Patents
Literature
33 results about "Nmr magnet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
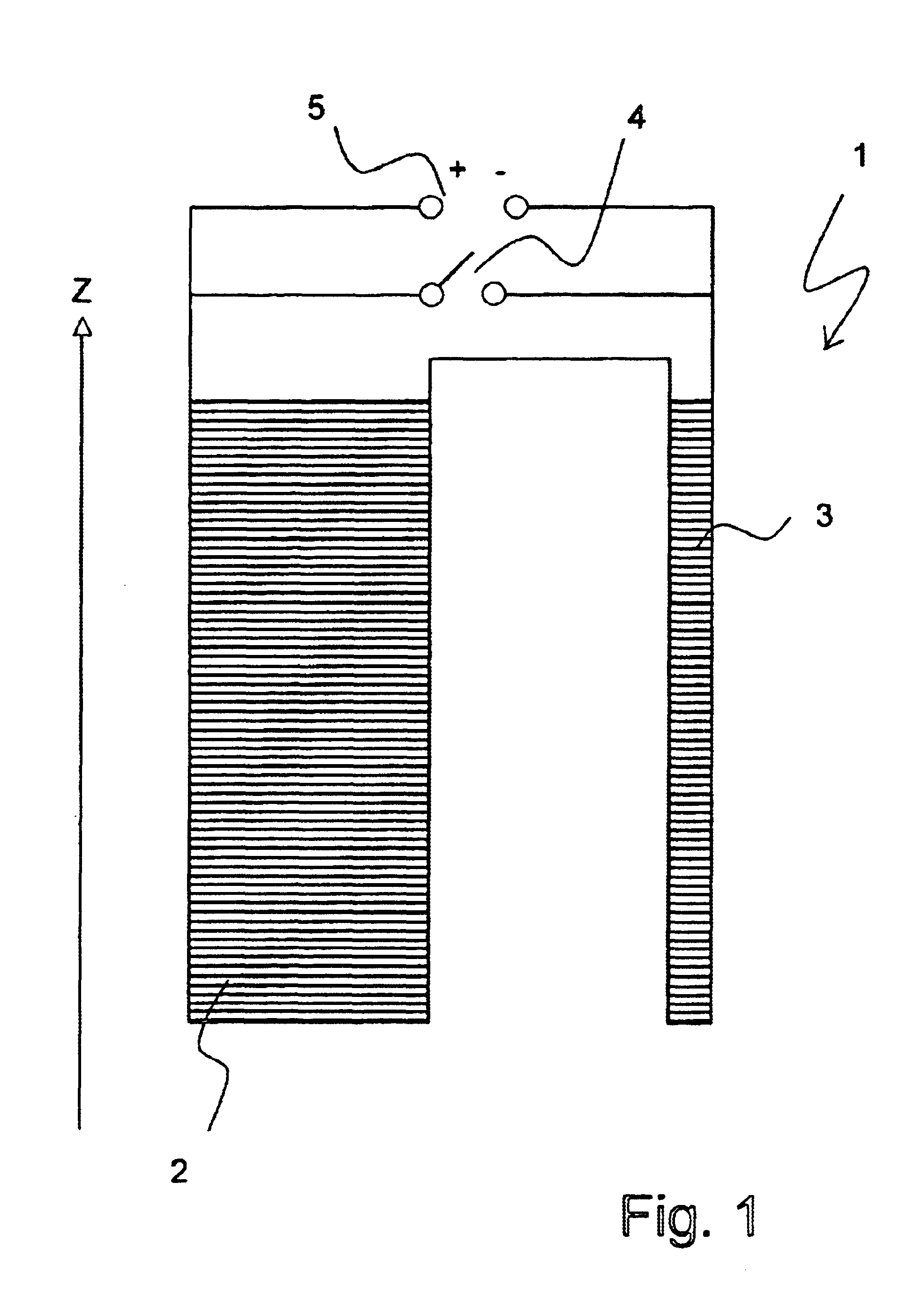
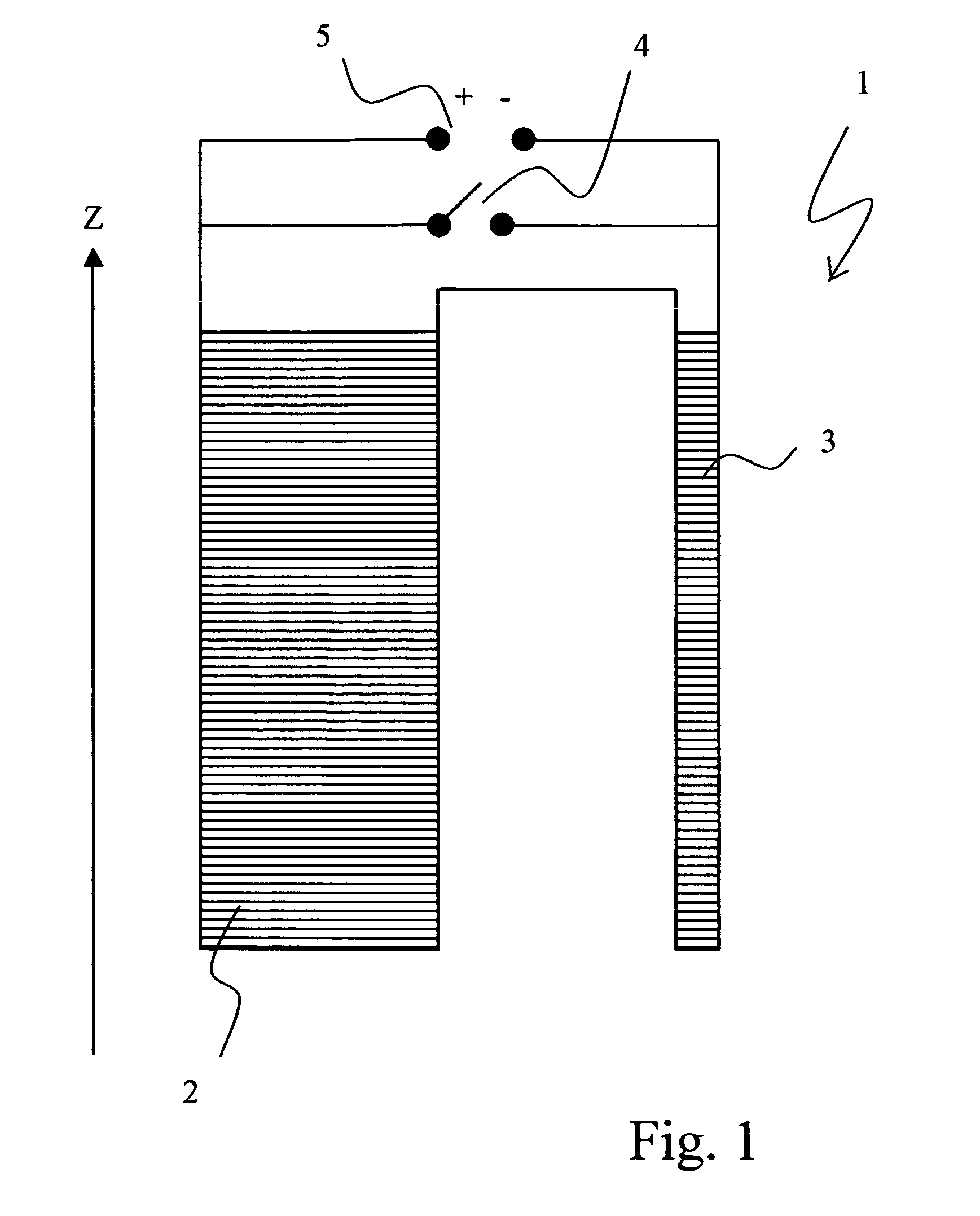
The NMR magnet is arguably the most important part of the NMR spectrometer. The NMR magnet is one of the most expensive components of the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer system. NMR magnet technology has evolved considerably since the development of NMR.
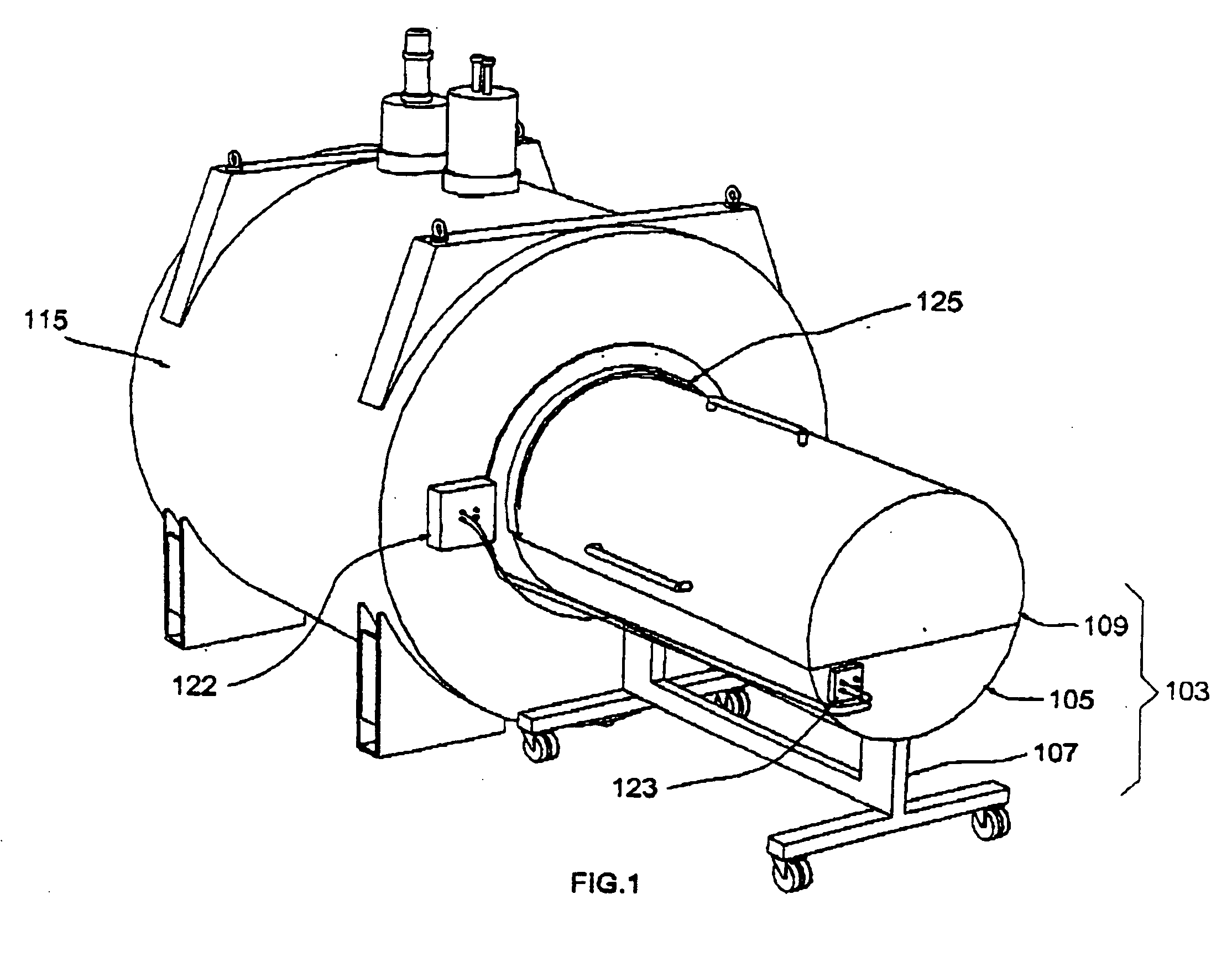
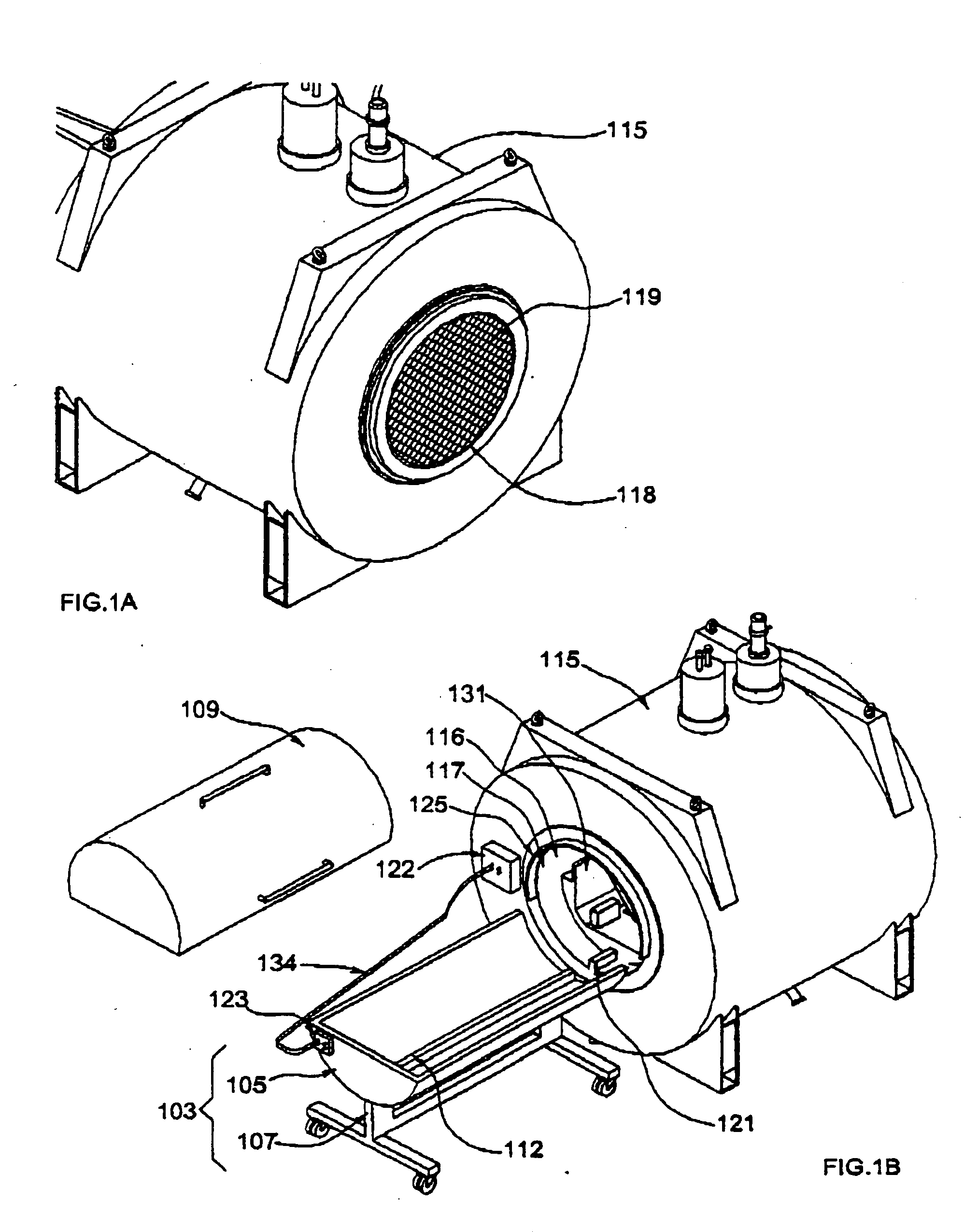
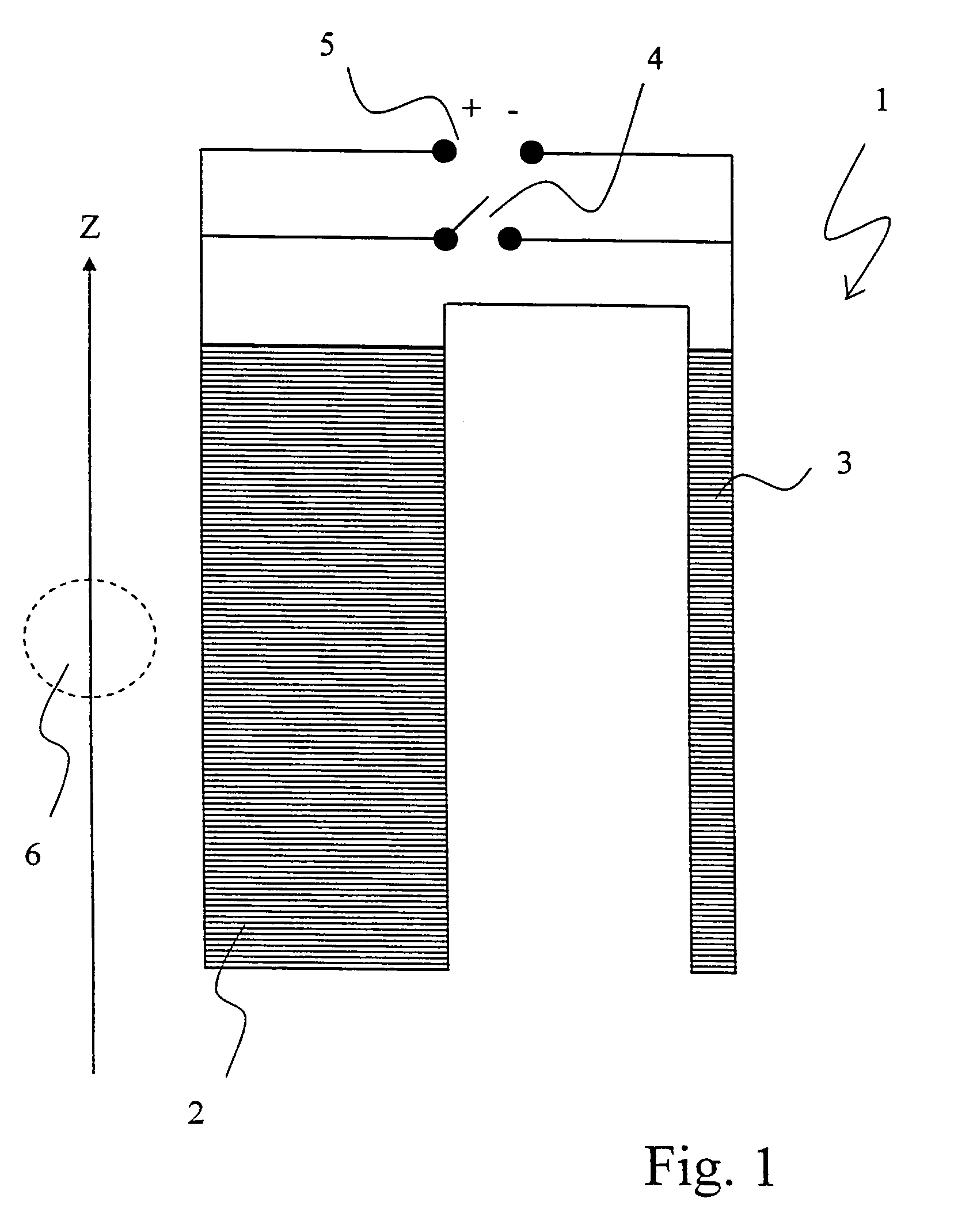
Radio frequency shield for nuclear magnetic resonance procedures
InactiveUS20030088175A1Magnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceEngineering
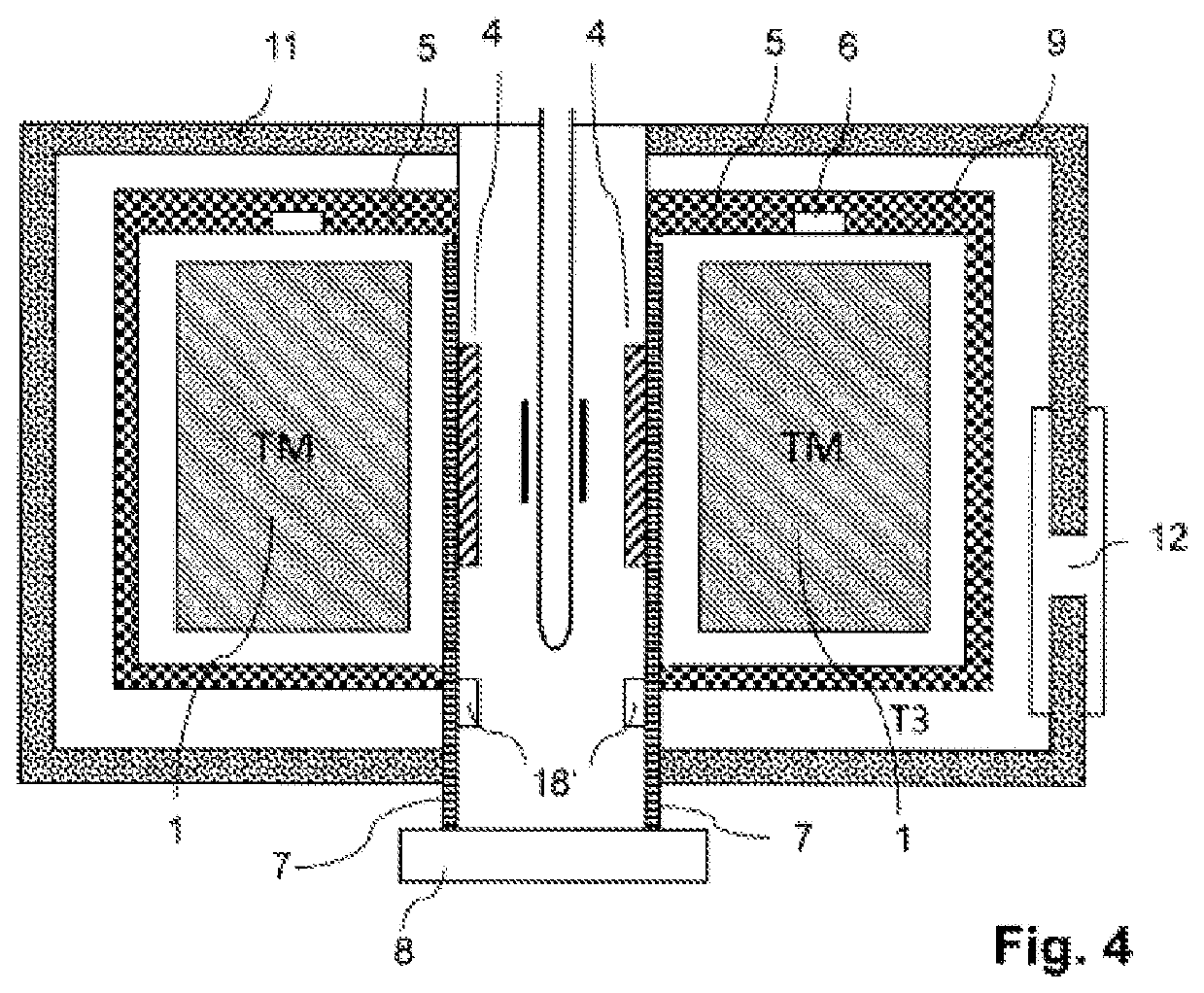
An apparatus and method for providing RF shielding for performing nuclear magnetic resonance ("NMR") procedures, comprising a radio-opaque holder in combination with radio-opaque magnet components to form an RF shield around a patient undergoing an NMR procedure. In embodiments, a radio-opaque holder having a radio-opaque bottom portion and a radio-opaque canopy is adjoined to an NMR magnet having a radio-opaque cryostat and a radio-opaque service end cap to form an RF shield. A patient is placed on a patient support unit located in the holder bottom portion. The patient support unit, including the patient, is then inserted into the cavity of the NMR magnet and a canopy is placed on top of the bottom portion of the holder. An RF shield is thus created comprising the canopy, the bottom portion, the cryostat of the magnet, and an end cap on the service end of the magnet.
