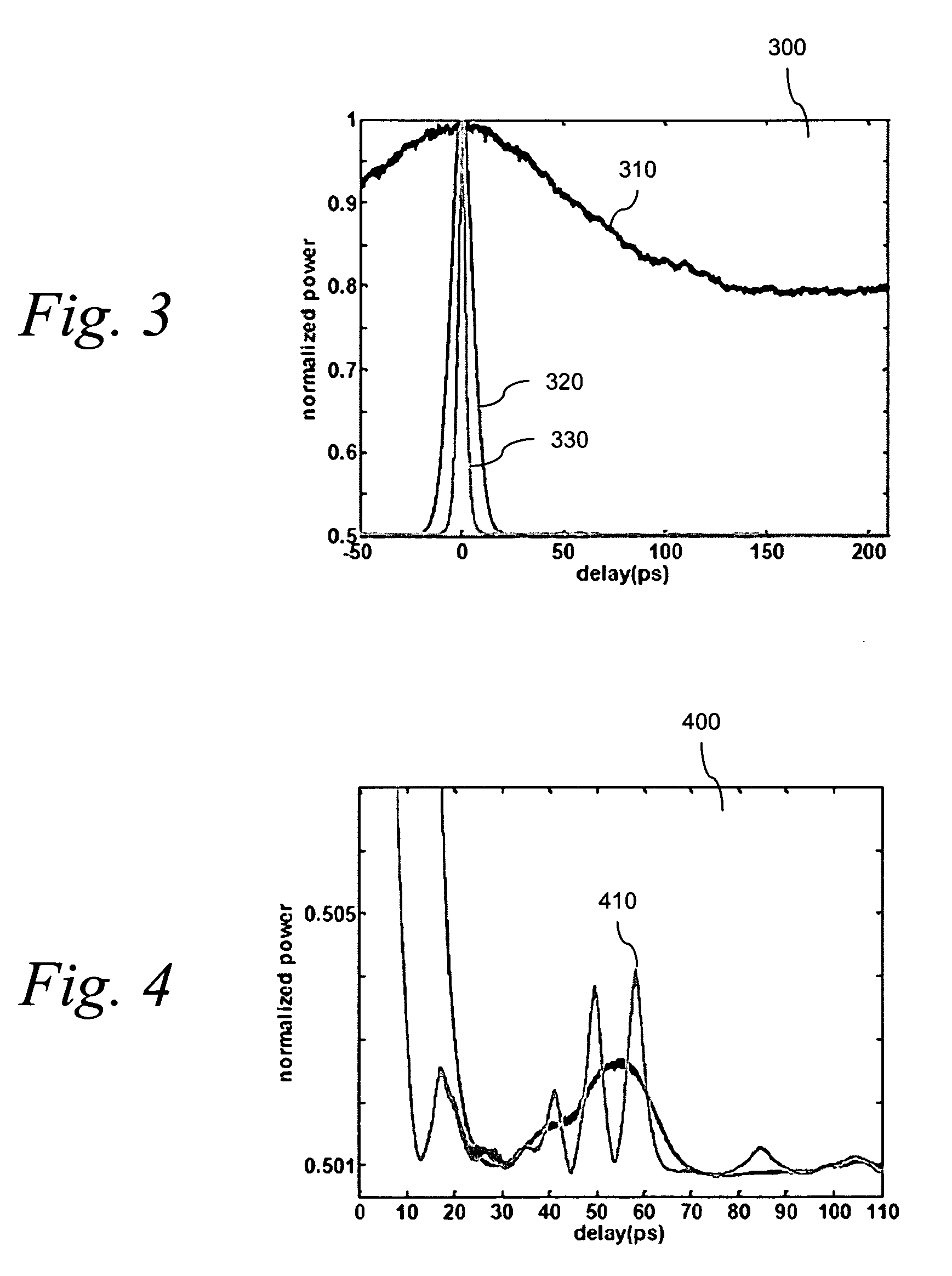
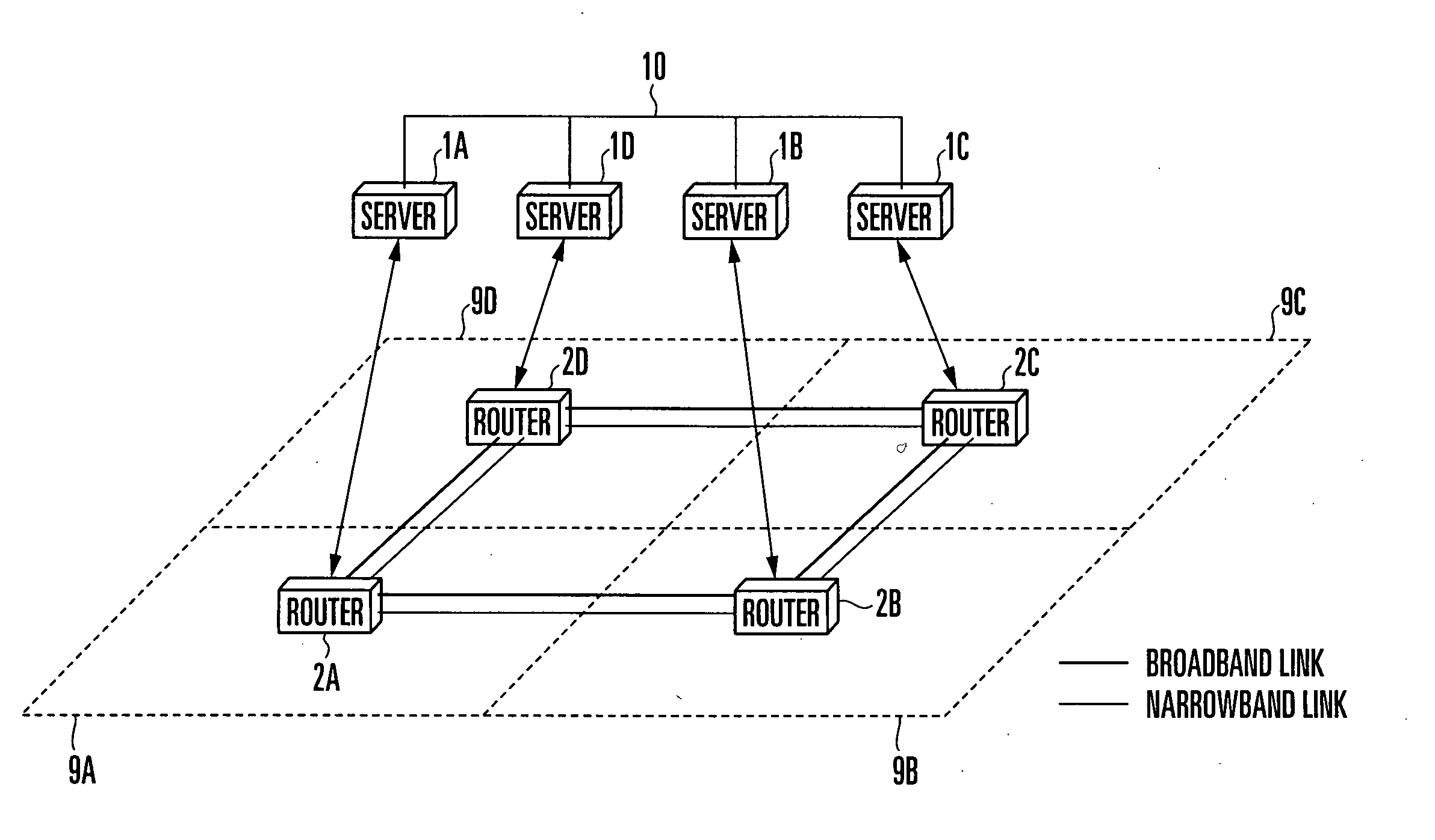
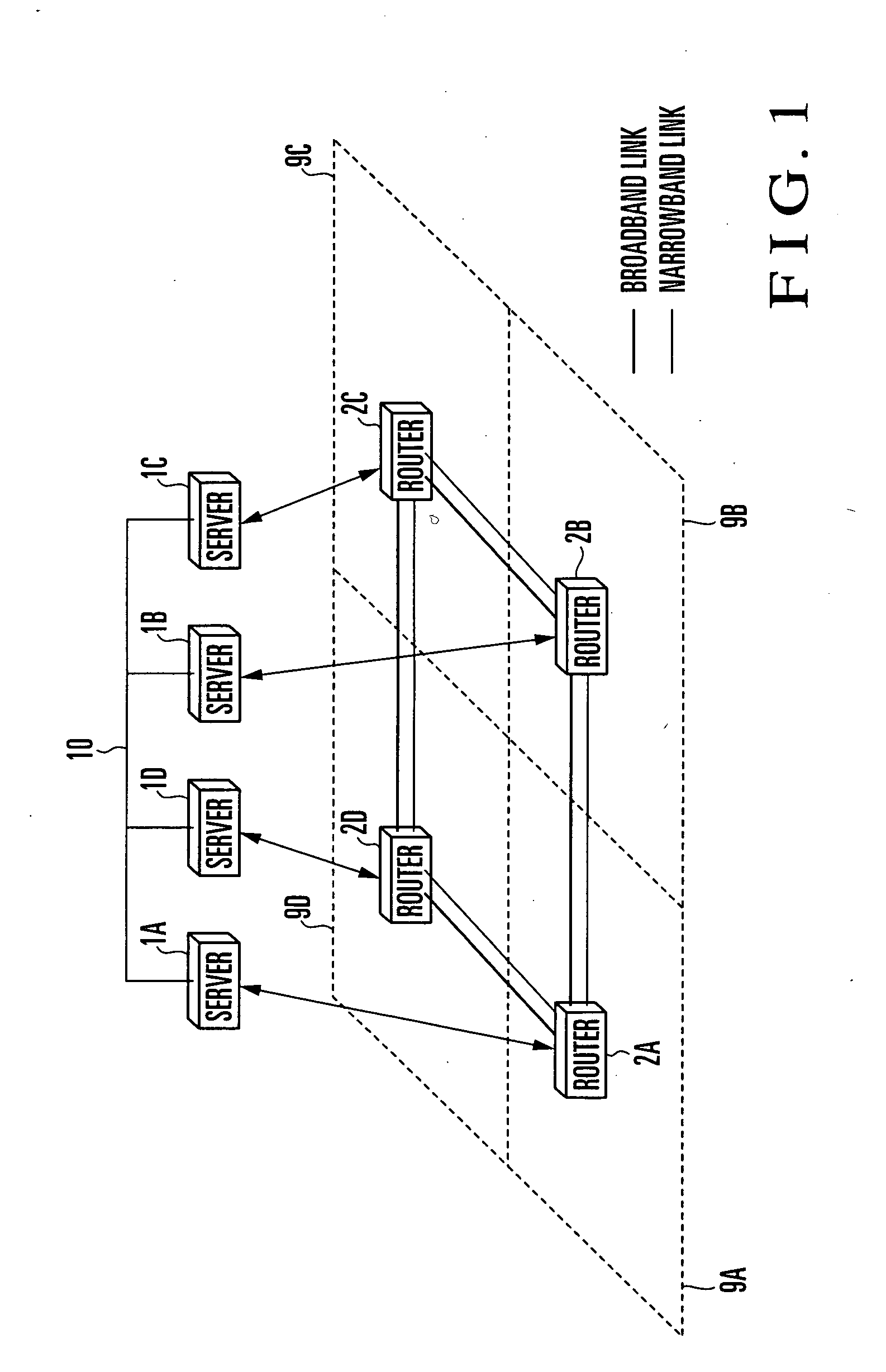
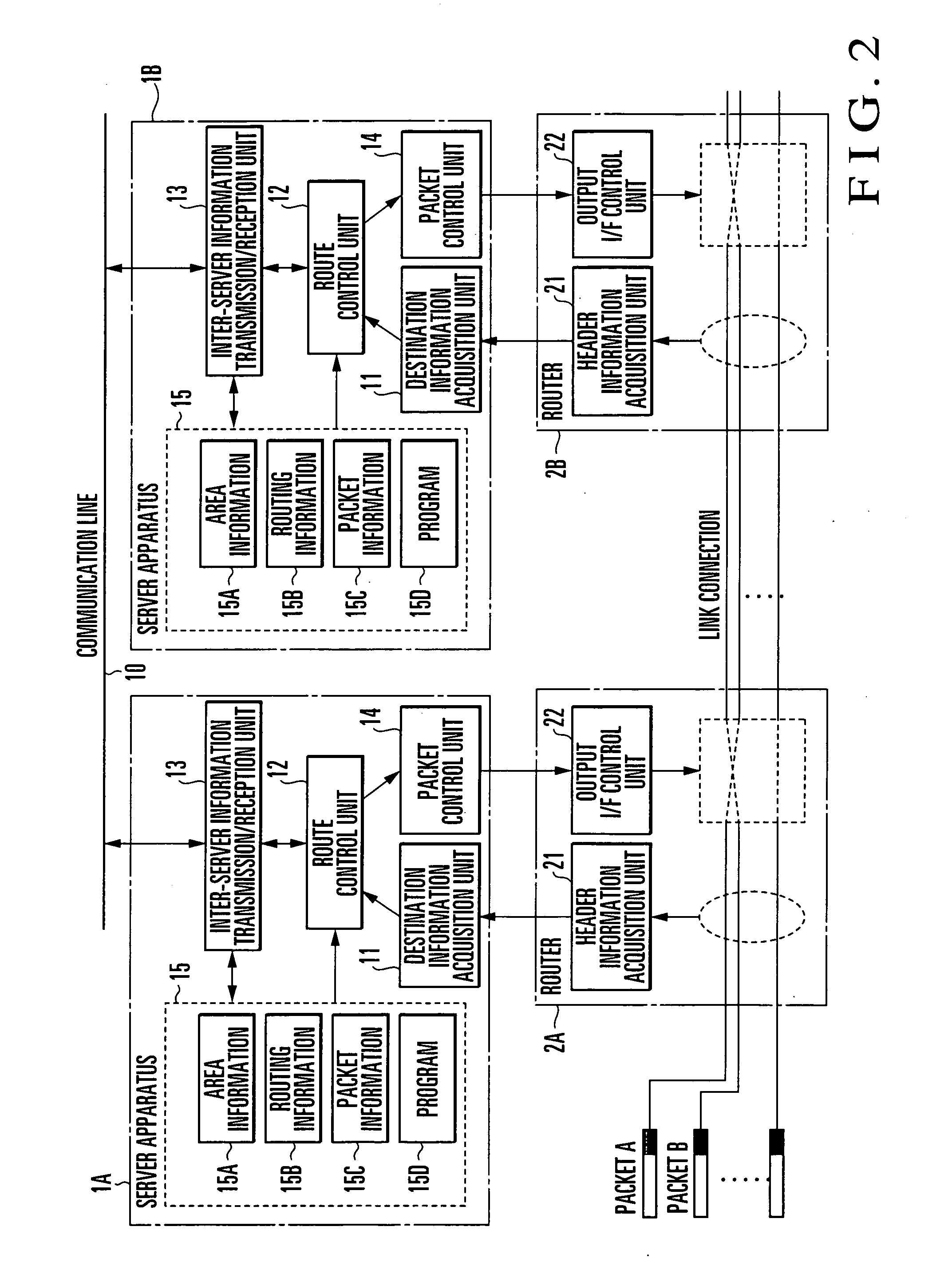
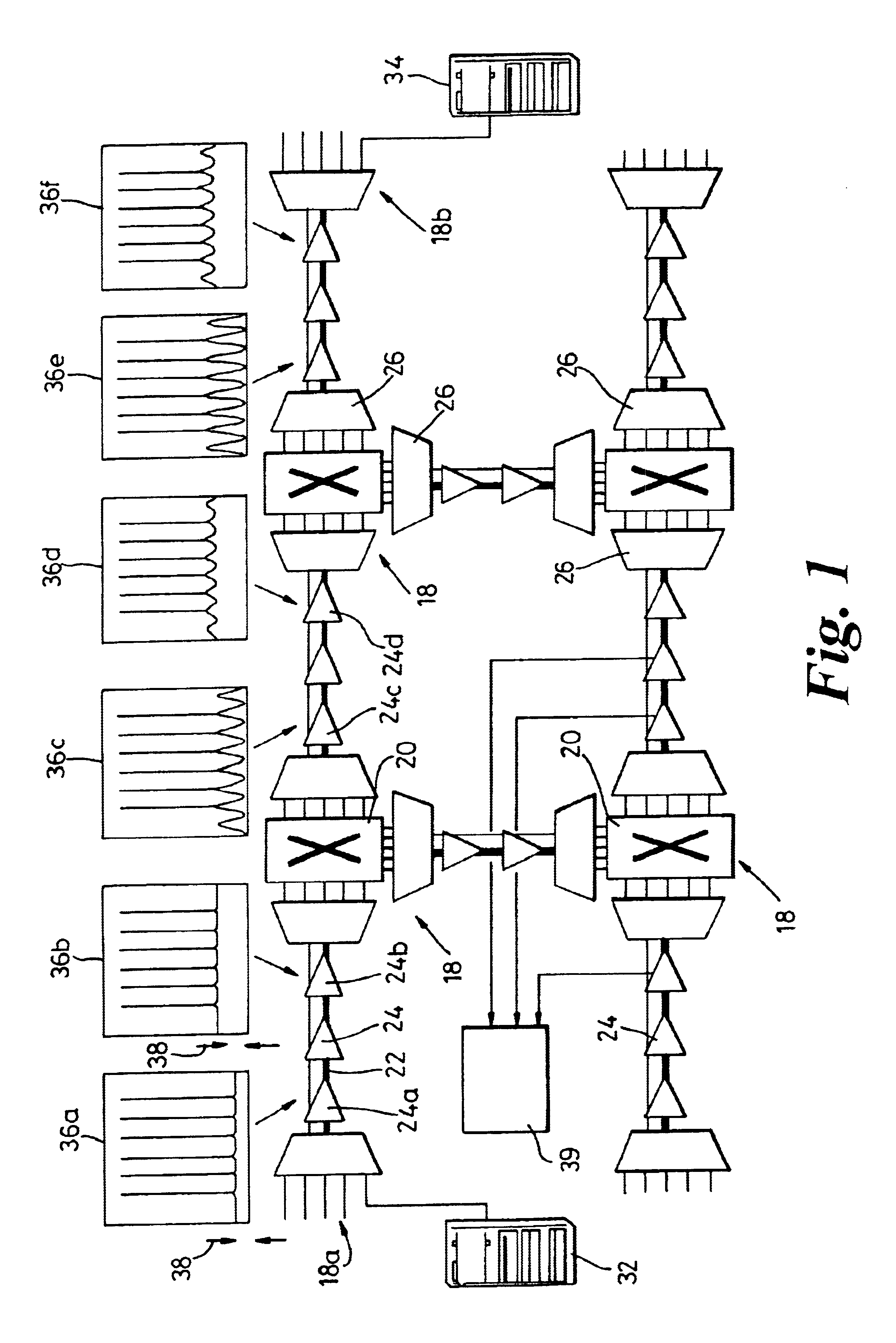
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Photonic network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Communications network
InactiveUS6714552B1Efficient routingSimple processTime-division optical multiplex systemsData switching by path configurationOptical packetNetwork routing
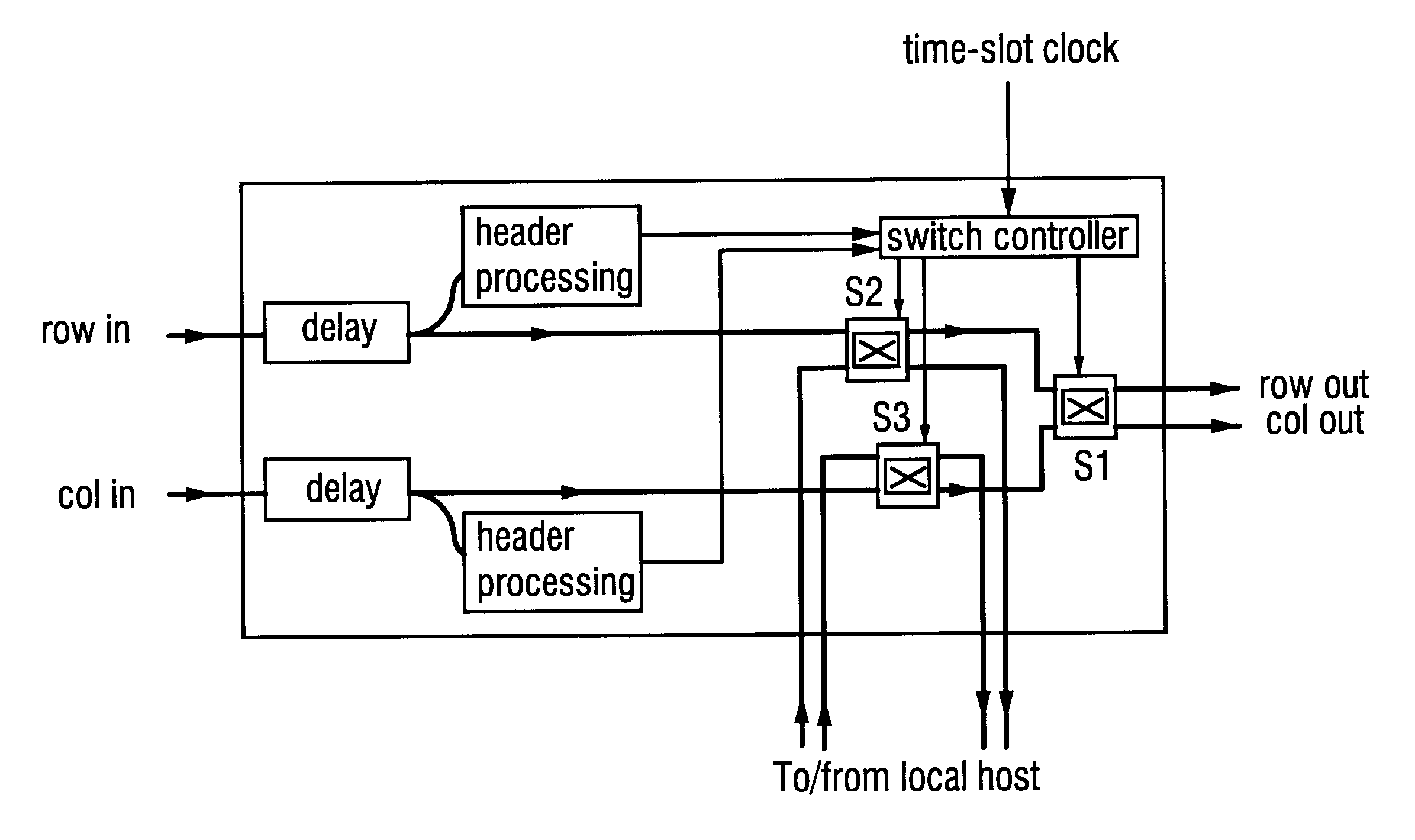
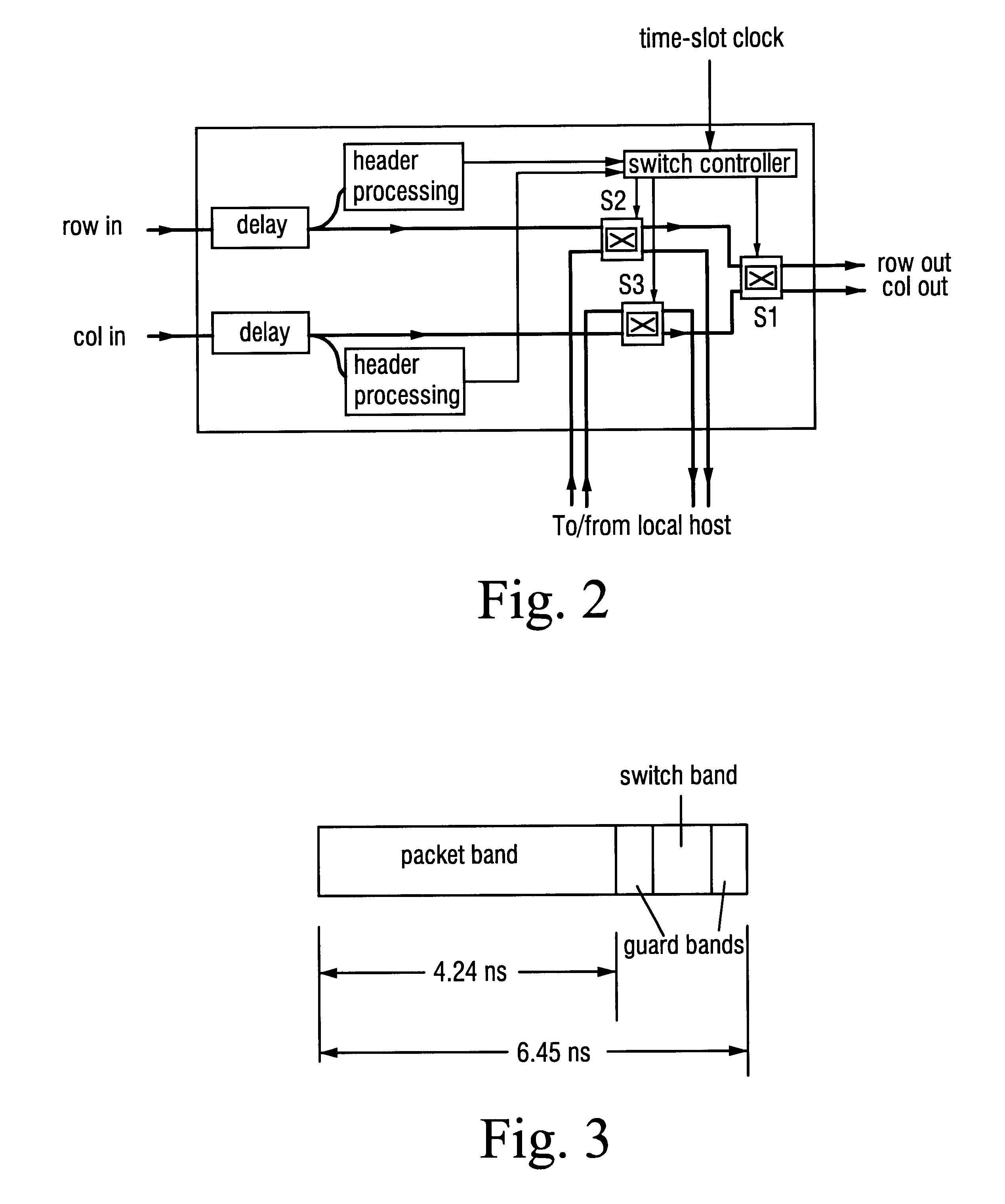
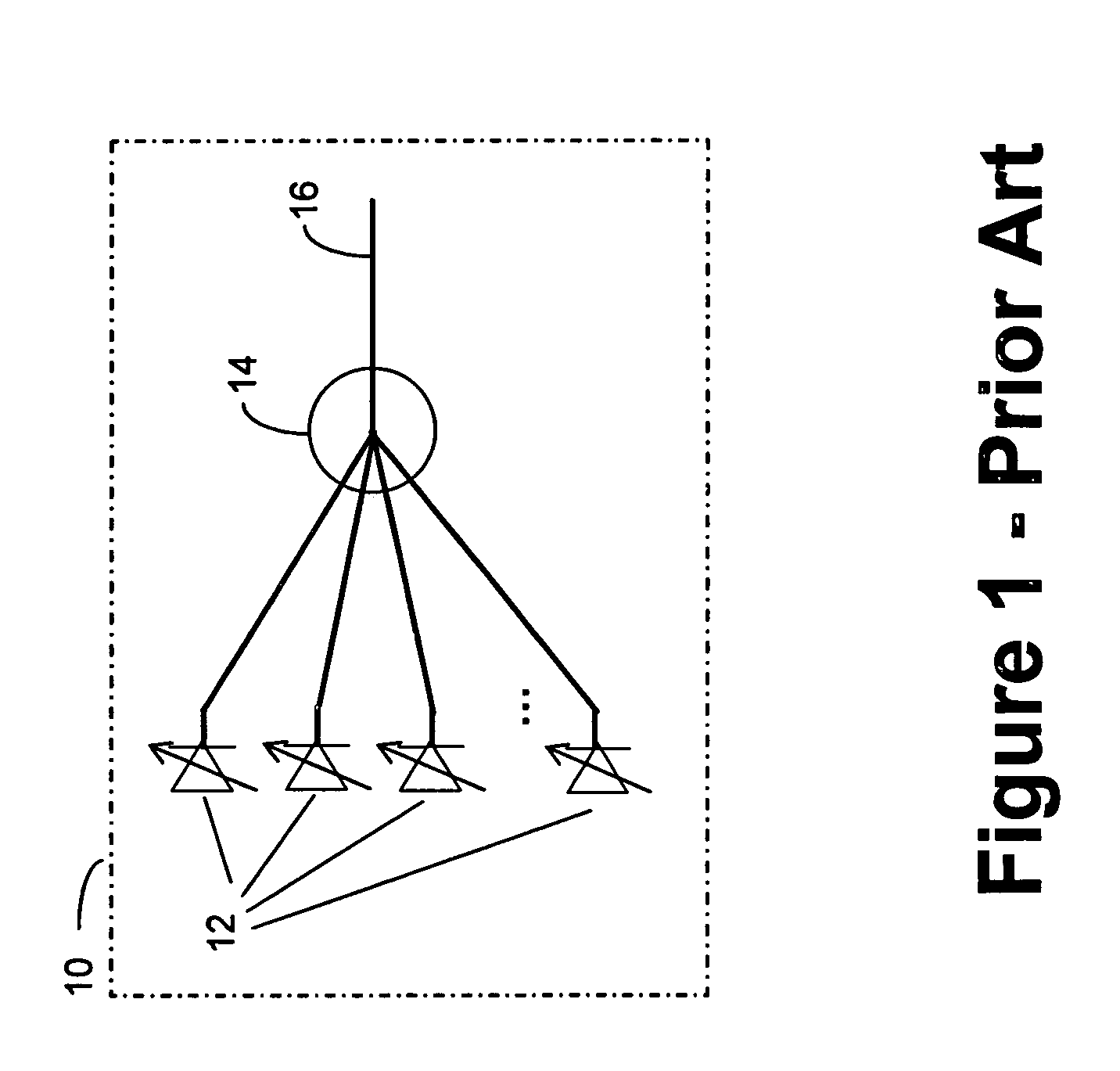
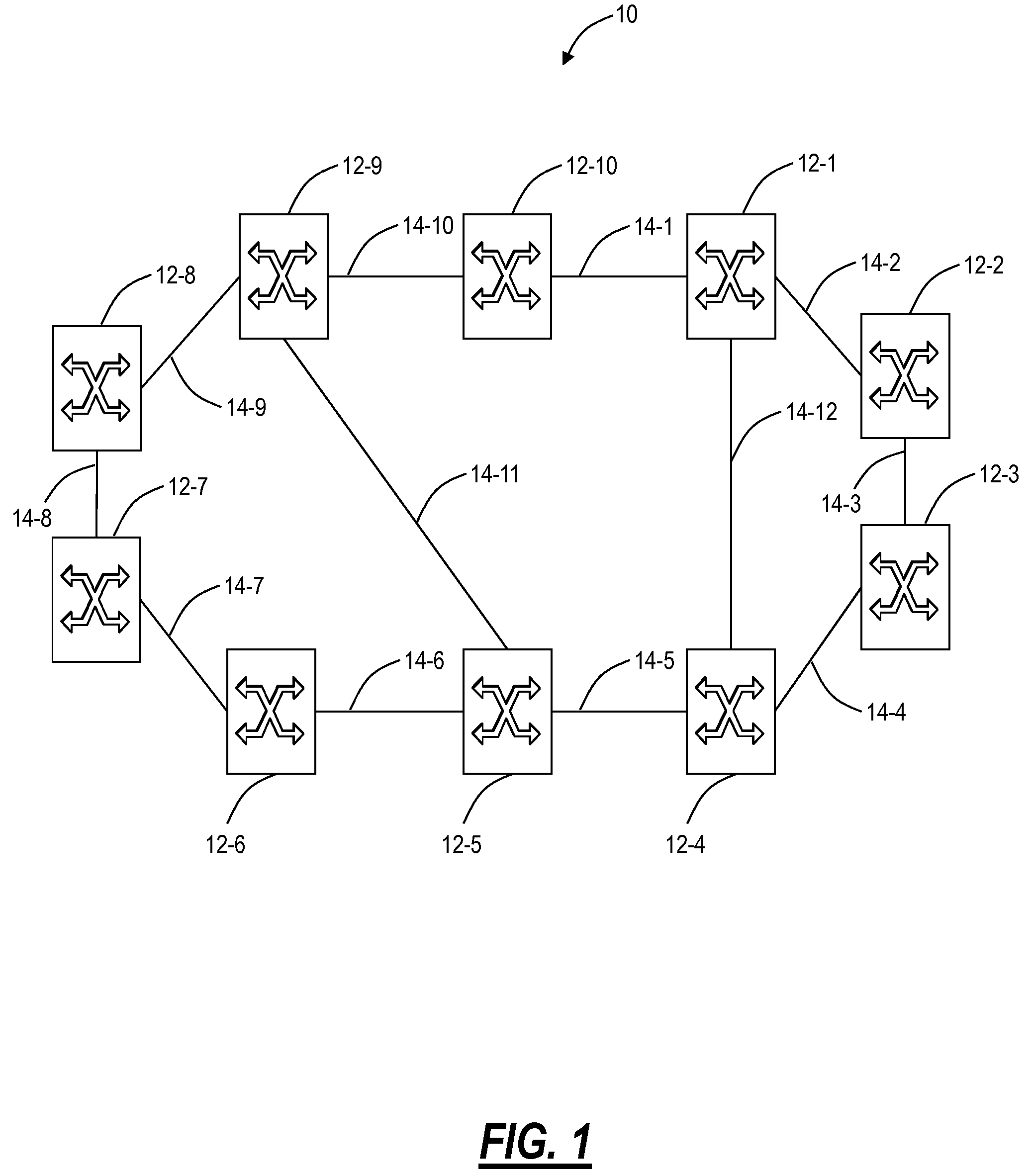
A communications network, suitable, for example, for linking computer processors, is formed from a number of nodes and links. The nodes and links are configured as a multiplicity of directed trails. Each directed trail spans some only of the nodes, but in combination the directed trails span every node of the network. Packets are routed through the network by selecting the appropriate one of the directed trails which links the source node and destination node, and by outputting the packet at the source node onto the selected trail. The nodes throughout the network may switch between predetermined and prescheduled switching states, and a given trail may be selected by choosing appropriately the time slot in which the packet is put onto the network. The network may be a photonic network carrying optical packets.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
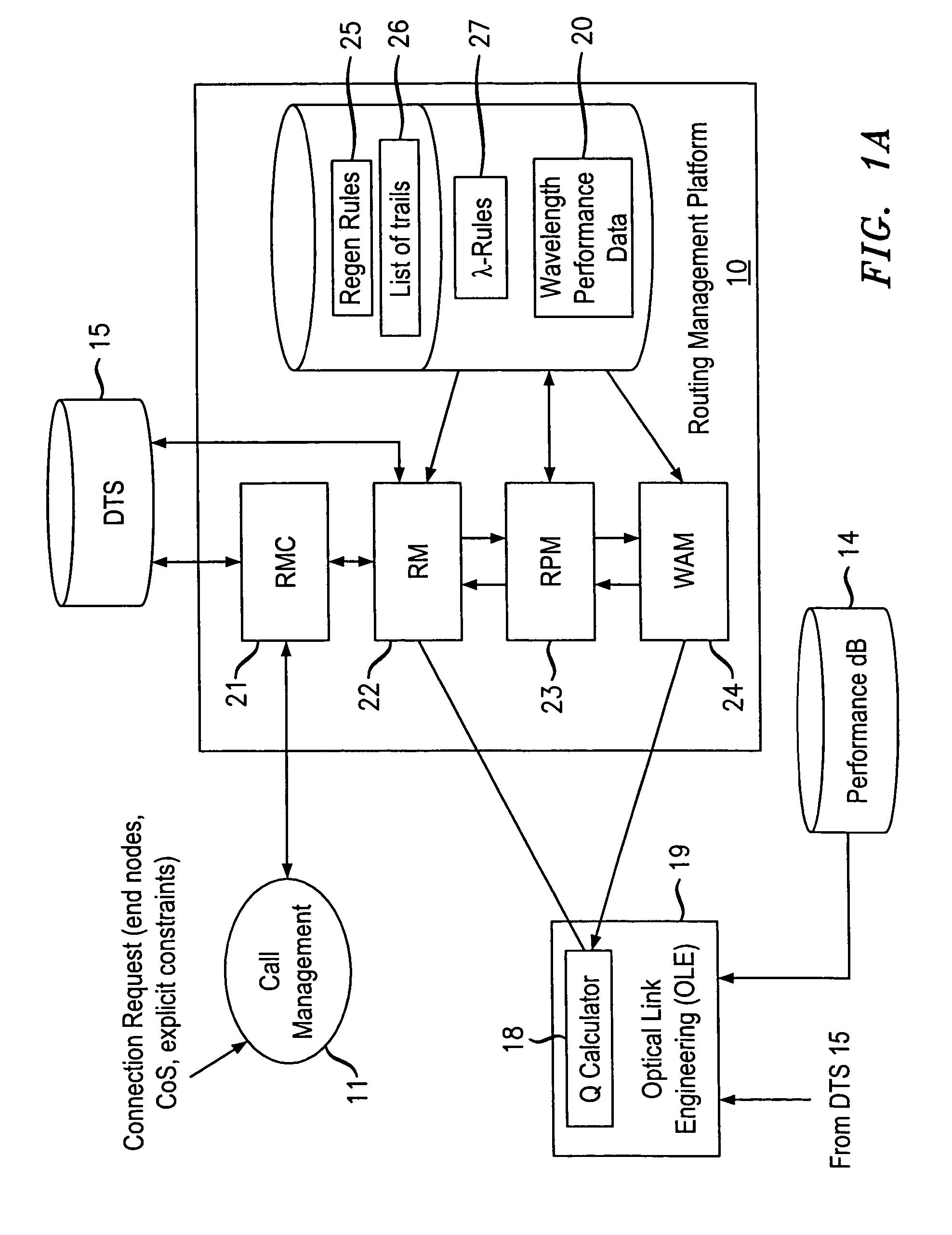
Architecture for dynamic connectivity in an edge photonic network architecture
ActiveUS7245829B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexerNetwork architecture
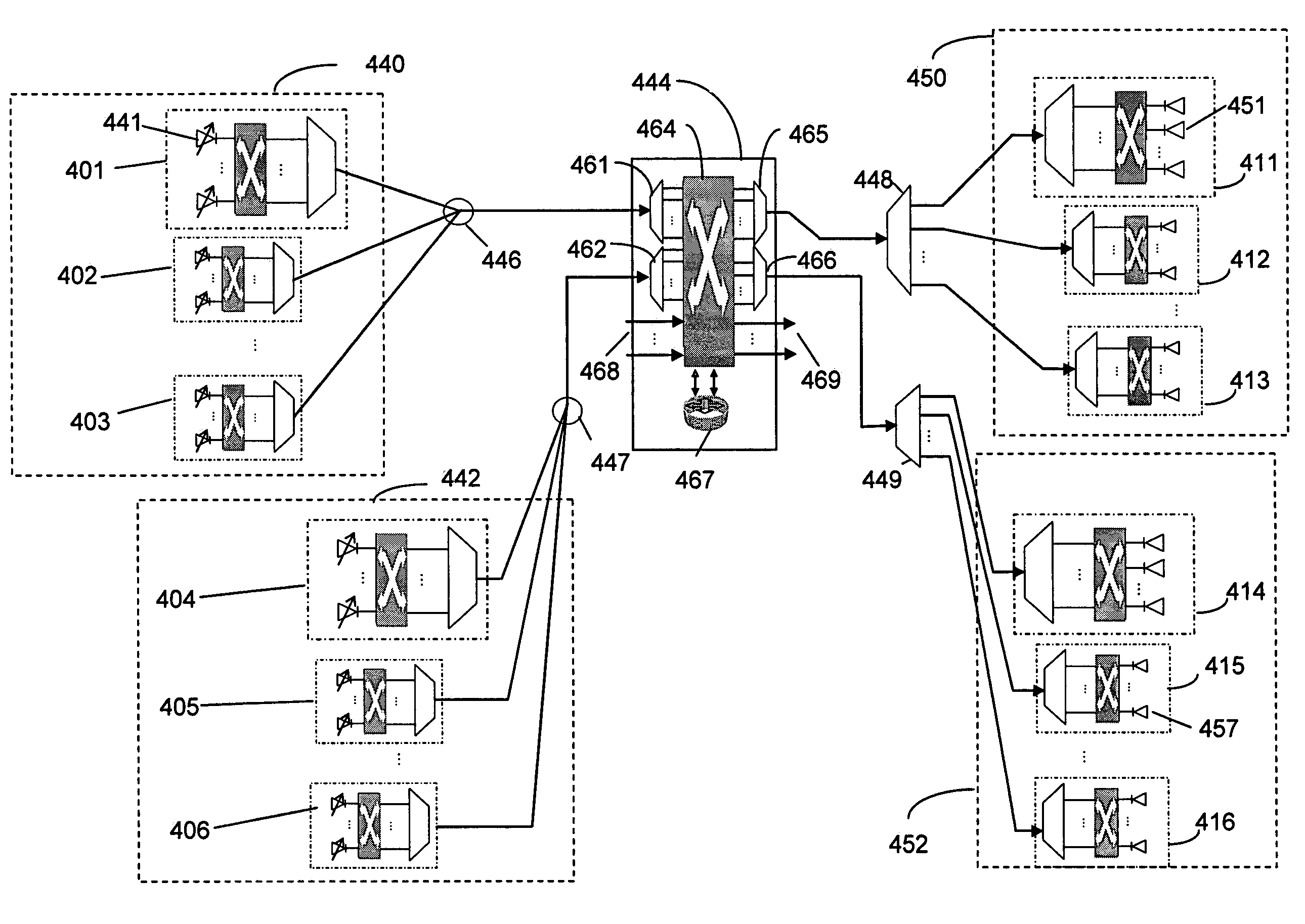
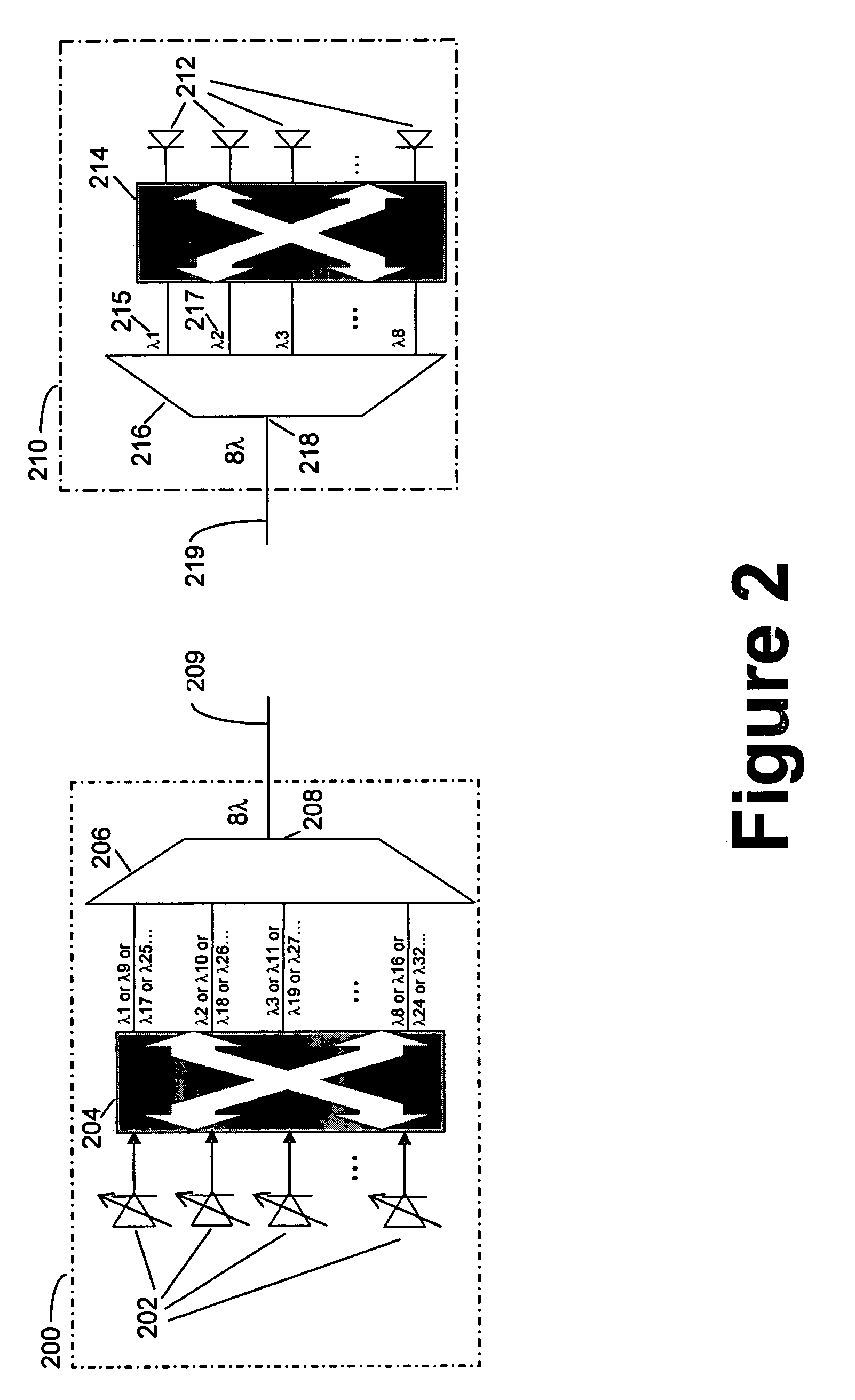
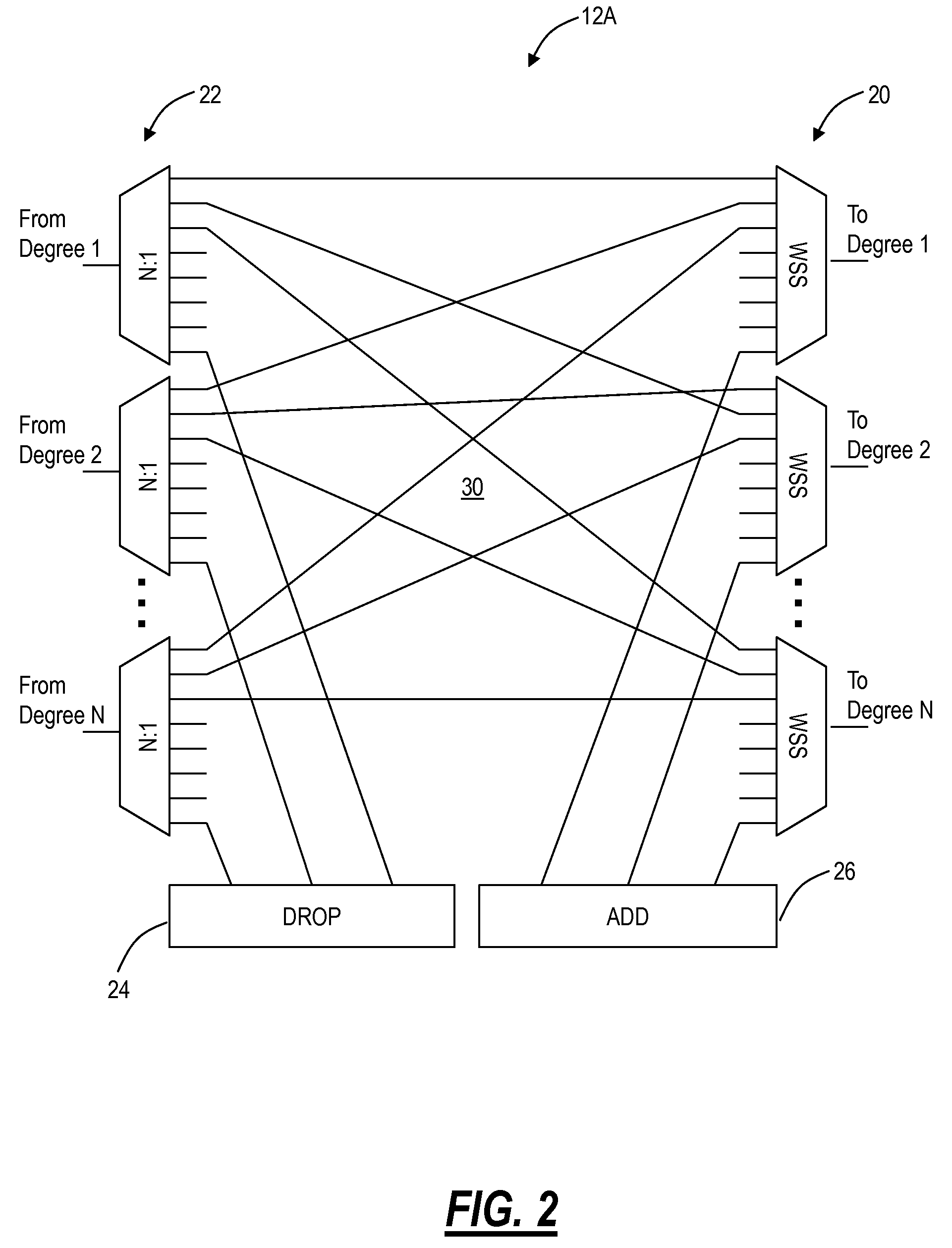
A network arrangement for aggregation of groups of tunable sources in a photonic network is disclosed. The network arrangement includes transmit edge elements having a plurality of tunable optical transmitters, an optical switch and a cyclic optical multiplexer, and receive edge elements having optical demultiplexers, optical switches and a plurality of optical receivers. A variety of arrangements are disclosed including protected and unprotected network architectures. The network arrangement disclosed is particularly useful for overcoming the problem of scaling a photonic network.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
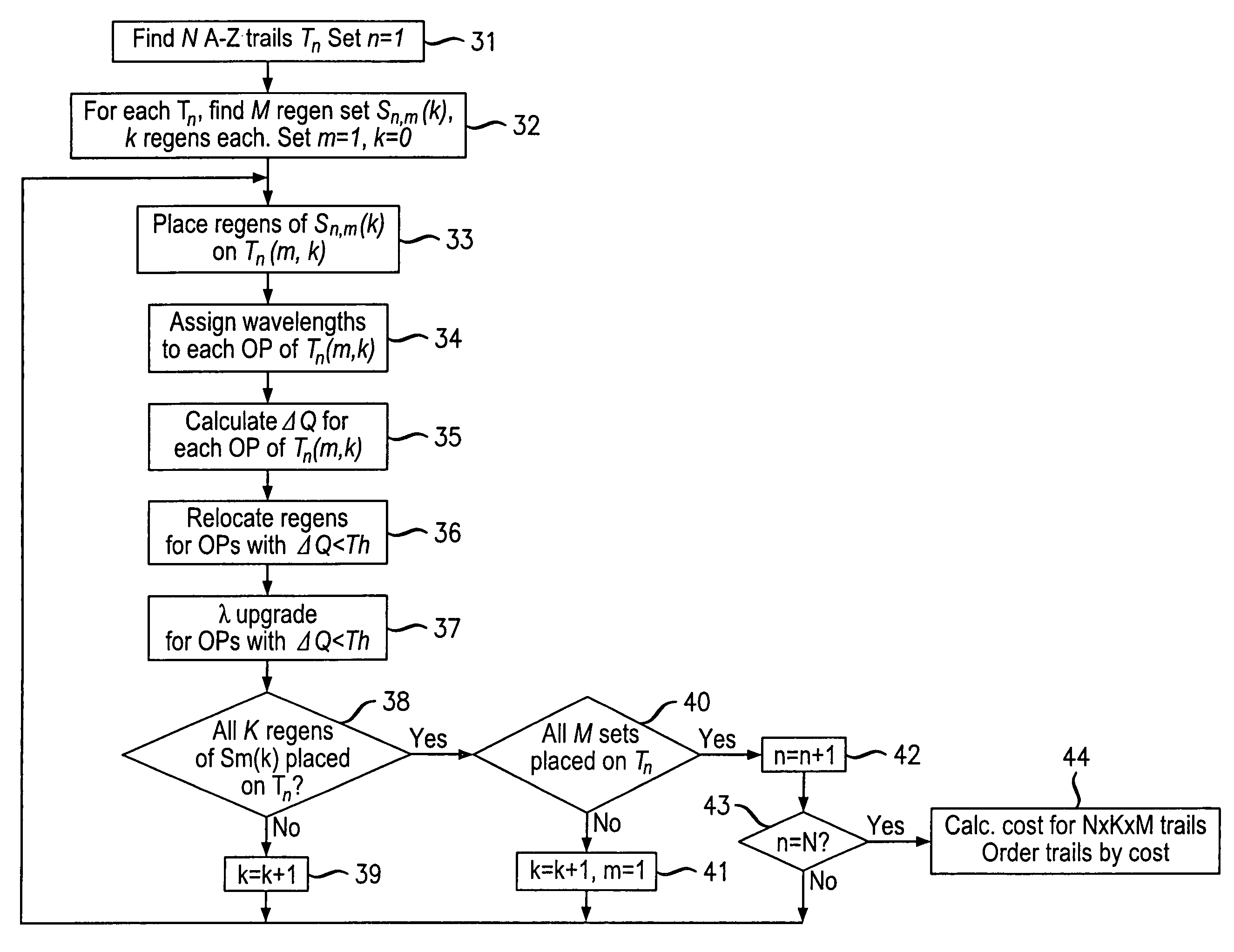
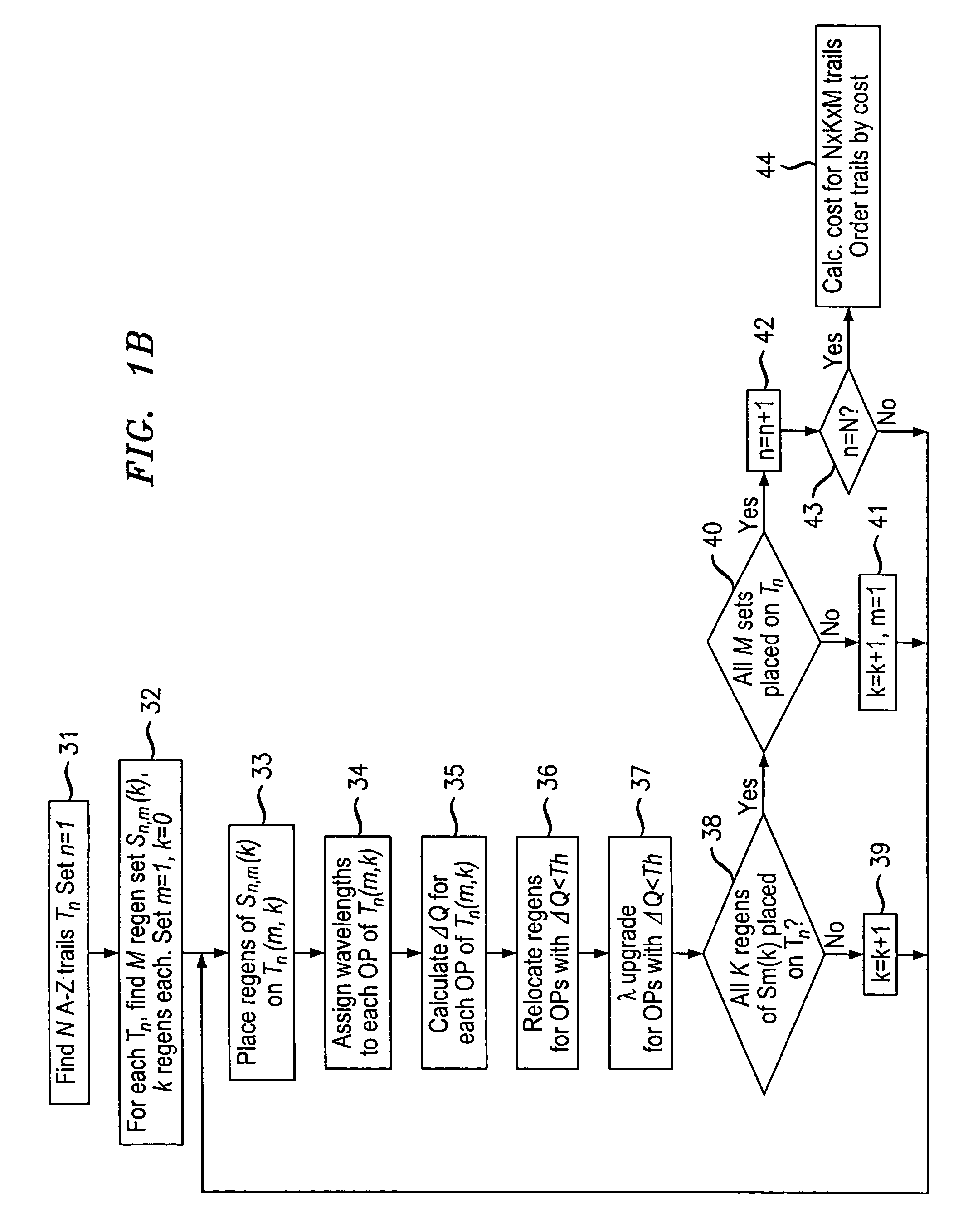
Wavelength routing and switching mechanism for a photonic transport network
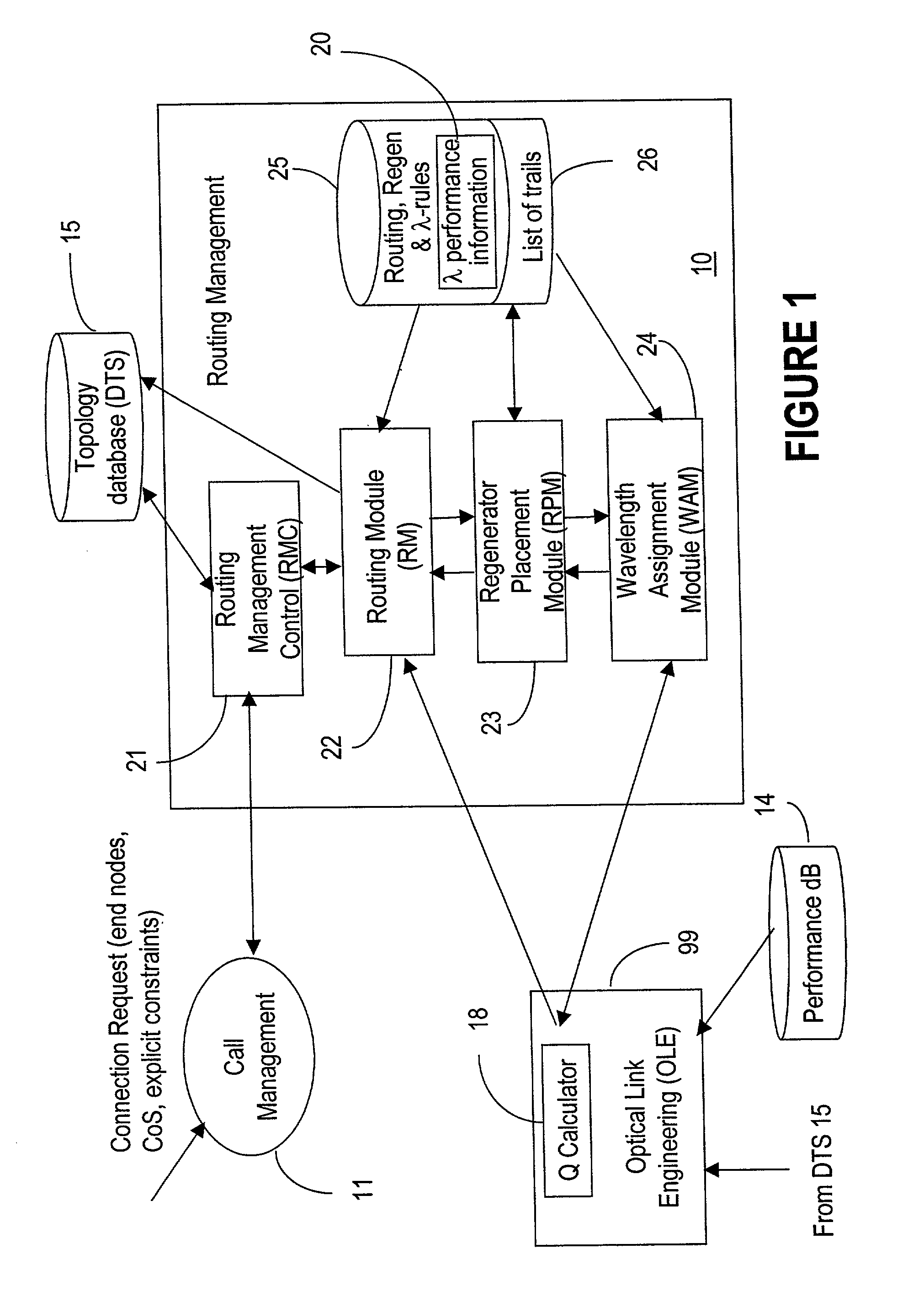
InactiveUS7171124B2Flexibility of provisioningLow costLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsPhoton transmissionAutomatic routing
