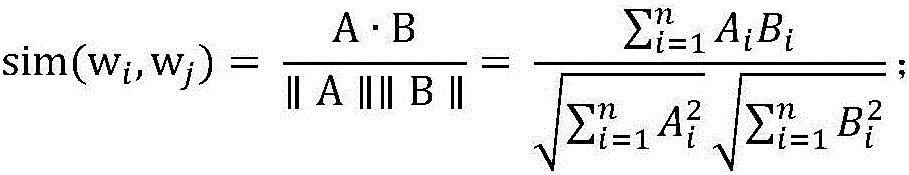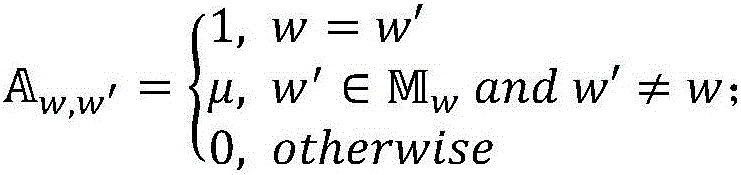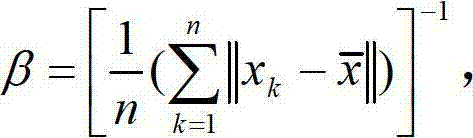Patents
Literature
150 results about "Random assignment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Random assignment or random placement is an experimental technique for assigning human participants or animal subjects to different groups in an experiment (e.g., a treatment group versus a control group) using randomization, such as by a chance procedure (e.g., flipping a coin) or a random number generator. This ensures that each participant or subject has an equal chance of being placed in any group. Random assignment of participants helps to ensure that any differences between and within the groups are not systematic at the outset of the experiment. Thus, any differences between groups recorded at the end of the experiment can be more confidently attributed to the experimental procedures or treatment.
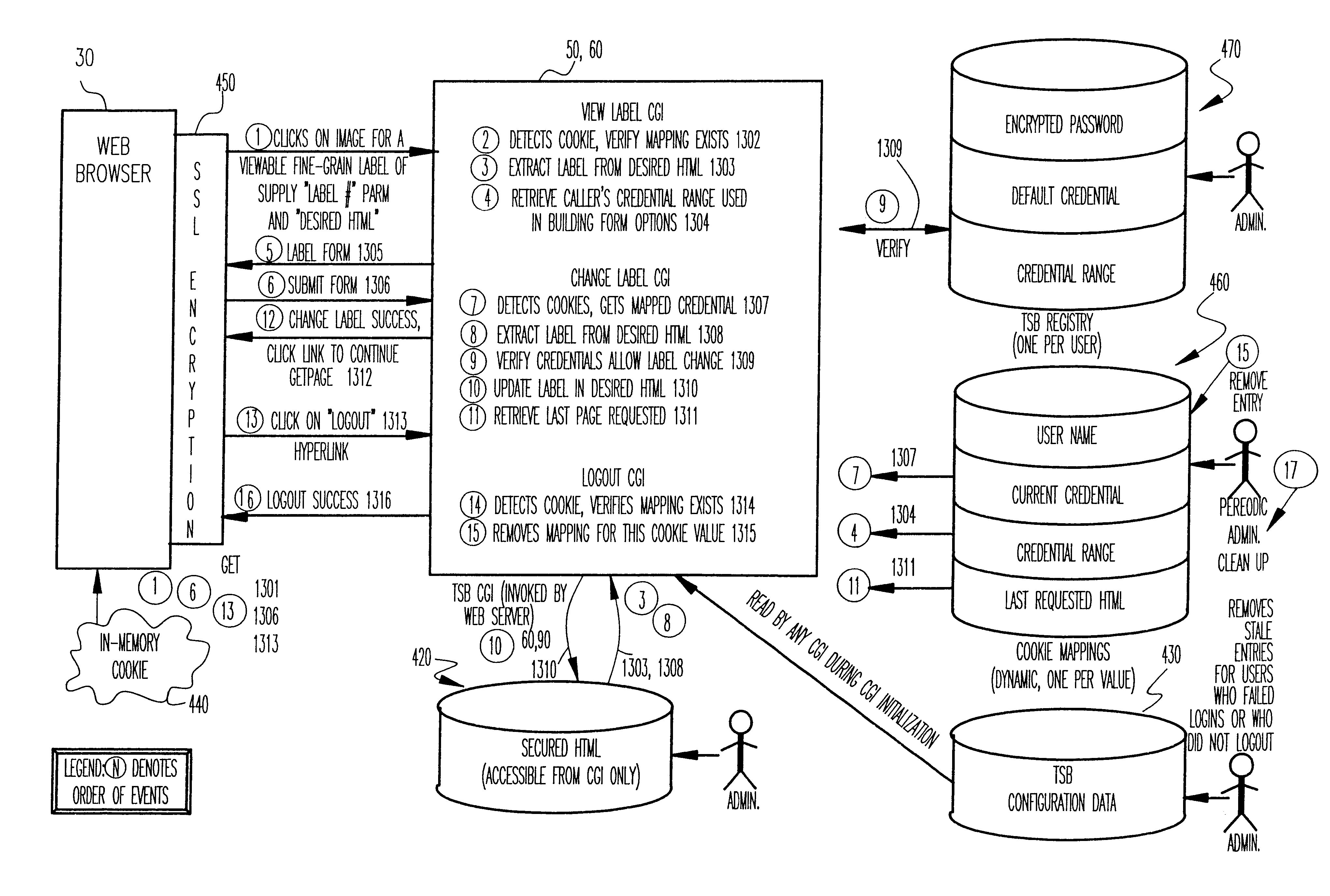
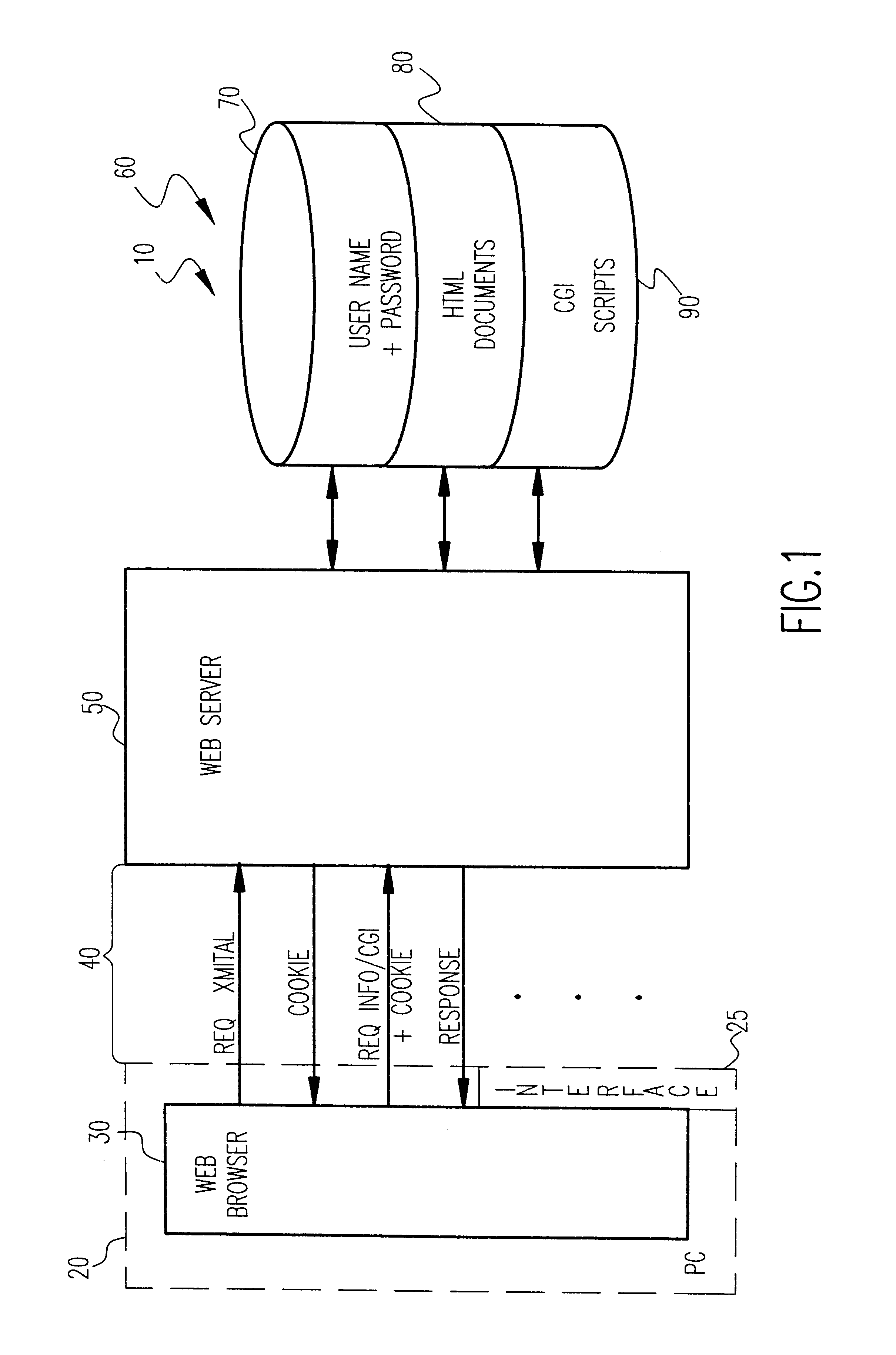
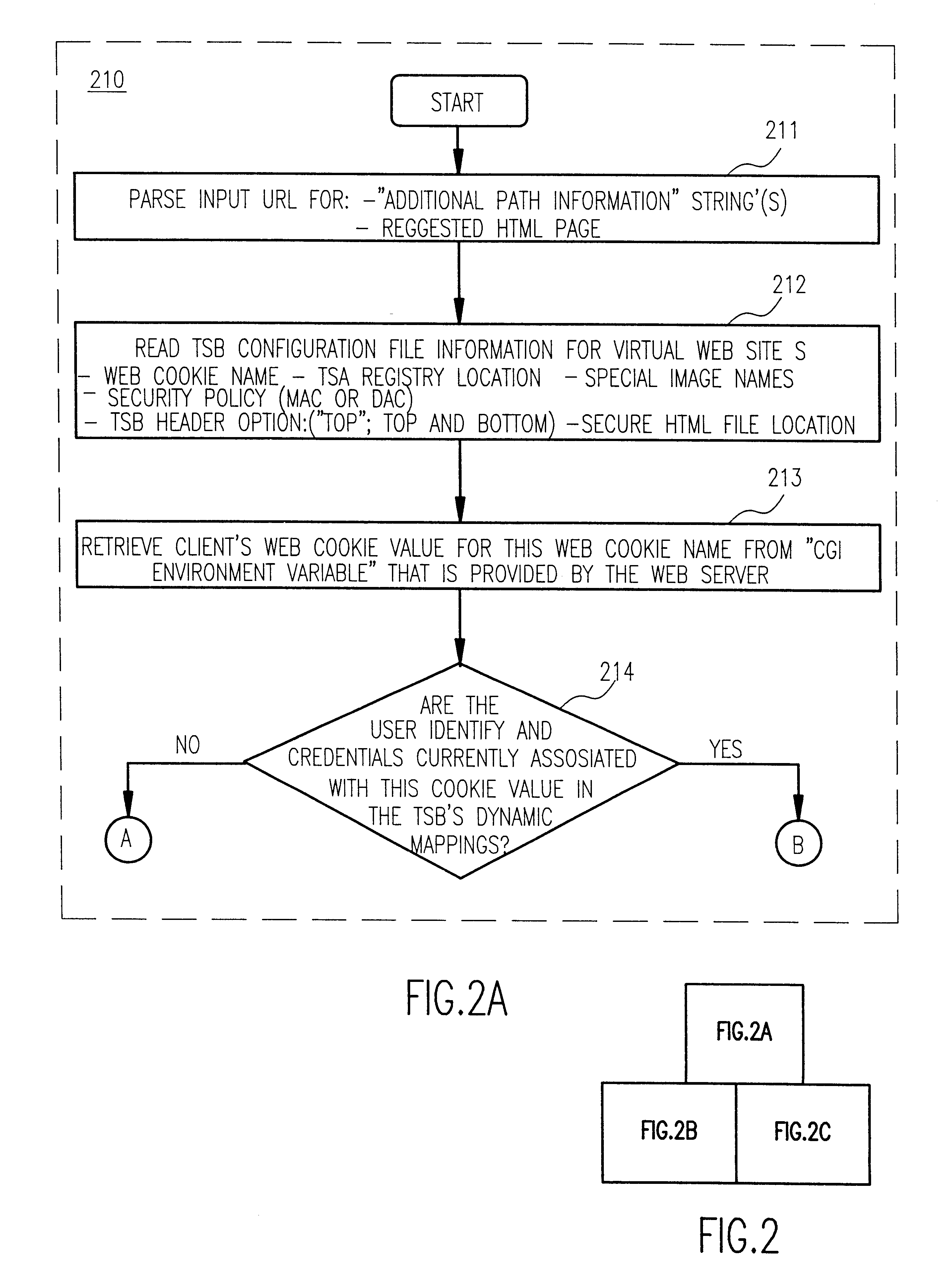
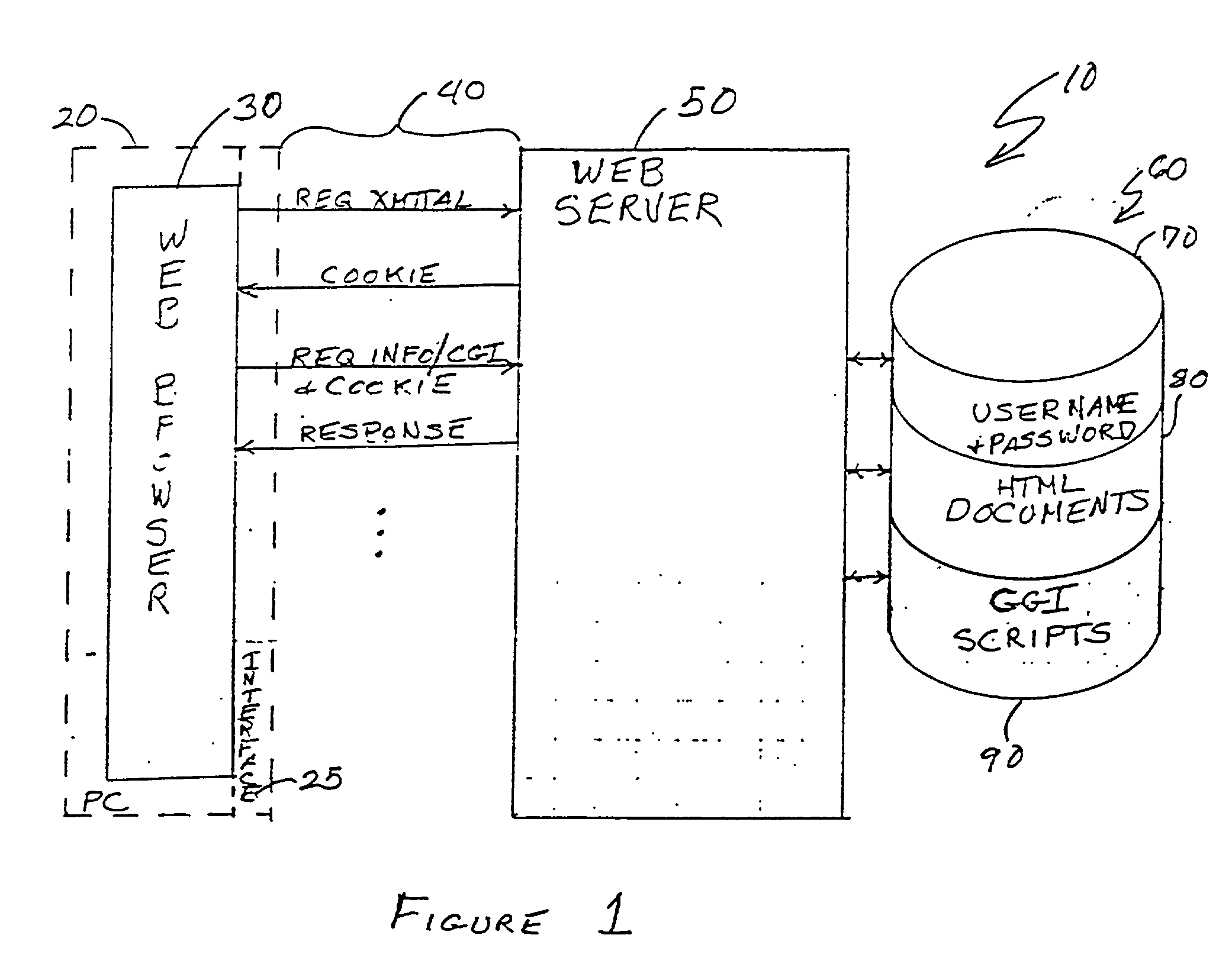
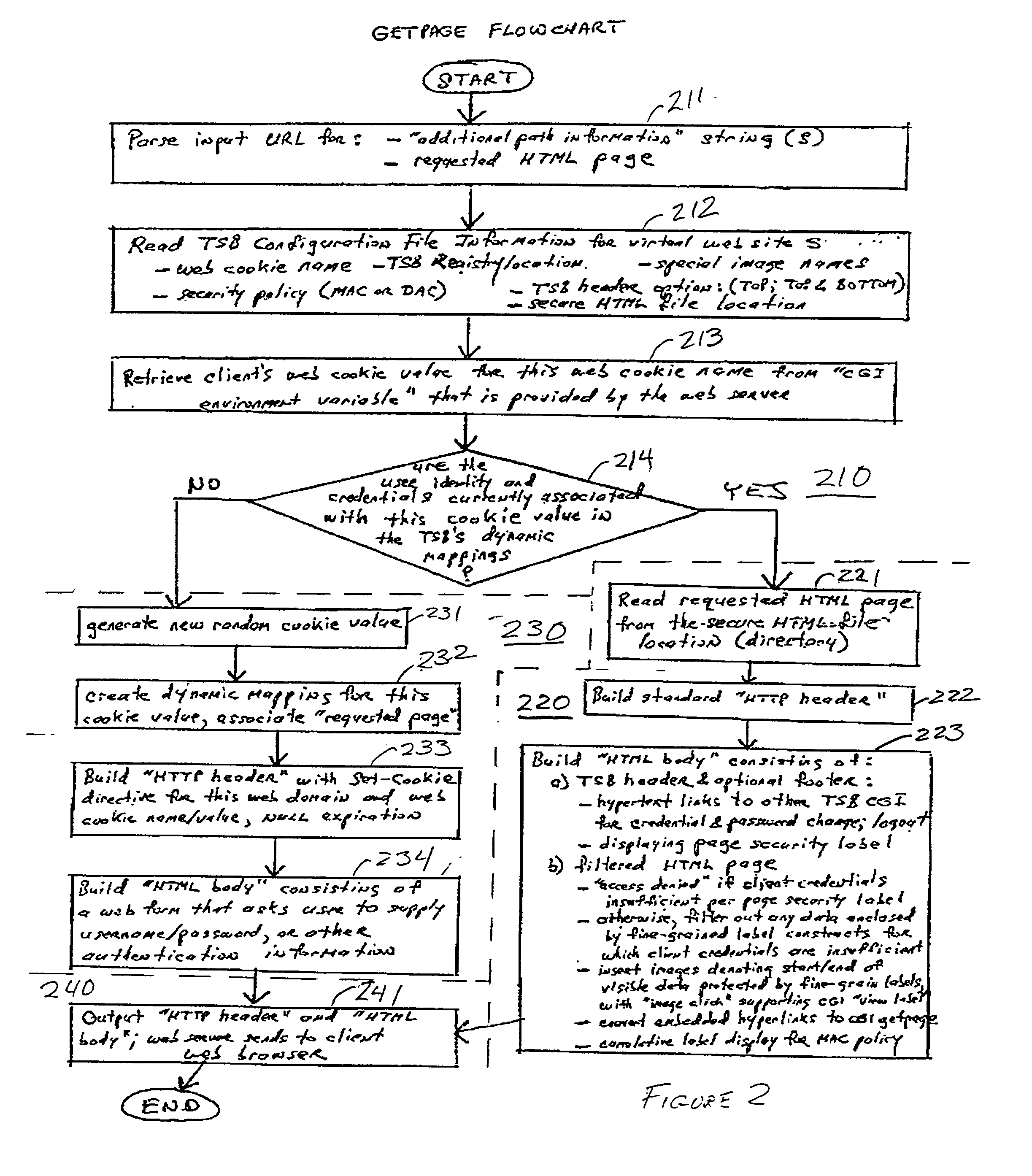
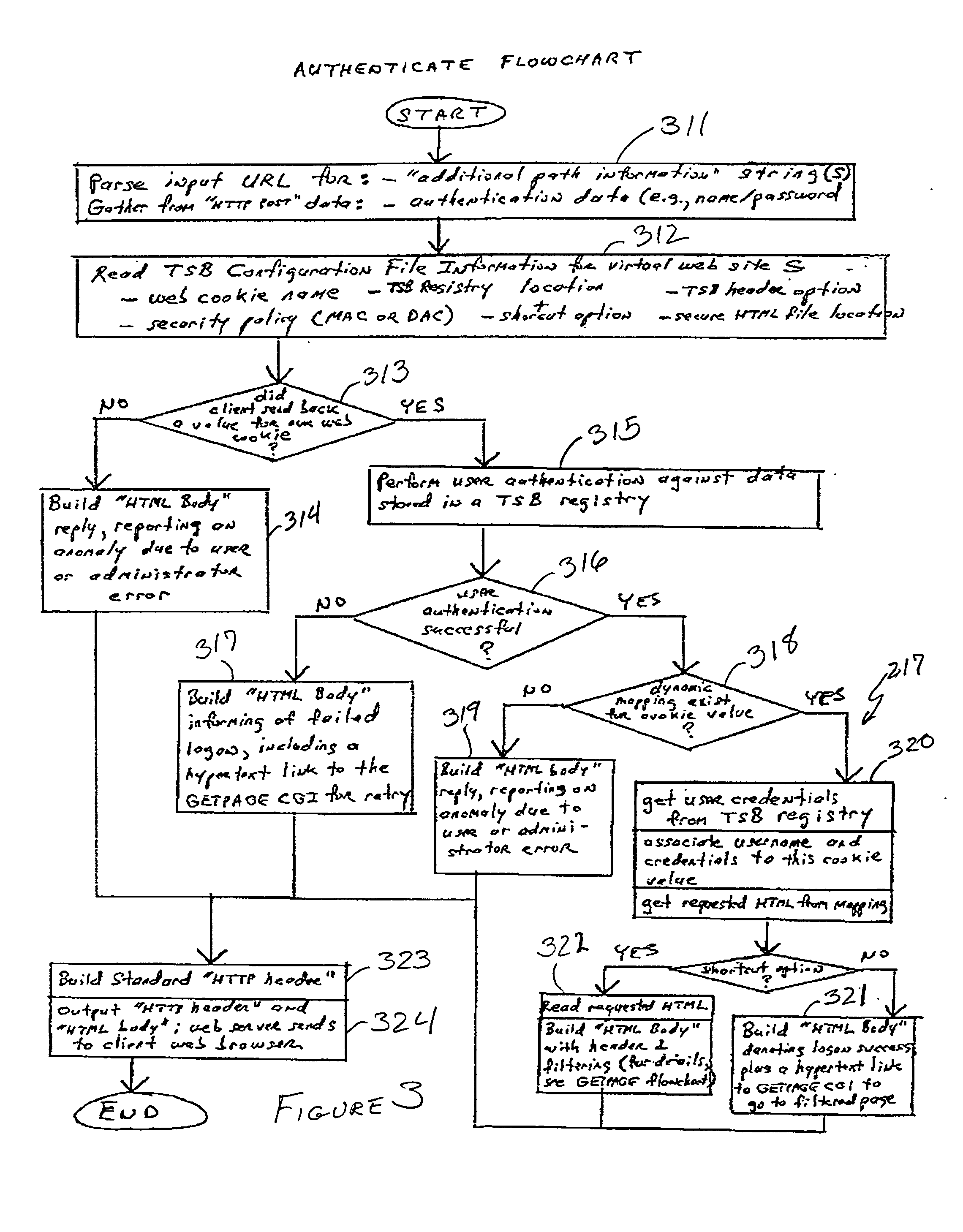
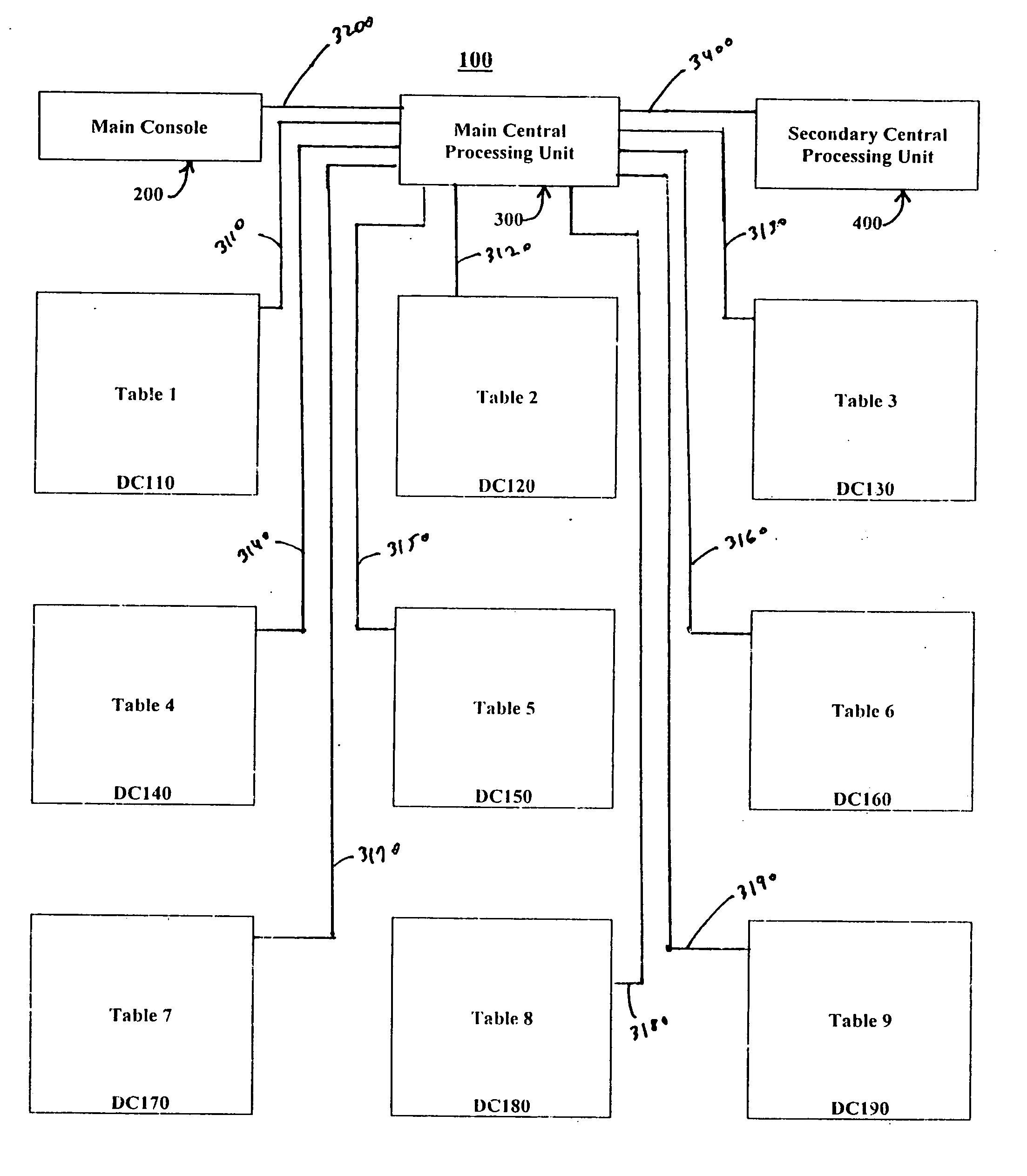
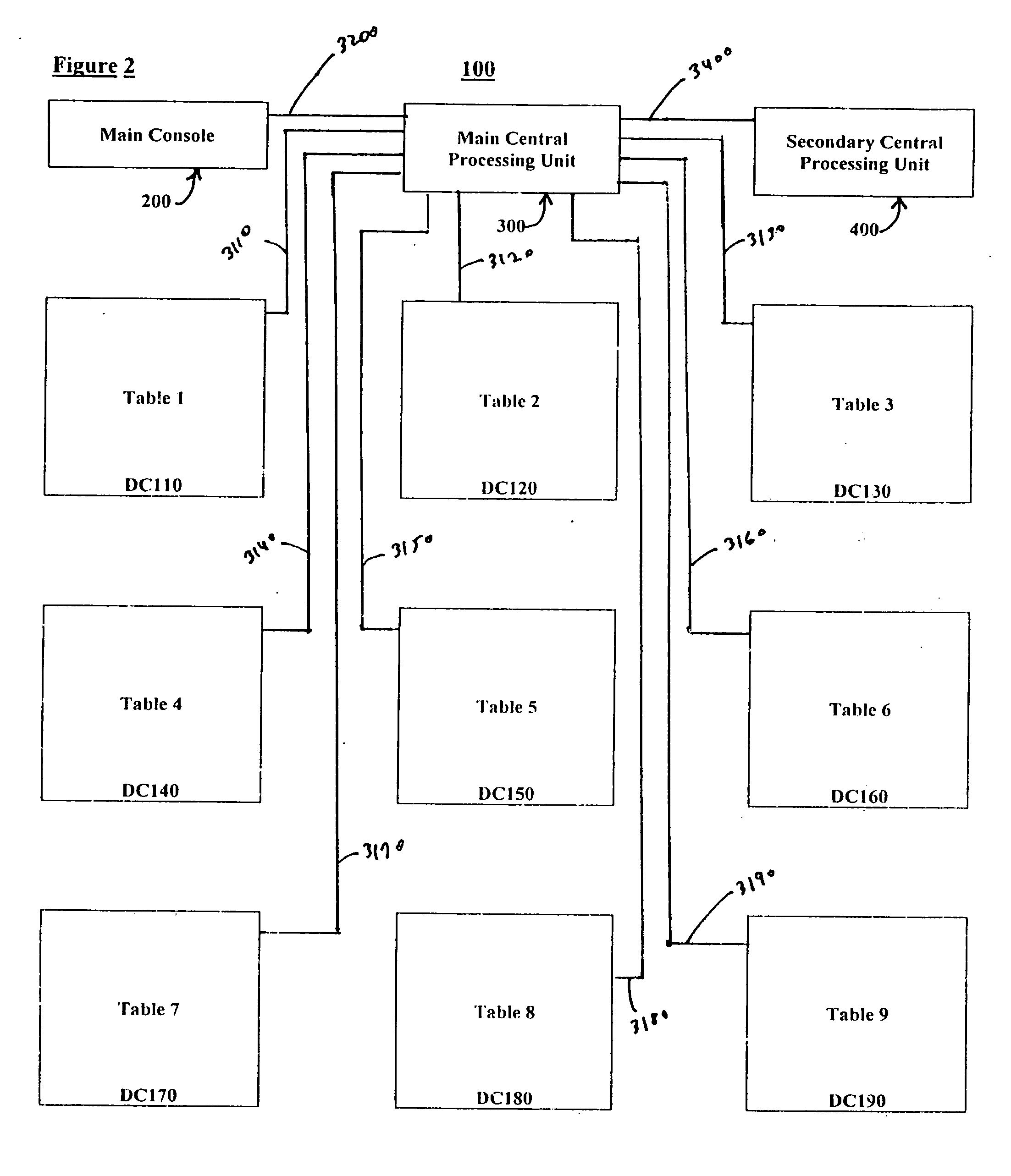
Trusted services broker for web page fine-grained security labeling
InactiveUS6311269B2Limit installationNeed to installWeb data retrievalDigital data processing detailsPasswordRandom assignment
Arbitrarily fine-grained limitation of access to information stored in a resource of a data processor network is provided in a manner compatible with existing network browsers by mapping user identity and credentials with randomly assigned security cookie information which thus serves as a surrogate credential accompanying each user request during a session. Labels are imbedded within HTML files / text which may embody any desired security policy, including mandatory access control (MAC) arrangements which are not available through native browser functions. Data is retrieved in response to a user request which includes a security cookie from a location in the resource which is not directly accessible through use of a URL; the location being stored in a configuration file which is hidden from users. The retrieved data is then filtered in accordance with labels provided for each page and / or embedded in the text and used to build a response which may include hypertext links or other user interfaces for transmission to the user. Provision is made for viewing or changing of labels, credentials and passwords.
