Patents
Literature
233results about "Magnetostrictive property measurements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
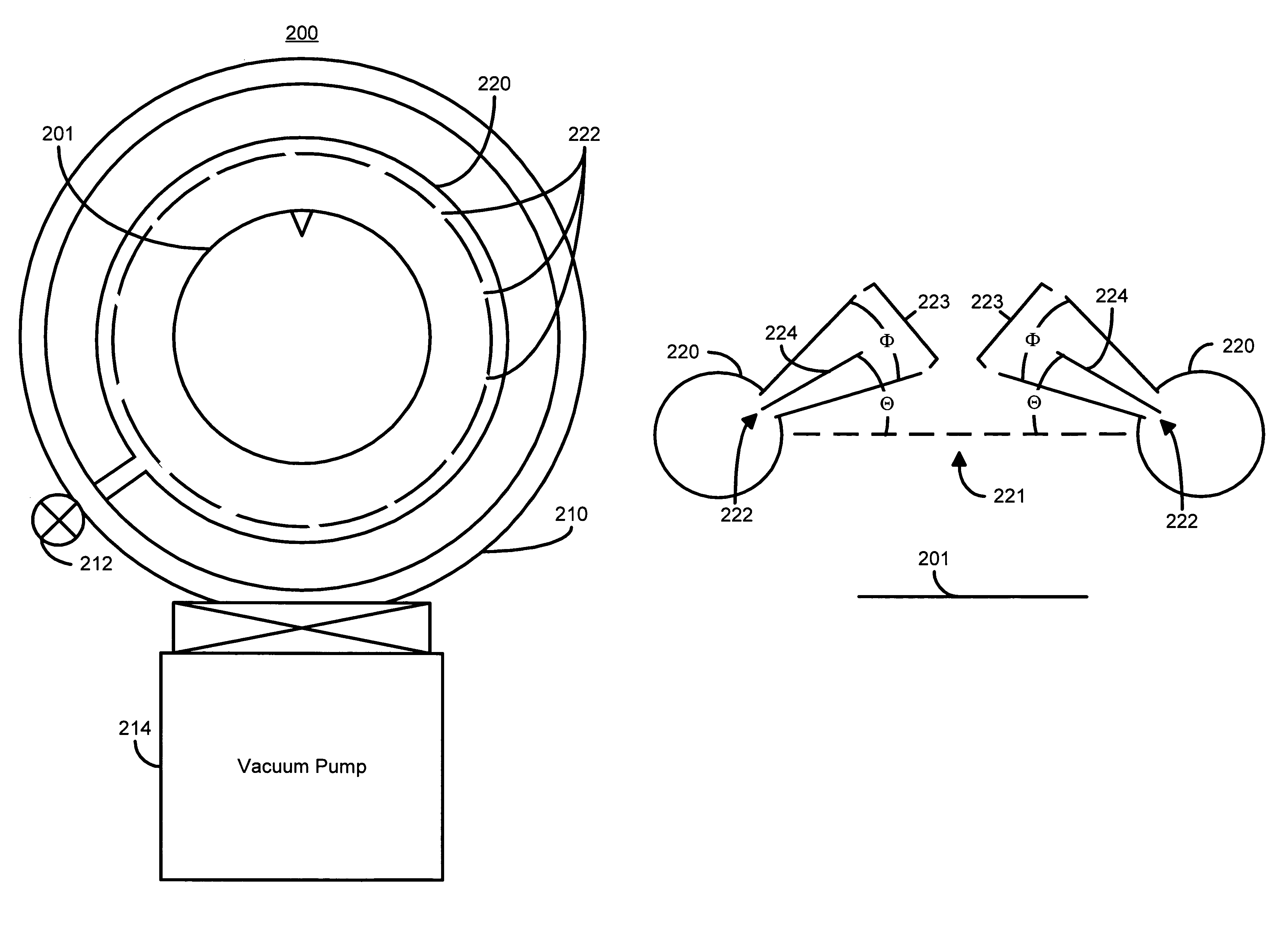
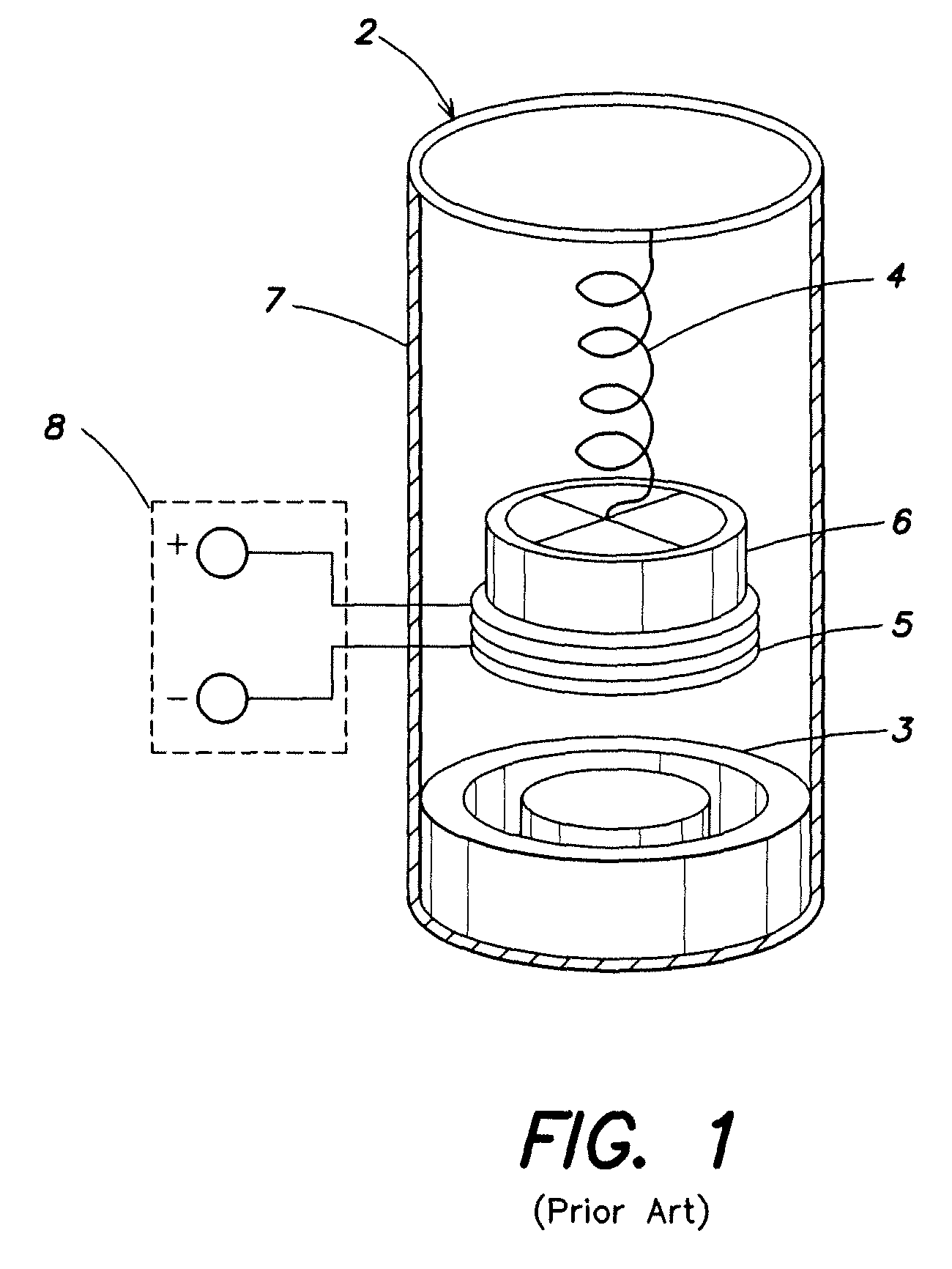
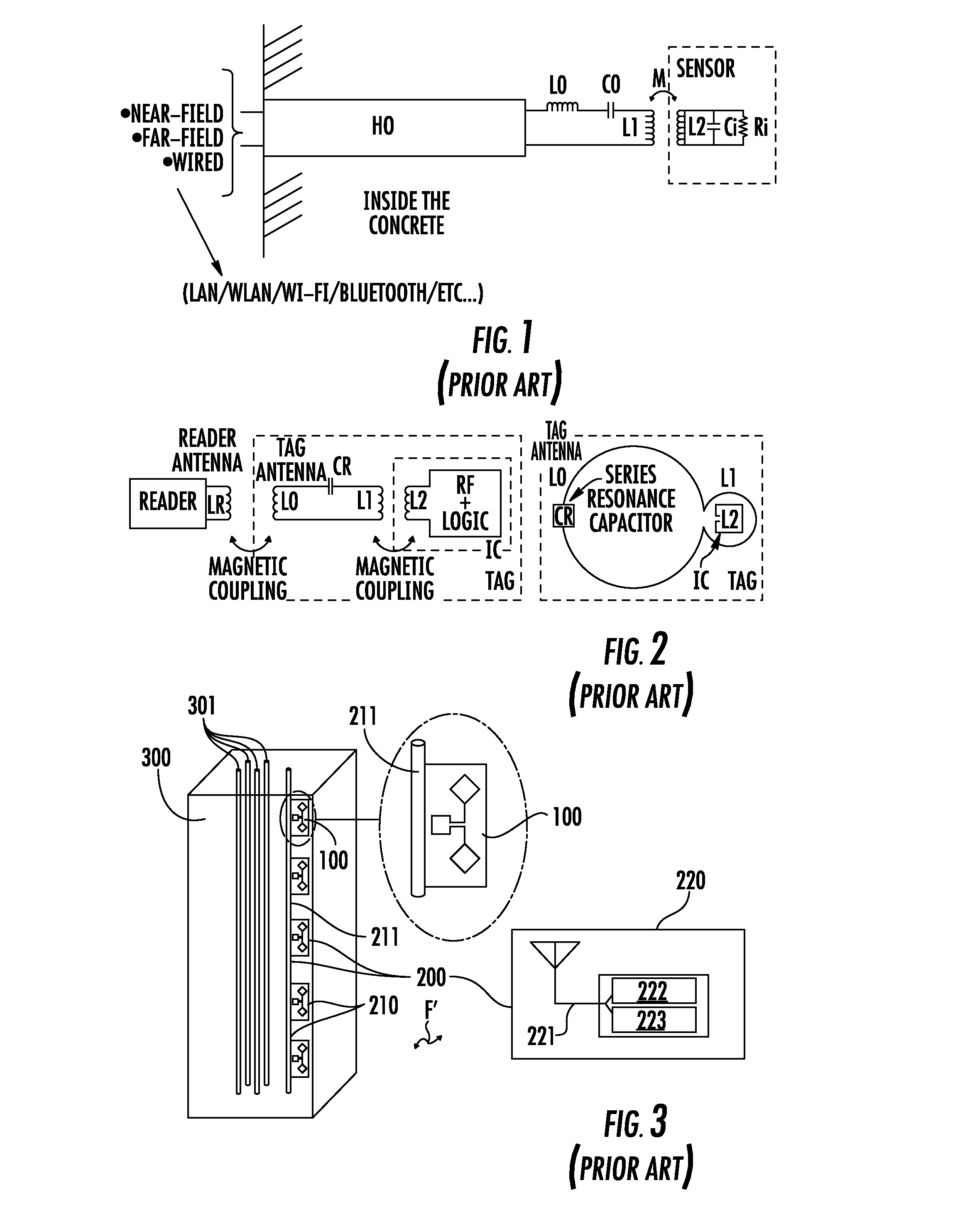
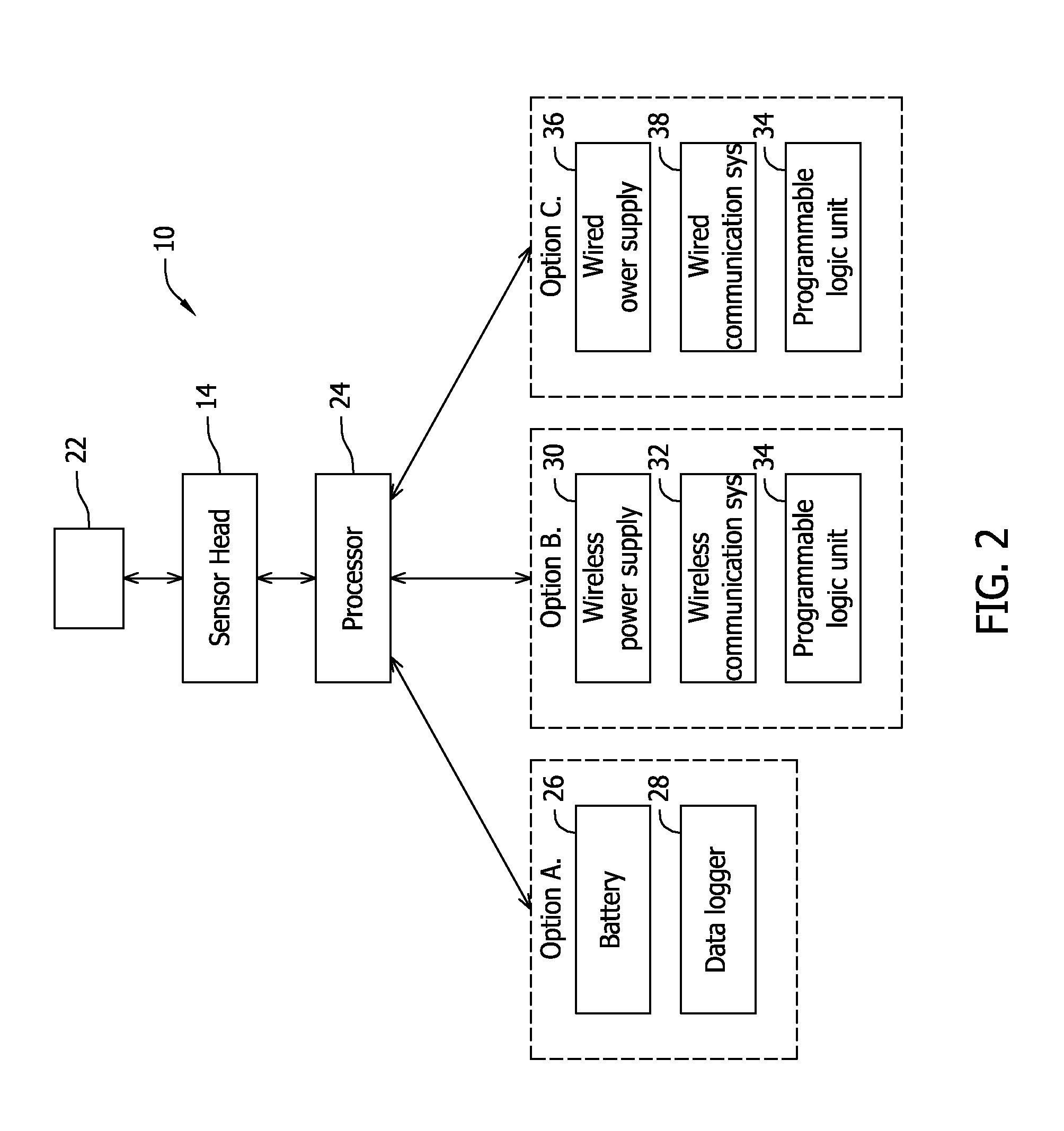
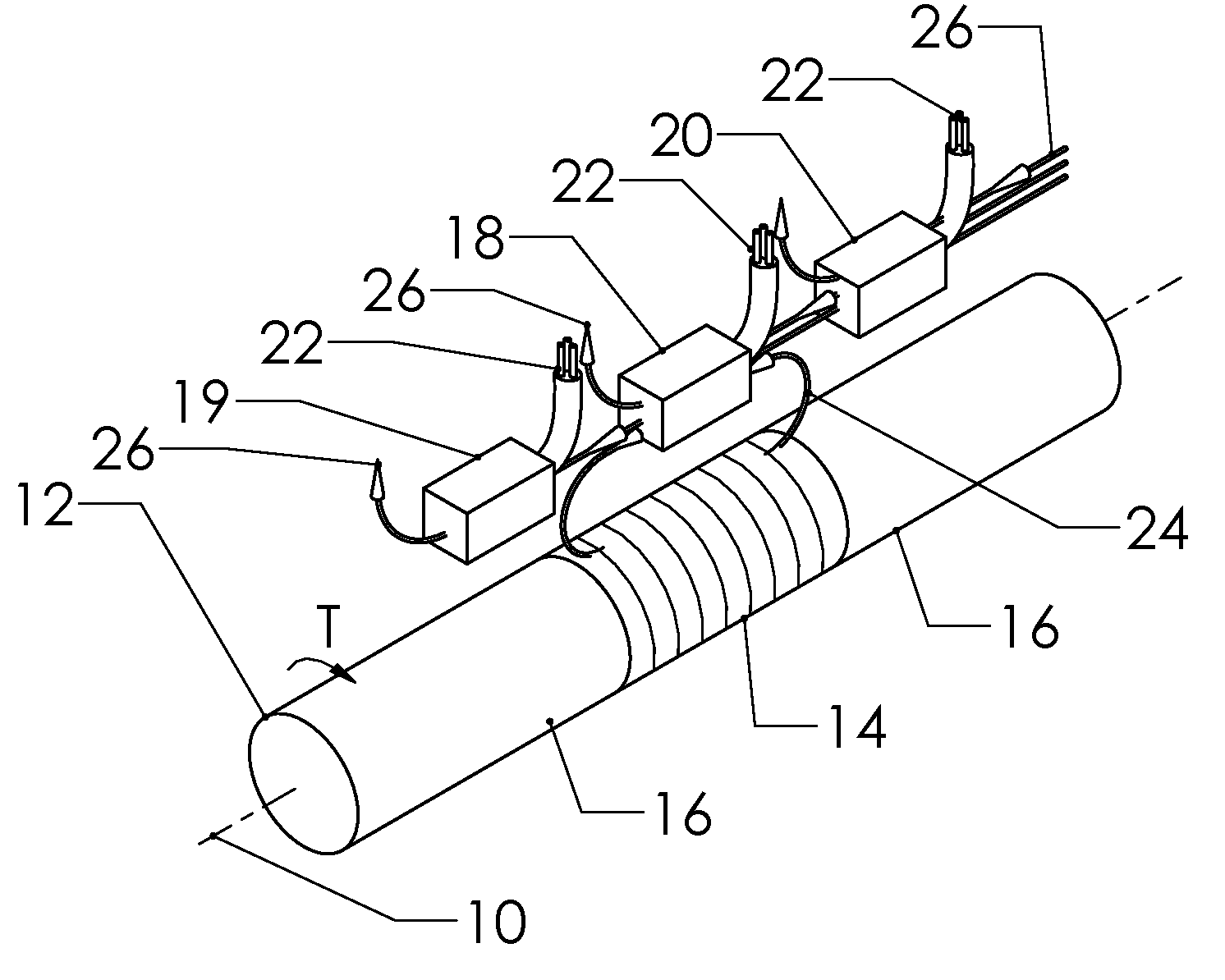
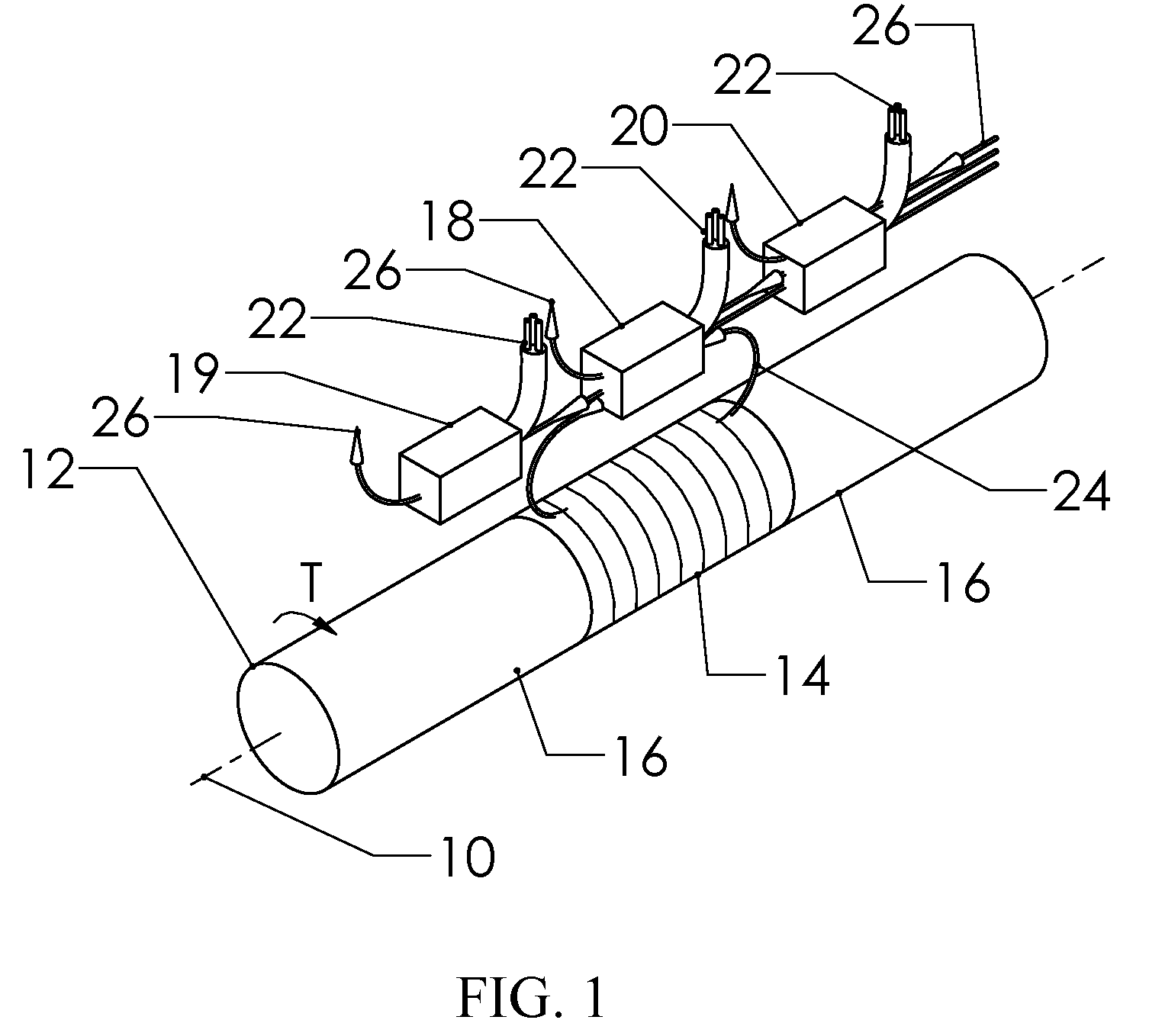
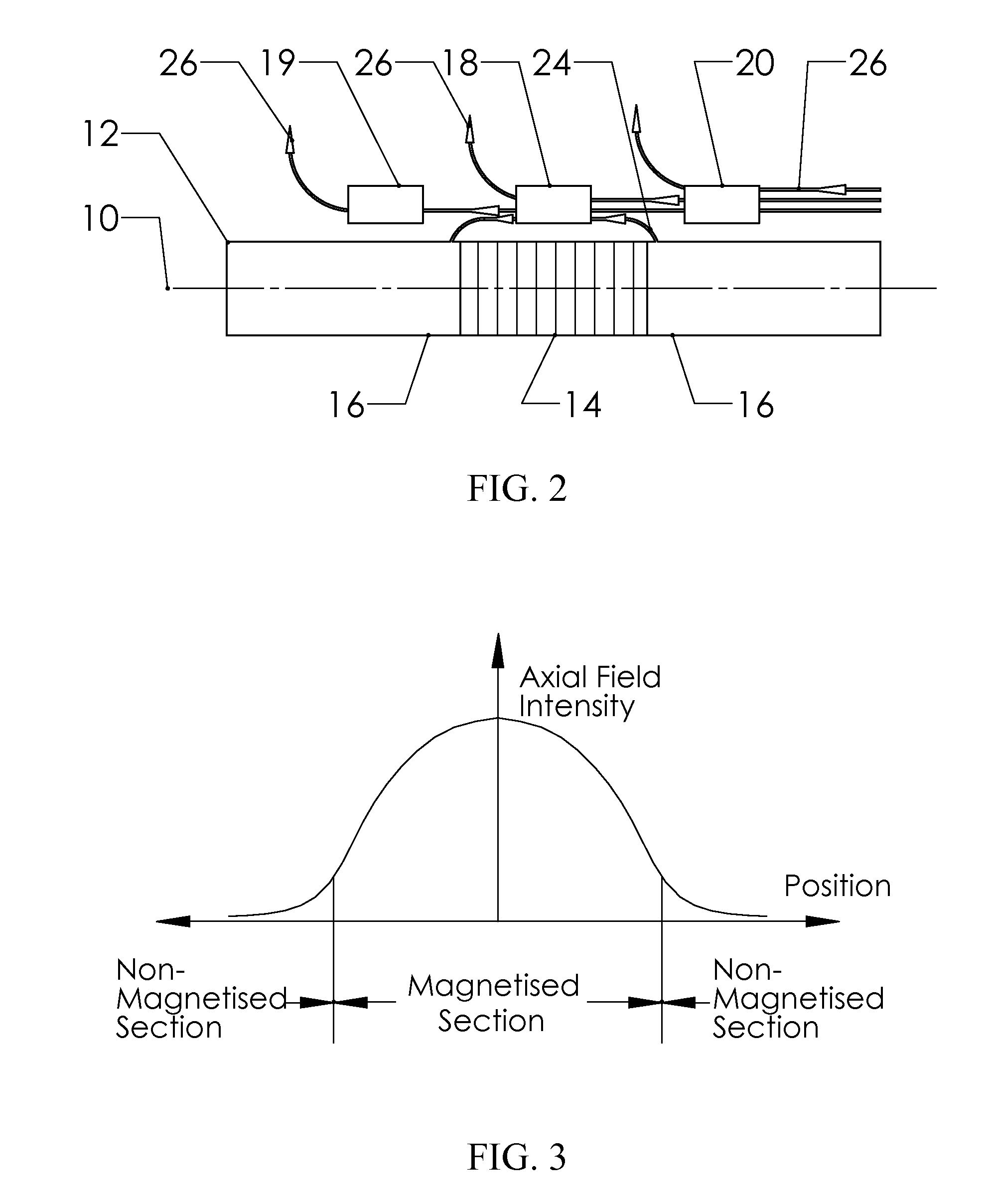
Method and apparatus for controlling magnetostriction in a spin valve sensor
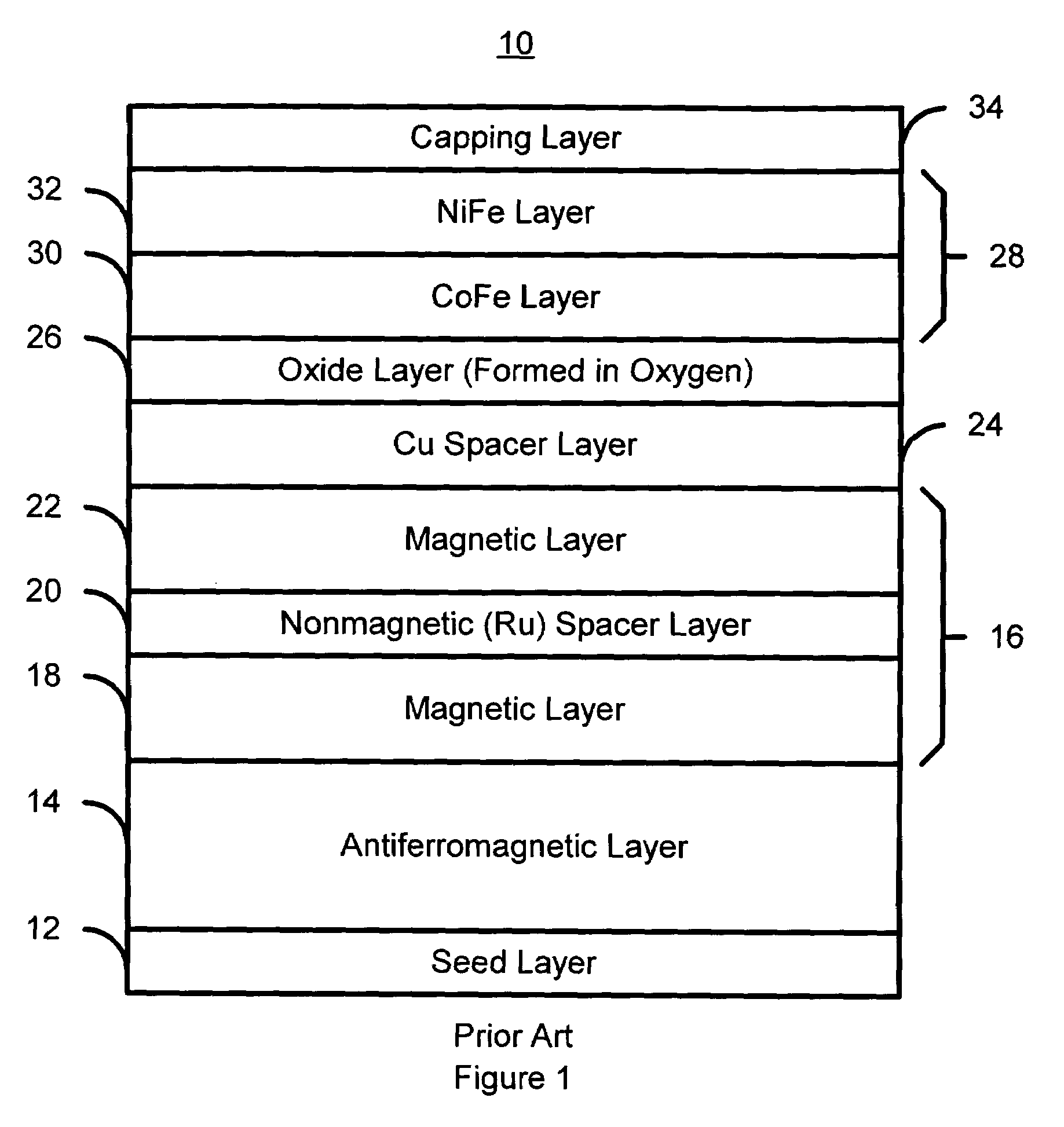
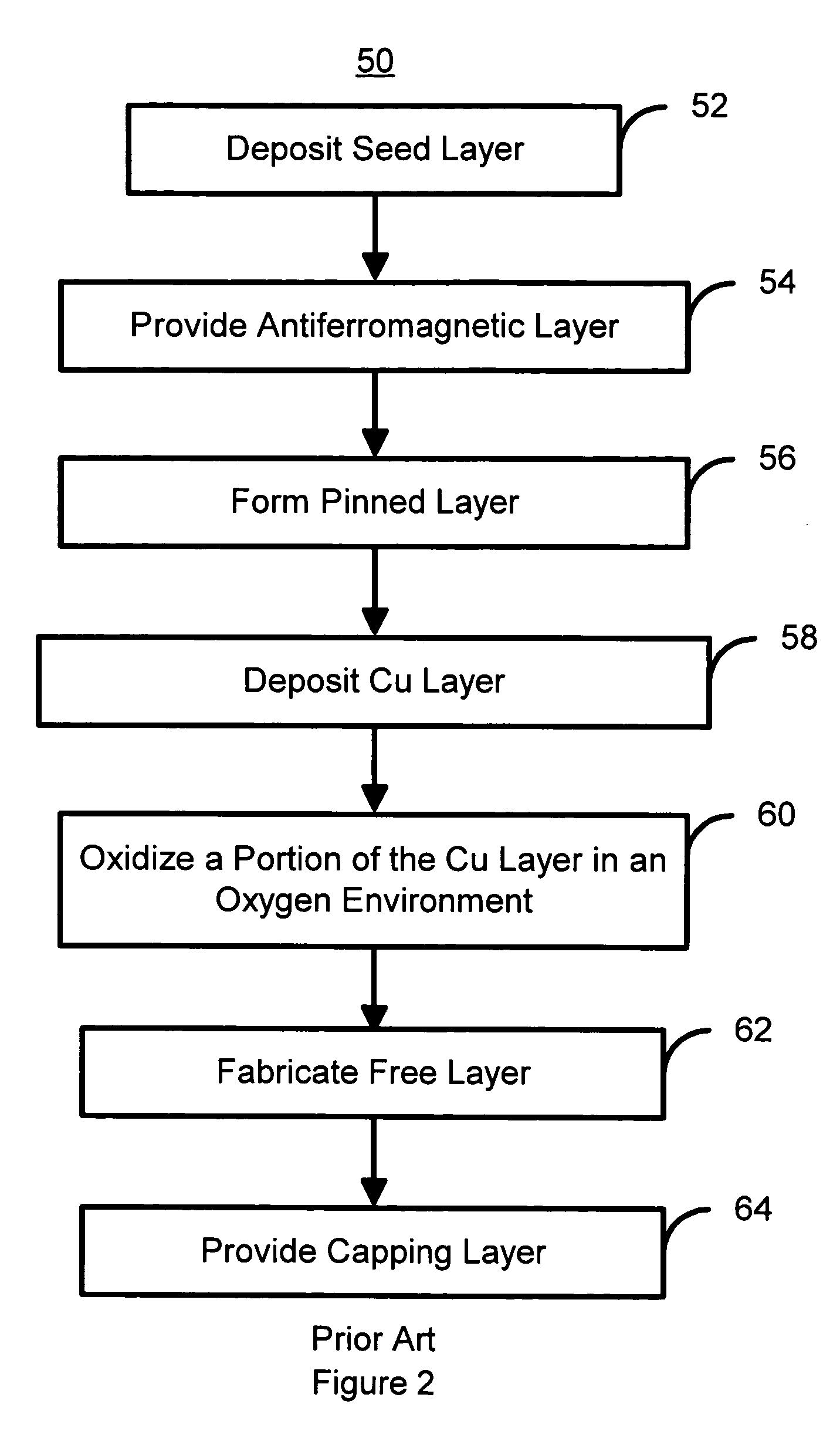
A method and system for providing a magnetic element are described. The method and system include providing a pinned layer, fabricating a metallic spacer layer and oxidizing a portion of the spacer layer in an environment including at least oxygen and a gas inert with respect to the spacer layer to provide an oxide layer. The method and system also include creating a free layer. The oxide layer is between a remaining metallic portion of the spacer layer and the free layer. In one aspect, the system includes a chamber and a gas diffusion apparatus within the chamber. The gas diffusion apparatus includes a plurality of nozzles and defines a plane. The gas exits each of the plurality of nozzles in a cone having an apex angle. The nozzles are directed at a nozzle tilt angle of at least half of the apex angle from the plane and the spacer layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Apparatus and method utilizing magnetic field
InactiveUS7952349B2Small and lightElectrotherapyMagnetostrictive property measurementsInertial massEnergy harvester
Apparatus and method for harvesting energy from the environment and / or other external sources and converting it to useful electrical energy. The harvester does not contain a permanent magnet or other local field source but instead relies on the earth's magnetic field of another source of a magnetic field that is external to the sensing device. One advantage of these new harvesters is that they can be made smaller and lighter than energy harvesters that contain a magnet and / or an inertial mass.
