Patents
Literature
325results about "Permanent superconductor devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
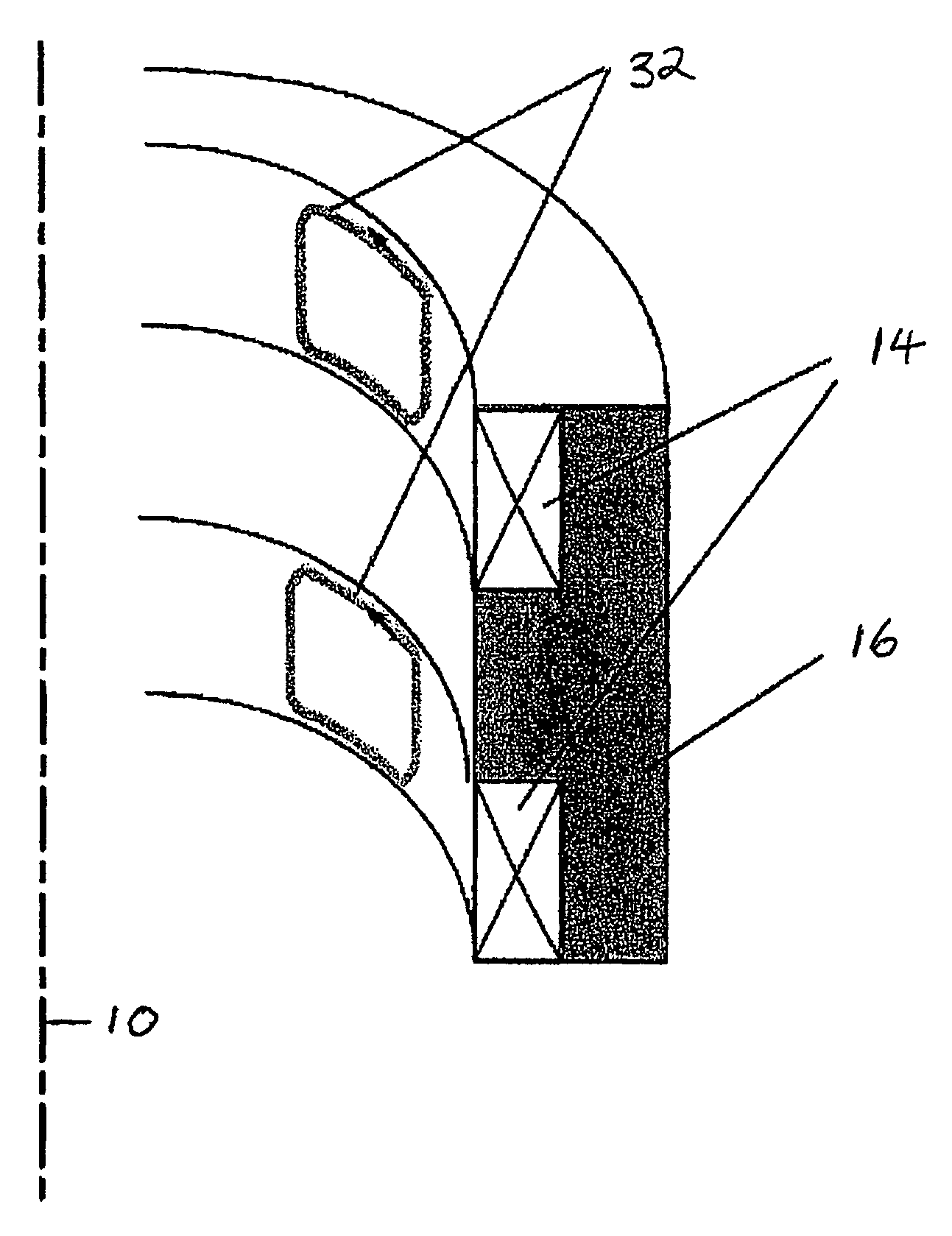
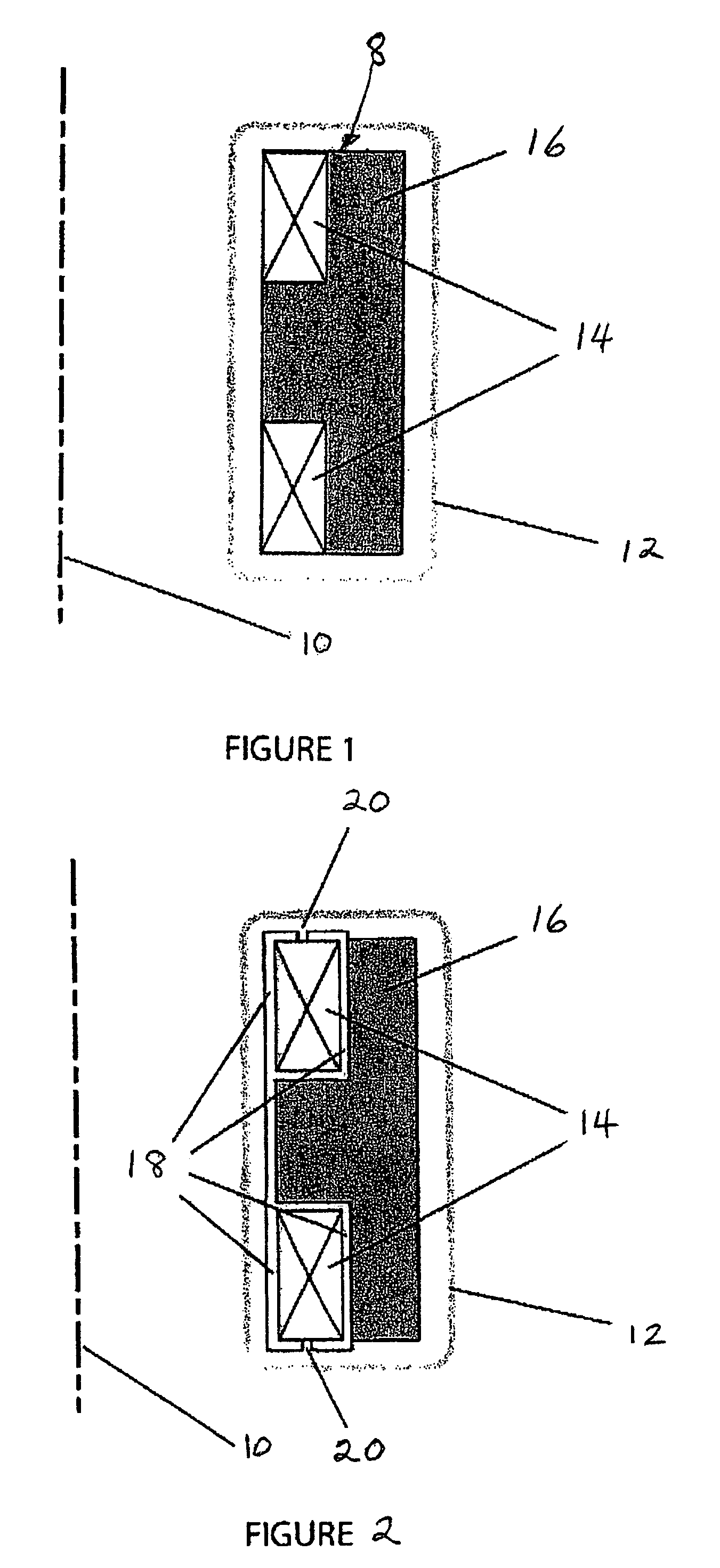
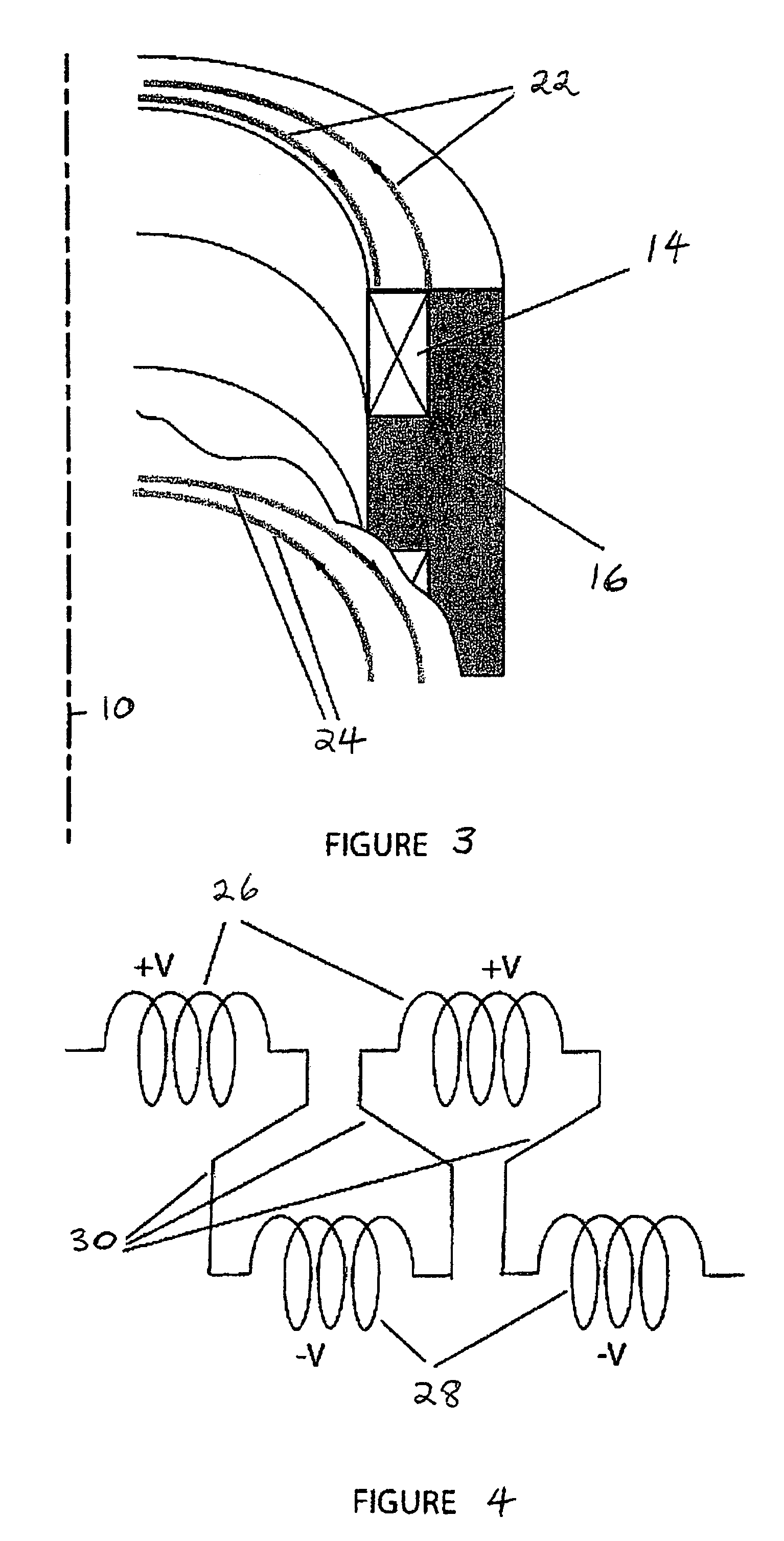
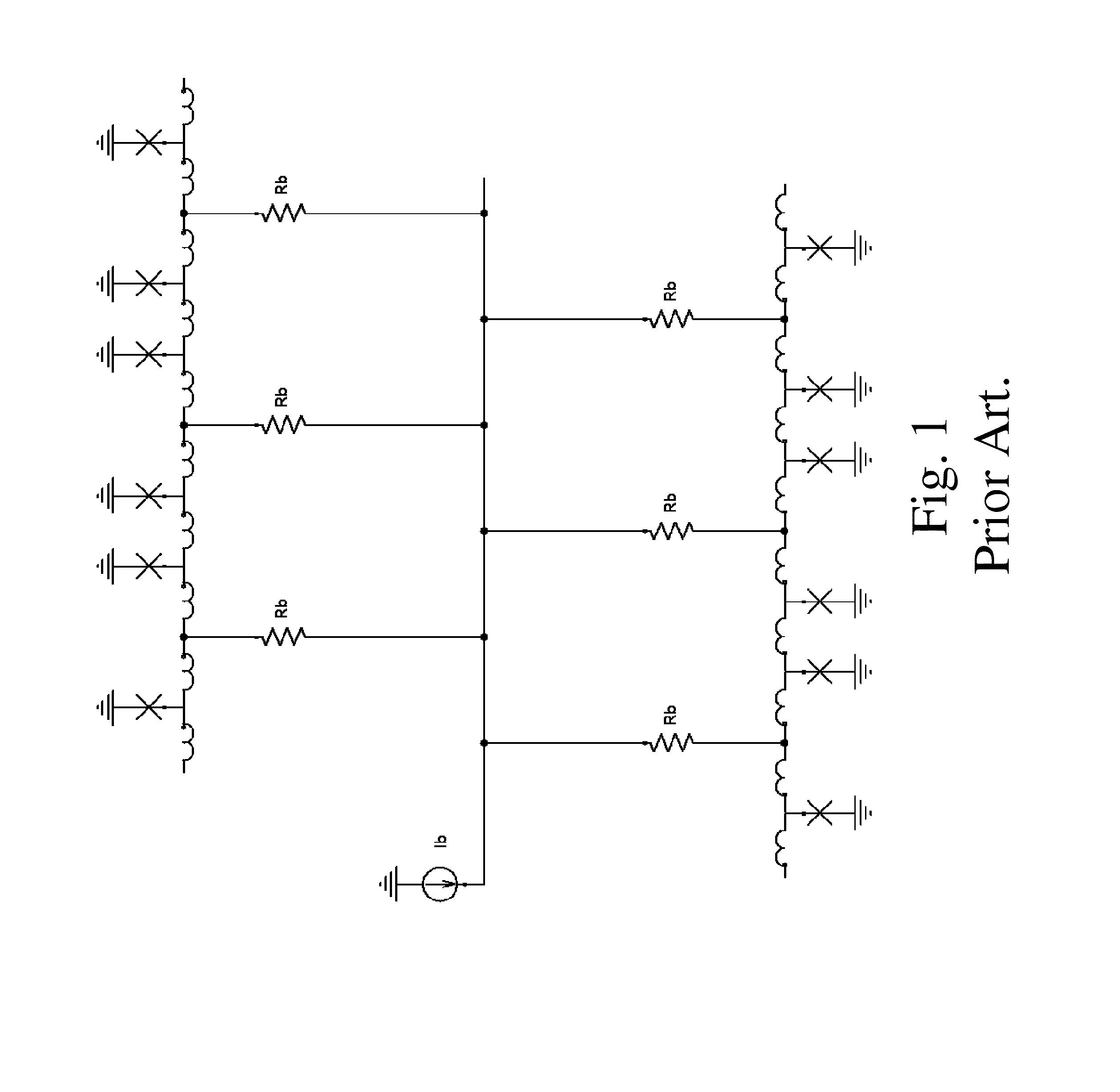
Inductive quench for magnet protection
ActiveUS7701677B2Effective heat conductionMagnetic measurementsMagnetsSuperconducting CoilsInternal energy
A coil system for inductively heating a superconducting magnet in order to provide an internal energy dump by uniformly quenching a high performance superconducting magnet. The quench-inducing system uses AC magnetic fields that require negligible reactive power. The system is especially suited for inducing a relatively uniform quench in dry superconducting magnets.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Low-loss superconducting devices
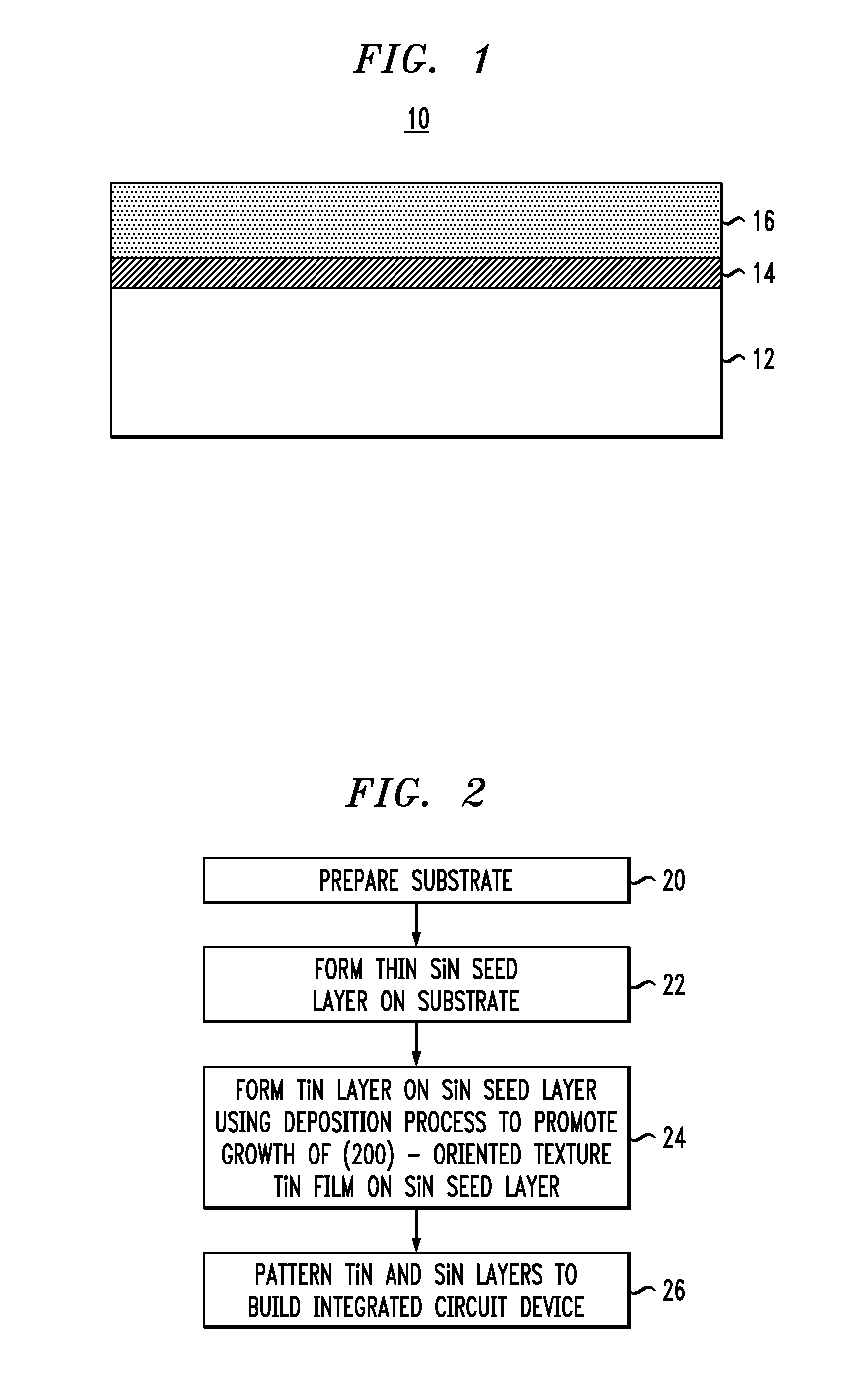
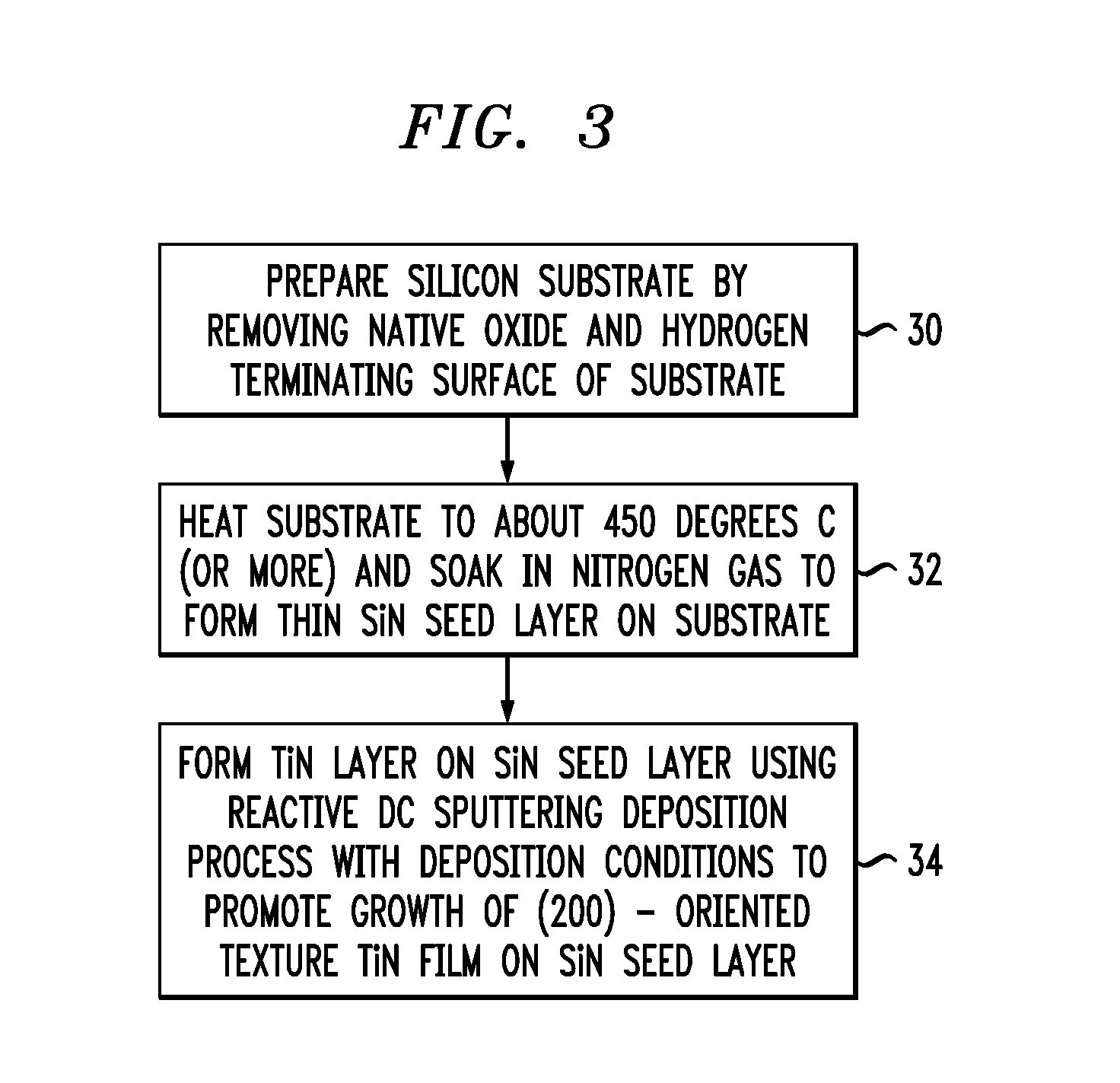
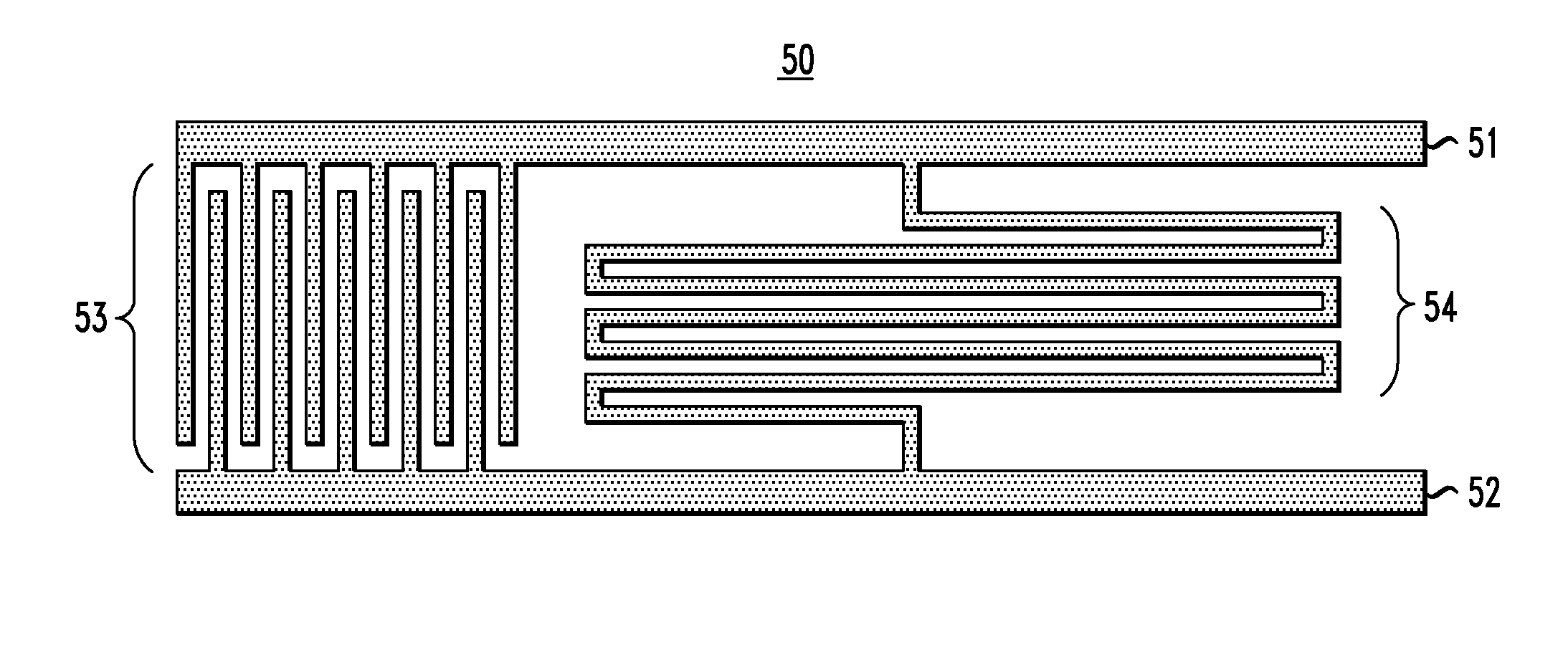
Low-loss superconducting devices and methods for fabricating low loss superconducting devices. For example, superconducting devices, such as superconducting resonator devices, are formed with a (200)-oriented texture titanium nitride (TiN) layer to provide high Q, low loss resonator structures particularly suitable for application to radio-frequency (RF) and / or microwave superconducting resonators, such as coplanar waveguide superconducting resonators. In one aspect, a method of forming a superconducting device includes foaming a silicon nitride (SiN) seed layer on a substrate, and forming a (200)-oriented texture titanium nitride (TiN) layer on the SiN seed layer.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
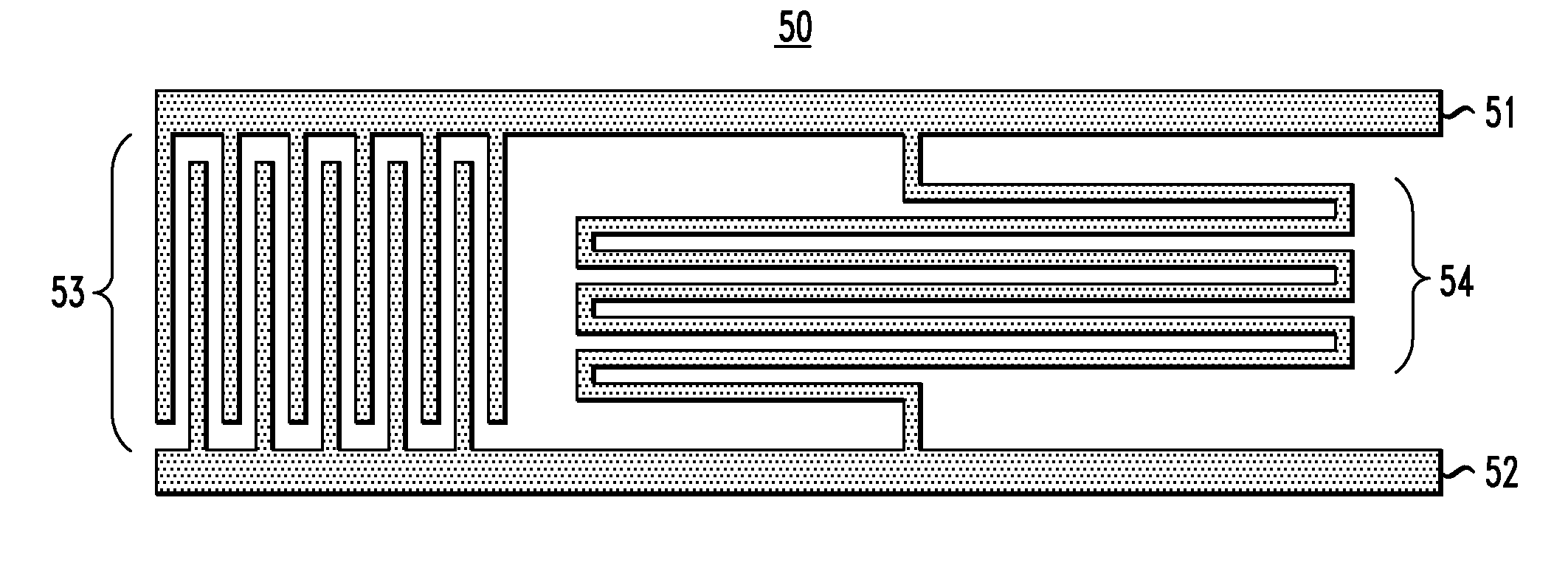
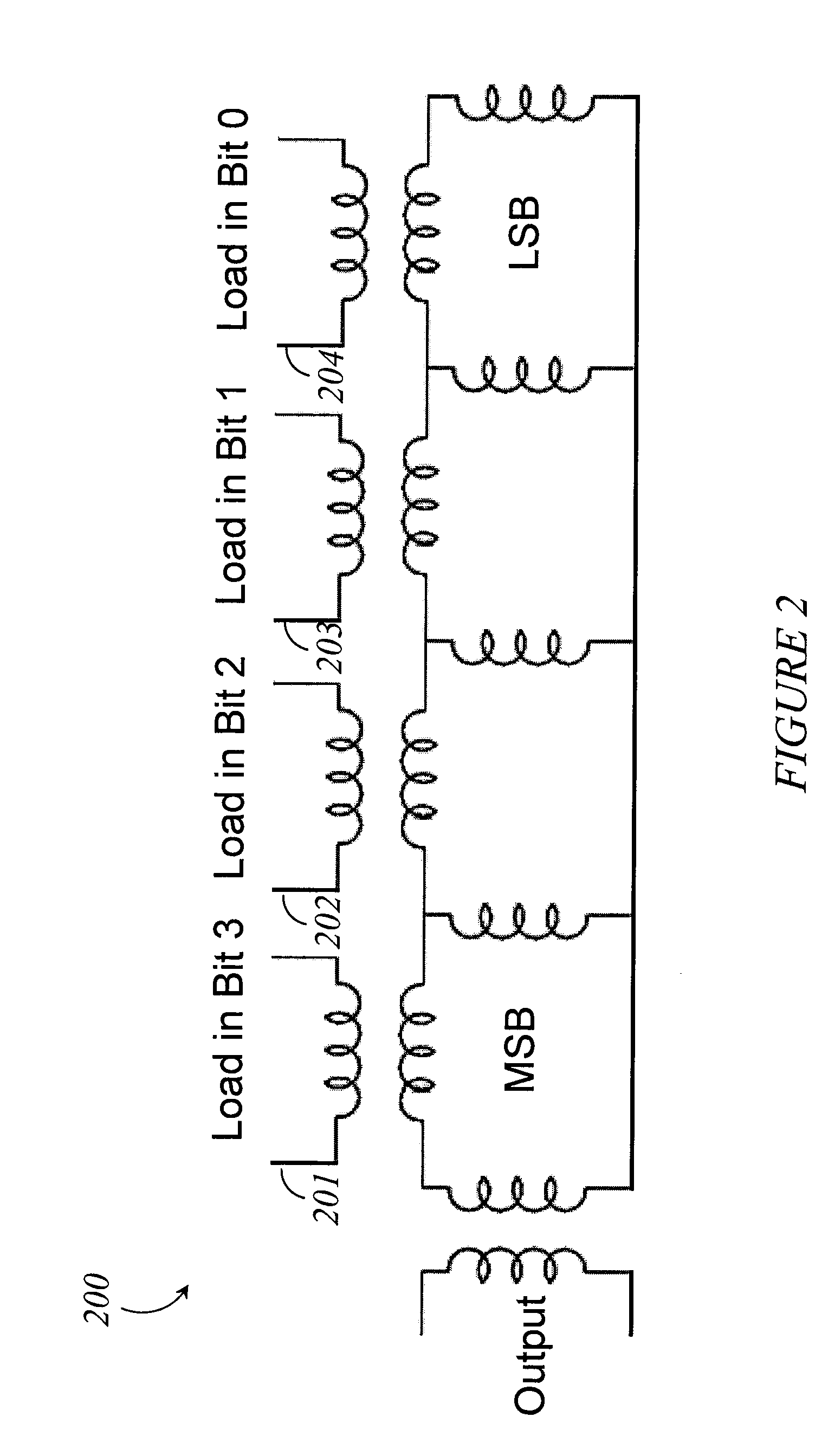
Systems, methods and apparatus for digital-to-analog conversion of superconducting magnetic flux signals
ActiveUS20090082209A1Fast switching speedShort calculation timeElectric signal transmission systemsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsShift registerData signal
A superconducting flux digital-to-analog converter includes a superconducting inductor ladder circuit. The ladder circuit includes a plurality of closed superconducting current paths that each includes at least two superconducting inductors coupled in series to form a respective superconducting loop, successively adjacent or neighboring superconducting loops are connected in parallel with each other and share at least one of the superconducting inductors to form a flux divider network. A data signal input structure provides a respective bit of a multiple bit signal to each of the superconducting loops. The data signal input structure may include a set of superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs). The data signal input structure may include a superconducting shift register, for example a single-flux quantum (SFQ) shift register or a flux-based superconducting shift register comprising a number of latching qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Low resistance conductors, processes of production thereof, and electrical members using same
