Patents
Literature
36results about How to "Sufficient signal to noise ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
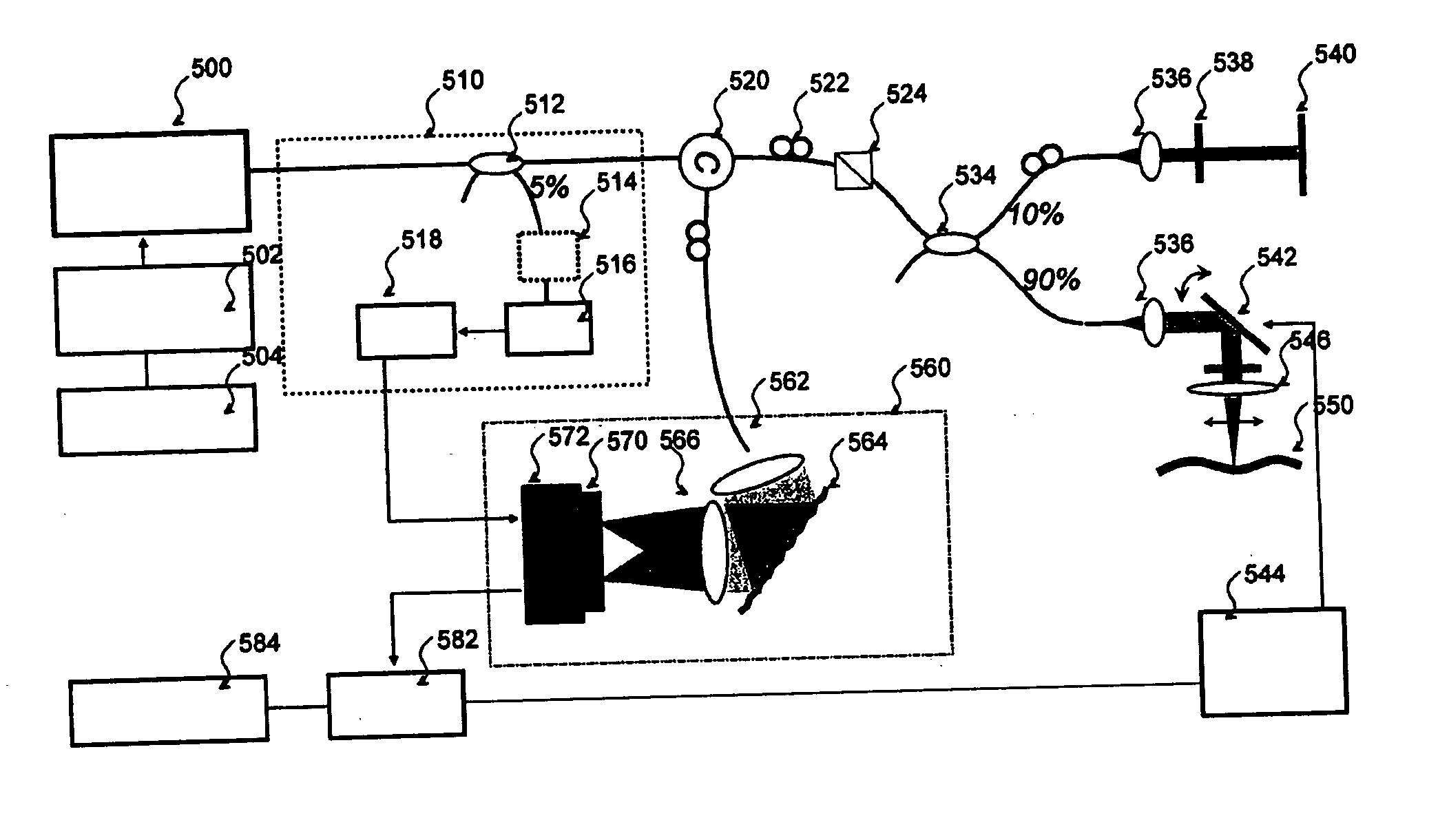
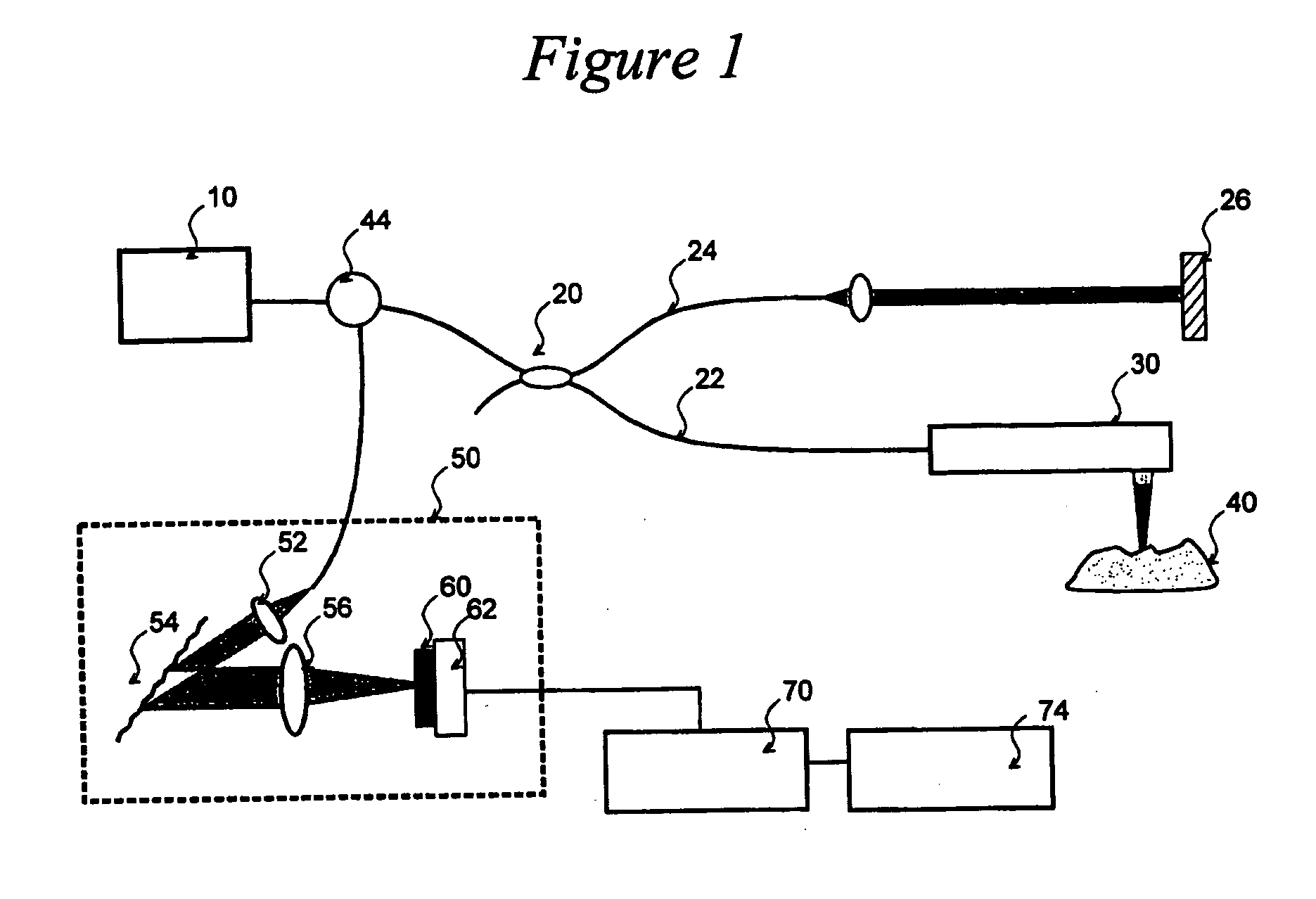
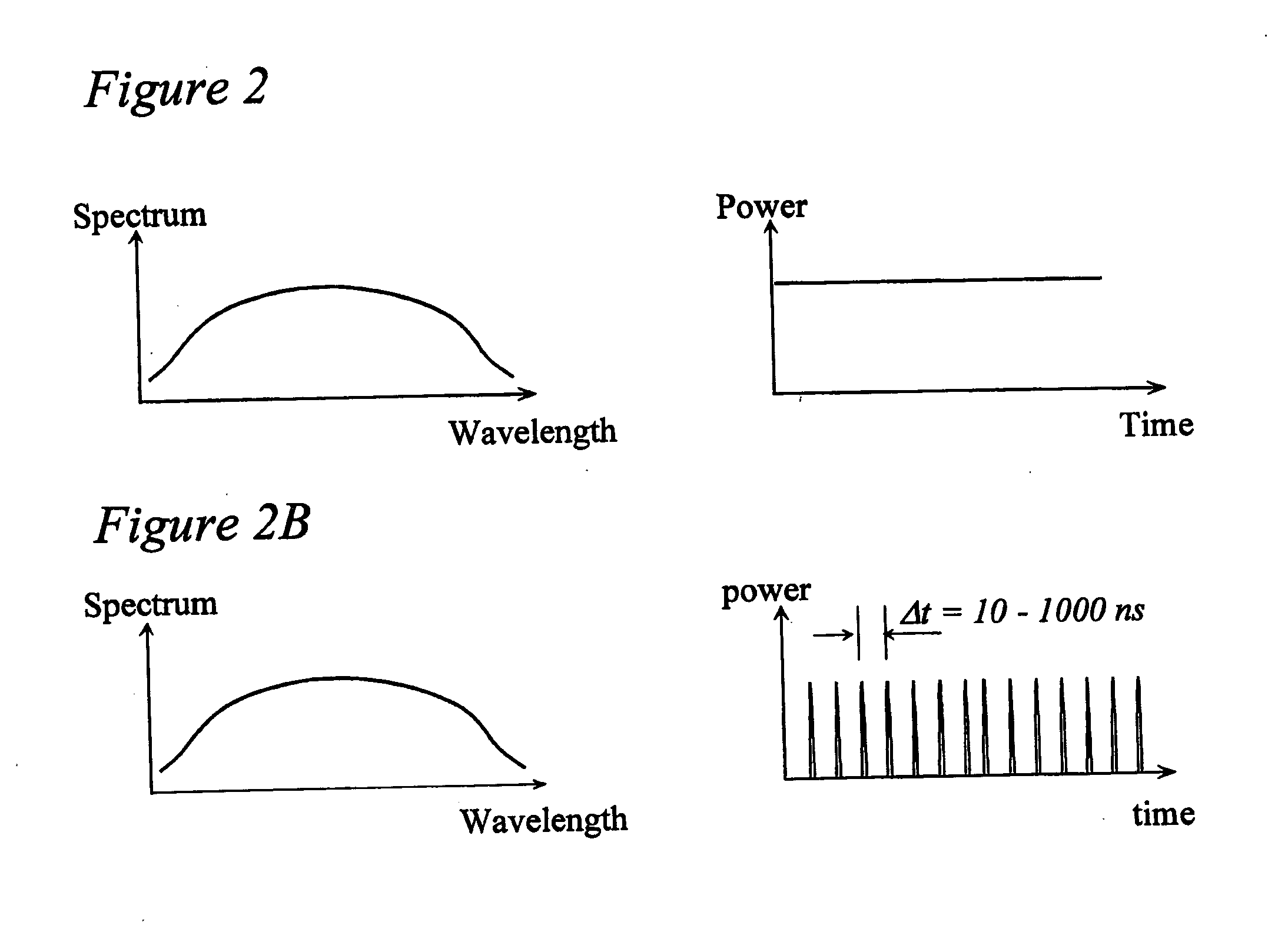
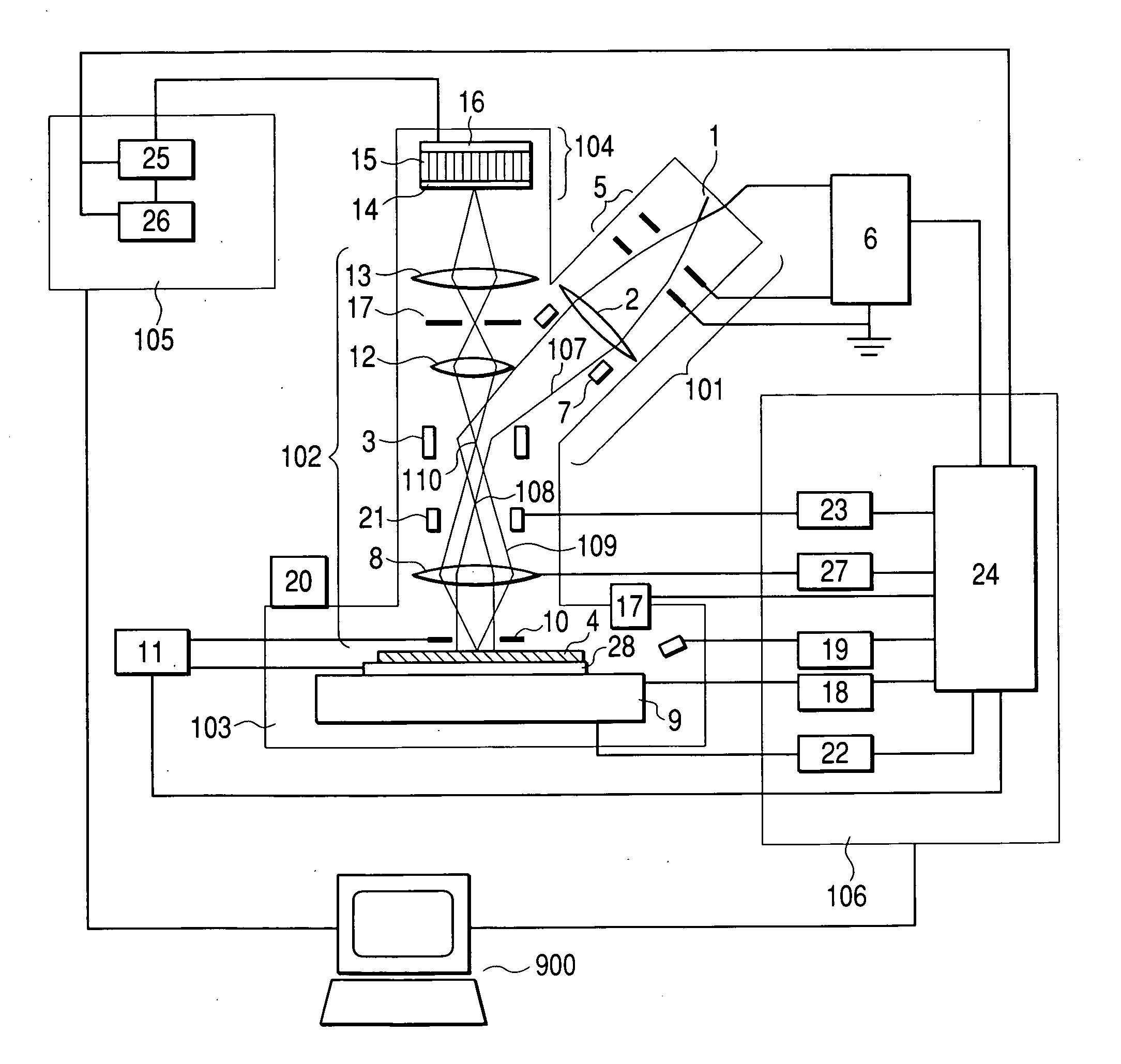
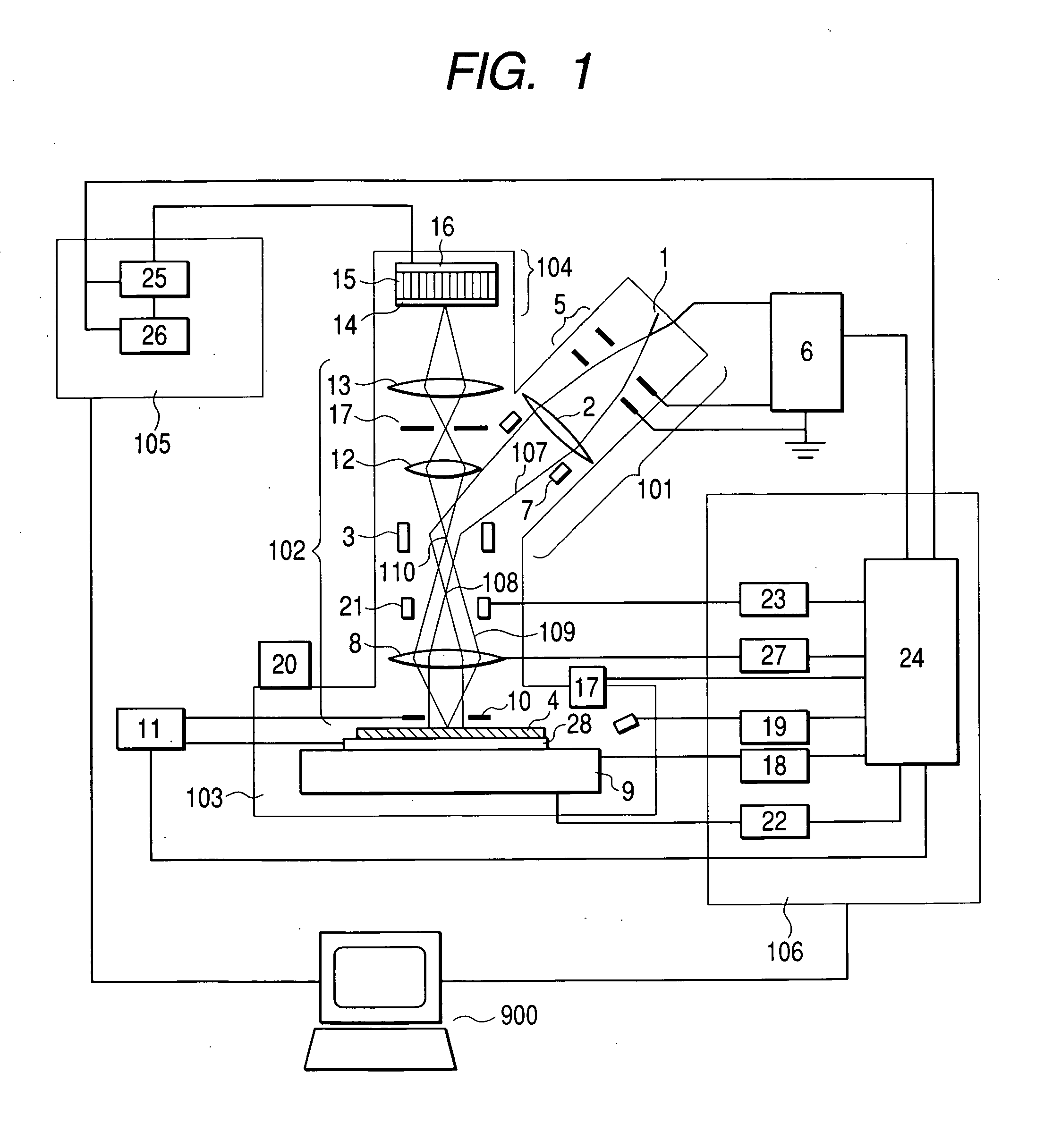
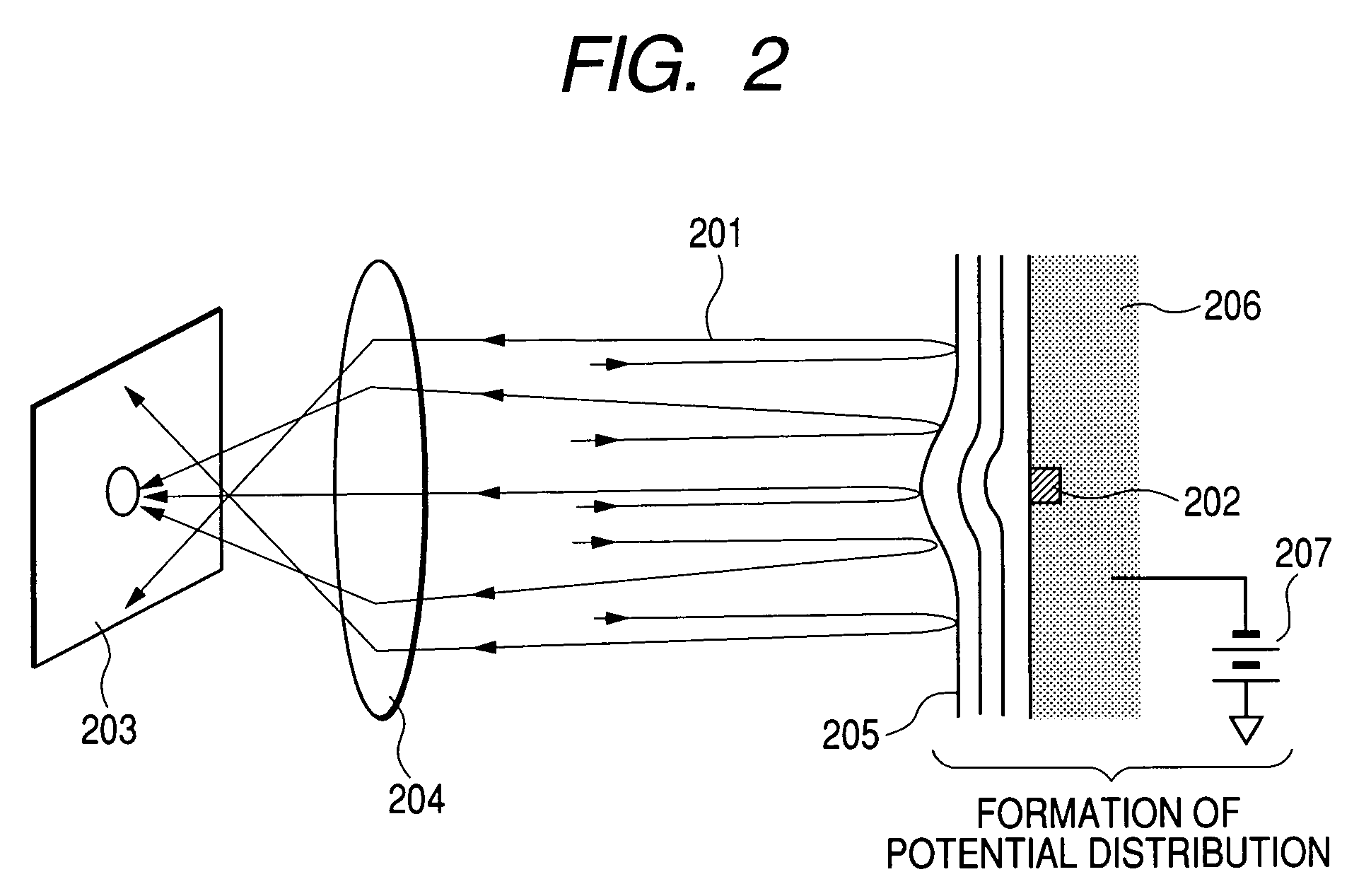
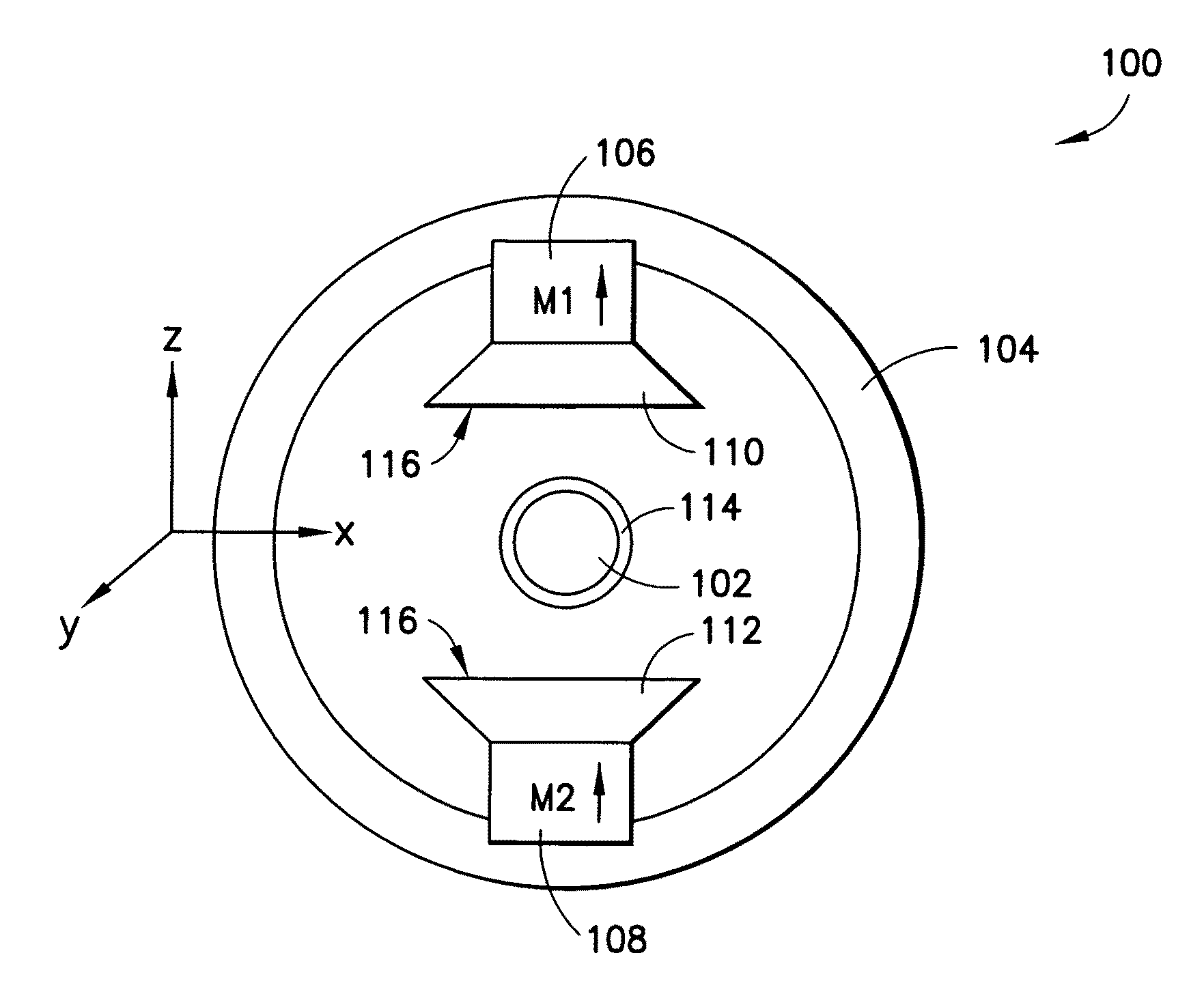
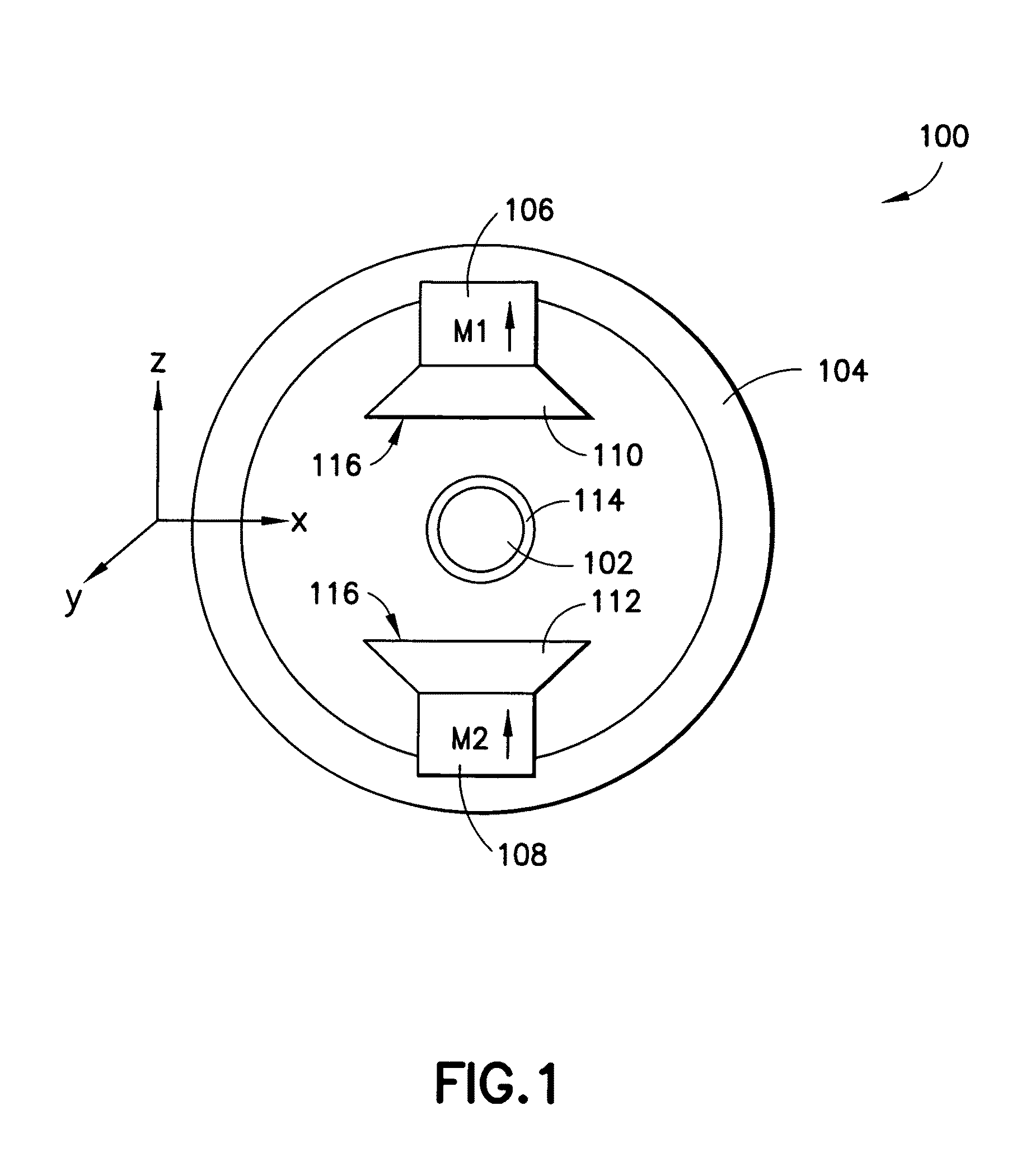
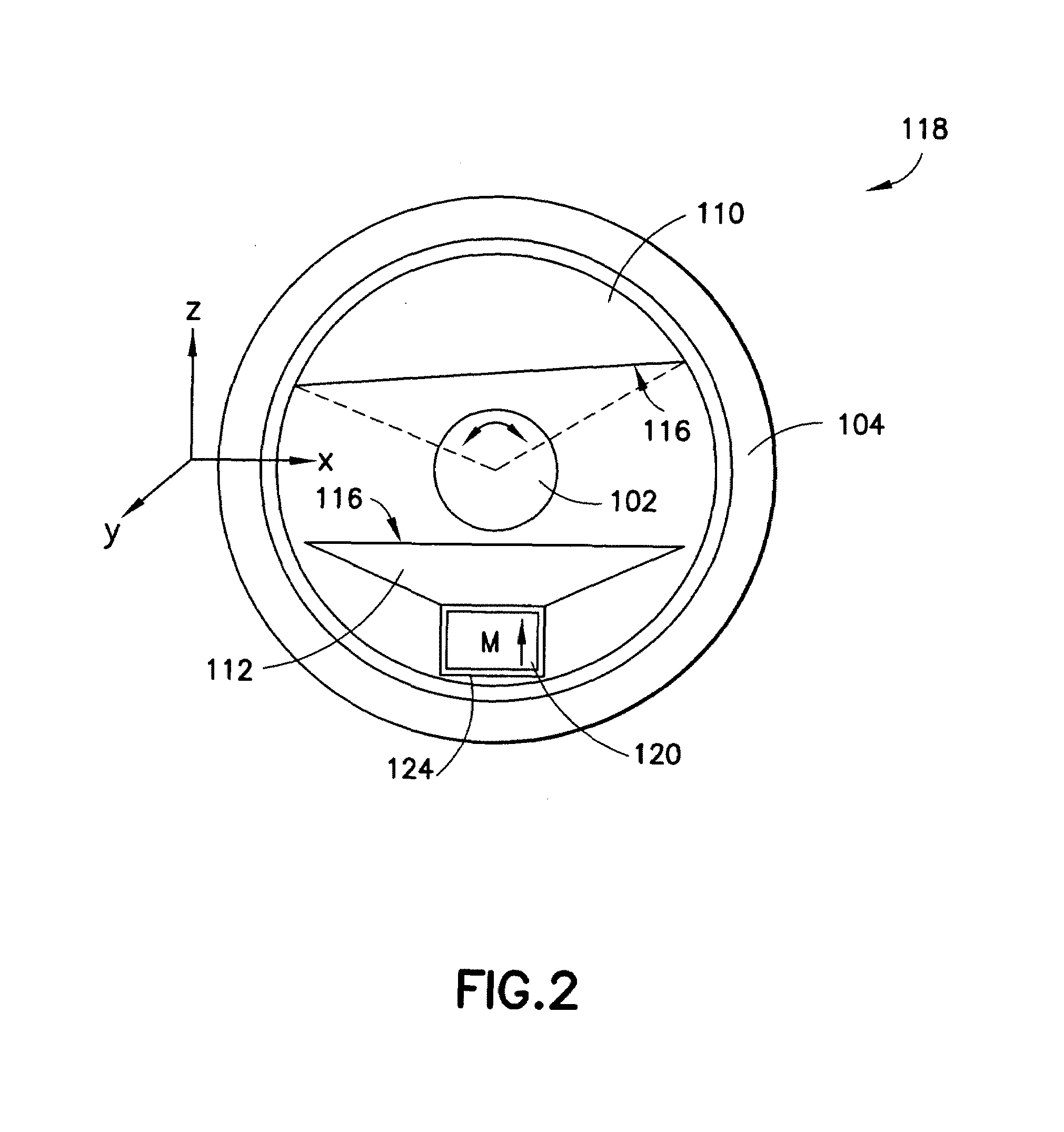
System and method for optical coherence imaging
ActiveUS20060055936A1Sufficient signal to noise ratioHigh sensitivityInterferometersScattering properties measurementsPhysicsCoherent imaging
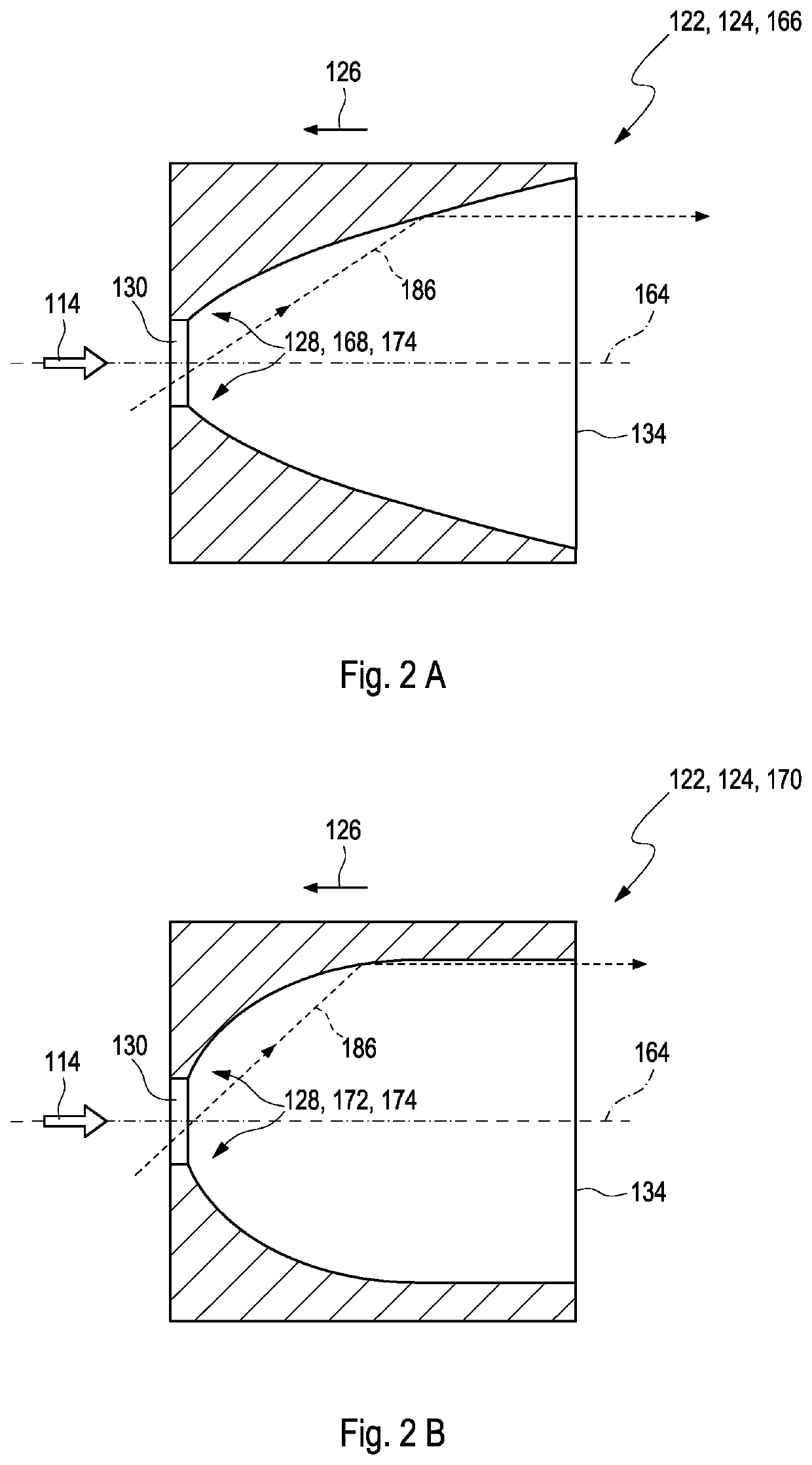
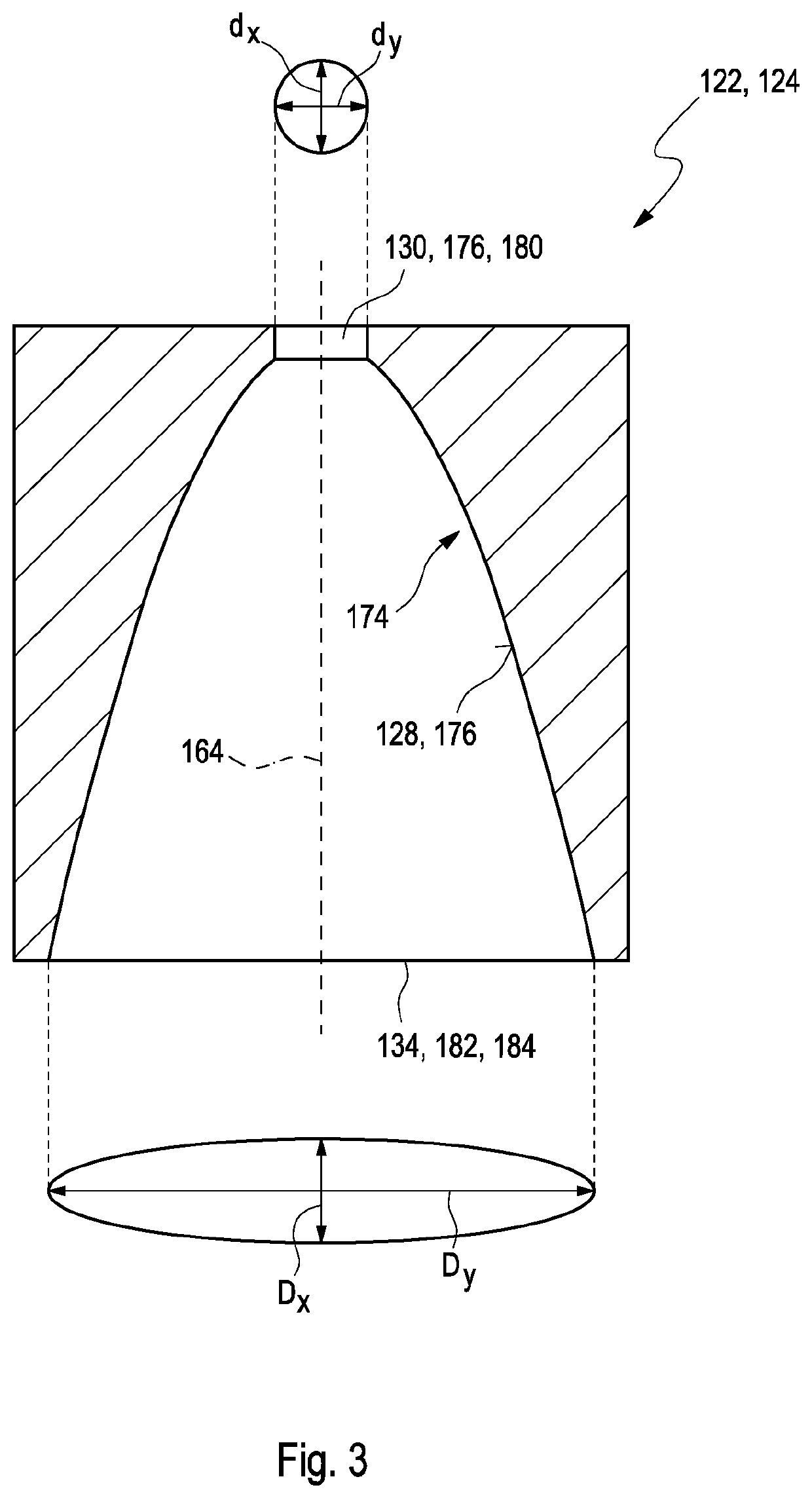
A system and method for imaging of a sample, e.g., biological sample, are provided. In particular, at least one source electro-magnetic radiation forwarded to the sample and a reference may be generated. A plurality of detectors may be used, at least one of the detectors capable of detecting a signal associated with a combination of at least one first electro-magnetic radiation received from the sample and at least one second electro-magnetic radiation received from the reference. At least one particular detector may have a particular electrical integration time, and can receive at least a portion of the signal for a time duration which has a first portion with a first power level greater than a predetermined threshold and a second portion immediately preceding or following the first portion. The second portion may have a second power level that is less than the predetermined threshold, and extends for a time period which may be, e.g., approximately more than 10% of the particular electrical integration time.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
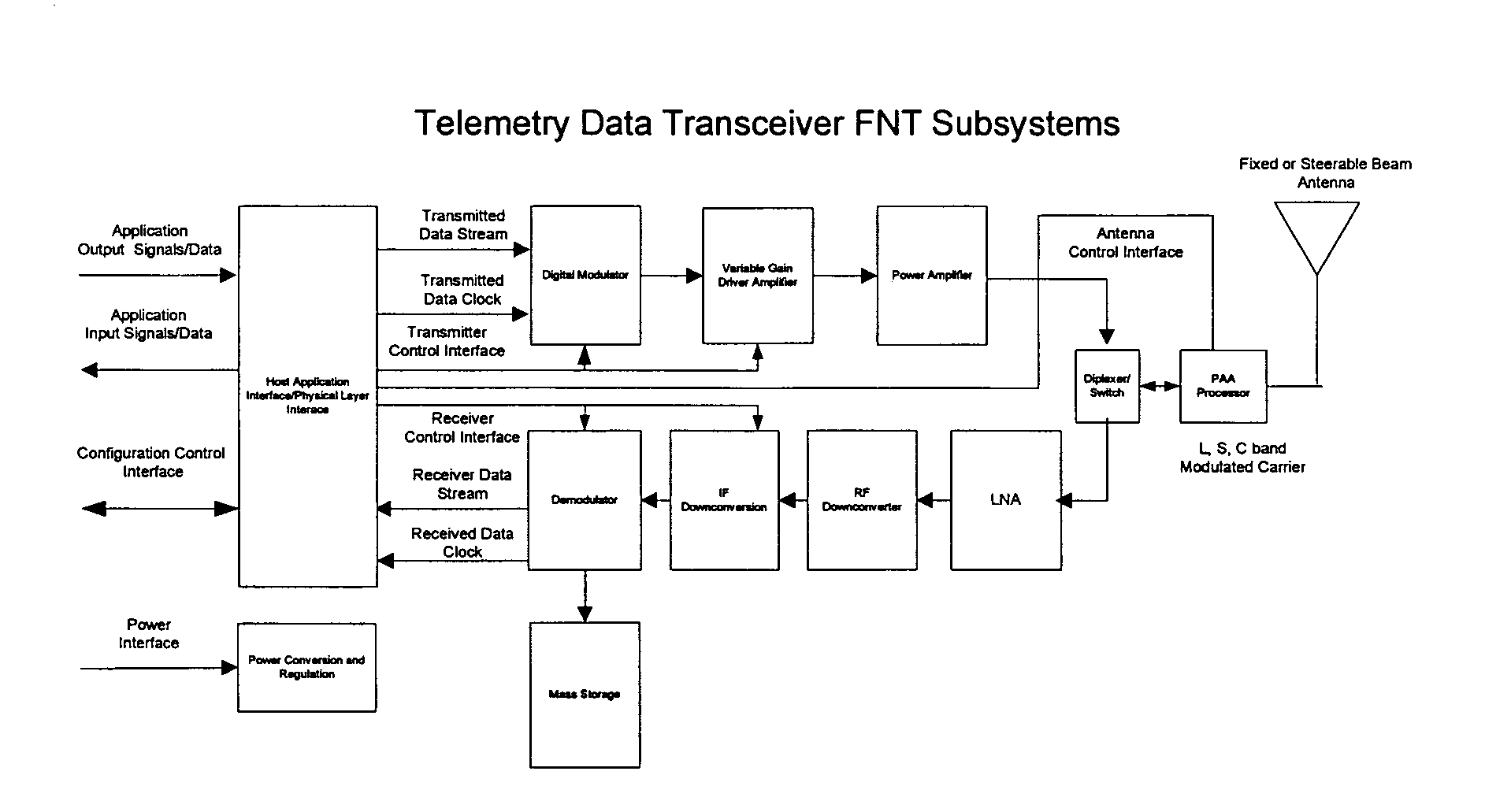
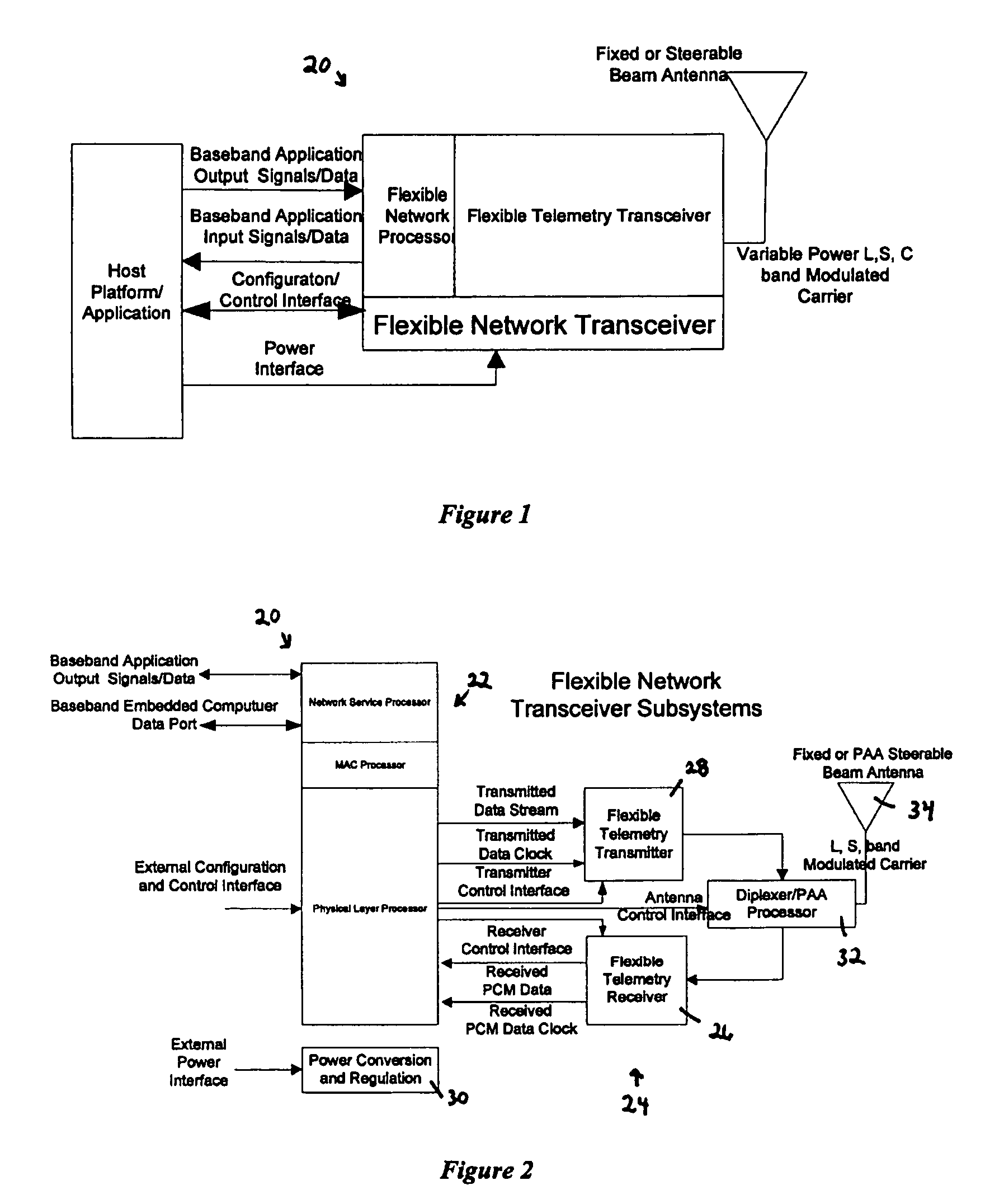
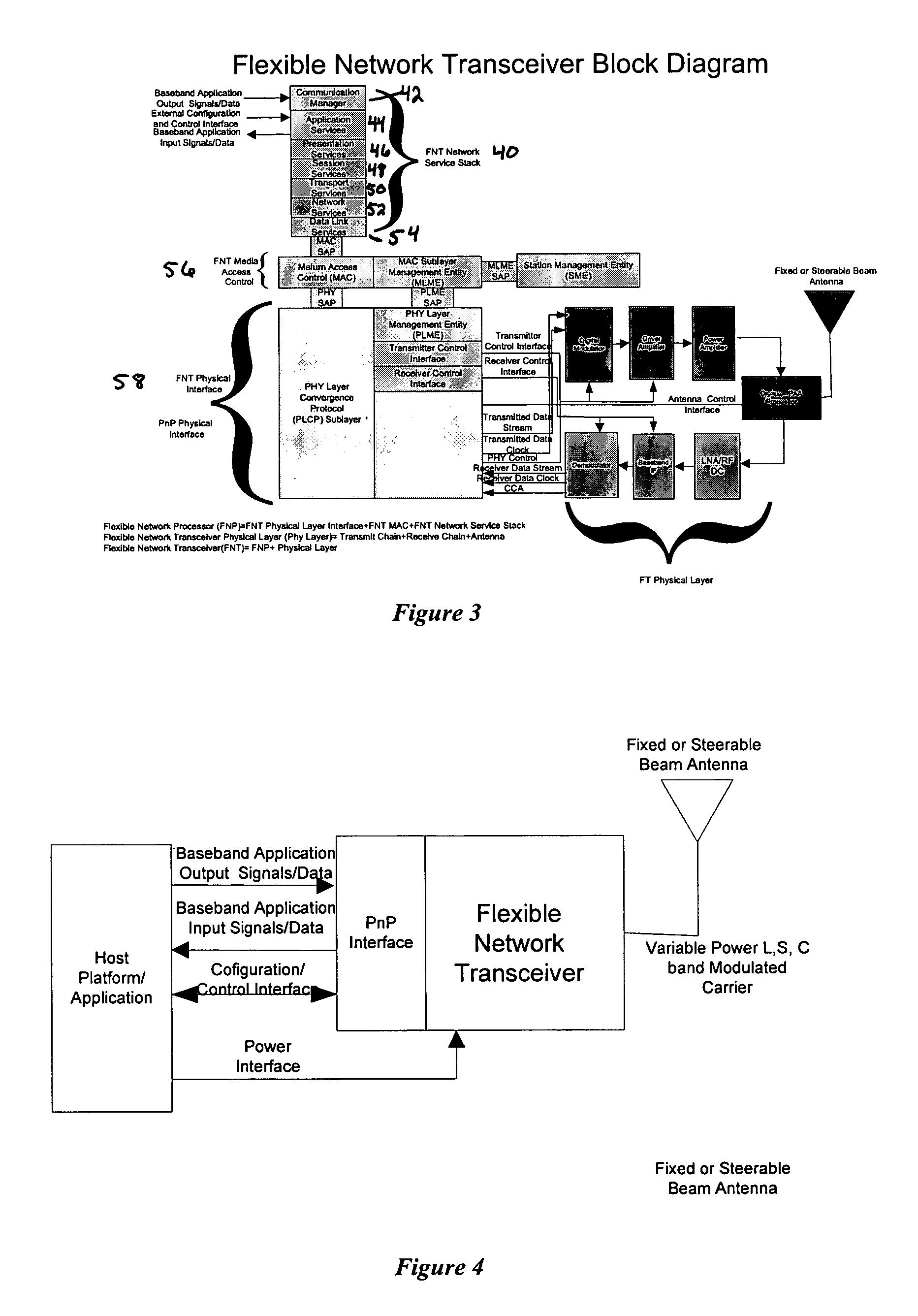
Flexible network wireless transceiver and flexible network telemetry transceiver
InactiveUS7408898B1Improve performanceIncrease data rateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransceiverGround vehicles
A transceiver for facilitating two-way wireless communication between a baseband application and other nodes in a wireless network, wherein the transceiver provides baseband communication networking and necessary configuration and control functions along with transmitter, receiver, and antenna functions to enable the wireless communication. More specifically, the transceiver provides a long-range wireless duplex communication node or channel between the baseband application, which is associated with a mobile or fixed space, air, water, or ground vehicle or other platform, and other nodes in the wireless network or grid. The transceiver broadly comprises a communication processor; a flexible telemetry transceiver including a receiver and a transmitter; a power conversion and regulation mechanism; a diplexer; and a phased array antenna system, wherein these various components and certain subcomponents thereof may be separately enclosed and distributable relative to the other components and subcomponents.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