Owner:FERRO SOLUTIONS
TMR device with low magnetostriction free layer
InactiveUS20090122450A1Increasing TMR ratioRaise the ratioNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsSputteringMagnetostriction
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
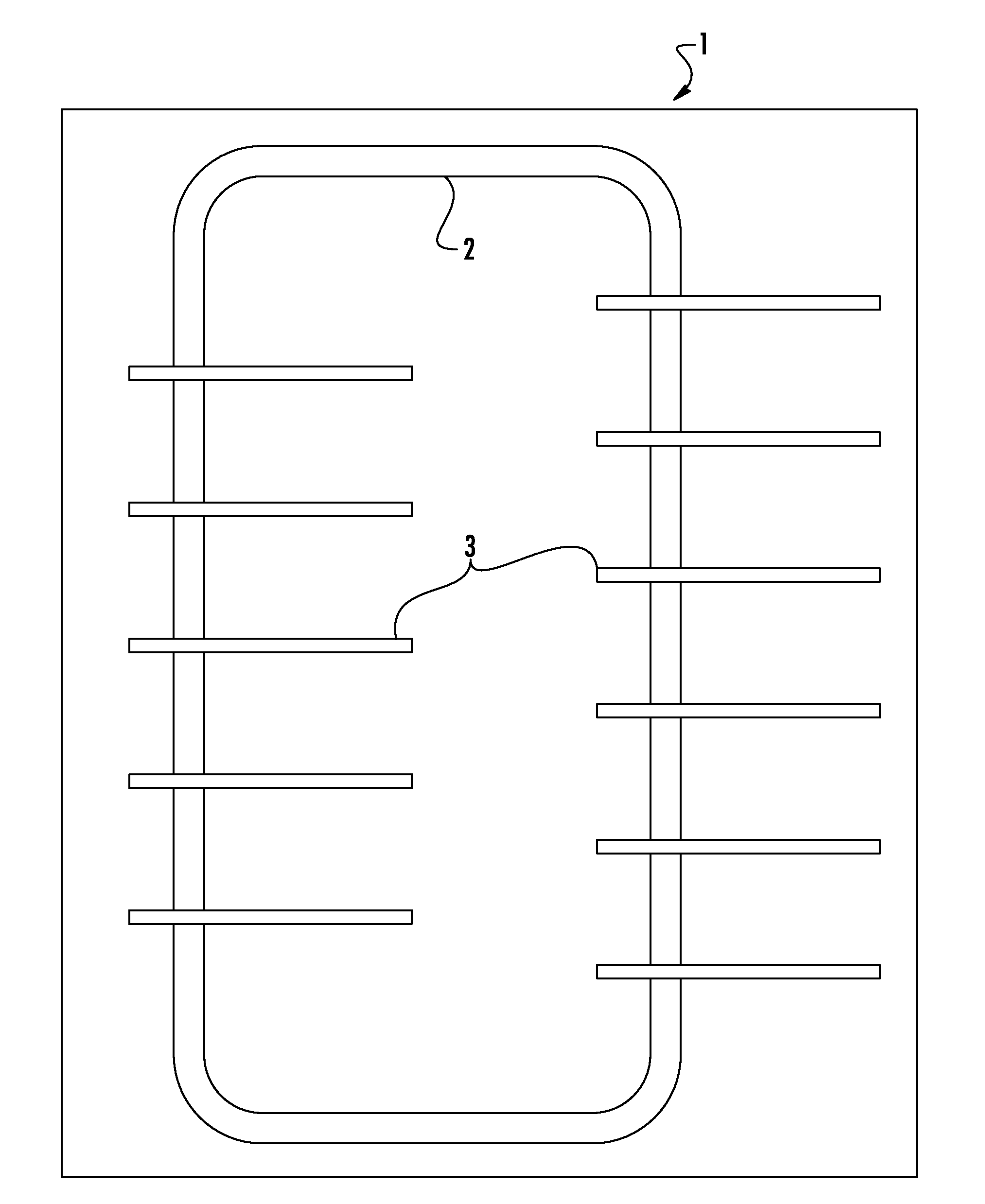
Block made of a building material
ActiveUS20140084909A1Using electrical meansMagnetostrictive property measurementsVoltageBuilding material
A building structure includes a block of building material and a magnetic circuit buried in the block of building material. The structure also includes a plurality of sensing devices buried in the block of building material. Each sensing device may include a contactless power supplying circuit magnetically coupled with the magnetic circuit to generate a supply voltage when the magnetic circuit is subject to a variable magnetic field.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Apparatus and method utilizing magnetic field
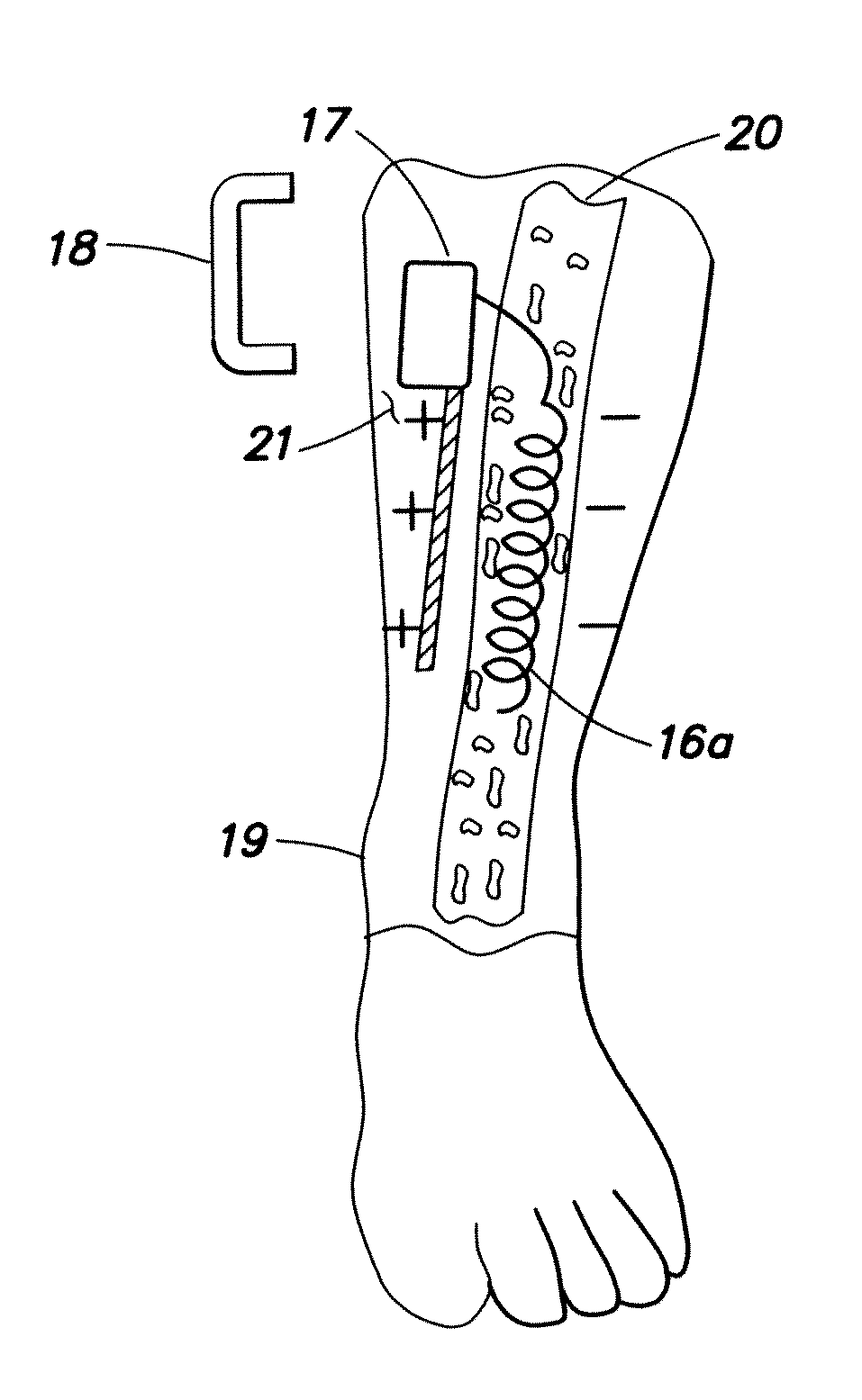
Apparatus and method for harvesting energy from the environment and / or other external sources and converting it to useful electrical energy. The harvester does not contain a permanent magnet or other local field source but instead relies on the earth's magnetic field of another source of a magnetic field that is external to the sensing device. One advantage of these new harvesters is that they can be made smaller and lighter than energy harvesters that contain a magnet and / or an inertial mass. A small implantable stimulator(s) includes at least one passive magnetostrictive / electro-active (PME) magnetic-field sensor for delivering electrical stimulation to surrounding tissue. The PME is charged utilizing a changing magnetic field from an external alternating magnetic field source at a frequency particular to the PME. The small stimulator provides means of stimulating a nerve, tissue or internal organ with direct electrical current, such as relatively low-level direct current for temporary or as needed therapy. The field source may be a hand-held device or a small antenna affixed to the wearer's skin, clothing or accessories. The stimulator may be configured to be small enough to be implanted through a surgical needle. Open- and closed-loop systems are disclosed with measurement of current flow and therapy through PME sensor function.
Owner:FERRO SOLUTIONS
Magnetic field sensor circuit
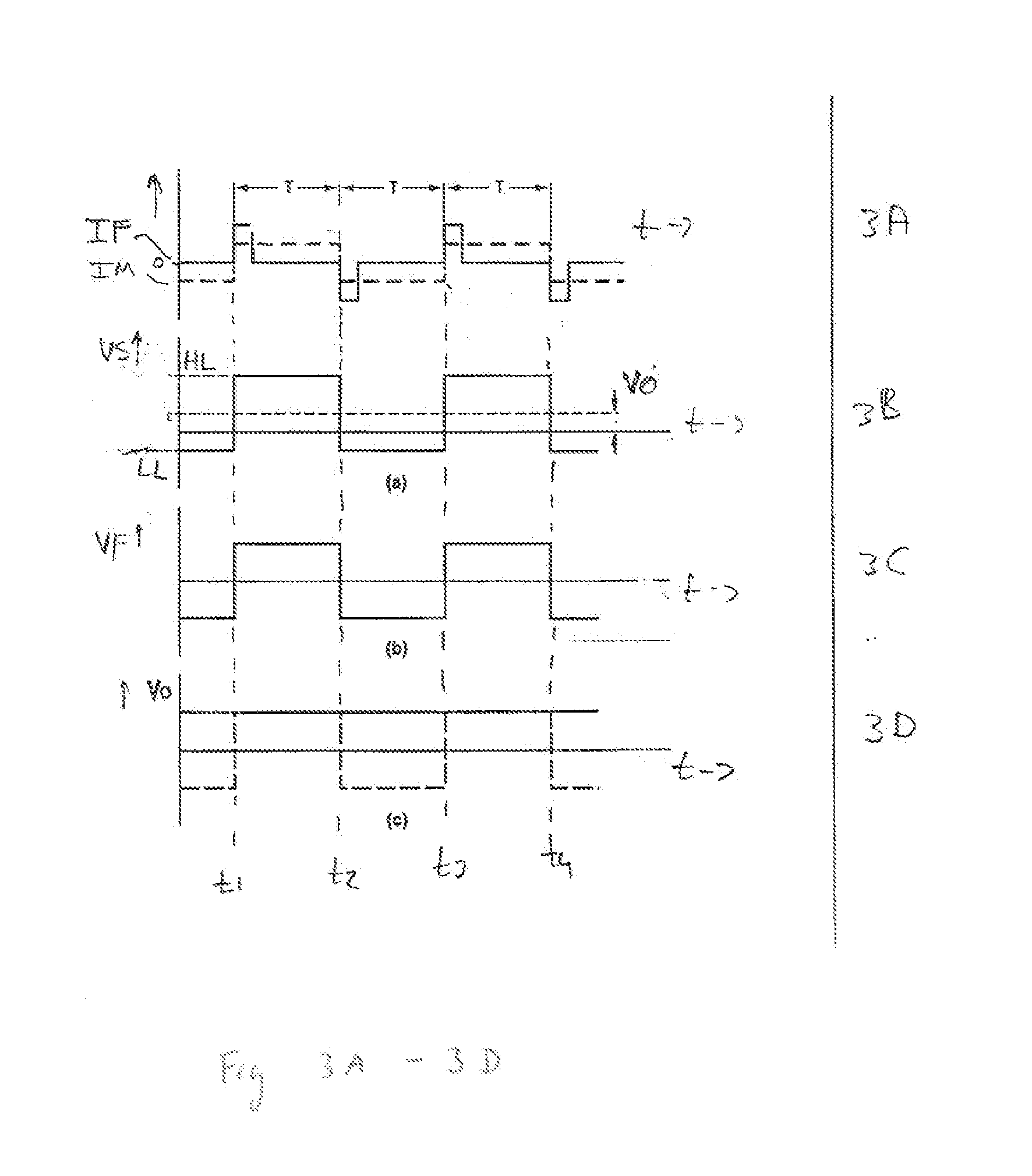
InactiveUS20100053789A1Improve performanceLess spaceNanomagnetismRecord information storageResistive sensorsPhase shifted
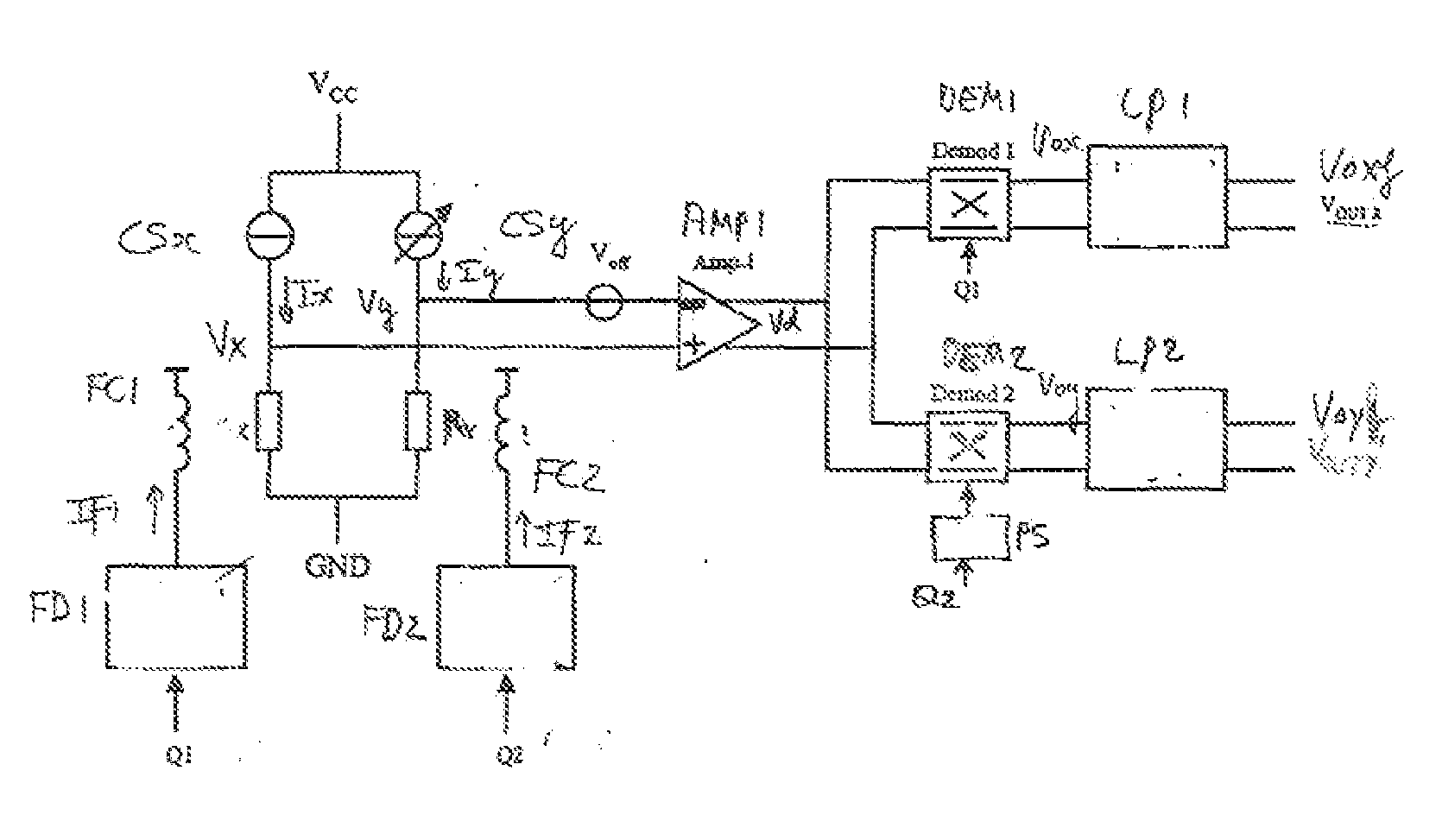
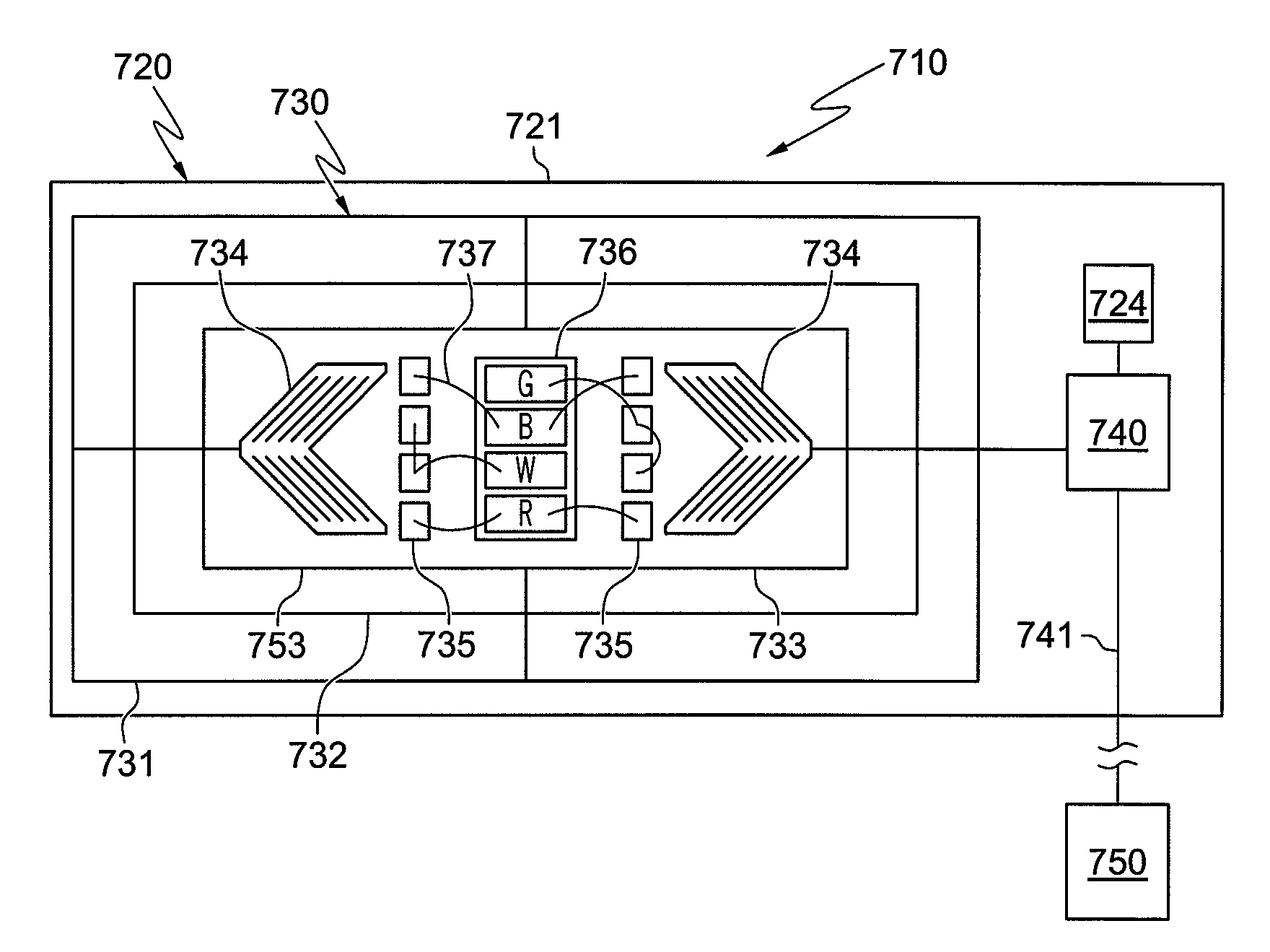
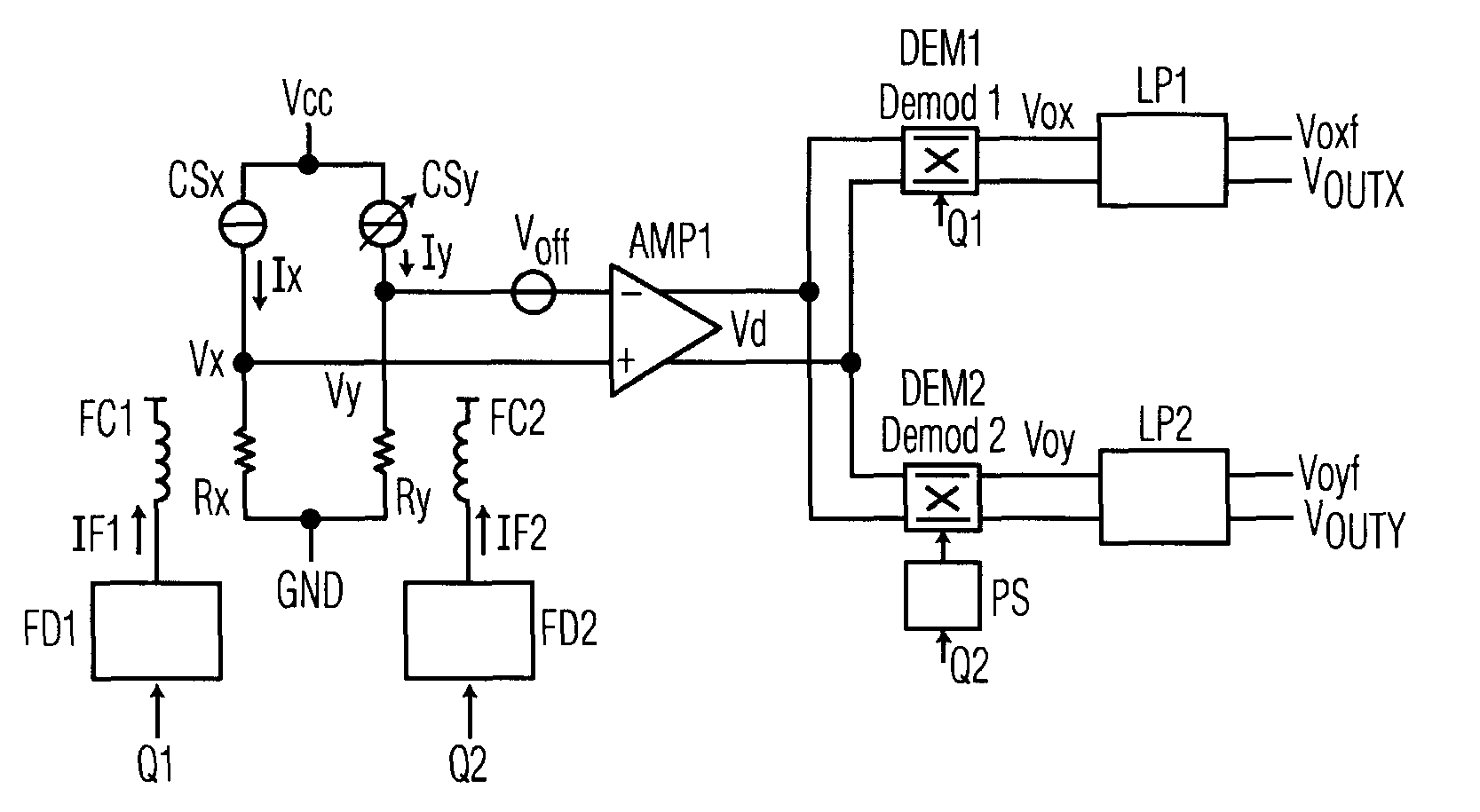
A magnetic field sensor circuit comprises a first magneto-resistive sensor (Rx) which senses a first magnetic field component in a first direction to supply a first sense signal (Vx). A first flipping coil (FC1) applies a first flipping magnetic field with a periodically changing polarity to the first magneto-resistive sensor (Rx) to cause the first sense signal (Vx) to have alternating different levels synchronized with the first flipping magnetic field. A second magneto -resistive sensor (Ry) senses a second magnetic field component in a second direction different than the first direction to supply a second sense signal (Vy). A second flipping coil (FC2) applies a second flipping magnetic field with a periodically changing polarity to the second magneto -resistive sensor (Ry) to cause the second sense signal (Vy) to have an alternating different levels synchronized with the second flipping magnetic field. The first flipping magnetic field and the second flipping magnetic field have a phase shift. A differential amplifier (AMP1) receives the first sense signal (Vx) and the second sense signal (Vy) to obtain a difference signal (Vd). A first synchronous demodulator (DEM1) receives the difference signal (Vd) and a first switching signal (Q1) being phase locked to the alternating different levels of the first sense signal (Vx) to supply a first output signal (Vox) indicating the first magnetic field component. A second synchronous demodulator (DEM2) receives the difference signal (Vd) and a second switching signal (Q2) being phase locked to the alternating different levels of the second sense signal (Vy) to supply a second output signal (Voy) indicating the second magnetic field component.