InactiveUS20030213611A1Low resistivityEconomical priceNon-insulated conductorsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical conductor
A conductor obtained by connecting a plurality of superconductors by normal conductivity or a conductor comprised of superconductors and normal conductors, said low resistance conductor using superconductors characterized in that an apparent specific resistance of said conductor at below a superconducting transition temperature of said superconductors is lower than the specific resistance of copper at that superconducting transition temperature.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
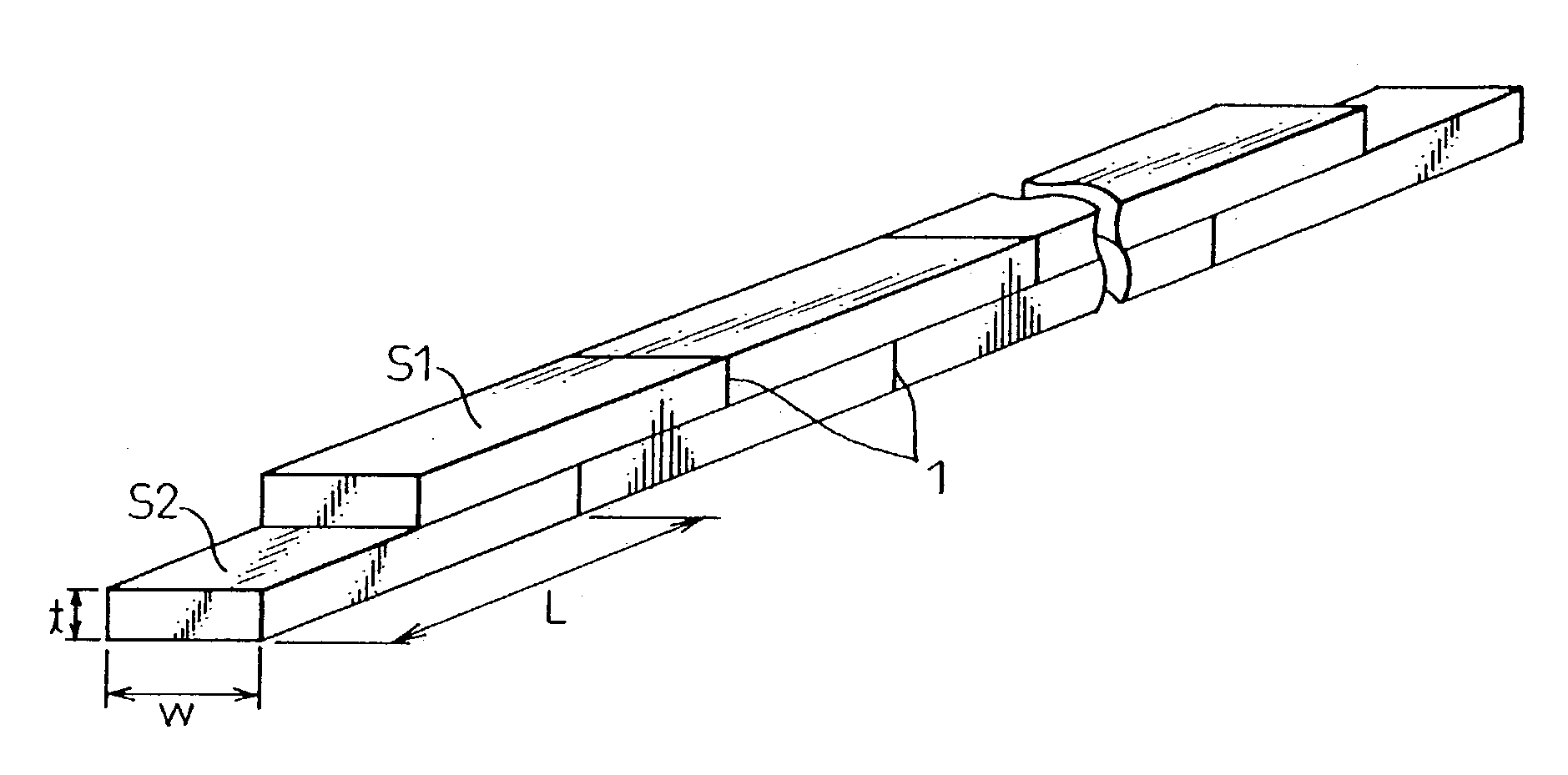
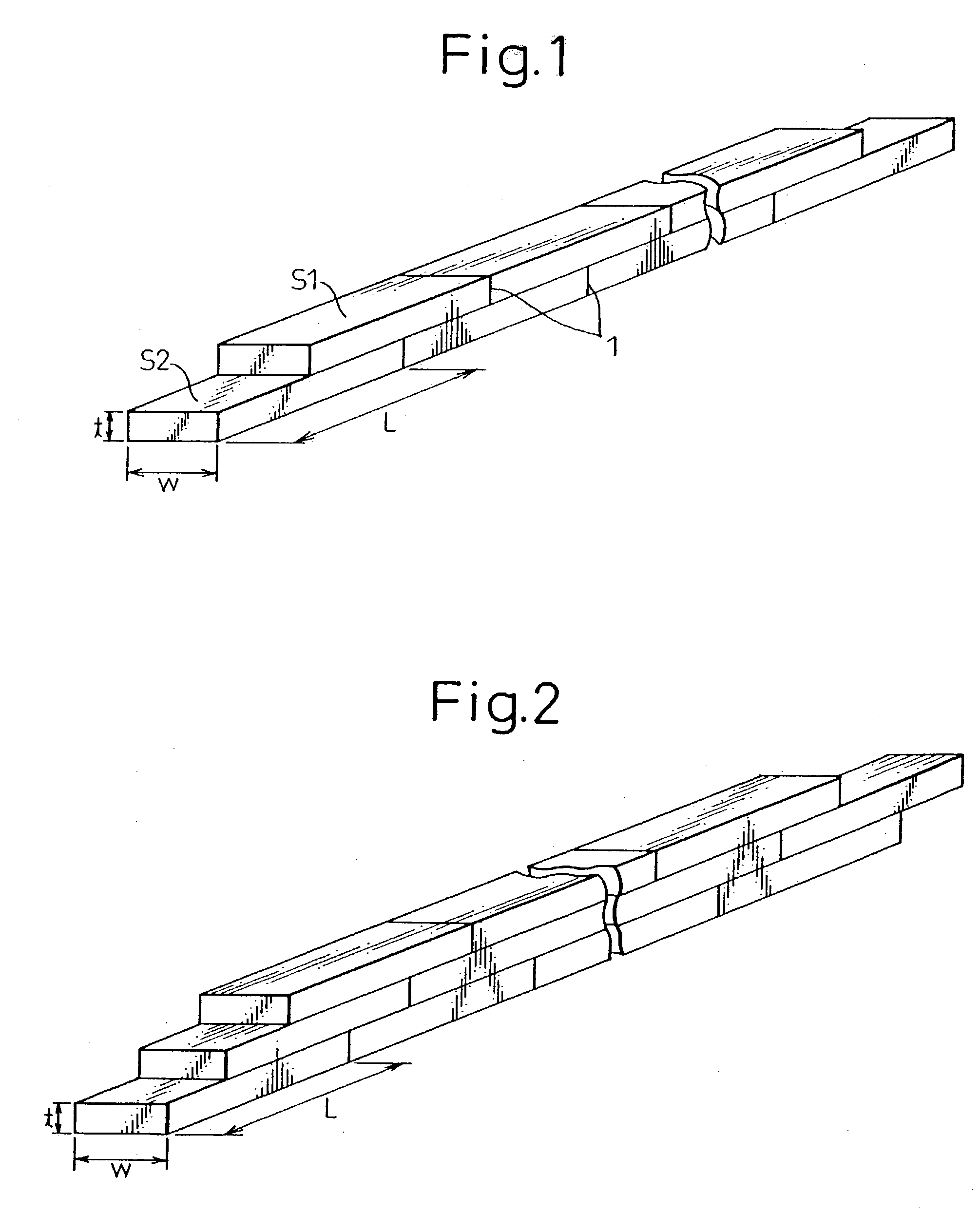
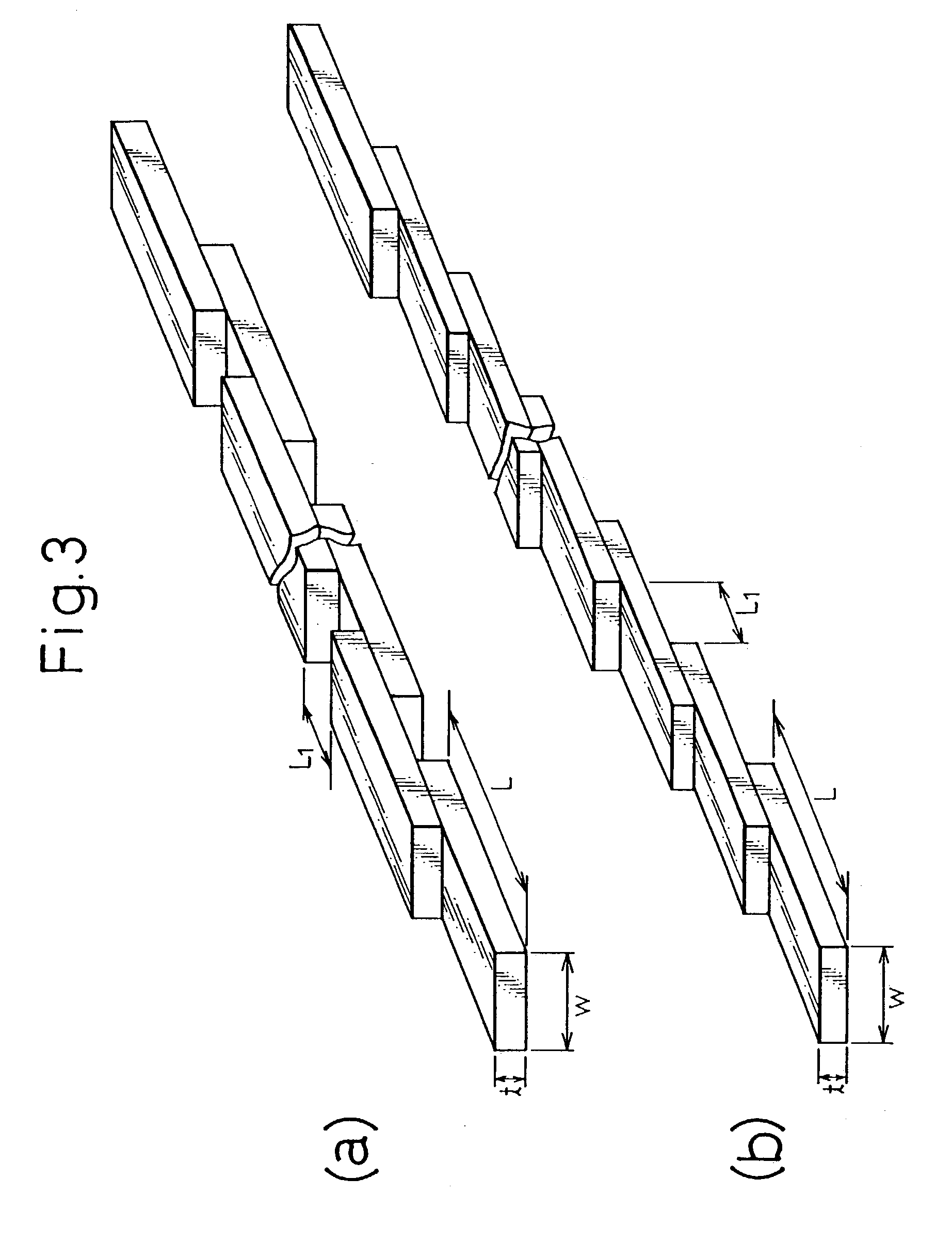
Low ac loss filamentary coated superconductors
InactiveUS20060040830A1Additive manufacturing apparatusSuperconductors/hyperconductorsOxide superconductorsPhysics
An article having low ac loss includes an elongated substrate having a length and a width; and a plurality of filaments comprising an oxide superconductor extending substantially along the length of the elongated substrate and spaced apart from one other filaments across the width of the elongated substrate, wherein at least one filament crosses over at least one other filament such that the at least one filament occupies a first position across the width of the elongated substrate before the crossover and a second position across the width of the elongated substrate after crossover.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
Low-power biasing networks for superconducting integrated circuits
ActiveUS8571614B1Maintain stabilityHigh dynamic impedanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSuperconducting integrated circuits
A superconducting integrated circuit, comprising a plurality of superconducting circuit elements, each having a variation in operating voltage over time; a common power line; and a plurality of bias circuits, each connected to the common power line, and to a respective superconducting circuit element, wherein each respective bias circuit is superconducting during at least one time portion of the operation of a respective superconducting circuit element, and is configured to supply the variation in operating voltage over time to the respective superconducting circuit element.
