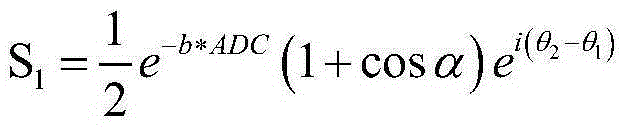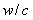Patents
Literature
255 results about "Transverse Relaxation Time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
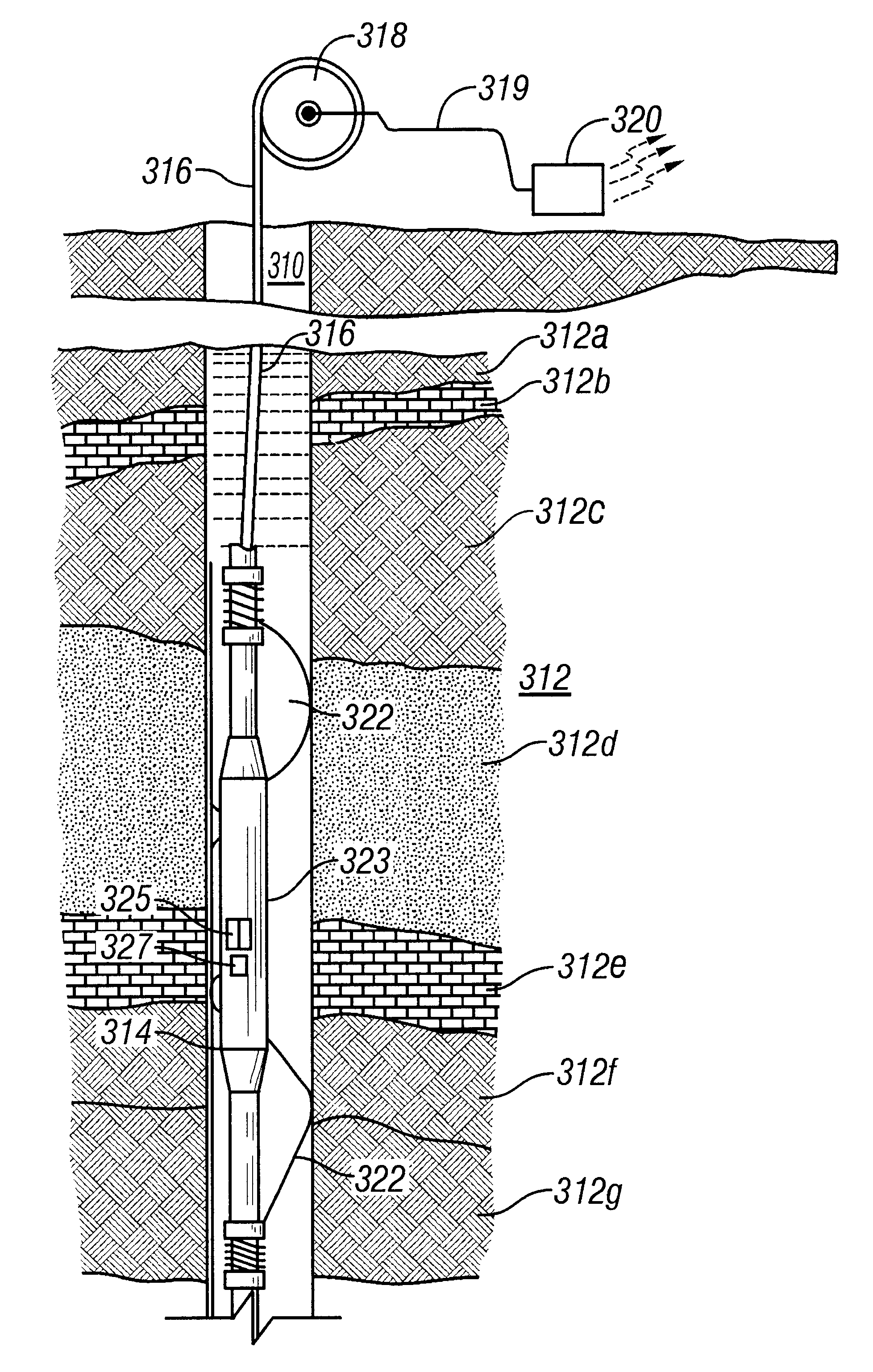
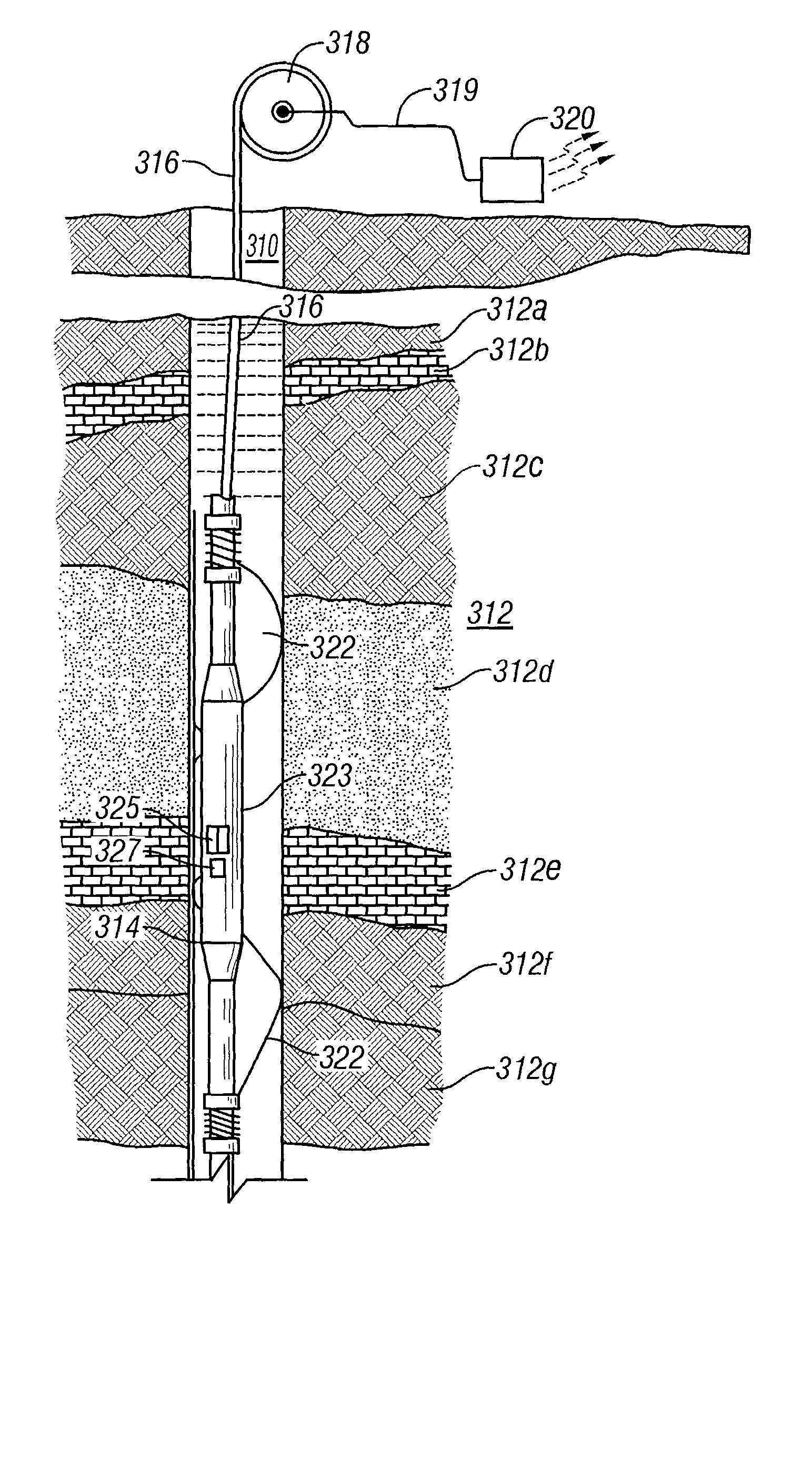
In-situ heavy-oil reservoir evaluation with artificial temperature elevation
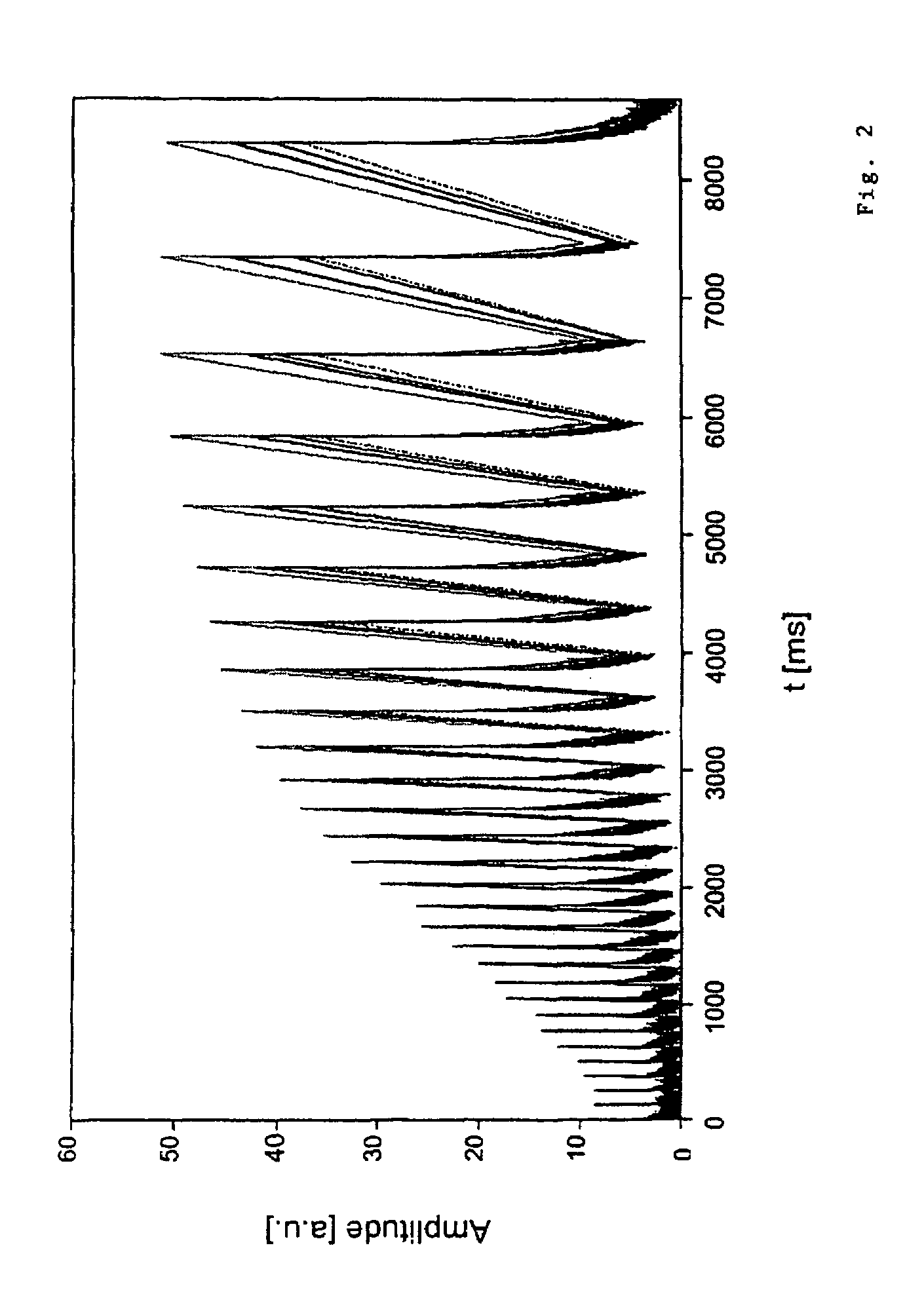
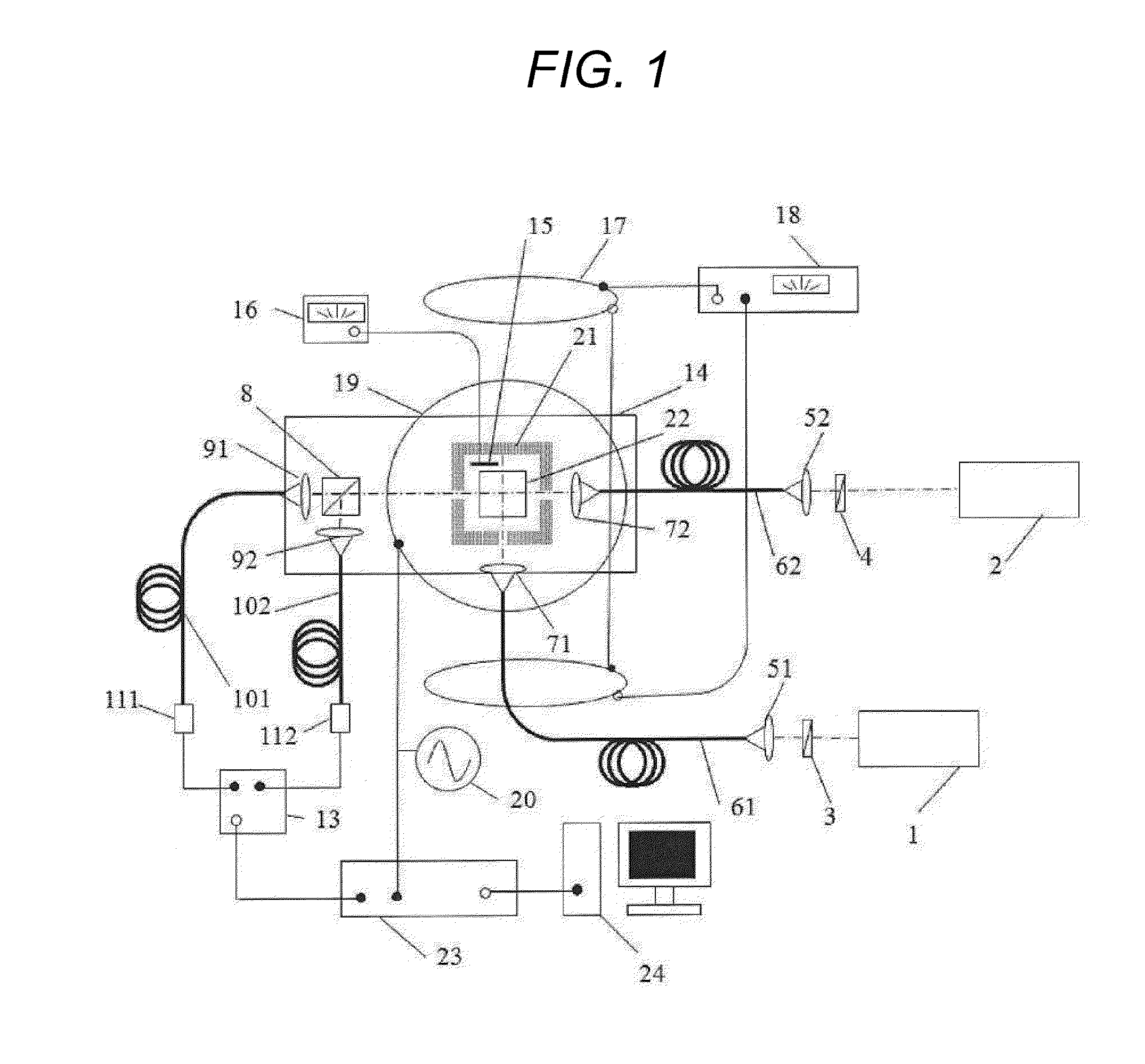
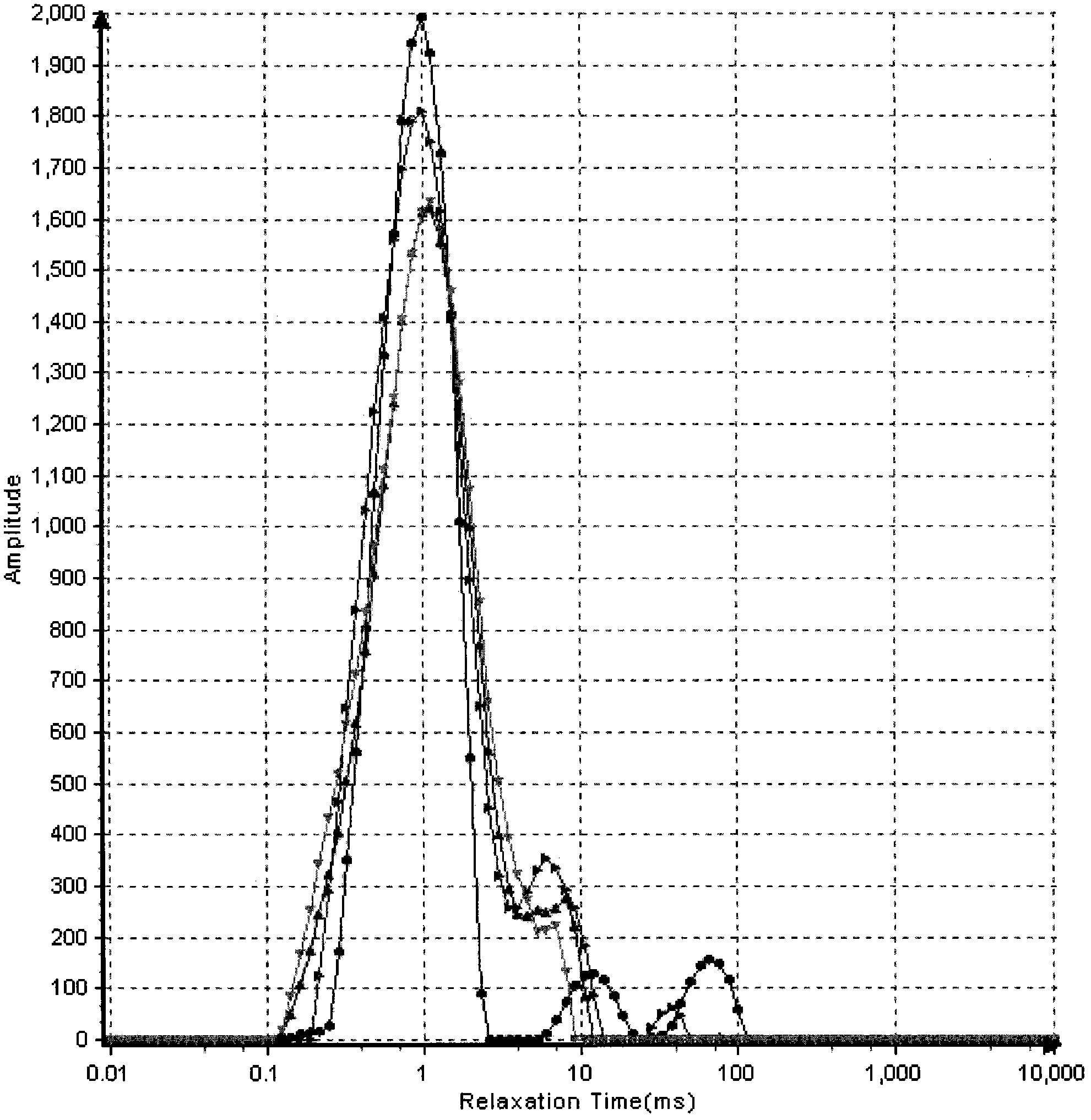
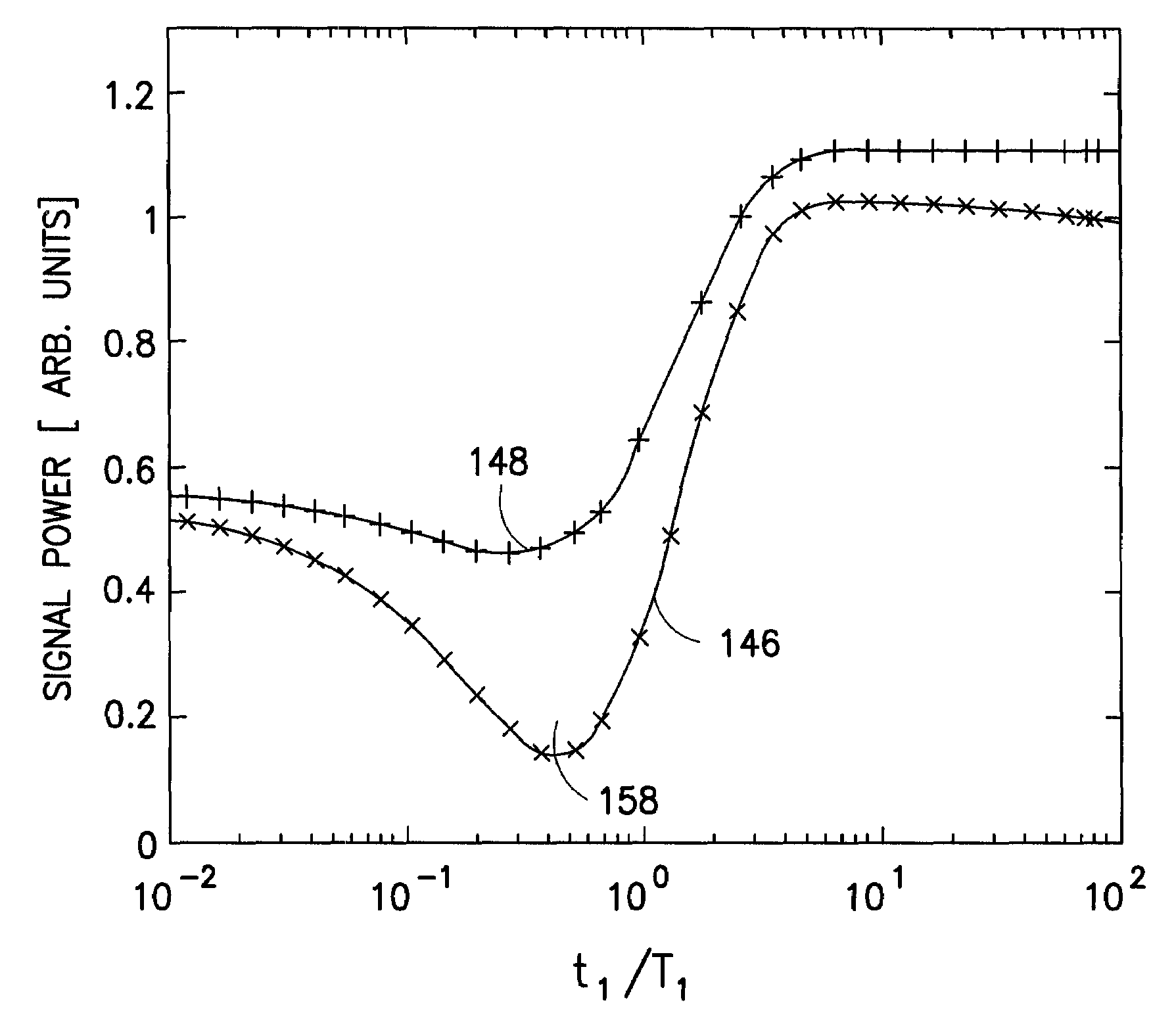
Many reservoirs of interest include heavy oil. In such reservoirs, parti at normal temperatures, many instruments commonly used for formation evaluation may not be able to distinguish between heavy oil and bound water in the formation. Passive or active heating is used to elevate the temperature of the fluids in the formation. At elevated temperatures, distinguishing between heavy oil and bound water is easier. Of particular interest is the increase in the resolvability of the transverse relaxation time T2 of NMR spin echo measurements. Additionally, the dielectric constant and the loss tangents of water and heavy oil show different temperature and frequency dependence.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
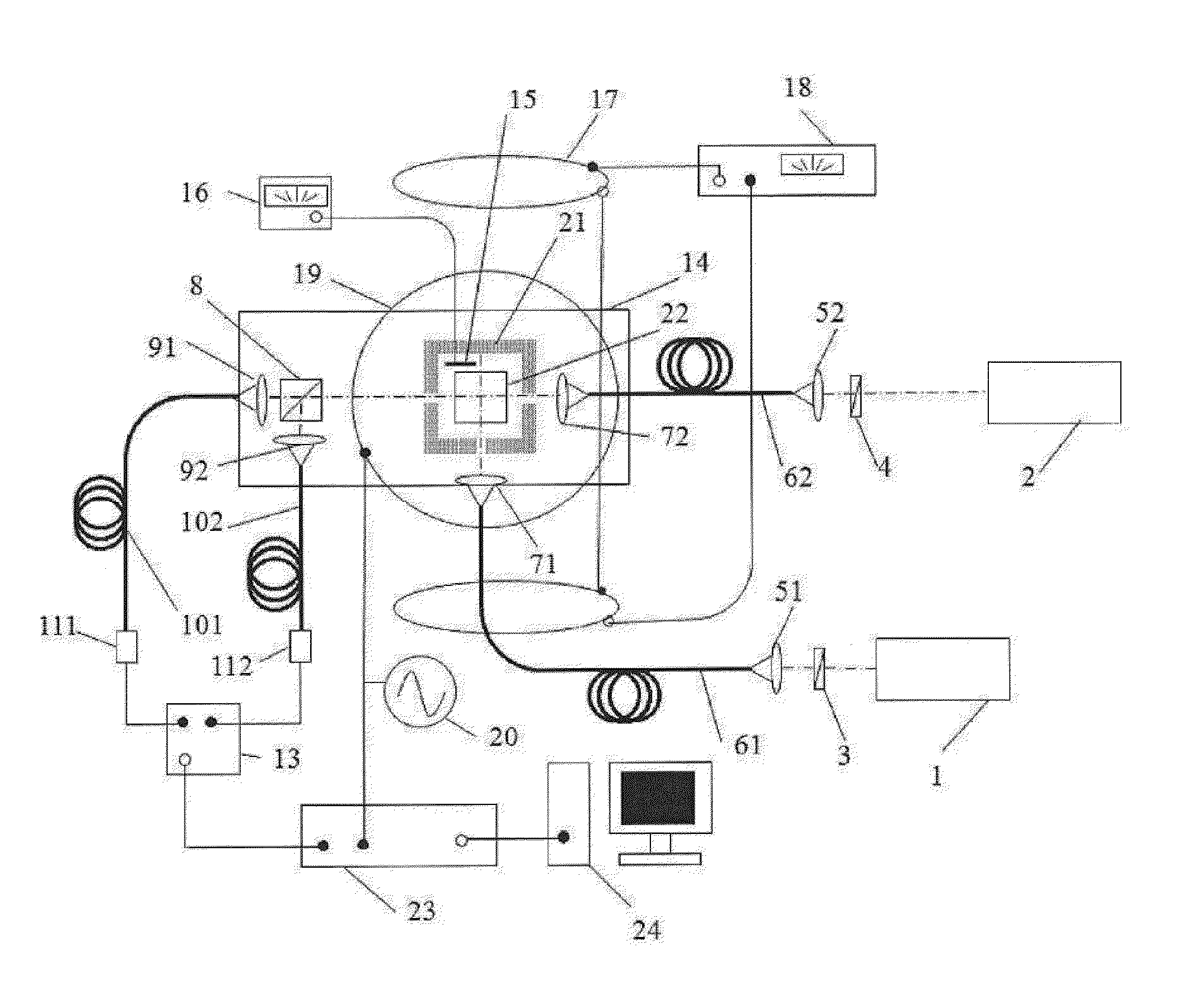
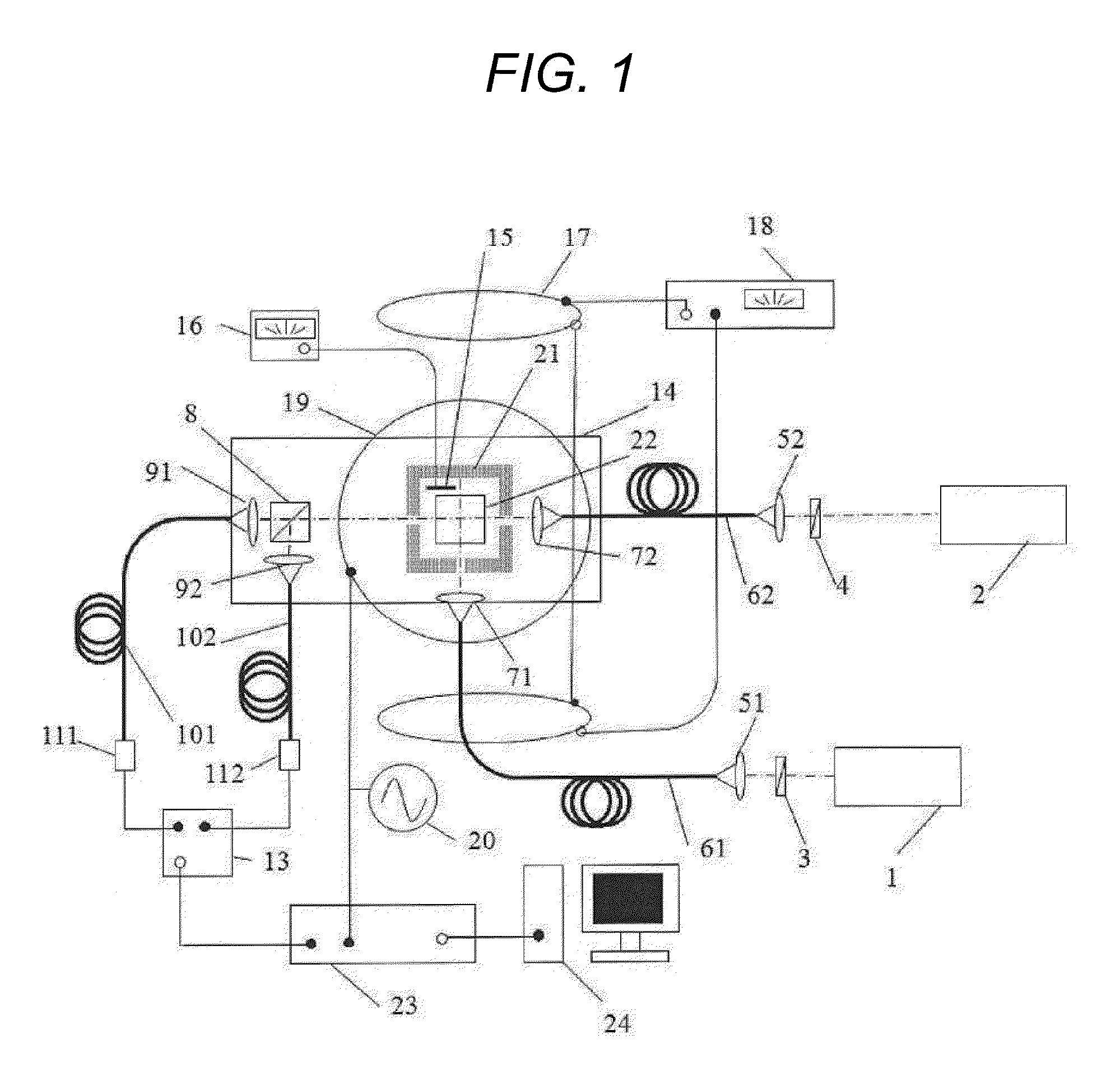
Nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer and nuclear magnetic resonance measuring method
ActiveCN102519999AAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceDiffusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer and a nuclear magnetic resonance measuring method. The analyzer comprises a radio frequency circuit, a magnet, a glass tube, a first coil and a second coil, wherein a sample to be measured is placed in the glass tube; the glass tube is fixedly arranged at a position opposite to the magnet and is placed in a magnetic field produced by the magnet; the first coil and the second coil are wound on the outer surface of the glass tube respectively and are connected with the radio frequency circuit; the first coil is placed at a uniform magnetic field produced by the magnet; and the second coil is placed at a gradient magnetic field produced by the magnet. Through the analyzer, distribution data of transverse relaxation time and longitudinal relaxation time of substances in the sample to be measured can be obtained, and distribution data of diffusion coefficients of the substances in the sample can be obtained.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
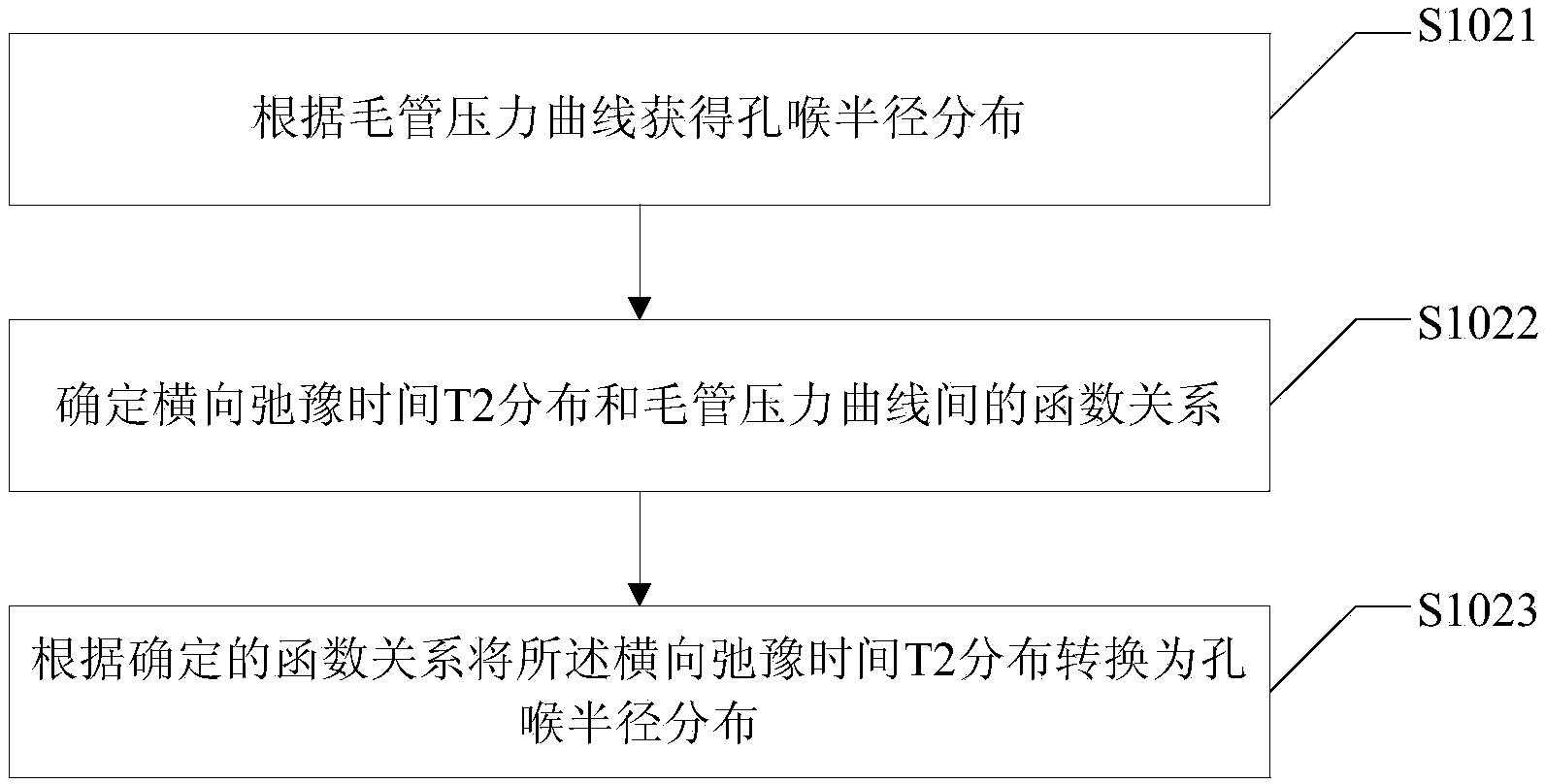
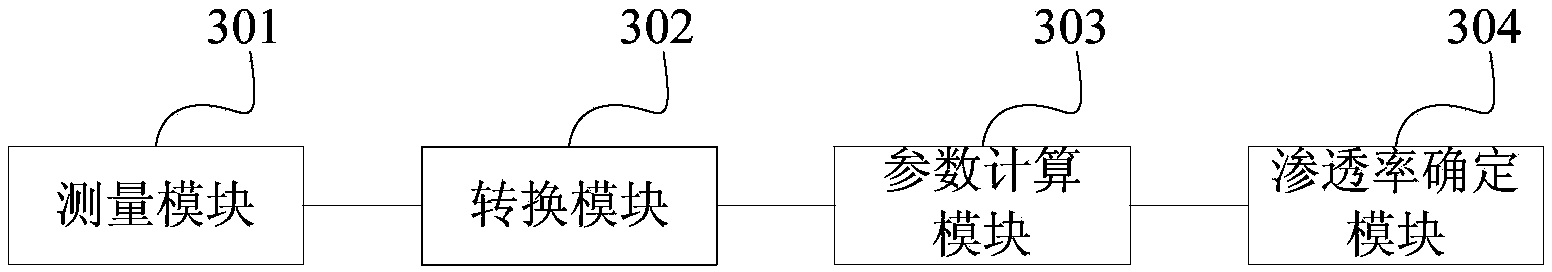
Method and device for confirming rock permeability
