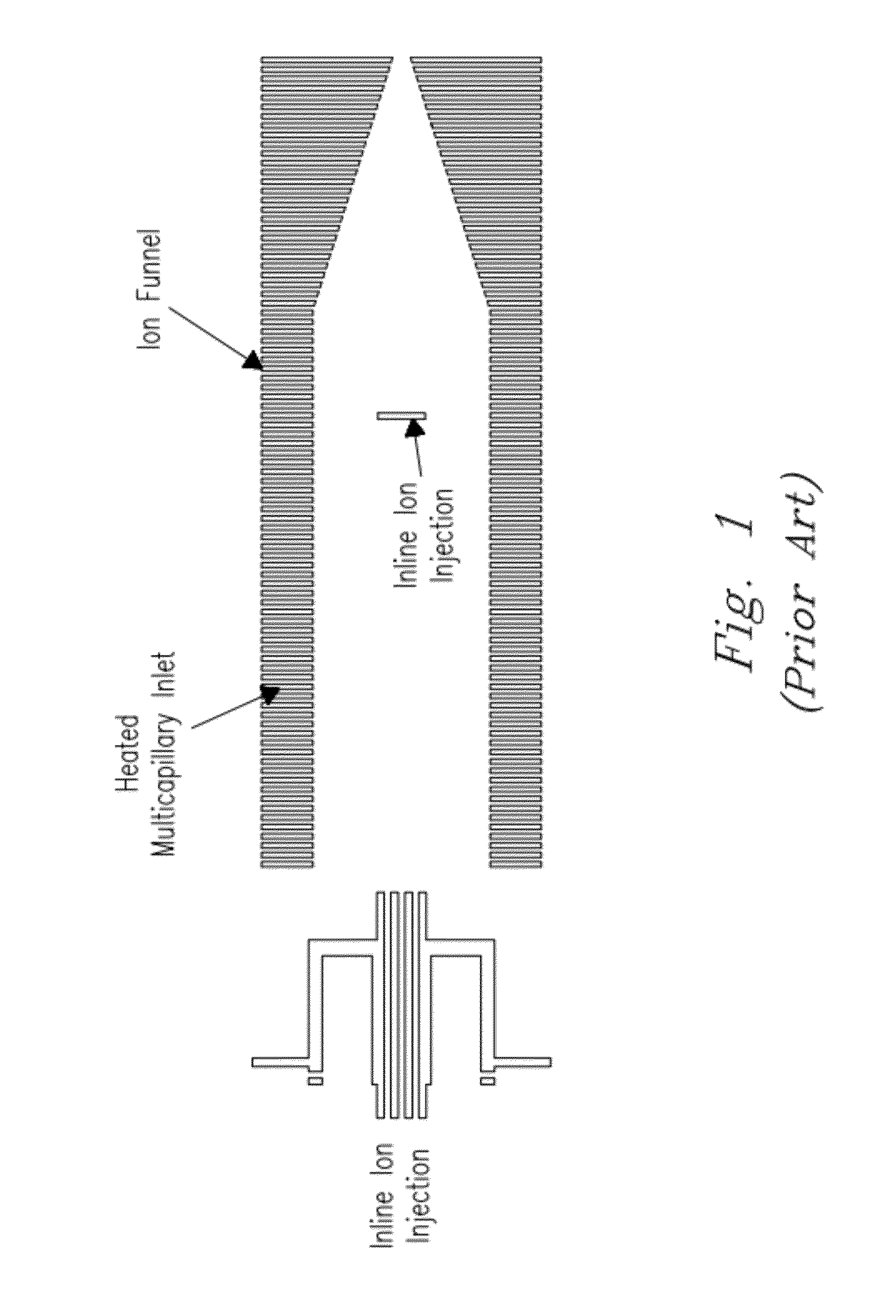
Orthogonal ion injection apparatus and process
ActiveUS20120298853A1High sensitivityReduce noiseIsotope separationTube electrostatic deflectionNoise levelIon transfer
An orthogonal ion injection apparatus and process are described in which ions are directly injected into an ion guide orthogonal to the ion guide axis through an inlet opening located on a side of the ion guide. The end of the heated capillary is placed inside the ion guide such that the ions are directly injected into DC and RF fields inside the ion guide, which efficiently confines ions inside the ion guide. Liquid droplets created by the ionization source that are carried through the capillary into the ion guide are removed from the ion guide by a strong directional gas flow through an inlet opening on the opposite side of the ion guide. Strong DC and RF fields divert ions into the ion guide. In-guide orthogonal injection yields a noise level that is a factor of 1.5 to 2 lower than conventional inline injection known in the art. Signal intensities for low m / z ions are greater compared to convention inline injection under the same processing conditions.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Apparatus and method for focusing ions and charged particles at atmospheric pressure
InactiveUS20020011560A1Samples introduction/extractionIsotope separationInductively coupled plasmaElectrospray
Improvements have been made for collection and focusing of ions generated from atmospheric pressure sources such as electrospray, atmospheric pressure chemical ionization, inductively coupled plasma, discharge, photoionization and atmospheric pressure matrix assisted laser desorption ionization. A high transmission electro-optical surface is placed between the source regions and the focusing regions to optimize the field geometries and strengths in each respective region. Compression ratios of greater than 5000 are capable of transferring virtually all ions from large volume dispersive ion regions into ion beam cross-sections of less than 1 mm. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when coupled to atmospheric pressure ionization sources.