Owner:ADVANCED VETERINARY TECH
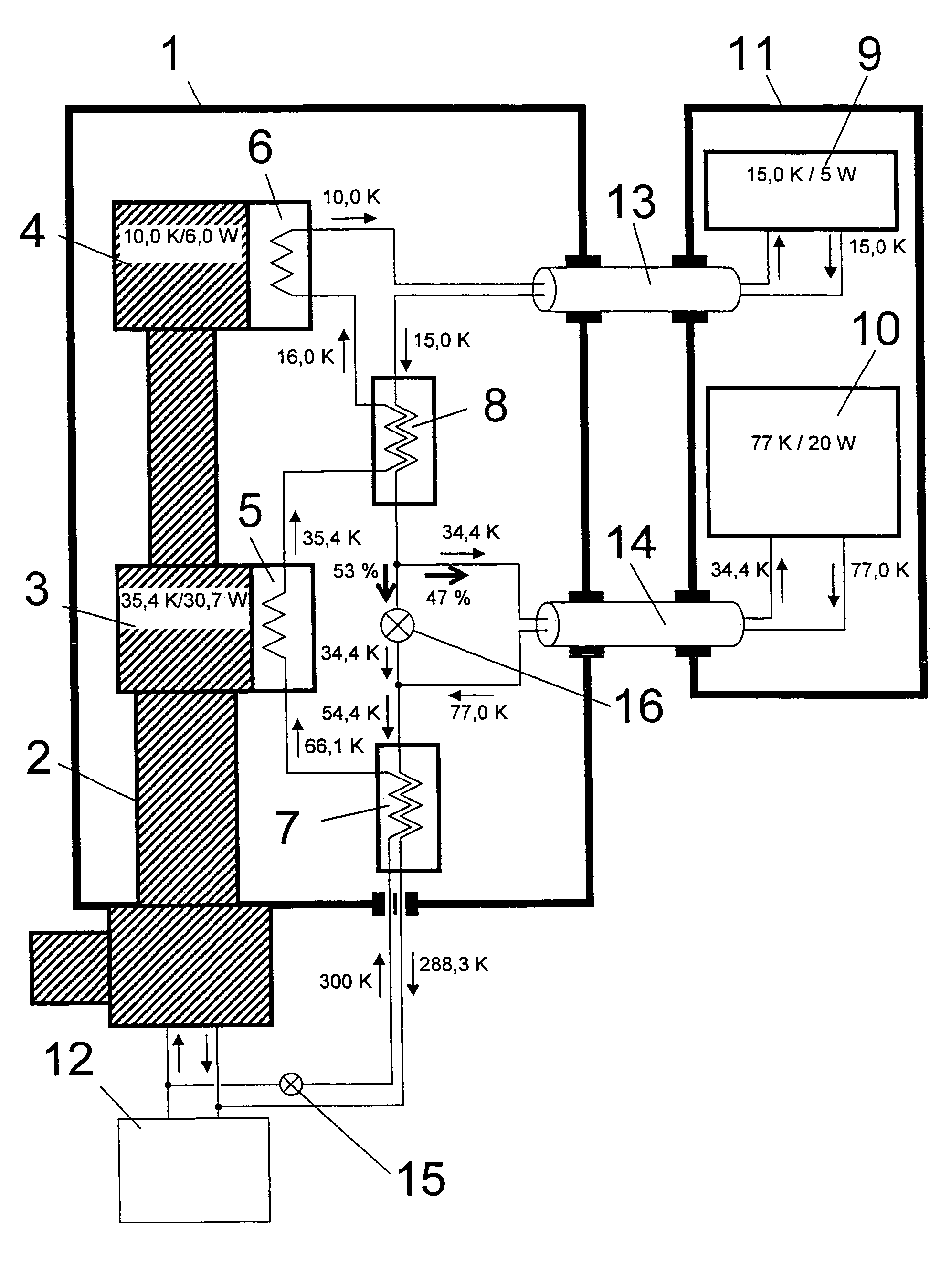
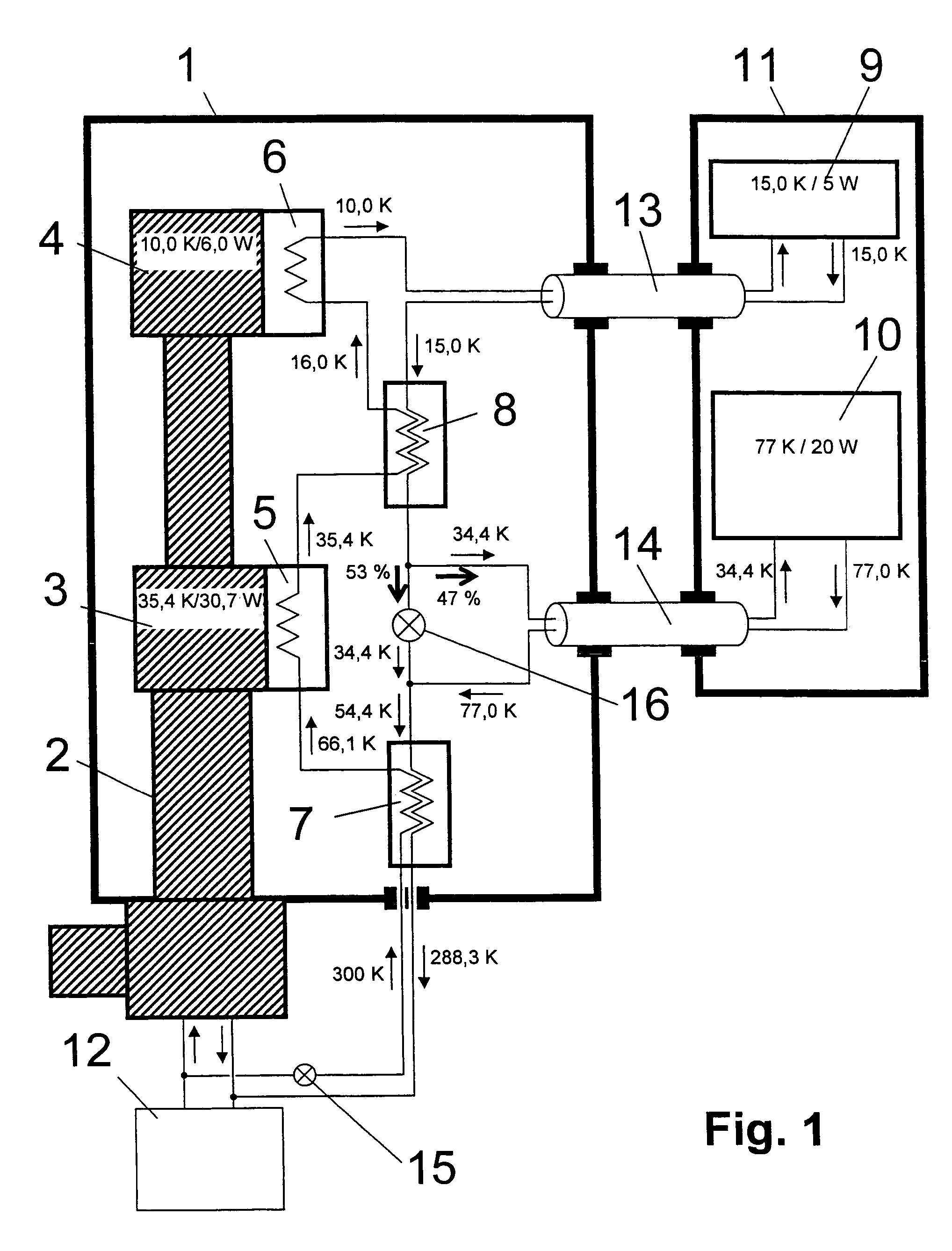
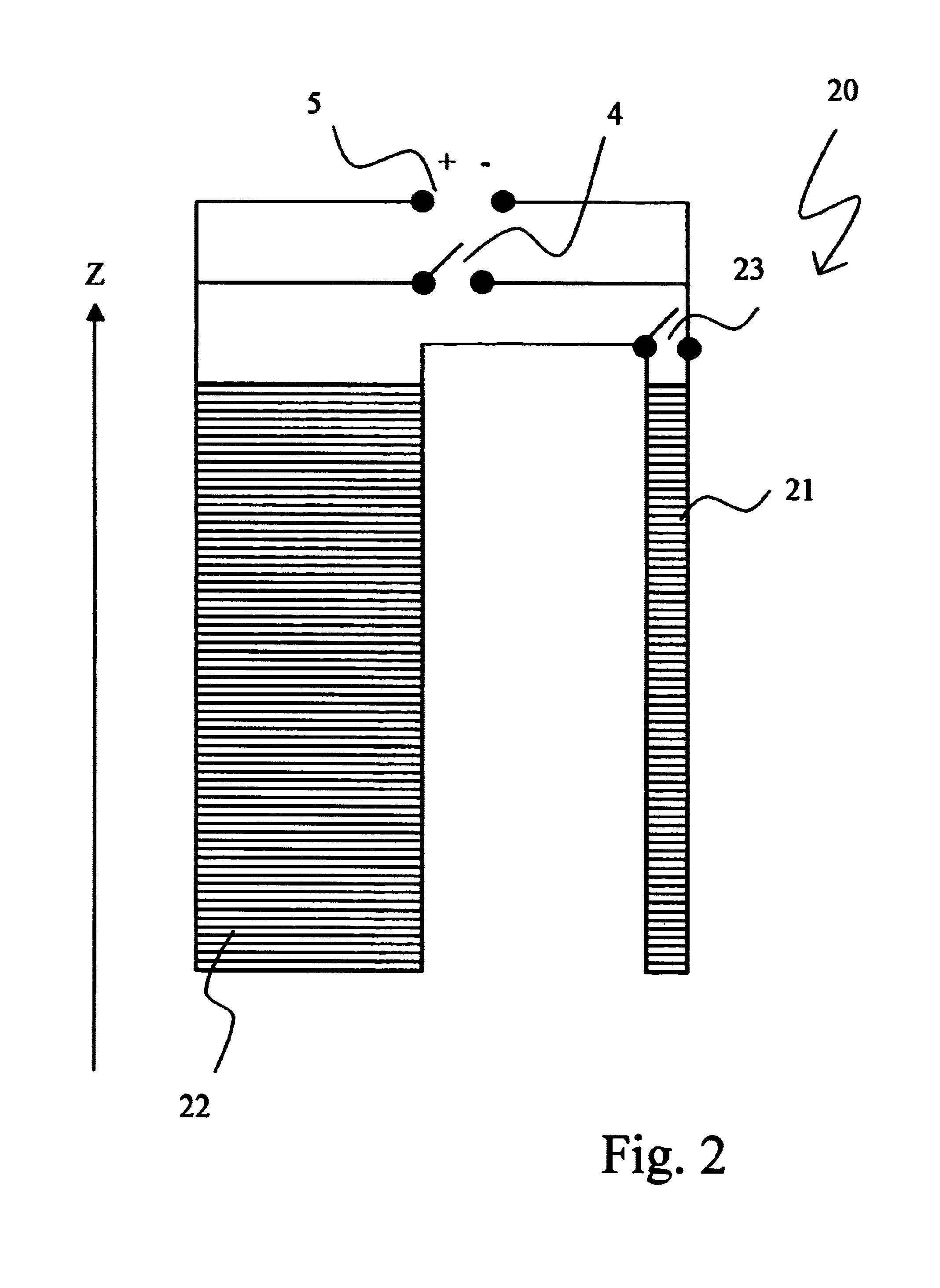
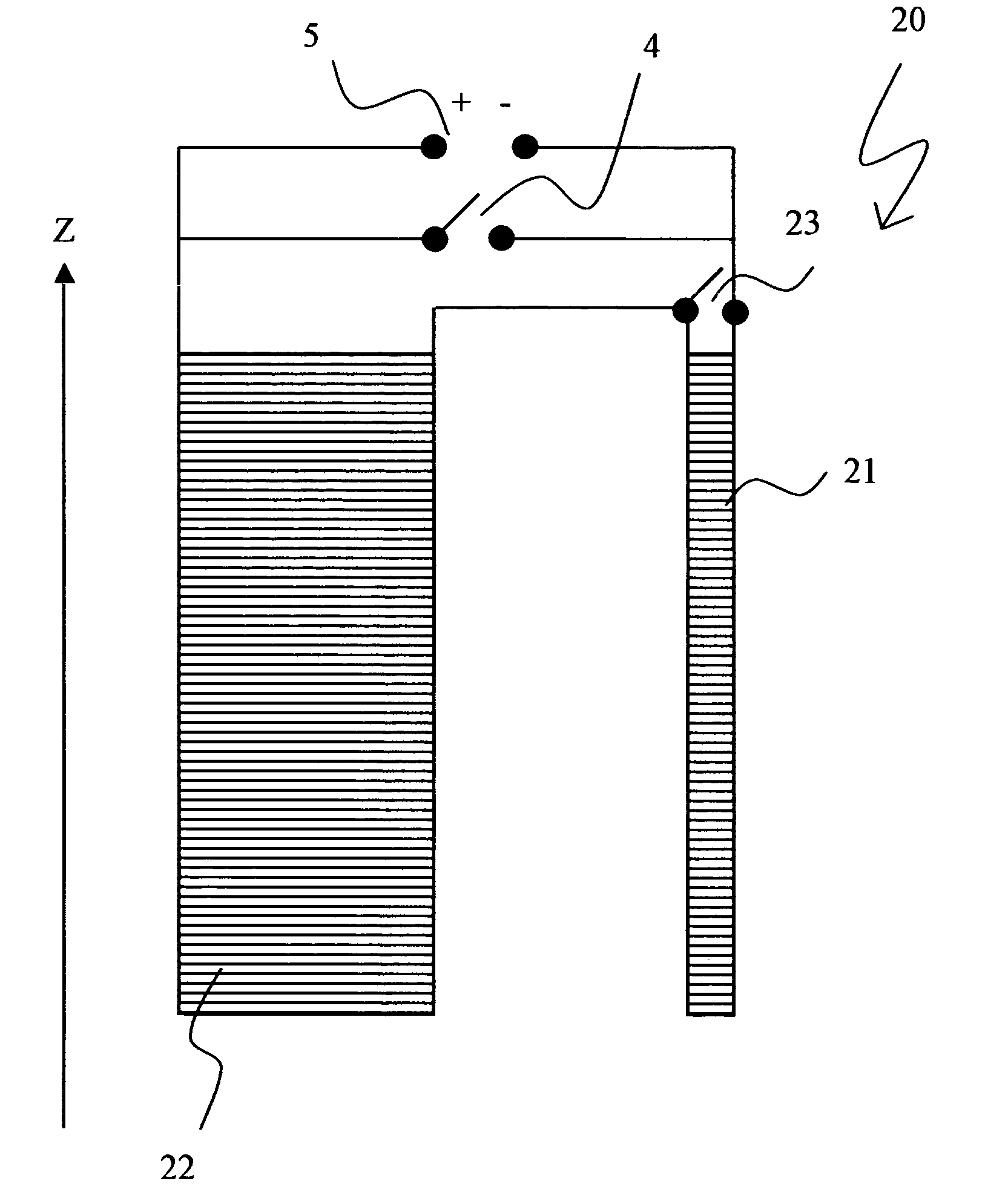
NMR spectrometer with refrigerator cooling
ActiveUS20060096301A1Reduce temperature lossReduce energy lossMagnetic measurementsCompression machinesEngineeringRefrigerated temperature
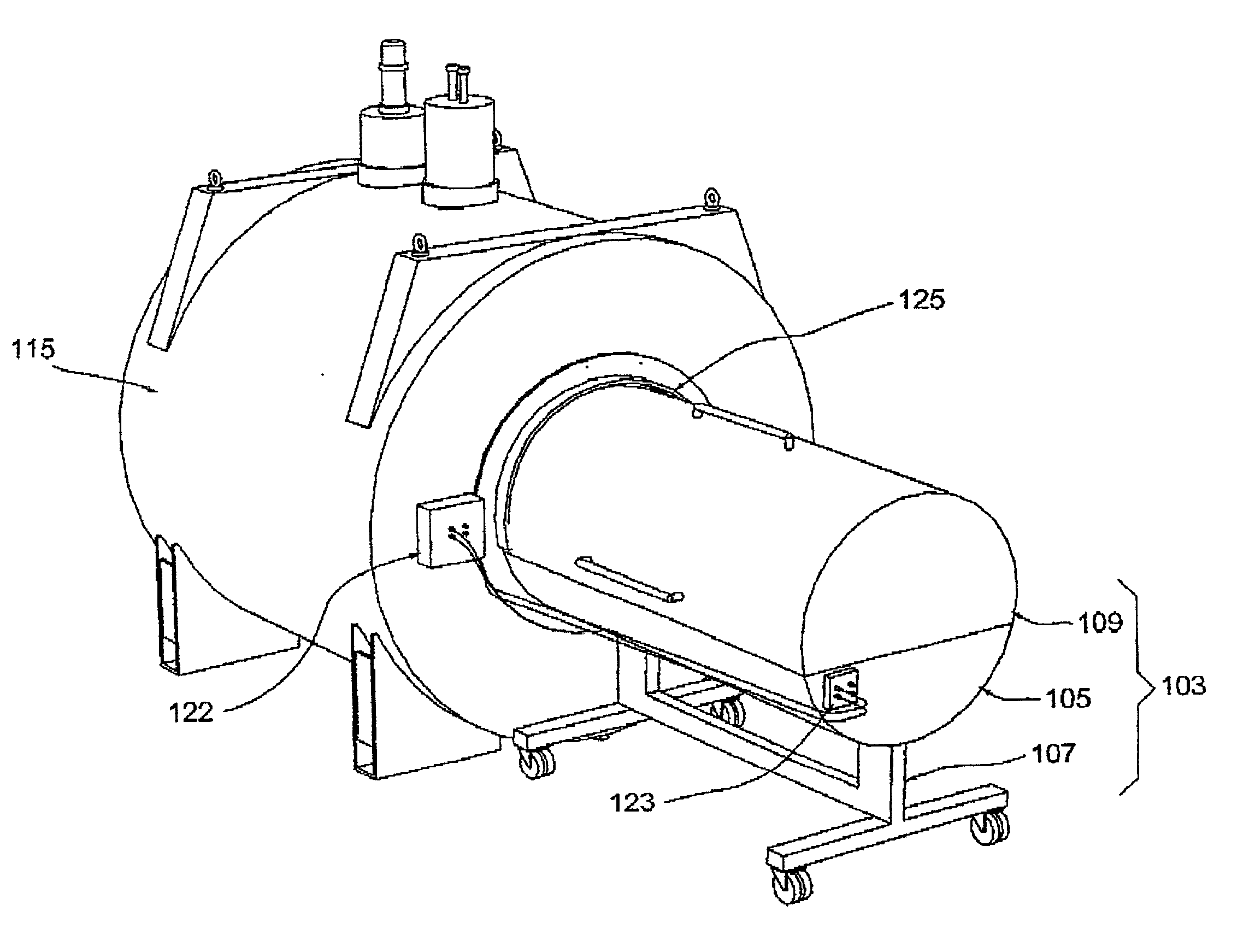
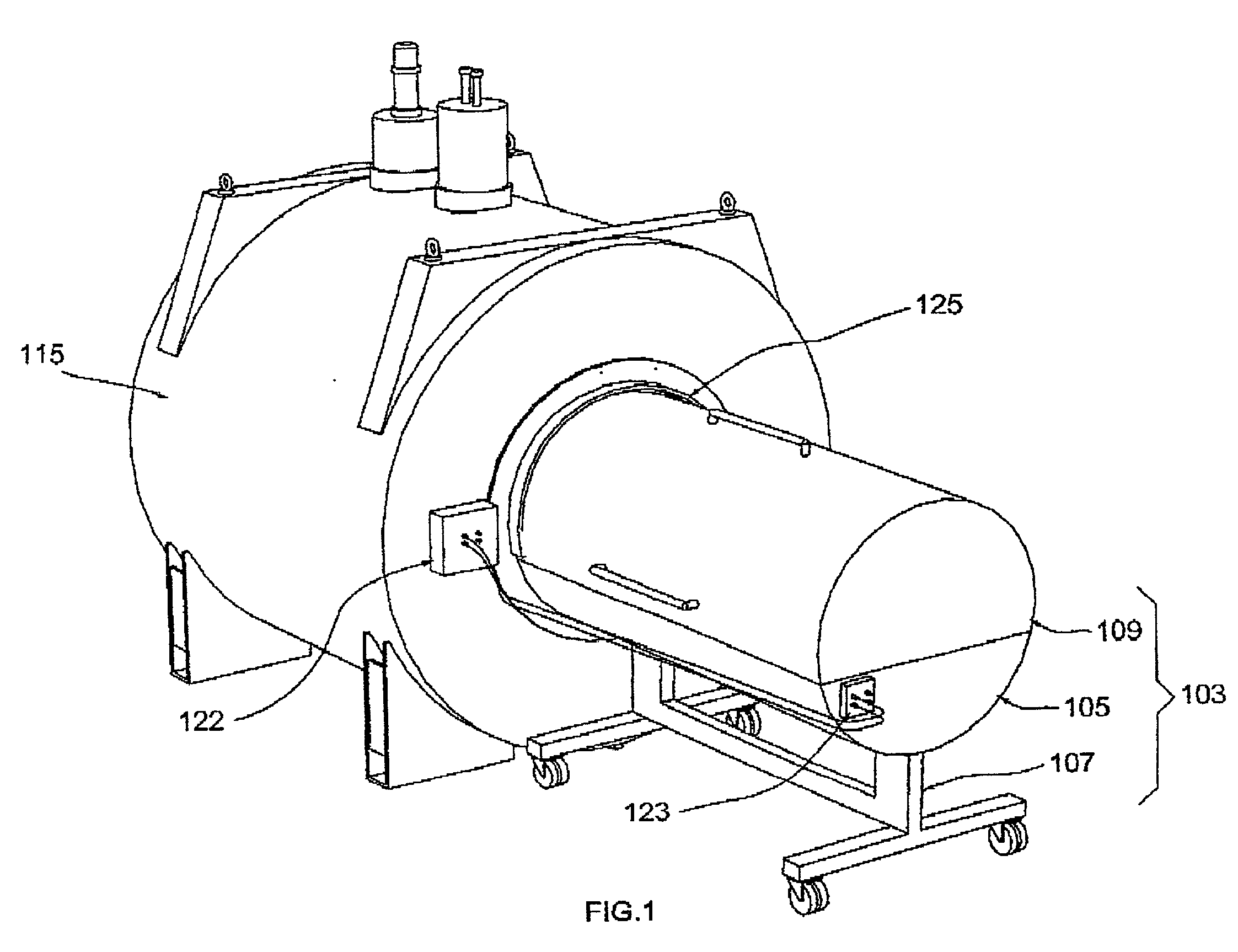
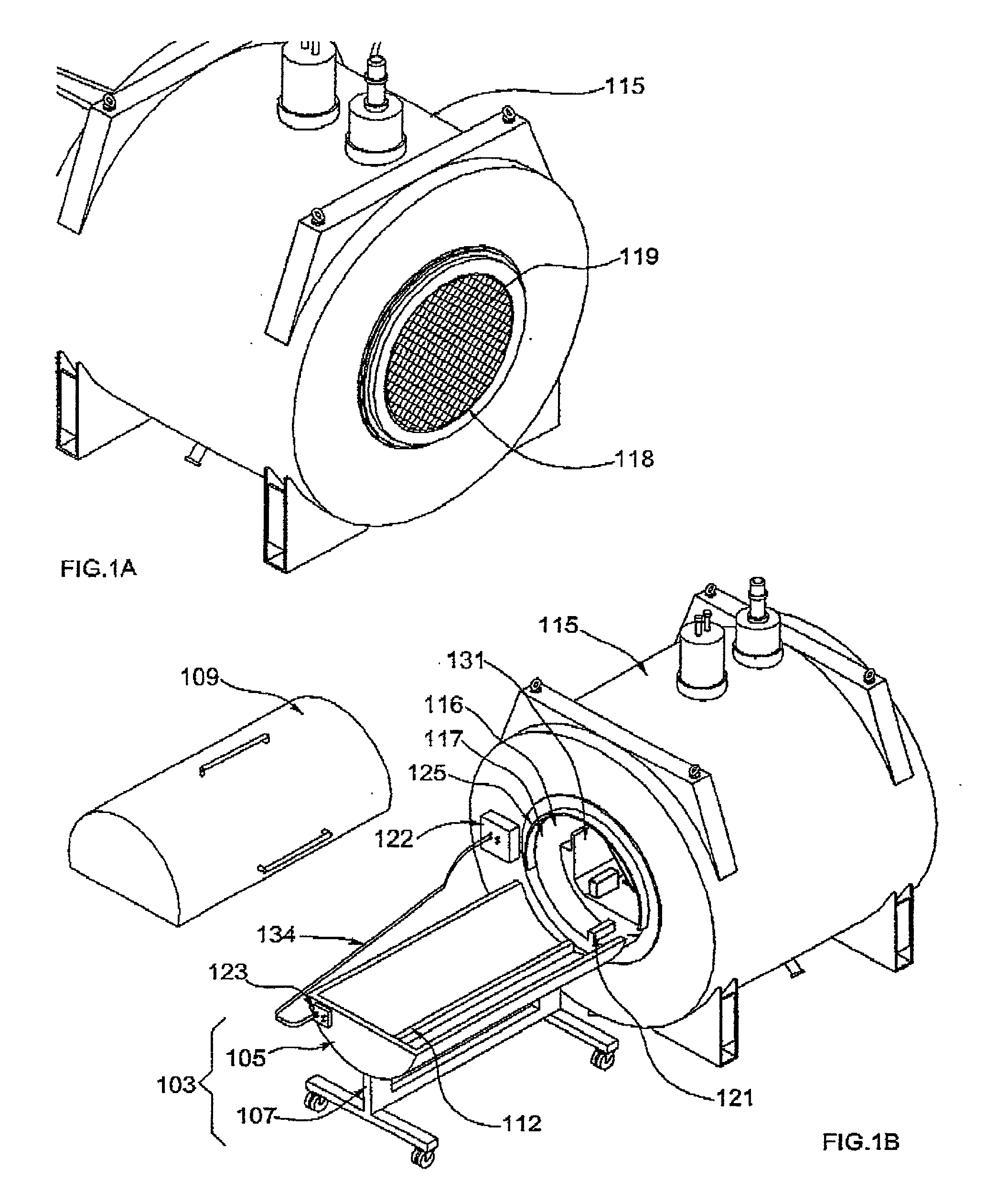
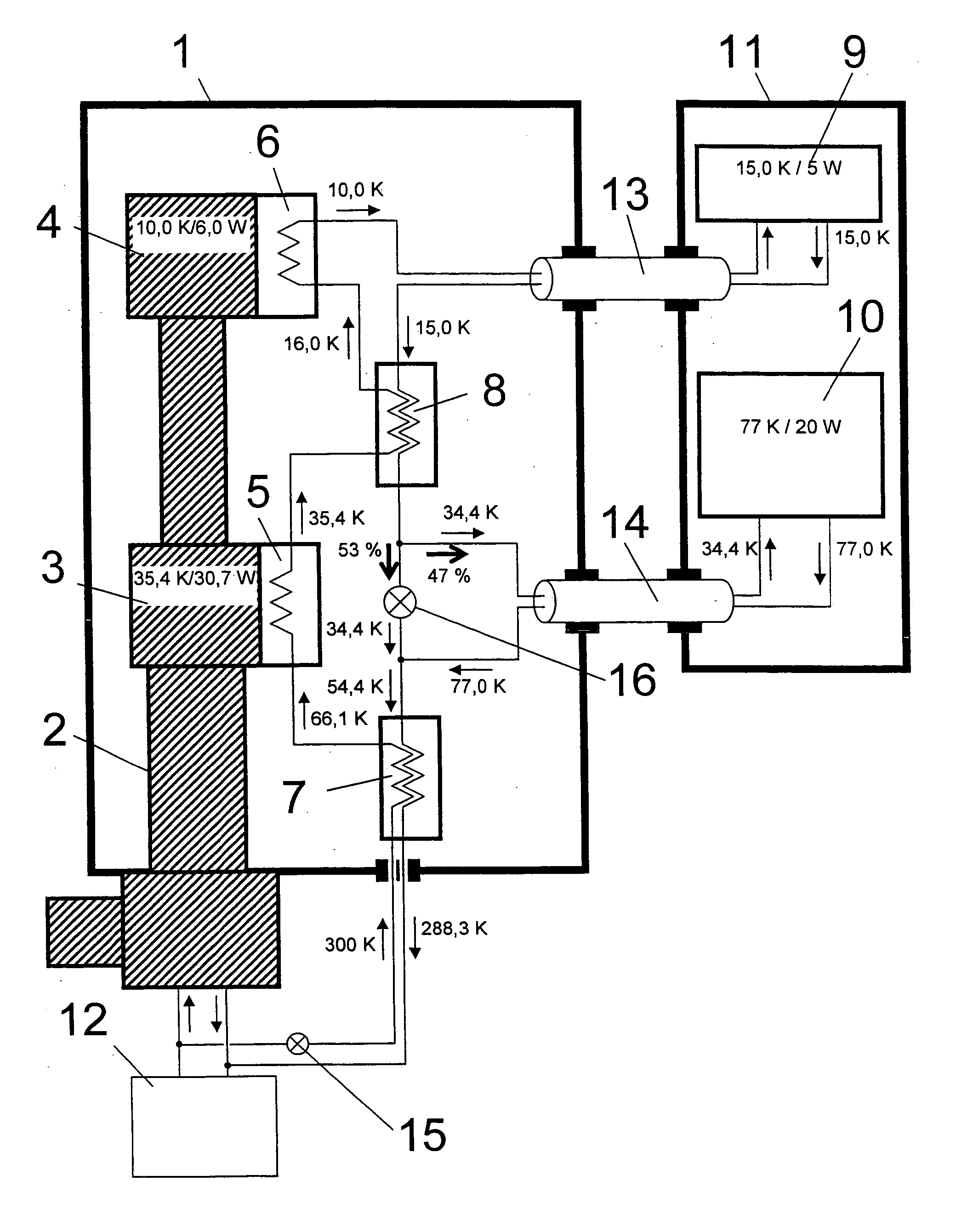
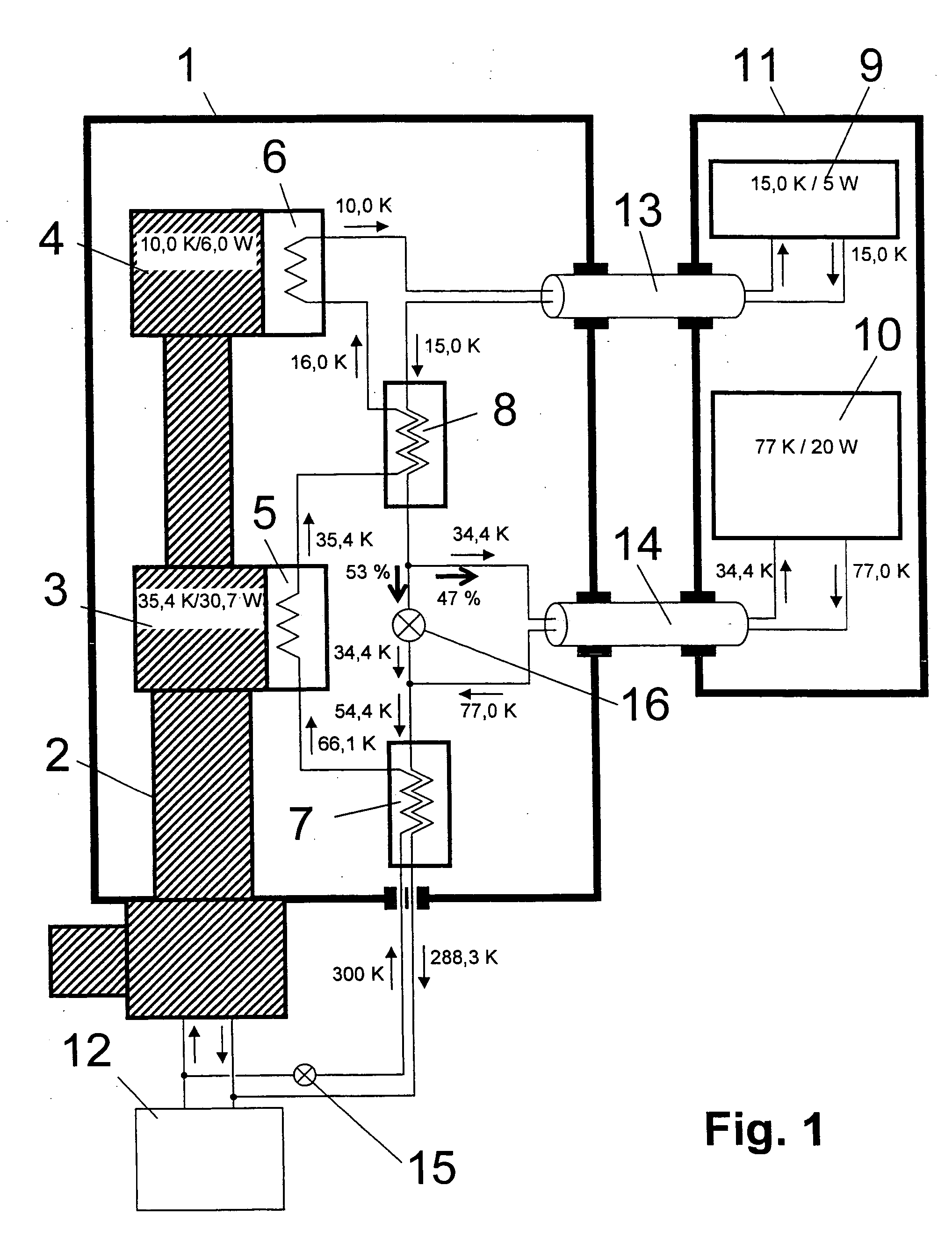
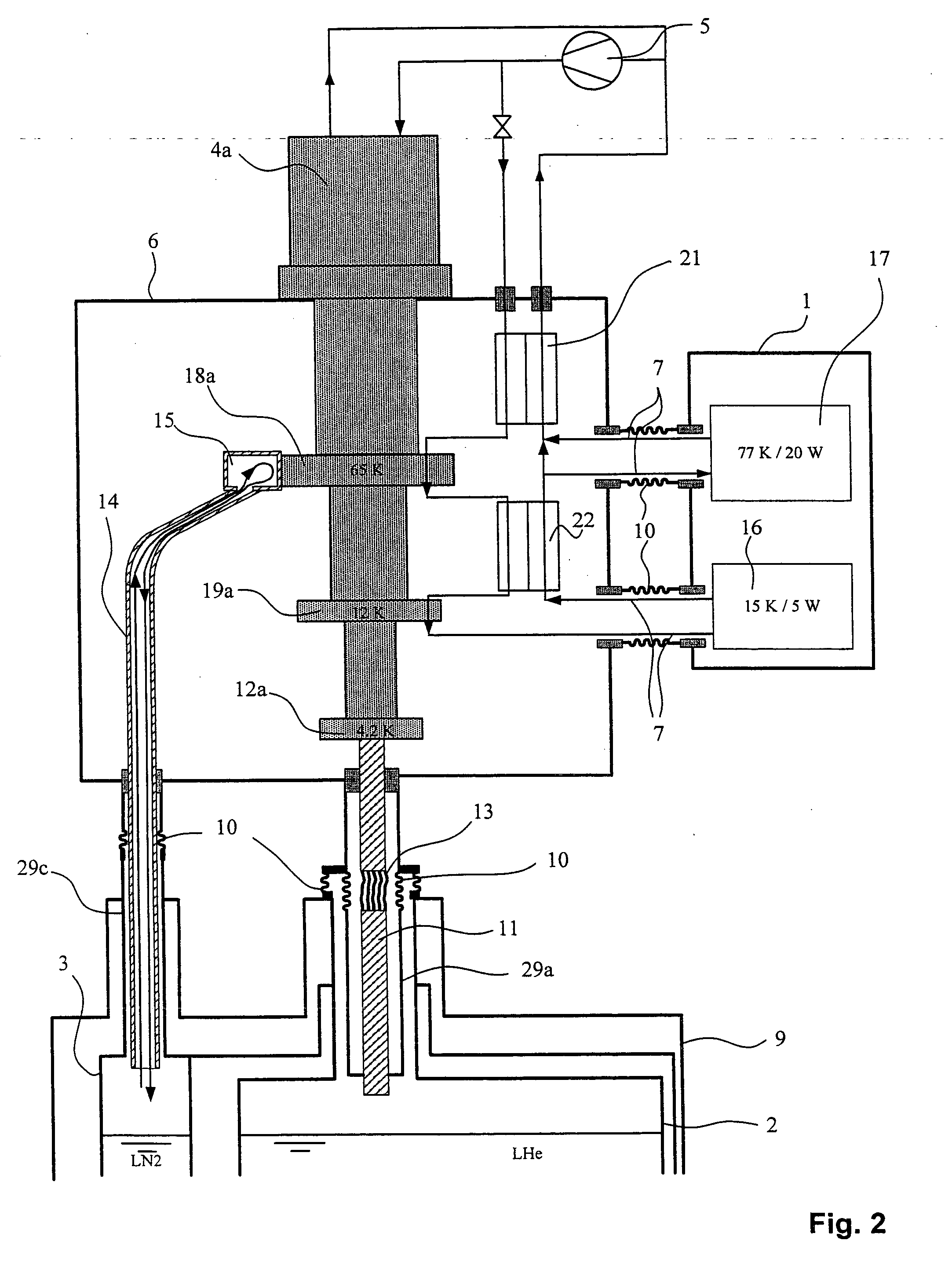
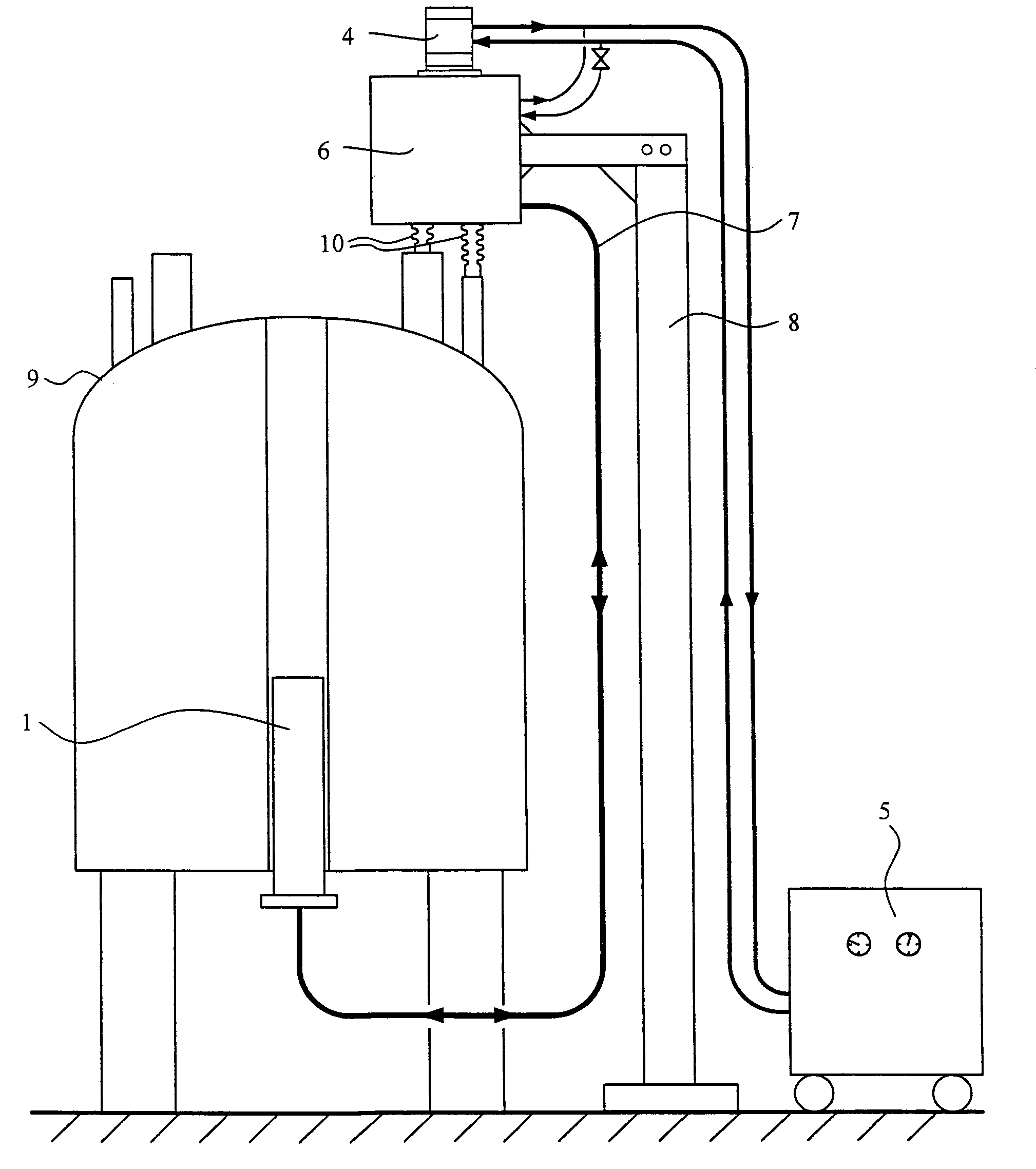
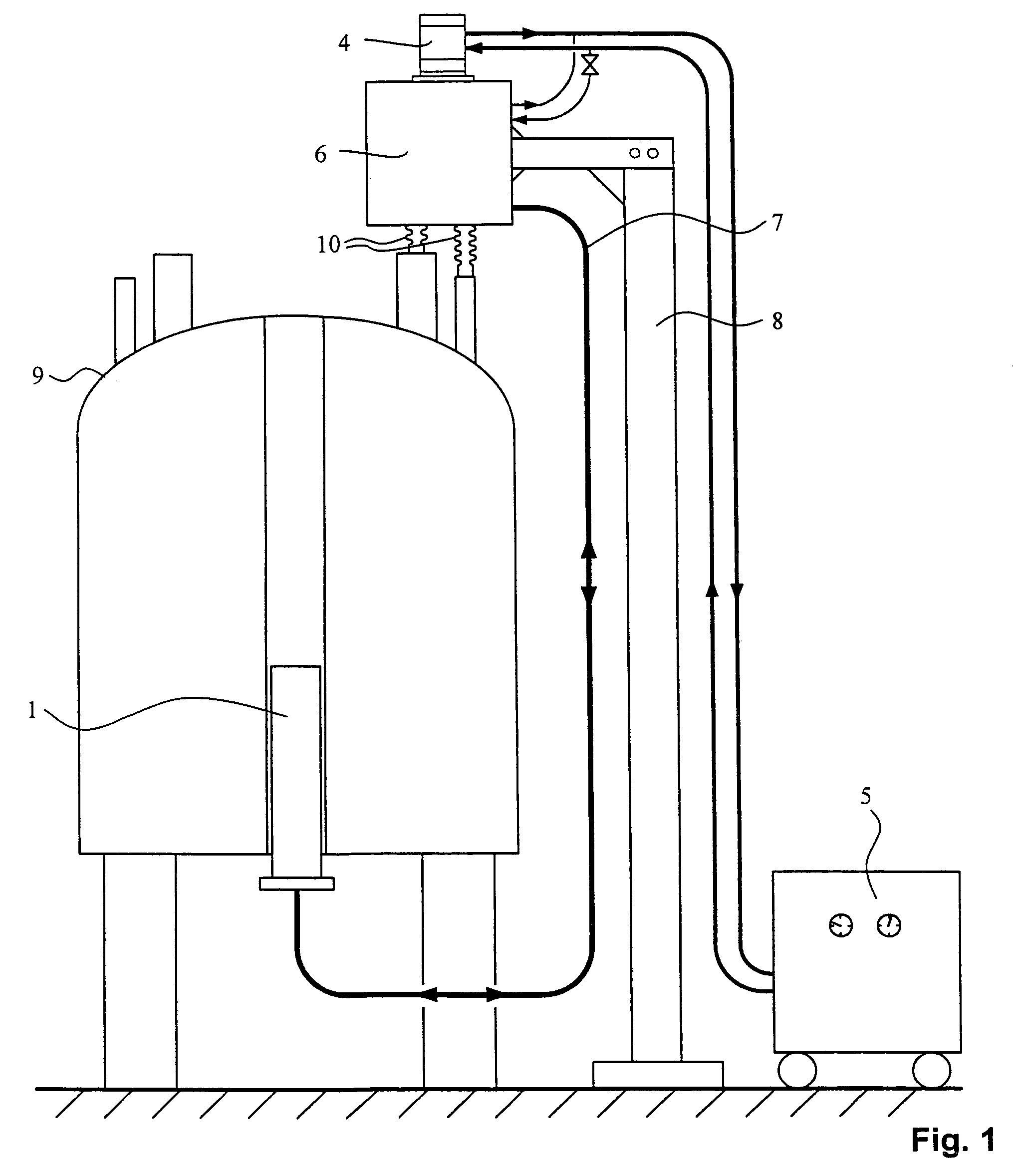
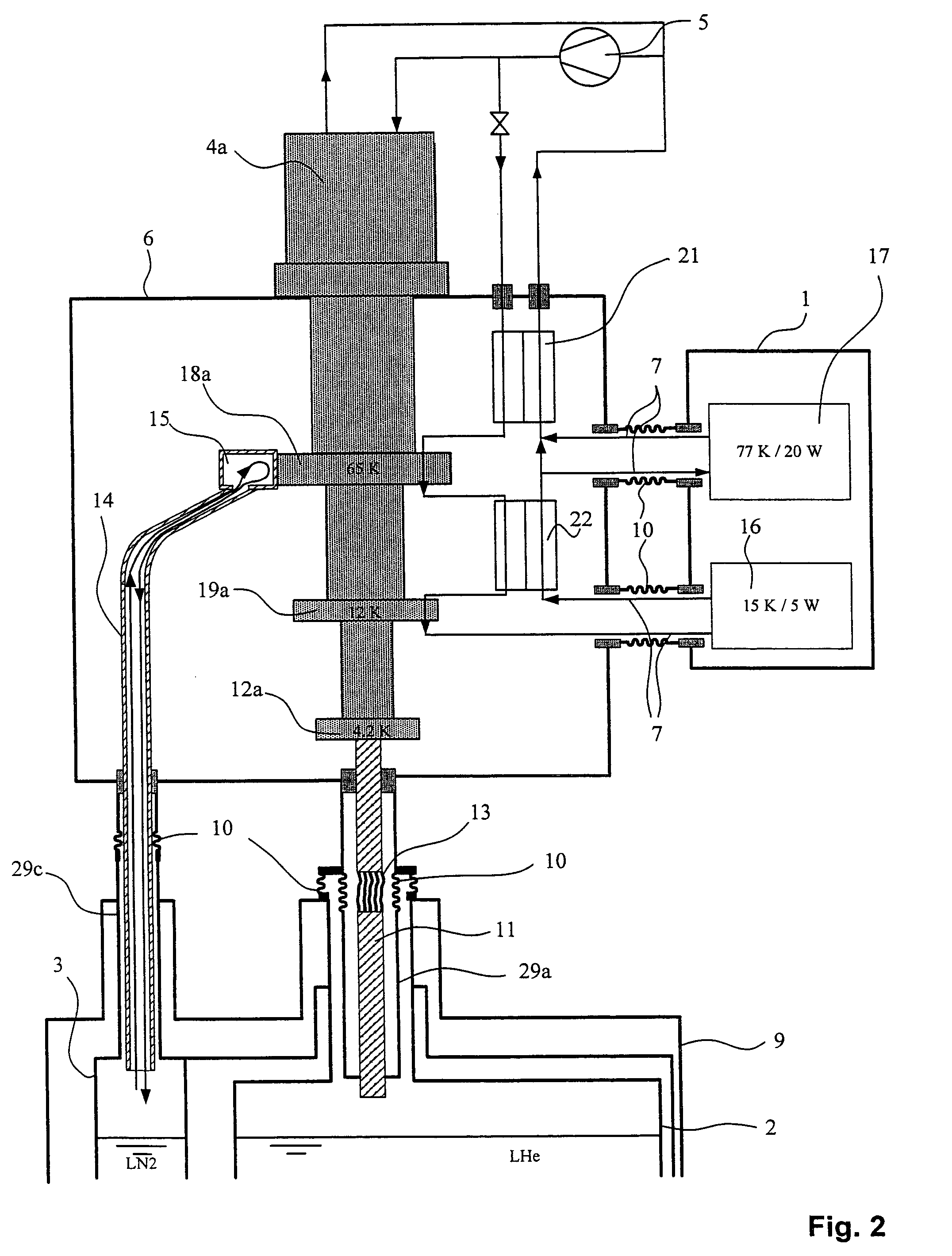
An NMR spectrometer comprising an NMR magnet system (27) disposed in a helium tank of a cryostat and an NMR probe head (11) disposed in a room temperature bore of the cryostat, which contains a cooled RF resonator (9) for receiving NMR signals from a sample to be investigated, and a cooled pre-amplifier (10), wherein the NMR probe head (11) is cooled by a common multi-stage compressor-operated refrigerator (2), wherein the refrigerator (2) comprises a cold head and several heat exchangers (5, 6) at different temperature levels, wherein the refrigerator (2) is disposed at a spatial separation from the cryostat in a separate, evacuated and thermally insulated housing (1) and wherein at least one cooling circuit with cooling lines, which are thermally insulated by a transfer line (13, 14) is disposed between the housing (1) containing the heat exchangers (5, 6) and the NMR probe head (11), is characterized in that additional cooling lines to an LN2 tank (18) or radiation shield (21) disposed in the cryostat and surrounding the helium tank are provided, and the refrigerator (2) also cools the LN2 tank (18) or the radiation shield (21). The inventive NMR spectrometer comprises a simple and inexpensive device for matching the holding time of LN2 to that of LHe through cooling the LN2 tank using the refrigerator provided for cooling the NMR probe head and without great expense.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
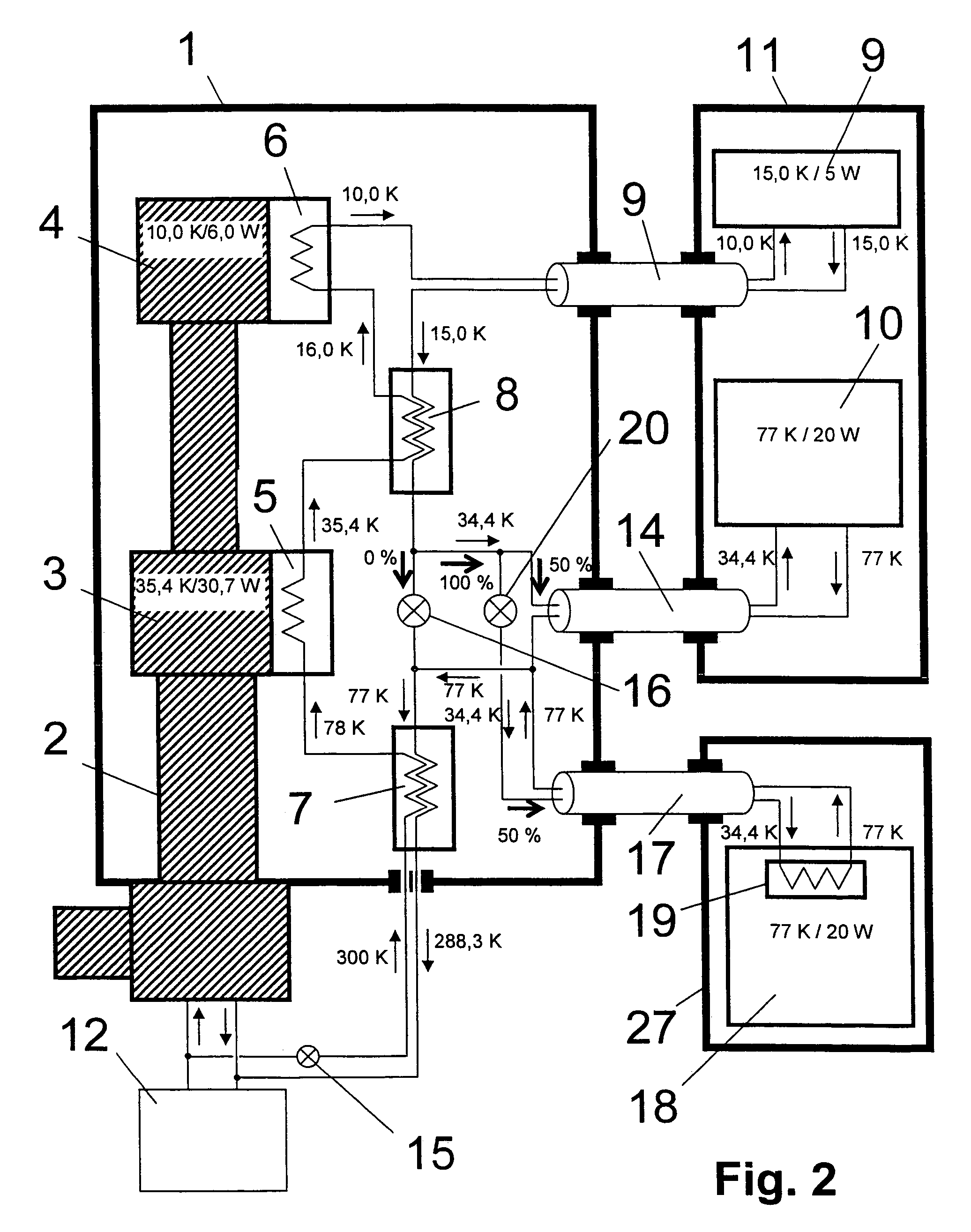
NMR apparatus with commonly cooled probe head and cryogenic container and method for the operation thereof
ActiveUS20070107445A1Improve thermodynamic efficiencyLow heat inputCompression machinesRefrigeration devicesEngineeringRadiation shield
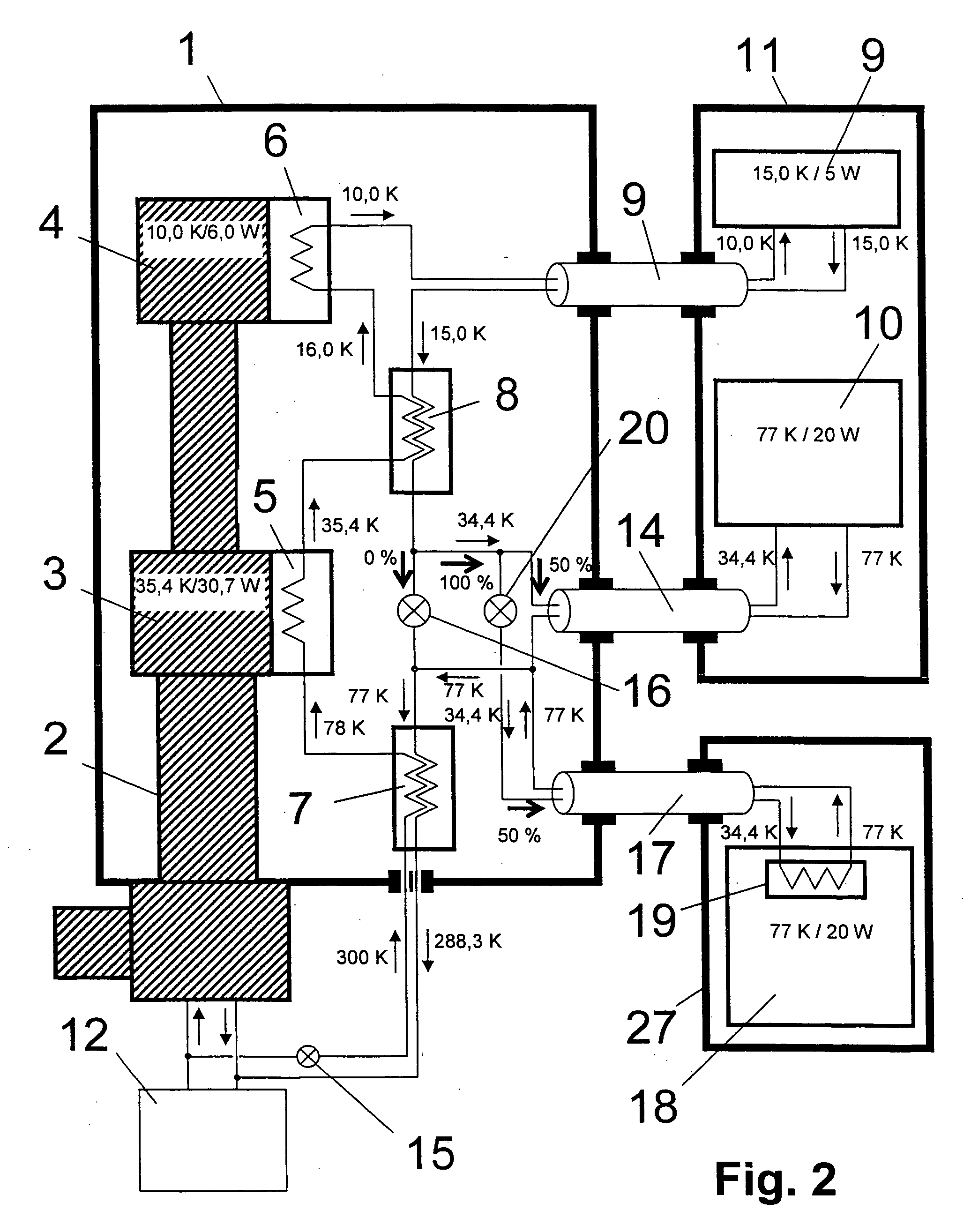
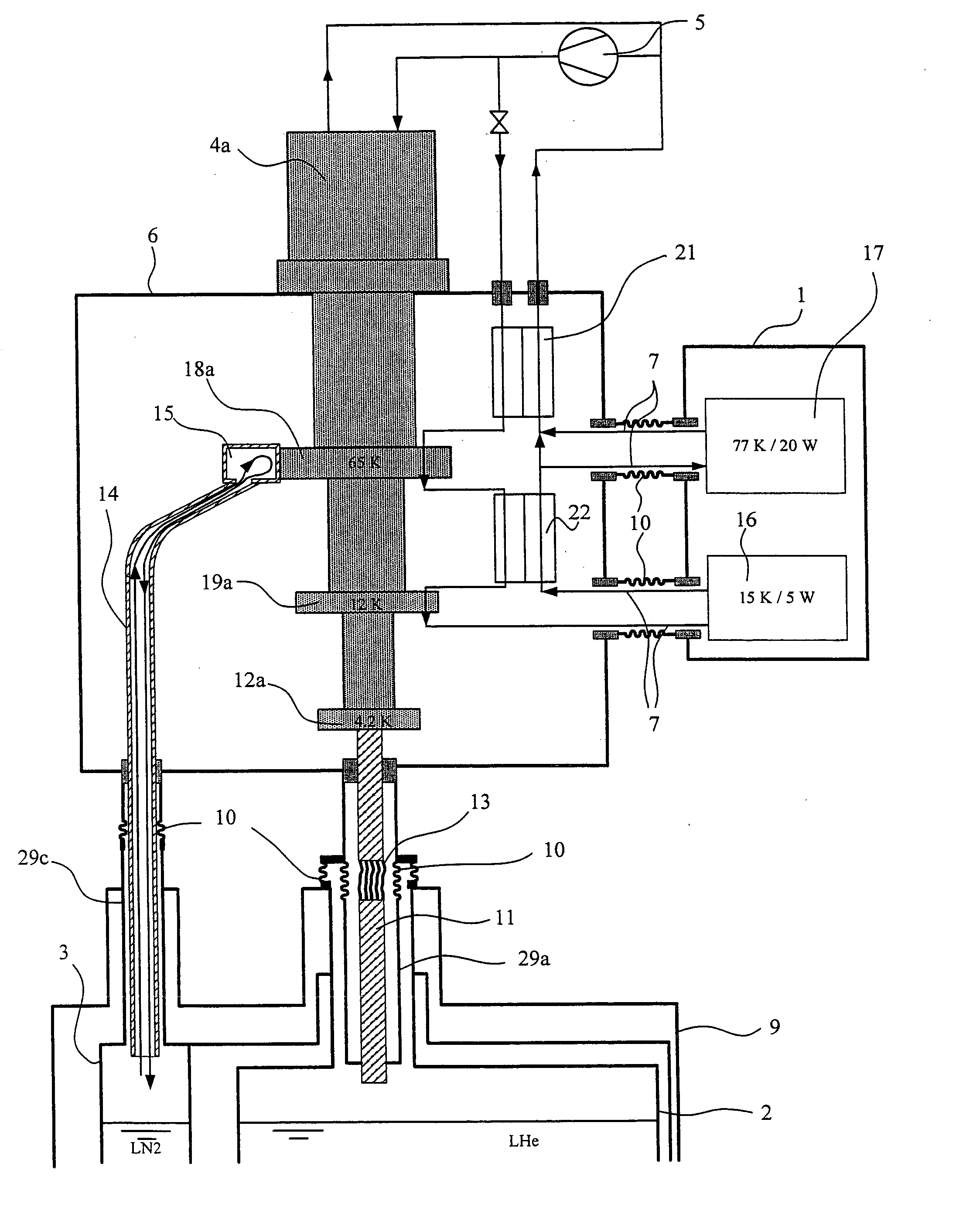
An NMR apparatus comprising an NMR magnet system disposed in a first cryocontainer (2) of a cryostat (9), and an NMR probe head (1), wherein the first cryocontainer (2) is installed in an evacuated outer jacket and is surrounded by a radiation shield (24) and / or a further cryocontainer (3), wherein a cooling device is provided for cooling the NMR probe head (1) and a cryocontainer (2, 3), which comprises a cold head (4, 4a, 4b, 4c) with several cold stages (12a, 12b, 12c, 18a, 18b, 18c, 19a), wherein one cold stage (12a, 12b, 12c, 18a, 18b, 18c, 19a) is connected to a heat-transferring device, and wherein a cooling circuit is provided between the cooling device and the NMR probe head (1), is characterized in that the cooling device is disposed in a separate, evacuated housing (6) which is positioned directly above the cryostat (9), wherein the heat-transferring device is inserted directly into suspension tubes (29a, 29c) of the cryocontainer (2, 3) and / or is in contact with the radiation shield (24). This effects a simple construction that is efficient for cooling an NMR apparatus.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
NMR apparatus with commonly cooled probe head and cryogenic container and method for the operation thereof
ActiveUS7474099B2Improve cooling effectReduce the presence of impuritiesCompression machinesRefrigeration devicesEngineeringRadiation shield
