Patents
Literature
59results about How to "Keep moving" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
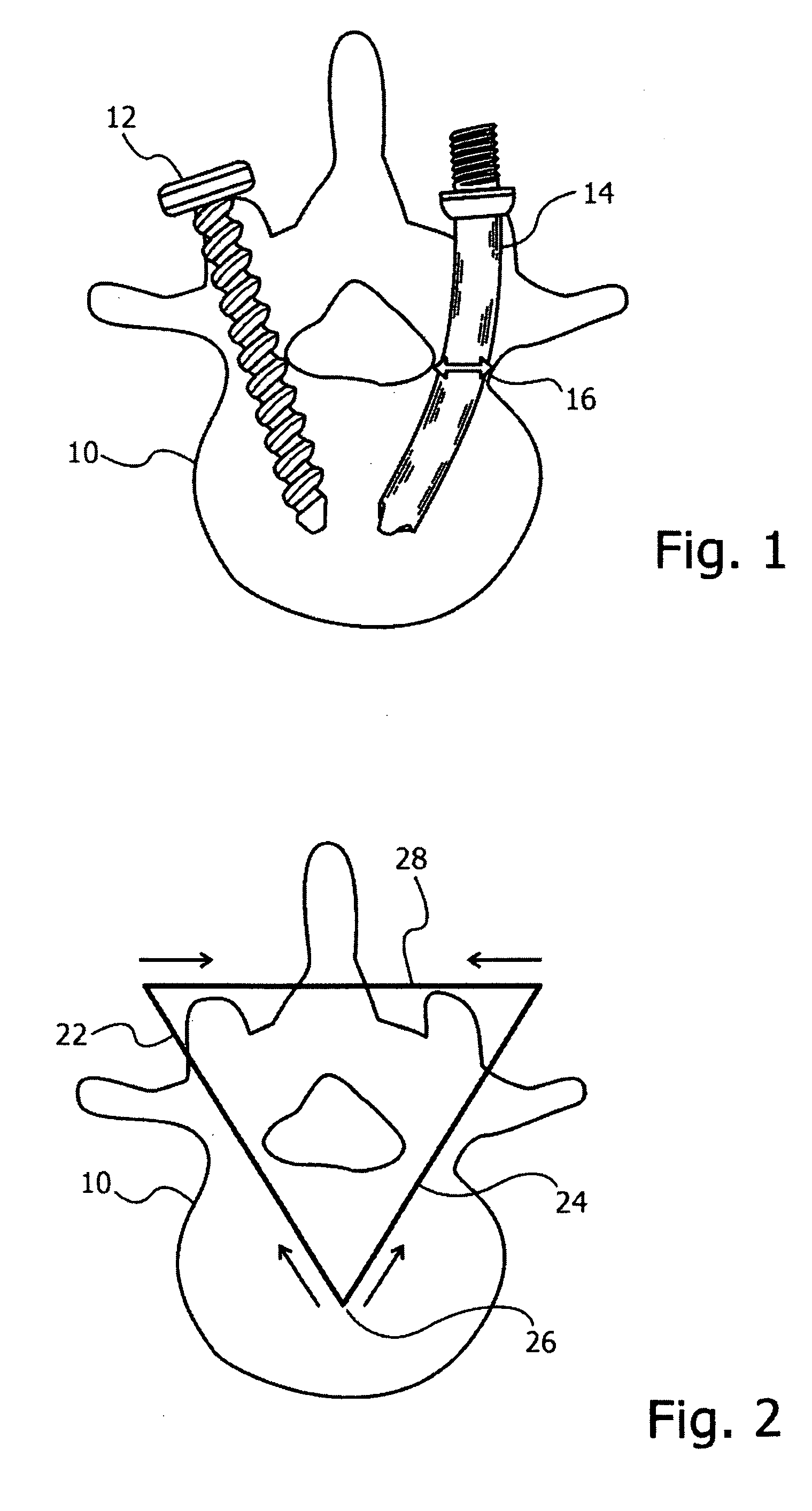
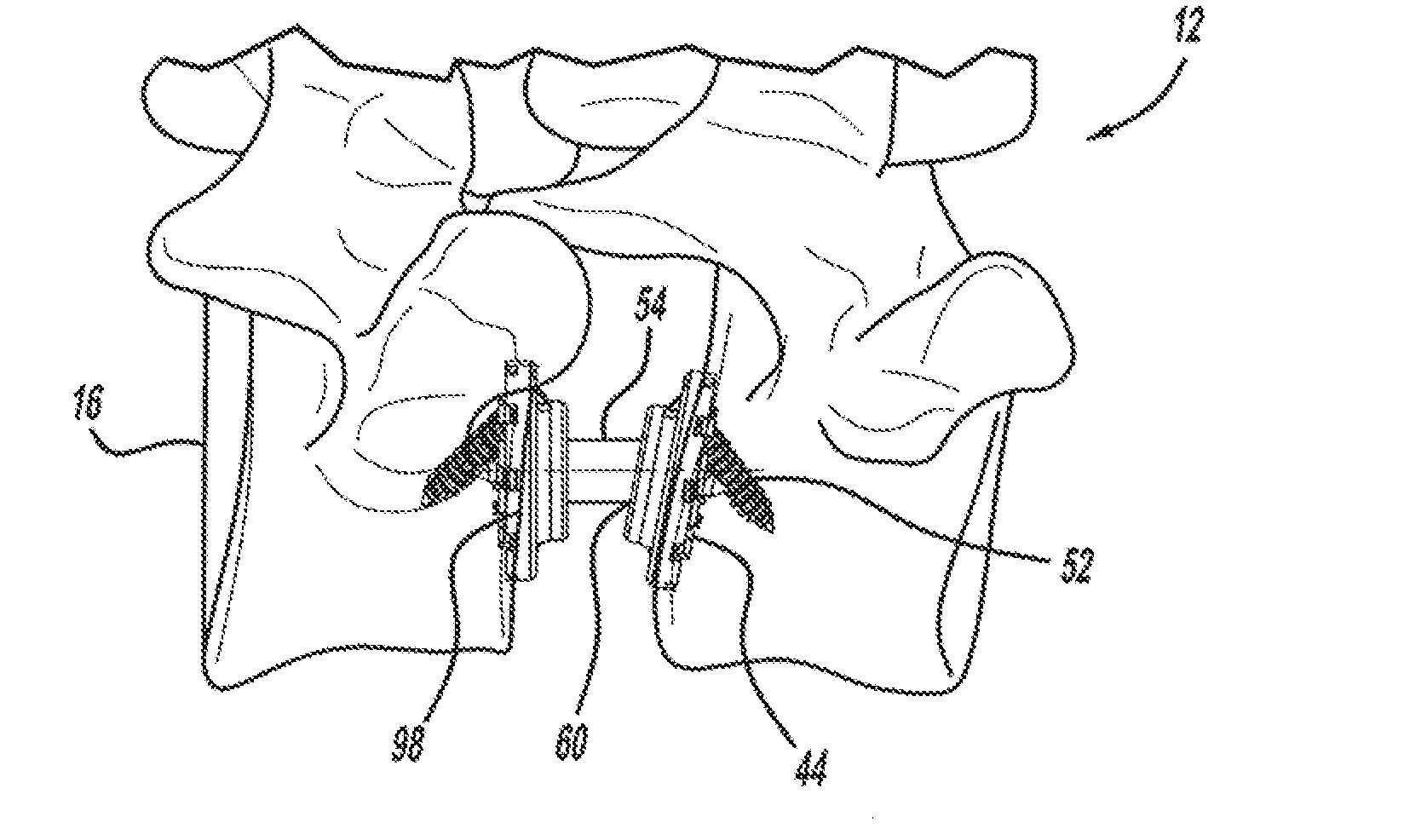
Systems and methods for posterior dynamic stabilization of the spine
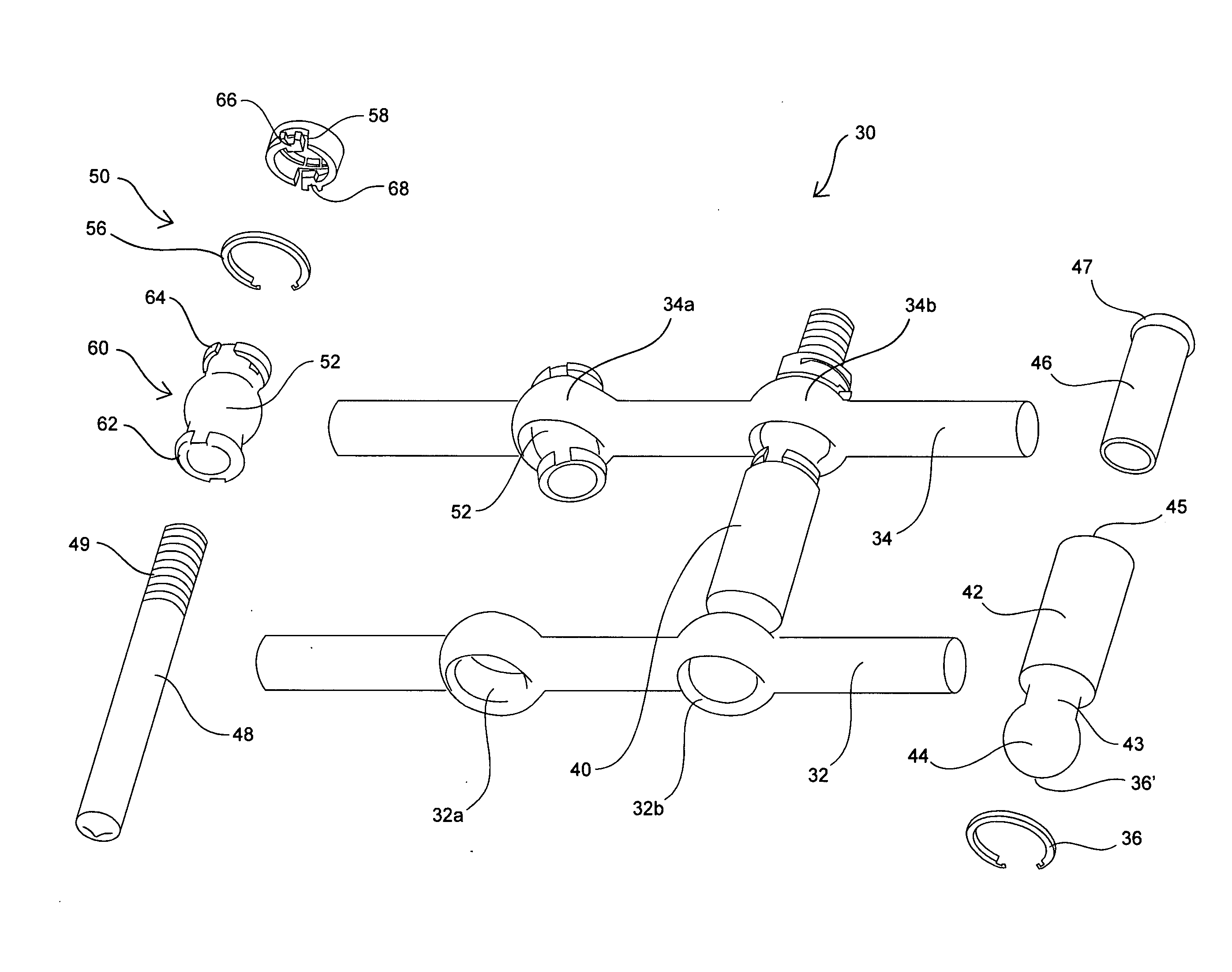
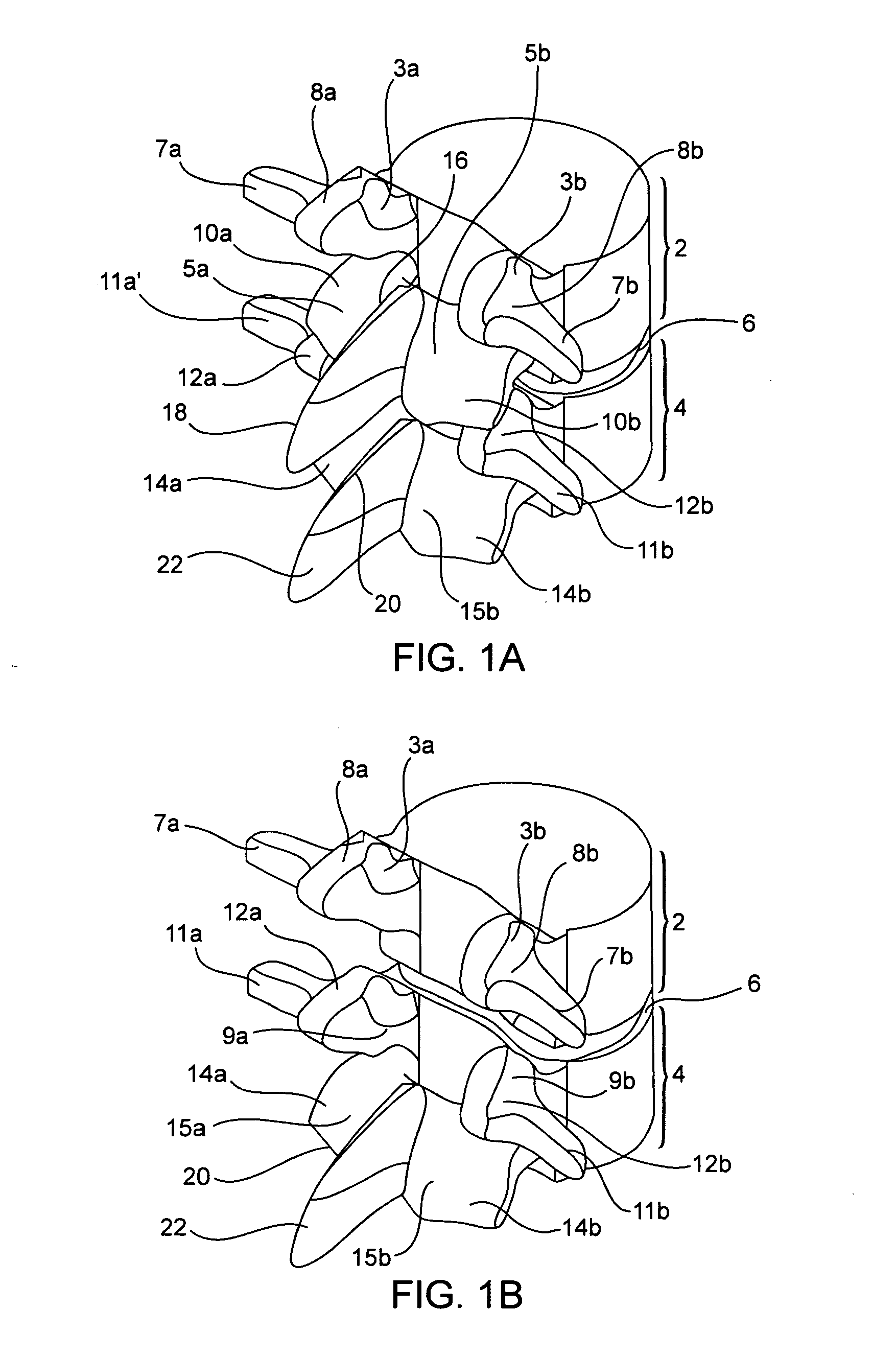
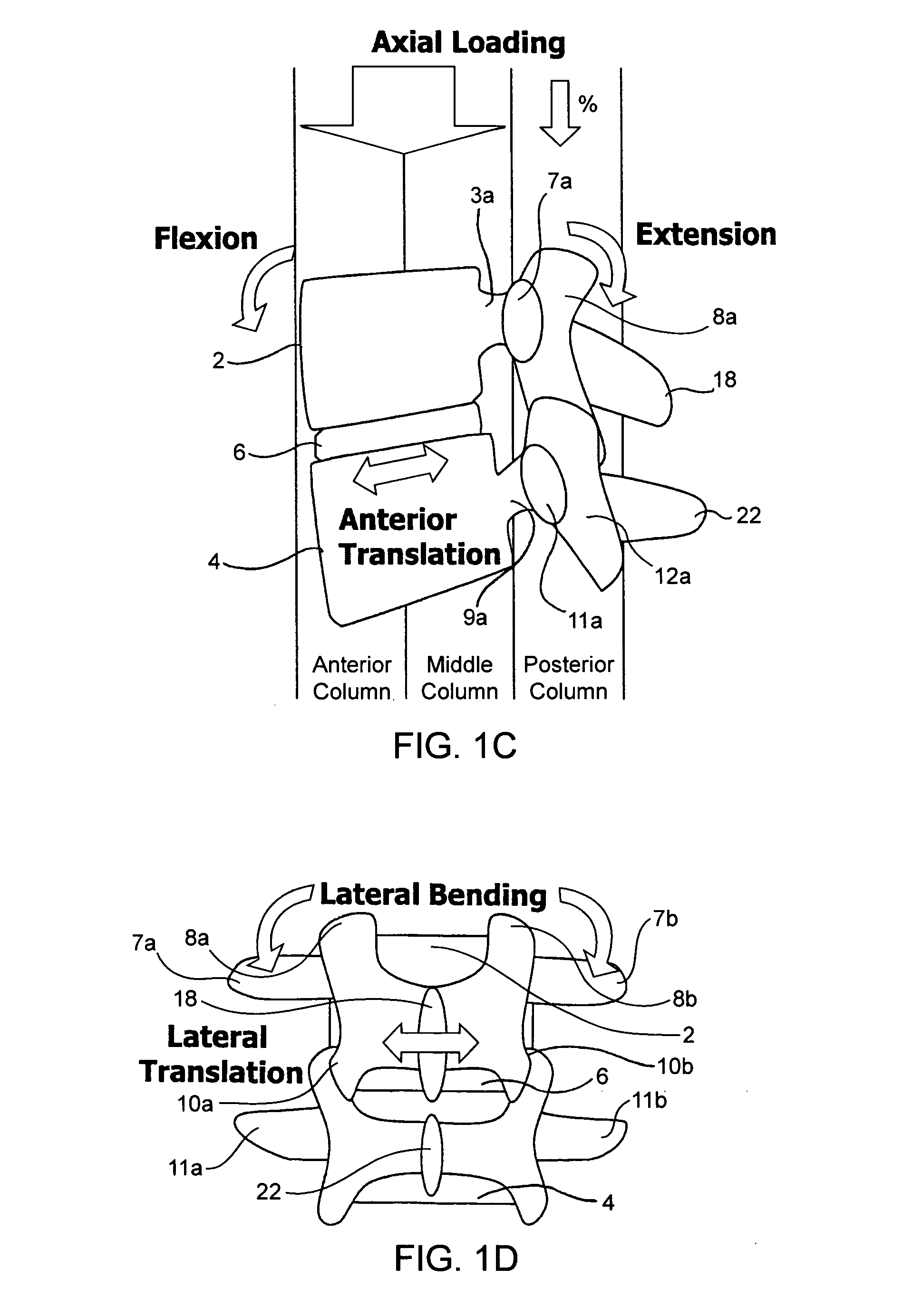
InactiveUS20080097441A1Reduces and eliminates facet painLiquidityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnInterconnection
Systems and devices for dynamically stabilizing the spine are provided. The systems include a superior component for attachment to a superior vertebra of a spinal motion segment and an inferior component for attachment to an inferior vertebral of a spinal motion segment. The interconnection between the two components enables the spinal motion segment to move in a manner that mimics the natural motion of the spinal motion segment while substantially offloading the facet joints of the spine. Methods are also provided for stabilizing the spine and for implanting the subject systems.
