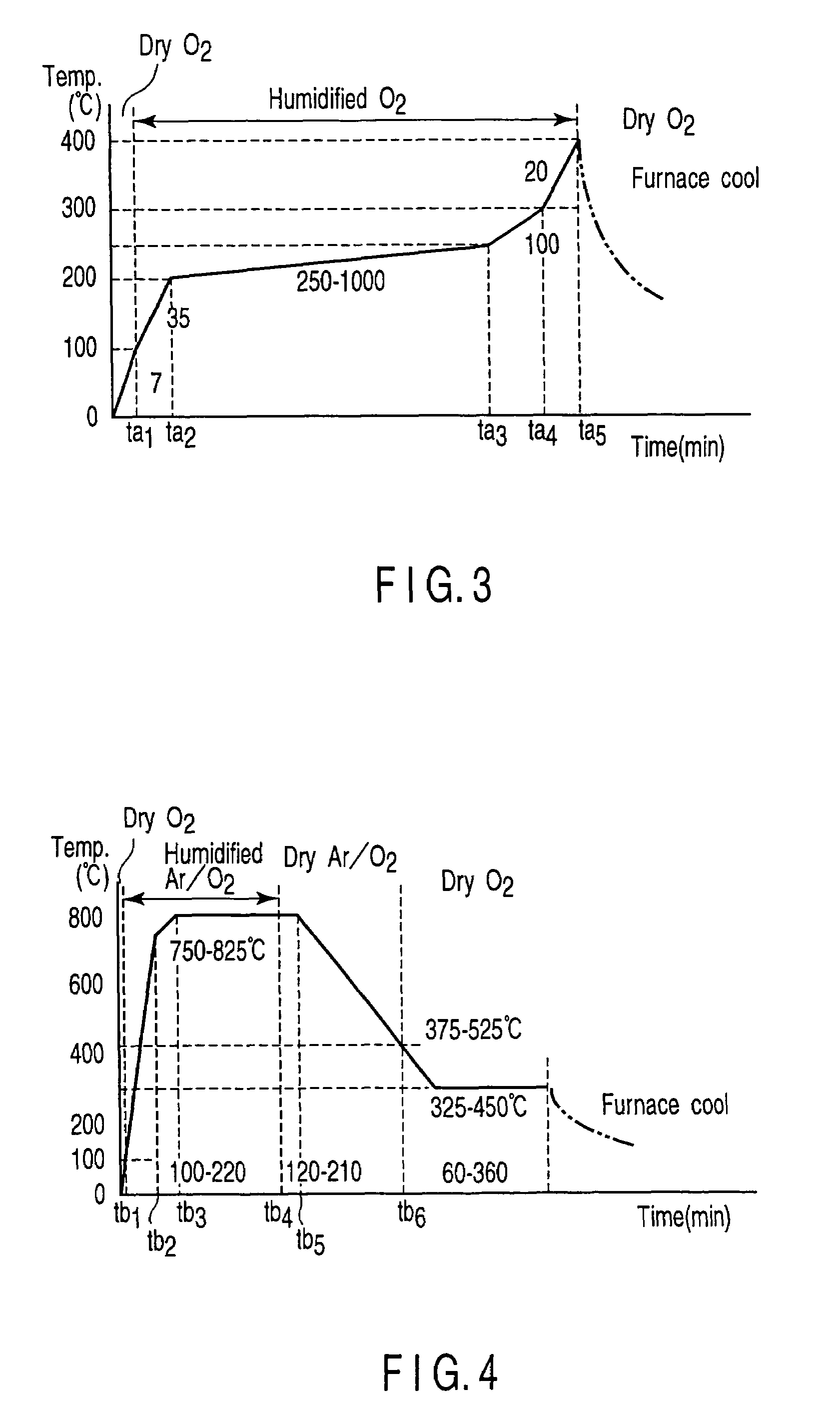
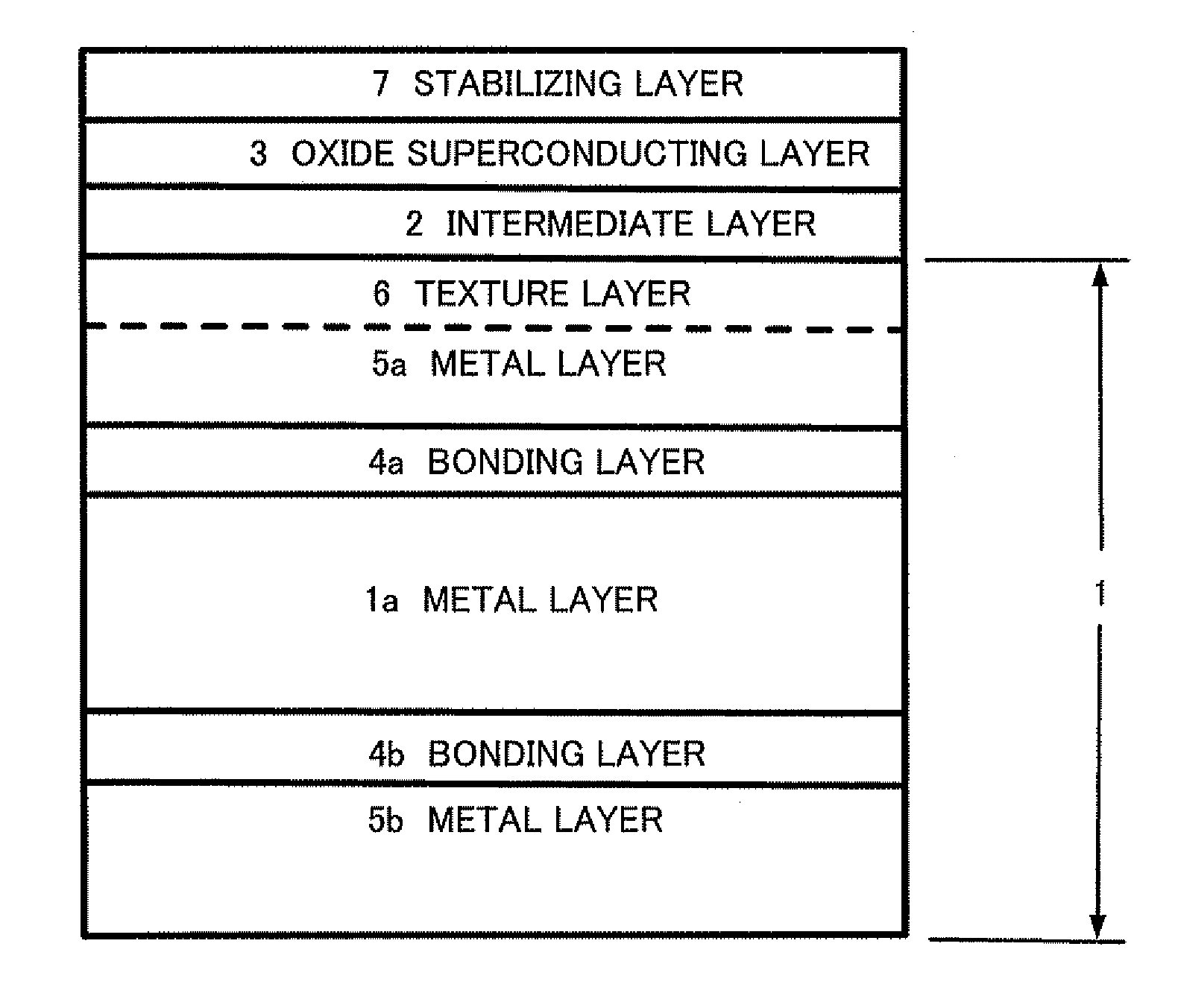
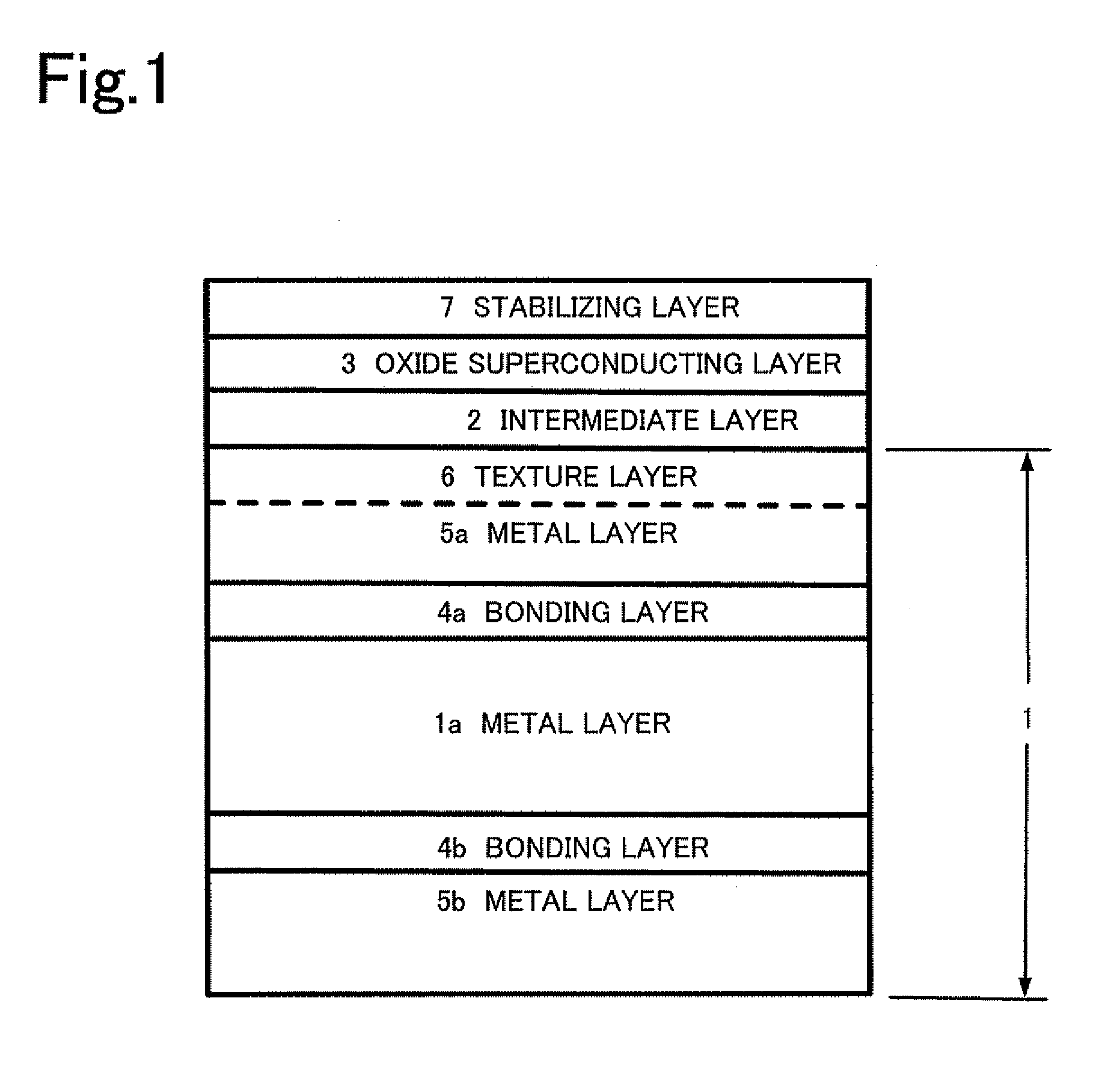
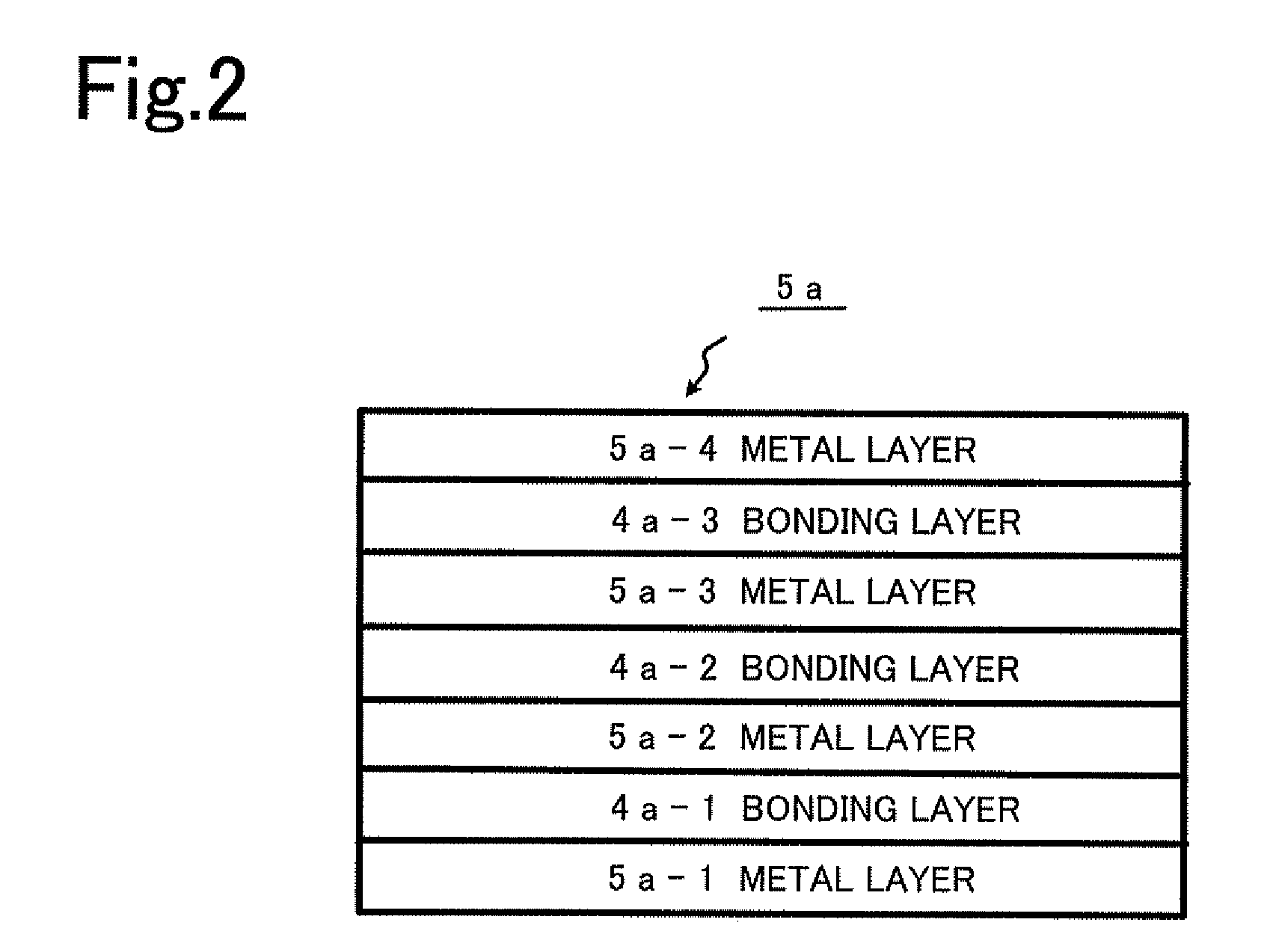
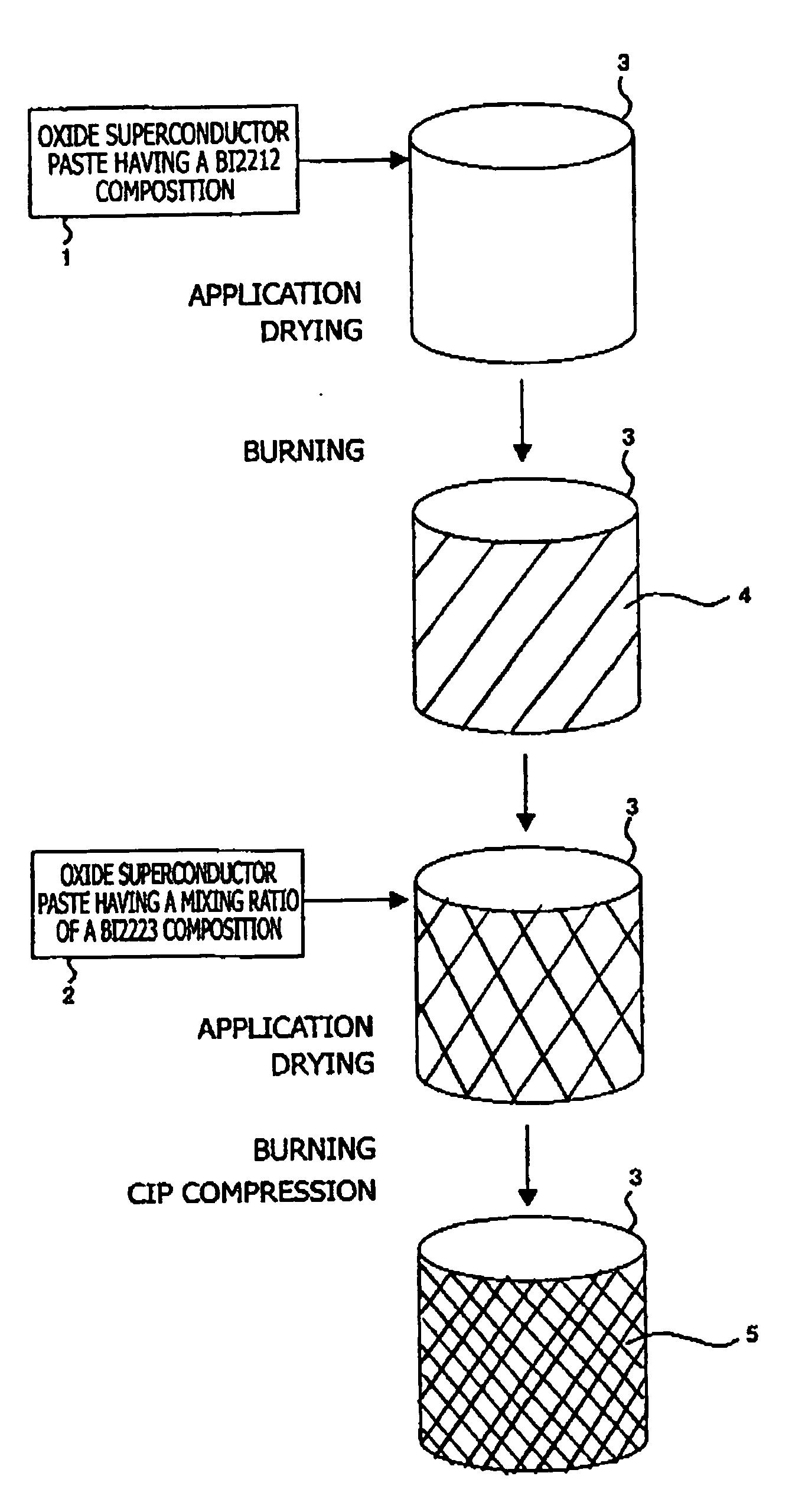
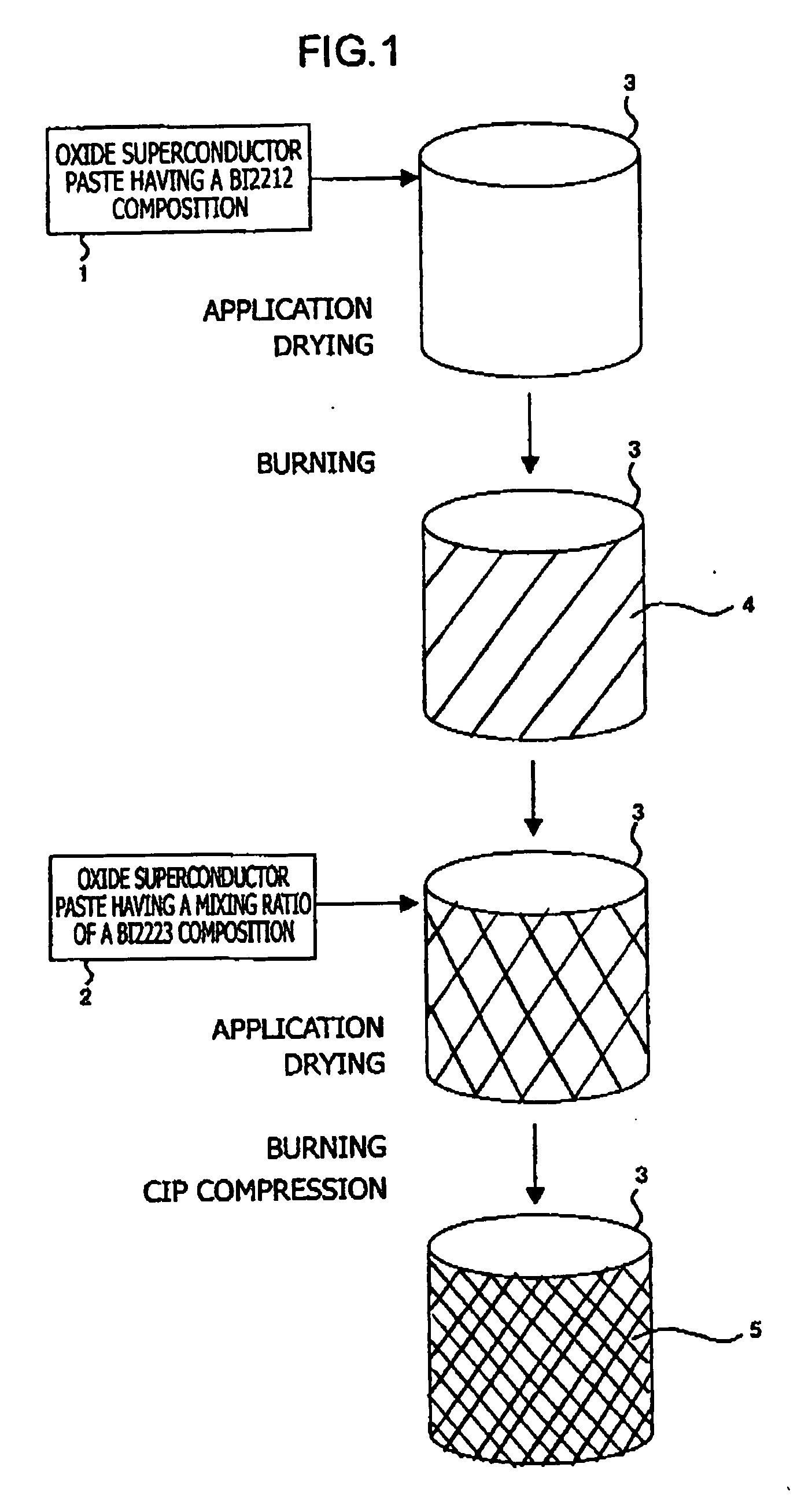
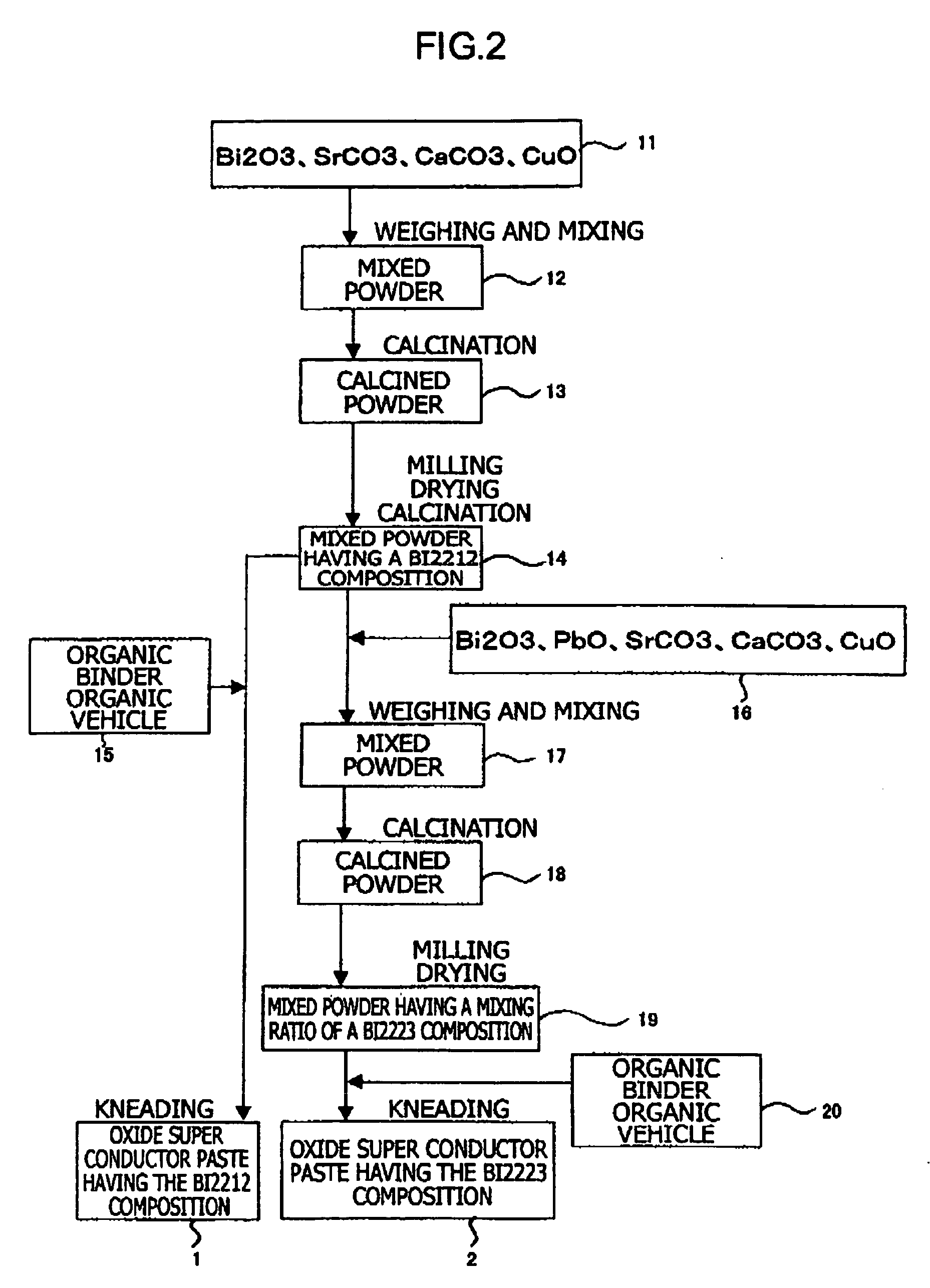
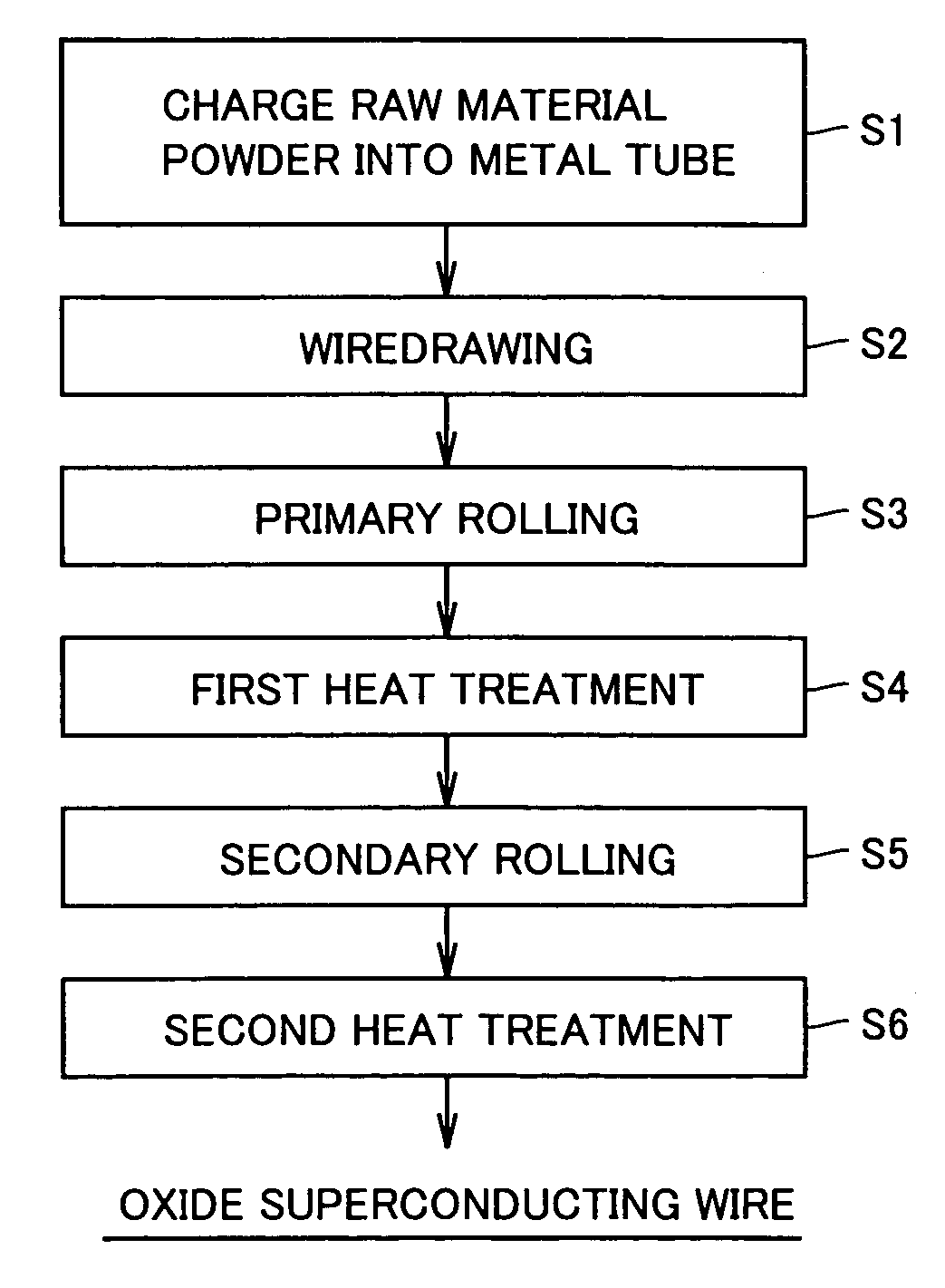
Patents
Literature
152 results about "Oxide superconductors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
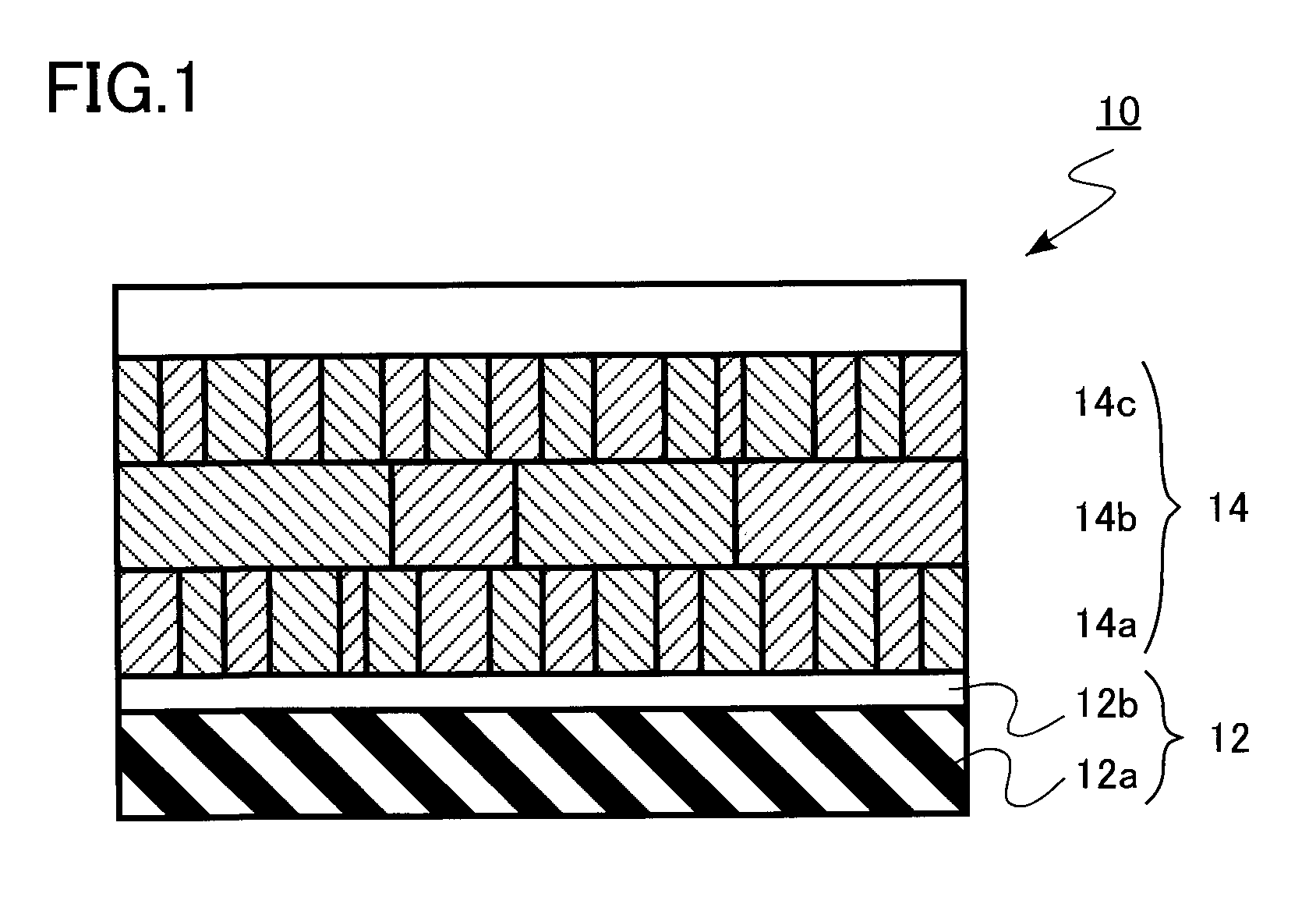
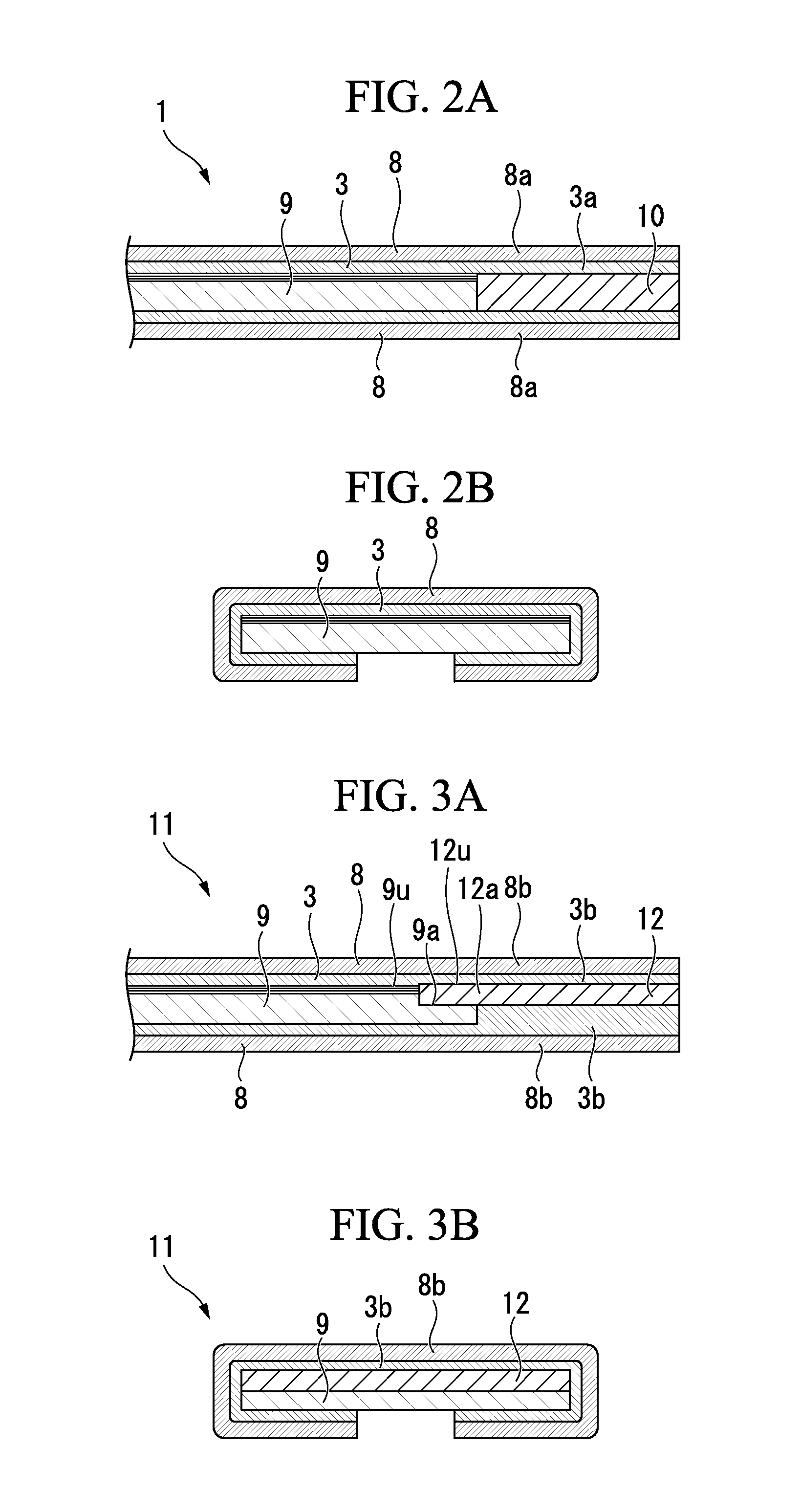
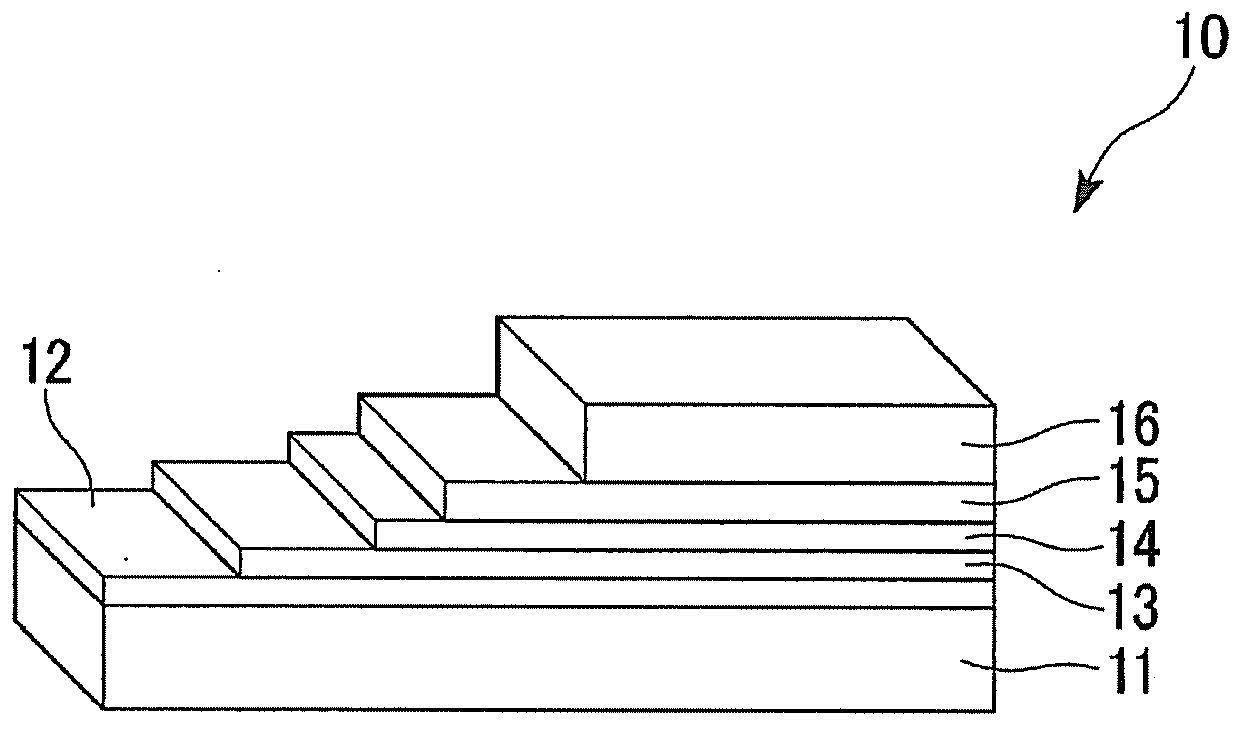
An oxide superconductor as recited in claim 3, wherein the oxide superconducting member comprises a substrate, and an oxide superconductor layer containing the oxide superconductor and coated over the substrate, the oxide superconductor layer having a thickness of about about 0.01 μm to about 2 μm.
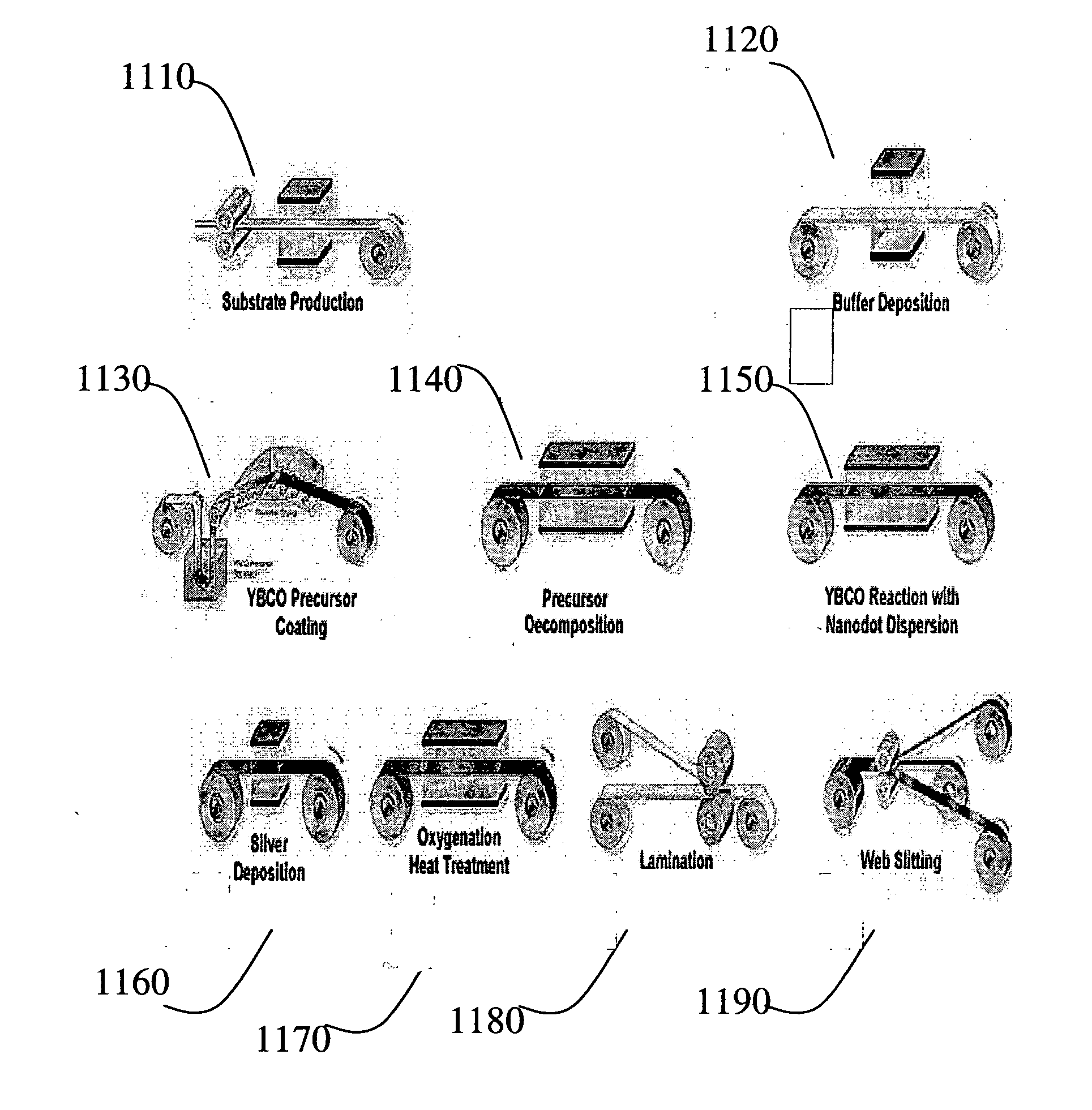
Low ac loss filamentary coated superconductors
InactiveUS20060040830A1Additive manufacturing apparatusSuperconductors/hyperconductorsOxide superconductorsPhysics
An article having low ac loss includes an elongated substrate having a length and a width; and a plurality of filaments comprising an oxide superconductor extending substantially along the length of the elongated substrate and spaced apart from one other filaments