Owner:SEEQC INC
Superconducting Wires and Cables and Methods for Producing Superconducting Wires and Cables
InactiveUS20090258787A1Easy and efficientSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentEngineeringHeat treated
Owner:HILLS CO
Systems, methods, and apparatus for multilayer superconducting printed circuit boards
ActiveUS20090099025A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBoard structureElectrical and Electronics engineering
Superconducting connections are provided to internal layers of a multi-layer circuit board structure, for example by superconducting vias.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Low-loss superconducting devices
Low-loss superconducting devices and methods for fabricating low loss superconducting devices. For example, superconducting devices, such as superconducting resonator devices, are formed with a (200)-oriented texture titanium nitride (TiN) layer to provide high Q, low loss resonator structures particularly suitable for application to radio-frequency (RF) and / or microwave superconducting resonators, such as coplanar waveguide superconducting resonators. In one aspect, a method of forming a superconducting device includes forming a silicon nitride (SiN) seed layer on a substrate, and forming a (200)-oriented texture titanium nitride (TiN) layer on the SiN seed layer.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP +1
Input/output systems and devices for use with superconducting devices
Systems and devices for providing differential input / output communication with a superconducting device are described. Each differential I / O communication is electrically filtered using a respective tubular filter structure incorporating superconducting lumped element devices and high frequency dissipation by metal powder epoxy. A plurality of such tubular filter structures is arranged in a cryogenic, multi-tiered assembly further including structural / thermalization supports and a device sample holder assembly for securing a device sample, for example a superconducting quantum processor. The interface between the cryogenic tubular filter assembly and room temperature electronics is achieved using hermetically sealed vacuum feed-through structures designed to receive flexible printed circuit board cable.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
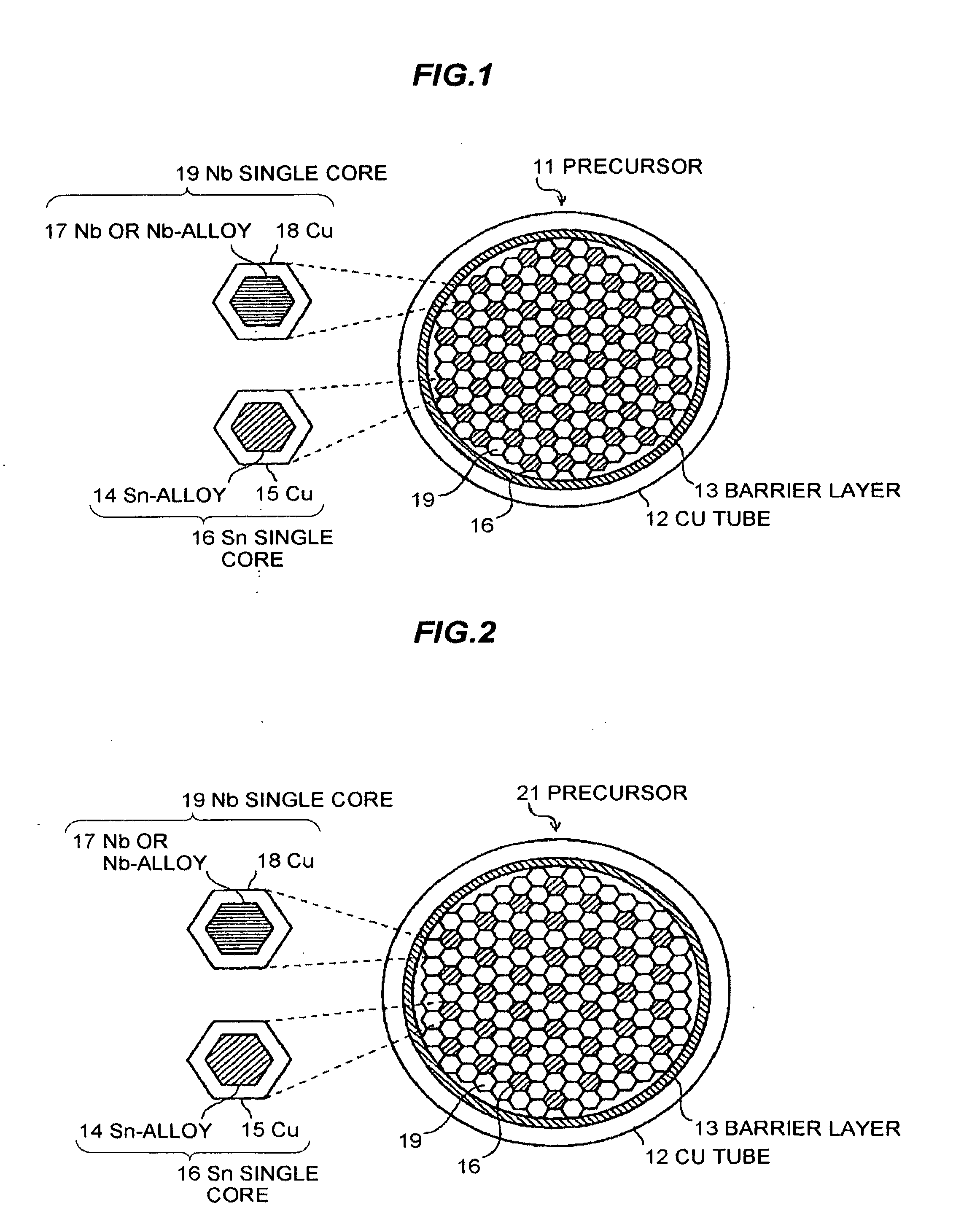
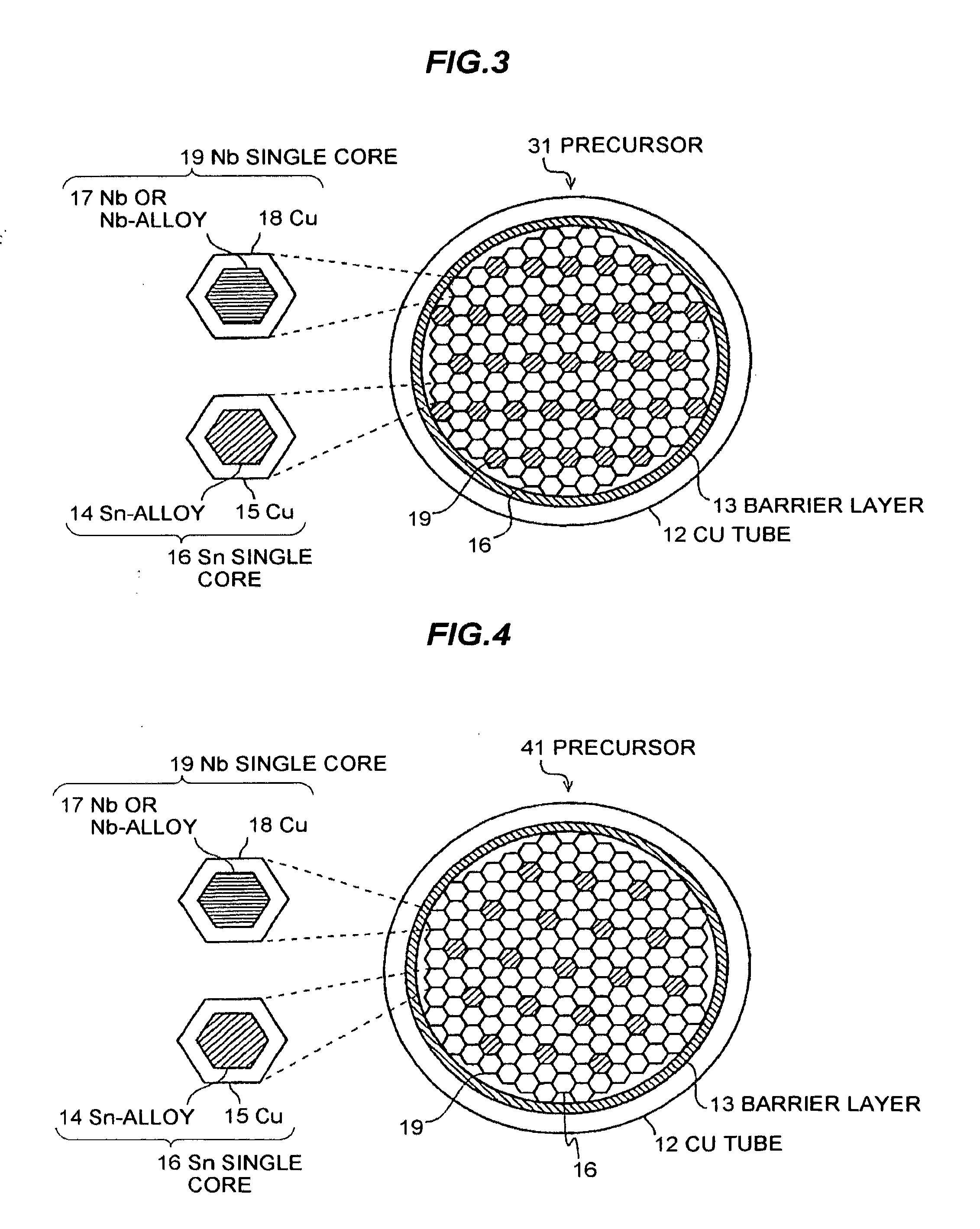
Nb3Sn SUPERCONDUCTOR WIRE AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING Nb3Sn SUPERCONDUCTOR WIRE
InactiveUS20130053250A1High densityDegradation rate of the critical current density)Superconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentAlloyMaterials science
An Nb3Sn superconductor wire is manufactured by heating a precursor for an Nb3Sn superconductor wire. The precursor includes a Cu tube made of Cu or Cu-alloy, assemblies, each of which includes Nb filaments disposed in the Cu tube, and each of the Nb filaments includes an Nb core made of Nb or Nb-alloy. Each of the assemblies also includes Sn filaments disposed in the Cu tube, and each of the Sn filaments includes a Sn core made of Sn or Sn-alloy. The precursor also includes reinforcing filaments disposed in the Cu tube for dividing the assemblies such that the assemblies are not adjacent to each other. By heating the precursor, Sn in the Sn core is diffused into the Nb core to produce Nb3Sn.