An NMR apparatus comprising an NMR magnet system disposed in a first cryocontainer (2) of a cryostat (9), and an NMR probe head (1), wherein the first cryocontainer (2) is installed in an evacuated outer jacket and is surrounded by a radiation shield (24) and / or a further cryocontainer (3), wherein a cooling device is provided for cooling the NMR probe head (1) and a cryocontainer (2, 3), which comprises a cold head (4, 4a, 4b, 4c) with several cold stages (12a, 12b, 12c, 18a, 18b, 18c, 19a), wherein one cold stage (12a, 12b, 12c, 18a, 18b, 18c, 19a) is connected to a heat-transferring device, and wherein a cooling circuit is provided between the cooling device and the NMR probe head (1), is characterized in that the cooling device is disposed in a separate, evacuated housing (6) which is positioned directly above the cryostat (9), wherein the heat-transferring device is inserted directly into suspension tubes (29a, 29c) of the cryocontainer (2, 3) and / or is in contact with the radiation shield (24). This effects a simple construction that is efficient for cooling an NMR apparatus.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
NMR spectrometer with refrigerator cooling
ActiveUS7222490B2Without additional expenseAvoid the needMagnetic measurementsCompression machinesEngineeringRefrigerated temperature
An NMR spectrometer comprising an NMR magnet system (27) disposed in a helium tank of a cryostat and an NMR probe head (11) disposed in a room temperature bore of the cryostat, which contains a cooled RF resonator (9) for receiving NMR signals from a sample to be investigated, and a cooled pre-amplifier (10), wherein the NMR probe head (11) is cooled by a common multi-stage compressor-operated refrigerator (2), wherein the refrigerator (2) comprises a cold head and several heat exchangers (5, 6) at different temperature levels, wherein the refrigerator (2) is disposed at a spatial separation from the cryostat in a separate, evacuated and thermally insulated housing (1) and wherein at least one cooling circuit with cooling lines, which are thermally insulated by a transfer line (13, 14) is disposed between the housing (1) containing the heat exchangers (5, 6) and the NMR probe head (11), is characterized in that additional cooling lines to an LN2 tank (18) or radiation shield (21) disposed in the cryostat and surrounding the helium tank are provided, and the refrigerator (2) also cools the LN2 tank (18) or the radiation shield (21). The inventive NMR spectrometer comprises a simple and inexpensive device for matching the holding time of LN2 to that of LHe through cooling the LN2 tank using the refrigerator provided for cooling the NMR probe head and without great expense.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
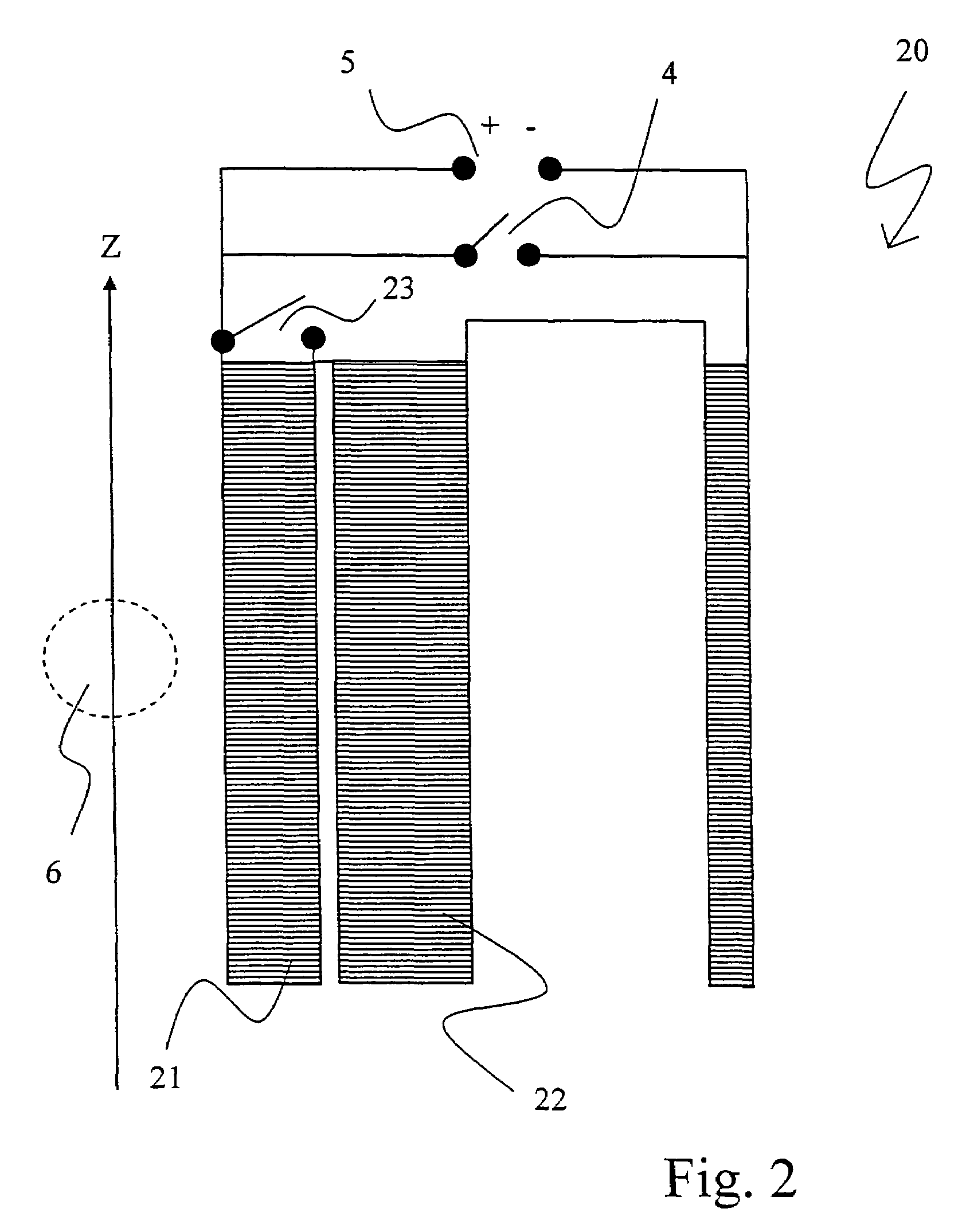
Radio frequency shield for nuclear magnetic resonance procedures
InactiveUS20040194989A1Electrically conductive connectionsMagnetic measurementsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceEngineering
An apparatus and method for providing RF shielding for performing nuclear magnetic resonance ("NMR") procedures, comprising a radio-opaque holder in combination with radio-opaque magnet components to form an RF shield around a patient undergoing an NMR procedure. In embodiments, a radio-opaque holder having a radio-opaque bottom portion and a radio-opaque canopy is adjoined to an NMR magnet having a radio-opaque cryostat and a radio-opaque service end cap to form an RF shield. A patient is placed on a patient support unit located in the holder bottom portion. The patient support unit, including the patient, is then inserted into the cavity of the NMR magnet and a canopy is placed on top of the bottom portion of the holder. An RF shield is thus created comprising the canopy, the bottom portion, the cryostat of the magnet, and an end cap on the service end of the magnet.
