Self-adaptive elastic ring optical buffer for variable length optical packet
An optical buffer and optical grouping technology, applied in the field of optical communication, can solve the problems of poor upgrade ability and adaptability, increase the minimum granularity T of the cache, and poor cache flexibility, etc., and achieve powerful congestion control, traffic engineering, and flexible level The effect of linking and expanding capabilities and eliminating restrictions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
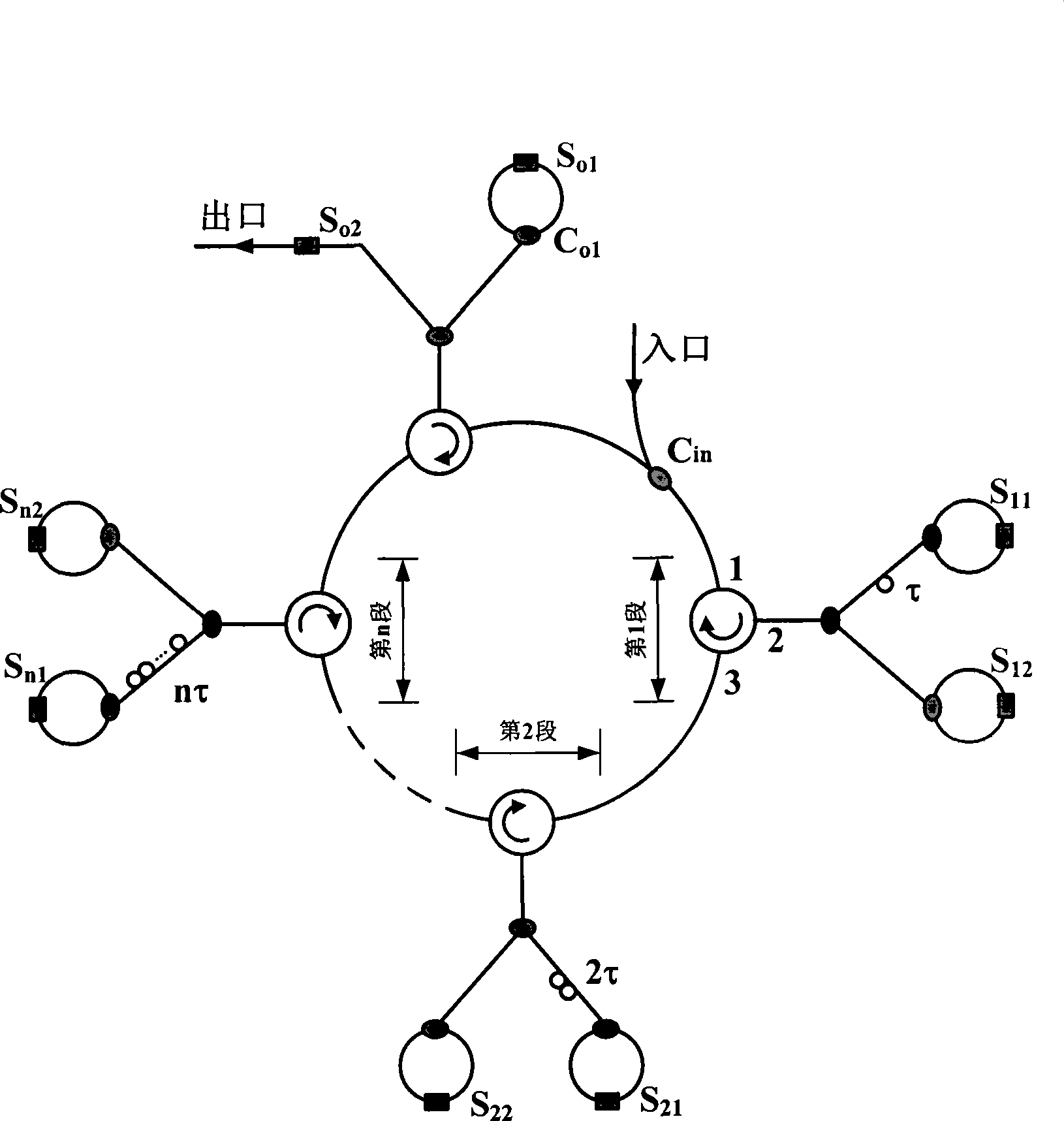
[0030] The caching function of the single-level buffer is implemented as follows:
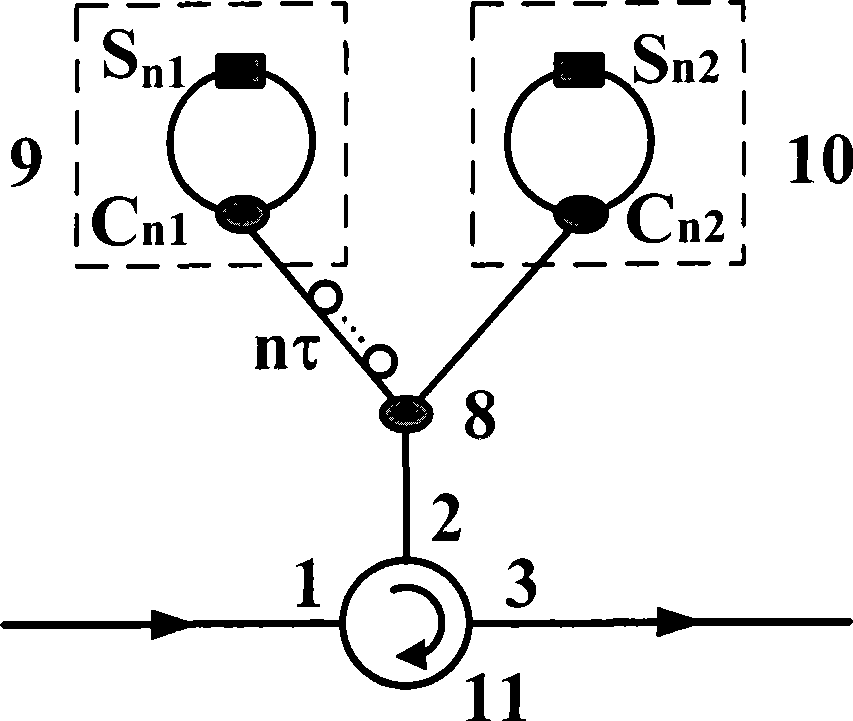
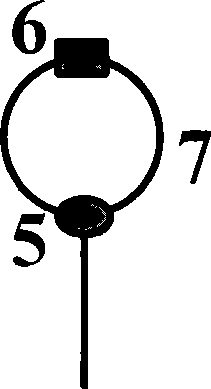
[0031] like figure 2 shown, setting S n1 Open S n2 off, the basic buffer unit completes the function of buffering optical packets for 2nτ; set S n1 Close S n2 On, the basic cache unit completes the non-caching function. Similarly, if Figure 4 As shown in the buffer exit structure, set S o1 Open S o2 Off, optical packets will continue to be buffered in the buffer; set S o1 Close S o2 On, the optical packet will be read out of the buffer. Therefore, if figure 1 As shown, for each basic buffer unit and outlet in the buffer, a pair of reverse electrical signals are used to control the buffer delay combination function and the buffer cycle number selection function of the buffer. E.g:
[0032] ①Set S in the first basic cache unit 11 Open S 12 Off, all others are set to S n1 Close S n2 open, the exit is S o1 Close S o2 On, the optical packet will be buffered in the buffer for 2τ t...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The caching function of the system-level cascaded buffer is realized in the following way (the cache structure is as follows Image 6 shown):
[0042] 1) The internal control mode of each level of buffer is the same as that of Embodiment 1;
[0043] 2) The two-way transmission capability of the ring structure and the separate "read / write" function enable the buffer to allow the optical packets in the rear to be directly output counterclockwise when buffering the optical packets without affecting the optical packets being buffered. For example: assuming that there are optical packets in the cache in the first-level and second-level buffers, when the optical packets in the second level are still in the buffer state, the optical packets in the first level can enter the first level through the exit of the first level. The entrance of level 2, and the counterclockwise direct output, enters the level 3 buffer. Where the length of the optical packet in the first level is l ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com