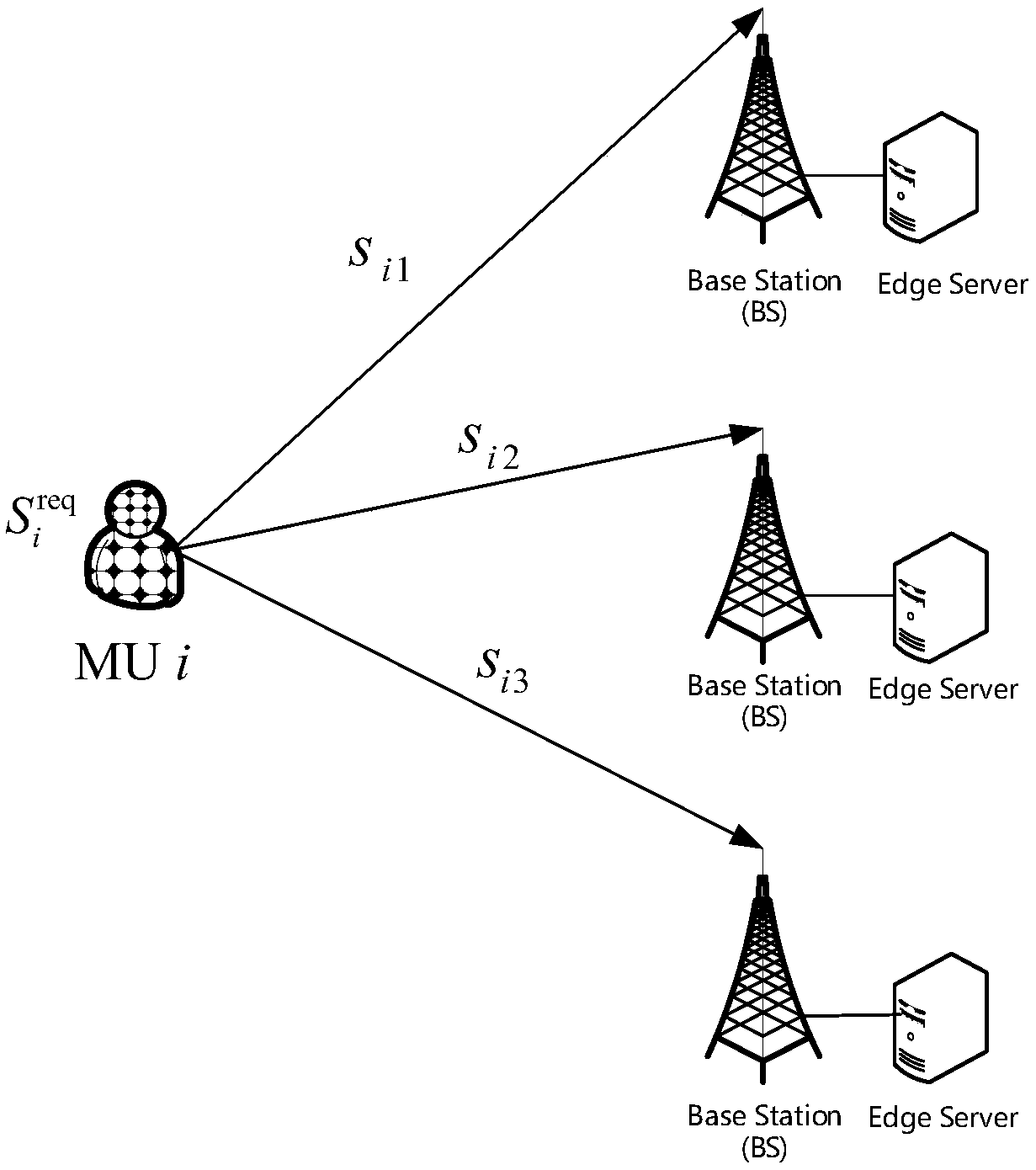
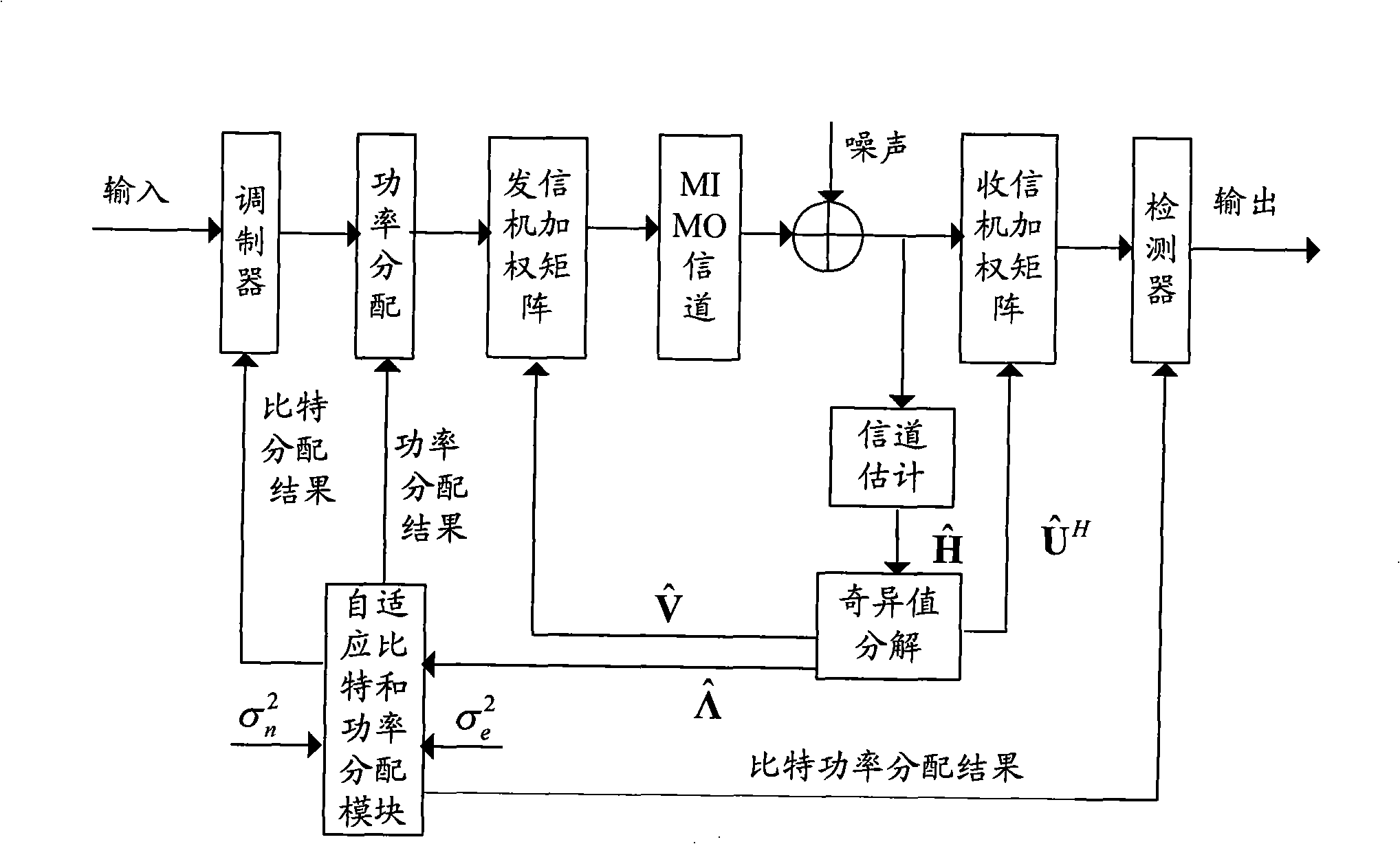
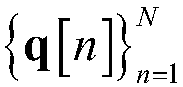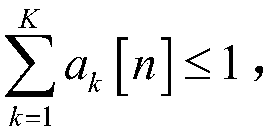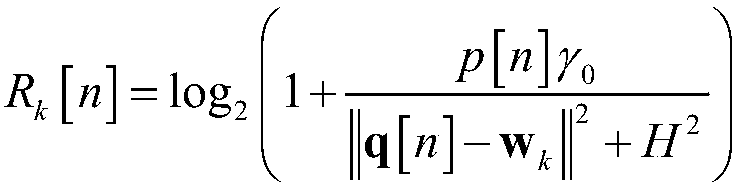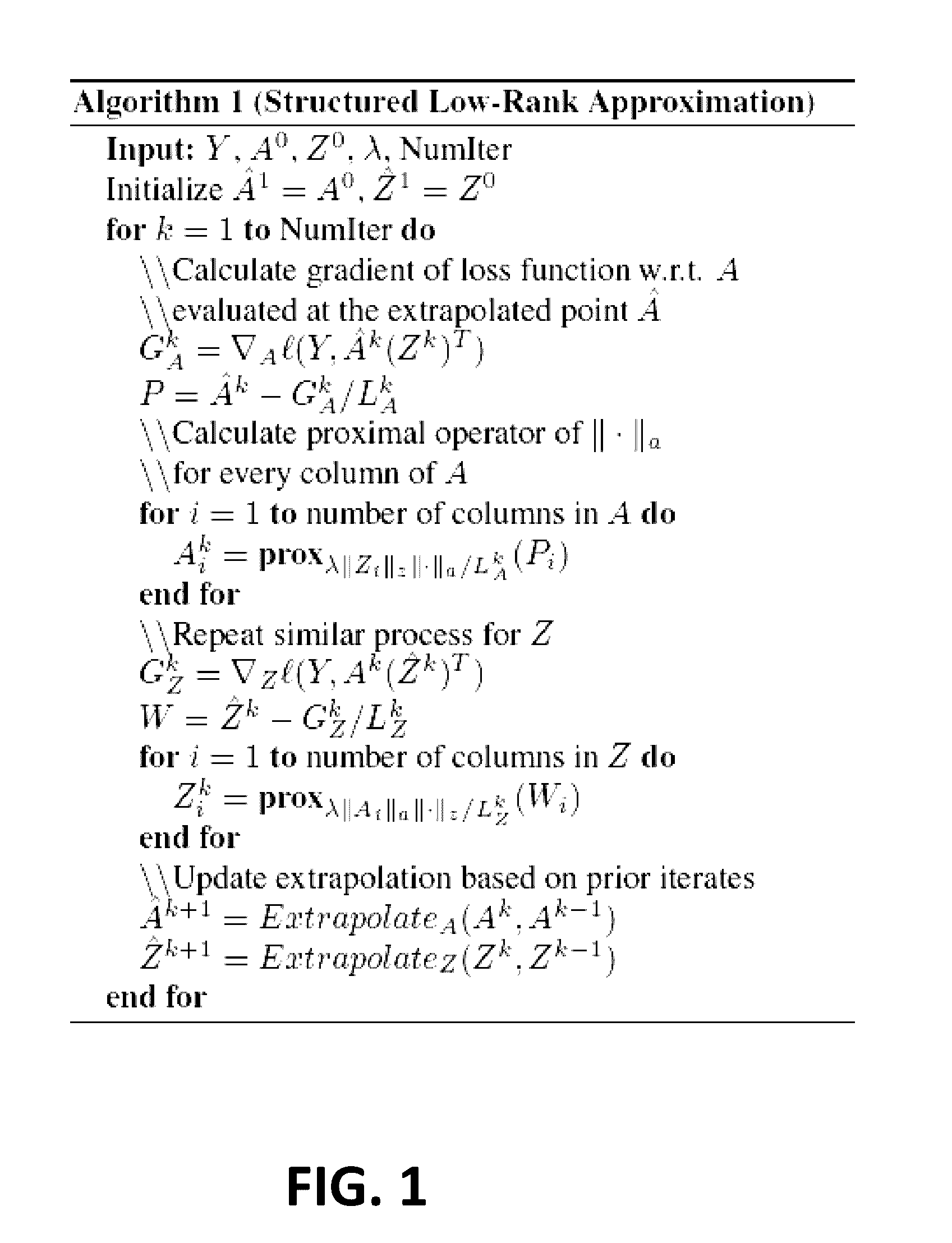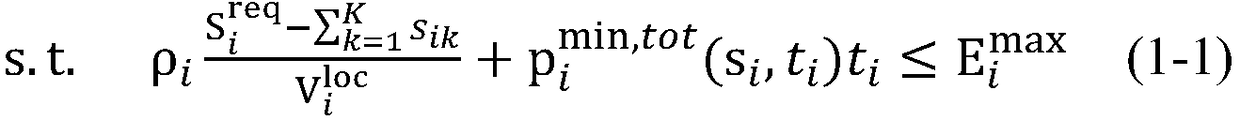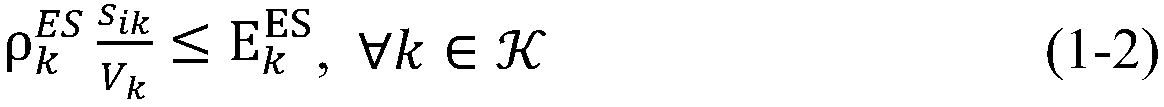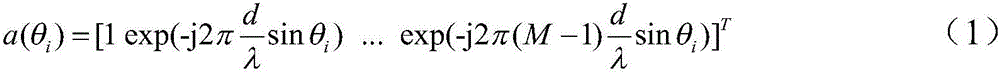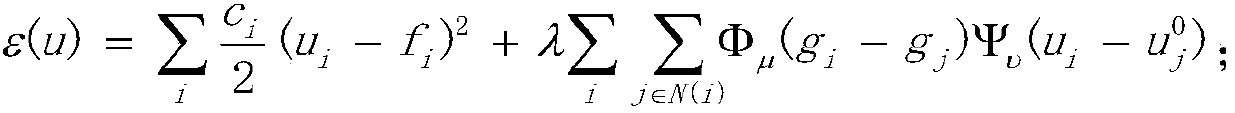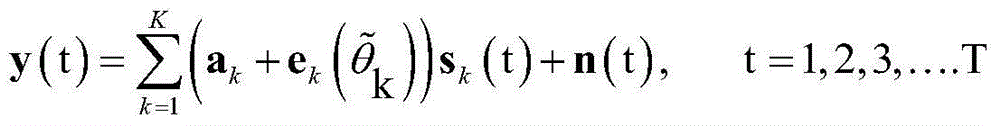Patents
Literature
184 results about "Non convex optimization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Non-convex optimization is now ubiquitous in machine learning. While previously, the focus was on convex relaxation methods, now the emphasis is on being able to solve non-convex problems directly.
UAV-assisted WSN, as well as method for designing node scheduling, route planning and power distribution of same
InactiveCN108566670APower managementInternal combustion piston enginesTransmitted powerNon convex optimization
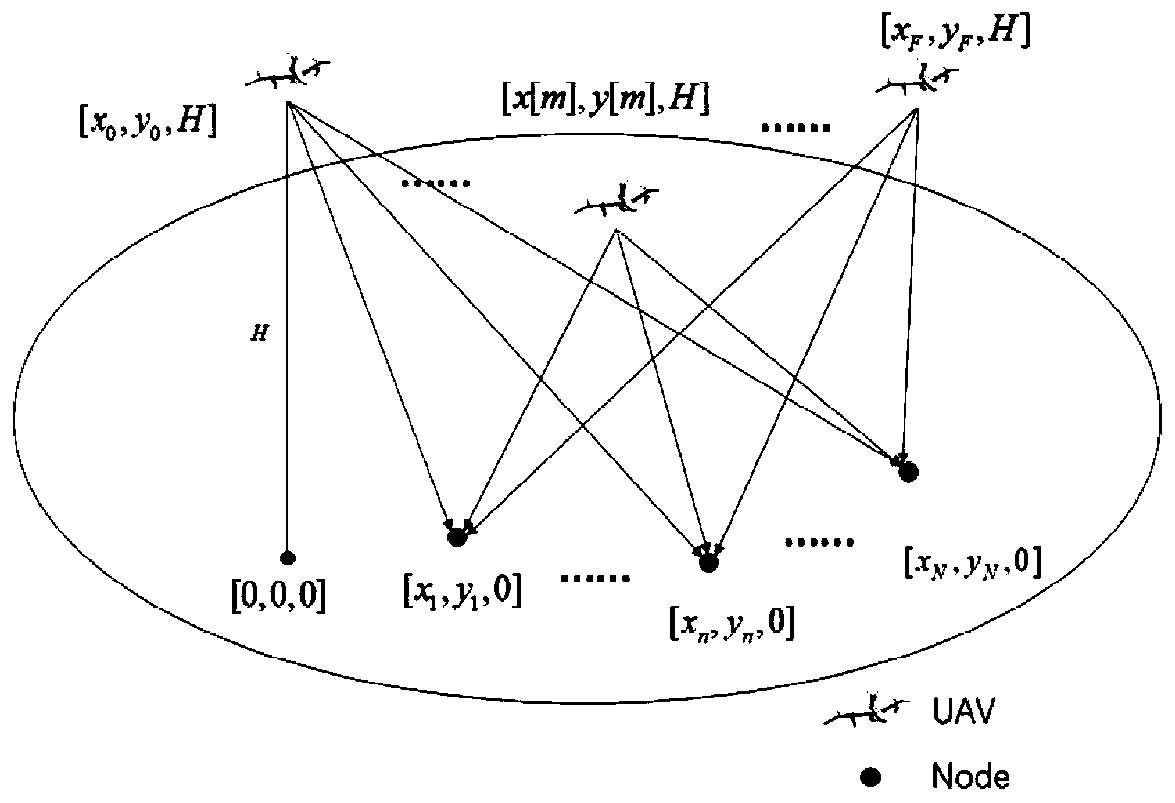
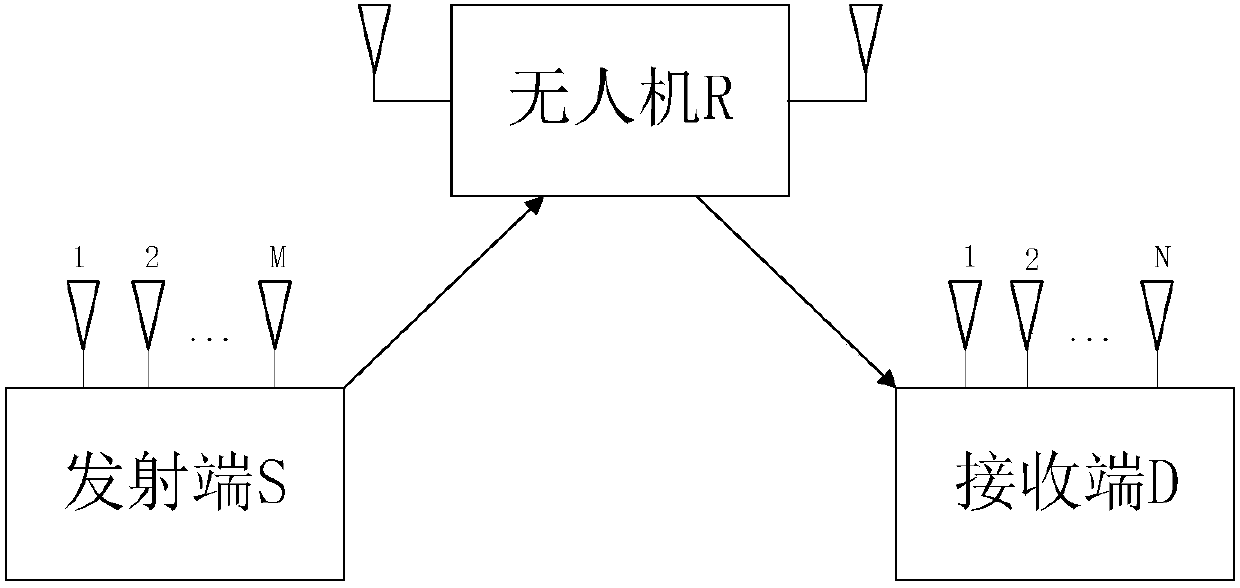
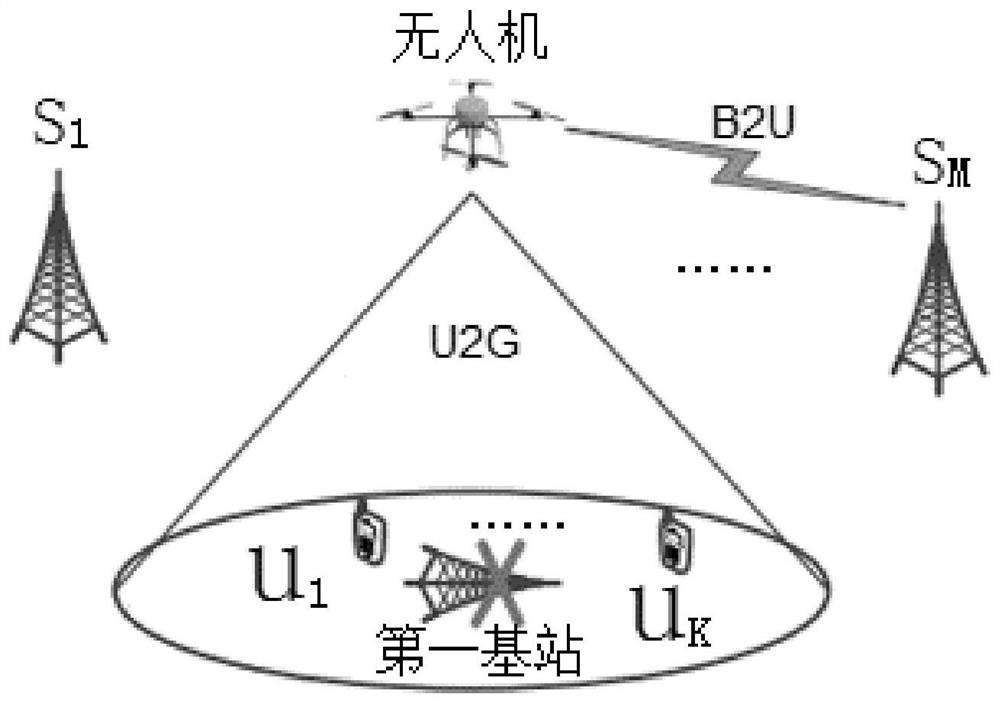
The invention discloses a UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle)-assisted WSN (Wireless Sensor Network), as well as a method for designing node scheduling, route planning and power distribution of the same, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication and IOT (Internet Of Things). The UAV-assisted WSN consists of a UAV aerial base station and K single-antenna ground terminal nodes. The method of the invention is characterized by aiming at minimizing system power consumption, considering constraint conditions such as a data transmission rate of the terminal node, a flight speed of the UAV and a transmitting power of the UAV, building a mathematical optimization model by taking a scheduling variable of the terminal node, a flying route of the UAV and a transmitting power variable of the UAV as parameters, respectively converting two sub-problems decomposed from a non-convex optimization problem of mixed integer variables into upper bound convex problems corresponding to the two sub-problems, alternately iterating sub-optimization problems through a block coordinate descent method and an interior point method, and obtaining a suboptimal parameter solution for scheduling of theterminal node, the flying route and the power distribution of the UAV.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF AERONAUTICS
Improved particle swarm-based power control optimization algorithm in cognitive radio network
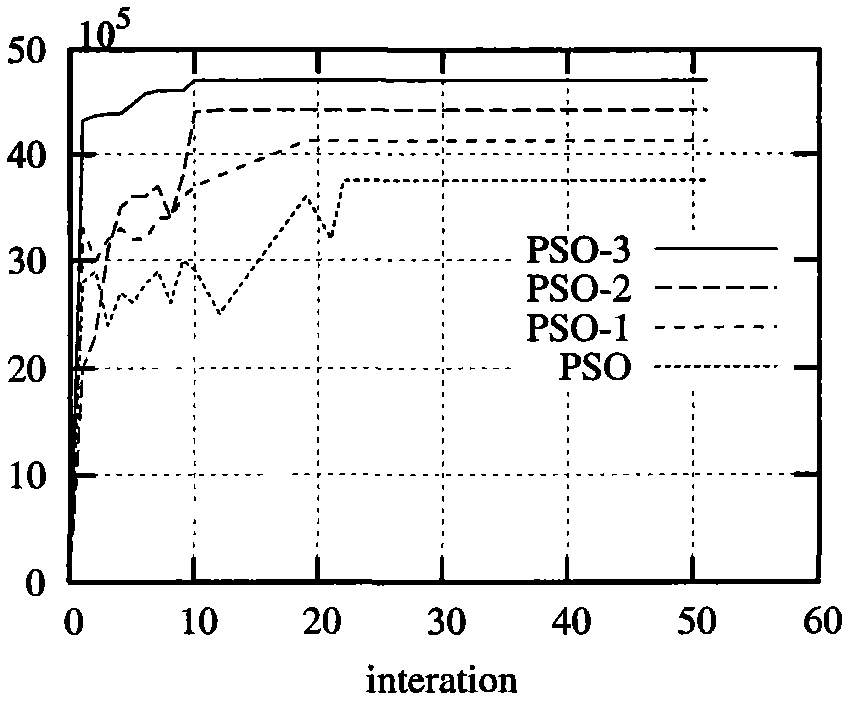
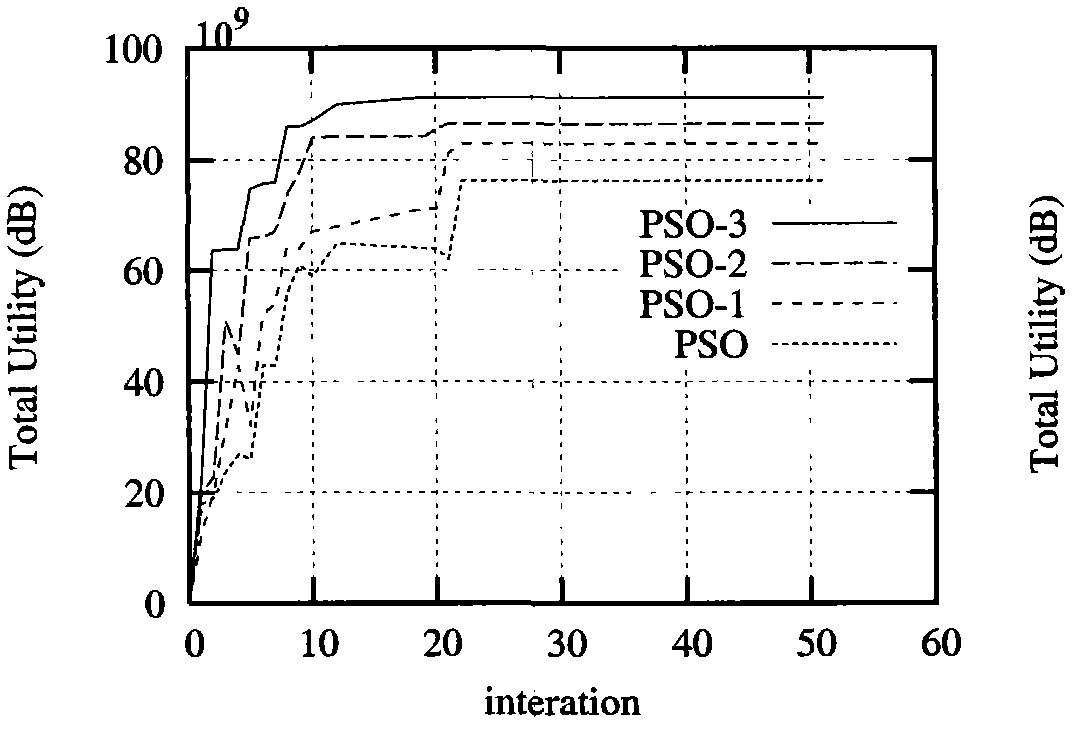
The invention relates to a power control optimization algorithm in a cognitive radio network, which belongs to the field of system resource allocation. The algorithm comprises the following steps: 1, initializing the iteration number of the algorithm, the positions and speed of particles and the basic parameters of the particle swarm; 2, calculating a fitness function value, setting the position Xa of an individual particle as the initial best position, and setting the particle with the best function value in the swarm as the initial best swarm position Gbestk; 3, searching based on a PSO algorithm, updating the best positions of the particles and the swarm and updating the speed and positions of the particles by using a fundamental formula of the particle swarm; and 4, setting a termination standard. The invention conducts study on the non-convex optimization problem controlled by the cognitive radio power and puts forward an improved particle swarm-based power control algorithm which allows utility functions such as an S-type function a convex function and the like to be non-concave, thereby conforming to the actual network better. Parameter adjustment is performed by the particle swarm algorithm to guarantee the global astringency of the algorithm. The algorithm of the invention has better validity and rapidity.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
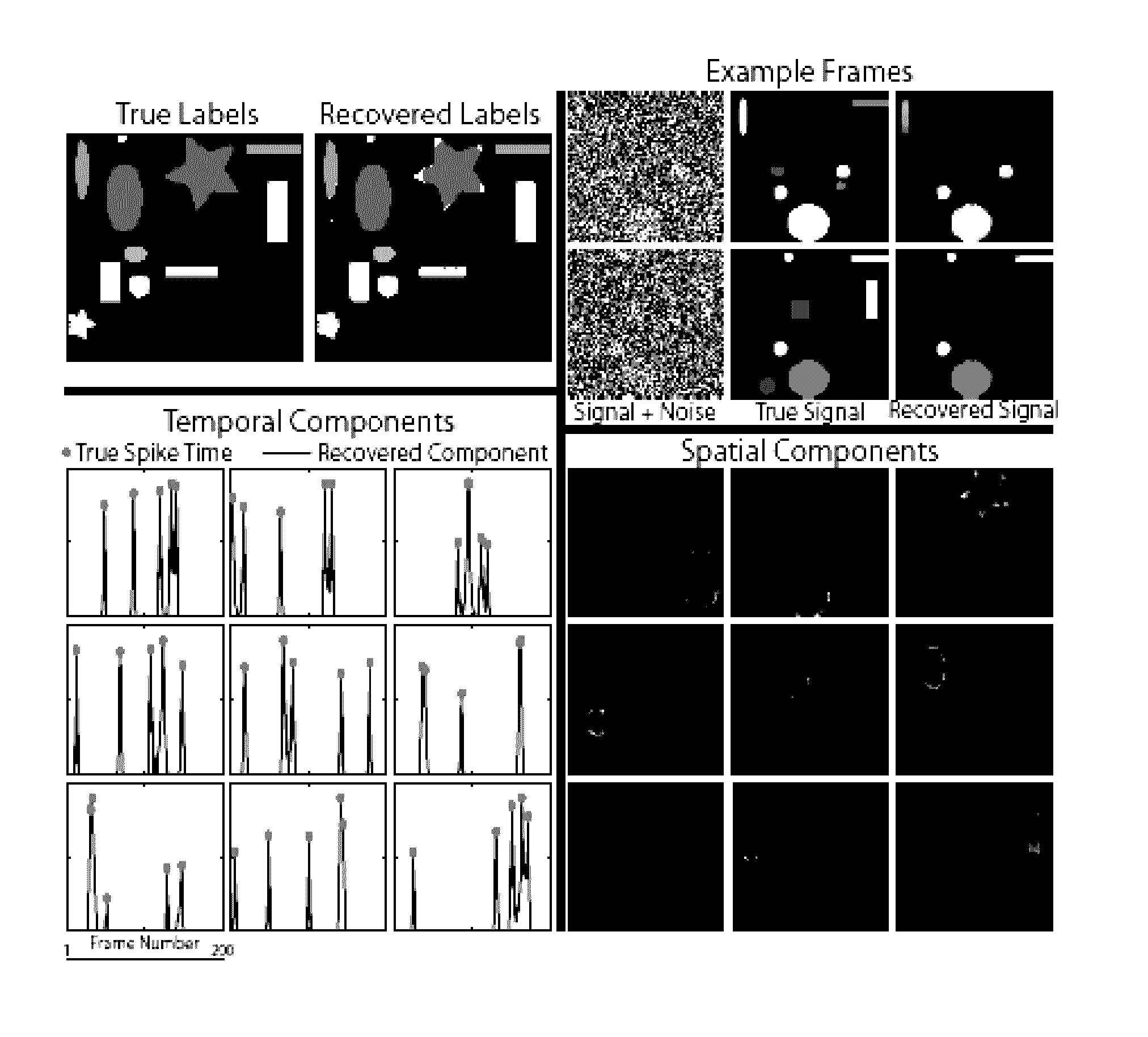
System and method for structured low-rank matrix factorization: optimality, algorithm, and applications to image processing
ActiveUS20160371563A1Character and pattern recognitionImaging processingLow rank matrix factorization
The present invention provides a system and method for structured low-rank matrix factorization of data. The system and method involve solving an optimization problem that is not convex, but theoretical results should that a rank-deficient local minimum gives a global minimum. The system and method also involve an optimization strategy that is highly parallelizable and can be performed using a highly reduced set of variables. The present invention can be used for many large scale problems, with examples in biomedical video segmentation and hyperspectral compressed recovery.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
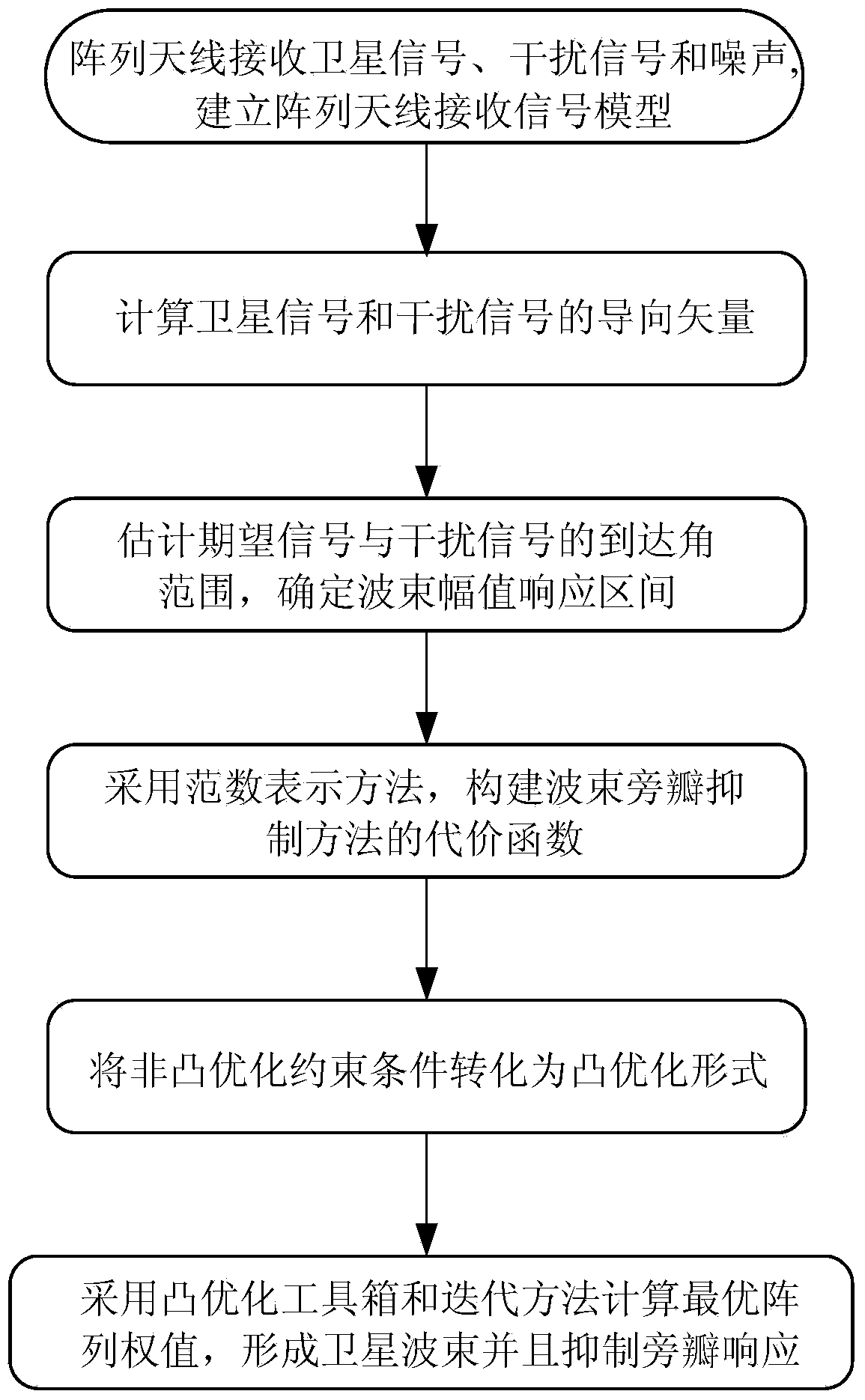
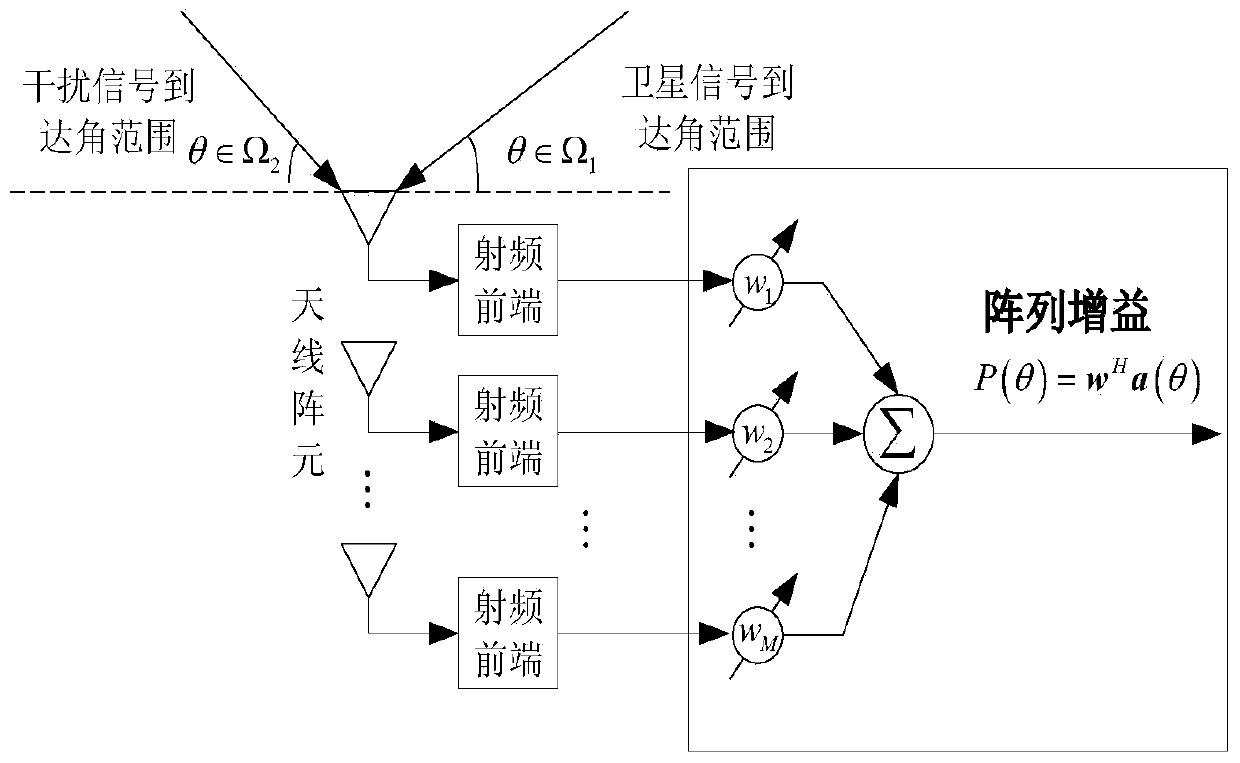
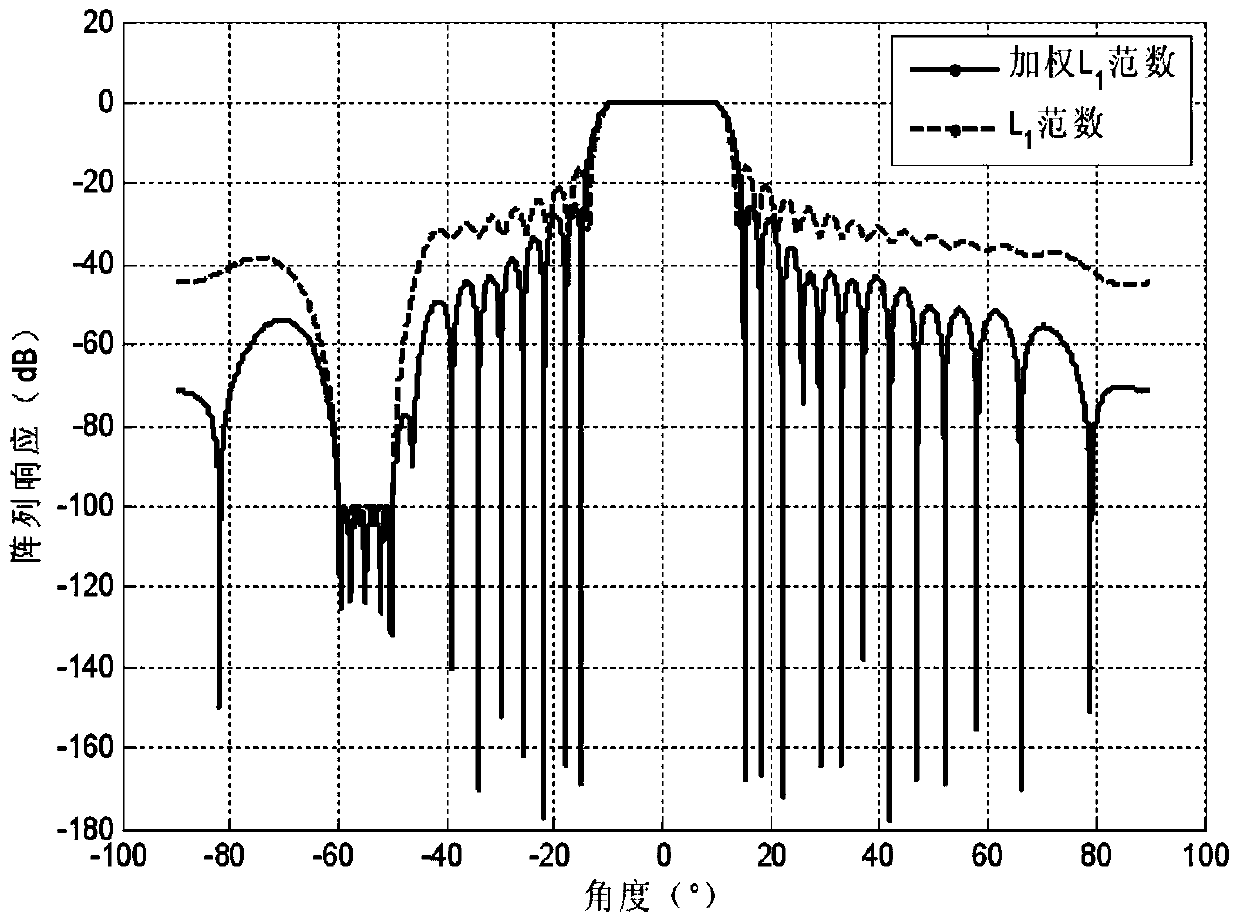
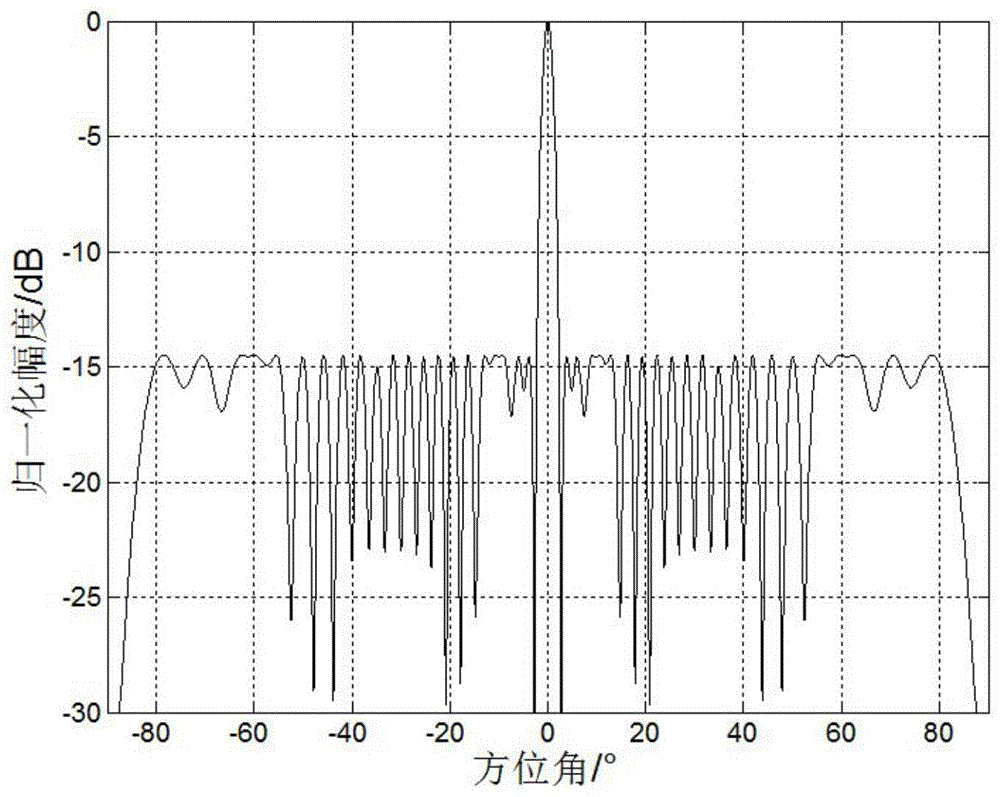
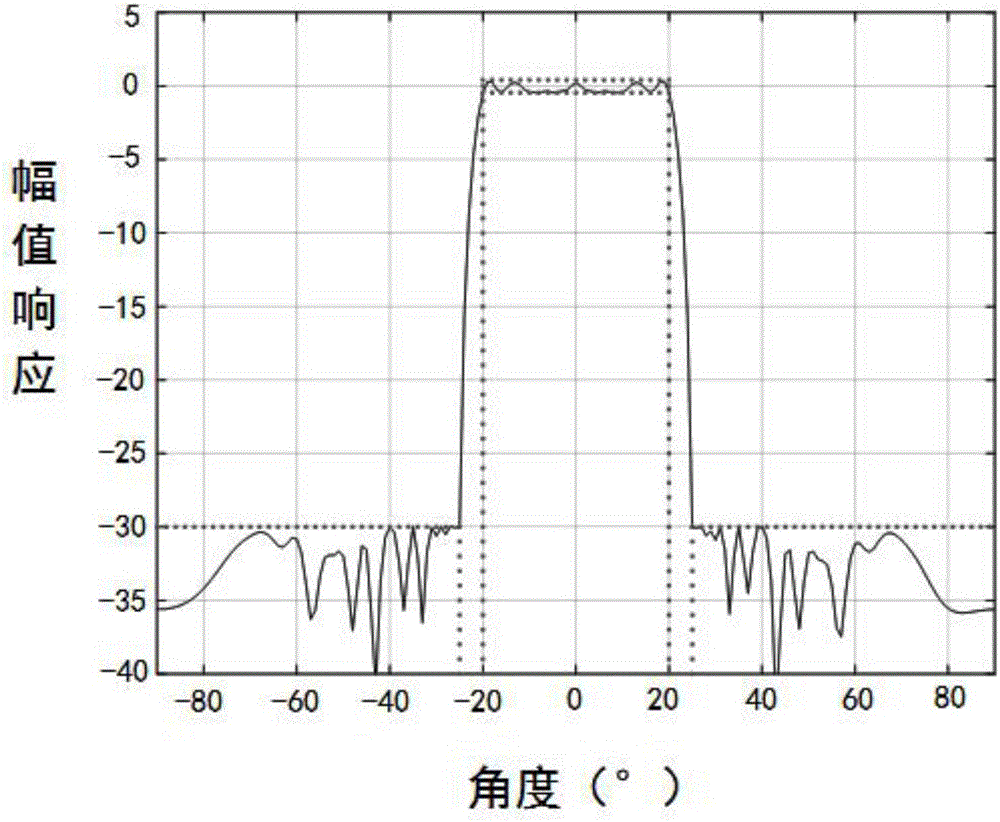
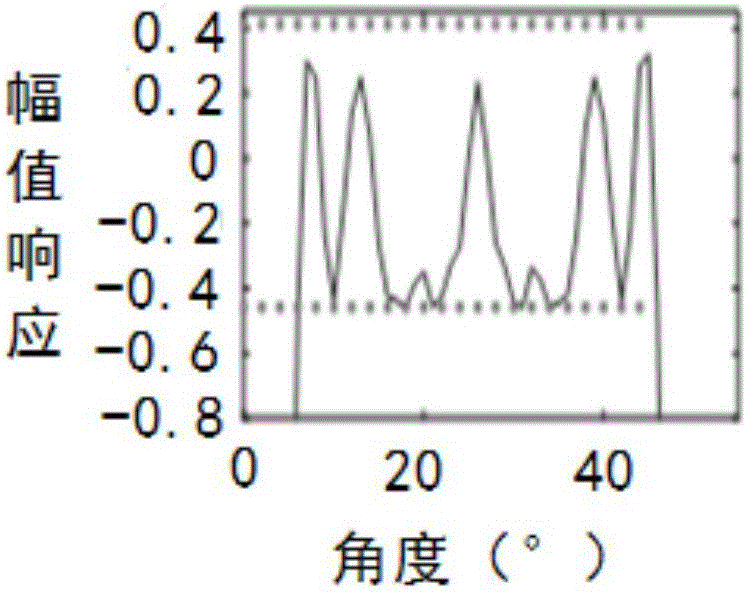
Beam sidelobe suppression method based on norm constraint
