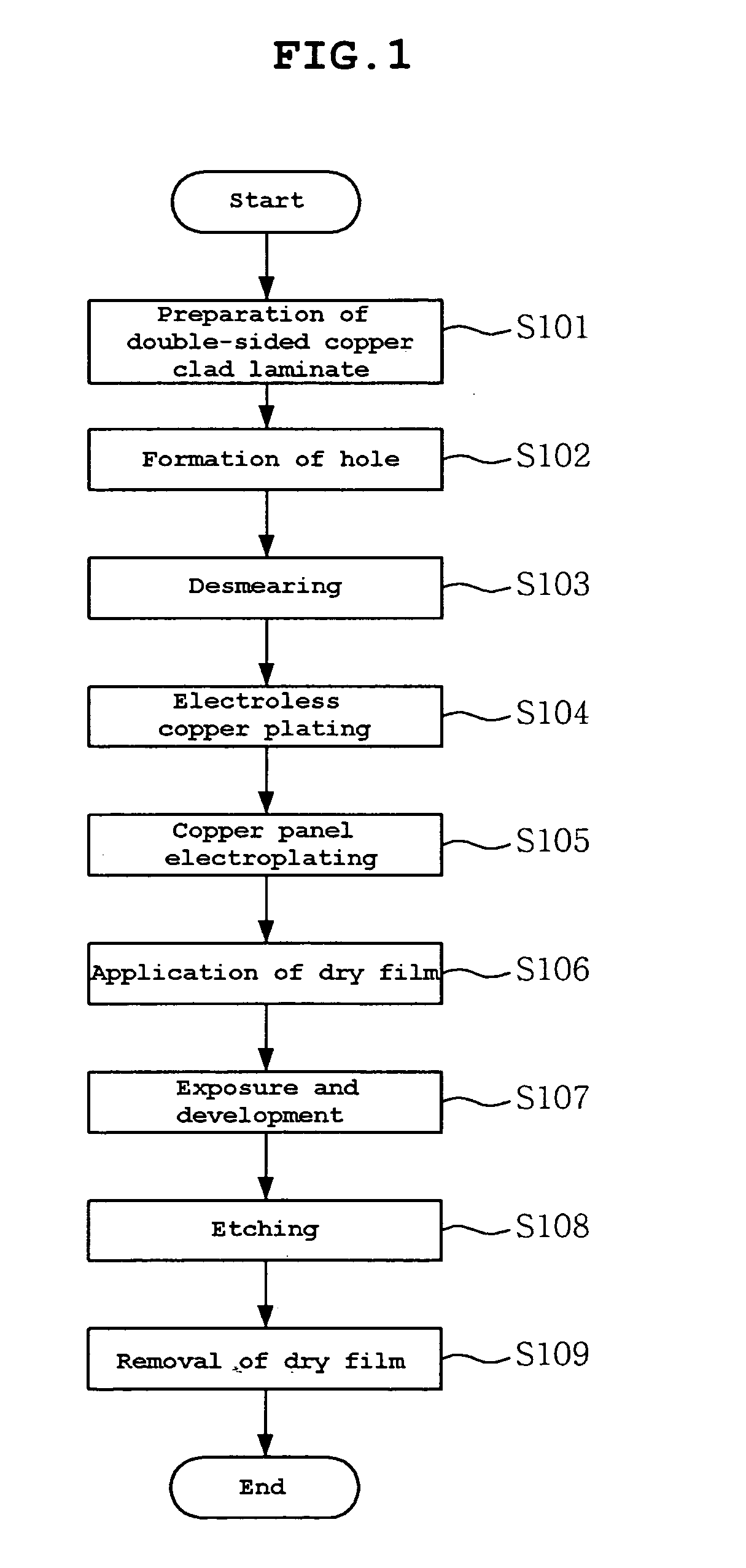
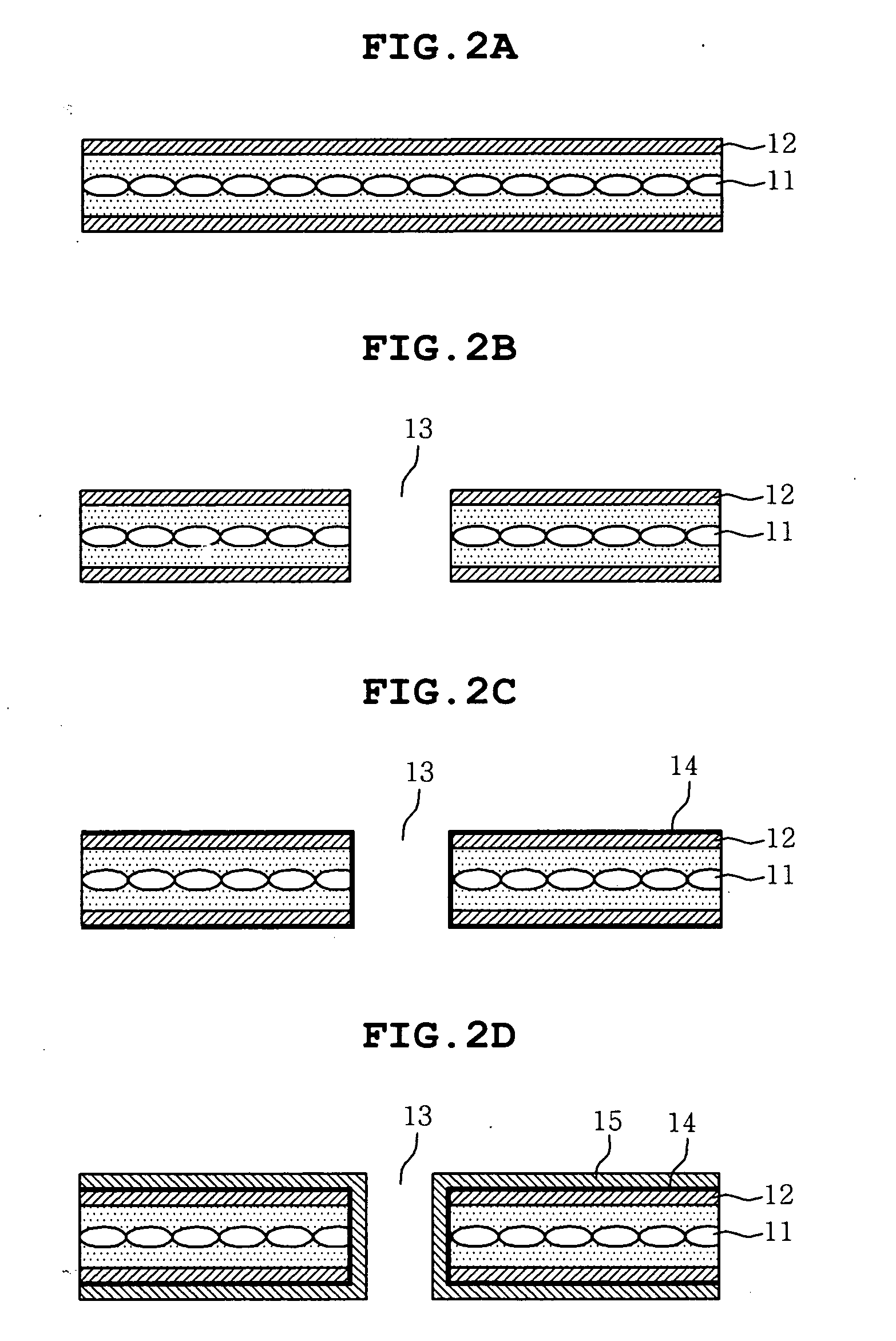
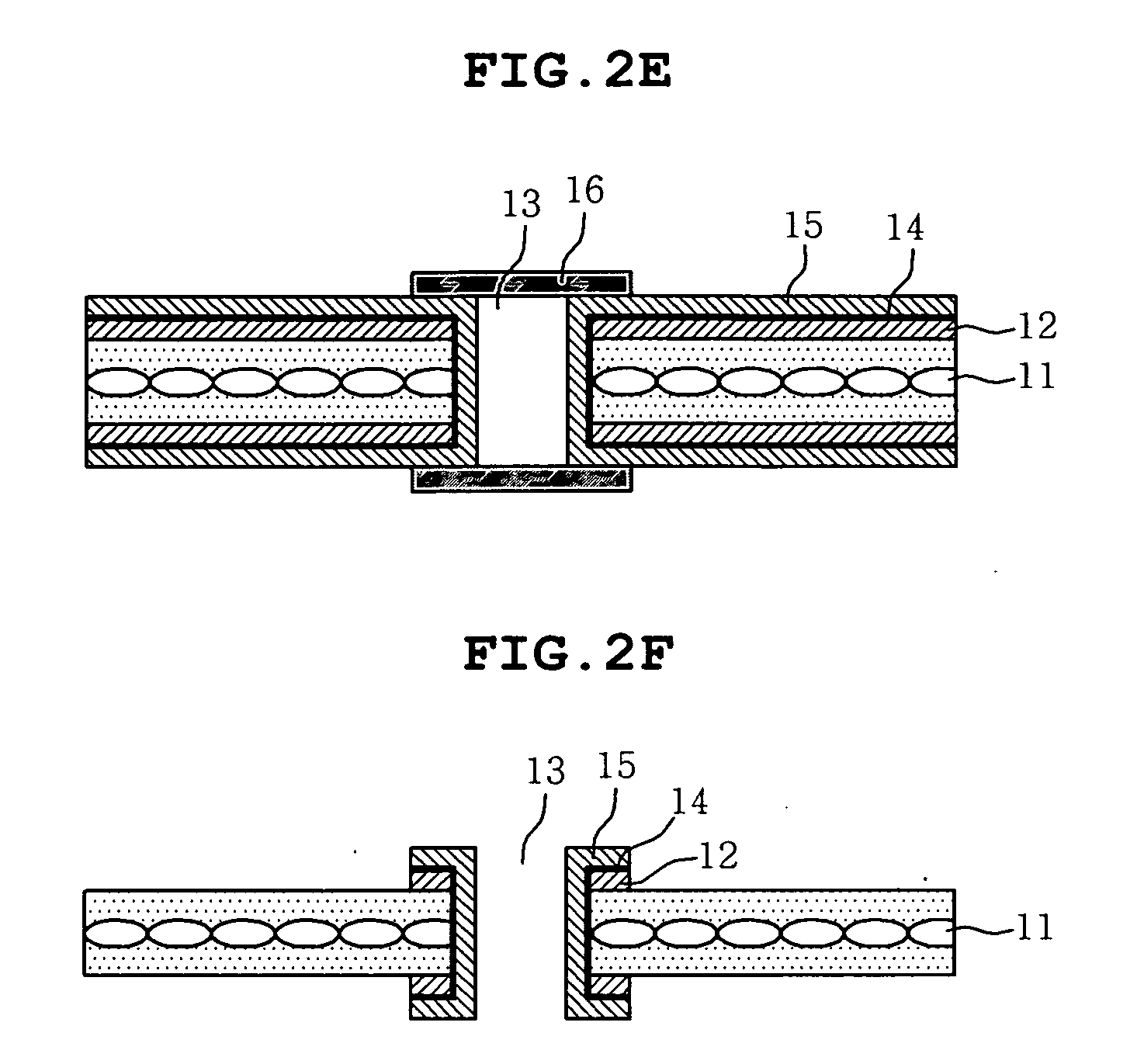
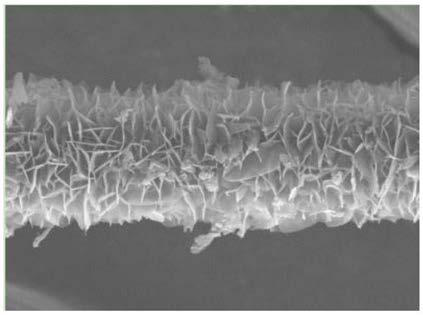
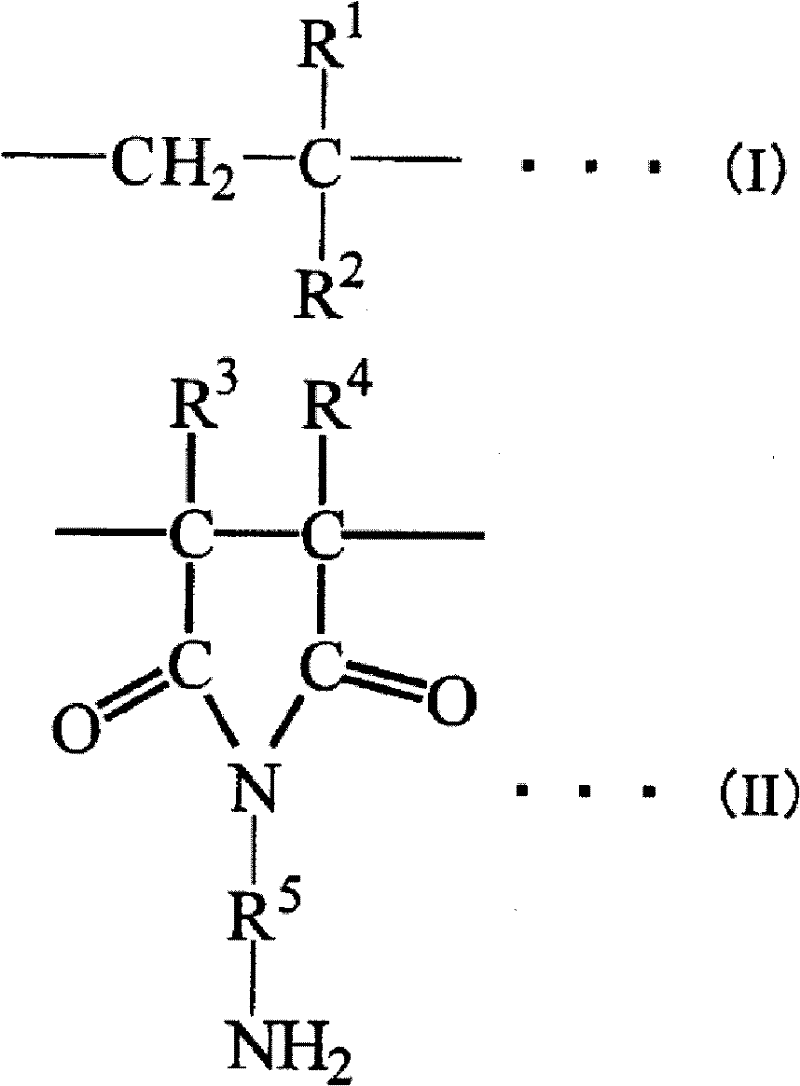
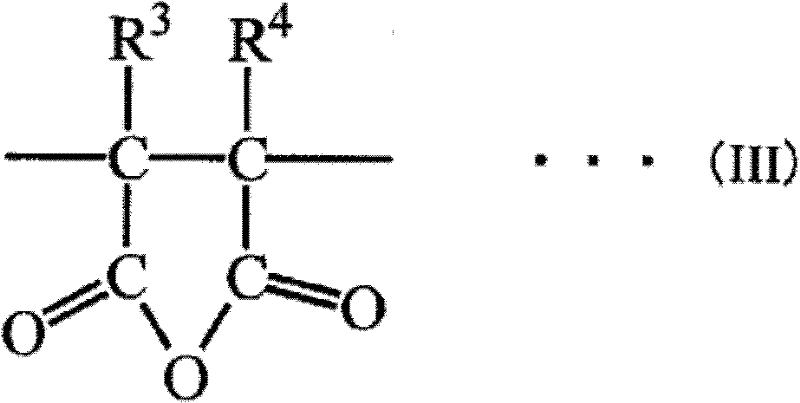
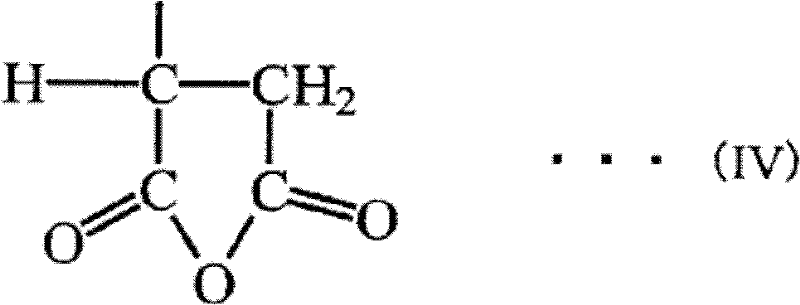
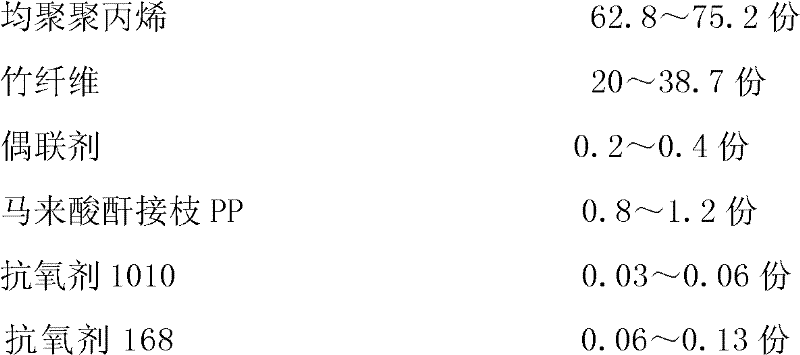Patents
Literature
319 results about "Interfacial adhesion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
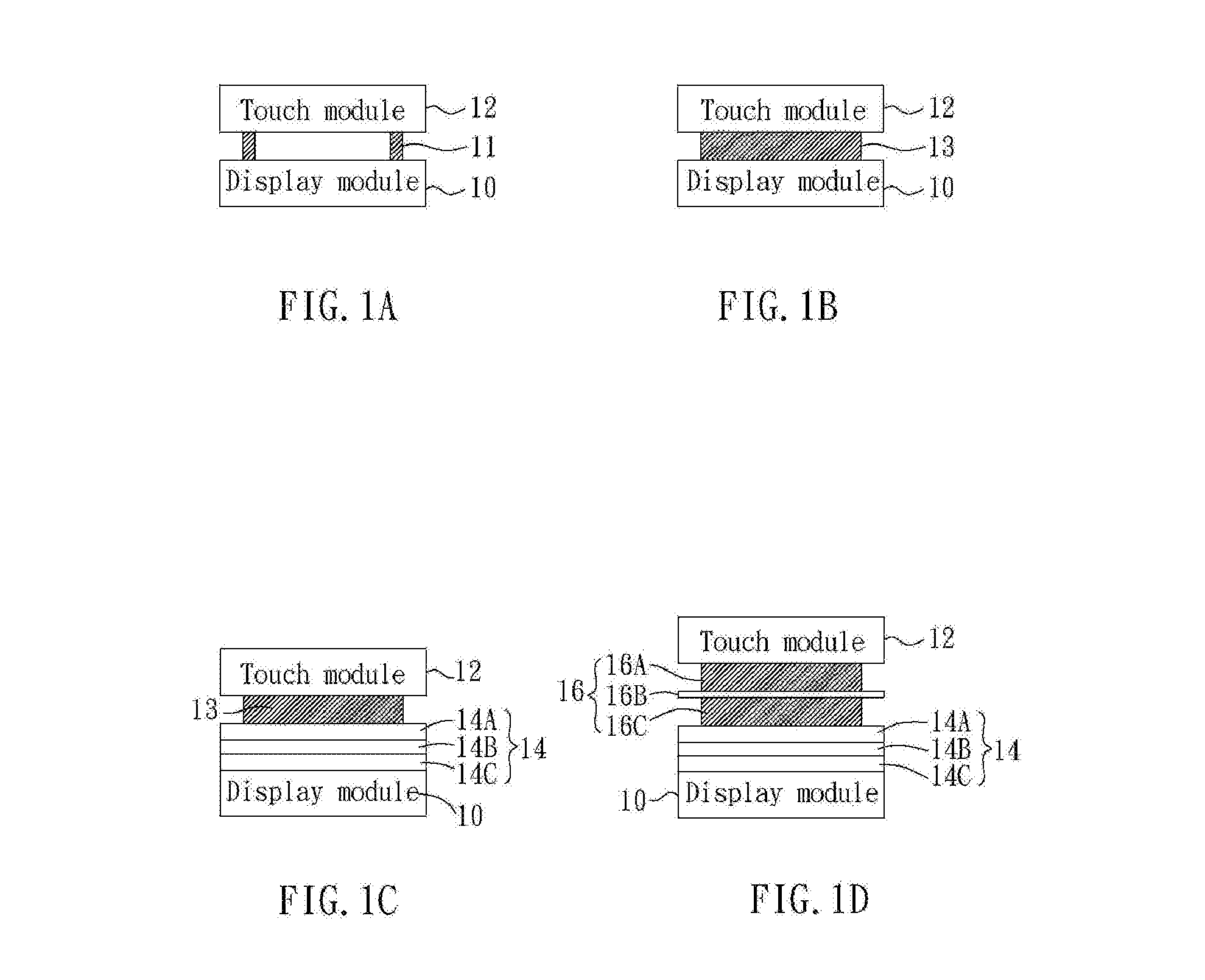
Polymer binders for flexible and transparent conductive coatings containing carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20050209392A1Decrease in optical transparencyDecrease in surface conductivityMaterial nanotechnologySpecial tyresThermoplasticCarbon nanotube
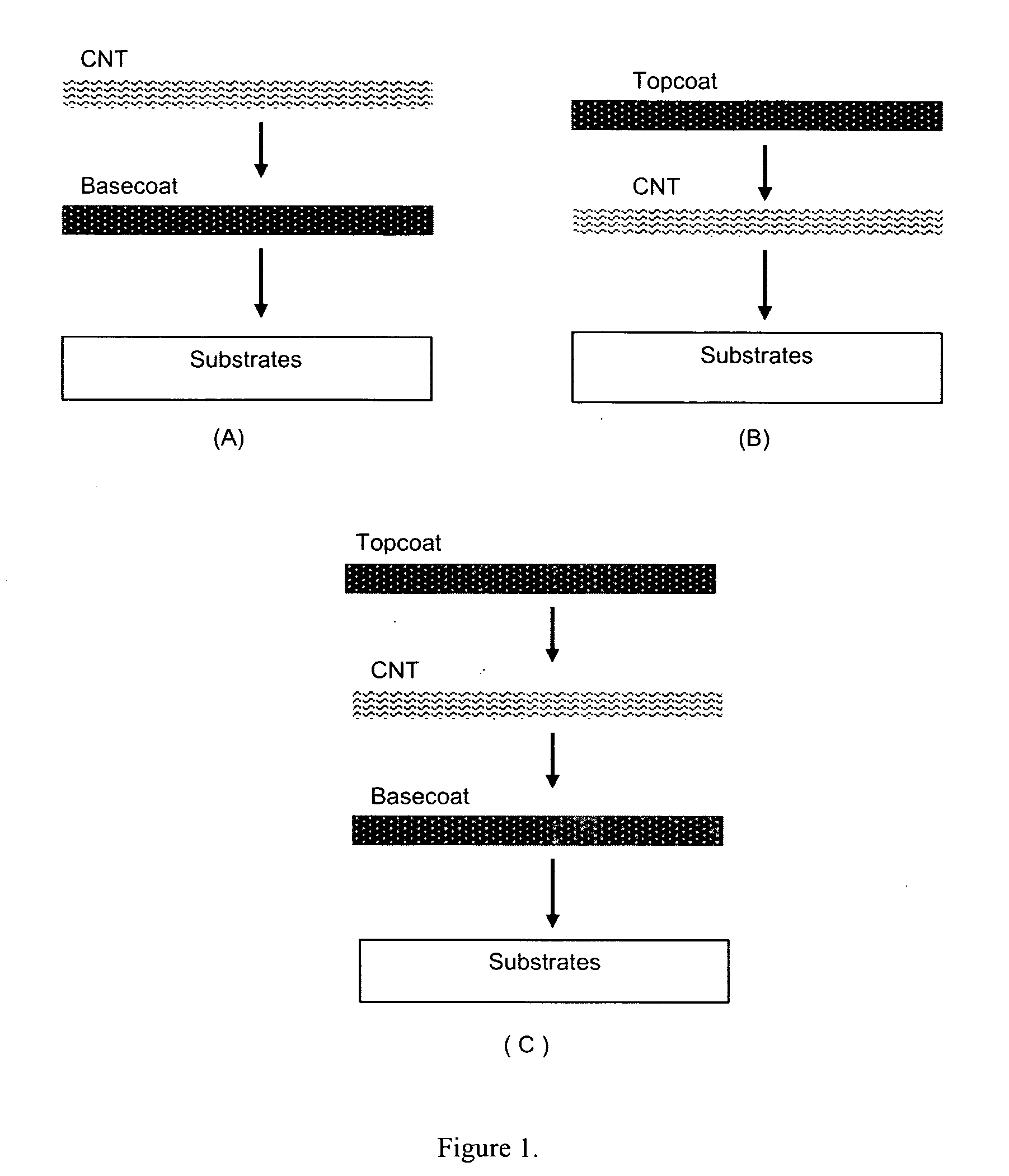
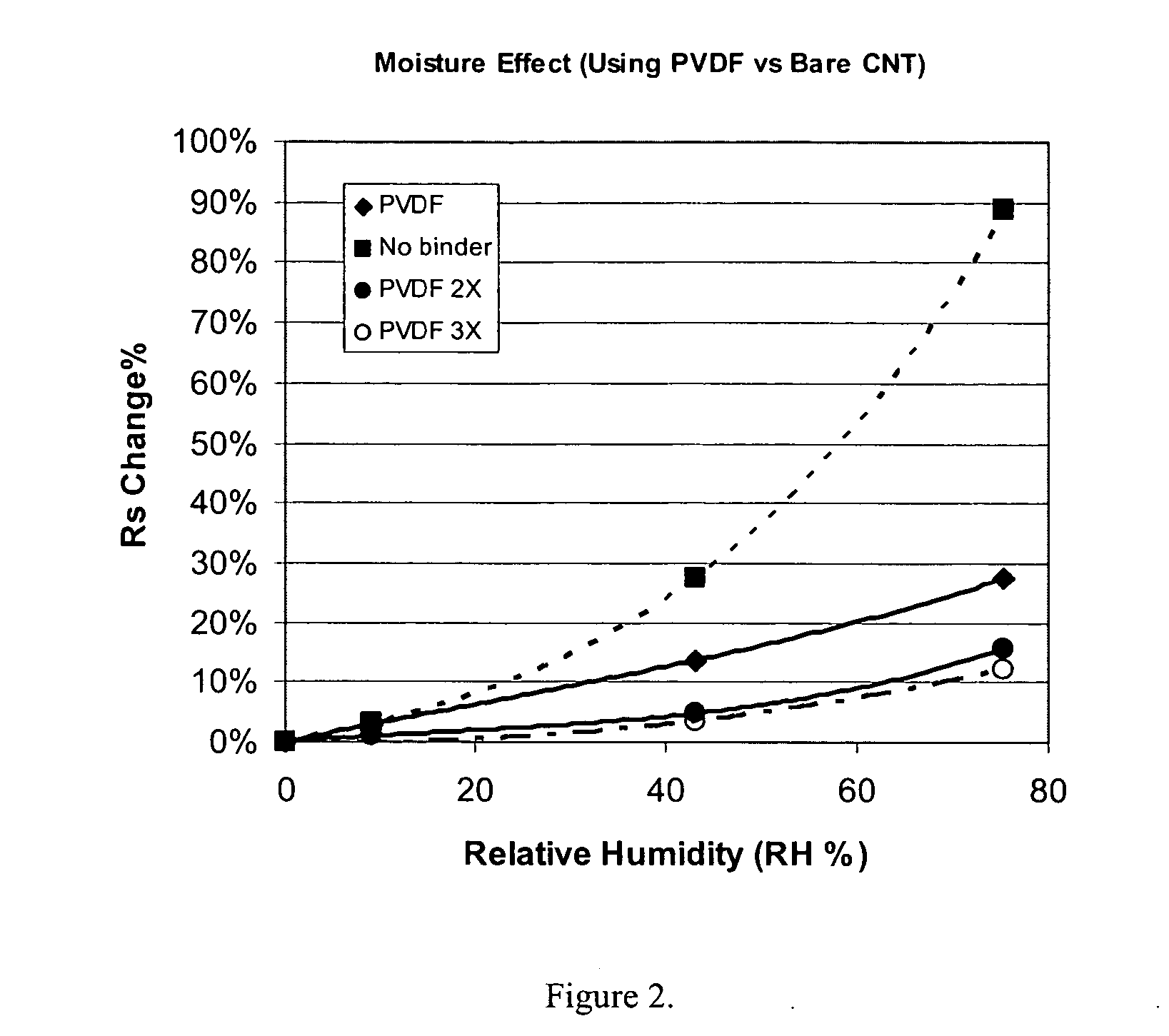
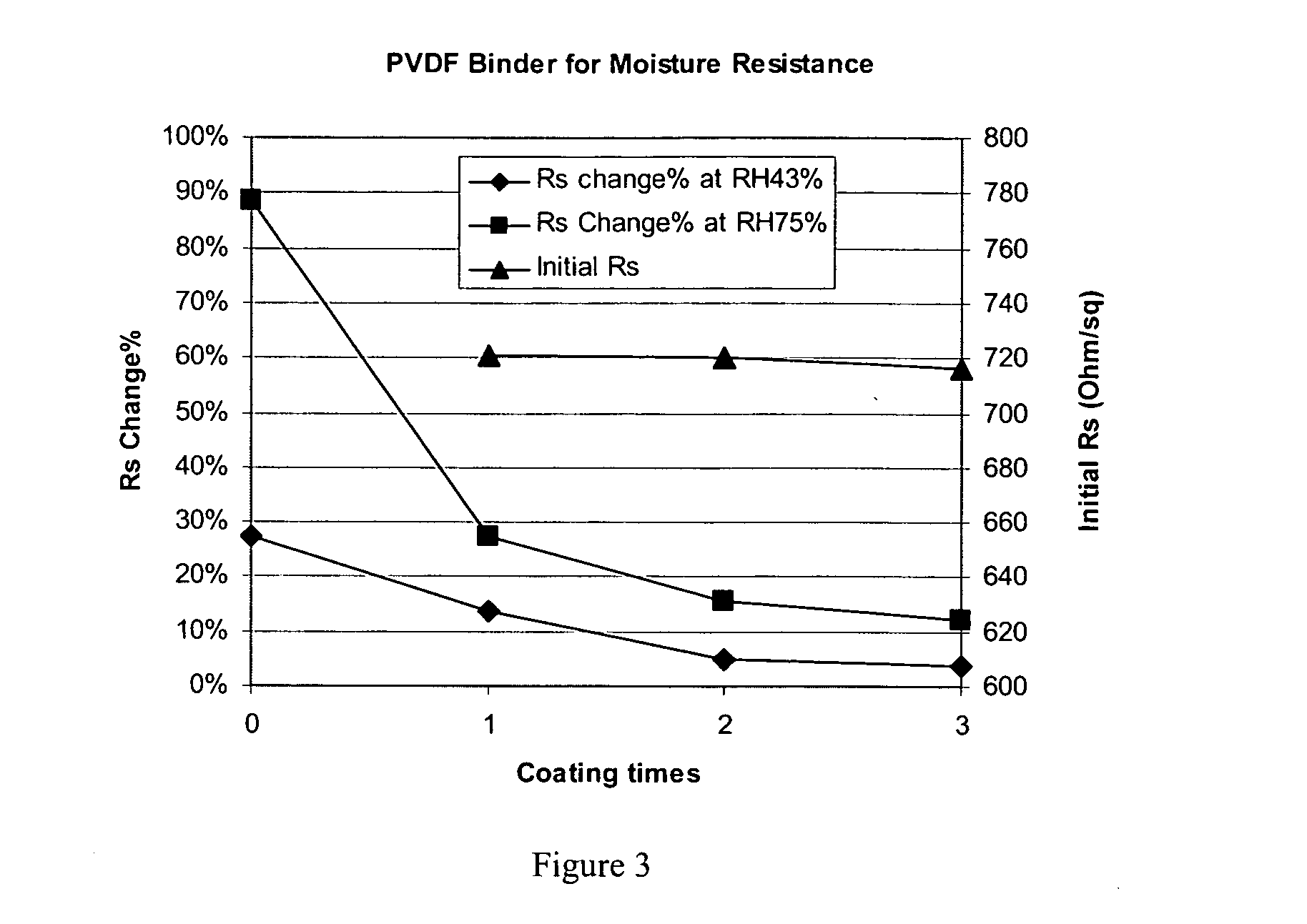
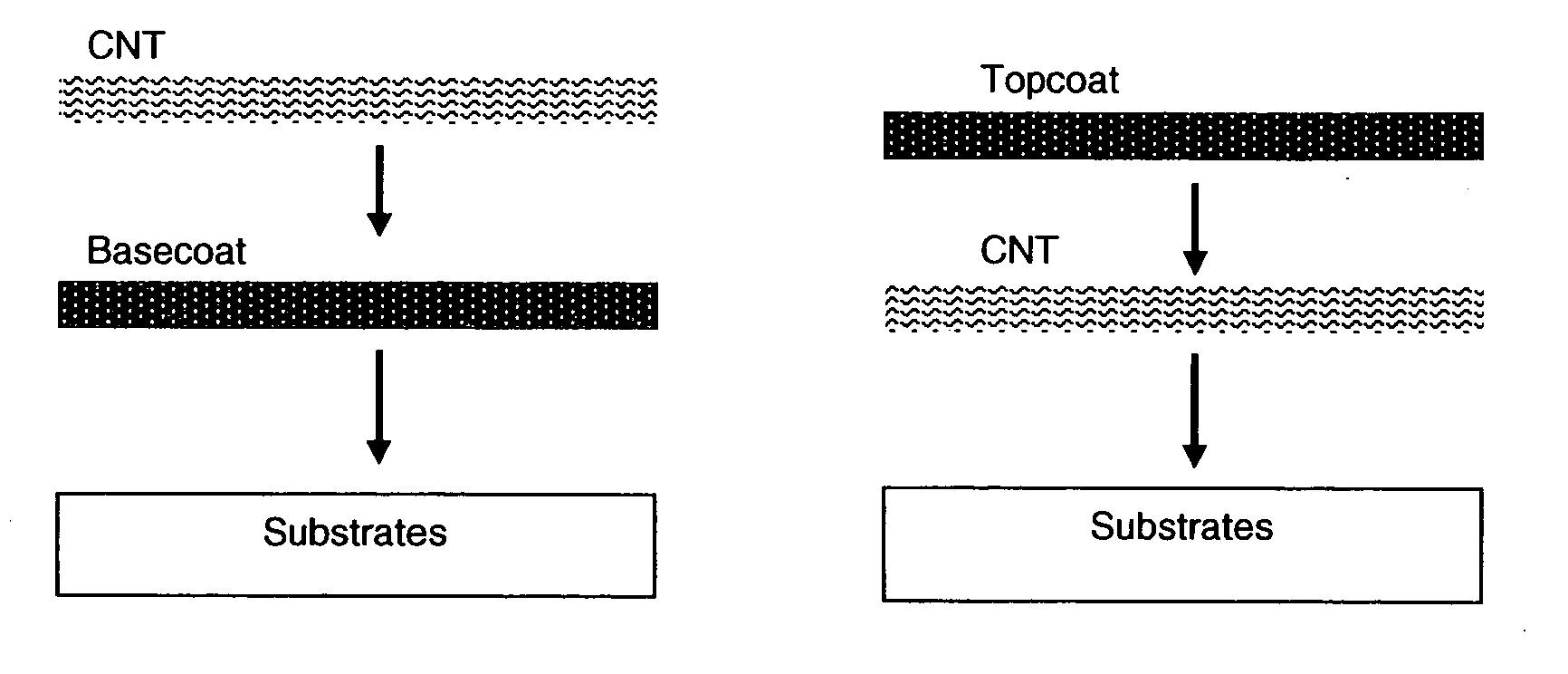
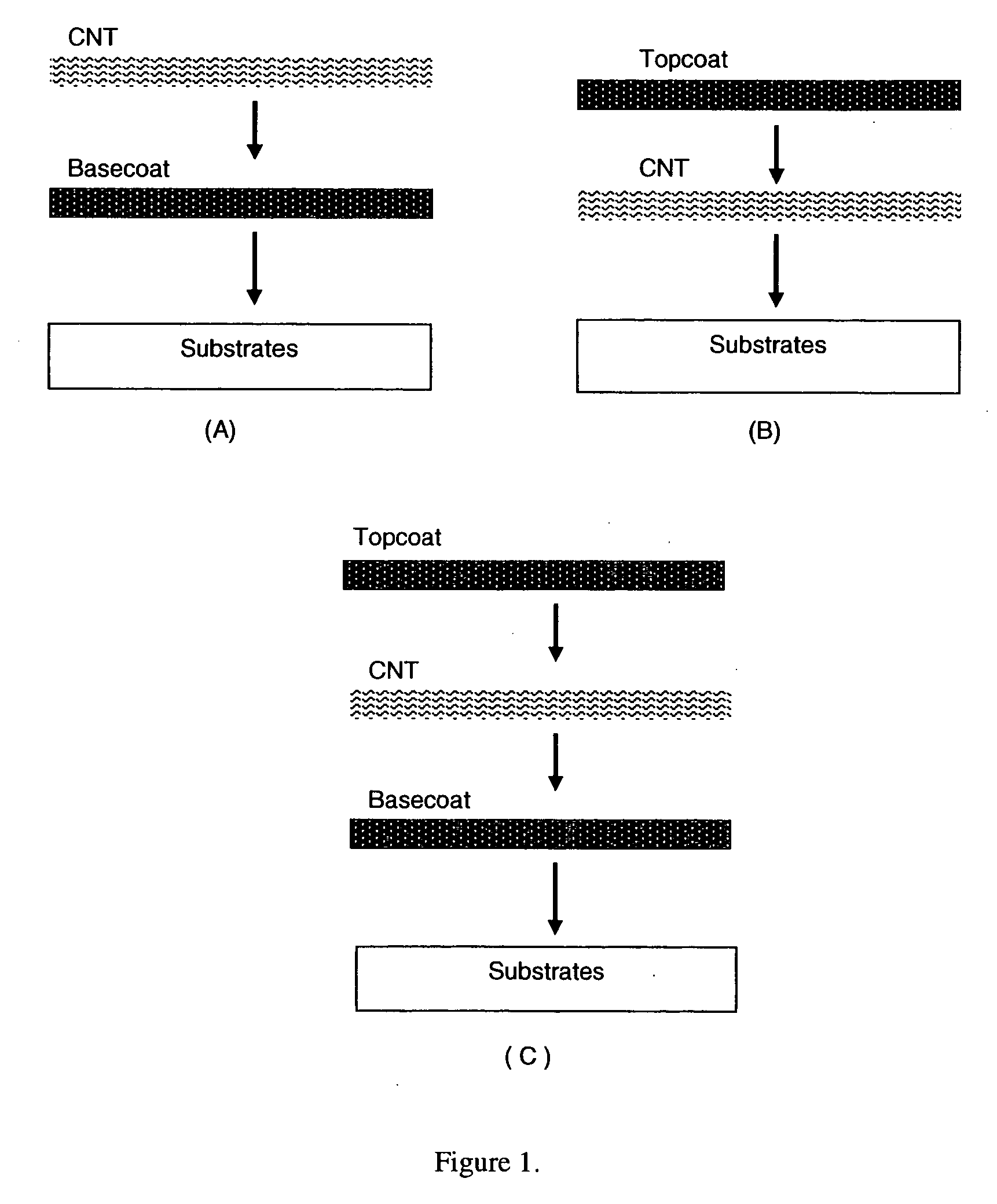
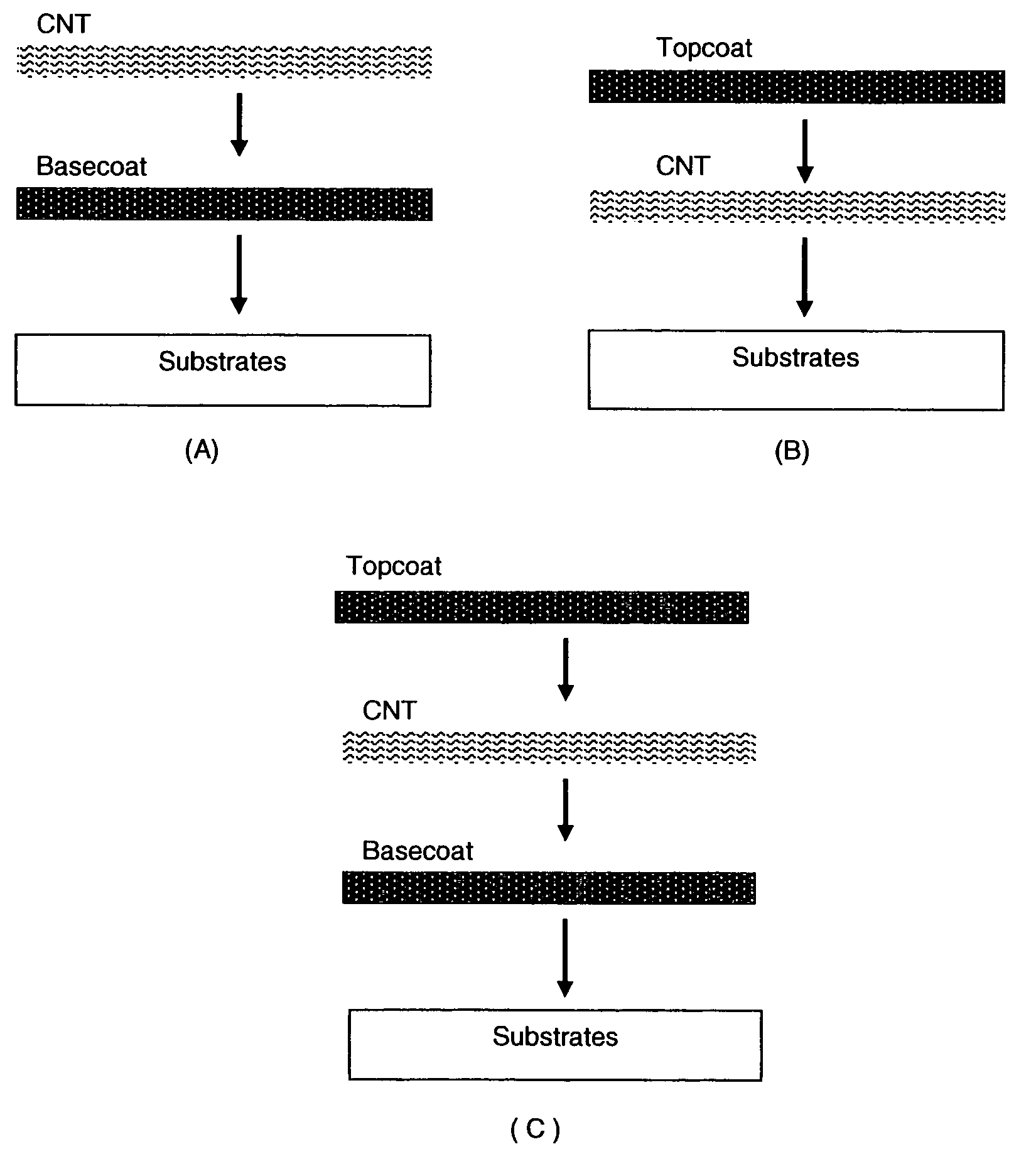
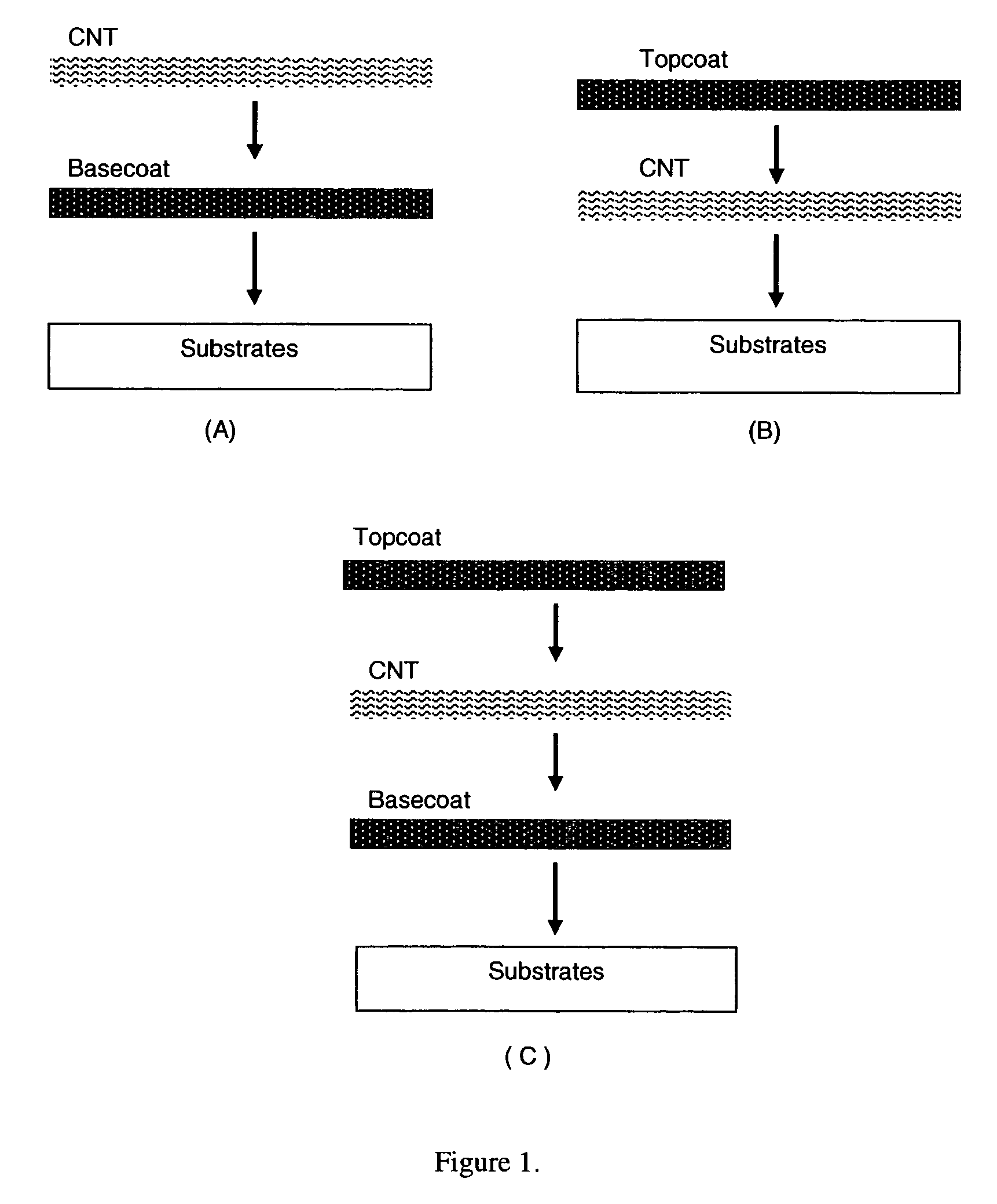
This invention relates to flexible, transparent and conductive coatings and films formed using single wall carbon nanotubes and polymer binders. Preferably, coatings and films are formed from carbon nanotubes (CNT) applied to transparent substrates forming one or multiple conductive layers at nanometer level of thickness. Polymer binders are applied to the CNT network coating having an open structure to provide protection through