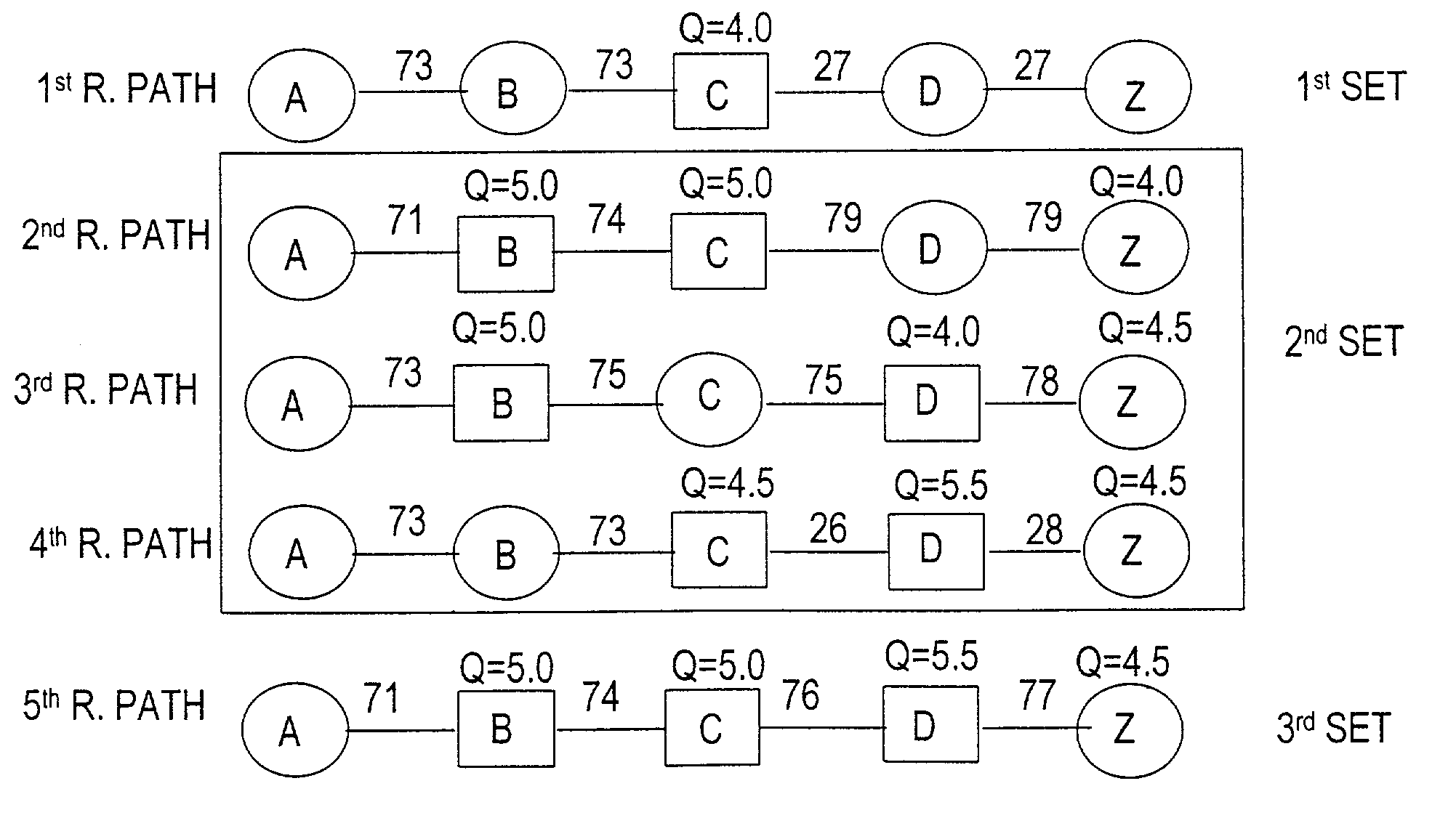
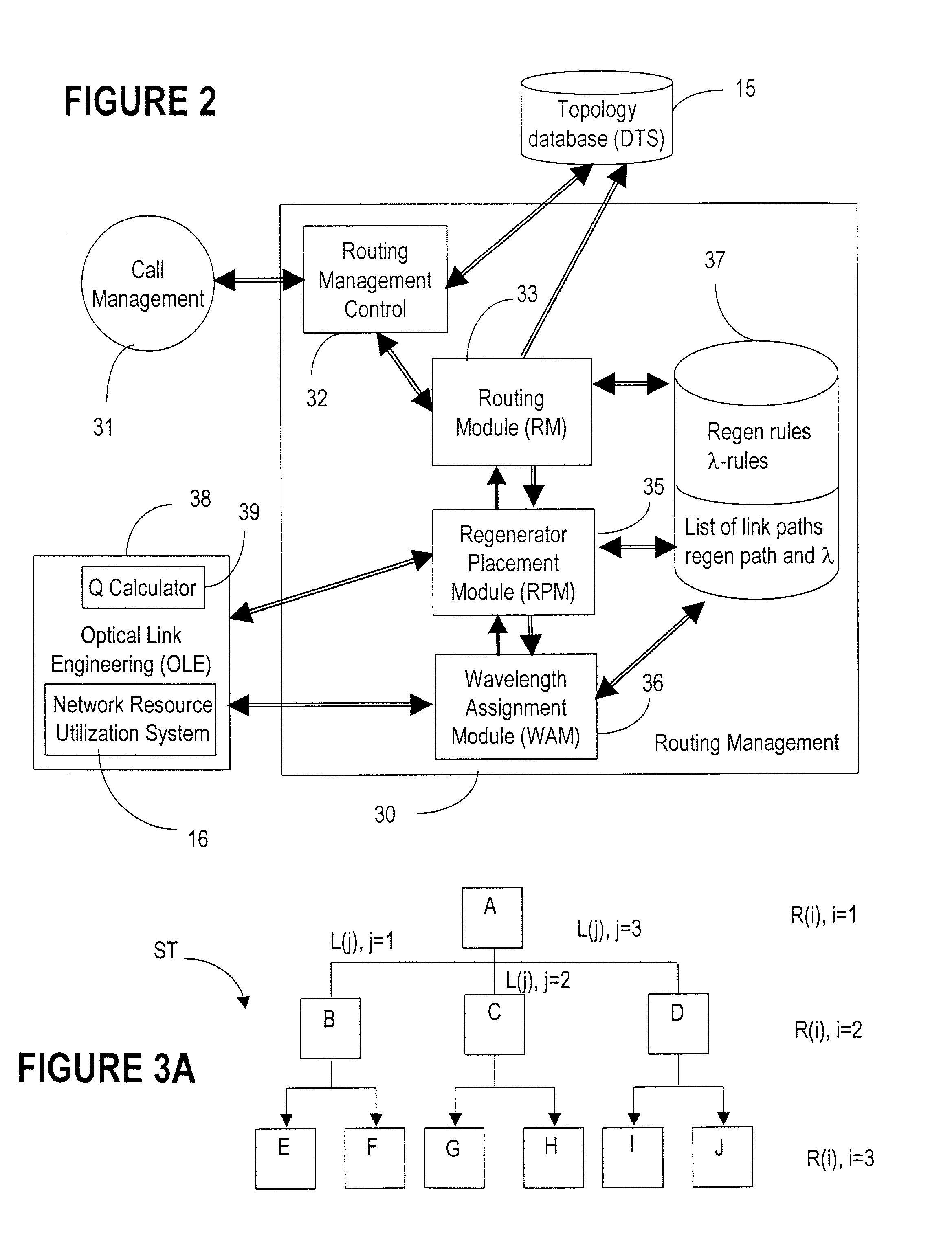
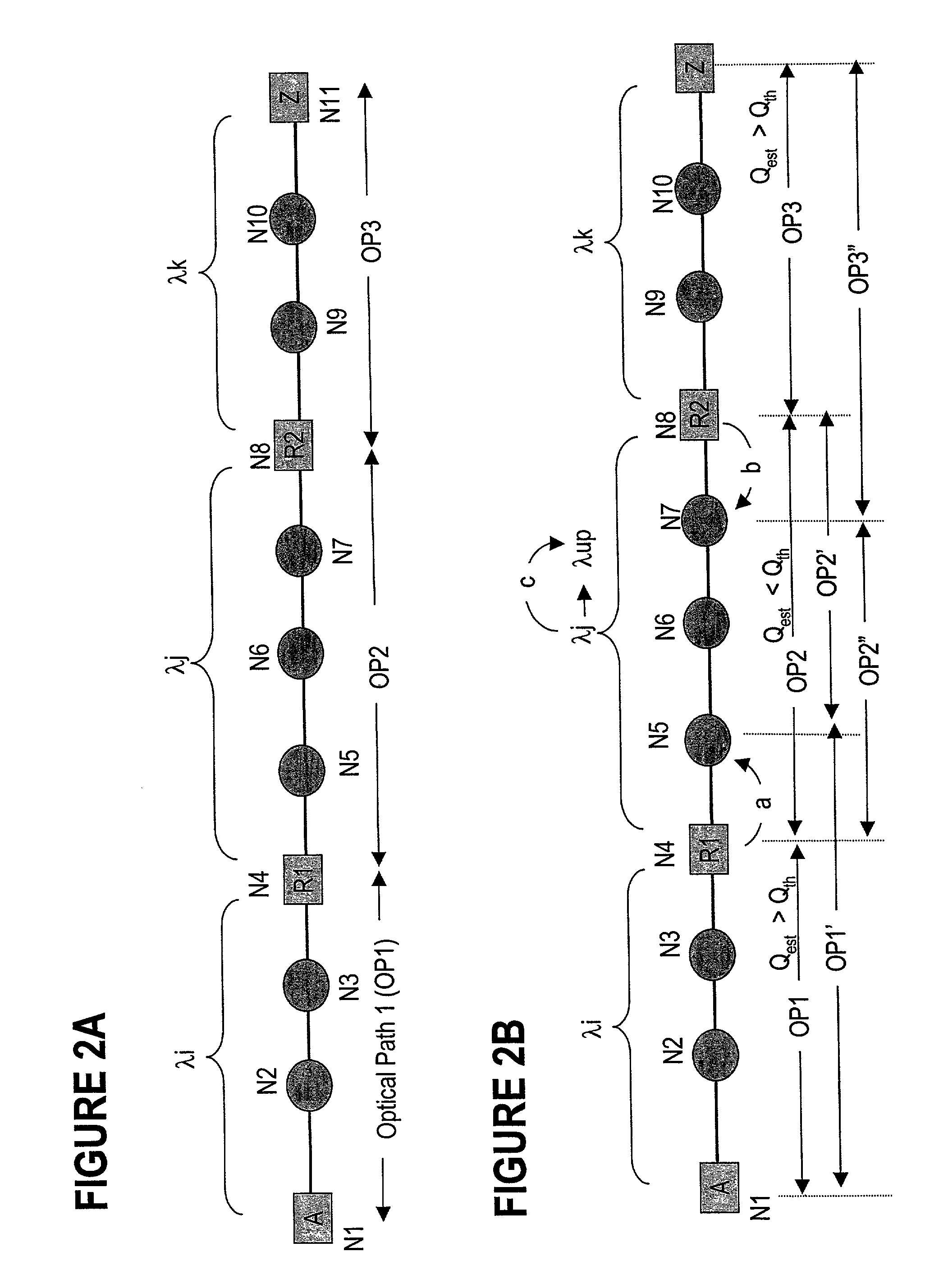
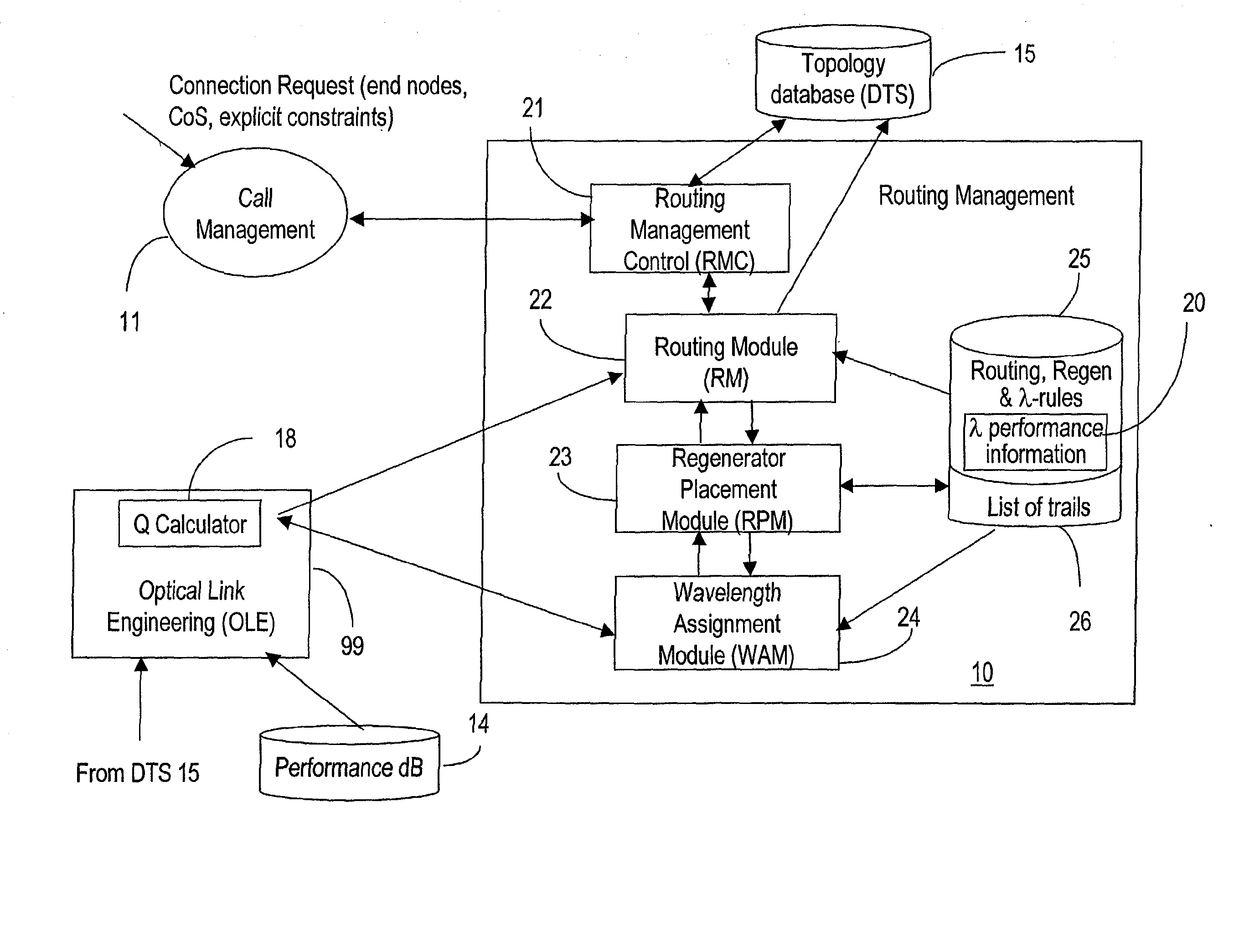
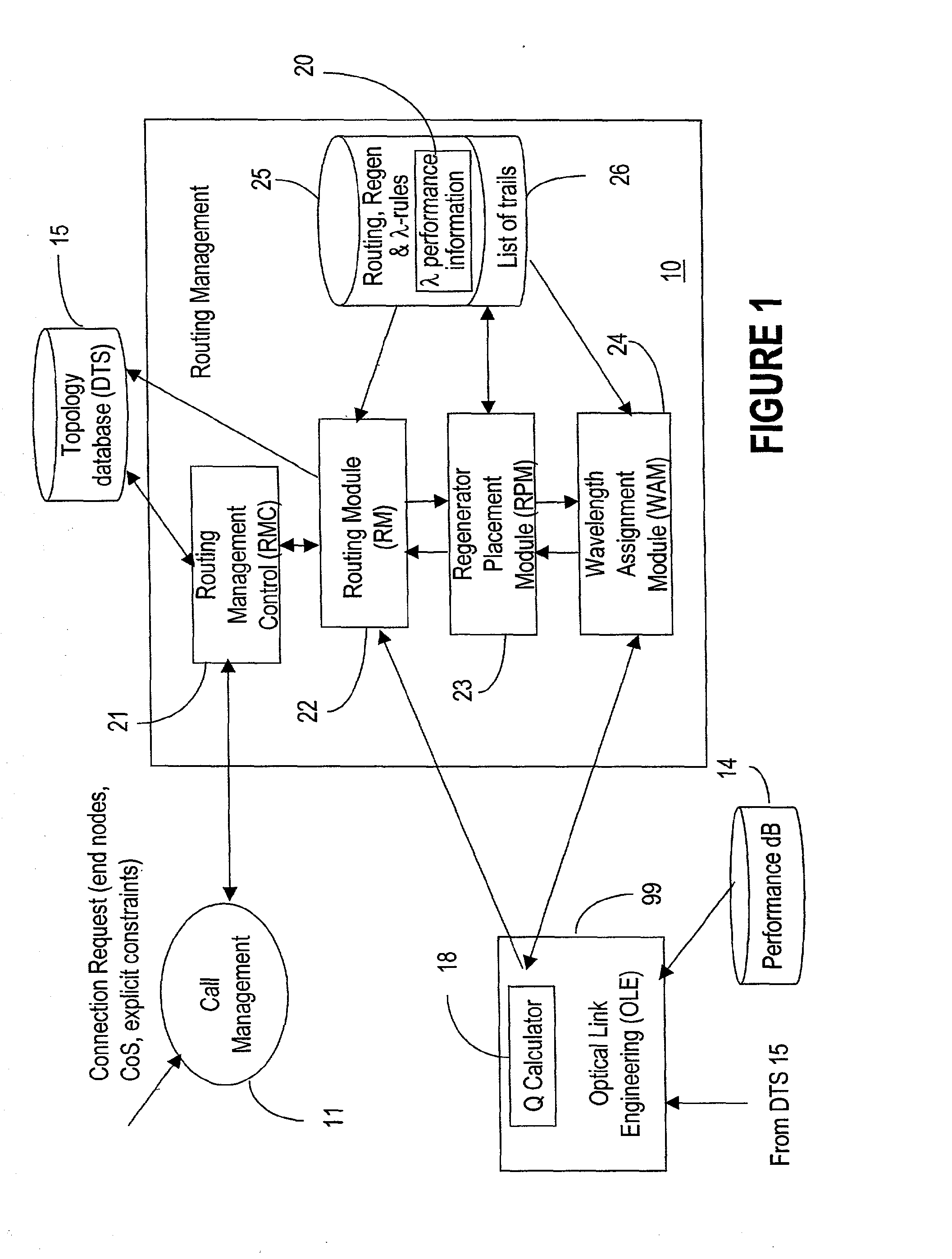
A connection between a source node and a destination node is automatically routed and switched in a WDM photonic network, on receipt of a connection request. A switching and routing mechanism selects a plurality of valid link paths using a path tree, where invalid branches are eliminated based on constraints received in the connection request, and on a link and path cost functions. A regenerator placement tree is used for determining a plurality of viable regenerator paths for each valid link path. On the regenerator placement tree, non-viable branches are eliminated based on constraints received with the request and on regenerator availability at the intermediate nodes along the respective path, and on the specification of these available regenerators. Next, the switching and routing mechanism assigns a set of wavelengths to each viable regenerator path, and estimates the performance of the path using a Q estimator. The regenerator paths are ordered according to their performance and the switching and routing mechanism attempts to setup a paths to serve the request, starting with the best path.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Hybrid photonic crystal fiber, and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20140178023A1Efficient manufacturing processKeep sizeGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreUltra-widebandFluorescence
The present invention relates to a hybrid photonic crystal fiber, into the core of which a functional material is injected. The hybrid photonic crystal fiber of the present invention comprises: a central hole having a diameter of 4 to 15 μm extending in the longitudinal direction; an inner cladding also formed in the longitudinal direction outside the central hole, having a hexagonal arrangement of air holes, each of which has a diameter of 2 to 5 μm and a lattice constant of 4.5 to 7 μm; an annular outer cladding surrounding the outer surface of the inner cladding; and a core formed by filling a functional material in some of the air holes including the central hole. According to the present invention, changes in the state, i.e. the liquid, liquid-crystal, or biofluid states, of the functional material that fills the core that has a variety of shapes may enable the modulation of light intensity, wavelength, phase, and polarization, and thus enable various photonic networks to be produced. The hybrid photonic crystal fiber of the present invention may serve as various optical sensors capable of sensing changes in refractive index caused by external stresses such as temperature and pressure. The hybrid photonic crystal fiber of the present invention may be used as a light source for a fluorescent dye laser for a visible ray zone using fluorescent dye, or for an ultra-wideband laser of 700 nm or higher using high nonlinear liquid.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Method of and system for routing in a photonic network
