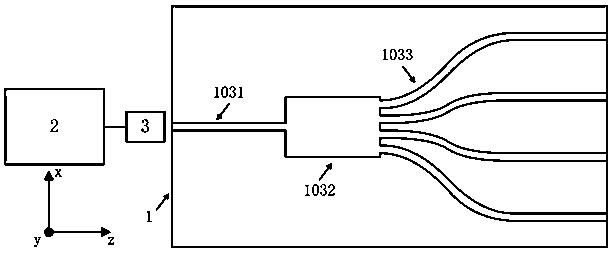
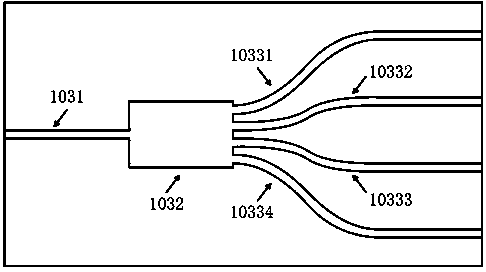
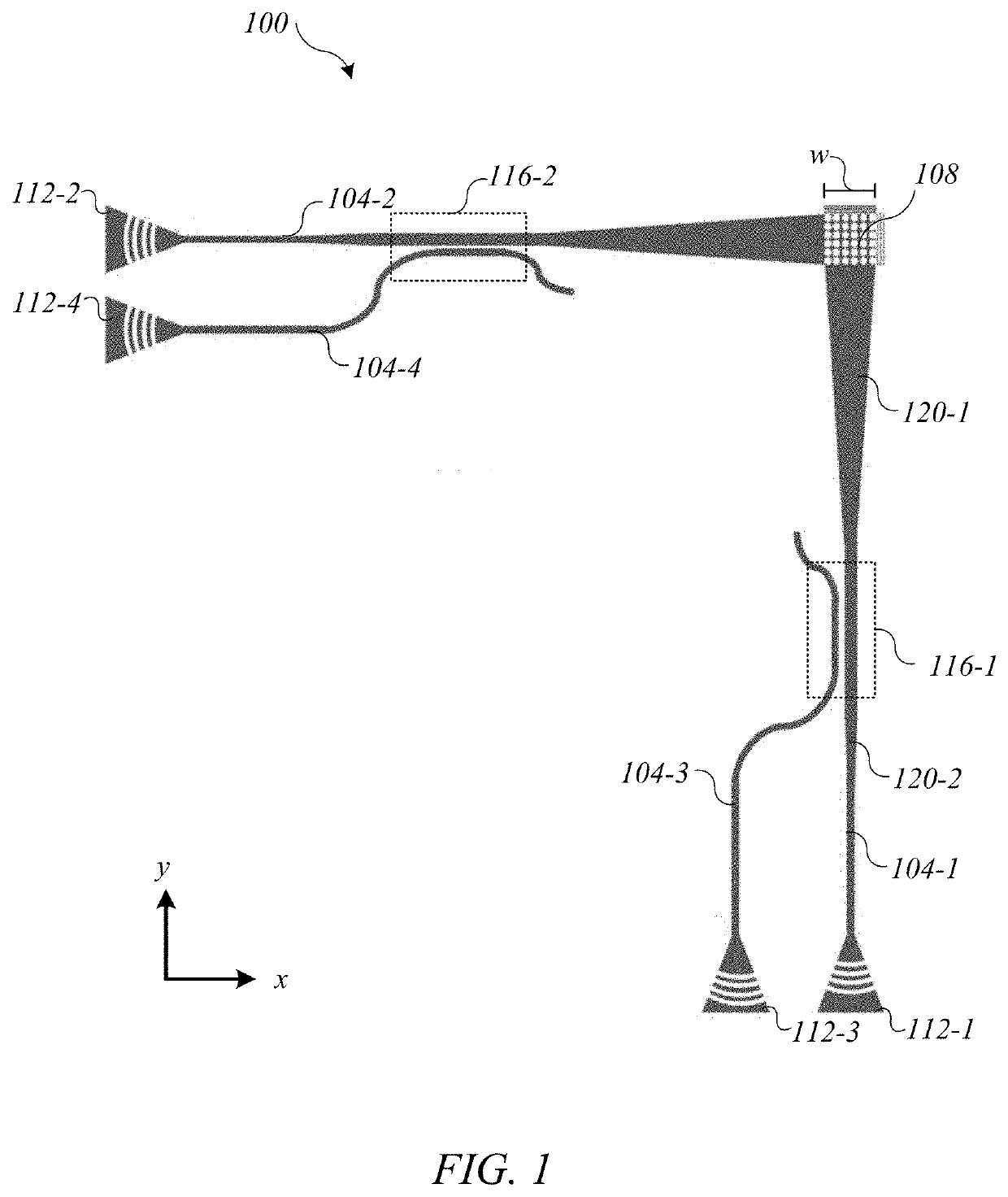
Patents
Literature
93 results about "Multimode waveguides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods and apparatus for imaging with multimode optical fibers
ActiveUS20150015879A1Radiation pyrometryOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingLight dispersionImage resolution
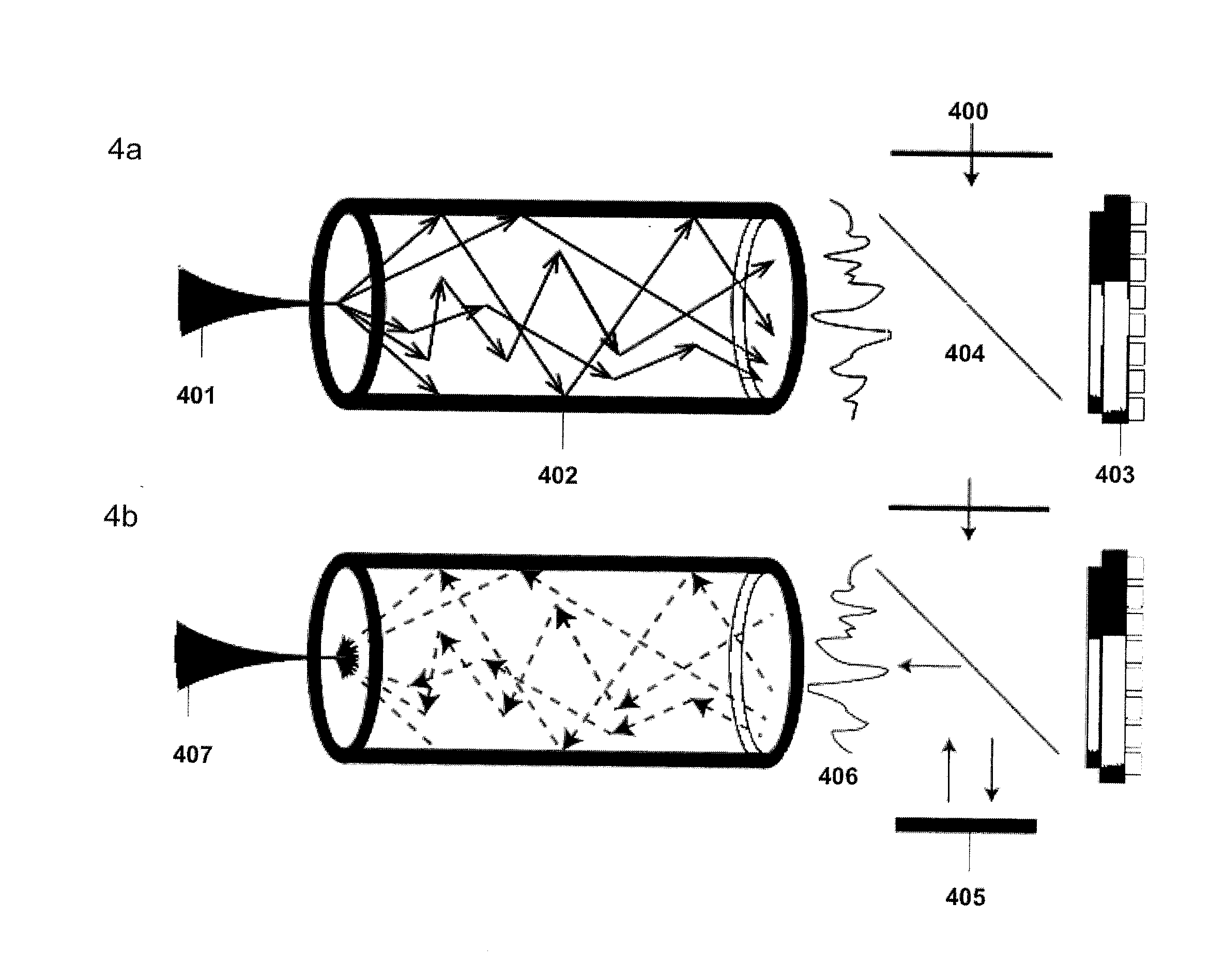
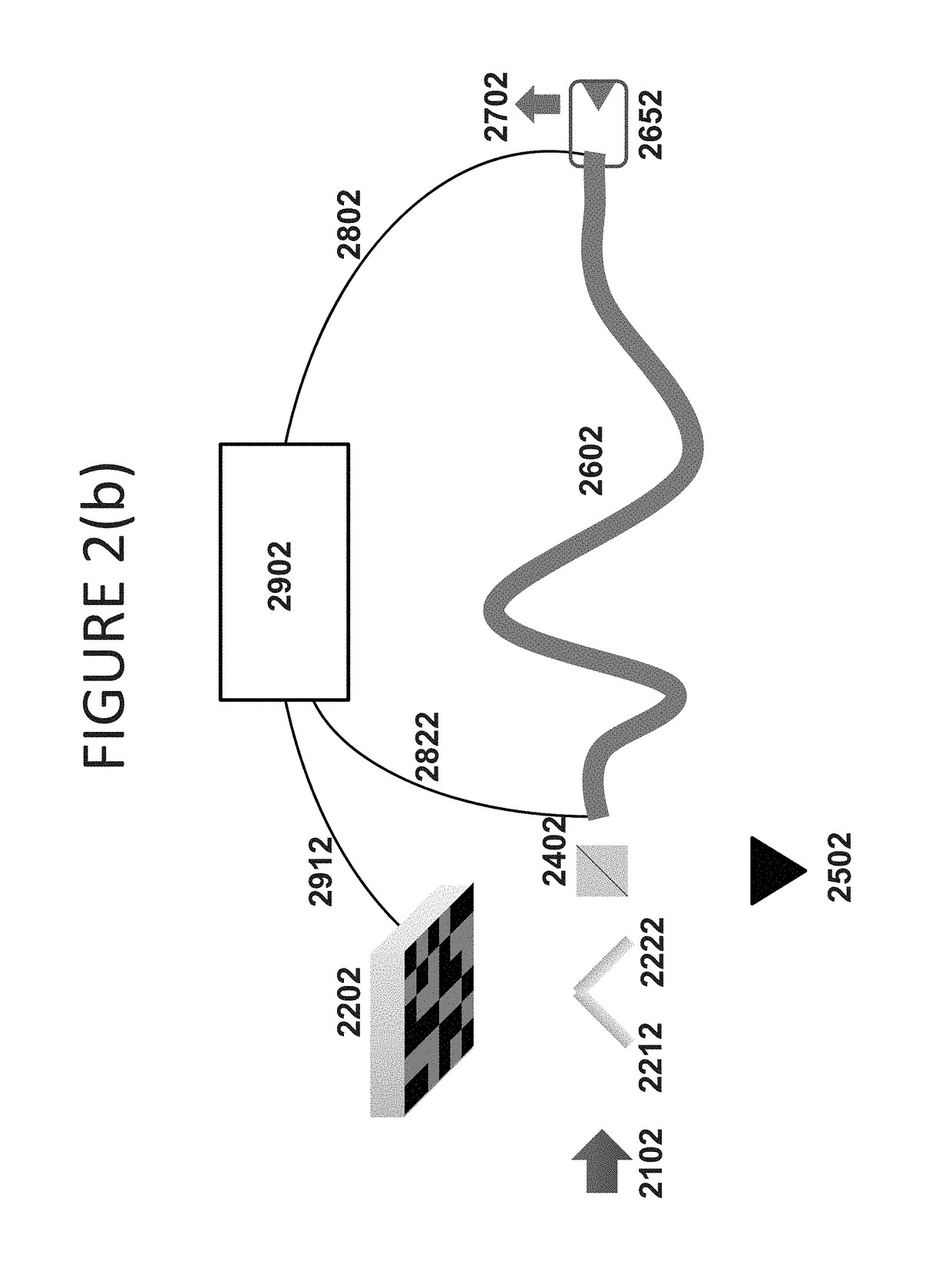
A multimode waveguide illuminator and imager relies on a wave front shaping system that acts to compensate for modal scrambling and light dispersion by the multimode waveguide. A first step consists of calibrating the multimode waveguide and a second step consists in projecting a specific pattern on the waveguide proximal end in order to produce the desire light pattern at its distal end. The illumination pattern can be scanned or changed dynamically only by changing the phase pattern projected at the proximal end of the waveguide. The third and last step consists in collecting the optical information, generated by the sample, through the same waveguide in order to form an image. Known free space microscopy technique can be adapted to endoscopy with multimode waveguide, such as, but not limited to, fluorescence imaging or Raman spectroscopy or imaging, 3D linear scattering imaging or two-photon imaging. Super-resolution, i.e., resolution below the diffraction limit, is achieved for example but not limited to, using the STimulated Emission Depletion microscopy (STED) technique or the Structured Illumination Microscopy (SIM) technique or a stochastic illumination based method (PALM, STORM) in combination with the multimode waveguide imaging method.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
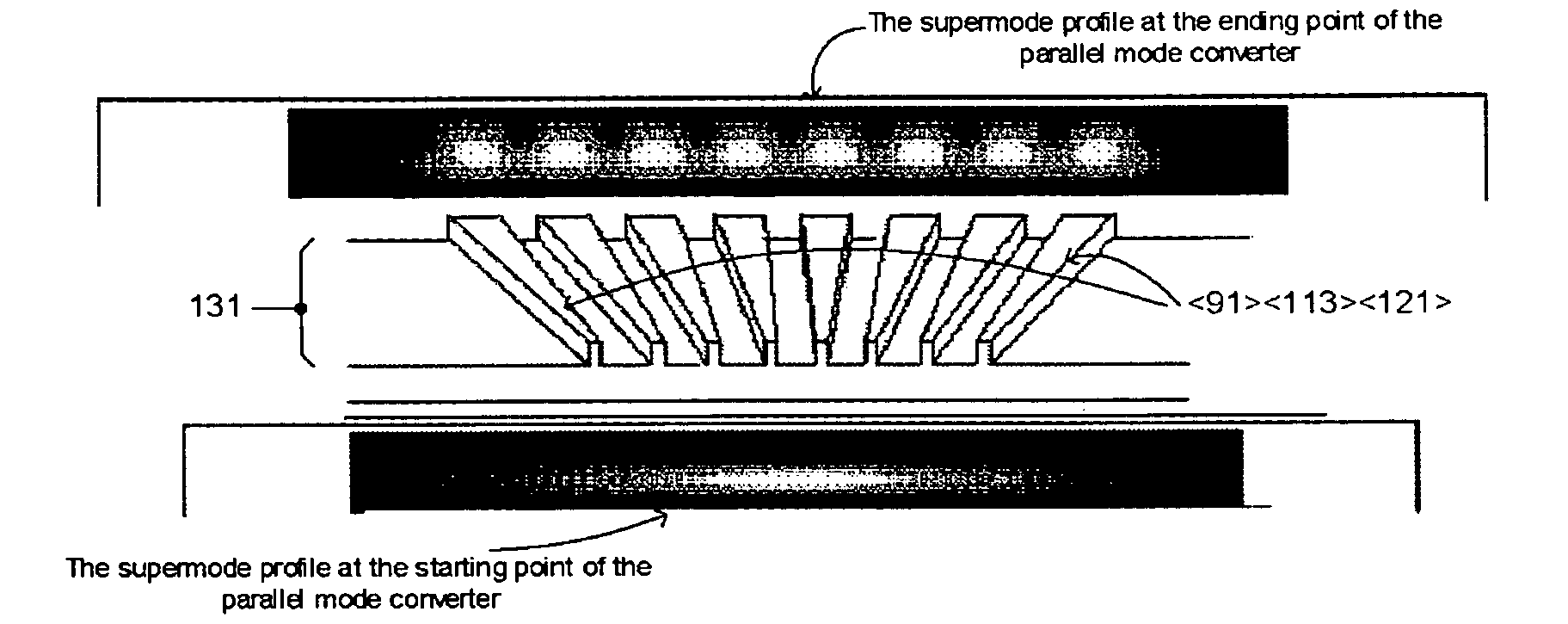
Single mode photonic circuit architecture and a new optical splitter design based on parallel waveguide mode conversion
ActiveUS20080002928A1Increase contrastSmall bend radiusNanoopticsCoupling light guidesRefractive indexWaveguide mode
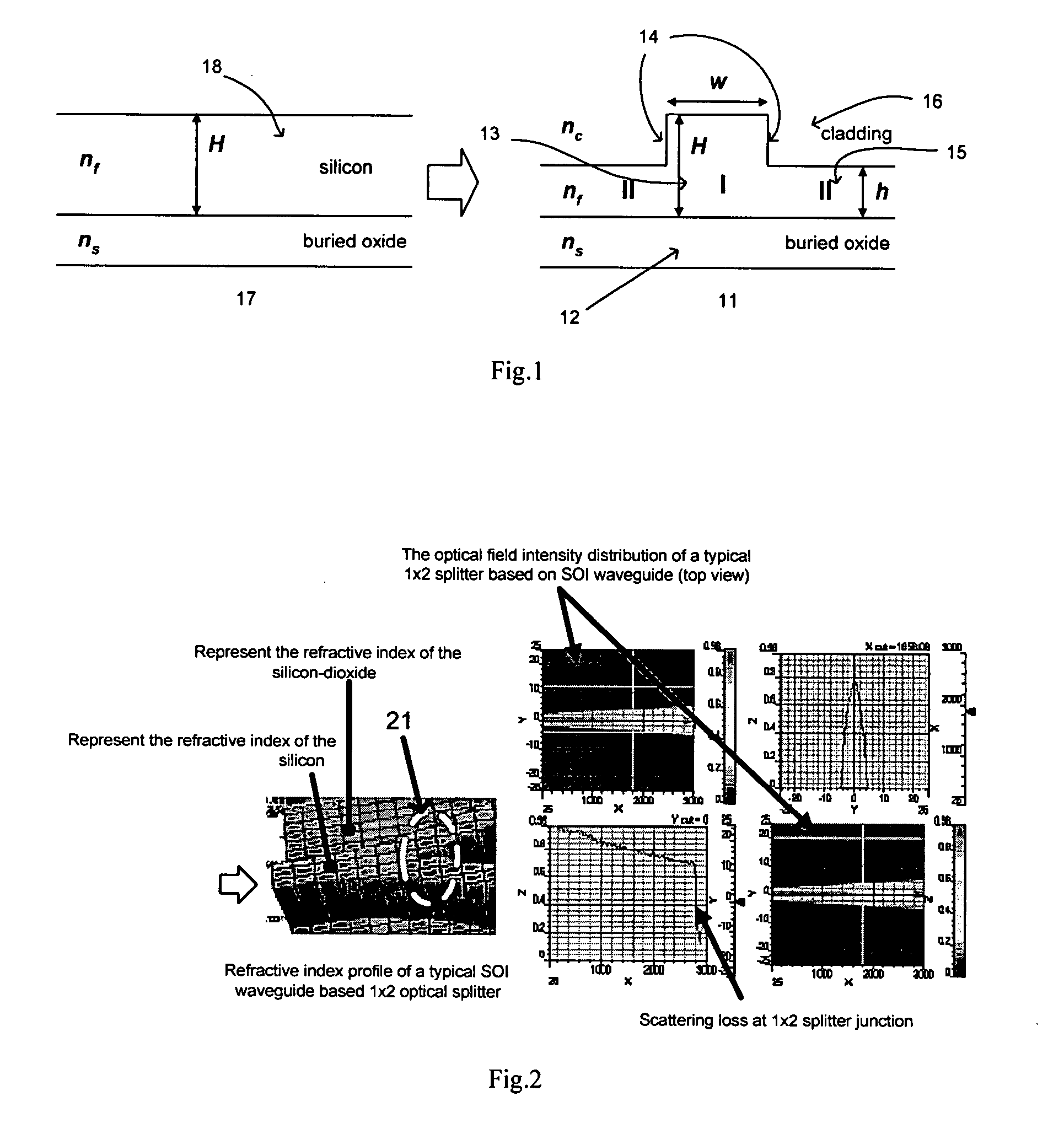
The new single mode circuit (SMC) architecture is invented for photonic integrated circuits (PIC). This architecture allows using multimode waveguides or structures to construct a single mode operated PIC. The multimode sections used in such SMC based PIC possess strong lateral confinement so that the PIC can have high circuit density and high optical performance at the same time. A parallel mode converter structure is also invented here. Based on this parallel mode converter, a low loss optical splitter can be constructed for high index contrast waveguide system.
