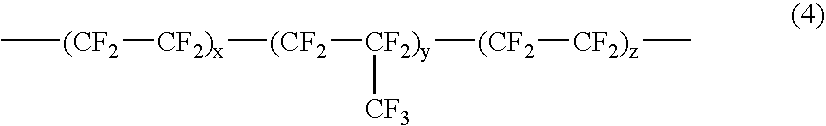Low refractive index fluoropolymer compositions having improved coating and durability properties
a fluoropolymer and composition technology, applied in the field of antireflection films, can solve the problems of poor abrasion and wear resistance, difficult and expensive continuous film processing, and low hardness of fluoropolymers, and achieve the effects of low refractive index, improved adhesion and high index polymer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0077] General Procedure: In a general procedure, the desired fluoropolymer mixture was dissolved in MEK or acetone at 10% solids and added to a MEK solution containing additional low index fluorinated materials such as perfluorocyclohexyl dihydroacrylate (PFCHA) and various other monomers, crosslinkers and particles as listed in Tables 4A and 4B below. The entire low index coating solution was diluted further to about 5% solids in the solvent system noted in Tables 4A and 4B. Typically methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK) was used. The amount of MIBK added was typically less than 50% wt of the solvent mixture, but its exact quantity could vary depending upon other conditions such as % relative humidity. The amount could be adjusted to obtain the desired coating quality. In addition, all low refractive index samples contained 2.0% by weight, based on solids, of Duracure 1173 as a photoinitiator unless noted otherwise. The low index solution were then coated on a hardcoated PET film and cur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com