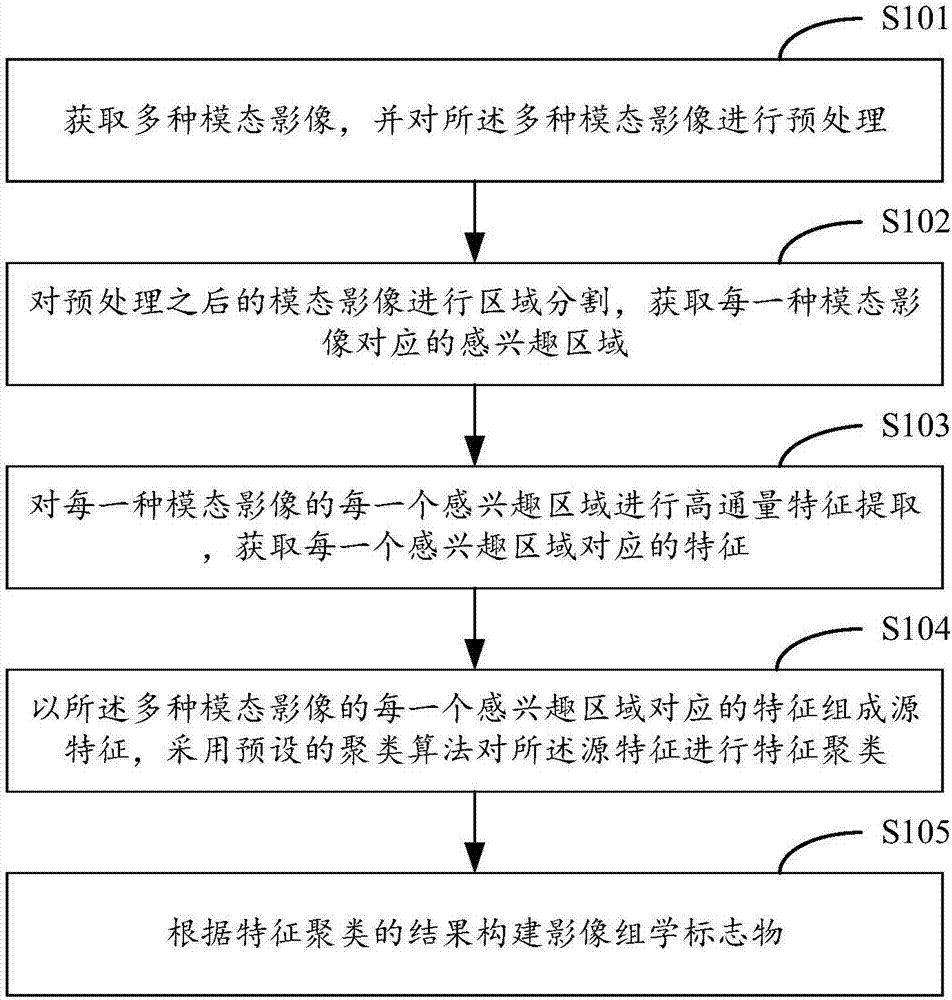
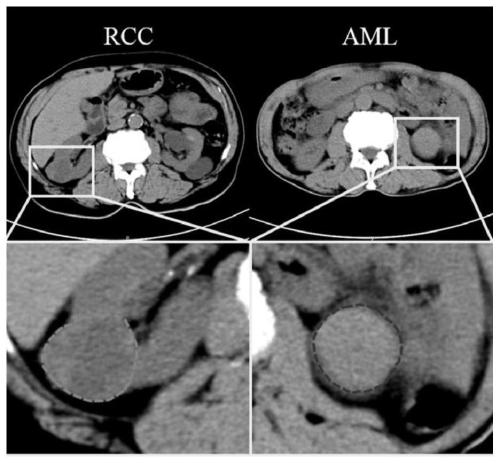
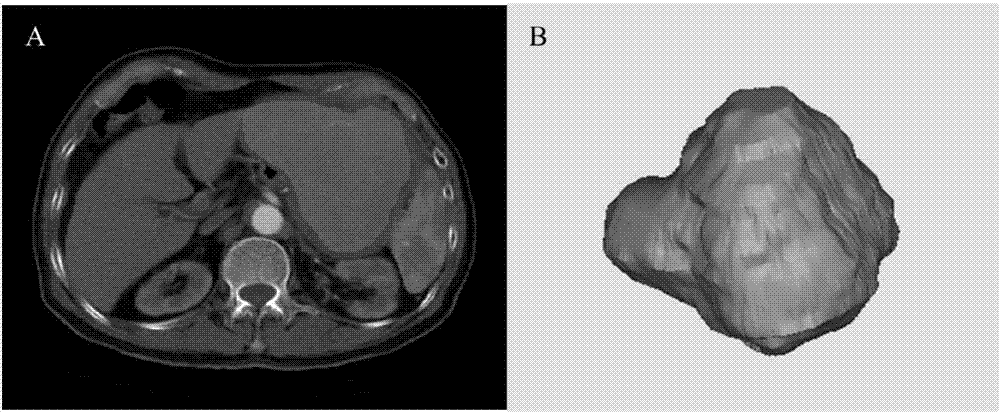
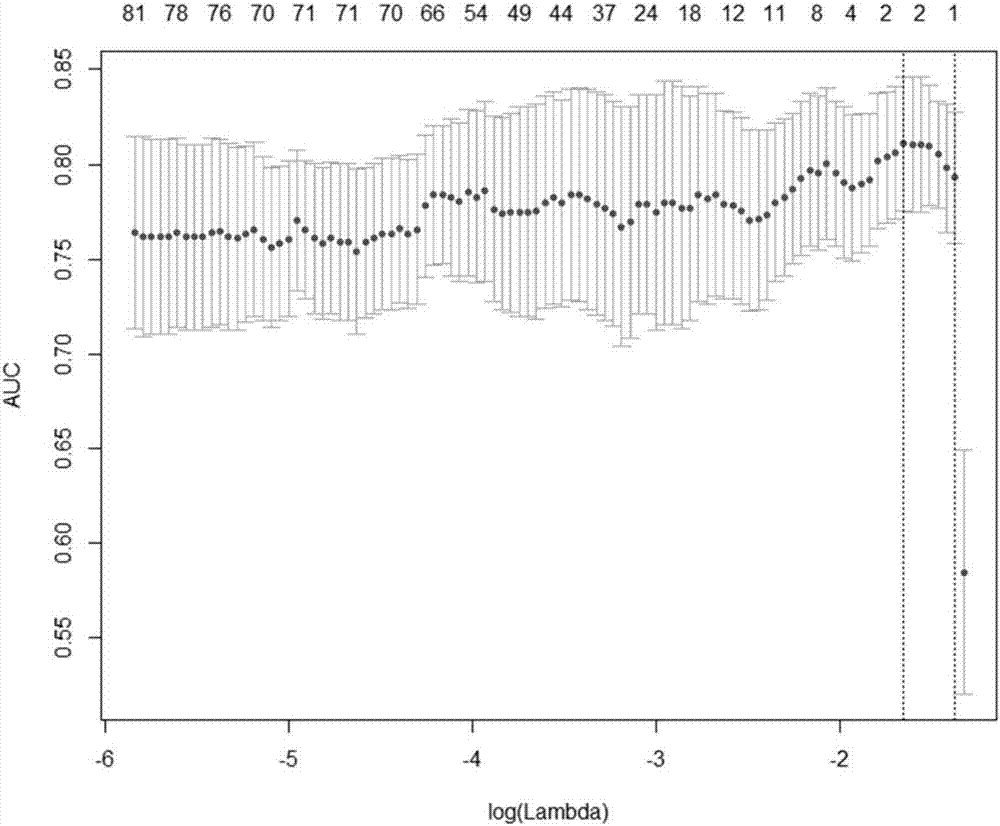
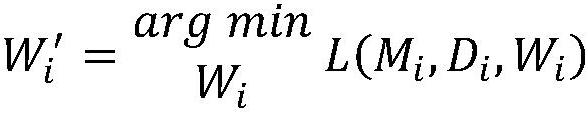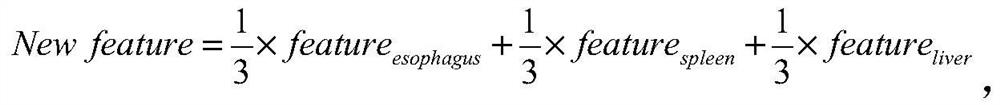Patents
Literature
146 results about "Radiomics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
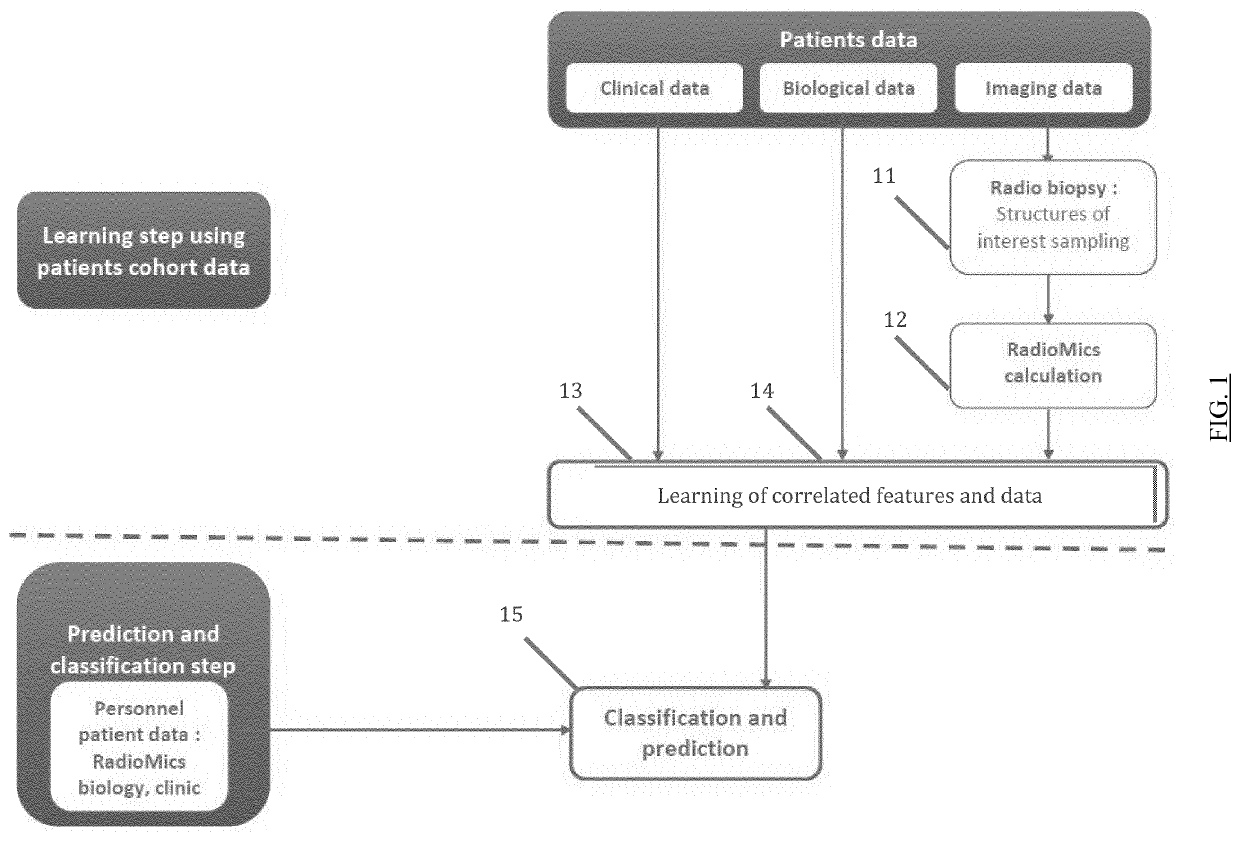
In the field of medicine, radiomics is a method that extracts large amount of features from radiographic medical images using data-characterisation algorithms. These features, termed radiomic features, have the potential to uncover disease characteristics that fail to be appreciated by the naked eye. The hypothesis of radiomics is that the distinctive imaging features between disease forms may be useful for predicting prognosis and therapeutic response for various conditions, thus providing valuable information for personalized therapy. Radiomics emerged from the medical field of oncology and is the most advanced in applications within that field. However, the technique can be applied to any medical study where a disease or a condition can be imaged.
Brain glioma molecular marker nondestructive prediction method and prediction system based on radiomics
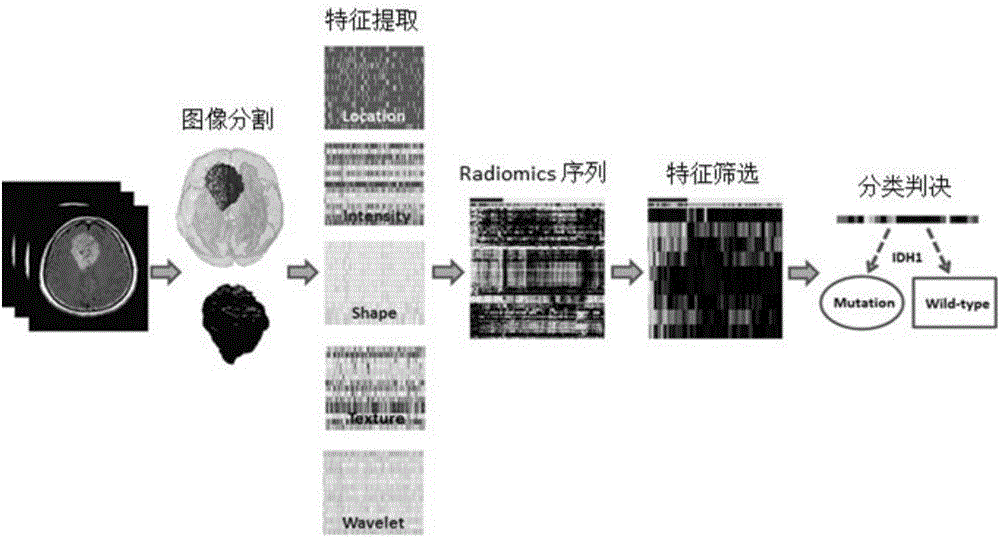
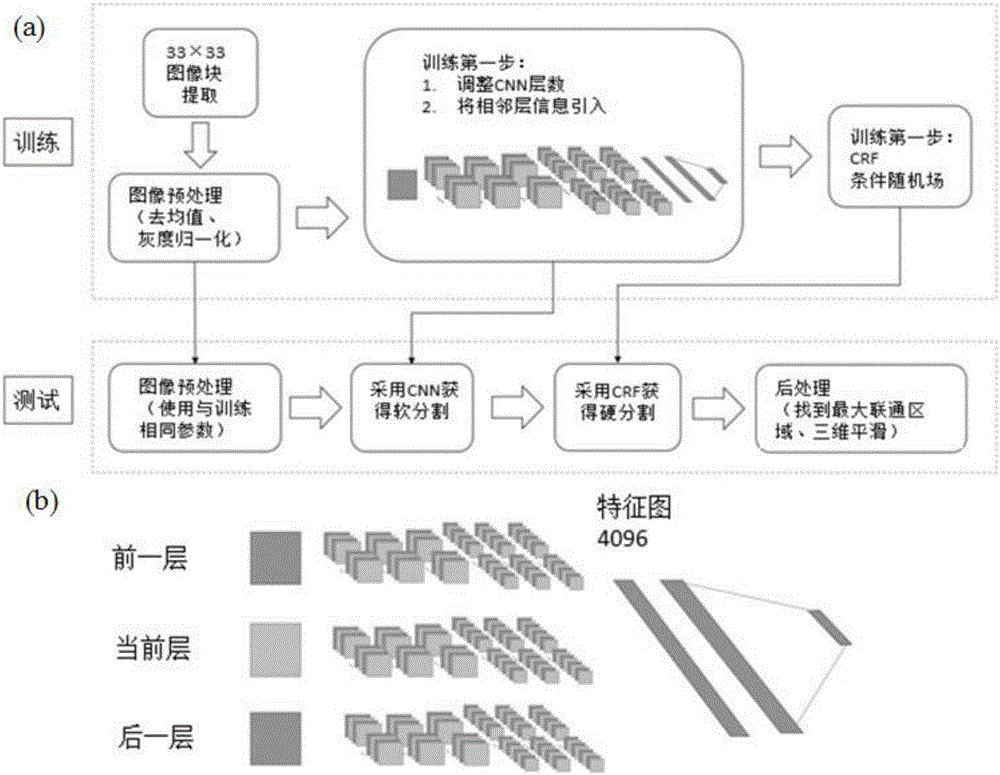
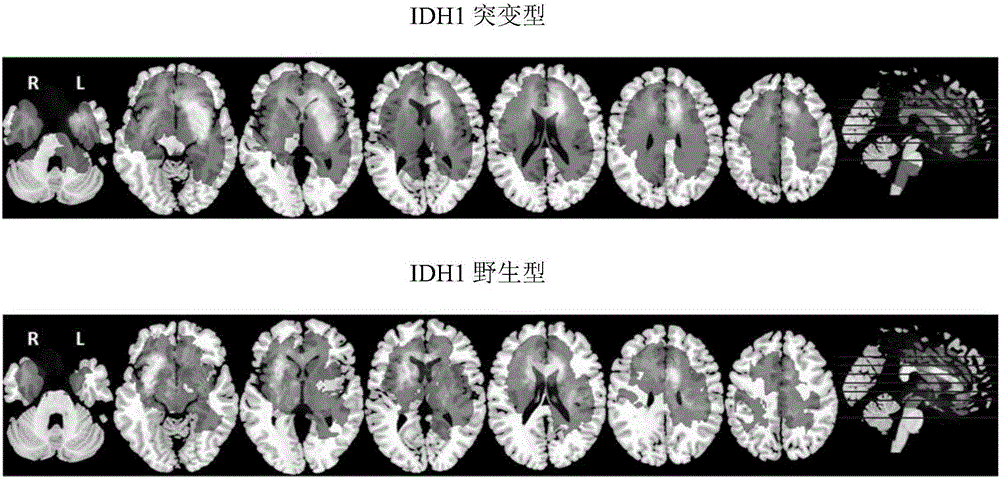
The invention belongs to the technical field of computer-aided diagnosis, and specifically relates to a brain glioma molecular marker nondestructive prediction method and a prediction system based on radiomics. The method comprises the following steps: adopting a three-dimensional magnetic resonance image automatic segmentation method based on a convolution neural network; registering a tumor obtained from segmentation to a standard brain atlas, and acquiring 116 position features of tumor distribution; getting 21 gray features, 15 shape features and 39 texture features through calculation; carrying out three-dimensional wavelet decomposition on the gray features and the texture features to get 480 wavelet features of eight sub-bands; acquiring 671 high-throughput features from the three-dimensional T2-Flair magnetic resonance image of each case; using a feature screening strategy combining p-value screening and a genetic algorithm to get 110 features highly associated with IDH1; and using a support vector machine and an AdaBoost classifier to get a classification of which the IDH1 prediction accuracy is 80%. As a novel method of radiomics, the method provides a nondestructive prediction scheme of important molecular markers for clinical diagnosis of gliomas.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Multi-modal, multi-resolution deep learning neural networks for segmentation, outcomes prediction and longitudinal response monitoring to immunotherapy and radiotherapy
PendingUS20210383538A1Faster training convergencePrevent overfittingImage enhancementImage analysisRadical radiotherapyAdversarial network
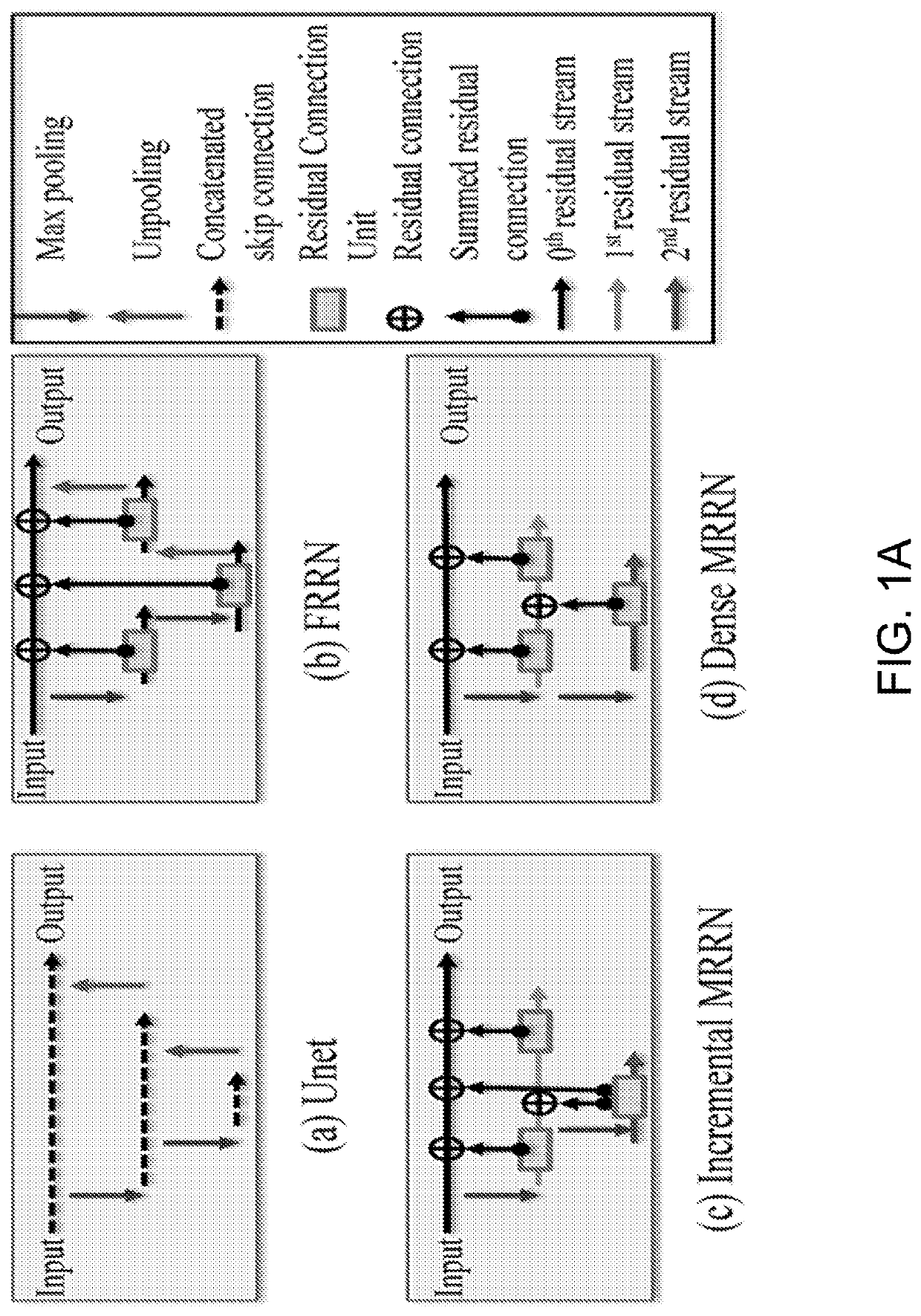
Systems and methods for multi-modal, multi-resolution deep learning neural networks for segmentation, outcomes prediction and longitudinal response monitoring to immunotherapy and radiotherapy are detailed herein. A structure-specific Generational Adversarial Network (SSGAN) is used to synthesize realistic and structure-preserving images not produced using state-of-the art GANs and simultaneously incorporate constraints to produce synthetic images. A deeply supervised, Multi-modality, Multi-Resolution Residual Networks (DeepMMRRN) for tumor and organs-at-risk (OAR) segmentation may be used for tumor and OAR segmentation. The DeepMMRRN may combine multiple modalities for tumor and OAR segmentation. Accurate segmentation is may be realized by maximizing network capacity by simultaneously using features at multiple scales and resolutions and feature selection through deep supervision. DeepMMRRN Radiomics may be used for predicting and longitudinal monitoring response to immunotherapy. Auto-segmentations may be combined with radiomics analysis for predicting response prior to treatment initiation. Quantification of entire tumor burden may be used for automatic response assessment.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Radiotherapy dosage verification method and system