Owner:LI BING
Wavelength stabilized laser
InactiveUS7212554B2Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsOptical radiationLight beam
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Wavelength stabilized laser
InactiveUS20050265416A1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsOptical radiationLight beam
A high power light source having an array, bundle or separate plurality of laser diodes coupled to a same number of multimode waveguides to collect beams of light emitted from the of laser diodes is provided. An optical combiner receives the beams of light and combines the beams of light into a single forward propagating beam of light so that substantially all optical radiation within each beam of light overlaps the optical radiation each other beam to form the single beam. A reflective element is located to receive the single forward propagating beam of light and transmits greater than 60% of the single forward propagating beam of light therethrough. The reflective element reflects between 3-40% of the single forward propagating beam back to the laser diodes as feedback to stabilize said laser diodes.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Optical device having a waveguide lens with multimode interference
In one embodiment, a waveguide lens of the invention has a pair of planar waveguides, e.g., a single-mode waveguide connected to a multimode waveguide. The widths of the two waveguides and the length of the multimode waveguide are selected such that particular mode coupling between the waveguides and multimode interference (MMI) effects in the multimode waveguide cause the latter to output a converging beam of light similar to that produced by a conventional waveguide lens. Advantageously, waveguide lenses of the invention may be used to implement low-loss, low-crosstalk waveguide crossings and / or compact waveguide turns. In addition, waveguide lenses of the invention can be readily and cost-effectively incorporated into waveguide devices designated for large-scale production.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Optical device structures based on photo-definable polymerizable composites