Owner:EXACTECH INC
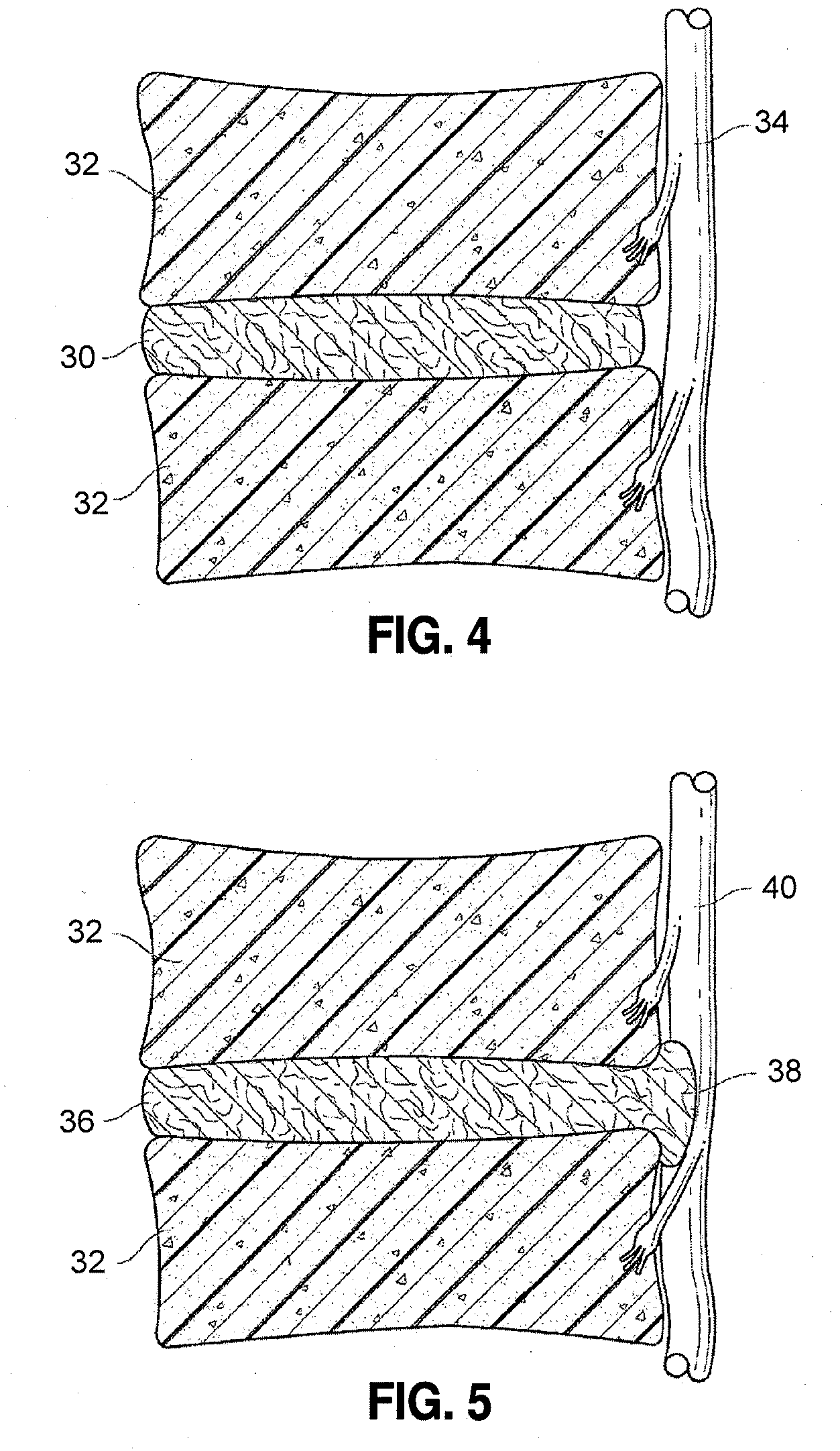
Spinal implants and methods
InactiveUS20090149959A1Reduce relative motionSmooth motionDiagnosticsBone implantPosterior regionIntervertebral disk
Owner:MAGELLAN SPINE TECH
Method and apparatus for path planning, selection, and visualization
InactiveUS20100241289A1Suffer from effectKeep movingProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorGraphicsThree-dimensional space
New and Improved methods and apparatus for robotic path planning, selection, and visualization are described A path spline visually represents the current trajectory of the robot through a three dimensional space such as a room By altering a graphical representation of the trajectory—the path spline—an operator can visualize the path the robot will take, and is freed from real-time control of the robot Control of the robot is accomplished by periodically updating the path spline such that the newly updated spline represents the new desired path for the robot Also a sensor that may be located on the robot senses the presence of boundaries (obstacles) in the current environment and generates a path that circumnavigates the boundaries while still maintaining motion in the general direction selected by the operator The mathematical form of the path that circumnavigates the boundaries may be a spline
Owner:SANDBERG ROY
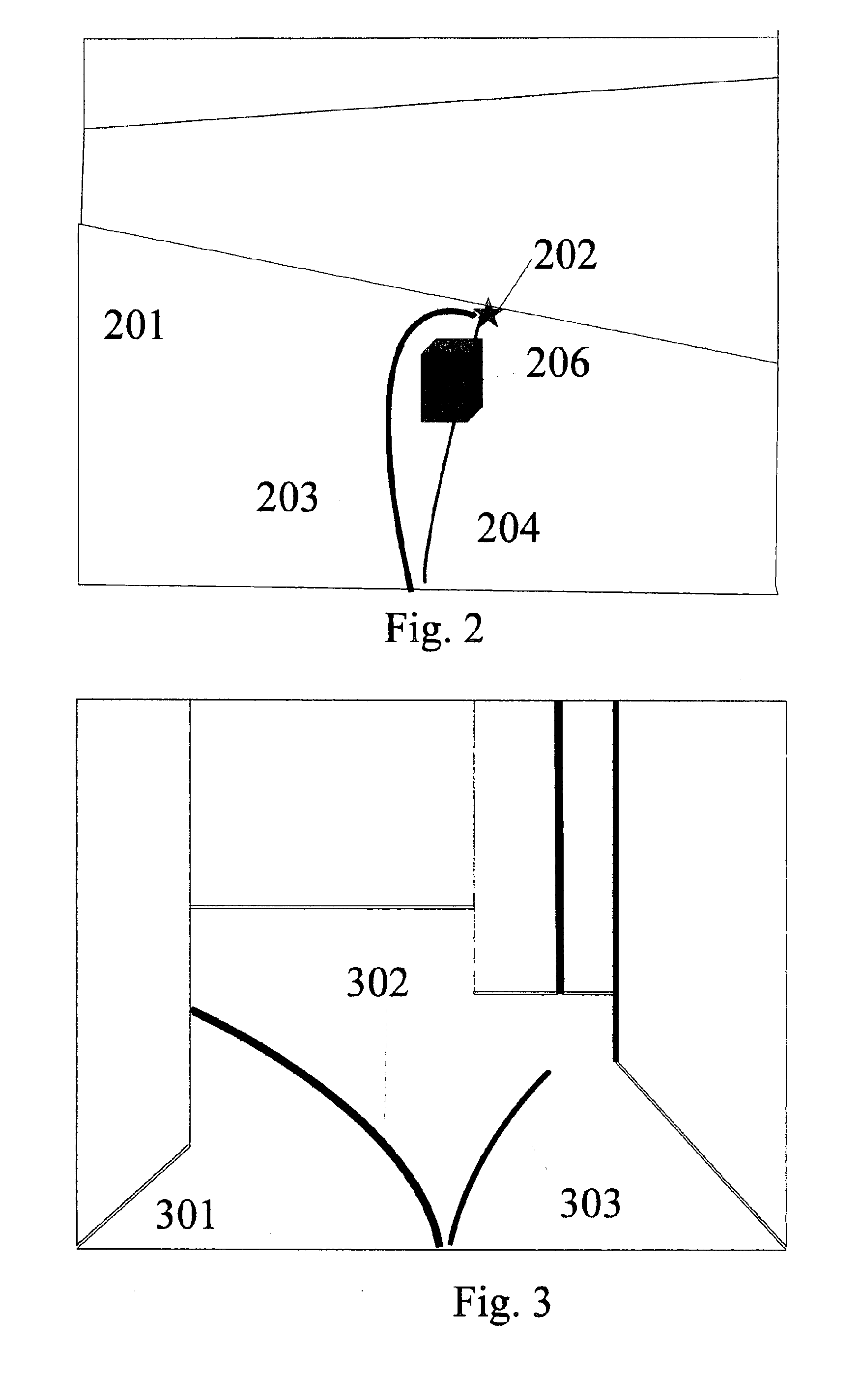
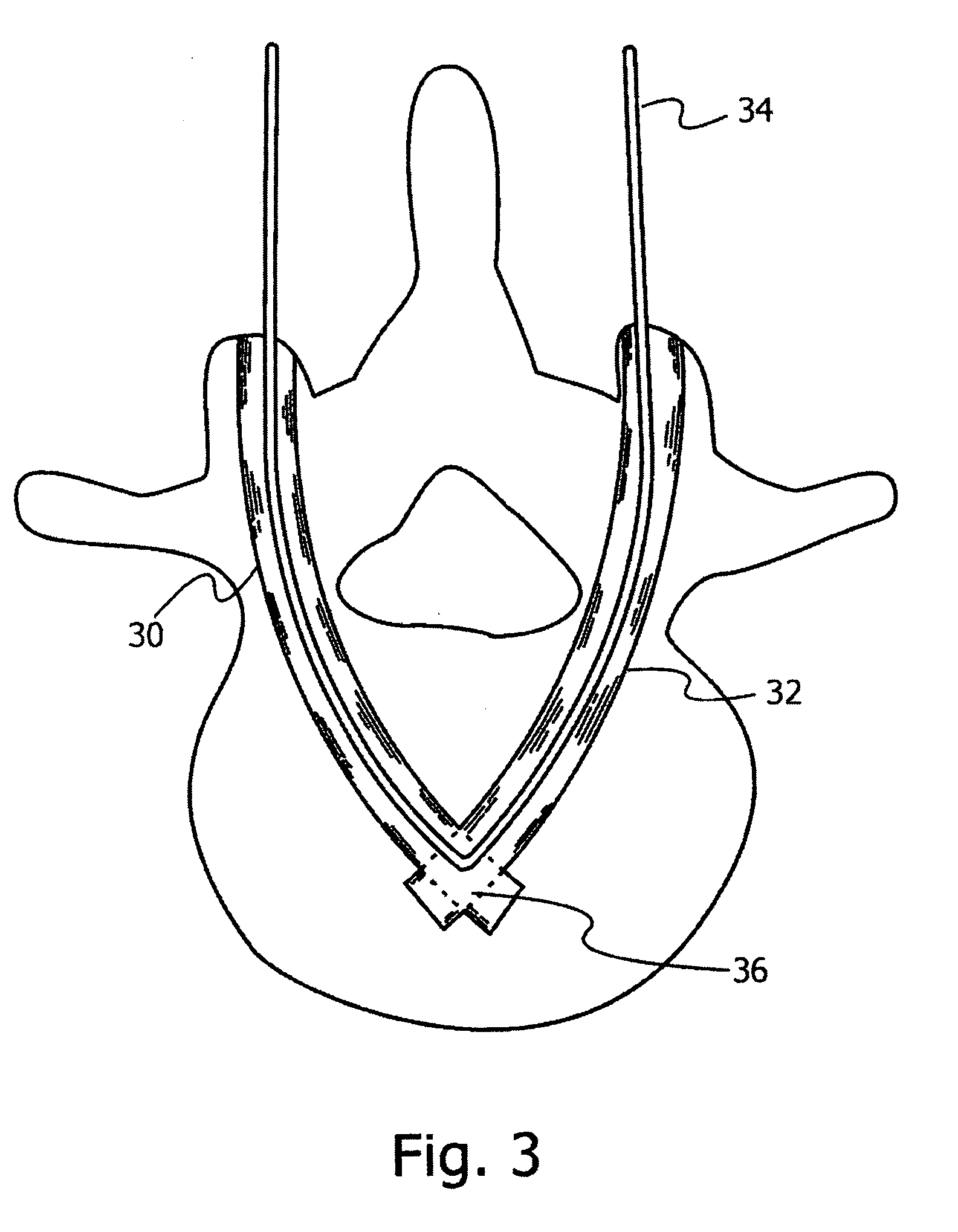
Bone anchoring system
InactiveUS20100305700A1Easy to deployReduces pull-out problemInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsIntervertebral spaceBone anchor
Methods and apparatus for connecting to a bone, which avoid the use of bone screws. A triangular shaped modular implant is used, with two sides of the structure and their respective vertex secured generally within the bone, with the base of the triangle outside the bone. These two arms, whether straight or arcuate, are cannulated, and are held together at their distal ends by a tightened cable that runs through both of the arms. The proximal ends of these arms are connected to a base side that completes the triangular structure. The device may be inserted into a vertebra and the base used for vertebral fusion. Alternatively, the arms themselves may be used to stabilize and fixate adjacent vertebrae, by insertion through adjacent vertebrae trans-segmentally. In the latter case, the vertex may be within the intervertebral space or within the vertebral body close to the intervertebral space.
Owner:SCORPION SURGICAL TECH
Spinal implants and methods
InactiveUS20090138015A1Reduce relative motionSmooth motionBone implantDiagnosticsPosterior regionIntervertebral disk
Spinal implants are disclosed that can be used for annular repair, facet unloading, disc height preservation, disc decompression, or for sealing a portal through which an intervertebral implant was placed. In some embodiments, an implant is placed within the intervertebral disc space, primarily within the region of the annulus fibrosus. In some embodiments, the implant is expandable. In some embodiments, the implant has a sealing tail structure comprising a tail flange and a linkage. In some embodiments, the sealing tail structure limits the extrusion or expulsion of disc material, either annulus fibrosus or nucleus, into the posterior region of the spine where it could impinge on nerves. In some embodiments, the tail structure is retained in place within the annulus fibrosus by means of an anchor. In some embodiments, the anchor is constructed from multiple components.
Owner:CONNER E SCOTT DR
Knee joint prosthesis for bi-compartmental knee replacement and surgical devices thereof
InactiveUS20080119938A1Improve rangePreventing malalignment and shakingJoint implantsKnee jointsFlexion deformitySacroiliac joint
There are provided a knee joint prosthesis for a bi-compartmental knee replacement and surgical devices thereof, wherein the knee joint prosthesis for the bi-compartmental knee replacement, which is performed on a patient with degenerative arthritis at any one of an inside compartment and an outside compartment of the knee and between the femur and the patella, is configured to position a femoral component at the inside or outside of the femur of the patient, to position a tibial component at the inside or outside of the tibia, and to properly position a tibial bearing member between the femoral component and the tibial component, thereby having the effects of improving the range of sense and motion after surgery by preserving other normal joints and reducing blood loss compared to a conventional prosthesis; improving the accuracy of the surgery to prevent the malalignment of the prosthesis, reduce the shaking of the prosthesis and extend the use life of the prosthesis; significantly improving a securing force compared to a conventional prosthesis; and using the knee joint prosthesis for the bi-compartmental knee replacement for patients with bi-compartmental arthritis, genu varum and genu valgum and flexion deformity, and anterior cruciate ligament loss.
Owner:OH SANG SOO
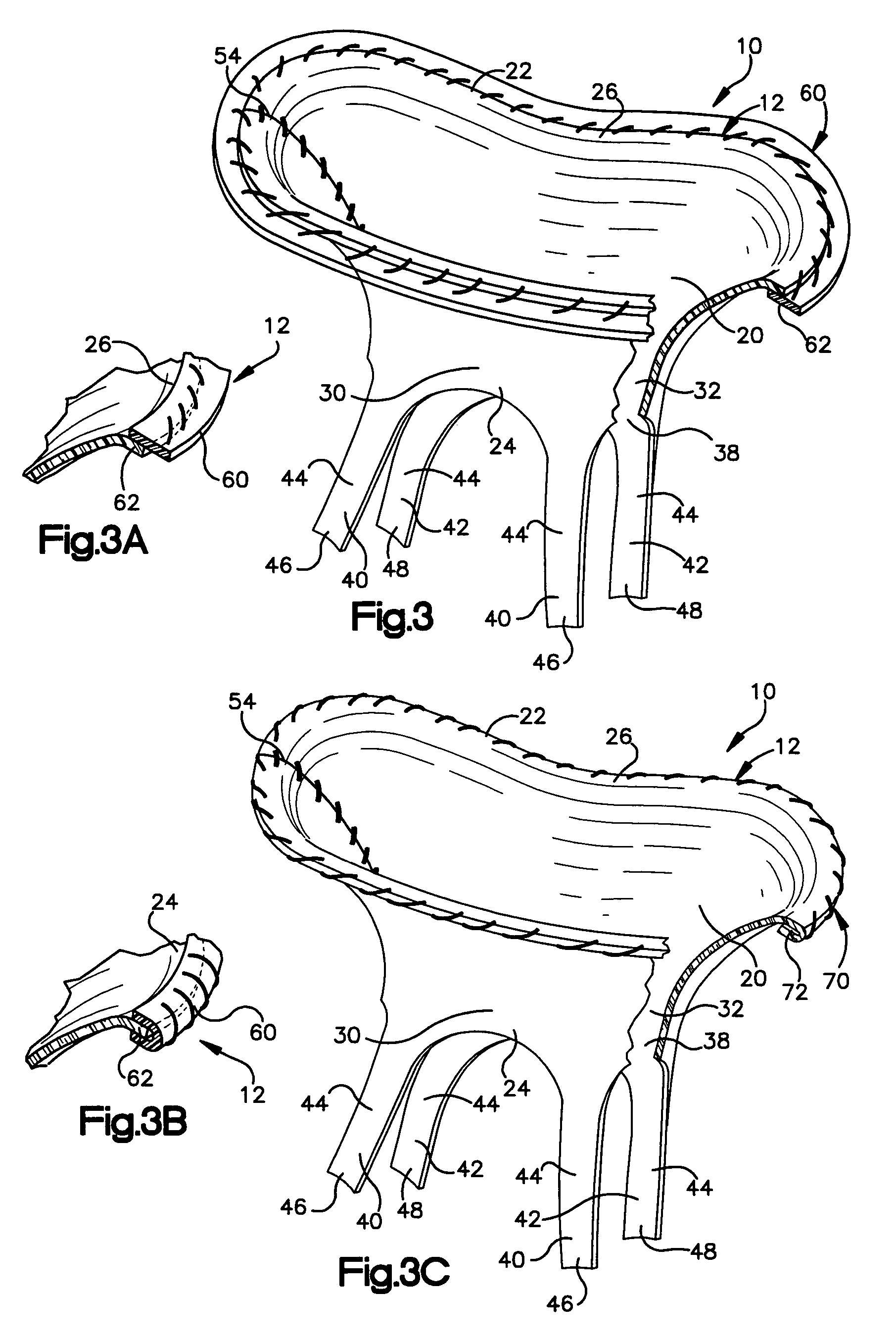
Stentless bioprosthetic valve having chordae for replacing a mitral valve
A stentless bioprosthetic valve includes at least one piece of biocompatible material comprising a bi-leaflet conduit having a proximal end and a distal end. The proximal end defines a first annulus for suturing to the valve annulus. The conduit includes first and second leaflets that mimic the native leaflets and extend between the conduit ends. The distal end defines a second annulus at which the first and second leaflets terminate. The conduit further includes first and second pairs of prosthetic chordae projecting from the leaflets at the second annulus. One of the first pair of prosthetic chordae extends from the first leaflet and has a distal end for suturing to a papillary muscle and the other of the first pair of prosthetic chordae extends from the first leaflet and has a distal end for suturing to another papillary muscles.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
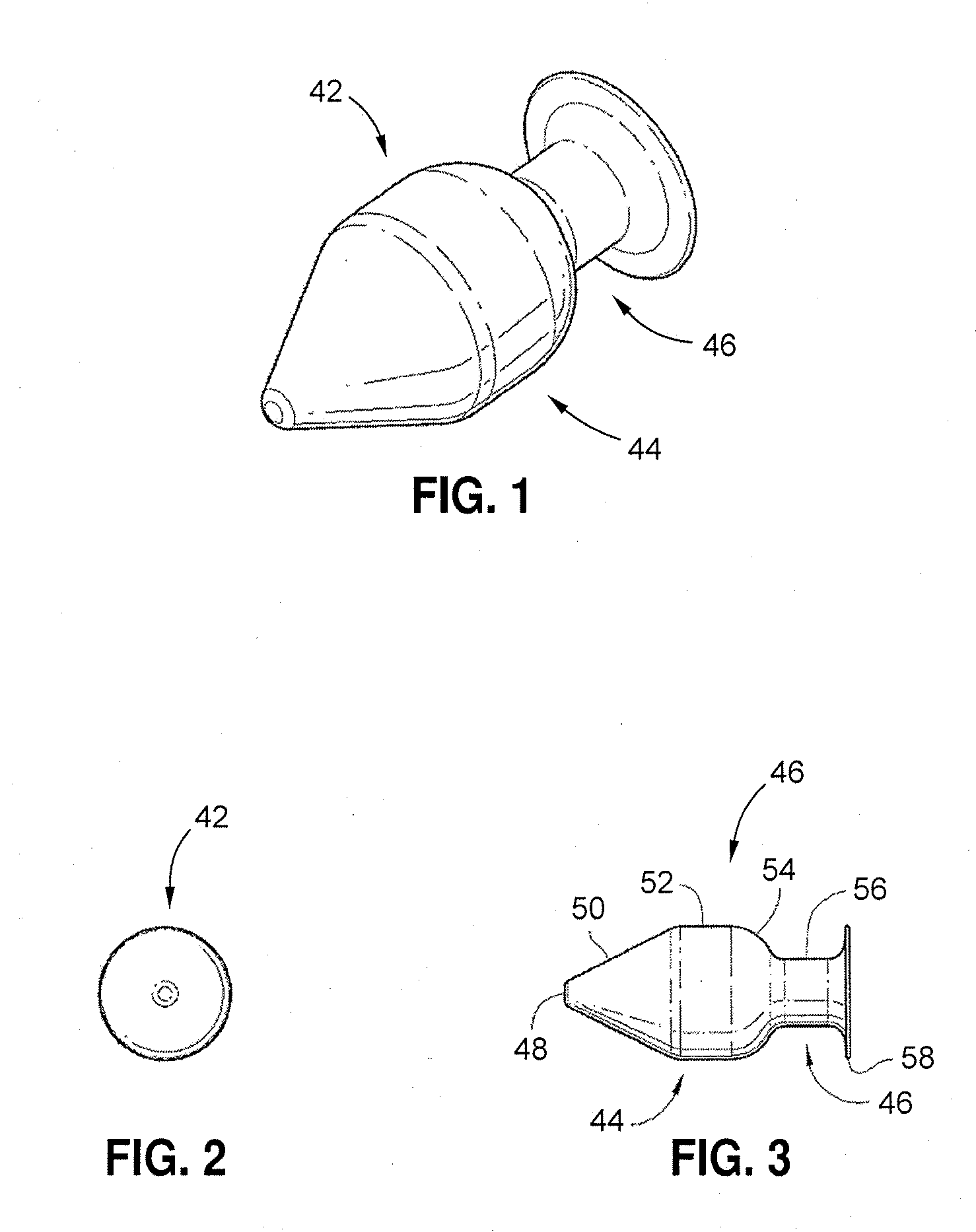
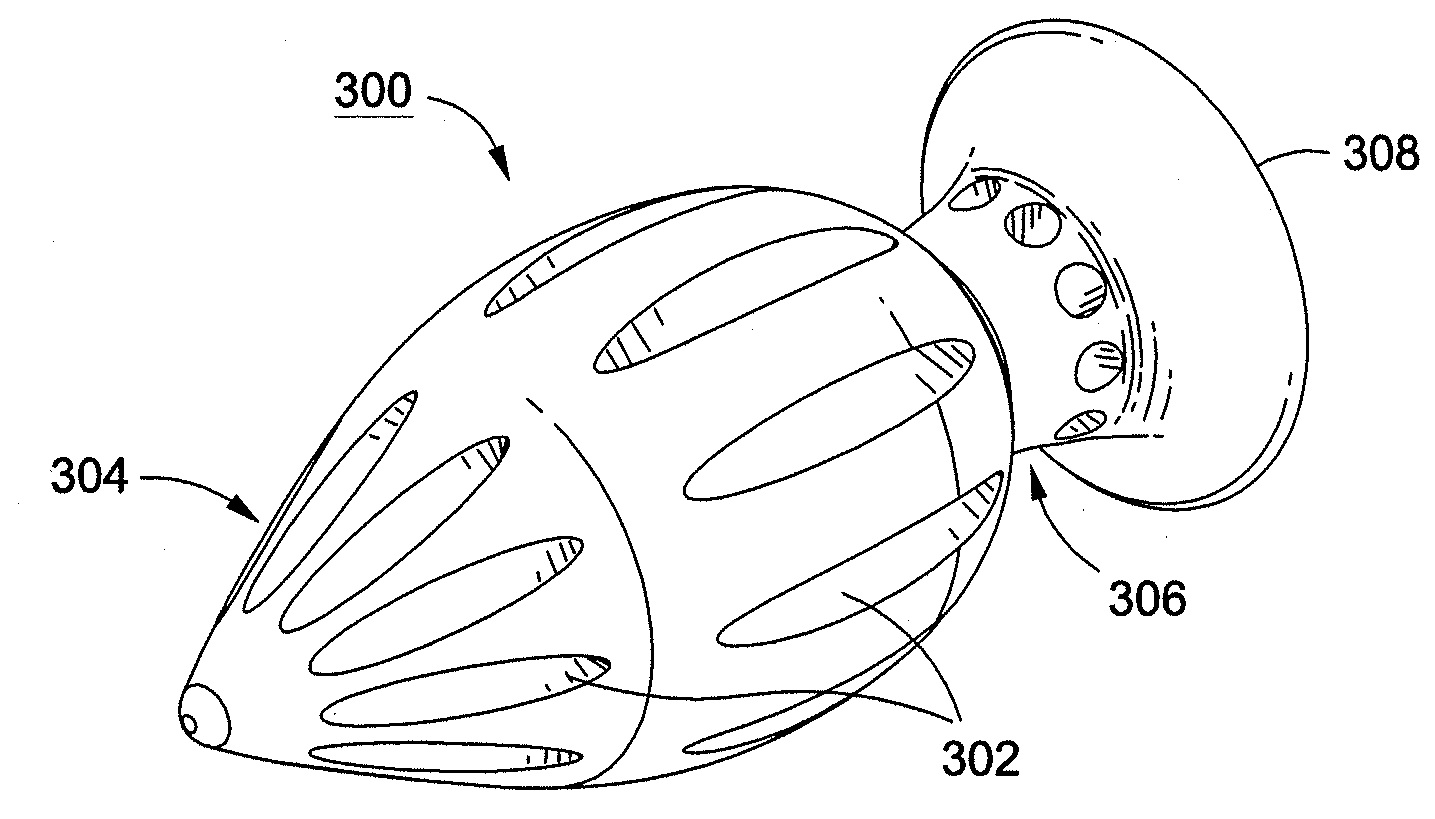
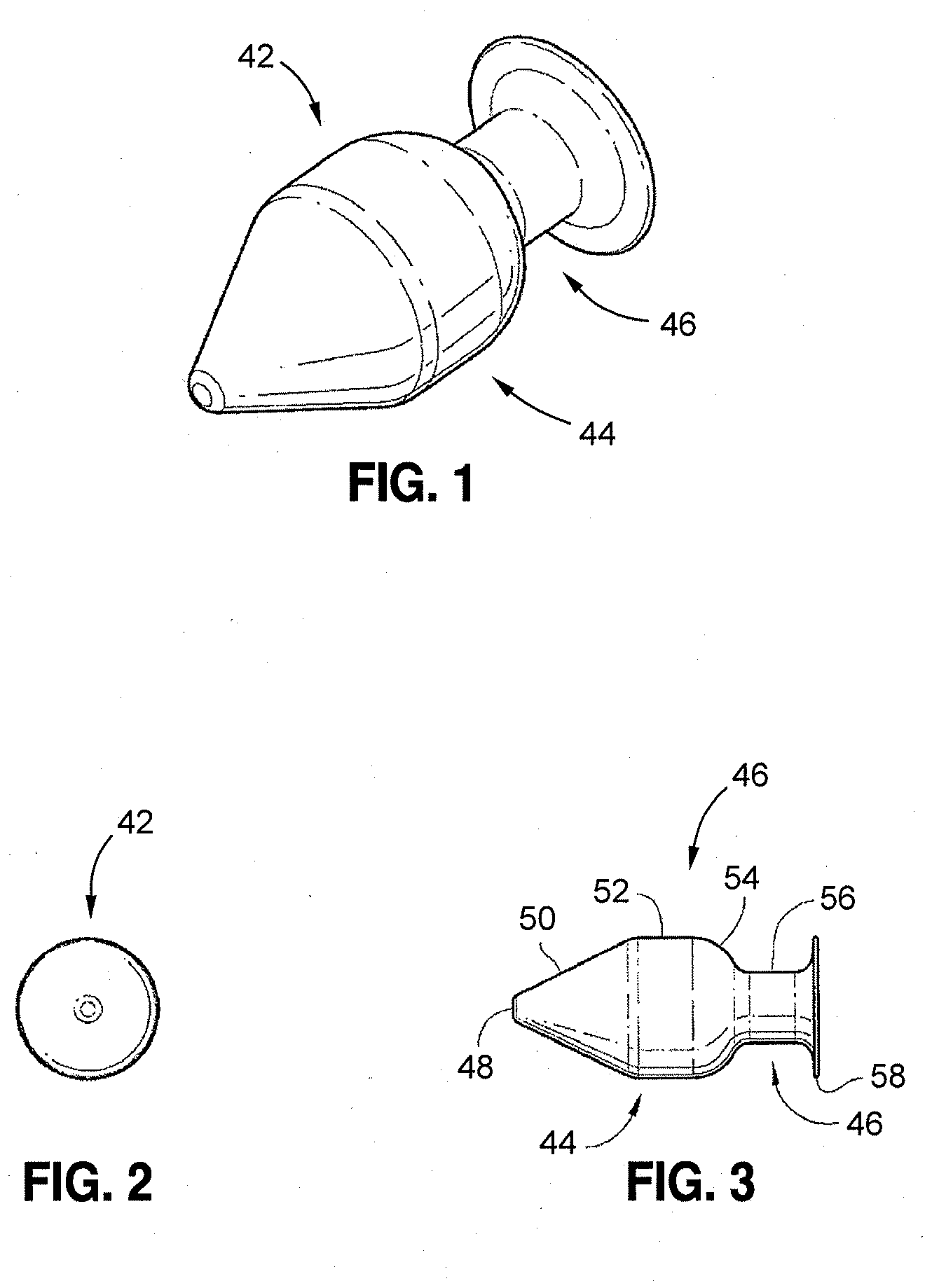
System and Method for Sizing, Inserting and Securing Artificial Disc in Intervertebral Space
InactiveUS20080103598A1Exceptional characteristicExceptional mechanical performanceSpinal implantsCoatingsMedicineIntervertebral space
A prosthetic spinal implant having a deployable securing mechanism that is deployable into a portion of the vertebral space for affixing the implant between the vertebrae, the securing mechanism having tactile feedback means comprising a surface for transmitting tactile feedback during deployment of the securing mechanism. A spinal implant having deployable securing means that interface with the implant to prevent the deployable securing means from retracting after deployment. An implant that utilizes its resilient properties to provide the user with tactile feedback with which the user may ascertain the position of the securing mechanism. A system and tools for sizing and implanting implants with the aforementioned characteristics.
