Sharing type optical packet switching node structure based on inside wavelength
An optical packet switching and node structure technology, applied in data switching networks, wavelength division multiplexing systems, selection devices for multiplexing systems, etc. The effect of solving the FDL competition problem, optimizing the packet loss performance, and compacting the node structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0014] In order to better understand the technical solutions of the present invention, the implementation manners will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
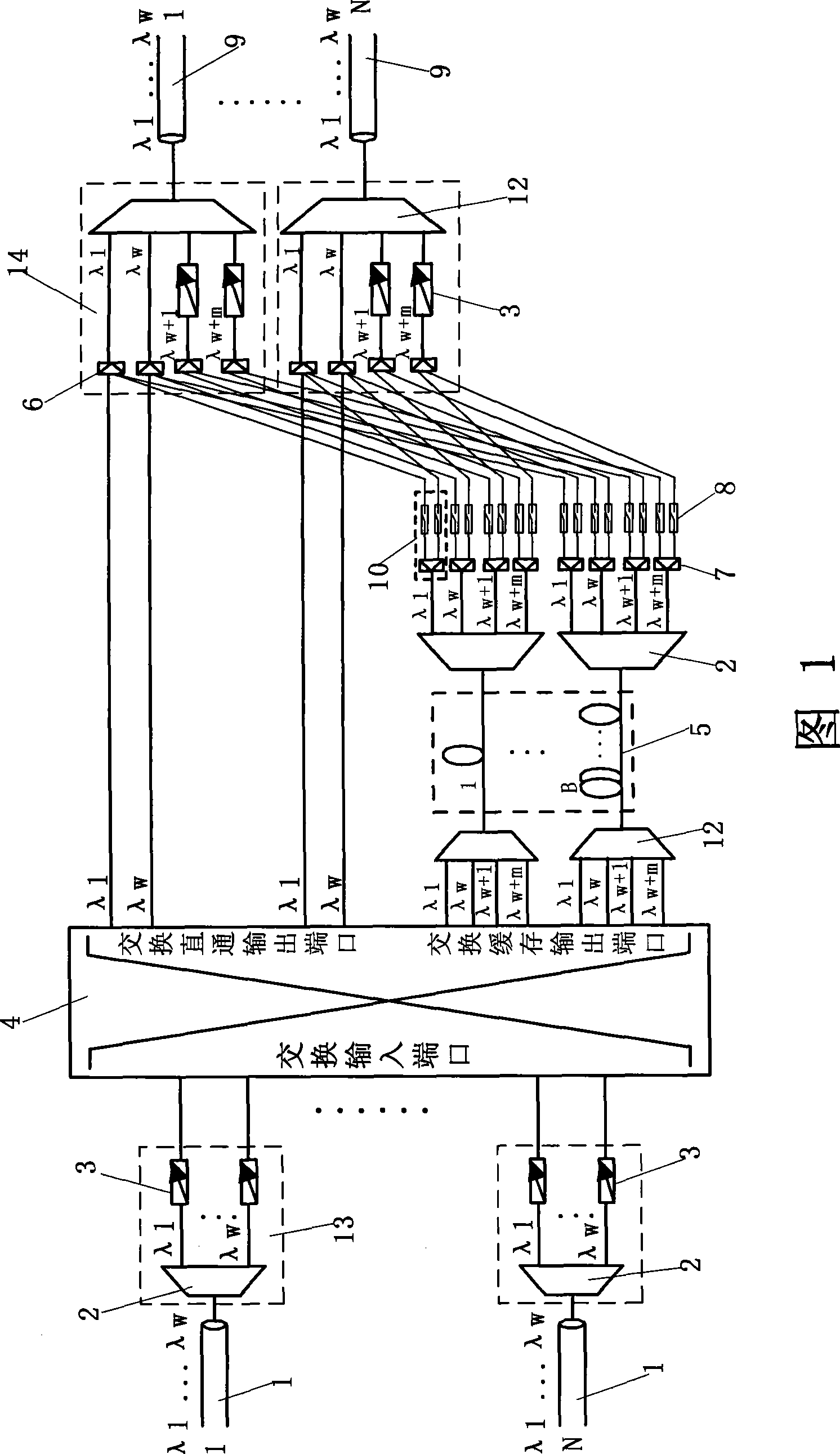
[0015] Optical packet switching node structure of the present invention as shown in Figure 1, by a plurality of wavelength division multiplexers 2, adjustable wavelength converter 3, optical switch matrix 4, wavelength division multiplexer 12, fiber delay line (FDL) 5. It consists of a splitter 7, a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) optical gate 8, a passive coupler 6 and connecting optical fibers.
[0016] There are N node input ports 13 on the left side of the switching node, and each node input port 13 is connected to an input optical fiber 1; there are N node output ports 14 on the right side of the switching node, and each node output port 14 is connected to an output optical fiber 9. W transmission wavelengths (λ j , j ∈ {1,...,W}). The core switching function of the switc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com