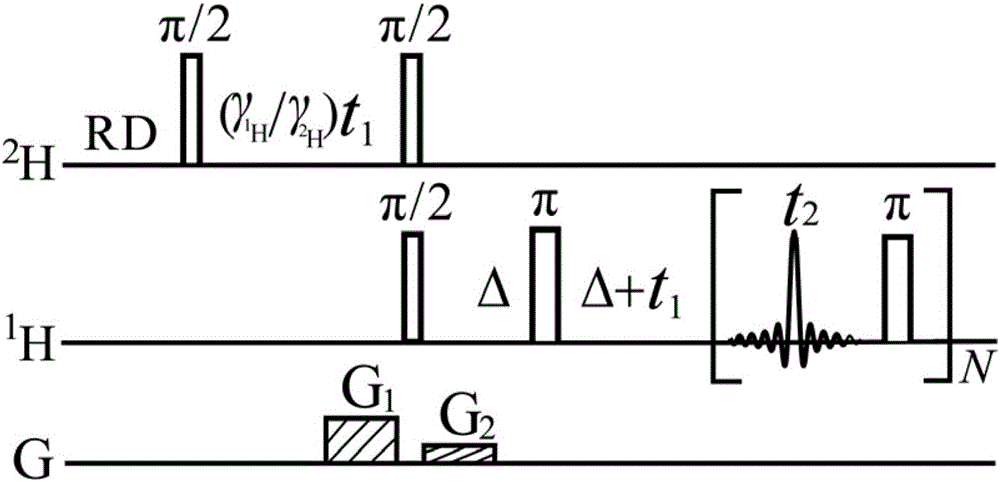
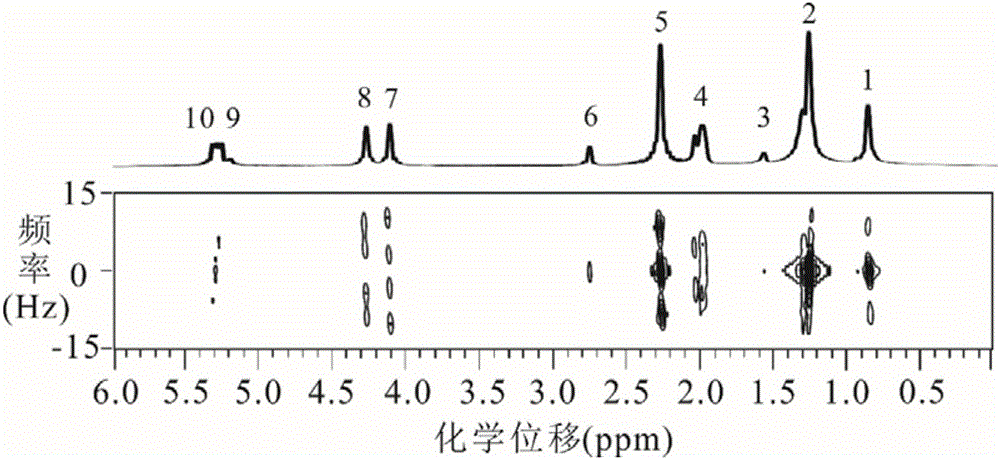
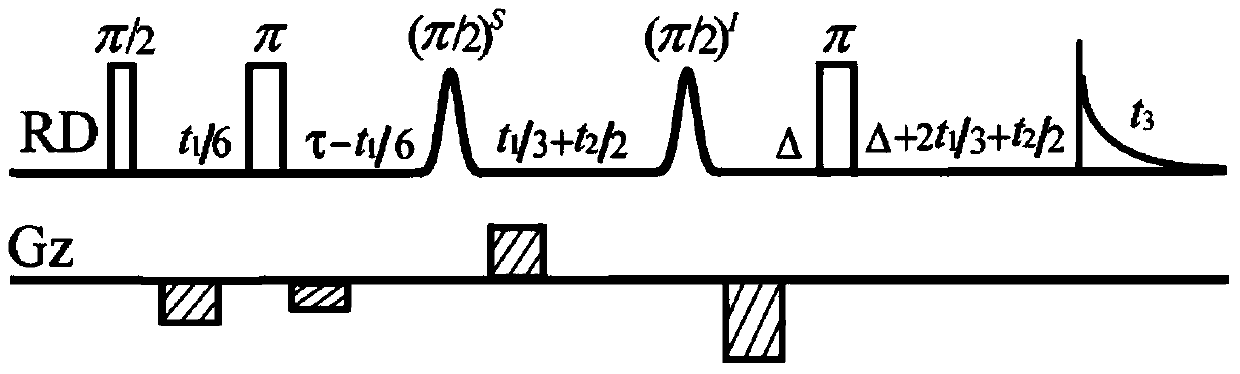
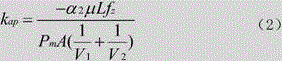Patents
Literature
332 results about "Nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, a machine called a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer is used to obtain information about the type, number, and arrangement of nuclei within a given sample.
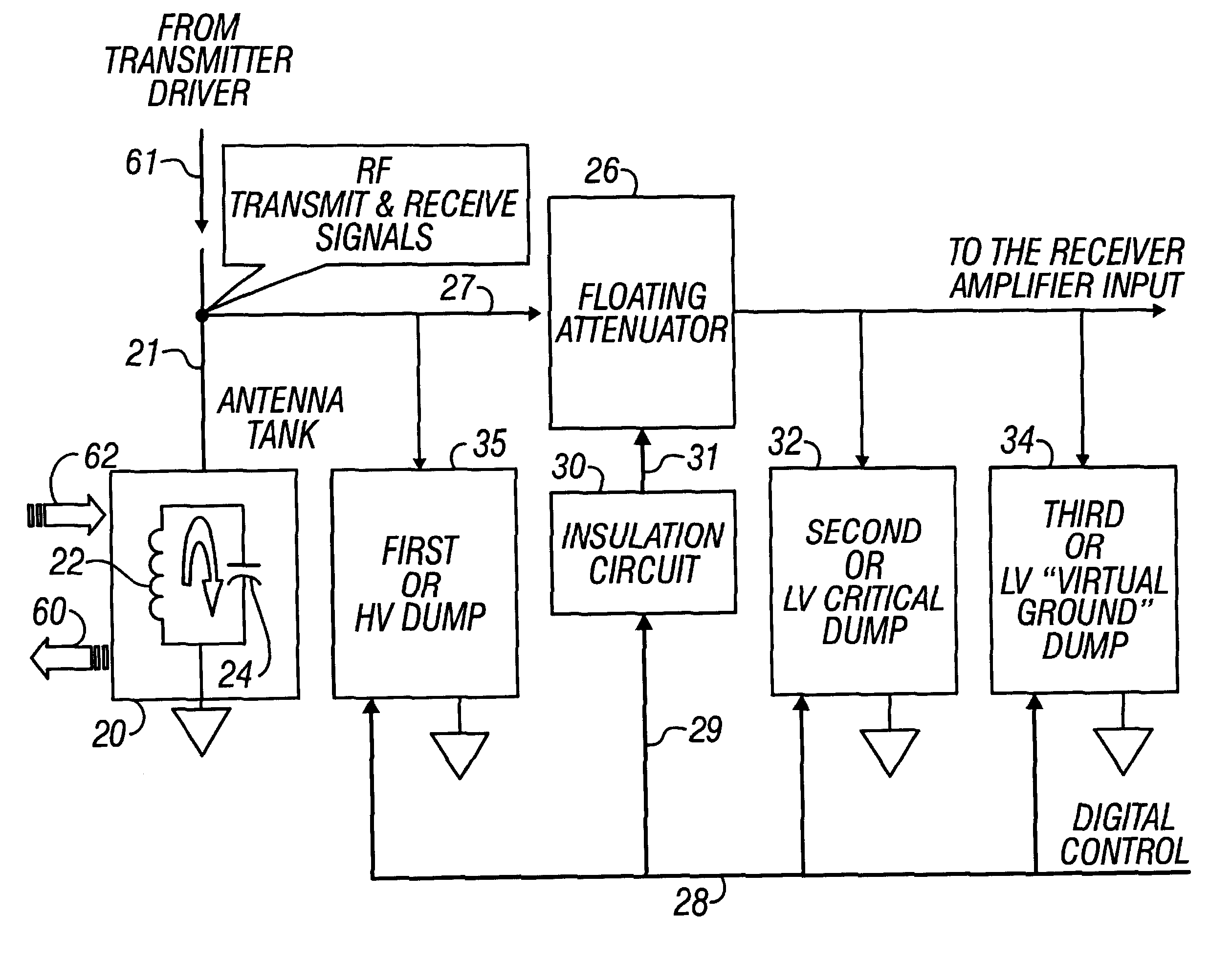
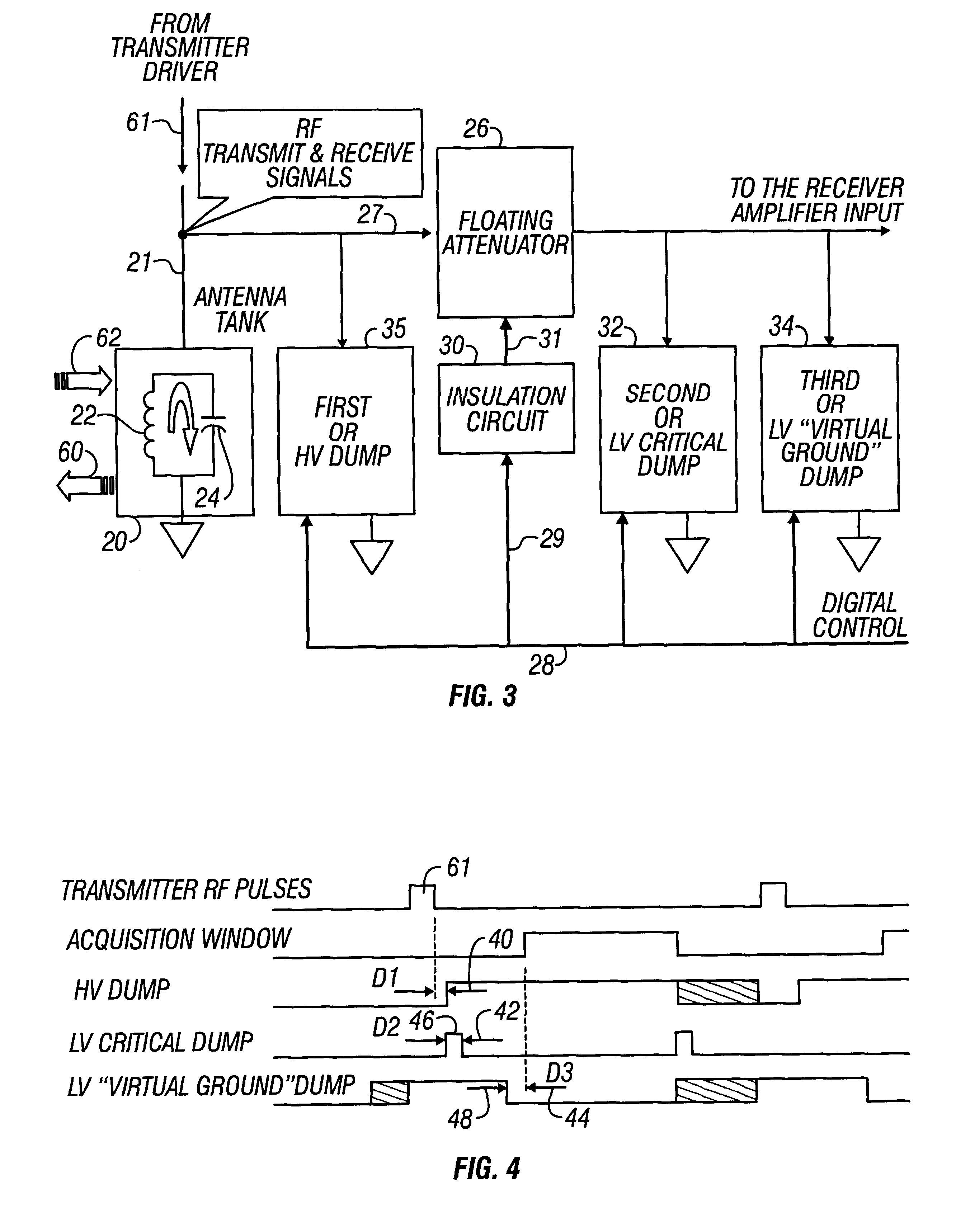
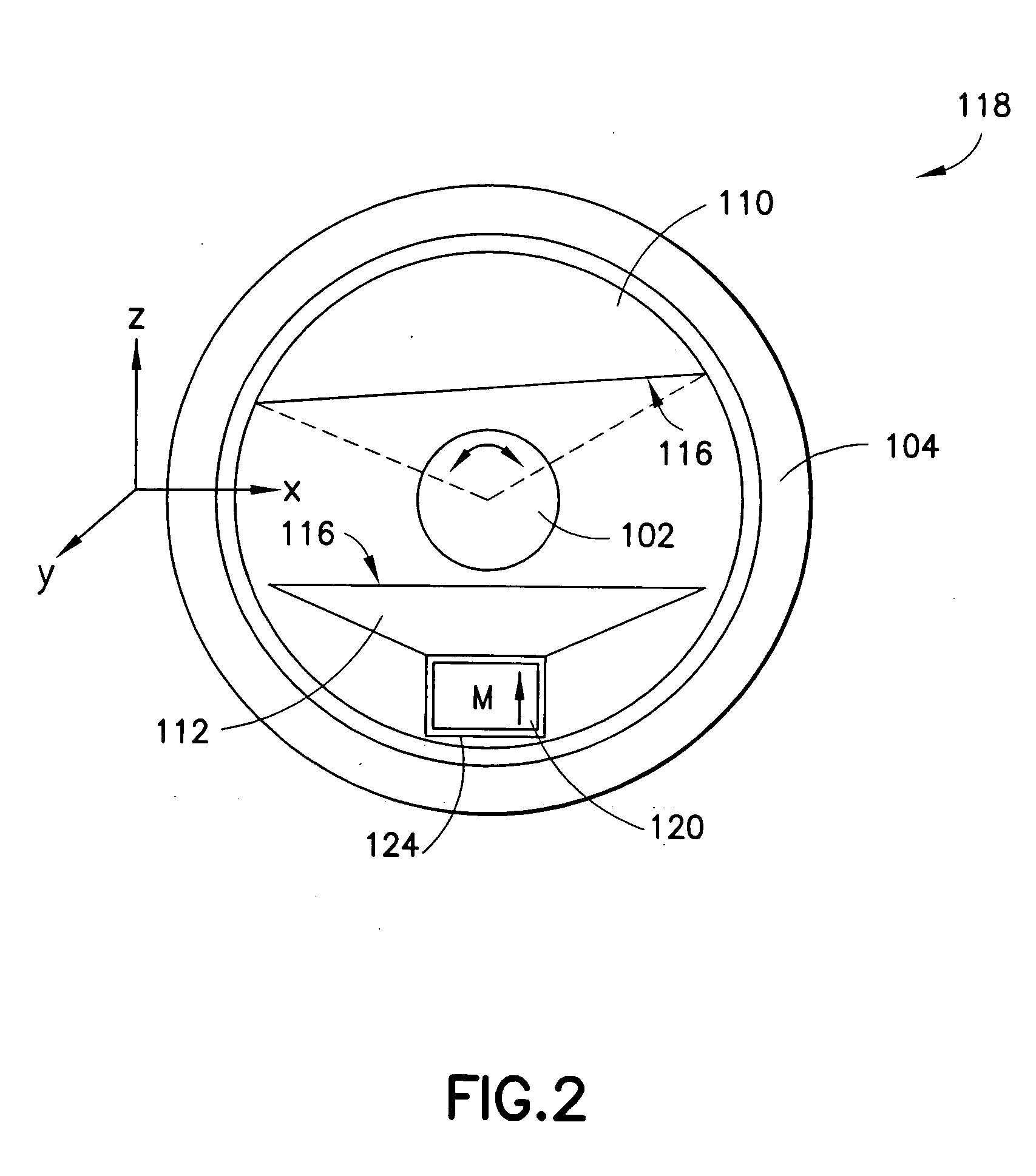
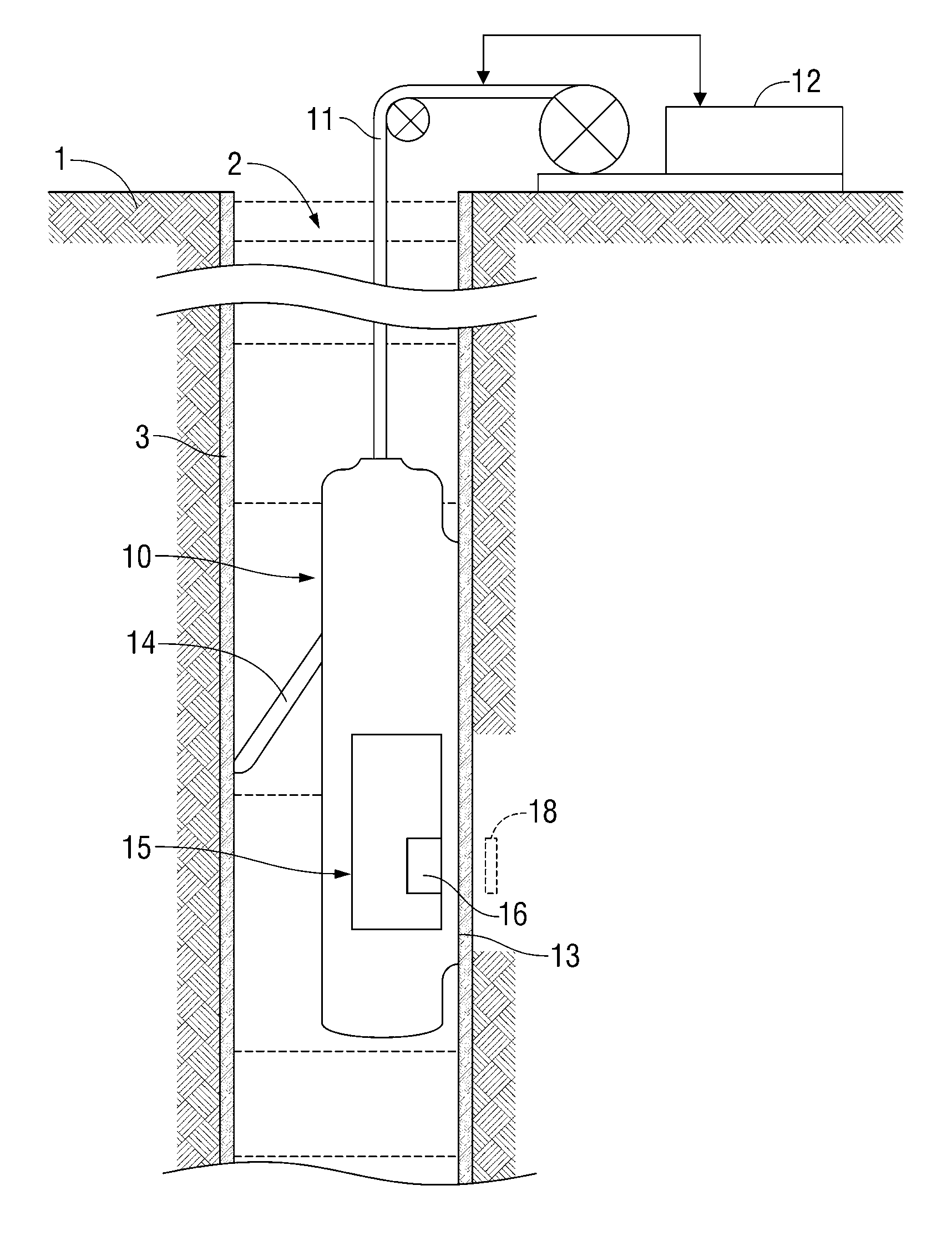
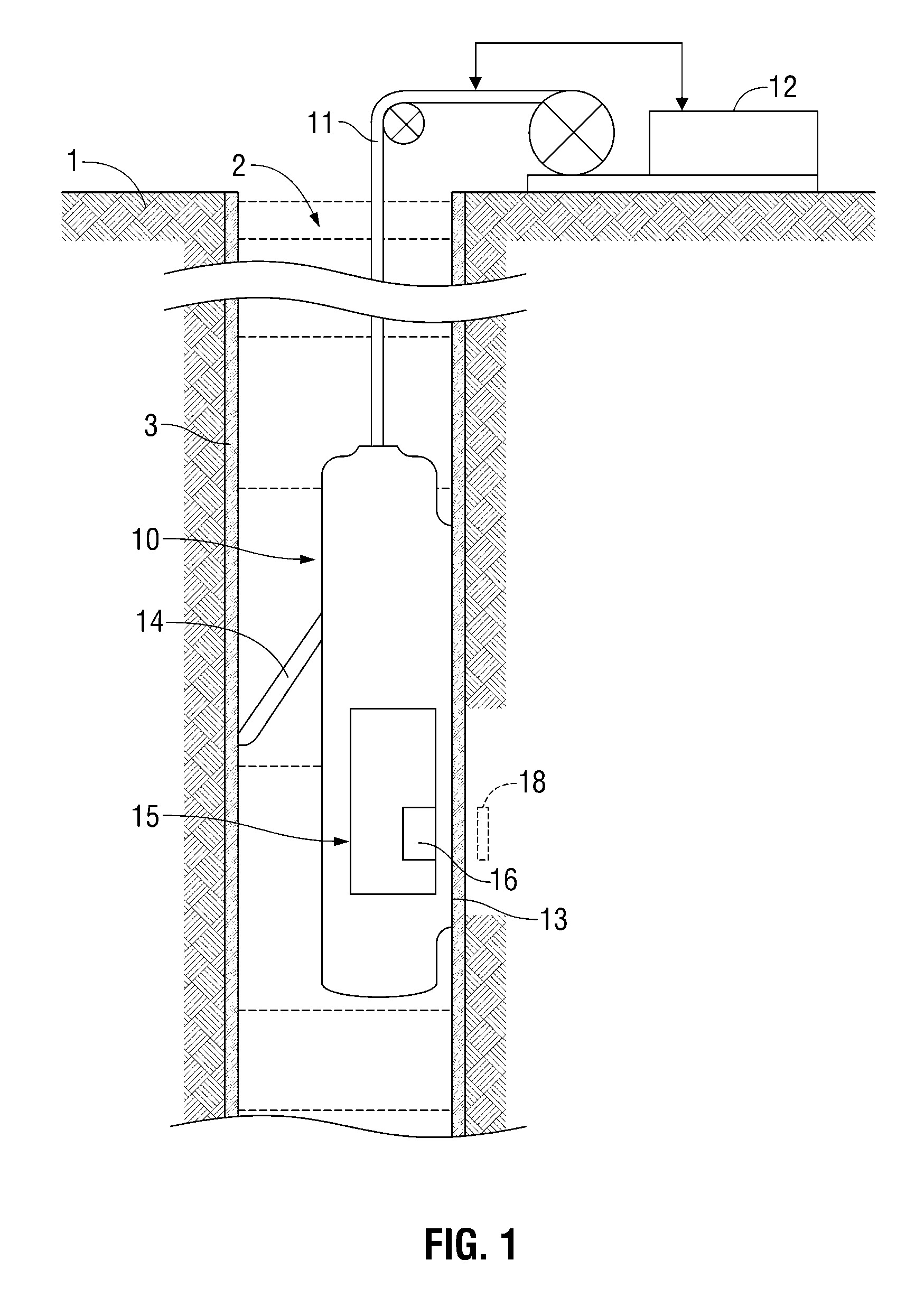
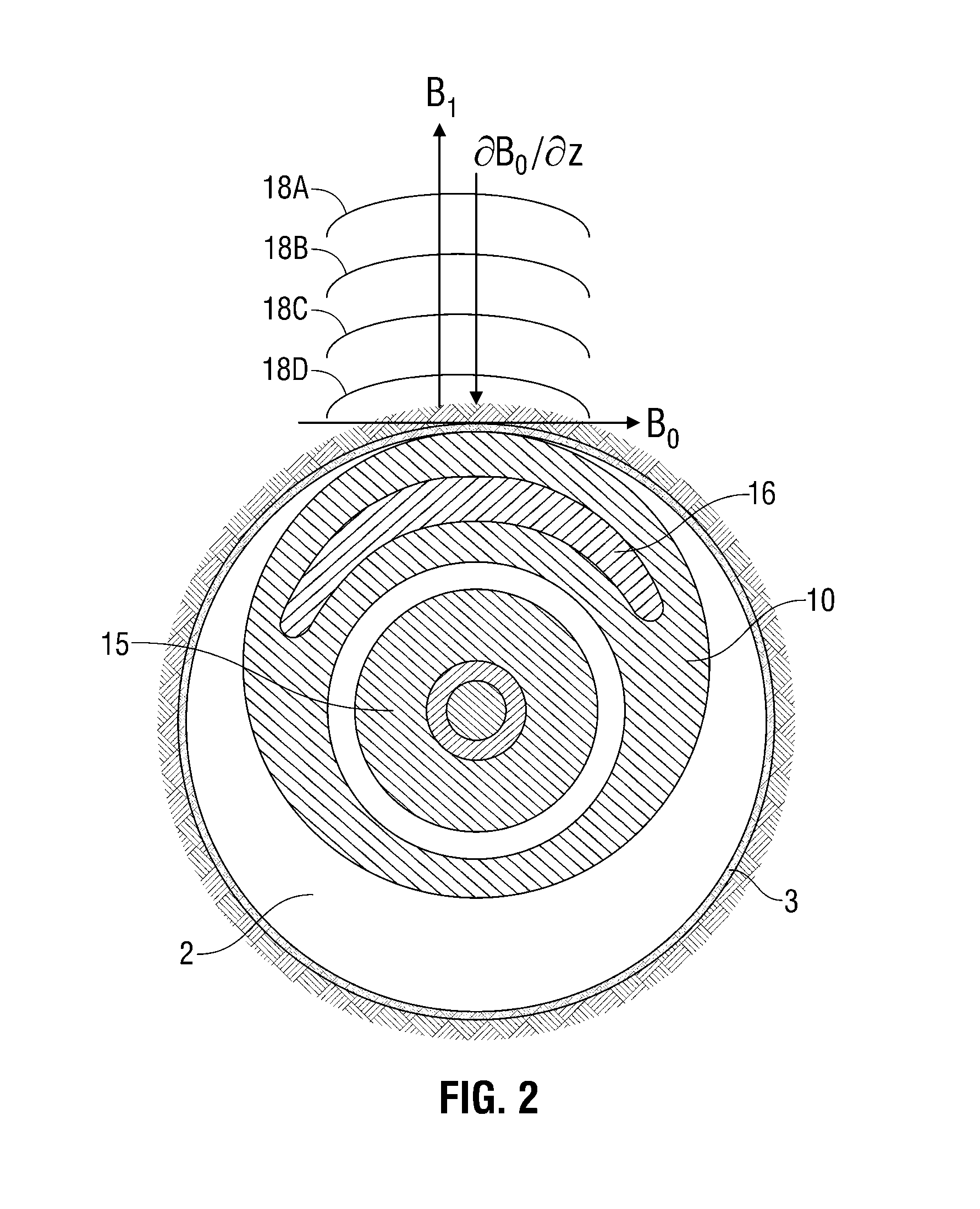
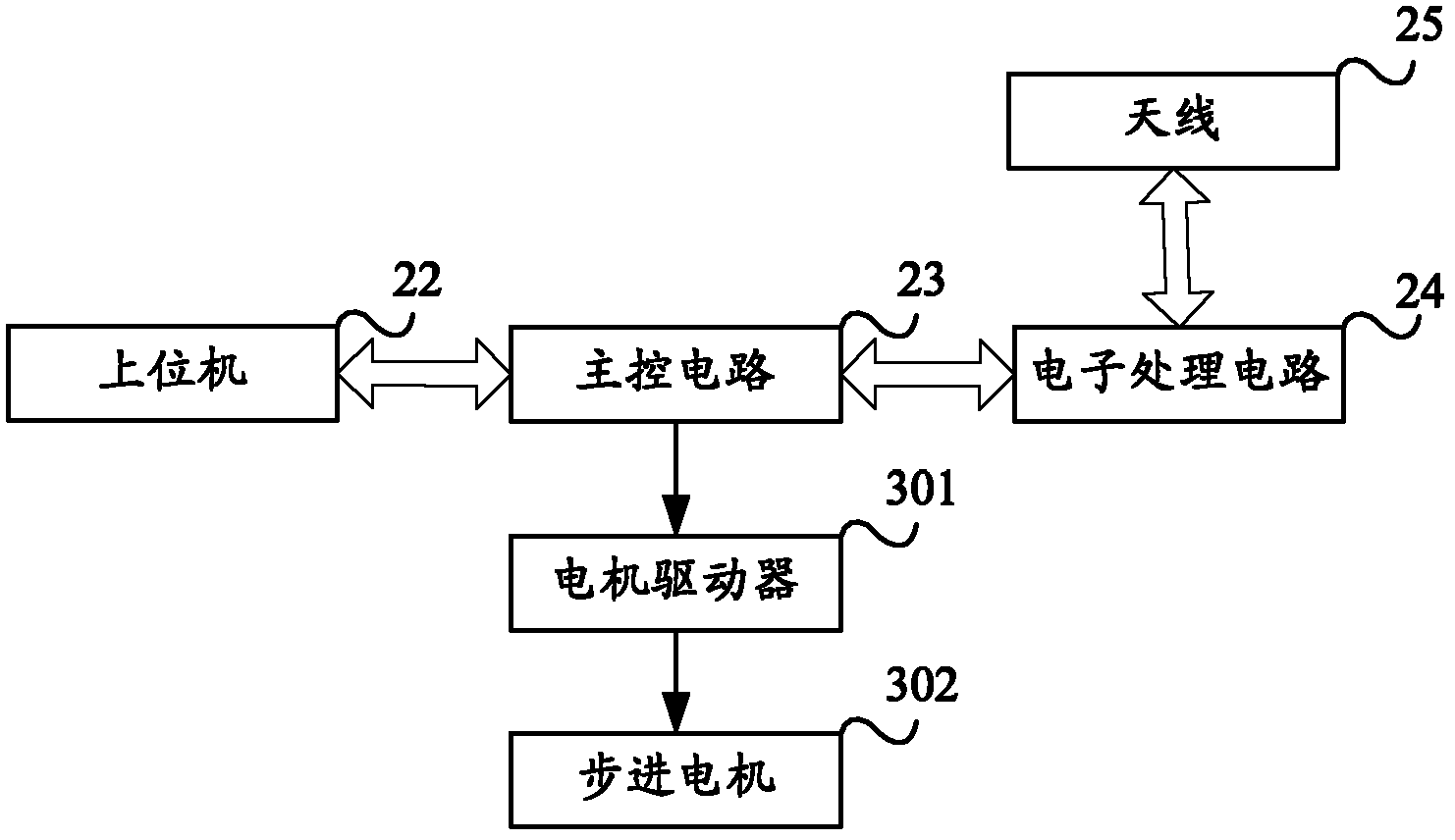
Active signal conditioning circuitry for well logging and monitoring while drilling nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometers
InactiveUS6603309B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceWell logging
NMR transmitter / receiver antenna active signal conditioning circuitry that enables receiver antenna circuit protection from high voltage RF transmitter pulses, provides energy dumping for the entire antenna in successive stages and eliminates re-tuning during sweeping of the antenna frequency.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
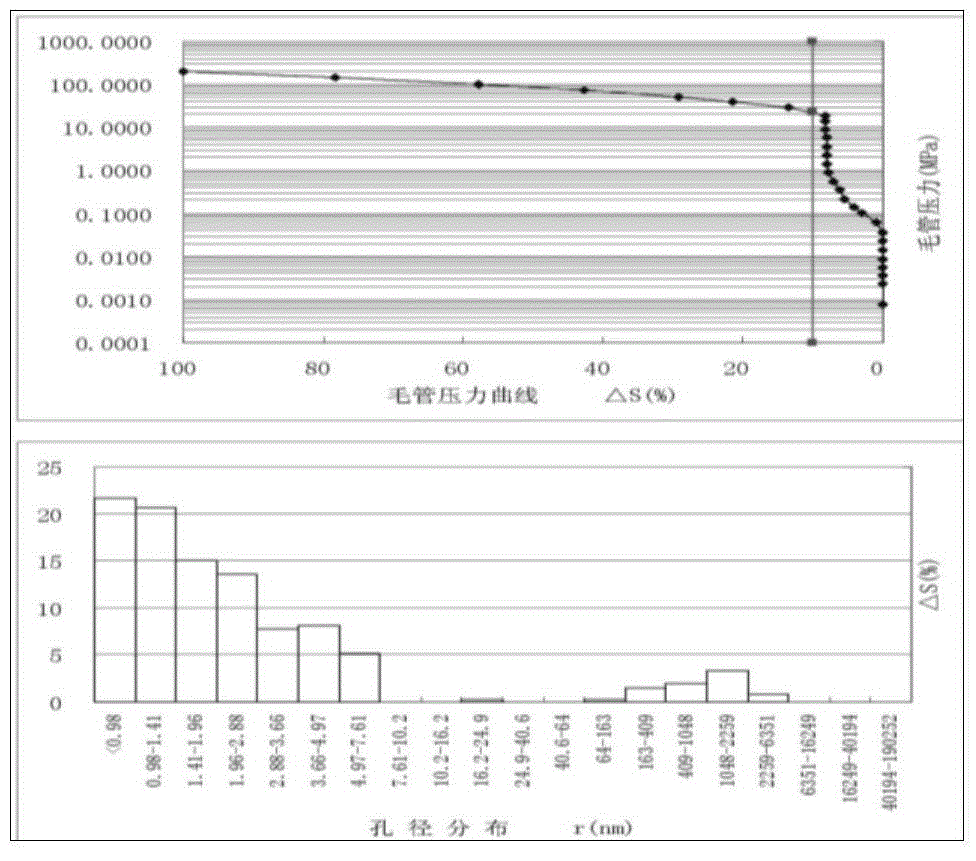
Shale micropore size and fluid distribution analysis method
ActiveCN104697915AAvoid damageGood reproducibilityWater resource assessmentAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceBound waterHydrogen
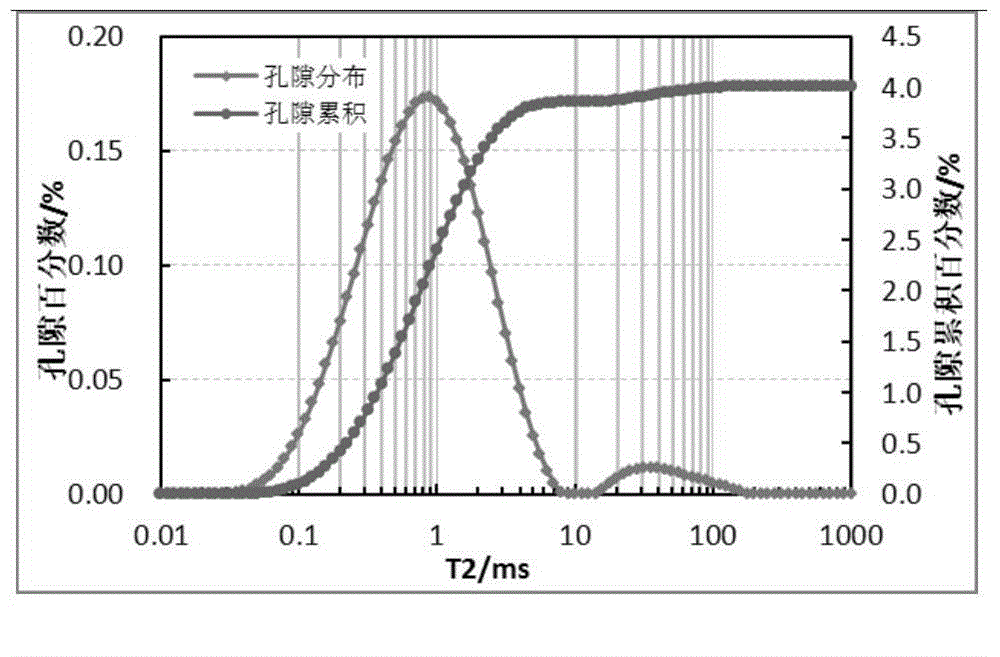
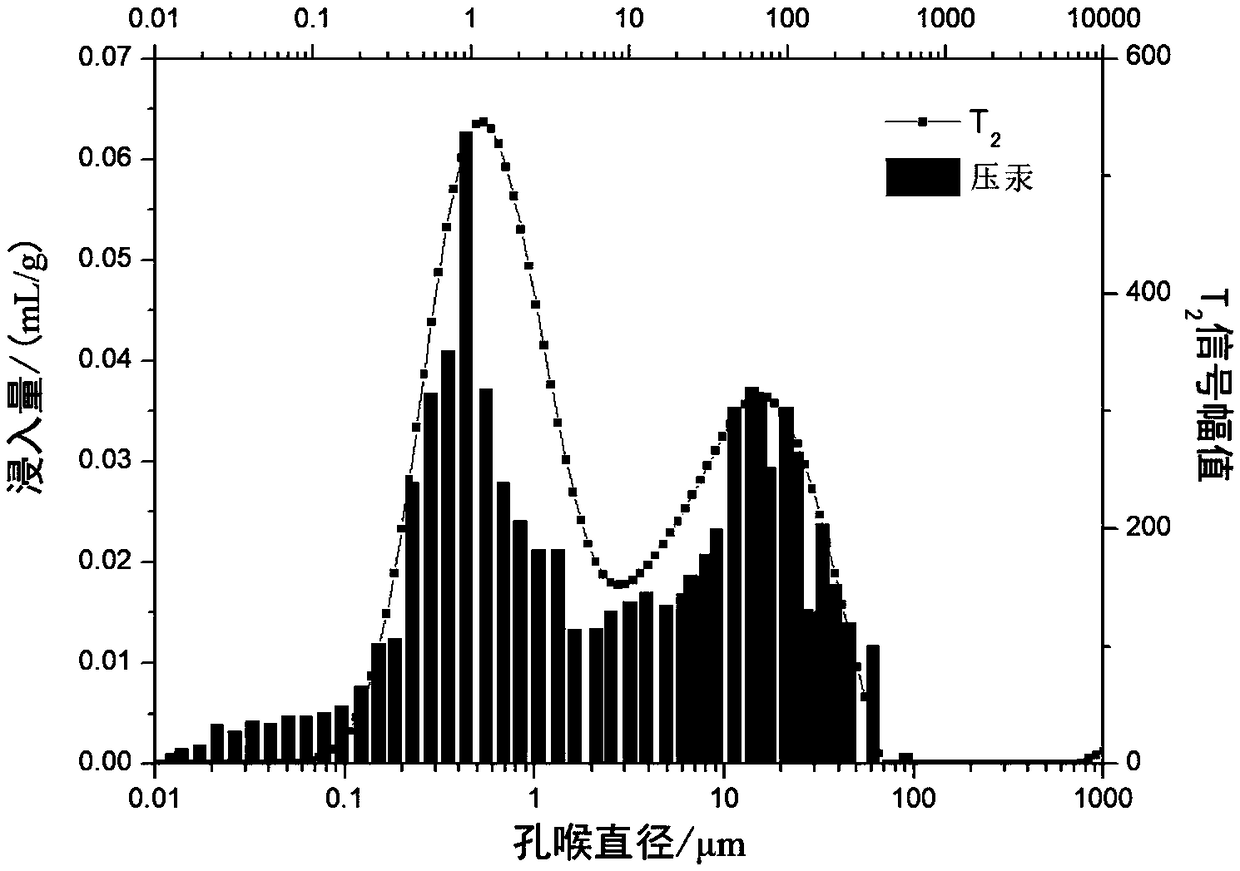
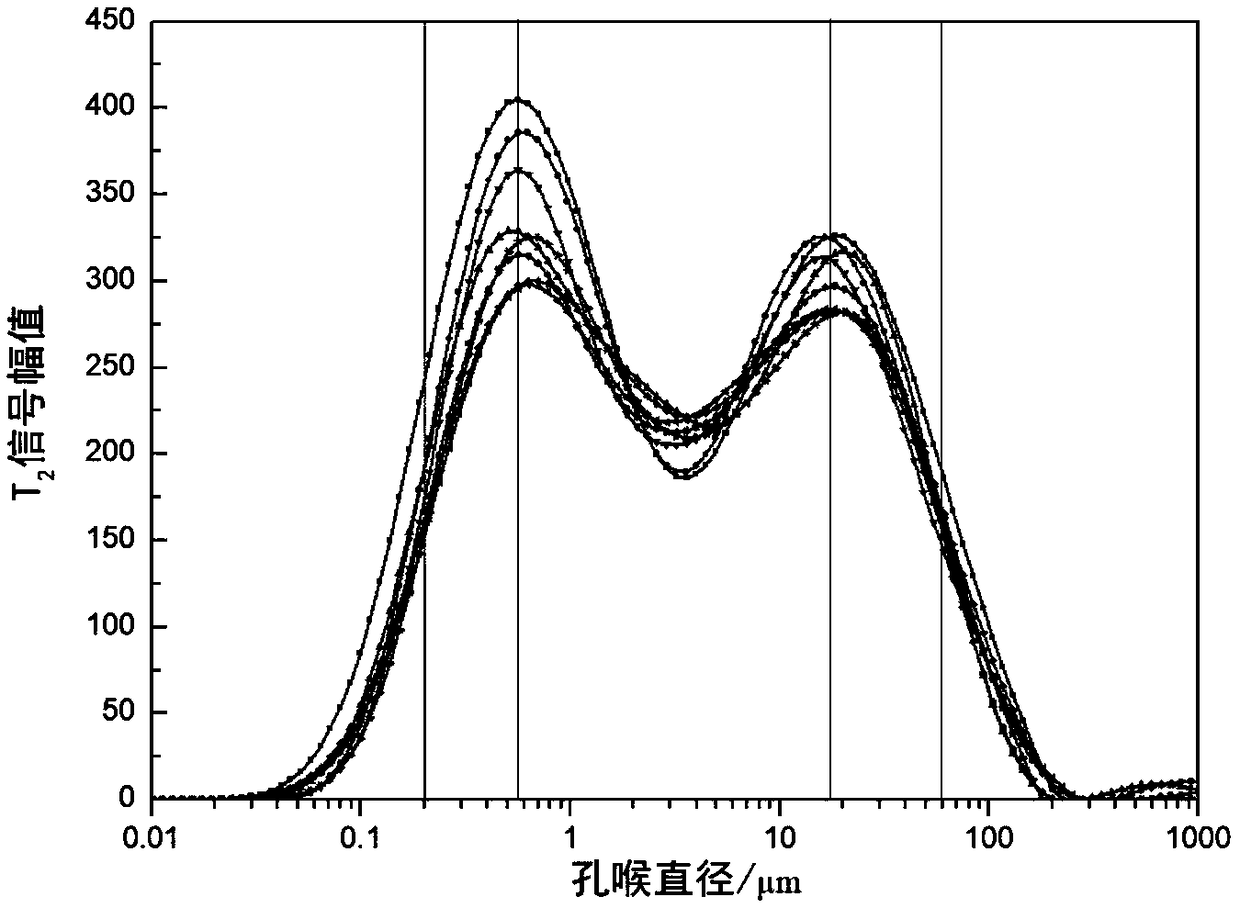
The invention discloses a shale micropore size and fluid distribution analysis method. The shale micropore size and fluid distribution analysis method comprises the following steps that shale gas reservoir rock is collected, and a natural core is manufactured; the relaxation characteristic of hydrogen-contained fluid in core pores is measured through a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, and a relaxation time T2 distribution map of clay water is obtained; the core is processed to obtain a saturated core, and a relaxation time T2 distribution map of saturated fluid and a summation curve are obtained; a T2 distribution map of effective fluid is obtained; a T2 distribution map of irreducible fluid and saturability Swi of bound water are obtained; a T2 distribution map of surplus water and water saturation Sw are obtained; the T2 distribution maps of the fluids are converted into a pore size distribution map, the shale clay deadline and the irreducible fluid deadline are obtained, and then the shale micropore size and fluid distribution are obtained. The nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer is adopted, the pore size and distribution of the shale and size and distribution positions of water drops in the pores are analyzed quantitatively and qualitatively, and the result is reliable.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Nuclear magnetic resonance module
ActiveUS20080150524A1Low cost designSufficient signal to noise ratioElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus that may be used in connection with a variety of different tools, including a down-hole side-wall coring tool as well as with manufacturing process controllers. In one embodiment, the nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus may include a magnet assembly constructed around a sample chamber. The magnet assembly is constructed and arranged to provide a non-uniform magnetic field having a known magnetic field gradient inside the sample chamber. The use of gradient fields may allow for a more flexible and robust magnet assembly design that may be suitable for a variety of different applications.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
System and method for emulating nuclear magnetic resonance well logging tool diffusion editing measurements on a bench-top nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer for laboratory-scale rock core analysis
InactiveUS20110234220A1Increase displacementPromote recoveryElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsWell loggingLaboratory scale
A laboratory NMR methodology (and corresponding laboratory apparatus) defines a sample volume. The method stores downhole tool data corresponding to a hydrocarbon-bearing sample collected from a given subsurface formation. The downhole tool data includes parameters pertaining to magnetic fields used by a downhole tool during a suite of NMR measurements of the given subsurface formation. The sample is positioned in the sample volume of the laboratory apparatus, which applies a static magnetic field in the sample volume. Furthermore, the laboratory apparatus applies a suite of NMR measurements to the sample volume to thereby determine a property of the sample. The NMR measurements of the suite each include a pulse sequence of oscillating magnetic field in conjunction with a pulsed-mode gradient field. The pulsed-mode gradient field is based on the stored downhole tool data corresponding to the sample. A laboratory NMR methodology for optimizing downhole NMR measurements is also described.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