Owner:TITAN INTELLIGENCE TECH LTD
Systems and methods for delivering electrical energy in the body
InactiveUS20090062886A1Minimally invasiveReduce expensesElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsSurgical operationHand held
Small implantable magnetostrictive-electroactive (ME) device for delivering electrical energy to surrounding tissue. The wireless ME device is activated by a changing magnetic field from an externally applied alternating magnetic field source. The ME device provides a means for stimulating a nerve, tissue or internal organ with direct electrical current, such as relatively low-level direct current for temporary or as needed therapy. The field source (e.g. small coil antenna) may be a hand-held device or affixed to the wearer's skin, clothing or accessories. The ME implant may be configured as pellets which are small enough to be implanted through a surgical needle. In one embodiment, the wireless energy transmission system can be used for stimulating bone growth.
Owner:FERRO SOLUTIONS
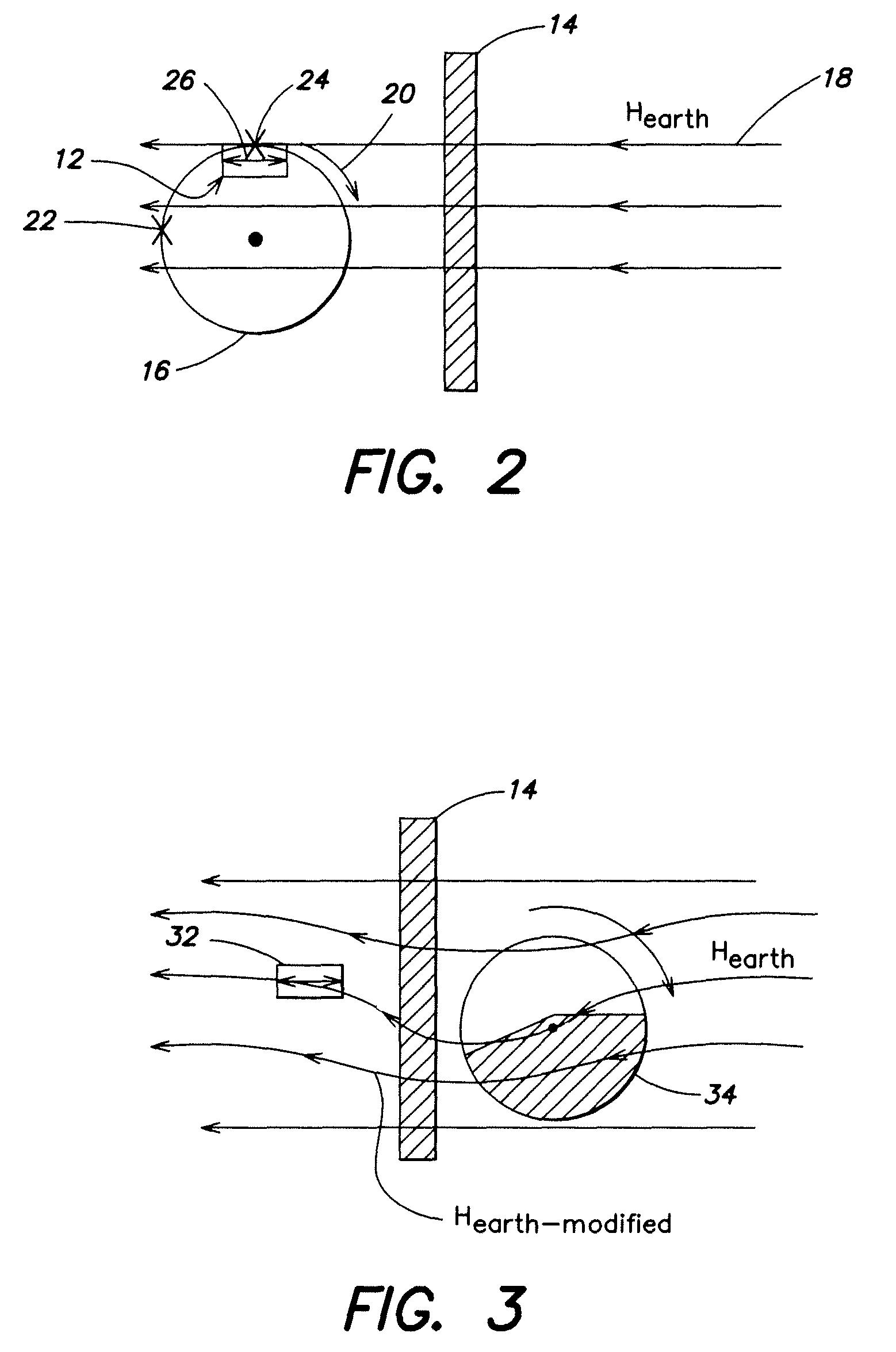
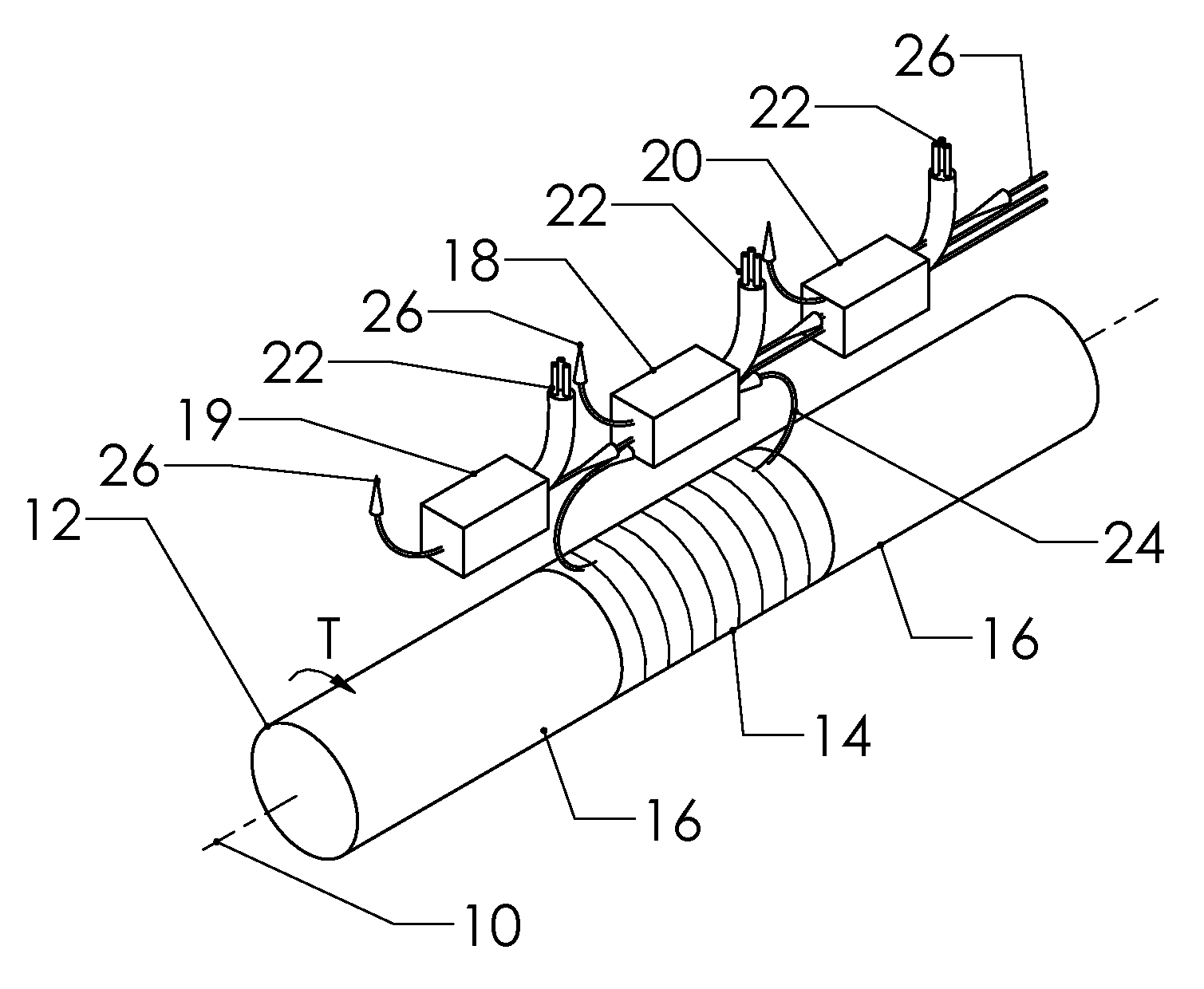
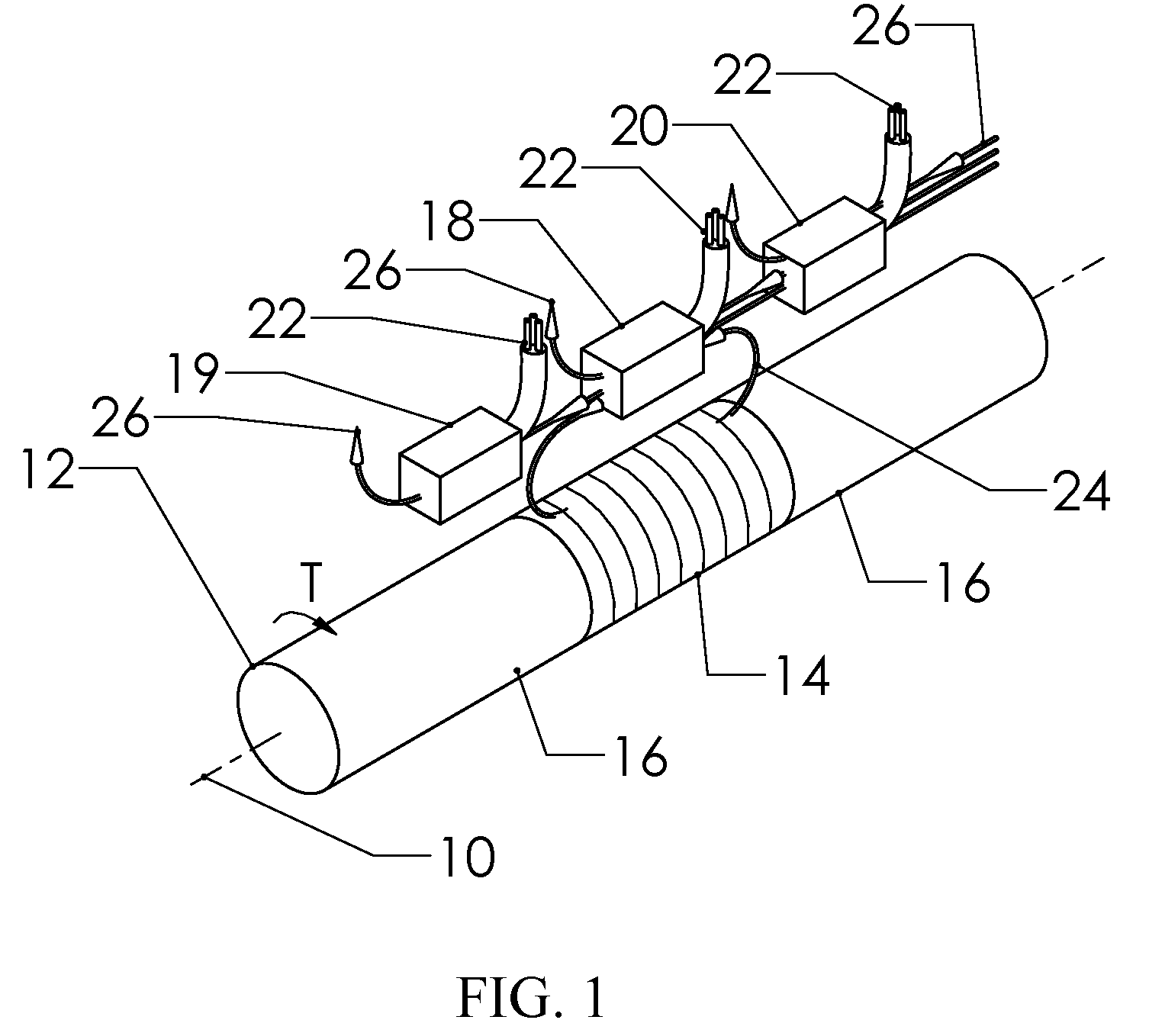
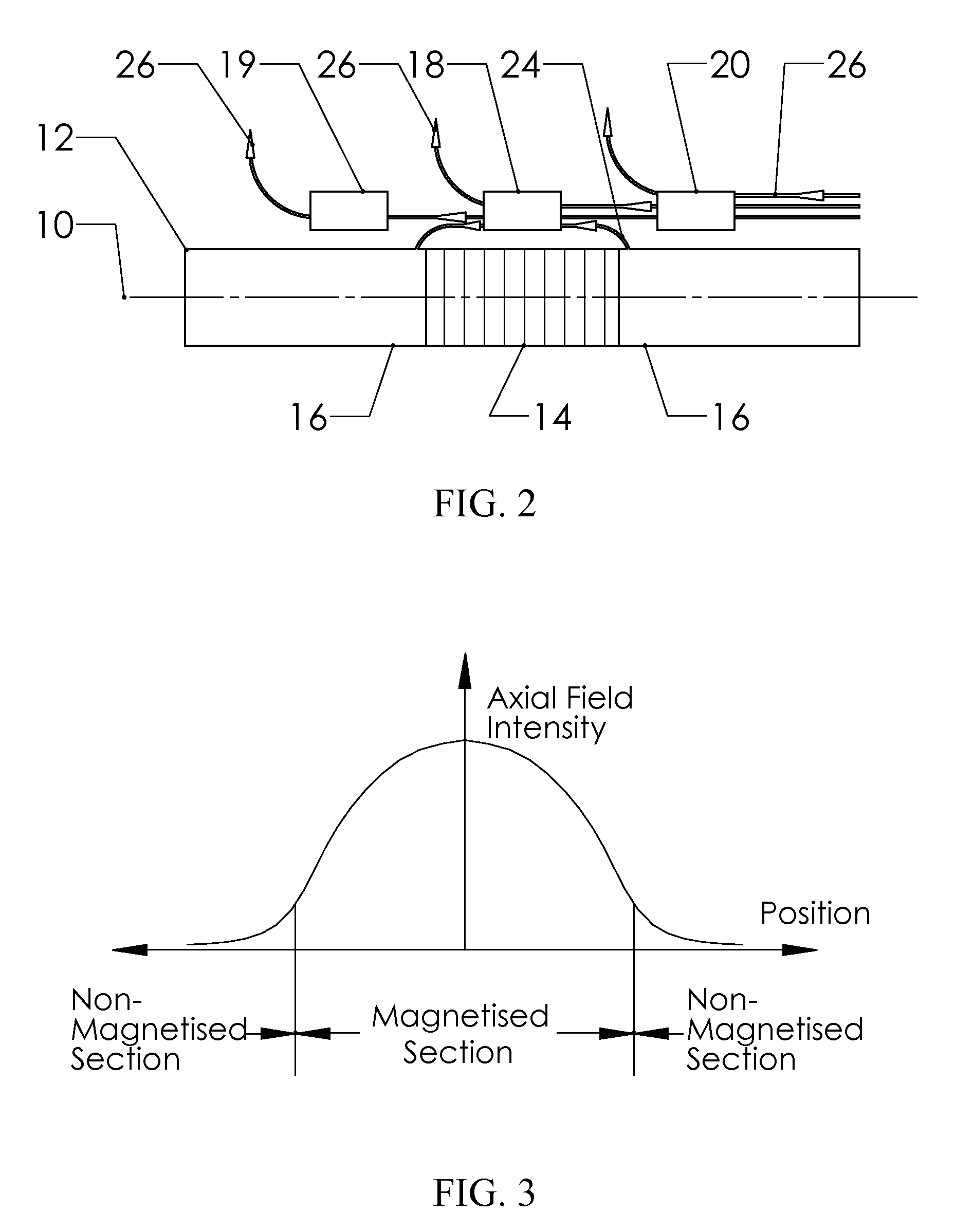
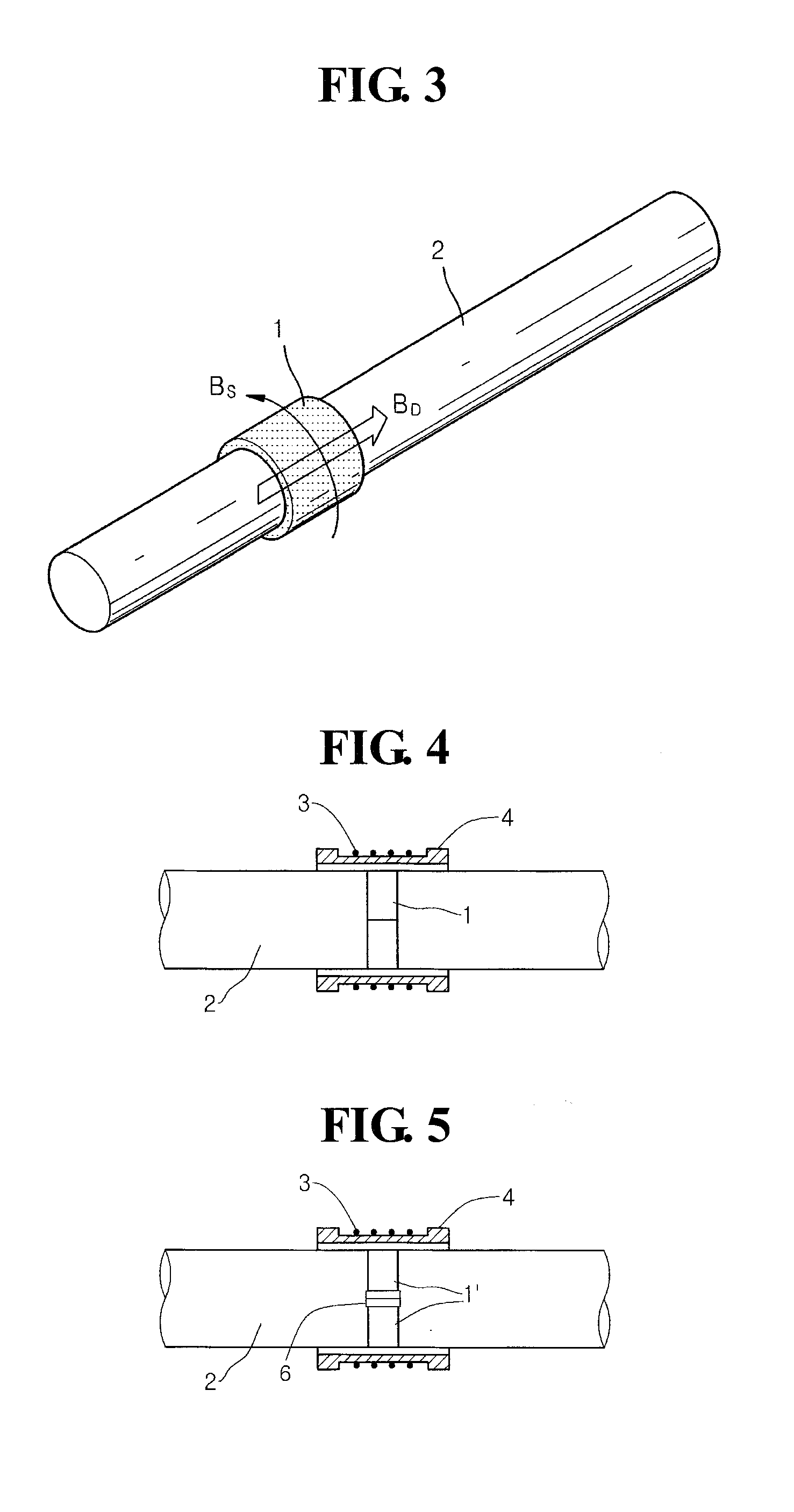
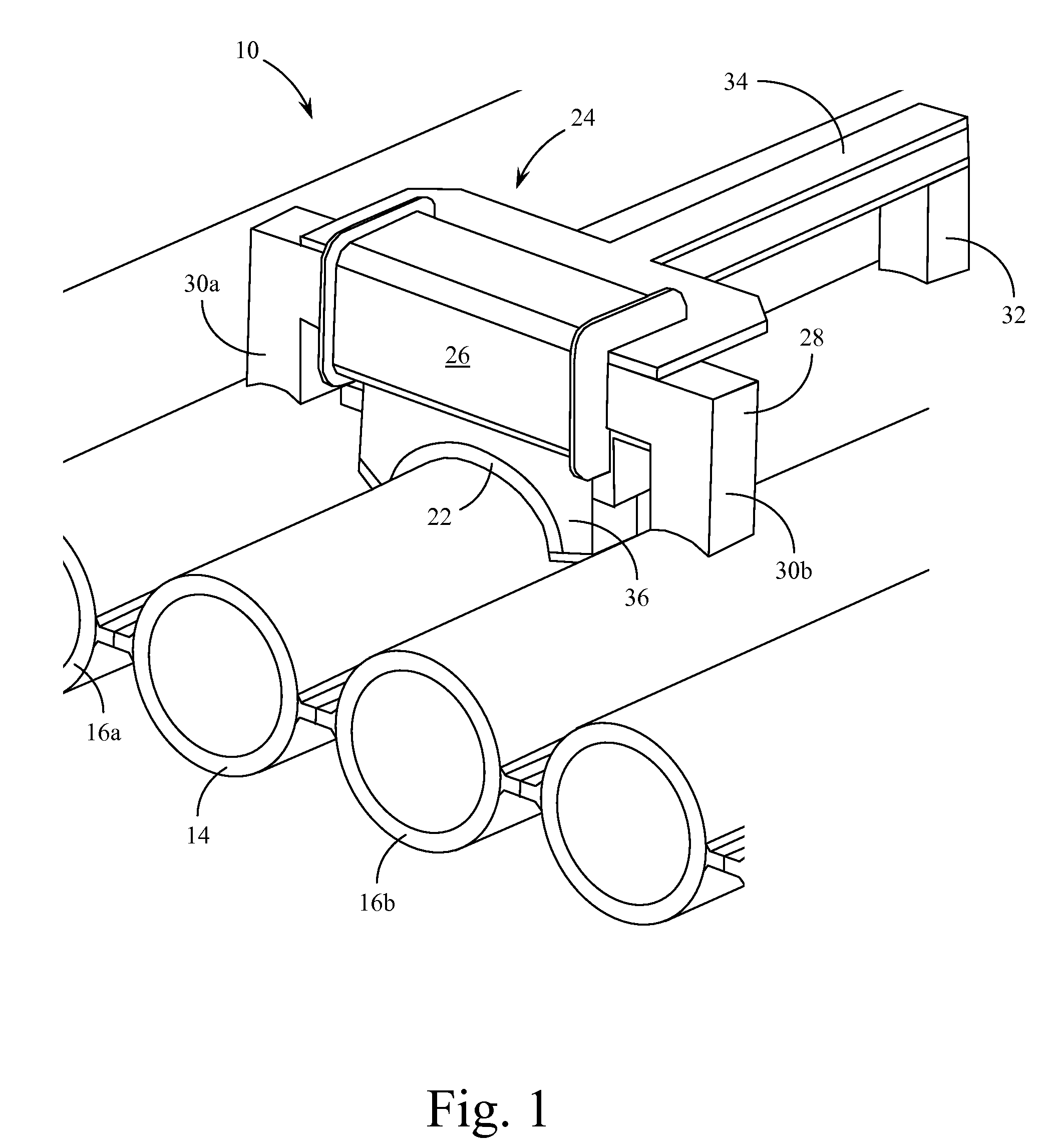
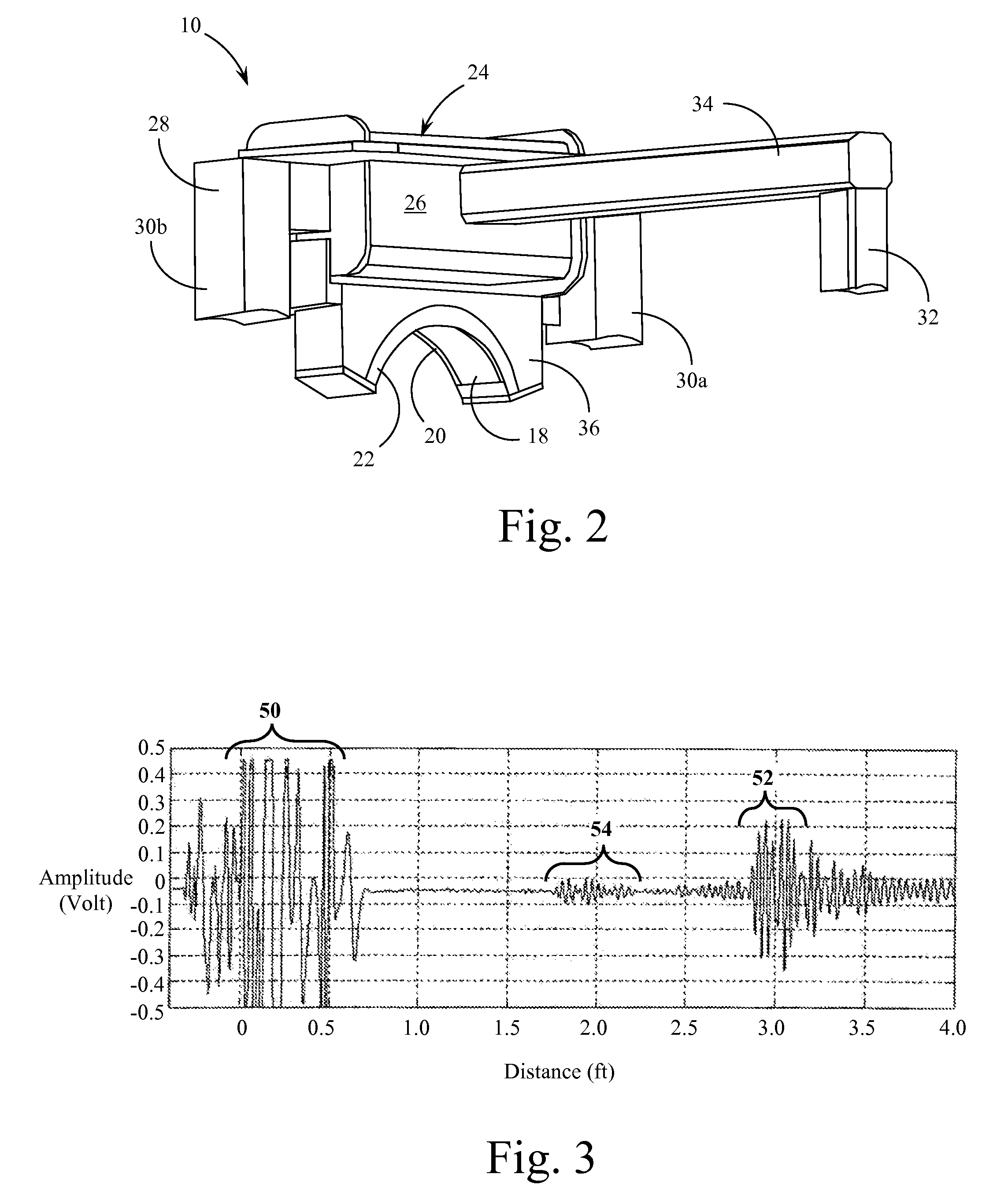
Method and apparatus generating and detecting torsional wave inspection of pipes or tubes
InactiveUS6917196B2High sensitivityLong rangeAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUsing electrical meansEngineeringMagnetostriction
A method and apparatus for implementing magnetostrictive sensor techniques for the nondestructive evaluation of pipes or tubes. A magnetostrictive sensor generates guided waves in a pipe or tube, which waves travel therethrough in a direction parallel to the longitudinal axis of the pipe or tube. This is achieved by using a magnetized ferromagnetic strip being pressed circumferentially against the pipe or tube. For improved efficiency, the strip may be made from an iron-cobalt alloy. The guided waves are generated in the strip and coupled to the pipe or tube and propagate along the length of said pipe or tube. For detection, the guided waves in the pipe or tube are coupled to the thin ferromagnetic strip and are detected by receiving MsS coils. Reflected guided waves may represent defects in the pipe or tube.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Energy harvester utilizing external magnetic field
InactiveUS7808236B1Small and lightEfficient couplingTransformersMagnetostrictive property measurementsInertial massEnergy harvester
Apparatus and method for harvesting energy from the environment and / or other external sources and converting it to useful electrical energy. The harvester does not contain a permanent magnet or other local field source but instead relies on the earth's magnetic field of another source of a magnetic field that is external to the sensing device. One advantage of these new harvesters is that they can be made smaller and lighter than energy harvesters that contain a magnet and / or an inertial mass.