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
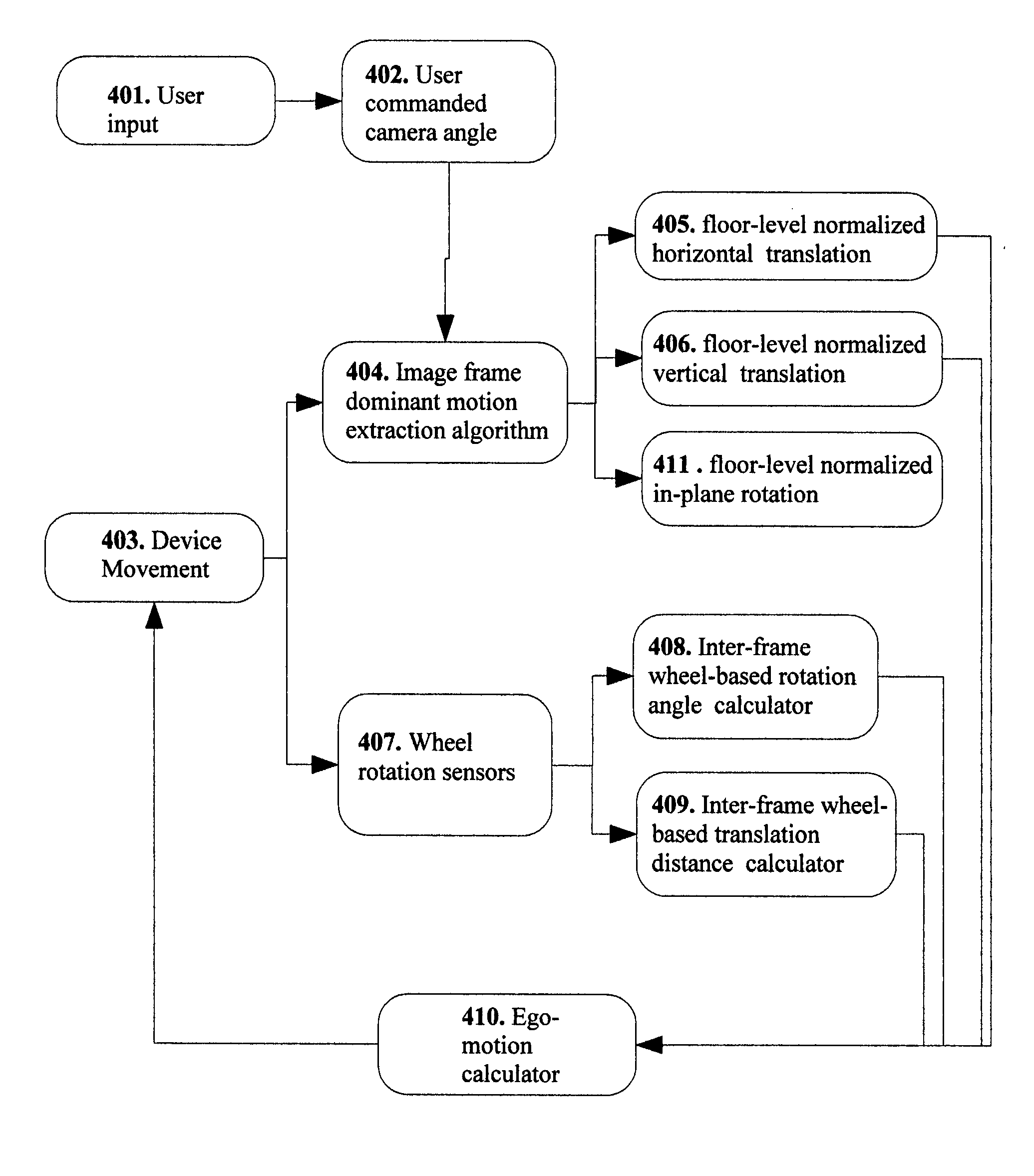
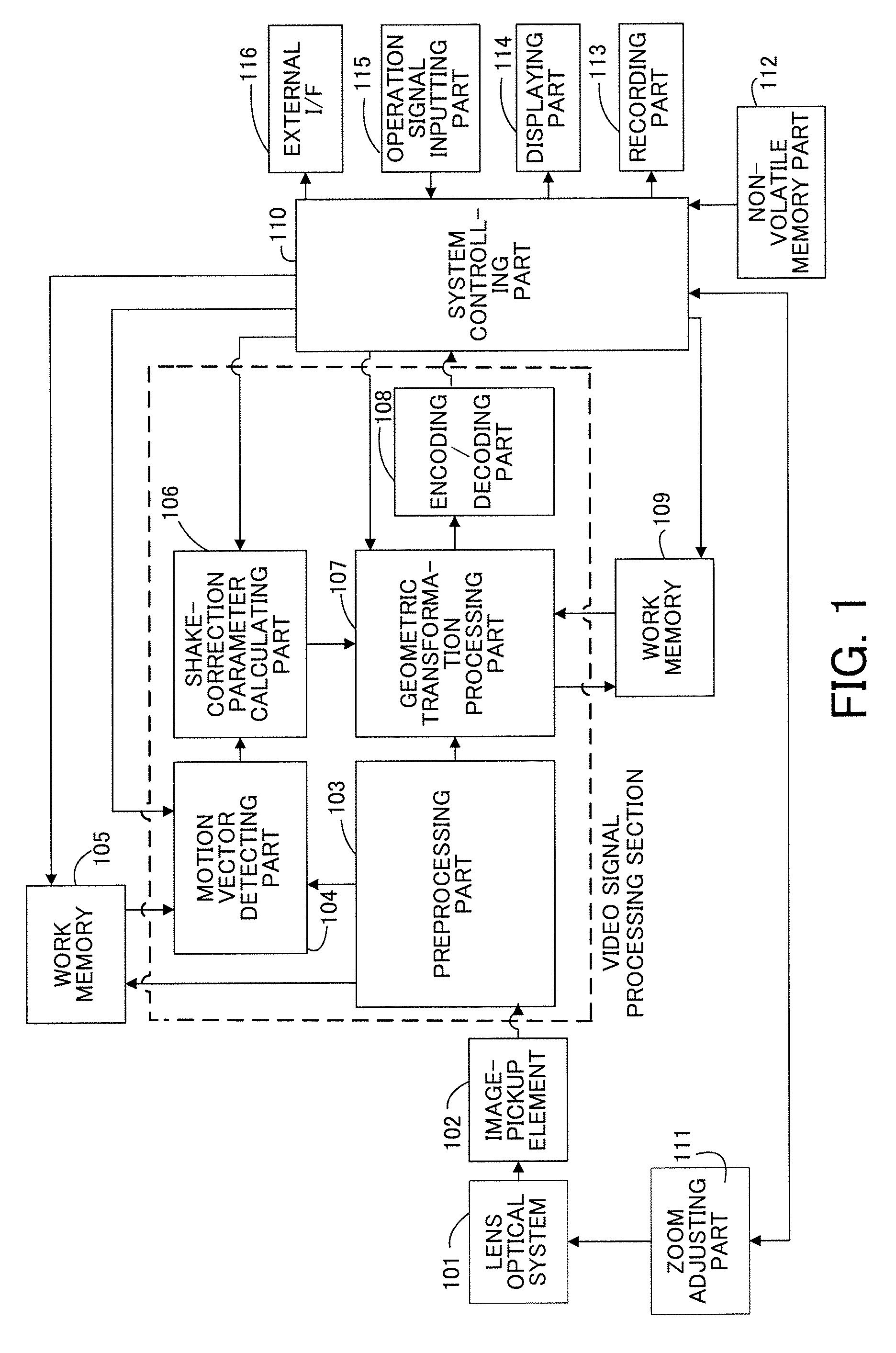
Image stabilizing apparatus, image-pickup apparatus and image stabilizing method
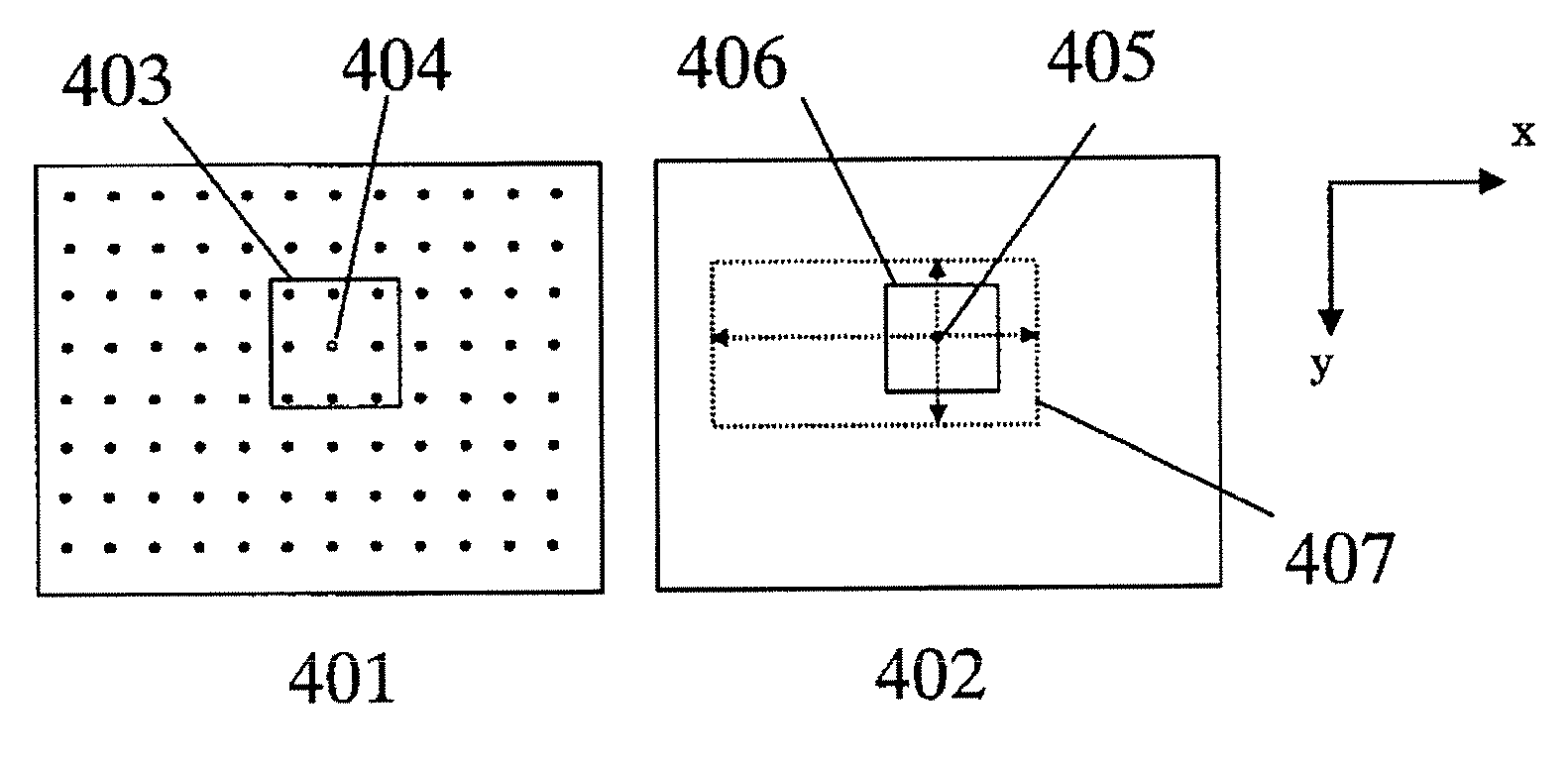
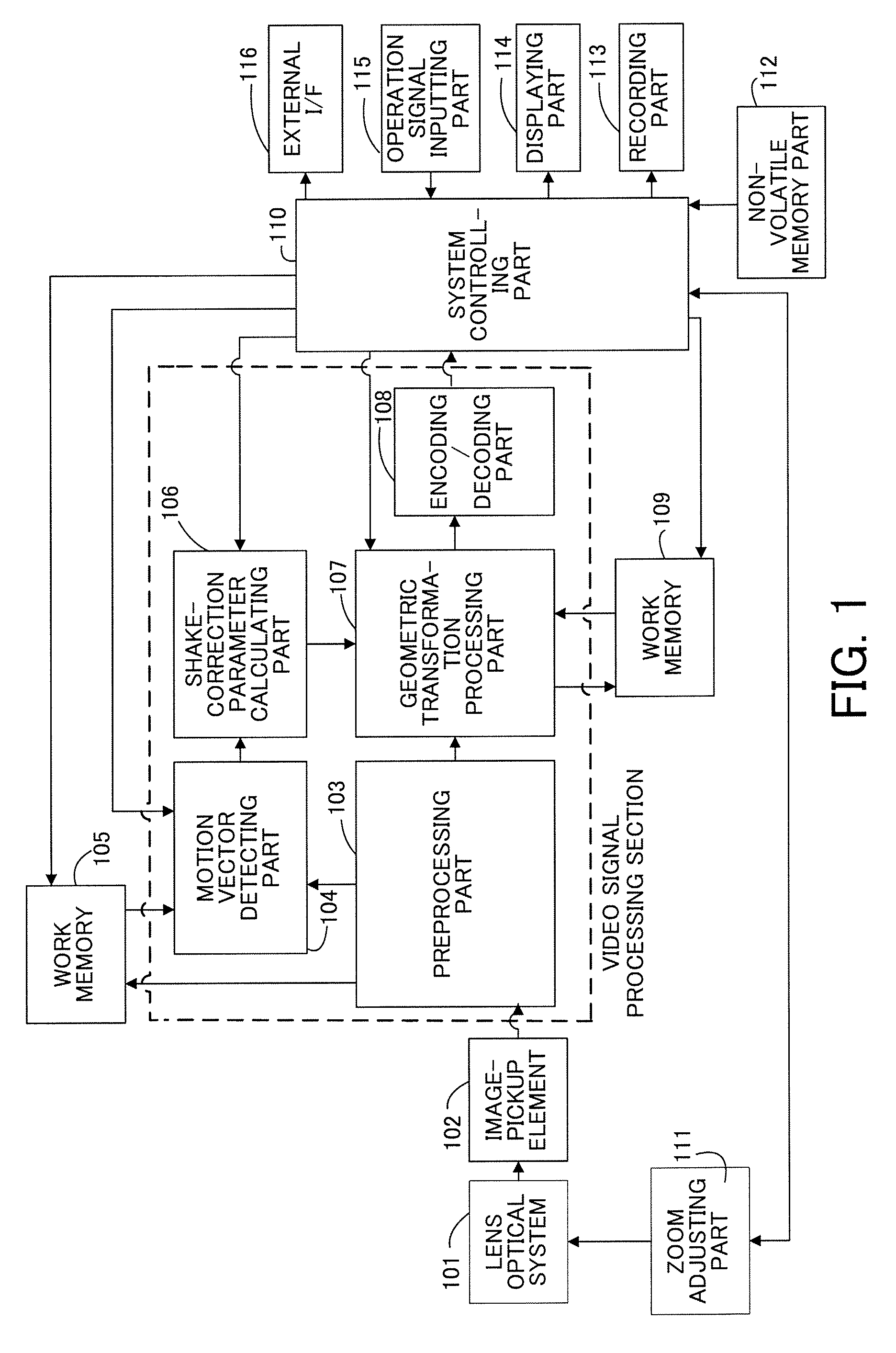
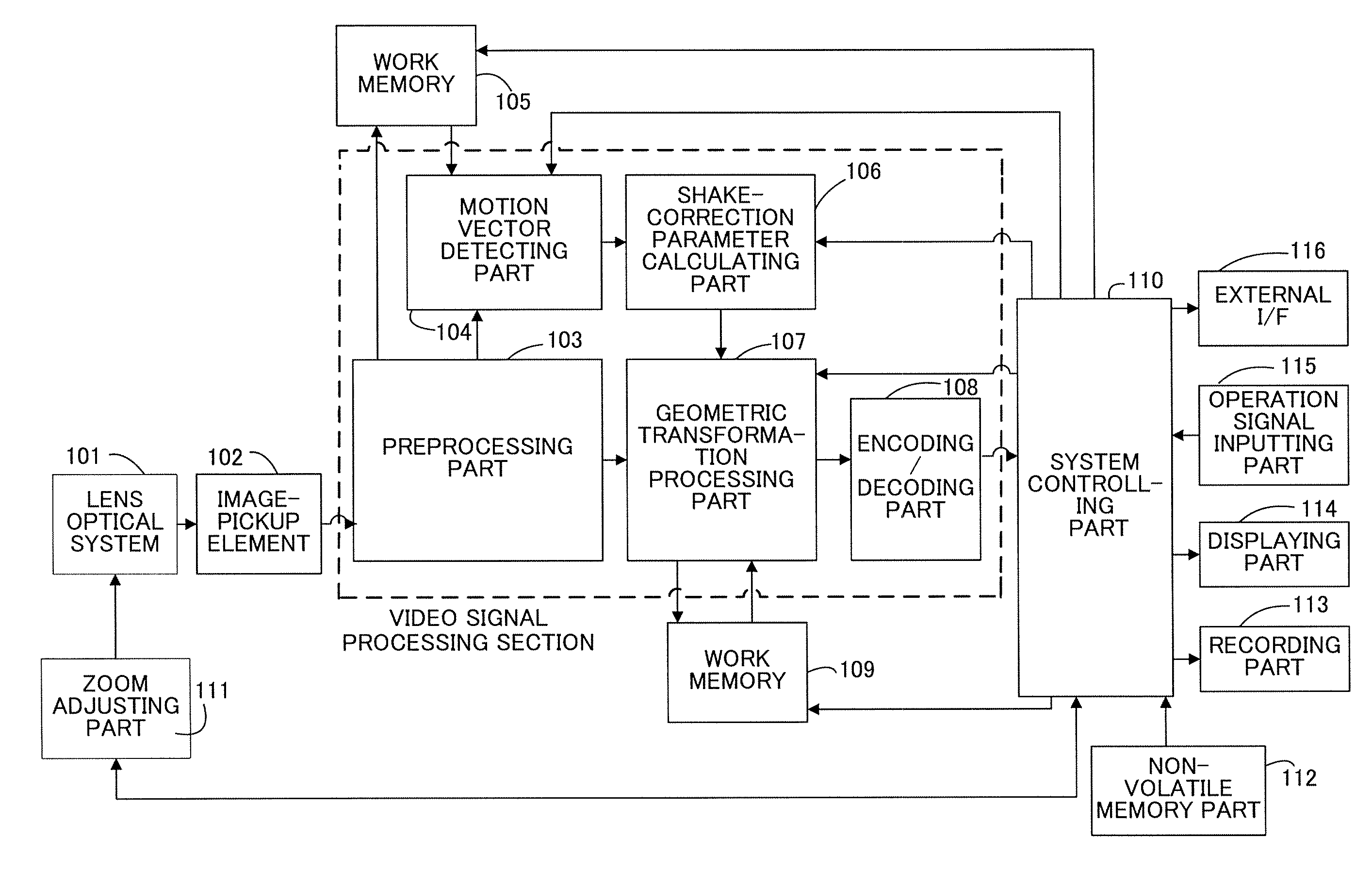
ActiveUS20080246848A1Keep movingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage stabilizationMotion vector
An image stabilizing apparatus includes a motion vector calculating part that calculates a motion vector between a plurality of images including a displacement caused by a motion of an image-pickup apparatus, a shake-correction parameter calculating part that receives the motion vector as input to calculate a shake correction amount, and an image transforming part that performs geometric transformation of the image in accordance with the shake correction amount. The shake-correction parameter calculating part performs variation amount calculation, variation amount correction and correction amount calculation based on the motion information between the plurality of images. The image stabilizing apparatus preserves a motion in video from an intended camera work and allows image stabilization for an unintended shake.