ActiveCN109966662AVerification results are reliableLight therapyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadiomicsRadiotherapy Dosages
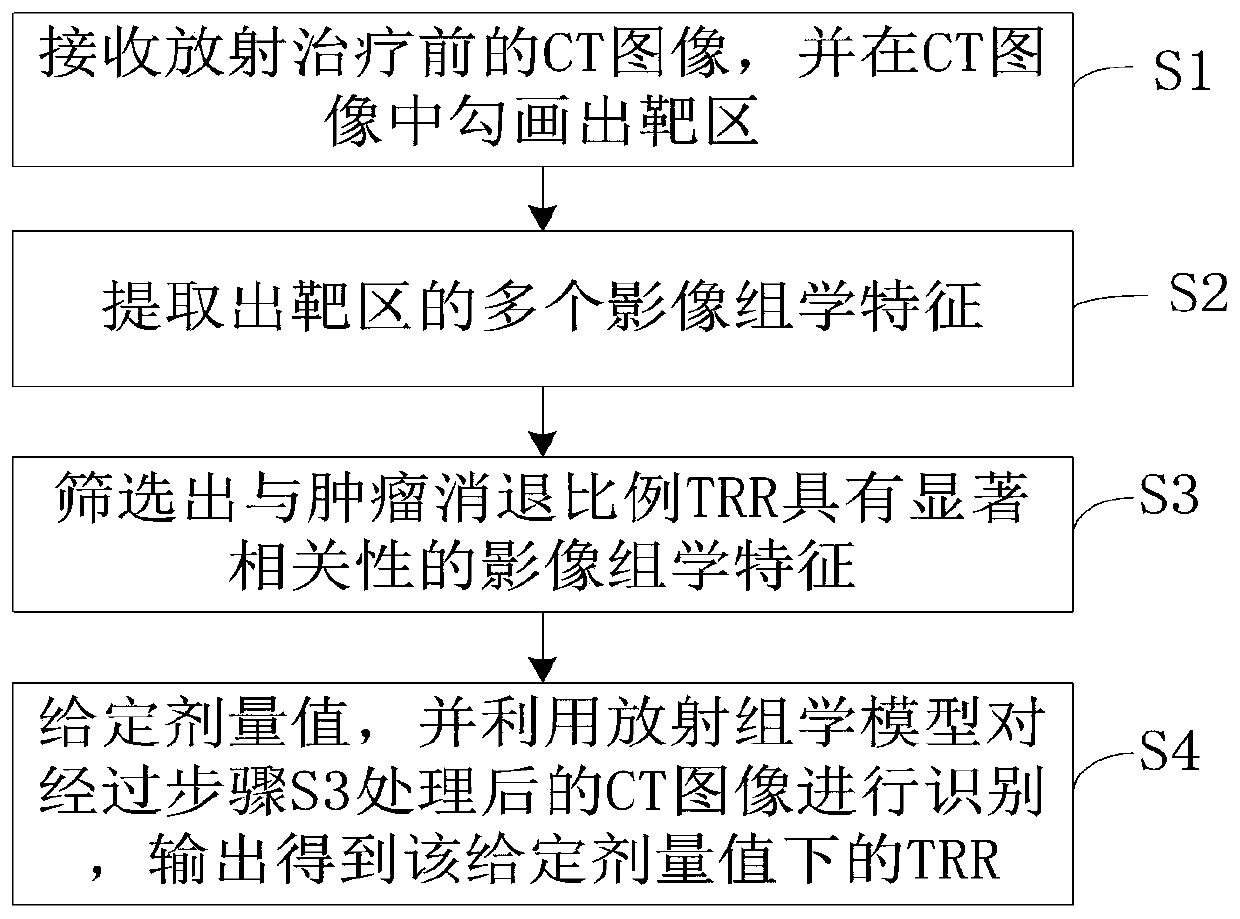
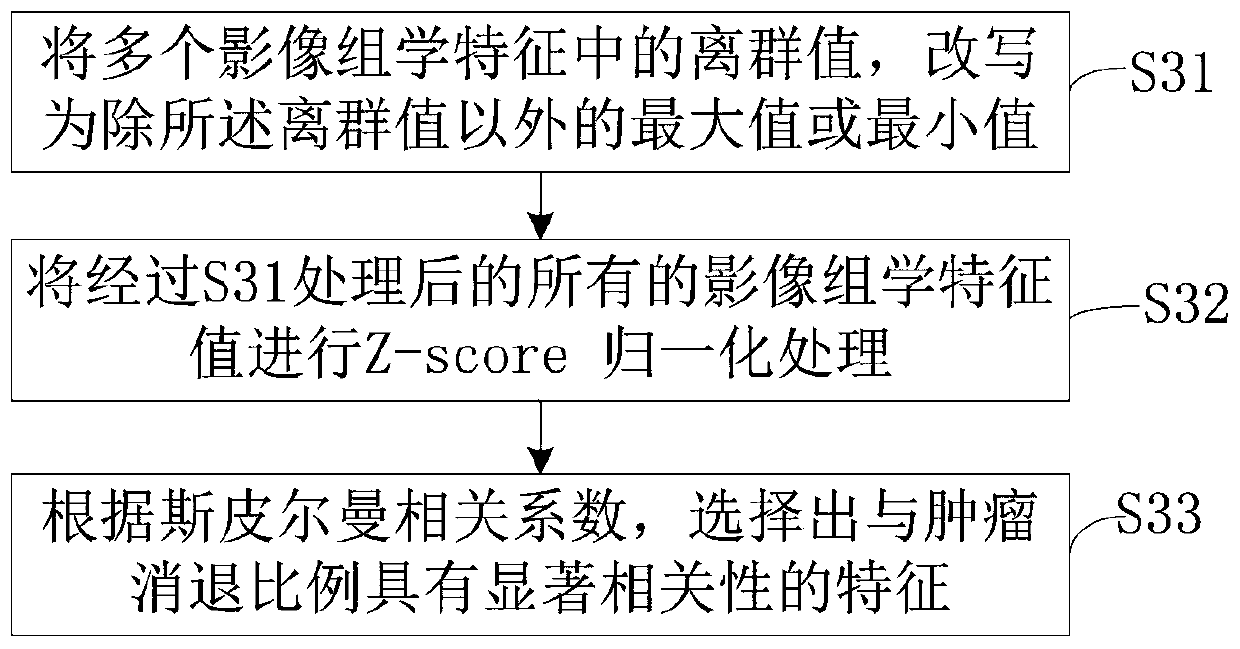
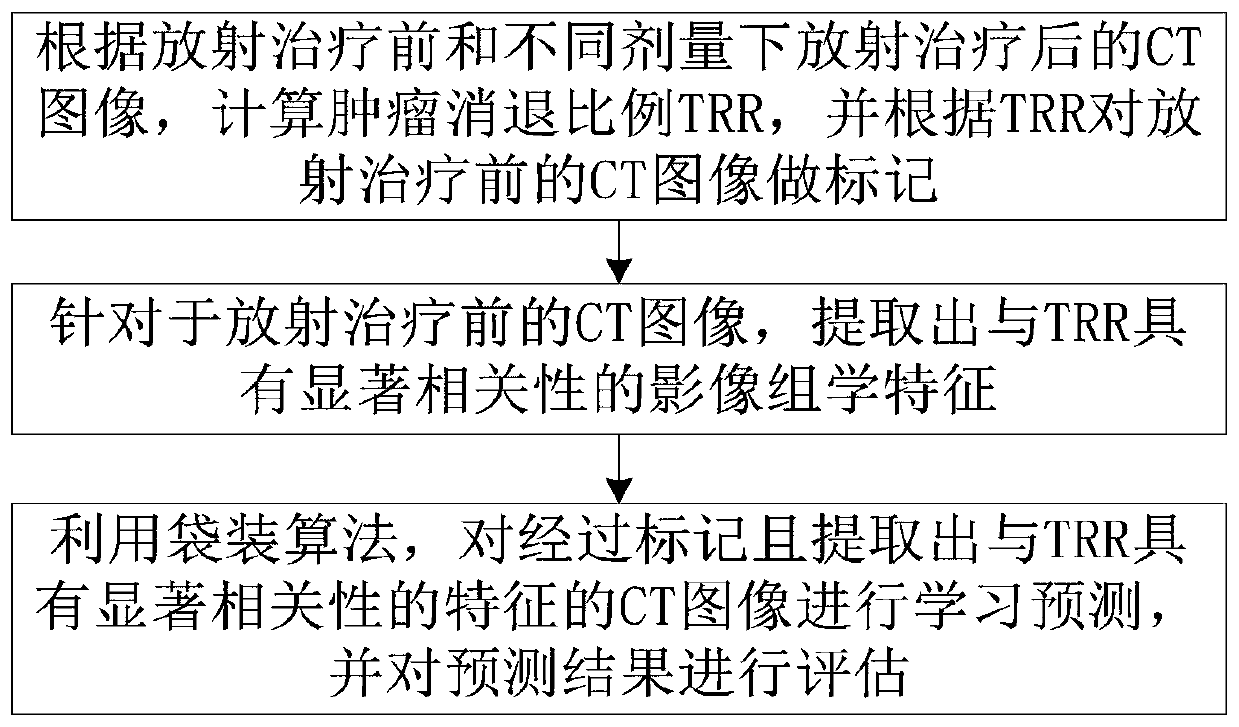
The invention relates to a radiotherapy dosage verification method and system. The method includes steps: S1, receiving a CT image obtained before radiotherapy, and sketching a target area in the CT image; S2, extracting a plurality of radiomics characteristics of the target area; S3, screening out the radiomics characteristics in remarkable relevance to TRR (tumor regression ratio) from the multiple extracted radiomics characteristics; S4, presetting a dosage value, recognizing the CT image processed in the step S3 by a pre-trained radiomics model, and outputting to obtain the TRR under the given dosage value. A novel idea is provided, the radiomics model is obtained by training based on a machine learning method, the given dosage value is verified by virtue of the TRR outputted by the radiomics model, a prediction result is insusceptible to single dosage, and high reliability of a verification result is realized.
Owner:SICHUAN CANCER HOSPITAL
Auxiliary assessment method for prognosis of nasopharynx cancer based on enhanced MRI radiomics
ActiveCN111657945ANo ionizing radiation damageClear structureDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsIndividualized treatmentNasopharyngeal cancer
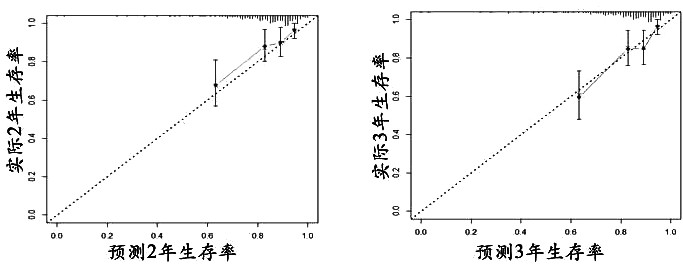
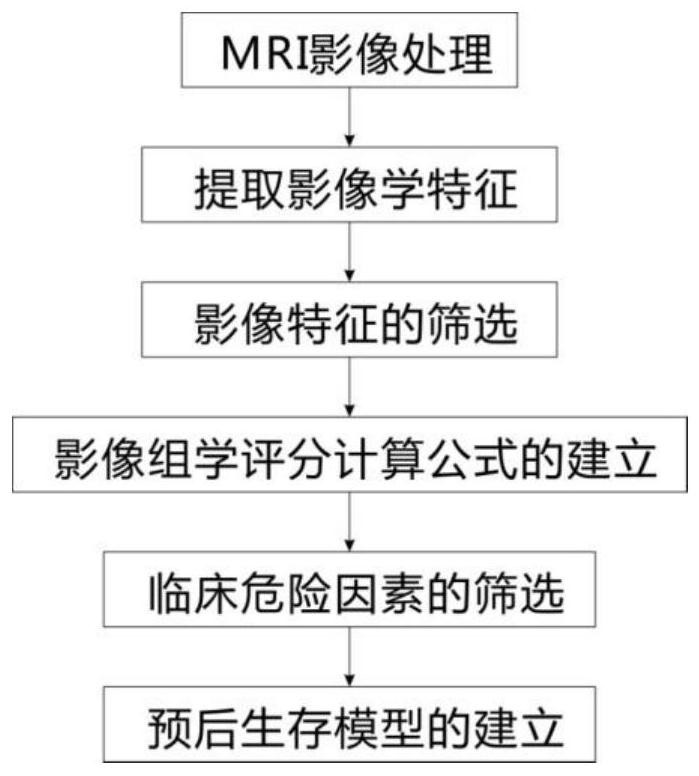
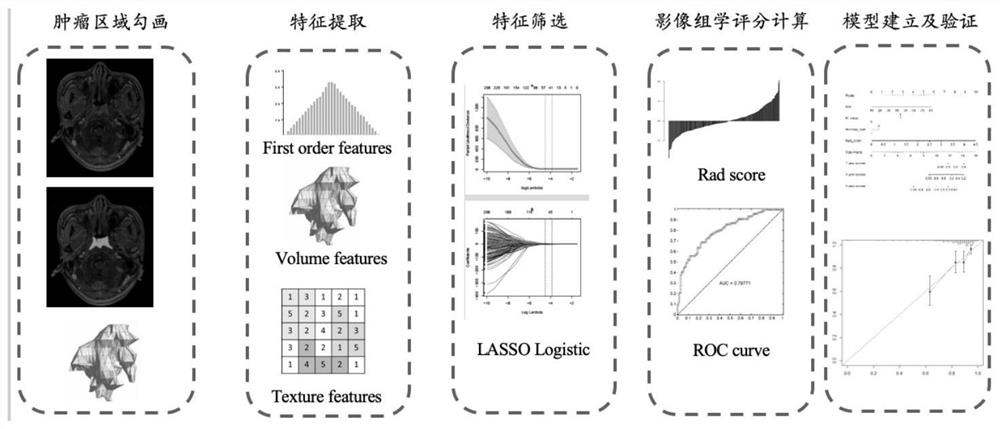
The invention relates to an auxiliary assessment method for prognosis of nasopharynx cancer based on enhanced MRI radiomics. The auxiliary assessment method comprises the steps of: (1), performing MRIimage processing; (2), extracting imaging features; (3), screening the imaging features; (4), establishing a radiomics scoring formula; (5), screening clinical risk factors; and (6), establishing a prognostic survival model: establishing a prognostic observation model through combination of a radiomics score and the clinical risk factors of a patient with nasopharynx cancer, performing qualitative and quantitative prediction on the PFS (progression free survival) of the patient, and furthermore, assessing the performance of the prognostic survival model. The auxiliary assessment method in theinvention has little harm to the image examination of the patient; qualitative and quantitative analysis on the survival time of a specific patient is carried out; therefore, a doctor is assisted tomake an individualized treatment and follow-up visit scheme; furthermore, the doctor is assisted to assess the survival and recurrence time of the patient; simultaneously, the performance of the obtained prognostic survival model is verified; and thus, the accuracy of a prognostic prediction model is ensured.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
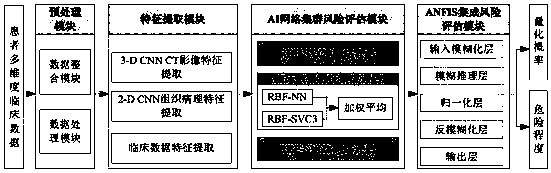
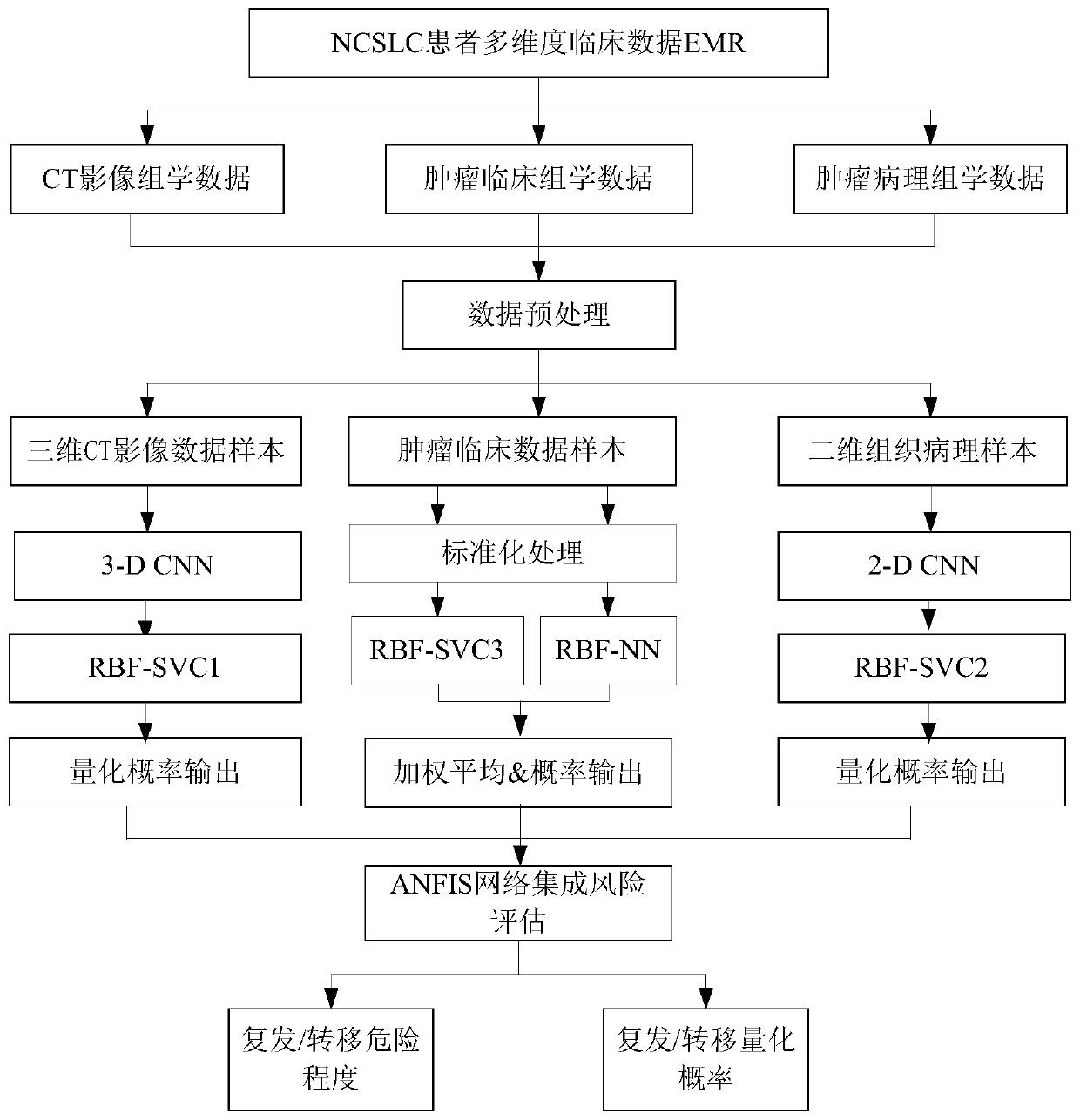
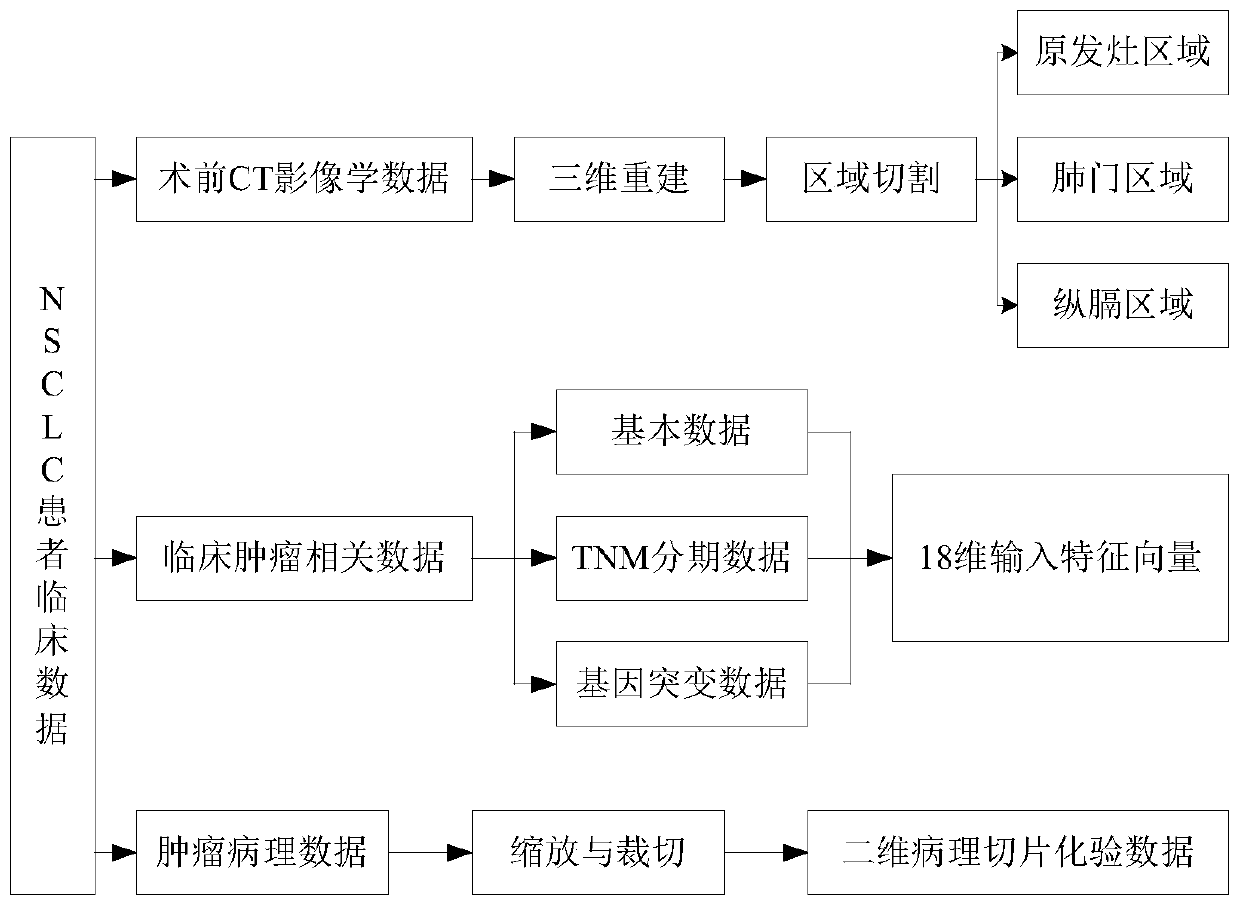
NSCLC patient postoperative short-period recurrence metastasis risk evaluating system
InactiveCN110111892AStrong clinical practicabilityImprove forecast accuracyMedical data miningHealth-index calculationLymphatic SpreadWilms' tumor
The invention provides an NSCLC patient postoperative short-period recurrence metastasis risk evaluating system which comprises a preprocessing module, a characteristic extracting module, an AI network cluster risk evaluating module and an ANFIS network integrated risk evaluating module. The preprocessing module is used for collecting and preprocessing multidimensional patient clinical data. The multidimensional patient clinical data comprise patient preoperative CT radiomics data, tumor histopathology data and tumor clinical. The characteristic extracting module is used for extracting the characteristic of the data sample after preprocessing. The AI network cluster risk evaluating module is used for performing recurrence risk probability evaluation on the extracted sample characteristic.The ANFIS network integrated risk evaluating module is used for using a recurrence risk probability evaluation result as an input characteristic vector, establishes an ANFIS network, uses a recurrence / metastasis risk quantification probability and dangerous degree as the output, and performs final integrated risk evaluation. The system can supply a reference for selecting a radial curing postoperative comprehensive treatment plan by a lung cancer patient and has high predicting accuracy.