A method of and system for determining a path through which to route a connection in a photonic network in which optically viable photonic paths of one or more physical links are determined and considered as “virtual” links in a “virtual” topology. Routing is then performed using the “virtual” topology rather than the physical topology to compute “virtual” paths of one or more “virtual” links.
Owner:CIENA
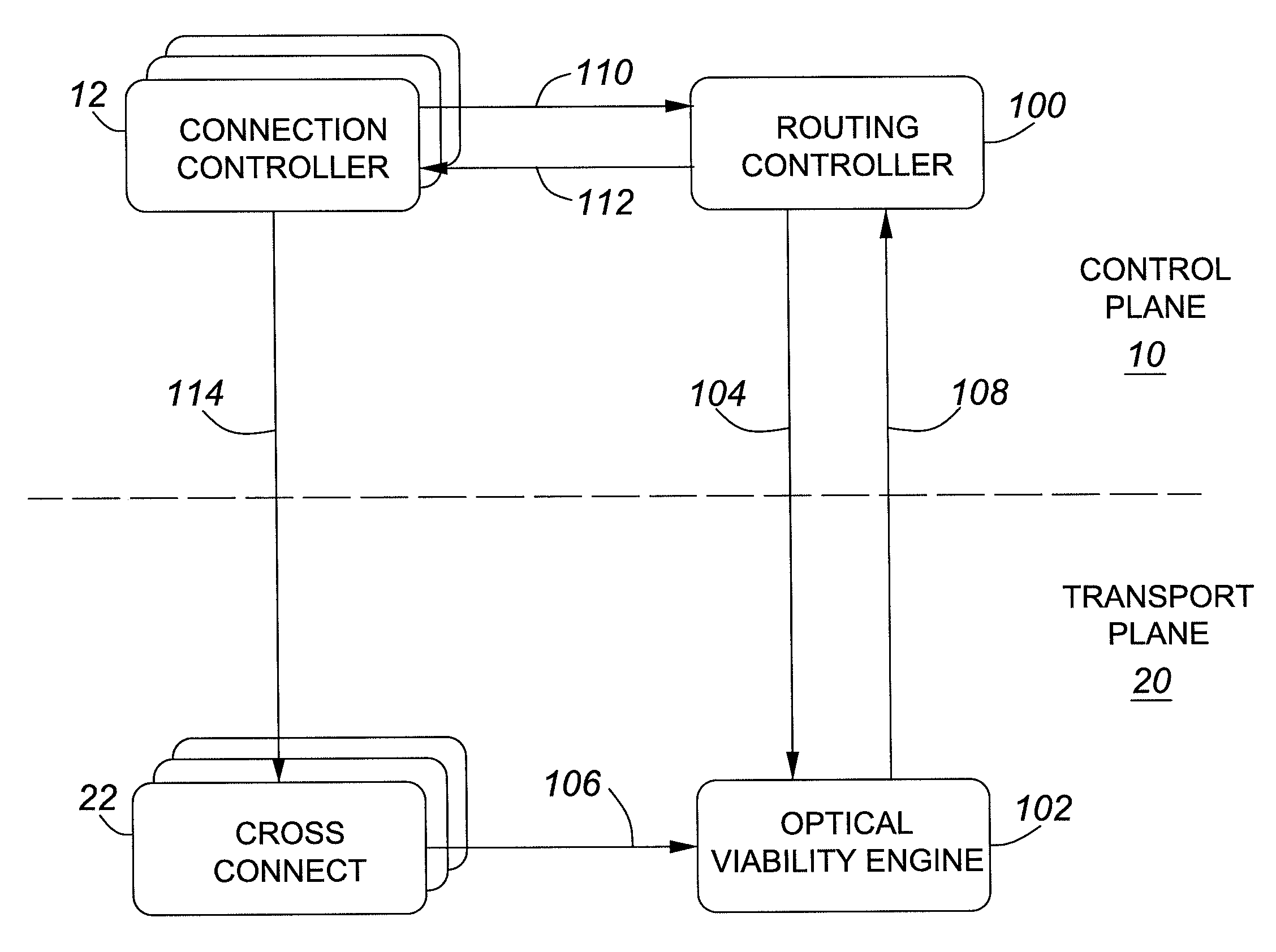
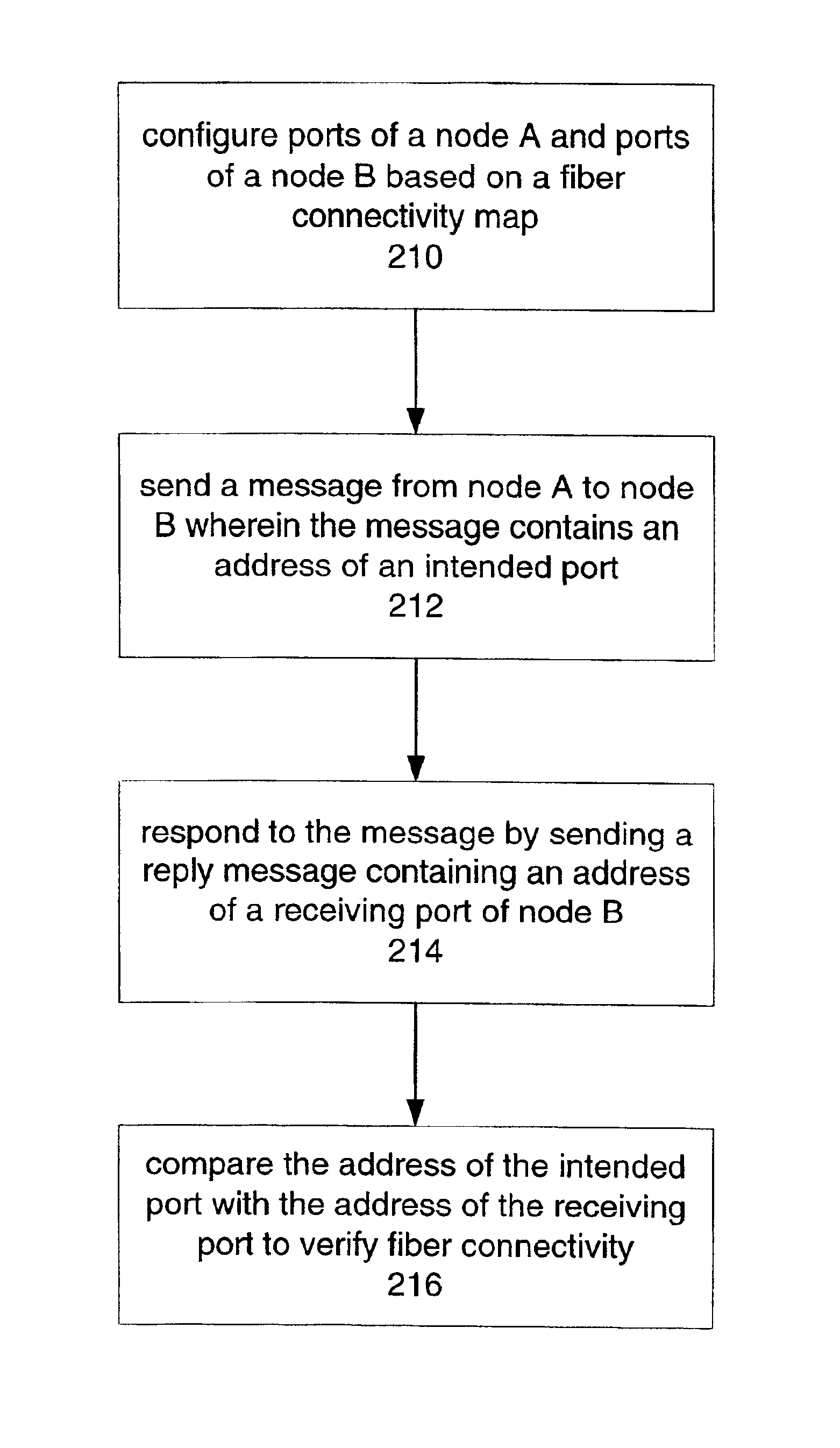
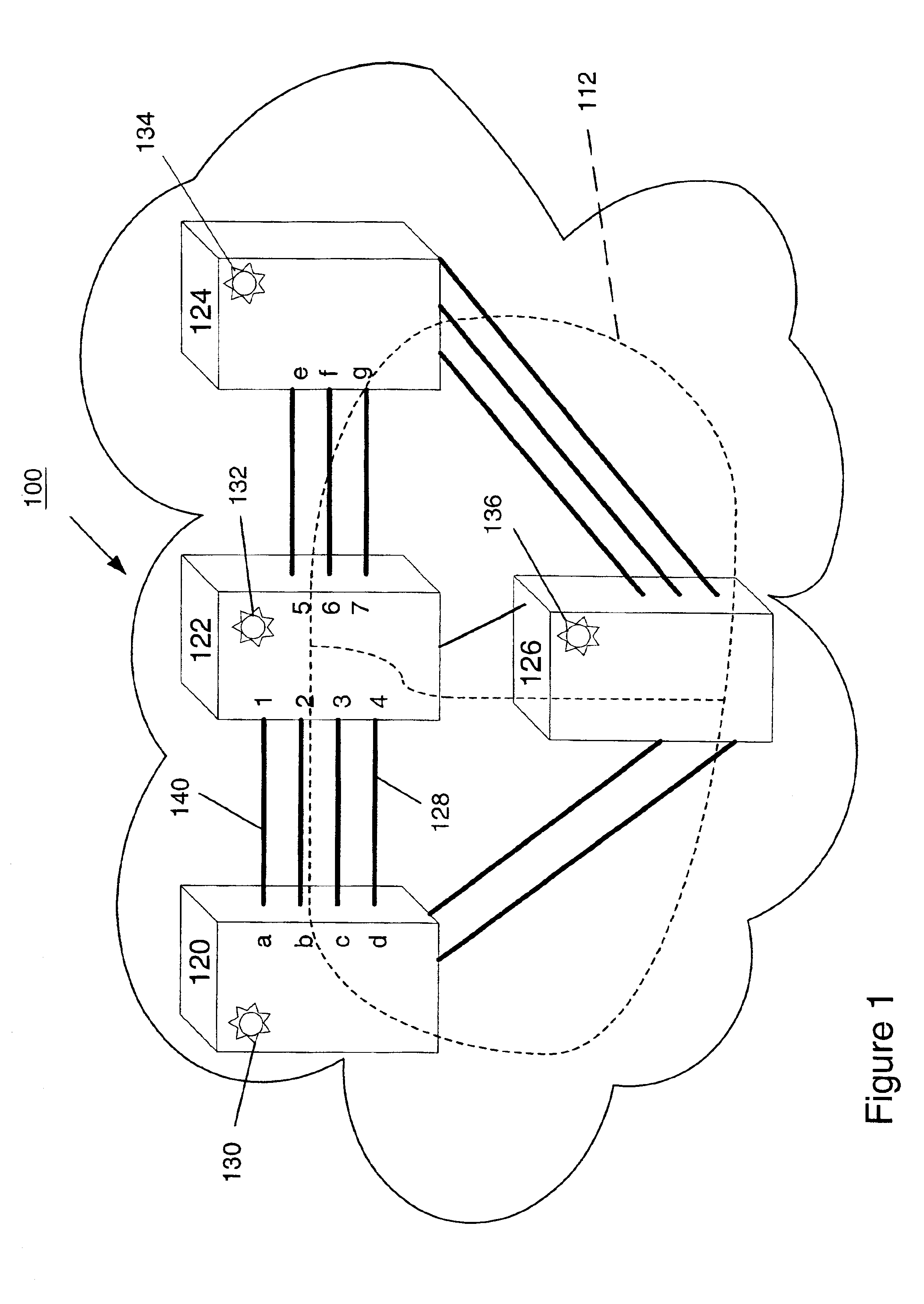
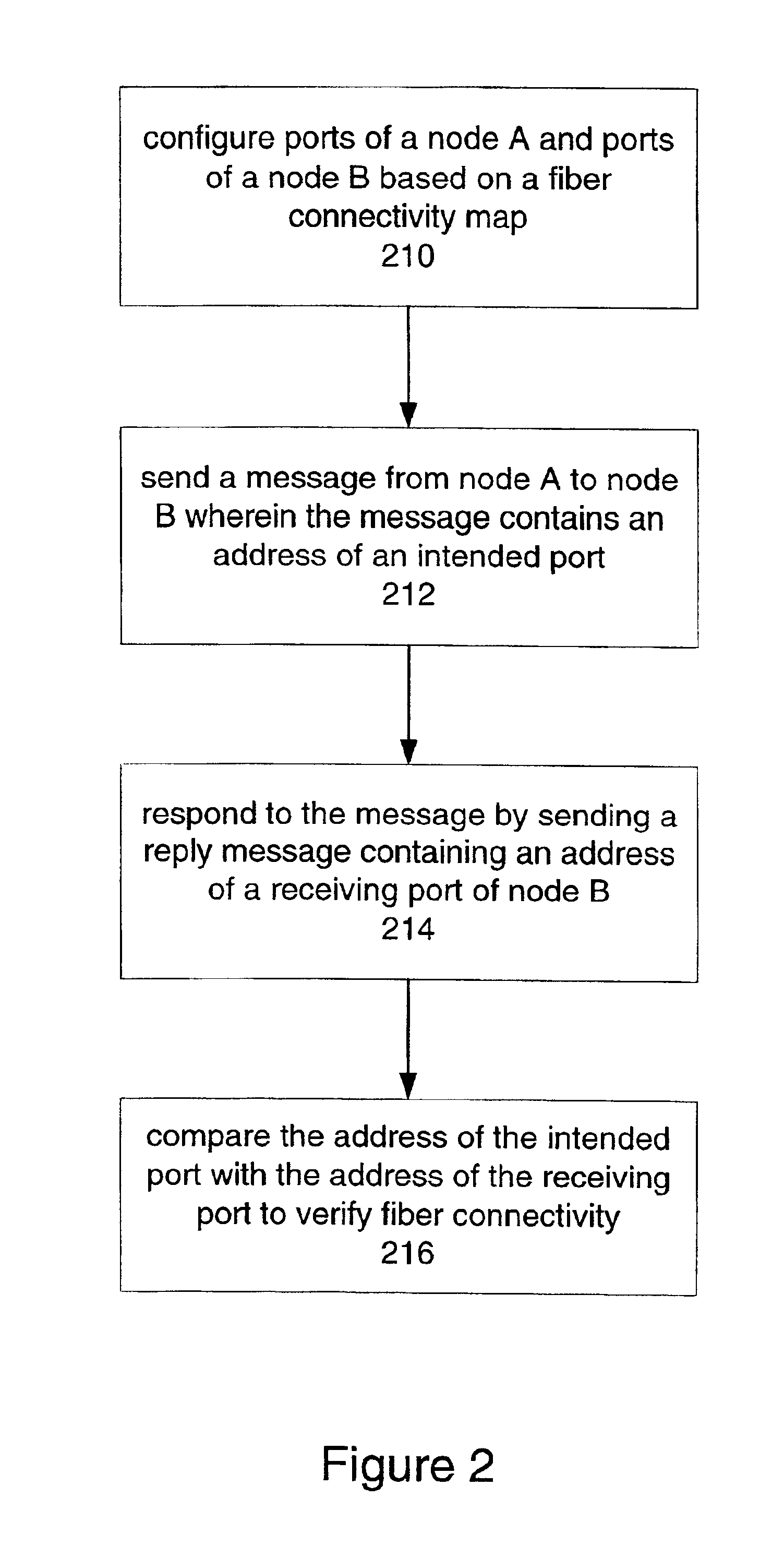
Technique for verifying fiber connectivity in a photonic network
ActiveUS6917763B1Guaranteed maximum utilizationTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsFiberComputer network
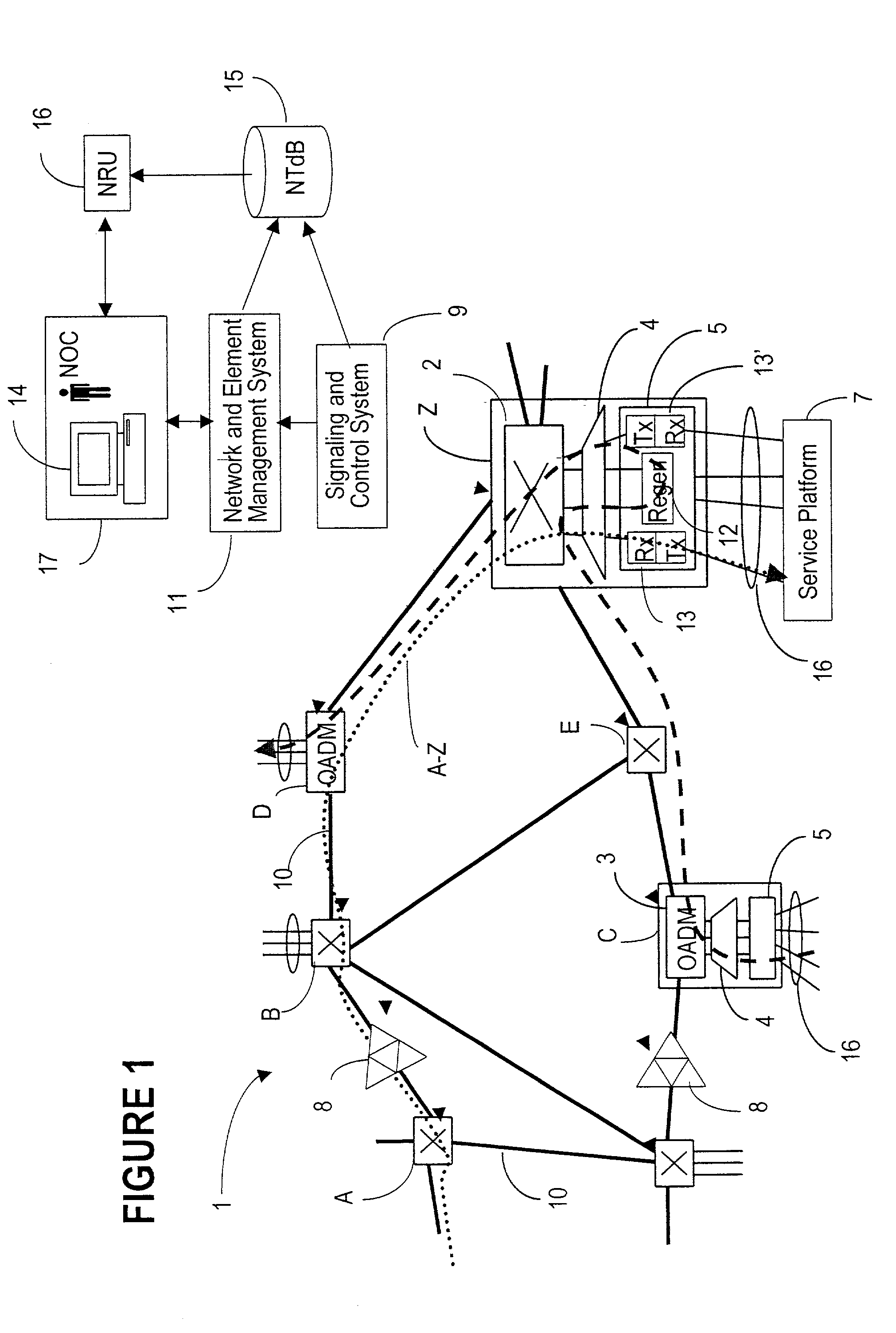
A technique for verifying fiber connectivity via an optical supervisory channel in a photonic network is disclosed. In one embodiment, the technique is realized by sending a first message from the first node to the second node, wherein the first message includes an address of an intended port of the second node; receiving a second message at the first node from the second node in response to the first message, wherein the second message contains an address of a receiving port of the second node; and comparing the intended port of the second node and the receiving port of the second node for verifying fiber connectivity between the first node and the second node.
Owner:CIENA
Method and apparatus for photonic resiliency of a packet switched network
A resilient photonic network includes a plurality of resilient switching nodes, each node comprising a photonic switch and one of a Layer-2 / 3 switch and router, and a plurality of bi-directional ports, each connected between the photonic switch the one of a Layer-2 / 3 switch and router, wherein at least one optical signal having a specific wavelength is transmitted through a first network port of a first one of the plurality of resilient switching nodes to an adjacent second one of the plurality of resilient switching nodes and the at least one optical signal is transmitted through a second network port of the first one of the plurality of resilient switching nodes to an adjacent third one of the plurality of resilient switching nodes to establish a bi-directional connectivity between the first, second, and third pluralities of resilient switching nodes.
