Patents
Literature
367 results about "Digital image correlation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Digital image correlation and tracking is an optical method that employs tracking and image registration techniques for accurate 2D and 3D measurements of changes in images. This method is often used to measure full-field displacement and strains, and it is widely applied in many areas of science and engineering, with new applications being found all the time. Compared to strain gages and extensometers, the amount of information gathered about the fine details of deformation during mechanical tests is increased due to the ability to provide both local and average data using digital image correlation.
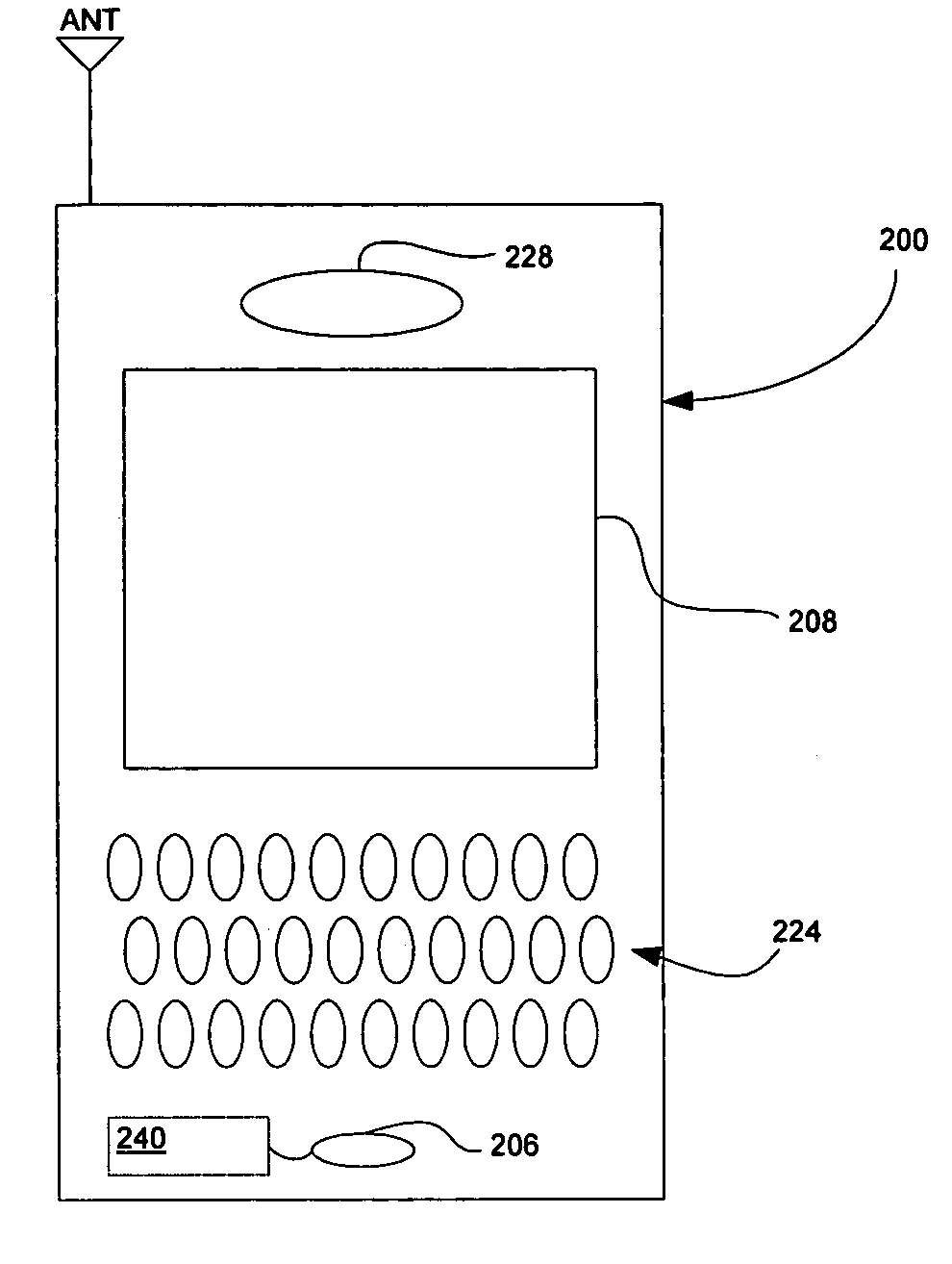
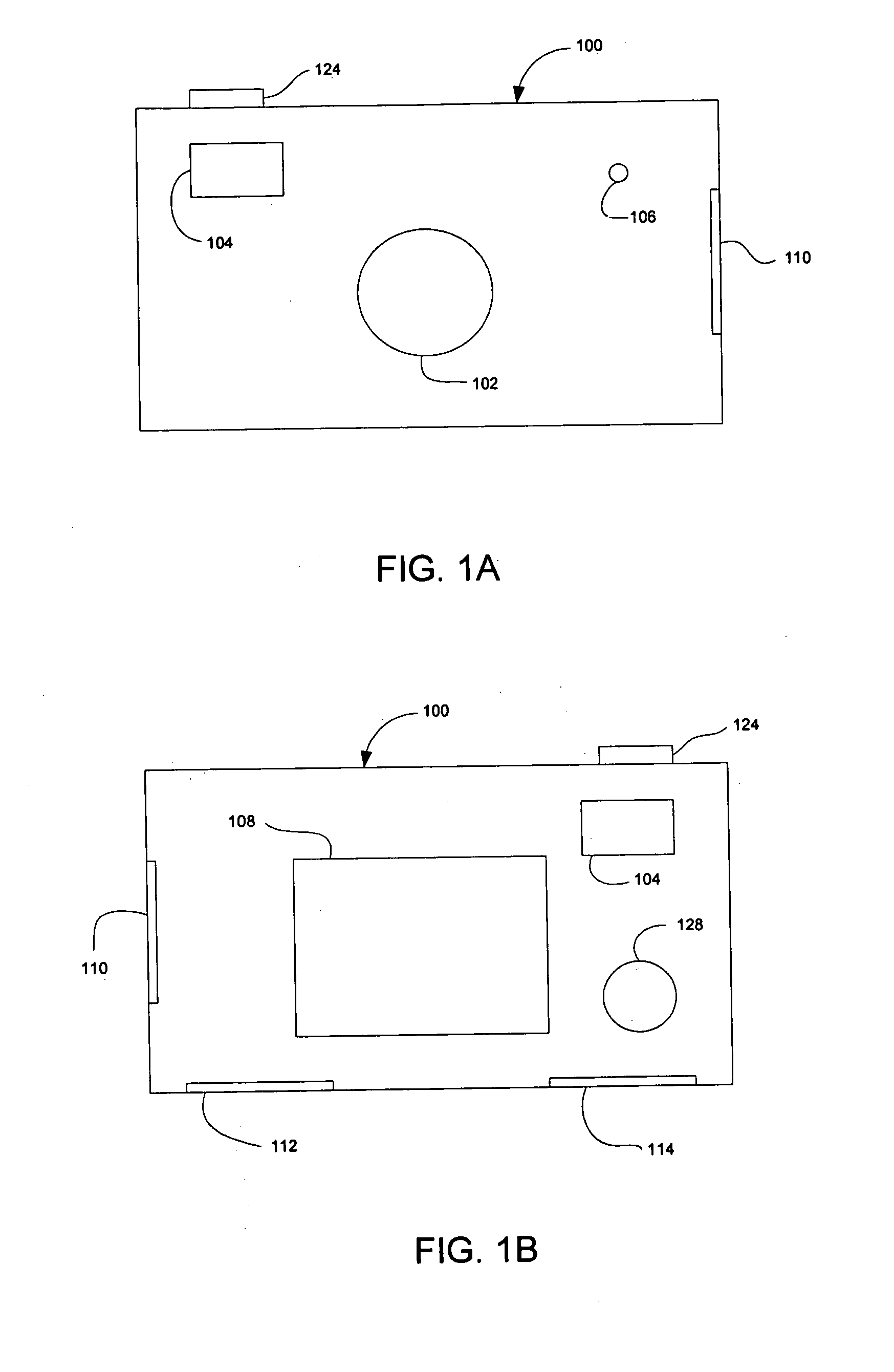
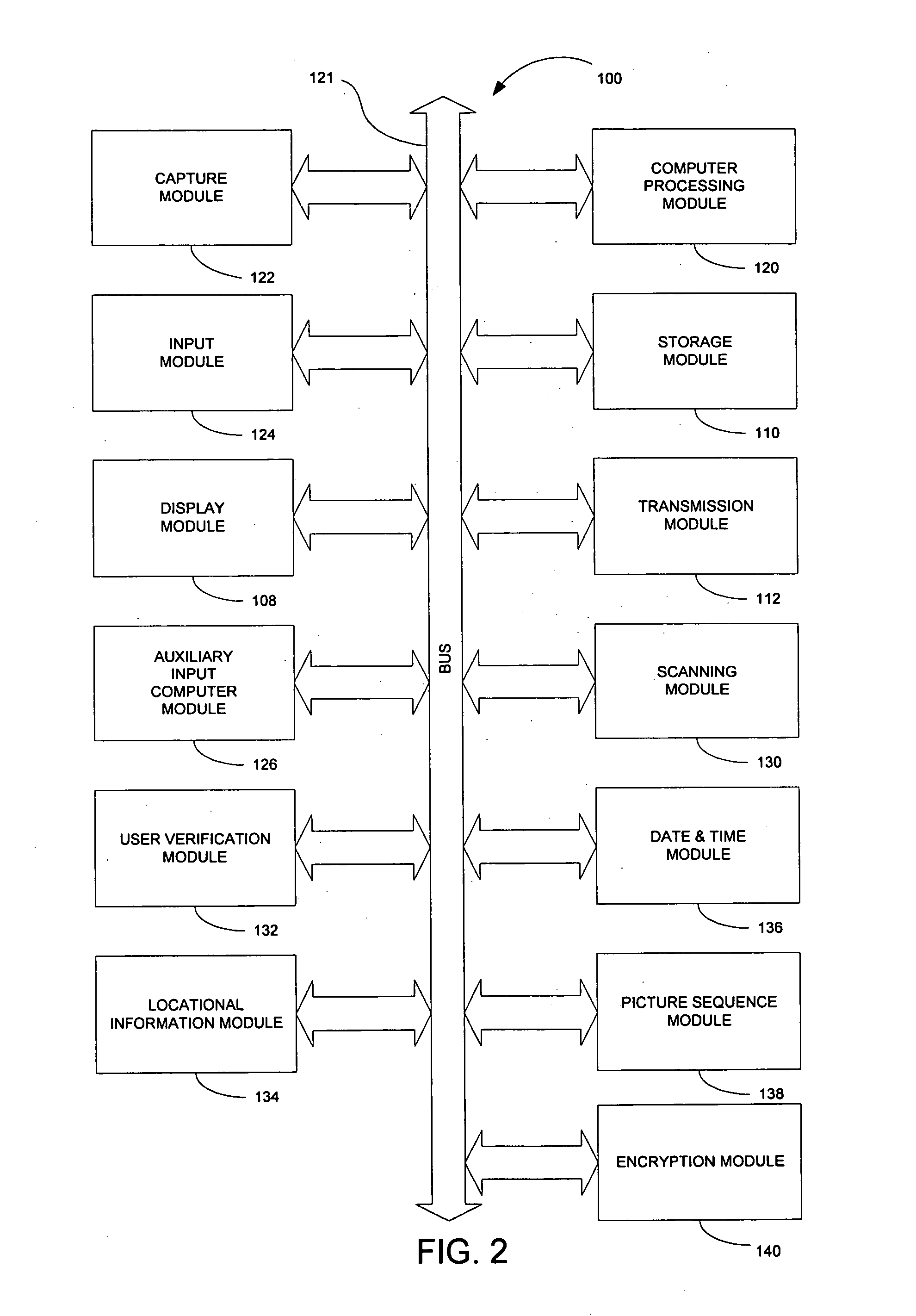
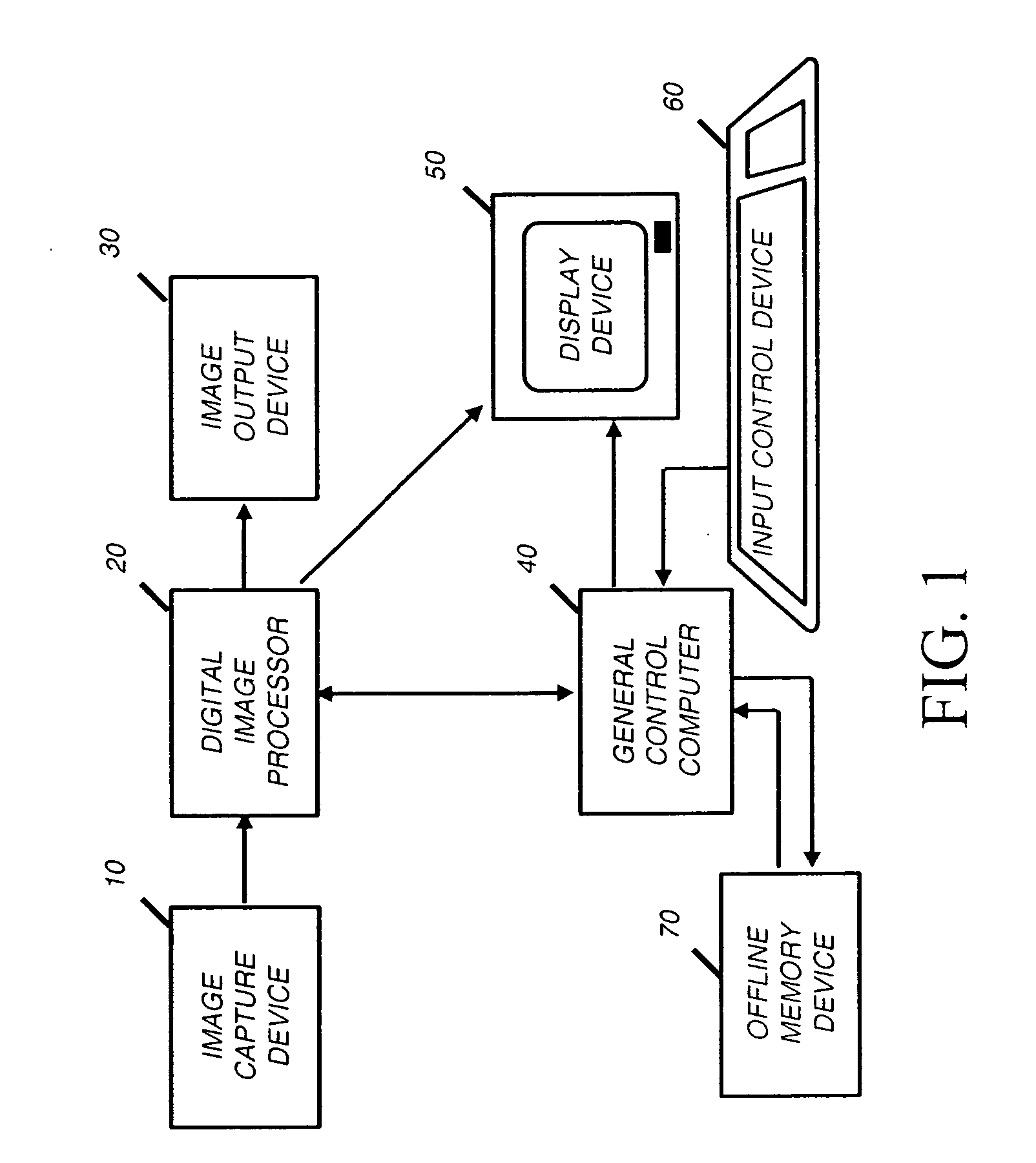
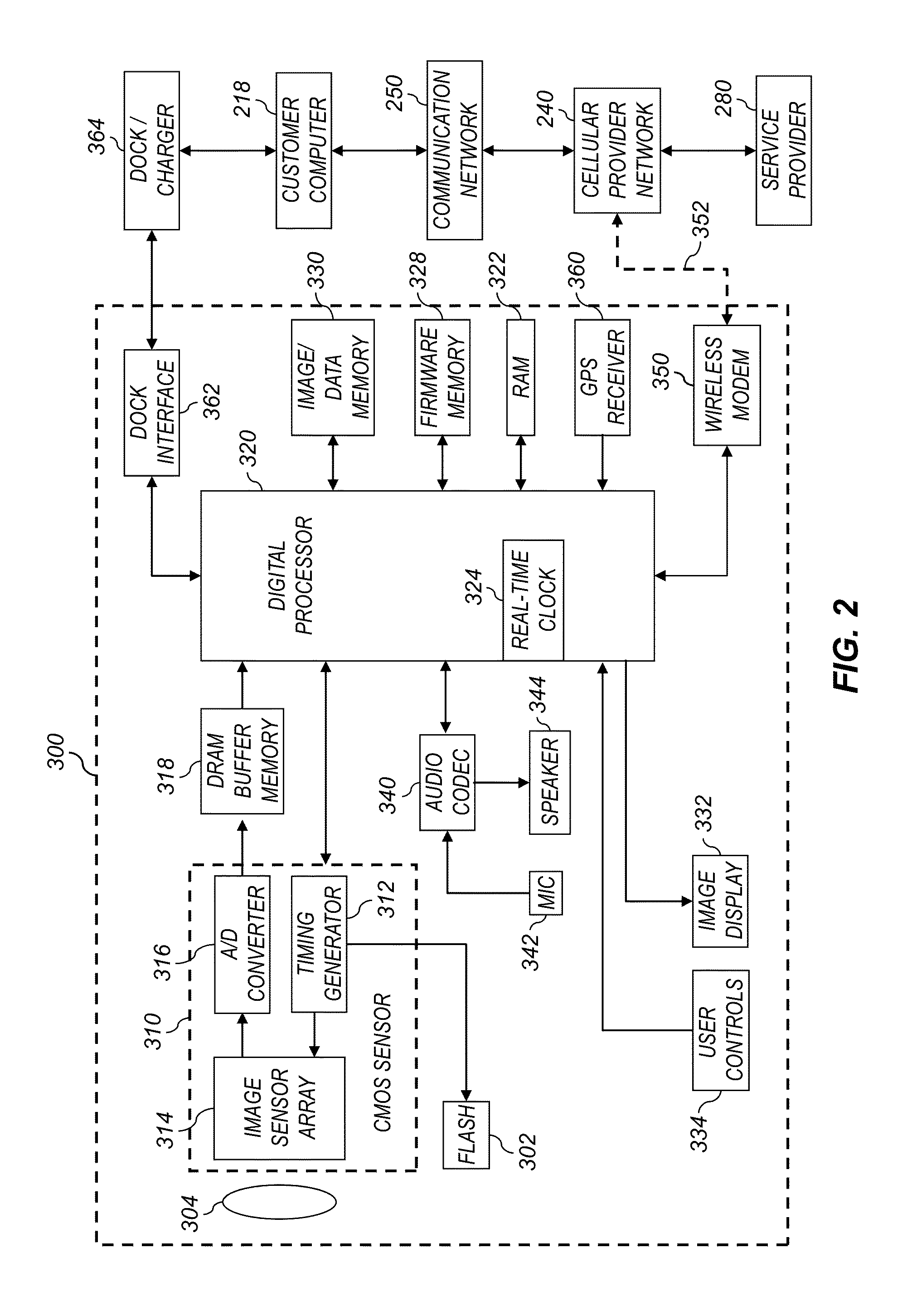
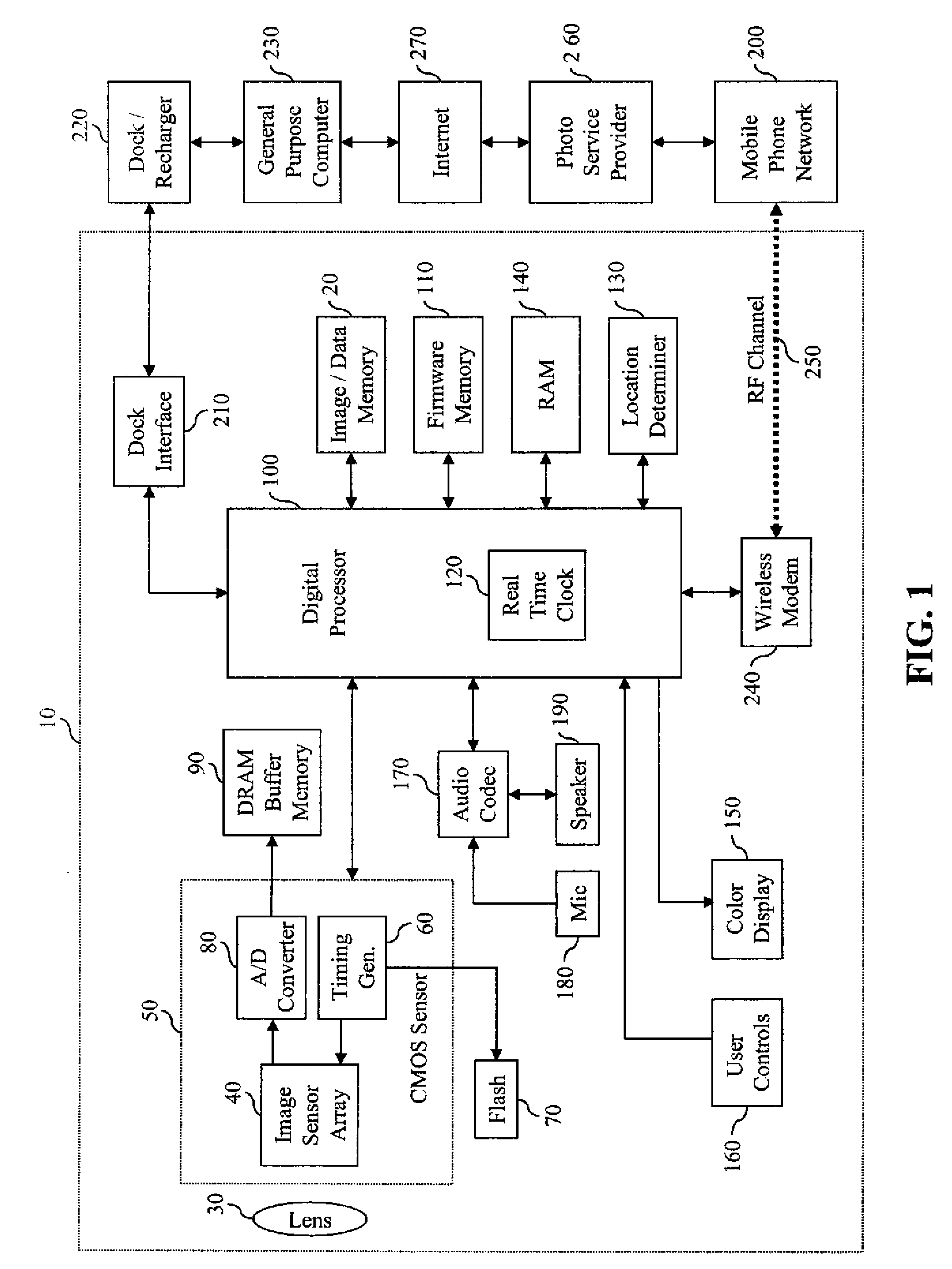
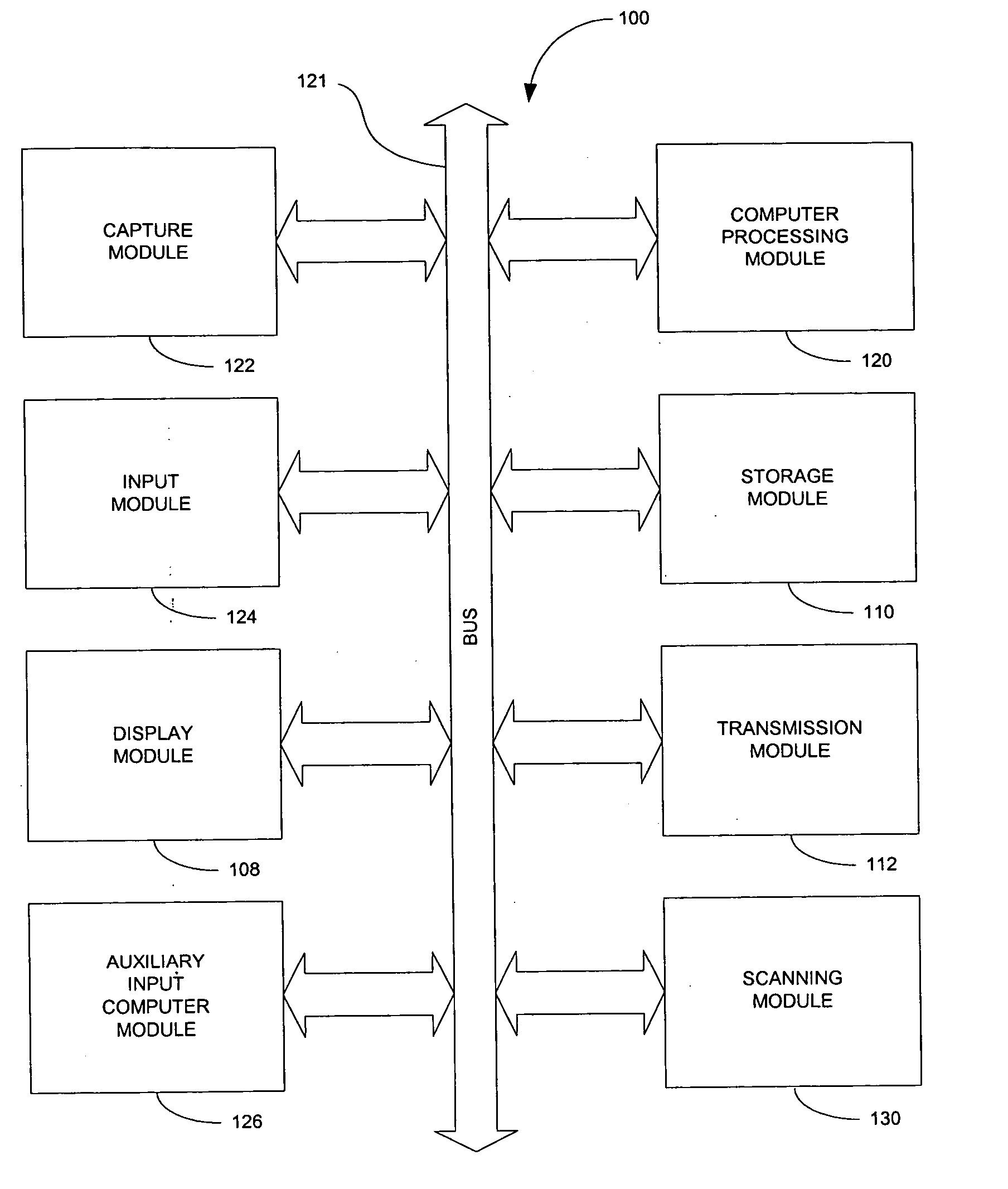
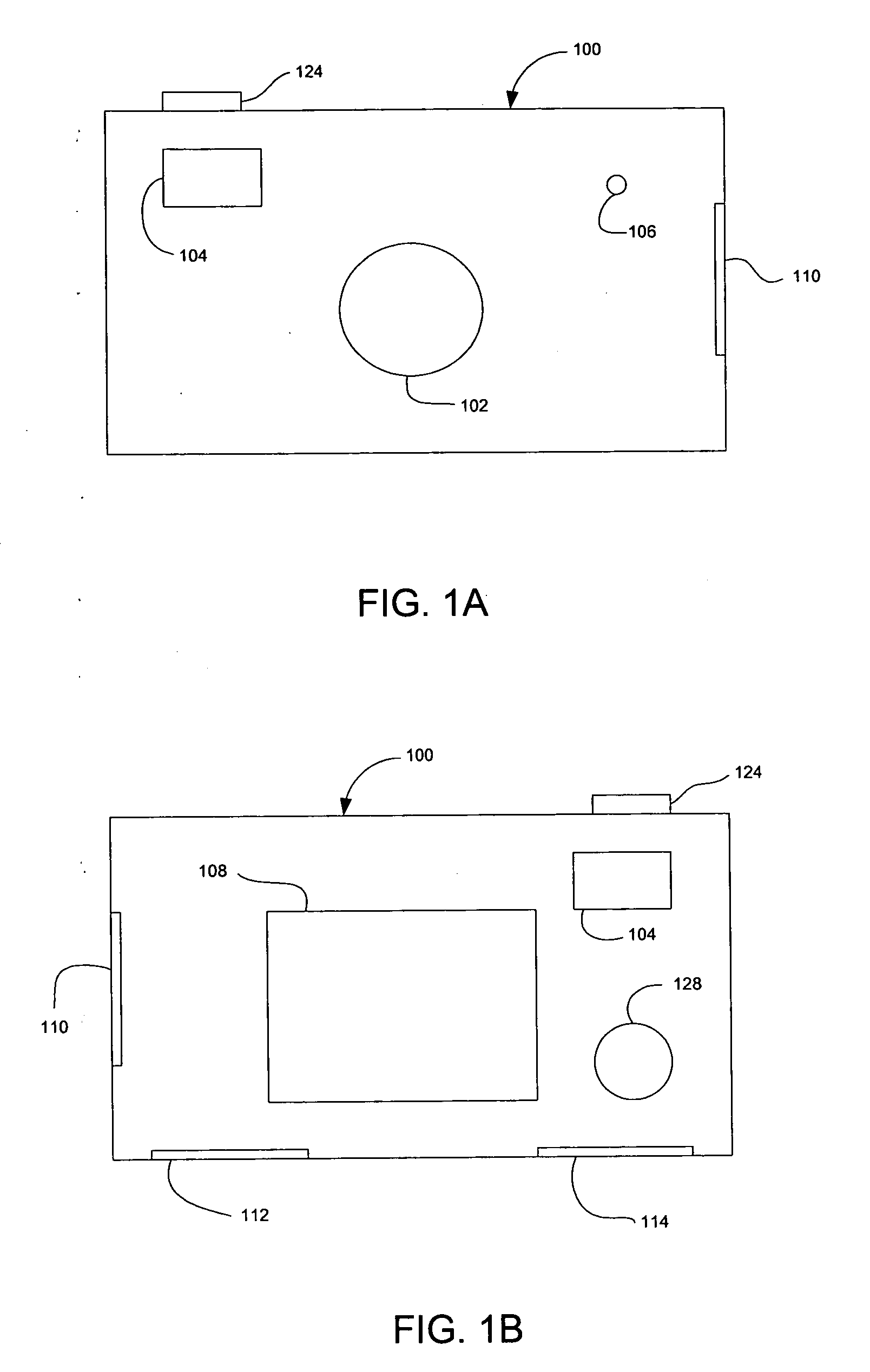
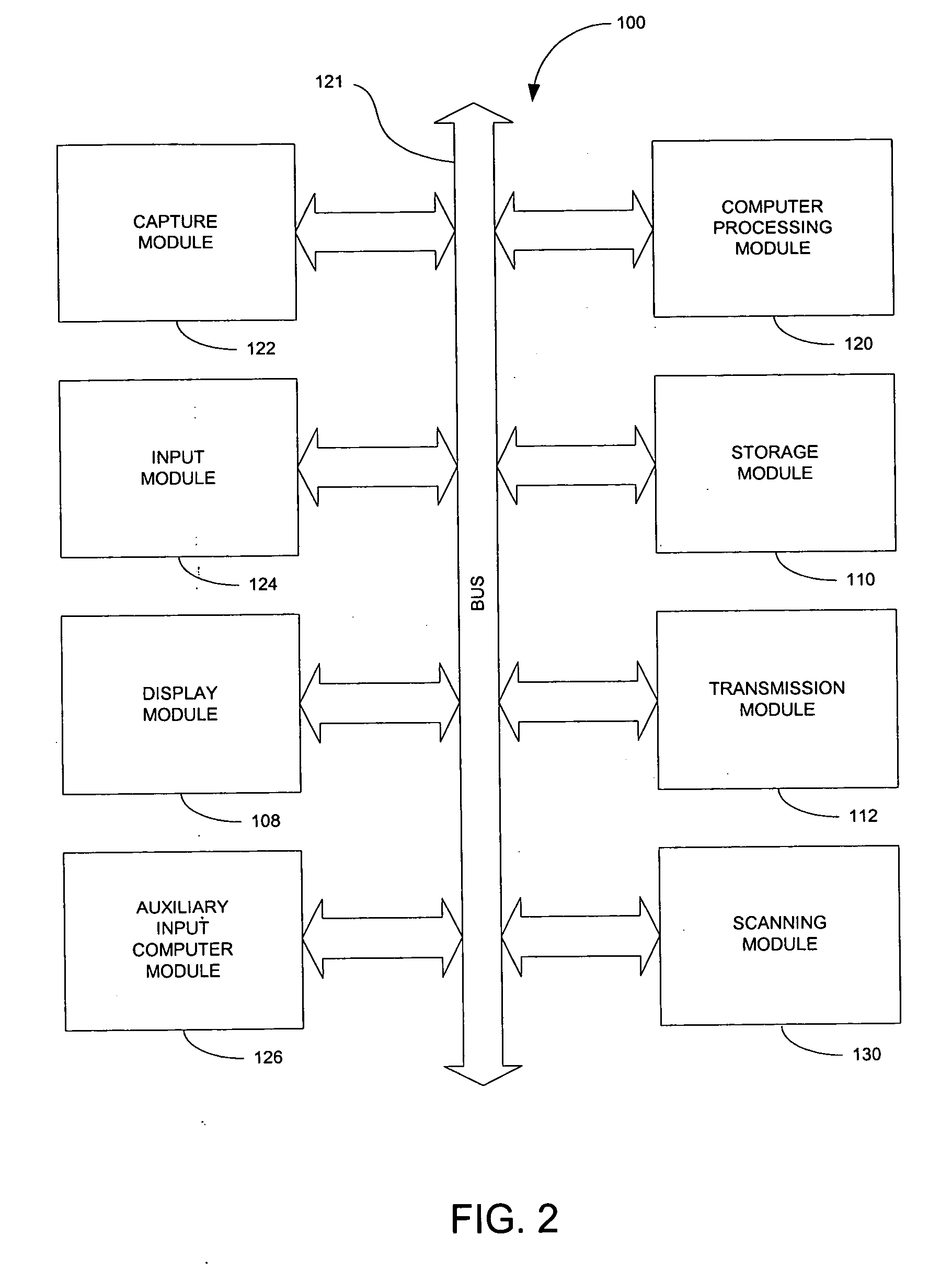
Device and method for embedding and retrieving information in digital images
InactiveUS20060114338A1Facilitate embedding informationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsUser verificationDigital imaging
A digital imaging device and method for embedding and retrieving of information in digital images are provided. The digital imaging device includes a capture module for capturing an image and creating a digital image file; a locational information module for determining a location of the device when capturing the image; and a processing module for associating the location information to the digital image file. The device further includes a user verification module for verifying an identity of a user of the device at a time of image capture and an encryption module for encrypting the digital image file and associated information. The method provides for securing information associated with the digital images and for verifying activities of a user.