across the width of the elongated substrate, wherein at least one filament crosses over at least one other filament such that the at least one filament occupies a first position across the width of the elongated substrate before the crossover and a second position across the width of the elongated substrate after crossover.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
Stacked filamentary coated superconductors
ActiveUS20060073975A1Promote growthAdditive manufacturing apparatusSuperconductor detailsMaterials scienceSecondary layer
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
Thick superconductor films with improved performance
ActiveUS20060094603A1Reduce metal contentLow costLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentRare-earth elementAlkaline earth metal
A method for producing a thick film includes disposing a precursor solution onto a substrate to form a precursor film. The precursor solution contains precursor components to a rare-earth / alkaline-earth-metal / transition-metal oxide including a salt of a rare earth element, a salt of an alkaline earth metal, and a salt of a transition metal in one or more solvents, wherein at least one of the salts is a fluoride-containing salt, and wherein the ratio of the transition metal to the alkaline earth metal is greater than 1.5. The precursor solution is treated to form a rare earth-alkaline earth-metal transition metal oxide superconductor film having a thickness greater than 0.8 μm. precursor solution.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
Dropwise deposition of a patterned oxide superconductor
InactiveUS20060040829A1Reduce AC-lossReduced ac lossesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsVacuum evaporation coatingElectrical conductorReaction zone
An oxide superconductor article having an oxide superconductor layer of a predetermined pattern is prepared by continuously advancing a wire having a textured surface into a deposition zone, dispensing droplets of a precursor solution to an oxide superconductor from a reservoir and the depositing droplets onto the textured surface of the wire that is introduced into the deposition zone, heating the wire or tape in the reaction zone under conditions to convert the precursor solution into an oxide superconductor; and collecting the wire after heating.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
Low Alternating-Current Loss Oxide Superconductor and Fabricating Method Thereof
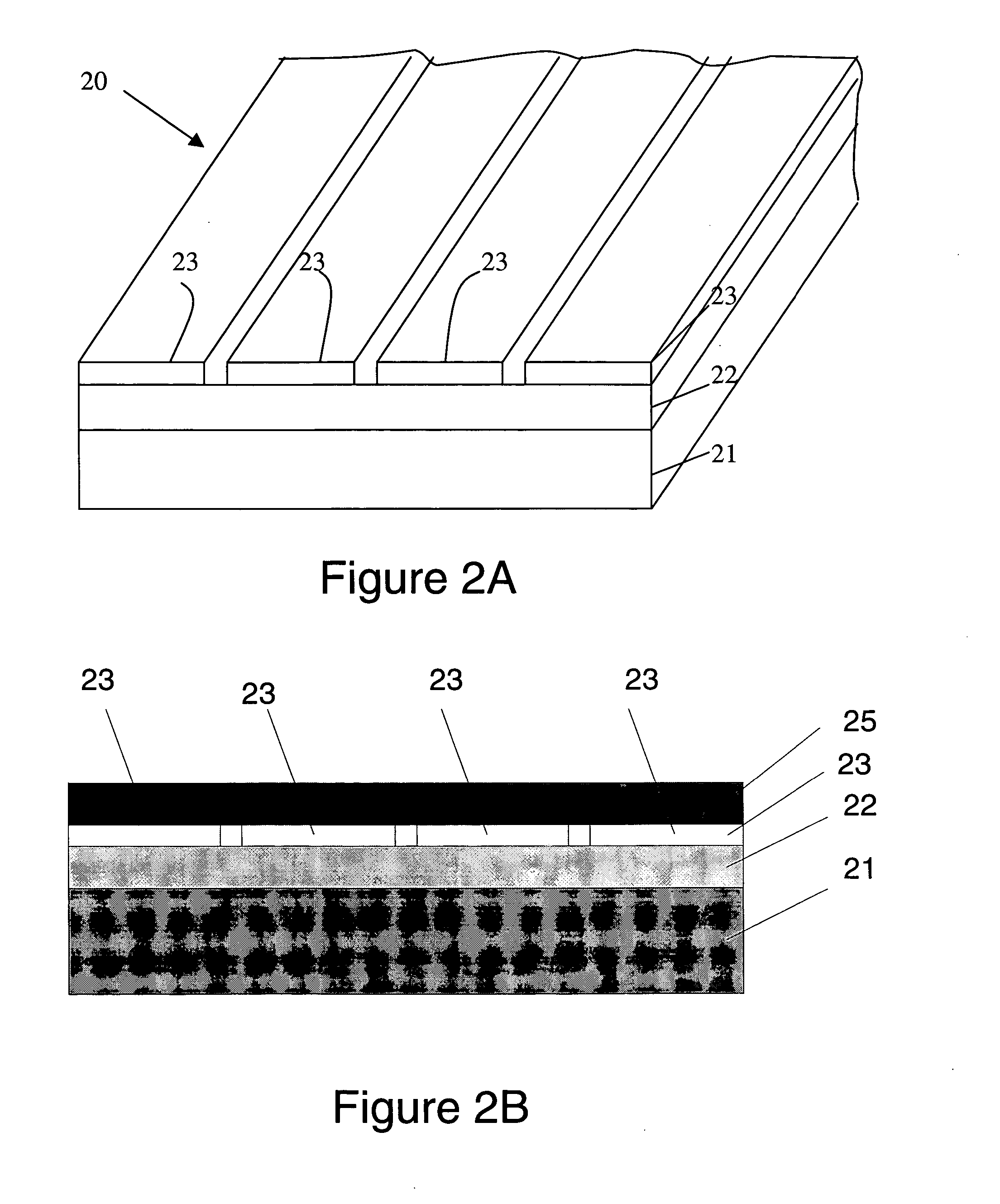
InactiveUS20070145100A1Reduce widthReduce lost timeCooking-vessel materialsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