The invention provides a method and a device for confirming the rock permeability. The method comprises the following steps: measuring a series of selected rock core samples to obtain rock permeability values; measuring transverse relaxation time T2 distribution and rock core capillary pressure curves of water-saturated rock core samples with different permeability values; confirming the relationship of the transverse relaxation time T2 distribution of the rock core samples and pore throat radius distribution of the rock core samples according to a function relationship of the transverse relaxation time T2 distribution and the rock core capillary pressure curves; uniformly dividing the transverse relaxation time T2 distribution and the pore throat radius distribution of the rock core samples into n groups; and calculating porosity components and average pore throat radiuses of the different groups of rock core samples. The rock permeability is confirmed by dividing the plurality groups of porosity components and average pore throat radius components through the nuclear magnetic resonance T2 distribution. The seepage characteristics of reservoir rocks are reflected in a relatively real manner through the permeability calculated by using the method and the device provided by the invention, the consistency with the rock core analysis permeability result is good, and the calculation result is accurate.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method and apparatus for reservoir fluid characterization in nuclear magnetic resonance logging
ActiveUS20060290350A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceWell logging
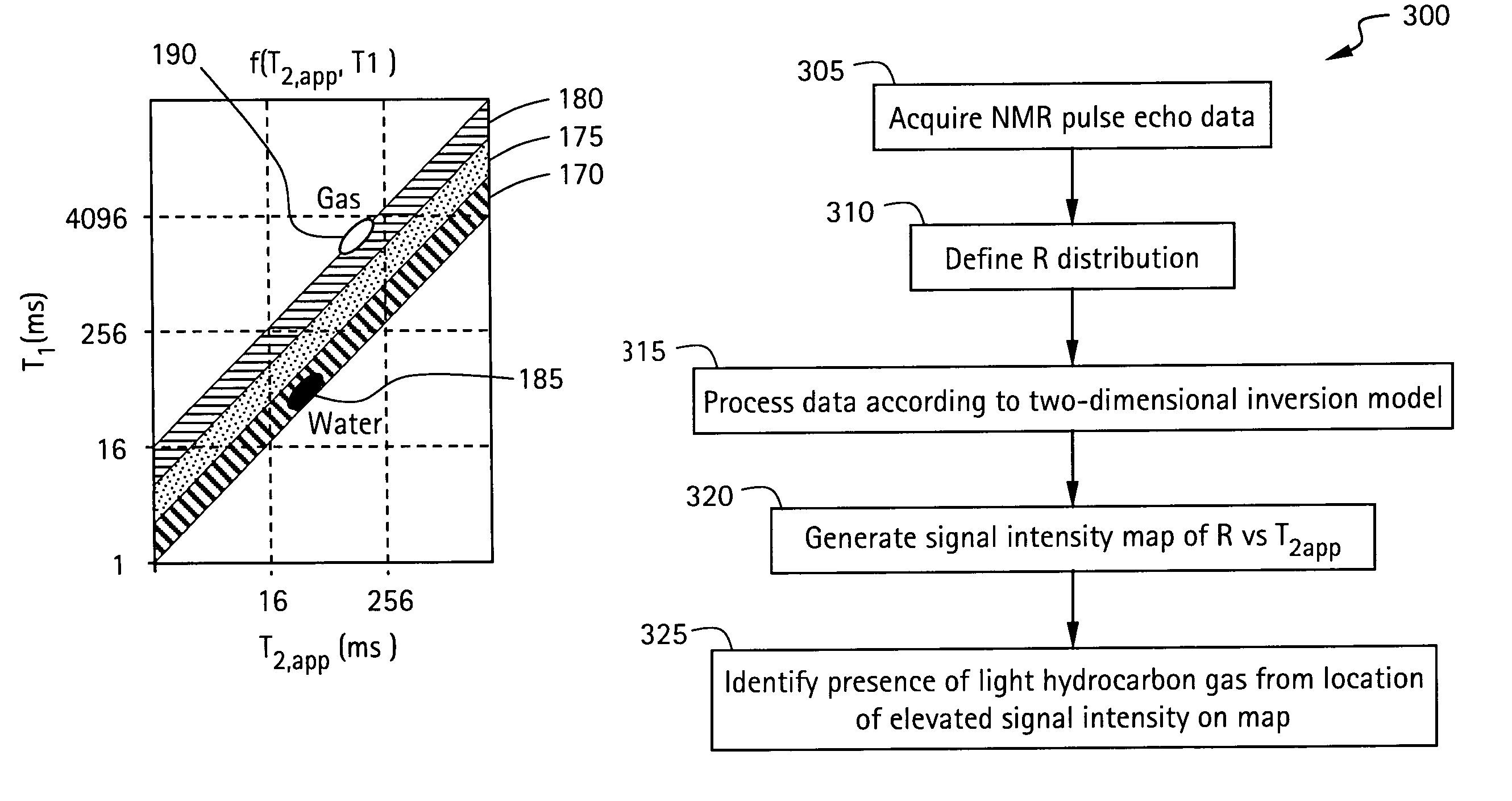
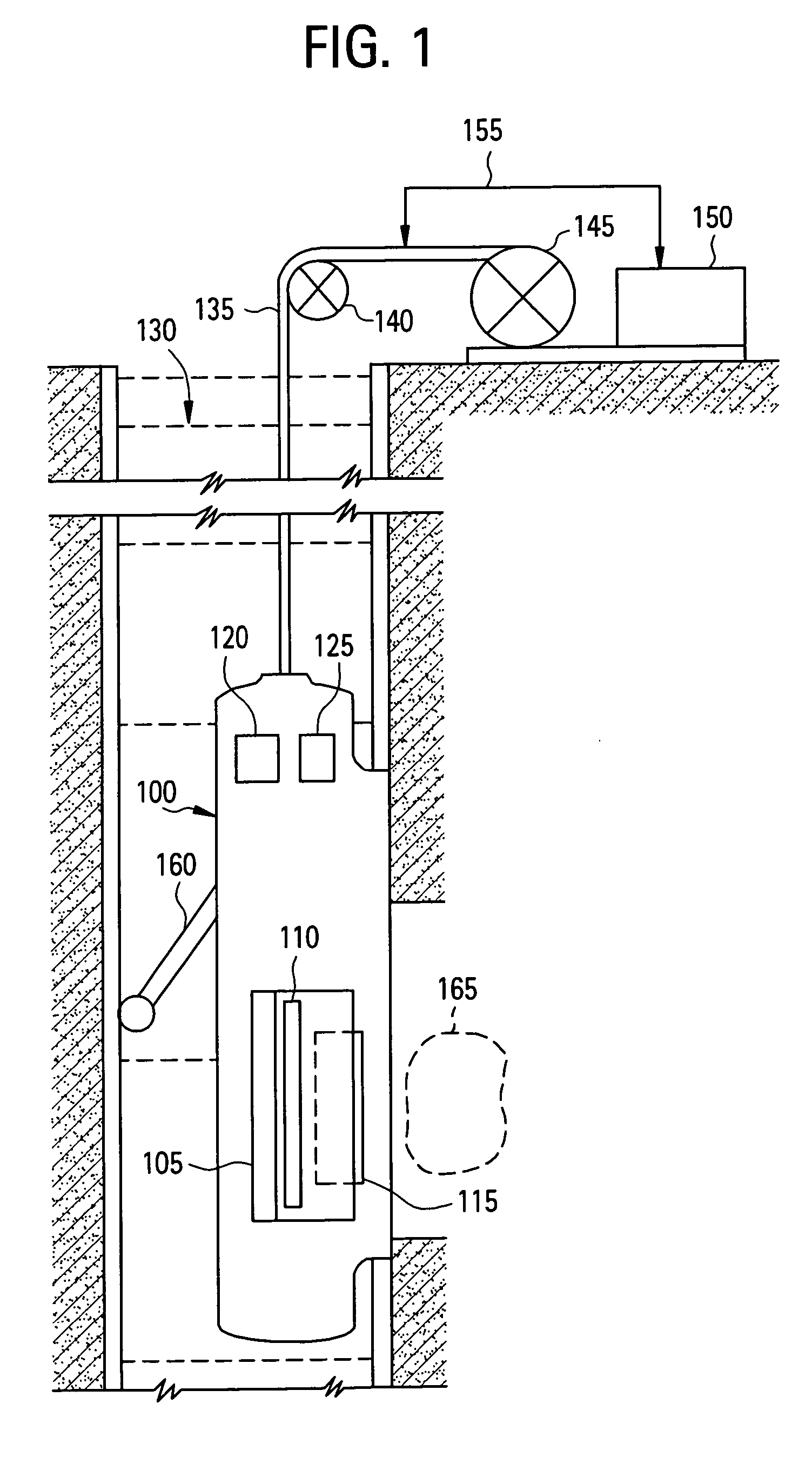
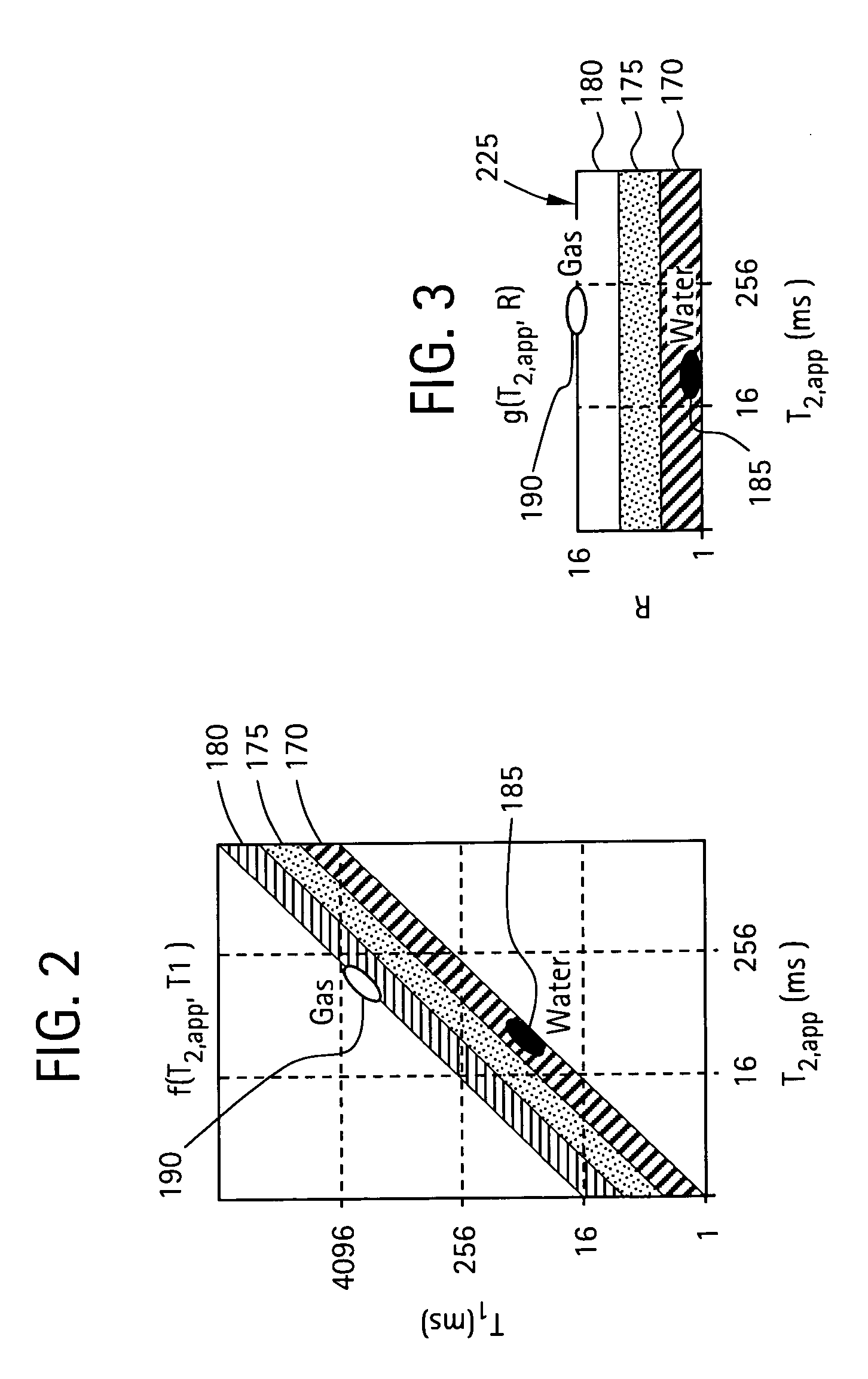
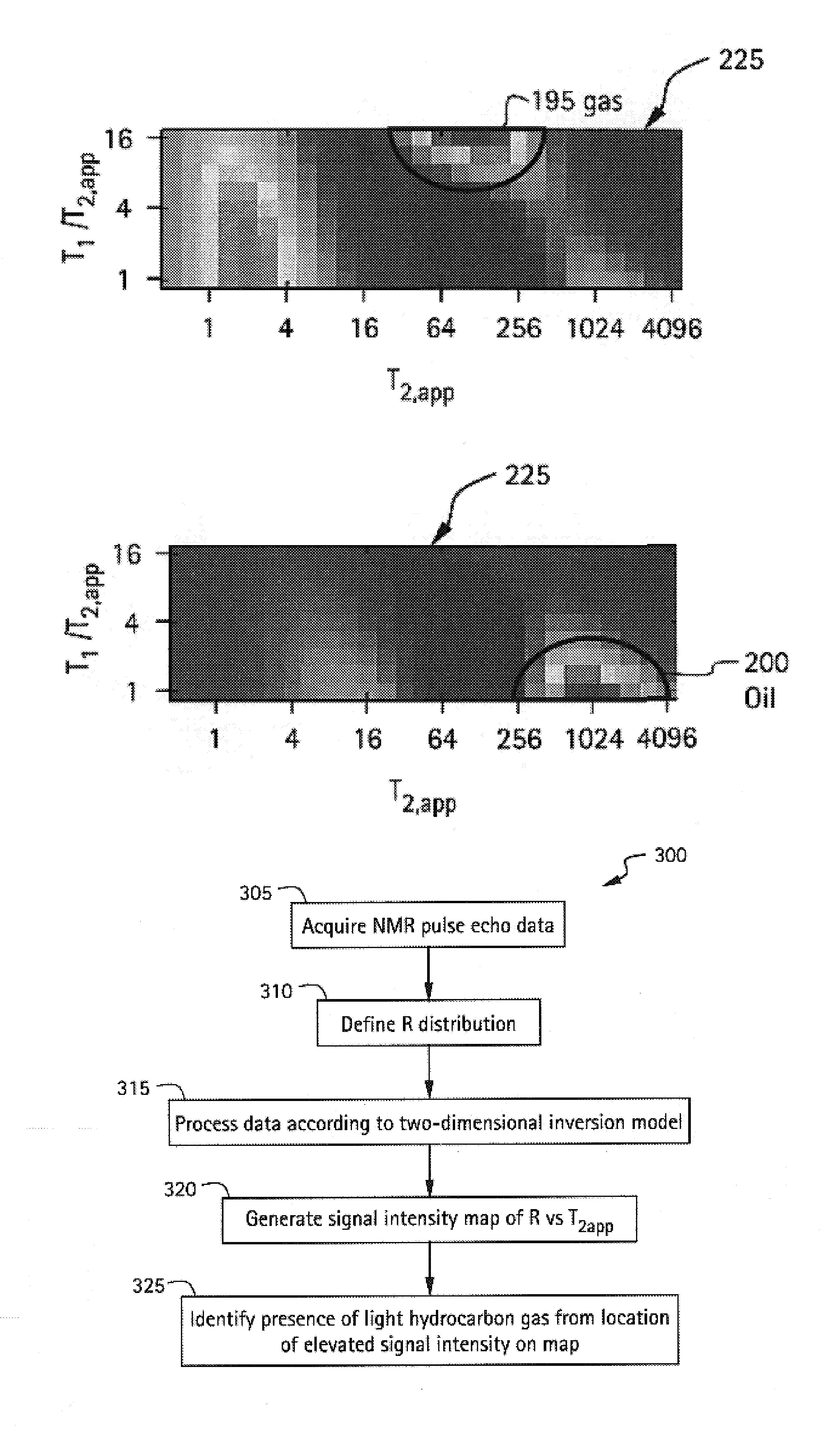
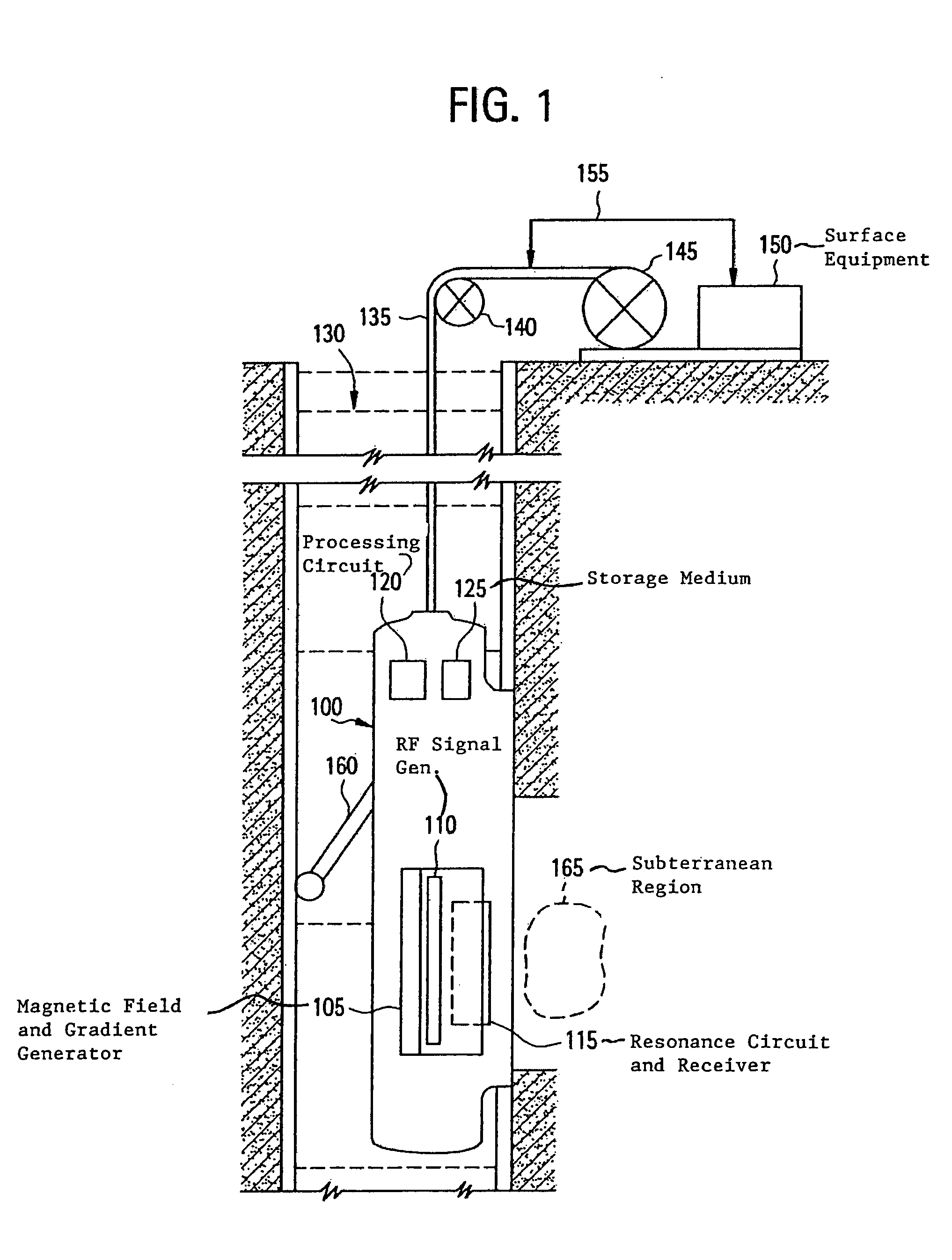
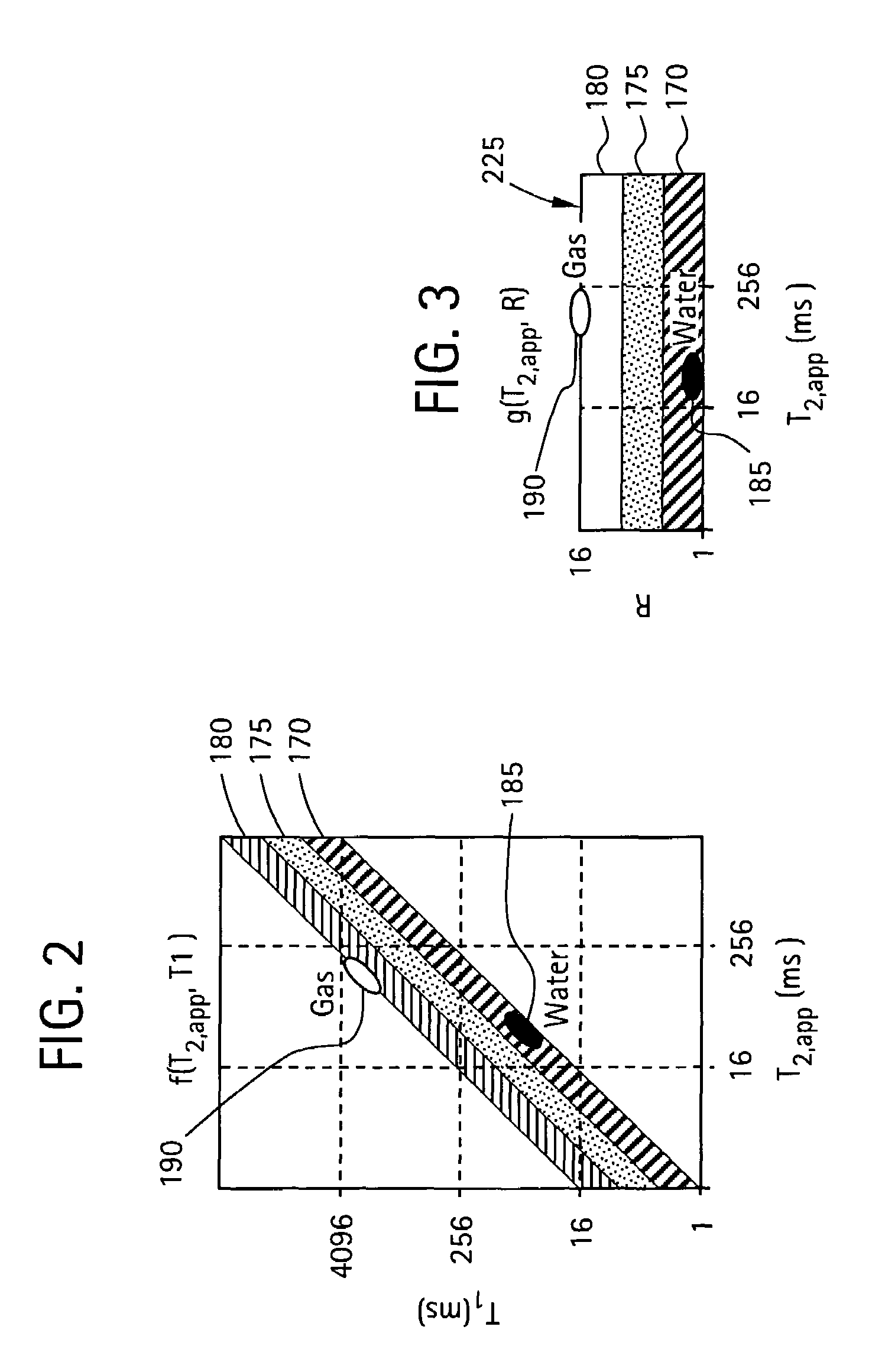
A method and apparatus for obtaining a parameter of interest relating to a region proximate a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) logging tool suitable for subterranean well logging is disclosed. The nuclei of the region are subjected to a pulsed NMR technique and are productive of NMR logging data, the nuclei of the region characteristically having a longitudinal relaxation time T1 distribution and an apparent transverse relaxation time T2app distribution. In response to the NMR logging data, an R distribution is defined as R=T1 / T2app, the T2app and R distributions are processed as separate bins, along with the NMR logging data, according to a two-dimensional inversion model, and a signal intensity map of R versus T2app is provided that is representative of the parameter of interest relating to the region. In response to a high-intensity signal on the map being within a first range of T2app values and a first range of R values, the presence of a light hydrocarbon within the region is identified.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method for judging wettability of reservoir rock