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Multi-modal, multi-resolution deep learning neural networks for segmentation, outcomes prediction and longitudinal response monitoring to immunotherapy and radiotherapy
PendingCN112771581AImage enhancementImage analysisGenerative adversarial networkRadical radiotherapy
Systems and methods for multi-modal, multi-resolution deep learning neural networks for segmentation, outcomes prediction and longitudinal response monitoring to immunotherapy and radiotherapy are detailed herein. A structure-specific Generational Adversarial Network (SSGAN) is used to synthesize realistic and structure-preserving images not produced using state-of-the art GANs and simultaneously incorporate constraints to produce synthetic images. A deeply supervised, Multi-modality, Multi-Resolution Residual Networks (DeepMMRRN) for tumor and organs-at-risk (OAR) segmentation may be used for tumor and OAR segmentation. The DeepMMRRN may combine multiple modalities for tumor and OAR segmentation. Accurate segmentation is may be realized by maximizing network capacity by simultaneously using features at multiple scales and resolutions and feature selection through deep supervision. DeepMMRRN Radiomics may be used for predicting and longitudinal monitoring response to immunotherapy. Auto-segmentations may be combined with radiomics analysis for predicting response prior to treatment initiation. Quantification of entire tumor burden may be used for automatic response assessment.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
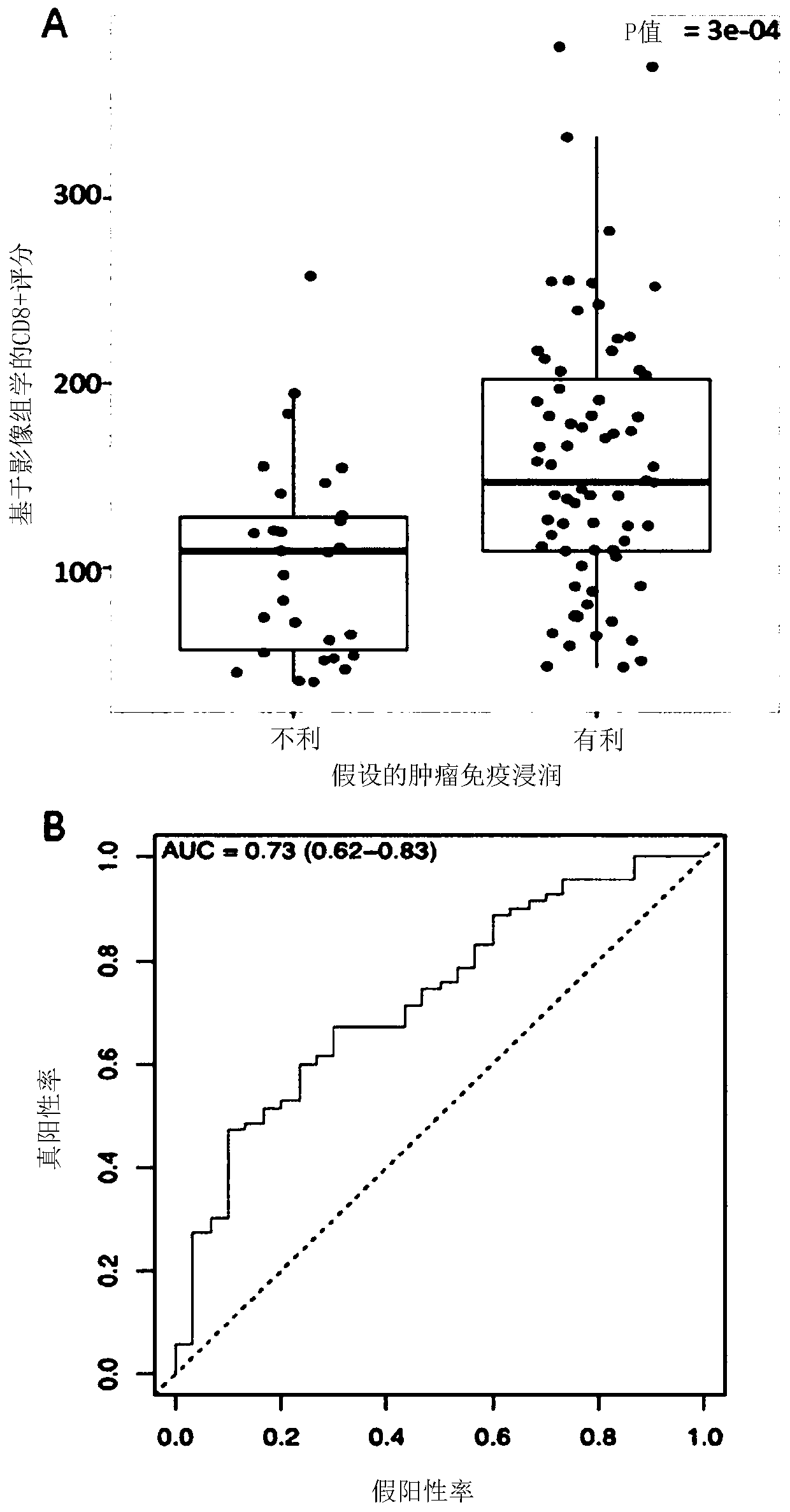
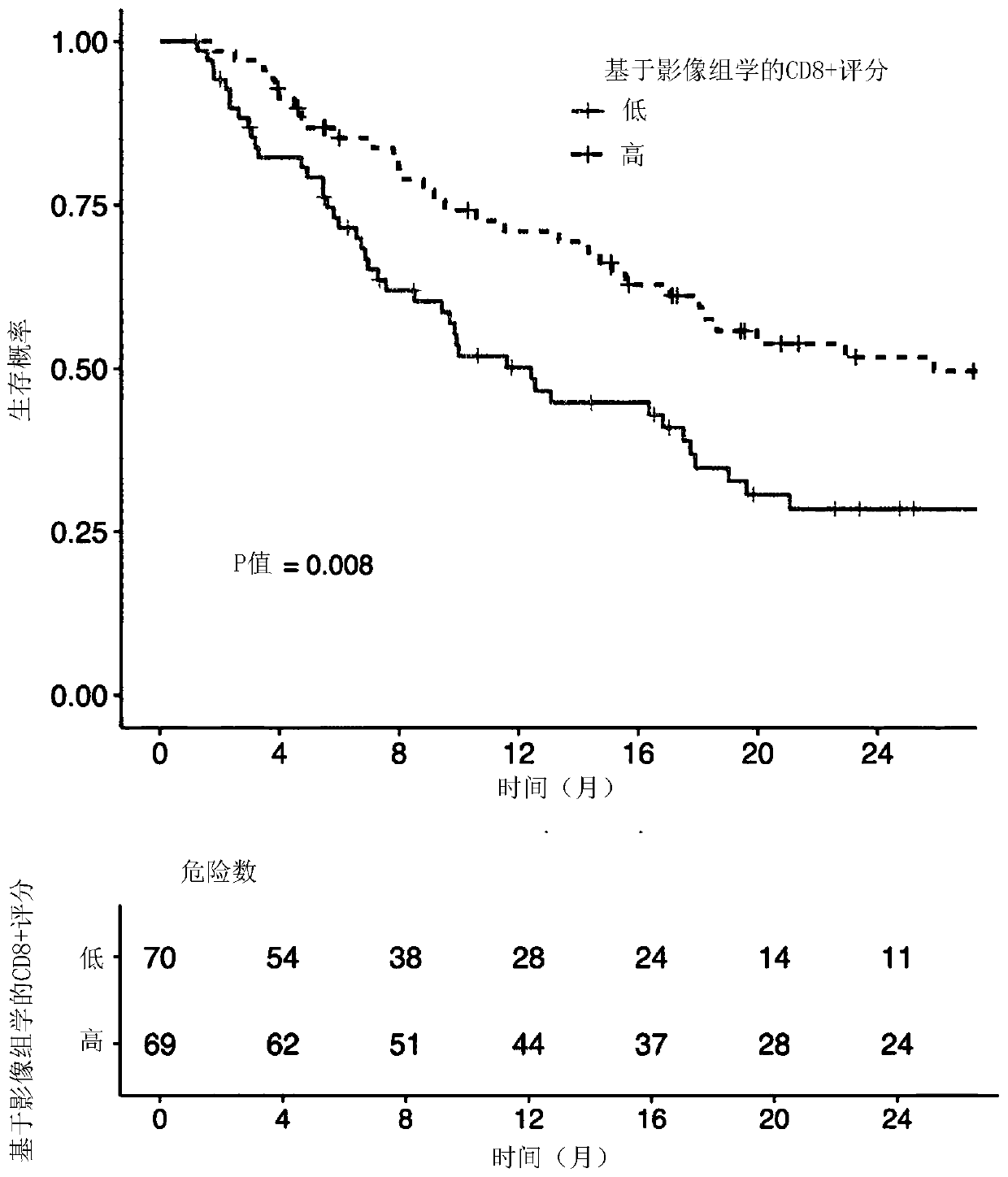
A radiomics-based imaging tool to monitor tumor-lymphocyte infiltration and outcome in cancer patients treated by anti-PD-1/PD-L1
PendingCN111094977AImprove conventional methodsReduced activityImage enhancementImage analysisCD8Therapy efficacy
The present invention proposes a radiomics-based biomarker for detecting the presence and the density of tumor infiltrating CD8 T-cells in a solid tumor without having to use any biopsy of said tumor.The invention also proposes to use this information to assess the immune phenotype of said solid tumor. In a particular embodiment, the invention proposes to prognose the survival and / or the treatment efficiency of cancer patients treated with immunotherapy such as anti-PD-1 / PD- L1 monotherapy.
Owner:INSTITUT GUSTAVE ROUSSY
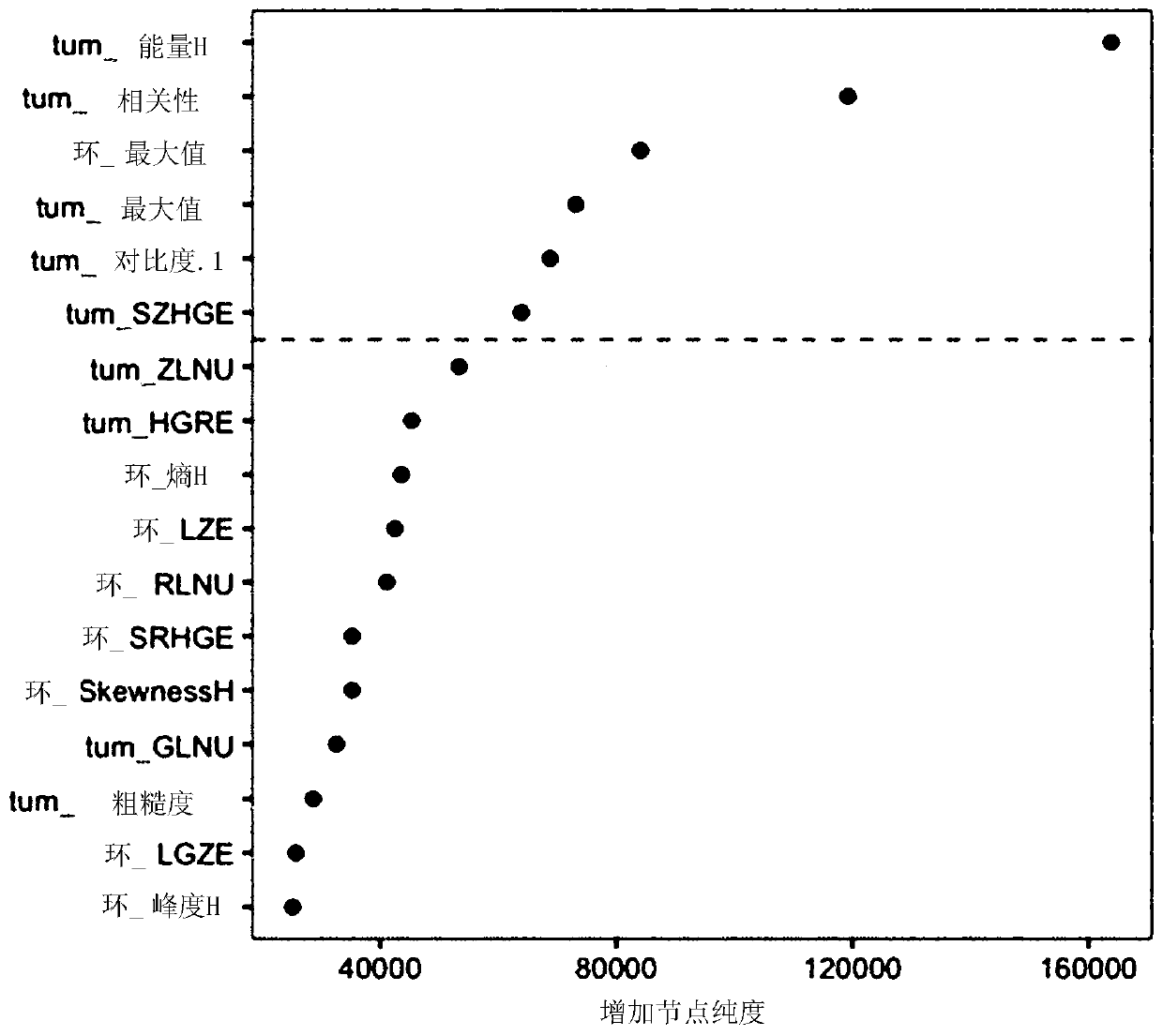
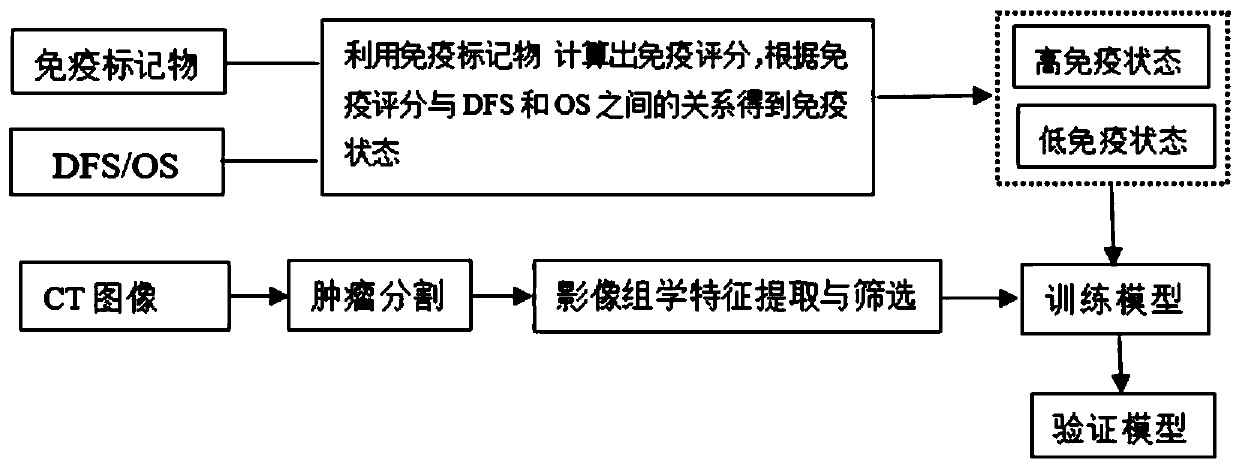
Method for quantifying tumor immune state based on radiomics
The invention discloses a method for quantifying a tumor immune state based on radiomics, wherein the method comprises the following steps: S1, collecting clinical information, immunohistochemical characteristics, overall survival OS and disease-free survival DFS of tumor patients; S2, obtaining a CT image sample group of solid tumors; S3, randomly dividing the patients into a training set and a test set in proportion; S4, calculating the immunoscore by an immune marker, and dividing the patients into a set with high immune state and a set with low immune state; S5, segmenting an interest region, and extracting radiomics characteristics of the solid tumors in the interest region; S6, screening the radiomics characteristics related to the immune state from the radiomics characteristics in the training set, and training a prediction model; and S7, predicting the image immunoscore of the tumor patients, obtaining the image immune state, and then predicting the DFS and the OS in the patients. The immune state of the solid tumors such as colorectal cancer, lung cancer, gastric cancer and breast cancer is predicted by the CT image characteristics, and the analysis of pathological sections and immunohistochemistry is reduced or avoided.