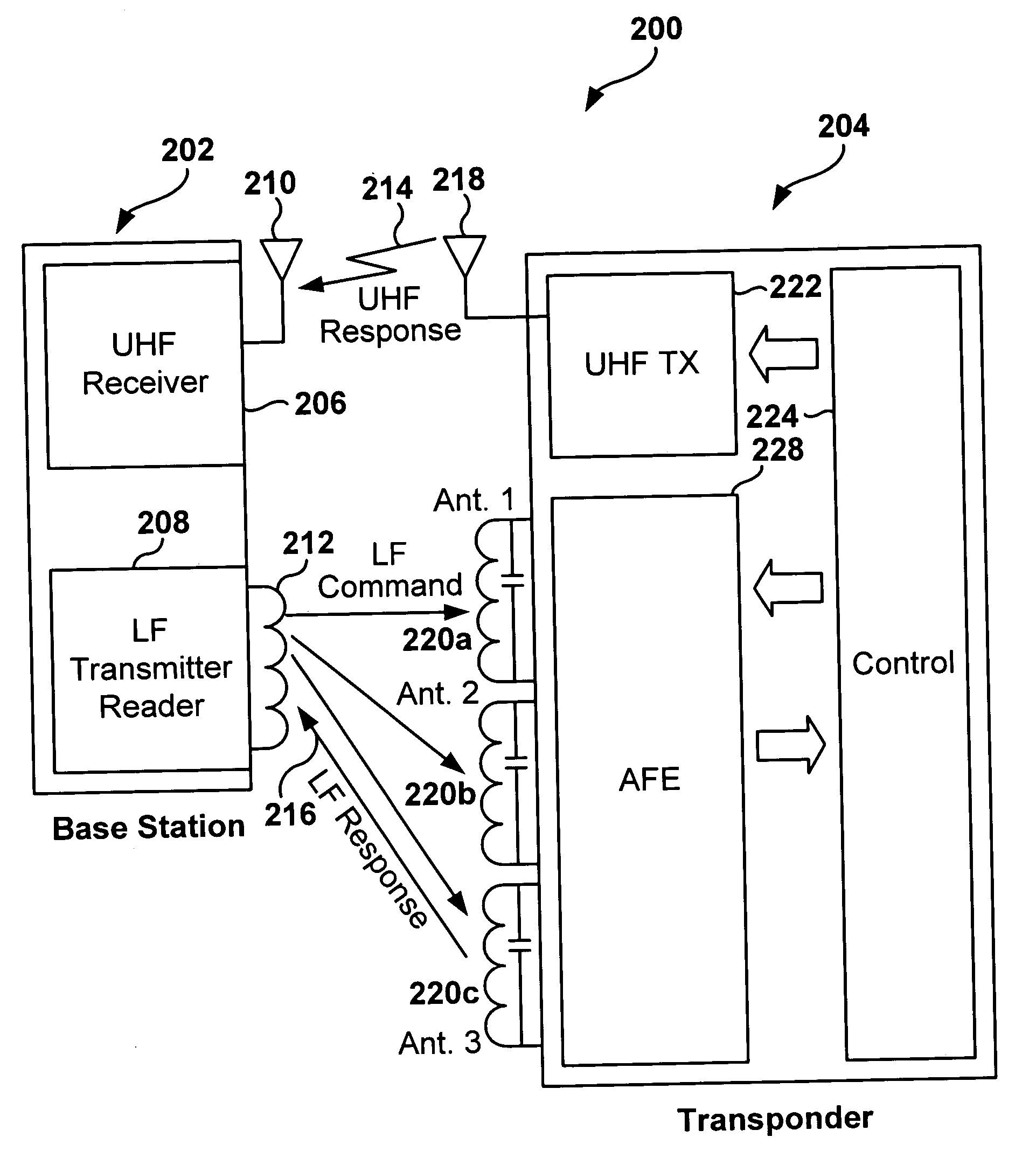
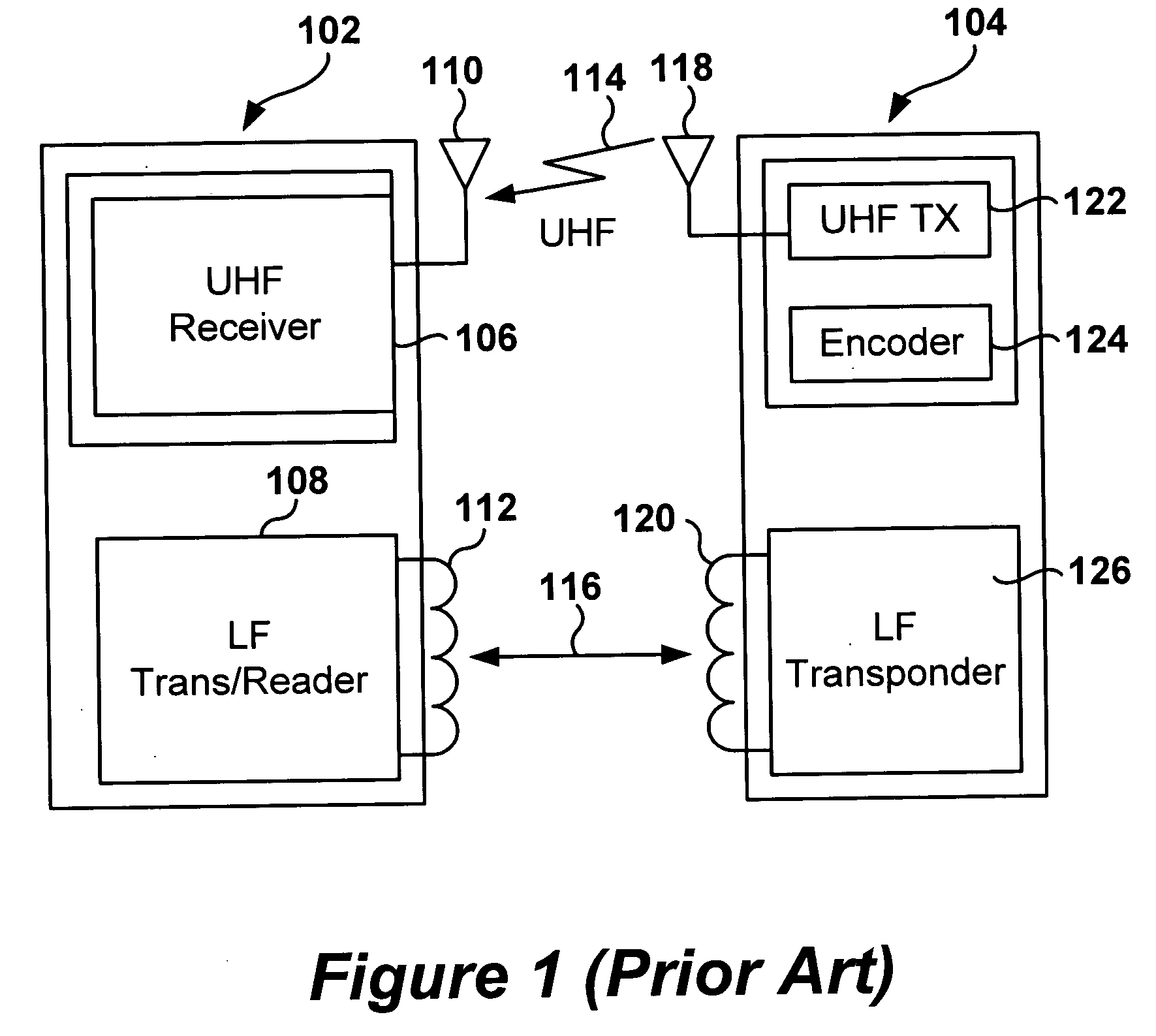
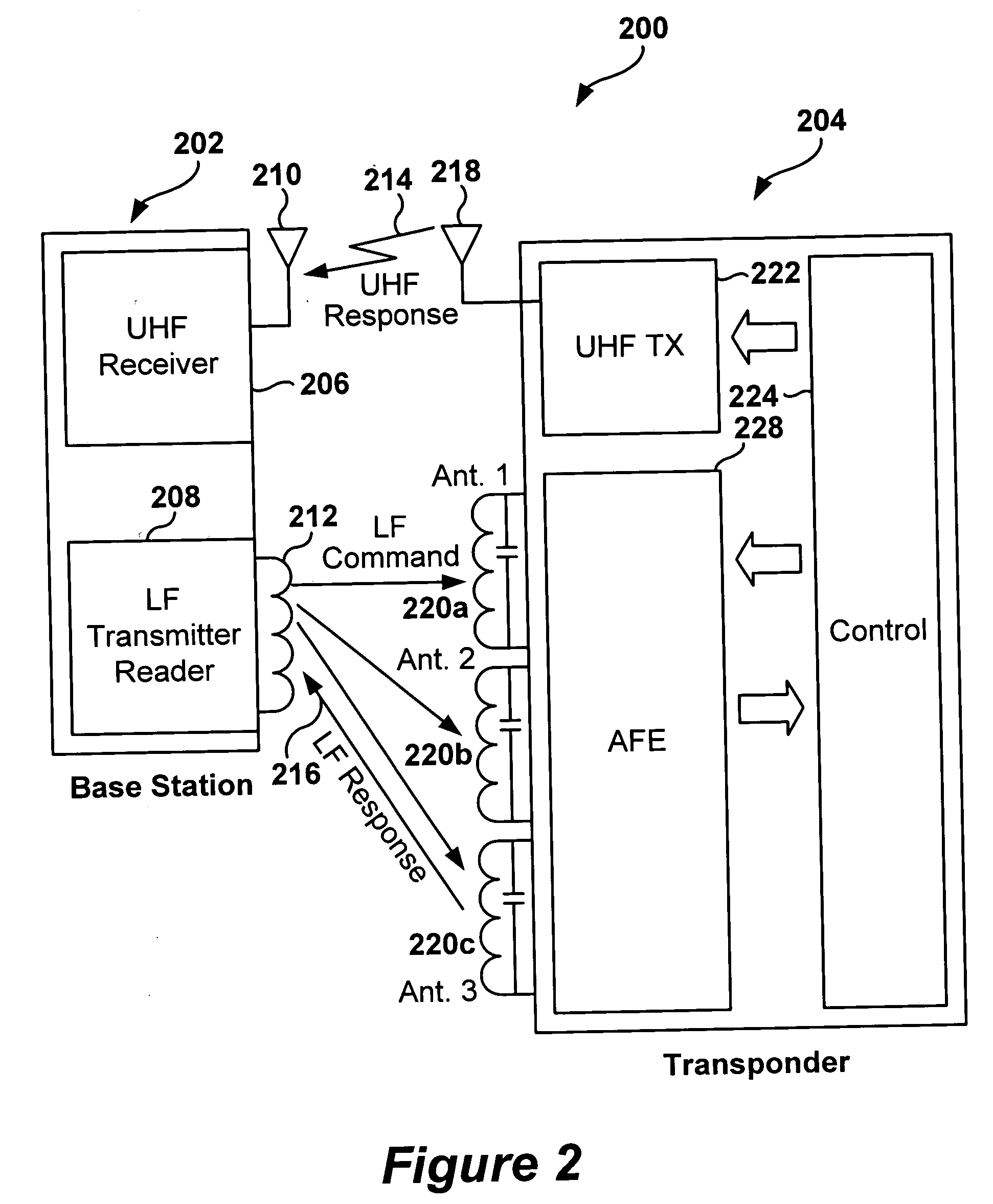
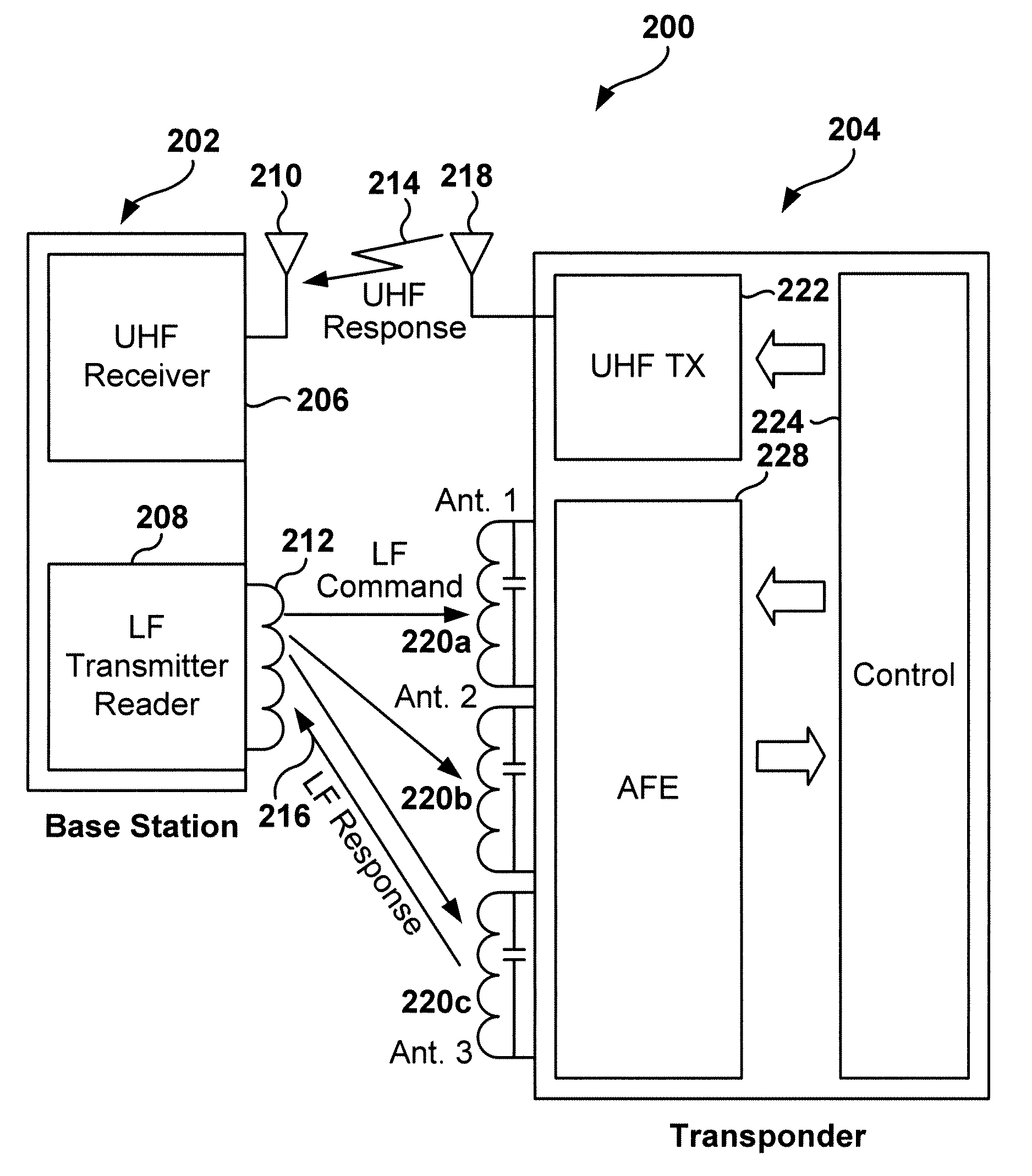
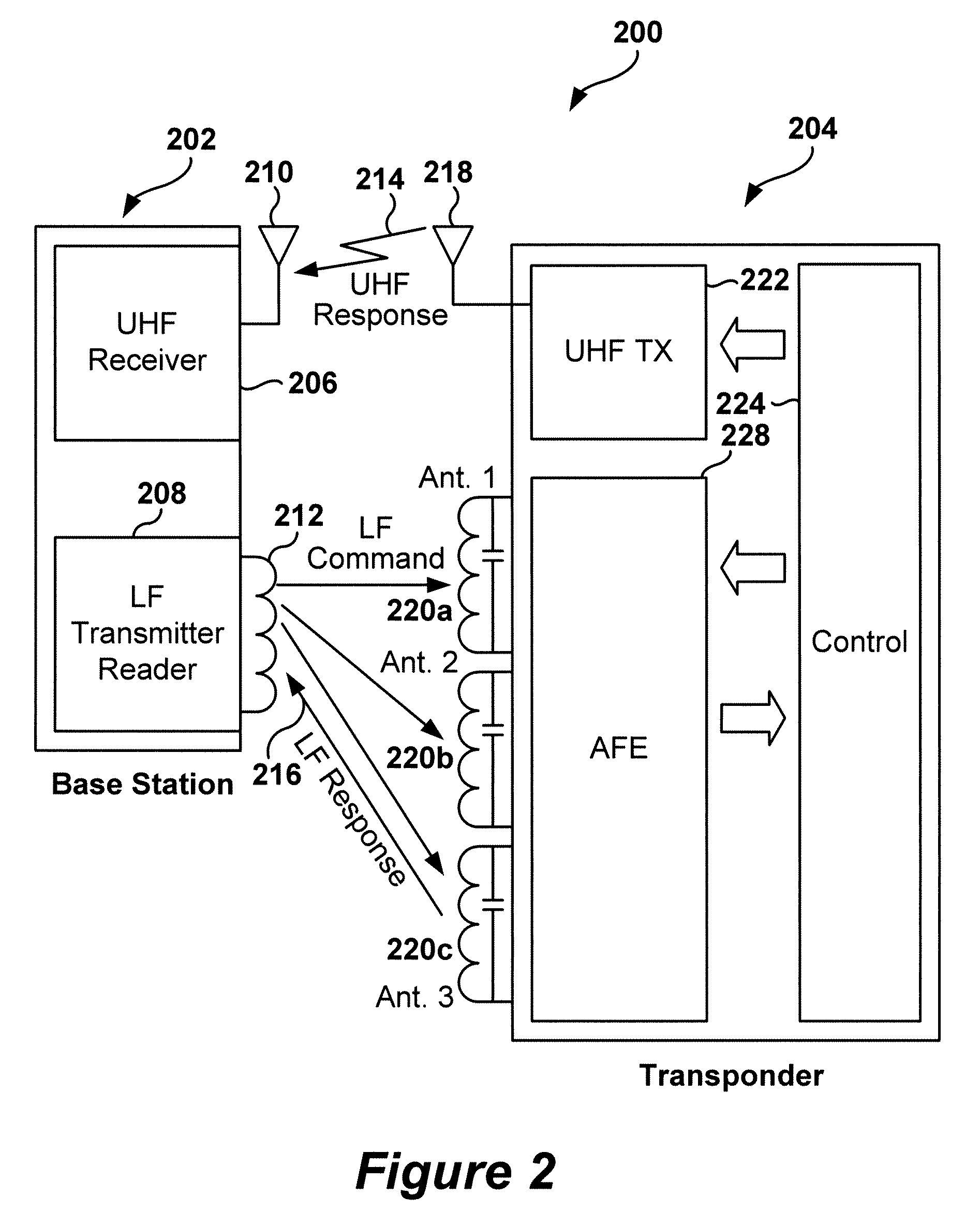
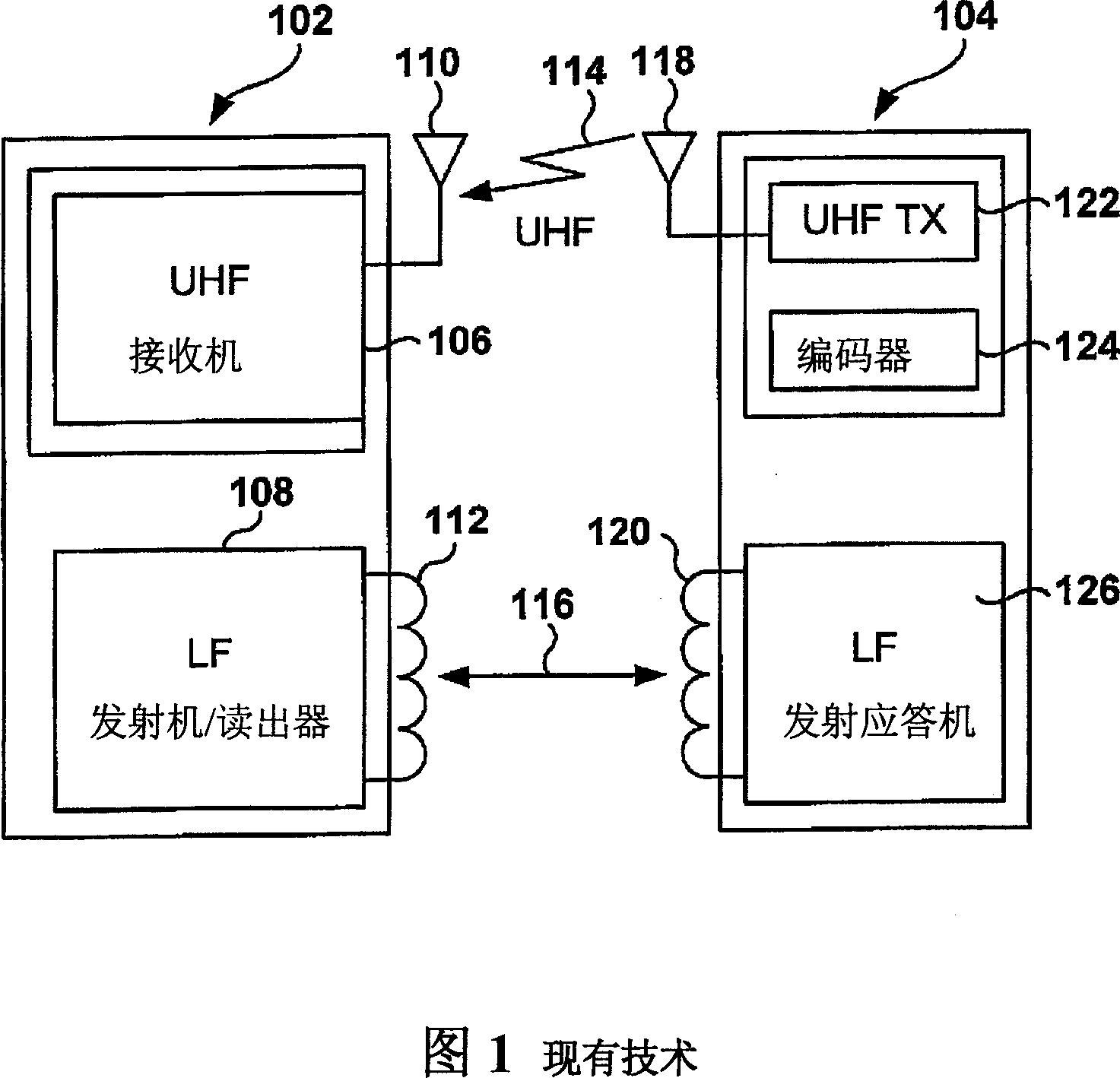
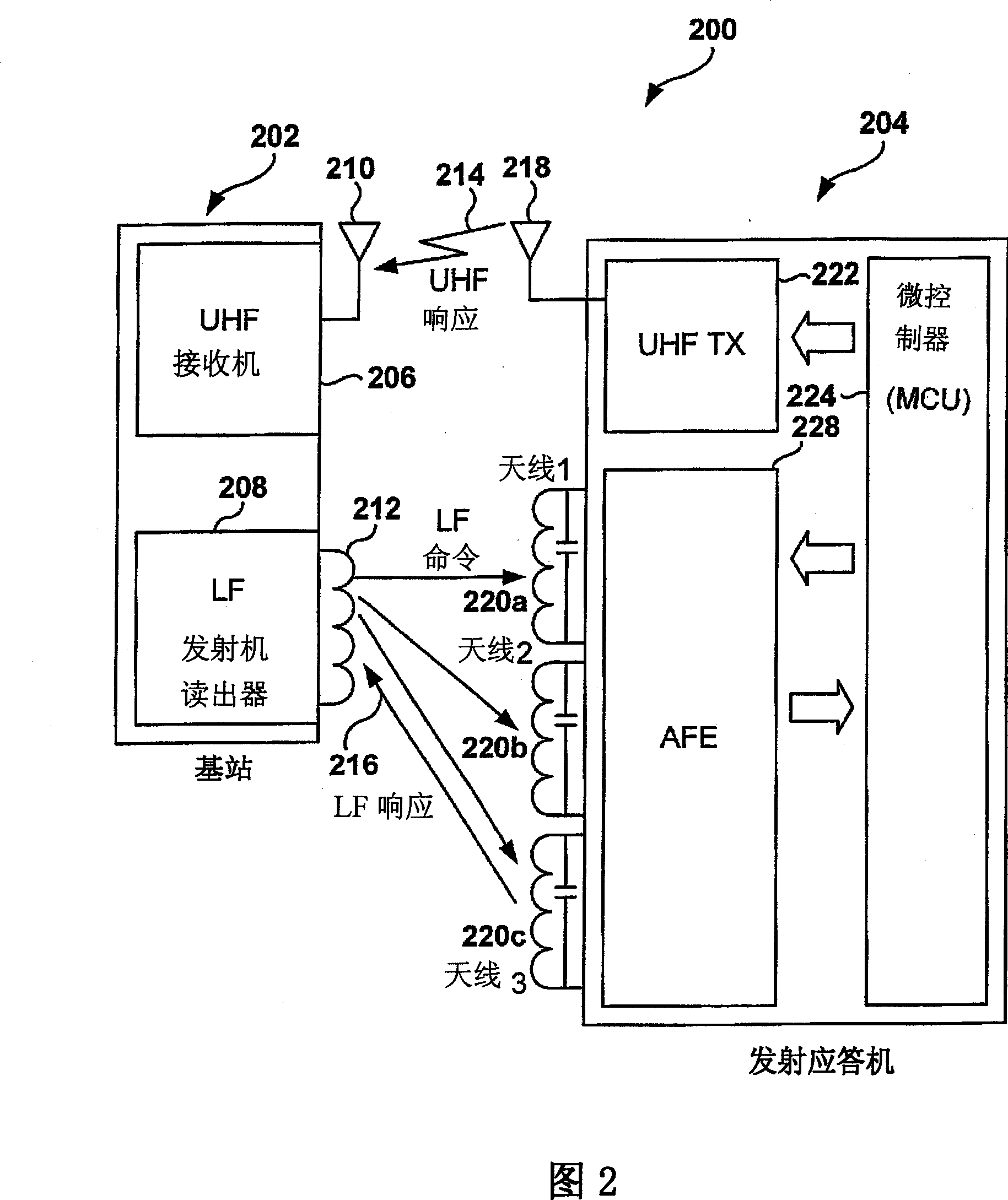
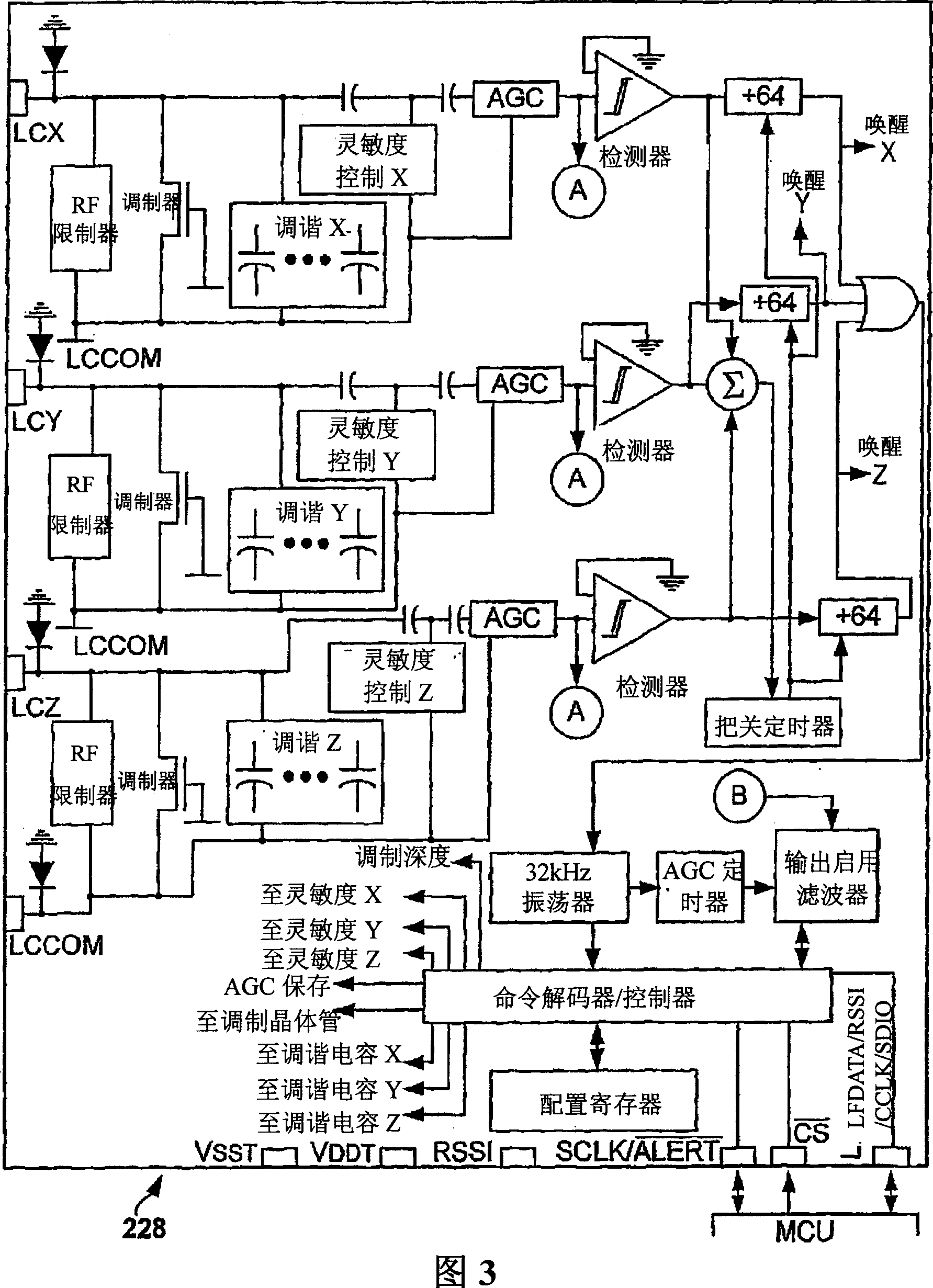
Dynamic configuration of a radio frequency transponder
ActiveUS20050237163A1Increased power consumptionShortened battery lifeElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsCapacitanceRadio frequency
A multi-channel remote keyless entry (RKE) transponder having dynamically re-configurable input channel selection, channel disable, settable sensitivity for each channel, wake-up filter timing parameters, automatic gain control hold, internal tuning capacitor selection for each channel's antenna, minimum modulation depth requirement for input signal and bi-directional talk-back. Programmable minimum modulation depth requirement reduces false wake-up of the RKE transponder. An antenna for each channel of the RKE transponder may be tuned with internal tuning capacitors for improved range and receiver sensitivity. The internal tuning capacitor parameters may be stored in a configuration register. Gain of the channel may be fixed while the antenna is tuned. The antennas may be de-queued for talk-back to a base station for low frequency bi-directional communications. An external control device may dynamically read from and write to the configuration registers via a serial communications interface.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Dynamic configuration of a radio frequency transponder
ActiveUS7602274B2Facilitate communicationImprove balanceElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsCapacitanceProcessor register
A multi-channel remote keyless entry (RKE) transponder having dynamically re-configurable input channel selection, channel disable, settable sensitivity for each channel, wake-up filter timing parameters, automatic gain control hold, internal tuning capacitor selection for each channel's antenna, minimum modulation depth requirement for input signal and bi-directional talk-back. Programmable minimum modulation depth requirement reduces false wake-up of the RKE transponder. An antenna for each channel of the RKE transponder may be tuned with internal tuning capacitors for improved range and receiver sensitivity. The internal tuning capacitor parameters may be stored in a configuration register. Gain of the channel may be fixed while the antenna is tuned. The antennas may be de-queued for talk-back to a base station for low frequency bi-directional communications. An external control device may dynamically read from and write to the configuration registers via a serial communications interface.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