Owner:FERRO SOLUTIONS
Non-contact magnetostrictive sensing systems and methods
ActiveUS20140184210A1Force measurement by measuring magnetic property varationWork measurementMagnetic fluxExcitation coil
A system for sensing stress in a ferromagnetic material is provided. The system includes at least one magnetic flux device configured to induce a conditioning magnetic flux in the ferromagnetic material. The system also includes a sensor positioned proximate to the ferromagnetic material. The sensor includes a core, at least one excitation coil configured to induce a second magnetic flux in the ferromagnetic material, and at least one detector configured to detect changes in the second magnetic flux.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Ultrasensitive magnetoelectric thin film magnetometer and method of fabrication
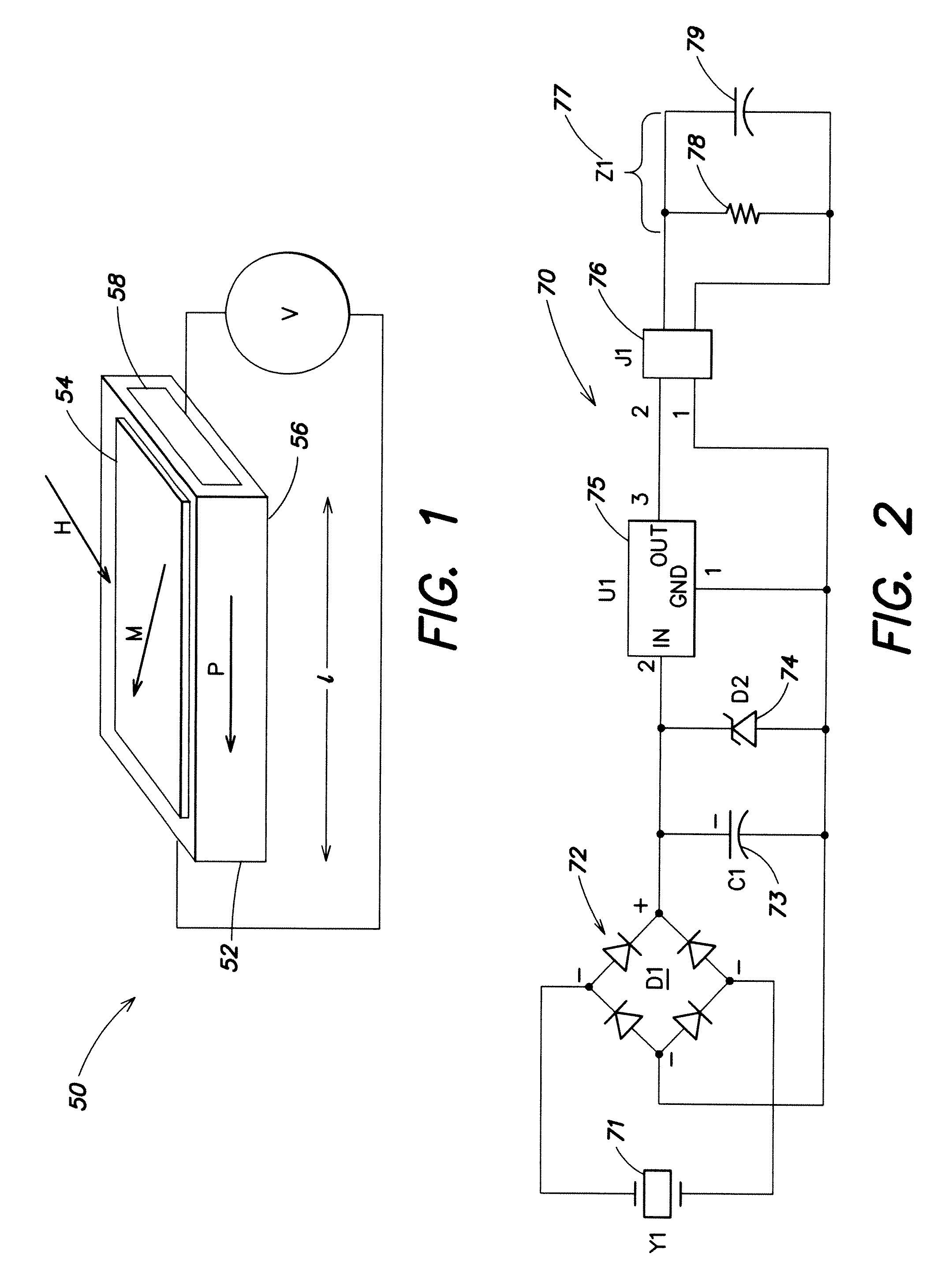
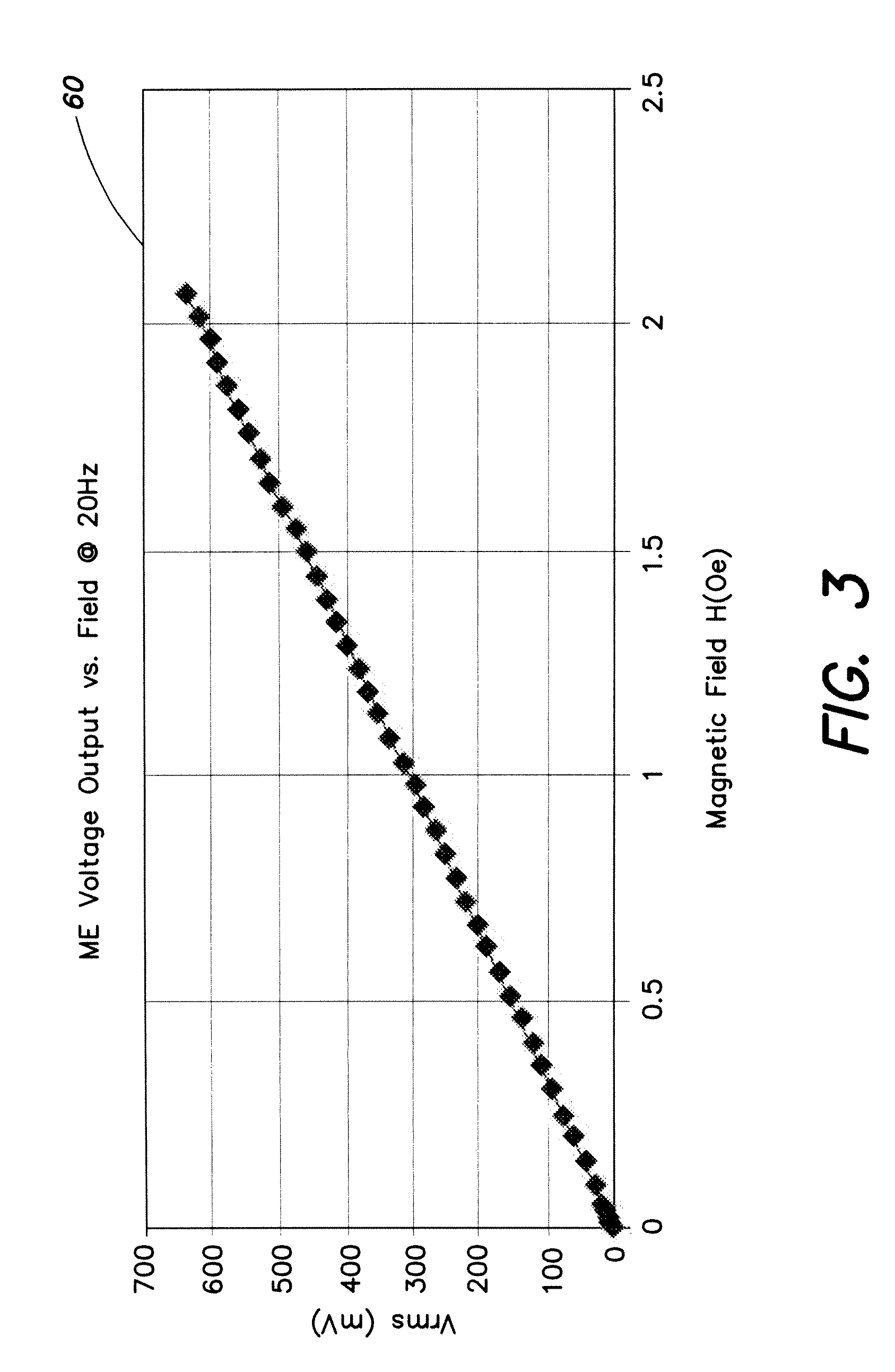
ActiveUS20070252593A1Improve operating characteristicsExcellent characteristicsDigital storageMagnetostrictive property measurementsElectricityRoom temperature
An ultrasensitive room temperature magnetoelectric thin film magnetometer is fabricated on a cantilever beam and includes an active magnetoelectric multilayer structure having a plurality of thin films formed at a region defined on the cantilever beam. Upon application of a magnetic field, the active magnetoelectric structure generates a corresponding response of an electrical nature which is a measure of a value of the applied magnetic field. The material of the cantilever beam may be removed beneath the active magnetoelectric multilayer structure to form a freestanding modification of the magnetometer with superior sensitivity. The active magnetoelectric multilayer structure is either a bi-layer structure which includes a piezoactive (piezoelectric and / or piezoresistive) thin film deposited in contact with a magnetostrictive thin film or a tri-layer active structure (in the free-standing implementation) including a piezoactive thin film sandwiched between a pair of magnetostrictive thin films.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
Magnetic field sensor with suspended stress gauge
ActiveUS20110304325A1Increased magnetic sensitivityStrong magnetic sensitivityNanotechUsing electrical meansPhysicsMagnetic field
A magnetic field sensor including a body including a magnetic mechanism capable of forming a torque applied on the body by action of an external magnetic field to be detected; a connector, separated from the body, mechanically connecting the body to an inlay portion of the sensor by at least one pivot link having an axis perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field to be detected; a detector detecting stress applied by the body by action of the torque, separated from the connector and including at least one suspended stress gauge including a first part mechanically connected to the inlay portion, a second part mechanically connected to the body, and a third part provided between the first and second parts and suspended between the inlay portion and the body.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
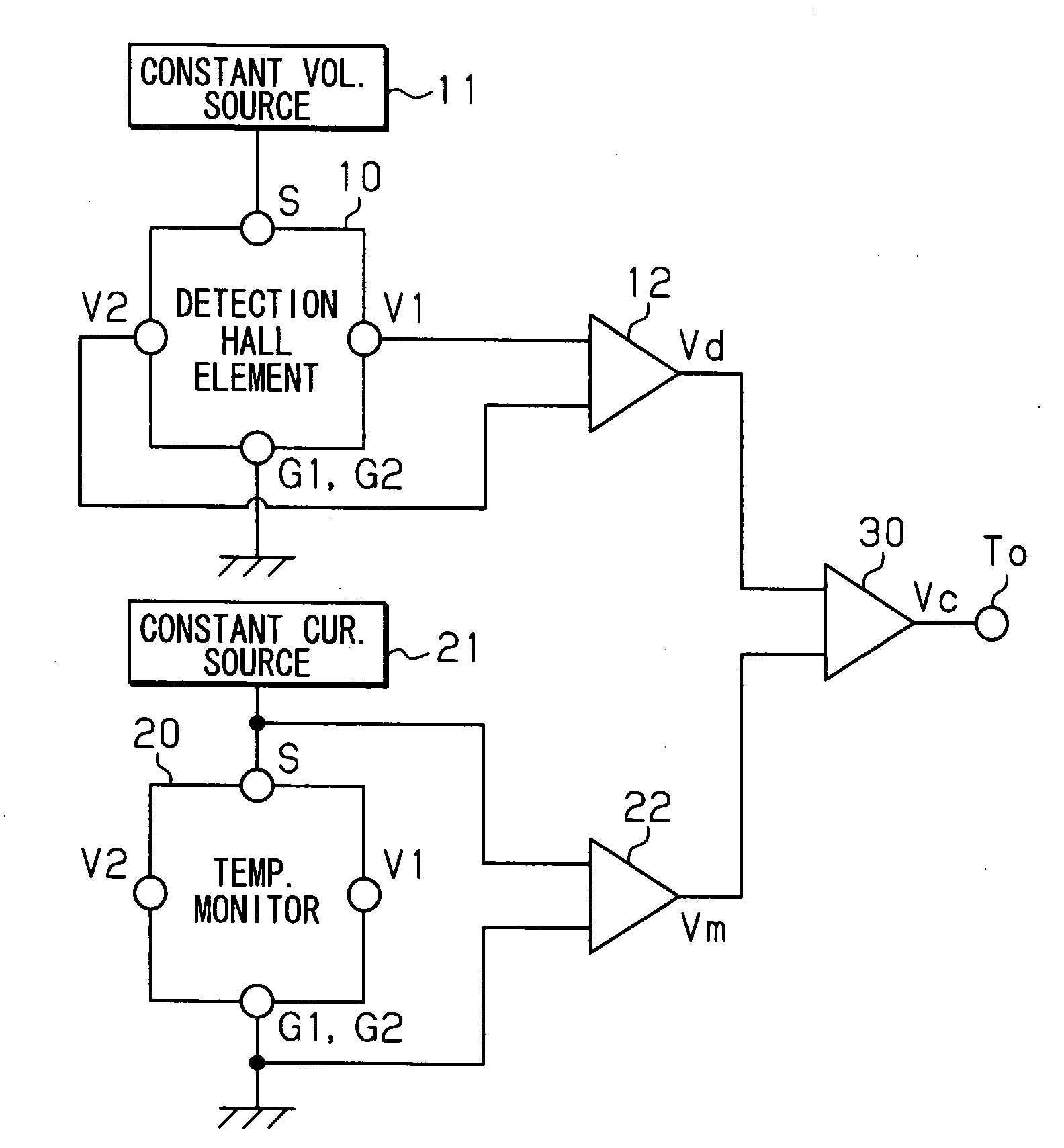
Semiconductor device, magnetic sensor, and physical quantity sensor
InactiveUS20080074106A1Improve linearitySuitable maintenanceSolid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesHall elementDevice material
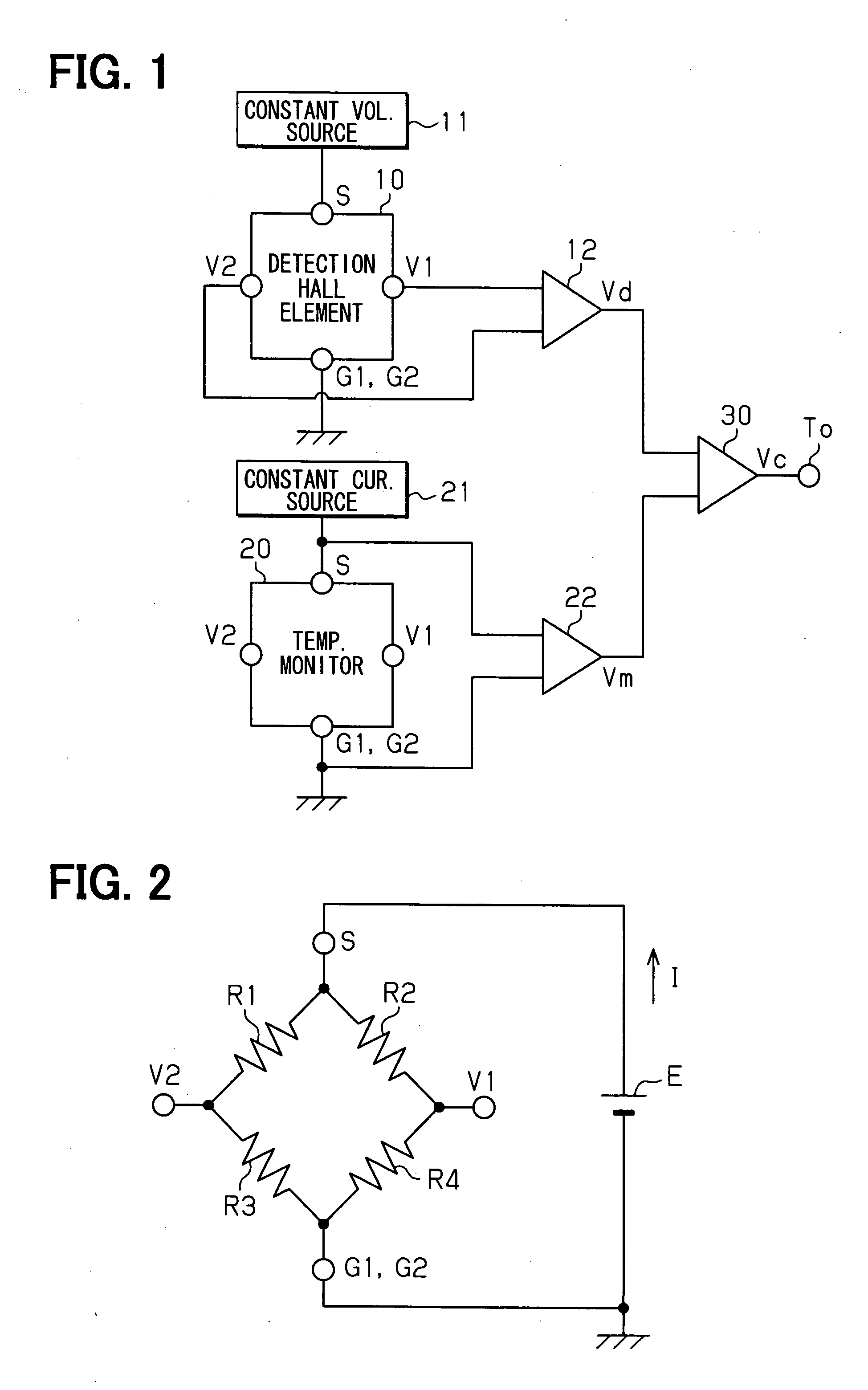
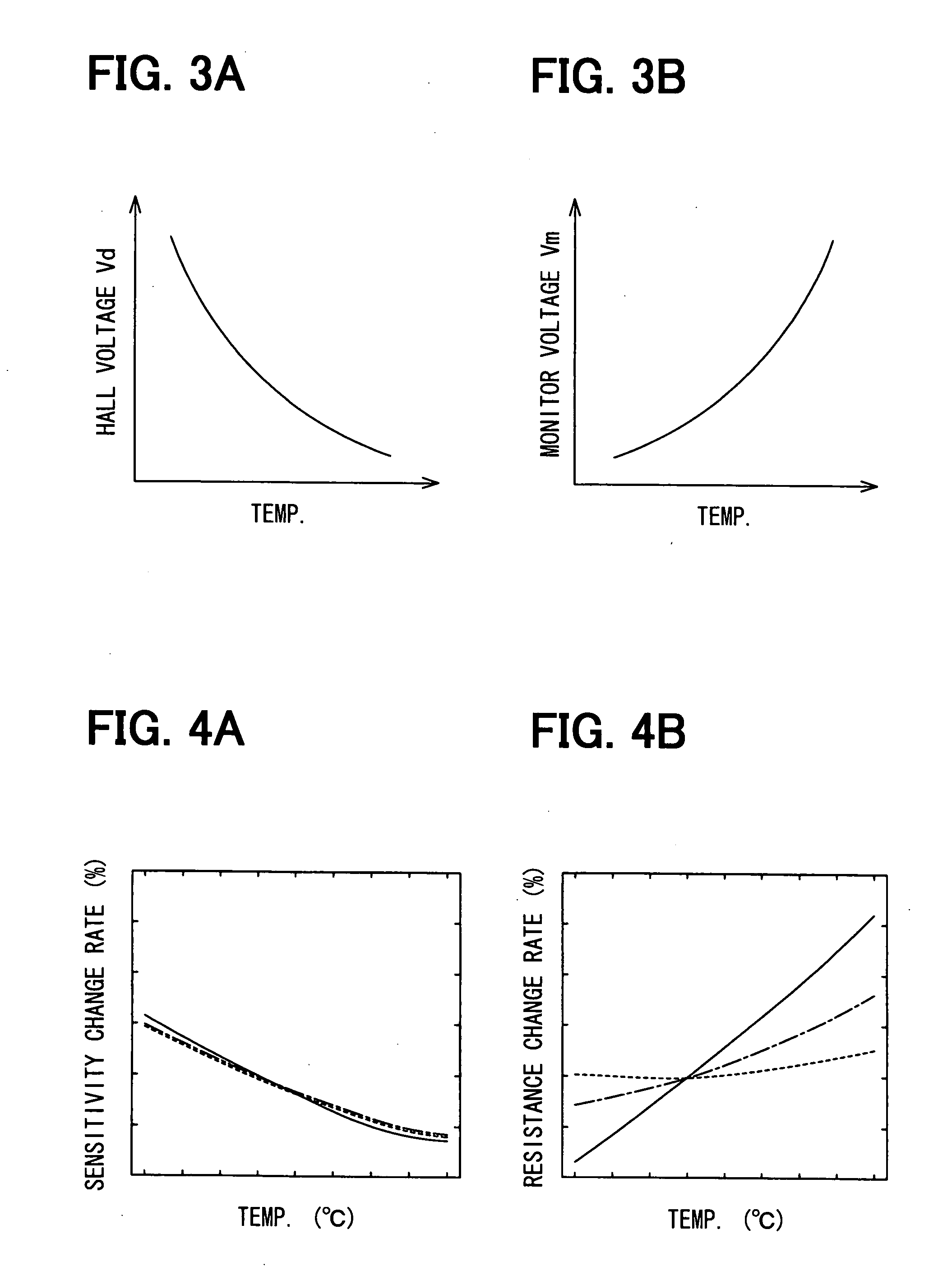
A semiconductor device includes: a detection Hall element for detecting a magnetic field; a temperature monitor Hall element; and a calculation circuit. The detection Hall element has a characteristic, which is almost a same as the temperature monitor Hall element. The detection Hall element is disposed near the temperature monitor Hall element. The detection Hall element outputs a Hall voltage. The temperature monitor Hall element includes a pair of driving signal supply terminals for outputting a temperature monitor voltage. The calculation circuit calculates to cancel a temperature characteristic of the Hall voltage based on the Hall voltage and the temperature monitor voltage.