InactiveCN104199052AGuaranteed distortion-free receptionEasy to solveSatellite radio beaconingAmplitude responseOptimal weight
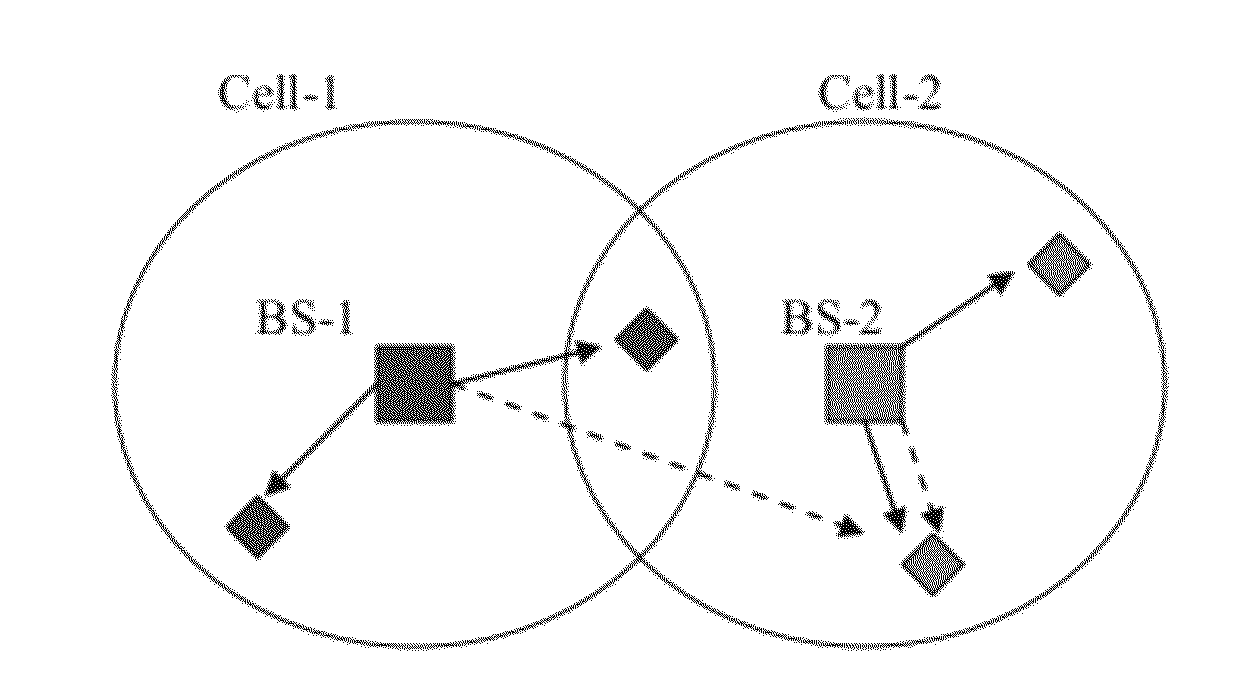
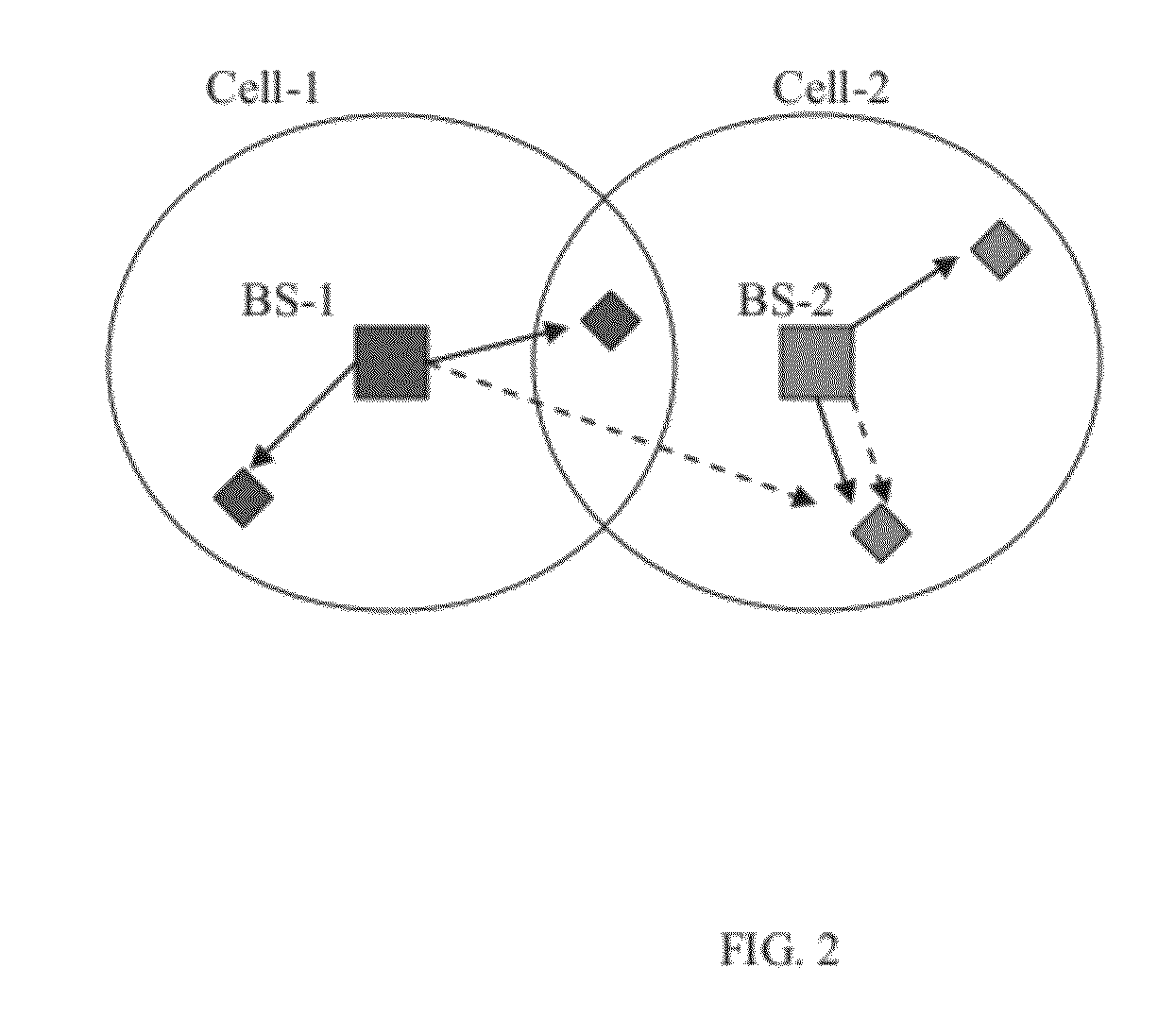
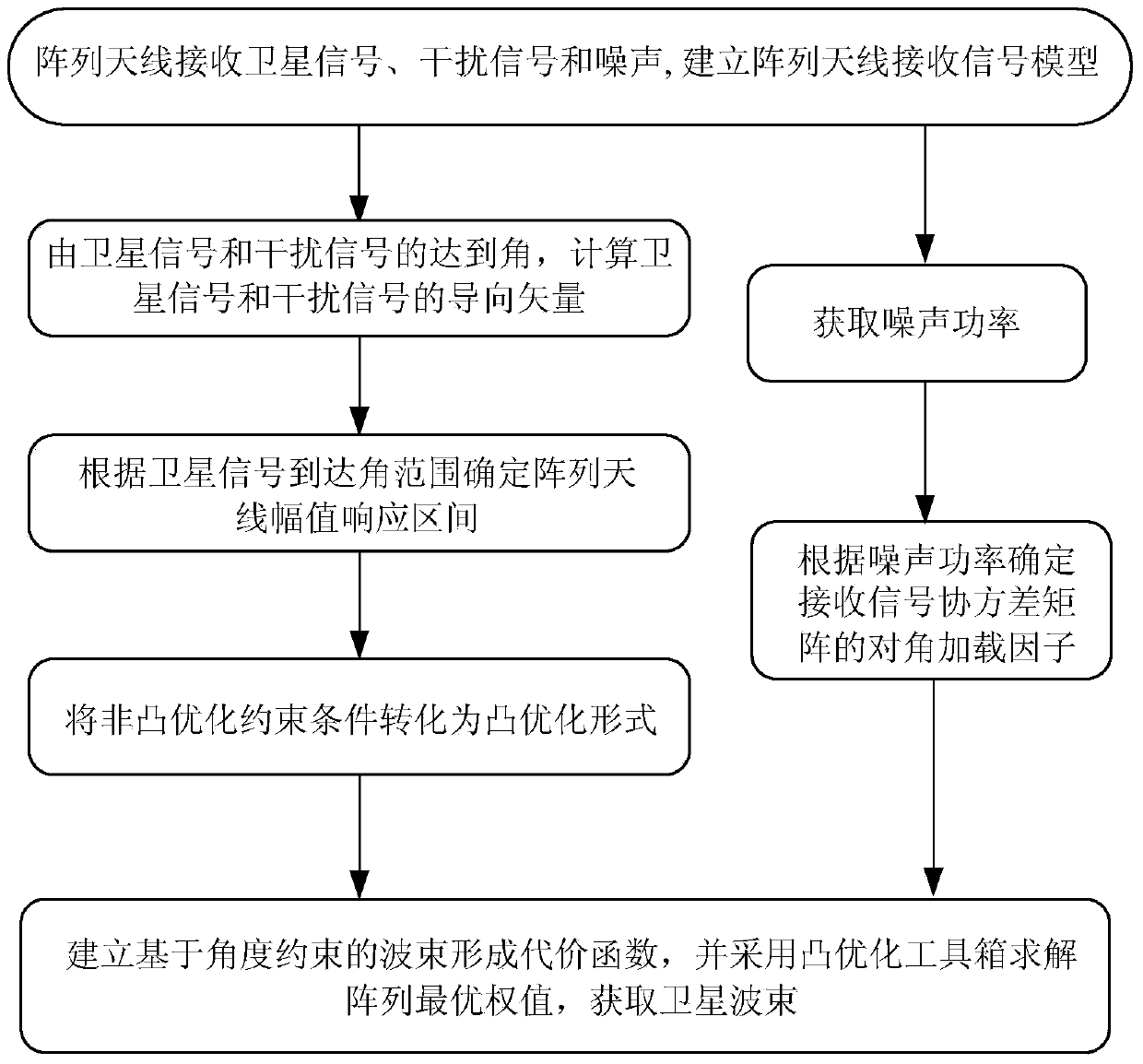
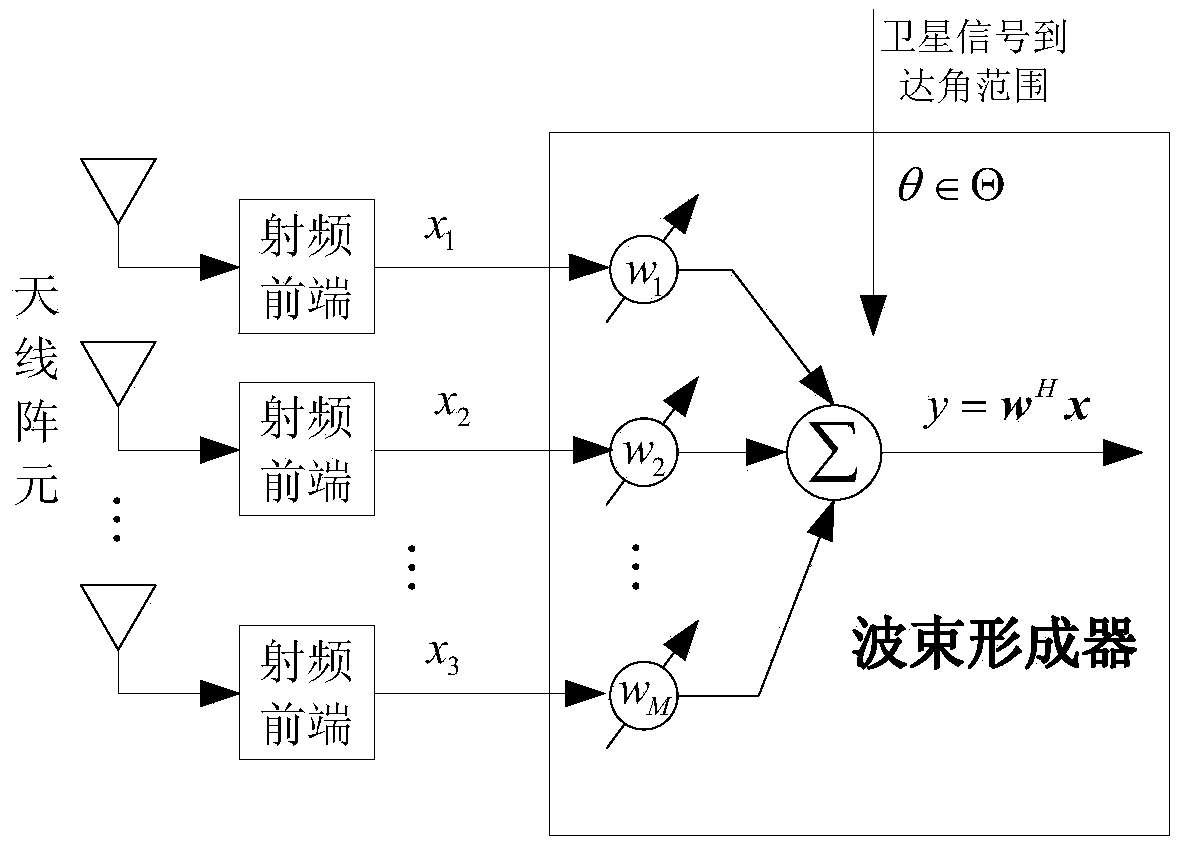
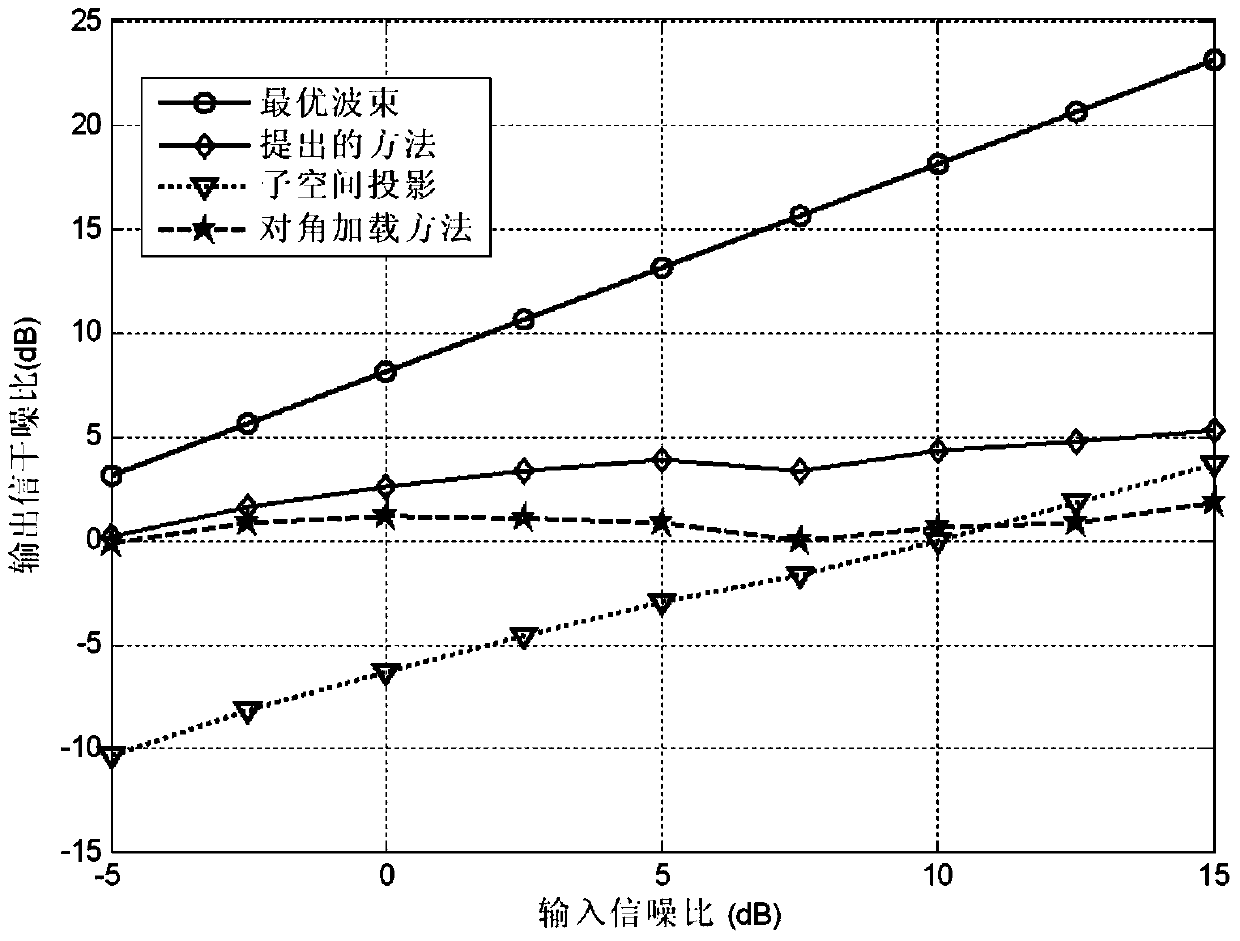
The invention relates to a beam sidelobe suppression method based on norm constraint. The method includes the steps of 1, establishing an array antenna signal-receiving model and calculating steering vectors of a satellite signal and an interfering signal; 2, determining array amplitude response constraint conditions according to angle-of-arrival ranges of the satellite signal and the interfering signal; 3, subjecting a whole angle space to sparse representation via norms, and determining a cost function of the method through the array amplitude response constraint conditions determined in the step 2; 4, converting non-convex optimization constraint conditions into convex optimization constraint conditions; and 5, calculating an array optimal weight by a weight iteration algorithm and a CVX toolbox to acquire a directional beam of the satellite signal and a directional null of the interfering signal.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
An unmanned aerial vehicle base station bandwidth and track joint optimization method with limited pushing power
ActiveCN109831797AMaximize the minimum average rateImprove resource utilizationNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionResource utilizationEngineering
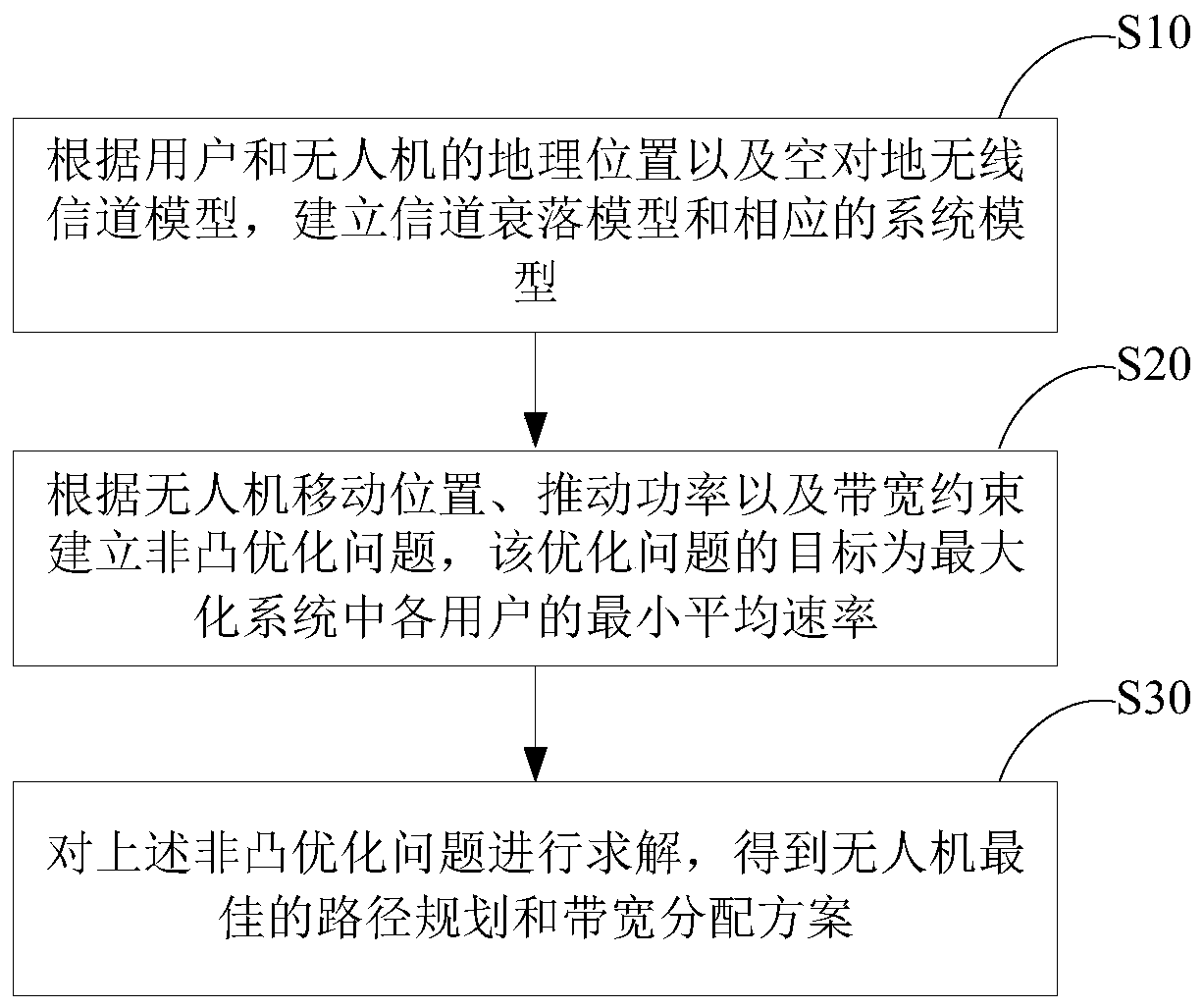
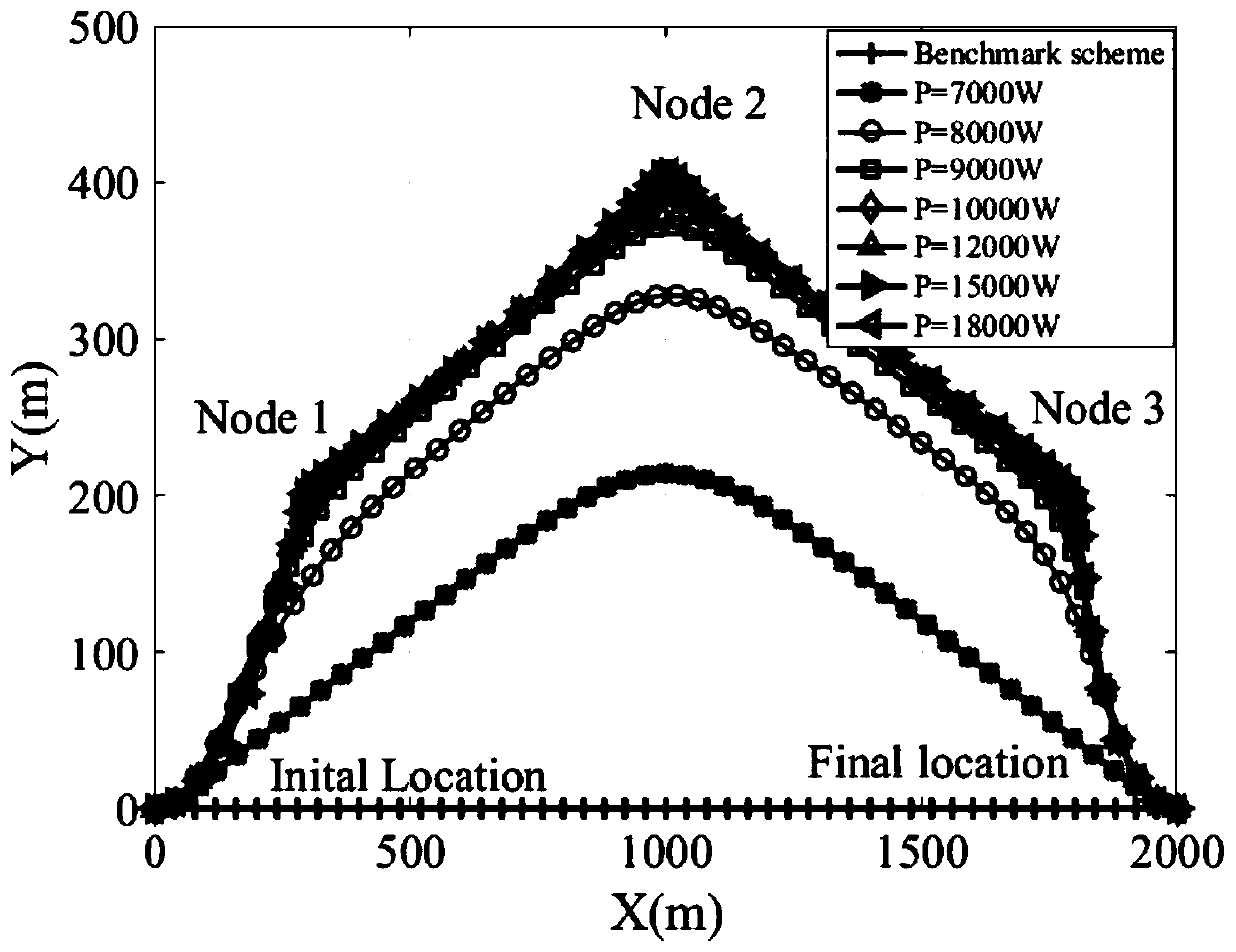
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle base station bandwidth and track joint optimization method with limited pushing power. The method is suitable for an unmanned aerial vehicle emergency communication scene. According to the invention, a single unmanned aerial vehicle is used as an air base station; in a scene of providing downlink transmission services for a plurality of users in aprocess of flying from a starting point to a terminal point, under the condition that the pushing power and the flight time of the unmanned aerial vehicle are limited; the minimum average rate of each user in the system is maximized by adjusting the flight path and the user bandwidth distribution; a non-convex optimization problem is established according to the moving position of the unmanned aerial vehicle, the pushing power and the bandwidth constraint, and the non-convex optimization problem is converted and solved by using a block coordinate descent and continuous convex approximation method, so that the minimum average rate of each user in the system is maximized, and the energy and frequency band resource utilization rate is maximized. The method has important guiding significancefor the unmanned aerial vehicle communication system under the condition that the pushing power and the total bandwidth are limited.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
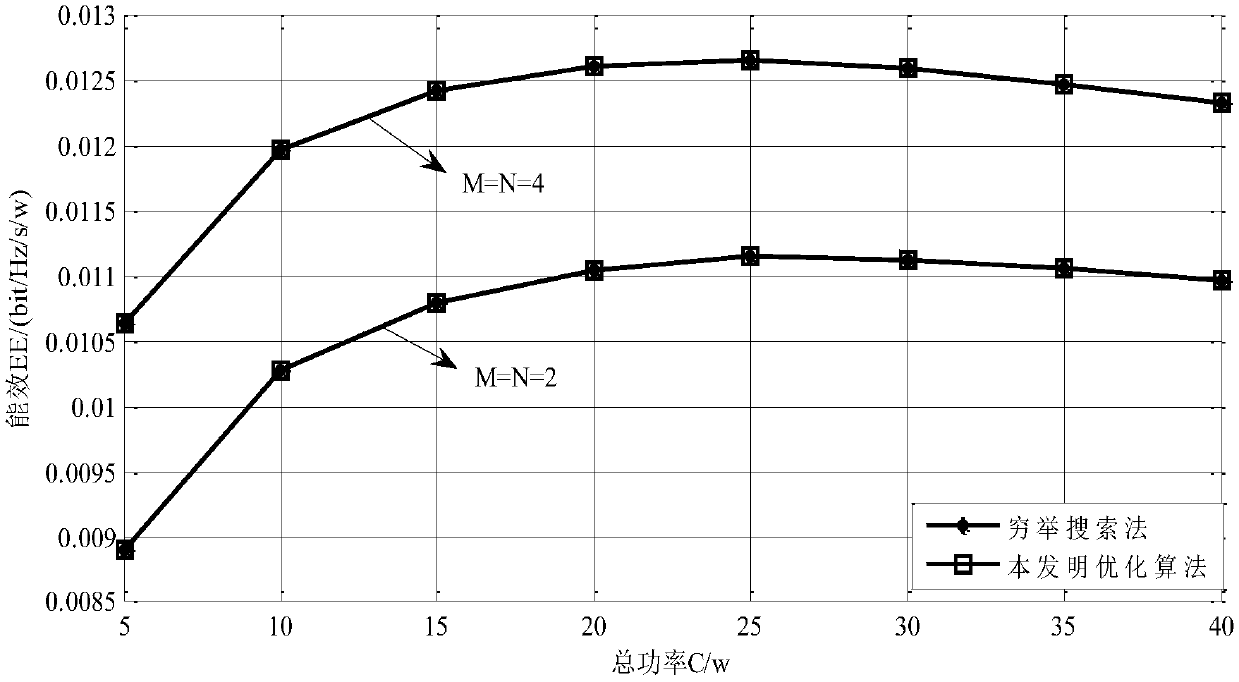
Power allocation algorithm for UAV relay system based on energy efficiency optimal criterion
ActiveCN108243431AReduce complexityImprove performancePower managementRadio transmissionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Allocation algorithm
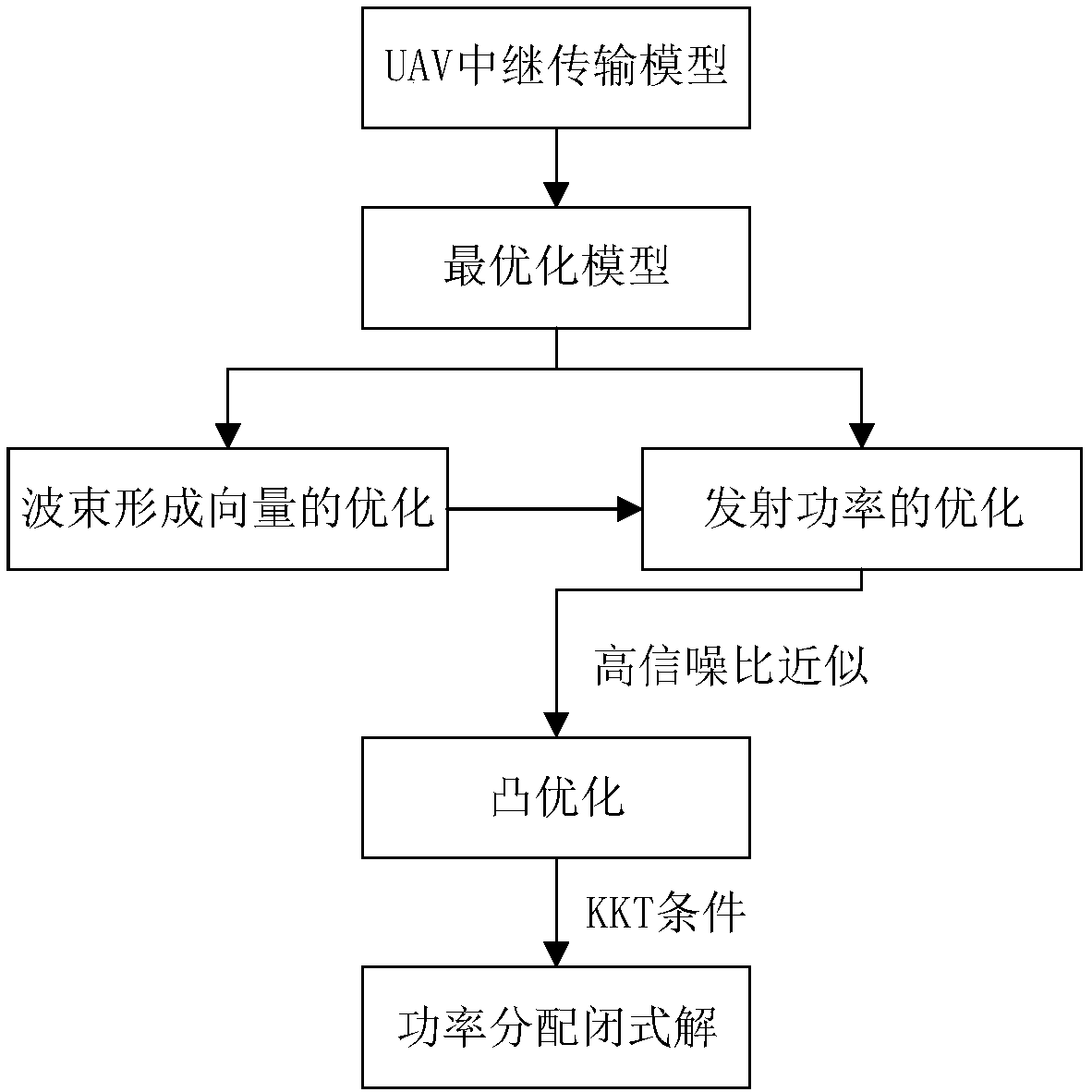
The invention discloses a power allocation algorithm for a UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) relay system based on an energy efficiency optimal criterion. Firstly, based on a double-hop amplification andrelay transmission model, an optimization model of power allocation is established, and a power allocation problem is converted into an optimization problem of the solution of maximum system energy efficiency. In the process of solving the optimal power allocation, firstly transmitted signal power is fixed to obtain a beamforming optimization scheme. Then, by a large signal-to-noise ratio intervalapproximation, an original non-convex optimization problem is converted into a convex optimization problem. Finally, a KKT condition is used, and a closed form solution of a power allocation scheme is calculated and obtained. A simulation experiment shows that the closed form solution obtained by the algorithm disclosed by the present invention is close to a loop iterative method, and thus the algorithm complexity is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
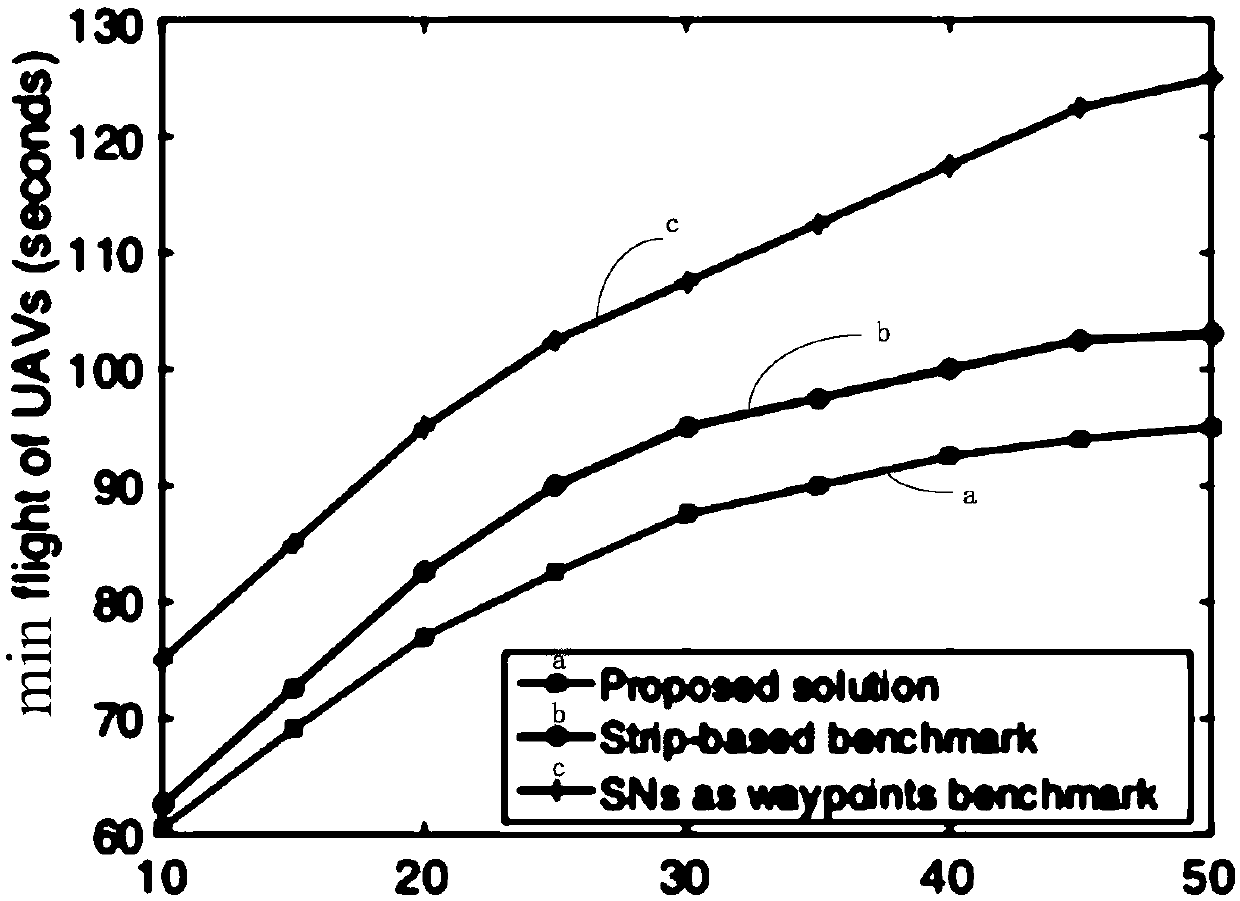
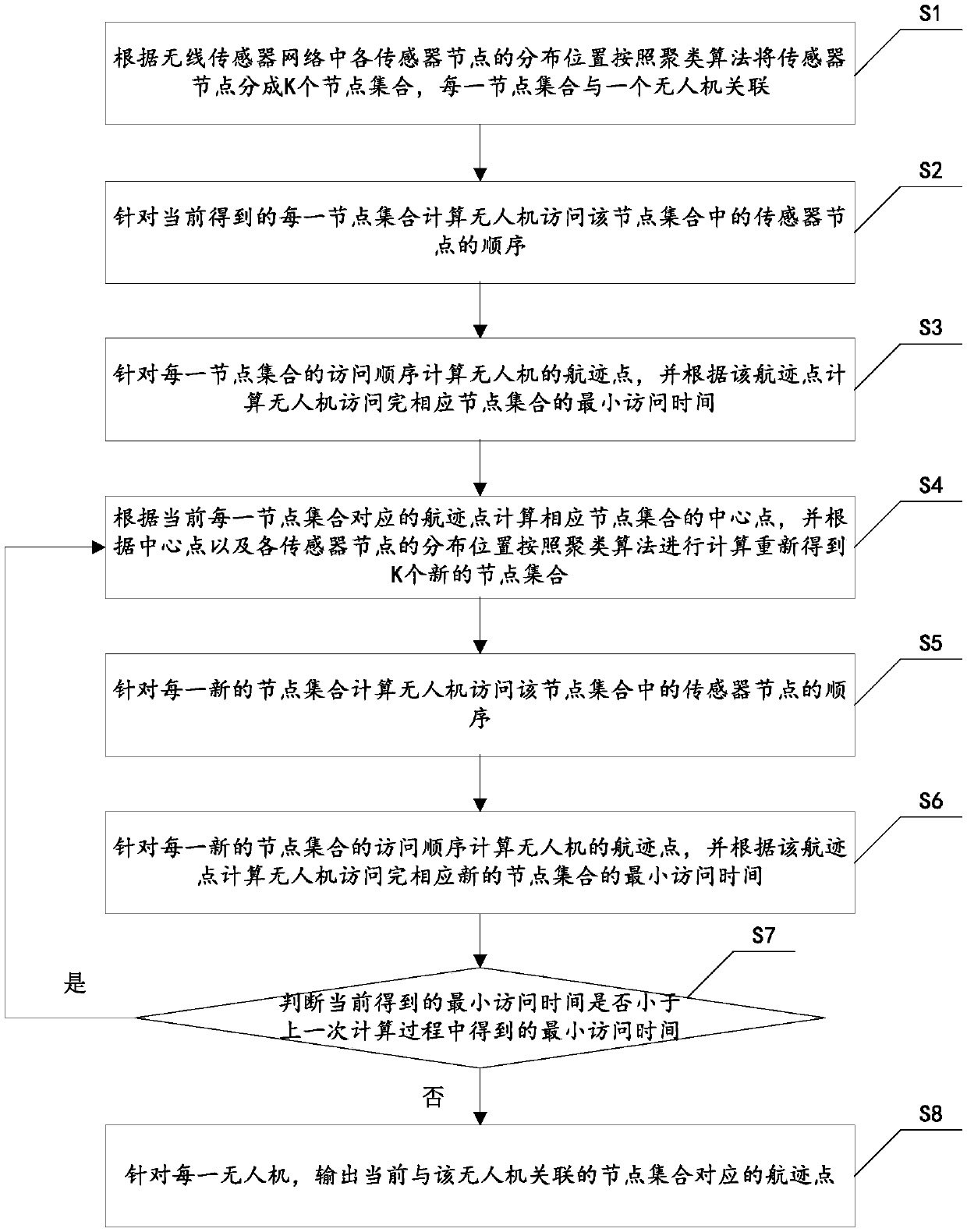
Trajectory planning method for unmanned aerial vehicle in wireless sensor network
ActiveCN109547938AReduce flight timeSolving Design DifficultiesNavigational calculation instrumentsParticular environment based servicesWireless mesh networkAccess time