Owner:SH COPPER PROD CO LTD
Superconductors and methods for making such superconductors
InactiveUS20050173679A1Simple manufacturing processInexpensive mass productionConductive materialOrganic conductorsElectrical conductorVolumetric Mass Density
This invention concerns an improvement of the supercurrent carrying capabilities, i.e. the increase of critical current densities, of polycrystalline superconductor structures, especially of high-Tc superconductors fabricated with a coated conductor technique to provide superconducting layers containing flat grains. A superconductor with superior critical current density is obtained by joining, i.e. pressing or otherwise bringing into intensive facial contact, preferably superconducting contact, two or more such superconducting layers.
Owner:MANNHART JOCHEN DIETER +4
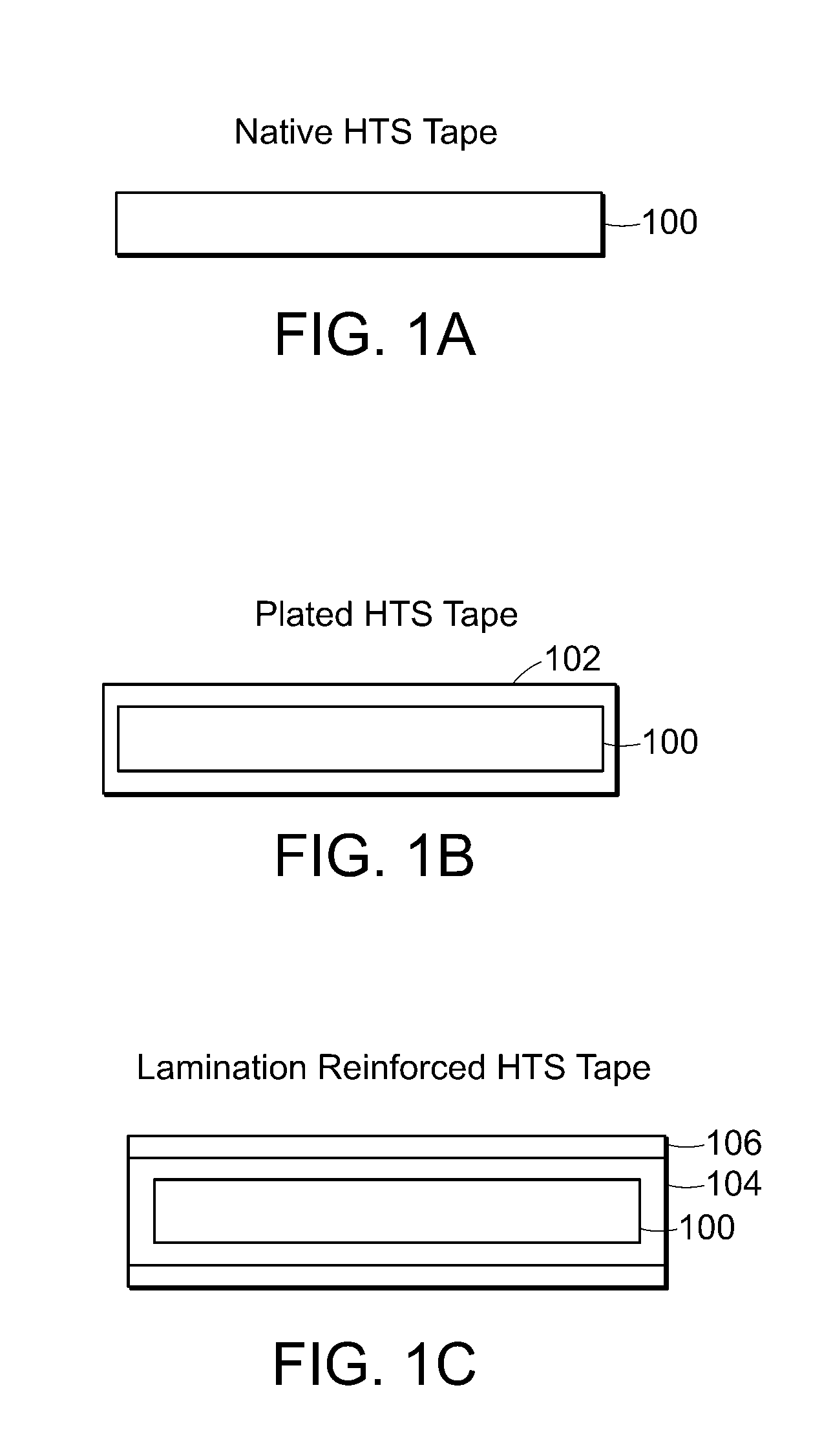
Superconducting articles having dual sided structures
ActiveUS7774035B2Prevent burnoutSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentPhysics
A superconducting article includes a substrate; first and second buffer layers overlying the substrate, such that the substrate is positioned so as to be interposed between the first and second buffer layers, first and second superconductor layers overlying the first and second buffer layers. Further, the first and second stabilizer layers respectively overlying the first and second superconductor layers, the first and second stabilizer layers adapted to conduct current and prevent burnout of the first and second superconductor layers when the first and second superconductor layers are in a non-superconductive state.
Owner:SUPERPOWER INC
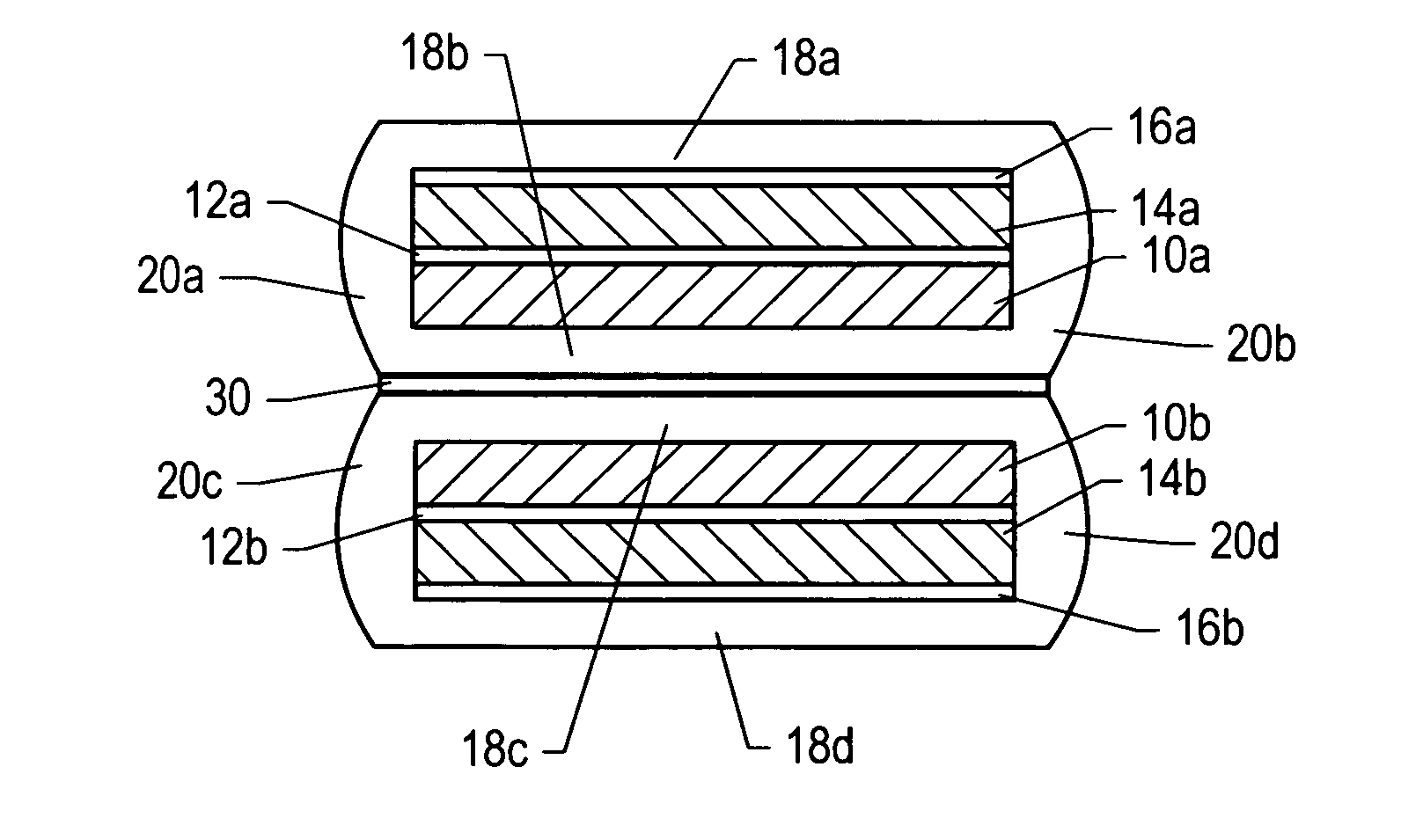
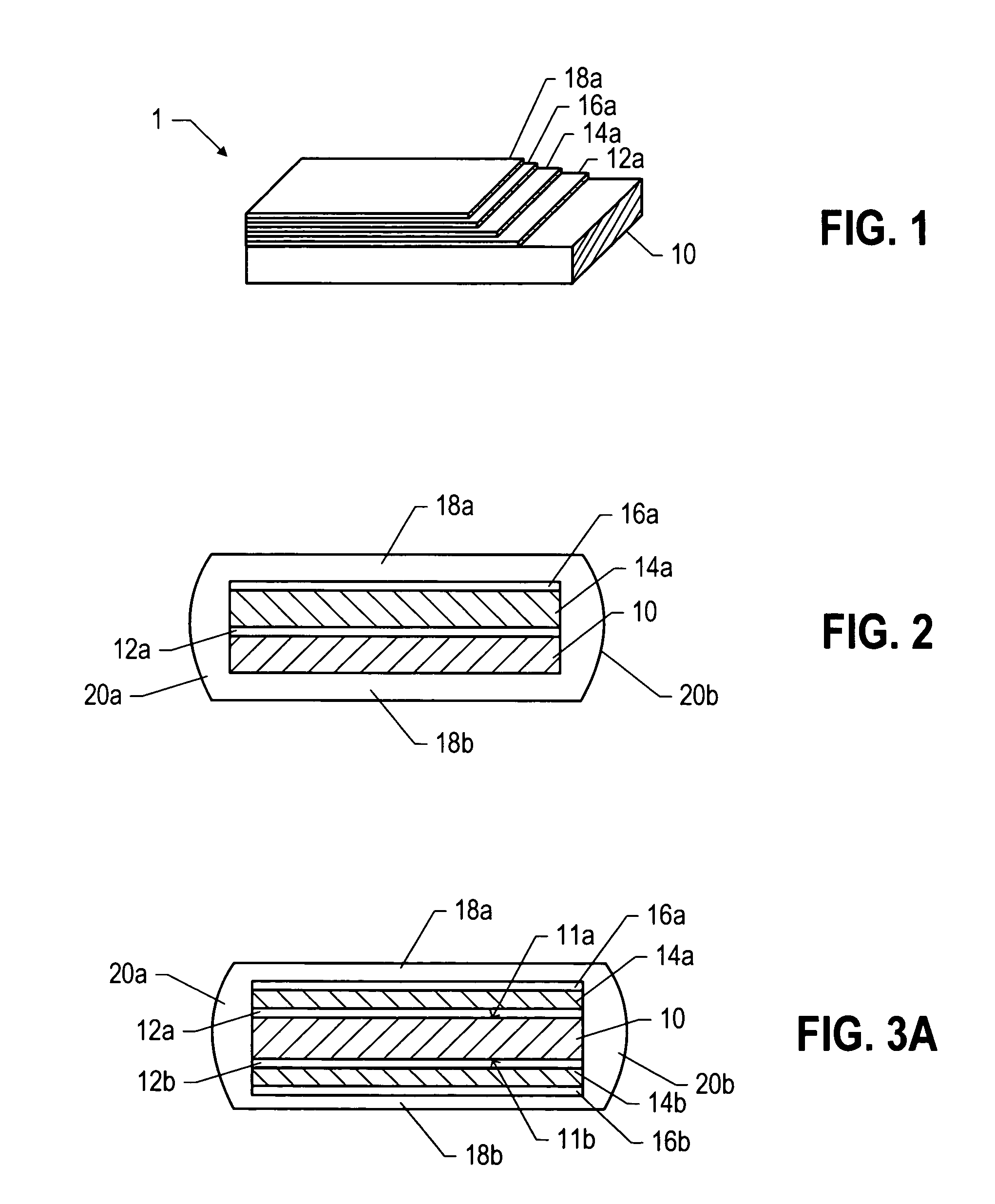
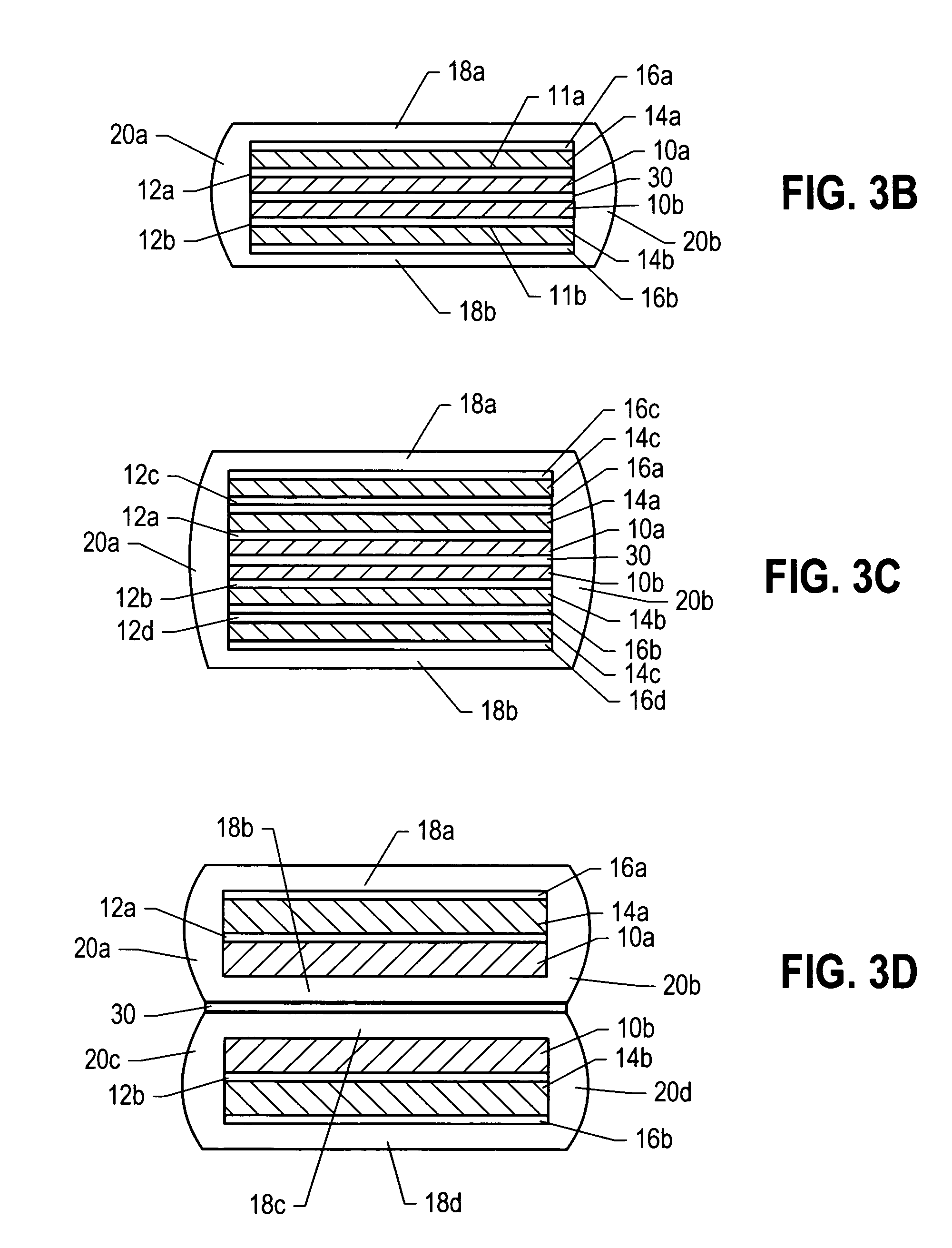
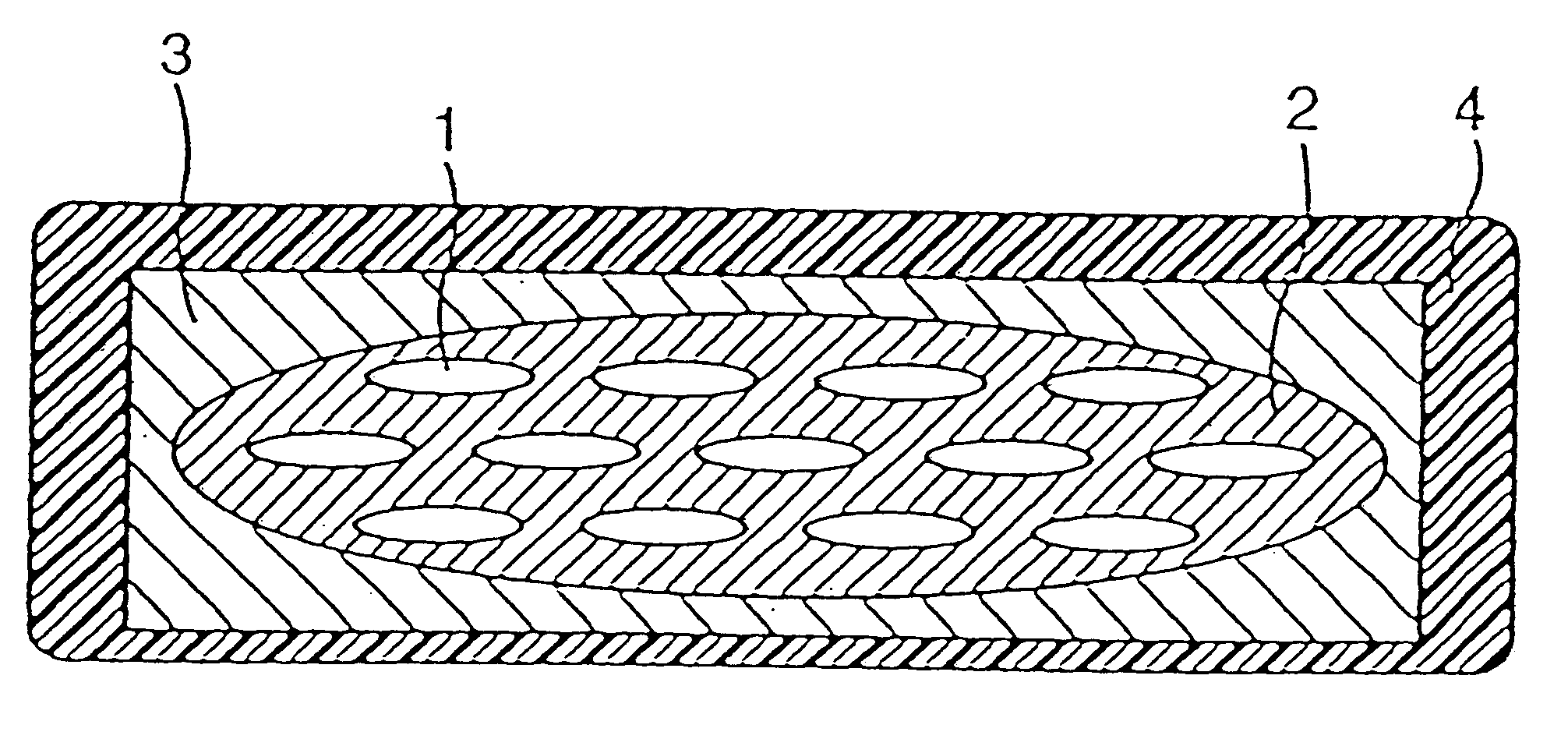
Oxide superconducting wire having insulating coat and production method thereof
InactiveUS6555504B1High strengthPrevent exertion of excessive mechanical strainSuperconductors/hyperconductorsTransformers/inductances detailsManganeseMaterials science
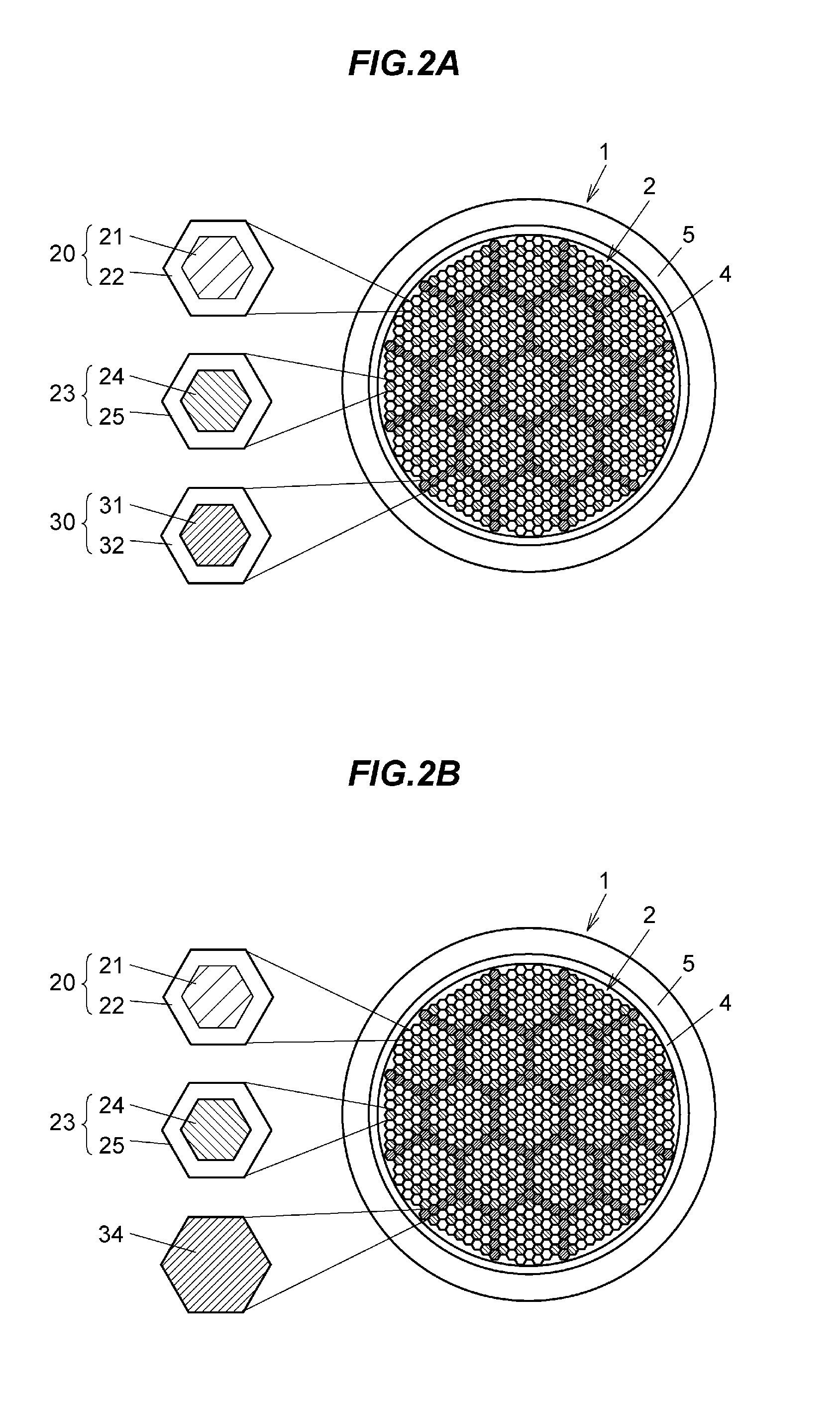
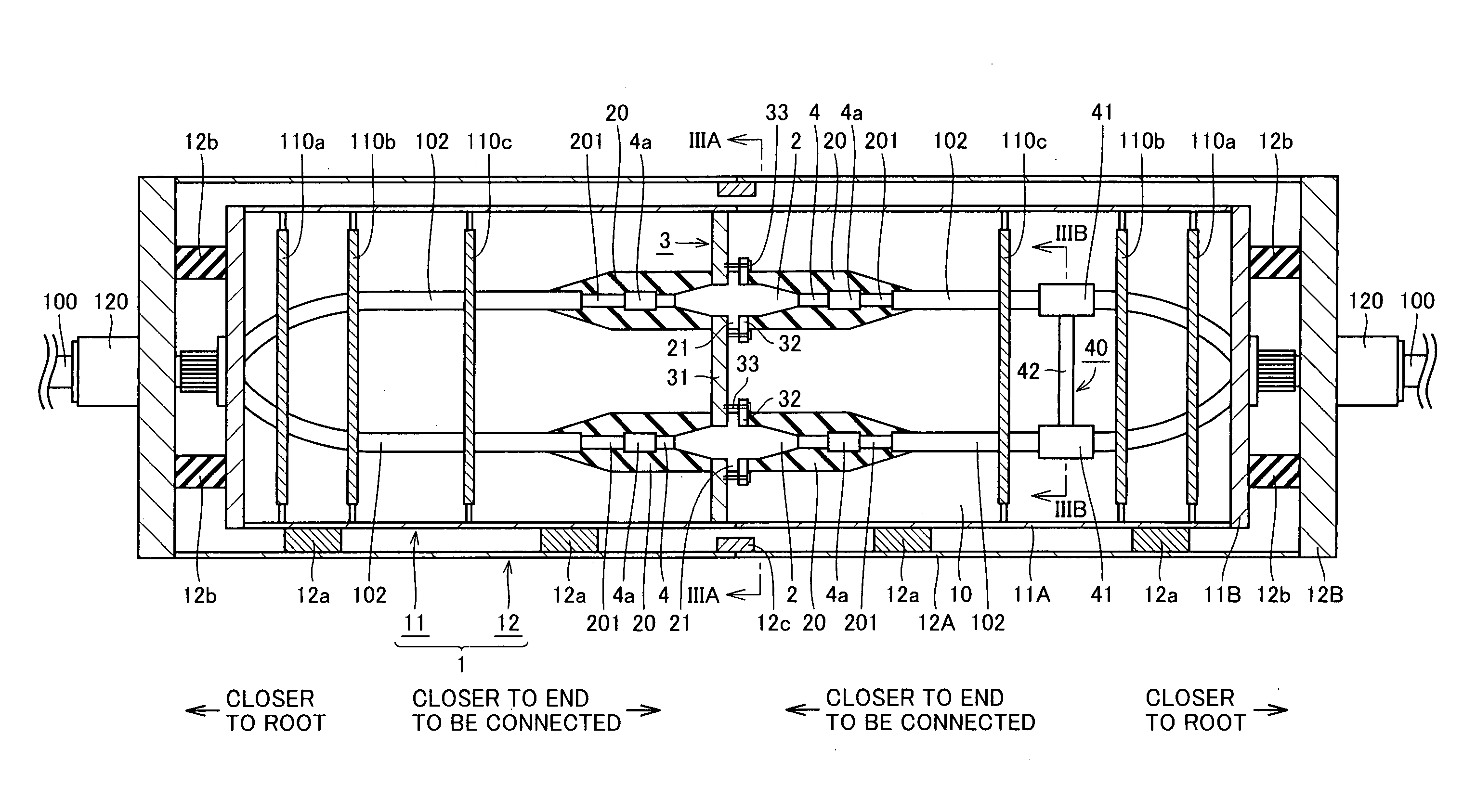
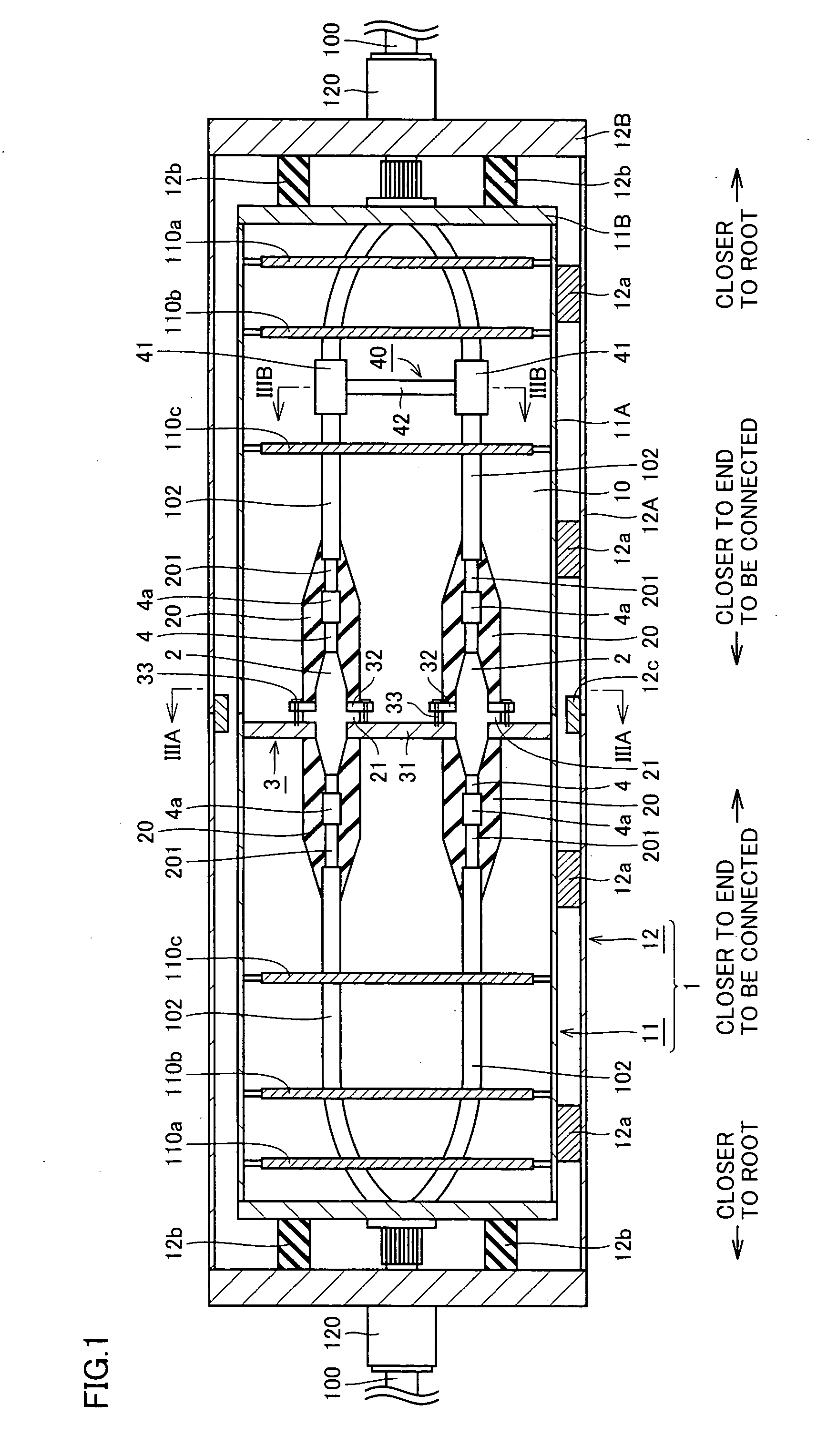
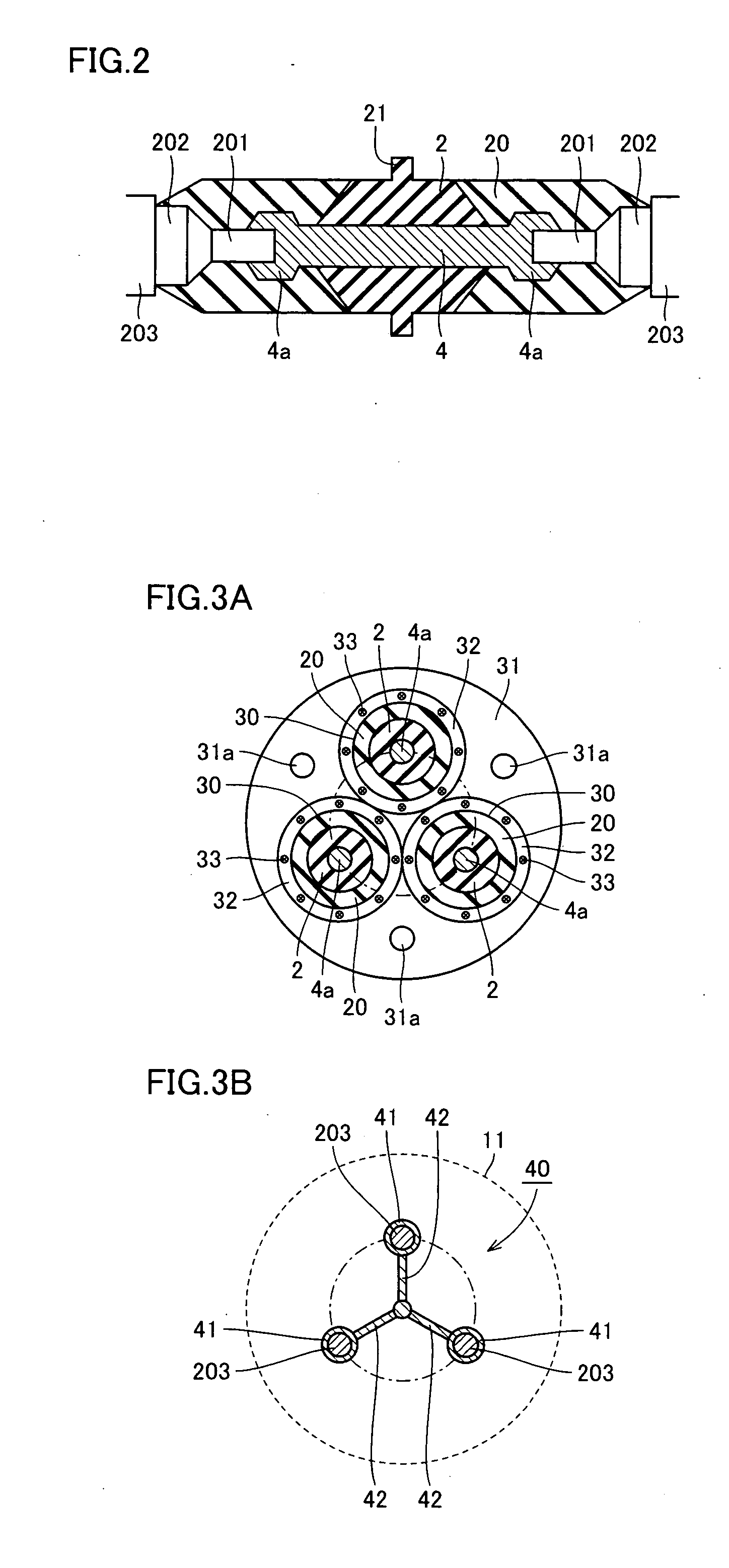
An oxide superconducting wire includes oxide superconducting filaments 1, a matrix 2, a covering layer 3, and an insulating layer 4. The matrix 2 is placed so as to enclose the oxide superconducting filaments 1 and is made of silver. The covering layer 3 is placed so as to enclose the matrix 2, contains silver and manganese, and has a thickness of 10 mum to 50 mum. The insulating layer 4 is placed so as to enclose the covering layer 3.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
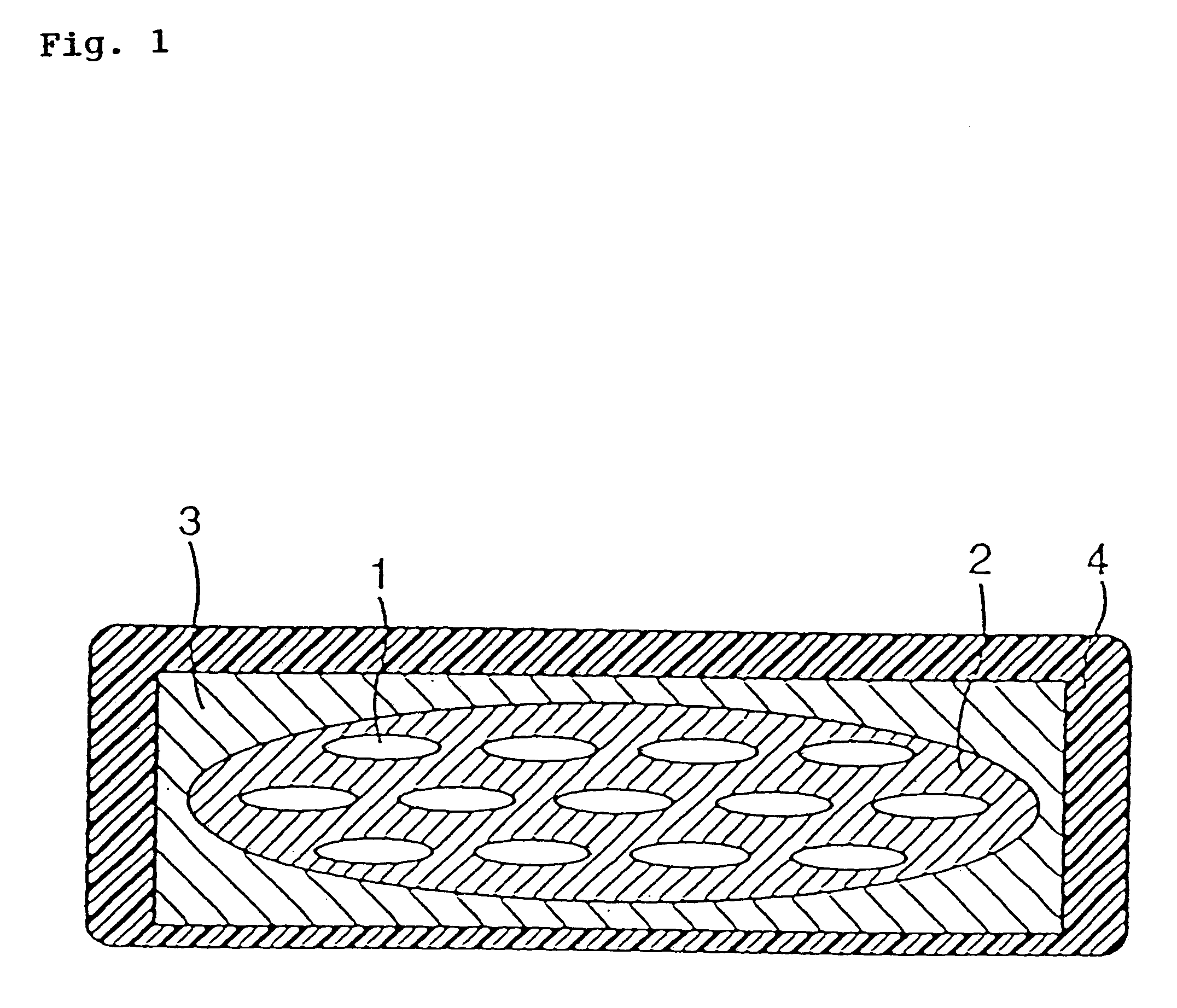
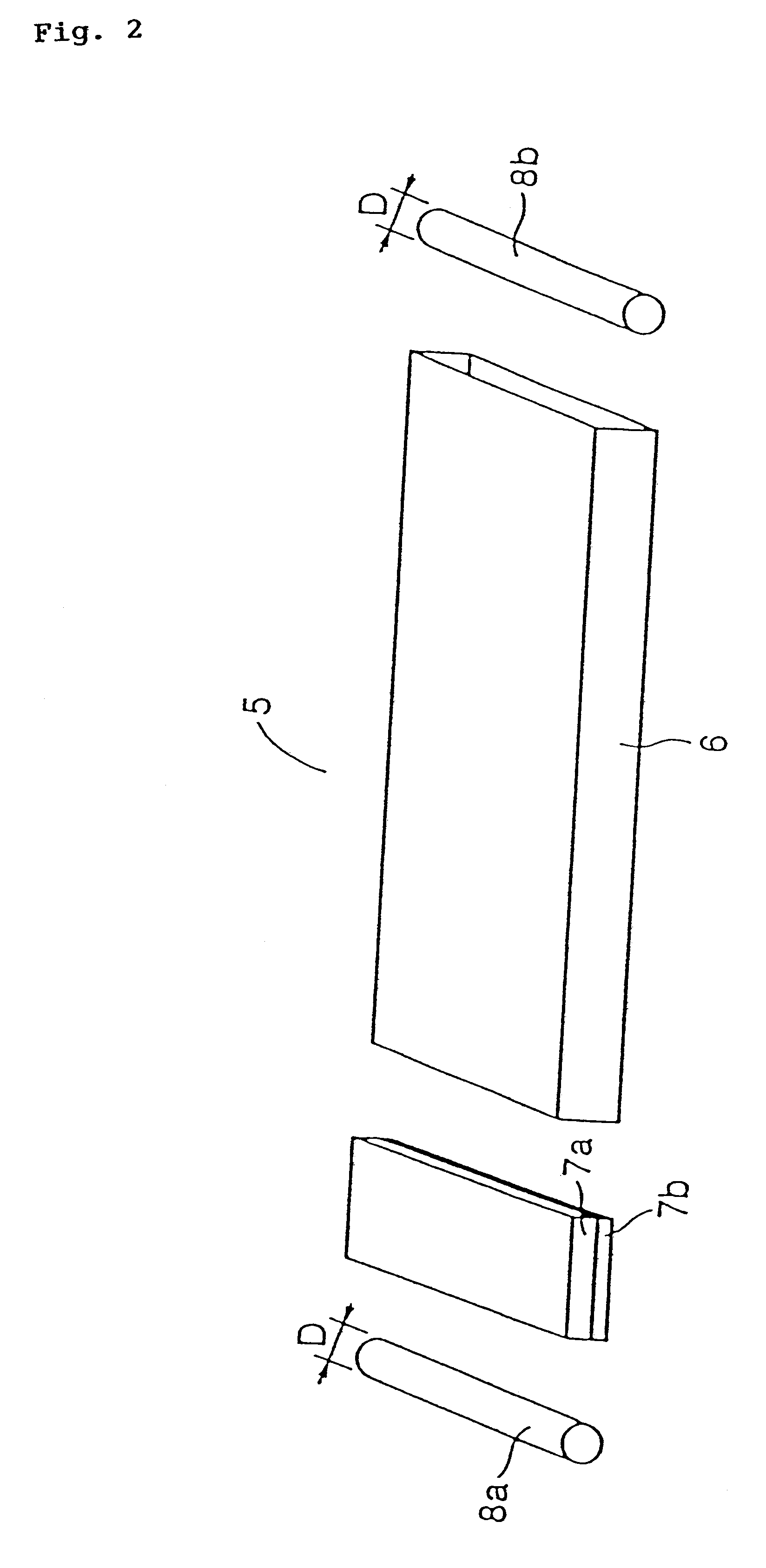
High-current, compact flexible conductors containing high temperature superconducting tapes