ActiveCN101915716AEasy to judge wettabilityWettability judgmentSurface/boundary effectAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceRock core
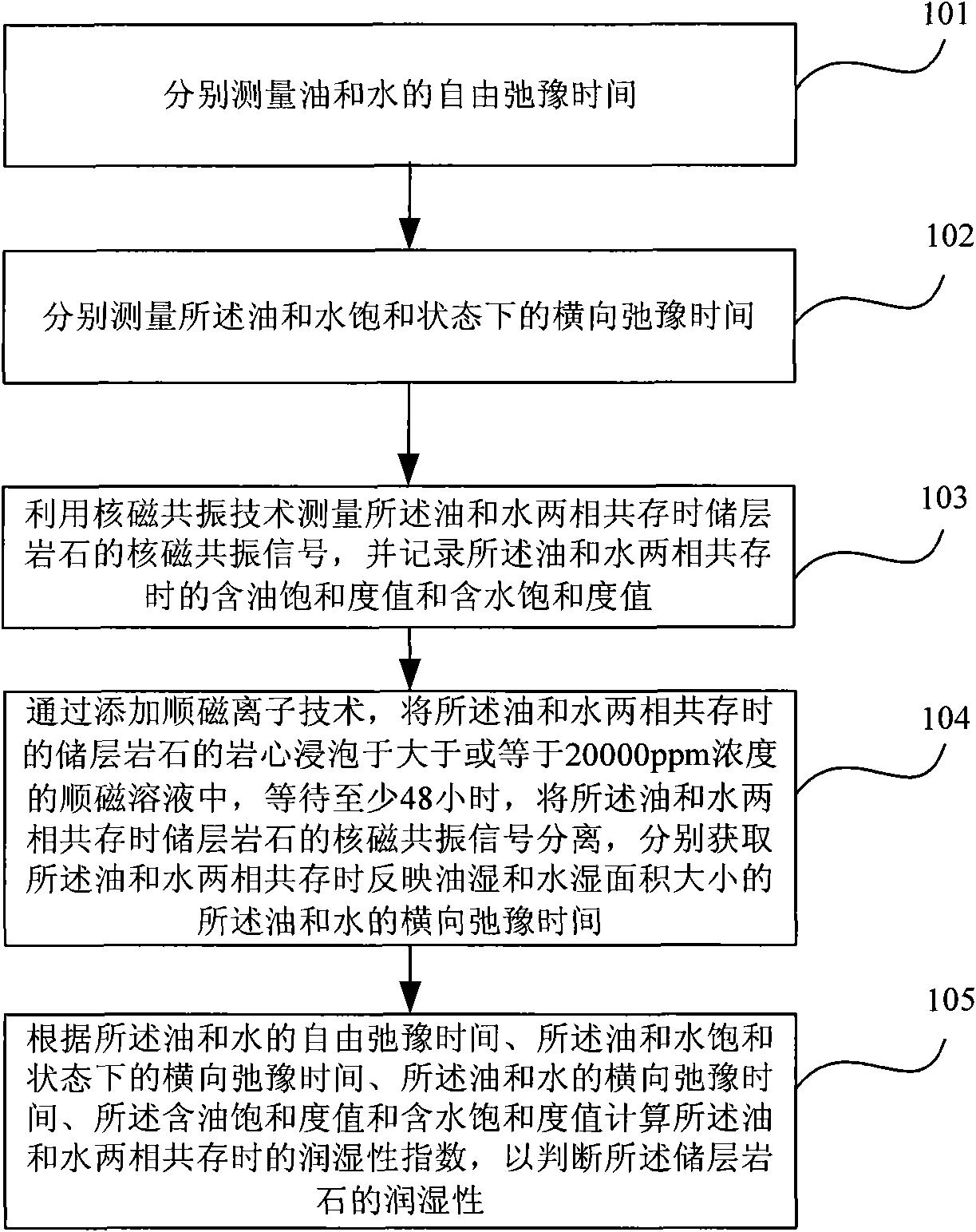
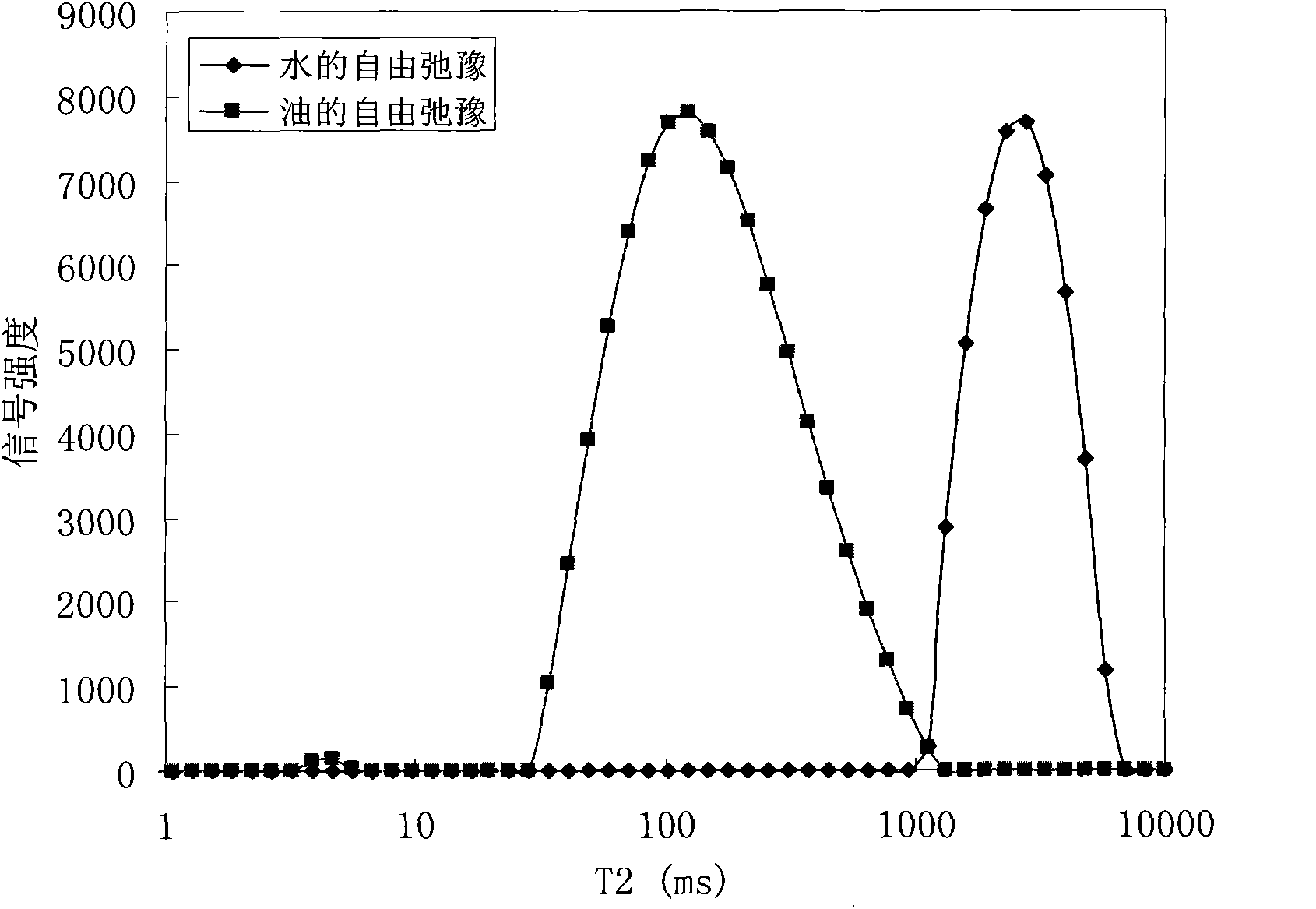
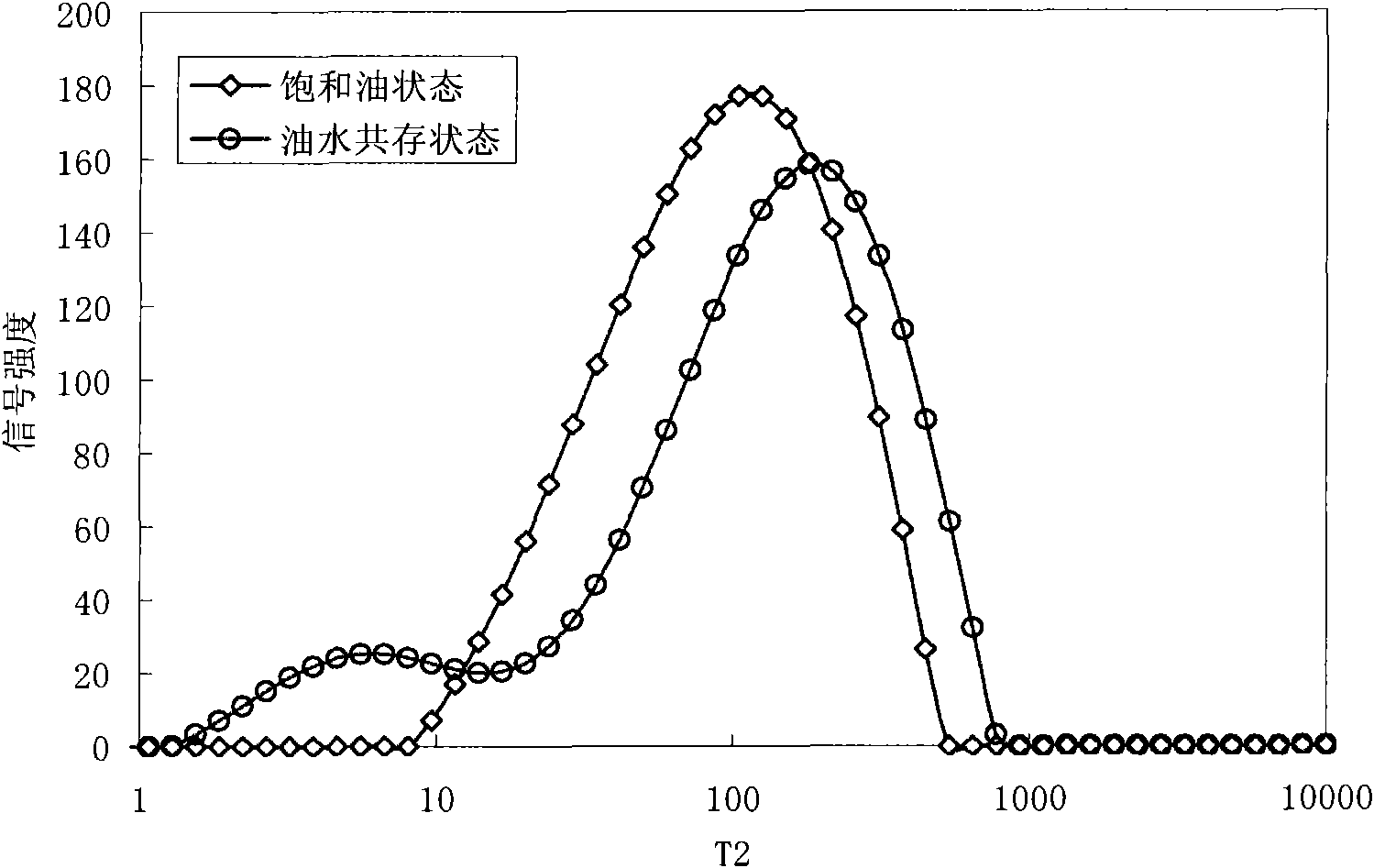
The invention provides a method for judging the wettability of a reservoir rock. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring free relaxation time of oil and water respectively; measuring transverse relaxation time of the oil and the water in saturated states respectively; measuring a nuclear magnetic resonance signal of the reservoir rock in the co-presence of an oil phase and a water phase by using nuclear magnetic resonance technology and recording an oil saturation value and a water saturation value in the co-presence of the oil phase and the water phase; dipping the rock core of the reservoir rock in the co-presence of the oil phase and the water phase in more than or equal to 20,000 ppm paramagnetic solution, waiting for at least 48 hours and separating the nuclear magnetic resonance signal of the reservoir rock in the co-presence of the oil phase and the water phase to obtain the transverse relaxation time of the oil and the water reflecting the size of an oil wet area and a water wet area; and calculating a wettability index in the co-presence of the oil phase and the water phase according to the free relaxation time of the oil and the water, the transverse relaxation time of the oil and the water in the saturated states, the transverse relaxation time of the oil and the water, the oil saturation value and the water saturation value so as to judge the wettability of the reservoir rock.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for determining the content of at least one component of a sample by means of a nuclear magnetic resonance pulse spectrometer
ActiveUS7397241B2Reliable measurementShort timeMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceTransverse relaxation
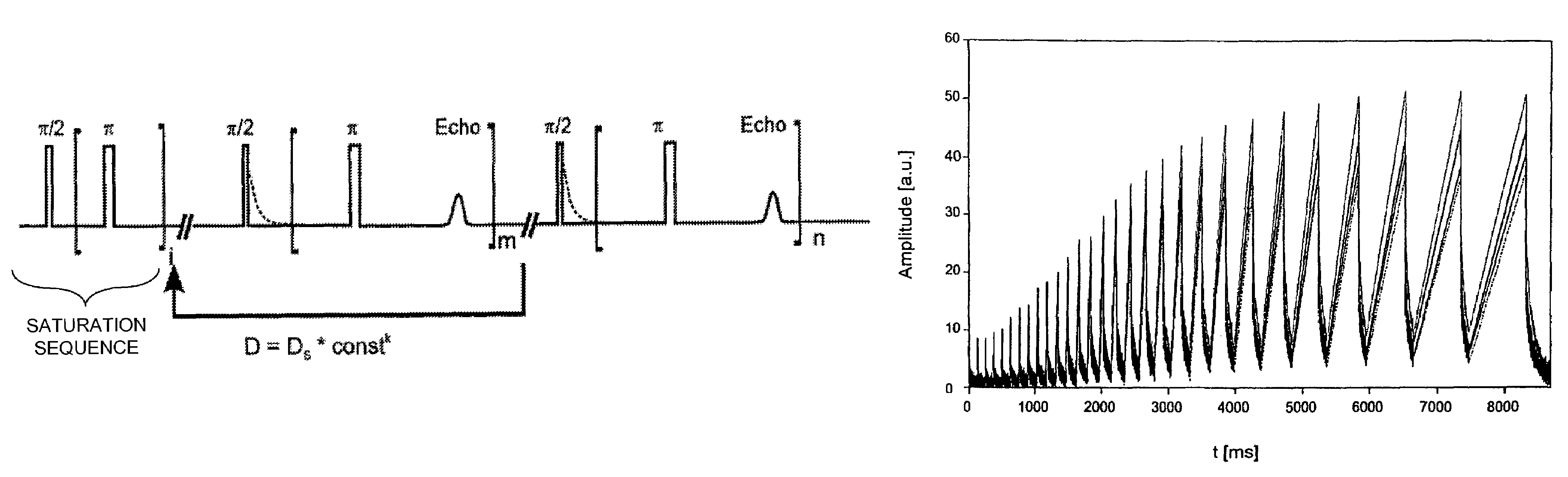
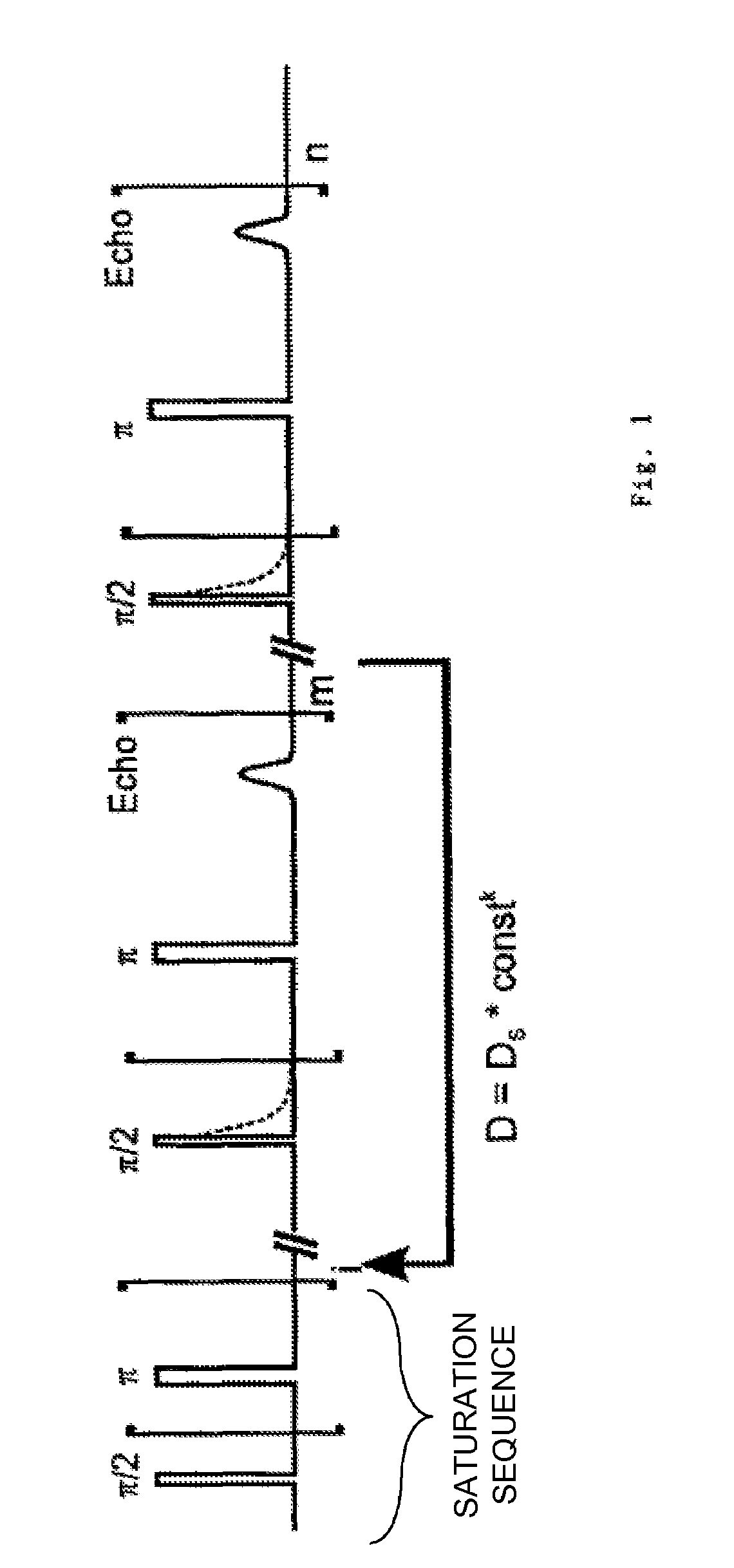
A method is described for determination of the content of at least one component of a sample by means of a nuclear magnetic resonance pulse spectrometer, with the magnetization of the sample being influenced by a sequence of radio-frequency pulses such that the signal amplitudes to be observed can be determined. The magnetization of the sample is initially saturated, and the signal amplitudes which are determined at each time by the longitudinal and transverse relaxation times T1 and T2 and / or T2* and / or T1p, from which a value for the content of the at least one component is determined, are measured at the same time in a cohesive experimental procedure.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Optical pumping magnetometer and magnetic sensing method