Owner:SHEEHAN EDWARD W +1
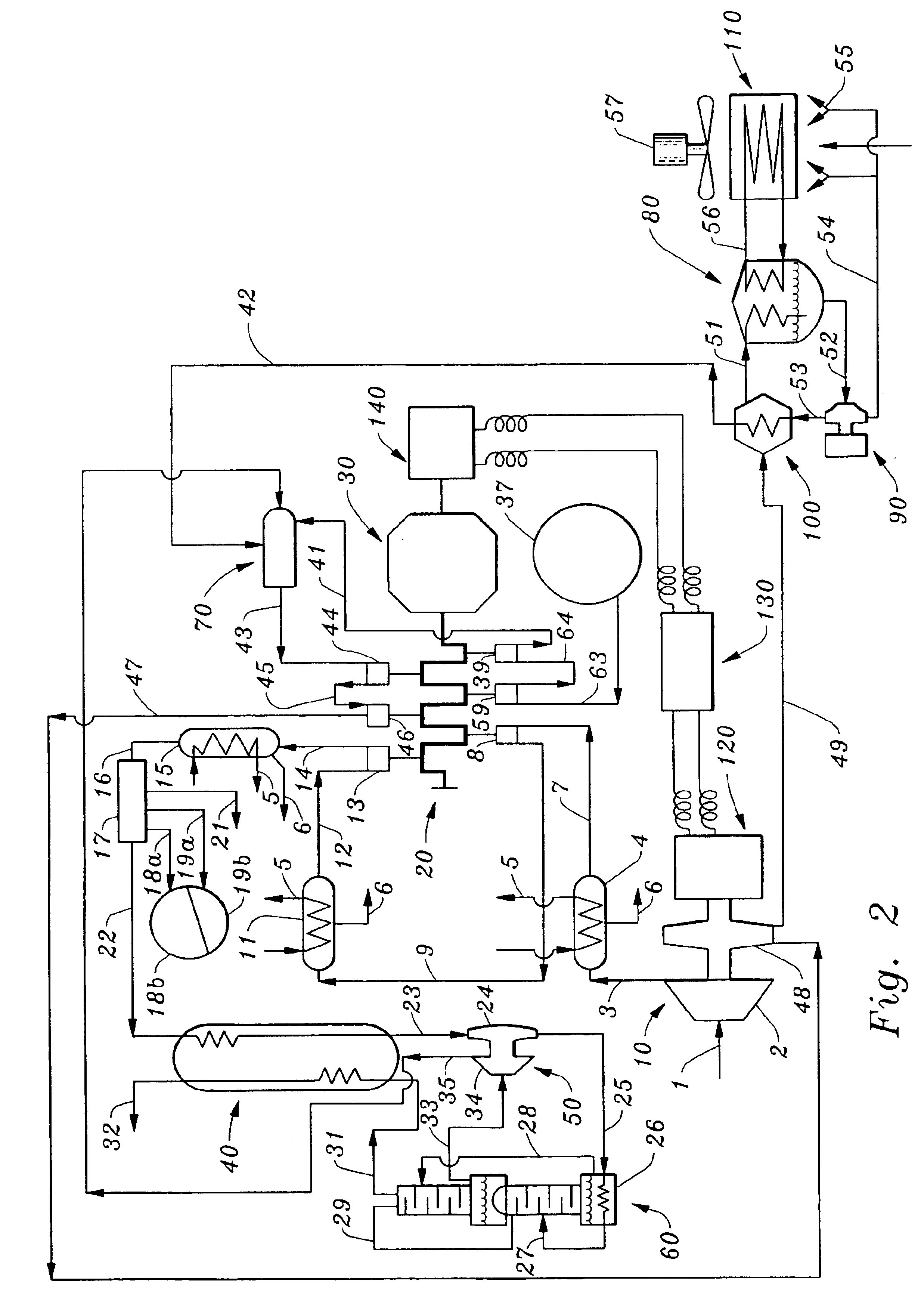
Ion Transfer Tube with Spatially Alternating DC Fields
ActiveUS20090321655A1Thermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersAxis of symmetryElectrical polarity
An ion transfer arrangement for transporting ions between higher and lower pressure regions of a mass spectrometer includes an electrode assembly (120) with a first plurality of ring electrodes (205) arranged in alternating relation with a second plurality of ring electrodes (210). The first plurality of ring electrodes (205) are narrower than the second plurality of ring electrodes (210) in a longitudinal direction, but the first plurality of ring electrodes have a relatively high magnitude voltage of a first polarity applied to them whereas the second plurality of ring electrodes (210) have a relatively lower magnitude voltage applied to them, of opposing polarity to that applied to the first set of ring electrodes (205). In this manner, ions passing through the ion transfer arrangement experience spatially alternating asymmetric electric fields that tend to focus ions away from the inner surface of the channel wall and towards the channel plane or axis of symmetry.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
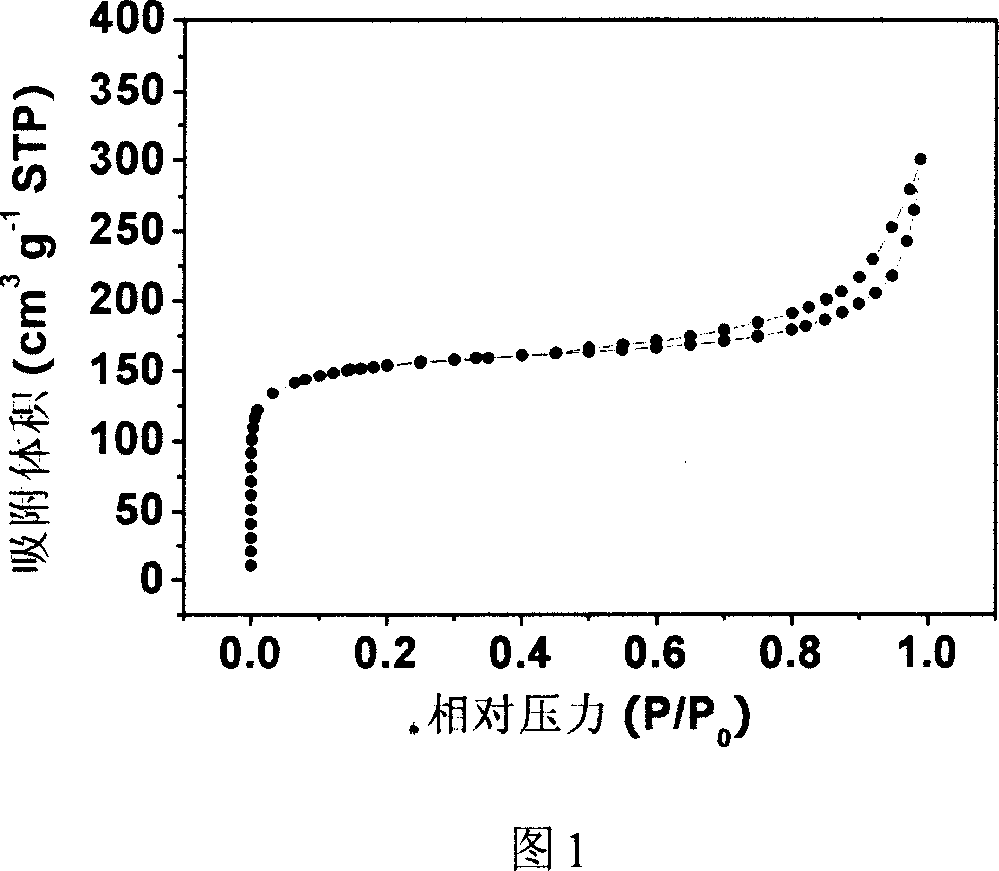
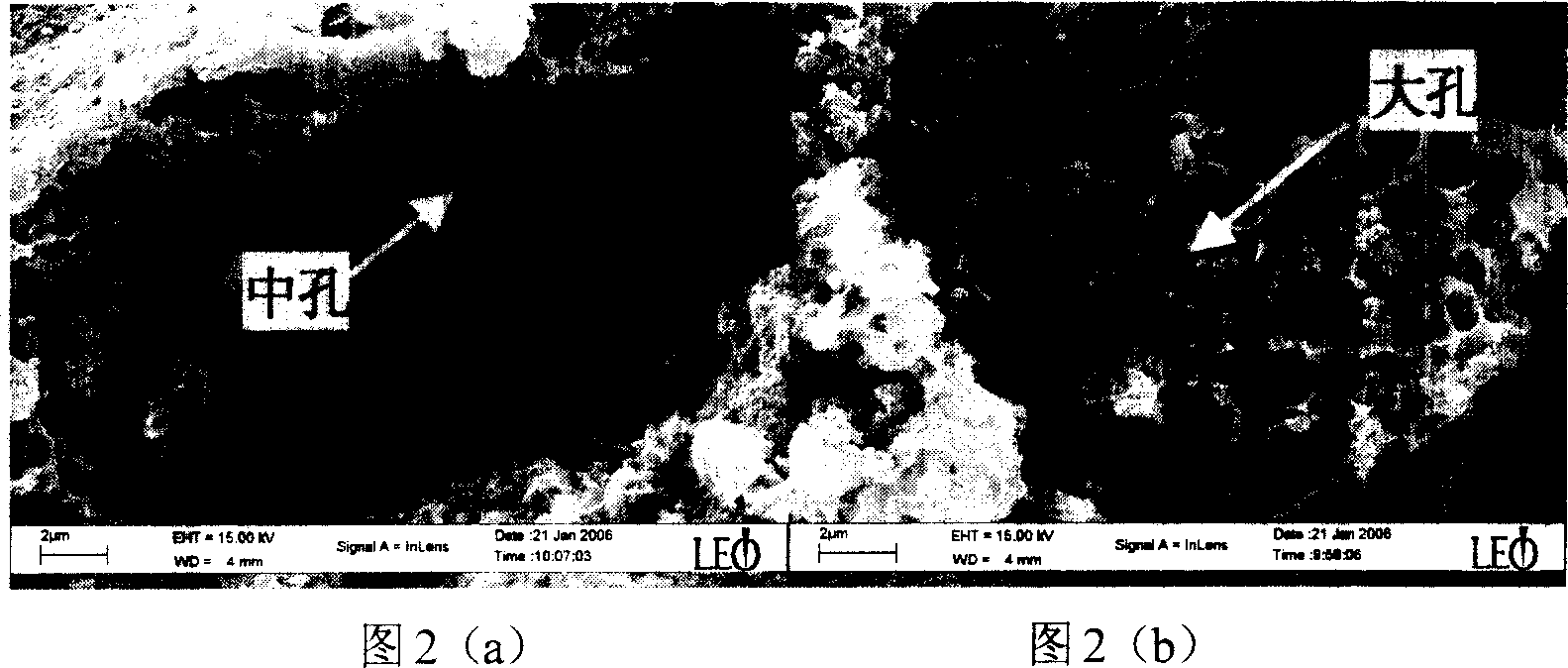
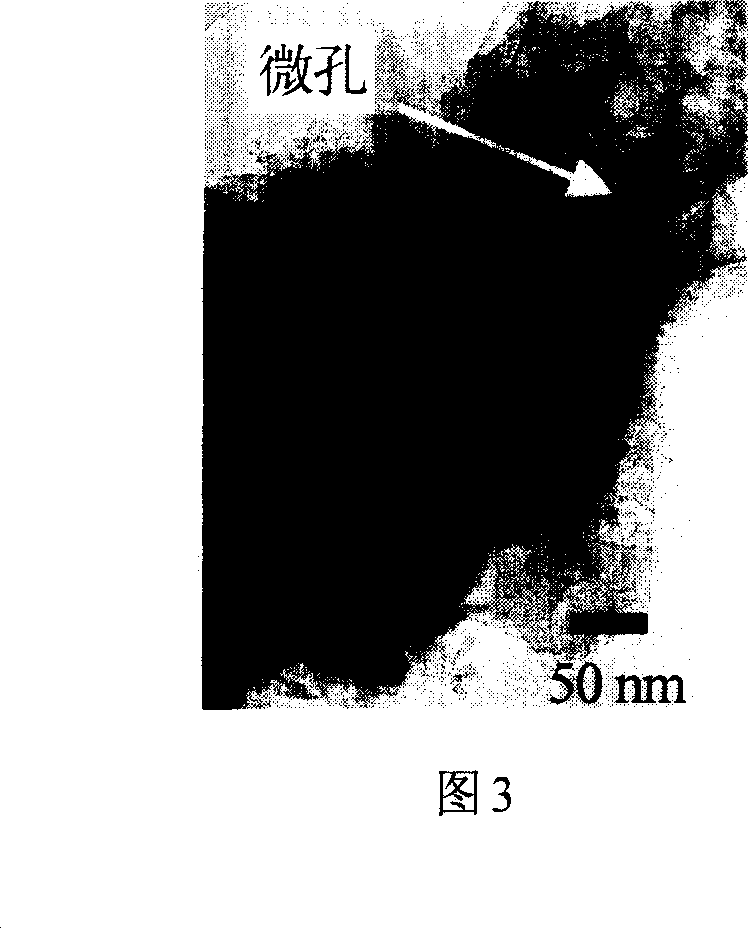
Layer combination controllable carbon material with nano pole of different scale, preparation method and application