Owner:LEIDOS INNOVATIONS TECH INC
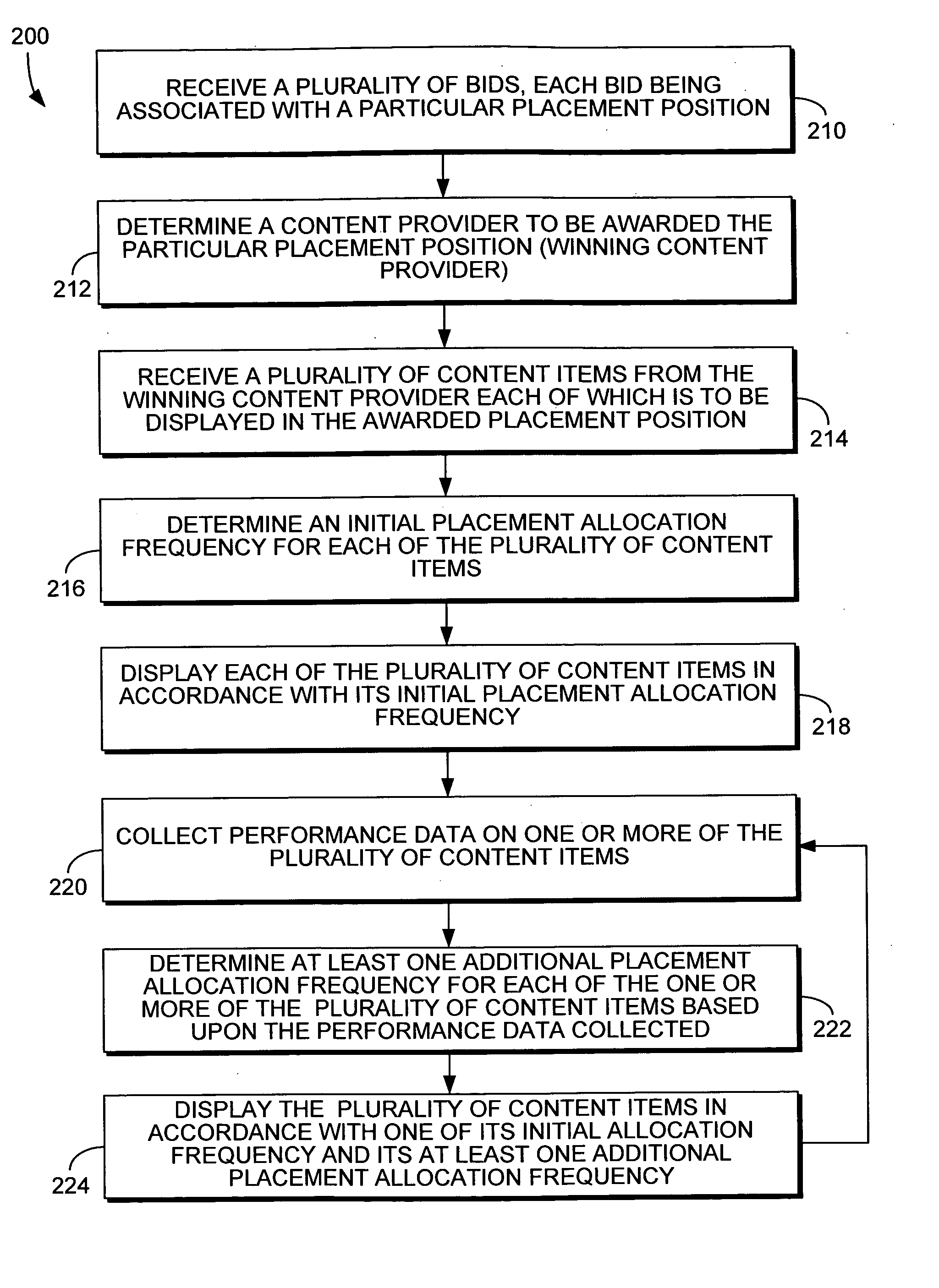
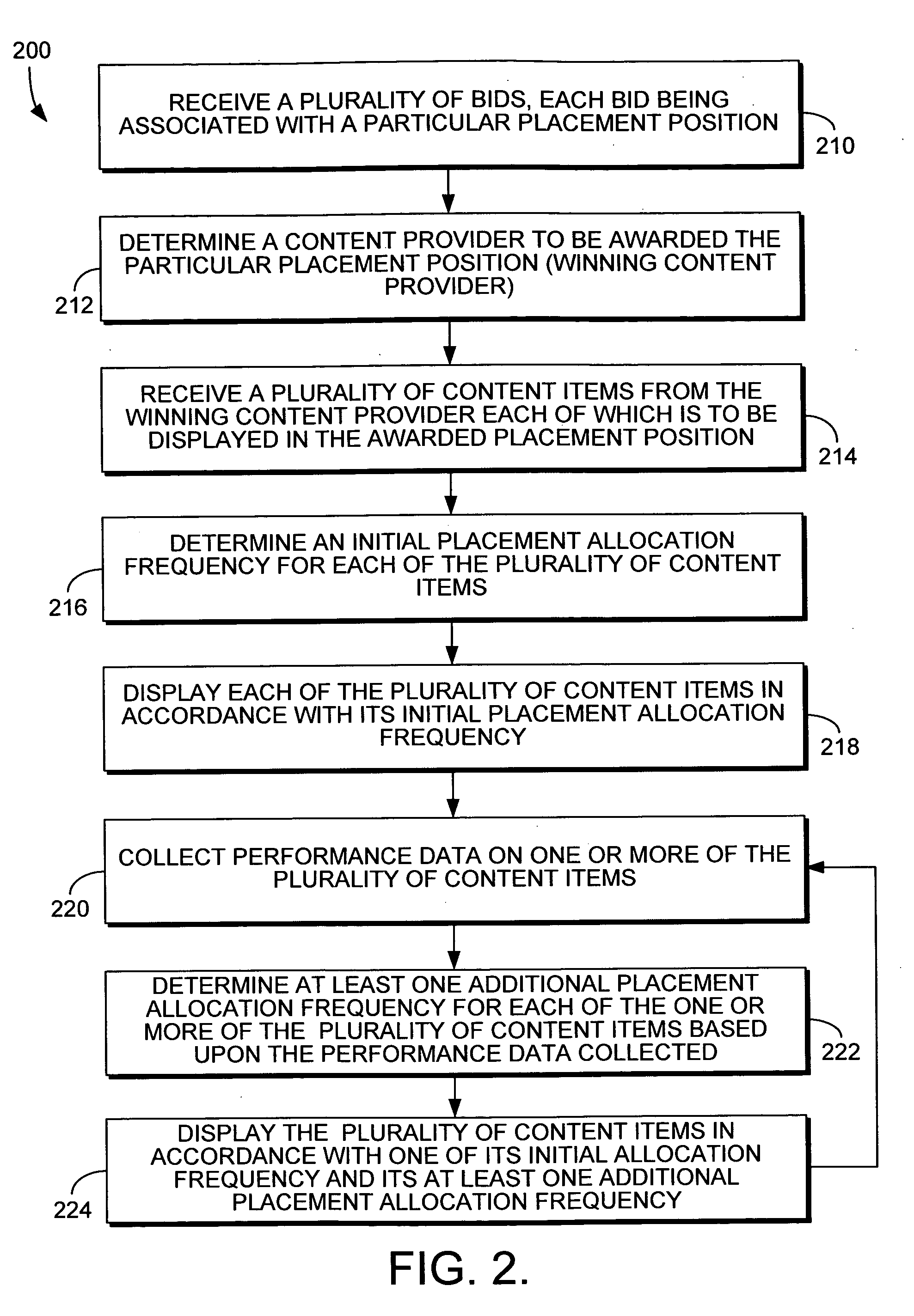
System and method for managing a plurality of content items displayed in a particular placement position on a rendered page
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
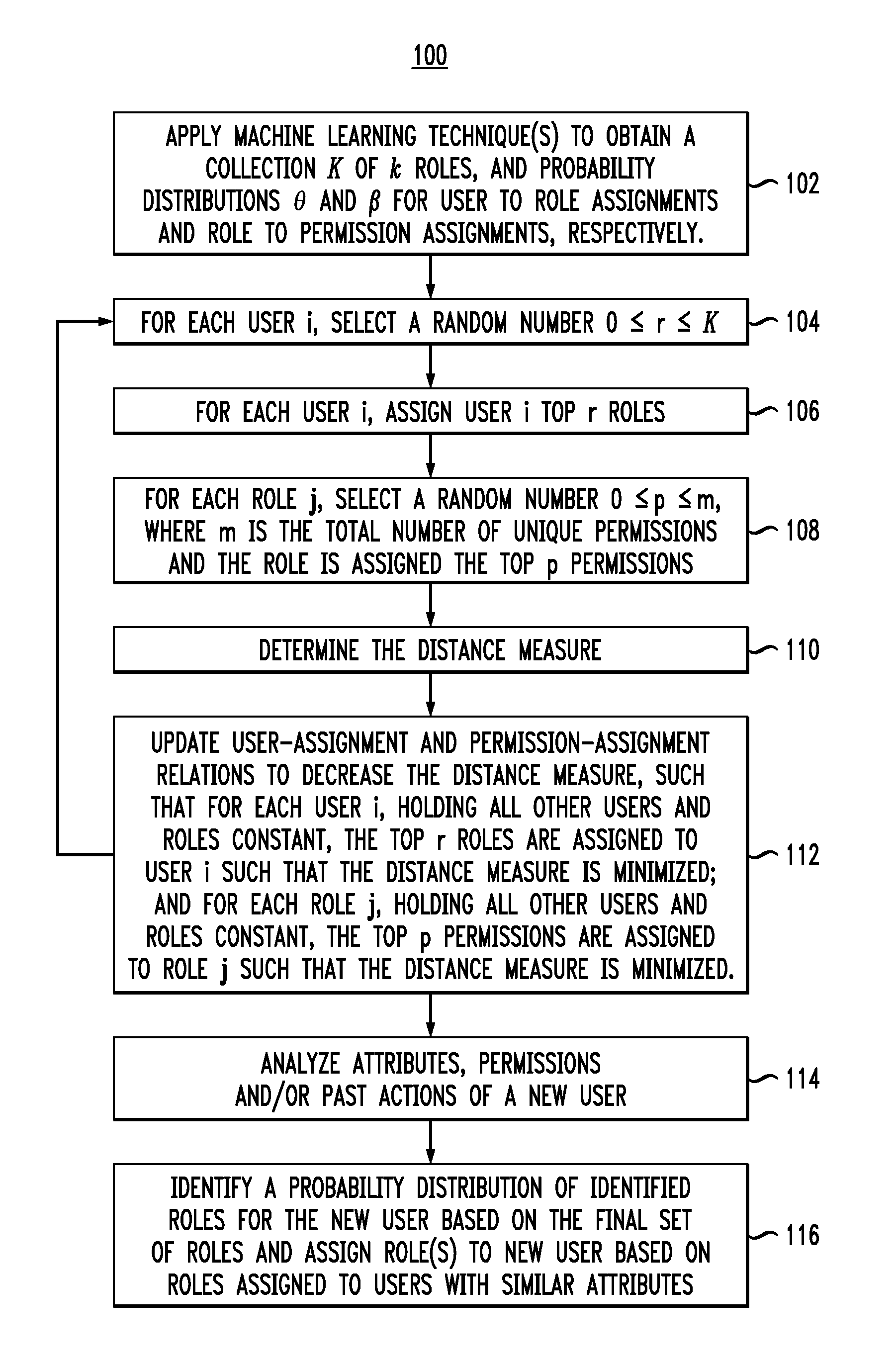
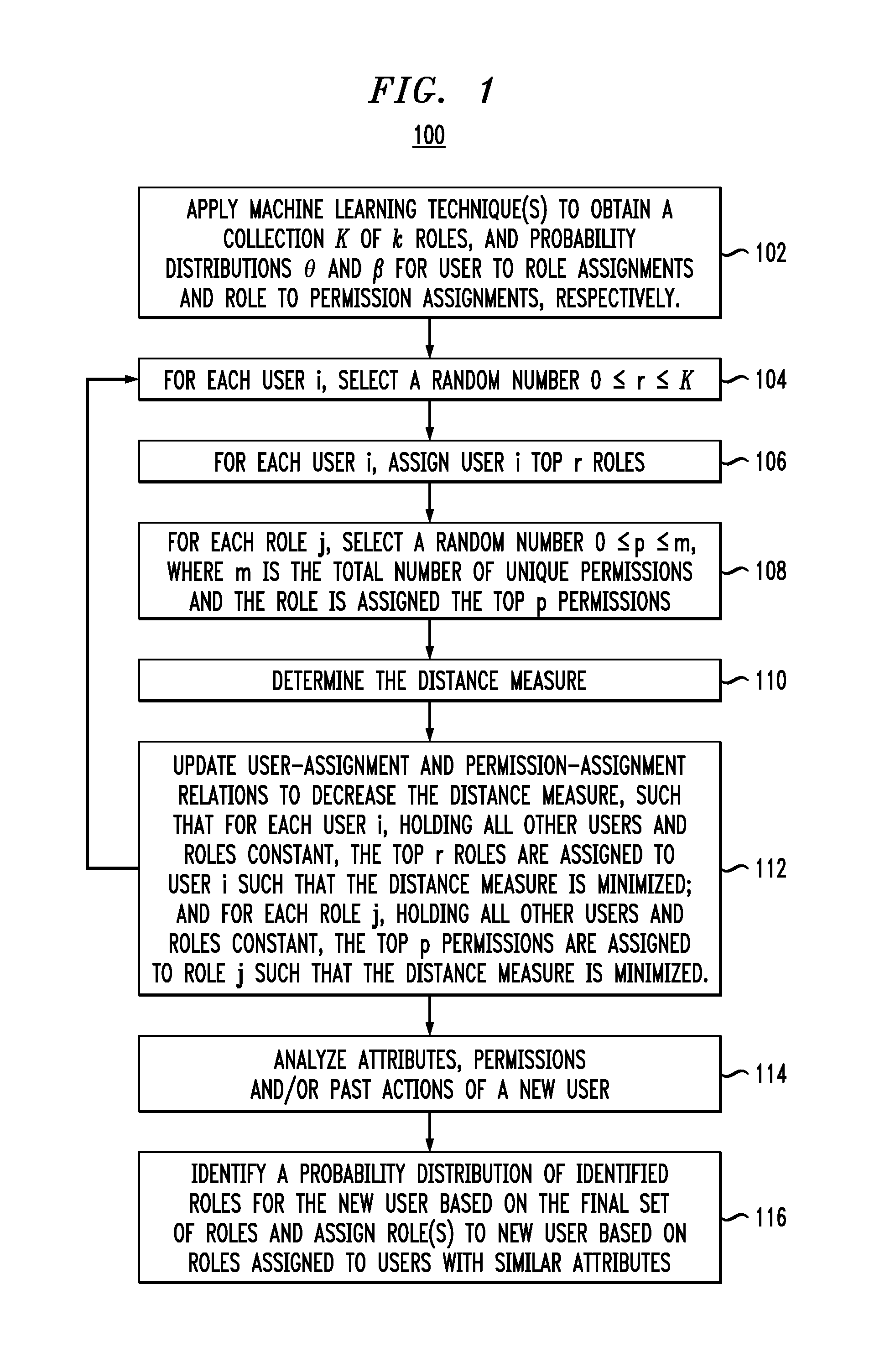
Role Mining With User Attribution Using Generative Models
ActiveUS20120246098A1Good conditionEasy to operateDigital computer detailsComputer security arrangementsRandom assignmentLatent Dirichlet allocation
Applications of machine learning techniques such as Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) and author-topic models (ATM) to the problems of mining of user roles to specify access control policies from entitlement as well as logs which contain record of the usage of these entitlements are provided. In one aspect, a method for performing role mining given a plurality of users and a plurality of permissions is provided. The method includes the following steps. At least one generative machine learning technique, e.g., LDA, is used to obtain a probability distribution θ for user-to-role assignments and a probability distribution β for role-to-permission assignments. The probability distribution θ for user-to-role assignments and the probability distribution β for role-to-permission assignments are used to produce a final set of roles, including user-to-role assignments and role-to-permission assignments.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and device for indicating future need for product replacement of random-use dispensing
ActiveUS20090204256A1Volume measurement and fluid deliveryHolders and dispensersRandom assignmentReliability engineering
Owner:GOJO IND INC
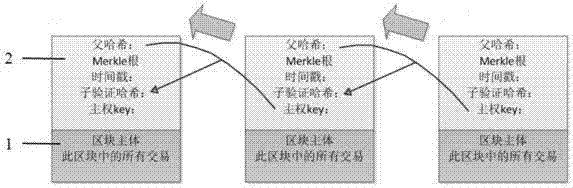
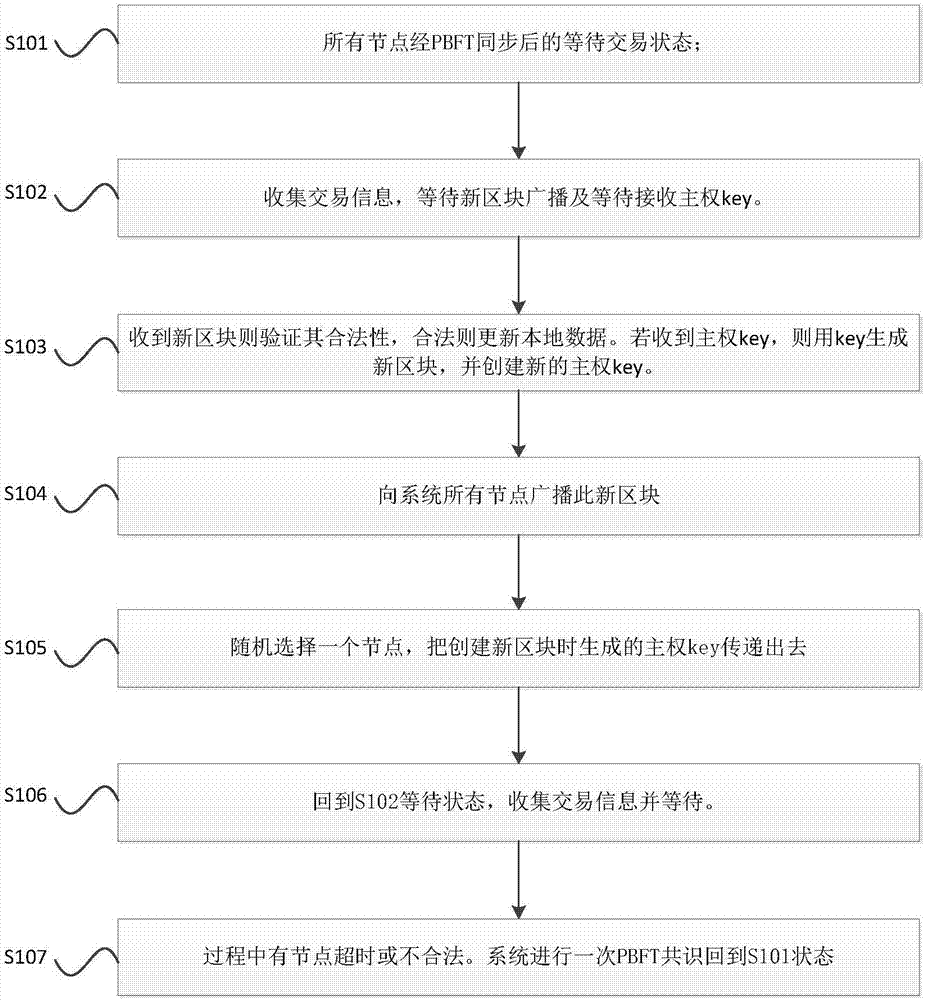
Quick consensus bookkeeping method and system based on blockchain alliance chain
InactiveCN107146087AAchieve any timeTransaction confirmation speed shortenedPayment architectureRandom assignmentDistributed computing
The invention aims to provide a quick consensus bookkeeping method and system based on a blockchain alliance chain. The method comprises the following steps that: when a system is initialized, the system generates a sovereignty key used for generating a new block; a node collects trade information and waits for a new block broadcast; after the node receives the new block broadcast, the new block is added into a local block; the node which receives the sovereignty key generates the new block, and a new sovereignty key is created; the new block is broadcast to all nodes of the system; and the new sovereignty key is transferred. By use of the method, through a method that the certain node of the system is randomly selected to transfer the sovereignty key, only a certain node which can not be determined in the system has power and permission for generating the new block at any time, bookkeeping rights are randomly distributed among all honest nodes so as to guarantee that the system can quickly reach consensus while the trade information can not be tampered, and trade confirmation speed is shortened into a second level from an original minute level.