ActiveUS20080180202A1Good flexibilityReduce weightDefensive equipmentElectromagnets without armaturesElectric power transmissionElectrical conductor
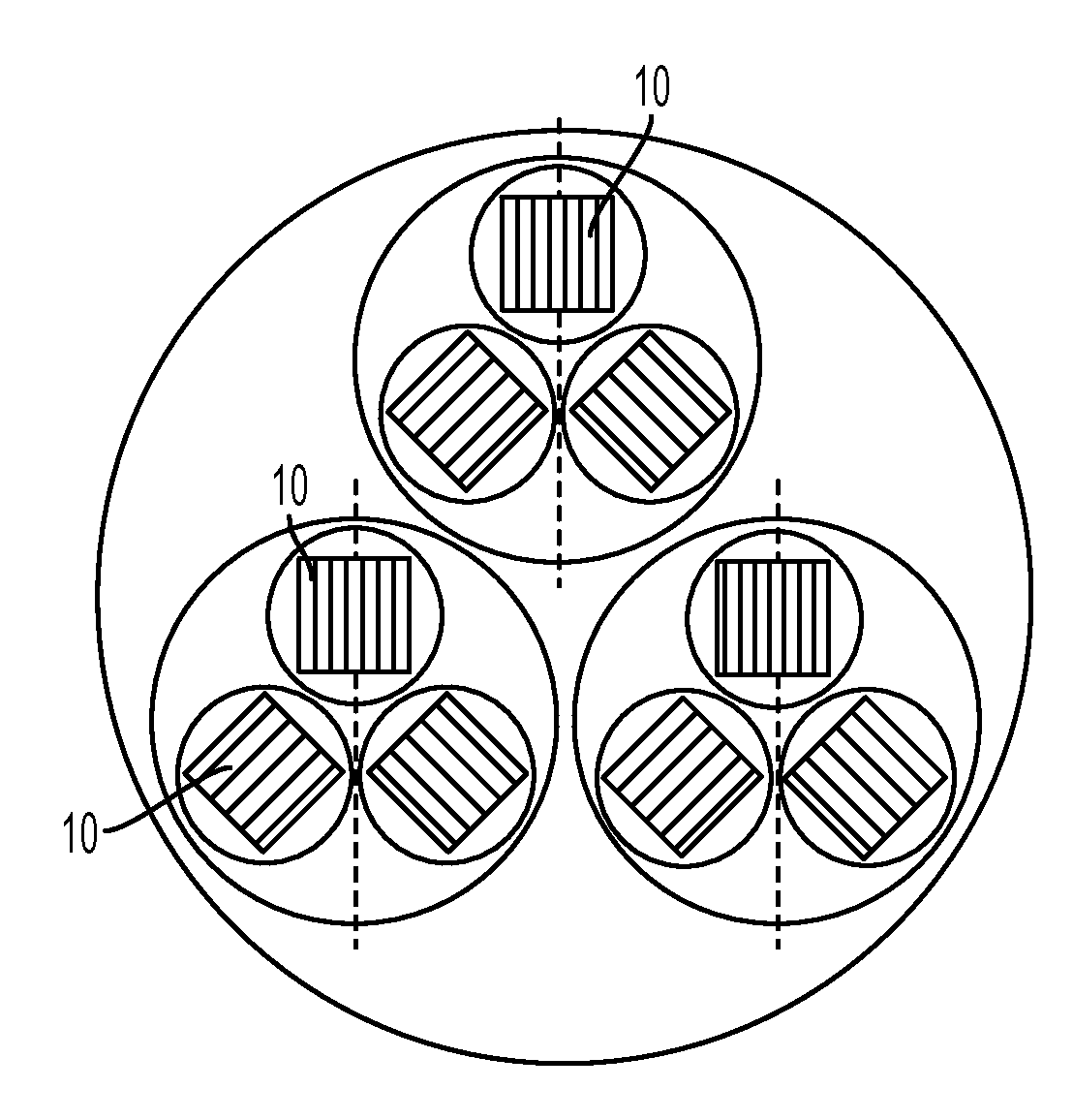
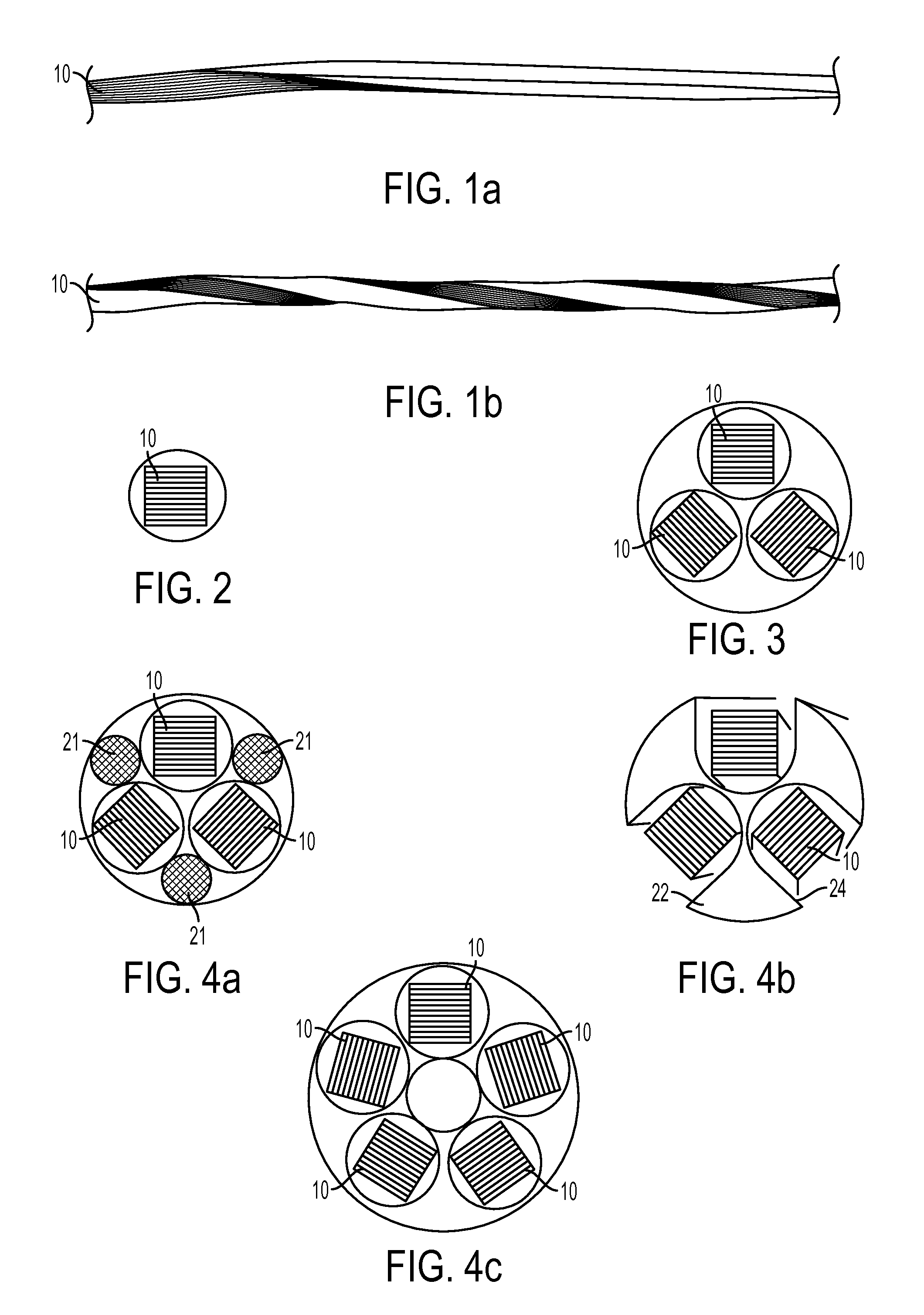
High-current, compact, flexible conductors containing high temperature superconducting (HTS) tapes and methods for making the same are described. The HTS tapes are arranged into a stack, a plurality of stacks are arranged to form a superstructure, and the superstructure is twisted about the cable axis to obtain a HTS cable. The HTS cables of the invention can be utilized in numerous applications such as cables employed to generate magnetic fields for degaussing and high current electric power transmission or distribution applications.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
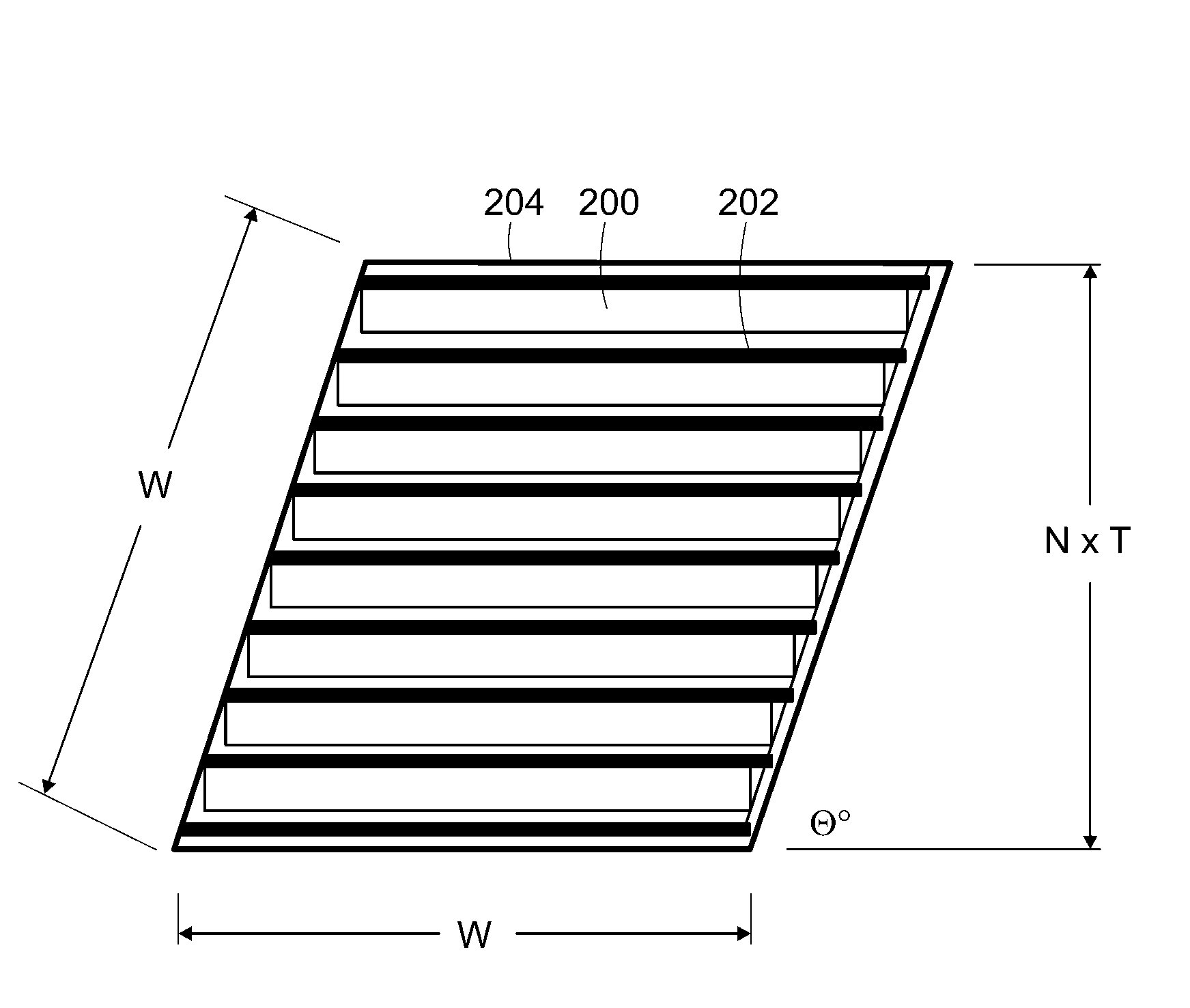
Segmented superconducting tape having reduced AC losses and method of making
ActiveUS20070191202A1Reduce AC-lossReducing AC losses in such tapesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentElectrical conductorHigh-temperature superconductivity
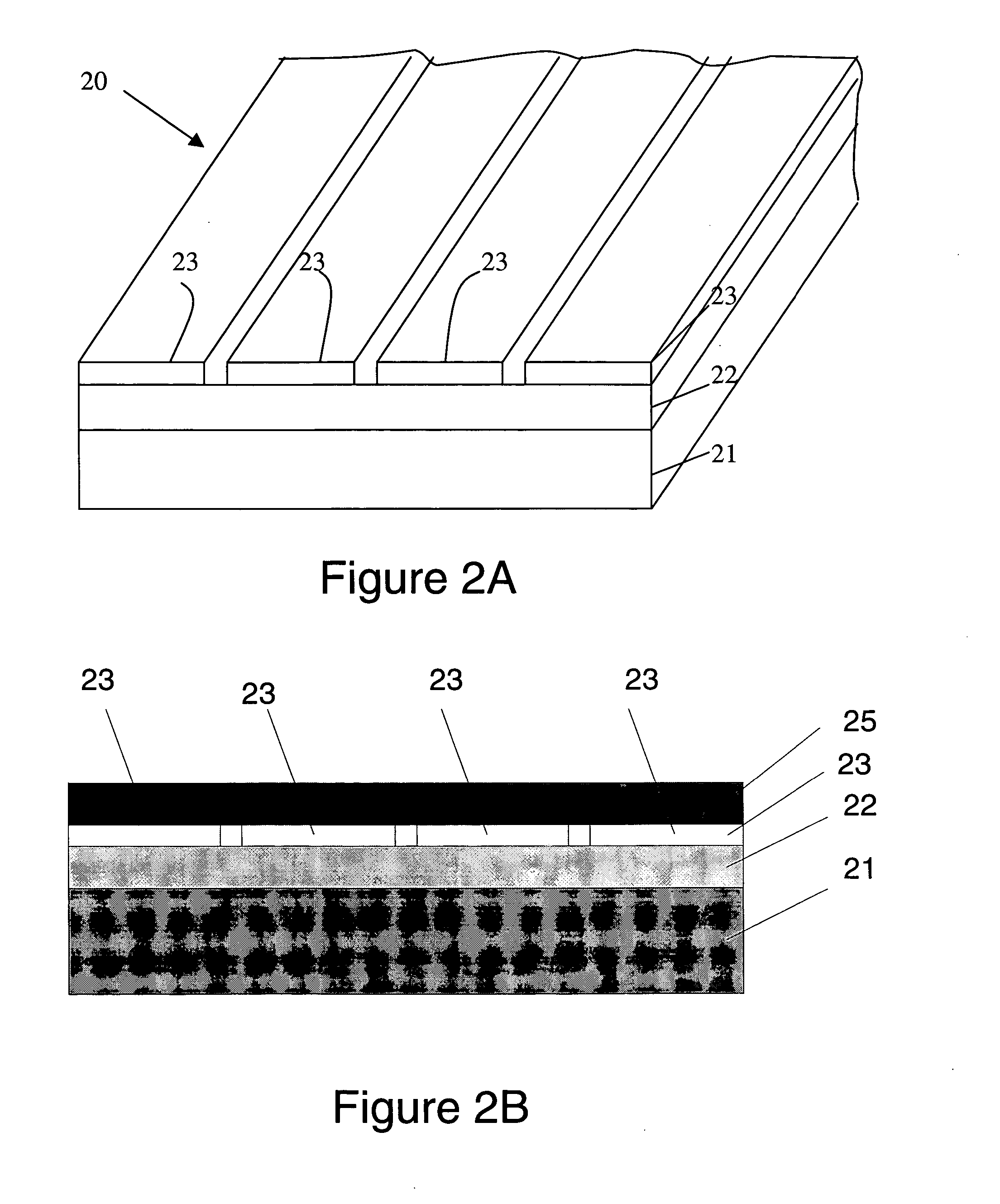
A superconducting tape having reduced AC losses. The tape has a high temperature superconductor layer that is segmented. Disruptive strips, formed in one of the tape substrate, a buffer layer, and the superconducting layer create parallel discontinuities in the superconducting layer that separate the current-carrying elements of the superconducting layer into strips or filament-like structures. Segmentation of the current-carrying elements has the effect of reducing AC current losses. Methods of making such a superconducting tape and reducing AC losses in such tapes are also disclosed.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Iron based superconducting structures and methods for making the same
InactiveUS20130196856A1Improve textureImprove superconductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThin membraneLattice constant
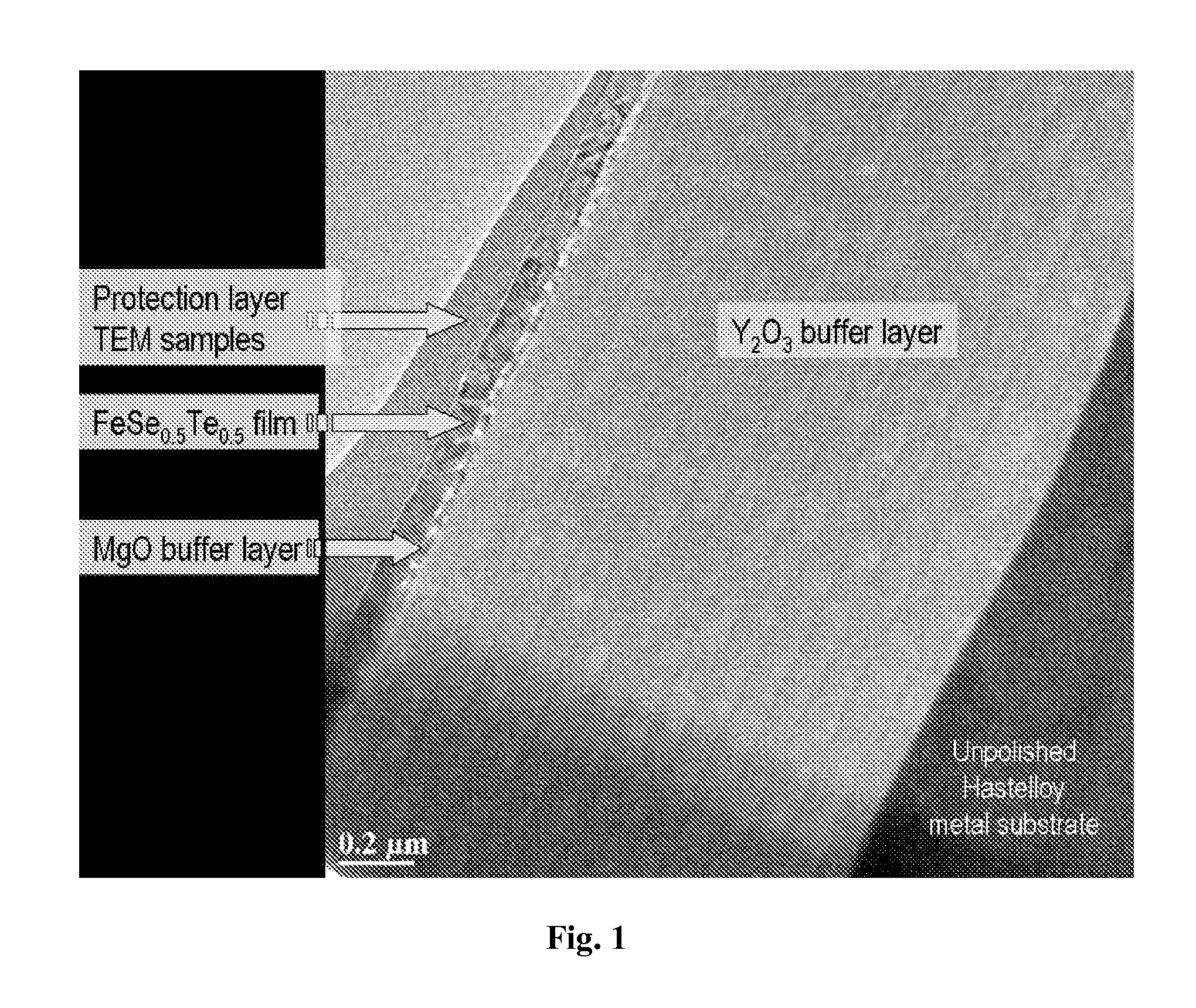
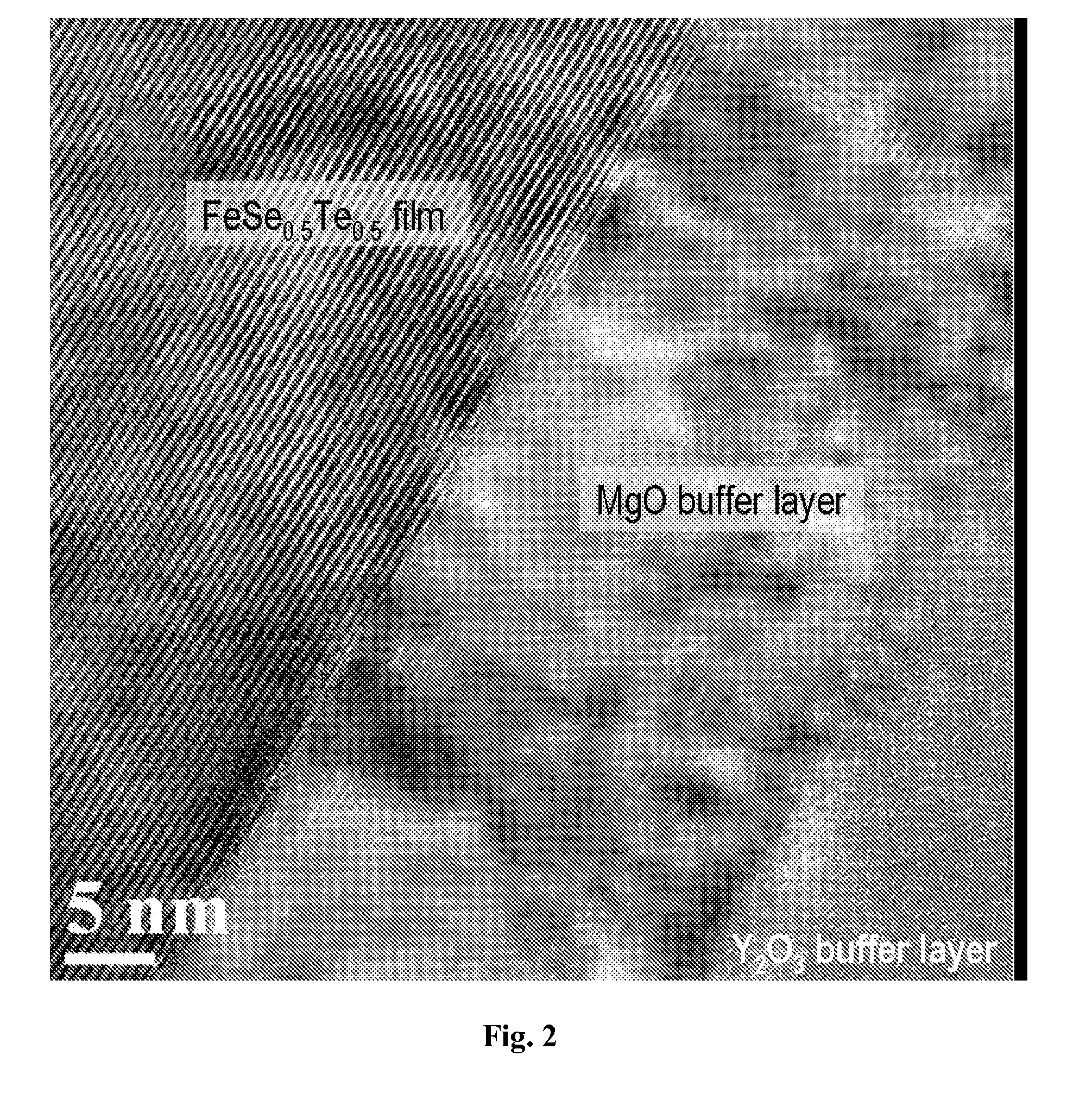
In some embodiments of the invention, superconducting structures are described. In certain embodiments the superconducting structures described are thin films of iron-based superconductors on textured substrates; in some aspects a method for producing thin films of iron-based superconductors on textured substrates is disclosed. In some embodiments applications of thin films of iron-based superconductors on textured substrates are described. Also contemplated is the formation of a film of iron-based superconductor having a thickness and an in-plane lattice constant formed on a textured substrate having a thickness and an in-plane lattice constant similar to the in-plane lattice constant of the iron-based superconductor.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
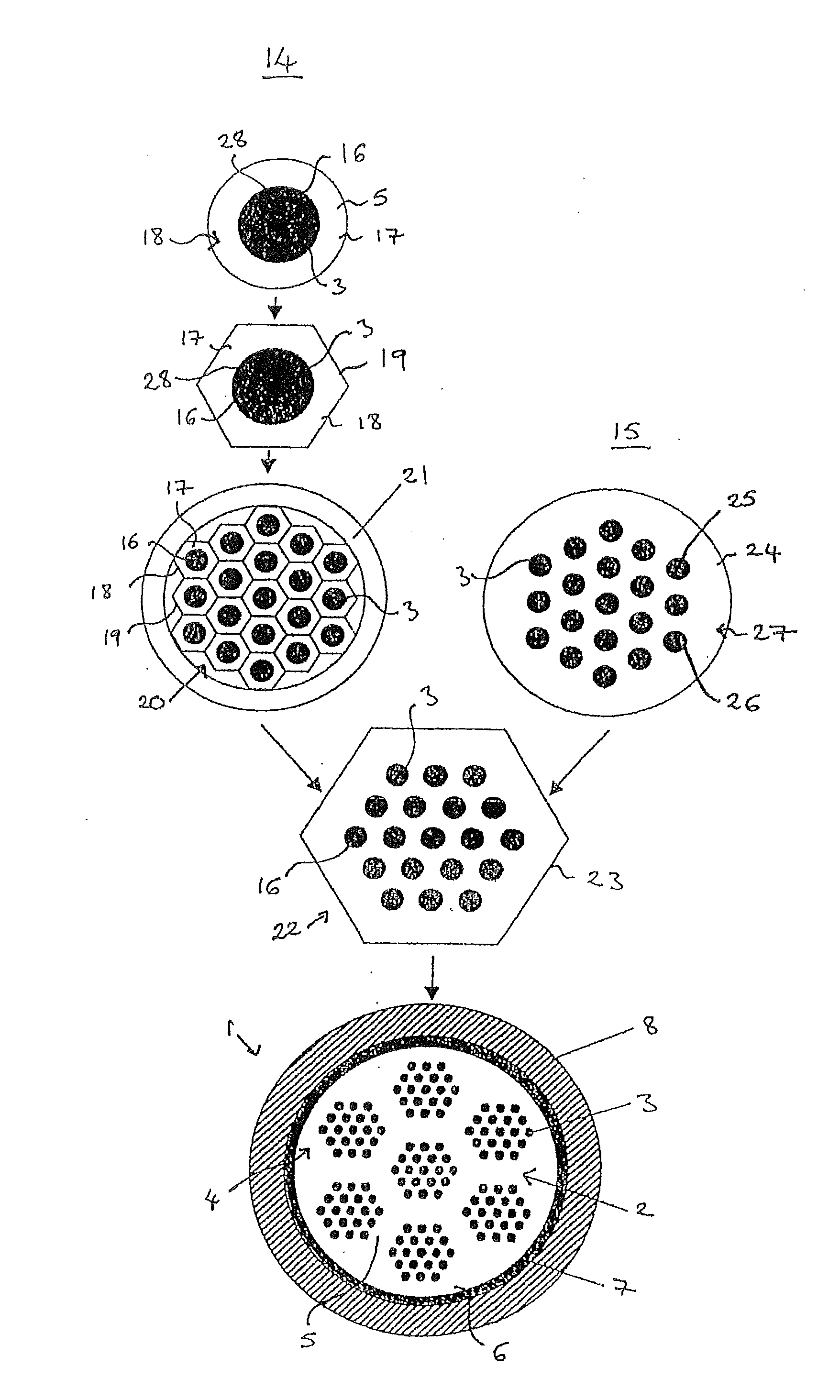
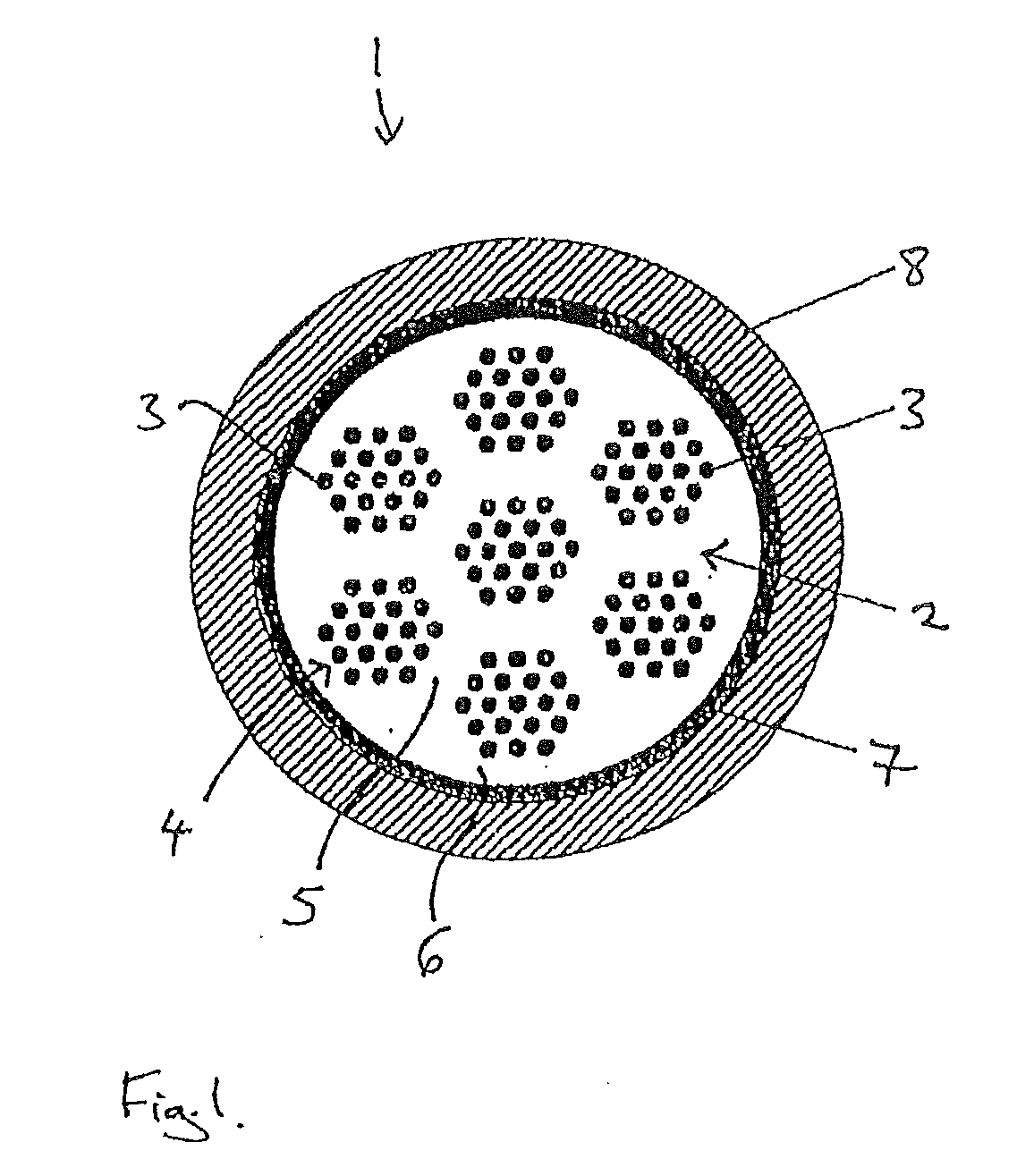
Superconductor cable
ActiveUS20100099570A1Minimizes strainStress minimizationSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsPower cableEngineering