ActiveUS9244137B2Improve responseHigh sensitivity measurementMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetic tension forceOptical pumping
An optical pumping magnetometer is provided that is capable of improving the response of the magnetometer with respect to a magnetic field that varies with a period shorter than the transverse relaxation time of electron spin of an alkali metal atom.
Owner:CANON KK
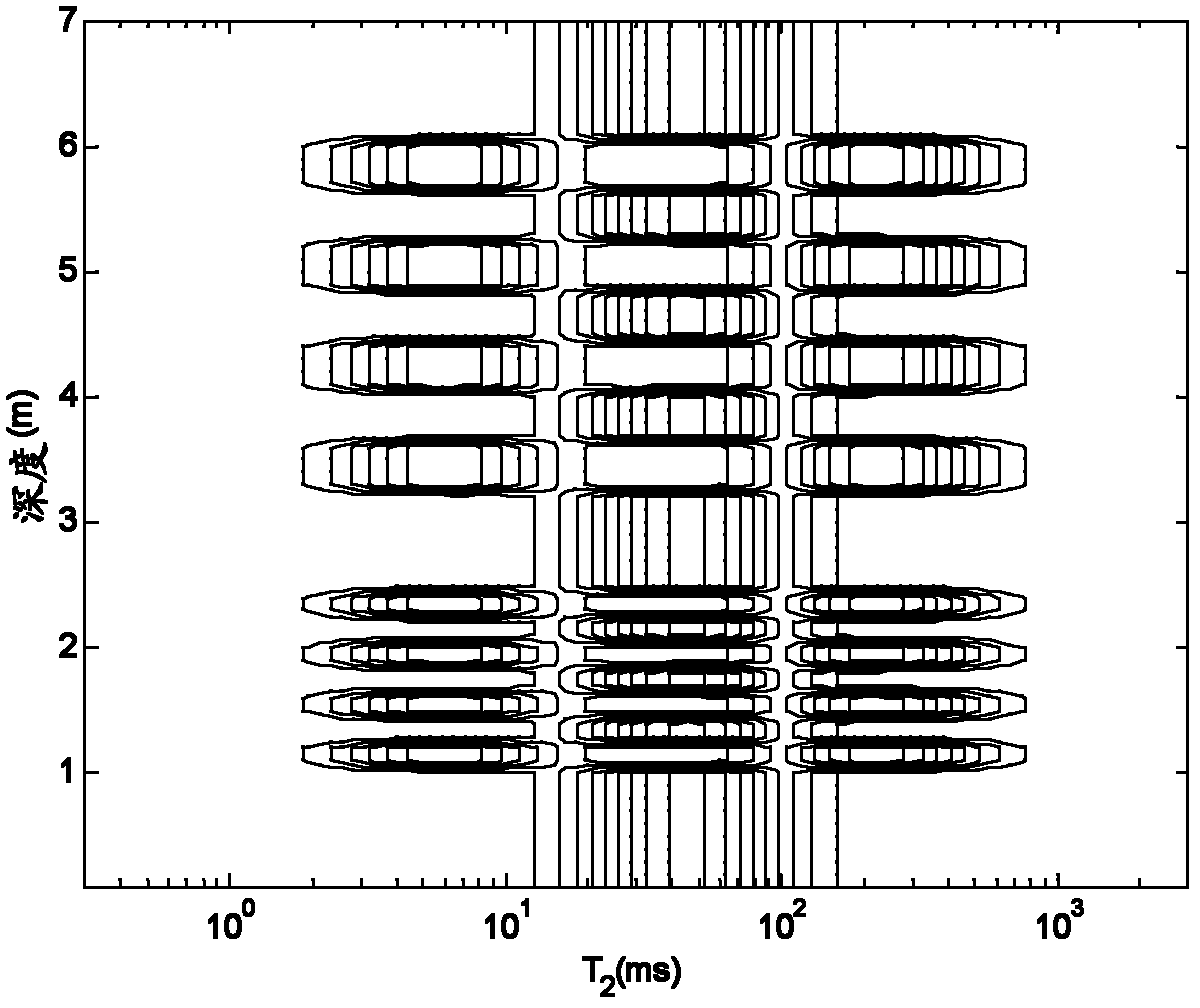
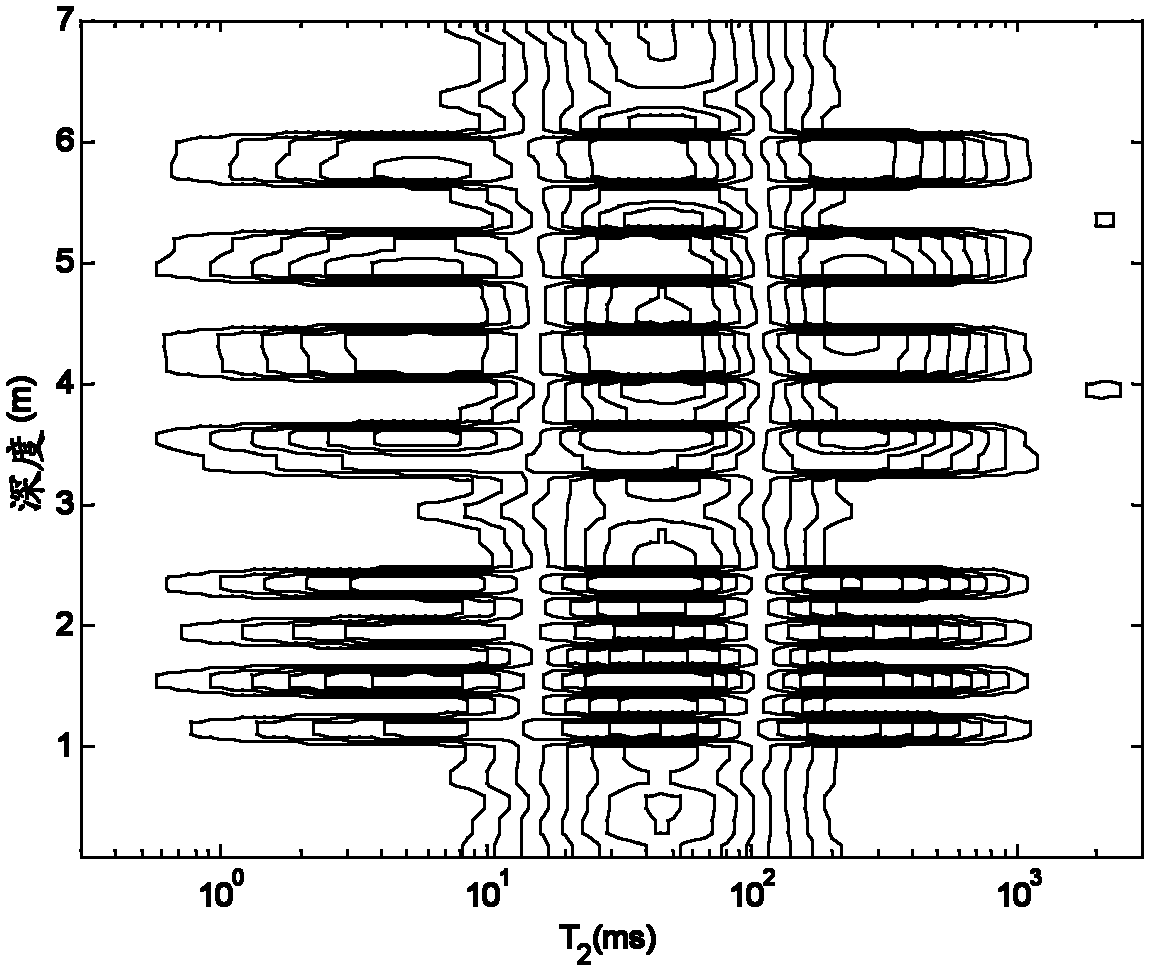
Method and device for obtaining transverse relaxation time spectrum by depth-dimension nuclear magnetic resonance inversion
ActiveCN102608664AIncrease vertical resolutionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceTransverse relaxation-optimized spectroscopy
The invention provides a method and device for obtaining a transverse relaxation time spectrum by depth-dimension nuclear magnetic resonance inversion. The method comprises the following steps of: for the spin echo string data of the stratum on multiple depth points, replacing the pore volume percentage of the pore with relaxation time T2 by multiple B spline primary functions on the T2 dimension, and expanding the data covering the stratum information on multiple depth points with a Walsh function on the depth dimension; constructing a kernel function for joint inversion according to the measurement parameter of an actual logging instrument and a longitudinal response function, and performing joint inversion to obtain the response parameter; and substituting the response parameter into the B spline primary function and the Walsh series of the Walsh function to obtain a nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum on multiple depth points. Through the scheme, the obtained nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum has relatively high longitudinal resolution, and a double sampling interval can be obtained for the horizontal layered stratum.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Optical pumping magnetometer and magnetic sensing method
ActiveUS20140320123A1Improve responseHigh sensitivity measurementMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMeasurements using magnetic resonanceOptical pumpingSpins
An optical pumping magnetometer is provided that is capable of improving the response of the magnetometer with respect to a magnetic field that varies with a period shorter than the transverse relaxation time of electron spin of an alkali metal atom.