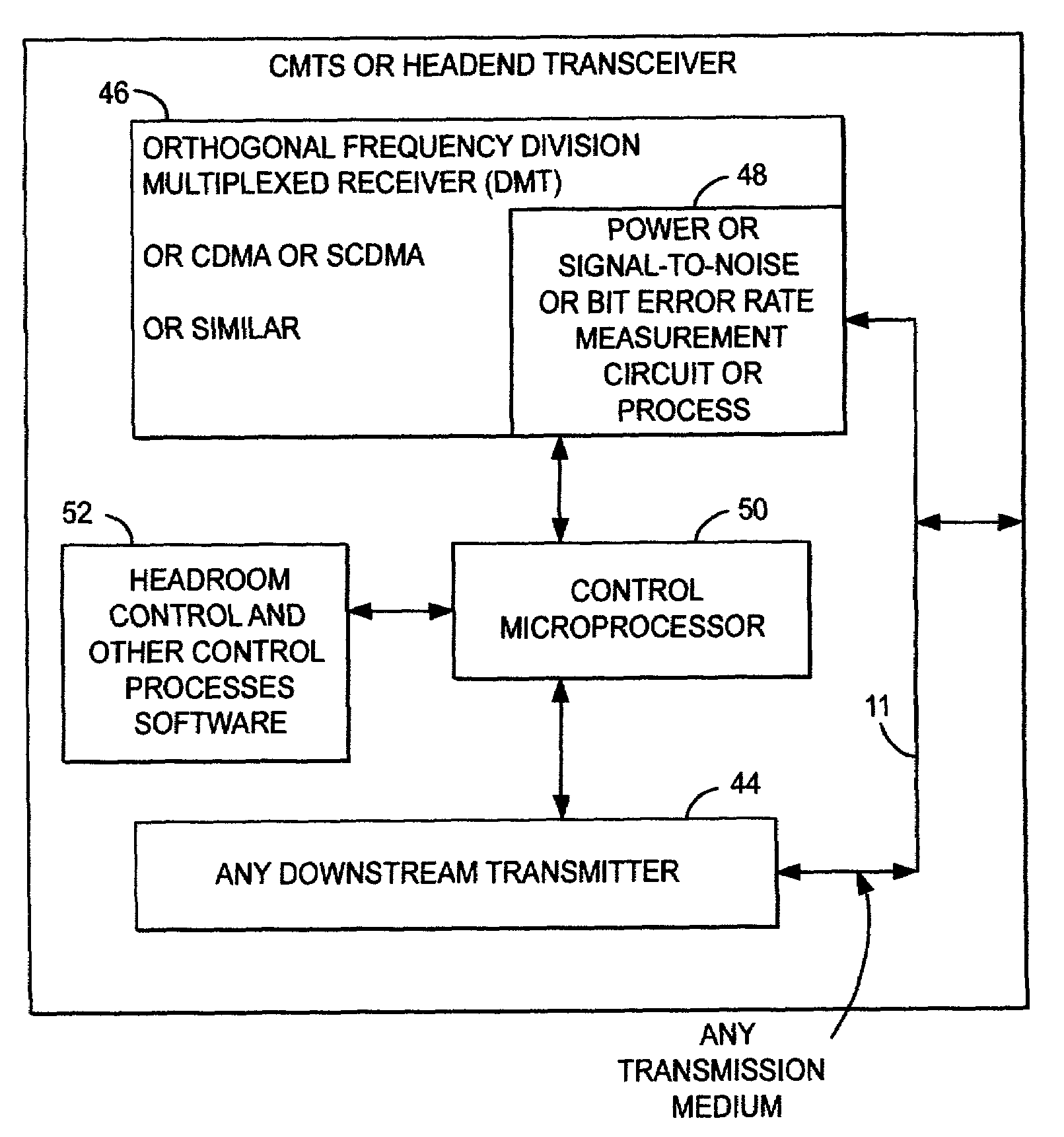
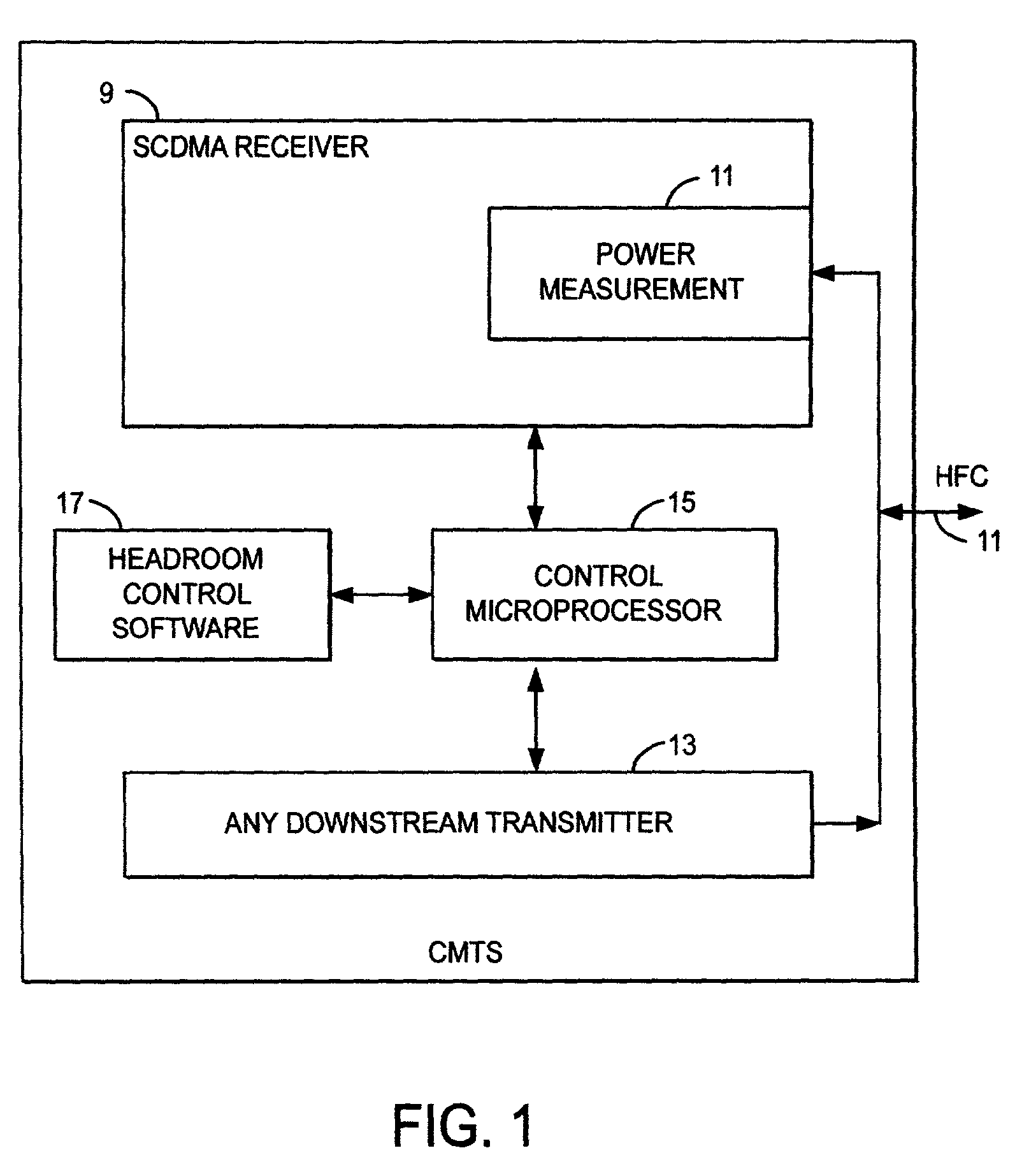
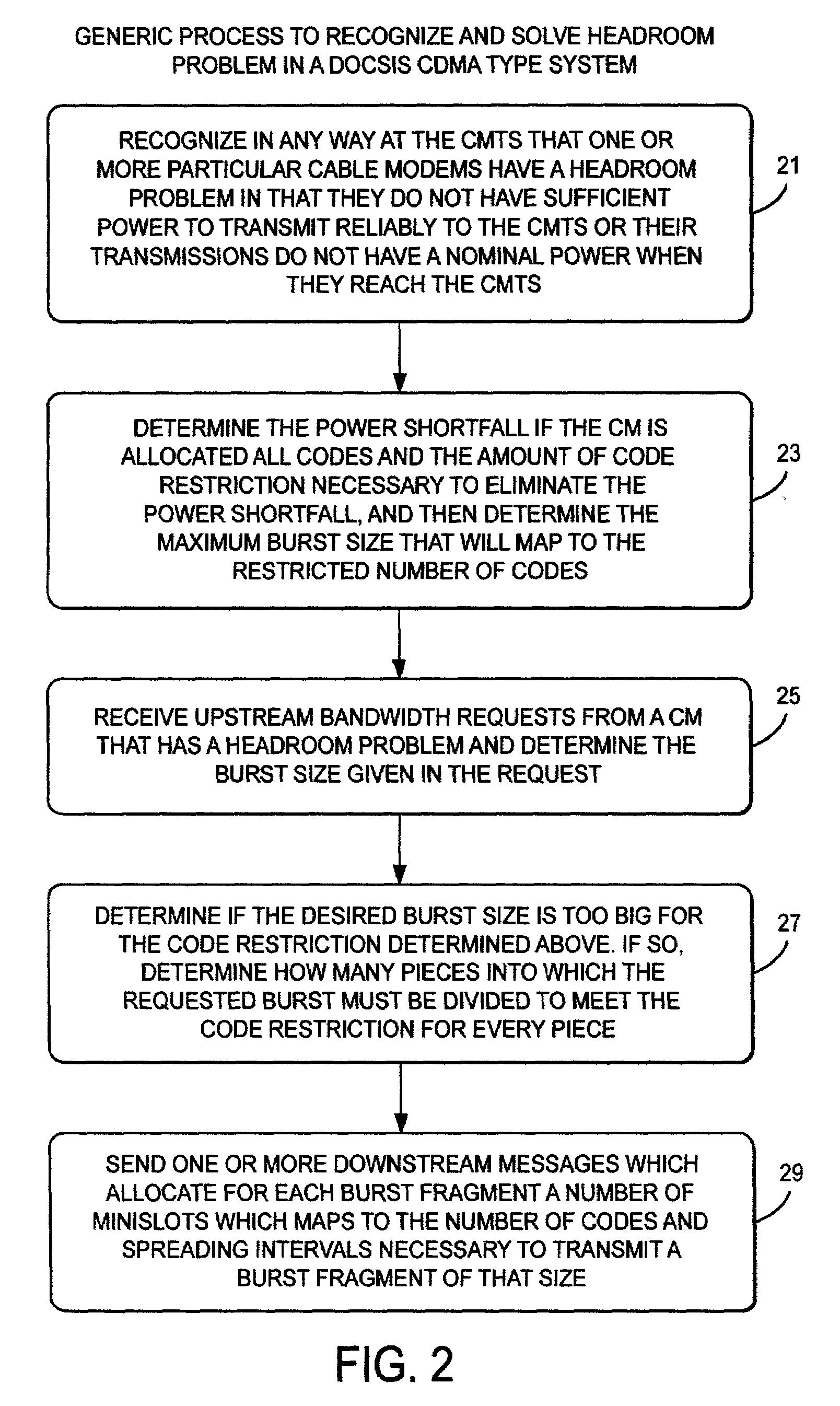
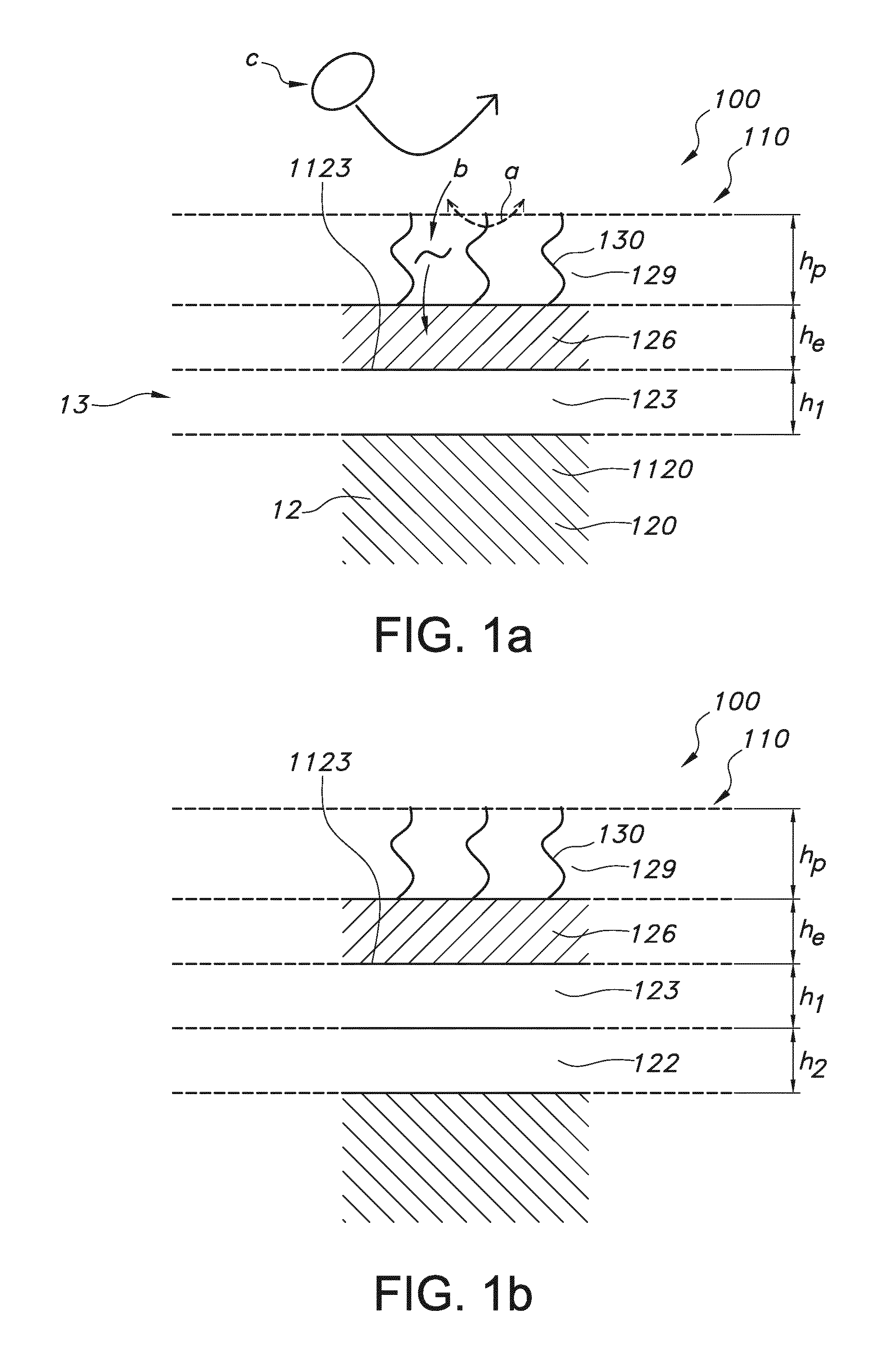
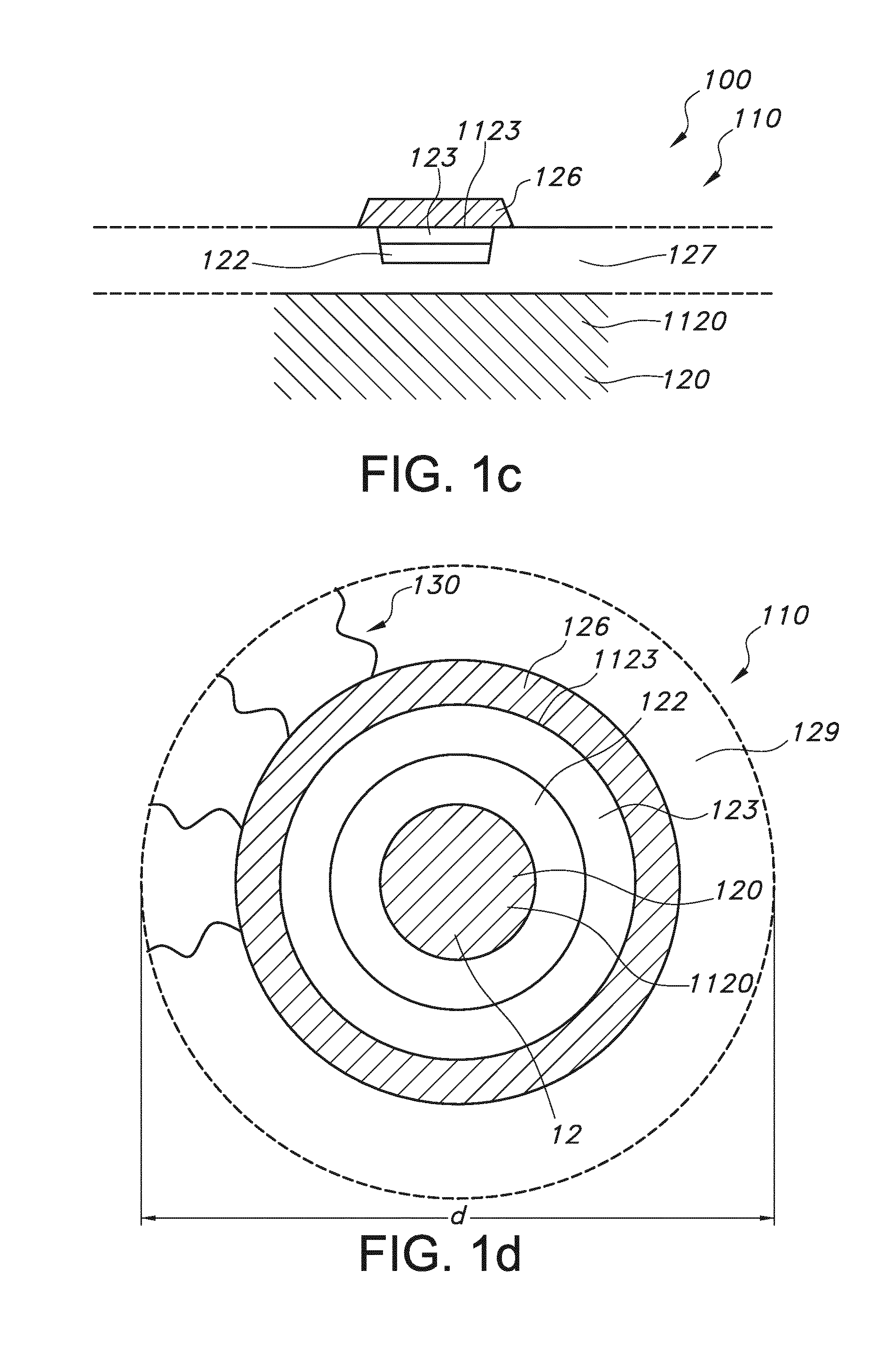
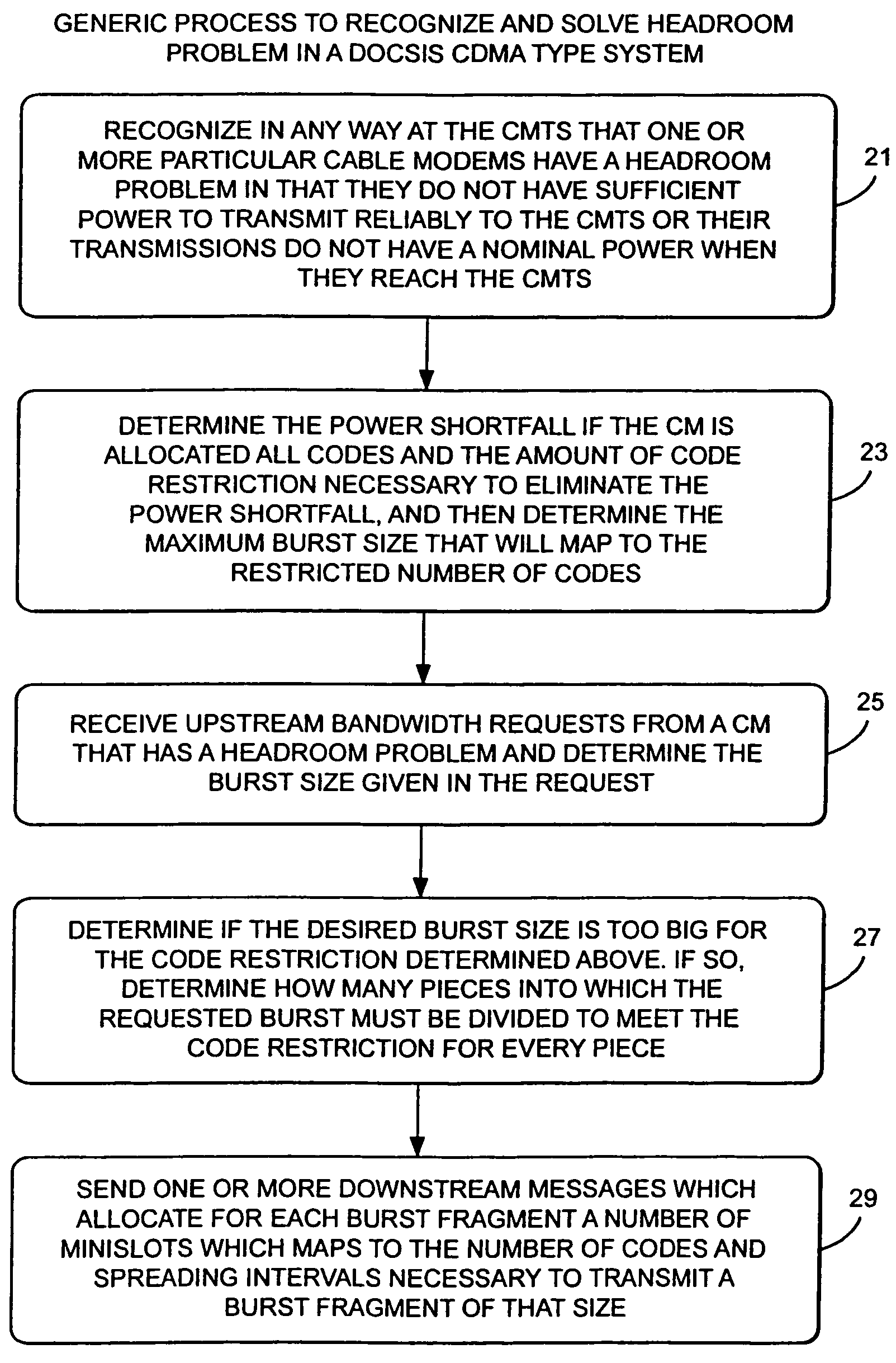
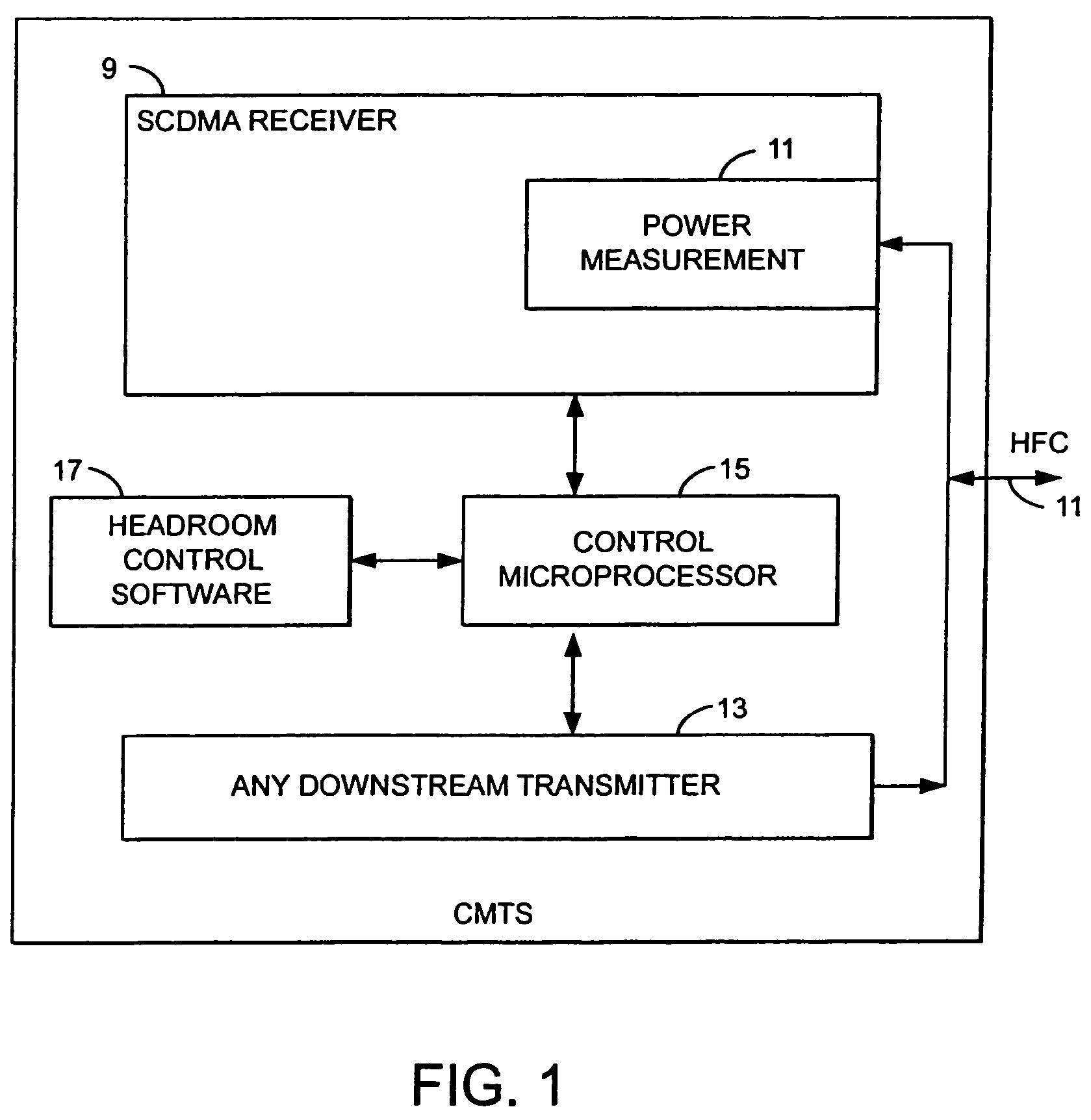
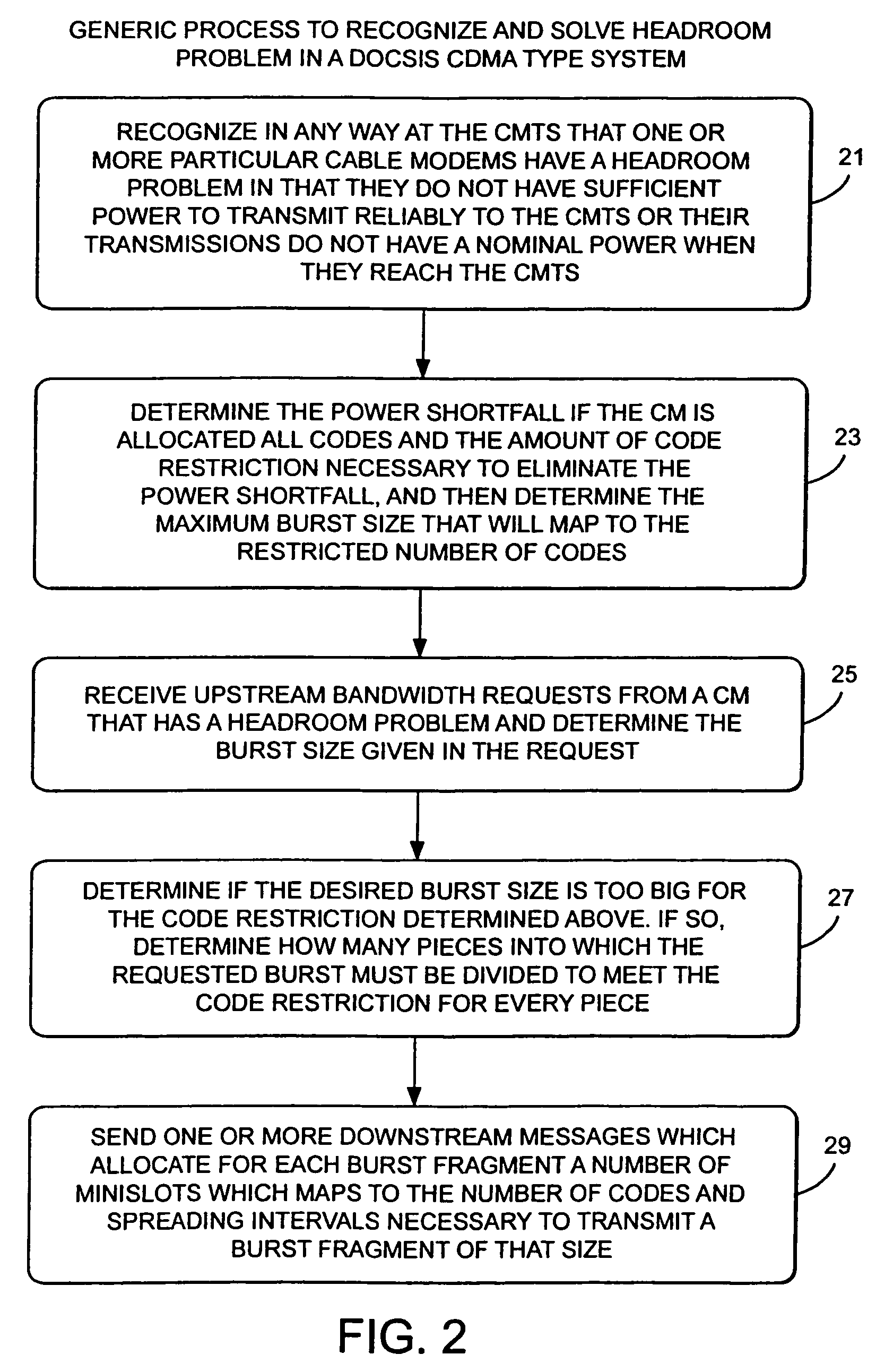
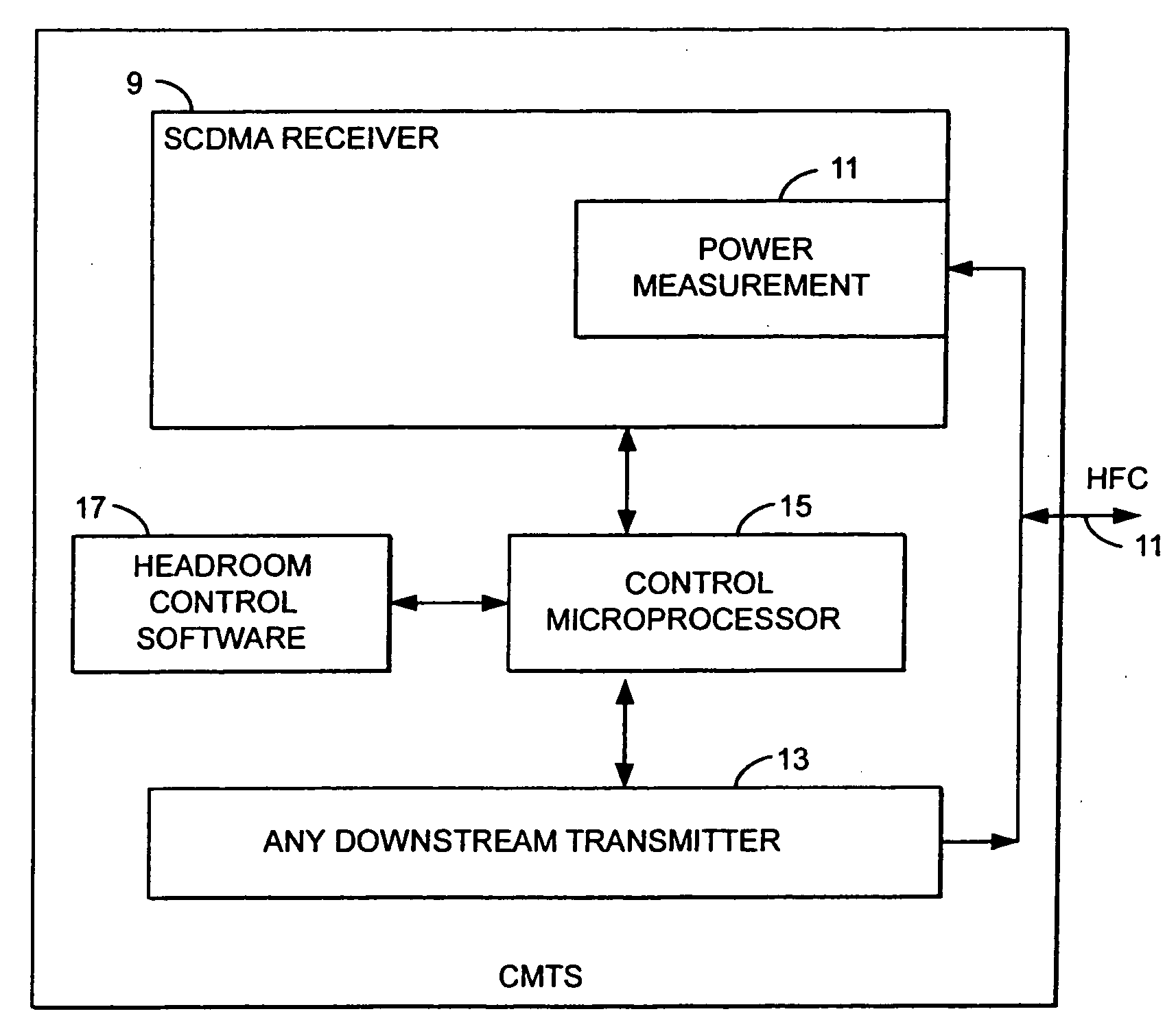
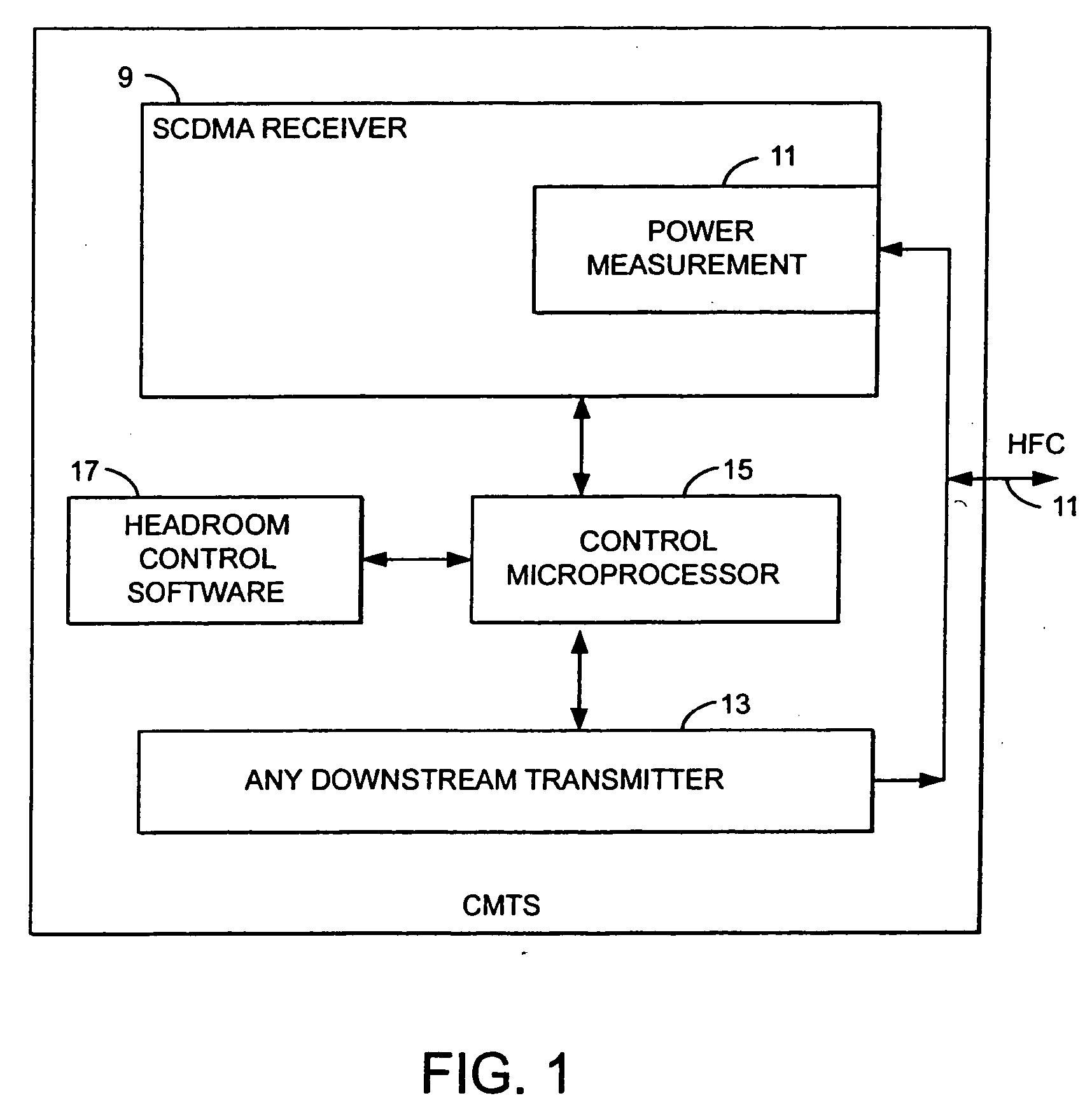
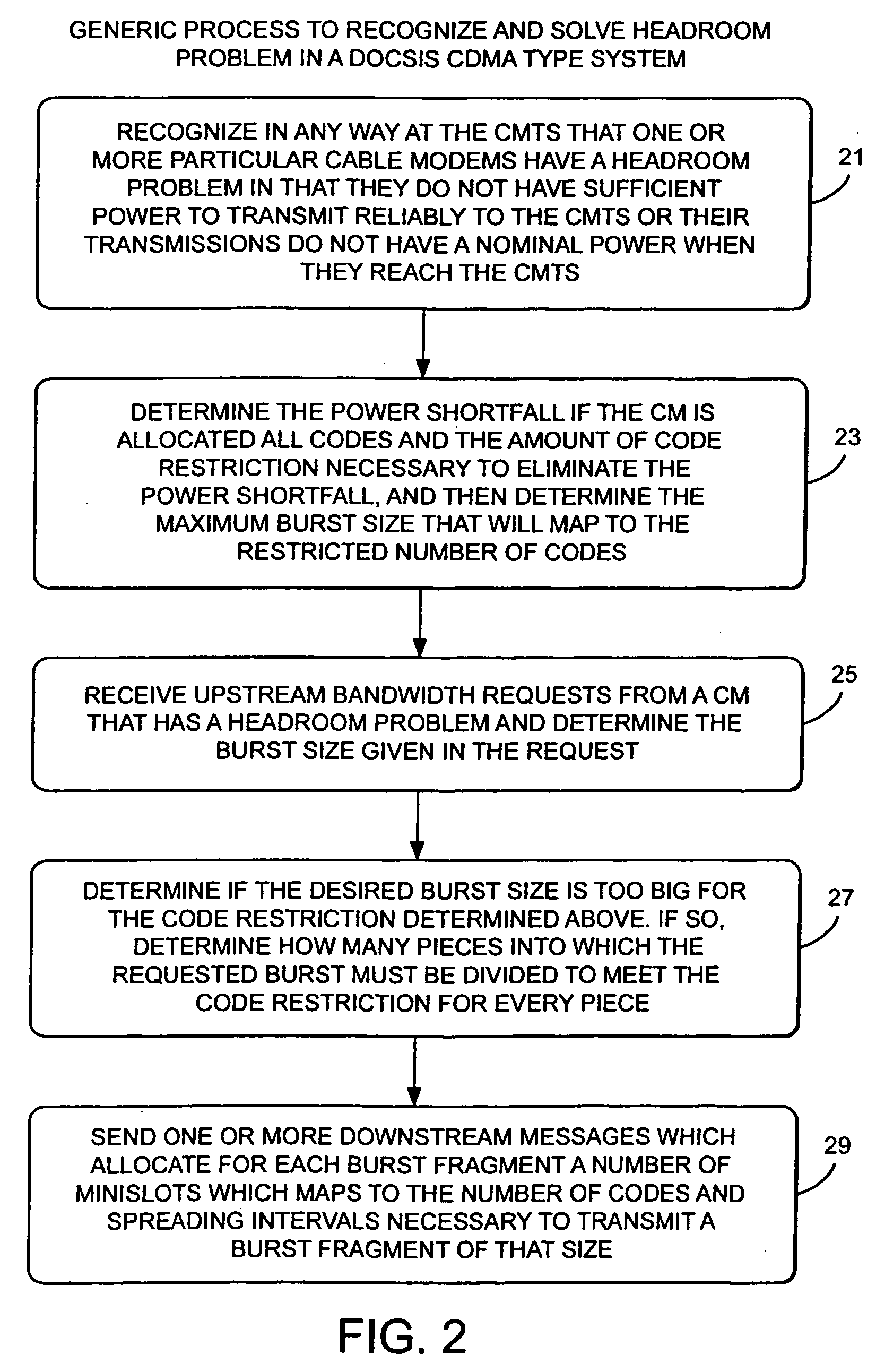
Method and apparatus to improve SCDMA headroom
ActiveUS7002899B2Increase receiving powerSufficient signal to noise ratioError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDigital dataModem device
A method of determining when cable modems in a distributed digital data delivery service over cable TV hybrid fiber coaxial cable network have a headroom problem and resolving said problem. The method involves measuring the burst power from each cable modem, and if the burst power is too low, requesting the cable modem whose burst power is too low to increase its transmit power, and keeping track of which modems have been requested to increase their power. If a predetermined number of requests to increase power have not resulted in the cable modem transmitting with sufficient power for reliable reception, the cable modem is listed as having a headroom problem. Subsequent requests for upstream bandwidth from all modems with headroom problems are analyzed to determine if the requested burst size is too large and will result in a headroom problem. If so, a calculation as to the maximum number of spreading codes that each modem with a headroom problem can simultaneously transmit on without a headroom problem. The requested burst is then broken down into smaller burst fragments, and appropriate upstream minislot assignments adequate to transmit the burst fragments are made and sent to the cable modem.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
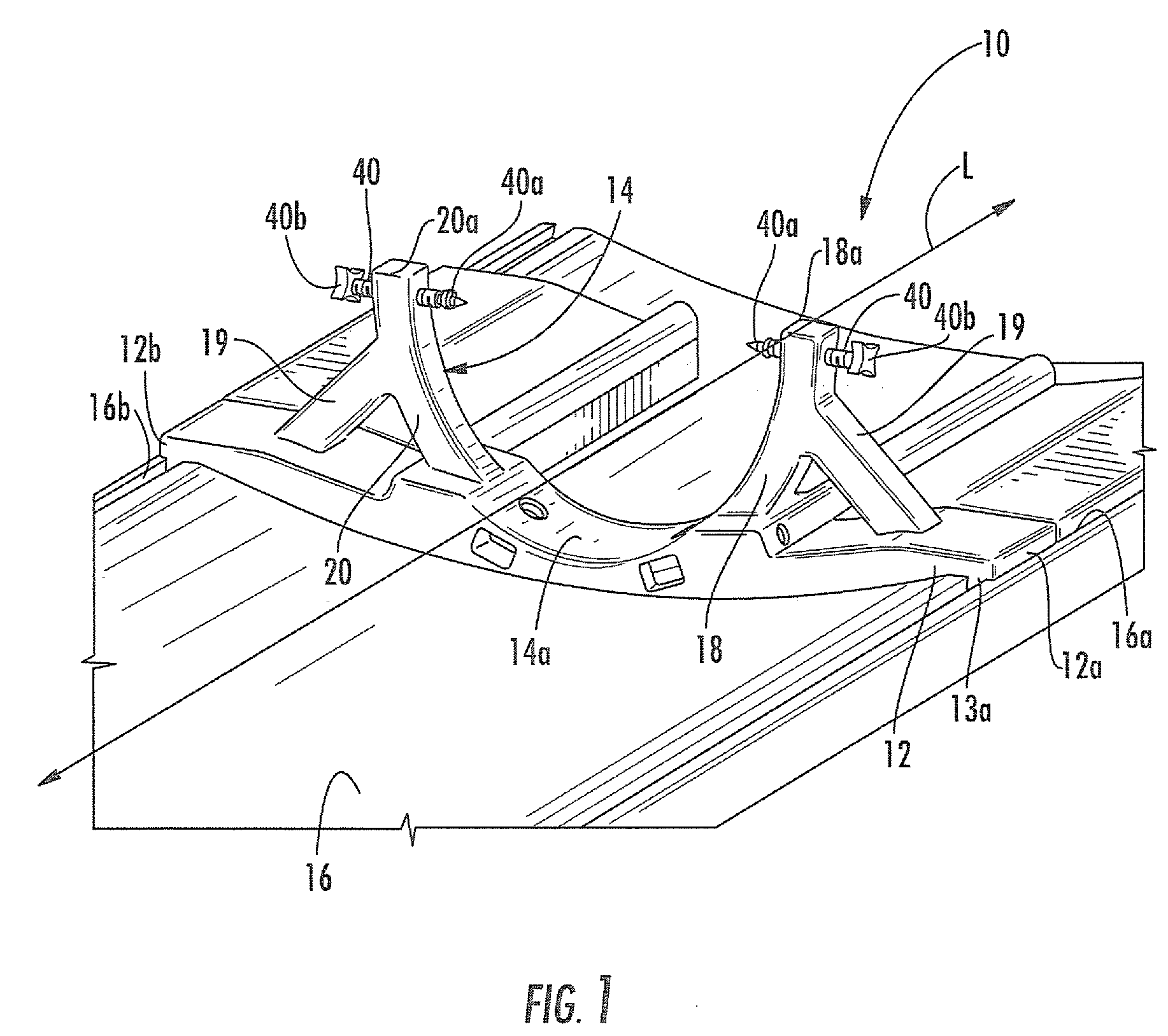
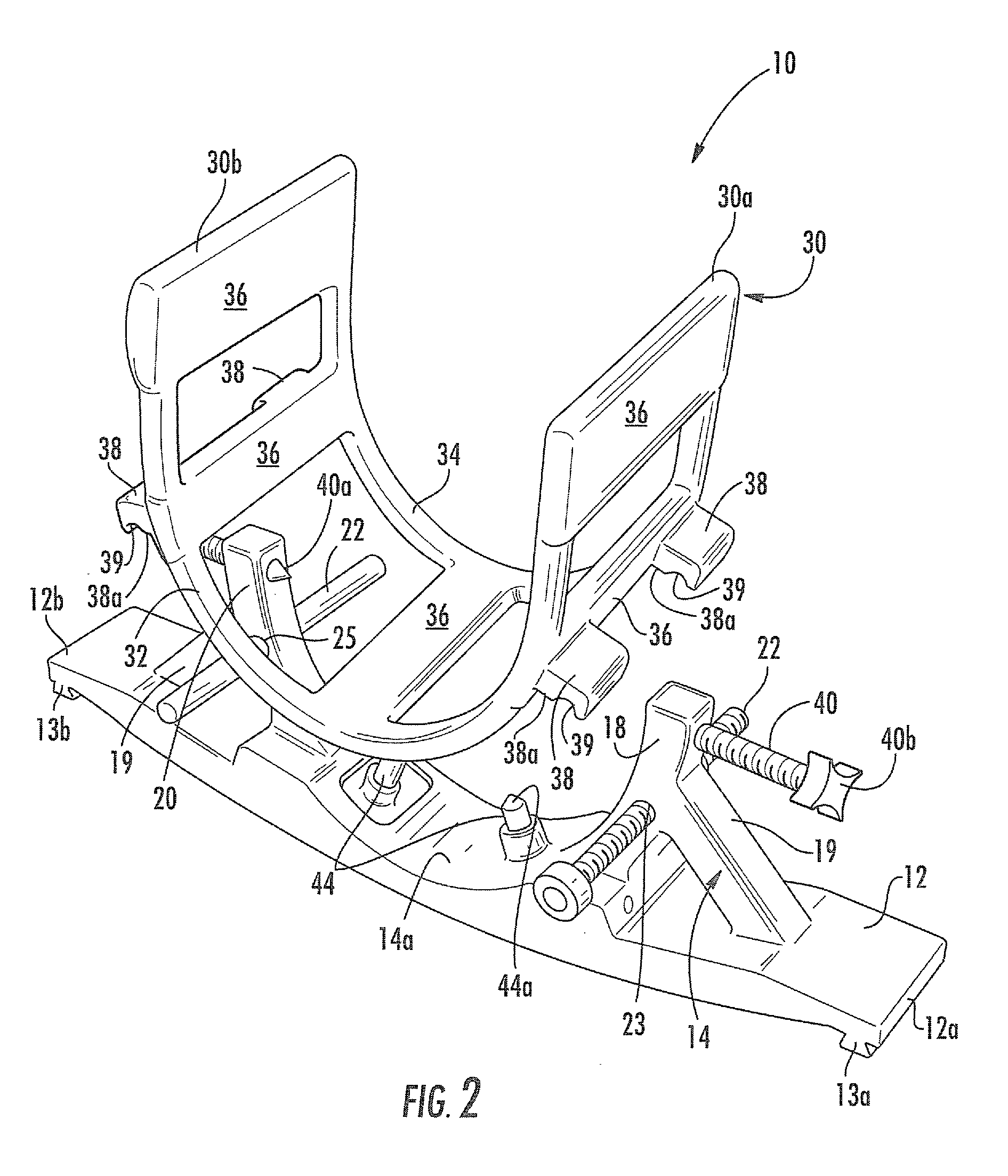
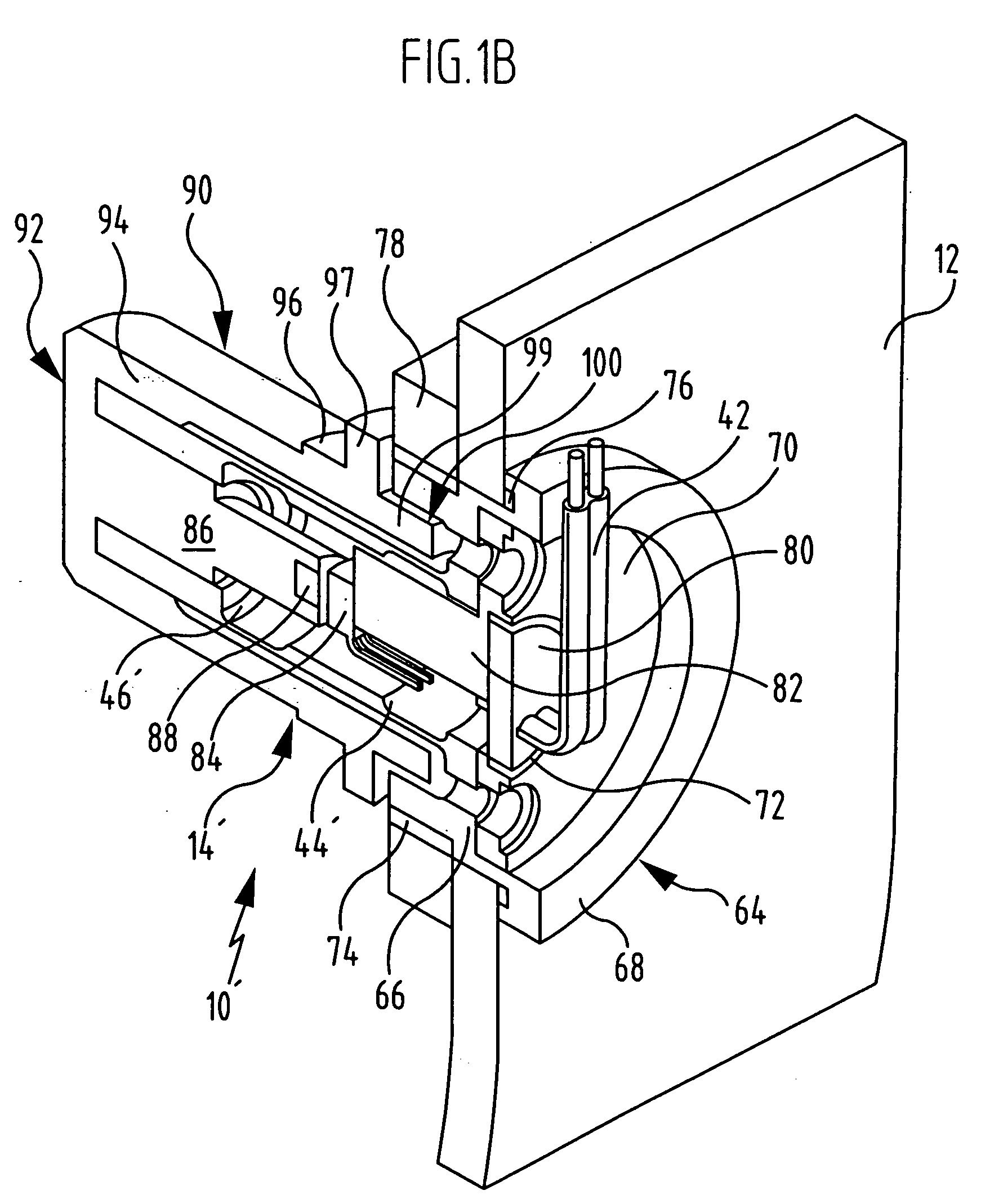
Mri-compatible head fixation frame with cooperating head coil apparatus
InactiveUS20090088627A1Easy accessSufficient signal to noise ratioComputer-aided planning/modellingDiagnostic recording/measuringHead fixationEngineering
A head support assembly includes a base configured to be removably secured to an MRI scanner gantry, a head support frame attached to the base, and a longitudinally extending head coil apparatus adjustably secured to the head support frame. The head support frame includes a pair of elongated arms that extend outwardly in adjacent, spaced-apart, substantially co-planar relationship to form an area for receiving the head of a patient. Each arm includes a respective free end, and a head engagement rod is adjustably associated with each respective arm free end. The head engagement rods are configured to engage a patients head within the head support frame. One or more additional head engagement rods may extend outwardly from the head support frame between the pair of arms.