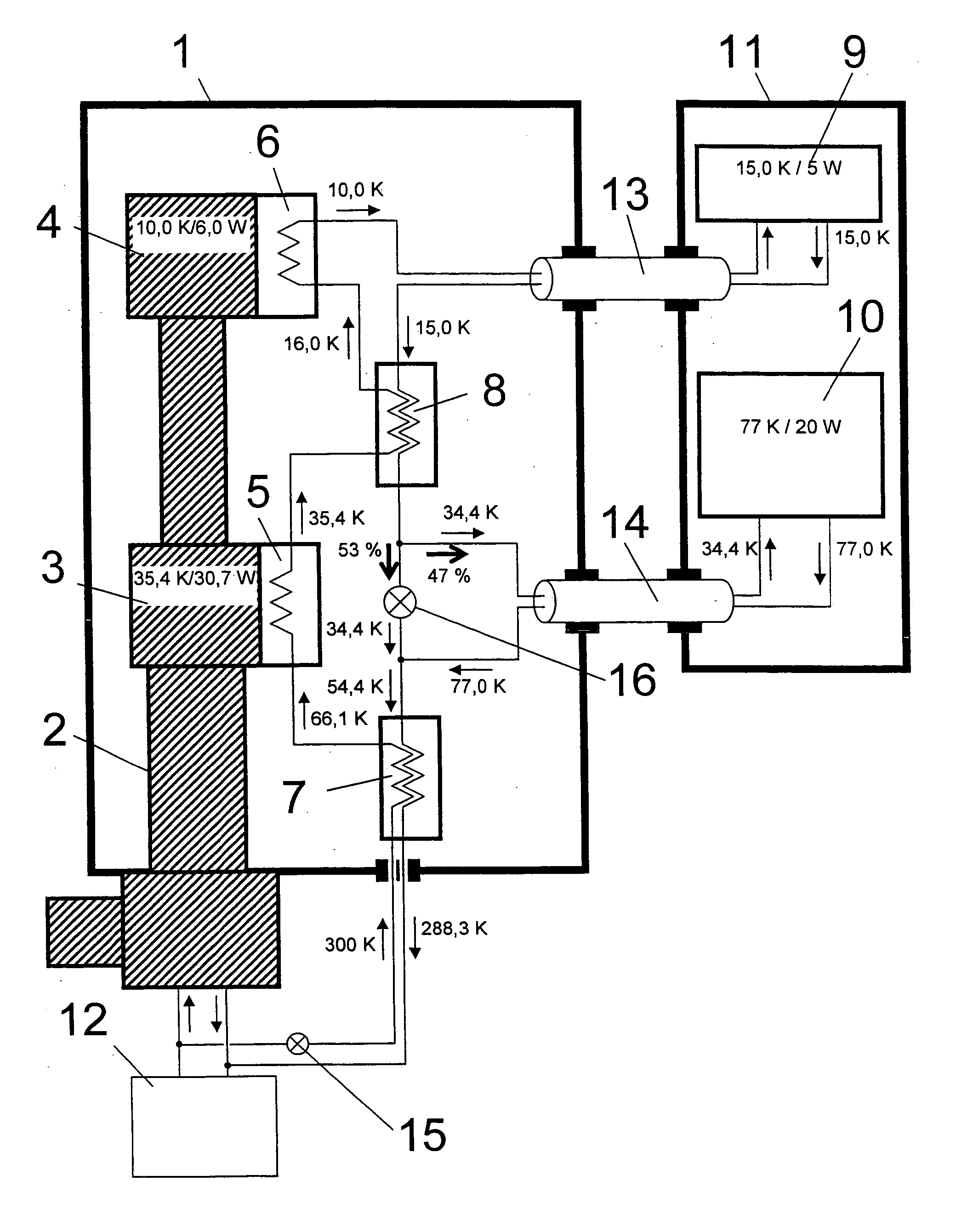
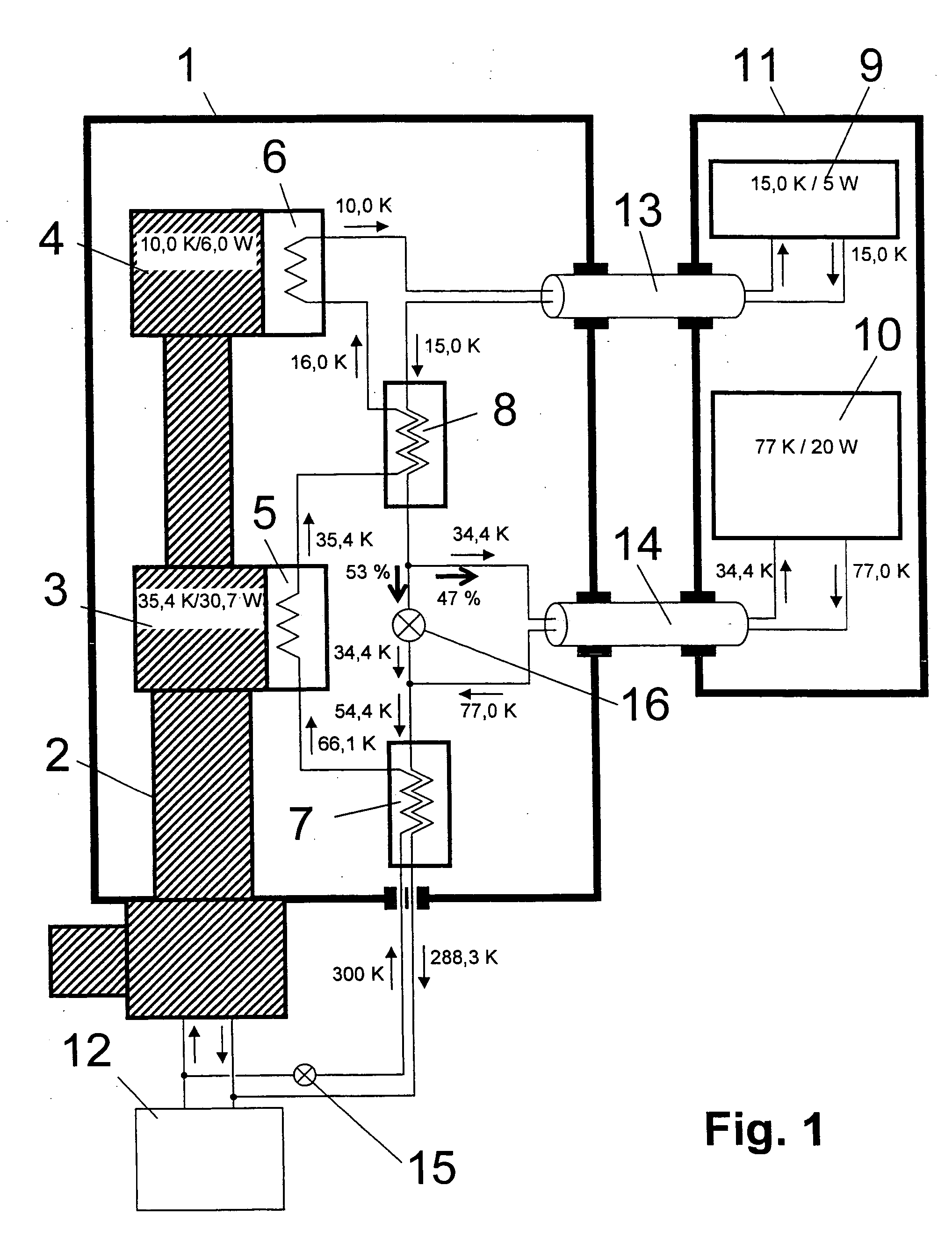
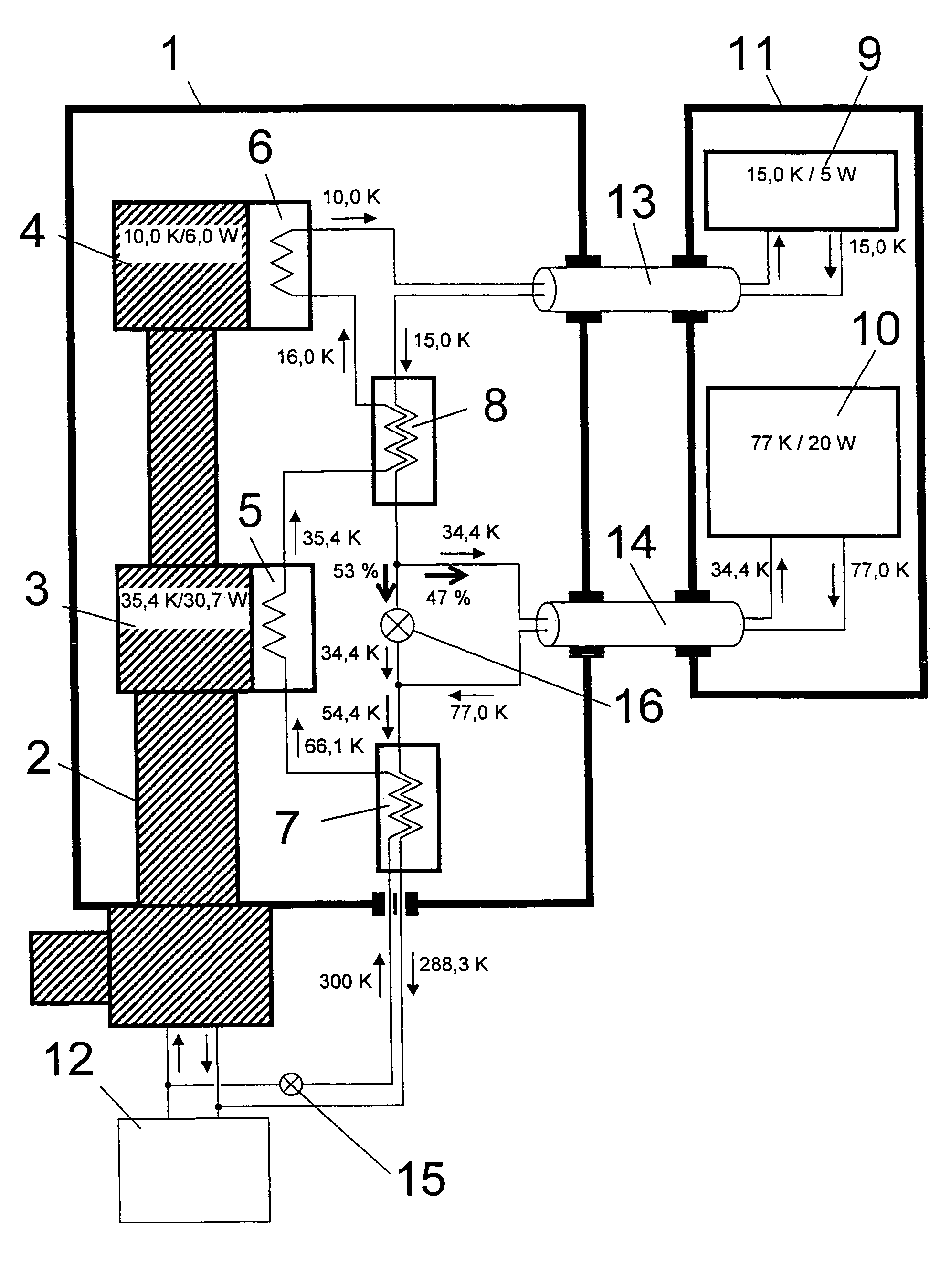
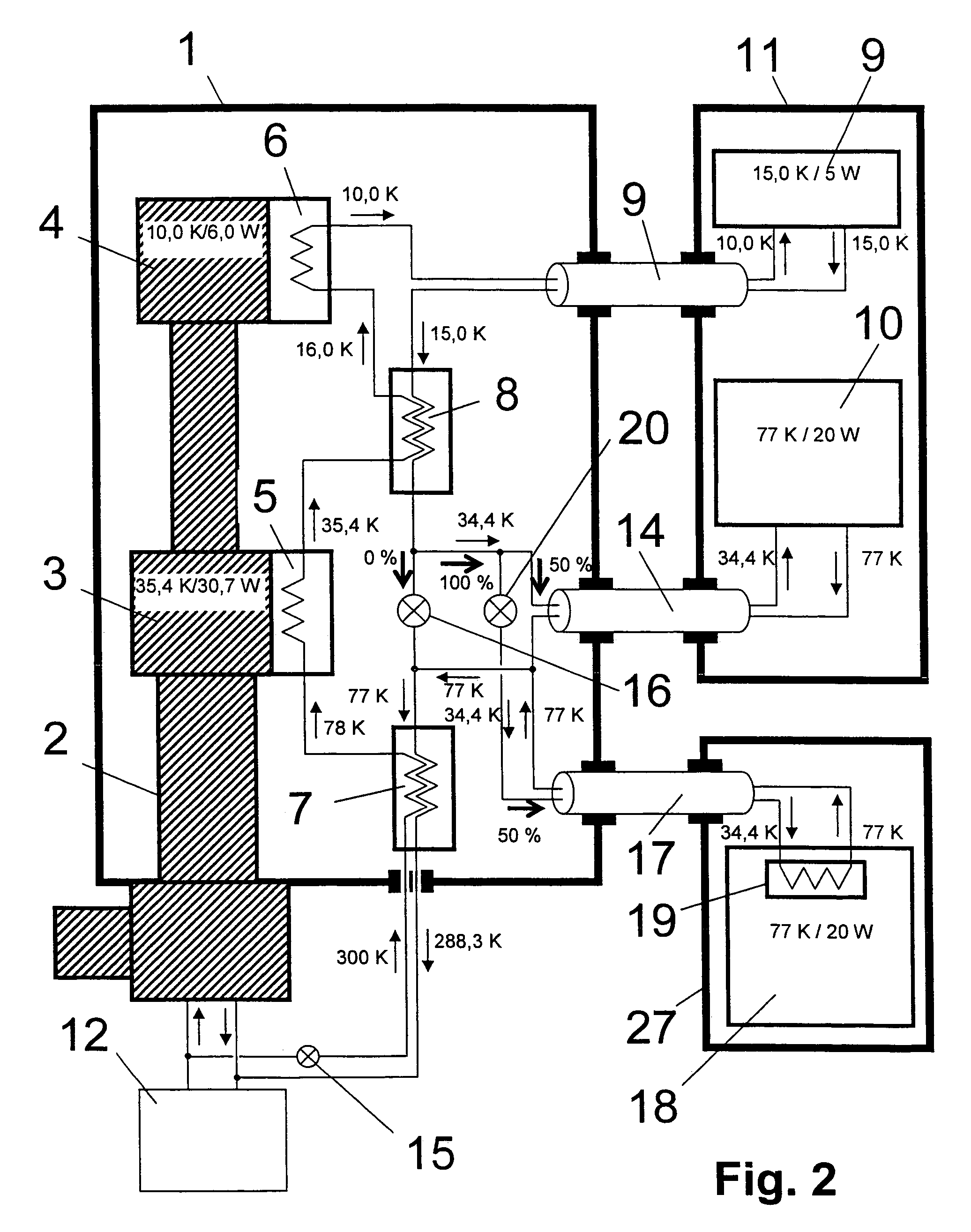
NMR spectrometer with refrigerator cooling
ActiveUS20060096301A1Reduce temperature lossReduce energy lossMagnetic measurementsCompression machinesEngineeringRefrigerated temperature
An NMR spectrometer comprising an NMR magnet system (27) disposed in a helium tank of a cryostat and an NMR probe head (11) disposed in a room temperature bore of the cryostat, which contains a cooled RF resonator (9) for receiving NMR signals from a sample to be investigated, and a cooled pre-amplifier (10), wherein the NMR probe head (11) is cooled by a common multi-stage compressor-operated refrigerator (2), wherein the refrigerator (2) comprises a cold head and several heat exchangers (5, 6) at different temperature levels, wherein the refrigerator (2) is disposed at a spatial separation from the cryostat in a separate, evacuated and thermally insulated housing (1) and wherein at least one cooling circuit with cooling lines, which are thermally insulated by a transfer line (13, 14) is disposed between the housing (1) containing the heat exchangers (5, 6) and the NMR probe head (11), is characterized in that additional cooling lines to an LN2 tank (18) or radiation shield (21) disposed in the cryostat and surrounding the helium tank are provided, and the refrigerator (2) also cools the LN2 tank (18) or the radiation shield (21). The inventive NMR spectrometer comprises a simple and inexpensive device for matching the holding time of LN2 to that of LHe through cooling the LN2 tank using the refrigerator provided for cooling the NMR probe head and without great expense.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
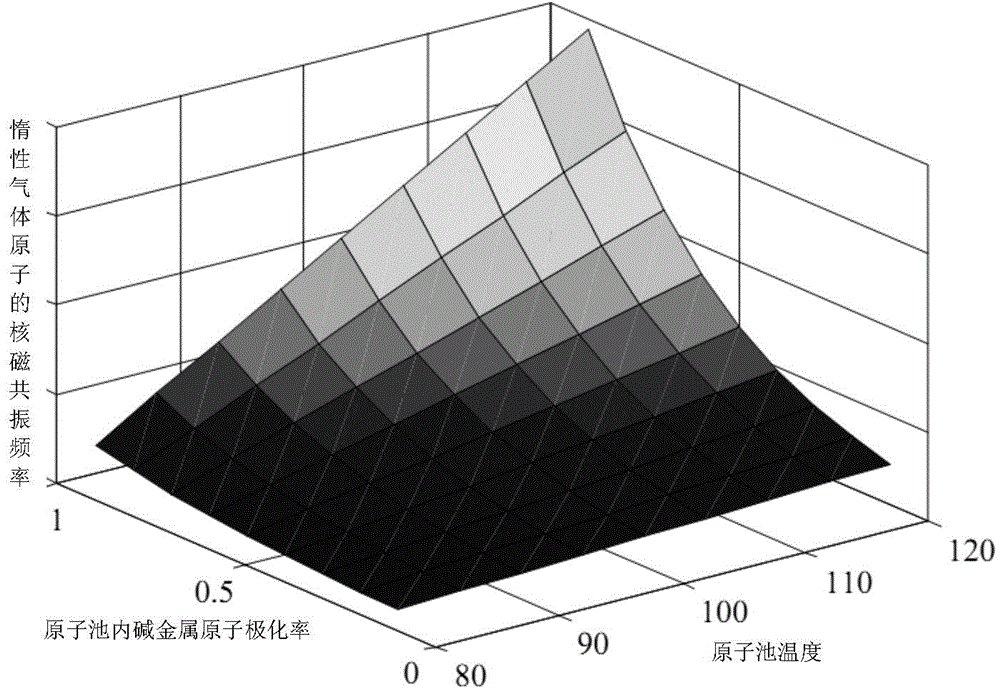
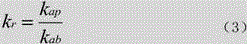
Method for measuring alkali metal atomic polarizability of nuclear magnetic resonance gyro in real time
ActiveCN104833690ADoes not affect the structureEasy to measureAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePolarizabilityProton NMR
The invention provides a method for measuring alkali metal atomic polarizability of a nuclear magnetic resonance gyro in real time and belongs to the field of atomic physics. The method includes: measuring alkali metal atomic densities of an atomic pool at different temperatures, measuring atomic nuclear magnetic resonance frequency of inert gas caused by polarization of alkali metal atoms, and thus acquiring polarizability of the alkali metal atoms in the atomic pool without changing the optical path structure of the nuclear magnetic resonance gyro and the magnetic field environment; building a three-dimensional model of changes in nuclear magnetic resonance frequency of the inert gas in the atomic pool along with temperature and the alkali metal atomic polarizability, measuring the frequency shift of atomic NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) of the inert gas at any temperature point while the nuclear magnetic resonance frequency normally runs, and thus calculating the polarizability of the alkali metal atoms in the atomic pool in real time. The method has the advantages that the method is simple, no influence is caused to the optical path structure of the nuclear magnetic resonance gyro and the method is of great significance to improving the performance of the nuclear magnetic resonance gyro.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Compacted rock gas phase relative permeability measurement device and method
ActiveCN106814018AReal-time monitoring and determination of stabilityAvoid systematic errorsWater resource assessmentPermeability/surface area analysisRock coreNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a compacted rock gas phase relative permeability measurement device and method. The measurement device comprises a rock core clamp, a confining pressure pump, a variable-volume upstream pressure chamber, a variable-volume downstream pressure chamber, a high-pressure gas source, a control table and a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, an air outlet of a high-pressure air source is connected with an inlet of the variable-volume upstream pressure chamber sequentially through a valve a, a first pressure controller and a valve b, an outlet of the variable-volume downstream pressure chamber is connected with the rock core clamp through a valve c, the rock core clamp is connected with an inlet of the variable-volume downstream pressure chamber through a valve d, an outlet of the variable-volume downstream pressure chamber is connected with a pressure relief opening through a valve f, and the rock core clamp is arranged in a measuring cavity of the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer. The invention provides a measurement method based on the measurement device. The measurement device has the advantages that gas relative permeability of compacted rocks can be rapidly and effectively measured.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