infiltration. This provides for the enhancement of properties such as moisture resistance, thermal resistance, abrasion resistance and interfacial adhesion. Polymers may be thermoplastics or thermosets, or any combination of both. Polymers may also be insulative or inherently electrical conductive, or any combination of both. Polymers may comprise single or multiple layers as a basecoat underneath a CNT coating, or a topcoat above a CNT coating, or combination of the basecoat and the topcoat forming a sandwich structure. Binder coating thickness can be adjusted by changing binder concentration, coating speed and / or other process conditions. Resulting films and articles can be used as transparent conductors for flat panel display, touch screen and other electronic devices.
Owner:EIKOS
Fluoropolymer binders for carbon nanotube-based transparent conductive coatings
InactiveUS20060113510A1Reduce conductivityFunction increaseNanoinformaticsConductive materialThermoplasticOptical transparency
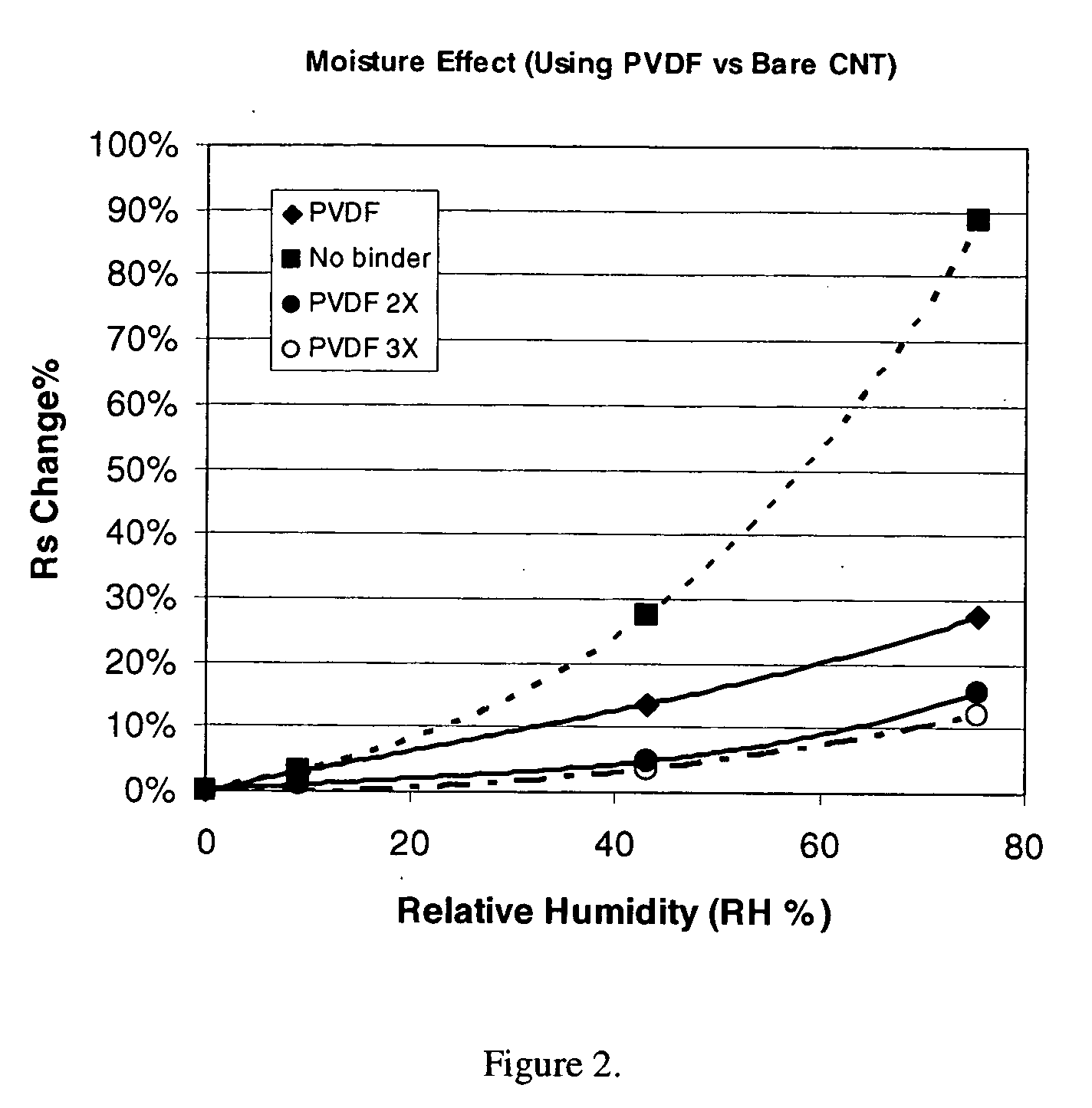
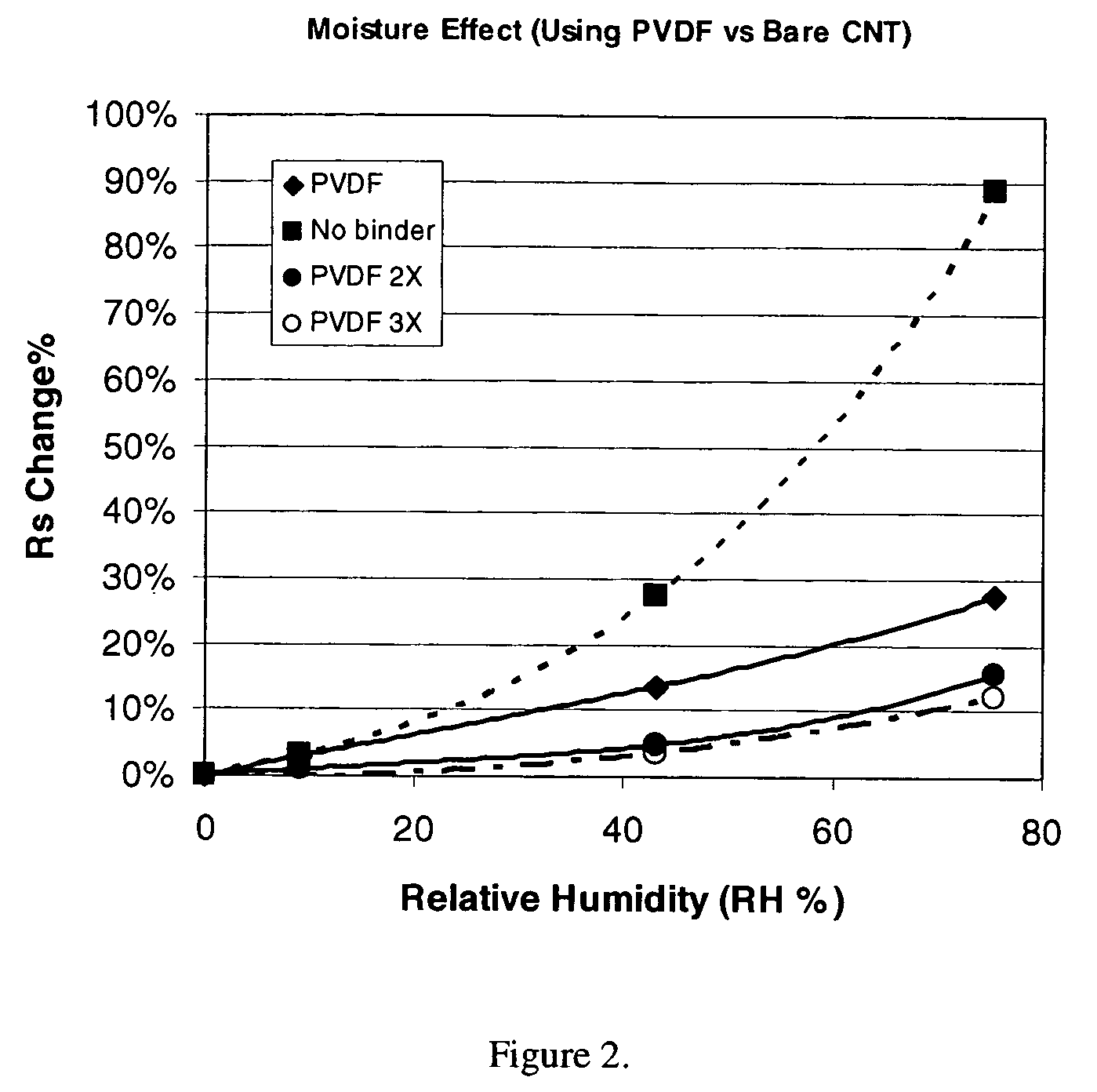
This invention relates to flexible, transparent and conductive coatings and films formed using carbon nanotubes (CNT) and, in particular, single wall carbon nanotubes, with polymer binders. Preferably, coatings and films are formed from carbon nanotubes applied to transparent substrates forming one or multiple conductive layers at nanometer level of thickness. Polymer binders are applied to the CNT network coating having an open structure to provide protection through infiltration. This provides for enhancement of properties such as moisture resistance, thermal resistance, abrasion resistance and interfacial adhesion. Polymers may be thermoplastics or thermosets, or a combination thereof. Polymers may also be insulative or inherently electrical conductive, or any combination of both. Polymers may comprise single or multiple layers as a basecoat underneath a CNT coating, or a topcoat above a CNT coating, or combination of the basecoat and the topcoat forming a sandwich structure. A fluoropolymer containing binder, which is a solution of one fluoropolymer or a blend of fluoropolymers, which may be formulated with additives, is applied onto a carbon nanotube-based transparent conductive coating at nanometer level of thickness on a clear substrate such as PET and glass. The fluoropolymers or blend can be either semi-crystalline (with low level of crystallinity) or amorphous, preferably to be amorphous with low refraction index. Binder coating thickness can be adjusted by changing binder concentration, coating speed and / or other process conditions. This binder coating significantly improves optical transparency, and also maintain or increases conductivity of the CNT-based coating. With other benefits such as abrasion, thermal and moisture resistance, this binder coating and the resulting products is used for display and electronic applications.