Owner:GUANGDONG GENERAL HOSPITAL
Analysis method and device for multi-mode radiomics, and terminal
ActiveCN106875401AImplement miningSolve the problem that image features cannot be extracted in many waysImage analysisCluster algorithmFeature extraction
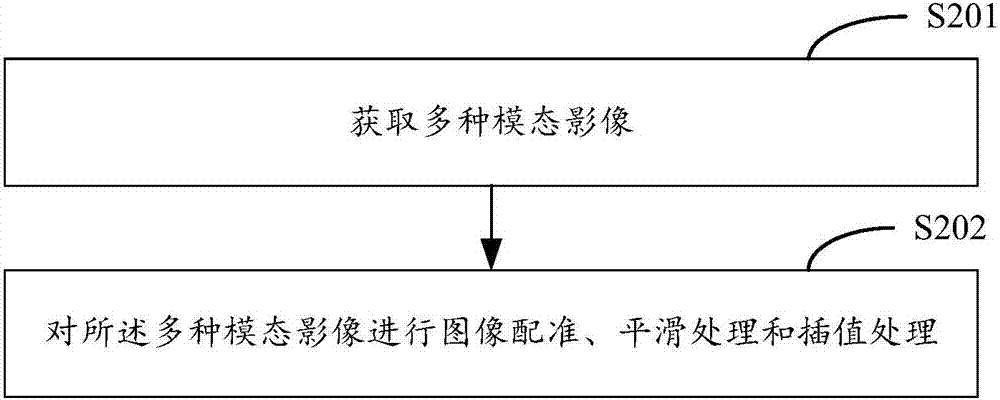
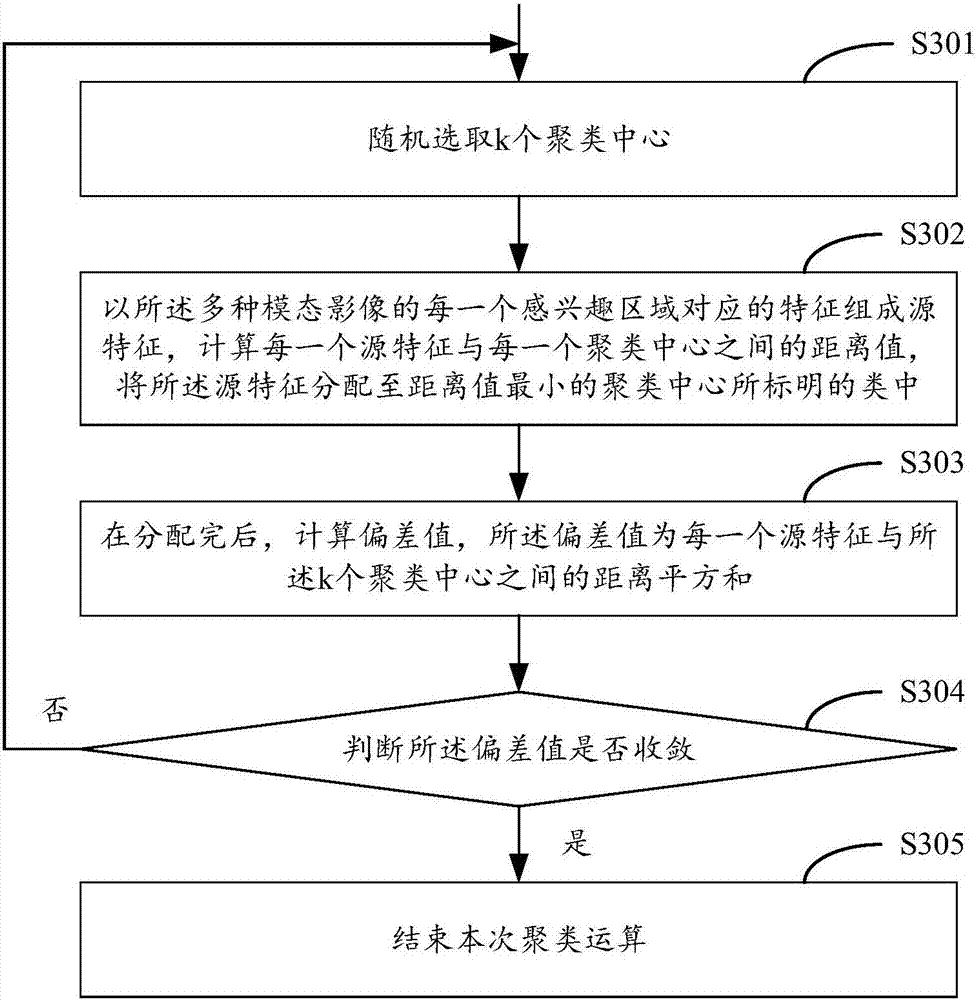
The invention provides an analysis method and device for multi-mode radiomics, and a terminal. The method comprises steps of obtaining multiple mode images, and preprocessing the multiple mode images; performing regional segmentation to the preprocessed mode images to obtain an area of interest corresponding to each mode image; for each area of interest of each mode image, performing high-pass feature extraction, and obtaining characteristics corresponding to each area of interest; grouping the characteristics corresponding to each area of interest of the multiple mode images into source characteristics, and using a preset clustering algorithm to perform characteristic clustering of the source characteristics; and according to the result of the characteristic clustering, constructing radiomics markers. Therefore, the problem that image characteristics cannot be extracted from multiple aspects in the radiomics research in the prior art is solved, the number of the source characteristics for the characteristic clustering and the representative characteristic kind after clustering are enriched, and the medical image information can be excavated to the greatest extent.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
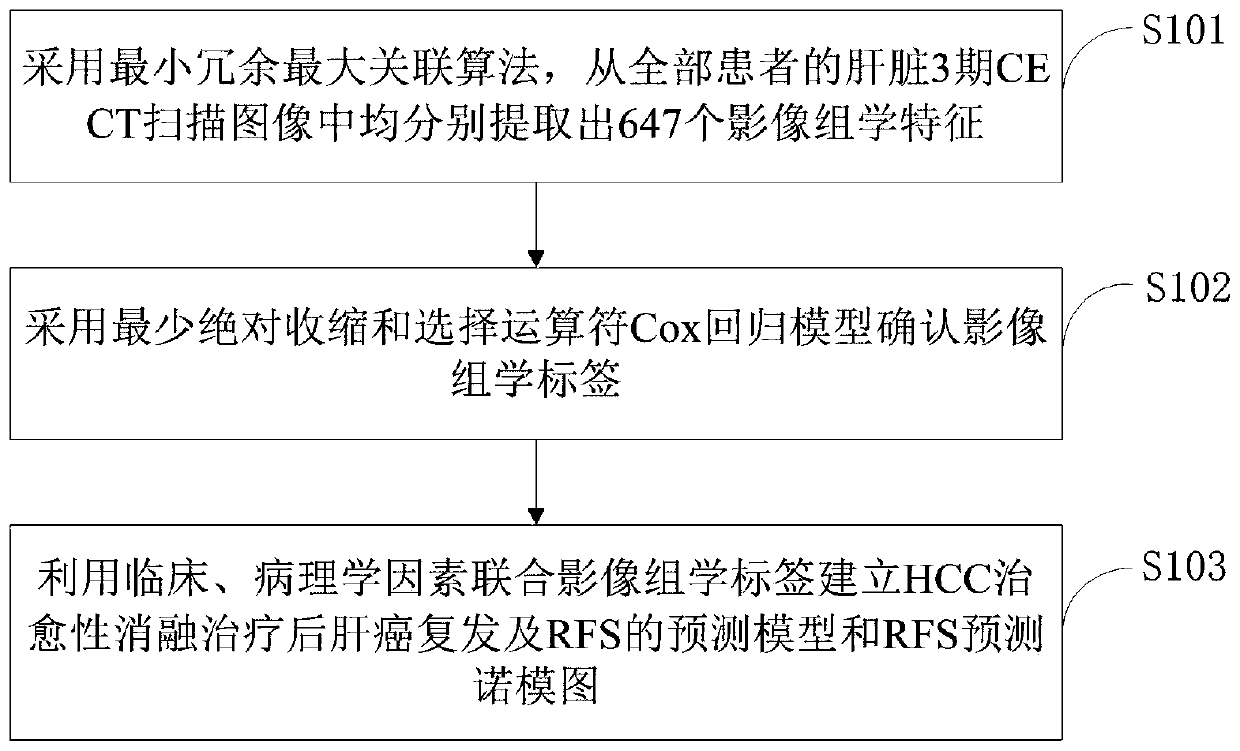
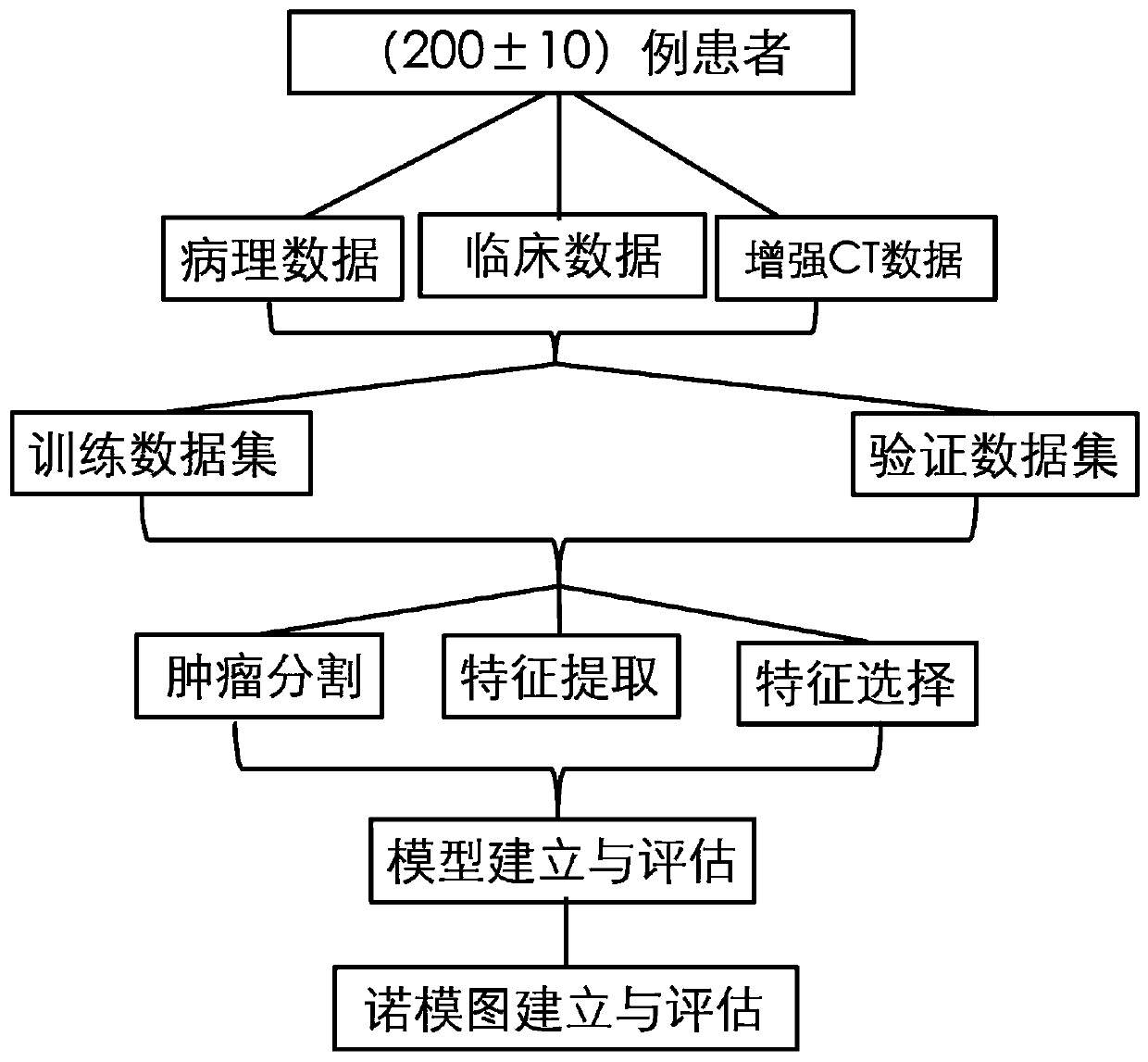
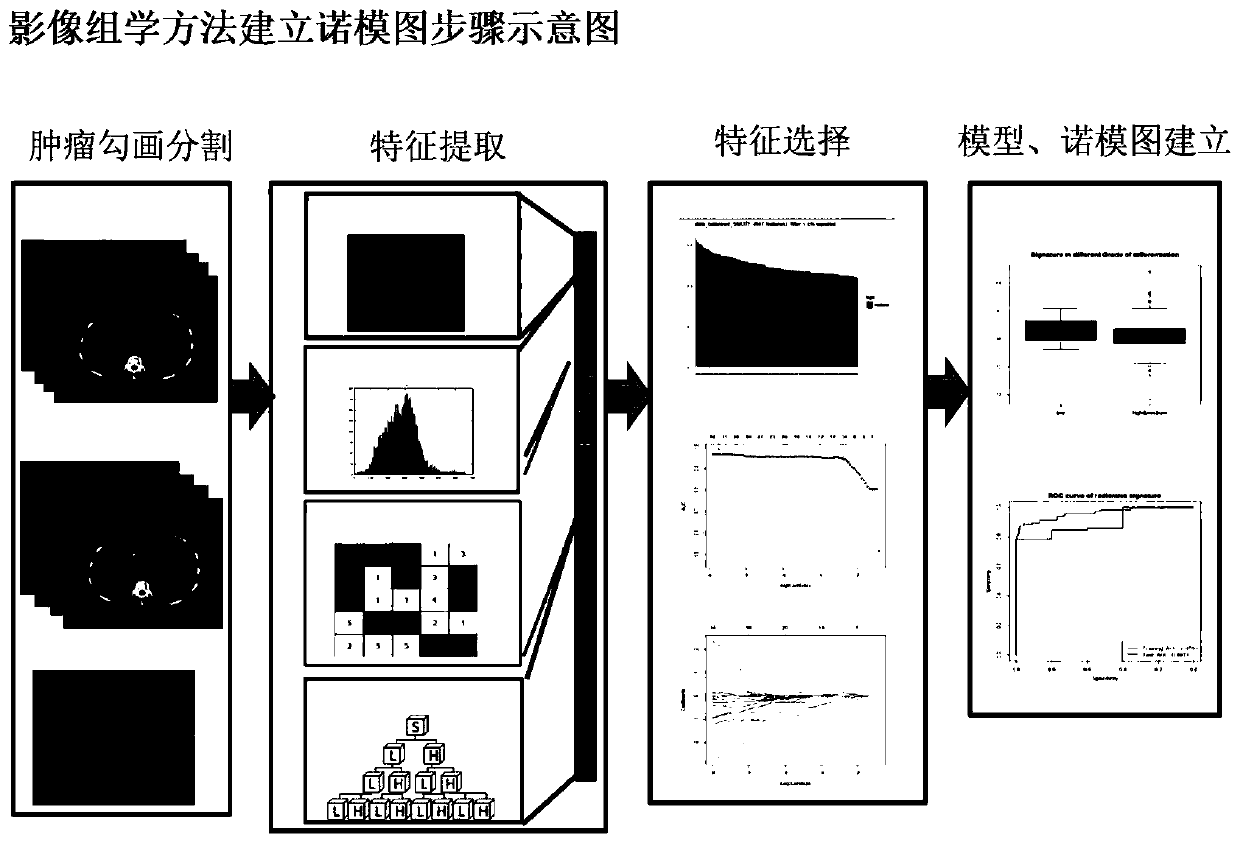
Constructing method of predicting model and nomograph for HCC recurrence and RFS and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of predicting model and nomograph construction technology, and discloses a constructing method of a predicting model and the nomograph for HCC recurrence and RFS and application thereof. The method comprises the steps of by means a minimum redundancy maximum relevance algorithm (MRMRA), respectively extracting 647 radiomics characteristics from liver 3-period enhanced CT scanning images of all patients; confirming a radiomics label by means of a least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO)-Cox regression model; and establishing a predicting model and a predicting naomograph for HCC recurrence after therapeutic ablation treatment and teh RFS by means of clinical and pathological factors and the radiomics label. According to the method of the invention, the predicting model and the predicting nomograph are constructed through the radiomics method. The method is used for predicting tumor recurrence and RFS of an HCC patient after therapeutic ablation treatment of a focus.