Owner:ROTHSCHILD DIGITAL CONFIRMATION LLC
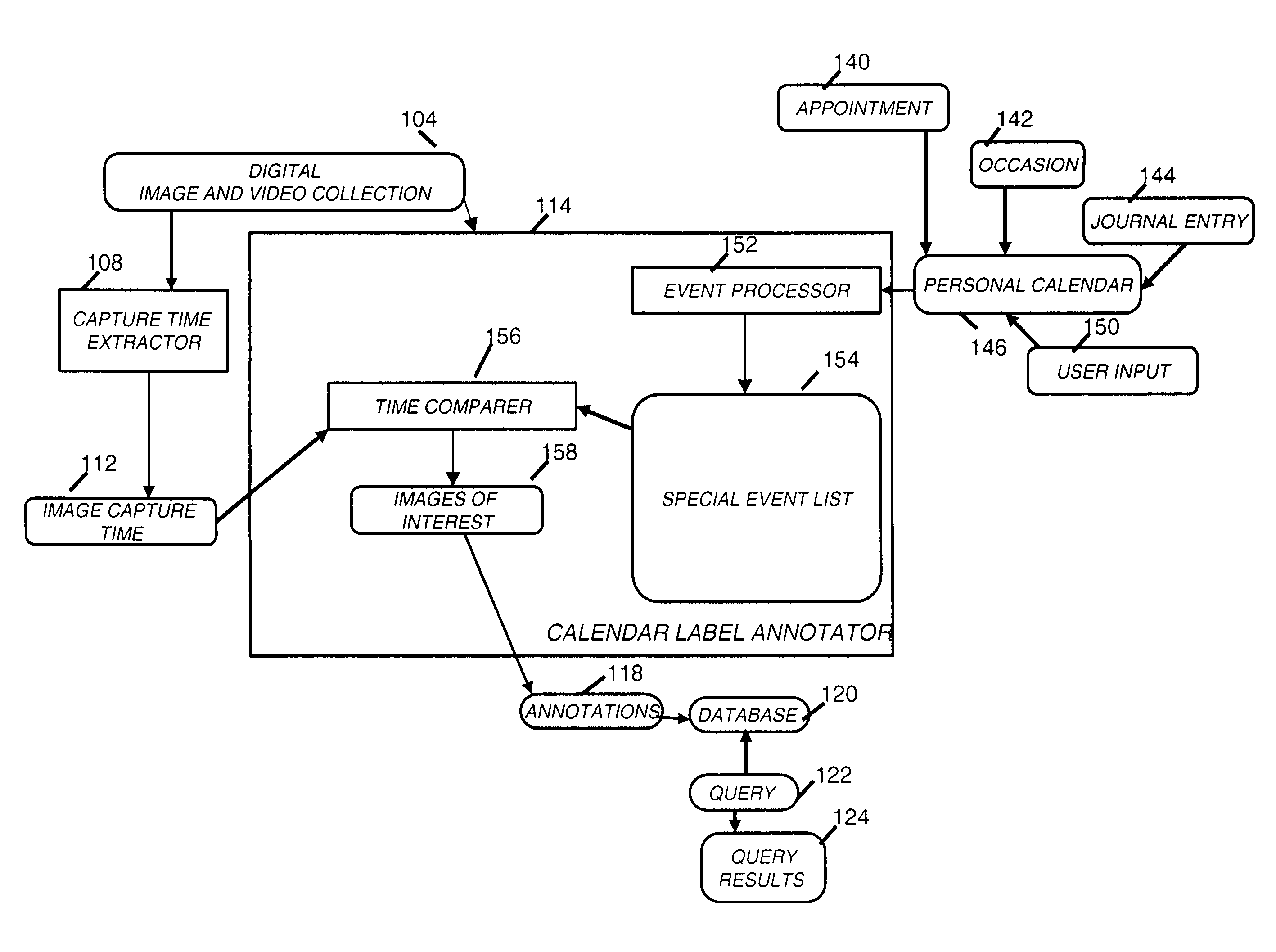
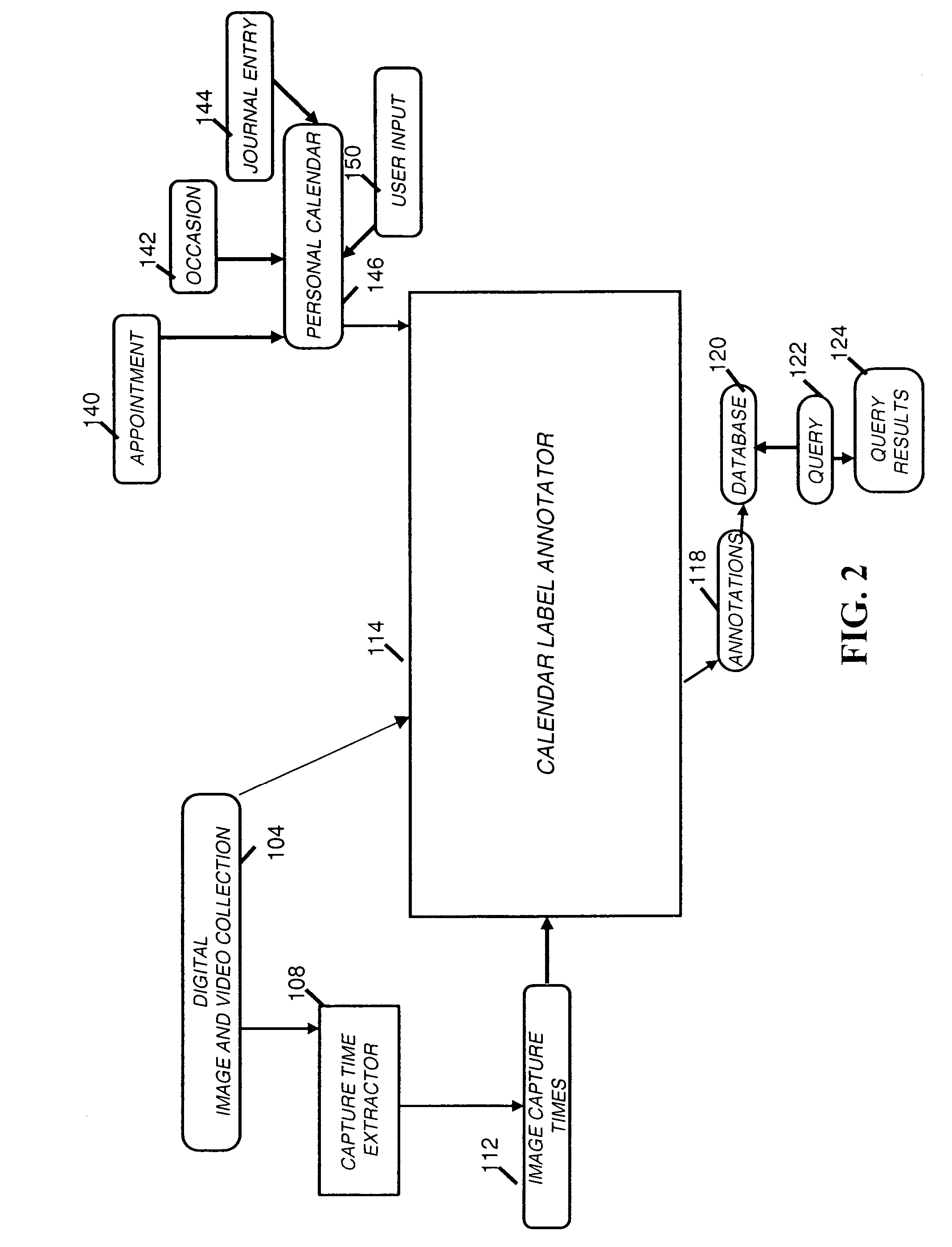
Identifying collection images with special events
InactiveUS20070008321A1Efficient searchImproved labelingCharacter and pattern recognitionAnimationDigital imageSpecial events
A method for associating event times or time periods with digital images in a collection for determining if a digital image is of interest, includes storing a collection of digital images each having an associated capture time; comparing the associated capture time in the collection with a special event time to determine if a digital image in the collection is of interest, wherein the comparing step includes calculation of a special event time associated with a special event based on the calendar time associated with the special event and using such information to perform the comparison step; and associating digital images of interest with the special event.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES FUND 83 LLC
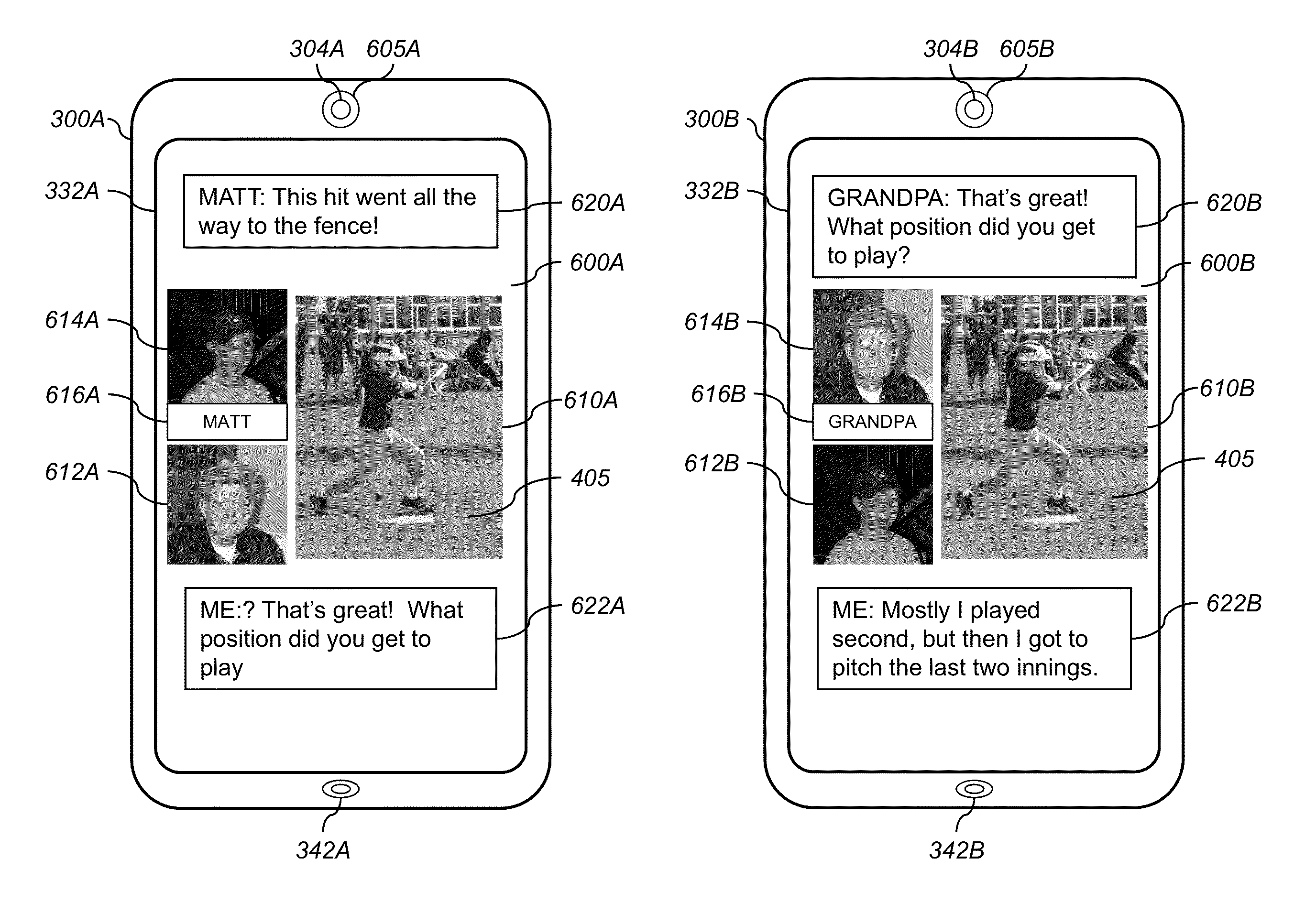
Forming a multimedia product using video chat
InactiveUS20130307997A1Capture reactionCapture emotionMetadata multimedia retrievalTwo-way working systemsVideo chatDigital image
A method for forming a composite multimedia product pertaining to a digital image captured of a scene. The method includes sharing the digital image with a remote user, and facilitating a conversation with the remote user across a communication network. A portion of the conversation that is relevant to the shared digital image is automatically extracted and combined with the digital image to form the composite multimedia product.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
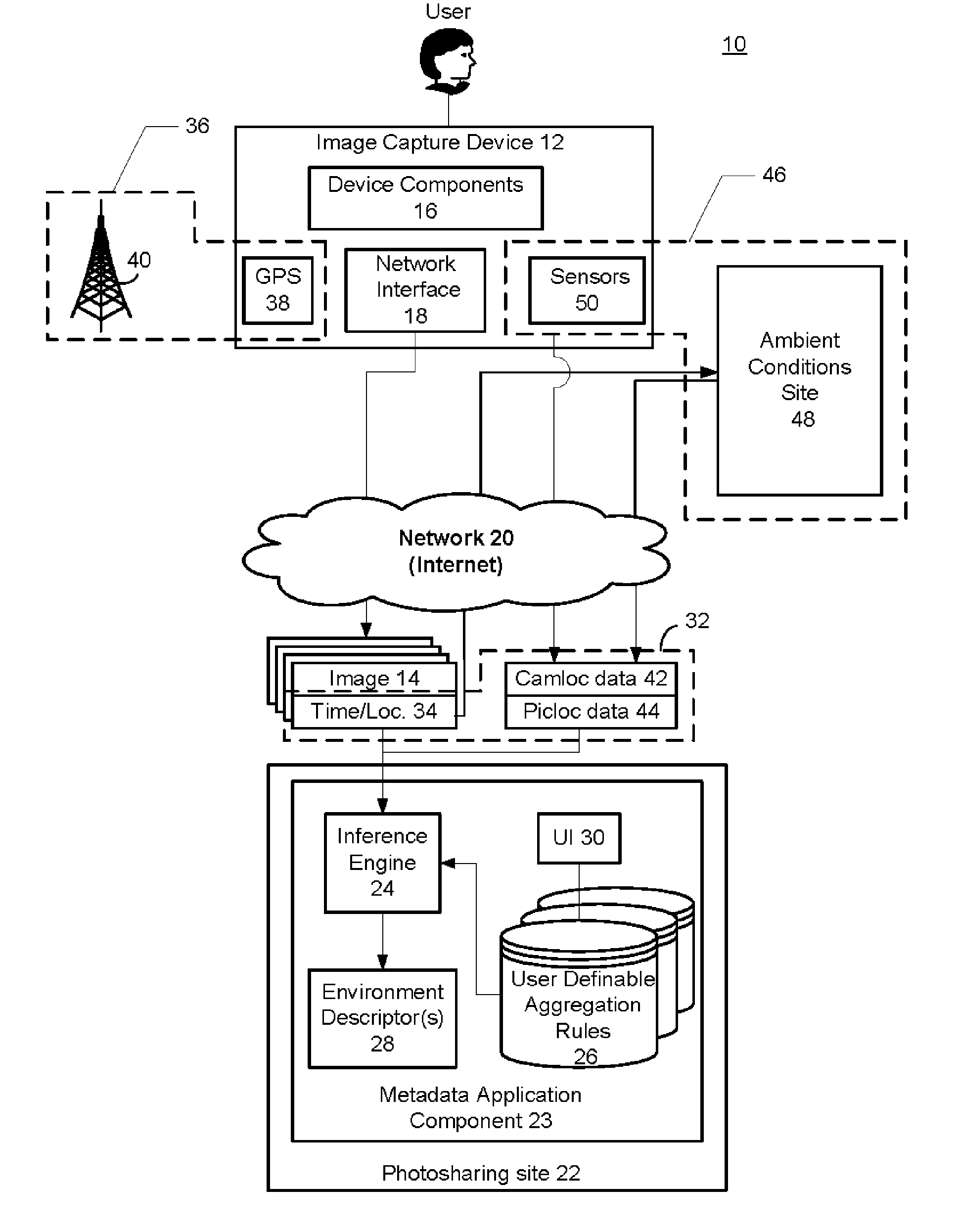
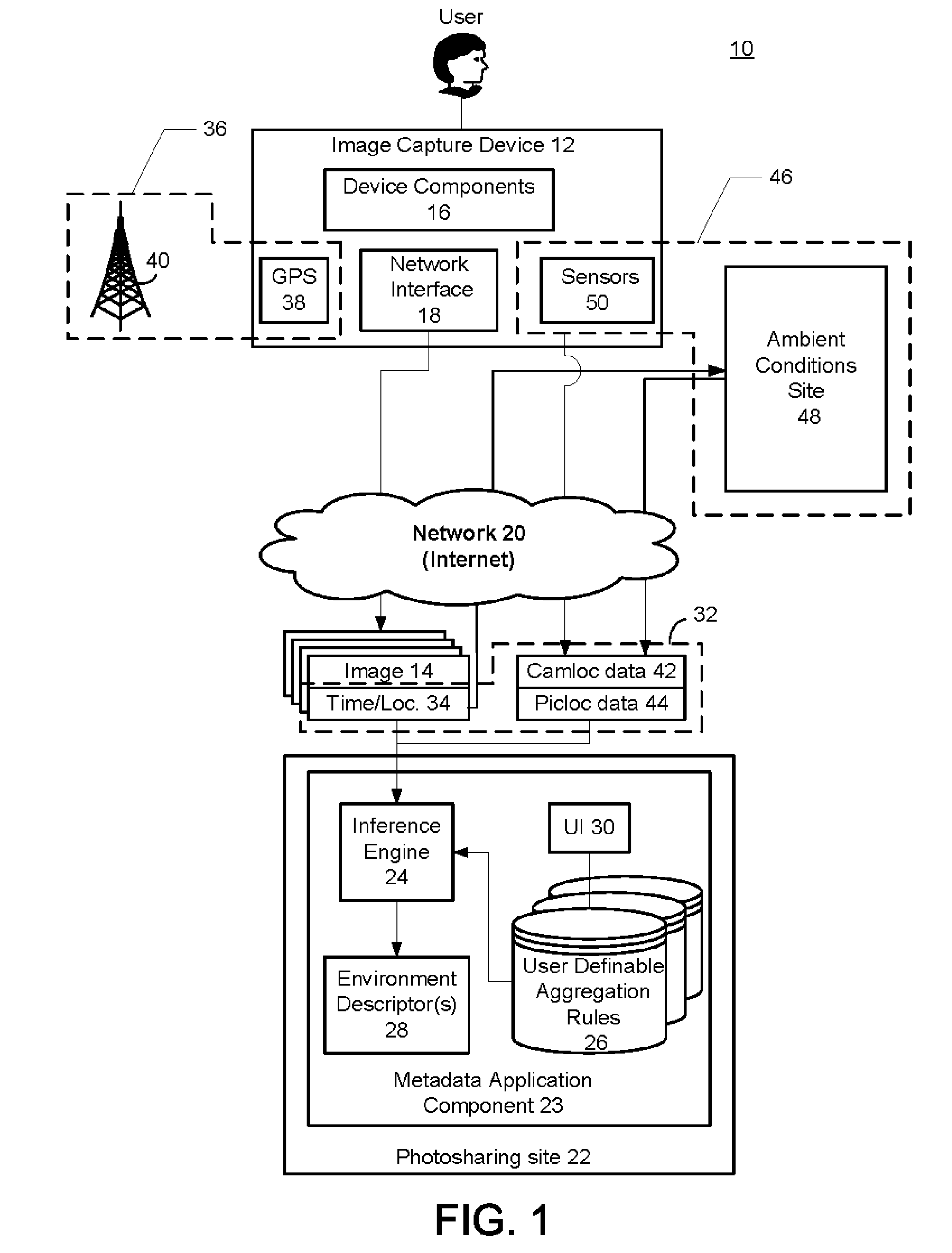
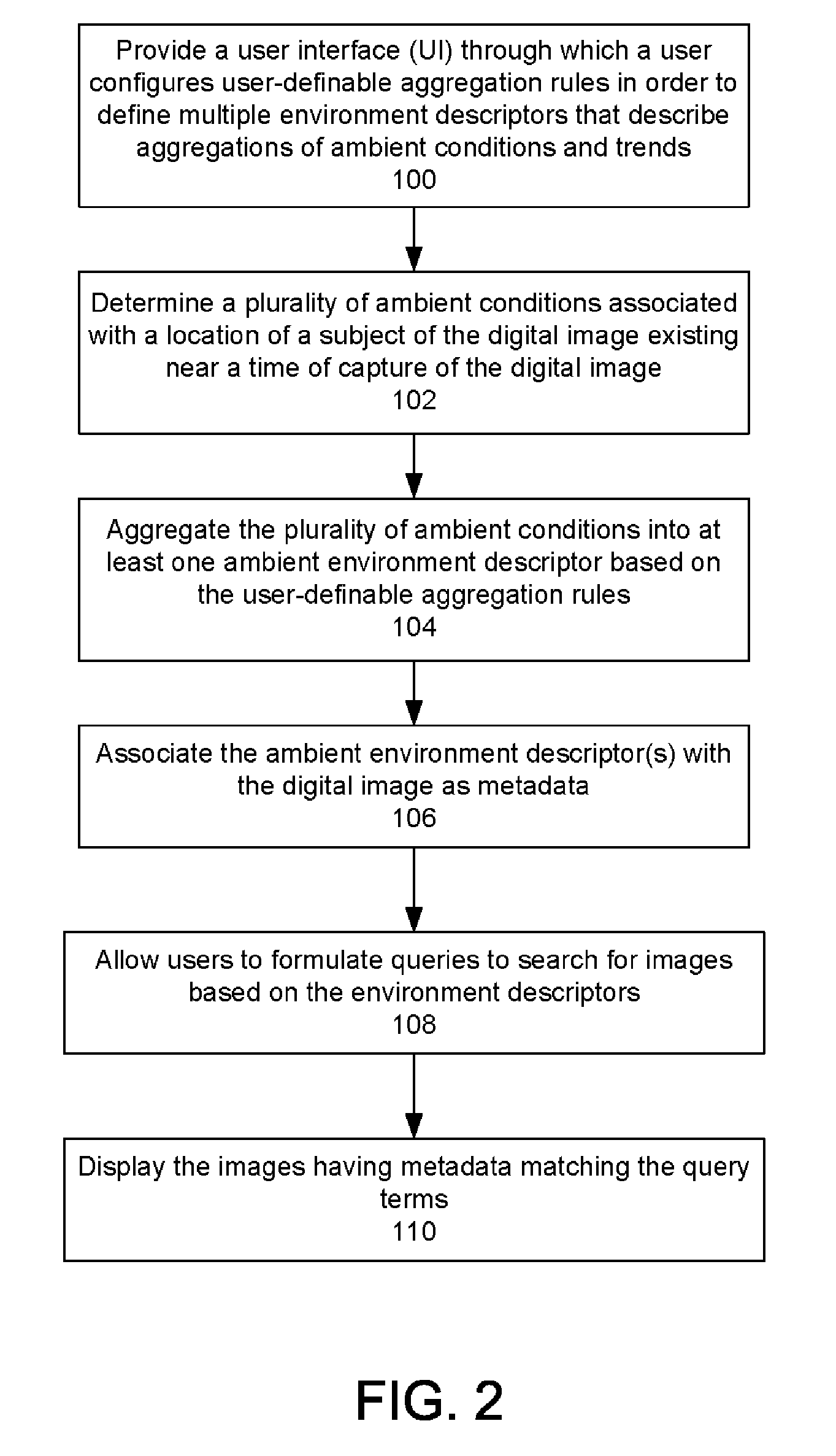
Automatic Generation Of Metadata For A Digital Image Based On Ambient Conditions
InactiveUS20070127833A1Easy retrievalMetadata multimedia retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Position dependent
A method and system is provided for automatically generating metadata for a digital image based on ambient conditions. Aspects of the preferred embodiment include determining a plurality of ambient conditions associated with a location of a subject of a digital image captured with a mobile image capture device, the ambient conditions existing at a time related to a time of capture of the digital image; aggregating the plurality of ambient conditions into at least one ambient environment descriptor based on user-definable aggregation rules; and associating the ambient environment descriptor with the digital image as metadata.