Owner:GUANGDONG YOUMAI INFORMATION COMM TECH
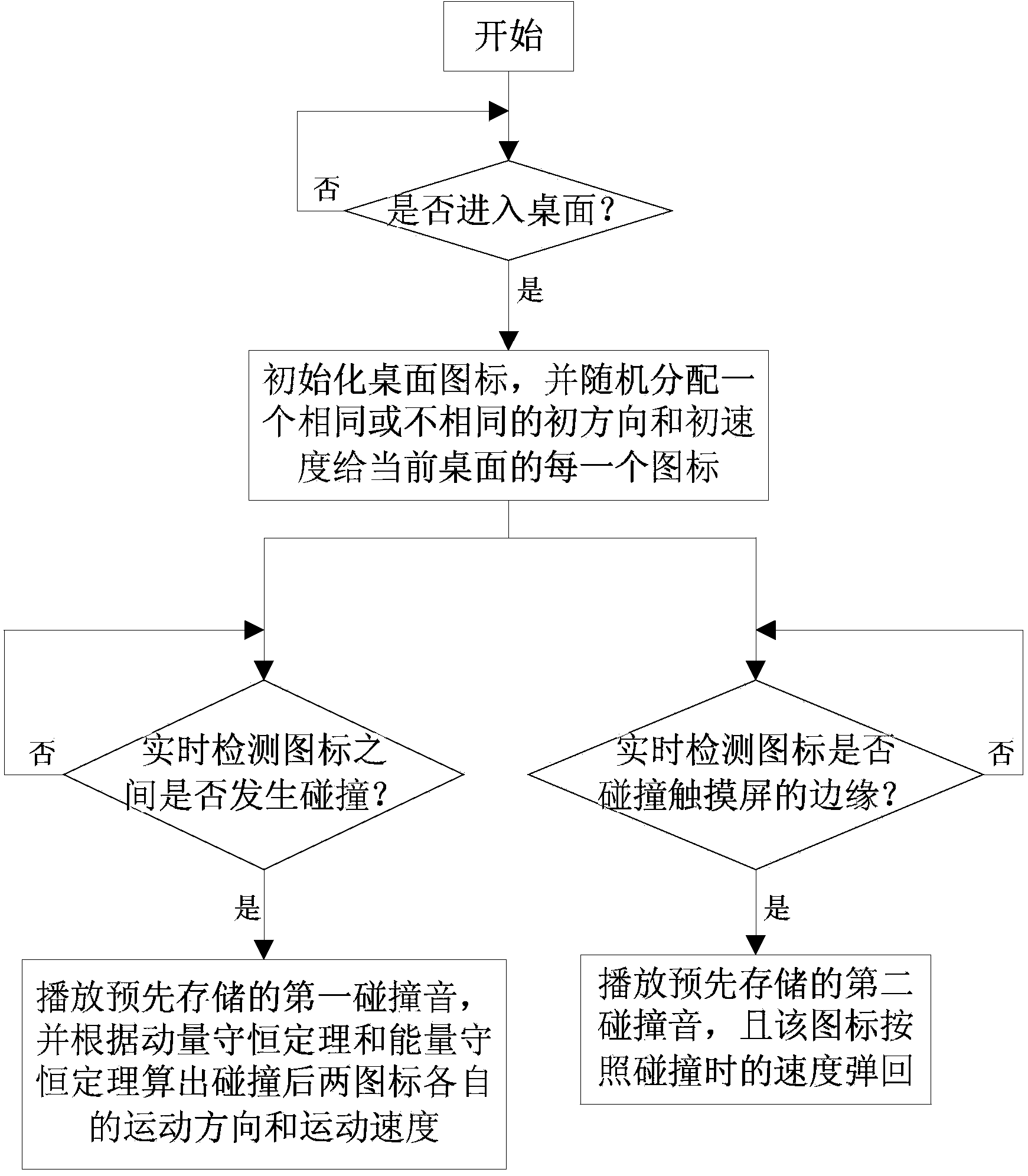
Vivid and interesting desktop icon displaying method and device
ActiveCN103838465AUnique displayImprove freshnessInput/output processes for data processingRandom assignmentTouchscreen
The invention discloses a vivid and interesting desktop icon displaying method and device. The method includes the following steps: when entering a desktop, initializing desktop icons, and randomly distributing same or different initial directions and initial speeds to all the desktop icons of the current desktop; detecting whether collision occurs among the icons or not in real time; if yes, playing a pre-stored first collision sound, and calculating respective motion directions and motion speeds of two collided icons according to the momentum conservation law and the energy conservation law; detecting whether the icons collide with the edge of a touch screen or not in real time; if yes, playing a pre-stored second collision sound, wherein the icons rebound in a collision speed. After the vivid and interesting desktop icon displaying method and device is applied, the terminal desktop displays showy dynamic effect and makes the icon collision sounds, and users can interact with the desktop and optionally change motion state of the icons, so that much interestingness is realized, and the users have a lot of fun and good use and operation experiences.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Trusted services broker for web page fine-grained security labeling
InactiveUS20010013096A1Need to installEnhance known web server functionsWeb data retrievalDigital data processing detailsPasswordRandom assignment
Arbitrarily fine-grained limitation of access to information stored in a resource of a data processor network is provided in a manner compatible with existing network browsers by mapping user identity and credentials with randomly assigned security cookie information which thus serves as a surrogate credential accompanying each user request during a session. Labels are imbedded within HTML files / text which may embody any desired security policy, including mandatory access control (MAC) arrangements which are not available through native browser functions. Data is retrieved in response to a user request which includes a security cookie from a location in the resource which is not directly accessible through use of a URL; the location being stored in a configuration file which is hidden from users. The retrieved data is then filtered in accordance with labels provided for each page and / or embedded in the text and used to build a response which may include hypertext links or other user interfaces for transmission to the user. Provision is made for viewing or changing of labels, credentials and passwords.
Owner:LEIDOS INNOVATIONS TECH INC
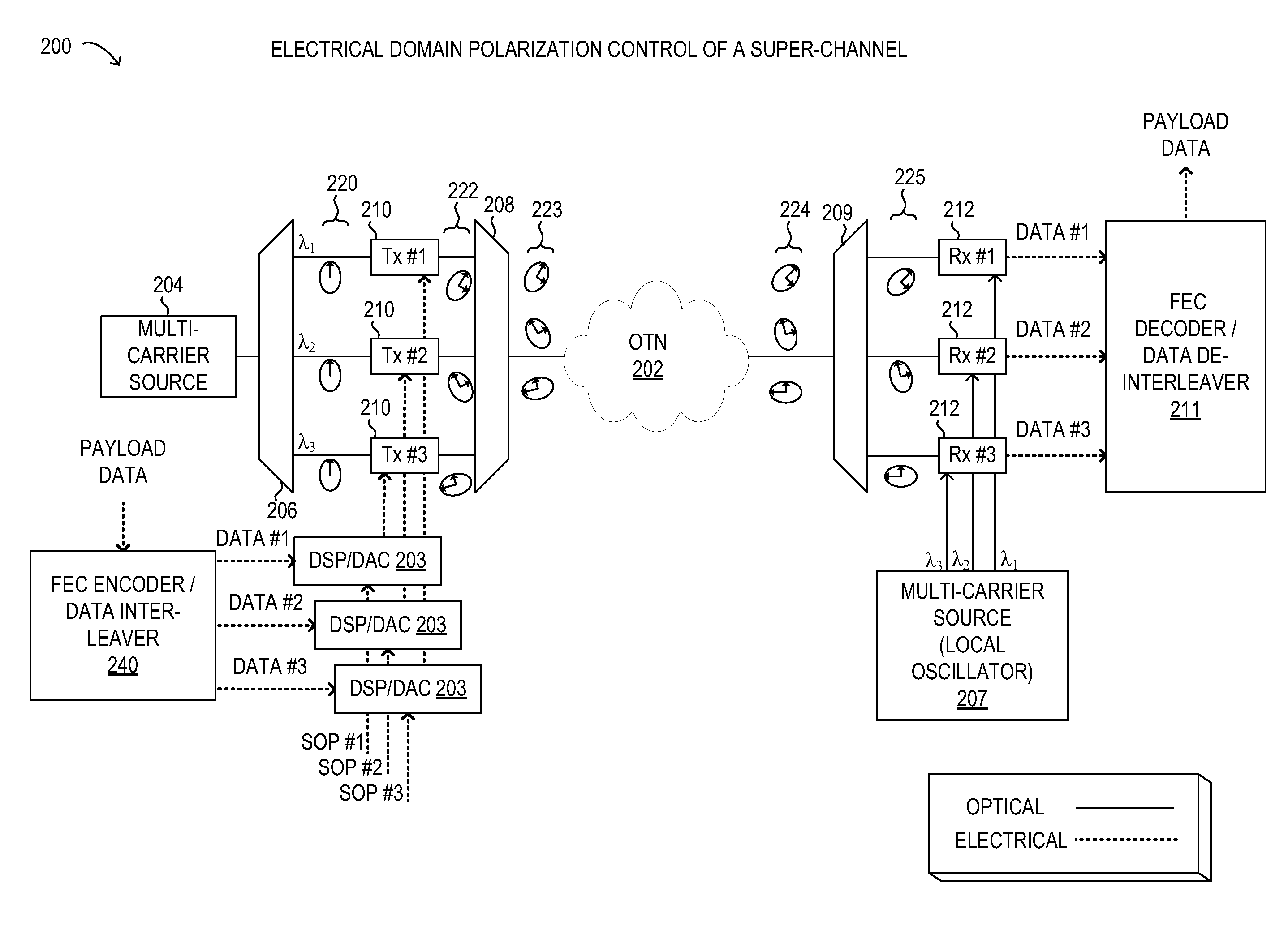
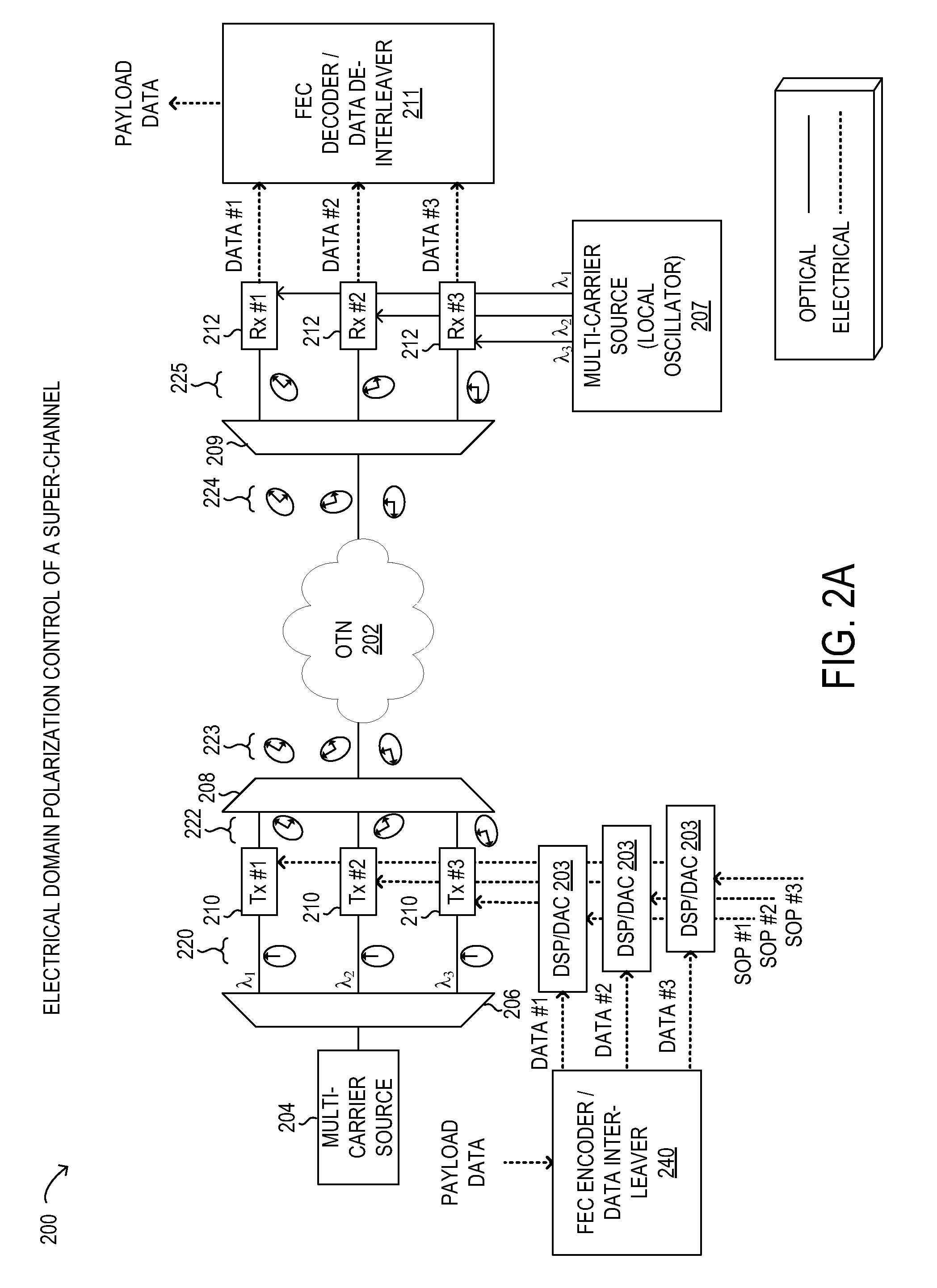
Mitigation of polarization dependent loss in optical multi-carrier/super-channel transmission
ActiveUS9112609B2Polarisation multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationSuper-channelCarrier signal
Methods and systems for mitigating effects of polarization dependent loss (PDL) in an optical network transmitting a multi-carrier optical signal comprising a plurality of subcarriers may involve assigning and modifying a state of polarization to each subcarrier prior to transmission. An assigned state of polarization for each subcarrier may be modified for the subcarrier in the digital domain and / or the optical domain. Various specific assignment methods may be used, including individual subcarrier assignment, subcarrier set assignment, arbitrary subcarrier group assignment, random assignment, and / or combinations thereof. The assigned states of polarization may be selected based on a resulting minimum PDL-induced peak-to-peak power variation over a sum of the subcarriers for all orientations of a principal axis of PDL.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
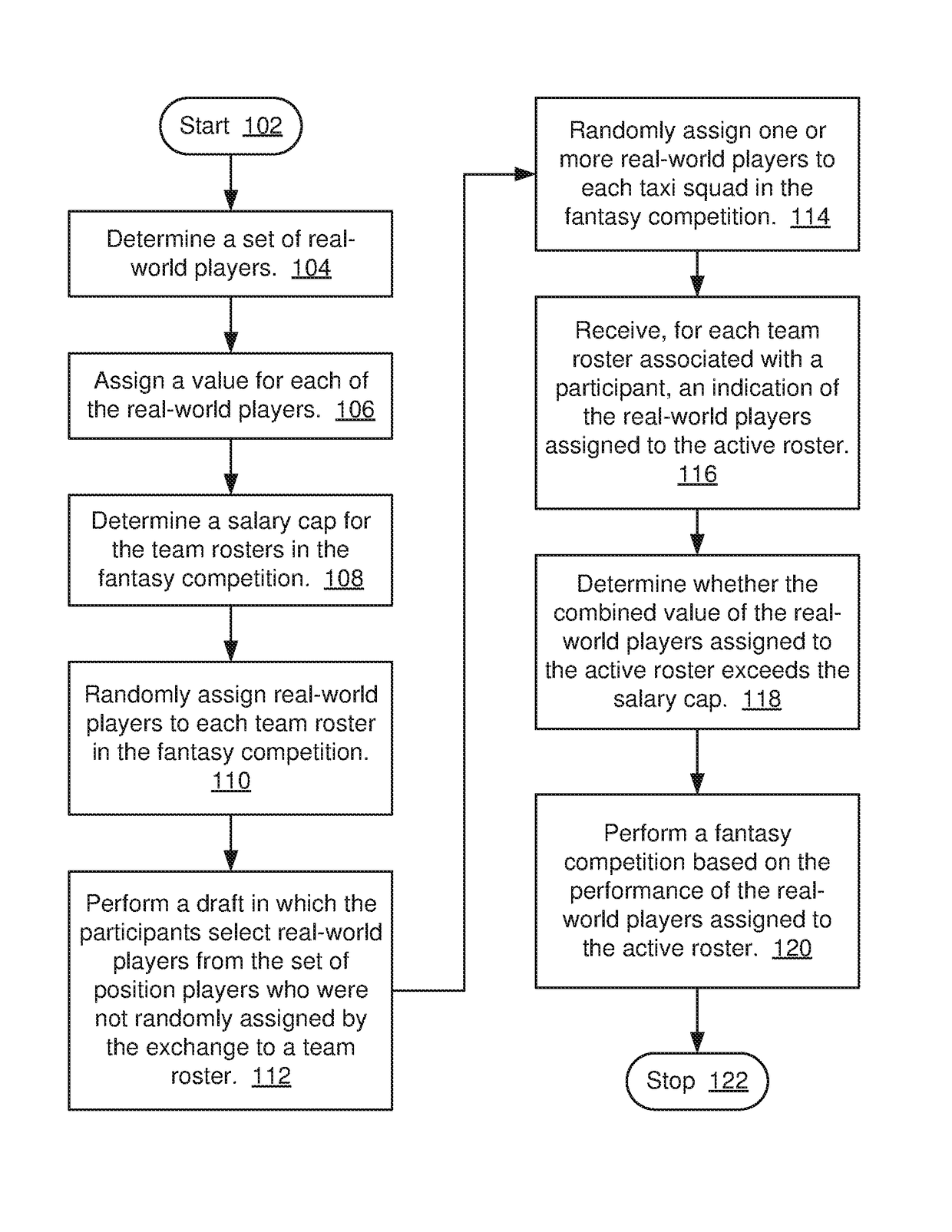
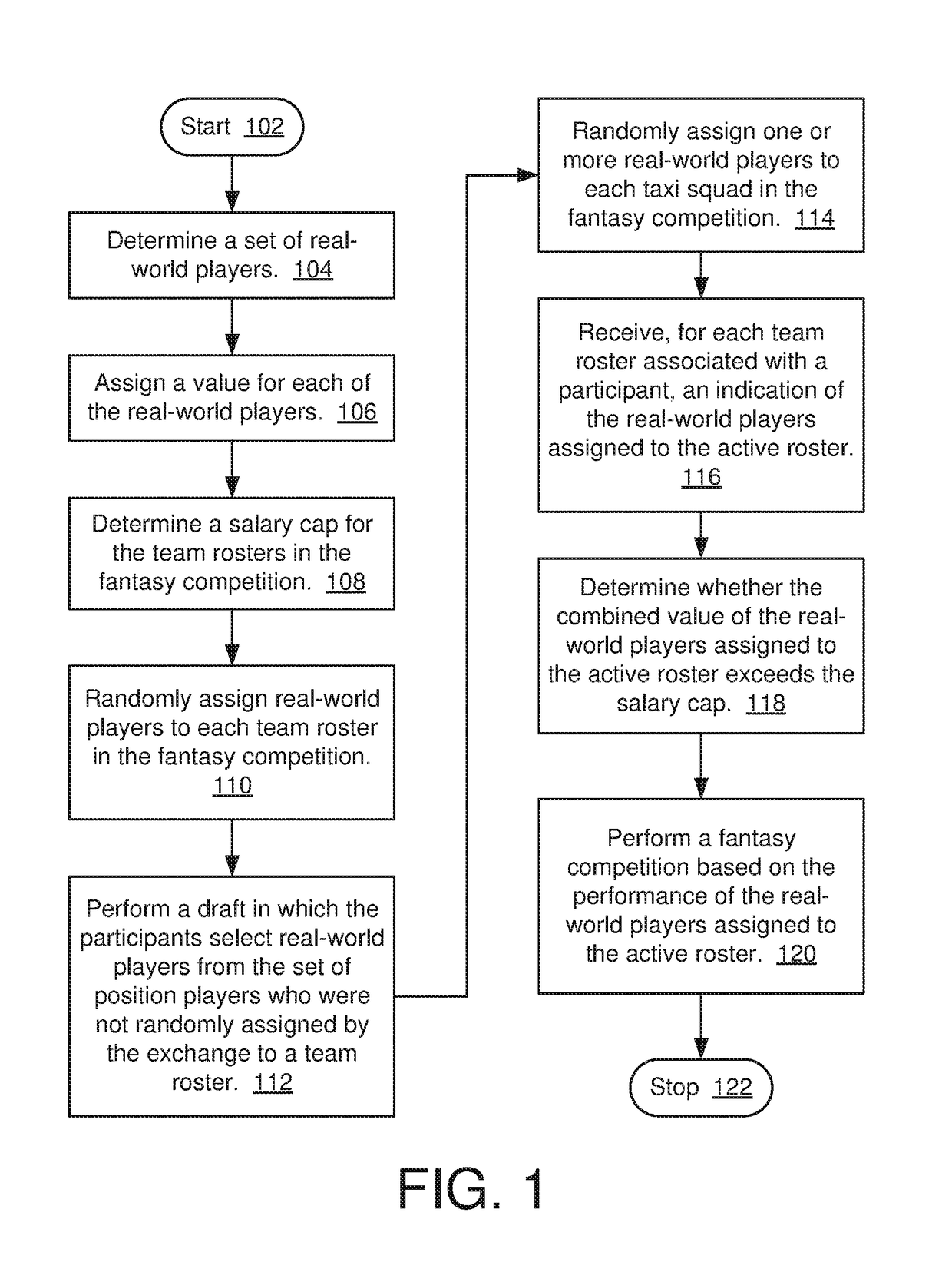
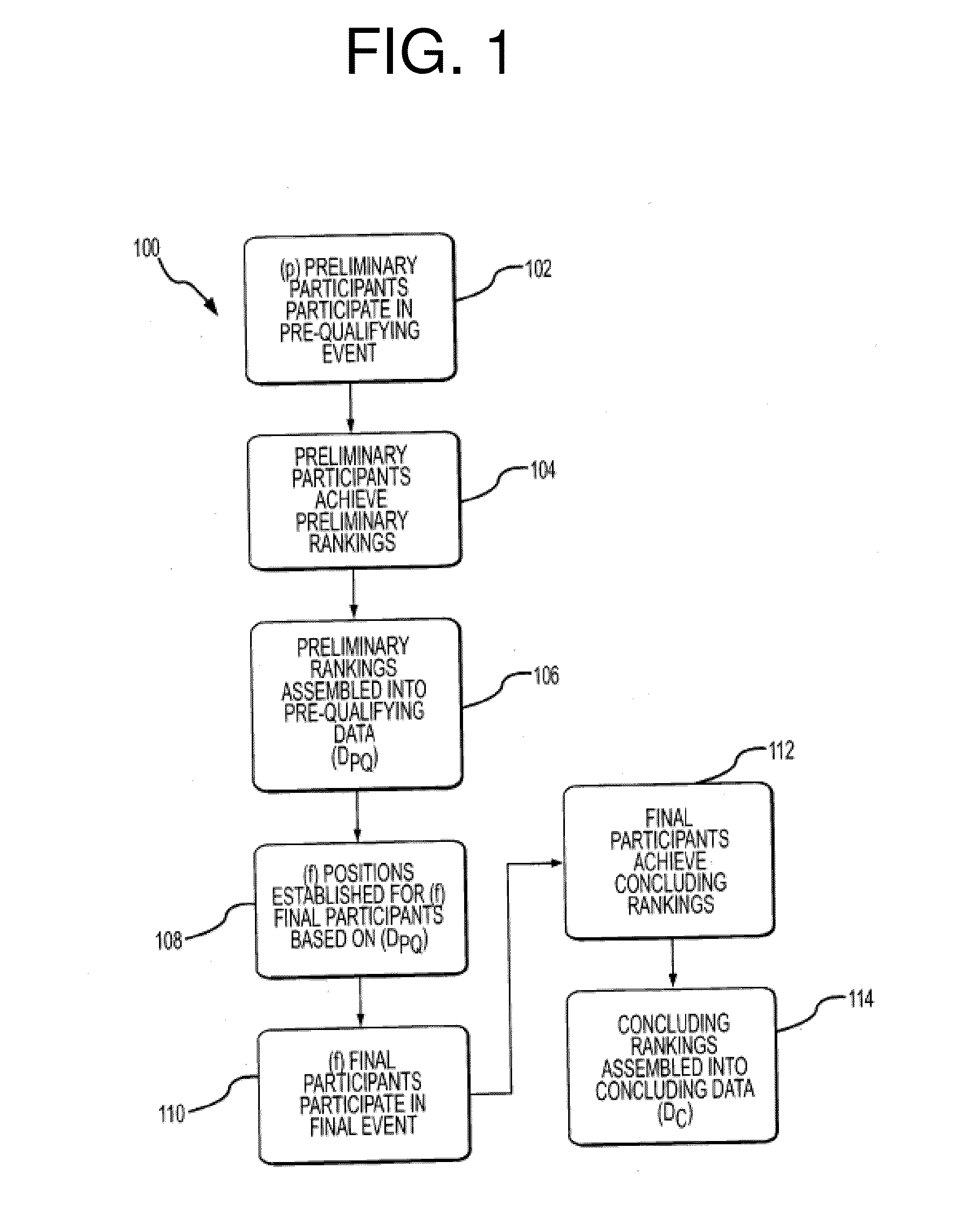
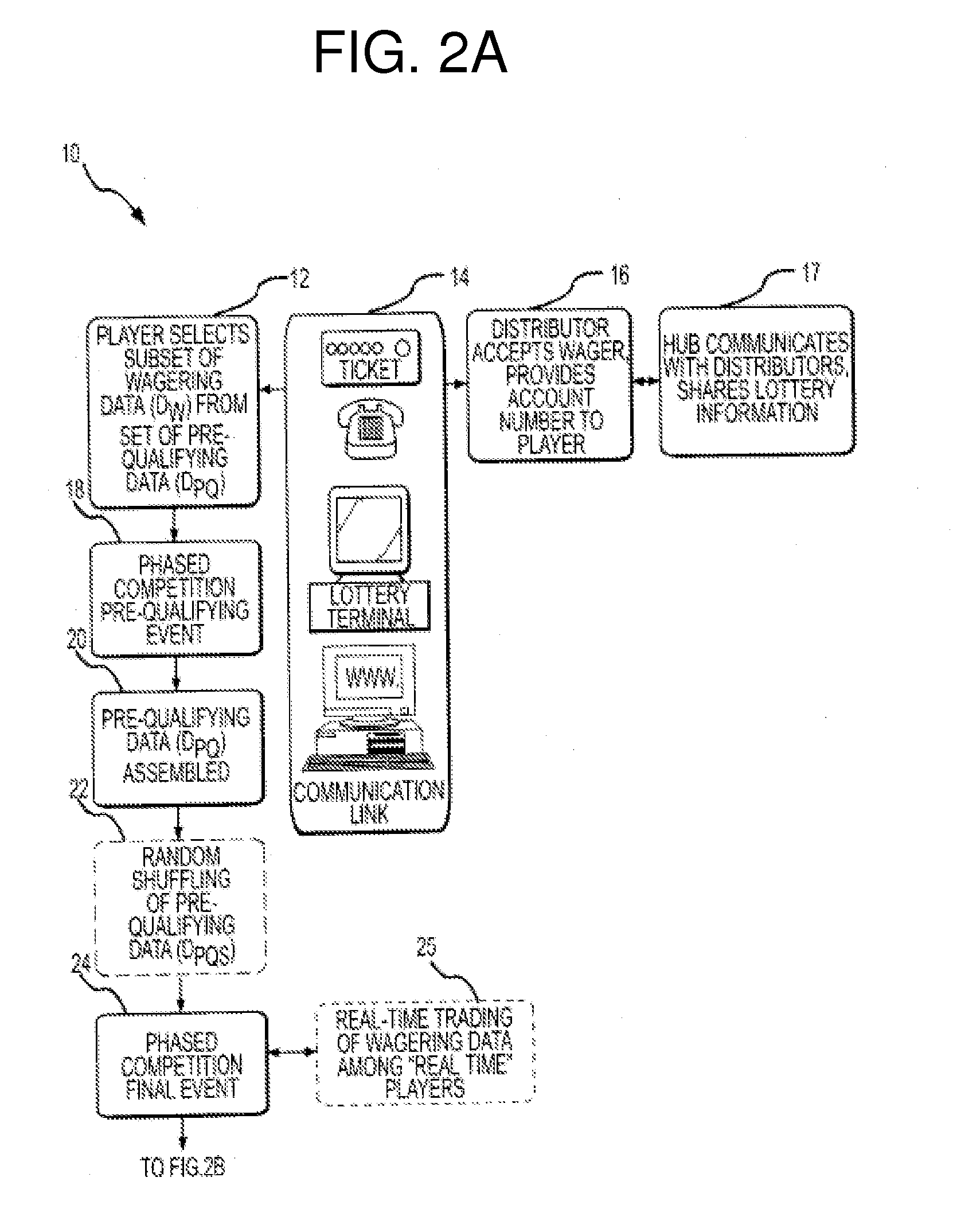
Method and system for providing fantasy competitions
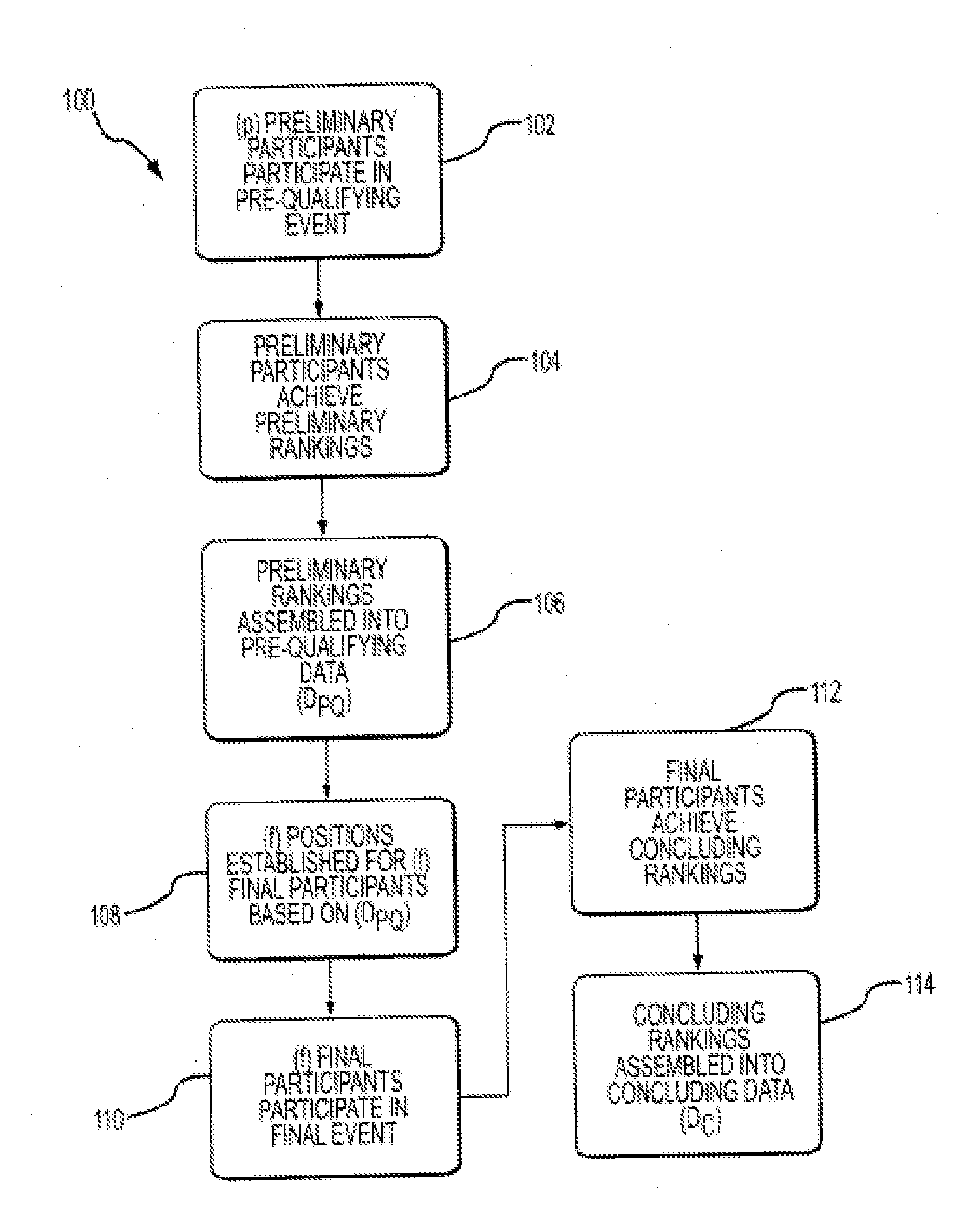
A method and system for providing a fantasy competition, in which the method includes determining a set of real-world players eligible for scoring in a fantasy competition; assigning a value for each of the real-world players; determining a salary cap for the fantasy competition; randomly assigning real-world players to a team roster; performing a draft in which the participants select real-world players who were not randomly assigned to a team roster; randomly assigning one or more real-world players to a taxi squad; receiving an indication of the real-world players assigned to the active roster; determining whether the combined value of the real-world players assigned to the active roster exceeds the salary cap; and performing a fantasy competition in which a score for each team roster associated with a participant is based on the performance, in one or more real-world events, of the real-world players assigned to the active roster.