Superconductor cable having a plurality of flat, tape-shaped ribbon superconductor wires assembled to form a stack having a rectangular cross section, the stack having a twist about a longitudinal axis of the stack. Multiple superconductor cables including twisted stacked-cables of the flat-tape-shaped superconductor wires, and power cable comprising the twisted flat-tape stacked cables are disclosed. Superconducting power cable disposed within and separated from an electrical insulator with a space passing cryo-coolant between the superconducting cable and insulator is also disclosed.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
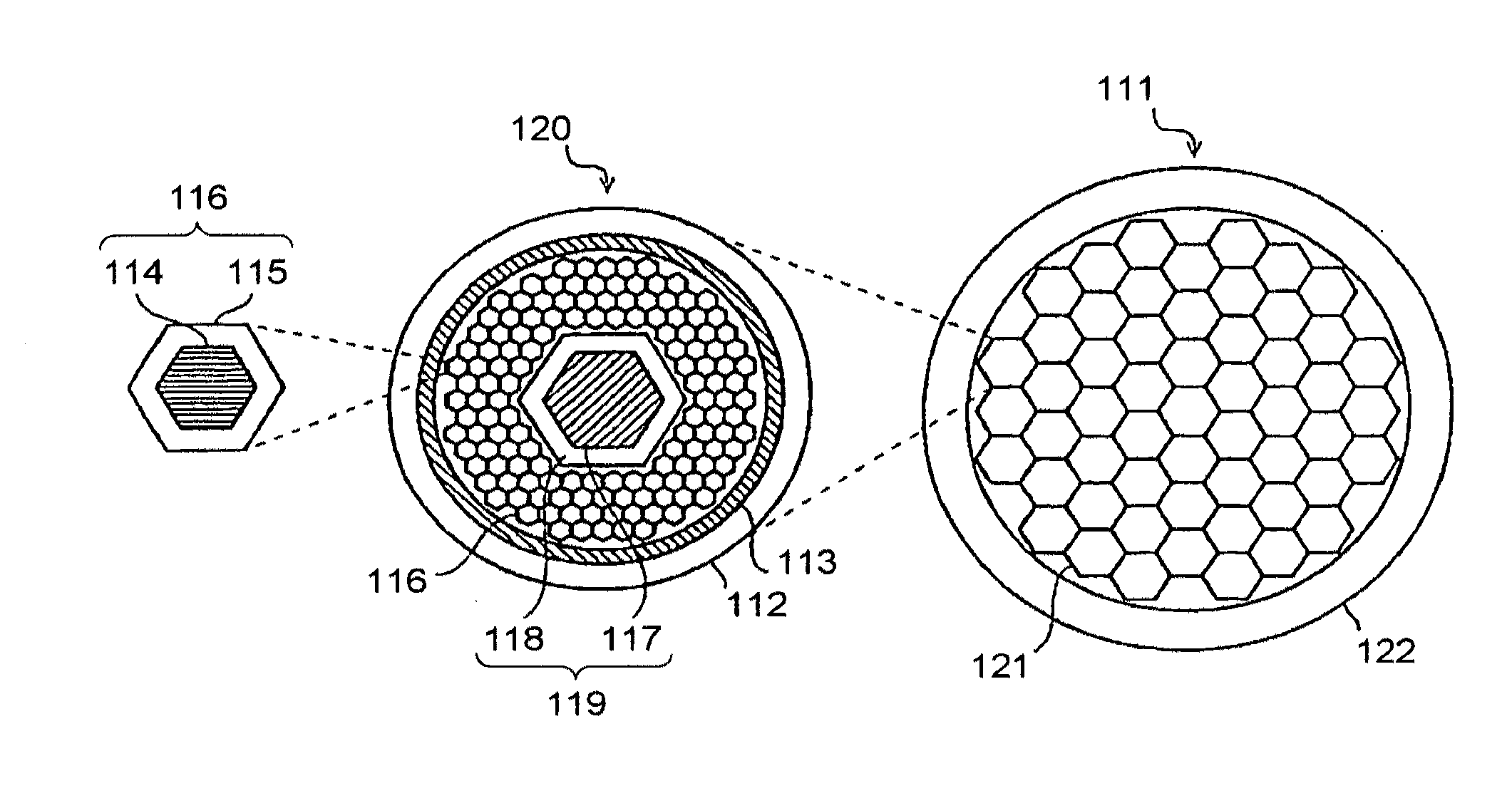
Precursor for Nb3Sn superconductor wire, superconductor wire using the same and method for manufacturing Nb3Sn superconductor wire
InactiveUS20120108437A1Easy to transformSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsAlloySingle-core
A precursor for a Nb3Sn superconductor wire is configured to be manufactured by the internal Sn diffusion method. The precursor includes a Cu tube including a barrier layer at an inner surface thereof. The barrier layer includes a metal selected from the group consisting of Ta, Ta-alloy, Nb and Nb-alloy. A plurality of Sn single cores are disposed in the Cu tube. Each of the Sn single cores includes Sn or Sn-alloy. A plurality of Nb single cores are also disposed in the Cu tube. Each of the Nb single cores includes Nb or Nb-alloy. The Sn single cores and the Nb single cores are arranged in the Cu tube such that the Sn single cores are not adjacent to each other.
Owner:SH COPPER PROD CO LTD
Composite Superconductor Cable Produced by Transposing Planar Subconductors
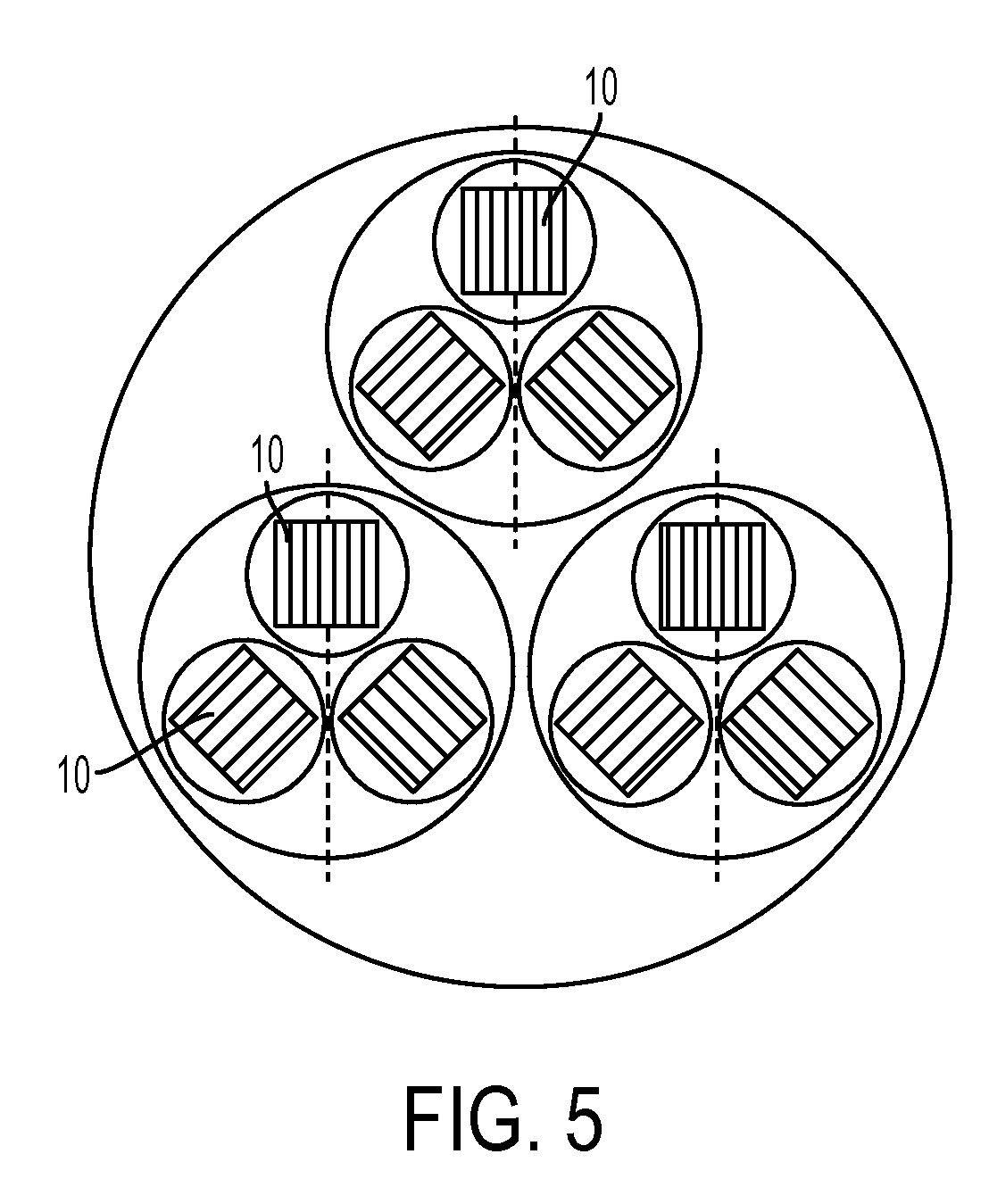
InactiveUS20080210454A1Superconductors/hyperconductorsTransformers/inductances detailsIn planeElectrical conductor
Owner:CALLAGHAN INNOVATION RES LTD
Susperconductive Multi-Phase Cable System, a Method of Its Manufacture and Its Use
ActiveUS20100227764A1Rational productionFlexible and efficient to useSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsElectrical conductorThermal insulation
The invention relates to a superconductive multi-phase, fluid-cooled cable system comprising a) a cable comprising at least three electrical conductors constituting at least two electrical phases and a zero- or neutral conductor, said electrical conductors being mutually electrically insulated from each other, and b) a thermal insulation defining a central longitudinal axis and having an inner surface and surrounding the cable, said inner surface of said thermal insulation forming the radial limitation of a cooling chamber for holding a cooling fluid for cooling said electrical conductors. The invention further relates to a method of manufacturing a cable system and to its use. The object of the present invention is to provide a simplified manufacturing and installation scheme for a fluid cooled cable system. The problem is solved in that said cable—at least over a part of its length—is located eccentrically relative to said central longitudinal axis when viewed in a cross section perpendicular to said longitudinal axis and where the eccentric location has the function of accommodating thermal shrinkage and expansion of the cable with respect to the thermal insulation.