Owner:ADVANCED VETERINARY TECH
NMR magnet device for solution analysis and NMR apparatus
InactiveUS20050253586A1High sensitivityHigh detection sensitivityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceSolution analysisMagnet device
A split type magnet device for a high-sensitivity NMR apparatus to be used for solution analysis generates a remarkably uniform magnetic field at the center portion of the magnet device used for determining a sample. The magnet device for NMR apparatus has first multilayer coils and second multilayer coils, which face each other with a predetermined distance being provided therebetween, each of pairs of the first and the second coils being substantially coaxial with respect to a central axis, and each of layers of each of the first and the second multilayer coils having at least one coil. An energizing current of at least one of the coils constituting an innermost layer of each of the first and the second multilayer coils is in a minus direction, when an energizing current of the coil used for generating a main magnetic field for NMR detection in the vicinity of a center portion of the apparatus is in a plus direction.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Split type NMR magnet device and NMR apparatus for solution analysis with at least an 11 T static magnetic field and different energizing directions of the NMR magnets
InactiveUS7053621B2Efficient and accurateHigh sensitivityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceSuperconducting CoilsSolution analysis
A split type magnet device configured for a high-sensitivity NMR apparatus and used for solution analysis generates a uniform magnetic field at the center portion of the magnet device of at least 11 T, which is used for determining a sample. The NMR magnet device has left and right solenoid superconducting magnets, which face each other with a predetermined distance being provided therebetween. The left solenoid superconducting magnets and the right solenoid superconducting magnets are substantially coaxial to a central axis, and constituted respectively by a plurality of outermost magnets and a separate plurality of innermost magnets. When a sample energizing current generates a main magnetic NMR detection field in the vicinity of a center portion of the apparatus the current direction in at least one of the plurality of innermost magnets is minus while the current direction in at least one of the plurality of outermost magnets is plus.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
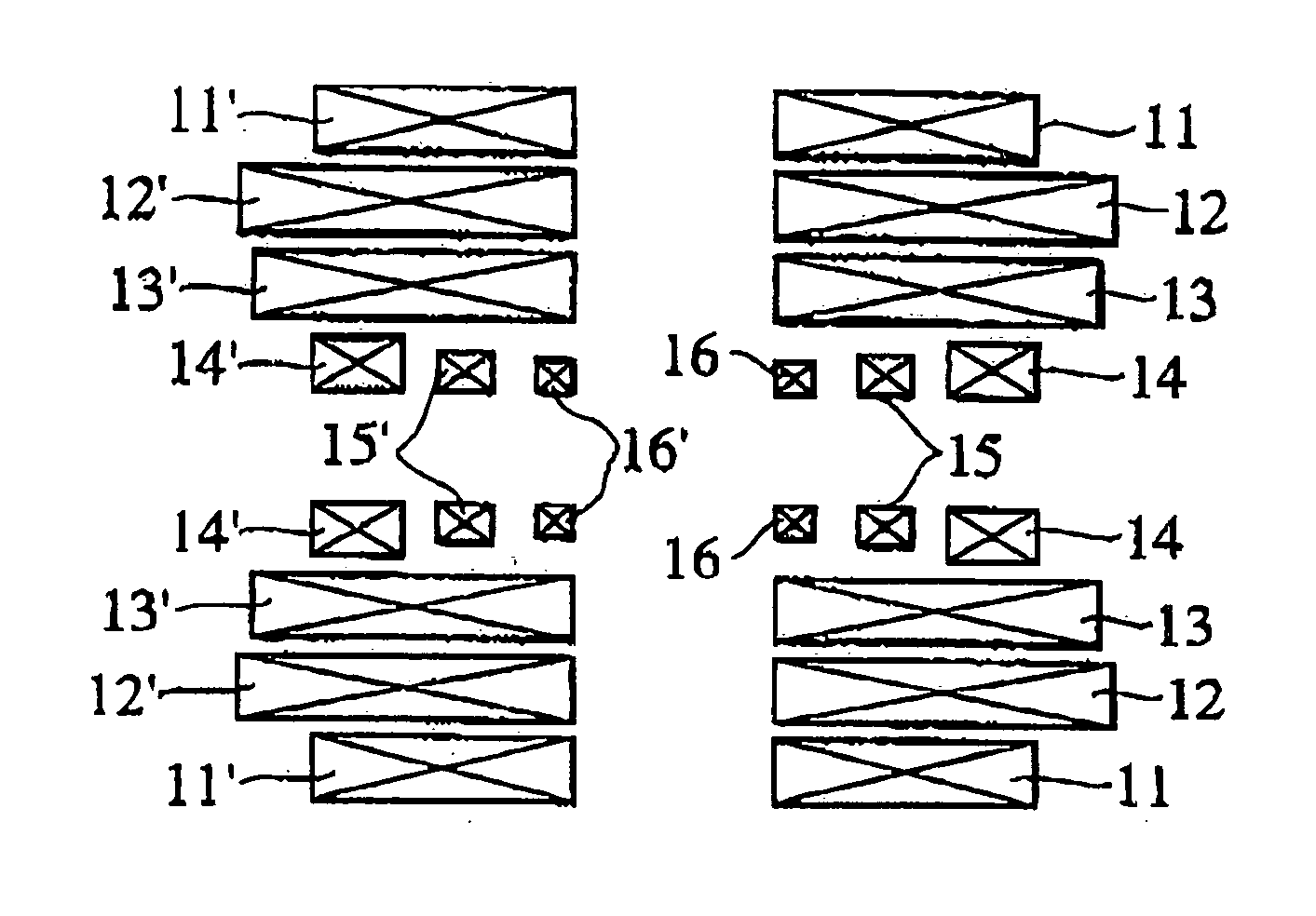
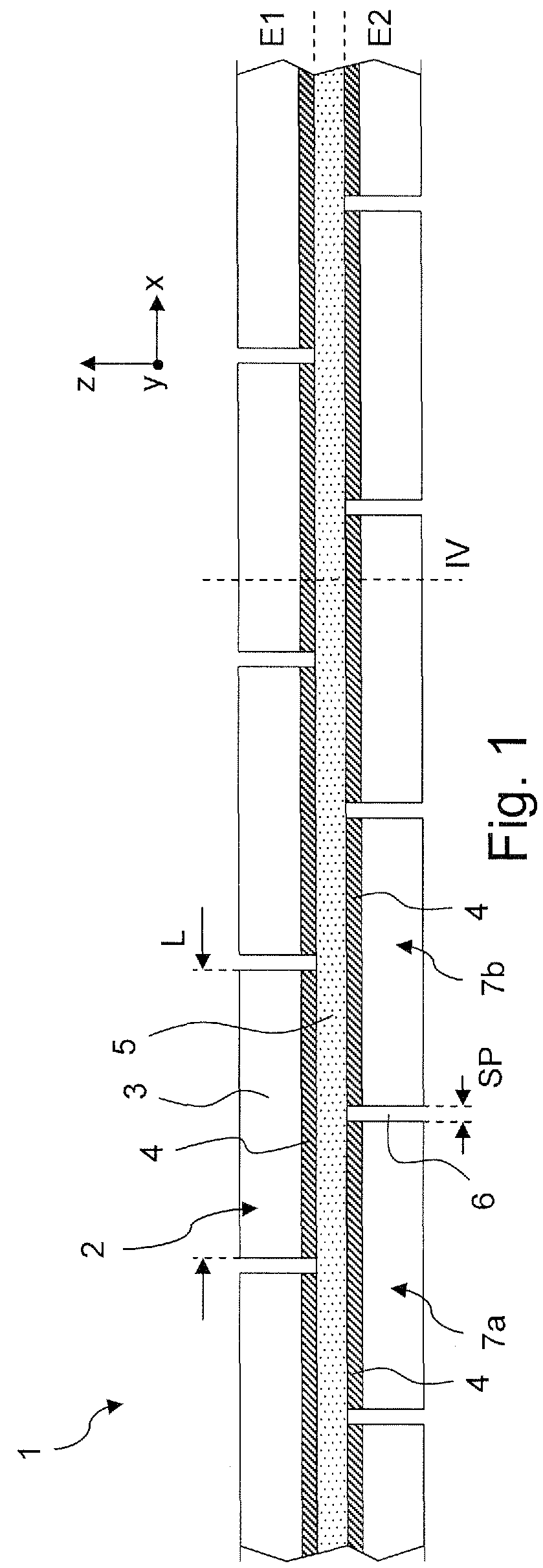
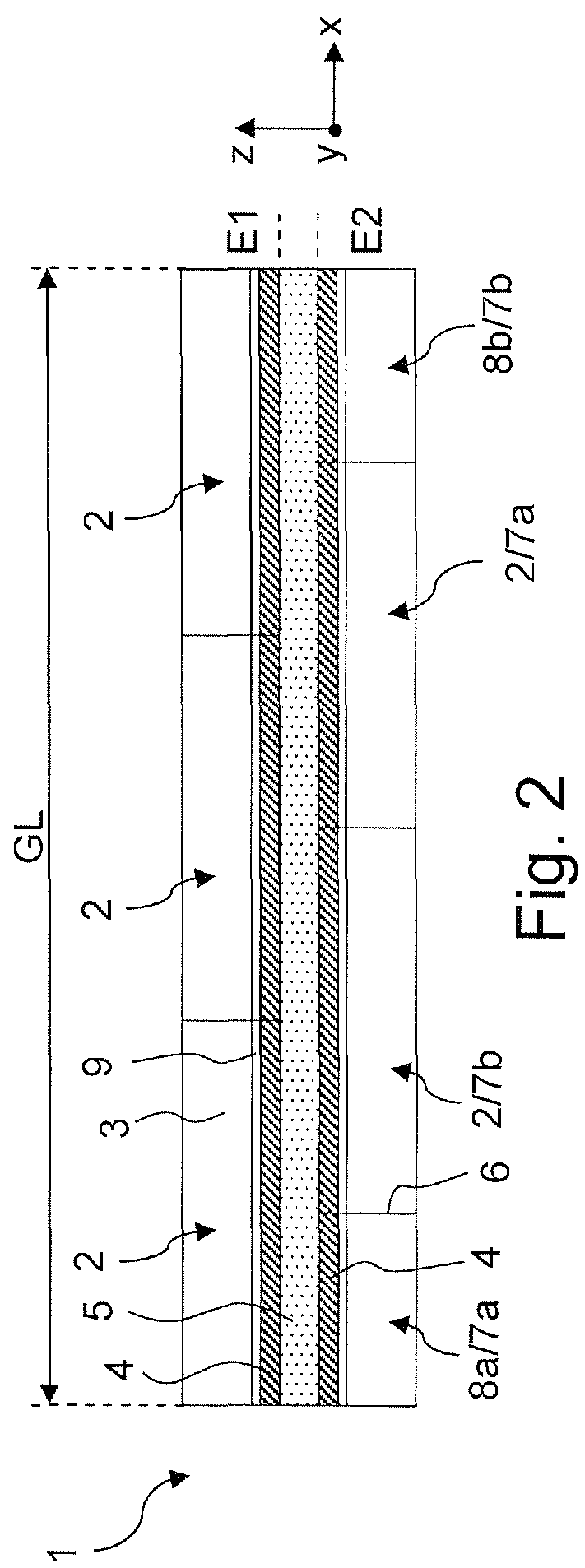
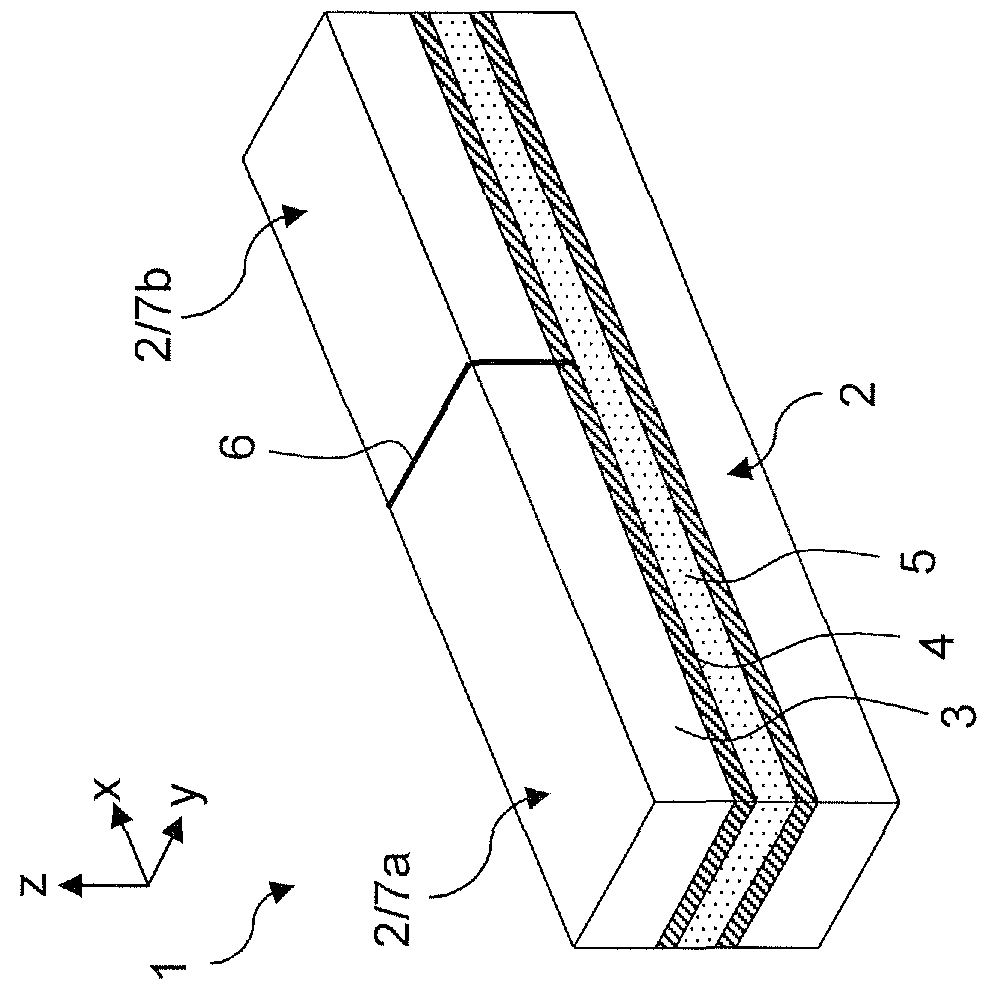
NMR Spectrometer comprising a superconducting magnetic coil having windings composed of a superconductor structure having strip pieces chained together
ActiveUS20160216348A1Need can be providedEliminating peak forceMeasurements using NMR spectroscopySuperconducting magnets/coilsElectrical conductorConductor Coil
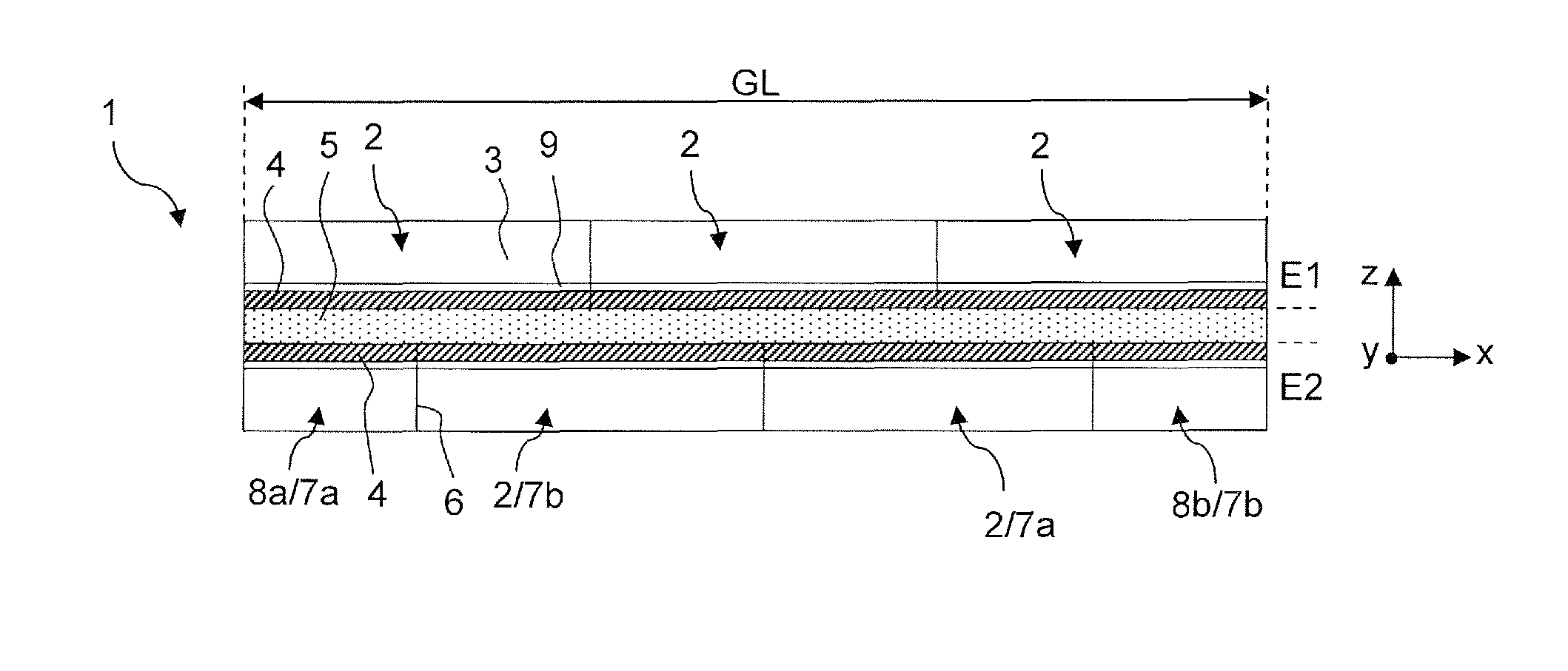
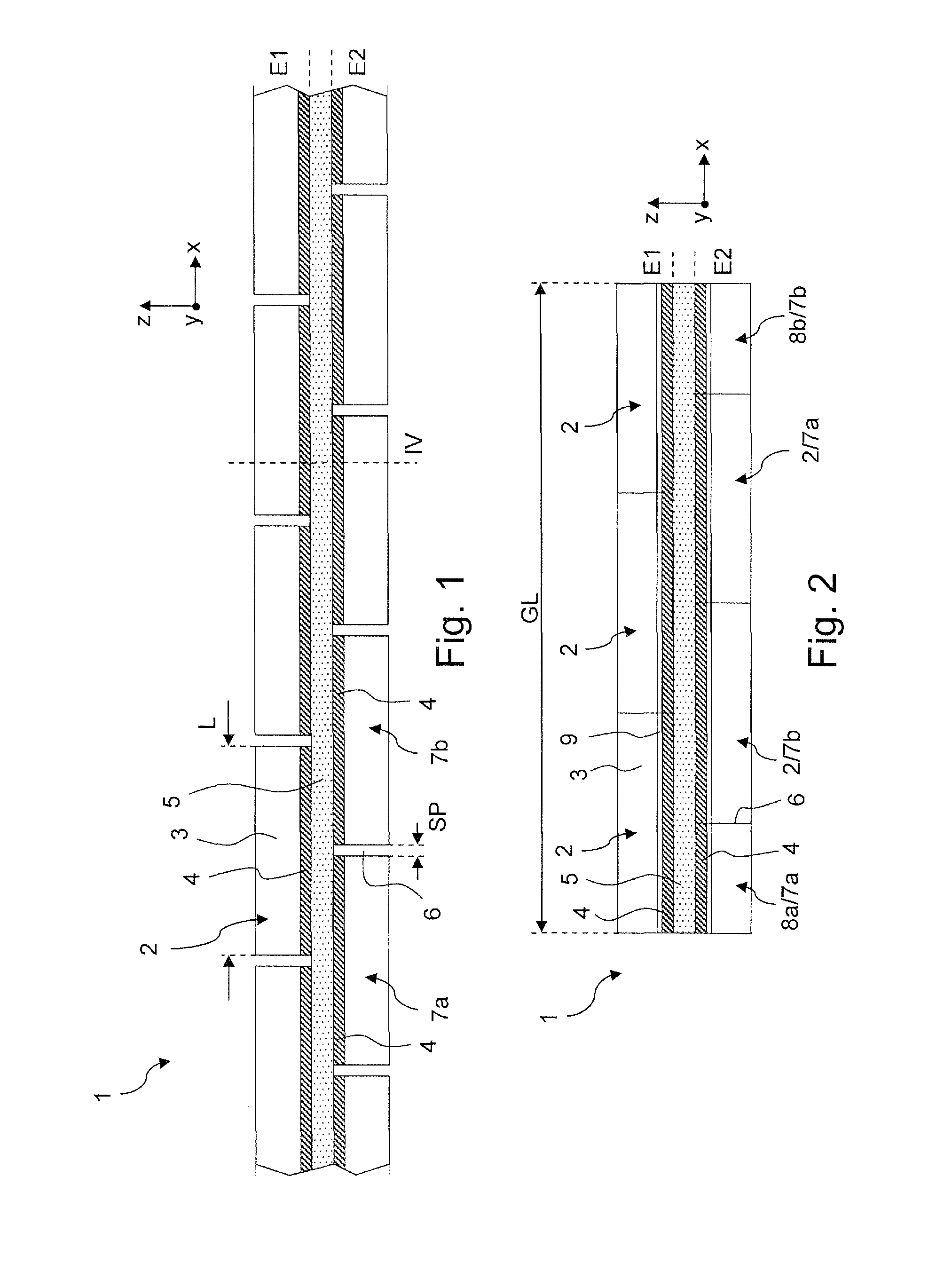
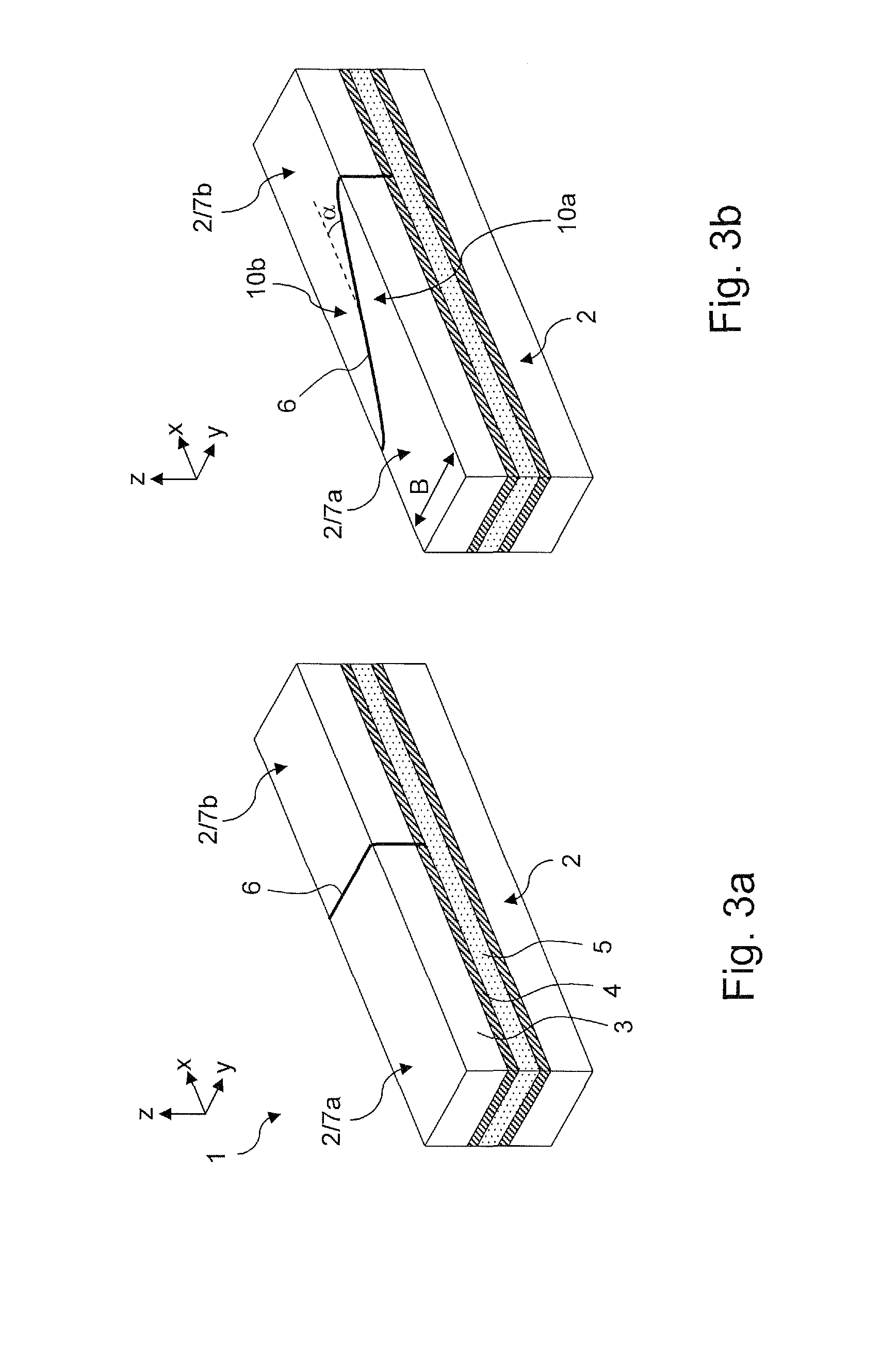
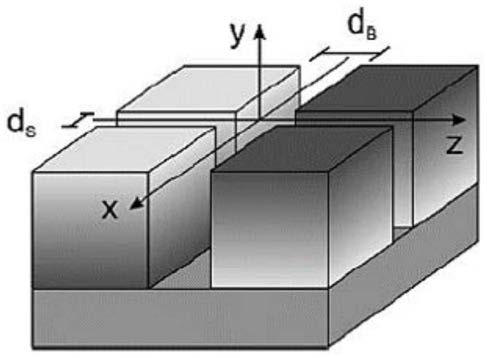
An NMR spectrometer (131) with an NMR magnet coil (91) having windings of a conductor with a superconducting structure (1), which have a plurality of band-segments (2, 2a, 7a-7e, 8a-8d, 15) made of band-shaped superconductor. Each band-segment (2, 2a, 7a-7e, 8a-8d, 15) has a flexible substrate (3) and a superconducting layer (4) deposited thereon, wherein the band-segments (2, 2a, 7a-7e, 8a-8d, 15) each have a length of 20 m or more. At least one of the band-segments (2, 2a, 7a-7e, 8a-8d, 15) forms a linked band-segment (2, 2a), and each linked band-segment (2, 2a) is connected to at least two further band-segments (7a-7e) in such a way that the combined further band-segments (7a-7e) overlap with at least 95% of the total length (L) of the linked band-segment (2, 2a). The magnet coil generates particularly high magnetic fields in a sample volume and has a low drift.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Method for fringe field compensation of an actively shielded superconducting NMR magnet
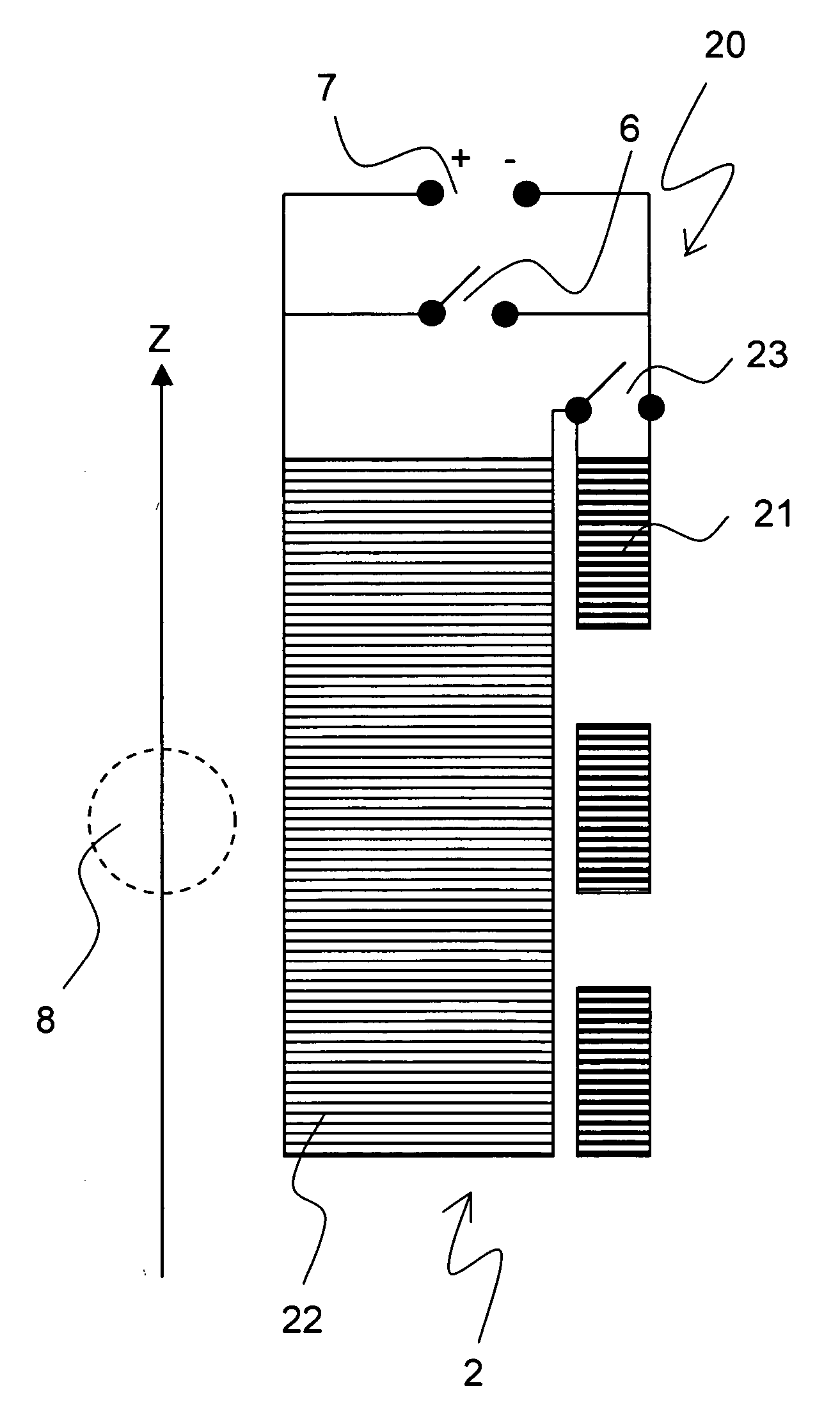
InactiveUS6987436B2Low costReduce the magnetic fringe fieldMagnetic measurementsMagnetsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceEngineering
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Method for fringe field compensation of an actively shielded superconducting nmr magnet
InactiveUS20050068033A1Easy to planMagnetic measurementsMagnetsInductive couplingElectromagnetic coil
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
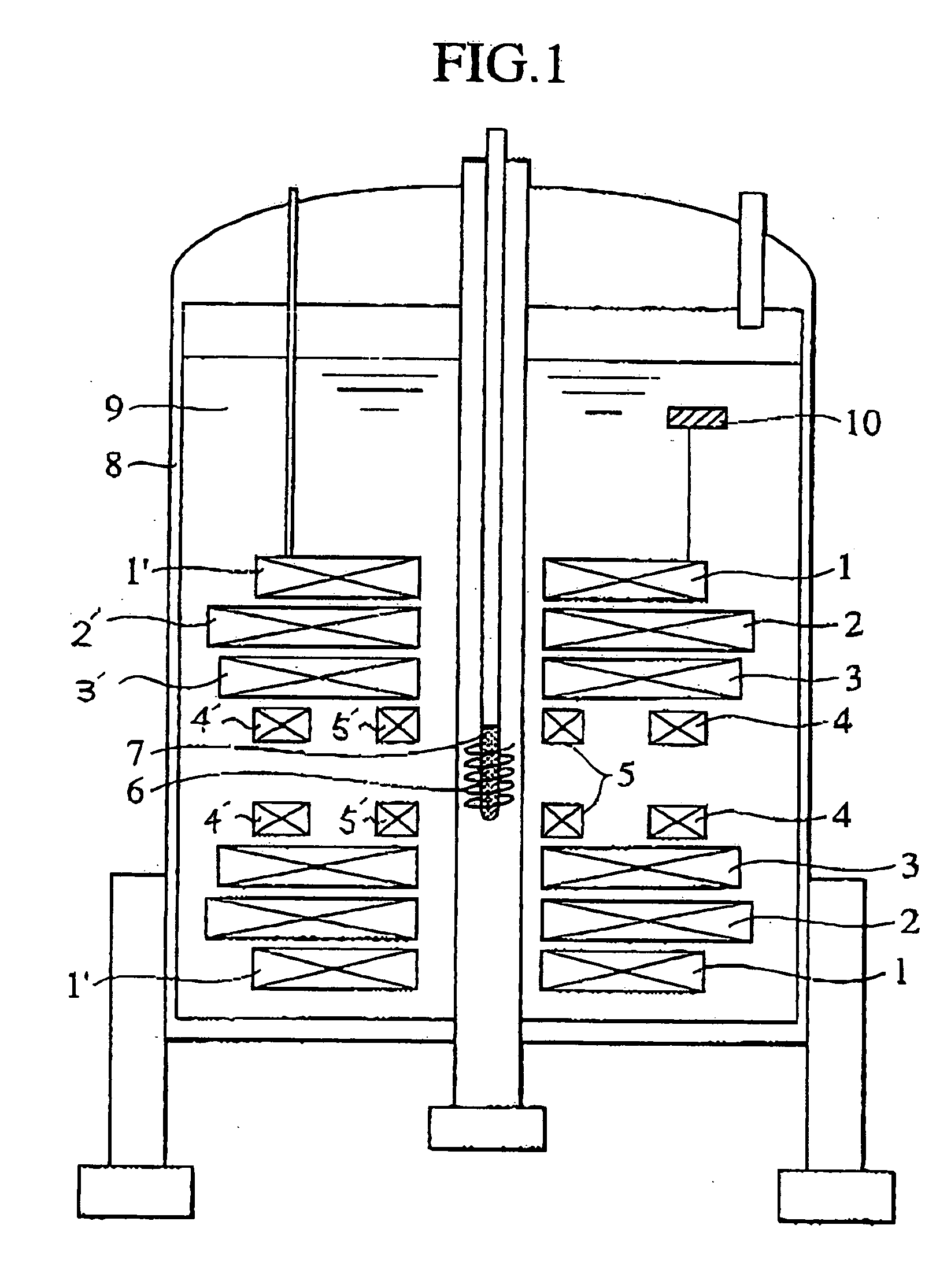