Owner:SCENERA MOBILE TEHNOLOGIES LLC
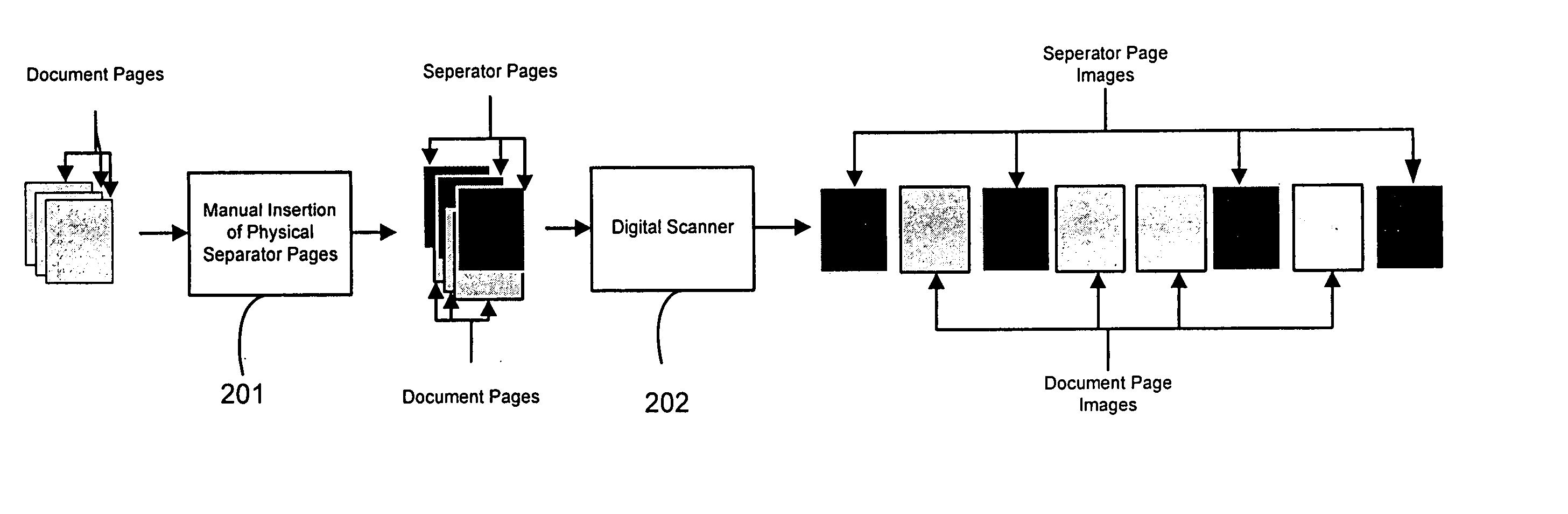
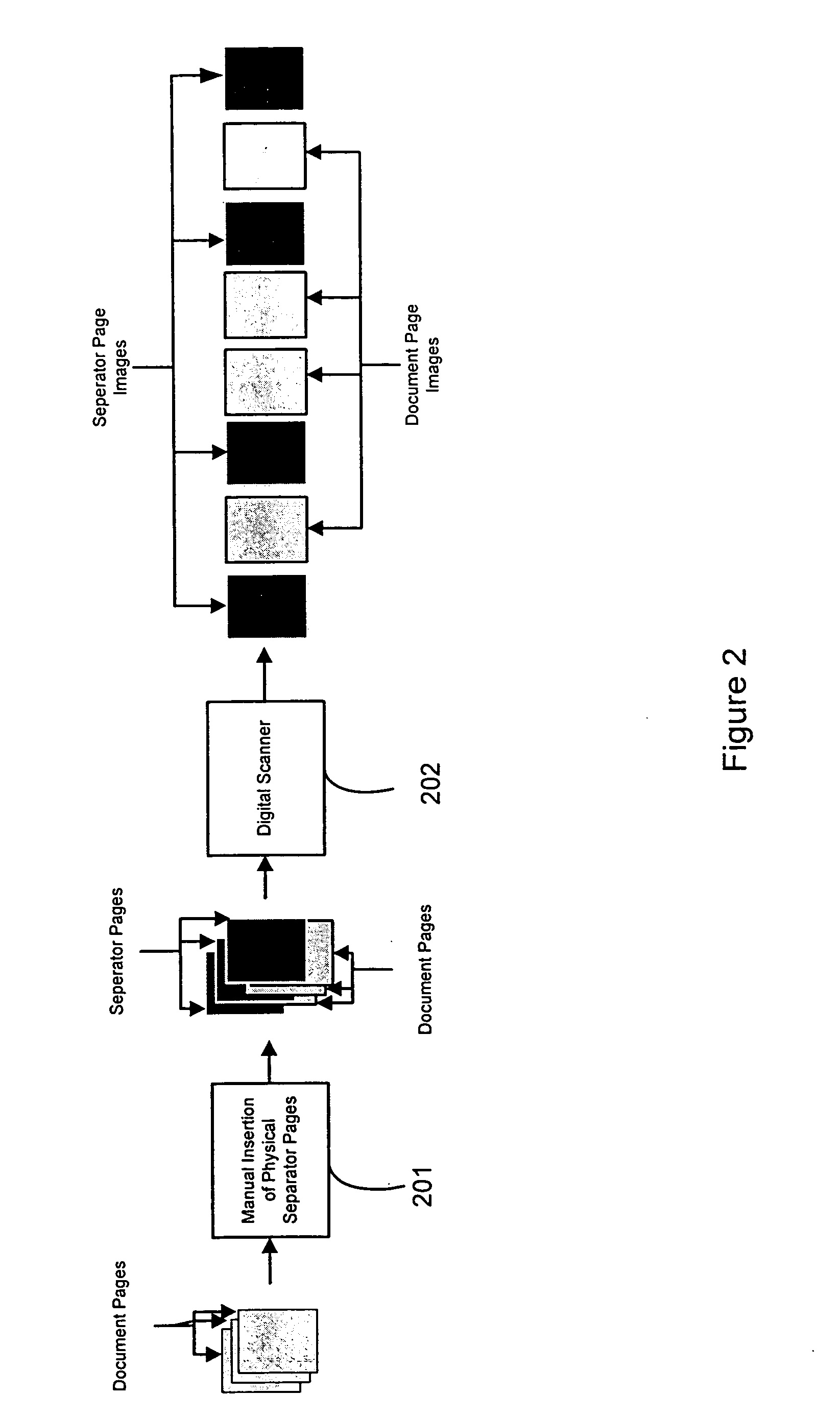
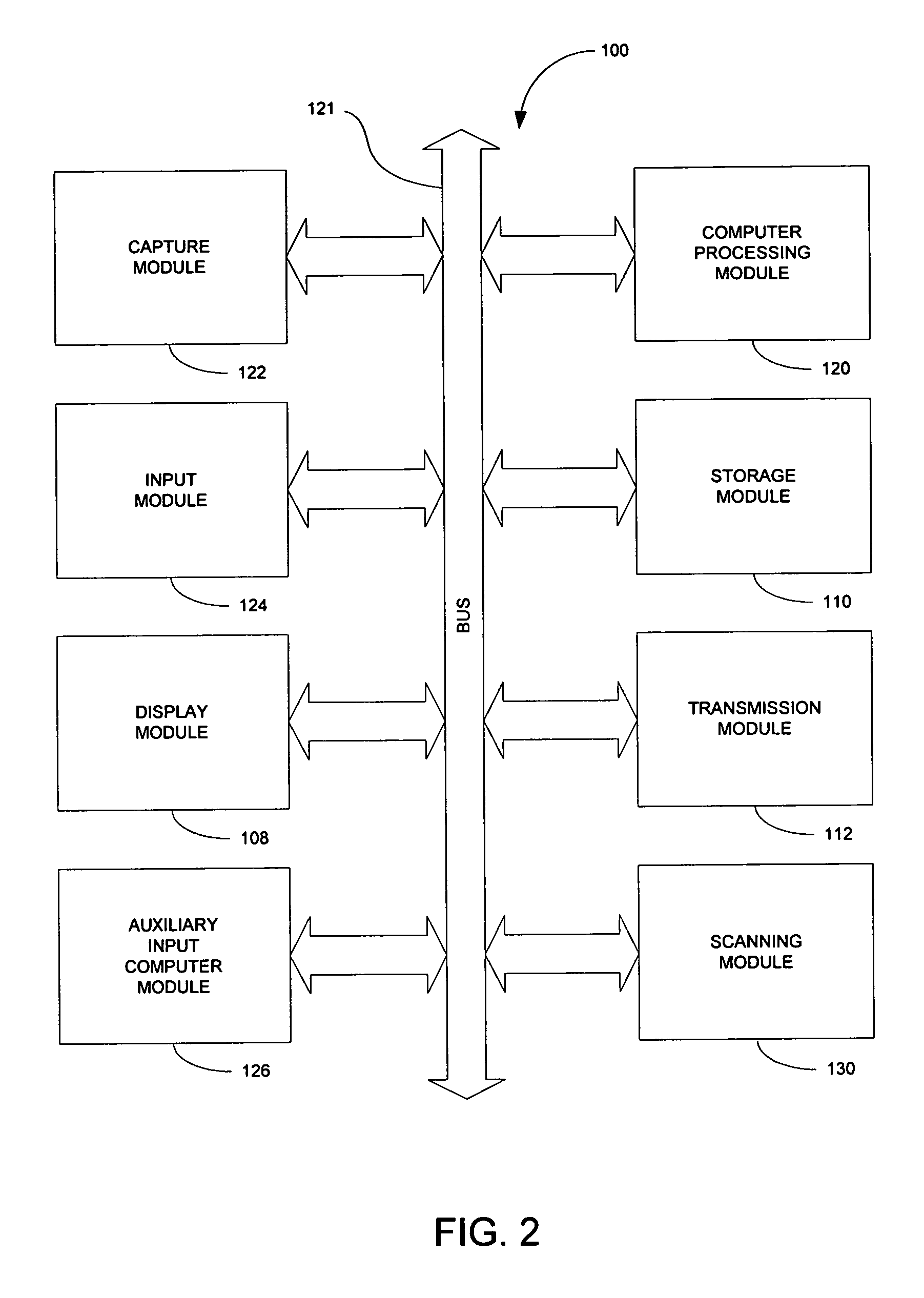
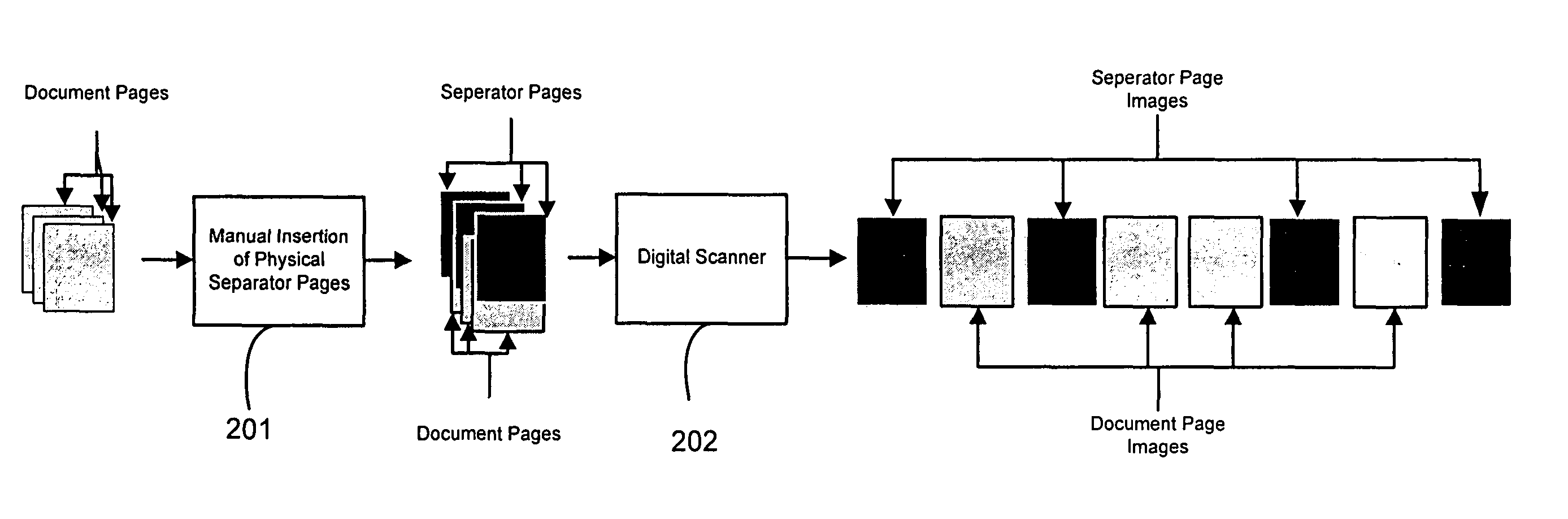
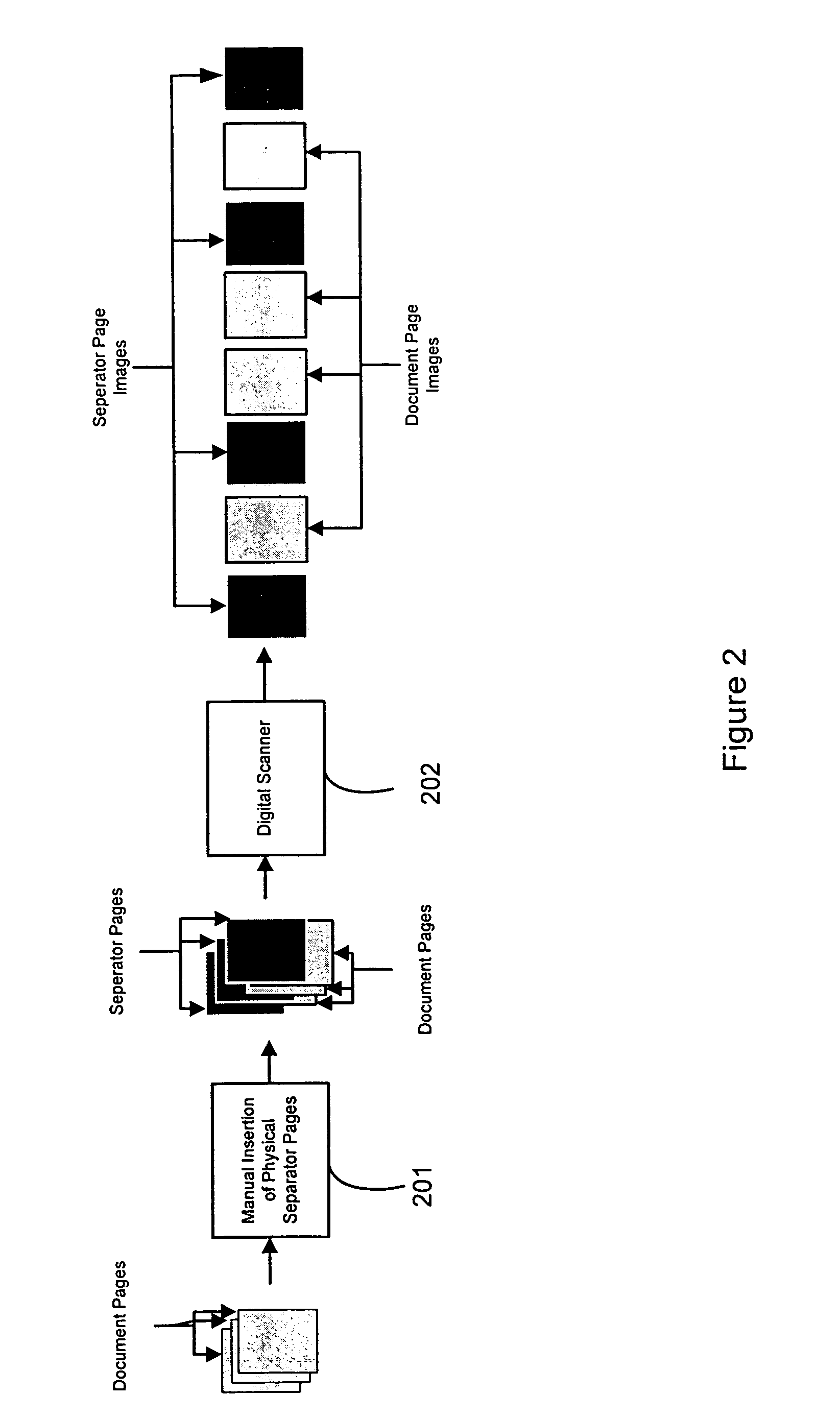
Automatic document separation
ActiveUS20050134935A1Easy maintenanceConfigurabilityImage analysisText processingPaper documentDigital image
A method and system for delineating document boundaries and identifying document types by analyzing digital images of one or more documents, automatically categorizing one or more pages or subdocuments within the one or more documents and automatically generating delineation identifiers, such as computer-generated images of separation pages inserted between digital images belonging to different categories, a description of the categorization sequence of the digital images, or a computer-generated electronic label affixed or associated with said digital images.
Owner:KOFAX
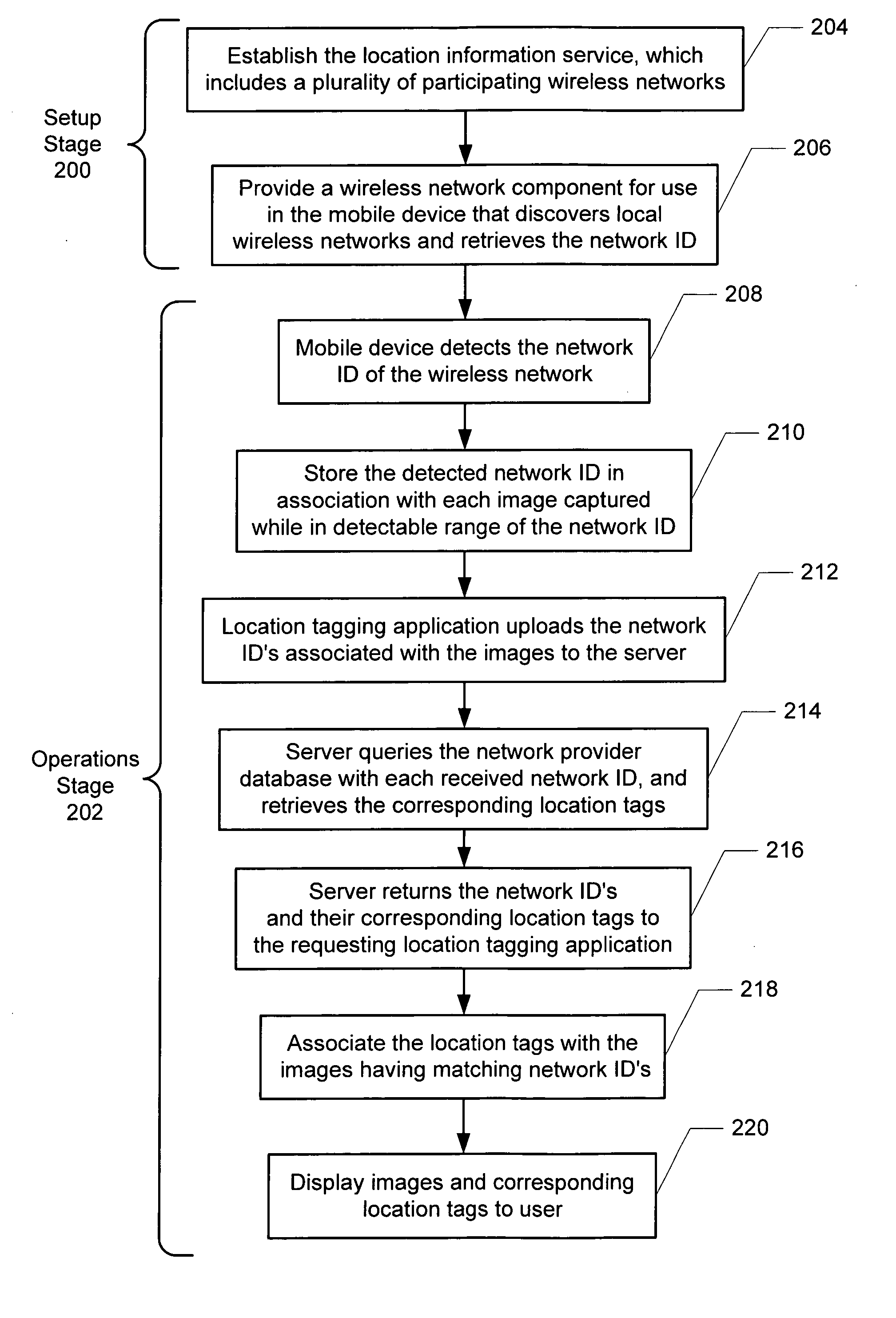
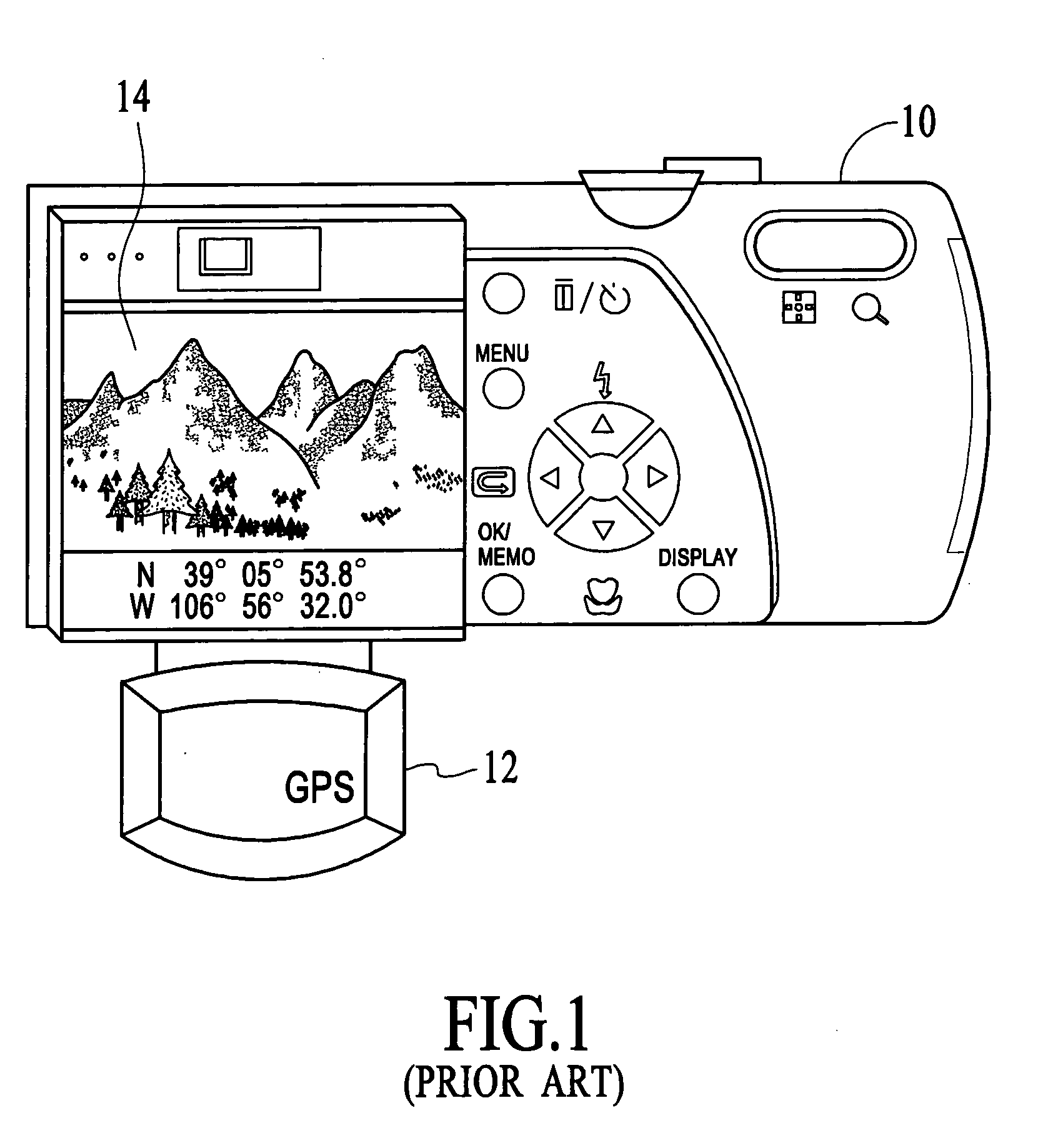
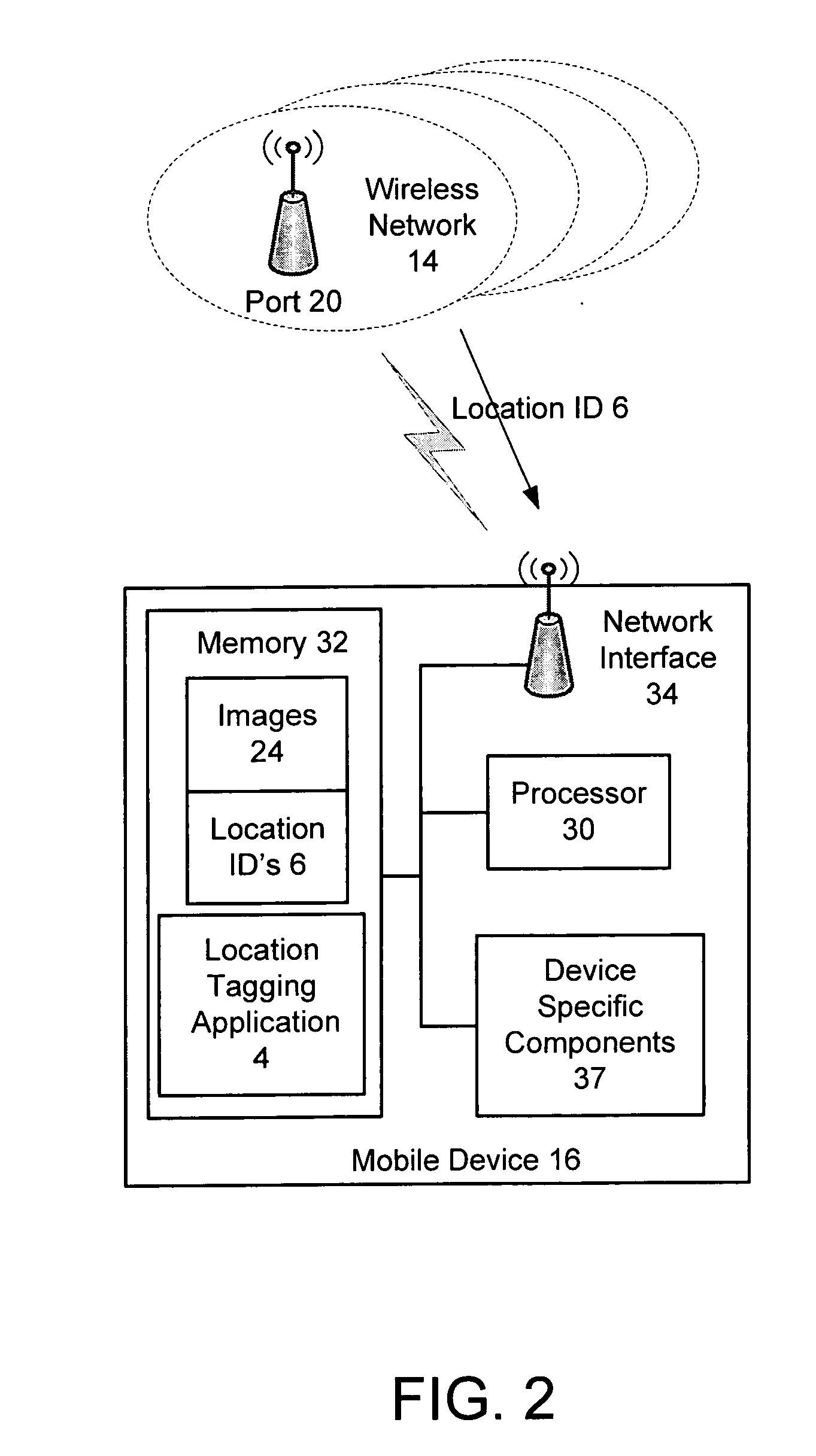
Using local networks for location information and image tagging
InactiveUS20060095540A1Information formatMultiple digital computer combinationsDigital imageImage capture
The present invention provides a method for establishing a location for a digital image without the use of a GPS unit. Aspects of the invention include broadcasting over a network a location identifier (ID) identifying a location of the network; detecting the location ID by a digital image capture device coupled to the network; and in response to the image capture device capturing a digital image when in communication with the network, associating the location ID with the digital image.