The invention relates to a method for design advanced materials with nano-scaled structure and techniques for preparing same. In particular, the invention relates to a carbon material capable of controllable laminated combination with the nano-holes of variable sizes and preparation and application thereof. The method comprises the steps of: preparing metal oxide sol in the alkali solution system, which is then mixed with an alcohol solution of an alcohol-soluble resin; the oxide sol being used as the template and water being the resin precipitation agent during the process to directly prepare resin / oxide sol composite system. After solvent removal, carbonization, activation and template removal processes, the carbon material with laminated nano-holes combination is prepared which is of controllable micro-holes proportion, controllable medium-holes aperture and proportion, controllable big-holes aperture and propotion and concentrated distribution of medium-holes and big-holes apertures. The carbon material capable of controllable laminated combination with the nano-holes of variable sizes prepared in the invention is characterized in laminated holes structure, excellent ion transfer performances and high electrochemical active specific surface area and the material is expected to be used as high energy density high power density electrochemical capacitor used electrode material.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microperfusion chamber assembly with base comprising silver chloride coated silver
InactiveUS6117291AImprove throughputLower requirementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAutosamplerIon transfer
Apparatus for carrying out patch clamp technique utilized in studying the effect of certain materials on ion transfer channels in biological tissue, and more particularly patch clamp apparatus utilizing an autosampler, such as those utilized with HPLC apparatus, to provide high throughput, is disclosed. The invention additionally includes novel microperfusion chamber assemblies capable of utilizing only small amounts of material to be tested and only small amounts of liquid carrier, thereby enabling many tests to be completed