Owner:BEIJING YOUAN HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
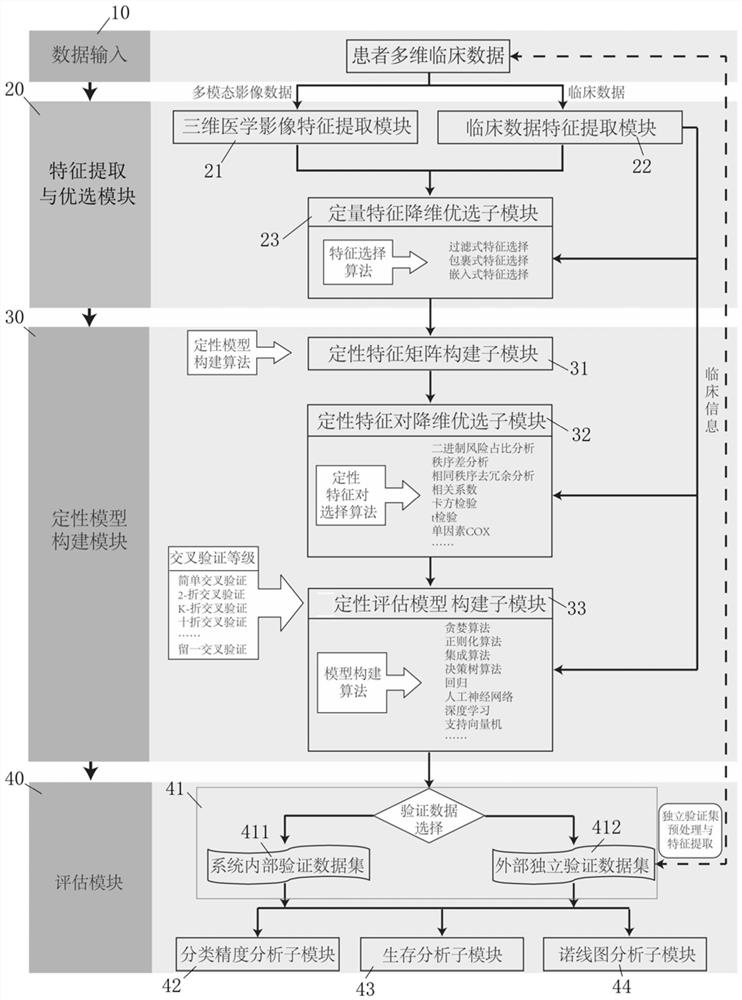
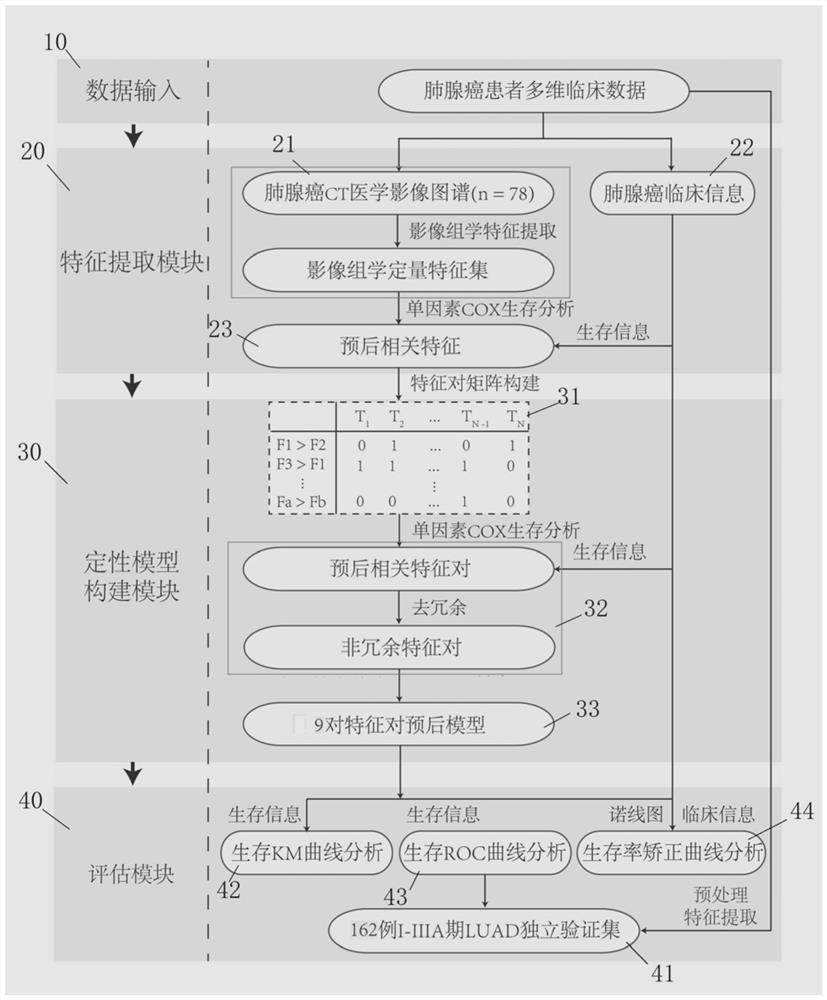
Cancer clinical index evaluation system constructed based on radiomics qualitative algorithm
ActiveCN112768072ANo additional medical expensesOvercoming Susceptibility to Batch EffectsMedical simulationImage enhancementFeature extractionData mining
The invention discloses a cancer clinical index evaluation system constructed based on a radiomics qualitative algorithm. The system comprises a data input module which is used for inputting multi-dimensional patient clinical data comprising a preoperative multi-modal medical image spectrum and clinical data of a patient; a feature extraction and optimization module connected with the data input module and used for extracting radiomics quantitative feature values and clinical data features and performing dimensionality reduction optimization on the quantitative feature values; a qualitative model construction module connected with the feature extraction and optimization module and used for constructing, through the radiomics qualitative algorithm, an evaluation model for predicting various clinical indexes of the cancer of the patient; and an evaluation module connected with the qualitative model construction module and used for providing noninvasive, accurate and non-subjective evaluation for early diagnosis, prognosis and drug effect subtypes of cancers.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
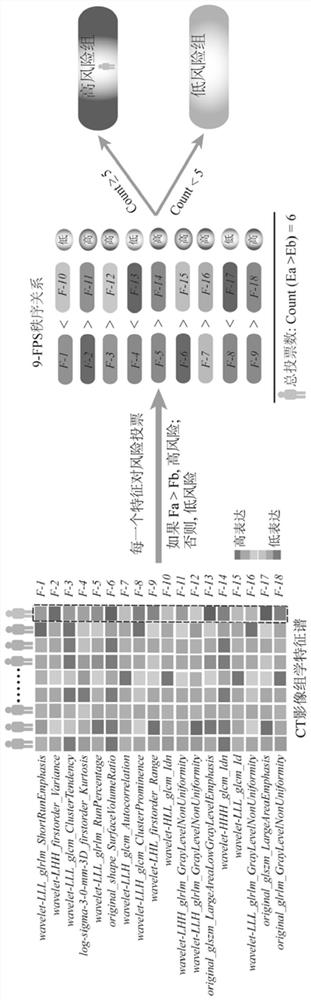
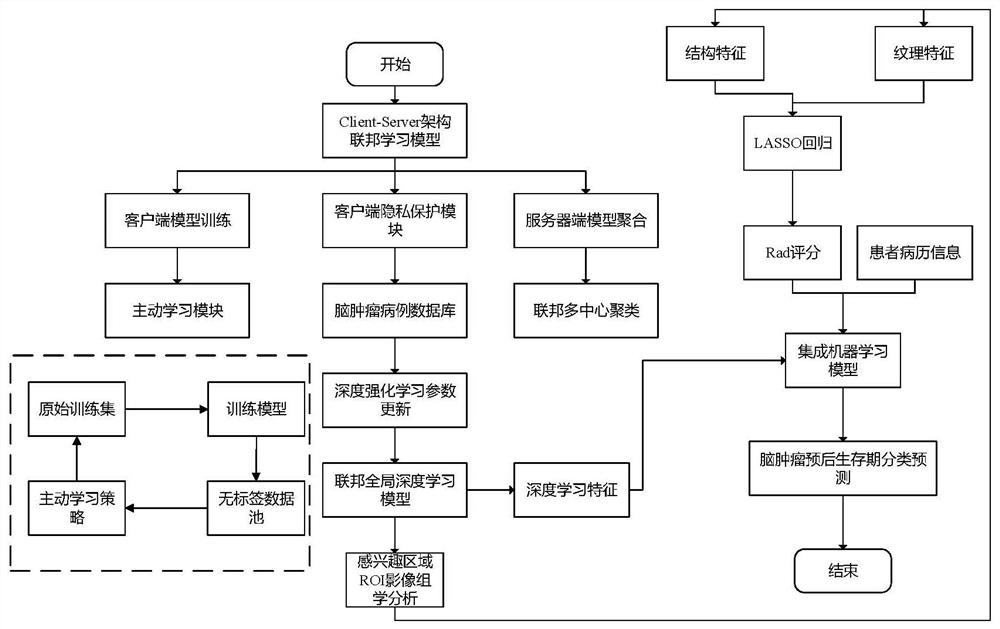
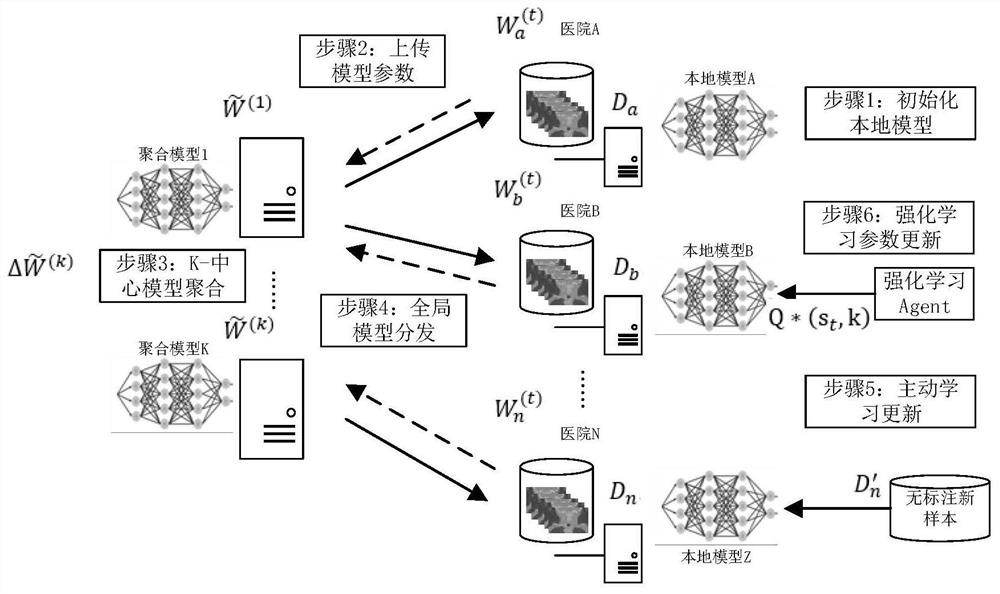
Multi-center brain tumor prognosis lifetime prediction method and system based on federated learning
PendingCN113571203AImprove accuracyGuaranteed image data privacyMedical data miningMedical imagesMedical recordLearning machine
The invention provides a multi-center brain tumor prognosis lifetime prediction method and system based on federated learning, and brain tumor prognosis lifetime prediction is carried out by using multi-scale information such as a multi-center multi-mode brain tumor image and omics information thereof, clinical medical record information of a patient and the like. The invention provides a multi-center federated learning mechanism based on active learning and reinforcement learning. According to the invention, a comprehensive brain tumor prognosis lifetime classification model is established by combining the patient electronic medical record information stored in each center in a distributed manner with the radiomics features and the deep learning features, and a reliable brain tumor prognosis lifetime prediction system with higher accuracy is realized on the basis of ensuring patient image data privacy.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
Non-invasive liver epithelioid vascular smooth muscle lipoma image classification device based on radiomics
InactiveCN113269225AEfficient use ofImage enhancementImage analysisEpithelioid angiomyolipomaBlood vessel
The invention discloses a non-invasive liver epithelioid vascular smooth muscle lipoma image classification device based on radiomics, and belongs to the technical field of medical image processing. The non-invasive liver epithelioid vascular smooth muscle lipoma image classification device includes: a sampling module which for collecting CT / MRI images of liver epithelioid vascular smooth muscle lipoma, liver cancer and liver focal nodule hyperplasia meeting requirements; a focus area extraction module which is used for extracting a focus area; a feature extraction module which is used for carrying out radiomics feature extraction on the focus area; a feature screening module which is used for screening radiomics features; a random forest network training module which is used for training a random forest model to obtain a radiomics label; a clinical index fusion module which is used for fusing the radiomics prediction label and the clinical indexes of the patient and training a multivariate logistic regression model; and a classification module which is used for obtaining a final prediction label in combination with a random forest network and a multivariate logistic regression model so as to realize the classification of the liver epithelioid vascular smooth muscle lipoma images. The device is high in recognition precision, high in recognition speed, safe and stable.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
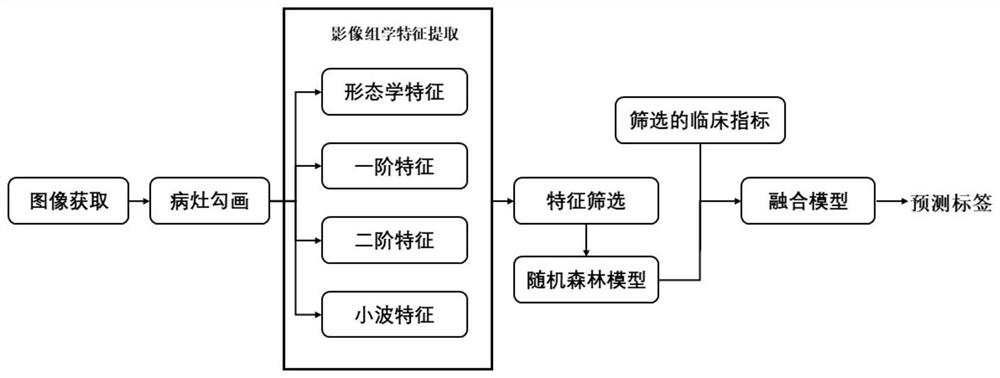
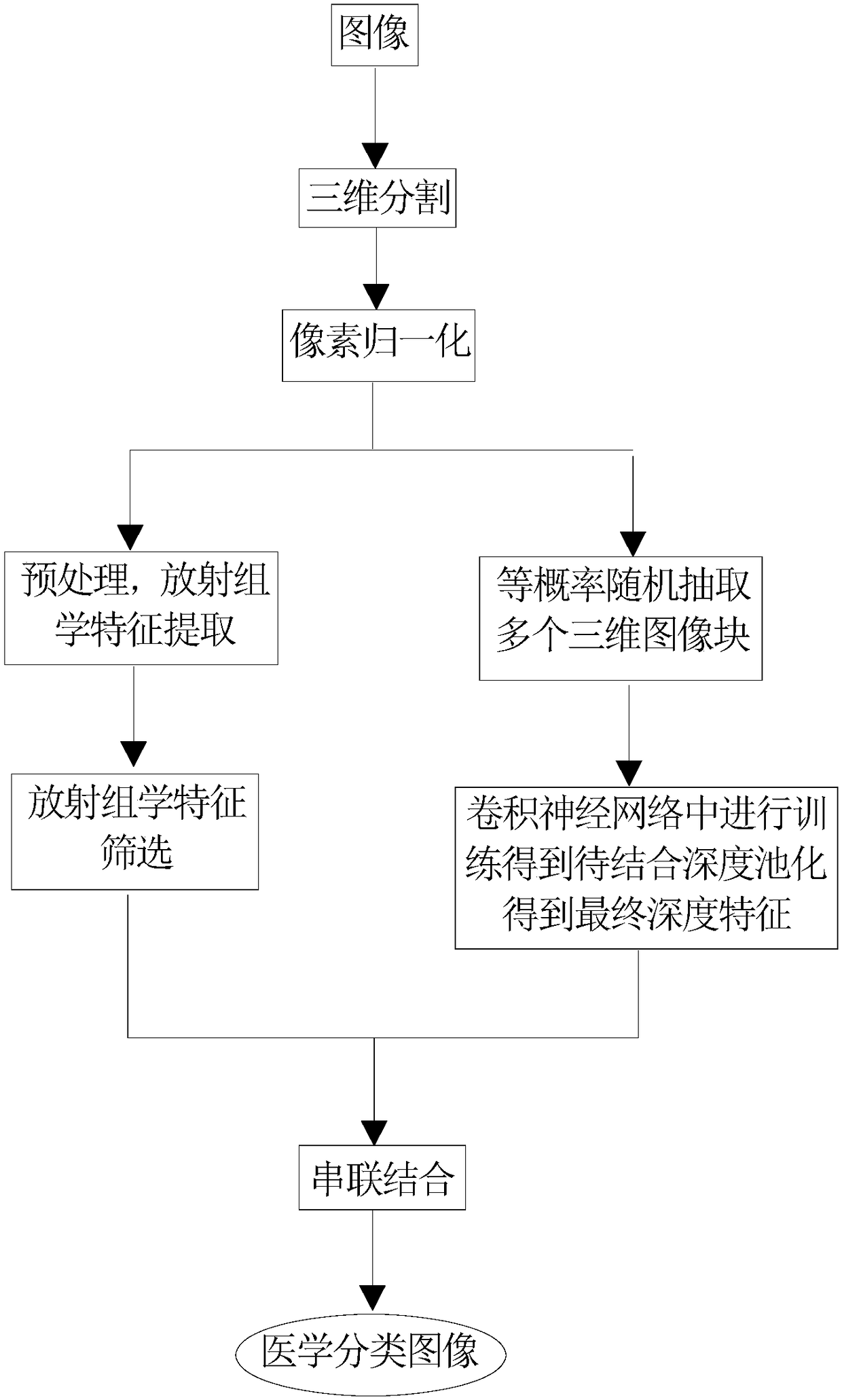
Image classification method fusing radiomics and deep convolution features
InactiveCN108596247AImprove accuracyMake up for the disadvantages of low classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesClassification methodsConvolution
An image classification method fusing radiomics and deep convolution features obtains medical classified images by virtue of 7 steps. The invention combines two technologies, namely radiomics and deeplearning, images are classified by combining global features provided by the radiomics and local features provided by the deep learning, the advantages of the radiomics and deep learning are inherited, and shortfalls of the radiomics and deep learning are also made up, so that medical image classification accuracy is enhanced. Meanwhile, the invention provides a strategy of pooling along an imageblock. The pooling technology makes up the abuse that classification accuracy is low as an image block technology is introduced due to the requirement of the deep learning on big data, and a foundation is provided for combination of depth features from the image block and other traditional features.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Radiomics-based hepatic venous pressure gradient (rHVPG) calculation model construction method
ActiveCN107480675AIncrease operational difficultyInvasive riskImage enhancementImage analysisMedicineQuality of life
The invention provides a radiomics-based hepatic venous pressure gradient (rHVPG) calculation model construction method, on this basis, a more advantageous hepatic venous pressure gradient calculation model can be constructed, and a new way is provided for the calculation of the early stage non-invasive index of a patient with portal hypertension. The invention also provides a radiomics-based hepatic venous pressure gradient calculation system. The invention overcomes the many limitations of current non-invasive measurement methods. The rHVPG calculation system proposed by the invention is feasible, is expected to provide a new idea for noninvasive measurement of portal pressure, and plays a positive role in improving the quality of life of the patient with portal hypertension and alleviating the disease burden of families and society.