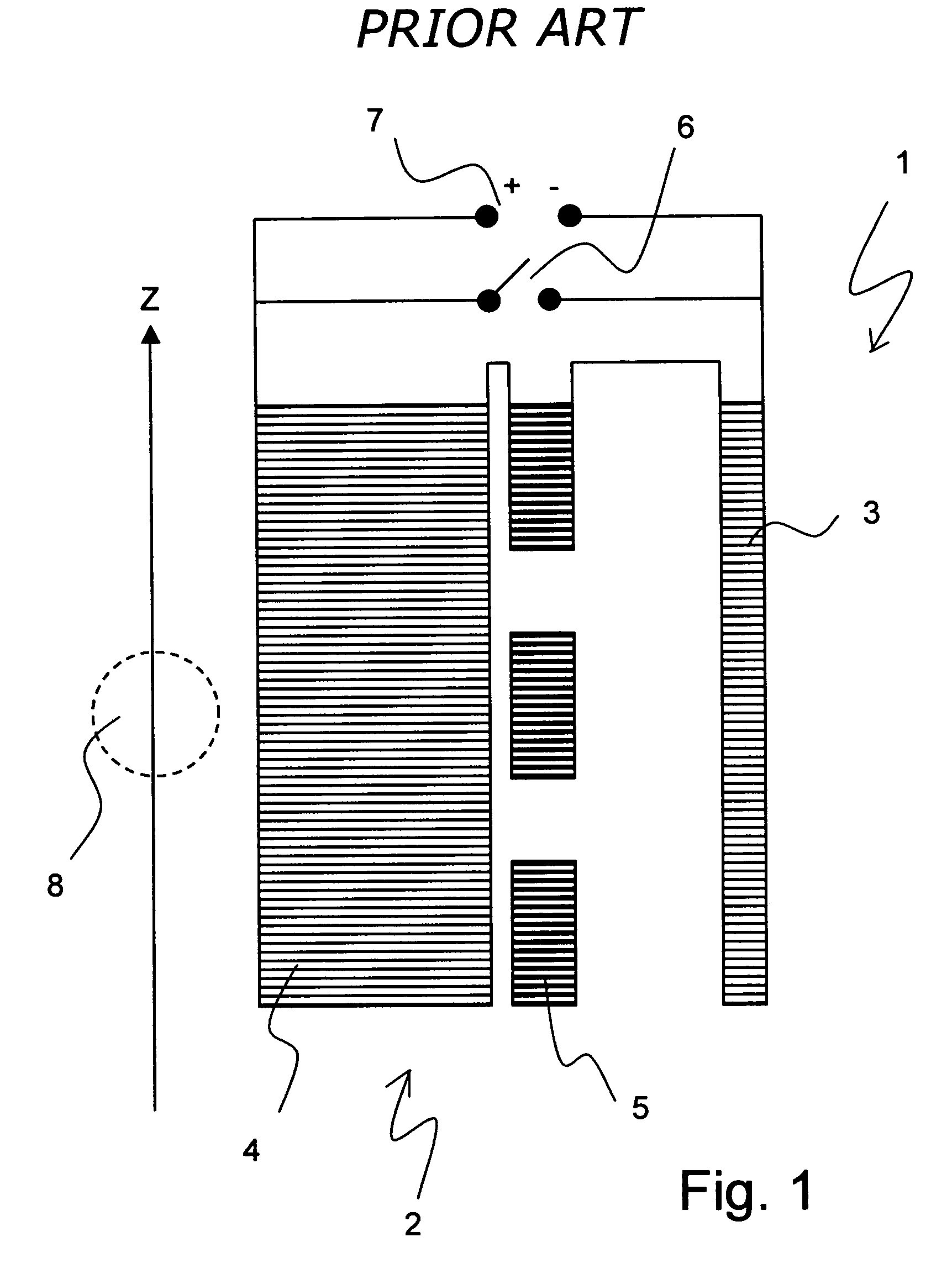
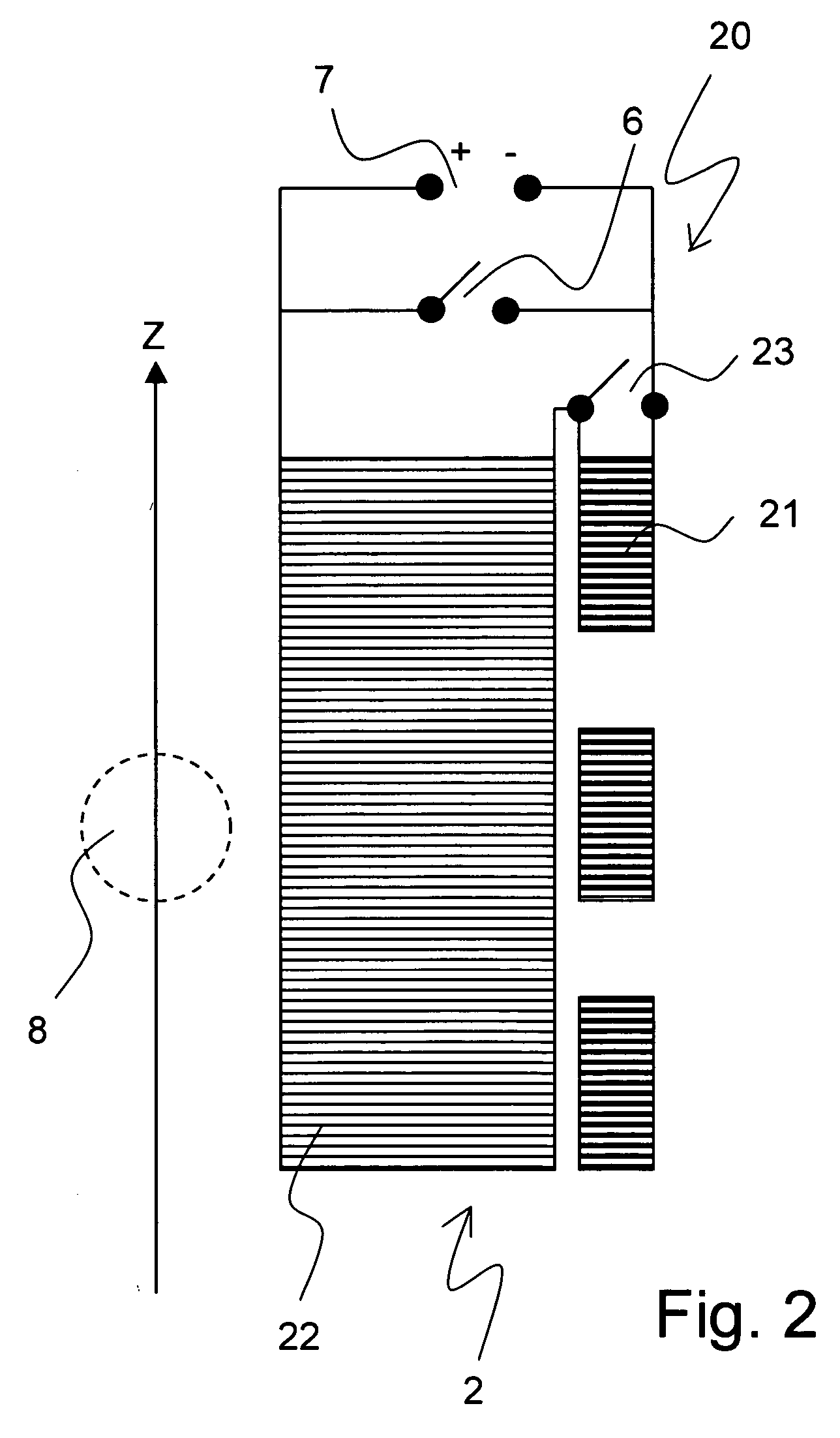
Method for homogenizing a super-conducting NMR magnet
InactiveUS6972652B2Improve basic homogeneityLow costMagnetic measurementsMagnetsMagnetic field gradientNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
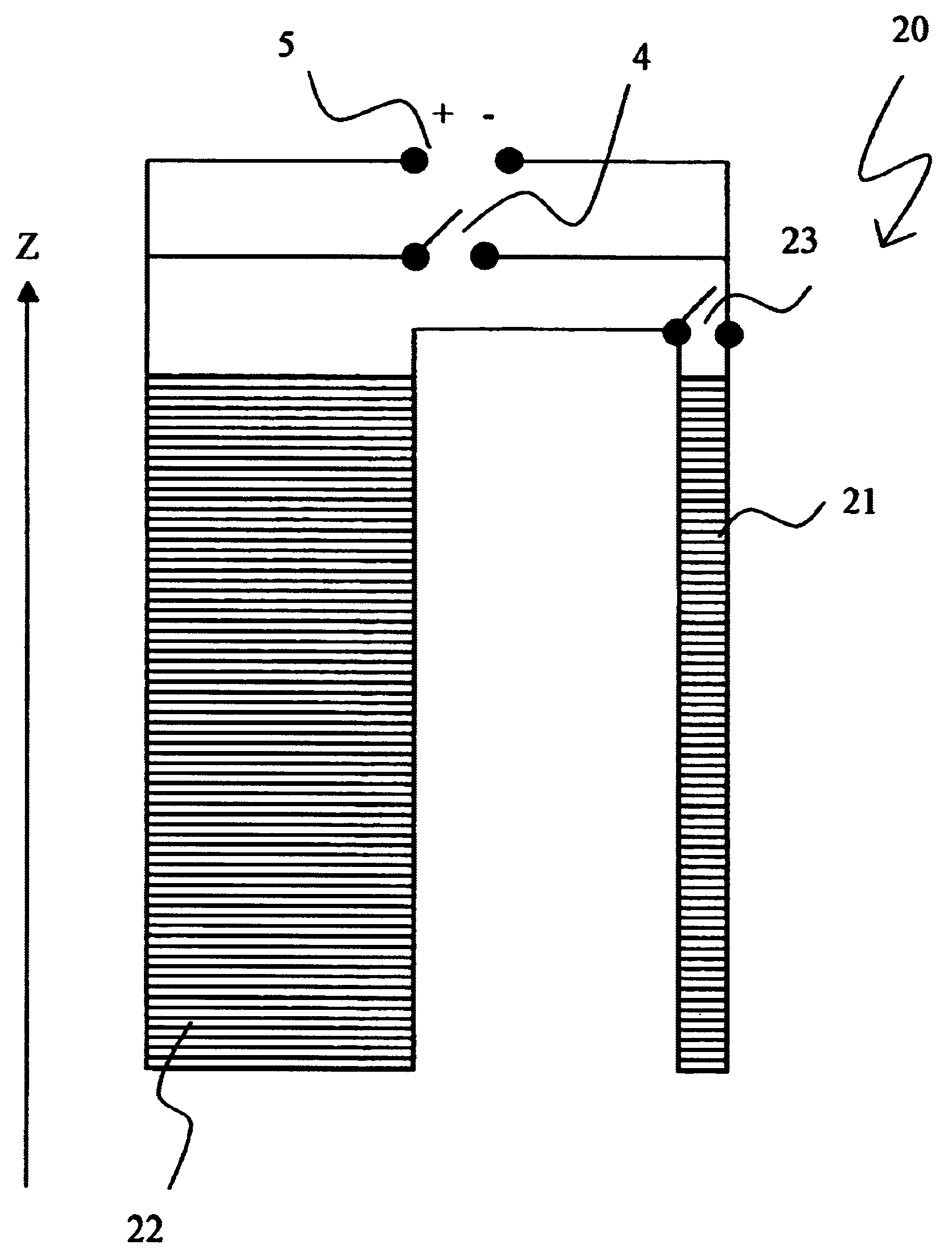
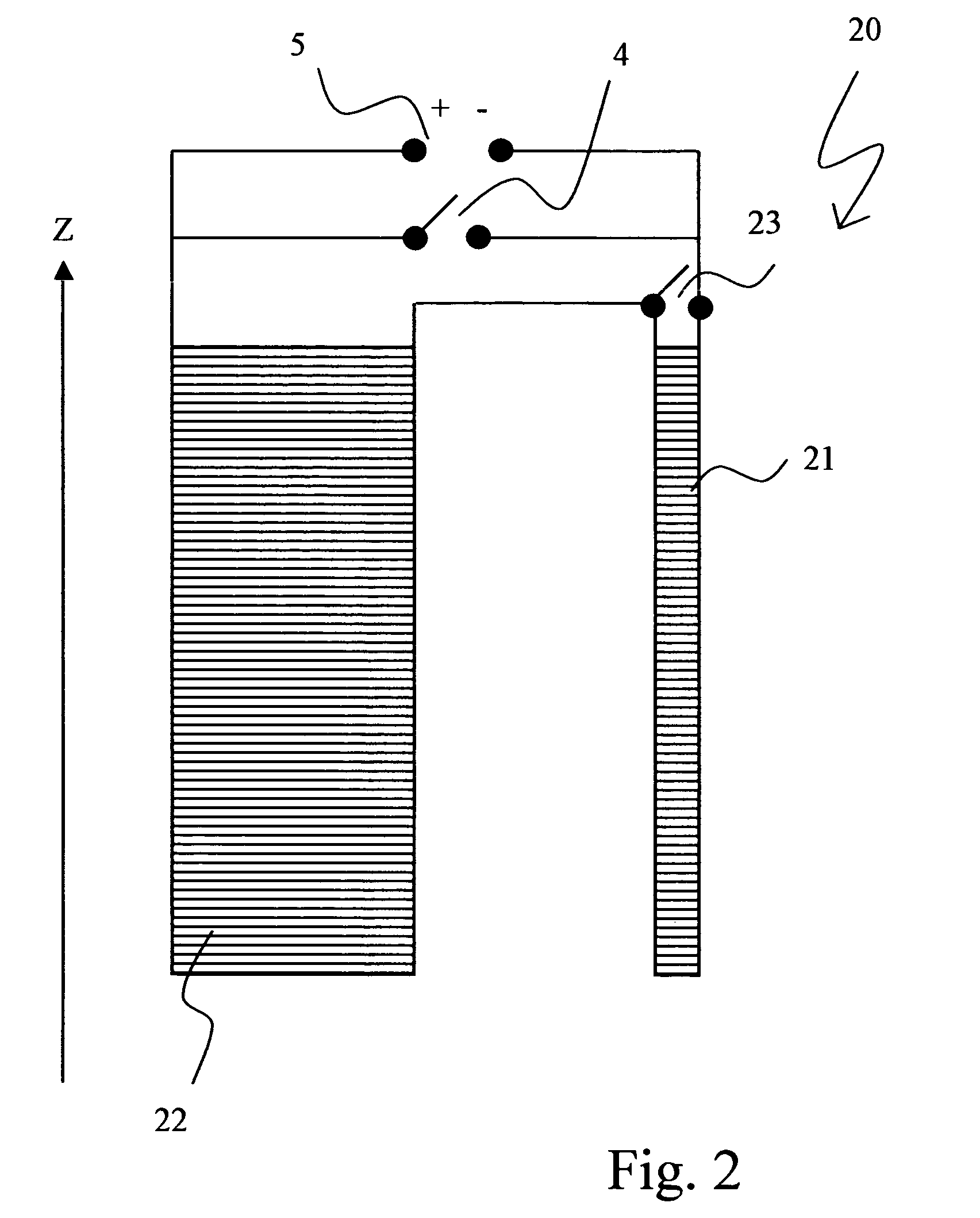
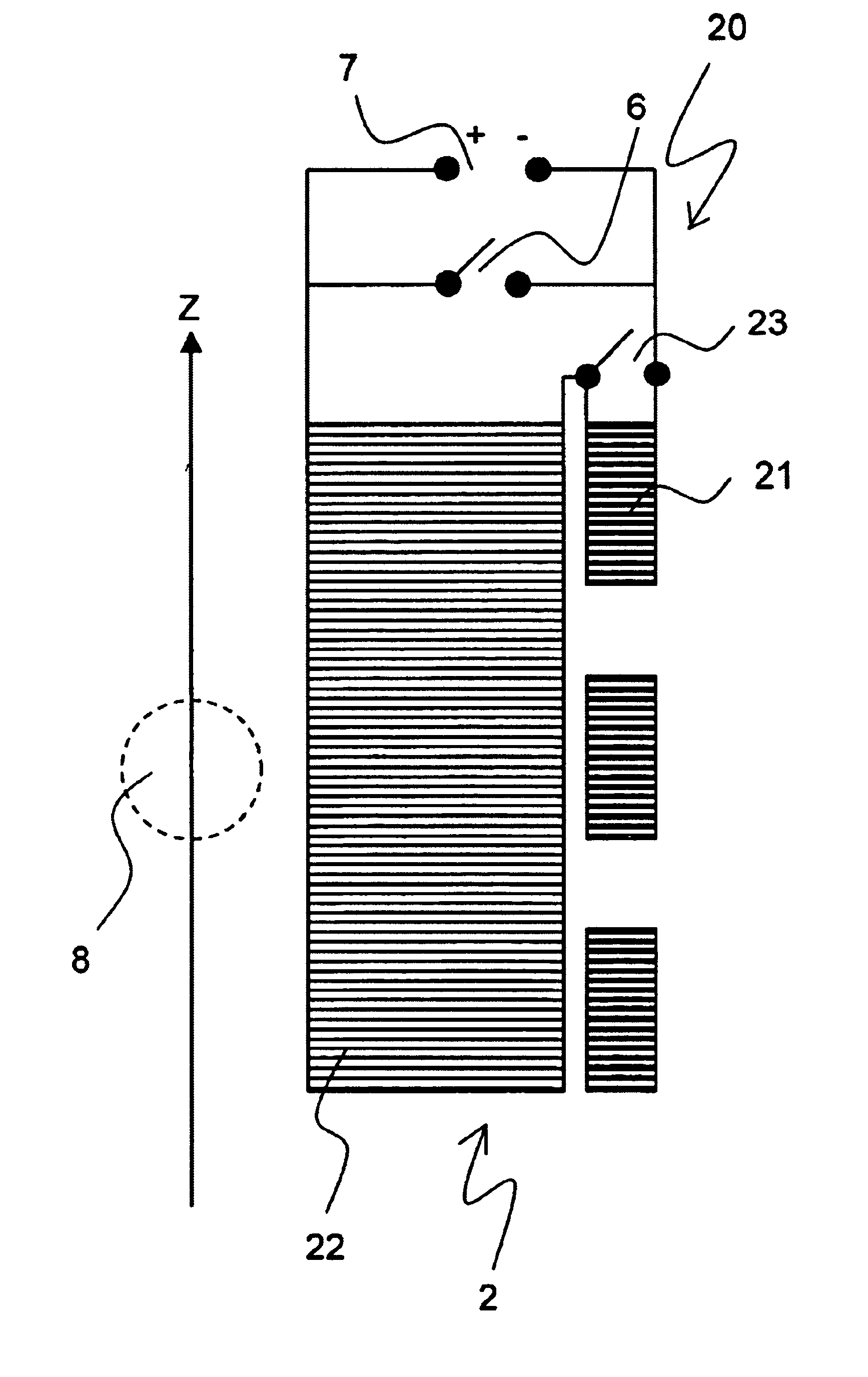
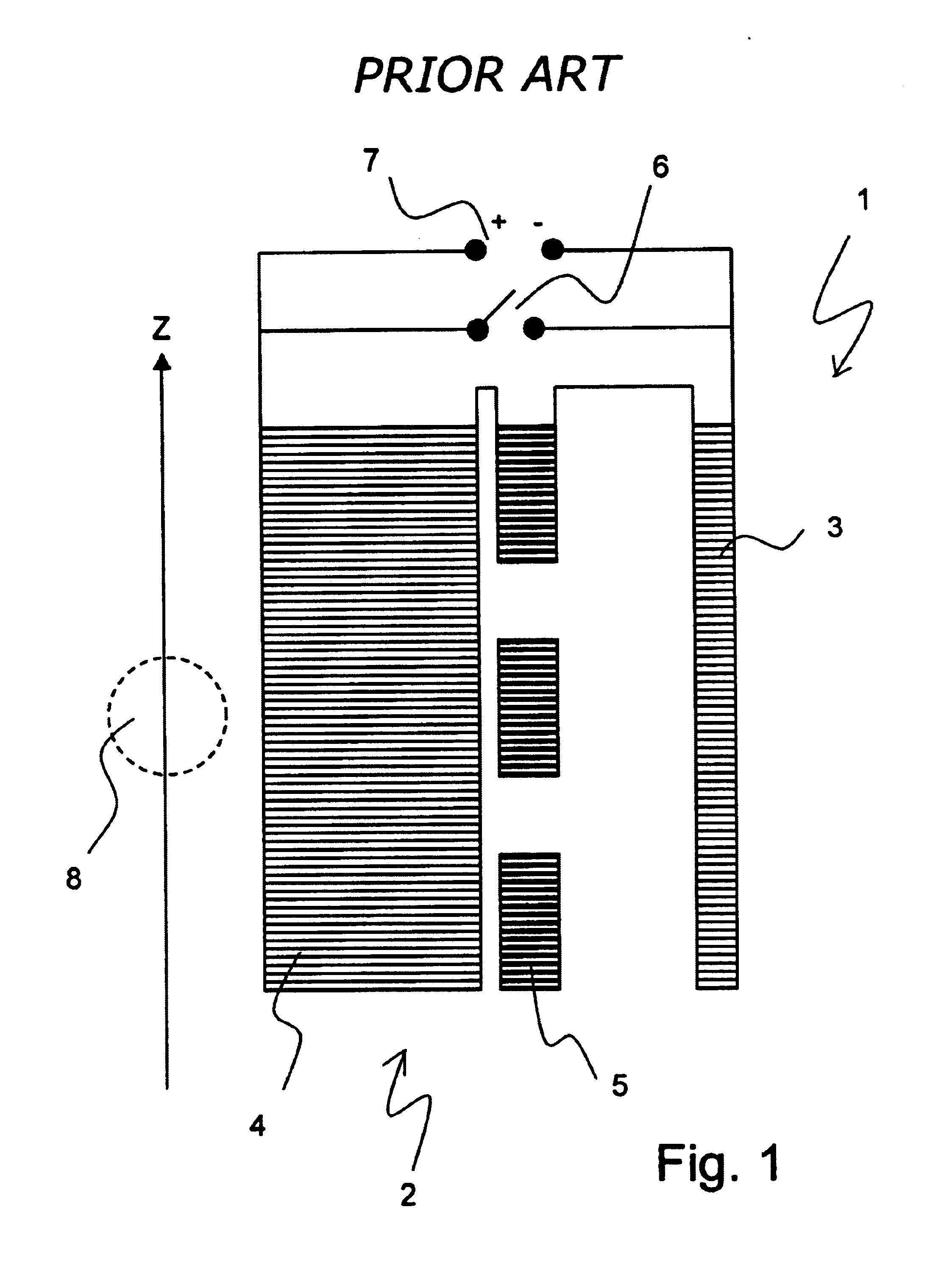
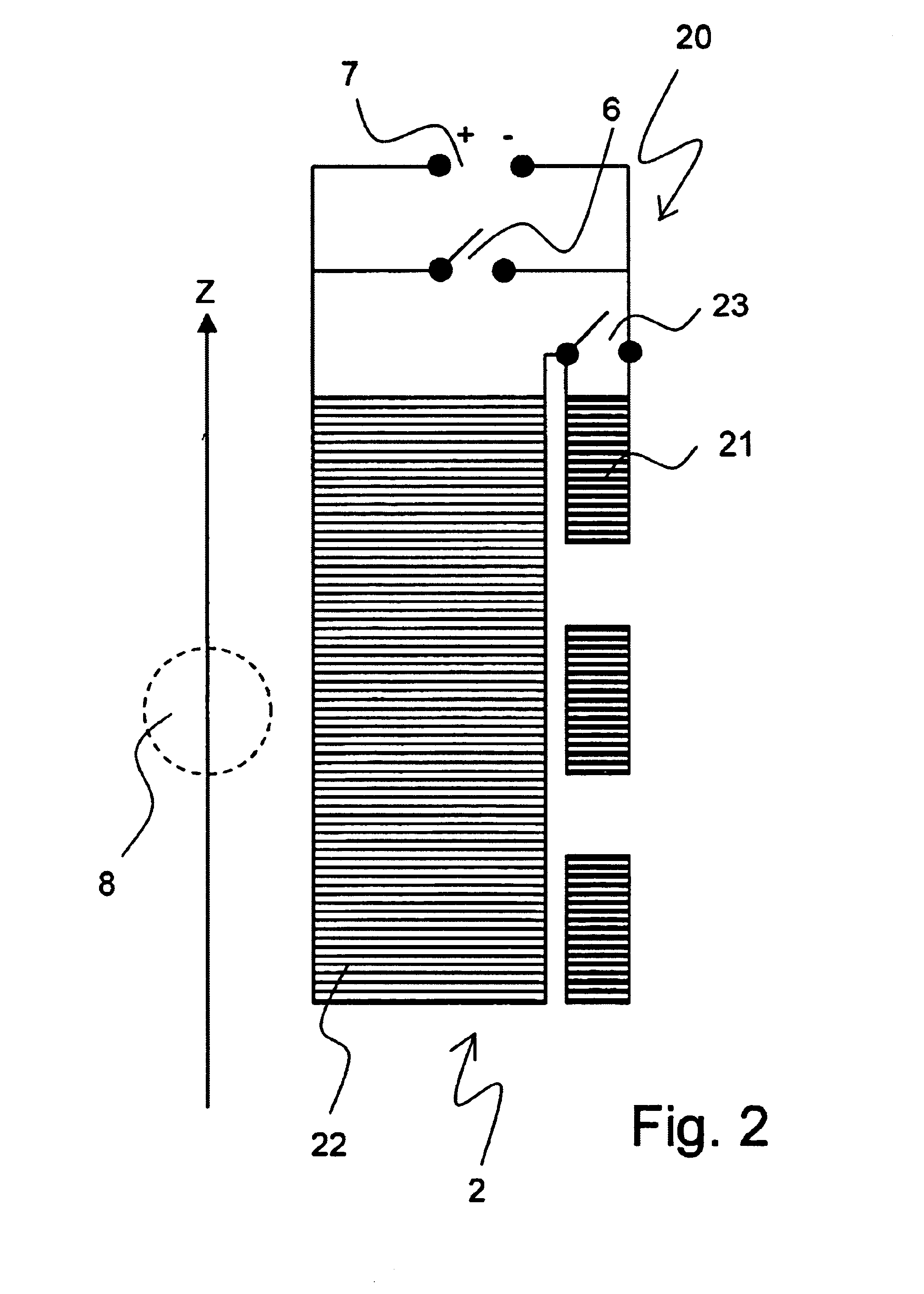
The invention concerns a method for charging a magnet arrangement (20) comprising a first partial region (21) which can be superconductingly short-circuited via an additional switch (23), and a second partial region (22), wherein the two partial regions (21, 22) generate, in an investigational volume (8), gradients of second order having different signs. A magnetic field dependence B* is measured close to the desired operating state of the magnet arrangement (20) and operating currents are determined for each of the two partial regions (21, 22) at which the overall magnetic field B in the volume (8) under investigation is freed from a magnetic field gradient of second order. These operating currents are set thereby taking into consideration the inductive coupling of the partial regions (21, 22) through initially charging of the overall magnet arrangement (20) and, after closing of the additional switch (23), through continuation of charging only in the second partial region (22). The magnetic field homogeneity of the magnet arrangement (20) can thereby be improved in a simple and inexpensive manner.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Fastening device for an NMR probe having a quick-release fastener
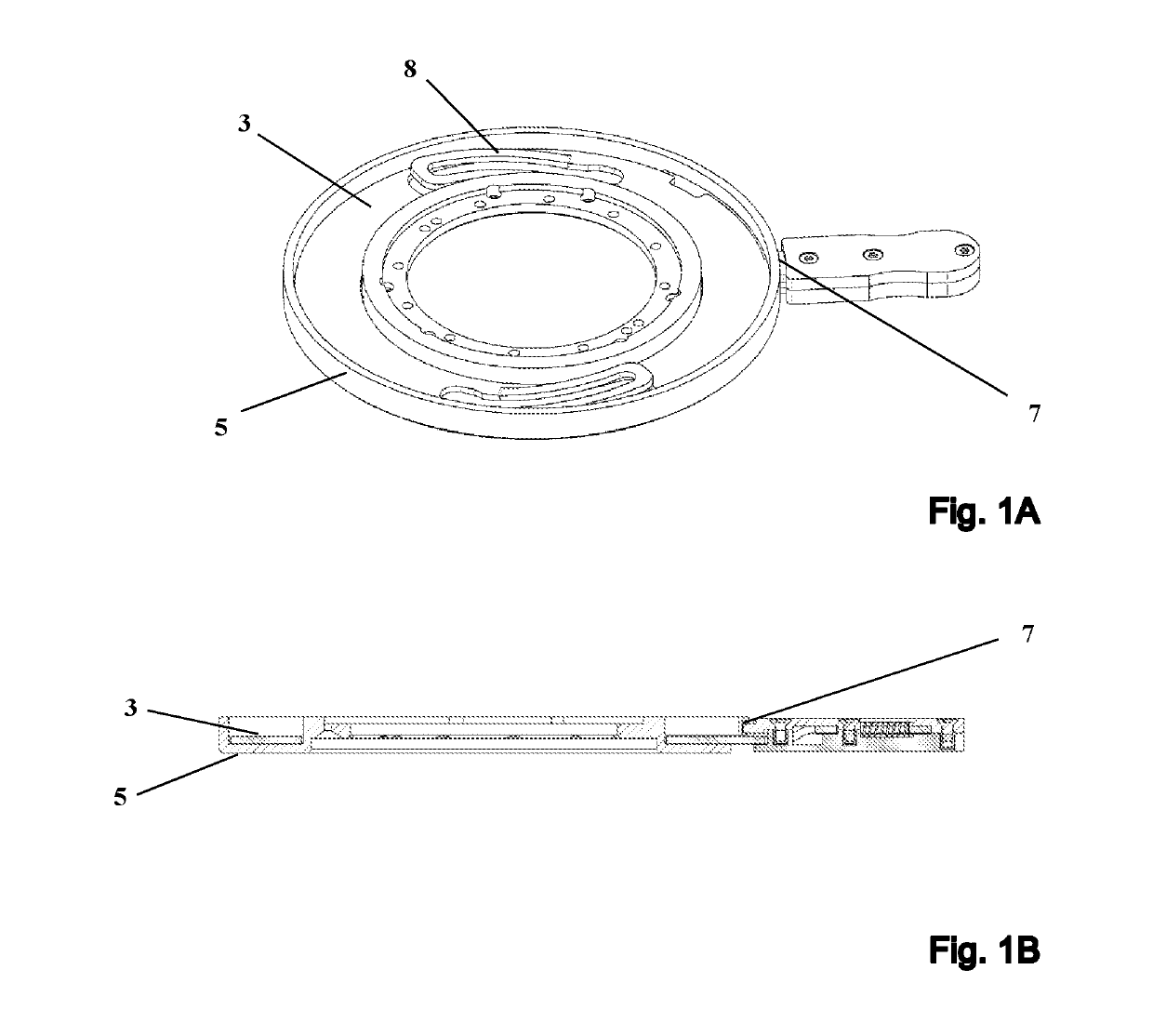
ActiveUS10379179B2Quality improvementReduce material costsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionEngineeringFixed length
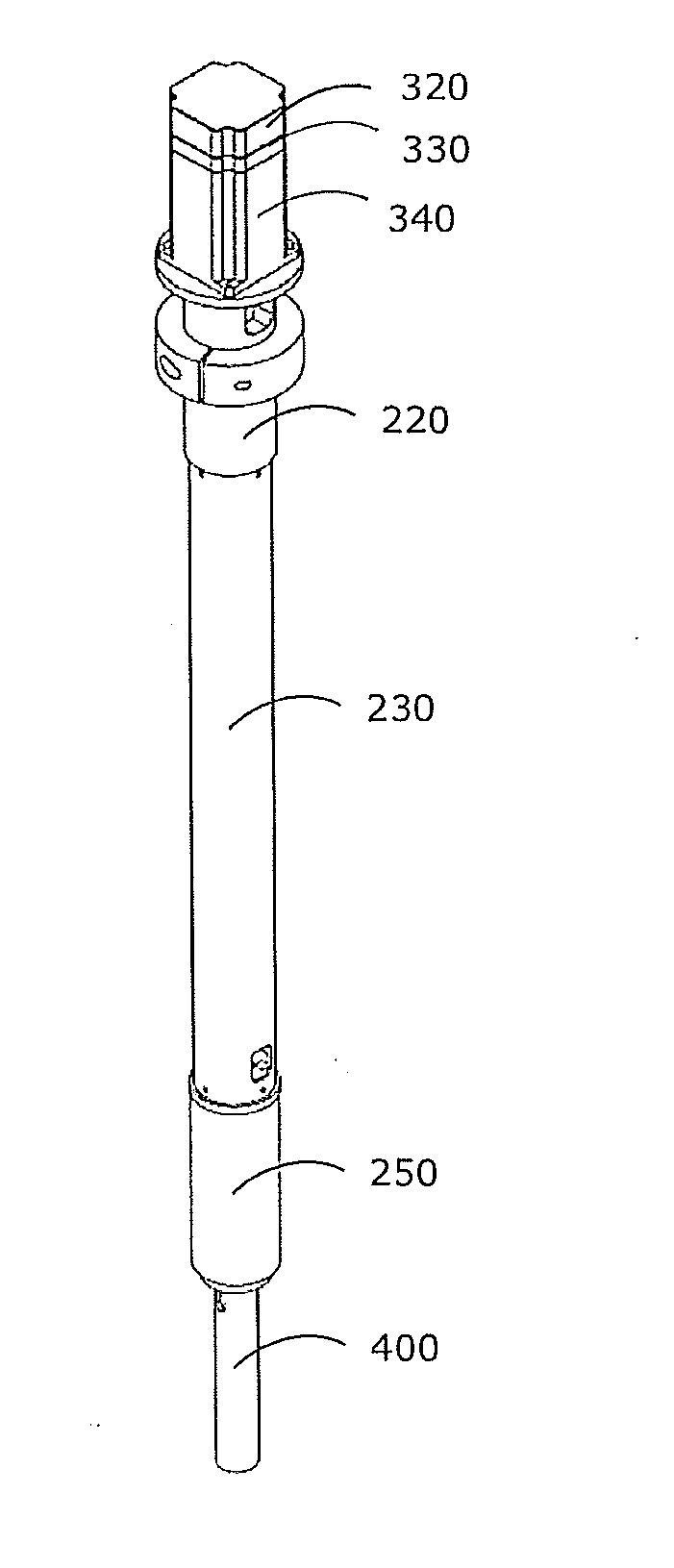
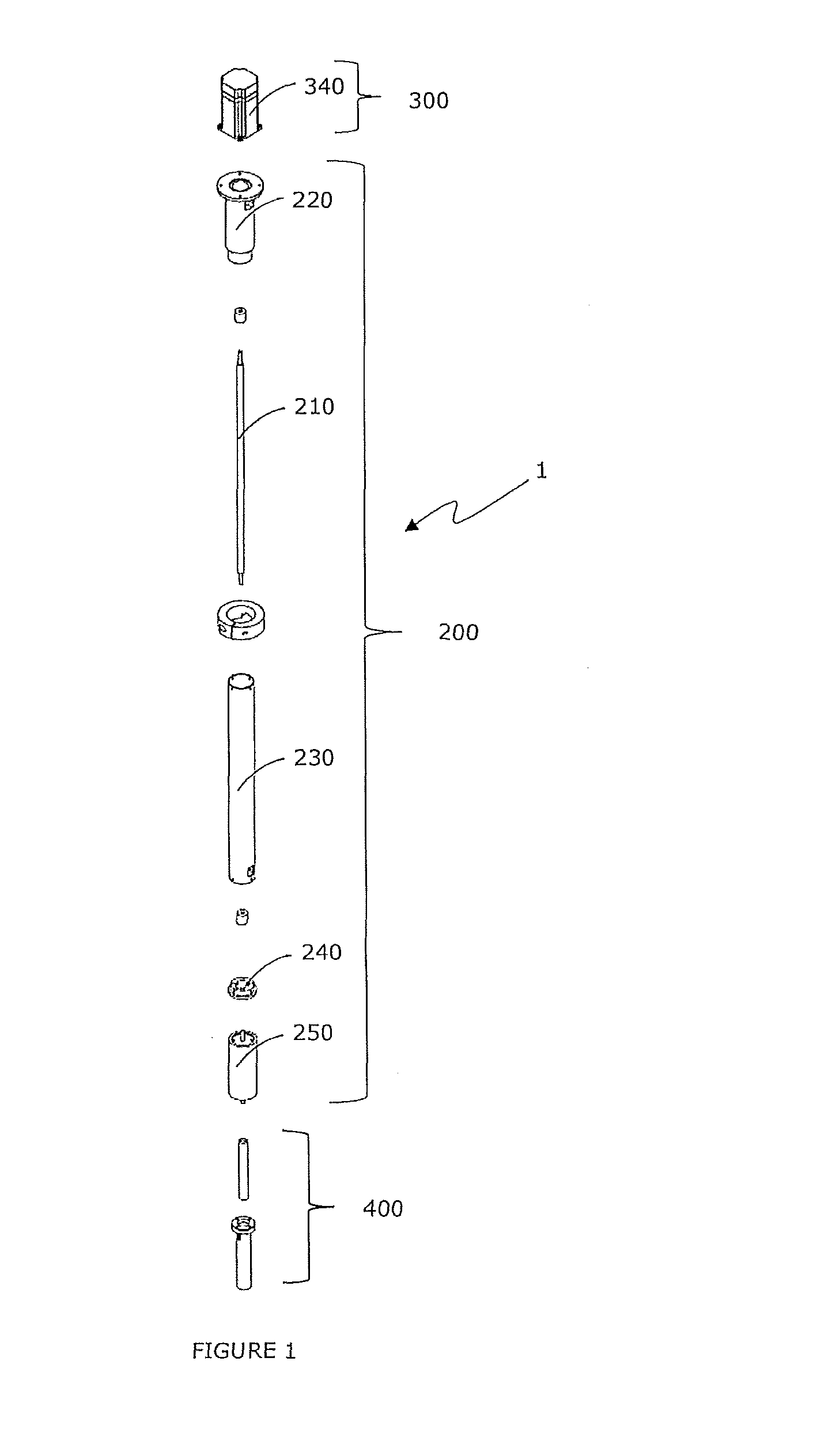
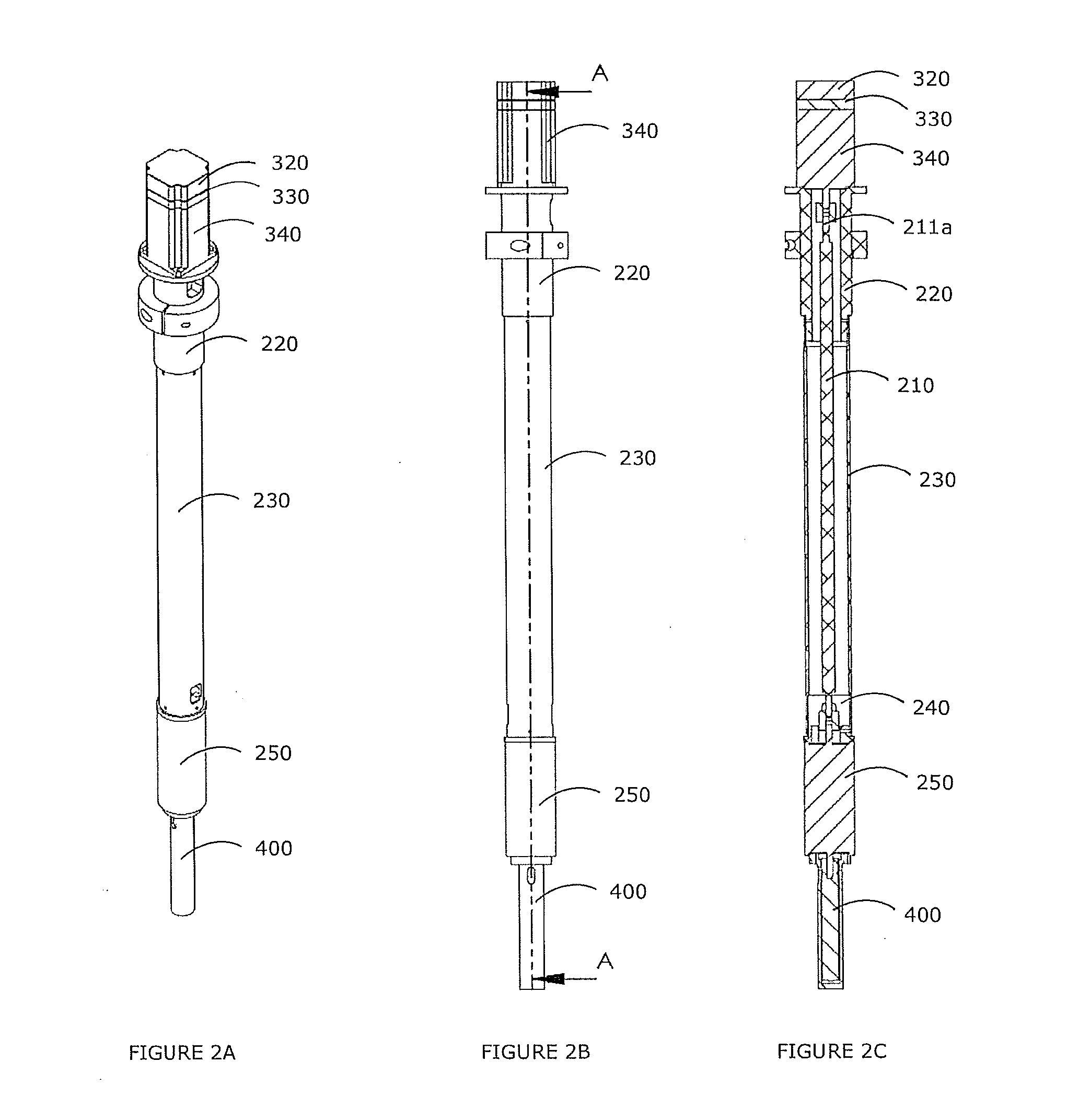
A fastening system for attaching an NMR probe to an NMR magnet includes a discoid insert and a retention system that is rigidly connected to the magnet and on which the insert can be mounted. A form-fitting, variable-force connection is established between the NMR probe and the retention system using a spring element. The probe attaches to the insert by a plurality of integral, rigid retaining elements that are of an invariable fixed length. The spring element and the retaining elements are designed geometrically such that in a first, opened state the connection between the insert and the retaining elements has a mechanical backlash between 0.5 mm and 5 mm when the spring element is relaxed. In a second, closed state the connection between the insert and the retaining elements has no mechanical backlash when the spring element is under mechanical tension.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
Method for testing a superconductor under increased current load in a series-produced and actively shielded superconducting NMR magnet
ActiveUS7368911B2Increase loadTemporal field stability of the magnet coil configurationSuperconductive properties measurementsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesCurrent loadInductance
A method for testing a new superconducting wire involves charging an actively shielded magnet coil configuration which comprises a first partial region which can be superconductingly short-circuited using an additional switch. A superconductor to be tested under increased current load is used in this first partial region, thereby preventing superconductor in the second partial region from being subjected to this increased current load. Operating currents are determined for both partial regions that have the desired excess current in the first partial region, with the overall field B0 only slightly differing from the standard operating field of the magnet coil configuration. The operating currents are adjusted through initial charging of the overall magnet coil configuration, thereby taking into consideration the inductive coupling between the partial regions and after closing of the additional switch, by continued charging or discharging in the second partial region only. The method permits inexpensive testing of a superconductor in a series-produced NMR magnet under NMR conditions.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
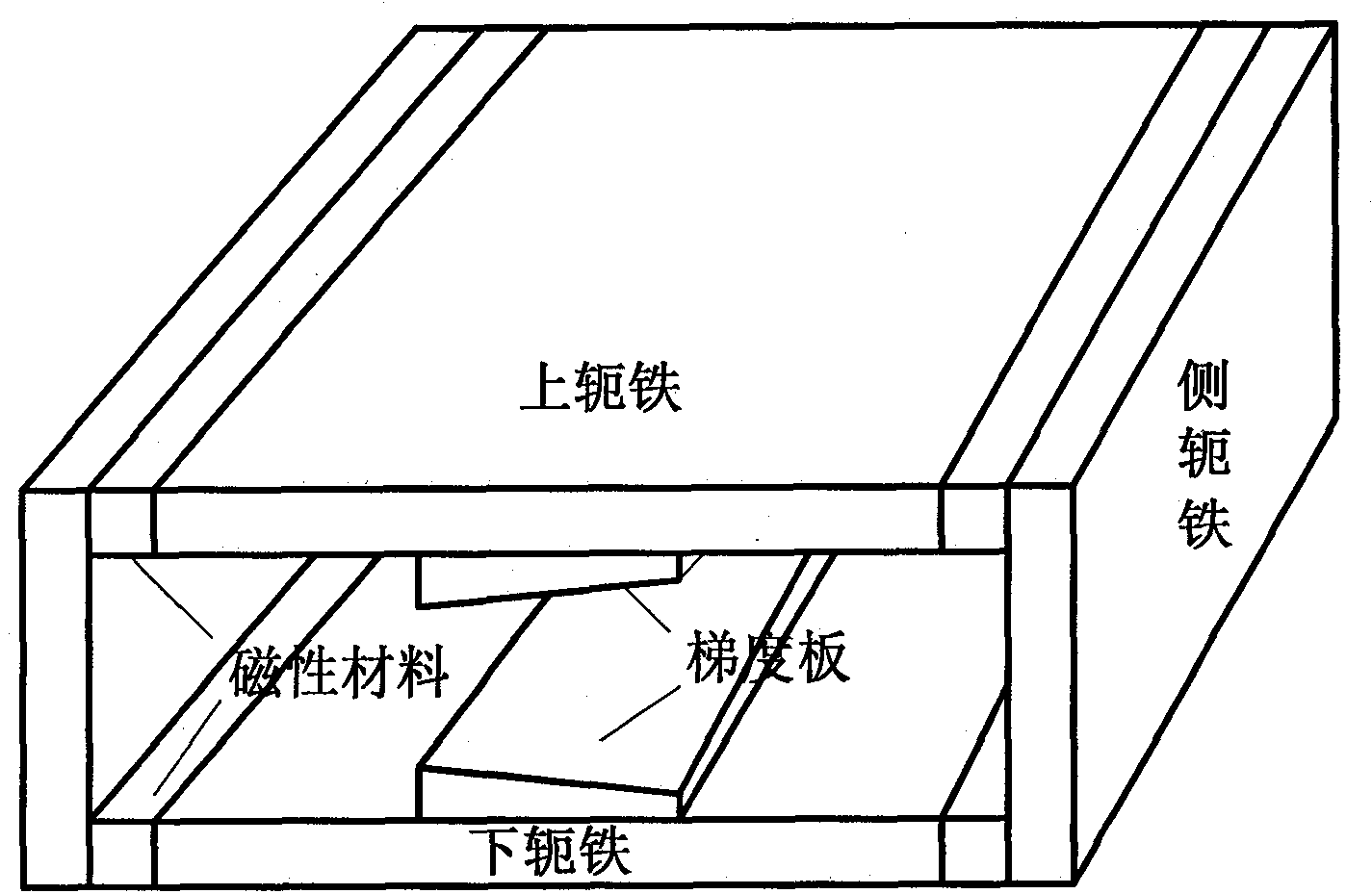
Fixed-gradient NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) magnet