Owner:BIDASK
Method for elliptic curve scalar multiplication
InactiveUS20090214023A1Improve the immunityImprove securityDigital data processing detailsSecret communicationPower analysisCountermeasure
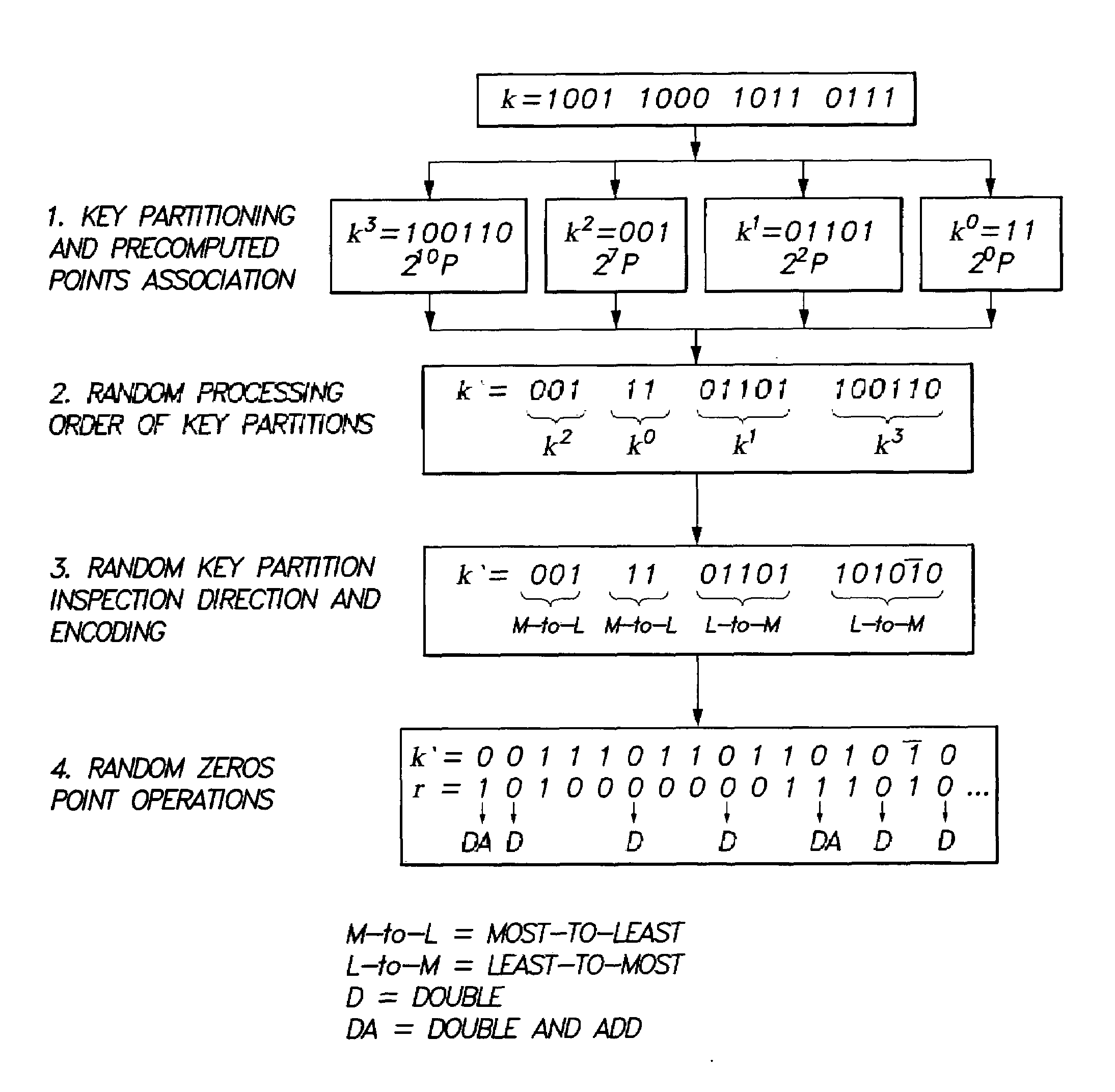
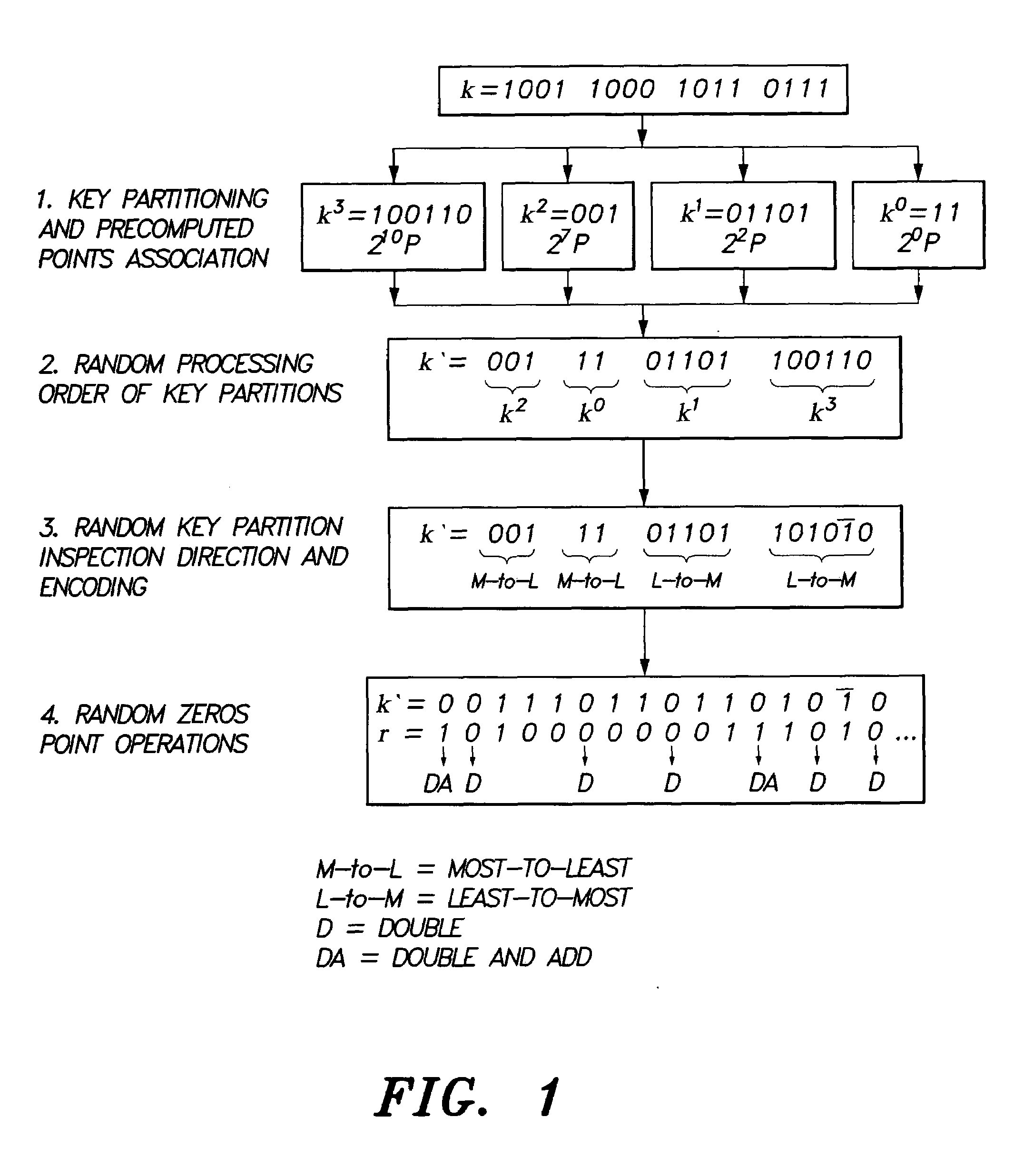
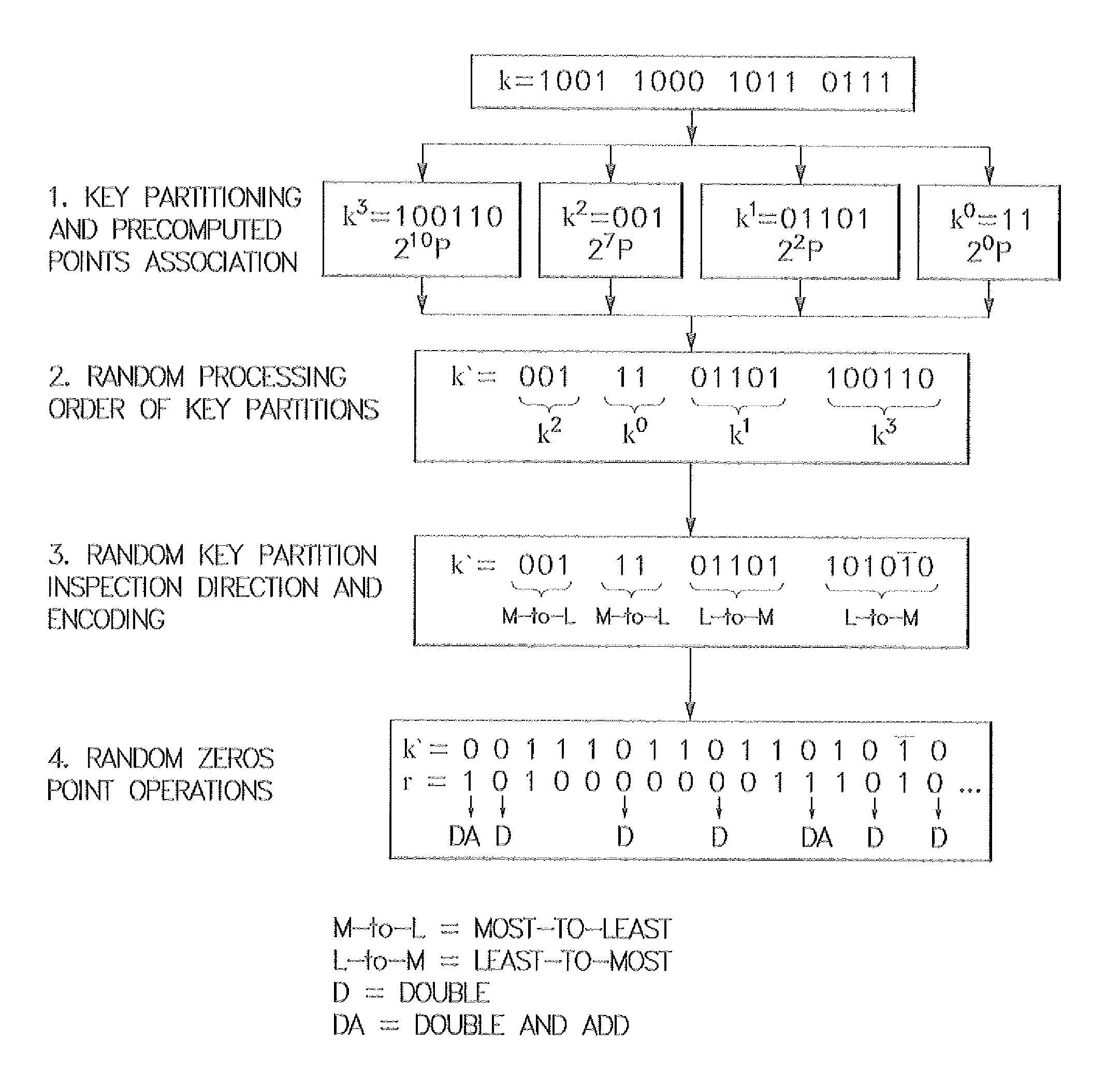
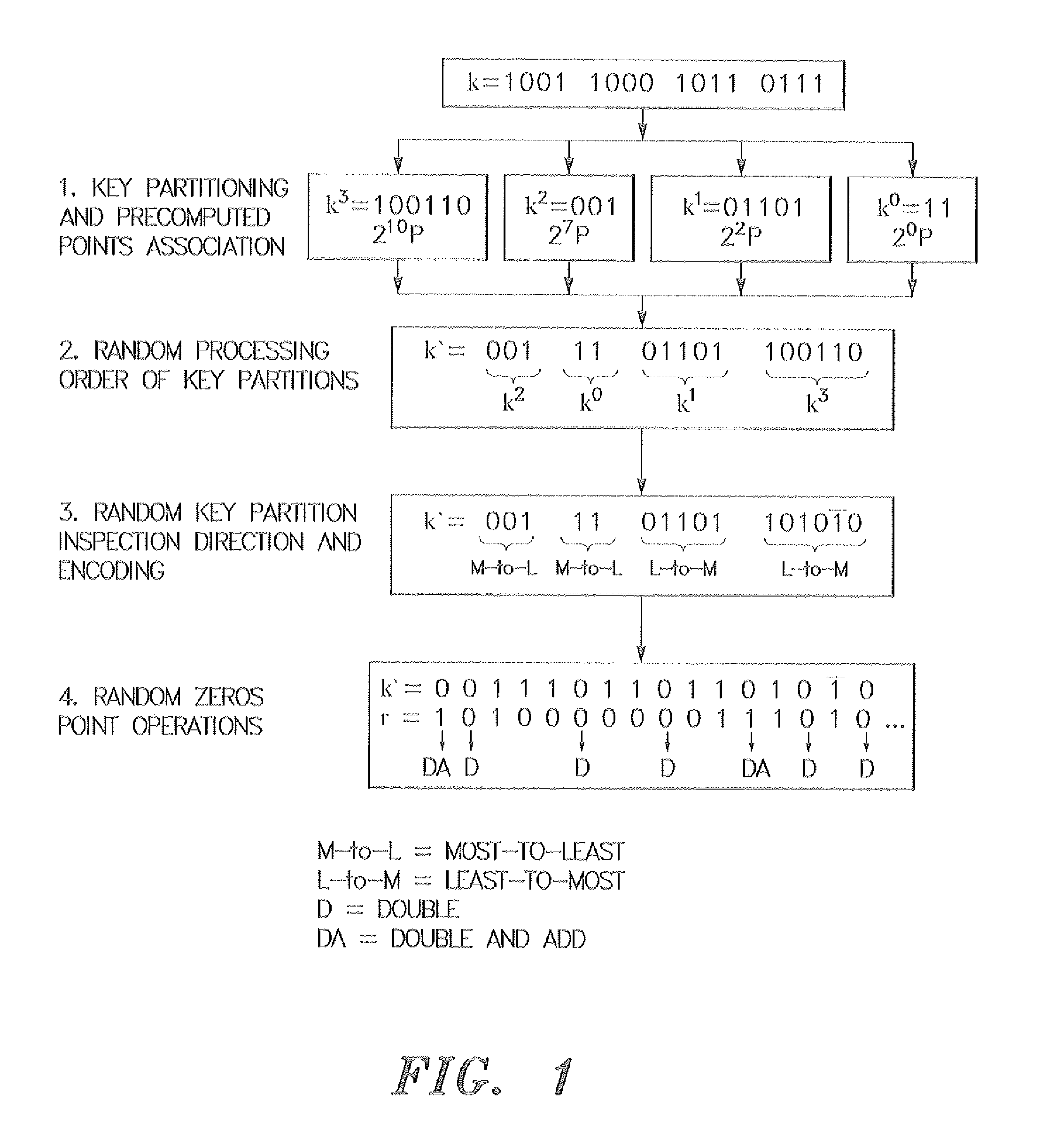
The method for elliptic curve scalar multiplication may provide several countermeasures to protect scalar multiplication of a private key k by a point P to produce the product kP from power analysis attacks. First, the private key, k, is partitioned into a plurality of key partitions, which are processed in a random order, the resulting points being accumulated to produce the scalar product kP. Second, in each partition, the encoding is randomly selected to occur in binary form or in Non-Adjacent Form (NAF), with the direction of bit inspection being randomly assigned between most-to-least and least-to-most. Third, in each partition, each zero in the key may randomly perform a dummy point addition operation in addition to the doubling operation. The method may be implemented in software, smart cards, circuits, processors, or application specific integrated circuits (ASICs) designed to carry out the method.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
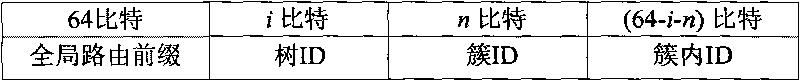
Method for achieving automatic configuration of IPv6 addresses for wireless sensor network
The invention provides a method for achieving the automatic configuration of IPv6 addresses for a wireless sensor network. In the method, the wireless sensor network is provided with four types of nodes including isolated sensor nodes, IPv6 access nodes, cluster head nodes and intra-cluster nodes, wherein one of the IPv6 access nodes and a plurality of the cluster head nodes form a dendritic structure. The wireless sensor network consists of a plurality of clusters, and each cluster comprises one cluster head node and a plurality of intra-cluster nodes. The IPv6 access nodes / cluster head nodes adopt a state-full address configuration scheme for recording address assignment to allocate the IPv6 addresses to the other cluster head nodes; the cluster head nodes adopt the state-full address configuration scheme for recording the address assignment and a state-less address configuration scheme for random assignment to allocate the IPv6 addresses to the intra-cluster nodes in the clusters to which the cluster head nodes belong; and when the cluster head nodes adopt the address configuration scheme for the random assignment to allocate the IPv6 addresses to the intra-cluster nodes in the clusters to which the cluster head nodes belong, repeat addresses of the allocated IPv6 addresses are only detected in the clusters.
Owner:JIANGSU TRIGIANT TECH
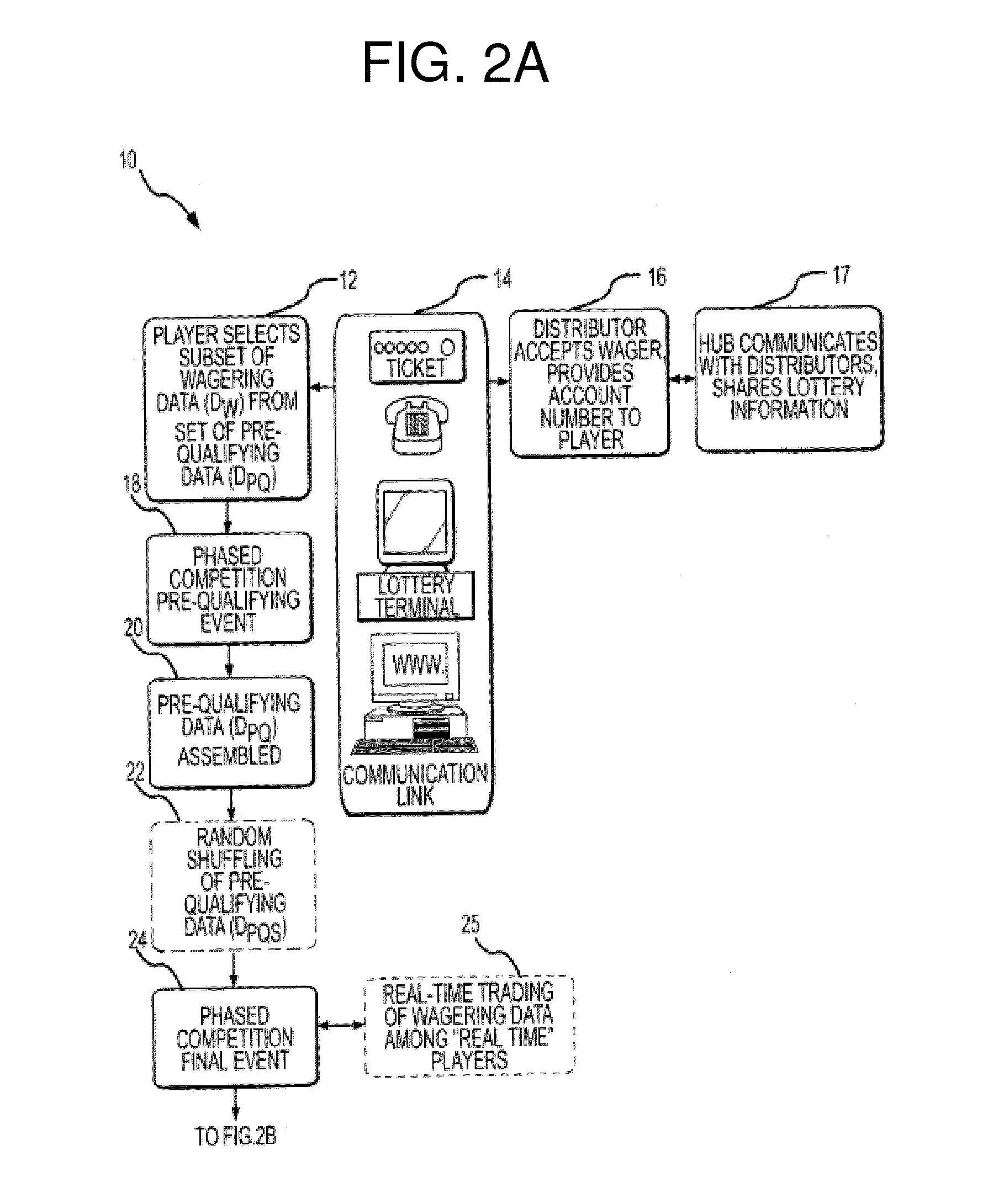
Method of Lottery Wagering on Real-World Events
InactiveUS20130079094A1Enhance current lottery systemIncrease salesLottery apparatusFinanceRandom assignmentData mining
Owner:ODOM JAMES M +1
Method for elliptic curve scalar multiplication
InactiveUS20120008780A1Improve the immunityImprove securityDigital data processing detailsSecret communicationSmart cardScalar multiplication
The method for elliptic curve scalar multiplication may provide several countermeasures to protect scalar multiplication of a private key k by a point P to produce the product kP from power analysis attacks. First, the private key, k, is partitioned into a plurality of key partitions, which are processed in a random order, the resulting points being accumulated to produce the scalar product kP. Second, in each partition, the encoding is randomly selected to occur in binary form or in Non-Adjacent Form (NAF), with the direction of bit inspection being randomly assigned between most-to-least and least-to-most. Third, in each partition, each zero in the key may randomly perform a dummy point addition operation in addition to the doubling operation. The method may be implemented in software, smart cards, circuits, processors, or application specific integrated circuits (ASICs) designed to carry out the method.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Poker tournament management method
InactiveUS20070135950A1Improve distributionPoker tournamentApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesRandom assignmentMaximum difference
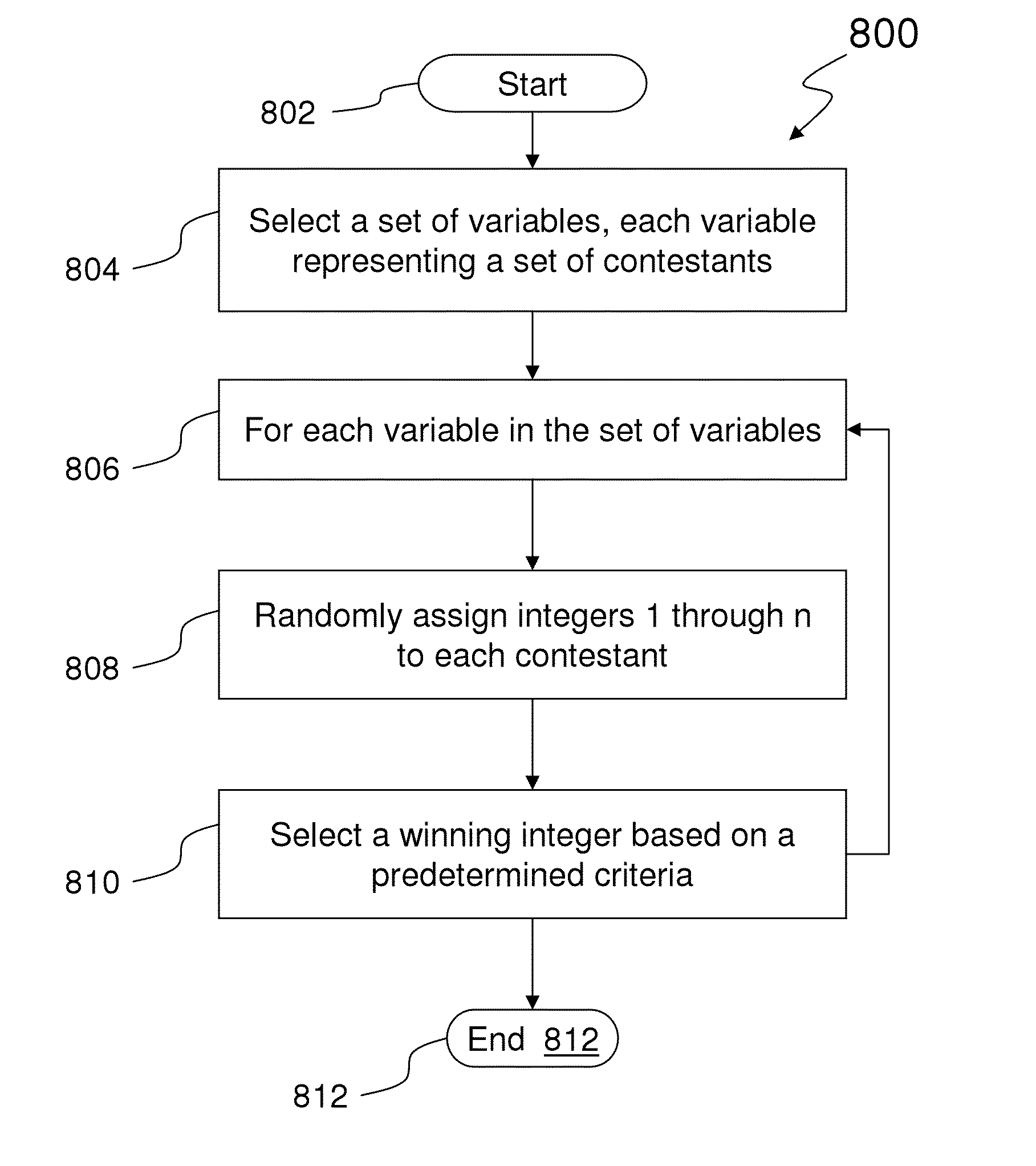
A Poker Tournament Management Method allows a plurality of players to enter a player-elimination poker tournament utilizing up to T poker tables designated tables T(1) to T(T), each poker table having up to P player positions designated P(1) to P(P); such METHOD comprising the steps of: Accessing the information for each entering player; Initially randomly assigning each entering player to a specific player position chosen from P(1) to P(P) at a specific poker table chosen from T(1) to T(T); storing said accessed entering player information, and storing said initially assigned player position and said initially assigned poker table for each entering player; and effecting the re-assignment of at least one randomly chosen player from at least one donor poker table to at least one donee poker table so that the resulting number of players assigned to each poker table differs by no more than a specified maximum difference.