Owner:SCENERA TECH
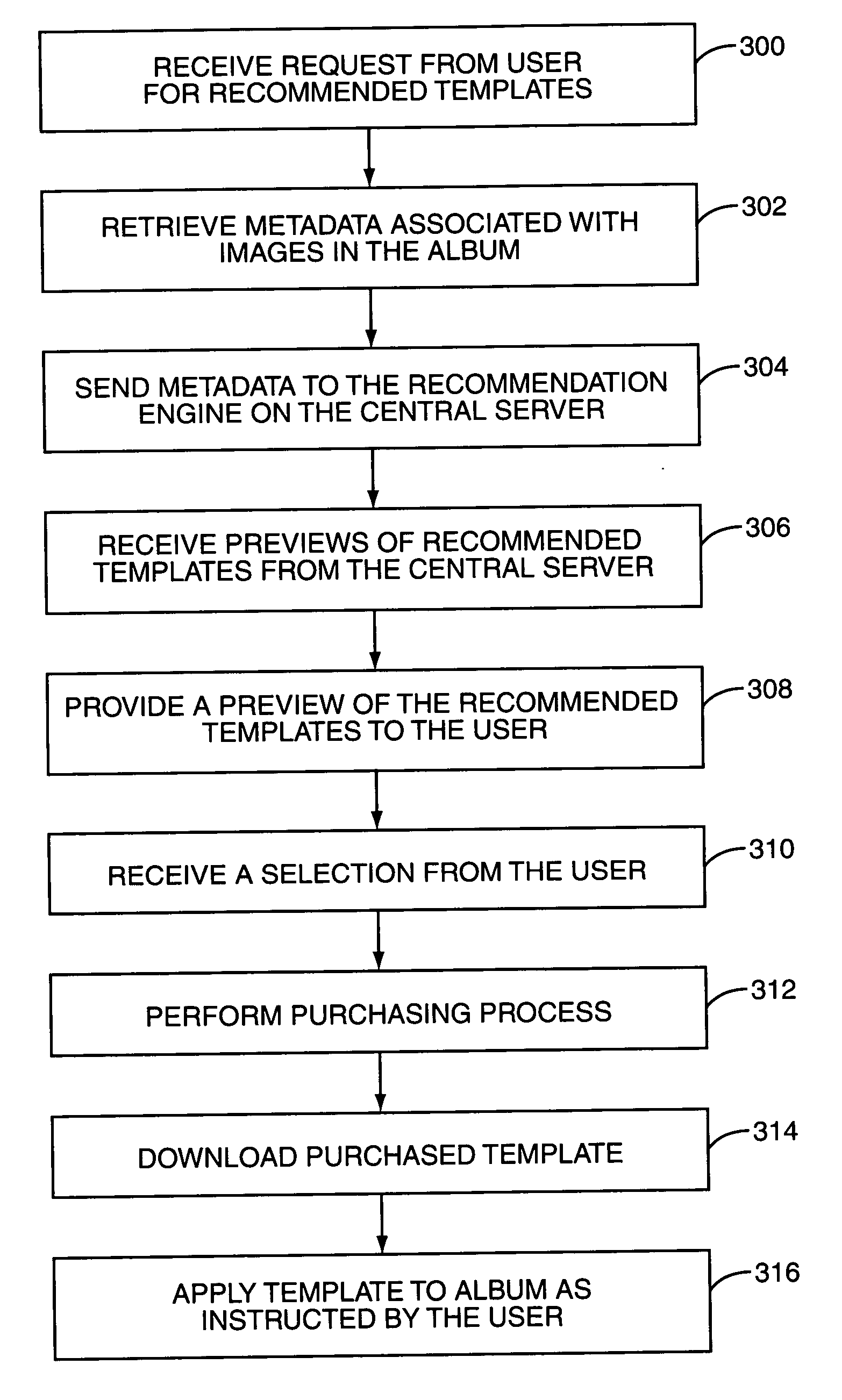
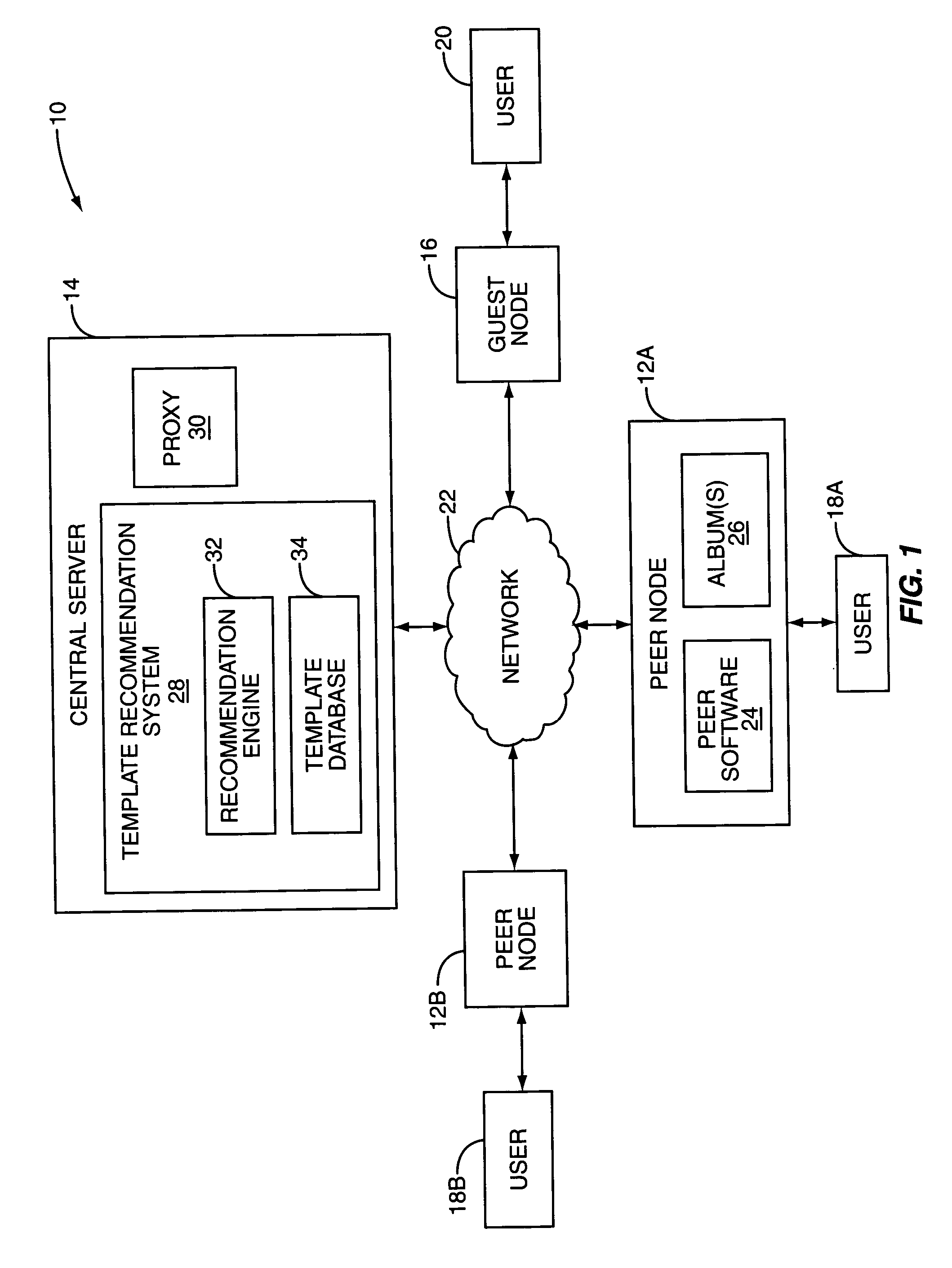
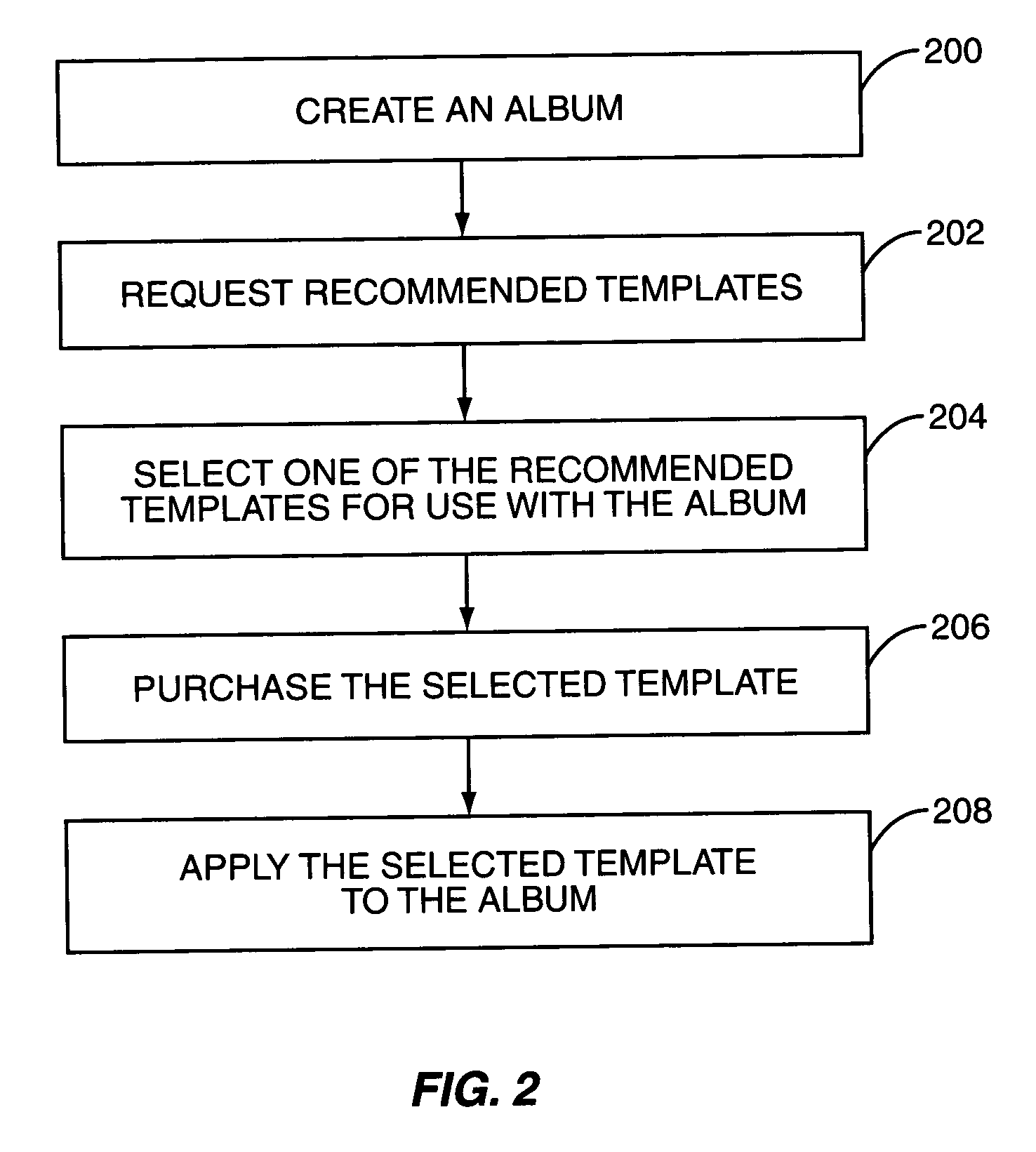
Real-time recommendation of album templates for online photosharing
InactiveUS20070064121A1Television system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsComputer graphics (images)Selection criterion
The present invention provides a system and method for recommending templates for electronic or online photo albums. In general, digital images are selected to form a photo album. The metadata associated with the digital images is analyzed to provide selection criteria. Using the selection criteria, one or more templates are selected from a template database as recommended templates. One of the recommended templates is selected and applied to the photo album.
Owner:QURIO HLDG
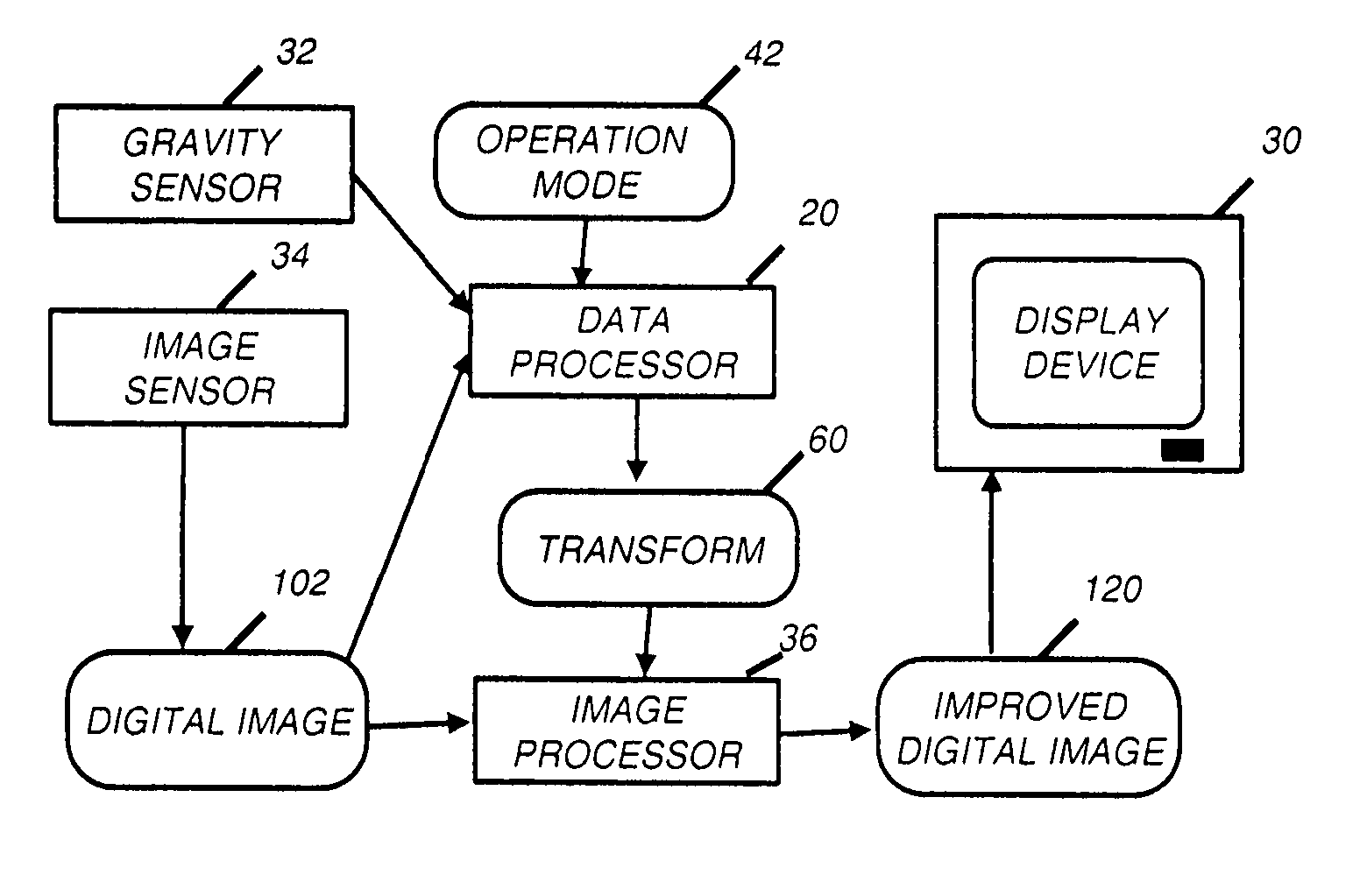
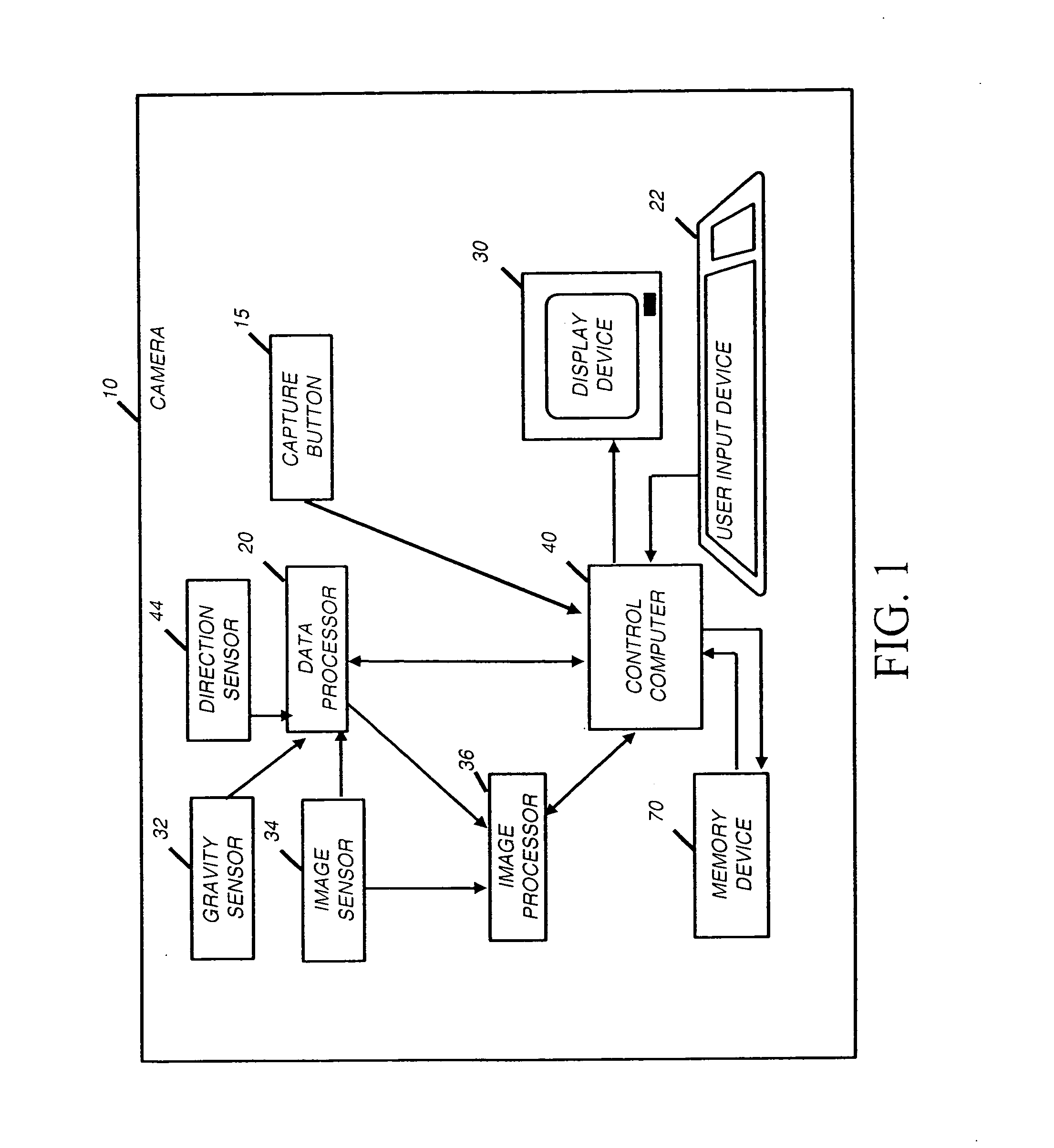
Image processing based on direction of gravity
ActiveUS20060078214A1Easy to optimizeReduce Perspective DistortionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingDigital image
A method of processing a digital image to produce an improved digital image, includes receiving the digital image captured with a camera; determining a first vanishing point associated with the digital image; determining a second vanishing point associated with the digital image corresponding to a direction orthogonal the first vanishing point; determining a transform for modifying the digital image based on the first vanishing point and the second vanishing point; and applying the transform to the digital image to produce an improved digital image.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Visualization, measurement and analysis of vibrating objects
InactiveUS20050279172A1Low costReduce the numberVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesObject motionFull field
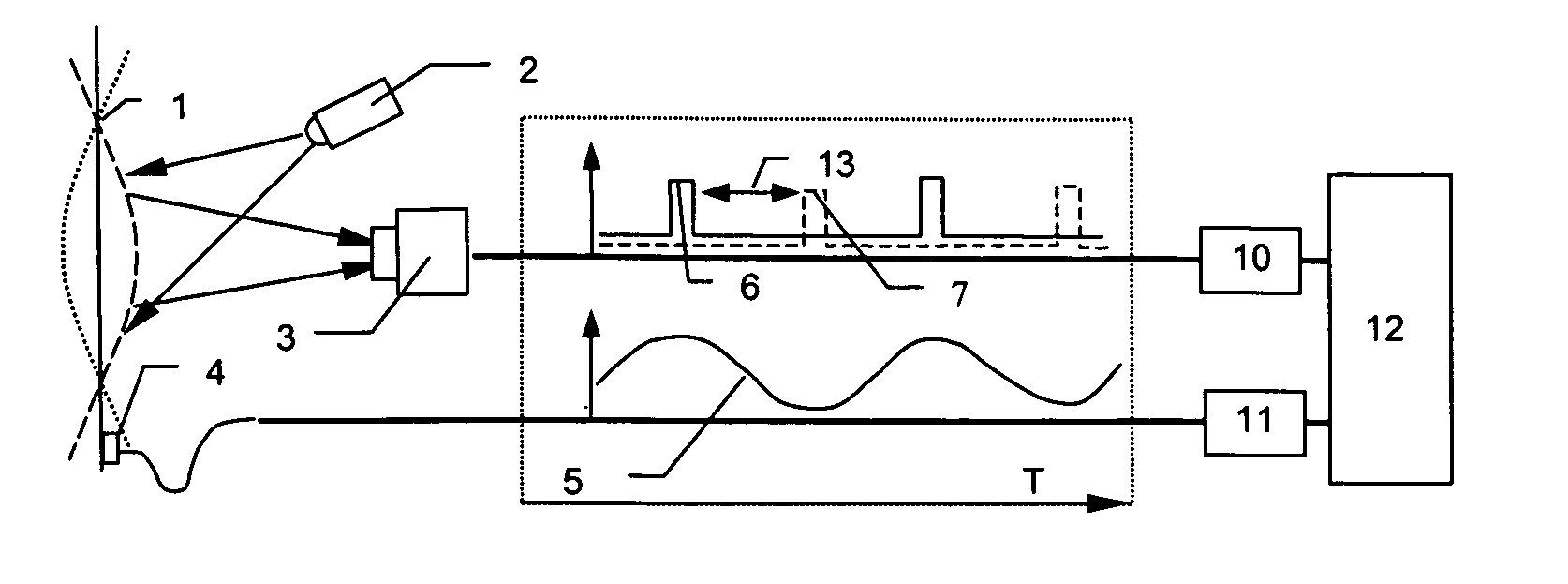
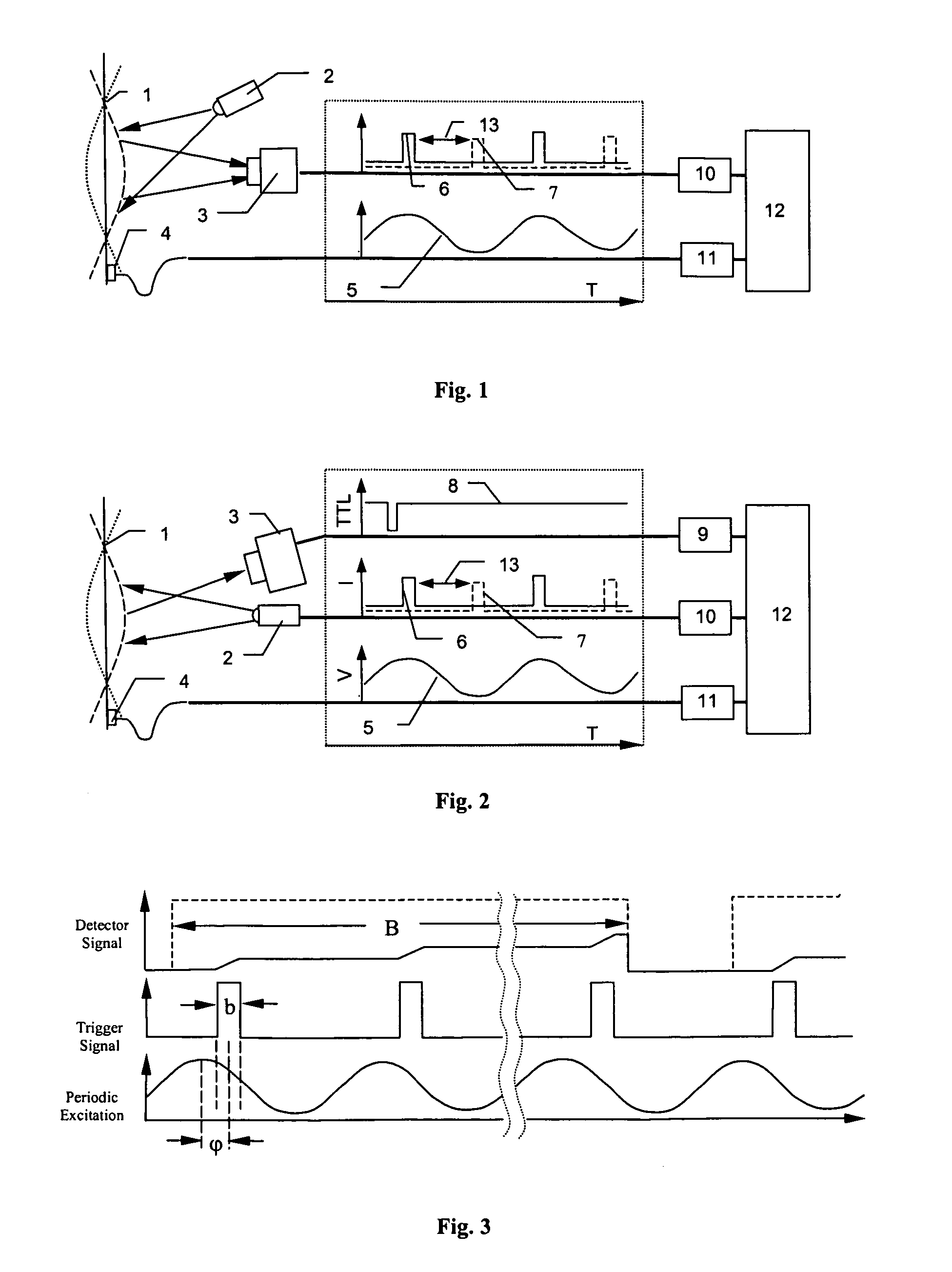
A simple, relatively inexpensive, non-contacting, full-field (total visible surface) measurement and visualization methodology is described to measure the object motions and the object stretches and object distortions (deformations) during oscillation of an object. The method is capable of full-field measurement of 1D, 2D and / or 3D object motions and the associated object surface deformations on vibrating objects. The methodology is based on a combination of stroboscopic image ascuisition and / or controlled image exposure time with a synchronization system to acquire the images at appropriate times during periodic oscillation of an object; the periodicity of the applied excitation is used to mitigate the requirement for high speed imaging. Then, image matching procedures, such as 3D digital image correlation, are used with software to extract full-field object motions and surface deformations at each time of interest.