in a short period of time. The invention more broadly relates to a novel electrophysiology drug handling and application set up for screening of chemical substances while providing high throughput and requiring only low volume of solutions and samples to be tested. The invention also comprises several novel procedures for utilizing the apparatus of the invention.
Owner:SOPHION BIOSCI
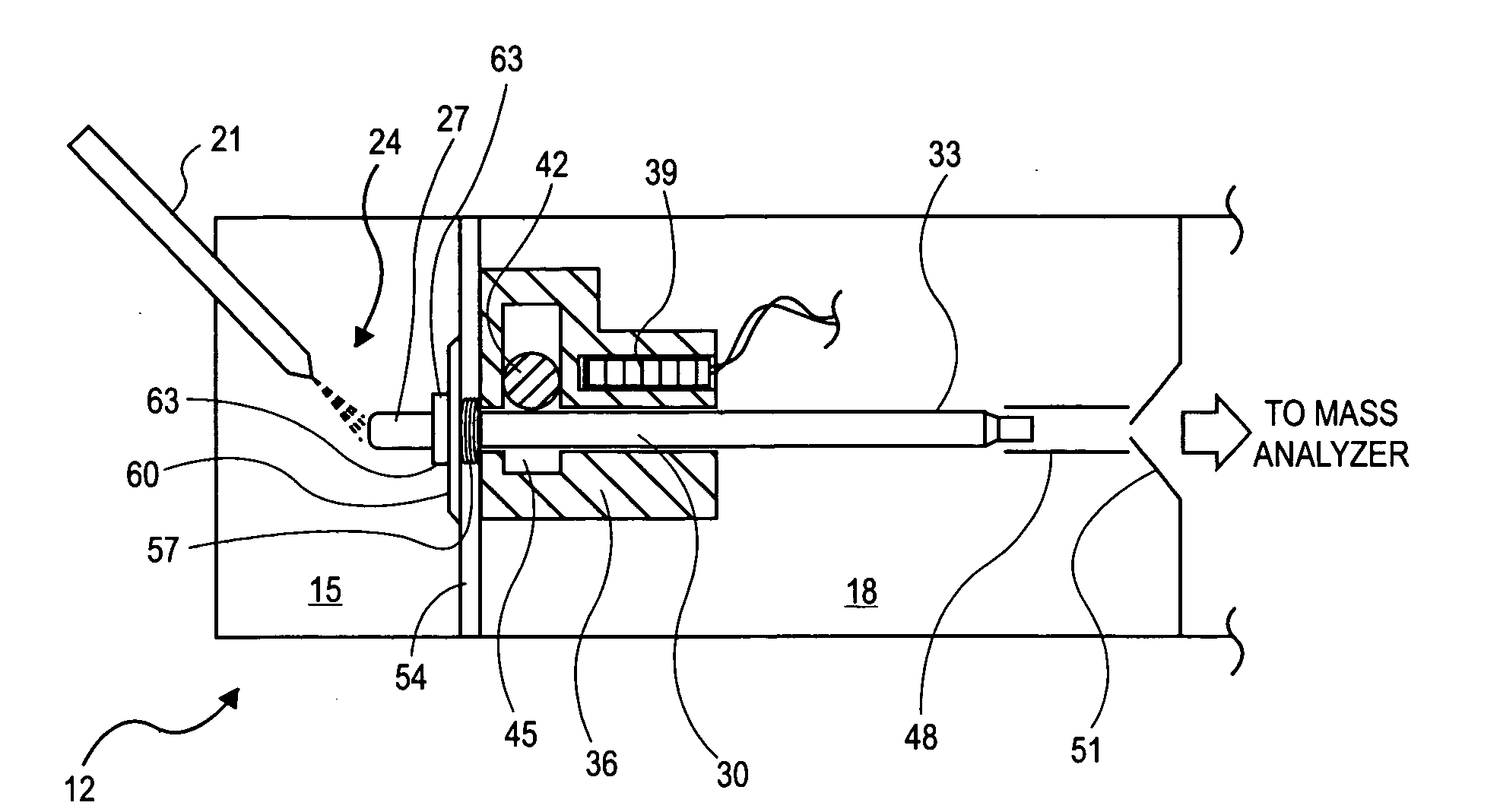
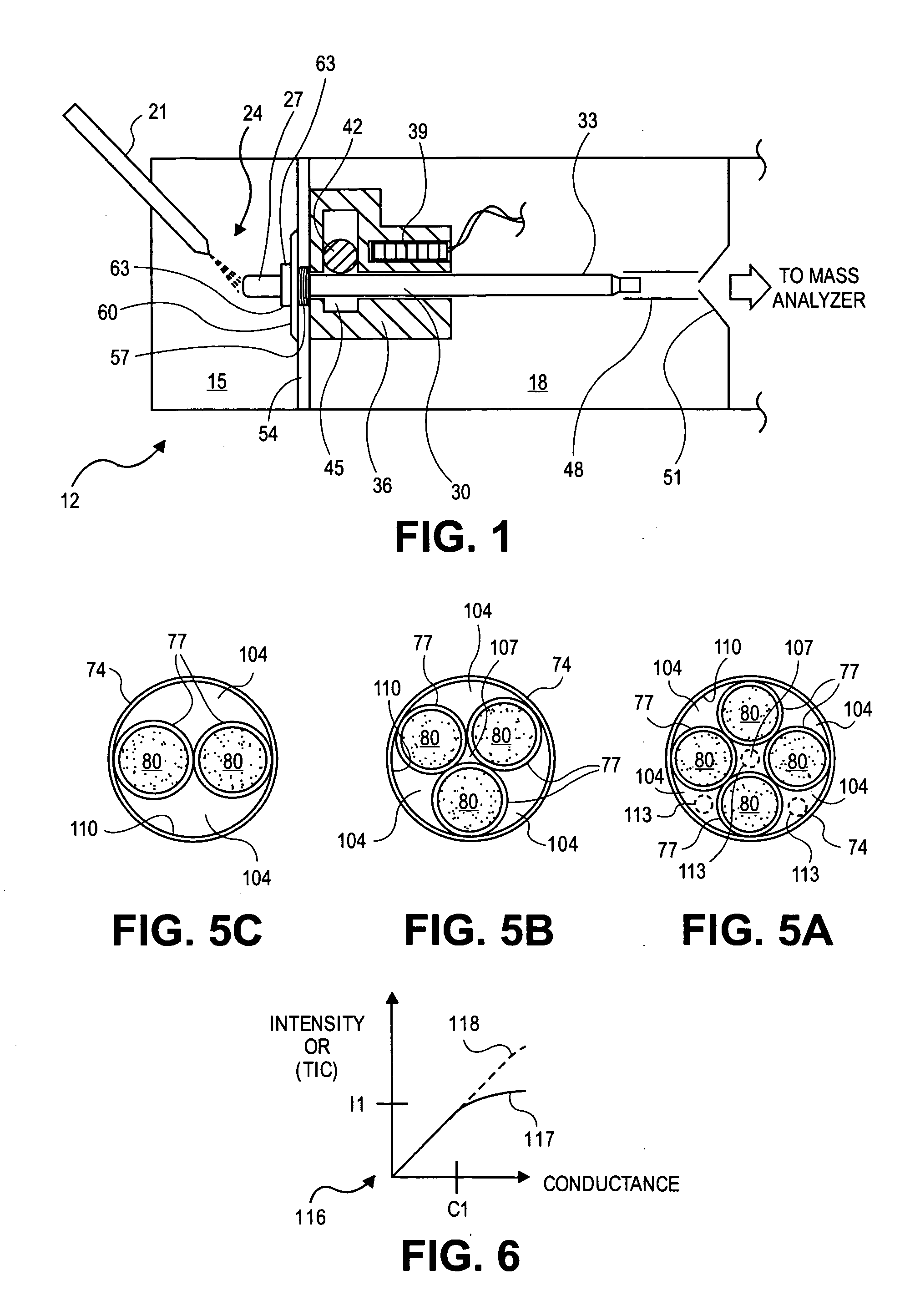
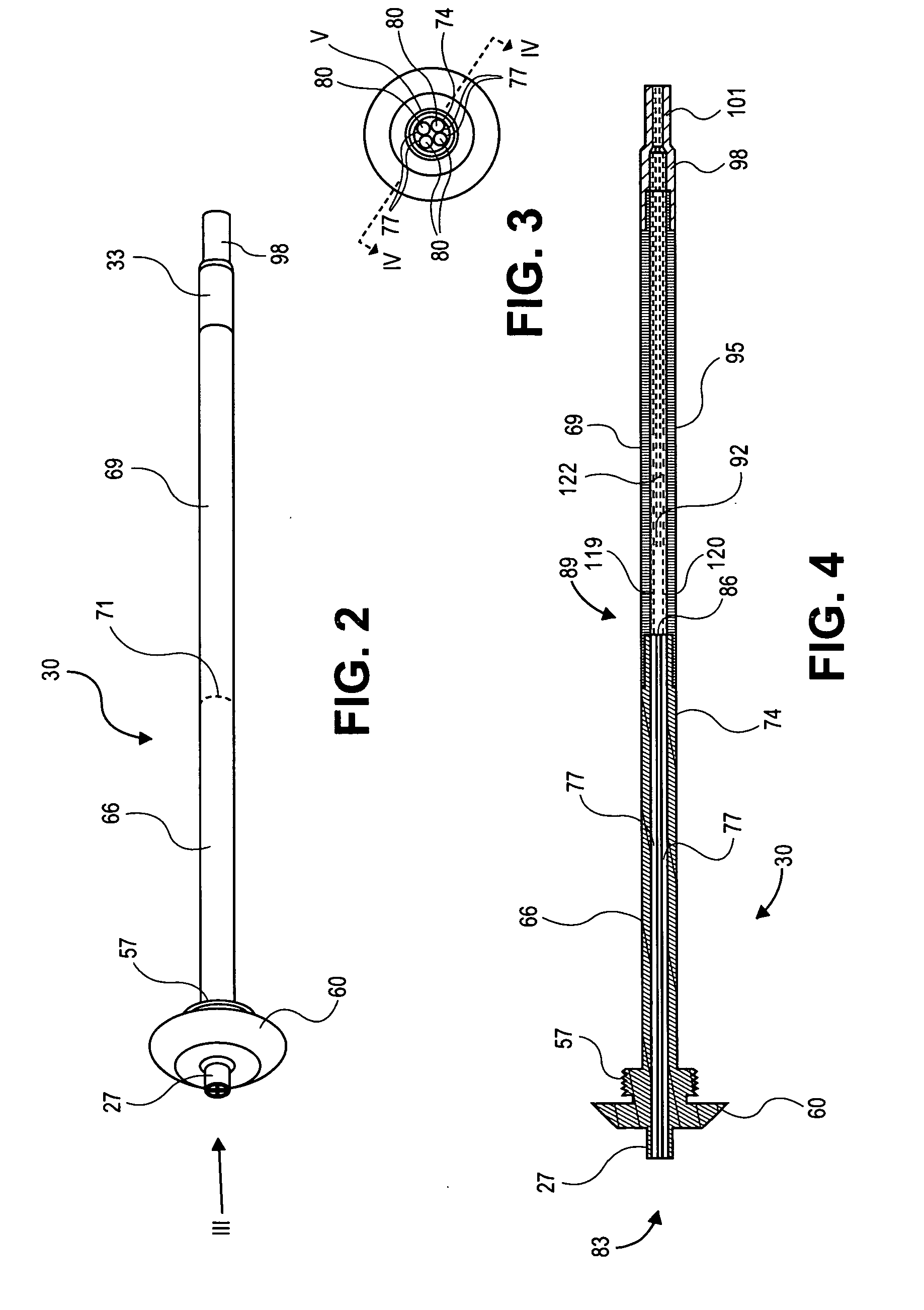
Plural bore to single bore ion transfer tube
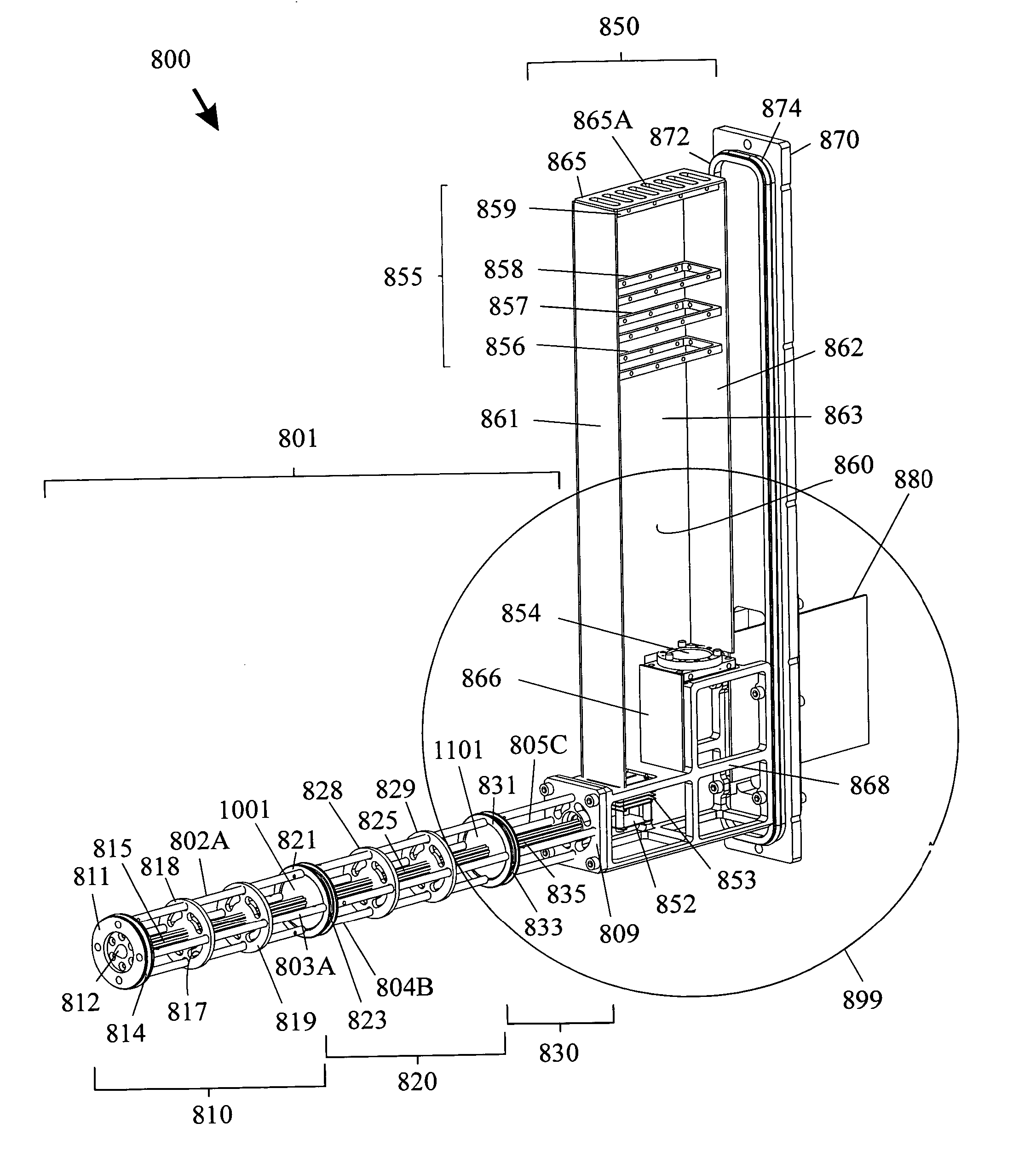
ActiveUS20080142698A1High ion/gas flow rateIncrease the number ofIsotope separationMass spectrometersIon transferEngineering
An ion source includes an ion transfer tube having two segments for transporting a sample fluid containing ions between a first chamber and a second chamber maintained at a reduced pressure relative to the first chamber. A first segment may include a plurality of channels and heat conductive walls forming the plurality of channels. The plurality of channels and walls forming the channels promote efficient convective heat transfer to the sample fluid, thereby enabling operation at relatively high sample fluid flow rates, resulting in an increase in the number of ions that may be delivered to a mass analyzer. A second segment forms a single common channel that receives a plurality of sample streams and enables them to combine into a single ion stream that may be introduced as a single gas stream expansion into the second chamber.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Hybrid mass spectrometer with branched ion path and switch
InactiveUS20090090853A1Easy to identifyStability-of-path spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsIon transferMass analyzer
