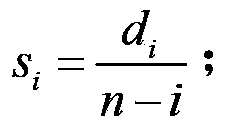Patents
Literature
35 results about "Point coordination function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
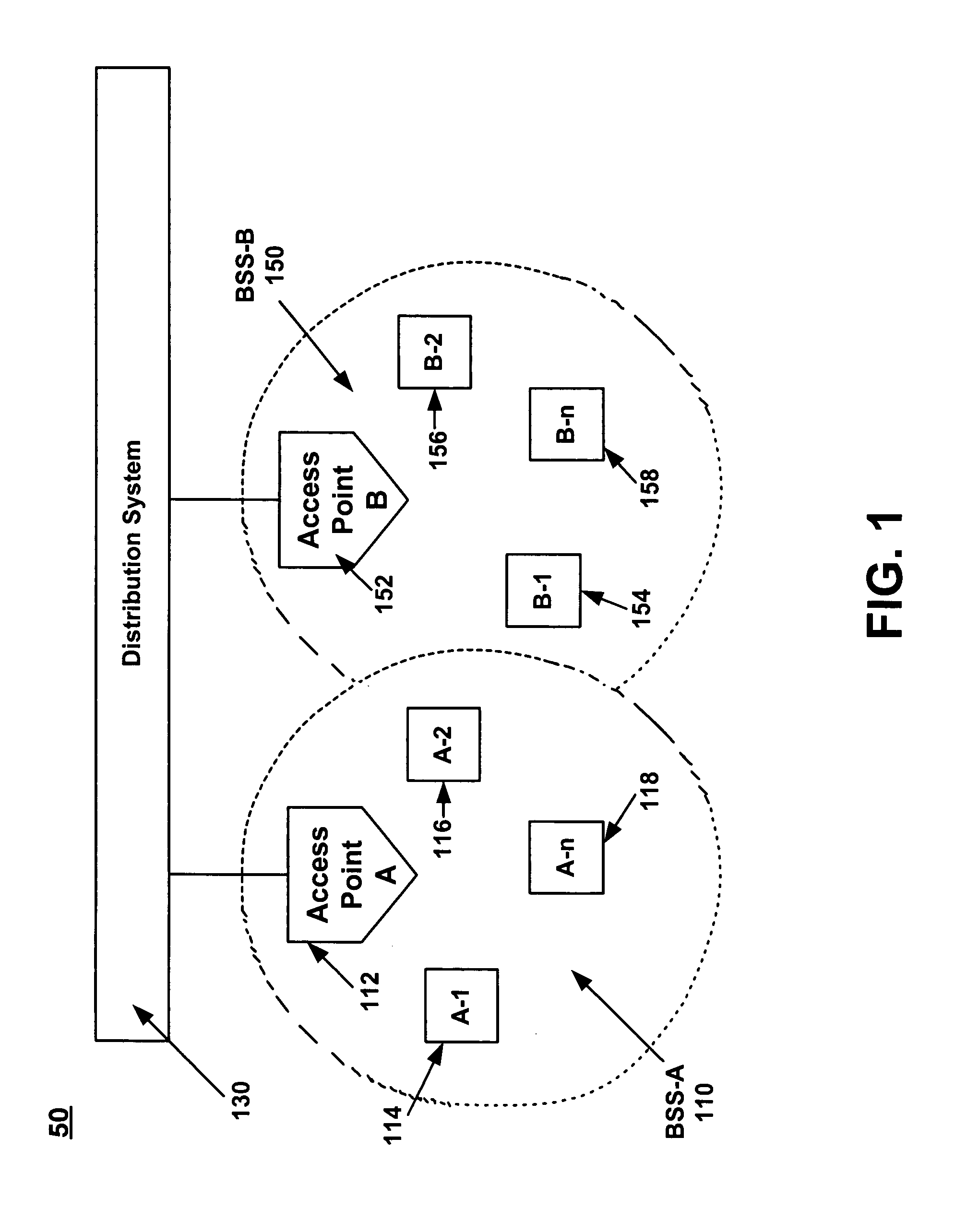
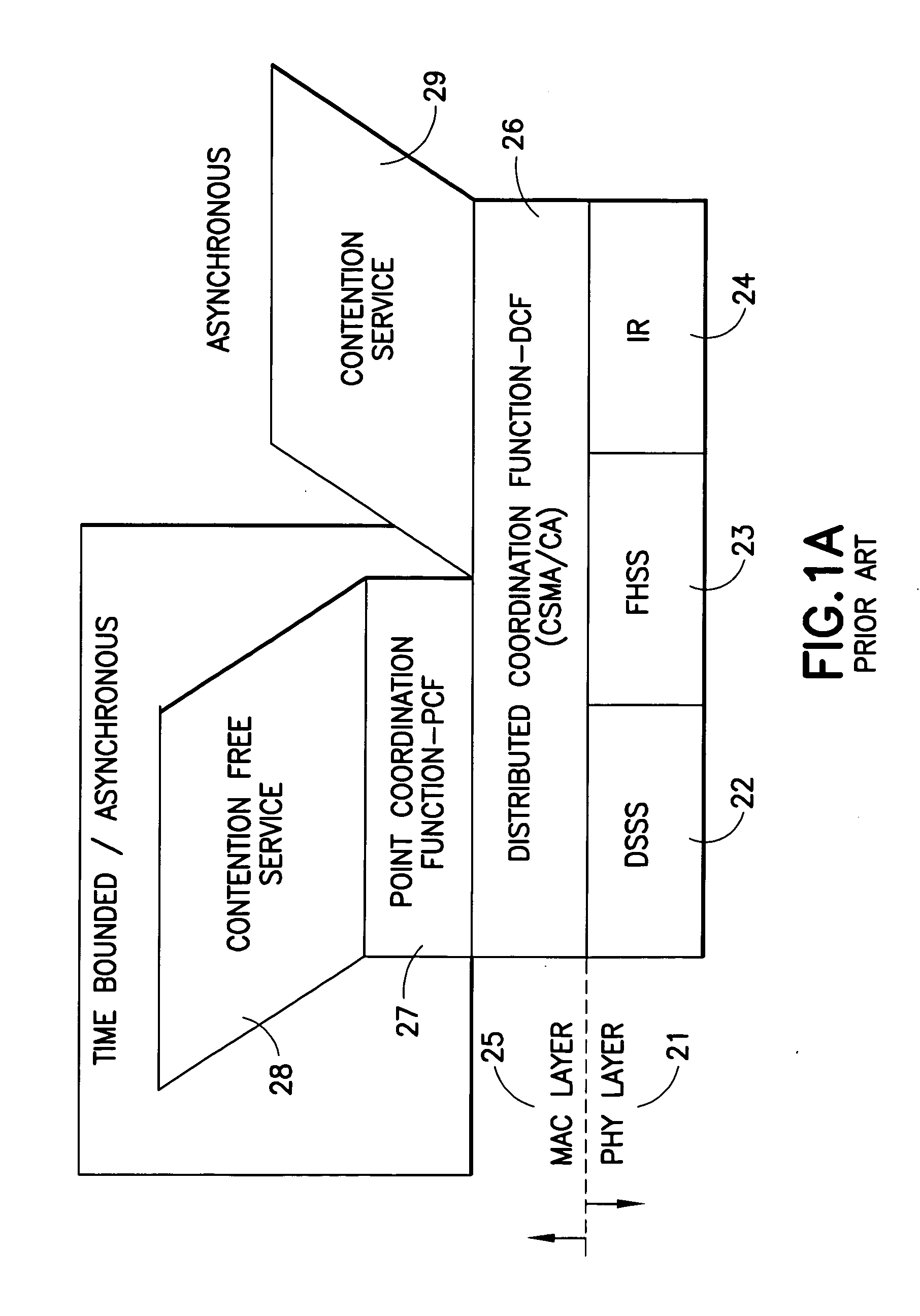
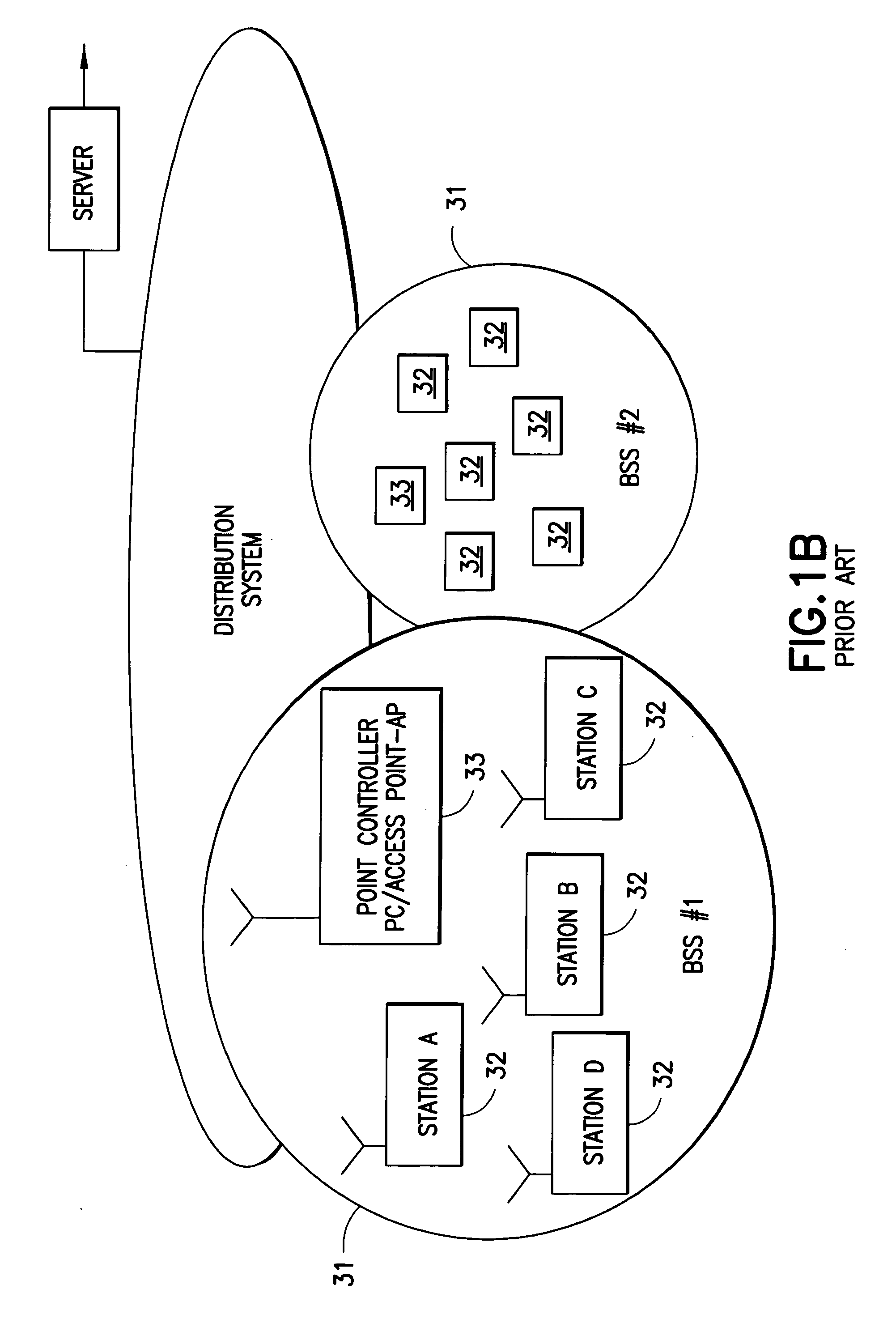
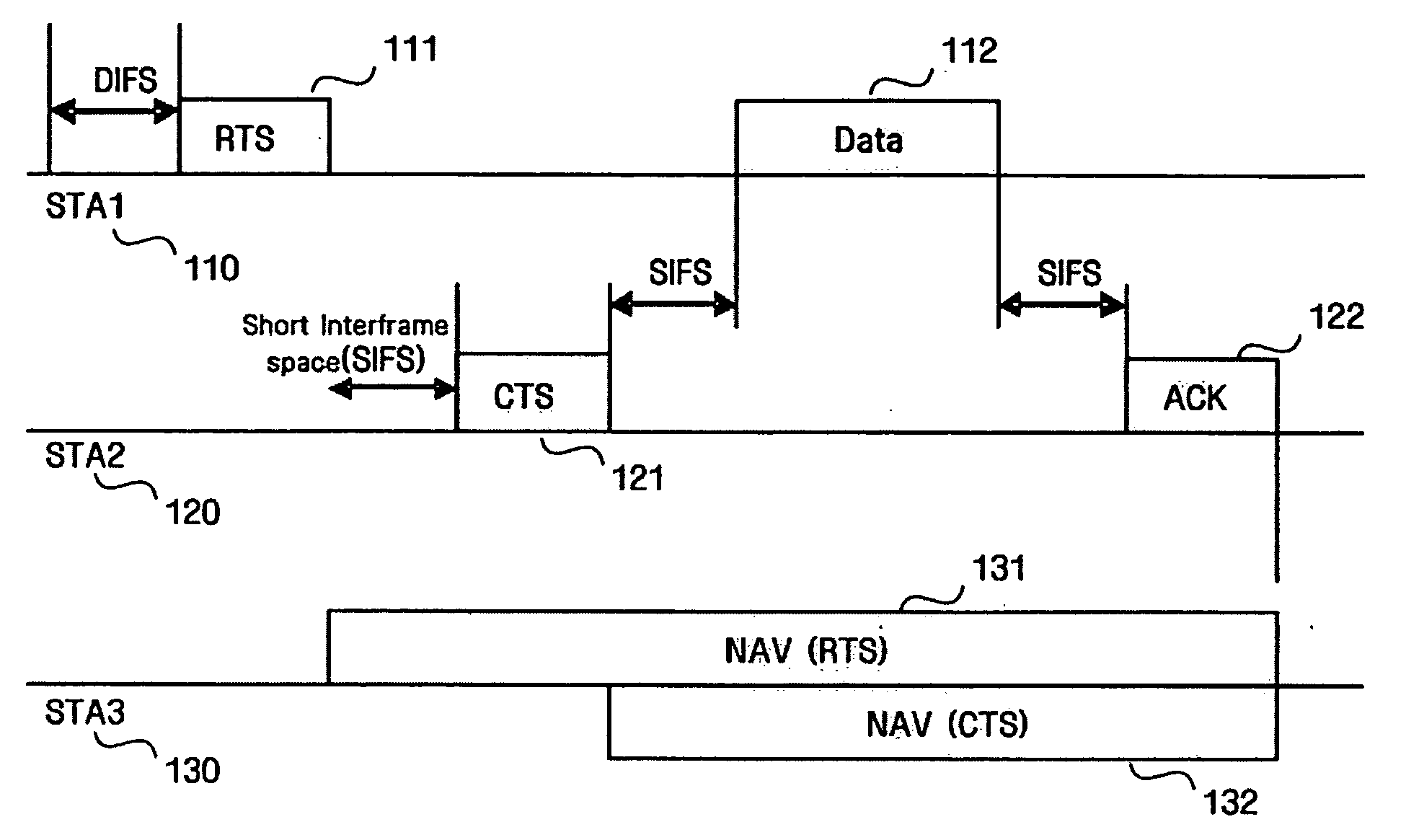
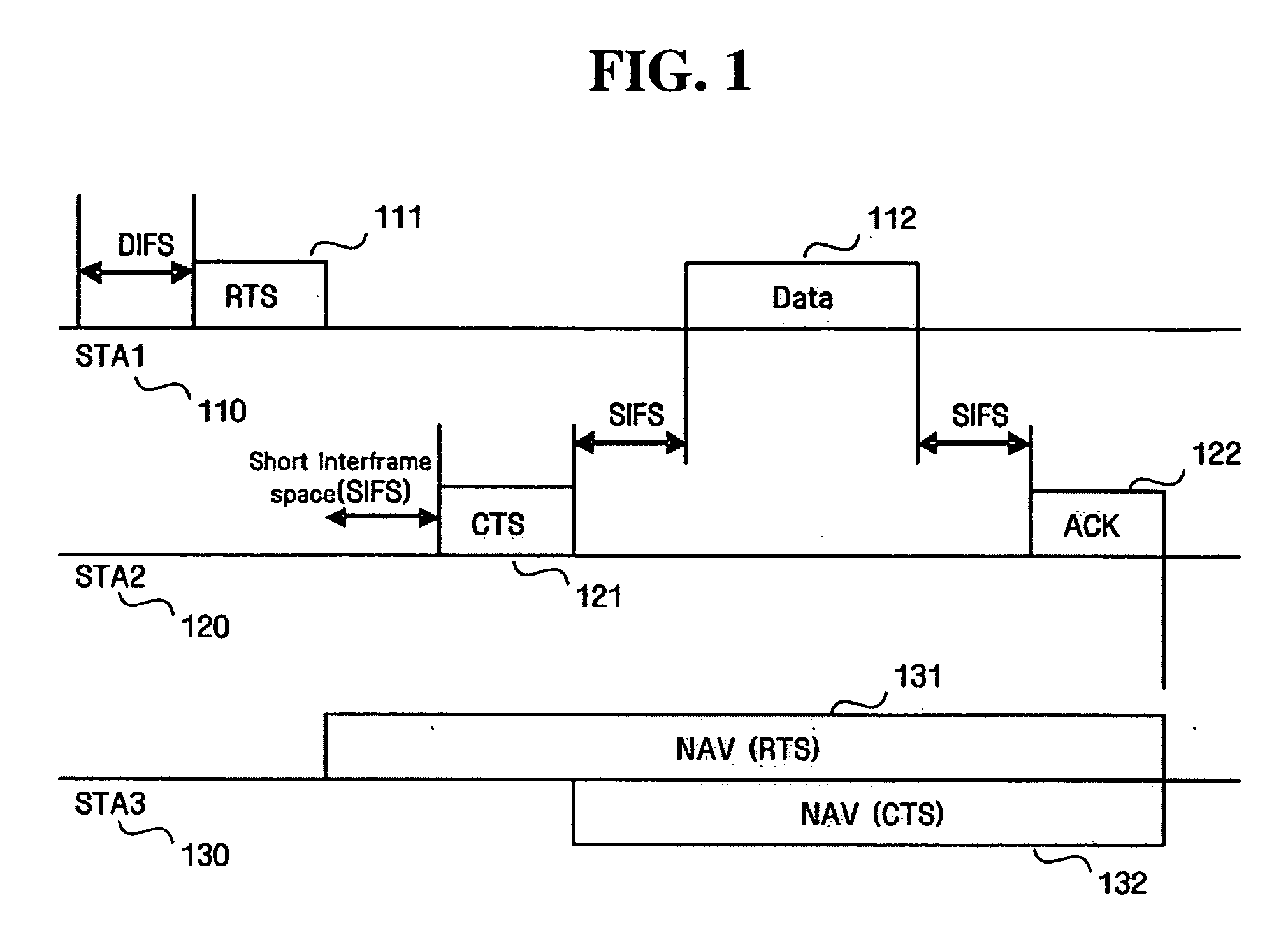
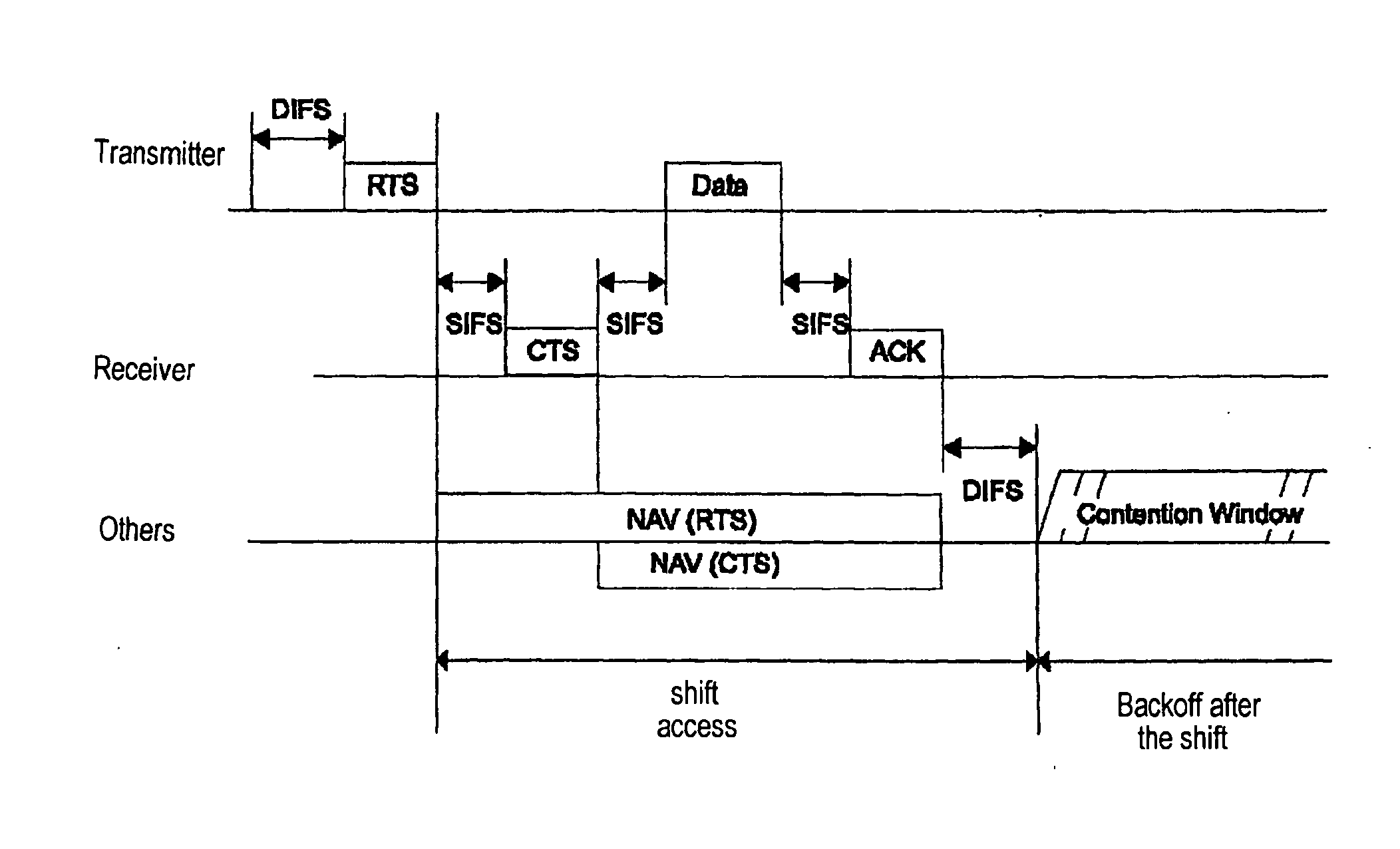
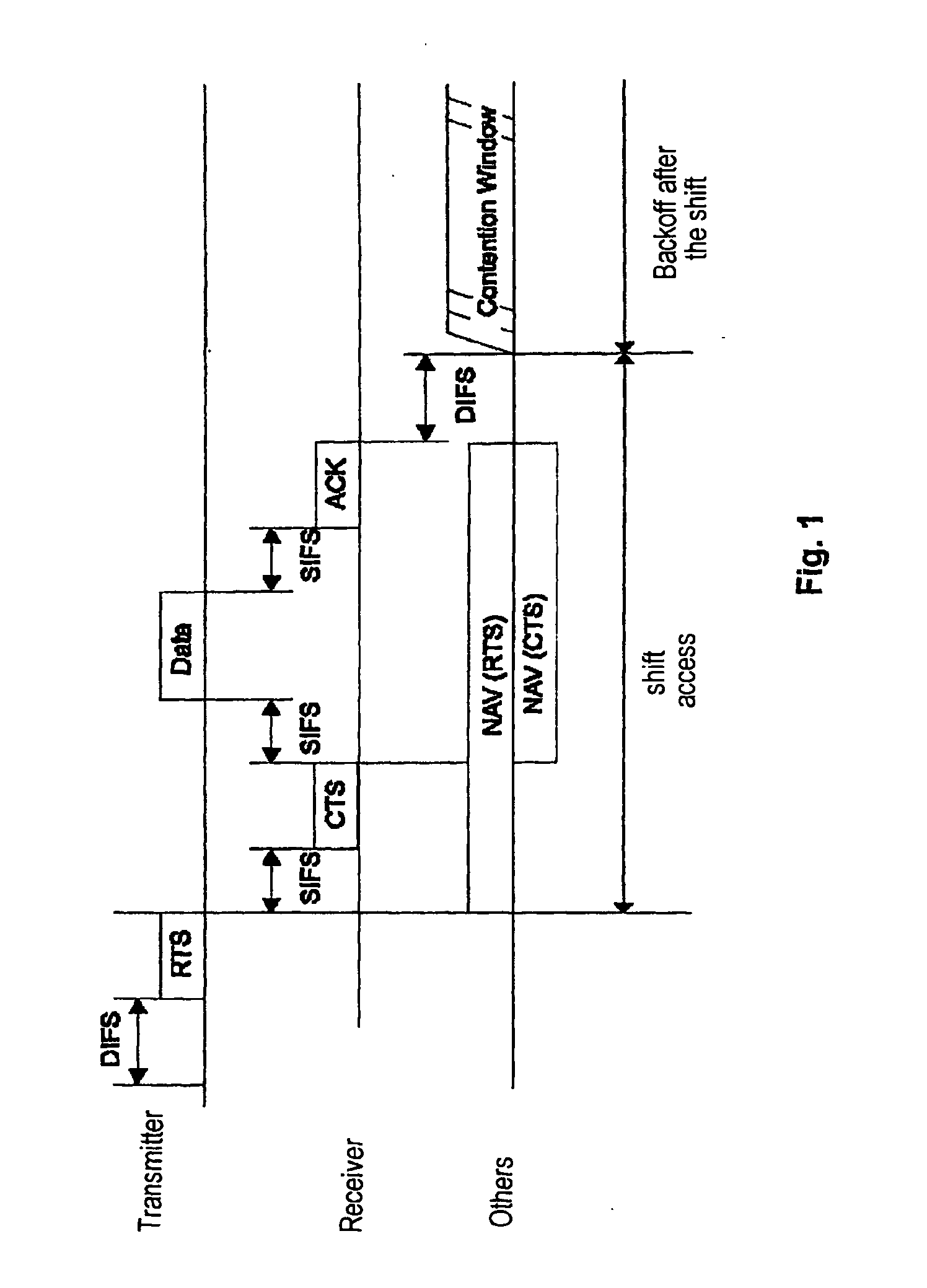
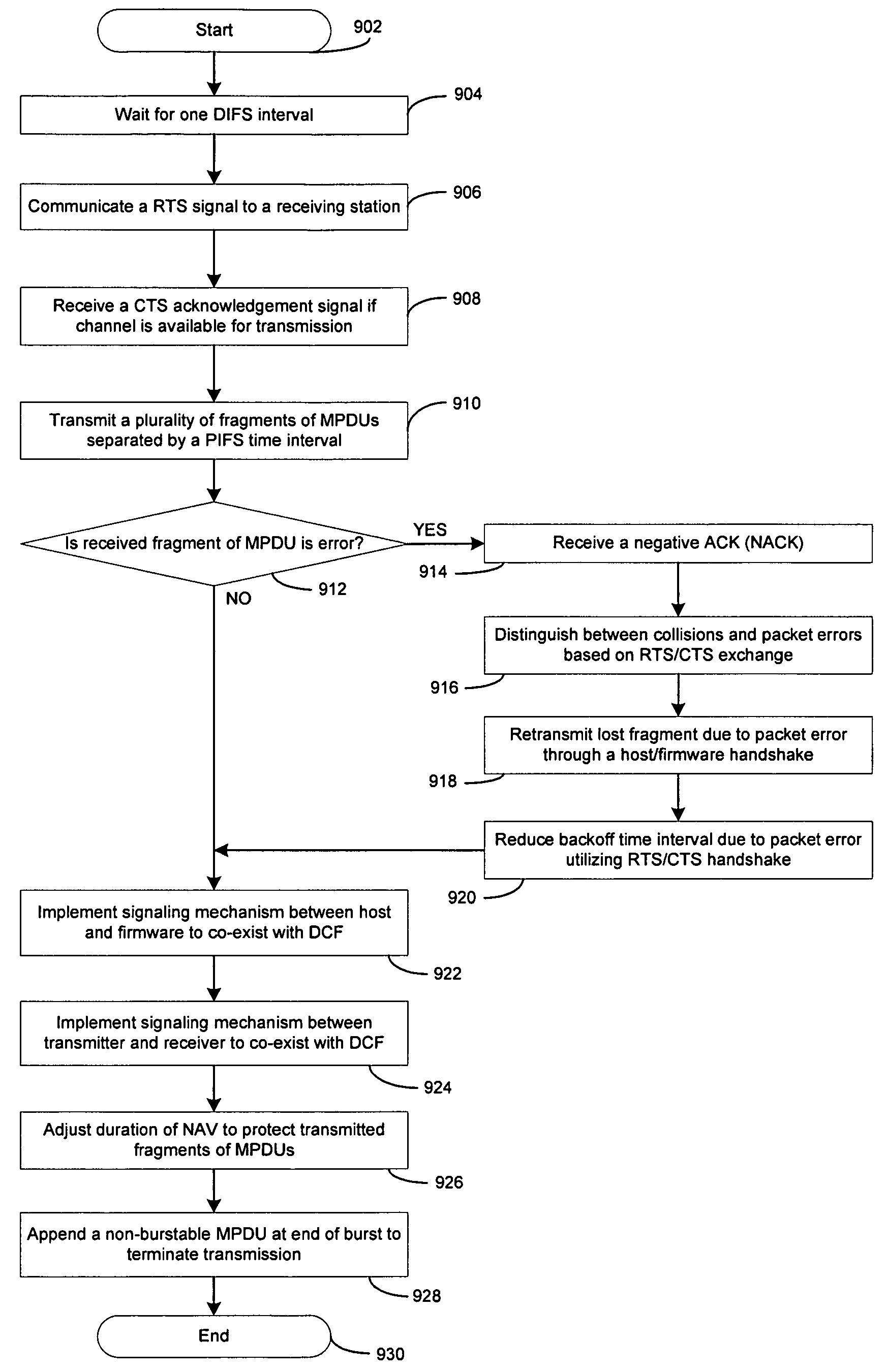
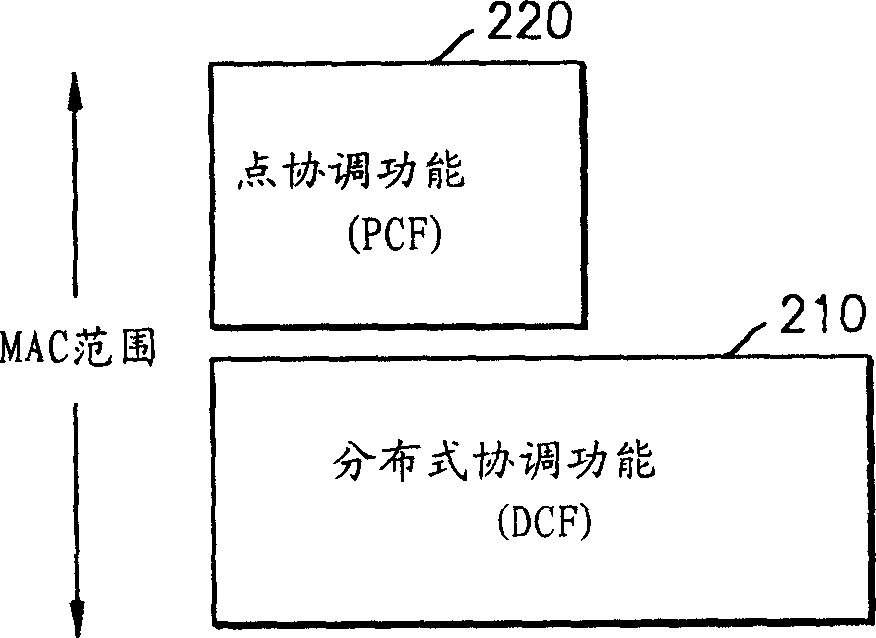
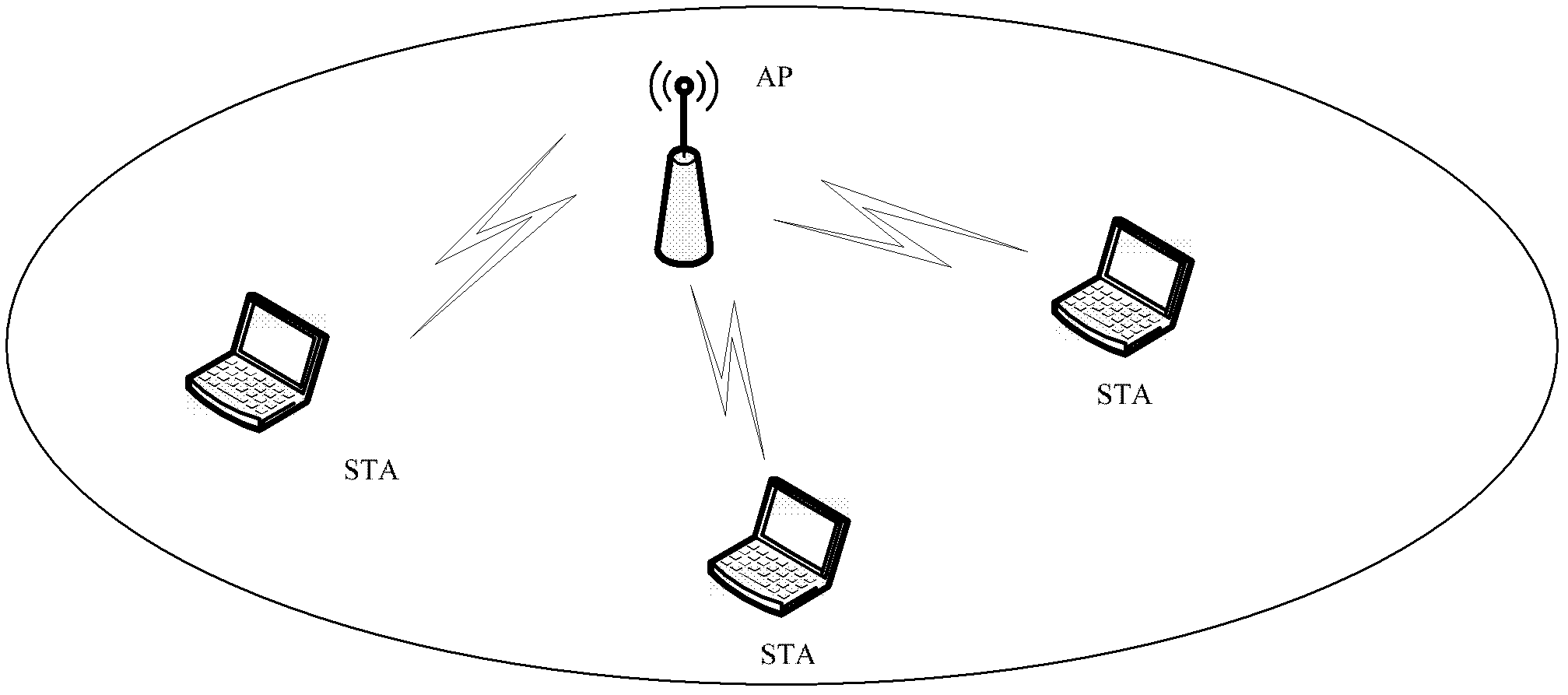
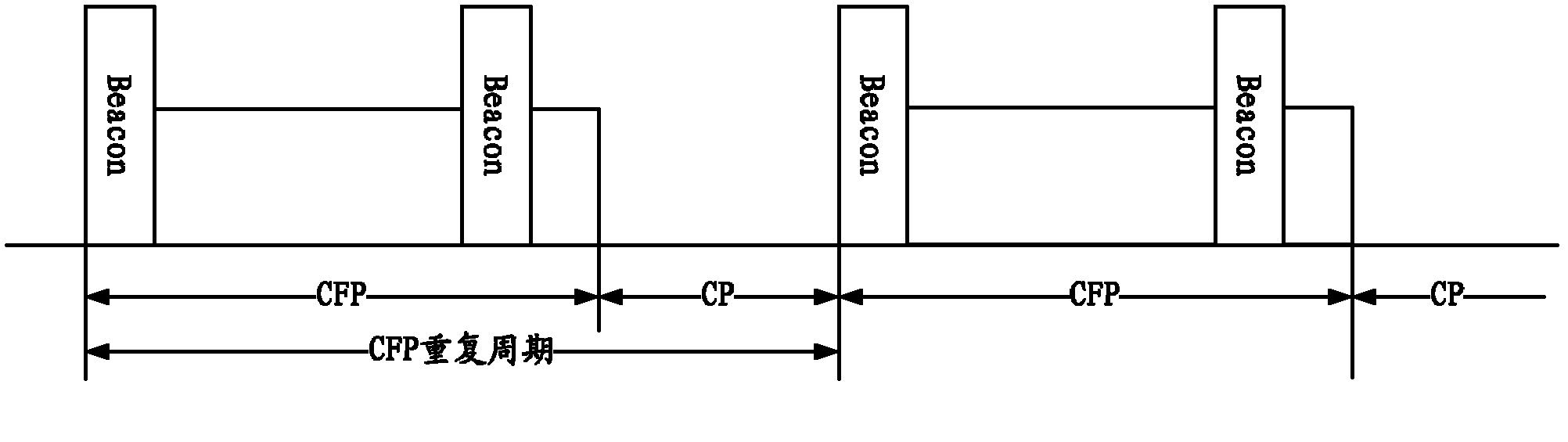
Point coordination function (PCF) is a media access control (MAC) technique used in IEEE 802.11 based WLANs, including Wi-Fi. It resides in a point coordinator also known as access point (AP), to coordinate the communication within the network. The AP waits for PIFS duration rather than DIFS duration to grasp the channel. PIFS is less than DIFS duration and hence the point coordinator always has the priority to access the channel.
Proxy active scan for wireless networks
InactiveUS20060092888A1Information obtainedAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsMobile station
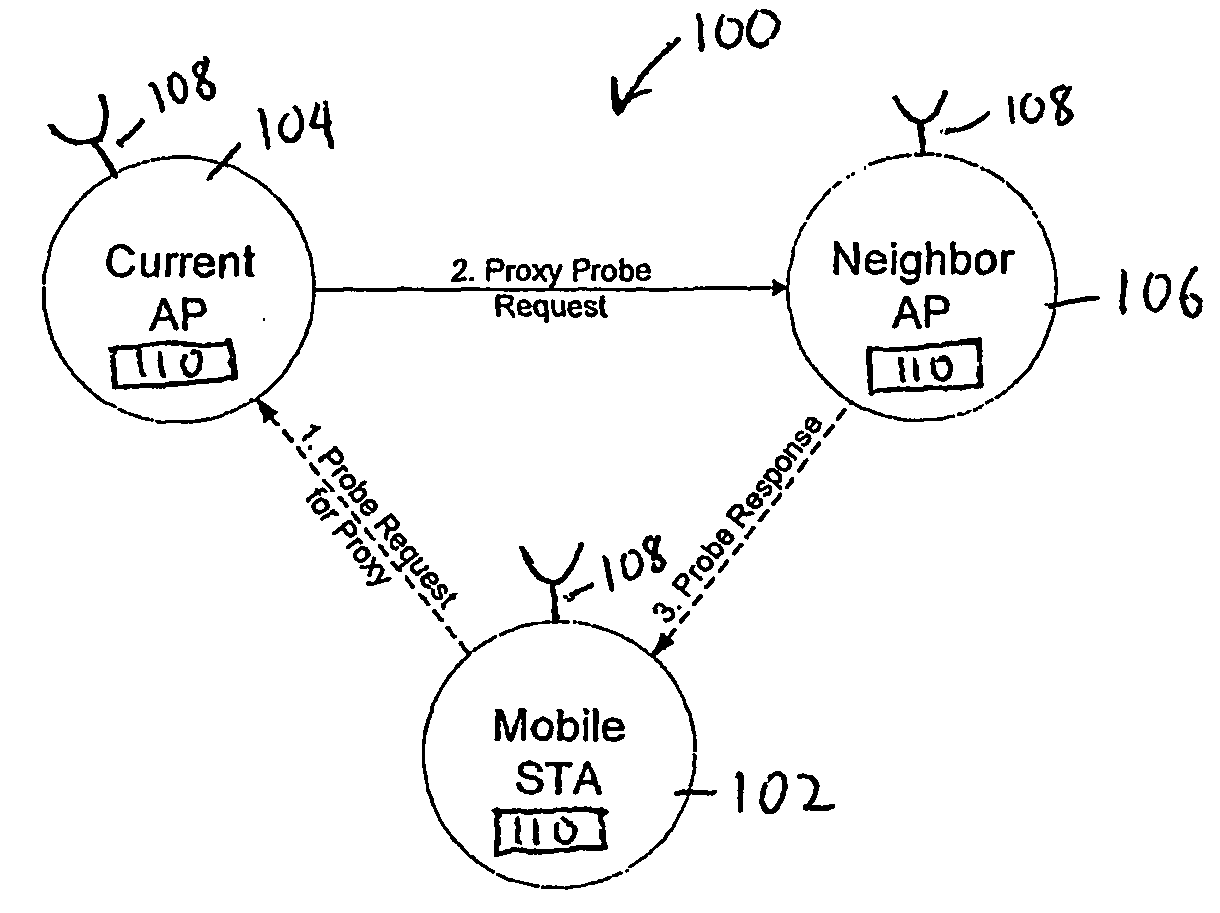
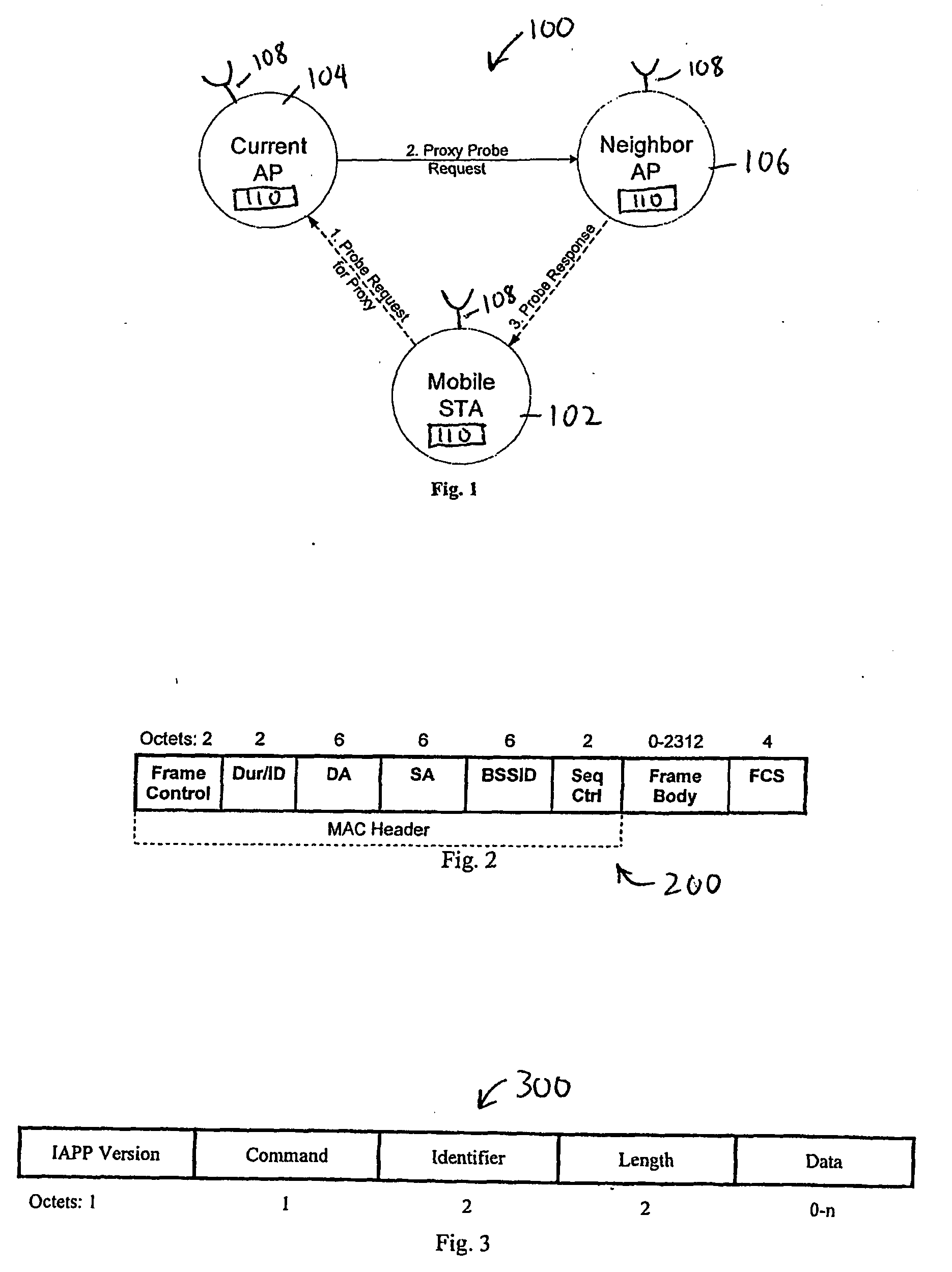
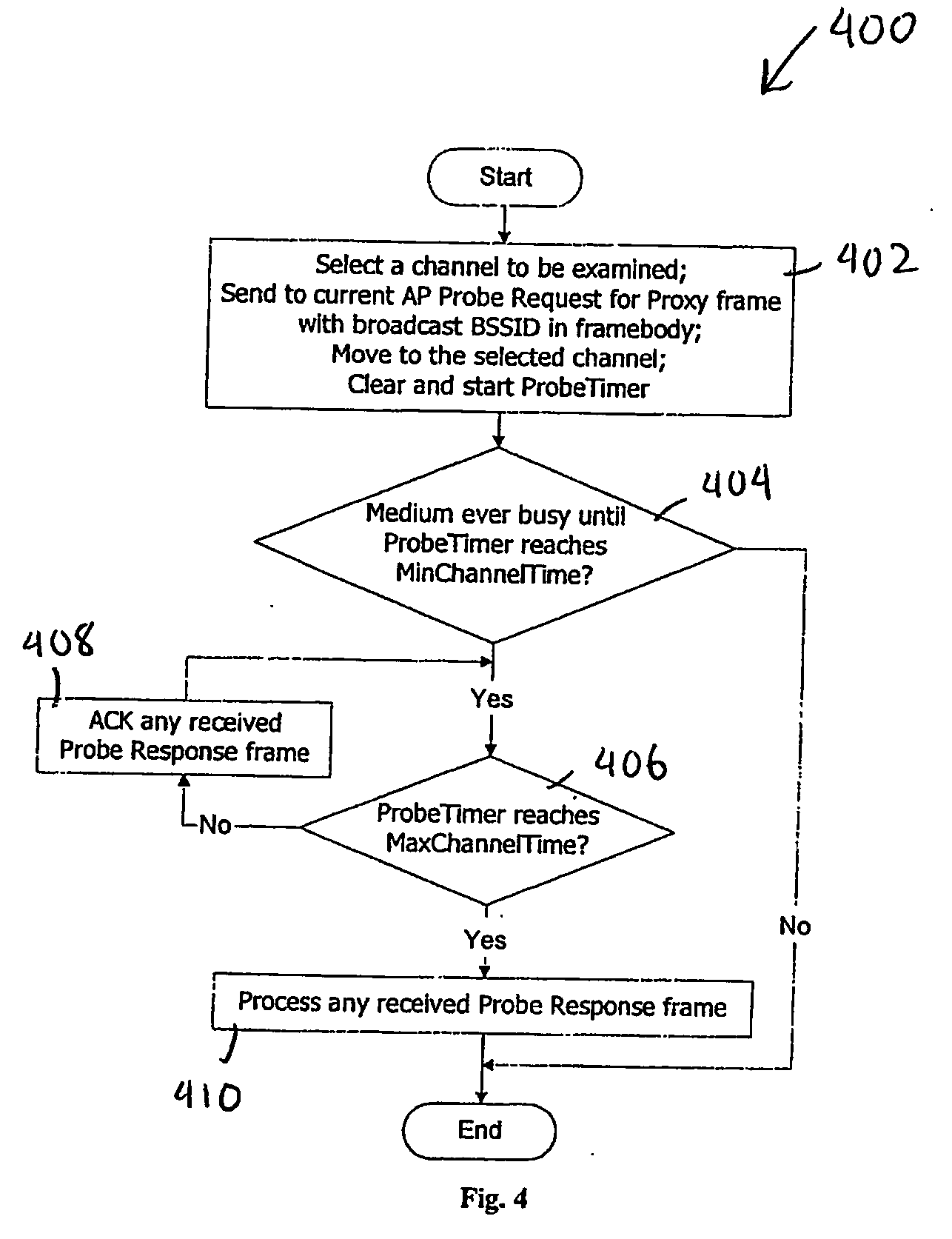
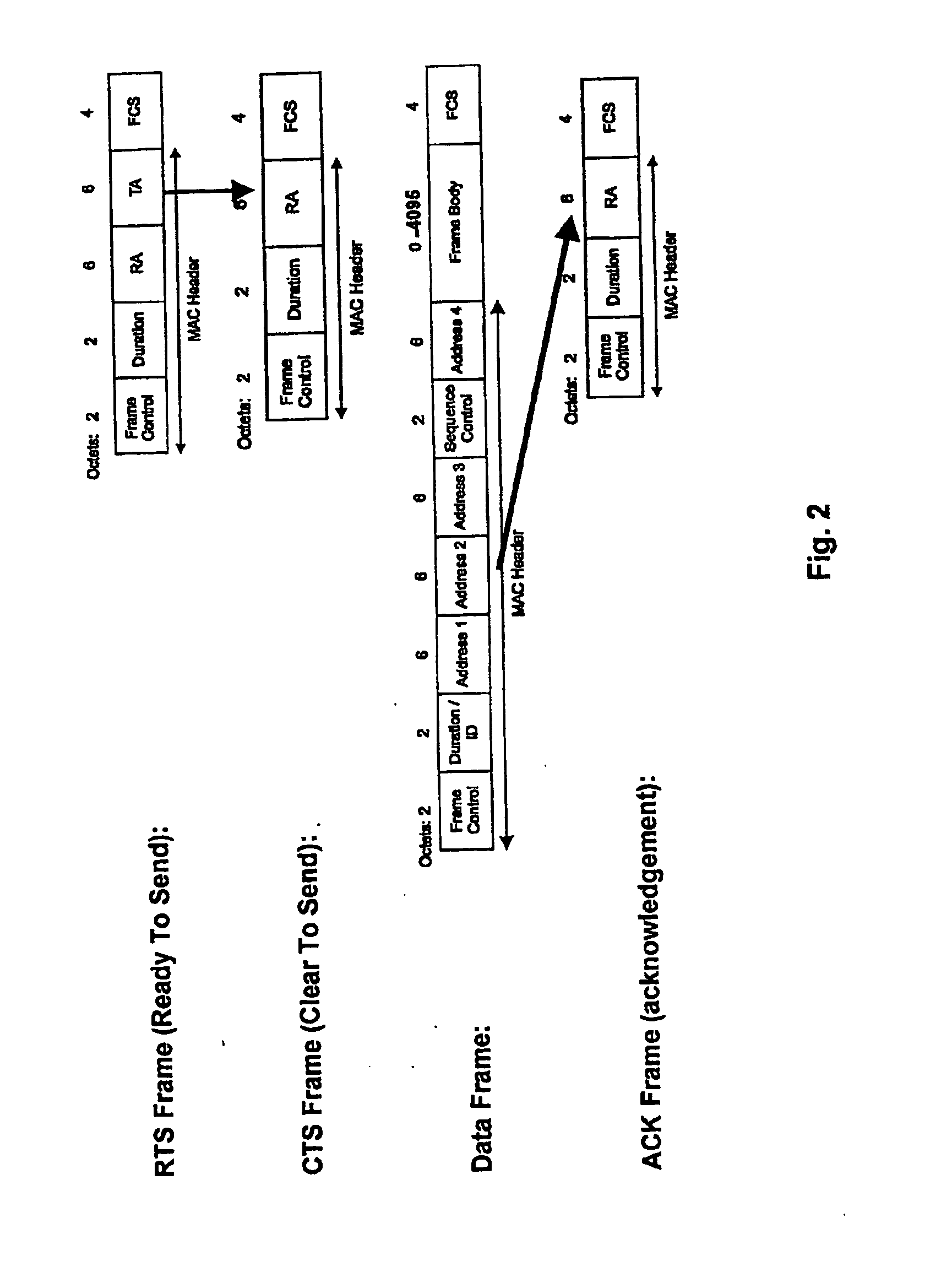
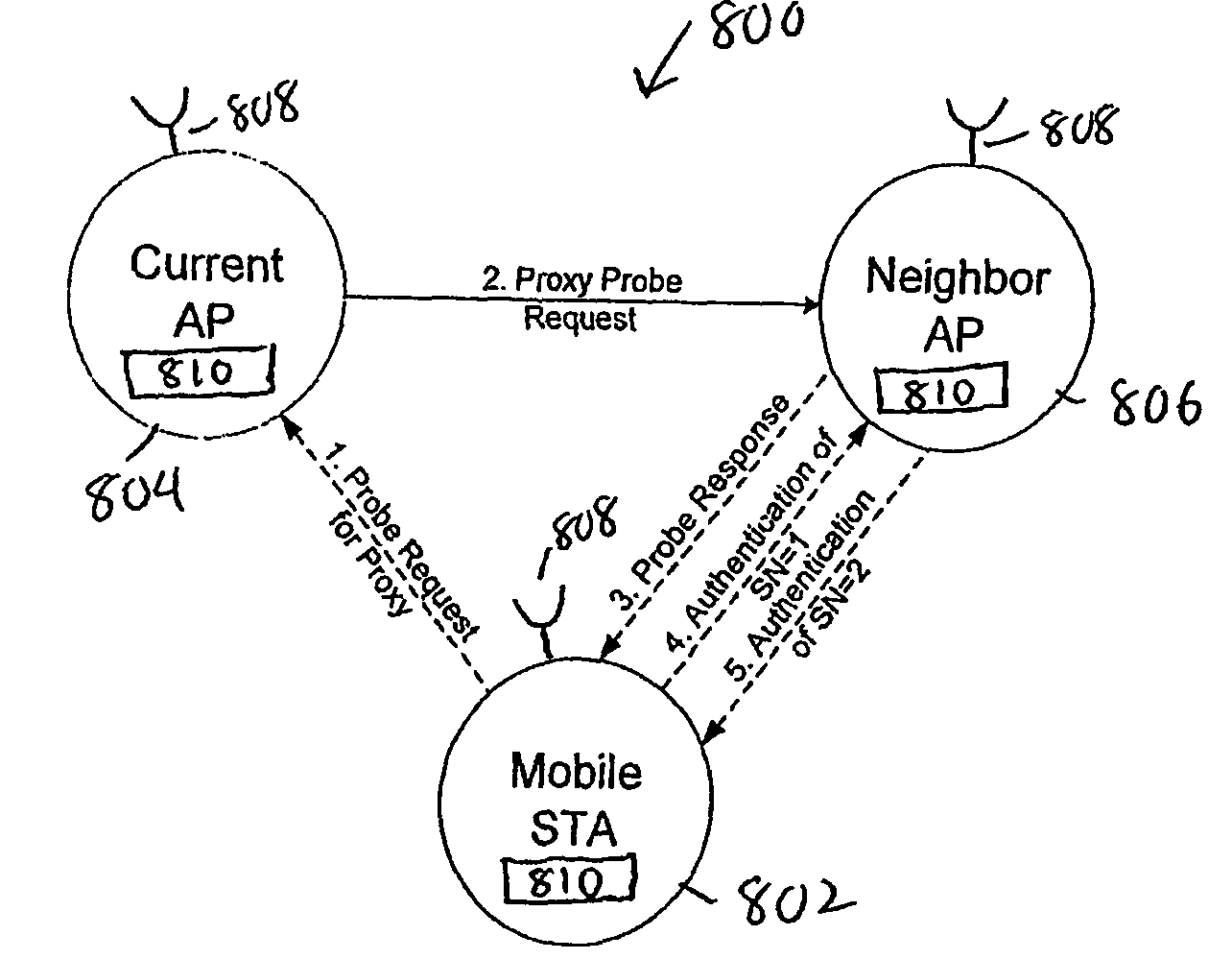
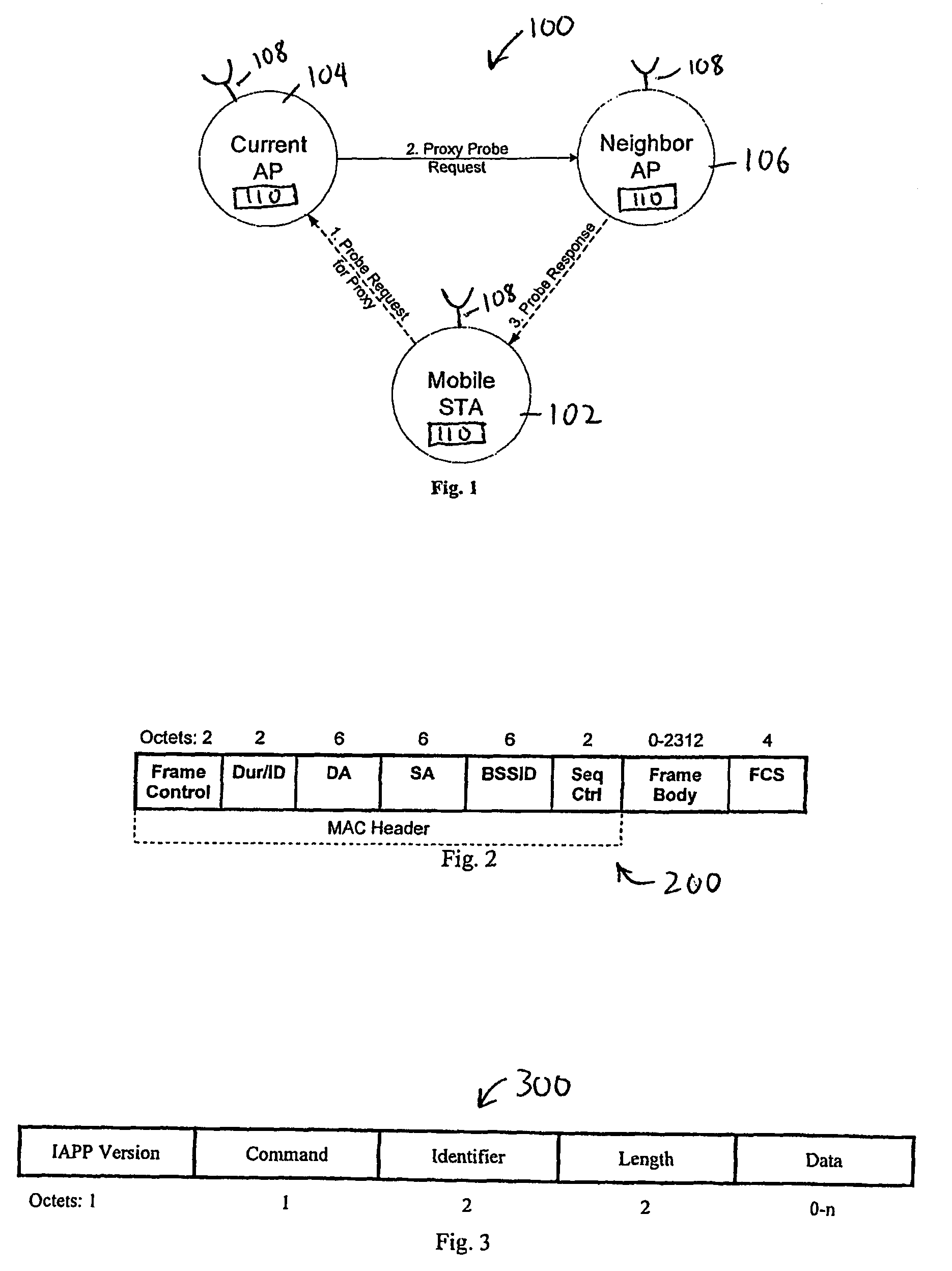
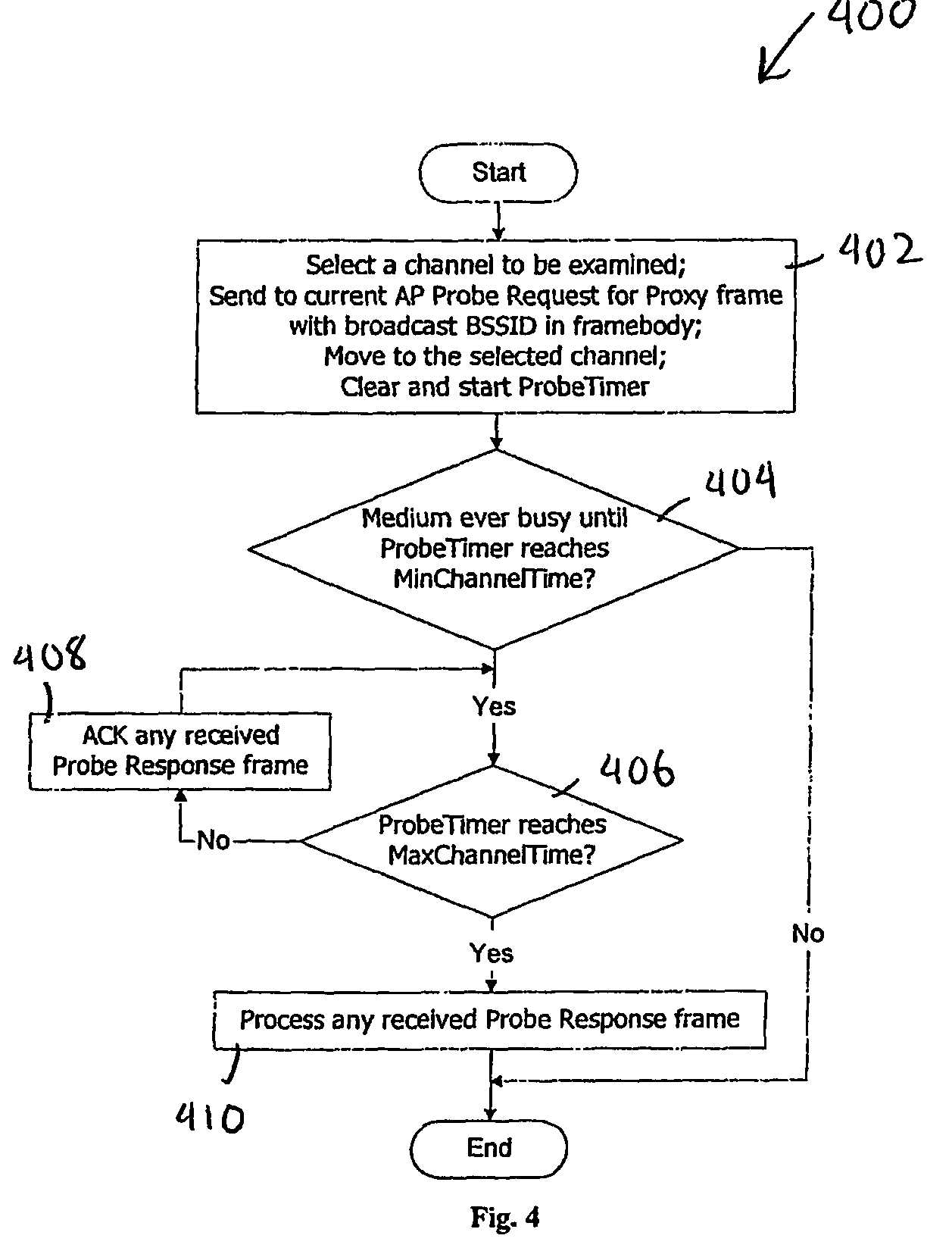
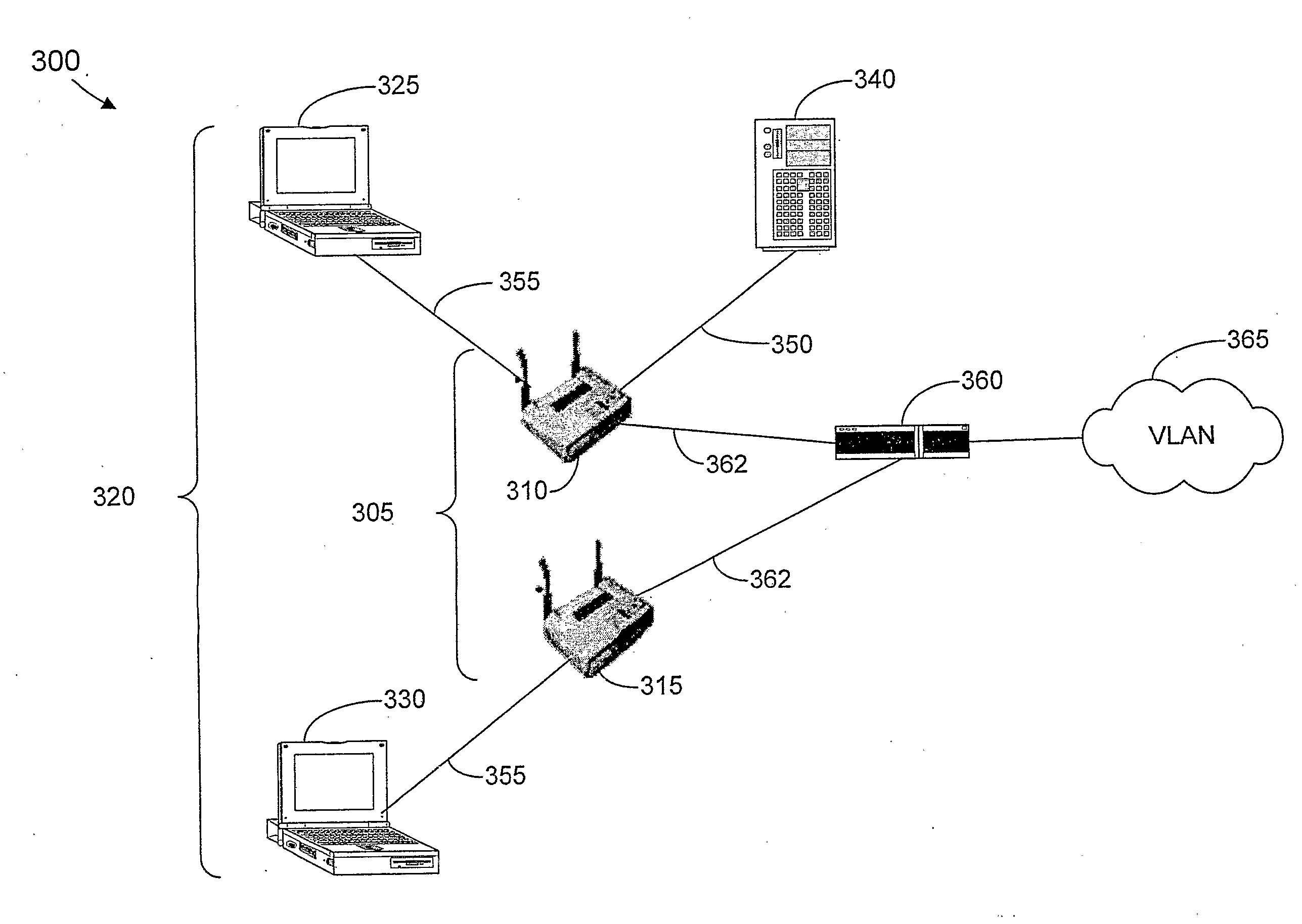
Active scanning method in a wireless network for fast determining available access points (106, 806) using inter-AP (Access Point) communication is described. In the scanning method, a mobile station (102, 802) sends Probe Request for Proxy frame to the current AP (104, 804) serving the mobile station (102, 802). In response to the Probe Request for Proxy frame, the current AP (104, 804) send Proxy Probe Request packet to the appropriate APs (106, 806). In response to the Proxy Probe Request packet, the neighbor APs (106, 806) send Probe Response frame to the mobile station (102, 802) on its operating channel. Since the mobile station (102, 802) moves to the