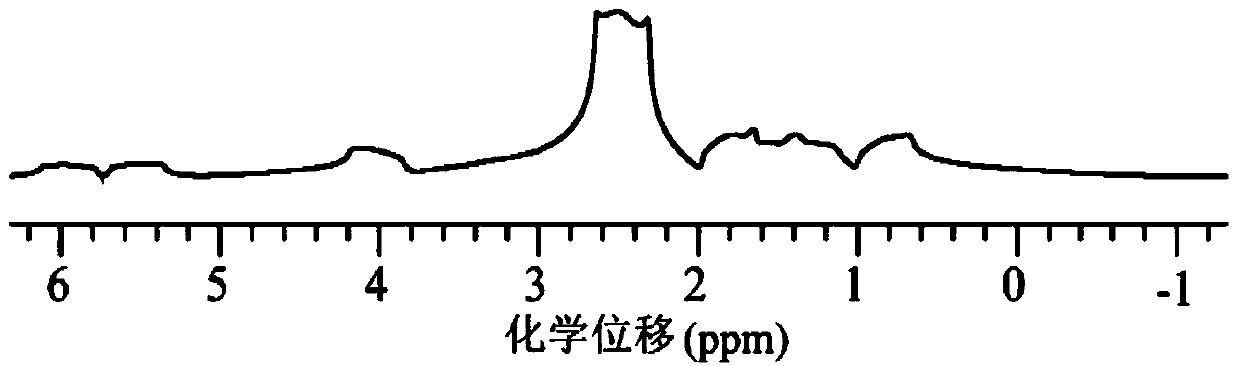
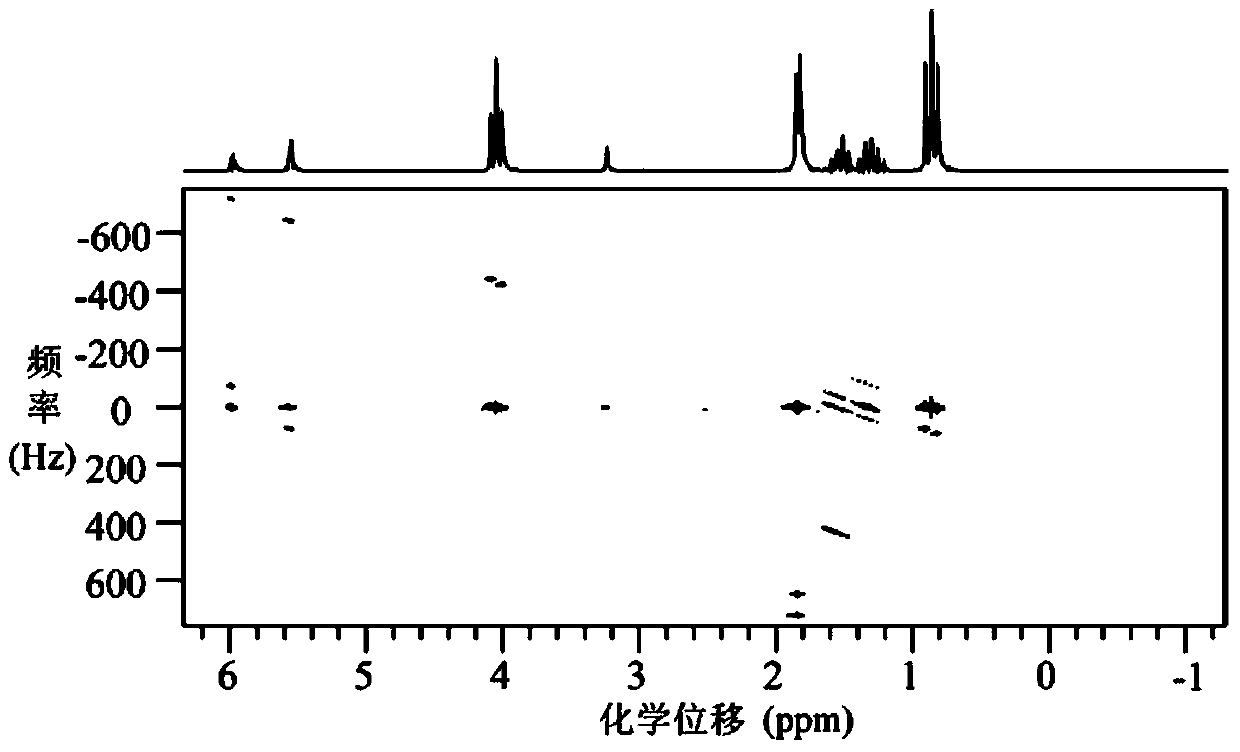
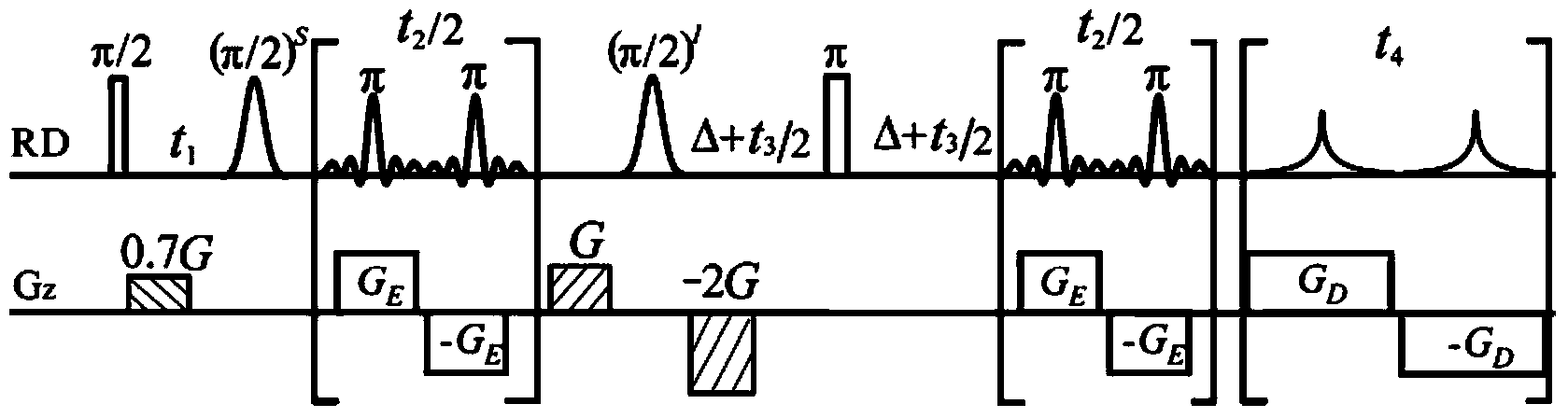
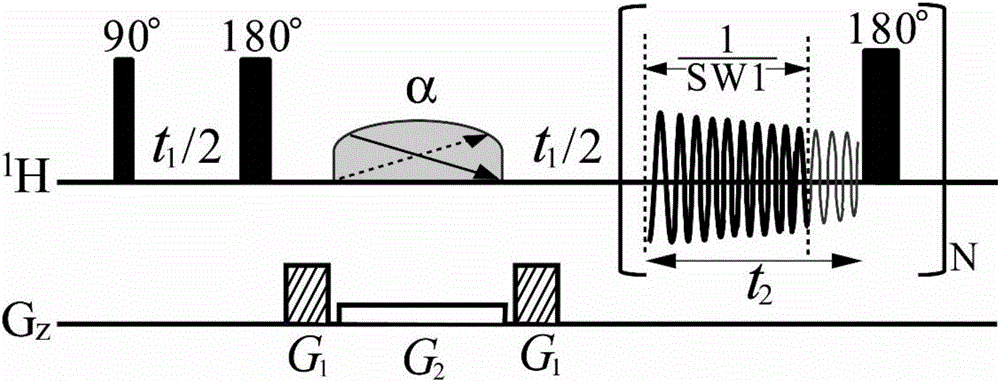
Method for obtaining nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimensional J-resolved spectroscopy in non-uniform magnetic field
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
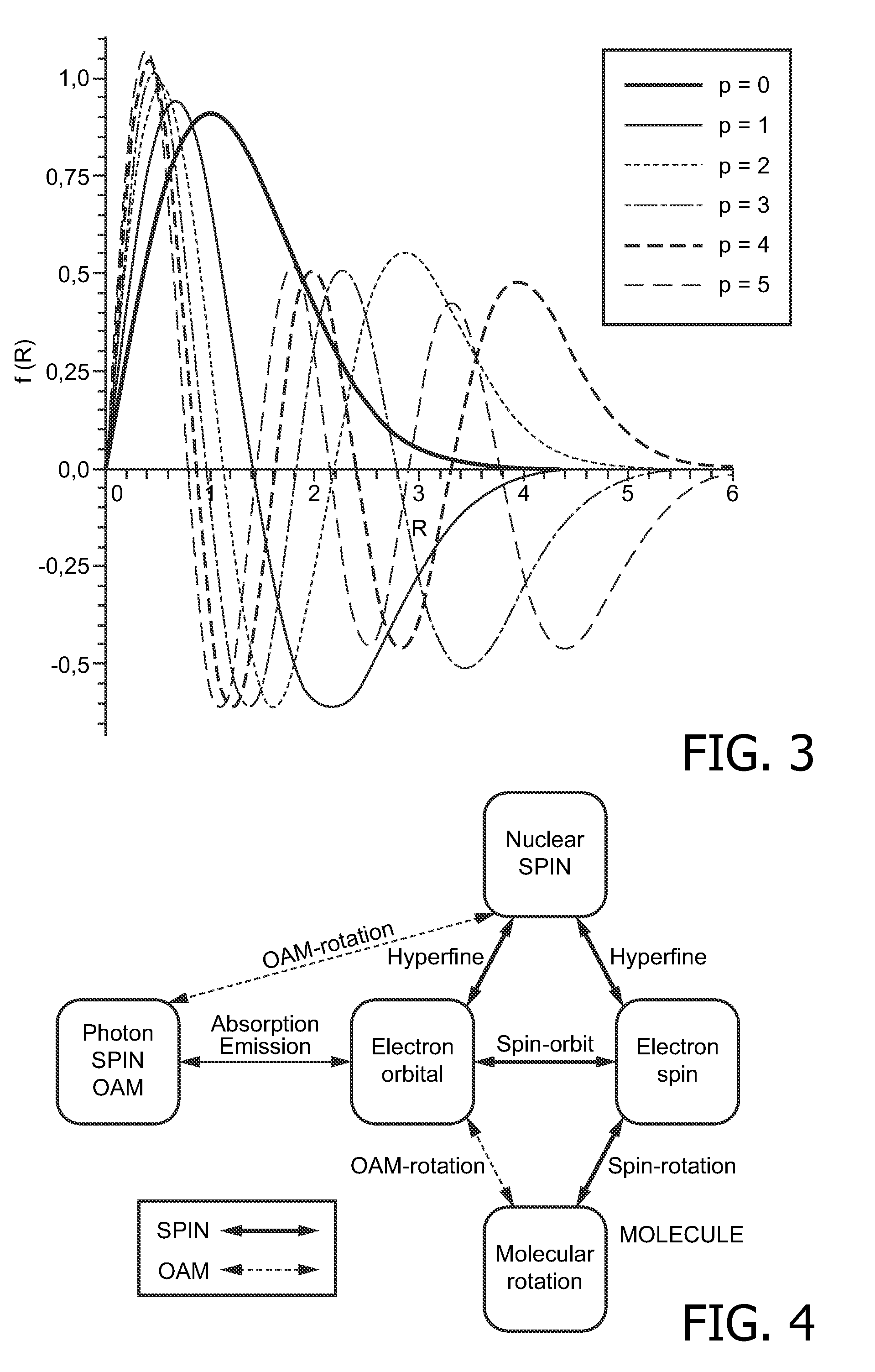
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy using light with orbital angular momemtum
InactiveUS20100327866A1Less noisyHigh resolutionLaser detailsAnalysis using optical pumpingTwo-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopySpectroscopy
The present invention relates to a device capable of producing a high resolution chemical analysis of a sample, such as fluid, based upon nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, where the nuclear magnetic polarizations of the sample are generated by sequentially illuminating the sample with a focused beam of light carrying angular orbital angular momentum (OAM) and possibly momentum (spin). Unlike in usual NMR used for magnetic nuclear resonance imaging (MRI) or spectroscopy, the invention does not make use of a strong magnet.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Magnetic-resonance compatible pneumatic puncture surgical robot
ActiveCN106388939AImprove accuracyImprove stabilitySurgical needlesSurgical robotsSurgical robotAutomatic control
The invention discloses a magnetic-resonance compatible pneumatic puncture surgical robot which comprises a location module, a puncture orientation module and a needle feed module which are sequentially connected, wherein the location module adopts a manner of arranging a shear fork type lift mechanism on an annular guide rail slide block, then arranging an annular guide rail on a rodless air cylinder and a linear guide rail slide block, so that the movable location of a puncture needle in a magnetic-resonance imaging device in the axial direction, the radial direction and the peripheral direction is achieved; the puncture orientation module can adjust and locate the puncture angle of the puncture needle based on being fixed to a rotation shaft through a parallel four-rod RCM mechanism; the needle feed module can achieve automatic control on needle feed and needle withdrawal of the puncture needle in a mode that two friction wheels are pushed by an air cylinder to drive the puncture needle. The magnetic-resonance compatible pneumatic puncture surgical robot is simple in structure, saves space, is safe and reliable, can work in a narrow space and a high-field-intensity magnetic field of a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, is smaller in interference on magnetic resonance imaging and effectively improves the accuracy and the stability of puncture operation.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Method for obtaining high-resolution two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum
InactiveCN106093099AAvoid signal excitationAvoid applicabilityAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceDecompositionLine width
The invention provides a method for obtaining a high-resolution two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum, and relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy detection method. The method comprises: loading a sample to be detected into a standard nuclear magnetic test tube, and conveying into the detection chamber of a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer; sampling the one-dimensional hydrogen spectrum of the sample to be detected, and obtaining the signal peak distribution area and the spectral line width so as to provide the reference for the spectral width parameter setting, wherein the line width value reflects the magnetic field uniformity condition; measuring the pulse width of a radio frequency pulse required by excitation of the sample to be detected; introducing a compiled pulse sequence on the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, opening the heteronuclear intermolecule multiple quantum coherent signal excitation module, the indirect dimensional evolving module, the spin echo fixed delay module and the J modulating fast sampling module of the pulse sequence, and setting the experiment parameters of various modules; skipping the artificial shimming operation process, and directly executing data sampling; and after completing the data sampling, calling data post-processing codes to carry out related data post-processing so as to obtain the high-resolution two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum being not affected by the inhomogeneous magnetic field.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for obtaining nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimension spin echo related spectrum under uneven magnetic field
ActiveCN103744042AOvercoming the influence of uneven magnetic fieldMagnetic measurementsLine widthPulse sequence