A hybrid mass spectrometer has a branched ion path. A first ion path within the branched ion path operates as a triple quadrupole instrument having a mass selection device, collision cell, and first mass analyzer and provides information on a specific m / z ratio corresponding to ions of interest in a sample. A second ion path within the branched ion path includes a second mass analyzer in the form of an electrostatic trap or other ion trap device. A branched ion transfer device may provide the branched ion path and may include the collision cell. A controller actuates an ion path switch in the branched ion transfer device and diverts from the first ion path to the second ion path in response to a triggering event. Ions at or near the m / z ratio of interest are then analyzed in the trap to obtain more detailed information of a full spectrum.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Mass spectrometry with multiple ionization sources and multiple mass analyzers
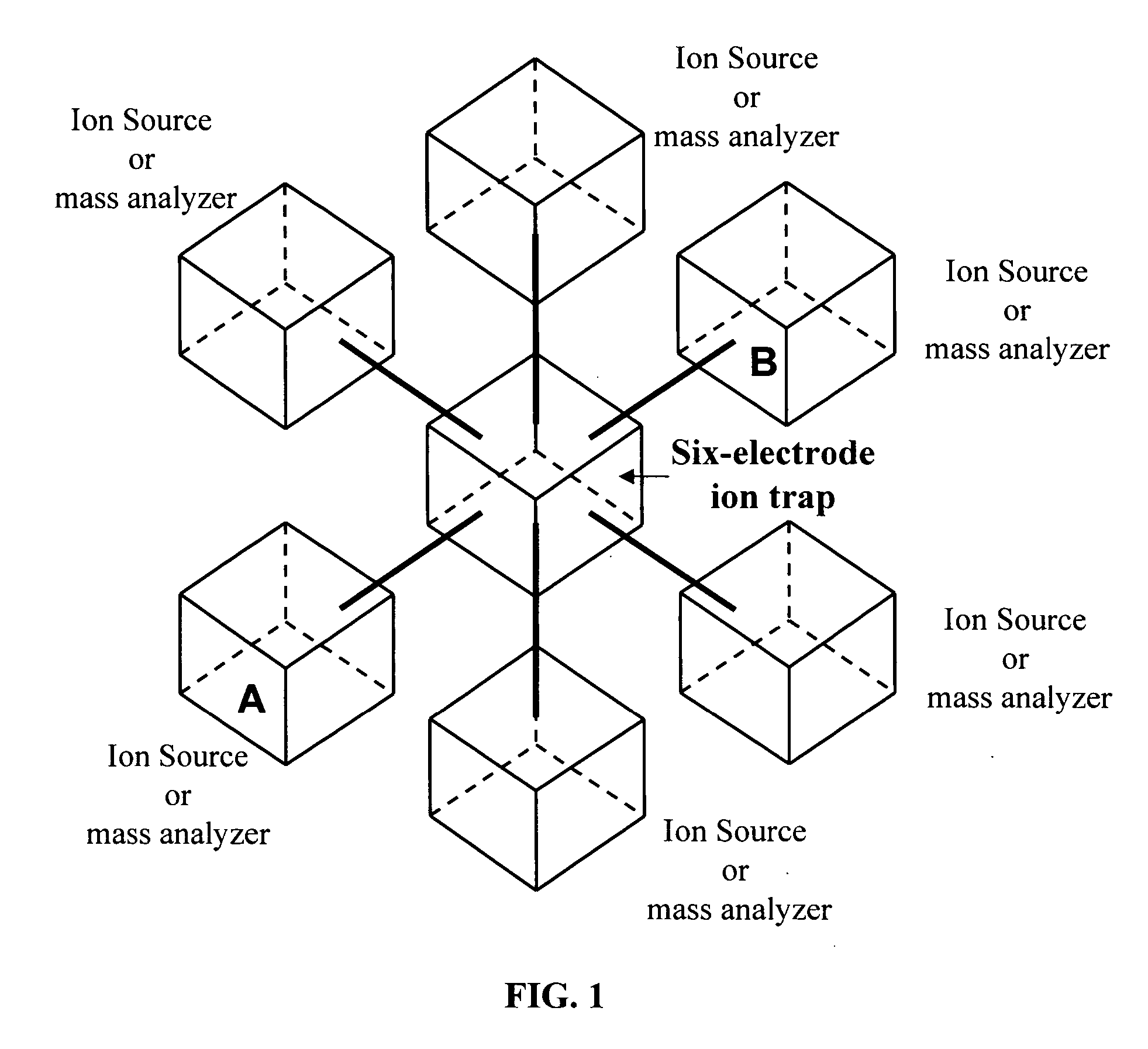
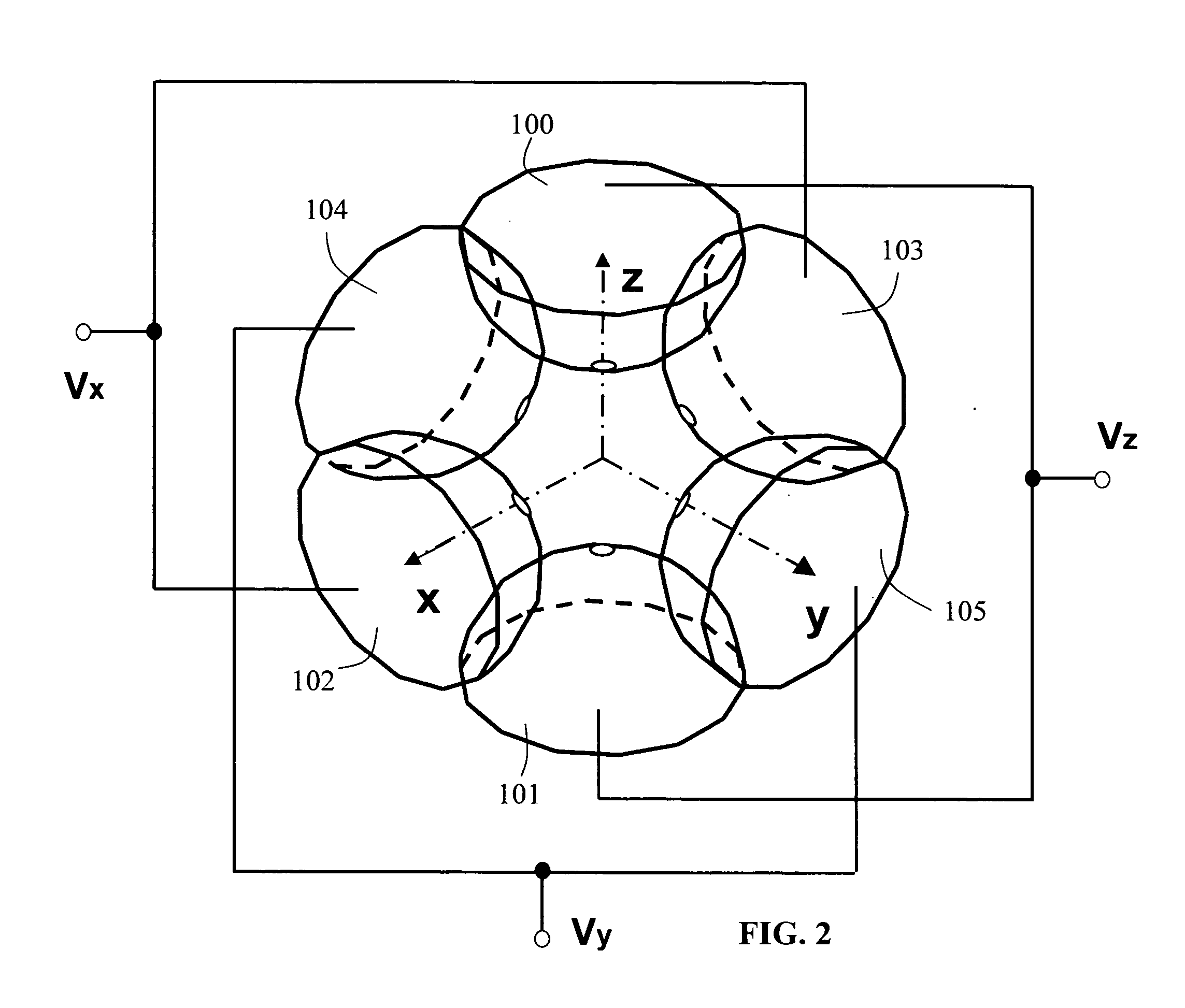
InactiveUS20070057172A1High duty-cyclesHigh sample throughputStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationMass analyzerProtein mass spectrometry
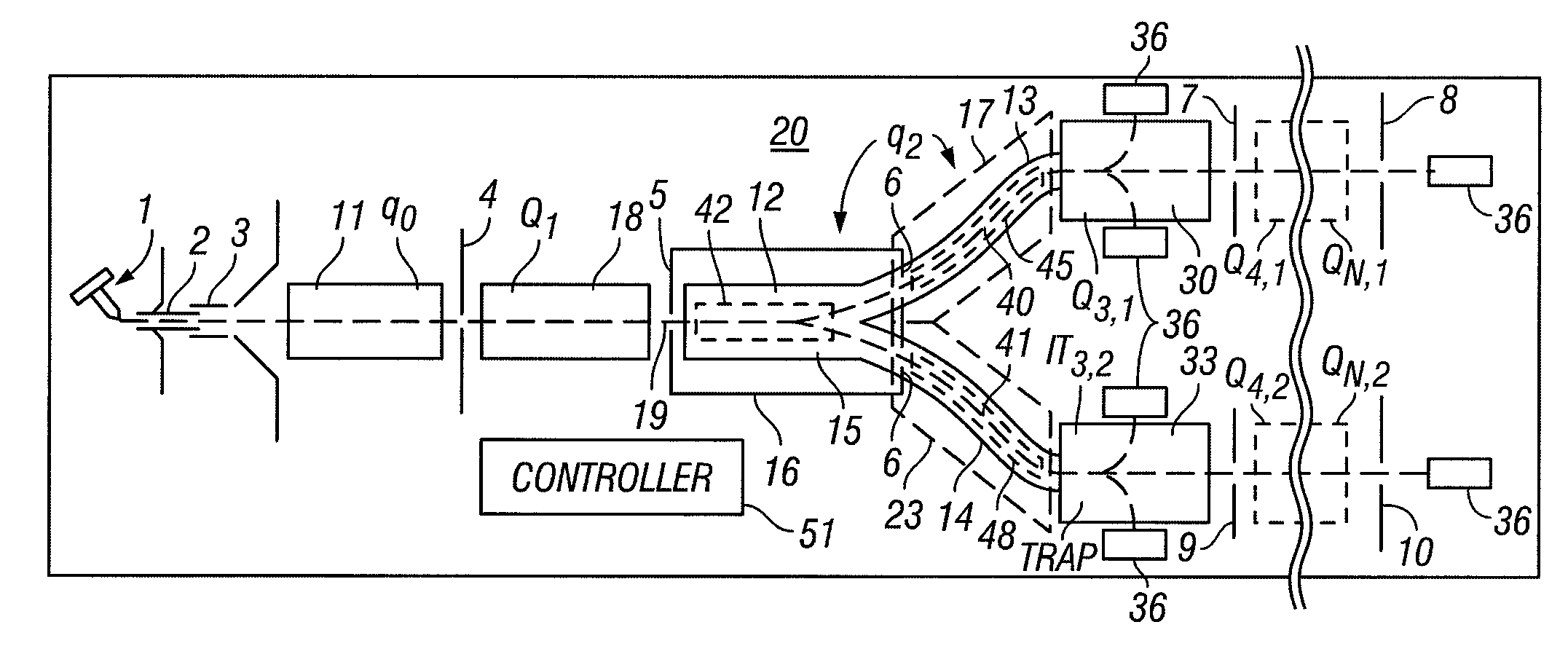
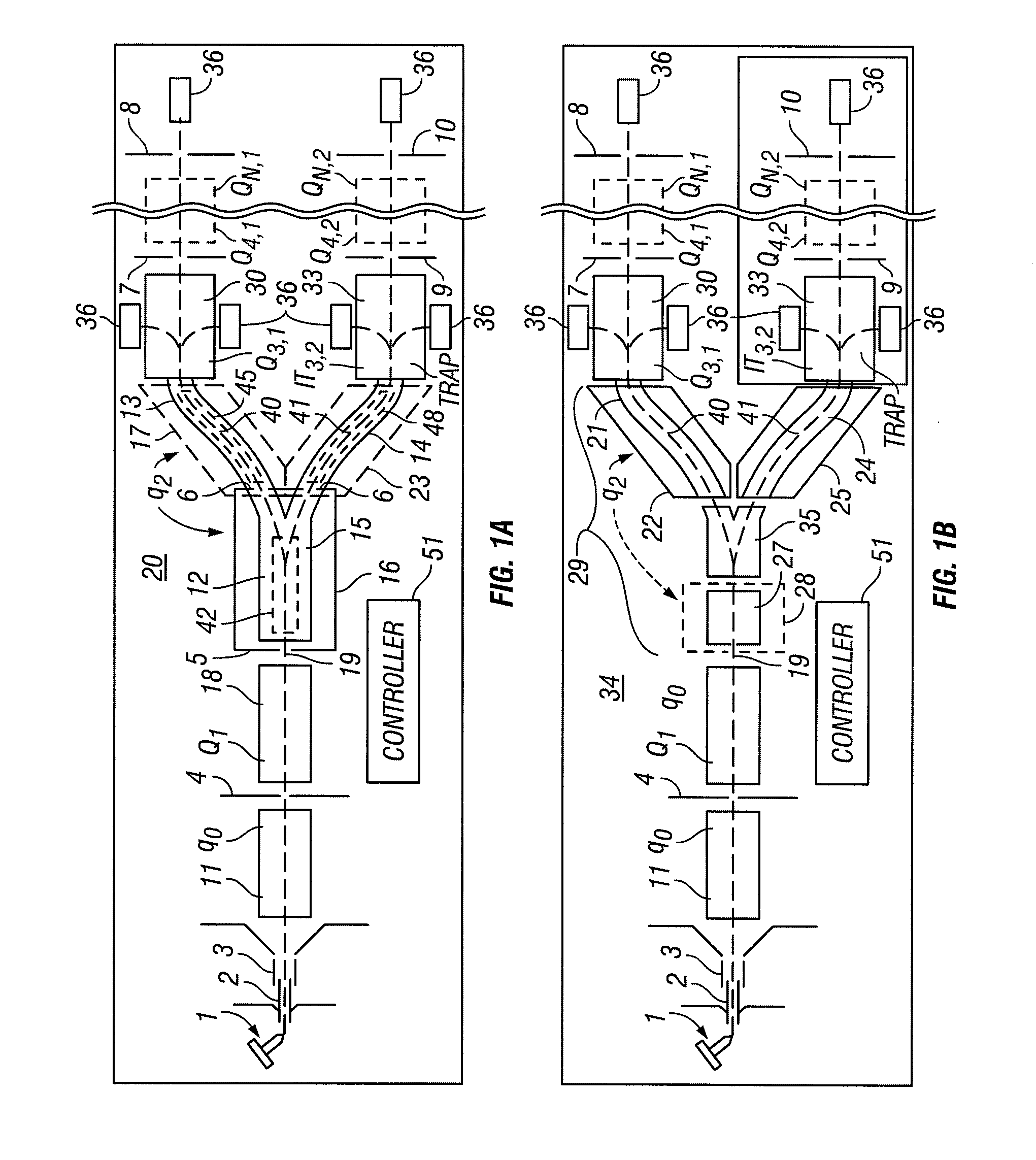
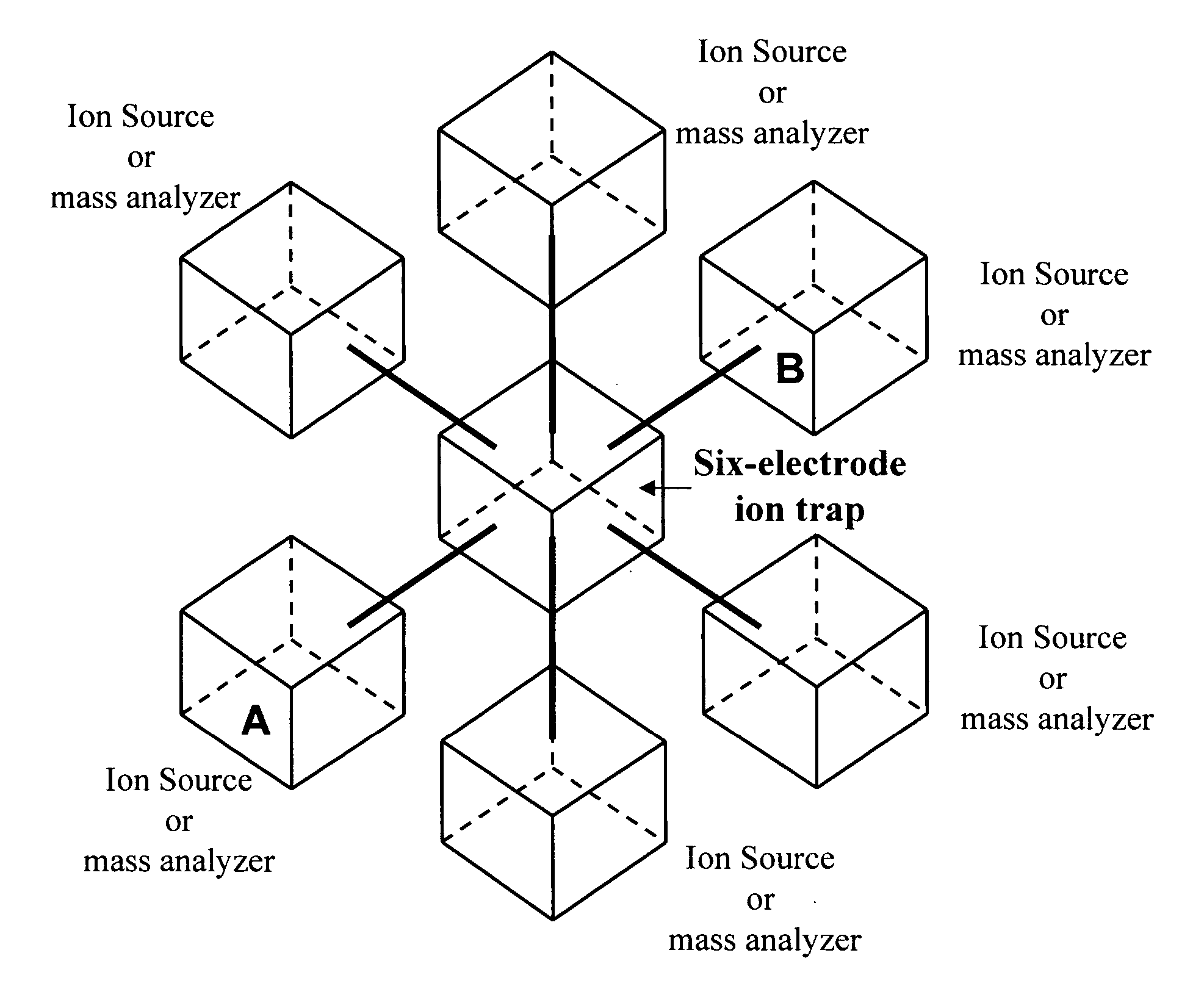
Multiple ionization ion sources and multiple mass analyzers are combined into one mass spectrometer instrument by a six-electrodes ion trap or an array of six-electrodes ion traps. The six-electrodes ion trap can be operated as an independent two-dimensional ion guide or linear ion tap in an arbitrarily selected direction among three orthogonal XYZ directions. The two-dimensional ion guide / linear ion trap can be alternated from one direction to another among the three orthogonal directions electrically. A six-electrodes ion trap generates six equivalent importing and exporting interfaces, each of the interfaces can be used to trap external ions and transfer the trapped ions to any of the other five interfaces. The six-electrodes ion trap provide a mass spectrometer with versatility, multiply functions, high duty-cycles and high sample throughput.