Owner:MRI INTERVENTIONS INC
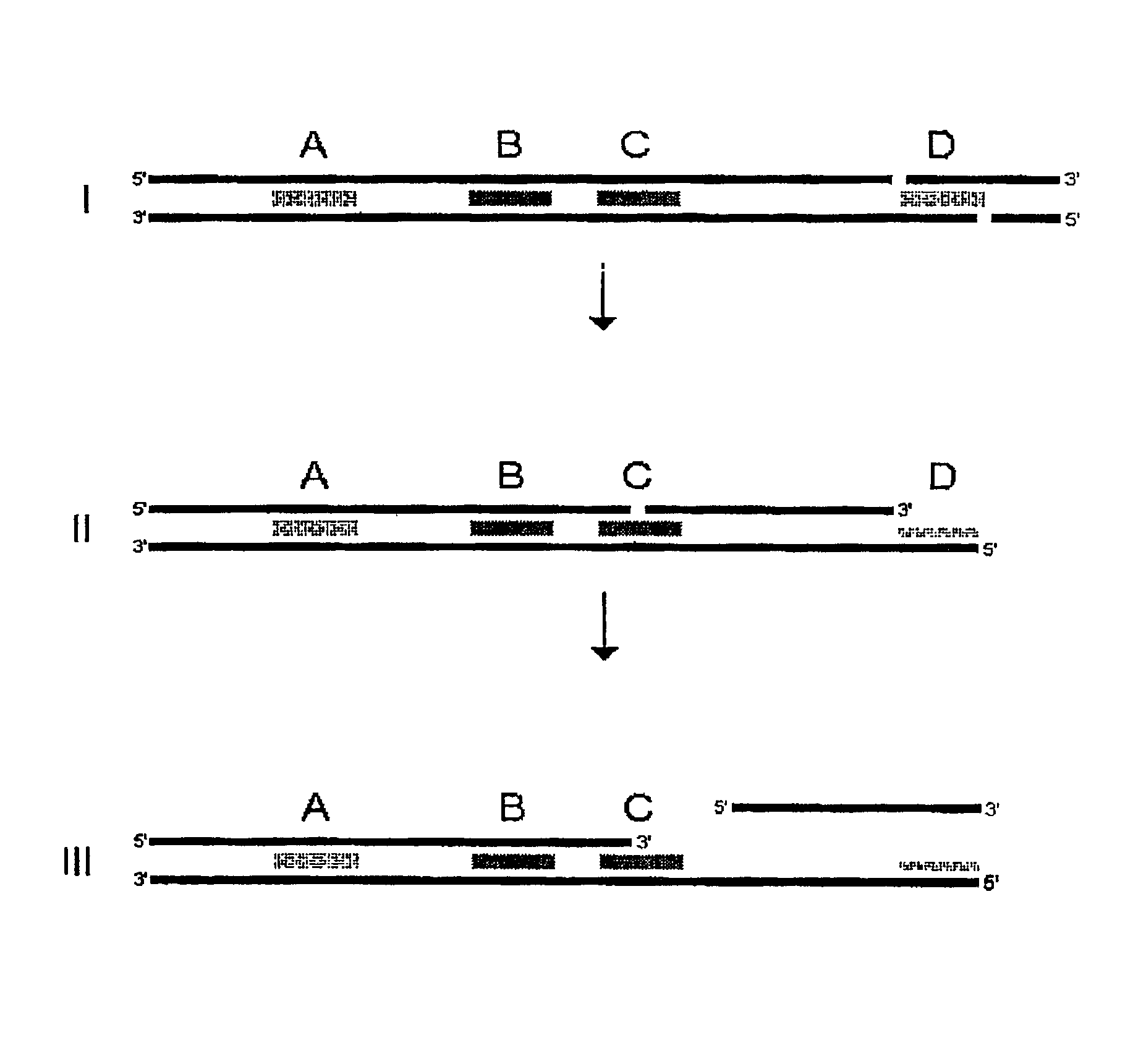
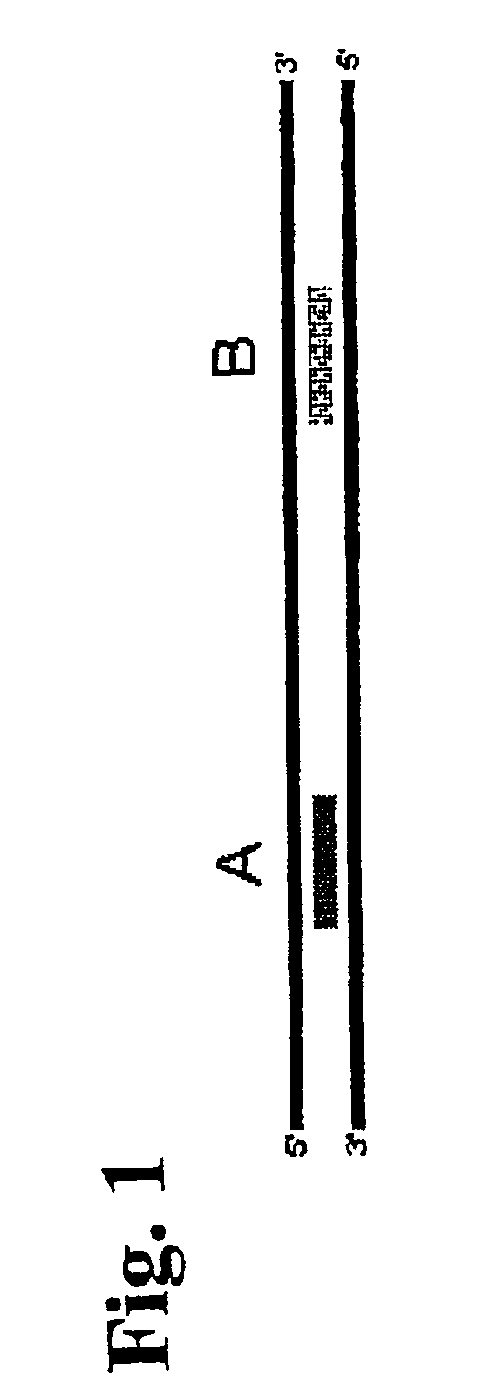
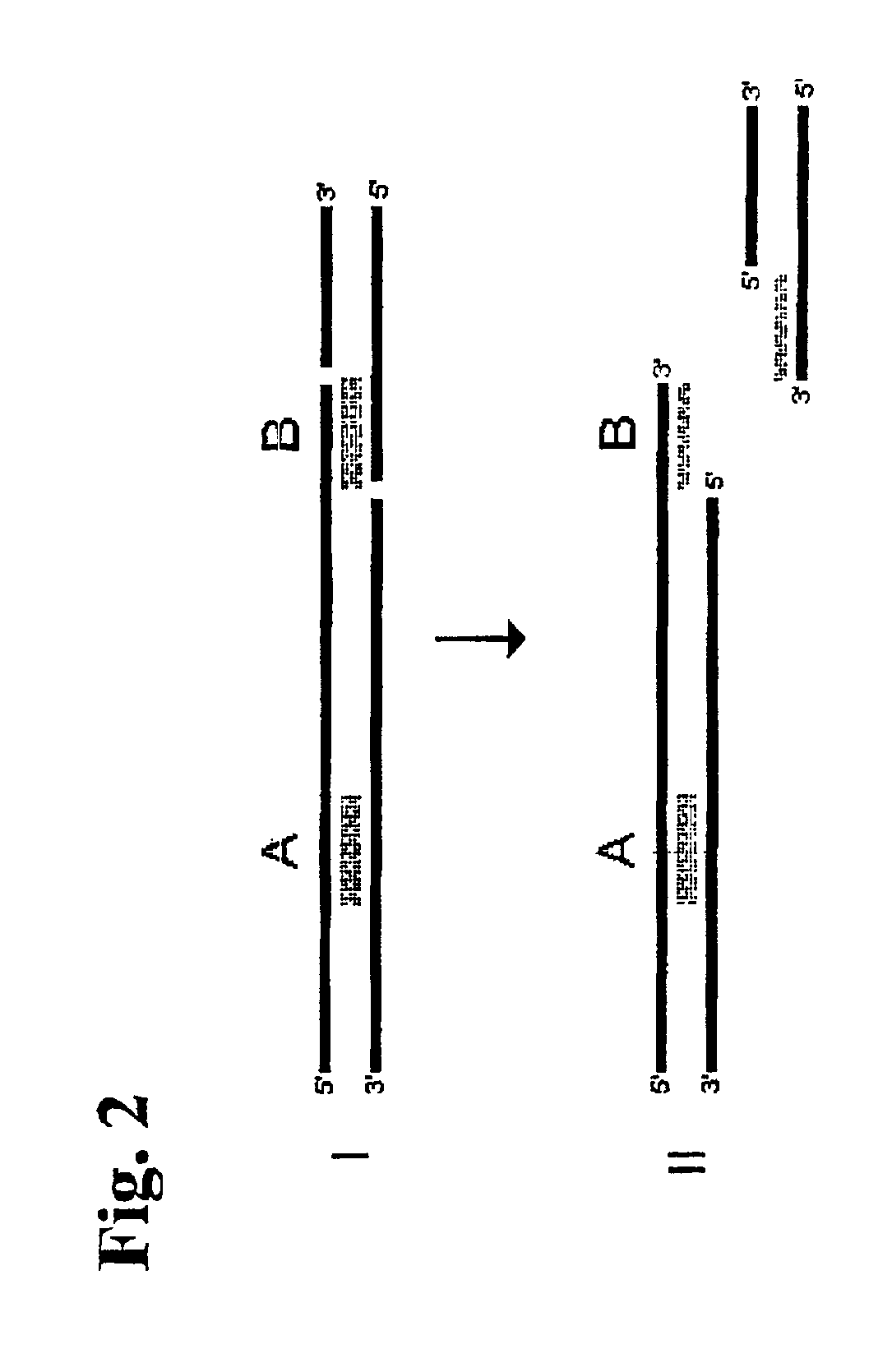
Single-stranded polynucleotide tags
InactiveUS6958217B2Simple counting statisticSufficient signal to noise ratioSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideGenetic Materials
It is one objective of the present invention to obtain reproducible representations of expressed mRNA molecules by exploiting a novel technique that relies on short, single stranded polynucleotide tags. In one preferred embodiment, only one polynucleotide tag is obtained from each mRNA molecule, and relatively simple counting statistics can thus be applied after identification and sampling of the different tags, or a subset of tags being present in the population of representative tags. The tags according to the present invention are preferably single stranded polynucleotide tags obtained by subjecting genetic material derived from a biological sample to at least one site-specific nicking endonuclease capable of i) recognizing a predetermined nucleotide motif comprising complementary nucleotide strands and ii) cleaving only one of said complementary strands in the process of generating the at least one single stranded polynucleotide tag. Accordingly, the present invention demonstrates that nicking endonucleases may advantageously be used for obtaining and isolating ssDNA tags. This novel approach in one embodiment eliminates the occurrence of any linker sequence in the ssDNA tag, and it eliminates the presence of a complementary strand in the isolated polynucleotide tag. The lack of linker sequence in the tag and the lack of any complementary strand serves to reduce the huge complexities associated with the analysis of expressed molecules in a biological sample.
Owner:GENOMIC EXPRESSION
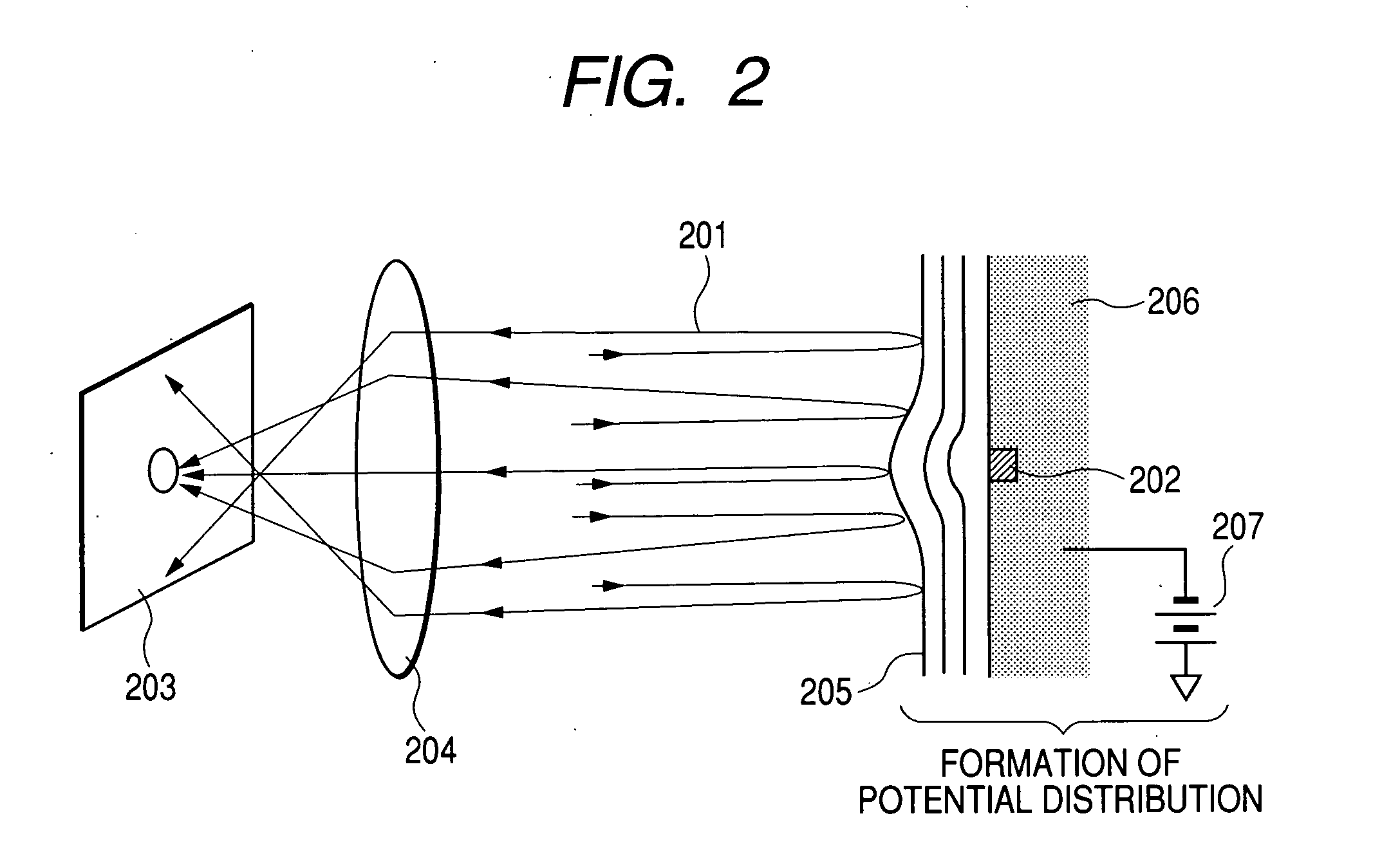
Patterned wafer inspection method and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS20050139772A1Reduce the number of pixelsReduce the burden onMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementImage resolutionImage signal
A defect inspection apparatus is provided which allows a technology for inspecting a pattern on a wafer by using an electron beam to implement a high-resolution and higher-speed inspection. A semiconductor wafer is irradiated with an electron beam and electrons reflected in the vicinity of the wafer are detected. The presence or absence of a defect and the location thereof are measured by forming an image from only a component which changes with a periodicity larger than a size of a circuit pattern or the repetition