A method for obtaining a nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimension spin echo related spectrum under an uneven magnetic field relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance wave spectrum detection method and comprises the steps of using a normal one-dimension pulse sequence to sample a one-dimension spectrum, obtaining the line width of spectral lines, and providing a basis for spectrum width parameter setting, wherein the line width value also reflects the uniformity condition of a magnetic field; introducing well precompiled two-dimension spin echo related spectrum pulse sequences onto a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer; opening a multi-quantum coherent signal selection module, a three-dimension sampled indirect dimension evolution period t1 combination and indirect dimension evolution period t2 combination and an echo delay module among the two-dimension spin echo related spectrum pulse sequences; setting each experiment parameter of the two-dimension spin echo related spectrum pulse sequences; executing the two-dimension spin echo related spectrum pulse sequences, of which the experiment parameters are set, for data sampling; after the data sampling is finished, performing related data postprocessing to obtain the two-dimension spin echo related spectrum uninfluenced by the uneven magnetic field. The method has no need of shimming operation and is simple, convenient and effective.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
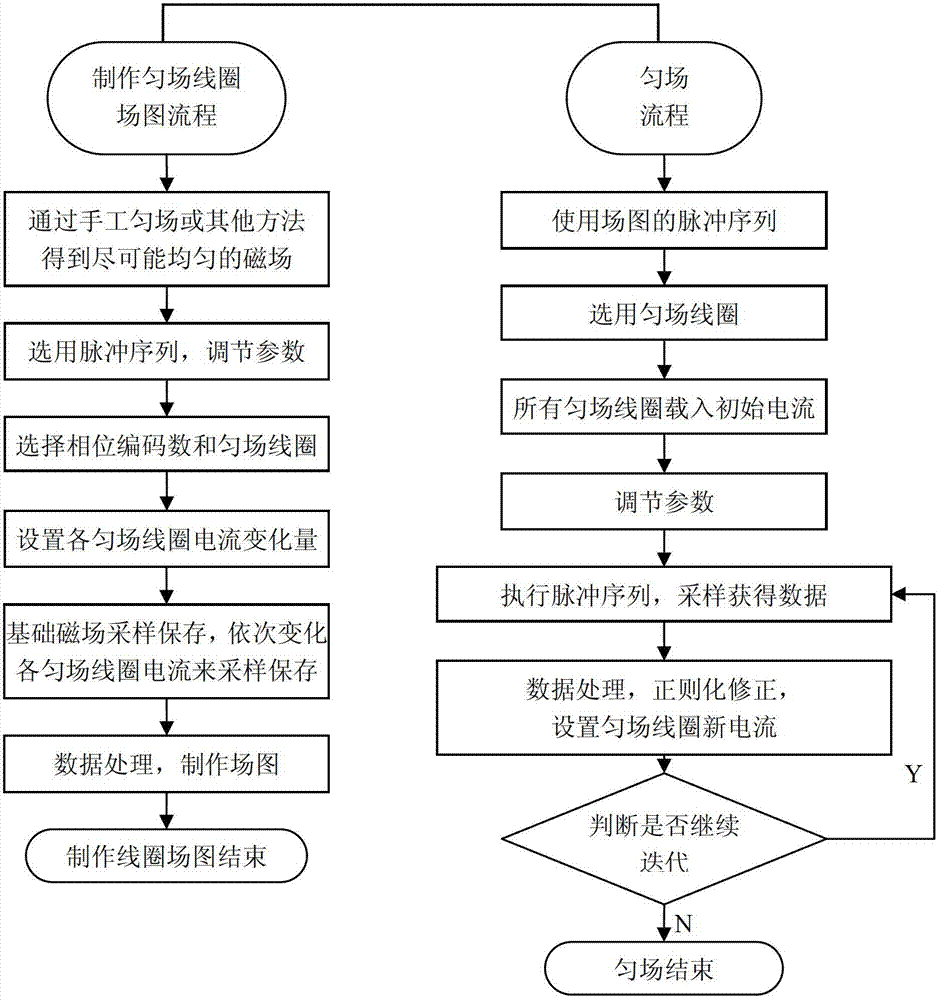
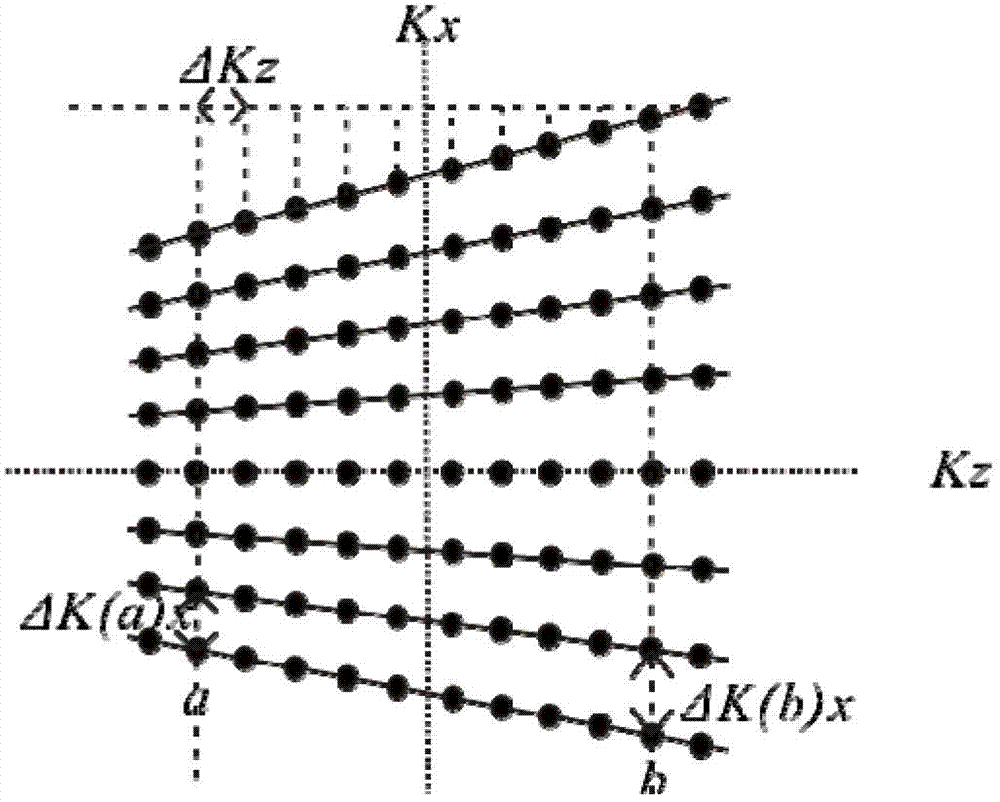
Rapid three-dimensional gradient shimming method for reducing phase encoding number on nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer
InactiveCN102768347AAvoid mutual interferenceGet rid of dependenceMeasurements using magnetic resonanceHydrogenSelective excitation
The invention discloses a rapid three-dimensional gradient shimming method for reducing phase encoding number on a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, which relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer. A method of shimming coils is selected according to the phase encoding number, X and Y high-order shimming coils are deducted, on this basis, a proper revised regularization method can be added to the calculation, a good shimming effect can still be achieved when the phase encoding number can be reduced to be 3*3 or 2*2. These few 2*2 and 3*3 phase codes are widely applied to all three-dimensional gradient shimming pulse sequences of the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, such as a three-dimensional gradient echo pulse sequence, a tilt three-dimensional gradient echo pulse sequence, and a pulse gradient field excitation echo pulse sequence. The mutual interference of multiple spectral peaks with farer chemical shifts can be overcome in the phase measurement. The three-dimensional gradient shimming in which the hydrogen nuclear is selectively excited enable the shimming method to get rid of the dependence on deuterium reagent, brings speed increase in cooperation with few phase encoding number and small-angle excitation, and has wide application range.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for obtaining high-resolution three-dimensional NMR spectrum under non-uniform magnetic field
InactiveCN103941204AMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceLine widthZero quantum coherence
The invention provides a method for obtaining a high-resolution three-dimensional NMR spectrum under a non-uniform magnetic field, and relates to nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometers. The method comprises the steps that (1) a one-dimensional spectrum is sampled by using a conventional one-dimensional pulse sequence and used for analyzing the condition of the non-uniformity of the magnetic field to obtain the line width of a spectral line and provide a basis for experimental spectral width parameter settings; (2) a precompiled intermolecular zero-quantum-coherence three-dimensional spectrum pulse sequence is guided into a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer; (3) an intermolecular zero-quantum-coherence signal selection module, an indirect dimension evolution period t1 module, an indirect dimension evolution period t2 module, an indirect dimension evolution period t3 module and a signal sampling period t4 module of the intermolecular zero-quantum-coherence three-dimensional spectrum pulse sequence are opened, and experiment parameters of all the modules of the pulse sequence are set; (4) the intermolecular zero-quantum-coherence three-dimensional spectrum pulse sequence in the step (3) after experimental parameter setting is executed, and data sampling is performed; (5) after data sampling is completed, relevant data post-processing is performed, so that the high-resolution three-dimensional NMR spectrum free of influence by the non-uniform magnetic field is obtained.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
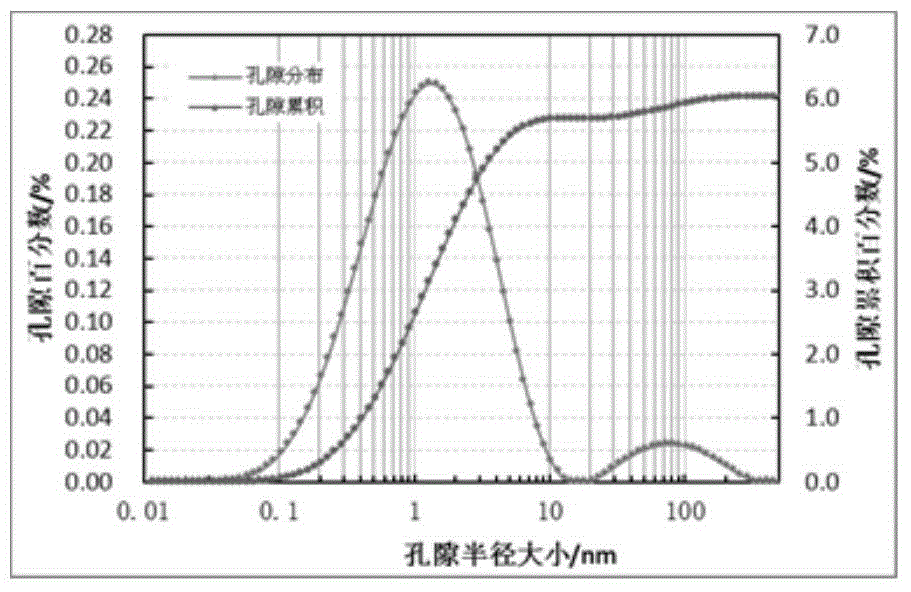