Owner:KOLEY BIKASH
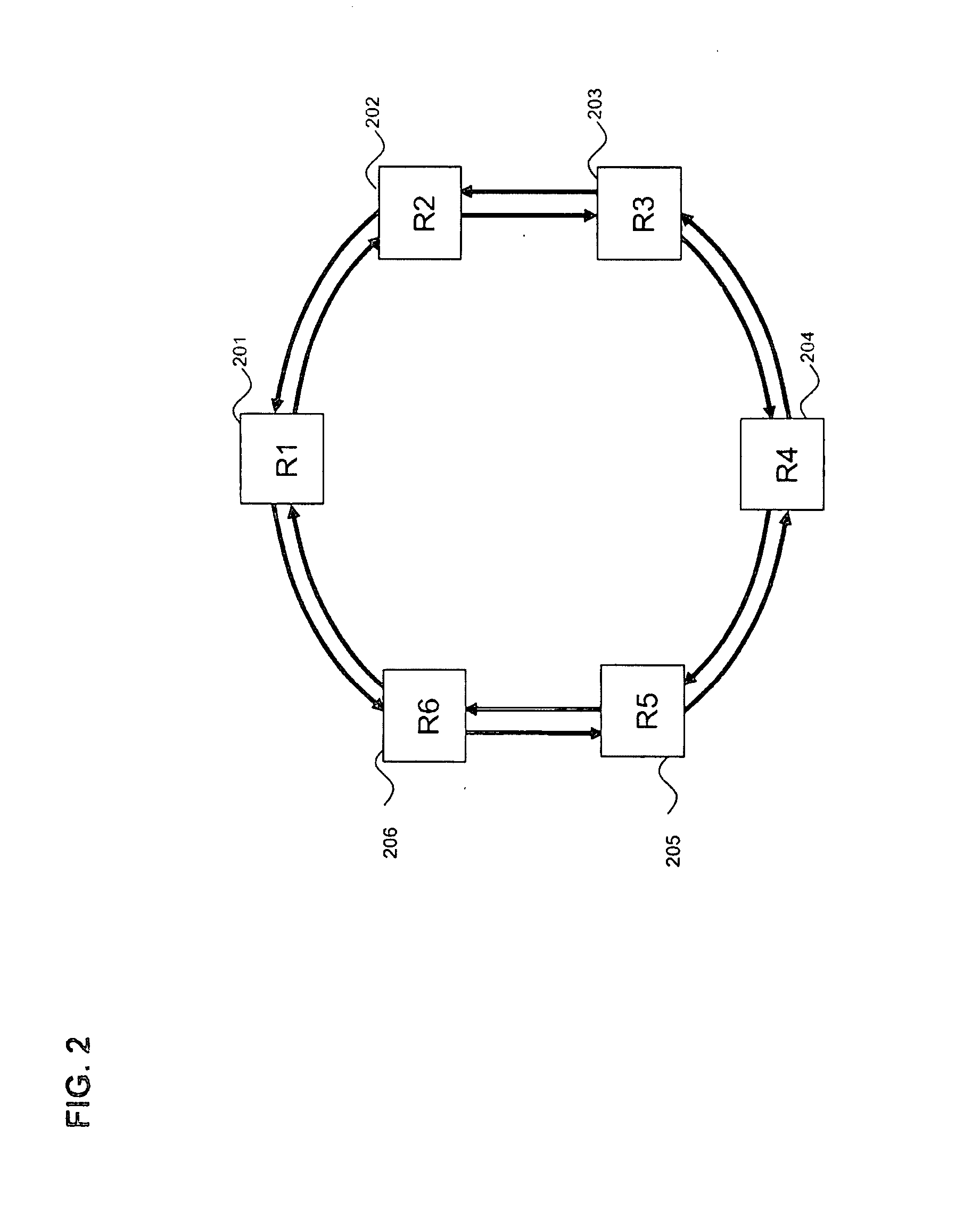
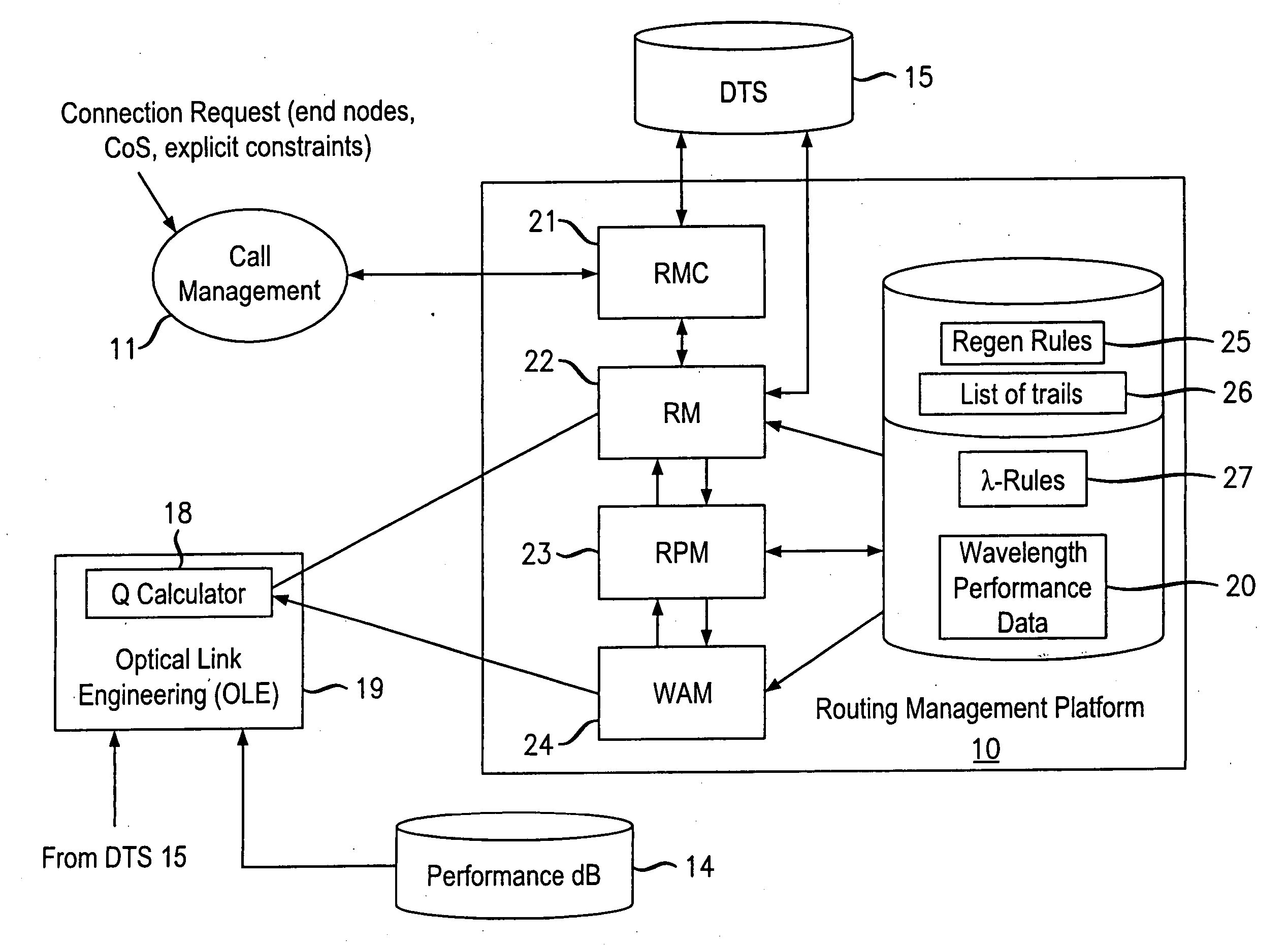
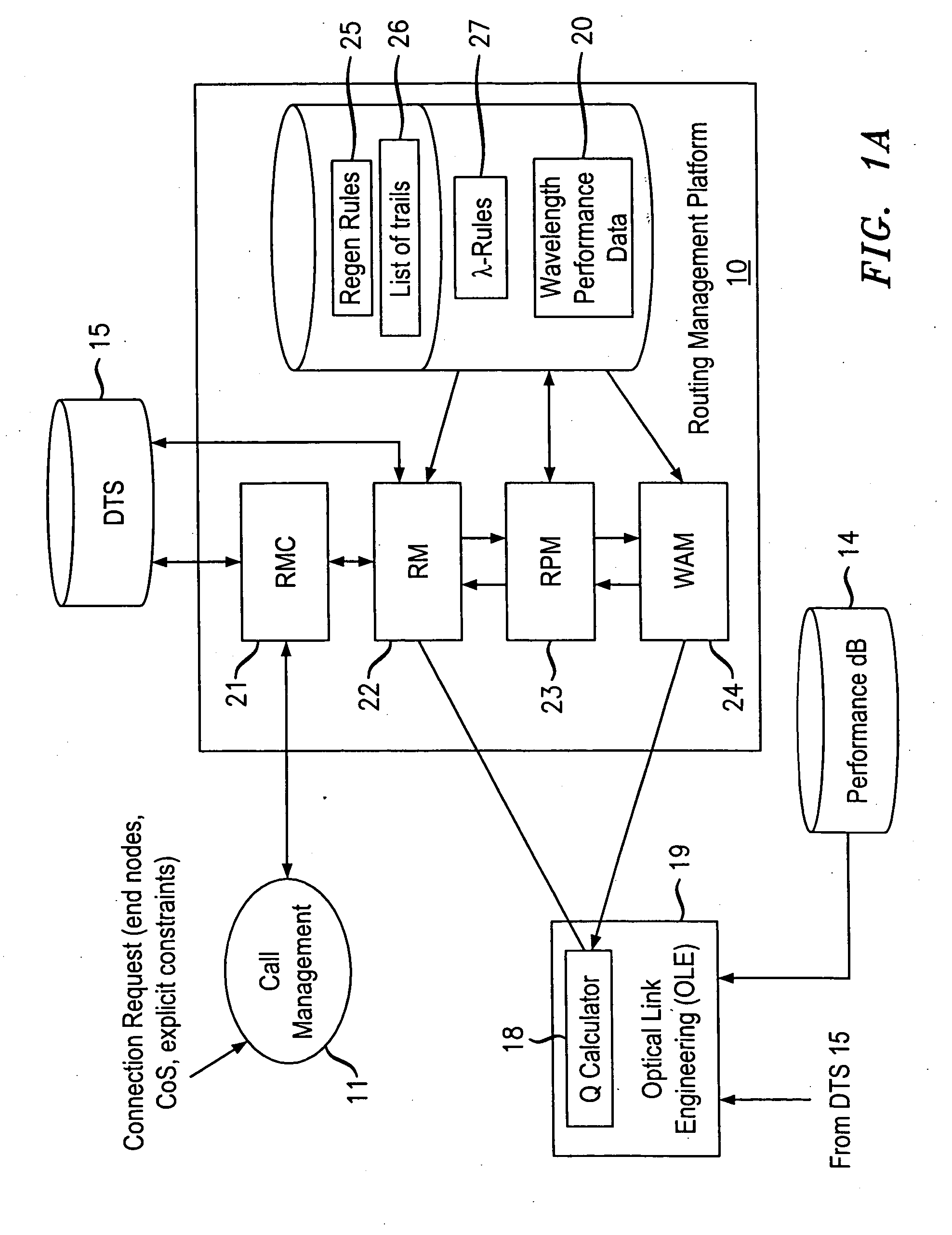
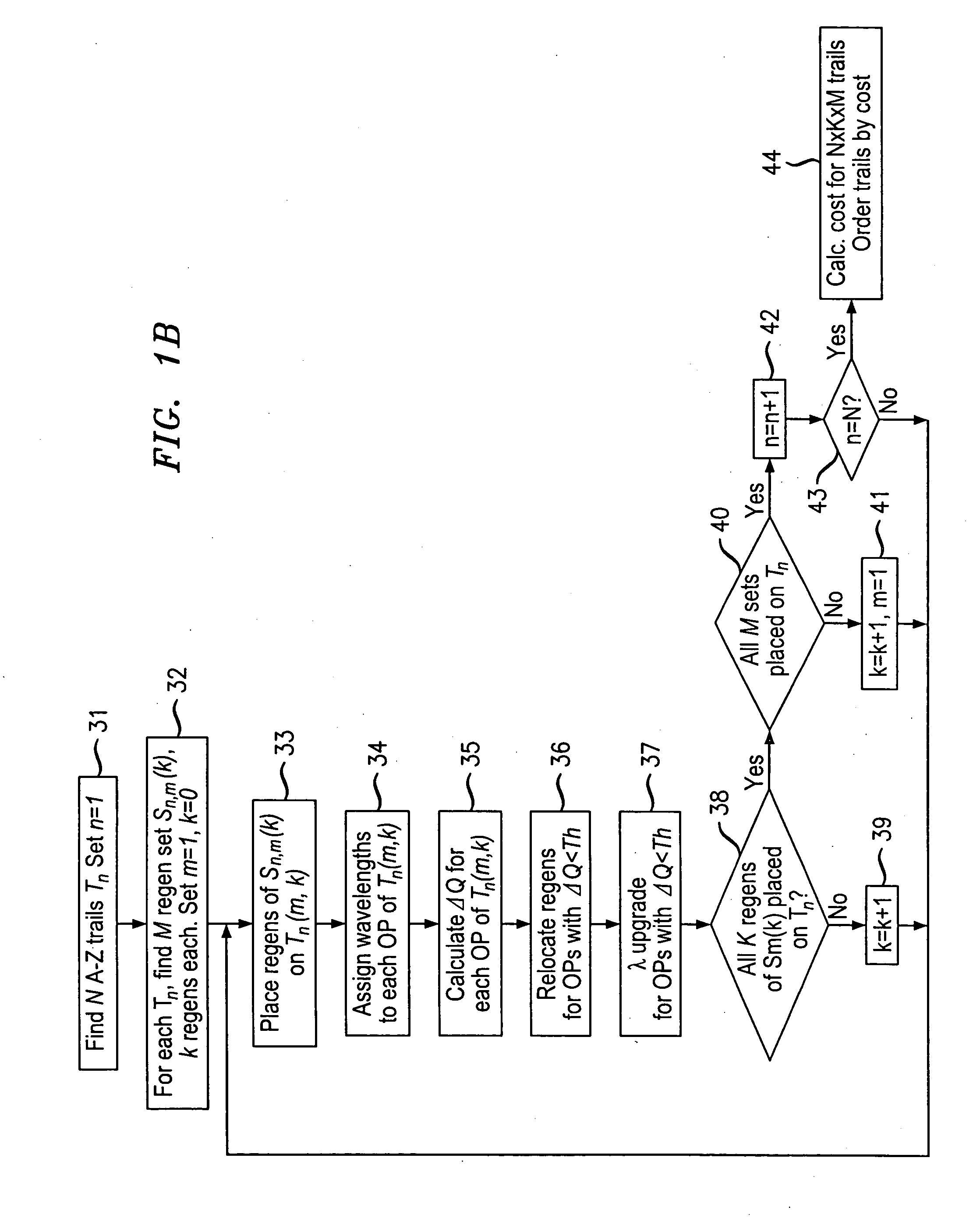
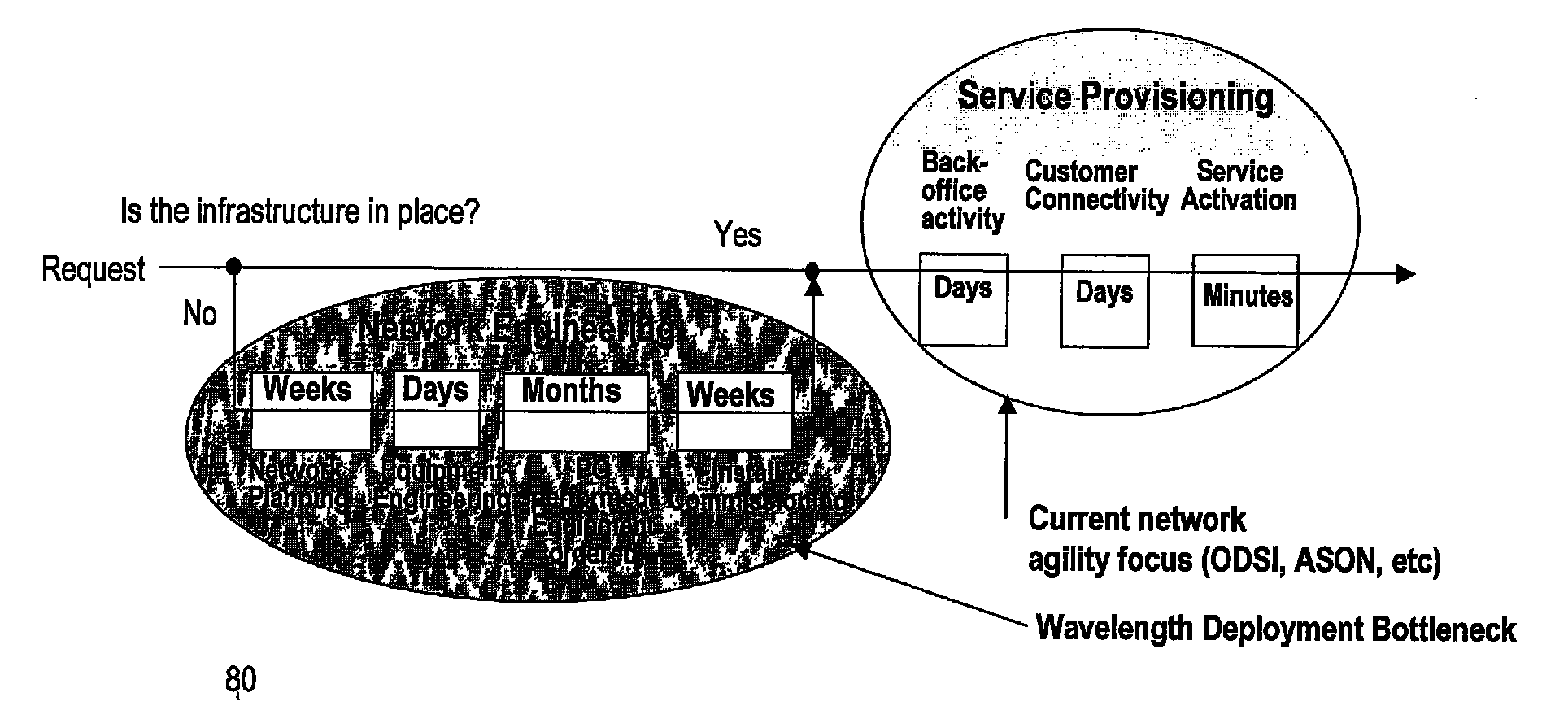
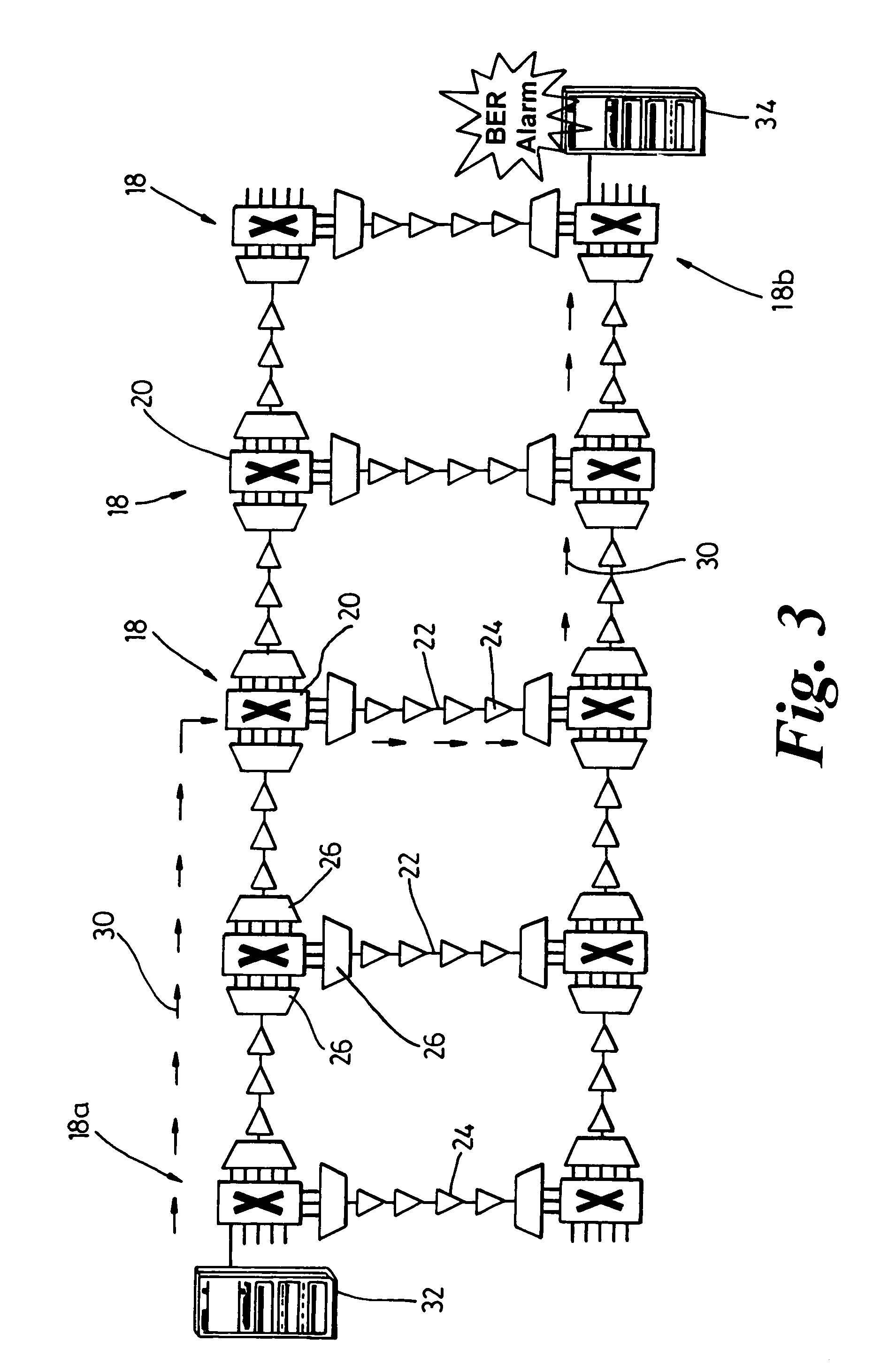
Trail engineering in agile photonic networks
ActiveUS20060002716A1Easy to useEfficient time-to-serviceOptical multiplexElectromagnetic transmissionPhotonicsNetwork architecture
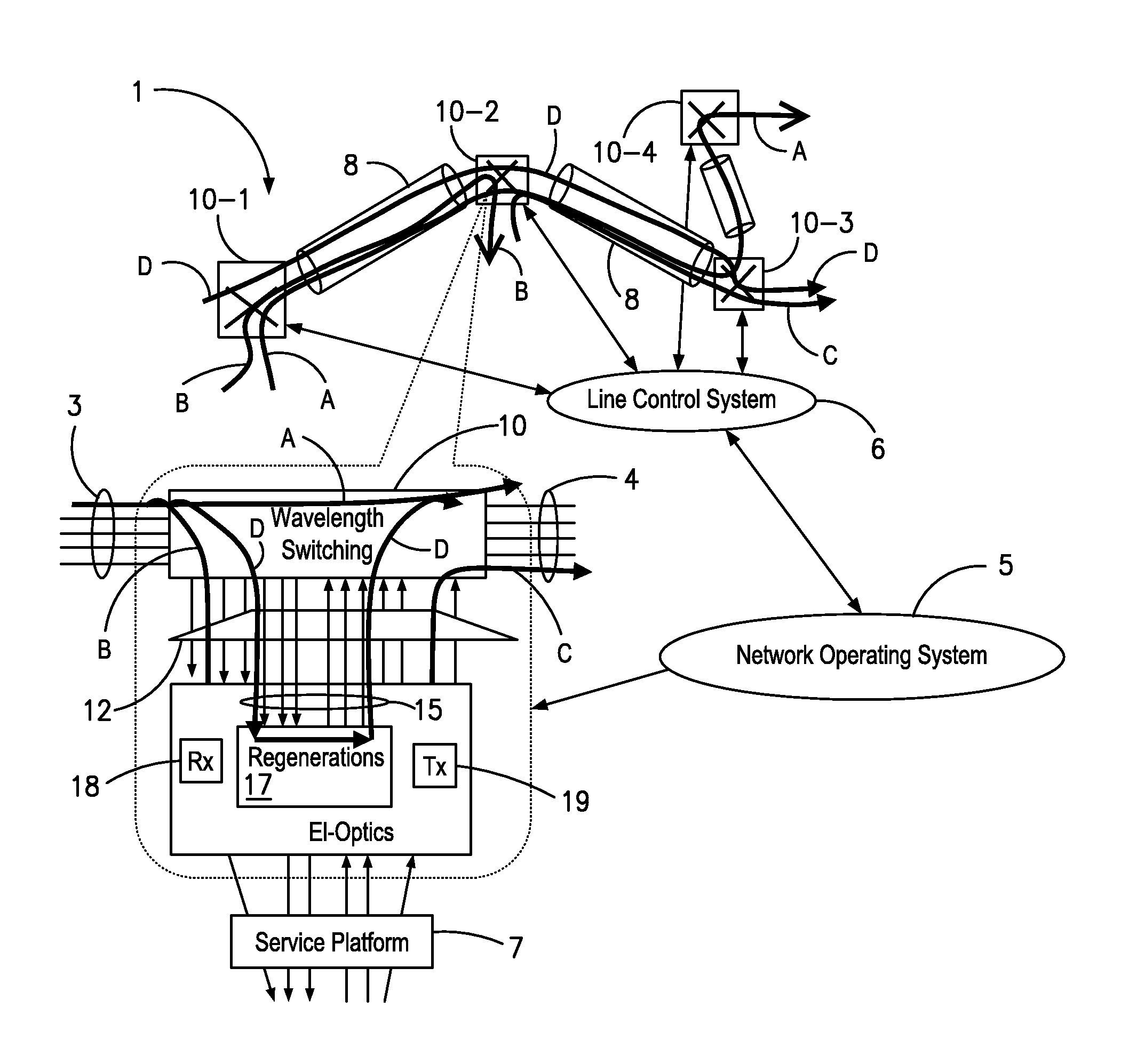
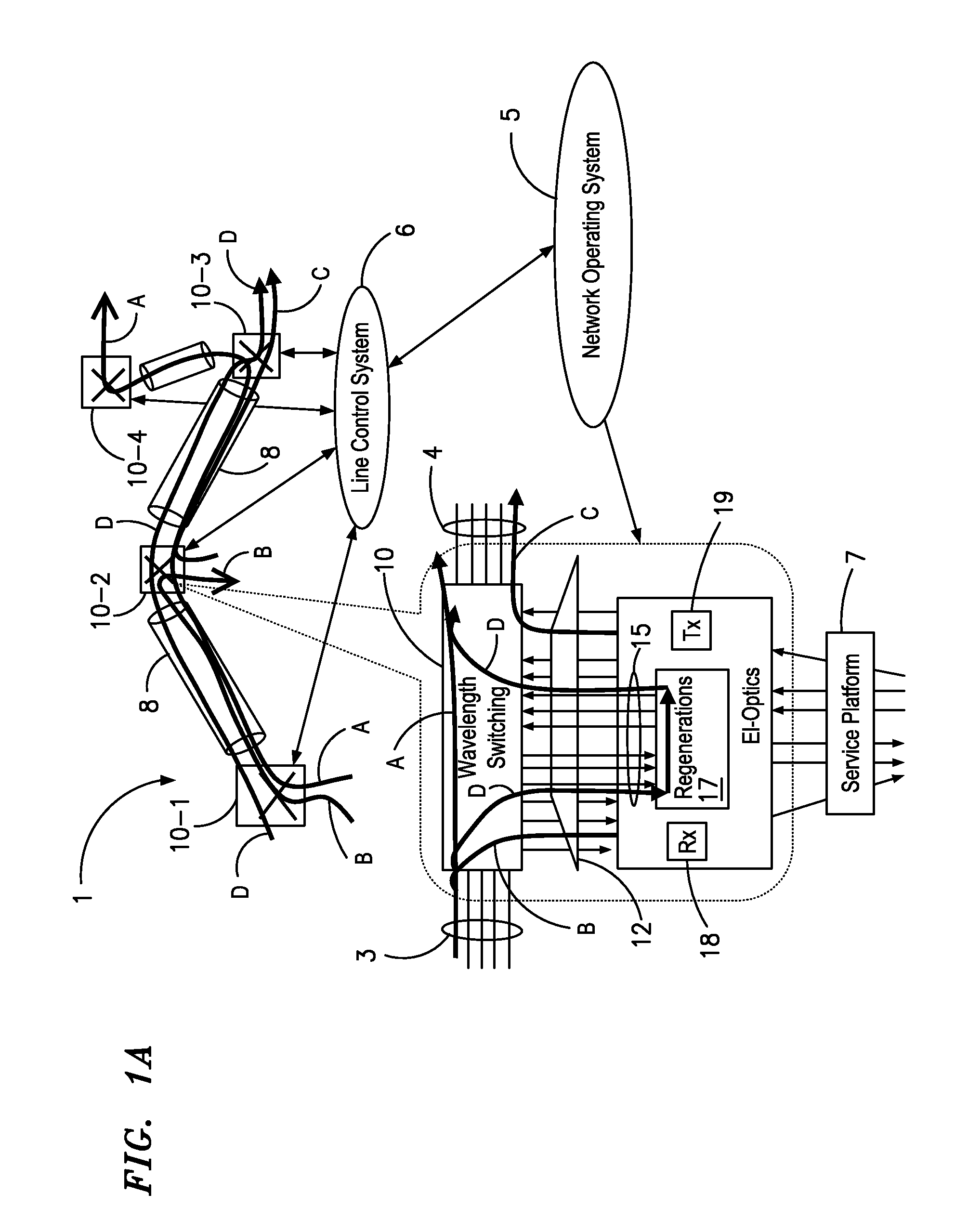
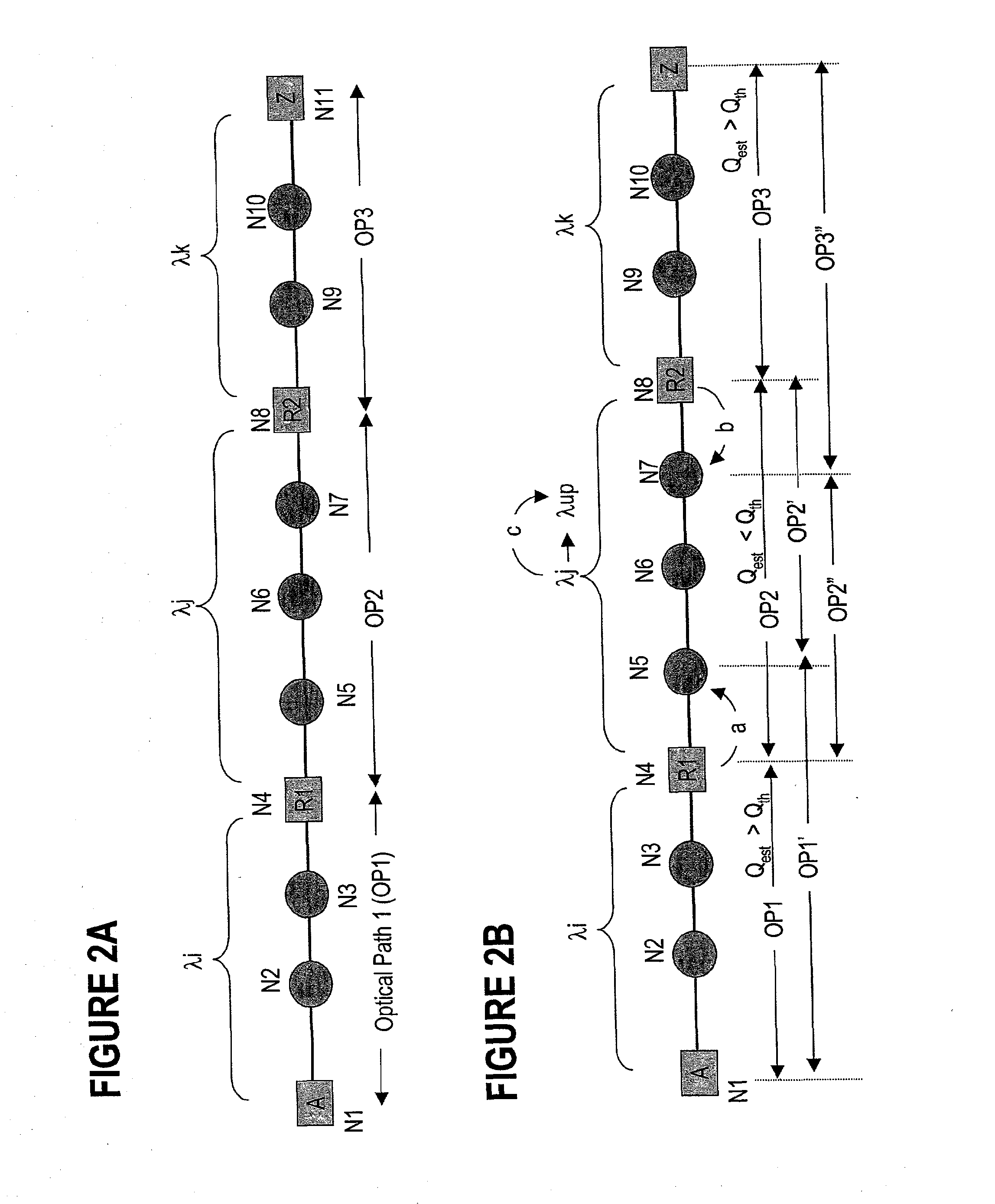
An agile transparent network with a trail routing and switching (also called “engineering”) mechanism is provided that enables efficient use of regenerators and wavelengths available in the network, while maintaining a very efficient time-to-service. The trail engineering mechanism allows fast, automatic establishment of new connections based on the current network architecture, connectivity and loading and also on conditions in the connection request. Selection of regenerator sites and of the wavelengths used on each regenerator segment is performed with optimal use of current network resources, while ensuring that the quality of the selected trail is adequate for the respective call. The mechanism provides for both distance and performance balancing, and it optimizes the network response time.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
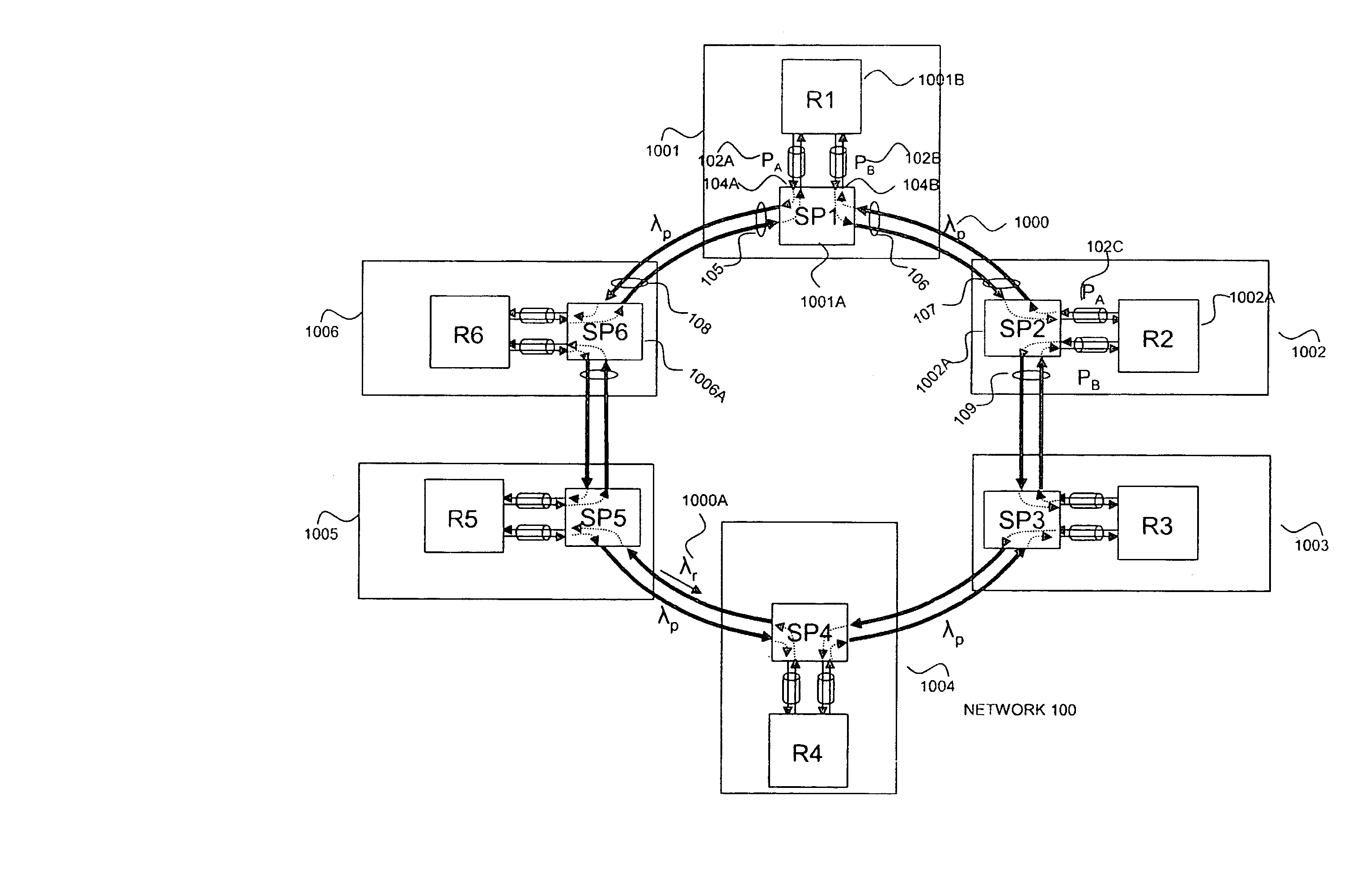
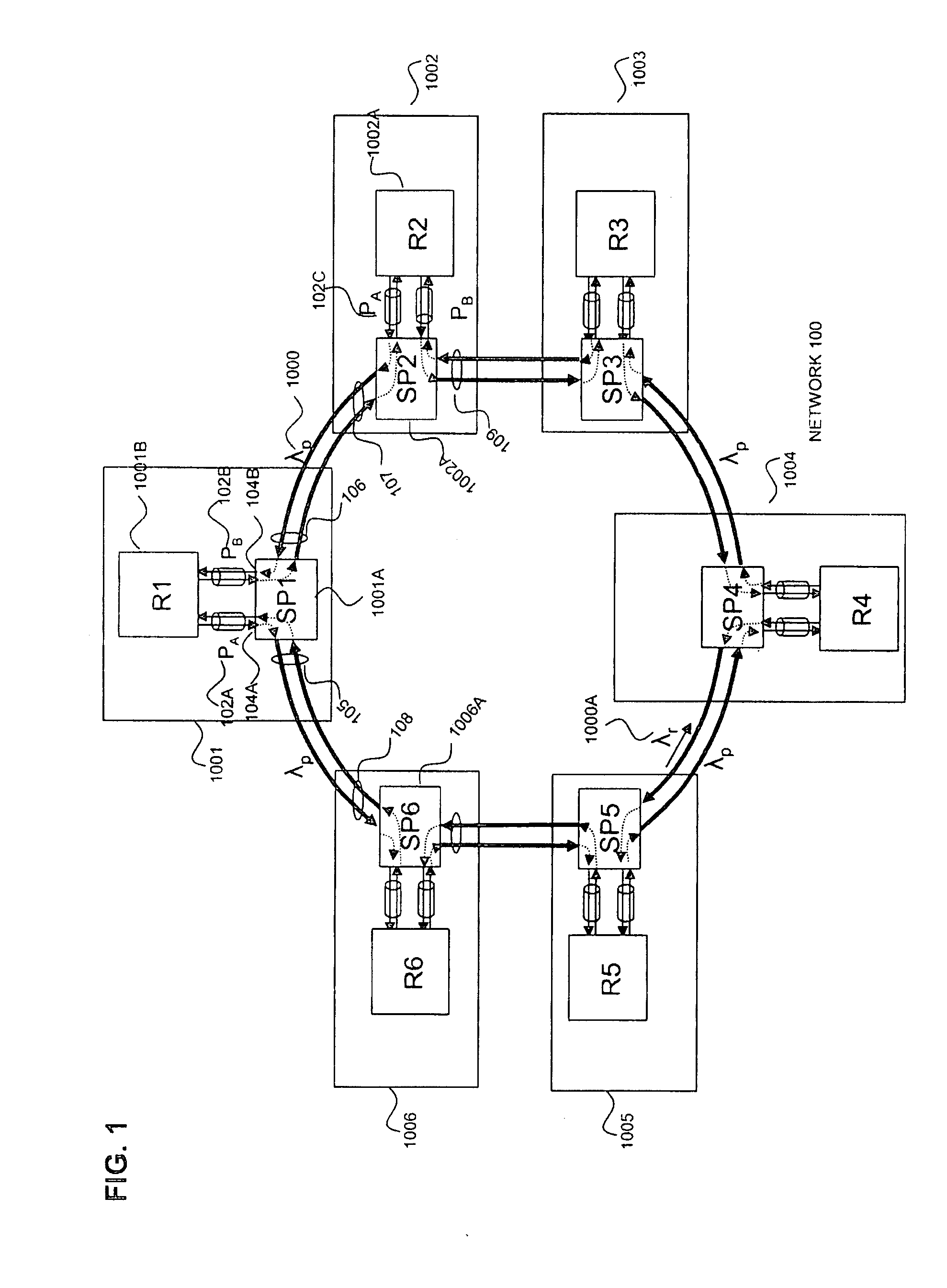
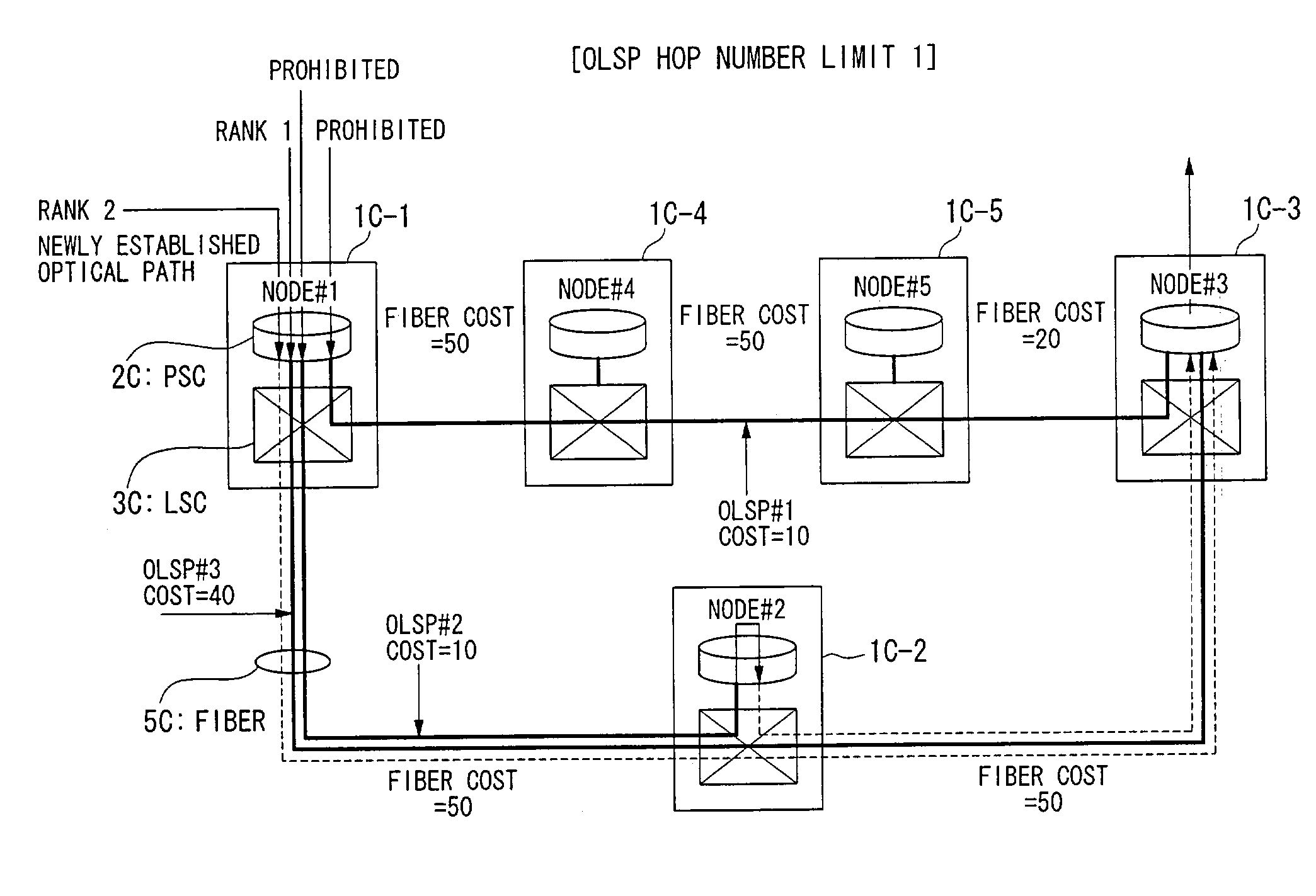
Node used in photonic network, and photonic network
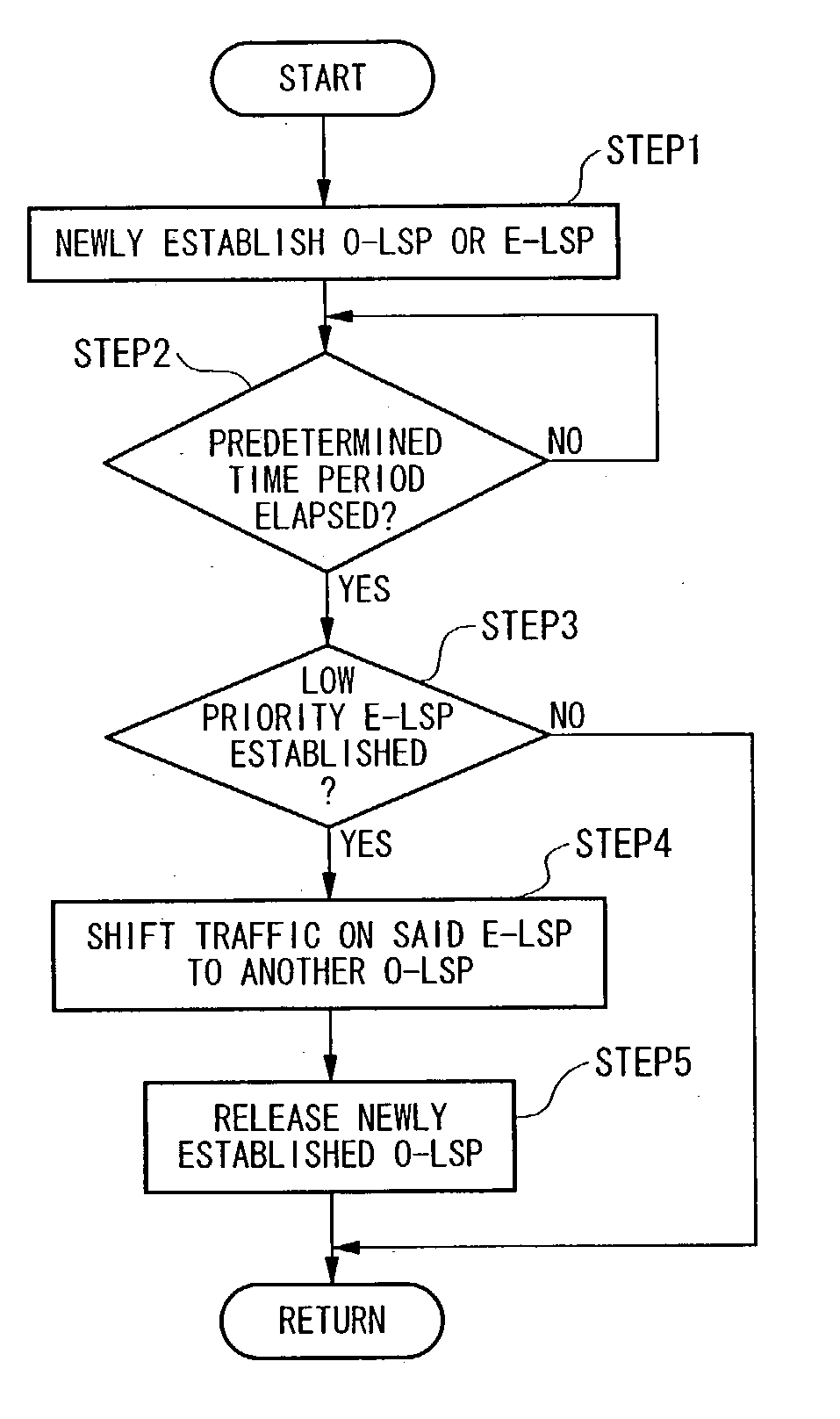
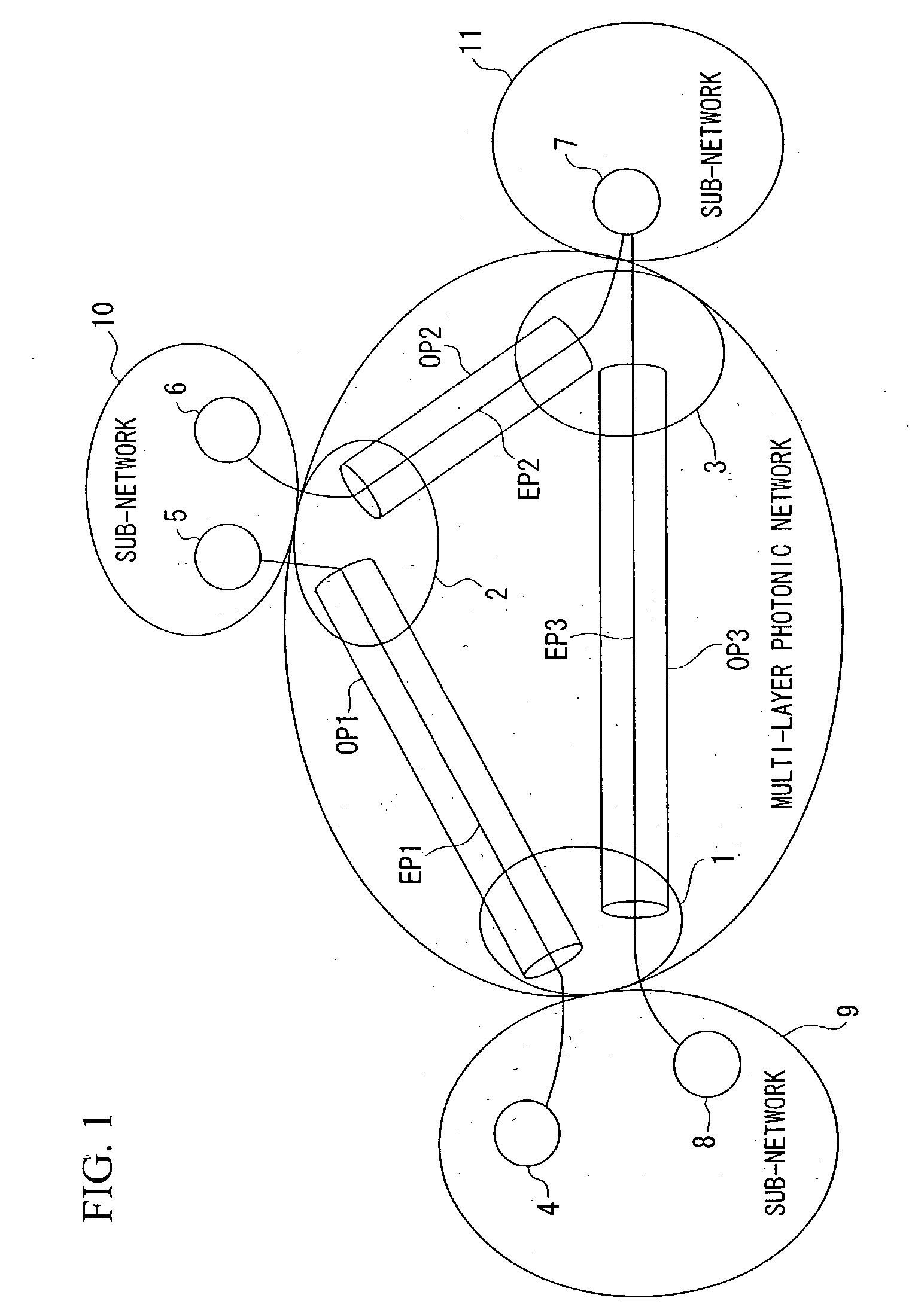
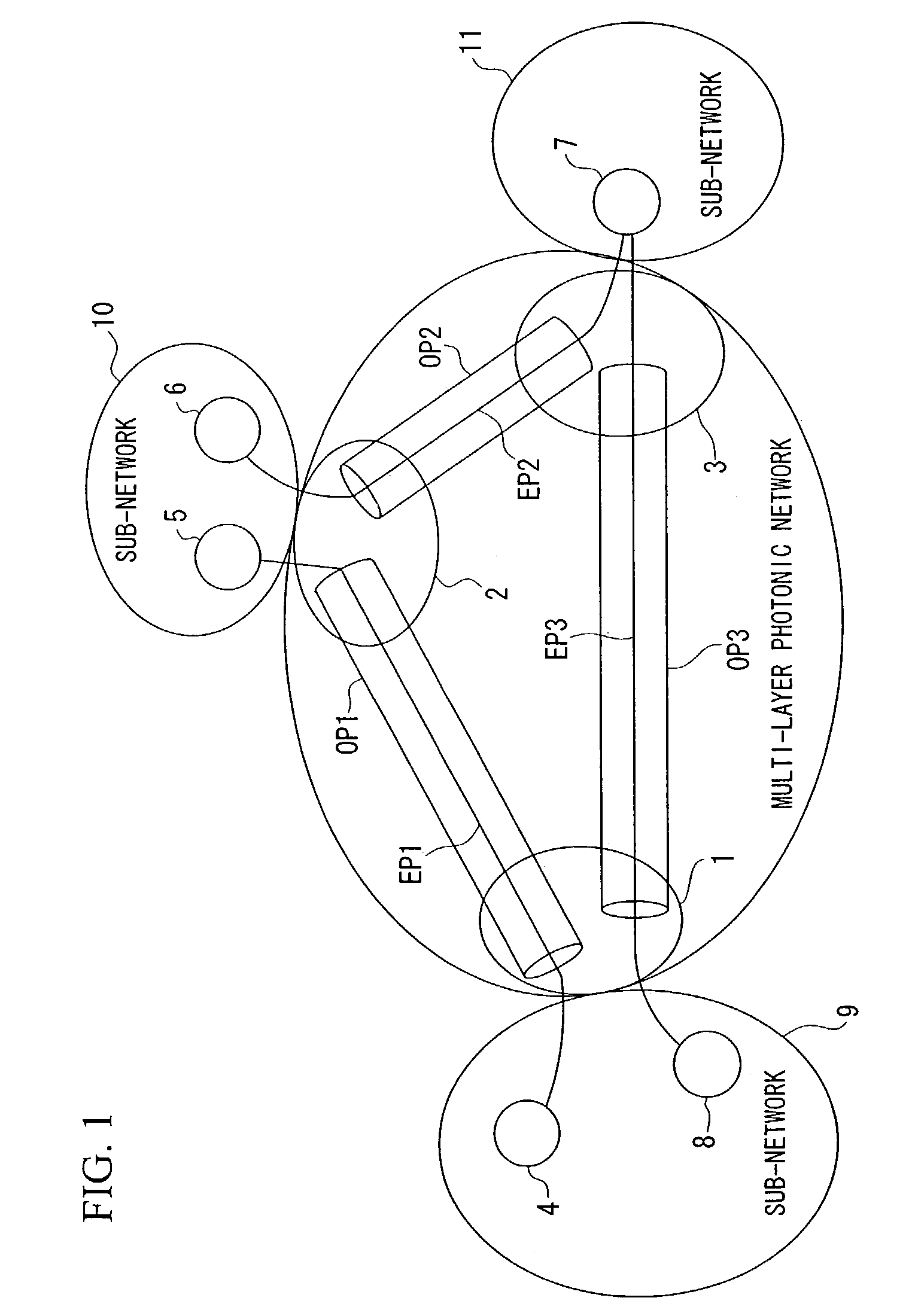
A multi-layer photonic network and nodes used therein are provided. The multi-layer photonic network comprises a packet network which performs switching and transfer in packet units, and a photonic network comprising optical transmission lines and photonic switches, and which accommodates the packet network. The multi-layer photonic network also has a two layer structure of optical wavelength links (O-LSPs) and packet links (E-LSPs). The O-LSPs are constituted by the optical transmission lines and comprise optical wavelength switching capability (LSC) which is capable of switching in optical wavelength units and packet switching capability (PSC) which is capable of switching in packet units at both their ends. The E-LSPs include the O-LSPs and PSCs at both their ends. Each node includes a section for automatically establishing an O-LSP according to an establishment request for an E-LSP while taking account of path information including path cost, resource consumption, and traffic quantity.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Photonic routing systems and methods for loop avoidance
A photonic network includes a plurality of nodes each supporting add and drop of at least Y wavelengths, a plurality of optical links interconnecting the plurality of nodes, the plurality of optical links support up to X wavelengths and Y≦X, an optical routing protocol configured to compute a loop-free path through the plurality of nodes on the plurality of links, the loop-free path is computed for one of the X wavelengths or a group of the X wavelengths using routing constructs adapted to a photonic domain, and optical components at each of the plurality of nodes configured to selectively block at least one of the X wavelengths based on the computed loop-free path. A photonic routing method and photonic node are also disclosed.