Owner:DENSO CORP
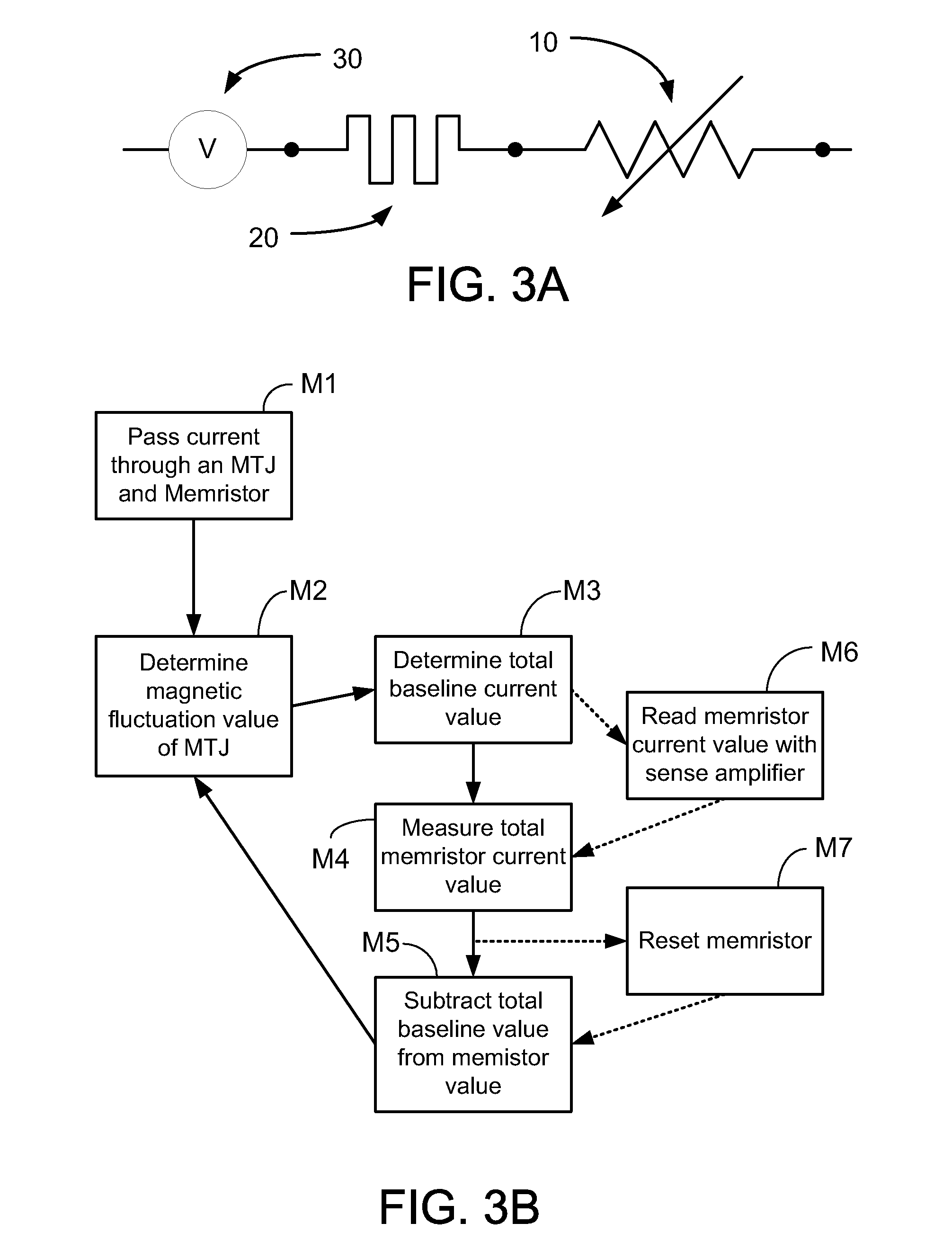
Magnetic Tunnel Junction and Memristor Apparatus
InactiveUS20100109656A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesHigh resistanceMagnetic memory
A magnetic memory device includes a magnetic tunnel junction having a free magnetic layer having a magnetization orientation that is switchable between a high resistance state magnetization orientation and a low resistance state magnetization orientation and a memristor solid state element electrically coupled to the magnetic tunnel junction. The memristor has a device response that is an integrated voltage versus an integrated current.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
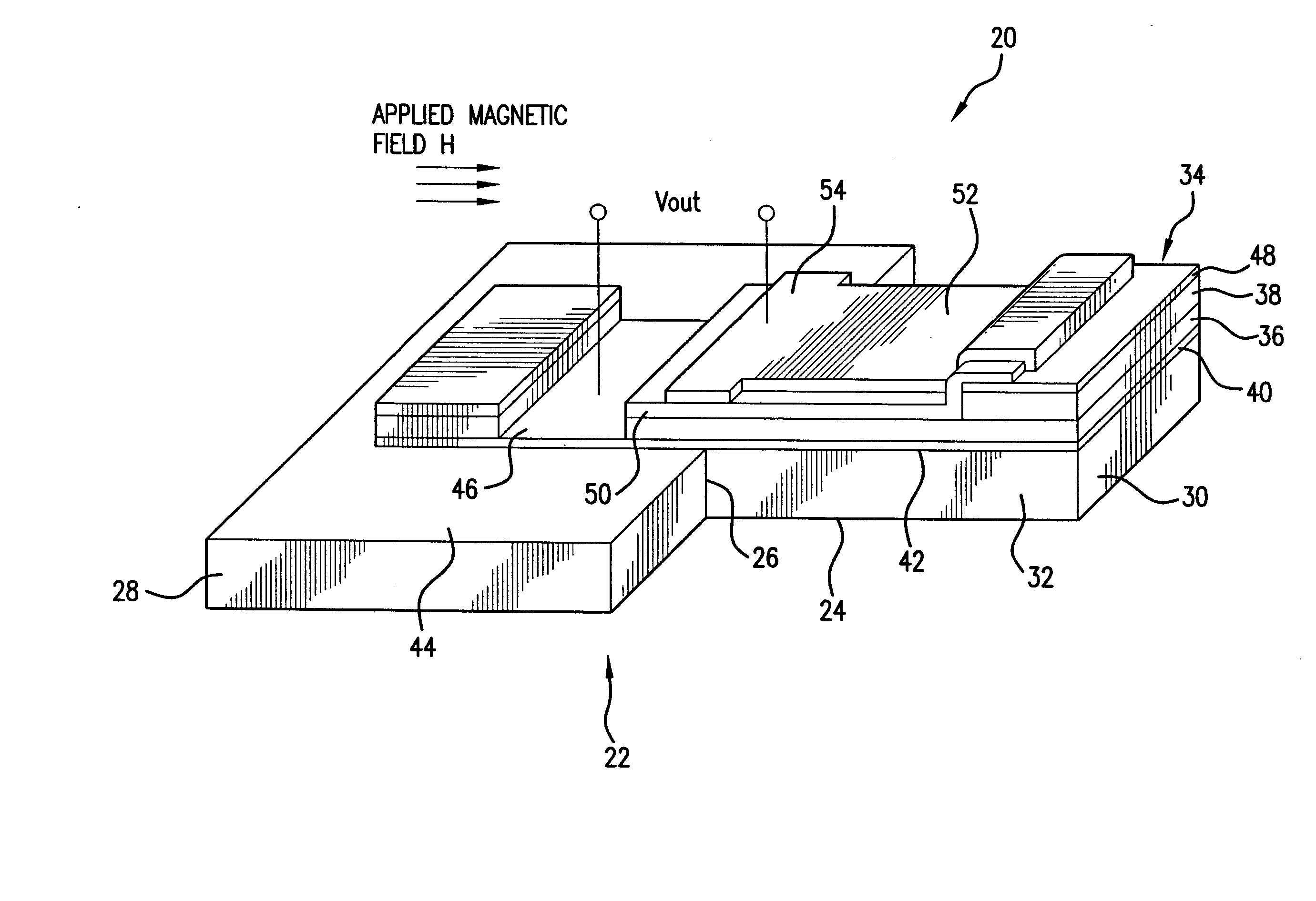
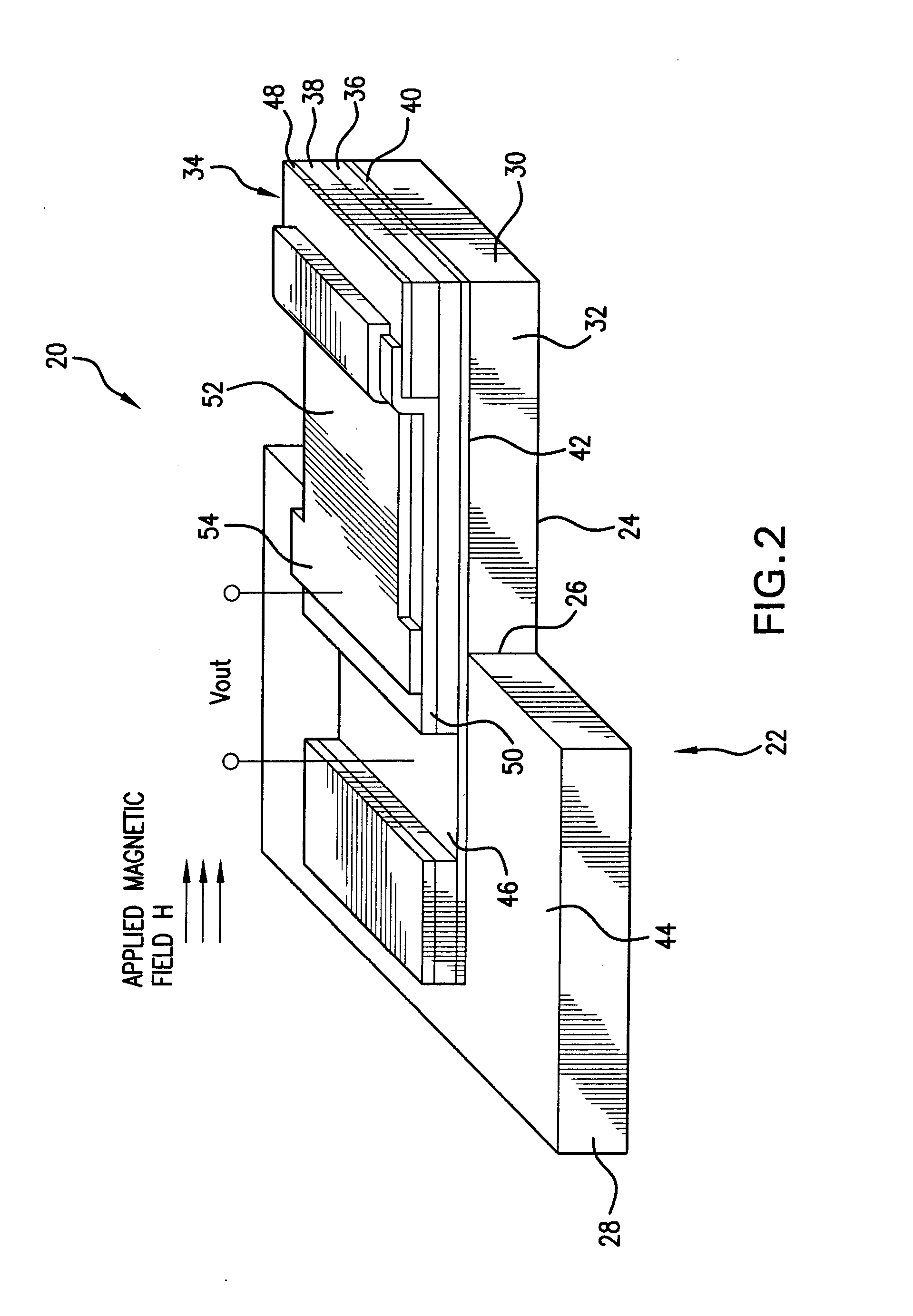
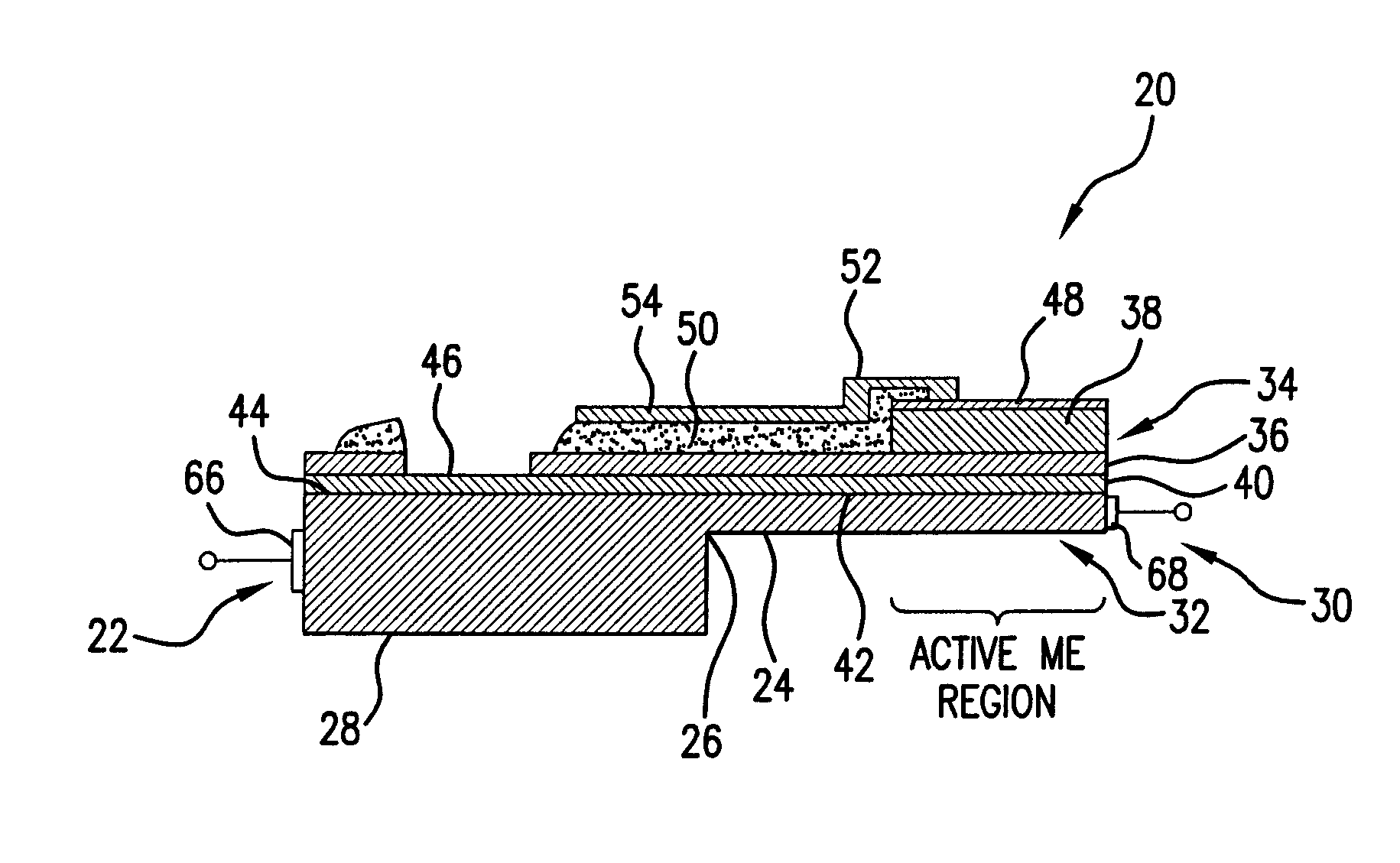
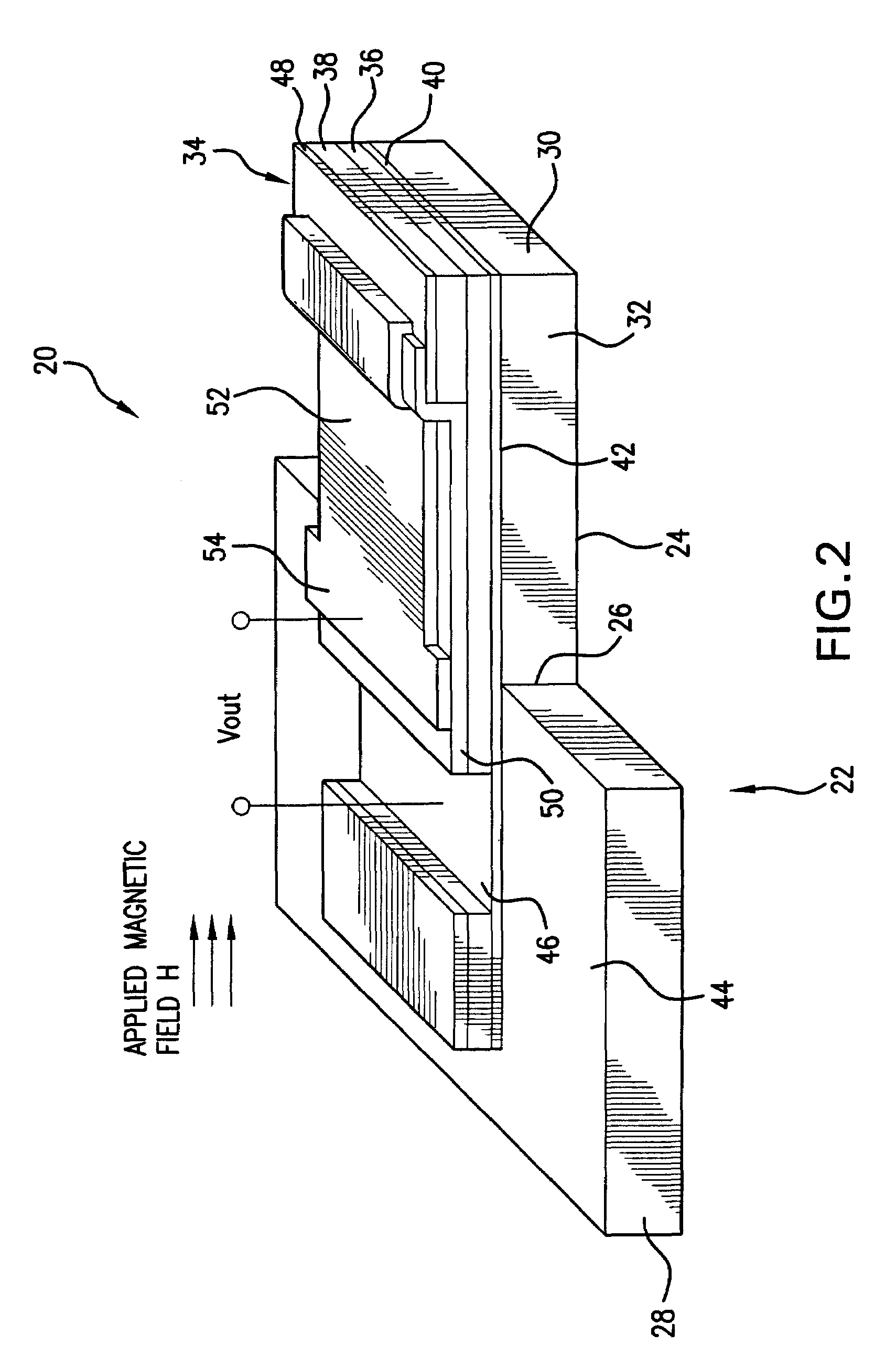
High sensitivity, passive magnetic field sensor and method of manufacture
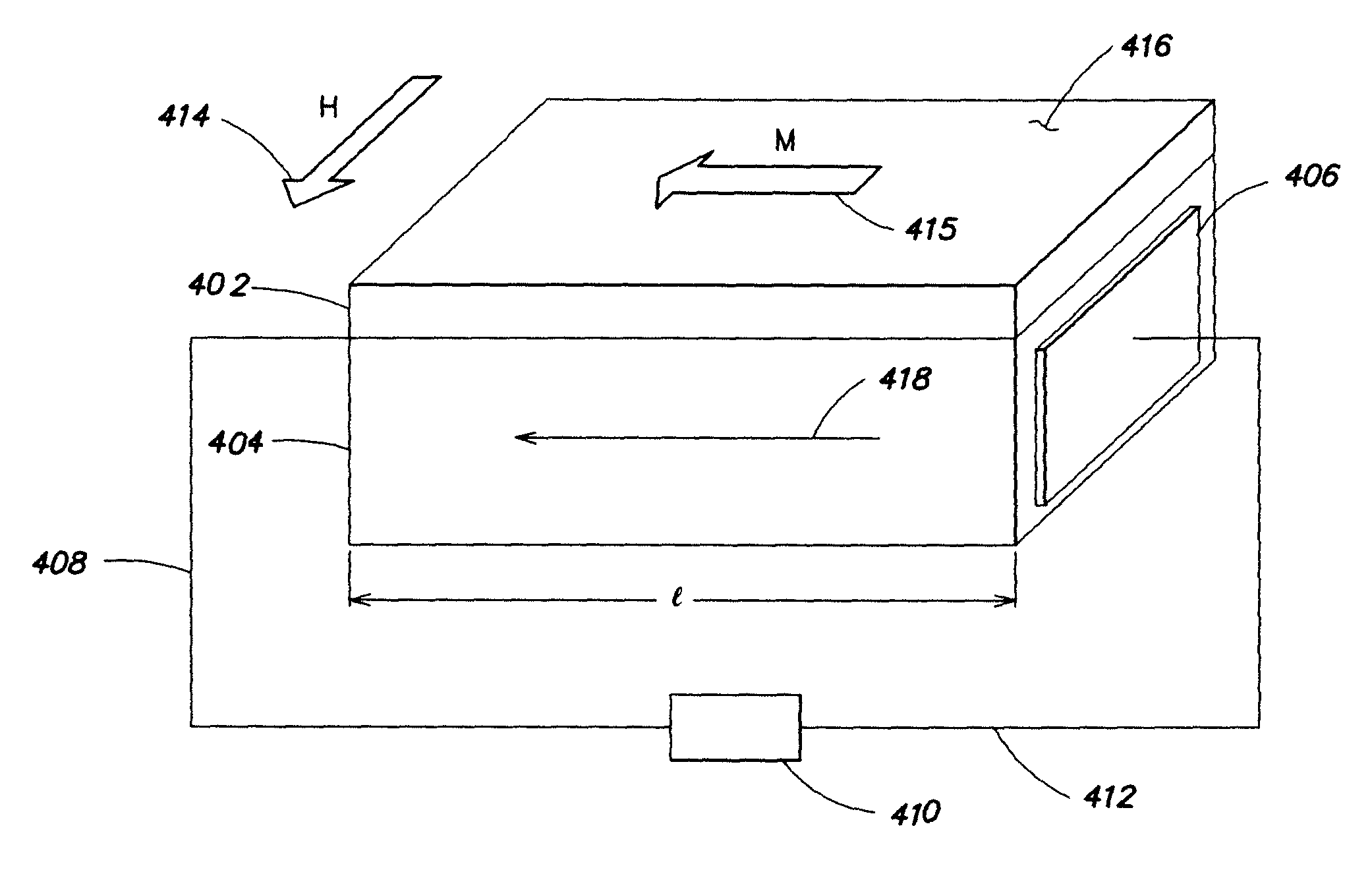
A magnetic field sensor comprises one or more magnetic layers of magnetostrictive material that is mechanically bonded to one or more layers of electroactive material. When a magnetic field is applied to the device, it rotates the magnetization that is present in the in the magnetostrictive material thereby generating a magnetostrictive stress in the material. The magnetostrictive stress generated by this layer, in turn, stresses the piezoelectric layer to which the magnetostrictive layer is bonded. In order to increase sensitivity, the voltage across the piezoelectric material is measured in a direction that is parallel to the plane in which the magnetization in the magnetic material rotates.
Owner:FERRO SOLUTIONS
Self-compensating magnetoelastic torque sensor system
InactiveUS8001849B2Improve reliabilityWork measurementMagnetostrictive property measurementsHigh magnetic field strengthMagnetic source
A magnetic torque transducer arrangement for self-compensating effects of external magnetic sources and temperature offset includes a shaft with at least one magnetized zone, at least one active magnetic field sensor and at least one passive magnetic field sensor disposed in such a way that the active field sensor is always in a position with higher magnetic field strength arising from applied torque than that of the passive sensor. Passive field sensors may also be placed on both sides of the active field sensor, or on only one side of the active field sensor. The transducer output is obtained by subtracting the output of the passive field sensors from that of the active field sensor, thus canceling out the effect of the interfering magnetic field flux and temperature offset on the torque transducer, and partially filtering out the temperature sensitivity drift and rotational dependant signal.