Shale pore structure detection method based on nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveCN106249306AClearly understand the changes in the size of poresAchieving Crack PredictionWater resource assessmentDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonancePore distributionWater state
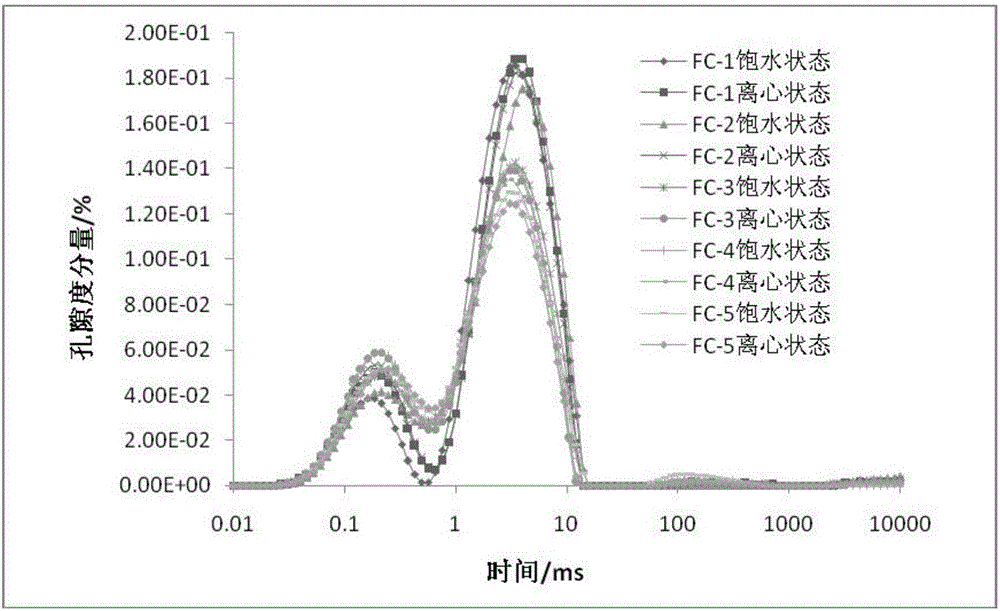
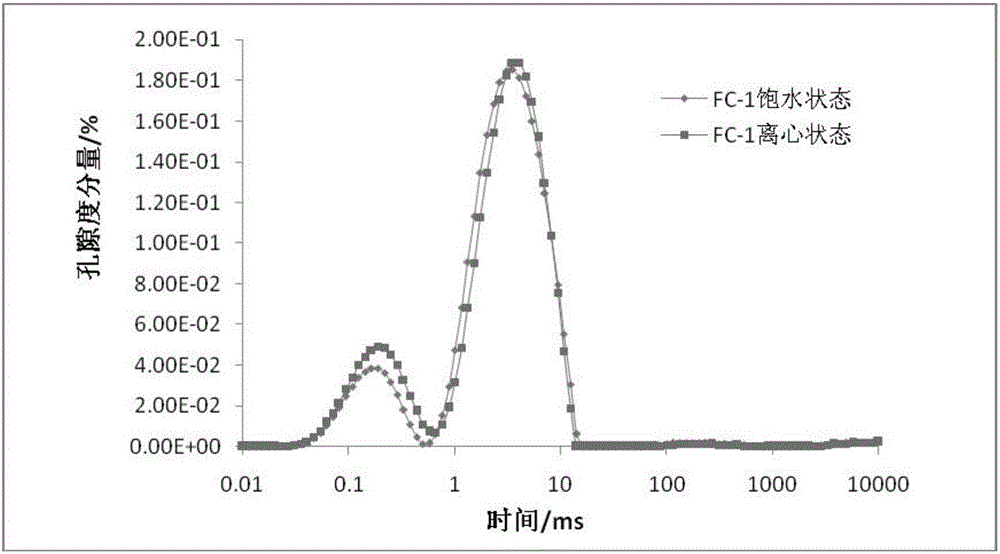
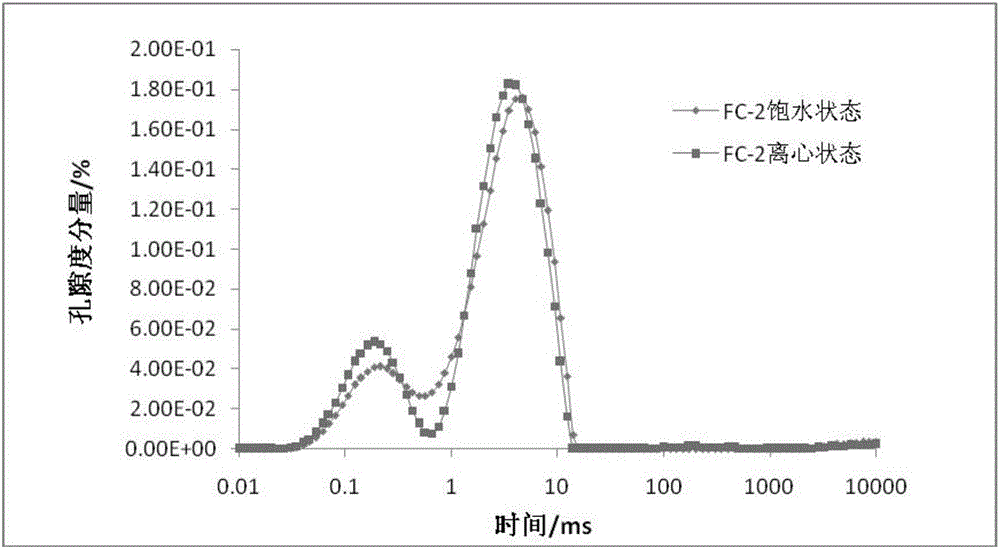
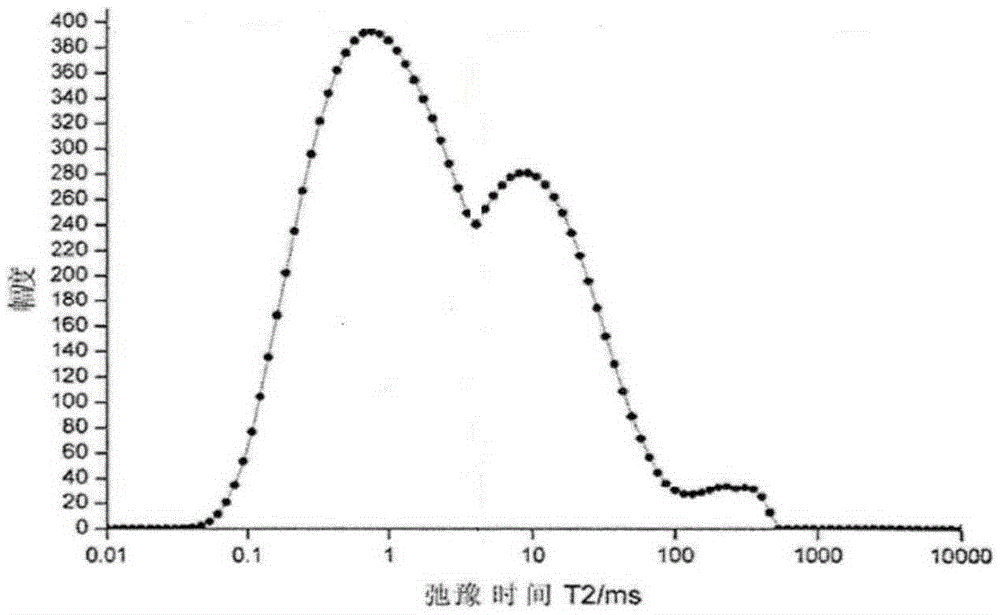
The invention provides a shale pore structure detection method based on nuclear magnetic resonance. The method comprises the steps that a sample is processed into a cylinder; the sample is saturated with water at normal pressure for 12h, and then is taken out; CPMG pulse sequence test is carried out on the sample to acquire a spin-echo-series attenuation signal; the spin-echo-series signal is inversed to acquire a T2 spectrum distribution diagram and the details of each peak; and the T2 spectrum of acquired same sample under water saturation and centrifugation is analyzed in a coordinate system to acquire the change of the volume and quantity of pores of the sample. The shale pore structure is mainly studied in a saturated water state in the prior art of nuclear magnetic resonance, and the problems that the study angle is single and limited; only pore distribution can be studied; and fracture prediction cannot be carried out are solved. The method provided by the invention belongs to the technical field of petroleum exploration and development.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
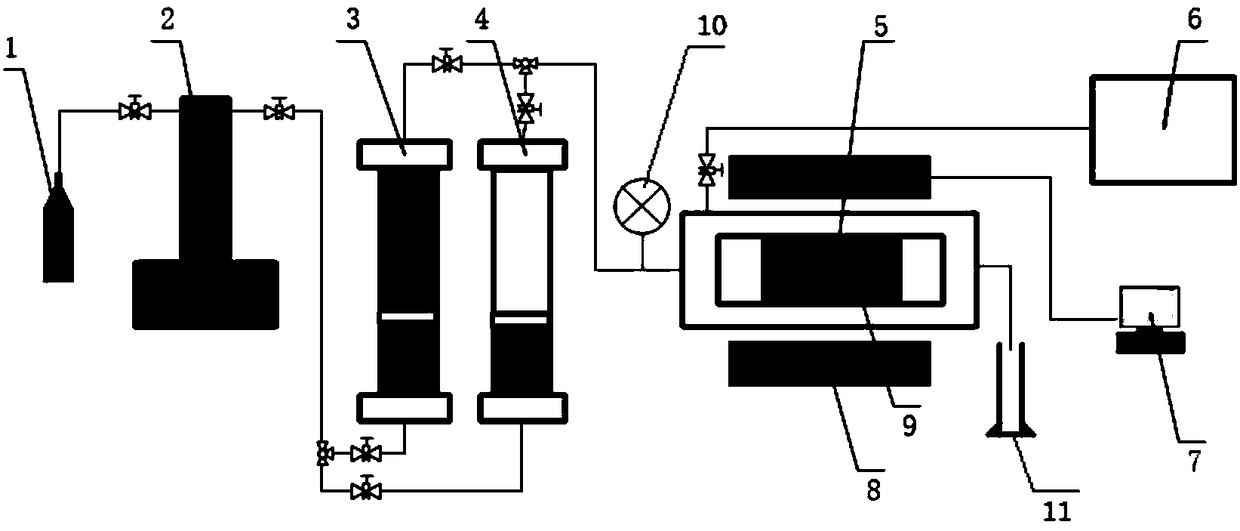
Nuclear magnetic resonance experiment device and method for multi-phase fluid flow characteristic in dense core porous media
InactiveCN109444201AAccurate Realistic Fluid Flow Study ResultsWater resource assessmentAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePorous mediumLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance experiment device and method for multi-phase fluid flow characteristic in dense core porous media, and belongs to the field of petroleum engineering and fluid research. The device consists of a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer system, a magnet system, a radio frequency system and a core displacement system. At present, a core displacement experiment in a laboratory only can calculate the oil discharge amount of a terminal, and a distribution state in the core and the pore throat utilization degree of different apertures cannot be obtained. According to the device, a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance technology is adopted to research fluid flow characteristics in the dense core porous media, the core displacement experiment andan online nuclear magnetic resonance technology are combined through a nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum analysis technology, the change characteristics of a fluid signal in the porous media canbe obtained through the online detection of the T2 spectrum so as to make the utilization characteristics of crude oil in the porous media clear, and an accurate and true research result of fluid flow in the dense core porous media is obtained.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Nuclear magnetic resonance quantitative analysis method for rock micro-crack damage variable
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
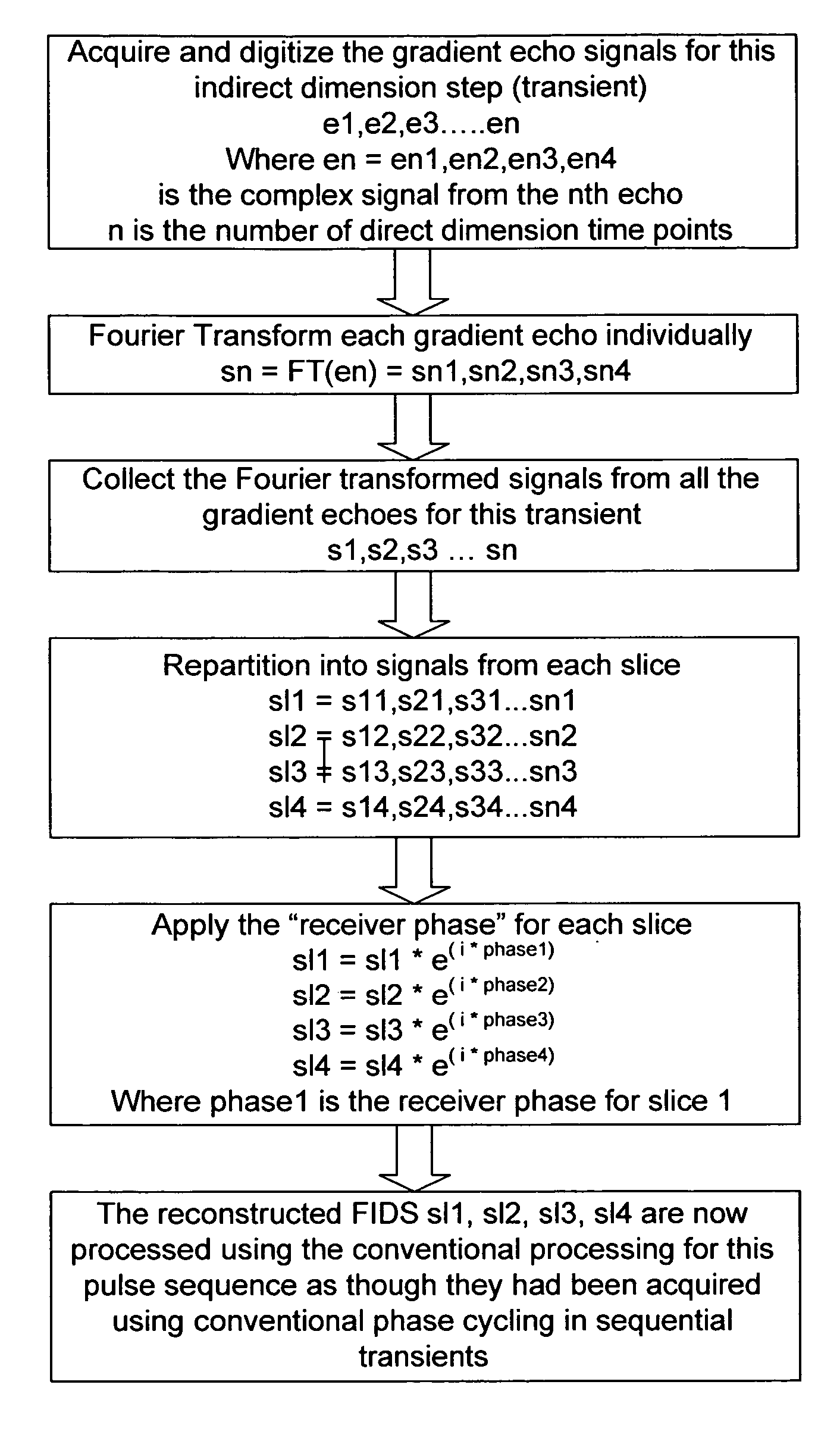
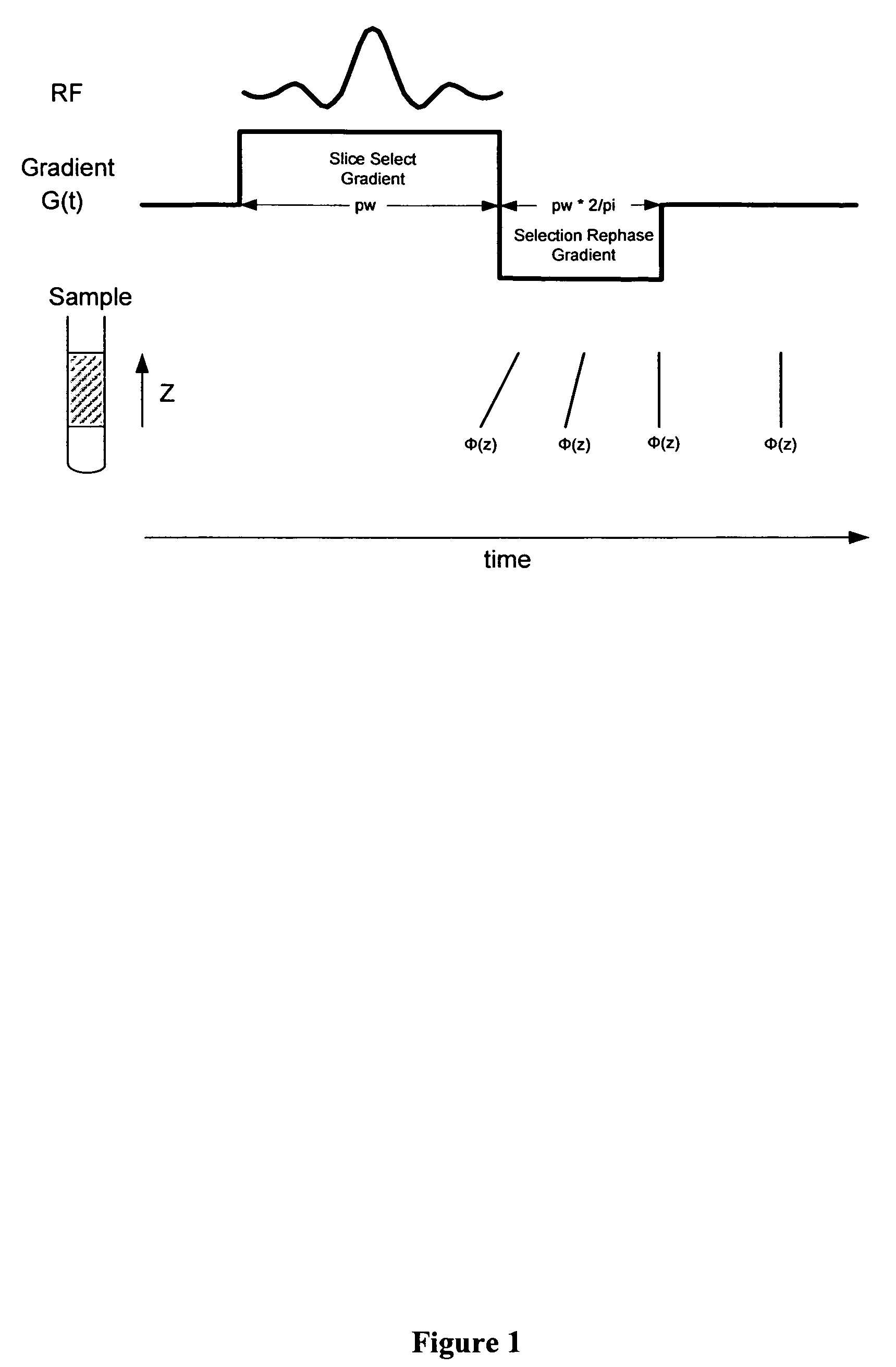
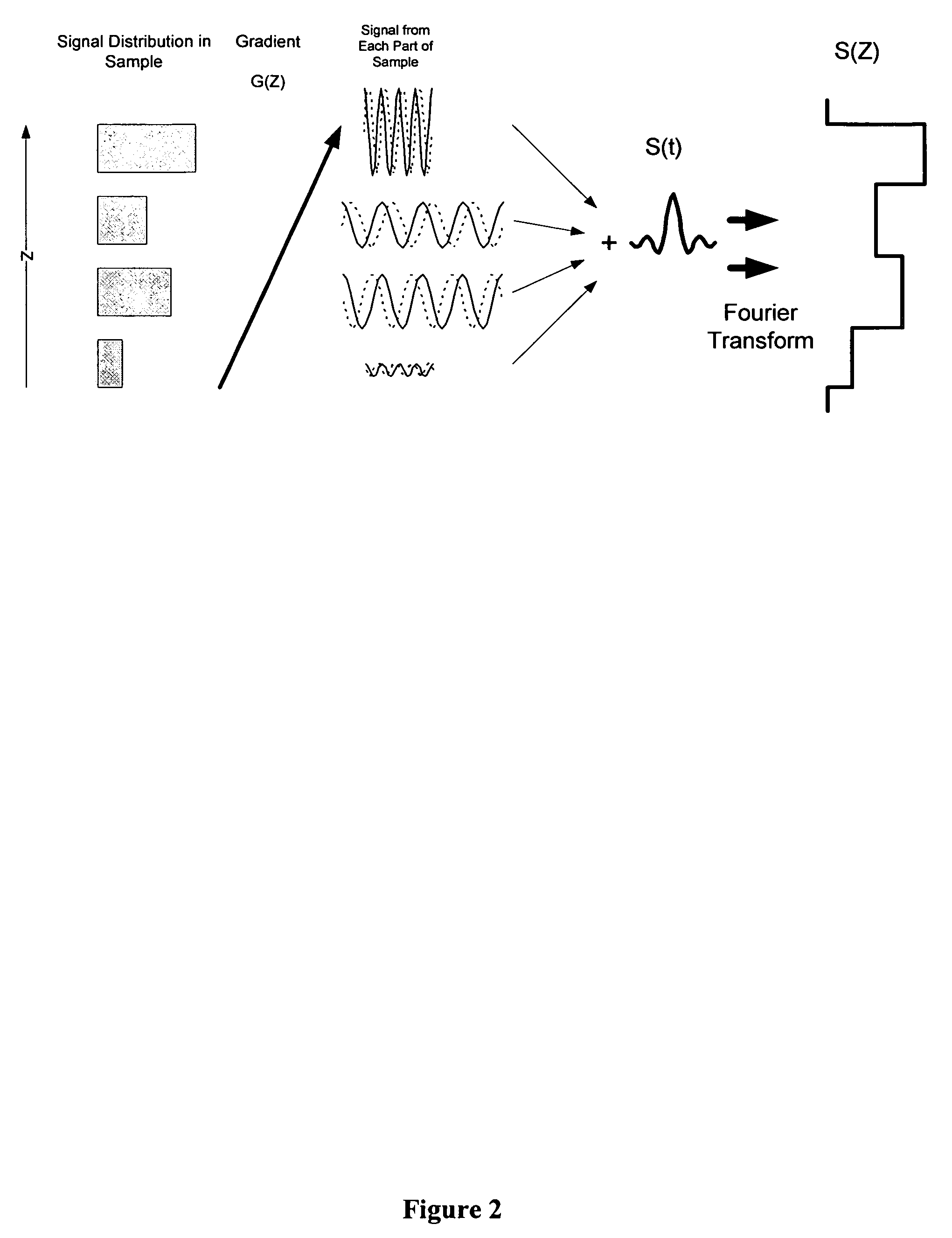
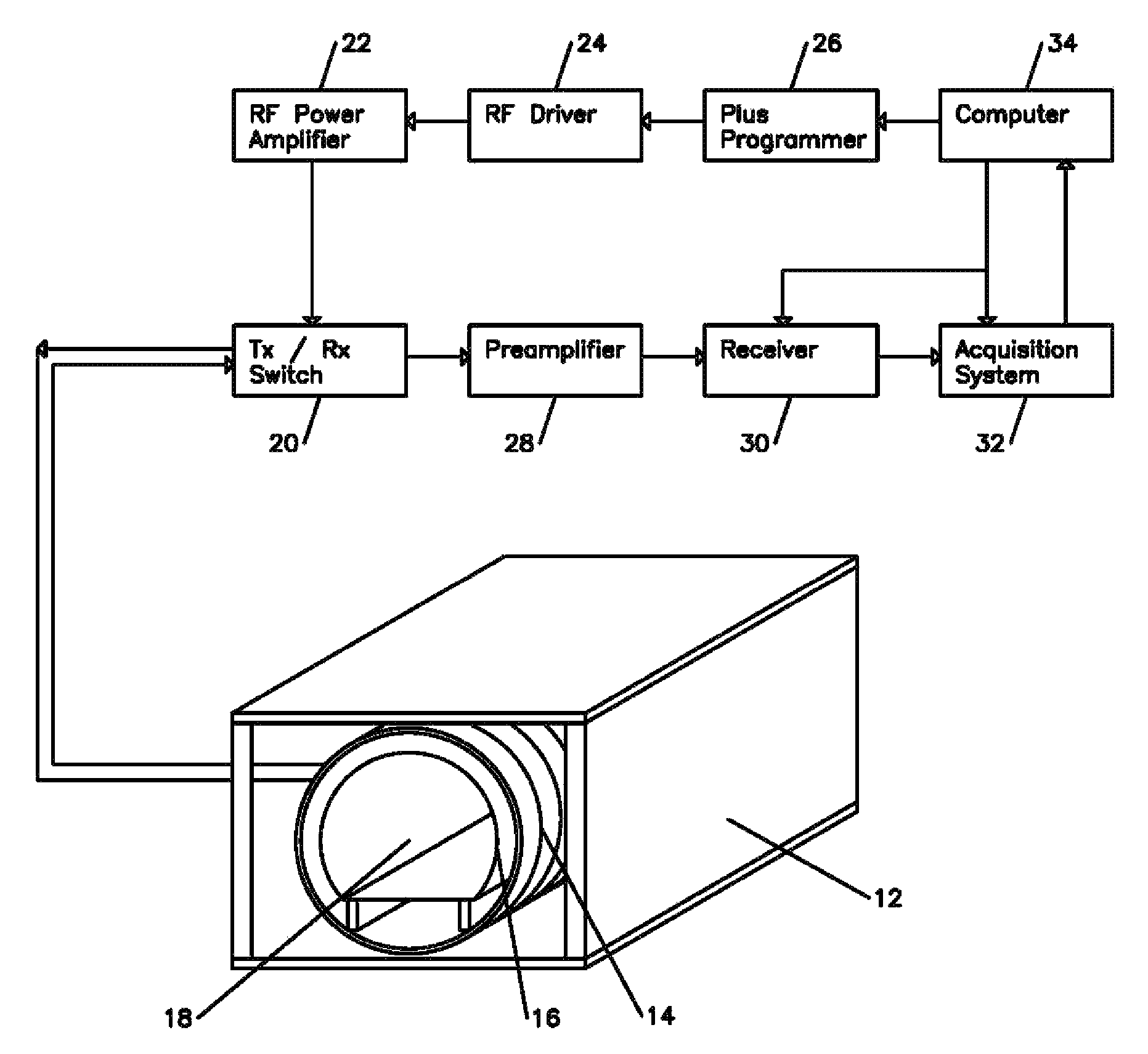
Simultaneous phase cycling for nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
InactiveUS7408346B2Less timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTwo-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopyProton NMR
The present invention discloses a method of simultaneously conducting more than one step of a radiofrequency phase cycle in a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiment. The method first involves providing a sample. Next, one or more radiofrequency pulses are applied to a plurality of spatially discrete slices of the sample under conditions effective to simultaneously conduct more than one step of a radiofrequency phase cycle in a single transient. Then, NMR signals generated from the step of applying the radiofrequency pulses are acquired. Finally, the NMR signals are processed to obtain an NMR spectrum.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Nuclear magnetic resonance method for body composition analysis
A method is disclosed for analyzing composition of a body part from nuclear magnetic resonance measurements made on the body part. The method includes exciting a predetermined sequence of nuclear magnetic resonance phenomena in the body part and measuring nuclear magnetic resonance signals from the body part. At least a part of the measured signals are composed into a measurement vector. The mass of the at least one constituent is determined as a predetermined function of the measurement vector. The predetermined function represents the at least one constituent and defines a standard for a range of at least one of compositional variations and temperature variations of the at least one constituent.