Owner:EIKOS
Benzoxazines, thermosetting resins comprised thereof, and methods for use thereof
InactiveUS7517925B2Improve adhesionSimple interfaceOrganic chemistrySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInterfacial adhesionThermal expansion
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided novel benzoxazine compounds and thermosetting resin compositions prepared therefrom. Invention compositions are particularly useful for increasing adhesion at interfaces within microelectronic packages. Invention benzoxazines are useful for the preparation of invention compositions with properties which are associated with increased adhesion at interfaces, such as, for example, low shrinkage on cure and low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). In another aspect of the invention, there are provided die-attach pastes having increased interfacial adhesion. Invention die-attach pastes include benzoxazine-containing thermosetting resin compositions. In further aspects of the invention, there are provided methods for enhancing adhesive strength of thermosetting resin compositions and methods for enhancing adhesion of a substrate bound to a metallic surface by a thermosetting resin composition.
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH
Method of forming fluoropolymer binders for carbon nanotube-based transparent conductive coatings
InactiveUS7378040B2Improve conductivityNanoinformaticsConductive materialThermoplasticOptical transparency
This invention relates to flexible, transparent and conductive coatings and films formed using carbon nanotubes (CNT) and, in particular, single wall CNT, with polymer binders. Preferably, coatings and films are formed from CNT applied to transparent substrates forming one or multiple conductive layers at nanometer level of thickness. Polymer binders are applied to the CNT network coating having an open structure to provide protection through infiltration, and may comprise a basecoat, a topcoat, or a combination thereof, providing enhanced optical transparency, conductivity, moisture resistance, thermal resistance, abrasion resistance and interfacial adhesion. Polymers may be thermoplastics, thermosets, insulative, conductive or a combination thereof. A fluoropolymer containing binder is applied onto a CNT-based transparent conductive coating at nanometer level of thickness on a clear substrate. The fluoropolymers or blend can be either semi-crystalline or amorphous. This binder coating and the resulting products can be used for display and electronic applications.
Owner:EIKOS
Interface adhesion improvement method
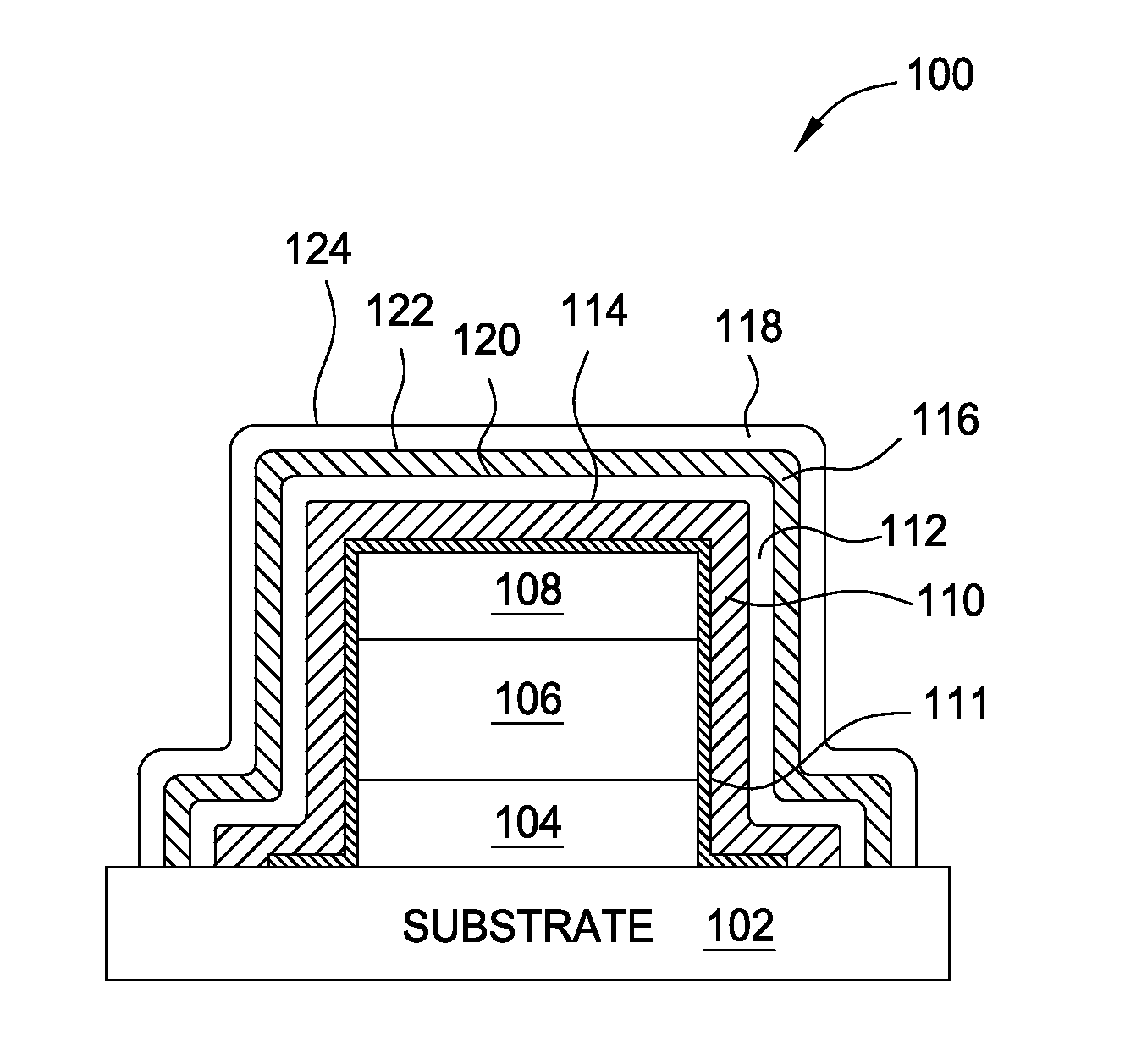
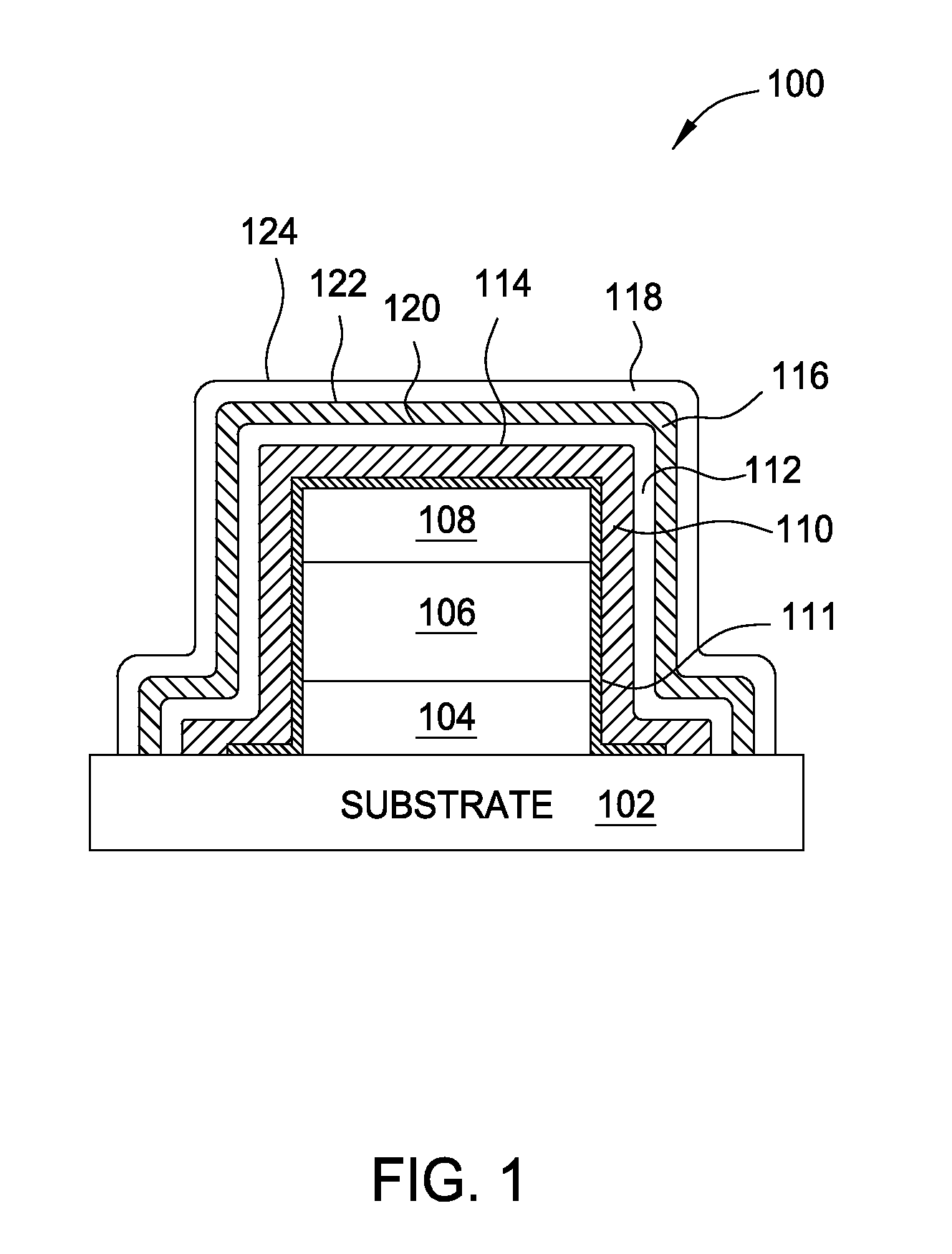
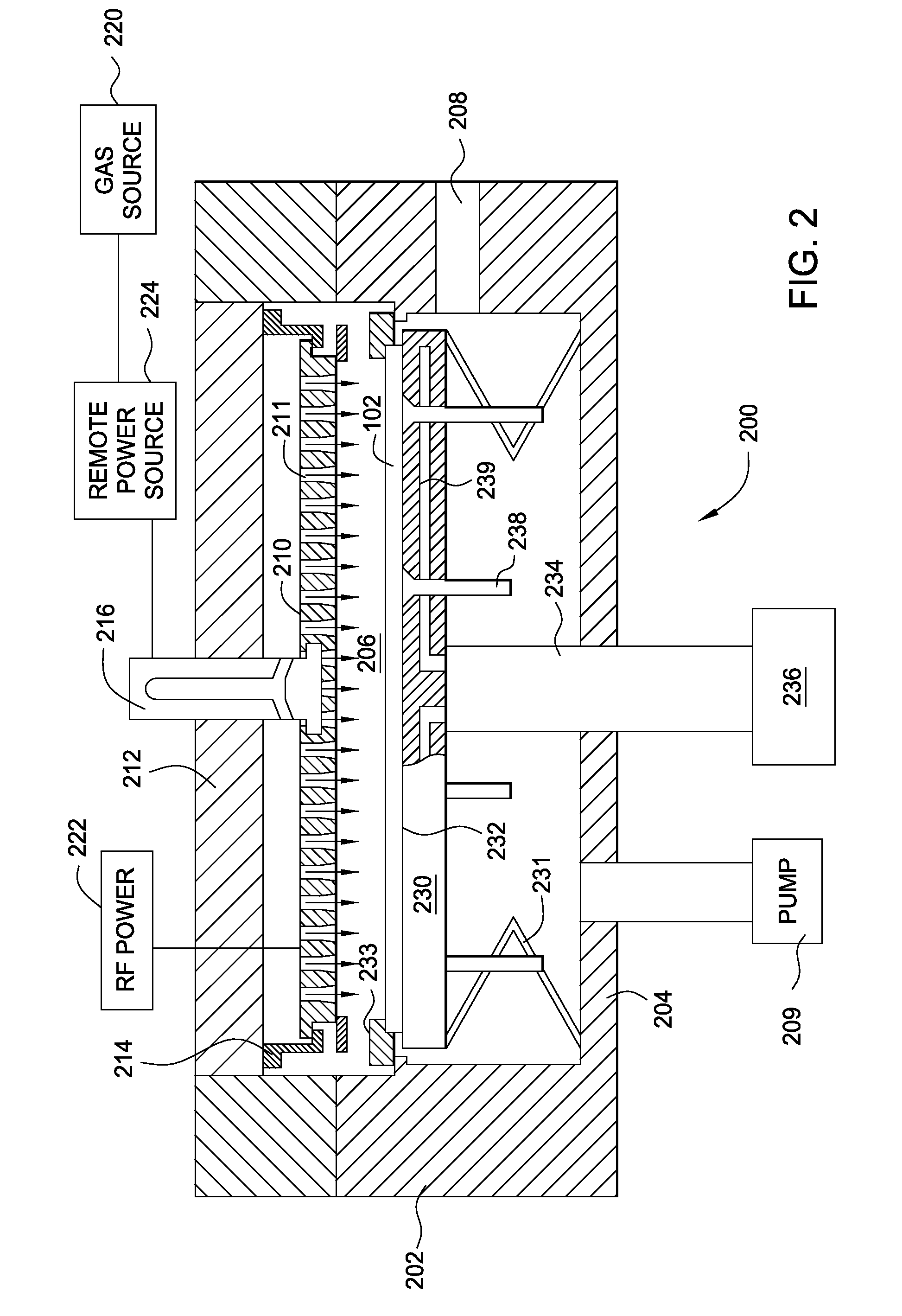
ActiveUS20140024180A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingPhysical chemistryThin membrane
Embodiments of the invention provide methods of an interface adhesion improvement methods used on a transparent substrate for OLED or thin film transistor applications. In one embodiment, a method of forming a buffer layer on a surface of a substrate includes providing a substrate having an planarization material disposed thereon in a processing chamber, supplying a buffer layer gas mixture including a silicon containing gas into the processing chamber, controlling a substrate temperature less than about 100 degrees Celsius, forming a buffer layer on the planarization material, supplying an encapsulating barrier layer deposition gas mixture including a silicon containing gas and a nitrogen containing gas into the processing chamber, and forming an encapsulating barrier layer on the buffer layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
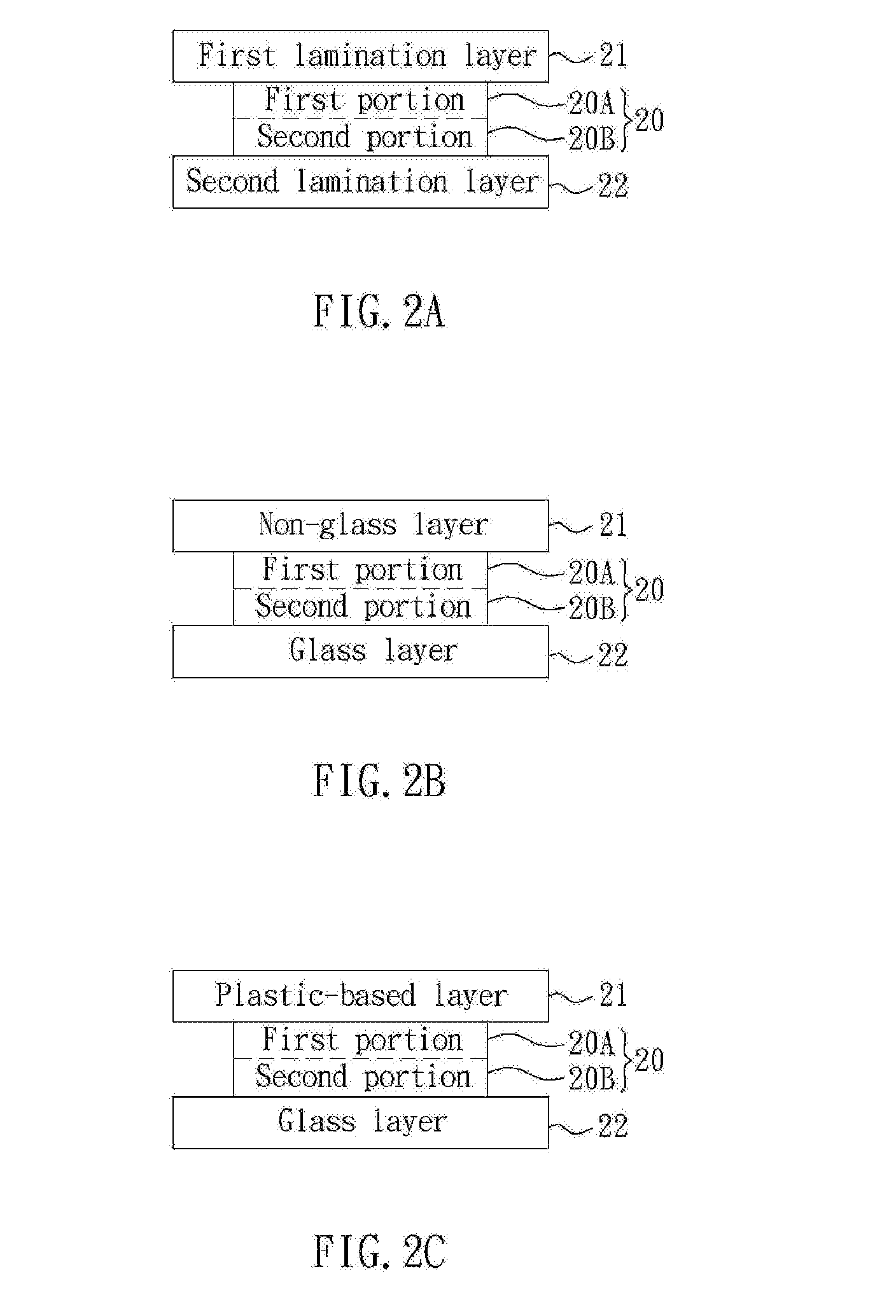