Owner:CANON KK
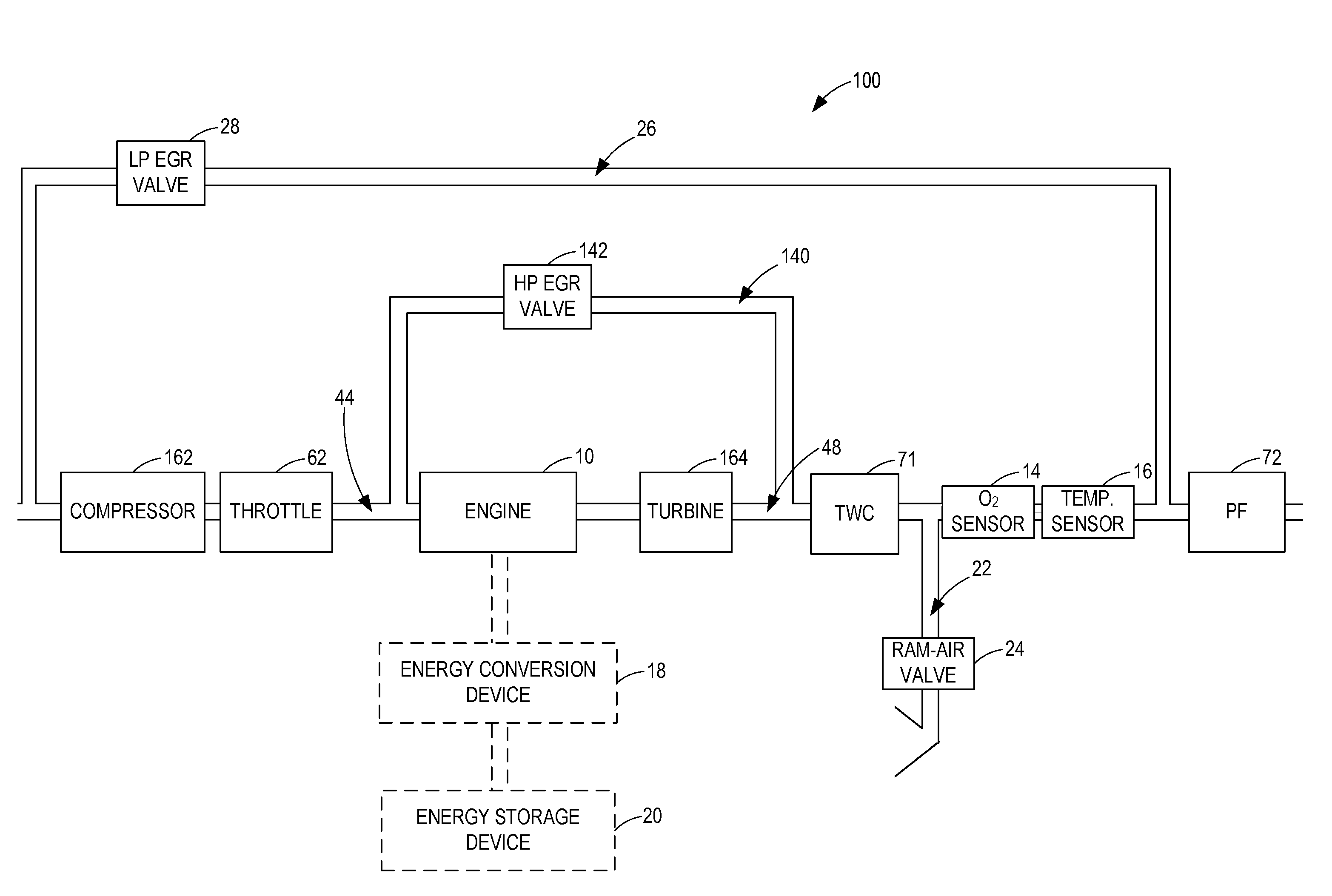
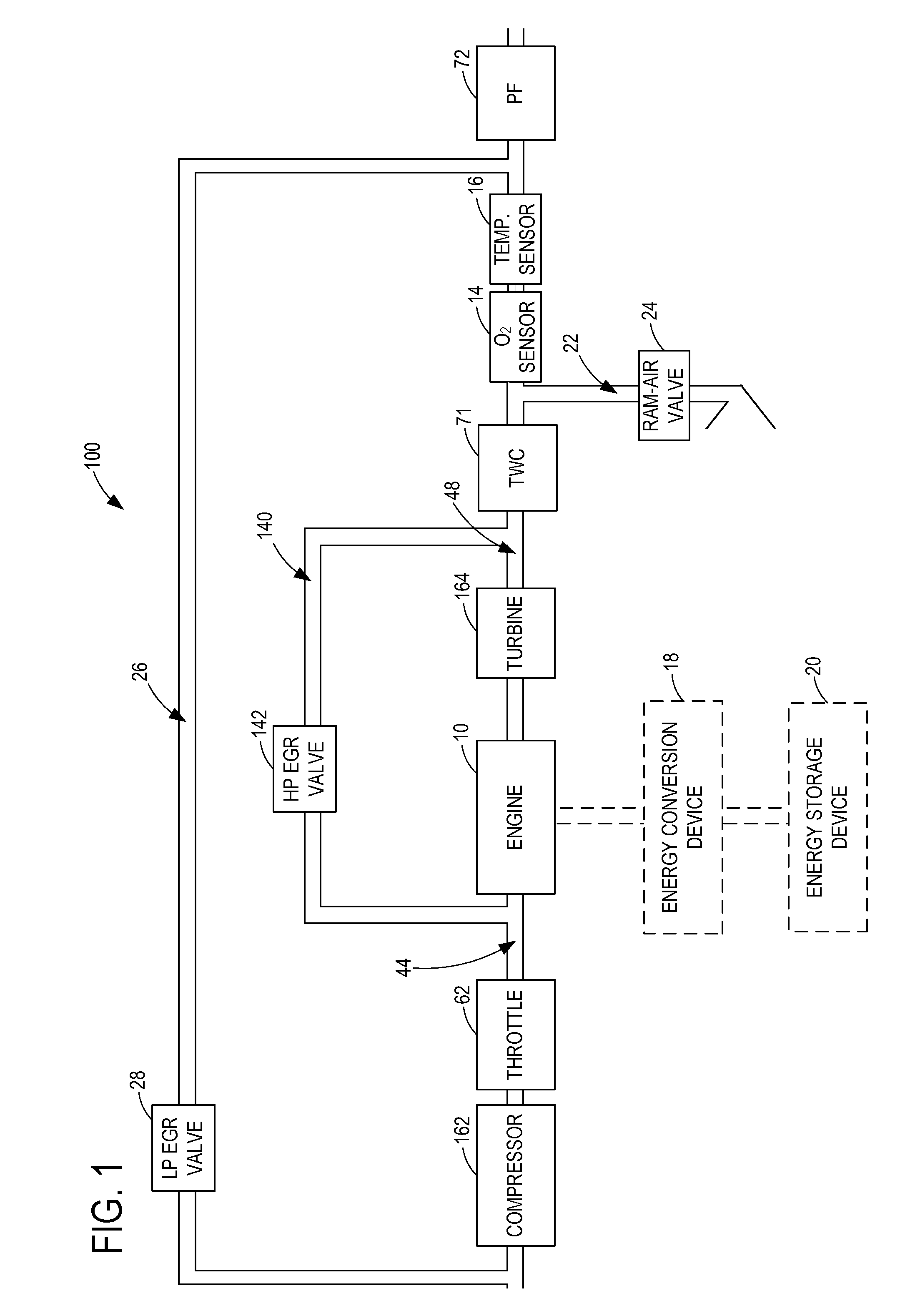
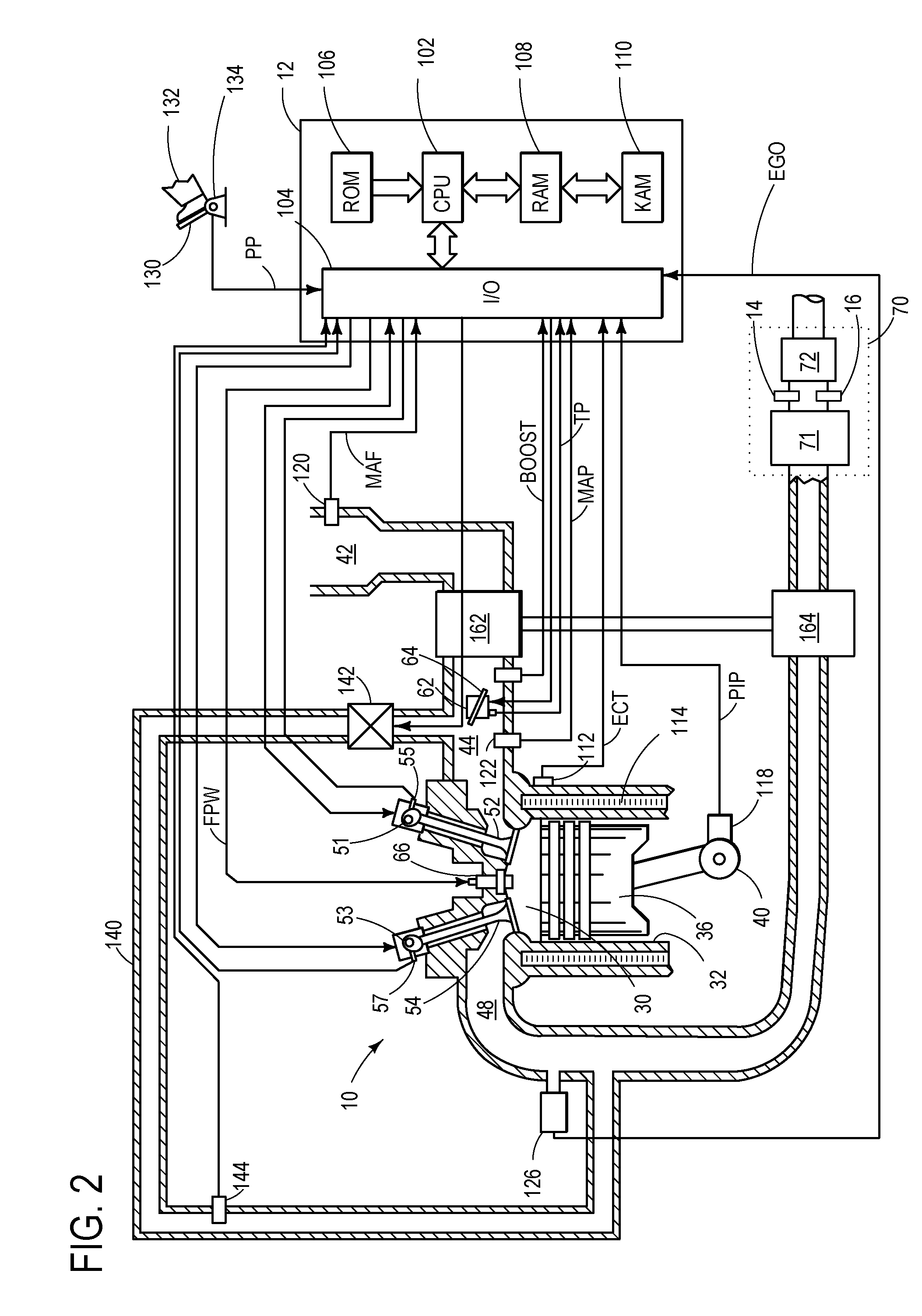
Particulate filter regeneration in an engine coupled to an energy conversion device
ActiveUS20110072791A1Reduce distractionsEmission reductionElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelParticulatesExcess oxygen
Systems and methods for controlling regeneration of a particulate filter downstream of an engine coupled to an energy conversion device are provided herein. One exemplary method includes, during first engine shutdown conditions, increasing excess oxygen to the particulate filter by spinning the engine with the energy conversion device, and regenerating the particulate filter. The method also includes, during second engine shutdown conditions, decreasing the excess oxygen to the particulate filter.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Methods and apparatus for accessing and treating the facet joint
InactiveUS20170189199A1Reduce pressureRelieve symptomsIncision instrumentsInternal osteosythesisDistractionDecortication procedure
Methods and systems are disclosed for accessing and treating the interior of the facet joint for vertebral distraction and immobilization. The systems include a number of tools that facilitate access to the facet joint, distraction of the articulating decortication of the articulating surfaces, and delivery of implants and agents into the facet joint for fusion.
Owner:PROVIDENCE MEDICAL TECH
Dynamically amplified micromachined vibratory angle measuring gyroscopes, micromachined inertial sensors and method of operation for the same
InactiveUS6928874B2Small amplitudeHigh amplificationAngles/taper measurementsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesParallel plateHigh amplitude
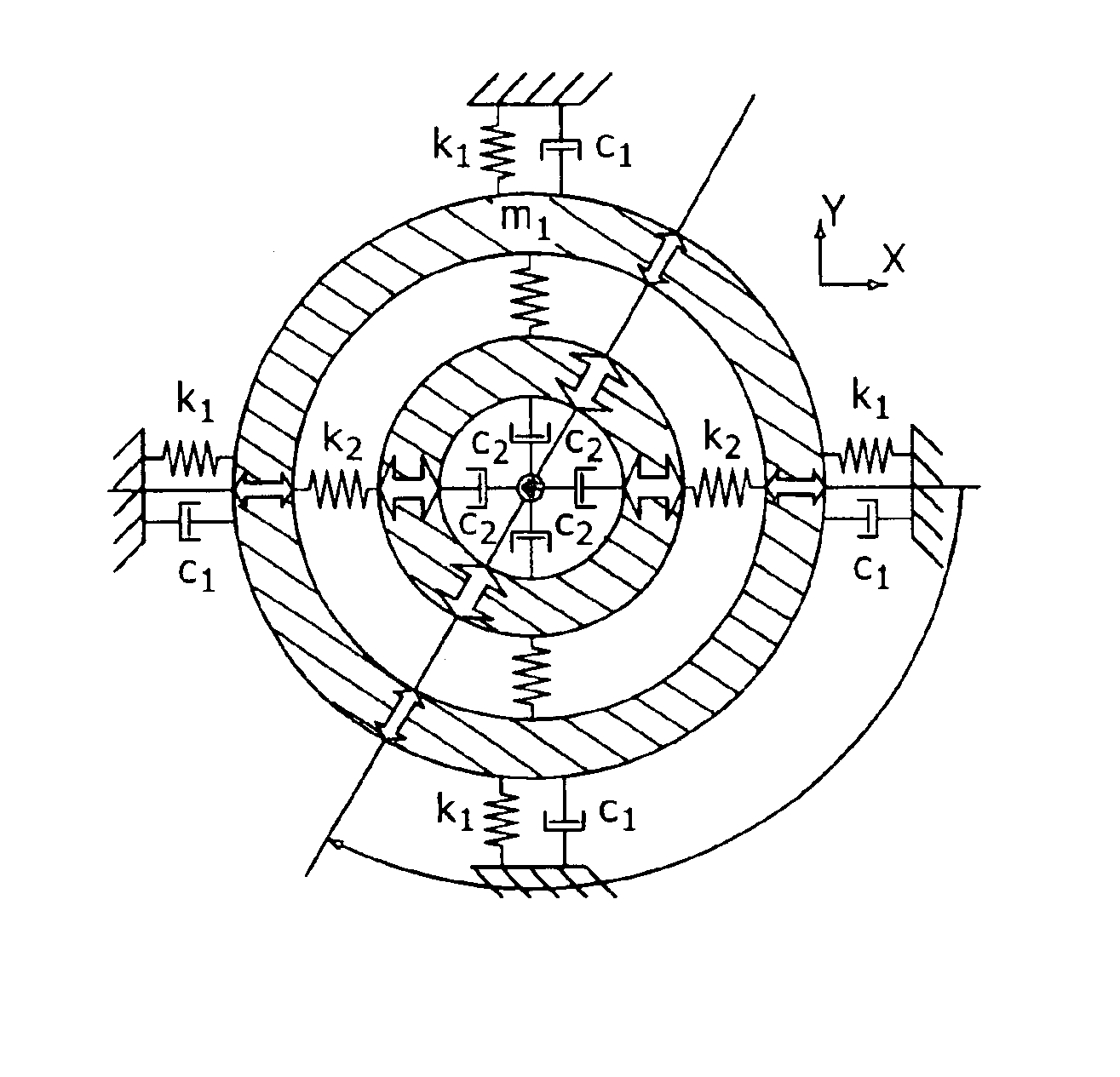
A micromachined angle measuring gyroscope using a dual mass architecture measures angular positions rather than angular rates. The invention decouples the effects of drive and sense through the use of a dual mass architecture, and is comprised of a single lumped drive mass, which is structurally coupled to a second lumped slave mass, where the drive mass is electrostatically driven at the first resonant frequency the system using parallel plate electrodes. The slave mass is driven to higher amplitudes than the drive mass. In the presence of rotation, the line of oscillation in both masses precesses, which is easily detectable in the slave mass due to the amplified motion, and is exactly equal to the angle of rotation. The two illustrated embodiments are z-axis realizations of this principle, where the first device uses an inner drive / outer sense architecture and the second uses an outer drive / inner sense architecture.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