Owner:CORRELATED SOLUTIONS
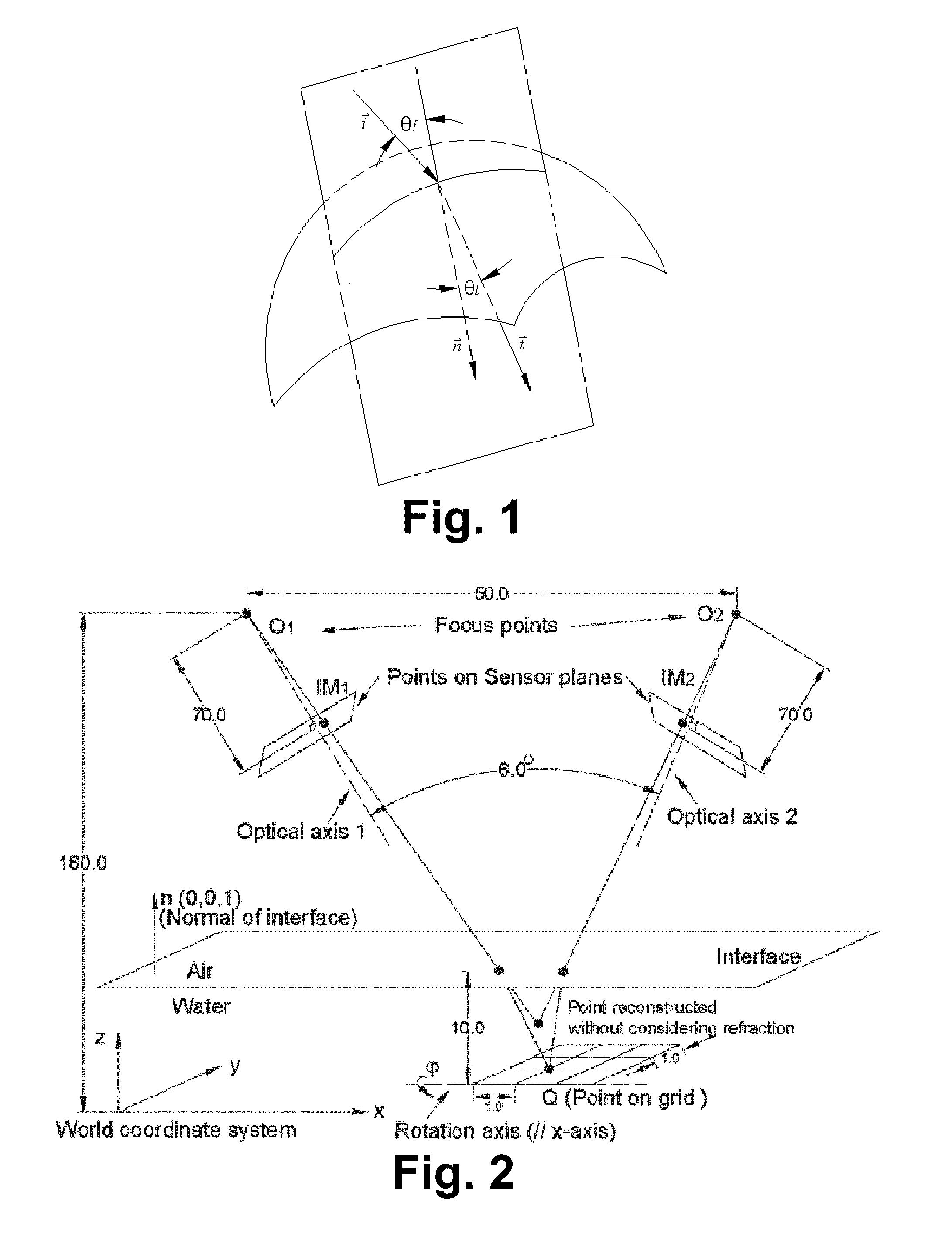
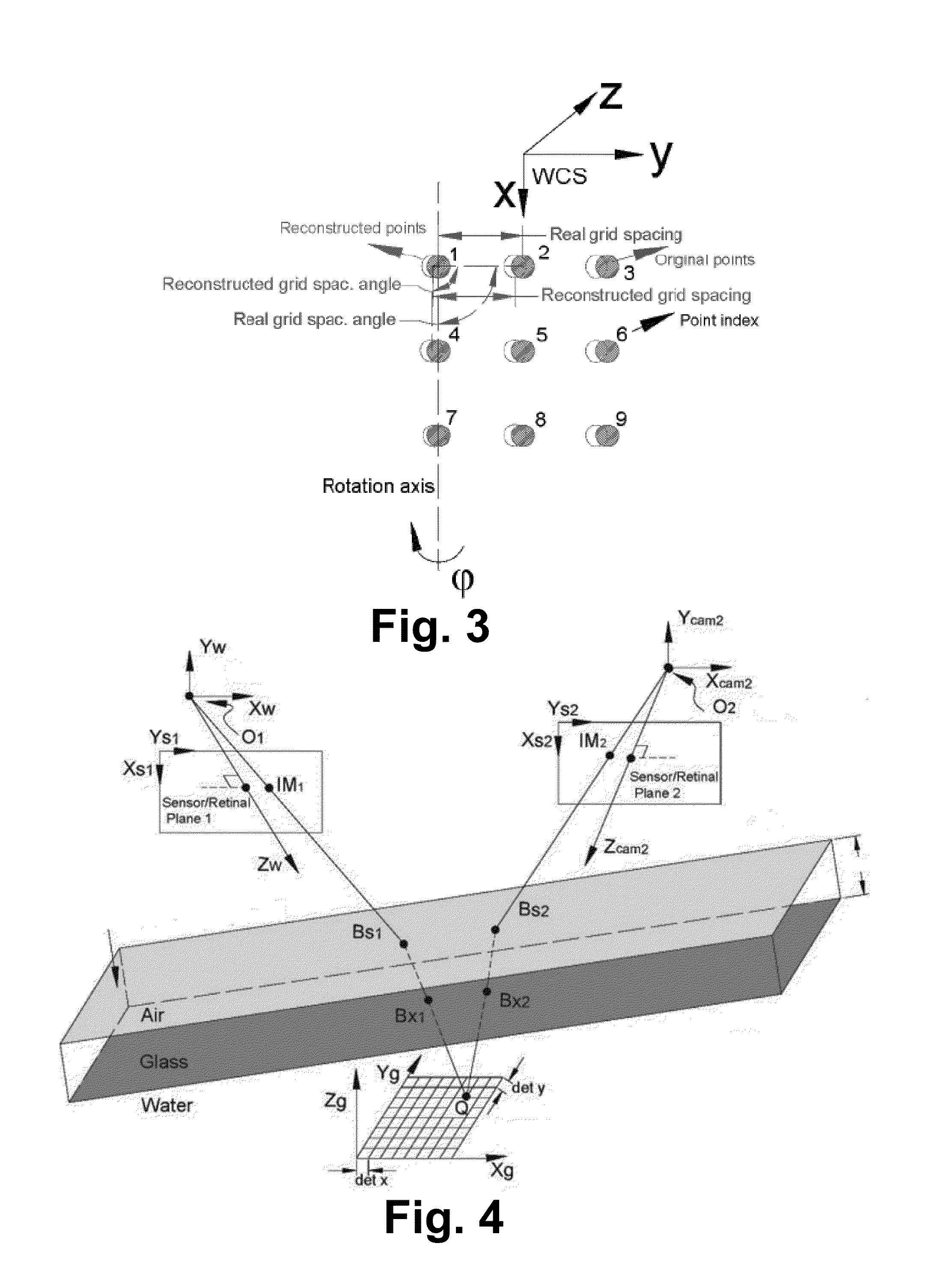
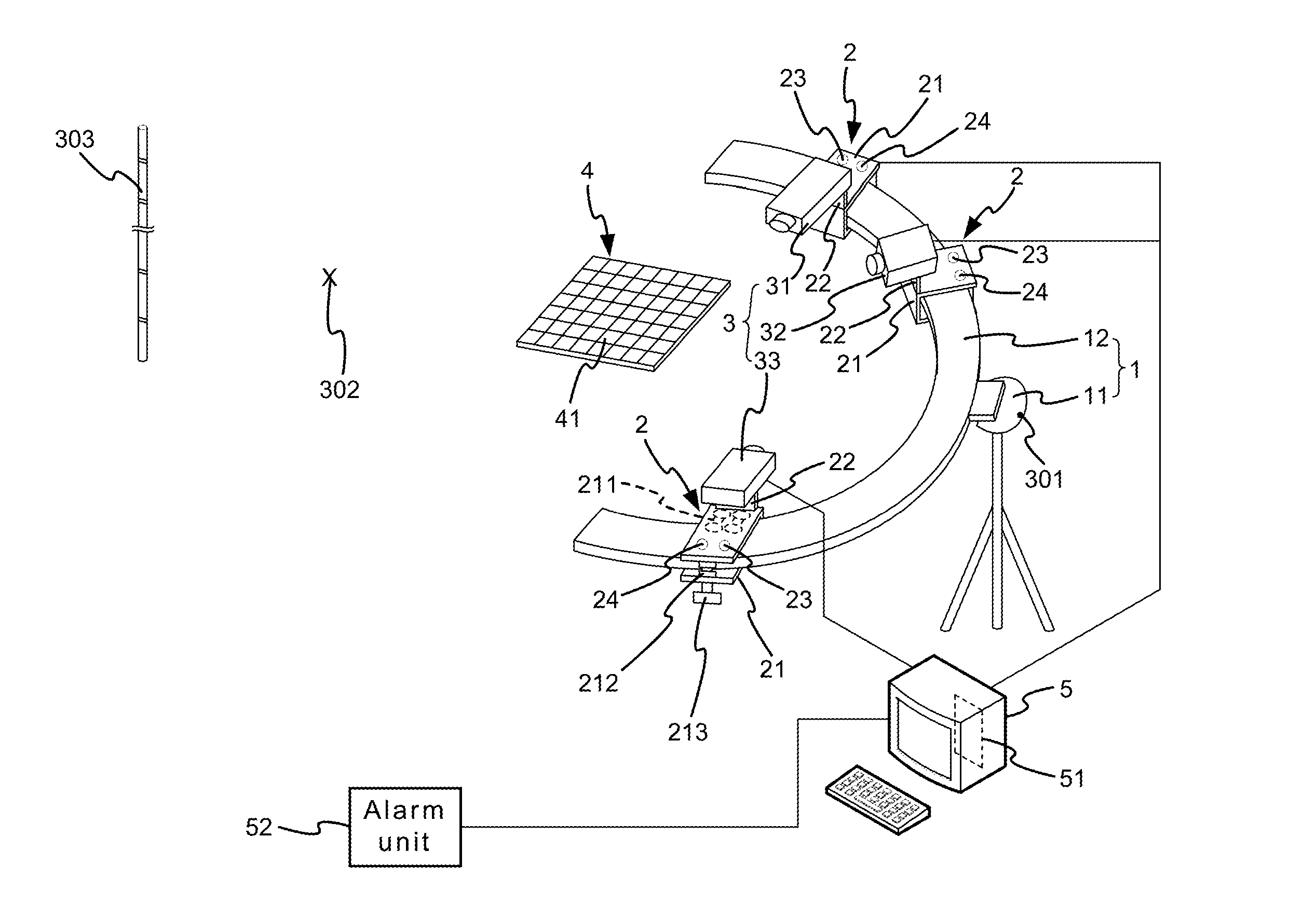
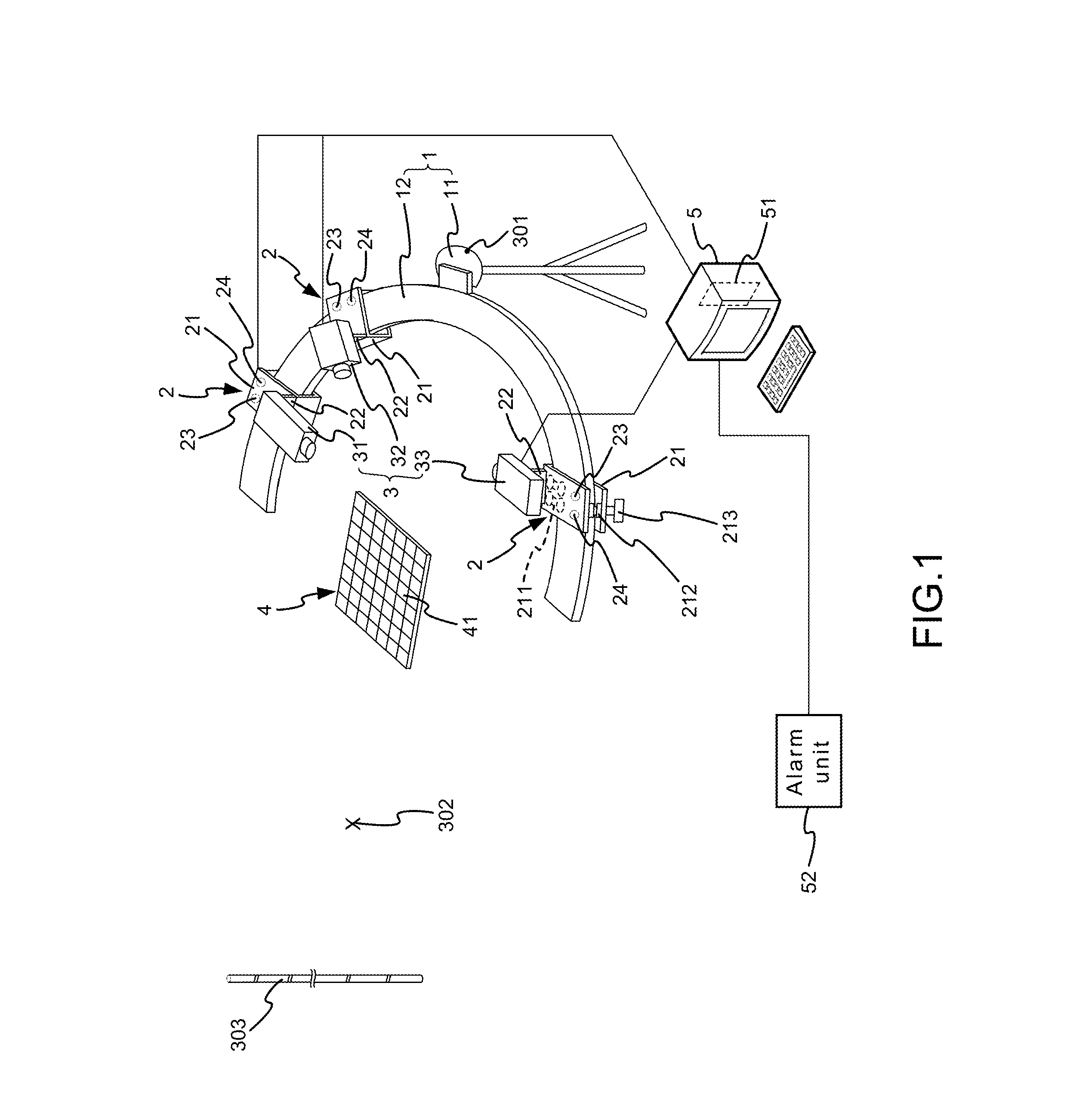
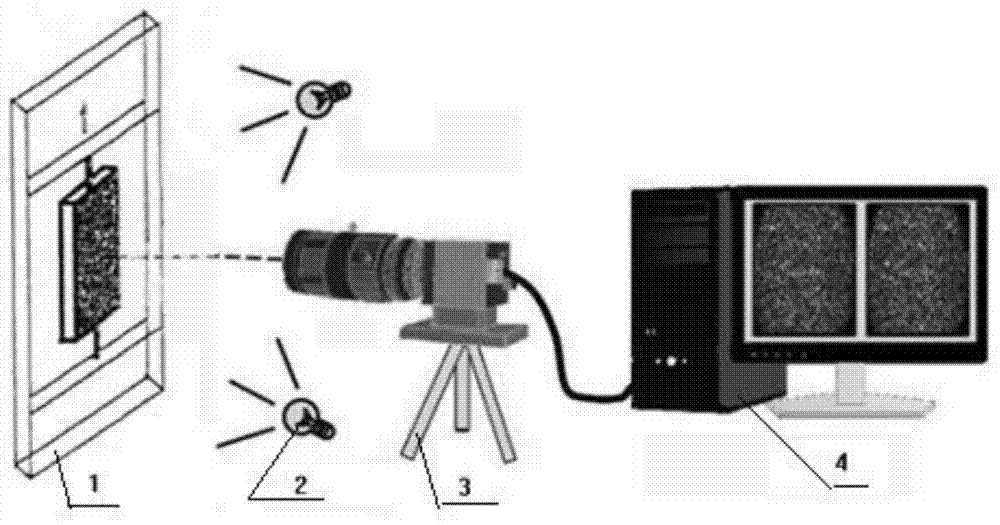
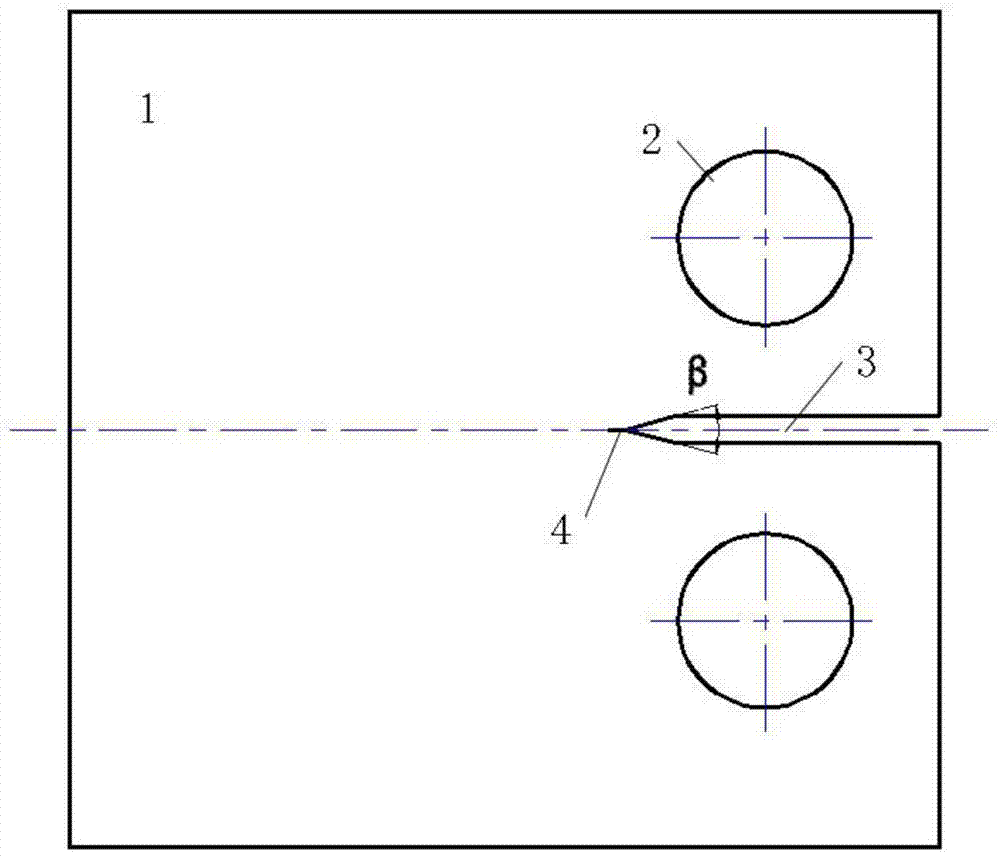
Robust Stereo Calibration System and Method for Accurate Digital Image Correlation Measurements
ActiveUS20100079598A1Maintain accuracyConvenient and accurateUsing optical meansTelevision systemsExplicit modelObject point
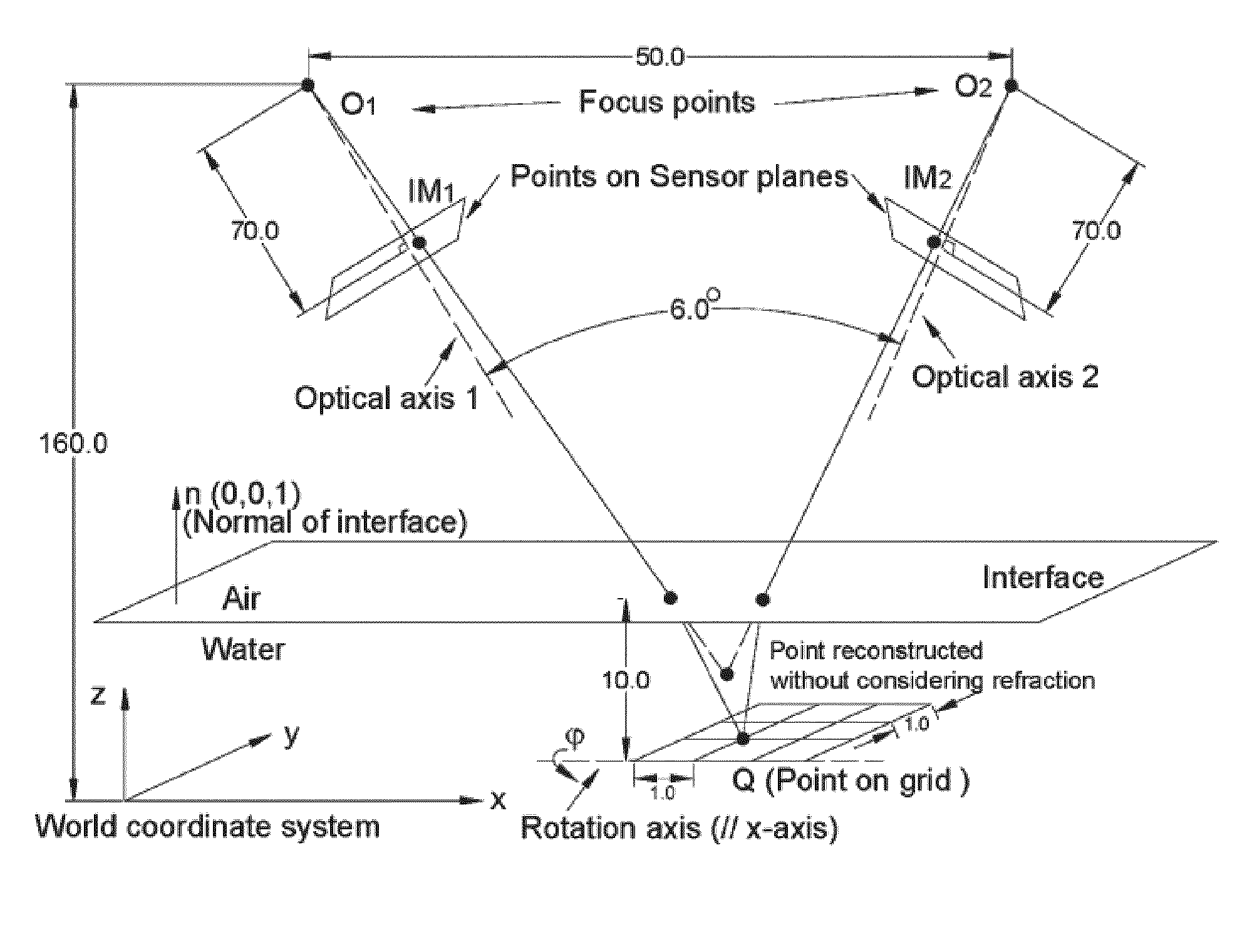
A stereo calibration method is proposed to calibrate an interface's shape and position when the measurement system is in one media and measures deformation and strain of an object that is submerged in a different media. After the interface's shape and position are modeled by parameters, an explicit model of object points as measurement is established taking account of refraction happening at the interface. Efficiency and convergence are assured by using measurement of object points to acquire initial estimates for refraction angles at the interface. Then, an optimization method is performed to get the optimized value of interface parameters. Last, based on the resulting interface parameters, 3-dimensional positions of object points in all the subsequent measurement could be reconstructed accurately. Therefore, the distortion induced by refraction in the measurement is corrected. Numerical simulations of the proposed calibration process confirm that it is both robust and accurate for a range of experimental conditions, even in the presence of Gaussian noise in the measurement.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
System and method for embedding and retrieving information in digital images and using the information to copyright the digital images
InactiveUS20060176516A1Facilitate embedding informationVisual presentationMetadata still image retrievalDigital imagingRelevant information
A system and method for embedding information in digital images and using the information to copyright the digital images are provided. The system includes a digital imaging capture device including a capture module configured to capture at least one digital image; a processing module configured to associate information to the digital image; and a transmission module configured to transmit the digital image and the associated information to a computing device; and the computing device including a communication device configured to receive at least one digital image file and associated information; and a processor configured to parse the associated information and store each piece of parsed information in at least one field of a record of a database, populate at least one field of a copyright registration form with information extracted from the database, and transmit the copyright registration form to a copyright office of a particular jurisdiction.
Owner:ROTHSCHILD MOBILE IMAGING INNOVATIONS
Automatic document separation
ActiveUS8693043B2Reduce effortReduce configuration timeDigitally marking record carriersImage analysisDigital imageDocumentation
Owner:KOFAX
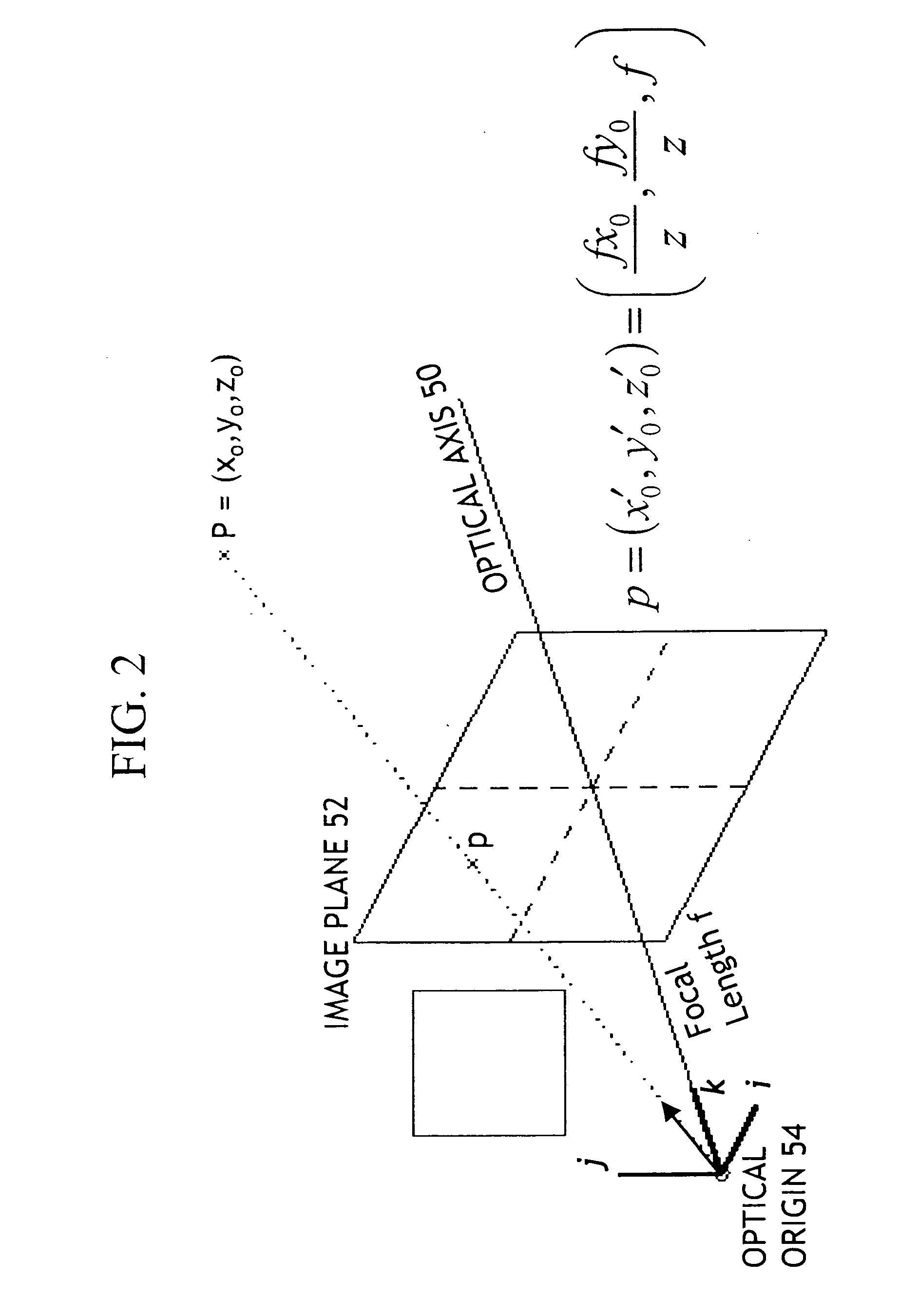
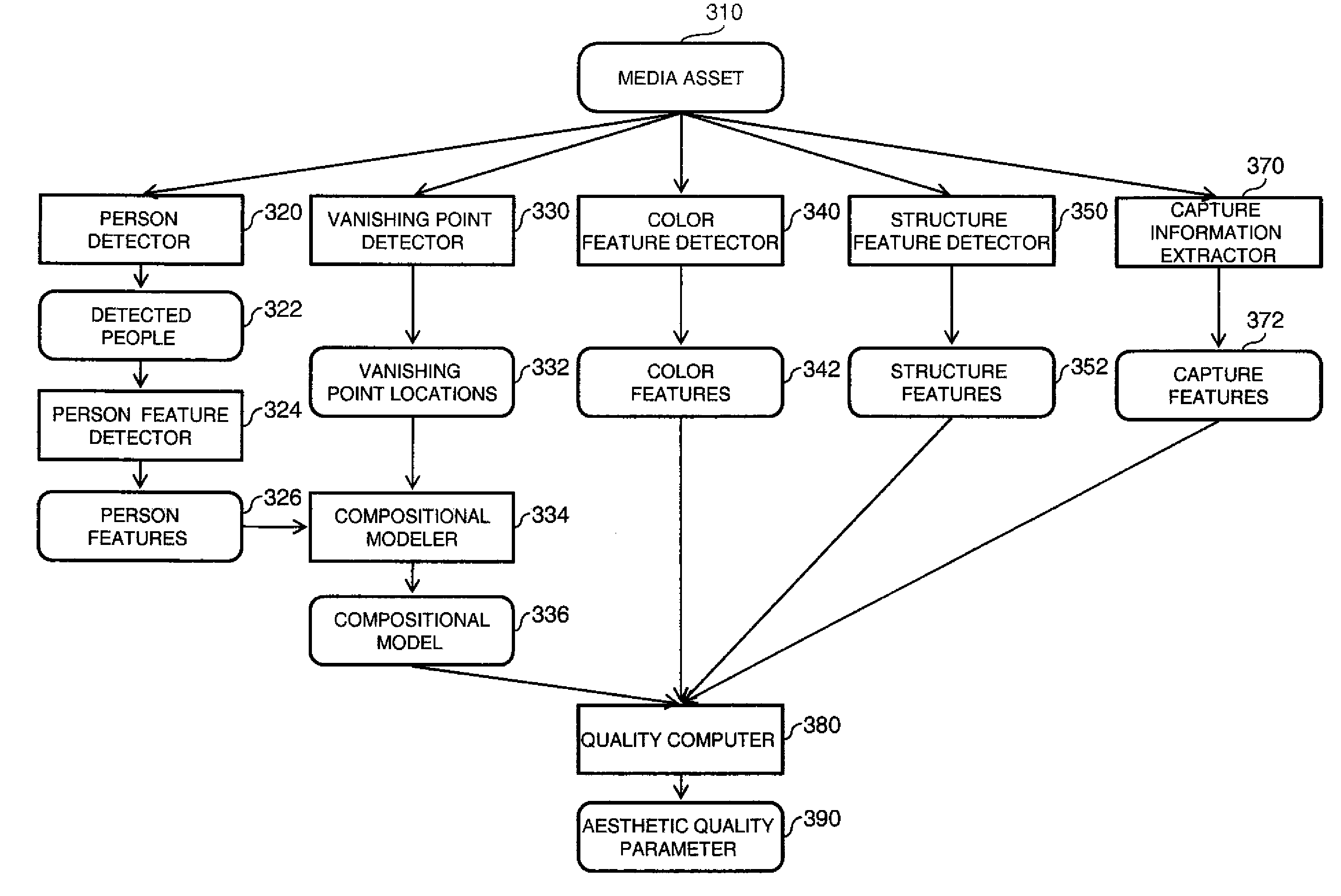
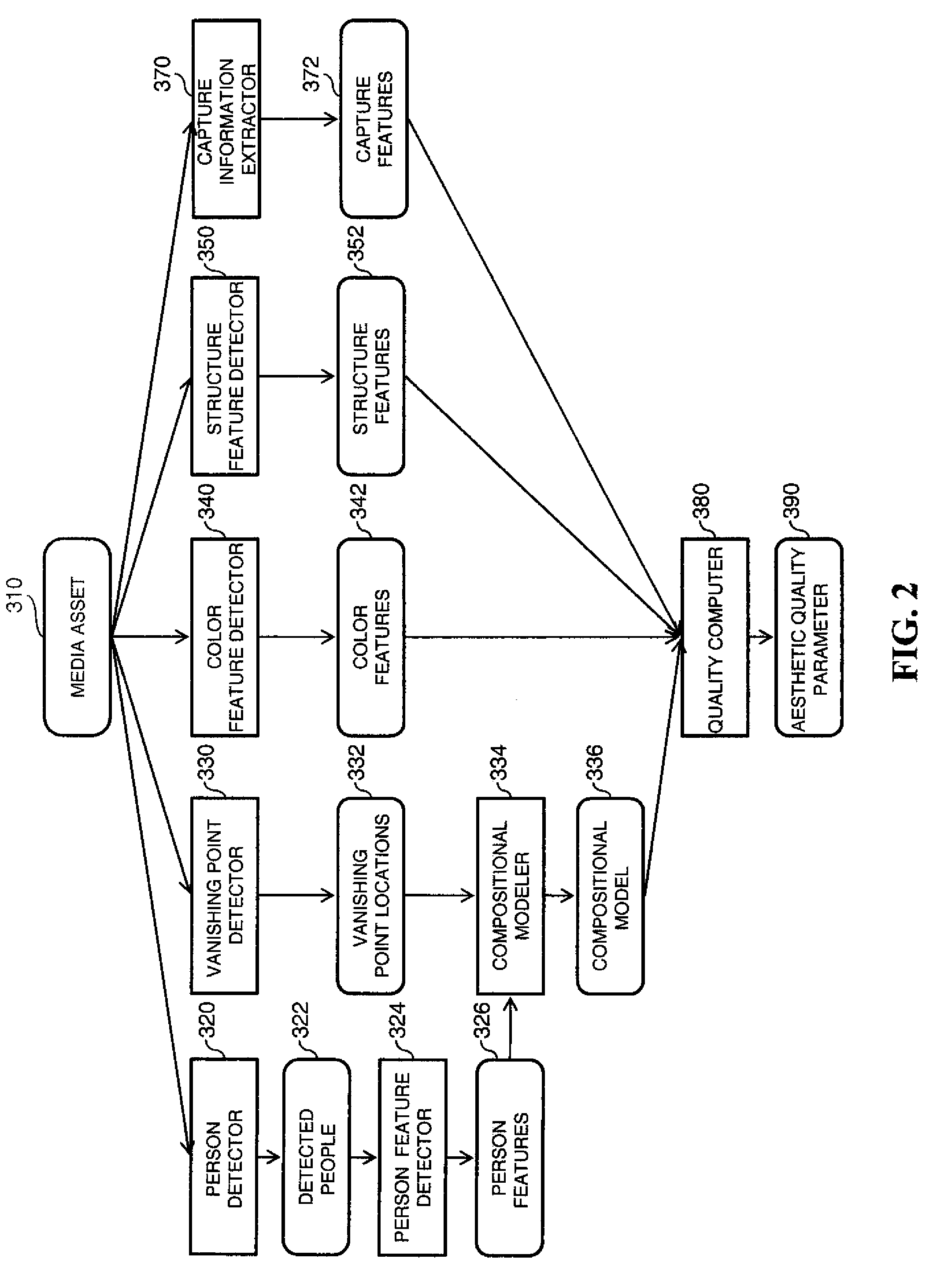
Estimating aesthetic quality of digital images
InactiveUS20110075917A1Improve aesthetic qualityHigh levelImage enhancementImage analysisDigital imageVanishing point
A method for estimating the aesthetic quality of an input digital image comprising using a digital image processor for performing the following: determining one or more vanishing point(s) associated with the input digital image by automatically analyzing the digital image; computing a compositional model from at least the positions of the vanishing point(s); and producing an aesthetic quality parameter for the input digital image responsive to the compositional model, wherein the aesthetic quality parameter is an estimate for the aesthetic quality of the input digital image.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Device and method for embedding and retrieving information in digital images
InactiveUS20060114337A1Facilitate embedding informationTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital imagingMobile phone
A digital imaging device and methods thereof that will enable the embedding and retrieving of information in digital images are provided. The digital imaging device includes a capture module for capturing an image and creating a digital image file; an input module for inputting information regarding the captured image; and a processing module for associating the inputted information to the digital image file. The device further includes a scanning module for reading a symbology associated with a printed digital image and wherein the processing module is adapted to use the symbology to retrieve the associated information of the digital image file. The device may be embodied as a digital camera, a mobile phone, personal digital assistant (PDA), etc.