The invention discloses a trajectory planning method for an unmanned aerial vehicle in a wireless sensor network. The method models the design problem of multiple unmanned aerial vehicle trajectoriesin the wireless sensor network into a mixed integer non-convex optimization problem. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, grouping sensor nodes based on an aggregation algorithm to forma plurality of node sets; calculating, for each node set, an access sequence of the sensor nodes accessed by the unmanned aerial vehicle in the node set; using a convex optimization technology to calculate a corresponding trajectory point for each access sequence, and using the trajectory point to calculate to obtain a center point so as to obtain a new node set; and based on the new node set, obtaining a corresponding new trajectory point according to the above process until the minimum access time is obtained, so that each unmanned aerial vehicle can reliably collect data from the corresponding sensor node set, and the flight time of all the unmanned aerial vehicles can be minimized.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
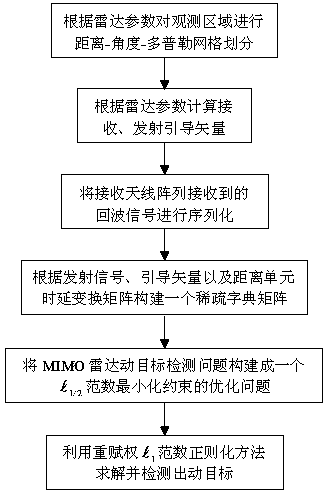
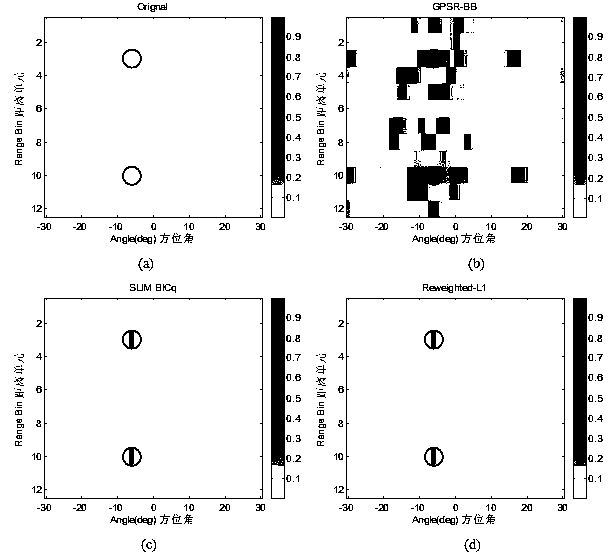
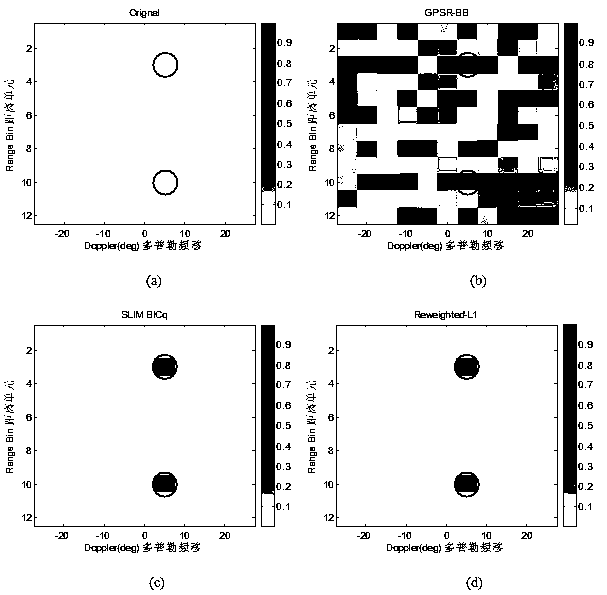
Non-convex optimization based MIMO radar moving object detection method
InactiveCN103744076AAccurate moving target detection resultsHigh resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar observationsImage resolution
The invention discloses a non-convex optimization based MIMO radar moving object detection method. The method comprises the following steps: according to radar parameters, performing distance-angle-Doppler grid dividing on an observation area; according to radar emission, the position of a receiving array, and radar observation area parameters, calculating emission and reception guiding vectors; according to emission signal waveforms, the guiding vectors and a distance unit time delay transformation matrix, constructing a sparse dictionary matrix; performing serialization on echo signals received by an antenna array; and according to an aforementioned model, constructing MIMO radar moving object detection to be an optimization problem of an L[1 / 2] norm minimizing constraint; and using a heavy weight determining L[1] norm regularization method to solve the optimization problem, obtaining distance-angle-Doppler imaging of a MIMO radar moving object, and detecting a moving object in the observation area. By using the method provided by the invention, a moving object detection result more accurate than a result by use of a convex optimization algorithm can be obtained, and the detection result is higher in resolution.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Brent delay optimization method for mobile edge computing based on non-orthogonal multiple access in multi-base station scenarios
ActiveCN109089272APremium quality of experienceImprove transmission efficiencyNetwork traffic/resource managementEdge serverMobile edge computing
The invention relates to a mobile edge computing Brent-type time delay optimization method based on non-orthogonal multiple access in a multi-base station scenario, comprising the following steps: (1)there is one mobile user in the coverage area of BSs of an integrated edge server, and the optimization problem is described as a multi-variable non-convex optimization problem; (2) decomposing the problem (DM i) into two levels of optimization problems; (3) According to the bottom DM-I-E-Sub problem, a split-search method based on Lagrange multiplier is proposed to optimize the overall delay ofmobile subscriber i under the condition of the transmission time ti of mobile subscriber i. (4) For top-level DM-I-E-Top problem, Brent method is proposed to optimize the transmission time ti of mobile subscriber i. (5) The problem (DM i) is solved by iteration of the bottom problem and the top problem. The invention improves the transmission efficiency of the system, saves bandwidth resources, and obtains higher quality wireless network experience quality.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Self-adaption bit and power distribution method with low complex degree
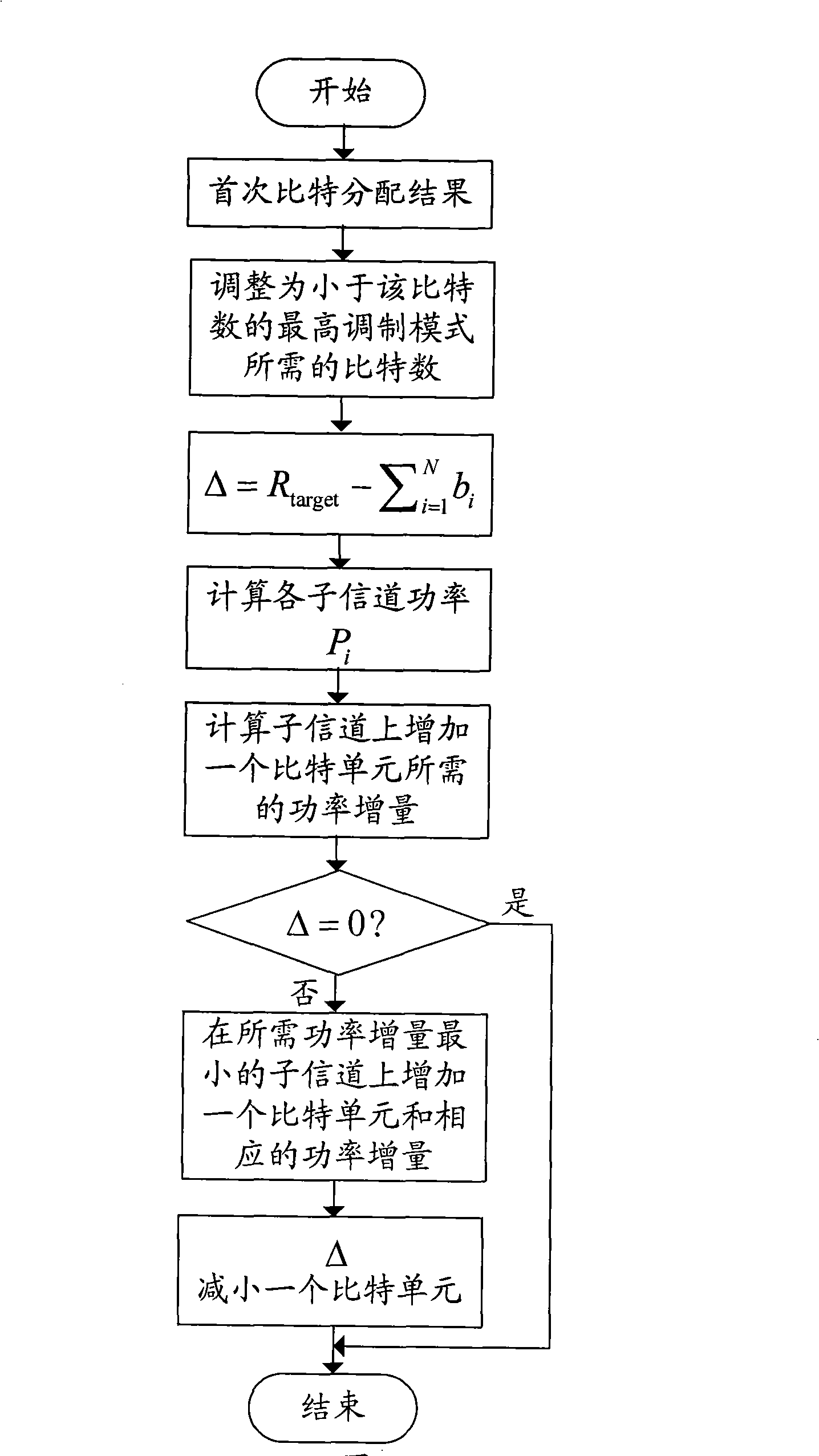
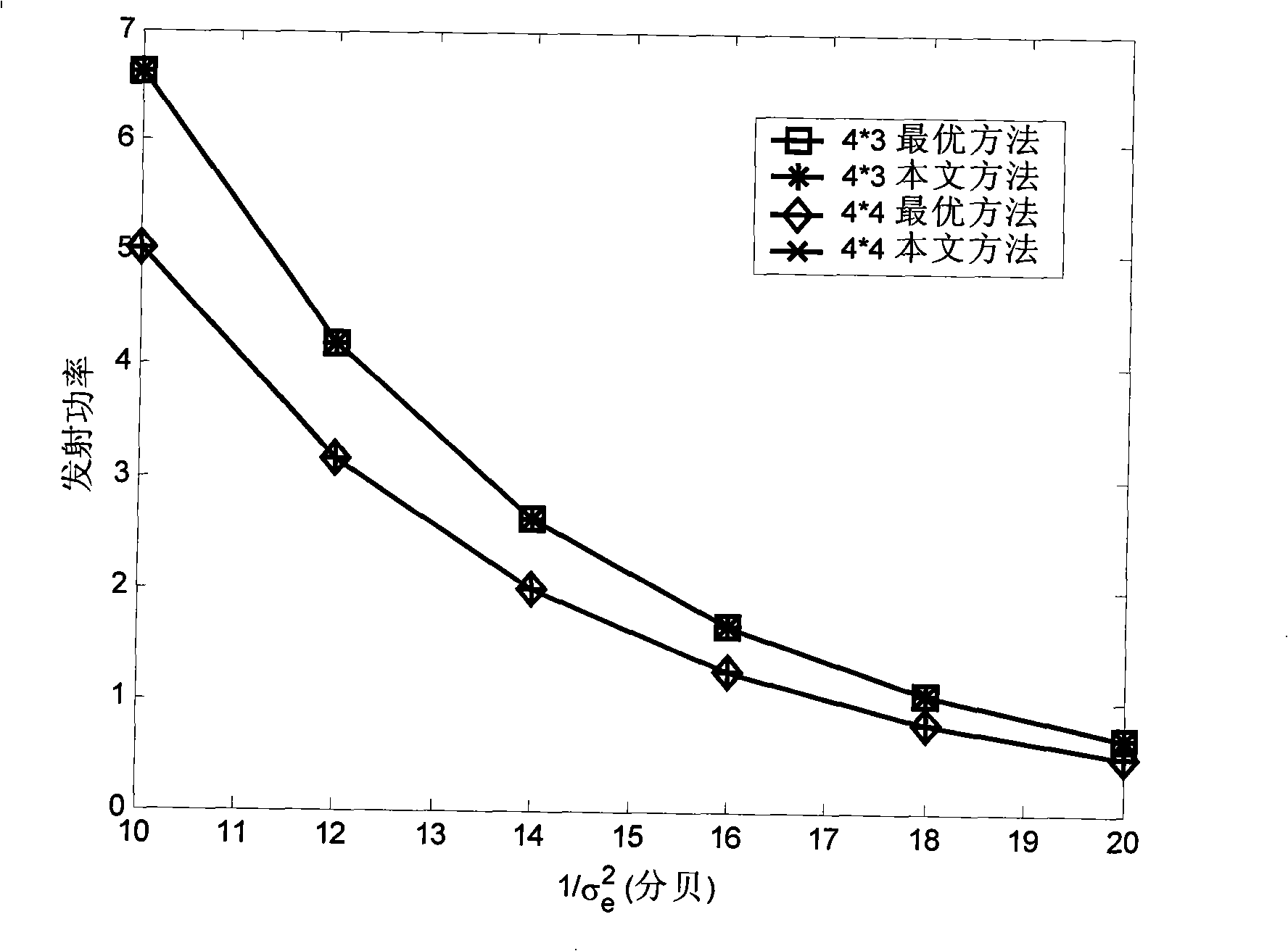
InactiveCN101304298AExcellent power efficiencyReduce operational complexityMulti-frequency code systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionBit allocationNon convex optimization
The invention discloses a self-adaptive bit and power allocation method with low complexity which is suitable for an MIMO system, and the method minimizes the total transmission power of the system under the condition that a sender cannot obtain an accurate channel state message and the bit error ratio of the system and the message transmission rate are restricted. The method is characterized in that signals to interference and noise ratios of equivalent sub-channels of the MIMO system under the condition of inaccurate channel state message are analyzed, thus obtaining an explicit relation between the transmission power of the sub-channels and the bit number; a non-convex optimization problem is converted into a convex optimization problem by adopting part monotonicity of functions, and then the closed optimal result in non-negative real number region of the optimization problem is calculated by adopting the Lagrangian approach; finally a real bit number is adjusted to a bit allocation result which requires the need of the real system and a corresponding power allocation is given. The invention is suitable for not only the MIMO system, but also an MIMO-OFDM system. The self-adaptive bit and power allocation method provided by the invention has the advantages of providing approximately optimal power efficiency under the condition of inaccurate channel state message and low operation complexity.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