channel being examined after sending the Probe Request for Proxy frame, it receives the Probe Response frame if it is in the coverage area of the neighbor AP (106, 806). The content of Probe Response frame provides the mobile station (102, 802) with the information to be used in handoff decision and network join procedures. Thus, the mobile station (102, 802) neither has to move to the channel to be examined nor send Probe Request frame on that channel. This enables active scan to be initiated even when the neighbor AP (106, 806) is operating in PCF (Point Coordination Function) and the network is in CFP (Contention Free Period), during which unassociated mobile stations (including the scanning mobile station) cannot send packets.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method and system for improving throughput over wireless local area networks with mode switching
InactiveUS6990116B1Improve throughputNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexDistributed coordination functionStation
A method and system for increasing the overall network throughput over a wireless local area network (WLAN). Specifically, in one embodiment of the present invention, the dynamic switching between the Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) and Point Coordination Function IEEE 802.11 access modes is determined according to the load conditions over the WLAN in a method and system. Stations and access points within a WLAN monitor conditions within the network to determine which access mechanism is most optimum for the current load conditions. Some factors to consider in determining the load conditions include but are not limited to the number of transmissions, number of receptions, and number of collisions.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
System topologies for optimum capacity transmission over wireless local area networks
ActiveUS7046651B2Improve rendering capabilitiesImprove functionalityError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementComputer scienceSystem topology
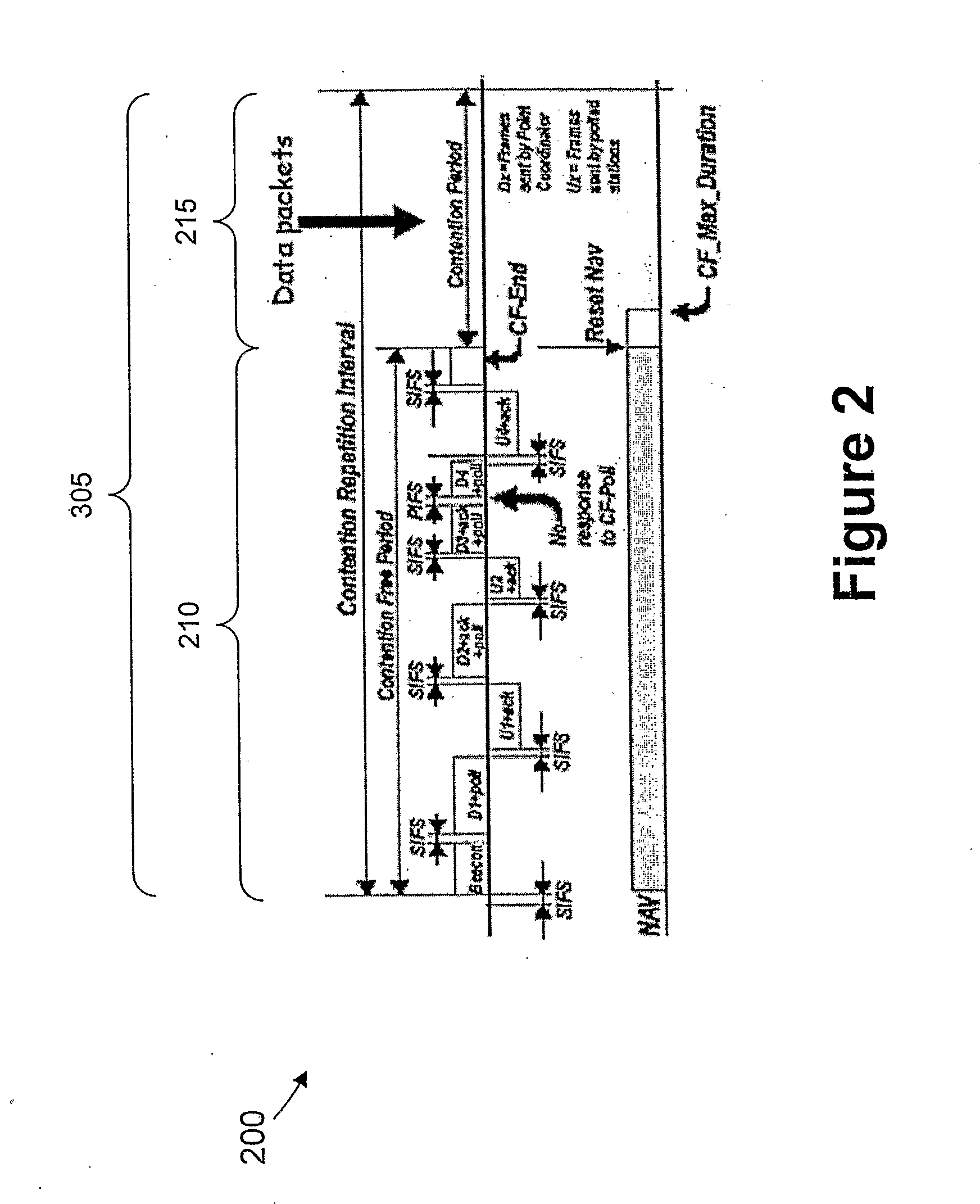
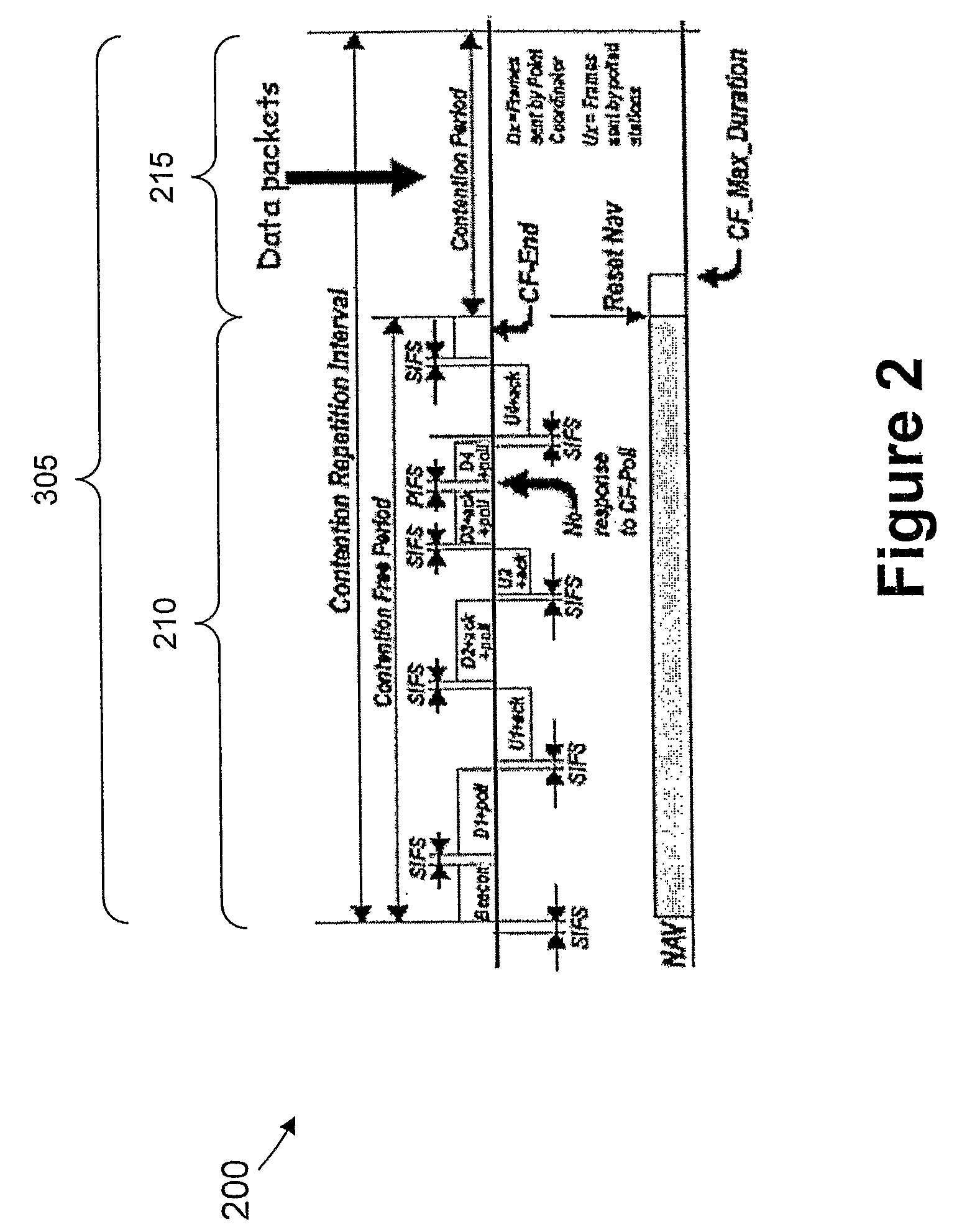