Owner:WENG WENSHENG
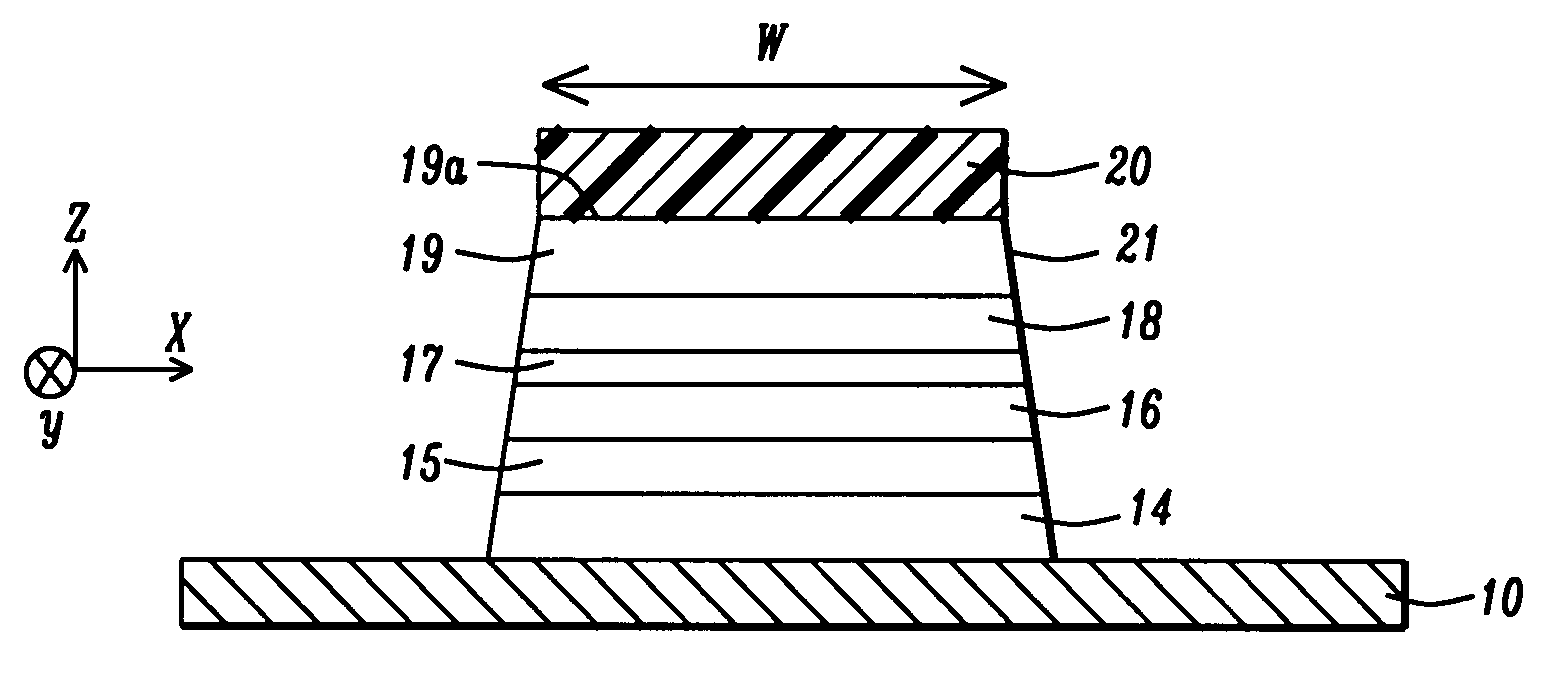
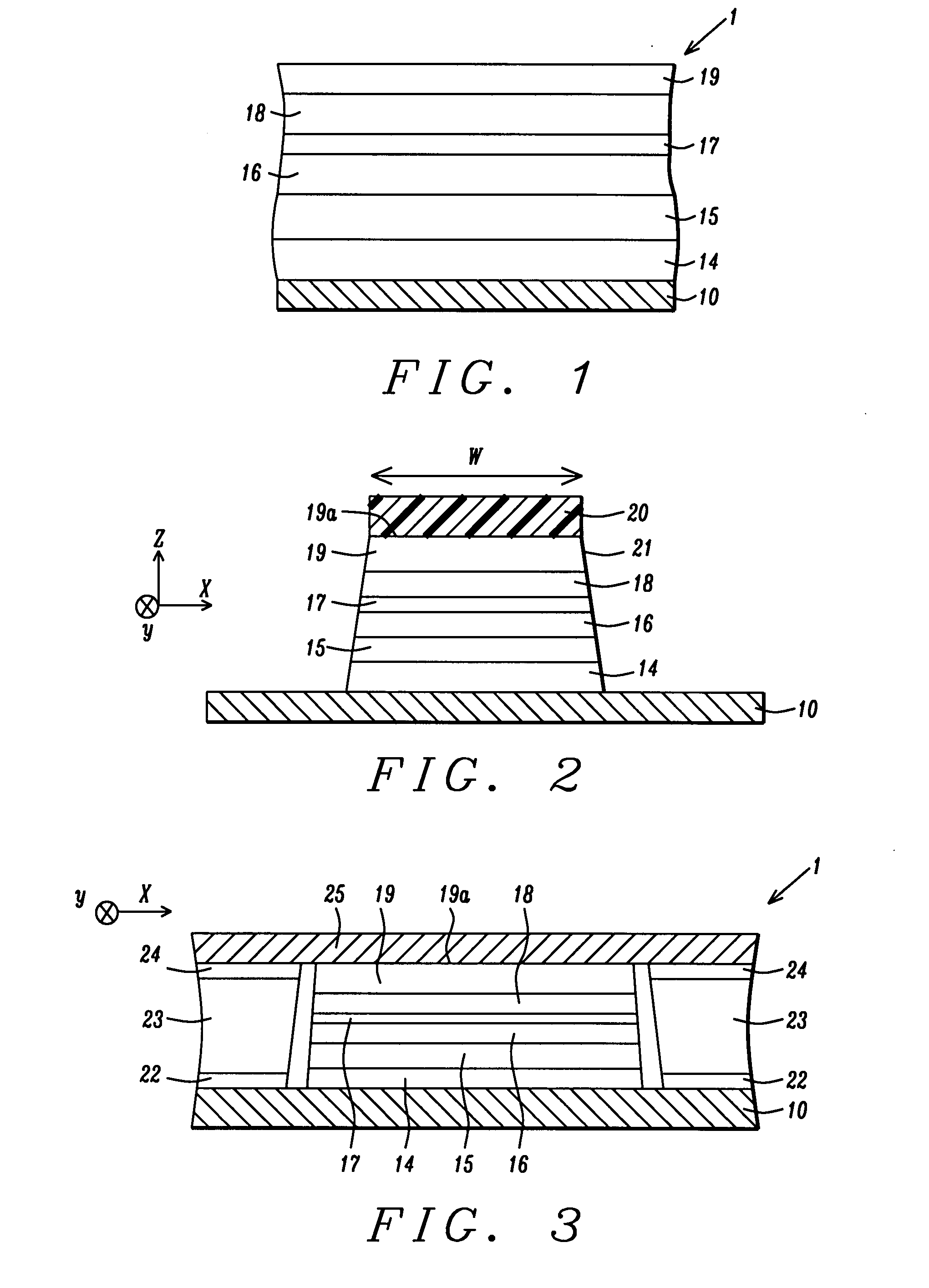
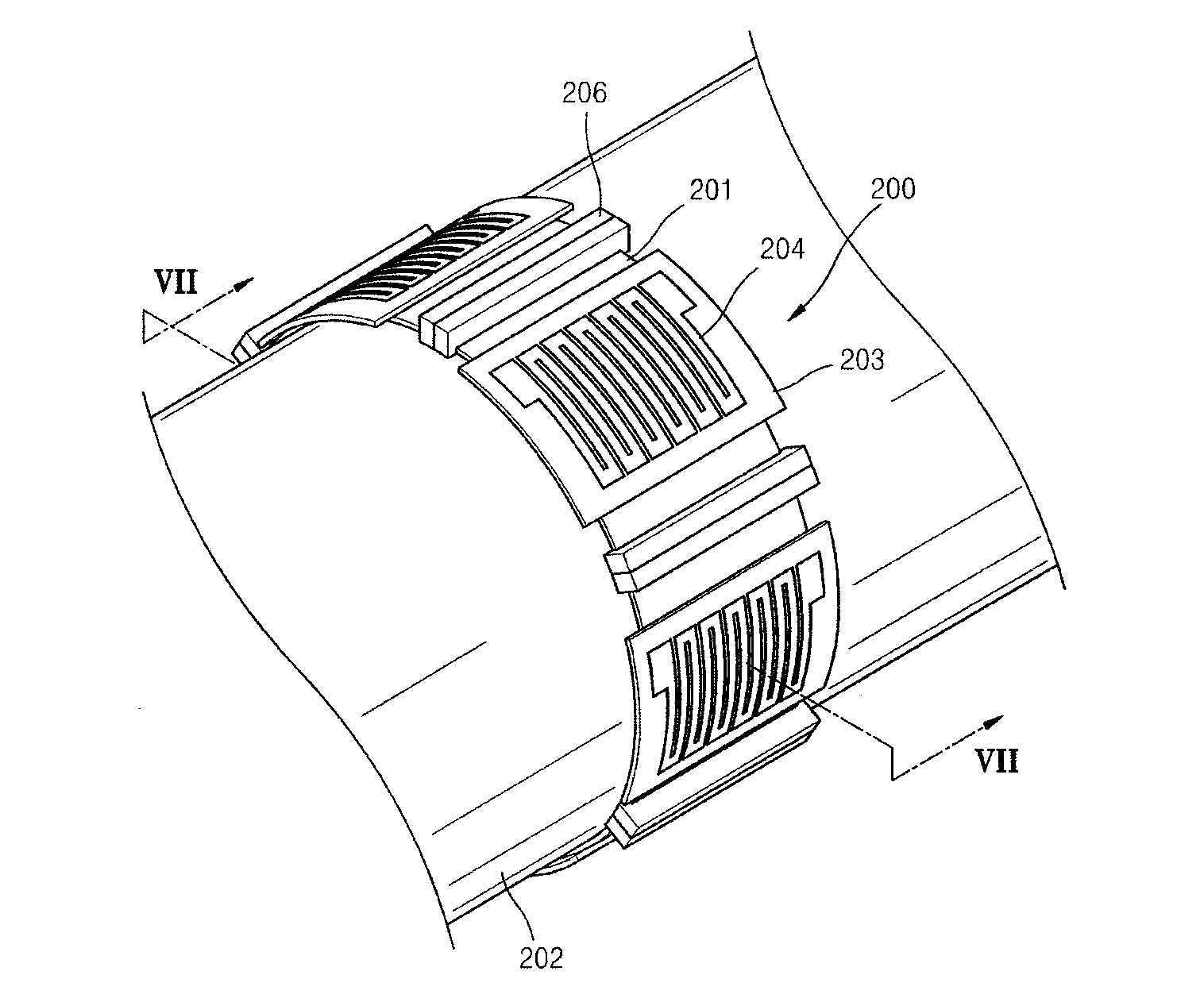
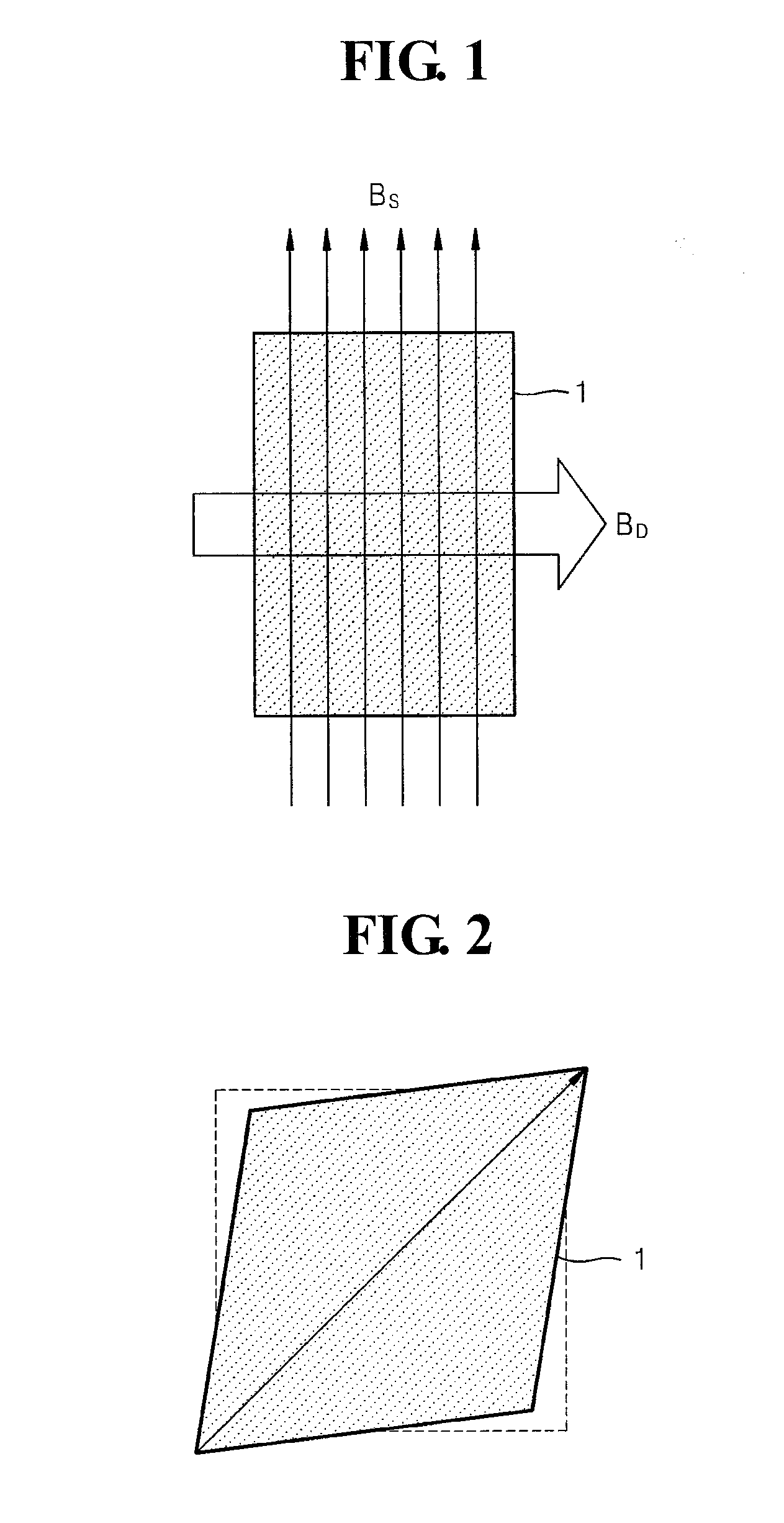
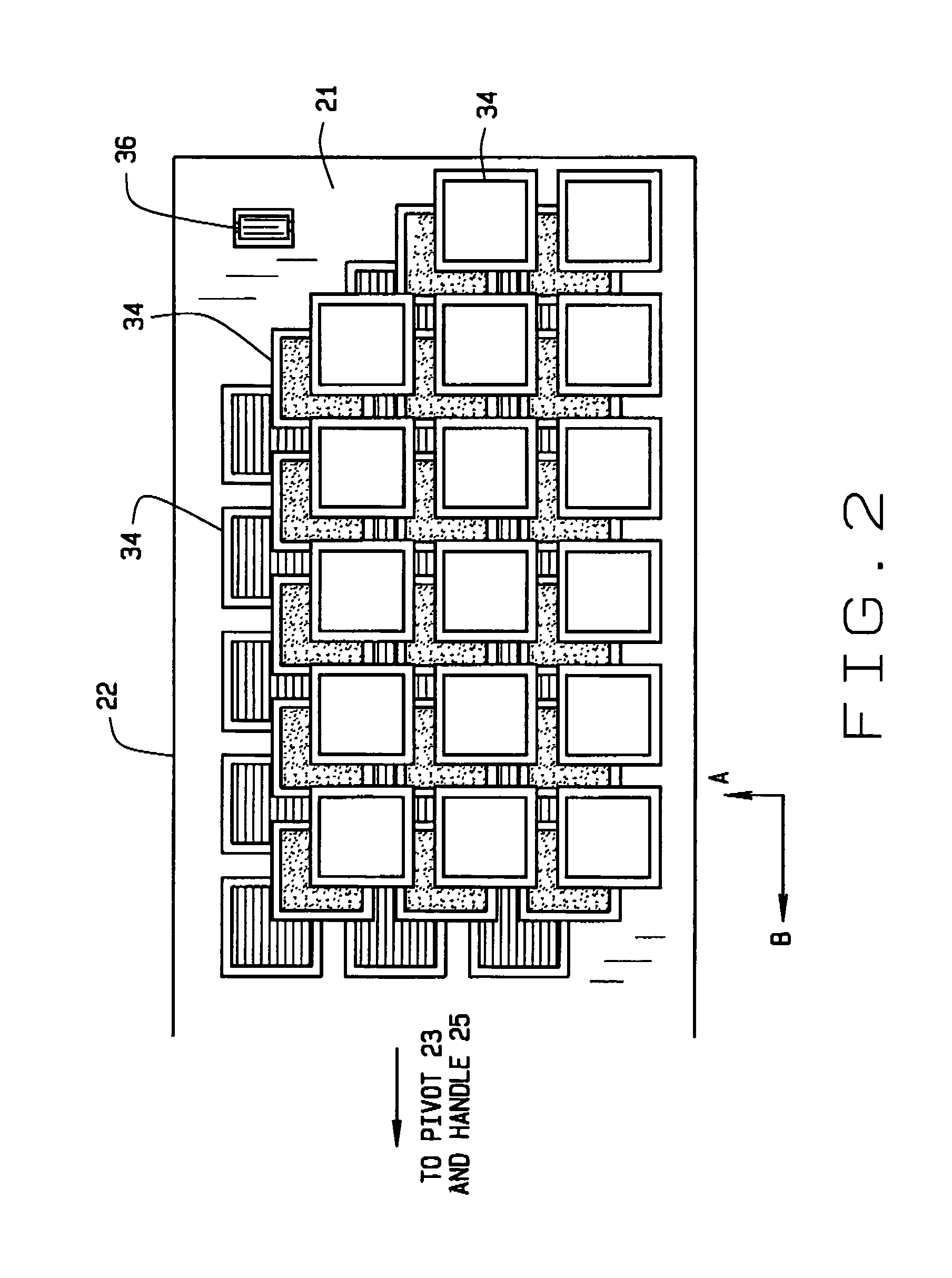
Segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer, apparatus for diagnosing structural fault by using the same, and method of operating the same
ActiveUS20100259252A1Accurate detectionDirection is limitedAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMagnetsPatch arrayMeander
A segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer capable of generating a high frequency shear wave in a structure such as a rod or a pipe, a structural fault diagnosing apparatus including the segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer, and a method of operating the segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer are shown. The segmented magnetostrictive patch array transducer includes a plurality of magnetostrictive patches attached along a circumference of a rod member; a plurality of insulators that are disposed on the magnetostrictive patches; a plurality of meander coils, each of the meander coils comprising a plurality of coil lines extending along the circumference direction of the rod member on each of the insulators, wherein a current flows through adjacent coil lines in opposite directions to one another; and a plurality of magnets that respectively form a magnetic field along the circumferential direction of the rod member on the magnetostrictive patches.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Energy harvester utilizing external magnetic field
InactiveUS20100253089A1Small and lightEfficient couplingTransformersMachines/enginesInertial massEnergy harvester
Apparatus and method for harvesting energy from the environment and / or other external sources and converting it to useful electrical energy. The harvester does not contain a permanent magnet or other local field source but instead relies on the earth's magnetic field of another source of a magnetic field that is external to the sensing device. One advantage of these new harvesters is that they can be made smaller and lighter than energy harvesters that contain a magnet and / or an inertial mass.
Owner:FERRO SOLUTIONS
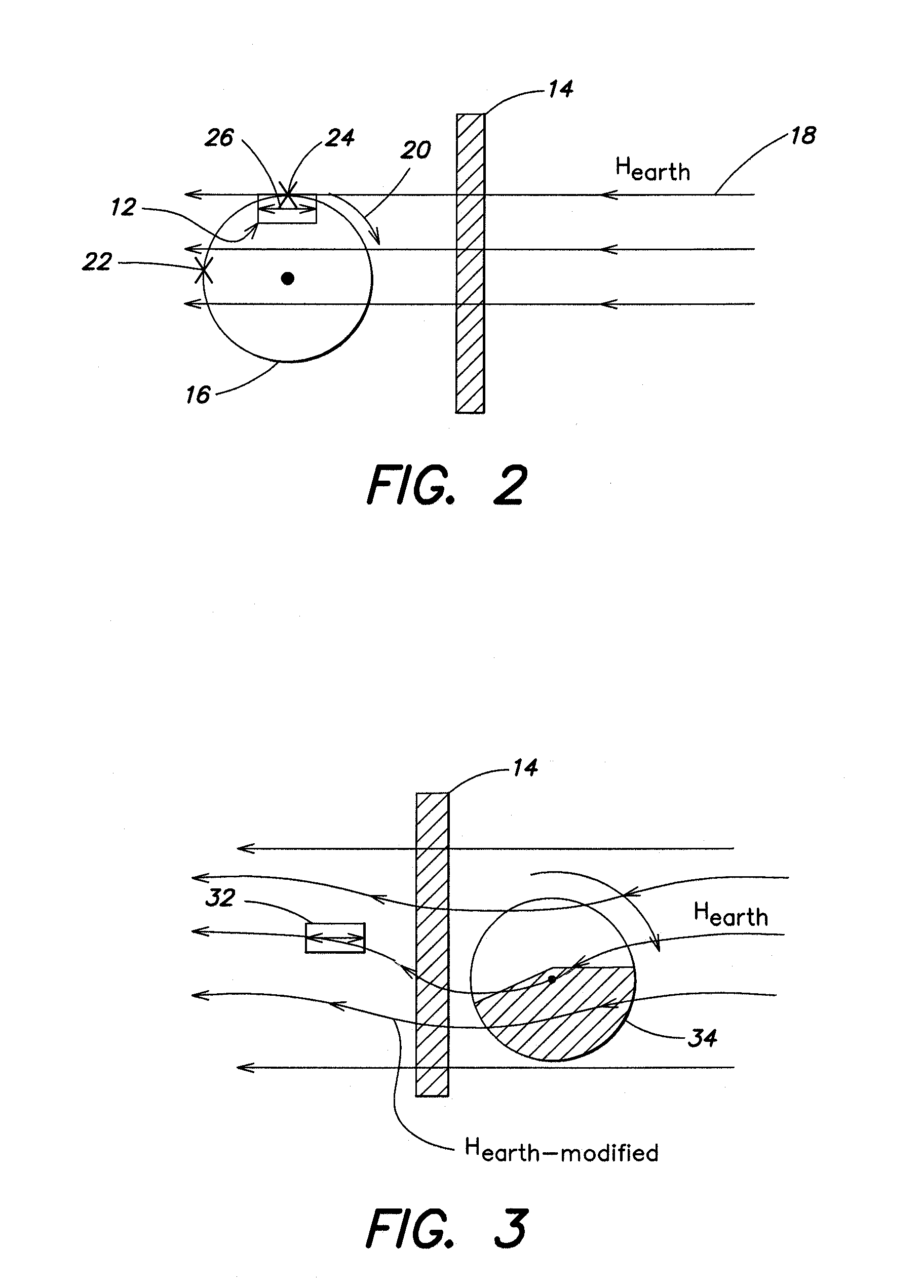
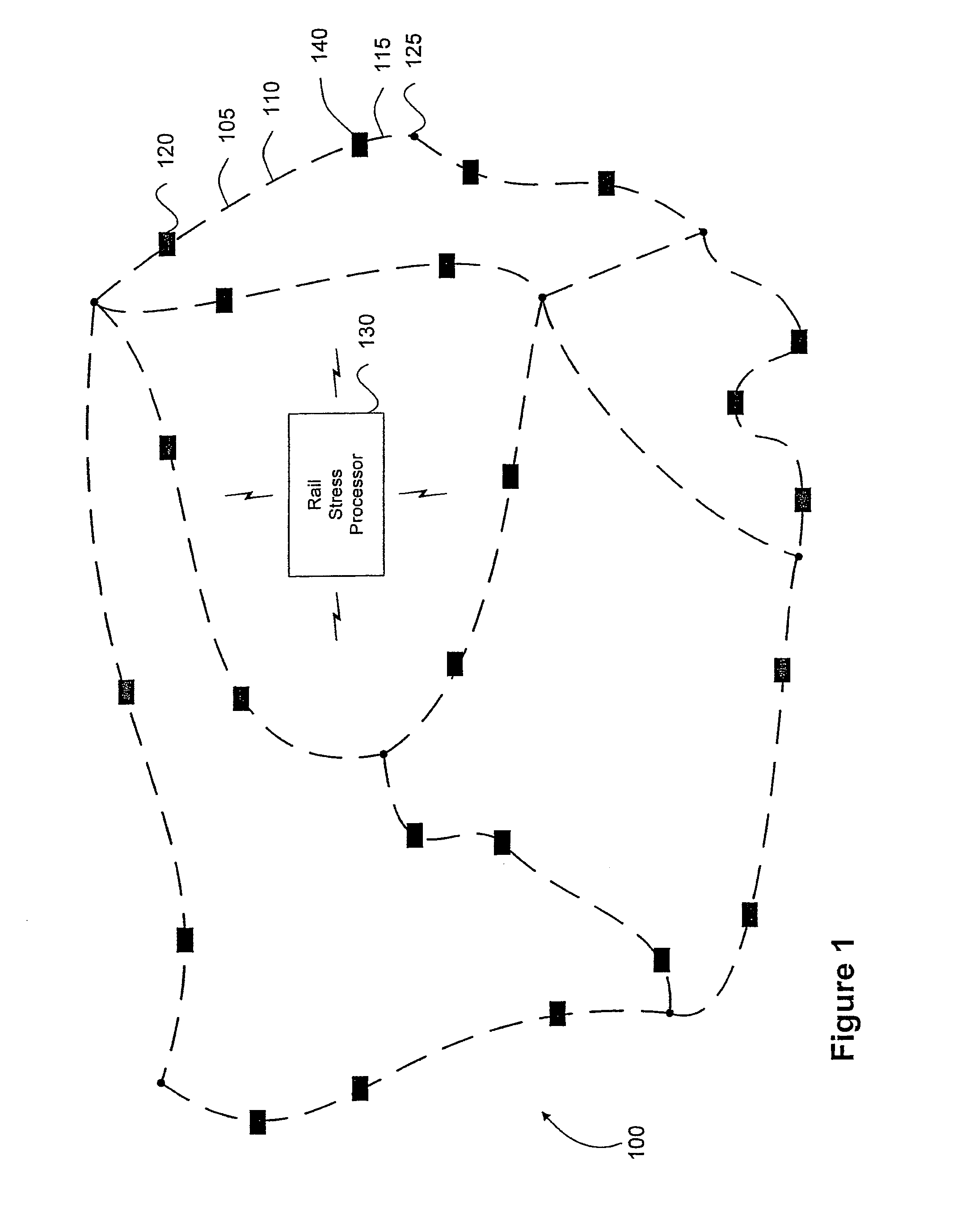
Stress monitoring system for railways
A rail stress monitoring system is disclosed. This system includes a sensor module that further includes a sensing device that is adapted to be mountable directly on a length of rail. The sensing device further includes a generally flat metal shim and at least one, and typically two or more, sensors mounted on one side of the shim. The sensors are typically strain gauges, which are mounted on the shim in a specific, predetermined configuration. At least one data acquisition module is in electrical communication with the sensing device and a data processing module receives and processes information gathered by data acquisition module.
Owner:SALIENT SYST
Self-compensating magnetoelastic torque sensor system
InactiveUS20100242626A1Improve reliabilityWork measurementMagnetostrictive property measurementsHigh magnetic field strengthMagnetic source
An improved magnetic torque transducer arrangement for self-compensating effects of external magnetic sources and temperature offset comprises a shaft with at least one magnetized zone, at least one active magnetic field sensor and at least one passive magnetic field sensor disposed in such a way that active field sensor always in a position with higher magnetic field strength arise from applied torque than that of passive sensor. Passive field sensors may also be placed in both sides of the active field sensor, or on one side of active field sensor only. The transducer output is obtained by subtract the output of passive field sensors from that of active field sensor thus cancel out the effect of interfering magnetic field flux and temperature offset on the torque transducer, and partially filter out temperature sensitivity drift and rotational dependant signal. The sensitivity of active and passive field sensors can also be electrically matched by calibrating them in a uniform magnetic field, thus a completely common mode rejection can be achieved. The sensor arrangements may also be utilized in other type of sensors that extract changes in magnetic fields to indirectly detect direction, speed, presence, force, linear position, or angle to cancel out interfering magnetic field and temperature offset effect.
Owner:WENG WENSHENG
Electromagnet inspection apparatus and method
ActiveUS20120306483A1Less sensitiveEfficient detectionPermeability measurementsUsing electrical meansPartial saturationComputer module
A method and apparatus for the inspection of electrically conductive components is described. The described apparatus comprises a sensor module having a magnetiser unit suitable for generating a variable DC magnetic field within the test component and an eddy current probe. The variable DC magnetic field and eddy current probe are configured to perform a partial saturation eddy current test upon the test component. The eddy current probe further comprises a magnetic field sensor that provides a means for measuring the permeability within the test component. Employing the magnetic field sensor provides apparatus that is more accurate and flexible in its modes of operation since such sensors provide a means for the actual permeability of a material being tested to be measured. The described methods and apparatus find particular application in the inspection of tubular components used in the oil and gas exploration and production industries.
Owner:SONOMATIC
Methods and apparatus for eddy current inspection of metallic posts
ActiveUS7026811B2Move preciselyReliable detectionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesEddy currentBiomedical engineering
An apparatus for inspecting a metallic post contoured in a single dimension for defects. The apparatus has a clamp having at least one jaw with a surface conforming to the contour to the metallic post. The conforming jaw or jaws also have a plurality of eddy current coils and the probe has at least one sensor configured to sense at least one of position or motion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ultrasensitive magnetoelectric thin film magnetometer and method of fabrication
ActiveUS7345475B2Excellent characteristicsImprove operating characteristicsDigital storageMagnetostrictive property measurementsElectricityRoom temperature
An ultrasensitive room temperature magnetoelectric thin film magnetometer is fabricated on a cantilever beam and includes an active magnetoelectric multilayer structure having a plurality of thin films formed at a region defined on the cantilever beam. Upon application of a magnetic field, the active magnetoelectric structure generates a corresponding response of an electrical nature which is a measure of a value of the applied magnetic field. The material of the cantilever beam may be removed beneath the active magnetoelectric multilayer structure to form a freestanding modification of the magnetometer with superior sensitivity. The active magnetoelectric multilayer structure is either a bi-layer structure which includes a piezoactive (piezoelectric and / or piezoresistive) thin film deposited in contact with a magnetostrictive thin film or a tri-layer active structure (in the free-standing implementation) including a piezoactive thin film sandwiched between a pair of magnetostrictive thin films.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
Robust detection of strain with temperature correction
ActiveUS7362096B2High strengthForce measurement by measuring magnetic property varationUsing electrical meansElectrical resistance and conductancePhase shifted
Owner:BWI CO LTD SA
Magnetic field sensor circuit
InactiveUS7818890B2Improve performanceLess spaceNanomagnetismRecord information storageResistive sensorsPhase shifted
A magnetic field sensor circuit comprises a first magneto-resistive sensor (Rx) which senses a first magnetic field component in a first direction to supply a first sense signal (Vx). A first flipping coil (FC1) applies a first flipping magnetic field with a periodically changing polarity to the first magneto-resistive sensor (Rx) to cause the first sense signal (Vx) to have alternating different levels synchronized with the first flipping magnetic field. A second magneto -resistive sensor (Ry) senses a second magnetic field component in a second direction different than the first direction to supply a second sense signal (Vy). A second flipping coil (FC2) applies a second flipping magnetic field with a periodically changing polarity to the second magneto -resistive sensor (Ry) to cause the second sense signal (Vy) to have an alternating different levels synchronized with the second flipping magnetic field. The first flipping magnetic field and the second flipping magnetic field have a phase shift. A differential amplifier (AMP1) receives the first sense signal (Vx) and the second sense signal (Vy) to obtain a difference signal (Vd). A first synchronous demodulator (DEM1) receives the difference signal (Vd) and a first switching signal (Q1) being phase locked to the alternating different levels of the first sense signal (Vx) to supply a first output signal (Vox) indicating the first magnetic field component. A second synchronous demodulator (DEM2) receives the difference signal (Vd) and a second switching signal (Q2) being phase locked to the alternating different levels of the second sense signal (Vy) to supply a second output signal (Voy) indicating the second magnetic field component.