periodicity thereof by using lenses and comparing an image signal with a preset value. Since only the component which changes with a periodicity larger than the size of the circuit pattern with a surface potential distortion and the repetition periodicity thereof is observed with a resolution lower than required to observe the pattern itself instead of detecting a defect through a comparison between extremely small pattern images, an inspection throughput can be increased exponentially compared with that of a conventional SEM inspection.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Dynamic configuration of a radio frequency transponder
ActiveCN1965323AReduce sensitivityShort lifeNear-field transmissionIndividual entry/exit registersProcessor registerEngineering
The invention discloses a multi-channel remote keyless entry (RKE) transponder having dynamically reconfigurable input channel selection, channel disable, settable sensitivity for each channel, wake-up filter timing parameters, automatic gain control hold, internal tuning capacitor selection for each channel's antenna, minimum modulation depth requirement for input signal and bi-directional talk-back. Programmable minimum modulation depth requirement reduces false wake-up of the RKE transponder. An antenna for each channel of the RKE transponder may be tuned with internal tuning capacitors for improved range and receiver sensitivity. The internal tuning capacitor parameters may be stored in a configuration register. Gain of the channel may be fixed while the antenna is tuned. The antennas may be de-queued for talk-back to a base station for low frequency bidirectional communications. An external control device may dynamically read from and write to the configuration registers via a serial communications interface.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
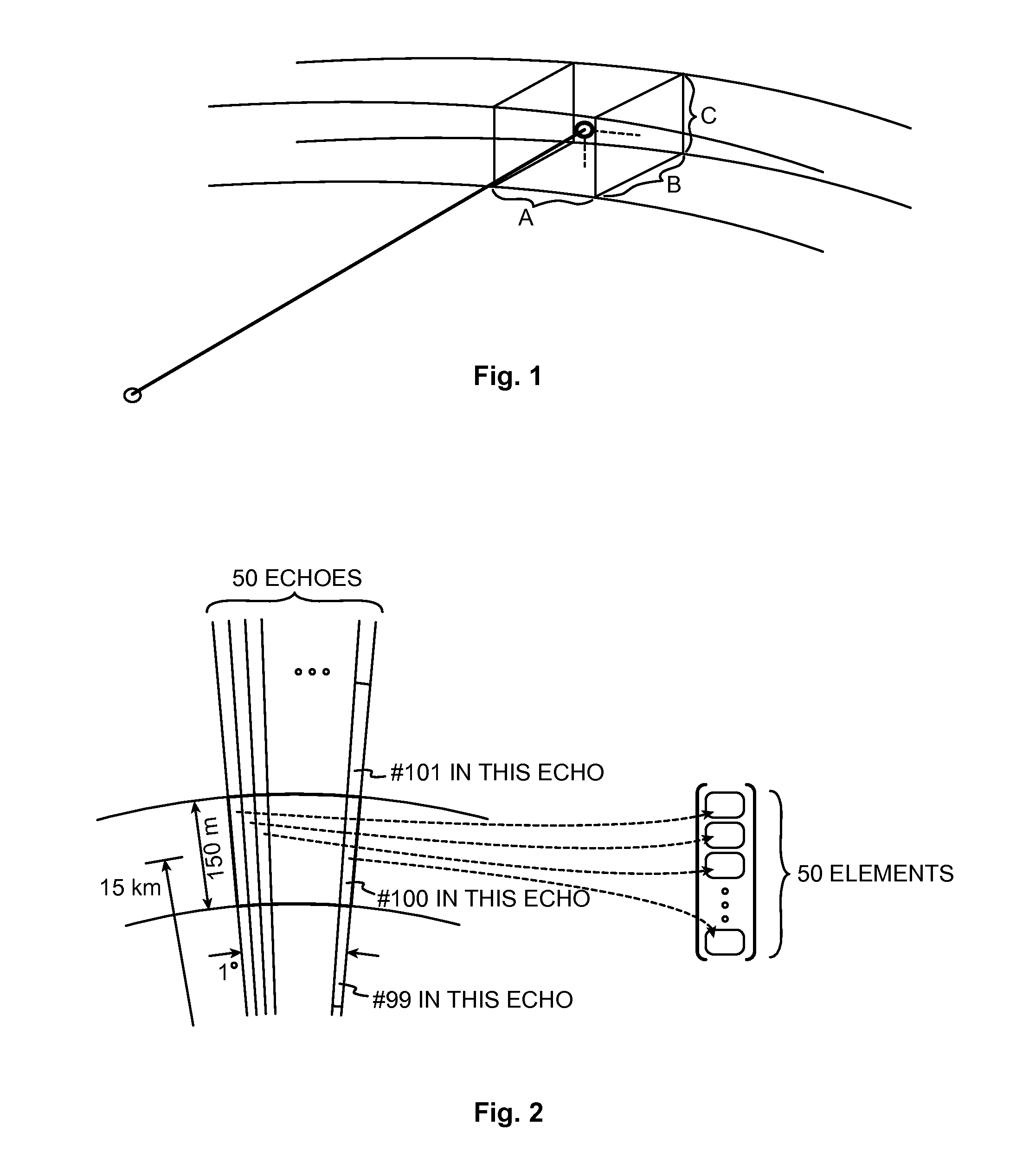
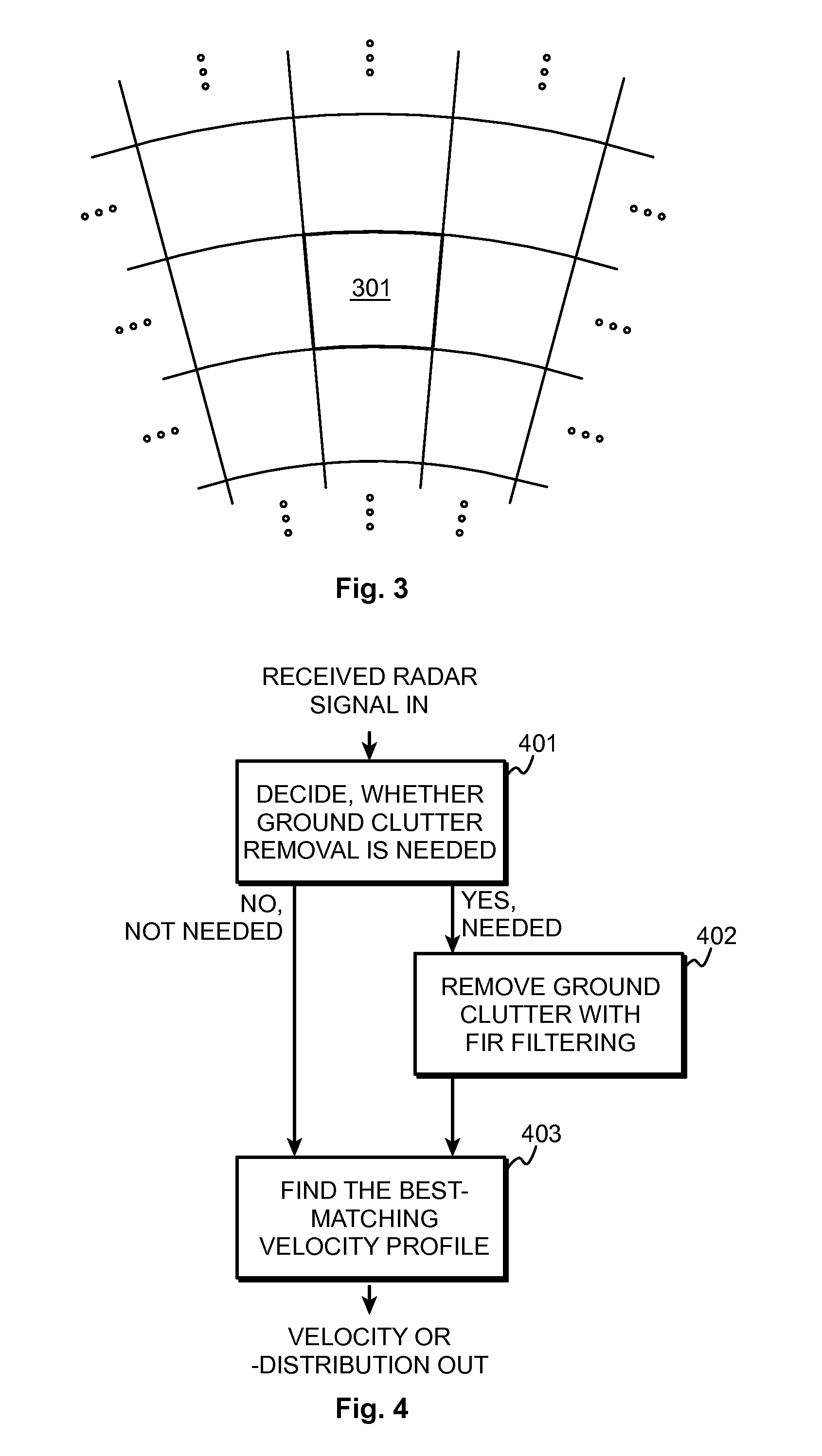
Method and arrangement for removing ground clutter
ActiveUS20140333475A1Signal to noise ratioSufficient signal to noise ratioICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarDigital filter
A digital radar receiver generates the input signal which is a stream of complex numbers. The input signal is rearranged and sorted by measurement volumes, resulting in Doppler data vectors. Doppler data vectors are filtered using a number of different digital filters. The output Doppler data vectors of the filters together with the original Doppler data vector are the candidate signals. Each candidate signal is analyzed using several criteria in order to find the one signal which is most likely to be caused by precipitation and has the ground clutter removed by the filtering. The selected signal is then used to calculate the meteorological products. The selected signal is also used to derive a velocity value or velocity distribution while taking into account the effects of the filtering performed earlier.