Owner:祁小龙
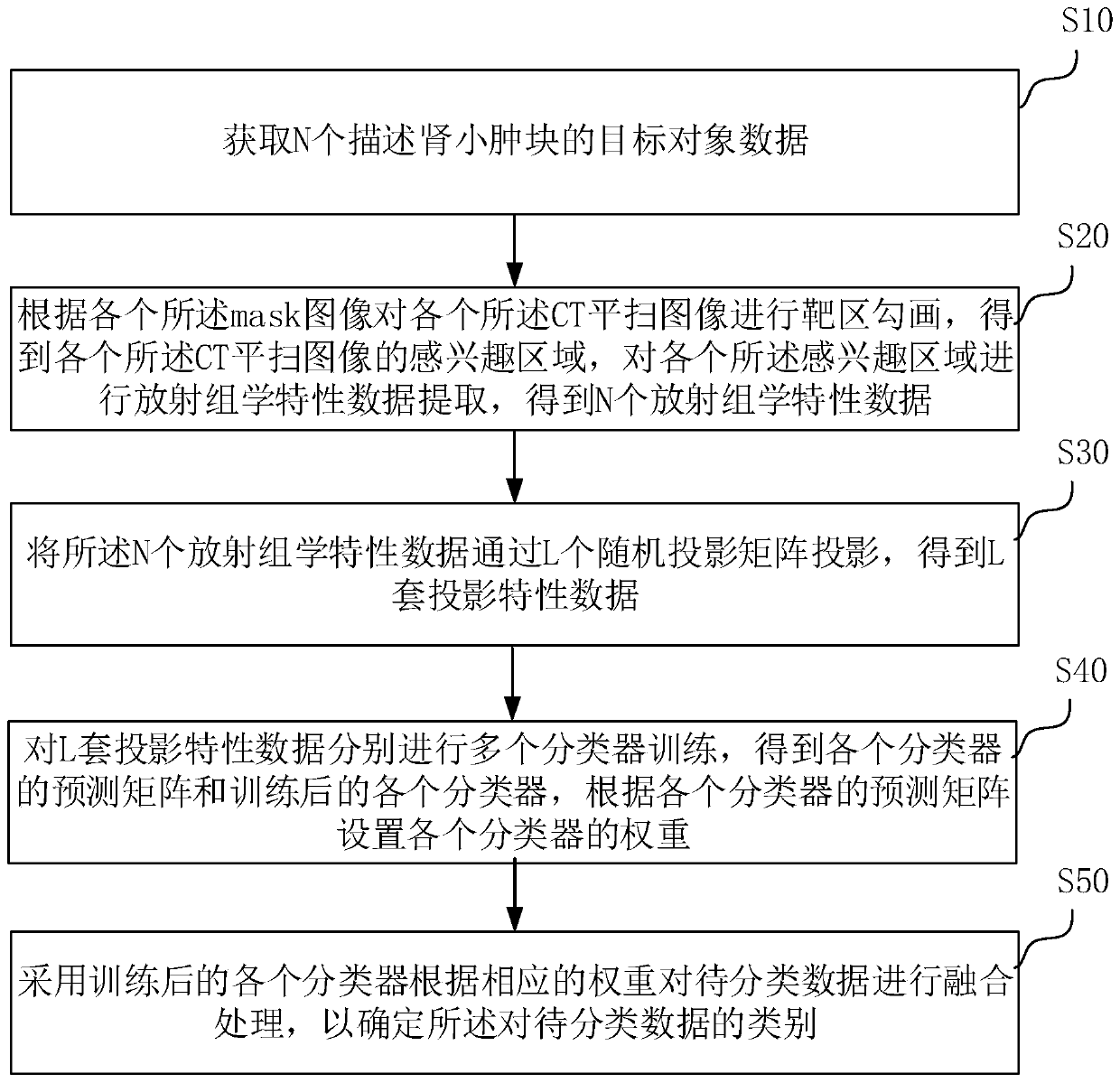
Kidney lump classification method based on random projection
ActiveCN111340135AImprove robustnessImprove reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisCategory recognitionData ingestion
Owner:甄鑫
Method for constructing gastrointestinal stromal tumor malignant potential classifying model based on radiomics
InactiveCN107368695ACapture heterogeneityNo extra costImage enhancementImage analysisStromal tumorData acquisition
The invention is a method of tumorology, imaging, and computer -assisted medicine, involving a method of building a model of malignant potential classification models based on radiological gastric and intestinal tumor.The construction method described in the present invention includes: data collection: abdominal enhancement phase of thin -layer CT image collection; extracting radiation group characteristics; statistical analysis; feature selection and radiation group characteristics model construction; radiology feature model verification and calibration.The method built by the method described by the present invention can classify the vicious potential classification model of gastrointestinal gastrointestinal tumor tumor tumor, which can accurately classify the GIST with different malignant potential, which is a non -invasive technology without increasing the additional cost of patients. Operations operation. Operations.Simple, convenient for clinical promotion.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
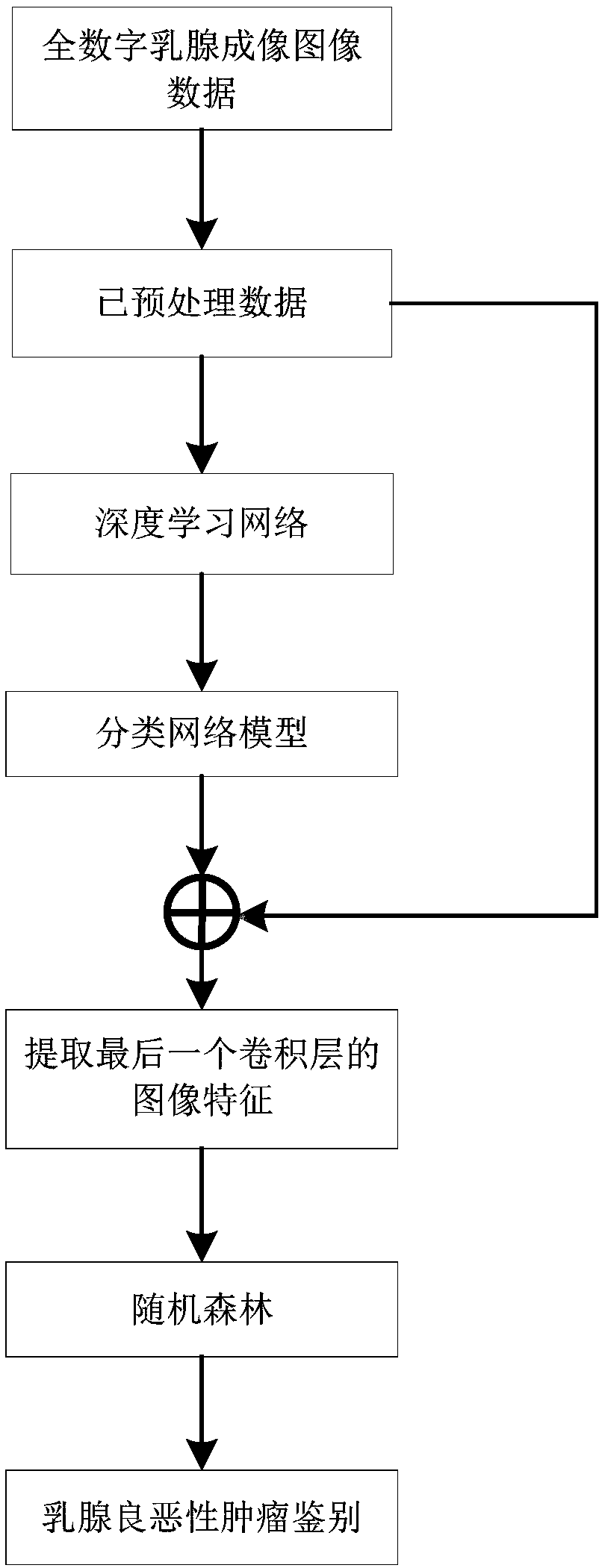
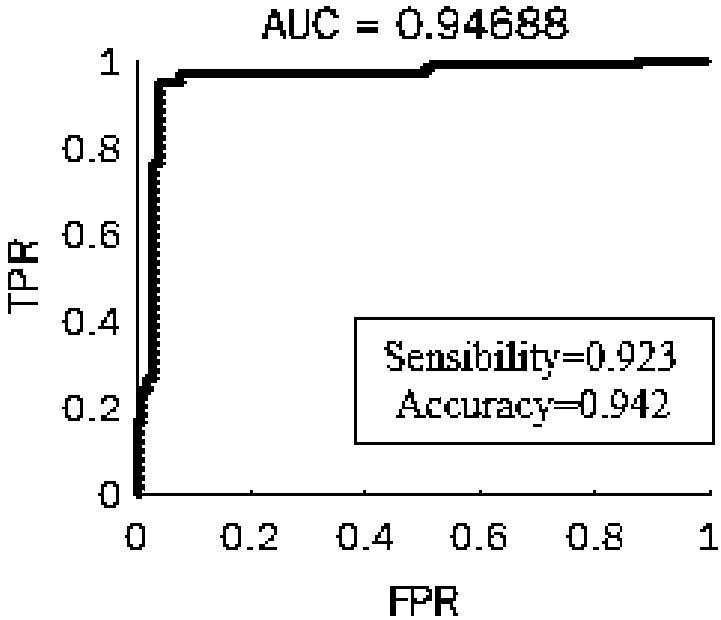
All-digital mammary gland imaging image radiomics method based on deep learning
InactiveCN108304889ADifferentiate benign from malignant tumorsRealize researchImage enhancementImage analysisFeature vectorFeature extraction
An all-digital mammary gland imaging image radiomics method based on deep learning includes the following specific steps: obtaining all-digital mammary gland imaging image data [mu]<datset>, preprocessing the all-digital mammary gland imaging image data [mu]<datset> to obtain preprocessed data [mu]<hdf5>, inputting the preprocessed data [mu]<hdf5> to a deep learning network Alexnet to perform training, establishing a classification network model M<alexnet>, inputting the preprocessed data [mu]<hdf5> to the classification network model M<alexnet> to perform feature extraction, obtaining a high-dimensional feature vector FeatureMap, inputting the high-dimensional feature vector FeatureMap to a random forest RF to perform training to obtain a high-performance tumor identification classifier. The method provided by the invention uses a deep learning network Alexnet framework to extract image features for identifying a tumor, and combined with radiomics, the random forest is adopted to learn the extracted features, thereby realizing research of all-digital mammary gland imaging image radiomics based on deep learning.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for early prediction of neurodegenerative decline
PendingUS20210228079A1Easy to useImage enhancementMedical imagingEarly predictionPredictive biomarker
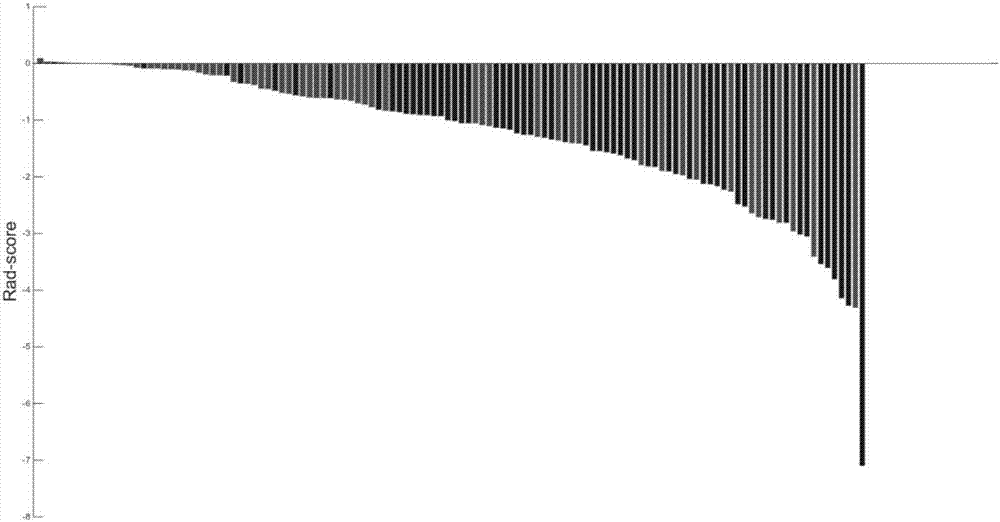
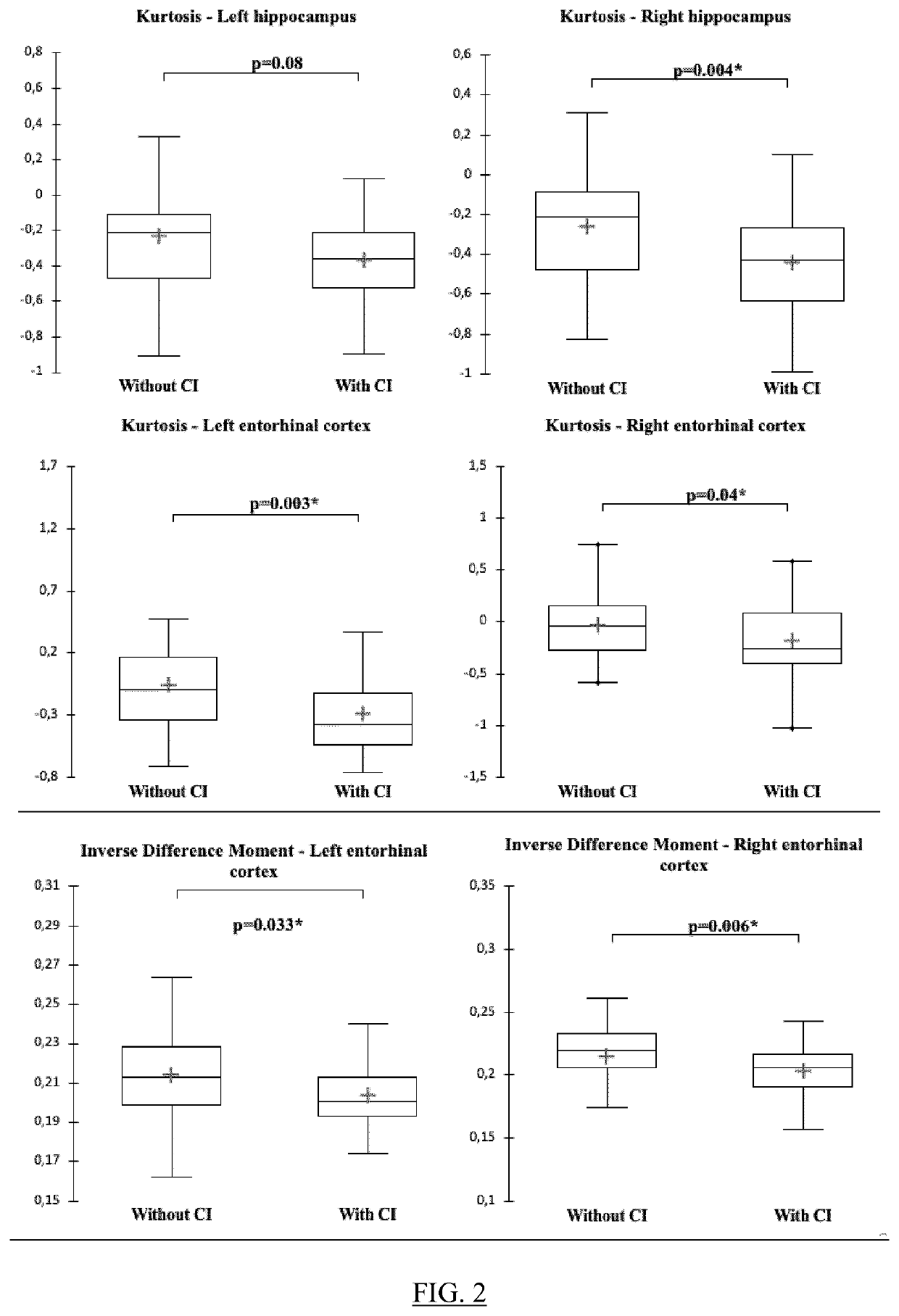
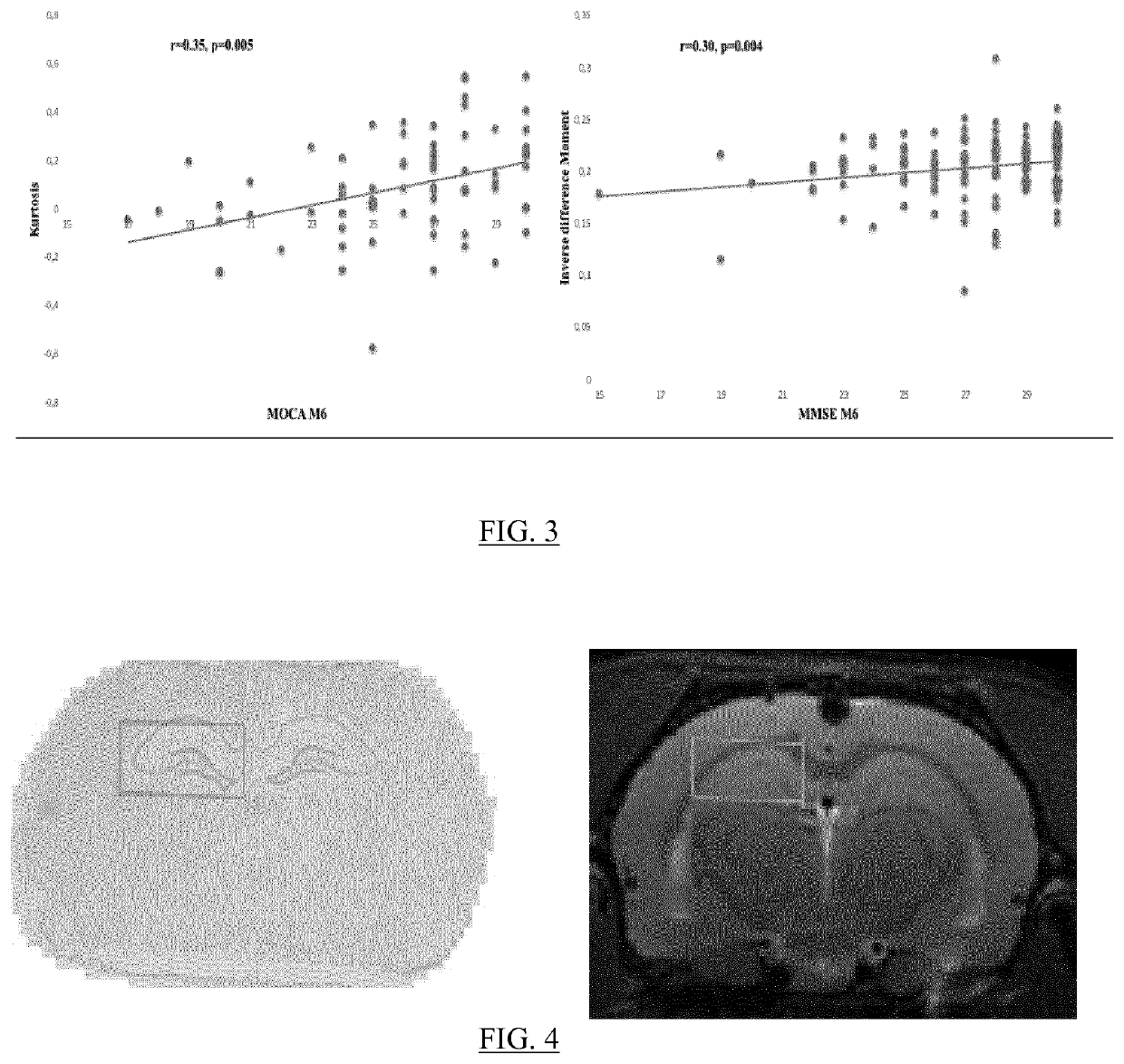
The present invention relates to a method for predicting neurodegenerative decline and / or its severity for a patient, especially of cognitive impairment (CI). Strokes and Parkinson's disease are frequently associated with occurrence of long-term cognitive impairment or dementia with still incompletely resolved mechanisms. The discovery of diagnostic and predictive biomarkers thus remains a major challenge. The method of the invention uses radiomics corresponding to texture features extracted from a plurality of previously-acquired medical brain images and correlated with previously-acquired clinical and / or biological data. A classifier is trained beforehand for learning these radiomics, and then operated on radiomics computed from at least one brain image of a patient to generate a score representative of its risks of neurodegenerative decline. By applying this method on a cohort of 160 MCI and non-MCI patients, the inventors show that MCI patients could be early predicted with a mean accuracy of 88%. In the same way, the method was able to discriminate very early stages of cognitive decline in a Parkinson's disease population of 100 patients.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
Colorectal cancer image classification method and system combining deep learning and radiomics
PendingCN114332577AAchieve integrationInterpretableEnsemble learningCharacter and pattern recognitionAutomatic segmentationClinico pathological
The invention provides a colorectal cancer image classification method and a colorectal cancer image classification system combining deep learning and imageomics, aiming at the problem of training a small sample by a deep learning model, the existing data is fully utilized to carry out data enhancement (rotation, translation, image transformation and the like) so as to solve the problem of time and labor consumption caused by manual marking by a doctor. An automatic segmentation network model of deep learning is introduced, and the region of interest is automatically marked from the image. In order to solve the problems that the explainability of the features extracted by the deep learning model is poor and the obtained feature information is not comprehensive, more and more comprehensive feature information is obtained by fusing the image omics features, the deep learning features and the clinical pathological information, and the classification accuracy and reliability of the image omics are further improved.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
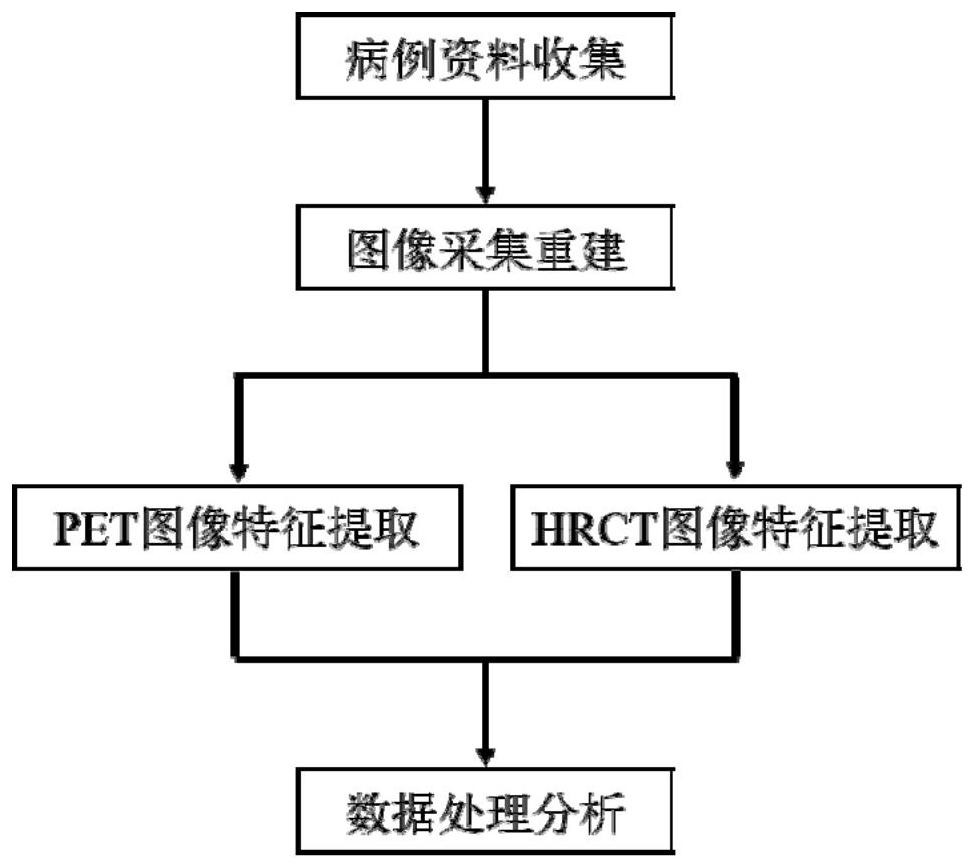
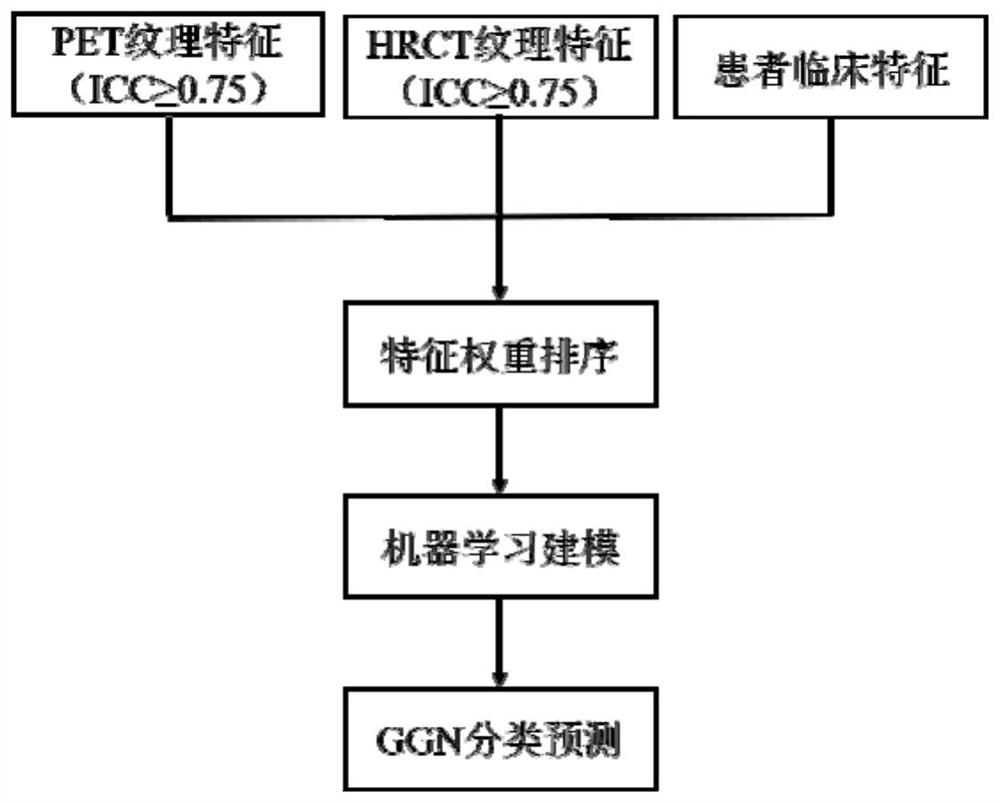
Machine learning-based bimodal image omics ground glass nodule classification method
PendingCN112767393AAids in clinical managementImprove predictive performanceImage enhancementImage analysisClassification methodsCt examination
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical treatment, and discloses a machine learning-based bimodal image omics ground glass nodule classification method, which comprises the following steps of: step 1, case data collection: collecting patients who receive 18F-FDG PET / CT examination due to suspicious ground glass nodules (GGN); step 2, image acquisition and reconstruction: performing image acquisition by adopting a PET / CT (positron emission tomography / computed tomography) imaging instrument; step 3, image feature extraction; and step 4, data processing and analysis. According to the method, the image omics model based on the combination of the PET image and the HRCT image is constructed by applying a machine learning method, the GGN is classified, including pre-infiltration lesion, micro-infiltration adenocarcinoma, infiltration adenocarcinoma and benign lesion, verification and testing, the method is good in robustness, high in accuracy, simple and feasible. According to the method, the functional metabolism information and the physical anatomical information of the molecular level of the focus are integrated, the prediction efficiency of traditional CT parameters and single CT radiomics is effectively improved, and clinical management of the GGN is facilitated.