Owner:WANG YANG
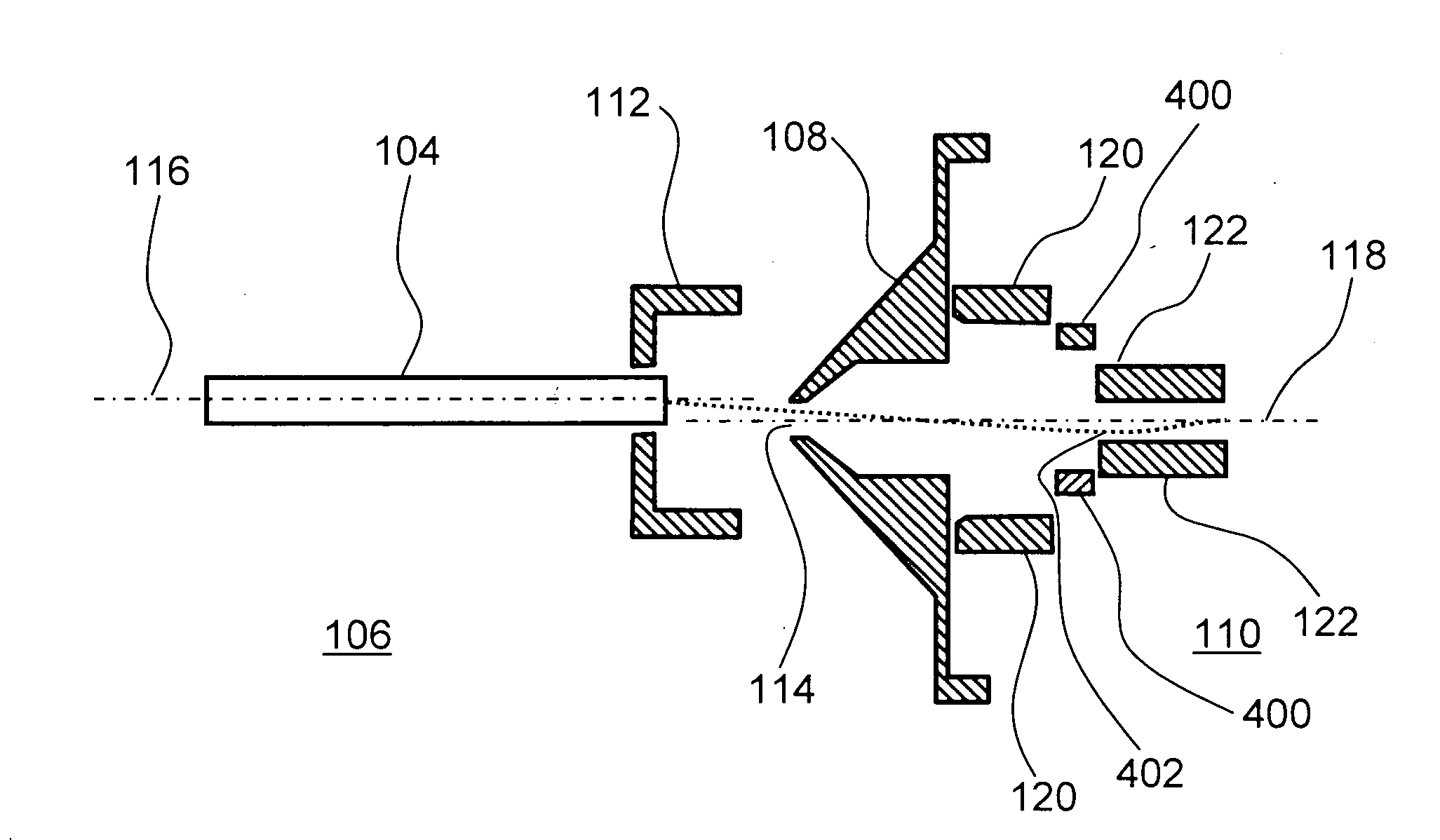
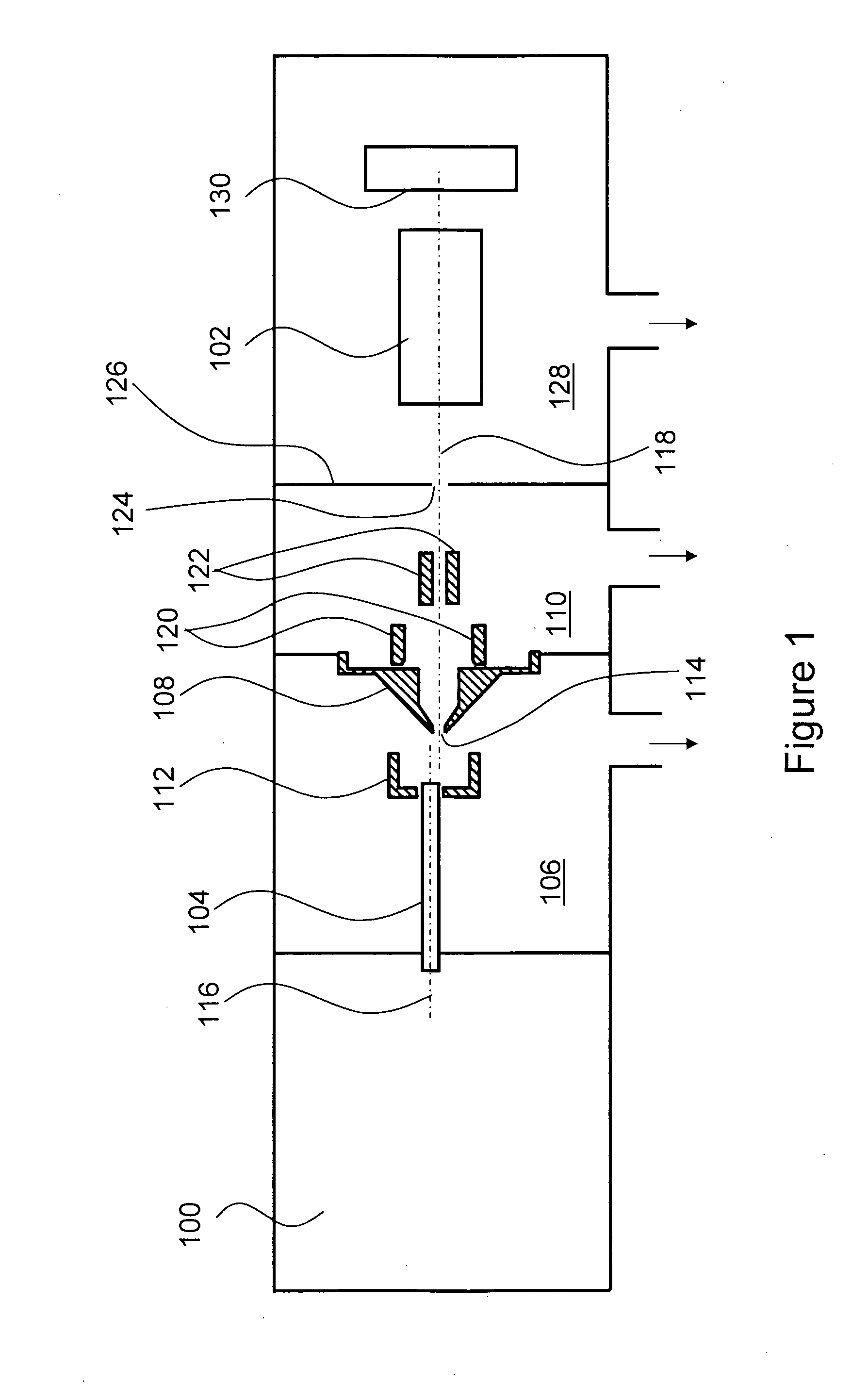
Apparatus and method for providing ions to a mass analyzer
A method and apparatus for directing ions from an ionization source to a mass analyzer is provided. The method includes producing ions from a sample in an ionization source. Some of the ions are transferred to a first region via a passageway that is in fluid communication with the ionization source. Next, some of the ions are sampled from the first region into a second region via an aperture that is defined thorough a partition element. The aperture is centered about a longitudinal axis that passes through an ion transfer element within the second region. An electric field is established for deflecting some of the ions that pass through the aperture of the partition element. In particular, the electric field is directed transverse to the longitudinal axis such that relatively more ions enter an input end of the ion transfer element compared to when the ions are not deflected.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
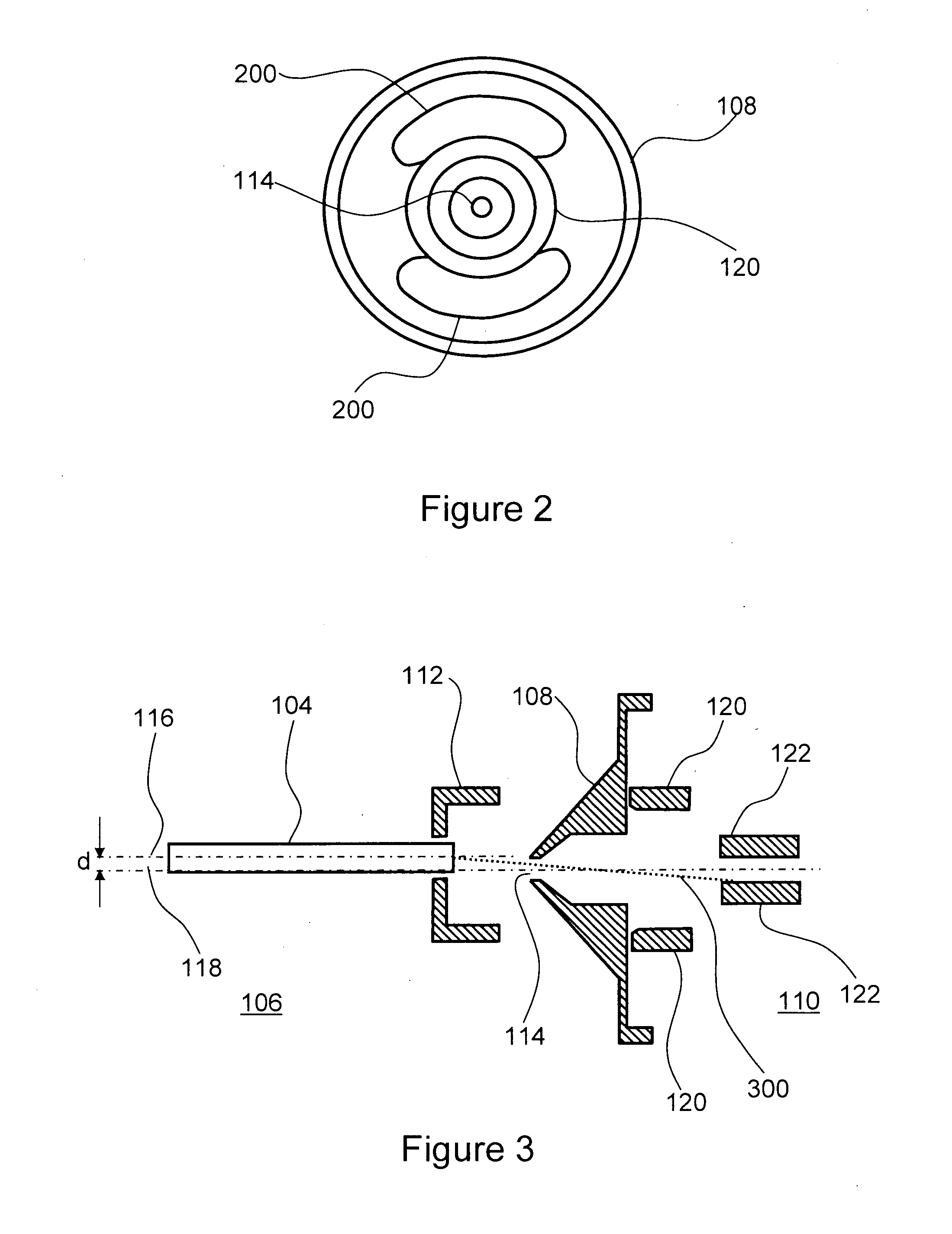
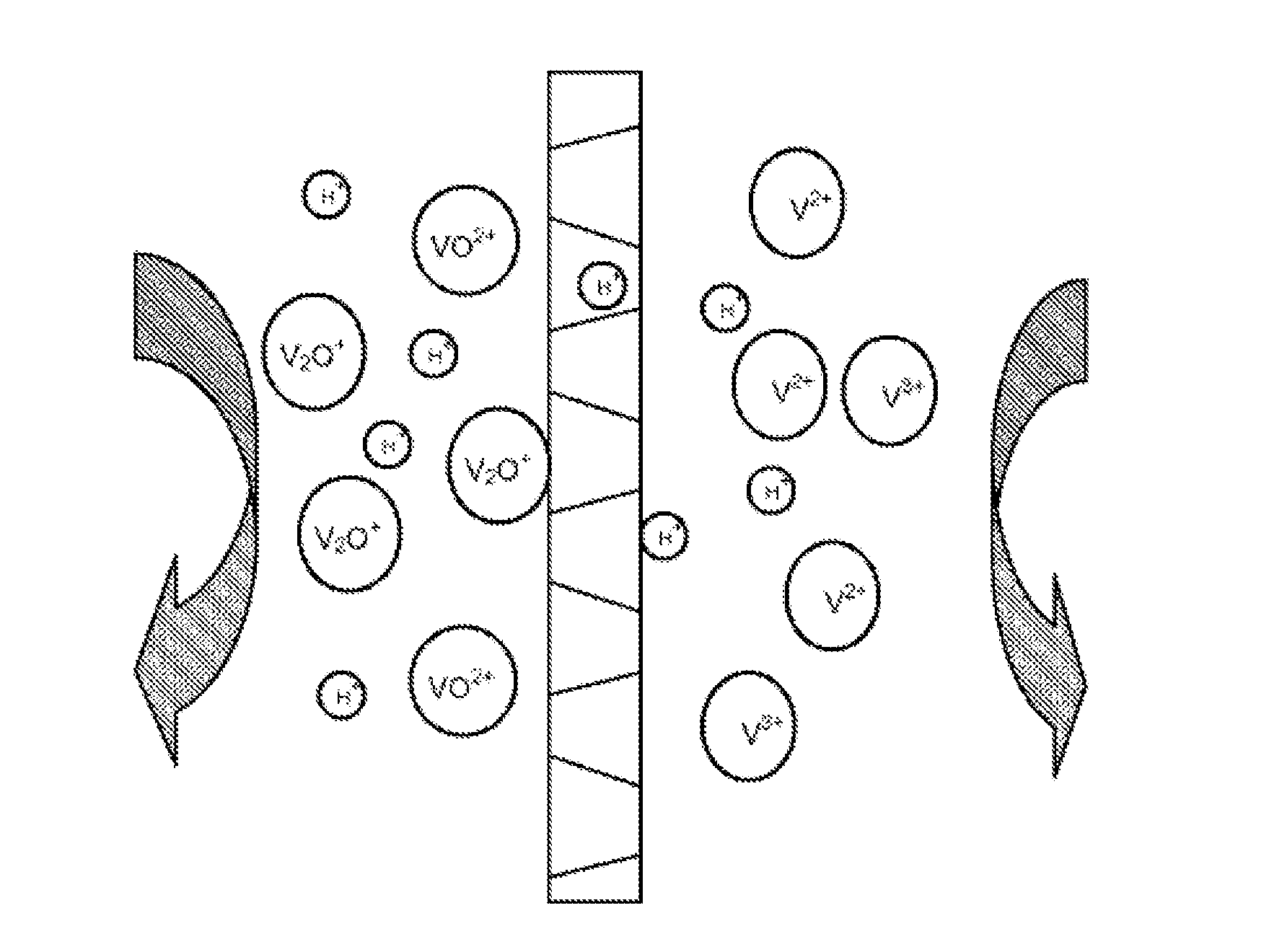
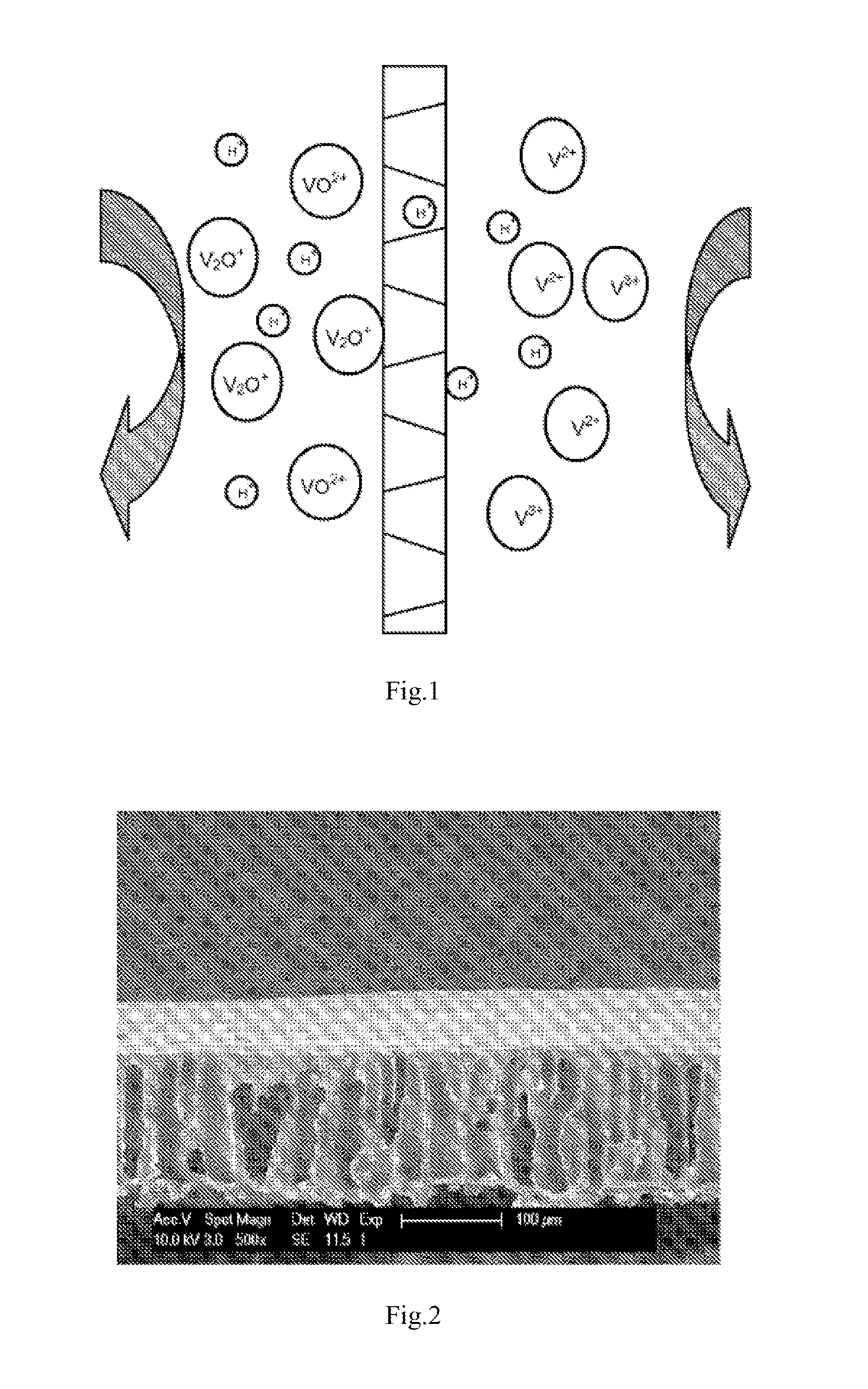
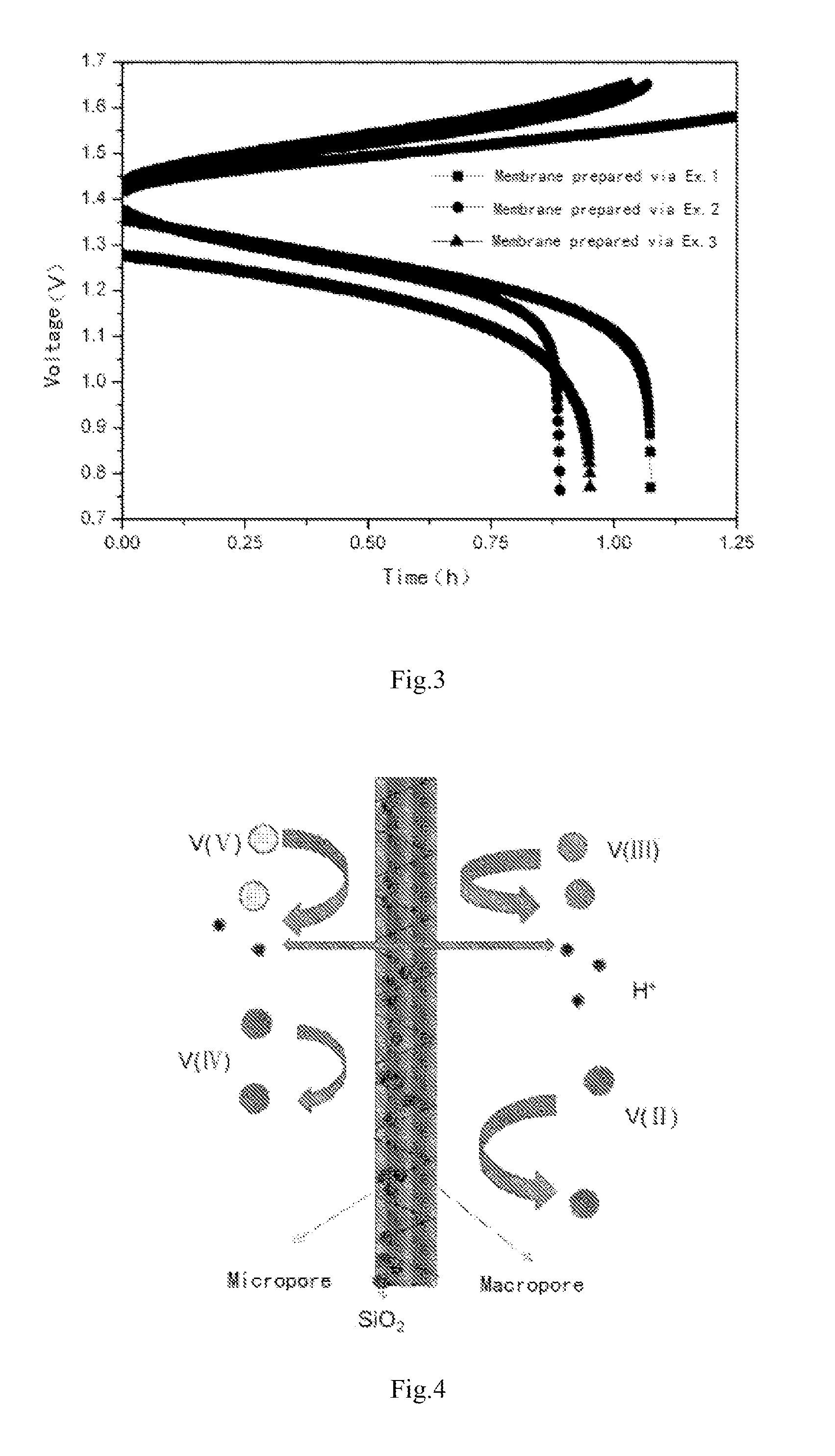
Use of porous membrane and composite membrane thereof in redox flow energy storage battery
ActiveUS20130252137A1Avoided low chemical stabilityMeet needsElectrolyte holding meansFinal product manufactureProtonIon transfer
Disclosed is use of a porous membrane and a composite membrane thereof in a redox flow batteries, and in particular the use thereof in a vanadium redox flow battery. The membrane can effectively realize the separation of ions with different valence states, and an ion transfer without any ion exchange group. The pore size and structure of the porous membrane can be controlled by filling an inorganic substance or grafting an ion exchange group in the pore, in order to improve the barrier properties of the porous membrane for vanadium ions and to increase proton conductivity.