Owner:OLIVERAS R MARTIN
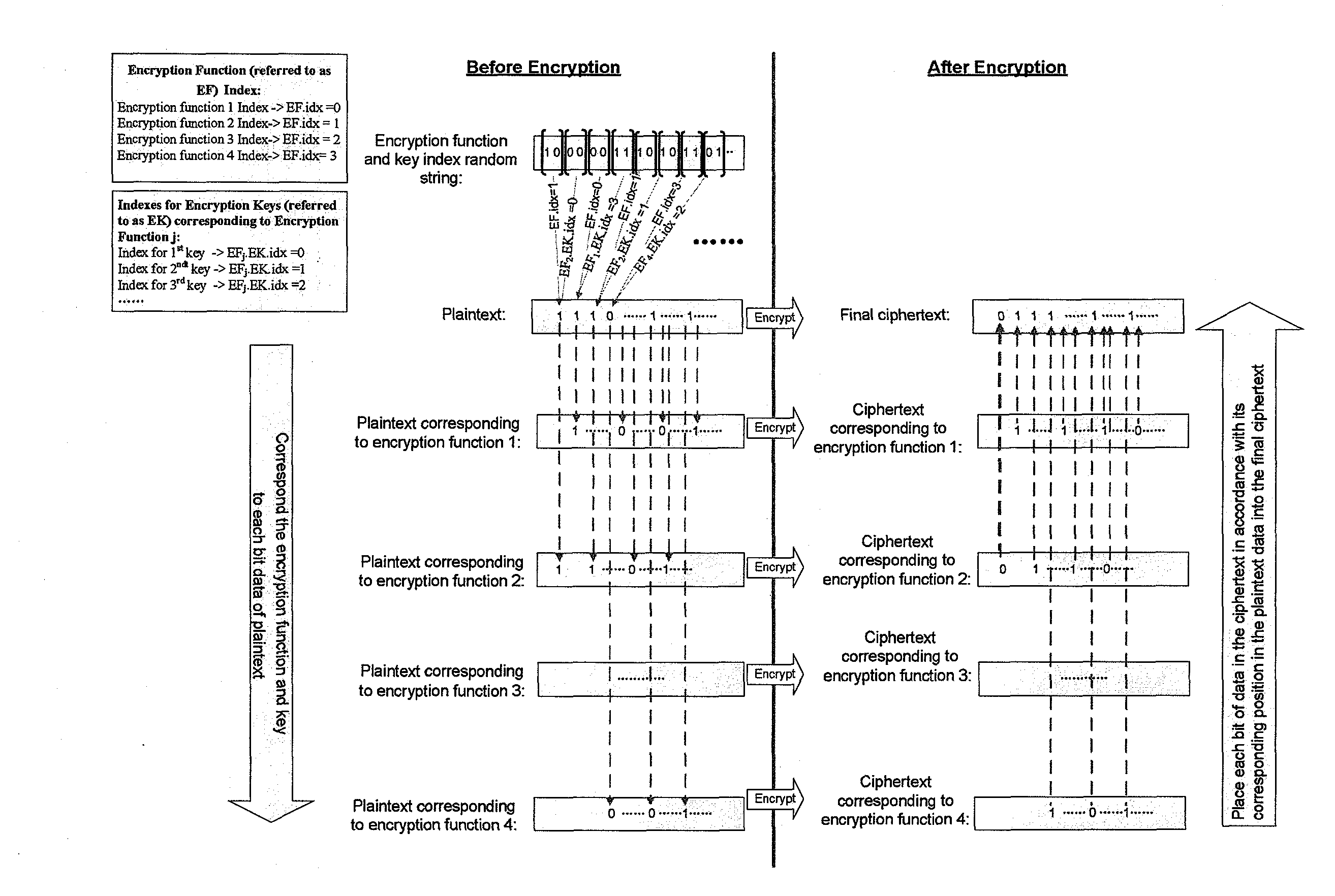
Data Encryption and Decryption Method and Apparatus
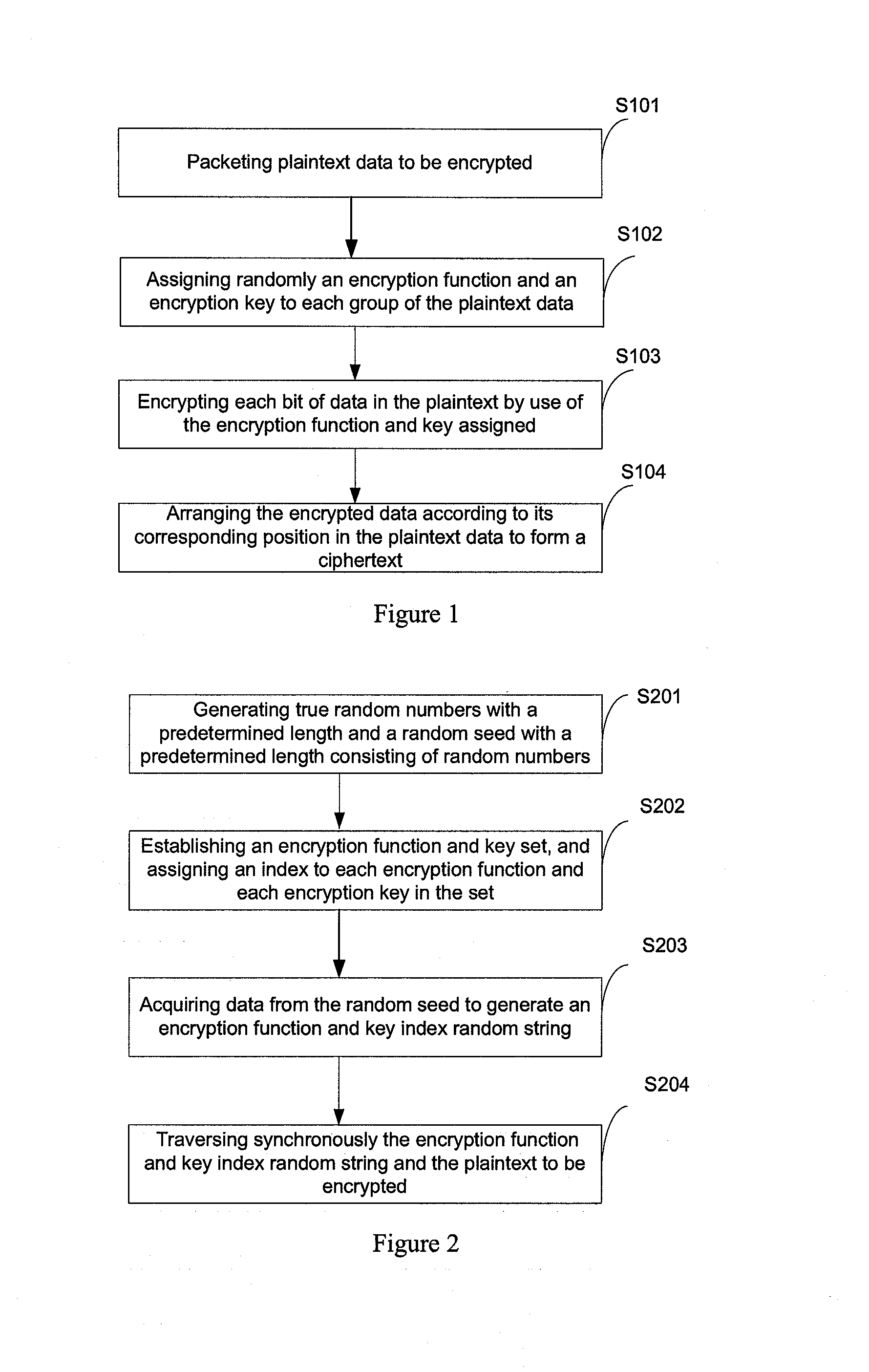
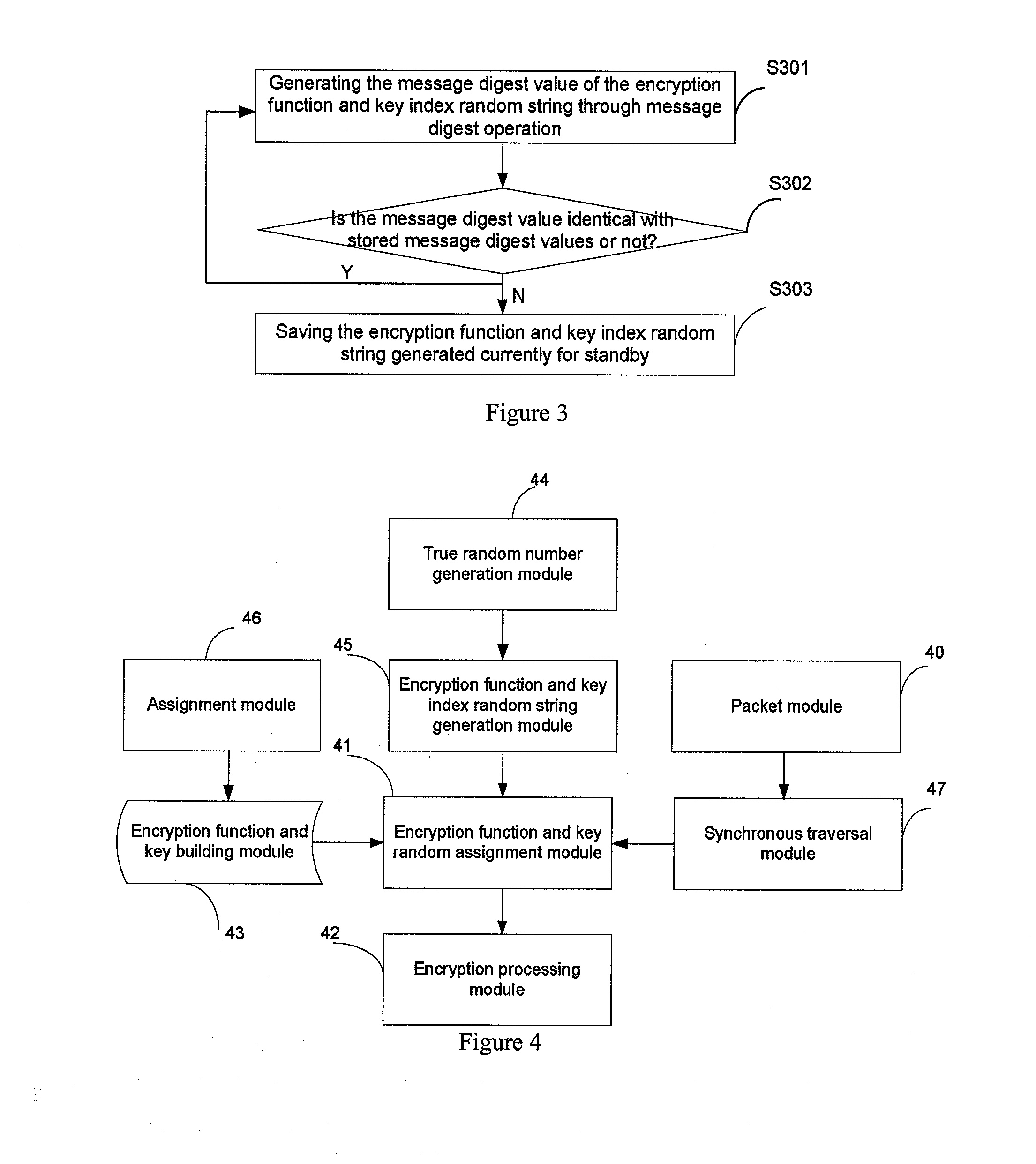
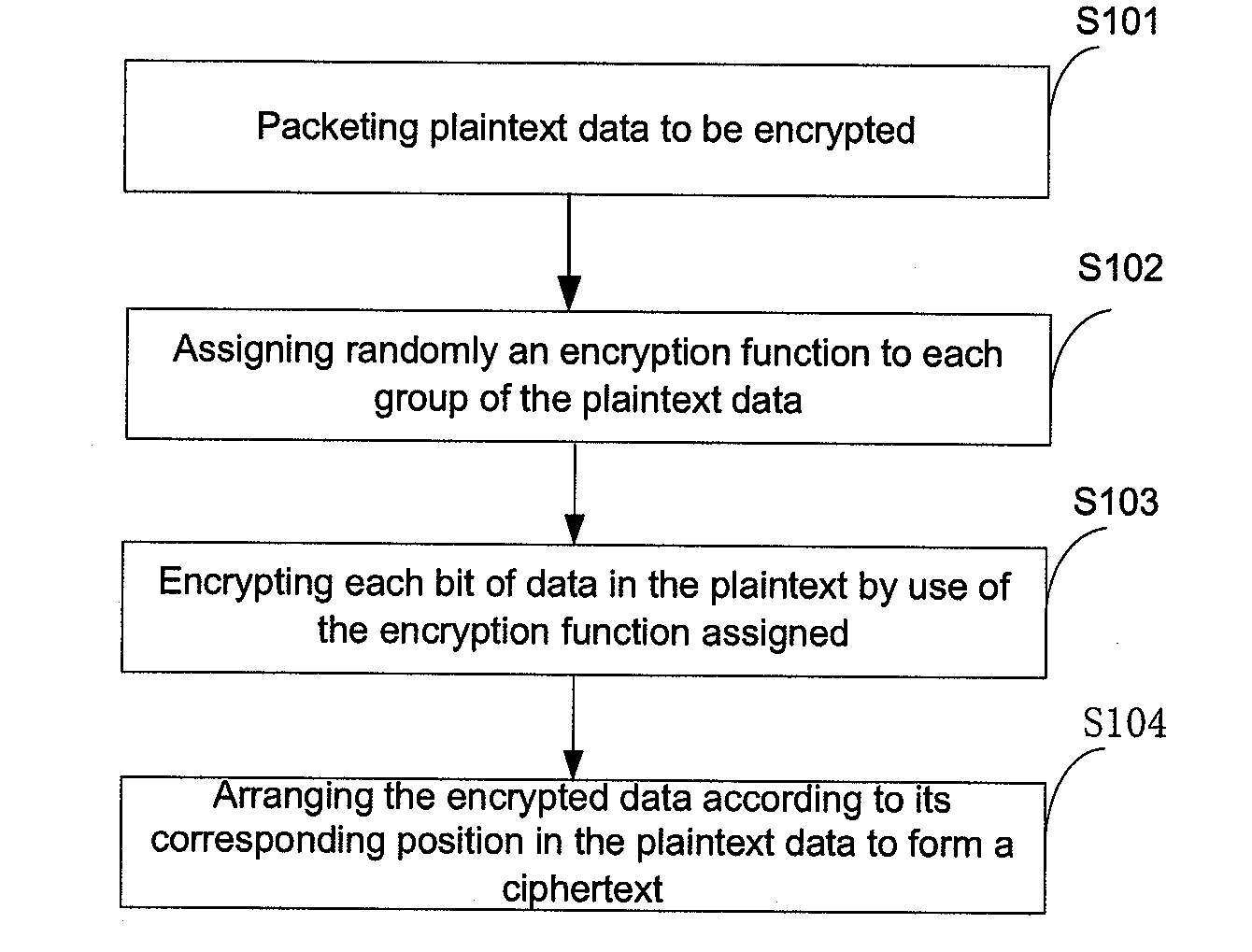
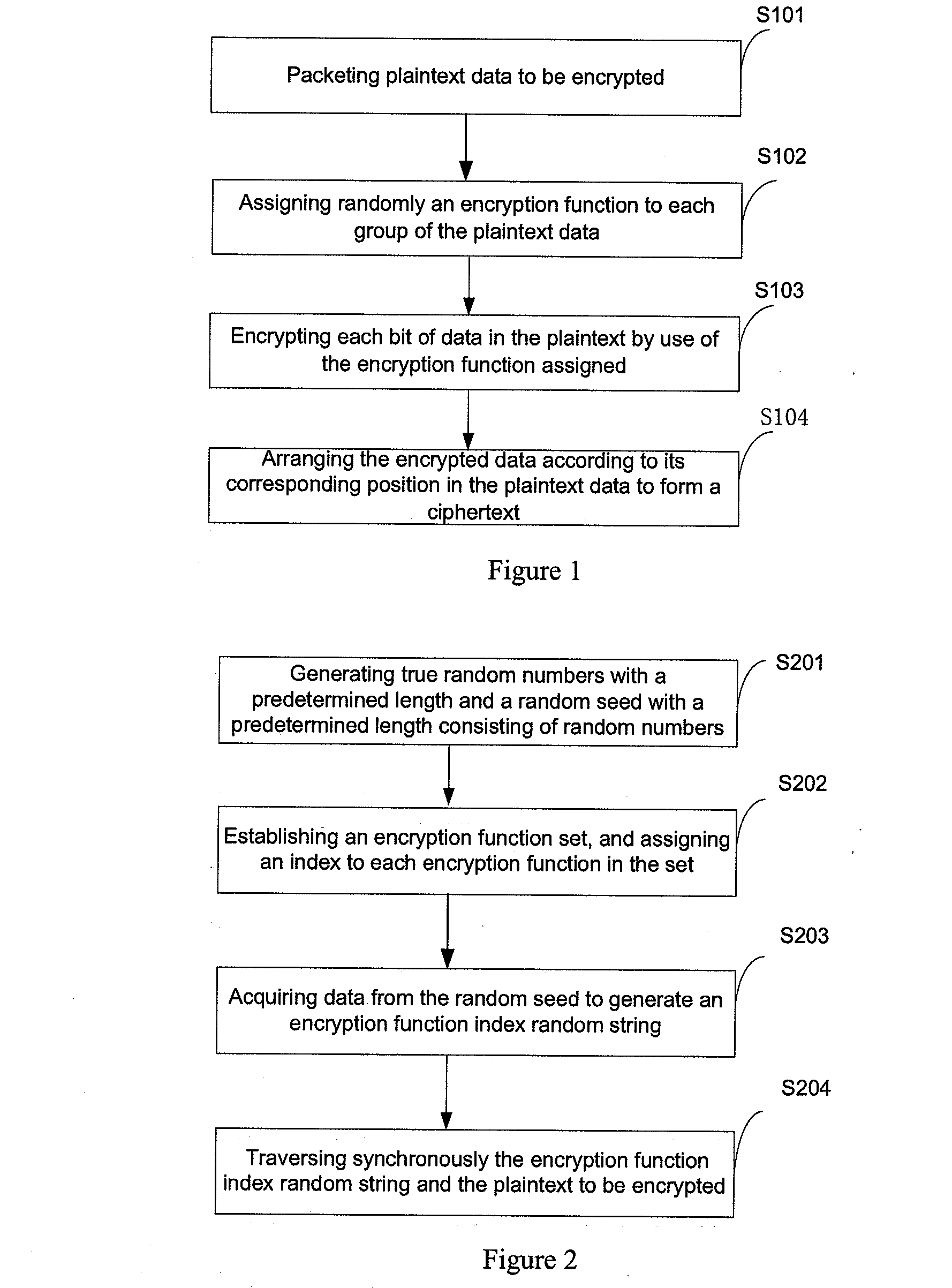
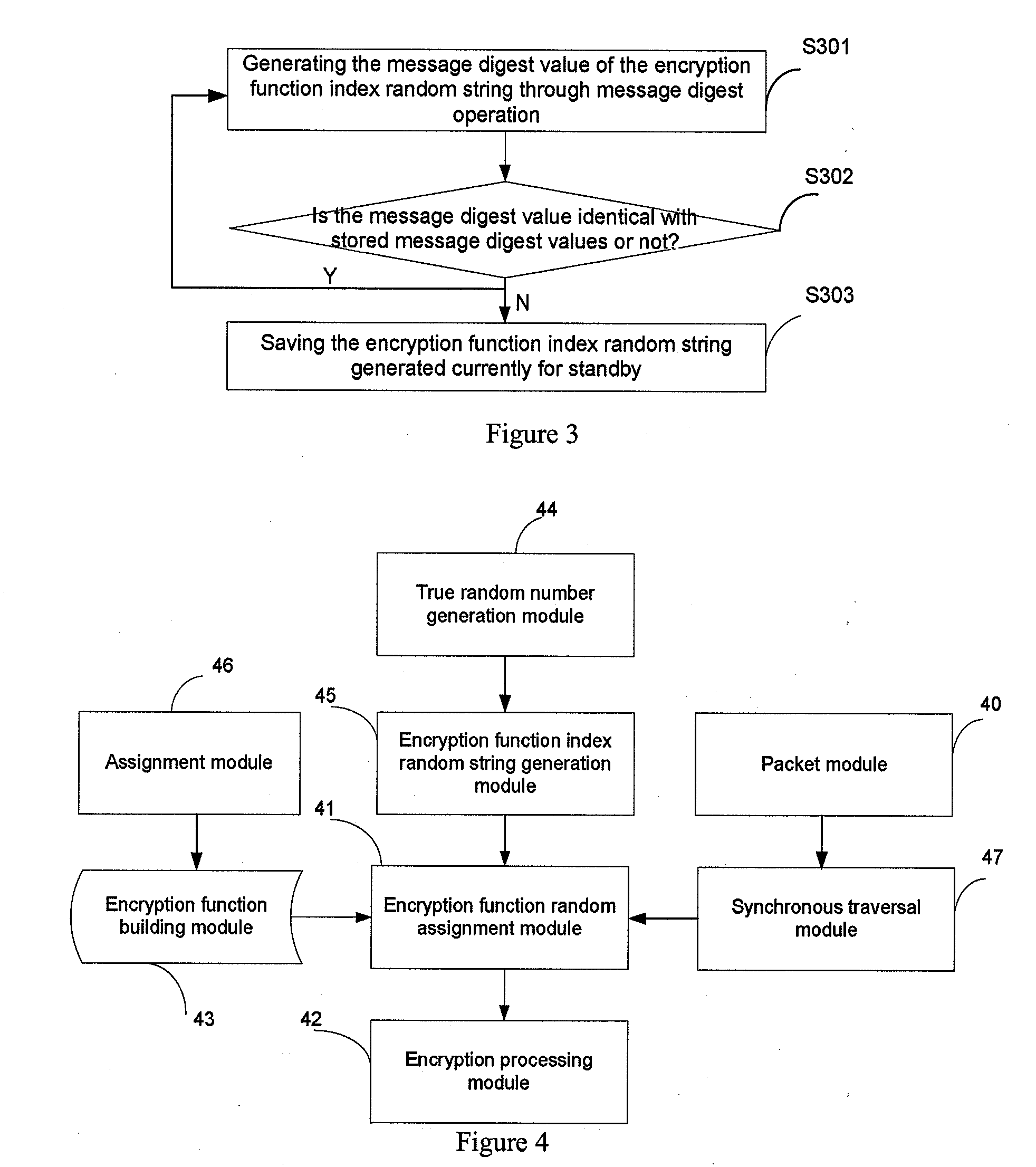
InactiveUS20140105382A1Improve data securityPerfect of dataSecret communicationSecuring communicationPlaintextComputer hardware
This present application relates to data encryption and decryption technology, and especially relates to a data encryption and decryption method and apparatus. The described encryption method comprises: packeting plaintext data to be encrypted, randomly assigning an encryption function an encryption key to each group of the plaintext data, encrypting each group of the plaintext data with the encryption function and key respectively, and arranging the encrypted data according to its corresponding position in the plaintext data to form a ciphertext. The encryption apparatus includes: packet module, encryption function and key random assignment module and encryption processing module. This application also provides a data decryption method and apparatus. This invention randomly assigns an encryption function and encryption key to the plaintext to be encrypted, and uses the assigned encryption function and key to encrypt the plaintext data to arrange and form a ciphertext, greatly strengthening the security of data storage, and achieving the perfect secrecy of data.