InactiveCN104215921AMagnetic measurementsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceUniform fieldSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention relates to a fixed-gradient NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) magnet and provides an NMR magnet system applied to non-uniform field NMR techniques. The system is capable of generating a fixed-gradient magnetic field in a measurement area; the fixed-gradient magnetic field is available for NMR two-dimensional imaging of liquid and solid samples. The system comprises four yokes made of pure iron, four pieces of rare-earth magnetic material, and two all-iron gradient plates. The four pieces of rare-earth magnetic material are placed in the yokes, every two of polarization directions of the four pieces of rare-earth magnetic material form two magnetic circuits; a more uniform measurement magnetic field is generated in the center of the system. The gradient plates are placed right over and under the measurement area; a uniformly decreasing one-dimensional gradient is generated in the measurement area.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for testing a superconductor under increased current load in a series-produced and actively shielded superconducting nmr magnet
ActiveUS20080084207A1Easy to set upIncrease loadSuperconductive properties measurementsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesMaterials scienceSuperconducting wire
A method for testing a new superconducting wire involves charging an actively shielded magnet coil configuration which comprises a first partial region which can be superconductingly short-circuited using an additional switch. A superconductor to be tested under increased current load is used in this first partial region, thereby preventing superconductor in the second partial region from being subjected to this increased current load. Operating currents are determined for both partial regions that have the desired excess current in the first partial region, with the overall field B0 only slightly differing from the standard operating field of the magnet coil configuration. The operating currents are adjusted through initial charging of the overall magnet coil configuration, thereby taking into consideration the inductive coupling between the partial regions and after closing of the additional switch, by continued charging or discharging in the second partial region only. The method permits inexpensive testing of a superconductor in a series-produced NMR magnet under NMR conditions.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
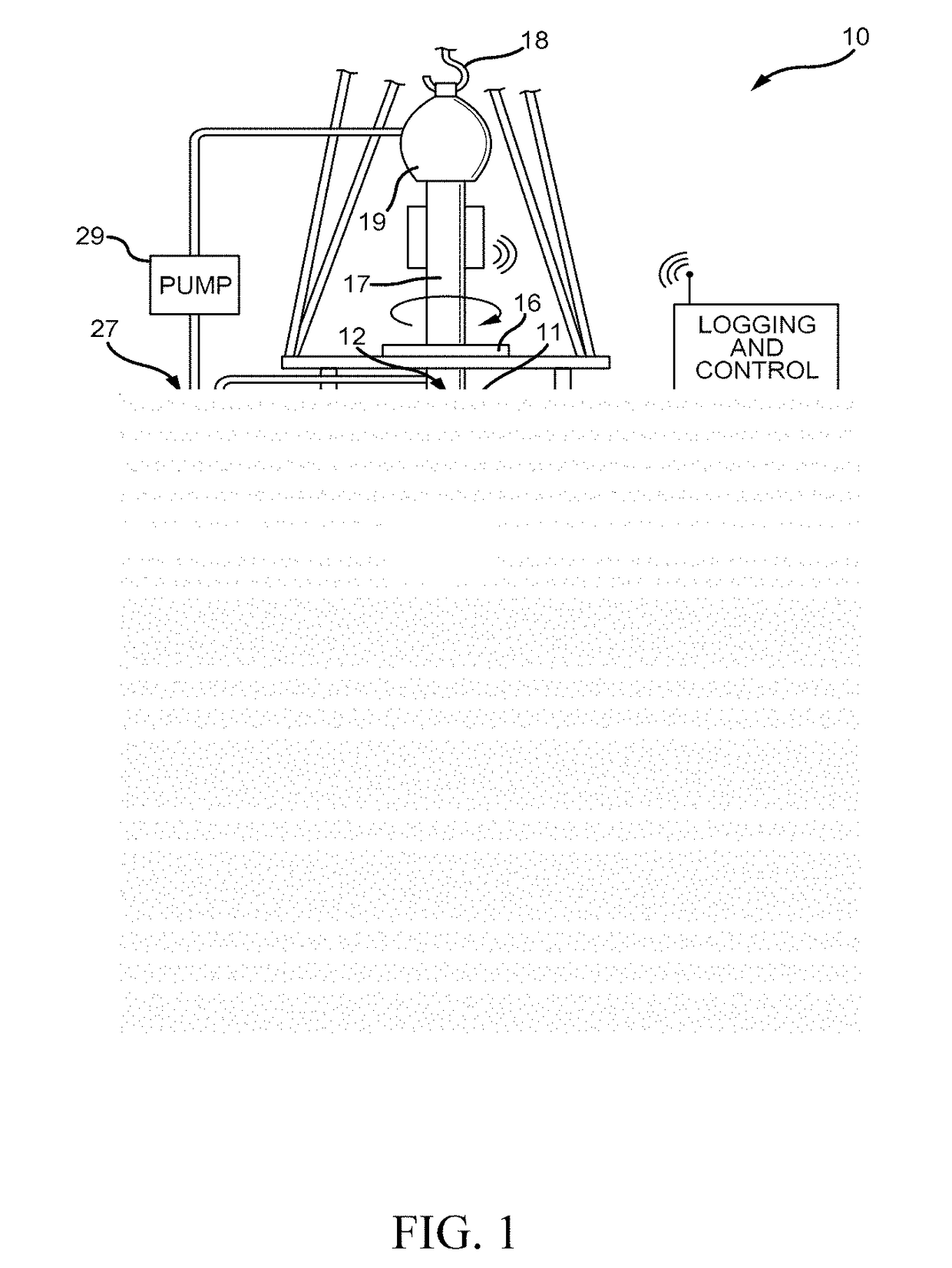
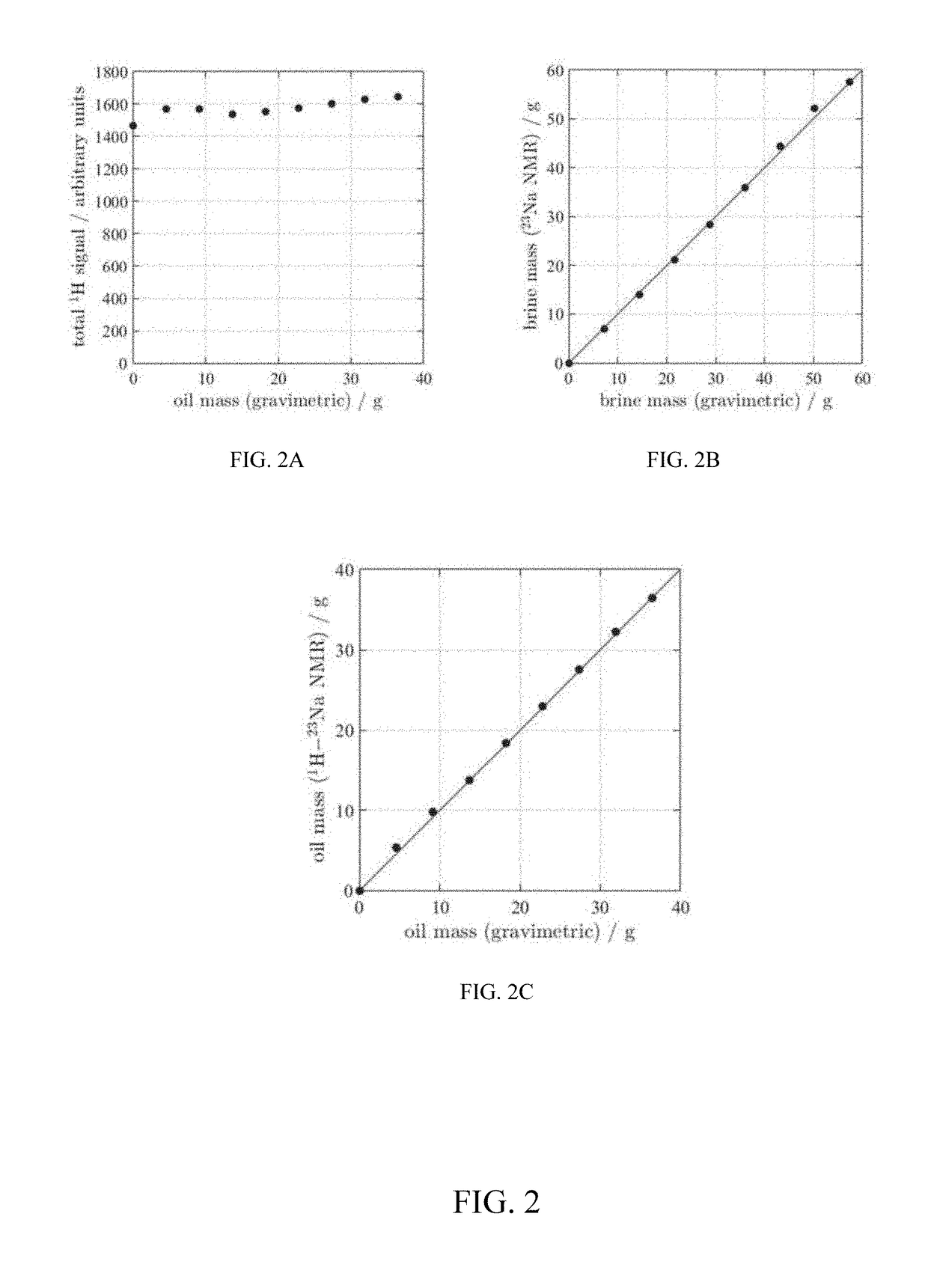
Methods for interpreting nmr data
ActiveUS20180203153A1Easy to analyzeEasy to explainElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingEarth material testingWell loggingRadio frequency
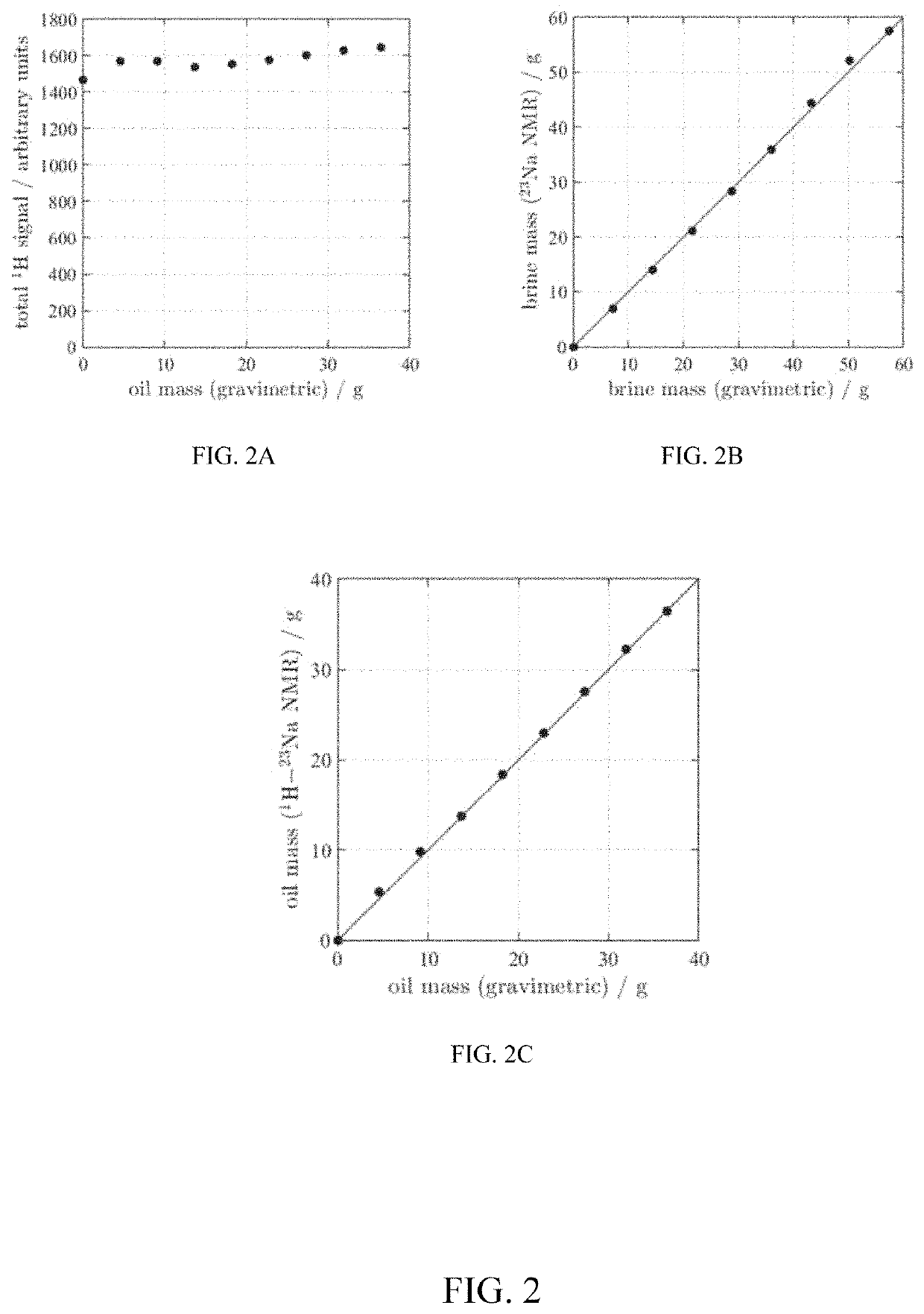
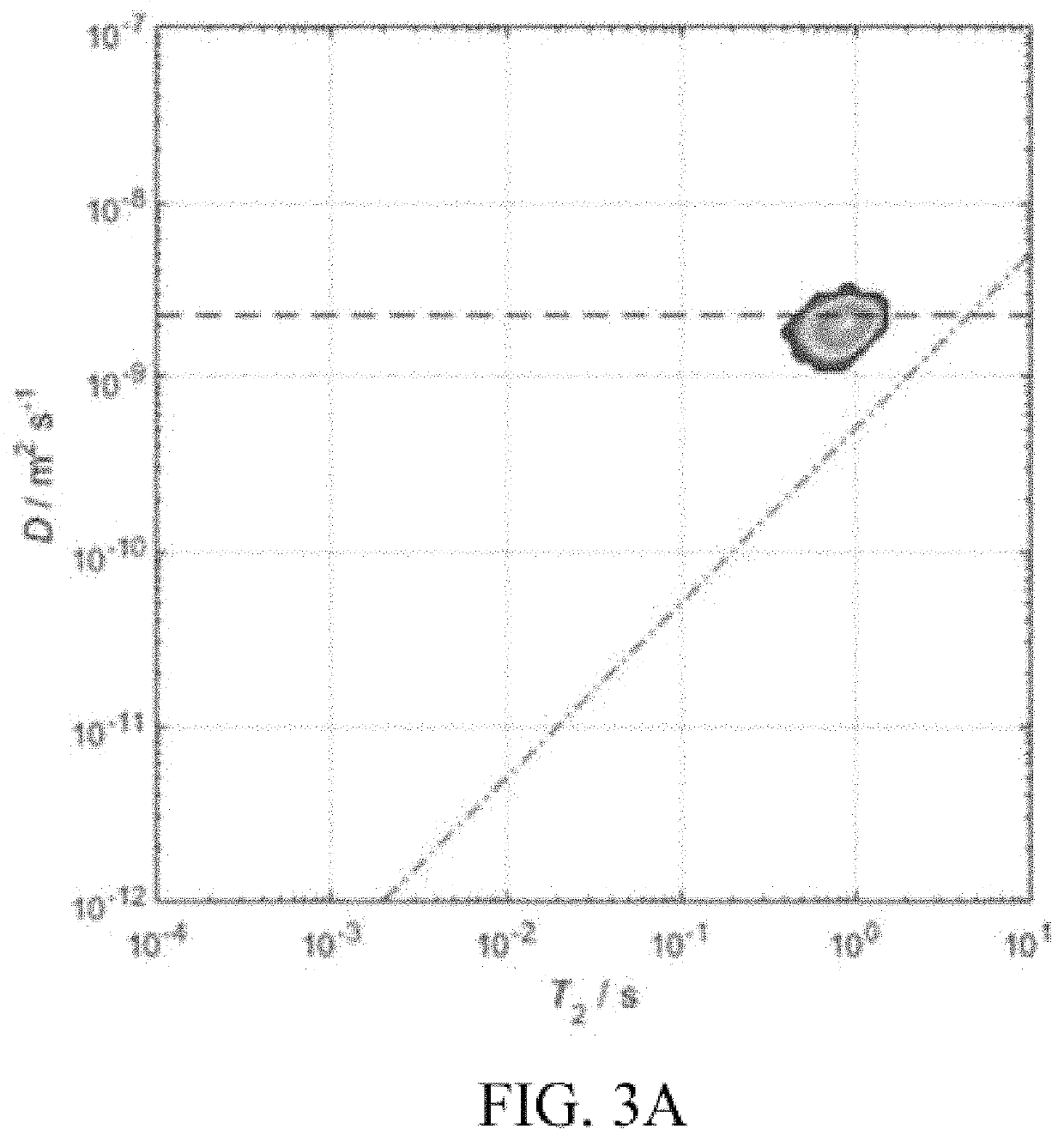
Methods for improved interpretation of NMR data acquired from industrial samples by simultaneously detecting more than one resonant nucleus without removing the sample from the sensitive volume of the NMR magnet or radio frequency probe are disclosed. In other aspects, the present disclosure provides methods for robust imaging / analysis of spatial distribution of different fluids (e.g., 1H, 23Na, 19F) within a core or reservoir rock. NMR data may be interpreted in real-time during dynamic processes to enable rapid screening, e.g. of enhanced oil recovery techniques and products and / or to provide improved interpretation of well-logs. Measurements of resonant nuclei other than 1H may be performed in the laboratory or downhole with a NMR logging tool. In other aspects, the present disclosure describes a novel kernel function to extract values for underlying parameters that define relaxation time behavior of a quadrupolar nucleus.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
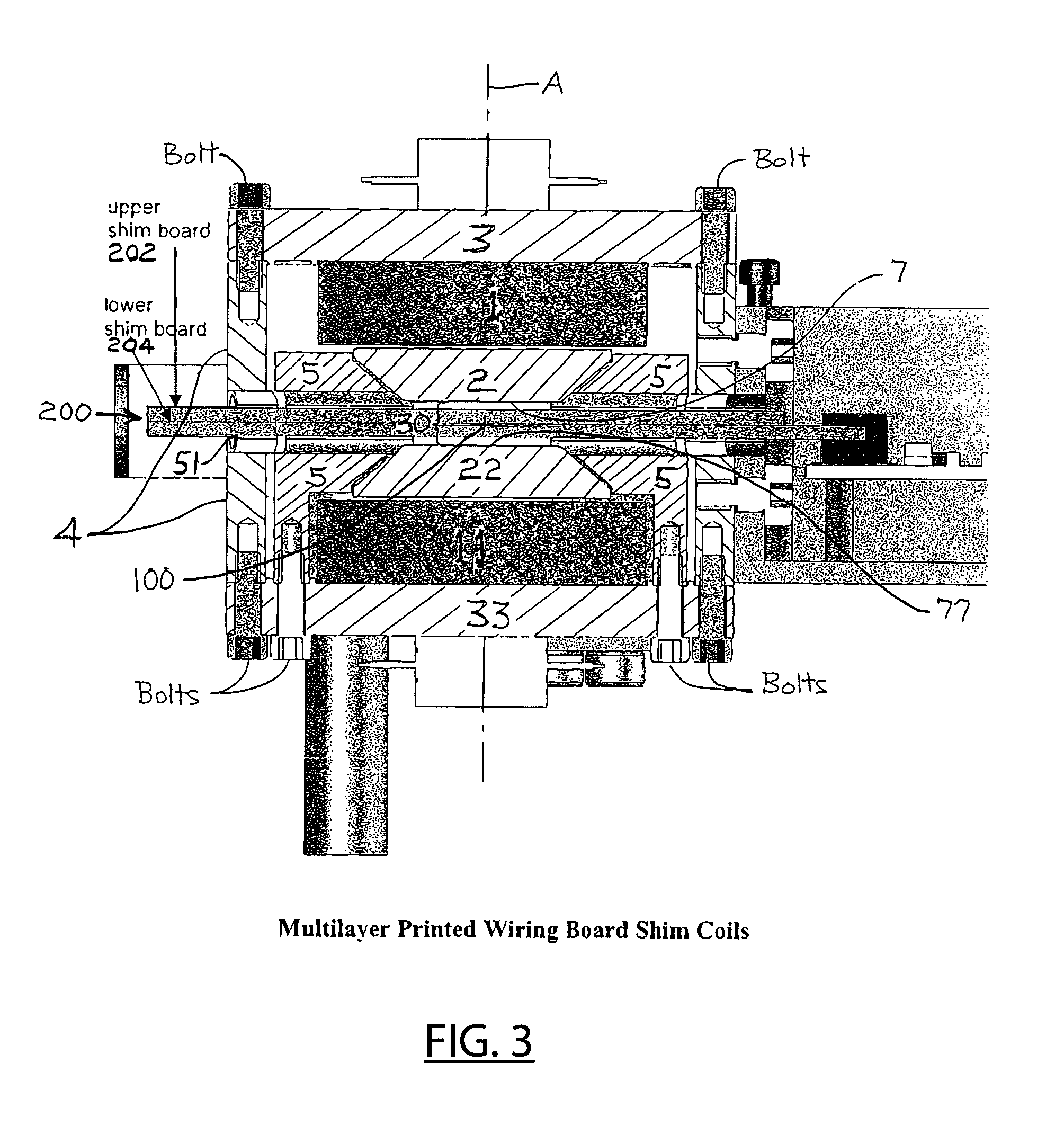
Shim coils and shimming miniaturized nuclear magnetic resonance magnets
ActiveUS8729898B2Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonancePole piece
A capillary cartridge assembly for positioning a sample fluid at a geometric center between juxtaposed pole pieces of a NMR magnet assembly for NMR analysis comprises a capillary captured in a channel in a printed circuit board assembly that is sized to fit between the pole pieces. The assembly includes a RF coil surrounding a portion of the capillary. Electric traces shaped to function as shim coils can be included in the printed circuit board. An end of the printed circuit board includes electrically conductive contacts that plug into a receptacle to connect the RF coil and traces to external electrical circuitry when the RF coil is in the geometric center. The capillary can be a continuous flow-through capillary or a closed cartridge.