Owner:CIENA
Interferometric method and apparatus for measuring optical signal quality in optical communications system
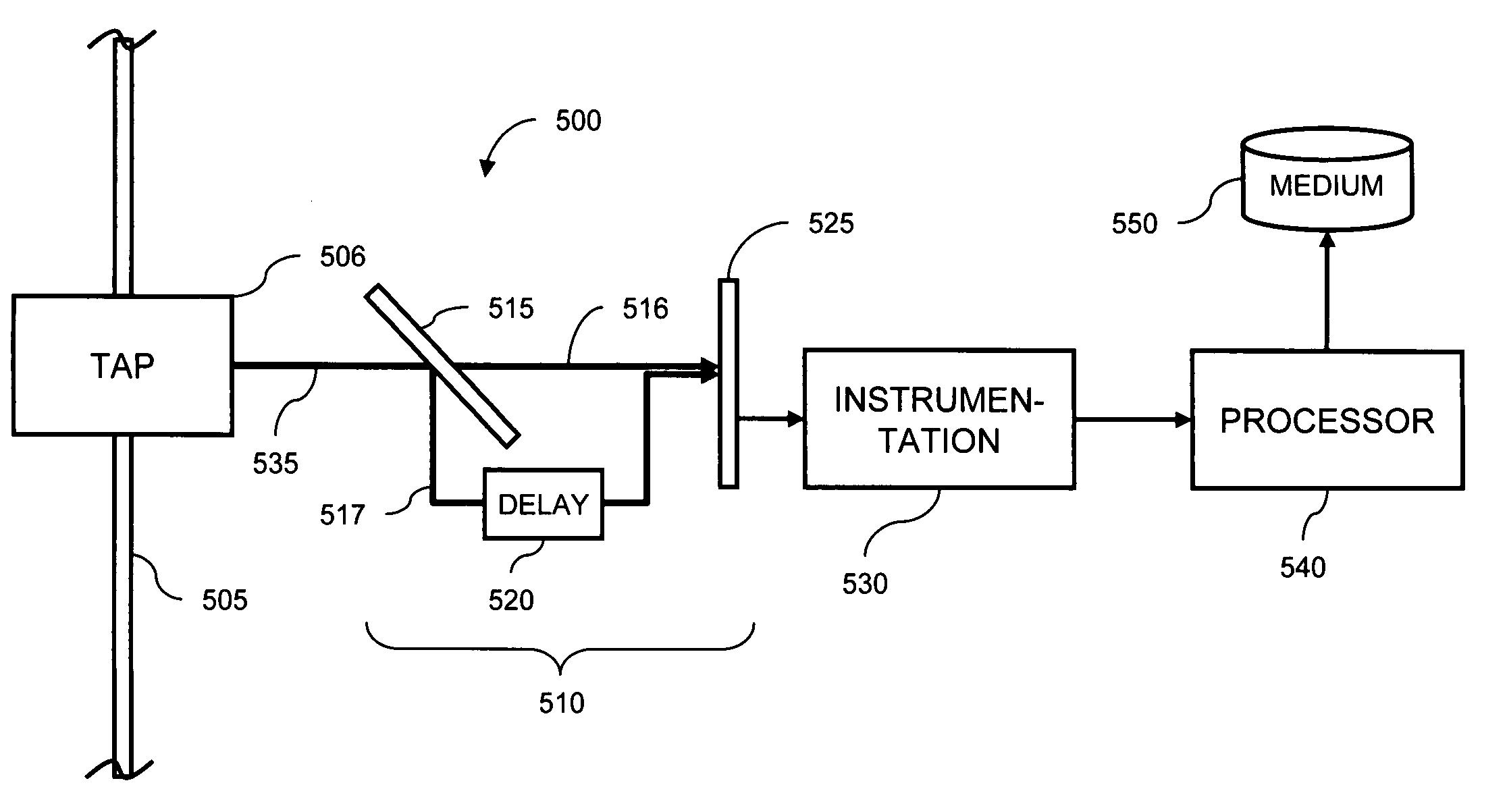
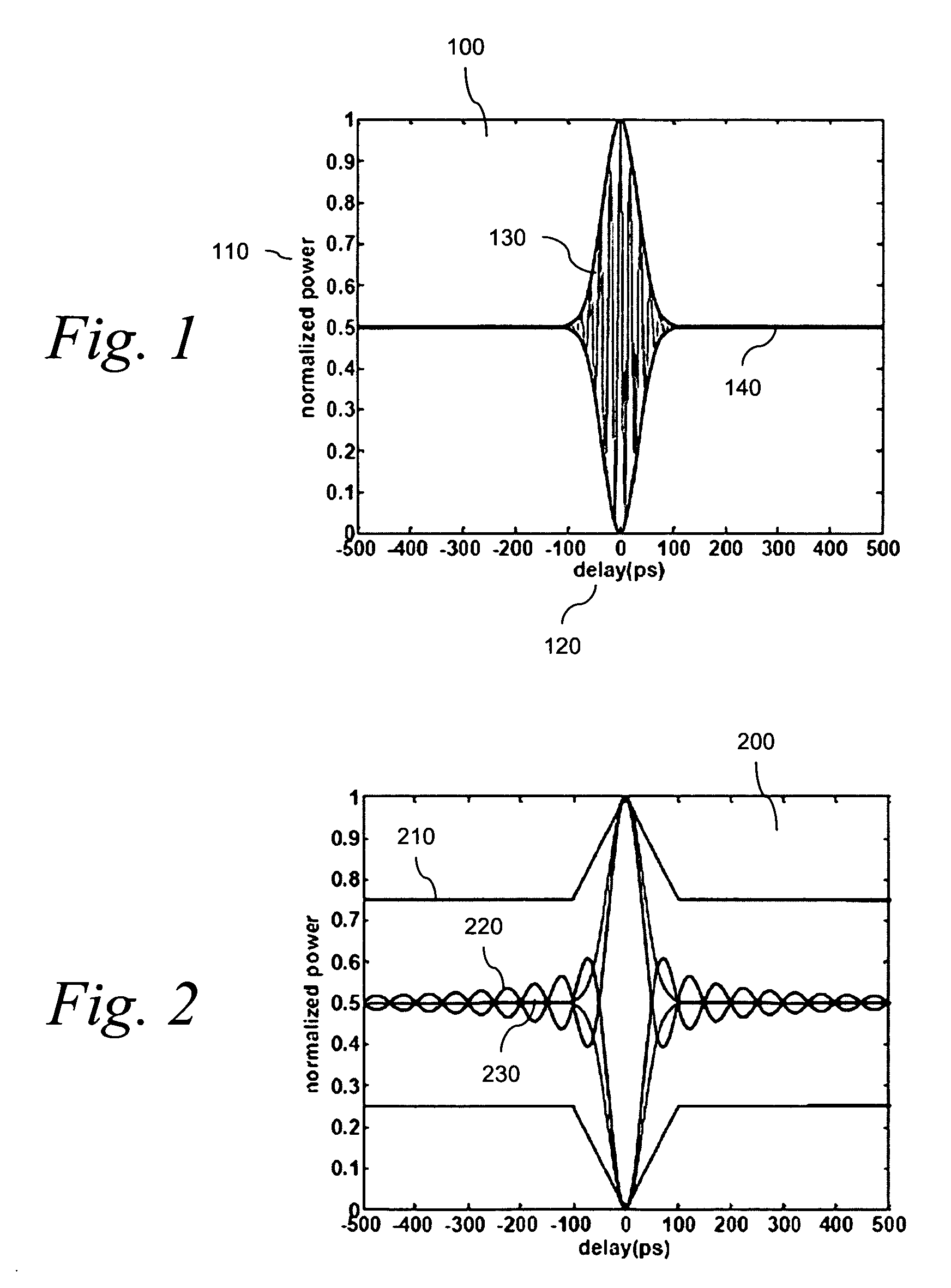
Differences in the interferometric patterns of modulated telecommunication signals and broadband optical noise sources are identified and are exploited in measuring the optical signal-to-noise measurements in reconfigurable photonic networks. A light output power from said interferometer corresponding to a specified delay setting in the interferometer is measured, and a coherent optical signal is distinguished from the incoherent optical noise based on the light output power measurement.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Packet communication network, route control server, route control method, packet transmission device, admission control server, light wavelength path setting method, program, and recording medium
InactiveUS20060053221A1Carrying efficiency is reducedAvoid problemsDigital computer detailsData switching networksPacket communicationLength wave
A route control server (1) sends destination information acquired by a router (2) in a managed area and transfer management information corresponding to the destination information to another route control server and determines the output interface of a packet on the basis of the destination information and transfer management information. A packet transfer apparatus (3) executes mutual conversion and transfer of an upper layer packet on a user terminal side and a lower layer frame on an optical wavelength path side. An admission control server (4) sets, of the optical wavelength paths of the photonic network, an optical wavelength path formed from a cut-through optical wavelength path which has a guaranteed band and directly connects packet transfer apparatuses of transmission source and destination in accordance with an optical wavelength path connection request from a transmission source user terminal.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Method and apparatus for measuring and estimating optical signal to noise ratio in photonic networks
InactiveUS6907197B2Accurate measurementWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringAudio power amplifierSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A WDM optical network comprising a plurality of nodes has a first apparatus for optical analysis at the site of a first optical amplifier upstream of the first node, a second apparatus for optical analysis at the site of a second optical amplifier at the downstream output of the first node, and a third apparatus for optical analysis at the site of a third optical amplifier further downstream of the first node, where knowledge of the optical sin to noise ratio (OSNR) is desired. The first, second and third apparatus are for measuring the signal level at frequencies both at and in-between the channel frequencies. The signal levels at the channel frequencies and between the channel frequencies at the first, second and third apparatus are used to derive the OSNR at the third apparatus. This enables the OSNR to be measured accurately at any site in the network, using calculations in which noise shaping of the nodes can be factored in to the calculation of OSNR.