Owner:ECHOMRI
Nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer and slide table thereof
InactiveCN102608145AUnlimited sizeSmall sizeAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceHomogeneous magnetic field
The invention discloses a nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer and a slide table thereof. The slide table comprises a main frame, a sample support and a driving mechanism, the main frame is provided with a non-magnetic platform, a magnet box of the nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer is placed on the non-magnetic platform, the sample support is fixedly connected onto the non-magnetic platform, a detected sample is placed on the sample support, and the driving mechanism is arranged on the main frame, is connected with the magnet box of the nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer, and is used for driving the magnet box of the nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer to move so as to change the position of the magnet box of the nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer relative to the detected sample. By the aid of the slide table of the nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer, phase positions of a magnet in the nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer and the detected sample can be changed, so that different portions of the sample to be detected is placed in a uniform magnetic field, nuclear magnetic resonance measurement to different portions of the sample to be detected is realized, the size of the sample to be detected is not limited, and the dimension range of detected samples which are in nuclear magnetic resonance measurement is expanded.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
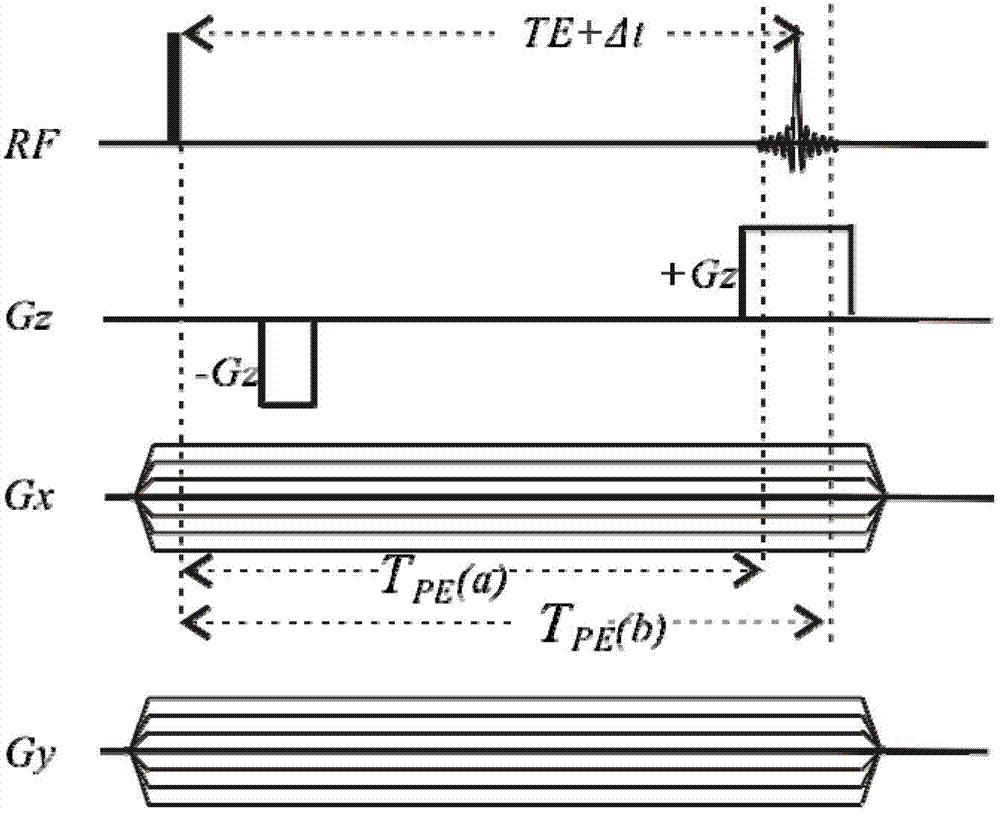
Method of obtaining one-dimensional high resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum under nonuniform magnetic field
The invention provides a method of obtaining a high resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum under a nonuniform magnetic field. The method comprises the steps of firstly applying a radio frequency pulse, rotating a magnetization vector from a Z axis to an XY plane, applying phase coding gradients along two directions, applying a sampling gradient of an echo plane spectrum imaging module on a third direction, collecting nuclear magnetic resonance signals, performing data permutation on the collected signals, and performing Fourier transform on a data matrix obtained by the permutation so as to obtain the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrums corresponding to a series of small voxels. The nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum corresponding to each small voxel is in high resolution; as the nonuniform magnetic field exists, the small voxels are directly projected in an accumulative mode, the obtain spectrums are in low resolution; the offset correction is performed on the spectrums corresponding to the small voxels, accumulative projection is then performed, the high resolution one-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum can be obtained, and the obtained high resolution spectrum facilitates chemical analysis in a heterogeneous system.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
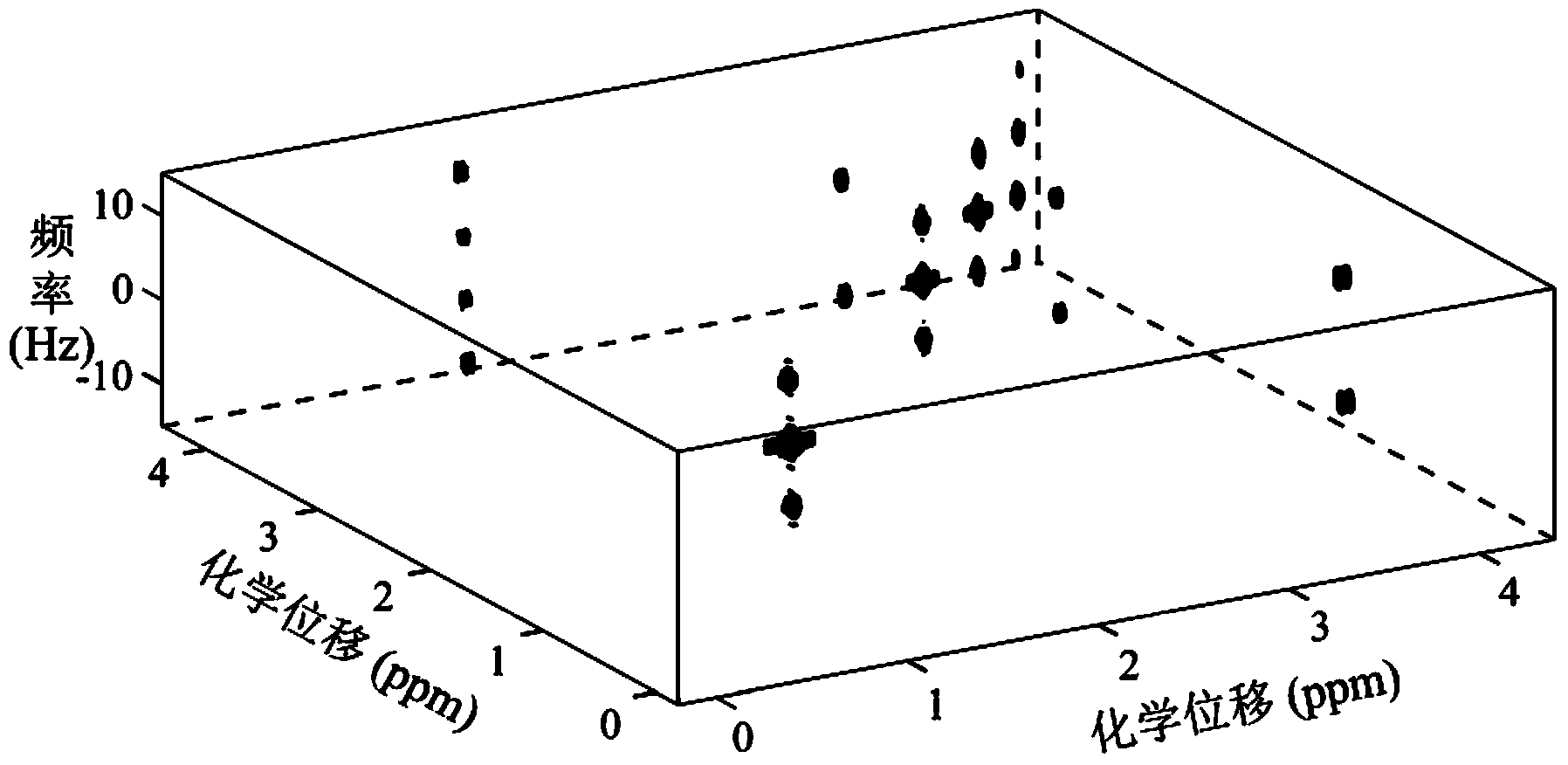
Method for obtaining nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimensional phase-sensitive J spectrum
ActiveCN106841270AHigh spectral resolutionImprove spectral qualityAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceFrequency spectrumData acquisition
The invention relates to a method for obtaining a nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimensional phase-sensitive J spectrum. The method comprises the following steps: putting a to-be-tested sample into a nuclear magnetic tube and conveying the nuclear magnetic tube loaded with the to-be-tested sample into a detection chamber of a magnetic resonance spectrometer; invoking a conventional one-dimensional hydrogen spectrum pulse sequence to acquire a one-dimensional hydrogen spectrum, obtaining signal peak distribution and spectrum width information, and measuring the non-selective 90-degree radio frequency pulse width; inputting a compiled two-dimensional phase-sensitive J spectrum pulse sequence into the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, opening a chiro pulse weak selection layer gradient combination module and a two-dimensional phase-sensitive J spectrum pulse sequence sampling module of the two-dimensional phase-sensitive J spectrum pulse sequence; setting two-dimensional phase-sensitive J spectrum pulse sequence experiment parameters, inspecting that the experiment parameters are set correctly, and then executing data sampling; after the completion of data sampling, performing corresponding data splicing and two-dimensional Fourier transform to obtain a two-dimensional frequency spectrum containing J coupling information and chemical displacement information; performing two-dimensional phase-sensitive treatment on the obtained two-dimensional frequency spectrum to obtain the two-dimensional phase-sensitive J spectrum.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
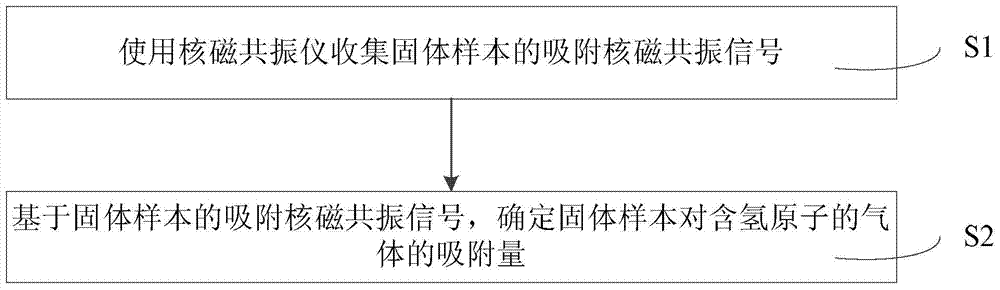
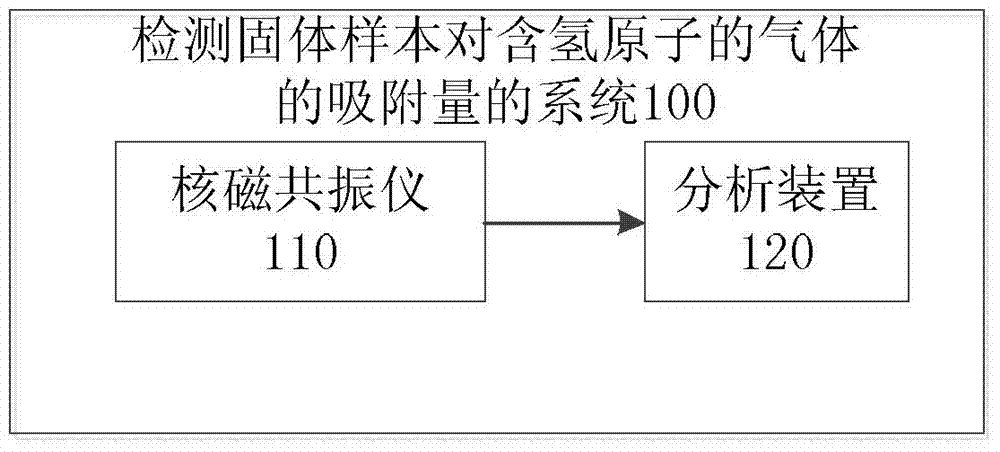
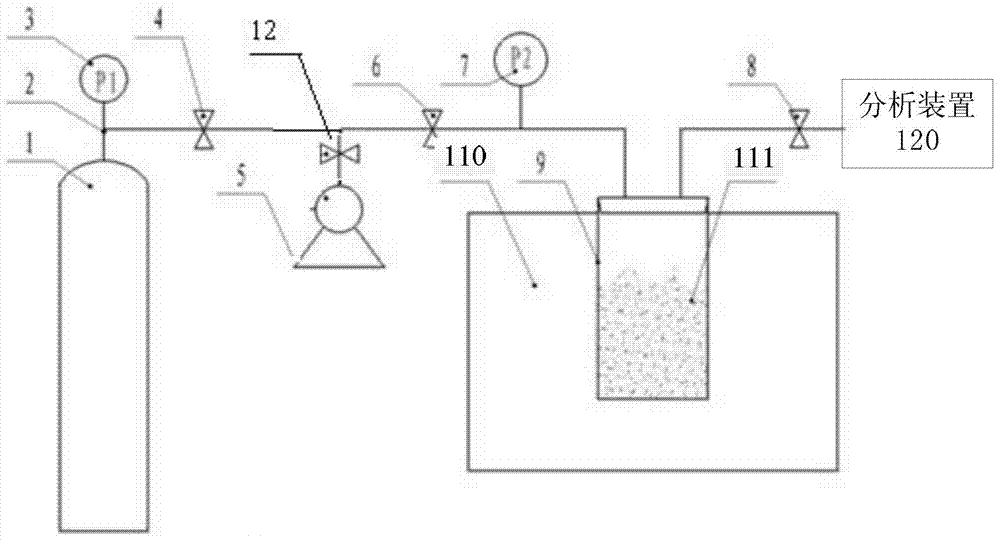
Method and system for detecting adsorption capacity of solid sample to hydrogen-atom-containing gas
ActiveCN104237283AEasy to operateHigh precisionAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePorosityNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a method for detecting the adsorption capacity of a solid sample to hydrogen-atom-containing gas. The method comprises the following steps: (1) collecting an adsorption nuclear magnetic resonance signal of the solid sample by using a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer; (2) determining the adsorption capacity of the solid sample to the hydrogen-atom-containing gas according to the adsorption nuclear magnetic resonance signal of the solid sample. The method disclosed by the invention is convenient to operate, simple in system, high in precision and low in cost, can be used for measuring the adsorption capacity of the solid sample to the hydrogen-atom-containing gas such as methane, so as to draw an adsorption-desorption curve, and can also be used for measuring contributions of different pores to adsorption / desorption so as to analyze the porosity characteristic of the solid sample. Correspondingly, the invention also provides a system for detecting the adsorption capacity of the solid sample to the hydrogen-atom-containing gas, a method for detecting the porosity of a solid and a method for drawing the adsorption-desorption curve of the solid sample to the hydrogen-atom-containing gas.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Two-dimensional diffusion-ordered nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy method used for any magnetic field environments
ActiveCN105651803ABreak through limitationsAchieve separationAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceLiquid separationSpectroscopySolvent