Owner:THE FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF CHANGZHOU
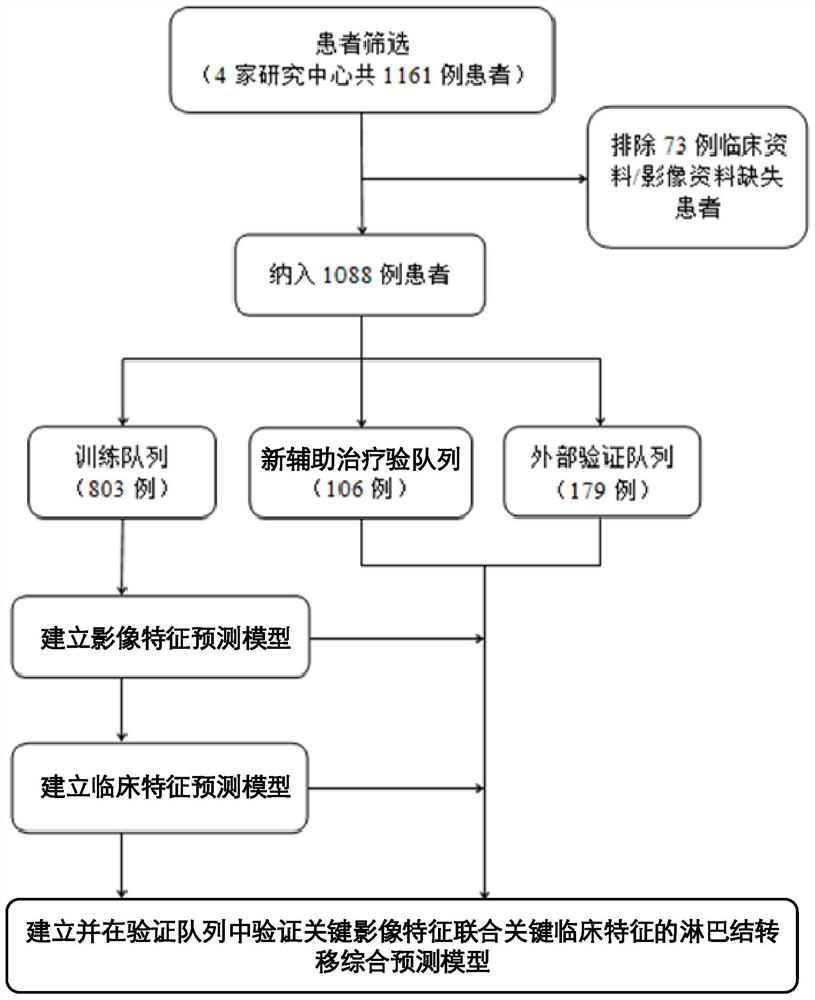
Method for constructing lymph node metastasis prediction model of breast cancer patient based on radiomics
PendingCN113555115AImprove stabilityImprove accuracyMedical data miningHealth-index calculationNode metastasisSingle factor analysis
The invention discloses a method for constructing a lymph node metastasis prediction model of a breast cancer patient based on radiomics. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring magnetic resonance image data and clinical feature data of the patient; extracting image features based on the magnetic resonance image data; screening the image features by using a random forest algorithm to obtain a plurality of key image features, and establishing an image feature prediction model based on the key image features by using a support vector machine algorithm; performing single-factor analysis screening on the clinical feature data to obtain key clinical features, and establishing a clinical feature prediction model according to the key clinical features by adopting a support vector machine algorithm; and establishing a lymph node metastasis comprehensive prediction model according to the key image features and the key clinical features by adopting a support vector machine algorithm. According to the embodiment, the model is established by adopting the random forest algorithm and the support vector machine algorithm, the prediction model can be established based on the structure risk minimum principle, and the problem of over-learning can be avoided, so that the constructed prediction model is more stable and accurate.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN MEMORIAL HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
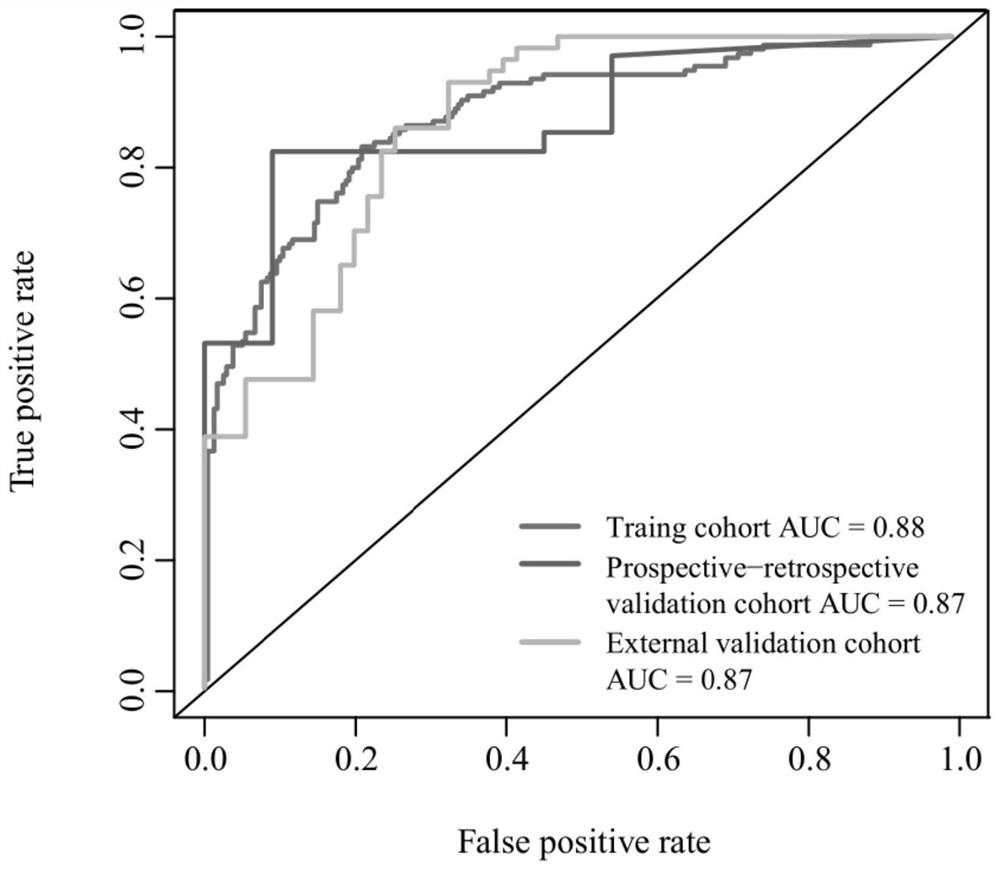
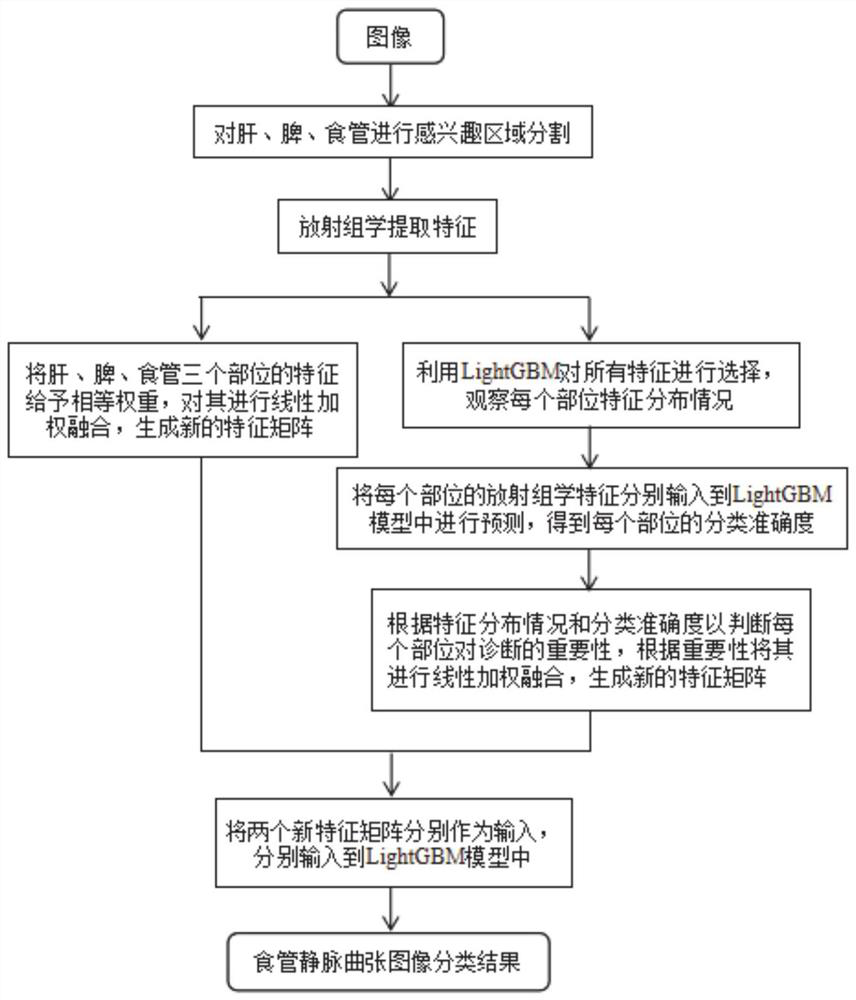
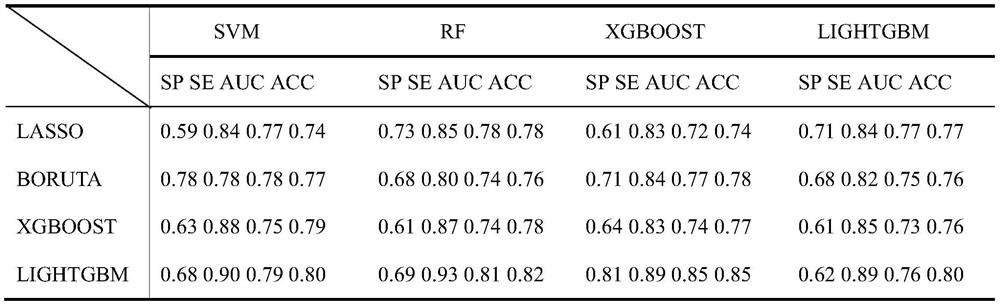
Esophageal varicosity classification system based on LightGBM and feature fusion
ActiveCN111881724AReduce complexityThe features are given equal weights, and the linear weighted fusion is used to give full play to them.Medical automated diagnosisRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsEsophageal varicesNuclear medicine
The invention discloses an esophageal varicosity classification system based on LightGBM and feature fusion. The esophageal varicosity classification system comprises a segmentation module for segmenting and extracting regions of interest of the liver, the spleen and the esophagus in a CT image; a feature extraction module performing radiomics feature extraction on the region-of-interest image ofeach part; a first weight distribution module distributing equal weights to the radiomics characteristics of each part to obtain a first characteristic matrix; a second weight distribution module judging the importance of each part to the varicose veins of the affected esophagus by adopting a LightGBM method according to the radiomics characteristics of each part, and performs weighted fusion on the radiomics characteristics of each part according to the importance to obtain a second characteristic matrix; a classification module training a LightGBM classification model for the first feature matrix and the second feature matrix, and classifies whether the to-be-detected CT image suffers from esophageal varicose veins. An esophageal varicosity classification model based on LightGBM and feature fusion is constructed on the basis of radiomics, the importance of each part is brought into play, and the classification performance is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
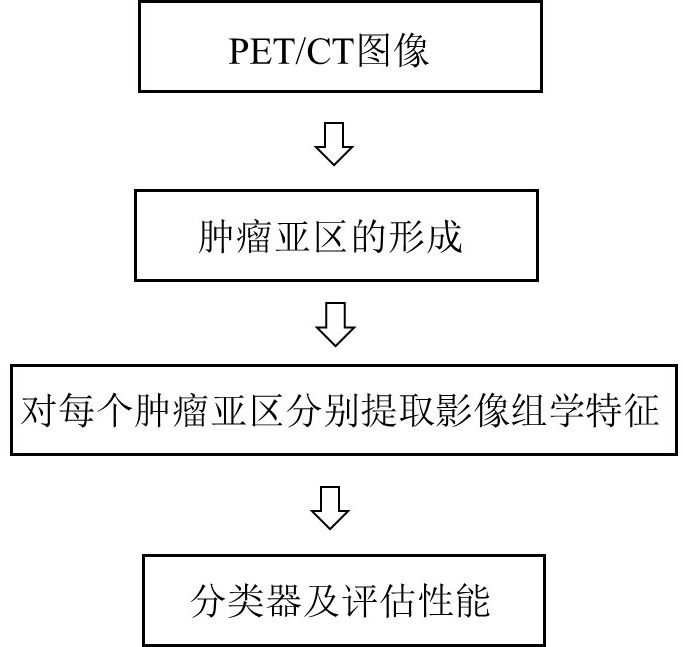
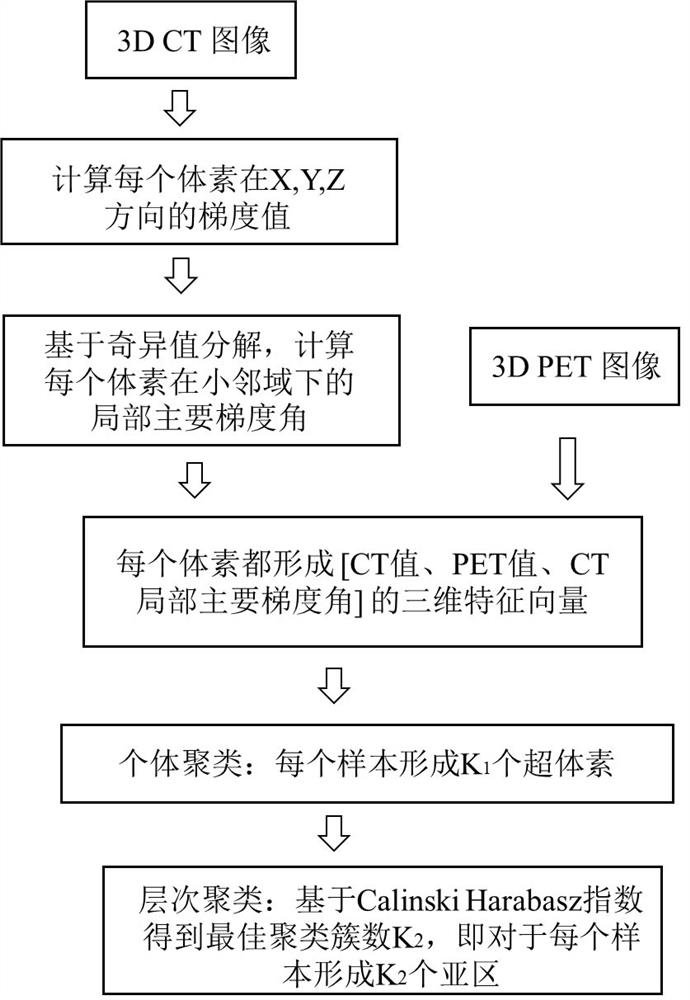
Lung gland squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis device based on PET/CT image sub-region imaging omics characteristics
ActiveCN112465824AImprove accuracyConsider heterogeneityImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelSquamous Carcinomas
The invention discloses a lung glandular squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis device based on PET / CT image subarea imaging omics characteristics, and belongs to the field of medical images. The diagnosisdevice comprises: a voxel three-dimensional feature extraction module, which is used for extracting a CT local main gradient angle feature value of each voxel of a lung tumor in a neighborhood in a PET / CT image, a CT value of the voxel and a PET value, and forming a three-dimensional feature vector of the voxel; a feature clustering module used for clustering the obtained three-dimensional feature vector of each voxel to obtain a tumor sub-region partition; a radios image omics feature extraction module used for extracting radios image omics features of each tumor sub-region in a partitioningmanner; and a classification module used for distinguishing whether the tumor is lung squamous cell carcinoma or lung adenocarcinoma according to the extracted radiomics characteristics of the radiomics. According to the diagnosis device, the heterogeneity in the tumor is better considered, and the accuracy of tumor diagnosis is effectively improved by extracting more effective imaging omics characteristics.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB +1
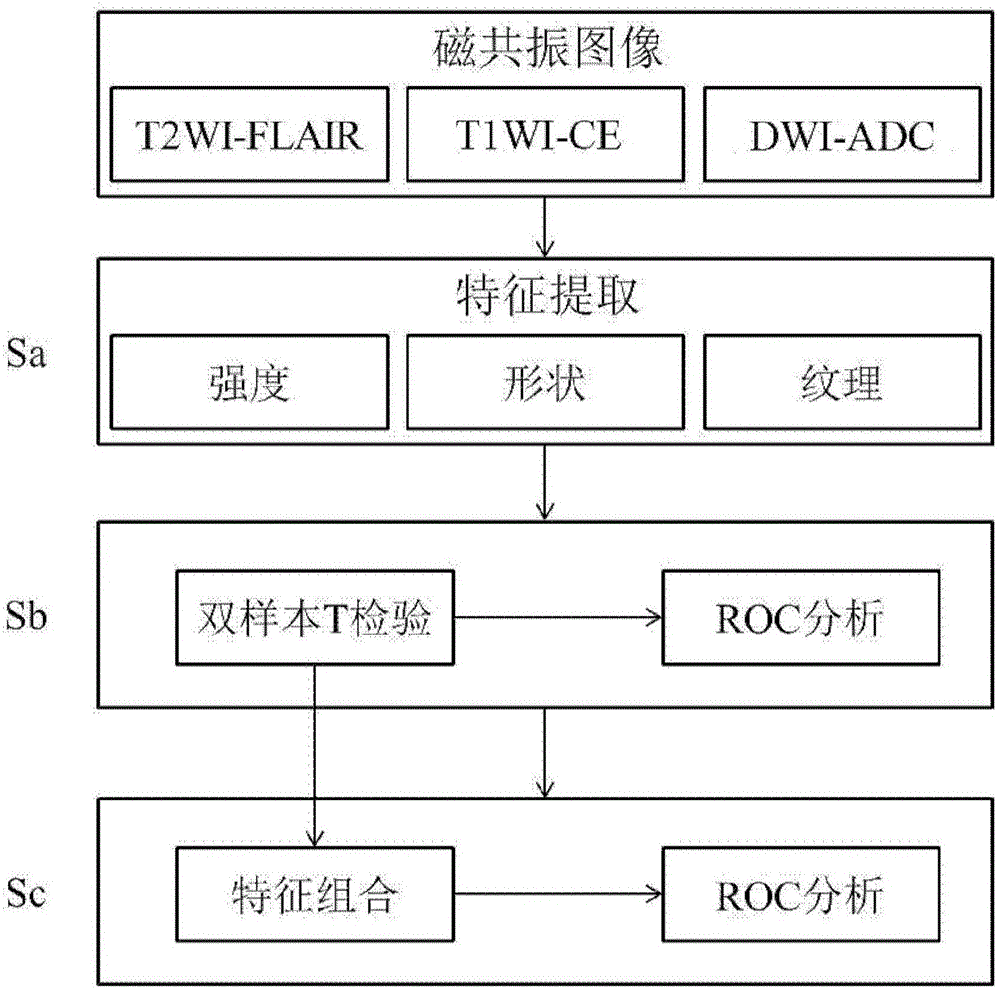
Radiomics based multi-modality magnetic resonance image difference detection method and device
ActiveCN105931221AIncrease differentiationImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisResonanceSample image
The invention discloses a radiomics based multi-modality magnetic resonance image difference detection method and device. The method comprises the steps that 1) two groups of sample images are pre-processed, ROIs (Regions of Interest) are sketched in T2WI-FLAIR, T1WI-CE and DWI-ADC sequences of each group of sample images, and image features of the ROI in the three sequences are extracted; 2) double-sample T test is carried out on each image feature between the two groups of sample images, features with inter-group difference between the two groups of sample images are obtained, capability of detecting difference, between the two groups of sample images, of the features with inter-group difference is determined; and 3) the features with inter-group difference are combined in the weighted manner to obtain a new feature, and an adaboost classifier is used for image classification. According to the invention, the multi-sequence multi-parameter feature of magnetic resonance imaging is utilized, different sequences are combined to obtain more information, and inter-group difference of magnetic resonance imaging can be detected accurately.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vertebral body bone mineral density classification method based on image omics and deep learning feature fusion