Owner:CANON KK
Nuclear magnetic resonance sensor used for nondestructive aging resonance of umbrella skirt of composite insulator
InactiveCN102735706ARealize non-destructive testingImprove performanceAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceComposite insulatorsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a nuclear magnetic resonance sensor used for the nondestructive aging resonance of an umbrella skirt of a composite insulator. The sensor comprises a permanent magnet structure and a plane radio-frequency coil, wherein the permanent magnet structure mainly consists of two cylindrical permanent magnet sheets of same specification, the two cylindrical permanent magnet sheets are oppositely and coaxially arranged, and the permanent magnet structure is used for producing a static state main field B0; and the permanent magnet structure is provided with a slide mechanism, so that the distance between the permanent magnet sheets can be adjusted so as to adapt to umbrella skirts of different thickness. The plane radio-frequency coil is formed by two spiral coils which are connected in series on a plane according to the reverse direction of the magnetic field, and the plane radio-frequency coil is used for generating radio-frequency magnetic field B1 orthometric with the main magnetic field in a target region, and detecting return signals produced by a sample to be tested. During the aging detection of the umbrella skirt of the composite insulator, the slide mechanism is adjusted to enable the sensor to clamp the umbrella skirt to be tested, so that the transverse relaxation time T2 of the umbrella skirt can be measured, and further, the aging degree of the umbrella skirt can be judged according to the transverse relaxation time T2. The open-type nuclear magnetic resonance sensor has the advantages of small volume, light weight, and convenience in engineering field detection.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
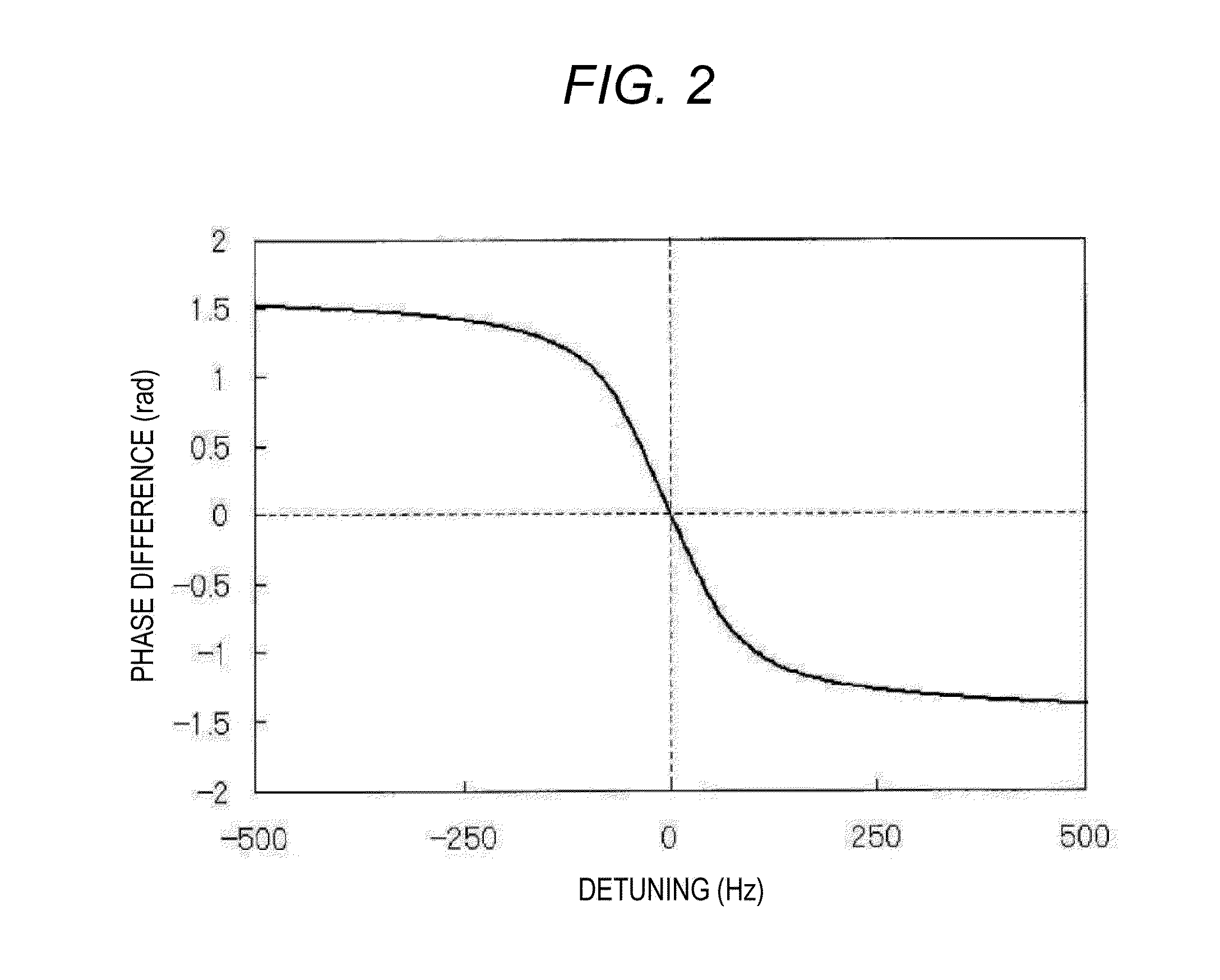
Method for measuring atomic transverse relaxation time based on electron resonance phase frequency analysis
InactiveCN106597338ASuppression of the effects of common coefficient fluctuationsExact transverse relaxation timeMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceFrequency spectrumTransverse magnetic field
The invention discloses a method for measuring atomic transverse relaxation time based on an electron resonance phase frequency analysis. In a strong-background magnetic field with almost neglected residual magnetization in a magnetic shielding barrel, a swept-frequency signal that has a bandwidth covering a resonance curve and has an amplitude enabling the resonance curve to have a clear curve under low polarizability is applied in a horizontal direction; an optical swing angle signal of a magnetometer is detected and a spectral analysis is carried out on an outputted signal in a polar coordinate system to obtain a phase frequency response function of the magnetometer; the phase frequency response function is fitted to a corresponding theoretical phase frequency curve of the magnetometer to obtain atomic spinning transverse relaxation time. Because the phase angle is a result obtained by quotient processing of a spinning transverse component, the influence of common coefficient fluctuation is suppressed, so that the phase frequency signal expression is more stable by being compared with amplitude-frequency signal expression. Besides, the theoretical phase frequency curve is not affected by the magnetic induction intensity of the transverse magnetic field and the atomic spinning longitudinal relaxation time, so that complexity of data processing can be reduced. Moreover, a lorenz curve widening risk caused by the transverse magnetic field can be eliminated.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance measurement techniques in non-uniform fields
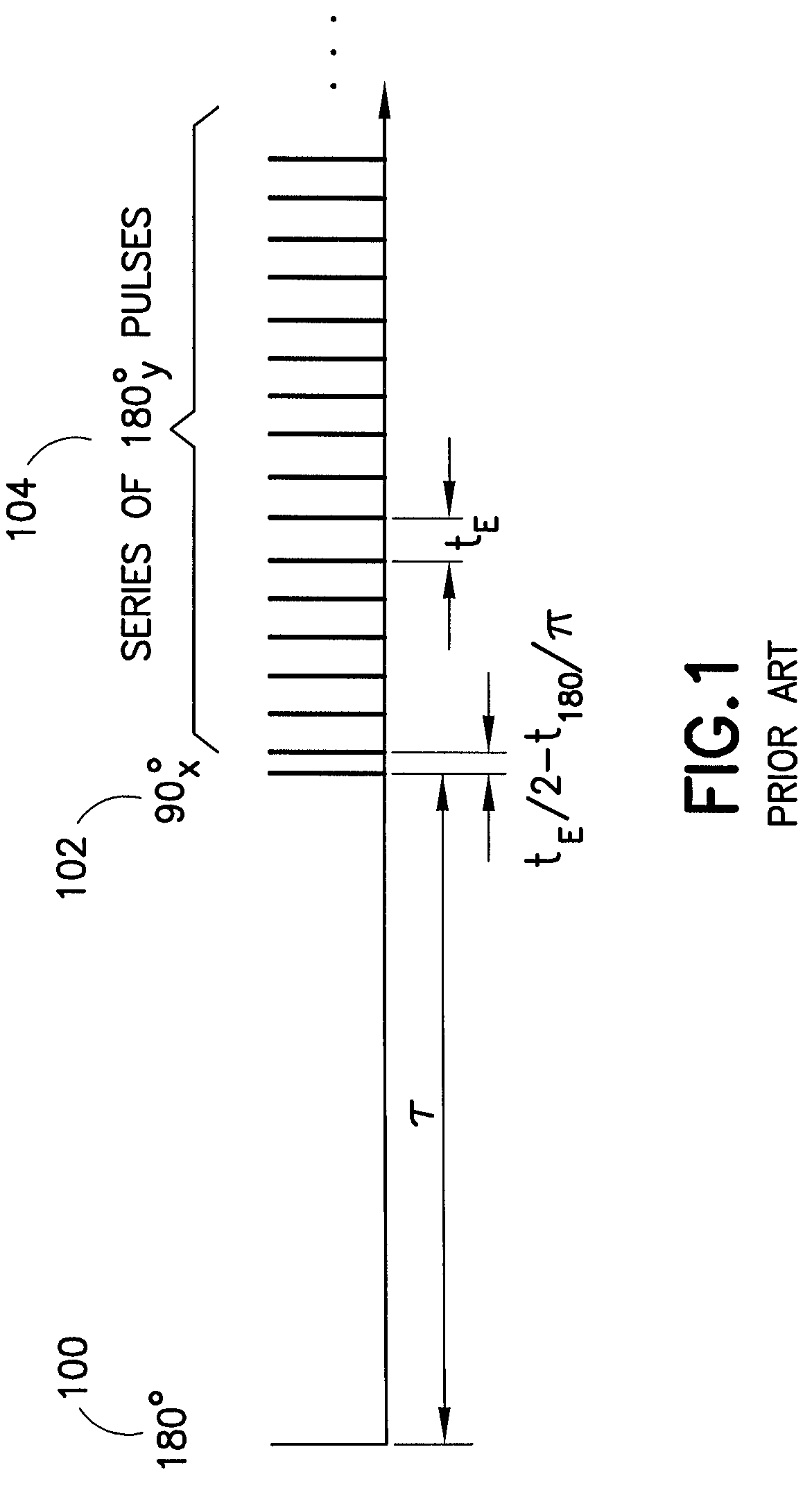
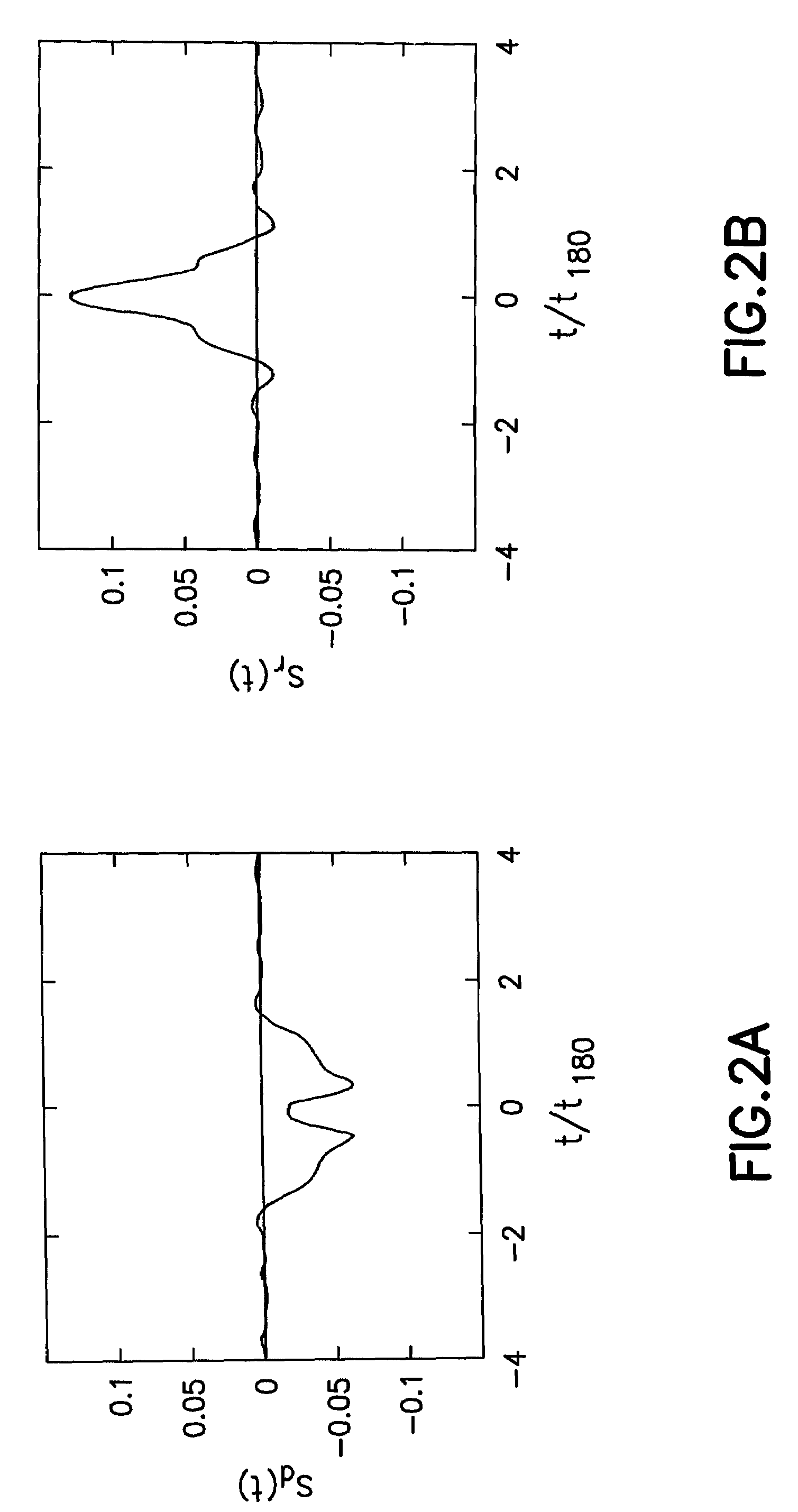
InactiveUS20080024128A1Easy to optimizeAccurate measurementElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsUniform fieldDiffusion
Methods and pulse sequences for facilitating nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements in grossly inhomogeneous fields. Methods and pulse sequences according to the invention may be used to accurately measure variables such as transverse relaxation time, longitudinal relaxation time, and diffusion, without the need for data at long recovery time, thereby allowing for faster measurements. In addition, methods and pulse sequences according to embodiment of the invention may allow simultaneous encoding of information in both the amplitude and the shape of echoes, so as to allow a single-shot measurement of multiple variables, e.g., both transverse relaxation time (from the decay of echo amplitudes) and longitudinal relaxation time (from the echo shape). CPMG detection may be used to overcome the often limited signal-to-noise ratio in grossly inhomogeneous fields.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
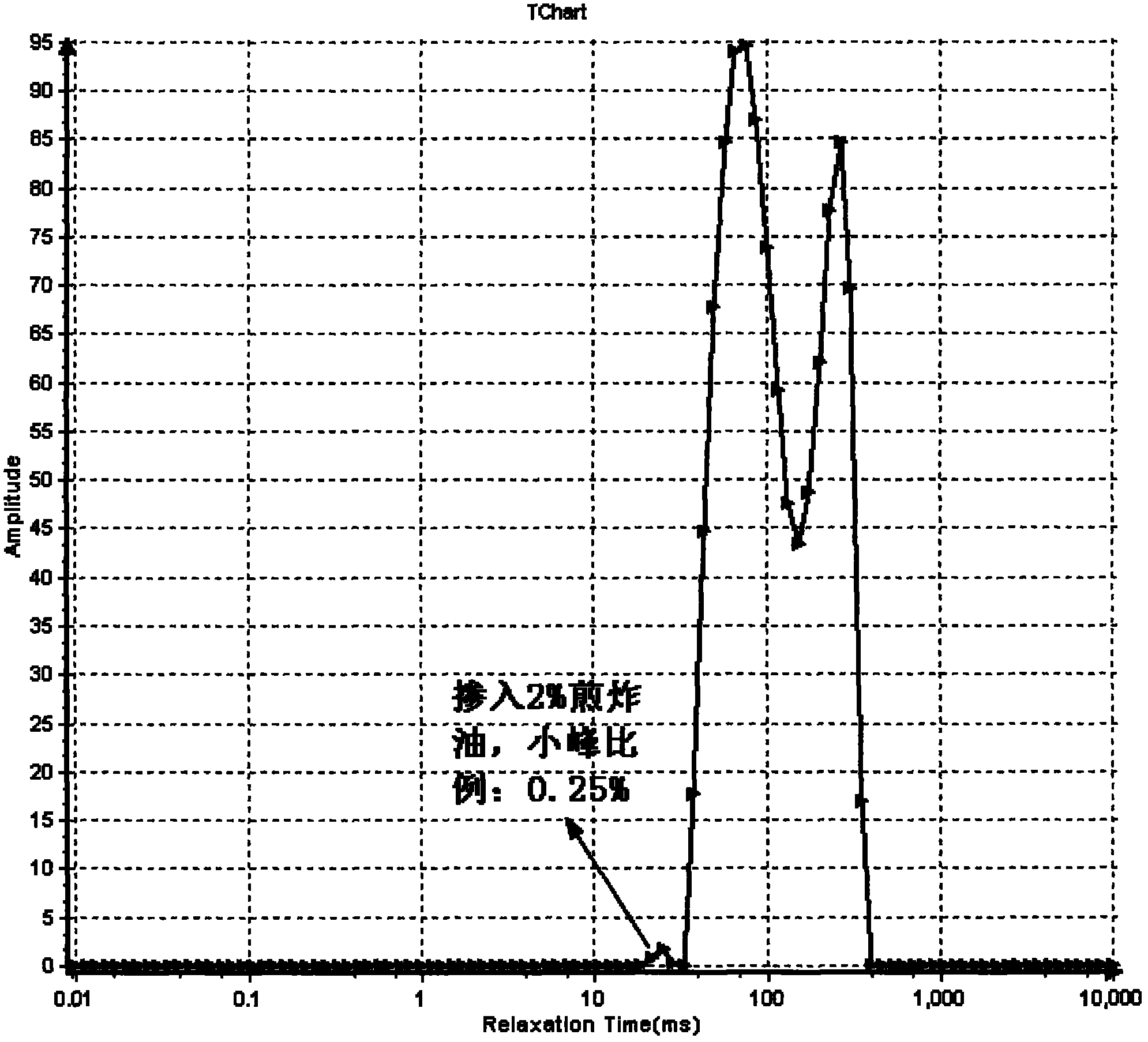
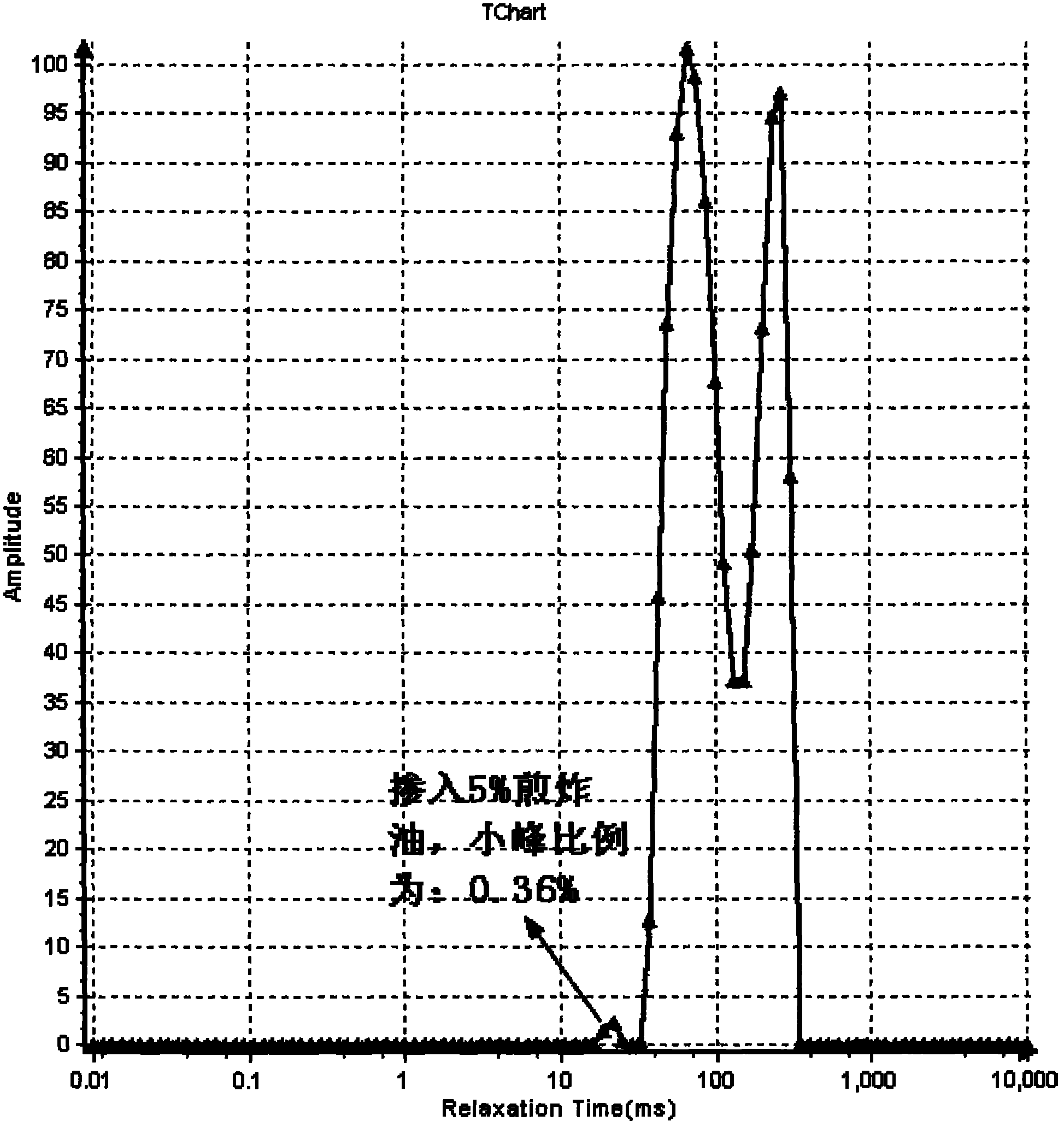
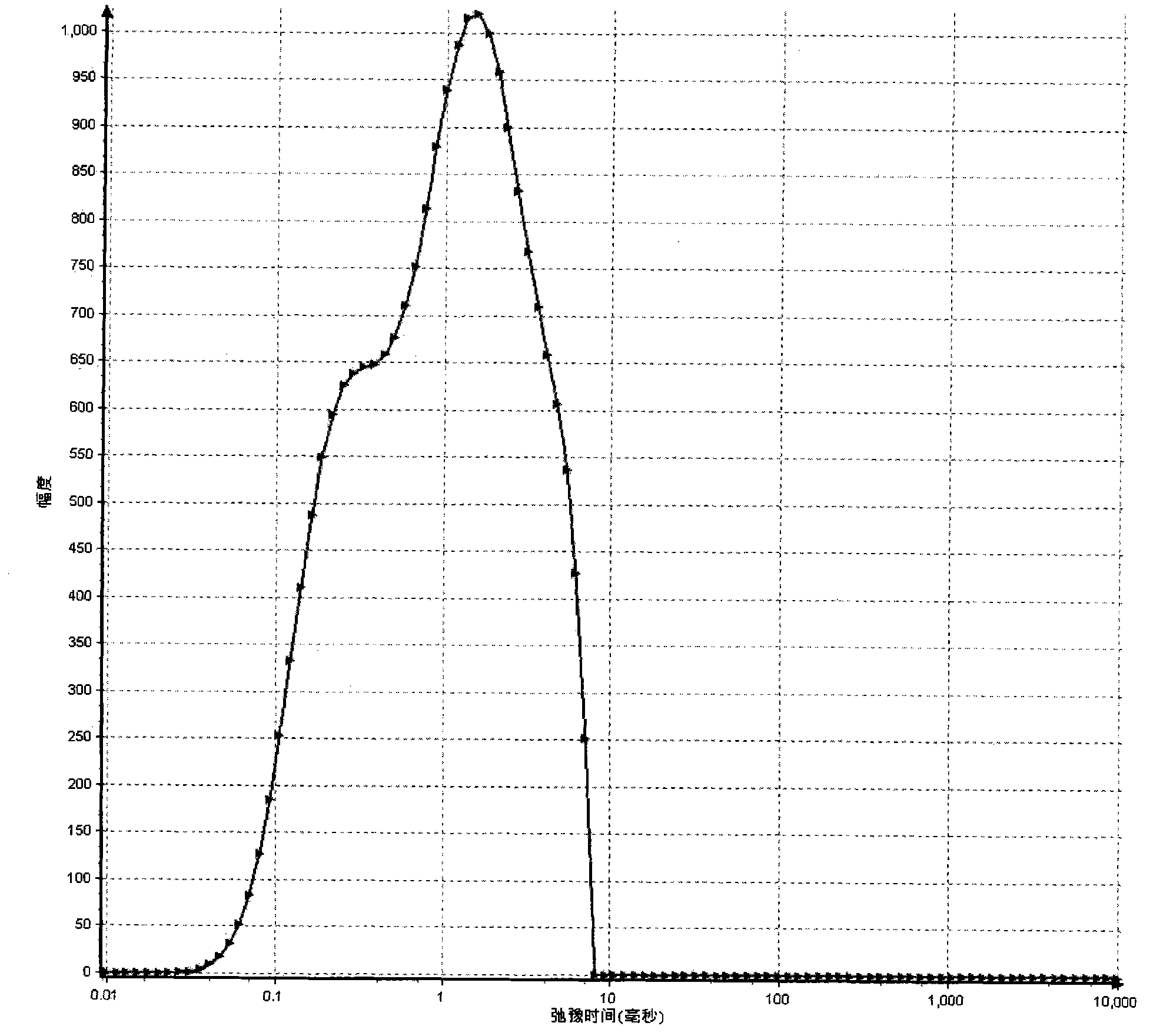
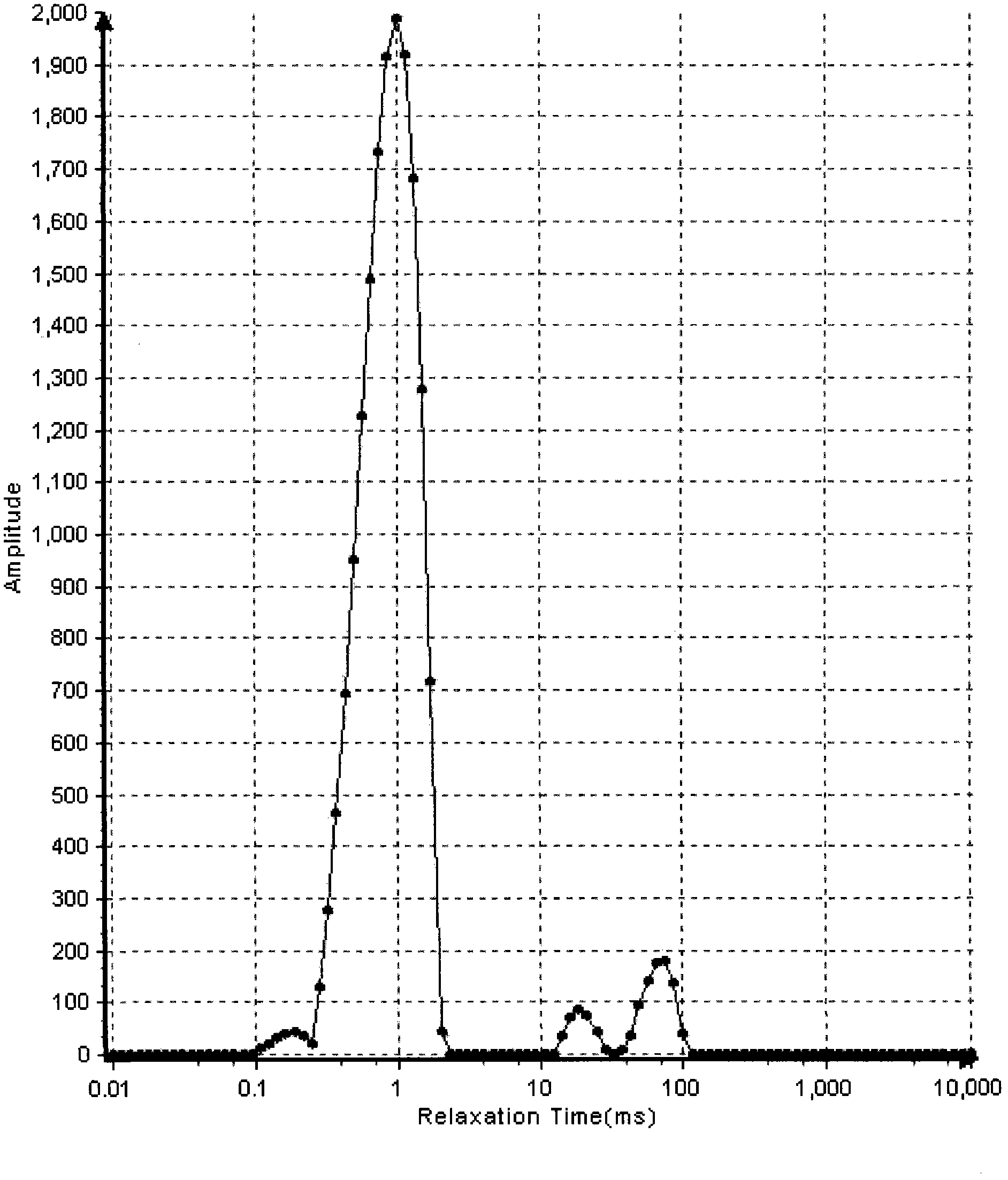
Method for identifying quality of edible oil with low-field NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance)
ActiveCN101975788ARapid identificationAccurate identificationAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a method for identifying the quality of edible oil with low-field NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance), suitable for identifying and measuring genuine edible oil and inferior drainage oil. The method rapidly and accurately identifies the genuine edible oil and the inferior drainage oil by using the difference between the relaxation time map data of the genuine edible oil and the inferior drainage oil as a main identification reference, using NMR signals of the genuine edible oil and the inferior drainage oil as main observation objects and using the comparison and the analysis of the transversal relaxation time map data of the genuine edible oil and the inferior drainage oil as main measures. The method of the invention has high measuring result accuracy, good repetition and stability, short duration, and the like, is beneficial to the realization of the one-site identification of the qualities of various kinds of edible oil and provides reliable oil quality information for detecting the qualities of various kinds of edible oil.