Owner:EIGENOR
Patterned wafer inspection method and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS7288948B2Sufficient signal to noise ratioReduce the number of pixelsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementImage resolutionImage signal
A defect inspection apparatus is provided which allows a technology for inspecting a pattern on a wafer by using an electron beam to implement a high-resolution and higher-speed inspection. A semiconductor wafer is irradiated with an electron beam and electrons reflected in the vicinity of the wafer are detected. The presence or absence of a defect and the location thereof are measured by forming an image from only a component which changes with a periodicity larger than a size of a circuit pattern or the repetition periodicity thereof by using lenses and comparing an image signal with a preset value. Since only the component which changes with a periodicity larger than the size of the circuit pattern with a surface potential distortion and the repetition periodicity thereof is observed with a resolution lower than required to observe the pattern itself instead of detecting a defect through a comparison between extremely small pattern images, an inspection throughput can be increased exponentially compared with that of a conventional SEM inspection.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
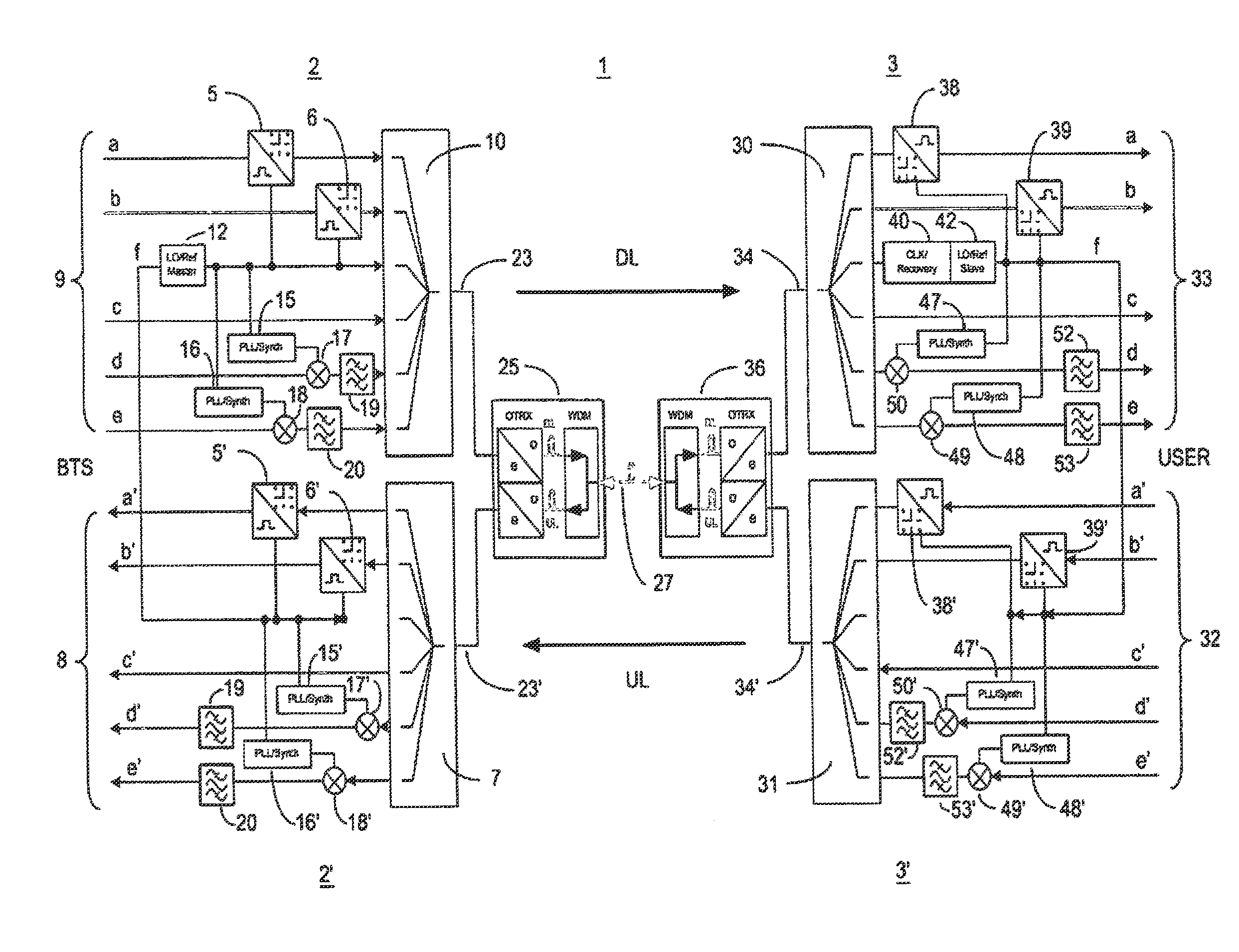
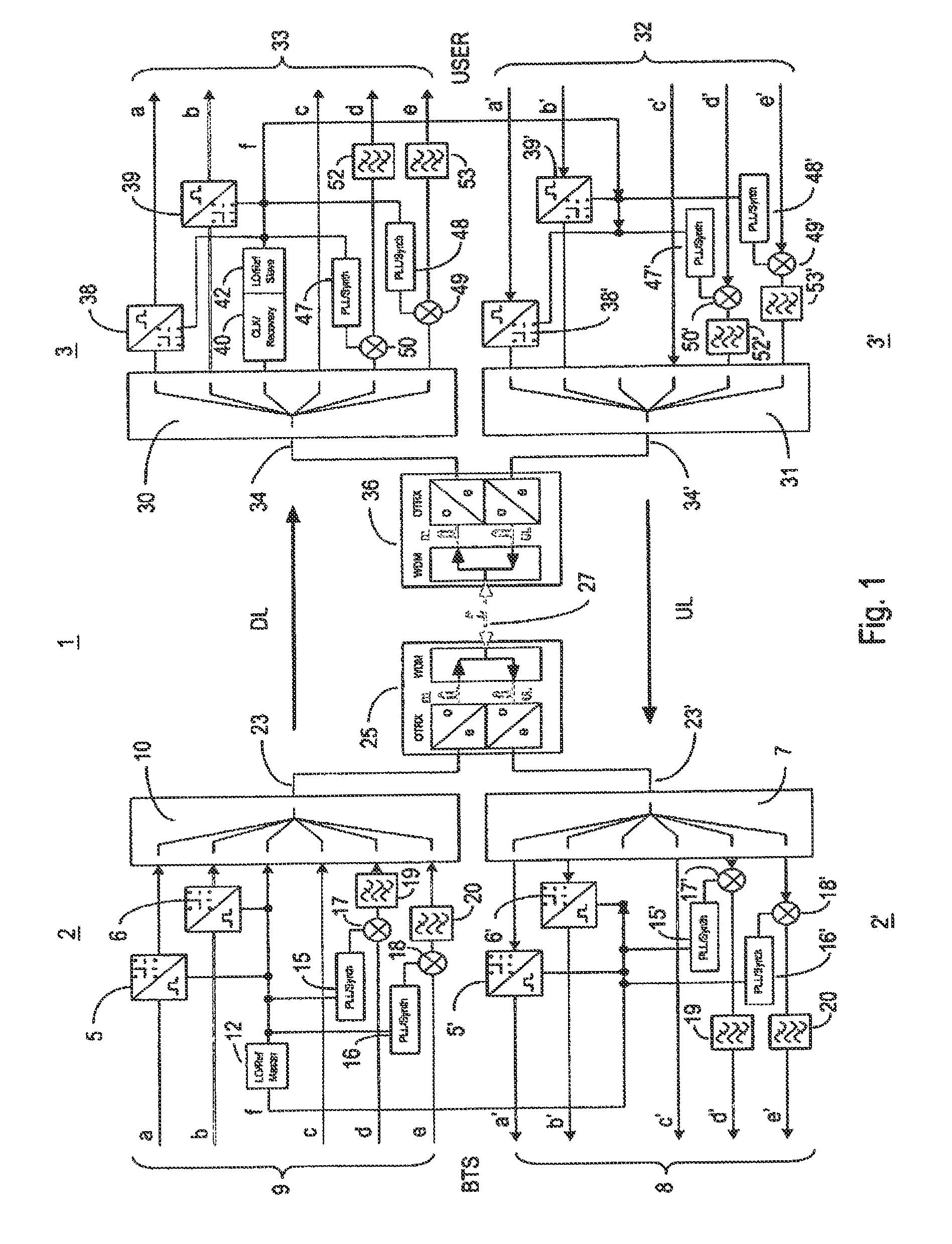
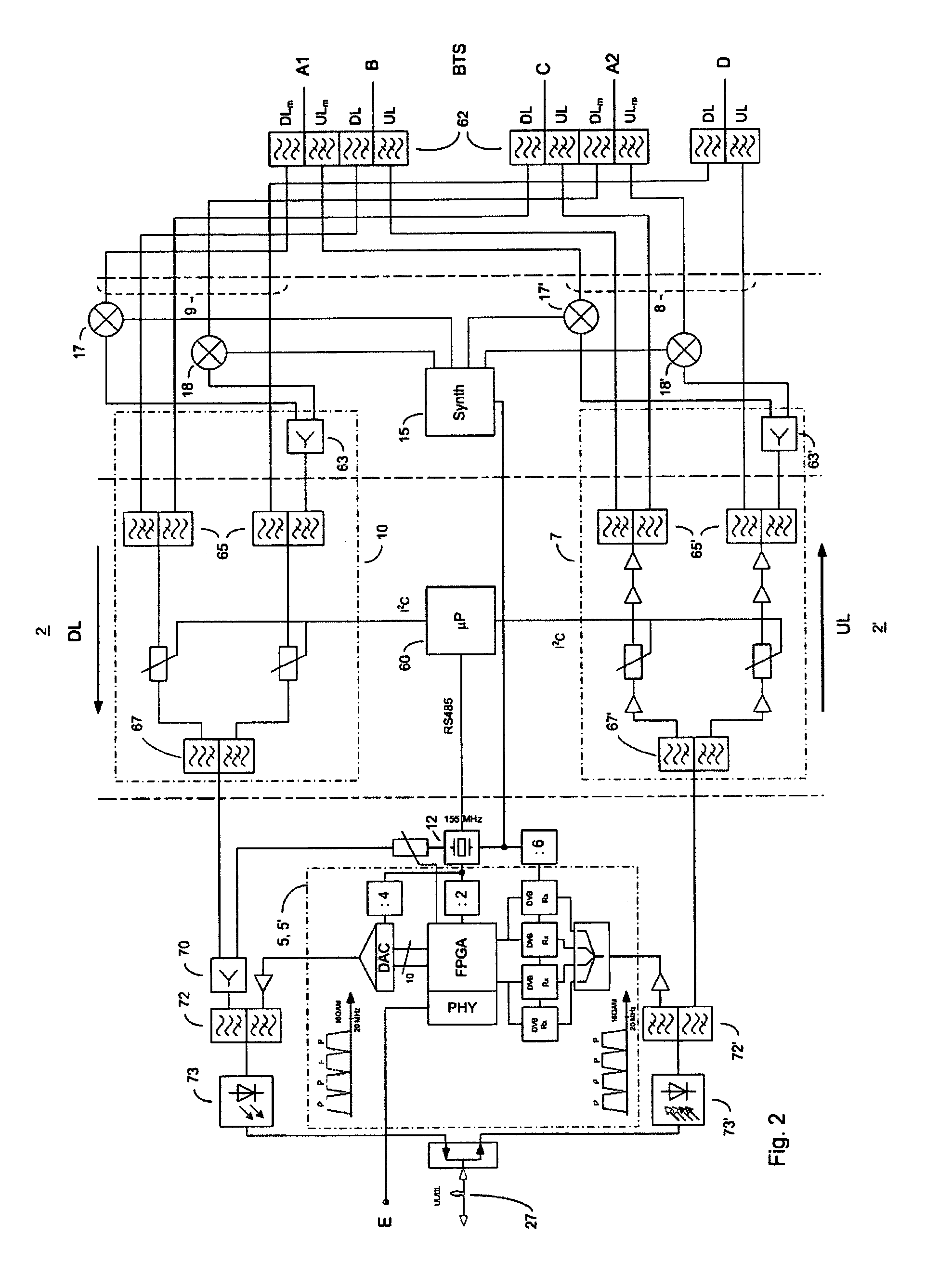
Master unit, remote unit and multiband transmission system
ActiveUS8681916B2Reduced strengthSufficient signal to noise ratioTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexModem deviceTransport system
A master unit and a remote unit is provided for a multiband transmission system for distributing and combining signals of at least one wireless communication network and at least one digital network. A reference frequency generator is arranged in the master unit, the reference frequency generator being designed to clock a master modem for converting the signals of the at least one digital network. The reference frequency signal emitted by the reference frequency signal is restored via a reference frequency receiver and is used for closing a remote modem that is located there for demodulation.
Owner:ANDREW WIRELESS SYST GMBH
Nuclear magnetic resonance module
ActiveUS7667462B2Flexible and low-field and relatively low-cost designReduce intensityElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus that may be used in connection with a variety of different tools, including a down-hole side-wall coring tool as well as with manufacturing process controllers. In one embodiment, the nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus may include a magnet assembly constructed around a sample chamber. The magnet assembly is constructed and arranged to provide a non-uniform magnetic field having a known magnetic field gradient inside the sample chamber. The use of gradient fields may allow for a more flexible and robust magnet assembly design that may be suitable for a variety of different applications.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
In-line fiber optic monitors responsive to optical intensity
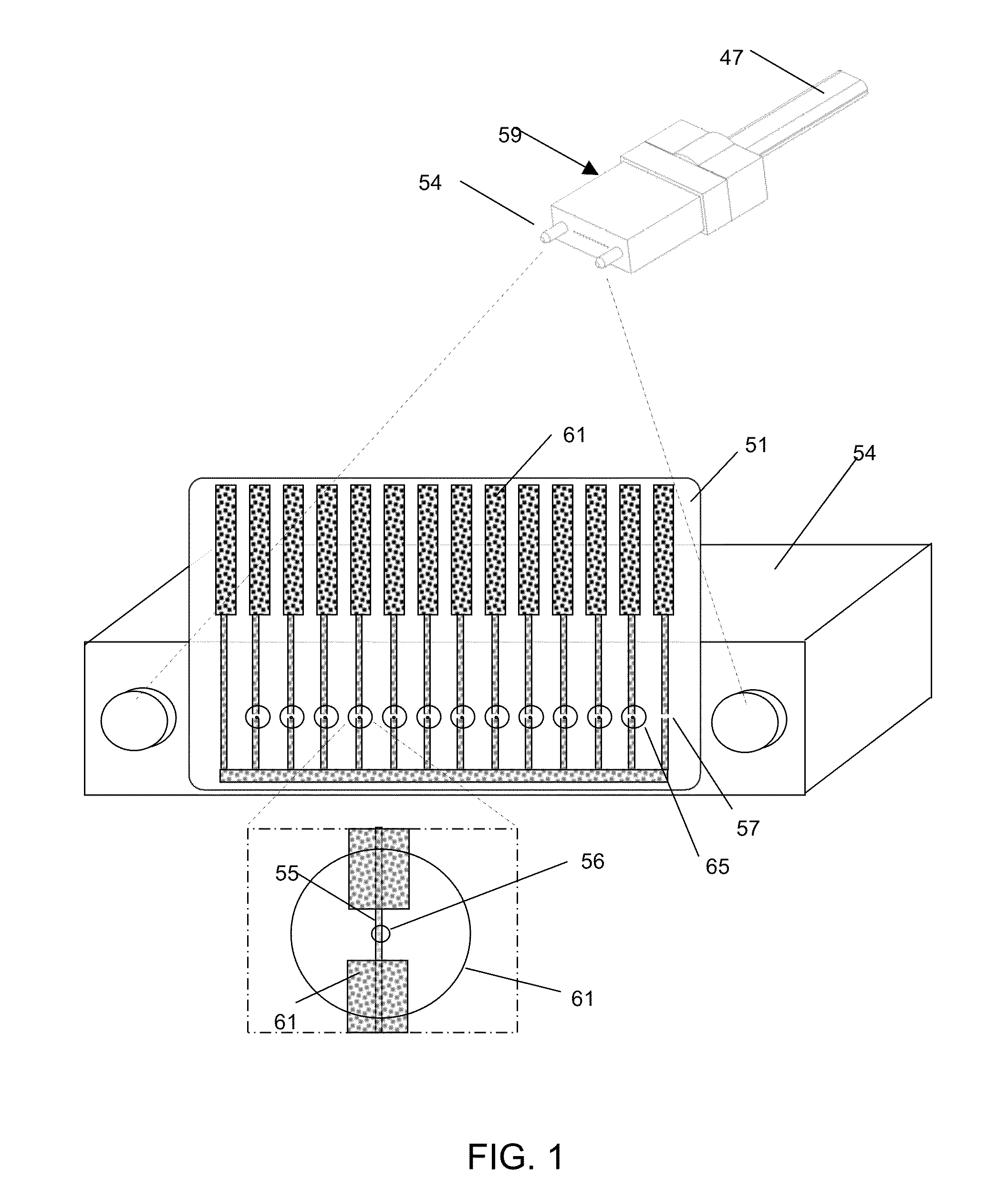
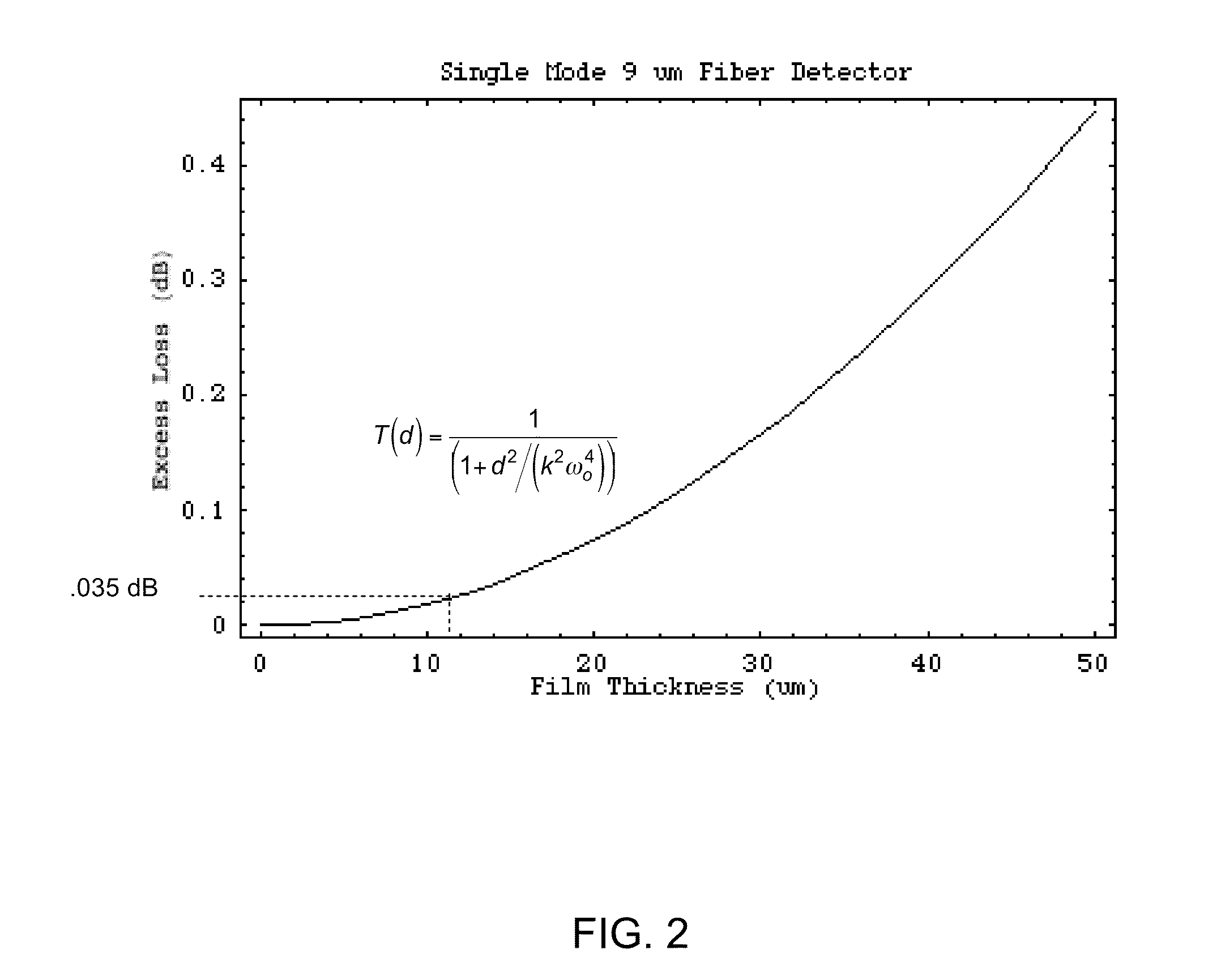
ActiveUS9110249B2Eliminate lossSufficient signal to noise ratioMaterial analysis by optical meansCoupling light guidesFiberConductive coating
Apparatus and methods to monitor optical intensity within optical fibers in a substantially non-invasive fashion are disclosed. Optical monitors are comprised of thin, conductive coatings applied to transparent substrates and patterned to form pairs of resistive elements, one of which intersects an optical beam propagating through optical fiber cables. Systems of distributed optical monitors interconnecting optical fiber links enable automated monitoring of the optical status across a communications networks.
Owner:TELESCENT
Dynamometric cell
InactiveUS20060053898A1High solution accuracySimple designForce measurement by measuring magnetic property varationPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementElectricityUltrasound attenuation
A dynamometric cell having an elastically deformable force transducer for receiving a weight force and a sensor arrangement for detecting the deformation of the force transducer and its conversion into an electric weight signal is disclosed, wherein the force transducer is connected to a mounting member at its first end and supports a force introduction member at its second end, such that it allows a more exact determination of weight force even when it is incorporated into narrow spaces and wherein the force transducer is designed as a hollow bar with two attenuation zones spaced in longitudinal direction of the bar.