Owner:CIENA
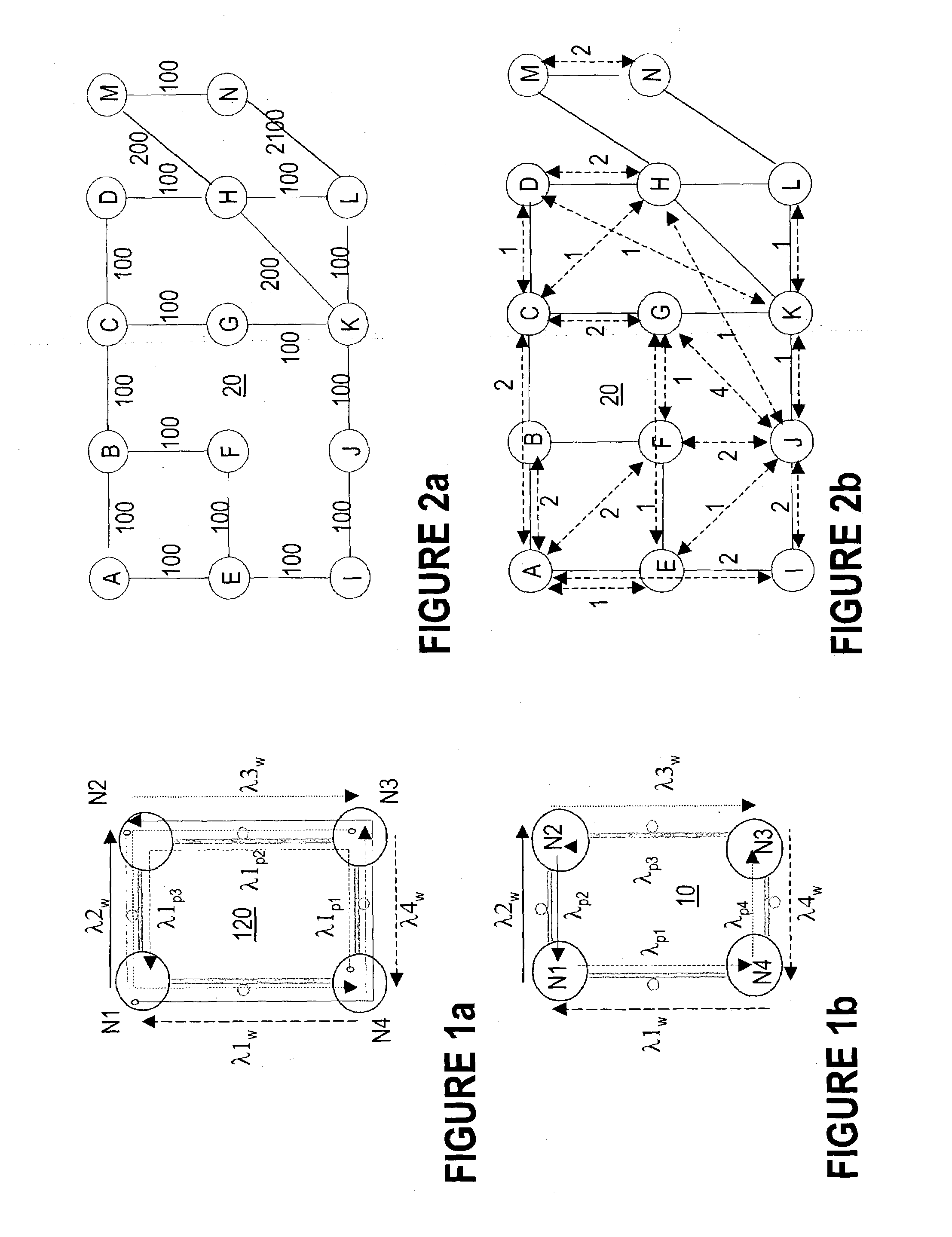
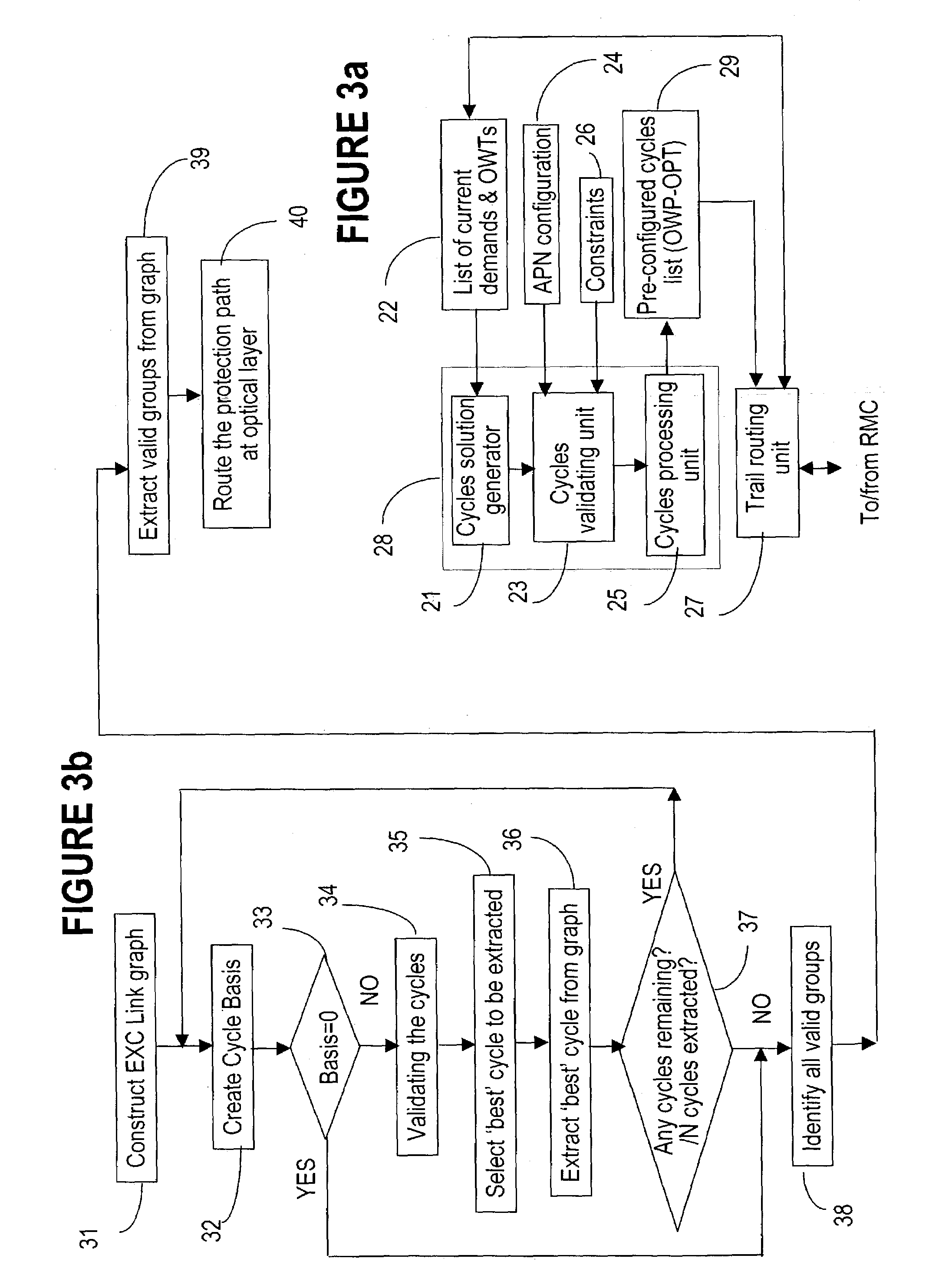
Method of preconfiguring optical protection trails in a mesh-connected agile photonic network
ActiveUS7224897B1Promote recoveryImprove utilizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsComputer sciencePhoton
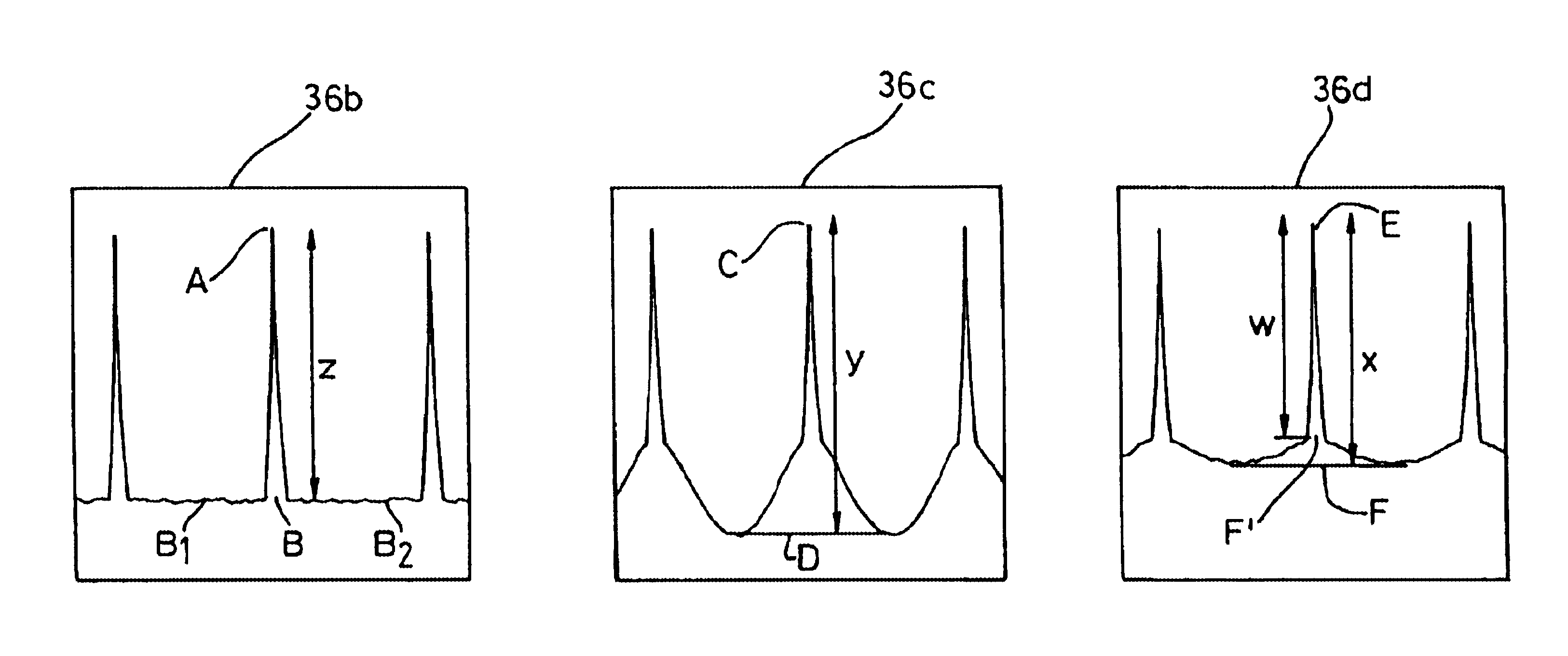
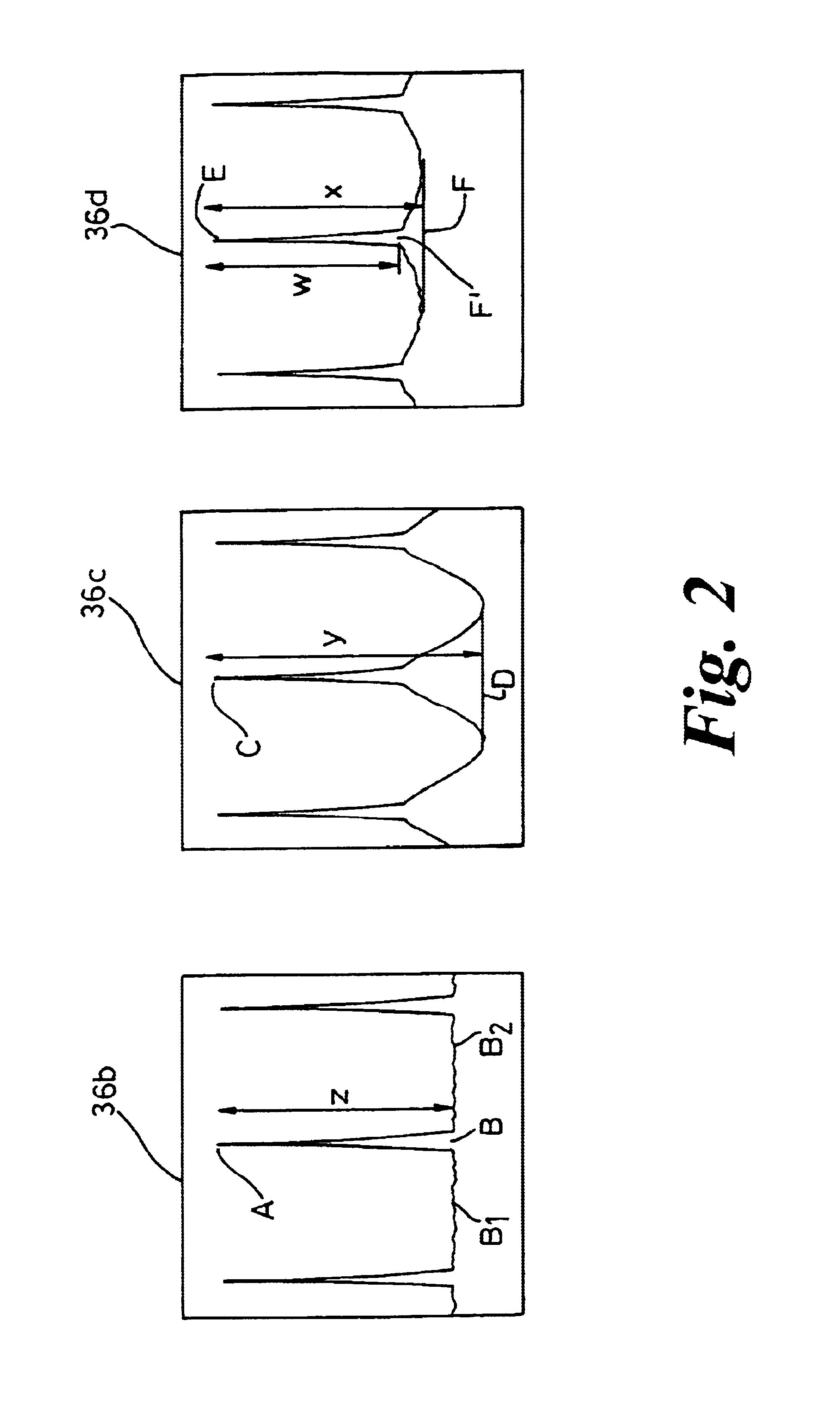
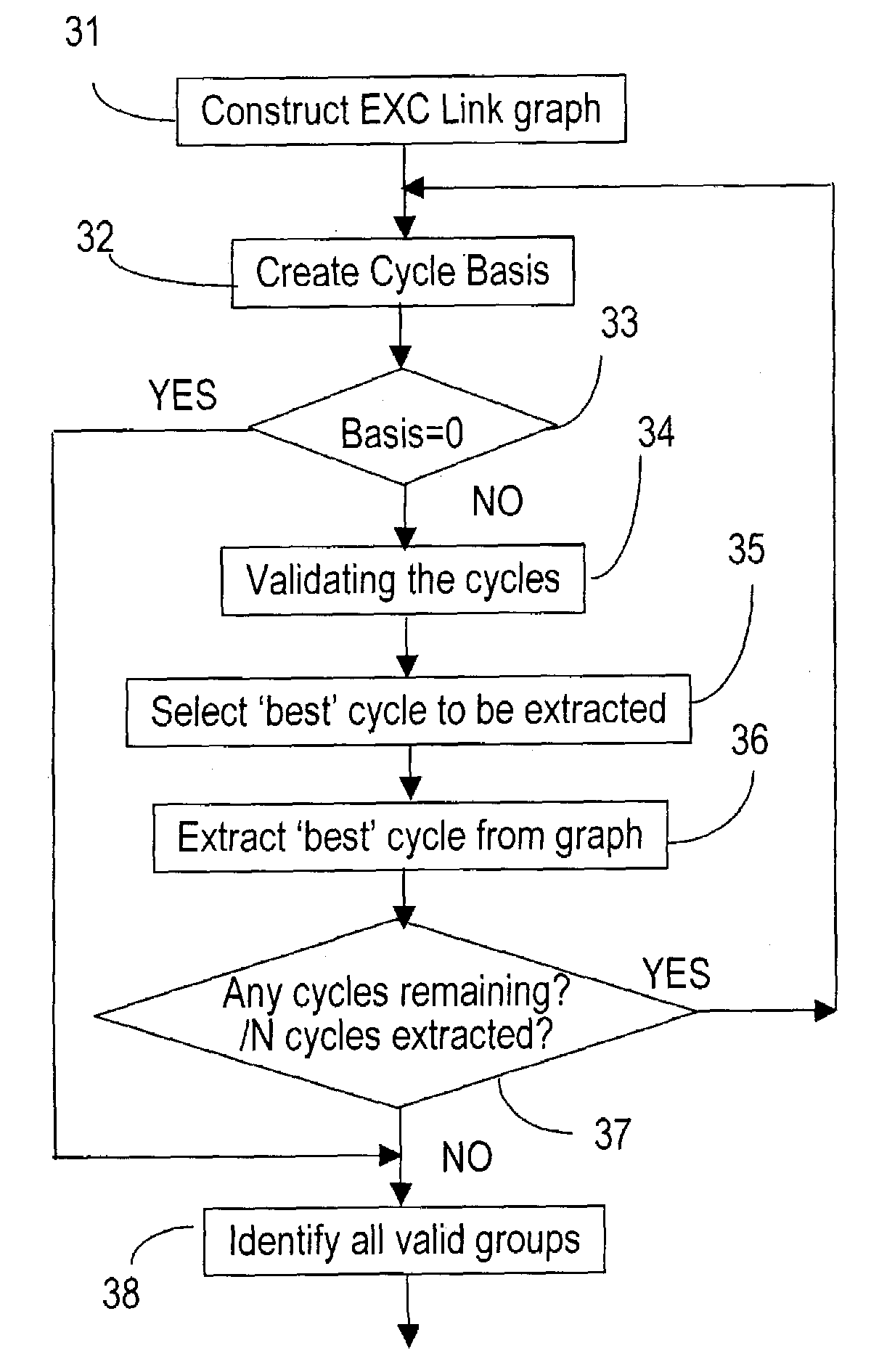
The method of pre-configuring the optical protect paths in an agile photonic network establishes a protection trail for each optical working path that may be set-up in the network. The pre-configuration is based on building an electrical layer (EXC) graph that takes into account all the connection demands in the network, and finding on this EXC graph a plurality of cycles. Next, the EXC cycles are validated at the optical layer, and are further validated against constraints. The method attempts to find an optimal cycles solution, without exhausting all possible variants.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
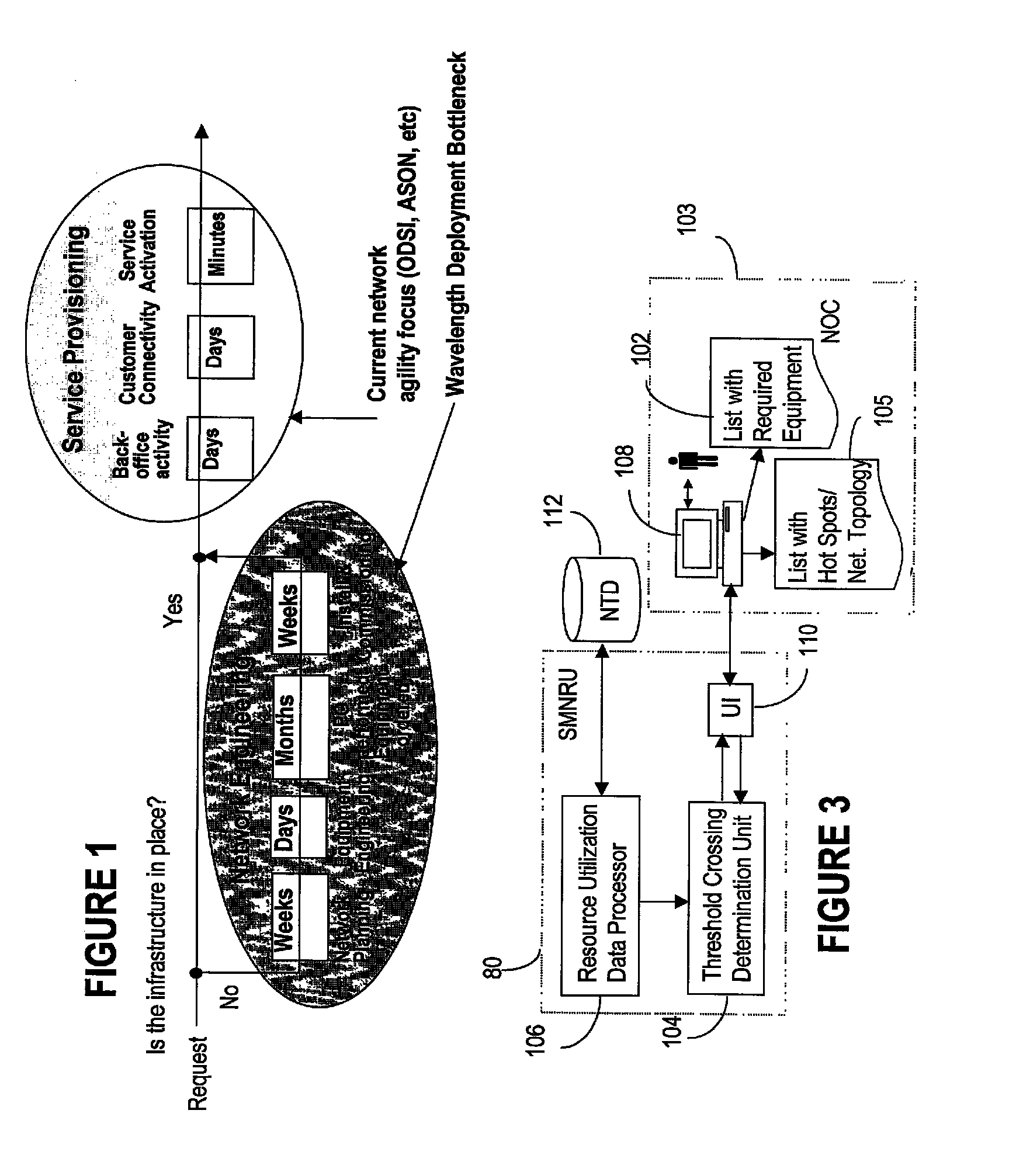
Method and system for monitoring network resources utilization
InactiveUS8676956B1Conserve costReadily apparentMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsResource utilizationUser interface
A system and method are provided for monitoring utilization of network resources in a photonic network. A monitoring threshold is set for monitoring utilization of network components of interest. A resource utilization data processor obtains resource utilization data indicating utilization of the network resources. A threshold crossing determination unit determines if threshold crossing has occurred based on the utilization data and the monitoring threshold. A user interface indicates the utilization of the network components in accordance with the determination of the threshold crossing.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Shortest path routing systems and methods for networks with non-fully meshed vertices
ActiveUS8854997B2Special service provision for substationError preventionMultiplexerDistributed computing
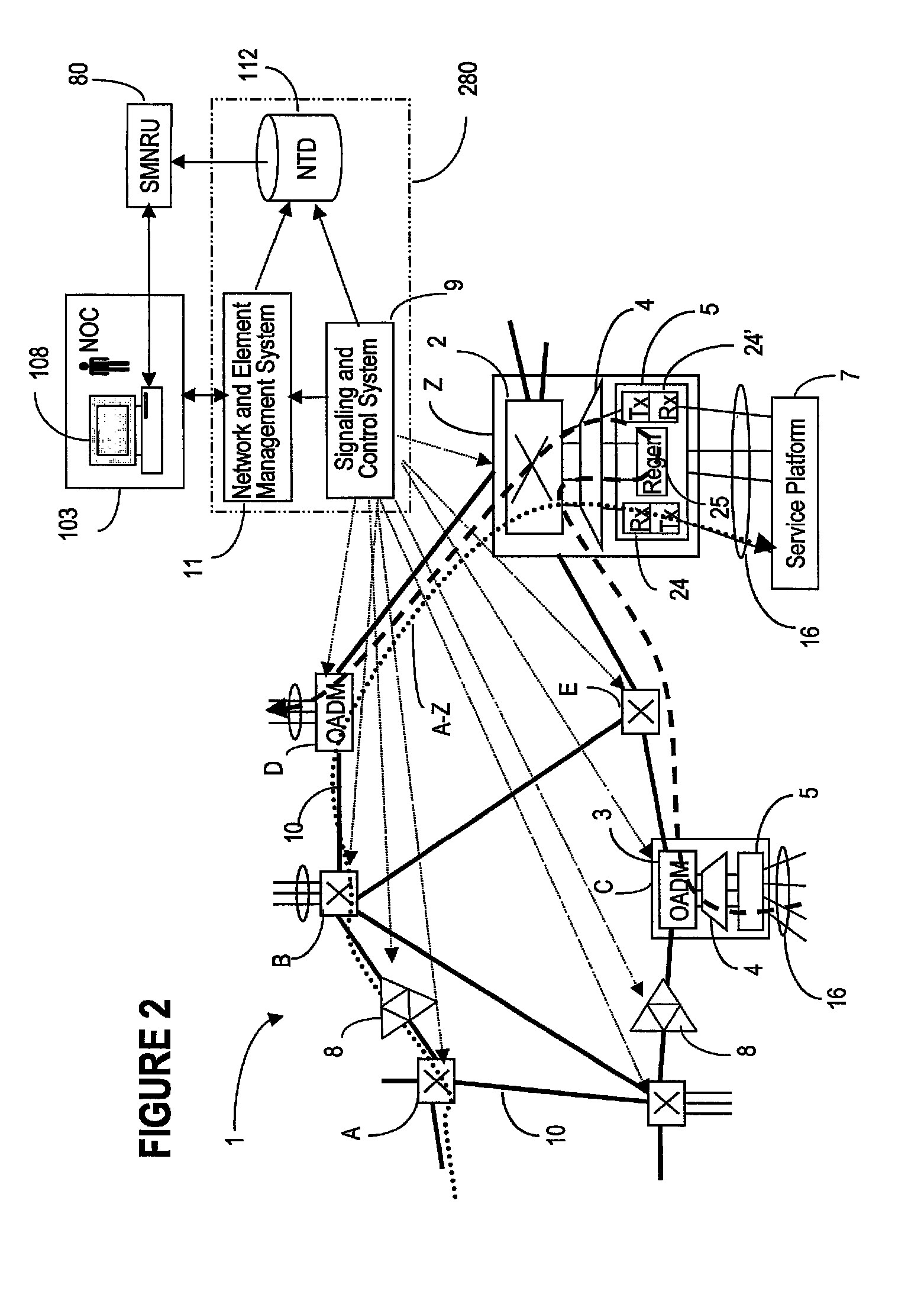
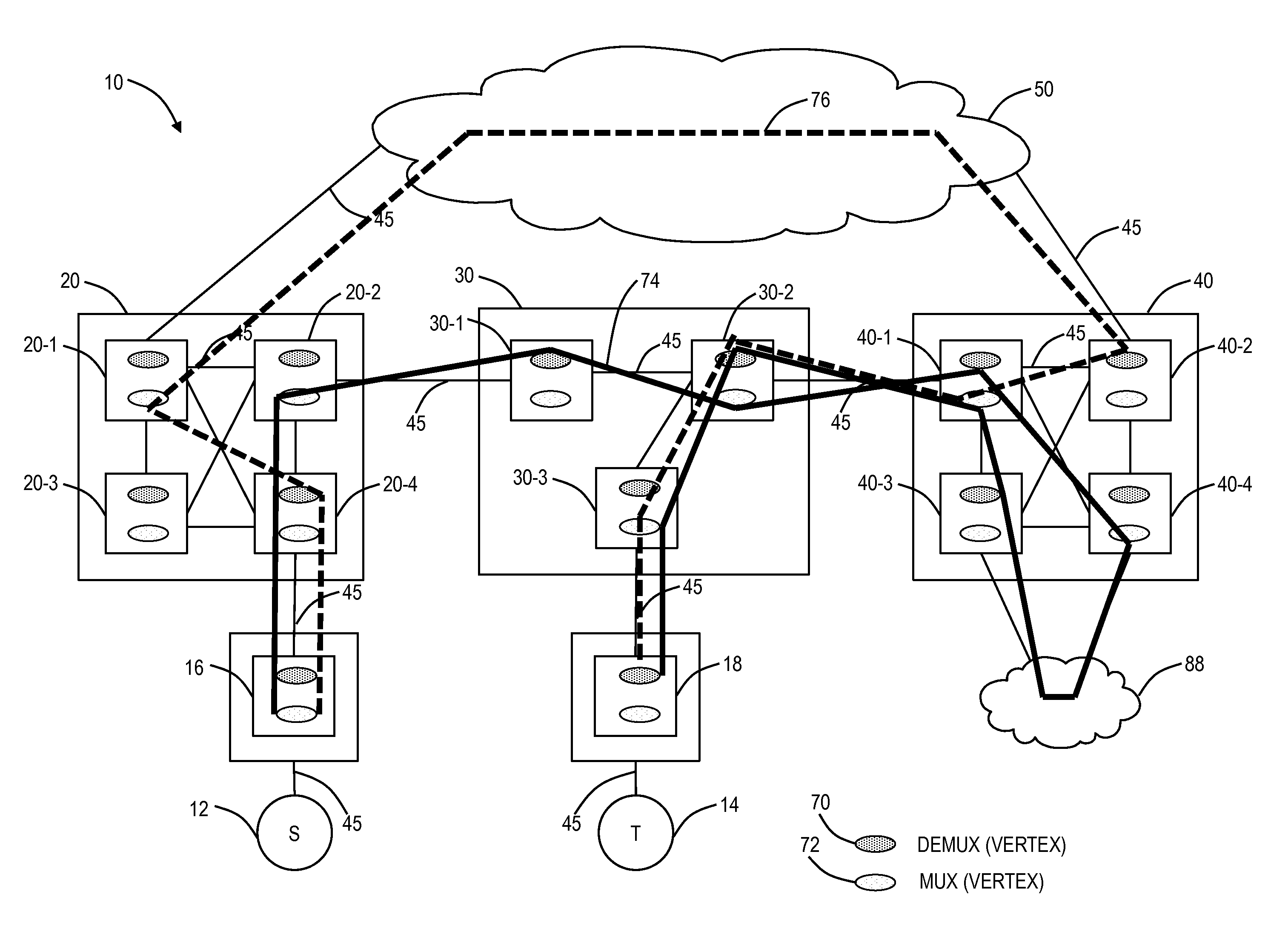
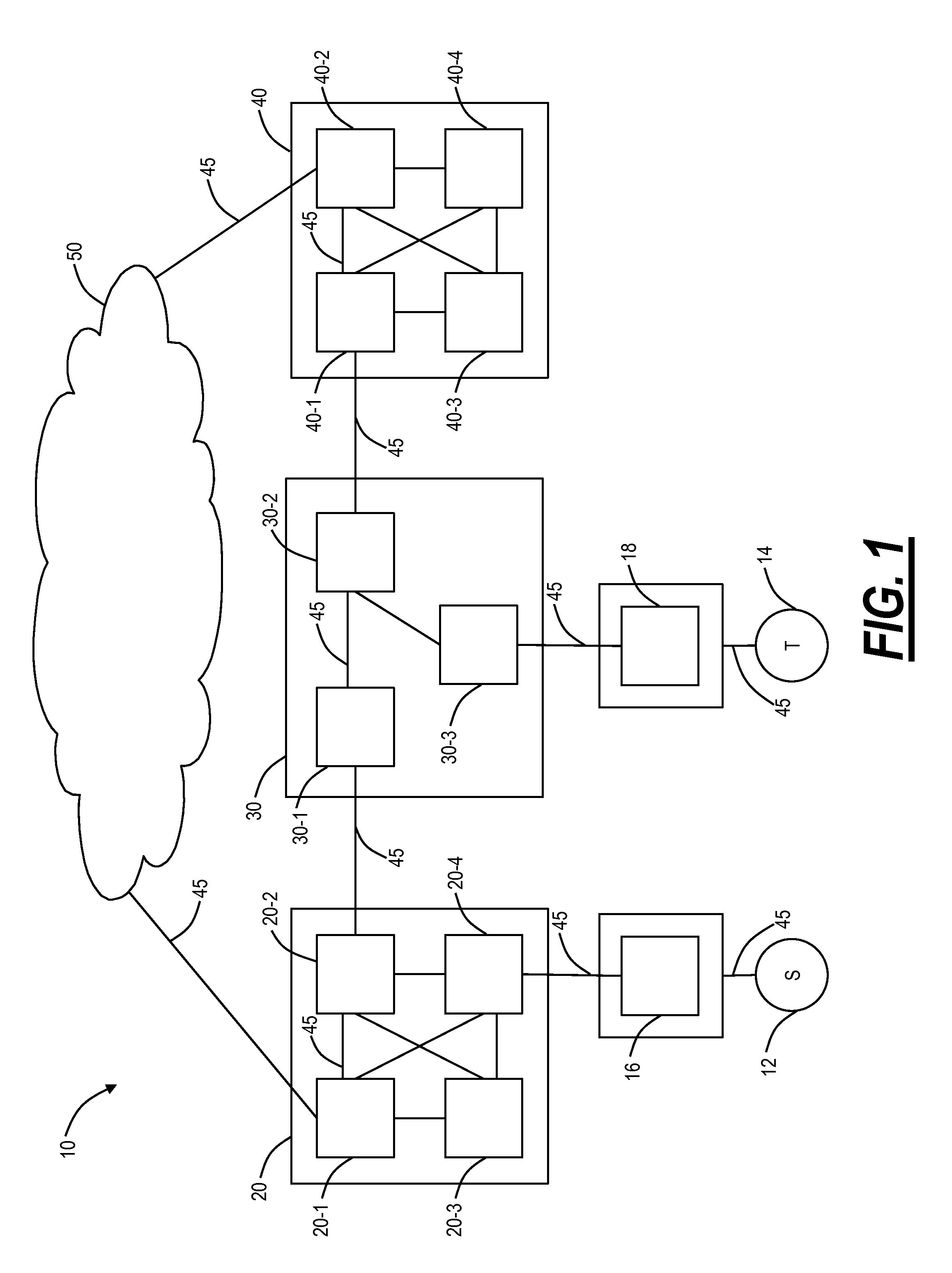
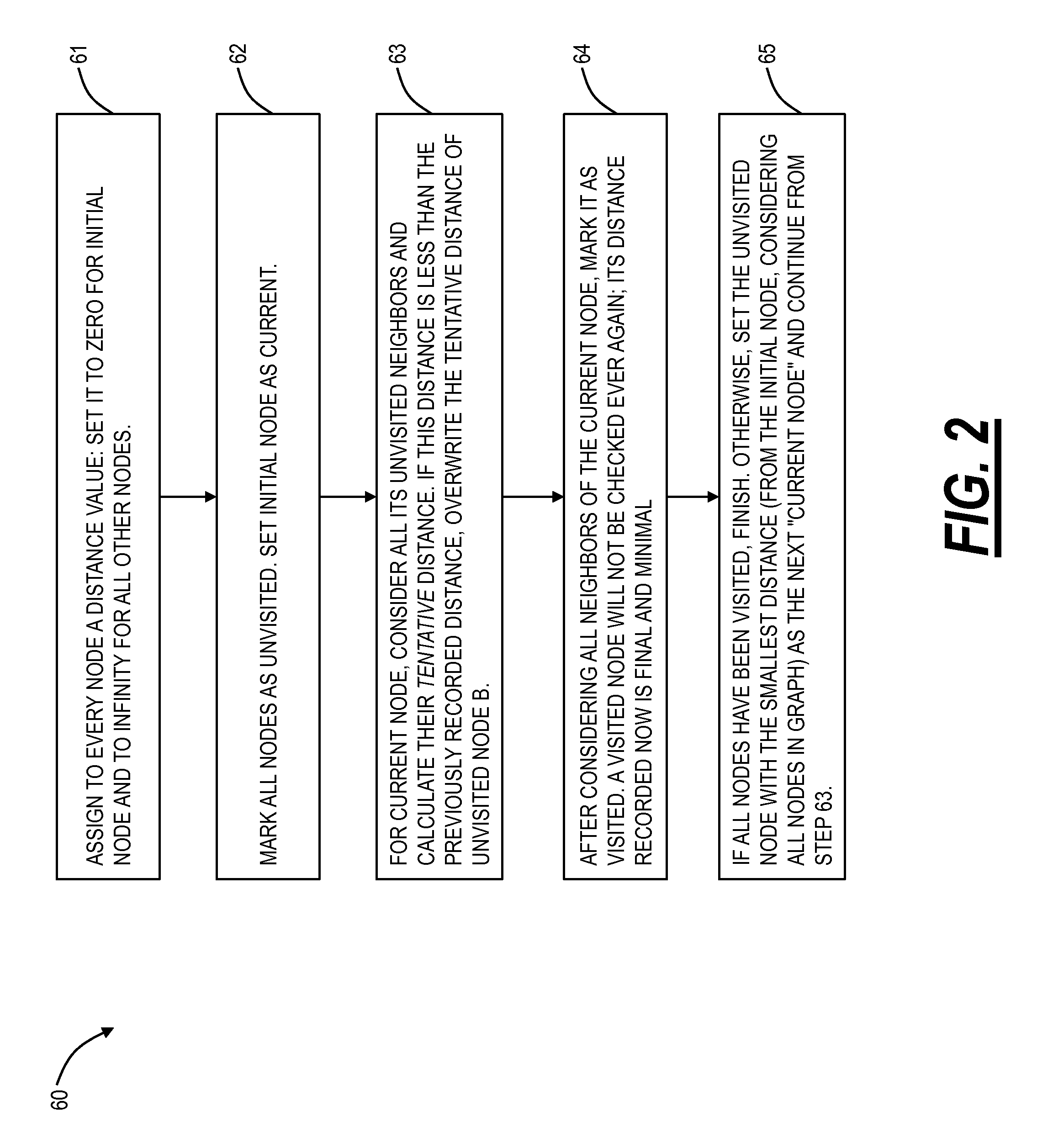
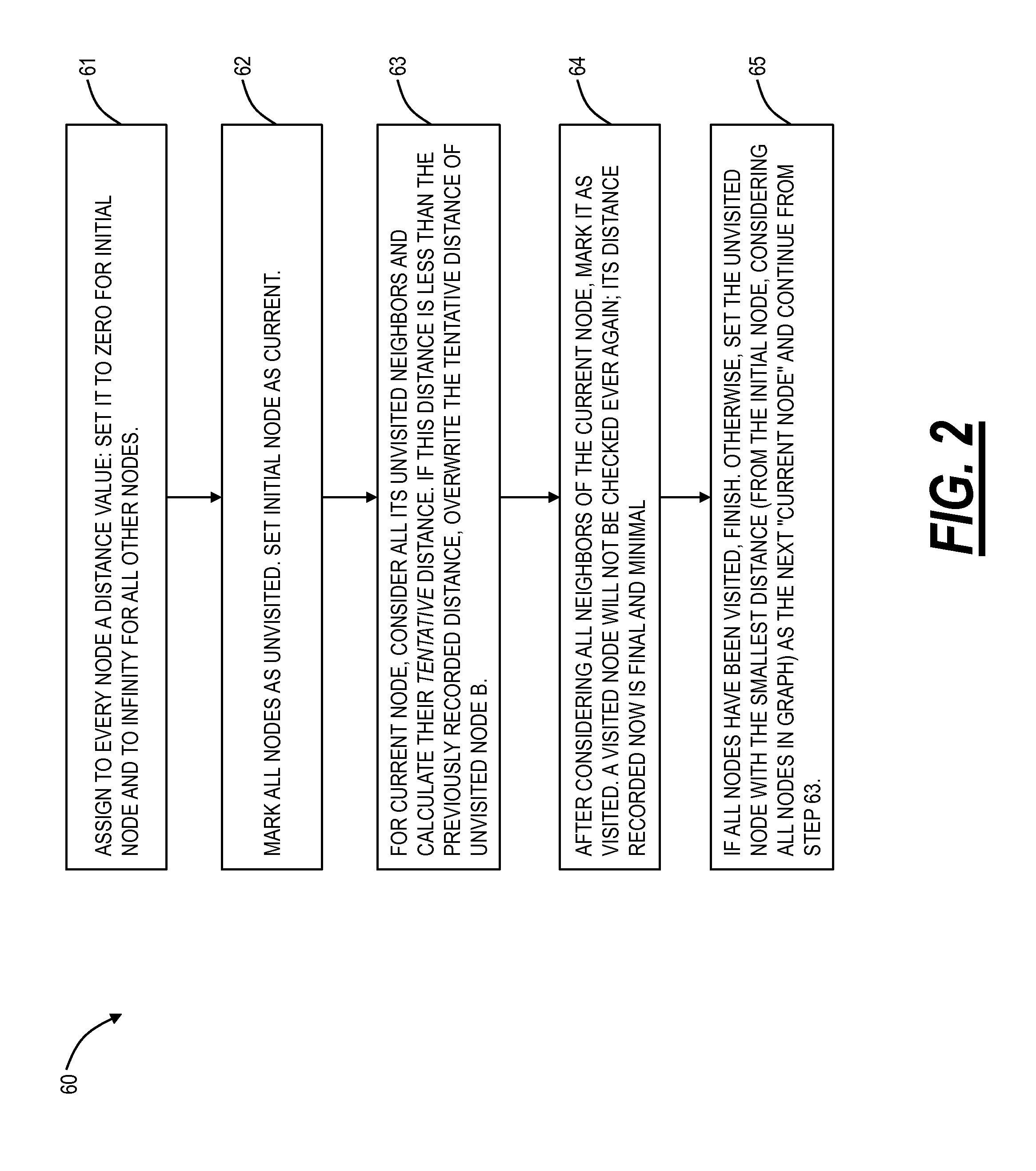
Shortest path routing systems and methods are presented for networks with non-fully meshed vertices or nodes. The systems and methods may include a shortest path routing method in a network with non-fully meshed vertices, a network with non-fully meshed vertices, and a system for implementing the shortest path routing methods. The shortest path routing systems and methods include modifications to the Dijkstra algorithm to more accurately model a network, such as an optical or photonic network. In an exemplary embodiment, the Dijkstra algorithm is modified to represent degrees at a site with an ingress vertex (e.g., a demultiplexer) and an egress vertex (e.g., a multiplexer). In another exemplary embodiment, in addition to representing degrees as ingress and egress vertices, the Dijkstra algorithm is modified to maintain knowledge of previously visited degrees to prevent revisiting a same degree in determining a shortest path.