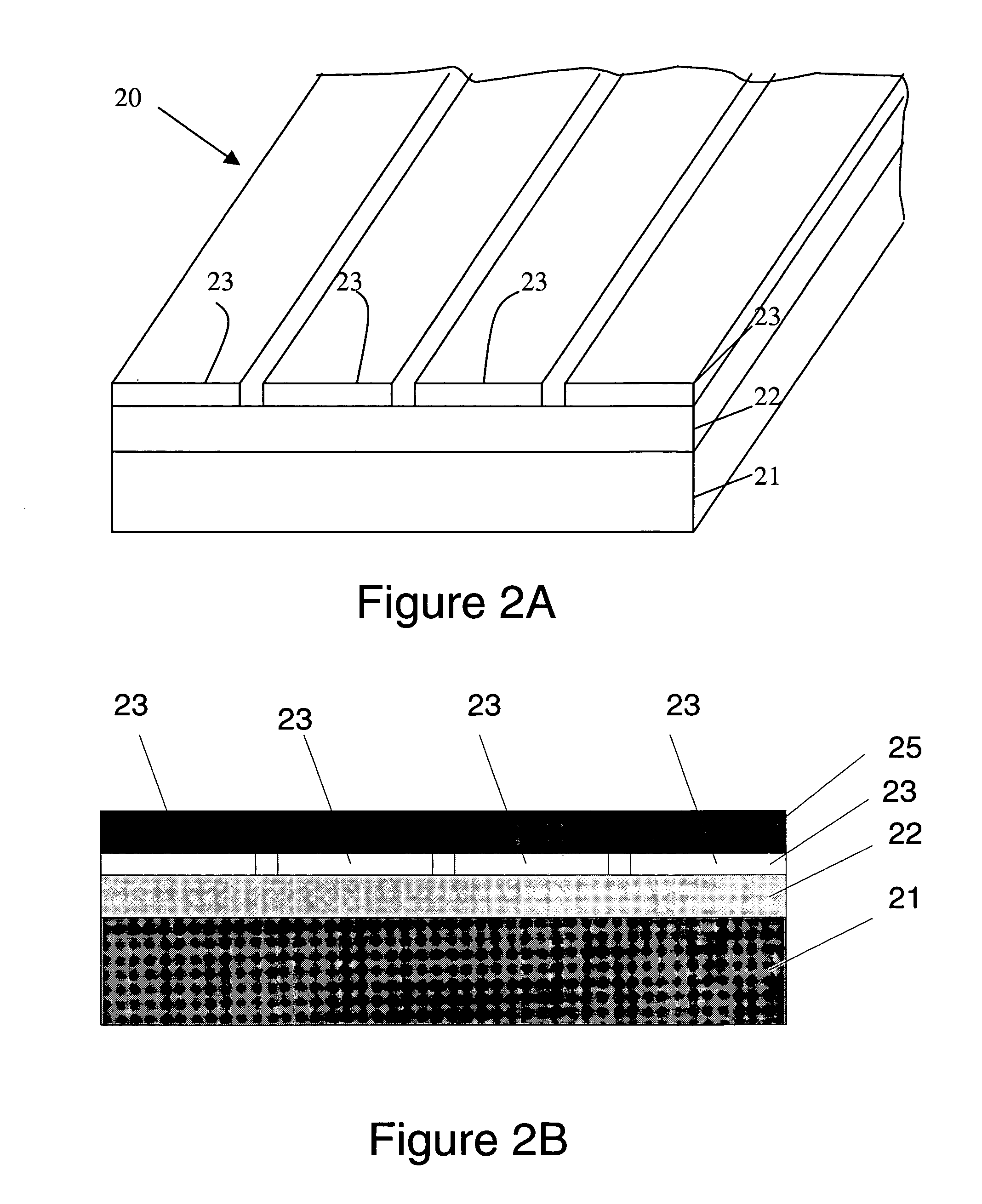
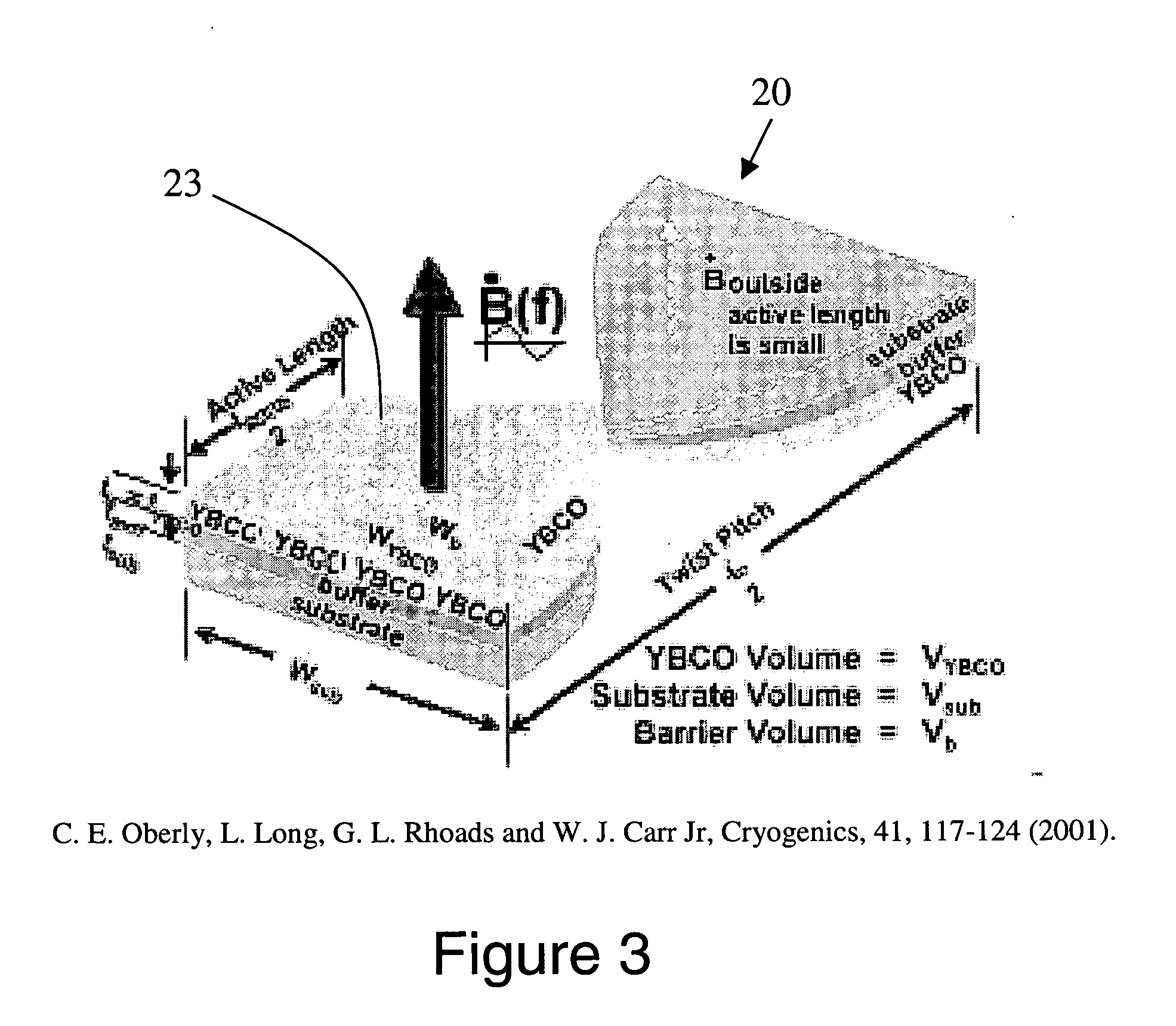
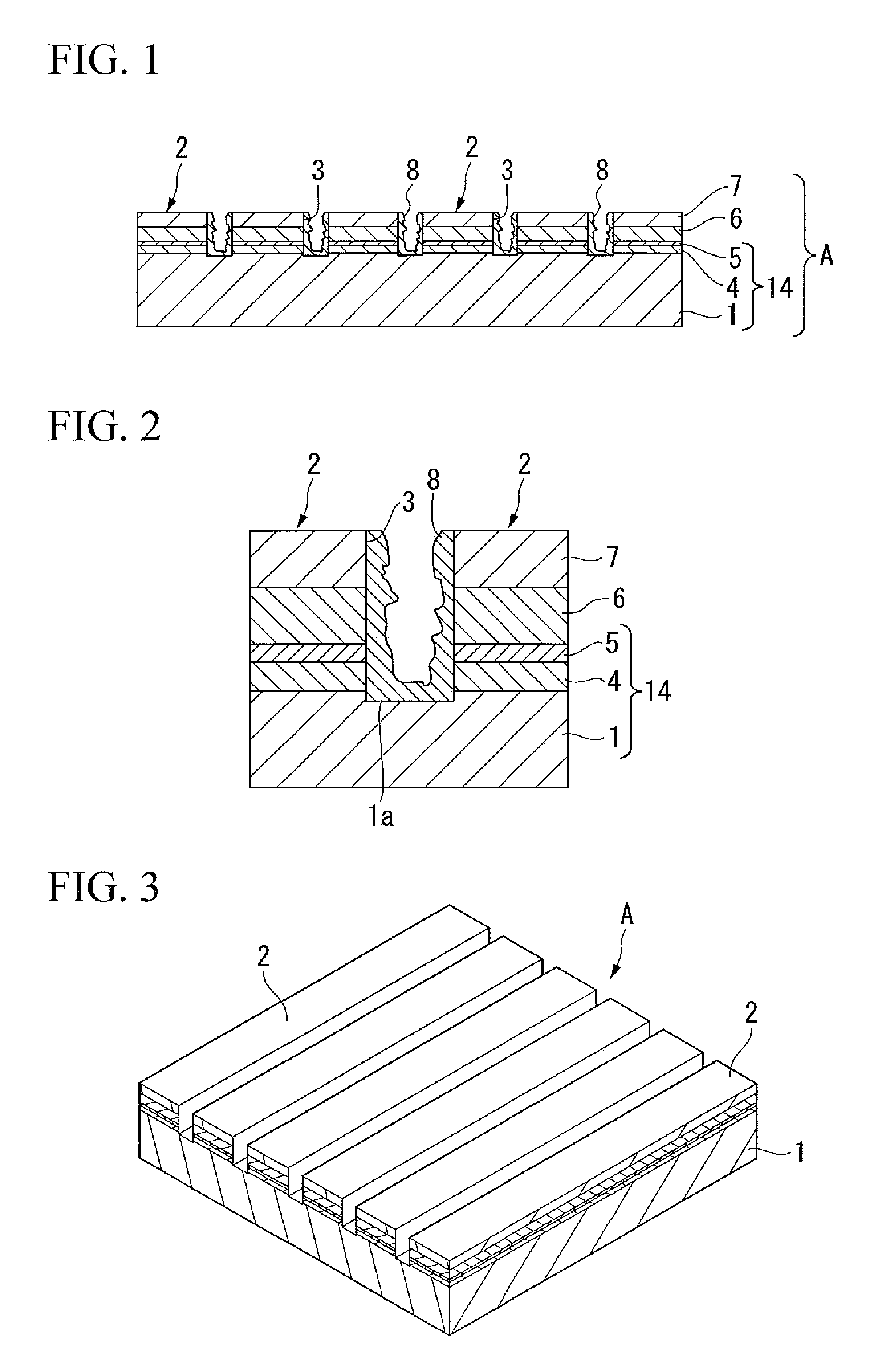
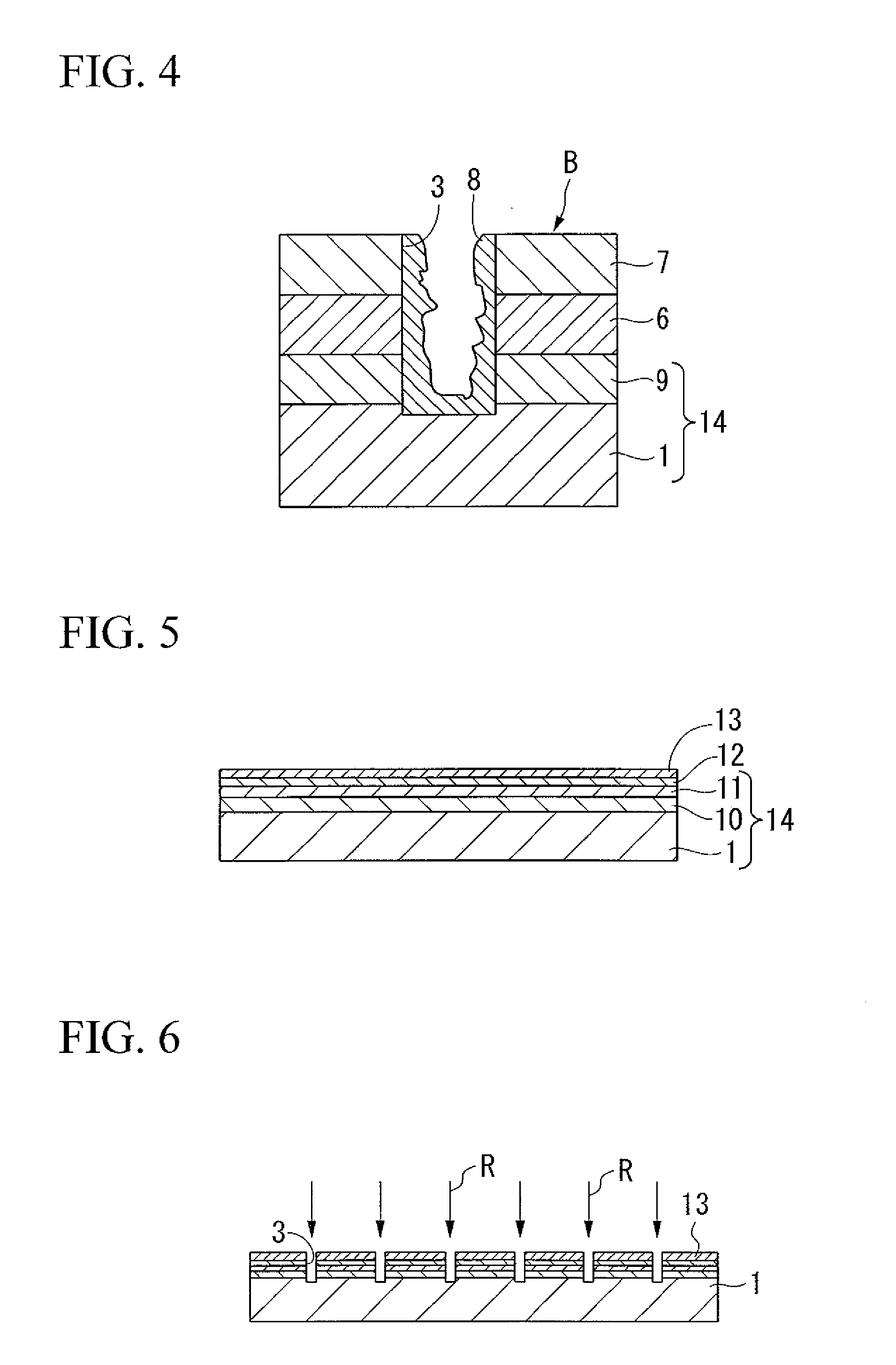
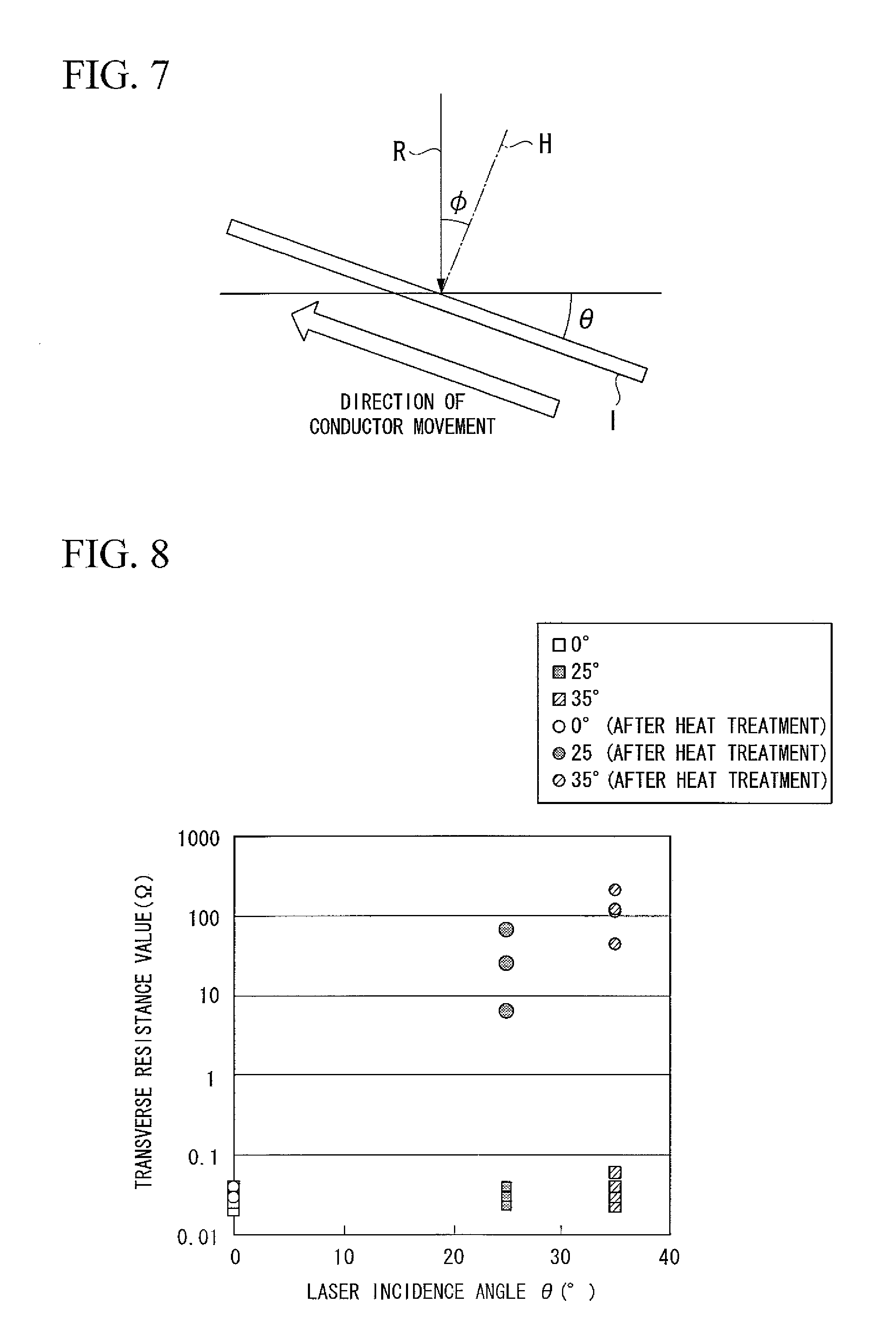
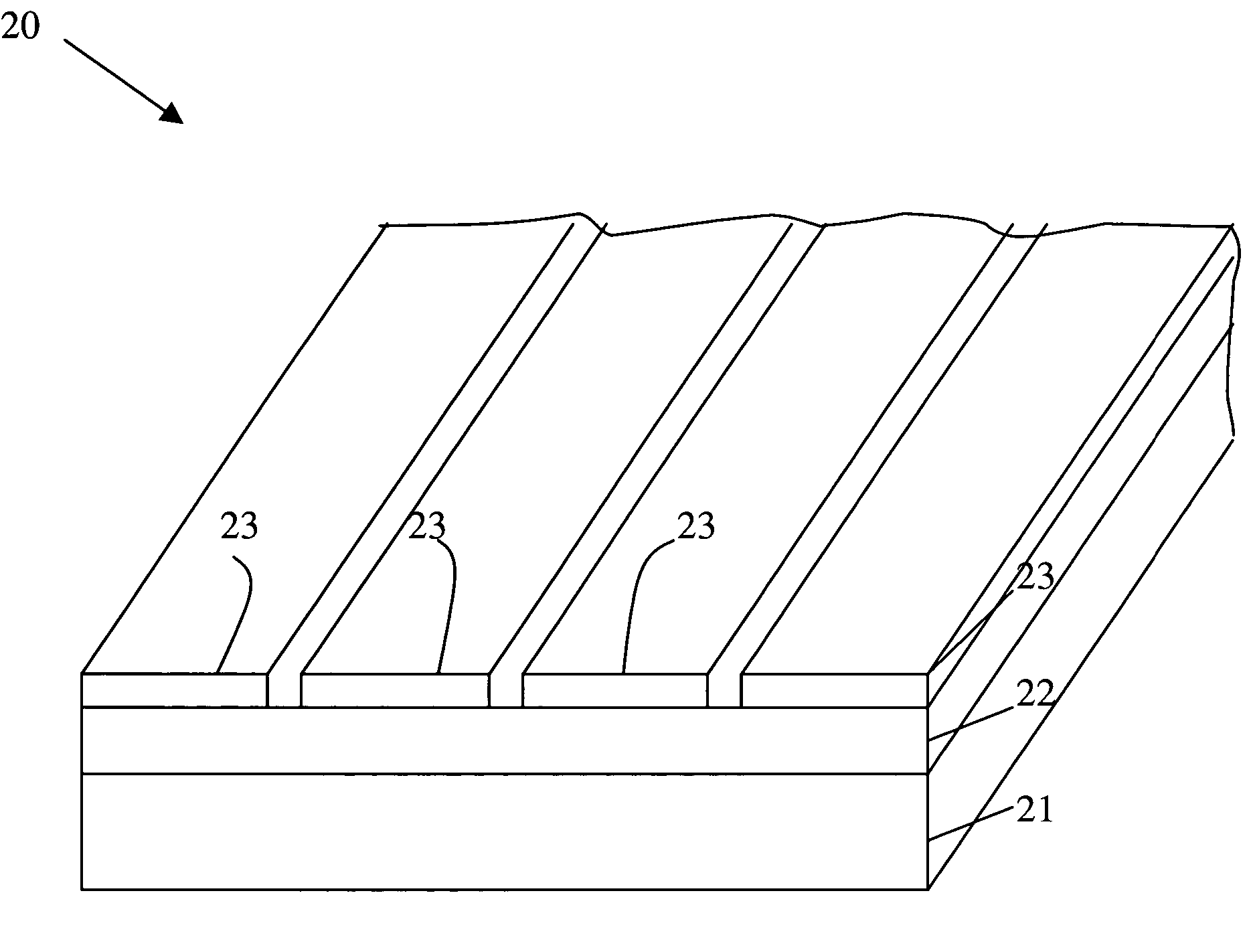
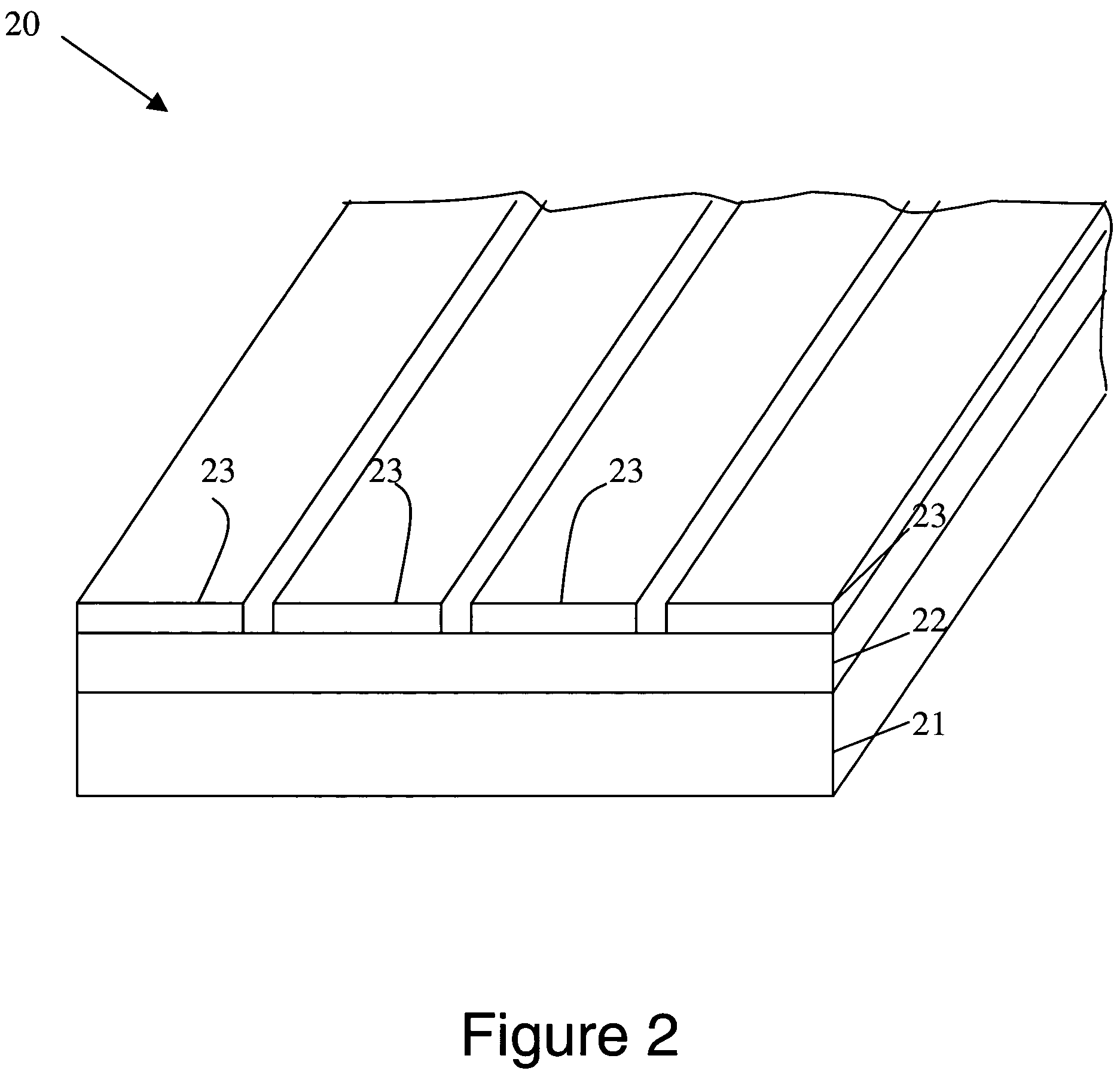
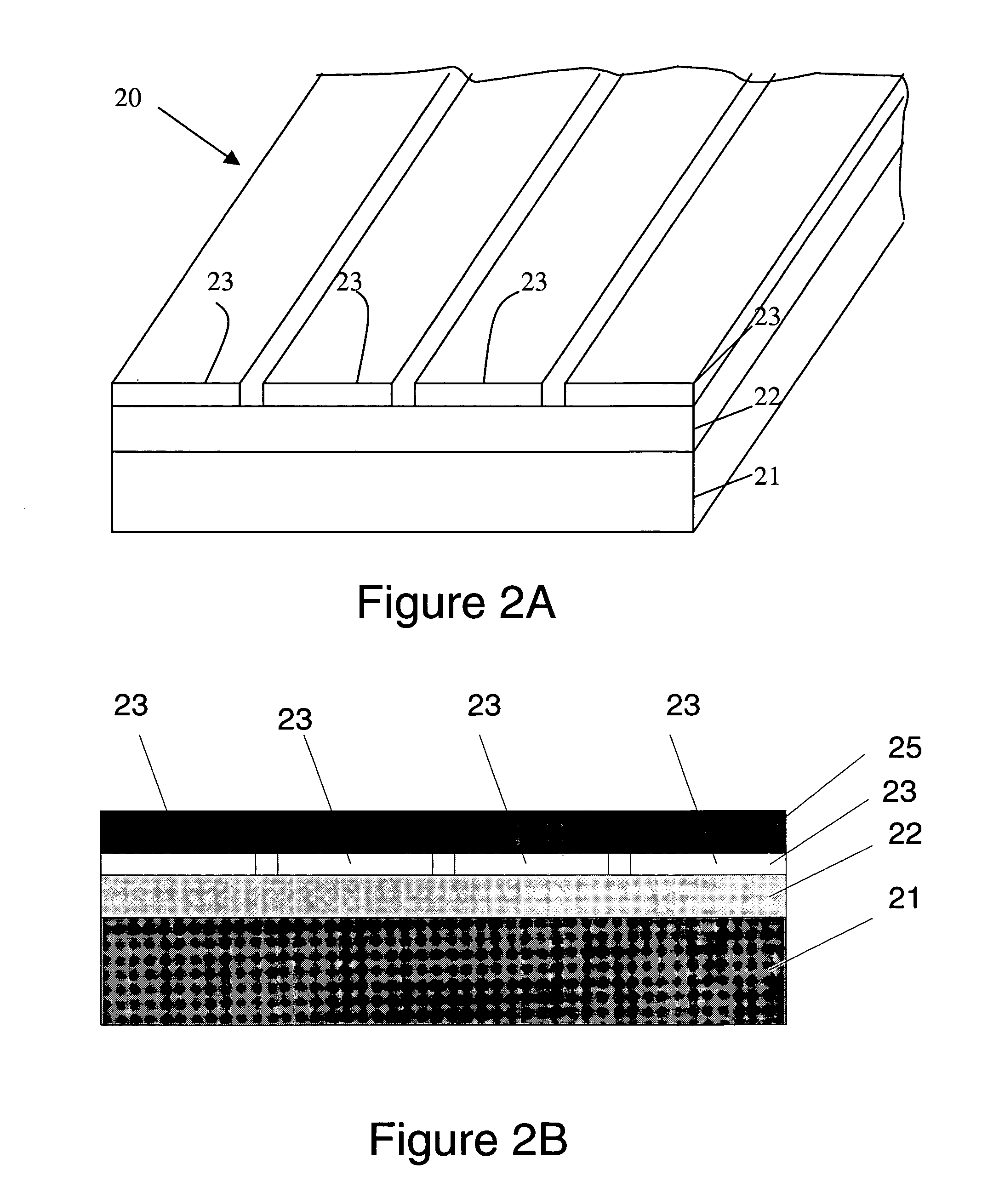
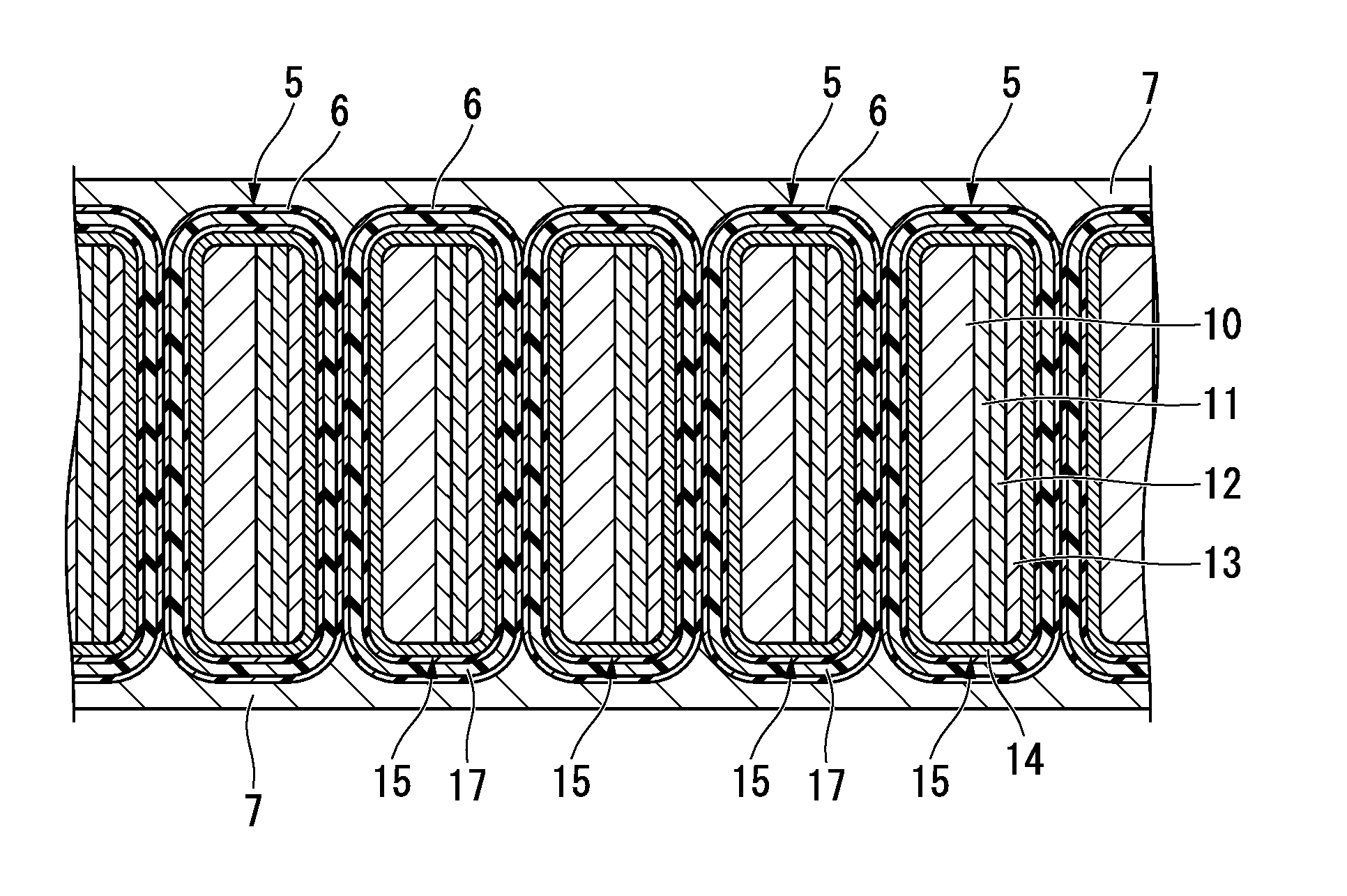
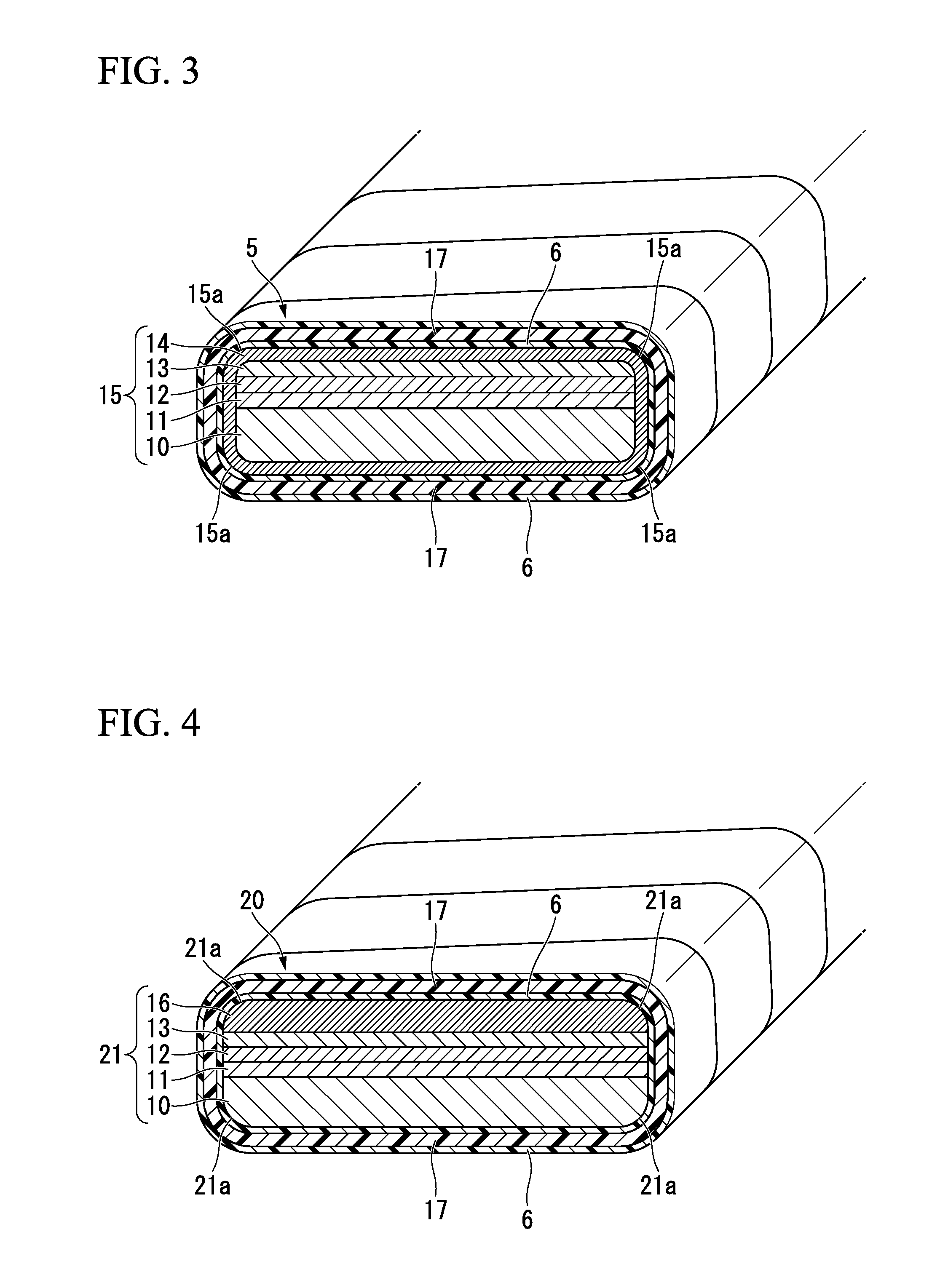
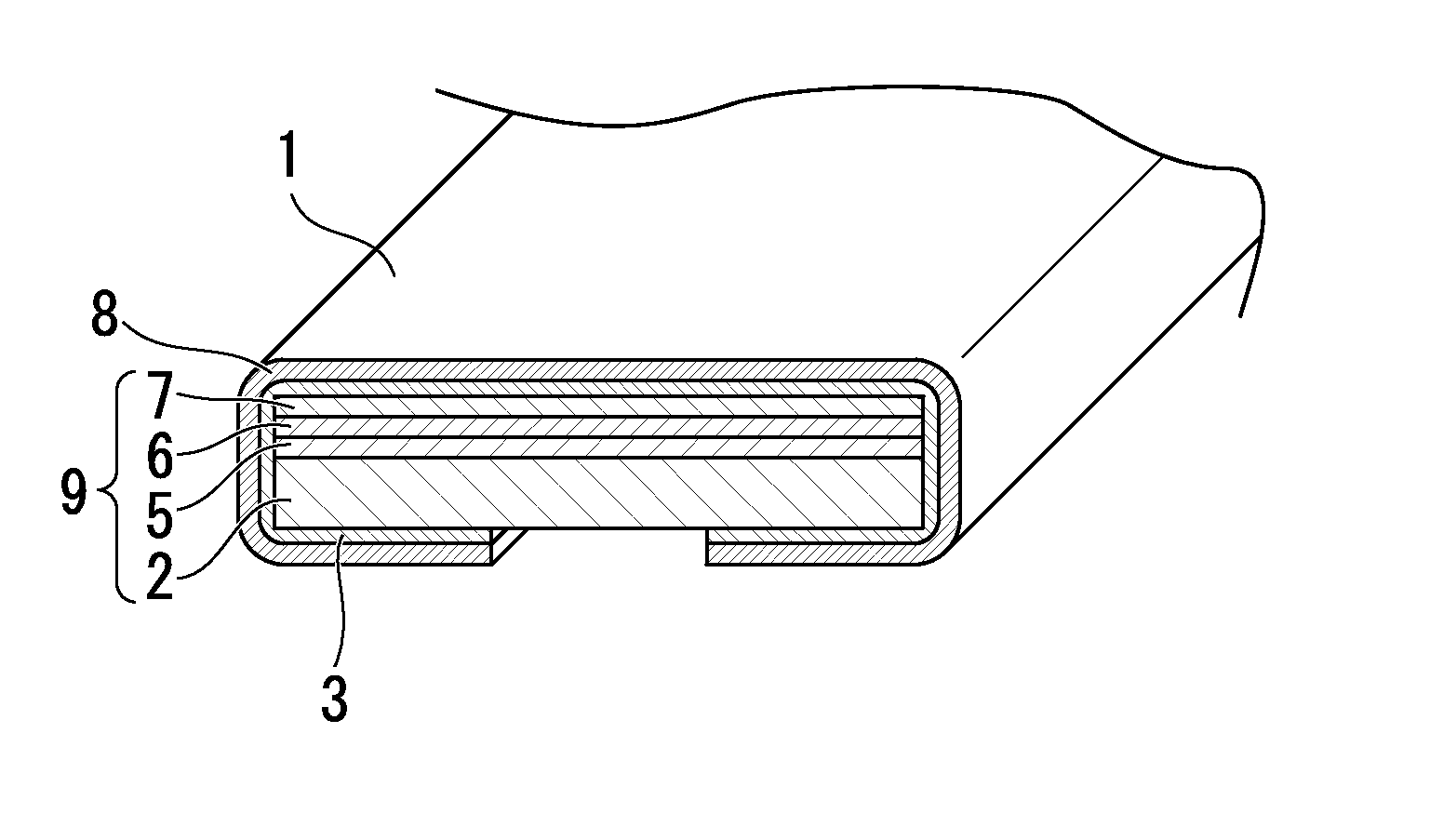
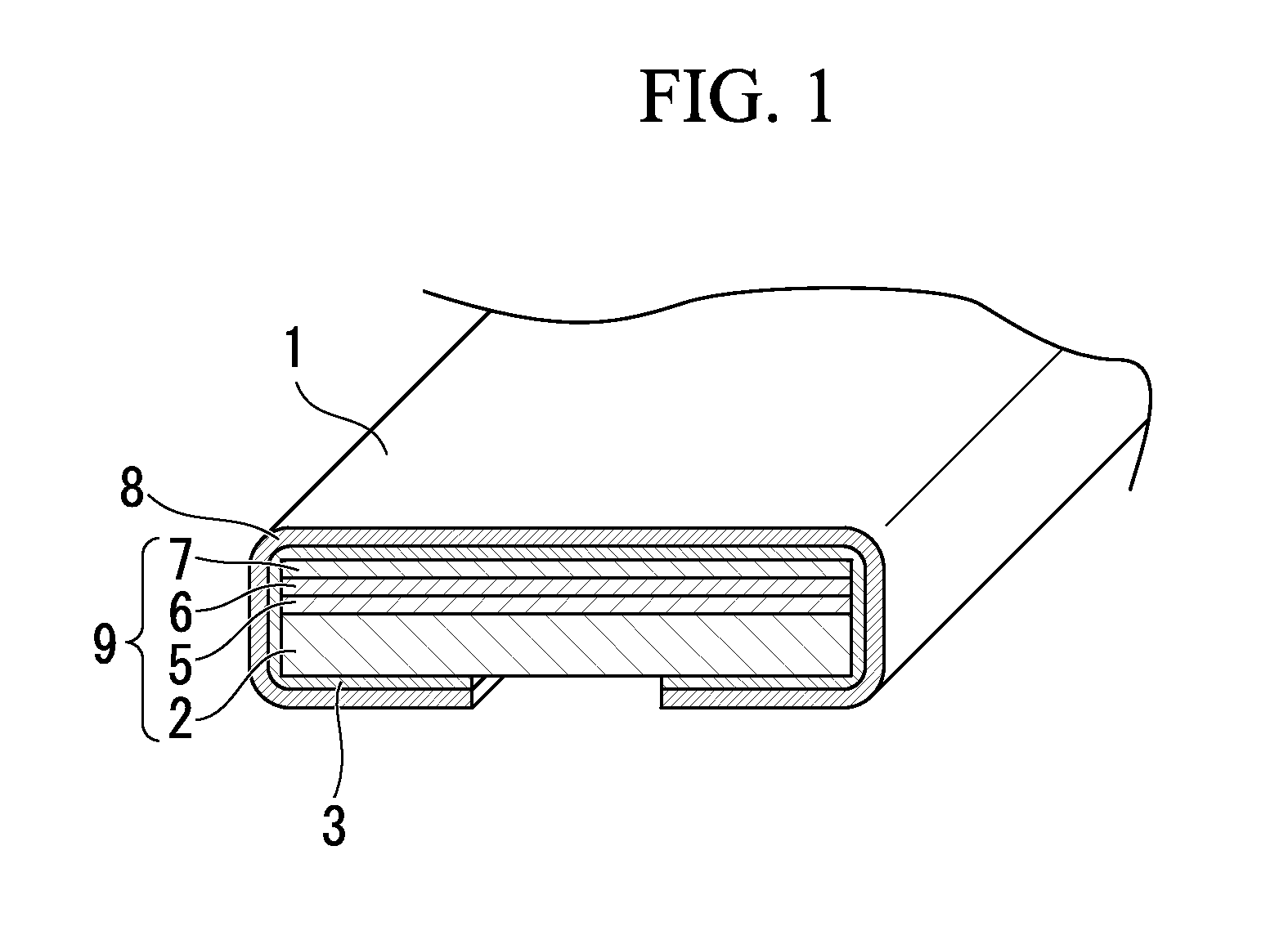
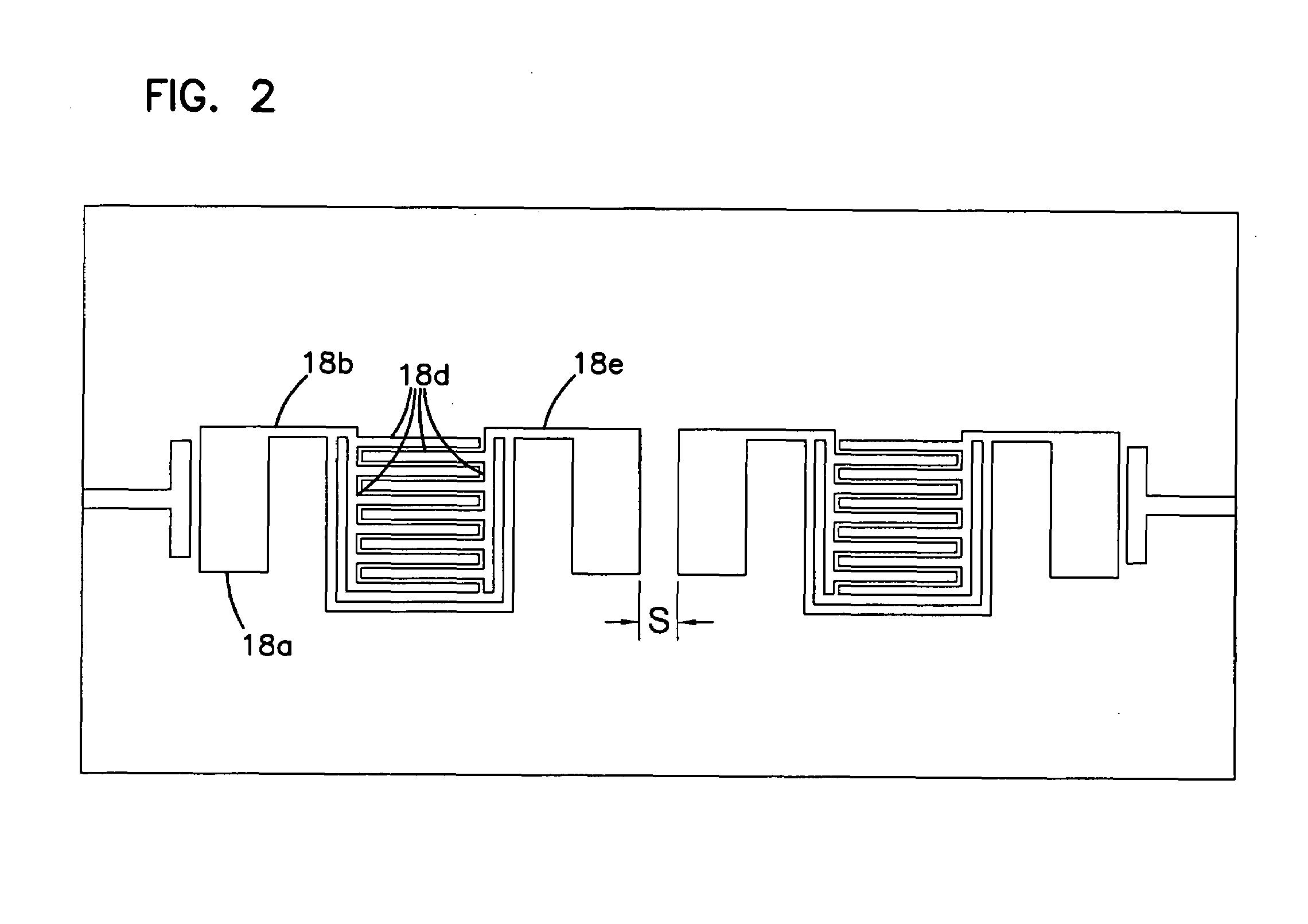
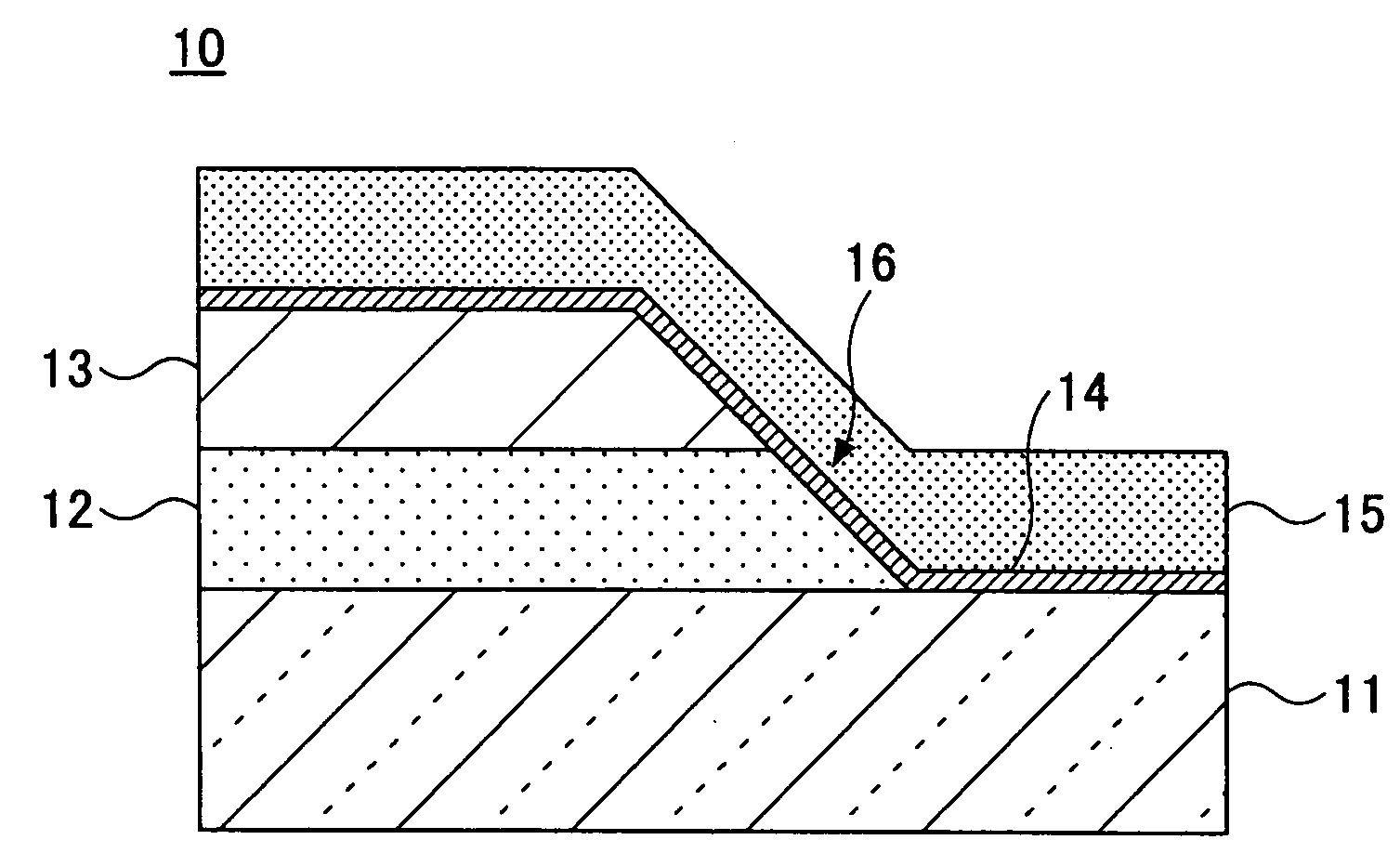
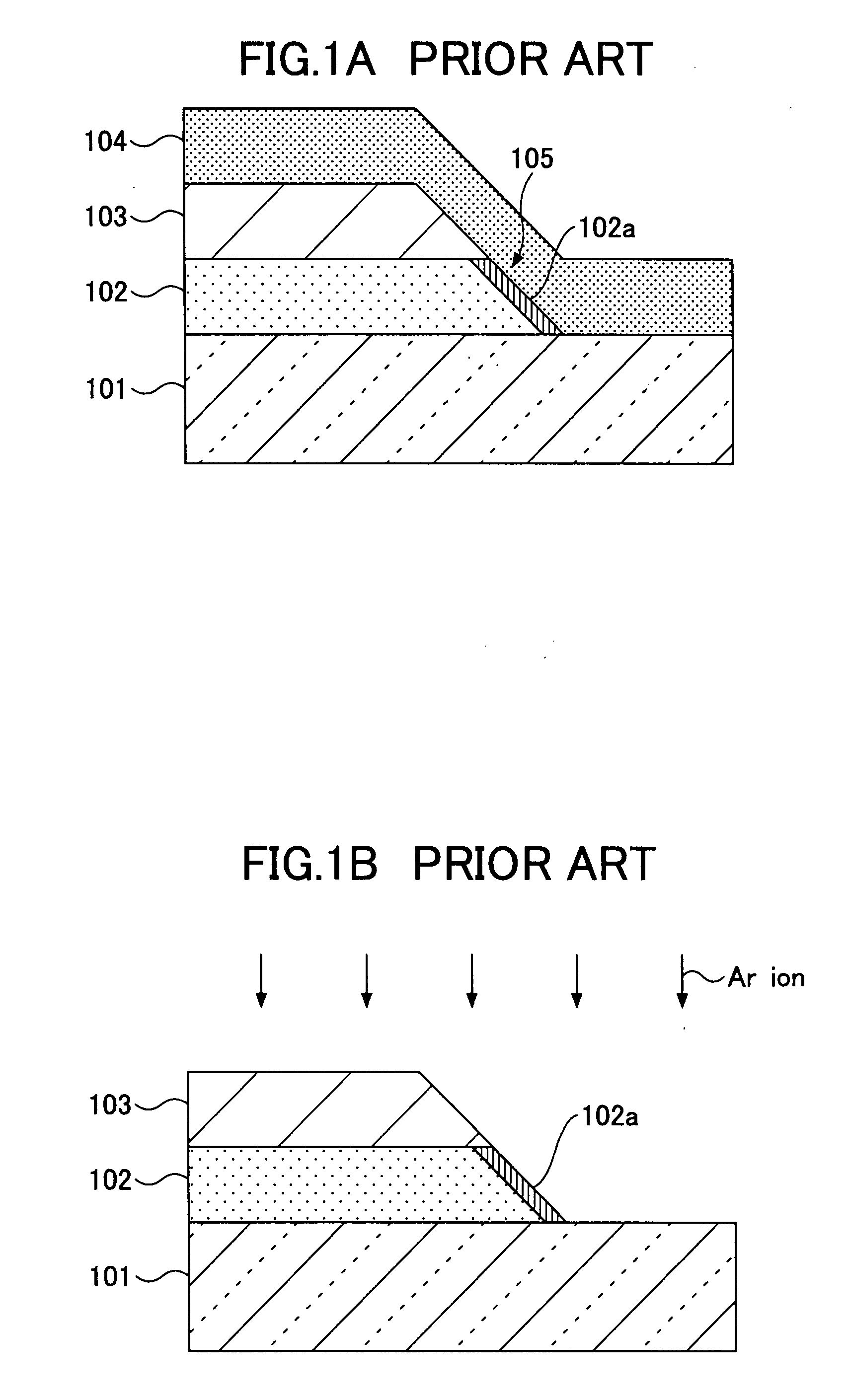
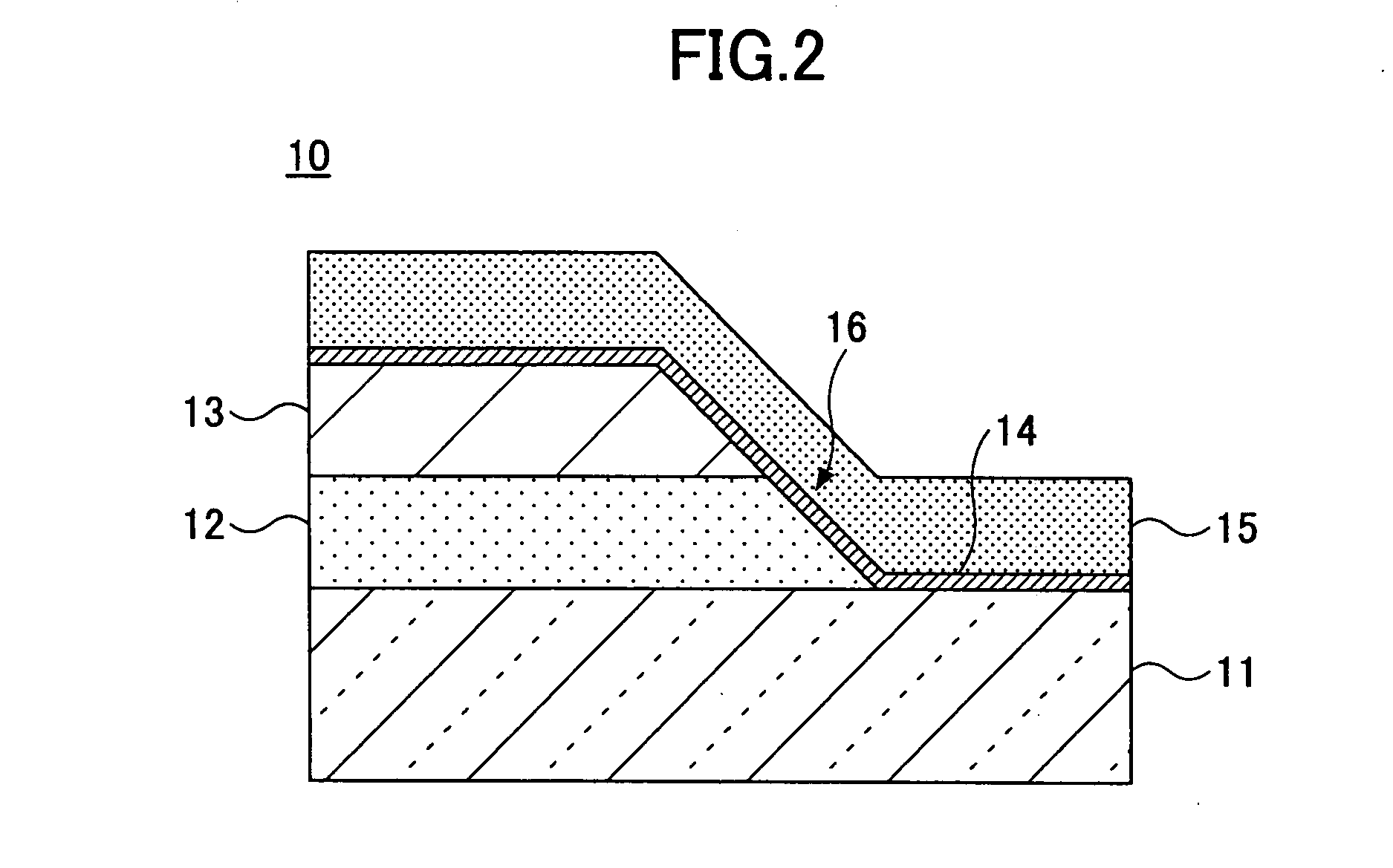
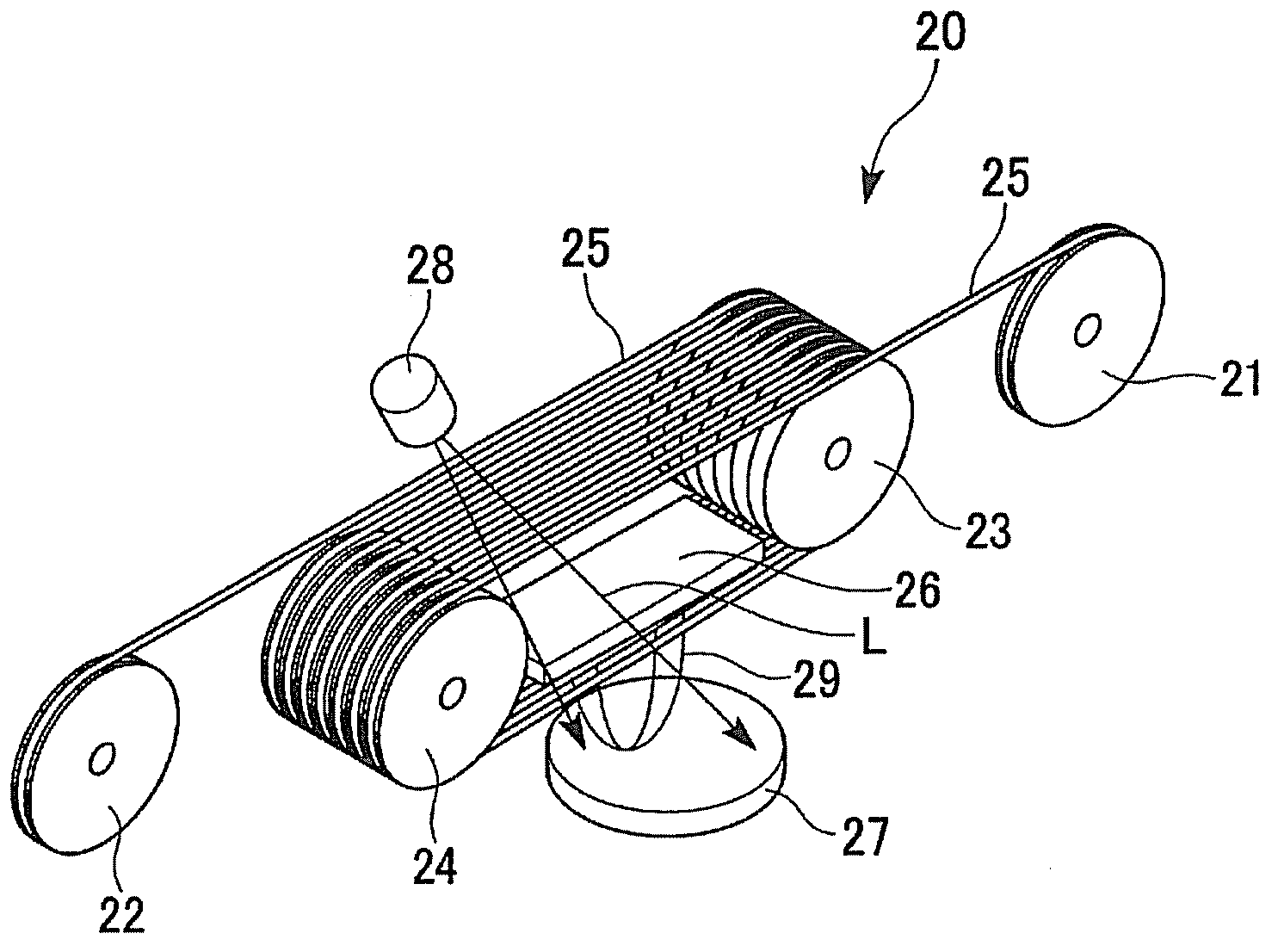
The present invention is configured such that, in a low AC loss oxide superconductor constituted by providing an oxide superconducting layer 6 on a substrate 1, said oxide superconducting layer 6 is separated into a plurality of filament conductors 2 in parallel to the lengthwise direction of said substrate 1 by dividing grooves 3 plurally formed in the widthwise direction of said substrate, and a high-resistance oxide 8 is formed in said dividing grooves 3. Because of the invention, it is possible to increase the insulation properties of individually divided mated filament conductors, and to obtain an oxide superconductor that has low AC loss.