An inventive method provides optimum topology for a multi-antenna system dedicated to higher throughput / capacity by bundling the Point Coordination Function (PCF) operation in infrastructure mode of the current and / or enhanced IEEE MAC with PHY specifications that employ some form of coherent weighting based on CSI at the transmitter in conjunction with the corresponding optimum receiver detection based on CSI. Specifically, CSI is measured from a control message, so data messages and control messages are separated. In the contention period of IEEE 802.11, the RTS / CTS exchange is used for CSI and the data message is sent following the CTS message. In the contention free period, a poll by the PC is separated from a data frame, which gives the polled station the first opportunity to send a data message. This change in topology results in various changes to the frame exchange format in the CFP for various scenarios of data and control messages to be exchanged.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
System topologies for optimum capacity transmission over wireless local area networks
InactiveUS20050147075A1Improve rendering capabilitiesImprove functionalityError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless lanSystem topology
An inventive method provides optimum topology for a multi-antenna system dedicated to higher throughput / capacity by bundling the Point Coordination Function (PCF) operation in infrastructure mode of the current and / or enhanced IEEE MAC with PHY specifications that employ some form of coherent weighting based on CSI at the transmitter in conjunction with the corresponding optimum receiver detection based on CSI. Specifically, CSI is measured from a control message, so data messages and control messages are separated. In the contention period of IEEE 802.11, the RTS / CTS exchange is used for CSI and the data message is sent following the CTS message. In the contention free period, a poll by the PC is separated from a data frame, which gives the polled station the first opportunity to send a data message. This change in topology results in various changes to the frame exchange format in the CFP for various scenarios of data and control messages to be exchanged.