Optical Level Composite Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive and an Apparatus Therewith
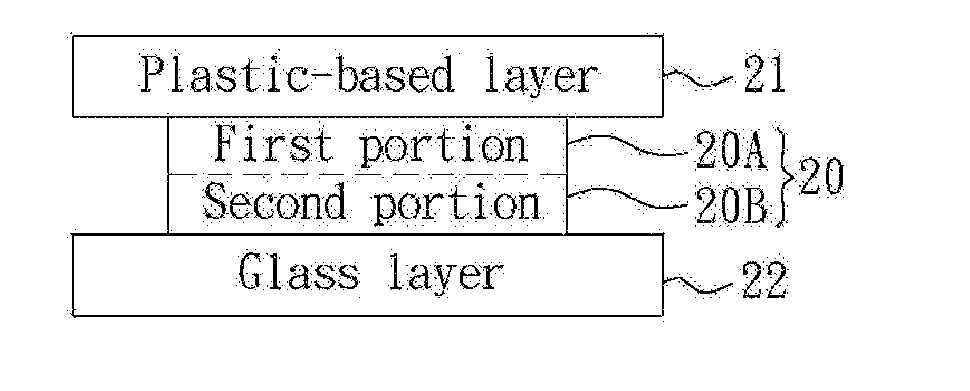
InactiveUS20120113361A1Improve effectivelyAdditional cost arid process timeSynthetic resin layered productsGlass/slag layered productsInterfacial adhesionEngineering
The present invention is directed to an optical level composite pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA), which includes a first portion and a second portion, which have different crosslinked densities and together form a mono-composite structure. The first portion and the second portion may be respectively bonded to a first lamination layer and a second lamination layer that are heterogeneous to each other. Accordingly, different interfacial adhesion and bulk rheology are generated at the interface of the first portion / first, lamination layer and the interface of the second portion / second lamination layer.
Owner:TRENDON TOUCH TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Low refractive index fluoropolymer compositions having improved coating and durability properties
InactiveUS20060148996A1Improve adhesionLow refractive indexNanoopticsCoatingsPolymer scienceRefractive index
A low refractive index composition that forms a low refractive index layer on an optical display is formed having a co-crosslinked interpenetrating polymer network of a fluoropolymer phase and an acrylate phase. The fluoropolymer phase is preferably formed from fluoropolymers based on THV or FKM and having either a degree of unsaturation and / or containing a reactive cure site monomer in its polymer backbone. The acrylate phase includes a multifunctional acrylate crosslinker, and more preferably includes a perfluoropolyether acrylate crosslinker. The formed low refractive index layer has improved interfacial adhesion to other layers or substrates contained in the optical display. Further, the mechanical strength and scratch resistance of the either of above low refractive index compositions can be further enhanced through the incorporation of surface functionalized inorganic particle into the formed layer.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Organic electroluminescence display and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050277355A1Improve interface adhesionImprove featuresMaterial nanotechnologyDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic layerInterfacial adhesion
A method of manufacturing an organic electroluminescence device whereby an encapsulating layer is formed by coating an encapsulating substrate with an encapsulating layer-forming composition and thermally processing the encapsulating substrate. A plasma treatment is performed on the encapsulating substrate having the encapsulating layer. A sealant is applied to at least one of the plasma treated encapsulating substrate and a substrate on which an organic electroluminescent unit including a first electrode, an organic layer, and a second electrode, which are sequentially stacked, is deposited. The sealing substrate and the substrate on which the organic electroluminescent unit is deposited are combined. Contaminants generated around the encapsulating layer and generated in the thermal process can be effectively removed by the cleaning process using plasma. Therefore, the interfacial adhesion between the sealant and the substrate is greatly improved, thereby preventing permeation of external air, moisture, etc., into the device.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
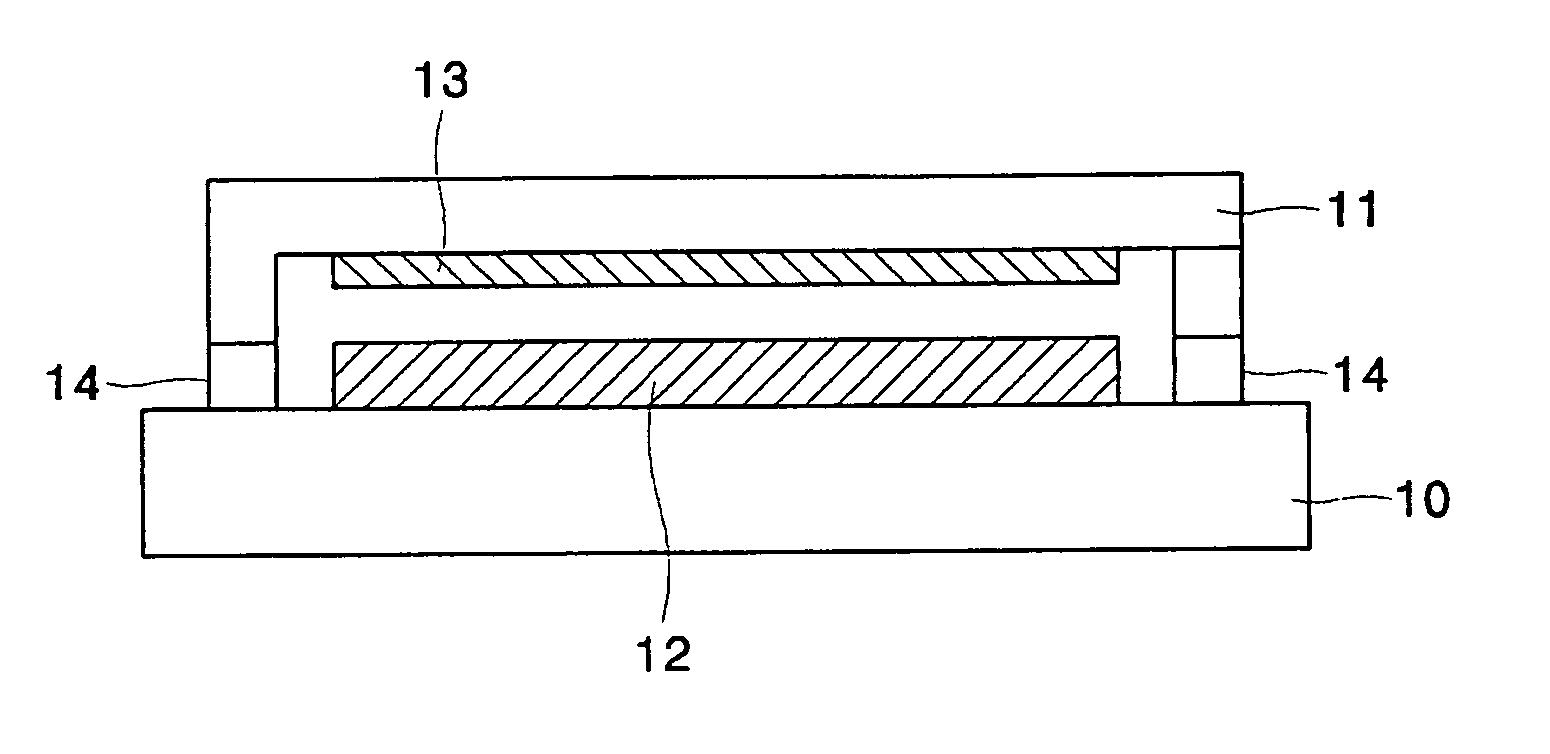
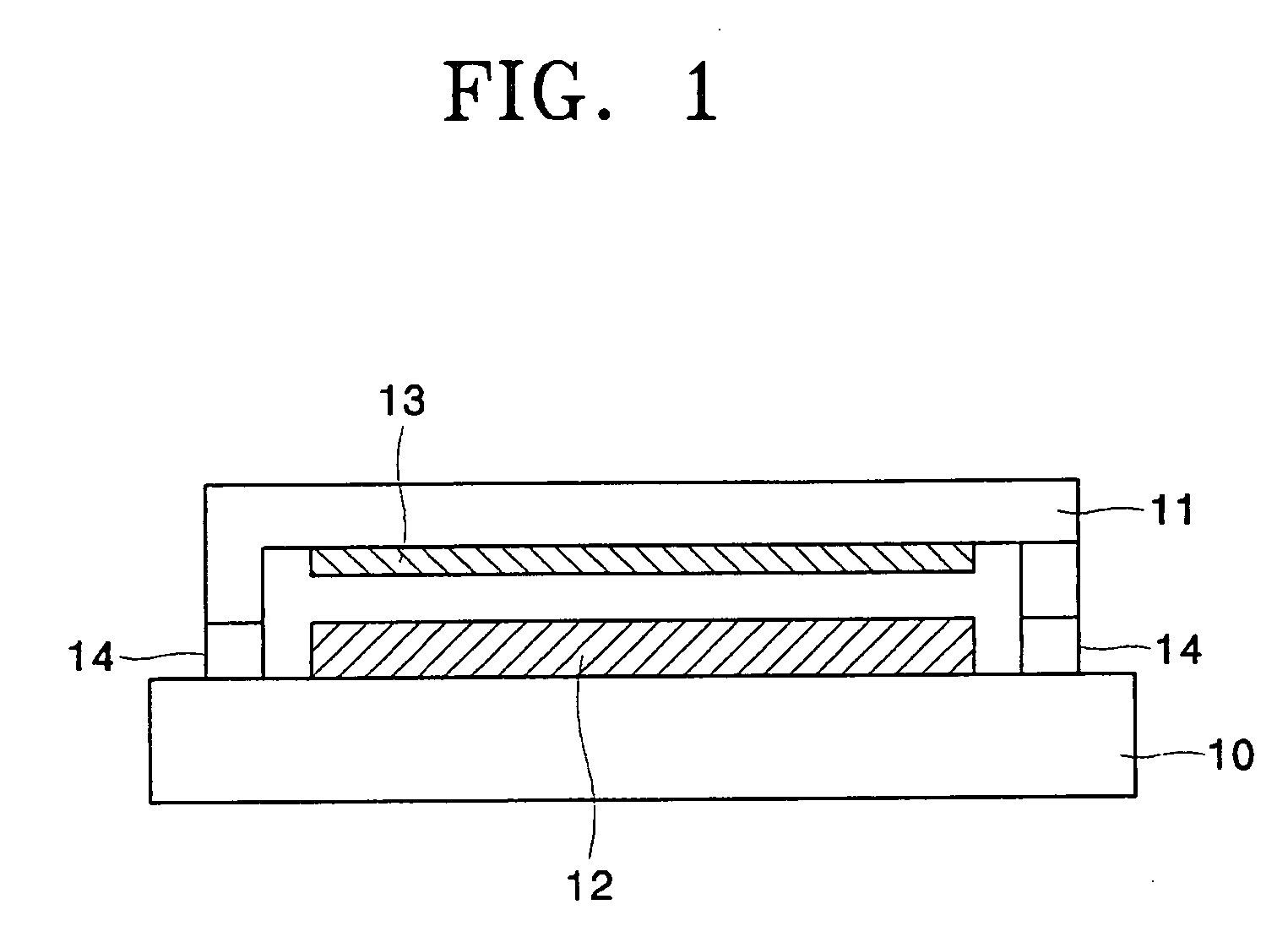
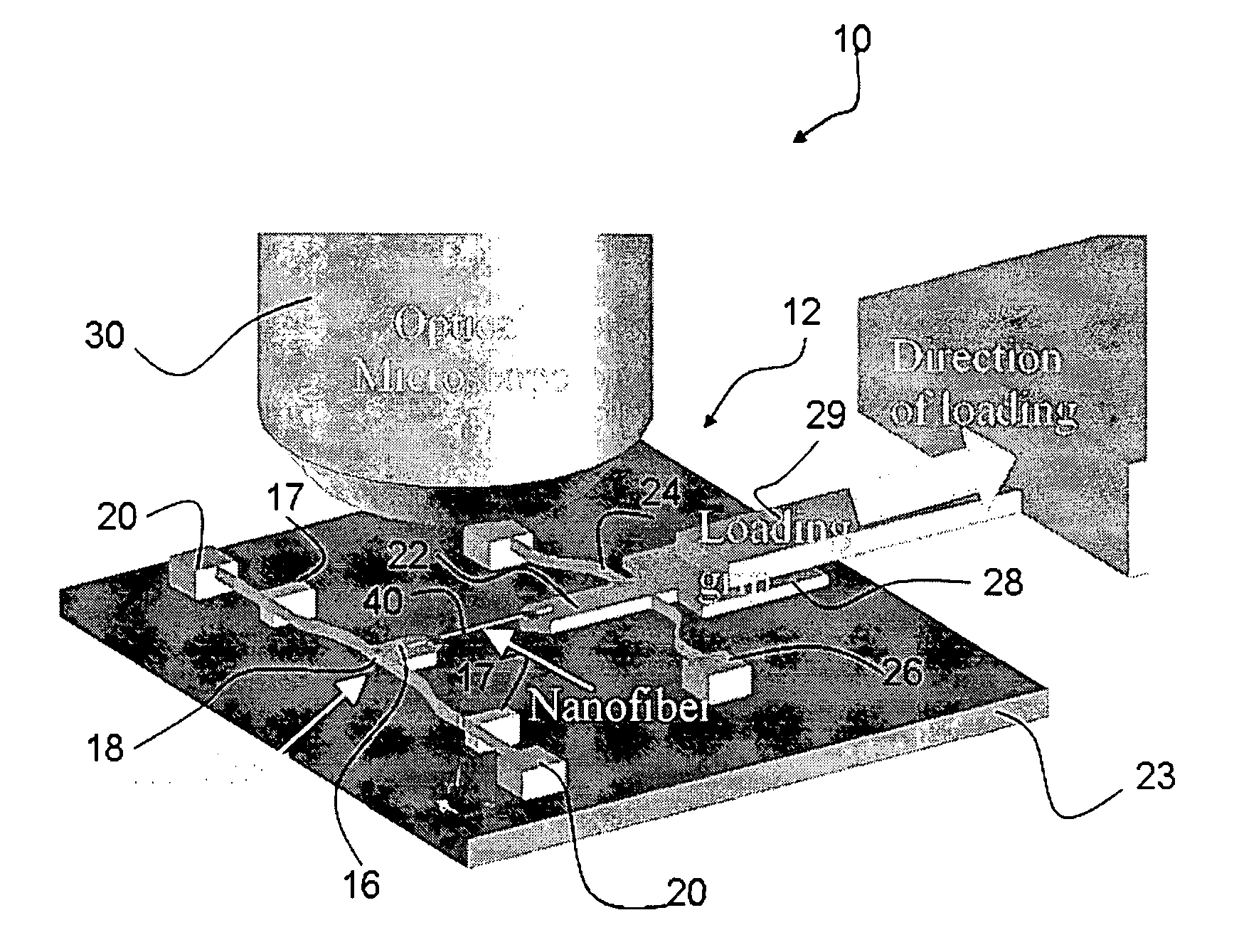
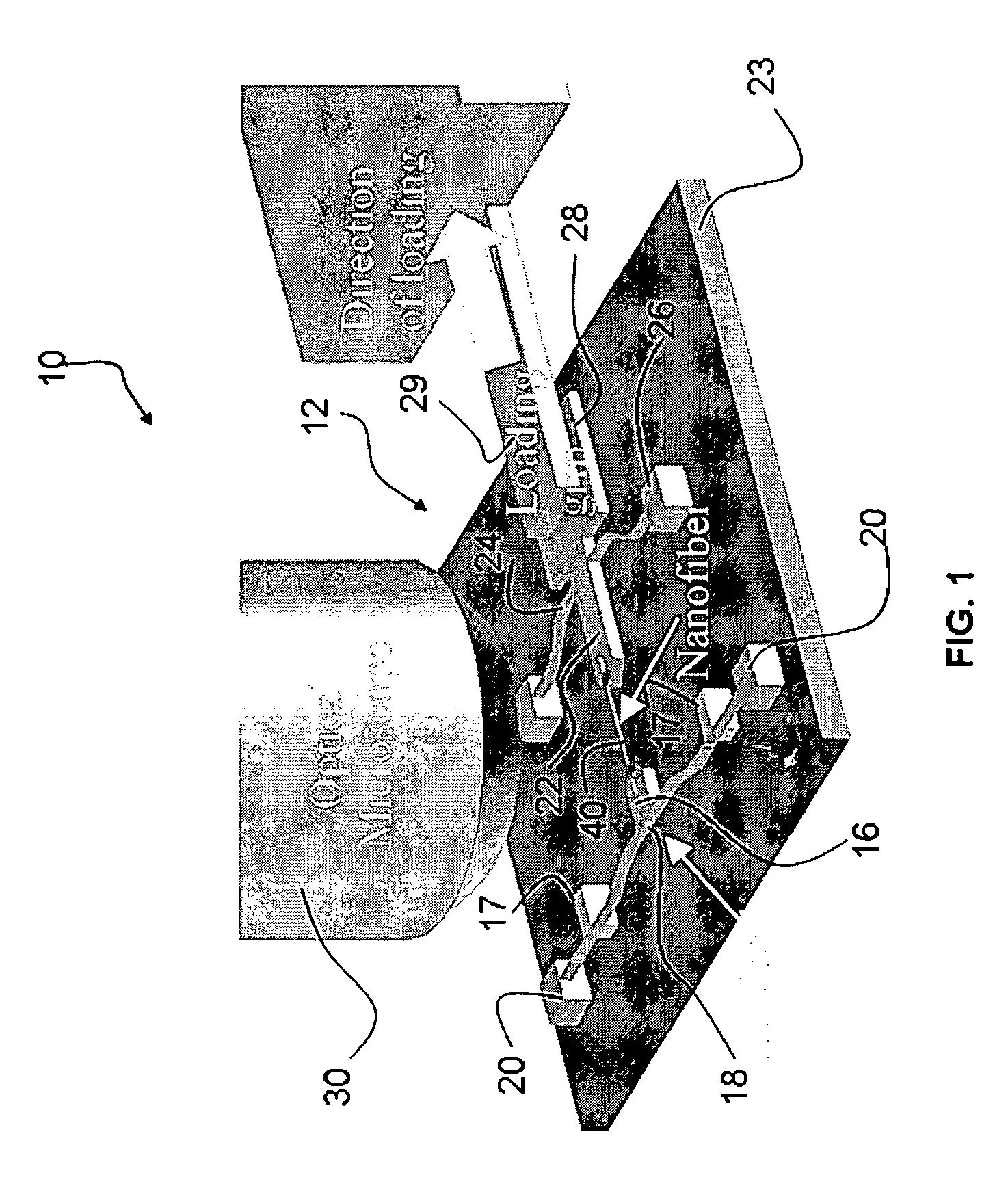
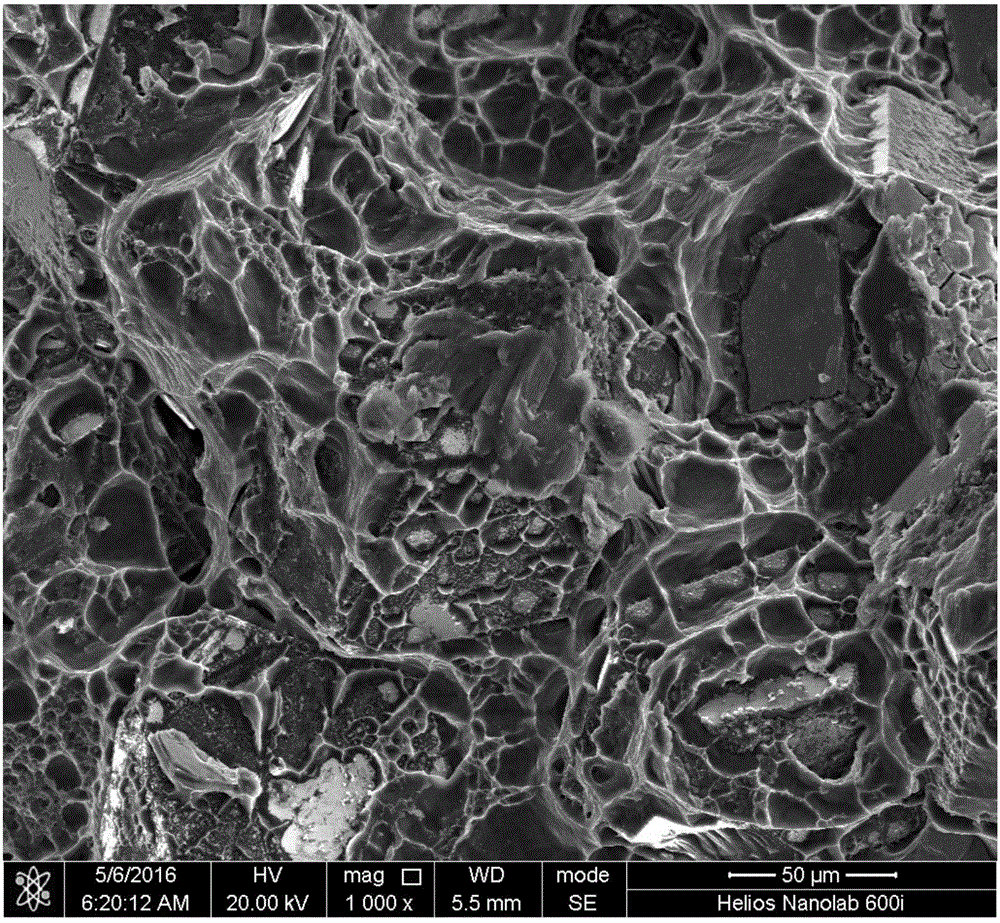
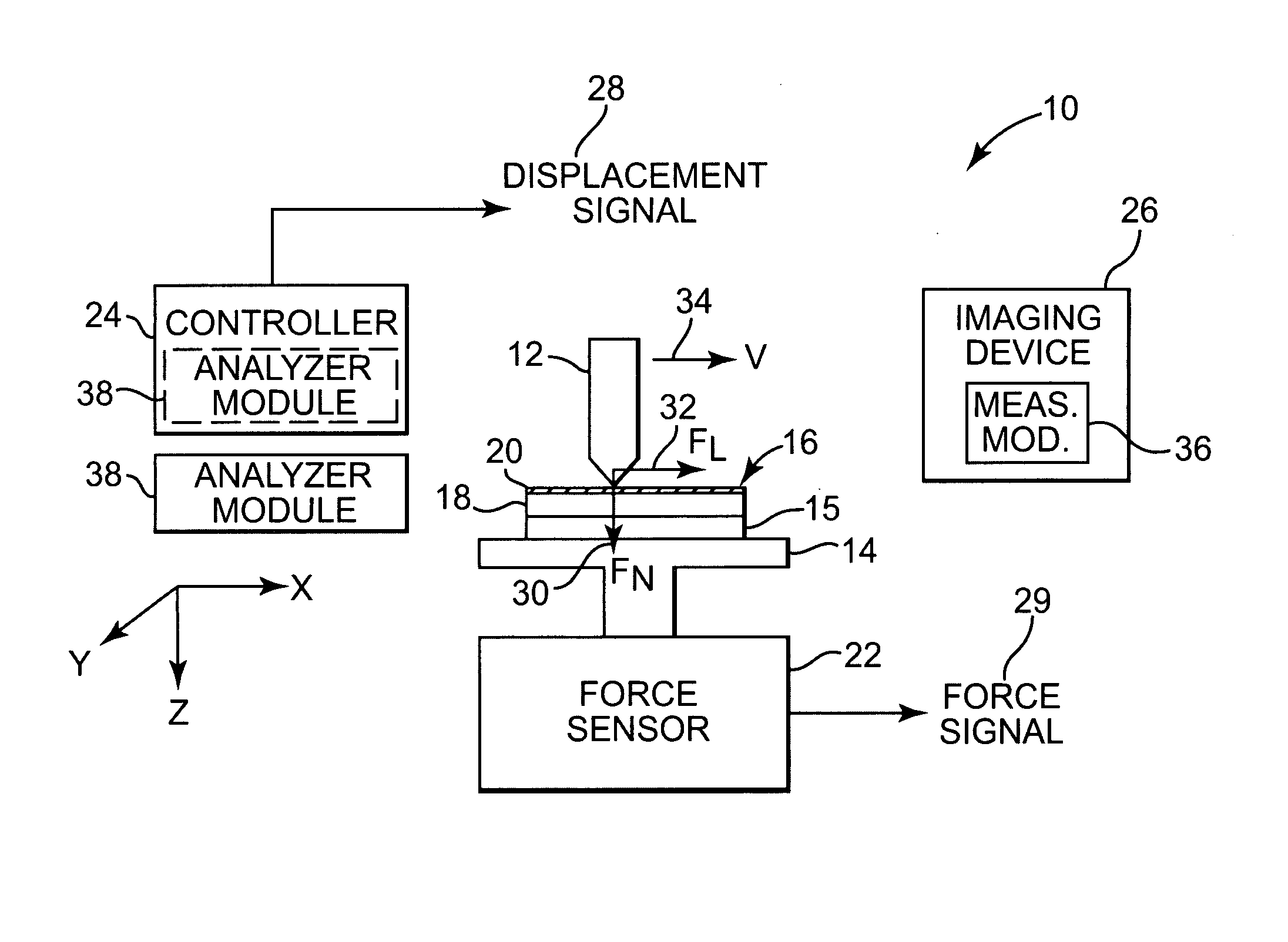