Owner:NKT CABLES ULTERA
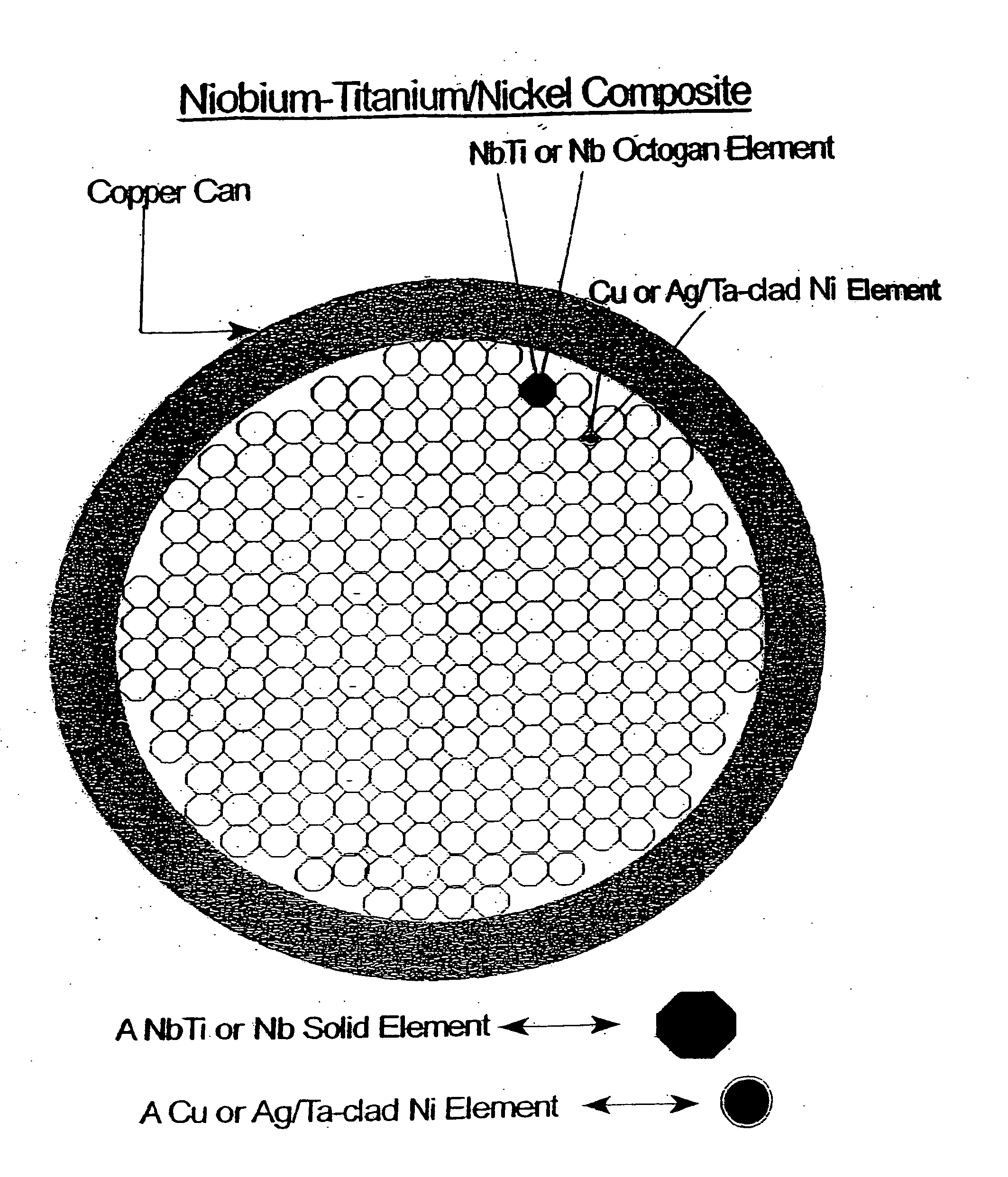
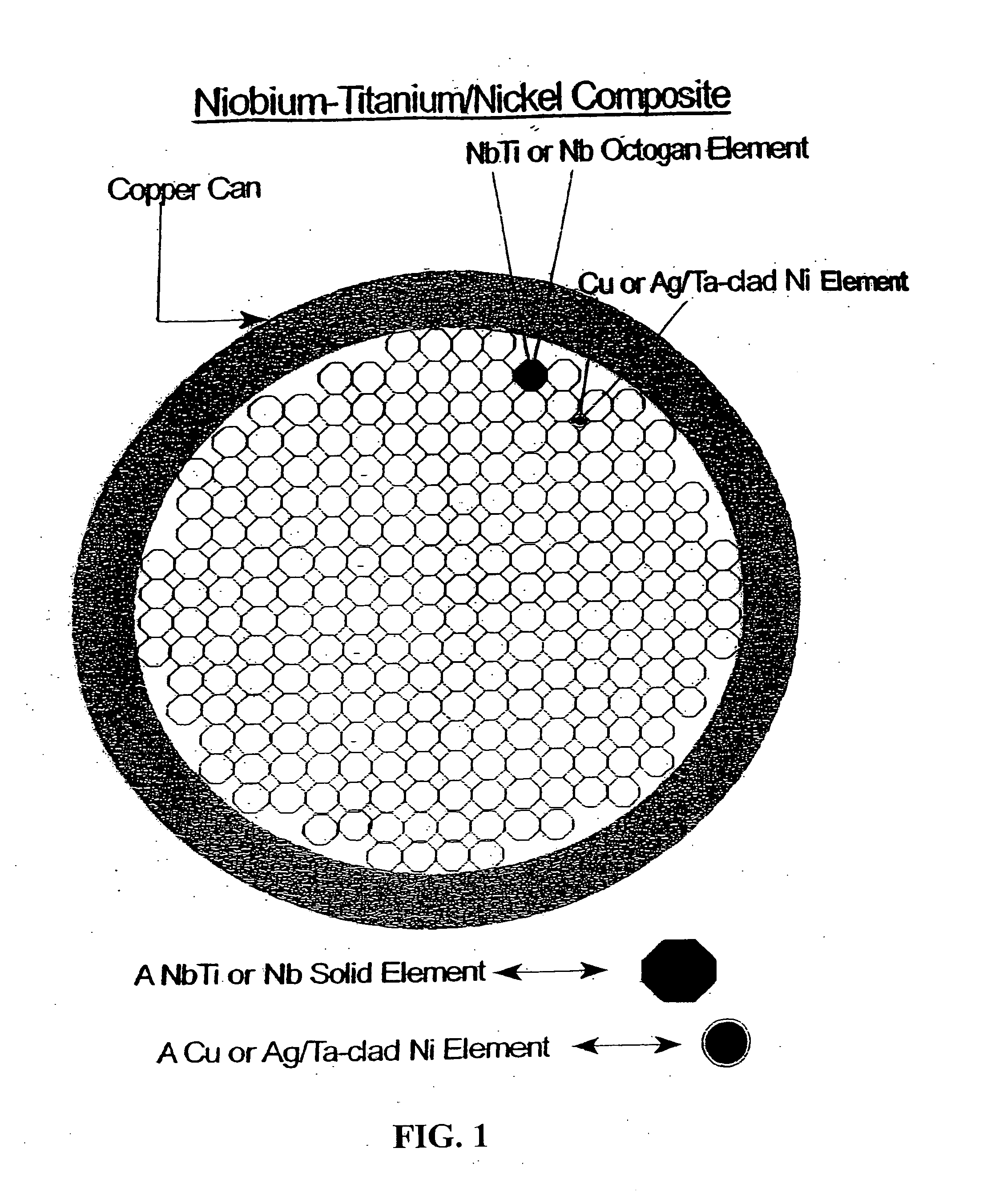
Composite conductors with improved structural and electrical properties
InactiveUS20080188372A1Improve featuresHigh strengthSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentElectrical performanceAlloy
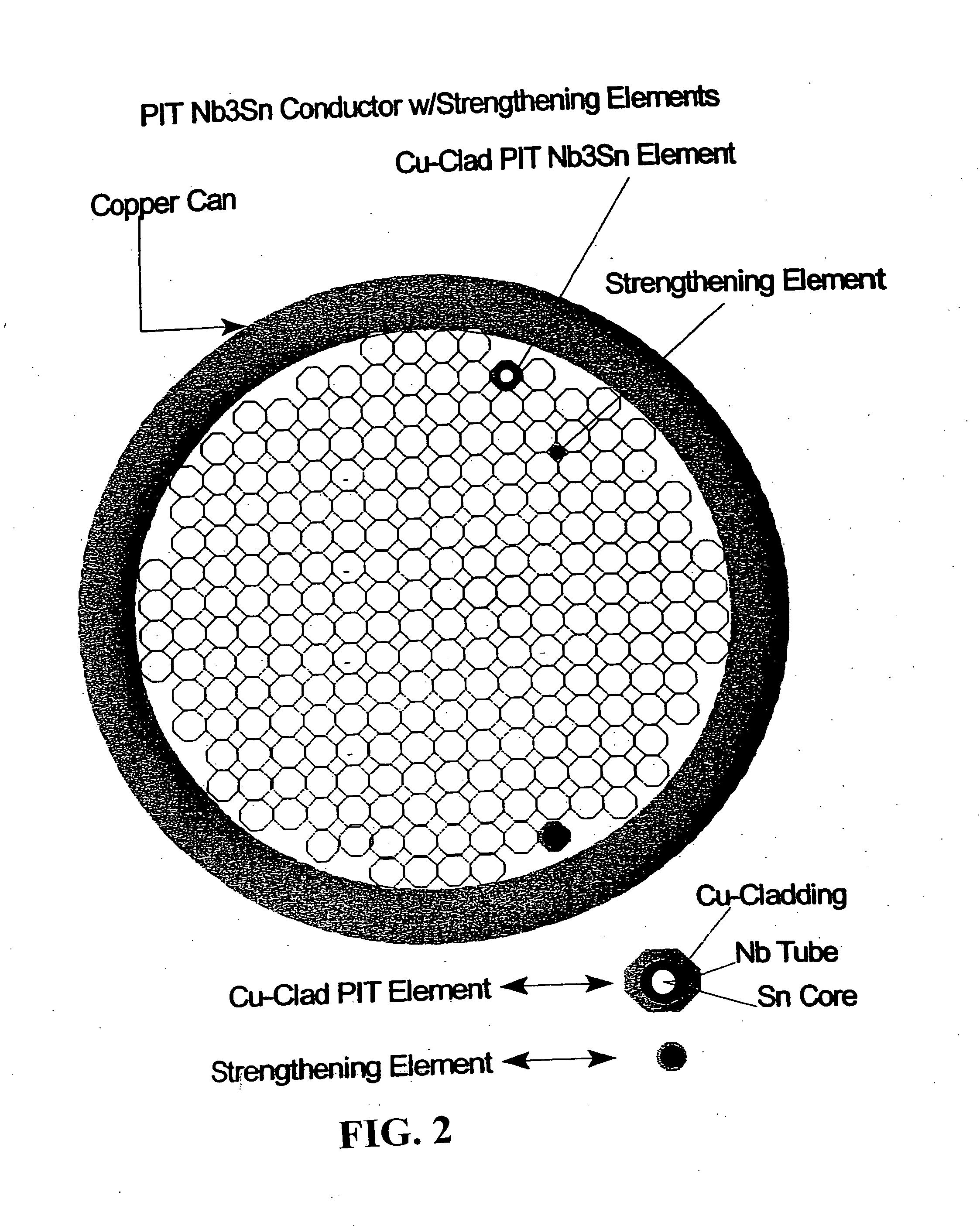
A method for forming improved superconducting composites having improved Jc values by assembling octagonal or curved octagonal elements which when assembled allow for formation of uniformly continuously spaced voids. The voids are then filled with a metal, alloy, intermetallic substance, or ceramic oxide. The assembly of the octagonal elements and the filling of the voids is performed in a metal can. Accordingly, the flexibility in design of the present invention allows control of the performance of the superconductor and is cost effective.
Owner:SUPRAMAGNETICS
Superconducting composite, preliminary product of superconducting composite and method for producing same
InactiveUS20100093546A1Minimizes and avoids damageImprove distributionSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentMagnesiumComposite material
Disclosed herein are superconducting composites, and preliminary products therefor, having a core comprising a superconducting phase, a first casing surrounding the core, and having an inner area abutting the core and having a first magnesium concentration and an outer area having a second magnesium concentration greater than the first magnesium concentration, wherein the second magnesium concentration is, on average, between 5 and 40 atomic percent. Desirably, the superconducting phase comprises a MgB2 phase. This arrangement allows for methods for producing the composites that reduce or eliminate subjecting the superconducting phase to mechanical stresses.
Owner:BRUKER EAS
Niobium based superconducting radio frequency(SCRF) cavities comprising niobium components joined by laser welding, method and apparatus for manufacturing such cavities
InactiveUS20120094839A1Improve performanceIncrease costWelding/cutting auxillary devicesSuperconductor detailsSurface finishAlloy
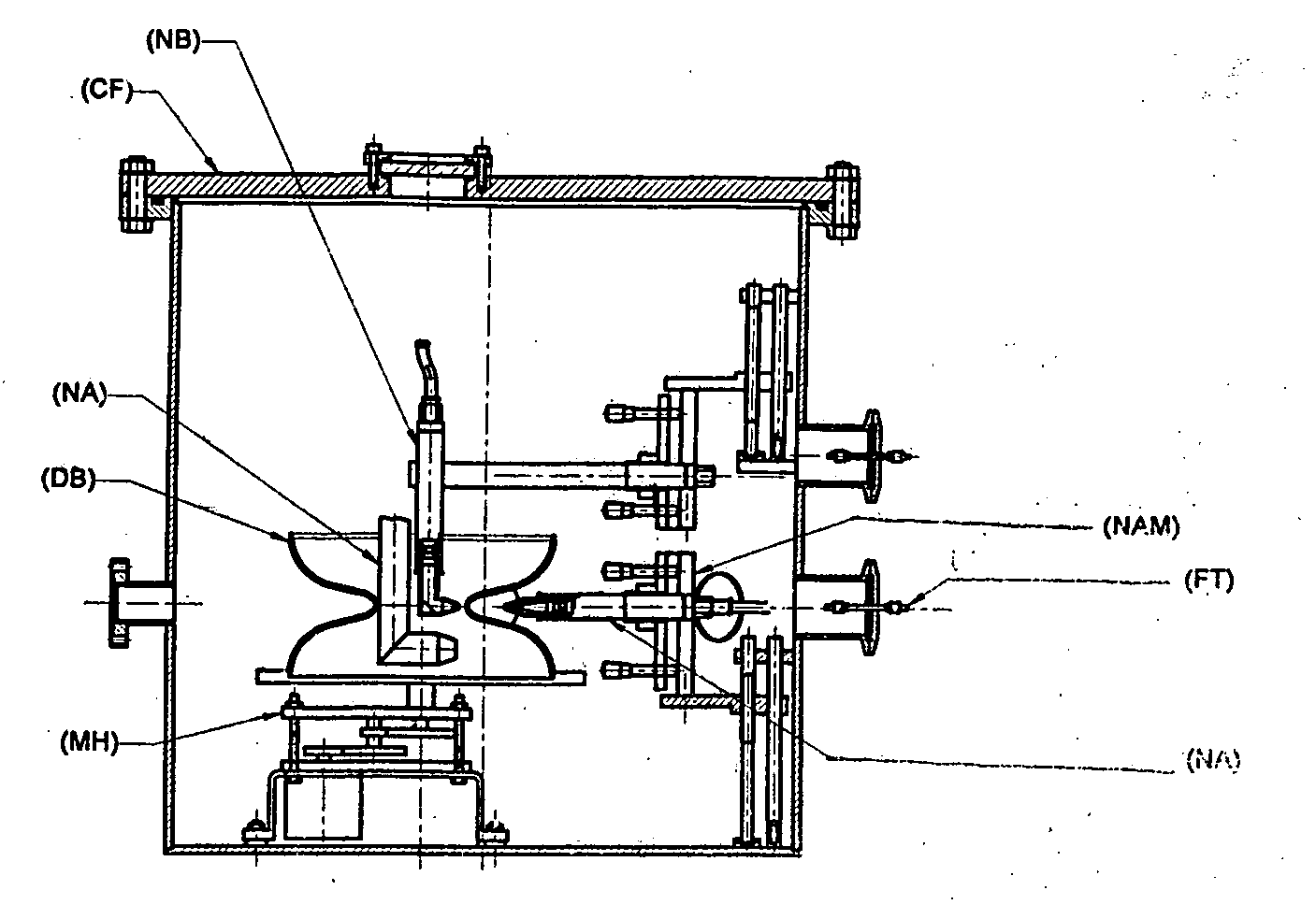
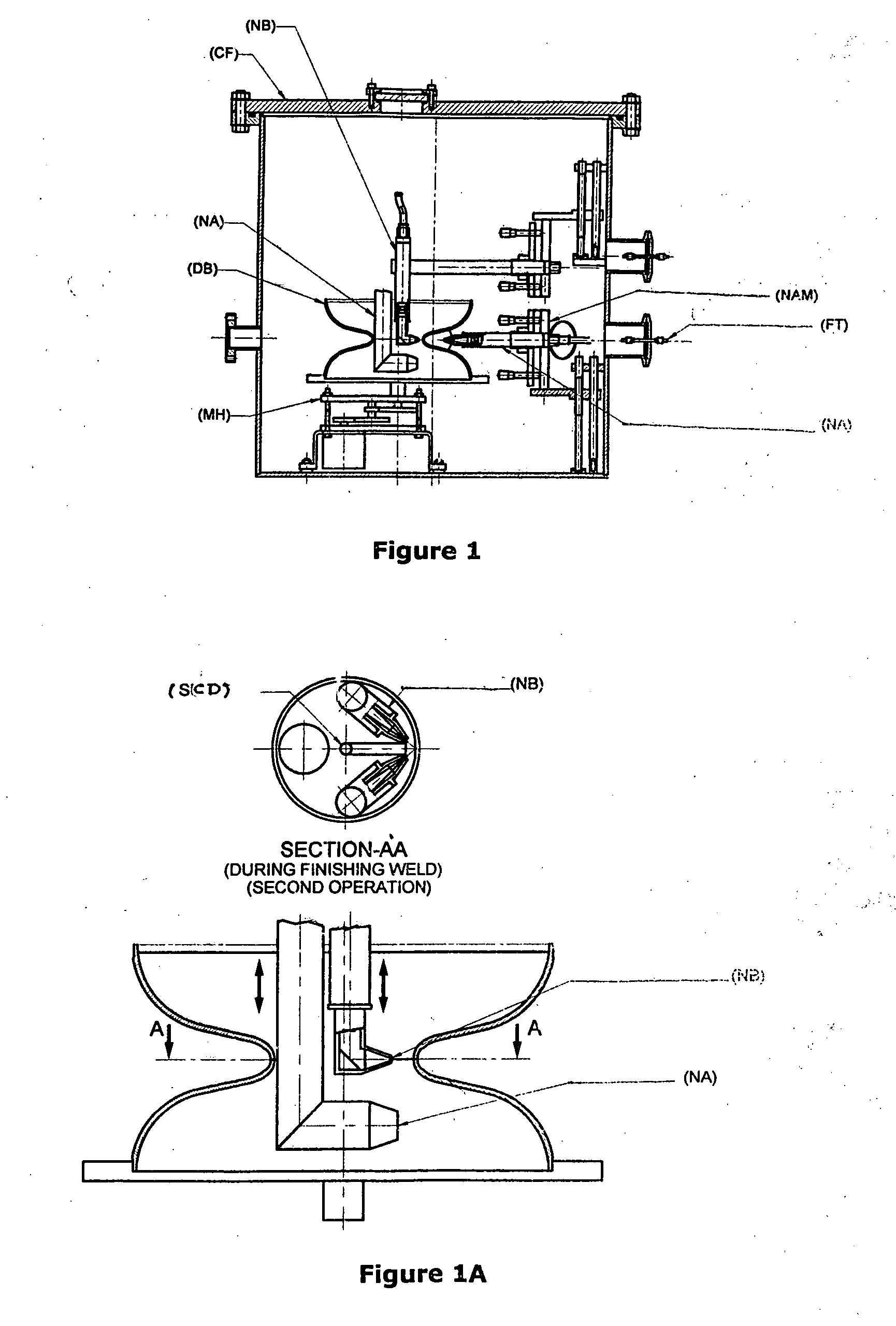
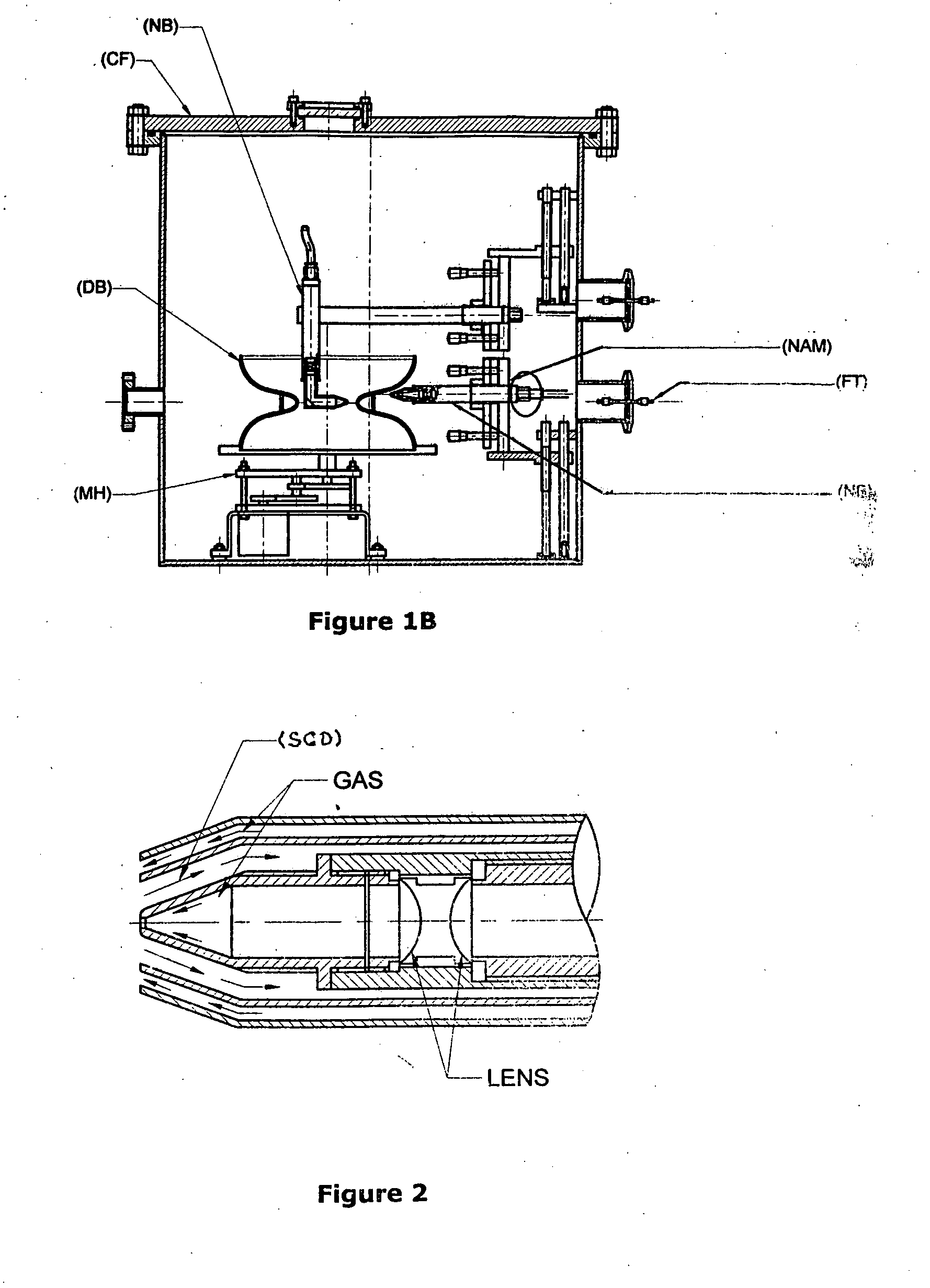
Niobium or its alloy based Superconducting Radio Frequency (SCRF) Cavities involving atleast one laser beam welded components in the SCRF cavity welded from inside surface of the wall of cavity directed to achieving more than half the thickness to full depth penetration with minimum HAZ, minimizing distortion and shrinkage. The method ensures improved weld quality and surface finish substantially free of any weld defects. Also disclosed is the welding nozzle system and welding rigs adapted to facilitate such laser welding of the Niobium or its alloy based Superconducting Radio Frequency (SCRF) Cavities. The invention is thus directed to enhancing productivity, ensuring consistent quality and reliability, enhanced weld penetration with minimum HAZ, smooth finish of weld joints at possible reduced costs.