InactiveUS20040101268A1Significant differenceSmall bending radiusOptical waveguide light guideLensRefractive indexSingle mode waveguides
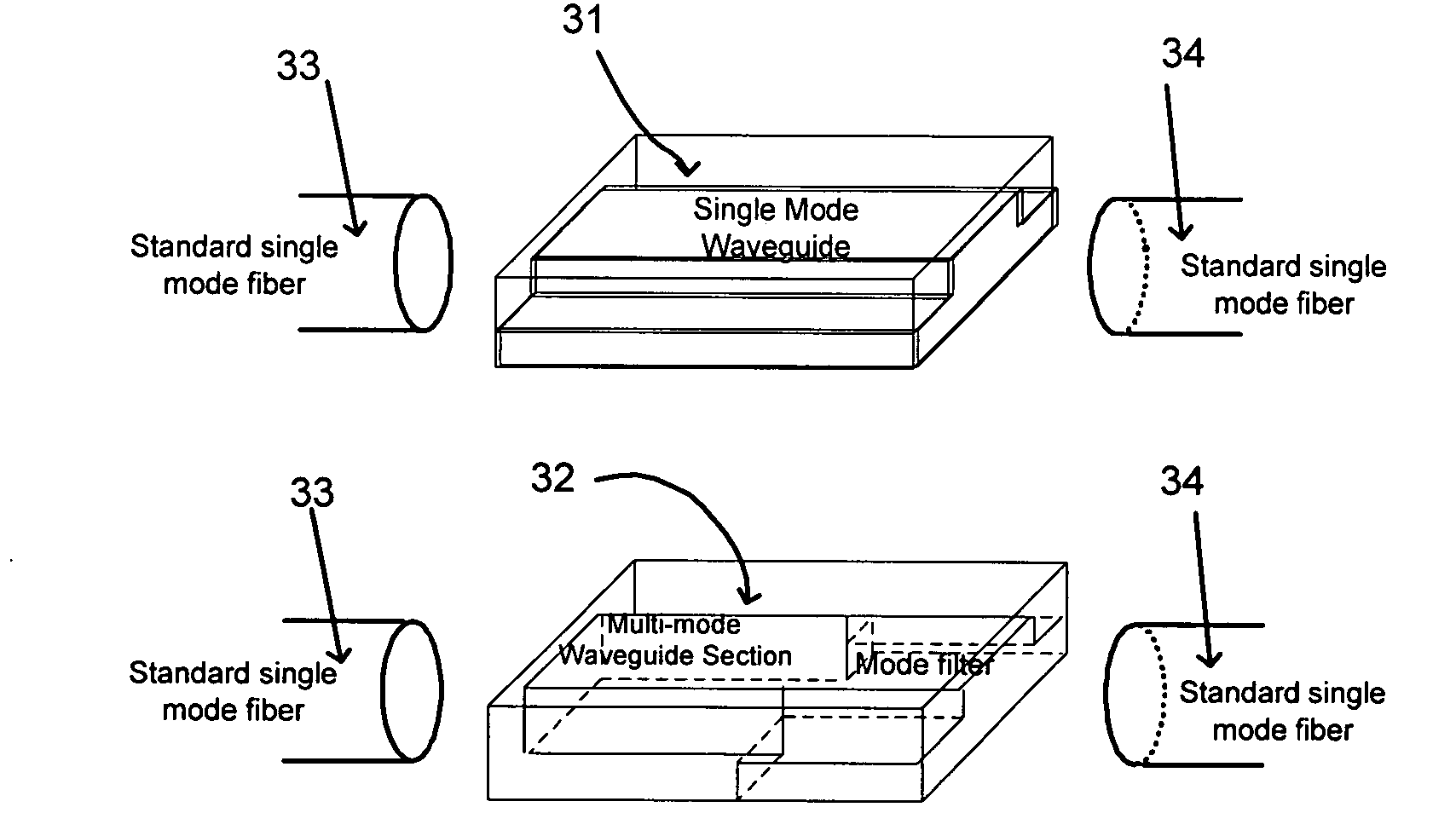
An optical device structure comprising a substrate and at least one topological feature. The topological feature comprises a polymeric composite material formed from a polymerizable binder and an uncured monomer. The topological feature has a controlled topological profile and a controlled refractive index across the topological feature. The optical device structure may be a multimode waveguide device, a single mode waveguide device, an optical data storage device, thermo-optic switches, or microelectronic mechanical system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
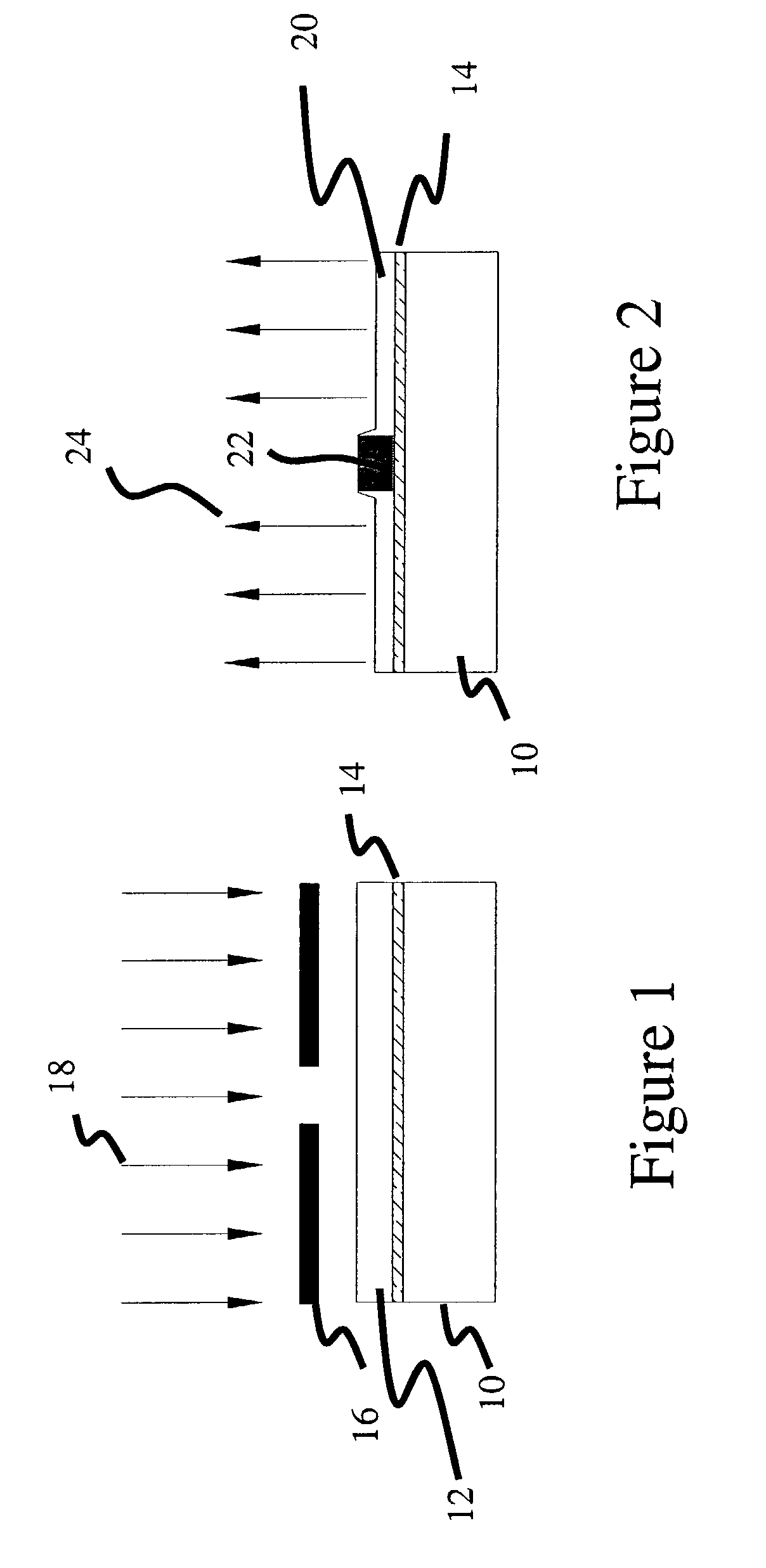
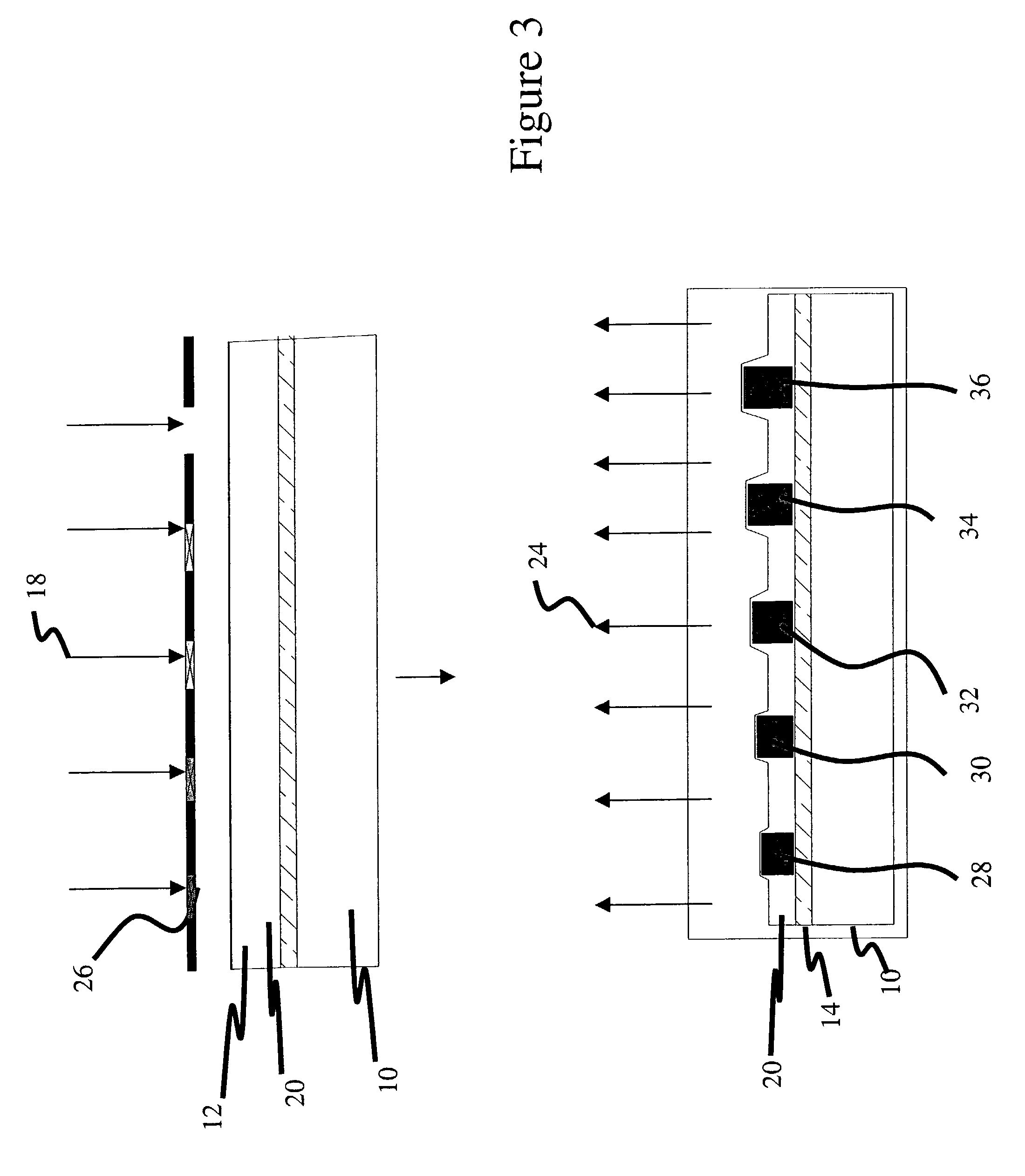
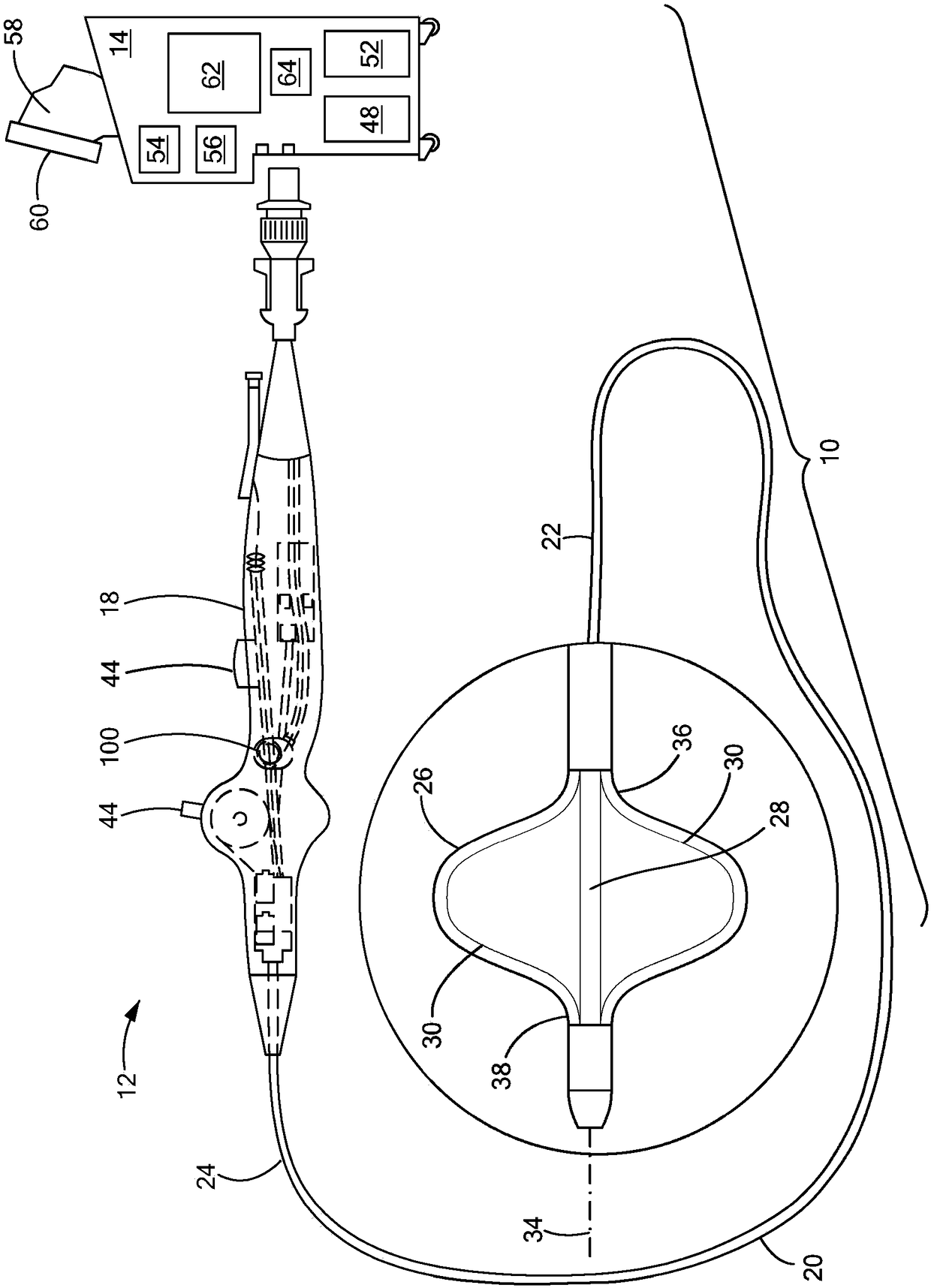
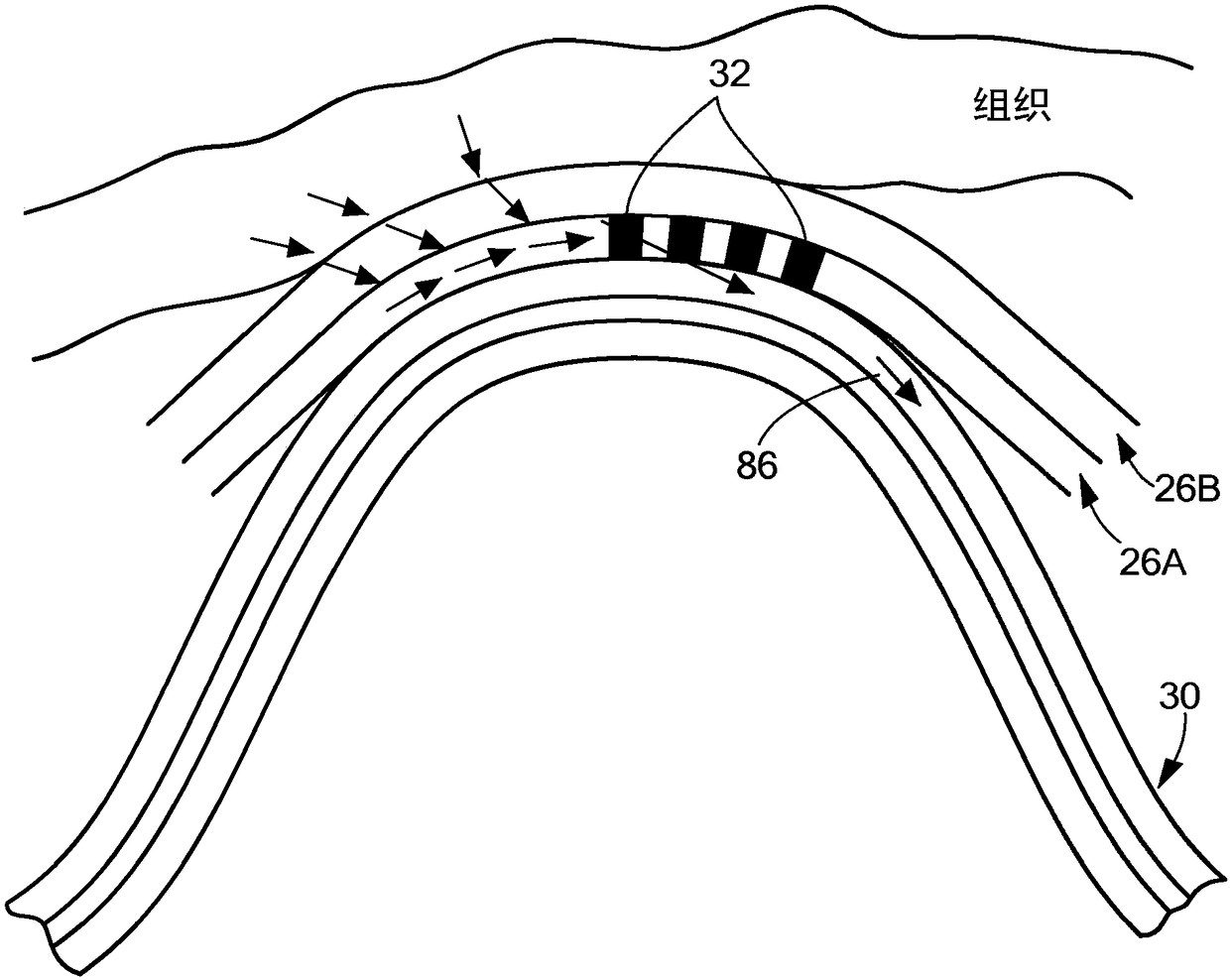
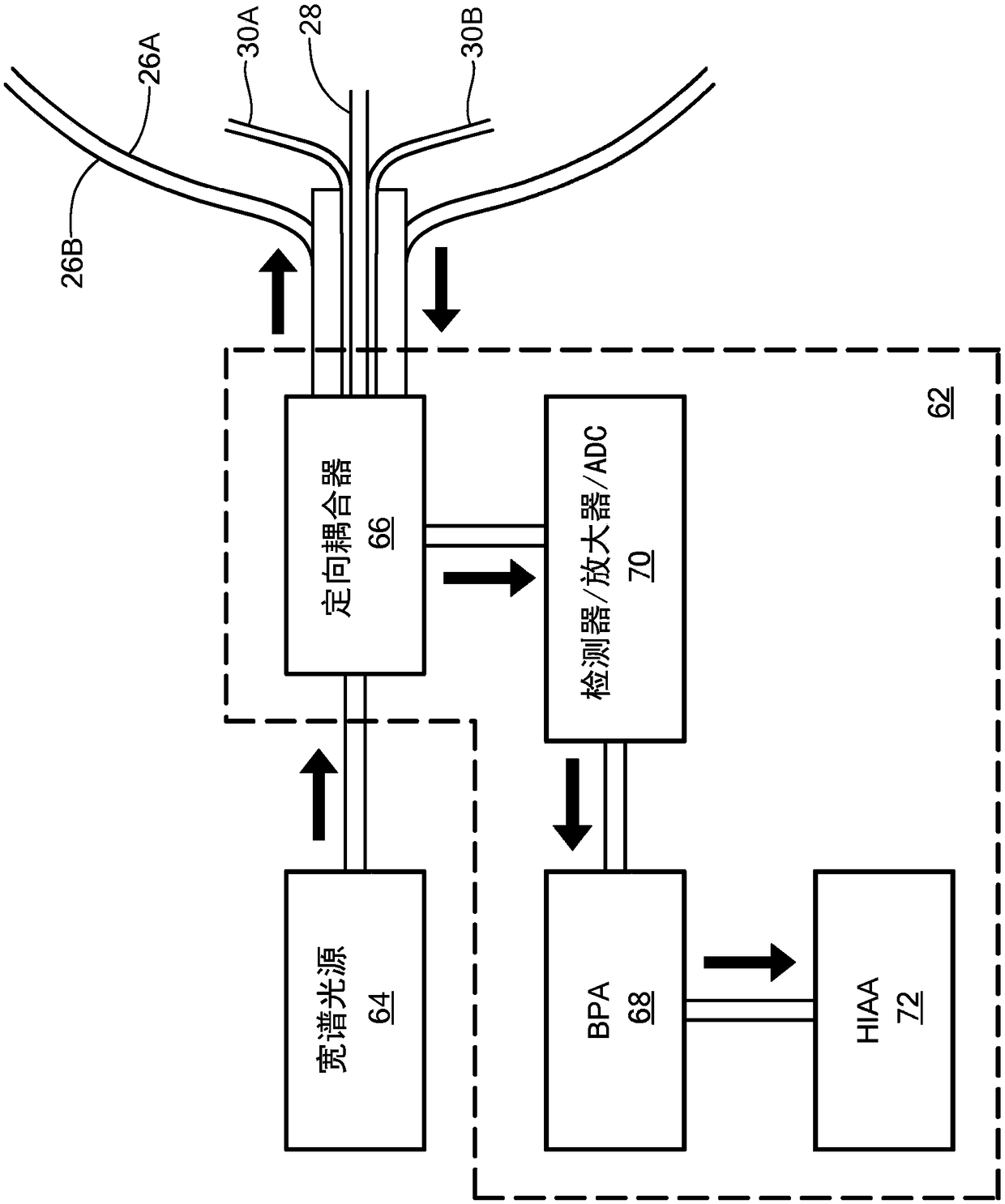
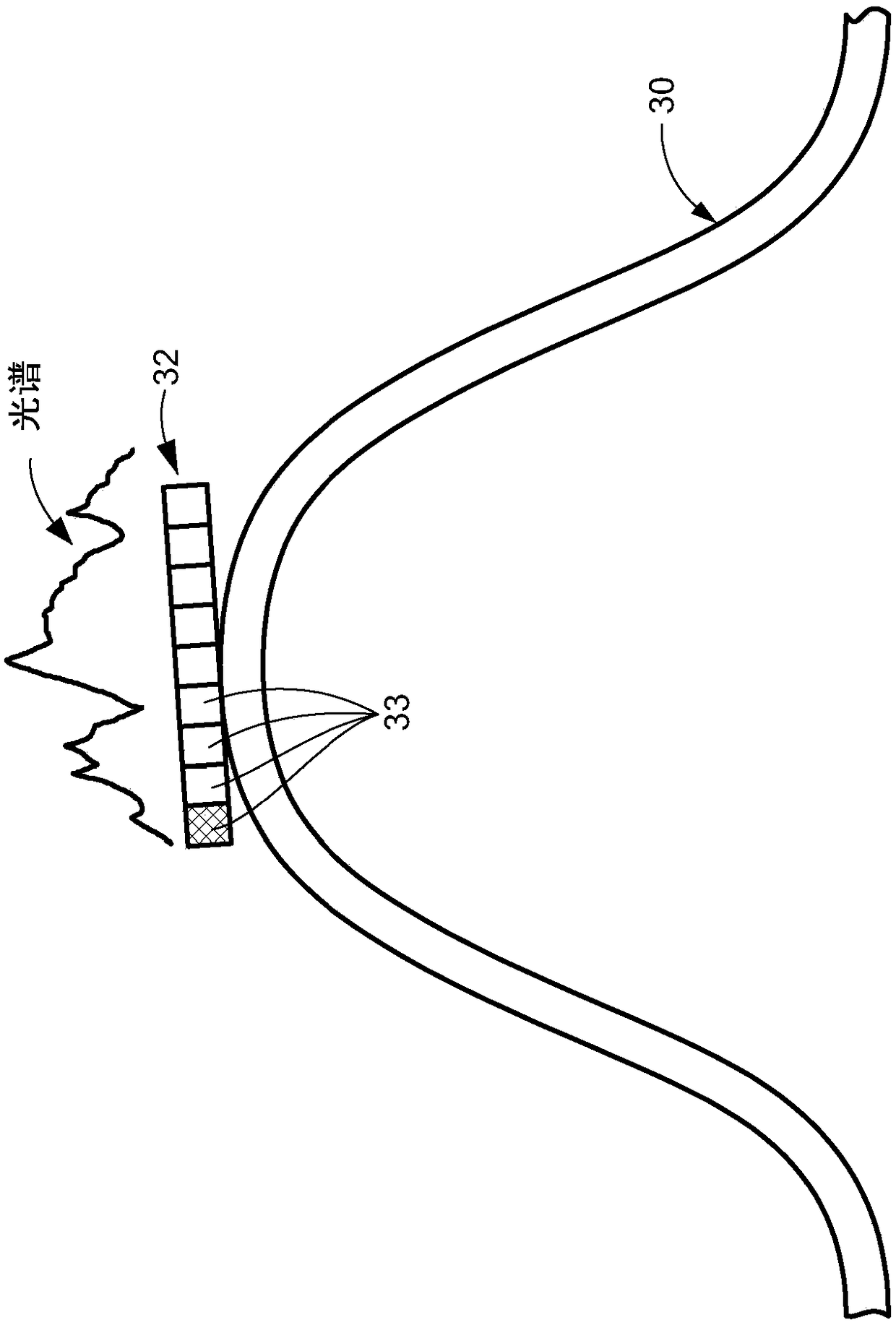
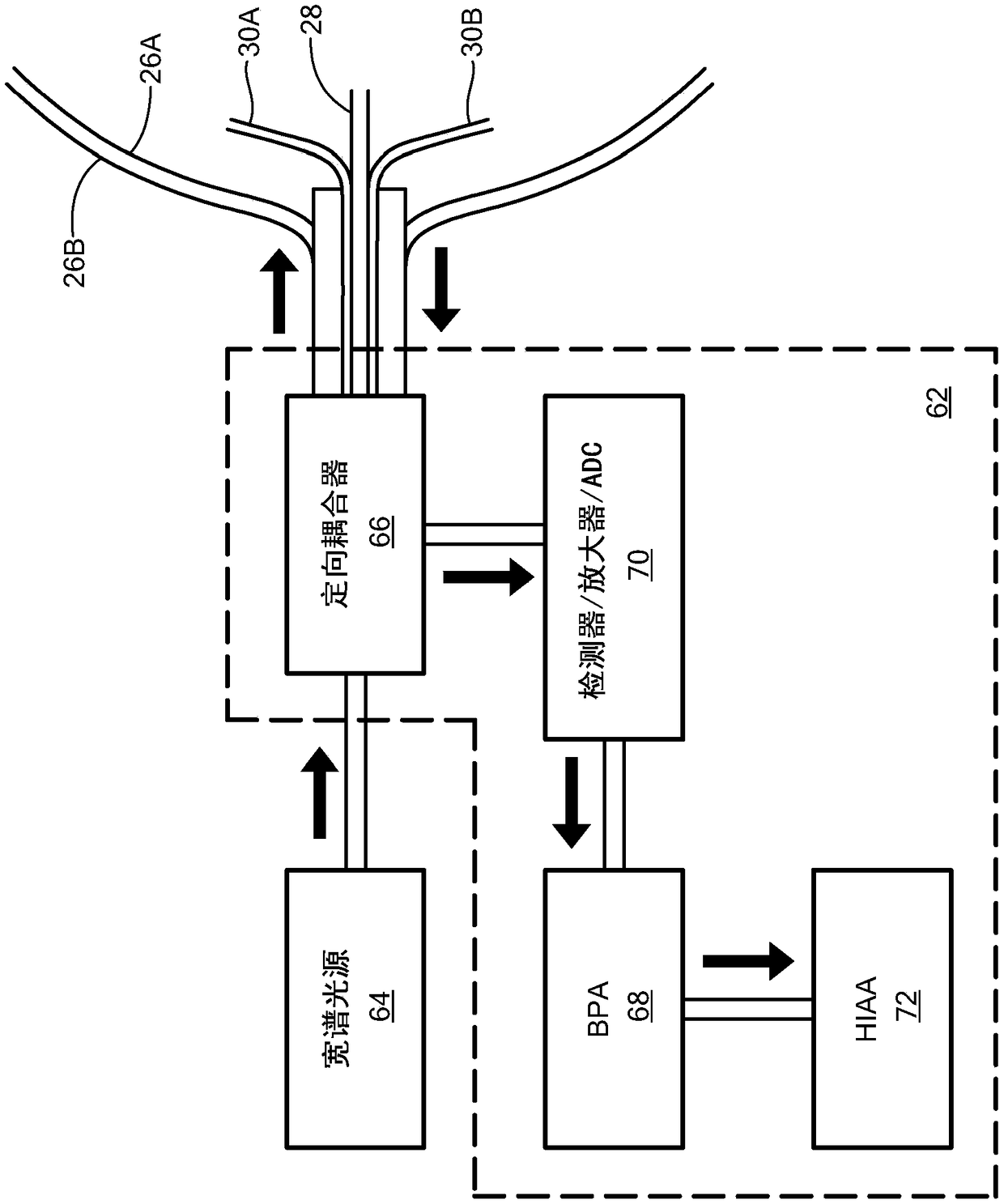
Temperature and strain measurement technique during cryoablation
Disclosed are a device, system, and method for identifying an area of ablated tissue and / or assessing contact between a treatment element and tissue and / or assessing occlusion of a body lumen by the treatment element. Specifically, the device, system, and method may include a device having one or more fiber sensors and a processing unit for receiving emitted and / or reflected light from tissue andmaking one or more determinations based on the received light regarding ablated tissue, tissue contact, and / or occlusion. Each of the fiber sensors may include at least one multi mode waveguide segment and at least one single mode waveguide segment, or each of the fiber sensors may be single mode waveguide including fiber Bragg grating for assessing strain of a treatment element by tissue contact.The processing unit may include a beam processing apparatus and a hyperspectral imaging and analysis apparatus, and may optionally include a light source.