ActiveCN114863165AGood distinctionImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImage segmentationNetwork classification
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Prostate image segmentation method and prostate cancer intelligent auxiliary diagnosis system
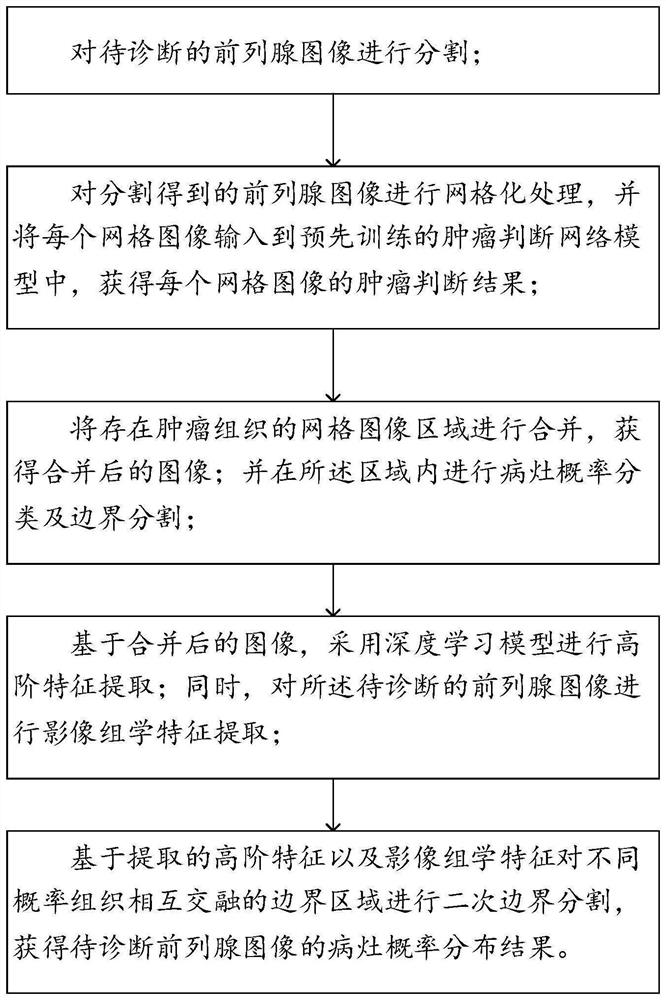
PendingCN114820520AImprove accuracyIncreased ancillary valueImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionProstate cancer
The invention provides a prostate image segmentation method and a prostate cancer intelligent auxiliary diagnosis system, and belongs to the technical field of prostate cancer intelligent auxiliary diagnosis, the prostate image segmentation method comprises the following steps: segmenting a prostate image to be diagnosed by using the prostate image segmentation method; performing meshing processing on the prostate images obtained by segmentation, and inputting the processed prostate images into a pre-trained tumor judgment network model to obtain a tumor judgment result of each grid image; combining the grid images with the tumor tissues to obtain a combined image; lesion probability classification and boundary segmentation are carried out in the region; based on the merged image, performing high-order feature extraction by using a deep learning model; meanwhile, image omics feature extraction is carried out on the prostate image to be diagnosed; and based on the extracted high-order features and radiomics features, carrying out secondary boundary segmentation on a boundary region where tissues with different probabilities are mutually fused to obtain a lesion probability distribution result of the prostate image.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH +1
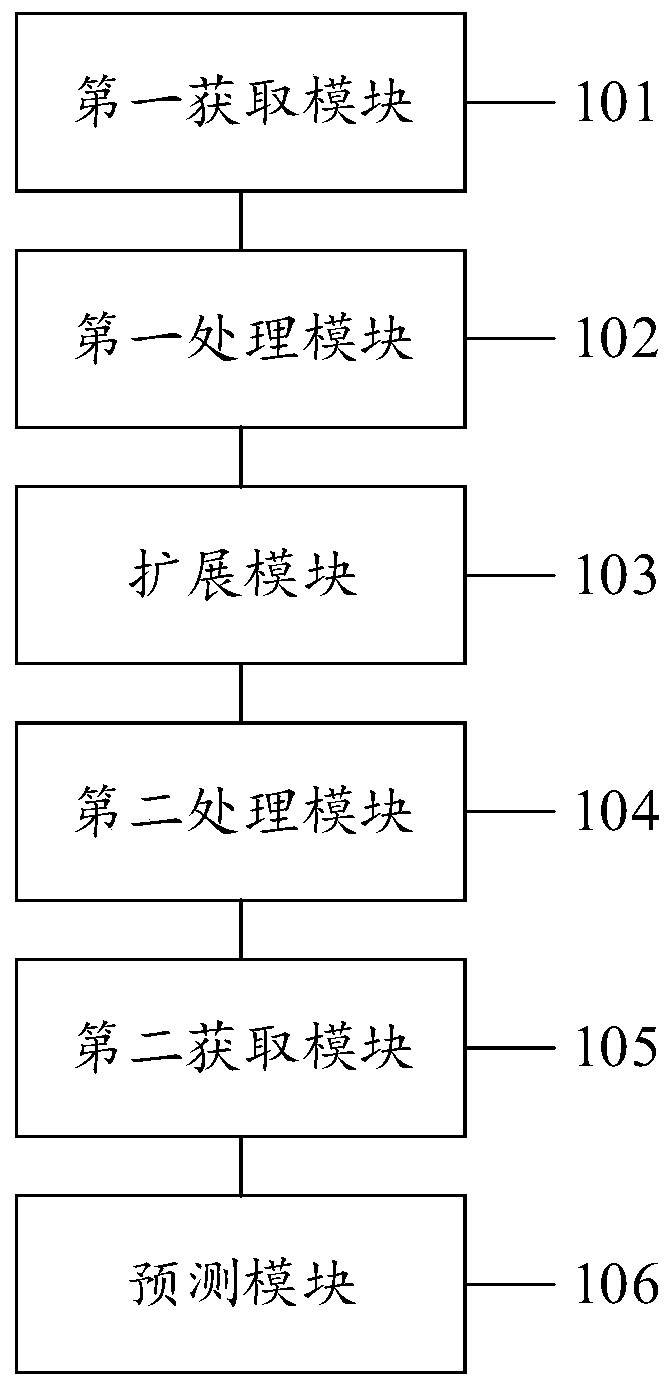
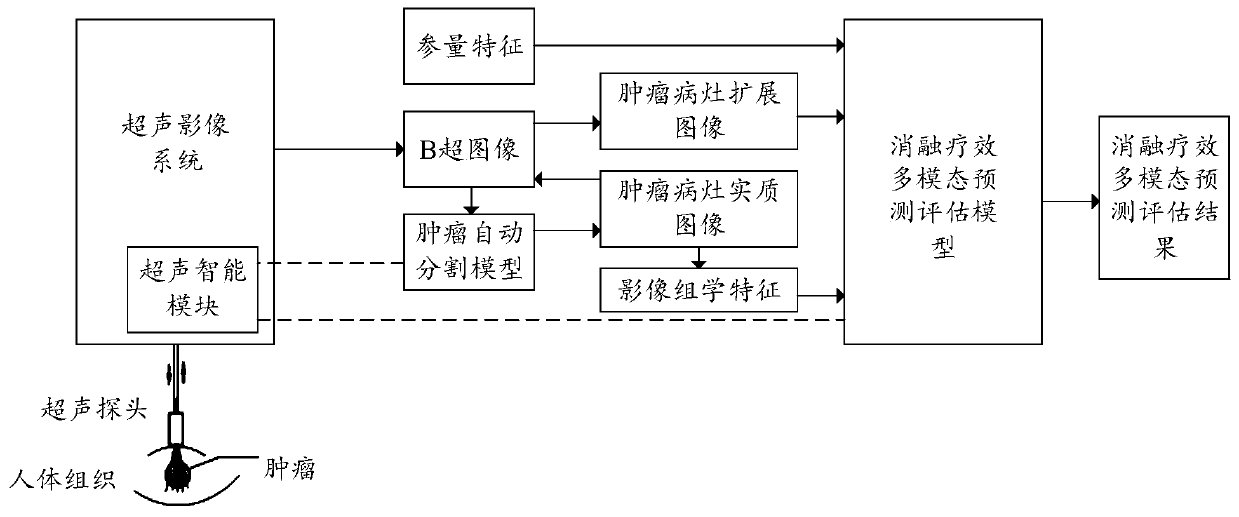
Tumor ablation curative effect prediction method, device, equipment and computer medium
PendingCN111528800AImprove accuracyOrgan movement/changes detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringFeature extractionExAblate
The invention discloses a tumor ablation curative effect prediction method, device and equipment and a computer medium. The tumor ablation curative effect prediction device includes a first acquisition module for acquiring an ultrasound image containing a tumor, a first processing module for processing the ultrasound image to obtain a tumor lesion parenchymal image, an expansion module used perform area expanding on the parenchymal image of the tumor lesion in the ultrasound image to obtain an expanded image of the tumor lesion, a second processing module for extracting and screening radiomicsfeatures of the parenchymal image of the tumor lesion to obtain target radiomics features, a second acquisition module for acquiring tumor-related parametric features except ultrasound images and a prediction module for performing tumor ablation curative effect prediction based on the tumor lesion expanded image, the target radiomics feature and parameter features to obtain prediction results oftumor ablation curative effect. Preoperative tumor ablation curative effect prediction can be performed based on ultrasound images and supplemented by parametric features, and limitations are small.
Owner:SONOSCAPE MEDICAL CORP
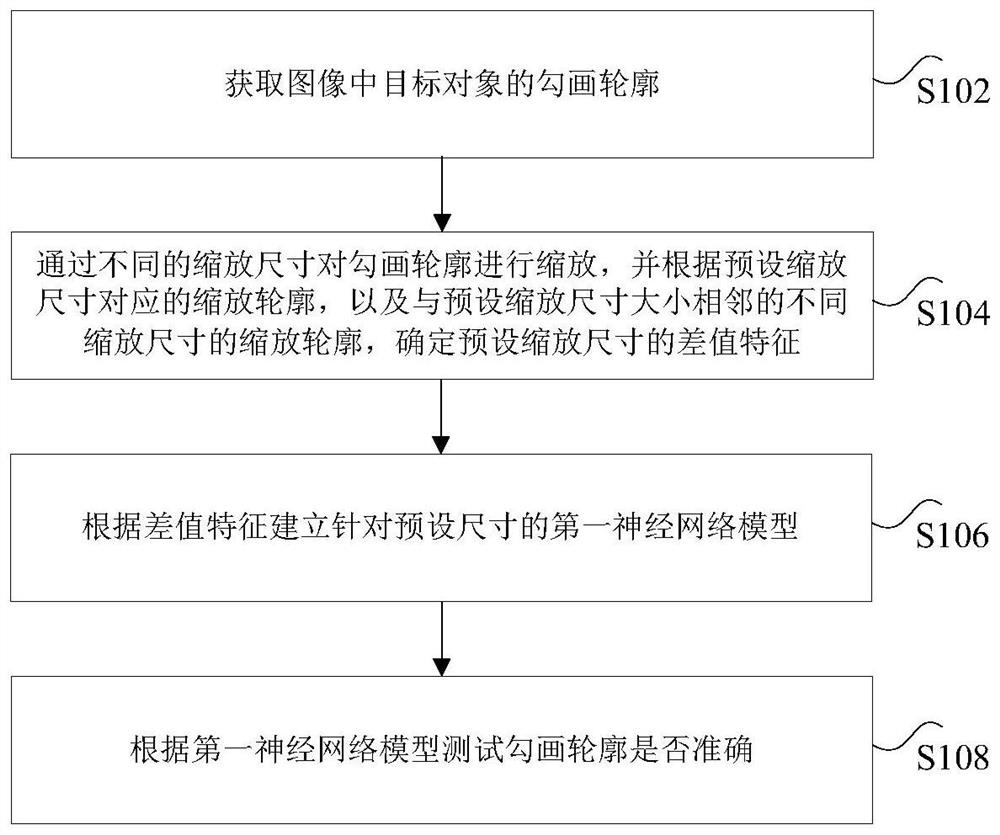
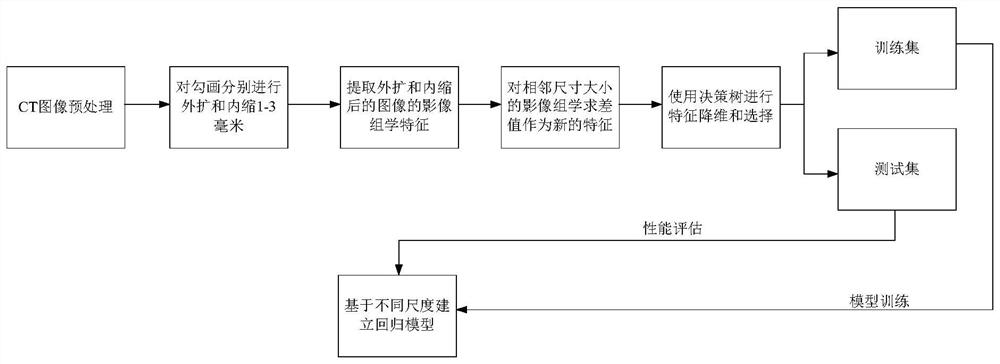
Target area and organ-at-risk outline sketching accuracy inspection method based on radiomics
ActiveCN113034528AImprove effectivenessImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionGraphics
The invention discloses a target area and organ-at-risk outline sketching accuracy inspection method based on radiomics. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a sketching contour of a target object in an image; scaling the delineated contour through different scaling sizes, and determining a difference feature of a preset scaling size according to the preset scaling size and scaling contours with different scaling sizes adjacent to the preset scaling size; establishing a first neural network model for a preset size according to the difference feature; and testing whether the sketched contour is accurate according to the first neural network model. According to the method and the device, the technical problems that the image sketching effect is poor, the accuracy and the stability are low and the sketching quality is difficult to evaluate quickly due to an image segmentation algorithm in related technologies, so that a graph sketching result needs to be artificially identified are solved.
Owner:MANTEIA TECH CO LTD
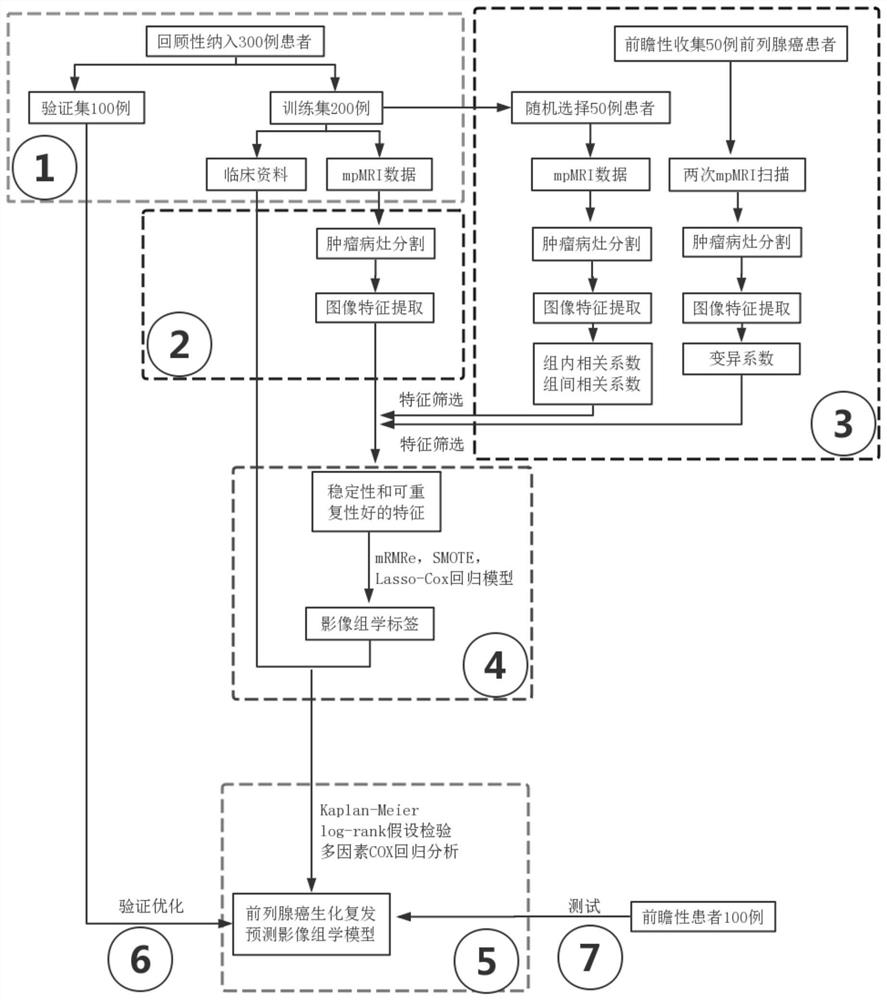
Method for predicting biochemical recurrence risk after prostatic cancer radical operation by MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) image
InactiveCN114121225AAchieving Prognosis Prediction of Biochemical RecurrenceGuaranteed reliabilityMedical automated diagnosisMedical imagesRecurrence predictionProstatectomy radical
The invention relates to the technical field of computer medicine, and discloses a method for predicting a biochemical recurrence risk after a radical prostatic cancer operation through an MRI image, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, collection and arrangement of prostatic cancer cases: firstly, carrying out the retrospective collection and arrangement of MRI data and clinical data of at least 300 patients subjected to the radical prostatic cancer operation according to a group entering standard, wherein 200 patients are used for constructing a radiomics model, and 100 patients are used for verifying and optimizing the radiomics model; according to the method, a retrospective and prospective combined mode is innovatively adopted, the optimized image group student recurrence prediction model is constructed and verified on the basis of a large number of prostate cancer cases which are collected in the past and are subjected to standardized scanning, and the accuracy of the model is tested by using prostate cancer radical cases collected prospectively, so that the reliability of the model is ensured. Meanwhile, retrospective and prospective data are creatively applied in the research, and the stability and repeatability of image features are evaluated by adopting multiple methods.
Owner:冯朝燕
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com