Owner:RAILWAY TECH RES INST +2
Oxide superconductor and method of fabricating same
ActiveUS20090247413A1High crystallinitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsElectrical conductorHigh density
An oxide superconductor with superconduction properties being improved by effectively introducing a pinning center thereinto and its fabrication method are disclosed. The superconductor has a high-crystallinity oxide superconductor film which is formed on a substrate with a <001> direction of crystal grain being oriented almost perpendicularly to the substrate and with (100) planes of neighboring crystal grains being oriented to form an oblique angle ranging from 0 to 4 degrees or 86 to 90 degrees. The film has a multilayer structure including a plurality of high-density magnetic field trap layers stacked in almost parallel to the substrate and a low-density magnetic field trap layer sandwiched therebetween. An average grain boundary width of the high-density trap layers in a cross-section horizontal to the substrate is 80 nm or less. The width is less than an average grain boundary width of the low-density trap layer in its cross-section horizontal to the substrate.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Oxide superconductor and method of preparing the same
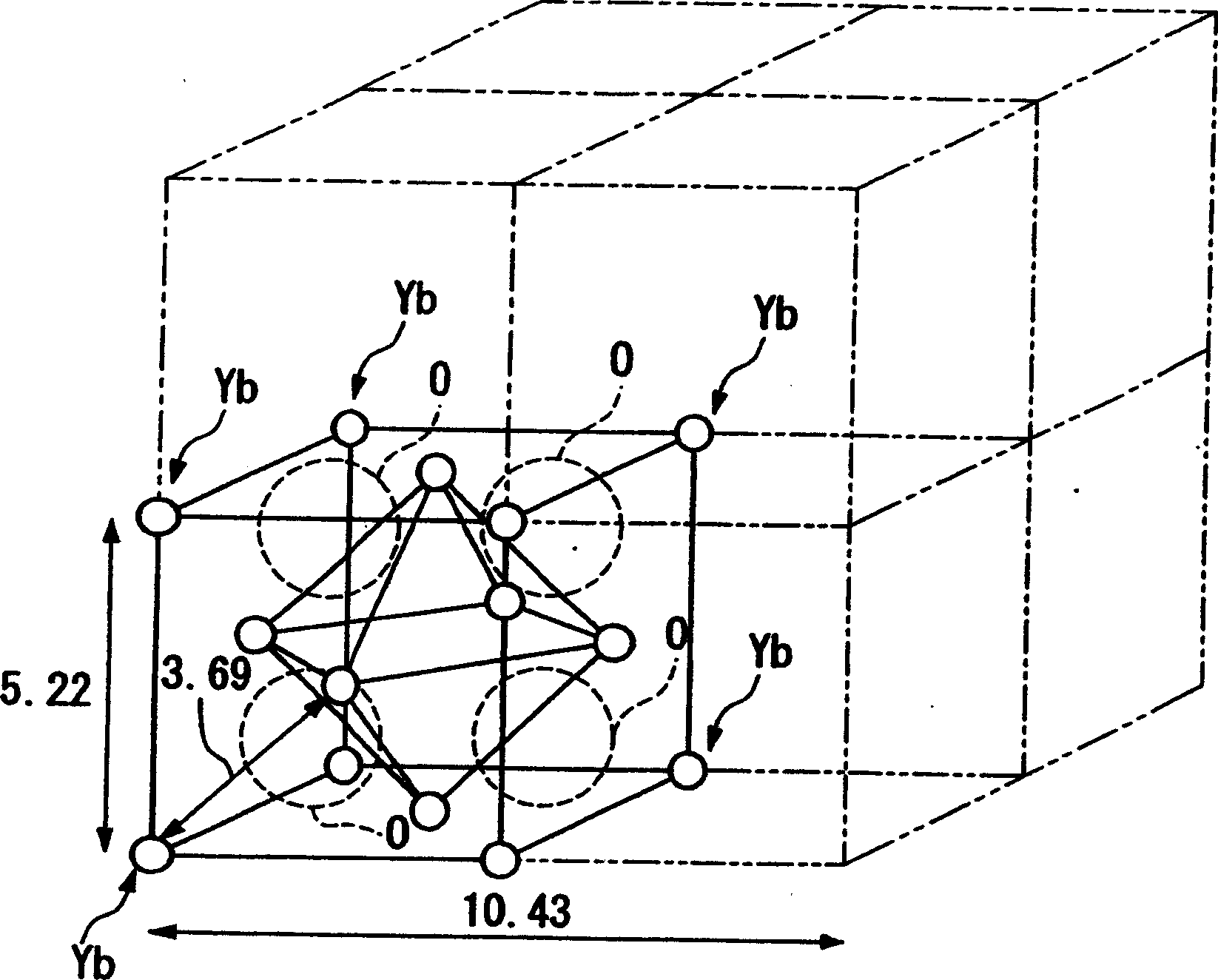
An oxide superconductor includes a main component represented by the following formula: LnBa2Cu3O7-x, where Ln comprises two or more types of elements selected from the group consisting of Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, and Y, and a content of each element is 10 to 90 mol %, and fluorine at a molar ratio of 10−2 to 10−6 with respect to copper.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Rare earth-type tape-shaped oxide superconductor and a composite substrate used for the same
InactiveUS20100099573A1Avoid deformationHigh mechanical strengthSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentComposite substrateBonding process
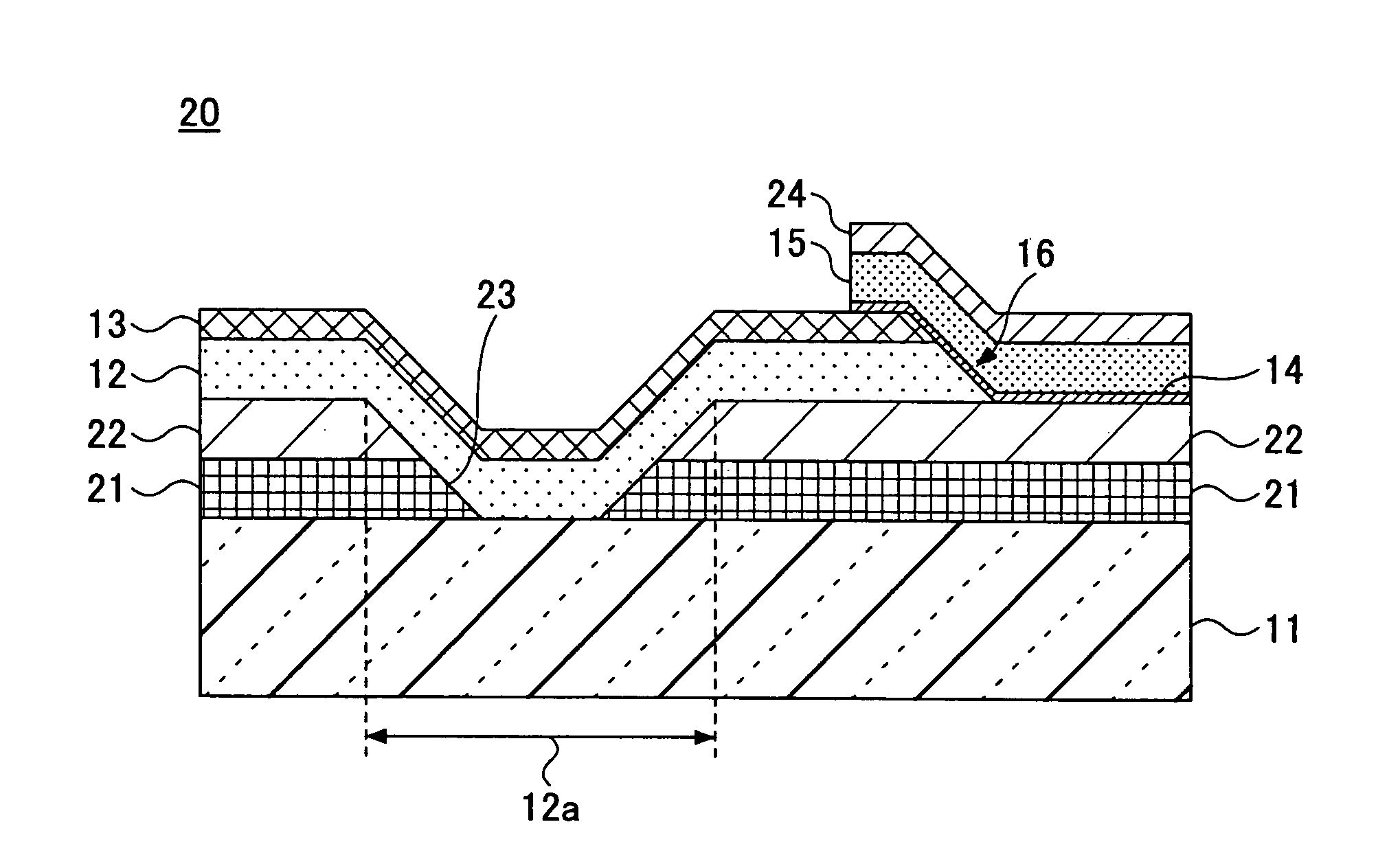
This invention provides a rare earth-type tape-shaped oxide superconductor having excellent mechanical strength and superconducting properties and a composite substrate using for the same. Non-oriented and non-magnetic Ni-9 at % W alloy tapes (11, 21) were bonded onto both sides of a non-oriented and non-magnetic hastelloy tape (100) by a normal temperature bonding process, and an Ni-3 at % W alloy tape (12) having a cubic texture was bonded onto the surface of the tape (11) by a normal temperature bonding process. Thereafter, the heat-treatment was given in a reducing atmosphere and a bonding layer (50a) etc. was formed on the adhesive interface of each layer. Next, a (Ce, Gd) O2 intermediate layer (13) and a Ce2Zr2O7 intermediate layer (14) by an MOD process, a CeO2 intermediate layer (15), a YBCO superconducting film (16) by a TFA-MOD method, and a silver stabilization layer (17) were stacked sequentially on the surface of the tape (12). A critical current value (Ic) of this superconductor showed 150 A.
Owner:SHOWA ELECTRIC WIRE & CABLE CO
Re123-based oxide superconductor and method of production of same
InactiveUS20110009273A1Good reproducibilitySuperior critical current characteristicVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingMethods of productionLaser
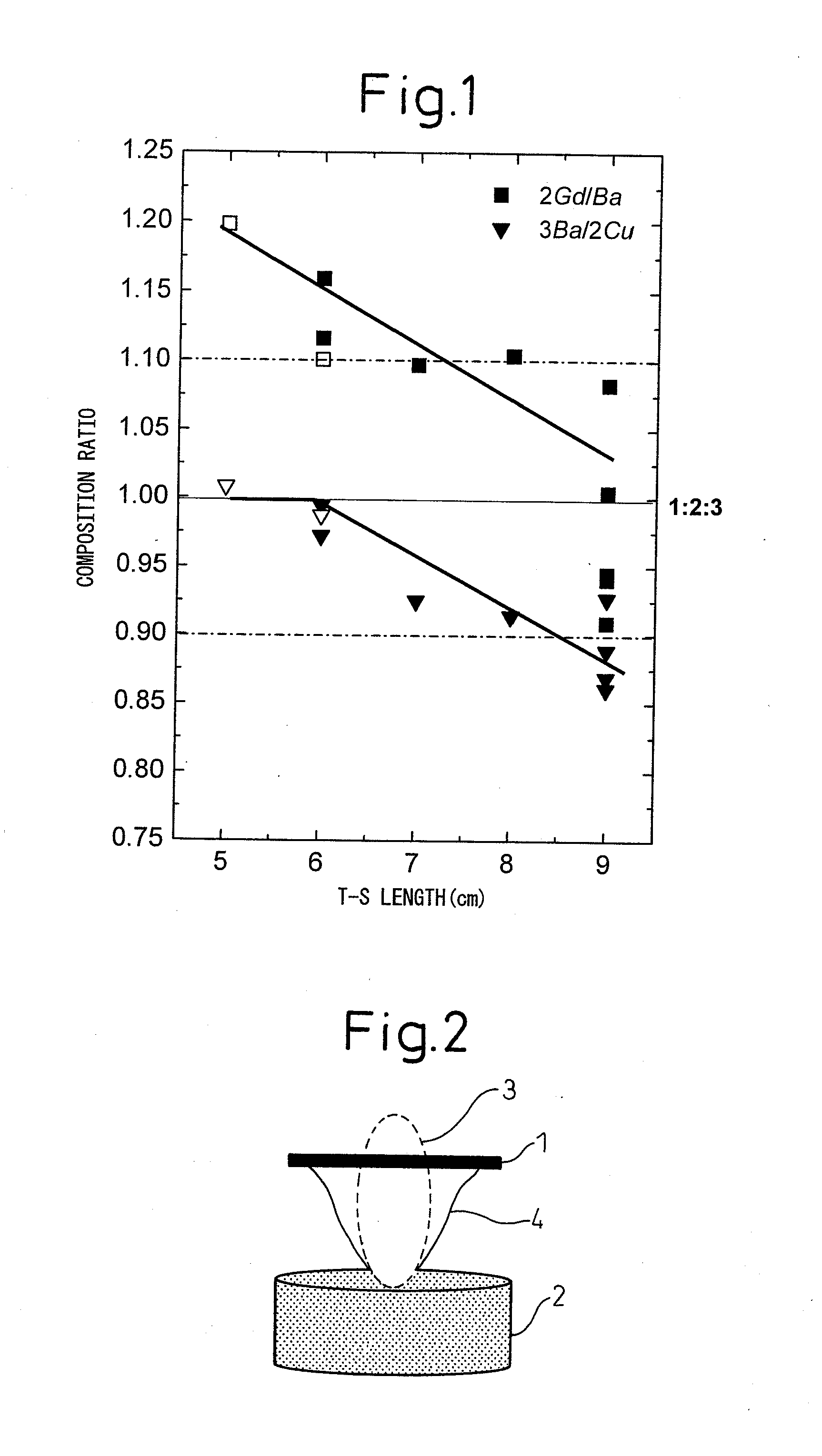
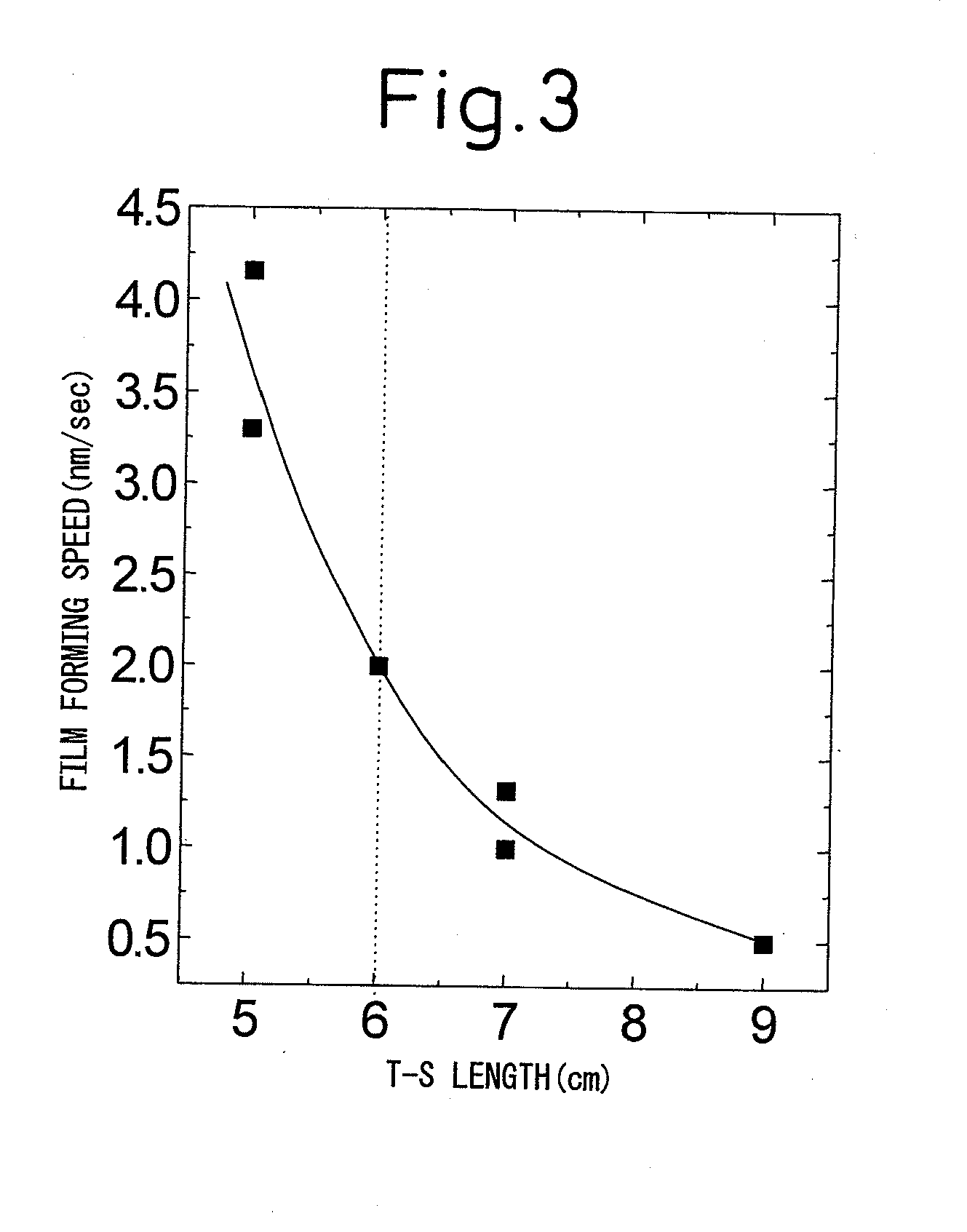
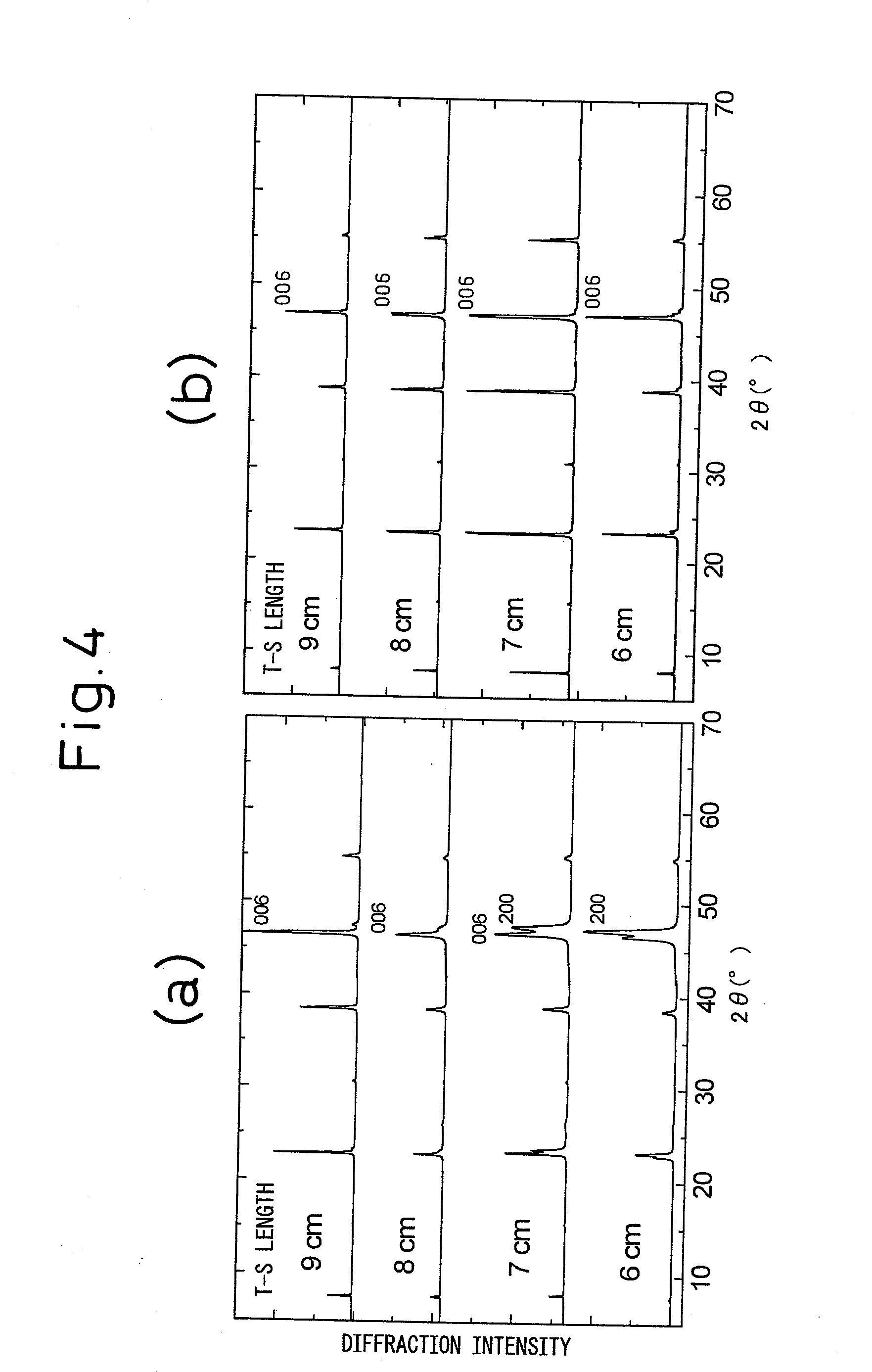
A method of production of a RE123-based oxide superconductor, said method of production of a RE123-based oxide superconductor characterized by comprising (i) firing a pulse laser at an oxide-based target including RE, Ba, and Cu satisfying the following formulas (1) and (2) to form a plume and (ii) holding a substrate in that plume to form an RE123-based oxide superconducting film:0.8≦2RE / Ba<1.0 (1)0.8≦3Ba / 2Cu<1.0 (2)where, RE is one or more of Y, La, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Dy, Ho, and Er
Owner:INT SUPERCONDUCTIVITY TECH CENT
Josephson device, method of forming Josephson device and superconductor circuit
InactiveUS8032196B2Improve IcRn productSuppress inconsistencySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsOxygenMaterials science
A Josephson device includes a first superconducting electrode layer, a barrier layer and a second superconducting electrode layer that are successively stacked. The first and second superconducting electrode layers are made of an oxide superconductor material having (RE)1(AE)2Cu3Oy as a main component, where an element RE is at least one element selected from a group consisting of Y, La, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb and Lu, and an element AE is at least one element selected from a group consisting of Ba, Sr and Ca. The barrier layer is made of a material that includes the element RE, the element AE, Cu and oxygen, where in cations within the material forming the barrier layer, a Cu content is in a range of 35 At. % to 55 At. % and an RE content is in a range of 12 At. % to 30 At. %, and the barrier layer has a composition different from compositions of the first and second superconducting electrode layers.
Owner:THE CHUGOKU ELECTRIC POWER CO INC +1
Method of joining together superconductors and a superconductor joined member produced by same
InactiveUS6561412B2Excellent current transmission performanceHigh currentSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsEngineeringTransmission performance
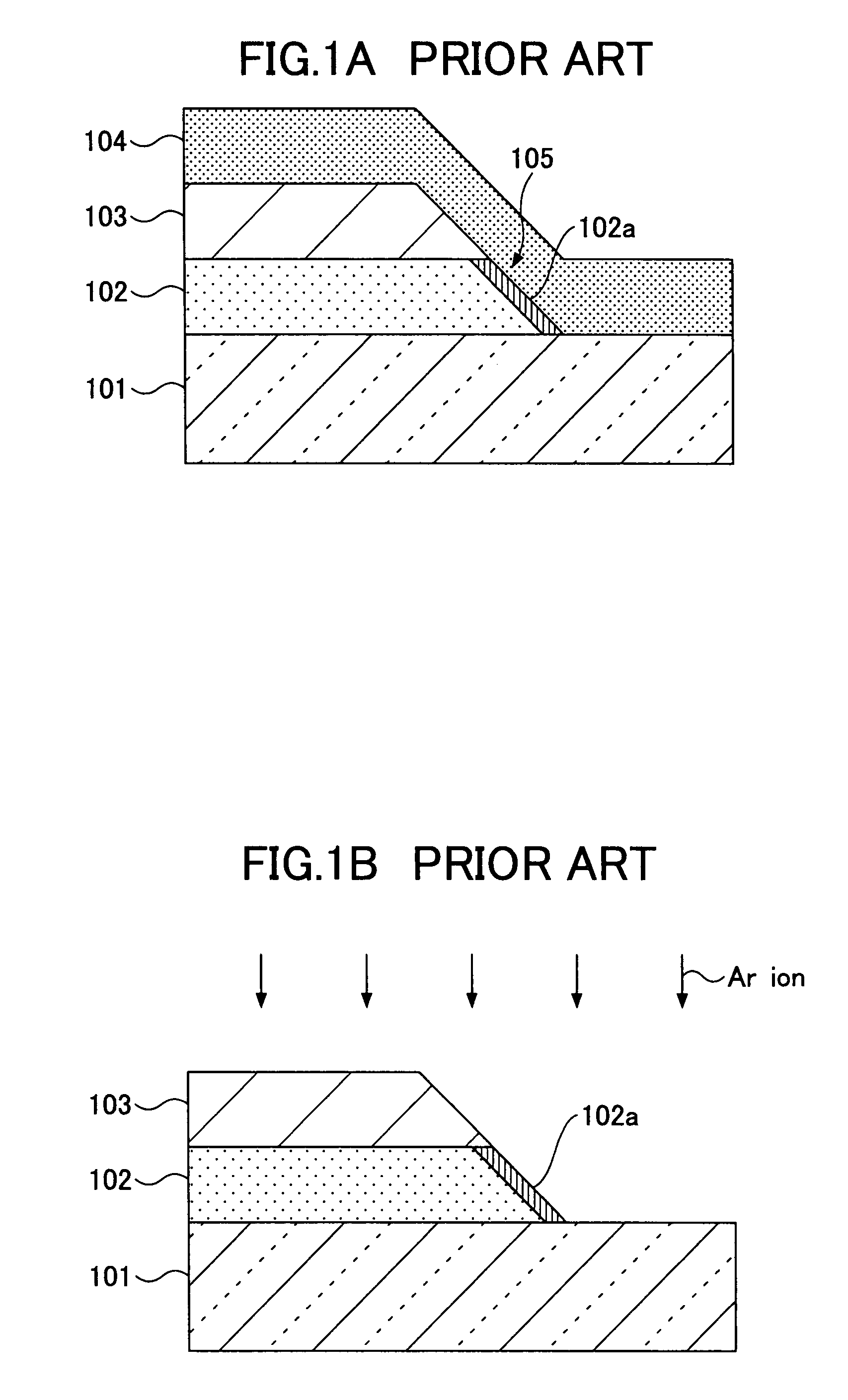
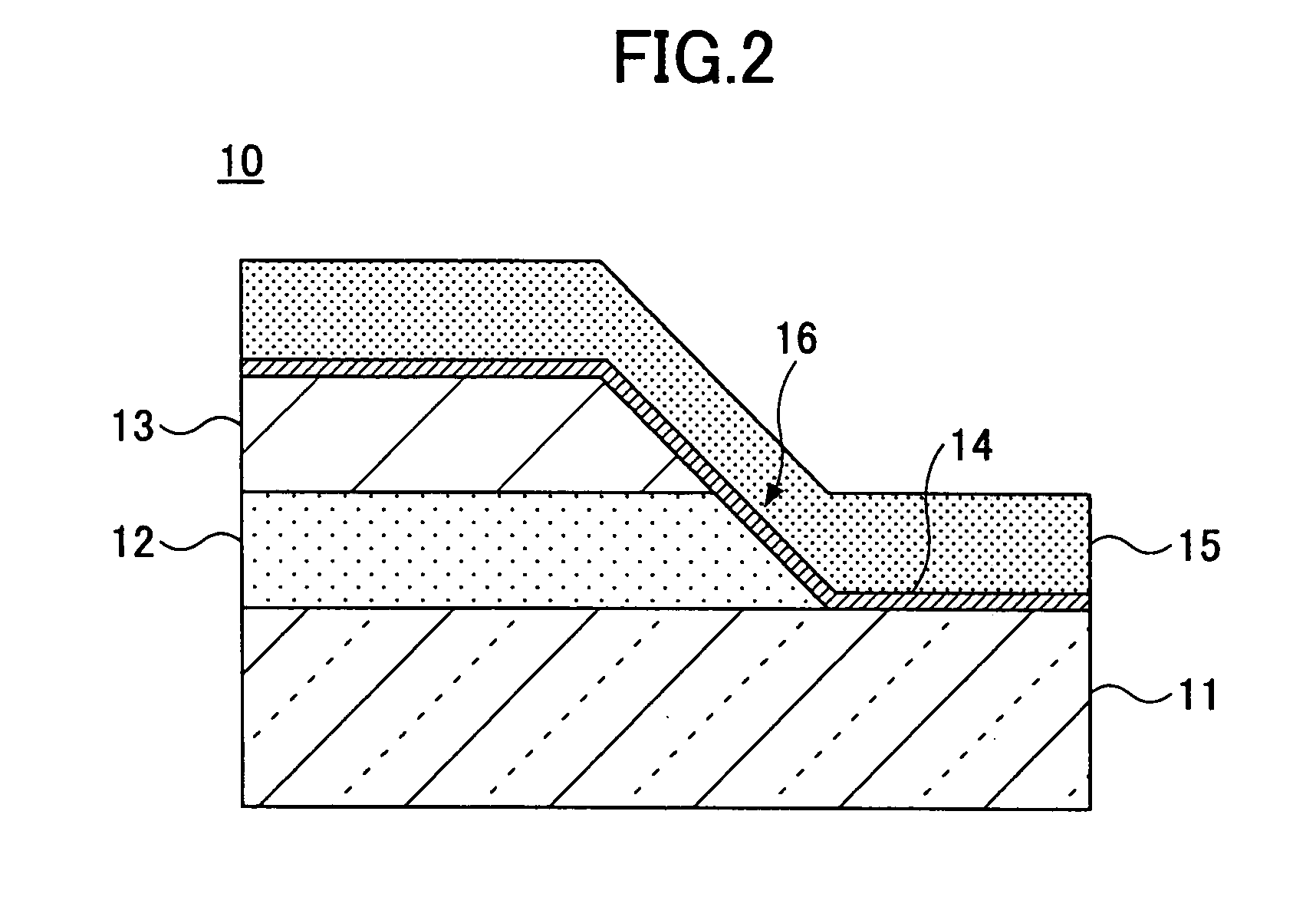
Methods for implementing production of an oxide superconductor joined member, excellent in electric current transmission performance, without a need of going through particularly complex steps, are provided. When joining together oxide superconductors by use of a solder composed of an oxide superconducting material, a finally solidified portion of the solder is positioned in a region where a transmission path of electric current flowing between oxide superconductor base materials as joined together is not obstructed by, for example, disposing the solder on a face of the oxide superconductor base materials, other than butting surfaces of the oxide superconductor base materials, so as to straddle both the base materials like bridge-building. Current flow is also not obstructed by, for example, shaping junction faces of the oxide superconductor base materials such that at least portions of the butting surfaces thereof are in the shape of sloped open faces, parting from each other. Further, an oxide superconductor joined member is made by joining the base materials with each other through the intermediary of an oxide superconductor, serving as a binder, disposed on at least a face of the base materials, other than butting surfaces thereof.
Owner:SUPERCONDUCTIVITY RES LAB
Chemical pinning centers for high temperature superconductors
InactiveUS6869915B2Improve responseSimple structureSuperconductors/hyperconductorsConductive materialElectrical conductorRoom-temperature superconductor
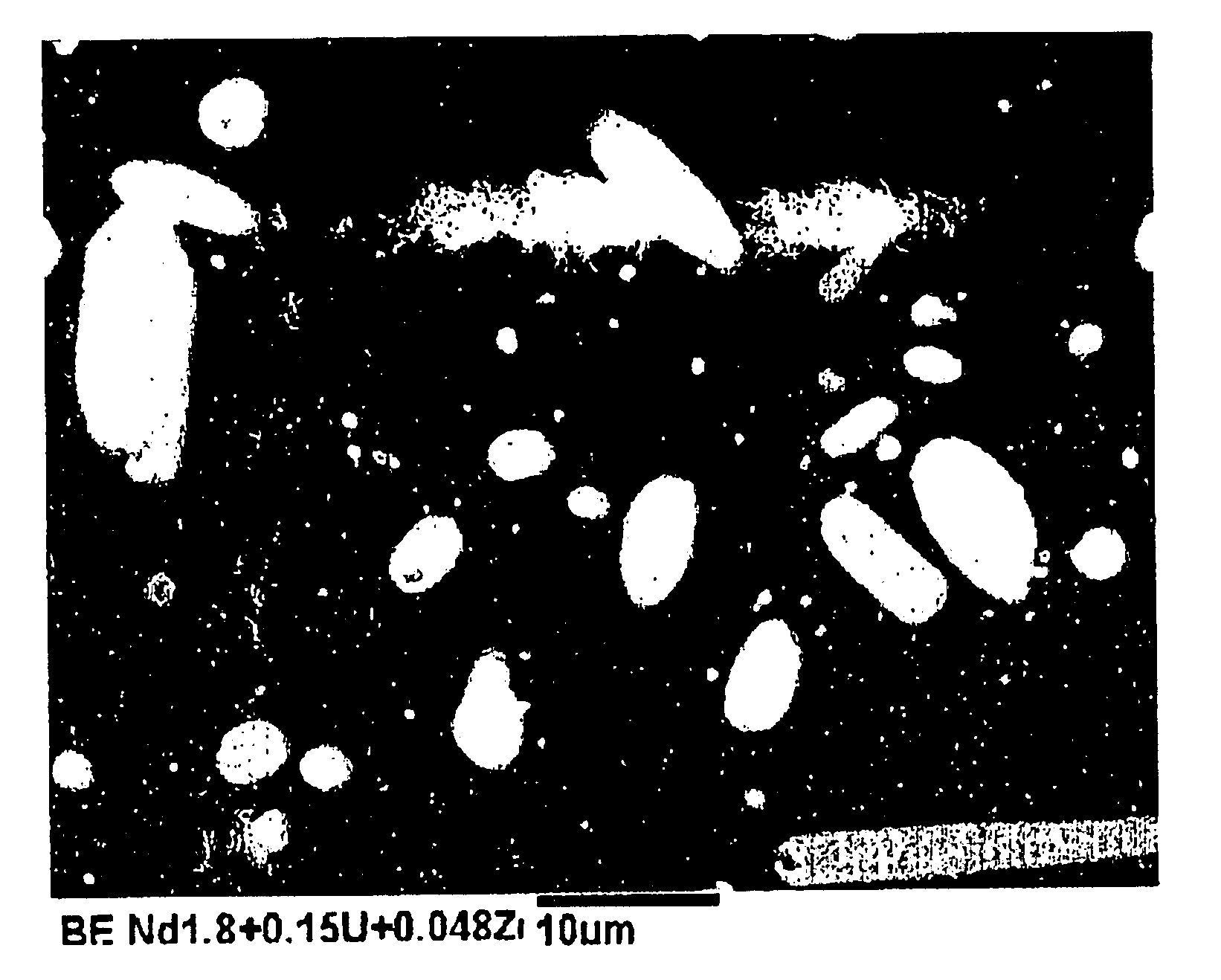
An oxide superconductor includes a textured superconducting material including an array of defects, where the defects are a compound of two elements foreign to the superconductor, plus other elements native to the superconductor. The two foreign elements include one from group A and one from group B (or alternately the two foreign elements include the element uranium and one element from group C), where group A includes Cr, Mo, W, or Nd, group B includes Pt, Zr, Pd, Ni, Ti, Hf, Ce and Th, and group C includes Zr, Pd, Ni, Ti, Hf, Ce and Th. The array of defects is dispersed throughout the superconducting material. The superconducting material may be the RE1Ba2Cu3O7−δ compound, wherein RE=Y, Nd, La, Sm, Eu, Gd, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu, Tb; the Bi2Sr2CaCu2Ox, (Bi, Pb)2Sr2CaCu2Ox, Bi2Sr2Ca2Cu3Ox (Bi, Pb)2Sr2Ca2Cu3Ox compounds; the HgBa2Ca2Cu3O8 and HgBa2CaCu2O6 compounds, the TlCaBa2Cu2Ox or Tl2Ca2Ba2Cu3Ox compounds and compounds involving substitution such as the Nd1+xBa2−xCu3Ox compounds.
