Piezoelectric Transducers and Inertial Sensors using Piezoelectric Transducers
a piezoelectric transducer and inertial sensor technology, applied in the field of microelectromechanical inertial sensor, can solve the problems of increasing the cost of the resulting mems-based device, reducing the accuracy of the piezoelectric transducer, and not being particularly compatible with the widely used standard cmos process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 60
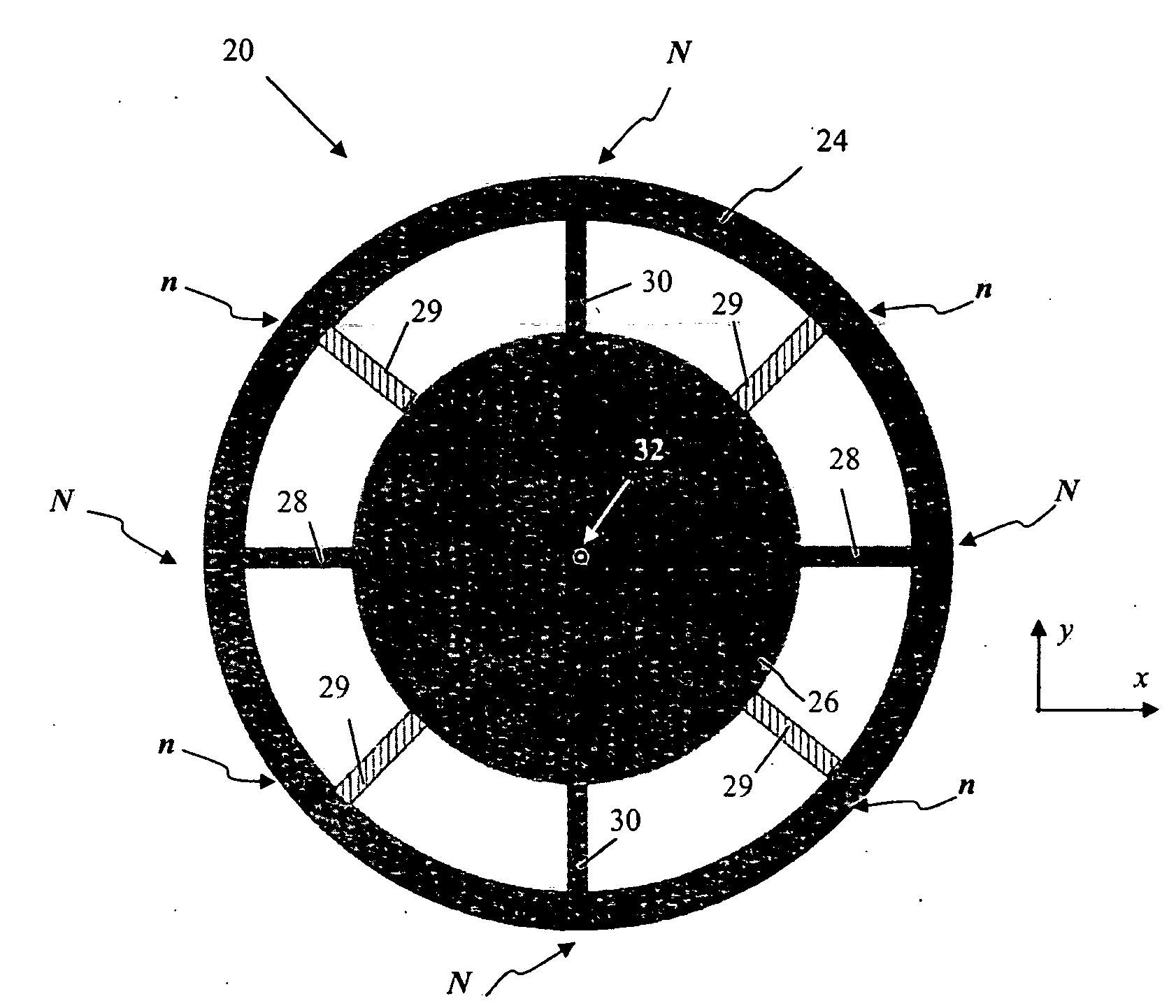
[0042]Configuration of transducers is further discussed with reference to FIGS. 9 and 10, illustrating some exemplary embodiments, with continuing reference to FIG. 8. Although the transducer operation is described below with reference to the driving transducers 50 of FIG. 8, the same description is equally applicable to the sensing transducers 58. FIG. 9A shows, in top view, a piezoelectric frame structure 60 of a transducer 50. As shown, the piezoelectric frame structure is elongated along x-axis, i.e. laterally with respect to a spoke 42 that connects the ring 24 of the gyroscope 40 to the hub 26. FIG. 9B offers a corresponding side view. The structure 60 is characterized by a substantially constant thickness t defined by the top and bottom substantially flat surfaces 46 and 62 that are parallel to a reference plane (the xy-plane in FIG. 9). Although the frame structure 60 is shown to possess two-fold symmetry (about the yz- and xz-planes, each of which is a plane of symmetry of ...