Owner:美敦力快凯欣有限合伙企业
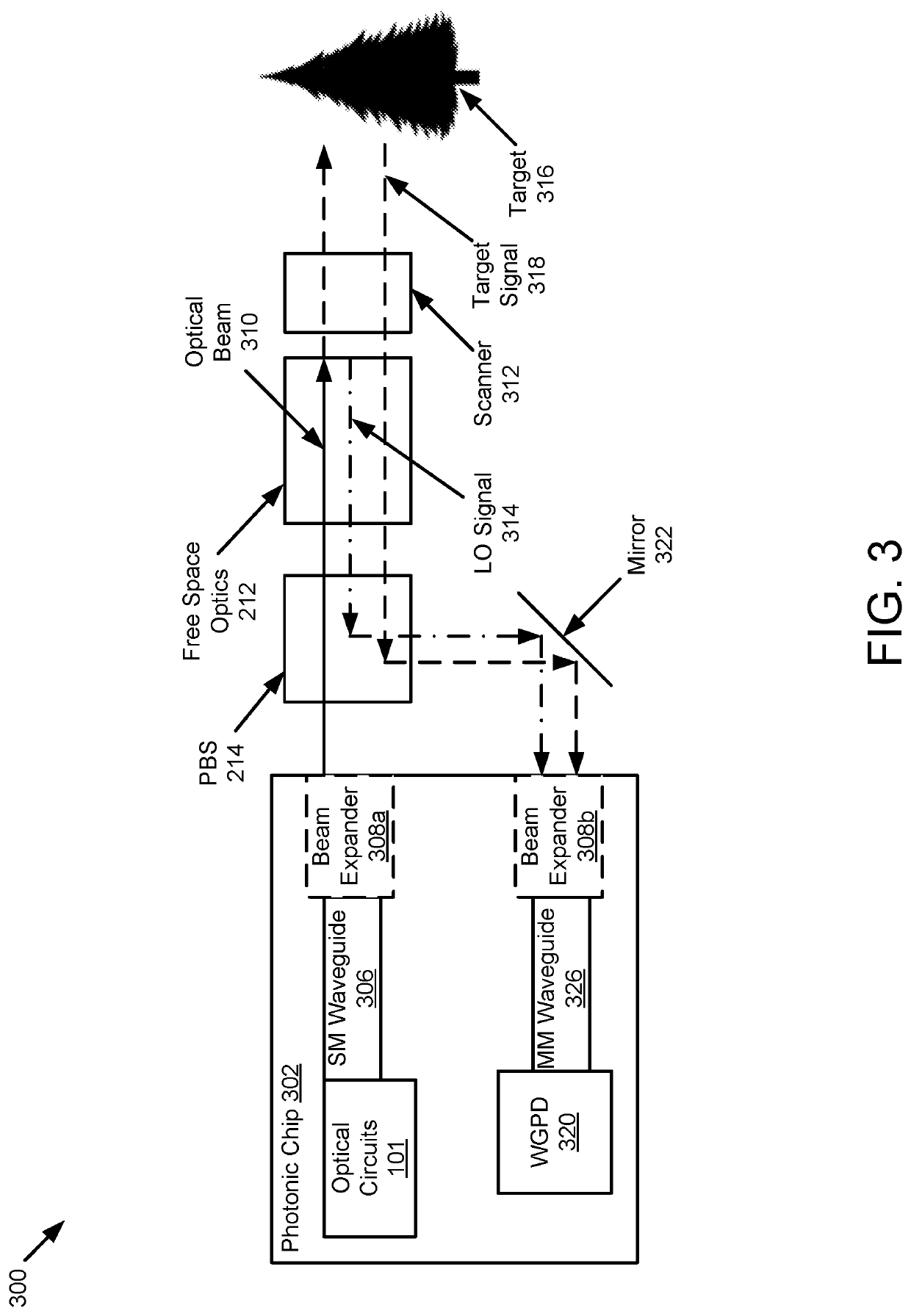
Lidar system with a multi-mode waveguide photodetector
ActiveUS20200319314A1Electromagnetic wave reradiationOptical elementsLocal oscillator signalTarget signal
A light detection and ranging (LIDAR) apparatus is provided that includes an optical source configured to emit an optical beam. The LIDAR apparatus further includes free space optics configured to receive a first portion of the optical beam as a target signal and a second portion of the optical beam as a local oscillator signal, and combine the target signal and the local oscillator signal. The LIDAR apparatus includes a multi-mode (MM) waveguide configured to receive the combined signal.
Owner:AEVA INC
Single mode photonic circuit architecture and a new optical splitter design based on parallel waveguide mode conversion
ActiveUS7668416B2Increase contrastSmall bend radiusNanoopticsCoupling light guidesRefractive indexEngineering
The new single mode circuit (SMC) architecture is invented for photonic integrated circuits (PIC). This architecture allows using multimode waveguides or structures to construct a single mode operated PIC. The multimode sections used in such SMC based PIC possess strong lateral confinement so that the PIC can have high circuit density and high optical performance at the same time. A parallel mode converter structure is also invented here. Based on this parallel mode converter, a low loss optical splitter can be constructed for high index contrast waveguide system.
Owner:LI BING
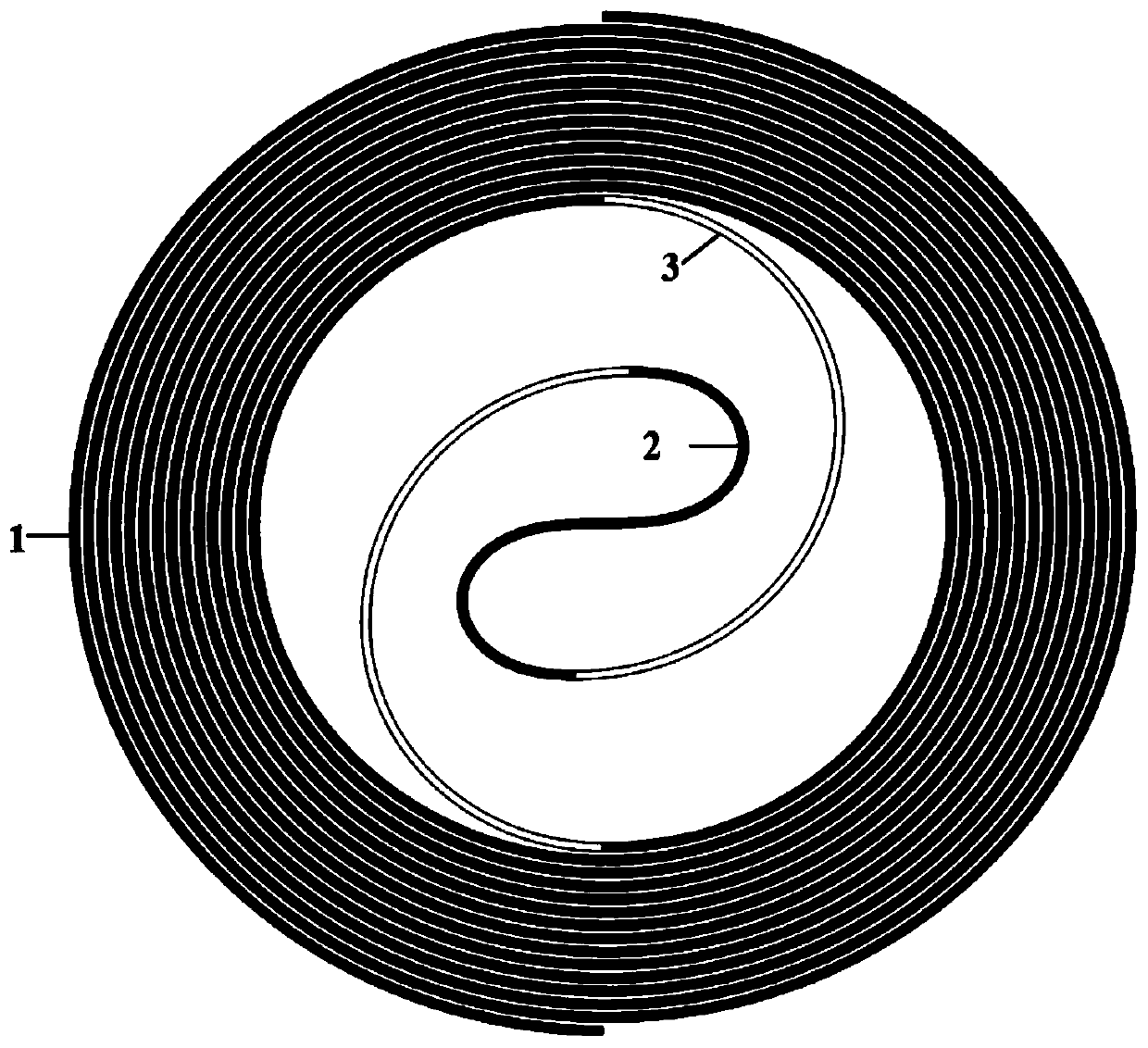
Silicon-based multimode helical waveguide delay line supporting low-loss fundamental mode transmission
ActiveCN110596813AExtended propagation distanceLow Intermodal CrosstalkCoupling light guidesScattering lossEngineering
The invention discloses a silicon-based multimode helical waveguide delay line supporting low-loss fundamental mode transmission. A curvature gradual change type S bending multimode waveguide is placed at the centers of curvature gradual change type helical bending multimode waveguides; and two curvature gradual change type helical bending multimode waveguides are annularly and helically arranged,an inner end of one curvature gradual change type helical bending multimode waveguide is connected with one end of the curvature gradual change type S bending multimode waveguide through a bending waveguide, the other end of the curvature gradual change type S bending multimode waveguide is connected with the inner end of the other curvature gradual change type helical bending multimode waveguidethrough another bending waveguide, and the entire silicon-based multimode helical waveguide delay line is arranged in a central symmetry manner. The silicon-based multimode helical waveguide delay line disclosed by the invention can effectively avoid mode mismatch loss and inter-mode crosstalk caused by the abrupt curvature change of the traditional structure, and can reduce the scattering loss introduced by a waveguide sidewall, thereby obtaining low-loss fundamental mode transmission in the silicon-based multimode helical waveguide, and the silicon-based multimode helical waveguide delay line has the advantages of low loss and compact structure and the like, and can be applied to optical buffers, optical delay lines and other systems.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Nonvolatile programmable integrated photonic device and design method thereof