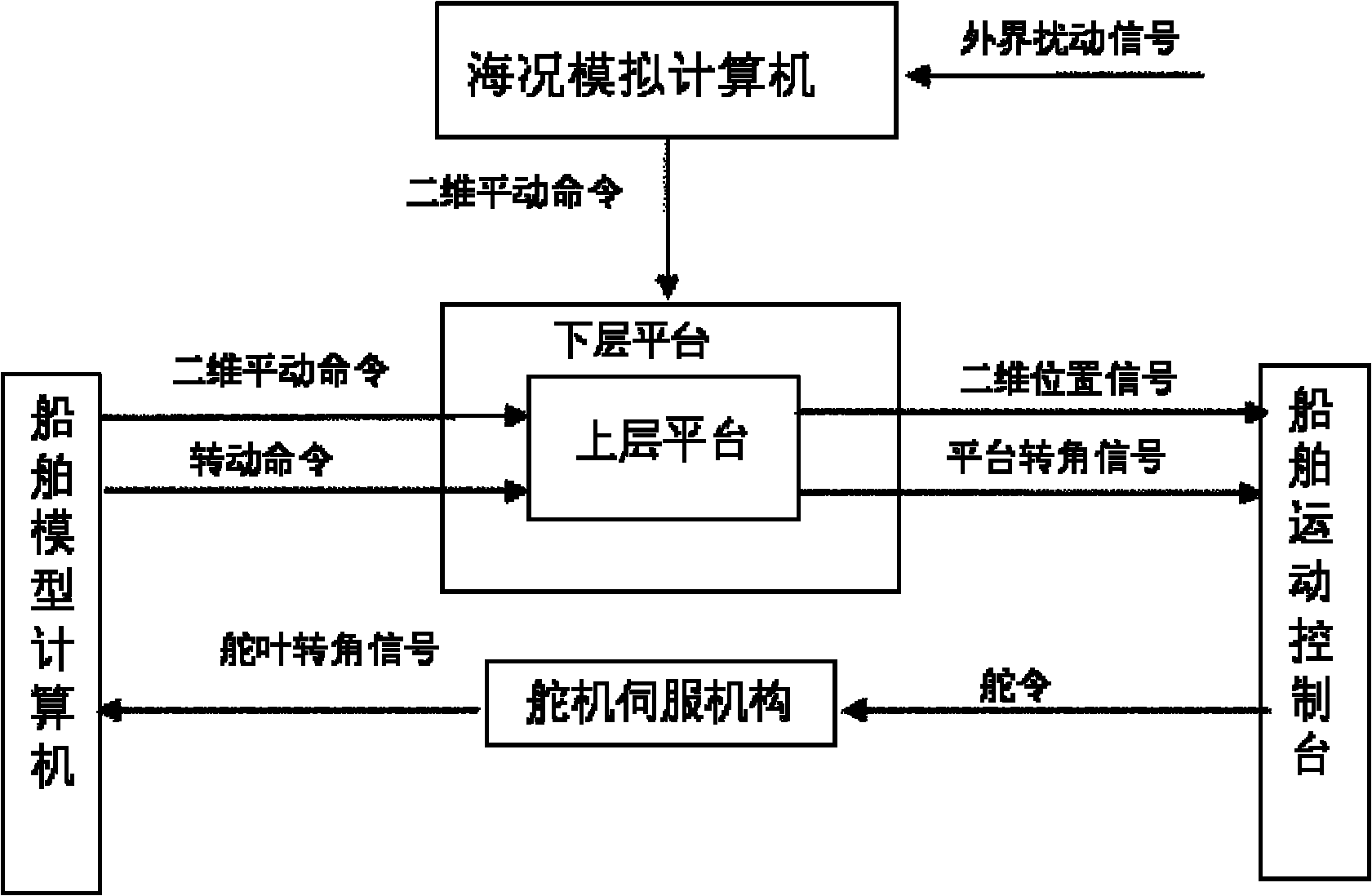
Ship position motion test platform
InactiveCN102074144AAchieving Dynamic PositioningRealize half-physical simulation experimentCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsAnalog computerRelative motion
The invention relates to a ship position motion test platform, which comprises upper and lower layers which make two-dimensional translation, wherein the upper and lower layers are controlled by a motion lock to make relative motion, and a position sensor, a compass and a global positioning system (GPS) are installed on a central platform; a sea condition simulation computer receives current sea conditions input by a keyboard, calculates and simulates the impact of external interference on a ship position and sends a two-dimensional translation command to control the lower layer to be used for simulating the sea conditions, and a ship motion console issues corresponding control commands to a rudder and a side thruster according to the detected ship position; and a ship model computer receives the commands issued by the ship motion console, obtains the current rubber angle and the position of a ship under the action of the side thruster by calculation, issues the two-dimensional translation commands to control the upper layer to move relative to the lower layer, issues rotating commands to control the central platform to rotate, and simulates the deflection of the ship under the action of the side thruster at the current rudder angle. In the ship position motion test platform, the ship parameters and the sea conditions can be arbitrarily set to realize the semi-physical simulation test of the dynamic positioning and automatic berthing or unberthing of the ship.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY +1
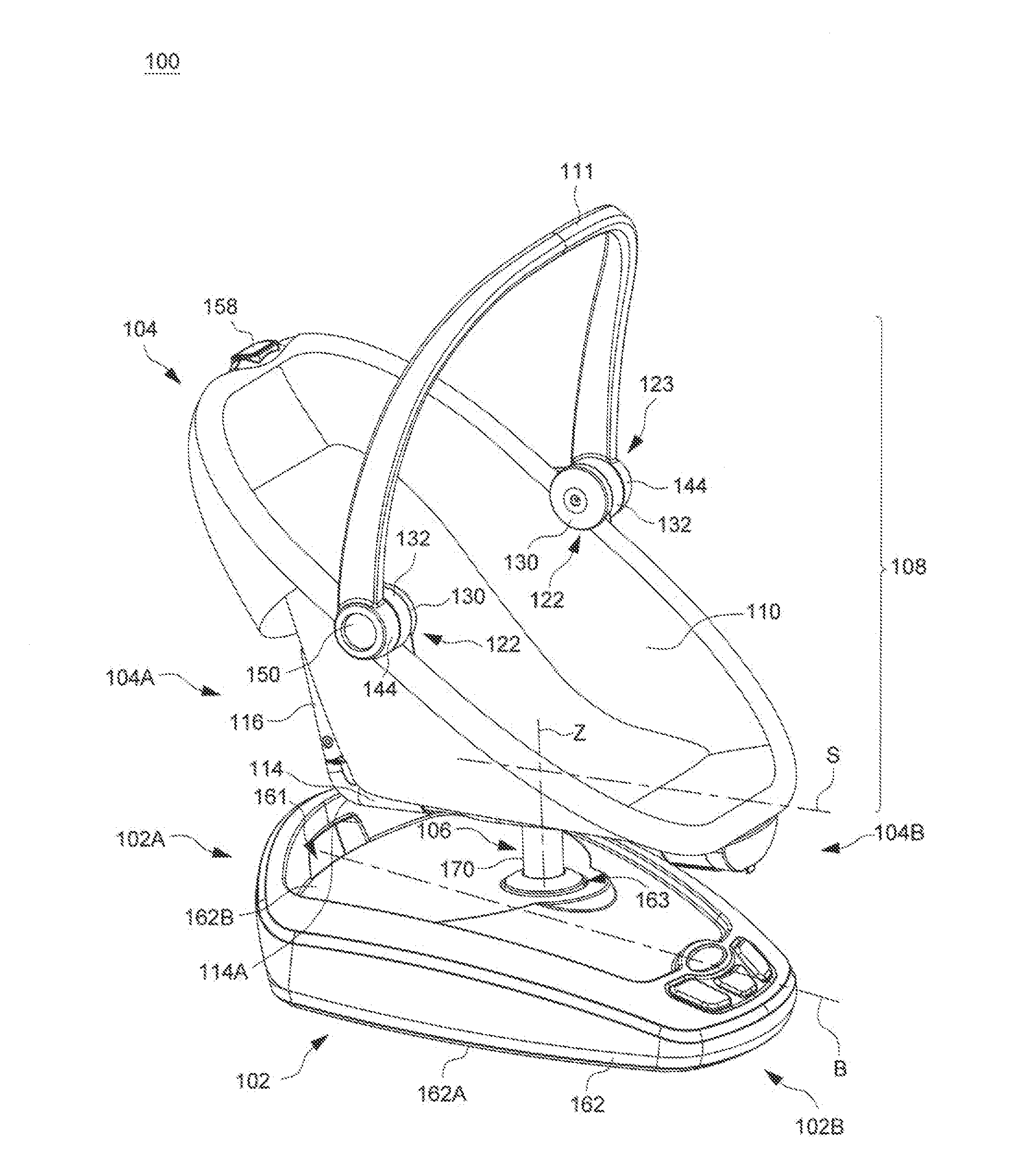
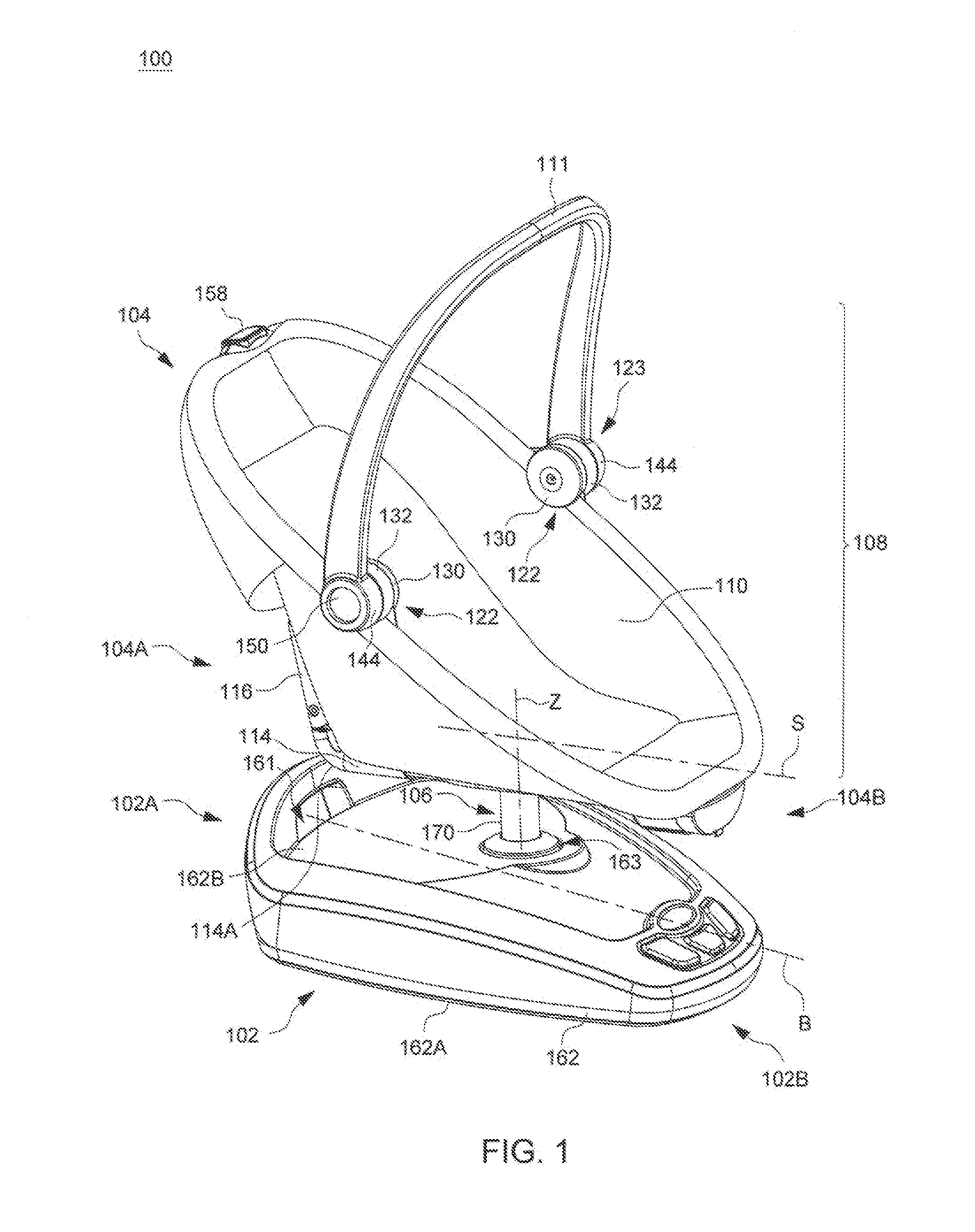
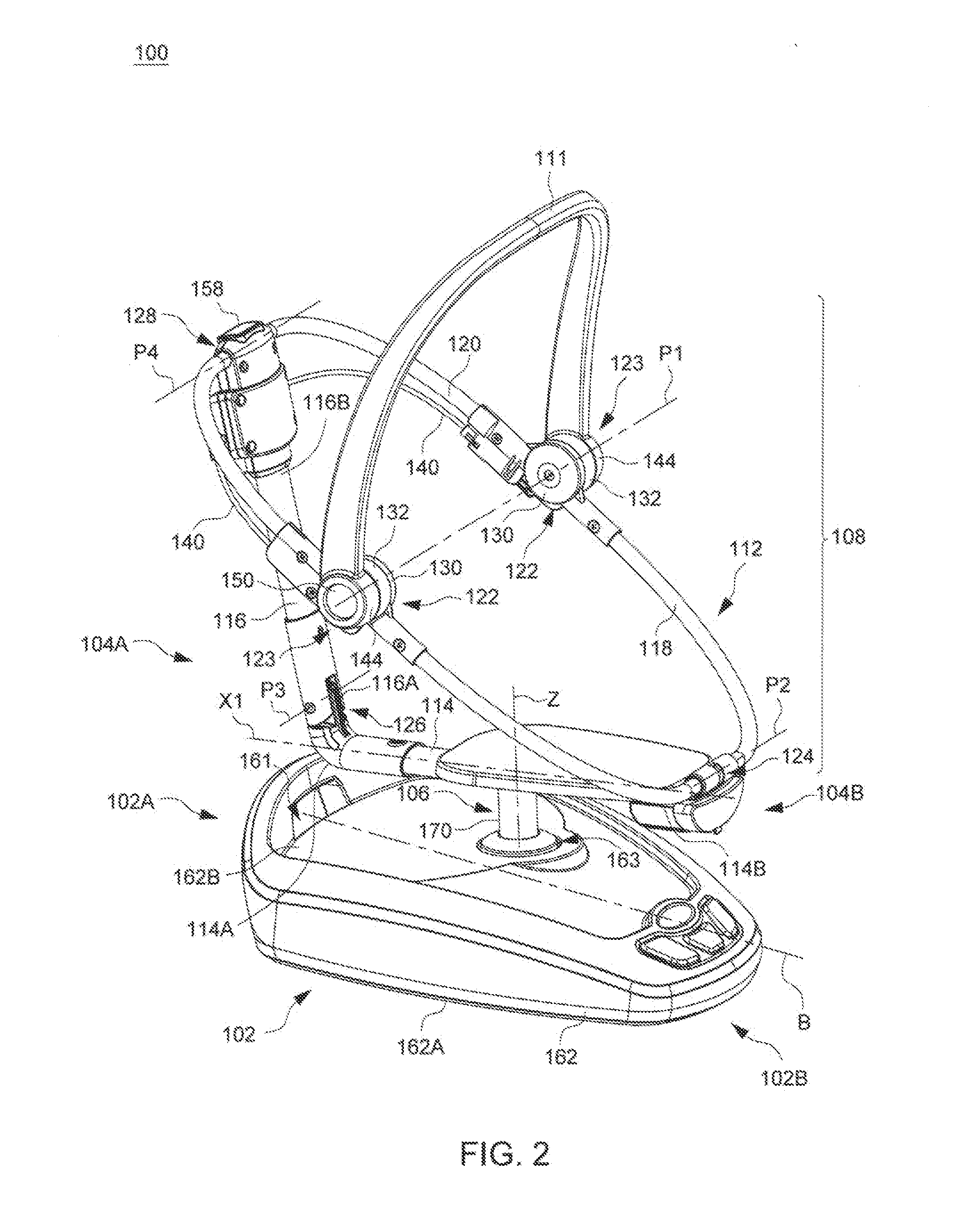
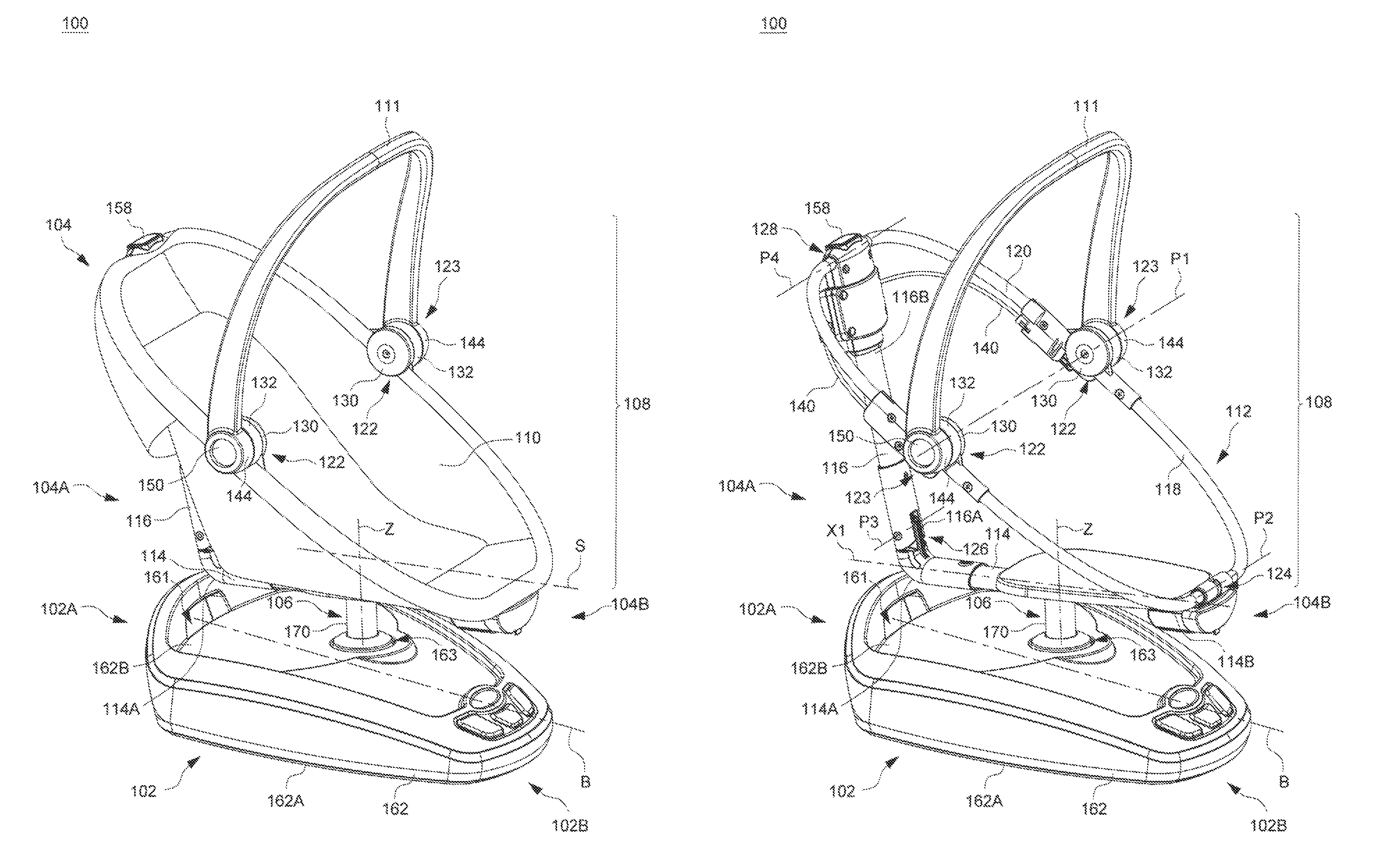
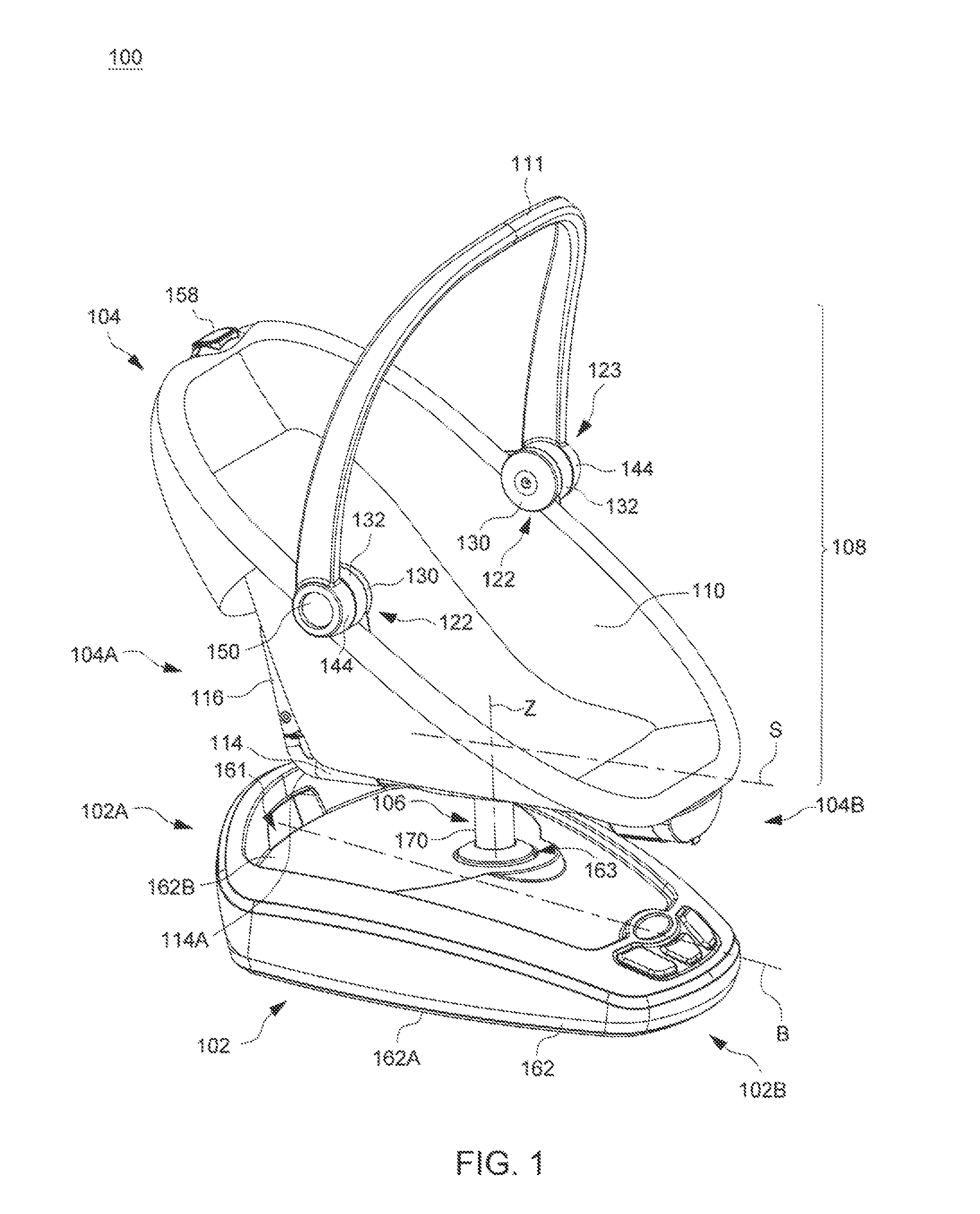
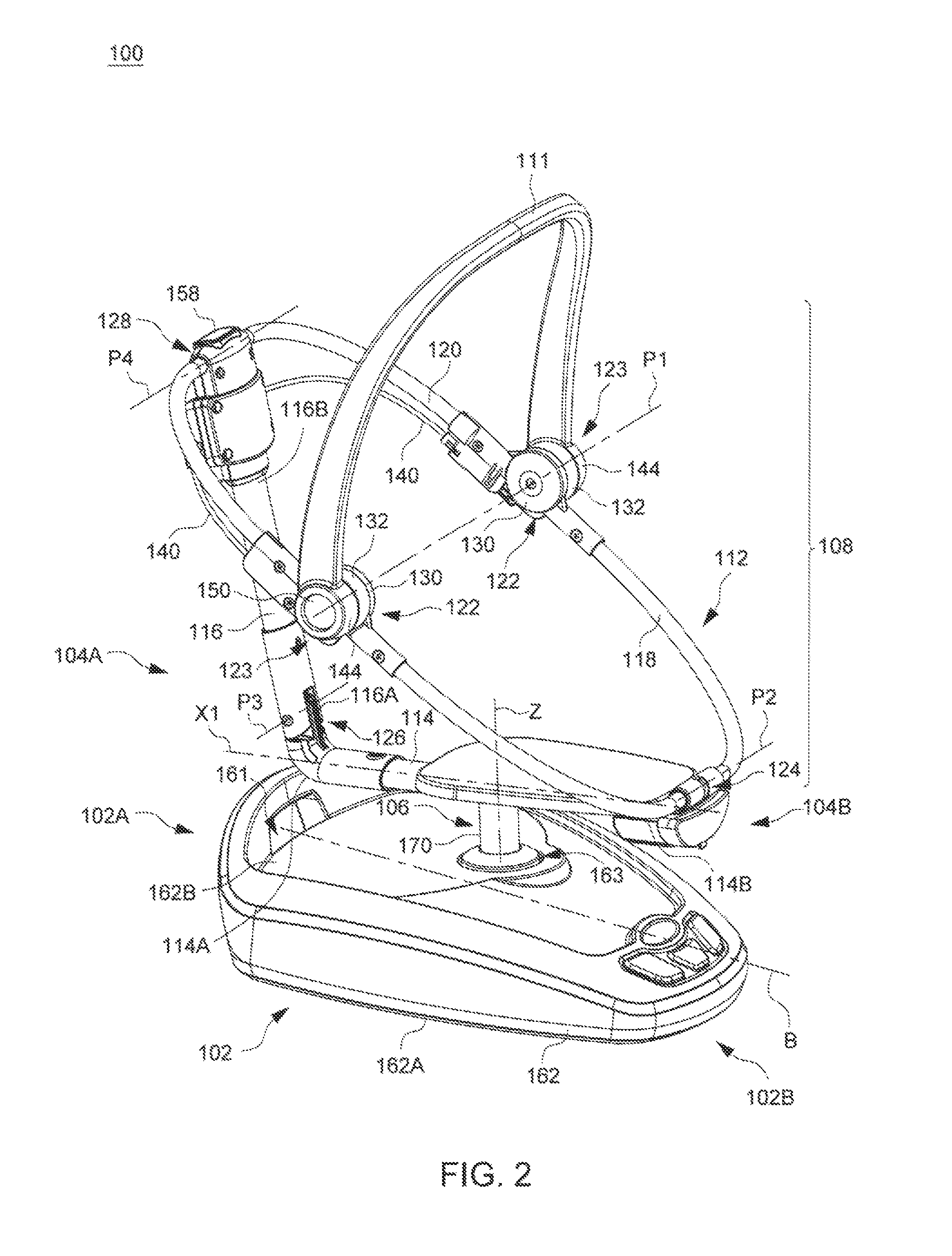
Child Motion Apparatus