Owner:SEC DEPT OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Input/output systems and devices for use with superconducting devices
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Fault Current Limiting HTS Cable and Method of Configuring Same
A cryogenically-cooled HTS cable is configured to be included within a utility power grid having a maximum fault current that would occur in the absence of the cryogenically-cooled HTS cable. The cryogenically-cooled HTS cable includes a continuous liquid cryogen coolant path for circulating a liquid cryogen. A continuously flexible arrangement of HTS wires has an impedance characteristic that attenuates the maximum fault current by at least 10%. The continuously flexible arrangement of HTS wires is configured to allow the cryogenically-cooled HTS cable to operate, during the occurrence of a maximum fault condition, with a maximum temperature rise within the HTS wires that is low enough to prevent the formation of gas bubbles within the liquid cryogen.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
Superconducting cable for alternating current
InactiveUS6417458B1Superconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentElectrical conductorSoftware engineering
A superconducting cable for alternating current, comprising conductor layers formed by a plurality of tape-shaped superconducting wires wound around a center member, an electric insulating layer formed outside the conductor layers, and a plurality of shielding layers formed outside the insulating layer, wherein, the conductor layers are formed, where N is a number of layers in the conductor layers and expressed by an integer, by gradually increasing a winding pitch of conductor layers in the same direction from an inner first layer to an N / 2 layer when the number of layers is even, or from an inner first layer to a (N-1) / 2 layer when the number of layers is odd, and then by gradually decreasing a winding pitch of conductor layers in an opposite direction to the inner layers from a N / 2+1 layer to an N layer when the number of layers is even, or from a (N+1) / 2 layer to an N layer when the number of layers is odd.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Multiphase superconducting cable connection structure and multiphase superconducting cable line
InactiveUS20050217878A1Help positioningHigh strengthSuperconductors/hyperconductorsCable fittings for cryogenic cablesElectrical conductorEngineering
A multiphase superconducting cable connection structure includes a connection box accommodating three conductor connects connecting a superconductor of a cable core of each phase extracted from a pair of 3-phase superconducting cables, a solid insulation member fixed to an outer circumference of each conductor connect, and a metal flange fixing the solid insulation member to the connection box. By fixing the metal flange to the connection box (a refrigerant vessel), the conductor connect can be positioned and the conductor connector's movement caused as the cable core thermally contracts can be reduced. The structure can help to position the conductor connect in the connection box and reliably hold it at a prescribed position.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Multifilament strand with Ag cladding and a coating of oxygen-permeable ceramic
InactiveUS6344430B1Improve breathabilityFilament decoupling is significantly improvedSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentOxygenTubing types
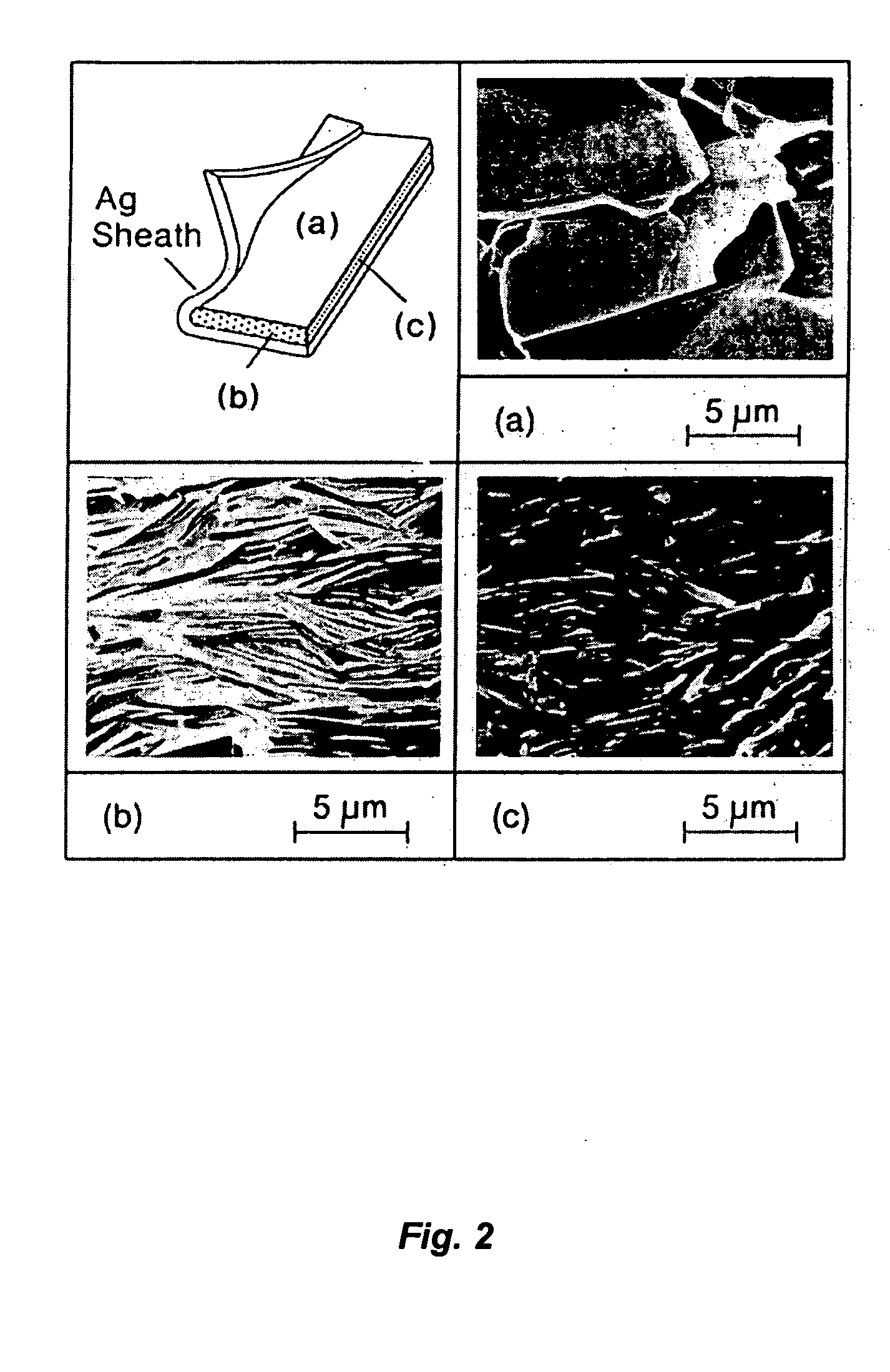
A powder in tube type method of making an HTc superconductive multifilament strand having a silver-based matrix, and an HTc superconductive multifilament strand having a silver-based matrix. The method includes, prior to the monofilament step, preparing a composite multilayer material is including at least one silver-based sheet, and at least one layer of non-superconductive ceramic material that is permeable to oxygen. During the monofilament step, a thickness of composite multilayer material is interposed between first and second thicknesses of silver-based material, thereby forming the first silver-based envelope.
Owner:NEXANS
Superconducting cable
ActiveUS20100099571A1Improve efficiencyReduction of AC lossesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentElectrical conductor
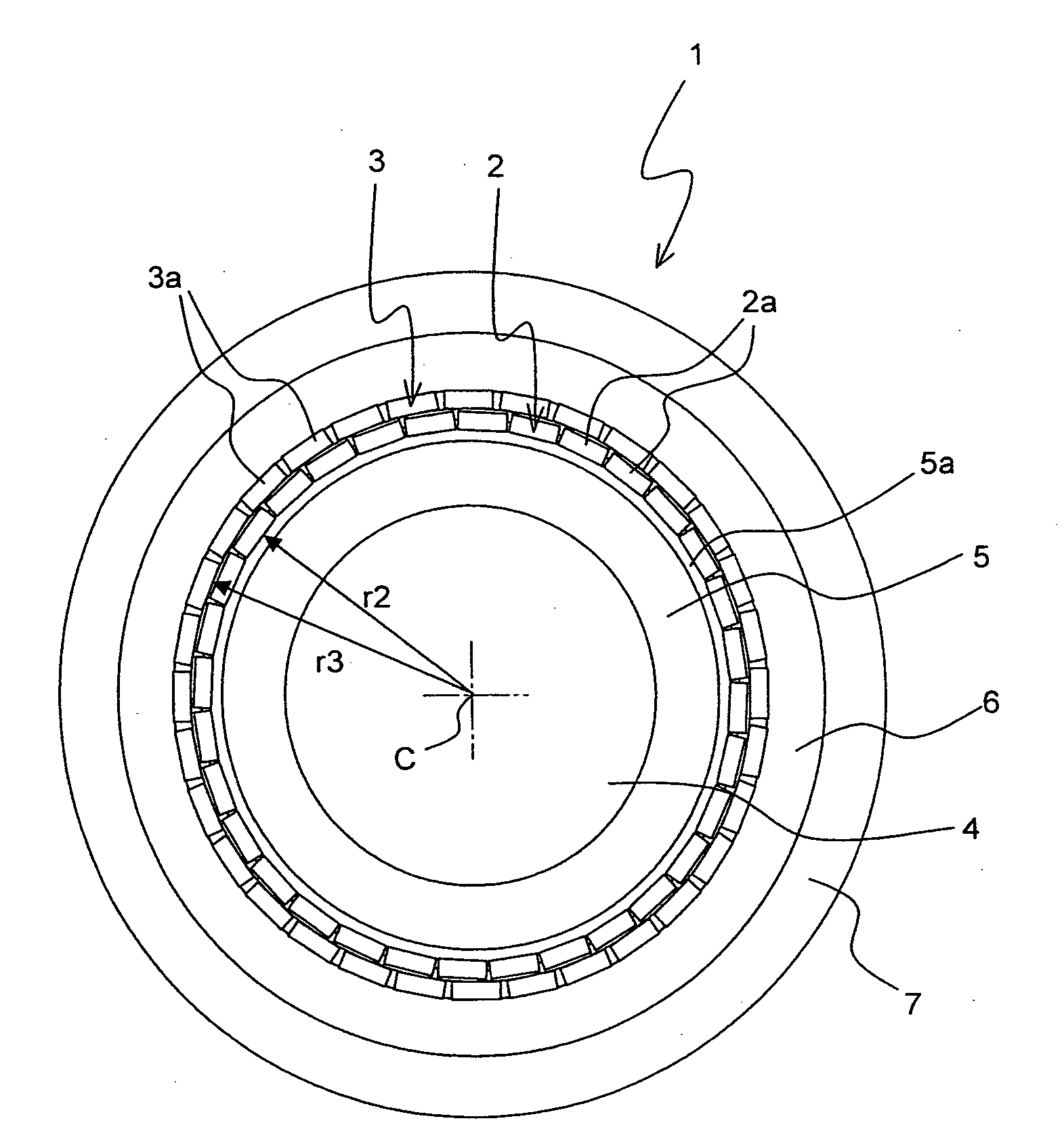
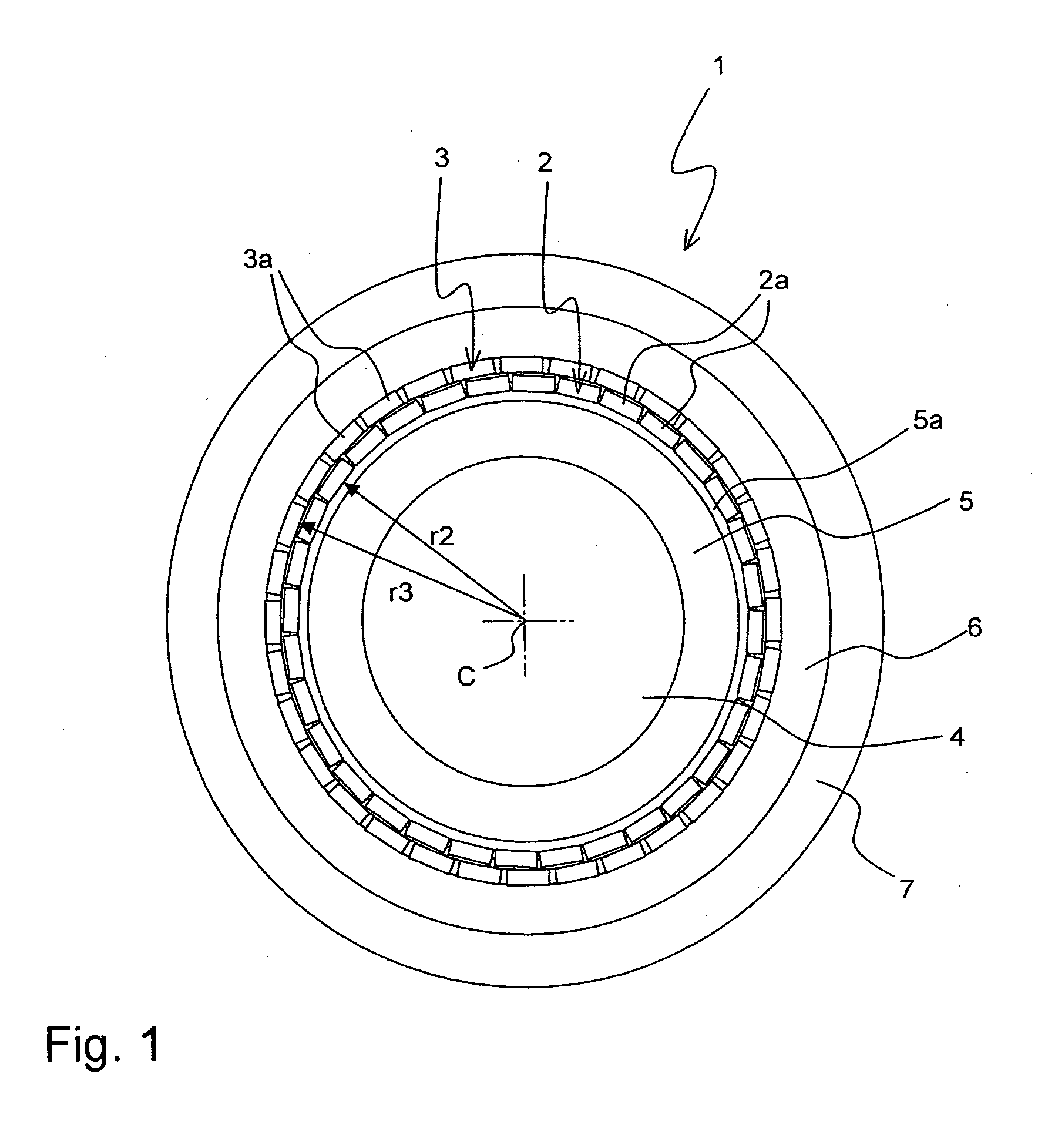
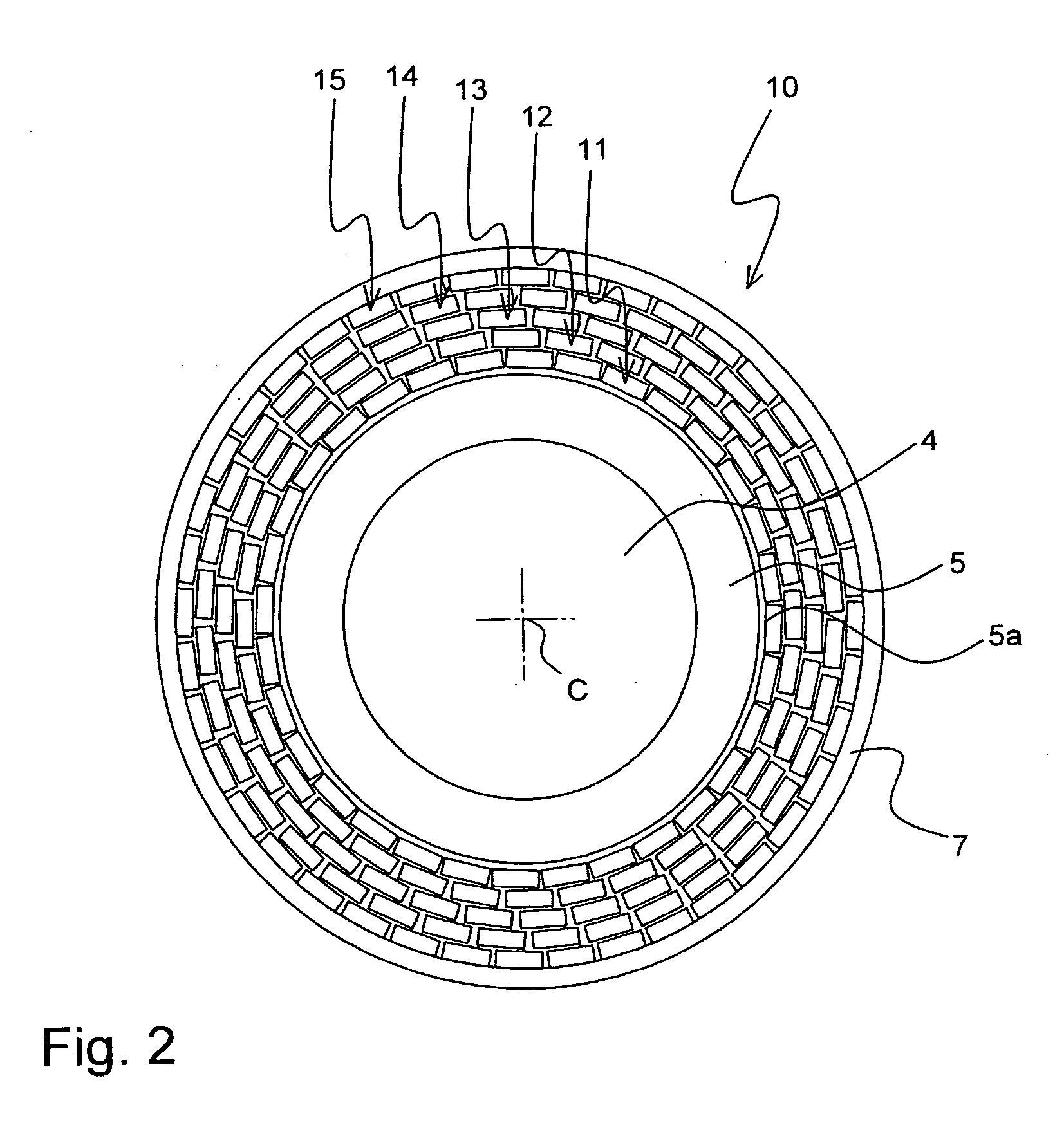
A superconducting cable (1; 10; 30) has a channel (4, 38) for a cooling liquid, a tubular support structure (5, 37), at least two layers (2, 3; 11-15; 31, 32, 35, 36) comprising high Tc conductors (2a, 3a) which comprise a high Tc material, and an insulation (7, 17), in particular a tubular insulation (7). The conductors (3a) of the outer layer (3; 13-15; 33, 36) comprise a first high Tc material that is different from a second high Tc material of the conductors (2a) of the inner layer (2; 11-12; 32, 35), wherein the first high Tc material exhibits lower AC losses as compared the second high Tc material, and that the high Tc conductors (3a) of the outer layer (3; 13-15; 33, 36) comprise normal-conducting interruptions (41, 42, 43). The superconducting cable exhibits reduced AC losses.
Owner:BRUKER HTS
Popular searches
Magnetic materials Permanent superconductor devices Superconducting magnets/coils Induction current sources Emergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/current Relays Superconductor elements usage Induction heating apparatus Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing Resonators
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com