Owner:TERRY JOHN
Method and apparatus for enhancing transfer rate using DLP and multi channels in wireless LAN using PCF and DCF
InactiveUS20050053015A1Reduce contentionData switching by path configurationWireless communicationWireless lanPrimary channel
A wireless network communication method and apparatus for enhancing a data transfer rate by using a direct link protocol (DLP) and multi channels during a point coordination function (PCF) period in wireless network communications in which an access point is employed in an infrastructure mode using both a contention-free period and a contention period. The wireless network communication method of the present invention including transmitting / receiving data among stations supporting a direct link, during a given duration, through the direct link using an independent channel; transmitting / receiving data among stations other than the stations supporting the direct link, during the duration, in a specific mode corresponding to the contention-free or contention period; switching the DLP stations to a primary channel after the given duration; and transmitting / receiving data among all stations including the DLP stations, during the remaining duration, in a specific mode corresponding to the contention-free or contention period.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
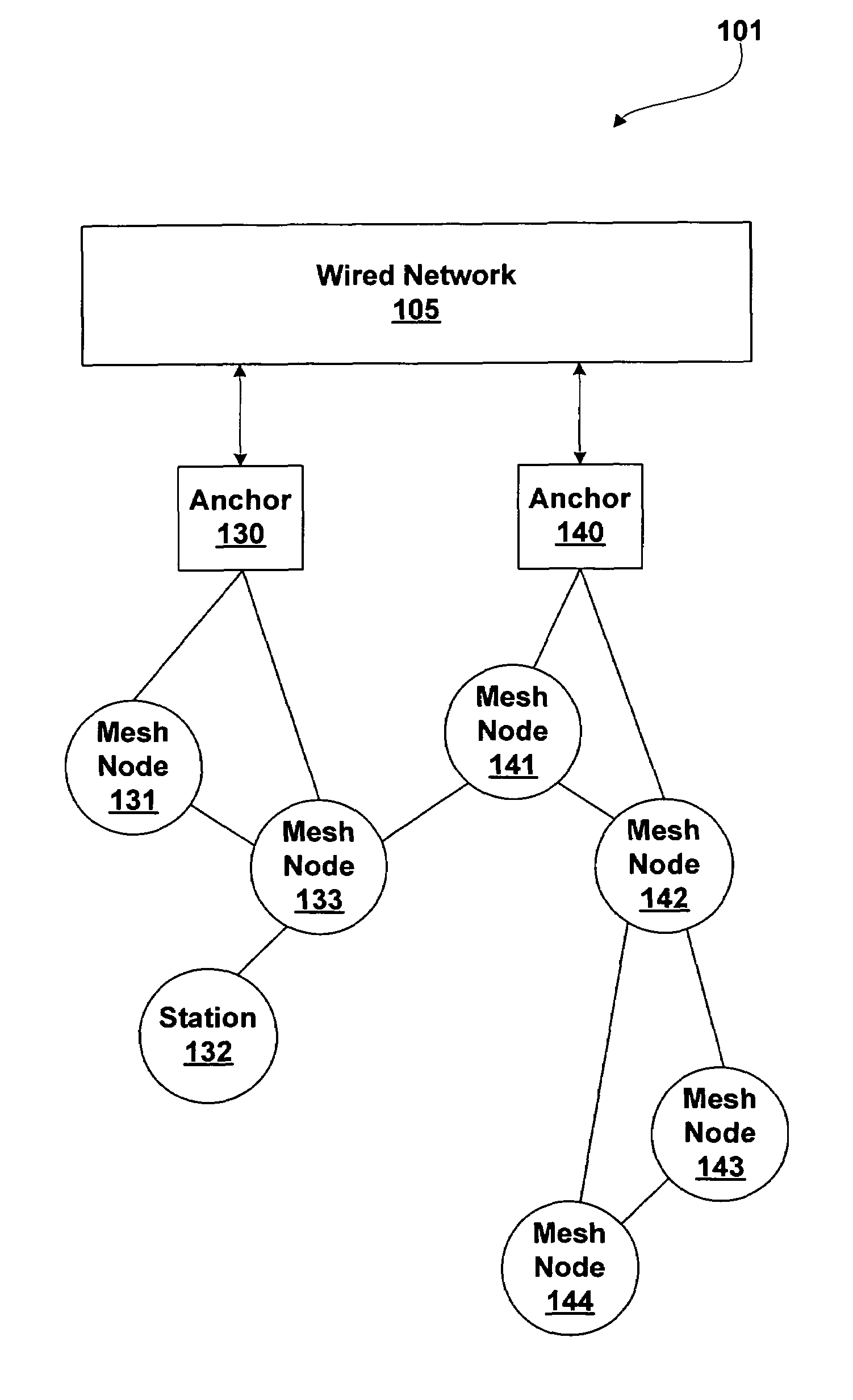
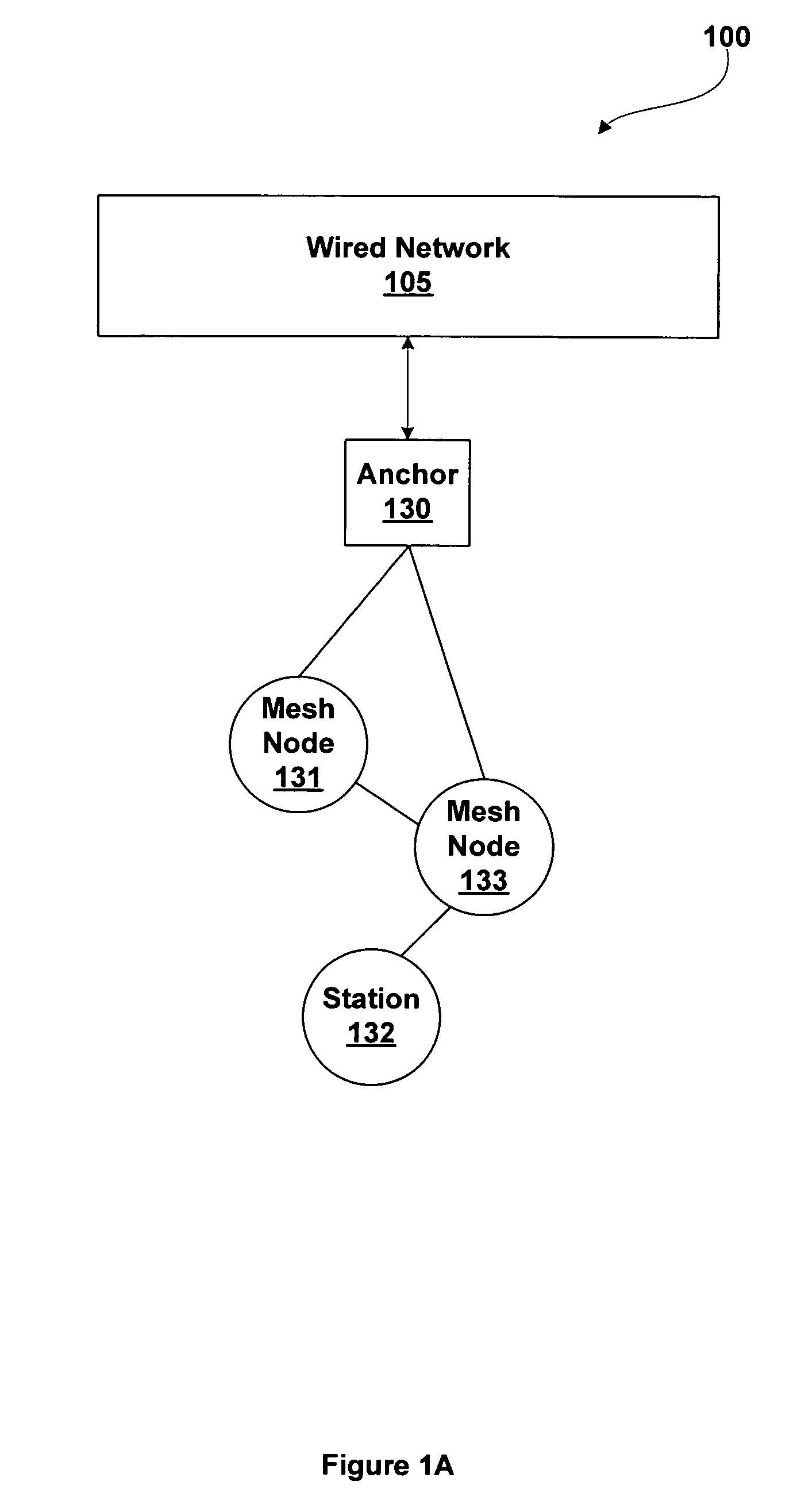
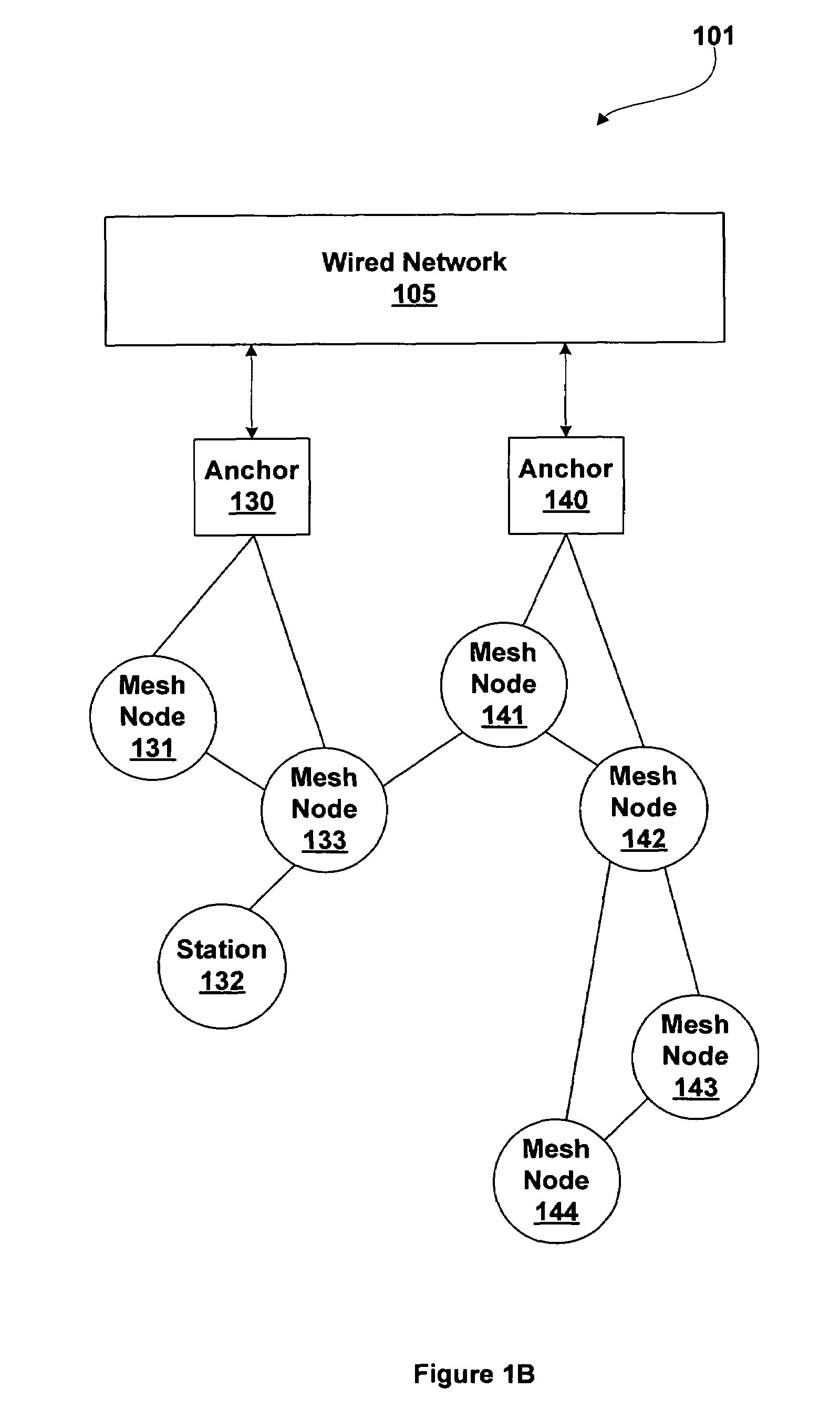
Mesh networking using point coordination function
ActiveUS7502354B1Raise the possibilityTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationGrid networkWireless computing
A system and methods for wireless computing devices to become mesh member nodes within a self-configuring mesh network includes mechanisms for neighbor discovery and sharing of a common topology database including mesh topology and mesh network information. Each mesh node may use the topology database to determine optimized routing paths within the mesh network. Mesh member nodes are configured to detect and communicate topology changes and measured mesh network attributes to other members of the self-configuring wireless network.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Carrier sense method and system
InactiveCN102595569AReduce power consumptionPower managementEnergy efficient ICTClear to sendMain channel
The invention discloses a carrier sense method and a system. According to the method, a transmitting terminal sends an idle channel to assess clear channel assessment (CCA) request frames on a main channel of a transmission channel which needs to be detected; the transmitting terminal sends request to send (RTS) frames on the transmission channel which needs to be detected after sending a point coordination function inter-frame space (PIFS) subsequent to transmission of the CCA request frame; and the transmitting terminal performs data transmission on the transmission channel transmitting clear to send (CTS) frames after receiving an indication that CTS frames are permitted to send. The invention also discloses the carrier sense system, which comprises a transmitting terminal and a receiving terminal. According to the method and the system, the power consumption of the receiving terminal is reduced and reliable CCA results of all transmission channels are provided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Adaptive modulation and other extensions of the physical layer in multiple access systems
ActiveUS20050141448A1Less susceptible to packet errorEasy to useTransmission control/equlisationFrequency-division multiplex detailsDistributed coordination functionCommunications system
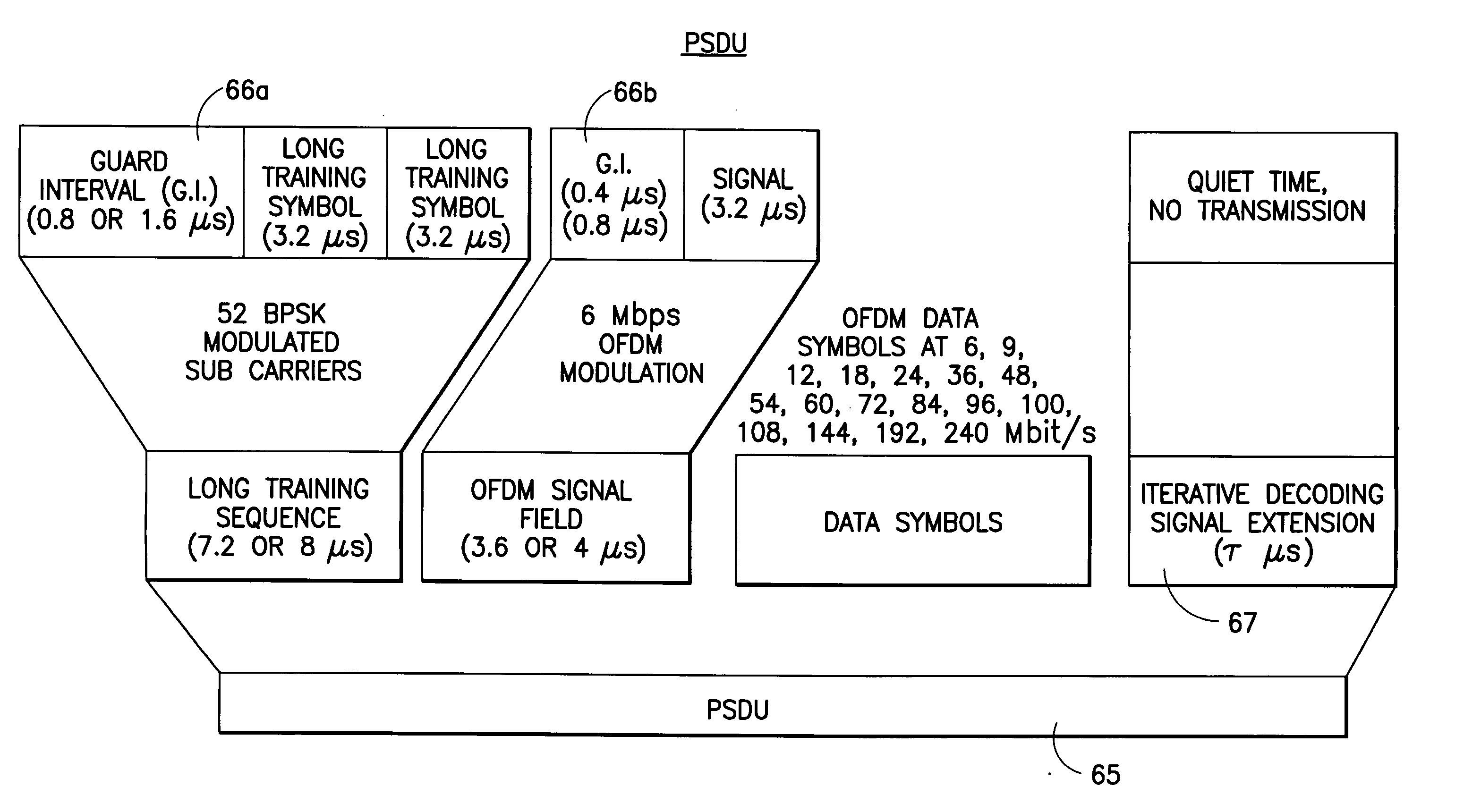
The present invention seeks to improve data exchange in a communications system that is especially standardized according to IEEE 802.11a. For this purpose, when the transmission medium, preferably an IEEE 802.11 system with a distributed coordination function (DCF) is accessed in a decentralized manner, pilot signals are transmitted from the transmitter to the recipients using a number of transmission modes and then an allocation table regarding the transmission modes is calculated by the recipient on the basis of the pilot symbols received. The recipient transmits the allocation table to the transmitter so that the subsequent data exchange can proceed on the basis of the allocation table. In the case of centralized access, preferably an IEEE 802.11 system with a point coordination function (PCF), data exchange is improved in that the subsequent data are adaptively modulated already when the allocation table is transmitted.