ActiveUS20150250330A1Easy to transportKeep movingCradleDismountable chairsEngineeringFront and back ends
Owner:WONDERLAND SWITZERLAND AG
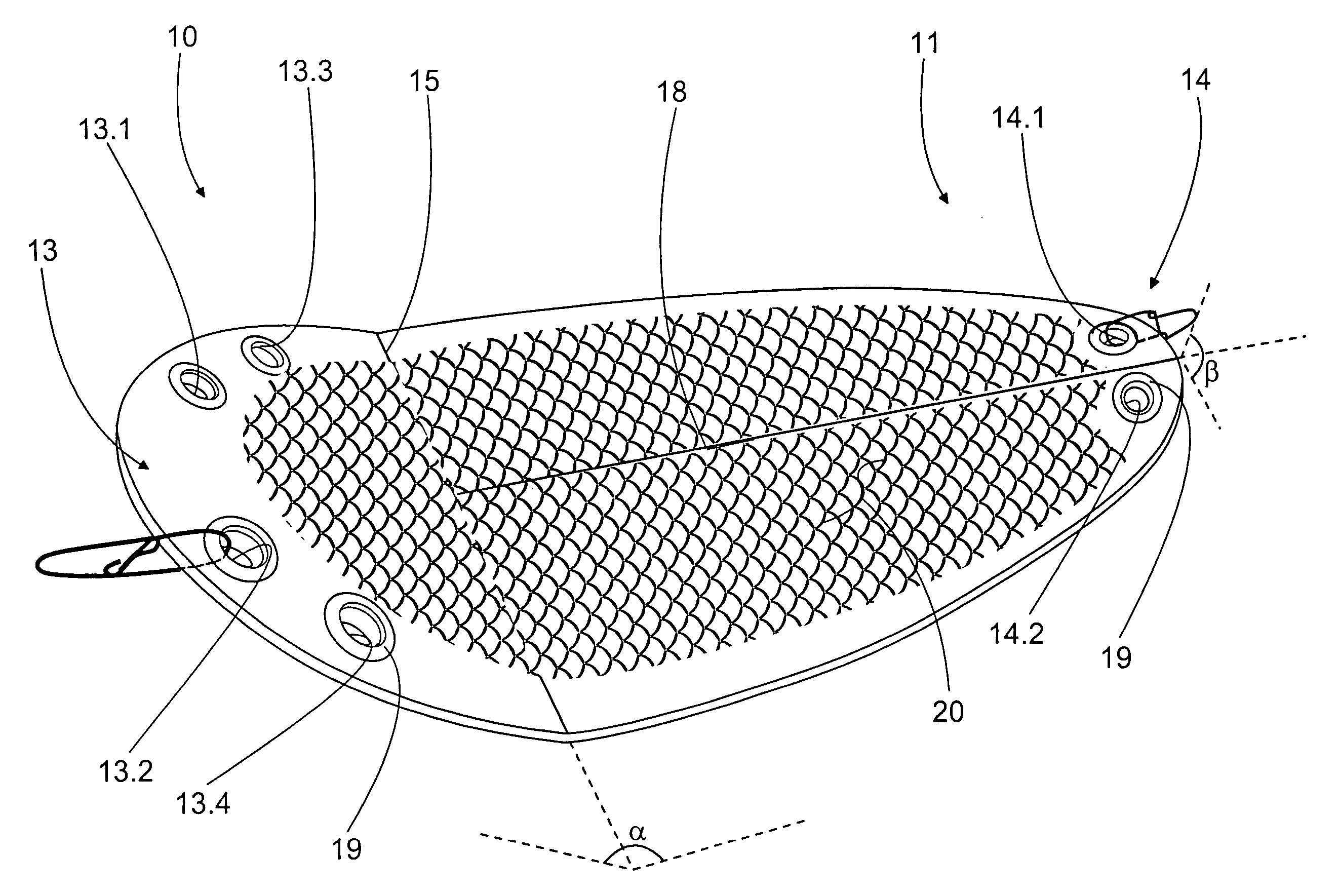
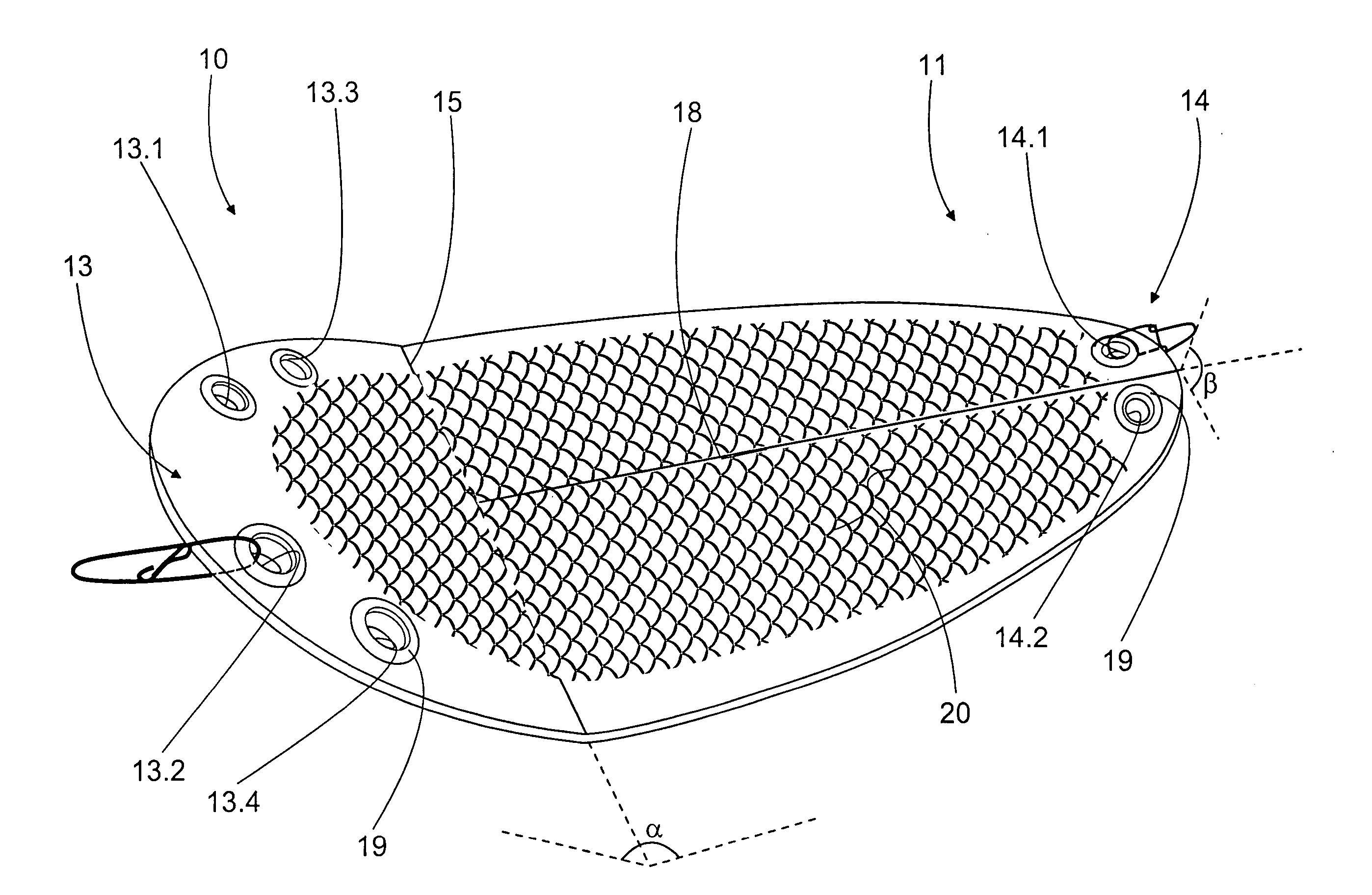
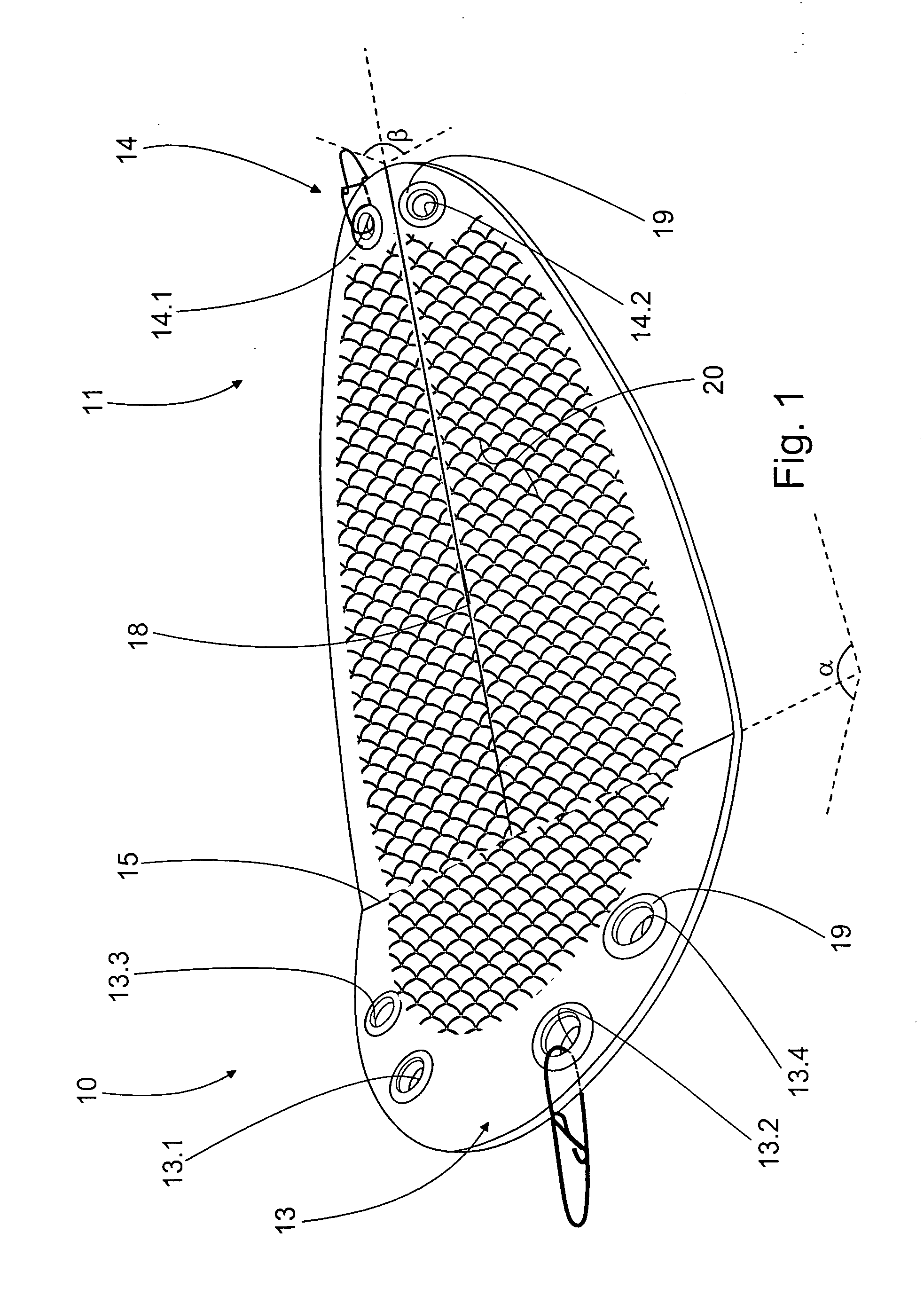
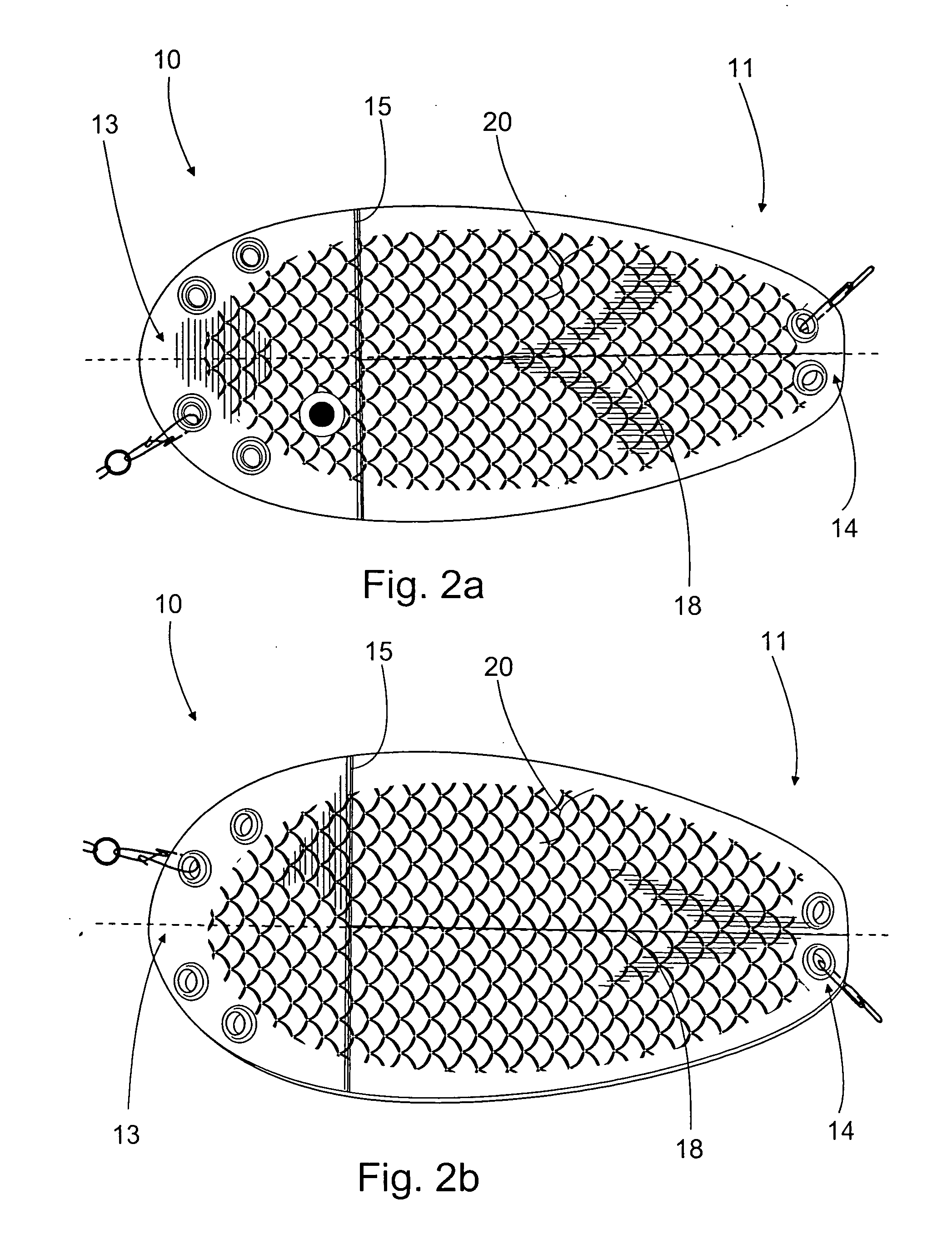
Flasher for fishing
A flasher for fishing is disclosed. The flasher is an elongated item with its width greater than thickness and with openings at its two opposite ends for the line used in fishing. The flasher is adapted drawable with the line fastened to the opening at the first end. At the first end there is a bending transversal in relation to the flasher centerline, and the opening at the first end is arranged to the side from the flasher centerline.
Owner:KAARIAINEN VESA +1
Methods and apparatus for accessing and treating the facet joint
InactiveUS20150201977A1Reduce pressureRelieve symptomsIncision instrumentsInternal osteosythesisDistractionDecortication procedure
Methods and systems are disclosed for accessing and treating the interior of the facet joint for vertebral distraction and immobilization. The systems include a number of tools that facilitate access to the facet joint, distraction of the articulating decortication of the articulating surfaces, and delivery of implants and agents into the facet joint for fusion.
Owner:PROVIDENCE MEDICAL TECH
Apparatus and method for rotating sleeve engine hydrodynamic seal
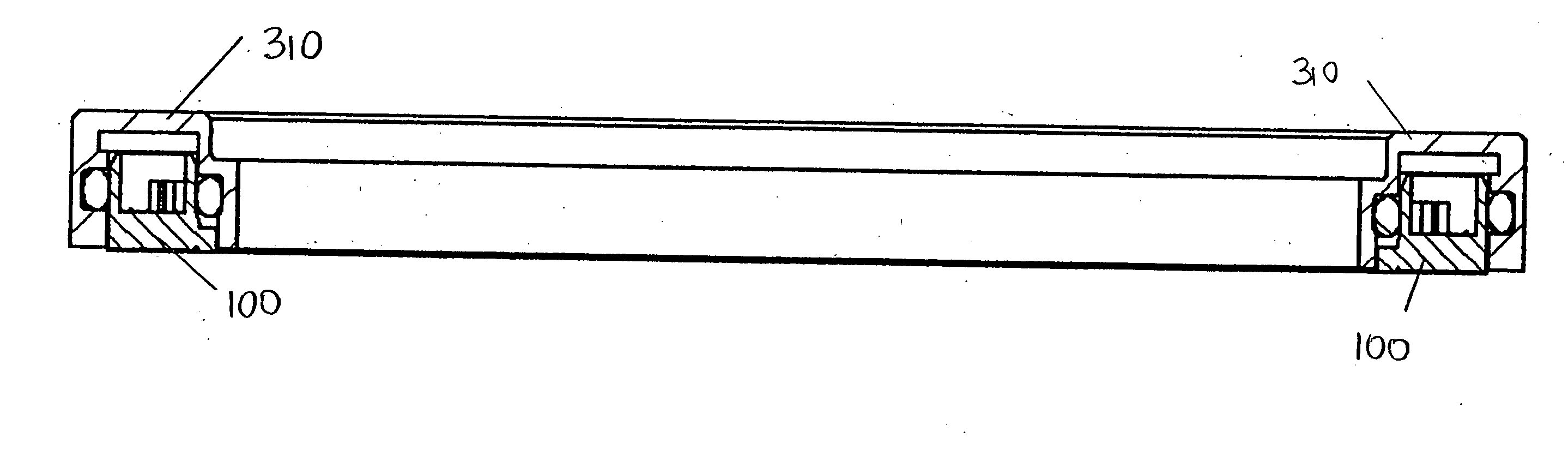
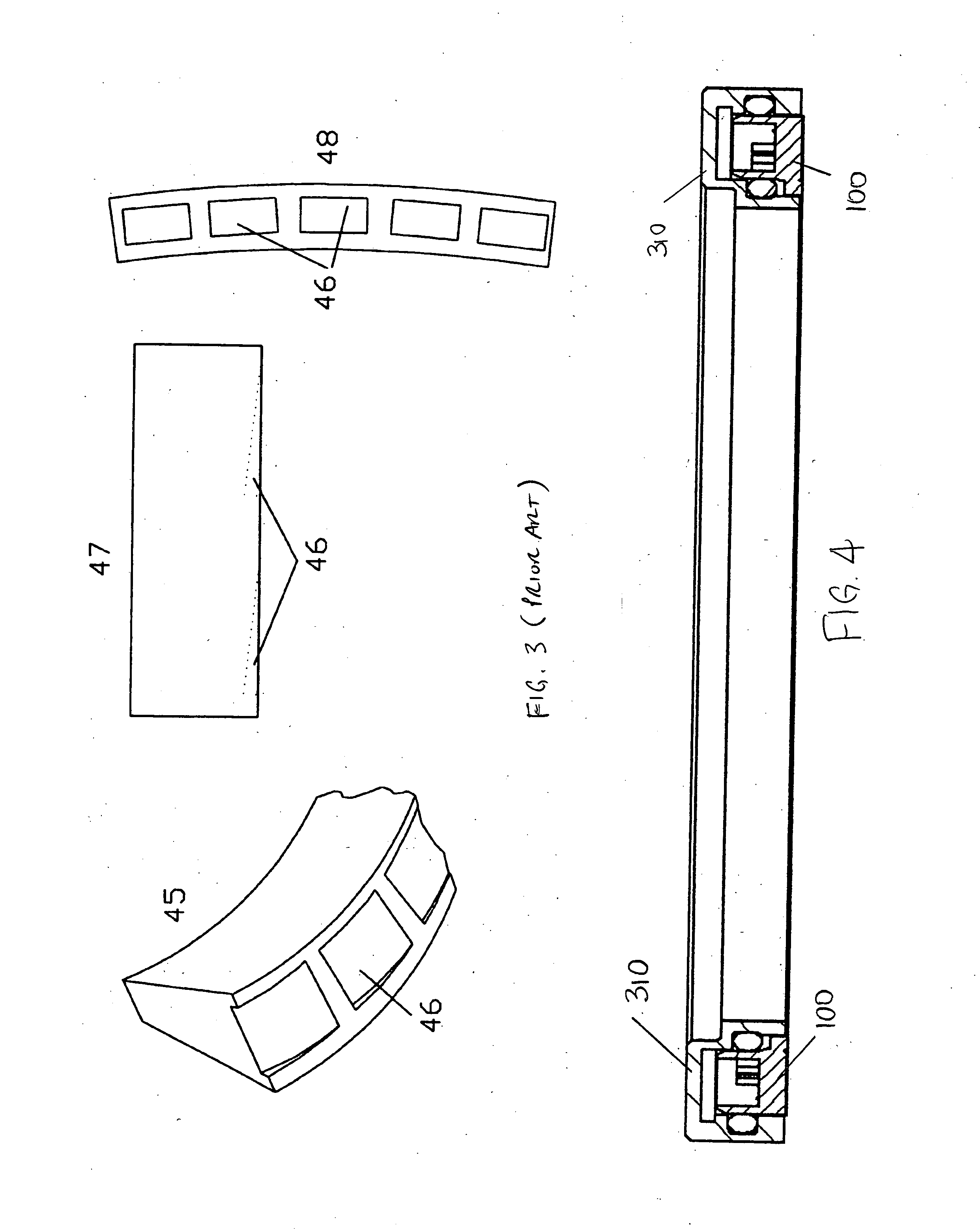
ActiveUS7004119B2Add partsMinimize and prevent expansionEngine sealsLubrication of auxillariesCombustionCylinder head
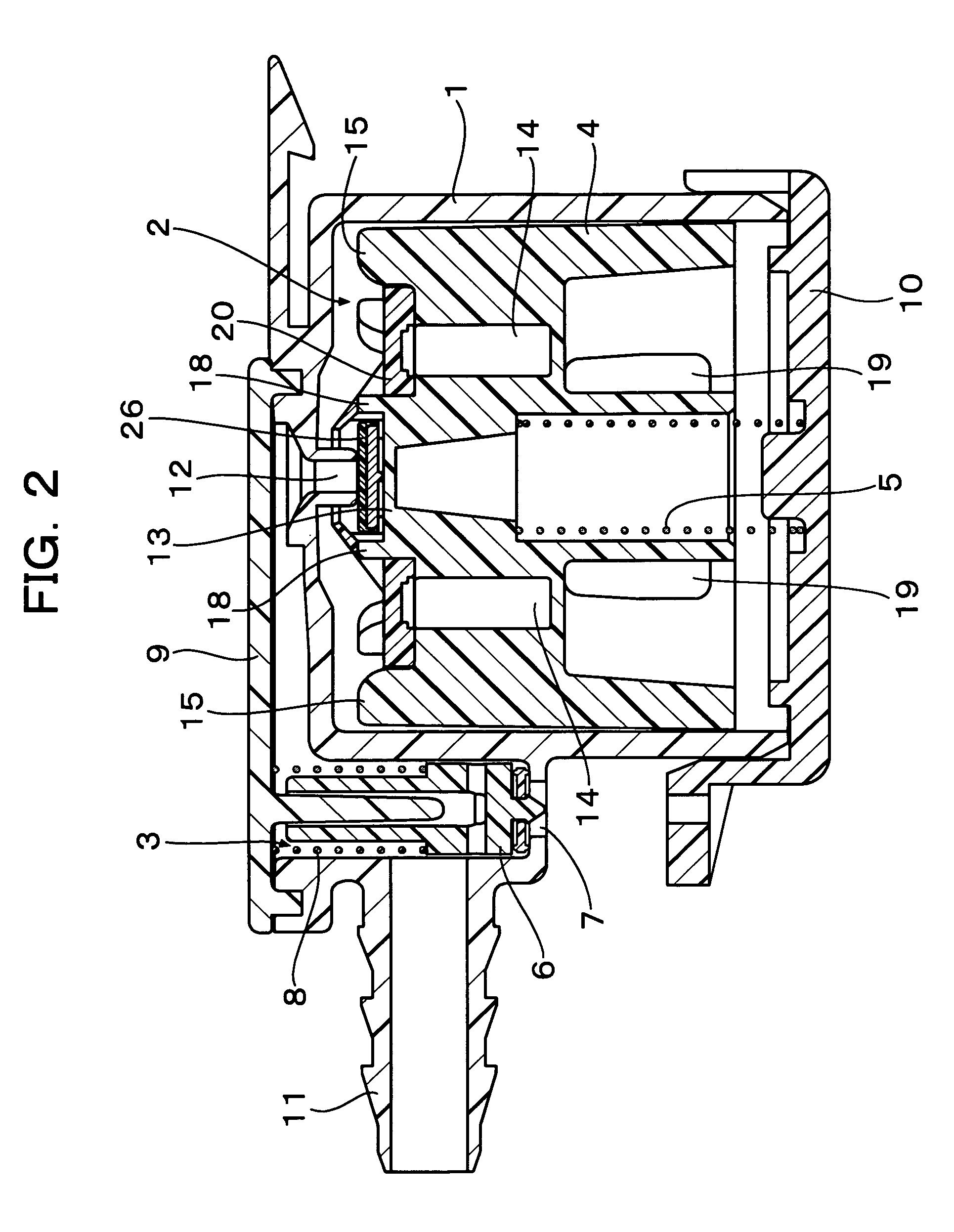
A hydrodynamic face seal 100 for sealing between the cylinder head 300 and rotating sleeve 200 of a rotating liner engine. The face of the face seal provides a sealing zone 130 for maintaining a lubricant layer of about 2 micrometers between the face seal and the sleeve; and a loading zone 132. The loading zone includes hydrodynamic lift features such as inclined pads 150 or recessed step pads 152. Oil is supplied to annular oil supply passage 142 between the sealing zone and the loading zone, and flows from the annular oil supply passage to radial passages 144 located between the step pads. A spring pre-load is provided to the seal. An outer secondary seal 190 is provided to contain the lubricant. One or more inner secondary seals is provided to contain lubricant and combustion gases. Spiral oil pumping grooves may be provided.