L1/2-norm-based sparse linear array optimization method
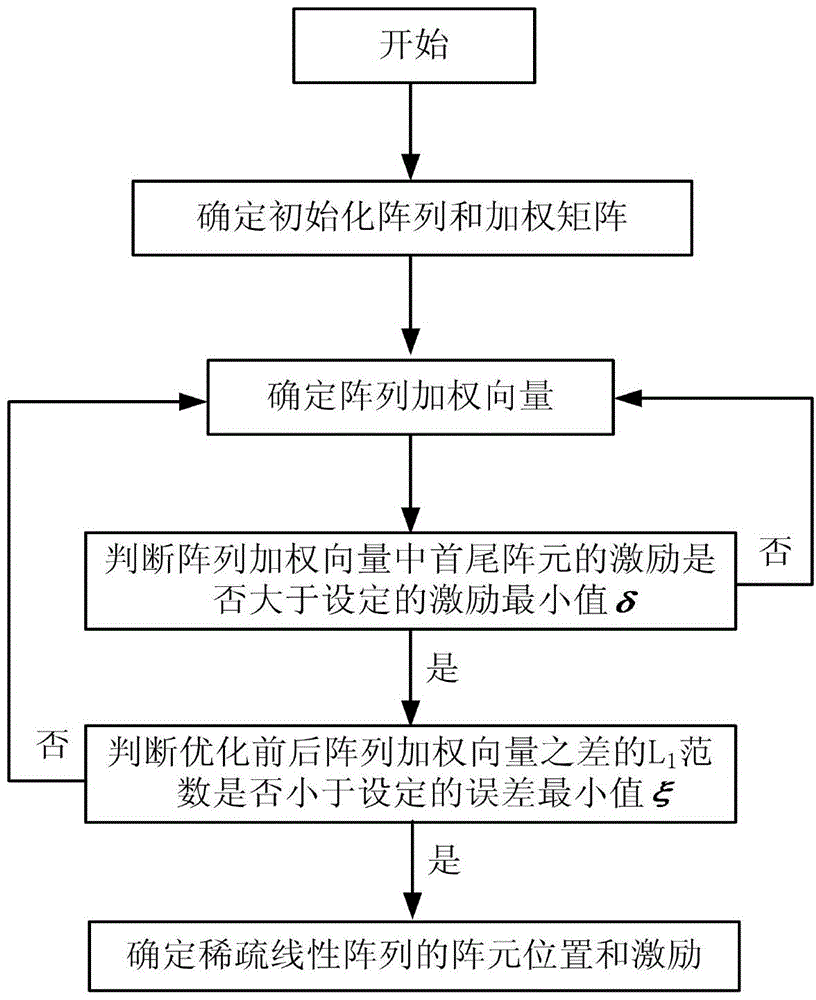
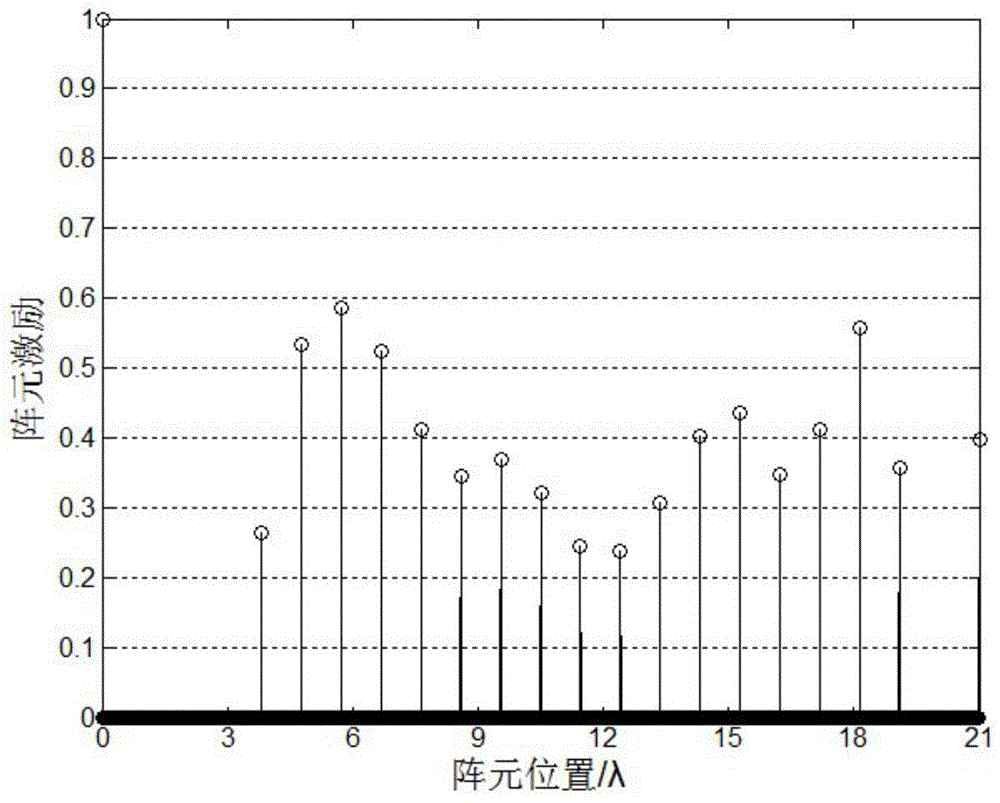
ActiveCN104392034AReduce sparsityMeet aperture requirementsSpecial data processing applicationsArray elementArray aperture
The invention relates to an L1 / 2-norm-based sparse linear array optimization method. The method is characterized by comprising the basic steps of determining an initial array and a weighting matrix, determining array weight vectors, judging whether the stimulus of head and tail array elements in the array weight vector is greater than a set stimulus minimum delta or not, judging whether an L1 norm for optimizing a difference between the previous and latter array weight vectors is smaller than a set error minimum xi or not, and determining the array element positions and stimulus of the sparse linear array. According to the method, the non-convex optimization problem of solution to an L1 / 2 norm is converted into a series of convex optimization problems of the L1 norm, so that a sparse array with lower sparsity can be obtained to reduce the number of actually required array elements on the premise of substantially keeping calculation unchanged; meanwhile, the head and tail array elements of the array are constrained and adaptively regulated under the condition of given array aperture, so that the problem of deficiency of the head and tail array elements of the sparse array in an iterative convex optimization process is well solved, and the method is particularly applied to the place of optimization of a large-sized antenna array.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
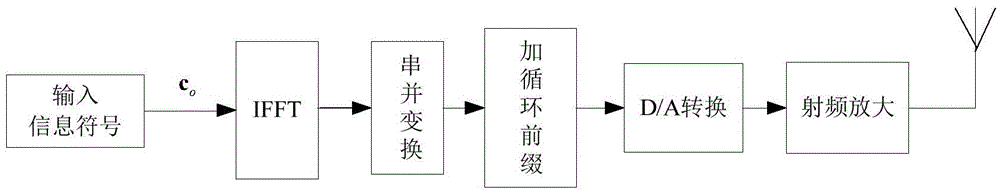
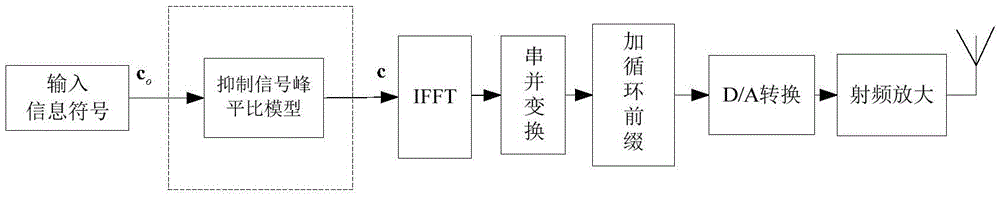
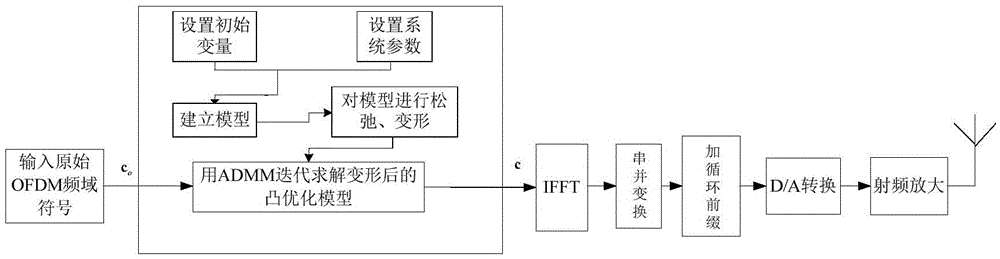
OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) signal peak-to-average power ratio inhibition method based on distributed implementation
ActiveCN105656830AReduce computational complexityCalculation speedMulti-frequency code systemsComputation complexityCyclic prefix
The invention discloses an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) signal peak-to-average power ratio inhibition method based on distributed implementation, mainly solving the problem of high complexity when the current inhibition OFDM system inhibits a peak-to-average power ratio. The method comprises the following steps: setting an OFDM system peak-to-average power ratio threshold, an idle subcarrier power amplitude limiting threshold and an OFDM symbol pilot subcarrier power constraint which meet requirements of an occasion of the system, and then combining with original OFDM frequency domain symbols and relevant initial variables to establish a non-convex optimization model; then, carrying out relaxation conversion on the model and solving to obtain an expected OFDM frequency domain symbol; and at last, enabling the expected OFDM frequency domain symbol to send out via an antenna after successively undergoing IFFT, parallel-serial conversion, cyclic prefix addition, D / A conversion and radio-frequency amplification. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the OFDM signal peak-to-average power ratio is effectively inhibited; and the method has relatively low computation complexity and can be used in signal transmission of communication field.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
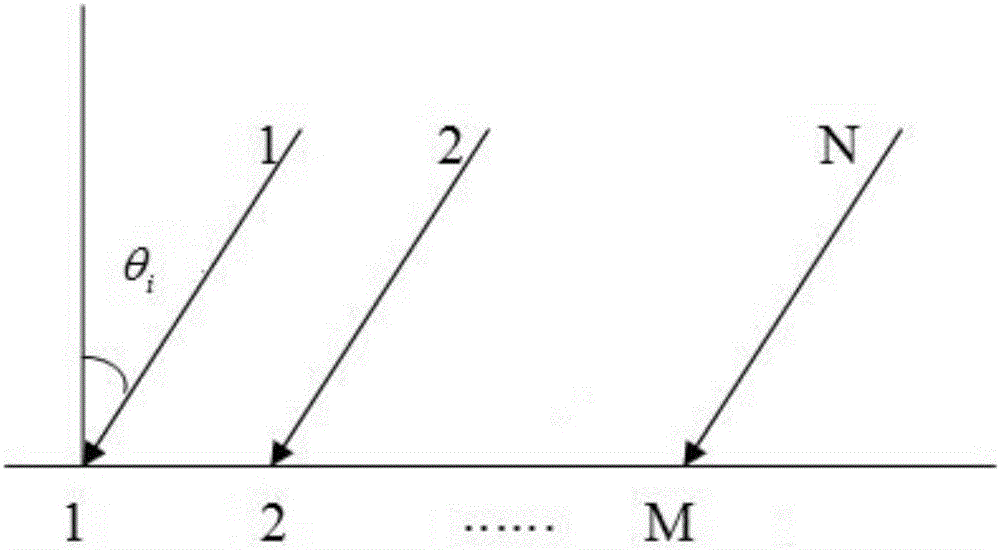
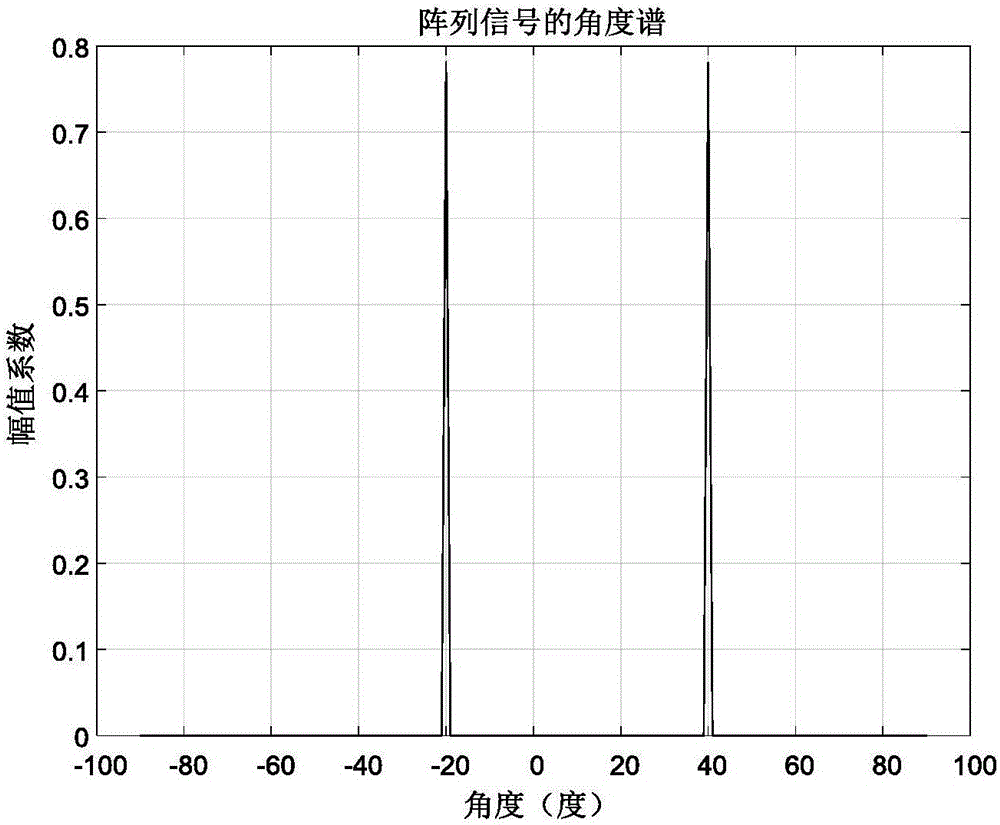
Signal angle-of-arrival high-precision estimation method under high sampling 1 bit quantification conditions
InactiveCN106842113AFew samplesEstimation is easy to implement in engineeringDirection findersSupport vector machineSparse constraint
The invention discloses a signal angle-of-arrival high-precision estimation method under high sampling 1 bit quantification conditions. The method includes the steps: firstly, generating a snapshot signal received by a uniform array comprising M array elements and performing 1 bit quantification sampling on the signal; secondly, building a sparse signal representation model taking a rho norm as a sparse constraint item and combining an insensitive epsilon-SVR (support vector regression) model, and performing sparse representation in original signal information by the aid of a non-convex optimization model; finally, resolving the non-convex optimization model by an ADMM (alternative direction multiplier method) to obtain a sparse representation coefficient for determining the arriving direction of the signal. According to the method, the arriving direction of the signal can be estimated in a high-precision manner without calculating an autocorrelation matrix and without reference to coherence of information sources when sampling quantity is small (such as single-snapshot), and signal arriving direction estimation based on the 1 bit quantification sampling conditions is more easily and rapidly implemented in engineering.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Unmanned aerial vehicle video relay system and method for minimizing energy consumption thereof