Owner:TITAN INTELLIGENCE TECH LTD
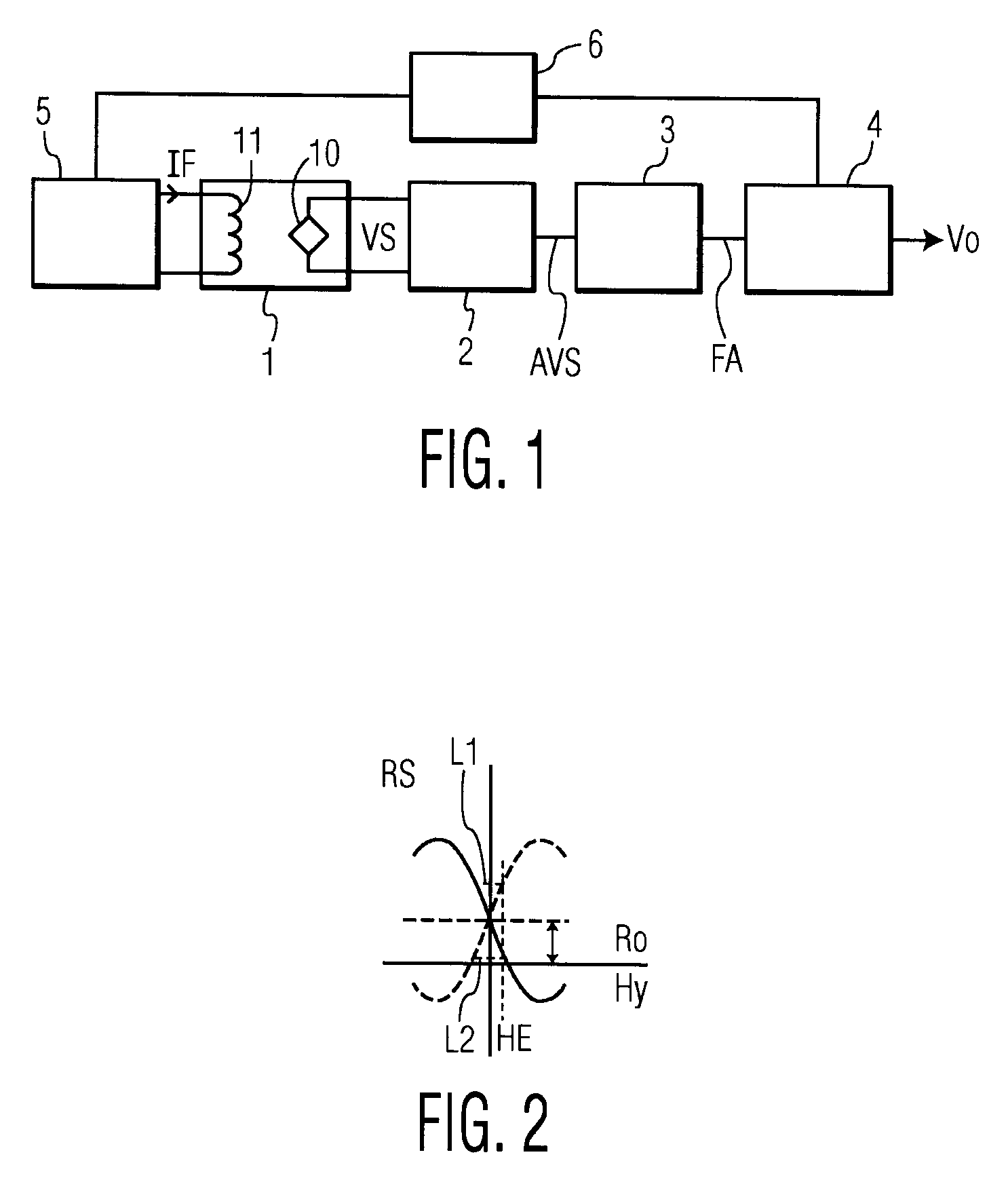
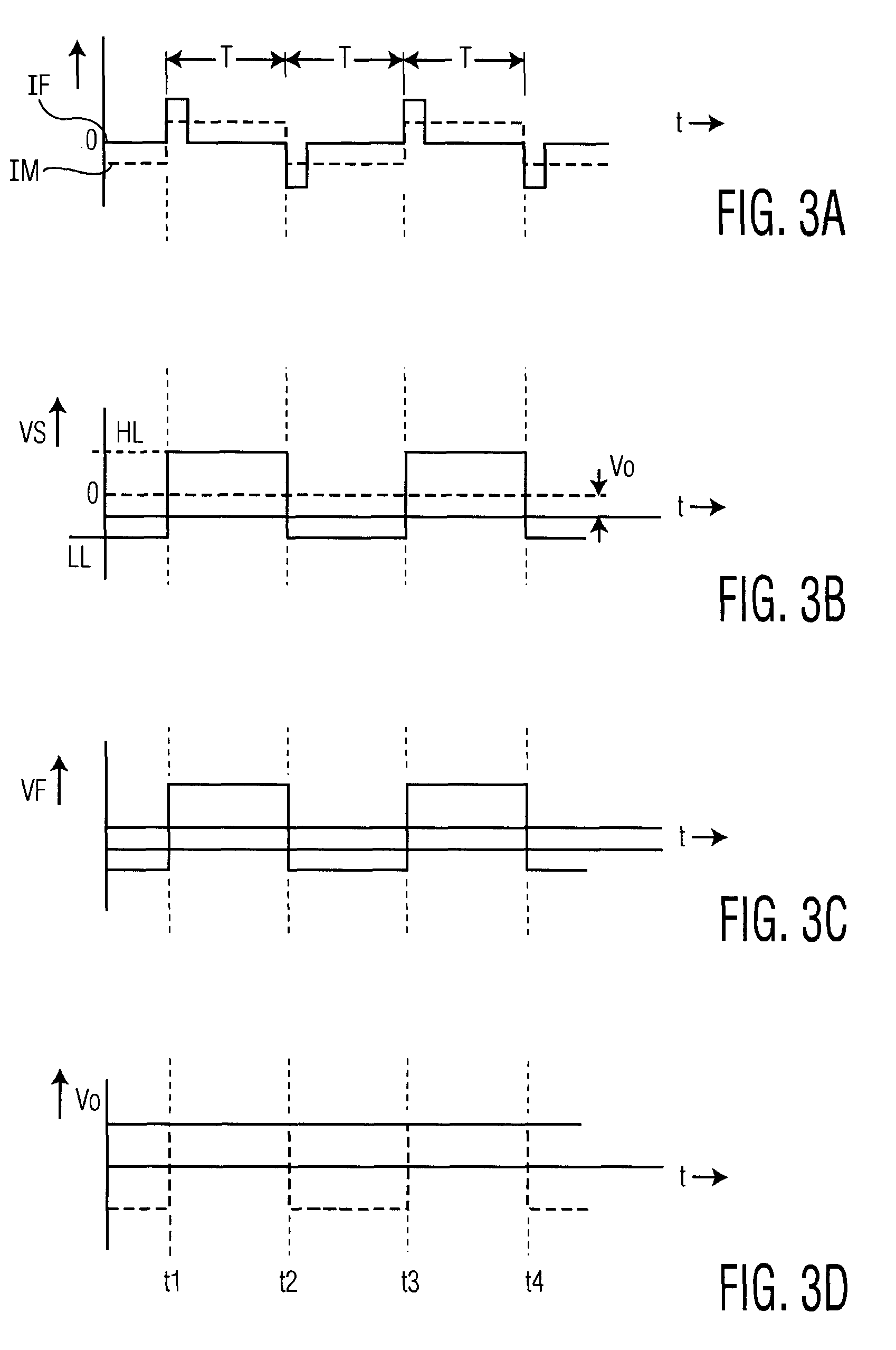
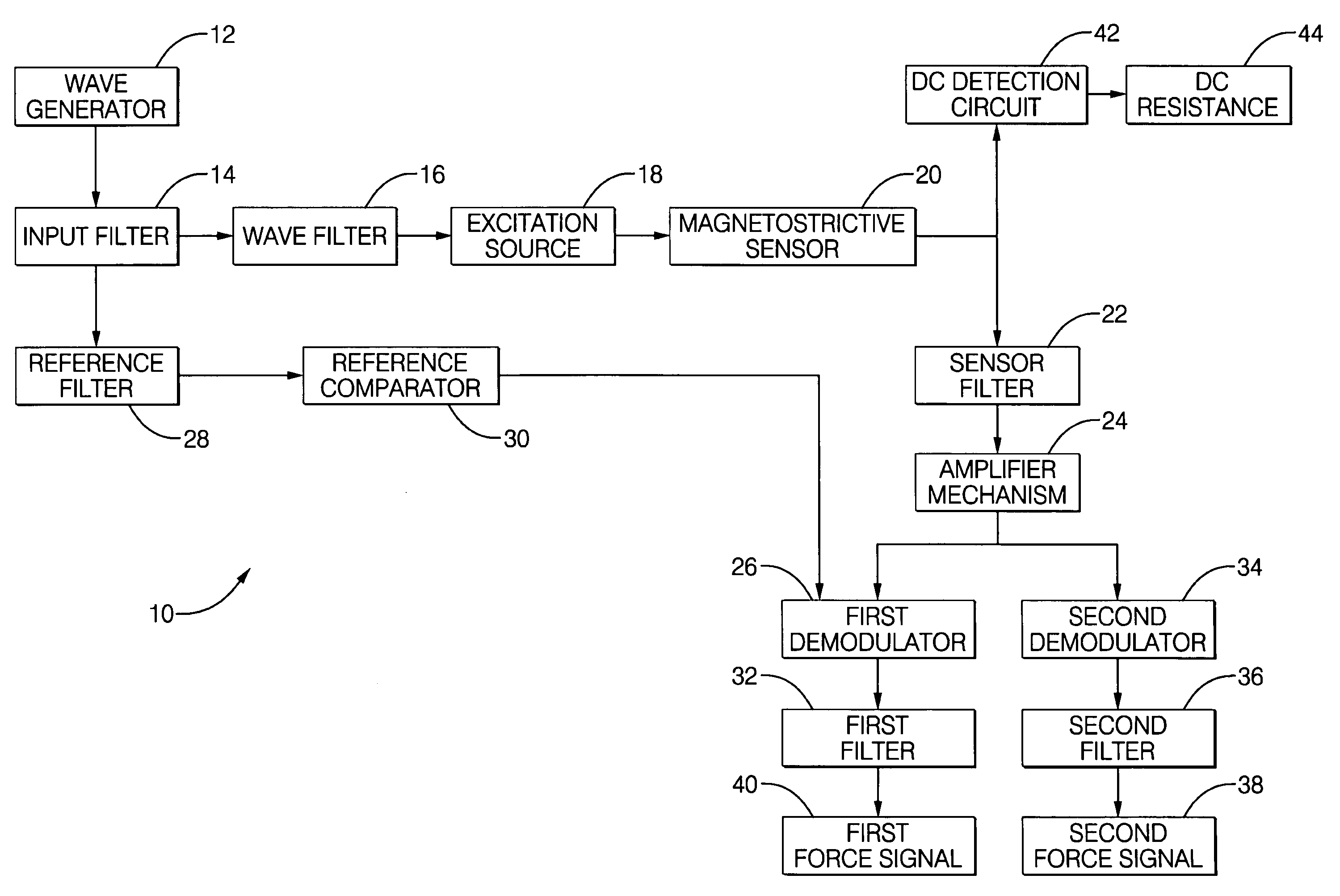
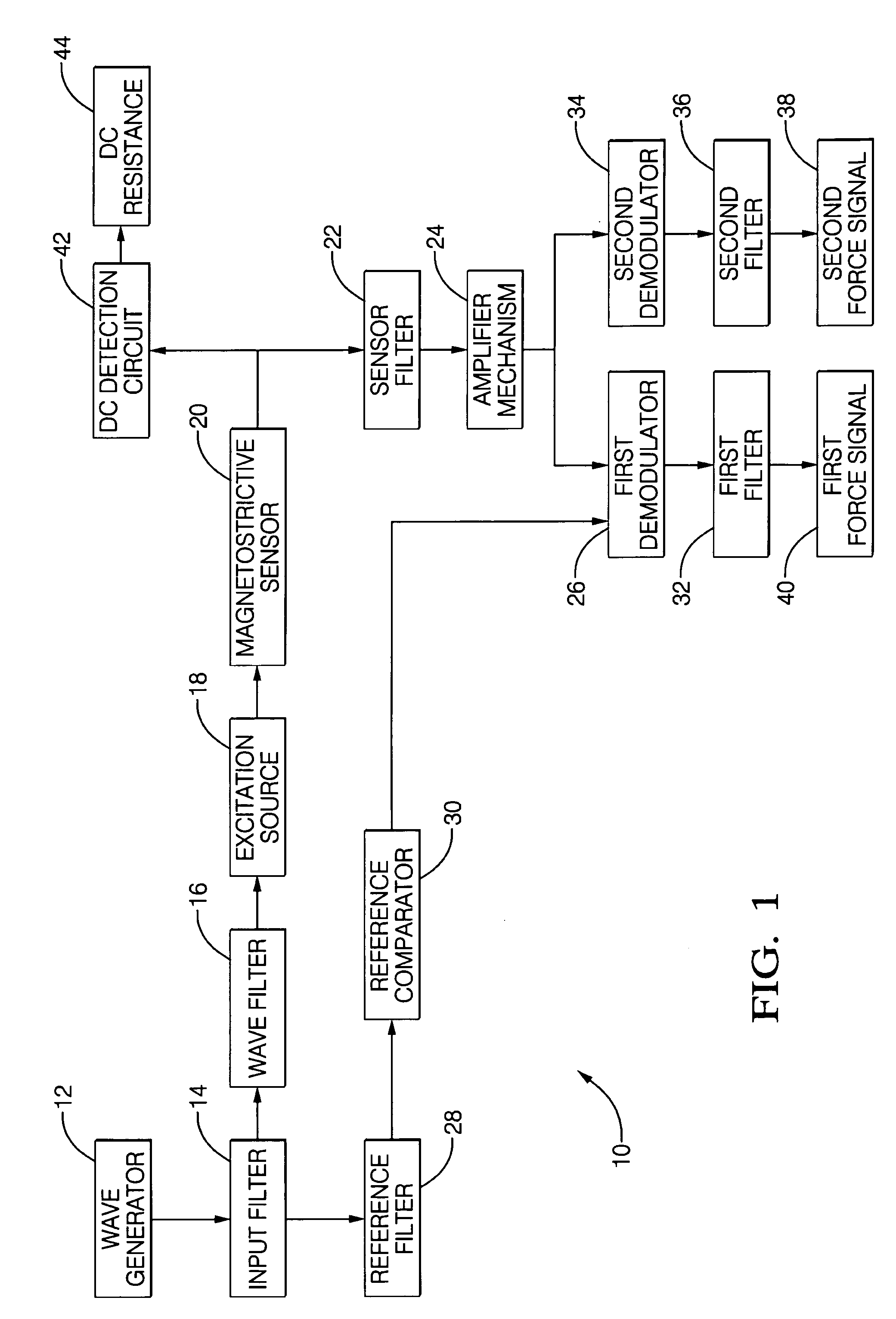
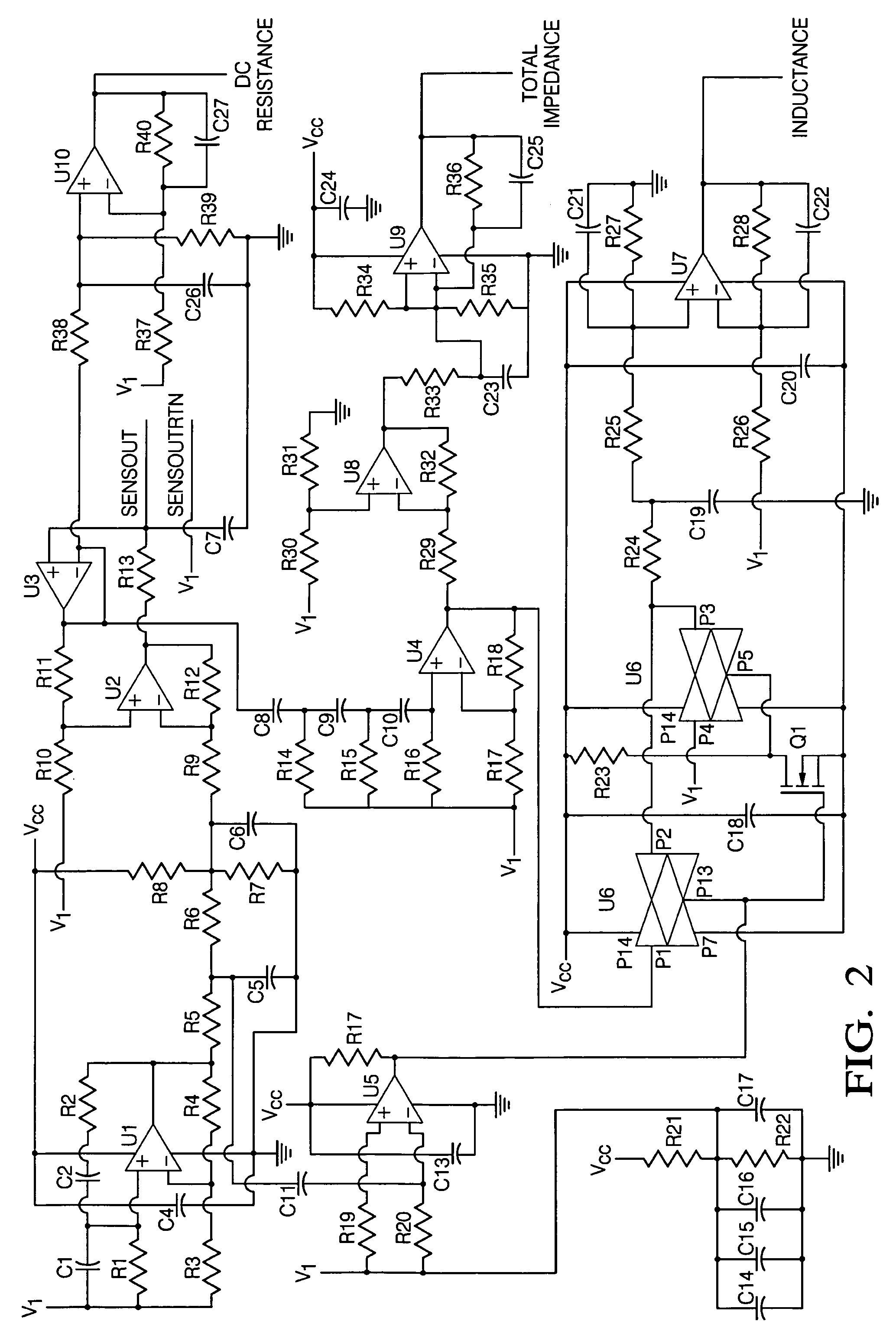
Robust detection of strain with temperature correction
ActiveUS20070096724A1High strengthForce measurementUsing electrical meansElectrical resistance and conductancePhase shifted
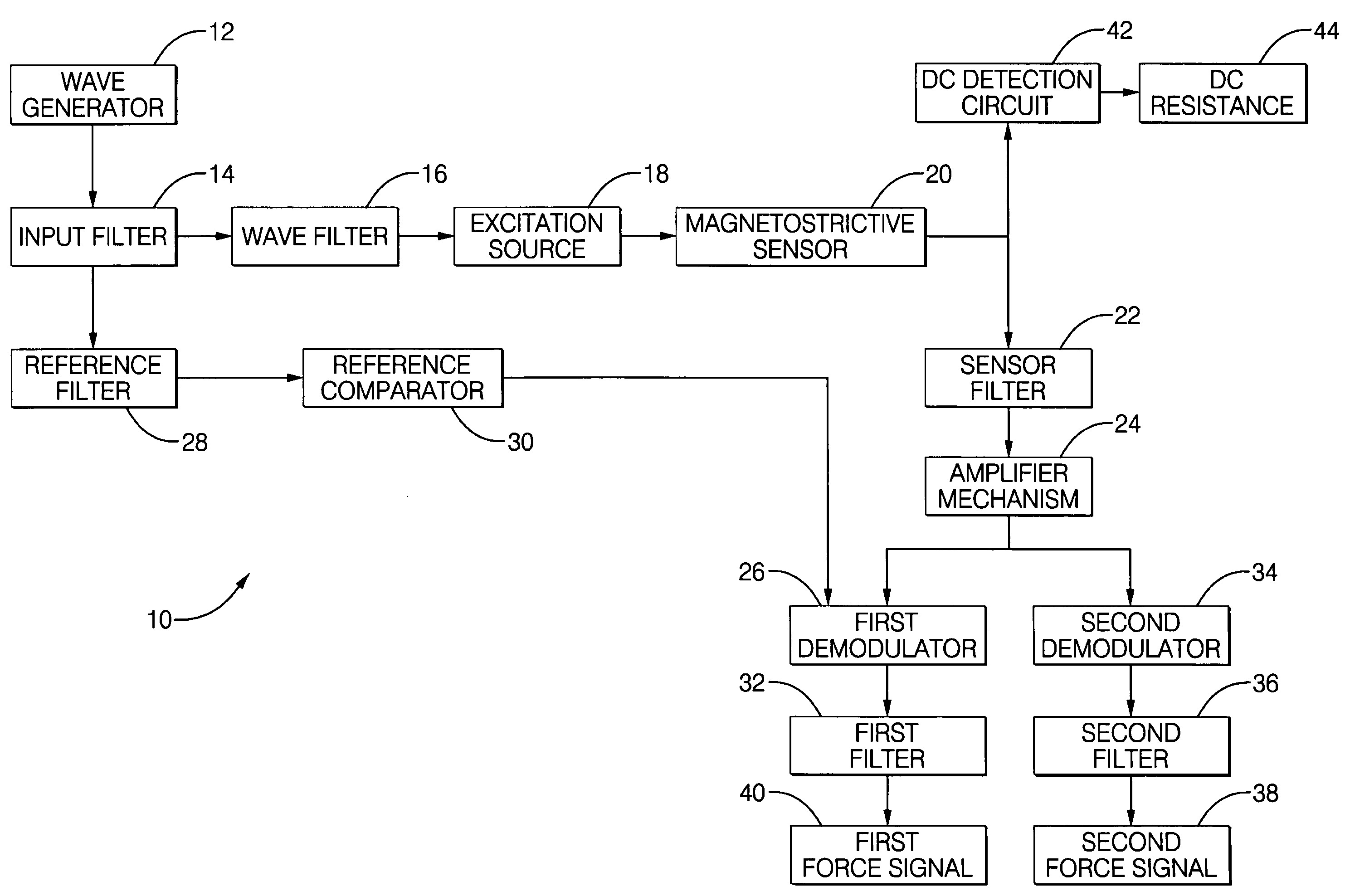
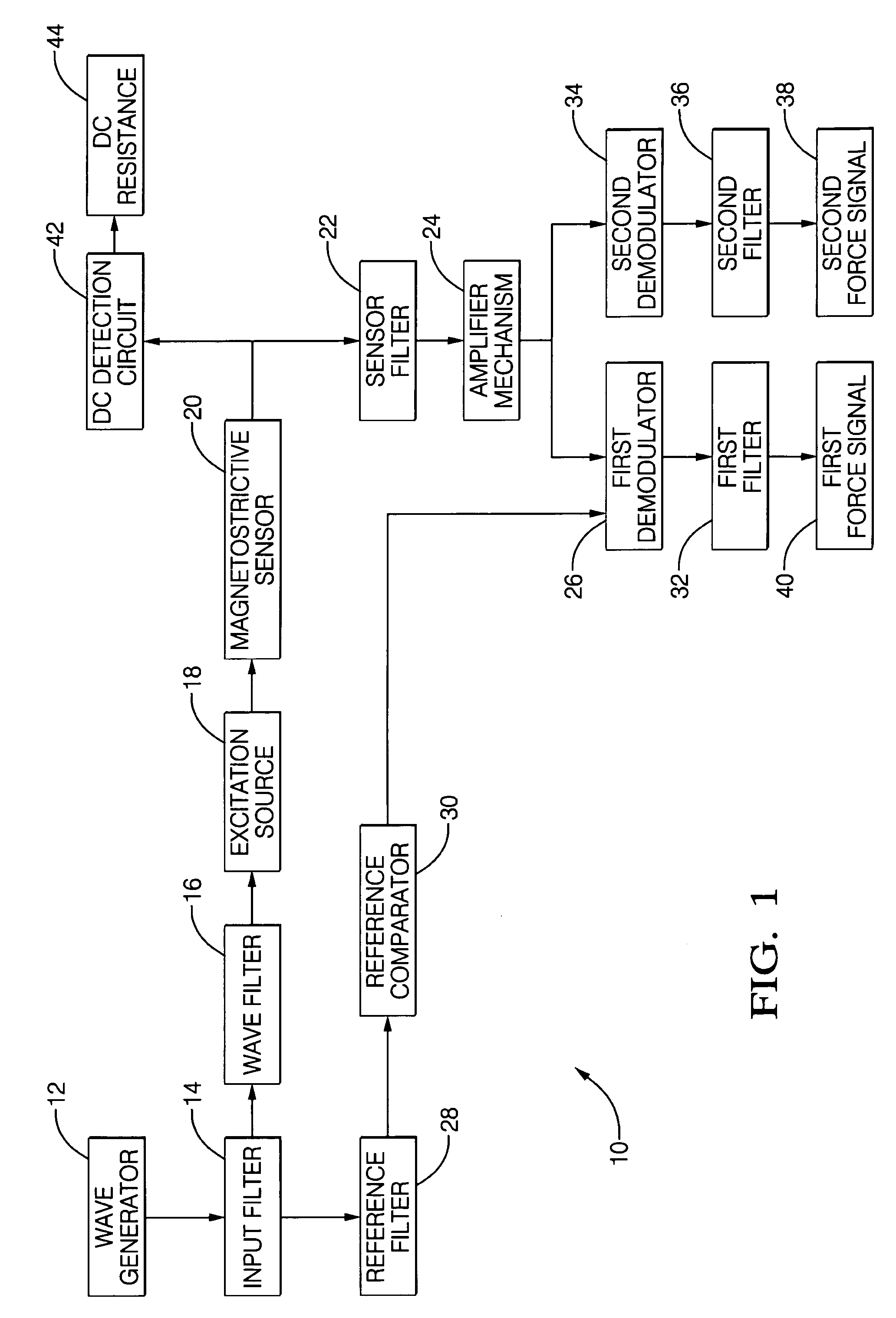
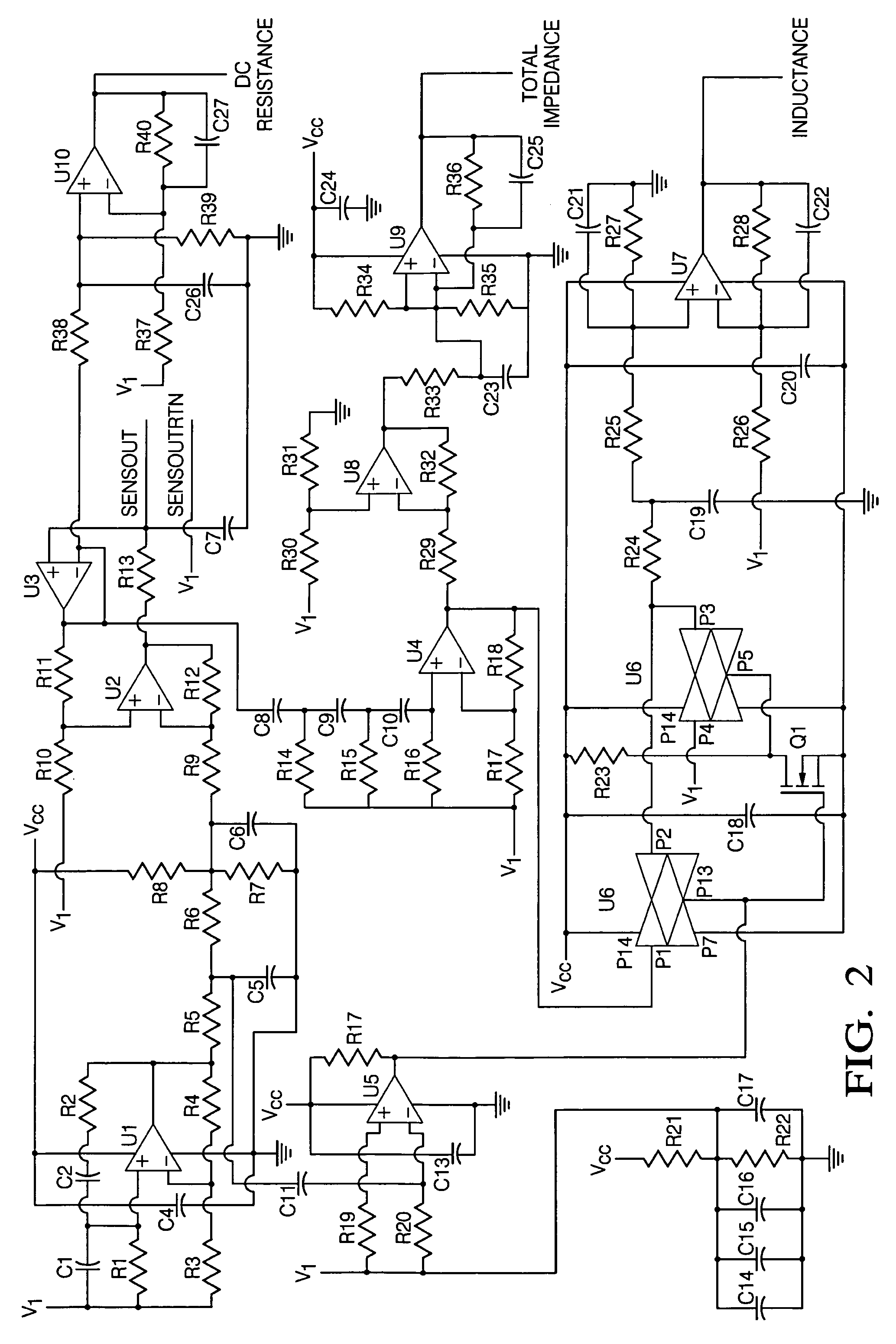
An apparatus (10) is set forth for measuring a return signal of a magnetostrictive sensor (20) that detects a force, torque, or pressure. The return signal includes noise, a DC resistance (44), an AC resistance and an inductance and the inductance is shifted ninety degrees from the AC resistance. The apparatus (10) includes a sensor filter (22) to remove the noise from the return signal. A sensor filter (22) shifts the return signal and more specifically, the inductance by an additional angle and the sum of the additional angle and the ninety degrees phase shift is defined as the final detection angle. To detect the inductance at the final detection angle, a wave filter (16) and a reference filter (28) shifts a reference signal by the final detection angle to trigger a first demodulator (26) to detect the inductance at the final detection angle. The inductance detected by the first demodulator (26) varies due to temperature. To remove the temperature from the measured inductance, the apparatus includes a DC detection circuit (42) to detect the DC resistance which is proportional to the temperature across the sensor (20). The DC resistance and the measure inductance are inserted into a correction equation to produce a corrected inductance which is independent of temperature. Instead of inductance, an AC resistance may be used in the equation.