Owner:GIGASET COMMUNICATIONS
Effective point coordination function in wireless lan
InactiveUS20060165021A1Reduce transmission delayEnhancing point coordination functionNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationWireless lanPoint coordination function
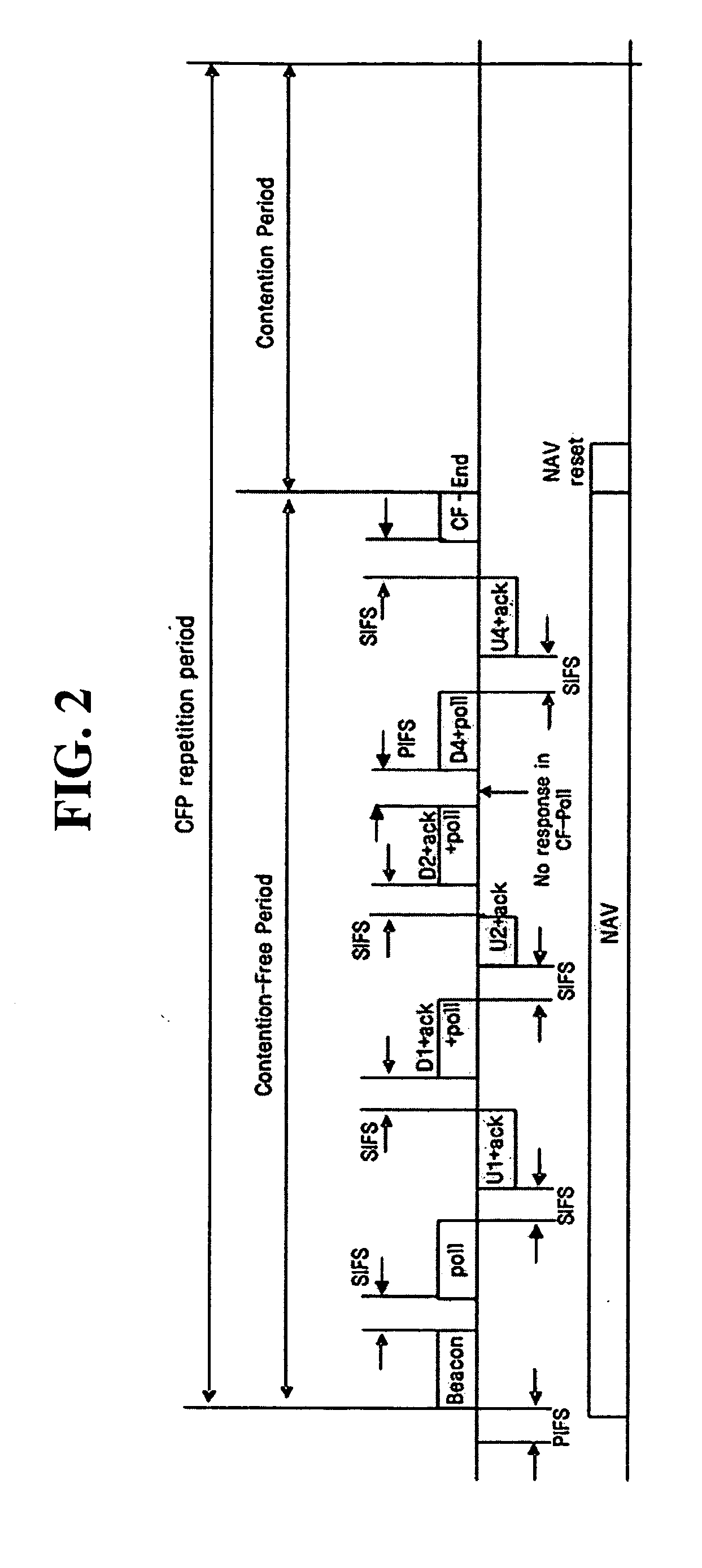
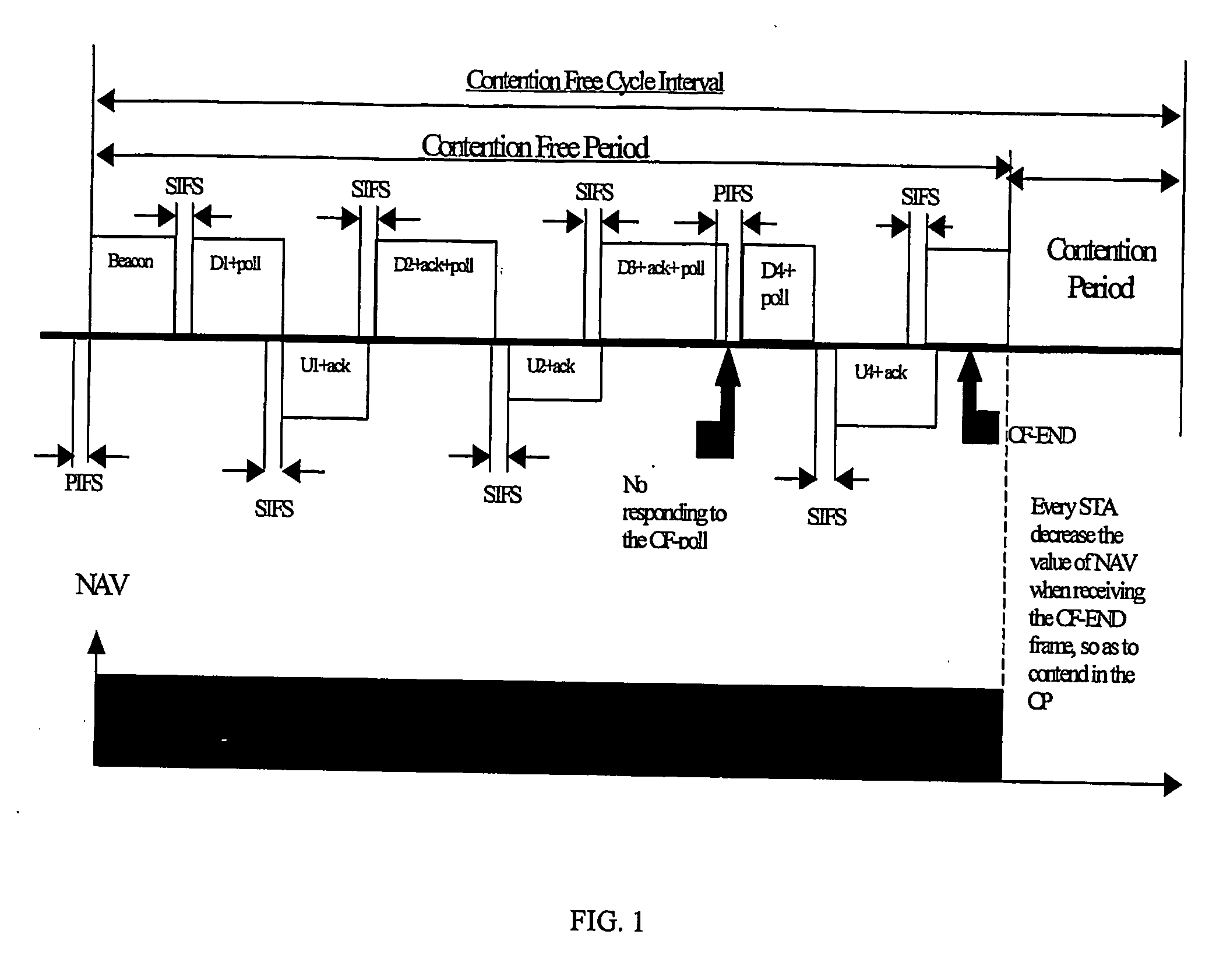
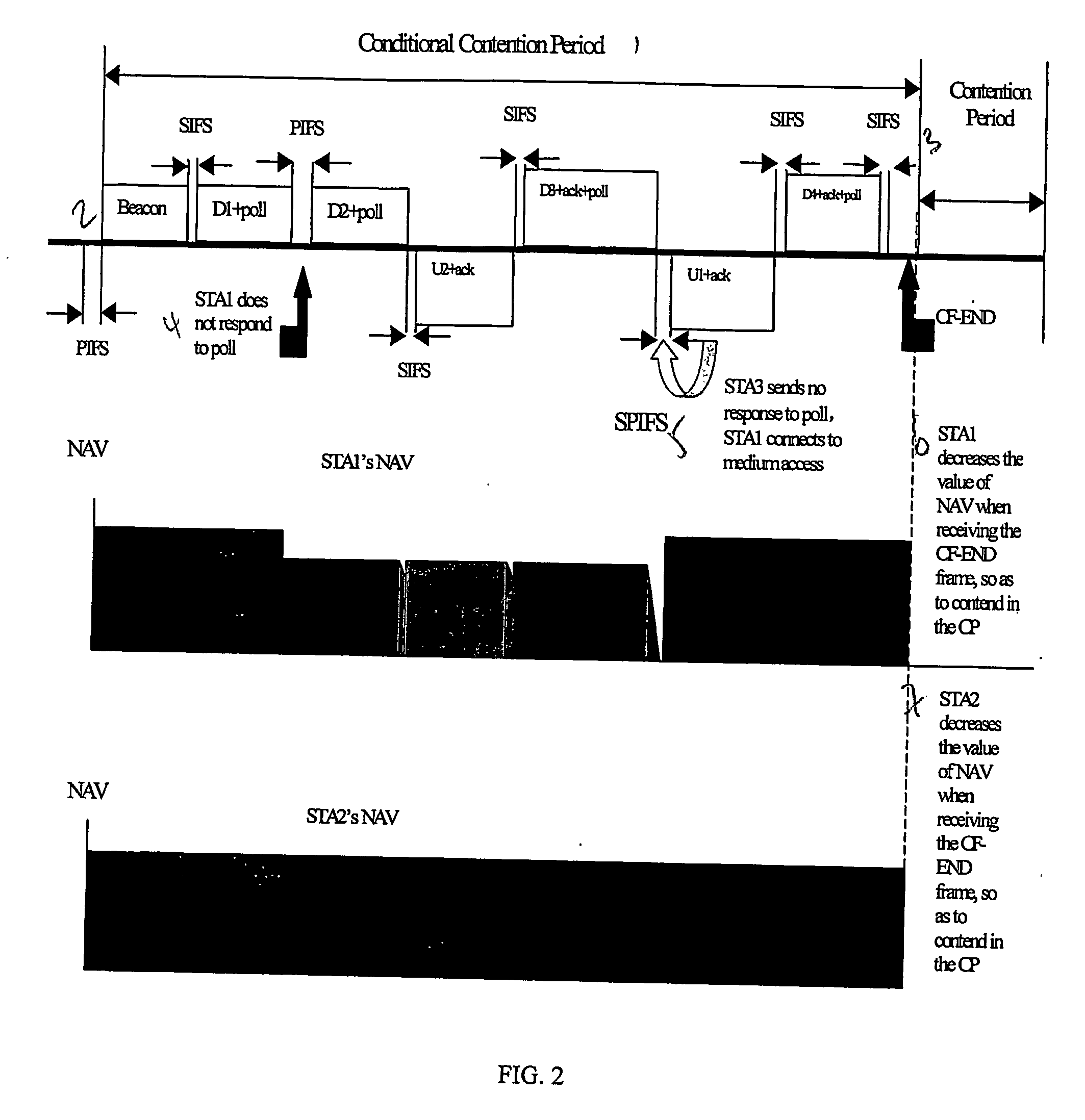
This invention provides a system and method for enhancing point coordination function in wireless LANs. A contention procedure is introduced into PCF in this invention. When the point coordinator (PC) polls the mobile terminal who has no frame to send, the terminal does not respond to the CF-Poll from PC, and will adjust its NAV and set it to a special value that is defined as SPIFS. When data is ready on this mobile terminal, the terminal can contend for accessing the medium. If it detects the medium to be idle for SPIFS period during the CFP, then the mobile terminal gains the control of medium and starts to send the ready data. So this mobile terminal can have another opportunity to gain the control of medium during this CFP instead of next CFP, and this can decrease the transmission delay.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Proxy active scan for wireless networks
InactiveUS8054798B2Information obtainedAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsWireless mesh network
Active scanning method in a wireless network for fast determining available access points (106, 806) using inter-AP (Access Point) communication is described. In the scanning method, a mobile station (102, 802) sends Probe Request for Proxy frame to the current AP (104, 804) serving the mobile station (102, 802). In response to the Probe Request for Proxy frame, the current AP (104, 804) send Proxy Probe Request packet to the appropriate APs (106, 806). In response to the Proxy Probe Request packet, the neighbor APs (106, 806) send Probe Response frame to the mobile station (102, 802) on its operating channel. Since the mobile station (102, 802) moves to the channel being examined after sending the Probe Request for Proxy frame, it receives the Probe Response frame if it is in the coverage area of the neighbor AP (106, 806). The content of Probe Response frame provides the mobile station (102, 802) with the information to be used in handoff decision and network join procedures. Thus, the mobile station (102, 802) neither has to move to the channel to be examined nor send Probe Request frame on that channel. This enables active scan to be initiated even when the neighbor AP (106, 806) is operating in PCF (Point Coordination Function) and the network is in CFP (Contention Free Period), during which unassociated mobile stations (including the scanning mobile station) cannot send packets.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
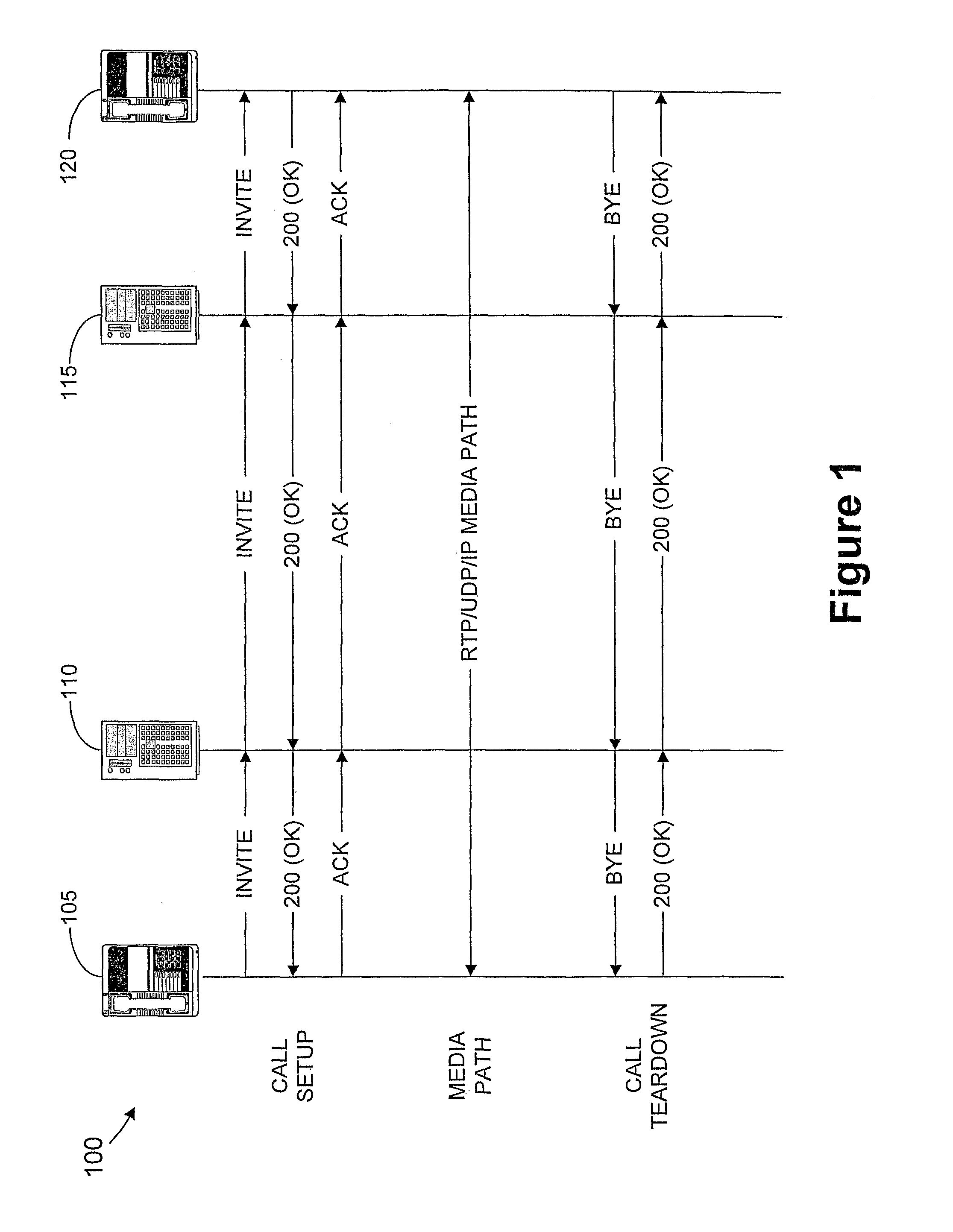
Method And Apparatus For Providing Quality Of Service To Voip Over 802.11 Wireless Lans
ActiveUS20070201409A1Connection managementData switching by path configurationFree accessSession Initiation Protocol
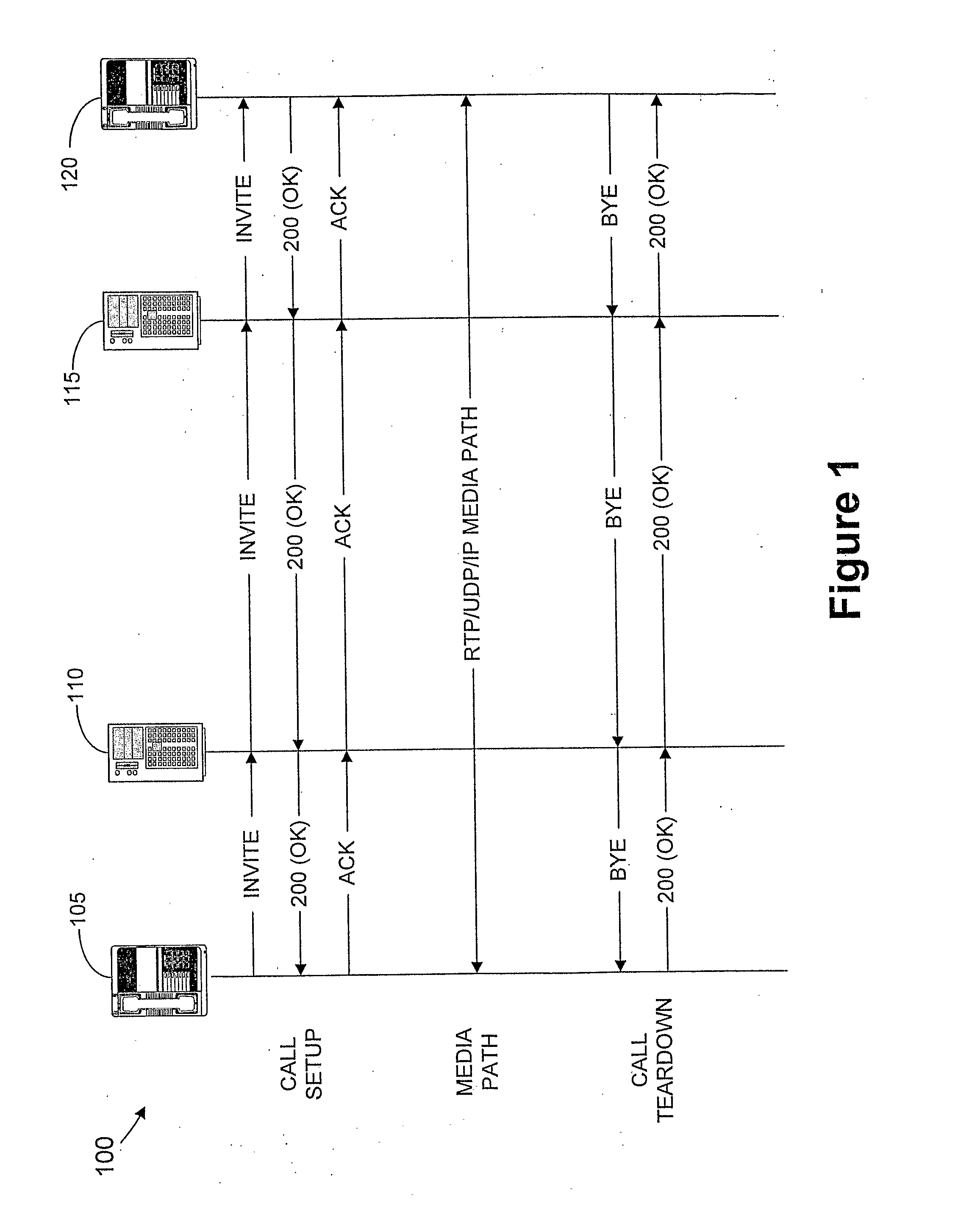
The present invention provides a method and system for providing quality-of-service to VoIP over a wireless local access network by providing periodic, contention-free access to a wireless link for voice packets. This is achieved by coupling Session Initiation Protocol (“SIP”) signaling for call setup with the Point Coordination Function mode of operation of the 802.11 medium access control. The result is that VoIP call signaling via SIP is tied with availability of periodic time-slots on the wireless medium. The periodic time-slots are used to guarantee contention-free access to the wireless link for voice packets. Accordingly, the present invention, in effect, merges two networking technologies: SIP-based VoIP and 802.11-based wireless LANs.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
Method and system for a bandwidth efficient medium access control (MAC) protocol
ActiveUS7706338B2Network traffic/resource managementWireless network protocolsClear to sendTelecommunications
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for providing quality of service to VoIP over 802.11 wireless LANs
ActiveUS7881310B2Connection managementData switching by path configurationFree accessQuality of service
The present invention provides a method and system for providing quality-of-service to VoIP over a wireless local access network by providing periodic, contention-free access to a wireless link for voice packets. This is achieved by coupling Session Initiation Protocol (“SIP”) signaling for call setup with the Point Coordination Function mode of operation of the 802.11 medium access control. The result is that VoIP call signaling via SIP is tied with availability of periodic time-slots on the wireless medium. The periodic time-slots are used to guarantee contention-free access to the wireless link for voice packets. Accordingly, the present invention, in effect, merges two networking technologies: SIP-based VoIP and 802.11-based wireless LANs.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
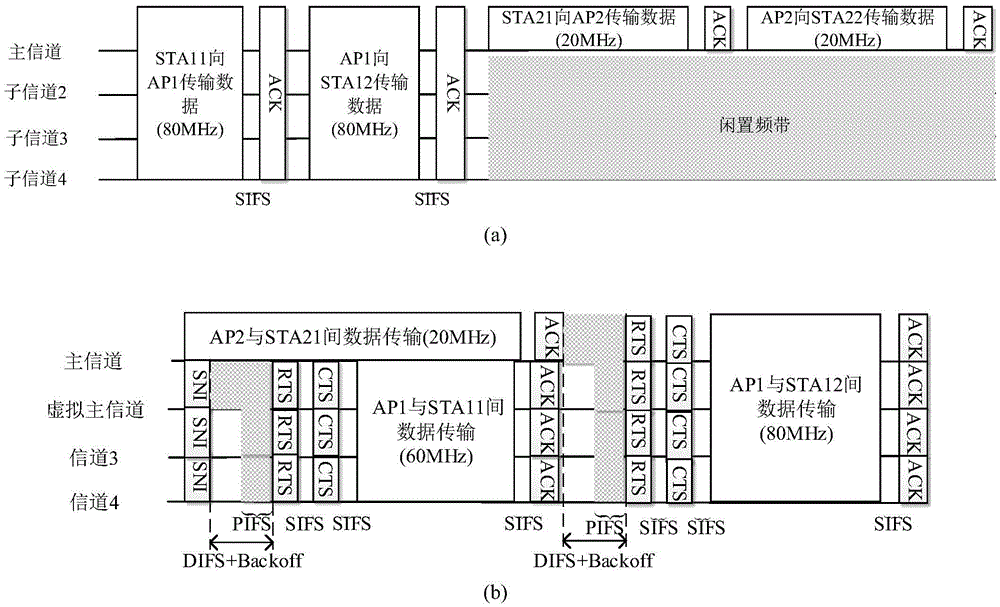
Media access control method based on WLAN system in 802.11ac protocol
ActiveCN105682247AImprove throughputImprove spectrum utilizationWireless communicationDistributed coordination functionFrequency spectrum
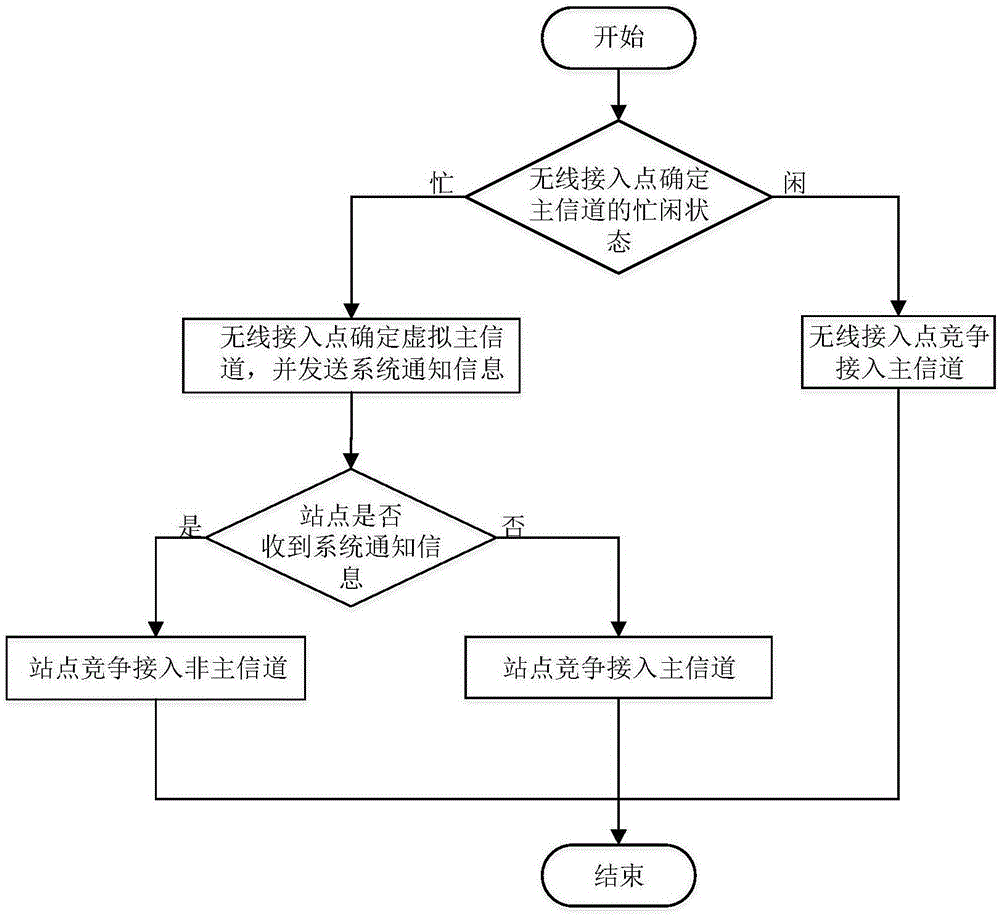
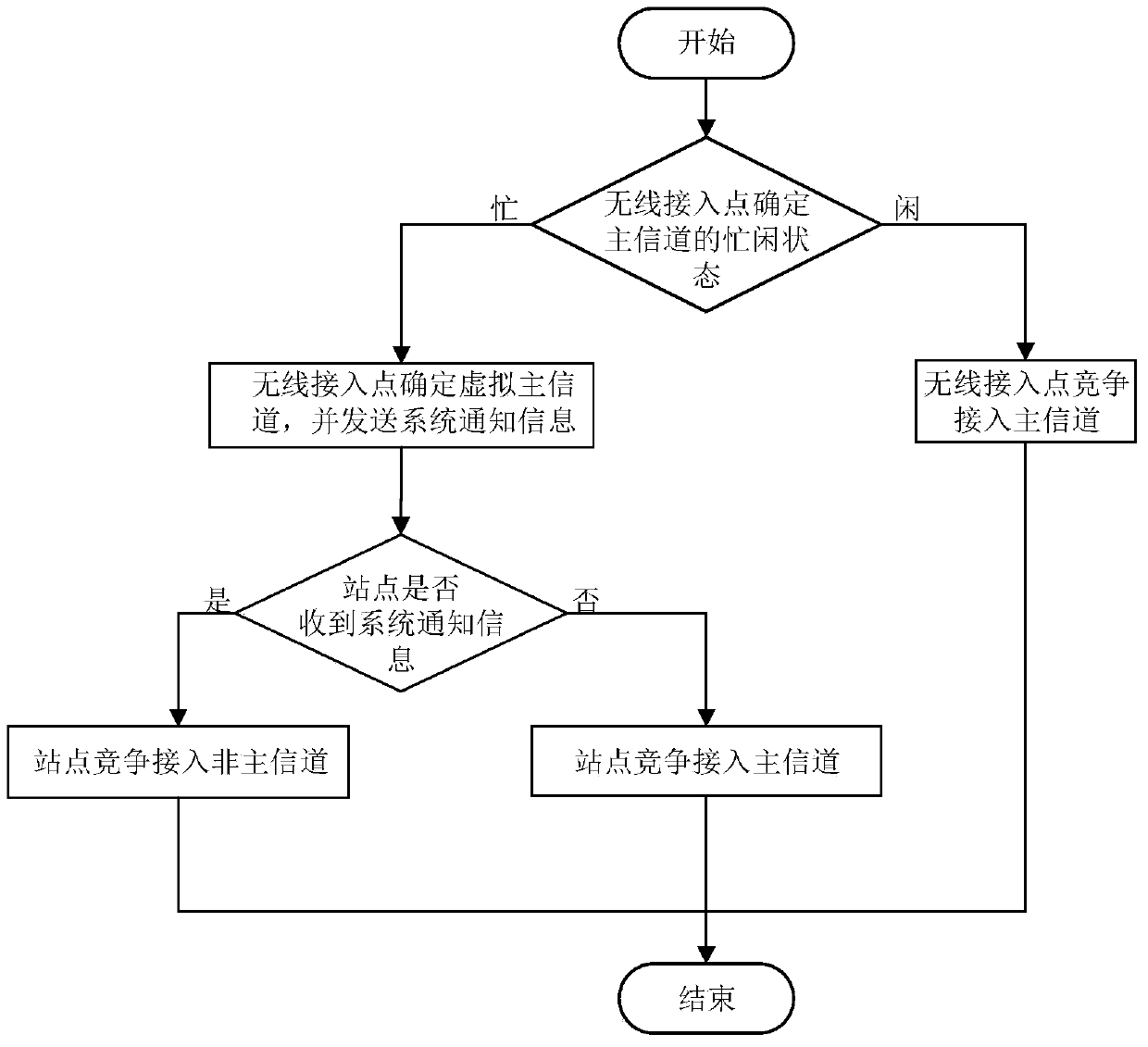
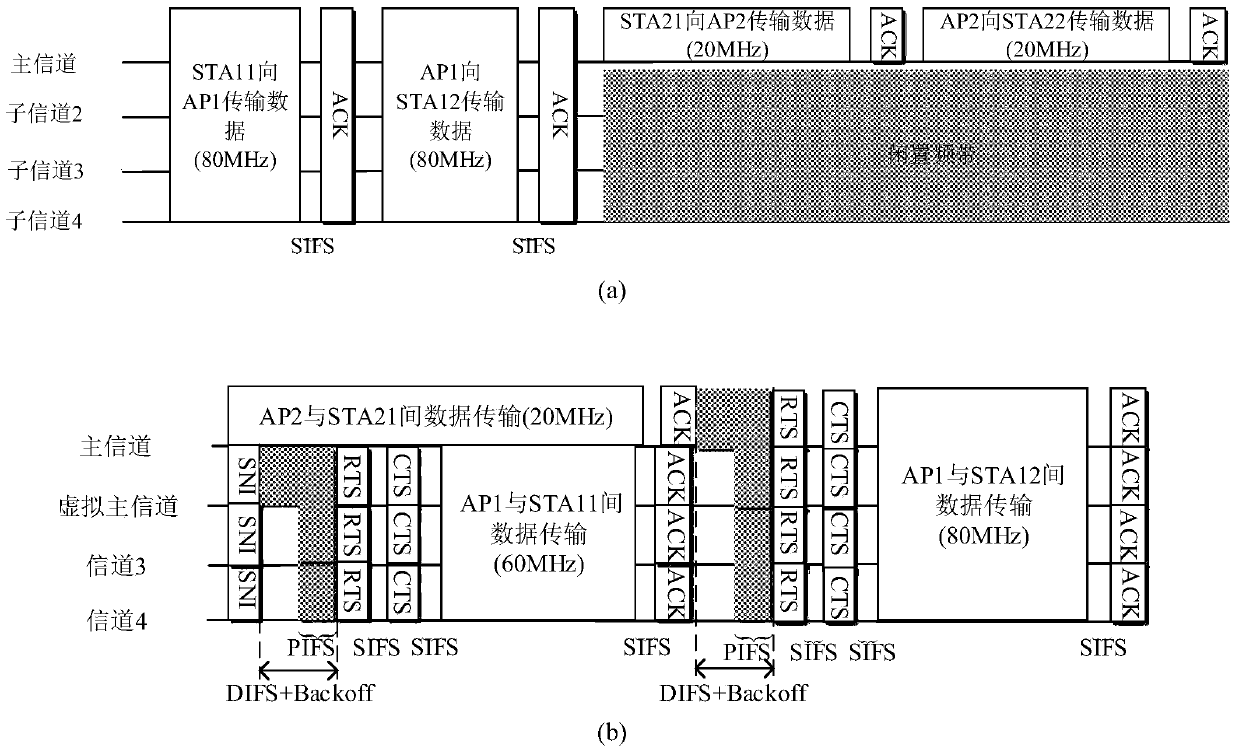