Owner:SUZHOU NIUMAG ELECTRONICS TECH +2
Method for measuring oil content of drilling fluid through low-field NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance)
ActiveCN101943669AAccurate analysisAccurate Analysis TestAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonanceCorrelation analysis
The invention discloses a method for measuring the oil content of drilling fluid through low-field NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance), suitable for measuring the content of crude oil with different densities in the drilling fluid. The method comprises the step of measuring the oil content of the drilling fluid by using the transverse relaxation time of the crude oil and the drilling fluid and different diffusion coefficients as main identification criteria, using the signal strength of NMR of the crude oil and the drilling fluid as a main observation object and using the transverse relaxation analysis of the drilling fluid and the correlation analysis of the diffusion coefficients and transverse relaxation as main measures. The method of the invention has the advantages of high measuring result accuracy, good stability, short time consumption, and the like, is easy to realize the online measurement of the oil content of the drilling fluid and provides reliable storage information of an oil layer for logging operation.
Owner:SUZHOU NIUMAG ELECTRONICS TECH
Method and apparatus for reservoir fluid characterization in nuclear magnetic resonance logging
ActiveUS7298142B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMagnetic property measurementsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceWell logging
A method and apparatus for obtaining a parameter of interest relating to a region proximate a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) logging tool suitable for subterranean well logging is disclosed. The nuclei of the region are subjected to a pulsed NMR technique and are productive of NMR logging data, the nuclei of the region characteristically having a longitudinal relaxation time T1 distribution and an apparent transverse relaxation time T2app distribution. In response to the NMR logging data, an R distribution is defined as R=T1 / T2app, the T2app and R distributions are processed as separate bins, along with the NMR logging data, according to a two-dimensional inversion model, and a signal intensity map of R versus T2app is provided that is representative of the parameter of interest relating to the region. In response to a high-intensity signal on the map being within a first range of T2app values and a first range of R values, the presence of a light hydrocarbon within the region is identified.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
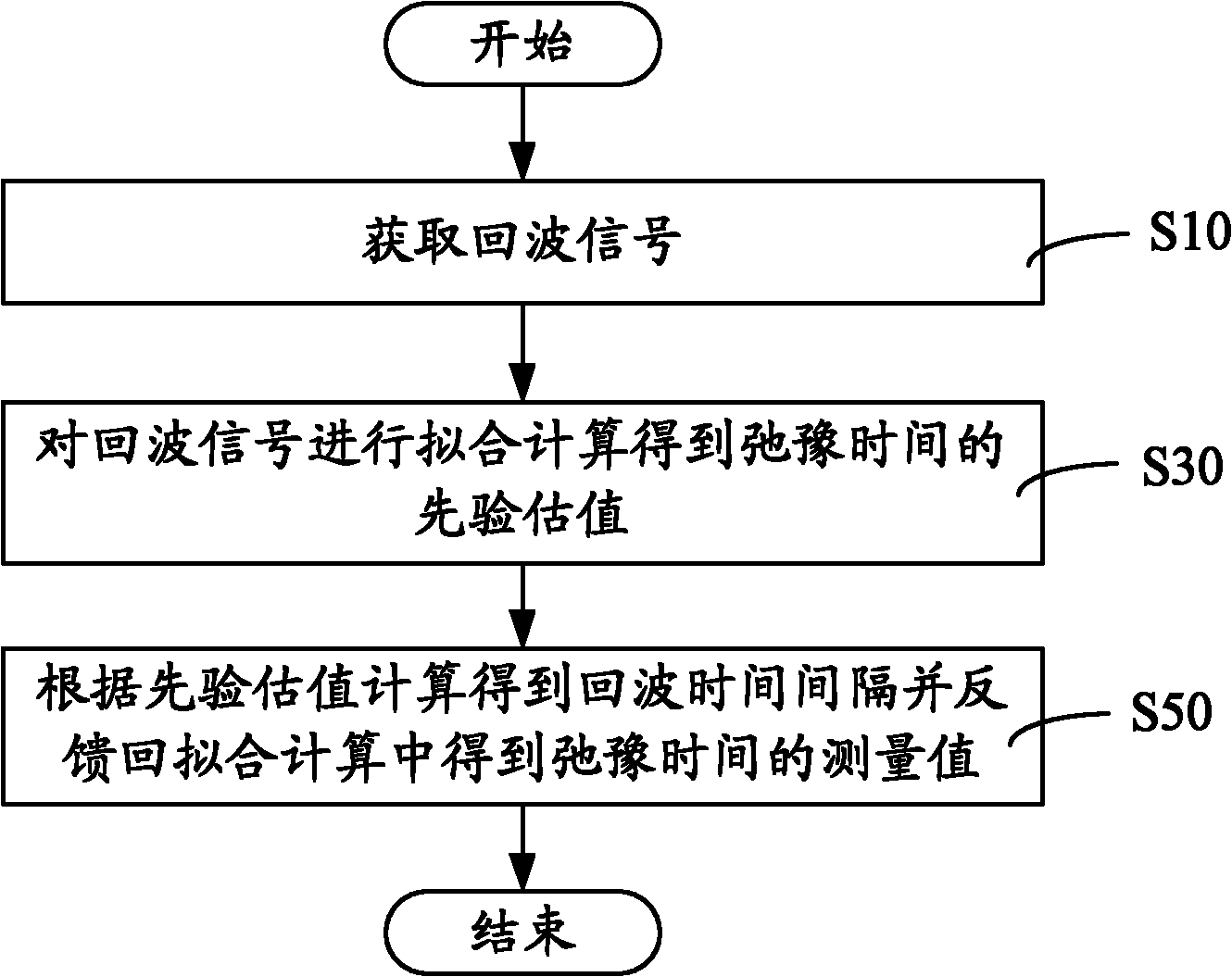
Transverse relaxation time measuring method and system
ActiveCN102116856ARelaxation time signal-to-noise ratio optimizationImprove accuracyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Signal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention provides a transverse relaxation time measuring method. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring an echo signal; fitting the echo signal to acquire a prior estimate value of the relaxation time; and calculating echo time interval according to the prior estimate value, and feeding the echo time interval to the fitting calculation to acquire a measurement value of the relaxation time. Through rough estimation on the relaxation by the fitting calculation, the transverse relaxation time measuring method and system realize optimization on the signal to noise ratio of the relaxation time in the echo signal, so that the accuracy of relaxation time measurement is effectively improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
In-situ heavy-oil reservoir evaluation with artificial temperature elevation
InactiveUS20030034777A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyBound waterRoom temperature
Many reservoirs of interest include heavy oil. In such reservoirs, parti at normal temperatures, many instruments commonly used for formation evaluation may not be able to distinguish between heavy oil and bound water in the formation. Passive or active heating is used to elevate the temperature of the fluids in the formation. At elevated temperatures, distinguishing between heavy oil and bound water is easier. Of particular interest is the increase in the resolvability of the transverse relaxation time T2 of NMR spin echo measurements. Additionally, the dielectric constant and the loss tangents of water and heavy oil show different temperature and frequency dependence.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method for measuring content of different state water in coal
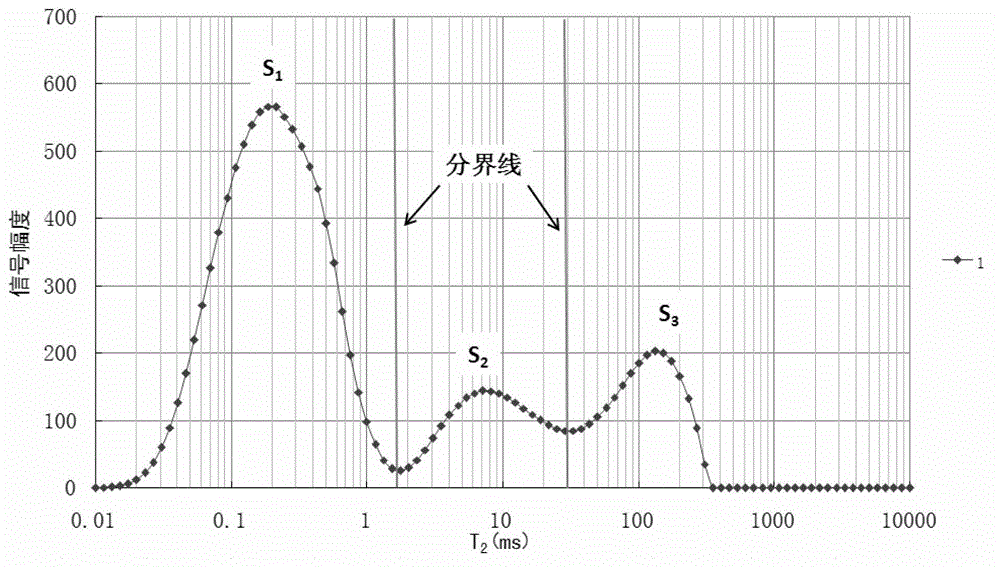
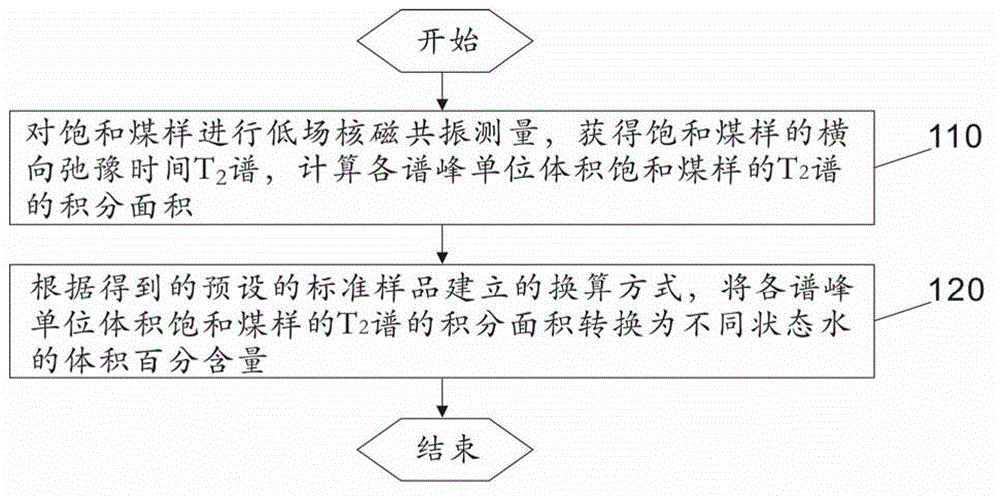
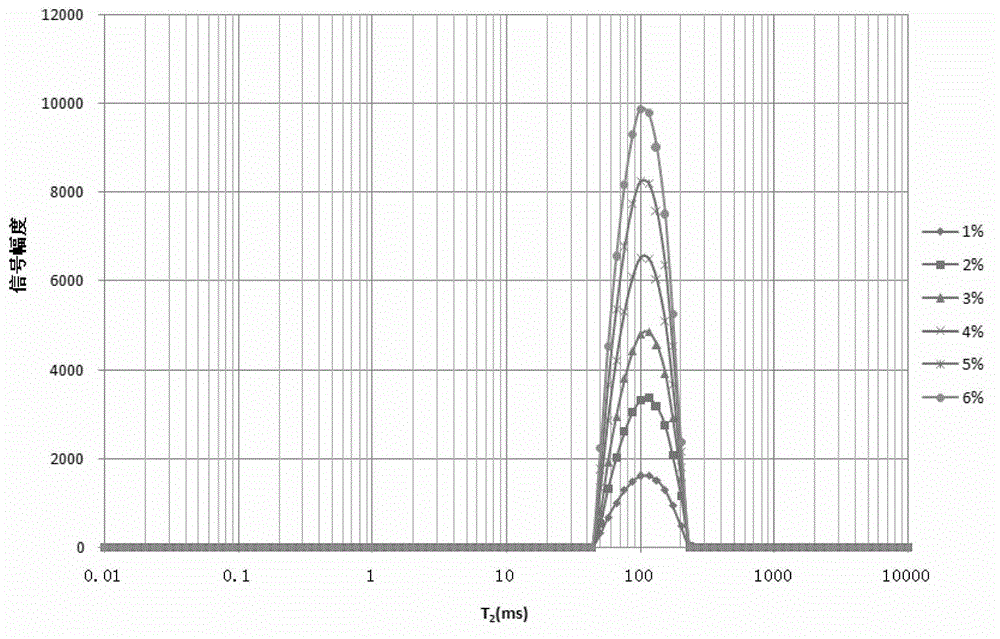
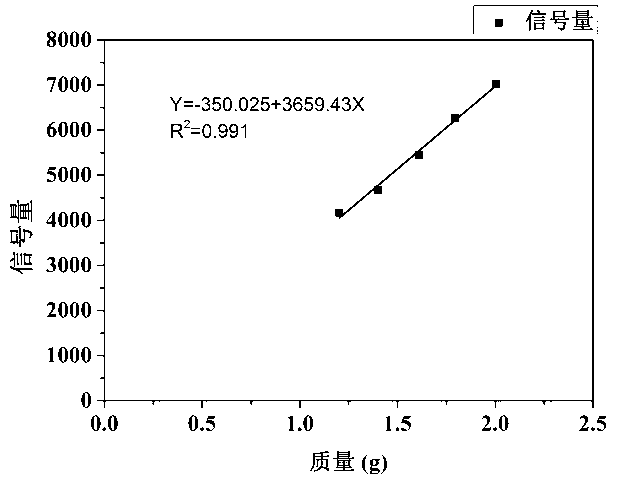
InactiveCN102944571AQuick measurementNon-destructive measurementAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonanceStandard samples
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of different state water in coal. The method comprises the steps of performing low field nuclear magnetic resonance measurement on a saturated coal sample to obtain a transverse relaxation time T2 spectrum of the saturated coal sample, calculating integral areas of the T2 spectrum of each spectral unit volume saturated coal sample; and conversing the integral areas of the T2 spectrum of each spectral unit volume saturated coal sample to the volume percent of the different state water according to obtained conversion modes established by preset standard samples. The method solves the problem that how to measure the content of different state water in the coal.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Quick measurement method for different forms of water in sludge
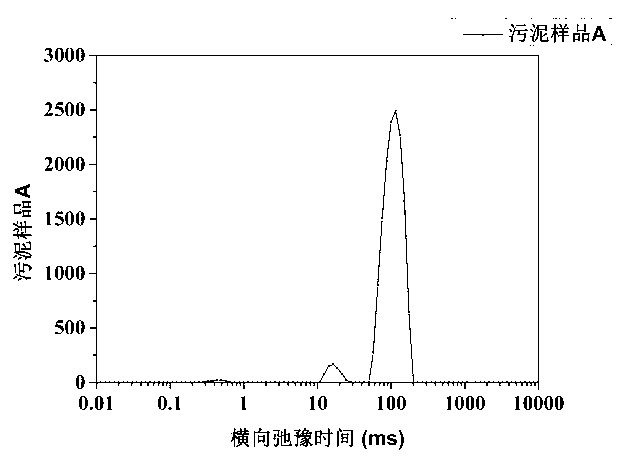
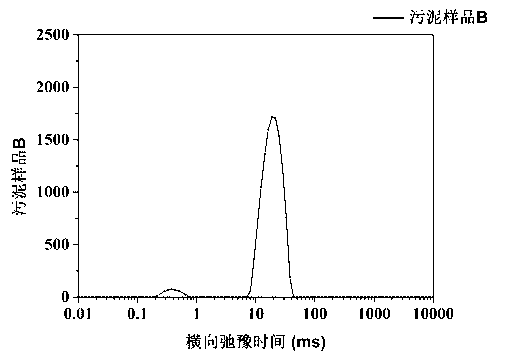
ActiveCN103308543ASimple and fast operationQuick measurementAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceInterstitial waterActivated sludge
The invention discloses a quick measurement method for different forms of water in sludge. The quick measurement method comprises the following steps of: (1) performing low-field nuclear magnetic resonance measurement on the sludge to obtain a transverse relaxation time T2 spectrum of different forms of water in the sludge; (2) stewing and settling activated sludge, preparing a standard sample by supernatant liquid at equal mass interval, and constructing a standard curve; (3) according to the obtained standard curve, matrixing the low-field nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time of the sludge to obtain three different forms of water, namely free water mass, interstitial water mass and surface combined water mass in the sludge; and (4) drying the sludge to be measured until the weight is balanced, subtracting the final mass from the initial mass, and calculating the fourth form of water in the sludge, namely the internal combined water mass. Compared with the conventional method, the quick measurement method for measuring the content of different forms of water in the sludge by a nuclear magnetic resonance technology has the advantages of short experiment time, harmlessness to experiment samples, precision of measurement and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and device for determining saturation exponent of tight sandstone
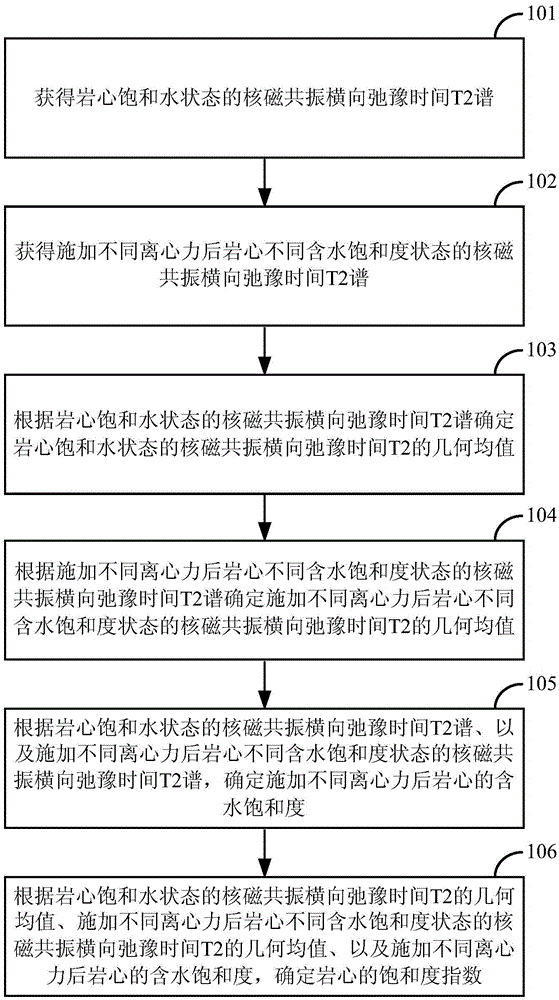
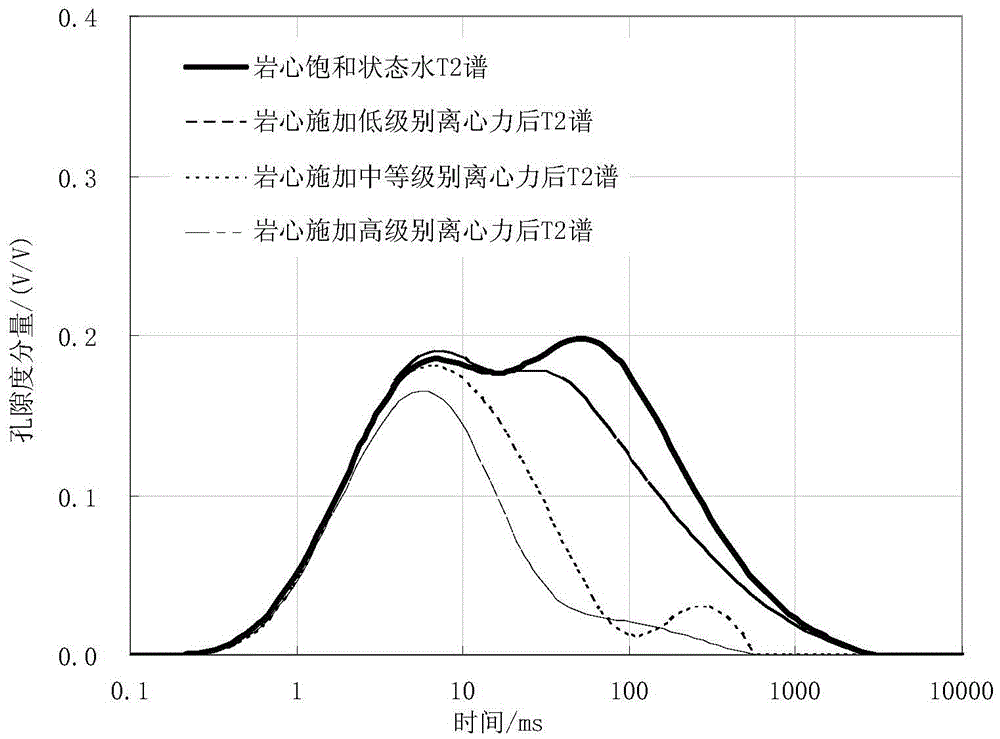
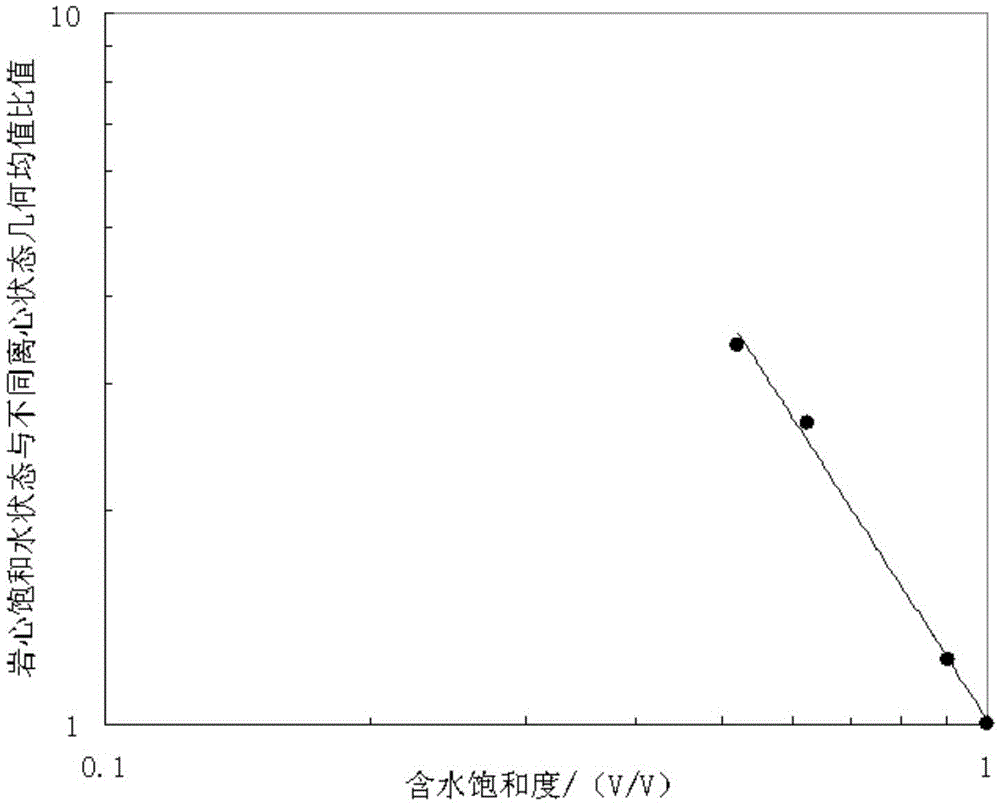
ActiveCN105464654AShort experiment cycleFast measurementAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceInformaticsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceCentrifugal force