Owner:BWI
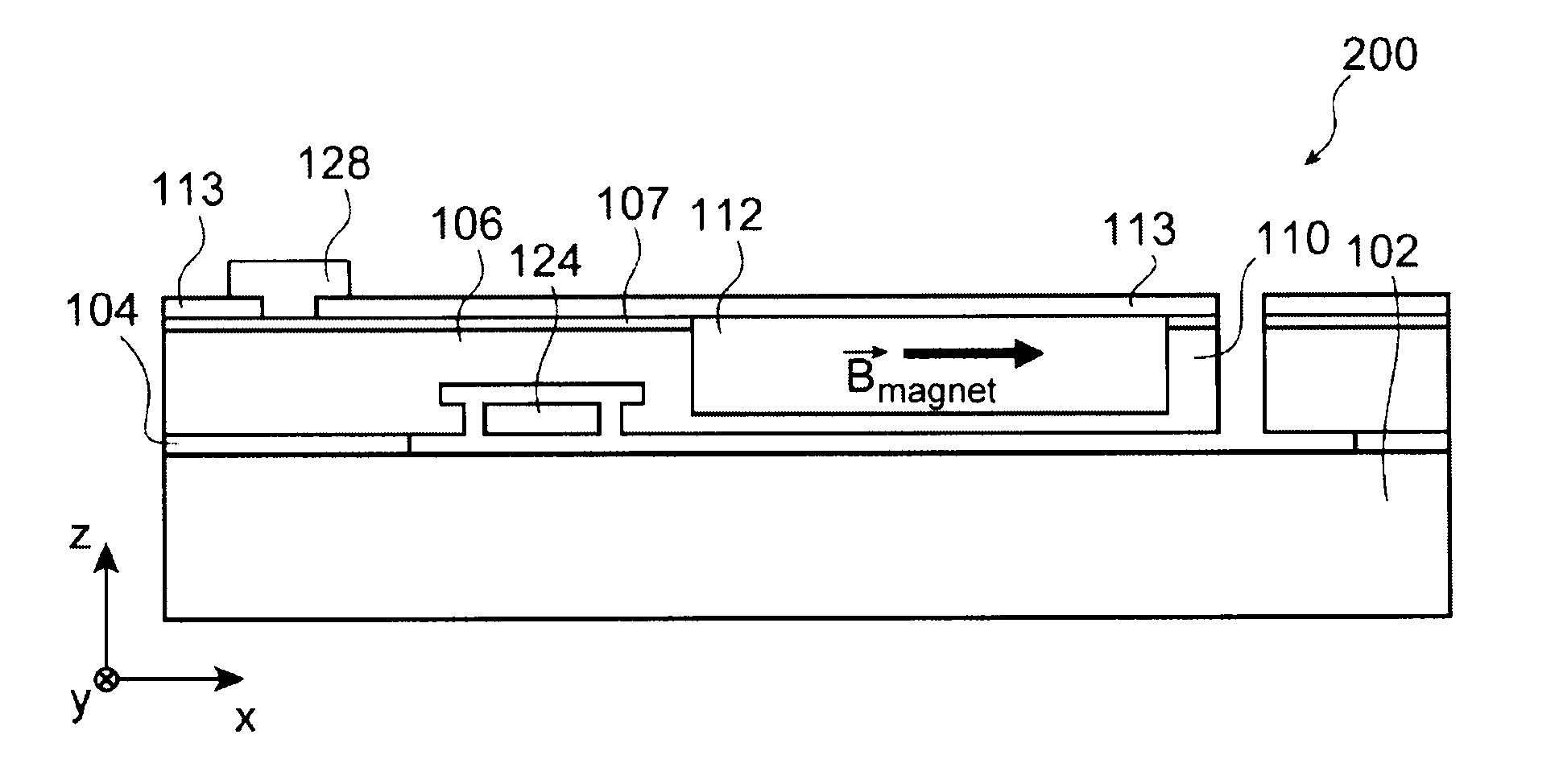
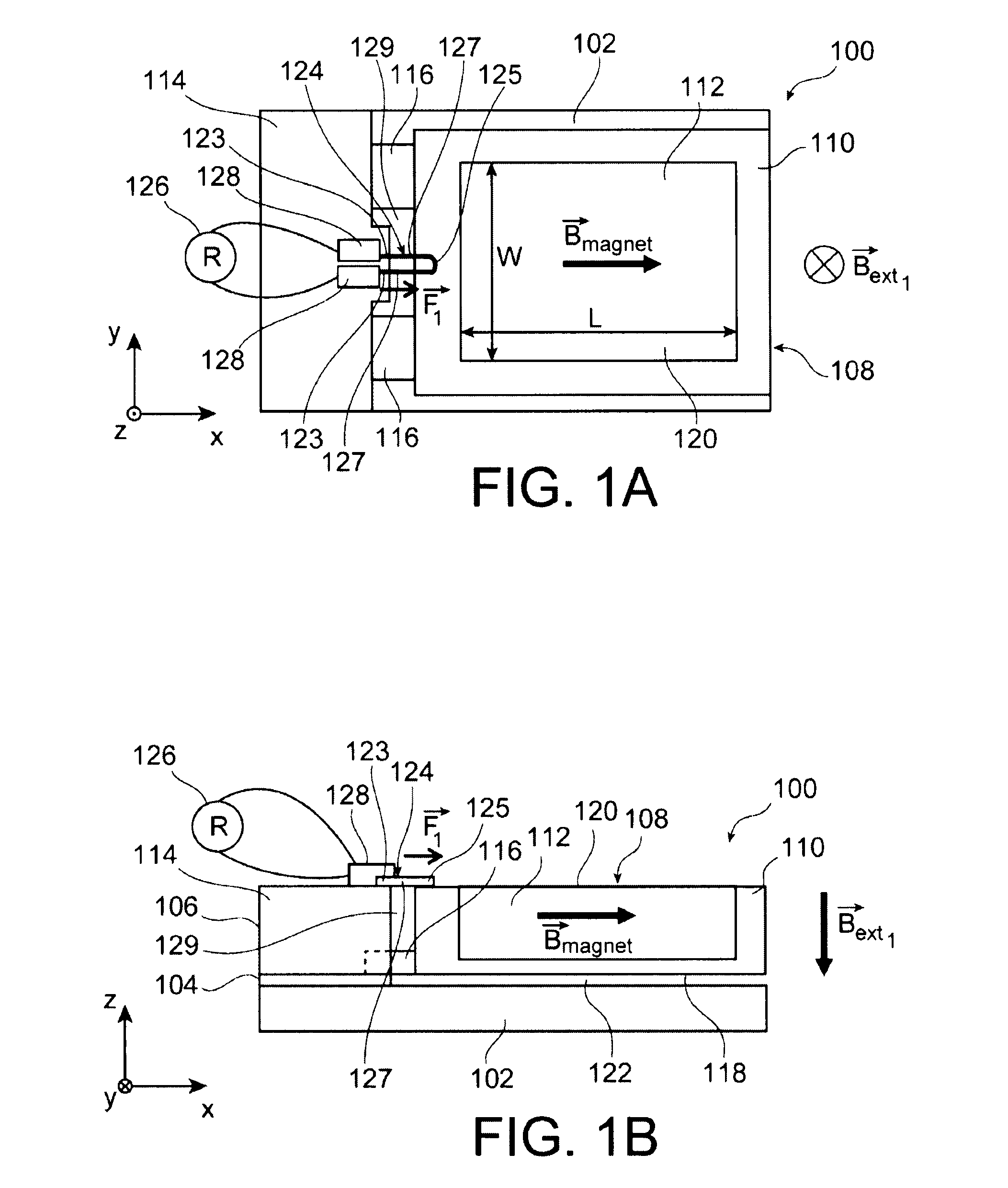
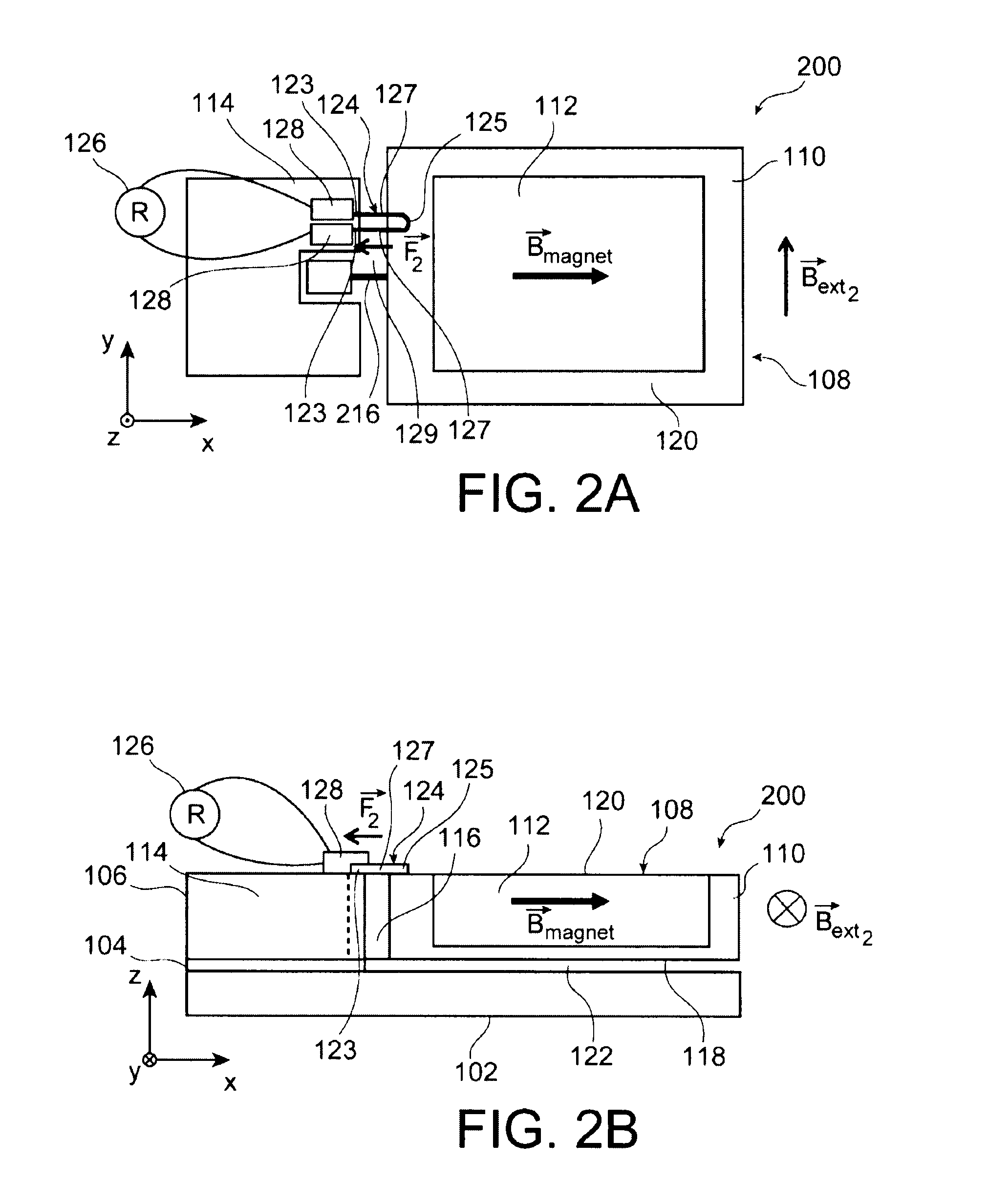
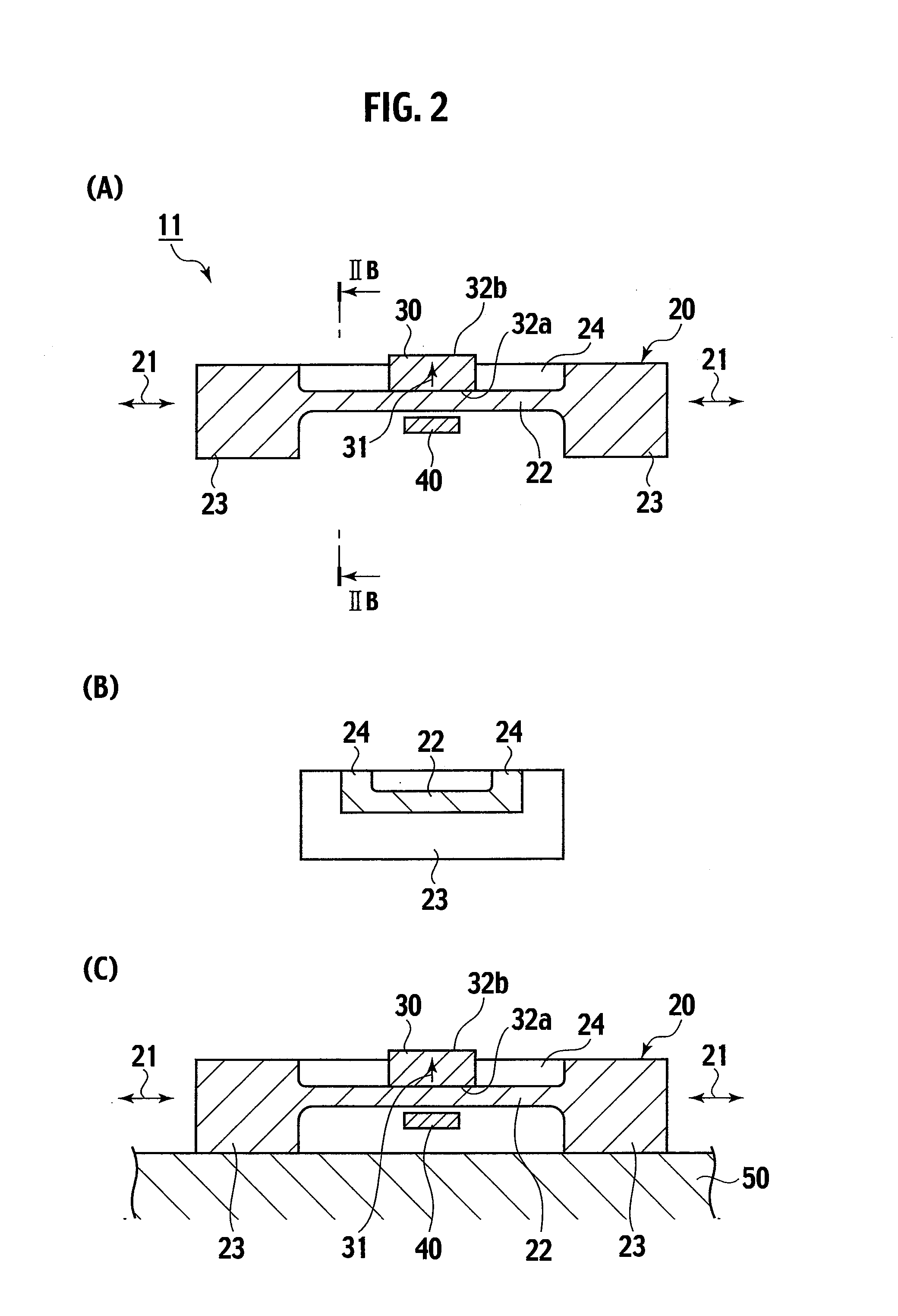
Magnetostrictive stress sensor
InactiveUS20100127698A1Detecting stress accurately and preciselyPrecise and accurate detectionForce measurementUsing electrical meansStress sensorMagnetic flux
A magnetostrictive stress sensor (11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16) includes: a magnetic member {20, (107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112)} having a magnetostriction; a permanent magnet (30, 35, 113) adjacent to the magnetic member; a magnetic sensor (40, 104A, 104B) for detecting a leak magnetic flux on a side opposite to the permanent magnet with respect to the magnetic member, wherein the leak magnetic flux changes according to a stress acting on the magnetic member and the magnetic sensor detects the change of the leak magnetic flux, to thereby detect the stress acting on the magnetic member, and a direction (21, 108A, 109A) of the stress acting on the magnetic member is substantially orthogonal to a magnetizing direction (31, 31, 113A) of the permanent magnet.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Method of diagnosing fatigue life of structural steelwork and a member of steelwork having life diagnostic function
InactiveUS6073493AEasily and accurately diagnosingEasy to diagnoseAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesForce measurementFatigue damageVoltage amplitude
In a method of diagnosing the fatigue life of structural steelwork according to the present invention, a Barkhausen noise measurement is performed under the condition of 5 mu m< / =d< / =1 mm where d is the detection depth of Barkhausen noise, by using a magnetic head constituted by an air-core coil detection head and a magnetic excitation head obtained by winding a copper wire such as an enameled wire on a U-shaped core made of a soft magnetic material such as a silicon steel sheet or an amorphous magnetic material. The degree of fatigue damage of a target measurement portion is diagnosed using the root-mean-square (RMS) voltage or voltage amplitude value of the Barkhausen noise. According to this method, the degree of fatigue and degradation by stress and strain in the structural steelwork can be accurately diagnosed prior to development of cracking without any limitation on diagnostic locations. A member of steelwork having a life diagnostic function is obtained by mounting the above magnetic head on a brace- or wall-like vibration-damping device made of very low-yield steel. According to this member of steelwork, the wall or covering material of a bridge or the like need not be removed even in practicing a fatigue life diagnosis. The degree of fatigue degradation in structural steelwork can be easily and accurately diagnosed prior to development of cracking even in a location where an operator cannot access due to the structural limitation.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Method and device for long-range guided-wave inspection of fire side of waterwall tubes in boilers
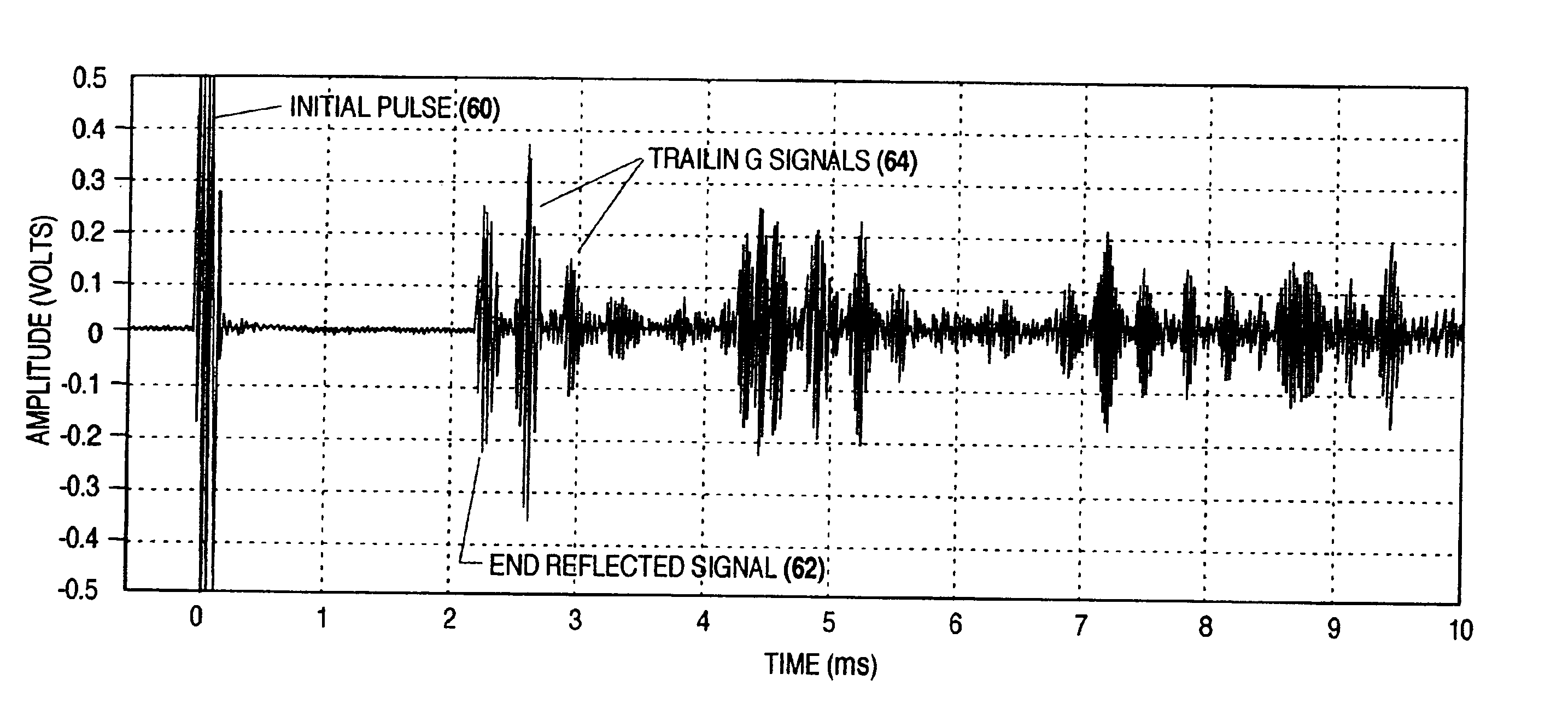
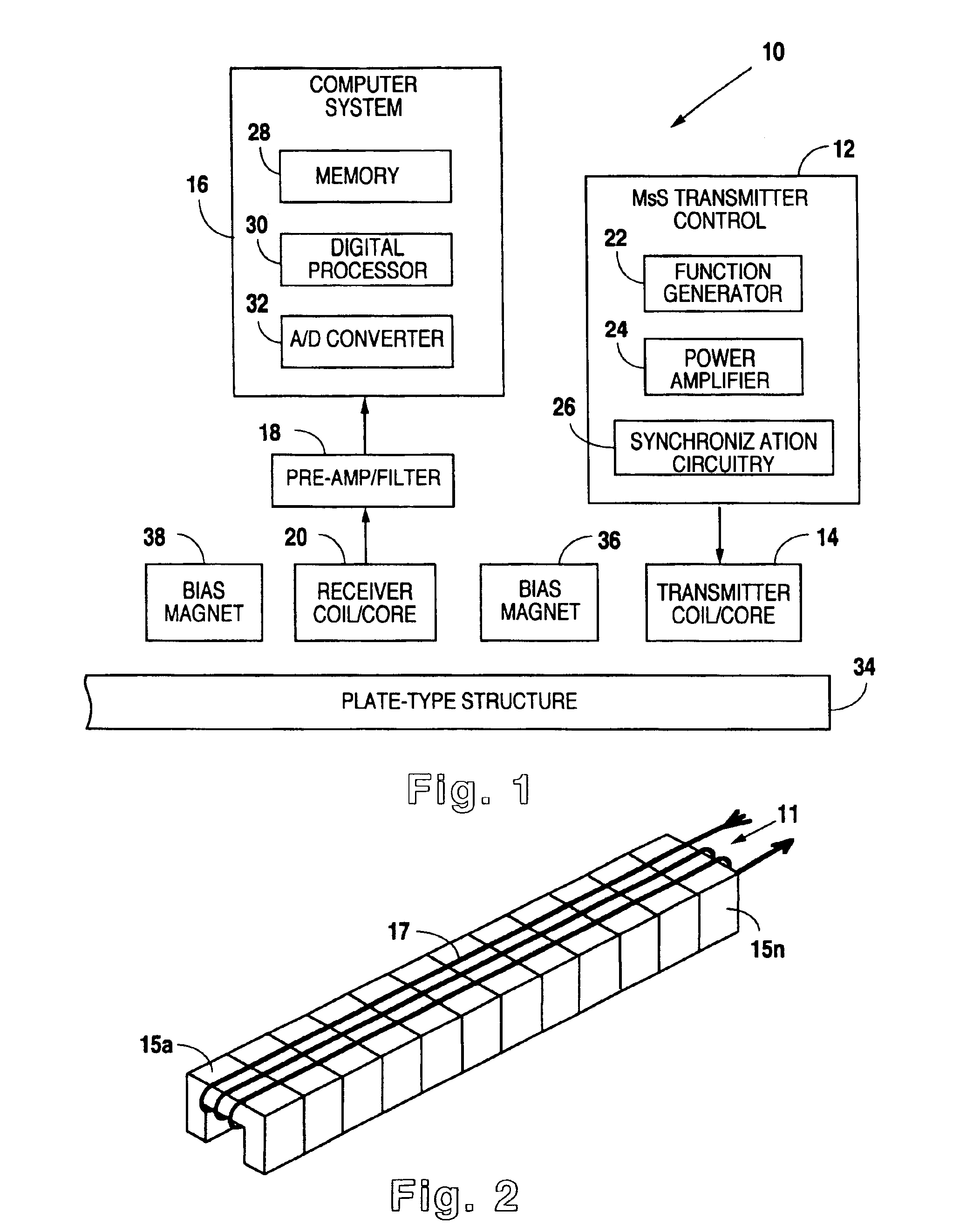
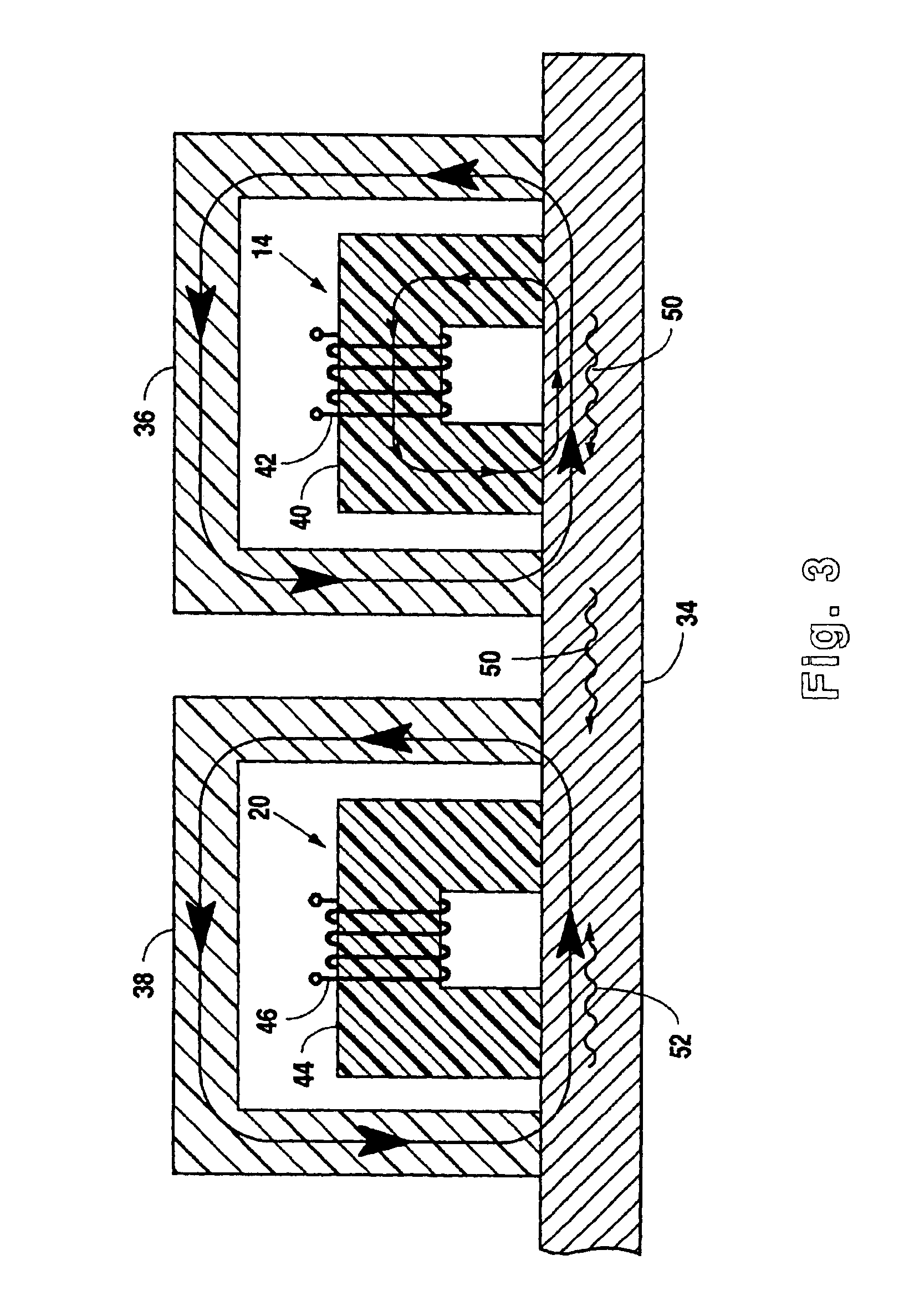
ActiveUS7474092B1Good mechanical couplingRapid investigationMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesStatic/dynamic balance measurementCouplingData acquisition
Methods and devices for inspecting waterwall tubes for the detection of fire side damage over a long length of the tube are described. The system of the invention uses a magnetostrictive strip and a flat coil-type plate magnetostrictive sensor (MsS) that are held in place on the waterwall using a specially designed frame and an electromagnetic circuit. The magnetostrictive strip and plate type MsS are positioned against a tube in the waterwall using an elastomeric pad or a fluid filled bladder to achieve close contact and good mechanical coupling between the magnetostrictive strip and the tube surface. When current activated, the electromagnet holds the entire assembly in place and provides a DC bias magnetic field required for plate magnetostrictive sensor probe operation. Long-range guided-waves are pulsed into the tube and reflected signals are detected within the same sensor structure. The received signal data representative of a long section of the tube under investigation is then analyzed for the presence of anomalies and defects. When data acquisition for a particular tube or tube section is completed the electromagnet is turned off and the entire device is moved to the next tube in the waterwall.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Applied and residual stress measurements using magnetic field sensors
InactiveUS7526964B2Promote accurate modelingIncrease capacityForce measurementUsing electrical meansSensor arrayStress distribution
Methods are described for the use of conformable eddy-current sensors and sensor arrays for characterizing residual stresses and applied loads in materials. In addition, for magnetizable materials such as steels, these methods can be used to determine carbide content and to inspect for grinding burn damage. The sensor arrays can be mounted inside or scanned across the inner surface of test articles and hollow fasteners to monitor stress distributions. A technique for placing eddy-current coils around magnetizable fasteners for load distribution monitoring is also disclosed.
Owner:JENTEK SENSORS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com