Owner:ROTHSCHILD MOBILE IMAGING INNOVATIONS
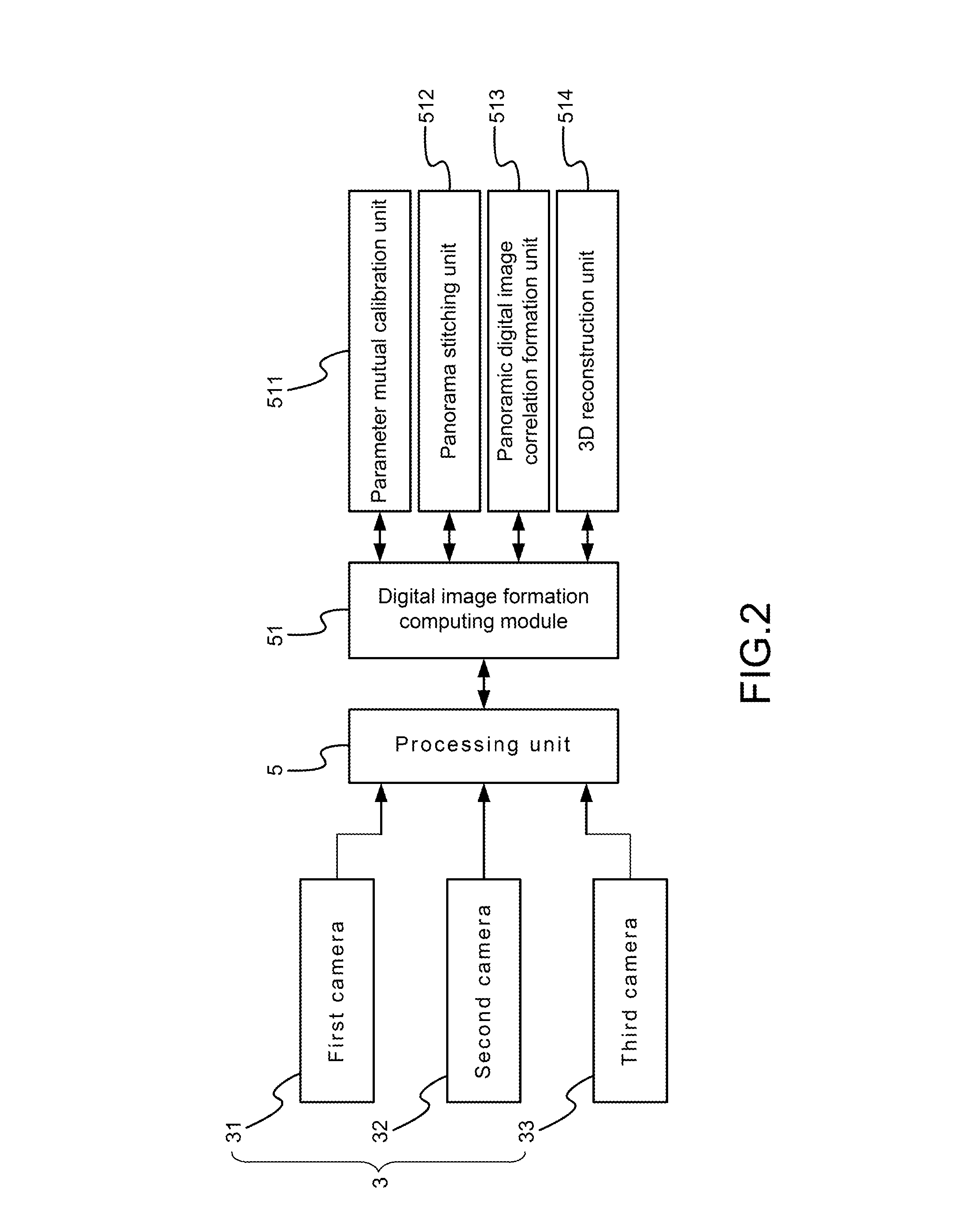
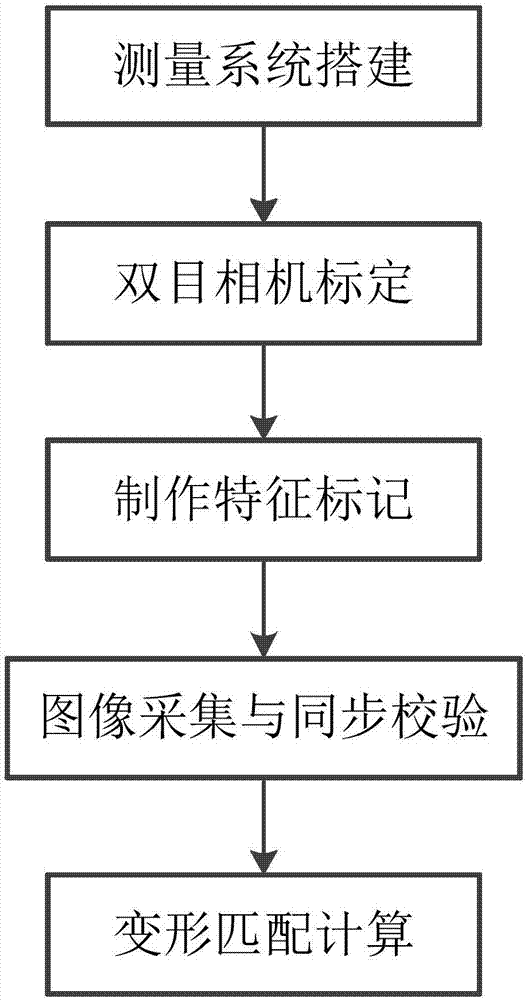
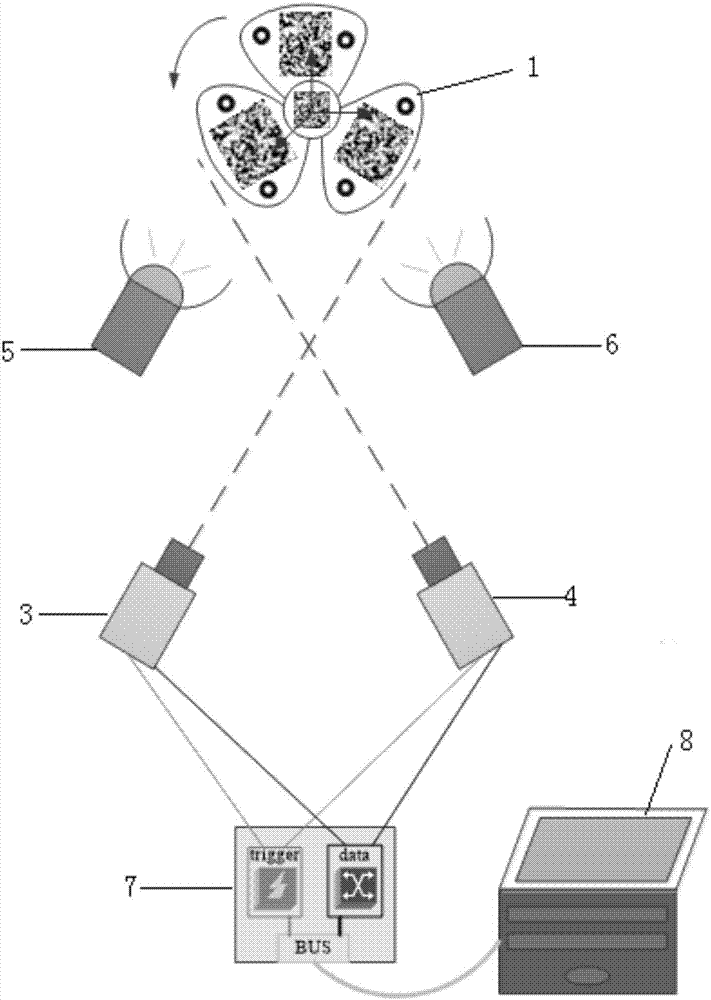
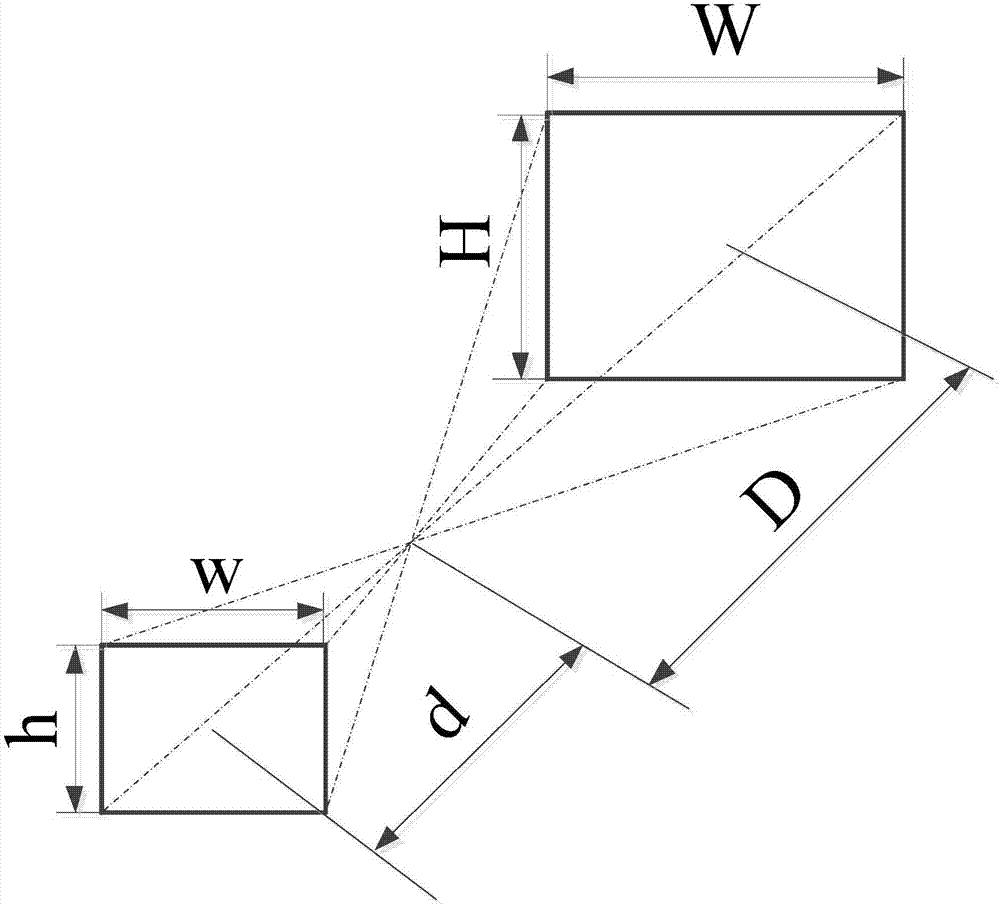
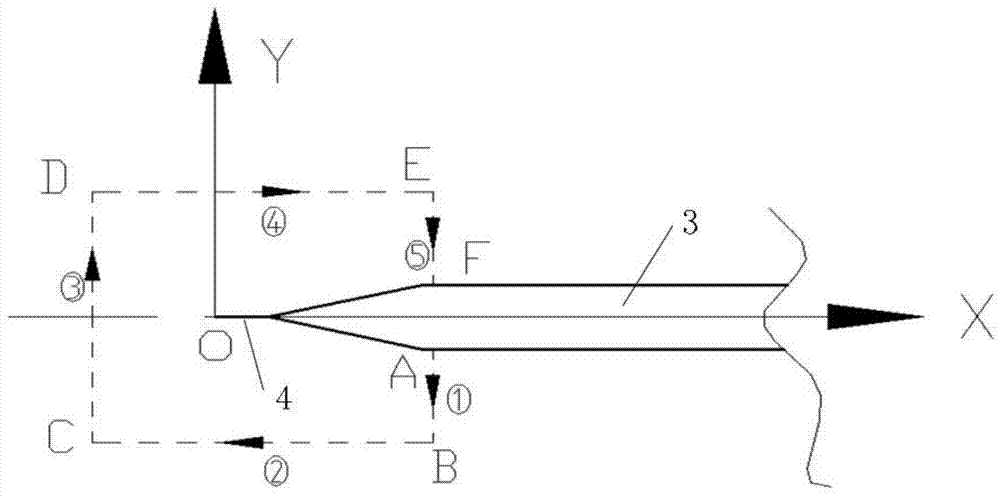
Formation Apparatus Using Digital Image Correlation
The present disclosure uses at least three cameras to monitor even a large-scale area. Displacement and strain are measured in a fast, convenient and effective way. The present disclosure has advantages on whole field, far distance and convenience.
Owner:NAT APPLIED RES LAB
Determining an interest level for an image
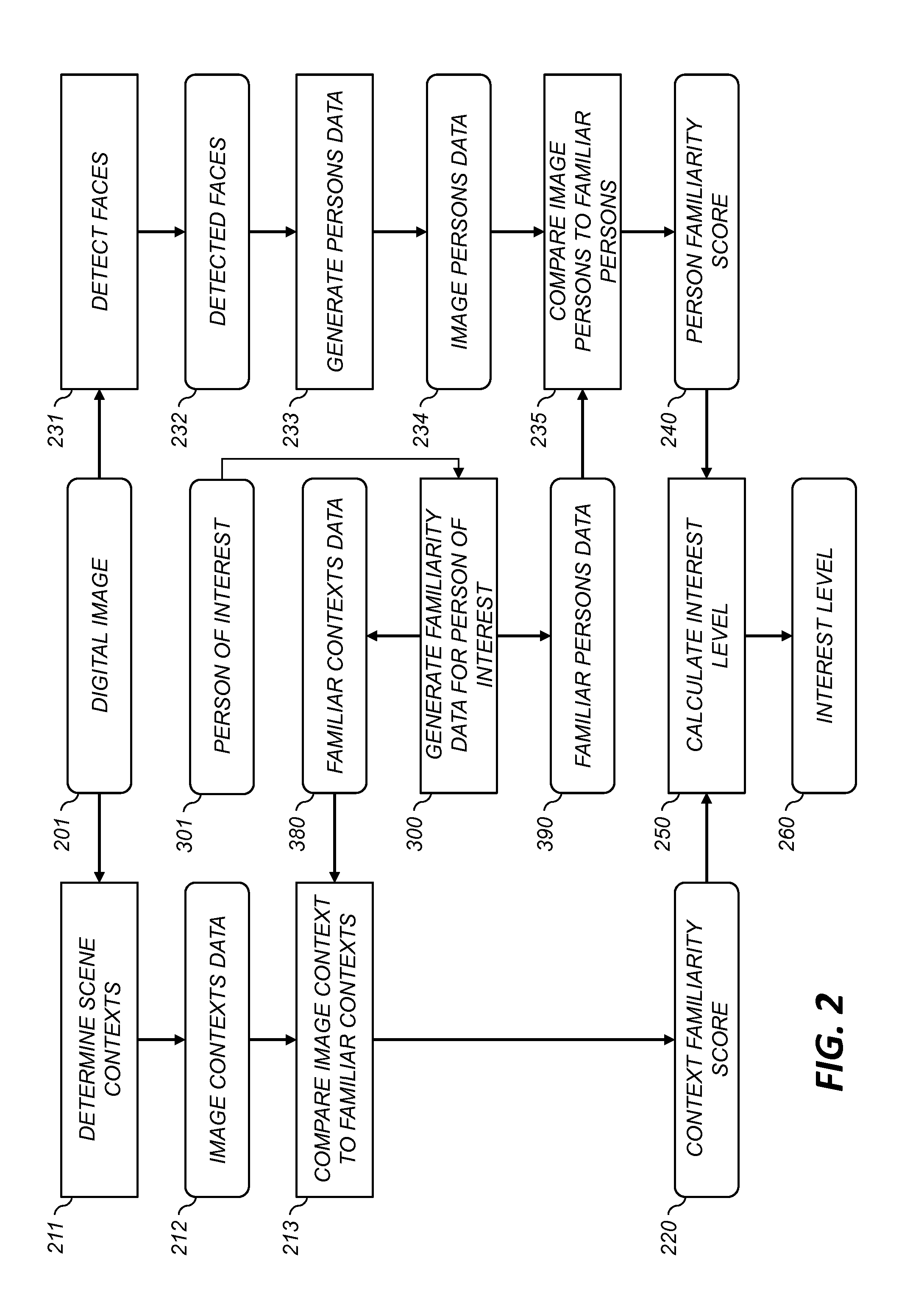
InactiveUS20140003648A1Capture and maintain attentionCharacter and pattern recognitionTransmissionDigital imageComputer vision
A method for determining an interest level of a digital image to a particular person. The digital image, or metadata associated with the digital image, is analyzed to designate one or more image elements in the digital image. Familiarity levels of the designated image elements to the particular person are determined. The interest level of the digital image to the particular person is then determined responsive to the determined familiarity levels. In some embodiments the image elements include persons and scene contexts, where digital images containing more familiar persons and less familiar scene contexts correspond to higher interest levels.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
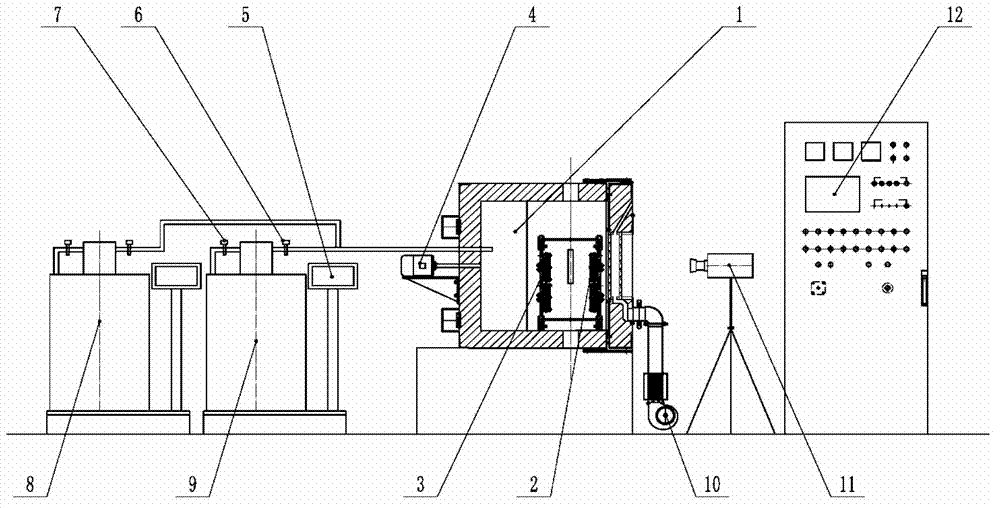
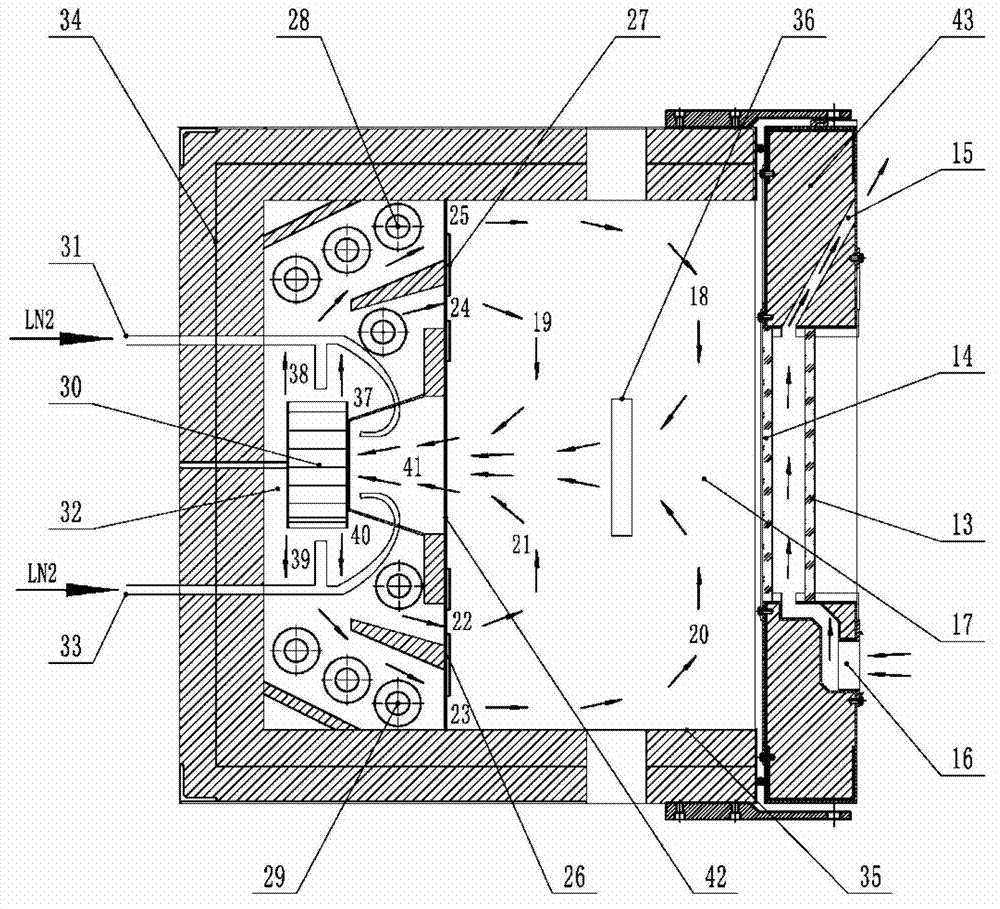
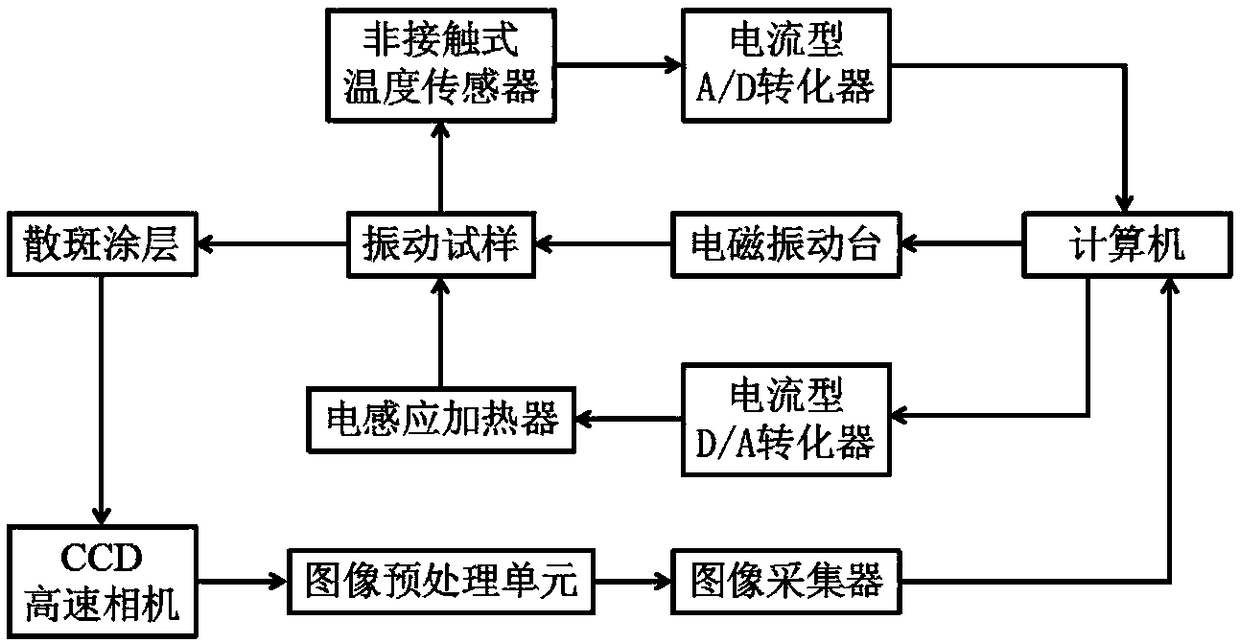
High-low temperature dynamic cold-hot circulation thermodynamic test system
InactiveCN102879278ARealize two-way cooling and heating cycleLow temperatureMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesLiquid nitrogen containerEngineering
The invention discloses a high-low temperature dynamic cold-hot circulation thermodynamic test system suitable for mechanics performance testing under a high-low temperature environment. A test box adopts a design of an inner cavity and an outer cavity; inner and outer cavity baffles are provided with four air outlets from top down and air suction holes in the center; the test box further comprises an optical strain observation window, a defrosting air heater and a multi-point direct-current illumination source; and in addition, the test system further comprises a dual-output PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) controller, a DIC (Digital Image Correlation) full strain measurement instrument and an automatic switchover liquid nitrogen refrigerating system. According to the high-low temperature dynamic cold-hot circulation thermodynamic test system, the defects that the conventional thermal steady state test system has no thermal transient state and thermal circulation functions and liquid nitrogen cannot be fed without interruption due to limitation of liquid nitrogen container volume on low-temperature refrigeration are solved, and the technical problems of interference and the like of high-temperature hot wave impact and low-temperature frost fog on full strain measurement are solved at the same time, so that the purposes of obtaining the mechanical performance of a test material under the high-low temperature environment in the processes of thermal steady state, thermal transient state, cold-hot circulation and the like and synchronously measuring a sample strain field are achieved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
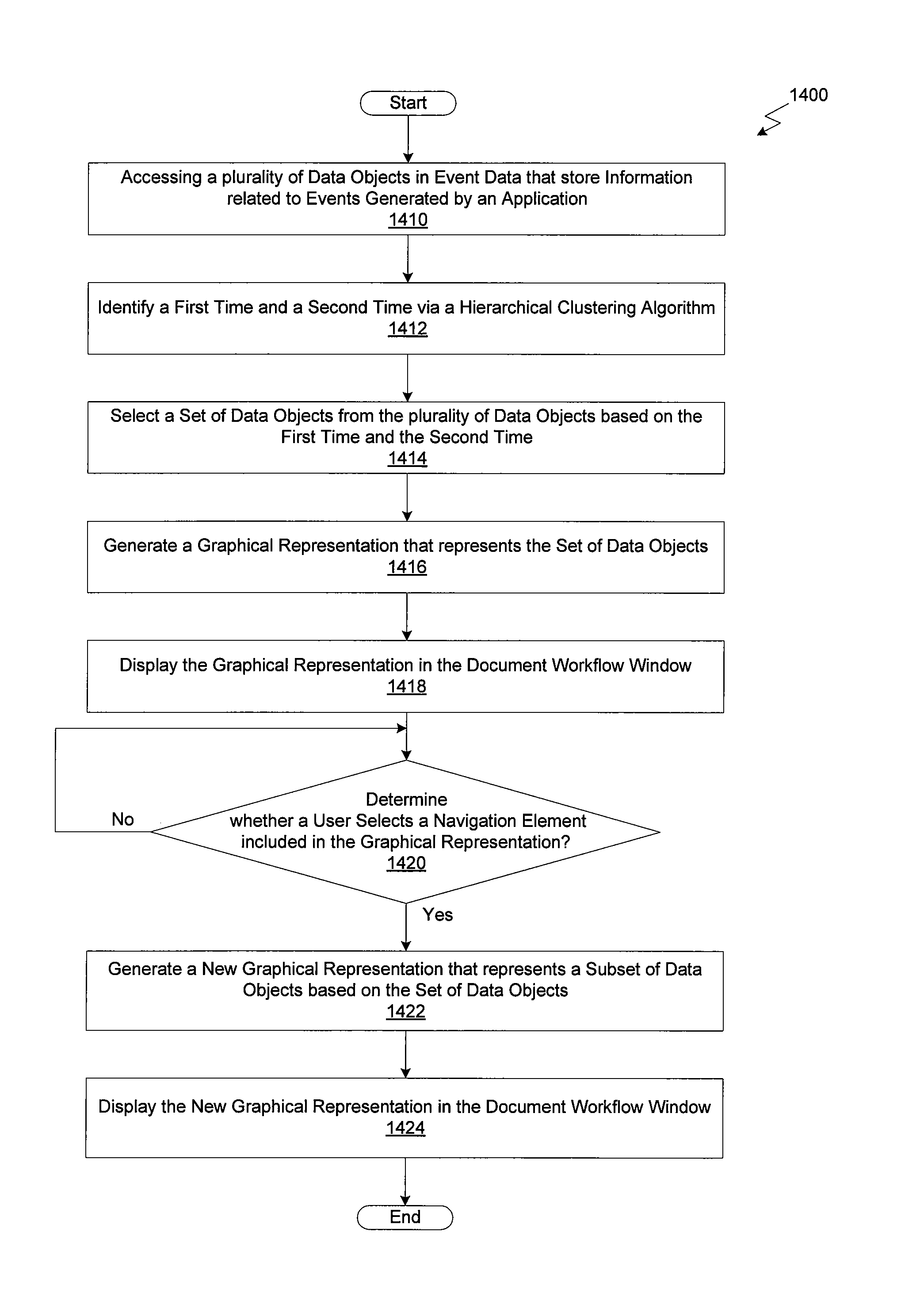
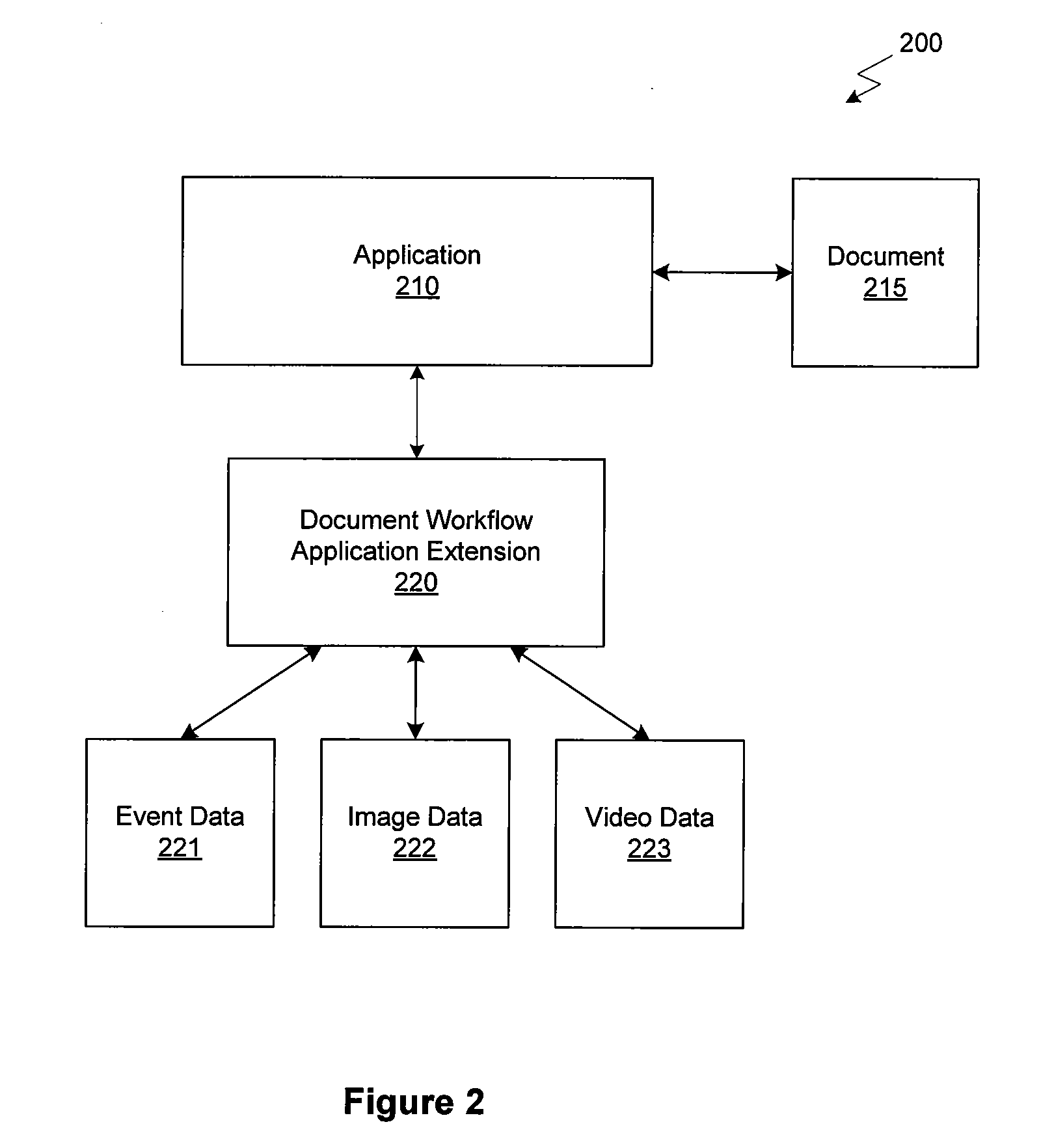
Hierarchical display and navigation of document revision histories
ActiveUS20120272173A1Electronic editing digitised analogue information signalsCarrier indicating arrangementsDigital videoGraphics
A system and technique for displaying a document's workflow history are disclosed. The system includes a graphical user interface for displaying one or more graphical representations of events generated by an application configured to edit a document. Each of the events generated by the application may be stored in a data structure that is associated with one or more portions of the document. The data structure may also be associated with a digital image that reflects the state of the document at the time the event was generated and one or more frames of digital video captured substantially simultaneously with the generation of the event. The system may display the stored events via graphical representations in the graphical user interface that represent a portion of the total document workflow history. A user may navigate through the graphical events based on a hierarchical algorithm for clustering events.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
System and method for measuring residual stress in real time
InactiveCN102072877AReal-time online drilling non-contact full-field measurementEasy to operateUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisElectric machineryEngineering
The invention relates to a system and a method for measuring residual stress in real time. The method comprises the following steps of: performing three-dimensional surface coordinate reconstruction on a test piece by three-dimensional digital image correlation, performing related research on a speckle image at the periphery of a hole before and after drilling the test piece, and calculating a three-dimensional displacement field before and after drilling; automatically feeding an electric spindle precisely through control over a stepping motor by a stepping motor controller and the translation of a worm gear and worm mechanism according to the drilling depth of the test piece; and calculating the residual stress of the test piece according to planar assumption of a drilling area of a curved surface by combining a theoretical formula for measuring the residual stress during drilling. The system can drill the hole precisely in real time, and measures the residual stress of the test piece with depth change in a stepping mode. The system and the method for measuring the residual stress have the advantages of real-time property, high precision, non-contact, whole-field displacement measurement, flexibility and convenience of operation, and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
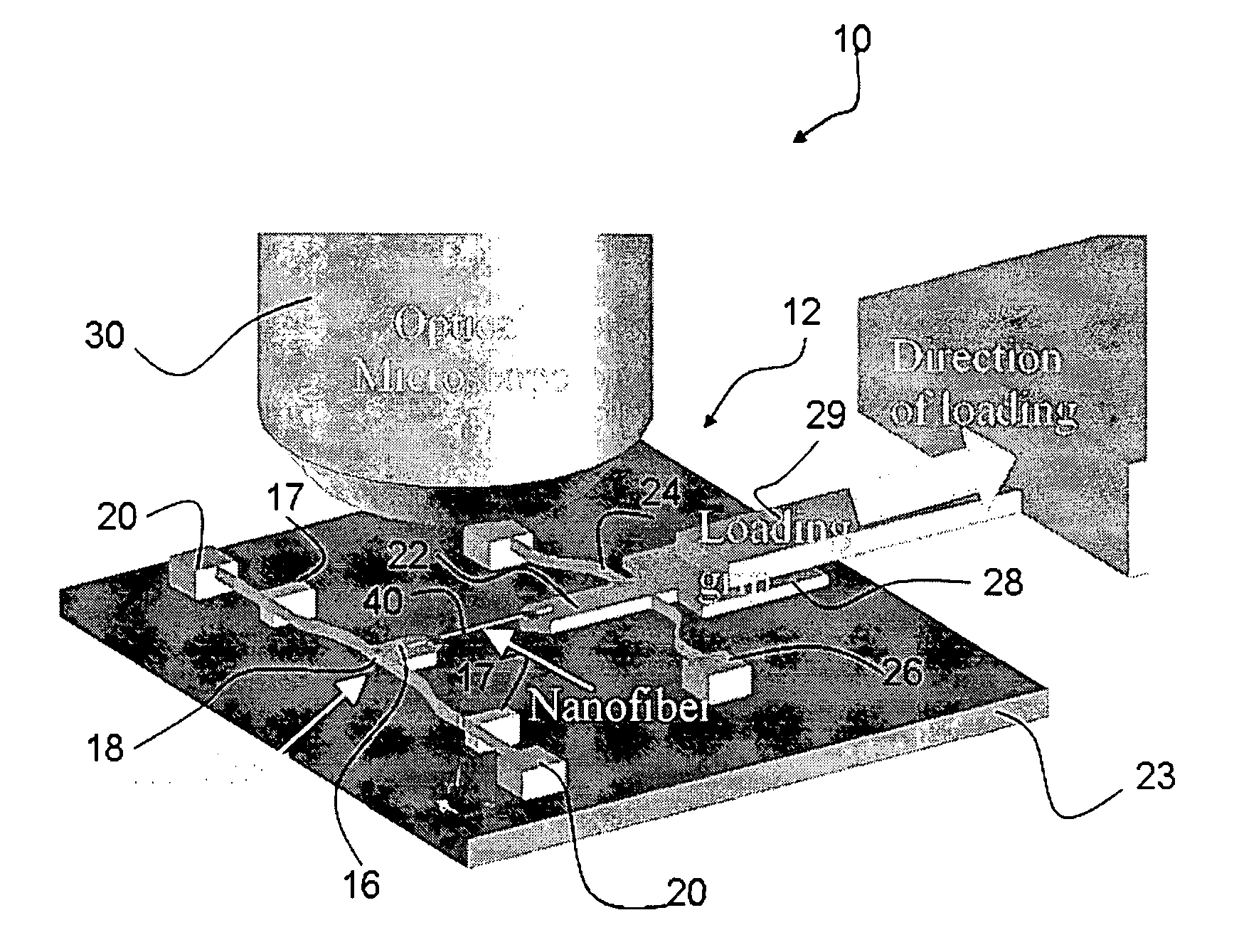
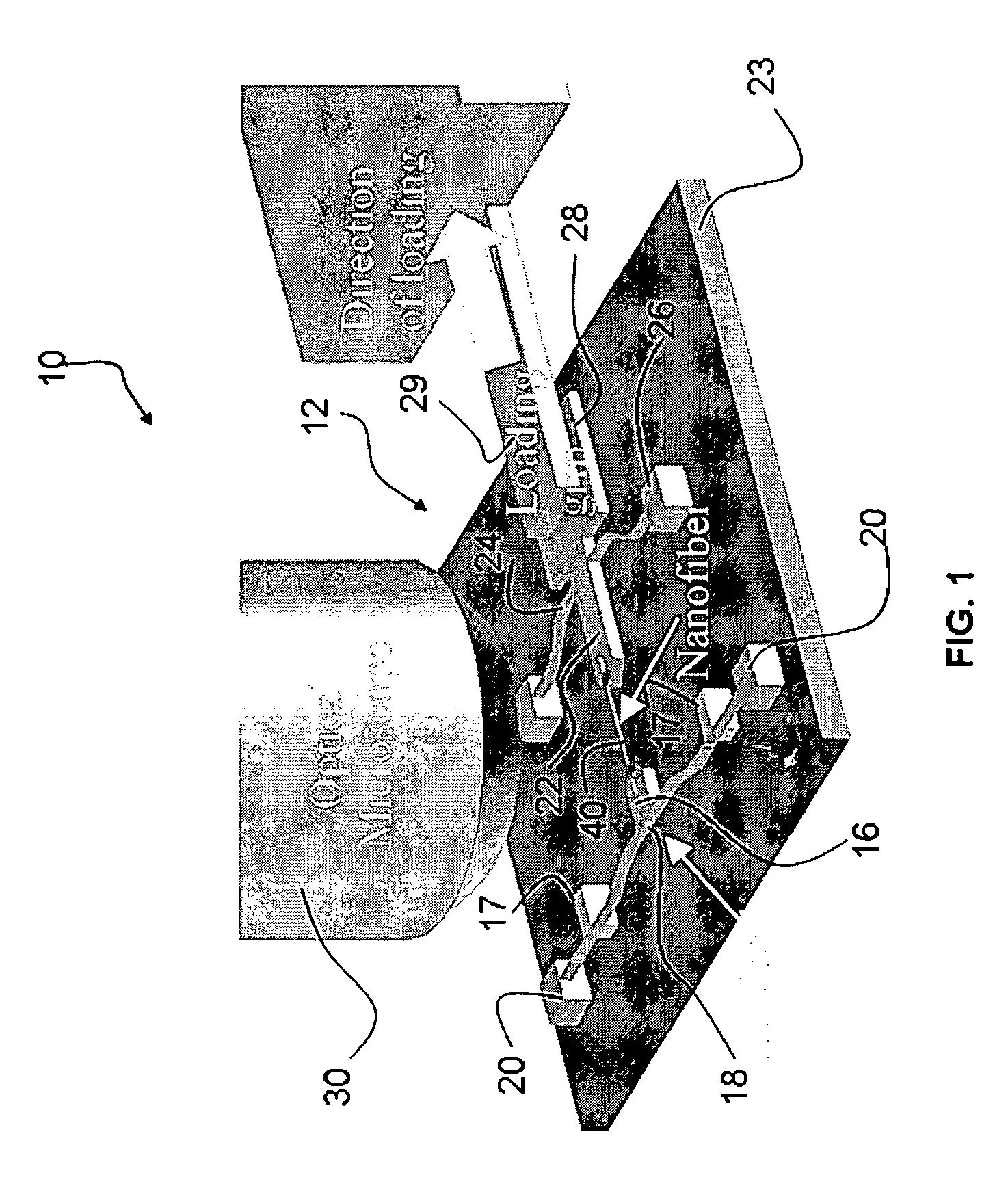
Stress micro mechanical test cell, device, system and methods
The invention provides a stress micro mechanical system for measuring stress and strain in micro- and nano-fibers tubes, and wires as well as for measuring the interface adhesion force and stress in nanofibers and nanotubes embedded in a polymer matrix. A preferred system of the invention has a substrate for supporting a MEMS fabrication. The MEMS fabrication includes freestanding sample attachment points that are movable in a translation direction relative to one another when the substrate is moved and a sample is attached between the sample attachment points. An optical microscope images surfaces of the MEMS fabrication. Software conducts digital image correlation on obtained images to determine the movement of the surfaces at a resolution much greater than the hardware resolution of the optical microscope. A preferred method for measuring stress and strain in micro- and nano-fibers, tubes, and wires, and / or measuring the force required to pull-out individual micro- and nano-fibers, tubes, and wires from a polymer matrix and to therefore measure interfacial adhesion is also provided. In the method a sample is attached between freestanding platforms in a MEMS device. Relative translational movement between the platforms is created and motion of the platforms is imaged with an optical microscope. Mechanical and adhesion properties of the sample are determined by applying a digital image correlation algorithm to the image data.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