Owner:PICOSPIN
NMR spectrometer comprising a superconducting magnetic coil having windings composed of a superconductor structure having strip pieces chained together
ActiveUS10042017B2Increase resistanceEasy to produceMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyPermanent superconductor devicesElectrical conductorConductor Coil
An NMR spectrometer (131) with an NMR magnet coil (91) having windings of a conductor with a superconducting structure (1), which have a plurality of band-segments (2, 2a, 7a-7e, 8a-8d, 15) made of band-shaped superconductor. Each band-segment (2, 2a, 7a-7e, 8a-8d, 15) has a flexible substrate (3) and a superconducting layer (4) deposited thereon, wherein the band-segments (2, 2a, 7a-7e, 8a-8d, 15) each have a length of 20 m or more. At least one of the band-segments (2, 2a, 7a-7e, 8a-8d, 15) forms a linked band-segment (2, 2a), and each linked band-segment (2, 2a) is connected to at least two further band-segments (7a-7e) in such a way that the combined further band-segments (7a-7e) overlap with at least 95% of the total length (L) of the linked band-segment (2, 2a). The magnet coil generates particularly high magnetic fields in a sample volume and has a low drift.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
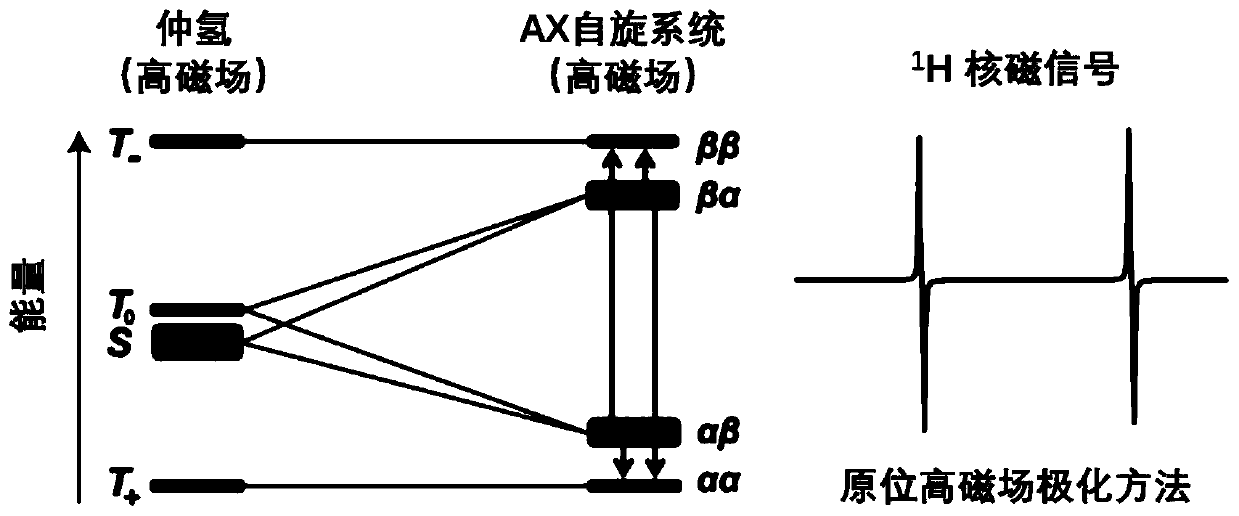
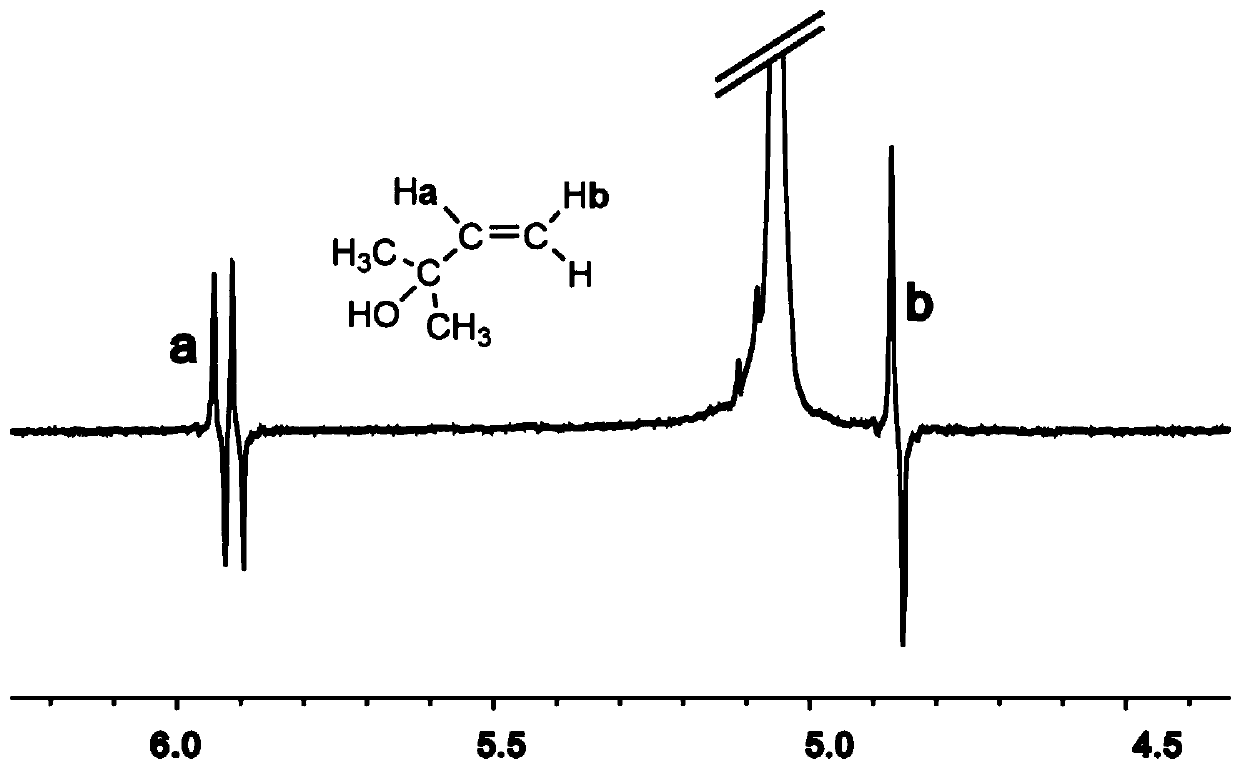
High-field in-situ polarization device and method utilizing parahydrogen to induce polarization
ActiveCN111580029ASimple structureImprove stabilityMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceEngineering
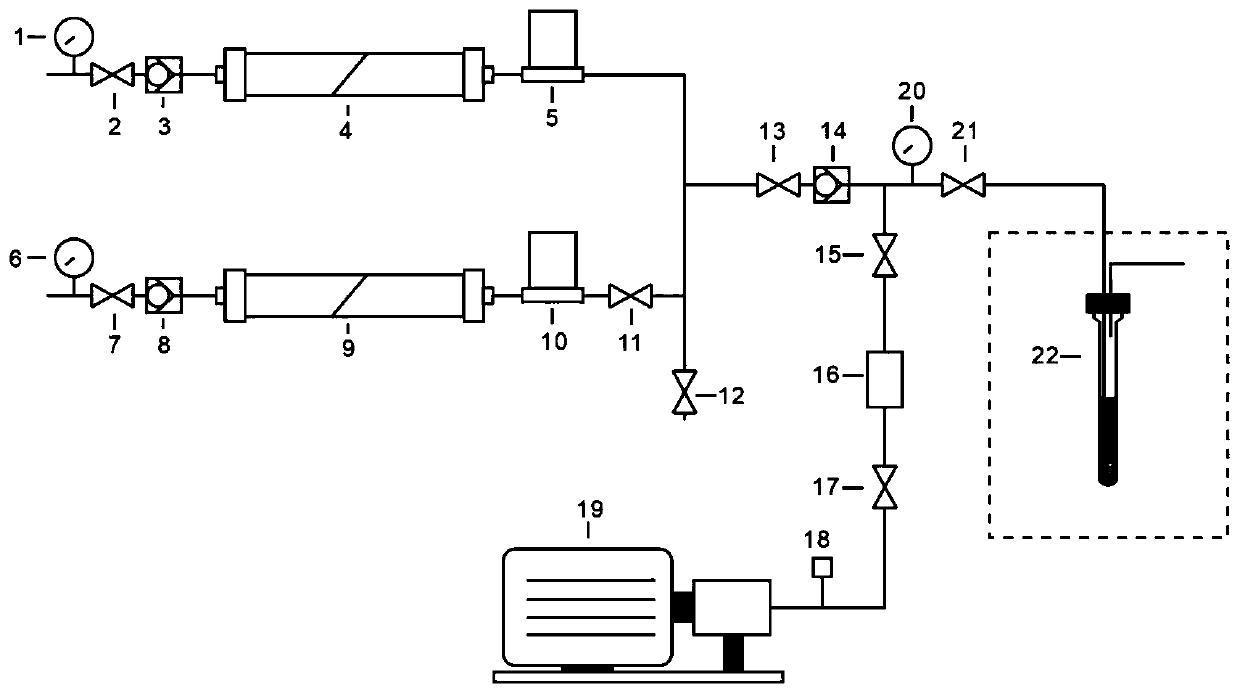
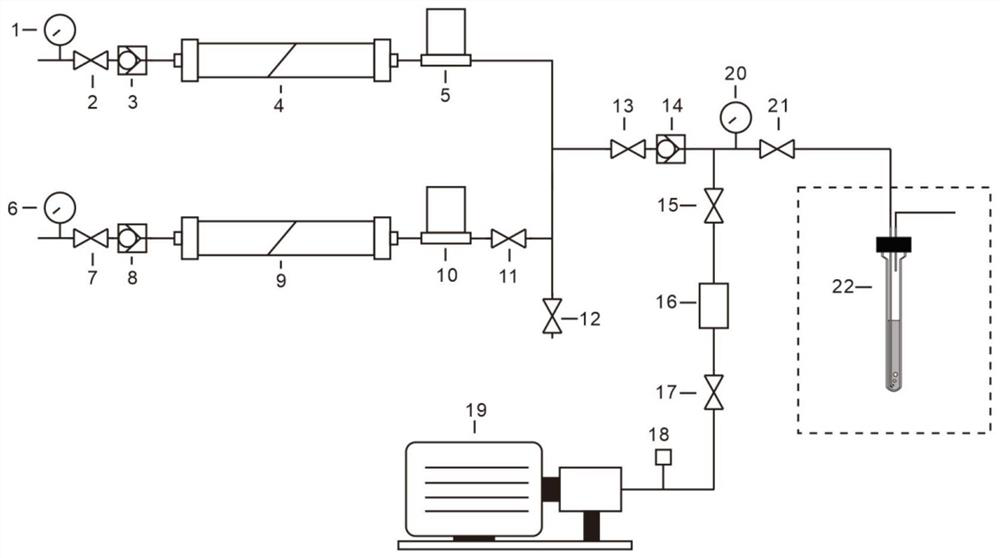
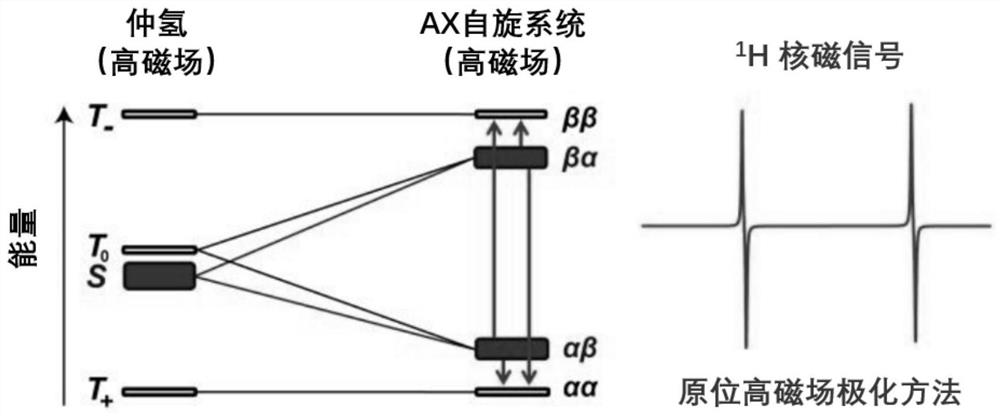
The invention discloses a high-field in-situ polarization device utilizing parahydrogen to induce polarization. The gas outlet end of the reaction gas inlet channel is connected with one end of a third straight-through valve; the other end of the third straight-through valve is respectively connected with the gas outlet end of the parahydrogen gas inlet channel, the fourth straight-through valve end and one end of a fifth straight-through valve; the other end of the fifth straight-through valve is connected with the inlet end of a third one-way valve; the outlet end of the third one-way valveis respectively connected with one end of an eighth straight-through valve and one end of a sixth straight-through valve; the other end of the eighth straight-through valve is connected with a reaction sampling pipe, the other end of the sixth straight-through valve is connected with a vacuum pump sequentially through a vacuum bin, a seventh straight-through valve and a vacuum gauge, a third pressure gauge is arranged at the end, connected with the outlet end of the third one-way valve, of the eighth straight-through valve, and the reaction sampling pipe is placed in a nuclear magnetic resonance magnet. The invention further discloses a high-field in-situ polarization method utilizing parahydrogen to induce polarization. The device is simple in structure and easy and convenient to controland operate, and efficient polarization generation and stable polarization nuclear magnetic spectrogram signal collection are achieved.
Owner:INNOVATION ACAD FOR PRECISION MEASUREMENT SCI & TECH CAS
Methods for interpreting NMR data
ActiveUS10725197B2Easy to explainQuick filterElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingEarth material testingRF probeNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Methods for improved interpretation of NMR data acquired from industrial samples by simultaneously detecting more than one resonant nucleus without removing the sample from the sensitive volume of the NMR magnet or radio frequency probe are disclosed. In other aspects, the present disclosure provides methods for robust imaging / analysis of spatial distribution of different fluids (e.g., 1H, 23Na, 19F) within a core or reservoir rock. NMR data may be interpreted in real-time during dynamic processes to enable rapid screening, e.g. of enhanced oil recovery techniques and products and / or to provide improved interpretation of well-logs. Measurements of resonant nuclei other than 1H may be performed in the laboratory or downhole with a NMR logging tool. In other aspects, the present disclosure describes a novel kernel function to extract values for underlying parameters that define relaxation time behavior of a quadrupolar nucleus.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
A High Field In Situ Polarization Method Using Parahydrogen Induced Polarization
ActiveCN111580029BSimple structureImprove stabilityMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceEngineering
The invention discloses a high-field in-situ polarization device using parahydrogen-induced polarization. The outlet end of the reaction gas inlet channel is connected to one end of a third through valve, and the other end of the third through valve is respectively connected to the parahydrogen inlet channel. The outlet end of the fourth through valve is connected to one end of the fifth through valve, the other end of the fifth through valve is connected to the inlet end of the third one-way valve, and the outlet end of the third one-way valve is connected to one end of the eighth through valve and one end of the eighth through valve respectively. One end of the sixth straight-through valve is connected, the other end of the eighth straight-through valve is connected to the reaction sampling pipe, the other end of the sixth straight-through valve is connected to the vacuum pump through the vacuum chamber, the seventh straight-through valve, and the vacuum gauge in sequence, and the eighth straight-through valve is connected to the third one-way valve. A third pressure gauge is arranged at one end connected to the outlet of the valve, and the reaction sampling tube is placed in the nuclear magnetic resonance magnet. The invention also discloses a high-field in-situ polarization method utilizing parahydrogen-induced polarization. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, convenient control and operation, and realizes efficient polarization generation and stable polarization nuclear magnetic spectrum signal collection.
Owner:INNOVATION ACAD FOR PRECISION MEASUREMENT SCI & TECH CAS
Pneumatic cable shuttle system for 2fnmr
ActiveUS20220326323A1Programme-controlled manipulatorMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyOptical spectrometerWinch
A transfer device is provided for shuttling an NMR sample container between at least two coaxially arranged NMR magnet systems of an NMR spectrometer comprising a guide tube positioned in a central bore of the magnet systems, a shuttle assembly arranged inside the guide tube for securely holding and shuttling the sample container and a drive system comprising a pulling drive and a winch cord attached to the drive system on one side and to the shuttle assembly on the other side, such that the shuttle assembly can travel inside the guide tube. The transfer device has a pneumatic pressurizing arrangement with an entry for pressurized gas arranged on a gas-tight body above the shuttle assembly that is adapted to maintain the winch cord under tension. The shuttle assembly comprises a piston design being moveable along the common axis of the coaxial magnet systems under the influence of the pressure.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
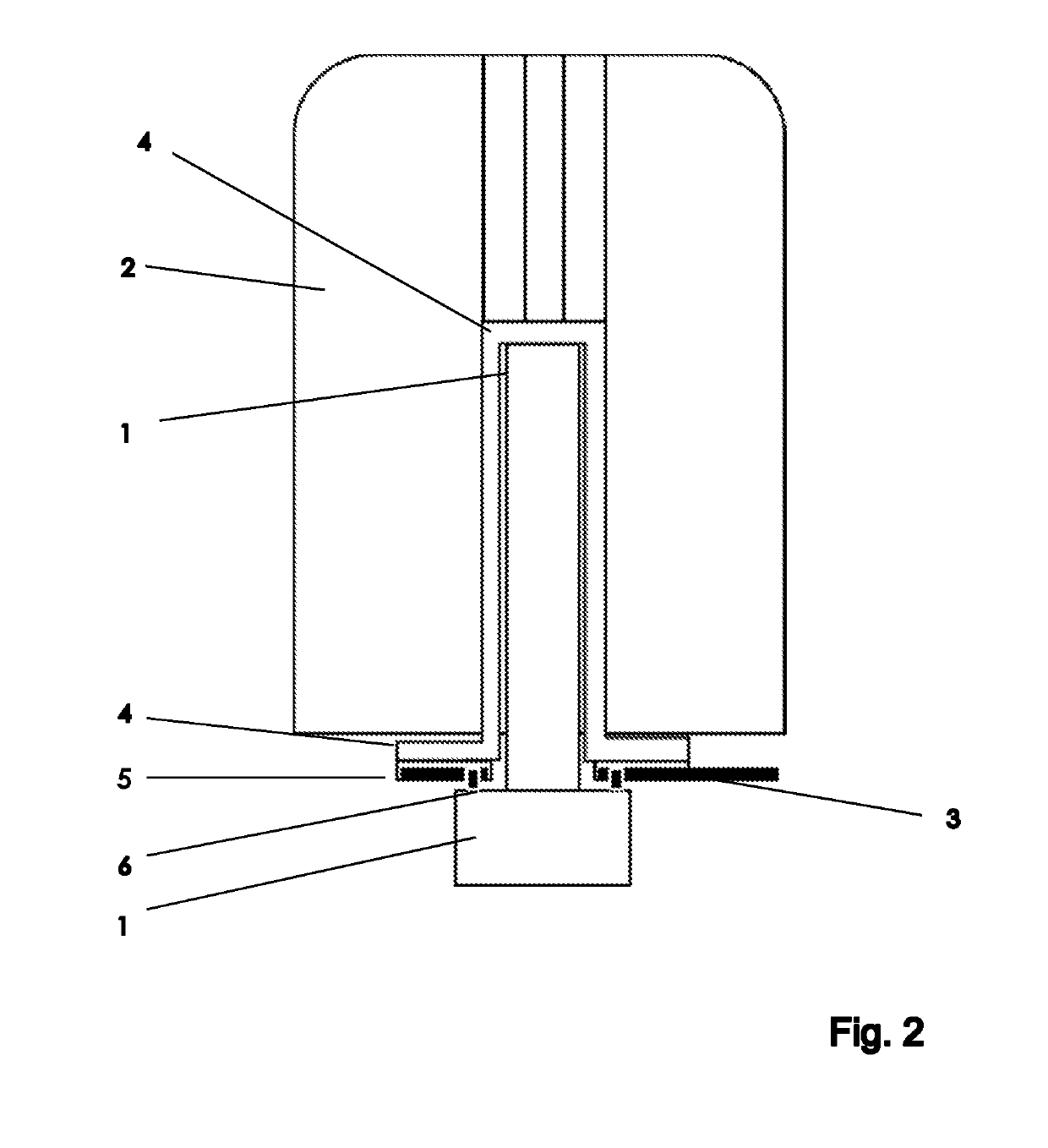
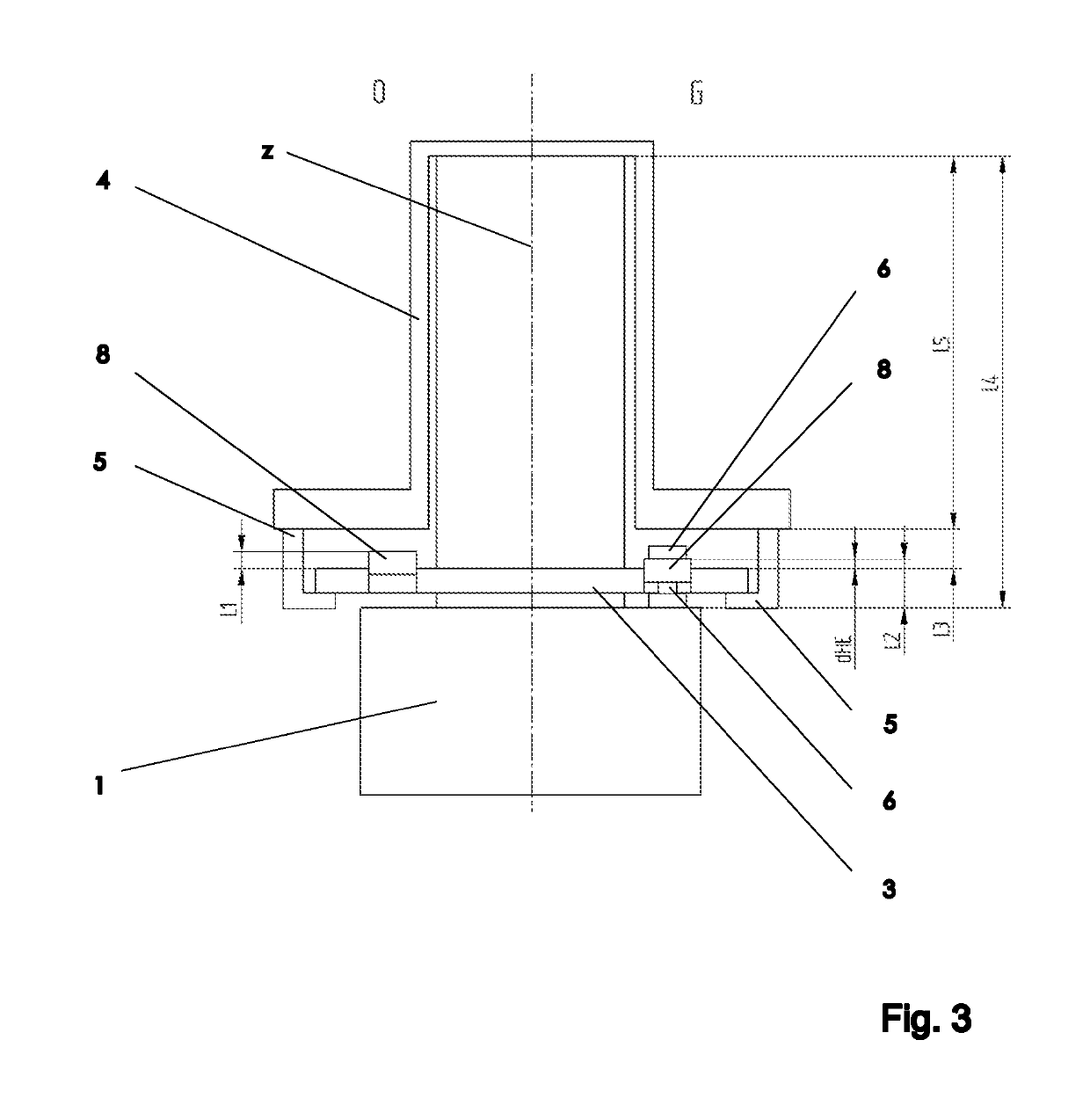
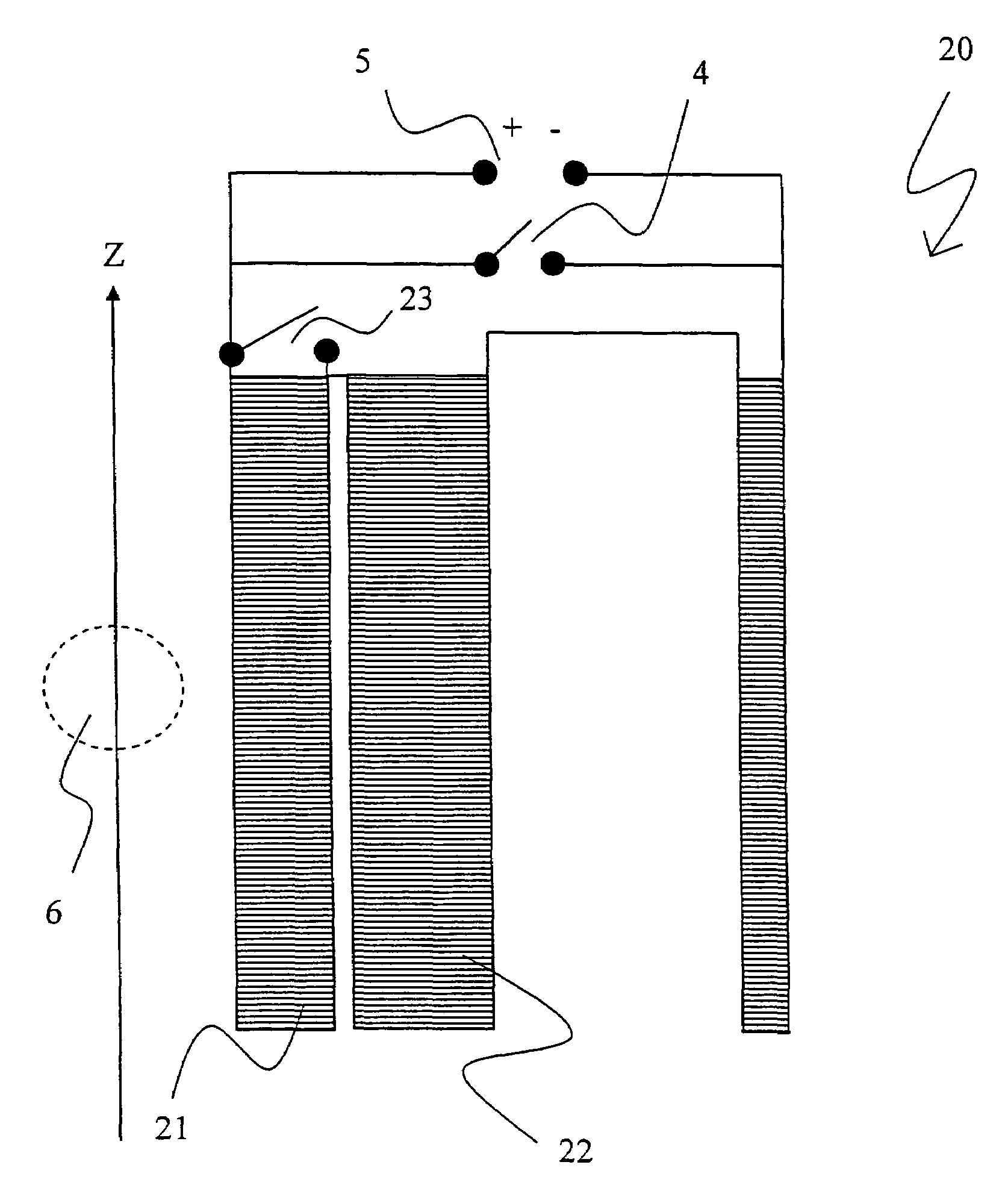
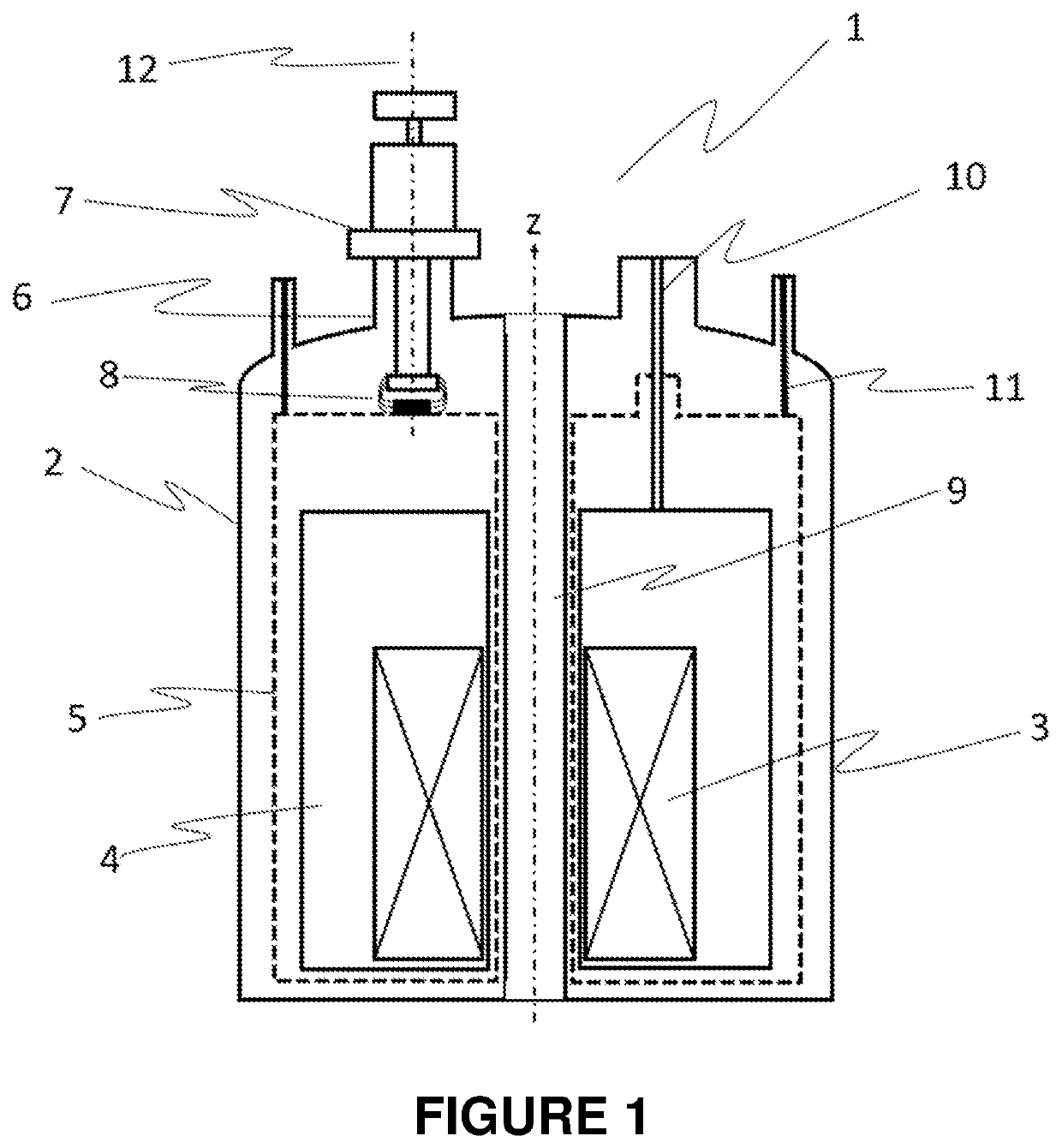
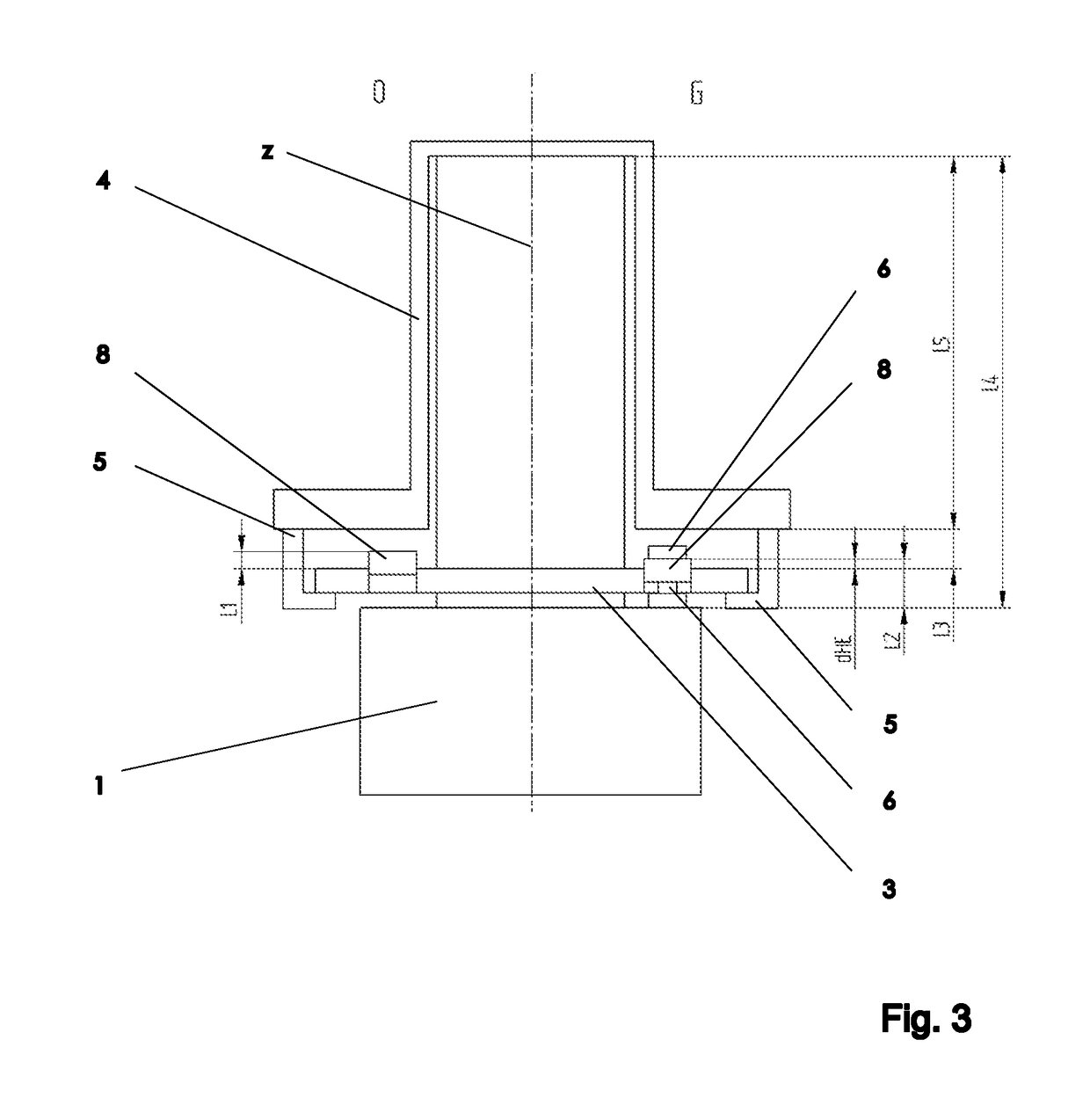
Temperature regulation system for MR devices with permanent magnet arrangements
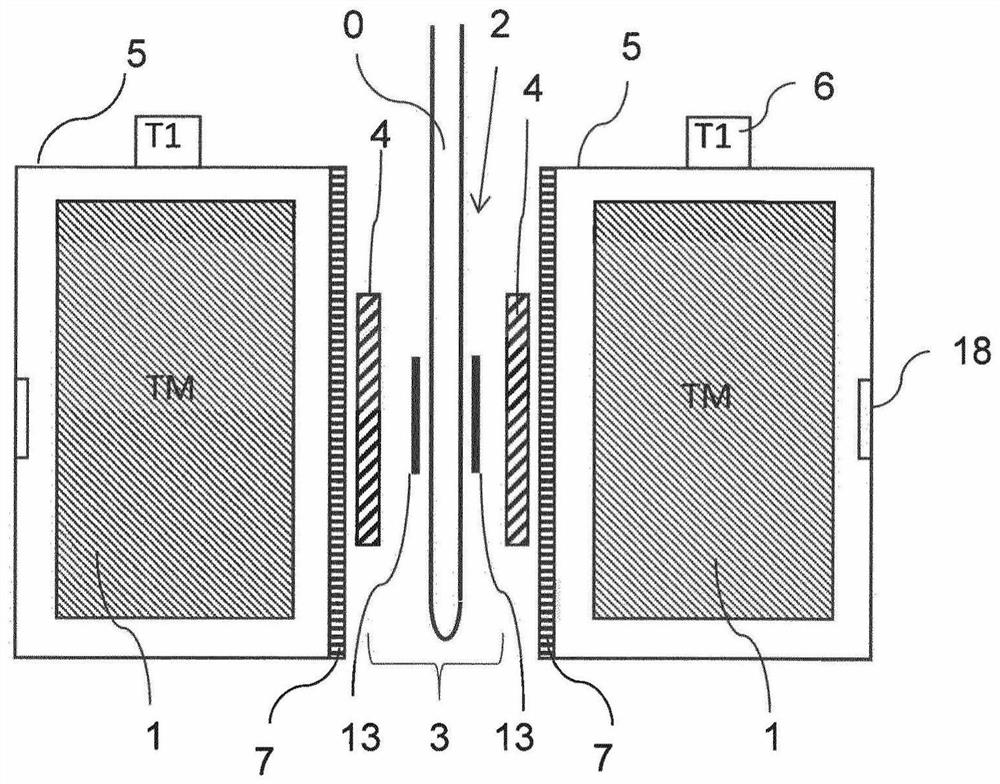
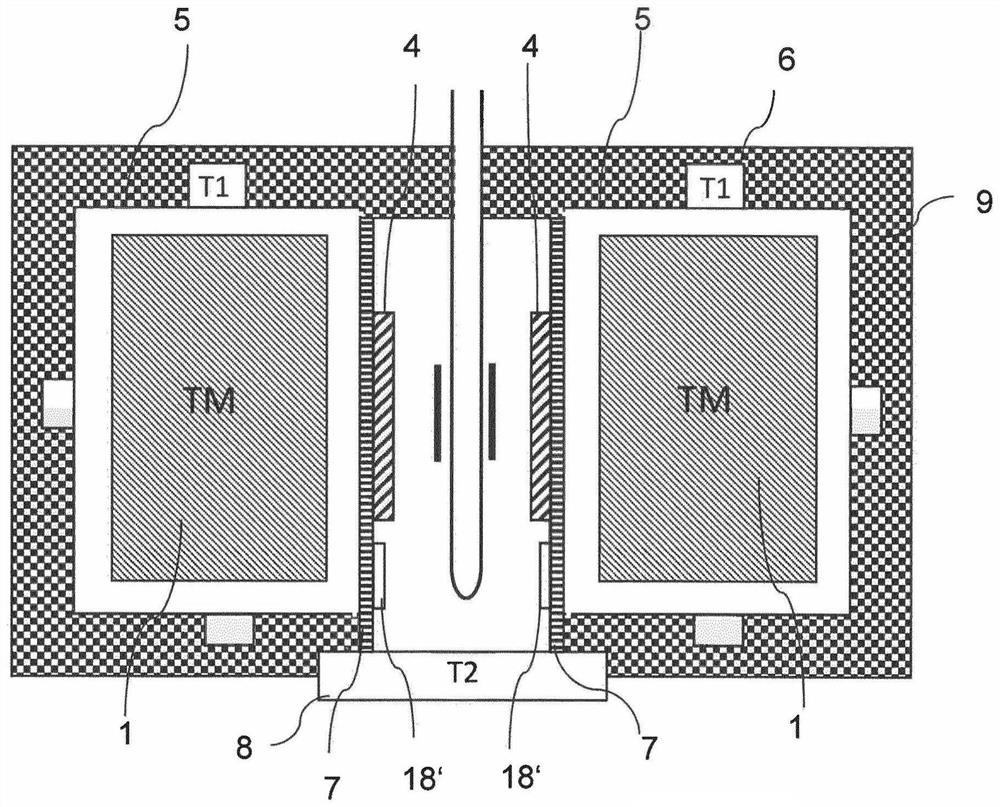
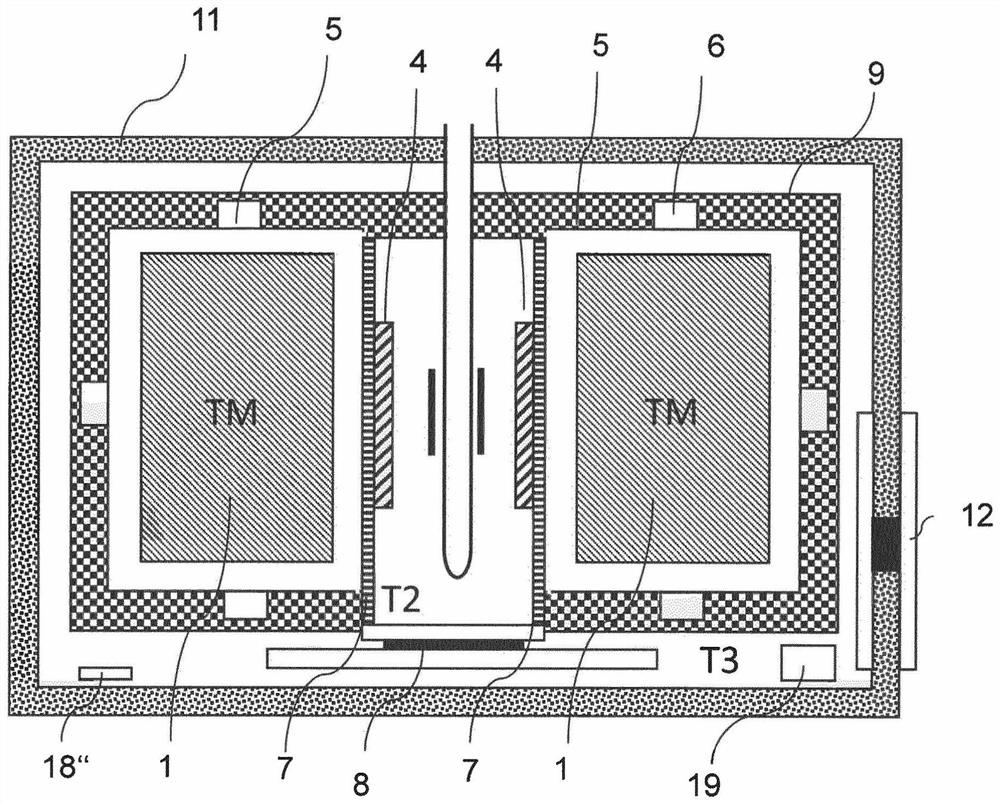