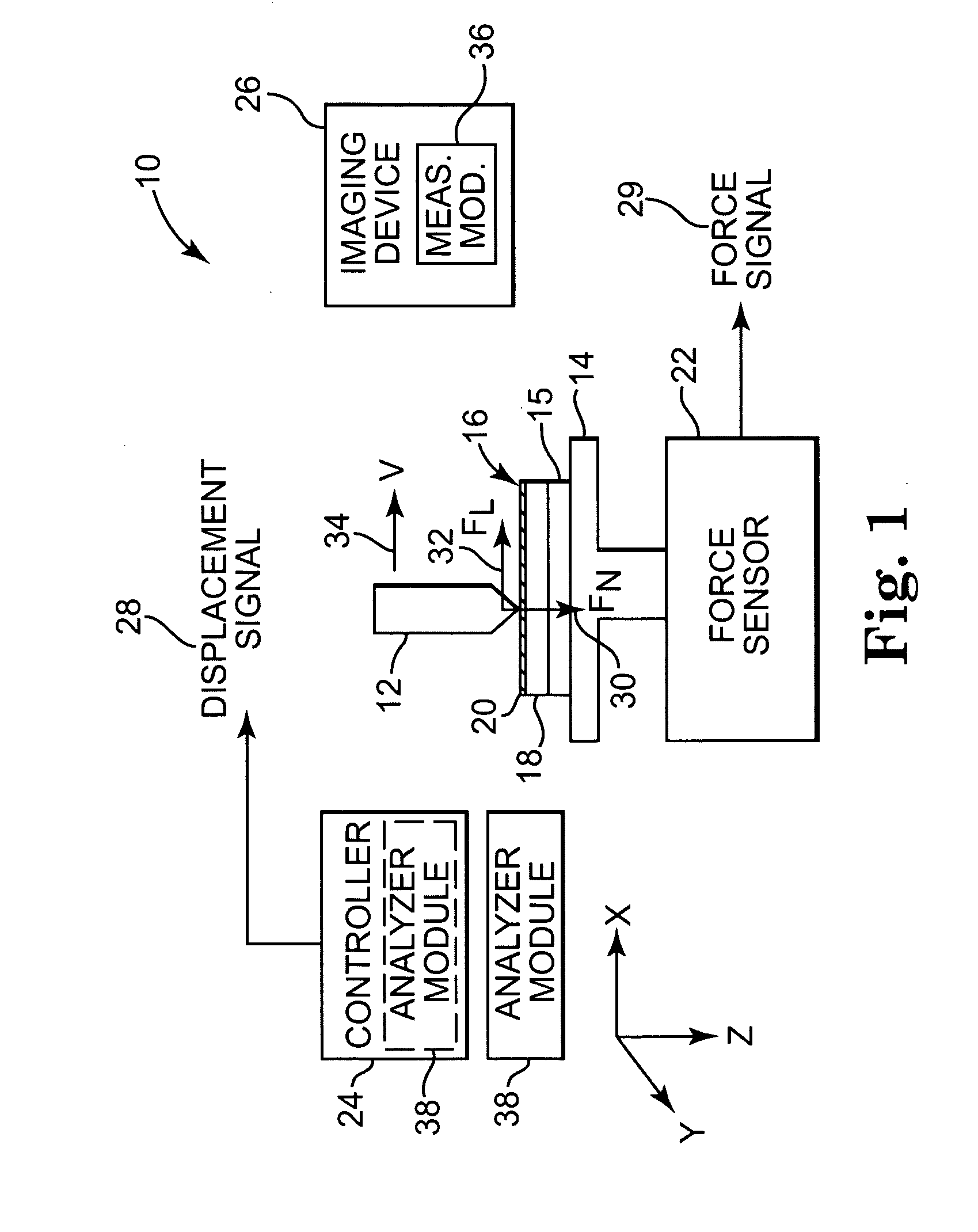
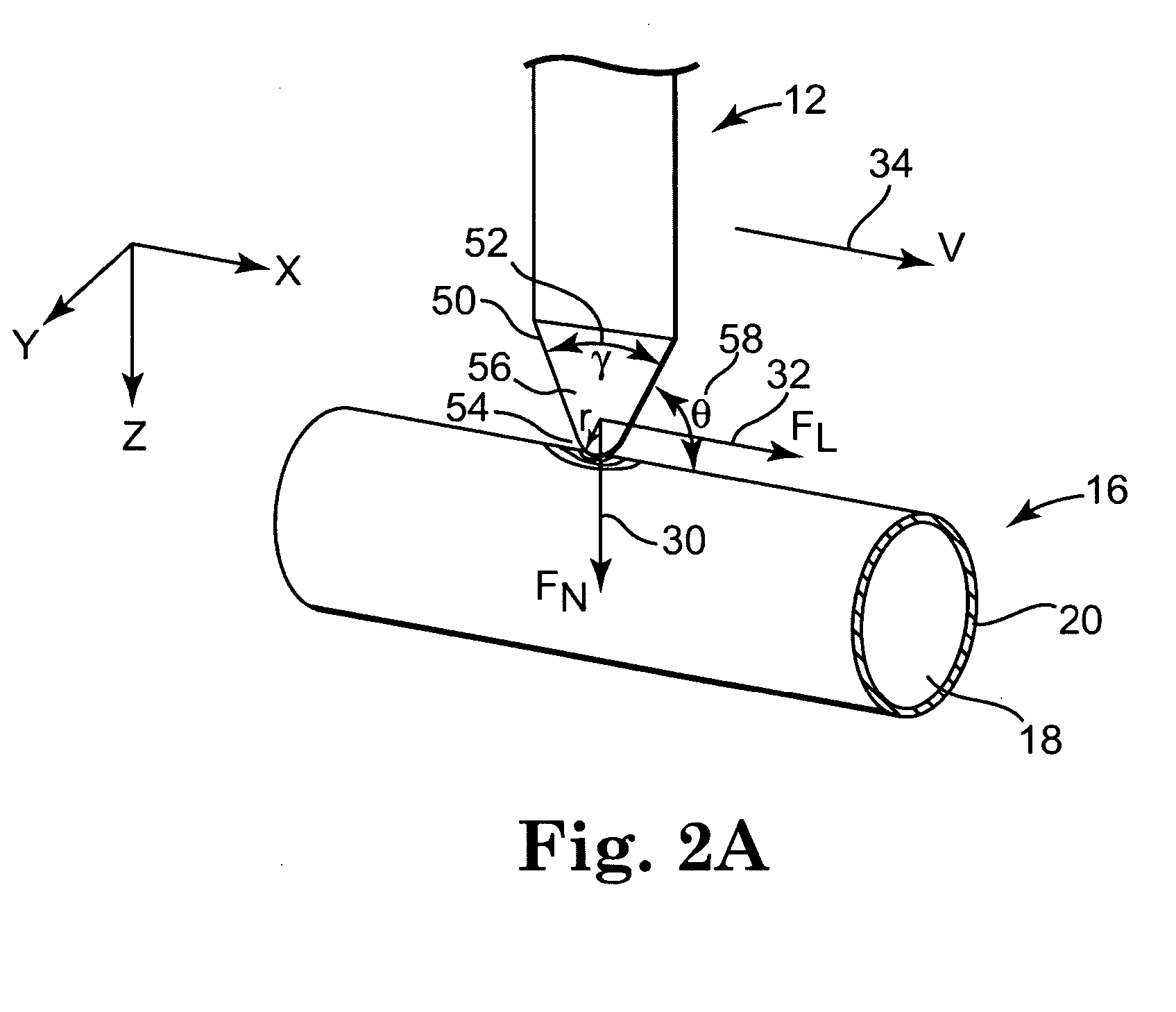
Stress micro mechanical test cell, device, system and methods
The invention provides a stress micro mechanical system for measuring stress and strain in micro- and nano-fibers tubes, and wires as well as for measuring the interface adhesion force and stress in nanofibers and nanotubes embedded in a polymer matrix. A preferred system of the invention has a substrate for supporting a MEMS fabrication. The MEMS fabrication includes freestanding sample attachment points that are movable in a translation direction relative to one another when the substrate is moved and a sample is attached between the sample attachment points. An optical microscope images surfaces of the MEMS fabrication. Software conducts digital image correlation on obtained images to determine the movement of the surfaces at a resolution much greater than the hardware resolution of the optical microscope. A preferred method for measuring stress and strain in micro- and nano-fibers, tubes, and wires, and / or measuring the force required to pull-out individual micro- and nano-fibers, tubes, and wires from a polymer matrix and to therefore measure interfacial adhesion is also provided. In the method a sample is attached between freestanding platforms in a MEMS device. Relative translational movement between the platforms is created and motion of the platforms is imaged with an optical microscope. Mechanical and adhesion properties of the sample are determined by applying a digital image correlation algorithm to the image data.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Carbon fiber bundle process for producing the same and thermoplastic resin composition and molded article thereof
A carbon fiber bundle is provided which can develop satisfactory interfacial adhesion to polyolefin-based resins, especially polypropylene resins. The carbon fiber bundle comprises a plurality of single fibers that was sized with a sizing agent comprising: a polymer having a main chain formed of carbon-carbon bonds, containing an acid group in at least part of side chains or at least a part of main chain ends, and representing an acid value of 23 to 120 mgKOH / g as measured in accordance with ASTM D1386; or a polymer having a main chain formed of carbon-carbon bonds and containing at least either of an epoxy group and an ester group in at least a part of side chains or at least a part of main chain ends.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Mixed Matrix Membranes Containing Low Acidity Nano-Sized SAPO-34 Molecular Sieves
InactiveUS20090149313A1High selectivityLost timeMembranesSemi-permeable membranesFiberPolymer science
The present invention discloses mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) containing polymer-functionalized low acidity, ultra low silica-to-alumina ratio, nano-sized SAPO-34 small pore molecular sieves and a continuous polymer matrix and methods for making and using these membranes. The surface functionalization of these molecular sieves provides a desired interfacial adhesion between SAPO-34 nano-particles and the continuous polymer matrix, which results in either no macrovoids or voids of less than 5 angstroms at the interface of the continuous polymer matrix and SAPO-34 in the MMMs. These MMMs, in the form of symmetric dense film, asymmetric flat sheet membrane, or asymmetric hollow fiber membranes, have good flexibility and high mechanical strength, and exhibit remarkably enhanced CO2 permeability (or CO2 permeance) and maintained CO2 / CH4 selectivity over the continuous polymer matrices for CO2 / CH4 separation. The MMMs of the present invention are suitable for a variety of liquid, gas, and vapor.