embodiment 80
[0044]It should be appreciated that a transducer of the invention can operate as part of either a driving element, generating an in-plane mode of oscillation of the ring of the inertial sensor as discussed above in reference to FIG. 7, or as part of a sensing element. The operation of a driving transducer of the invention is further discussed in reference to FIGS. 11 and 12, with continuing reference to FIG. 10. FIGS. 11A and 11B schematically illustrate, in side views, a cross-section of a portion of the frame of the embodiment 80 of FIG. 10 with a an electric potential of cyclically alternating polarity applied between the top electrode and the corresponding bottom electrode (in this example, the electrodes 82 and 82′) that sandwich the frame comprised of the piezoelectric material. The instantaneous electrostatic field, associated with the potential difference applied between the electrodes, is denoted as E. It should be appreciated that, to enhance the driving operation of the t...
embodiment 110
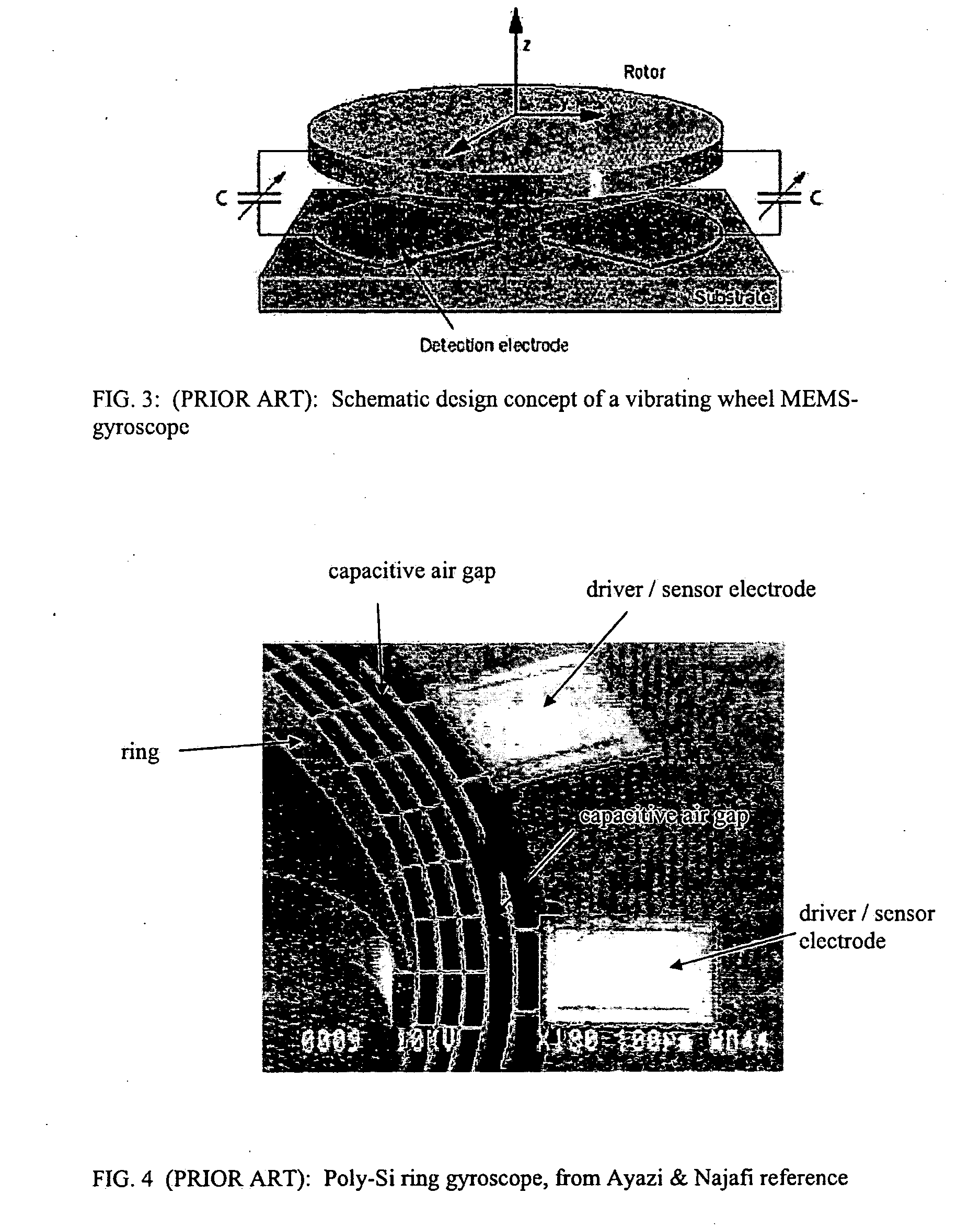
[0051]The embodiments of the invention described above are intended to be merely exemplary; numerous variations and modifications will be apparent to those skilled in the art based on the teachings of this disclosure. Piezoelectric drivers and / or sensors of the type described above (e.g., with reference to FIGS. 6,8-10,13) can be used in other types of inertial sensors and are not limited to ring gyroscopes. For example, piezoelectric transducers of the invention may be used in linearly resonating MEMS-based structures such as linear resonator gyroscopes. Although the operation of the inertial sensor of the invention was described in reference to an embodiment of FIG. 8 containing four driving elements 52 and four sensing elements 54, it should be understood that there is no theoretical limitation on the number of driving and sensing elements or a particular fashion in which the driving elements operate. For example, in reference to FIG. 8, the ring 24 of the inertial sensor may be ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| symmetry | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrostatic energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com