Owner:DARDALIS DIMITRIOS
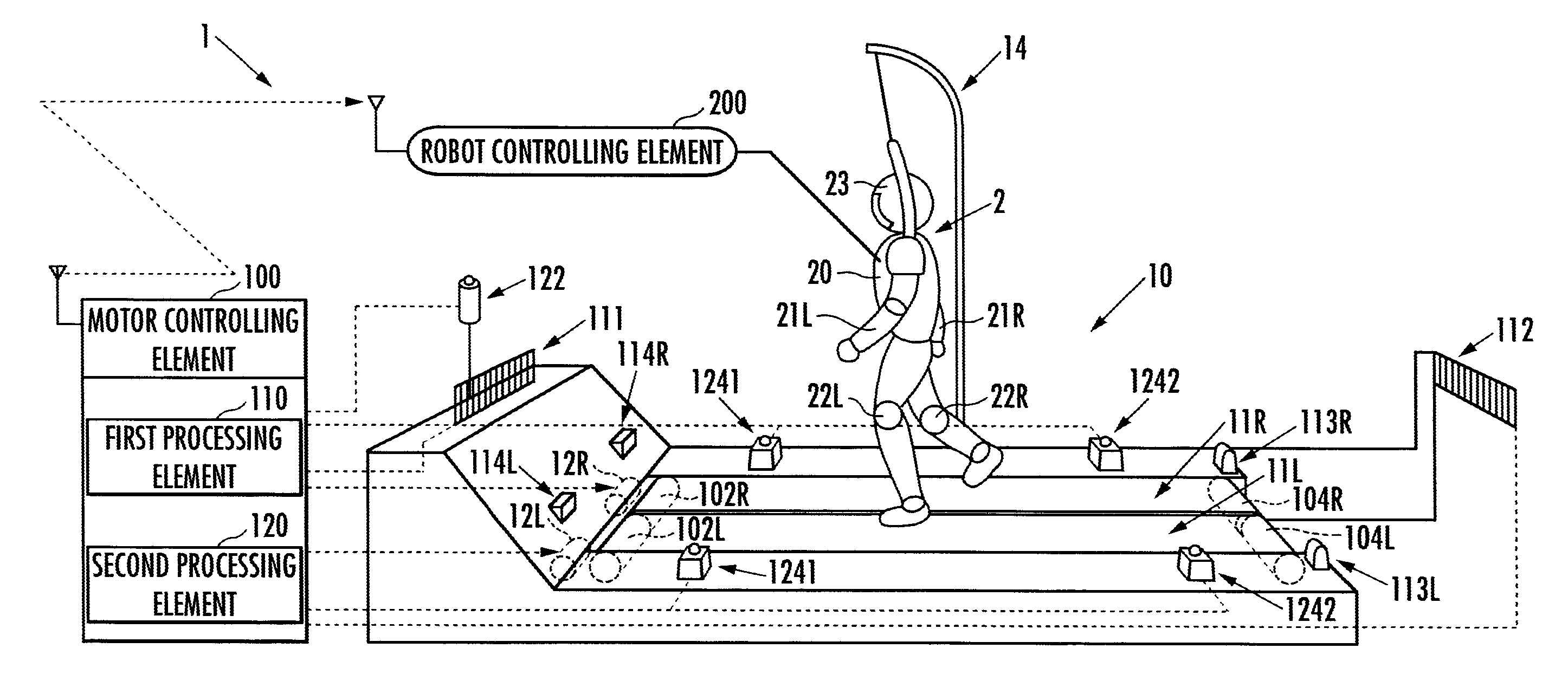
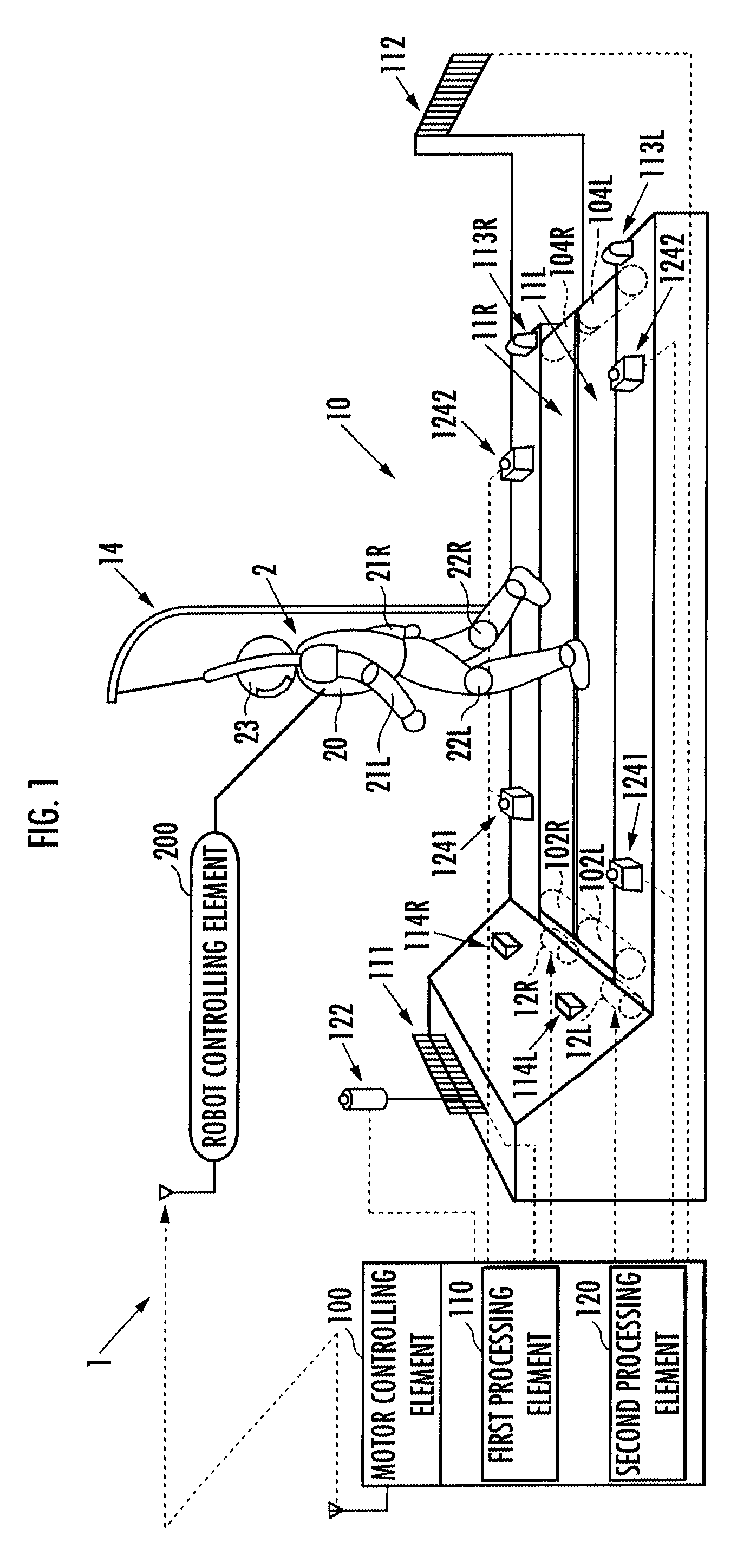
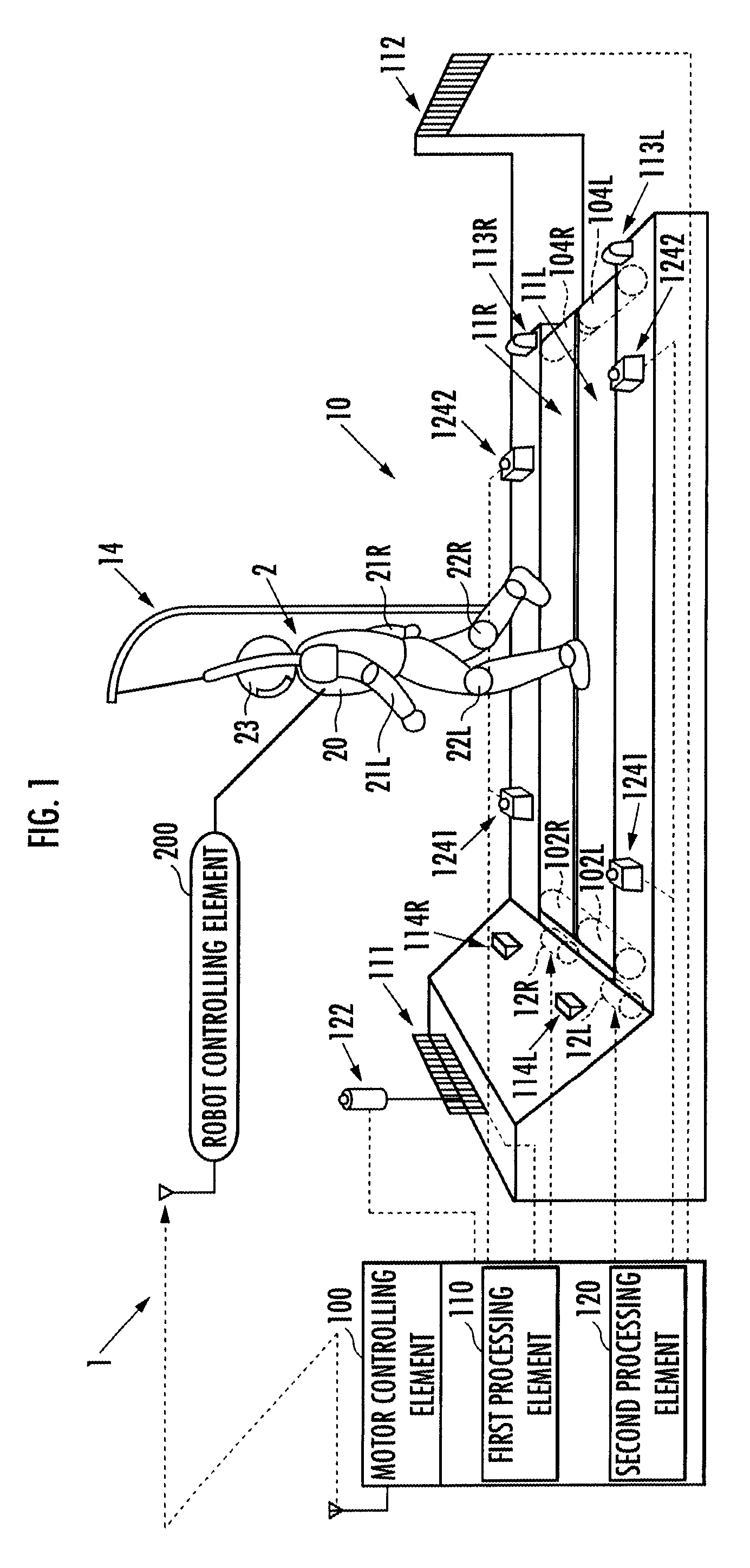
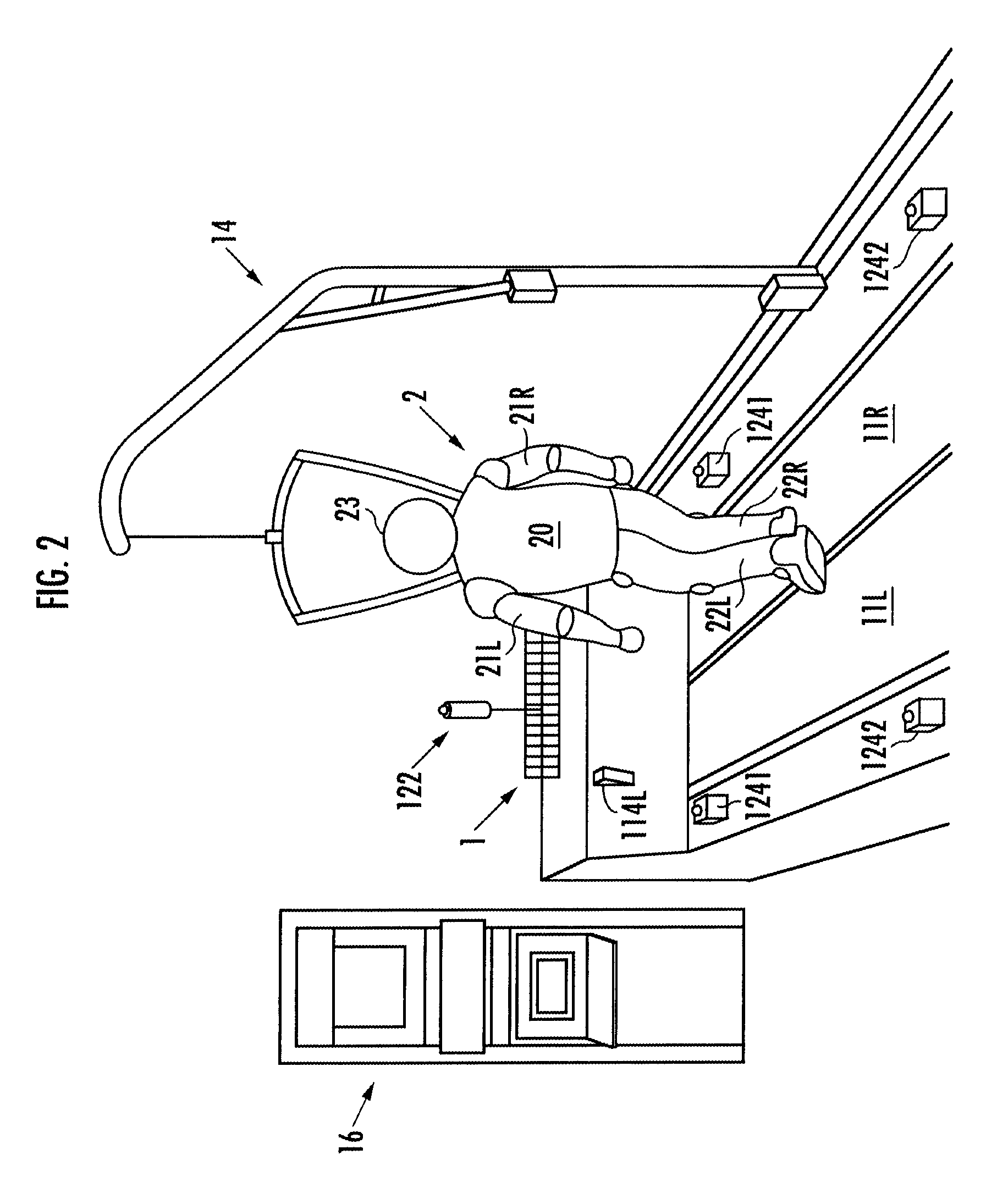
Locomotive performance testing apparatus
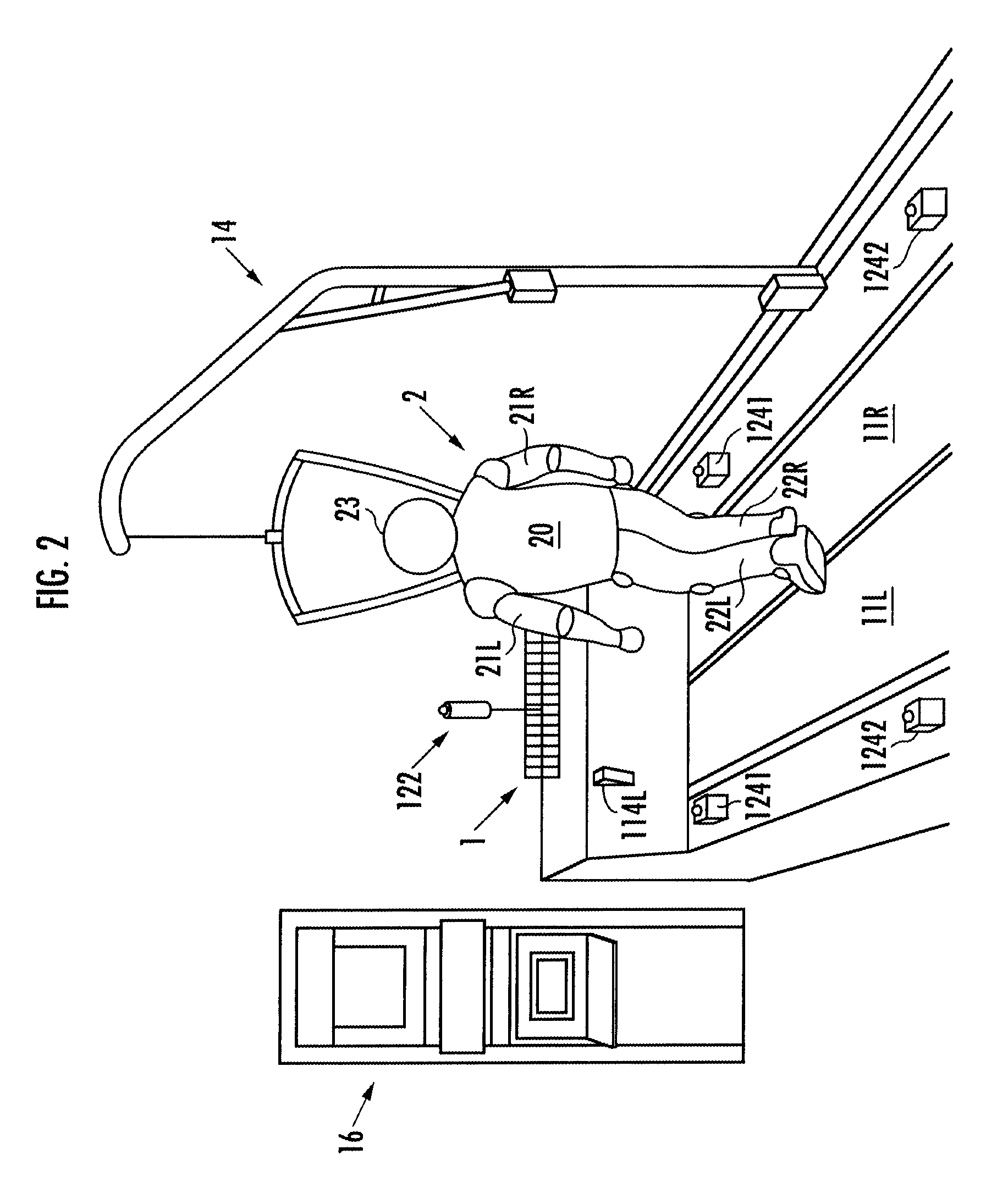
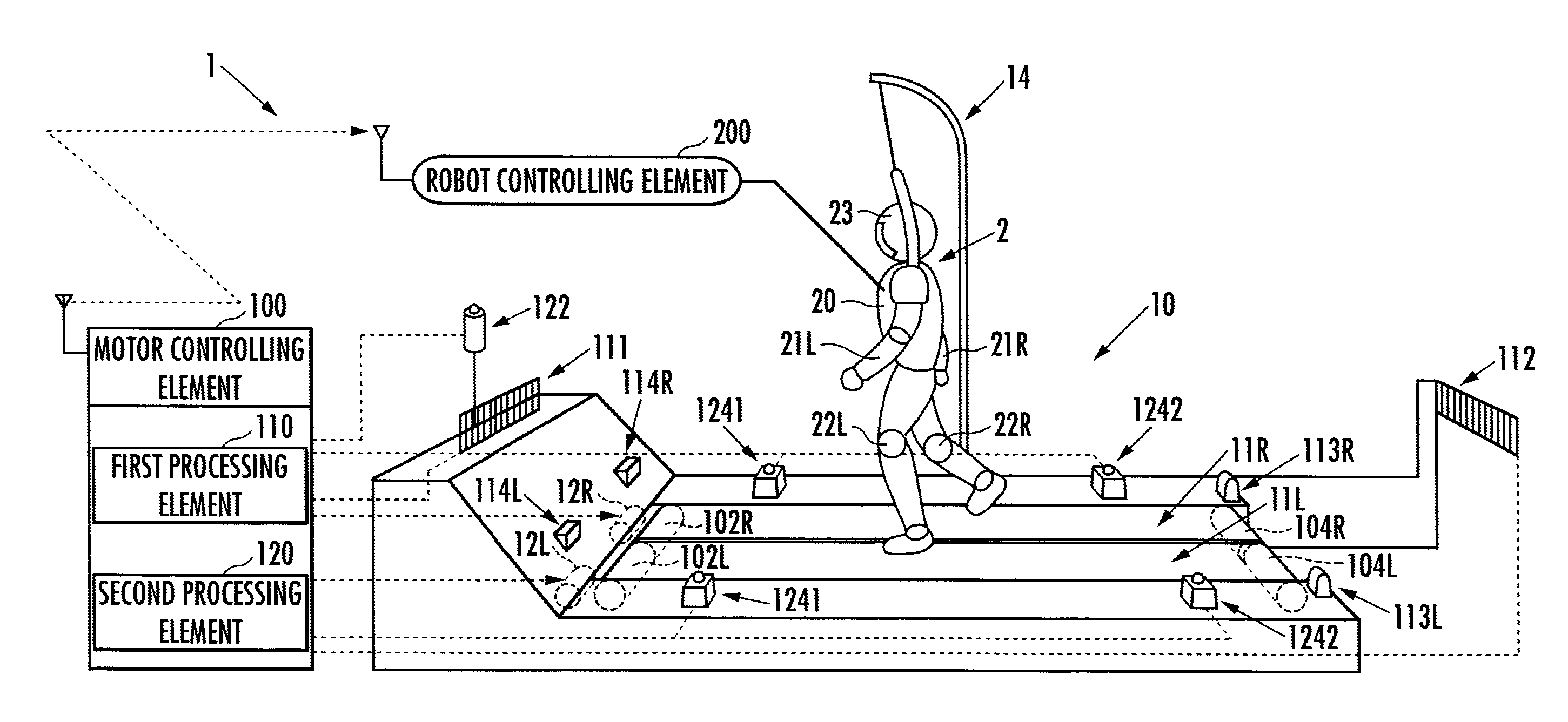
ActiveUS20100000345A1Keep movingStructural/machines measurementUsing mechanical meansRobot motion planningRhythm
Provided is a testing apparatus capable of testing locomotive performance of a robot while harmonizing motions of the apparatus with that of the robot. According to the locomotive performance testing apparatus (1), a motor working plan is made on the basis of a robot motion plan, and a motor (12) is driven according to the motor working plan. As a result, an alteration pattern of a driving velocity of an endless belt (11) can be controlled according to an alteration pattern of a moving velocity of a robot (2) whose locomotive performance is being tested on the endless belt (11). Moreover, a motion tempo of the endless belt (11) and a motion tempo of the robot (2) are so harmonized that the former tempo may approach the latter tempo, and the locomotive performance of the robot (2) can be stably tested in that state.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Apparatus and method for rotating sleeve engine hydrodynamic seal
ActiveUS20040256809A1Add partsPreventing and minimizing sleeve expansionEngine sealsLubrication of auxillariesCombustionCylinder head
A hydrodynamic face seal 100 for sealing between the cylinder head 300 and rotating sleeve 200 of a rotating liner engine. The face of the face seal provides a sealing zone 130 for maintaining a lubricant layer of about 2 micrometers between the face seal and the sleeve; and a loading zone 132. The loading zone includes hydrodynamic lift features such as inclined pads 150 or recessed step pads 152. Oil is supplied to annular oil supply passage 142 between the sealing zone and the loading zone, and flows from the annular oil supply passage to radial passages 144 located between the step pads. A spring pre-load is provided to the seal. An outer secondary seal 190 is provided to contain the lubricant. One or more inner secondary seals is provided to contain lubricant and combustion gases. Spiral oil pumping grooves may be provided.
Owner:DARDALIS DIMITRIOS
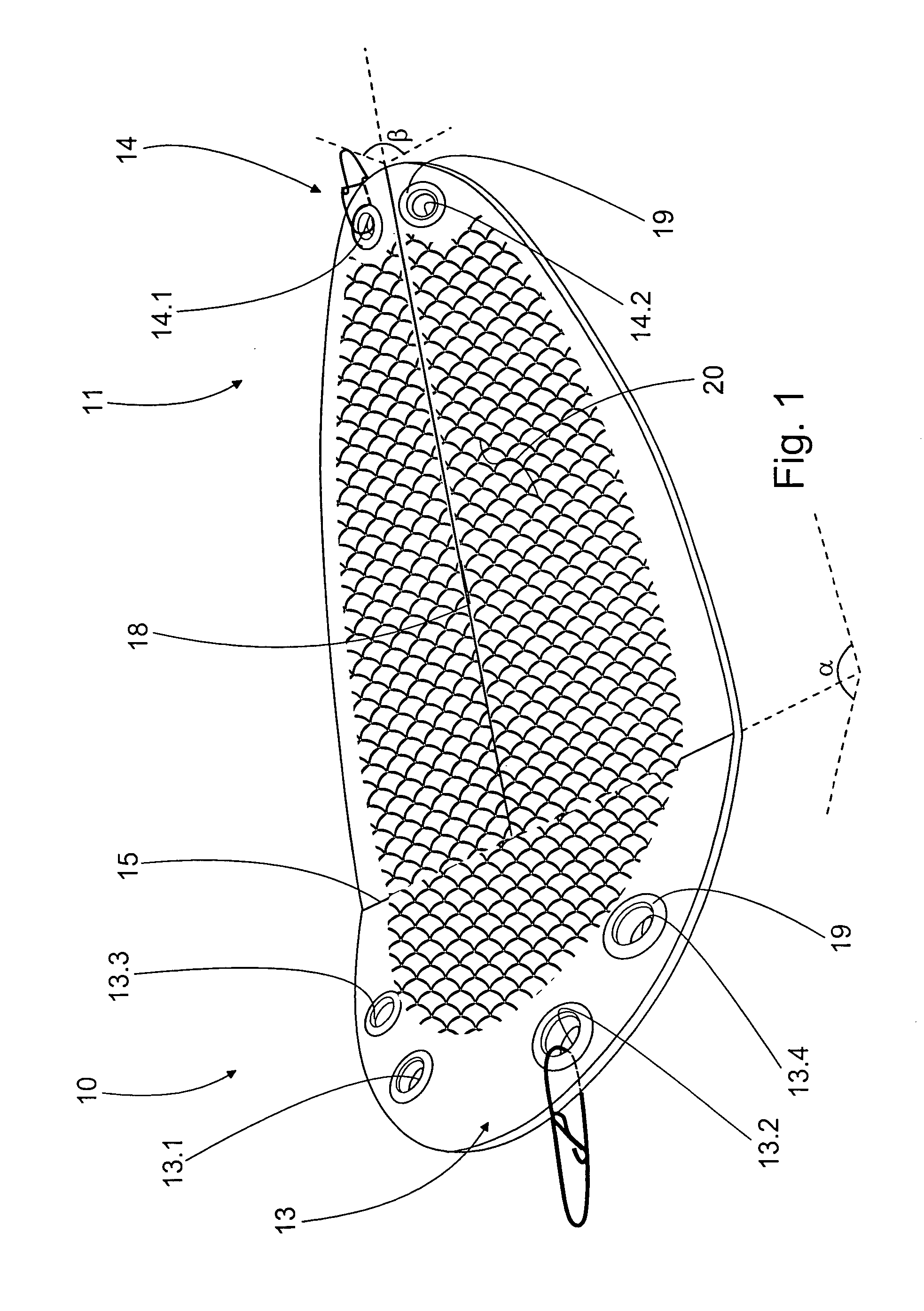
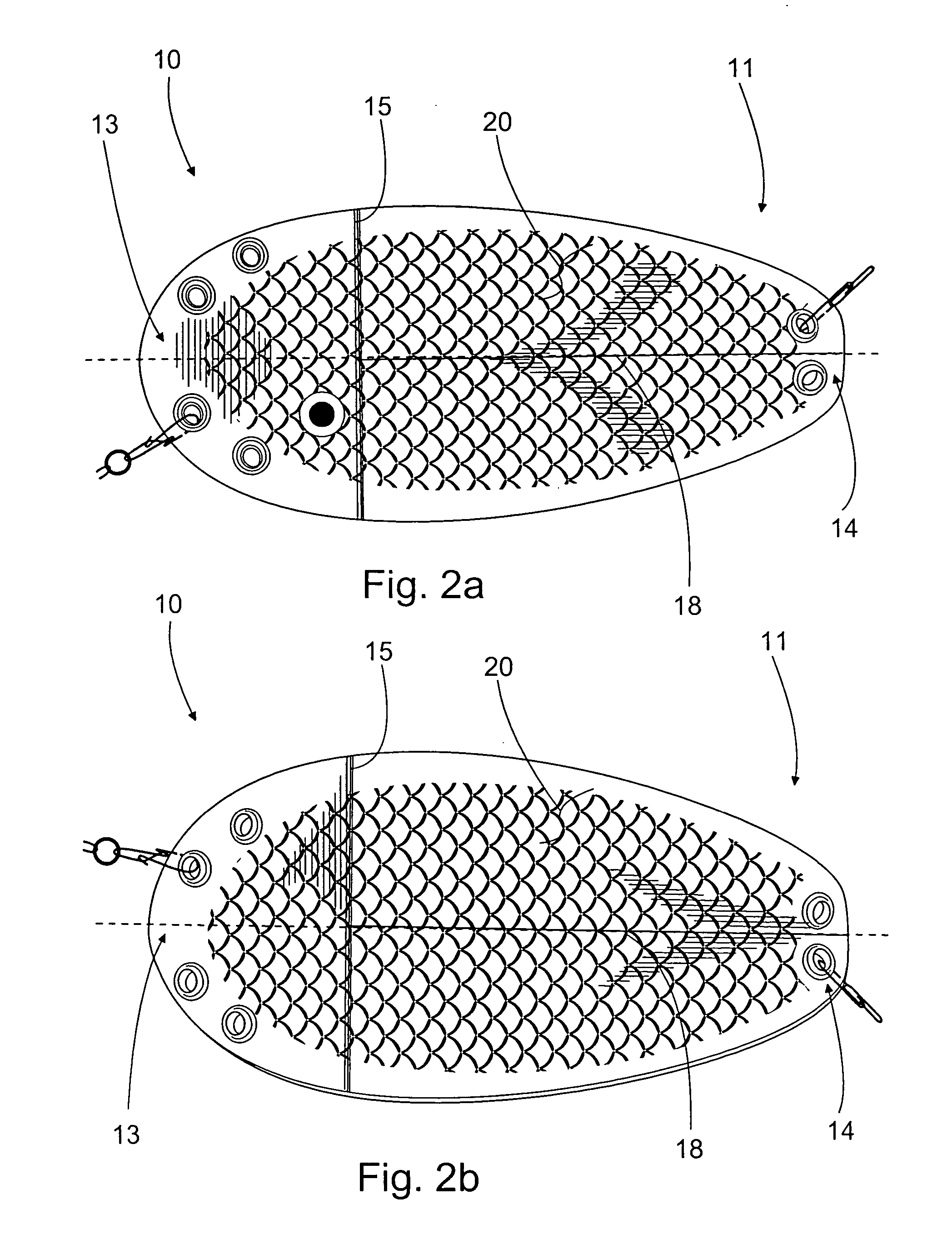
Flasher for fishing
A flasher for fishing is disclosed. The flasher is an elongated item with its width greater than thickness and with openings at its two opposite ends for the line used in fishing. The flasher is adapted drawable with the line fastened to the opening at the first end. At the first end there is a bending transversal in relation to the flasher centerline, and the opening at the first end is arranged to the side from the flasher centerline.