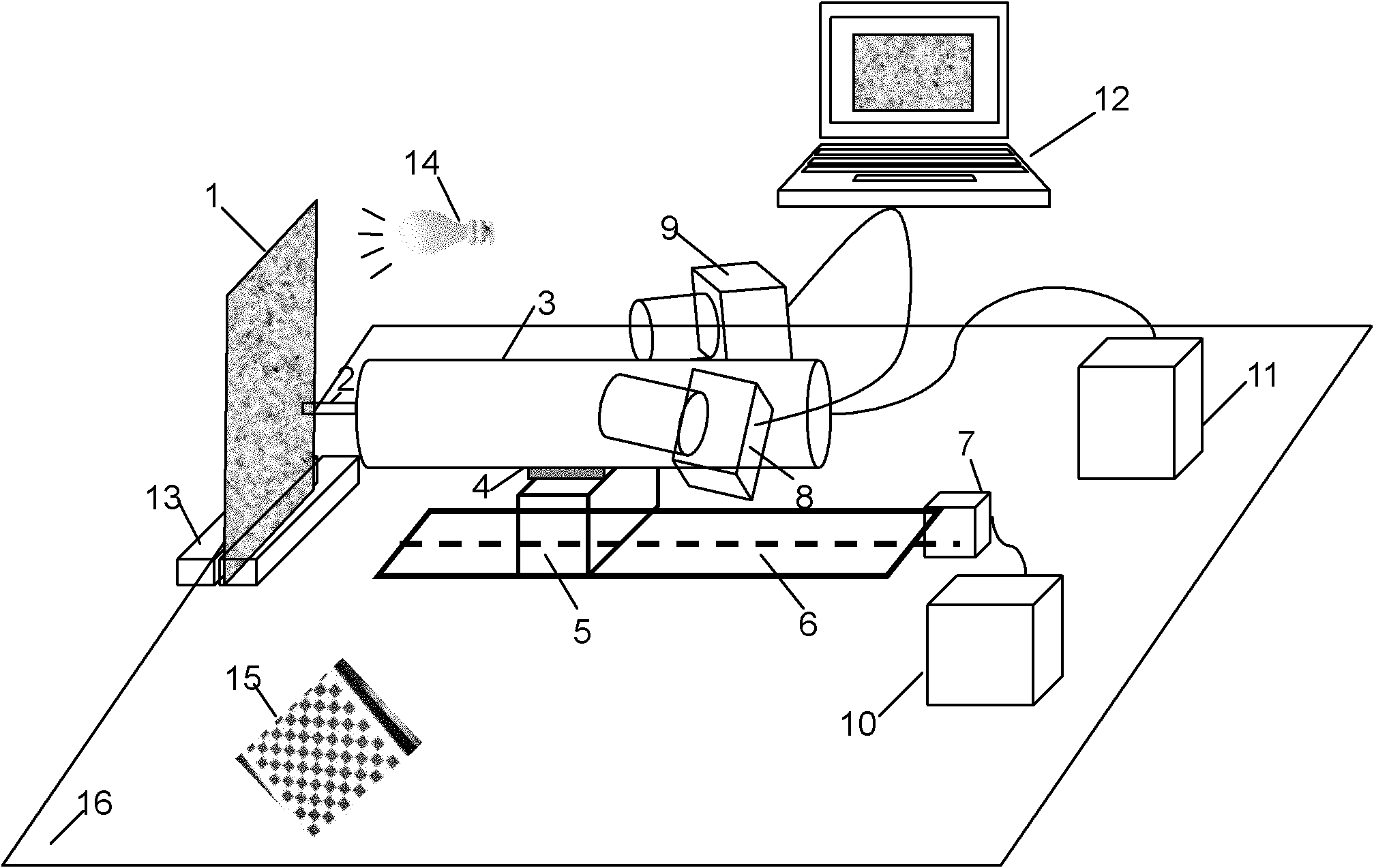
Optical method based high-speed aircraft hot surface full-field deformation measuring device
InactiveCN103558243ARealize deformation measurementGood test resultsUsing optical meansMaterial thermal analysisEngineeringRadiant heat
The invention provides an optical method based high-speed aircraft hot surface full-field deformation measuring device. The optical method based high-speed aircraft hot surface full-field deformation measuring device comprises a double-layer quartz lamp heating array, a thin-wall high-speed aircraft shell, a square transparent window, speckle particles, a thermocouple sensor, a signal amplifier, a temperature control computer, a driving power supply, a CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) camera, a lens, a narrow-band-pass optical filter and an image processing computer. In order to solve the problem of signal blockage caused by a high temperature radiant heat source between the CMOS camera and the surface of the high-speed aircraft shell, the vertical double-layer quartz lamp heating array is designed and the square transparent window with small area is formed, so that the optical camera lens can obtain images of the hot surface of the high-speed aircraft through the transparent window. The interference light ray of the quartz lamp heating array is shielded by selecting the narrow-band-pass optical filter with specific wave length, so that speckle images with high quality and no degeneration on the hot surface of the high-speed aircraft is obtained; a digital image correlation method is utilized for analyzing the speckle images under different temperatures to realize full measurement on the displacement field and the strain field of the hot surface of the high-speed aircraft in a high temperature environment.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
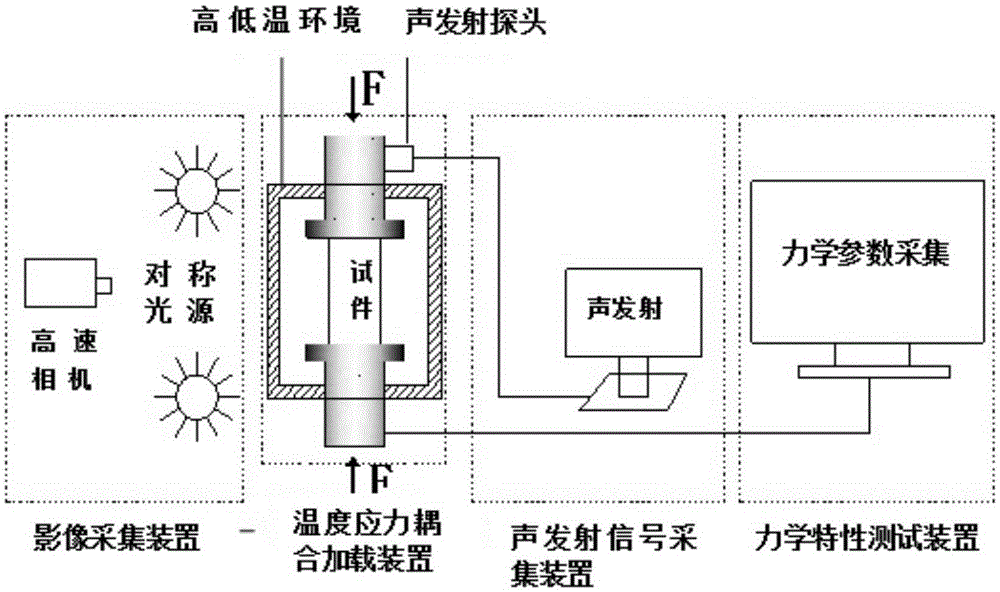
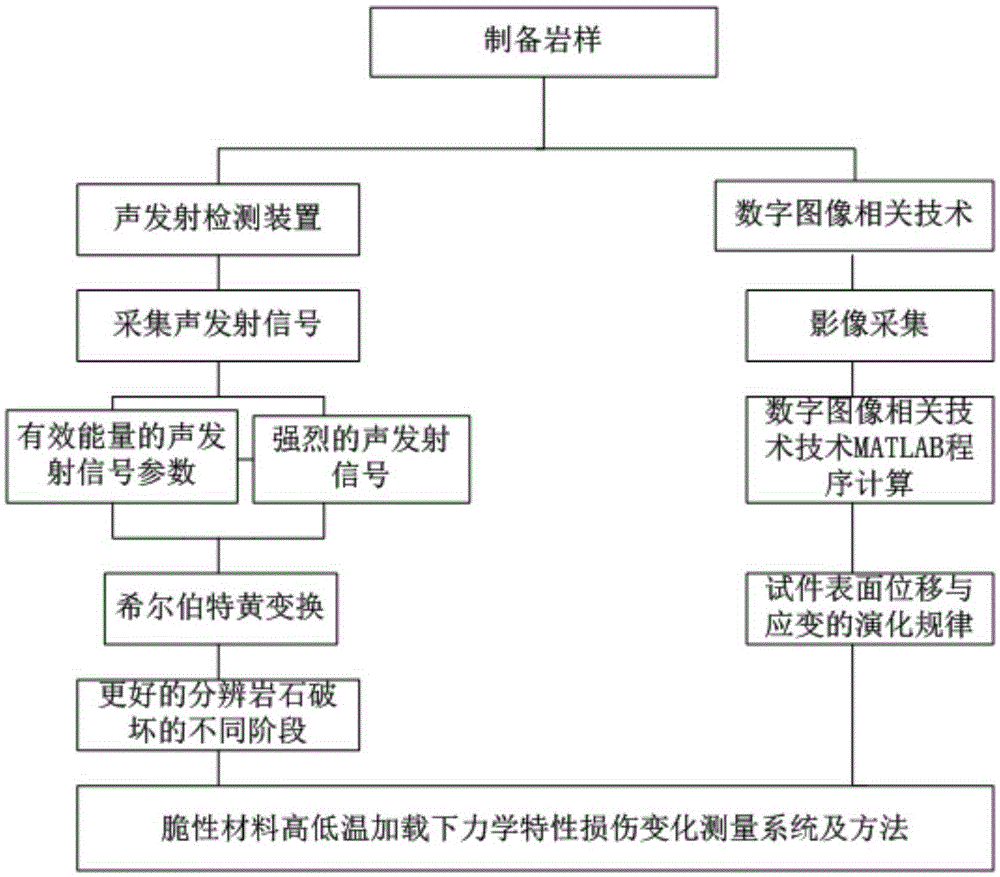
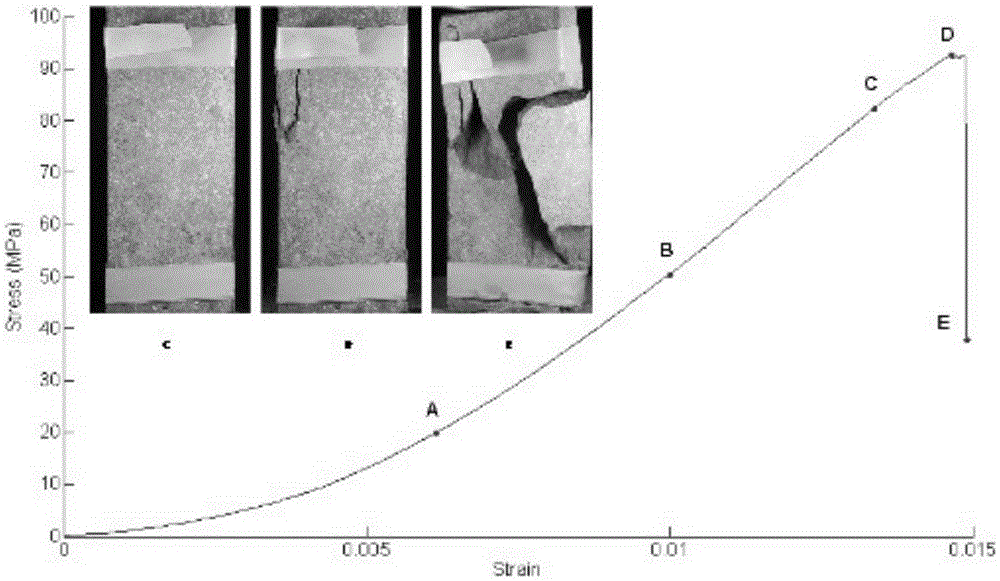
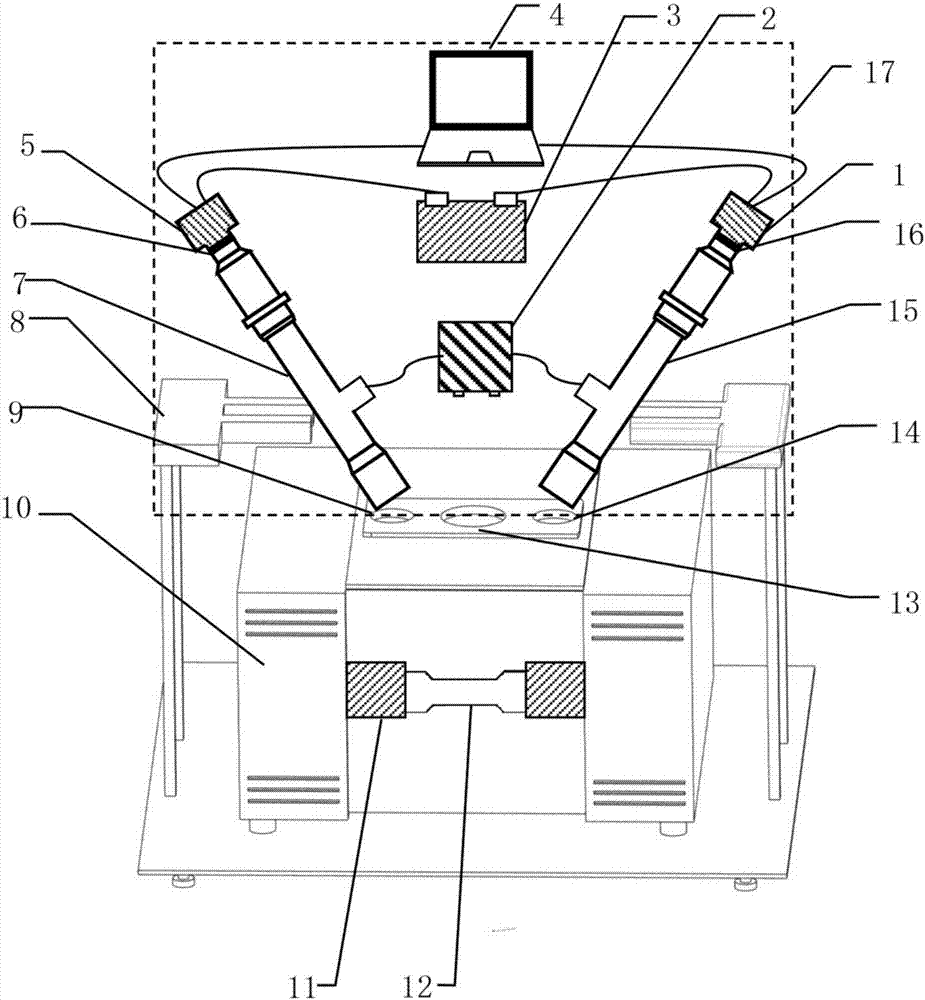
Mechanical property damage change measurement system and method for fragile materials under high-temperature and low-temperature load
InactiveCN105277428ACollection method is simpleHigh precisionStrength propertiesOriginal dataEngineering
The invention provides a mechanical property damage change measurement system and a mechanical property damage change measurement method for fragile materials under high-temperature and low-temperature load and belongs to fragile material measurement system and method. According to the system, a temperature stress coupling and loading device, an acoustic emission signal acquisition device and an image acquisition device are additionally arranged; the temperature stress coupling and loading device is utilized, and an experiment environment is relatively close to an actual environment, such as an environment of deep rocks, so that an experiment research result has a relatively good reference value; the image acquisition device is combined with a digital image correlation technology to obtain a partial displacement field and a strain field of a test piece in a testing process; and the measurement method has the advantages of non-contact and full-field measurement, wide application, high precision, simple acquisition manner on original data, low requirements on measurement environments, and convenience for realizing automation of the whole system. The acoustic emission signal acquisition device is used for detecting the formation and evolution of cracks through measuring cracking energy, so that the damages and attenuation of the fragile materials, such as the rocks, can be described macroscopically and microcosmically under a loading environment.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Ultrahigh temperature multi-dimensional multi-functional strain measurement system based on ultraviolet imaging DIC and measurement method
ActiveCN107255454AUniform brightnessClear imagingUsing optical meansUltraviolet lightsThree dimensional measurement
The invention relates to an ultrahigh temperature multi-dimensional multi-functional strain measurement system based on an ultraviolet imaging digital-image-correlation(DIC) method and measurement method. The strain measurement system comprises ultraviolet cameras (1,5), coaxial long-working distance microscopic lenses (7,15), a monochromatic source (2), narrowband pass filters (6,16) having wavelengths corresponding to that of the monochromatic source, and high temperature speckles or friction scratch spots on a surface of a test piece. A high temperature image observation furnace and a matched high temperature mechanical testing device are used to apply force and thermal load on the test piece having a rectangular cross section or a cylindrical surface. A coaxial ultraviolet light active illumination test piece is adopted, and the ultrahigh temperature multi-dimensional multi-functional strain measurement system based on the ultraviolet imaging digital-image-correlation(DIC) method is used to acquire the surface image of the test piece. By adopting the DIC method, the two-dimensional or three-dimensional measurement of the high-precision real-time millimeter to micron-level visual field of the strain of the surface of the test piece is carried out. A principle is simple, and a structure is compact. By adopting cooperation between a high temperature image furnace and a high temperature stretching device, the real-time, high-precision measurement of the deformation of the surface of the test piece and the mechanical performance of the test piece in environment at a temperature in a range from indoor temperature to ultrahigh temperature of 2000 DEGC is carried out.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
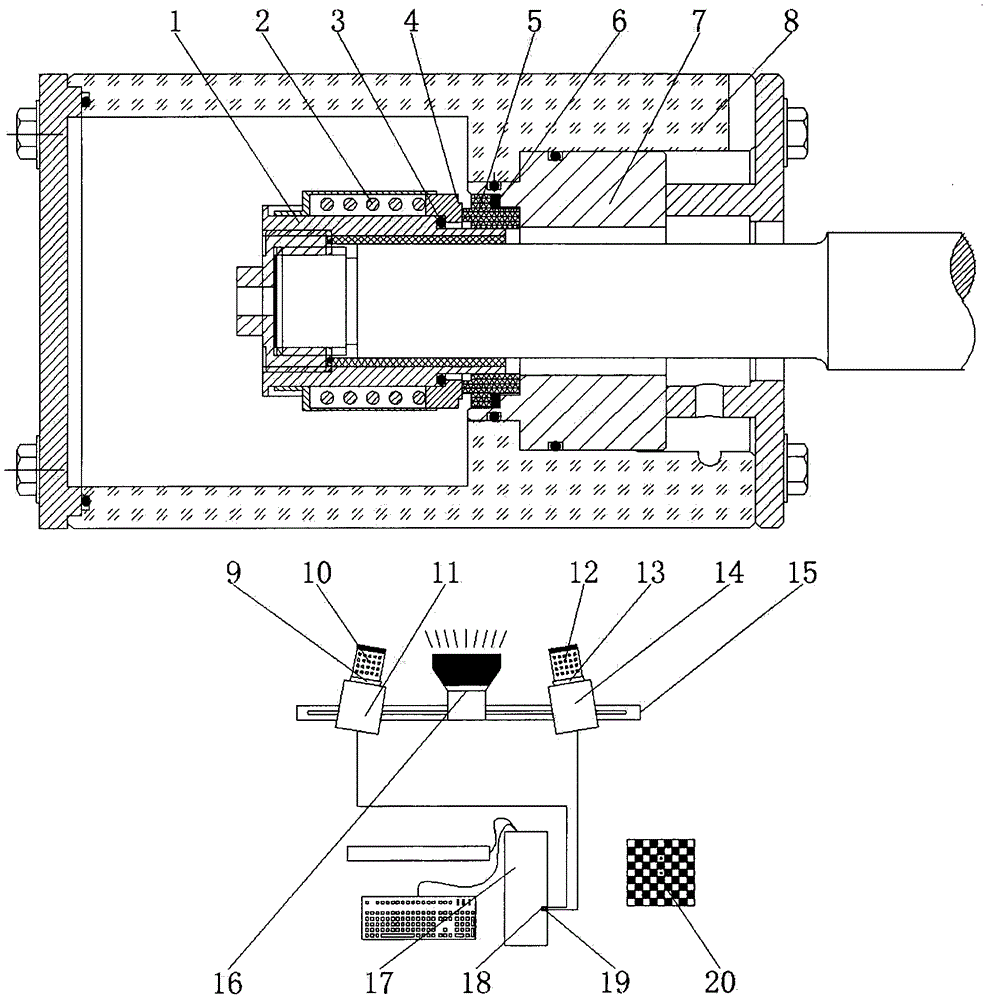
Device and method for detecting high-temperature vibration fatigue characteristics of aero-engine blade
ActiveCN108519225AMonitoring of Vibration Fatigue CharacteristicsGuaranteed accuracyMachine part testingVibration testingAviationFull field
The invention provides a device and a method for detecting high-temperature vibration fatigue characteristics of an aero-engine blade. A vibration loading system is used to apply a vibration load to an aero-engine blade, and the aero-engine blade is heated and controlled by an electric induction heating system; a three-dimensional digital image correlation method is utilized to detect and analyzethe vibration fatigue characteristics of the aero-engine blade under a high temperature vibration load. The invention utilizes the three-dimensional digital image correlation method of non-contact optical full-field deformation measurement, and can adapt to measurement under various scales and various conditions; the accuracy of the detection result is ensured; vibration fatigue monitoring of theaero-engine blade can be achieved at different temperatures and different frequencies; and the comprehensiveness of the experimental result can be ensured.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