ActiveCN111999802AReduce energy consumptionIncreased Design FreedomOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsPhotonic crystal structureRefractive index
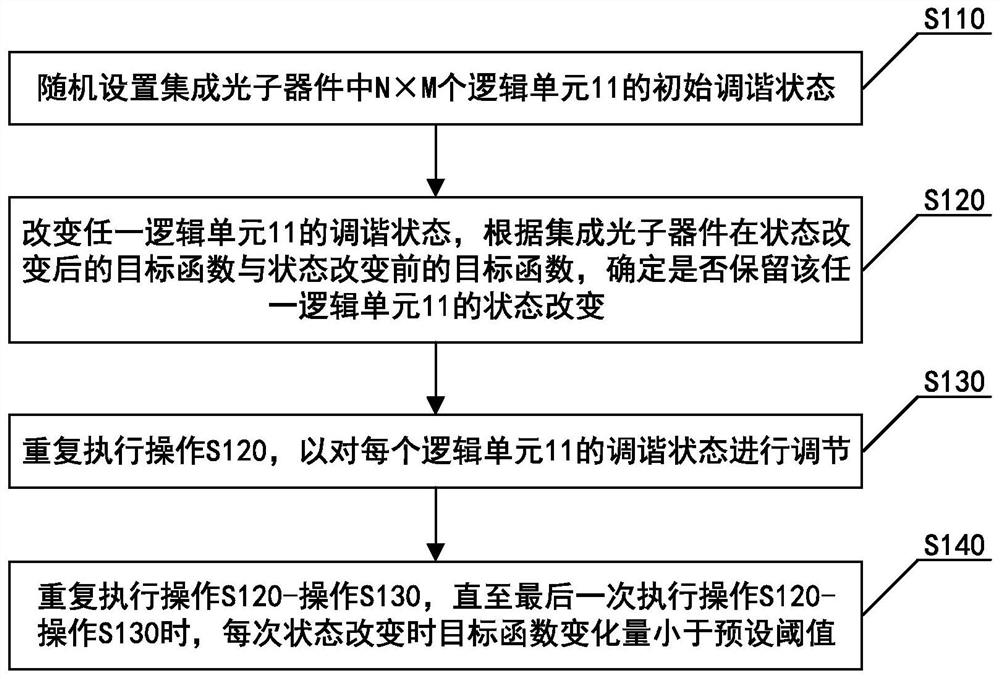
The invention discloses a nonvolatile programmable integrated photonic device and a design method thereof, and belongs to the field of photonic devices. A multimode waveguide of the integrated photonic device comprises N*M logic units capable of independently adjusting tuning states, and N and M are positive integers; each logic unit comprises a cuboid structure which is provided with a groove andmade of silicon and a filling structure which is filled in the groove and made of a phase change material, and each logic unit is of a sub-wavelength size structure. By adjusting the tuning state ofeach logic unit, the distribution of the refractive indexes of the device is adjusted and controlled in the sub-wavelength scale, and photonic devices with different functions are realized. The phasechange material is combined with a photonic-like crystal structure; the non-volatile and programmable ultra-small integrated photonic device is realized by utilizing the non-volatile and reconfigurable characteristics of the phase change material and utilizing the light field regulation and control capability of the sub-wavelength scale of the photonic-like crystal structure, the device size and energy consumption are reduced, and more tuning functions are realized, so that different functional purposes are realized.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Optical cross-connect device
InactiveUS6947626B2Simple structureMeet the requirementsMultiplex system selection arrangementsDigital storageFiberCross connection
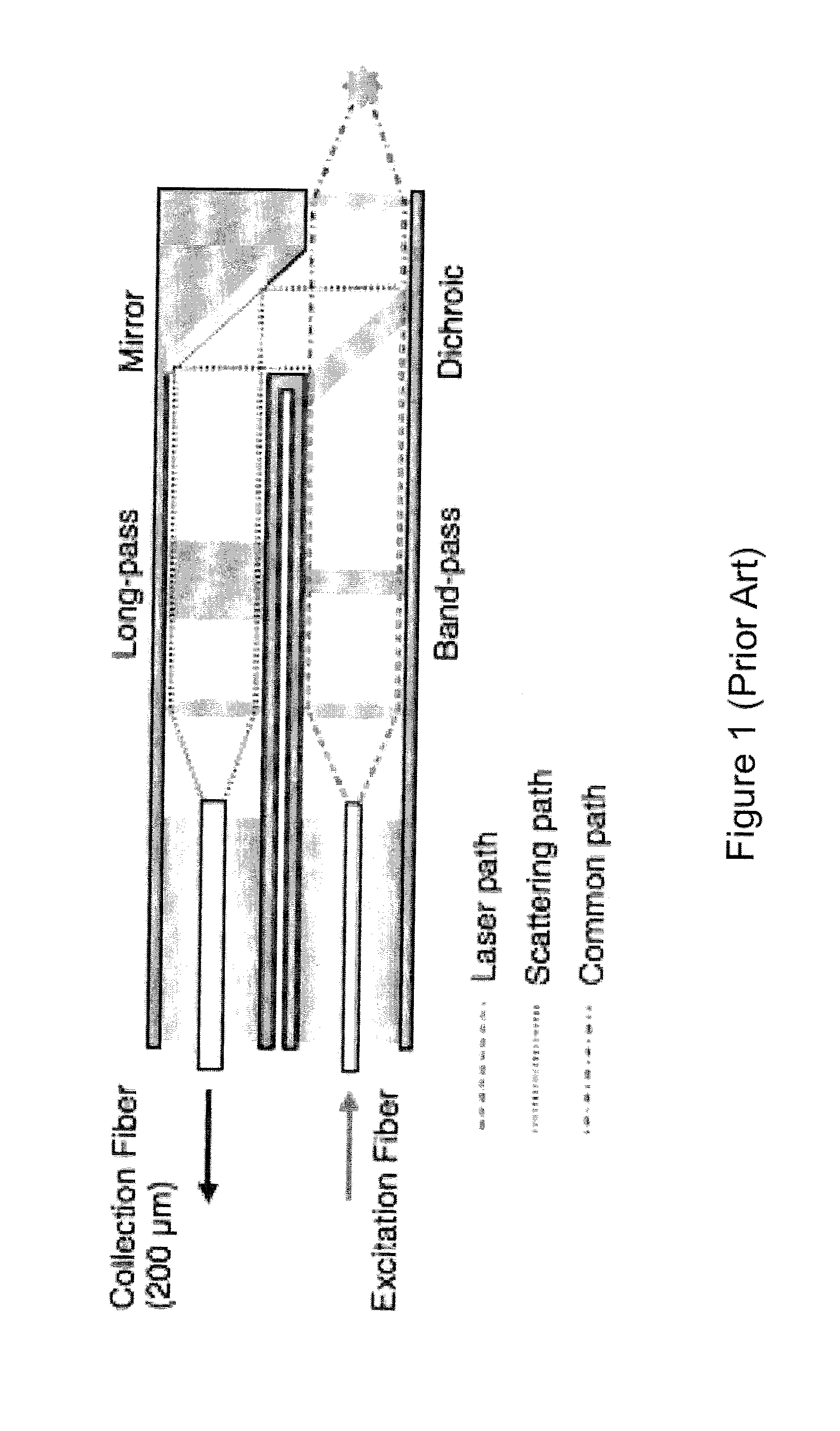
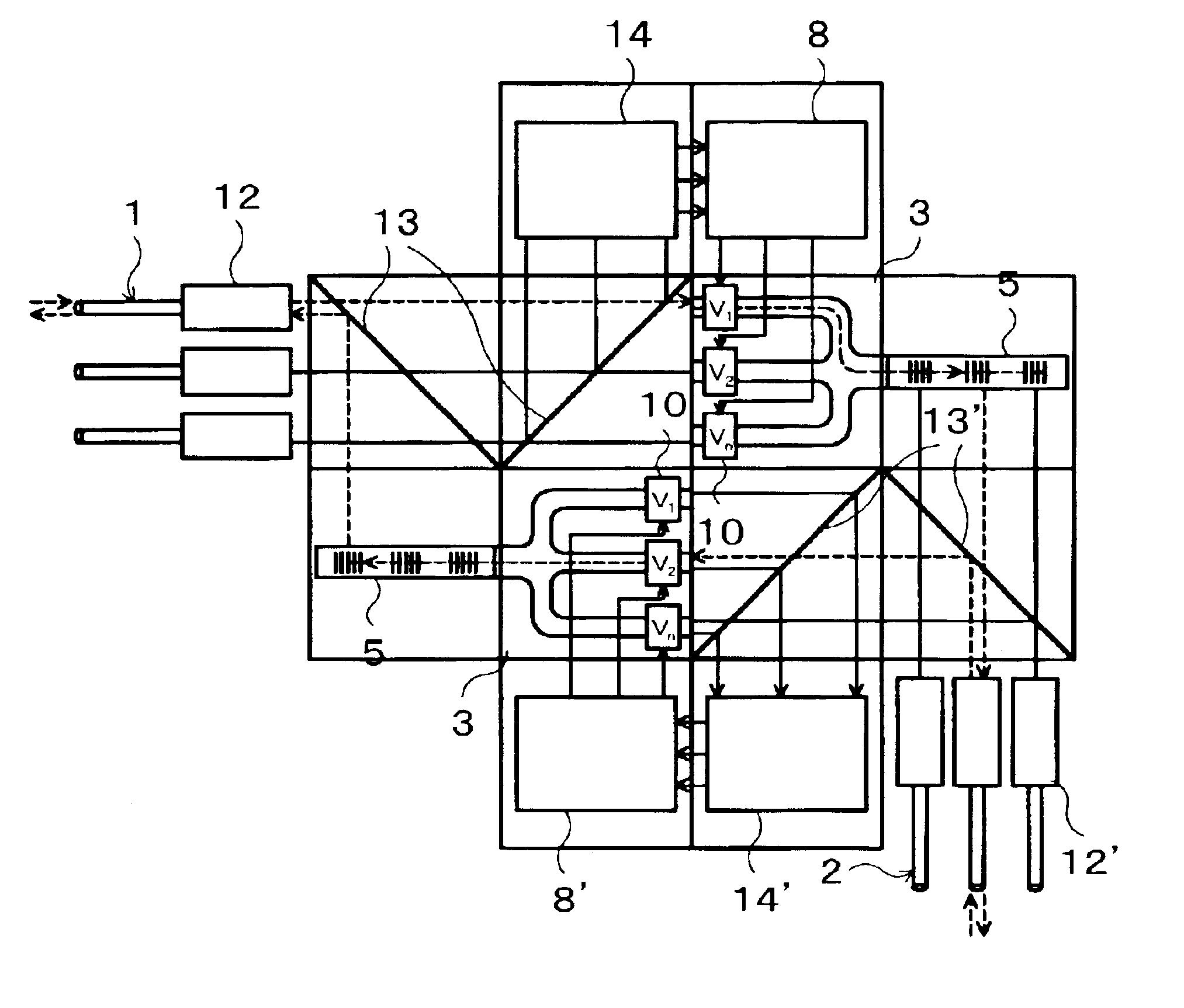
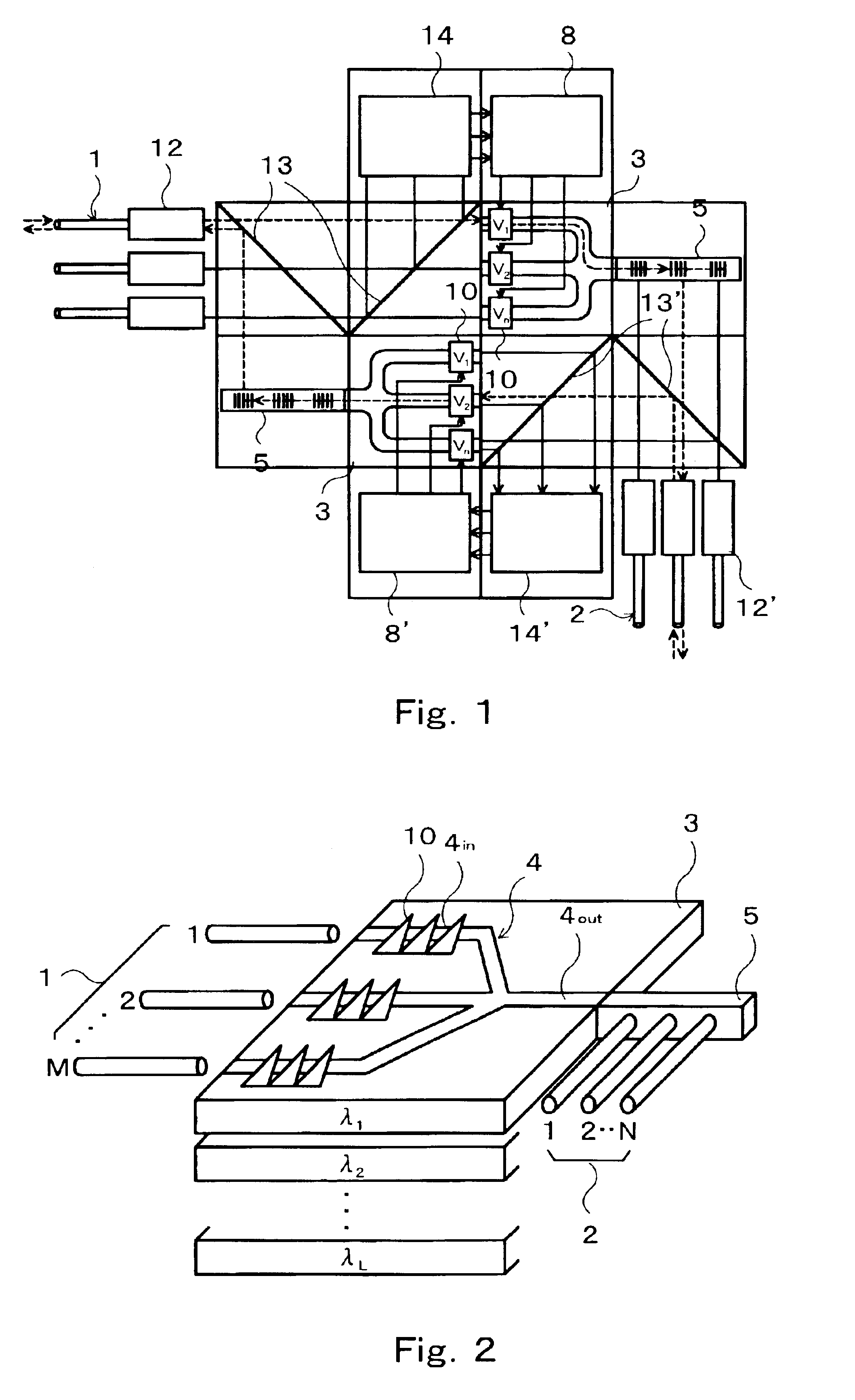
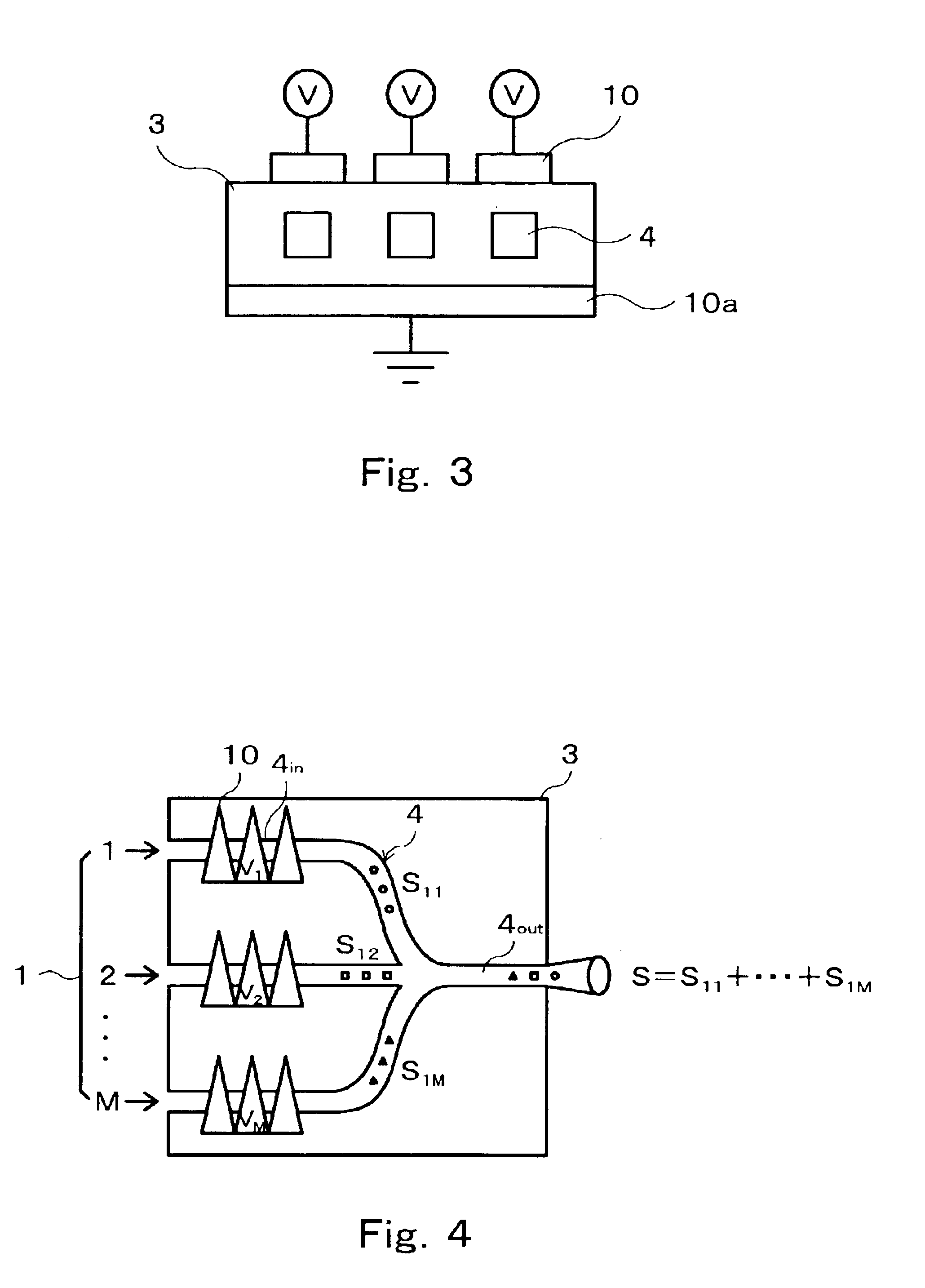
An optic switch for cross-connecting input light signals incoming from inlet fiber cables to outlet fiber cables is disclosed that makes use of a holographic filter (5) having a series of preformed different speckle patterns, each in the form of a hologram (H1, H2, . . . ). Associated with input light signals guided past respective inlet passages (4in) of a multimode waveguide (4), different speckle patterns are formed by applying different control voltages across respective electrode pairs (10, 10a) provided thereon. These speckle patterns past a single outlet passage (4out) of the multimode waveguide (4) into which the inlet passages (4in) converge are joined together and enter the holographic filter (5) in which an input light signal is selectively switched, addressed and cross-connected to an outlet waveguide (2) through a region thereof where a formed speckle pattern coincides with a preformed speckle pattern. The multi mode waveguides (4) is formed in, e. g., a LiNbO3 photorefractive substrate (3).