Owner:CIENA
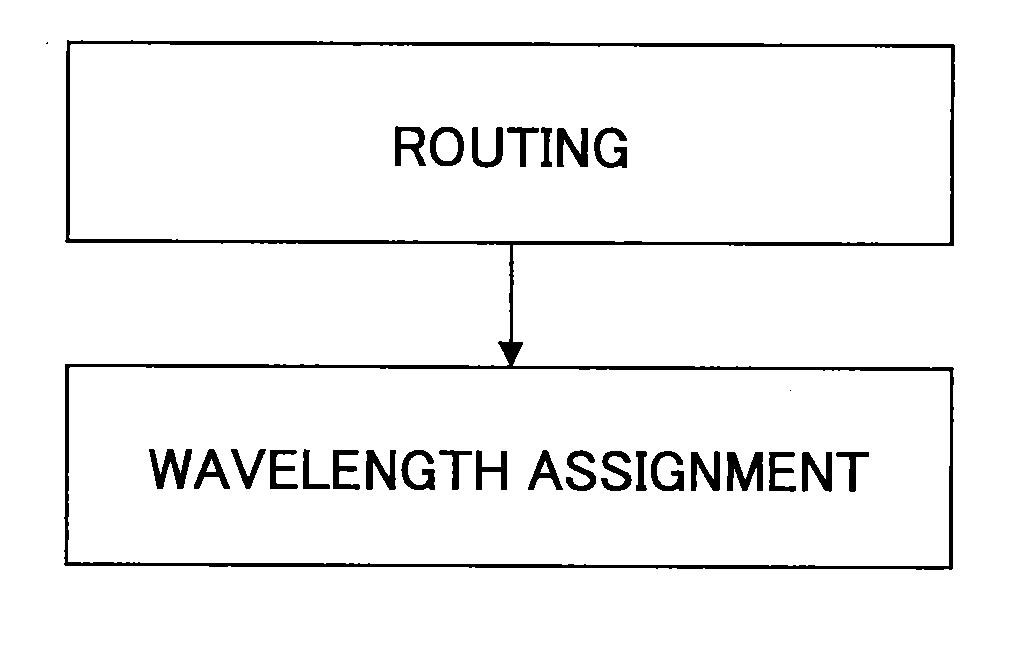
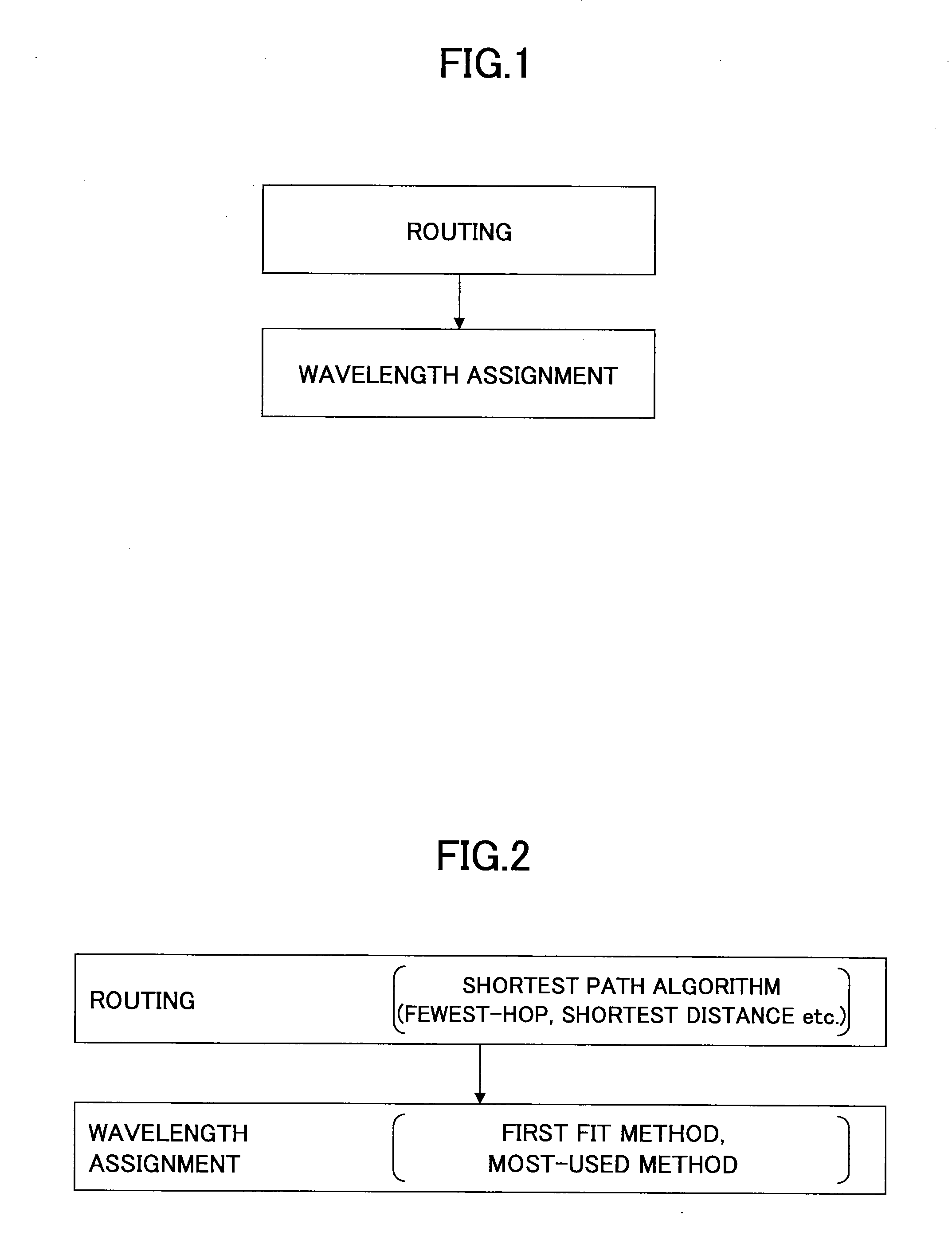
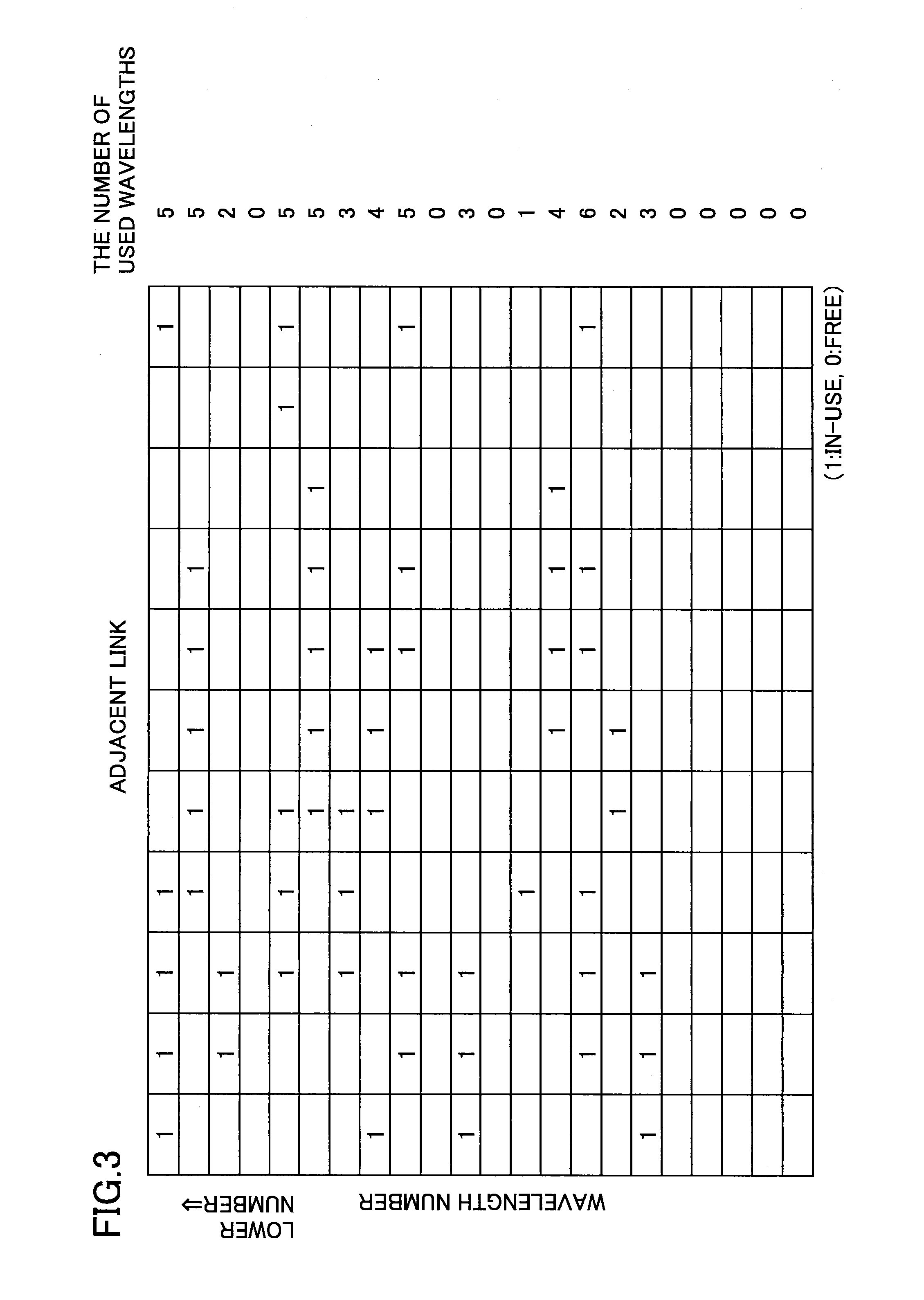
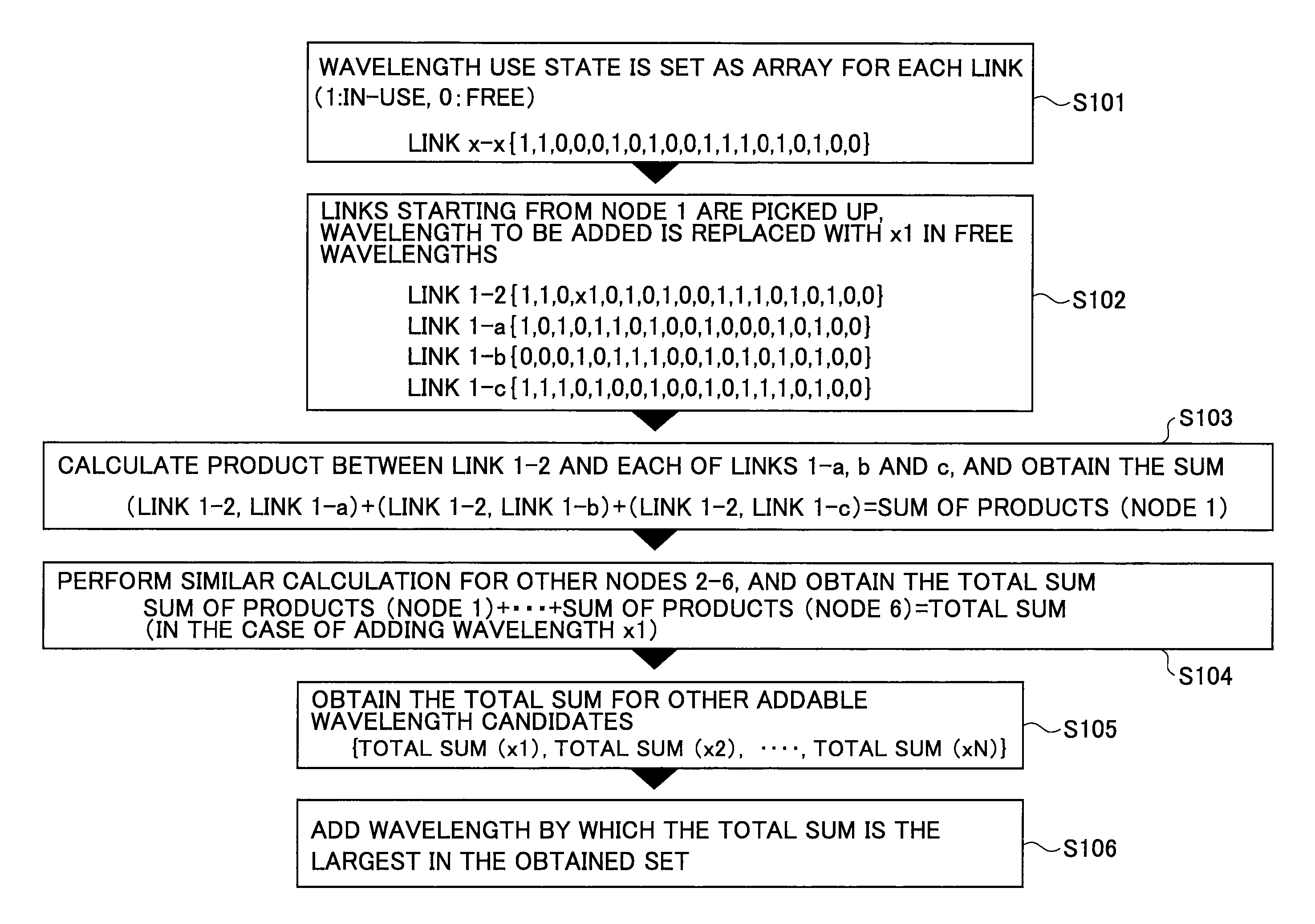
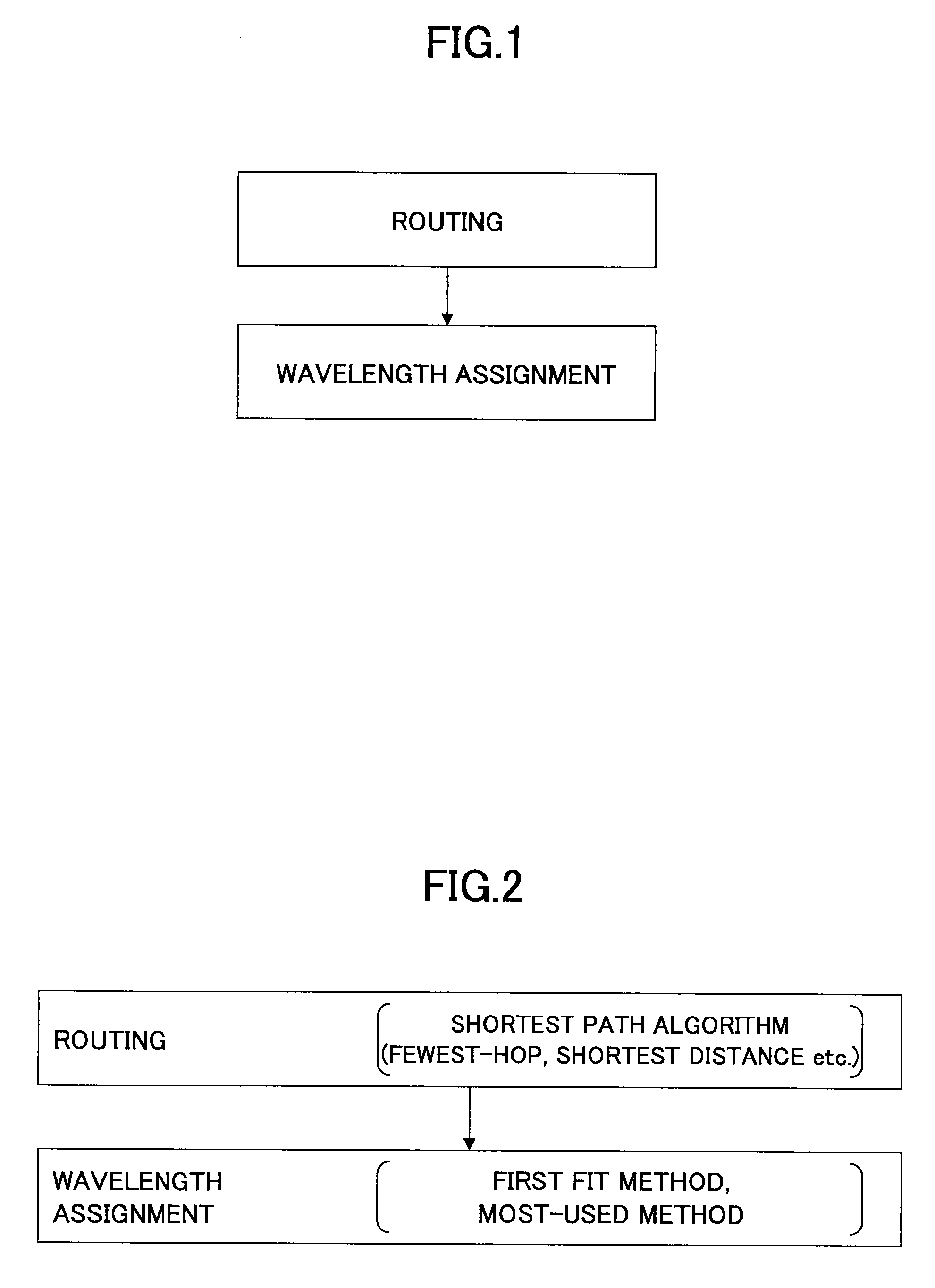
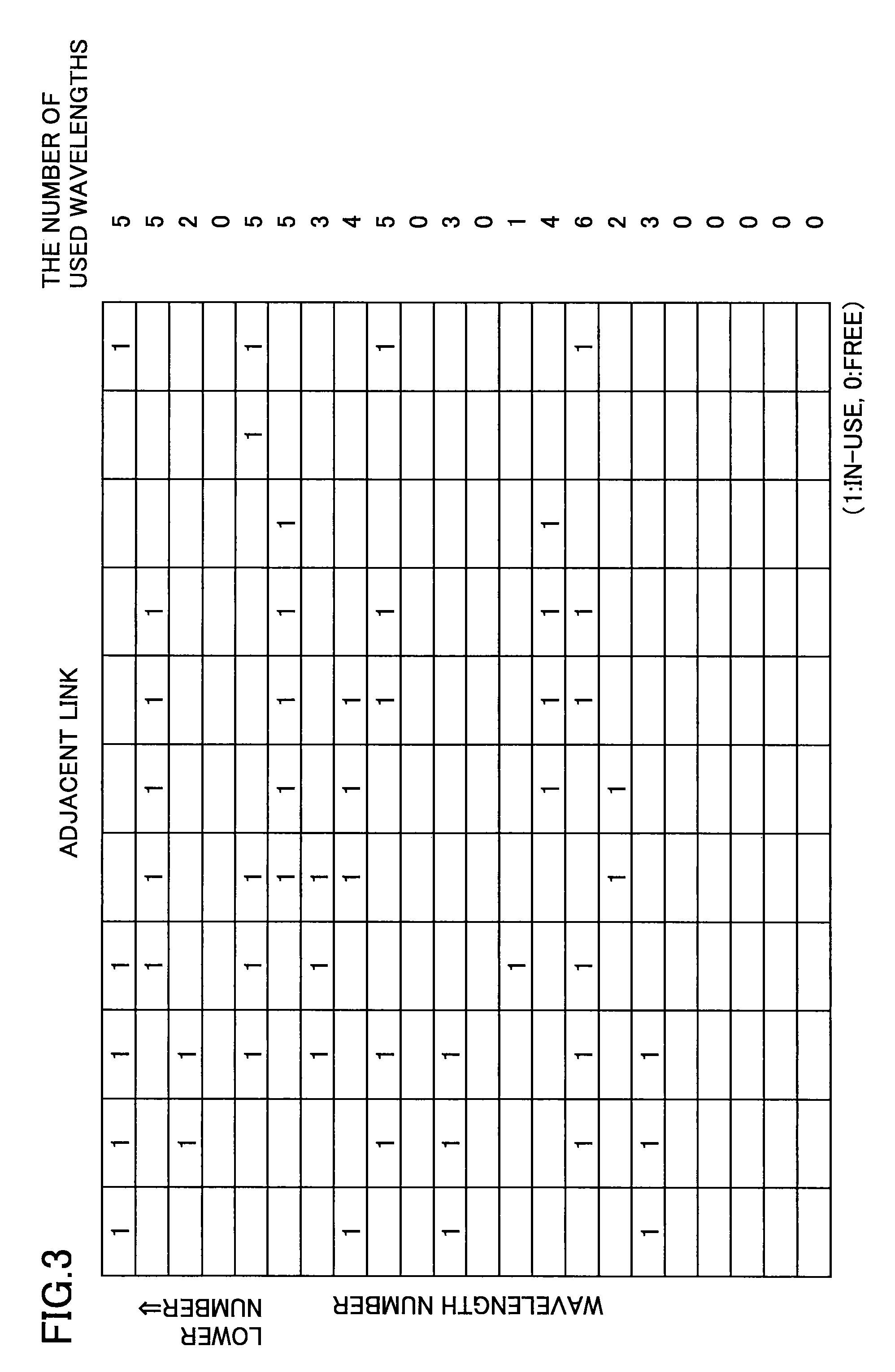
Frequency assignment method and apparatus
ActiveUS20130216226A1InhibitionImprove utilization efficiencyWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmissionElectricityLength wave
A frequency assignment method for selecting a frequency width used on a route connecting between a start point and an end point when the start point and the end point of an optical signal are supplied in a photonic network including an optical node that includes an optical switch for switching the optical signal without electrically terminating the optical signal is disclosed. The frequency assignment method includes steps of: obtaining a correlation amount of use state of wavelength or frequency between adjacent links by referring to a route calculation result; determining a fixed frequency width or variable frequency width to be set for a communication route based on the correlation amount; and assigning the fixed frequency width or the variable frequency width on the route.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Node used in photonic network, and photonic network
InactiveUS7313328B2Efficient managementMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsPhotonicsPath cost
A multi-layer photonic network and nodes used therein are provided. The multi-layer photonic network comprises a packet network which performs switching and transfer in packet units, and a photonic network comprising optical transmission lines and photonic switches, and which accommodates the packet network. The multi-layer photonic network also has a two layer structure of optical wavelength links (O-LSPs) and packet links (E-LSPs). The O-LSPs are constituted by the optical transmission lines and comprise optical wavelength switching capability (LSC) which is capable of switching in optical wavelength units and packet switching capability (PSC) which is capable of switching in packet units at both their ends. The E-LSPs include the O-LSPs and PSCs at both their ends. Each node includes a section for automatically establishing an O-LSP according to an establishment request for an E-LSP while taking account of path information including path cost, resource consumption, and traffic quantity.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Method and apparatus for rapidly measuring optical transmission characteristics in photonic networks
InactiveUS6980737B1Quick checkAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsElectronic circuit testingFast measurementPhotonics
An apparatus for determining an error ratio of individual channels of a WDM optical signal comprises a wavelength-selective filter for separating the individual channels of the WDM signal and a measurement circuit for measuring an error ratio of one channel using a first decision threshold level. The measurement circuit is operable to cycle through all channels, taking an error ratio measurement for each channel in sequence with a predetermined decision threshold level. Control circuitry alters the decision threshold level for successive cycles of the measurement circuit.The apparatus measures error ratio values for each channel in turn, building up an error ratio vs. threshold pattern enabling the Q value to be obtained. Although the time taken to build up the error ratio pattern for an individual channel is not shortened, measurements are taken on each channel at much shorter intervals. This means that signal degradations can be detected much more rapidly, as these signal degradations will be reflected in each error ratio measurements, and do not require a completely updated error ratio pattern to be obtained.
Owner:CIENA
Trail engineering in agile photonic networks
ActiveUS7599621B2Easy to useEfficient time-to-serviceOptical multiplexElectromagnetic transmissionPhotonicsNetwork architecture
An agile transparent network with a trail routing and switching (also called “engineering”) mechanism is provided that enables efficient use of regenerators and wavelengths available in the network, while maintaining a very efficient time-to-service. The trail engineering mechanism allows fast, automatic establishment of new connections based on the current network architecture, connectivity and loading and also on conditions in the connection request. Selection of regenerator sites and of the wavelengths used on each regenerator segment is performed with optimal use of current network resources, while ensuring that the quality of the selected trail is adequate for the respective call. The mechanism provides for both distance and performance balancing, and it optimizes the network response time.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
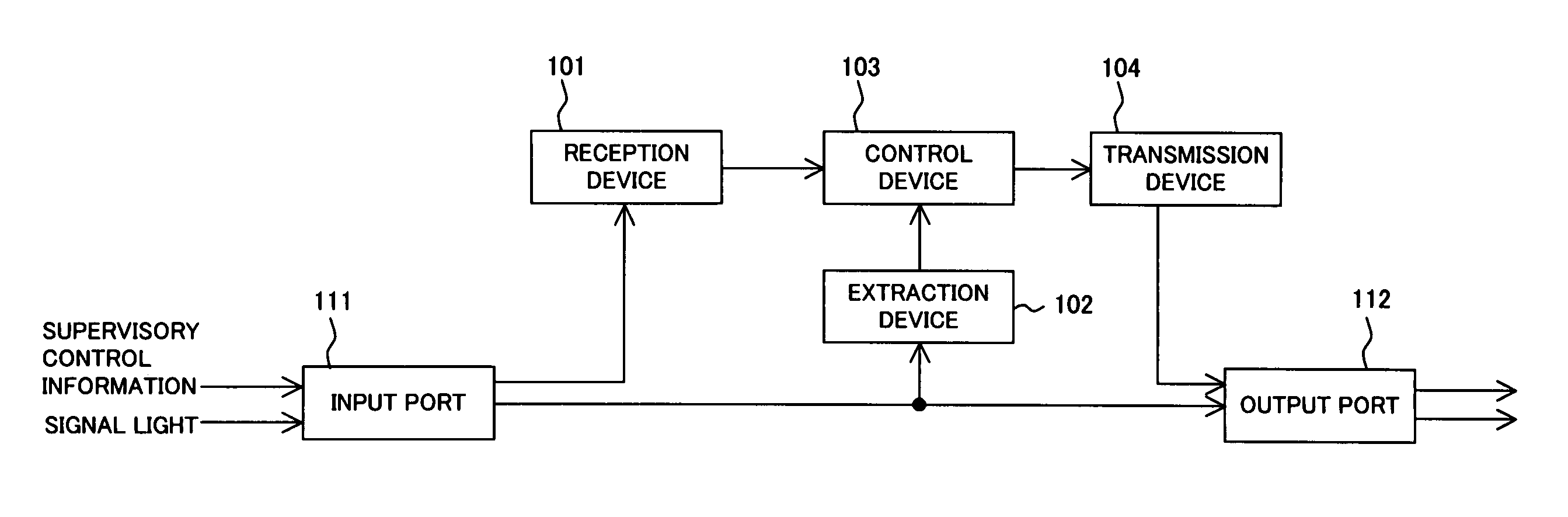
Node device for transfering supervisory control information in photonic network
InactiveUS20060209854A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexSignal lightEngineering
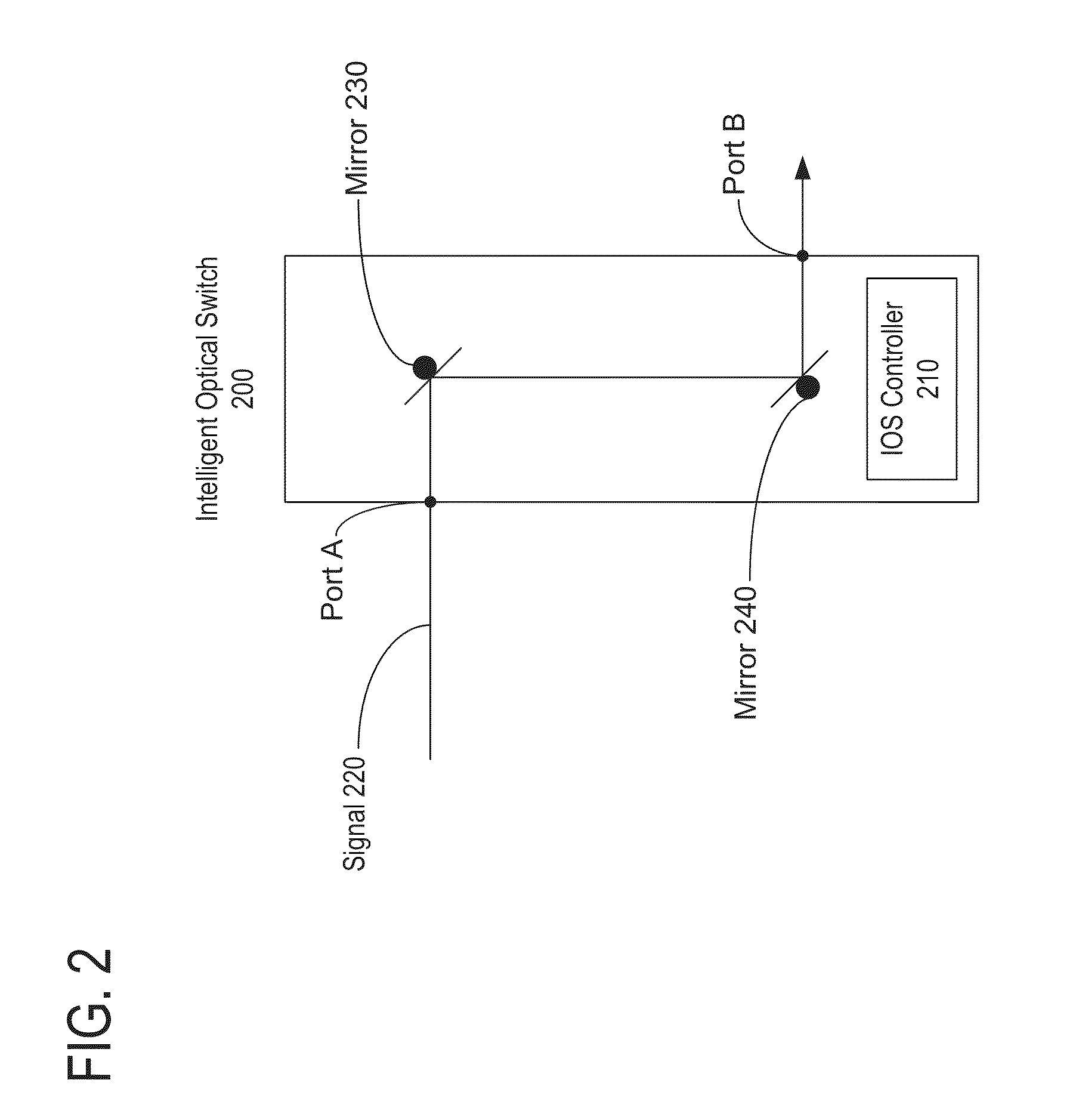
A node device receives supervisory control information on a dedicated wavelength different from a wavelength of signal light, which is input from an input port together with the signal light, and extracts, from signal light to be output from an output port, information superposed on an optical main signal of the signal light. Then, it is confirmed whether or not the signal light to be output and the supervisory control information correspond by using the extracted information, and supervisory control information corresponding to the signal light to be output is transmitted on the dedicated wavelength from the output port.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and system for managing optical distribution network
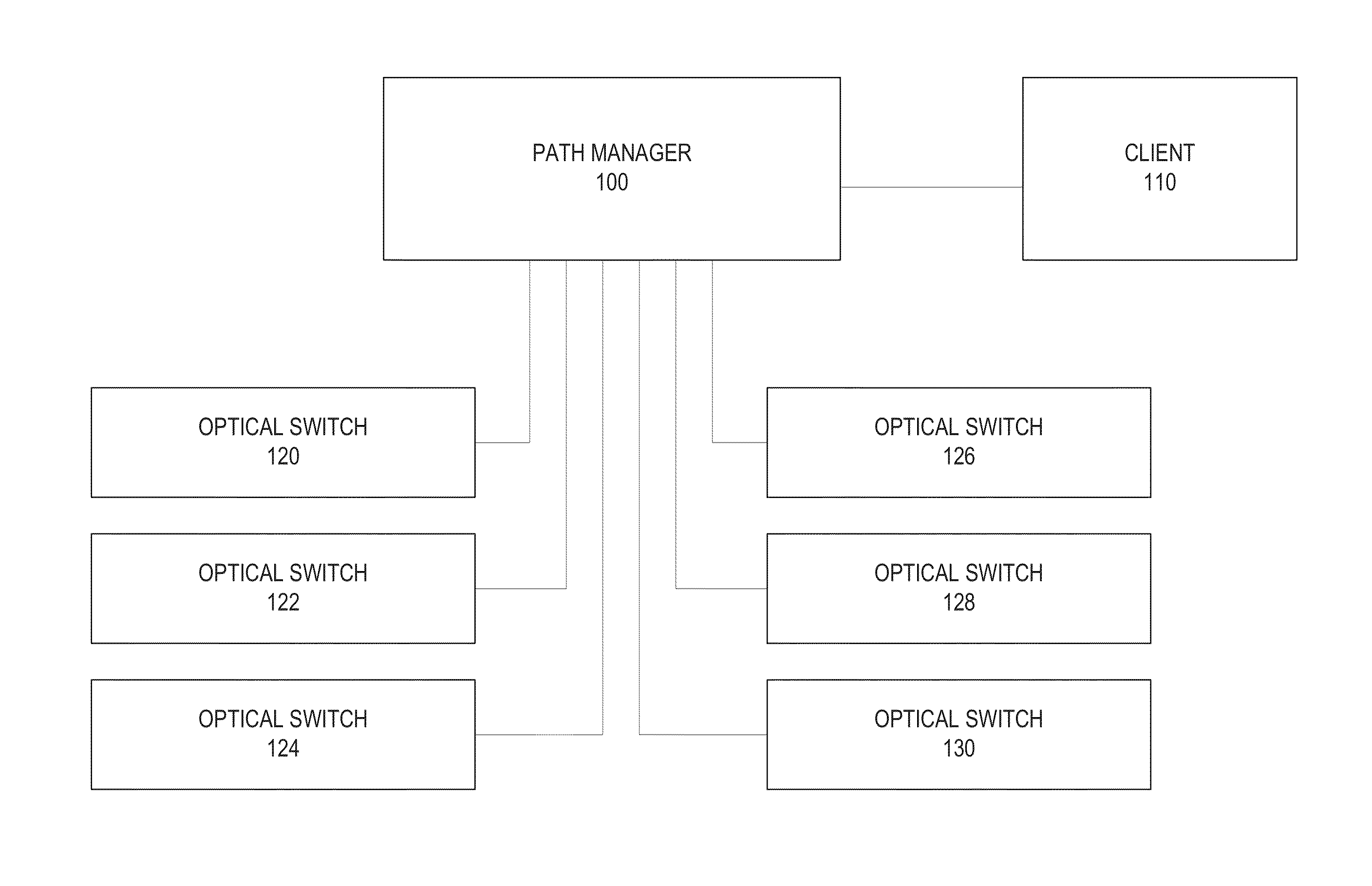
InactiveUS20130094855A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexDistributed computingDistribution networks
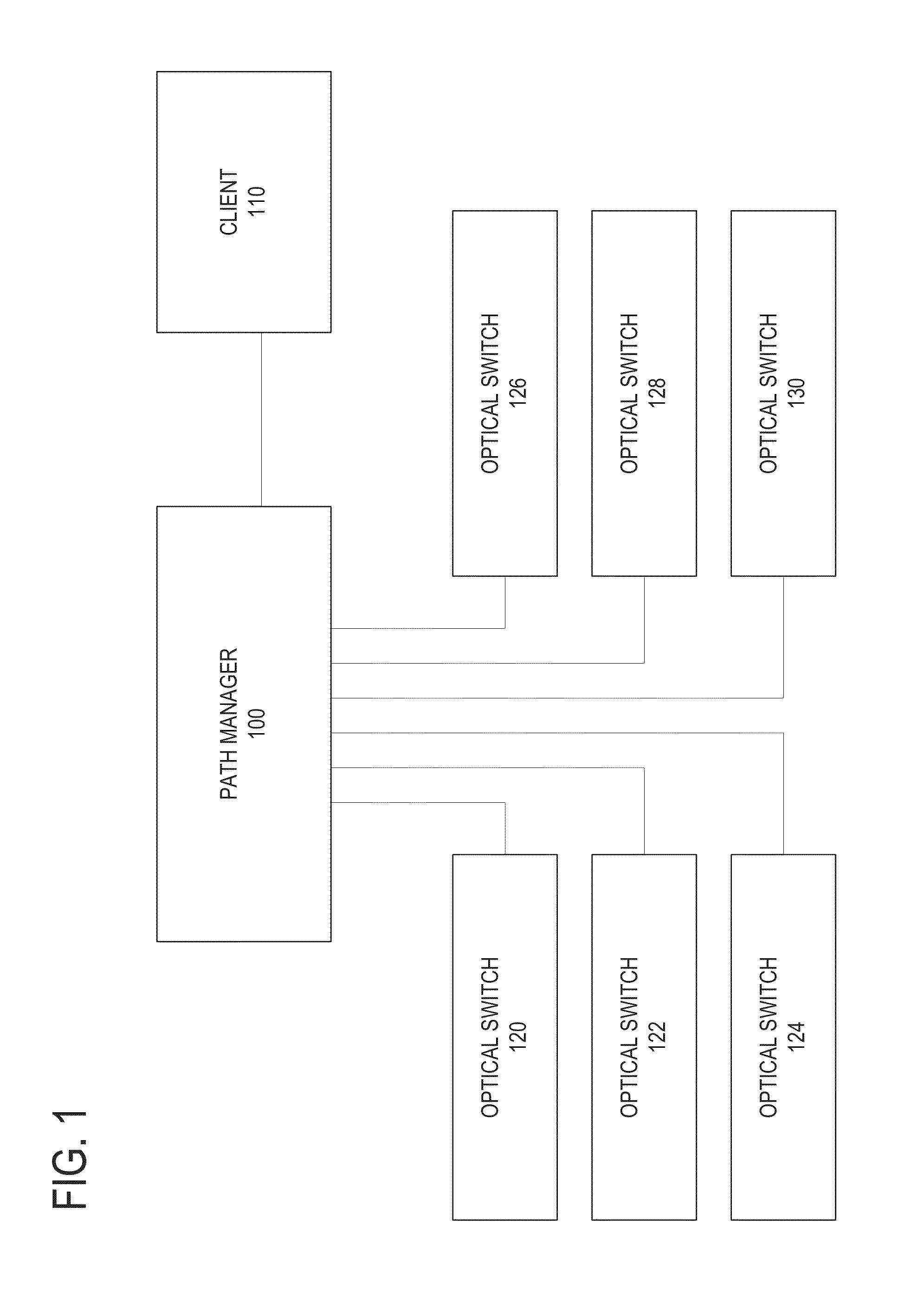
A method for generating optical paths in a photonic network is provided. A model of a photonic network is used to store relationship information that describes the relationships between photonic network elements, as well as configuration information about the elements of the photonic network. A path manager receives a request to generate one or more paths based on an input port and one or more output ports. Using the information stored in the photonic network model, the path manager generates one or more candidate paths.