The invention discloses a two-dimensional diffusion-ordered nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy method used for any magnetic field environments and relates to nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy detection methods. The method includes the steps of 1), measuring pi / 2 nonselective radiofrequency pulse width and (pi / 2) solvent selective radiofrequency pulse width required by sample stimulation; 2), importing a nuclear magnetic resonance pulse sequence on a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer; 3), turning on an intermolecular zero-quantum coherence signal selection module, a time-invariant evolution module and a diffusion order module of the nuclear magnetic resonance pulse sequence and setting experiment parameters of all modules; 4), executing data sampling; 5), performing data post-processing to obtain high-resolution two-dimensional diffusion-ordered spectroscopy. The two-dimensional diffusion-ordered nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy method used for any magnetic field environments does not need any shimming operation, a sample preprocessing process and any special hardware devices, is simple, convenient and feasible and is applicable to any conventional nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometers.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
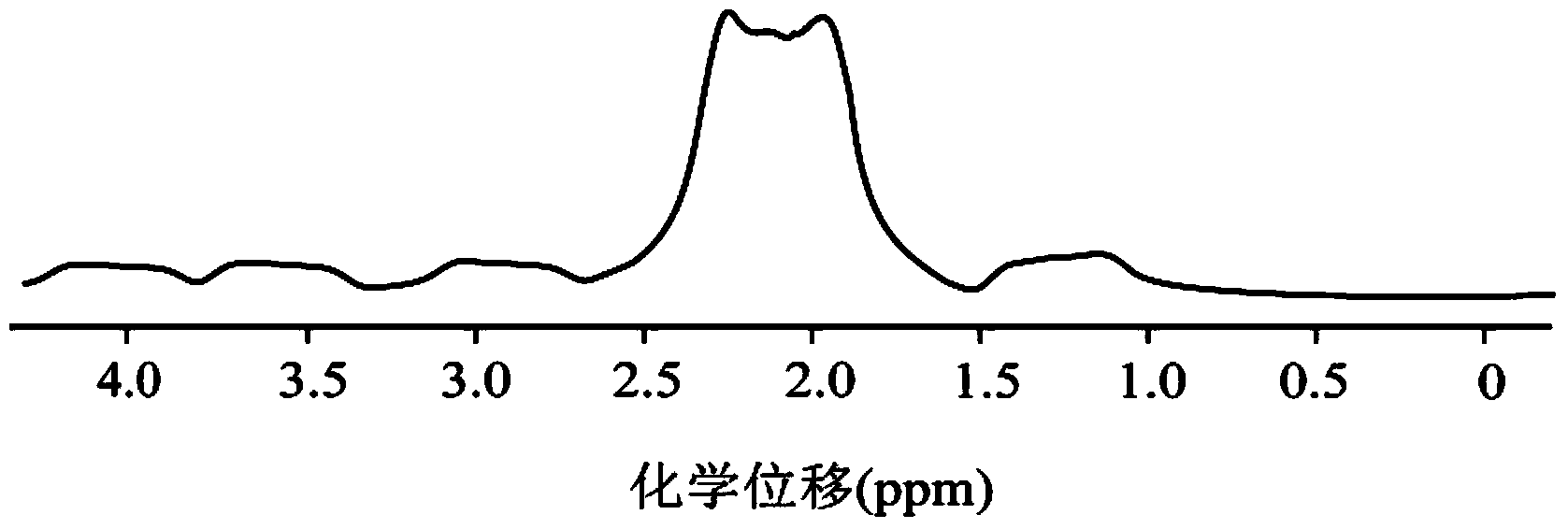
Nuclear magnetic resonance detection method for biological tissue
ActiveCN105158289AFast samplingThe influence of magnetic field inhomogeneity is overcomeAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceSpectral width
The invention discloses a nuclear magnetic resonance detection method for biological tissue, and relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy detection method. A biological tissue sample to be detected is put into a nuclear magnetic test tube, and then the test tube containing the sample is put into a detection magnetic body of a nuclear magnetic spectrometer; a one-dimensional spectrum is sampled through a conventional one-dimensional pulse sequence, the width of the spectral line is obtained to provide a basis for setting a spectral width parameter, and meanwhile a line width value reflects the nonuniformity situation of a magnetic filed of the biological tissue sample; a pulse sequence which is well compiled in advance is introduced onto a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer; an intermolecular zero-quantum coherent signal selection module, a folding-correction module, a solvent suppression module and a J modulating signal sampling module of the pulse sequence are started, and experiment parameters of all the modules are set; after setting of the experiment parameters is completed, the artificial shimming operation process is skipped, and data sampling is directly executed; after data sampling is completely completed, related data post-processing is conducted, and a high-resolution two-dimensional J resolution spectrum which is free of the influence of a nonuniform magnetic field is obtained.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
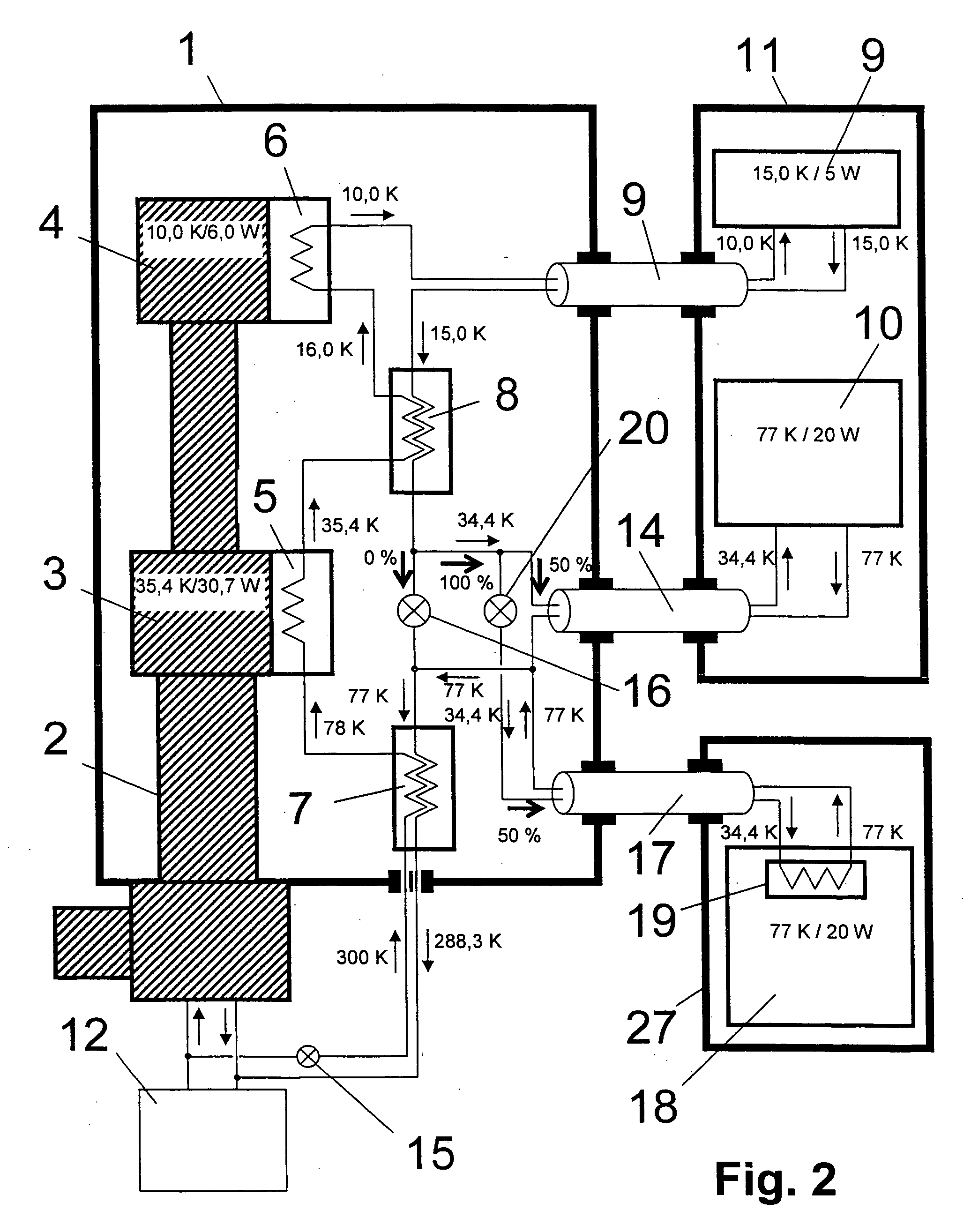
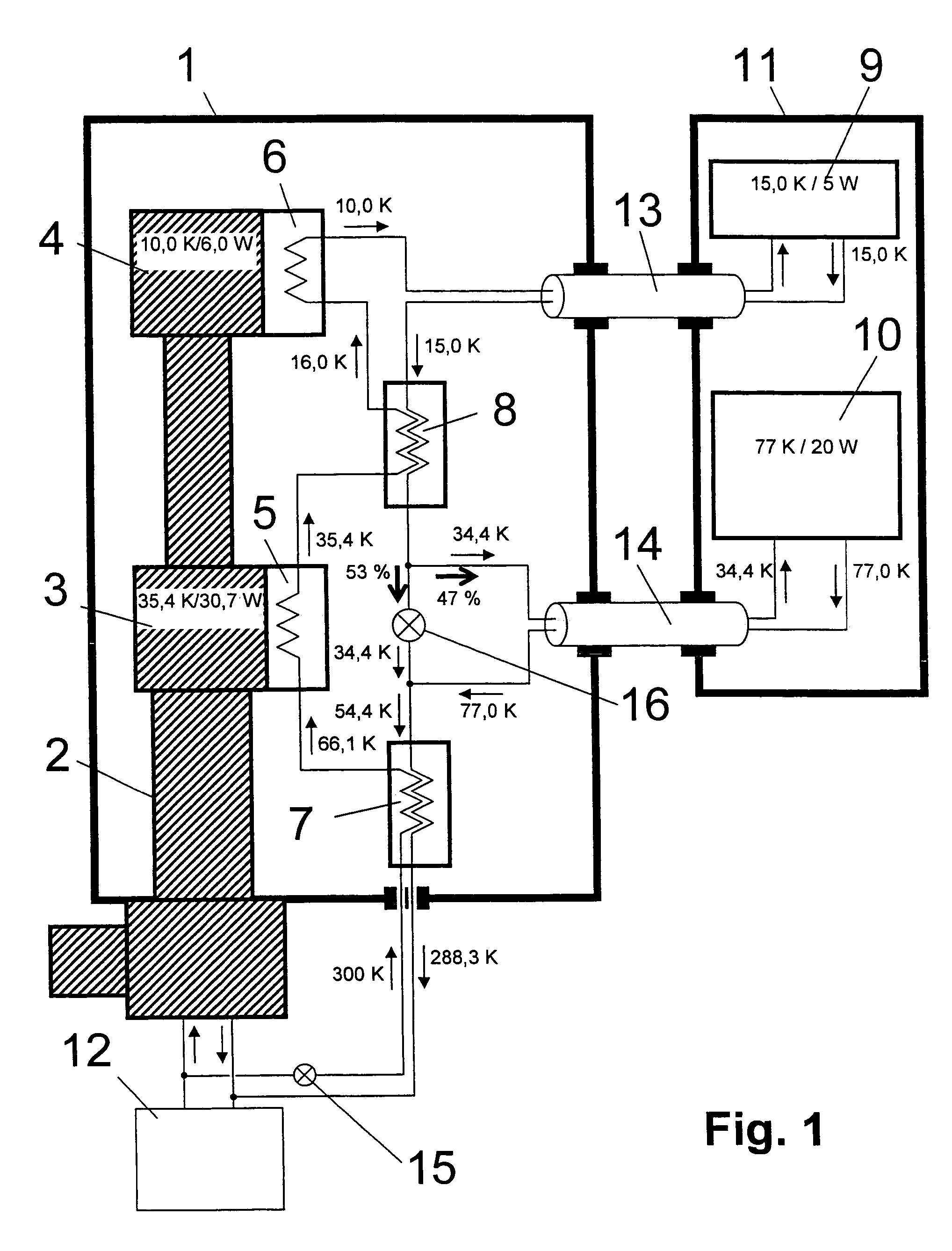
NMR spectrometer with refrigerator cooling
ActiveUS7222490B2Without additional expenseAvoid the needMagnetic measurementsCompression machinesEngineeringRefrigerated temperature
An NMR spectrometer comprising an NMR magnet system (27) disposed in a helium tank of a cryostat and an NMR probe head (11) disposed in a room temperature bore of the cryostat, which contains a cooled RF resonator (9) for receiving NMR signals from a sample to be investigated, and a cooled pre-amplifier (10), wherein the NMR probe head (11) is cooled by a common multi-stage compressor-operated refrigerator (2), wherein the refrigerator (2) comprises a cold head and several heat exchangers (5, 6) at different temperature levels, wherein the refrigerator (2) is disposed at a spatial separation from the cryostat in a separate, evacuated and thermally insulated housing (1) and wherein at least one cooling circuit with cooling lines, which are thermally insulated by a transfer line (13, 14) is disposed between the housing (1) containing the heat exchangers (5, 6) and the NMR probe head (11), is characterized in that additional cooling lines to an LN2 tank (18) or radiation shield (21) disposed in the cryostat and surrounding the helium tank are provided, and the refrigerator (2) also cools the LN2 tank (18) or the radiation shield (21). The inventive NMR spectrometer comprises a simple and inexpensive device for matching the holding time of LN2 to that of LHe through cooling the LN2 tank using the refrigerator provided for cooling the NMR probe head and without great expense.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
Method for detecting illegal cooking oil
ActiveCN102706915AQuick checkEasy to operateAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceOil and greaseSolvent
The invention discloses a method for detecting illegal cooking oil and relates to the method for detecting fat. The method comprises the steps of: sampling, weighing a liquid oil sample to be measured, dissolving the liquid oil sample by a deuterated solvent, transferring the solution to a nuclear magnetic tube, and collecting hydrogen spectrum and carbon spectrum data of the sample through a high-field nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer; analyzing data, leading out a nuclear magnetic spectrogram, judging normal edible oil and drainage oil by comparison of a specific fingerprint area, and refining the illegal oil just the same as the fingerprint area; distinguishing by concrete fatty acid constituents, carrying out aggregate analysis on concrete data of total hydrogen quantity of saturated fatty acids, concrete content of various fatty acids, relative content of oxide and relative content of free acid in different edible oil obtained by data analysis, analyzing the spectrogram by a stoichiometry method to obtain a result, collecting the spectrogram of an oil product by NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance), and then comprehensively distinguishing the illegal cooking oil according to each constituent in the oil product by a plurality of indexes.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
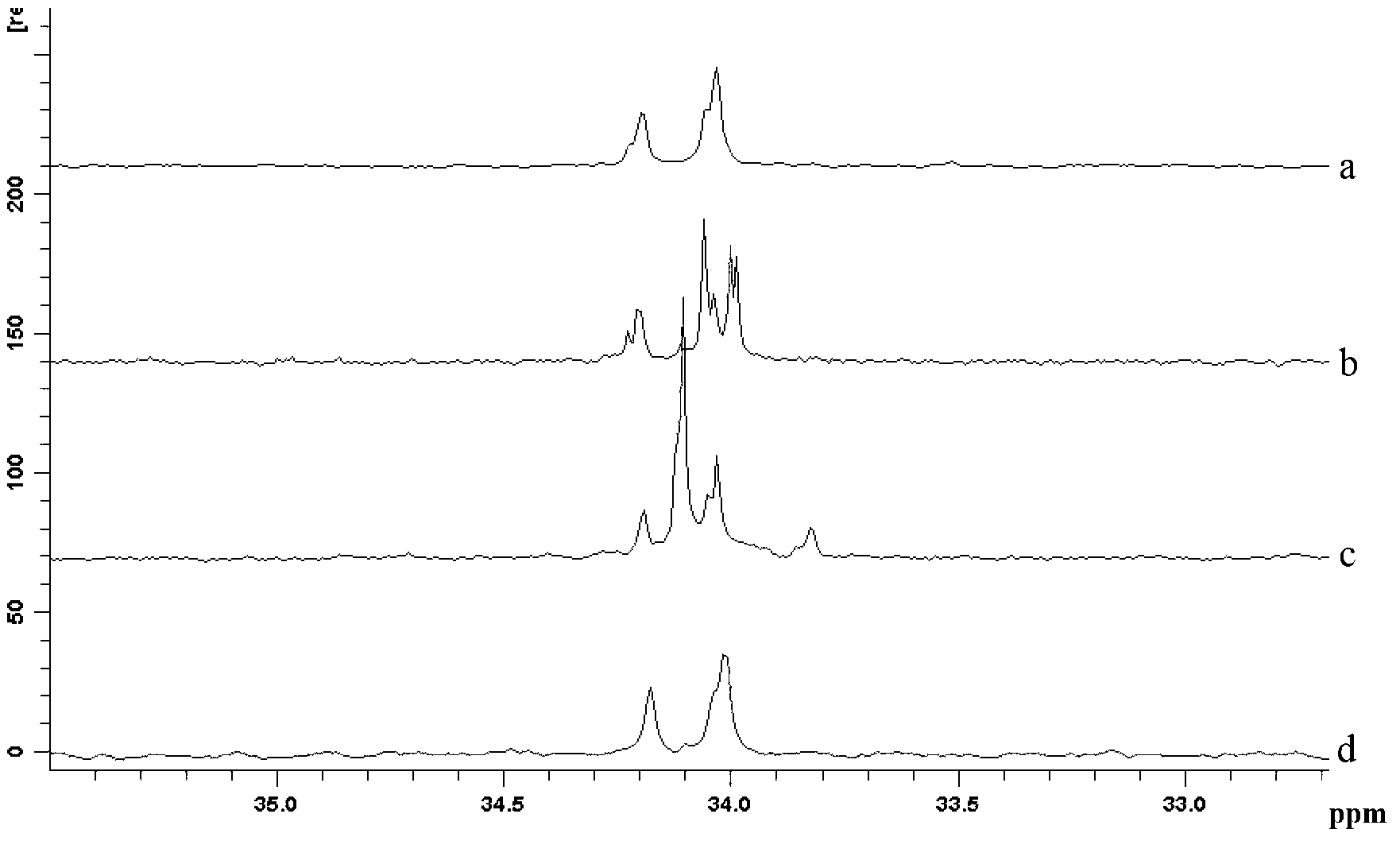
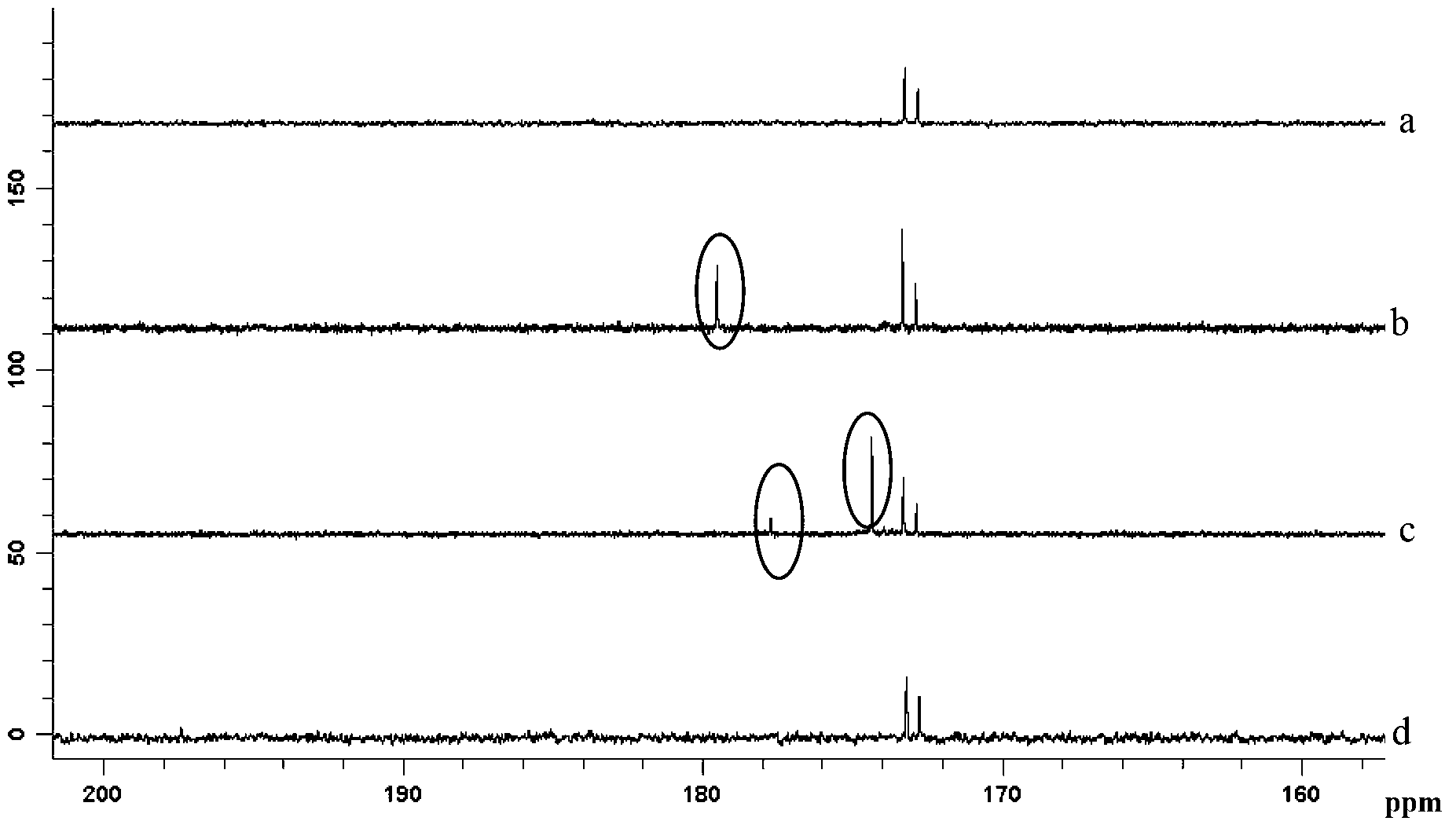
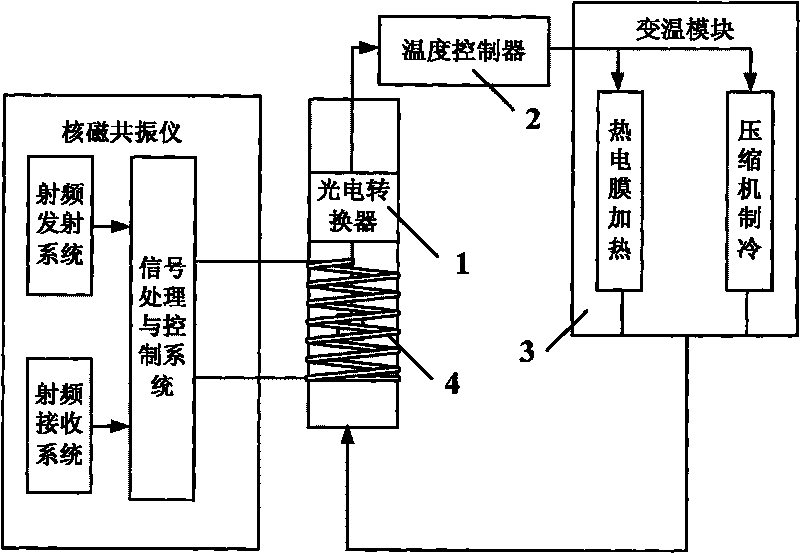
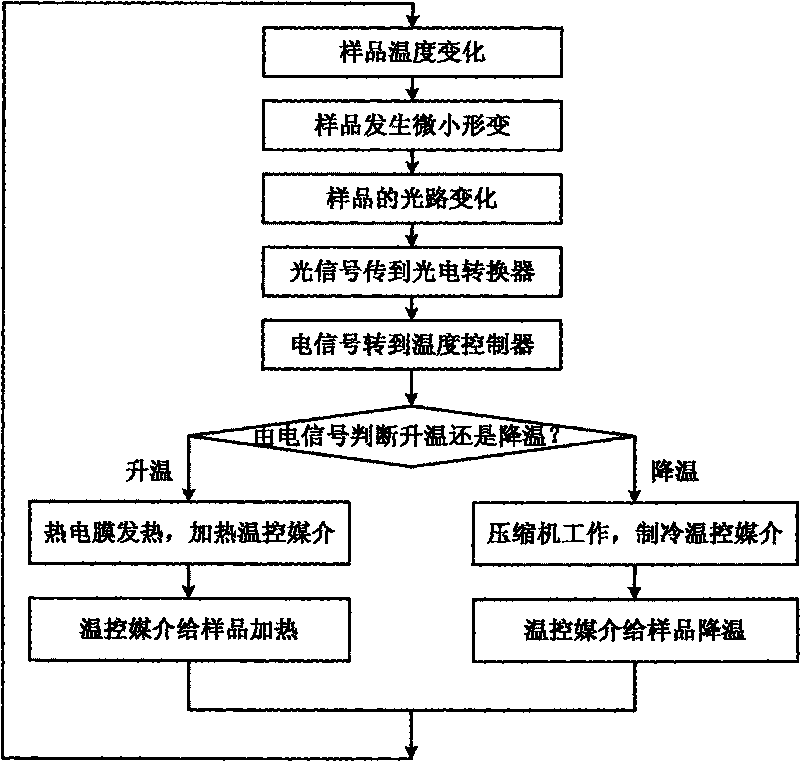
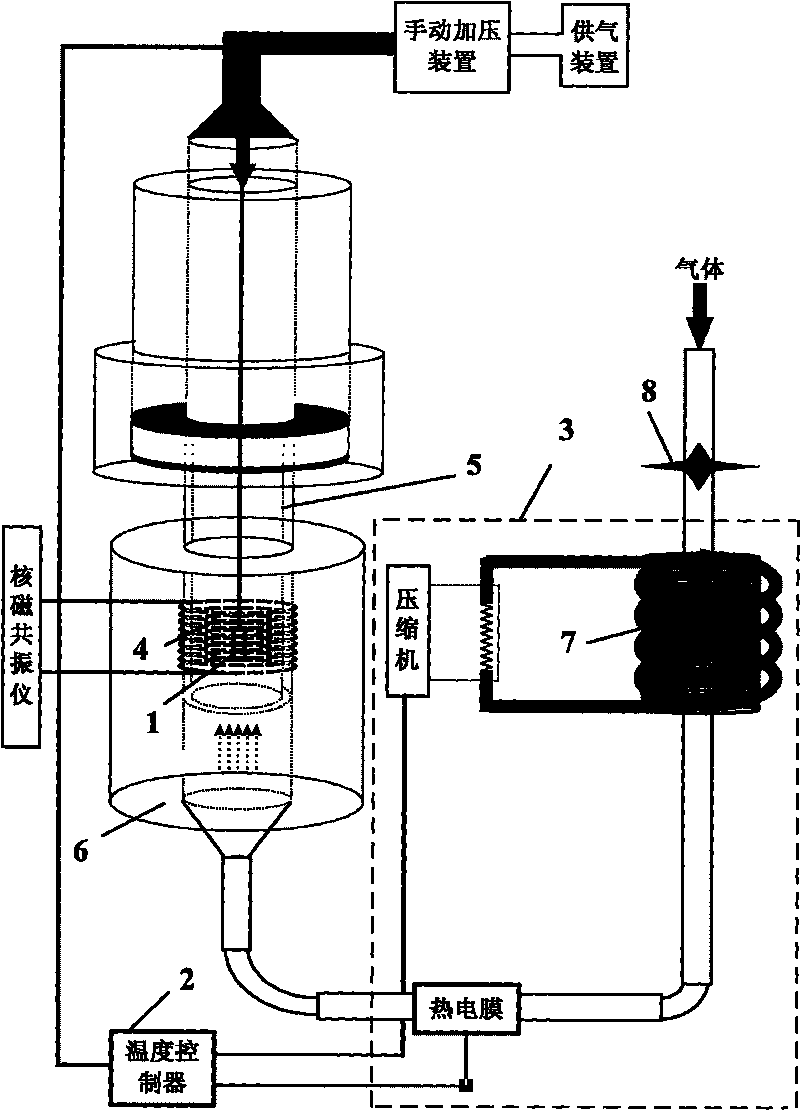
Temperature control system for nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer
InactiveCN101692122AGood repeatabilityImprove stabilityMeasurements using magnetic resonanceTemperature controlControl system
The invention discloses a temperature control system for a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, which comprises a photoelectric transducer, a temperature controller, and a temperature change module; the temperature change of a sample to be detected causes the deformation of the sample so as to cause the change of an optical path; optical signals generated by the change of the optical path are transmitted to the photoelectric transducer through an optical fiber; the photoelectric transducer converts the optical signals to electric signals and transmits the electric signals to the temperature controller; and the temperature controller generates corresponding control signals according to the input electric signals to control the temperature change module to adjust the temperature of the sample, wherein the temperature change module comprises a refrigeration module, a heating module and a heat exchange pipeline. The temperature control system can ensure that the temperature in the sample testing process is maintained to be constant, also can freely set the temperature of the sample in a temperature range allowed by experiments, and can conveniently and accurately control the temperature of the sample according to the experiment requirements so as to meet the requirements of special experiments, and has no influence on the work of the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer.