ActiveCN111953407AReduce energy consumptionMeet video quality of experience requirementsPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementEnergy consumption minimizationDynamic resource
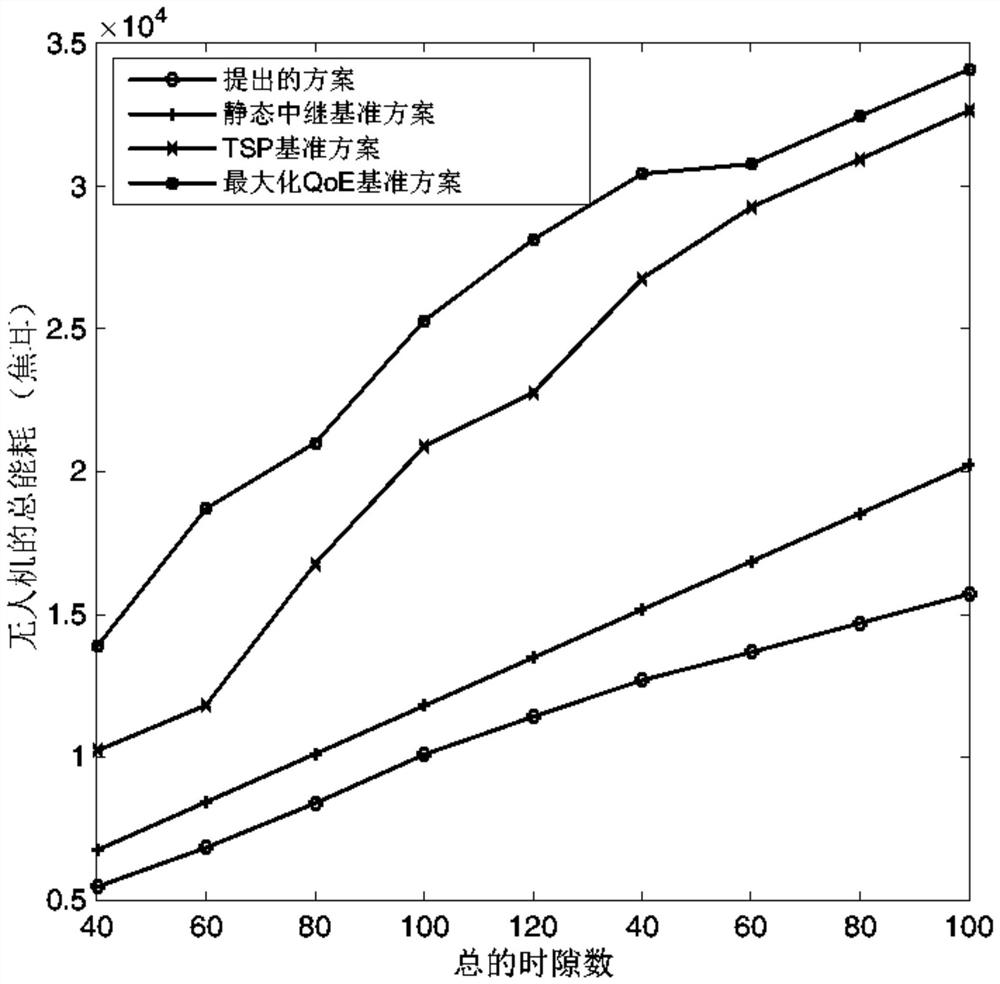
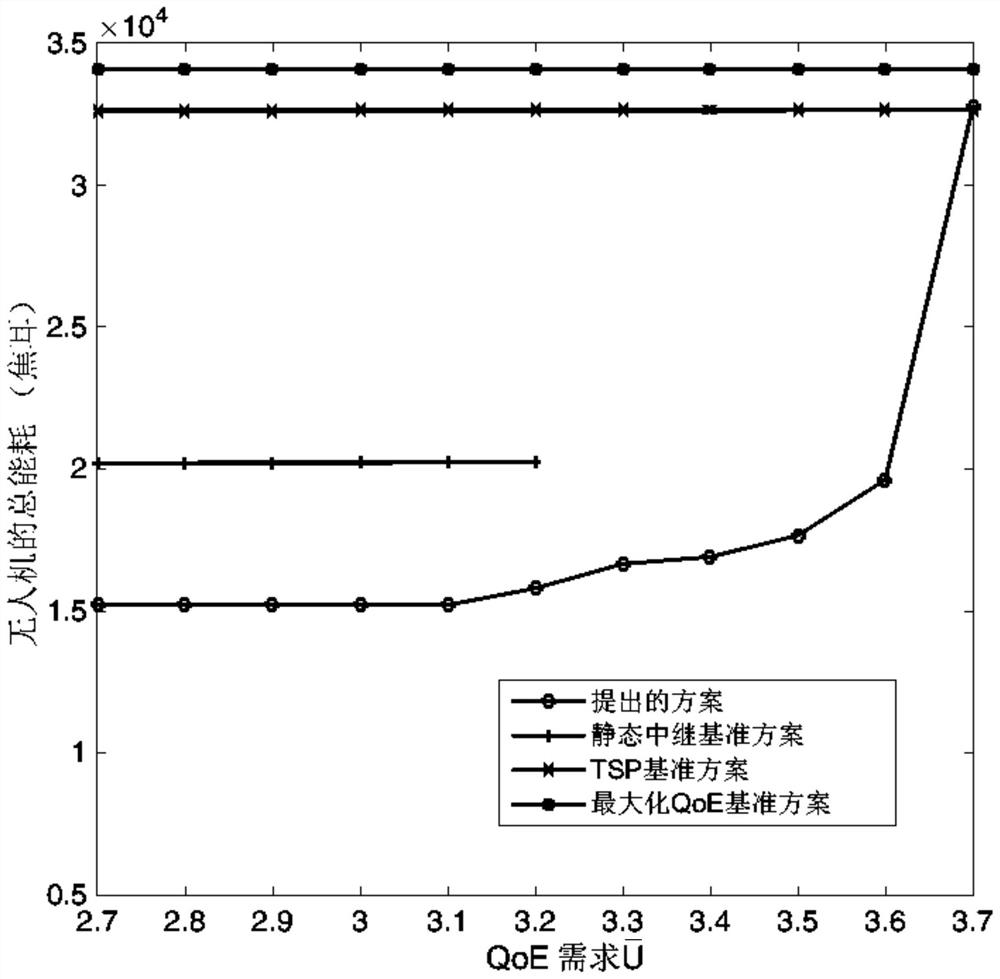
The invention relates to the technical field of unmanned aerial vehicle video relay, and particularly discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle video relay system and an energy consumption minimization method thereof. Under the condition that a first base station does not work, an unmanned aerial vehicle serves as a relay node to communicate a second base station and a user, and bandwidth is dynamically allocated between the second base station and the user; the method is based on the unmanned aerial vehicle video relay system, firstly, a dynamic resource allocation strategy is adopted to perform transmission bandwidth and power allocation, and the transmission bandwidth and power allocation is combined with the flight path of the unmanned aerial vehicle, so that a problem is modeled into a non-convex optimization problem; further the problem is decomposed into two sub-problems, namely a transmitting power and bandwidth allocation optimization sub-problem and an unmanned aerial vehicle trajectory optimization sub-problem; and finally, the two sub-problems are solved by using successive convex approximation and alternating optimization technologies to obtain a sub-optimization solution meeting a KKT condition. Experiments show that the energy consumption of the unmanned aerial vehicle can be significantly reduced by 30%, and meanwhile, the video experience quality requirements of users can be well met.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Optimization method for artificial noise direction modulation based on frequency control array
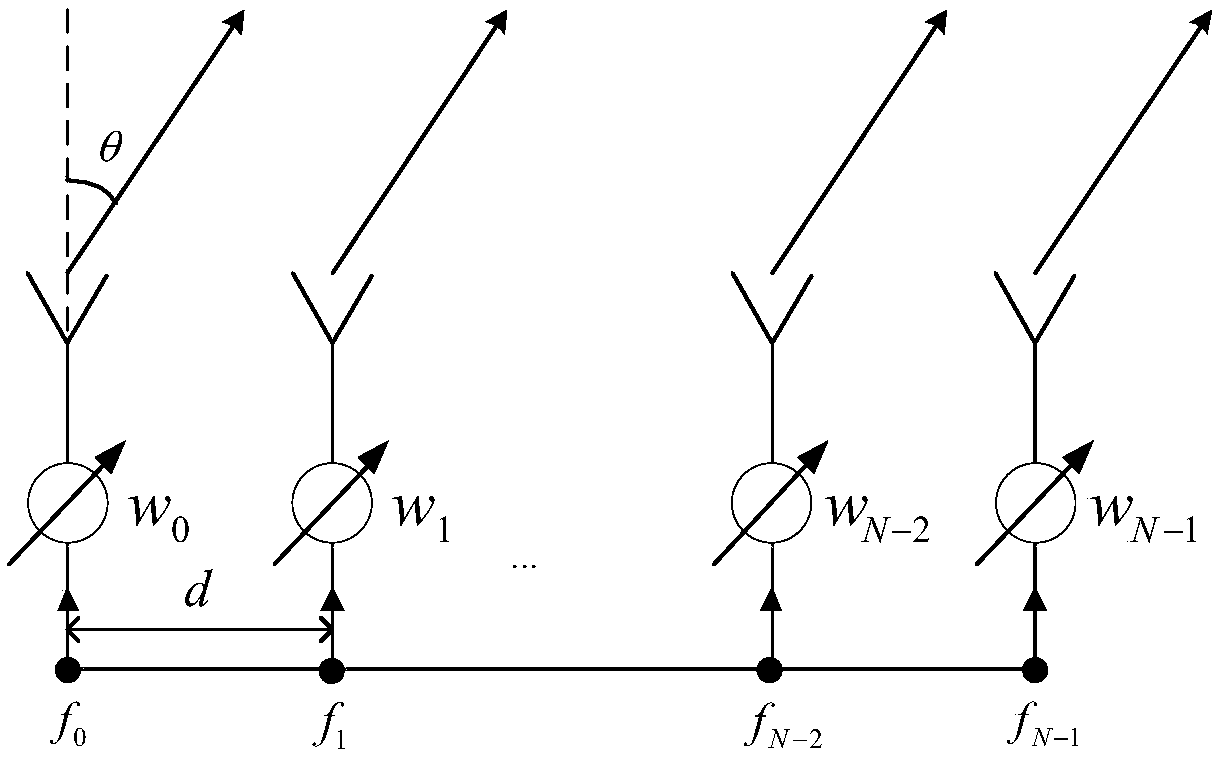
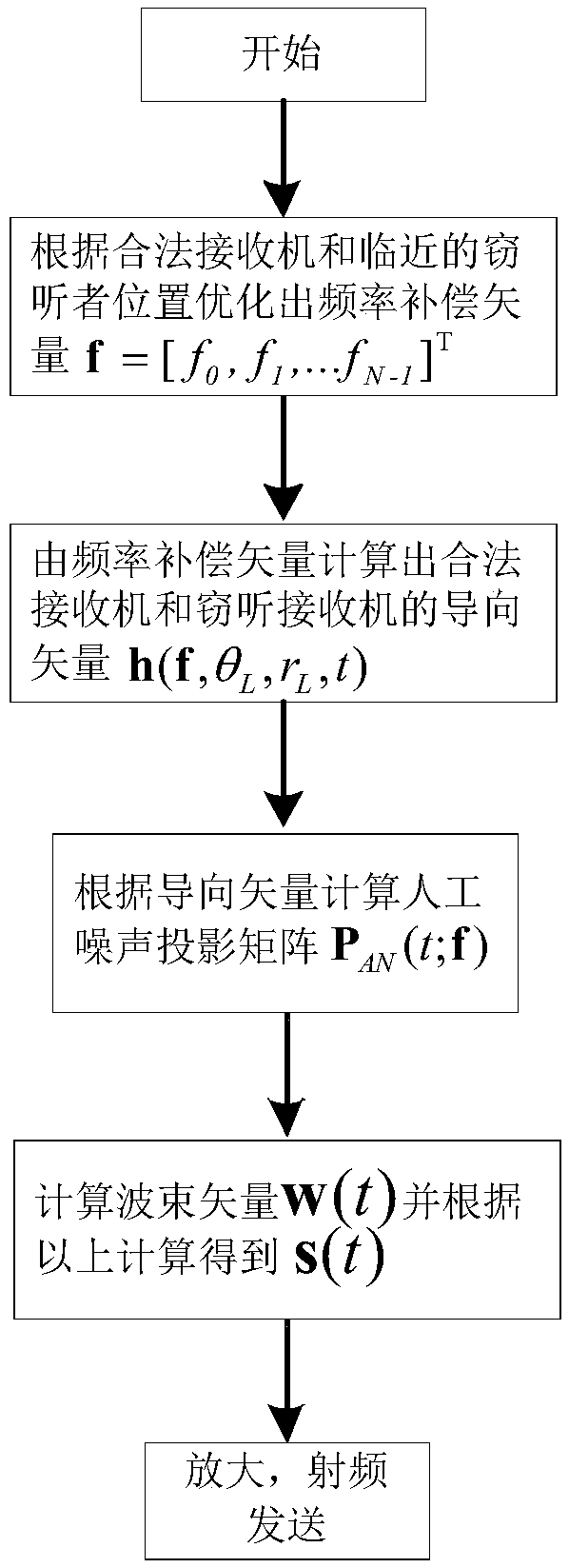
ActiveCN109245811AMaximize confidentiality rateReduce signal to noise ratioSpatial transmit diversityMultiple carrier systemsHat matrixFrequency compensation
The invention provides an optimization method for artificial noise direction modulation based on a frequency control array. The method comprises the steps: enabling a transmitting end to obtain the azimuth and distance of a legal receiver, and extracting a normalized beam vector; calculating the maximum confidential rate difference between a maximum legal receiver and an adjacent eavesdropping receiver; calculating a frequency compensation vector with the maximum confidential capability through a non-convex optimization algorithm, and then calculating a legal receiver guide vector; calculatinga normalized artificial noise projection matrix according to the orthogonality of the artificial noise and the legal receiver guide vector, and obtaining an artificial noise baseband signal based onthe frequency control array. The method realizes the dual control of angle and distance, and realizes the maximum confidential rate difference between the legal receiver and the adjacent eavesdroppingreceiver, and ensures higher-precision physical layer wireless security communication.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Design method for designing two-path orthogonal graph filter group
ActiveCN107256537AHigh stopband attenuationImprove frequency characteristicsImage enhancementImage analysisUltrasound attenuationIterative method
The invention discloses a design method for designing a two-path orthogonal graph filter group, models a design problem of the two-path orthogonal graph filter group into a band constraint optimization problem, takes the reconstruction error of a filter as a target function and takes stopband attenuation as a constraint condition. Therefore, an iterative method is adopted to solve the problem. In single-step iteration, through a Taylor formula and functional approximation, a highly nonlinear non-convex target function is converted into a convex quadratic function, and a non-convex optimization problem is approximate to the subproblem of convex optimization. By use of the method, the two-path orthogonal graph filter group with better integral performance can be obtained.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Coordinated linear beamforming in downlink multi-cell wireless networks
ActiveUS20120163332A1Improve spectral efficiencySecret communicationRadio transmissionFrequency-division multiple accessNon convex optimization
System and methods are disclosed for optimizing wireless communication for a plurality of mobile wireless devices. The system uses beamforming vectors or precoders having a structure optimal with respect to the weighted sum rate in a multi-cell orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) downlink. A plurality of base stations communicate with the mobile devices and all base stations perform a distributed non-convex optimization exploiting the determined structure.