Owner:KAARIAINEN VESA +1
Image stabilizing apparatus, image-pickup apparatus and image stabilizing method
InactiveUS7929043B2Keep movingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsMotion vectorImage stabilization
An image stabilizing apparatus includes a motion vector calculating part that calculates a motion vector between a plurality of images including a displacement caused by a motion of an image-pickup apparatus, a shake-correction parameter calculating part that receives the motion vector as input to calculate a shake correction amount, and an image transforming part that performs geometric transformation of the image in accordance with the shake correction amount. The shake-correction parameter calculating part performs variation amount calculation, variation amount correction and correction amount calculation based on the motion information between the plurality of images. The image stabilizing apparatus preserves a motion in video from an intended camera work and allows image stabilization for an unintended shake.
Owner:CANON KK
Fuel leakage preventing valve
Disclosed is a fuel leakage preventing valve, involving no variations in valve closing characteristics, in which a vertically movable float valve is arranged in a chamber defined inside a housing and in which a valve seat of the housing communicating with an outside is opened and closed by the float valve, which has a protruding step portion formed upwardly at the center of an upper surface of the float valve, a retainer fixed to the upper surface side of the float valve, the retainer having a flange portion covering the upper surface of the float valve and a cage portion raised from the flange portion to define an accommodating space in conjunction with the protruding step portion of the float valve; and a valve body for opening and closing the valve seat of the housing is rockably accommodated in the accommodating space defined by the cage portion.
Owner:PIOLAX CO LTD +1
System and method for sizing, inserting and securing artificial disc in intervertebral space
InactiveUS8597357B2PerformancePerforms betterSpinal implantsCoatingsIntervertebral discIntervertebral spaces
A prosthetic spinal implant having a deployable securing mechanism that is deployable into a portion of the vertebral space for affixing the implant between the vertebrae, the securing mechanism having tactile feedback means comprising a surface for transmitting tactile feedback during deployment of the securing mechanism. A spinal implant having deployable securing means that interface with the implant to prevent the deployable securing means from retracting after deployment. An implant that utilizes its resilient properties to provide the user with tactile feedback with which the user may ascertain the position of the securing mechanism. A system and tools for sizing and implanting implants with the aforementioned characteristics.
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
Spinal implants and methods
InactiveUS20090138084A1Reduce relative motionSmooth motionBone implantDiagnosticsPosterior regionIntervertebral disk
Spinal implants are disclosed that can be used for annular repair, facet unloading, disc height preservation, disc decompression, or for sealing a portal through which an intervertebral implant was placed. In some embodiments, an implant is placed within the intervertebral disc space, primarily within the region of the annulus fibrosus. In some embodiments, the implant is expandable. In some embodiments, the implant has a sealing tail structure comprising a tail flange and a linkage. In some embodiments, the sealing tail structure limits the extrusion or expulsion of disc material, either annulus fibrosus or nucleus, into the posterior region of the spine where it could impinge on nerves. In some embodiments, the tail structure is retained in place within the annulus fibrosus by means of an anchor. In some embodiments, the anchor is constructed from multiple components.
Owner:MAGELLAN SPINE TECH
Method and implant device for grafting adjacent vertebral bodies
ActiveUS20160354213A1Easy to assembleEasy to insertBone implantJoint implantsImplanted deviceEngineering
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
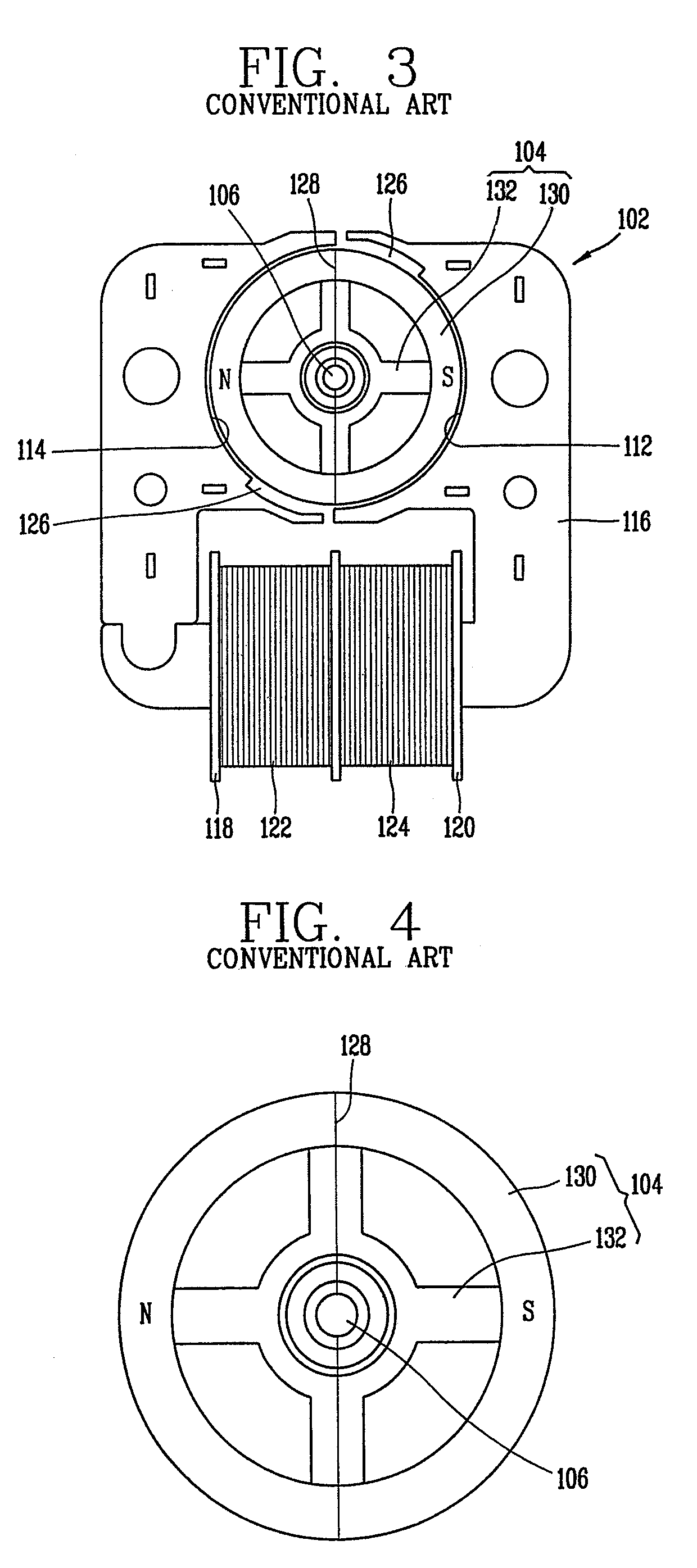
Skeleton type BLDC motor
A rotor of a BLDC motor includes: a rotor divided into a north pole and a south pole on the basis of a magnetic pole separating line; and a stator at which the rotor is disposed with an air gap, the stator having a first pole shoe, a second pole shoe and a pair of detent grooves at its inner surface, wherein an air gap forming portion for enlarging an air gap between the rotor and the detent grooves is formed at both end portions of the rotor where the magnetic pole separating line passes, so that the rotor can maintain the motor performance and reduce resonance noise by reducing only higher degree of cogging torque from cogging torque generated when the motor is driven.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Child motion apparatus
Owner:WONDERLAND SWITZERLAND AG
Passive exercise apparatus
InactiveUS20110152731A1Inhibition decreasedKeep movingChiropractic devicesEye exercisersPassive exercisesReciprocating motion
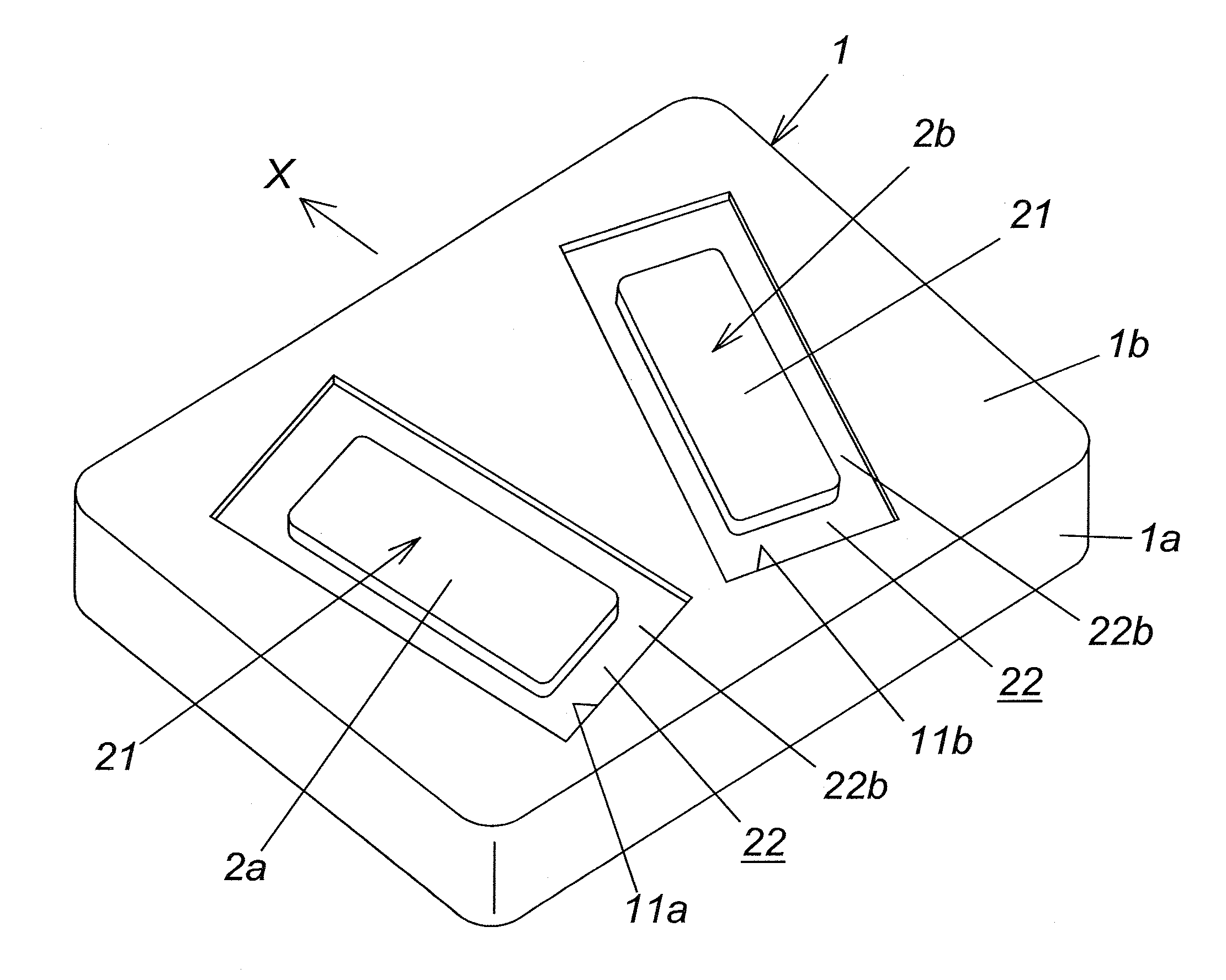
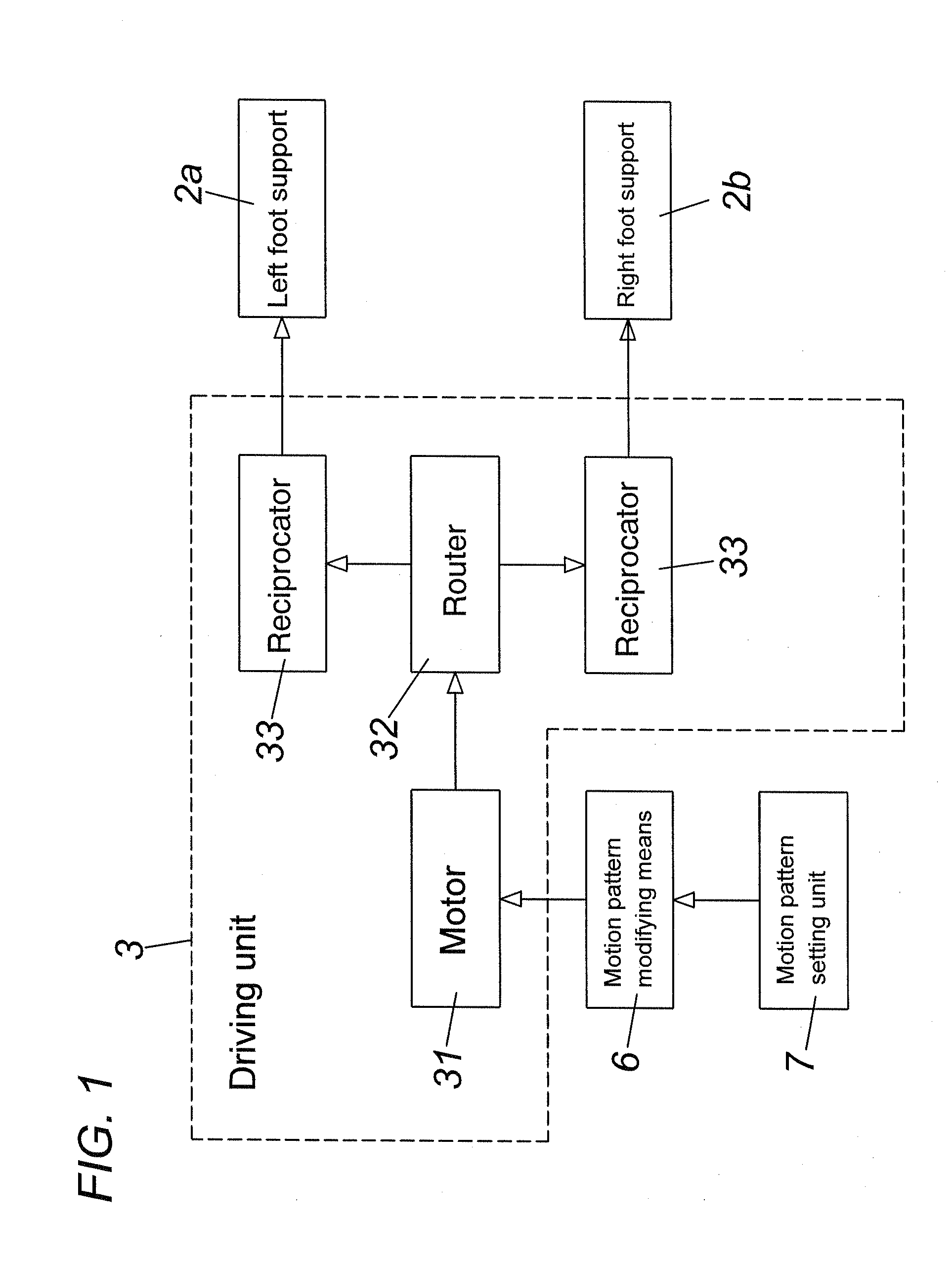
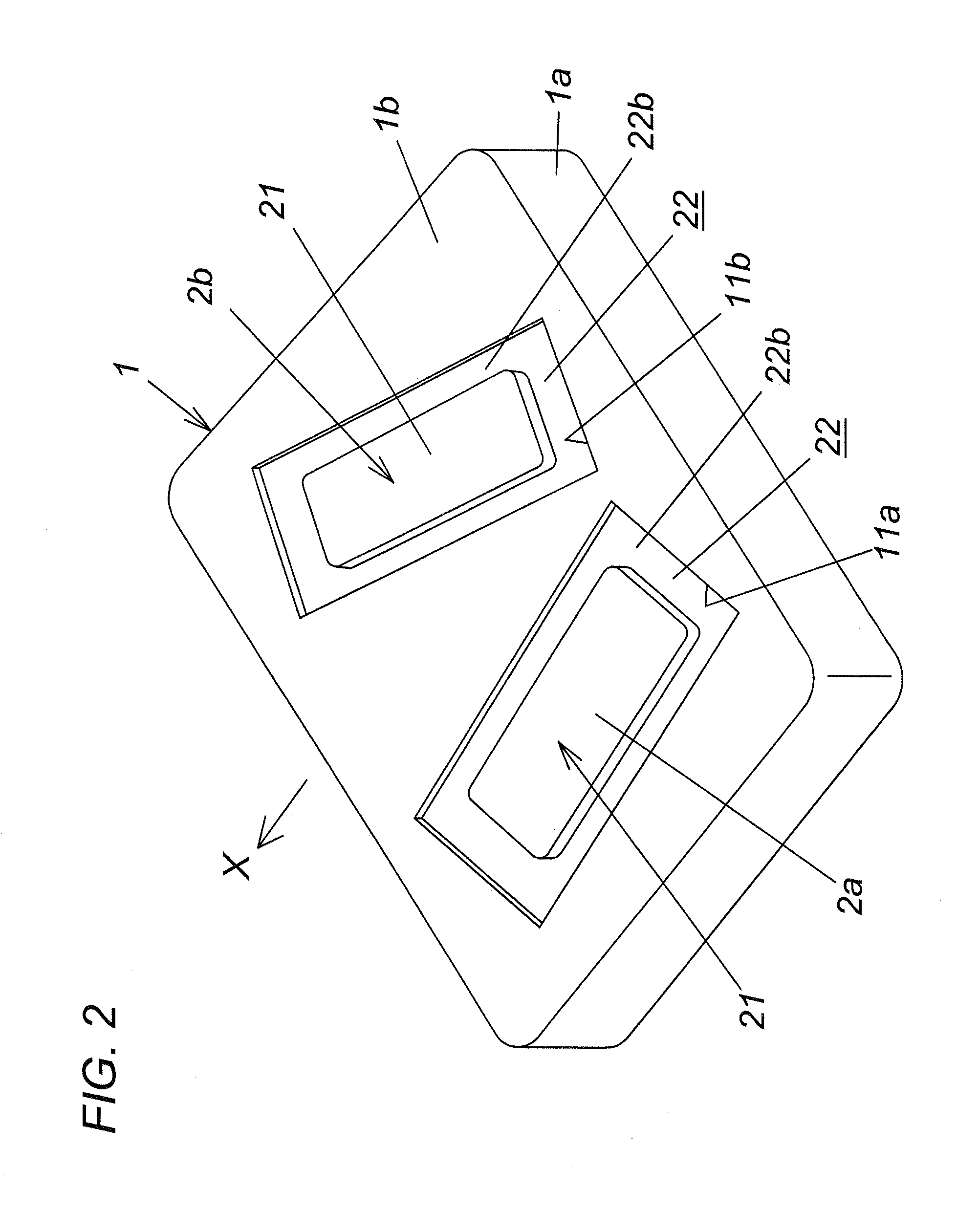
This invention has an object to provide a passive exercise apparatus which is driven to help user to stretch and contract various muscles of his / her feet by a driving force generated at a driving unit while not lowering positive effects in his / her exercise. This passive exercise apparatus in the present invention comprises a left foot support 2a, a right foot support 2b, a driving unit 3, and a motion pattern modifying means 6. The left foot support and the right foot support are provided to support user's left foot and right foot respectively. The driving unit is configured to give a reciprocatory motion along a predetermined path to each of the left foot support and the right foot support according to a predetermined motion pattern defined by frequency, phase, and amplitude of the reciprocatory motion. The motion pattern modifying means is configured to modify at least one of the frequency, the phase, and the amplitude. The motion pattern modifying means is configured also to modify the motion pattern in accordance with inputs at a motion pattern setting unit 7.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Methods and devices for preserving motion in an articulating prosthetic disc
ActiveUS20060229728A1Keep movingSurgical adhesivesSkeletal disorderArticular surfacesIntervertebral disc
The present invention overcomes the problem of undesirable bone growth and / or unwanted scar tissue formation on the articulating surfaces and in the articulating spaces of prosthetic intervertebral discs. The invention comprises a method for preserving motion in a prosthetic disc having at least one articulating surface comprising applying an anti-infiltration agent on and around an articulating surface of the prosthetic disc. Suitable anti-infiltration agents include but are not limited to, hemostatic compounds, anti-adhesion compounds, bone-formation inhibiting compounds, or any combination thereof.
Owner:SDGI HLDG
Locomotive performance testing apparatus
ActiveUS8082811B2Keep movingStructural/machines measurementUsing mechanical meansRobot motion planningTester device
Provided is a testing apparatus capable of testing locomotive performance of a robot while harmonizing motions of the apparatus with that of the robot. According to the locomotive performance testing apparatus (1), a motor working plan is made on the basis of a robot motion plan, and a motor (12) is driven according to the motor working plan. As a result, an alteration pattern of a driving velocity of an endless belt (11) can be controlled according to an alteration pattern of a moving velocity of a robot (2) whose locomotive performance is being tested on the endless belt (11). Moreover, a motion tempo of the endless belt (11) and a motion tempo of the robot (2) are so harmonized that the former tempo may approach the latter tempo, and the locomotive performance of the robot (2) can be stably tested in that state.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com