Owner:PEGASUSNET
Multi-mode interference optical switch with controlled input position and preparation method of multi-mode interference optical switch
ActiveCN103777283AChange the resonance phenomenonChange the interference relationshipCoupling light guidesFiber arrayEngineering
The invention discloses a multi-mode interference optical switch with the controlled input position. The multi-mode interference optical switch comprises a plane optical wave optical path chip, a light source, an input optical fiber array and an electric and automatic core adjusting device. The plane optical wave optical path chip comprises a silicon substrate, a silicon dioxide buffer layer, a waveguide and a covering layer. The waveguide comprises an input-stage single-mode waveguide, a middle-stage multi-mode waveguide and n output-stage single-mode waveguides. The light source is connected with the input end of the input optical fiber array. The output end of the input optical fiber array is connected with the input end of the input-stage single-mode waveguide. The output end of the input-stage single-mode waveguide is connected with the input ends of the n output-stage single-mode waveguides through the middle-stage multi-mode waveguide. The input optical fiber array is fixedly connected to the electric and automatic core adjusting device. The on-off mode of the optical switch is adjustable, the technology and the structure are simple, and the cost is low. The invention further discloses an adjusting method of the multi-mode interference optical switch with the controlled input position. The adjusting method is simple and capable of rapidly adjusting the on-off mode of the optical switch.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Multimode waveguide grating coupler
ActiveUS20200333535A1Improve communication bandwidthOptical mode multiplex systemsElectromagnetic network arrangementsRefractive indexEngineering
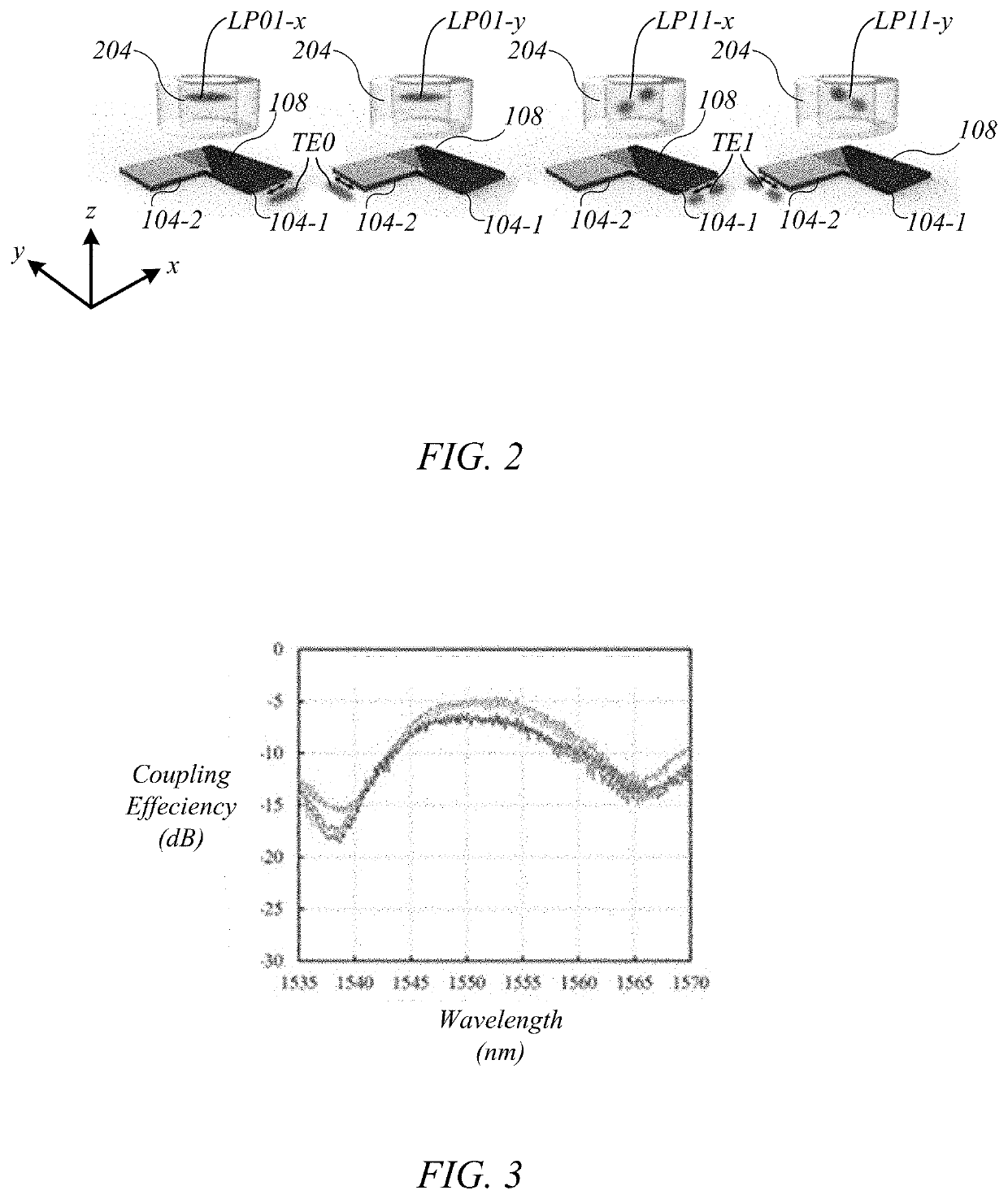
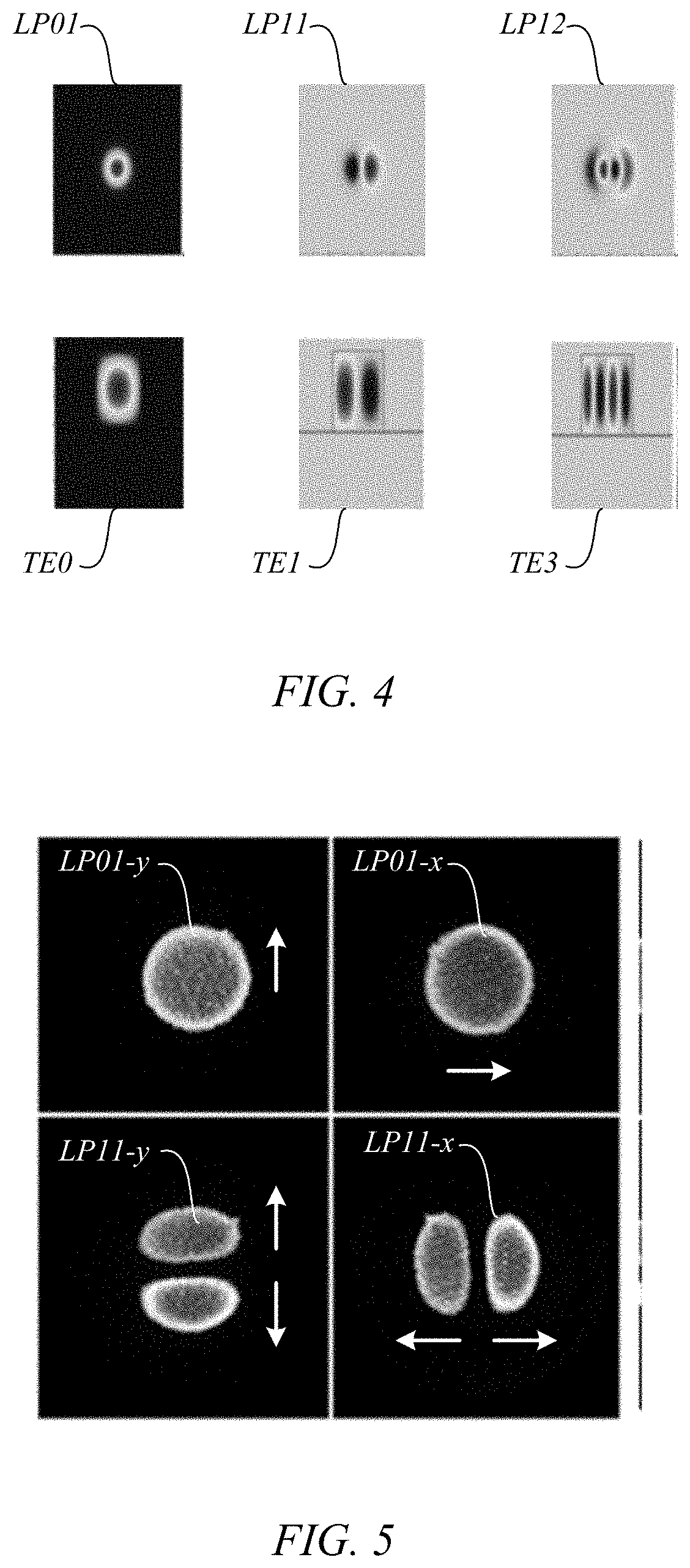
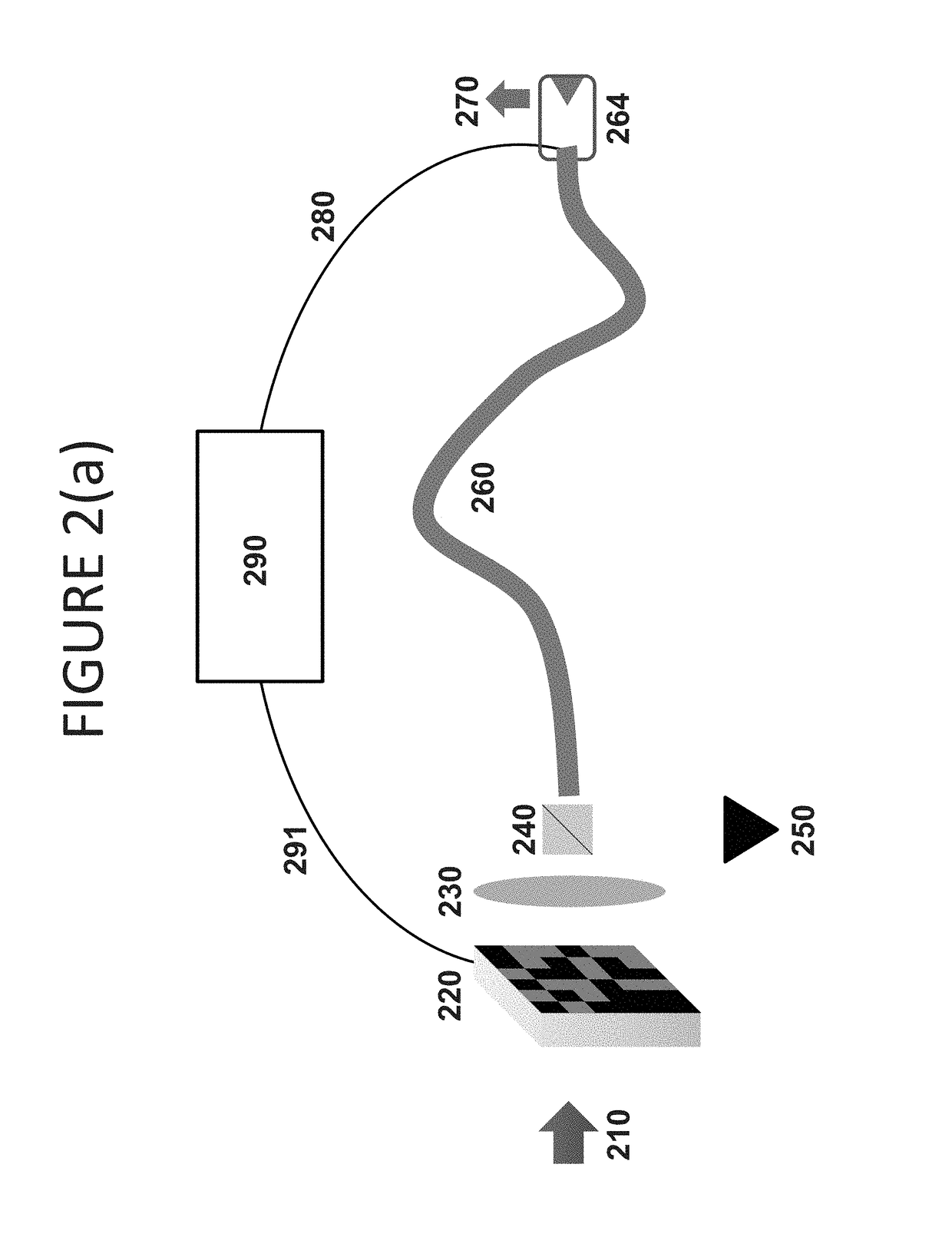
We describe a high coupling-efficiency waveguide grating coupler for use in the optical interface between a planar multimode waveguide and a multimode optical fiber in mode division multiplexed optical communication systems. The multimode waveguide grating coupler can launch light from the different modes of the planar waveguide into the different modes of the multimode optical fiber and vice-versa. A silicon based multimode waveguide grating coupler was used to couple two polarizations of a multimode silicon waveguide into the LP01 mode and LP11 mode from a step index multi-mode fiber (MMFs). Simulations of the preliminary design predicted the coupling efficiency to be −4.3 dB for LP01 mode and −5.0 dB for the LP11 mode. Experimental coupling efficiency of −4.9 dB and −6.1 dB were obtained for LP01 and LP11, respectively. The multiplexer can be passive.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Apparatus and method for controlling propagation and/or transmission of electromagnetic radiation in flexible waveguide(s)
ActiveUS10228556B2Easy to operateMechanical apparatusSpectrum investigationEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
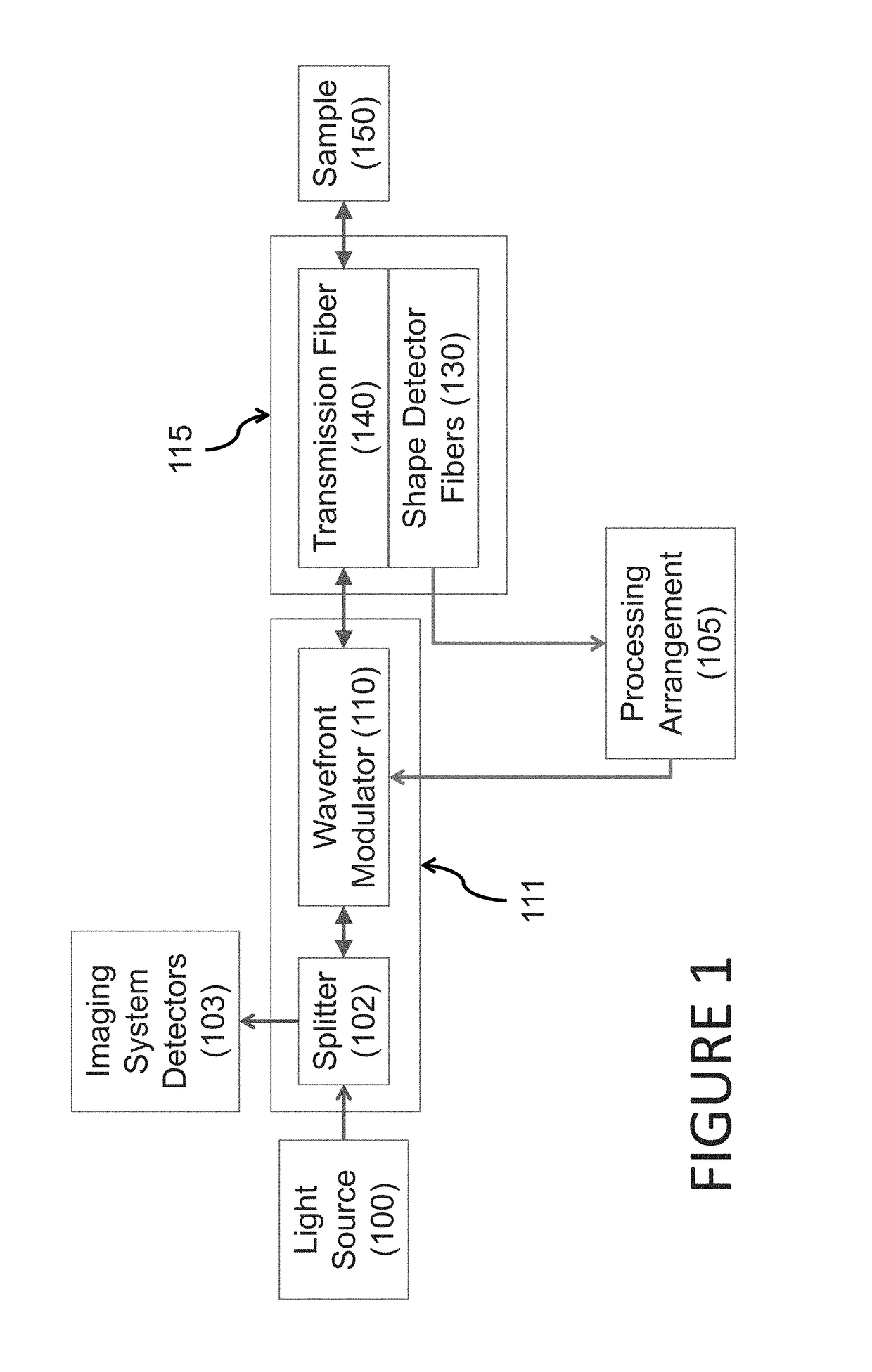
According to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure, apparatus and process for providing at least one radiation can be provided. For example, with at least one multi-mode waveguide, it is possible to transmit the radiation(s). In addition, with a shape sensing arrangement, it is possible To dynamically measure a shape of the multi-mode waveguide(s). Further, with a specifically programmed computer arrangement, it is possible to control a light modulator arrangement based on the dynamically-measured shape to cause the radiation(s) transmitted through the multi-mode waveguide(s) to have at least one pattern.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Three-dimensional hybrid multiplexing signal all-optical wavelength conversion device on silicon substrate
ActiveCN113484952AReduce lossImprove transmission capacityOptical waveguide light guideBeam splittingEngineering
The invention discloses a three-dimensional hybrid multiplexing signal all-optical wavelength conversion device on a silicon substrate. The wavelength conversion device is mainly composed of a transverse magnetic mode demultiplexer, three transverse electric mode demultiplexers, two transverse electric mode multiplexers, two polarization beam splitting rotators and two multimode nonlinear waveguides, the signal light with dual polarization, dual modes and multiple wavelengths and the pump light are input into the wavelength conversion device at the same time, and after passing through the wavelength conversion device, the signal light and the pump light are subjected to all-optical wavelength conversion to generate the idle frequency light carrying the same data as the signal light. According to the invention, multiple paths of signals can be loaded to a fundamental mode and a first high-order mode of a same multimode waveguide at the same time to form the mode multiplexing, and meanwhile, the all-optical wavelength conversion of the mixed multiplexing signals is realized by combining a polarization multiplexing technology and utilizing the dispersed and optimized multimode nonlinear waveguide, so that the transmission capacity of a communication system and the flexibility of a dynamic wavelength routing network are improved. The device can be used in the fields of wavelength routing, ultra-large capacity signal processing and the like in an all-optical communication network.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Photon convolution accelerator based on mode multiplexing
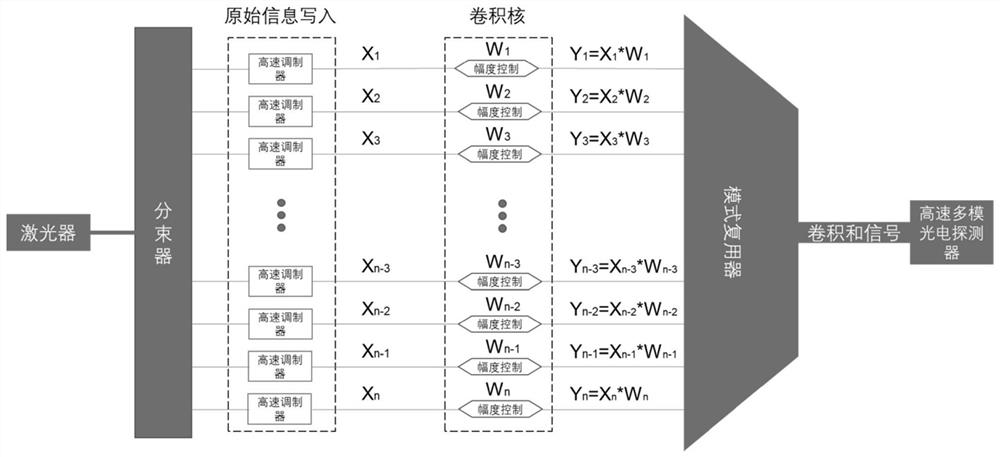
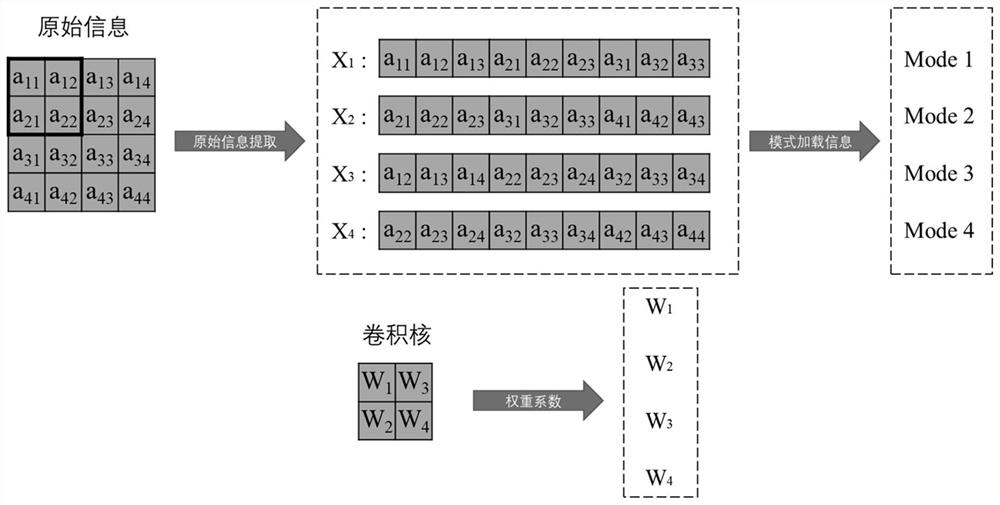
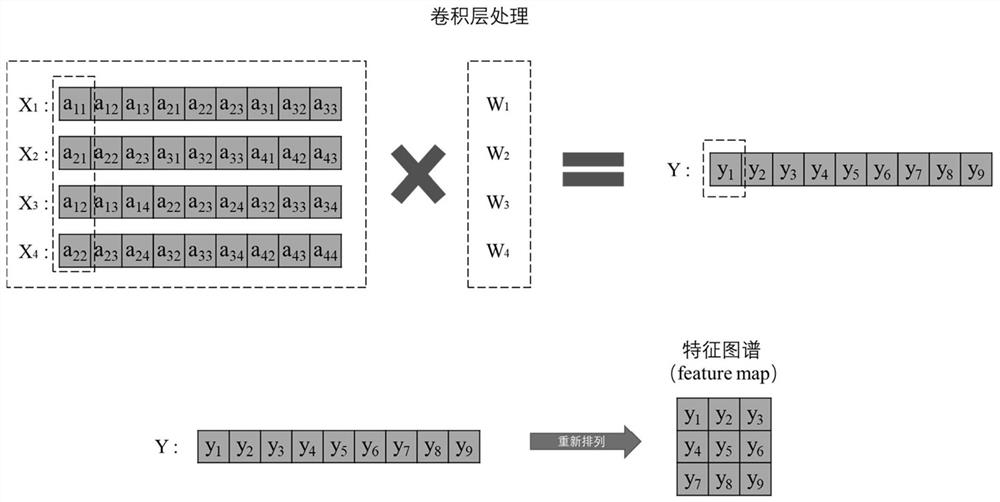
PendingCN114819089AImprove computing powerWide range of application scenariosNeural architecturesPhysical realisationSoftware engineeringAmplitude control
The invention discloses a photon convolution accelerator based on mode multiplexing, and belongs to the field of optical calculation. Light output by a laser enters different corresponding waveguides after being split, the light in the different waveguides is written into picture information through an information writing unit, and then the product of signals and weights in corresponding convolution kernels is achieved through amplitude control. And the light after amplitude control is multiplexed to a multimode waveguide through a mode multiplexer to form different modes to be detected by a high-speed multimode photoelectric detector to output a convolution sum signal, and finally convolution layer processing on picture information is realized. According to the method, information is processed in parallel by using orthogonality of different modes in the waveguide, the capability that a traditional electronic chip cannot achieve parallel processing is broken through, convolutional layer processing in the convolutional neural network is accelerated, a brand new thought and a framework are provided for optical calculation processing of the convolutional neural network, and the method has a wide application prospect in the field of optical calculation and has a wide application prospect in the field of optical calculation. And the blank in the related technical field is filled.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Lightguide tamper seal
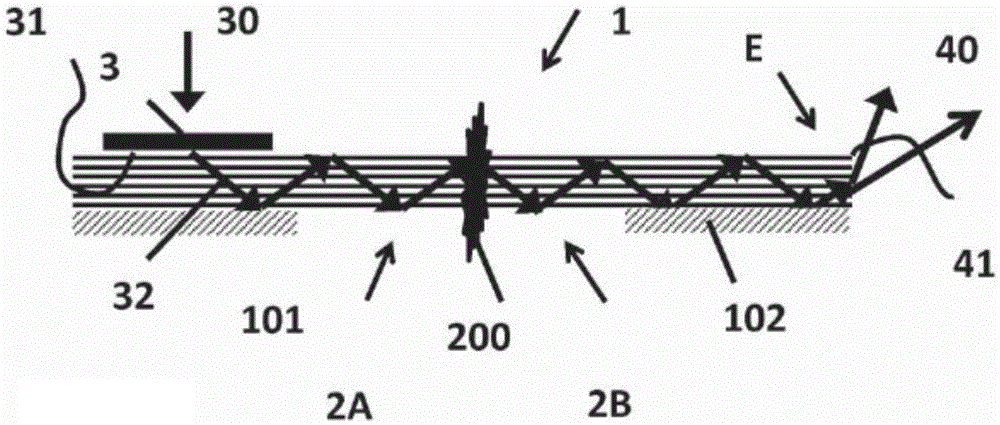
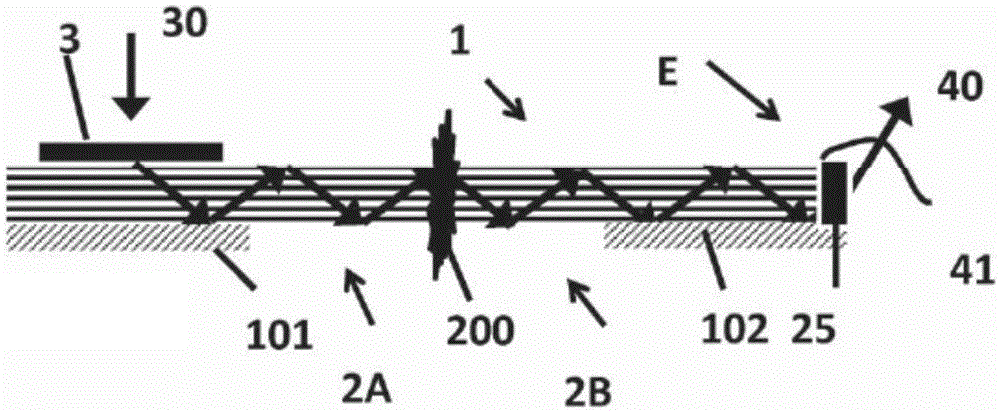
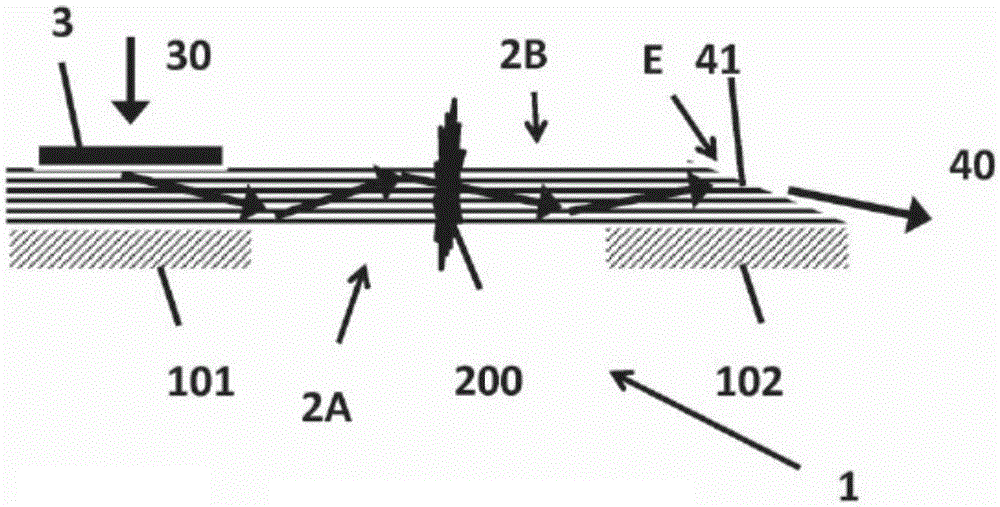
The invention concerns a tamper seal (1) comprising an optical waveguide (2) arranged to guide a propagating light-beam along a propagation direction, comprising at least a first portion (2A) and a second portion (2B) intended to be respectively arranged on a first part and on a second part of an object, said first and a second parts being movable relative to each other. Said optical waveguide (2) is a multimode waveguide comprising at least a waveguide core that has its smallest dimension, defined perpendicular to said propagation direction, greater than 10 [mu]m and smaller than 10mm. Said first portion (2A) comprises an input coupler (3) arranged to couple incident light into said optical waveguide (2) and wherein said second portion (2B) comprises at least one outcoupling surface arranged to couple out at least partially light guided in the optical waveguide (2). Said input coupler (3), said optical waveguide (2) and said outcoupling surface are arranged so as to transmit light from said input coupler (3) to said outcoupling surface, said optical waveguide (2) being further designed to be at least partially disruptable between said two portions, said optical waveguide (2) losing or changing at least partially its optical guiding properties after its disruption.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