Owner:BEIJING Z & W TECH CONSULTING
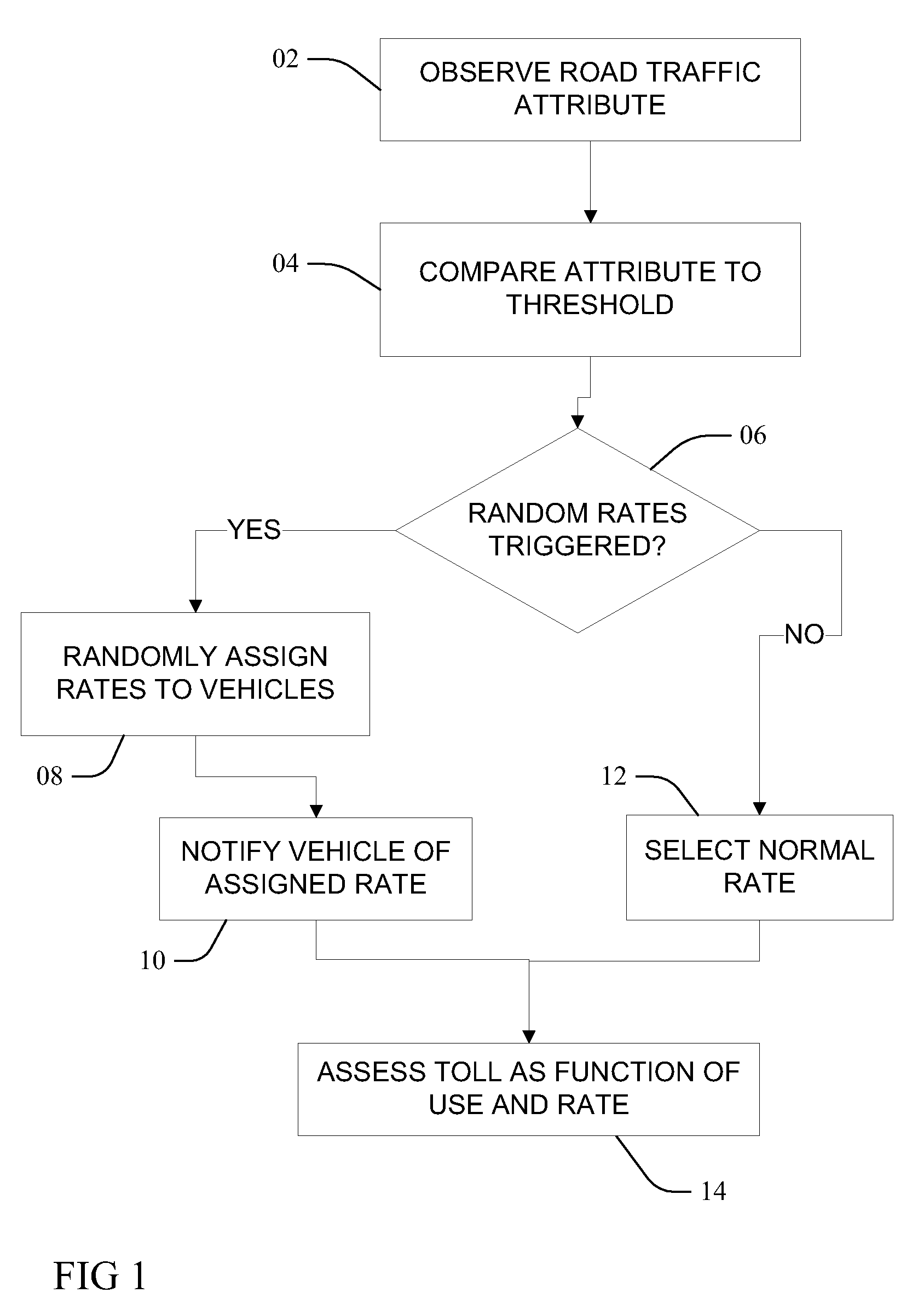
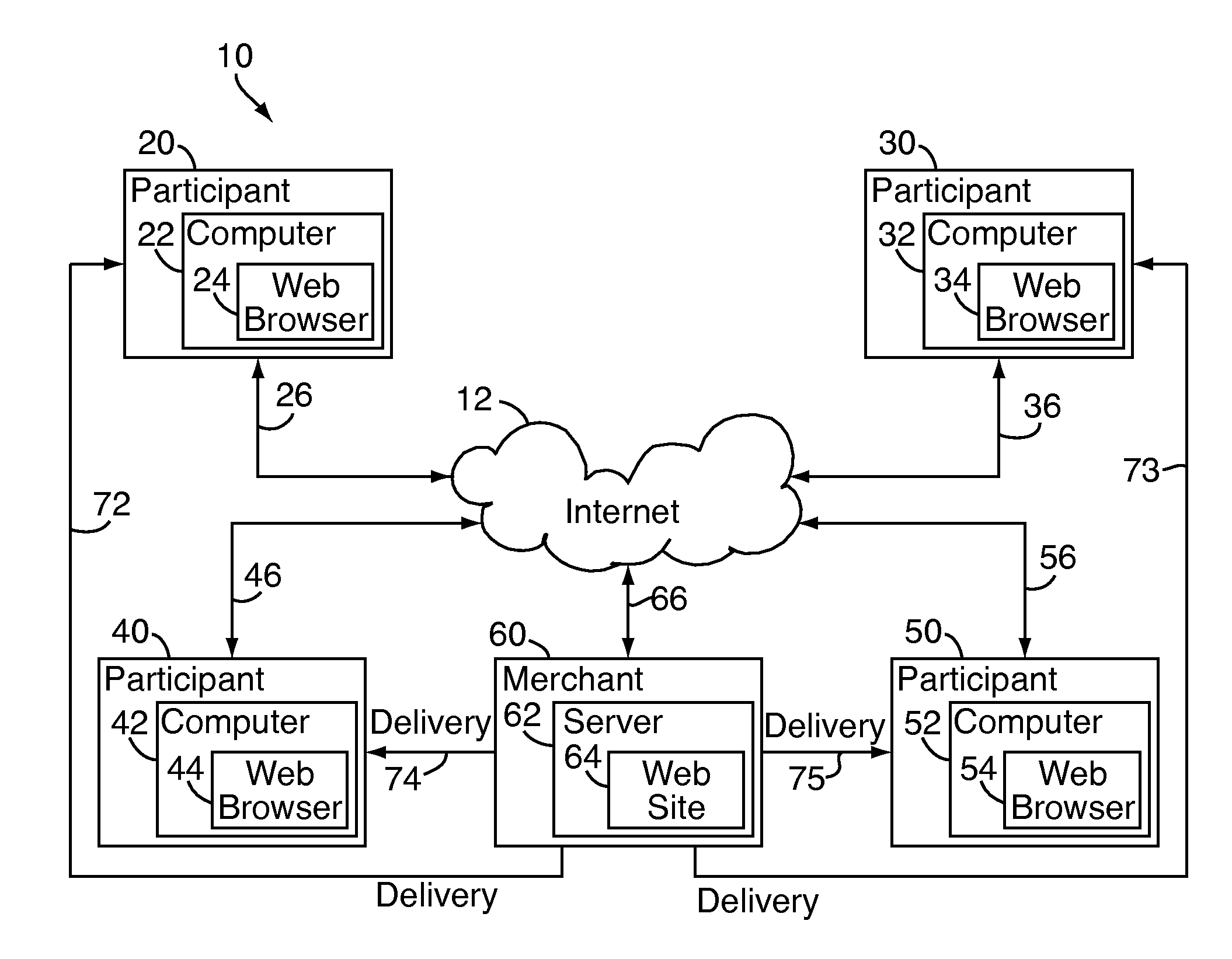
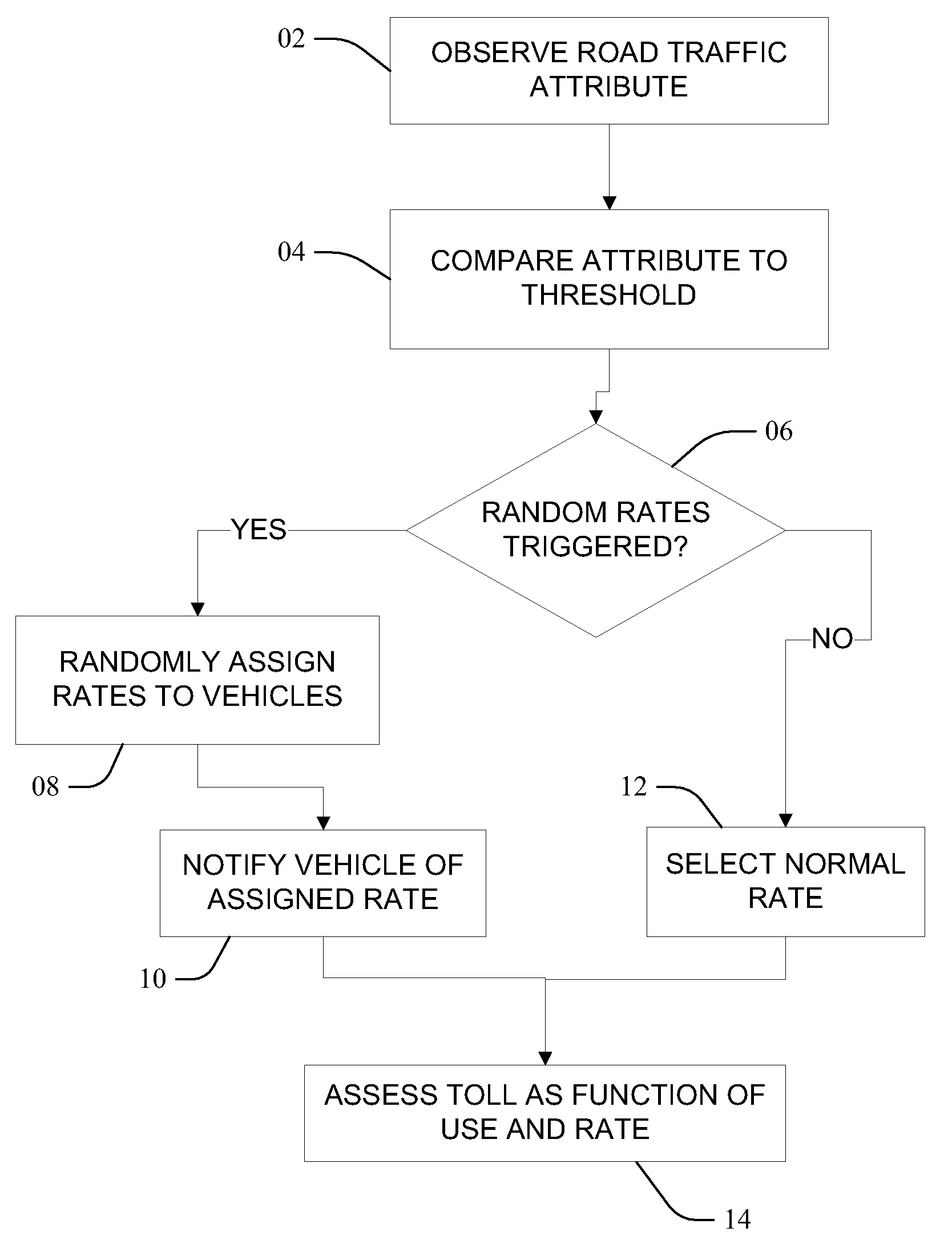
Random and deterministic travel fees
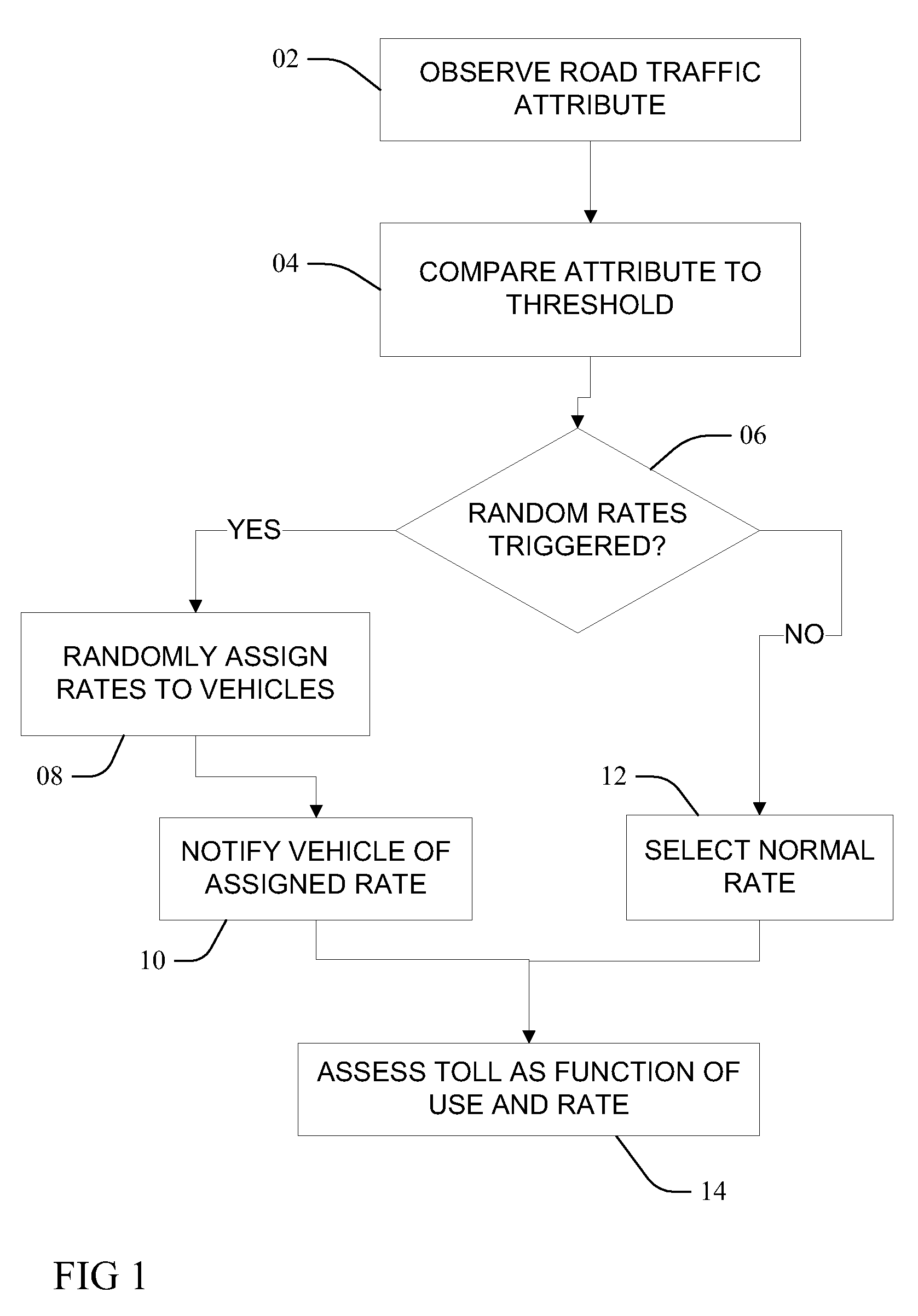
InactiveUS8200529B2Ticket-issuing apparatusRoad vehicles traffic controlRandom assignmentReal-time computing
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
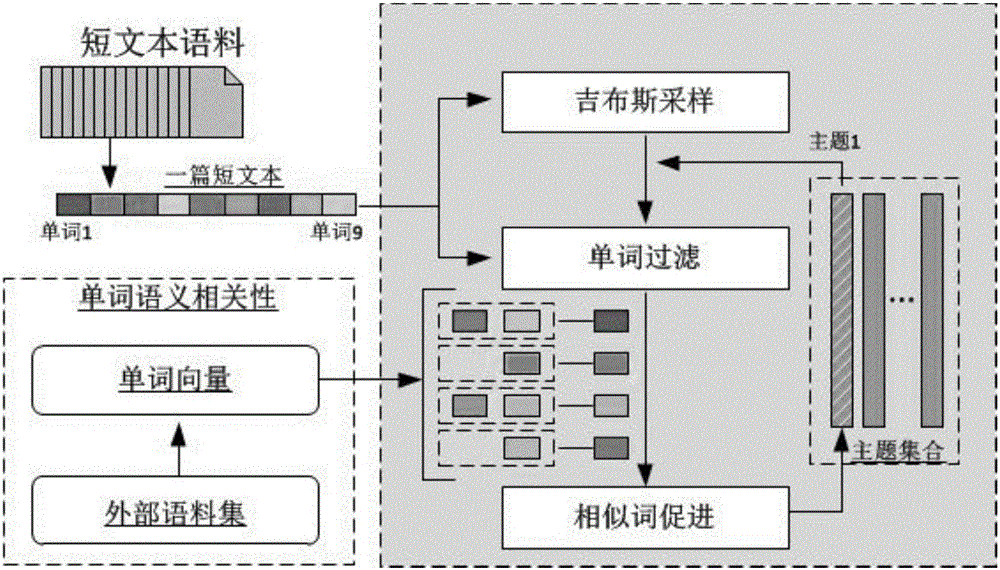
Short text topic modeling method based on word semantic similarity
ActiveCN105955948AImprove classificationImprove clustering accuracySemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorGibbs sampling
The invention discloses a short text topic modeling method based on word semantic similarity. The method comprises: according to word semantic similarity provided by external, establishing a similar word set of short text centralized words; determining the number of topics used in modeling; randomly distributing the topic of each short text; through a Gibbs sampling process, iteratively determining the topic of each short text and the distribution of the words in the topic; according to a final distribution result of the above variable, feeding back the word distribution under each topic and the topic associated to each short text. The method preferably solves problems of sparse information contents of short texts and unclear semantic expression. According to the model result, short texts can be preferably expressed as topic vectors, and the topic vectors are used as final feature vectors of a short essay. The topic vector-based expression has good semantic interpretability, and can be used as algorithm basis of various applications. The method can be widely applied in various short text data, and has wide actual meaning and commercial values.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
System and method for group gift exchanges
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
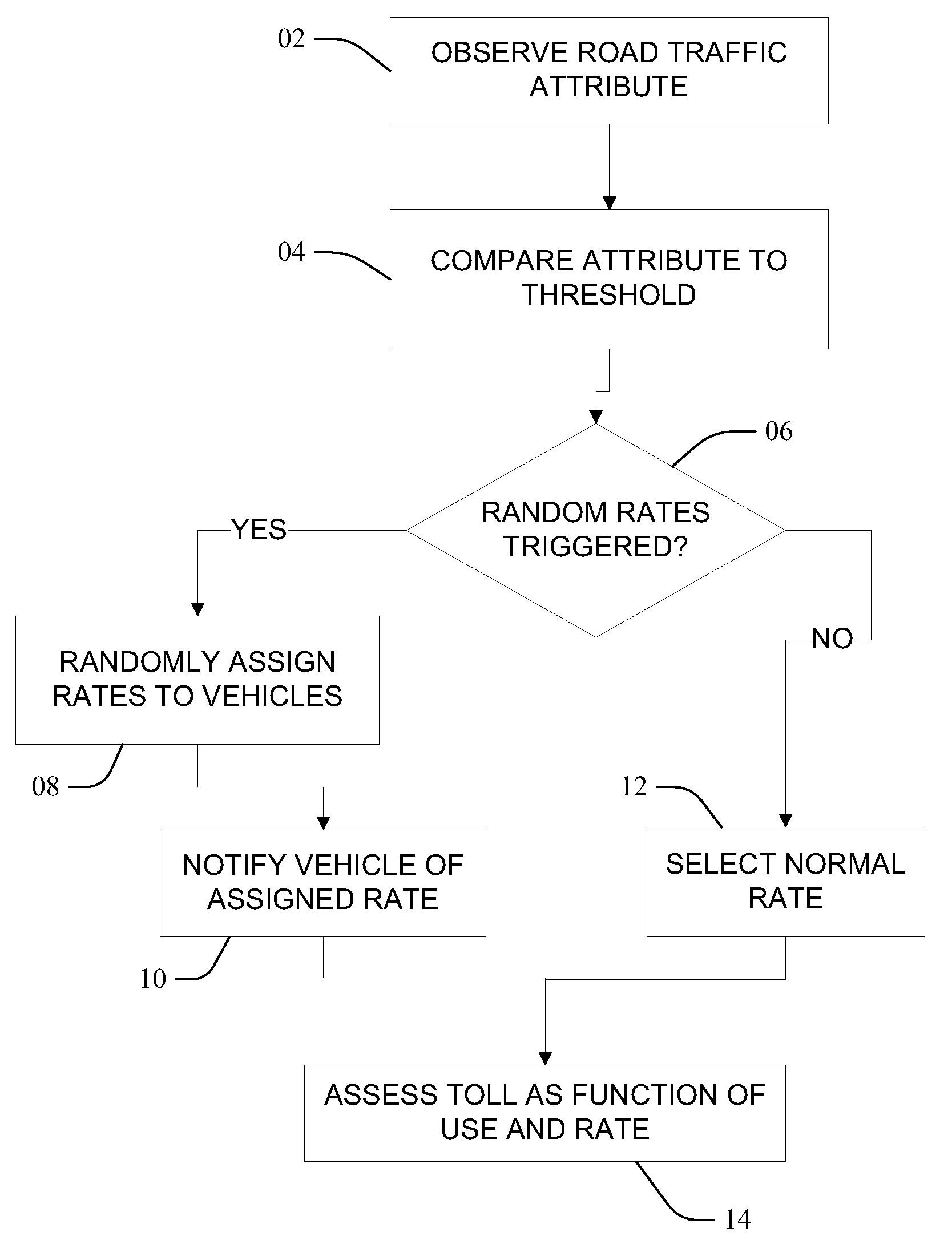
Random and deterministic travel fees
InactiveUS20100153125A1Ticket-issuing apparatusRoad vehicles traffic controlToll roadRandom assignment
Methods, including service methods, articles of manufacture, systems, articles and programmable devices are provided for randomly setting a travel fee. A usage attribute of vehicle traffic travelling upon a toll thoroughfare is observed and compared to a threshold. As a function of comparing the attribute to the threshold, a plurality of different toll rates are randomly assigned to each of a plurality of vehicles, each of the vehicles either travelling upon the toll thoroughfare or potentially entering the toll thoroughfare. An occupant of a vehicle is notified of a toll rate randomly assigned, and fees or credits associated with travel by the occupant's vehicle are charged (levied or awarded) at the randomly assigned toll rate.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method of Lottery Wagering on Real-World Events
InactiveUS20110098096A1Enhance current lottery systemIncrease salesOther printing matterLottery apparatusRandom assignmentComputer science
Owner:ODOM JAMES M +1
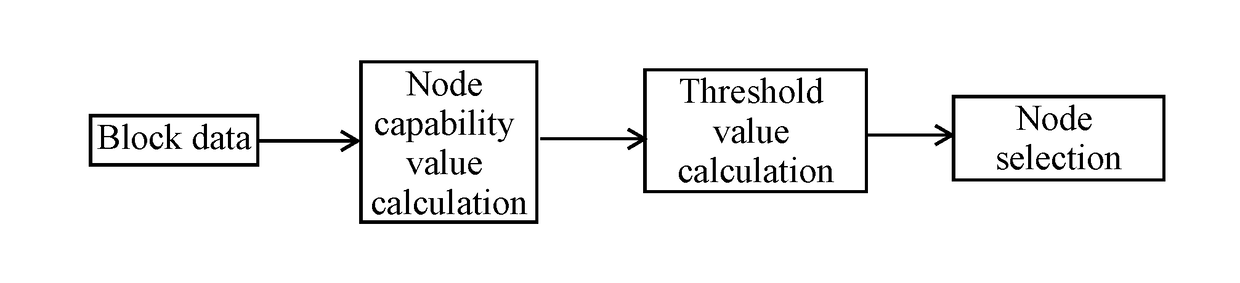
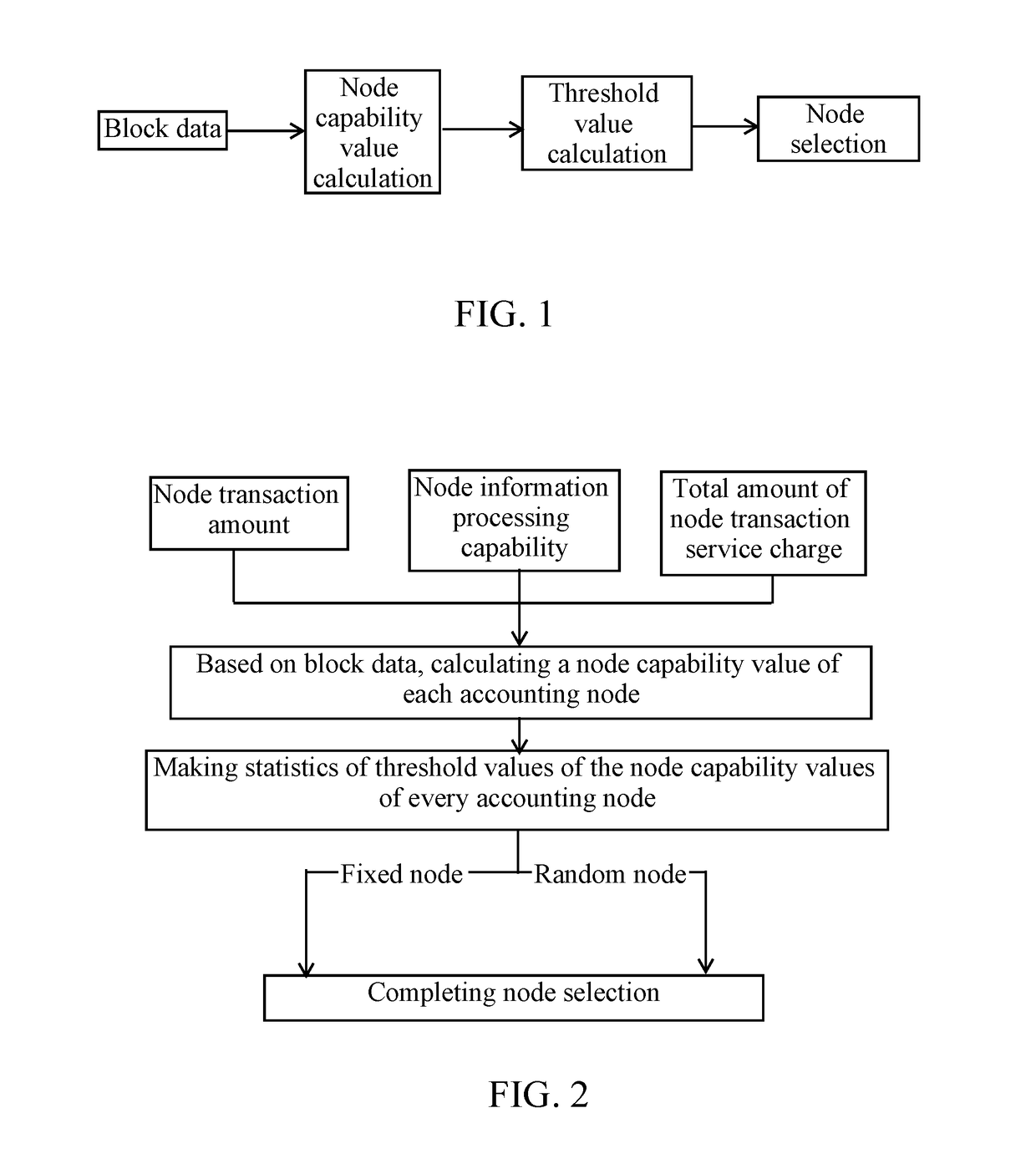
Method for intelligently selecting accounting node of blockchain
InactiveUS20180300694A1Improve securityGreat transaction amountCryptography processingDigital data protectionRandom assignmentData mining
A method for intelligently selecting an accounting node of a blockchain, relating to fields of blockchain, virtual currency and artificial intelligence, is provided, including steps of: (1), based on block data, calculating a node capability value of each accounting node; (2), making statistics of threshold values of the node capability values of every node; and (3), according to the threshold values, determining a current accounting node, and thereafter randomly selecting other nodes, so as to complete node selection. According to the present invention, based on block data and miner data of various dimensions, an intelligent distribution mechanism of accounting rights or mining rights is adopted; and meanwhile, a random distribution of accounting rights or mining rights is also adopted for avoiding hacker attacks. Therefore, on a premise of guaranteeing fairness, decentration and safety of the blockchain, problems of energy waste and low accounting efficiency due to mining conflict are solved.
