Method for achieving automatic configuration of IPv6 addresses for wireless sensor network
A wireless sensor and automatic configuration technology, applied in wireless network protocols, network topology, wireless communication, etc., can solve the problems of a large number of control packet overhead, consumption of storage resources, consumption of network resources, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
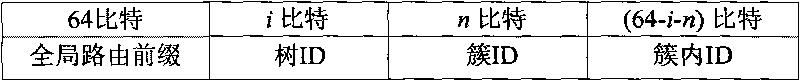
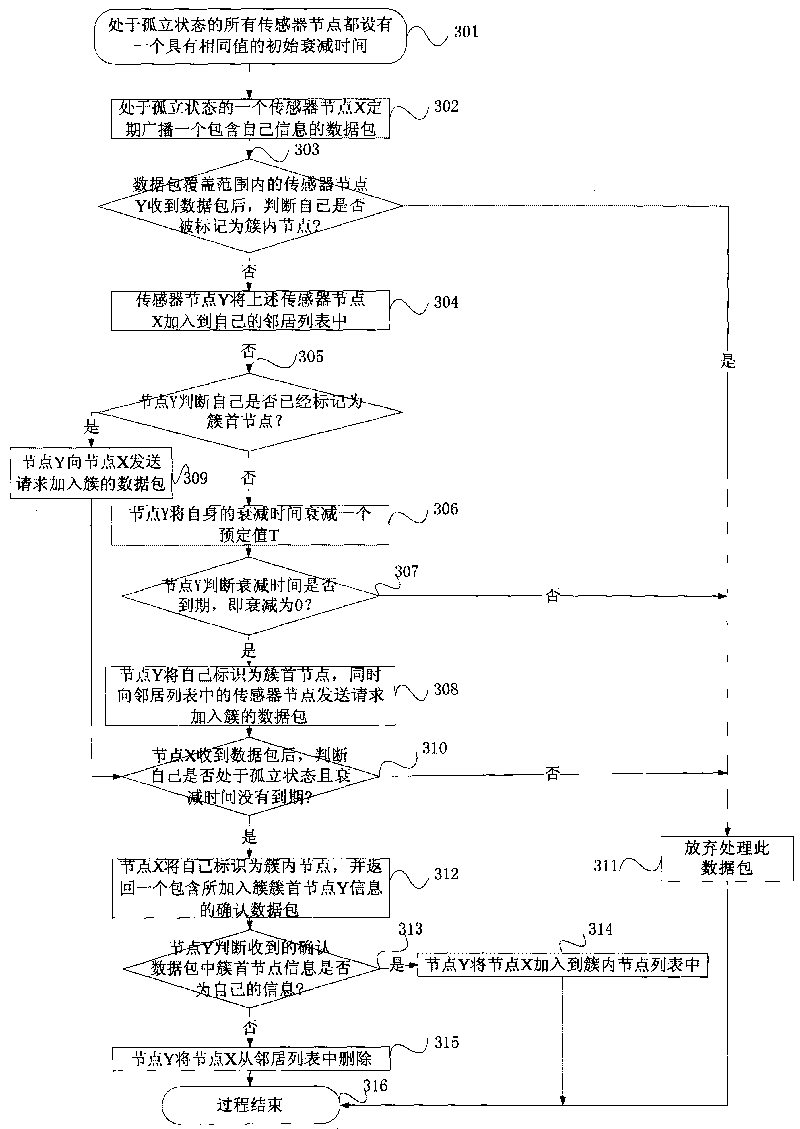
[0049] The present invention provides a method for realizing automatic configuration of a wireless sensor network IPv6 address. In the method, each sensor node in the wireless sensor network can obtain a globally unique IPv6 address, and the IPv6 network node uses the IPv6 address of the wireless sensor node Realize the communication with each other and obtain the data information collected by the sensor nodes.
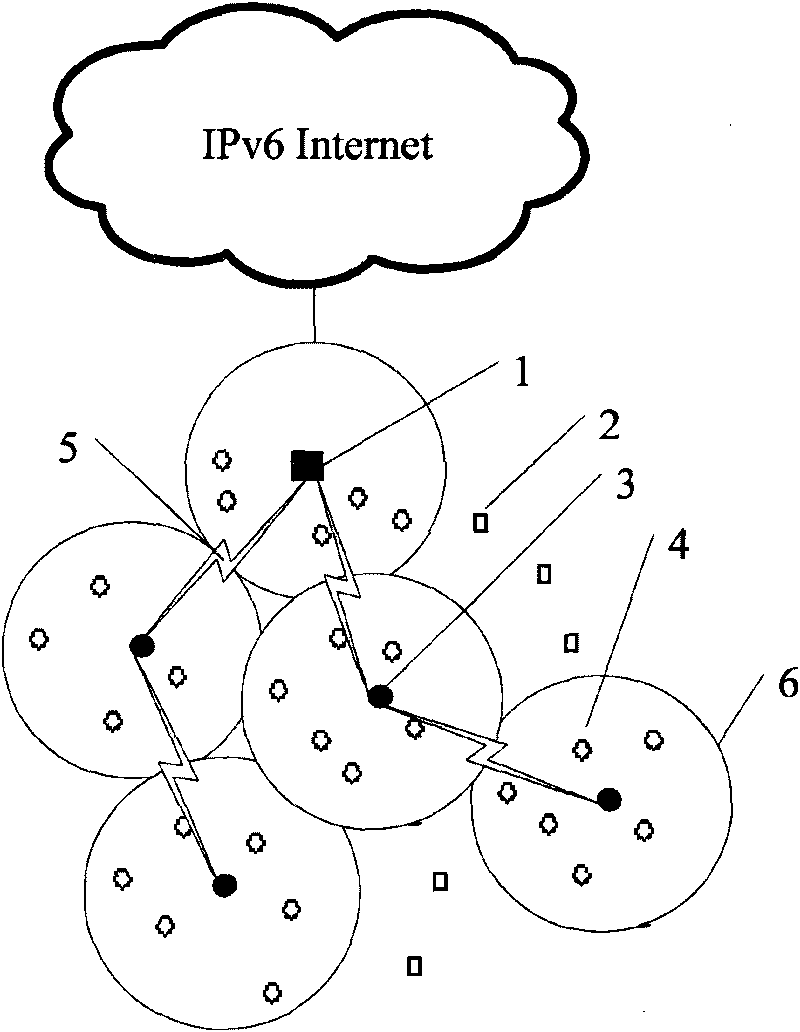
[0050] figure 1 Shown is the tree topology schematic diagram of IPv6 access node and cluster head node described in the present invention, wireless sensor network among the present invention is provided with four types of nodes: isolated sensor node 2, IPv6 access node 1, cluster head The node 3 and the node 4 in the cluster, wherein, an IPv6 access node 1 and a plurality of cluster head nodes 3 form a tree structure 5, the IPv6 access node 1 is the root node of the tree structure, and the cluster head node 3 is the The middle and leaf nodes of the tree structure, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com