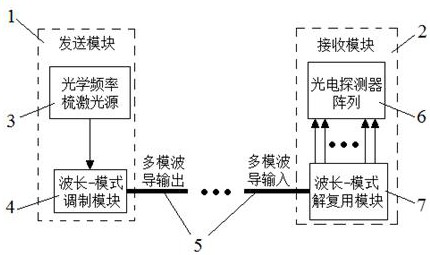
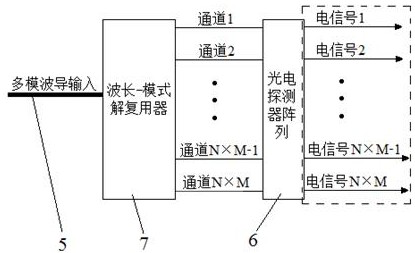
Silicon nitride assisted lithium niobate thin film waveguide-based full-integrated optical transceiving system
InactiveCN111880267AReduce processing difficultyReduce manufacturing costWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsFrequency combLithium niobate
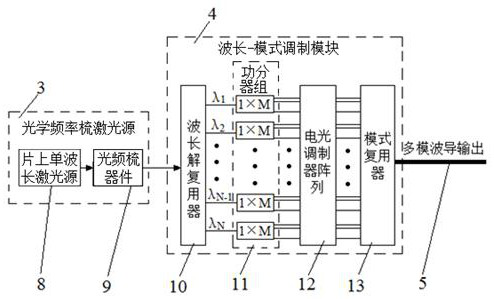
The invention provides a silicon nitride assisted lithium niobate thin film waveguide-based full-integrated optical transceiving system. The system comprises a transmitting module and a receiving module which are connected through a multimode waveguide, the optical frequency comb laser source comprises an on-chip single-wavelength laser source and an optical frequency comb device which are connected. The wavelength-mode modulation module comprises a wavelength demultiplexer, a power divider group, an electro-optical modulator array and a mode multiplexer which are connected in sequence; the optical frequency comb device is connected with the wavelength demultiplexer, and the mode multiplexer is connected with the wavelength mode demultiplexing module through the multimode waveguide. According to the optical system, full integration of devices such as a multi-wavelength laser, an electro-optical modulator, a wavelength (demultiplexing) device, a mode (demultiplexing) device and a photoelectric detector can be achieved on the same chip only by using a standard commercial CMOS process, so that the process difficulty and the manufacturing cost of the chip are greatly reduced. The communication capacity of the system is greatly expanded, and the processing speed of the system is multiplied.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
On-chip mode multiplexing and demultiplexing device
ActiveCN108196339ALarge toleranceCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideMultiplexingEngineering
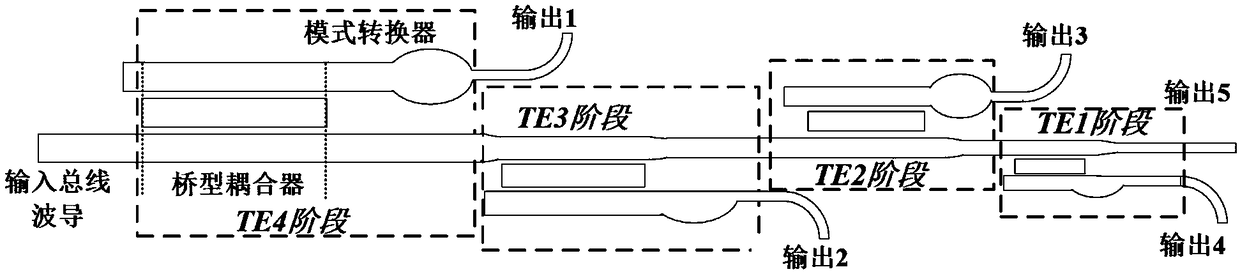
The invention discloses an on-chip mode multiplexing and demultiplexing device which comprises a plurality of demultiplexing units. Each demultiplexing unit comprises a bridge coupler and a mode converter, each bridge coupler comprises three multimode waveguides A, B and C in parallel placement, a mode m is a highest-order mode in the bridge coupler of an ith demultiplexing unit, the mode m formsa supermode with three effective refractive indexes being an arithmetic progression in the waveguides A, B and C of the bridge coupler of the ith demultiplexing unit, and length of the bridge couplerof the ith demultiplexing unit meets a condition of only outputting the mode m in a coupled manner; the waveguide C of each bridge coupler serving as a mode output end is connected with a mode converter which is used for converting input modes into fundamental modes and outputting the fundamental modes in a coupled manner, and each two adjacent demultiplexing units are connected through the corresponding waveguides A. A multiplexing device is completely symmetric with a demultiplexing structure, but the using method is the other way round. Performance of the mode multiplexing device is improved greatly.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
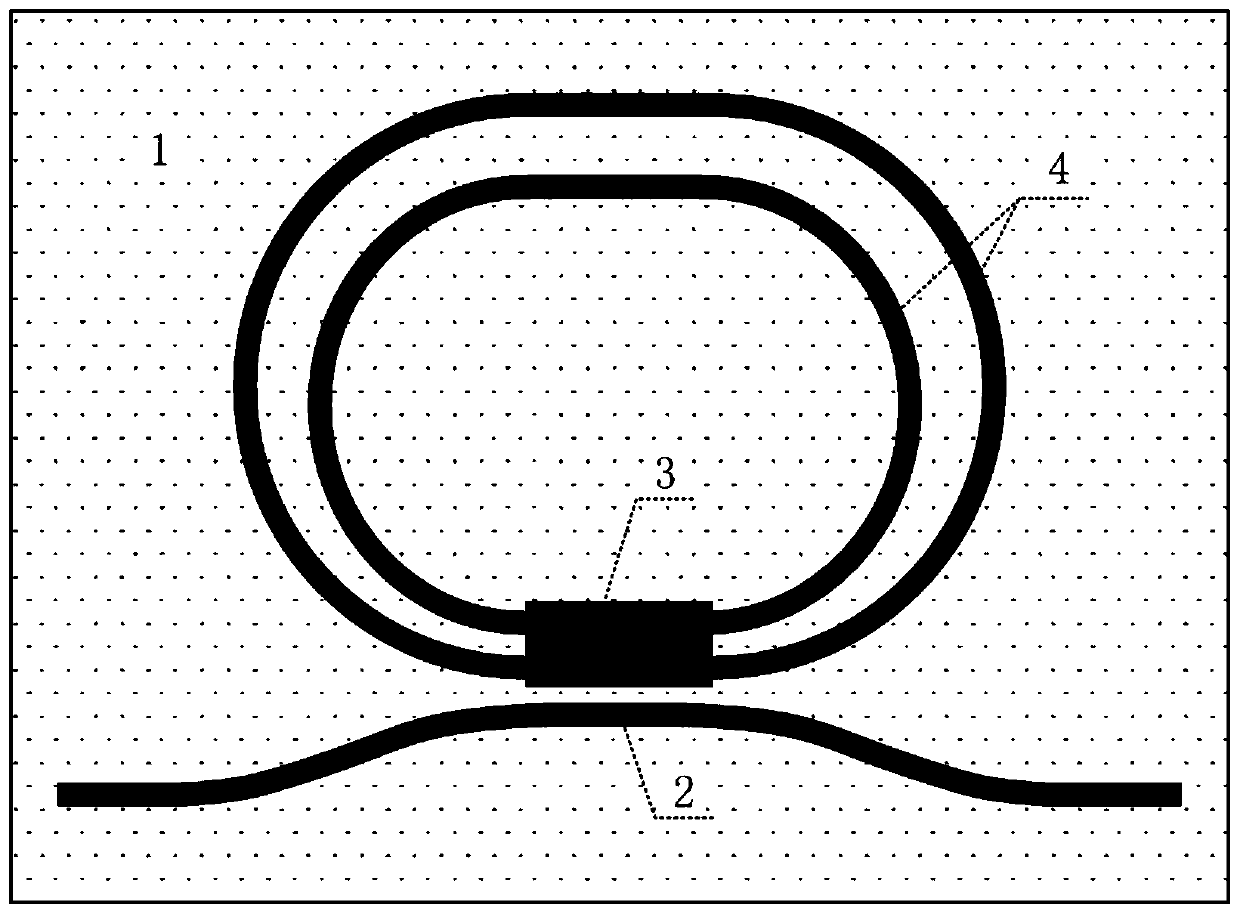
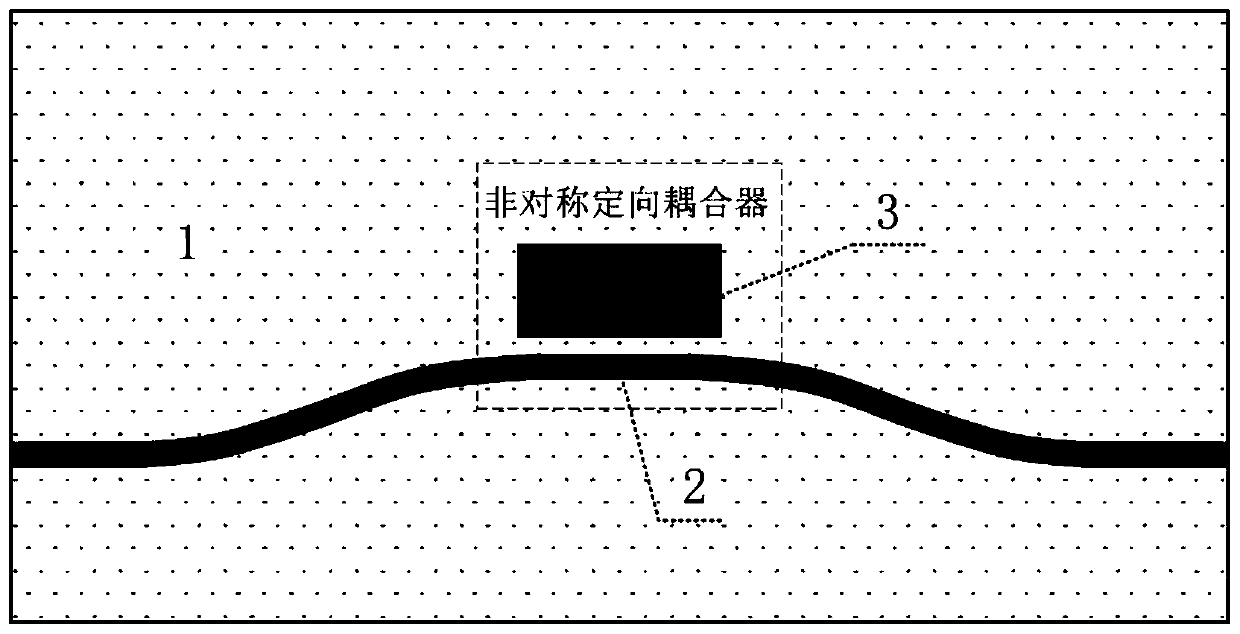
Optical waveguide ring resonator based on asymmetric directional coupler
The invention discloses an optical waveguide ring resonator based on an asymmetric directional coupler, and is applied to the fields of optical communication, optical information processing and optical sensing to realize wave filtering, delay, sensing and other functions. The optical waveguide ring resonator comprises a main waveguide, a multimode waveguide and a ring waveguide, the main waveguideand the multimode waveguide form an asymmetric directional coupler, and a plurality of ring waveguide resonant cavities can be coupled to the main waveguide at the same time by using the asymmetric directional coupler so that the FSR can be increased by utilizing the vernier effect, the high-performance ring resonator is realized, the structure of the ring resonator is easy to expand, the numberof the utilized ring resonant cavities can be expanded from two to three or even more by designing different asymmetric couplers, and the size of the device cannot be obviously increased. The ring resonator is compact in structure, high performance can be achieved with a small size, application of the ring resonator in the fields of optical communication, optical information processing, optical sensing and the like is further promoted, important technical support is provided for the fields and the ring resonator has high application value.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Integrated polarization beam splitter based on thin-film lithium niobate waveguide
ActiveCN111399118AAchieve separationSimple structureOptical light guidesPhase shiftedMultimode interference
The invention discloses an integrated polarization beam splitter based on a thin-film lithium niobate waveguide. A 1*2 multimode interference coupler, a multistage phase shifter and a 2*2 multimode interference coupler are sequentially cascaded to form a Mach-Zehnder interferometer structure. The 1*2 multimode interference coupler is composed of a first conical waveguide, a second conical waveguide, a third conical waveguide and a multimode waveguide. The 2*2 multimode interference coupler is composed of a first conical waveguide, a second conical waveguide, a third conical waveguide, a fourthconical waveguide and a multimode waveguide. The multi-stage phase shifter is composed of a first interference arm and a second interference arm. The first interference arm is formed by sequentiallyconnecting a first connecting waveguide, a first phase shift waveguide, a second connecting waveguide, a second phase shift waveguide and a third connecting waveguide. The second interference arm is formed by sequentially connecting a fourth connecting waveguide, a third phase shift waveguide, a fifth connecting waveguide, a fourth phase shift waveguide and a sixth connecting waveguide. The integrated polarization beam splitter has the characteristics of high extinction ratio, low loss, simple structure, simple design and simple processing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Mode multiplexer/demultiplexer, mode demultiplexing method and mode multiplexing method
ActiveCN111025468AStructural process tolerance is largeSmall sizeOptical waveguide light guideInterference (communication)Multimode interference
A mode multiplexer / demultiplexer, a mode demultiplexing method and a mode multiplexing method relate to the technical field of optical communication devices. The mode multiplexer / demultiplexer comprises a multimode interference waveguide which is asymmetric and variable in width, a multimode waveguide which is connected to the left side of the multimode interference waveguide, and two transmissionwaveguides which are connected to the right side of the multimode interference waveguide, wherein a first port is formed in the left end of the multimode waveguide, and a second port is formed in thesingle-mode waveguide at the right end of each transmission waveguide. The mode multiplexer / demultiplexer has the advantages that internal interference points can be adjusted by adjusting the shape of the multimode interference waveguide, mode multiplexing and demultiplexing are achieved, the structural process tolerance is large, the size is small, no fine waveguide structure exists, the machining precision requirement is not high, and the manufacturing cost is low.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD +1
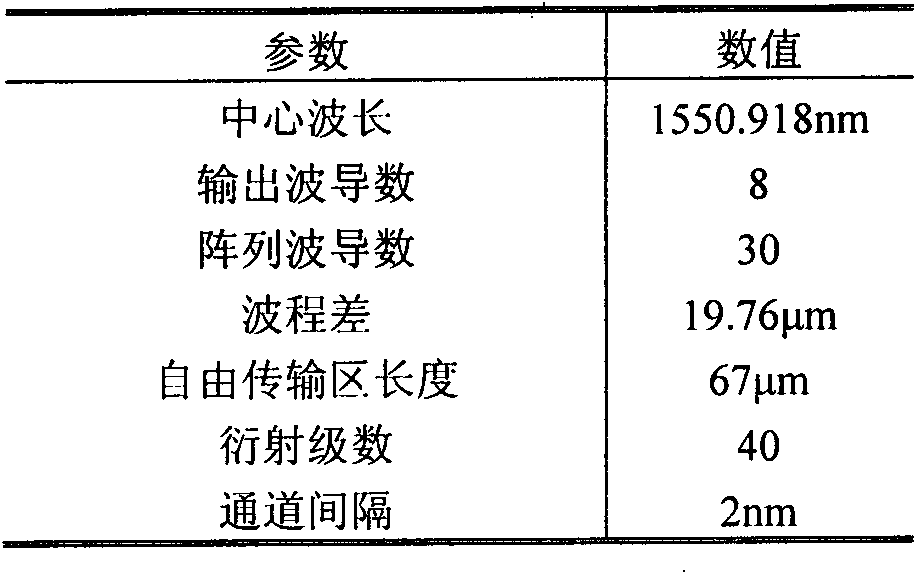
Method for flattening output spectra of arrayed waveguide grating
The invention discloses a method for flattening the output spectra of an arrayed waveguide grating. The method adopts a design combining tapered multimode waveguides and input / output waveguides in a tapered to-be-widened structure. The method is characterized in that the tapered multimode waveguides are connected to the tail ends of the input waveguides, and one section of tapered to-be-widened waveguides is inserted respectively before the tapered multimode waveguides and after the output panel waveguides of the arrayed waveguide grating. The method for flattening the output spectra of the arrayed waveguide grating has the advantages of higher design freedom, capability of obtaining the flattened spectra of low chromatic dispersion, lower output crosstalk and low losses. Meanwhile, 3dB bandwidth can be increased to more than 60% of the original channel spacing after spectra flattening.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Reconfigurable mode converter based on Mach-Zehnder interferometer