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method and apparatus for ion manipulation using mesh in a radio frequency field
ActiveUS8373120B2Easy to buildSmall scaleTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationIon chromatographyDesorption
Owner:LECO CORPORATION
System and Methods for Ionizing Compounds using Matrix-assistance for Mass Spectometry and Ion Mobility Spectometry
ActiveUS20130306856A1Facilitated ionizationLow costSamples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansVacuum assistedGas phase
An ionization method for use with mass spectrometry or ion mobility spectrometry is a small molecule compound(s) as a matrix into which is incorporated analyte. The matrix has attributes of sublimation or evaporation when placed in vacuum at or near room temperature and produces both positive and negative charges. Placing the sample into a region of sub-atmospheric pressure, the region being in fluid communication with the vacuum of the mass spectrometer or ion mobility spectrometer, produces gas-phase ions of the analyte for mass-to-charge or drift-time analysis without use of a laser, high voltage, particle bombardment, or a heated ion transfer region. This matrix and vacuum assisted ionization process can operate from atmosphere or vacuum and produces ions from large (e.g. proteins) and small molecules (e.g. drugs) with charge states similar to those observed in electrospray ionization.
Owner:MSTM LLC
Ion Transfer Tube Having Single or Multiple Elongate Bore Segments and Mass Spectrometer System
ActiveUS20120043460A1Maximize transfer efficiencySamples introduction/extractionArc welding apparatusIon transferMass analyzer