The invention discloses a media access control method based on a WLAN system in an 802.11ac protocol. The method mainly is used for solving the problem of low spectrum utilization rate resulted from overlapped basic service sets. The method comprises that a wireless access point AP invokes a carrier monitoring mechanism on a master channel so as to determine the busy and idle states of the master channel; when the master channel is in an idle condition, the wireless access point and stations STA access the master channel by a distributed coordination functional channel access method; when the master channel is in a busy condition, the wireless access point selects a first channel in non-master channels as a virtual master channel and sends system notice information SNI to the stations in a basic service set in which the wireless access point is located; SNI copies are sent to the other non-master channels; and the stations access the non-master channels on the virtual master channel according to a point coordination functional interframe interval channel access algorithm. According to the method provided by the invention, the non-master channel is utilized fully; the spectrum utilization rate and system throughput are improved; and the method can be used for optimizing the MAC layer protocol in the 802.11ac protocol.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
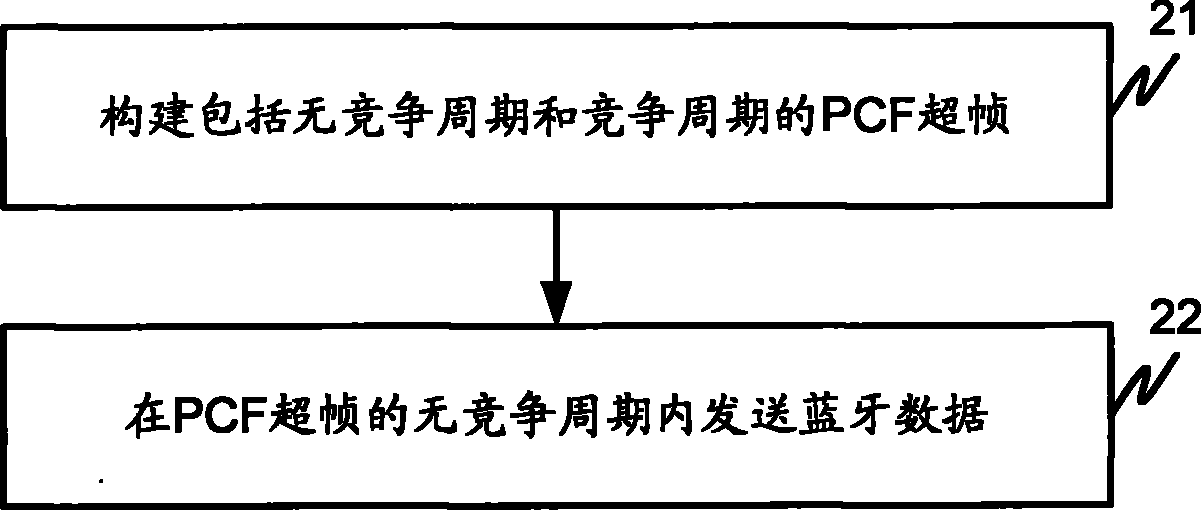
Data transmission method and device thereof
The embodiment of the invention relates to a data transmission method and a device thereof. The data transmission method comprises the following steps: constructing a point coordination function PCF superframe comprising a competition-free period and a competition period; and transmitting Bluetooth data in the competition-free period of the PCF superframe. The data transmission method and the device thereof realize Bluetooth data transmission in the competition-free period, and avoid mutual interference of transmitted between Wi-Fi data and Bluetooth data.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
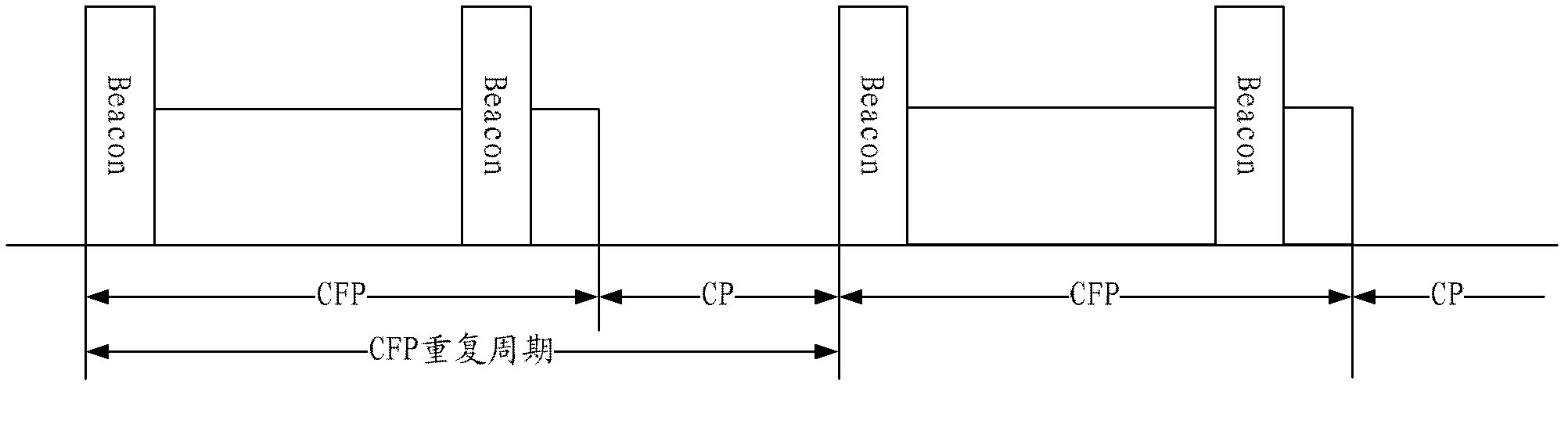
Wireless network with contention and contention-free periods
InactiveUS20100014472A1Improve performanceImprove reliabilityWireless commuication servicesData switching networksWireless mesh networkAccess method
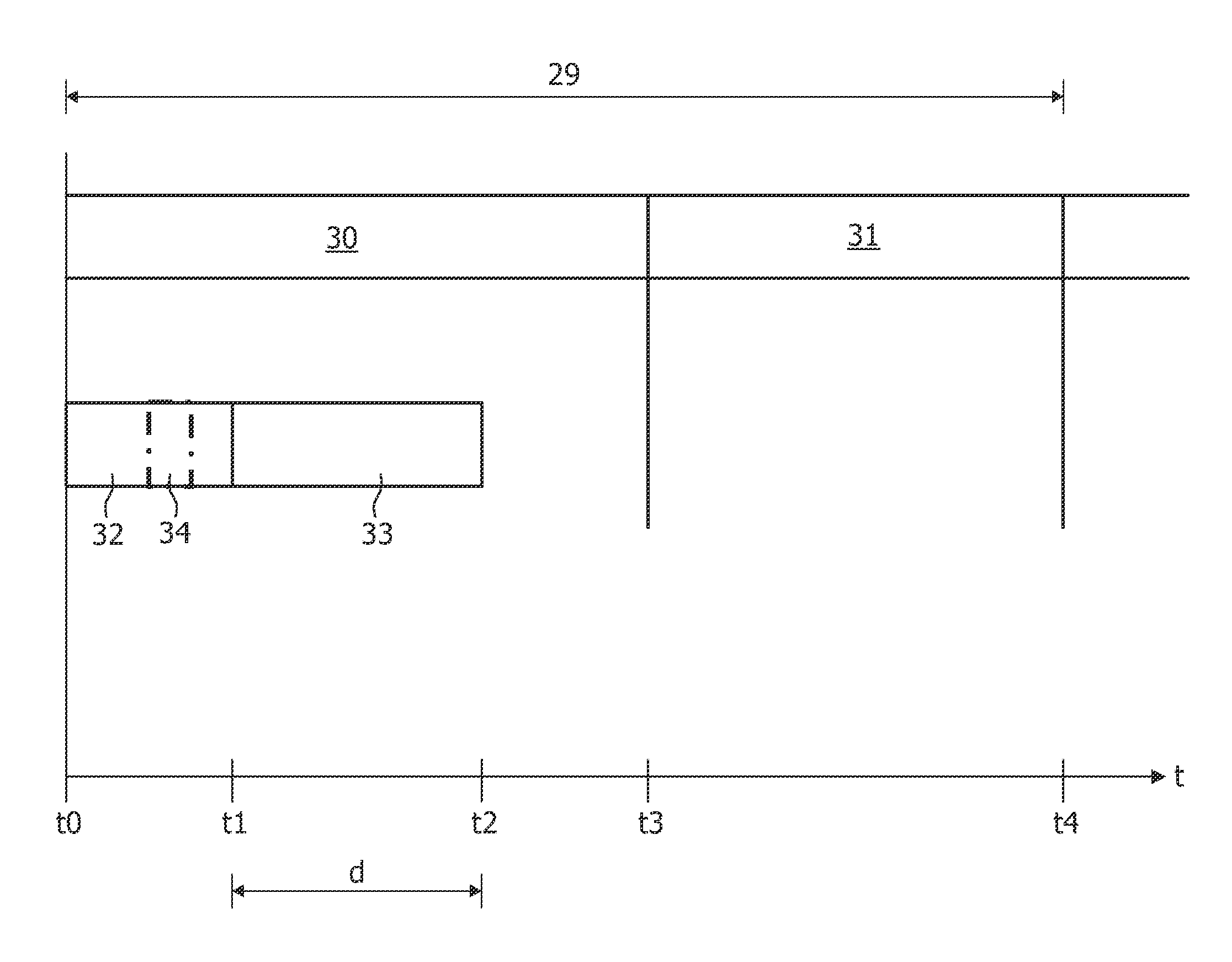
A wireless network (1) comprises mesh devices and non-mesh devices. A medium access control architecture incorporates at least a point coordination function as an access method, wherein the point coordination function starts a contention-free period (30) with a beacon (32) so that a non-polled transmission by the non-mesh devices is prevented. Further, the mesh devices are enable to communicate during the contention-free period (30). Hence, communication between the mesh devices is priorisized so that a high reliability is achieved and utilization of the wireless network (1) is optimized.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method of transmitting multimedia data over wlan and point coordinator in wlan
InactiveCN1523846ASuccessfully transmittedReduce overheadSpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelDistributed coordination functionDistribute coordination function
Transmitting multimedia data over a wireless local area network (WLAN), guaranteeing the full length of a multimedia point coordination function (mPCF) period in a WLAN, and dynamically allotting a length of the mPCF period, by receiving a request for multimedia resource from a predetermined device connected to the WLAN, during a distributed coordination function (DCF) period when a right to use a channel is distributed through contention and unilaterally transmitting the requested multimedia resource to the predetermined device during the mPCF period when the right to use a channel is distributed in a centralized manner.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Bandwidth control method, device and network bridge
ActiveCN102098225AMeet bandwidth requirementsSpecial service provision for substationDistributed coordination functionComputer terminal
The invention provides a bandwidth control method, a bandwidth control device and a network bridge. The invention provides a bandwidth control method based on point-to-multipoint network bridge. The method comprises the following steps that: the beacon cycle with the scheduled length is divided into a distributed coordination function cycle and a point coordination function cycle; based on the scheduled unit bandwidth, the size of the scheduled unit pocket and the point coordination function cycle, minor time slice units comprising a plurality of minor time slices are judged; in the distribution type coordination function cycle, when a registration request message of terminal access equipment is received, the number of the minor time slice units distributed for the bandwidth is calculated according to the bandwidth of the thermal access equipment, and a mark comprising the terminal access equipment and the information item of the number of the minor time slice units are written in the current registration terminal list, and a registration response message is constructed and transmitted; in the point coordination function cycle, taking the minor time slices as a unit, according to the scheduled scheduling algorithm, the terminal access equipment indicated by the mark of the terminal access equipment of each information item in the current registration terminal list is polled.