The invention discloses a method and a device for determining saturation exponent of tight sandstone. The method comprises: according to nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time T2 spectrum of a core in a water saturation state and nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time T2 spectrum of cores in different water saturation states after different centrifugal forces are applied, determining geometric mean value of the nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time T2, the geometric mean value of the nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time T2 of the cores in different water saturation states after different centrifugal forces are applied on the cores, and water saturation of the cores after different centrifugal forces are applied; and according to the geometric mean value of the nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time T2 of the core in a water saturation state, and the geometric mean value of the nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time T2 of the cores in different water saturation states after different centrifugal forces are applied, and the water saturation of the cores after different centrifugal forces are applied, determining saturation exponent of the cores. The method and the device can accurately and efficiently determine the saturation exponent of tight sandstones.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
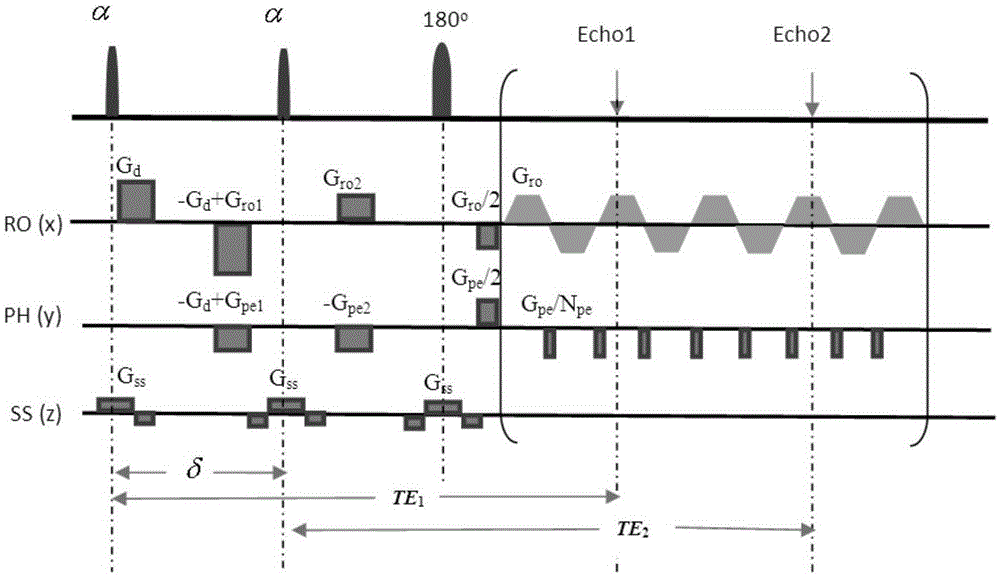
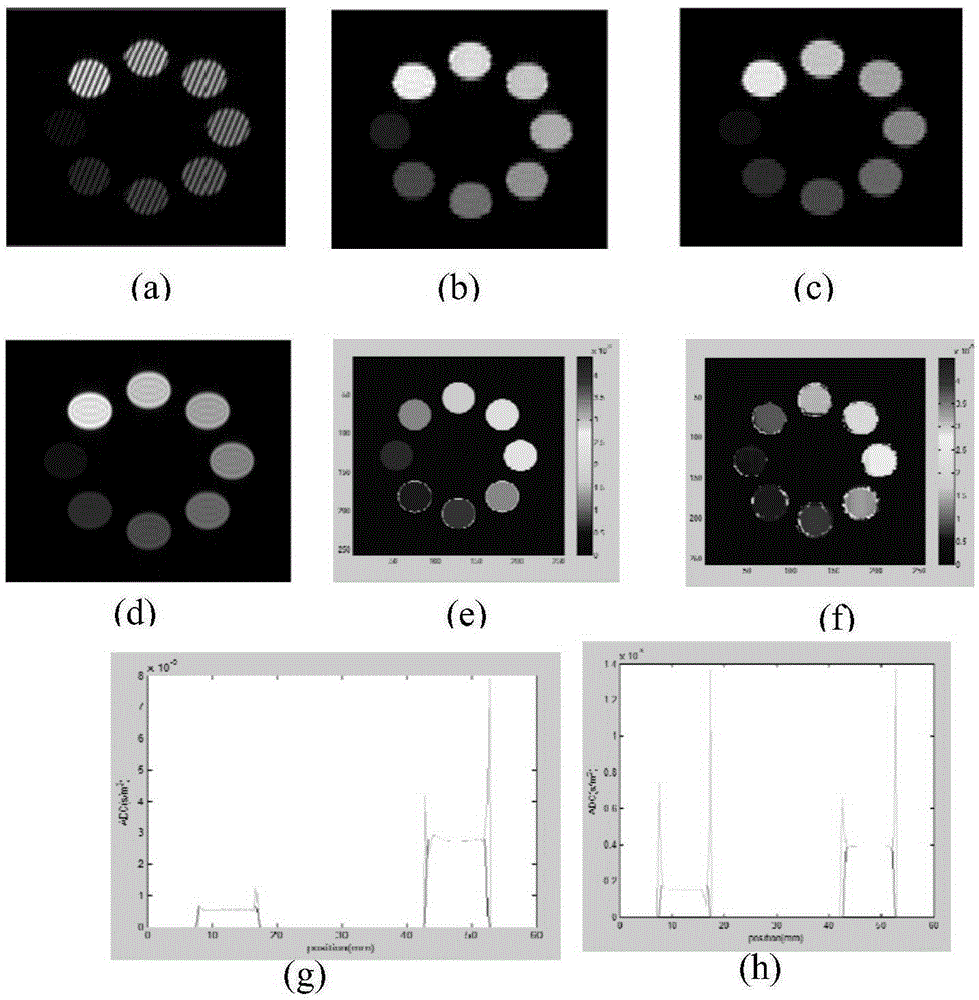
Single-scanning quantitative magnetic resonance diffusion imaging method based on dual echoes
The invention provides a single-scanning quantitative magnetic resonance diffusion imaging method based on dual echo, and relates to a magnetic resonance imaging method. According to the method, two echoes with the same evolution time are generated through two small-angle excitation pulses with the same turning angle, so that the same transverse relaxation time is achieved; a displacement gradient is added after each excitation pulse to achieve central displacement of the two echo signals in a signal space, and a diffusion gradient is added after the first excitation pulse, so that diffusion reduction only exists in the first echo signal; accordingly, signals under different diffusion factors are obtained. The two echo signals are from one imaging slice, so that the two echo signals can be separated through priori knowledge of the two echo signals by matching sparse conversion with a corresponding separation algorithm. Finally, a quantitative ADC image is obtained by performing apparent diffusion coefficient calculation on two signals obtained through separation. Single-scanning quantitative ADC imaging is obtained through the method, and the quality of the obtained ADC image is good.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for simultaneously quantitatively analyzing water and oil in oily sludge through low-field NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance)
InactiveCN104807847AFast testThe test result is accurateAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceCorrection algorithmSludge
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously quantitatively analyzing water and oil in oily sludge through low-field NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance). The method comprises steps as follows: deionized water and crude oil are taken as standard samples to perform low-field NMR measurement, and calibration curves of water and oil are established; a to-be-measured sample which is uniformly stirred is divided into two parts and put in containers respectively, a reagent capable of realizing signal partition of oil and water is added to one part, and the mixture is uniformly stirred to form a sample a; the other part keeps unchanged and is taken as a sample b; the two samples are subjected to low-field NMR measurement to obtain an echo attenuation curve, and transverse relaxation time T2 curves of the two samples are obtained through inversion with a joint iterative correction algorithm; the transverse relaxation time T2 curves of the two samples are subjected to area integration and calculation to obtain integral areas of a water peak and an oil peak, and the calibration curves of water and oil are substituted to calculate water content and oil content of the to-be-measured sample b. The method can be suitable for measurement of content of water and oil in various kinds of oily sludge, and the measurement result is high in accuracy and good in repeatability and consumes short time.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
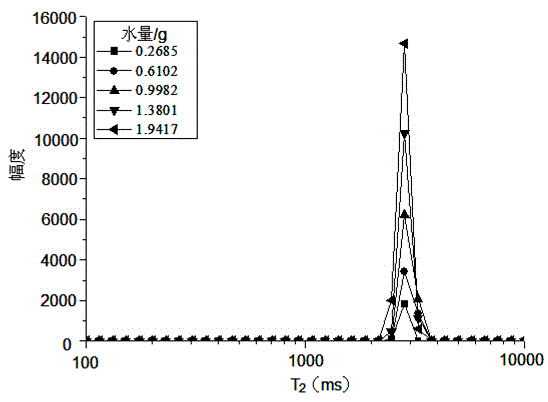
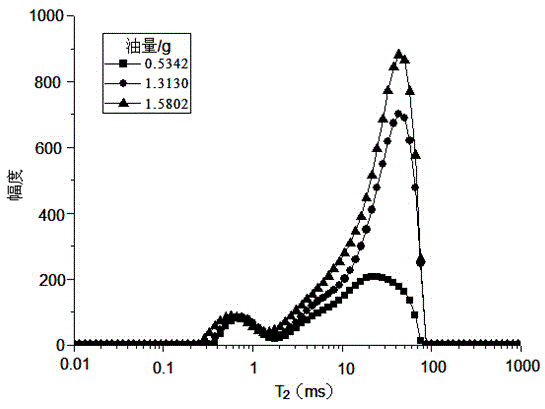
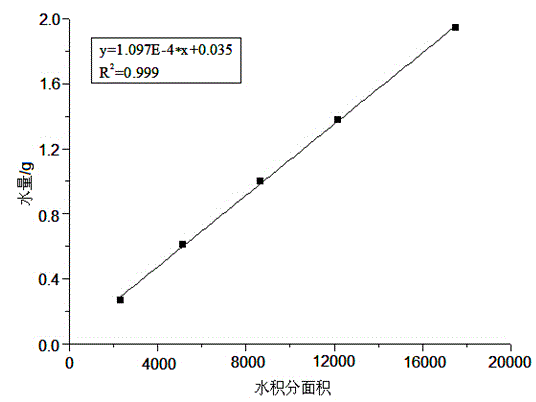
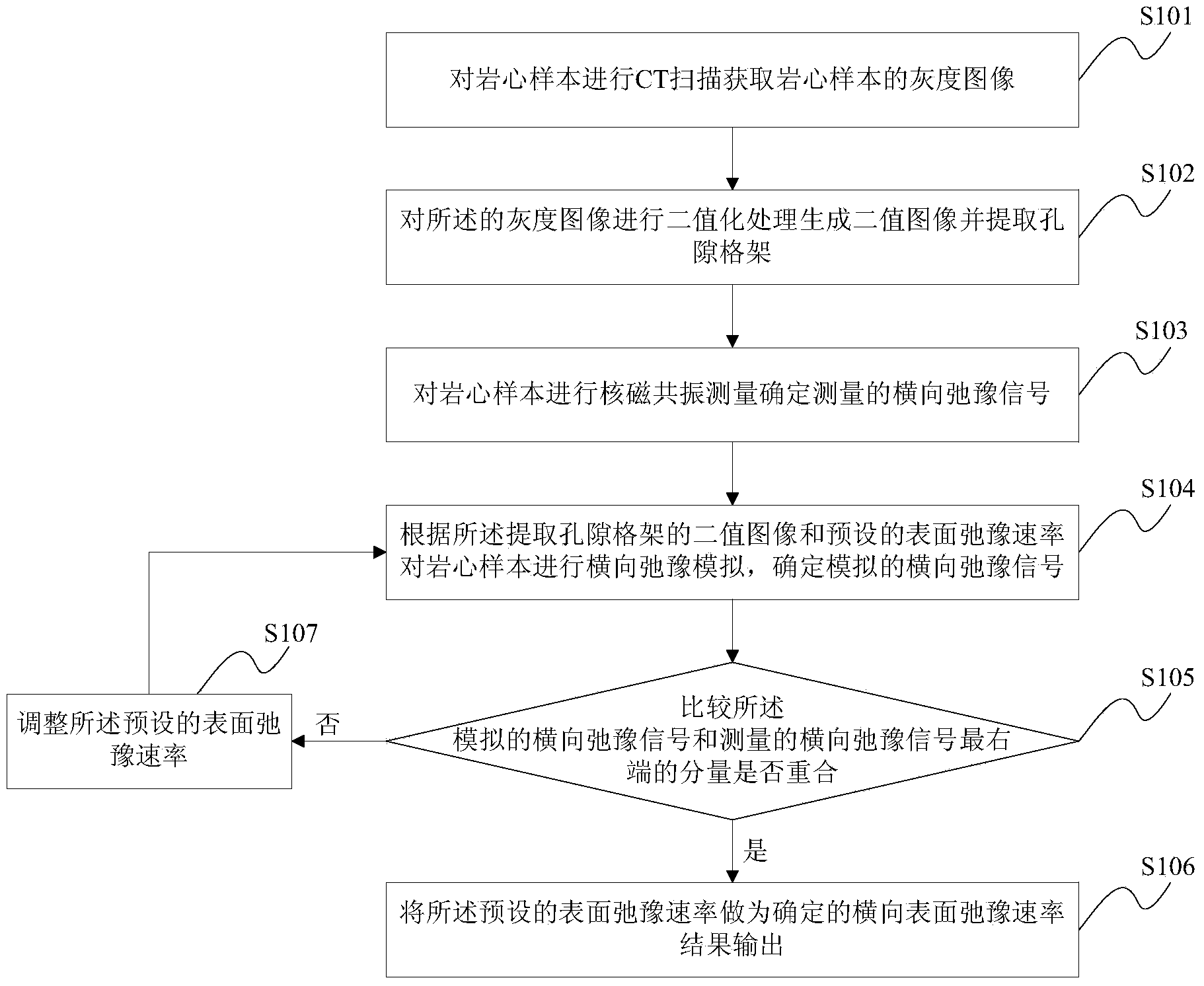
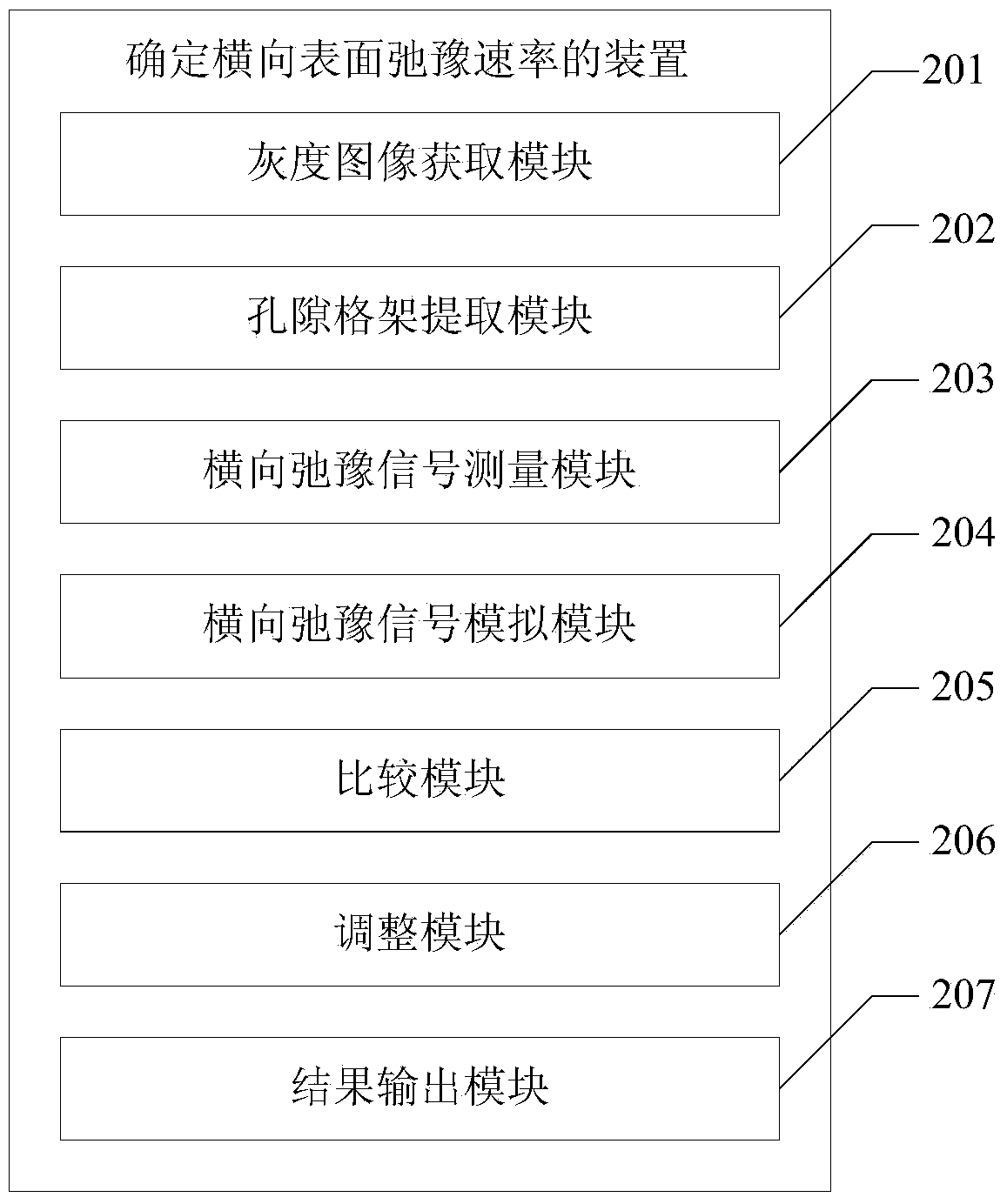
Method and device for determining horizontal surface relaxation rate
ActiveCN103513285AThe principle of the method is reliableSimple calculationElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceRock core
The invention provides a method and device for determining horizontal surface relaxation rate. The method comprises the step of carrying out CT scanning on a rock core sample to acquire a gray level image of the rock core sample, carrying out binarization processing on the gray level image to generate a binary image and extract a hole grillage, carrying out nuclear magnetic resonance measurement on the rock core sample to determine measured horizontal relaxation signals, carrying out relaxation simulation on the rock core sample according to the extracted binary image of the hole grillage and the preset surface relaxation rate to determine simulated horizontal relaxation signals, comparing whether the simulated horizontal relaxation time signals coincide with the components at the right-most ends of the measured horizontal relaxation time signals, and choosing the preset surface relaxation rate as the determined horizontal surface relaxation rate of the rock core sample to be outputted when the simulated horizontal relaxation time signals coincide with the component of the right-most ends of the measured horizontal relaxation time signals. The method and device for determining horizontal surface relaxation rate has the advantages of being more reliable in principle, simple in calculating process, easy to achieve, strong in actual operability and the like.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
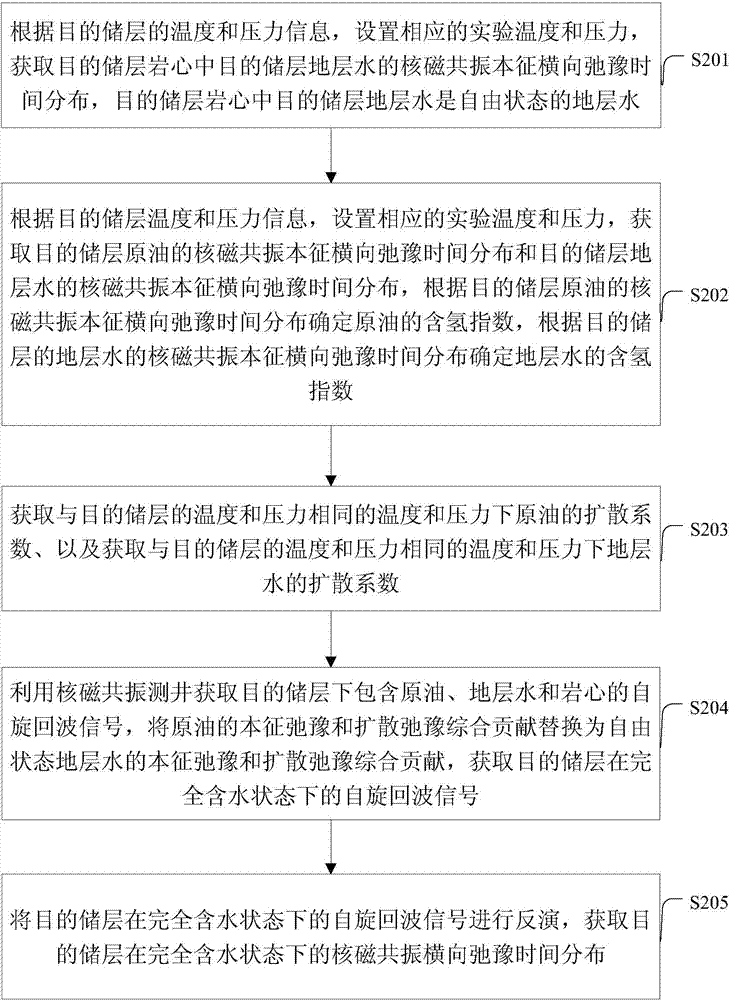
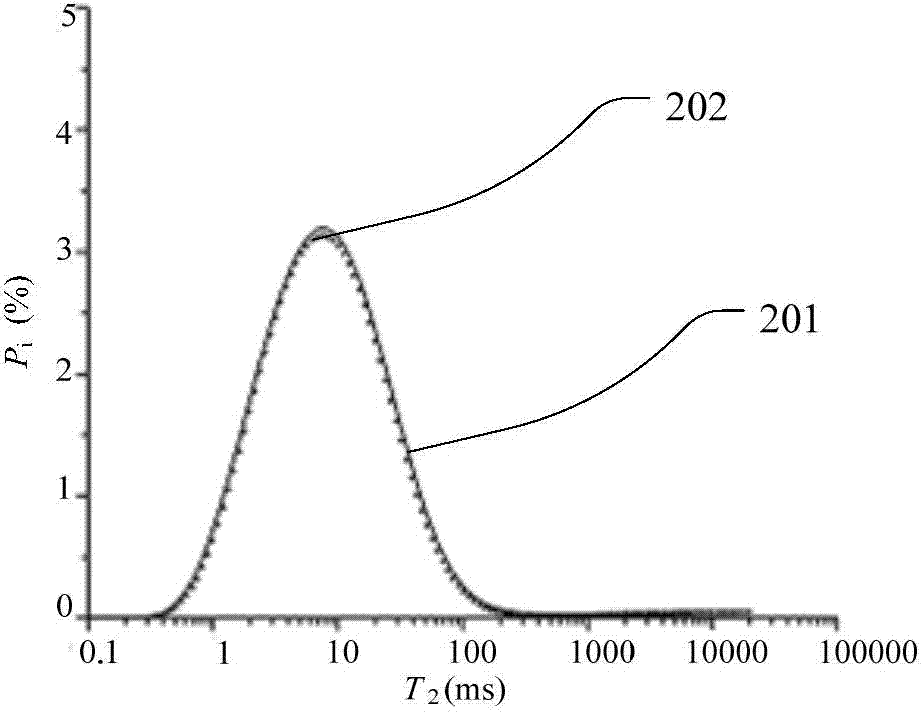
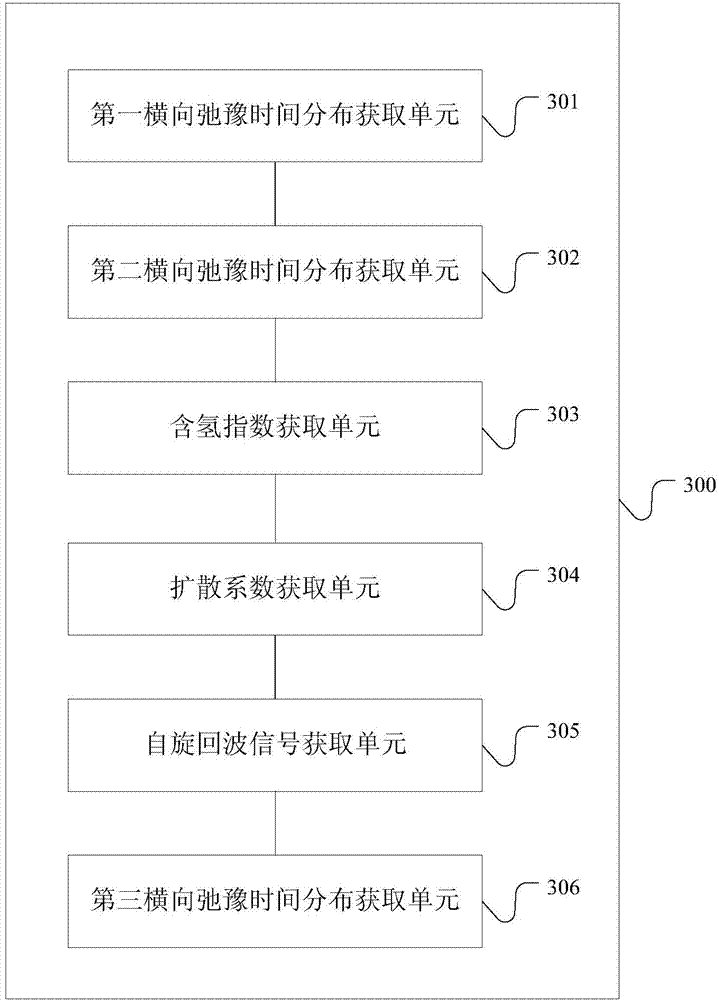
Method and device for obtaining transverse relaxation time distribution of target storage layer
ActiveCN104330433AImprove the accuracy of evaluationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentDiffusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and a device for obtaining transverse relaxation time distribution of a target storage layer. The method comprises the steps of setting corresponding experiment temperature and pressure according to temperature and pressure information of the target storage layer, and obtaining nuclear magnetic resonance intrinsic transverse relaxation time distribution of free state formation water of the target storage layer, nuclear magnetic resonance intrinsic transverse relaxation time distribution of crude oil of the target storage layer and nuclear magnetic resonance intrinsic transverse relaxation time distribution of formation water of the target storage layer; and calculating a hydrogen-containing index of the crude oil, a hydrogen-containing index of formation water, a diffusion coefficient of the crude oil and a diffusion coefficient of the formation water, then replacing intrinsic relaxation and diffusion relaxation comprehensive contribution of the crude oil by intrinsic relaxation and diffusion relaxation comprehensive contribution of the free state formation water, acquiring a rotating echo signal of the target storage layer under a complete water containing state, and performing inversion on the rotating echo signal to obtain the nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time distribution of the target storage layer under the complete water containing state.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Nuclear magnetic resonance measurement techniques in non-uniform fields