ActiveCN112859240AImprove reconfigurabilityIncrease or decrease the quantityOptical waveguide light guideConvertersSoftware engineering
The invention discloses a reconfigurable mode converter based on a Mach-Zehnder interferometer, which comprises a third-order mode demultiplexer and a third-order mode multiplexer connected with each other. The third-order mode demultiplexer and the third-order mode multiplexer are both connected with a Mach-Zehnder interferometer switch group; the demultiplexer is used for demultiplexing the multimode waveguide, the Mach-Zehnder switch is used for controlling mode output, and the multiplexer is used for multiplexing modes in the Mach-Zehnder switch into the multimode waveguide. According to the reconfigurable mode converter, a scheme is provided for flexible conversion between different modes in a mode multiplexing technology in optical communication, and the problem of efficient utilization of the device area caused by increasing scale of an optical information network is effectively solved. The device can be highly integrated, is compact in structure, is good in reconfigurability, and can play an important role in the application of the optical interconnection network.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
High-power soliton frequency comb chip and pulse generation system and method thereof
PendingCN112526673AMeet high power requirementsAchieving net signal gainElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptical light guidesFrequency combGain
The invention relates to a high-power soliton frequency comb chip and a pulse generation system and method thereof. The soliton frequency comb chip comprises a substrate, a micro-ring resonant cavityand a straight waveguide, the straight waveguide sequentially comprises a multimode waveguide, a multimode single-mode transition cone waveguide, a single-mode waveguide and a single-mode slot waveguide from one end to the other end, the wide end of the multimode single-mode transition cone is connected with the multimode waveguide, and the narrow end of the multimode single-mode transition cone is connected with one end of the single-mode waveguide. The other end of the single-mode waveguide is in coupling connection with the single-mode lot waveguide through a linear striptolot mode converter; and the micro-ring resonant cavity is positioned on one side of the multimode waveguide and is in coupling connection with the multimode waveguide. According to the invention, the thought of lasercoherent ranging is combined, the frequency comb micro-cavity structure is integrated on the micro-nano waveguide, and the generated soliton frequency comb is subjected to on-chip light amplificationto realize signal gain amplification, so that the novel integrated design of the ranging transmitting end optical system is realized, and the measurement efficiency is effectively improved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Double-cantilever inverted cone spot-size conversion structure for waveguide coupling
PendingCN114397730APrevent leakageImprove alignment toleranceOptical waveguide light guideBeam splittingEngineering
The invention discloses a double-cantilever inverted-cone spot-size conversion structure for waveguide coupling, and the structure consists of an input waveguide, a multimode waveguide interference region, two output waveguides, and parabolic inverted-cone structures at the rear ends of the output waveguides. The self-mapping effect is utilized to enable input light waves to generate a plurality of images on the cross section of the output waveguide, the light waves after beam splitting are spread in the output waveguide, and the cross section of the output waveguide passing through the parabola-shaped inverted cone structure is gradually reduced, so that the light waves of several output waveguides are diffused into the cladding so as to be conveniently coupled with a large-size waveguide. Compared with a traditional single inverted-cone-shaped coupler, the double-cantilever parabola-shaped inverted-cone-shaped structure is adopted, the alignment tolerance is improved, a small mode field of light transmitted by a small-size waveguide can be converted into a large mode field so that the light can be efficiently coupled into a large-size waveguide, meanwhile, a cladding layer where the parabola-shaped inverted-cone-shaped structure is located is suspended, substrate leakage is avoided, and the coupling efficiency is improved. And the loss during optical signal transmission is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Post ablation tissue analysis technique
A device, system, and method for identifying an area of ablated tissue. Specifically, the device, system, and method may include a device having one or more fiber sensors and a processing unit for receiving emitted and / or reflected light from tissue and making one or more determinations based on the received light regarding ablated tissue, tissue contact, and / or occlusion. Each of the fiber sensors may include at least one multimode waveguide segment and at least one singlemode waveguide segment, or each of the fiber sensors may be singlemode waveguide. Further, each fiber sensor may have a core with long-period grating for optically coupling light from tissue to the fiber sensor. The processing unit may include a beam processing apparatus and a hyperspectral imaging and analysis apparatus, and may optionally include a light source.
Owner:美敦力快凯欣有限合伙企业
A polarization-insensitive waveguide grating filter based on double-layer structure
ActiveCN113075766BSmall sizeLarge toleranceOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsMaterials scienceWaveguide filter
The invention discloses a polarization-insensitive waveguide grating filter based on a double-layer structure; it includes a polarization-insensitive filter unit, and the polarization-insensitive filter unit includes a silicon waveguide apodized grating layer and a silicon nitride waveguide apodized A grating layer, where the TE signal is filtered by the silicon waveguide apodized grating and the TM signal is filtered by the silicon nitride apodized grating. The polarization-insensitive filter unit can be realized by using a multimode waveguide filter, or by a grating-assisted filter; the filter of the present invention can realize simultaneous filtering of TE mode and TM mode, and realize polarization-insensitive grating filter, and the device size can be effectively reduced by half compared to the traditional solution using a polarization rotator. In addition, the present invention is based on silicon-based and silicon nitride waveguide grating filters, with large tolerance and small insertion loss, and the central wavelength adjustment range is not limited by FSR, and filters with different bandwidths can be realized by setting different coupling coefficients.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Polarization insensitive waveguide grating filter based on double-layer structure
ActiveCN113075766ASmall sizeLarge toleranceOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsMaterials scienceWaveguide grating
The invention discloses a polarization insensitive waveguide grating filter based on a double-layer structure. The filter comprises a polarization insensitive filter unit, the polarization insensitive filter unit comprises a silicon waveguide apodized grating layer and a silicon nitride waveguide apodized grating layer, the silicon waveguide apodized grating filters TE signals, and the silicon nitride waveguide apodized grating filters TM signals. The polarization insensitive filter unit can be realized by adopting a multi-mode waveguide type filter and also can be realized by adopting a grating auxiliary type filter; according to the filter, simultaneous filtering in a TE mode and a TM mode can be achieved, a grating filter insensitive to polarization is achieved, and the device size can be effectively reduced by half compared with a traditional scheme adopting a polarization rotator. In addition, based on a silicon substrate and a silicon nitride waveguide grating filter, the filter is large in tolerance and small in insertion loss, the adjustment range of the central wavelength is not limited by FSR, and filters with different bandwidths can be achieved by setting different coupling coefficients.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com