Owner:BEIJING HAN NETWORKS TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for transmitting a beacon and communicating a frame
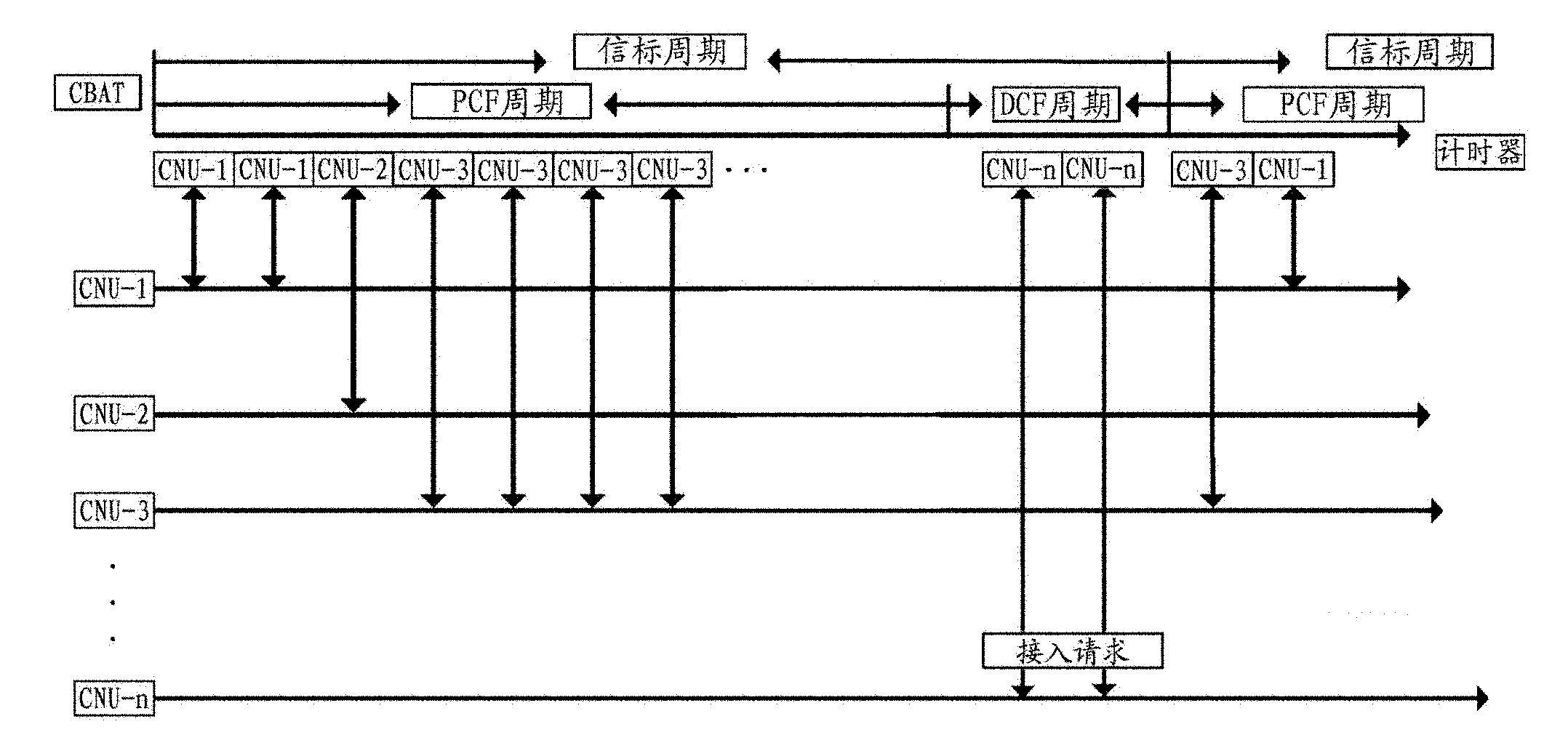
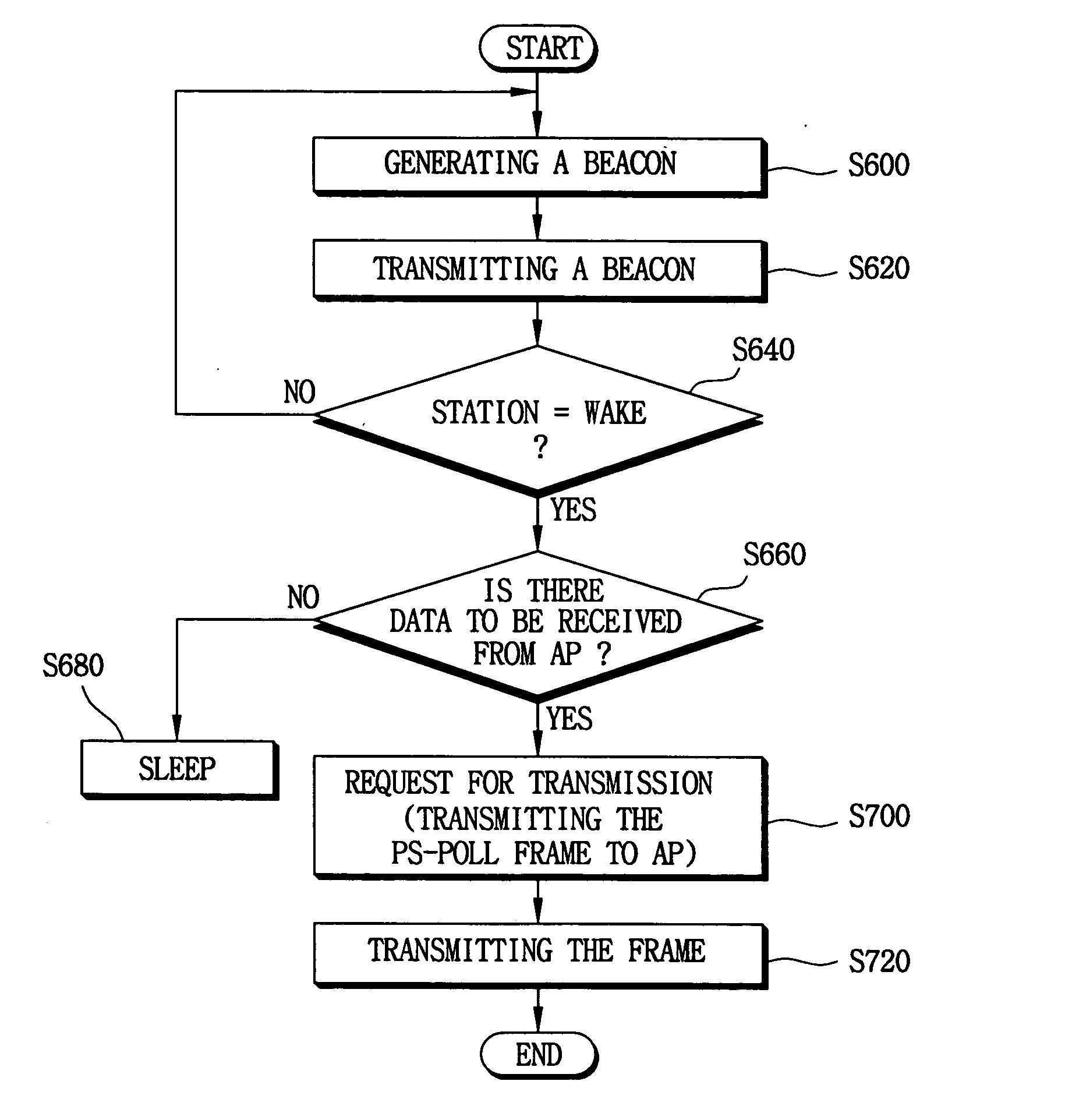
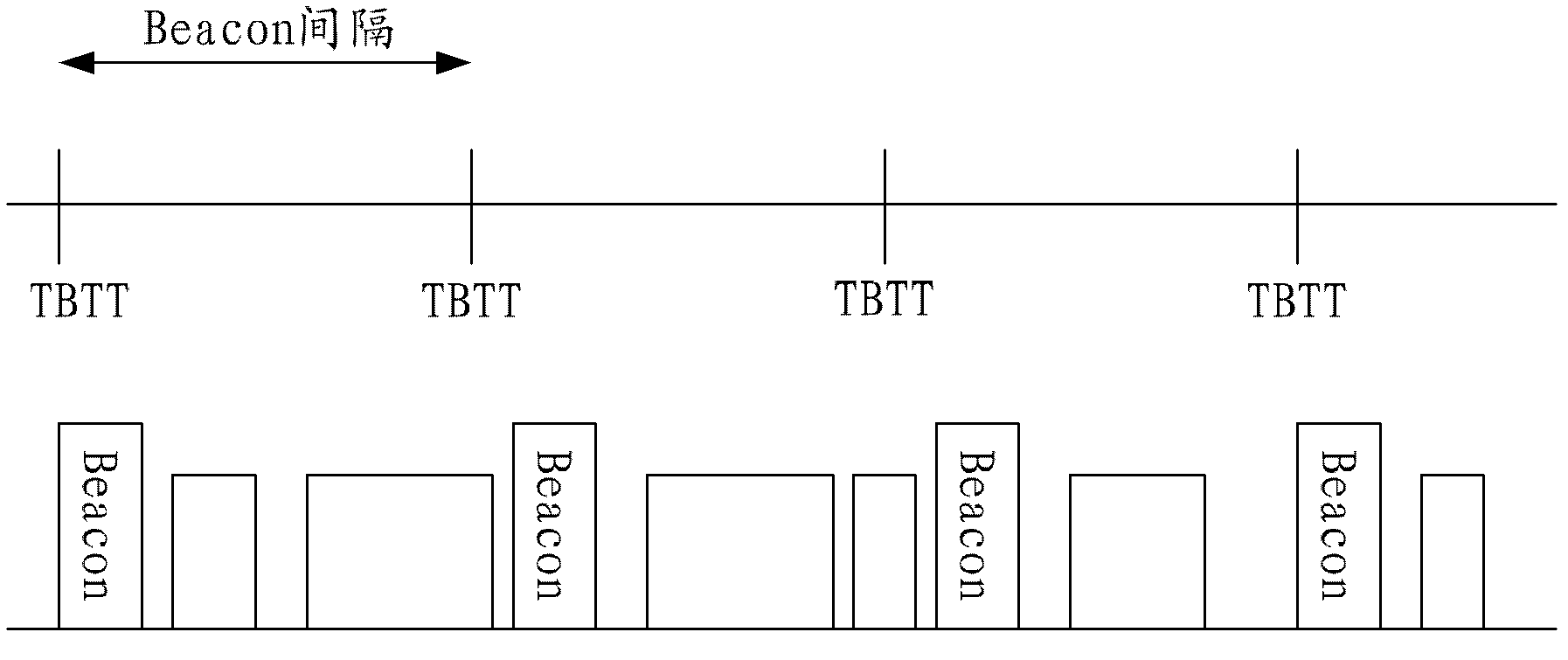
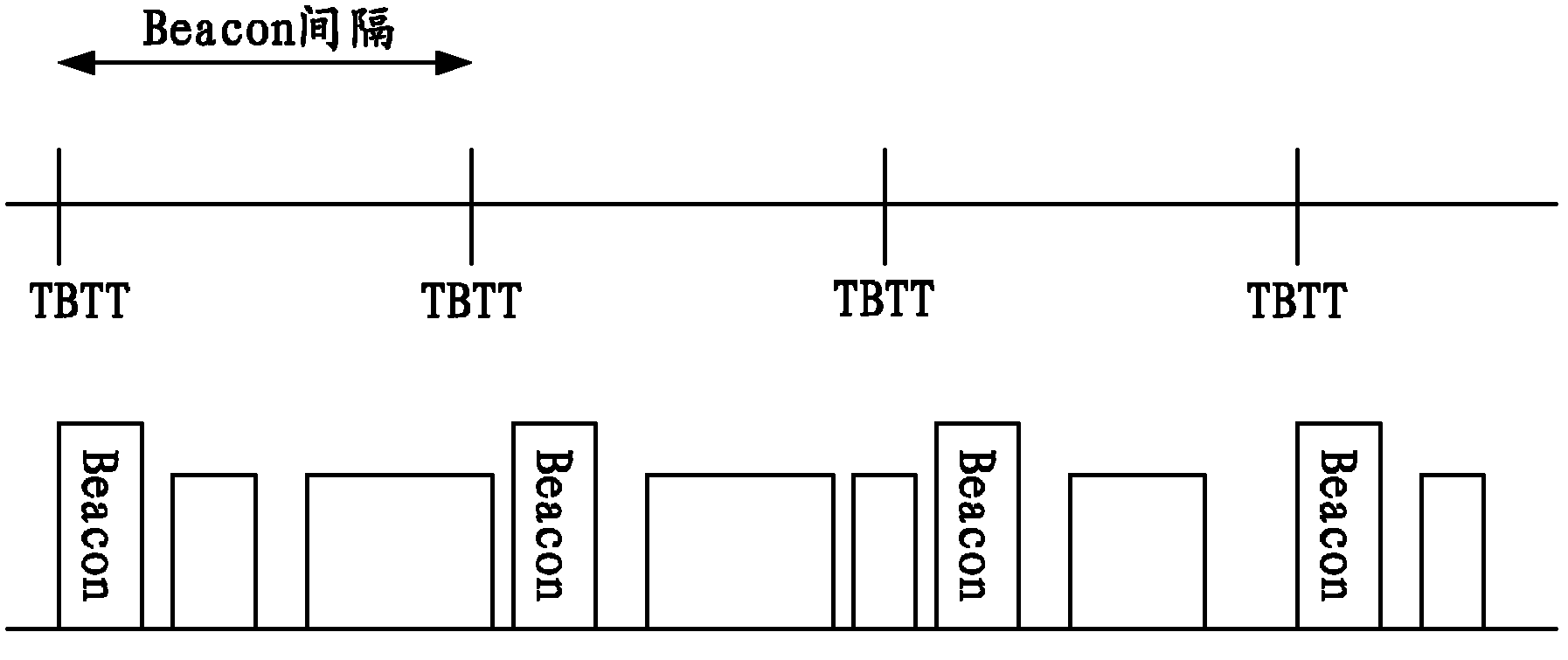
InactiveUS20050036473A1Reduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTTransmission systemsPoint coordination functionBeacon interval
A beacon having a traffic indication map (TIM) and information concerning a beacon interval is generated. The generated beacon is transmitted to stations prior to lapse of Point Coordination Function Interframe Space (PCF IFS) after detecting the condition of the channel. The beacon is transmitted prior to the lapse of PIFS from the time of detecting the condition of the channel to the stations. Therefore, the beacon is transmitted to the stations prior to a frame having a data is transmitted to the stations.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for avoiding network congestion in transmission process of 802.11 polling type data
The invention discloses a method for avoiding the network congestion in transmission process of 802.11 polling type data. The method comprises the following steps of: after association of an infrastructure BSS (Basic Service Set) network at the STA and before polling of the STA by adopting a point coordination function (PCF) or a hybrid coordinate controlled channel access (HCCA) mode through an access point (AP) of the infrastructure BSS network, respectively affiliating the alternative each STA in the infrastructure BSS network to at least one priority group; and polling the STA by adopting the PCF or the HCCA mode and transmitting data according to the priority group in which each STA is arranged. According to the method discloses by the invention, before the STA is polled by adopting the PCF or the HCCA mode and the data are transmitted, various STAs in the infrastructure BSS network are classified according to the priority by adopting a mode of the priority group; and when the polling for a large amount of STAs and the data transmission are carried out, under the condition that the network congestion is avoided, part of important STAs in high priority can be ensured to be preferably polled or polled for multiple times so as to finish data transmission at the earliest and avoid the network congestion.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF INFORMATION & COMM
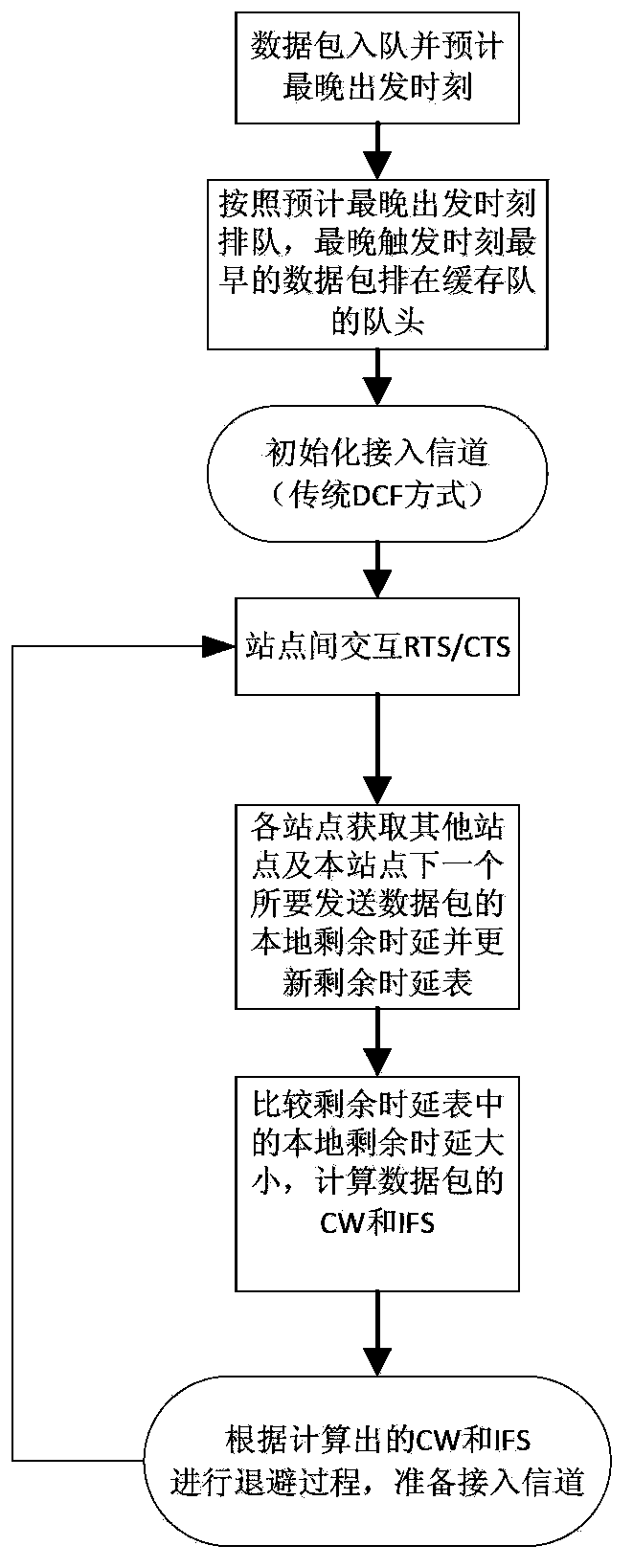
Wireless medium access methods for DCF (distributed coordination function)/PCF (point coordination function) on basis of residual delays
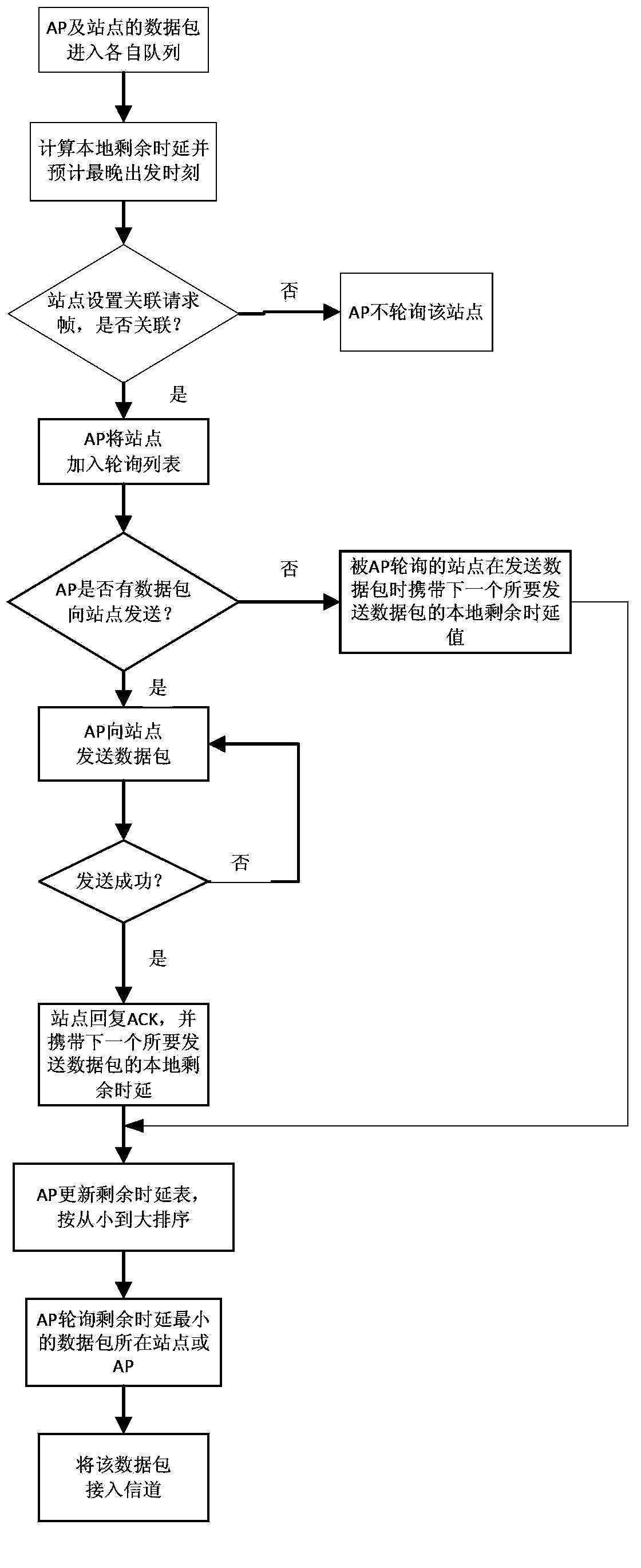
ActiveCN103428772AMeet transmission delay requirementsImprove service qualityNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceDistributed coordination function
The invention discloses wireless medium access methods for a DCF (distributed coordination function) / a PCF (point coordination function) on the basis of residual delays. Local residual delay values are computed according to the end-to-end residual delays of data packets and routing states of the data packets in the methods, and positions of the data packets in buffer queues are determined according to the local residual delay values of the data packets. The wireless medium access method for the DCF includes comparing the local residual delays of the next to-be-transmitted data packets of various websites to determine competition windows and interframe spaces of the various data packets so that the probability that the certain data packet with the small local residual delay value can preferably access a channel is high. The wireless medium access method for the PCF includes comparing the local residual delays of the next to-be-transmitted data packets of the various websites to obtain a polling list and polling sequences of the websites in each competition-free period so that the certain data packet with the minimum local residual delay value can preferably access the channel. The methods have the advantages that the certain website with the small local residual delay can assuredly preferably access the channel, and the end-to-end service quality of networks can be improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
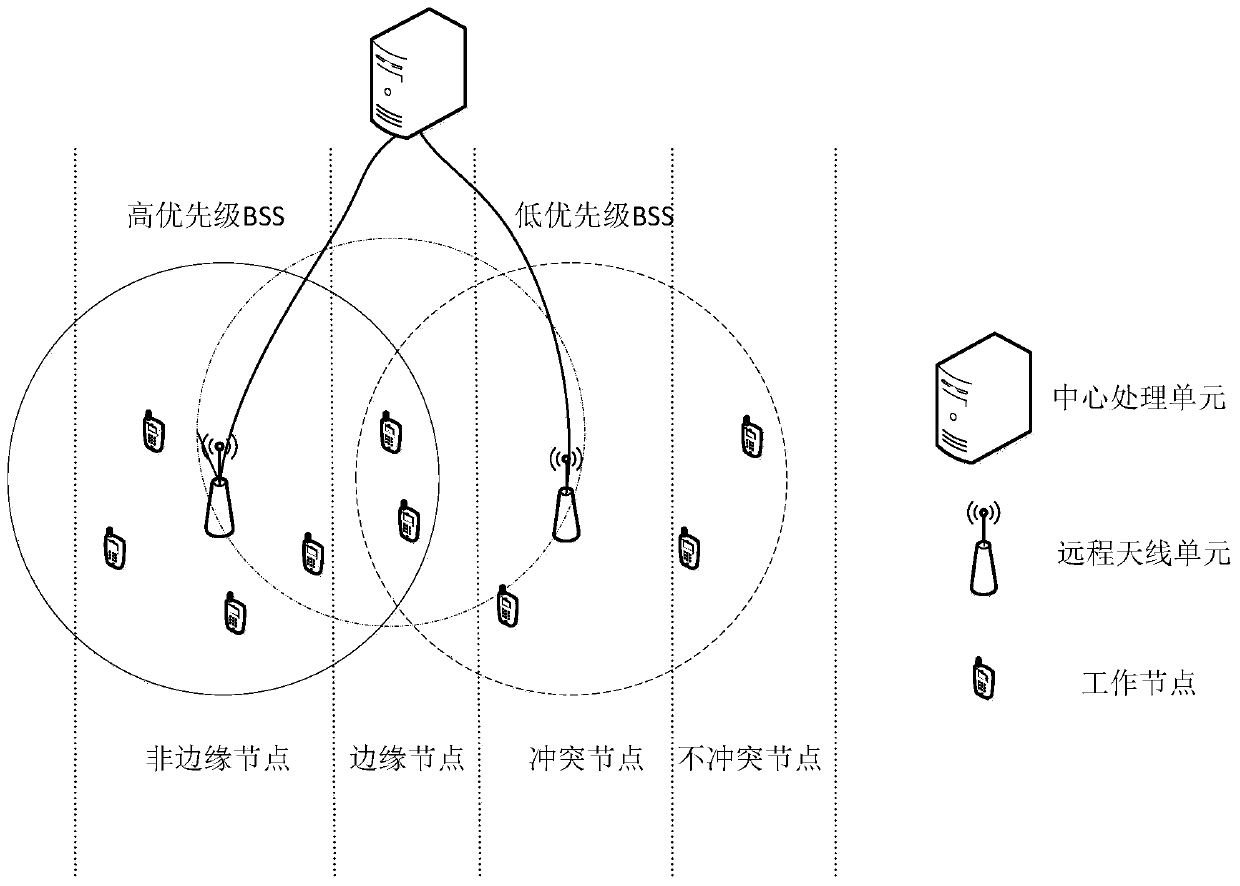
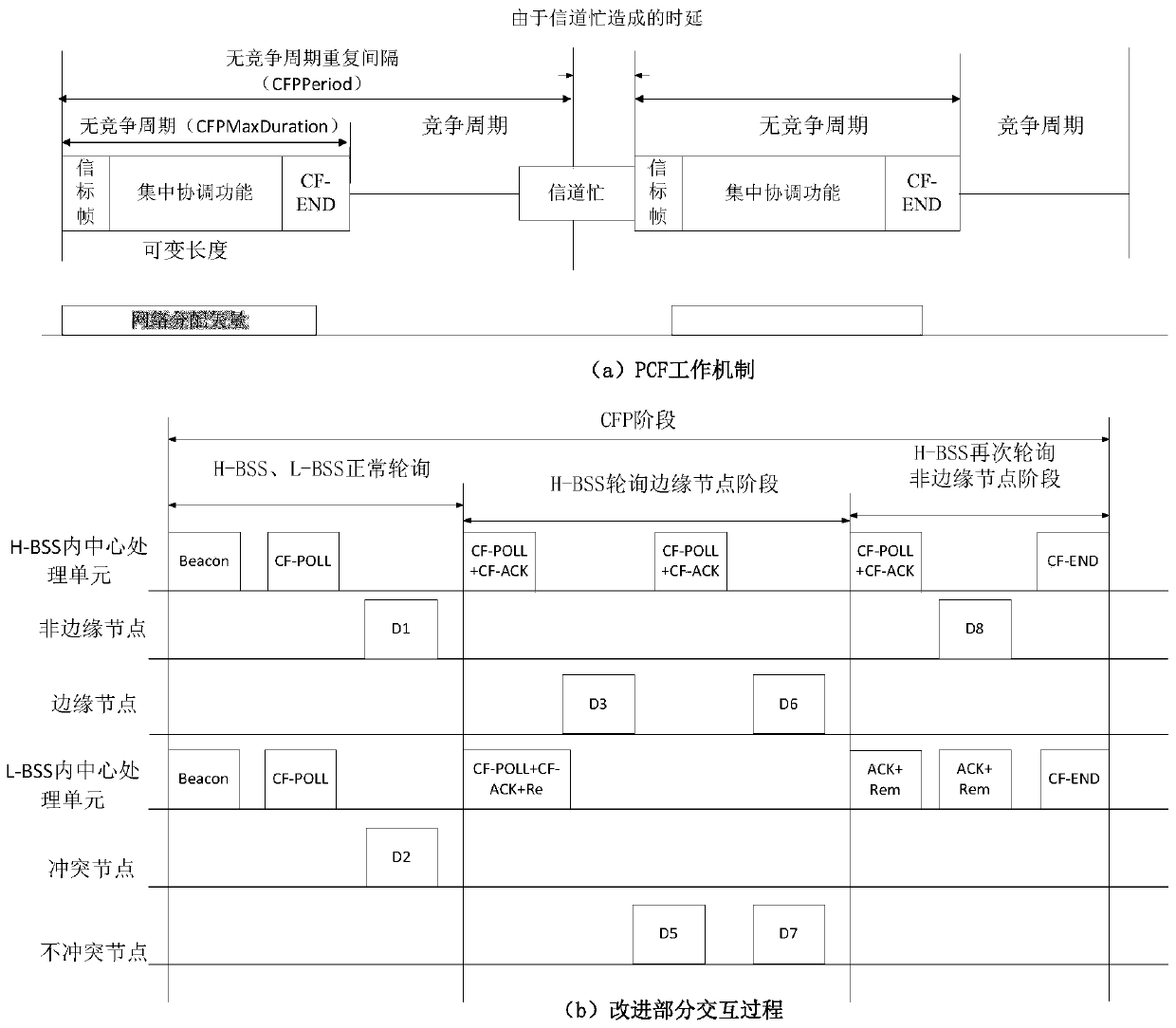
Distributed antenna system MAC protocol improvement method based on IEEE802.11
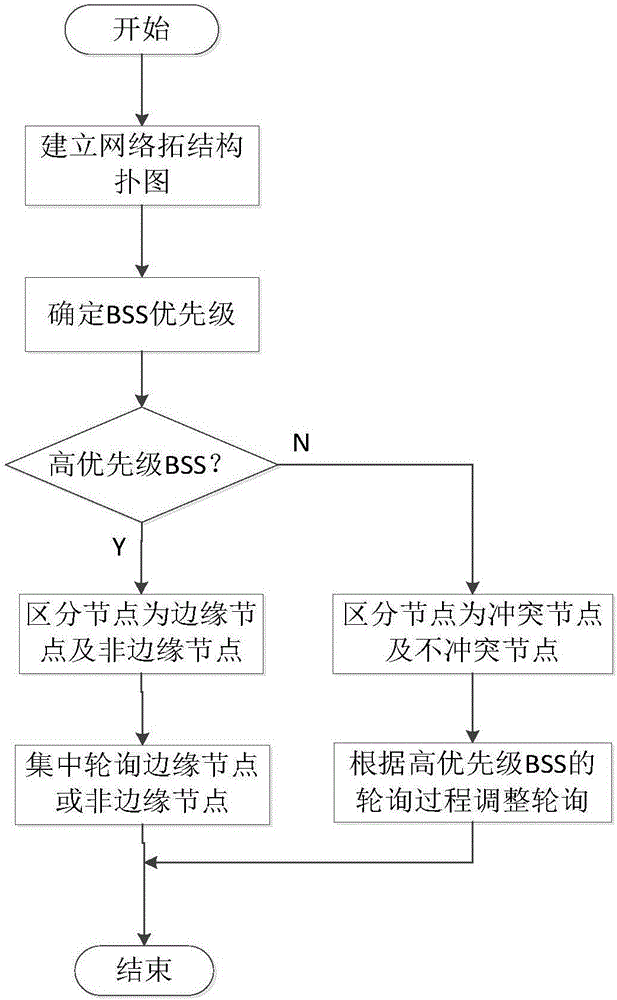
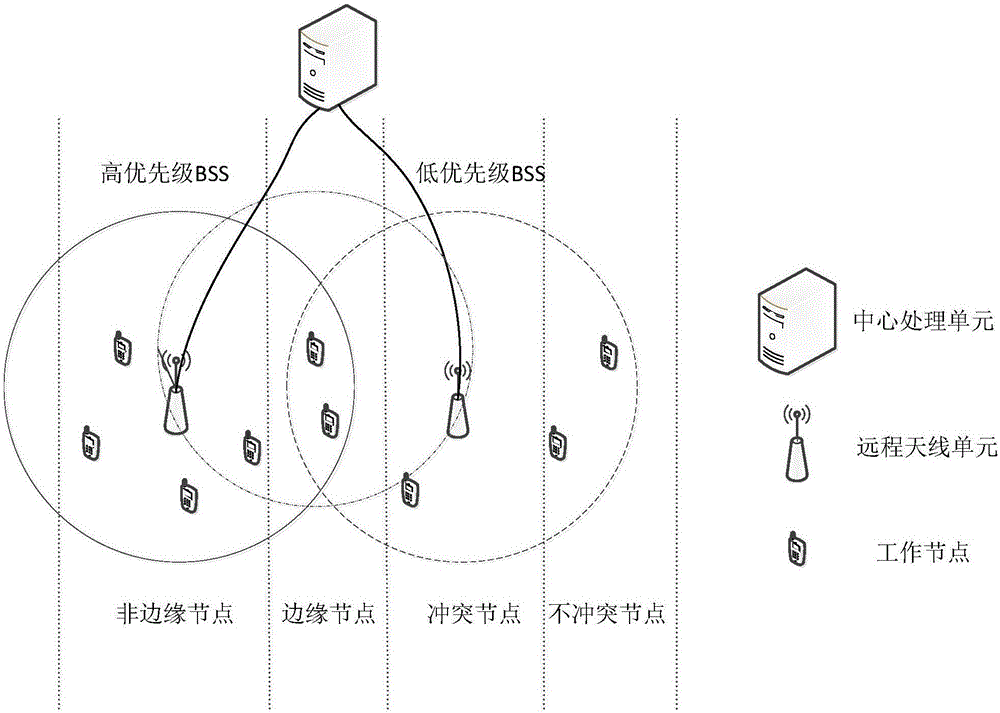
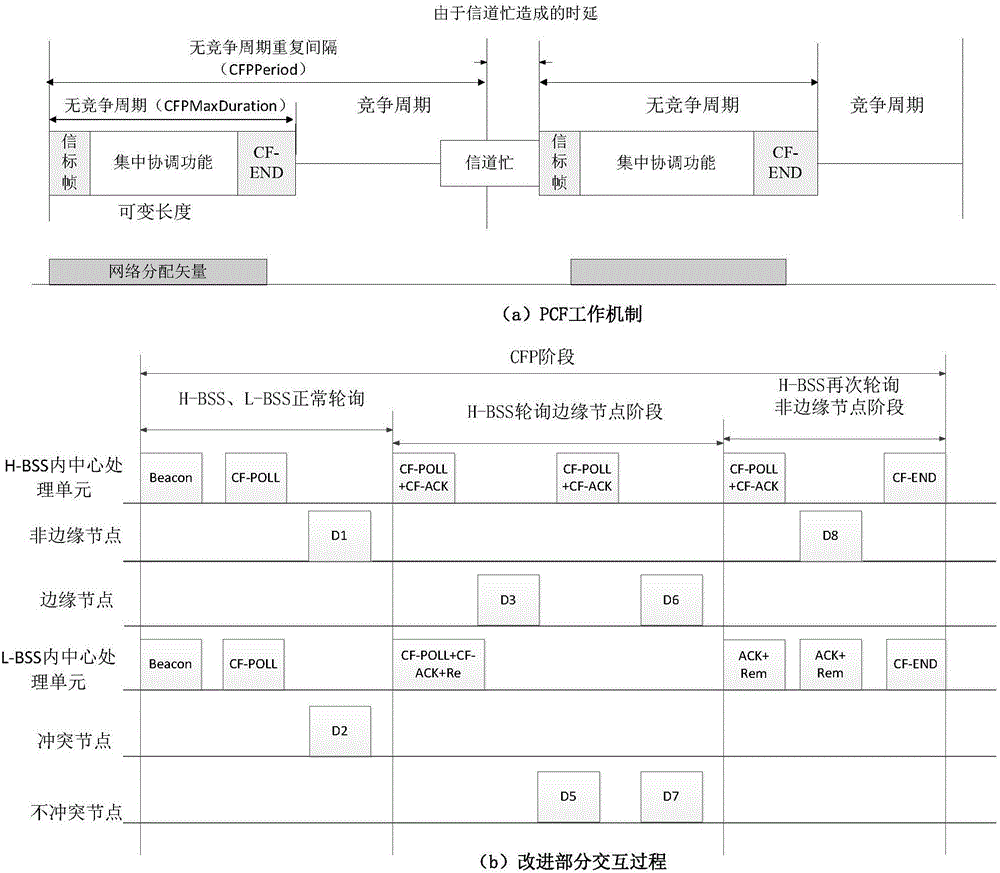
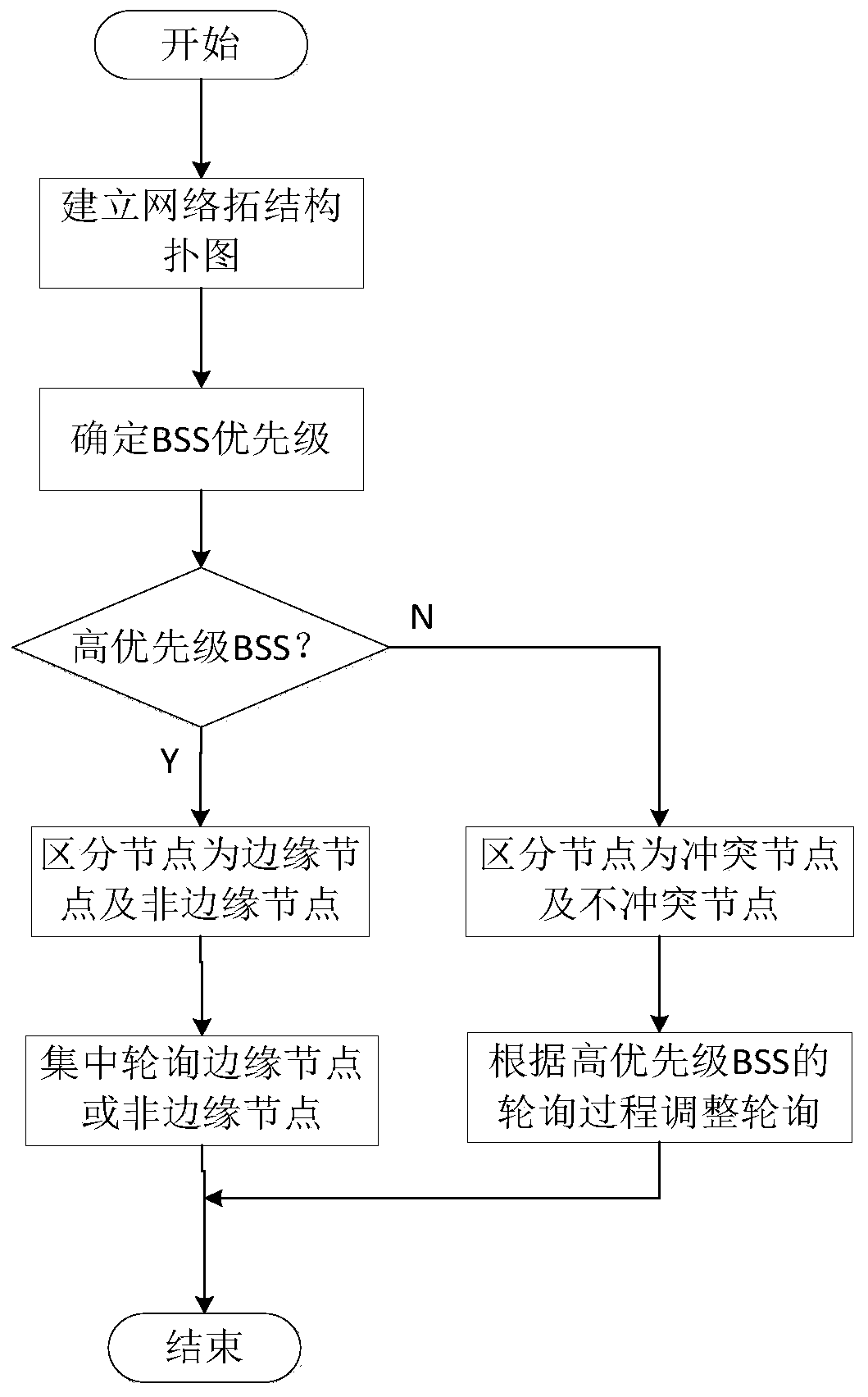
ActiveCN106850587AImprove throughputReduce retransmission performanceTransmissionDistributed antenna systemTime delays
The invention belongs to the technical field of a wireless communication network and relates to a distributed antenna system MAC protocol improvement method based on IEEE802.11. Under a point coordination function PCF mechanism, conflicts among RAU coverage areas are reduced. The method comprises the steps of S1, establishing a network topology structure diagram; S2, dividing priorities and node types of basic service sets, wherein the BSSs are divided into high priority BSSs and low priority BSSs, interior nodes of the high priority BSSs are divided into edge nodes and non-edge nodes, and the interior nodes of the low priority BSSs are divided into non-conflict nodes and conflict nodes; S3, establishing a polling list according to the network topology structure diagram and marking the nodes in the polling list, the high priority BSSs carry out conventional polling according to the polling list; and S4, the low priority BSSs adjust own polling processes according to the polling processes of the high priority BSSs. According to the method, under the condition of sacrificing the time delay performance in a relatively low degree, the total retransmission performance of the system is reduced, and the edge node throughput is improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
WLAN date retransmission method, equipment and system
ActiveCN103248462AReduce the chance of collisionIncrease profitNetwork topologiesError prevention/detection by transmission repeatPoint coordination functionReal-time computing
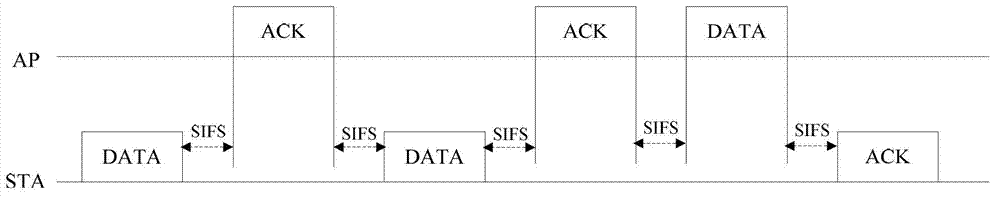
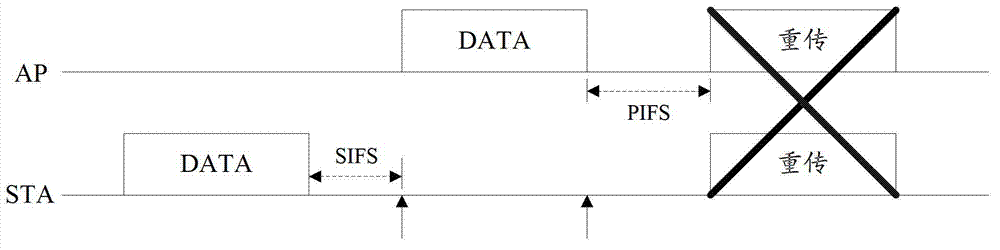
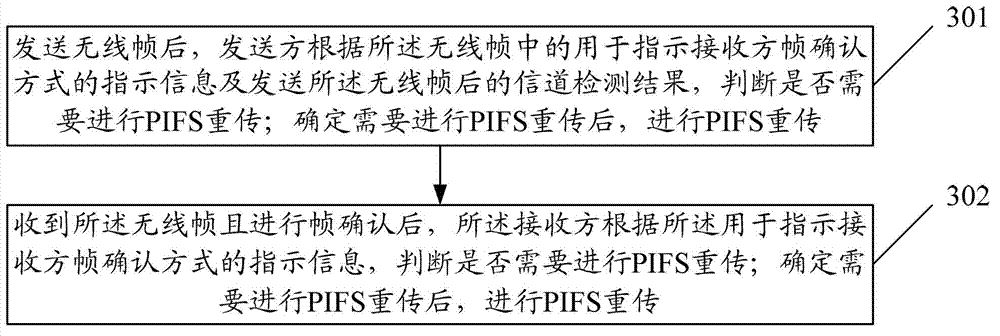
The invention discloses a WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) date retransmission method. The method comprises the following steps: after sending out wireless frames, a sender judges whether PIFS (Point coordination function Interframe Space) retransmission is needed according to the indication information, used for indicating the frame acknowledgment mode for a receiver, of the wireless frames and the detection result of an information channel through which the wireless frames are sent out; and performing PIFS retransmission after determining that PIFS retransmission is needed. The invention further discloses WLAN date retransmission equipment and a WLAN date retransmission system. Through the adoption of the method, the equipment and the system provided by the invention, the probability of collision in date retransmission in quick frame exchange is effectively reduced, and further the utilization ratio of the information channel is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
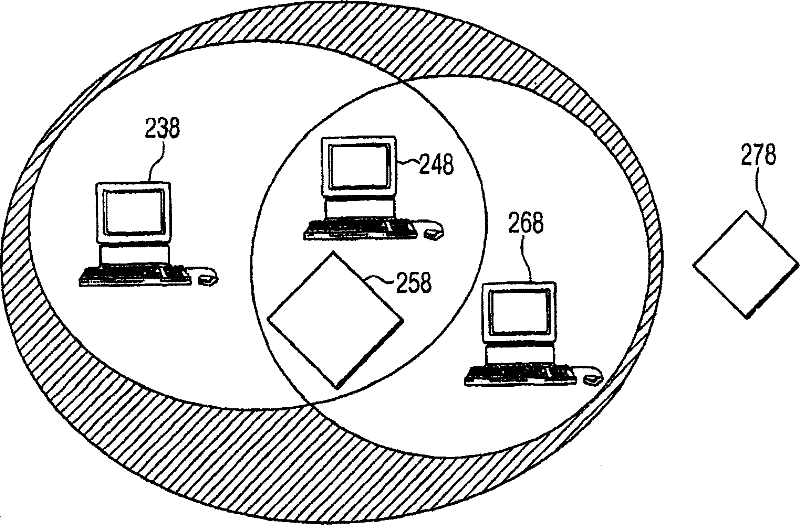
Method, system to achieve fast active scan in WLAN, access point and mobile station
ActiveCN1823501BReduce hardware complexityLower latencyNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationMobile stationPoint coordination function