Owner:GLIMMERGLASS NETWORKS
Dynamic assignment of wavelengths in agile photonic networks
InactiveUS8521022B1Fast and automatic establishmentImprove the quality of selectionMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexPath lengthGranularity
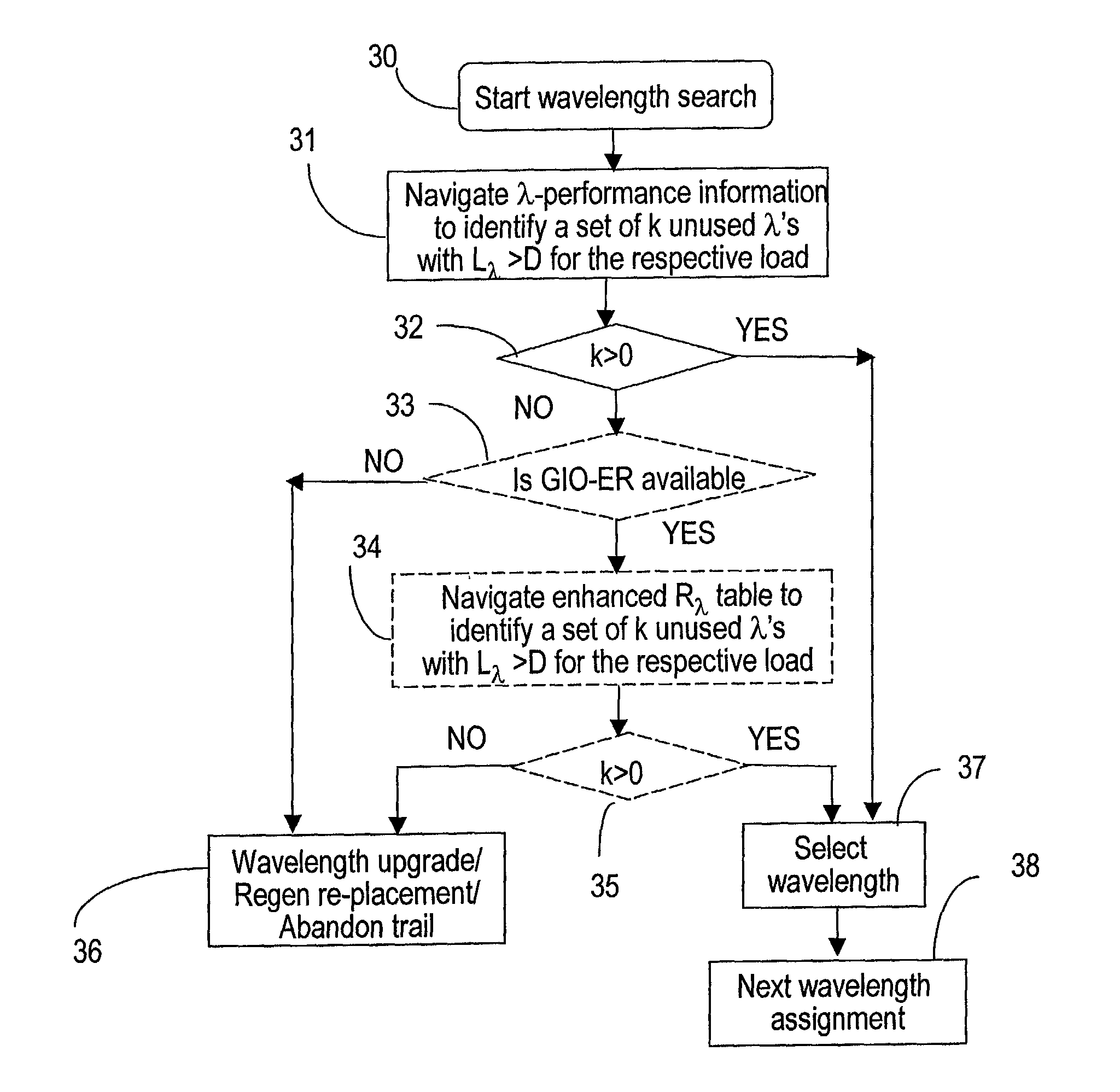
In an automatically switched optical network, the wavelengths are assigned to optical path based on their intrinsic physical performance and on the current network operating parameters. The wavelength performance information is organized in binning tables, based primarily on the wavelength reach capabilities. A network topology database provides the distance between the nodes of the network, which is used to determine the length of the optical path. Other network operating parameters needed for wavelength selection are also available in this database. Once a bin corresponding to the path length is identified in the binning table, the wavelength for that path is selected based on length only, or based on the length and one or more additional parameters. The optical path performance is estimated for the selected wavelength, and the search continues if the estimated path performance is not satisfactory. Several available wavelengths are searched and of those, the wavelength that is most used along the optical path in consideration or alternatively network-wide is selected and assigned. This method helps minimize wavelength fragmentation. The binning tables may have various granularities, and may be organized by reach, or by reach, wavelength spacing, the load on the respective optical path, the fiber type, etc.
Owner:PROVENANCE ASSET GRP LLC
Method For Engineering Connections In A Dynamically Reconfigurable Photonic Switched Network
InactiveUS20110182576A1Cost optimizationImprove performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsChannel powerPhotonics
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method for engineering connections in a dynamically reconfigurable photonic switched network
InactiveUS7941047B2High network costReduce networking costsMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsChannel powerPhotonics
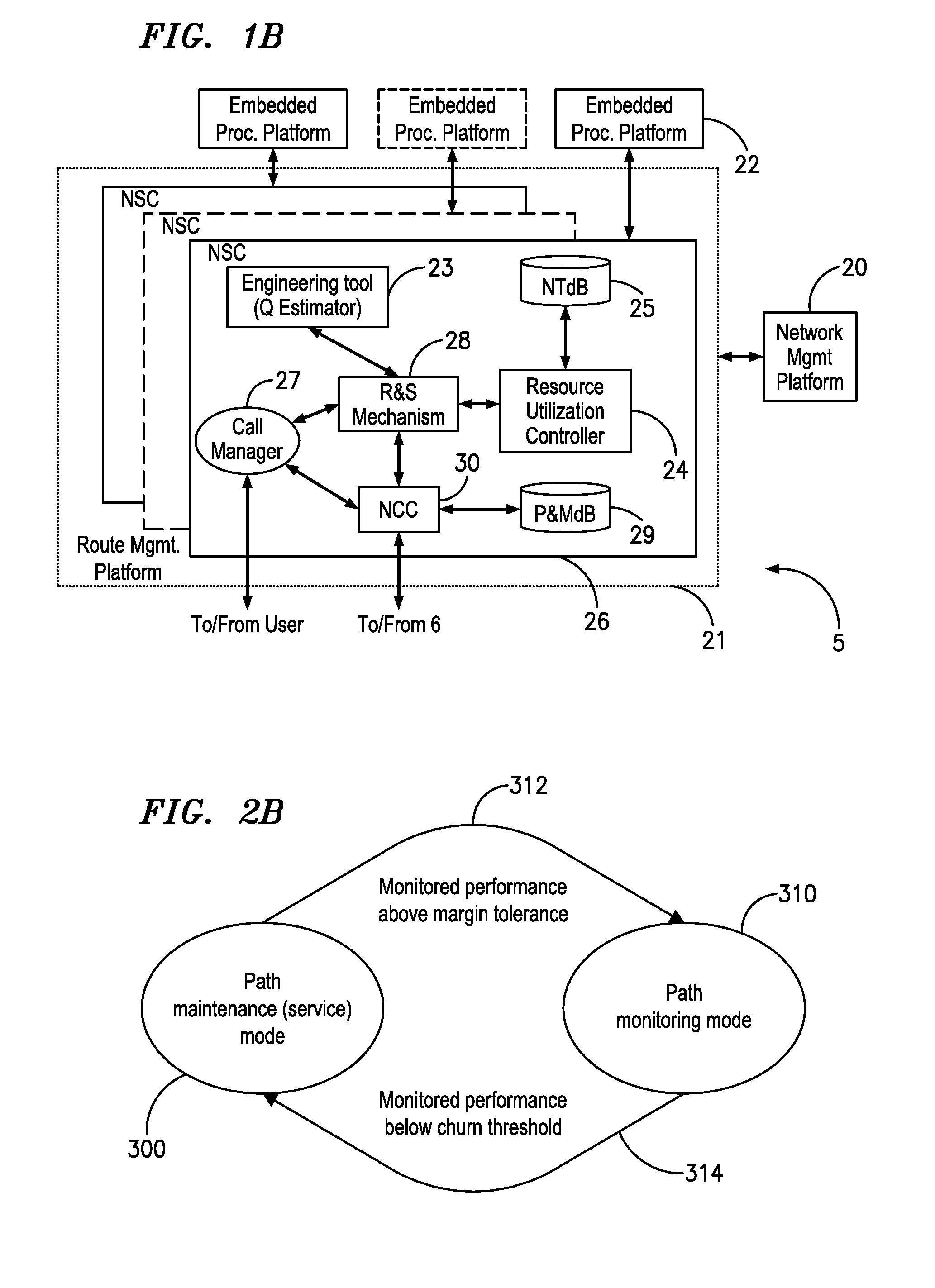
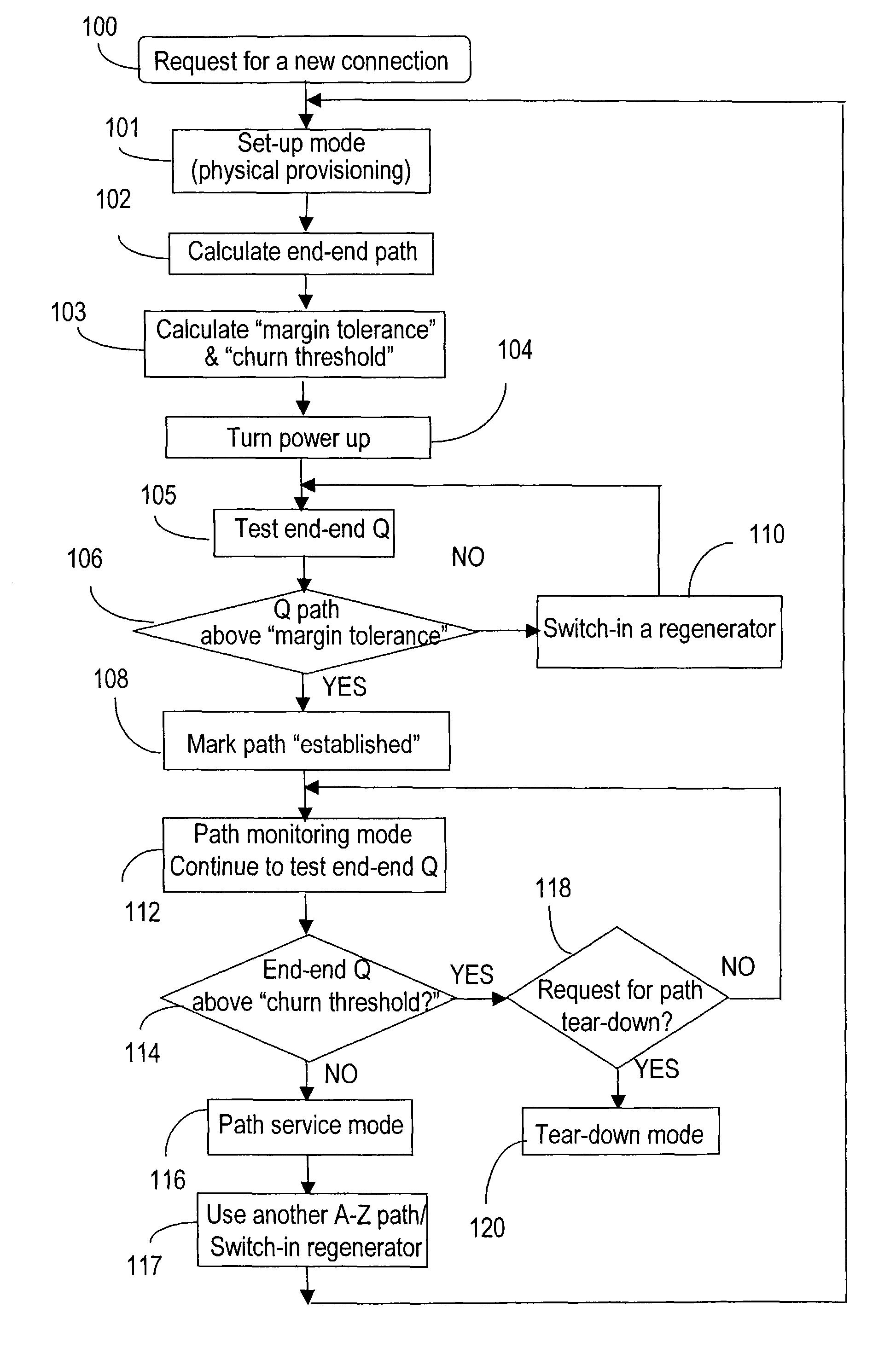
A method for engineering of a connection in a WDM photonic network with a plurality of flexibility sites connected by links comprises calculating a physical end-to-end route between a source node and a destination node and setting-up a communication path along this end-to-end route. An operational parameter of the communication path is continuously tested and compared with a test threshold. The path is declared established whenever the operational parameter is above the margin tolerance. The established path is continuously monitored by comparing the operational parameter with a maintenance threshold. A regenerator is switched into the path whenever the operational parameter is under the respective threshold, or another path is assigned to the respective connection. An adaptive channel power turn-on procedure provides for increasing gradually the power level of the transmitters in the path while measuring an error quantifier at the destination receiver until a preset error quantifier value is reached. As the connection ages, the power is increased so as to maintain the error quantifier at, or under the preset value. The path operation is controlled using a plurality of optical power / gain control loops, each for monitoring and controlling a group of optical devices, according to a set of loop rules.
Owner:PROVENANCE ASSET GRP LLC +1
Wavelength division multiplexing optical transmission system
InactiveUS20060039703A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesTransfer systemNetwork management
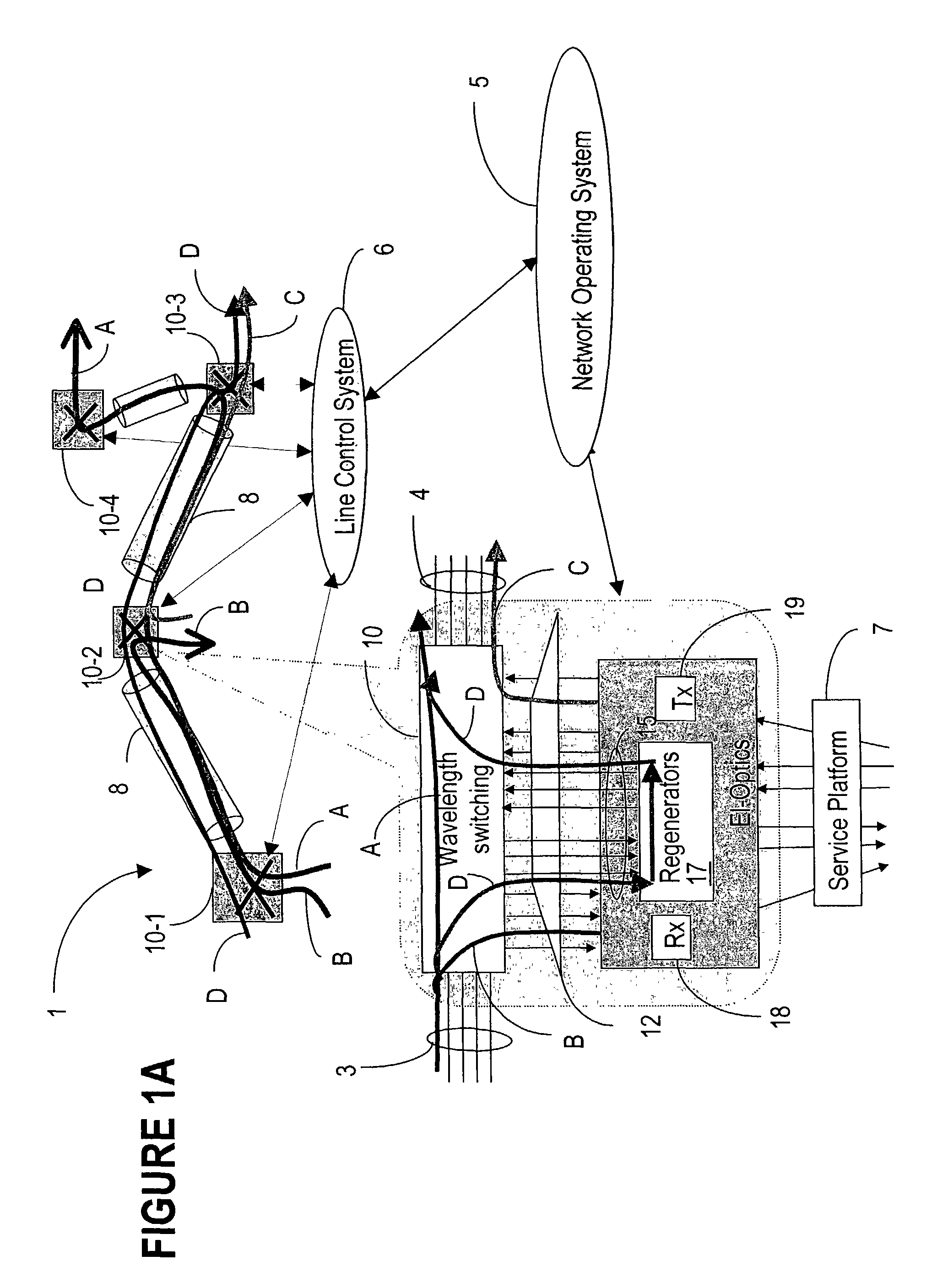
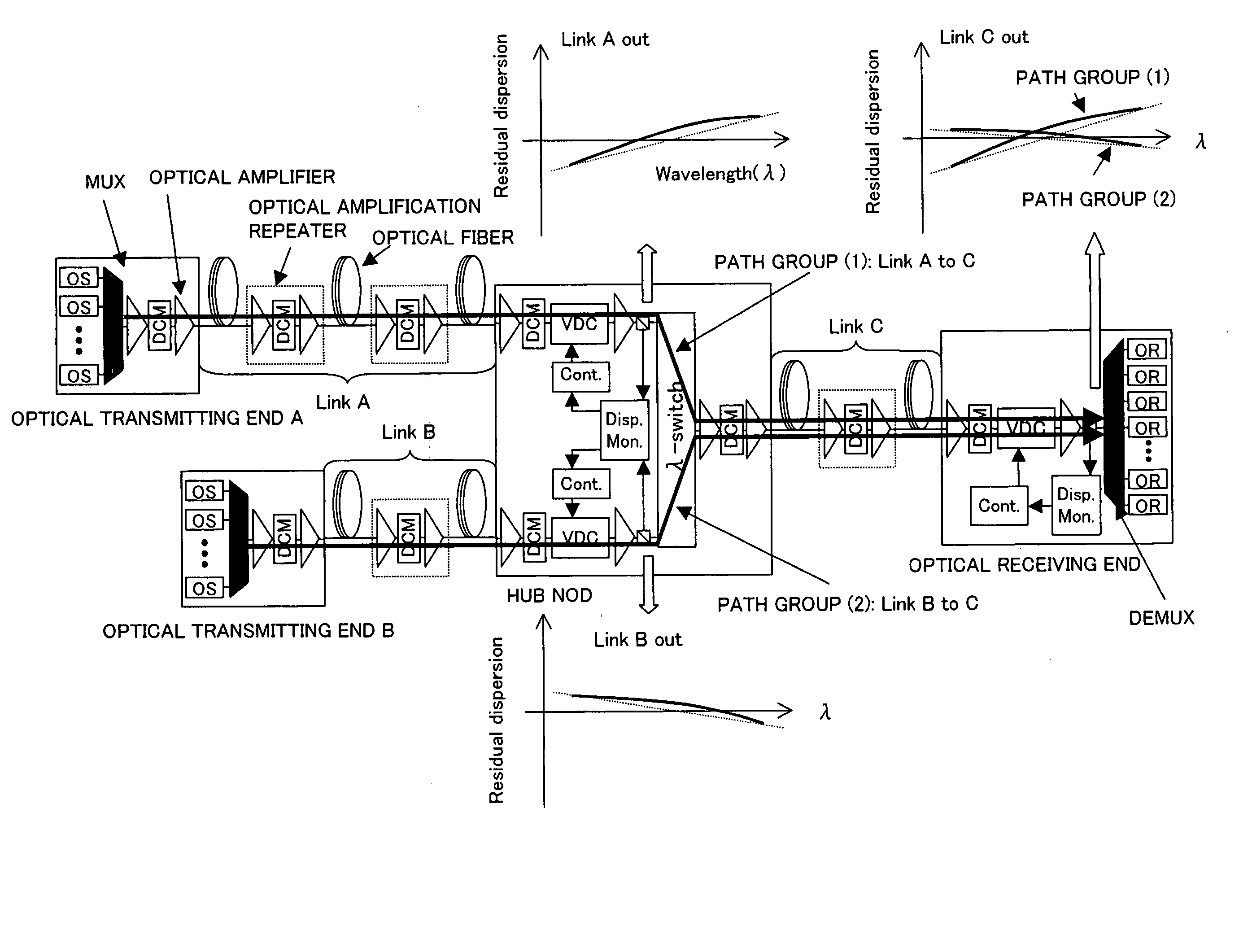
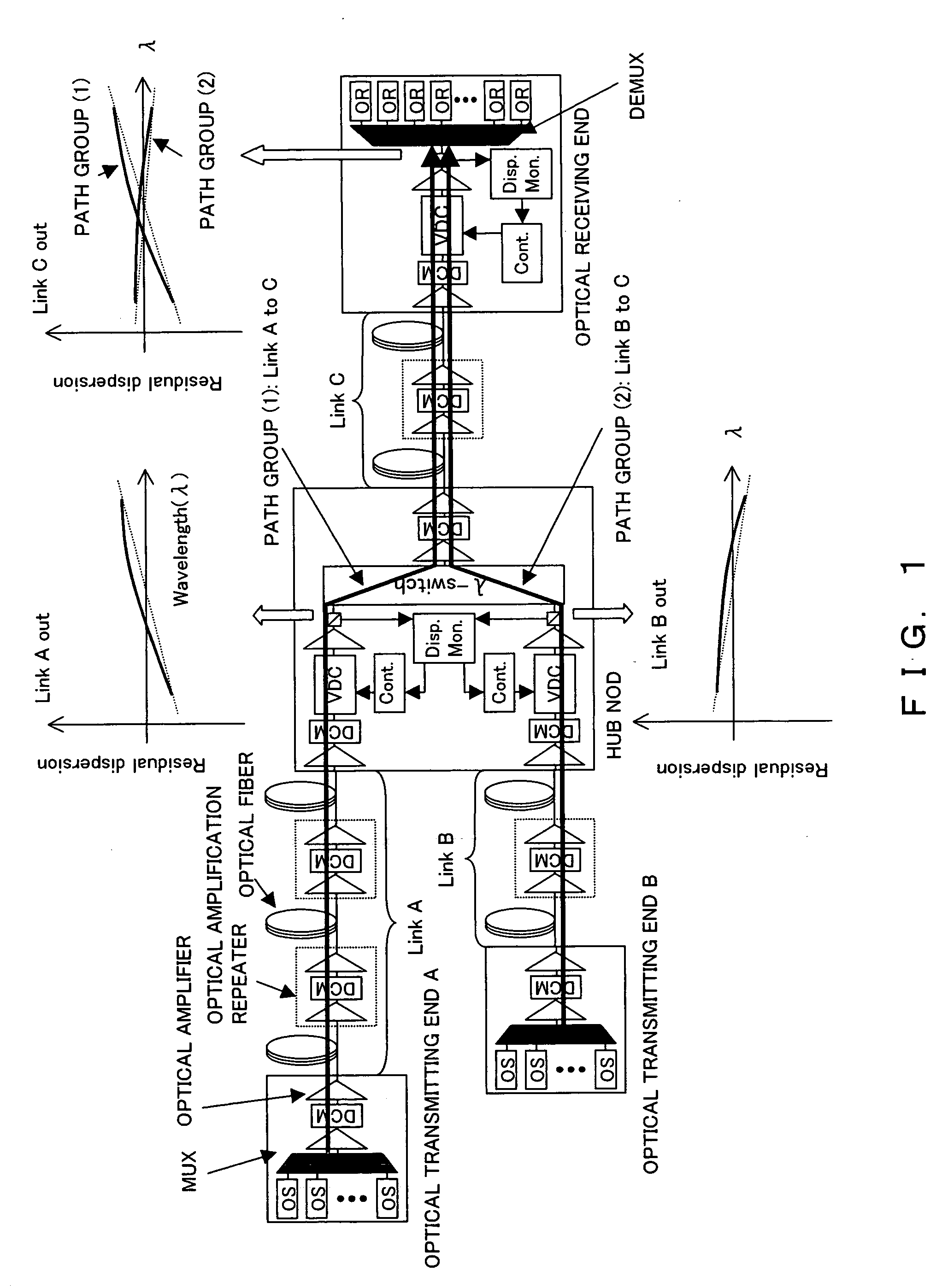
The objective of the present invention is to realize a chromatic dispersion compensation method which does not depend on a wavelength path in a photonic network to which a HUB node is applied and its monitoring control. In order to achieve this purpose, the present invention controls a plurality of variable chromatic dispersion compensators arbitrarily disposed in the photonic network based on the measured results of a plurality of chromatic dispersion monitors arbitrarily disposed in the photonic network and wavelength path information kept by the network management system which manages the entire photonic network. Here, the variable chromatic dispersion compensator within the network that should be controlled and the chromatic dispersion compensated quantity thereof are determined based on the measured results of the chromatic dispersion monitor and the wavelength path information kept by NMS.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Shortest path routing systems and methods for networks with non-fully meshed vertices
ActiveUS20130070617A1Maintain topologyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNODALMultiplexer
Shortest path routing systems and methods are presented for networks with non-fully meshed vertices or nodes. The systems and methods may include a shortest path routing method in a network with non-fully meshed vertices, a network with non-fully meshed vertices, and a system for implementing the shortest path routing methods. The shortest path routing systems and methods include modifications to the Dijkstra algorithm to more accurately model a network, such as an optical or photonic network. In an exemplary embodiment, the Dijkstra algorithm is modified to represent degrees at a site with an ingress vertex (e.g., a demultiplexer) and an egress vertex (e.g., a multiplexer). In another exemplary embodiment, in addition to representing degrees as ingress and egress vertices, the Dijkstra algorithm is modified to maintain knowledge of previously visited degrees to prevent revisiting a same degree in determining a shortest path.
Owner:CIENA
Dynamic Assignment Of Wavelengths In Agile Photonic Networks
InactiveUS20130302033A1Fast and automatic establishmentQuality improvementMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexPath lengthGranularity
In an automatically switched optical network, the wavelengths are assigned to optical path based on their intrinsic physical performance and on the current network operating parameters. The wavelength performance information is organized in binning tables, based primarily on the wavelength reach capabilities. A network topology database provides the distance between the nodes of the network, which is used to determine the length of the optical path. Other network operating parameters needed for wavelength selection are also available in this database. Once a bin corresponding to the path length is identified in the binning table, the wavelength for that path is selected based on length only, or based on the length and one or more additional parameters. The optical path performance is estimated for the selected wavelength, and the search continues if the estimated path performance is not satisfactory. Several available wavelengths are searched and of those, the wavelength that is most used along the optical path in consideration or alternatively network-wide is selected and assigned. This method helps minimize wavelength fragmentation. The binning tables may have various granularities, and may be organized by reach, or by reach, wavelength spacing, the load on the respective optical path, the fiber type, etc.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Path-number-balanced universal photonic network
Owner:LIGHTMATTER INC
Frequency assignment method and apparatus
ActiveUS9154257B2InhibitionImprove utilization efficiencyWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionLength waveComputer science
A frequency assignment method for selecting a frequency width used on a route connecting between a start point and an end point when the start point and the end point of an optical signal are supplied in a photonic network including an optical node that includes an optical switch for switching the optical signal without electrically terminating the optical signal is disclosed. The frequency assignment method includes steps of: obtaining a correlation amount of use state of wavelength or frequency between adjacent links by referring to a route calculation result; determining a fixed frequency width or variable frequency width to be set for a communication route based on the correlation amount; and assigning the fixed frequency width or the variable frequency width on the route.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com