Owner:WEINSTEIN ROY
Dropwise deposition of a patterned oxide superconductor
InactiveUS7582328B2Reduced ac lossesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsVacuum evaporation coatingElectrical conductorReaction zone
An oxide superconductor article having an oxide superconductor layer of a predetermined pattern is prepared by continuously advancing a wire having a textured surface into a deposition zone, dispensing droplets of a precursor solution to an oxide superconductor from a reservoir and the depositing droplets onto the textured surface of the wire that is introduced into the deposition zone, heating the wire or tape in the reaction zone under conditions to convert the precursor solution into an oxide superconductor; and collecting the wire after heating.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
Stacked filamentary coated superconductors
ActiveUS7463915B2Promote growthAdditive manufacturing apparatusSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMaterials scienceOxide superconductors
An elongated article comprising a first layer of oxide superconductor filaments extending substantially along the length of the elongated article and spaced apart from one another across the width of the elongated substrate; a second layer of oxide superconductor filaments extending substantially along the length of the elongated article and spaced apart from one another across the width of the elongated article, wherein the first filament layer is positioned above the second filament layer; and a barrier layer positioned between the first and second filament layers, wherein the filaments of the first and second filament layers are positioned such that at least one filament of the first layer crosses at least one filament of the second layer.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
Oxide superconductor wire and superconducting coil
ActiveUS20140155269A1Superconductors/hyperconductorsPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsElectrical conductorSuperconducting Coils
An oxide superconductor wire includes: a superconductor laminate that comprises a substrate which is formed in a tape shape and an intermediate layer, an oxide superconductor layer, and a metal stabilizing layer which are laminated on the substrate; and an insulating coating layer that covers an outside surface of the superconductor laminate, Also, either the entire outside surface or the entire inside surface of the insulating coating layer is coated with a coating layer formed of a fluororesin.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Superconductive nanocomposite
InactiveUS20110021360A1Low densityReadily apparentMagnetic/electric field screeningThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsLow-density polyethyleneLinear low-density polyethylene
The superconductive nanocomposite is a composition formed by nanoparticles of a high temperature superconductor blended with a polymer matrix containing natural rubber and polyethylene. The high temperature superconductor is preferably a bismuth-based superconductor (BSCCO) having a particle size of about 21 nm, but may be any other high temperature or Type II ceramic, metal oxide superconductor. The superconductor nanoparticles comprise about 15% of the weight of natural rubber in the composition. The polyethylene is preferably low density polyethylene and may comprise between 0% up to about 40% of the weight of natural rubber in the composition. The nanocomposite may be prepared by blending the components and roll milling the rubber. Depending upon the percentage of polyethylene present in the matrix, the nanocomposite has useful applications as a double thermistor (both positive and negative coefficients of electrical resistivity), for antistatic charge dissipation, and for electromagnetic shielding in the microwave region.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ UNIV
Oxide superconductor wire, connection structure thereof, and superconductor equipment
InactiveUS20150332812A1Line/current collector detailsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsElectrical conductorBand shape