Owner:BEIJING EASY AI TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
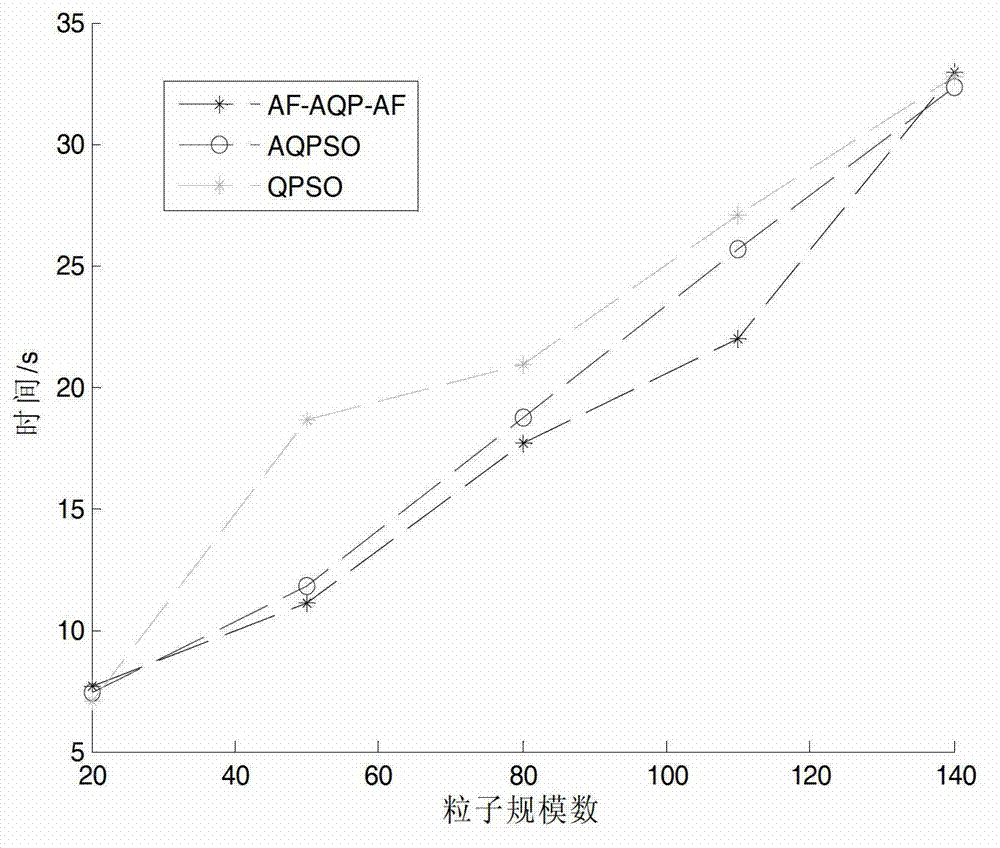
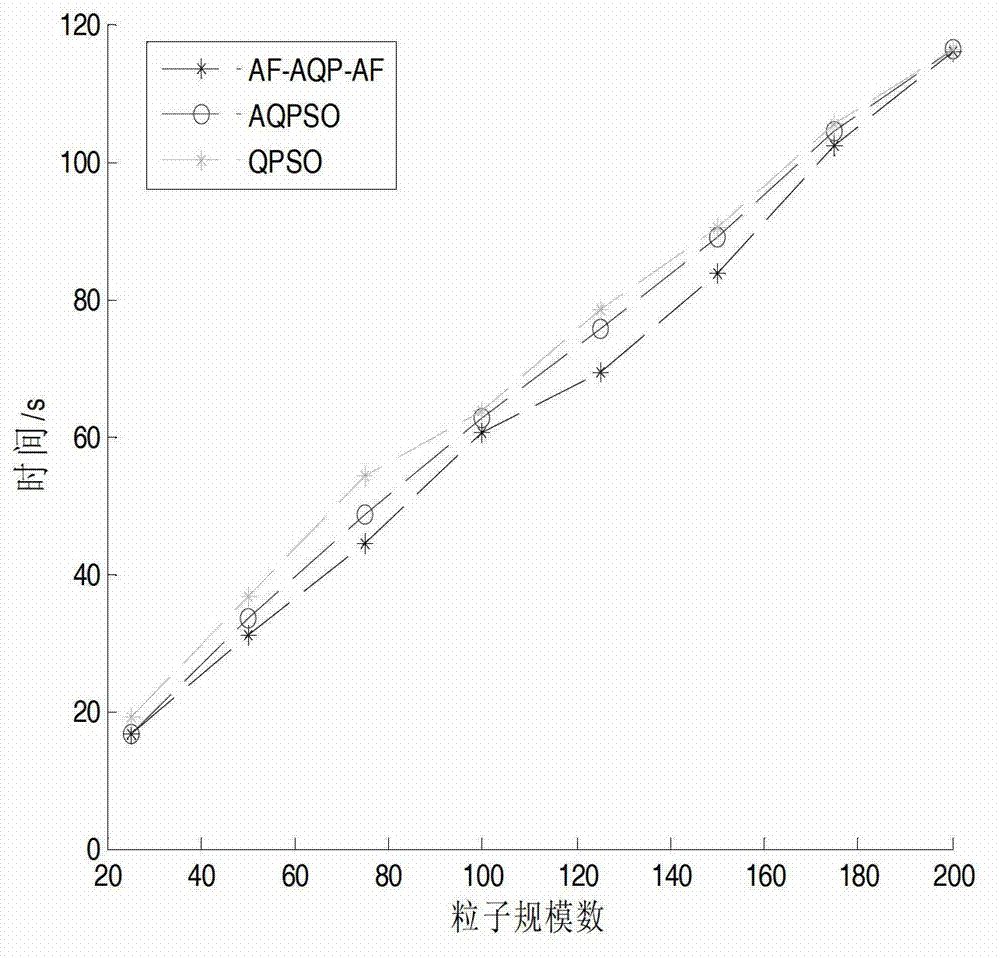
Improved fuzzy C-mean clustering method based on quantum particle swarm optimization
ActiveCN102831474AImprove Fuzzy AccuracyImprove convergence accuracyBiological modelsCanopy clustering algorithmCluster algorithm
The invention relates to a clustering method, in particular relates to an improved fuzzy C-mean clustering method based on quantum particle swarm optimization, and belongs to the technical field of data mining and artificial intelligence. The improved fuzzy C-mean clustering method comprises the steps of: firstly, based on the conventional fuzzy C-mean clustering algorithm, improving the fuzzy accuracy of the conventional clustering algorithm by using a novel distance standard in place of a Euclidean standard; meanwhile classifying singly and quickly through using an AFCM (Adaptive Fuzzy C-means) algorithm to replace a randomly distributed initial clustering center to reduce the sensitivity of the clustering algorithm on the initial clustering center; and finally, introducing a QPSO (AQPSO (Adaptive-Quantum Particle Swarm Optimization)) parallel optimization concept based on distance improvement in a clustering process, so that the clustering algorithm has relatively strong overall search capability, relatively high convergence precision, and can guarantee the convergence speed and obviously improve the clustering effect.
Owner:重庆高新技术产业研究院有限责任公司
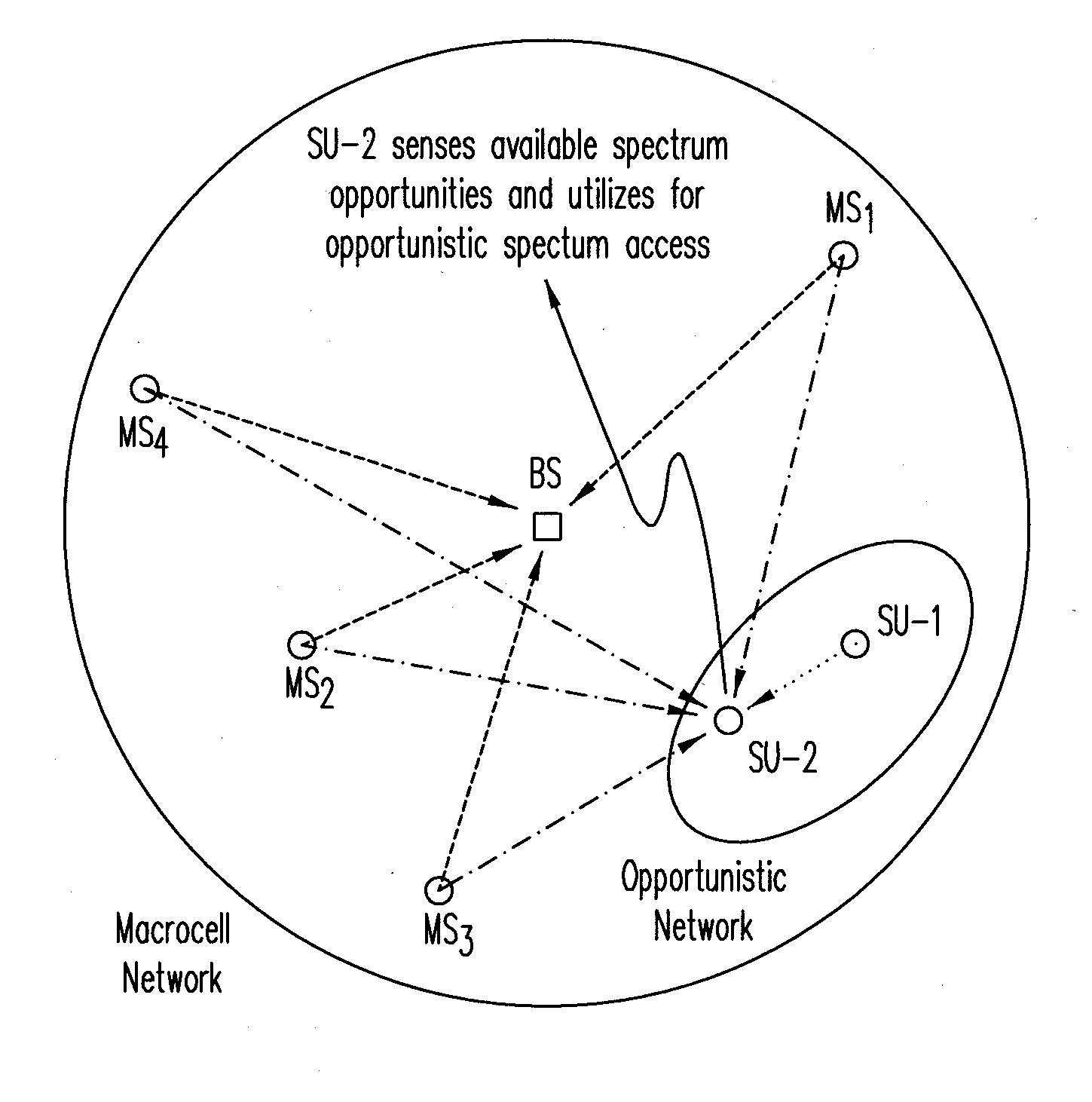
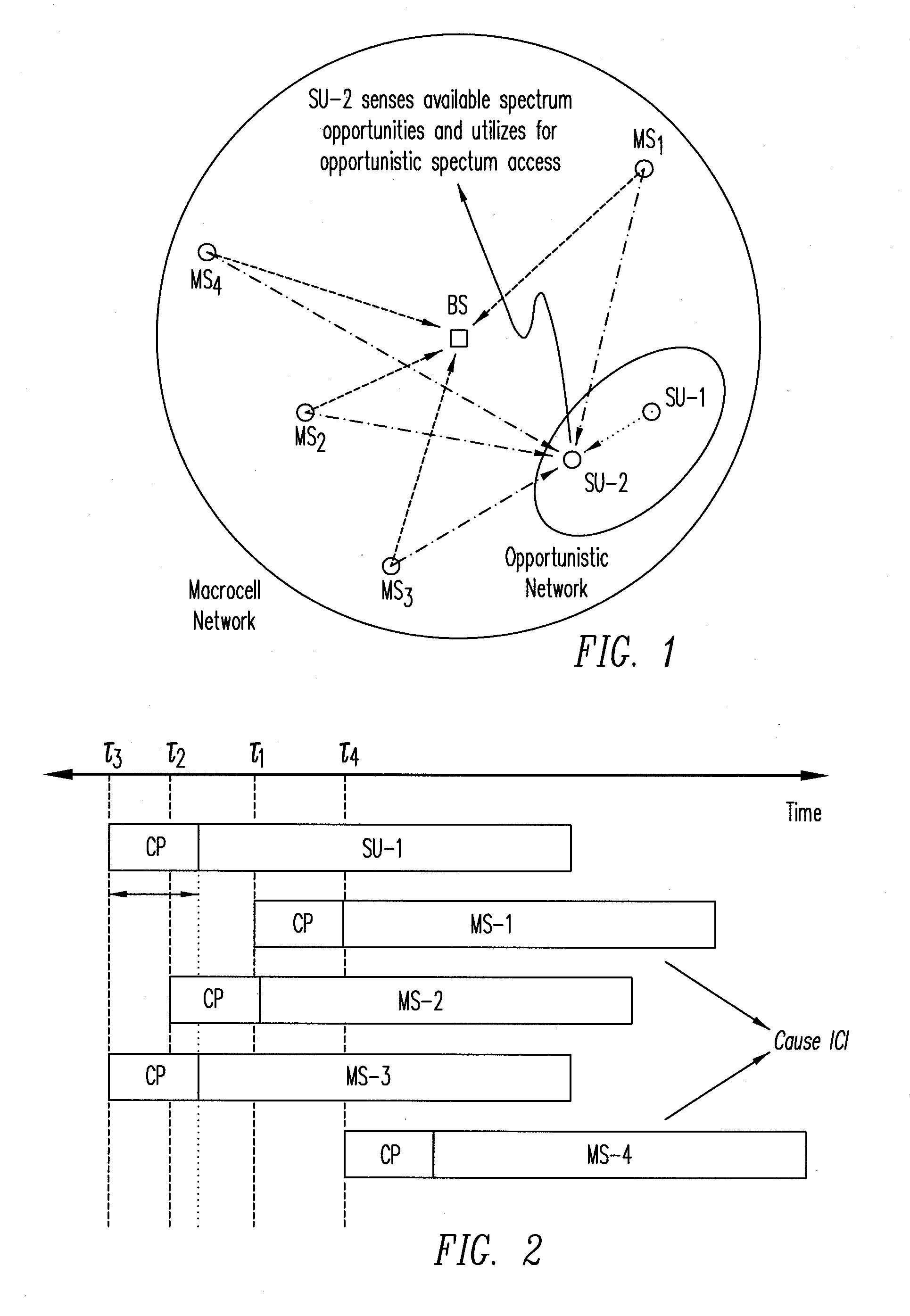
Method for interference-minimizing resource block-size selection at a macrocell, a microcell and a femtocell
ActiveUS20100056167A1Avoid interferenceWasteTransmission path divisionNetwork topologiesFrequency spectrumResource block
A method for an opportunistic network within a coverage area of a primary network includes (a) spectrum-sensing signals from users in the primary network to identify unused spectrum resources in a spectrum shared between the opportunistic network and the primary network; and (b) based on the spectrum resources identified, assigning the identified spectrum resources to be used among the users of the opportunistic network in one or more block sizes determined from expected interference from the users of the primary network. The method is applicable to a primary network whether or not spectrum resources are assigned to its users using a block-wise subcarrier assignment scheme or a randomized allocation scheme. The identified unused spectrum resources that are to be assigned to the users of the opportunistic network exclude un-used subcarriers adjacent to subcarriers used by the users of the primary network to avoid interference. The opportunistic network may assign the identified unused spectrum resources using a scheme that selects a block size for an adaptive modulation and coding scheme or for avoidance of waste of spectrum resources.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Data Encryption and Decryption Method and Apparatus
InactiveUS20120134492A1Improve data securityPerfect of dataMultiple keys/algorithms usageSecret communicationComputer hardwarePlaintext
This present application relates to data encryption and decryption technology, and especially relates to a data encryption and decryption method and apparatus. The described encryption method comprises: packeting plaintext data to be encrypted, randomly assigning an encryption function to each group of the plaintext data, encrypting each group of the plaintext data with the encryption function respectively, and arranging the encrypted data according to its corresponding position in the plaintext data to form a ciphertext. The encryption apparatus includes: packet module, encryption function random assignment module and encryption processing module. This application also provides a data decryption method and apparatus. This invention randomly assigns an encryption function to the plaintext to be encrypted, and uses the assigned encryption function to encrypt the plaintext data to arrange and form a ciphertext, greatly strengthening the security of data storage, and achieving the perfect secrecy of data.
Owner:BEIJING Z & W TECH CONSULTING
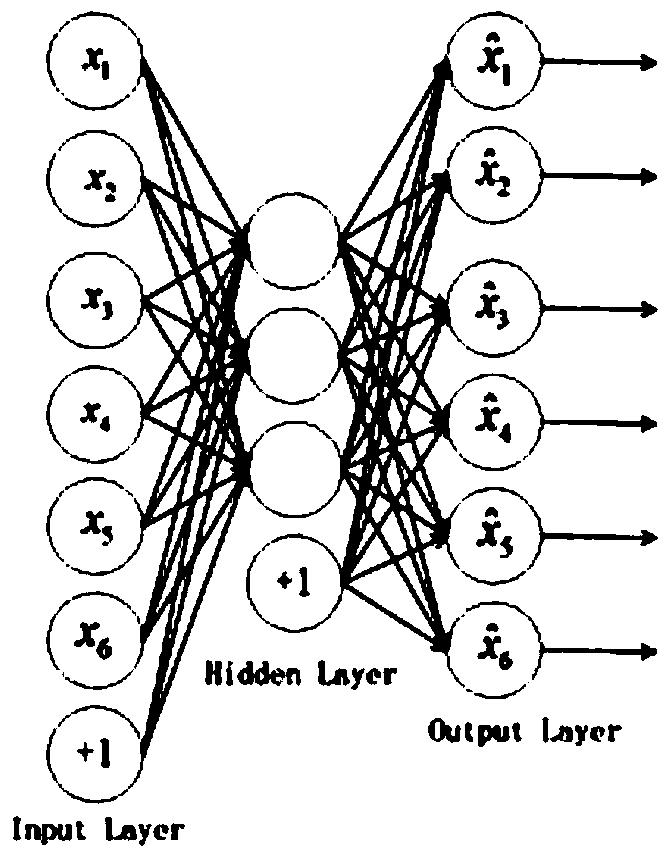
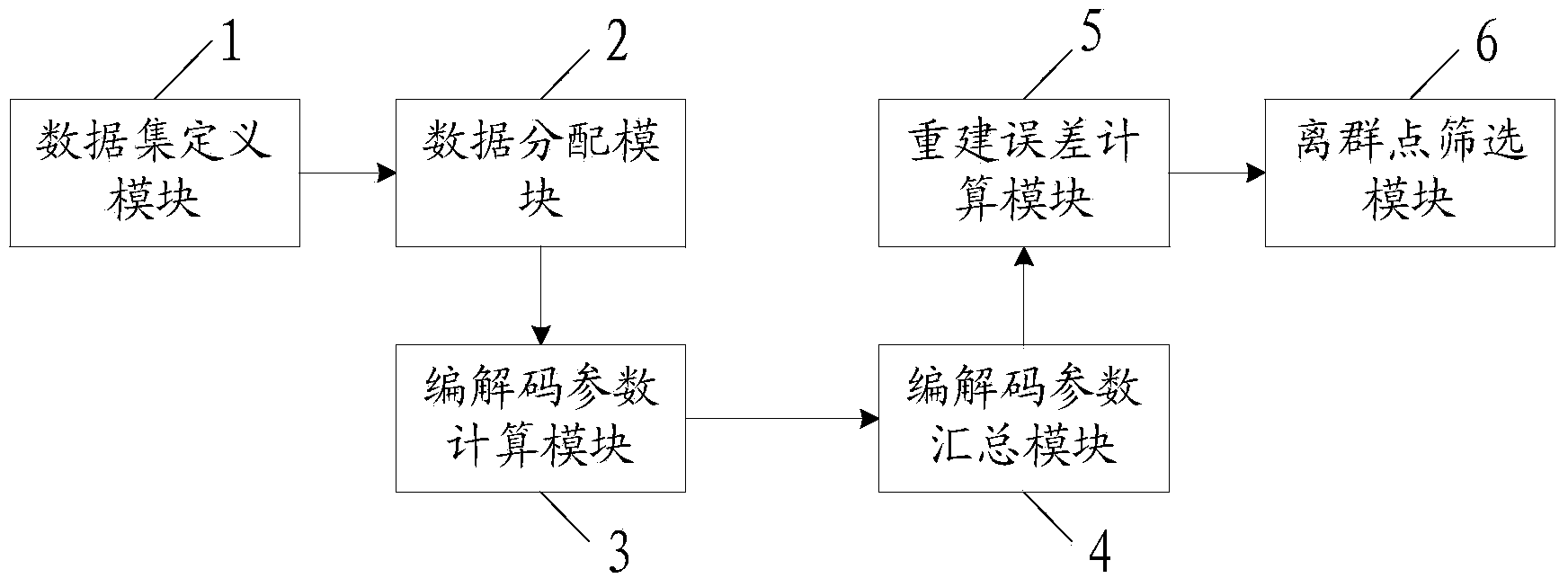
Distributed outlier detection method and system based on automatic coding machine
InactiveCN104008420AReduce computing timeImprove flexibilityNeural learning methodsData setRandom assignment
The invention relates to a distributed outlier detection method and system based on an automatic coding machine. The method includes the steps that a training data set and a testing data set are defined; training data of the training data set are distributed to a plurality of calculation units randomly; the calculation units conduct parallel execution, and each calculation unit solves coding and decoding parameters; the coding and decoding parameters of each calculation unit are summarized to obtain a final coding and decoding parameter, and a self-duplication model is built; the self-duplication model is applied to the testing data set, and concurrent computation is conducted on reconstruction errors of all testing data; the testing data are arranged according to a descending order of the reconstruction errors, and the testing data with the reconstruction errors larger than a predetermined threshold value are outliers. According to the method, the total time required for processing and the number of processed samples are independent, and the total time and the number only depend on the required accuracy of parameter solution. The distributed outlier detection method and system based on the automatic coding machine are very suitable for detecting outliers on large-scale data sets on the basis of MapReduce frameworks, and have good flexibility and good expansibility.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CAS