An ion transfer tube for a mass spectrometer comprises a tube member having an inlet end and an outlet end; and at least one bore extending through the tube member from the inlet end to the outlet end, the at least one bore having a non-circular cross section. A method of forming an ion transfer tube comprises the steps of providing a tube member having a length and an internal bore, the internal bore having a wall of circular cross section; and etching or eroding portions of the tube member adjacent to the wall so as to form an enlarged bore having a non-circular cross section.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Mass Spectrometer
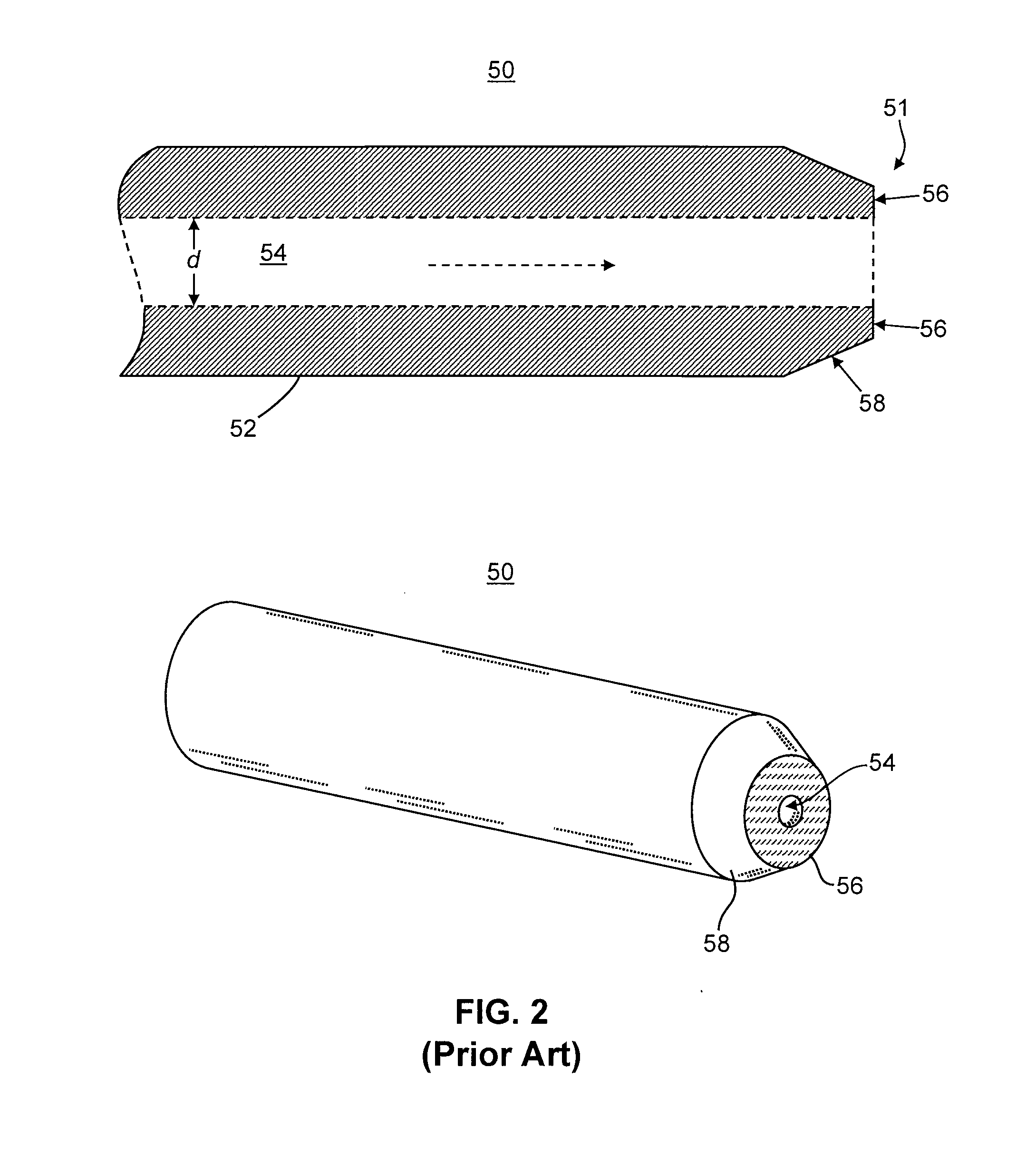
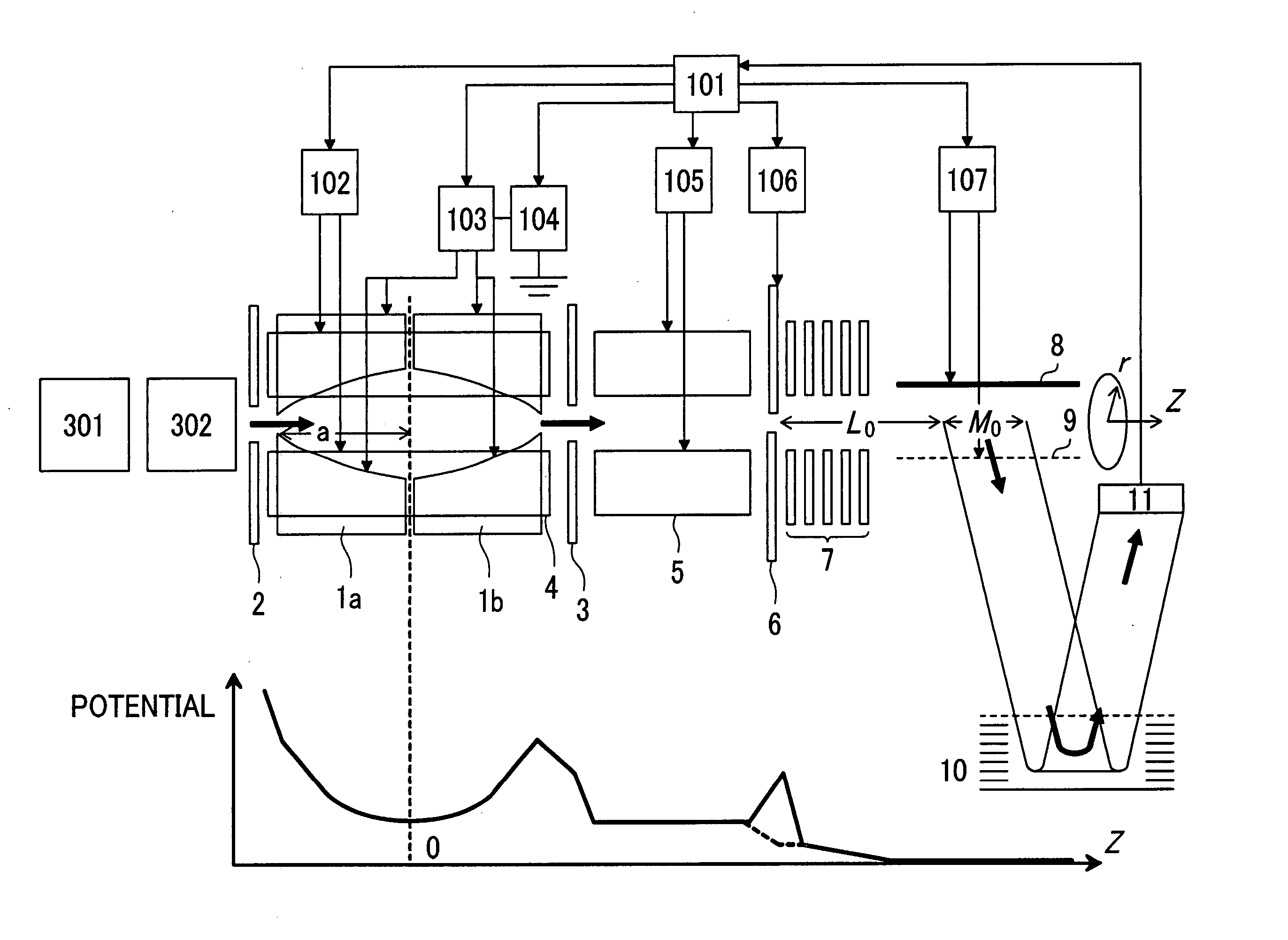
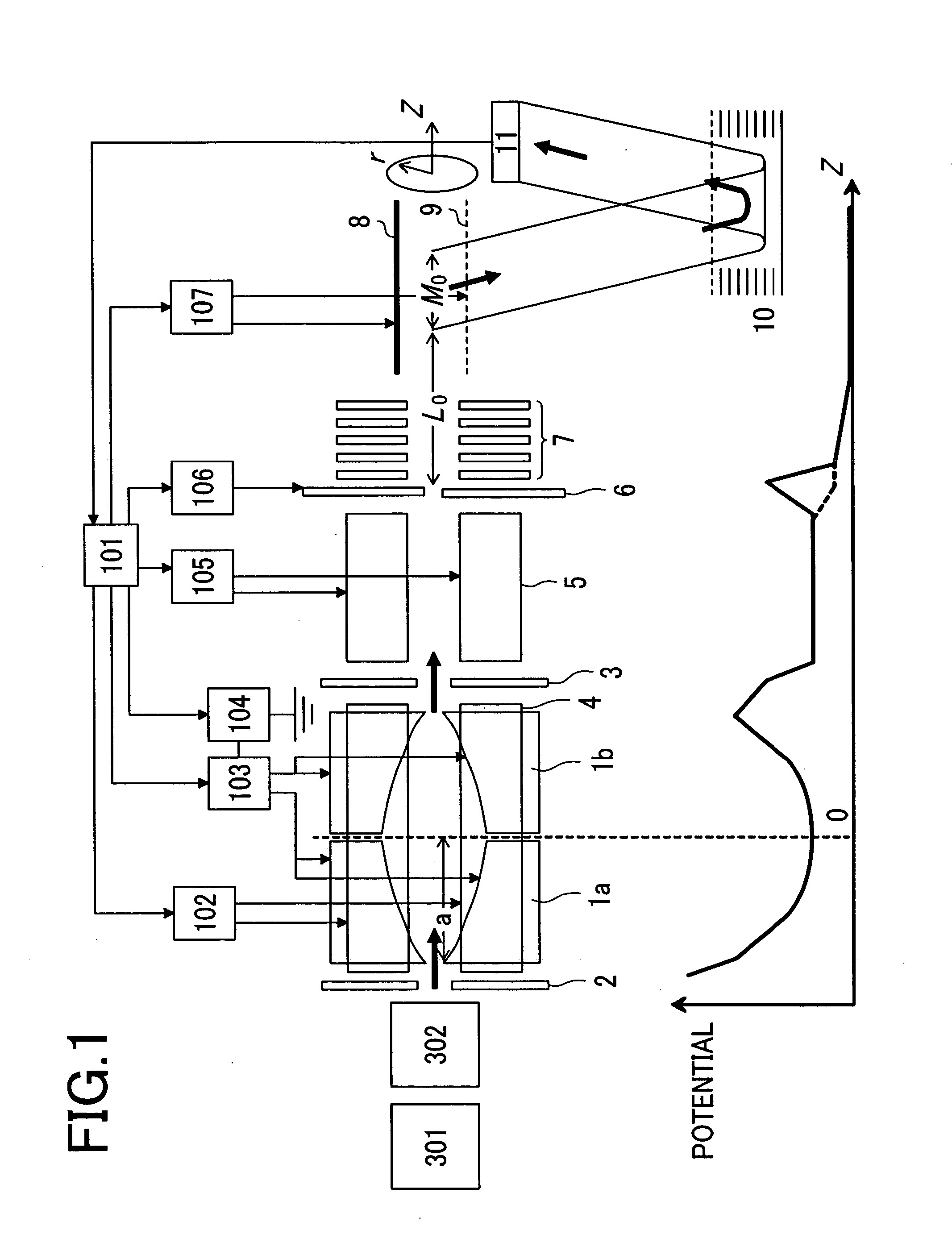
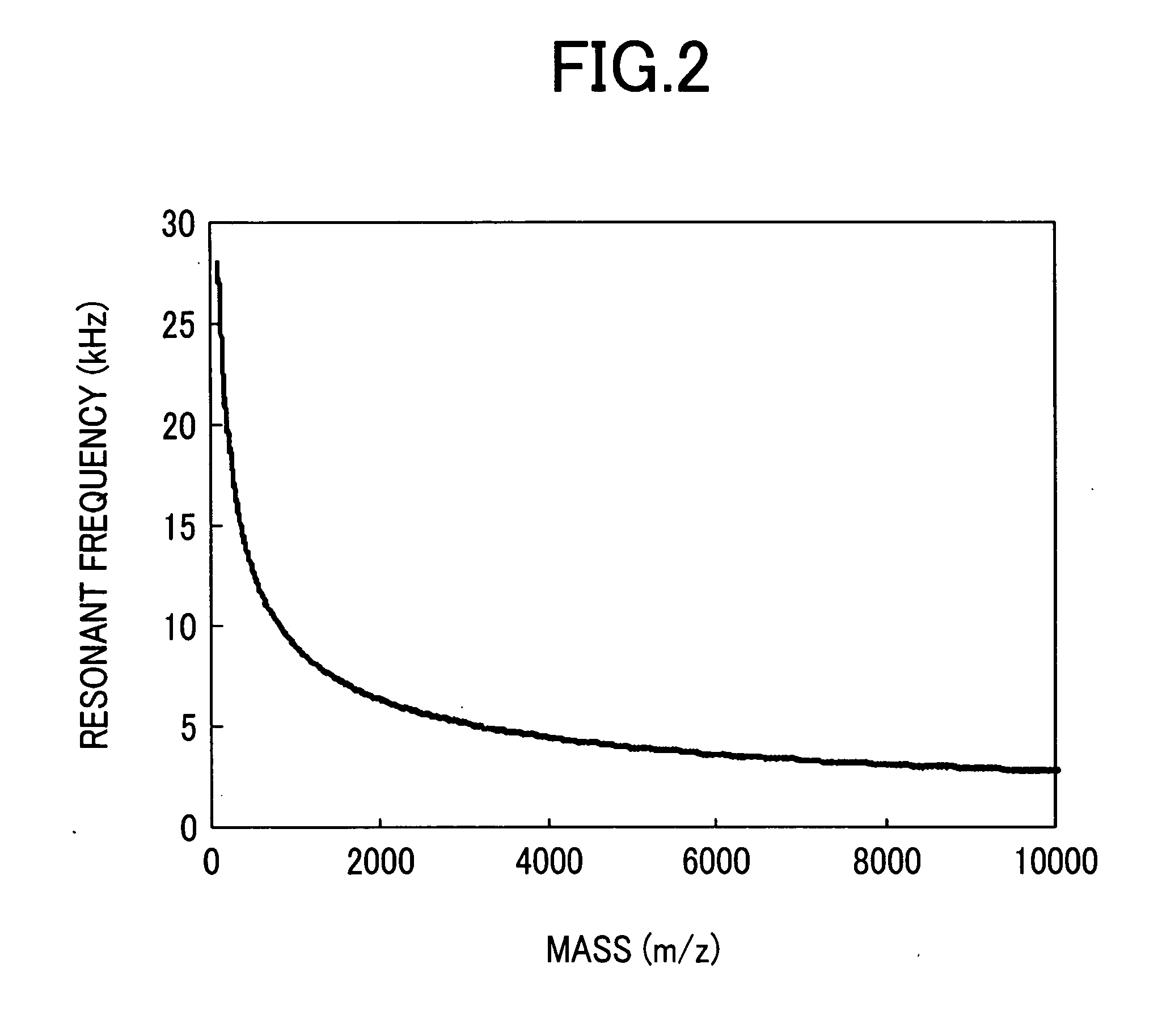
ActiveUS20050127290A1High sensitivityHigh mass accuracyStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersDelayed timeMass analyzer
A mass spectrometer capable of analyzing a wide mass range with high sensitivity and high mass accuracy. A mass spectrometer has an ionization source generating ions; an ion transfer optics transferring the ions; a first linear trap accumulating the ions and ejecting the ions in the specific mass range; a second linear trap having an end electrode disposed at the exit end ejecting the ions to change a DC potential gradient relative to a DC potential of the end electrode and trapping the ions ejected from the first linear trap to repeatedly eject them in pulse form; a time-of-flight mass spectrometer accelerating the ions ejected from the second linear trap in the orthogonal direction to detect them; and a controller changing the time duration of the ions in which the ions are ejected from the second linear trap or delay time from the completion of ejection to application of an accelerating voltage of the time-of-flight mass spectrometer according to the mass range of the ions ejected from the first linear trap to the second linear trap.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com