Owner:NEC CORP
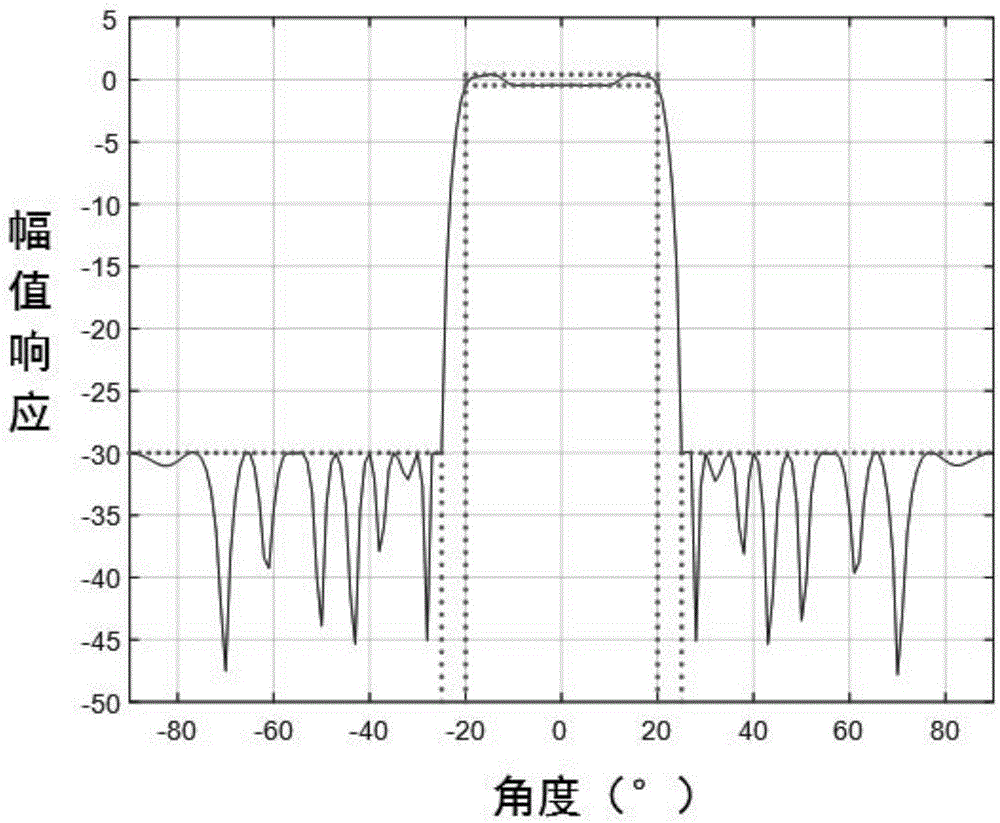
Robust beam forming method based on constraint of direction of arrival of satellite signal
ActiveCN104199053AGuaranteed distortion-free receptionSolve the blockageSatellite radio beaconingLoading factorAmplitude response
The invention relates to a robust beam forming method based on the constraint of the direction of arrival of a satellite signal. The method includes the steps of 1, establishing an array antenna signal-receiving model and calculating steering vectors of the satellite signal and an interfering signal; 2, determining array antenna amplitude response constraint conditions according to a range of the direction of arrival of the satellite signal; 3, converting non-convex optimization constraint conditions obtained in step 2 into convex optimization constraint conditions; 4, according to noise power, determining a diagonal loading factor Nu of a covariance matrix of a signal received by an array antenna; and 5, establishing a beam forming cost function based on angle constraint, and solving and calculating an array antenna optimal weight by a convex optimization tool to obtain a directional beam of the satellite signal and a directional null of the interfering signal.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Unmanned aerial vehicle track and signal transmitting power joint optimization method for wireless relay
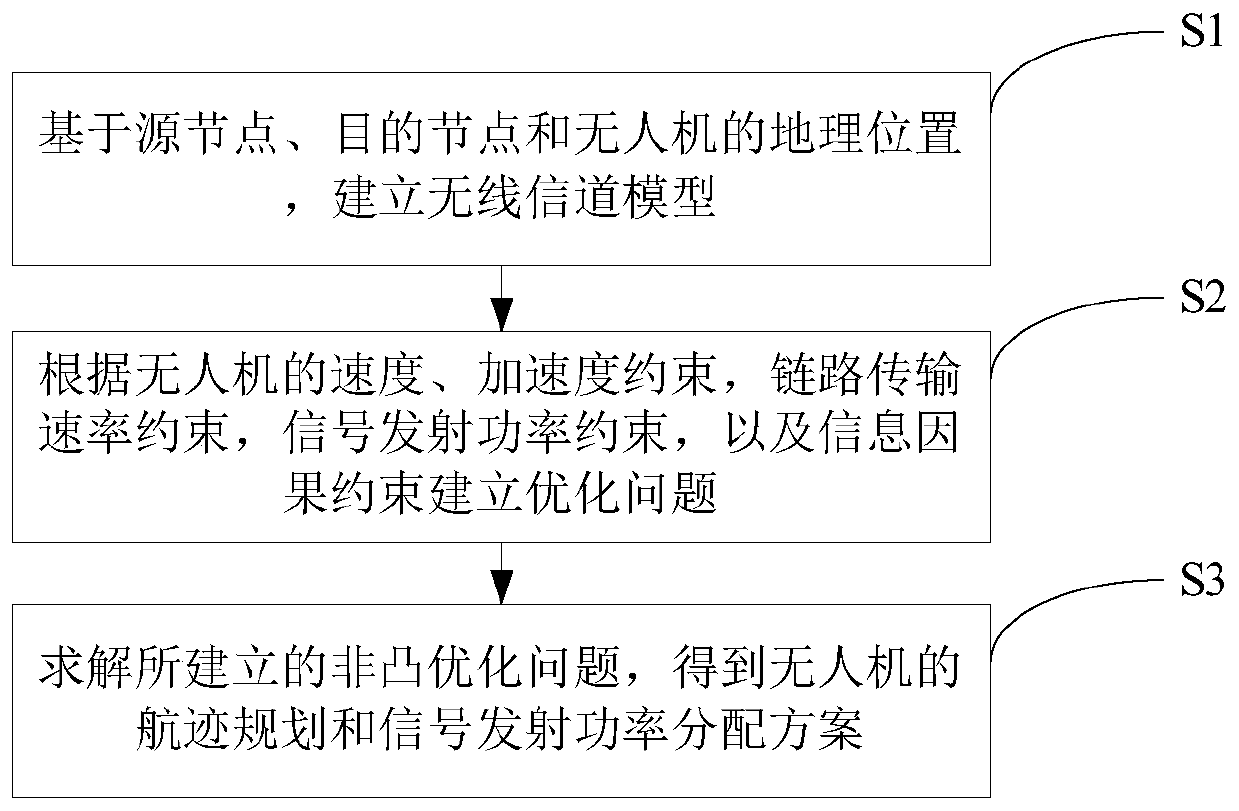
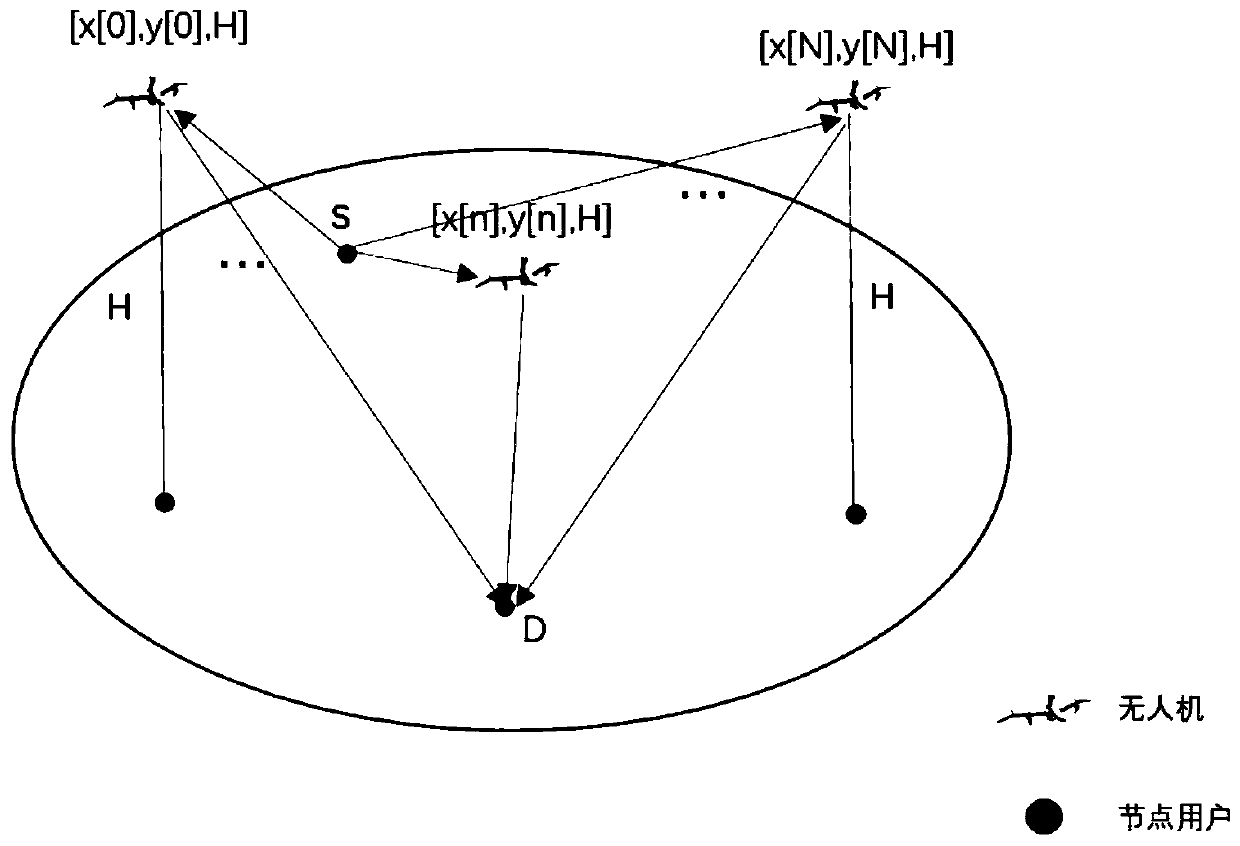
ActiveCN110138443AReduce energy consumptionEfficient use ofRadio transmissionTransmission monitoringTerrainEngineering
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle track and signal transmitting power joint optimization method for wireless relay. According to the method, a wireless network taking an unmanned aerial vehicle as a relay is considered; in the process that the unmanned aerial vehicle flies from a starting point to a terminal point, a signal sent by a source node is forwarded to a target node, andunder the conditions that the signal transmitting power of the unmanned aerial vehicle is limited, the flight time is limited, the information causal constraint and the link transmission rate constraint are limited, the total energy consumption of the unmanned aerial vehicle is optimized by adjusting the track and the signal transmitting power of the unmanned aerial vehicle. As the obtained problem is a non-convex optimization problem and is difficult to directly solve, the method provided by the invention uses a Successive Convex Approximation (SCA) method to convert and solve the problem. The method is suitable for areas with complex terrains, difficult deployment of ground base stations or poor communication quality, and the unmanned aerial vehicle is used as a mobile relay to provide services for user equipment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
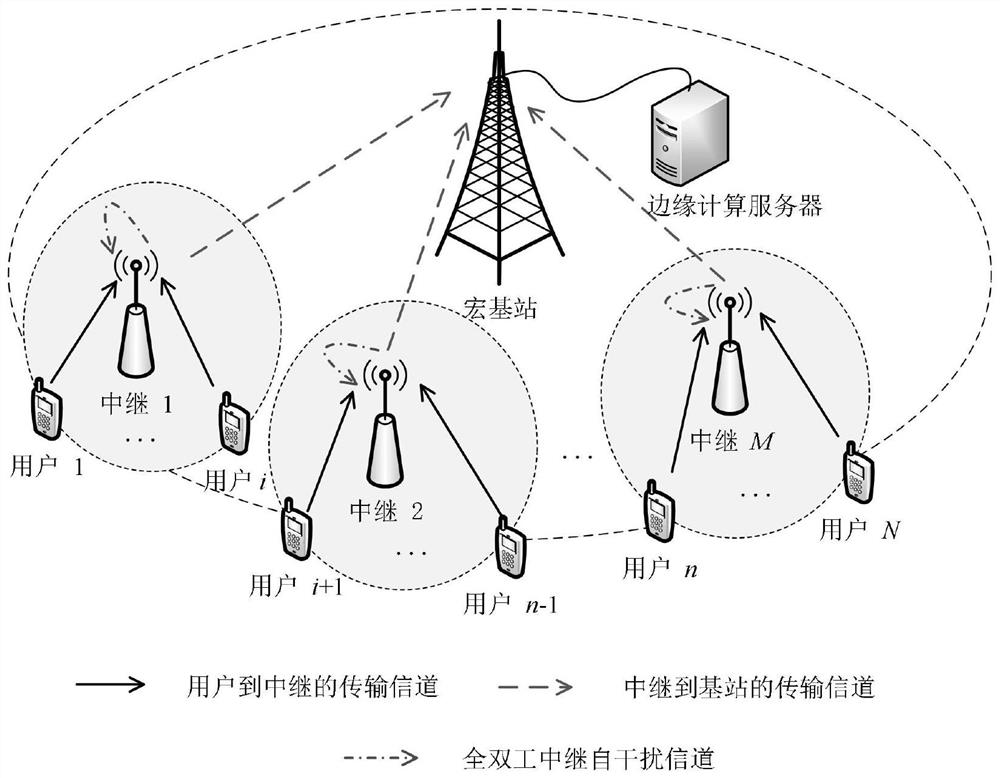
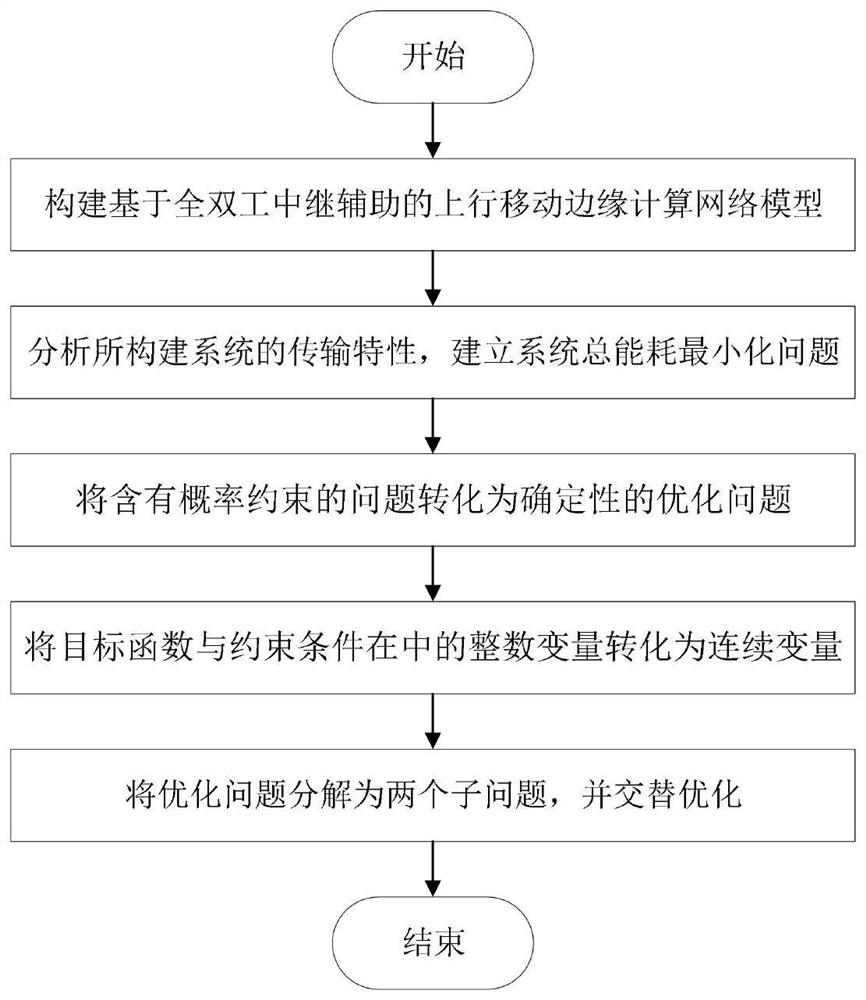
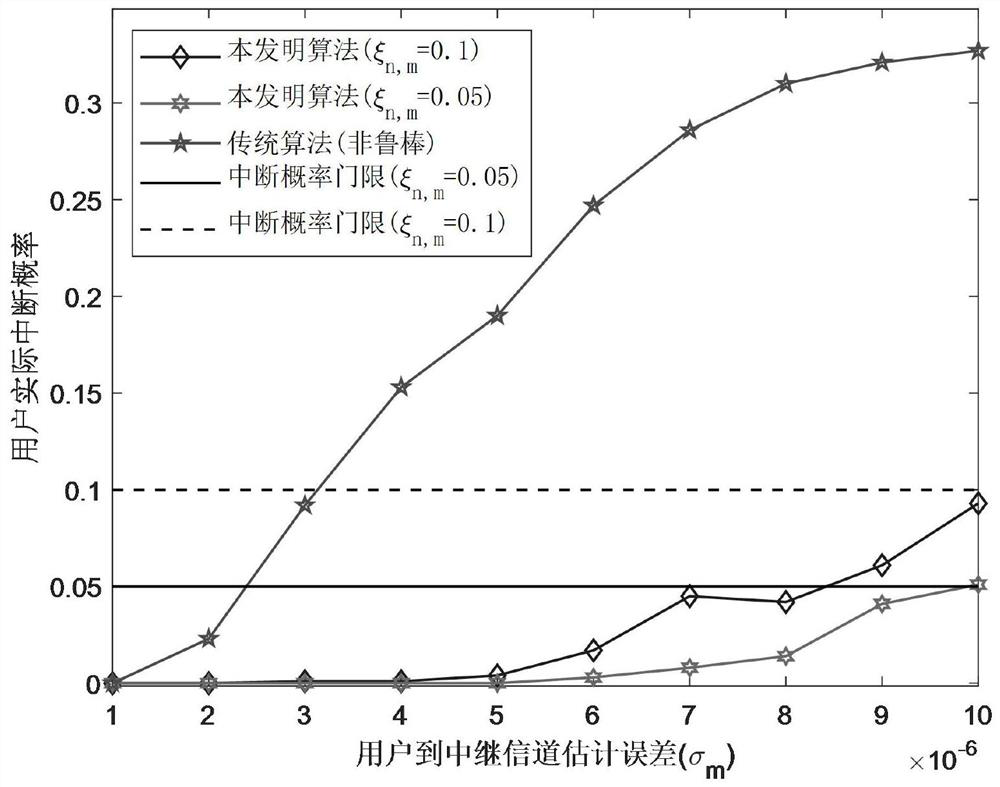
Mobile edge computing network resource allocation method based on full duplex relay
ActiveCN111988806AImprove utilization efficiencyImprove experienceData switching networksHigh level techniquesQuality of serviceEnergy consumption minimization
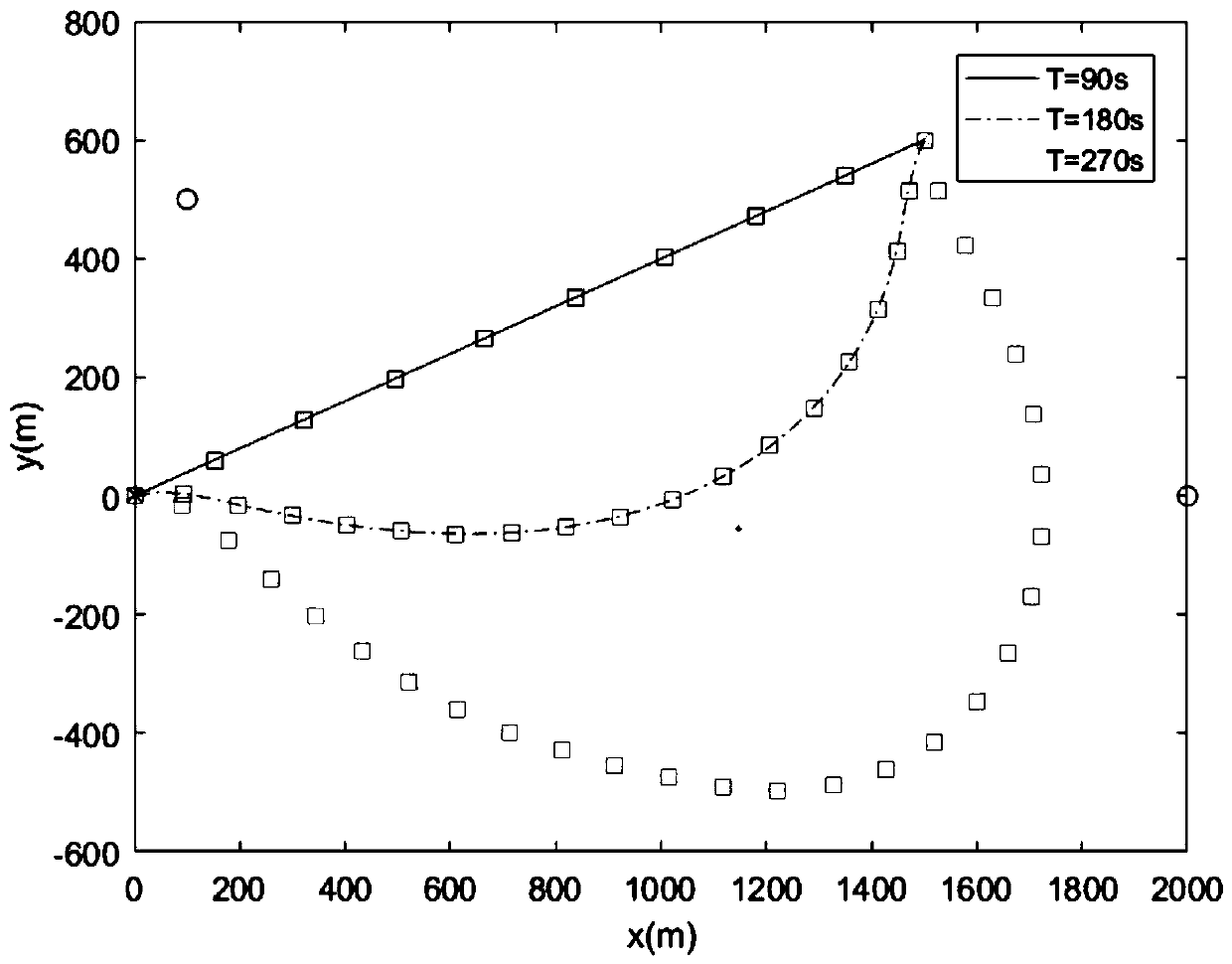
The invention relates to a mobile edge computing network resource allocation method based on full duplex relay, and belongs to the field of mobile edges. The method comprises the following steps: constructing an uplink mobile edge computing network model assisted by a full duplex relay; analyzing transmission characteristics of the constructed system, jointly optimizing a user matching strategy, auser task unloading coefficient and transmission power when constraints such as user computing task delay, user outage probability, user maximum computing power and maximum transmitting power are met, and establishing a system total energy consumption minimization optimization problem; decomposing an original non-convex optimization problem into two deterministic convex optimization sub-problemsto be solved by utilizing a worst criterion and an alternate iteration method. According to the method, the pressure of executing tasks with large calculation data volume and low time delay request bythe user can be effectively relieved, the service quality of the user is improved, and compared with the prior art, the consumption of executing the calculation tasks can be effectively reduced, theinterruption probability of the system is reduced, and the stubborn performance of the system is improved.
Owner:成都国恒空间技术工程股份有限公司
Network section optimization method in wireless access network
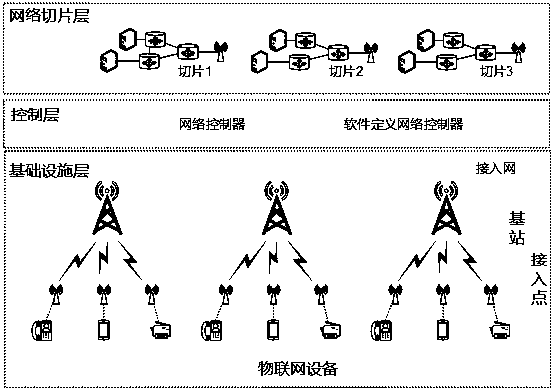
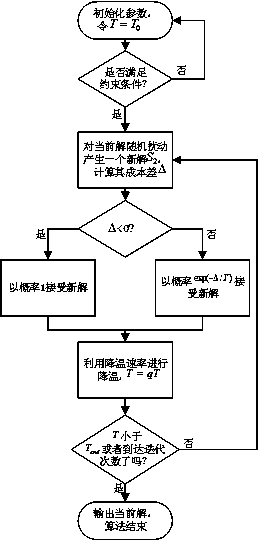
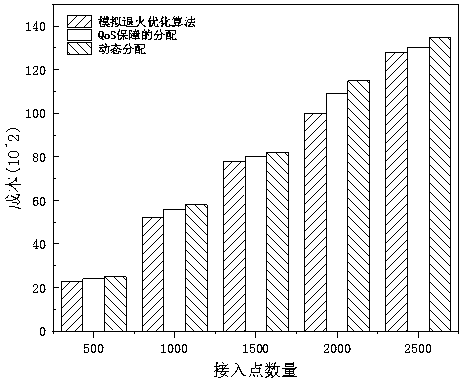
InactiveCN109379754AEasy to controlAchieve separationWireless communicationWireless mesh networkNon convex optimization
The invention relates to a network section optimization method in a wireless access network, and belongs to the field of mobile communications. The network section optimization method comprises the following steps: Step I, building a combined and non-convex optimized model in combination with the cost, service isolation and return capacity constraints; and Step II, solving the model by using a simulated annealing optimization algorithm according to the theory of an iterative adaptive heuristic probability search algorithm. The invention discloses a network resource optimized distribution method for a wireless virtual resource distribution mechanism; separation of control and forwarding is realized through an SDN (Software Defined Network) technology; and network resources are sensed and scheduled by using a network control plane. Customization of end-to-end services is supported on the basis of an SDN and a network section; independent and mutually isolated virtual networks are established according to network service requirements; and hardware resources in a network are dynamically deployed, which enables a plurality of virtual networks to share one physical network, thereby realizing sharing of the hardware resources of the network.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
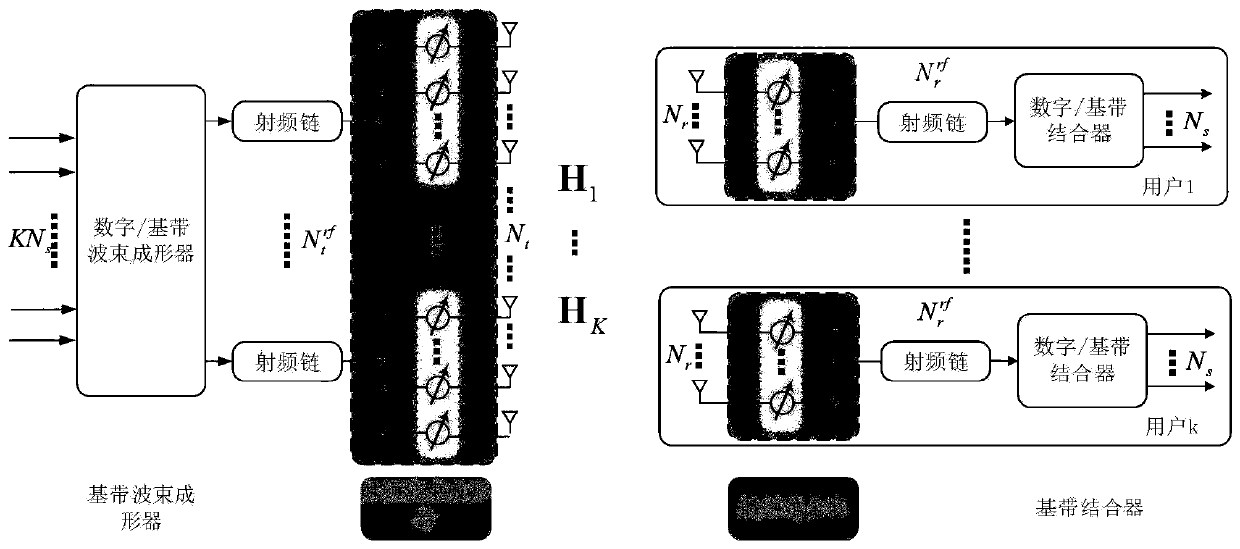
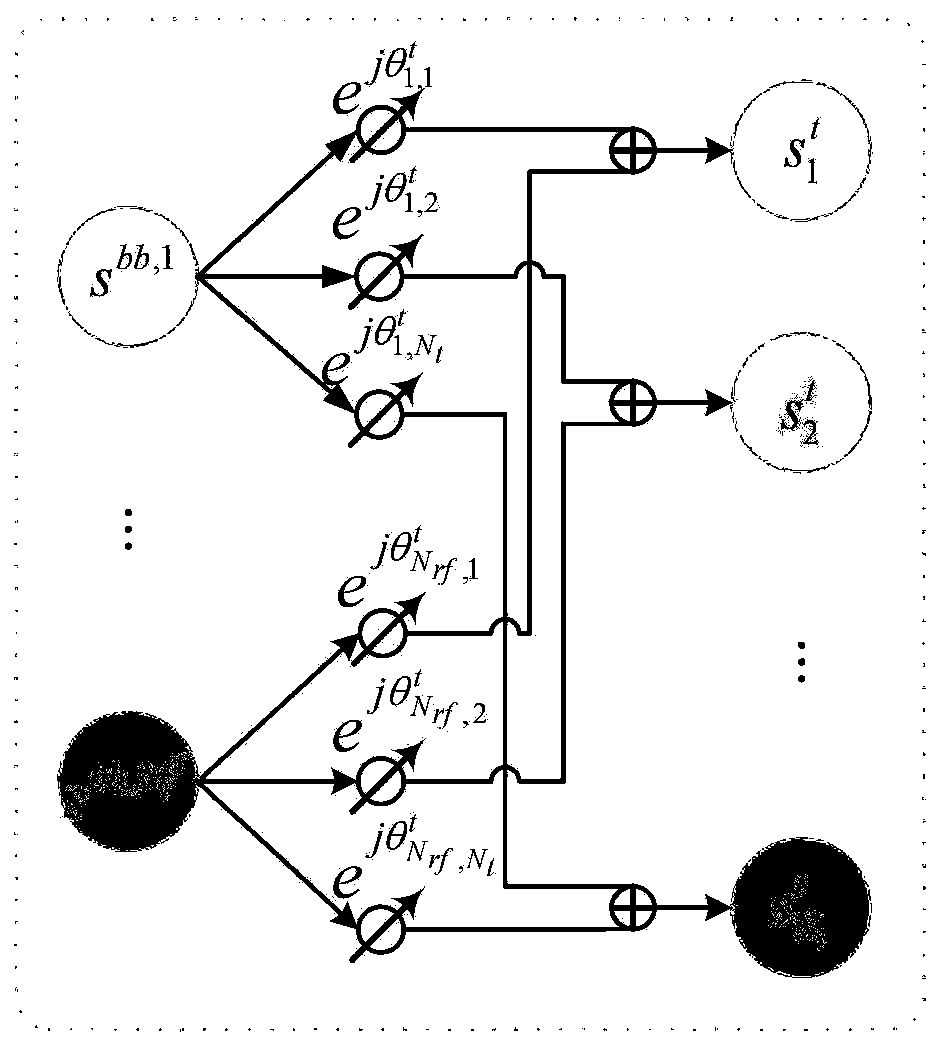
Millimeter wave MIMO hybrid beam forming optimization method based on deep learning
ActiveCN110535500AChange the priority factorChange optimization prioritySpatial transmit diversityHybrid beamformingEngineering
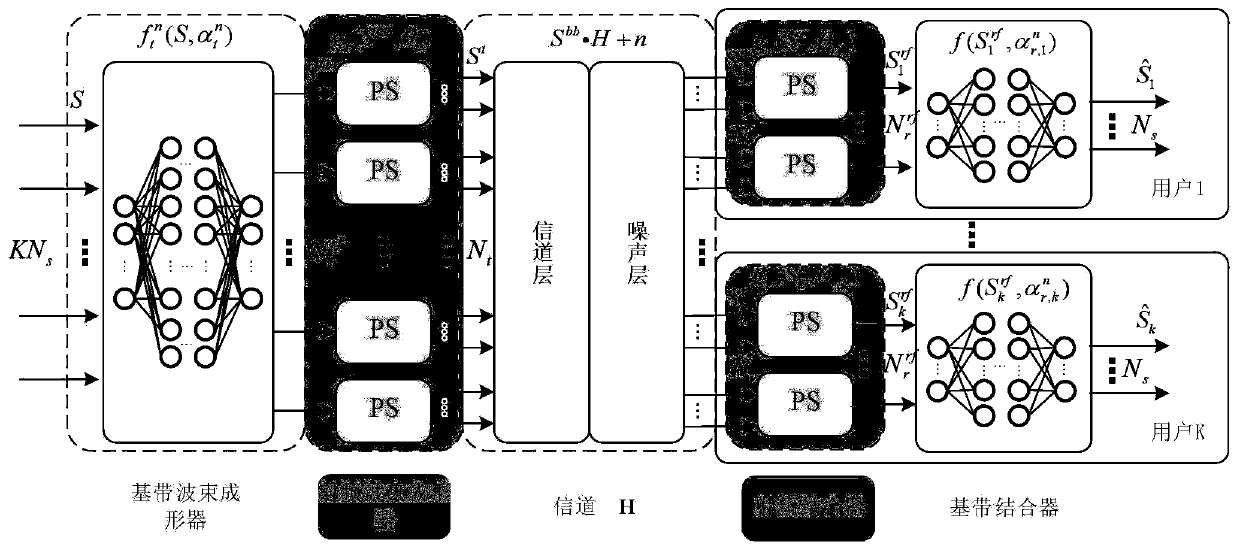