Information modeling and projection for geographic regions having insufficient sample size
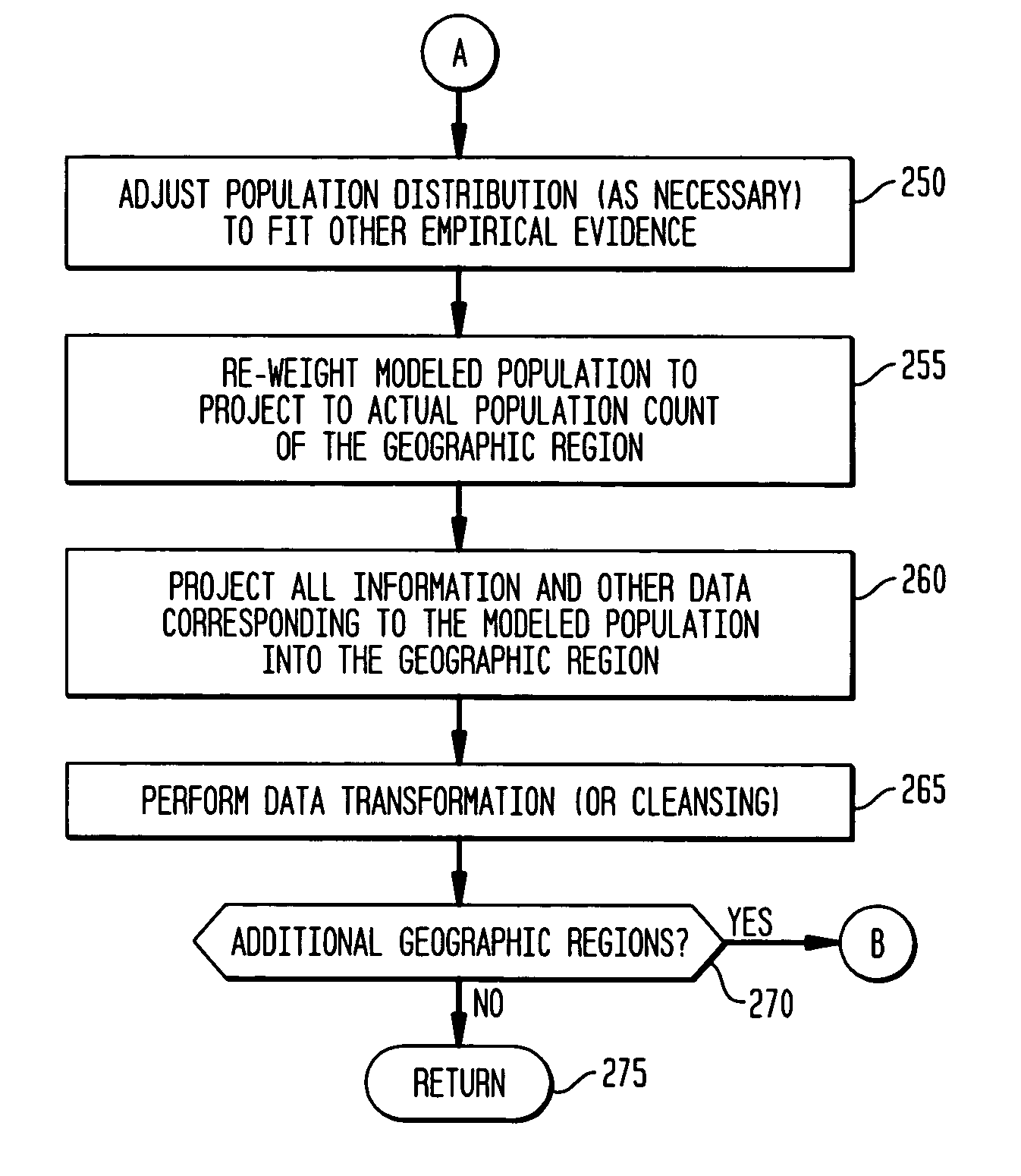
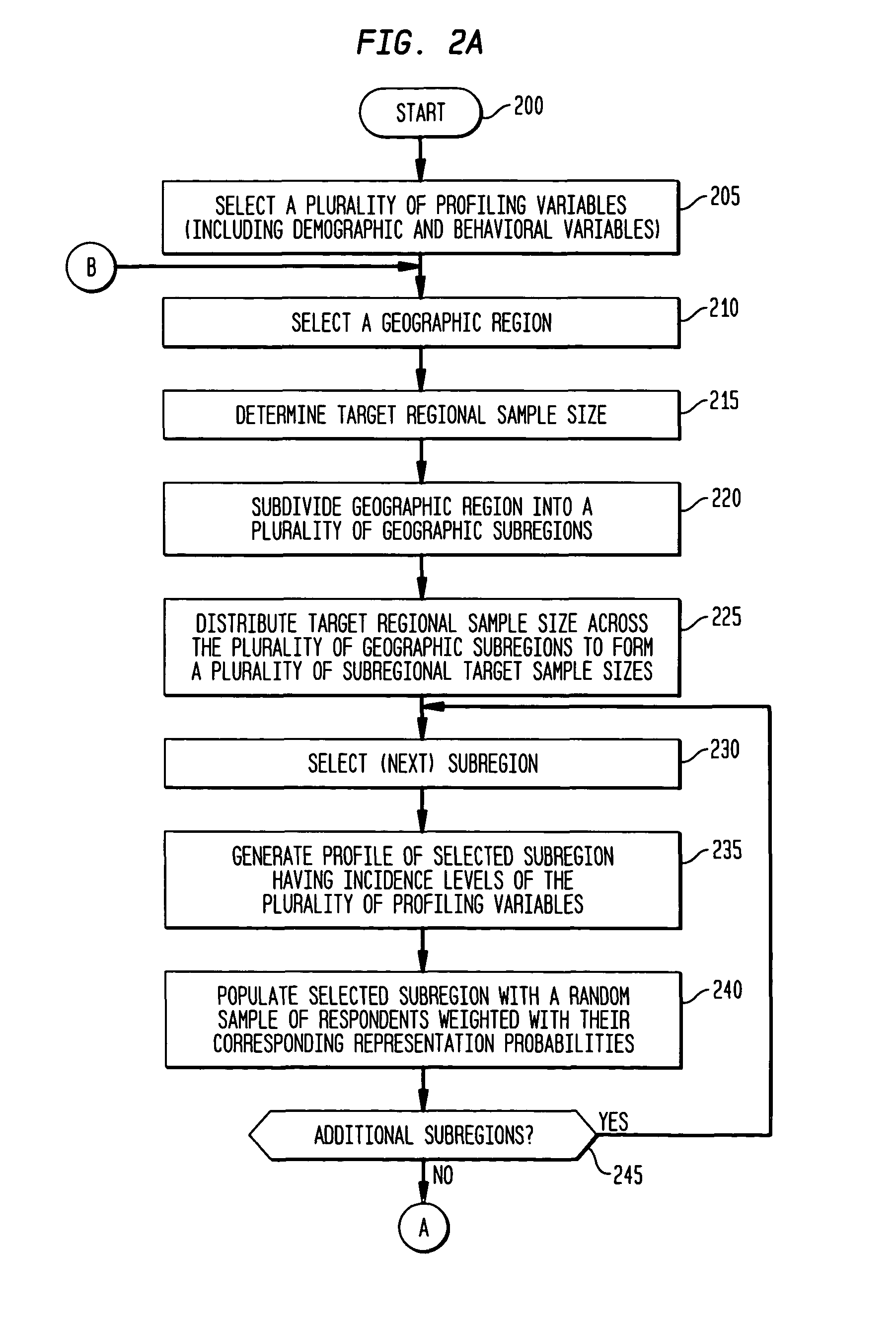
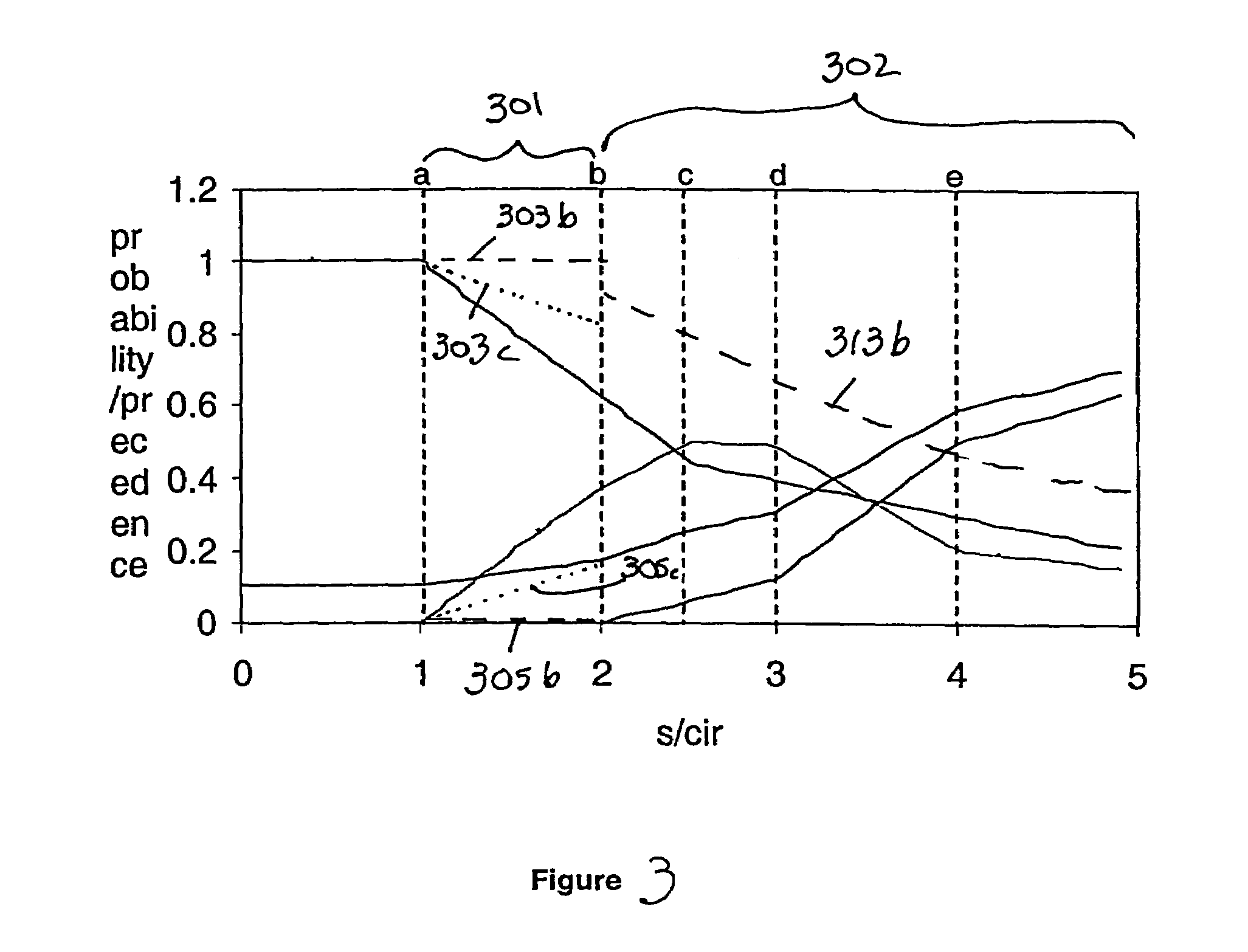
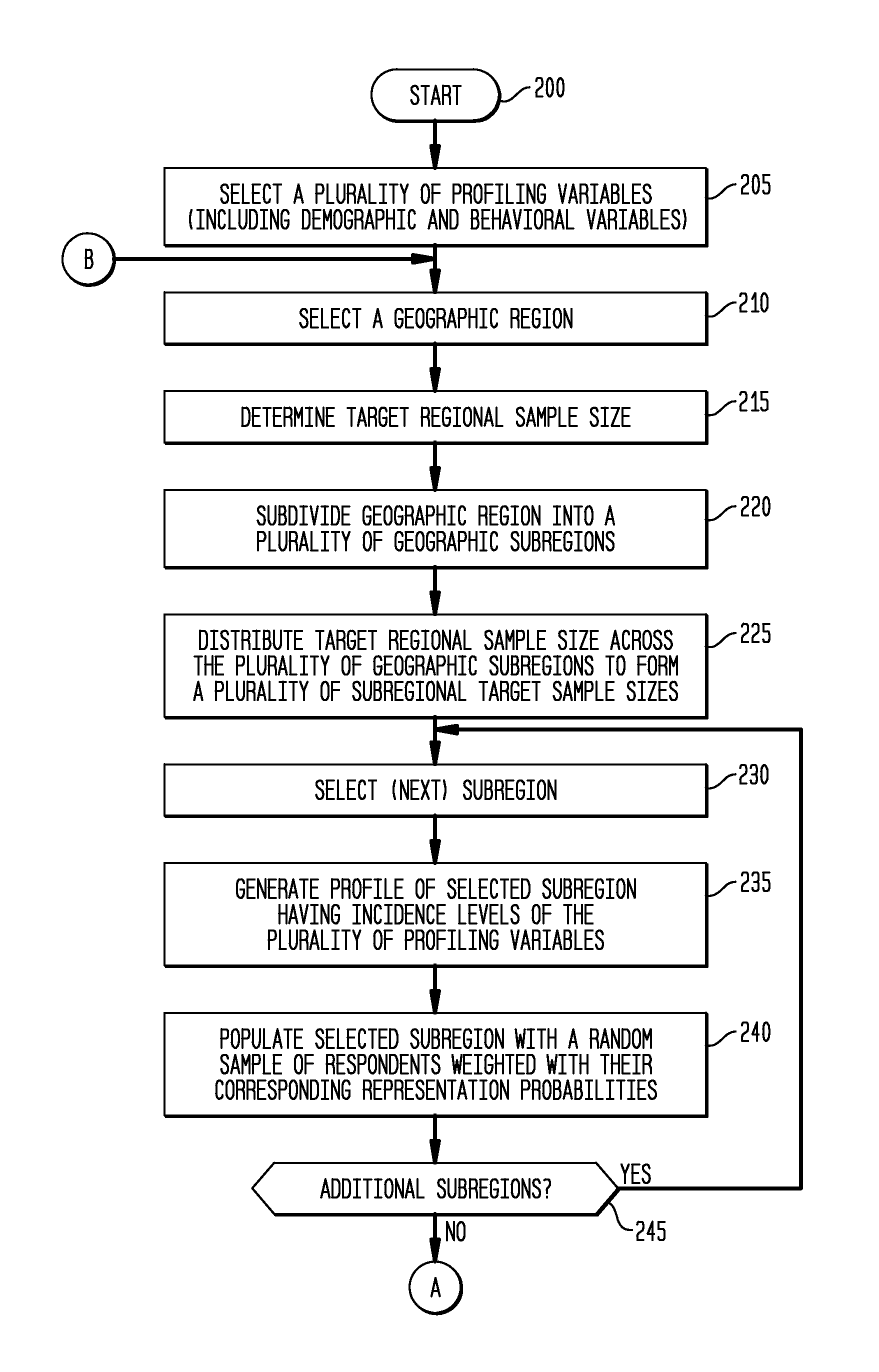
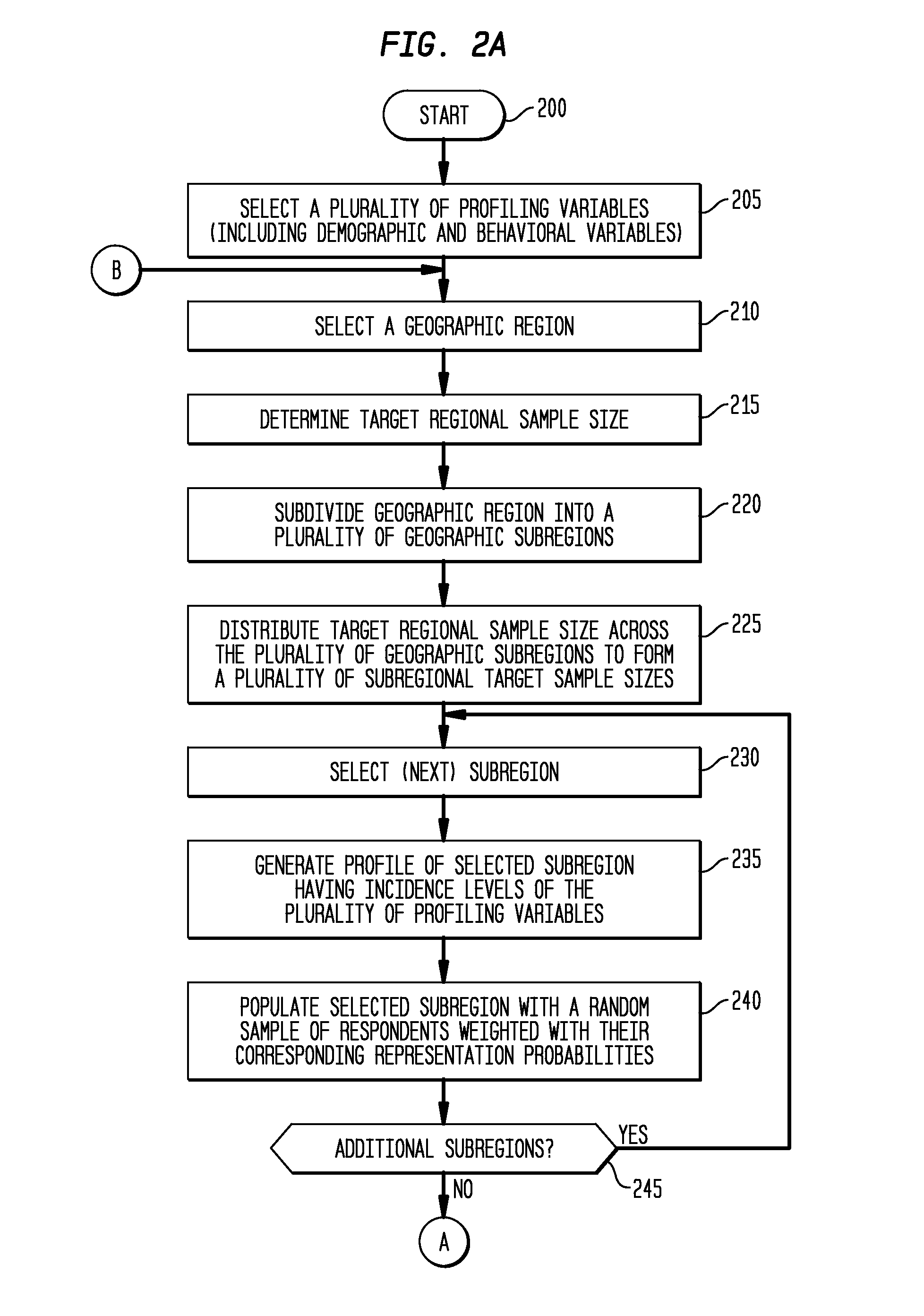
InactiveUS8341009B1Accurate projectionAccurate and representative modelingMarket predictionsGeographic regionsInsufficient Sample
The various exemplary embodiments provide a method for projecting survey information into a geographic region. The geographic region is divided into a plurality of geographic subregions, each of which are profiled using a plurality of profiling variables to form a selected geographic subregion profile. The profiling variables include both demographic and behavioral variables. A plurality of survey respondents are then randomly assigned into the selected geographic subregion to form a modeled population, with the random assignment weighted based on a representation probability of each of the corresponding plurality of survey respondents for the selected geographic subregion profile, with the representation probabilities having been determined using a sample balancing algorithm. Following such profiling and assignment for all subregions, survey information corresponding to the modeled population is projected into the geographic region.
Owner:GFK US MRI LLC
Automatic layout method for urban development land with best road accessibility
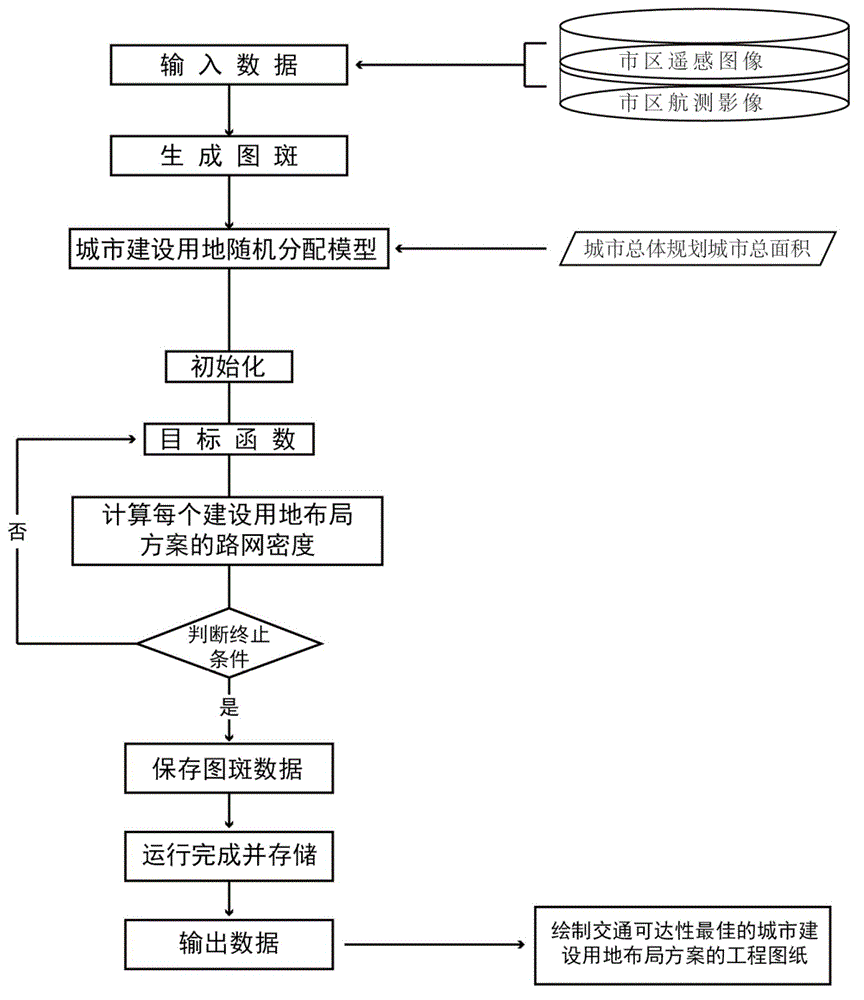
ActiveCN103150680AImprove transportation accessibilityShorten planning work timeData processing applicationsInformation processingControllability
The invention discloses an automatic layout method for urban development land. The method comprises the following steps of establishing an urban development land random distribution model by using an information processing system of which the core is a high performance computer, taking geographical data of urban areas as model input data and taking land use span pattern spots as a model processing unit, performing circulation calculation by using the random distribution model, and combining to generate all possible layout schemes of the urban development land through exhaustion; by taking road network density as a detection condition, automatically detecting the road network density of the urban development land in each layout scheme, and saving the layout scheme with the highest road network density; and automatically outputting an engineering drawing, which can be directly used by urban controllability detailed planning, by using plotting equipment. The method overcomes the defects of subjectivity and randomness generated because urban spatial layout is decided by intellectual activity of human brains in urban construction engineering practice.
Owner:南京东南大学城市规划设计研究院有限公司
Method and apparatus for random packet marking for differentiated services
InactiveUS7277388B1Improve fairnessError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDifferentiated servicesDifferentiated service
Owner:NOKIA INTERNET COMM
Information modeling and projection for geographic regions having insufficient sample size
InactiveUS8694359B2Accurate projectionAccurate and representative modelingMarket predictionsGeographic regionsInsufficient Sample
The various exemplary embodiments provide a method for projecting survey information into a geographic region. The geographic region is divided into a plurality of geographic subregions, each of which are profiled using a plurality of profiling variables to form a selected geographic subregion profile. The profiling variables include both demographic and behavioral variables. A plurality of survey respondents are then randomly assigned into the selected geographic subregion to form a modeled population, with the random assignment weighted based on a representation probability of each of the corresponding plurality of survey respondents for the selected geographic subregion profile, with the representation probabilities having been determined using a sample balancing algorithm. Following such profiling and assignment for all subregions, survey information corresponding to the modeled population is projected into the geographic region.
Owner:GFK US MRI LLC
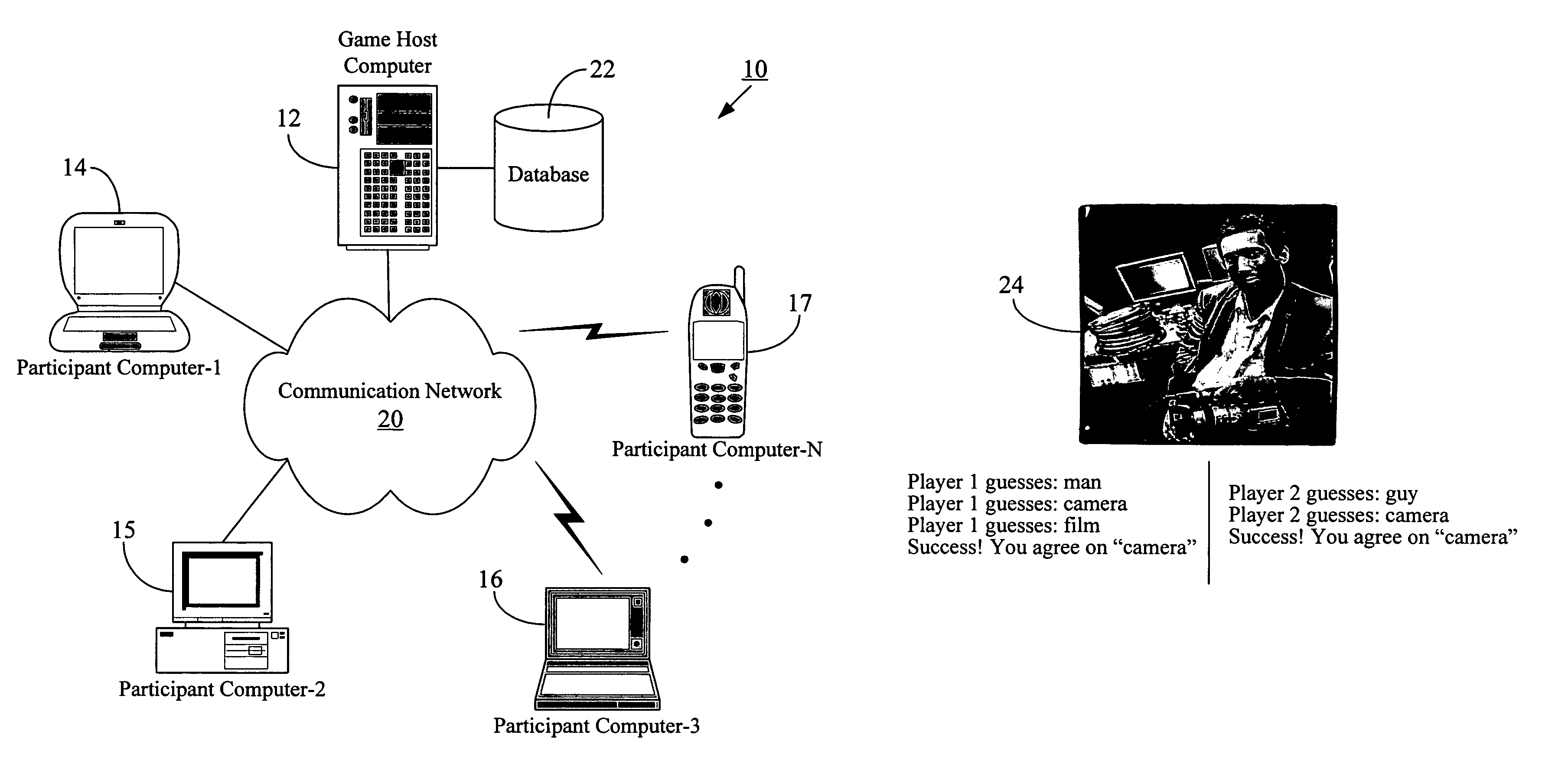
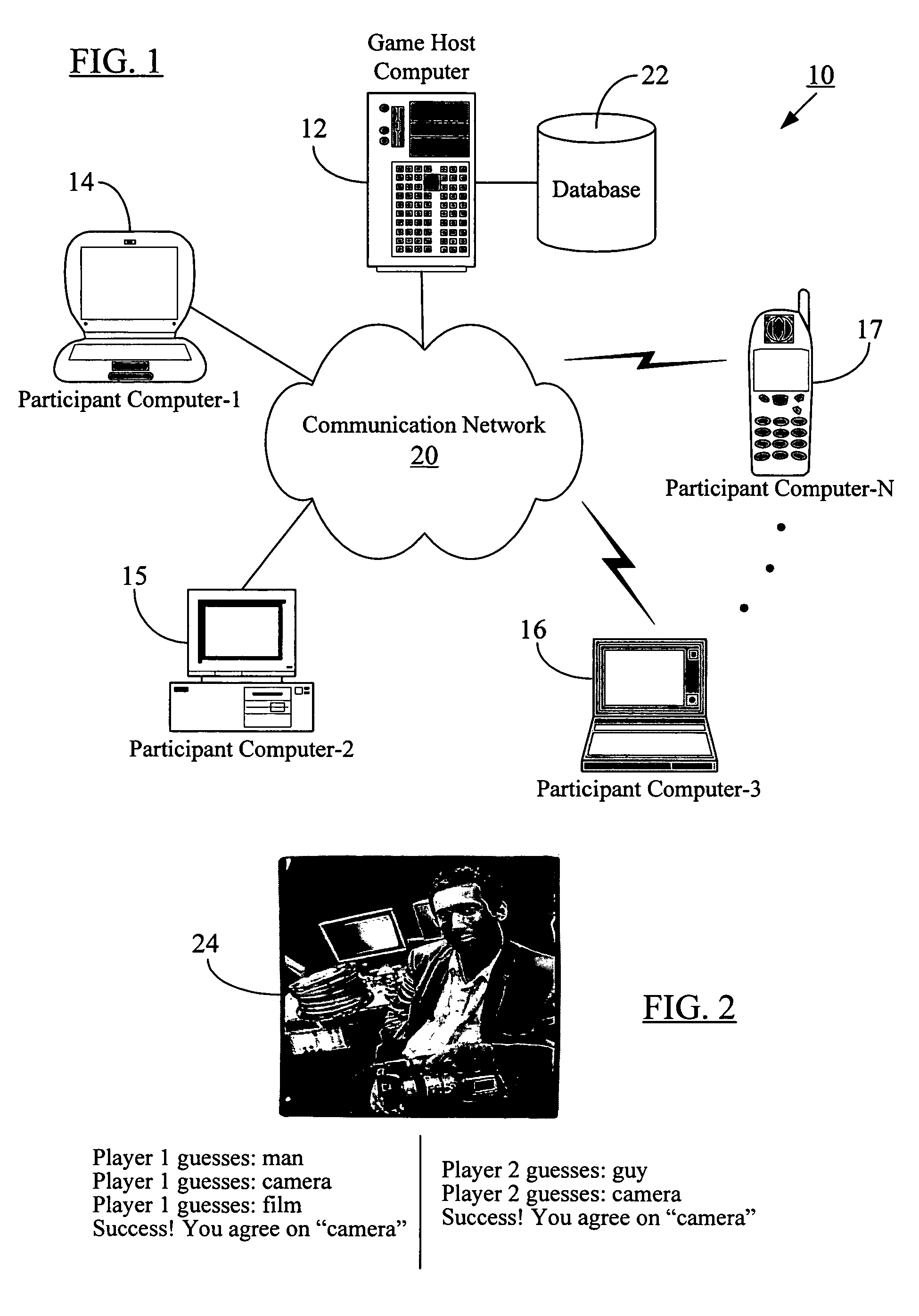
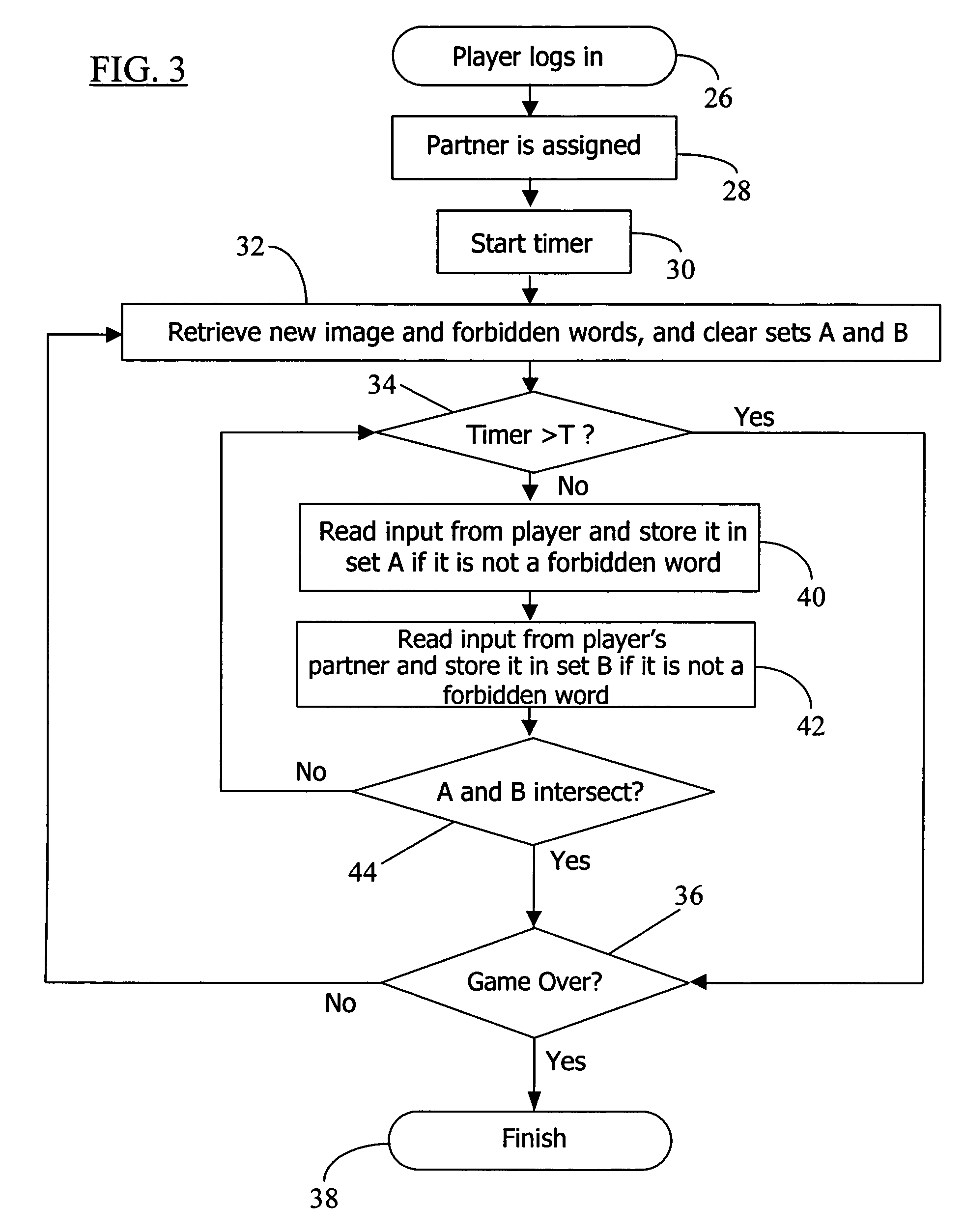
Method for labeling images through a computer game
A methodology to determine the contents of an image uses an online game that is played by a large number of people at once. Each player may be randomly assigned a partner to form a pair. Partners do not know each other's identity and cannot communicate with one another. Players cannot see what their partners are typing, and the only thing the two partners have in common is an image that they can both see. One object of the game is to have each player type exactly what his or her partner is typing or has already typed. Once both players type the same string of words or letters, they receive a new image (the players are not required to type the string at the same time). The string upon which the two players agree is used as a label for that image. When trying to agree on a word, players may not be able to type certain specific strings of characters or “forbidden words”. When humans play the electronic game (online or over the Internet), they help computers determine the contents of images. If played by a large number of people, this game could provide a resource capable of classifying a vast portion of images on the World Wide Web. Because of the rules governing abstracts, this abstract should not be used to construe the claims.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com