An oxide superconductor wire including: a superconductor laminate including a tape-shaped substrate, an interlayer, an oxide superconductor layer, and a protection layer which are formed on the substrate; a metal stabilization layer covering the periphery of the superconductor laminate; a first electrically conductive joint material arranged between the superconductor laminate and the metal stabilization layer; and a sealing member formed from a metal foil, connected to a terminal of the superconductor laminate, and extending in the longitudinal direction of the superconductor laminate, wherein the metal stabilization layer includes an extension part formed so as to cover the periphery of the sealing member, and wherein the first electrically conductive joint material includes an extension part arranged between the extension part of the metal stabilization layer and the sealing member and formed so as to cover the periphery of the sealing member.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
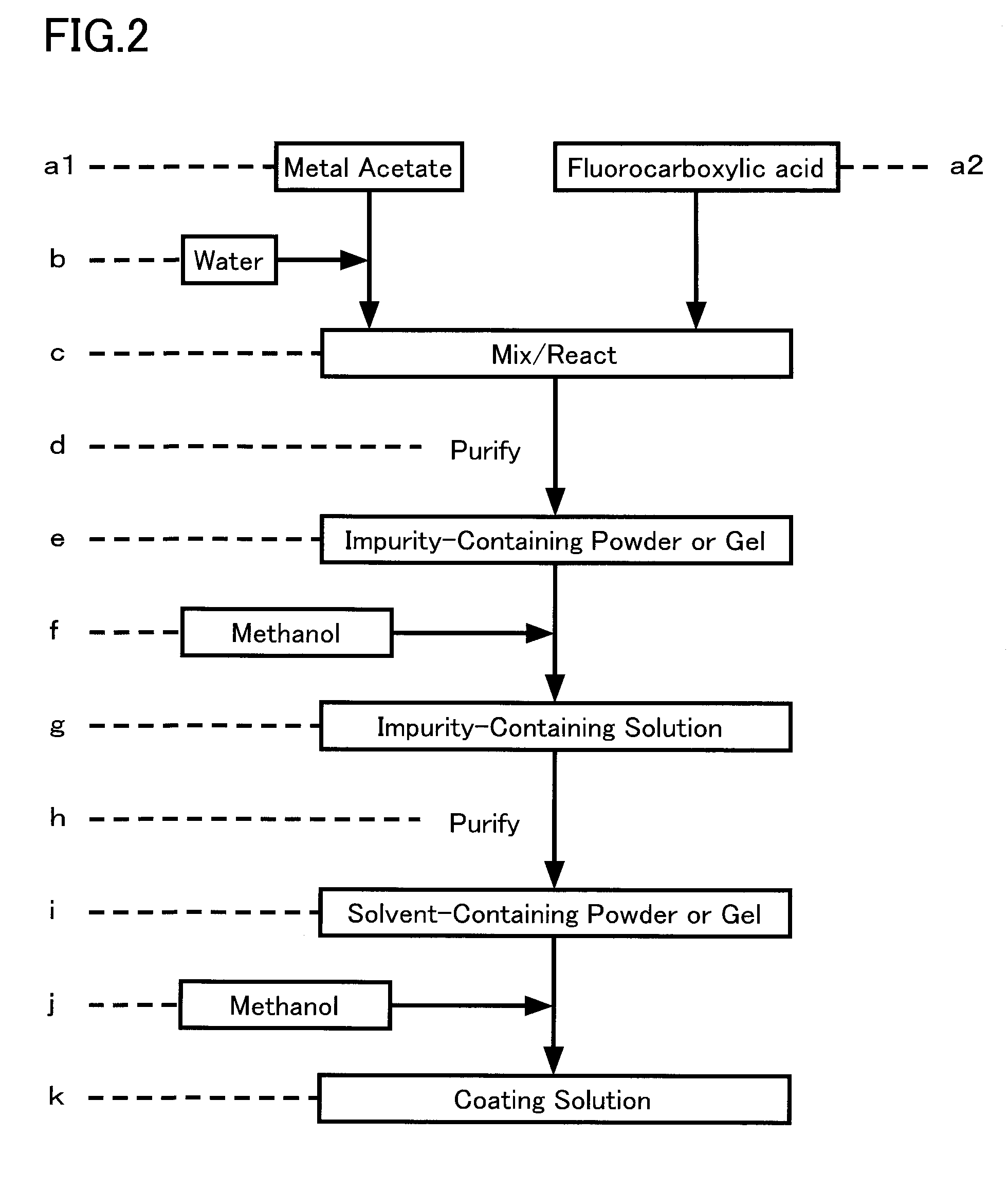
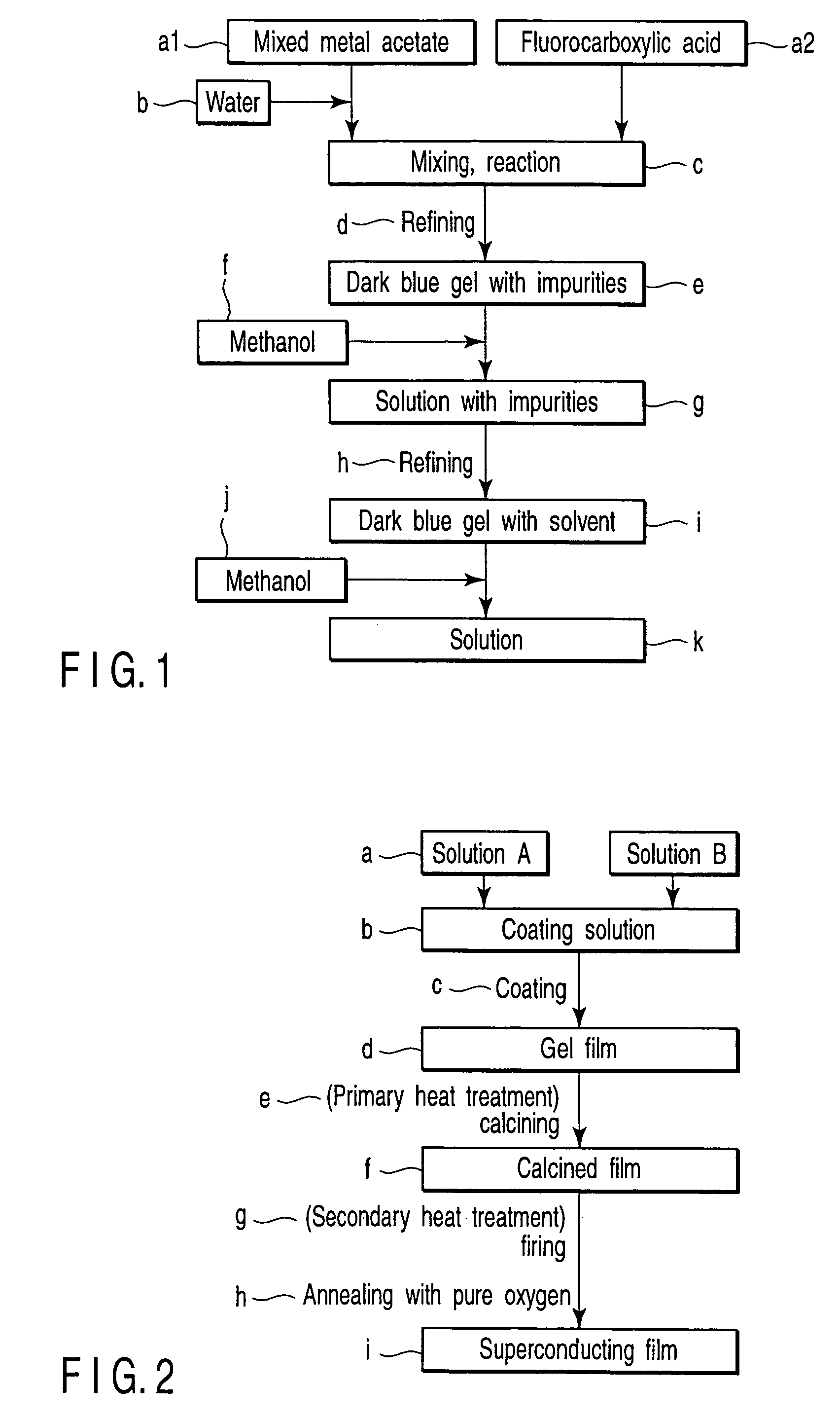
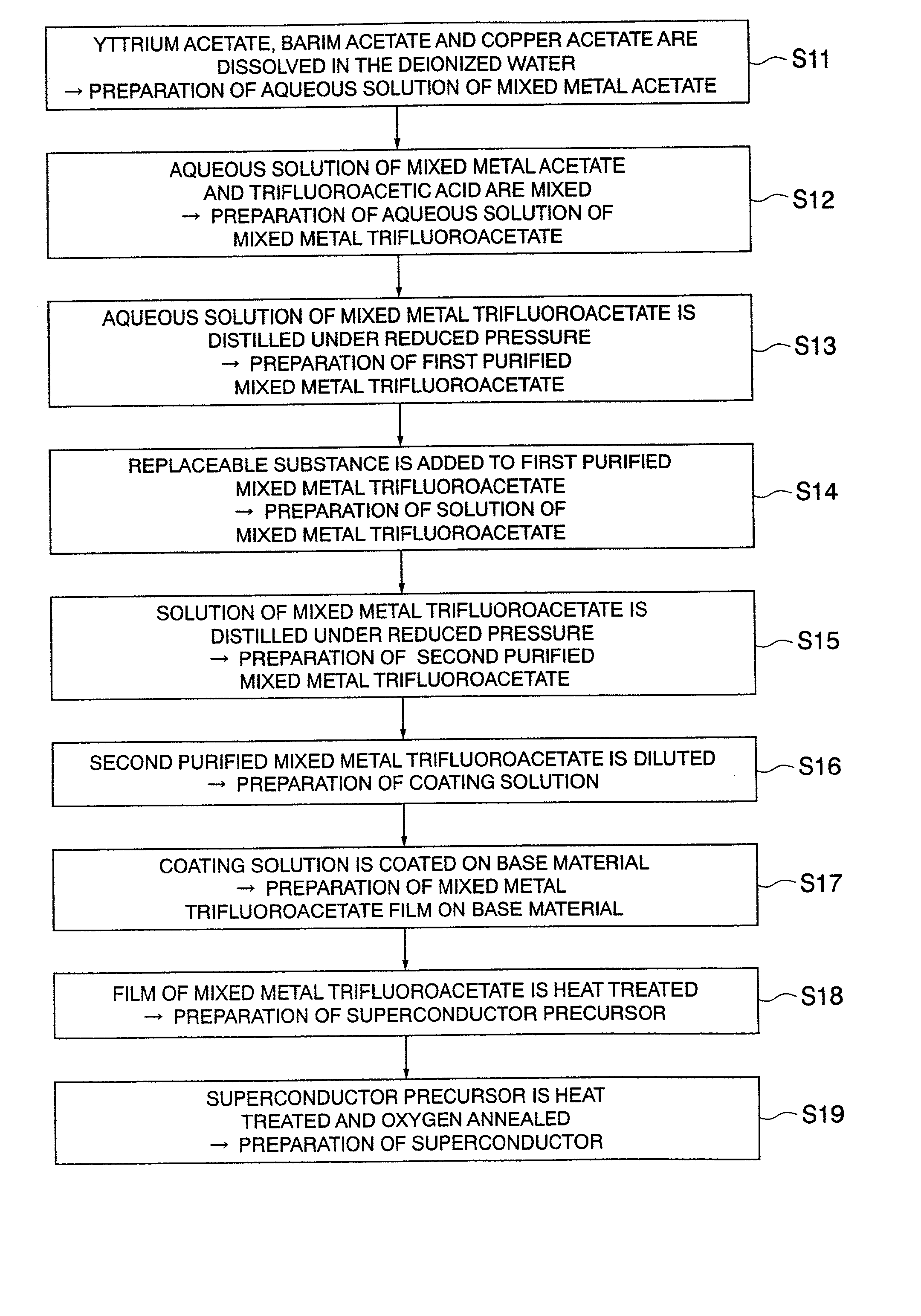
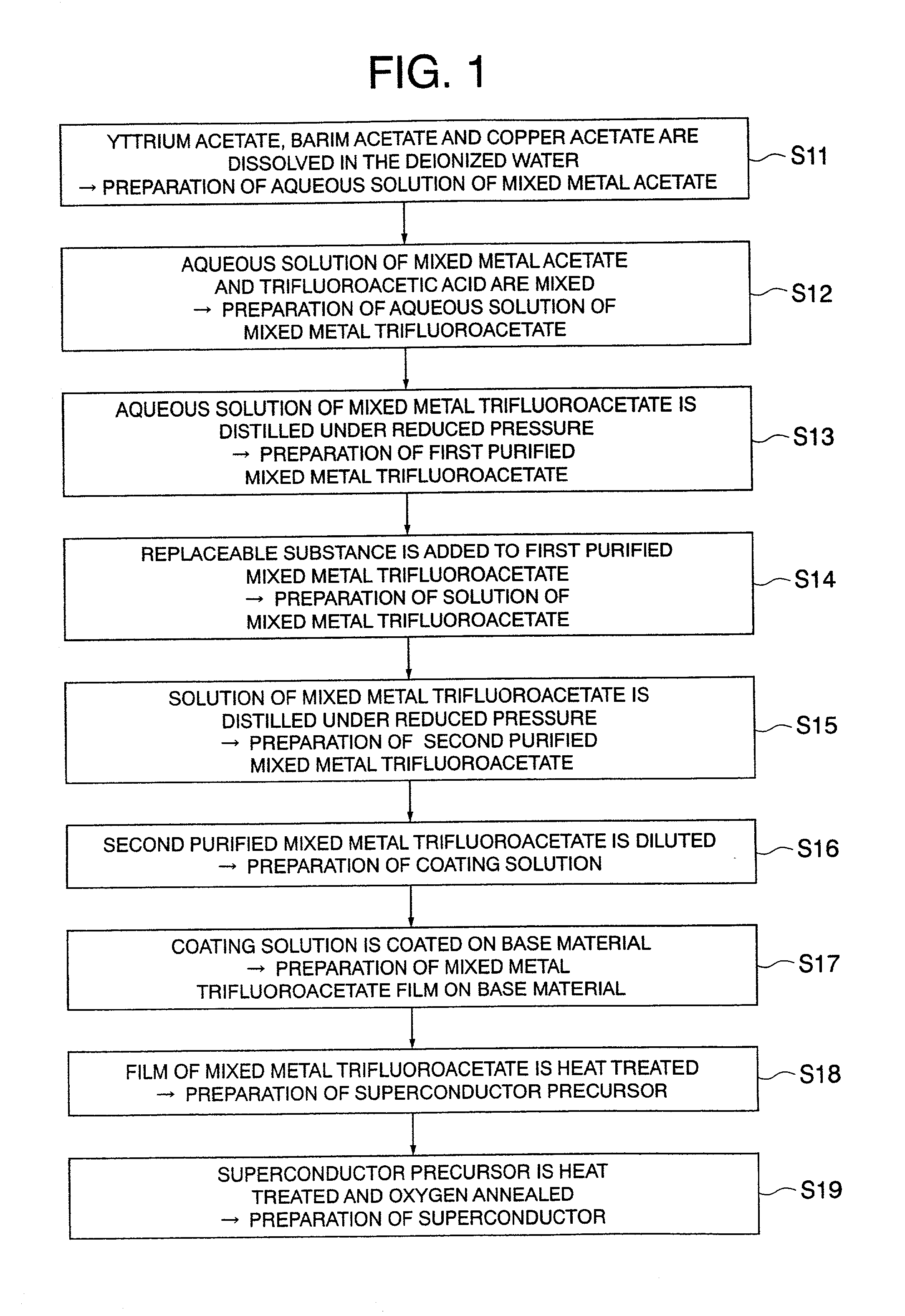
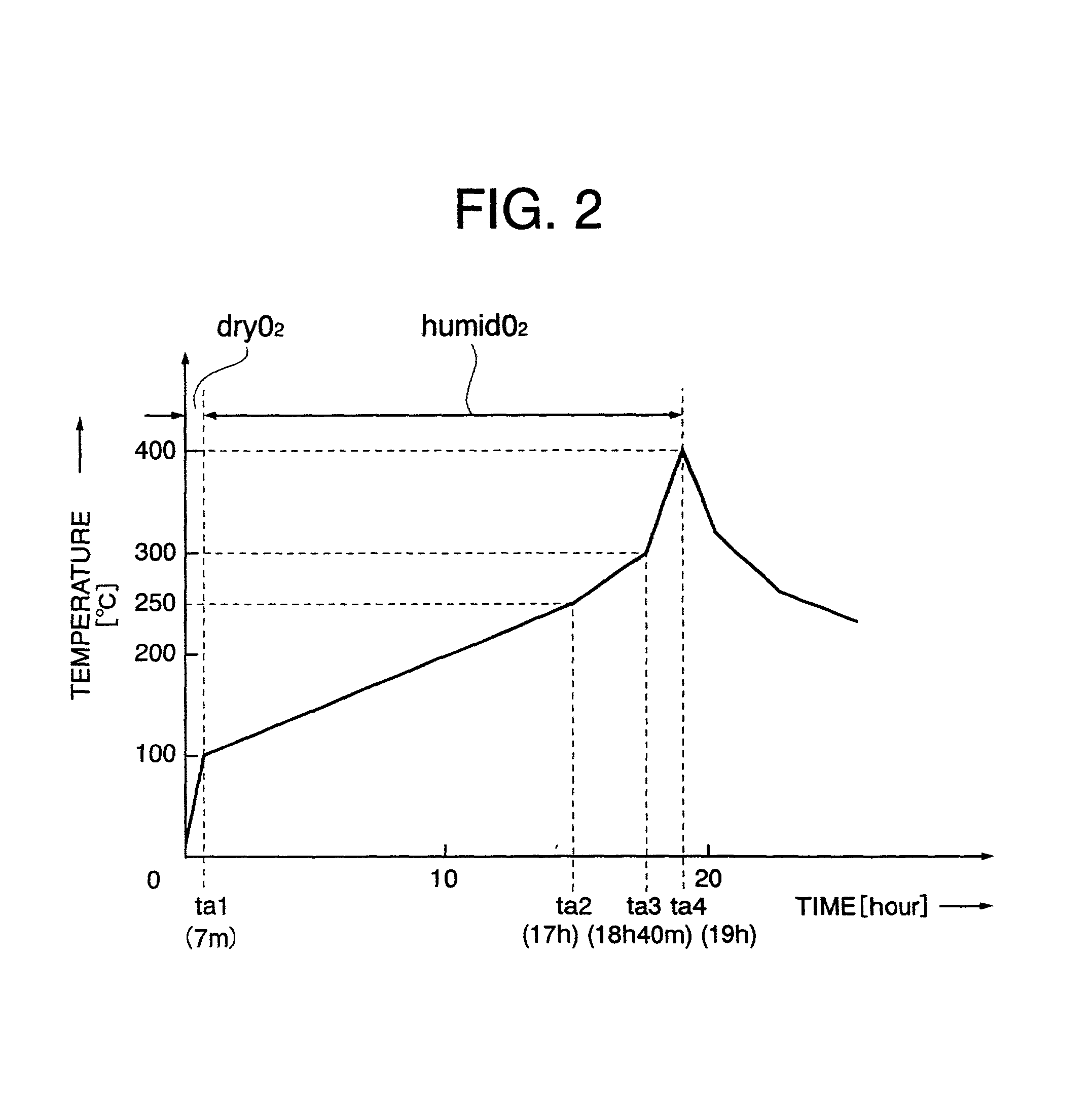
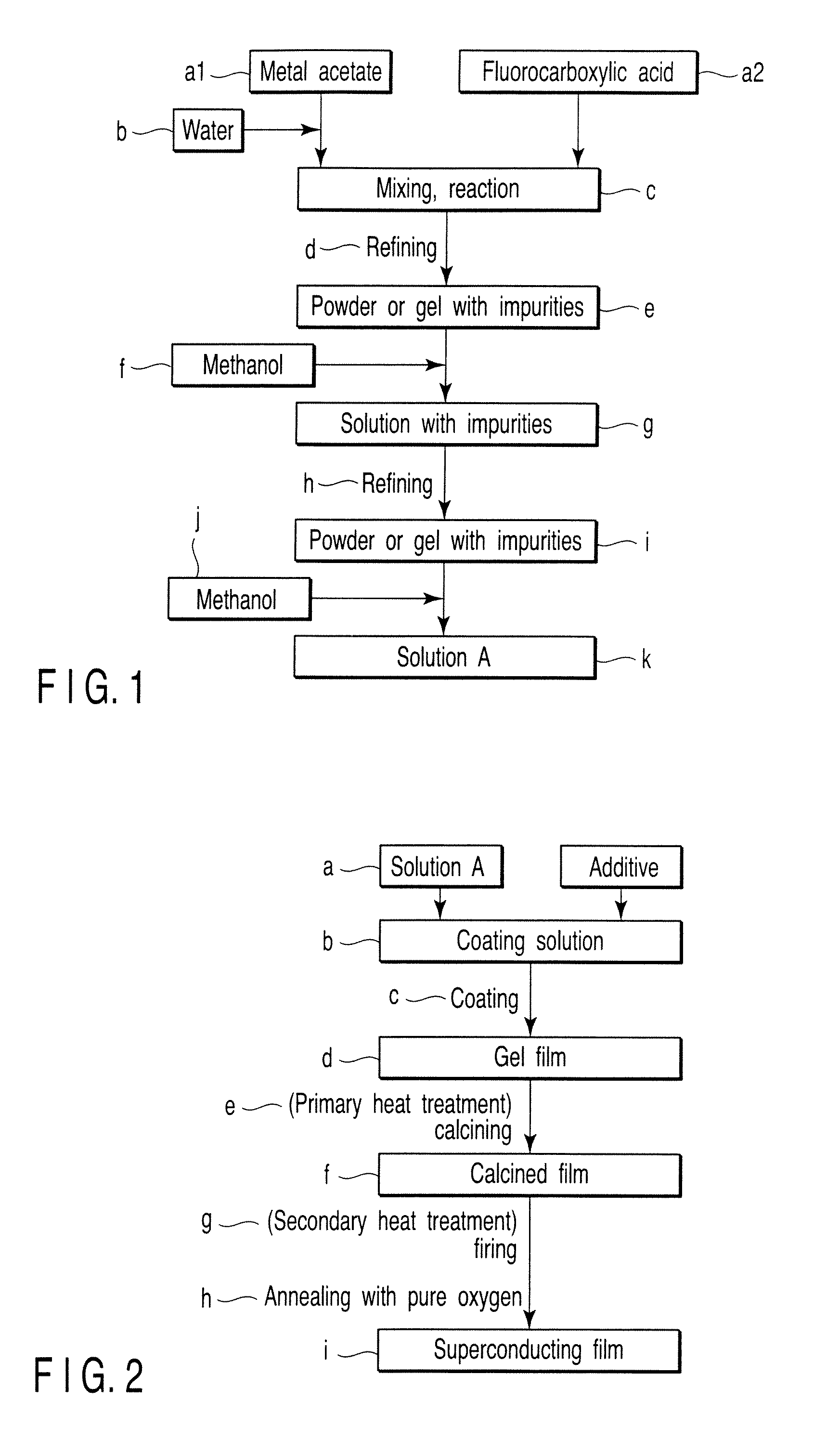
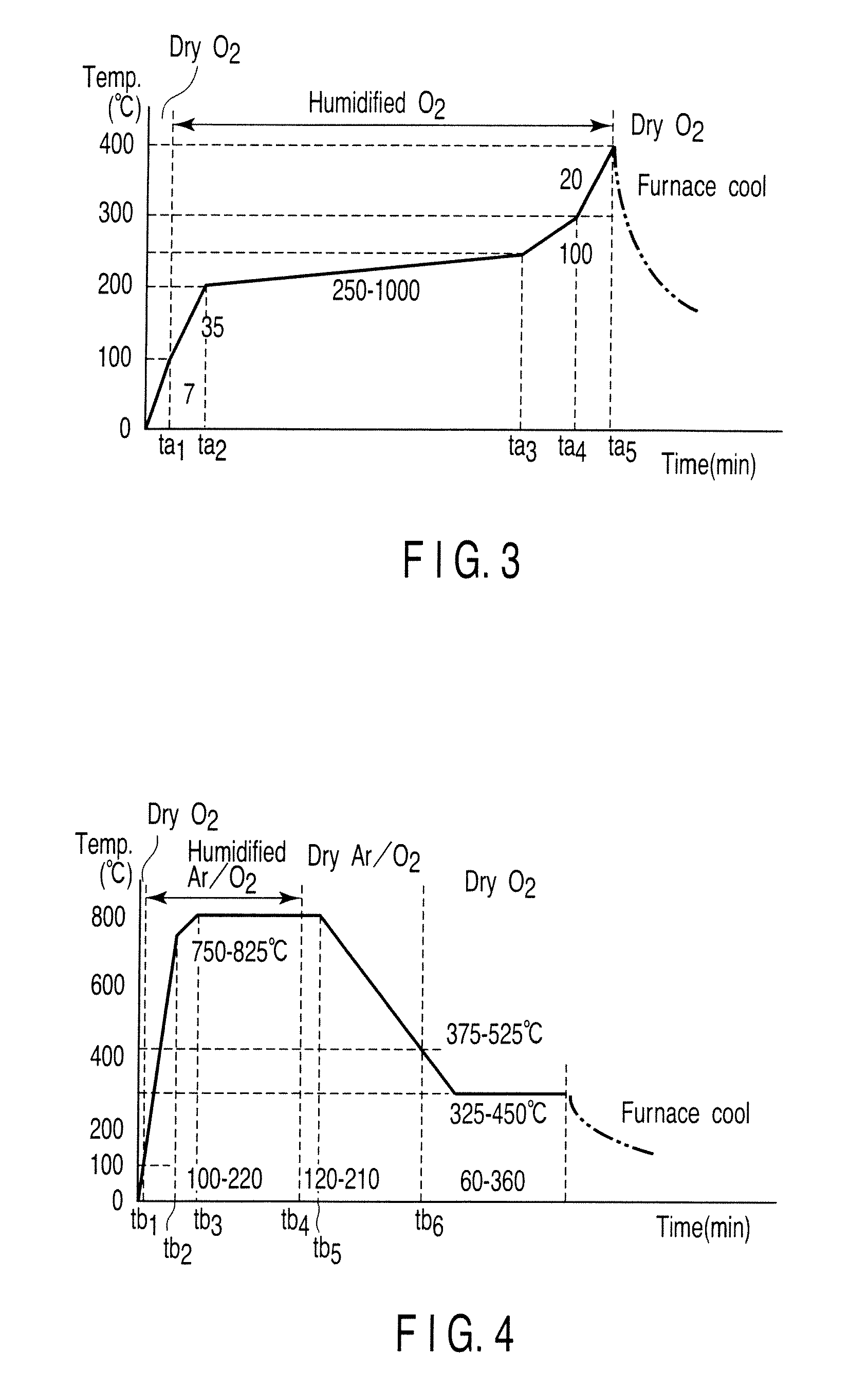
Preparing method of oxide superconductor, raw material for oxide superconductor, and preparing method of raw material for oxide superconductor
InactiveUS20020086799A1Improve performanceReduce contentPolycrystalline material growthOxide conductorsAcetic acidTrifluoroacetic acid
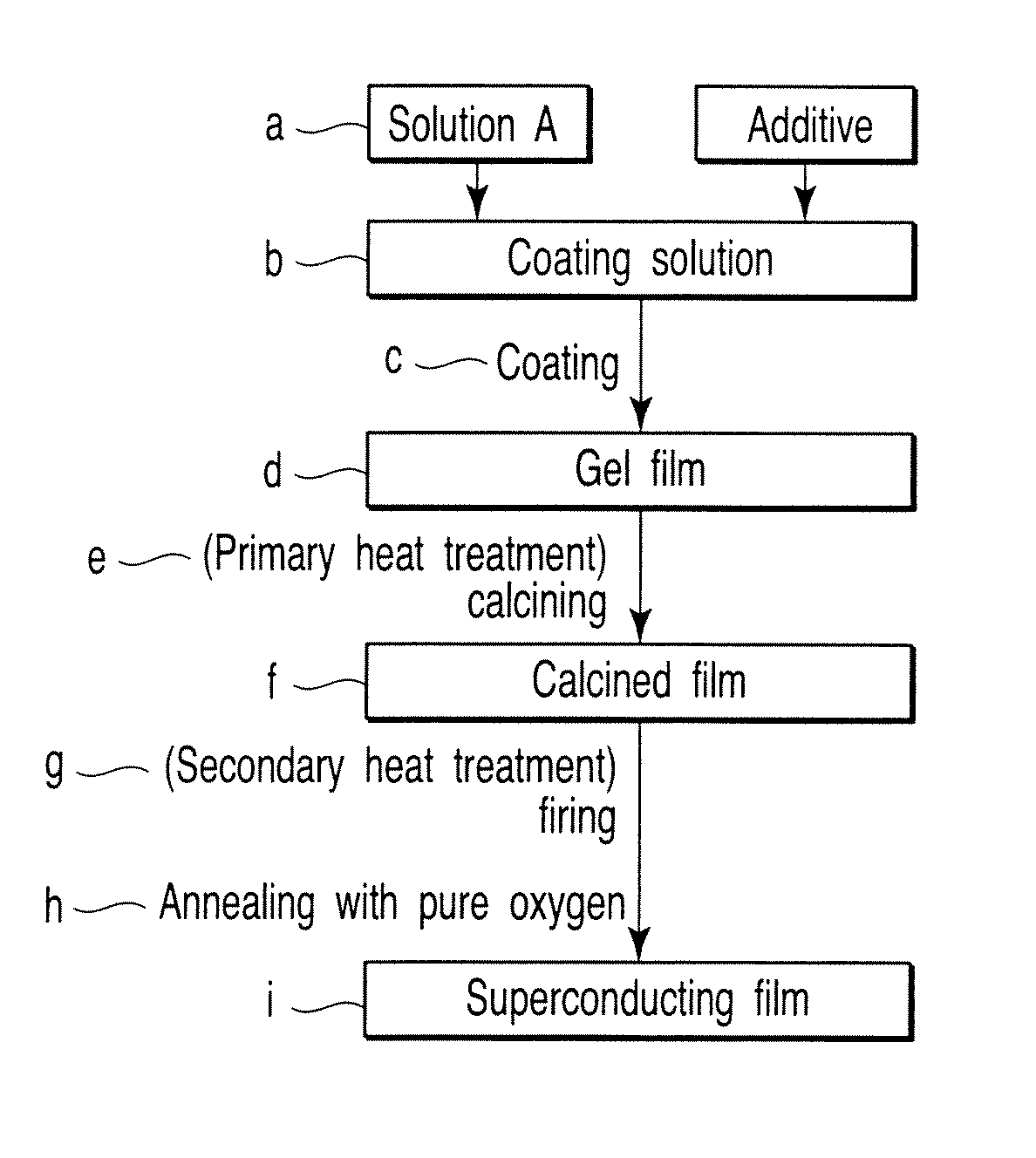
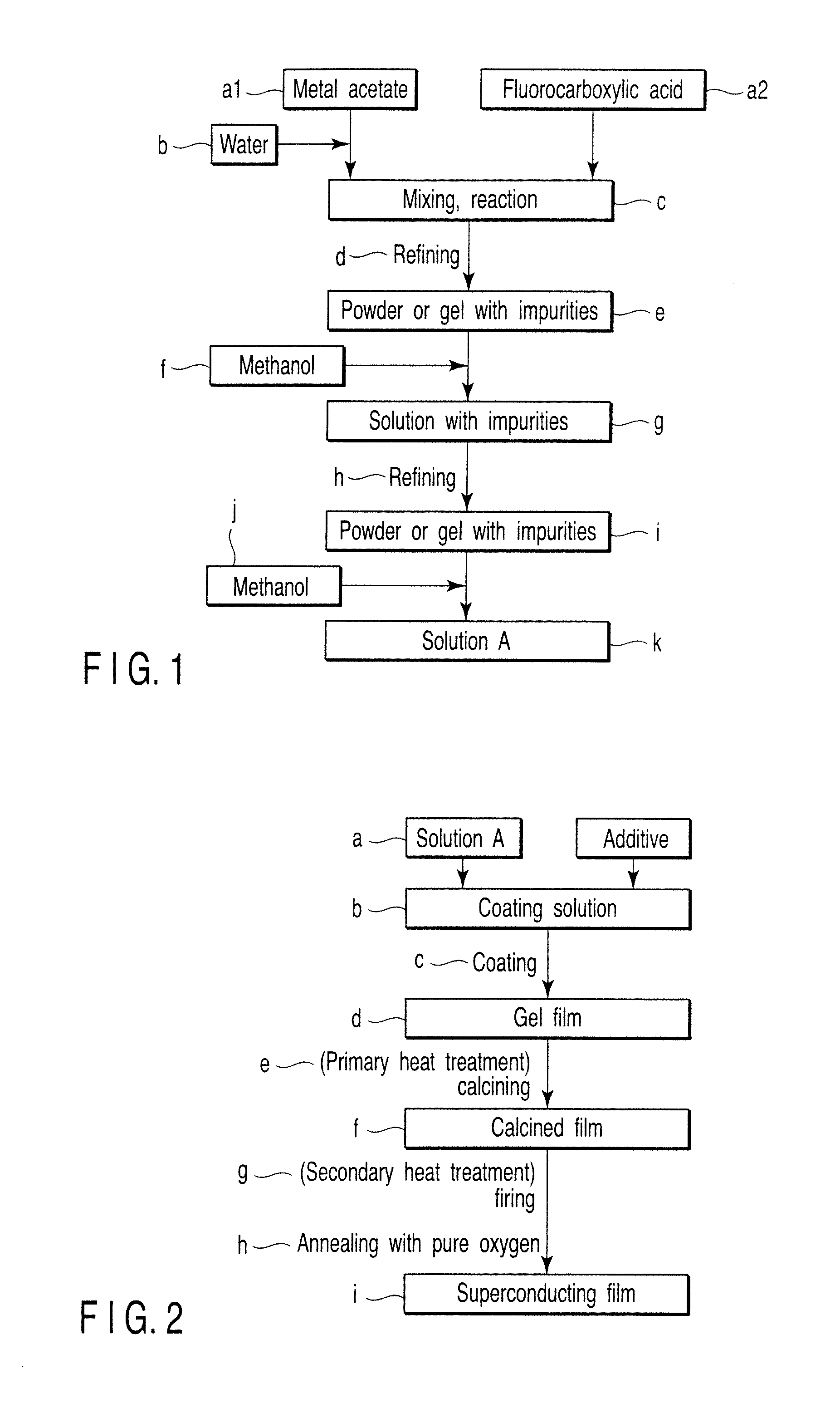
An aqueous solution of mixed metal acetate including one kind or more of element selected from lanthanide series and yttrium, barium and copper is mixed with trifluoroacetic acid to prepare a solution of mixed metal trifluoroacetate. From a solution of mixed metal trifluoroacetate obtained thus, purified mixed metal trifluoroacetate of which total content of water and acetic acid is 2% by weight or less is prepared. With purified mixed metal trifluoroacetate, an oxide superconductor of excellent performance may be prepared.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Oxide superconductor thick film and method for manufacturing the same
Owner:DOWA ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CO LTD +1
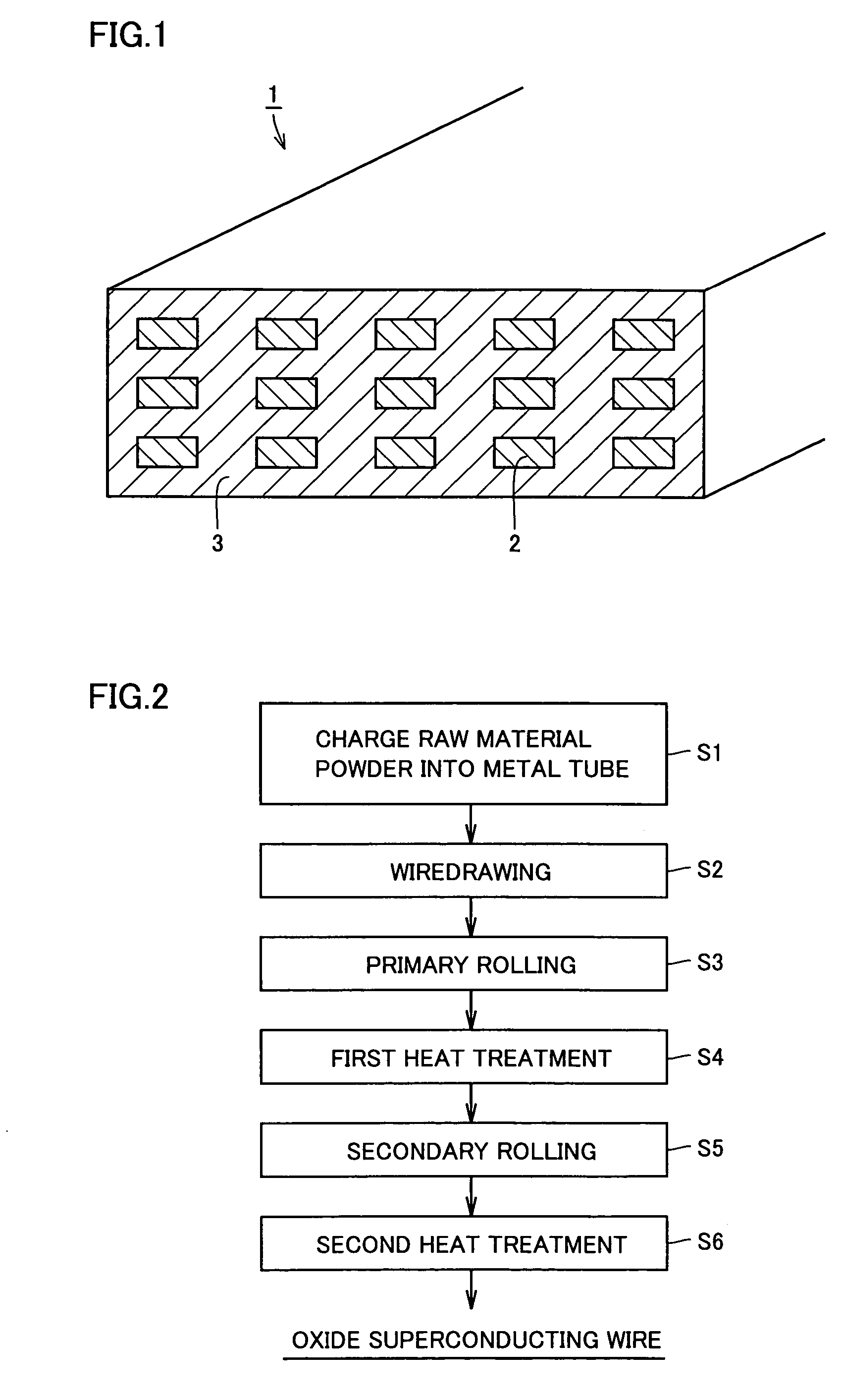
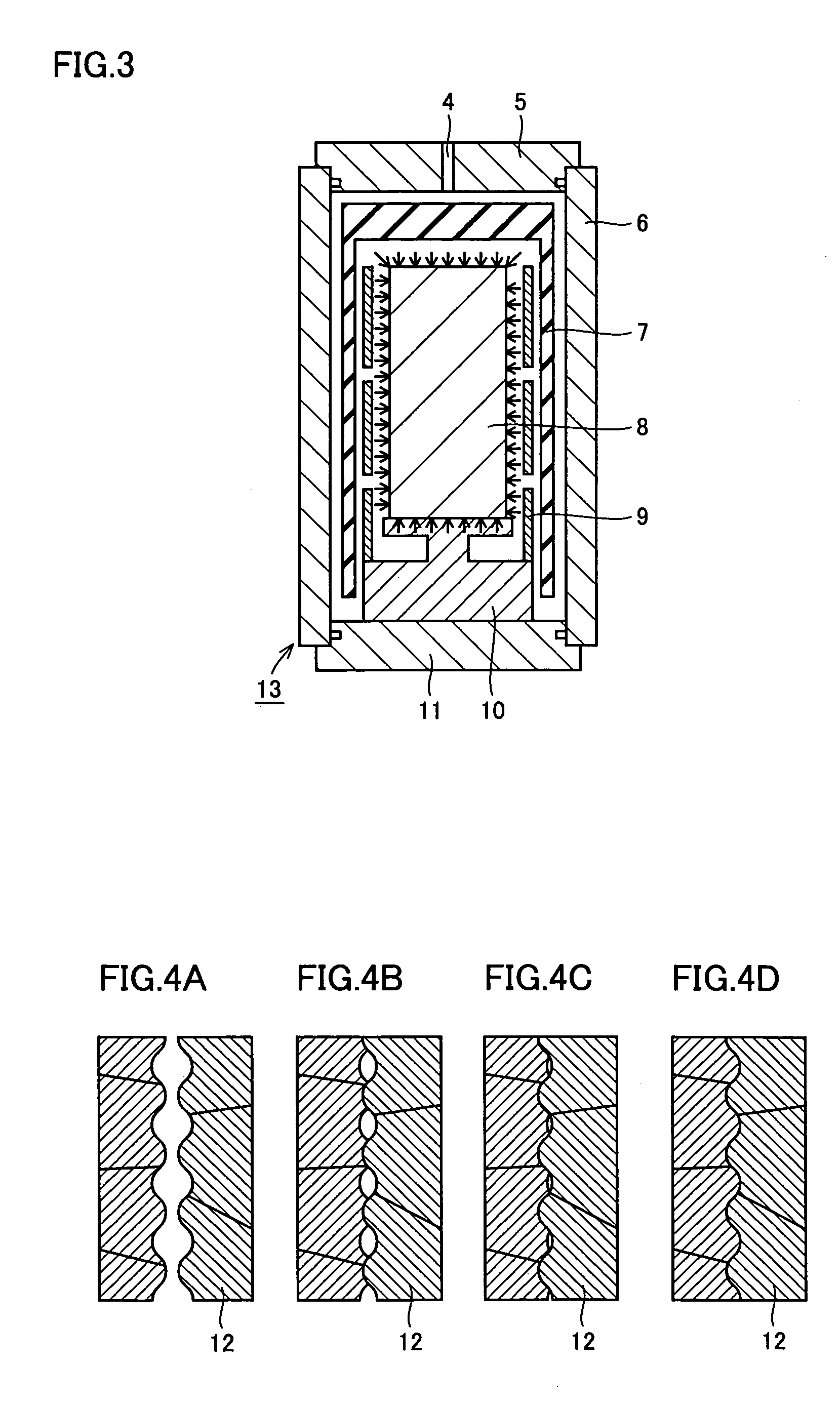
Method of manufacturing oxide superconducting wire
InactiveUS6993823B2High densityEasy to controlLine/current collector detailsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsBlistersMaterials science
The inventive method of manufacturing an oxide superconducting wire comprises a step (S1, S2) of preparing a wire formed by covering raw material powder of an oxide superconductor with a metal and a step (S4, S6) of heat-treating the wire in a pressurized atmosphere, and the total pressure of the pressurized atmosphere is at least 1 MPa and less than 50 MPa. Thus, formation of voids between oxide superconducting crystals and blisters of the oxide superconducting wire is suppressed while the partial oxygen pressure can be readily controlled in the heat treatment, whereby the critical current density can be improved.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
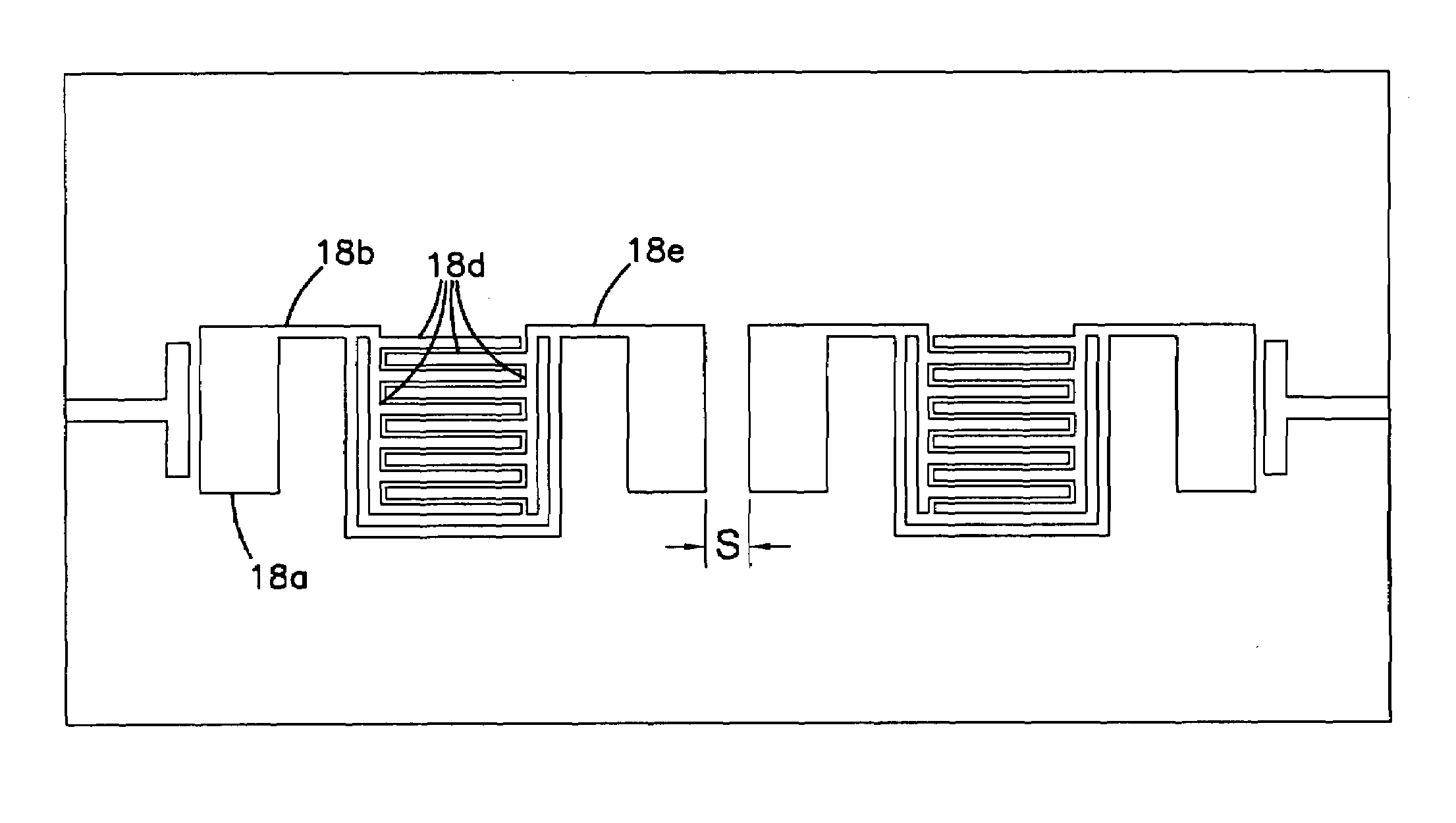
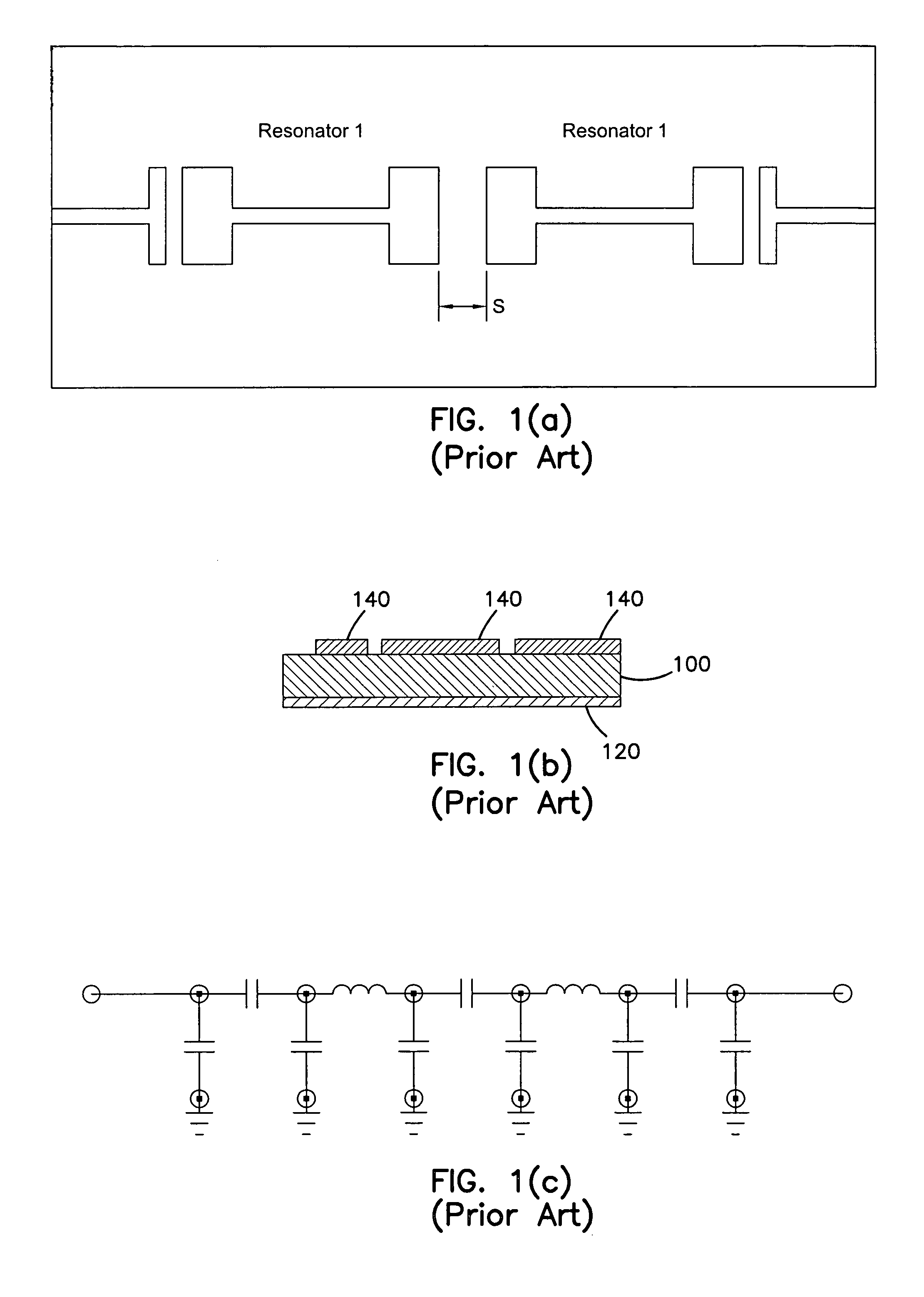
Superconductive filter with capacitive patches providing reduced cross-coupling
InactiveUS7437187B1Wide manufacturing toleranceMore layout flexibilityMultiple-port networksSuperconductors/hyperconductorsState of artShunt capacitors
A resonator of a planar circuit type is provided for receiving a signal from an input end and transmitting a signal to an output end. The resonator includes: (a) a dielectric substrate; (b) a ground plane including a layer of conductive material formed on the bottom surface of the substrate; (c) an inductor formed on the top surface of the substrate and connected to the input and output ends; and (d) a series capacitor connected in parallel to the inductor, wherein the series capacitor includes two patches of conductive material formed on the top surface of the substrate, each patch being connected to one respective end of the resonator. Each patch also forms a shunt capacitor with the ground plane, and the capacitance of the shunt capacitor constitutes the majority of capacitance between the ground plane and the end of the resonator that is connected to the patch. The conductive material may be a superconductor, including oxide superconductors. Filters utilizing multiple resonators of the invention are also described. The integration of the series and shunt capacitors results in a more compact resonator and filter layout, allows broader manufacturing tolerances, and allows for more layout flexibility than is attainable with the technology of the prior art.