The invention discloses a millimeter wave MIMO hybrid beam forming optimization method based on deep learning. According to the millimeter wave MIMO hybrid beam forming optimization method based on deep learning, constraint conditions in a traditional millimeter wave large-scale MIMO hybrid beam forming optimization problem can be mapped into a neural network, and a multi-user hybrid beam formingsystem is completely converted into an equivalent neural network. Therefore, a complex non-convex optimization problem in hybrid beam forming can be converted into end-to-end unsupervised optimizationsimilar to an auto-encoder, and joint optimization can be carried out on a plurality of beam forming matrixes.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Depth image high-resolution reconstruction method based on Kinect camera
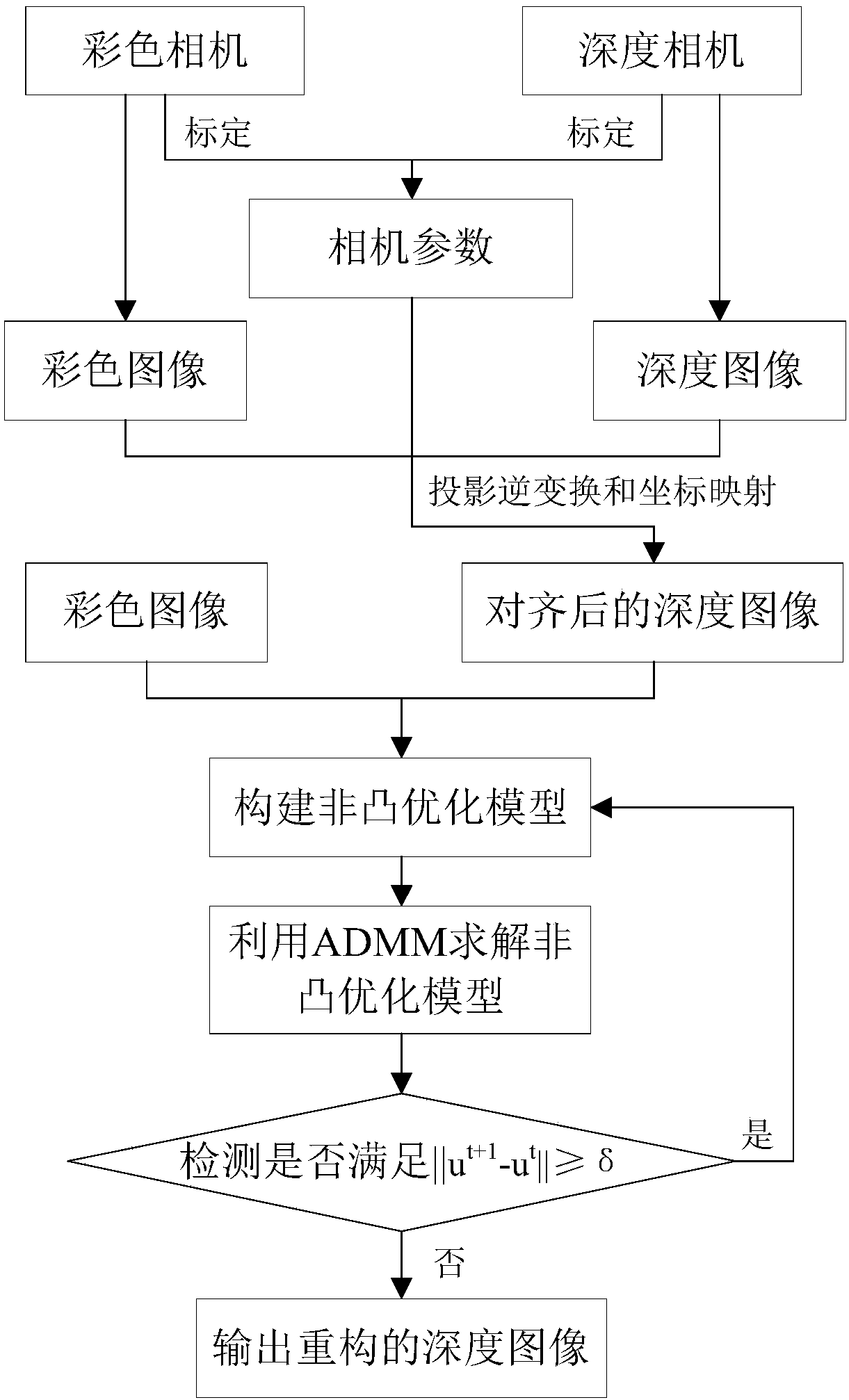
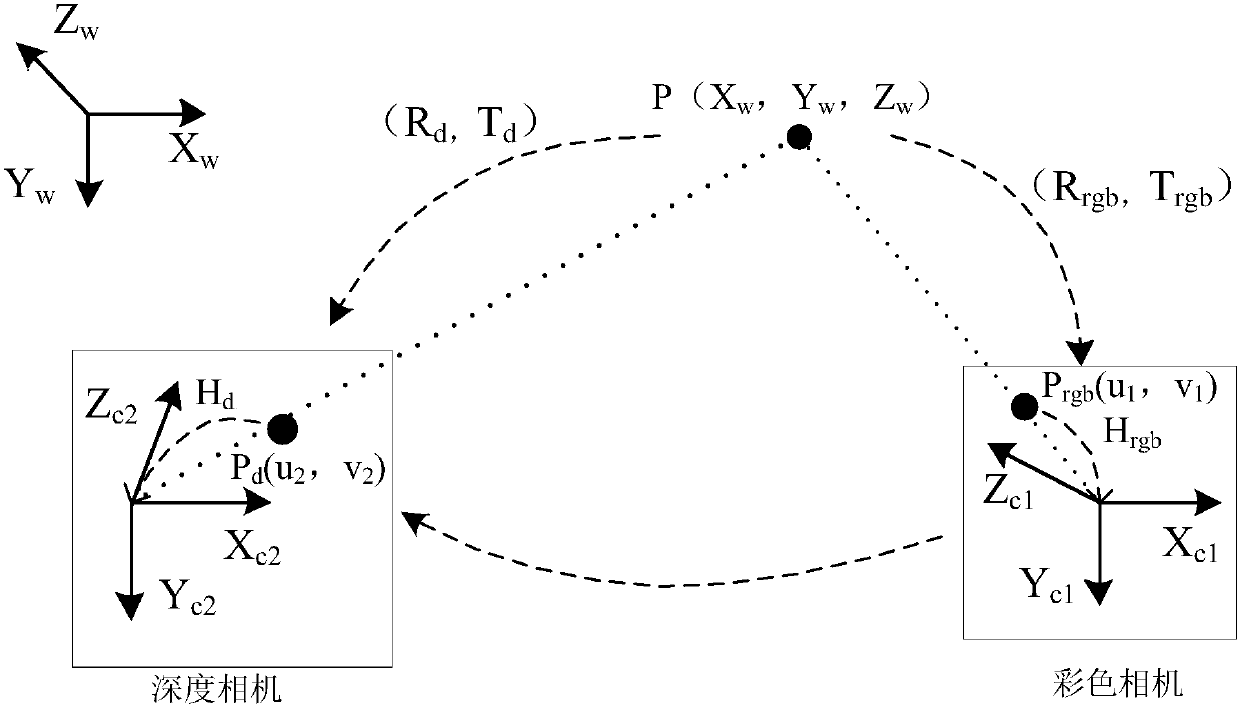
ActiveCN107680140AImprove detection accuracyHigh positioning accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageImaging processing
The invention discloses a depth image high-resolution reconstruction method based on a Kinect camera and relates to the image processing field. The method comprises the steps that a color camera and adepth camera of the Kinect camera are calibrated, and camera parameters of the Kinect camera are acquired; a color image and a depth image of a target object are acquired through the color camera andthe depth camera of the Kinect camera respectively; the depth image is mapped into a color image pixel coordinate system where the color image is located according to the camera parameters of the kinect camera, and an after-alignment depth image is obtained; a non-convex optimization model is constructed according to the color image and the after-alignment depth image; and an alternate directionmultiplier algorithm is utilized to solve the non-convex optimization model to obtain a reconstructed depth image. Through the method, high-resolution reconstruction of the depth image under the guidance of the color image in a natural scene can be realized, and good edges can be obtained and kept smooth and robust while quick convergence is guaranteed.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
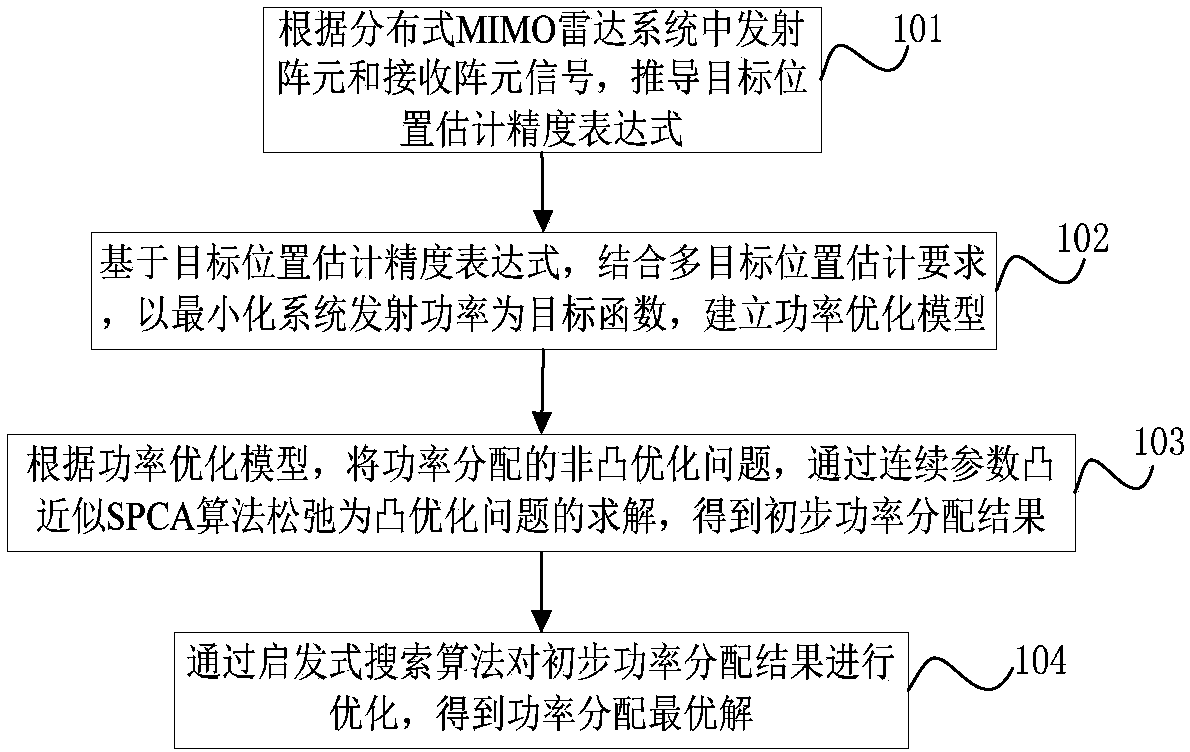
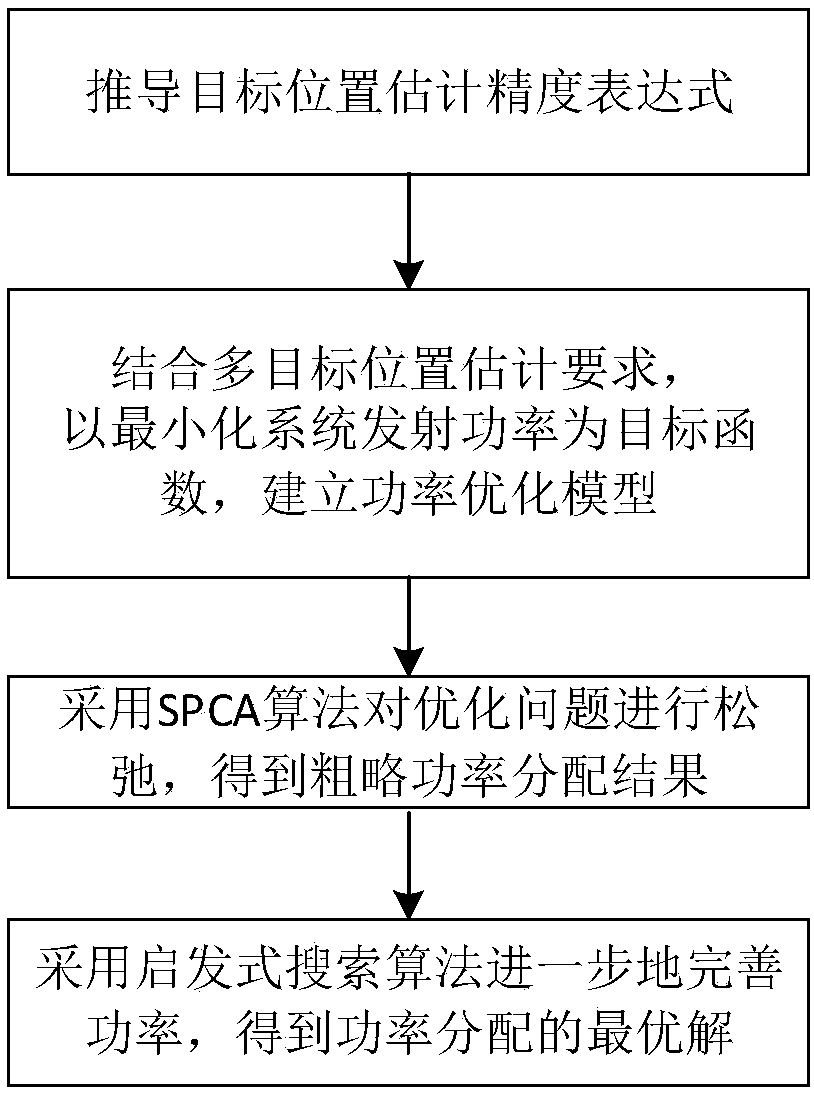
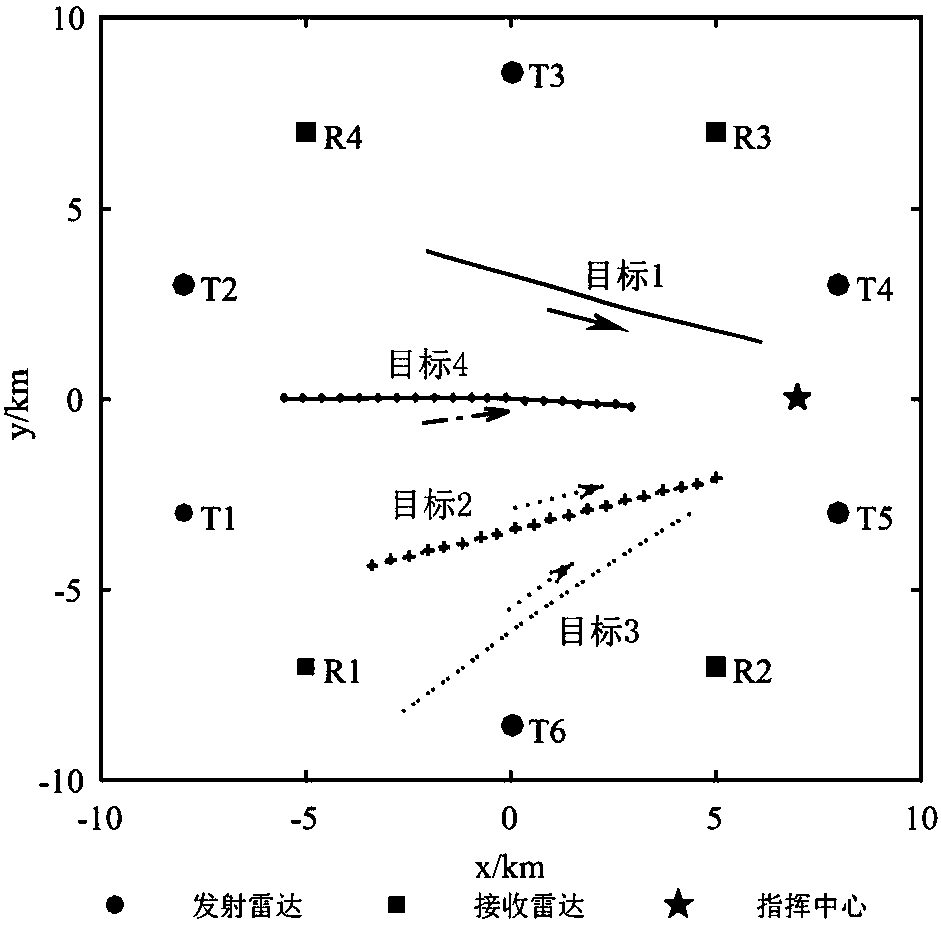
Power optimization method for multi-target position estimation of distributed MIMO radar system
ActiveCN107863997AReduce consumptionImprove resource utilizationWave based measurement systemsRadio transmissionRadar systemsResource utilization
The invention relates to a power optimization method for multi-target position estimation of a distributed MIMO radar system. The method comprises the following steps of taking minimum radar system transmitting power as a target function, and establishing a transmitting power optimization model under the constraints of different position estimation accuracy requirements for multiple targets and anupper limit of radar transmitting power; loosening a non-convex optimization problem of power distribution to be a convex optimization problem through an SPCA algorithm, and solving an approximate solution of power distribution; and adopting a heuristic search algorithm to carry out further optimization on a power distribution result in order to obtain an optimal power distribution result. According to the method, the resource utilization rate can be maximized and the minimum power resources are consumed under the condition that the different position estimation requirements for multiple targets are met; less system consumption can be used, the resource utilization rate is improved while the calculation amount of the system is reduced; through controlling the target number and the position estimation precision requirement, the higher the target tracking precision requirement is, the more stable the performance is, and the more the number is, the more obvious the advantages are; and the method has better application value.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
Sparse beam pattern comprehensive designing method
InactiveCN106682293AReduce complexityOvercome limitationsDesign optimisation/simulationMulti-objective optimisationWeight coefficientEngineering
The invention discloses a sparse beam pattern comprehensive designing method. The method specifically includes: step 1, in an actual array signal system, according to designing requirements, building a weight optimization objective model taking p norm (0<p<2) as sparse constraint, and setting constraint conditions of main lobe width, ripple wave width and side lobe limitation according to requirements; step 2, after the step 1 is completed, aiming at a non-convex optimization model, adopting an alternating method multiplier method to iteratively sparse weight coefficient w; step 3, utilizing the sparse weight coefficient w acquired in the step 2, and combining computer simulation software to make beam pattern according to designing requirements. By the method, the problems of boundedness and inaccuracy in the prior art are solved, and complexity of an actual array system and actual application cost are lowered.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
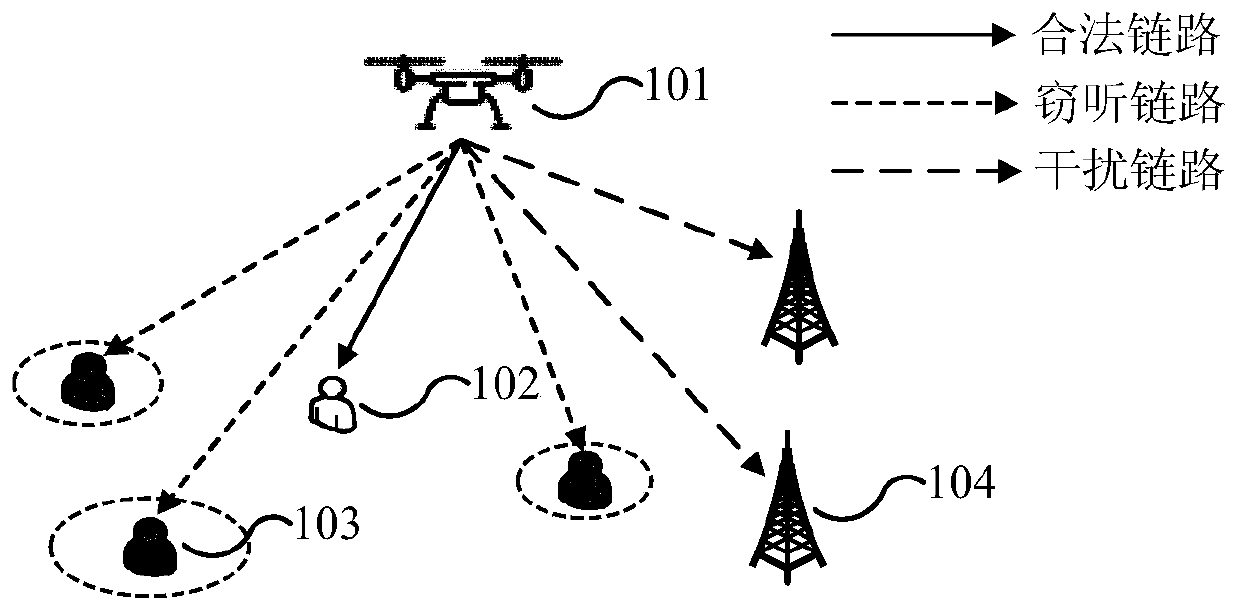
Method for controlling communication security of unmanned aerial vehicle assisted cognitive radio network
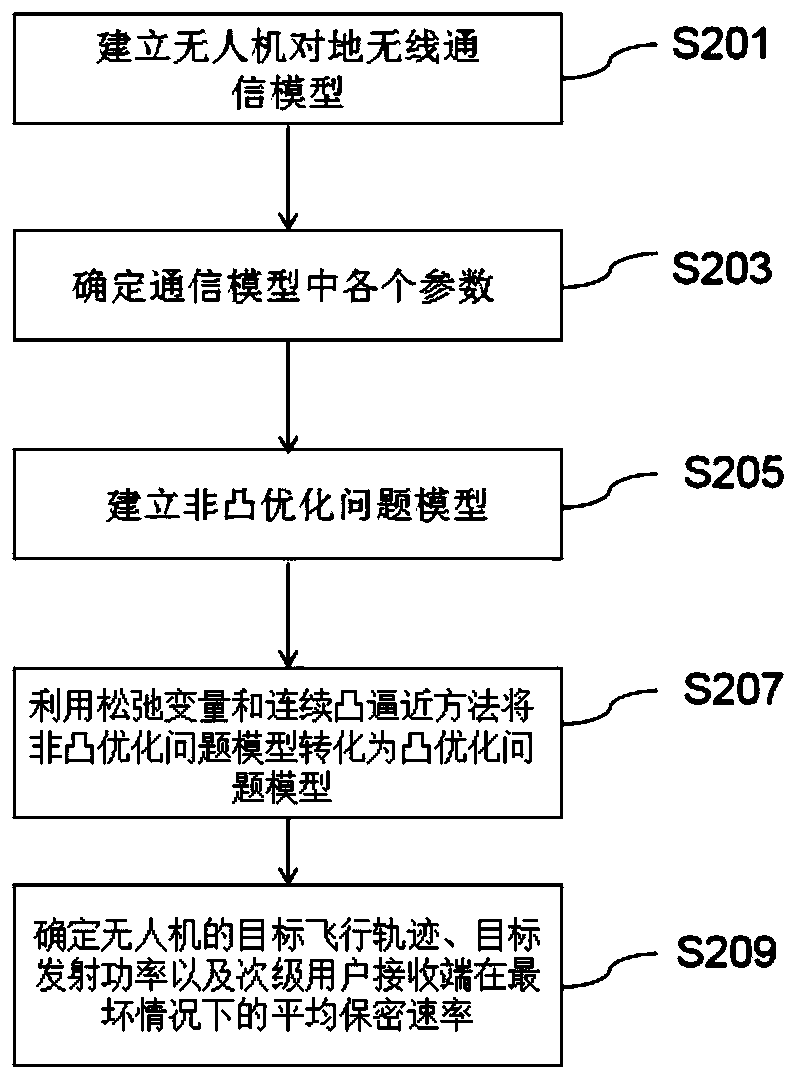
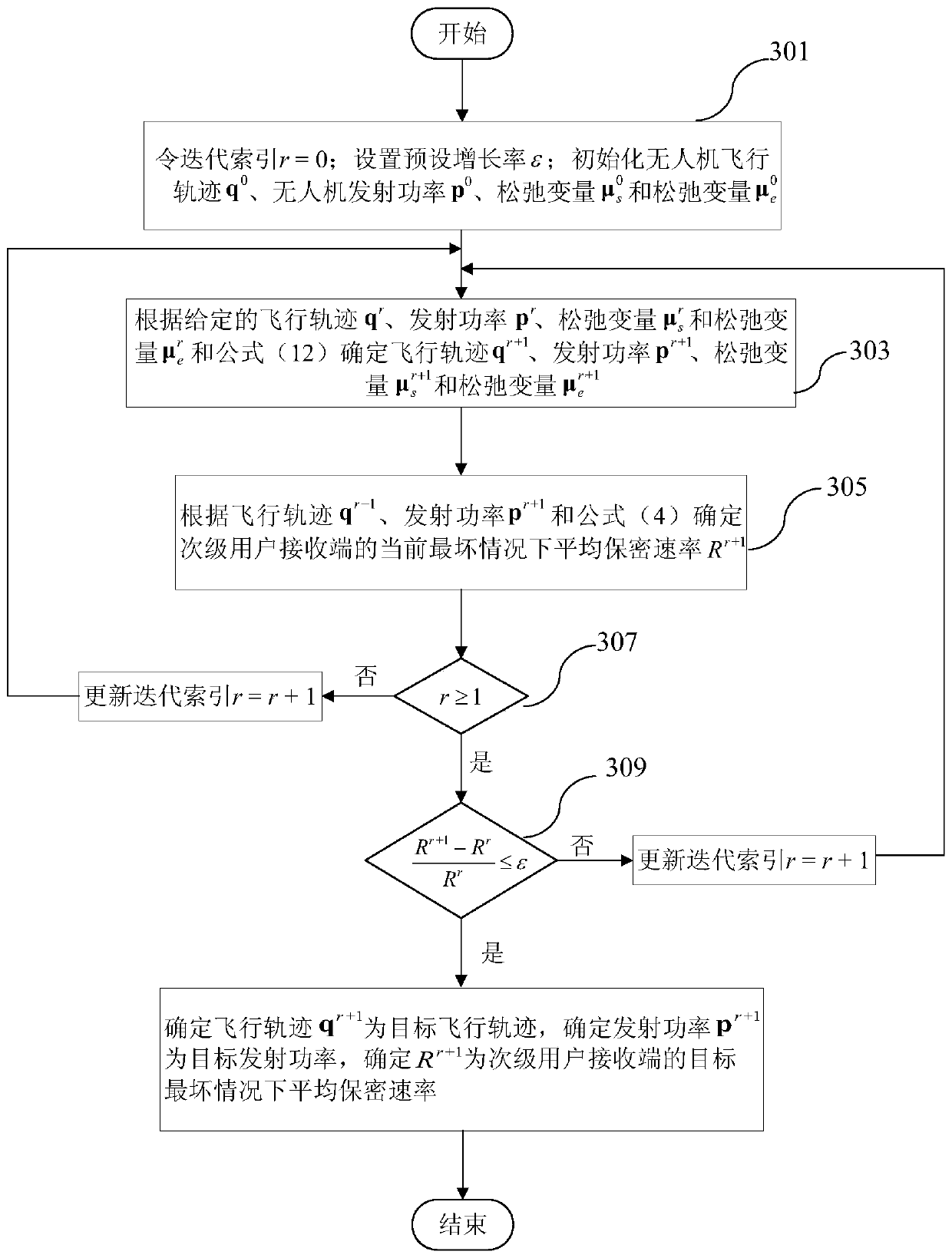
InactiveCN111343712AEnsure secure transmissionPower managementInternal combustion piston enginesCommunications securityTransmitted power
The invention relates to a method for controlling the communication security of an unmanned aerial vehicle assisted cognitive wireless network. The method comprises the following steps: step S201, establishing a communication model of unmanned aerial vehicle-to-ground wireless communication; step S203, determining each parameter in the communication model; s205, establishing a non-convex optimization problem model according to each parameter in the communication model; s207, converting the non-convex optimization problem model into a convex optimization problem model by using a slack variableand a continuous convex approximation method; and S209, according to the convex optimization problem model, determining the target flight path and the target transmitting power of the unmanned aerialvehicle and the average secrecy rate of the secondary user receiving end under the worst condition. According to the method, the average secrecy rate of the secondary user receiving end under the worst condition is maximized by jointly optimizing the flight path and the transmitting power of the unmanned aerial vehicle within the given flight time, so that safe transmission of information is effectively guaranteed.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
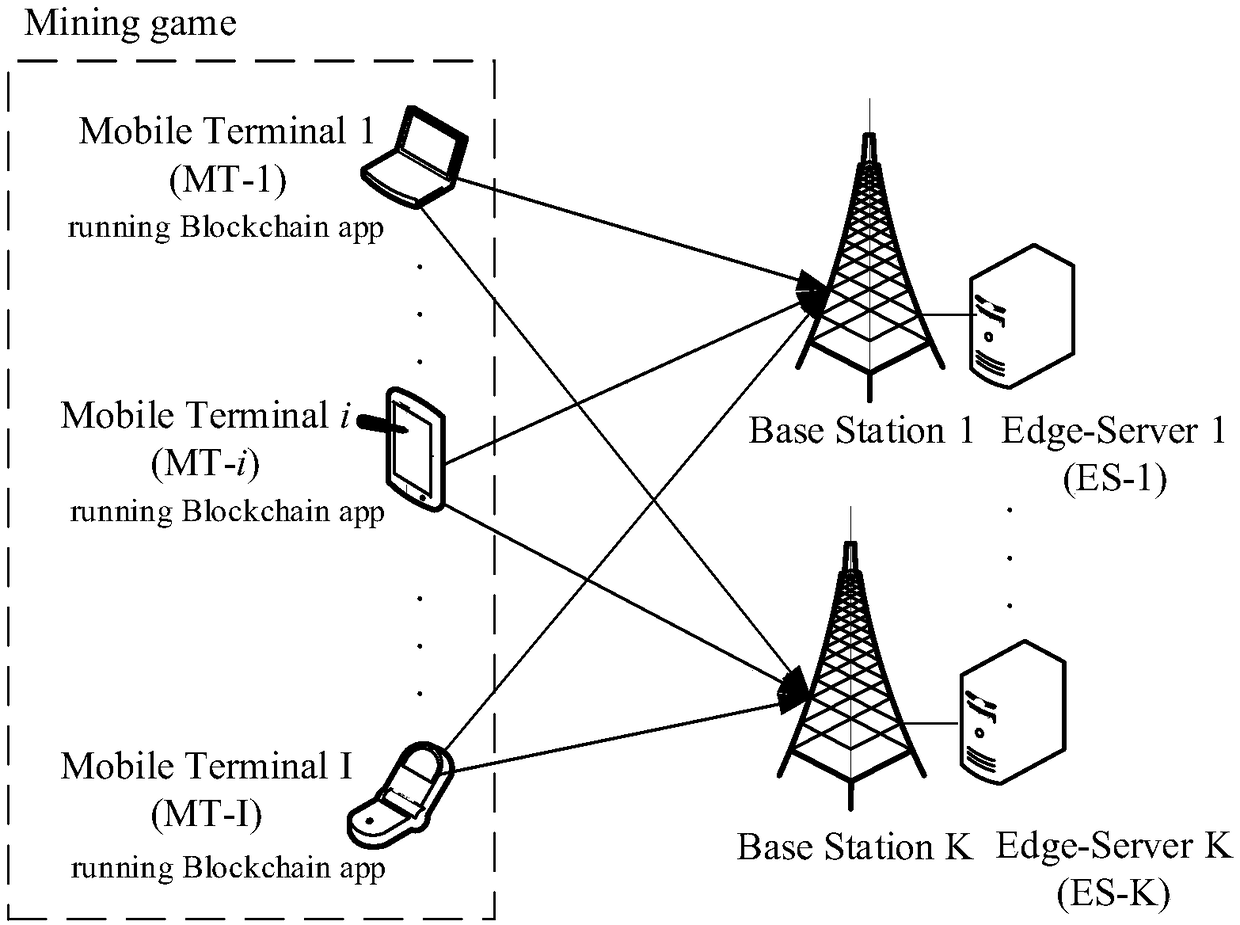