Owner:SUZHOU NIUMAG ELECTRONICS TECH
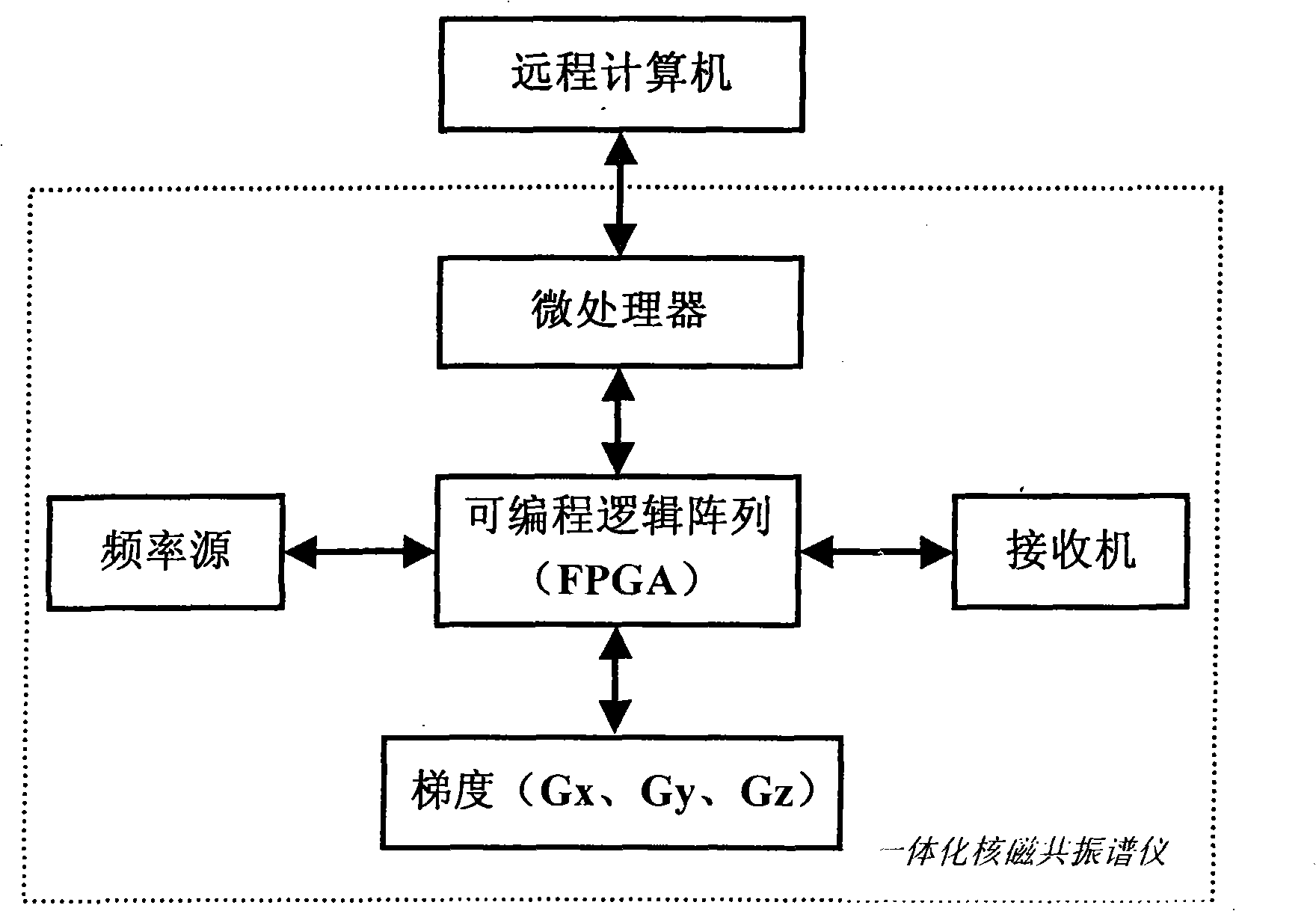
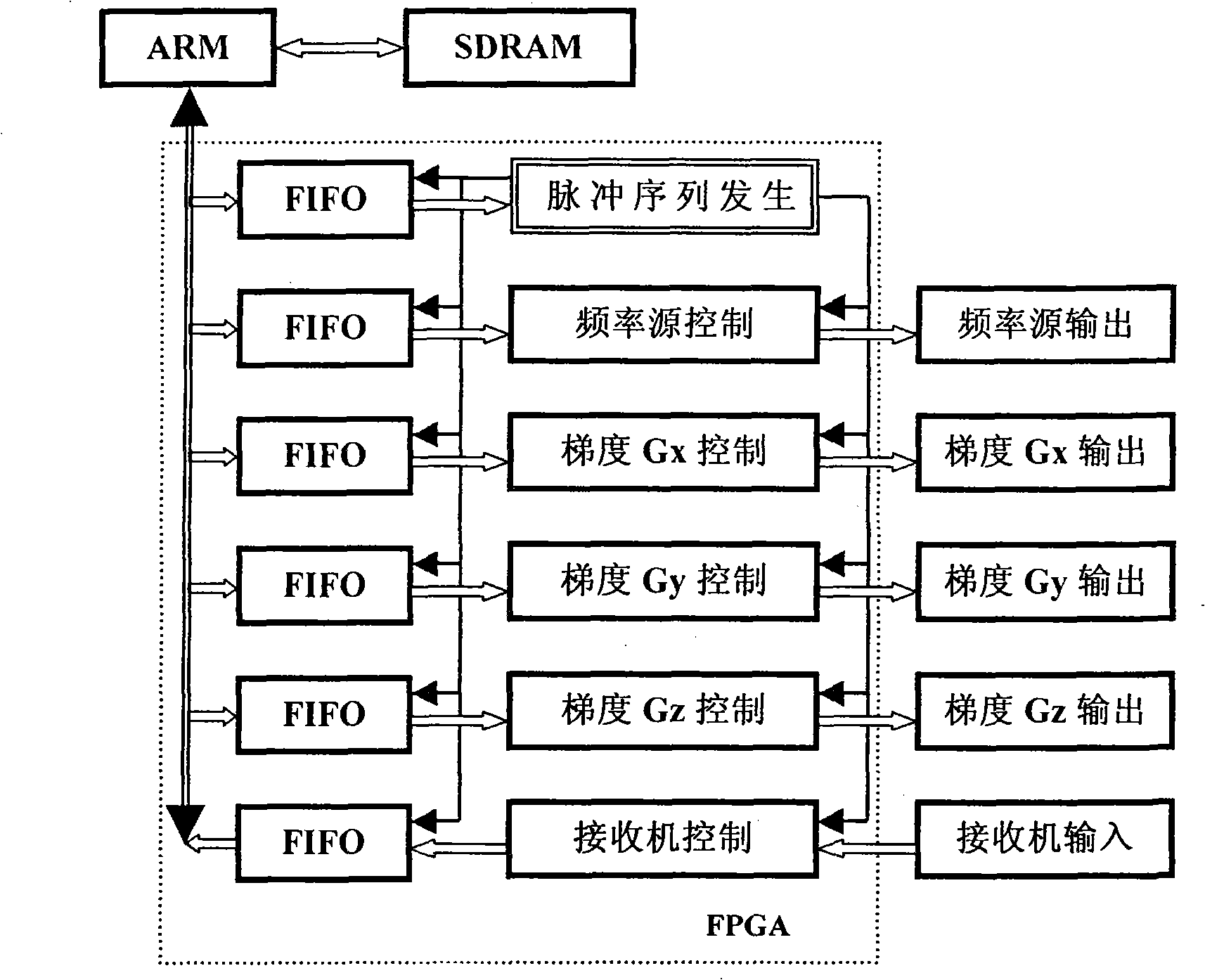
Control method for integrated nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer data communication
InactiveCN101271076AHighly integratedReduce development costsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMRNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceProgrammable logic device
The invention specifically relates to a control method of the data exchange of an integrated nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, and the method adopts a large-scale programmable logic device FPGA aiming at the nuclear magnetic resonance and real-time needs of an imaging test thereof as well as each function module of the spectrometer, comprising a digital frequency source, a digital receiver, a gradient waveform generator and a pulse sequence generator, etc. The interior of the FPGA is constructed with an independent FIFO (or a dual port RAM), the data of the initial part of the sequence is firstly written into the FIFO according to the needs of the different pulse sequences, the data in each FIFO is carried out the real-time reading and is output and the corresponding function is further realized under the control of the pulse sequence generator. The control method has the advantage that one ARM chip is used as a CPU of the whole system, which is coordinated with the FPGA to work by a single bus, at the same time, all the function modules are controlled, then the whole nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer system is concentrated on a single plate, the hardware of the system is not dependent on a PC machine, thus having more portable and smaller table type nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer and having high integration level and saving development cost.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
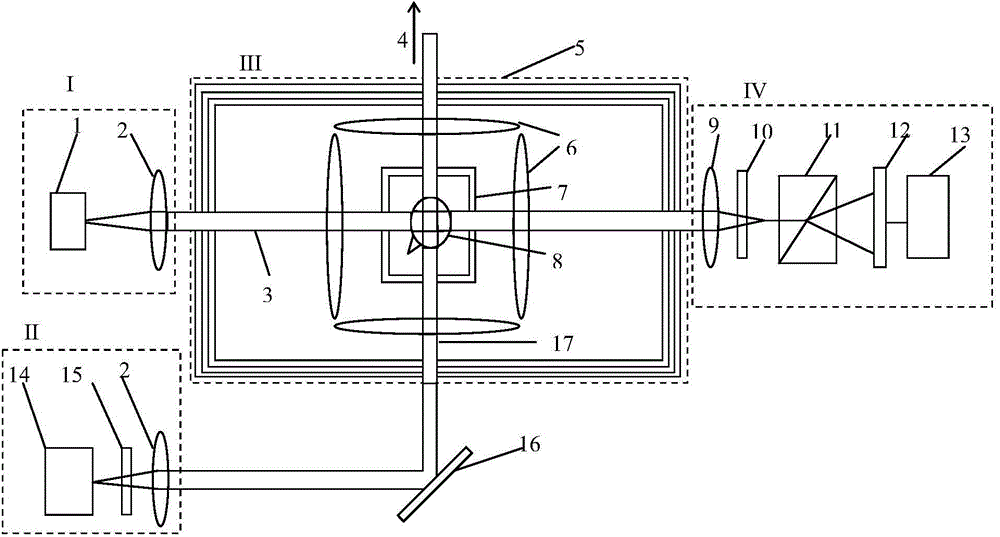
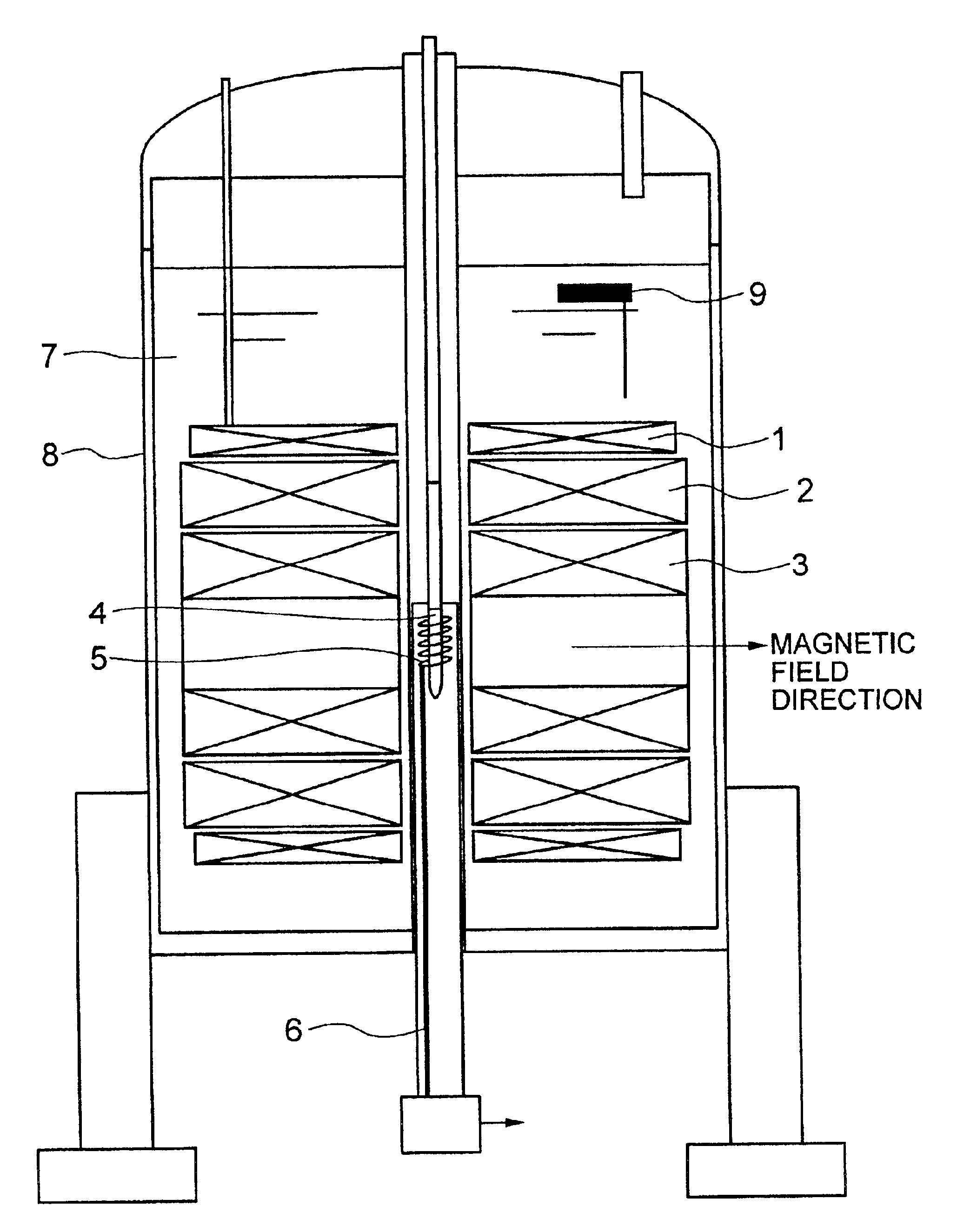
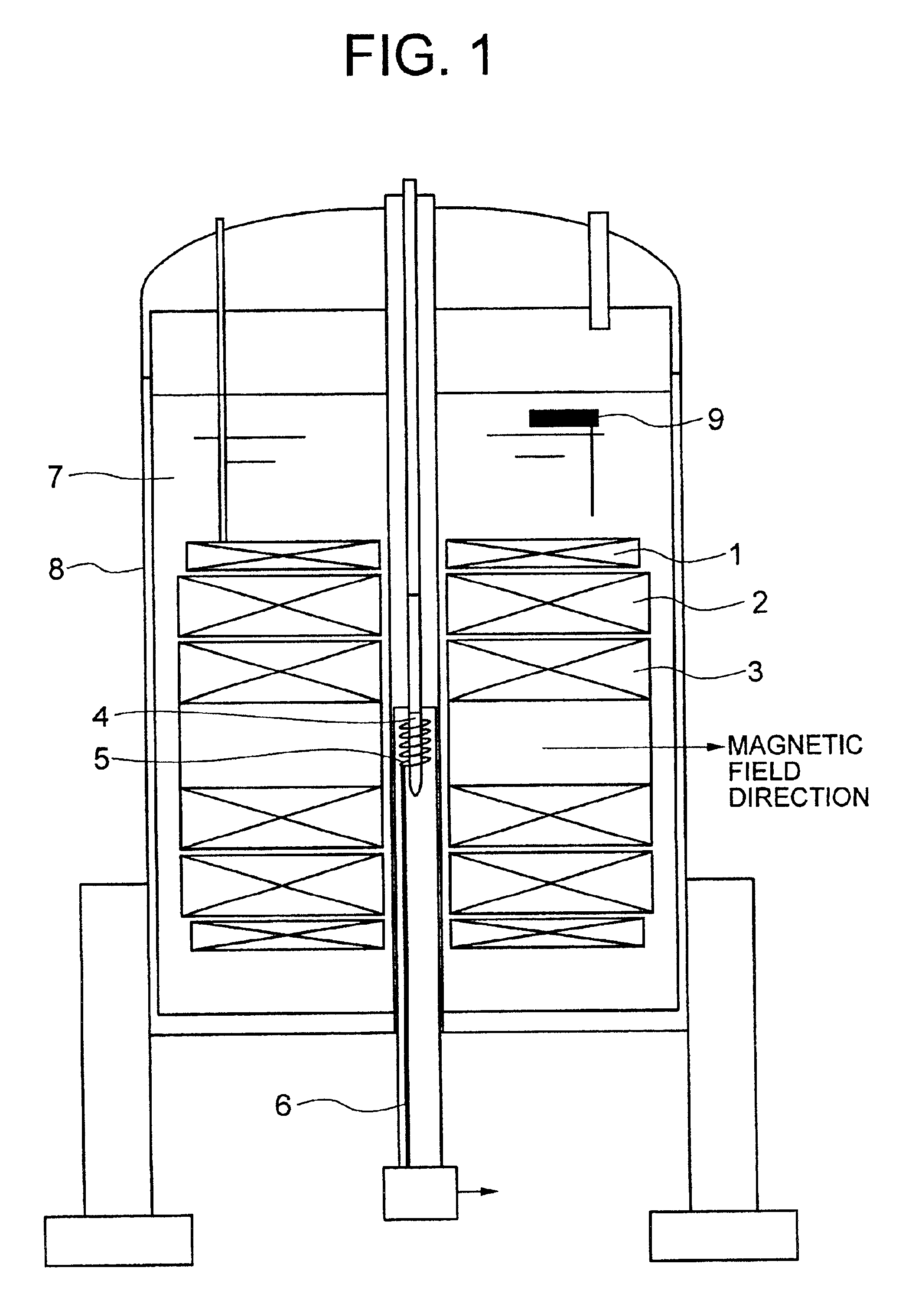
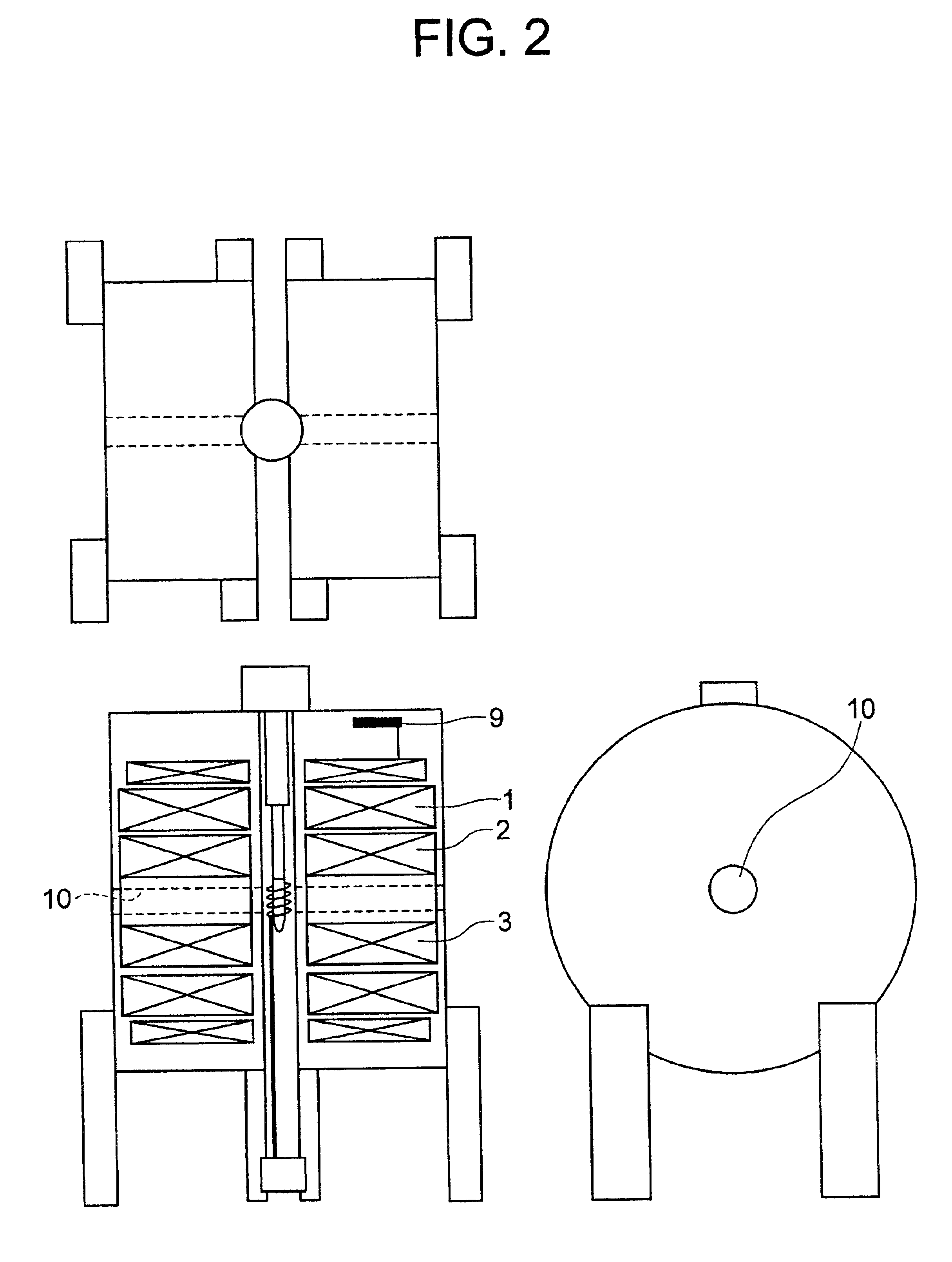
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer for liquid-solution
InactiveUS6897657B2Maintain compatibilityImprove the uniformity of the magnetic fieldElectromagnets without armaturesAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceSplit magnetAir core
In a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, the shape of a detection coil is changed from a conventional cage type to a solenoid type of higher sensitivity. Accordingly, differing from the conventional superconductive magnet of multilayer air core solenoids, a superconductive magnet is right and left divided to split magnets for generating 11 T, preferably, 14.1 T in the horizontal direction, and the magnetic field uniformity is set to 0.001 ppm or less and the temporal stability is set to 0.001 ppm or less.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com