A method for fast active scanning and an Access Point apparatus that reduces the delay in convention active scanning. The method includes the step of giving an AP higher priority to transmit a probe response than is currently known. This priority comes at the delay of transmission of the probe response, so preferably the probe response can be delayed by just the time that the AP needs to prepare the response plus the time, if any, for the frame already in the air to finish. According to the invention, a method can include steps for: sending a uni-cast probe request message by an (STA) 238, 248, 268 on a particular channel having at least one Access Point (AP) 258, 278 in communication therewith; receiving by one particular (AP) 278 the probe request message sent by the (STA); sensing by the particular (AP) 278 of a point coordination function (PCF) interframe space (PIFS) 325 of the particular channel; and sending by the particular (AP) 278 of a probe response message to the (STA) 238in response to the probe request message after the PIFS. As the probe request is uni-cast, there is no need for a backoff interval as only one AP will respond. Since normal traffic utilizes the longer DIFS space plus backoffs to avoid collisions, the AP will always be able to respond to a probe request of scan faster than other items can respond on the channel, thus giving the AP priority when sending the probe response message.
Owner:网络系统技术有限责任公司
Channel interception method and related device
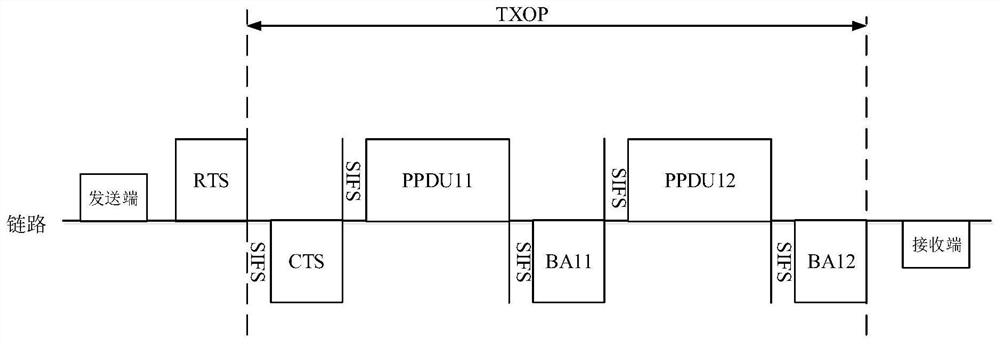
The embodiment of the invention discloses a channel interception method and a related device, which can avoid the influence of the sending action of other links on the channel interception result by adjusting the channel interception time, thereby realizing the link error recovery in a communication scene in which NSTR MLD (Non Short Term Rate Multilink Device) cannot be simultaneously transmitted and received. The method is applied to an NSTR MLD, the NSTR MLD comprises a first station STA and a second station STA, the first STA transmits a first frame on a first link, and the second STA transmits a second frame on a second link; the NSTR MLD determines transmission failure of at least one of the first frame and the second frame; the first STA performs channel interception at a first inter-frame interval after the first frame ends, the time length of the first inter-frame interval being less than or equal to the time length of a point coordination function inter-frame interval (PIFS), or the second STA performs channel interception at a second inter-frame interval after the second frame ends, and the time length of the first inter-frame interval is less than or equal to the time length of the point coordination function inter-frame interval (PIFS). The time length of the second inter-frame interval is greater than or equal to the time length of the short inter-frame spacing (SIFS) and less than or equal to the time length of the PIFS.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Wireless network with contention and contention-free periods
InactiveUS8451782B2Improve performanceImprove reliabilityWireless commuication servicesData switching networksAccess methodWireless mesh network
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
A method of medium access control based on 802.11ac protocol
ActiveCN105682247BImprove throughputImprove spectrum utilizationWireless communicationDistributed coordination functionFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a media access control method based on a WLAN system in an 802.11ac protocol. The method mainly is used for solving the problem of low spectrum utilization rate resulted from overlapped basic service sets. The method comprises that a wireless access point AP invokes a carrier monitoring mechanism on a master channel so as to determine the busy and idle states of the master channel; when the master channel is in an idle condition, the wireless access point and stations STA access the master channel by a distributed coordination functional channel access method; when the master channel is in a busy condition, the wireless access point selects a first channel in non-master channels as a virtual master channel and sends system notice information SNI to the stations in a basic service set in which the wireless access point is located; SNI copies are sent to the other non-master channels; and the stations access the non-master channels on the virtual master channel according to a point coordination functional interframe interval channel access algorithm. According to the method provided by the invention, the non-master channel is utilized fully; the spectrum utilization rate and system throughput are improved; and the method can be used for optimizing the MAC layer protocol in the 802.11ac protocol.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Improved Method of MAC Protocol in Distributed Antenna System Based on IEEE 802.11
ActiveCN106850587BImprove throughputReduce retransmission performanceTransmissionTime delaysDistributed antenna system
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method for avoiding network congestion in transmission process of 802.11 polling type data
The invention discloses a method for avoiding the network congestion in transmission process of 802.11 polling type data. The method comprises the following steps of: after association of an infrastructure BSS (Basic Service Set) network at the STA and before polling of the STA by adopting a point coordination function (PCF) or a hybrid coordinate controlled channel access (HCCA) mode through an access point (AP) of the infrastructure BSS network, respectively affiliating the alternative each STA in the infrastructure BSS network to at least one priority group; and polling the STA by adopting the PCF or the HCCA mode and transmitting data according to the priority group in which each STA is arranged. According to the method discloses by the invention, before the STA is polled by adopting the PCF or the HCCA mode and the data are transmitted, various STAs in the infrastructure BSS network are classified according to the priority by adopting a mode of the priority group; and when the polling for a large amount of STAs and the data transmission are carried out, under the condition that the network congestion is avoided, part of important STAs in high priority can be ensured to be preferably polled or polled for multiple times so as to finish data transmission at the earliest and avoid the network congestion.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF INFORMATION & COMM
Method and device for cooperative transmission in wireless local area network
ActiveCN107040356BSolve the problem of mutual influence of data transmissionImprove accuracyError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork topologiesStationWireless lan
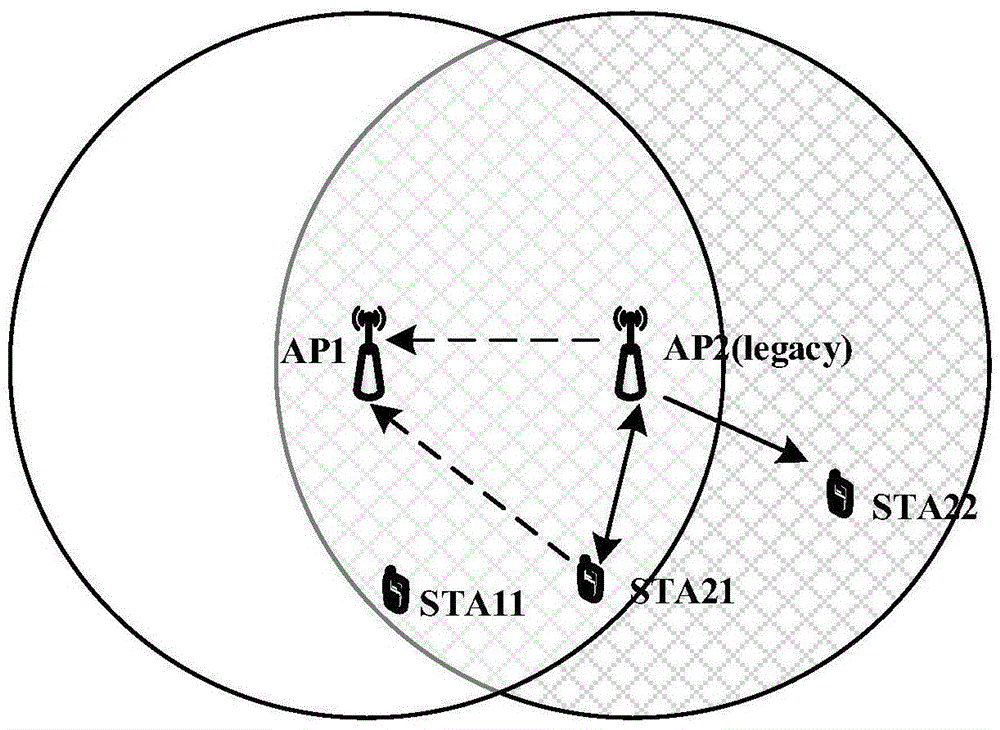
The present invention provides a method and device for coordinated transmission in a wireless local area network. The method comprises: a first access point receives first data from a station, wherein the first data carries information for indicating enabling of a multi-point coordination function, and the station and the first access point pertain to a same basic service set; the first access point receives second data forwarded by a second access point, wherein the second access point and the first access point pertain to a same multi-point coordination group, and the second data is from the basic service set to which the first access point pertains; the first access point makes a judgment on the first data and the second data, and sends, according to the judgment result, to the station, an acknowledgment message for indicating accurate reception of the first data. The present invention resolves the problem in the related art of interaction among OBSSes due to data transmission between stations, thereby improving the accuracy of data transmission.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com