A simulated annealing-based mobile blockchain optimization hashrate allocation method in multiple edge computing server scenarios
ActiveCN109388492AMeet needsIncrease the probability of being the first to complete the proof-of-workResource allocationEnergy efficient computingMultiple edgesEdge server
A simulated annealing-based mobile blockchain optimization hashrate allocation method in multiple edge computing server scenarios comprises the following steps: (1) there are n mobile users in total under the coverage of multiple edge computing servers, and an optimization problem is described as a non-convex optimization problem, in which the computational power of the optimal system mobile terminal is allocated and the system revenue is maximized under the limited computational power resources of the edge servers; (2) the TRO problem is transformed into TRO-sub problem equivalently under thecondition of given vi; (3) the TRO Sub problem is discussed and , based on simulated annealing method, the global optimal solution is obtained and the maximum system benefit is obtained. For the mobile terminal, the invention greatly improves the probability of completing the workload proof first by using the edge computing technology. For the edge computing server, under the condition of limitedcomputing resources, it meets the needs of mobile terminals; Increased the ultimate benefits of the system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Wave-beam forming method based on cognitive hybrid two-way relay
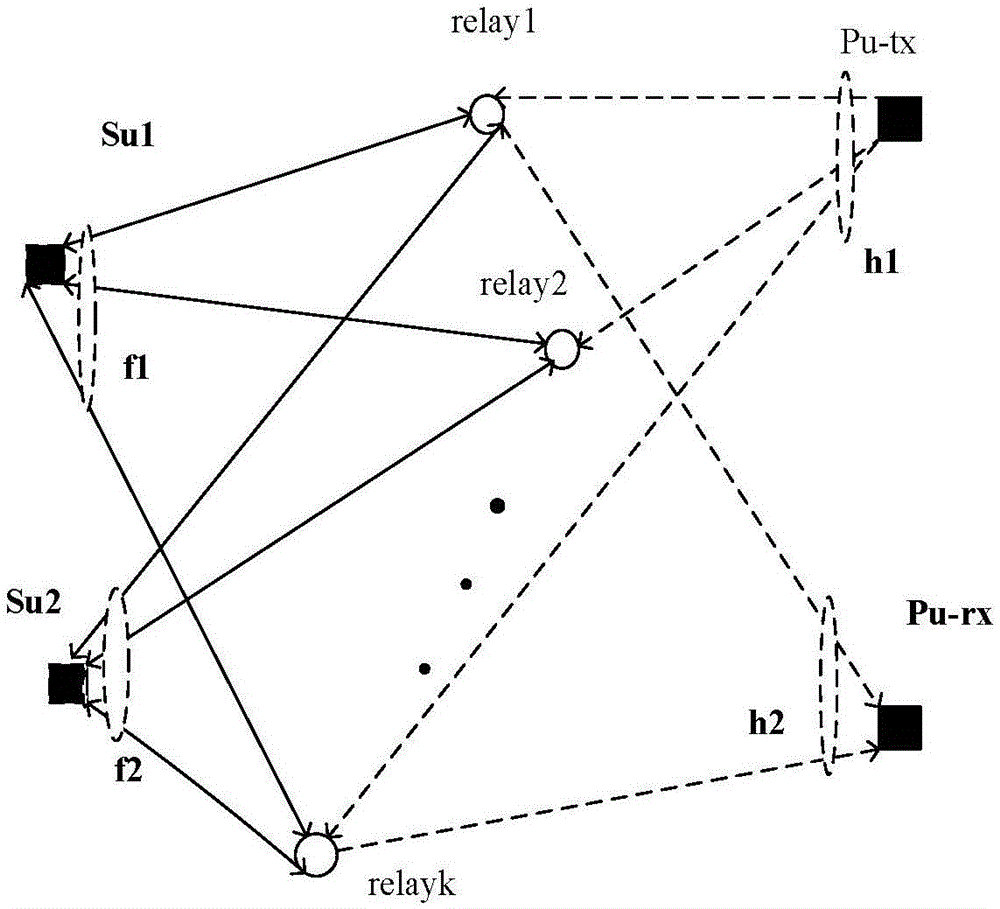
ActiveCN105656537AReduce distractionsImprove the problem of noise amplificationSpatial transmit diversityNetwork planningCognitive userSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
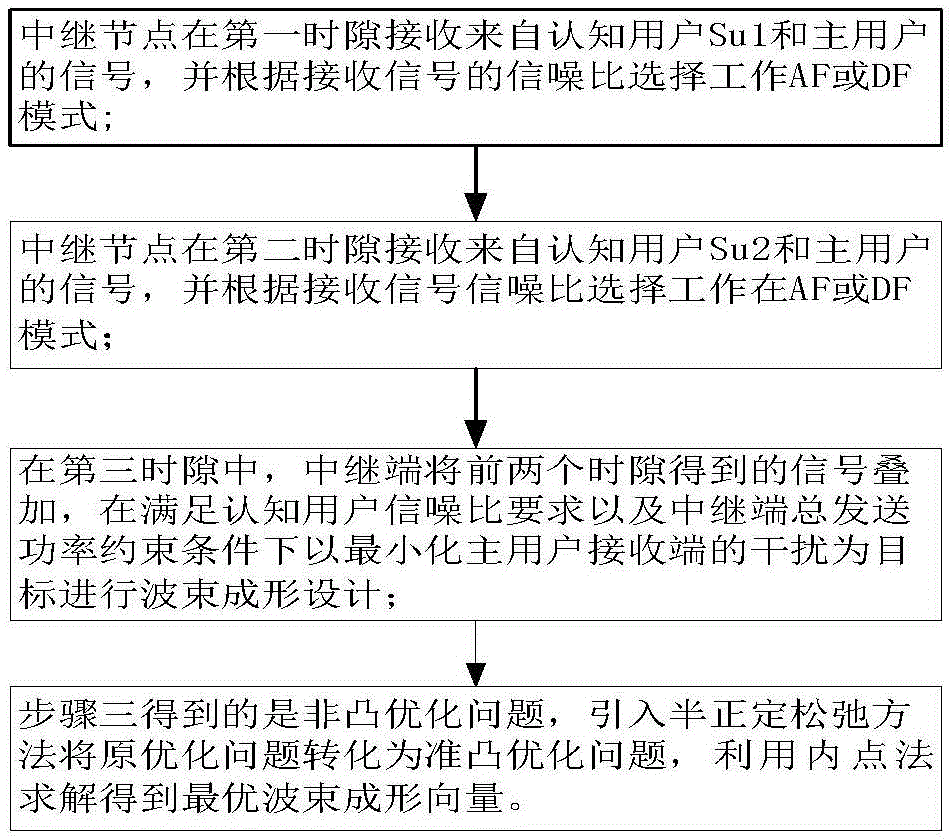
The invention discloses a wave-beam forming method based on a cognitive hybrid two-way relay. The wave-beam forming method comprises the following steps that: (1) a relay node receives signals from a cognitive user Su1 and a main user in a first time slot and chooses to work in an amplifying-forwarding and decoding-forwarding mode according to the signal-to-noise ratio of the received signals; (2) the relay node receives signals from a cognitive user Su2 and the main user in a second time slot and chooses to work in an amplifying-forwarding or decoding-forwarding mode according to the signal-to-noise ratio of the received signals; (3) in a third time slot, the relay end superposes the signals obtained in the former two time slots and carries out wave-beam forming design with the target of minimizing the interference of the receiving end of the main user under the condition of meeting the requirement of the signal-to-noise ratio of the cognitive user and the constraint condition of the total transmitting power of the relay end; and (4) the non-convex optimization problem is obtained from the step (3), a semi-definite relaxation method is introduced to convert the original optimization problem into a quasi-convex optimization problem, and an interior point method is utilized for solving to obtain an optimized wave-beam forming vector. The wave-beam forming method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the intersystem interference is reduced and the system performance can be improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
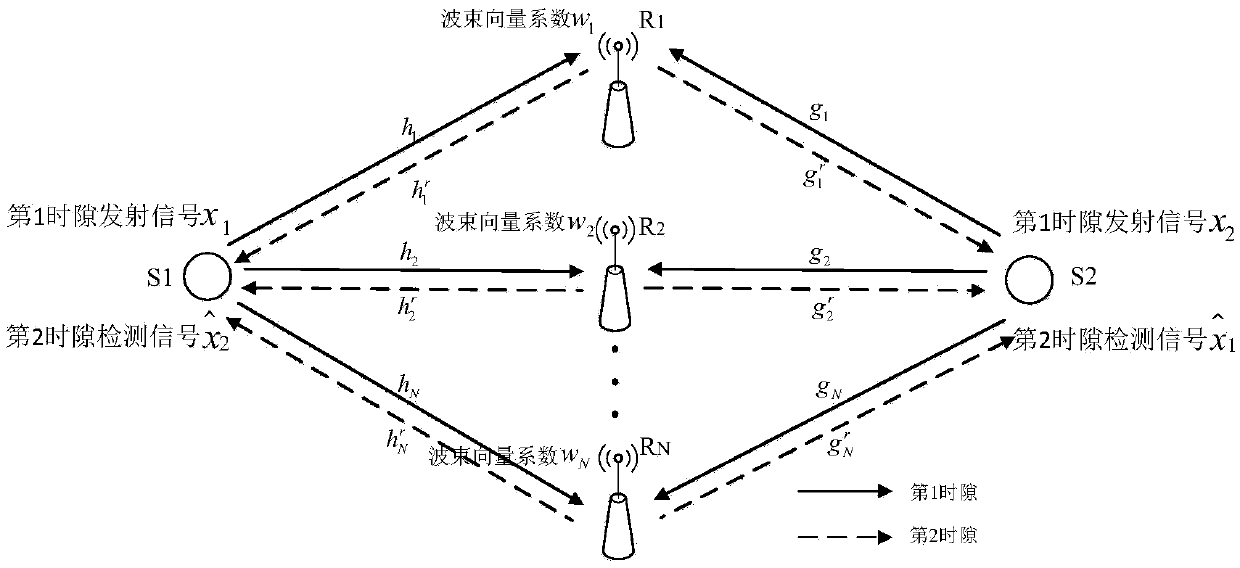
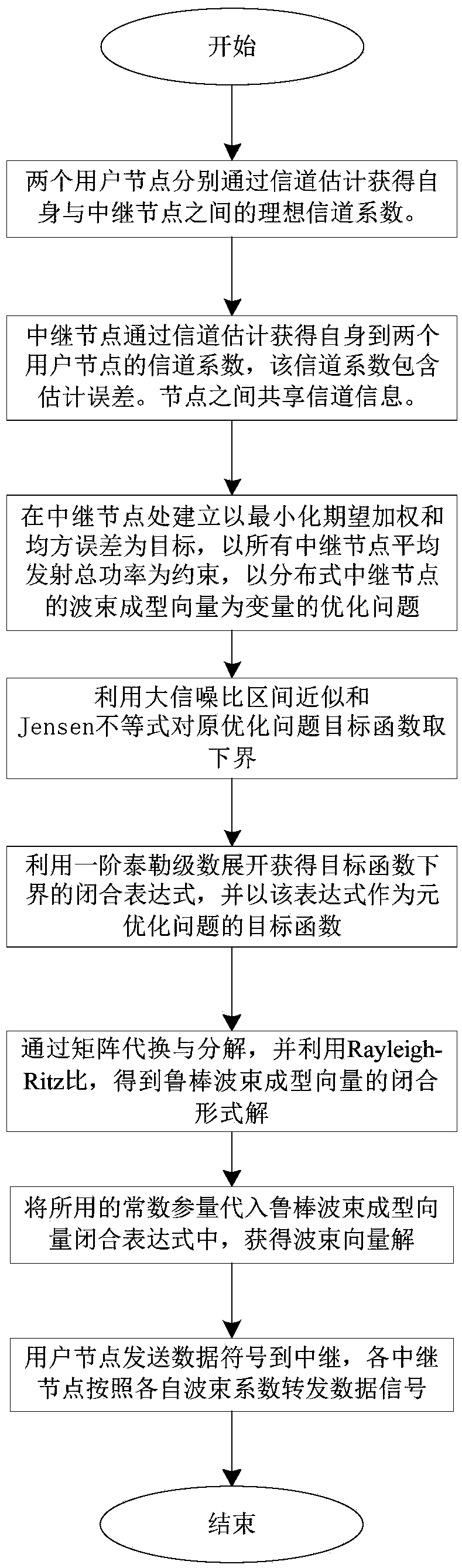
Robust wave beam molding method based on distributed bidirectional relay system
ActiveCN105281817ABest Received Symbol Detection PerformanceReduce complexitySite diversitySpatial transmit diversityLower limitSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
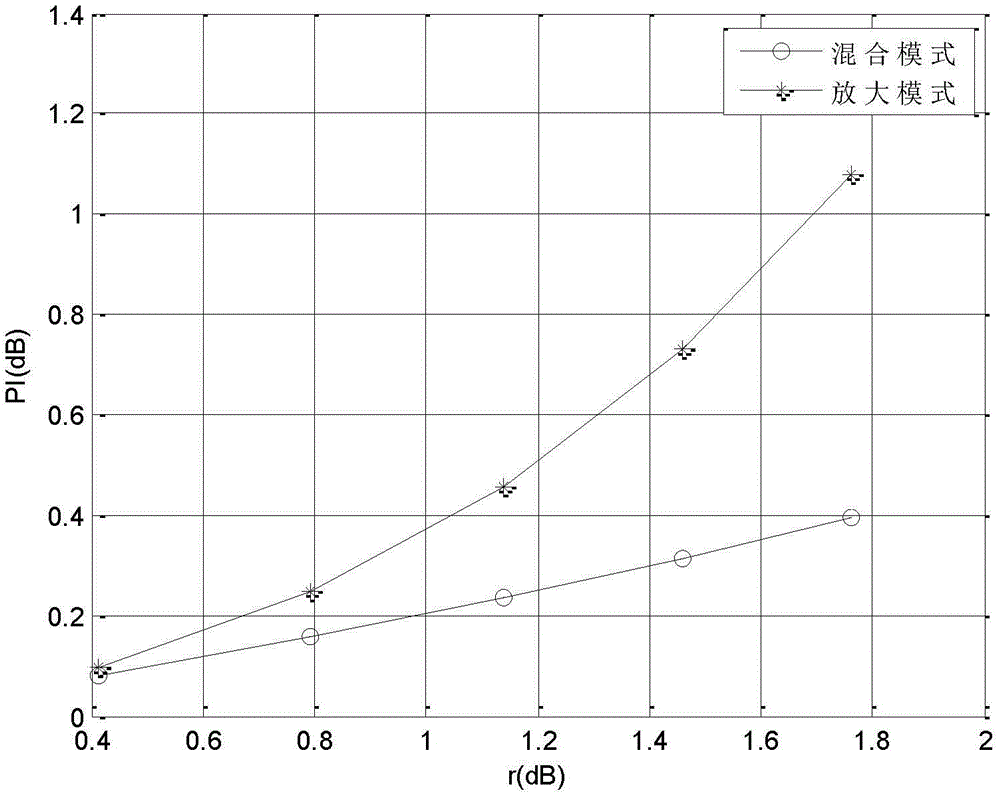
The invention discloses a robust wave beam molding method based on a distributed bidirectional relay system. The system consists of two user nodes and a plurality of bidirectional relay nodes distributed at different positions, wherein all nodes are respectively provided with a single antenna. Two users complete information exchange within two time intervals through a relay, which is shown in an attached map. Considering that a relay node is a non-ideal signal channel, the invention proposes a robust wave beam molding optimization scheme which takes the maximization of the expectation weight and mean square error of a received signal as the objective, takes the mean transmission total power of all relay nodes as the constraint. Because an objective function in an optimization problem has no precise analysis mode, the method solves the lower limit of the objective function through the approximation in a large signal to noise ratio section and a Jensen inequation, and obtains the approximate expression of the lower limit through a one-order Taylor series expansion, and enables a non-convex optimization problem to be gradually changed into a convex problem which is easy to solve. Finally, the method obtains the closed-form solution of a robust wave beam vector through matrix substitution and decomposition.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Steady direction of arrival estimation method based on sparse representation and covariance fitting
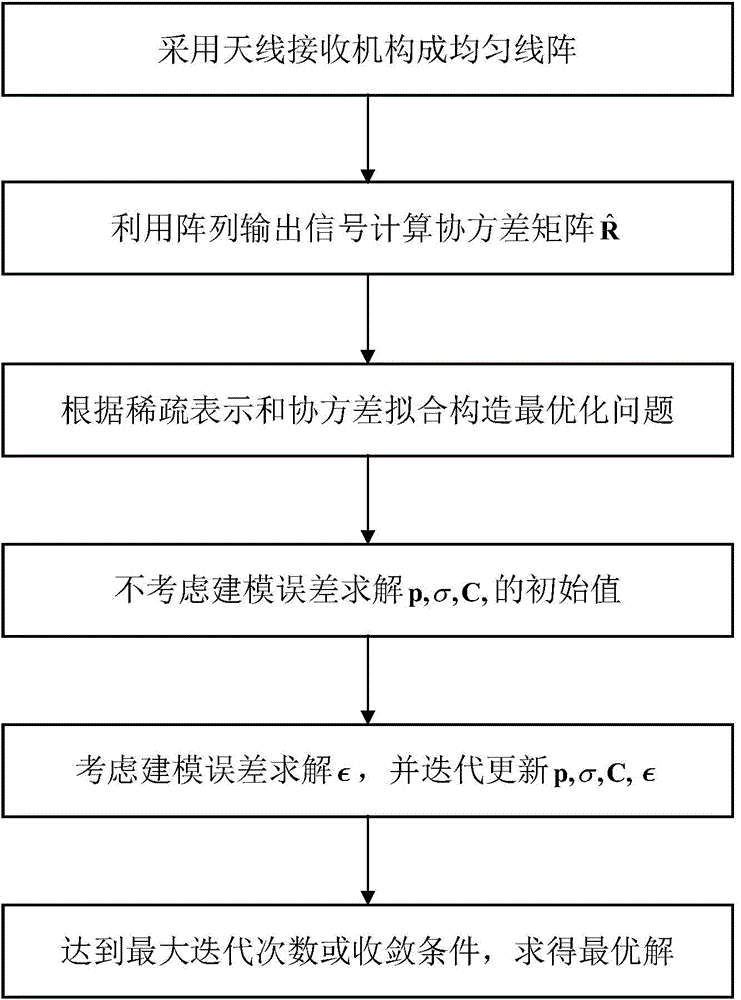
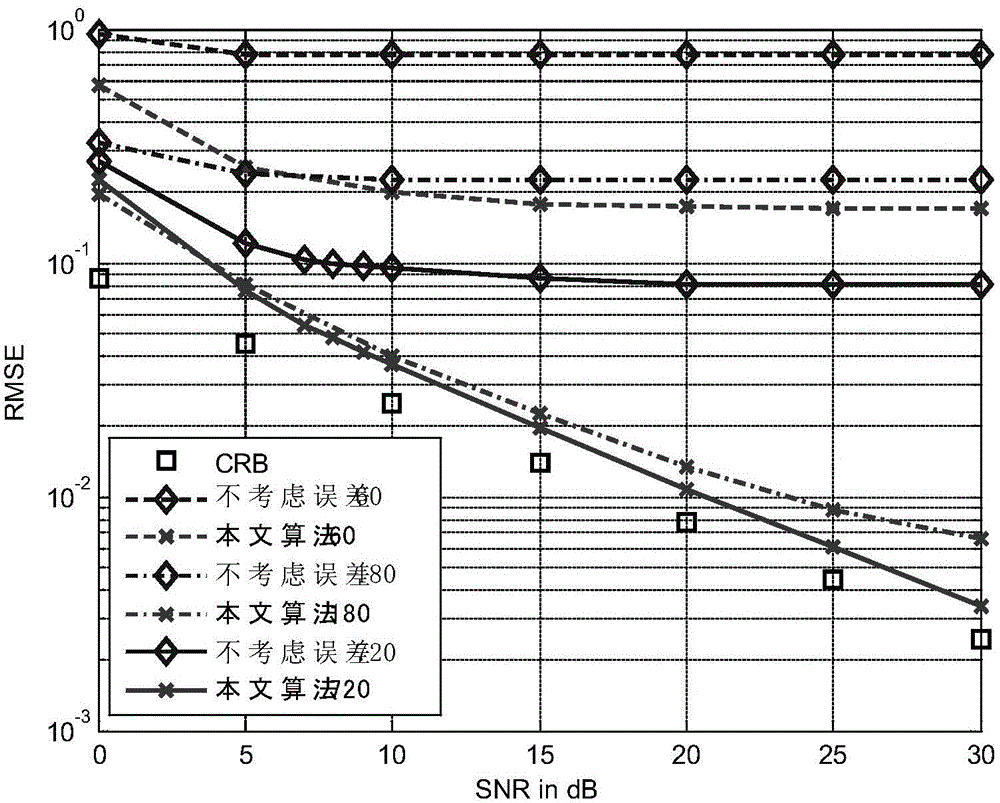
ActiveCN104539340ARobust Continuous Sparse Iterative Estimation MethodImprove estimation accuracySpatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringEstimation methodsCovariance function
The invention provides a steady direction of arrival estimation method based on a sparse representation and covariance fitting. The steady direction of arrival estimation method based on the sparse representation and the covariance fitting mainly comprises the steps that a sparse spatial spectrum representation model is established according to antenna array receipt signals, a parameterization representation is carried out on model errors, and an optimization problem is established according to a covariance fitting criterion. The obtained problem is non convex optimization, therefore, the transformation and solution of the problem can be performed through equivalent transformation, parameter increase and step-by-step solution. Without considering the model errors at first, an original problem can be simplified as a convex optimization problem. The convex optimization problem is quickly solved by an existing method, and an initial solution is obtained. Iteration solving is carried out on the original problem, a model error parameter is estimated and an initial estimation is renewed. The steady direction of arrival estimation method based on the sparse representation and the covariance fitting can obtain a precise DOA estimation by low complexity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com