Owner:UOP LLC
Carbon fiber molding material, molding material, and carbon fiber-strengthening composite material
InactiveCN103975003AGood adhesionCovalent bond formation promotionFibre typesWoven fabricsFiberPolymer science
A carbon fiber molding material is provided that exhibits excellent interfacial adhesion between the carbon fibers and a thermosetting resin, and that yields a molded product exhibiting excellent mechanical properties. The carbon fiber molding material is either (Z) a prepreg containing sizing agent-coated carbon fibers and a thermosetting resin, or (Y) a material for forming woven fabric or braided cords that employs sizing agent-coated carbon fibers. The sizing agent is characterized by containing the following components (A) and (B): component (A) is an epoxy compound having two or more epoxy groups, or two or more functional groups; component (B) is a compound containing one or more of the group consisting of a tertiary amine compound, a tertiary amine salt, a quaternary ammonium salt, a quaternary phosphonium salt, and a phosphine compound. The sizing agent is obtained by blending 0.1-25 parts by mass of the compound (B) with 100 parts by mass of the compound (A).
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Semi-flexible pavement material, preparation method therefor and semi-flexible pavement
InactiveCN106587842AImprove crack resistanceImprove adhesionIn situ pavingsPolymer scienceCrack resistance
The invention discloses a semi-flexible pavement material, a preparation method therefor and a semi-flexible pavement. The semi-flexible pavement material is prepared from the raw materials, i.e., a cement grouting material and an asphalt mixture in parts by mass, wherein the cement grouting material contains 15-20 parts of cement, 8-10 parts of emulsified asphalt, 0.03-0.06 part of water reducing agent, 0.06-0.2 part of polypropylene fibers, 10-15 parts of mineral powder, 30-35 parts of sand, 8-10 parts of fly ash, 0.06-0.12 part of expanding agent and 0.03-0.06 part of interface modifier. According to the semi-flexible pavement material disclosed by the invention, the cement grouting material is added with the emulsified asphalt, the fly ash, the polypropylene fibers, the mineral powder, the water reducing agent, the expanding agent and the interface modifier which are mutually compounded and are in synergism, so that the cement grouting material can be easily subjected to dry shrinkage, the condition that the interfacial adhesion performance of cement-asphalt concrete is poor is improved, and thus, the crack resistance is improved. In addition, asphalt of the asphalt mixture is rubber asphalt, so that the crack resistance and adhesion property of the asphalt mixture are improved.
Owner:江苏北极星交通产业集团有限公司
Carbon fiber bundle, process for producing the same, and thermoplastic resin composition and molded article thereof
A carbon fiber bundle is provided which can develop satisfactory interfacial adhesion to polyolefin-based resins, especially polypropylene resins. The carbon fiber bundle comprises a plurality of single fibers that was sized with a sizing agent comprising: a polymer having a main chain formed of carbon-carbon bonds, containing an acid group in at least part of side chains or at least a part of main chain ends, and representing an acid value of 23 to 120 mgKOH / g as measured in accordance with ASTM D1386; or a polymer having a main chain formed of carbon-carbon bonds and containing at least either of an epoxy group and an ester group in at least a part of side chains or at least a part of main chain ends.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
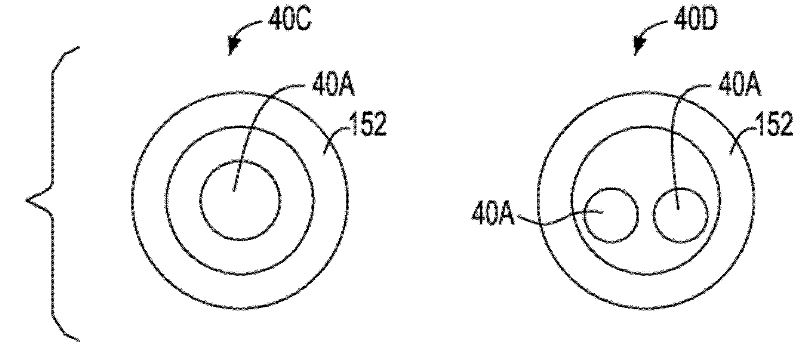
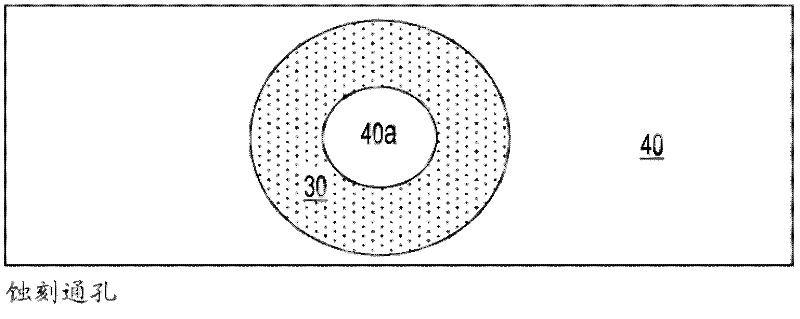
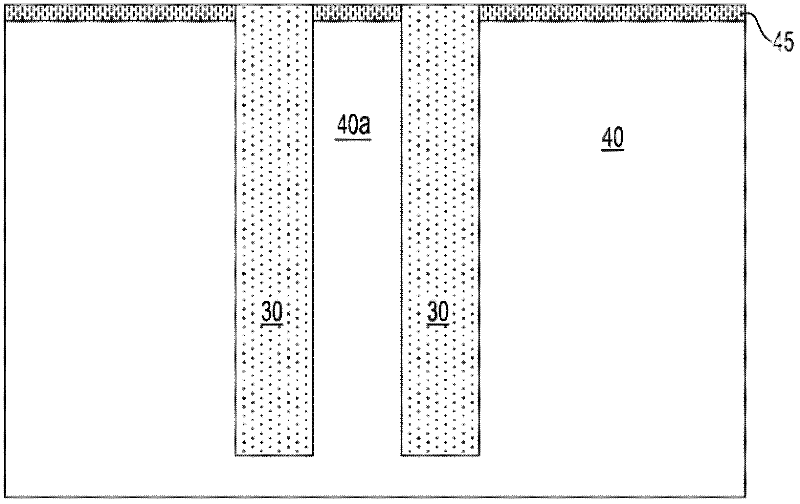
Coaxial through-silicon via
ActiveCN102598245AOvercome any defect of leakageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityElectrical conductor
A through-silicon via (TSV) structure forming a unique coaxial or triaxial interconnect within the silicon substrate 40. The TSV structure is provided with two or more independent electrical conductors 50, 60 insulated from another and from the substrate. The electrical conductors can be connected to different voltages or ground, making it possible to operate the TSV structure as a coaxial or triaxial device. Multiple layers using various insulator materials can be used as insulator, wherein the layers are selected based on dielectric properties, fill properties, interfacial adhesion, CTE match, and the like. The TSV structure overcomes defects in the outer insulation layer that may lead to leakage. A method of fabricating such a TSV structure is also described.
Owner:IBM CORP
Carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin composition, molding material, prepreg, and methods for producing same
ActiveUS20140228519A1Improve dynamic characteristicsInterfacial adhesionFibre treatmentWood working apparatusEpoxyFiber
Provided are a carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin composition excellent in interfacial adhesion between carbon fiber and a thermoplastic resin and excellent in dynamic characteristics, and a molding material, a prepreg, and a method for producing the same. The carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin composition includes the following components (A) and (B), carbon fiber and a thermoplastic resin; component (A): (A1) a bifunctional or higher functional epoxy compound and / or (A2) an epoxy compound which has a monofunctional or higher epoxy group and has one or more taypes of functional groups selected from a hydroxyl group, an amide group, an imide group, a urethane group, a urea group, a sulfonyl group and a sulfo group; and component (B): 0.1 to 25 parts by mass, based on 100 parts by mass of the component (A), of at least one reaction accelerator selected from the group consisting of [a] a specific tertiary amine compound (salt) (B1), [b] a specific quaternary ammonium salt (B2) and [c] a quaternary phosphonium salt and / or phosphine compound (B3).
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Carbon/carbon fiber-silicon, boron, carbon and nitrogen ceramic composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a carbon / carbon fiber-silicon, boron, carbon and nitrogen ceramic composite material and a preparation method thereof. The invention relates to a short carbon fiber reinforced silicon, boron, carbon and nitrogen ceramic composite material and a preparation method thereof. The invention aims to solve the problem that the existing fiber reinforced silicon, boron, carbon and nitrogen ceramic composite material is complex in preparation process and high in cost, and the strengthening and toughening effect of the fibers is not remarkable due to over-strong interfacial adhesion. The product is prepared from short carbon fibers, phenolic resin, acetone and silicon, boron, carbon and nitrogen ceramic composite powder. The preparation method comprises the following steps: I, dissolving phenolic resin in acetone to prepare dipping liquor; II, putting the short carbon fibers in the dipping liquor to dip, and then splitting in an argon atmosphere to obtain carbon coating-coated short carbon fibers; III, putting silicon powder, graphite and hexagonal boron nitride in a ball mill to ball-mill and mix to obtain composite powder; and IV, after mixing the carbon coating-coated short carbon fibers with the composite powder, carrying out hot pressed sintering to obtain the carbon / carbon fiber-silicon, boron, carbon and nitrogen ceramic composite material.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Preparation method for functional fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin composite material
The invention belongs to the field of nanotechnology, and particularly relates to a preparation method for a functional fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin composite material. The preparation method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: purifying carbon nanotubes, then carrying out carboxylation and acylation, carrying out a reaction on the acylated carbon nanotubes and a coupling agent with an active amino to obtain carbon nanotubes grafted with the coupling agent on the surface, and carrying out a reaction with fiberglass to obtain a functional fiberglass reinforcement body; and compounding the functional fiberglass reinforcement body with an epoxy resin base body to obtain the functional fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin composite material. The preparation method has simple reaction steps, and utilizes the strength and toughness of carbon nanotubes to modify fiberglass; and the prepared reinforcement body can strengthen and toughen the resin base body and significantly improve the interfacial adhesion strength and the mechanical properties of the composite material. The composite material prepared by the preparation method provided by the invention can be widely applied in the technical fields of aerospace, automobile shipping, transport and communication, mechanical electronics, civilian devices, etc.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Preparation method of W-plated diamond/aluminum composite
ActiveCN105886849AAvoid introducingLong melting timeVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingInterfacial adhesionFlexural strength
A preparation method of W-plated diamond / aluminum composite relates to a preparation method of a metal-based composite. In order to solve the technical problem that since diamond and aluminum react to produce Al4C3, the obtained composite has poor interfacial adhesion and low heat conductivity. The method includes: first, coating the surface of diamond particles with W; second, preheating; third, infiltrating under pressure: applying a pressure of 10-15 Mpa with an intra-furnace press so that molten aluminum infiltrates the W-coated diamond particles, cooling at a speed of 100 DEG C / h to below 300 DEG C, relieving pressure, turning off a vacuum furnace, and demolding to obtain the W-plated diamond / aluminum composite; diamond is 55-65% in volume fraction, > / =98% in compactness, up to 622 W / (m.K) in heat conductivity, down to 7.08*10-6 / K in thermal expansion coefficient and up to 304 Mpa in flexural strength. The invention belongs to the field of preparation of composites.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method of measuring interfacial adhesion properties of stents
A method for measuring toughness of interfacial adhesion including applying a normal force with a probe to a surface of a coating joined to a major surface of a substrate of a medical stent, wherein the surface is substantially parallel to the major surface, and applying a lateral force to the coating with the probe by laterally moving a position of the probe relative to the major surface such that the probe forms at least one delaminated region in the coating as the position of the probe moves laterally across the major surface, the delaminated region having a starting point and an ending point. The method further includes measuring a magnitude of the lateral force over time, and determining a toughness of interfacial adhesion between the coating and the major surface based on changes in magnitude of the lateral force as the position of the probe moves from the starting point to ending point.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Preparation method of sisal hemp cellulose nanowhisker/polylactic acid biological composite material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a sisal hemp cellulose nanowhisker / polylactic acid biological composite material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: grafting a polylactic oligomer on the surface of the sisal hemp cellulose nanowhisker through adopting a grafting treatment method; and forming good interfacial adhesion by means of compatibility between the polylactic oligomer which is grafted on the surface of the sisal hemp cellulose nanowhisker and polylactic acid and preparing the sisal hemp cellulose nanowhisker / polylactic acid biological composite material by adopting an in-situ composite technique. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple in preparation process and green and environmental friendly, and the prepared sisal hemp cellulose nanowhisker / polylactic acid biological composite material has excellent mechanical properties and biocompatibility.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
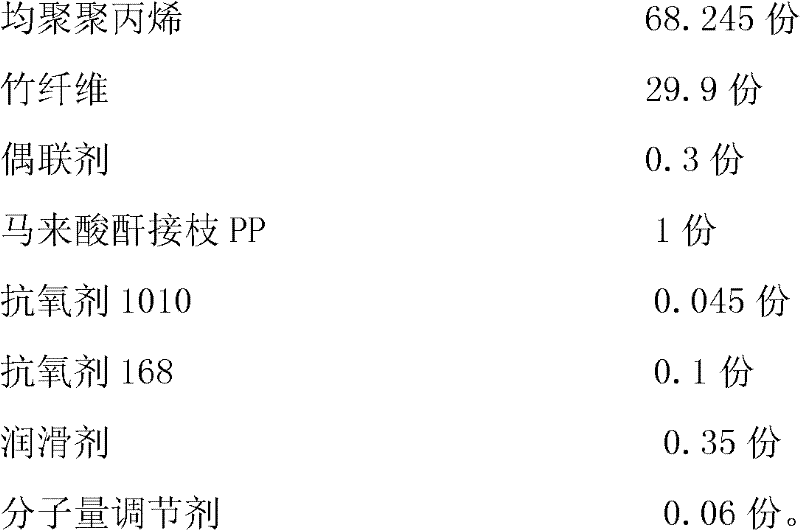
Novel bamboo fiber/polypropylene composite material and method for preparing same
The invention discloses a novel bamboo fiber / polypropylene composite material and a method for preparing the novel bamboo fiber / polypropylene composite material. The novel bamboo fiber / polypropylene composite material is prepared by treating the surface of bamboo fiber, adding a graft, an antioxidant, a lubricant and a molecular weight regulator into homopolymerized polypropylene as a substrate, and fully mixing according to proportion. The surface of the bamboo fiber is treated, thus the compatibility of the bamboo fiber and the polypropylene is improved, and the novel bamboo fiber / polypropylene composite material has excellent mechanical properties. In addition, the plasticizing properties of the polypropylene is improved, the melt viscosity is reduced, the flowability is improved, the compatibility and dispersibility of components of a system are effectively improved, and the interfacial adhesion of the material system is improved. Moreover, the aging resistance and the processing performance of the product are also improved, the polypropylene has thermal stability, and the rigidity of the polypropylene is greatly enhanced. Due to the addition of the lubricant and the molecular weight regulator, the flowability and the flow rate of the novel bamboo fiber / polypropylene composite material are improved. The novel bamboo fiber / polypropylene composite material is suitable for the process for extruding plastics into sheets, plates and pipes and also suitable for the process for injecting and molding small house appliance shells and bases.