Owner:SUPERCONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGIES INC
Low ac loss filamentary coated superconductors
InactiveUS7496390B2Additive manufacturing apparatusSuperconductors/hyperconductorsOxide superconductorsPhysics
An article having low ac loss includes an elongated substrate having a length and a width; and a plurality of filaments comprising an oxide superconductor extending substantially along the length of the elongated substrate and spaced apart from one other filaments across the width of the elongated substrate, wherein at least one filament crosses over at least one other filament such that the at least one filament occupies a first position across the width of the elongated substrate before the crossover and a second position across the width of the elongated substrate after crossover.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
Oxide superconductor and method for producing the same
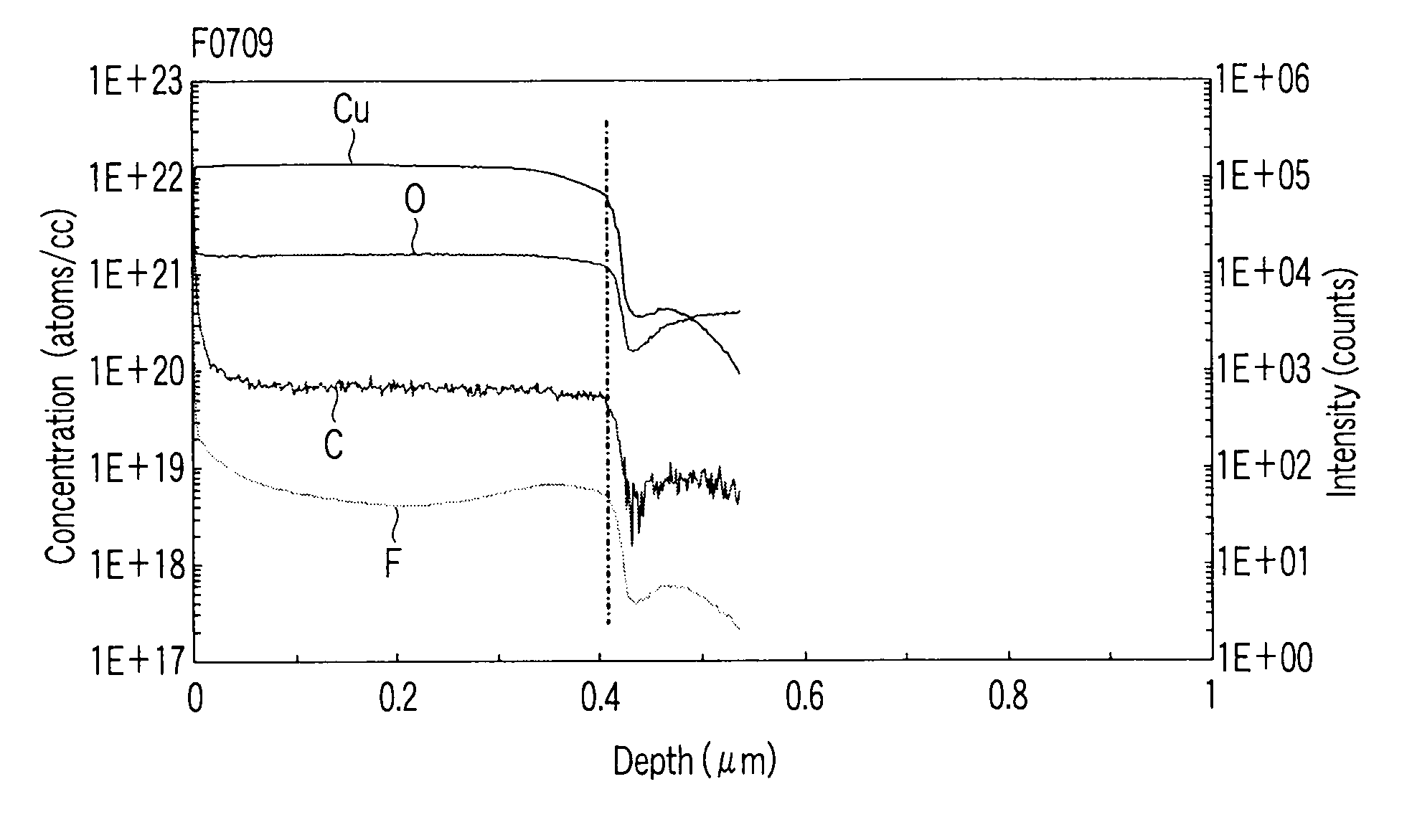
An oxide superconductor film formed on a substrate includes an oxide containing at least one metal M selected from the group consisting of yttrium and lanthanoid metals, provided that cerium, praseodymium, and promethium are excluded, and barium and copper, in which the film has an average thickness of 350 nm or more, an average amount of residual carbon of 3×1019 atoms / cc or more, and an amount of residual fluorine in a range of 5×1017 to 1×1019 atoms / cc, and in which, when divided the film into a plurality of regions from a surface of the film or from an interface between the film and the substrate, each region having a thickness of 10 nm, atomic ratios of copper, fluorine, oxygen and carbon between two adjacent regions are in a range of ⅕ times to 5 times.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Josephson device, method of forming Josephson device and superconductor circuit
ActiveUS20080051292A1Improve IcRn productSuppress inconsistencySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsOxygenMaterials science
A Josephson device includes a first superconducting electrode layer, a barrier layer and a second superconducting electrode layer that are successively stacked. The first and second superconducting electrode layers are made of an oxide superconductor material having (RE)1(AE)2Cu3Oy as a main component, where an element RE is at least one element selected from a group consisting of Y, La, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb and Lu, and an element AE is at least one element selected from a group consisting of Ba, Sr and Ca. The barrier layer is made of a material that includes the element RE, the element AE, Cu and oxygen, where in cations within the material forming the barrier layer, a Cu content is in a range of 35 At. % to 55 At. % and an RE content is in a range of 12 At. % to 30 At. %, and the barrier layer has a composition different from compositions of the first and second superconducting electrode layers.
Owner:THE CHUGOKU ELECTRIC POWER CO INC +1
Oxide superconductor and method for producing the same
An oxide superconductor film formed on a substrate includes an oxide containing at least one metal M selected from the group consisting of yttrium and lanthanoid metals, provided that cerium, praseodymium, promethium and ruthenium are excluded, and barium and copper, in which the film has an average thickness of 350 nm or more, an average amount of residual carbon of 3×1019 atoms / cc or more, and an amount of residual fluorine in a range of 5×1017 to 1×1019 atoms / cc, and in which, when divided the film into a plurality of regions from a surface of the film or from an interface between the film and the substrate, each region having a thickness of 10 nm, atomic ratios of copper, fluorine, oxygen and carbon between two adjacent regions are in a range of 1 / 5 times to 5 times.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Thick superconductor films with improved performance
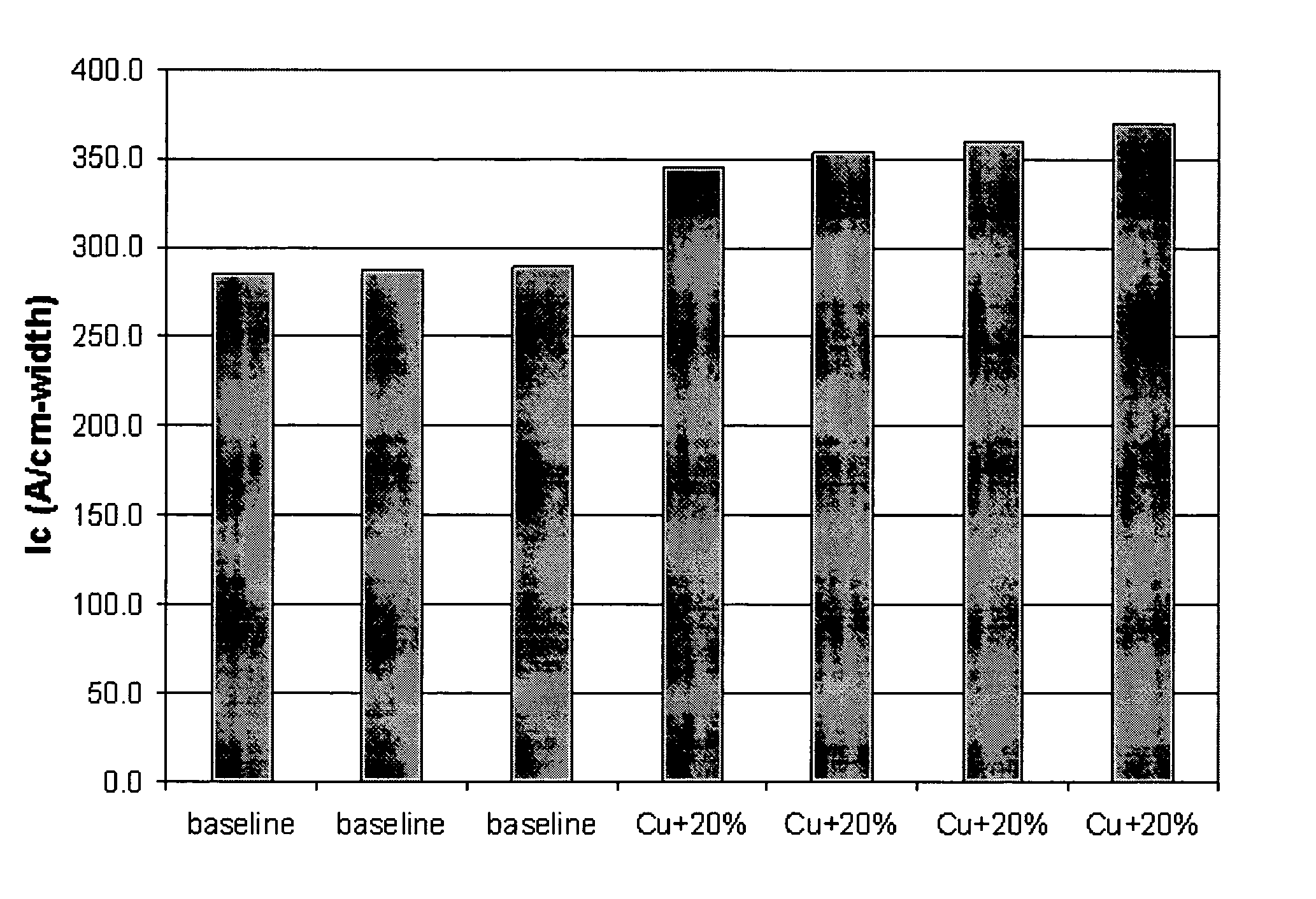
ActiveUS7622424B2Low costIncrease contentSuperconductors/hyperconductorsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingRare-earth elementAlkaline earth metal
A method for producing a thick film includes disposing a precursor solution onto a substrate to form a precursor film. The precursor solution contains precursor components to a rare-earth / alkaline-earth-metal / transition-metal oxide including a salt of a rare earth element, a salt of an alkaline earth metal, and a salt of a transition metal in one or more solvents, wherein at least one of the salts is a fluoride-containing salt, and wherein the ratio of the transition metal to the alkaline earth metal is greater than 1.5. The precursor solution is treated to form a rare earth-alkaline earth-metal transition metal oxide superconductor film having a thickness greater than 0.8 μm. precursor solution.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
Oxide superconductor and production method for same
InactiveCN102844823AReduce anisotropyAvoid changeSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesRare-earth elementStructural formula
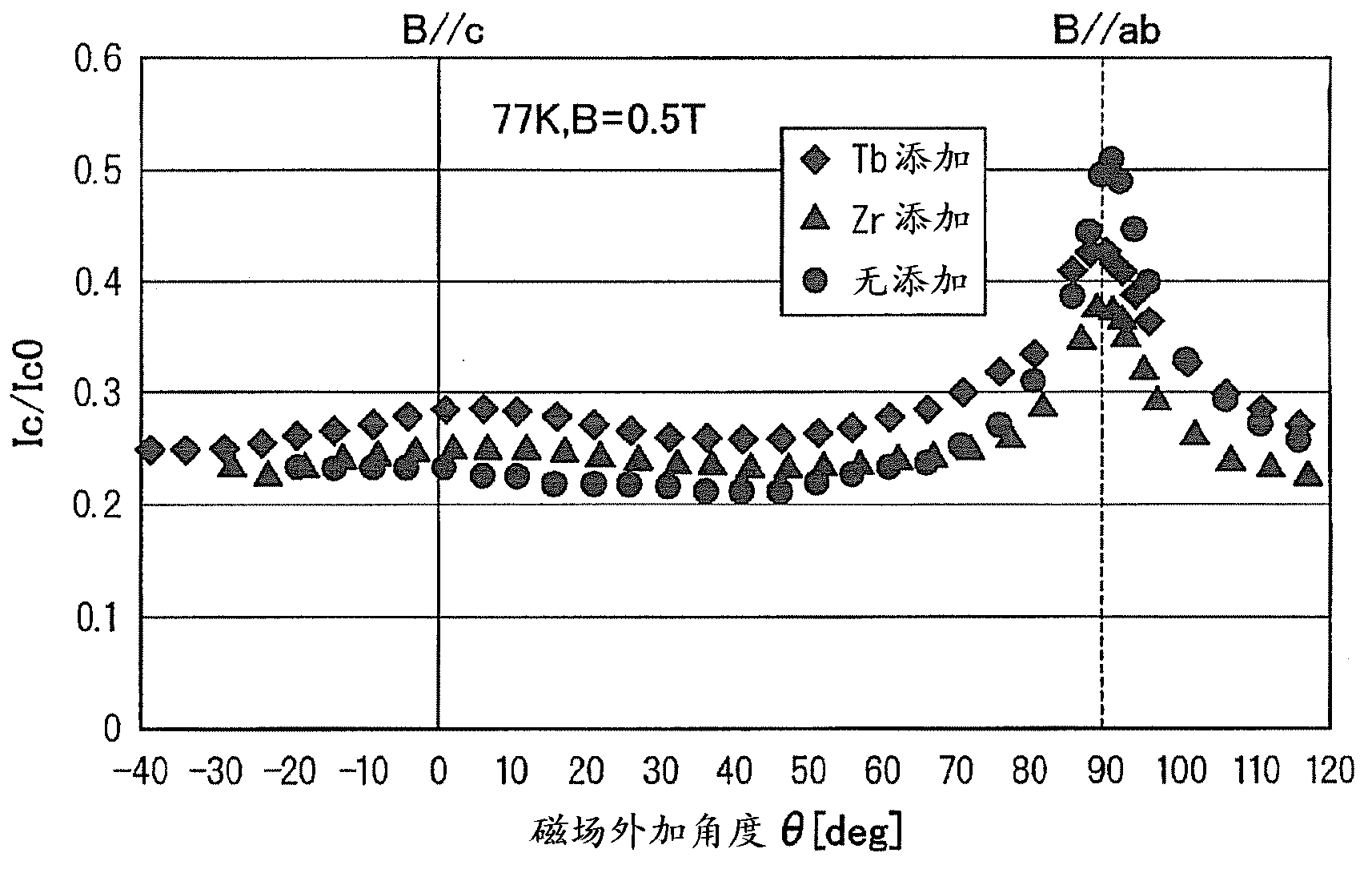
The disclosed oxide superconductor is provided with a substrate and an oxide superconducting layer which is formed on the substrate. The oxide superconducting layer is formed from an oxide superconductor represented by the structural formula: RE1Ba2Cu3Oy (in the formula RE represents a rare earth element, and 6.5<y<7.1), and has a Tb-containing hetero-phase dispersed therein.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
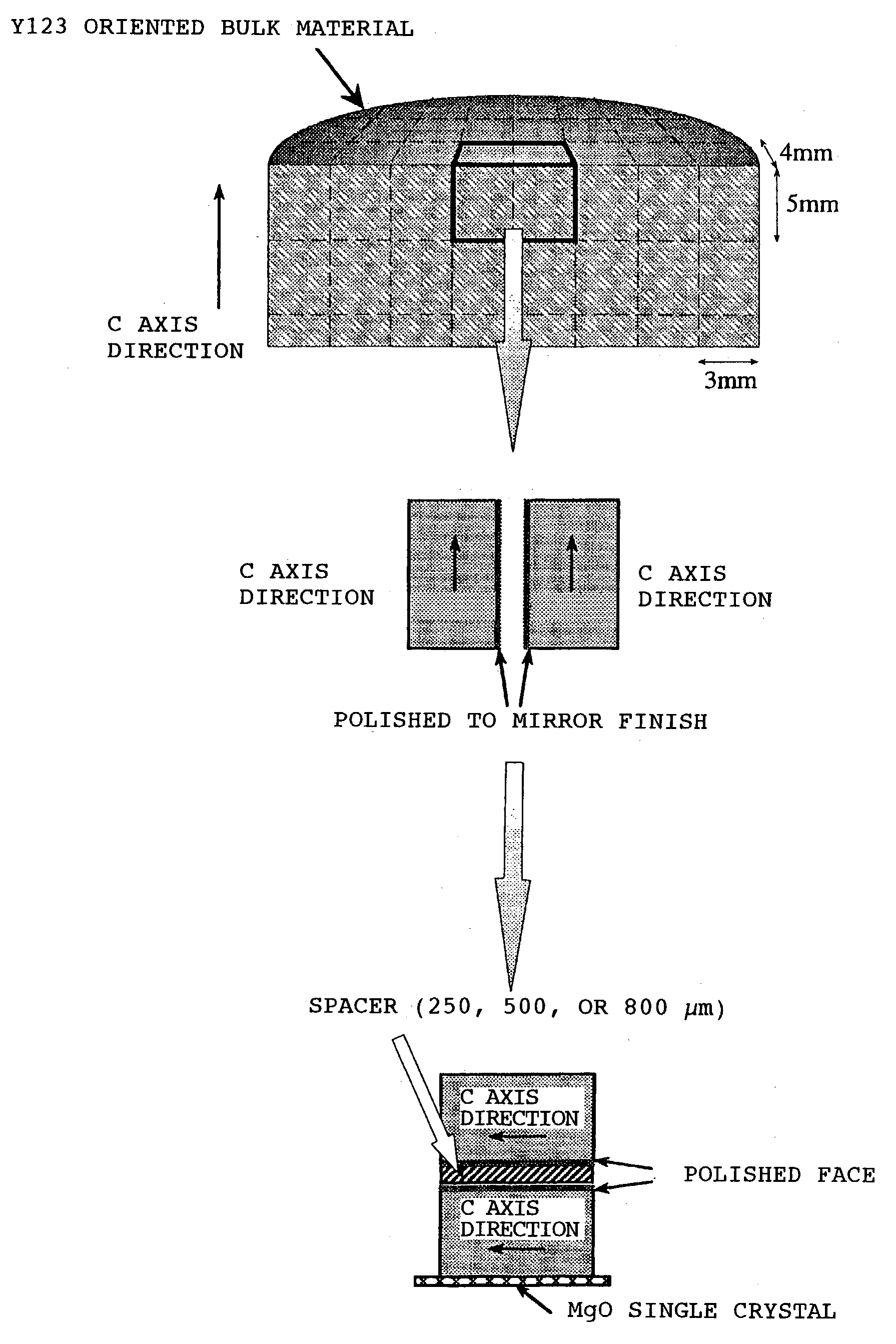
Method of joining oxide superconductors and oxide superconductor joiner
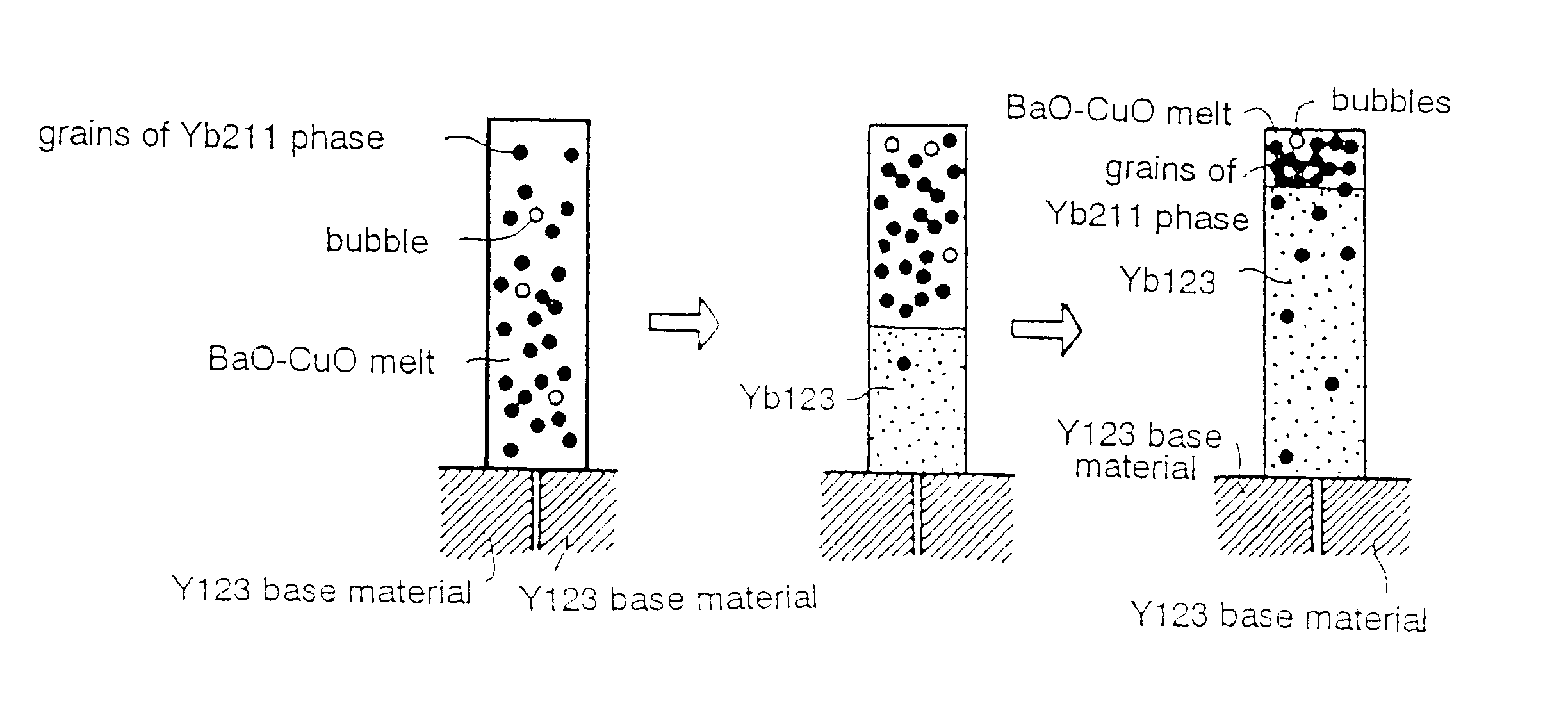
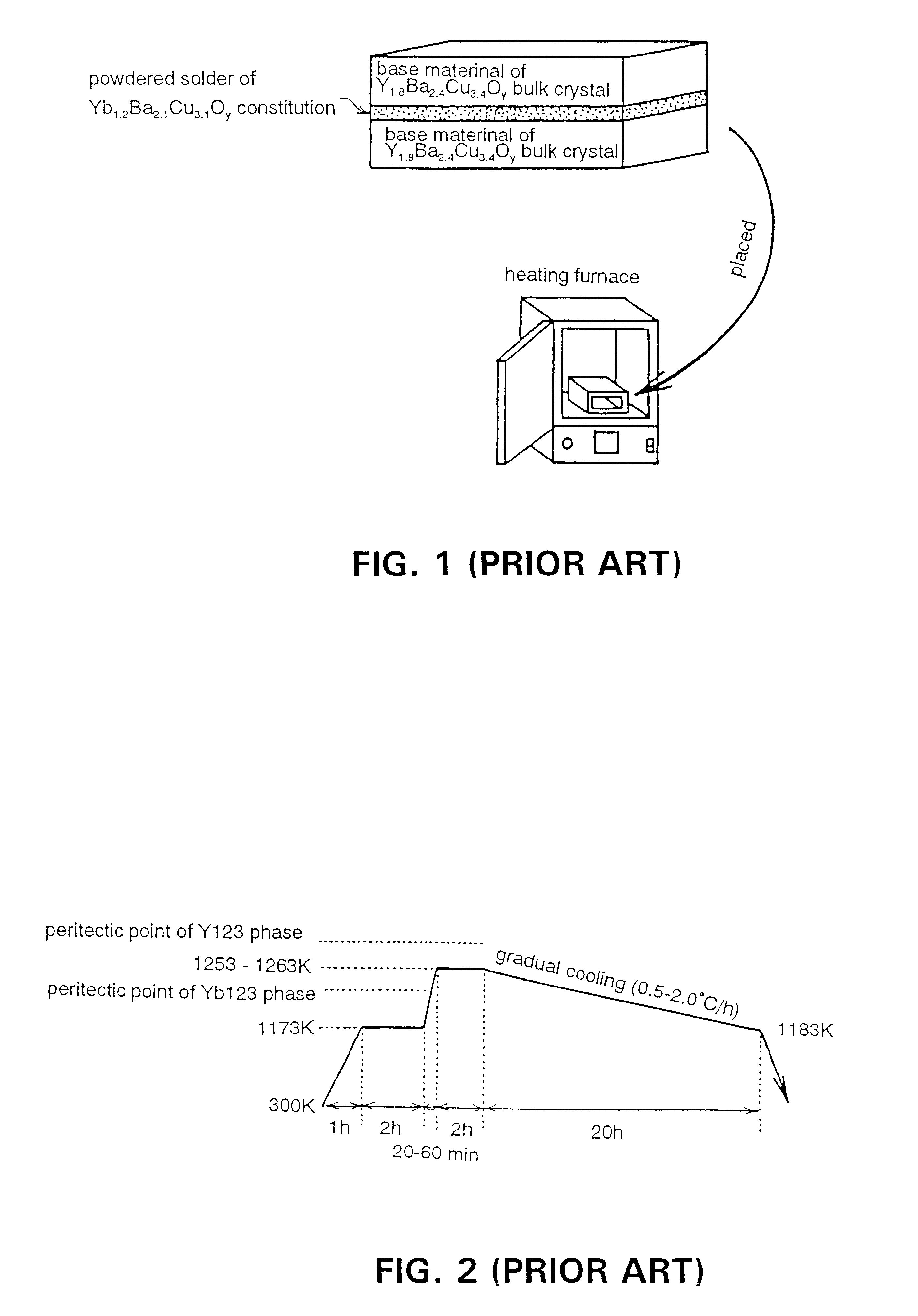
The present invention provides a method for joining an RE123 oxide superconductor matrix obtained by a melt process by the use of a solder material. The (110) plane of an RE123 oxide superconductor matrix obtained by a melt process is used as the plane to be joined, a solder material composed of an RE123 oxide superconductor having a lower melting point than the above-mentioned RE123 oxide superconductor is interposed between the planes to be joined, and this solder material is melted and then solidified to form a joining layer, thereby joining the matrices. The solder material can be a sinter, a melt-processed material, a powder, a slurry, or a molded powder.
Owner:INT SUPERCONDUCTIVITY TECH CENT
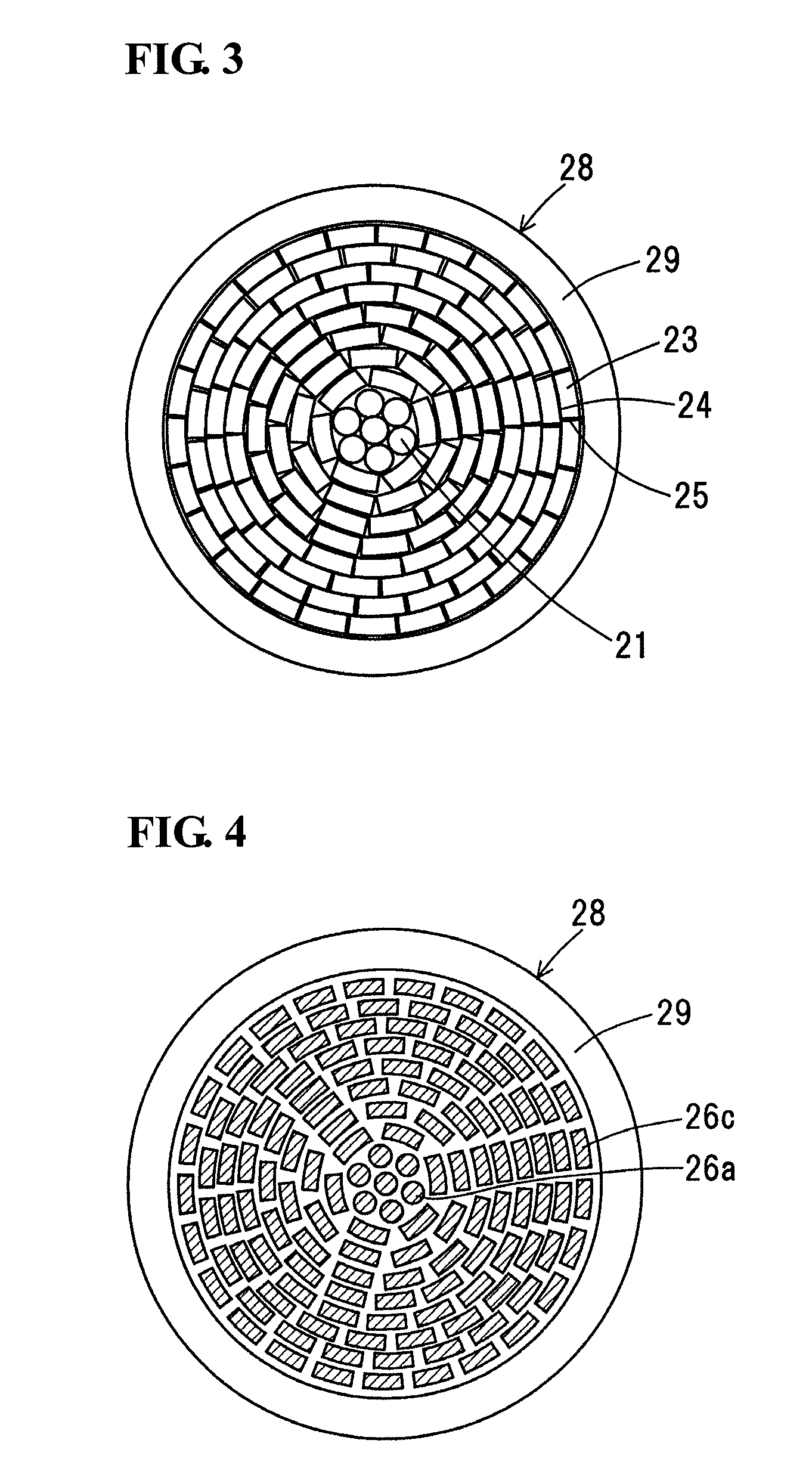
Precursor wire of oxide superconducting wire and production method thereof and oxide superconducting wire produced by using the precursor wire
ActiveUS20110136673A1High critical current densityReduce thicknessSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsBand shapeAlloy
A precursor wire of an oxide superconducting wire includes a first sheath made of silver or silver alloy, a center portion in the first sheath, and a plurality of peripheral segments placed close to one another at the inside of the first sheath so as to surround the center portion. Each of the peripheral segments is formed as a monofilamentary segment that has an arch-shaped cross section and that includes a ribbon-shaped filament made of a precursor of an oxide superconductor and covered with a second sheath made of silver or silver alloy. The multiple peripheral segments are placed in a multilayer state in the form of concentric circles such that wide-width surfaces of the peripheral segments surround the center portion.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Manufacturing method of polycrystal film and manufacturing method of oxide superconductor
InactiveCN1478919AEasy generationImprove superconductivityPolycrystalline material growthSuperconductors/hyperconductorsCrystal orientationIon beam
In the production method for a polycrystal thin film, when a polycrystal thin film is deposited on a polycrystal base material, the temperature of the polycrystal base material is set to the range of 150 to 250[deg.]C, the ion beam energy of an ion beam is controlled to the range of 175 to 225eV, and the ion beam is applied to the normal of the face to be film-formed in the polycrystal base material at an incident angle of 50 to 60 degrees. By the production method, the polycrystal thin film in which the inclination of grain boundaries composed by the same crystal axes of the crystal grains of the polycrystal thin film along the face parallel to the face to be film-formed in the polycrystal base material is suppressed to <=20 degrees, and having high crystal orientation properties can stably be produced.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com