Owner:BAG BIZERBA AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
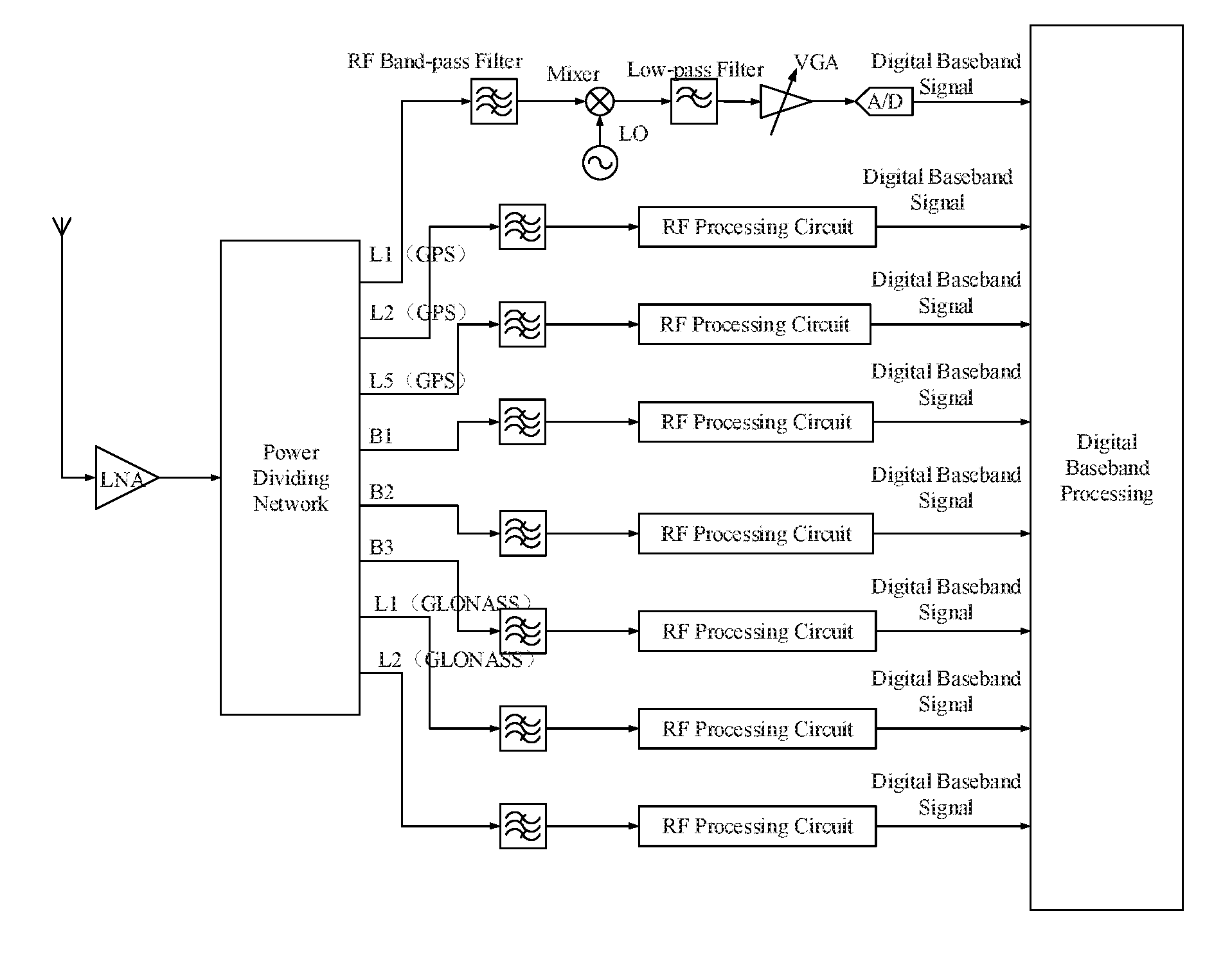
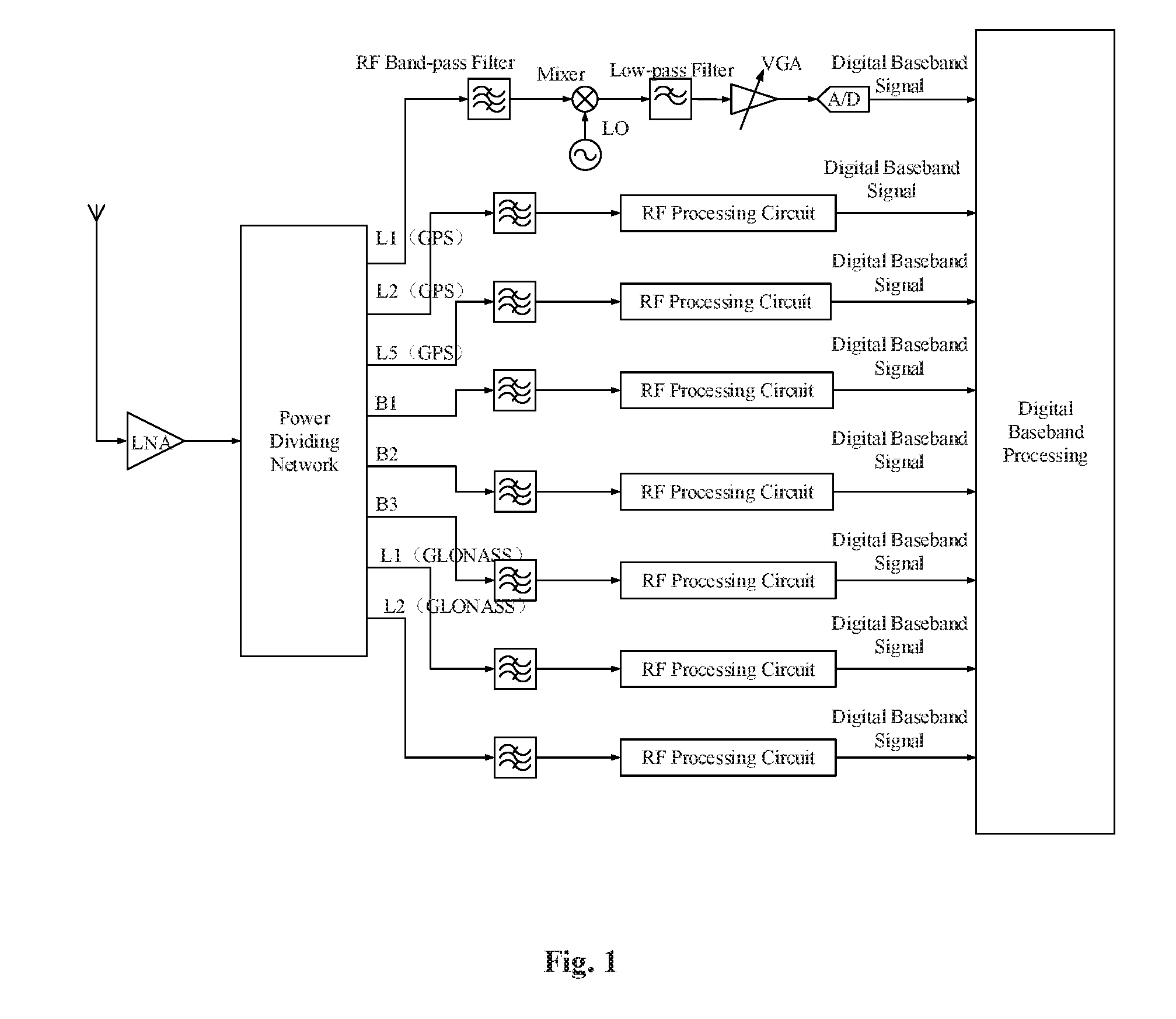
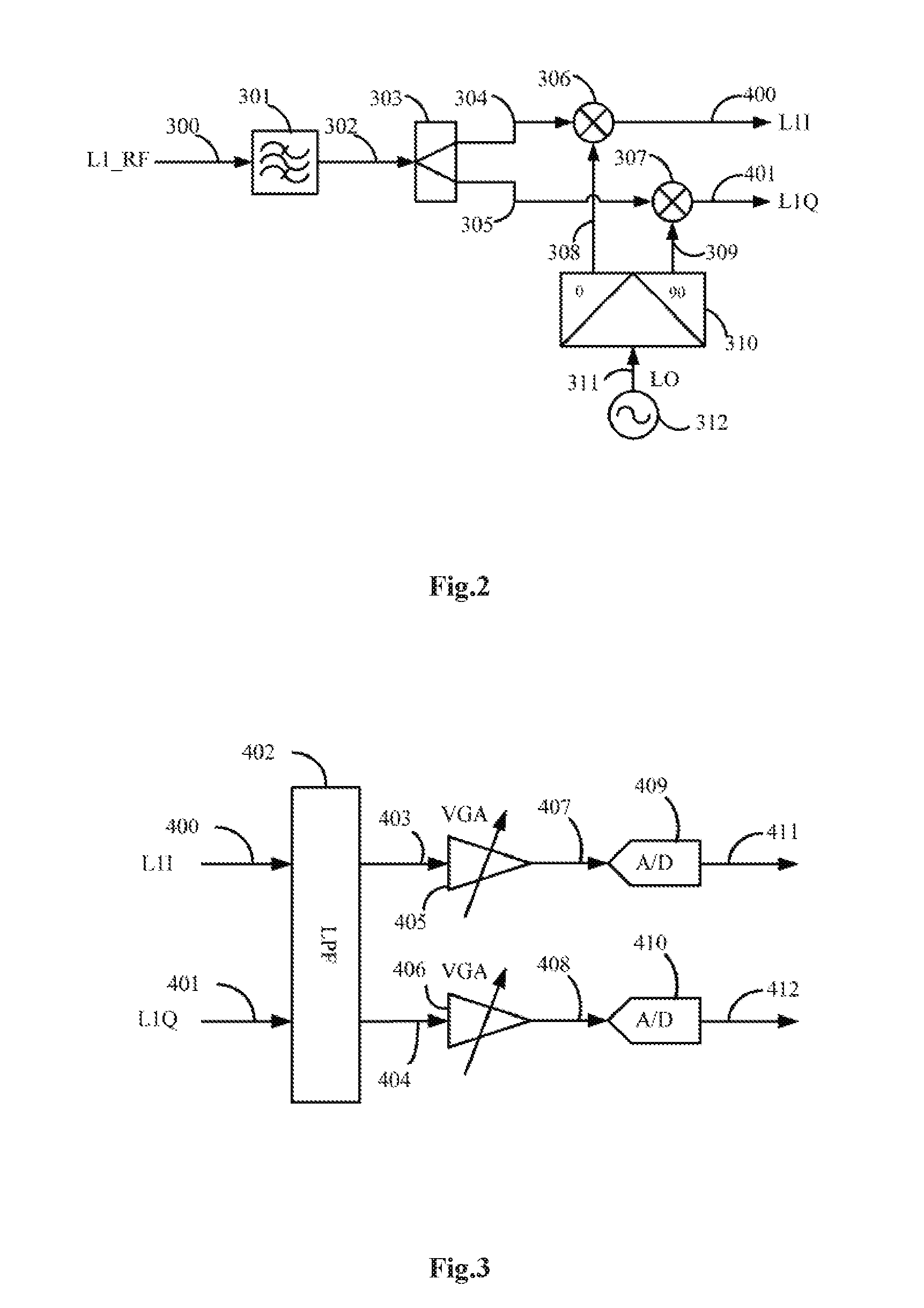
Radio frequency circuit structure for implementing function of converting GNSS satellite signal into baseband signal
ActiveUS20160195620A1Reduce crosstalkReduce complexitySatellite radio beaconingLocal oscillator signalSignal quality
The present invention relates to a radio frequency circuit structure for implementing a function of converting a satellite signal of a global navigation satellite system into a baseband signal. The radio frequency circuit structure comprises a channel dividing function module, a plurality of frequency converting function modules, a plurality of local oscillator signal modules, and a plurality of analog-to-digital convertor modules. The channel dividing function module is used for dividing a satellite signal of the global navigation satellite system received by an antenna into satellite signals in a plurality of channels. Each of the frequency converting function modules is used for performing frequency conversion on the satellite signals in the corresponding channels to form near zero-frequency signals. Each of the local oscillator signal module is used for generating a local oscillator signal and outputting the local oscillator signal to the frequency converting function module. By using the radio frequency circuit structure for implementing a function of converting a satellite signal of a global navigation satellite system into a baseband signal, frequency conversion and follow-up signal processing can be performed on the satellite signals in each frequency band separately, the signal quality insured, a sufficient signal to noise ratio is provided for a baseband processing circuit, thereby providing a wider application range.
Owner:COMNAV TECH
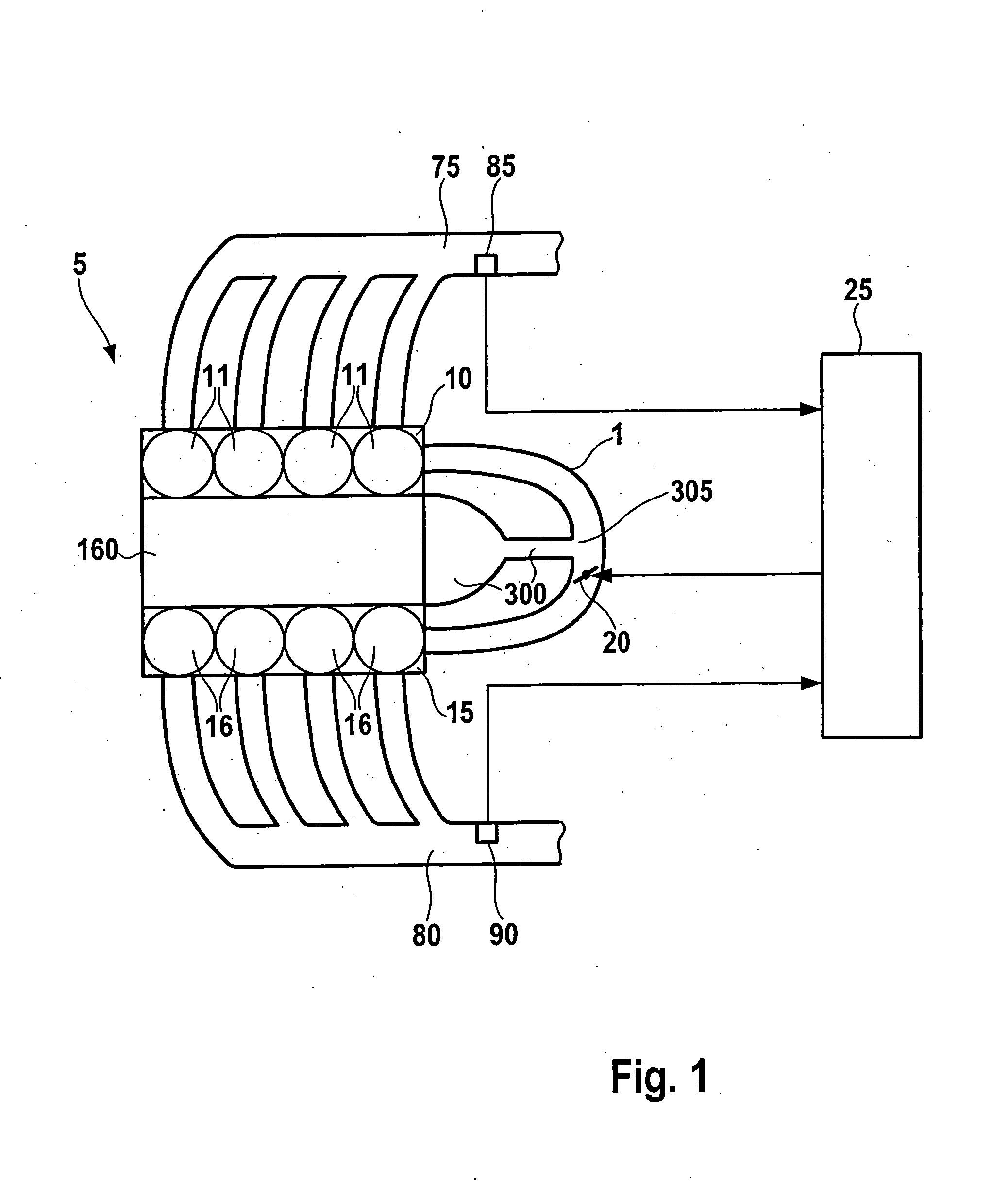
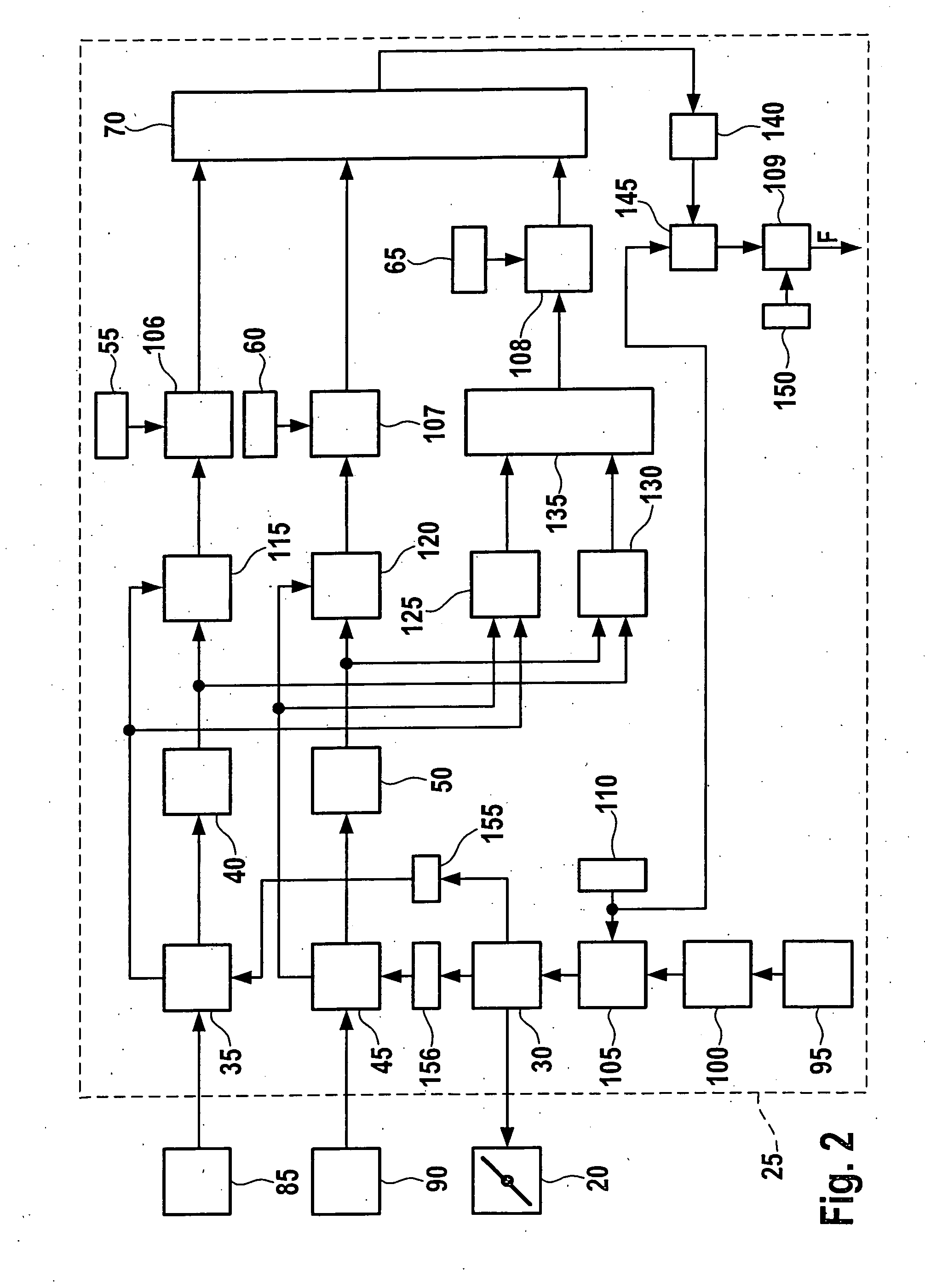
Method and device for diagnosing a crankcase ventilation of an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7567867B2Simple and reliable and economical mannerStable operating pointAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlExternal combustion engineEngineering
A method and device for diagnosing a crankcase ventilation of an internal combustion engine, which enable a diagnosis of a malfunction of an actuator of the crankcase ventilation. The internal combustion engine has at least two cylinder banks to which the crankcase ventilation is supplied, and an actuator is provided via whose position the distribution of the crankcase ventilation to the at least two cylinder banks is influenced. In a first position of the actuator, a different distribution of the crankcase ventilation to the at least two cylinder banks comes about than in a second position of the actuator that differs therefrom. Given simultaneously activated operation of the at least two cylinder banks, the actuator is switched over at least one between the two different positions. For at least one of the at least two cylinder banks, a characteristic variable of the internal combustion engine influenced by the crankcase ventilation is determined prior to and following the switchover operation. A minimum value for a change in the characteristic variable of at least one of the at least two cylinder banks and / or the ratio of the characteristic variable between the at least two cylinder banks is specified for the switchover-related change in the distribution of the crankcase ventilation to the at least two cylinder banks. A malfunction of the actuator is detected if at least one change derived from the ascertained values for the characteristic variable undershoots its assigned expected minimum value in quantitative terms.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Rod shaped implantable biosensor
InactiveUS20150366493A1Improve conductivityIncrease contactContact member manufacturingVacuum evaporation coatingEngineeringBiosensor
A biosensor includes a biosensor unit with an electrode, wherein the electrode is rod-shaped, wherein the electrode further comprises a support with an electrically conductive first layer and an exclusion layer, wherein the electrically conductive first layer is configured between the support and the exclusion layer. A sensing system can include such biosensor.
Owner:BRAINS ONLINE HLDG
Method and apparatus to improve SCDMA headroom
InactiveUS7580346B2Sufficient signal to noise ratioIncrease powerError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDigital dataModem device
A method of determining when cable modems in a distributed digital data delivery service over cable TV hybrid fiber coaxial cable network have a headroom problem and resolving said problem. The method involves measuring the burst power from each cable modem, and if the burst power is too low, requesting the cable modem whose burst power is too low to increase its transmit power, and keeping track of which modems have been requested to increase their power. If a predetermined number of requests to increase power have not resulted in the cable modem transmitting with sufficient power for reliable reception, the cable modem is listed as having a headroom problem. Subsequent requests for upstream bandwidth from all modems with headroom problems are analyzed to determine if the requested burst size is too large and will result in a headroom problem. If so, a calculation as to the maximum number of spreading codes that each modem with a headroom problem can simultaneously transmit on without a headroom problem. The requested burst is then broken down into smaller burst fragments, and appropriate upstream minislot assignments adequate to transmit the burst fragments are made and sent to the cable modem.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Touch and stylus sensing
InactiveUS20190187856A1Increase effortSufficient signal to noise ratioStatic indicating devicesDigital output to display deviceEngineeringCapacitive sensing
A trackpad for a dual user interface has capacitive sensing and inductive sensing capabilities, charge transfer measurement circuitry, a set of a plurality of sensing electrode structures, a set of a plurality of inductive receiving coils and at least one inductive transmit coil. The set of sensing electrode structures is used with the charge transfer measurement circuitry for capacitive sensing and the capacitive sensing is used to discern user input via finger proximity or touch. The set of inductive receiving coils is used with the charge transfer measurement circuitry for inductive sensing and the inductive sensing is used to discern user input via a stylus.
Owner:AZOTEQ PTY LTD
Method and apparatus to improve SCDMA headroom
InactiveUS20060123452A1Sufficient signal to noise ratioIncrease powerError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDigital dataModem device
A method of determining when cable modems in a distributed digital data delivery service over cable TV hybrid fiber coaxial cable network have a headroom problem and resolving said problem. The method involves measuring the burst power from each cable modem, and if the burst power is too low, requesting the cable modem whose burst power is too low to increase its transmit power, and keeping track of which modems have been requested to increase their power. If a predetermined number of requests to increase power have not resulted in the cable modem transmitting with sufficient power for reliable reception, the cable modem is listed as having a headroom problem. Subsequent requests for upstream bandwidth from all modems with headroom problems are analyzed to determine if the requested burst size is too large and will result in a headroom problem. If so, a calculation as to the maximum number of spreading codes that each modem with a headroom problem can simultaneously transmit on without a headroom problem. The requested burst is then broken down into smaller burst fragments, and appropriate upstream minislot assignments adequate to transmit the burst fragments are made and sent to the cable modem.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and device for diagnosing a crankcase ventilation of an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20080201062A1Simple and reliable and economical mannerStable operating pointAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlExternal combustion engineEngineering
A method and device for diagnosing a crankcase ventilation of an internal combustion engine, which enable a diagnosis of a malfunction of an actuator of the crankcase ventilation. The internal combustion engine has at least two cylinder banks to which the crankcase ventilation is supplied, and an actuator is provided via whose position the distribution of the crankcase ventilation to the at least two cylinder banks is influenced. In a first position of the actuator, a different distribution of the crankcase ventilation to the at least two cylinder banks comes about than in a second position of the actuator that differs therefrom. Given simultaneously activated operation of the at least two cylinder banks, the actuator is switched over at least one between the two different positions. For at least one of the at least two cylinder banks, a characteristic variable of the internal combustion engine influenced by the crankcase ventilation is determined prior to and following the switchover operation. A minimum value for a change in the characteristic variable of at least one of the at least two cylinder banks and / or the ratio of the characteristic variable between the at least two cylinder banks is specified for the switchover-related change in the distribution of the crankcase ventilation to the at least two cylinder banks. A malfunction of the actuator is detected if at least one change derived from the ascertained values for the characteristic variable undershoots its assigned expected minimum value in quantitative terms.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
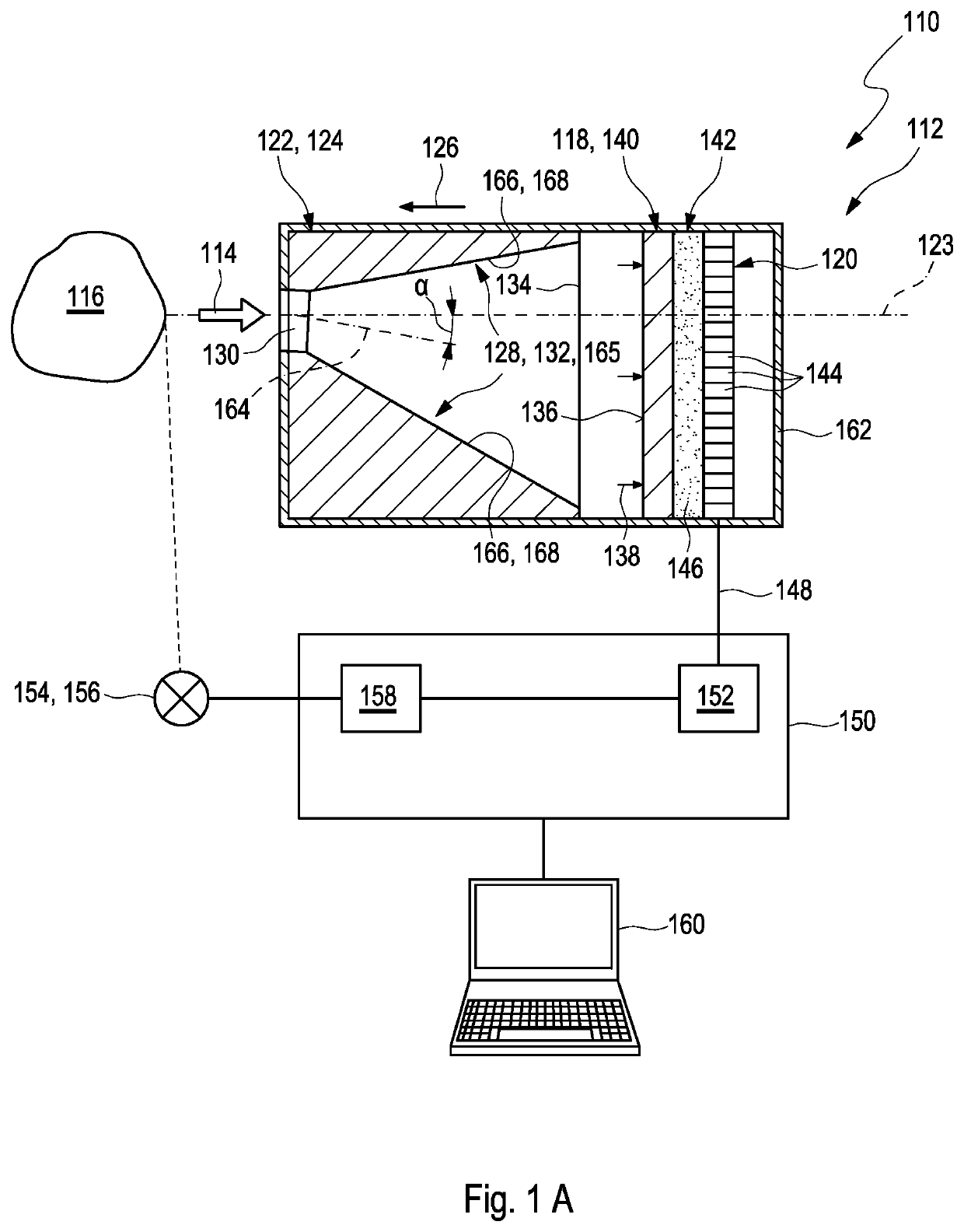
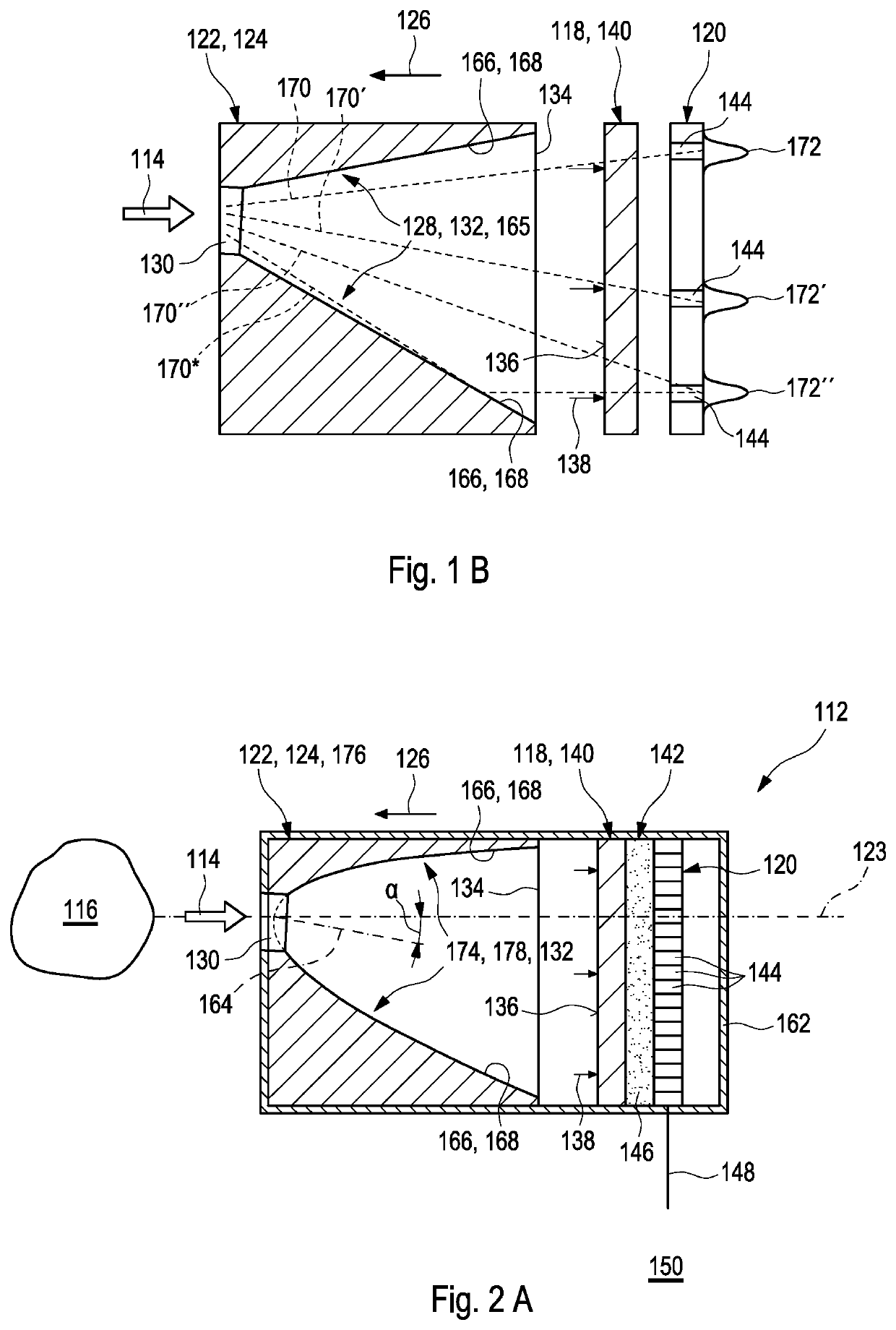
Spectrometer device and system
ActiveUS20210072082A1High strengthSufficient signal-to-noise ratioSpectrum investigationSensing radiation from gases/flamesHigh concentrationOptical spectrometer
Described herein are a spectrometer system and a spectrometer device, which are suited for investigation or monitoring purposes, in particular, in the infrared (IR) spectral region, and for a detection of heat, flames, fire, or smoke.The spectrometer device) allows capturing incident light from object and transferring the incident light to a length variable filter with a particularly high concentration efficiency. Apart from the spectrometer device the spectrometer system further includes an evaluation unit designated for determining information related to a spectrum of an object by evaluating the detector signals provided by the spectrometer device.
Owner:TRINAMIX GMBH
Dynamometric cell
InactiveUS7380475B2High solution accuracySimple designForce measurement by measuring magnetic property varationPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementUltrasound attenuationEngineering
A dynamometric cell having an elastically deformable force transducer for receiving a weight force and a sensor arrangement for detecting the deformation of the force transducer and its conversion into an electric weight signal is disclosed, wherein the force transducer is connected to a mounting member at its first end and supports a force introduction member at its second end, such that it allows a more exact determination of weight force even when it is incorporated into narrow spaces and wherein the force transducer is designed as a hollow bar with two attenuation zones spaced in longitudinal direction of the bar.