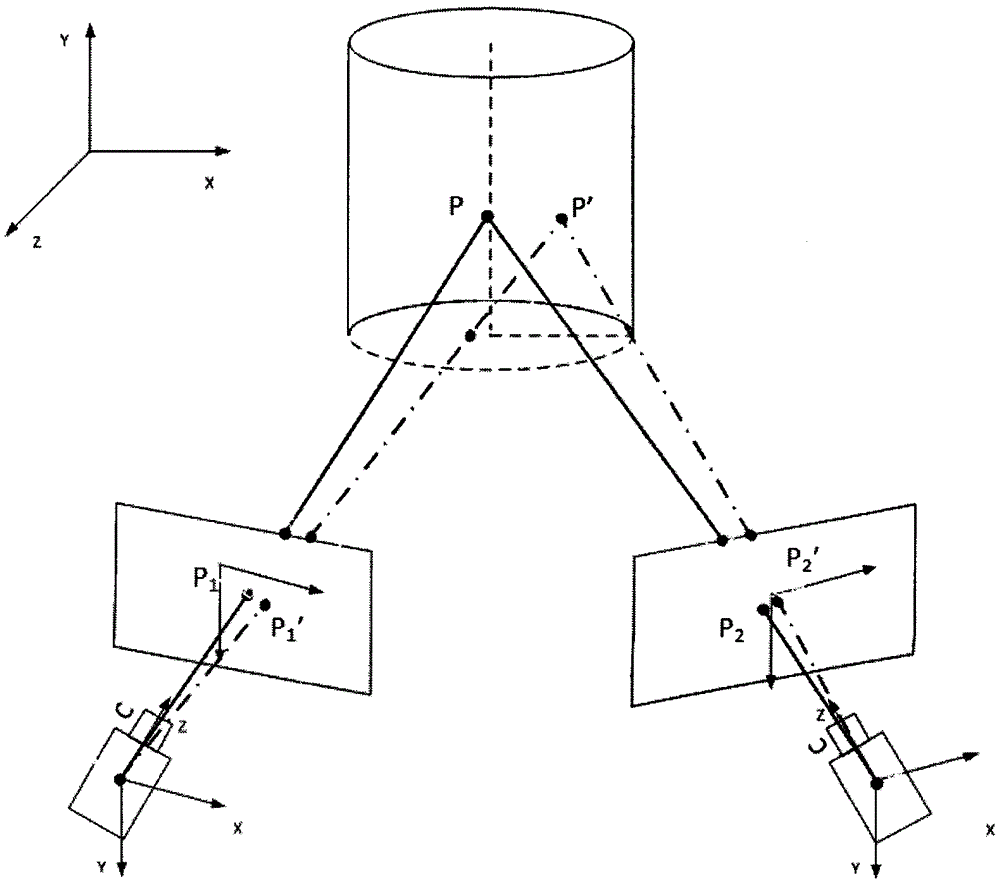
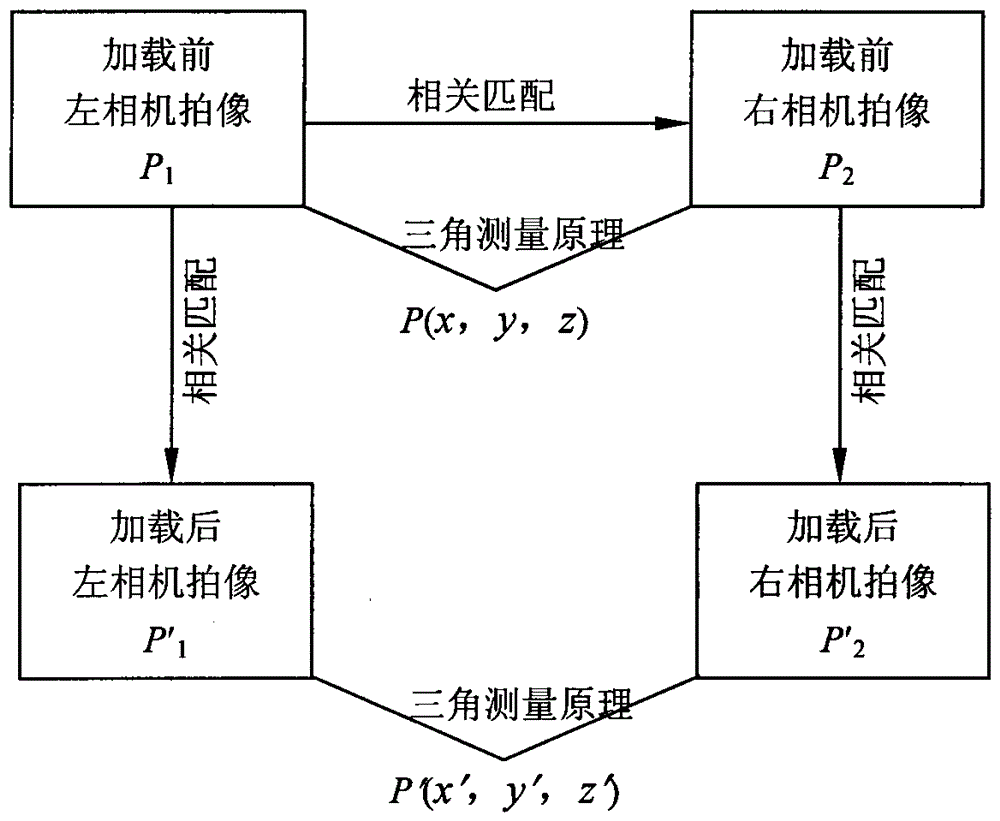
Mechanical sealing end surface deformation measurement system based on binocular vision DIC and measurement method thereof
InactiveCN104634266ARealize full-field measurementAvoid the downside of measuring in pointsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesUsing optical meansFull fieldThree dimensional shape
The invention discloses a mechanical sealing end surface deformation measurement system based on binocular vision DIC and a measurement method thereof. The system comprises a mechanical sealing test device, high-speed digital cameras, lenses, acquisition cards, a light source, a calibration plate, a support system, and a server for digital image acquisition and correlation analysis and processing. The measurement method altogether comprises eight steps. A speckle image on the surface of a mechanical sealing static ring in an operation condition can be acquired, the image can be analyzed and processed by directly using the binocular vision digital image correlation method, and thus, a three-dimensional shape on the surface of the mechanical sealing static ring, and a three-dimensional deformation field under effects of force and thermal load can be acquired. According to the method, the use is convenient, the measurement precision is high, the full-filed measurement problem of surface deformation under effects of force and thermal load of mechanical sealing can be effectively solve4d, and foundation is laid for making a research on key factors influencing mechanical sealing deformation and exploring measures for reducing deformation.
Owner:NANJING COLLEGE OF CHEM TECH
Vision measurement method used for overall motion tracking of rotating object
The invention relates to a vision measurement method used for overall motion tracking of a rotating object. The method combines binocular vision and a digital image correlation method. Speckles are sprayed on the surface of the measured object, and a small number of mark points are attached. The rotation parameters of the center coordinate of a mark point image before and after solving are used to carry out corresponding rotation transformation on speckle images or subsegment sets, wherein the speckle images or subsegment sets are collected before and after. Similar subsegments are searched and matched. The problem of difficult matching caused by large subsegment rotation angle is solved. According to the method provided by the invention, the space coordinate of any position on the feature surface in each state can be accurately acquired to realize tracking and deformation measurement.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
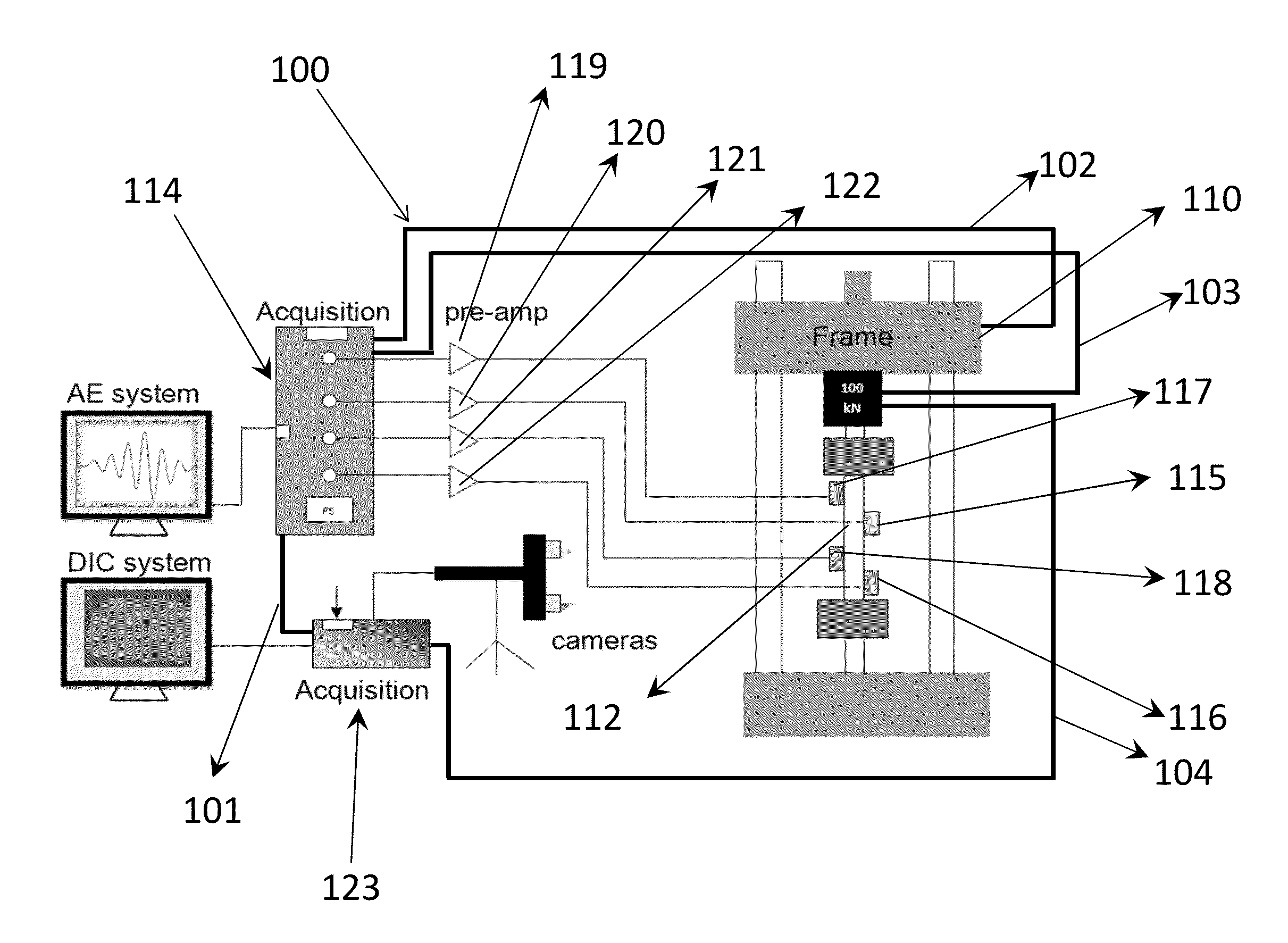
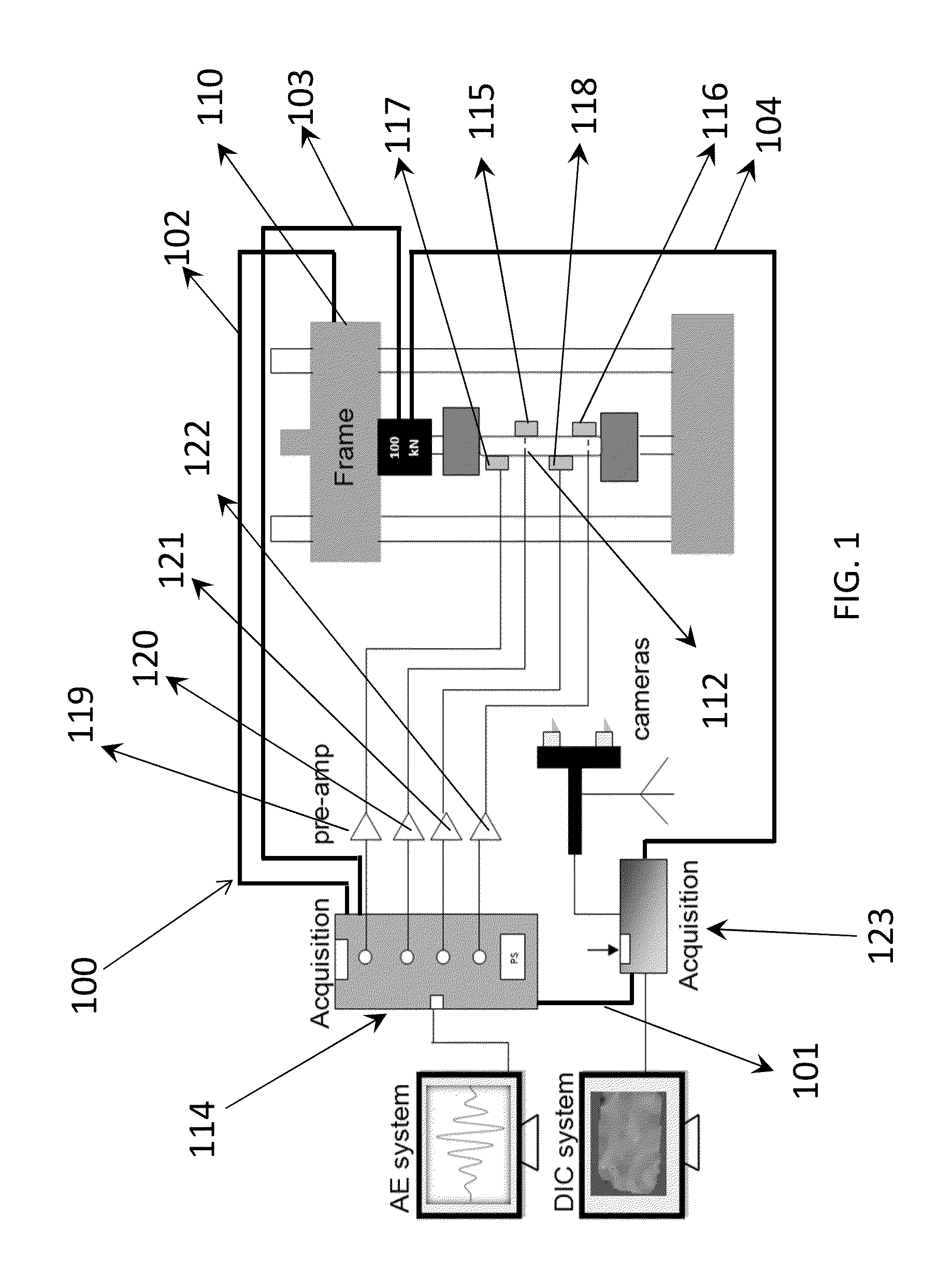
Integration of Digital Image Correlation with Acoustic Emission
An inventive approach is disclosed to integrate Digital Image Correlation (DIC) with the Acoustic Emission method that may be used for structural health monitoring and assessment of critical structural components in civil, mechanical, and aerospace industries. The inventive approach relies on passively recording acoustic emission across the specimen being tested and activating the DIC cameras automatically to measure deformation on the specimen's surface. The resulting acousto-optic system can be used to determine damage initiation, progressive damage development, identify critical regions and make lifetime predictions of the tested specimen.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Method for measuring J integration of cracks on basis of digital-image correlation
InactiveCN104502198AEasy accessImprove efficiencyMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesPhase correlationData information
The invention discloses a method for measuring the J integration of cracks on the basis of digital-image correlation, belongs to the field of fracture mechanics and engineering application and relates to the method for measuring the J integration of cracks on the basis of digital-image correlation. The method comprises the following steps: by a digital-image correlation technology, measuring and calculating a displacement field and a strain field under different loads on the surface containing crack defects, acquiring information of the displacement field and the strain field, and storing into an Excel; writing an MATLAB program, calling data information in the Excel, carrying out numerical-integration calculation and further obtaining the J integration value of the cracks. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the digital-image correlation, an MATLAB technology and J-integration calculation are combined, the strain of a test piece with the cracks is acquired by the digital-image correlation technology, a calculation result of digital-image correlation is extracted by MATLAB, and numerical integration is calculated; the method has the advantages of high efficiency and strong practicability, is suitable for calculating various test pieces which contain micro-deformation cracks and have elasticity and small-range yield, and is strong in universality.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Quick digital image correlation measurement method based on stochastic parallel gradient descent optimization technology
InactiveCN102221341AQuick measurementRealize real-time online measurementUsing optical meansCorrelation coefficientDifferential coefficient
The invention provides a quick digital image correlation measurement method based on stochastic parallel gradient descent optimization technology, comprising the following steps of comprehensively considering related parameters such as displacement, differential coefficient and the like of any one point in a speckle field of an object to be measured; and utilizing the stochastic parallel optimization technology to realize quick digital image correlation measurement. In the method, by adopting stochastic parallel disturbance on a deformation parameter, the correlation coefficient is convergentto a global unique extremum, thus obtaining the deformation parameter. The method has a simple principle, can be realized easily, is a DIC (digital image correlation) measurement method with totally new concept, can realize the aim of quickly measuring DIC with high precision and high reliability, and is expected to realize the real-time online measurement on the DIC.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
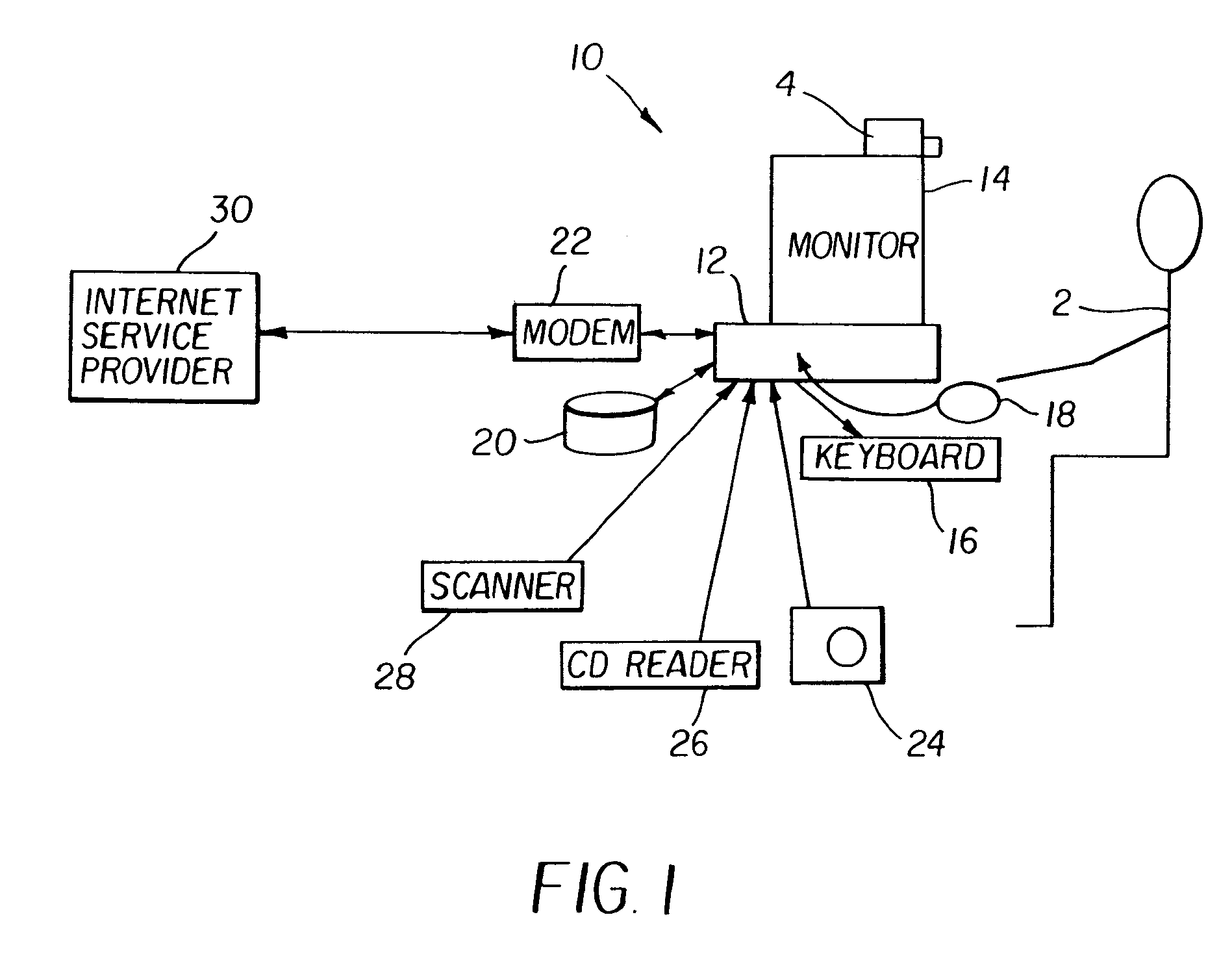
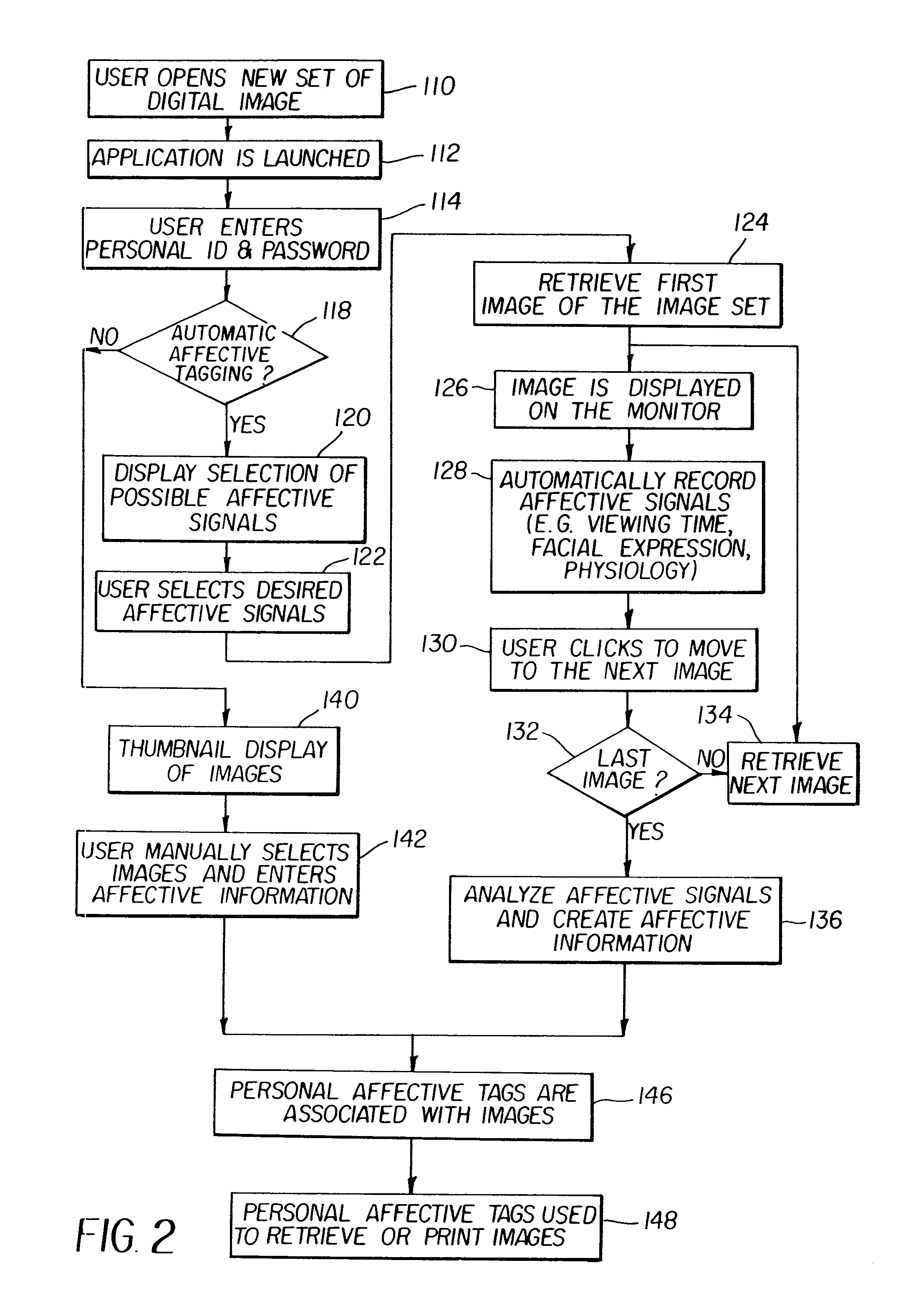
Method for creating and using affective information in a digital imaging system
InactiveUS7620270B2Image enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital imagingComputer graphics (images)
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com