Owner:苏州晋圣博高分子材料科技有限公司
Polymer composite structure
InactiveUS6852424B2Synthetic resin layered productsConstructions elementsPolymer scienceInterfacial adhesion
Two-component polymer composite structures are described, such as a composite structure that includes a first polymer structure and a second polymer structure adhered to one another through interfacial adhesion provided by a semicrystalline random copolymer with 70-88 mole % propylene units and alpha olefin units having 2 or from 4 to 10 carbon atoms, the semicrystalline random copolymer having a heat of fusion of from 2 to 90 J / g and a crystallinity of from 2% to 65% of the crystallinity of isotatic polypropylene.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
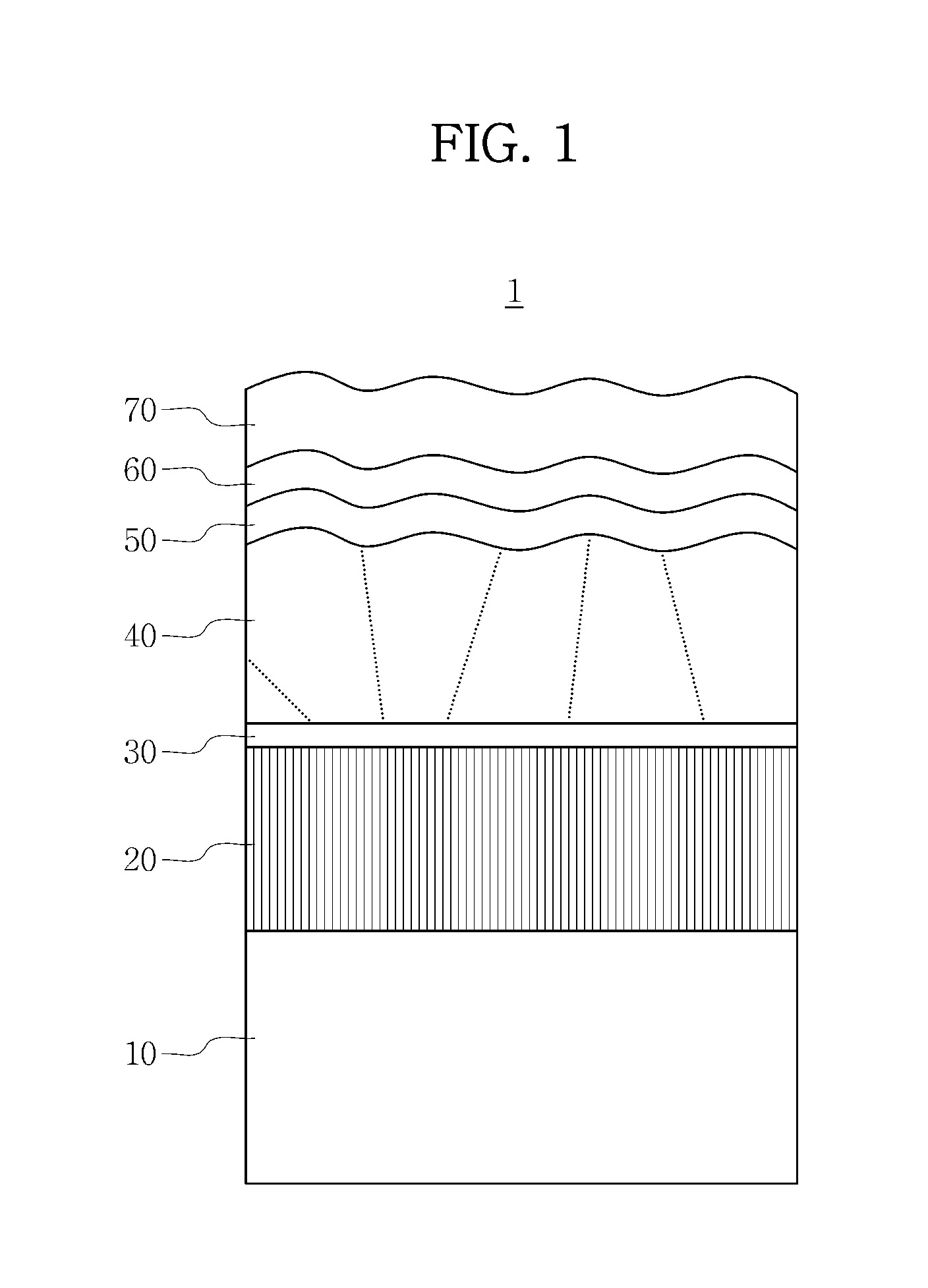
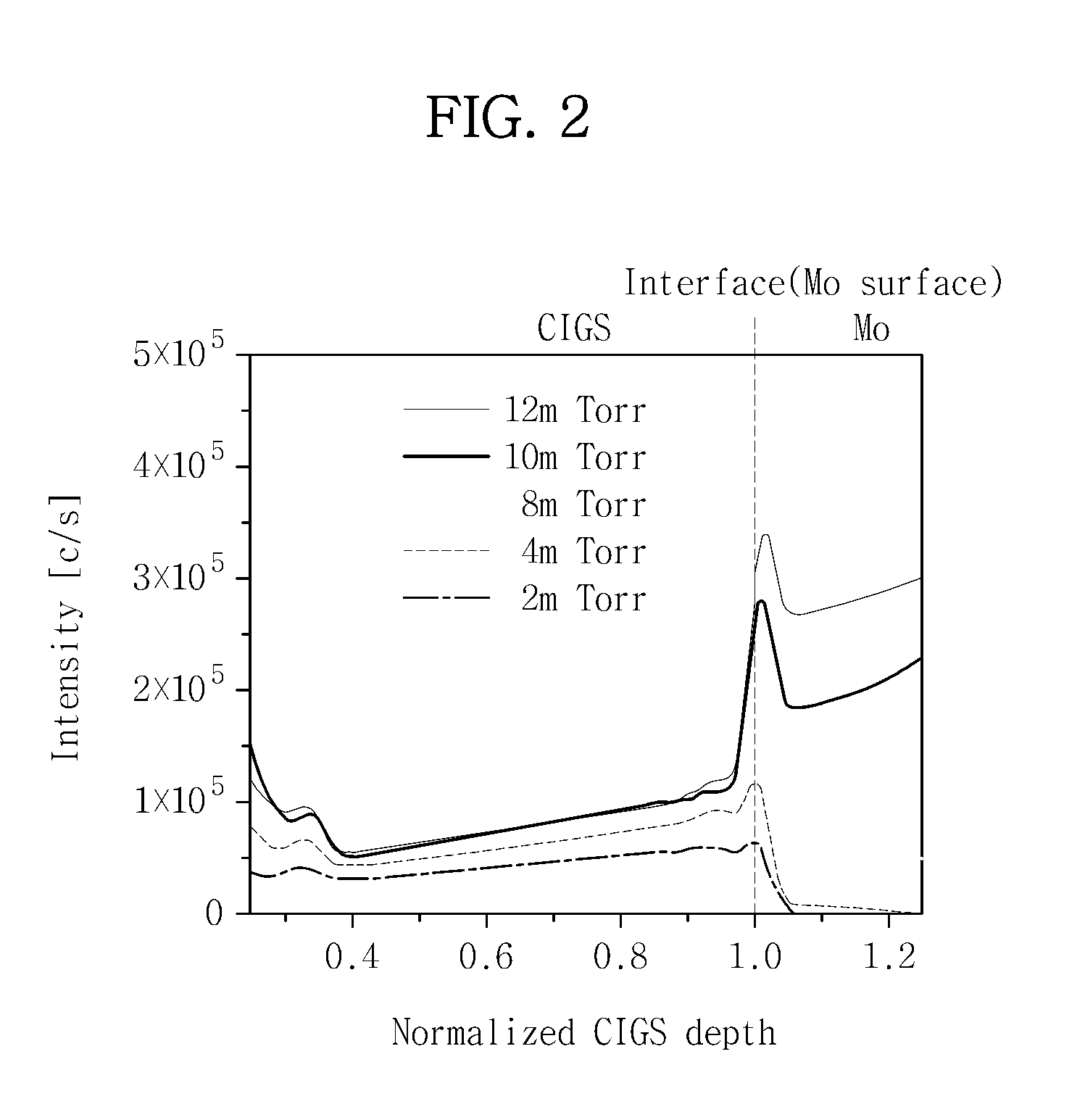
Se OR S BASED THIN FILM SOLAR CELL AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING THE SAME
InactiveUS20130104972A1Reduce unevennessGuaranteed smooth progressFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSulfurInterfacial adhesion
Provided is a Se- or S-based thin film solar cell, including a substrate, a rear electrode formed on the substrate, a light absorbing layer formed on the rear electrode and containing at least one of selenium (Se) and sulfur (S), and an rear electrode top layer. The rear electrode top layer is formed between the rear electrode and the light absorbing layer, and contains a large amount of oxygen (O) to control diffusion of sodium (Na) through the rear electrode to the light absorbing layer. In this manner, it is possible to improve the electrical conductivity and interfacial adhesion of the rear electrode while stimulating diffusion of sodium (Na) to improve the efficiency of a thin film solar cell.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Reacting nano inorganic particle/polymer composite material
This invention discloses a kind of reactive inorganic nanoparticle / polymer composite materials which comprises 1~5wt% inorganic nanoparticles, 2.5~10wt% reactive compatilizers and 85~96.5wt% polymer matrix. In this invention, reactive compatilization technology is adopted, that is, inorganic nanoparticles react with polymer in situ during ordinary blending to produce grafted compounds, which greatly enhances the interfacial effect between inorganic nanoparticles and polymer matrix so that both the interfacial adhesion strength and the dispersion of inorganic nanoparticles in the matrix are greatly improved and mechanical properties of the prepared composite materials are effectively promoted. This invention requires no special apparatus or technique the composite materials with good comprehensive properties can be obtained with only common facilities.
Printed circuit board and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070141310A1Highly reliable fine circuitImprove interface adhesionDielectric materialsSynthetic resin layered productsCopper platingInterfacial adhesion
Disclosed are a printed circuit board and a method of manufacturing the same, in which a fluorine resin coating layer is formed on a resin substrate, and then a copper layer is formed using a dry process including ion beam surface treatment and vacuum deposition instead of a conventional wet process including surface roughening and electroless copper plating. According to this invention, the interfacial adhesion of the substrate material may be increased without changing the surface roughness thereof, thus realizing a highly reliable fine circuit. As well, a low dielectric constant and a low loss coefficient may be obtained thanks to the formation of the fluorine resin layer. Further, a wet process is replaced with a dry process, whereby the copper plating layer may be formed in an environmentally friendly manner.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Method for modifying carbon fiber surface by assembly of aromatic fused ring molecules and preparation method of carbon fiber interface reinforced resin matrix composite
The invention provides a method for modifying a carbon fiber surface by assembly of aromatic fused ring molecules and belongs to the technical field of carbon fiber modification. The method comprisesthe following steps: aromatic fused ring dianhydride and diamine are subjected to imidization, and an aromatic fused ring imide molecule assembly liquid is obtained; carbon fibers are soaked in the aromatic fused ring imide molecule assembly liquid, the aromatic fused ring imide molecules are combined with the carbon fibers, and the carbon fibers with surfaces subjected to assembly modification are obtained. Chemical activity of the surfaces of the carbon fibers can be improved with the modification method. The invention further provides a preparation method of a carbon fiber interface reinforced resin matrix composite. The obtained carbon fibers with the surfaces subjected to assembly modification are compositely cured with resin, and the aromatic fused ring molecule assembly-modified carbon fiber interface reinforced resin matrix composite is obtained. The interface reinforced resin matrix composite obtained with the preparation method has good interfacial adhesion strength and interfacial shear strength.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Carbon fiber bundle and method for producing same
ActiveCN102597360AImprove interface bonding performanceCarbon fibresCoatingsFiber bundlePolymer science
Disclosed is a carbon fiber bundle in which an amino group-containing modified polyolefin resin adheres to a carbon fiber bundle and the amount of the amino group-containing modified polyolefin resin adhering to the carbon fiber bundle is 0.2-5.0% by mass. The carbon fiber bundle is able to be produced by having 0.2-5.0% by mass of an amino group-containing modified polyolefin resin adhere to the surface of a carbon fiber bundle. The carbon fiber bundle exhibits excellent interfacial adhesion to polyolefin resins, especially to polypropylene resins, and is useful for the reinforcement of polyolefin resins. Also disclosed is a method for producing the carbon fiber bundle.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Preparation method of C/C composite material
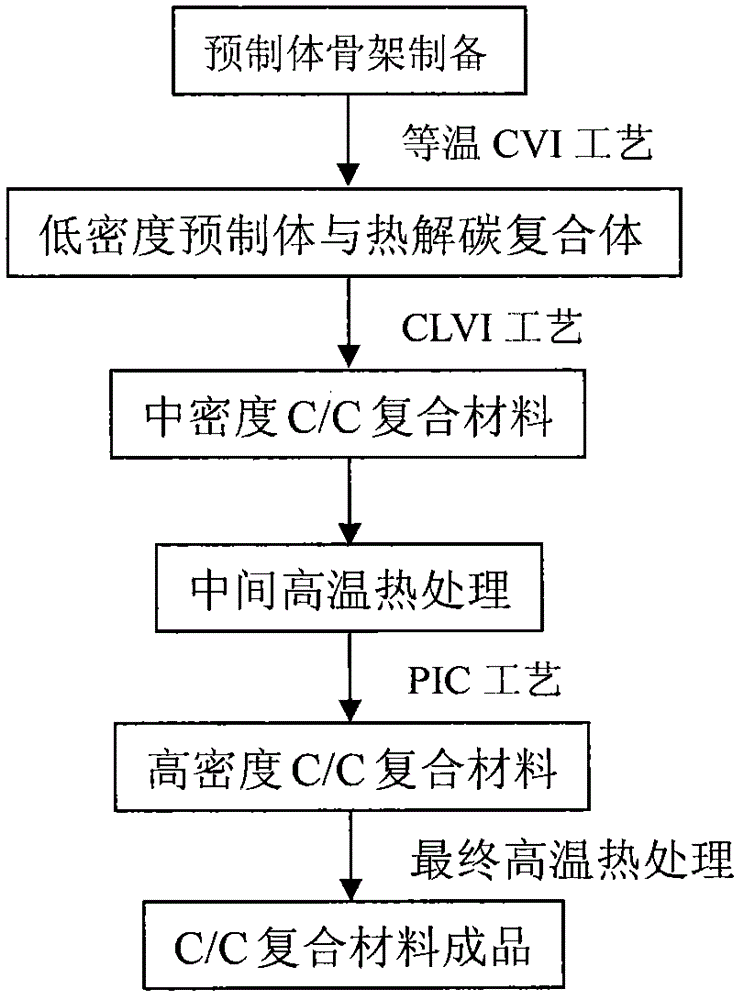
The invention relates to a preparation method of a C / C composite material. The C / C composite material is prepared by combining advantages of three processes: a chemical vapor infiltration process, a chemical liquid vapor infiltration process and a resin impregnation and carbonization process. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a preform; 2) preparing a low-density preform and a pyrolytic carbon complex by using the chemical vapor infiltration process; 3) preparing a medium-density C / C composite material by using the chemical liquid vapor infiltration process; 4) carrying out medium high-temperature treatment to improve the porosity so as to facilitate further densification; 5) finally densifying by adopting PIC to obtain a high-density C / C composite material; and 6) carrying out final high-heat treatment to obtain the C / C composite material finished product. The prepared C / C composite material is good in fibrous / interfacial adhesion and excellent in performance, and moreover, the preparation period is greatly shortened, the production efficiency and the utilization ratio of the raw materials are improved, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AEROSPACE HONGGANG MACHINERY
Method for evaluating snow and ice melting capacity of anti-freezing asphalt mixture
InactiveCN105806778AChange the status quo of no quantitative evaluation of ice and snow melting effectLowering the freezing pointUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisAnti freezingInterfacial adhesion
The invention discloses a method for evaluating snow and ice melting capacity of an anti-freezing asphalt mixture. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a Marshal test piece by adopting an anti-freezing asphalt mixture, simulating the site freezing conditions, and testing the anti-drawing strength of the test piece. Because the adopted anti-freezing asphalt mixture during test piece preparation contains salts, chloride ions in the salts are gradually separated out of the surface of the test piece, and an isolating layer is formed on the surface, so that the ice point of the solution is reduced; and therefore, the cohesive force of the ice layer and the test piece surface of the anti-freezing asphalt mixture is greatly reduced. According to the test method disclosed by the invention, the interfacial adhesion strength of the test piece and the ice layer is tested, the snow and ice melting effect is further evaluated, and the lower the anti-drawing strength is, the higher the snow and ice melting capacity is. The actual conditions can be simulated indoors, and the snow and ice melting effects of different anti-freezing asphalt mixtures can be quantitatively evaluated; and moreover, the method has the advantages that operating steps are simple and data is accurate and reliable.
Owner:JIANGSU SINOROAD ENG TECH RES INST CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com