Owner:BAG BIZERBA AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
Communications devices, infrastructure equipment and methods
ActiveUS9866247B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioEarly terminationTransmission path divisionWireless commuication servicesComputer scienceCommunication device
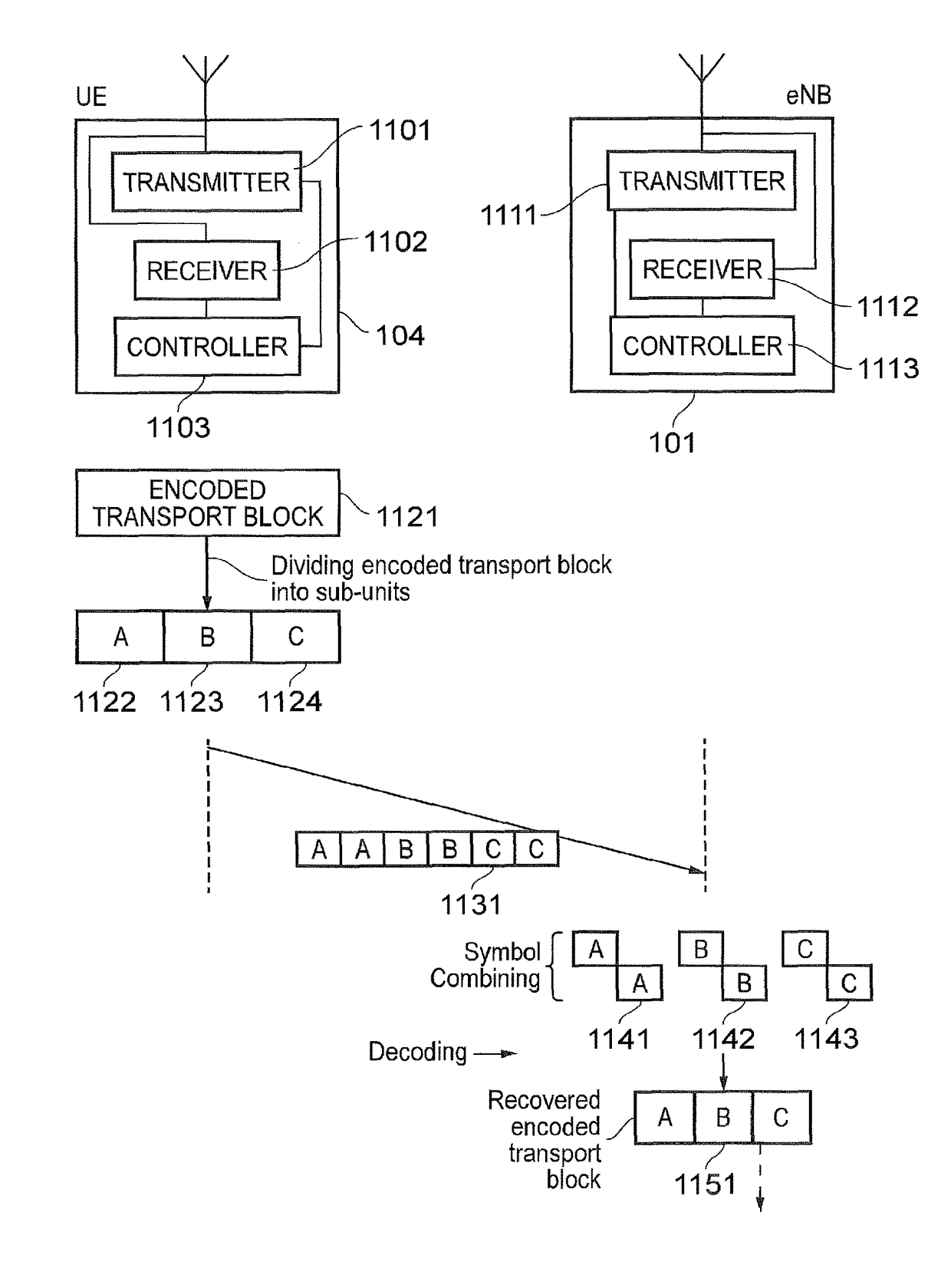
A communications device including a receiver configured to receive a plurality of sub-units of an encoded transport block of data in a plurality of time-divided units within frequency resources of a wireless access interface allocated to the mobile terminal, each of the sub-units being received a repeated number of times within a repetition cycle; and circuitry configured to combine a same sub-unit received the repeated number of times to form a composite sub-unit to recover the transport block.
Owner:SONY CORP
Spectrometer device and system
InactiveUS20210190585A1High degreeImprove concentration efficiencySpectrum investigationSensing radiation from gases/flamesHigh concentrationOptical spectrometer
Described herein are a spectrometer system and a spectrometer device, which are suited for investigation or monitoring purposes, in particular, in the infrared (IR) spectral region, and for a detection of heat, flames, fire, or smoke.The spectrometer device allows capturing incident light from an object and transferring the incident light to a length variable filter with a particularly high concentration efficiency. Apart from the spectrometer device, the spectrometer system further includes an evaluation unit designated for determining information related to a spectrum of an object by evaluating the detector signals provided by the spectrometer device.
Owner:TRINAMIX GMBH
Communications devices, infrastructure equipment and methods
ActiveUS20180109276A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioEarly terminationTransmission path divisionPayload allocationComputer terminalComputer science
A communications device including a receiver configured to receive a plurality of sub-units of an encoded transport block of data in a plurality of time-divided units within frequency resources of a wireless access interface allocated to the mobile terminal, each of the sub-units being received a repeated number of times within a repetition cycle; and circuitry configured to combine a same sub-unit received the repeated number of times to form a composite sub-unit to recover the transport block.
Owner:SONY CORP
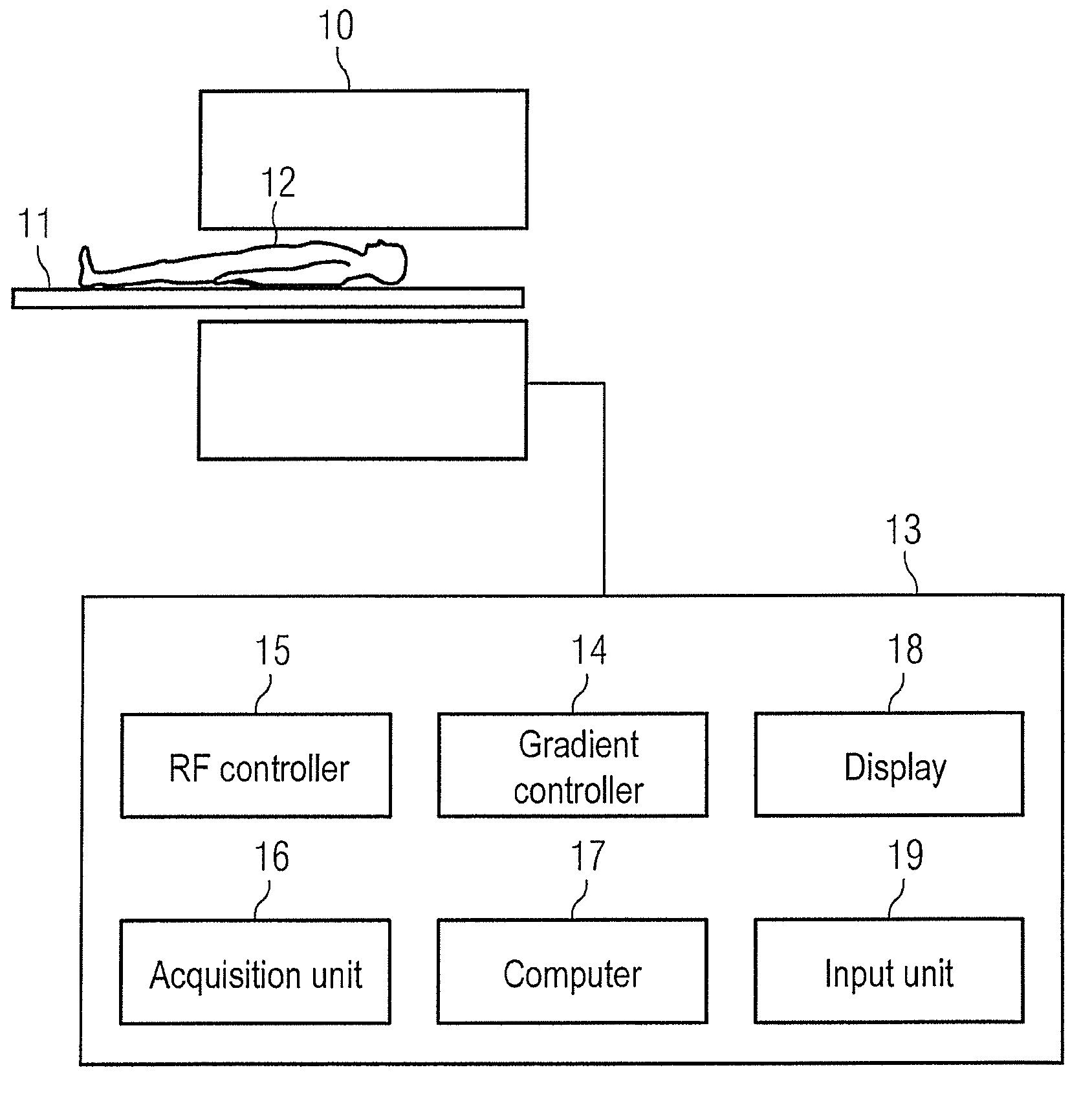
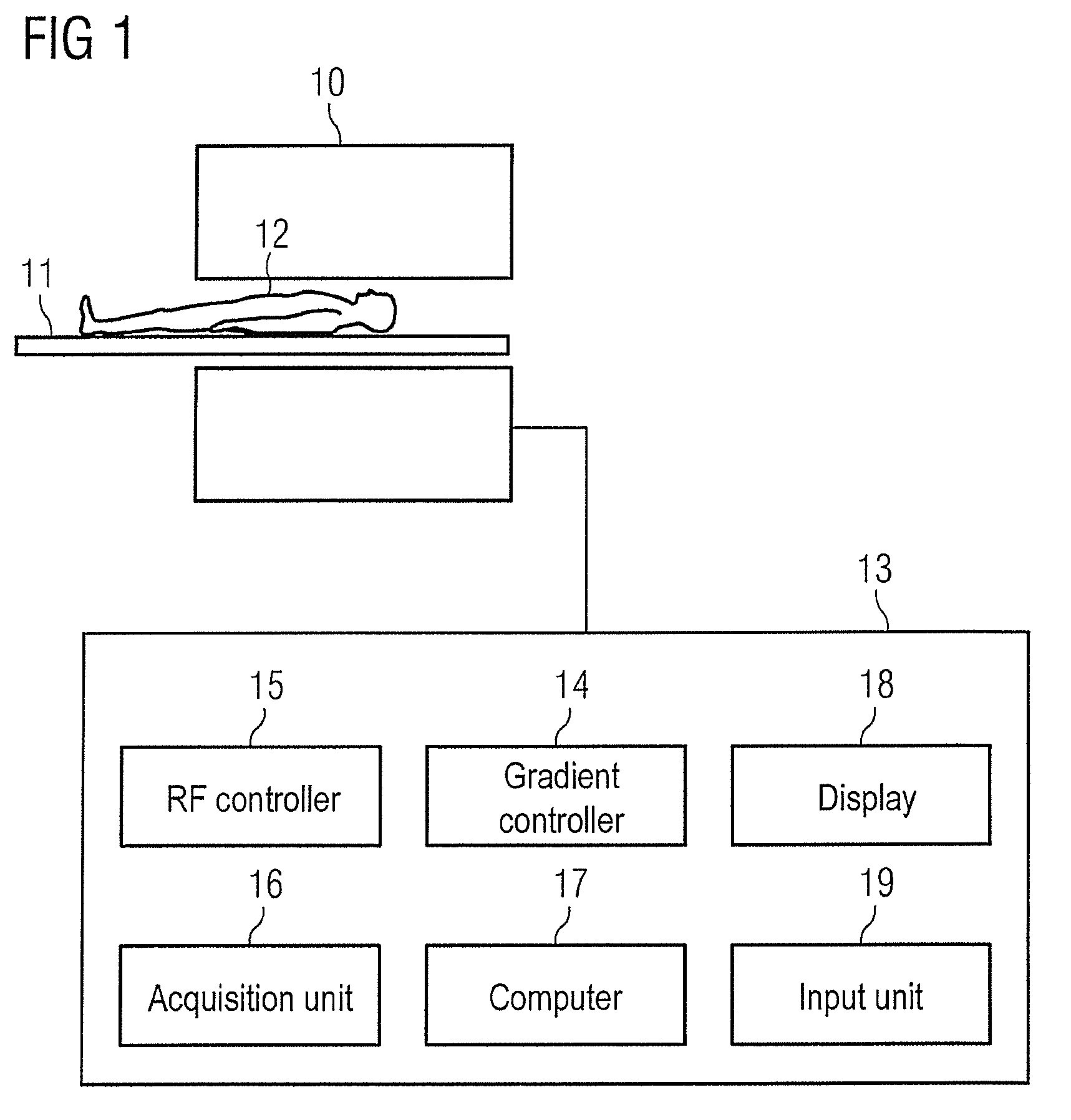
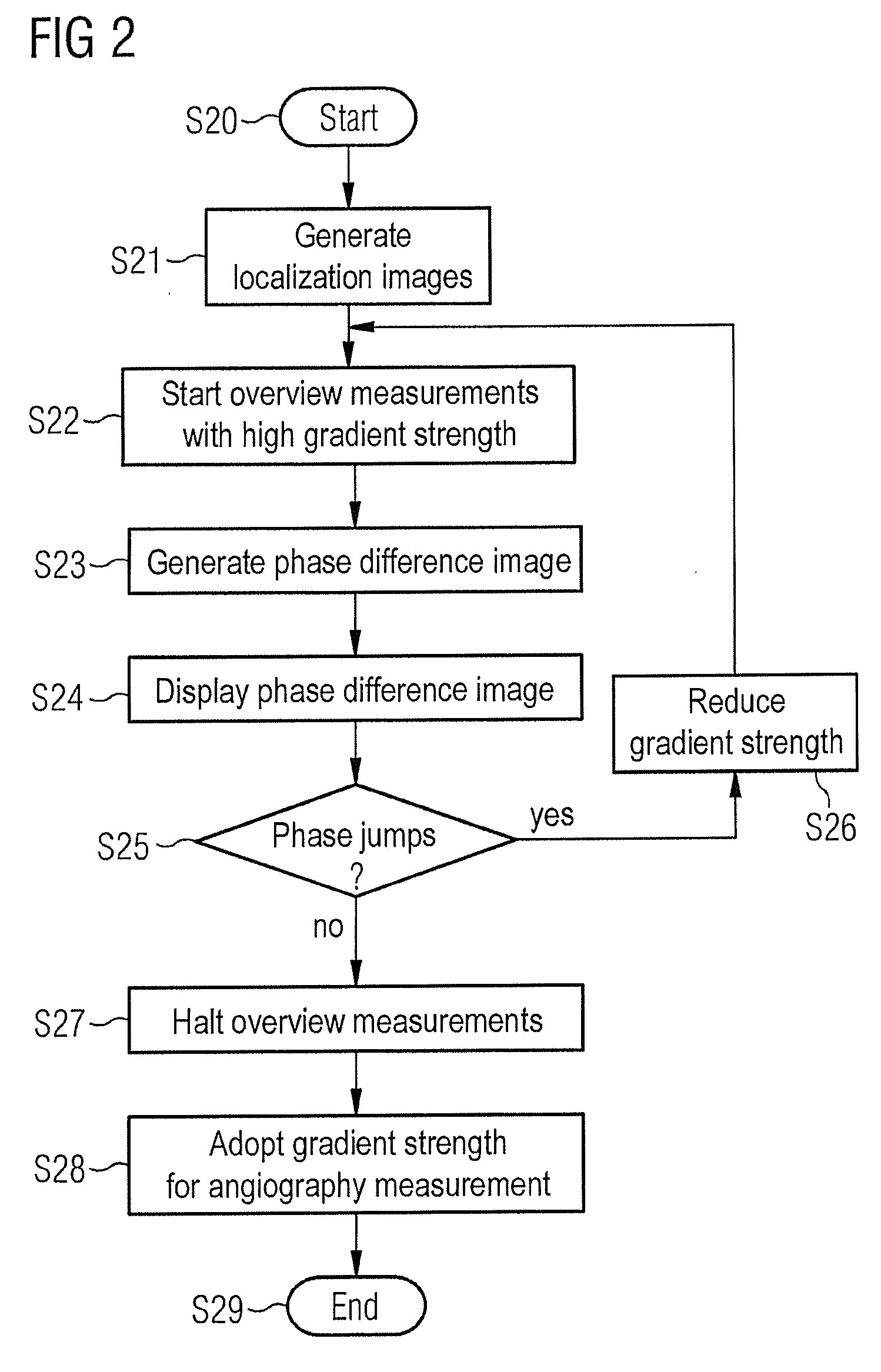
Dynamic adaptation of a dephasing gradient pair
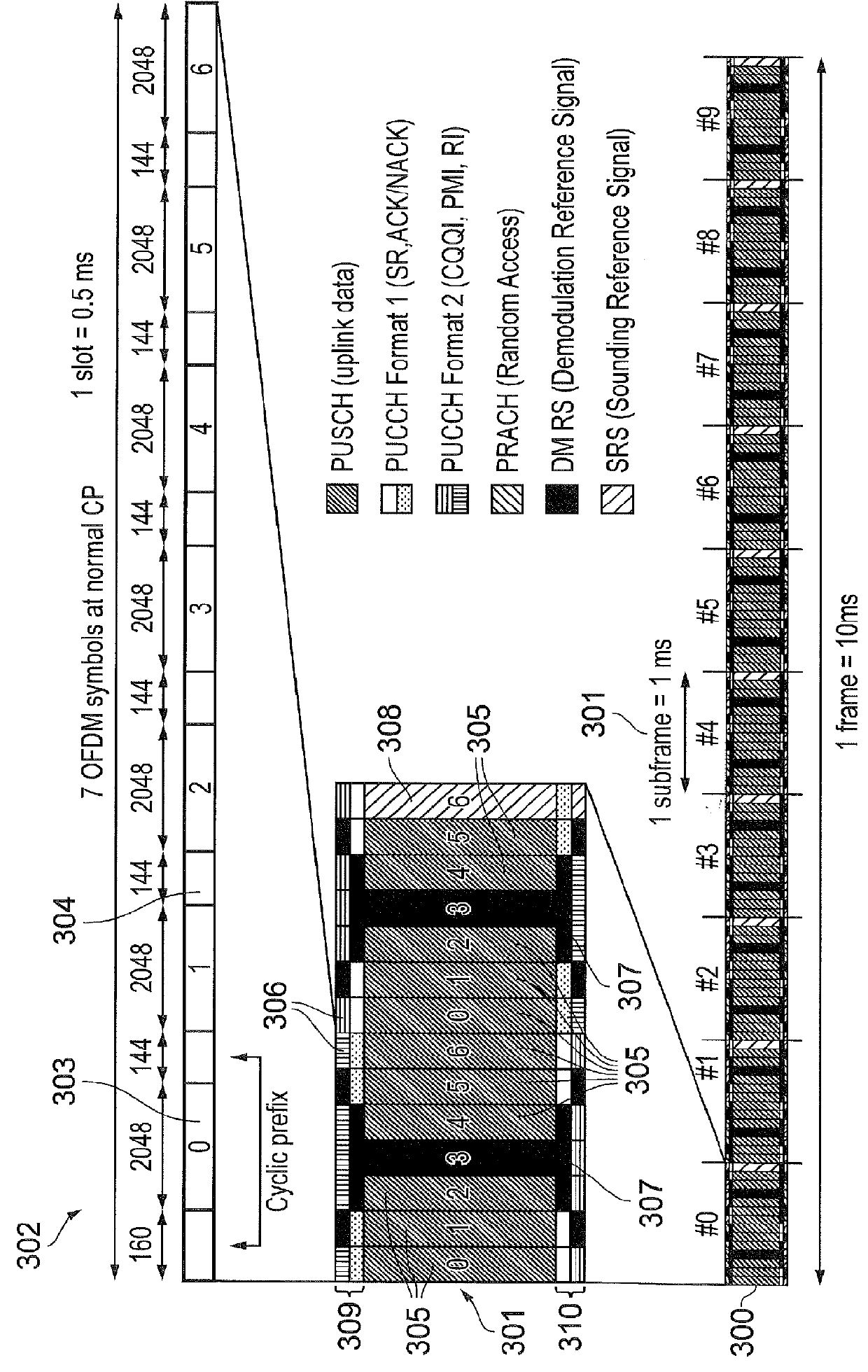
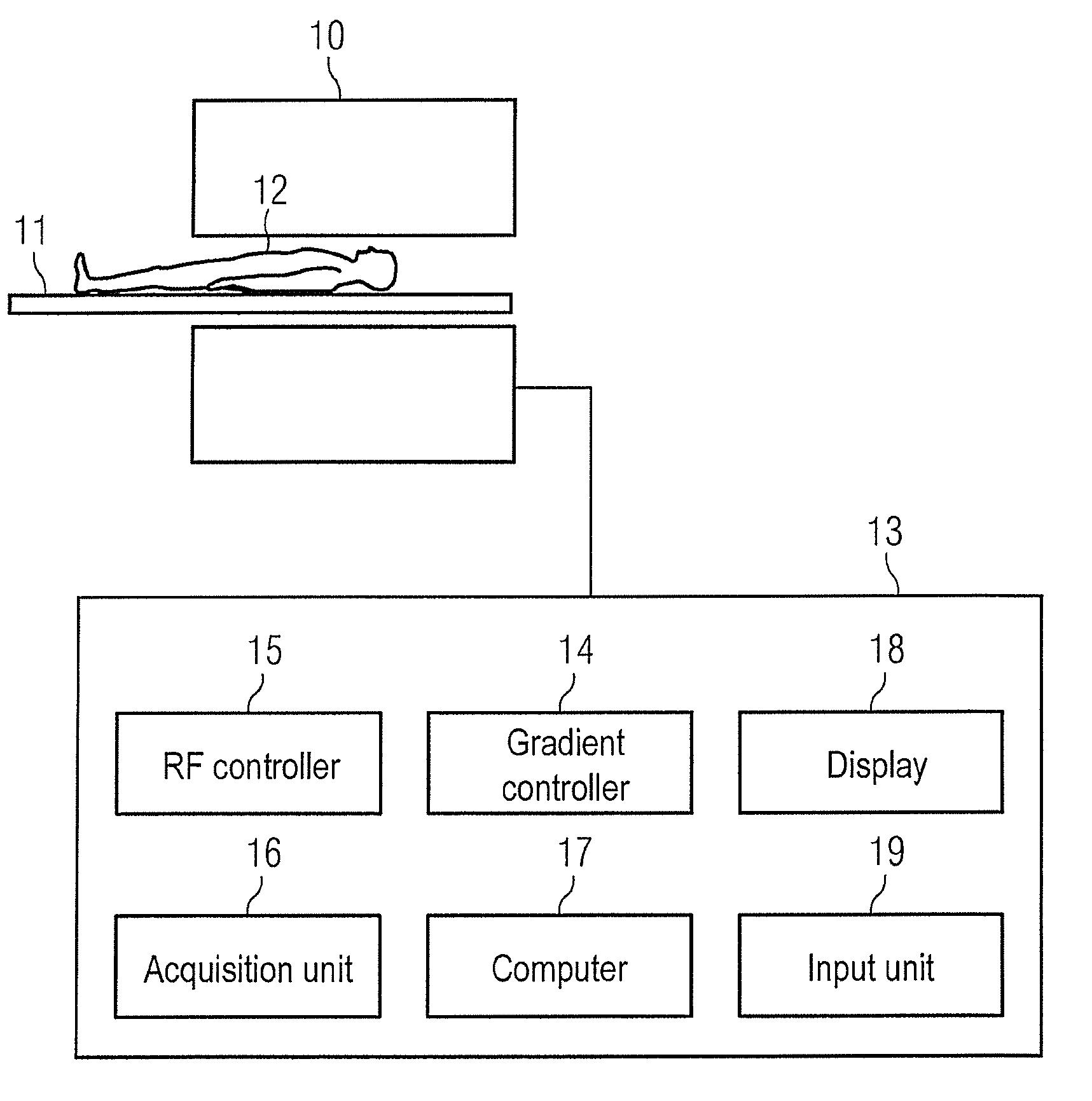
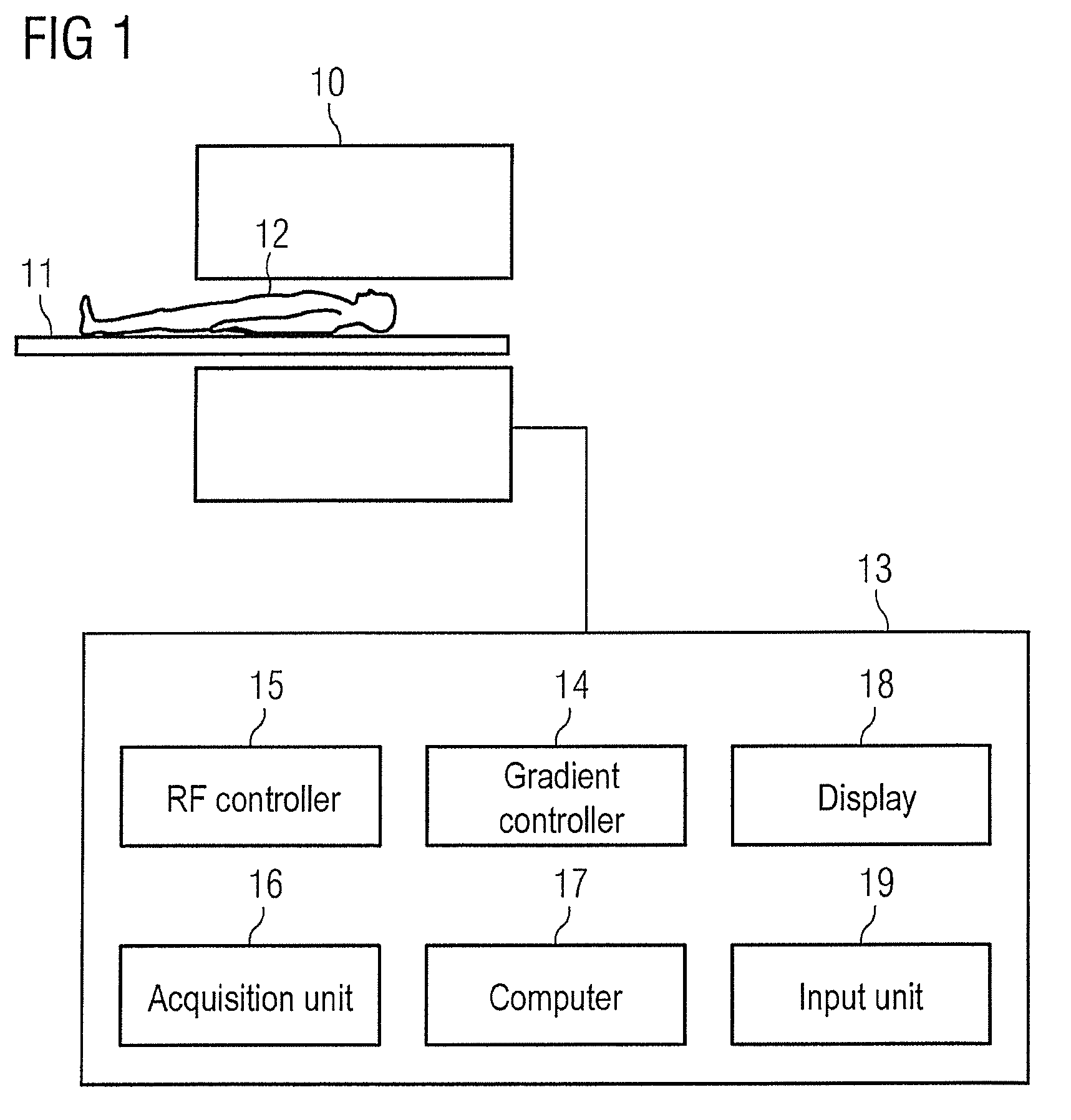
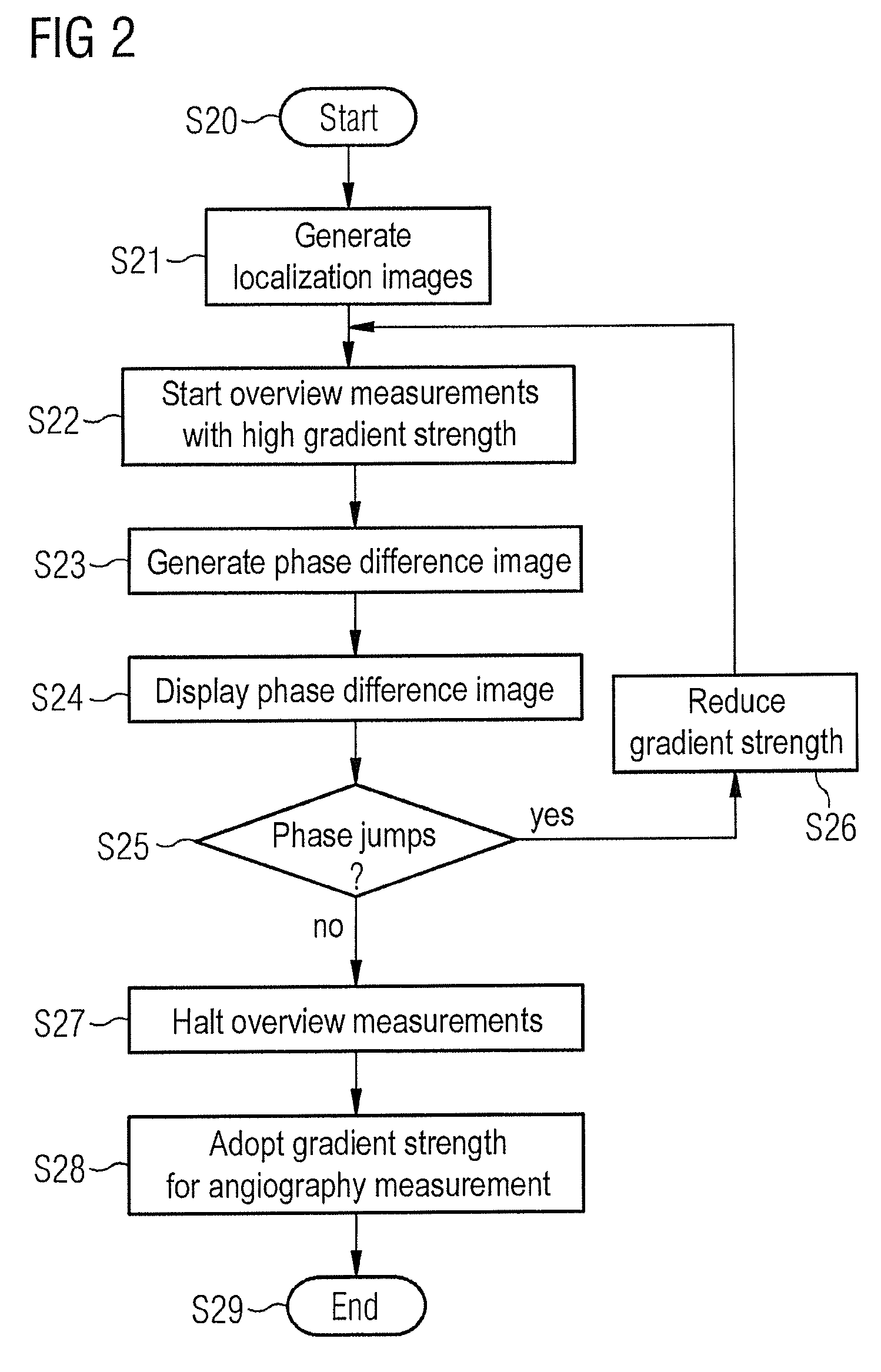
InactiveUS8975893B2Speed up searchIncrease probabilityCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringResonancePhase difference
In a method for optimization of a flow coding with switching of an additional bipolar dephasing gradient pair, used in a magnetic resonance (MR) phase contrast angiography, the strength of the flow coding is selected depending on the flow velocity in the vessels that should be depicted. MR signals of an examination region are acquired with continuously running overview measurements, with an operator-selected flow coding strength. After the selected flow coding strength is adopted automatically for the next measurement of the continuously running overview measurements, and two partial measurements with different flow codings are implemented for each selected strength and a phase difference image from the two partial measurements is calculated and depicted in real time, and the selected flow coding strength is automatically adopted for the MR phase contrast angiography.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Dynamic adaptation of a dephasing gradient pair
InactiveUS20120268125A1Speed up searchIncrease probabilityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRPhase differenceResonance
In a method for optimization of a flow coding with switching of an additional bipolar dephasing gradient pair, used in a magnetic resonance (MR) phase contrast angiography, the strength of the flow coding is selected depending on the flow velocity in the vessels that should be depicted. MR signals of an examination region are acquired with continuously running overview measurements, with an operator-selected flow coding strength. After the selected flow coding strength is adopted automatically for the next measurement of the continuously running overview measurements, and two partial measurements with different flow codings are implemented for each selected strength and a phase difference image from the two partial measurements is calculated and depicted in real time, and the selected flow coding strength is automatically adopted for the MR phase contrast angiography.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Detector array and a spectrometer system
PendingUS20220357202A1High strengthSufficient signal-to-noise ratioSpectrum investigationSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionOptical spectrometerDetector array
Disclosed herein are a detector array, a spectrometer system including the detector array and a method of using of the spectrometer system. The detector array includes a substrate; and a plurality of detector pixels applied to a surface of the substrate, where each detector pixel has a sensor region which is designated for receiving a partition of incident light, where each detector pixel is designated for generating a sensor signal depending on an intensity of the partition of the incident light received by the sensor region of the detector pixel, where at least two adjacent detector pixels share a single connection to a common electric potential, and where the sensor regions of at least two of the detector pixels differ with respect to each other by an area of the corresponding sensor region.
Owner:TRINAMIX GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com