The invention relates to a temperature regulating system for an NMR magnet system. The device comprises a permanent magnet arrangement (1) having a central air gap (2) for generating a uniform static magnetic field in a measurement volume inside the central air gap (2), an NMR sample head (3) for emitting HF pulses and receiving HF signals from a measurement sample (0), comprising frequency detection in the NMR sample head and HO coils for varying the amplitude of the static magnetic field, and a shimming system (4) in the central air gap for further homogenizing the magnetic field in the measurement volume, in which a first isolation chamber (5) surrounds the permanent magnet arrangement in a thermally shielded manner, the first isolation chamber comprises means (6) for adjusting the temperature T1 of the first isolation chamber, the shimming system, the HO coil and the NMR sample head are arranged in the central air gap outside the first isolation chamber, and at least one heat conductor (7) is arranged between the shimming system and the HO coil on the one hand and the permanent magnet arrangement on the other hand. Therefore, the field stability and the drifting-free property of the arrangement structure are obviously improved.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
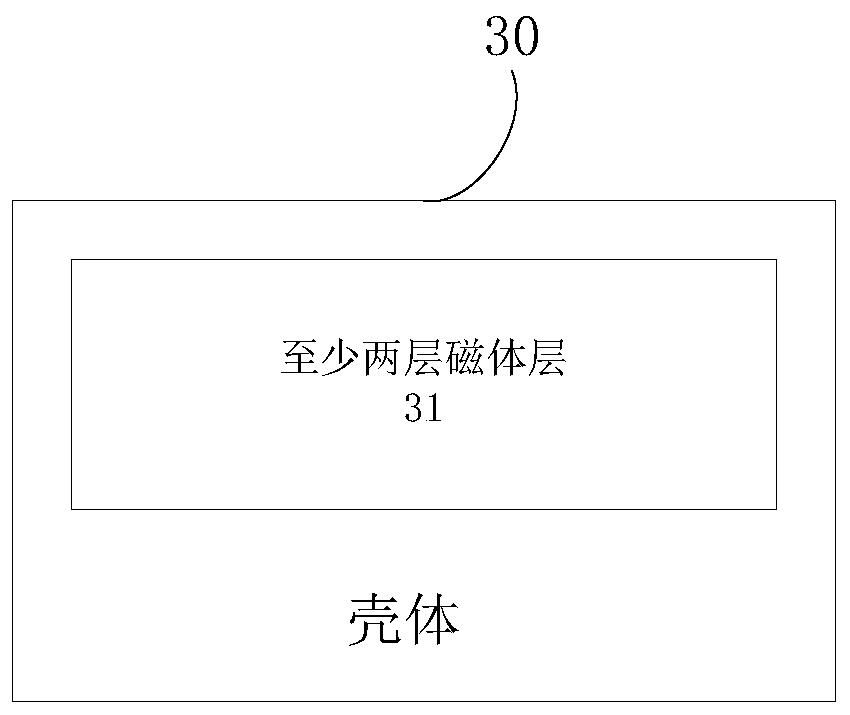
High magnetic field strength, high uniformity nuclear magnetic resonance magnet structure and measuring device
ActiveCN108931748BImprove uniformityHigh strengthPermanent magnetsMeasurements using magnetic resonanceHigh magnetic field strengthNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention provides a high-magnetic-field-strength and high-uniformity nuclear magnetic resonance magnet structure and a measuring device. The magnet structure comprises a housing and at least twomagnet layers which are arranged in the housing, wherein at least two magnet layers are vertically stacked in the housing. The magnetization directions of at least two magnet layers are same. According to the invention, through vertically stacking two or more magnet layers with the same magnetization directions in the housing, the nuclear magnetic resonance magnet structure is formed. The magneticfields which are generated by two or more magnet layers are stacked, thereby generating a static magnetic field together. Compared with a static magnetic field which is generated by a single layer ofmagnet, the static magnetic according to the invention has advantages of improving magnetic field uniformity and magnetic field strength, and increasing the area of a uniform area and detecting distance. Through cooperative use of a specific RF antenna and the magnet structure, layered heterogeneous samples and homogeneous samples can be effectively measured, thereby expanding application range of a nuclear magnetic resonance measurement device.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Temperature-control system for mr apparatuses with a permanent magnet arrangement
PendingUS20220171004A1Avoid disadvantagesImprove stabilityMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyTemperature controlTest sample
A temperature-control system for an NMR magnet system. A permanent magnet arrangement (1) with a central air gap (2) generates a homogeneous static magnetic field inside the air gap. A probehead (3) transmits RF pulses and receives RF signals from a test sample (0). An H0 coil changes the amplitude of the static magnetic field. A shim system (4) in the air gap further homogenizes the magnetic field. A first insulation chamber (5) surrounds and thermally shields the permanent magnet arrangement and includes an arrangement (6) controlling a temperature Ti of the first insulation chamber. The shim system, the H0 coil and the NMR probehead are arranged outside the first insulation chamber in the air gap. A heat-conducting body (7) is arranged between the shim system and the H0 coil on one side and the permanent magnet arrangement on the other, thereby enhancing field stability and suppressing drift.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
Rheological measurement device with torque sensor
InactiveUS20160209311A1Flow propertiesAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurement deviceDrive shaft
The invention relates to a rheological measurement device adapted for use in a bore of an NMR magnet. The measurement device comprises a drive shaft, a drive shaft housing in which the drive shaft is located, and a torque sensor directly or indirectly attached to the drive shaft. The torque sensor is positioned substantially in line with the drive shaft.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
Method for homogenizing a super-conducting NMR magnet
InactiveUS20050007229A1Improve accuracyArrangement is more flexibleMagnetic measurementsMagnetsMagnetic field gradientInductance
The invention concerns a method for charging a magnet arrangement (20) comprising a first partial region (21) which can be superconductingly short-circuited via an additional switch (23), and a second partial region (22), wherein the two partial regions (21, 22) generate, in an investigational volume (8), gradients of second order having different signs. A magnetic field dependence B* is measured close to the desired operating state of the magnet arrangement (20) and operating currents are determined for each of the two partial regions (21, 22) at which the overall magnetic field B in the volume (8) under investigation is freed from a magnetic field gradient of second order. These operating currents are set thereby taking into consideration the inductive coupling of the partial regions (21, 22) through initially charging of the overall magnet arrangement (20) and, after closing of the additional switch (23), through continuation of charging only in the second partial region (22). The magnetic field homogeneity of the magnet arrangement (20) can thereby be improved in a simple and inexpensive manner.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Nmr magnet system with stirling cooler
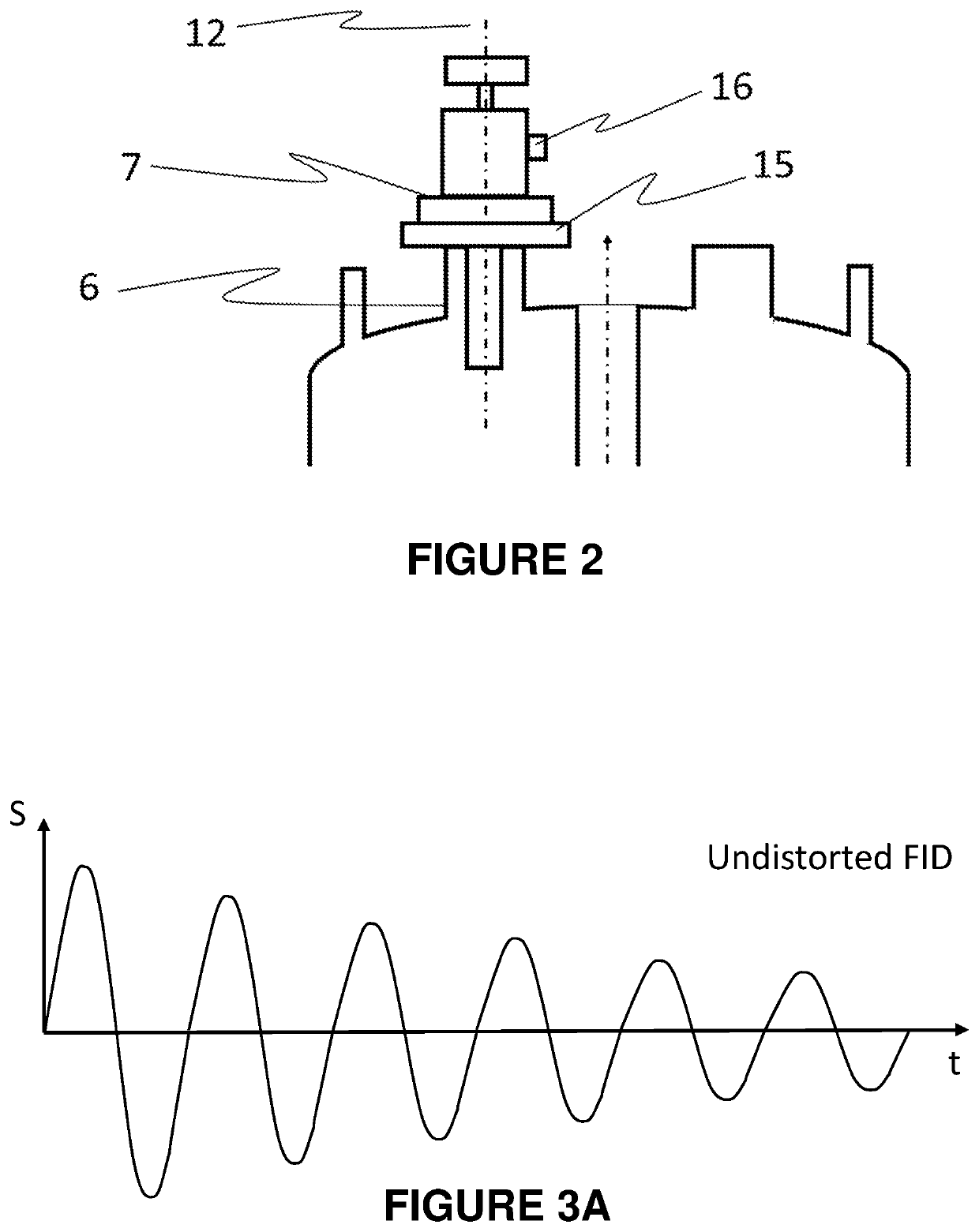
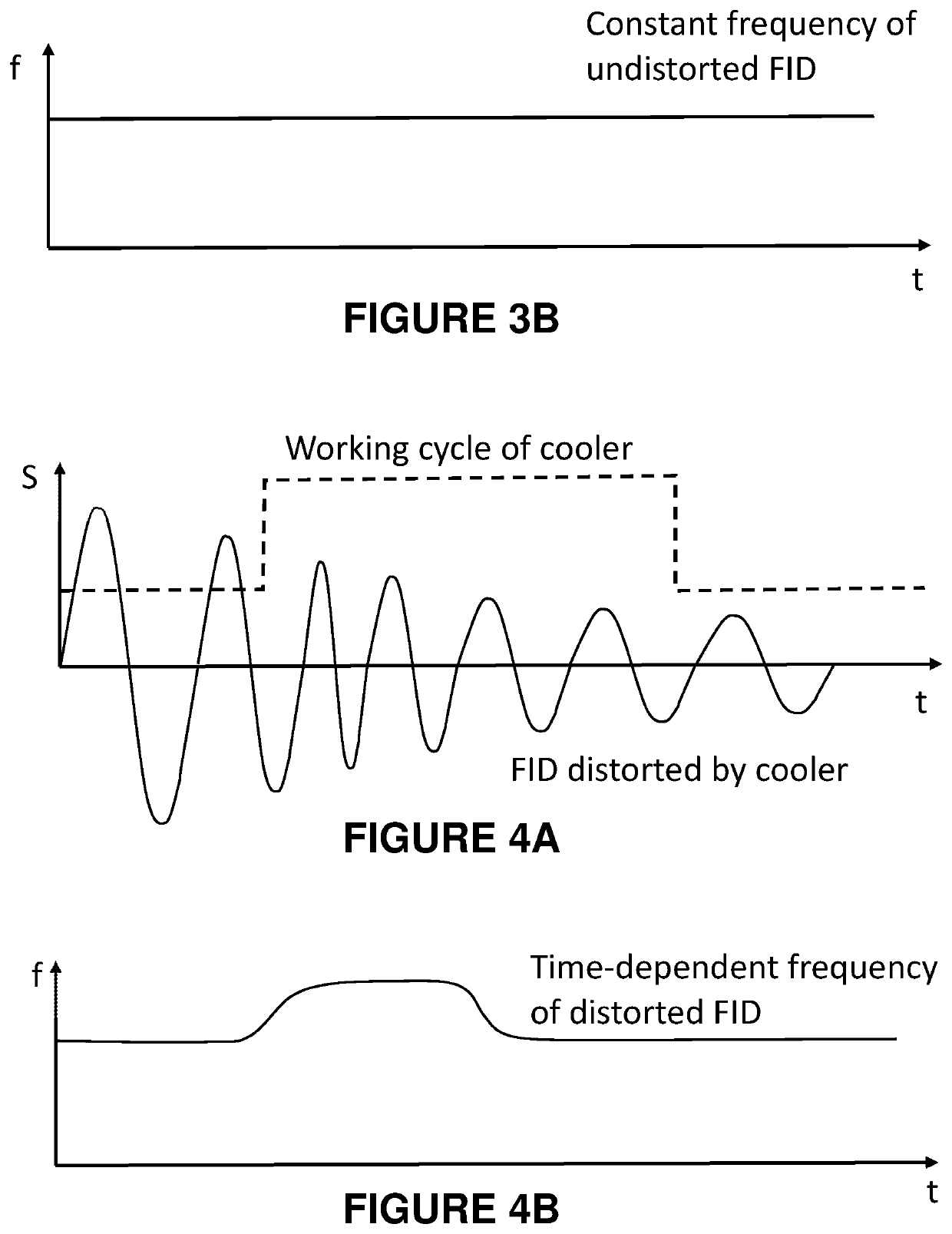
ActiveUS20220291307A1Low costMinimal effectCompression machinesMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceCold shield
An NMR magnet system uses a Stirling cooler having a cold head that extends into a housing of the system to cool a cold shield surrounding a cryogen vessel. The system may have a damper located between the cooler and the cold shield to reduce a transmission of vibration from the cooler to a magnet coil immersed in the cryogen. The damper may be passive, or may be part of an active damping system that uses an acceleration sensor to drive an active damper that compensates for cooler vibration. A compensation apparatus may use a stored characteristic of a signal distortion caused by the vibration and, in response to a trigger signal from the cooler, apply compensation to an excitation signal provided to a sample by an NMR probe in a bore of the magnet coil, or to an FID signal from the sample that is detected by the probe.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Fastening device for an nmr probe having a quick-release fastener
ActiveUS20190072625A1Quality improvementReduce material costsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using magnetic resonanceFast releaseGeometric design
A fastening system for attaching an NMR probe to an NMR magnet includes a discoid insert and a retention system that is rigidly connected to the magnet and on which the insert can be mounted. A form-fitting, variable-force connection is established between the NMR probe and the retention system using a spring element. The probe attaches to the insert by a plurality of integral, rigid retaining elements that are of an invariable fixed length. The spring element and the retaining elements are designed geometrically such that in a first, opened state the connection between the insert and the retaining elements has a mechanical backlash between 0.5 mm and 5 mm when the spring element is relaxed. In a second, closed state the connection between the insert and the retaining elements has no mechanical backlash when the spring element is under mechanical tension.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com