InactiveUS7622919B2Accurate measurementEasy to measureElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsUniform fieldDiffusion
Methods and pulse sequences for facilitating nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements in grossly inhomogeneous fields. Methods and pulse sequences according to the invention may be used to accurately measure variables such as transverse relaxation time, longitudinal relaxation time, and diffusion, without the need for data at long recovery time, thereby allowing for faster measurements. In addition, methods and pulse sequences according to embodiment of the invention may allow simultaneous encoding of information in both the amplitude and the shape of echoes, so as to allow a single-shot measurement of multiple variables, e.g., both transverse relaxation time (from the decay of echo amplitudes) and longitudinal relaxation time (from the echo shape). CPMG detection may be used to overcome the often limited signal-to-noise ratio in grossly inhomogeneous fields.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Hydration degree measurement method for cement-based materials based on nuclear magnetic resonance
ActiveCN103399027AReduce mistakesEasy to operateAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMuffle furnaceWater content
The invention discloses a hydration degree measurement method for cement-based materials based on nuclear magnetic resonance, which belongs to the technical field of cement material measurement. The hydration degree measurement method disclosed by the invention adopts a nuclear magnetic resonance technique to test nuclear magnetic signals of the cement-based materials at different ages; a relation between transverse relaxation time and the nuclear magnetic signals is obtained by inverse analysis; furthermore, a ratio of nuclear magnetic semaphores of left and right peaks is taken as a nuclear magnetic signal ratio of gel pore water and capillary pore water, and then the hydration degree of the cement-based materials to be detected at the age is solved according to a Powers model. Compared with traditional methods including a muffle furnace method and the like, the hydration degree measurement method disclosed by the invention is a nondestructive testing method, can reduce operation steps of a test greatly and shorten a testing period greatly, and can be used for monitoring samples continuously so as to ensure that the errors of test results are small; meanwhile, the method disclosed by the invention does not need to calibrate nuclear magnetic resonance semaphores and sample water content and directly adopts the ratio of the nuclear magnetic semaphores of the left and right peaks, namely a microstructure factor, as a parameter to represent the hydration degree, and therefore, measurement procedures and errors are reduced.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance quantitative analysis method for rock micro-crack damage variable
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
MR Imaging System for Discriminating Between Imaged Tissue Types
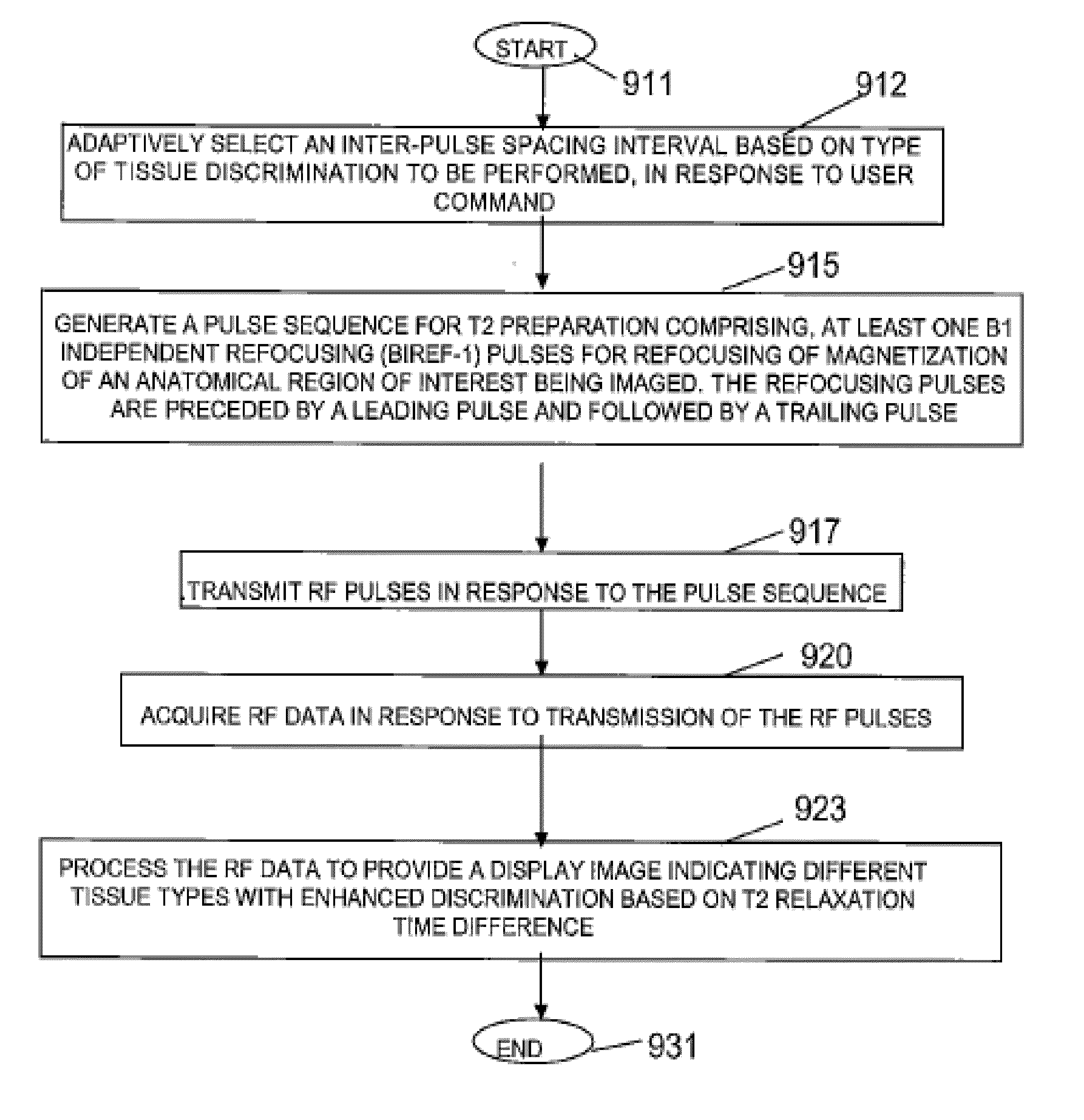
ActiveUS20120194186A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionInversion recoveryMagnetization
A system provides B1- and B0-insensitive, blood flow and motion-robust T2-preparation and T2-preparation combined with inversion recovery. An MR imaging system discriminates between imaged tissue types based on transverse relaxation time (T2) or transverse relaxation time combined with longitudinal recovery time (T1). A signal generator generates a pulse sequence for T2 preparation or combined T2-preparation with inversion recovery comprising one or more B1 independent refocusing (BIREF-1) pulses for refocusing of magnetization of an anatomical region of interest being imaged, and different combinations of adiabatic or non-adiabatic tip-down and flip-back pulses. Multiple RF coils transmit RF pulses in response to the pulse sequence and acquire RF data in response to transmission of the RF pulses. A processing system processes the RF data to provide a display image indicating different tissue types with enhanced discrimination based on T2 relaxation time difference or combined T2 and T1 time difference.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
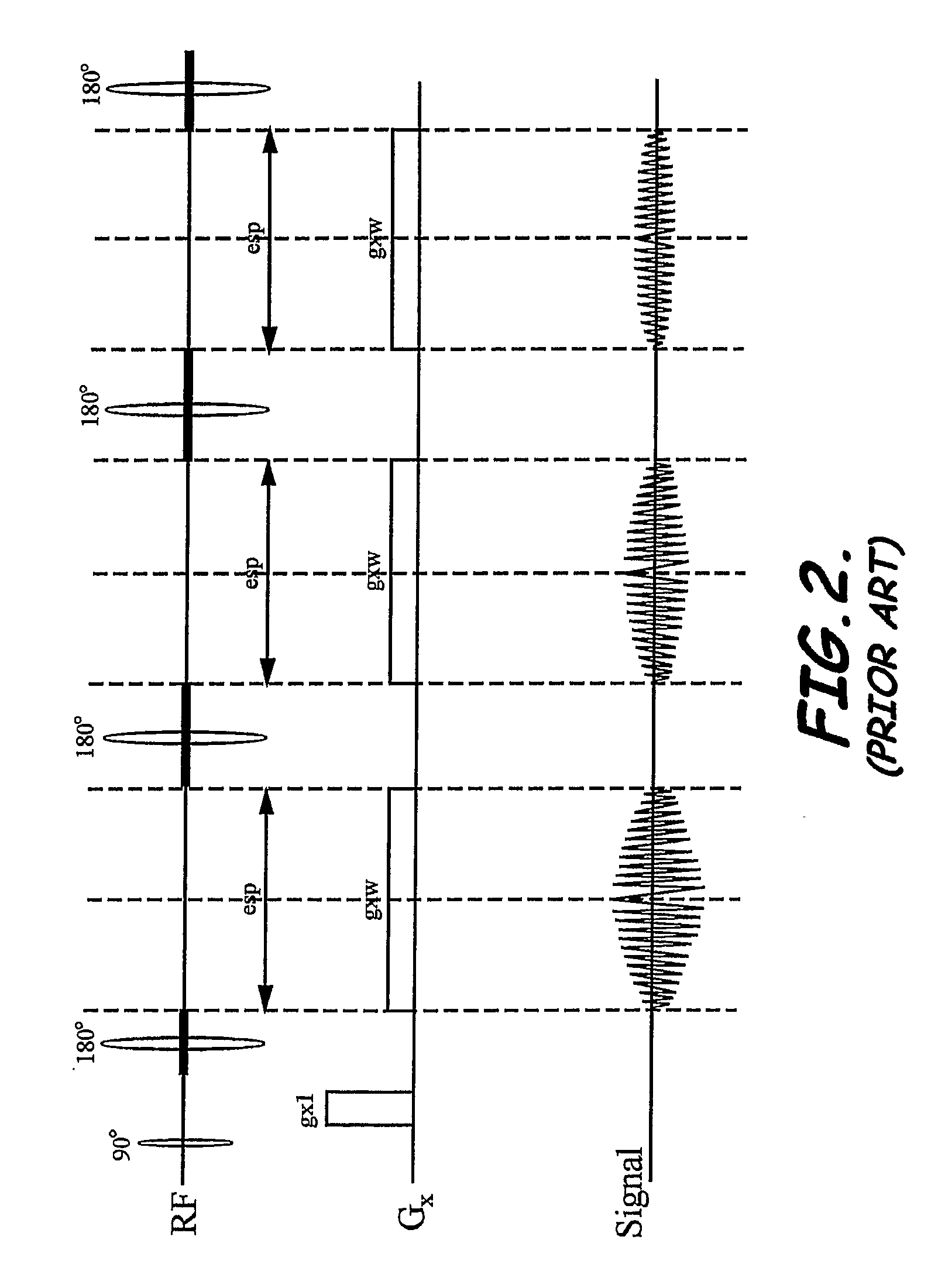
System, program product, and method of acquiring and processing MRI data for simultaneous determination of water, fat, and transverse relaxation time constants
ActiveUS20090093704A1Extension of timeEfficiently determine separateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSingle imageRelaxation time constant
A system, program product, and method to determine water, fat, and transverse relaxation time constants in MRI scanning are provided. A method includes initiating readout gradient pulses to collect echo signals with identical phase encoded gradients to thereby produce a plurality of images, instead of a single image with a single readout gradient. A receiver bandwidth used for collecting the echo signals can be determined responsive to an acquisition matrix size along the readout axis and a time duration for water and fat signals to evolve by a preselected phase angle. In a modified FSE implementation, for example, a method includes using readout gradient pulses that use substantially all of the echo spacing time periods between successive refocus RF pulses. By exploiting the phase and the amplitude relationship between the images, the method can include processing the images to generate separate water and fat images, as well as quantitative maps of transverse relaxation time constants.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
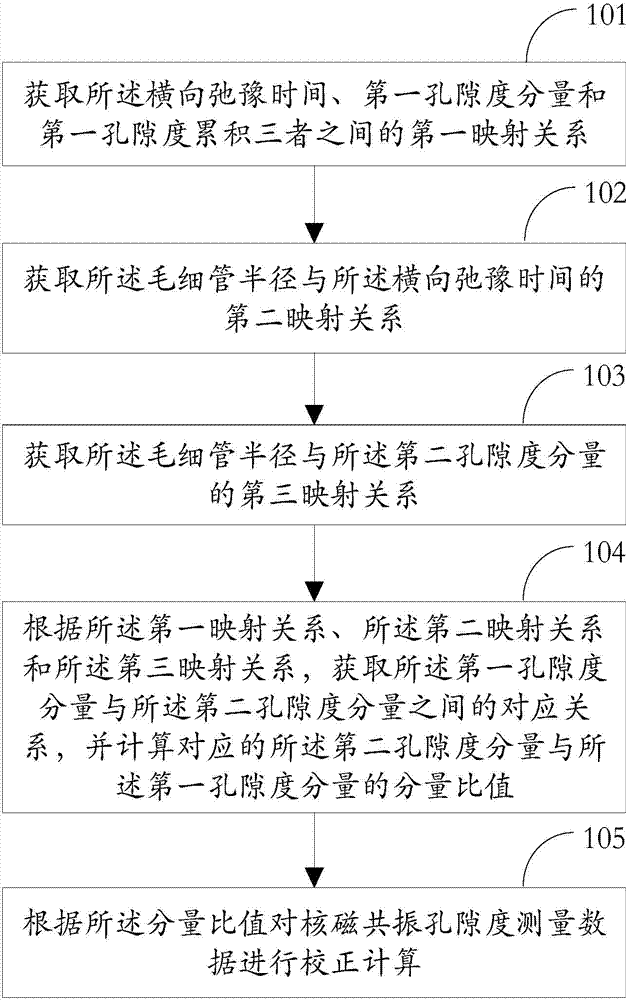
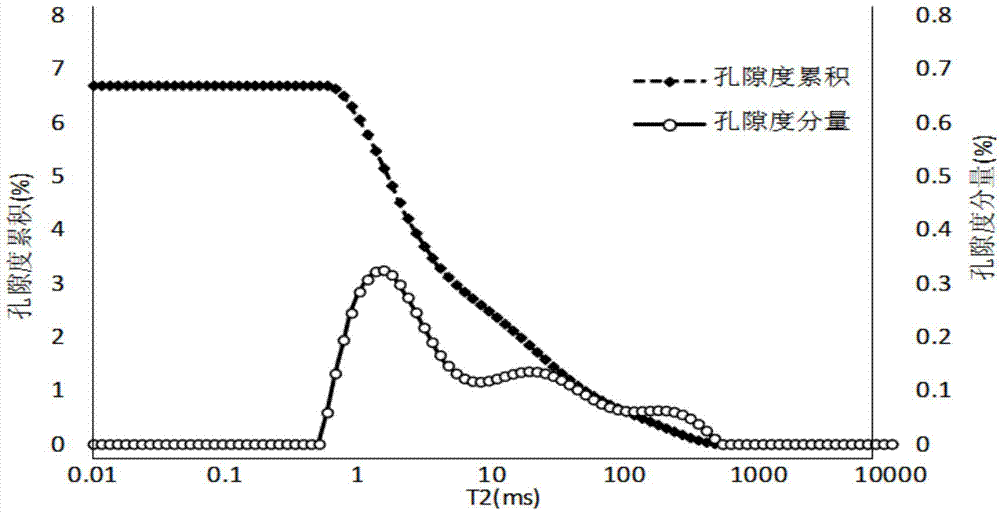
Method, device and system for correcting measurement of nuclear magnetic resonance porosities
ActiveCN103674811AHigh precisionAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePermeability/surface area analysisPorosityNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention relates to the field of well logging technology and discloses a method, device and system for correcting measurement of nuclear magnetic resonance porosities. A first mapping relation among transverse relaxation time, a first porosity component and first porosity cumulation is obtained, so that a second mapping relation between a capillary radius and the transverse relaxation time is obtained and further a third mapping relation between the capillary radius and a second porosity component is obtained; according to the first mapping relation, the second mapping relation and the third mapping relation, the corresponding relation between the first porosity component and the second porosity component is obtained, and the component ratio of the second porosity component to the first porosity component is calculated; according to the component ratio, the correction computation is performed on the measurement data of nuclear magnetic resonance porosities, so that the accuracy of the existing measurement of nuclear magnetic resonance porosities is improved.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com